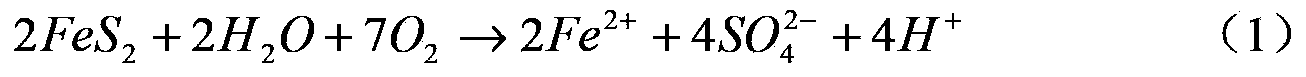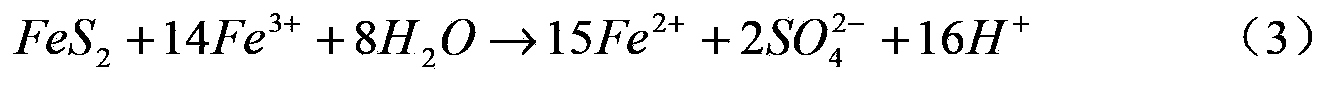Patents
Literature
57 results about "Acidophilic bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
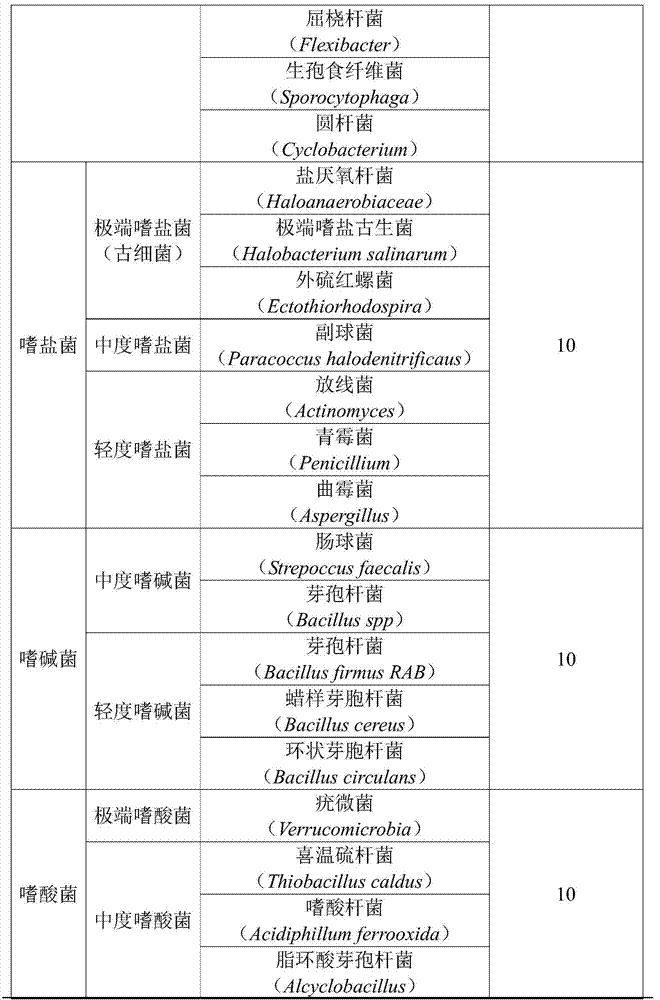
Organisms which require a significant acidity of the environment. Acidophilic bacteria include acetic-acid bacteria which grow well in a medium having a pH of 3.3; lactic bacteria which live on milk substrates (a medium with a pH of 3.4); and chemoautotrophic bacteria which oxidize sulfur in ores to sulfuric acid and multiply with a pH of 1–2.
Method for leaching valuable metals in waste circuit board by acidophilic bacteria mixed culture
InactiveCN101962712AEliminate Growth Inhibitory FactorsHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionMixed culture
The invention discloses a method for leaching valuable metals in a waste circuit board by acidophilic bacteria mixed culture, comprising steps of: (1) preparing metal concentrate powders from the waste circuit board; (2) preparing the acidophilic bacteria mixed culture: collecting acid mine drainage from a sulfide ore mine, inoculating the pit water to 9K culture medium according to the inoculation amount of 5-40% by volume, culturing the culture medium in shaking conditions until a large number of reddish-brown precipitates are produced, filtering the solution and obtaining the acidophilic bacteria mixed culture; (3) leaching metals in the metal concentrate powders by the acidophilic bacteria mixed culture. The method of the invention has the advantages of high target metal recovery, low energy consumption, improves the leaching yield of copper by 98% or more during 2 days and the leaching yield of zinc and aluminum by 90% or more during 4 days, simplifies the treatment process and reduces the cost without separating and purifying microbial strains, can recycle the leach liquor repeatedly and substantially realizes zero-pollution emission.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Sulfide ore treatment technology by thermoacidophile
InactiveCN1827805AReduced Cooling NeedsFast oxidationProcess efficiency improvementMetaboliteSulfide
The invention relates the technology of using thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria to treat sulphide field, comprising the following steps: screening and domesticating the thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria to get the high effective biooxidation strain; training it to get inoculation liquid whose thalline density is above 1X108 per liter; mixing the inoculation liquid, sulphide powder and culture medium of thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria, carrying out biological oxidation reaction, and when the copper ion of chalcopyrite in sulphide powder dissolving out above 70%, or 70% lattice structure of chalcopyrite destroyed, terminating the reaction. The technology uses the microbe direct oxidation action and metabolite indirect oxidation action to oxygenize the sulphide in ore to sulphate, destroying the sulphide lattice and discharging the precious metal ion.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for extracting and preparing peat fulvic acid and drug application
InactiveCN103588977AAvoid high temperatureAvoid high pressureFungiOrganic chemistryPeatExtreme thermophile
The invention discloses an extraction method of peat fulvic acid and drug application. A method A is that mixing peat, hyperthermophilic baceria (3-13 CFU), barophilic baceria (5-11 CFU), halophilic baceria (6-12 CFU), basophilic baceria (7 to 13 CFU) and acidophilic bacteria (3-10 CFU) under three conditions including the condition I (10-130 DEG C and 0.05-0.18 MPa), the condition II (5-75 DEG C and 0.05 to 0.12 MPa) and the condition III (5-65 DEG C and 0.05 to 0.12 MPa) and treating for 1-2, 1-3 and 1-2 days respectively; a method B is that mixing the peat and part of the baceria under the conditions I and II for 1-2 and 1-3 days respectively, and mixing with the acidophilic bacteria under the condition III for 1-2 days; a method C is that mixing the peat, the hyperthermophilic baceria and the barophilic baceria under the condition I for 1-3 days, mixing with the halophilic baceria and the basophilic baceria under the condition II for 1-3 days, and mixing with the acidophilic bacteria under the condition III for 1-2 days. Fulvic acid prepared by the method is high in purity.
Owner:云南联合药业有限责任公司 +1
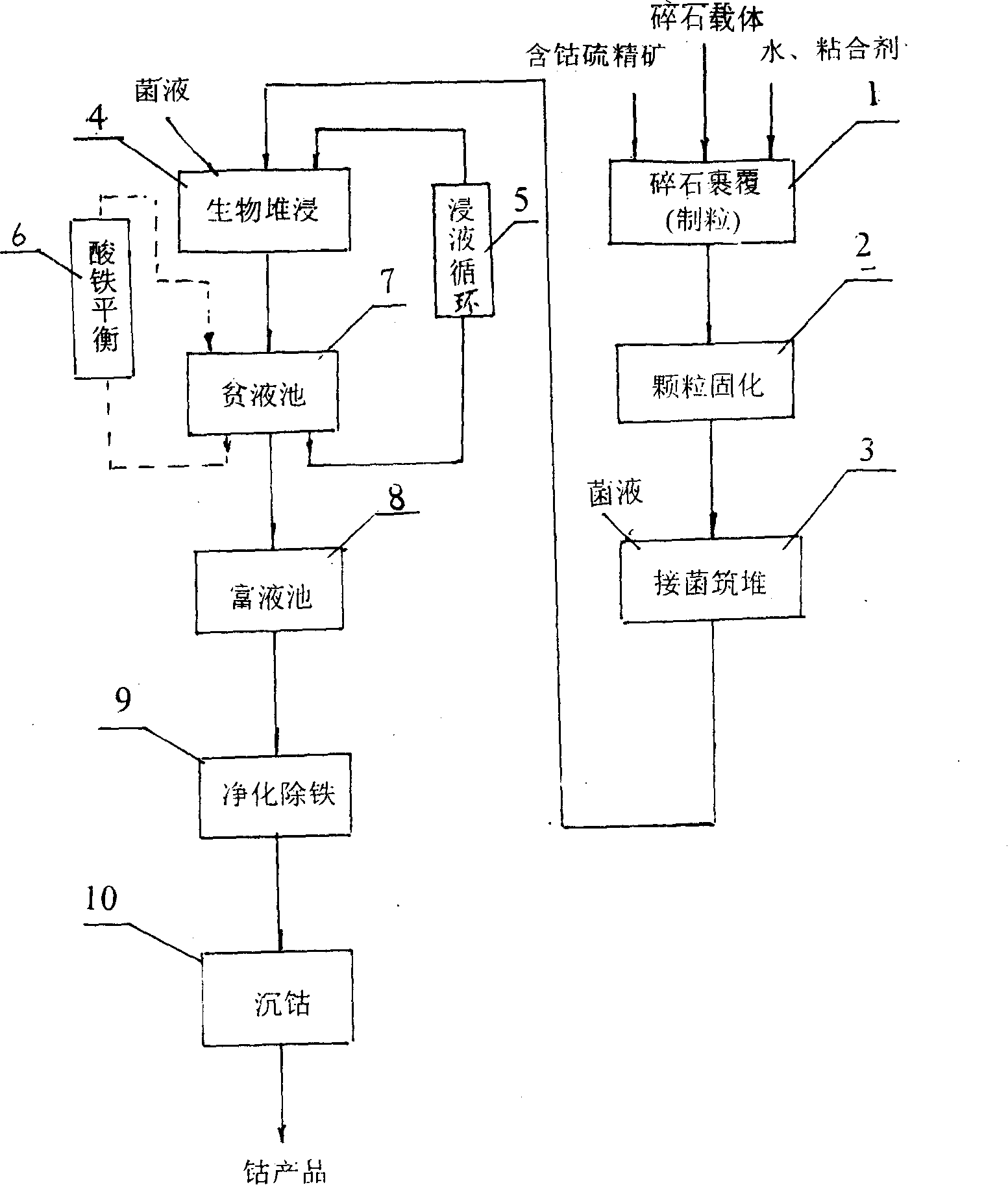
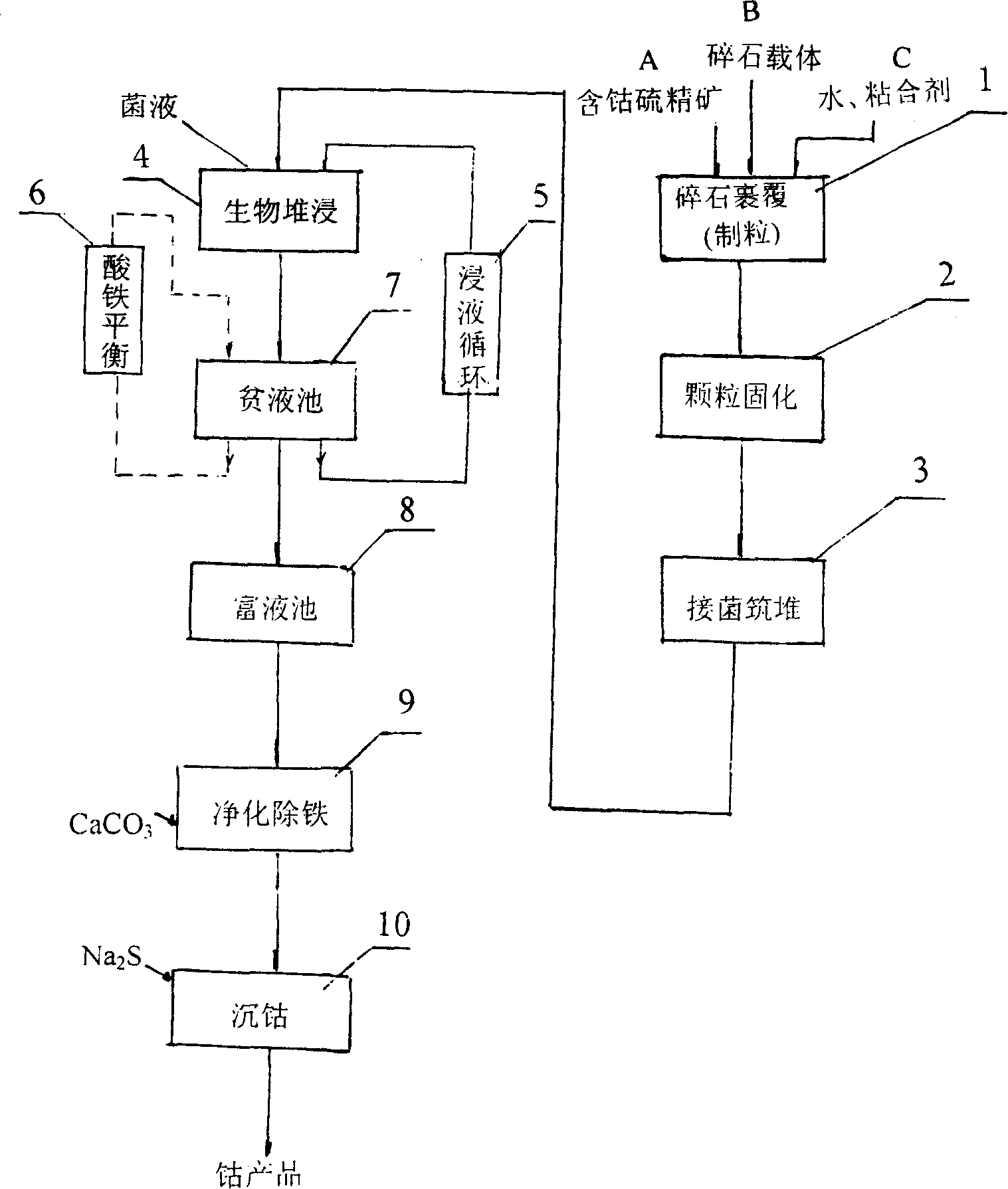
Mesophilic acidophilic bacteria and biological heap leaching technique for low-grade cobalt-containing sulfur concentrate
InactiveCN101191122AEfficient recyclingLow investment costBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansCobalt sulphate
