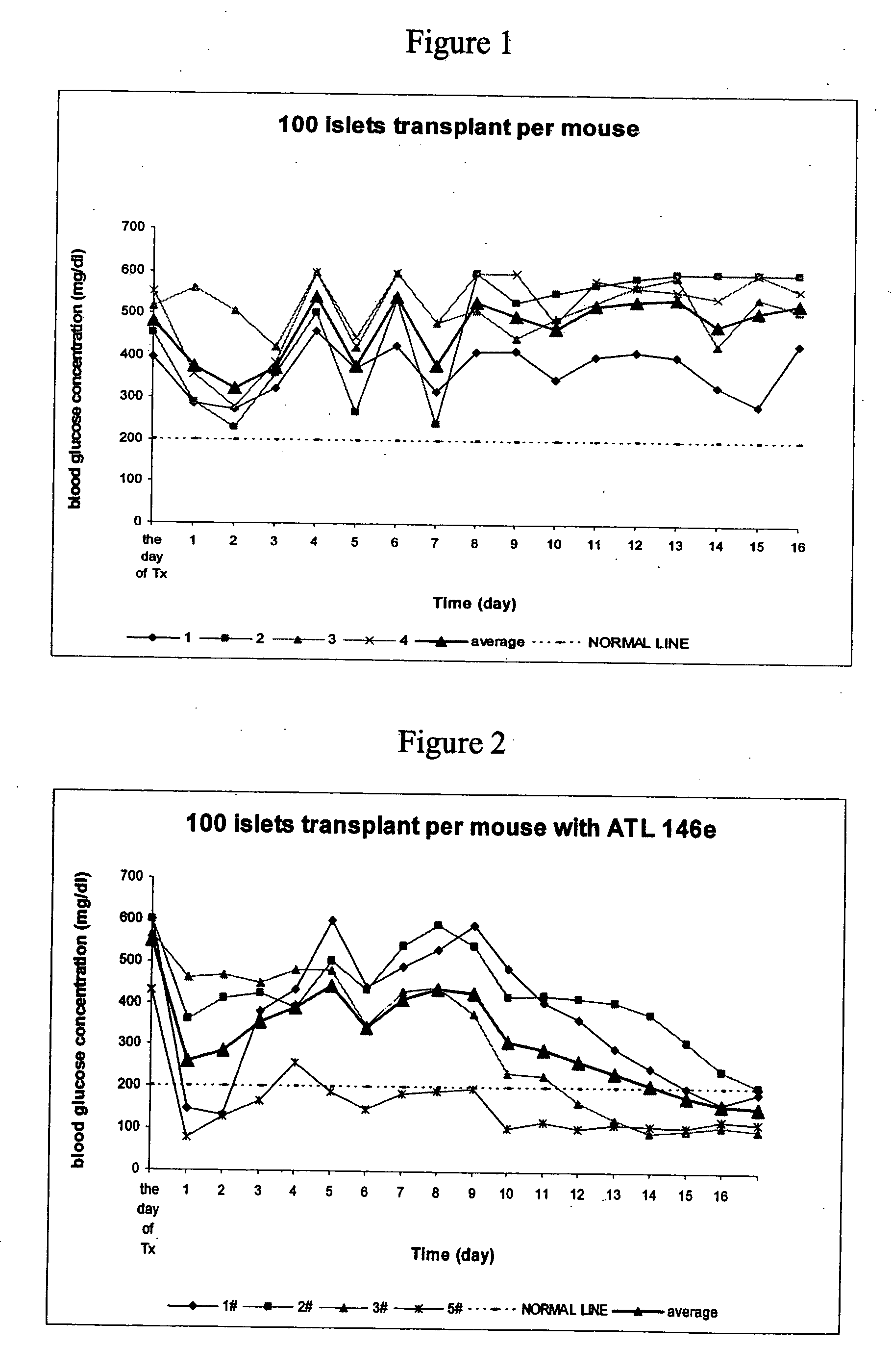
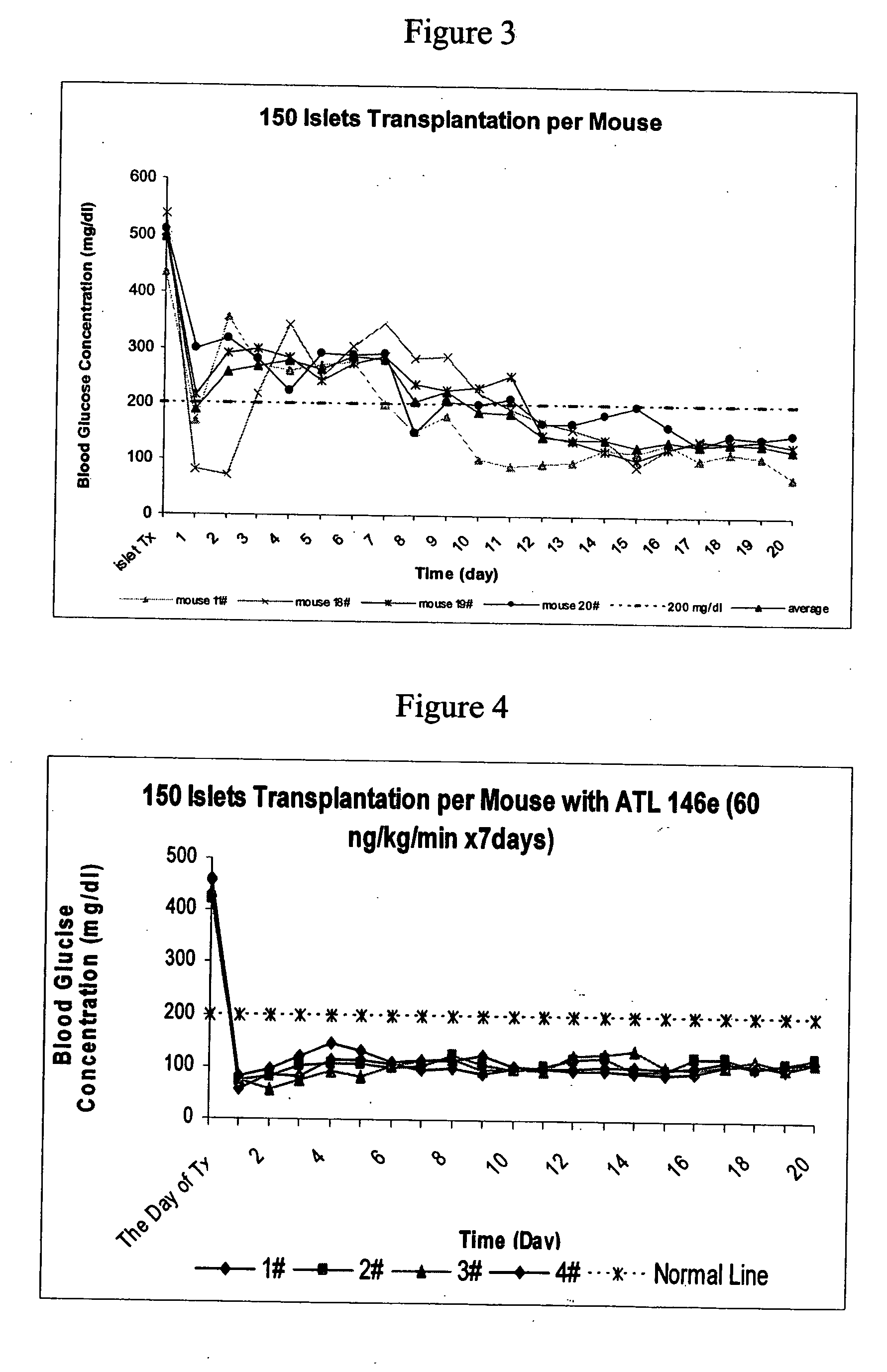
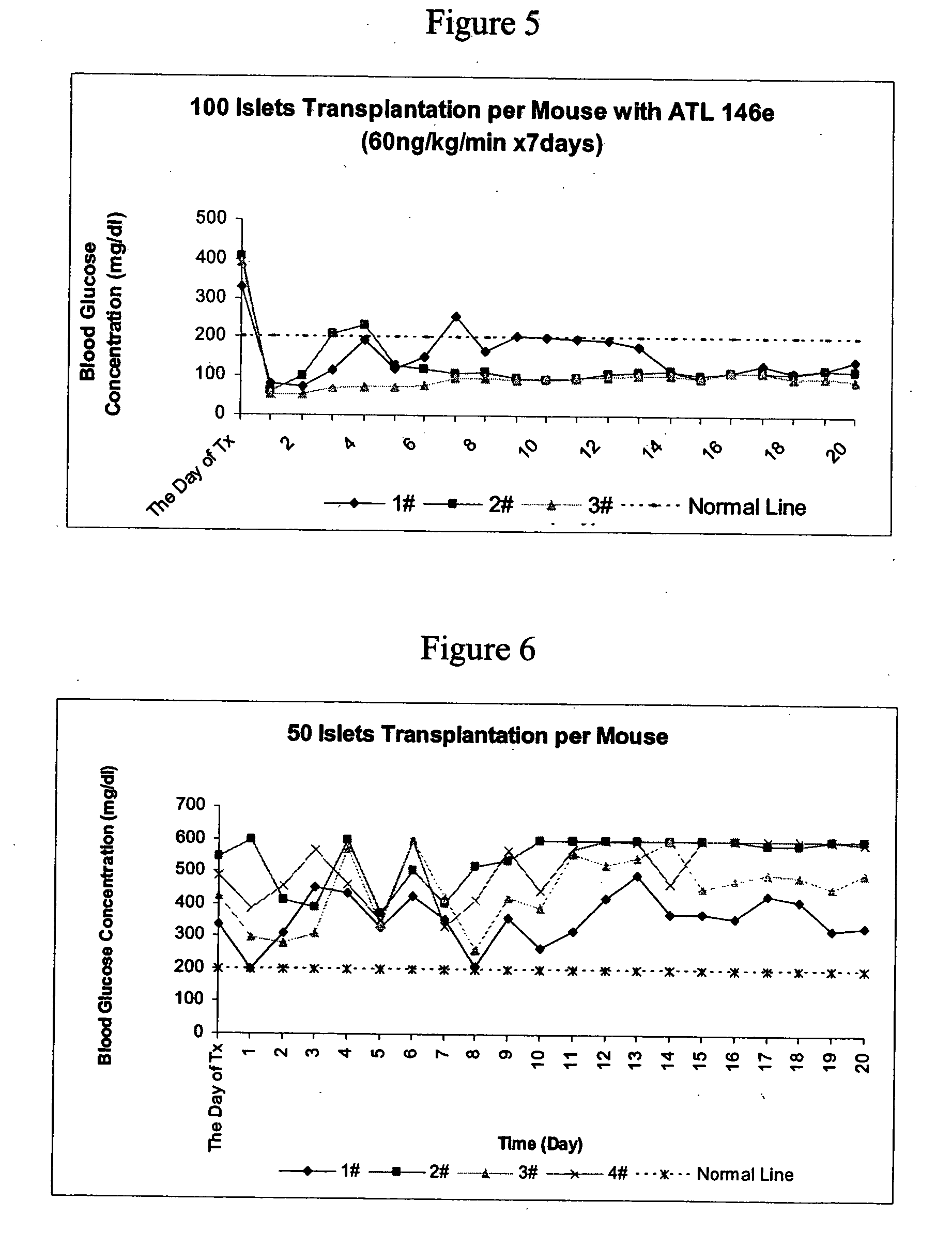
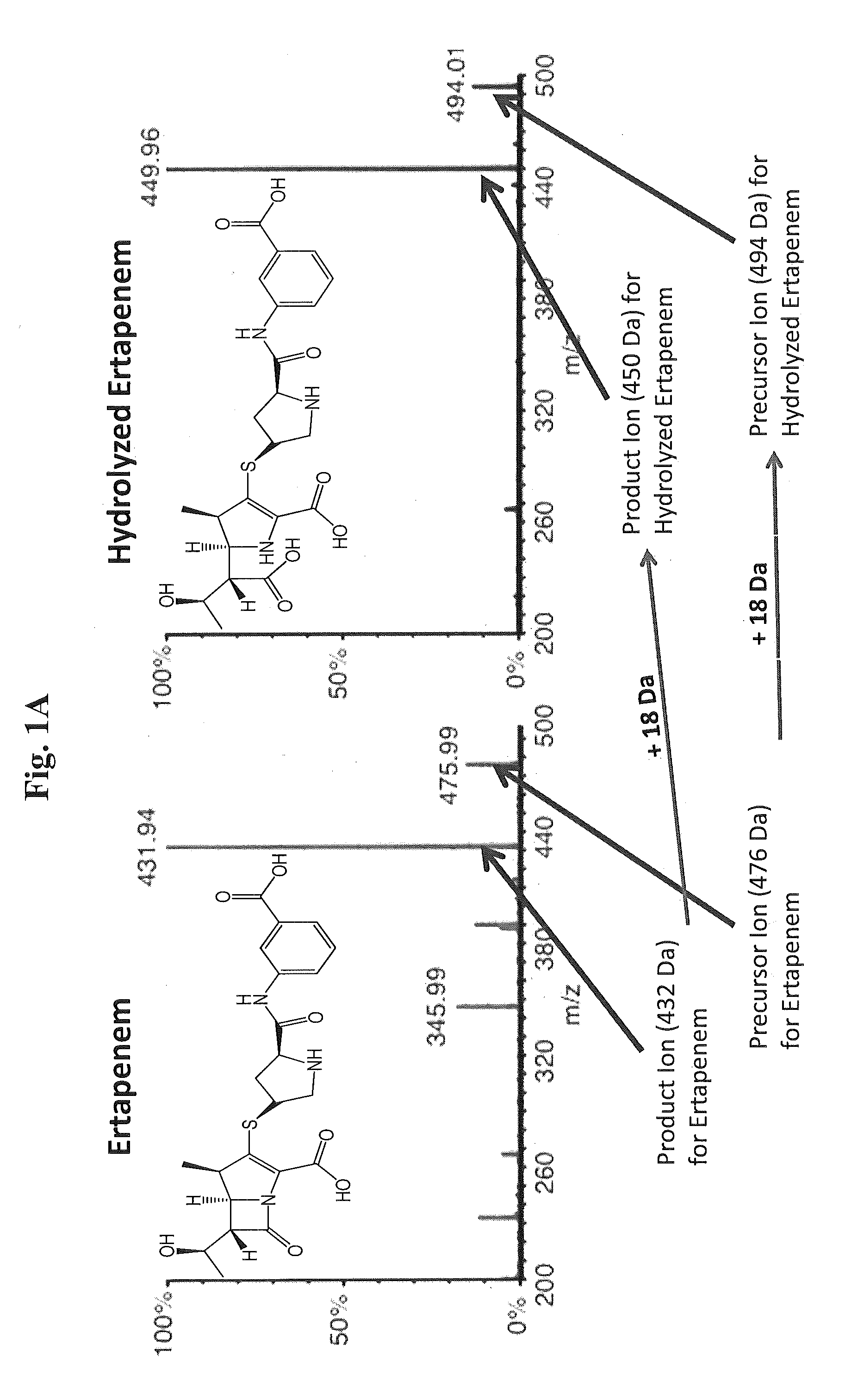
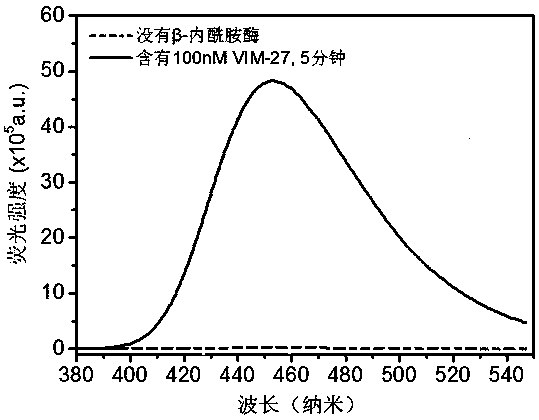
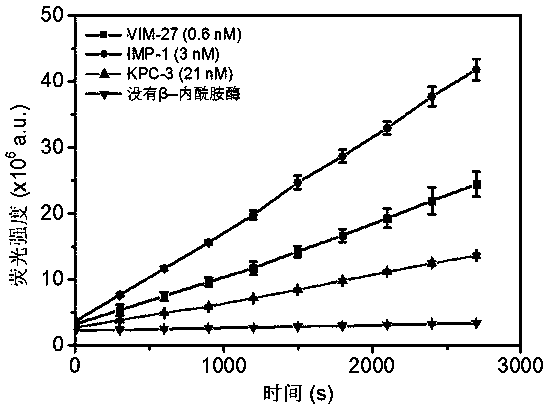
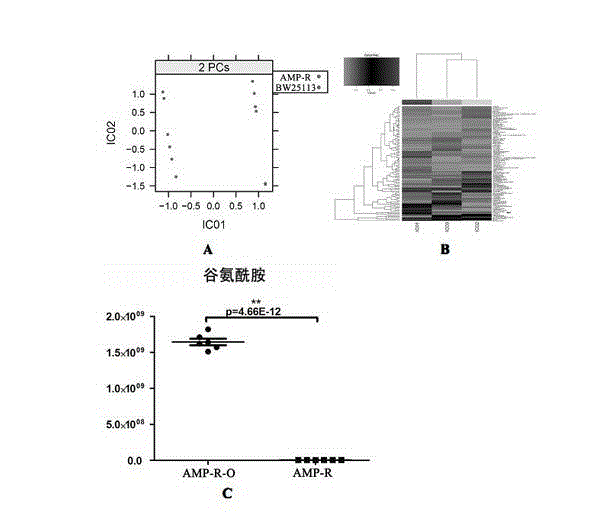
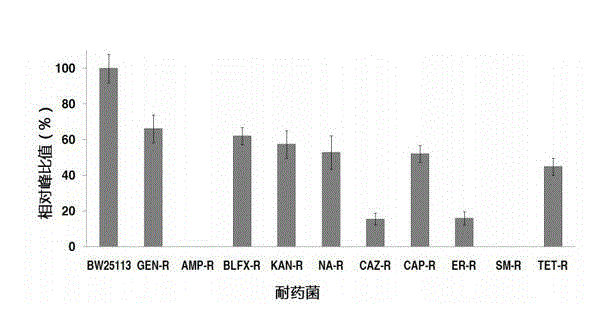
Patents
Literature
1032 results about "Resistant bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
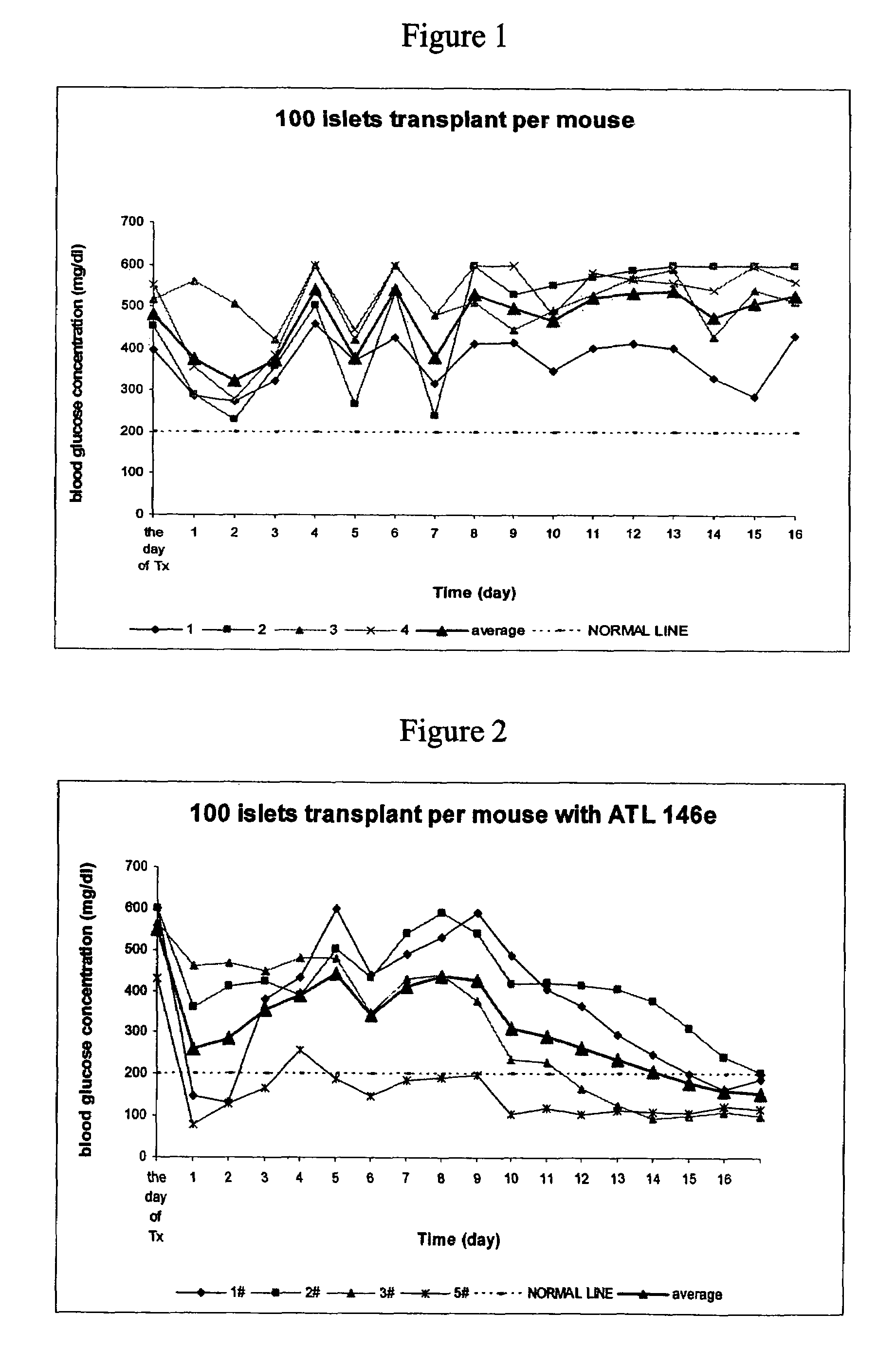
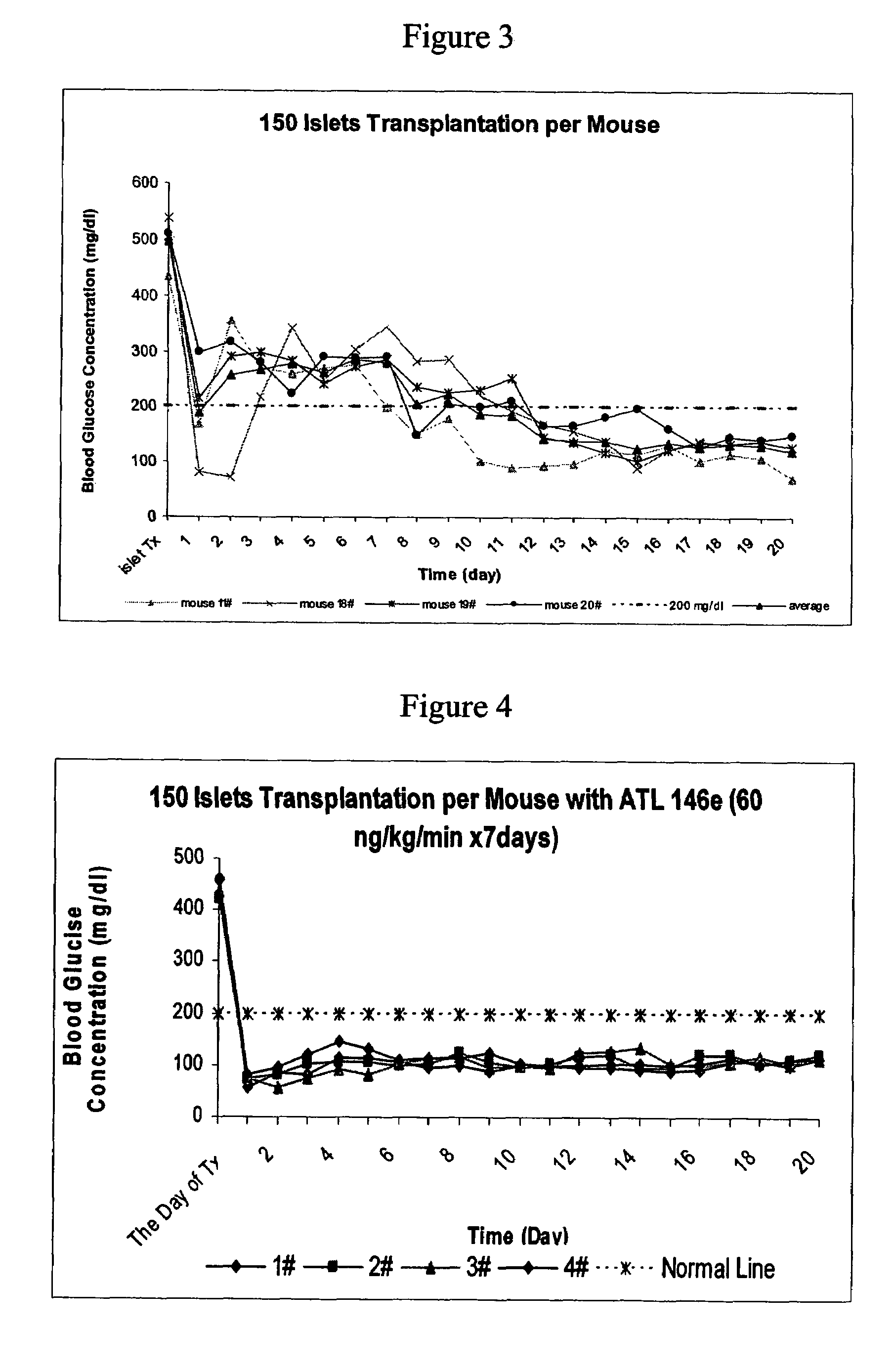
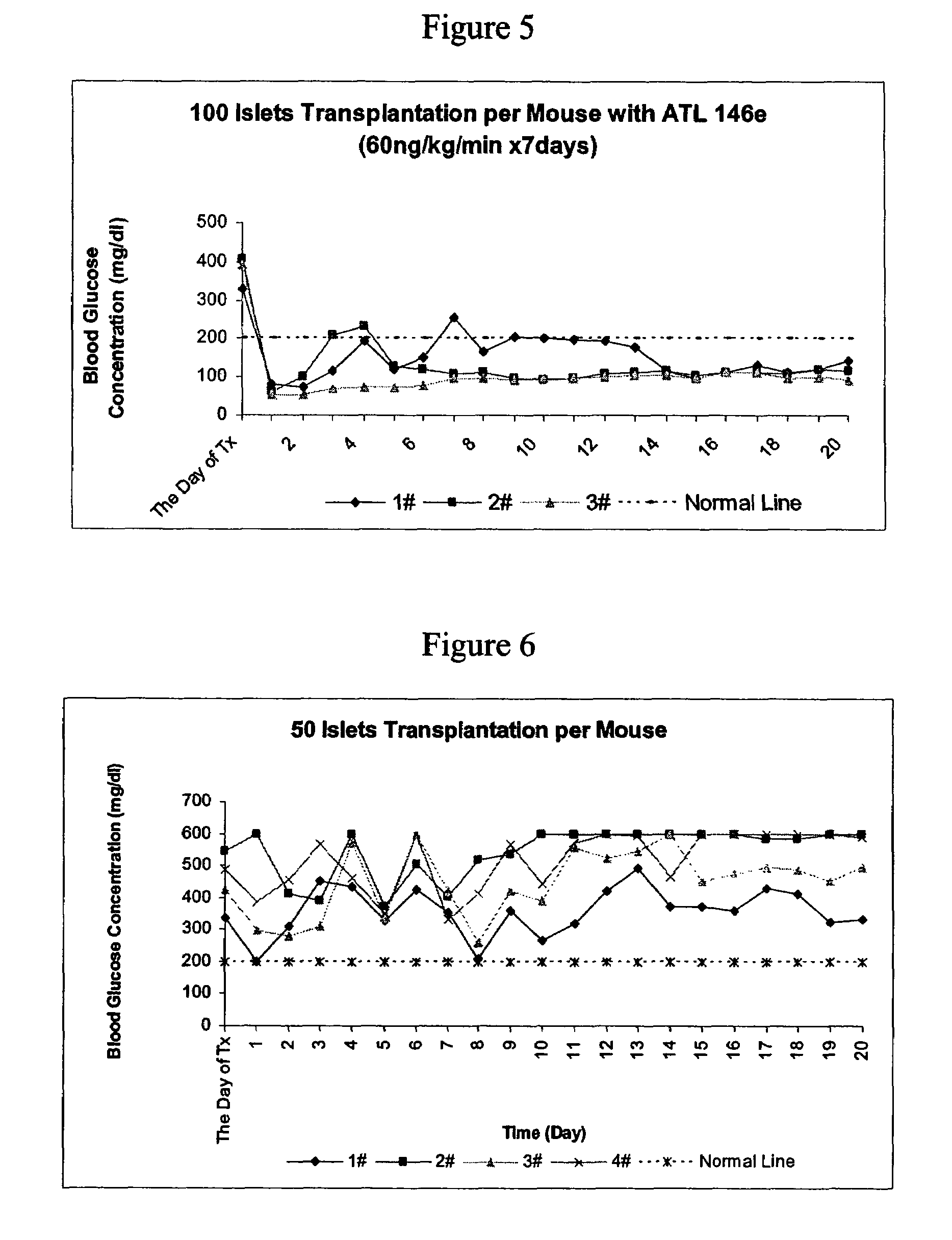
Method to reduce inflammatory response in transplanted tissue
InactiveUS20050182018A1Inhibit inflammationLower immune responseBiocideSugar derivativesPandrug resistant bacteriaDisease cause
The present invention provides a therapeutic method for treating biological diseases that includes the administration of an effective amount of a suitable antibiotic agent, antifungal agent or antiviral agent in conjunction with an A2A adenosine receptor agonist. If no anti-pathogenic agent is known the A2A agonist can be used alone to reduce inflammation, as may occur during infection with antibiotic resistant bacteria, or