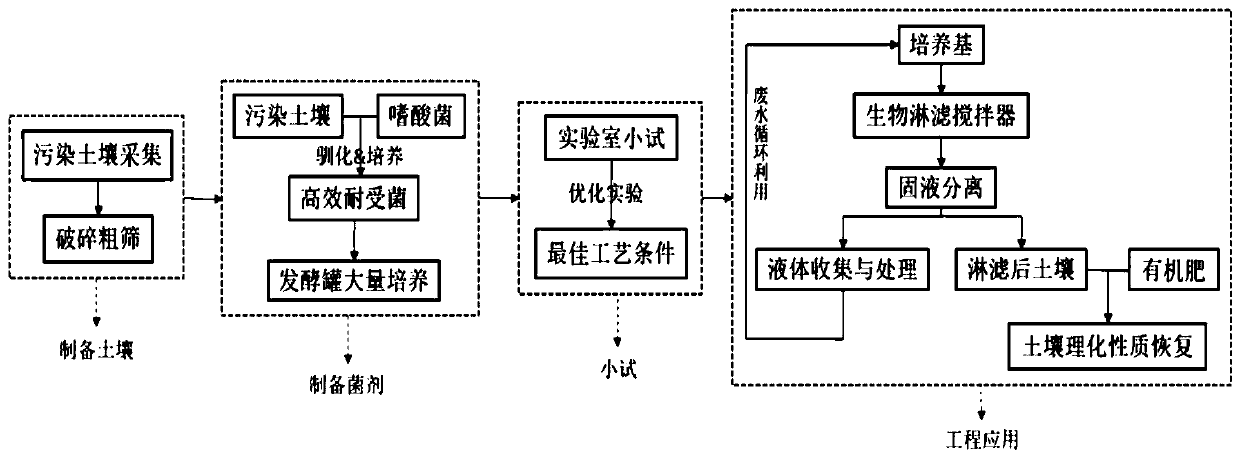
Method for removing heavy metal in different forms in polluted soil through acidophilic bacteria leaching
A technology for contaminated soil and heavy metals, applied in the field of microbial remediation, can solve the problems of slow remediation process, low treatment efficiency, poor environmental adaptability, etc., and achieve the effect of low operating cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Comparison of the removal effects of strains on heavy metals in soil before and after domestication:
[0035] (1) Strain domestication
[0036] (2) Leachate (medium) components: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 : 3g / L, K 2 HPO 4 : 0.5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O: 0.5g / L, KCl: 0.5g / L, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 : 0.01g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O: 40g / L, pH value is 2, leaching culture is carried out at 30°C and 120rmp / min.
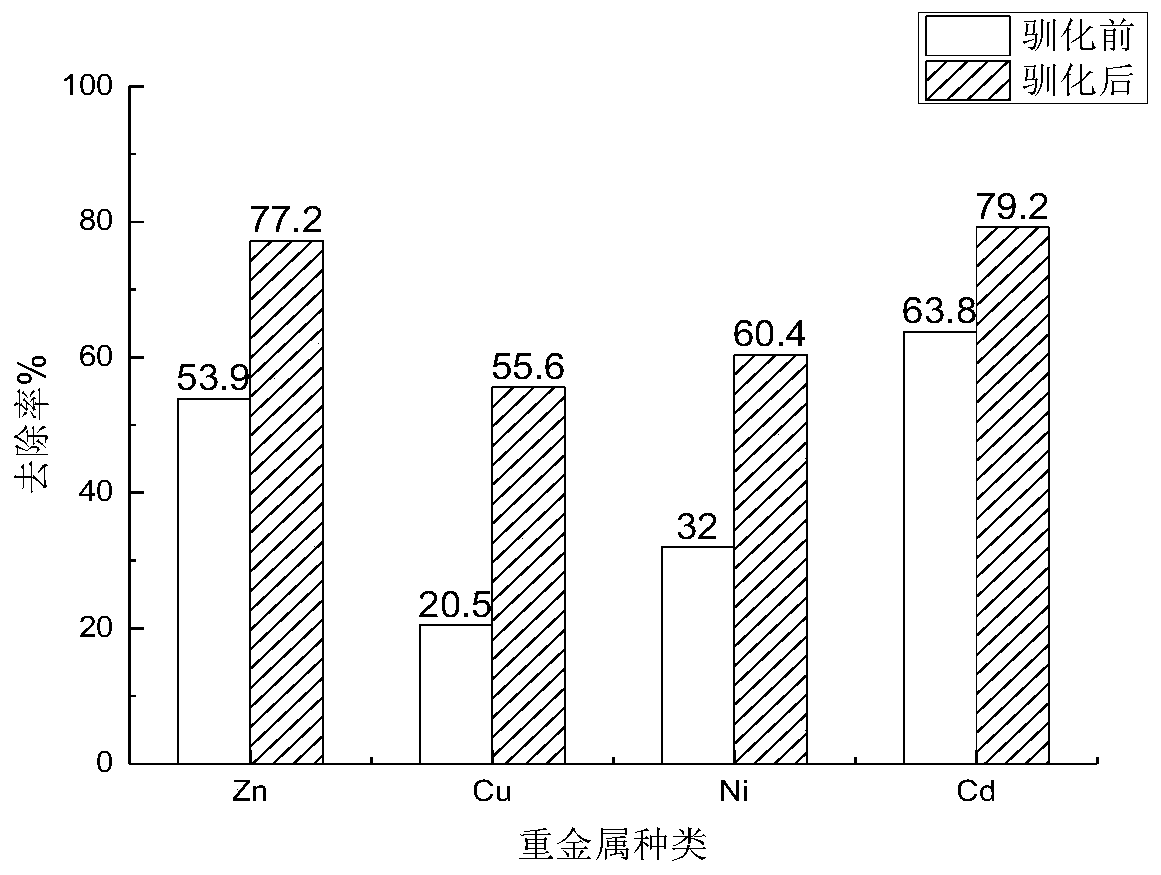
[0037] (3) Add 2% (v / v) strains before and after domestication to the leaching device, put the leaching device into a constant temperature shaker incubator, and leaching for 8 days at 30°C and 120rmp / min, the leachate The amount of soil in the medium is 5g / L, finally analyze the