The invention relates to mesophilic acidophilic bacteria and a biological heap leaching technology for low-grade cobaltiferous sulfide ore concentrates. The mesophilic acidophilic bacteria have a name of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Retech V and a collection registration number of CCTCC NO: M202039, and has been stored and collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (in Wuhan University). The biological heap leaching technology is that: mineral grains which are suitable for biological heap leaching are obtained after coating of crushed stones and solidification of the mineral grains of the low-grade cobaltiferous sulfur-bearing ore concentrates. Cobalt sulphates are obtained through procedures of embankment, heap leaching and trickling by adoption of bacteria with two different growth temperatures, lixivium circulation, purification and deferrization of cobalt pregnant solution, cobalt settlement and so on of the mineral grains. The temperature of 10 to 55 DEG C, the PH value of 1.2 to 1.8 and the adequate Fe concentration of a storage yard in a heap leaching system during the leaching out process are favorable for activity of leaching bacteria. The invention has the advantages of capability of fully utilizing low-grade cobaltiferous sulfide ore resources in old mines, improvement of comprehensive utilization level of mines, conservation of cost, and improvement of profit. The invention is applied in developing cobaltiferous sulfide ore resources in remote areas.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
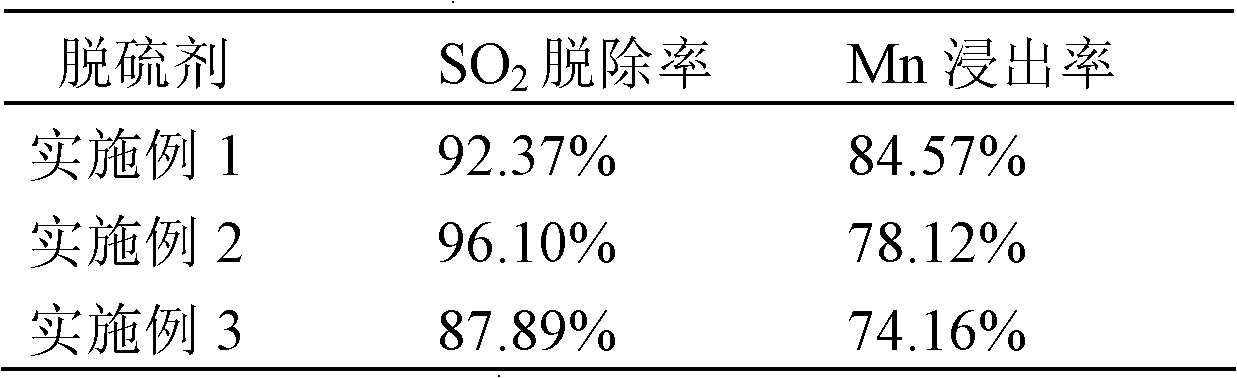
Microbial flue gas desulfurizer
InactiveCN102179167AImprove oxidation efficiencyReduce outputDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementMicroorganismPyrolusite
The invention relates to a microbial flue gas desulfurizer, which is characterized by comprising bacterial solution of active bacteria of Alicyclobacillus BM No.CGMCC 4500 and active bacteria of any one or more acidophilic bacteria which get energy from ferrous ions and / or reduced sulfur and / or element sulfur. Compared with the conventional pure-pyrolusite desulfurizer, the desulfurizer provided by the invention can improve the SO2 oxidization rate due to the addition of microbes which can oxide the reduced sulfur and fermentation liquor containing rich iron ions, improves the yield of manganese(II) dithionate serving as a byproduct and thus improves removal rate.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chromium reducing method based on iron-containing sulphide ore under action of acidophilic bacteria
ActiveCN104498713AHuge storageLow priceProcess efficiency improvementSulfate radicalsChemical reaction
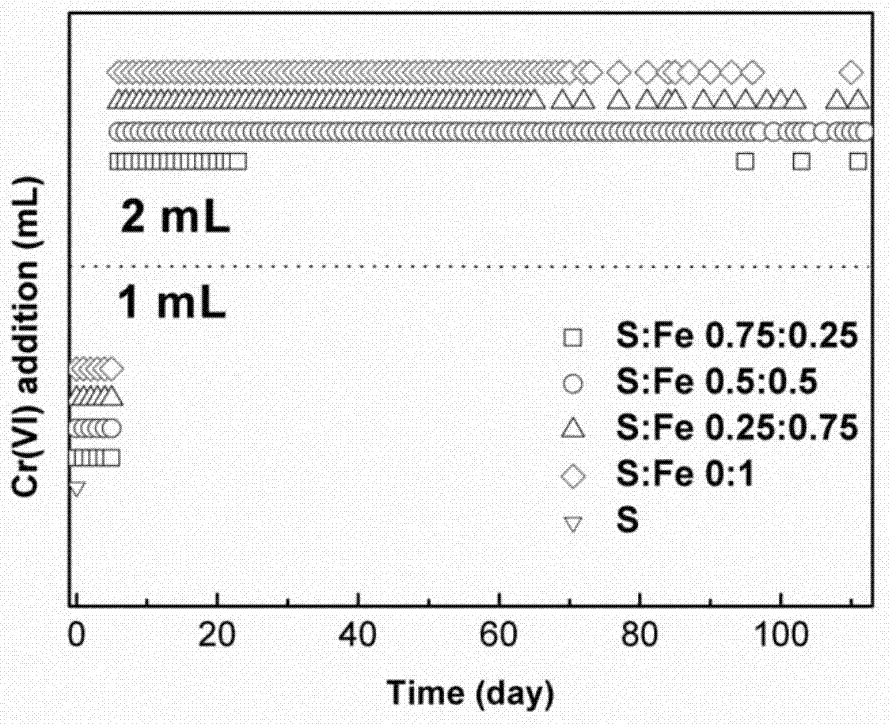
The invention discloses a chromium reducing method based on iron-containing sulphide ore under action of acidophilic bacteria, belonging to the wastewater treatment technology of the environmental engineering field. The chromium reducing method comprises the following steps: introducing thermoacidphilic iron-sulfur oxidizing bacteria into a chromium reducing process of the iron-containing sulphide ore, and adhering a biological membrane on the surface of the pyrite. The chromium reducing method can be used for effectively relieving a passivation layer on the surface of the pyrite, overcoming the problem that the raw material utilization efficiency of the pure chemical reaction is low, greatly quickening kinetics of reduction, and completely utilizing the pyrite. After being reduced, the chromium, an iron ion and sulfate radical in the system can form precipitates such as jarosite and schwertmannite which are filtered and separated, so that the trivalent chromium ion in the system can be removed. The reduction government mode is wide in scope of application, low in site requirement and long in operation period and has large-scale industrial application potential.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Two-phase biological deodorization method and two-phase biological deodorization device
InactiveCN106799164AReduce typesAvoid competitive inhibitionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationMulti pollutantNutrient solution
The invention relates to a two-phase biological deodorization method and a two-phase biological deodorization device. According to the two-phase biological deodorization method, malodorous gas is sequentially subjected to humidification treatment, acid treatment and neutral treatment, wherein the humidification treatment refers to using a nutrient solution to carry out spray treatment on the malodorous gas; the acid treatment refers to using acidophilic bacteria and fungi to degrade the malodorous gas; the neutral treatment refers to using neutral heterotrophic bacteria to degrade the malodorous gas. The method and the device can effectively and thoroughly degrade multiple pollutants in the malodorous gas; furthermore, the land area occupied by a reactor is reduced, and the investment and treatment cost are lowered.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE
Gene chip for analyzing microbial group structure and function under acid environment
InactiveCN101074449AMonitor function activityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobial profilingFunctional genes