certain viruses such as those that cause SARS or Ebola. Optionally, the method includes administration of a type IV PDE inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Heavy-metal polluted soil united directional restoration method by using plant-microorganism
InactiveCN101181715AImprove repair effectLow costContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismResistant bacteria
The invention relates to a method for remediation of heavy metals contaminated soil by a plant-microorganism joint direction method. The detailed steps of the method of the invention are that: firstly, resistant bacteria of plant and microorganism is sifted, so as to obtain plant and microorganism bacteria strains with heavy metal resistance; and then the seeds of the resistant plant is soaked and coated in microorganism resistant bacteria solution; finally, the seeds are planted in the soil contaminated by heavy metal, therefore the soil can be remedied. The method has the advantages of good remediation effect, low cost, easy management and operation, no secondary pollution and broad application prospect, therefore, the method is the most important development direction of soil remediation technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
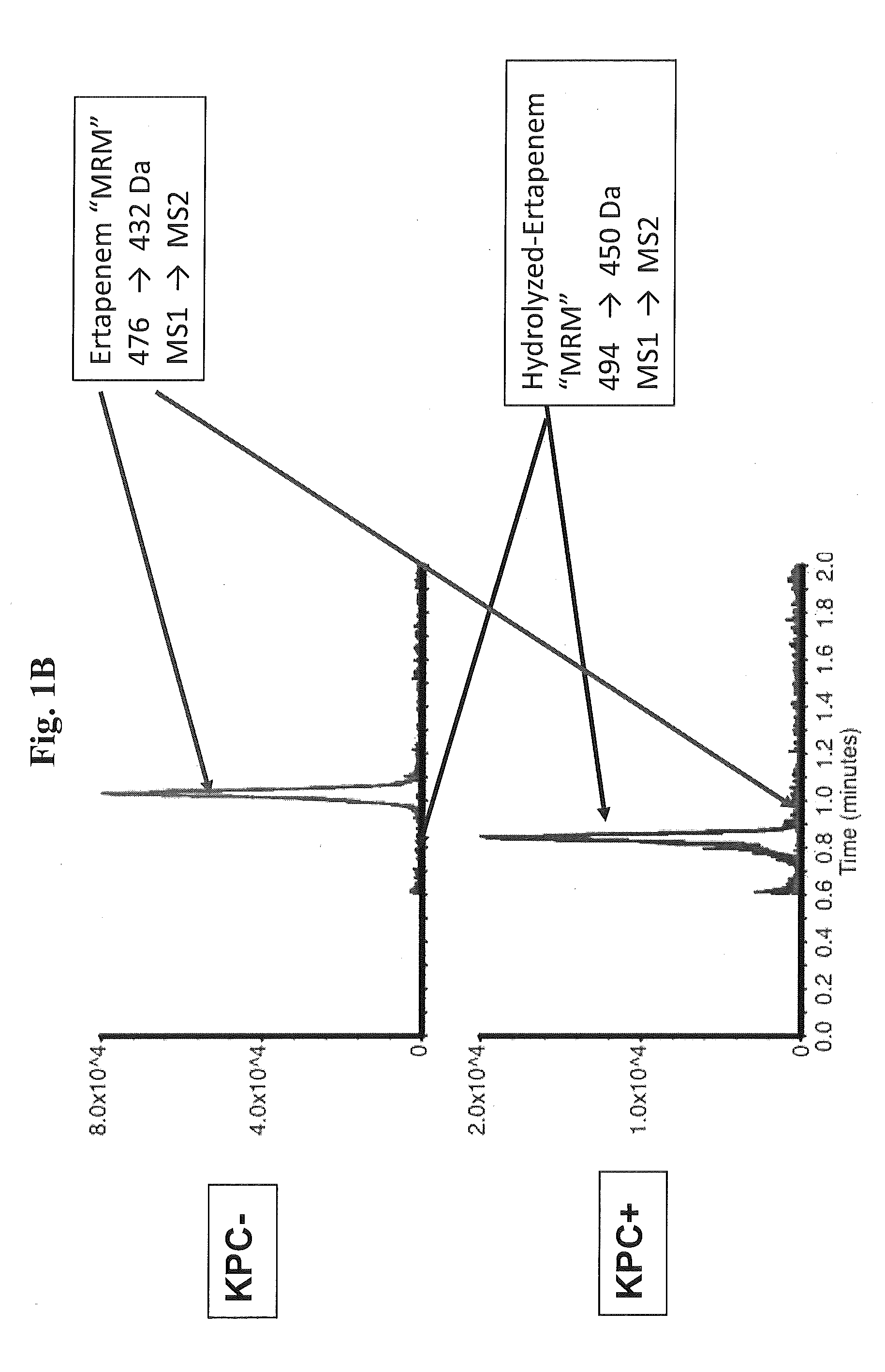
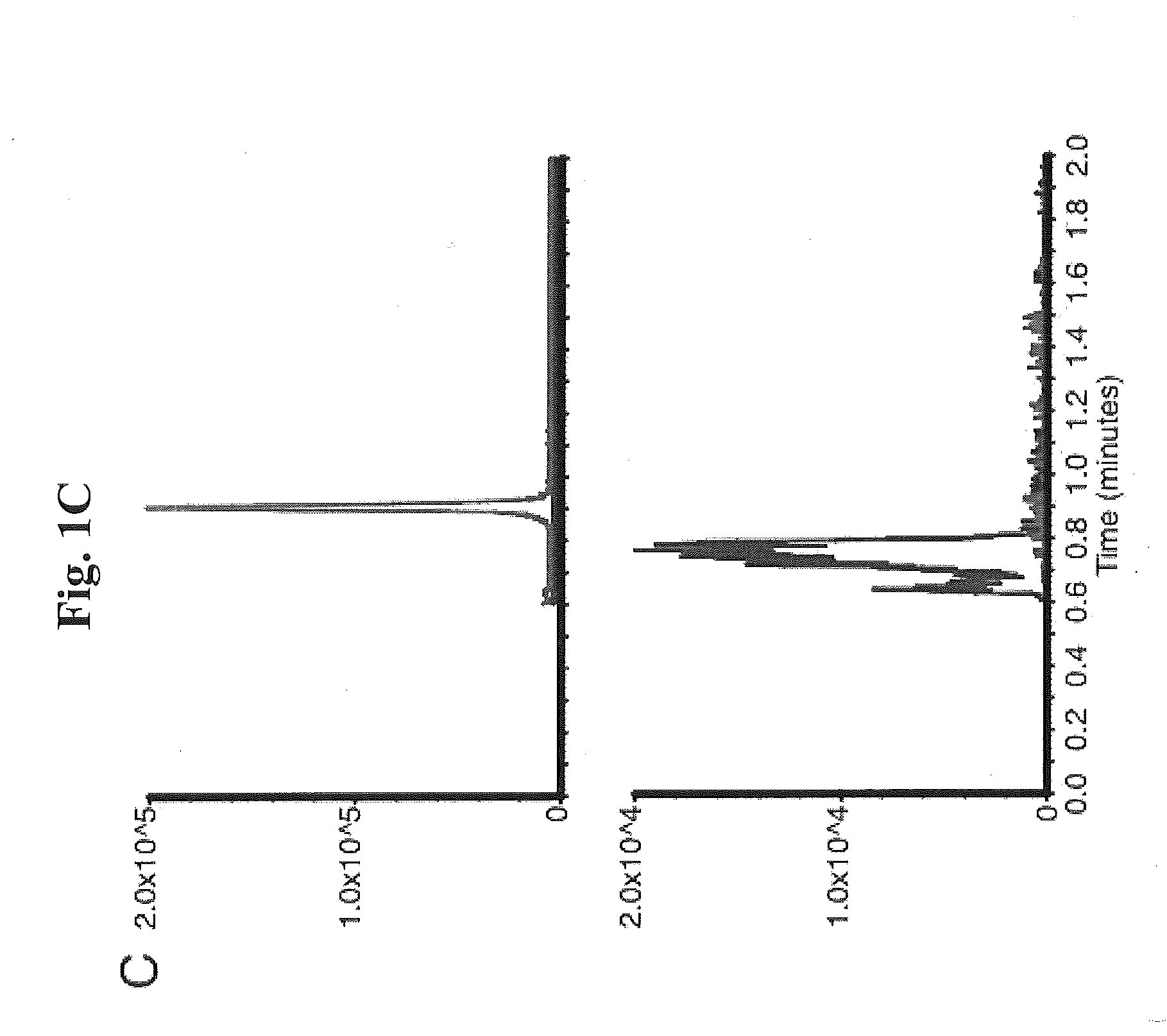
Methods and Kits for Detection of Antibiotic Resistance
InactiveUS20120196309A1Promotes bacterial resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisResistant bacteriaMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to a method of detecting antibiotic resistant bacteria in a sample. The method includes the steps of analyzing a sample derived from bacteria via mass spectrometry to produce a data set, and determining from the data set the presence or absence of a covalently modified antibiotic compound in the sample, wherein the presence of a covalently modified antibiotic compound in the sample is indicative that the bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic. The present invention also relates to a kit for determining the presence or absence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in a sample. The kit includes reagents for preparing and performing the assay, and instructions for the set-up, performance, monitoring, and interpretation of the assay.