content change of heavy metal in the leachate, the result is as follows figure 2 As shown, the removal effect of acidophilus on various heavy metals was improved after domestication, the removal rate of Zn increased from 53.9% to 77.2%, the removal rate of Cu increased from 20.5% to 55.6%, and the removal rate of...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Changes of heavy metal content in leachate during acidophilus leaching process:
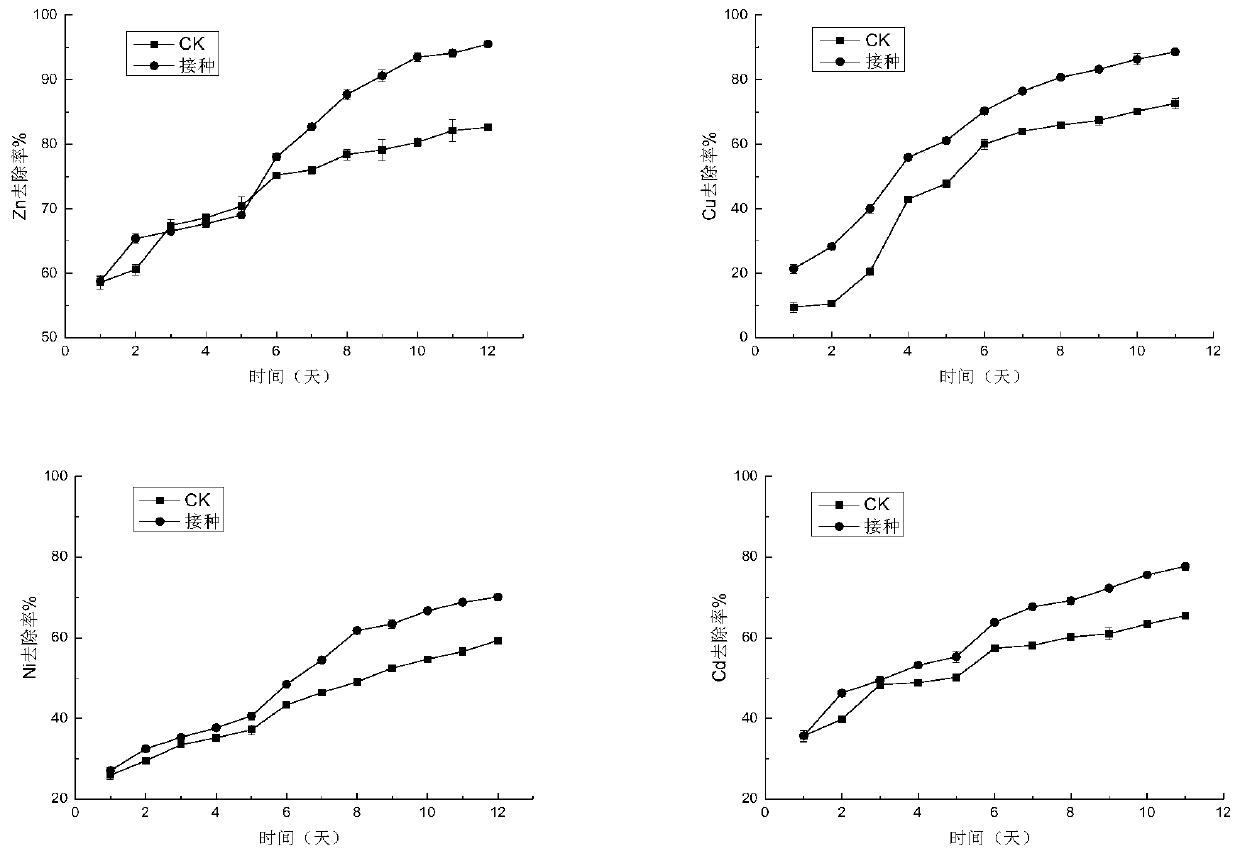
[0040] Set different single factor conditions (solid-liquid ratio, inoculum size, initial pH, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O content), the leaching device was placed in a constant temperature shaking incubator, and leached at 28-35°C and 120rmp / min for 12 days. From the first day, a 1ml sample was taken quantitatively every day. image 3 For the leachate (medium) component: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 : 3g / L, K 2 HPO 4 : 0.5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O: 0.5g / L, KCl: 0.5g / L, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 : 0.01g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O: 40g / L, pH value 2, solid-liquid ratio 100:1, inoculum size 1% (v / v), leaching culture at 30°C, 120rmp / min for 12d. Each group has 3 parallels, and a control CK (not inoculated with strains). The results show the changes in the removal rates of heavy metals Zn, Cu, Ni, and Cd under different leaching culture times. It can be seen that as the leaching time becomes longer, the removal rates of Zn, Cu, Ni, and...
Embodiment 3
[0042] When the inoculation amount is 1% (v / v), acidophilus changes the form of heavy metals in soil:
[0043] The example operation steps are the same as in Example 1, about 10 days of leaching, the soil after the leaching is collected, and the change situation of its heavy metal form is detected, the results are as follows Figure 4 shown. Compared with the soil before leaching, the contents of various forms of heavy metals in the soil after leaching were significantly reduced. Compared with the control CK group not inoculated with bacteria, it can be seen that the stable oxidizable state and residue state are transformed into the exchangeable or reducible state that is easier to remove under the action of acidophilus, in which the heavy metal Cd After filtration, each heavy metal form could not be detected because the content was too low. It can effectively remove 80% to 95% of the exchangeable state, 75% to 90% of the reducible state, 70% to 90% of the oxidizable state a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com