A gene chip for analyzing microbiocoenosis structure and function in acid environment is fast, sensitive and correct. The probe of the gene chip consists of acidophilic microbe 16S rRNA sequence and gene relating to carbon, nitrogen and iron metabolism, metal resistance and film, transposon and IST etc. functional gene sequence and minor human gene as negative contrast and quantitative contrast. It is constructed by 754-1072 oligomeric nucleotide sequences. It has high flux and less labor strength. It's easy to separate and culture acidophilic bacteria.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for rapidly processing large-scale piggery wastes
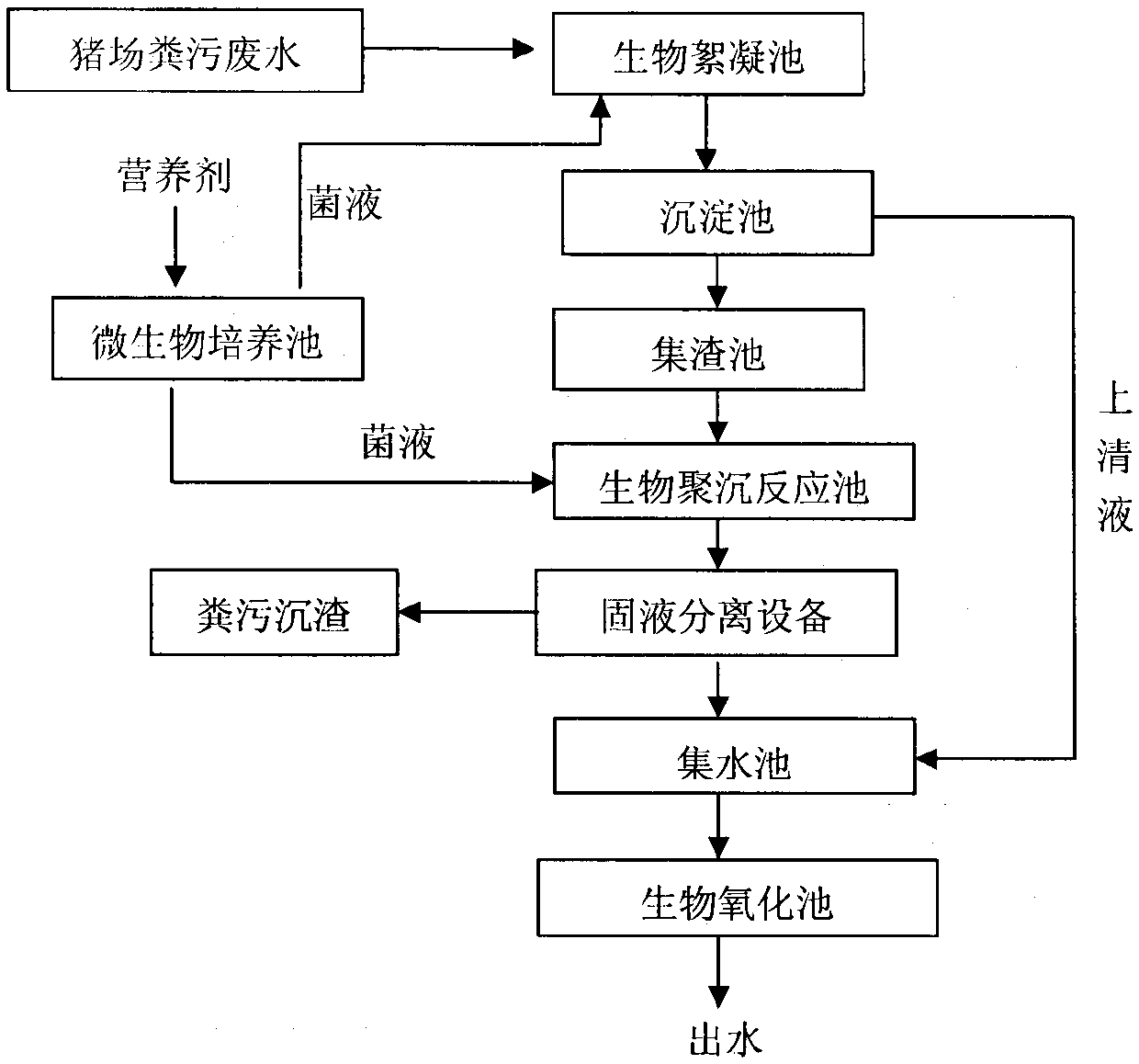
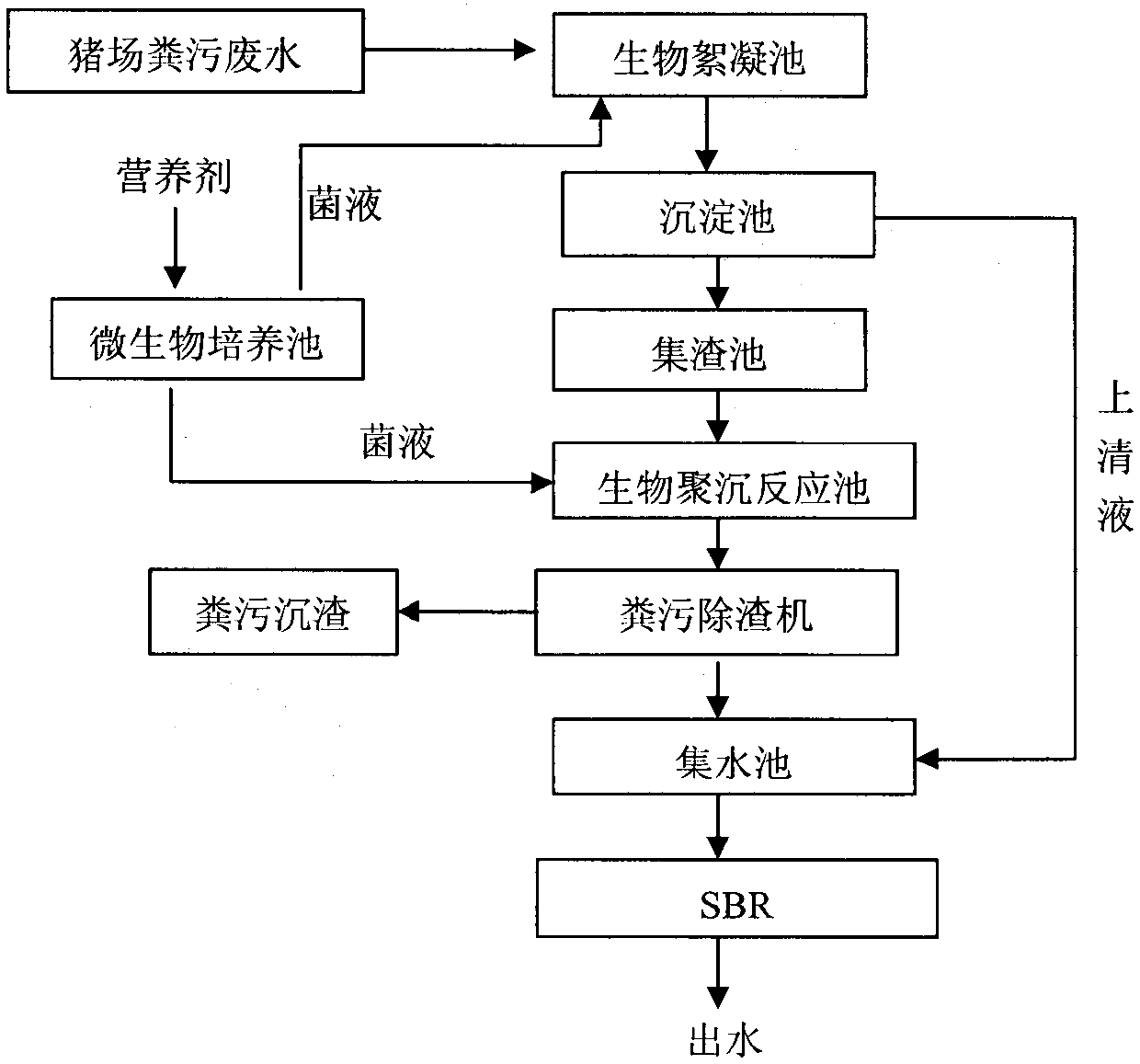
ActiveCN105502802AImprove dehydration effectEasy to handleTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsFlocculationBiological oxidation
The invention provides a method for rapidly processing large-scale piggery wastes. The method is specifically a biological coagulation oxidation technology. Main facilities contain a biological flocculation tank, a sedimentation basin, a slag collection tank, a biological coagulation reaction tank, solid-liquid separation equipment, a microbial cultivation tank, a collecting basin and a biological oxidation tank. The method is characterized in that specific heterotrophic microbes (acidophilic bacteria JZ6, preservation number: CGMCC No. 11036) are utilized to generate a biological flocculant; through adsorption bridging effect, charge neutralization effect and sweeping effect, the biological flocculant and SS, COD, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus in piggery waste water undergo polymerization to be deposited, and dehydration performance of piggery wastes is improved; separation is further carried out by the utilization of solid-liquid separation equipment; separated piggery wastes are used in production of organic fertilizers; and separated wastewater undergoes further biological oxidation treatment to realize up-to-standard release.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
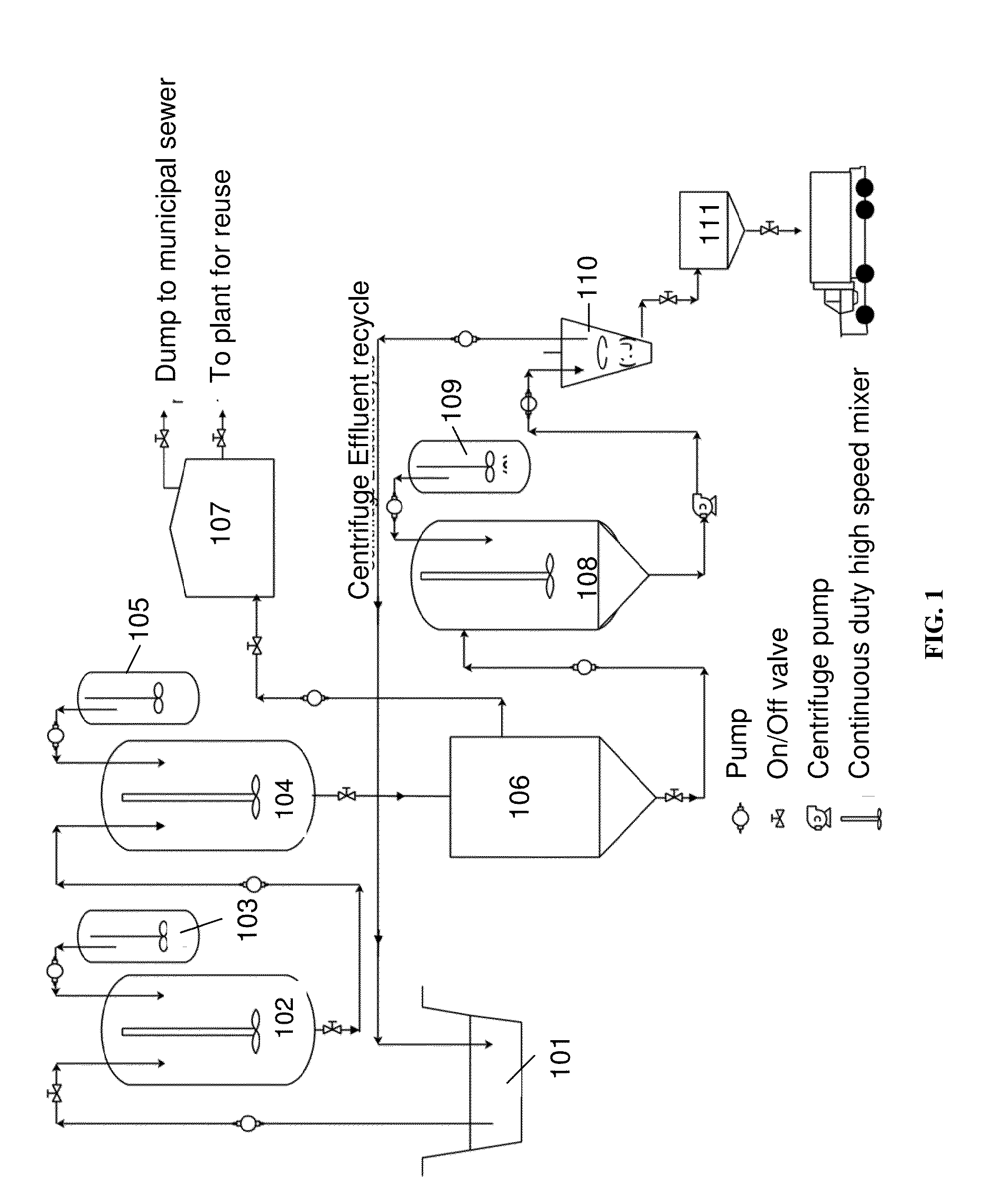
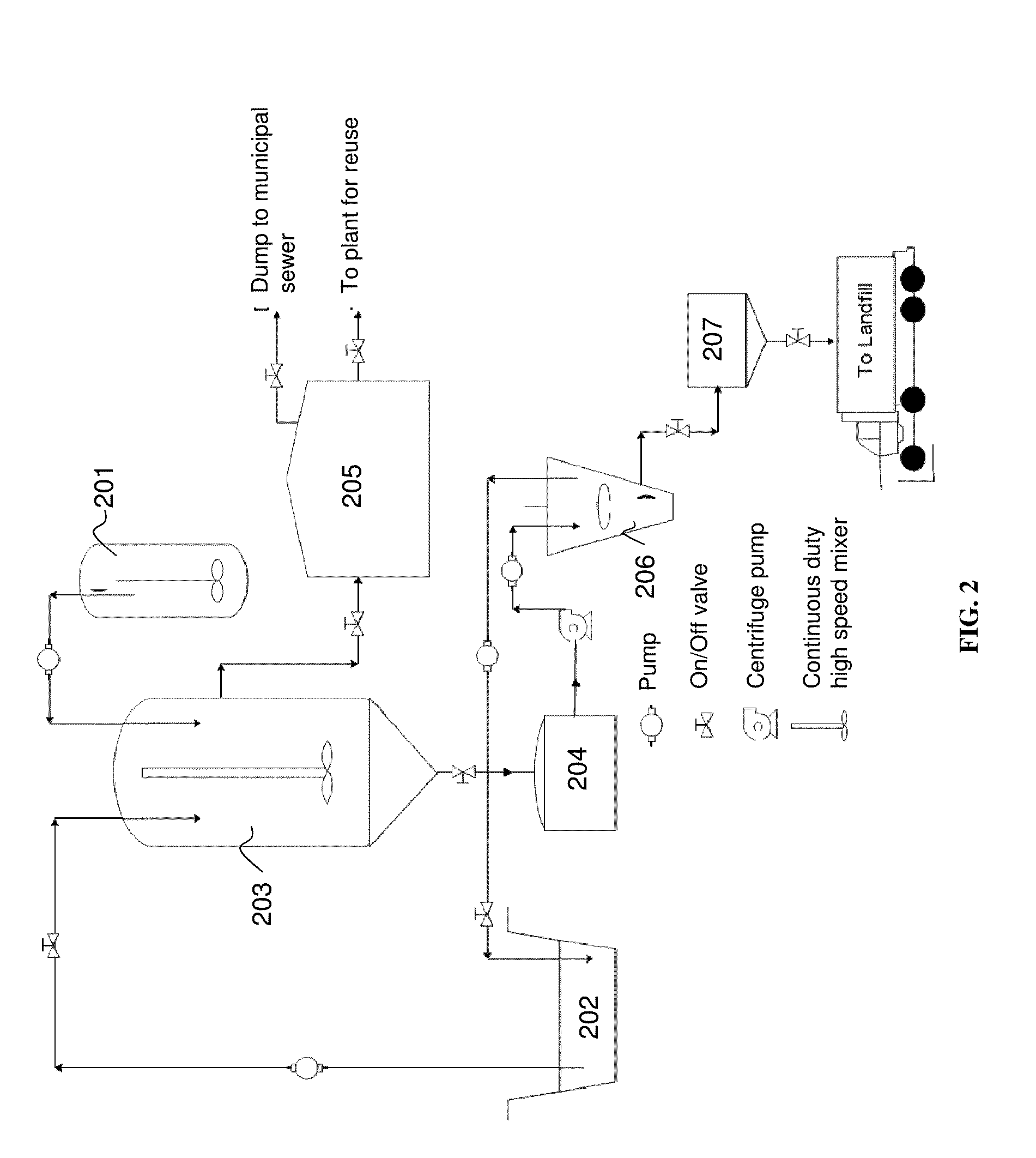
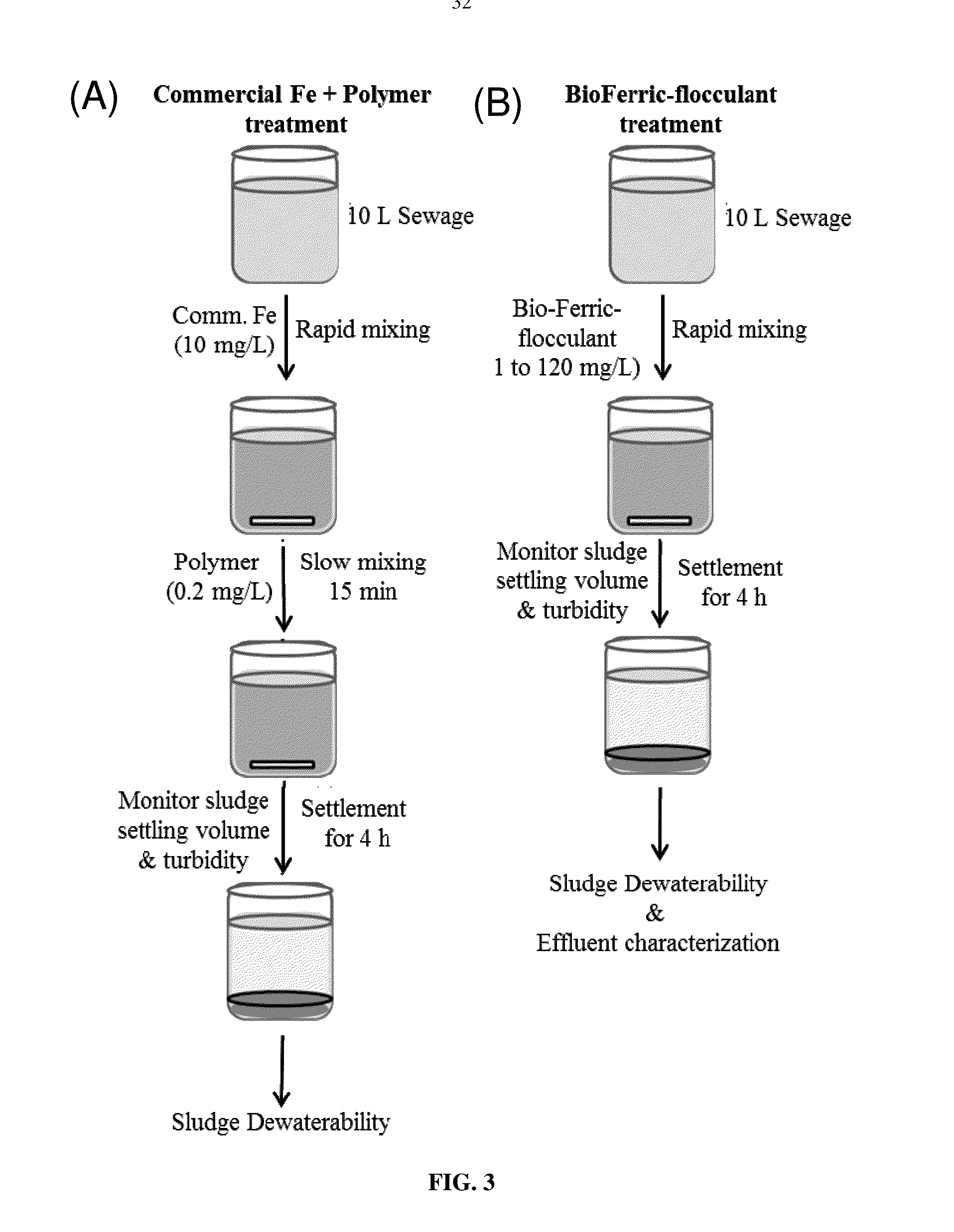
BioFerric-Flocculant Enhanced Primary Treatment Process (BEPT) for Sewage Treatment
ActiveUS20160023933A1Simple processMinimizes stepBacteriaWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationSludge
The present invention relates to one step “BioFerric flocculant enhanced primary treatment” (BEPT) process for domestic sewage treatment. More particularly, it relates to a novel composite flocculant consisting of acidophilic bacteria, and bacteriogenic flocculants for sewage flocculation and settling that enhanced the sewage treatment process by minimizing the chemical uses and steps and direct dewatering of sludge without preconditioning.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Rapid nano PCR detection method for heat-proof acid-resistant bacterium in concentrated fruit juice
InactiveCN101096707AHigh sensitivityPromote amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant bacteriaFruit juice
The invention discloses a rapid nano-PCR detecting method of thermotolerant acid-resistant bacteria, which comprises the following steps: (1)separating thermotolerant acidophilic bacteria from the concentrated juice; (2)extracting the whole genome from thermotolerant acidophilic bacteria; (3)allocating rapid PCR system depended on nanometer silver; (4)setting and operating the rapid PCR condition; (5)detecting the PCR product with total time at 7.5h. The invention can monitor the thermotolerant acid-resistant bacteria of the condensed juice in the industrializing manufacturing effectively, which enlarges the directly economic benefit of export trade.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
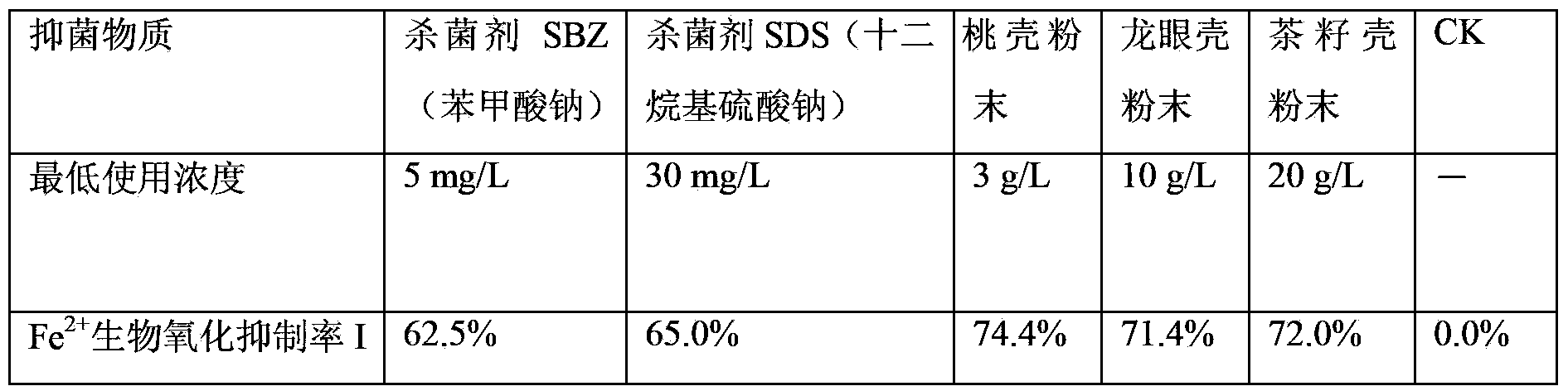
Method for performing in situ treatment on acid mine water by using crop seed husks
InactiveCN103362550AProduction slows down and suppressesExtend design service lifeMining devicesFerric hydroxidePollution
The invention provides a method for performing in situ treatment on acid water of a mine by using crop seed husks. The method comprises the steps that an acid generation point or a fissure surface where the acid water seeps in a mine shaft is detected; a biological inhibitor and alkali flocculation mixed liquor are prepared; the surface of the acid water of the mine shaft is sprayed by the biological inhibitor or subjected to brushed in batch; and continuous seepage of the acid water in the shaft can be eliminated by spraying the alkali flocculation mixed liquor onto an inhibitor layer at intervals for 1-3 times finally. According to the method, the oxidative activity of acidophilic bacteria in an acid water generation environment is inhibited by the biological inhibitor, generation of the acid water is slowed down or inhibited, and the alkali flocculation mixed liquor is used for spraying continuously to form ferric oxide or ferric hydroxide flocculent settling to form a protective film on the surface of pyritic sulfide, so that the acid water generated due to biological and chemical oxidation of sulfur-bearing minerals is avoided completely. The method has the advantages that waste is recycled, neither poison nor secondary pollution to an environment is caused, and the method is low in cost and simple to apply and operate.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