Owner:YALE UNIV
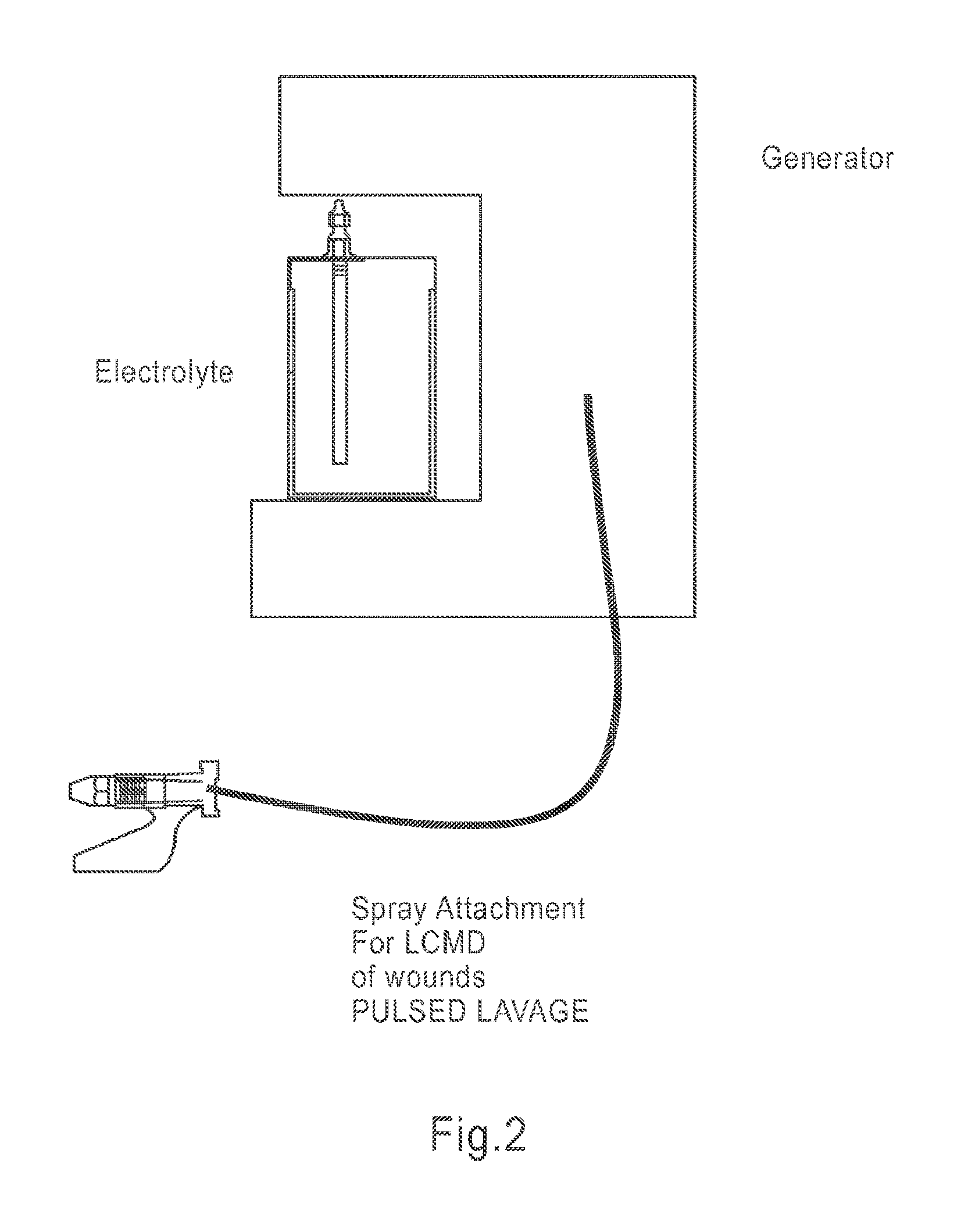
Apparatus and method for wound, cavity, and bone treatment
InactiveUS20130261534A1Environment safetyPromote formationElectrolysis componentsCannulasWound dressingWound care
Owner:PURICORE
Lead and cadmium tolerant bacteria and method for plants renovation of soil pollution by heavy metal
InactiveCN101153272AHas nitrogen fixationWith characteristicsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPhosphateAntibiotic resistance
The invention relates to a heavy metal lead and cadmium antibiotic-resistant bacterium and a method for strengthening lead and cadmium heavy metals in the vegetable extraction soil, and belongs to the agricultural and environmental pollution treatment technical field. The J62 culture stain is appraised as the Burkholderia sp, has antibiotic resistance to a plurality of heavy metals, in particular to lead and cadmium, respectively reaching Pb<2+>1000mg / L and Cd<2+>2000mg / L. The invention has the characteristics of nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilizing, and can promote the growth of the plant and improve the stress resistance of the plant. The effective living microbial numbers of the liquid preparation are above a billion per millimeter, and the effective living microbial numbers of the solid preparation are 200 millions per gram. When the seeds of the plant are seminated in humid soil containing heavy metals, 10 to 20mL of the bacteria liquid of 10<8> bacteria J62 / mLs is inoculated in each grams of soil once or in two times. The invention promotes the growth of the plant, strengthens the enrichment of heavy metal lead and cadmium of the plant, and improves the extraction and recovery efficiency of the plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
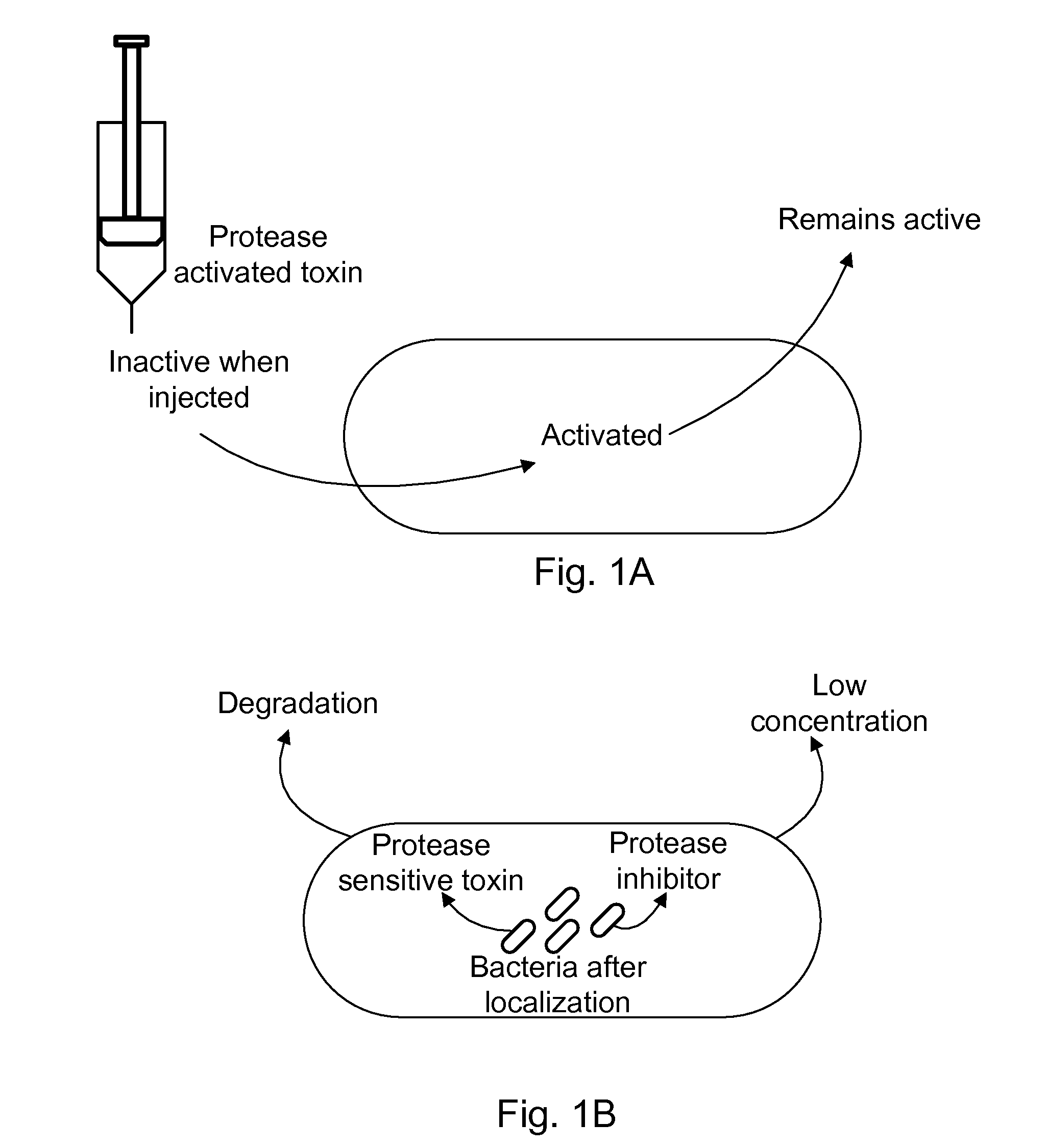
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Method for associating plants and microorganisms to accumulate heavy metal cadmium in soil and application thereof
ActiveCN103350105APromote growthImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationResistant bacteriaMicroorganism
The invention relates to a method for associating plants and microorganisms to accumulate heavy metal cadmium in soil. The method comprises the following steps: firstly planting cadmium accumulated plants in cadmium polluted soil; then inoculating cadmium-resistant bacteria in rhizosphere soil of the cadmium accumulated plants; conventionally culturing, watering and moisturizing; enriching cadmium in cadmium accumulated soil by utilizing the absorption effect of the cadmium accumulated plants to the cadmium and reinforcing effect of the cadmium-resistant bacteria; repeating the process so that the purpose of repairing the cadmium polluted soil can be achieved. The soil repairing method is good in effect, low in cost, easy to manage and operate, and free of secondary pollution, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Antibiotic testing and screening system