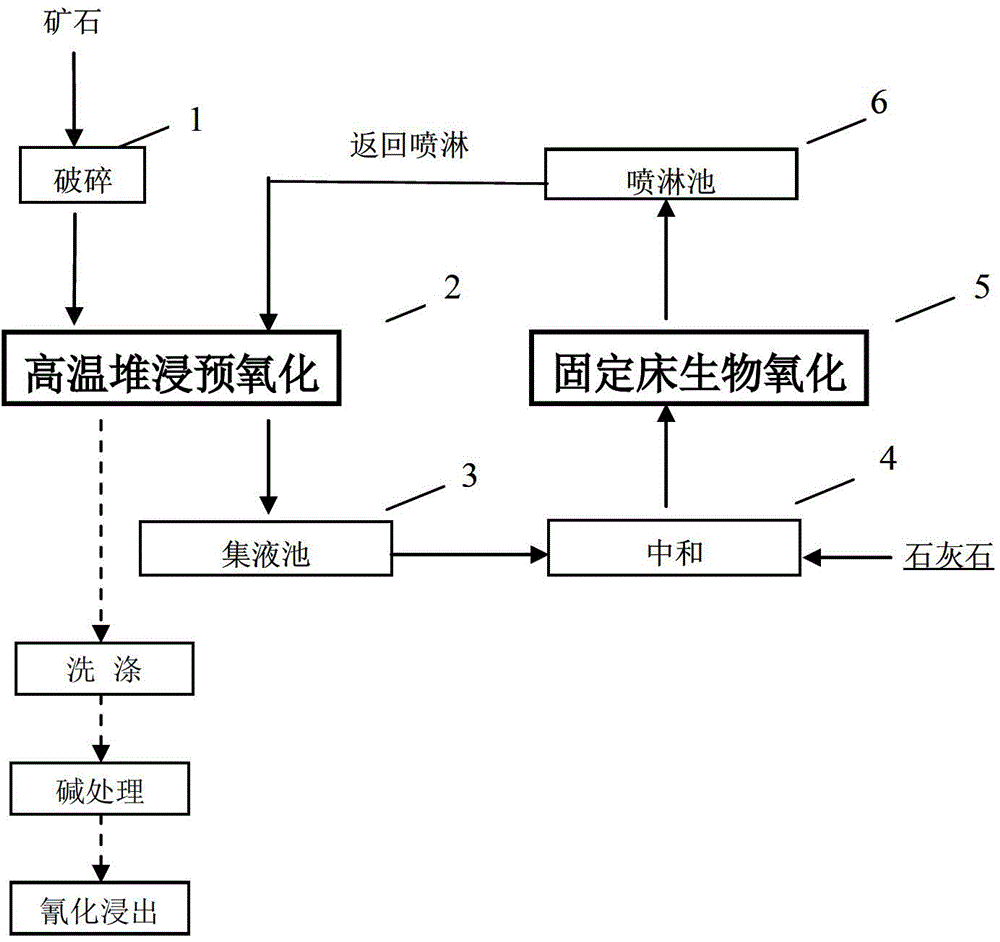
Heap-leaching based biological pre-oxidation method for refractory gold ore
ActiveCN104419827AFully exposedImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementBiological pumpHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a heap-leaching based biological pre-oxidation method for refractory gold ore. The heap-leaching based biological pre-oxidation method for refractory gold ore comprises the following steps: (1) breaking raw ore into pieces, heaping the broken ore, spray-leaching the heaped low-grade refractory gold ore, and controlling the temperature of a leachate to be above 45 DEG C; (2) neutralizing the leachate to increase the pH value thereof to 1.5-1.9 if the pH value of the leachate is lower than 1.5; (3) feeding the neutralized leachate into a biological fixed bed, oxidizing ferrous iron into ferric iron with acidophilic bacteria adsorbed by the biological fixed bed, and obtaining a high-potential oxidation solution after the oxidation-reduction potential of a solution is more than 850mV; and (4) spaying the high-potential oxidation solution obtained in the step (3) onto the low-grade refractory gold ore circularly until the pre-oxidation of the refractory gold ore is finished. The process provided by the invention is simple, and the procedure parameters of the process are easy to control. By adopting the process, the dissolution of a large amount of pyrite can be promoted effectively, the oxidation efficiency can be improved, and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction method of acidophilic bacteria genome DNA in wet method metallurgy
The invention provides a novel, fast and stable method for extracting genome DNA from pulp acidophilic bacteria. It comprises following steps: centrifuging cultured pulp, washing with 0.2 M sulfate and SET buffer solution respectively; adding lysozyme and treating for 30 minutes at 37 Deg. C, adding protein enzyme K and SDS and treating for 45 minutes at 50 Deg. C, adding glass balls and vortexing for 1 minute to crack cell completely, then extrcting protein with chloroform, washing with waterless alcohol precipitation and alcohol of 75% and getting pure genome DNA, which can be used for PCR gene operation.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
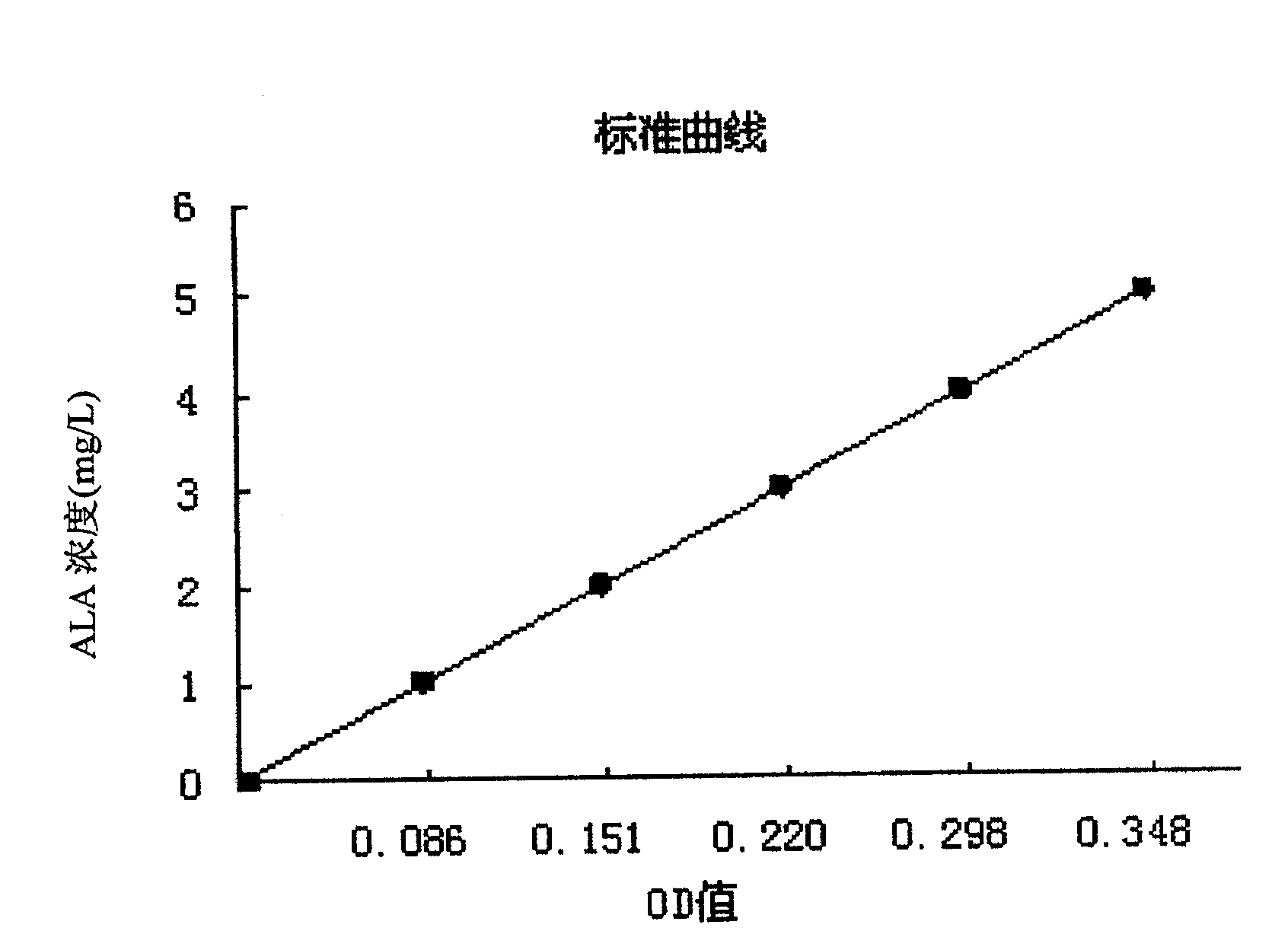
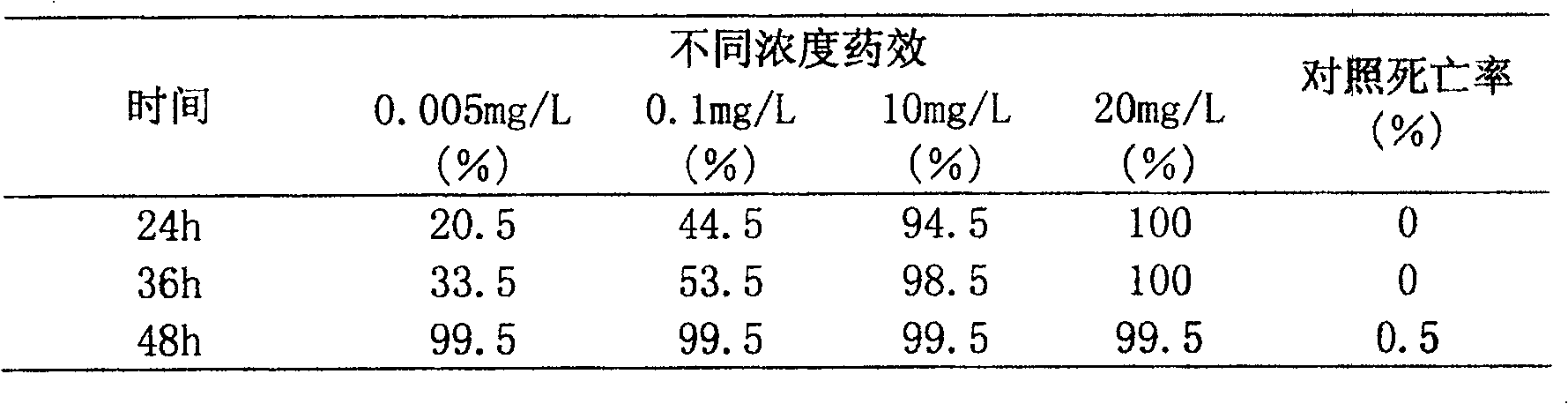
Microbial insecticide for controlling wireworm and application thereof
The invention relates to a microbial nematicide. Microbial nematicides are the fermentation products of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodoblastus acidophilus CCTCC M 206124, in which 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-Aminolevulinic acid or δ -Aminolevulinic acid, referred to as ALA). The biological nematocide of the present invention is a pure biological preparation, and can be used for biological control of plant parasitic nematodes such as pine wood nematodes, root-knot nematodes, soybean cyst nematodes, and sweet potato stem nematodes. The nematocide of the invention has no adverse effects on the environment and all organisms such as plants, humans and animals, has low production cost, simple production process and does not pollute the environment. Microbial nematicides have no phytotoxicity to tobacco, pepper, cucumber and ramie within the test concentration range, but can promote and stimulate the growth of these crops, with no residue and good safety. The invention has extremely important significance for the biological control of plant nematodes, the development and application of microbial nematicides and the pollution-free production of agricultural products.
Owner:HUNAN PLANT PROTECTION INST
Method for rapidly oxidizing Fe<2+> in acid process in-situ leaching uranium mining solution by psychrotolerant and acidophilic bacteria at low temperature
InactiveCN108913890AMaintain oxidation activityPromotes rapid oxidationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological activationMoving bed
The invention discloses a method for rapidly oxidizing Fe<2+> in an acid process in-situ leaching uranium mining solution by psychrotolerant and acidophilic bacteria at a low temperature. The method is characterized in that psychrotolerant and acidophilic thiobacilli are adopted as an oxidizing agent, a biological ceramsite with high acid resistance and specific surface area is adopted as a film hanging carrier of the thiobacilli, and a moving bed bioreactor is adopted for immobilization culture of the bacteria, thereby achieving the purpose of rapidly and continuously oxidizing Fe<2+> in adsorption tail liquid. The method specifically comprises the operation steps of activation of the psychrotolerant and acidophilic bacterium solution, carrier pretreatment, film hanging, rapid and continuous oxidation and adsorption of Fe<2+>+ in the adsorption tail liquid, and regeneration of ceramsite carriers. The bred psychrotolerant and acidophilic bacteria can still keep oxidization activity ofthe bacteria at a low temperature environment of 5-20 DEG C, and rapidly oxidize ferrous ions. By adopting the adsorption tail liquid as a nutritional ingredient for the bacteria, a culture medium isadopted as a bacterium nutrient substance simply during biological ceramsite film hanging, and any nutrient substance is added in a normal running period, so that the production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
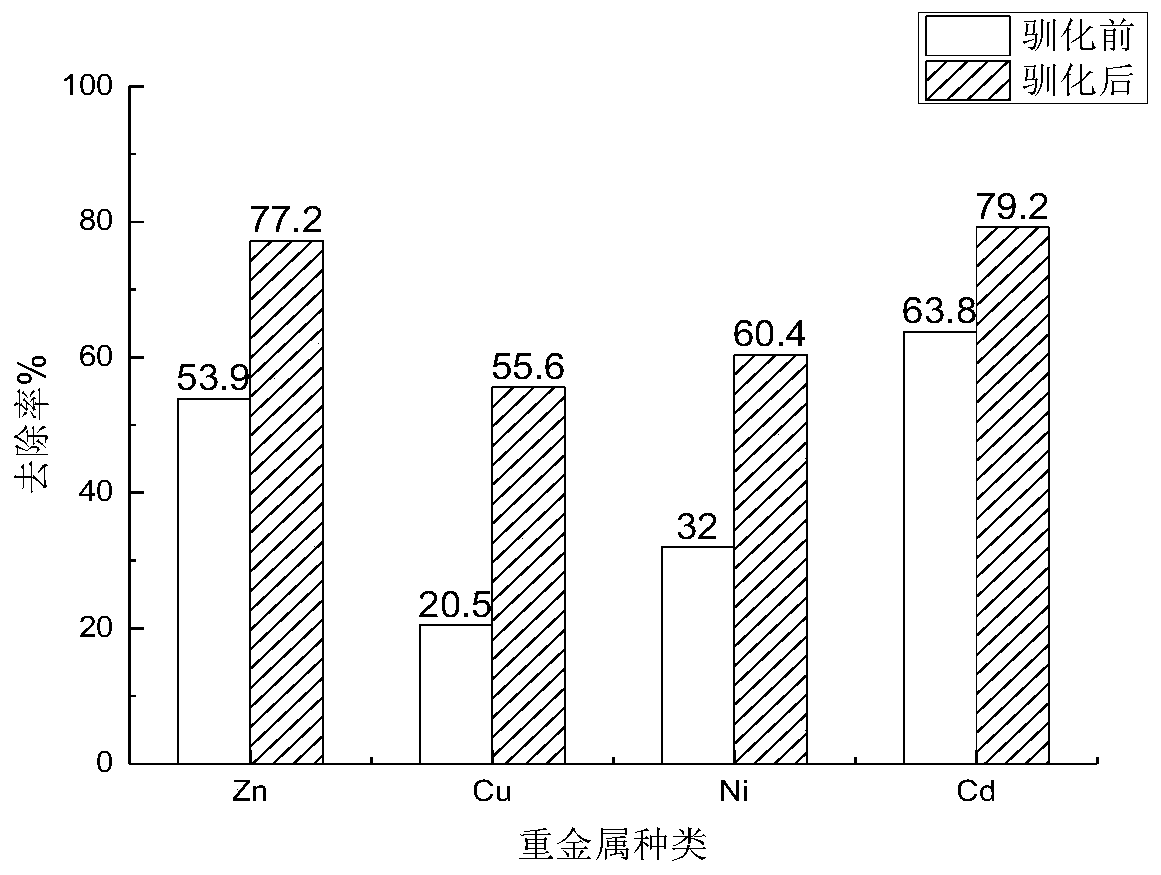
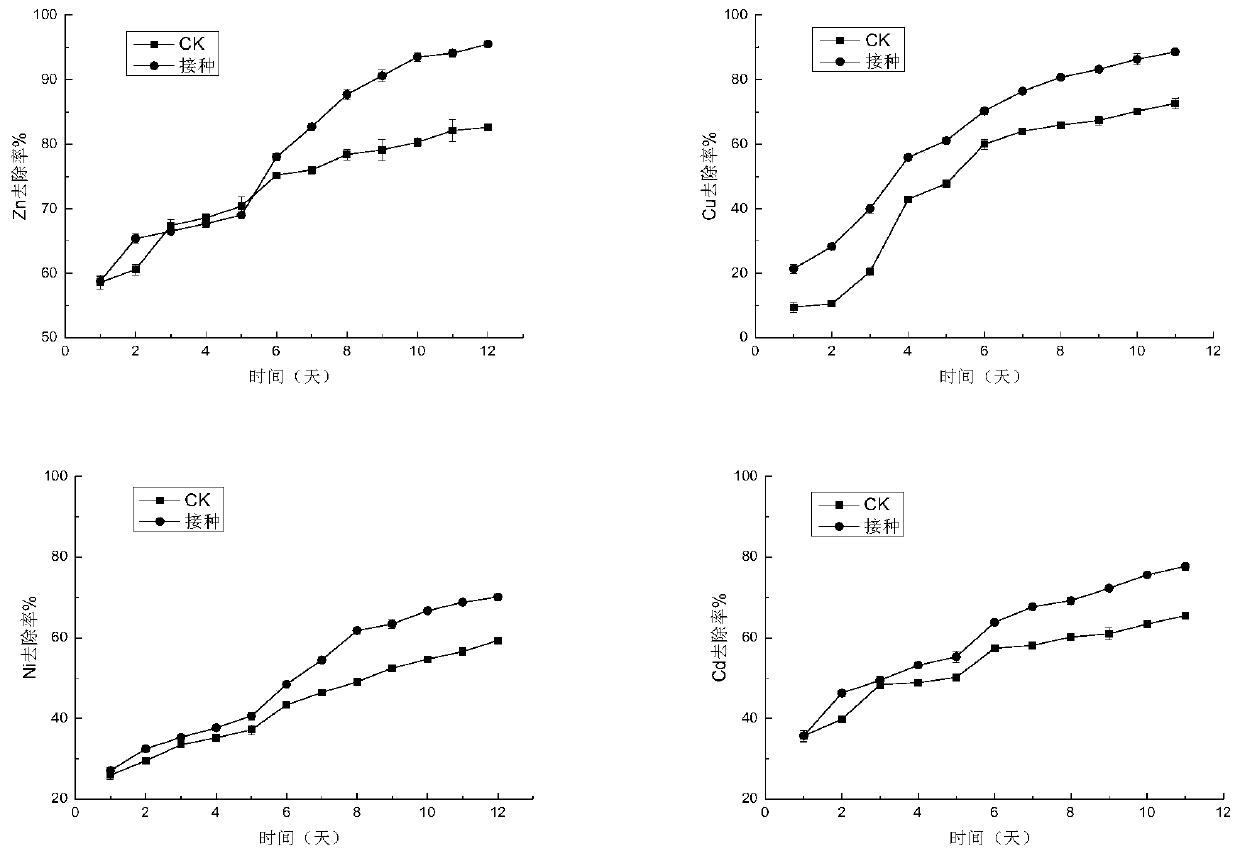
Method for removing heavy metal in different forms in polluted soil through acidophilic bacteria leaching
InactiveCN110523770AEfficient removalEfficient repairContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilCopper
The invention discloses a method for removing heavy metal in different forms in polluted soil through acidophilic bacteria leaching. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, strains areacclimatized, then the acclimatized strains are inoculated into a culture solution containing the heavy metal highly-polluted soil, leaching culture is conducted under certain parameter conditions, and by changing the occurrence form of the heavy metal in the soil, the heavy metal highly-polluted soil is repaired. The method utilizes acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to remove the heavy metal in different forms in the heavy metal highly-polluted soil, and has the advantages that operation is easy, the cost is low, the repairing effect is good, a bacteria solution can be secondarily utilized, andsecondary pollution to the environment is avoided, the good removing effect on zinc, chromium, copper and nickel with the high content in the soil is achieved, and the problems that in an existing heavy metal polluted soil repairing technology, the strains only have tolerance and leaching capability for single heavy metal, heavy metal tolerance is poor, reducing of toxicity of the heavy metal is small, the operation cost is high, and the environment condition requirements are harsh are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
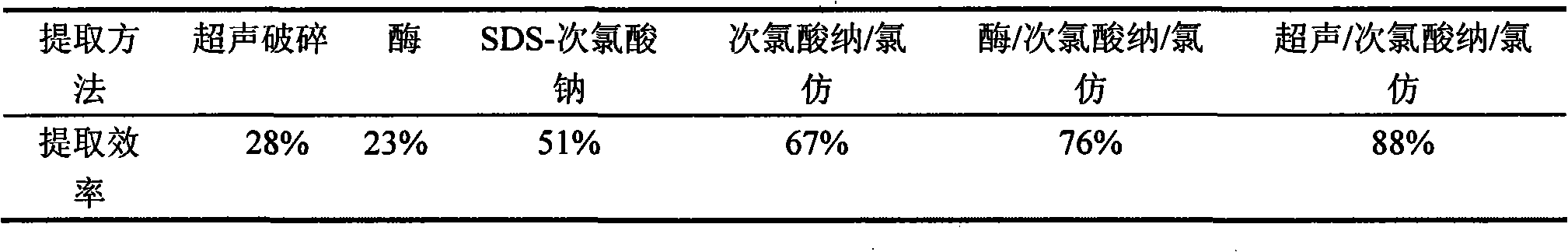
Method for extracting concealed acidophilic bacteria cohesive action-beta-hydroxy-butanoic acid ester
The invention relates to a method for abstracting poly-Beta-hydroxybutyrate in the acidiphilium cryptum bacteria cell. The method mainly comprises the steps of thallus gathering, ultrasonication, chloroform / sodium hypochlorite abstracting, and the deposition is obtained after centrifugation by filling the alcohol and drying. By adopting the invention, the abstracting rate of the PHB in the Acidiphilium cryptum bacteria cell can be up to 88 percent, which is increased by 12 percent in comparison with the method for abstracting sodium hypochlorite and chloroform solely.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Bacillus velezensis HP-24 and application thereof in preparation of liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch
ActiveCN113755393AOpen up new ways of biological controlEffective controlBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacilli
The invention relates to bacillus velezensis HP-24 and application thereof in preparation of liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch, which can effectively solve the problem of bacterial liquid for preventing and treating fruit blotch caused by melon pathogenic bacteria Acidovorax citrulli and can realize biological prevention and treatment of fruit blotch. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 is classified and named as bacillus velezensis and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation number is CGMCC NO.22973, the preservation date is July 28, 2021, and the preservation address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 has the function of apoptosis of melon pathogenic bacteria watermelon acidophilus, is effectively used for preparing liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch, and realizes prevention and treatment of fruit blotch. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 and the application thereof can effectively prevent and treat melon bacterial fruit blotch caused by watermelon acidophilic bacteria, develop a new way for biological prevention and treatment of fruit blotch, and have remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY +1
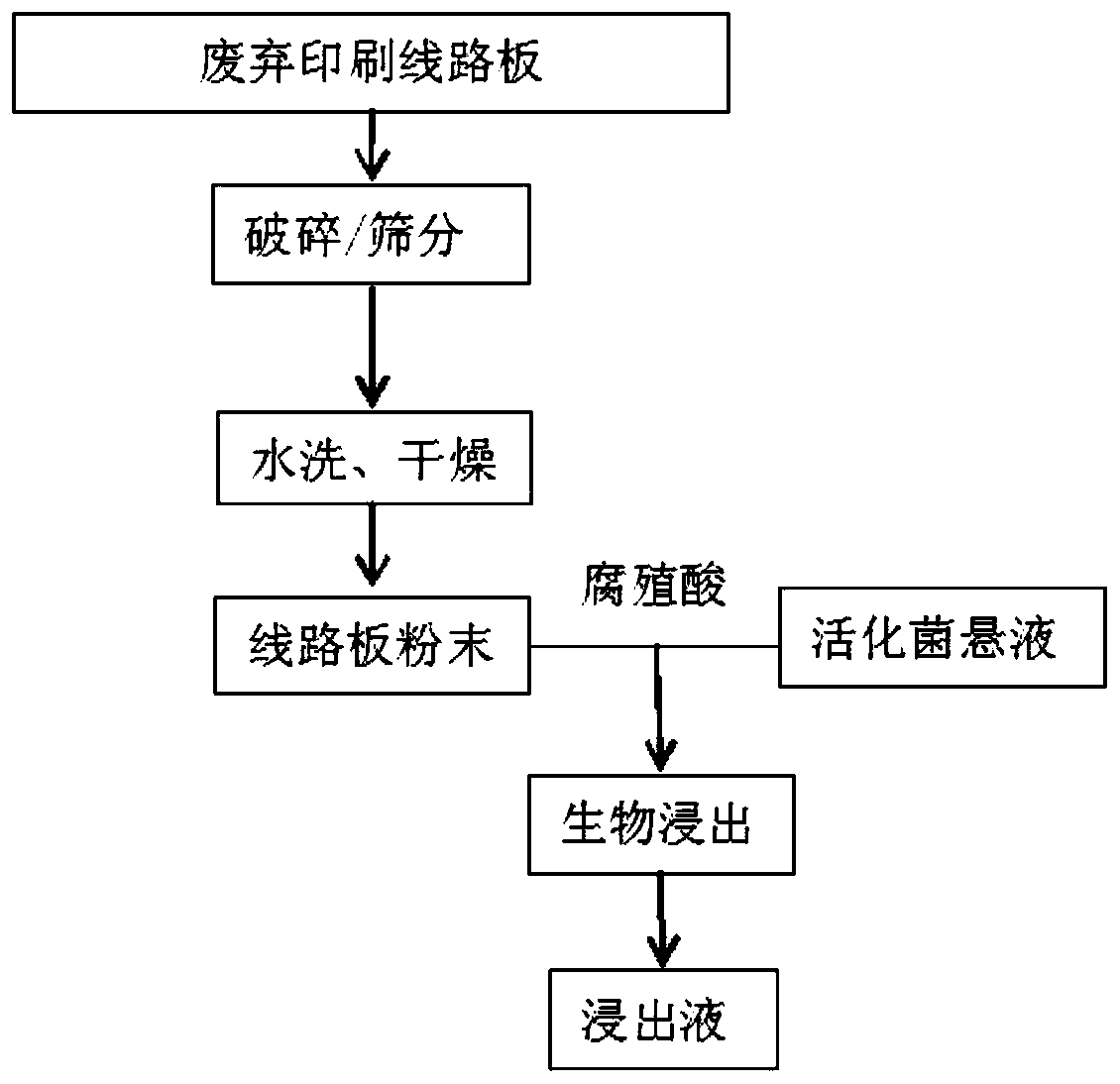
Method capable of improving bioleaching efficiency of valuable metals in waste printed circuit boards
ActiveCN109722537AModerate molecular weightImprove bindingProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental engineeringAcidophilic bacteria
The invention relates to a method capable of improving the bioleaching efficiency of valuable metals in waste printed circuit boards, and belongs to the technical field of solid waste recycling. The method comprises the steps that 1) broken waste printed circuit boards are ultrasonically cleaned and then placed in a drying oven for drying; 2) activated culture is carried out on mixed acidophilic bacteria by using a 9K medium at medium temperature; 3) the crushed waste printed wiring board powder and humic acid are placed in a microbial reactor containing mixed acidophilic bacteria for bioleaching of the valuable metals. The equipment required by the method is simple, and the method is low-cost and environmentally friendly, and can greatly improve the efficiency of leaching valuable metalsfrom waste printed wiring boards by utilizing microorganisms.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