ActiveUS20180245125A1Decrease antibiotic permeabilityEliminates and reduces bindingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant bacteriaIn vivo
The present invention provides a platform technology for testing, screening, selecting and evaluating antibiotics by using genetically engineered strains with identified, individual or combined, resistance mechanisms, prepared from fully susceptible clinical isolates. This antibiotic testing and screening system of the present invention can efficiently and effectively evaluate antibiotics against specified resistance mechanisms in vitro and in vivo, and is suitable on the novel antibiotic development in against multidrug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:KEMYTH BIOTECH CO LTD
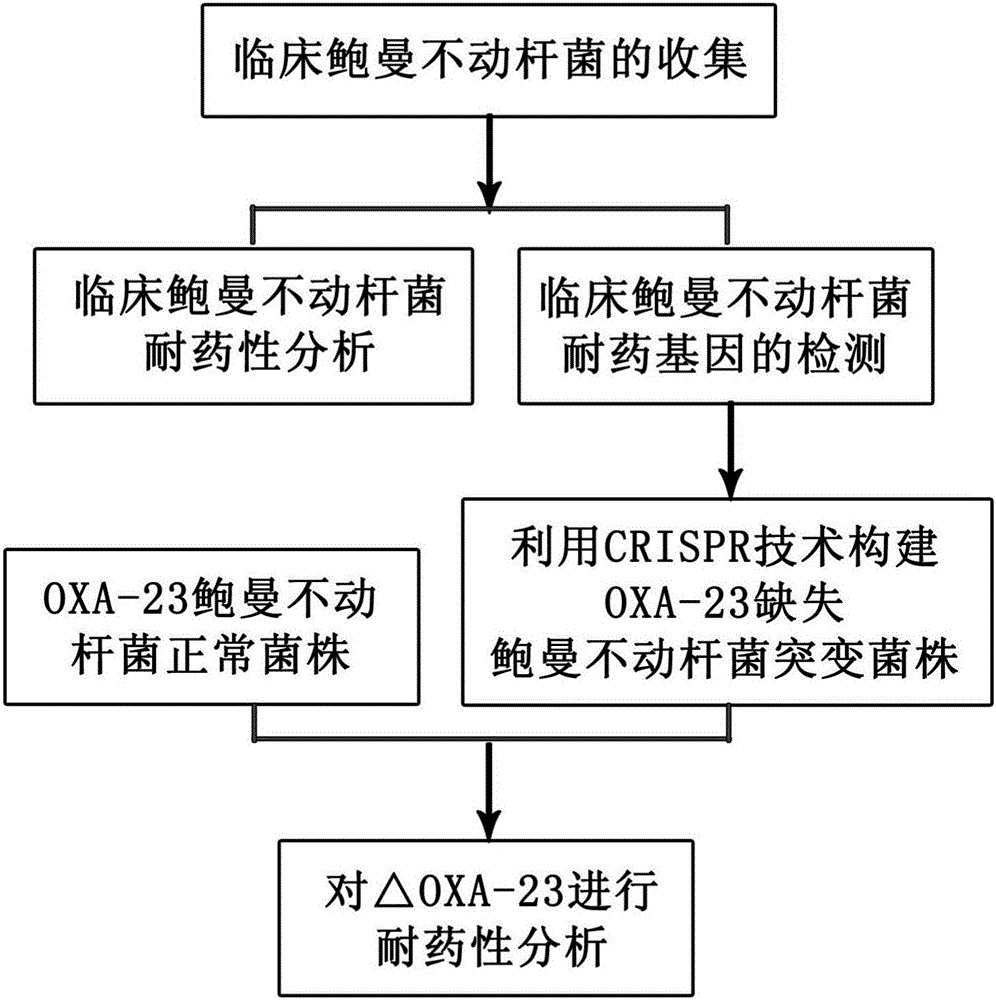
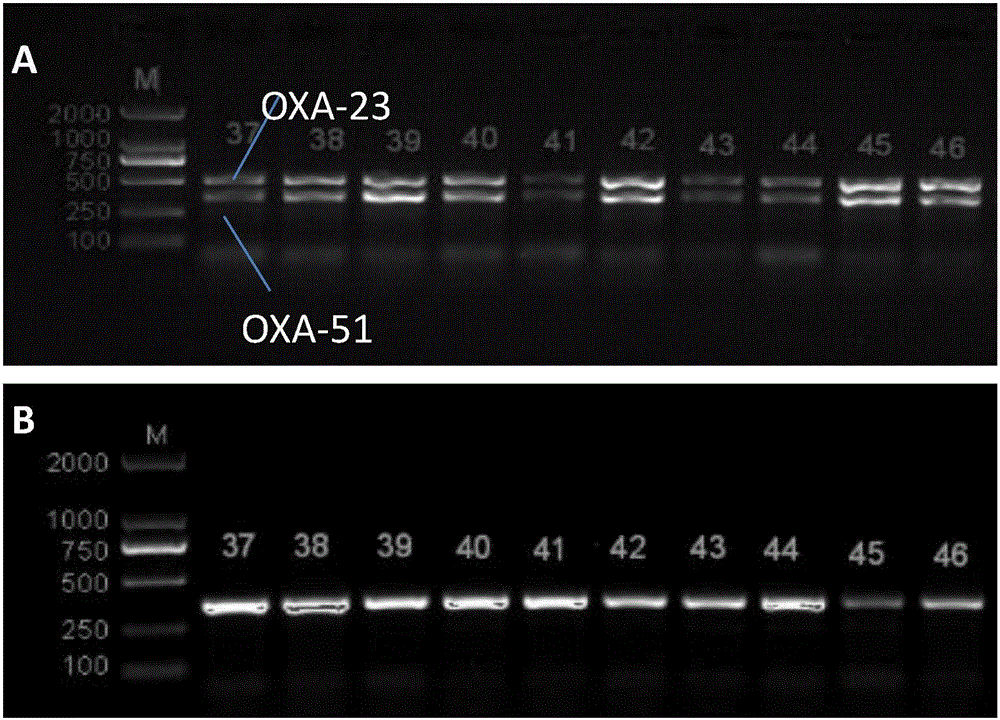
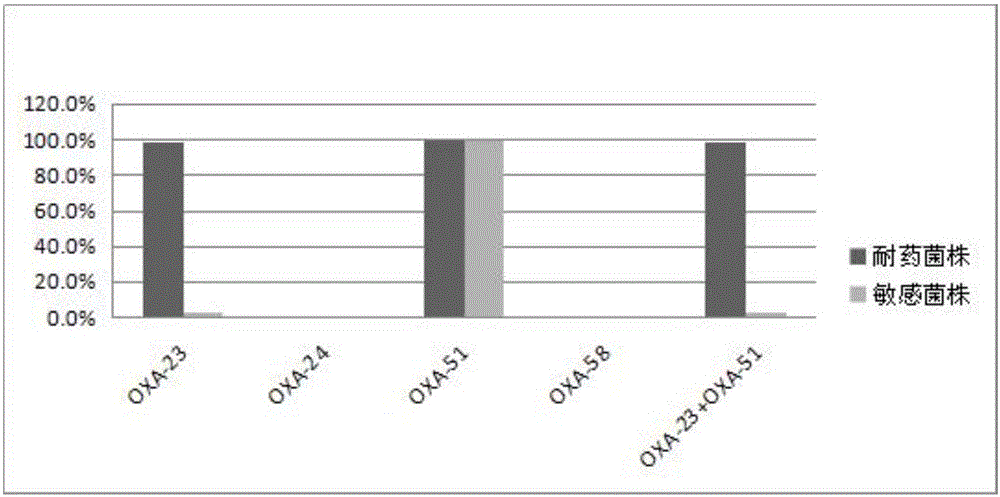
Method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN106544353ASensitivity reversalEasy to operateVectorsMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMulti drug resistant
The invention discloses a method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9. The method comprises the steps that firstly, AB is collected clinically, and drug resistance analysis and statistics are conducted after the AB is subjected to drug resistance measurement through a drug sensitive slip method; secondly, the multi-drug resistant AB is subjected to DNA extraction through a lysis-boiling method, and then amplification analysis is conducted by mean of well designed drug resistant gene primers of the AB; and thirdly, according to drug resistant gene detection in the former step, the AB containing an OXA-23 gene is selected, CRISPR / Cas9 and sgRNA plasmids are established and transferred into the AB containing the OXA-23 gene, an OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain is established, and drug resistance analysis is conducted on the OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain. The method is easy to operate and high in knocking-out efficiency, and a novel method and a novel concept are provided for preventing spreading of the drug resistant genes and treating drug resistant bacteria.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
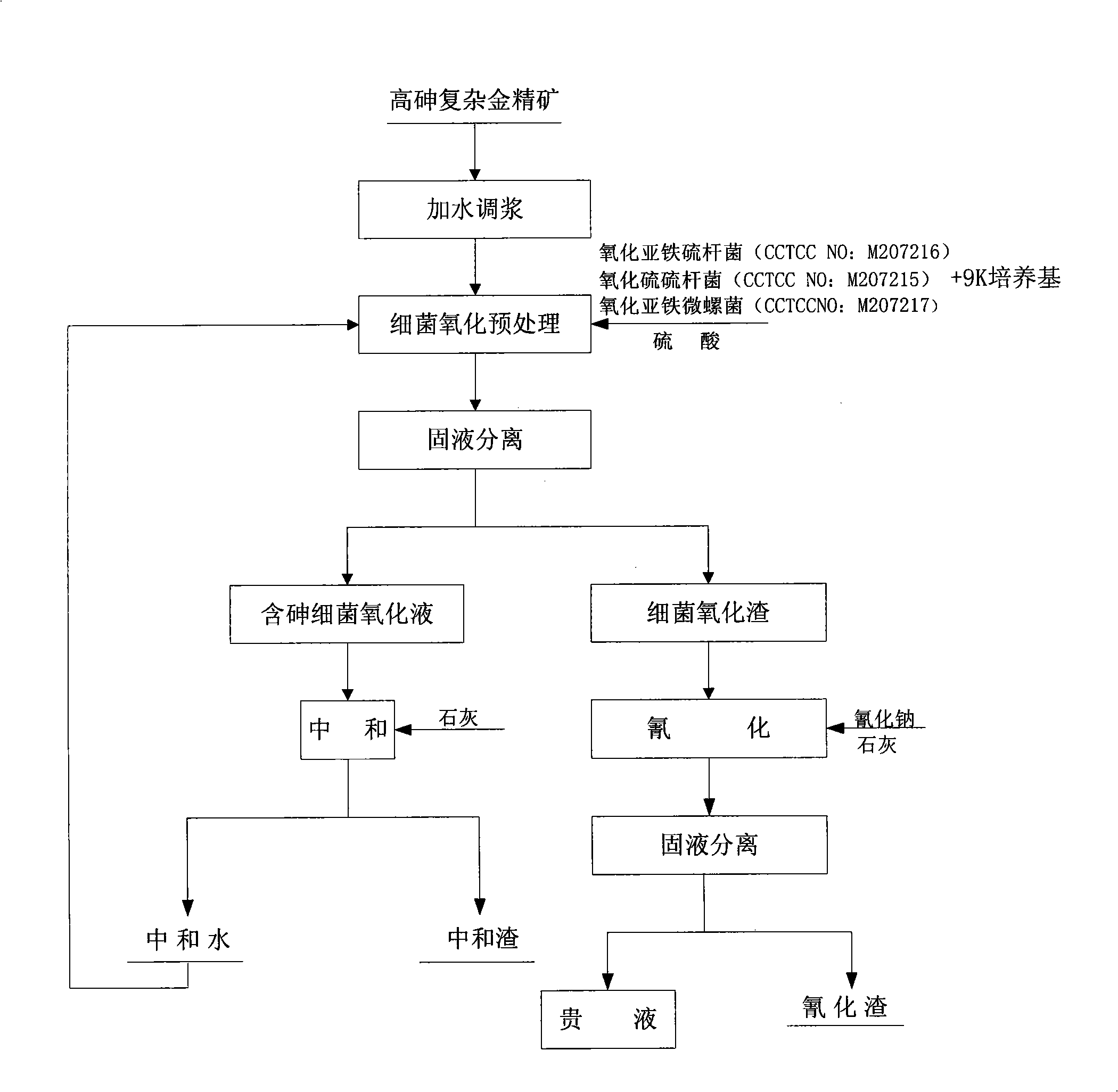
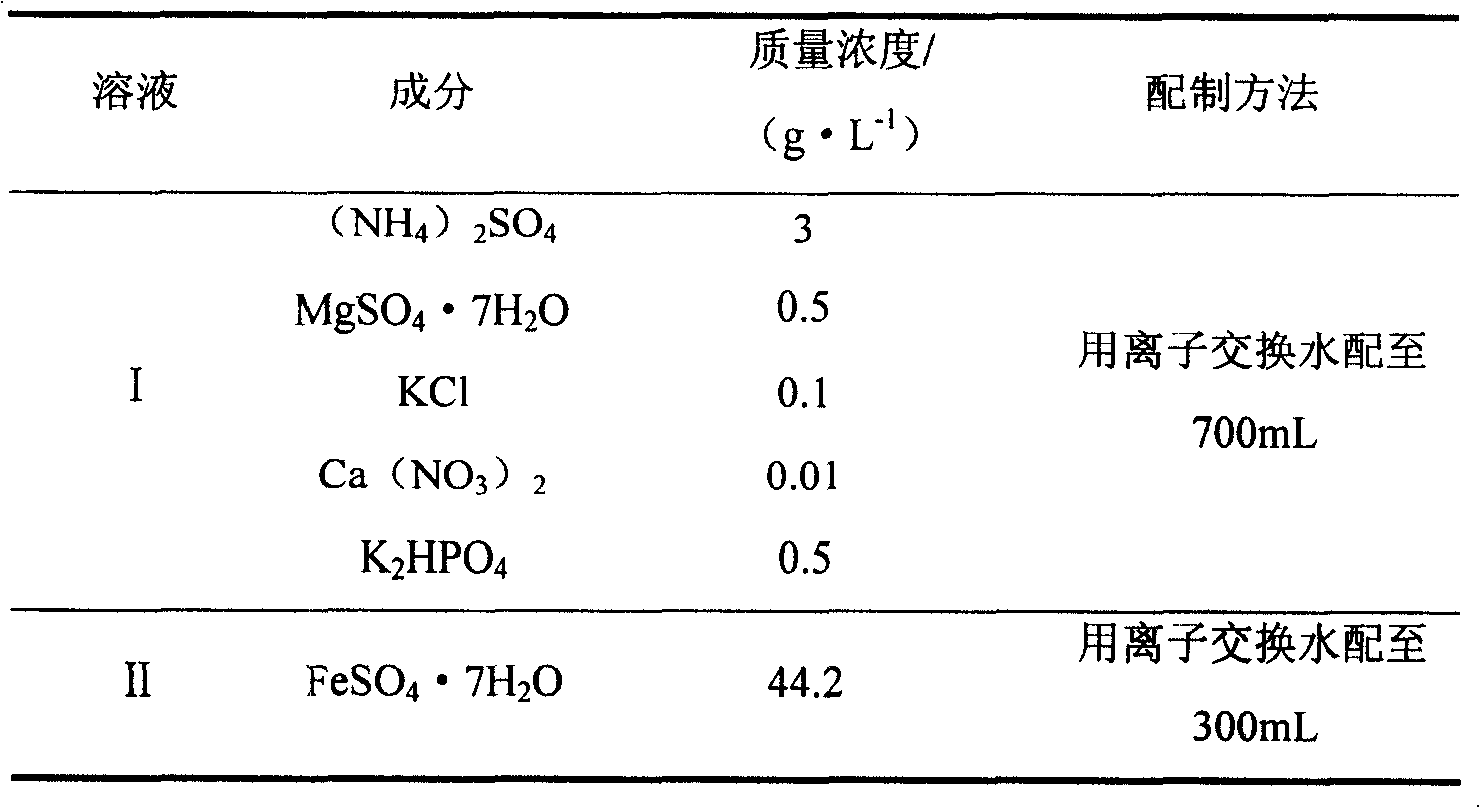
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
ActiveUS9068187B1Direct cytotoxicDirect inhibitoryBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesSurface display
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Methods, compositions and kits for detection and analysis of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
InactiveUS20090081663A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant bacteriaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention relates generally to detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in a sample. In particular, the invention provides methods, compositions and kits for detecting and analyzing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other methicillin-resistant bacteria in a sample.