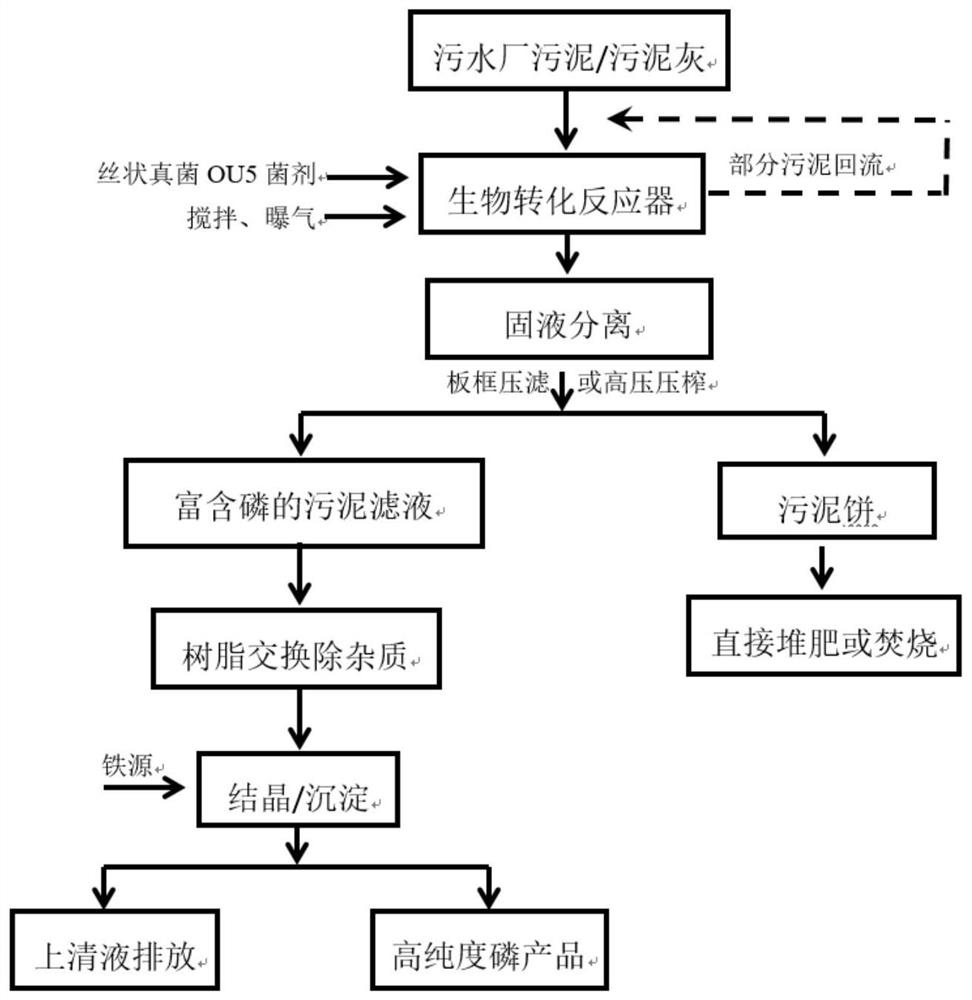
Filamentous fungi and method for recovering phosphorus in sludge by using filamentous fungi
ActiveCN114644985ANon-pathogenicEconomical and practicalFungiWater contaminantsBiotechnologySludge cake
The invention belongs to the technical field of sludge recycling, and relates to filamentous fungi and a method for recovering phosphorus in sludge by using the filamentous fungi. Aiming at the technical bottlenecks that in the prior art, extraction of phosphorus from sludge by a microbiological method mostly depends on the action of acidophilic bacteria, the treatment period is long, the effect is unstable and the recycling degree is not high, the filamentous fungus strain Talaromyces tracerspermus OU5 is rich in hypha structure and does not need to be added with any nutritional agent or acid-base medicament, and the method has the advantages that the method is simple, the cost is low, and the production cost is low. The DOM of the sludge can be directly used as a nutrient for rapid growth. The scheme also provides a method for recovering phosphorus from sludge by using filamentous fungi, the strain OU5 is inoculated in sludge, the three-dimensional space floc structure of the sludge is destroyed by using the dual effects of biological disintegration and biological acidification of the strain OU5, phosphorus in the solid phase of the sludge is released and enters the liquid phase, then the sludge floc rich in phosphate is obtained, and then the sludge floc rich in phosphate is dehydrated and separated, so that the phosphorus is recovered from the sludge by using the filamentous fungi. A phosphorus-rich water solution and a sludge cake are obtained. The filamentous fungi are efficient and stable in sludge phosphorus recovery and high in economic practicability.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Screening, identification and biocontrol activity determination methods for acidophilic PGPR strains
InactiveCN112280703AImproving the biological control effect of bacterial wiltPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses screening, identification and biocontrol activity determination methods for acidophilic PGPR strains. The screening method comprises the following steps of: 1, screening of theacidophilic PGPR strains: adjusting the pH value of a nutrient agar culture medium plate to 5.5 for screening of acidophilic bacteria, wherein rhizosphere soil sample suspension is not subjected to heat treatment at 80 DEG C; and 2, determination of the bacteriostatic activity of the strains under different pH conditions: (1) preparing fermentation liquor of test strains, namely inoculating activated strains into NB with different pH values in 1.1. The invention relates to the technical field of tobaccos. The screening, identification and biocontrol activity determination methods for the acidophilic PGPR strains are based on treatment of bacteria with bacteria, bacteriostatic activity, disease prevention and growth promotion effects and related biocontrol characteristics of the strains onralstonia solanacearum are studied under acidic and neutral conditions respectively, the strains are classified and identified by combining BIOLOG-GEN-III identification and 16SrDNA gene sequence homology analysis, and a foundation is laid for providing efficient microbial resources for improving the biocontrol effect of tobacco bacterial wilt in acidic soil and application of the efficient microbial resources.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
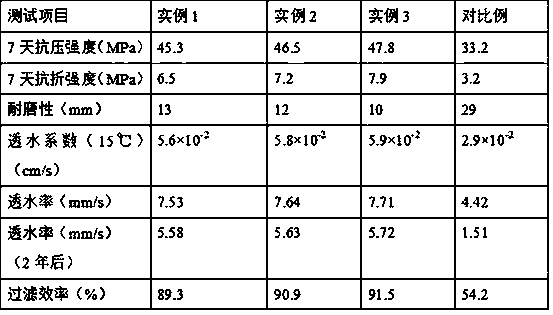
Production method of high-strength zeolite water-permeable bricks
The invention relates to the technical field of the production of water-permeable bricks, in particular to a production method of high-strength zeolite water-permeable bricks. The production method has the advantages that resin is carbonized and crushed, hydroxylation modification is performed, tetraethyl orthosilicate is added into the mixed liquid of alkali, aluminum source sodium metaaluminateand modified carbonized framework particles to synthesize carbonized framework particles, the adsorption activity of molecular sieves is increased under the effect of potassium thiocyanate, the carbonized framework particles with high-adsorption-activity zeolite molecular sieves deposited on the surfaces, lemon juice, tartaric acid and acidophilic bacteria are subjected to blending fermentation, the hydrophilic property of zeolite is increased and self-made water-permeable filler is obtained, the self-made water-permeable filler, cement, a sodium silicate solution and the like are compounded and injected into dies, and solidification is performed to obtain the high-strength zeolite water-permeable bricks; the generation of high-bond-energy chemical bonds greatly enhances cohesion inside the water-permeable bricks, the mechanical strength of the water-permeable bricks is thus increased, and the production method is promising in application prospect.
Owner:仇颖超
Method for fixing acidophilic bacteria
InactiveCN1884511AHigh strengthImprove toughnessBacteriaOn/in organic carrierConcentration ratioPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to an acidophile fixation method. The method includes heating the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and sodium alginate with finite concentration ratio and consolving in the water, after cooling, mixing with acidophile, directly dripping the said miscible liquids into sulfate -dipping acid buffer solution, reacting them to form particles, and obtaining granulation carrier after desalting with deionized water. The new method for preparation of spherical carrier can be widely used in acidophilic microorganism immobilization.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
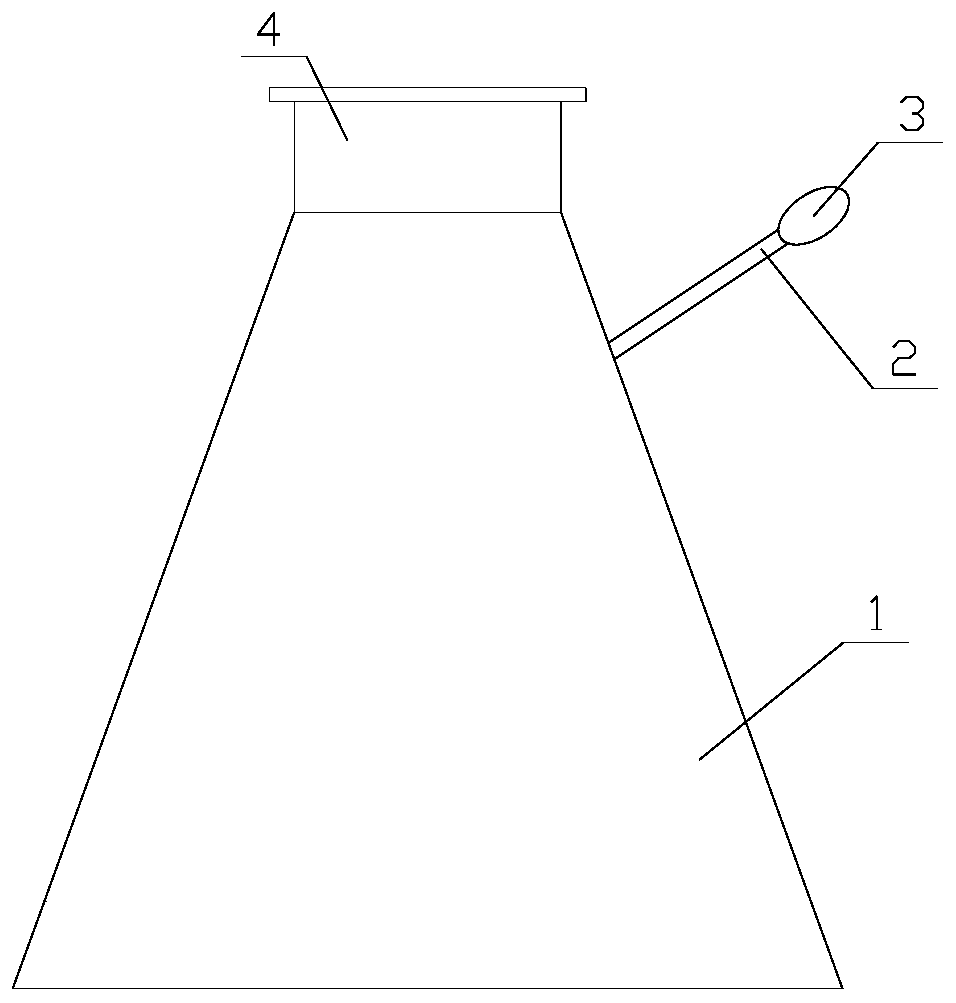
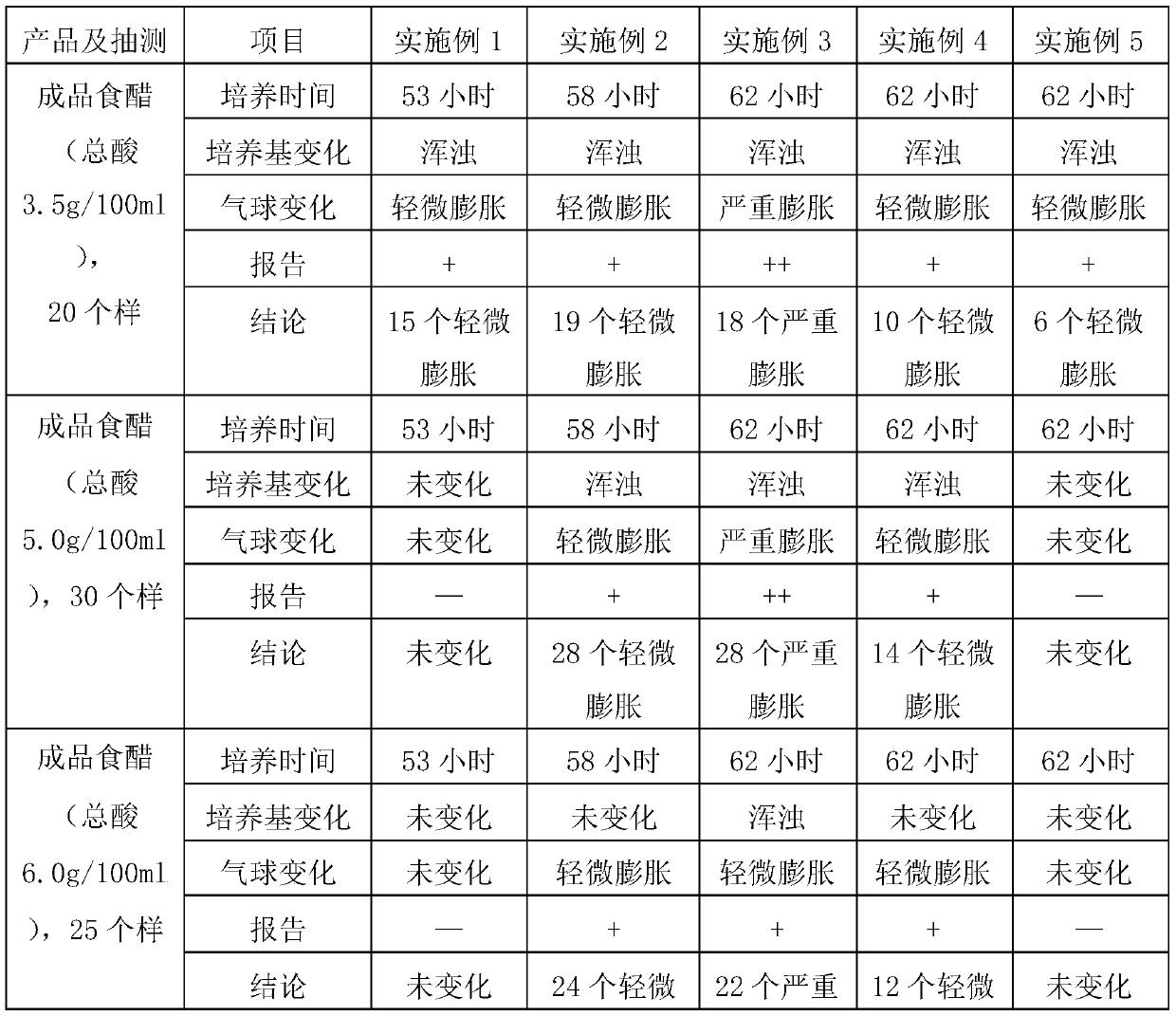
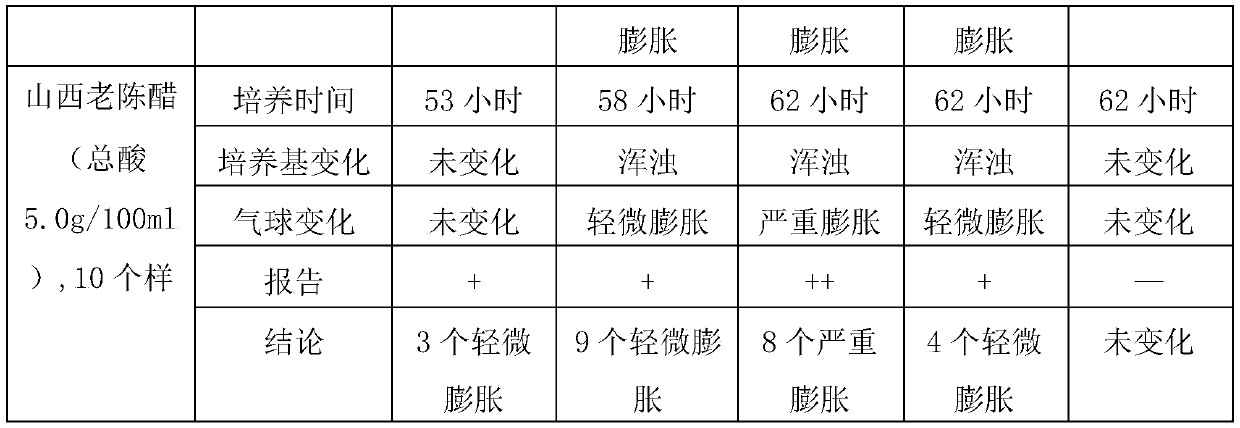
Method for detecting gas-producing acidophilic bacteria in vinegar
ActiveCN109929906AEasy to operateReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for detecting gas-producing acidophilic bacteria in vinegar. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding the finished vinegar to a reactor containing a medium, and then connecting a balloon to a glass tube of the reactor in the sealing mode; (2) conducting shake culture on the reaction liquid in the reactor at different temperature and rotation speed; (3)after shaking culture, judging whether the finished vinegar contains gas-producing bacteria according to whether the culture medium becomes cloudy or whether the balloon is expanded. According to themethod, whether a vinegar product contains gas-producing acidophilic bacteria can be detected rapidly. The method has high detection efficiency and good specificity and is simple in operation, therebyeffectively ensuring the quality of the vinegar product.