Owner:MOLECULAR DETECTION
Modified polypeptides with therapeutic activity and methods of use
InactiveUS20050118678A1High bactericidal activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFatty acidBiochemistry
Polypeptides modified by fatty acid conjugation and methods of using such modified polypeptides in treating bacterial infections, including the treatment of antibiotic resistant bacterial infections, are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
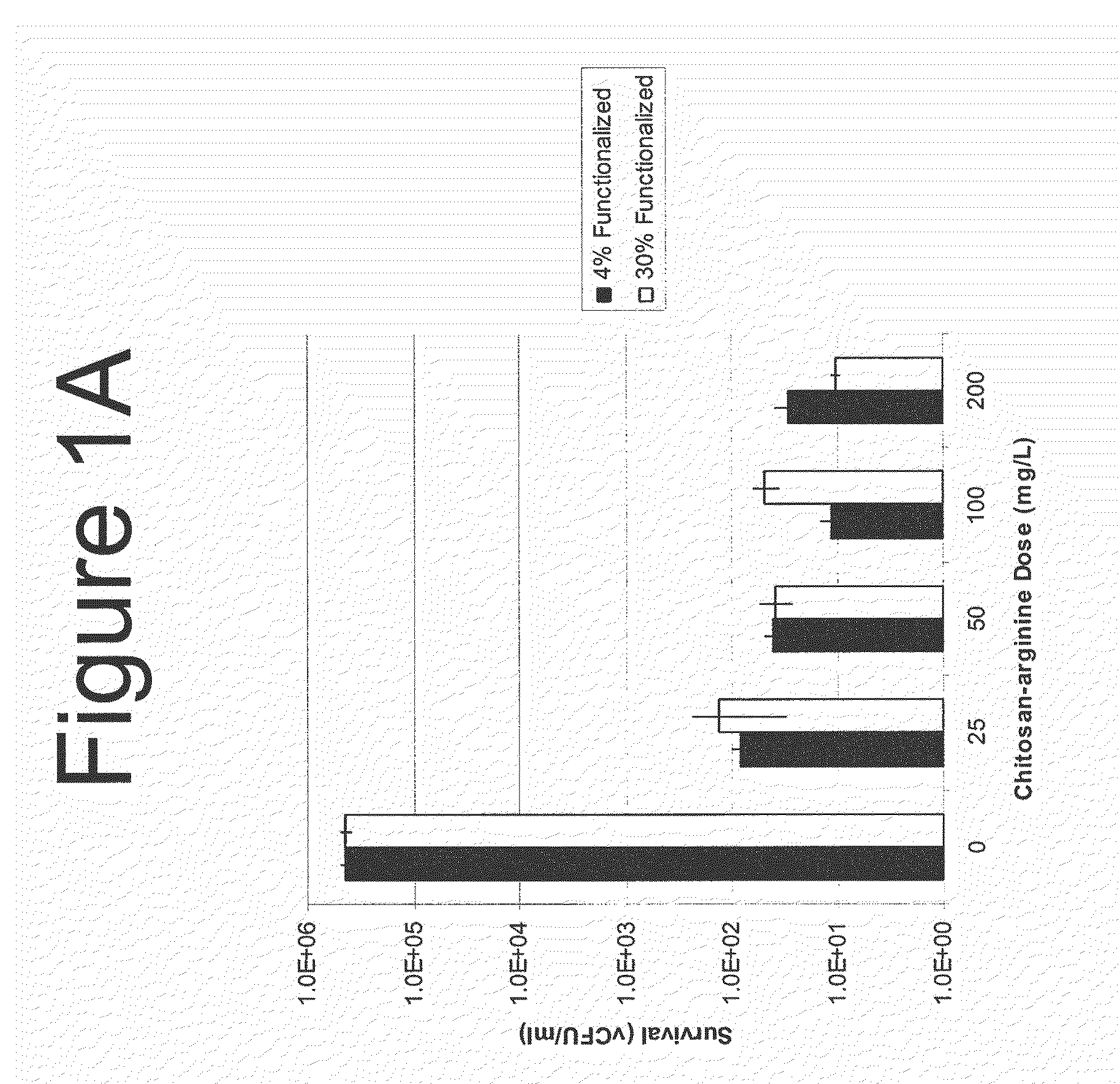
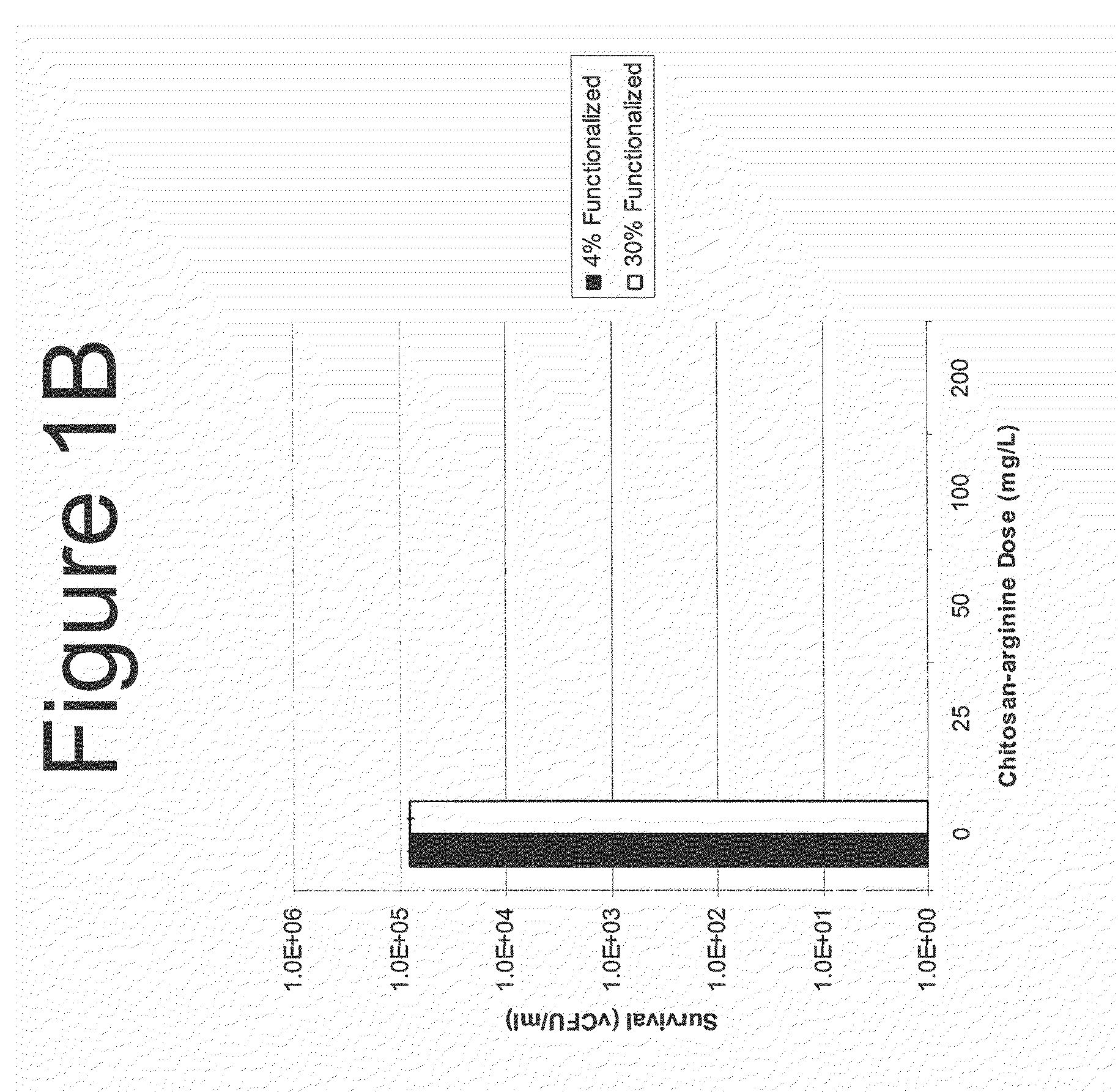
Methods and Compositions for the Prevention of and Treatment of Infections Utilizing Chitosan-Derivative Compounds
The present invention is directed to the treatment and prevention of nosocomial infections or MRSA infections utilizing soluble chitosan or chitosan derivative compounds. These chitosan-derivative compounds, e.g., chitosan-arginine and chitosan-acid amines, exhibit bactericidal activity against bacterial pathogens, e.g., drug resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Owner:SYNEDGEN
Method to reduce inflammatory response in transplanted tissue
InactiveUS7427606B2Lower immune responseGood effectBiocideSugar derivativesResistant bacteriaAntibiotic Agents
The present invention provides a therapeutic method for treating biological diseases that includes the administration of an effective amount of a suitable antibiotic agent, antifungal agent or antiviral agent in conjunction with an A2A adenosine receptor agonist. If no anti-pathogenic agent is known the A2A agonist can be used alone to reduce inflammation, as may occur during infection with antibiotic resistant bacteria, or certain viruses such as those that cause SARS or Ebola. Optionally, the method includes administration of a type IV PDE inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
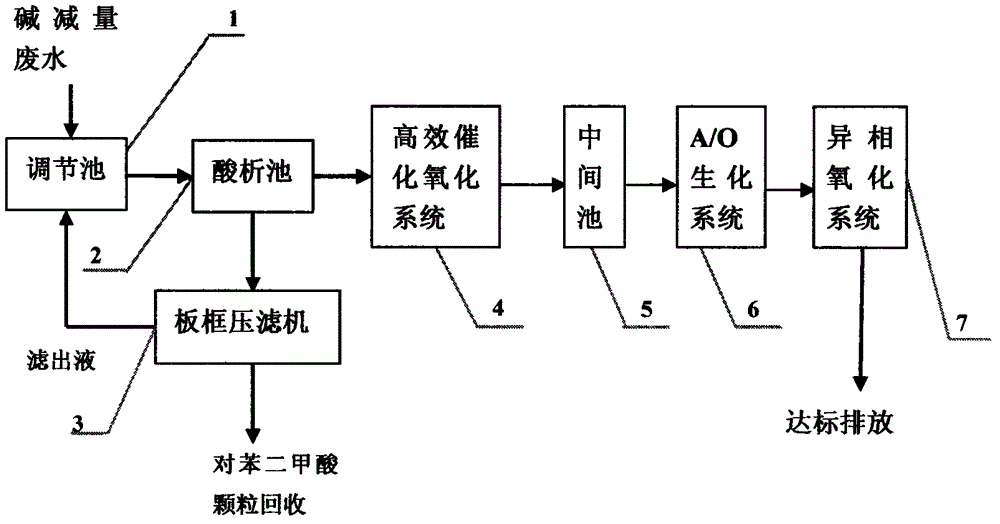
Resourceful treatment process for alkali-minimization waste water
InactiveCN104926018AReduce processing costsSolve the problems that cannot be dealt with separatelyMultistage water/sewage treatmentResistant bacteriaWastewater
The invention discloses a resourceful treatment process for alkali-minimization waste water. The resourceful treatment process is used for recycling terephthalic acid which is difficult to be degraded, is capable of reducing treatment cost, and is combined with an efficient oxidation technology and a bioaugmentation technology for aerobic degradation of organic matters which cannot be degraded in a biochemistry manner; the possibility that waste water is degraded in the biochemistry manner is realized; high-salt resistant bacteria are introduced into the bioaugmentation technology, so that the problem that high-salt alkali-minimization waste water is difficult to be degraded in the biochemistry manner is solved; the process effluent CODcr is controlled to be less than 200 mg / L; the problem that single alkali-minimization waste water treatment cannot reach the standard is effectively solved.
Owner:宁波沐德环境科技有限公司
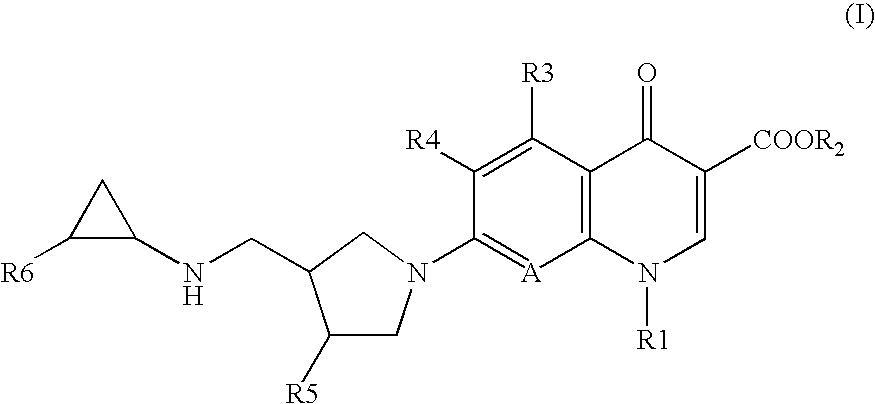
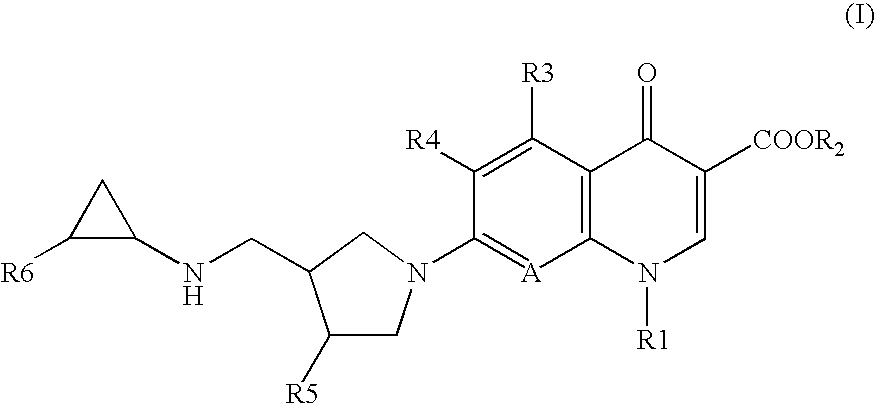
7-(4-Substituted-3-cyclopropylaminomethyl-1 pyrrolidinyl) quinolonecarboxylic acid derivative
ActiveUS20060281779A1Strong antibacterial activityEasy to useAntibacterial agentsBiocideResistant bacteriaAcid derivative
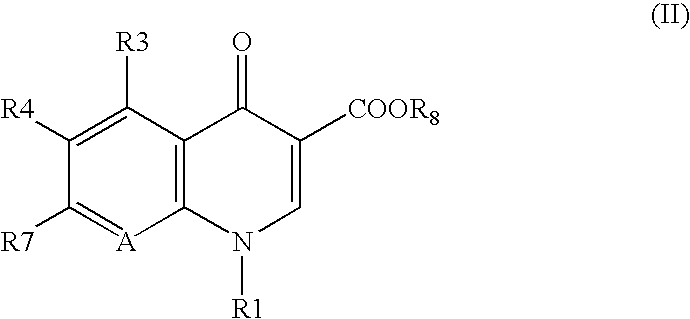
OBJECT To provide novel quinolonecarboxylic acid compounds serving as safe, strong antibacterial agents that are effective against drug-resistant bacteria that are less susceptible to conventional antibacterial agents. SOLVING MEANS There are provided 7-(4-substituted-3-cyclopropylaminomethylpyrrolidinyl)quinolonecarboxylic acid derivatives (such as 1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3S,4S)-3-cyclopropylaminomethyl-4-fluoro-1-pyrrolidinyl]-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid) that exhibit strong antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria, such as MRSA, PRSP and VRE, while being safe. The compounds are shown by the following general formula (I):
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD
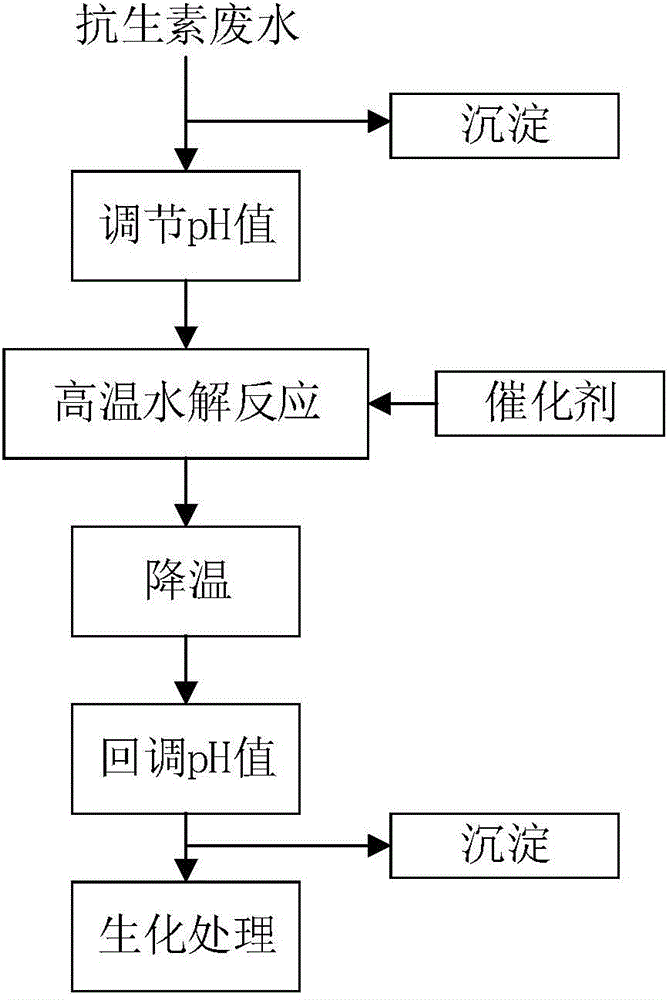
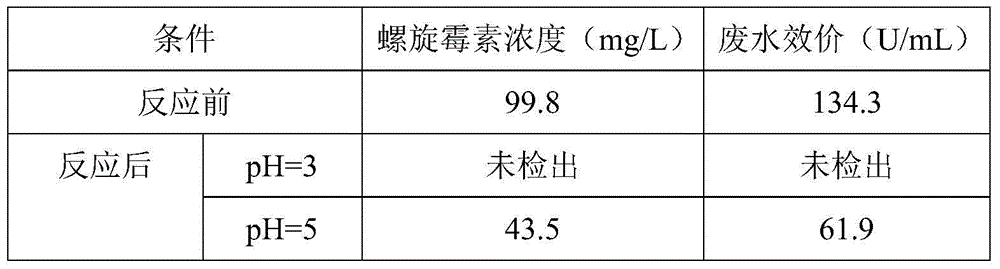
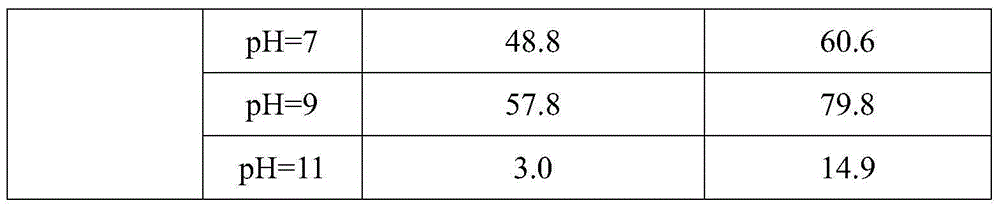
Pretreatment method for removing antibiotics in ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater
ActiveCN105084442ALower titerEfficient decompositionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by heatingMicroorganismResistant bacteria
The invention provides a pretreatment method for removing antibiotics in ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater. The method removes antibiotics in the ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater mainly through adjustment of the pH value of the wastewater and high-temperature catalytic hydrolysis, and the treated pharmaceutical wastewater without antibiotics can enter a subsequent biochemical treatment process for treatment. The method provided by the invention can basically remove antibiotics in the pharmaceutical wastewater, reduce inhibition effect of high-concentration antibiotics on microbes, lower down difficulty in treatment of the wastewater by using the subsequent biochemical process and decrease generation of drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant genes in subsequent biochemical treatment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Separating and screening method for saline-alkaline-resistant bacteria degrading petroleum hydrocarbon
InactiveCN104877930AImprove the quality of micro-ecological environmentNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture fluidBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for separating and screening a saline-alkaline-resistant pure bacterial strain degrading petroleum hydrocarbon from oily soil. The method comprises the steps: firstly collecting soil polluted by salinized petroleum hydrocarbon from an oil field, adding the collecting soil according to an amount of 10% into an inorganic salt culture medium which takes crude oil as a unique carbon source, and carrying out enrichment culture in a constant temperature shaker; then inoculating a 10% enriching liquid into a fresh crude oil inorganic culture medium and continuously carrying out habituated culture under a same condition for 4-5 times, wherein the pH, salinity and crude oil content of the culture medium in the domestication process are gradually raised; after diluting the culture liquid after domestication in a gradient manner, coating the culture liquid to a LB-agar panel, after bacterial colonies grow, picking up single colonies in different shapes, and lineating and purifying and separating single bacteria; and finally, spreading the separated single bacteria to a crude oil inorganic salt-agar panel and detecting whether the bacterial colonies grow or not, if so, the bacterial strain is the bacteria degrading petroleum hydrocarbon; determining the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation rate of the single bacterial strain and carrying out 16Sr DNA molecular identification on the bacterial strain so as to determine the species relationship of the bacterial strain.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