Owner:QIANHE CONDIMENT & FOOD CO LTD
Composite agricultural microorganism bacteria and method for applying composite bacteria to lotus root planting
InactiveCN105331555ARich varietyEasy to adaptBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLysobacter antibioticus
The invention provides composite agricultural microorganism bacteria and a method for applying composite bacteria to lotus root planting. All strains of compound bacteria comprise, by weight, 20% of rhodospirillum, 10% of nitrospira, 10% of azotobacter, 10% of bacilli, 10% of thermoactinomyces, 10% of xanthomonas, 10% of lysobacter, 10% of acidophilic bacteria and 10% of novosphingobium. The composite bacteria are used for lotus root planting, the yield of lotus roots is increased, and the quality of the lotus roots is improved.
Owner:NANPING CP OREEZYME BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
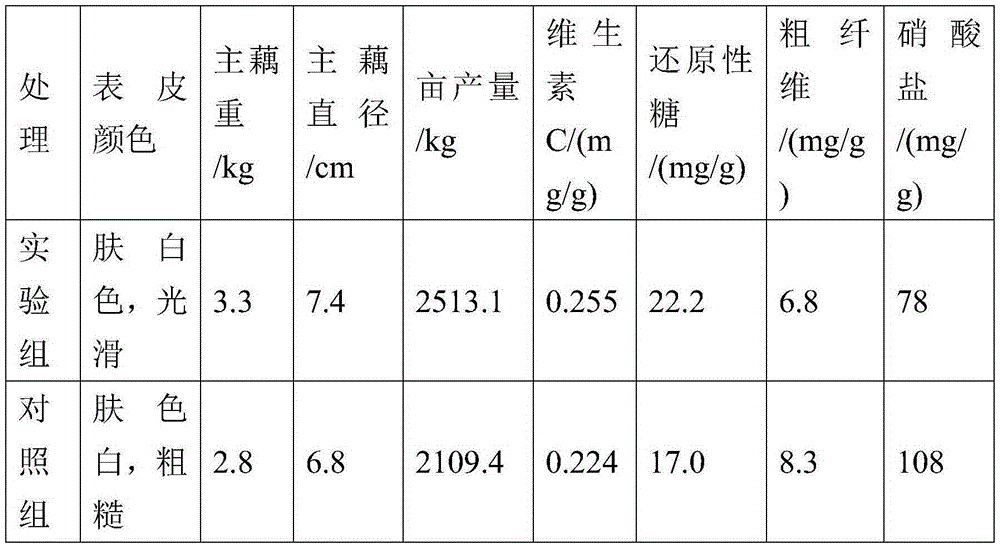
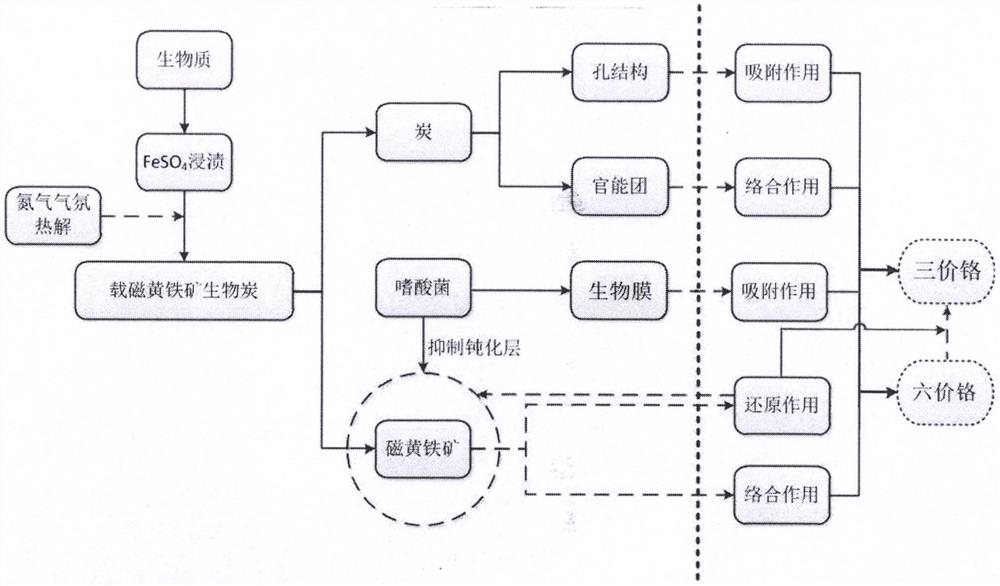
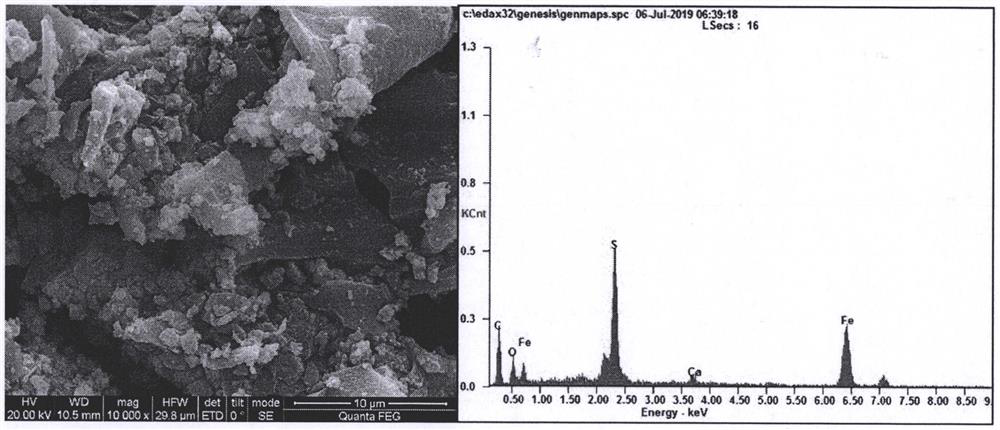
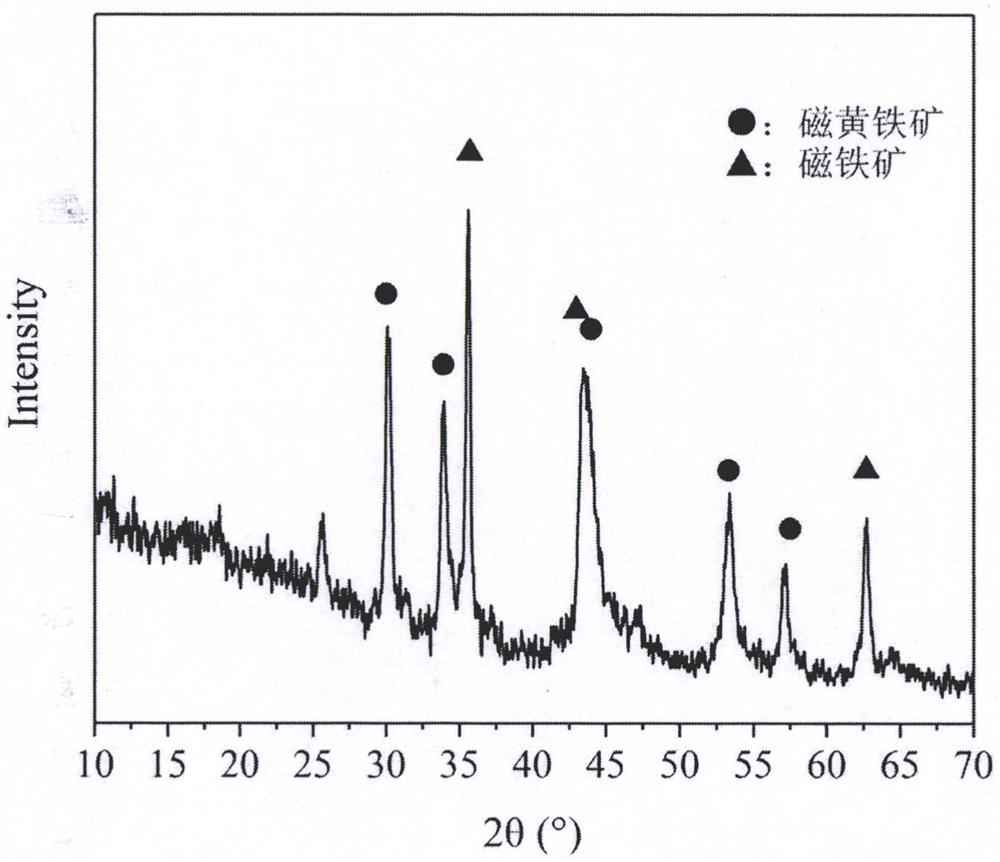
Method for treating hexavalent chromium wastewater based on pyrrhotite biochar loaded acidophilic bacteria biological membrane
PendingCN112624528ALarge specific surface areaImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiofilmEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for treating hexavalent chromium wastewater based on a pyrrhotite biochar-loaded acidophilic bacteria biological membrane, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing pyrrhotite-loaded biochar: crushing biomass, soaking the crushed biomass in FeSO4, and pyrolyzing in a tubular furnace; (2) culturing acidophilic bacteria and preparing a biological membrane: adding the pyrrhotite-loaded biochar into an acidophilic bacteria culture medium, and adsorbing the acidophilic bacteria on the surface of pyrrhotite after oscillation to form the biological membrane; and (3) wastewater treatment: adding the pyrrhotite biochar loaded with the acidophilic bacteria biofilm into the wastewater containing hexavalent chromium, controlling the temperature to be 20-60 DEG C, carrying out air or oxygen aeration by using an aeration device, and filtering the solution when the wastewater does not contain hexavalent chromium. The method has the advantages of low cost, mild reaction, simple process and high chromium removal rate, and can be applied to treatment of hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater in electroplating plants, smelting plants, electronic plants and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
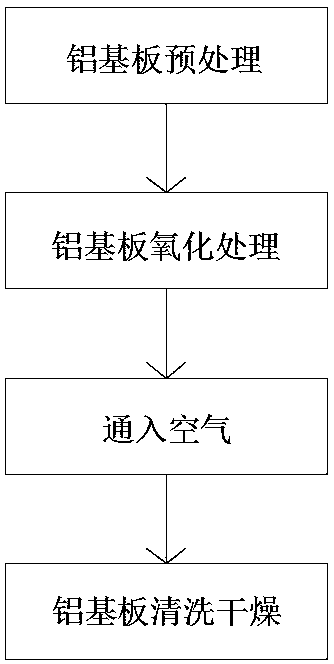
Aluminum substrate surface biological treatment oxidation process
InactiveCN110565086AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove bindingDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsProcess efficiencyPre treatment
The invention discloses an aluminum substrate surface biological treatment oxidation process. The process comprises the following steps that, S1, an aluminum substrate is pretreated, oil removal treatment is carried out on the surface of the aluminum substrate, and washing is carried out; S2, oxidation treatment is carried out on the aluminum substrate, biological bacteria treatment oxidation is carried out on the pretreated aluminum substrate, an alumina dense film is generated, wherein oxidation treatment comprises the step of immersing the aluminum substrate in aqueous liquid containing acidophilic bacteria, the adding amount of the acidophilic bacteria is 50-500 g / L, the pH of the aqueous liquid is 2-6, and the immersion time is 5-10 h; S3, air is introduced into immersion liquid in the oxidation treatment process, and the introduction amount of the air is 1-5 L / h; and S4, the aluminum substrate is cleaned and dried. According to the process, the oxidized aluminum substrate is cleaned and dried through a cleaning and drying device, the process efficiency is improved, the production speed is increased, manual participation is not needed, the labor cost is greatly reduced, and the corrosion resistance of the aluminum substrate oxide film can be improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU AOHONG ELECTRONICS
Biological treatment oxidation process for aluminum substrate
InactiveCN107841741AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove bindingMetallic material coating processesInorganic ChemicalHigh energy
The invention relates to a method using biological oxidation. An aluminum substrate is treated through acidophilic bacteria in an acid environment and is washed with circulation water, so that a compact alumina film is formed on the aluminum substrate. High-pollution and high-energy-consumption inorganic chemical oxidation and electro-oxidation are avoided, a compact aluminum oxide layer is formedon the surface of the aluminum substrate, higher insulation and heat conduction properties are achieved, the compact oxide layer has the characteristics of uniformity, stability and consistency, theheat conduction and insulation properties of an aluminum-based copper clad plate are greatly improved, and industrial pollution and energy loss are not generated.
Owner:乾乐欣展新材料技术(上海)有限公司
Microbial sludge dehydrating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN114409225AEasy to dehydrateTo achieve the purpose of deep dehydrationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBiological sludge treatmentBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a microbial sludge dehydrating agent and a preparation method thereof. The sludge dehydrating agent comprises an acidophilic bacteria solution, an aspergillus tubingensis solution, a bacteria secreted extracellular enzyme solution, a lysozyme solution, polyacrylate, wood cellulose, tourmaline powder, a polyacrylamide solution, a sludge stripping agent solution, a sludge wall breaking agent solution and a sludge surface structure modifier solution. By adding the acidophilic bacteria solution, the aspergillus tubingensis solution, the bacterial secreted extracellular enzyme solution and the lysozyme solution, under the combined action of acidophilic bacteria, aspergillus tubingensis, bacterial secreted extracellular enzyme and lysozyme, the adsorption and wrapping effects of sludge extracellular polymeric substances on water can be thoroughly destroyed, so that the sludge is easier to dehydrate, and the water content is reduced. And the biological cell wall structure in the sludge can be destroyed, so that the sludge floc structure is thoroughly disintegrated, water in the sludge can be fully released, and the purpose of deep dehydration of the sludge is achieved.
Owner:南京瑞特莱生态环境有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com