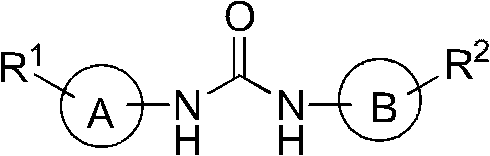
N,N'-asymmetric diayl substitution urea compound and preparation method and purpose thereof
InactiveCN103130686ALow structural requirementsOmit the isocyanate stepAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryArylResistant bacteria
The invention relates to N,N'-asymmetric diayl substitution urea compound of a general formula (I). A and B independently represent aryl, one-substitution or multi-substitution aryl, miscellaneous aryl and one-substitution or multi-substitution miscellaneous aryl. R1 and R2 independently represent hydrogen or C1-C8 alkyl or C1-C8 alkoxy or aromatic alkoxy or acyl or non-aromatic heterocycle substitution group or halogen or nitryl or trifluoromethyl or cyan. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the compound, active component medicine composition of the compound and application of the compound in preparing medicine for restraining new delhi metallo beta-lactamase (NDM-1) drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE +1
Novel pleuromutilin derivate, preparation method and medical use thereof
ActiveCN102229580AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMethyl palmoxirate
The invention discloses a pleuromutilin derivate, a preparation method and medical use thereof. The pleuromutilin derivate is a compound, which is obtained by coupling pleuromutilin to alkyl acylamino-thiazole-4-methyl merecaptan with 2-different substitutional amino. Pharmacological experimental results show that: compared with the pleuromutilin, the pleuromutilin derivate disclosed by the invention has better antimicrobial and antibiotic resistant bacteria activities; and therefore, the compound is possibly applicable for curing a plurality of infection and inflammatory diseases on clinic.
Owner:南通药享科技有限公司
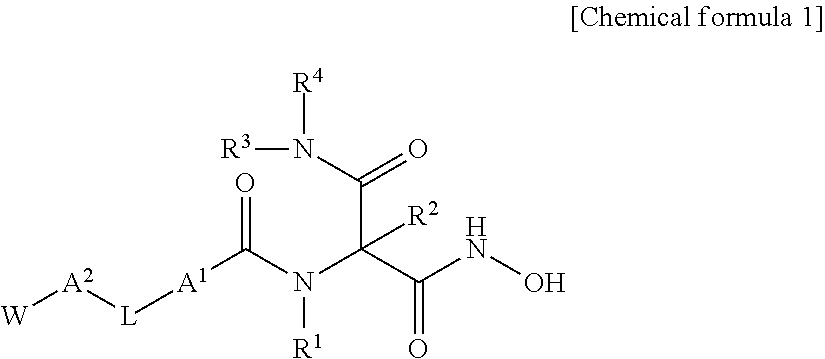
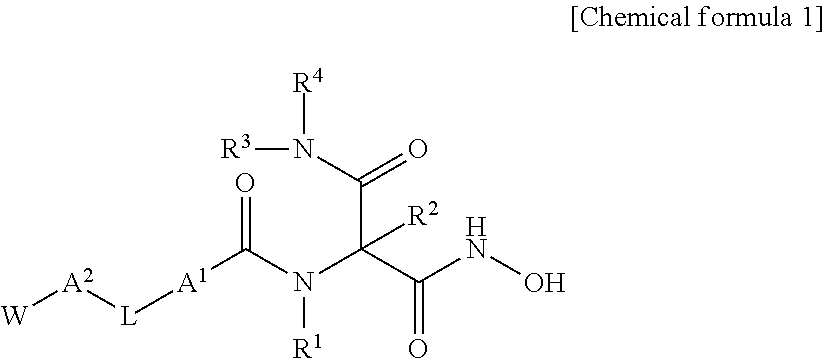
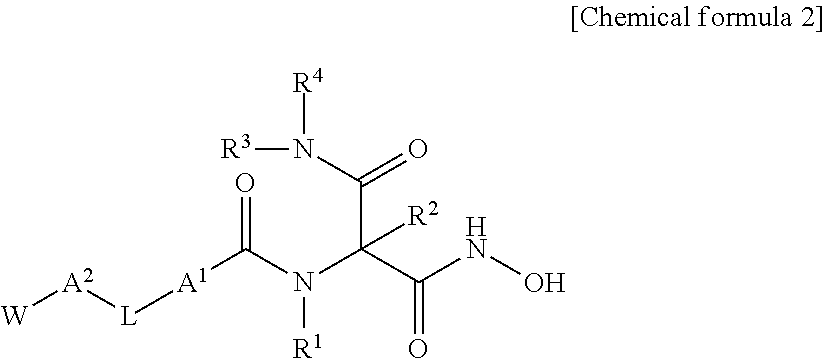
Novel hydroxamic acid derivative
ActiveUS20130072677A1Strong LpxC-inhibiting actionHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaHydroxamic acid
Provided is a novel compound which is useful as a pharmaceutical composition by inhibiting an LpxC activity, thereby exhibiting potent antimicrobial activity against gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its drug resistant bacteria. Provided is a hydroxamic acid derivative represented by the following general formula [1] or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
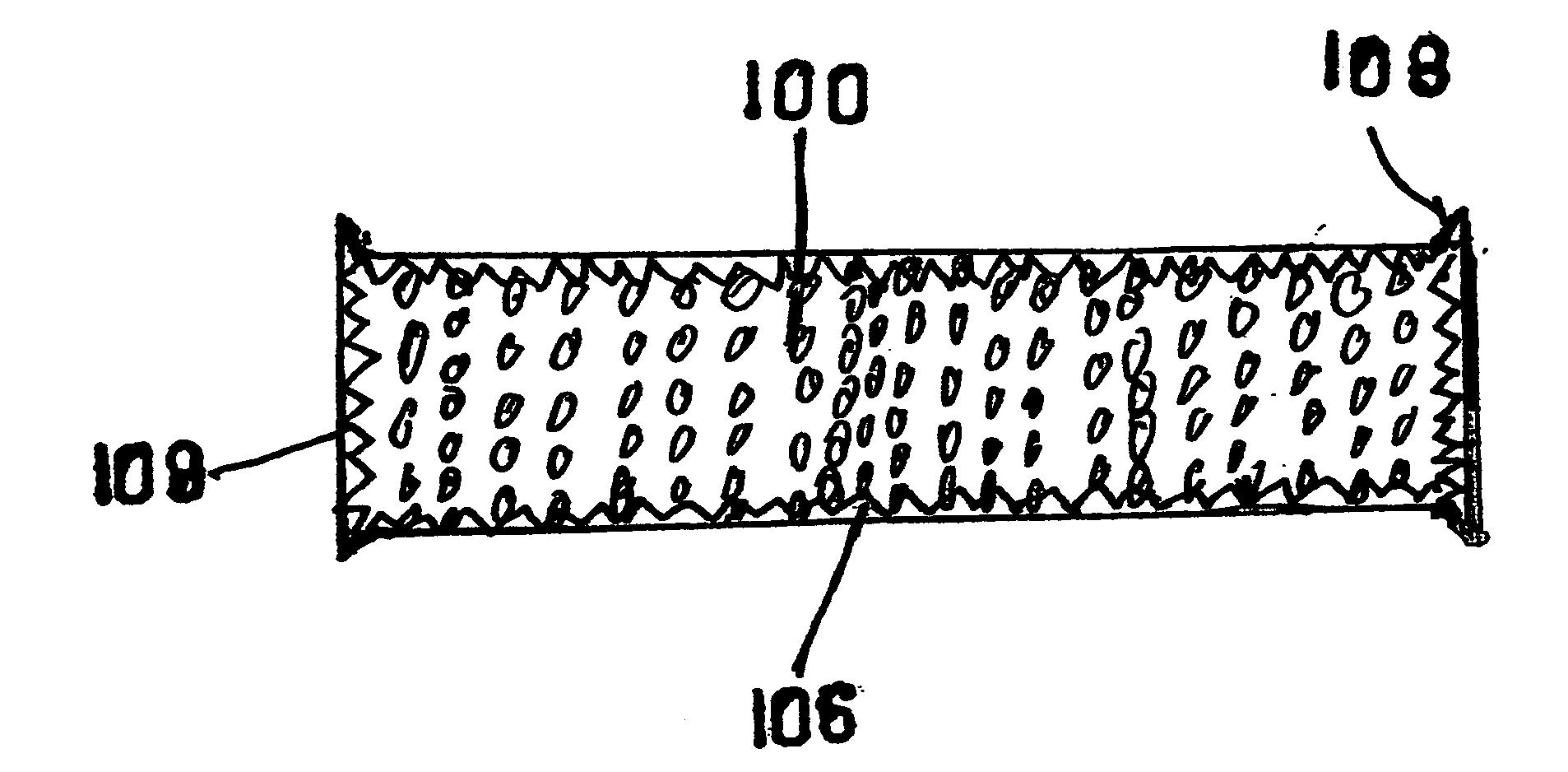
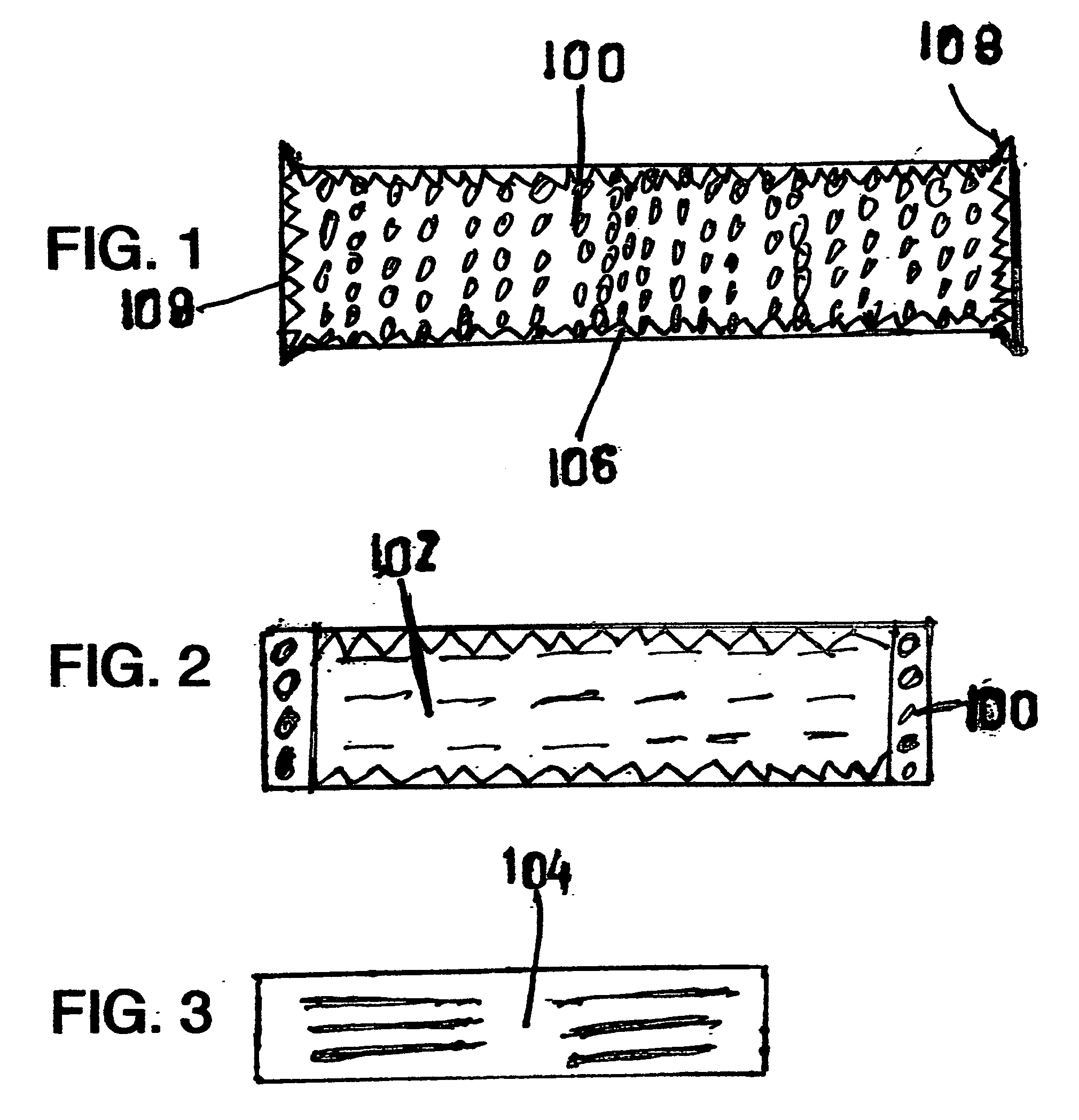
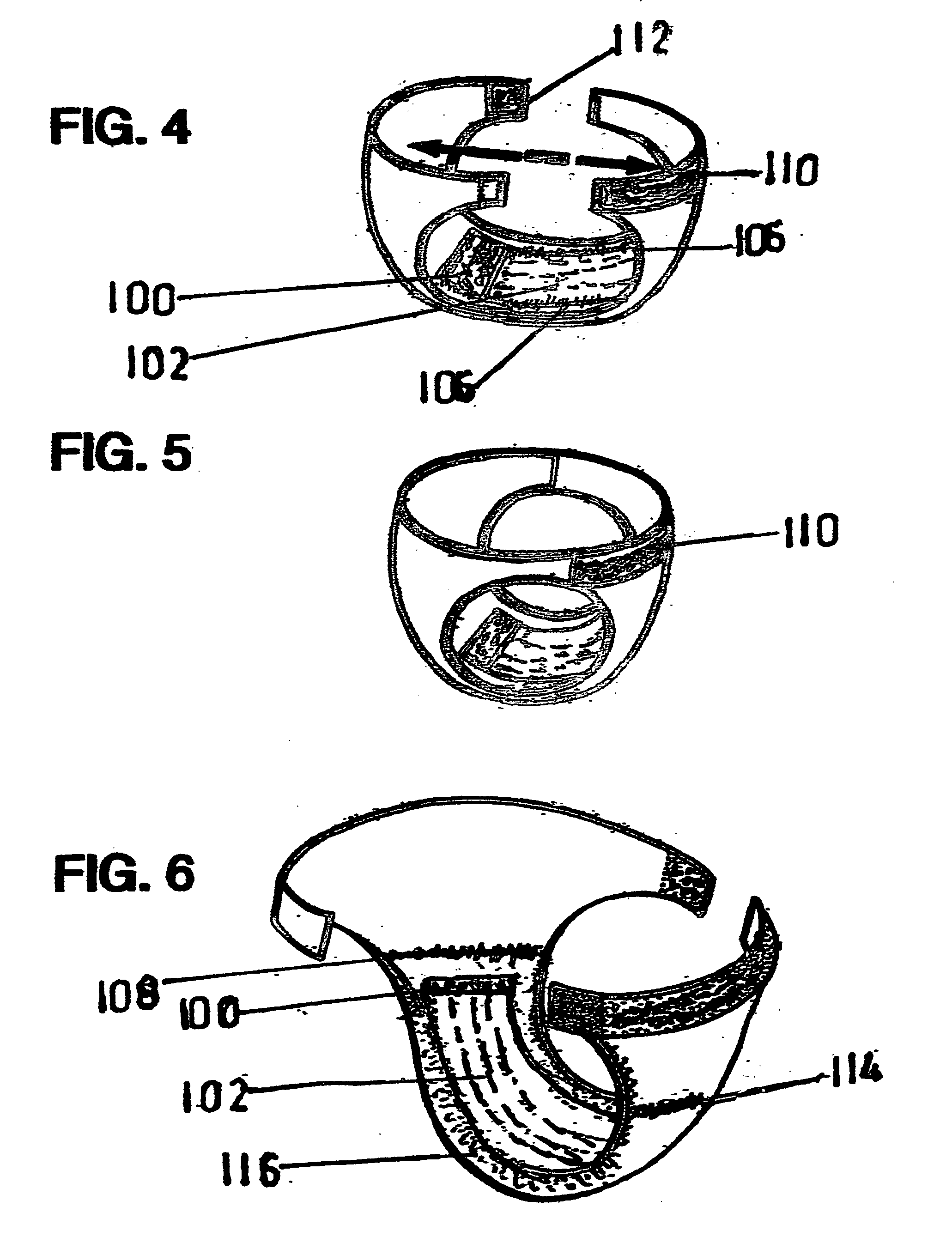
Incontinence garments with a silver lining infection stopper
InactiveUS20100021512A1Avoid painSimple structureBiocideInorganic active ingredientsBacteroidesResistant bacteria
Antibiotics used to cure Uterine Tract Infections have resulted in the growth of MRSA. and other antibiotic resistant bacteria. The CDC guidelines state “Disposable diapers cause 95% of all UTI'S”. The procedures used for “prevention” are ineffective because millions of bacteria in incontinence garments continue to double every 20 minutes. Silver ions in bandages are used to cure severly damaged skin, such as in burns. The best two in a large scale test achieved results in just 30 minutes. This Invention uses silver ions in linings next to the skin to stop the growth of over 250 kinds of infectious bacteria on it's surface and the body parts it touches. It achieves results in 30 minutes, equal to the most highly rated bandages . . . for every level of incontinence for both sexes.
Owner:ARRON STANLEY
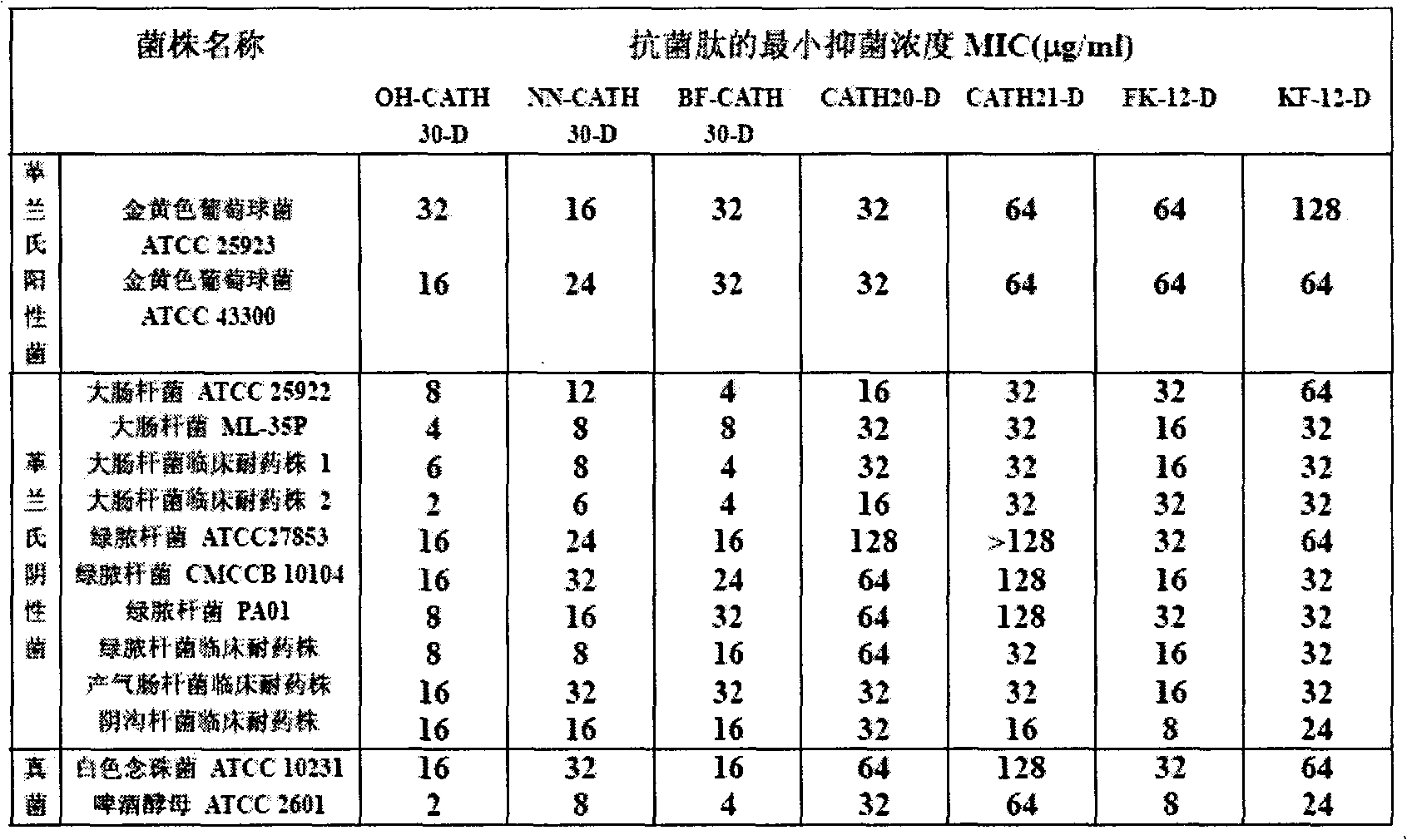
Non-natural fully D-type snake venom cathelicidin antibacterial peptide and derivative, preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102311492AEasy to degradeRetain antimicrobial activityCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRetention time
The invention provides sequences of a snake venom cathelicidin antibacterial peptide consisting of non-natural fully D-type amino acid, which cannot be easily degraded by protease, and a derivative thereof and a preparation method thereof, and also provides application of the snake venom cathelicidin antibacterial peptide consisting of the non-natural fully D-type amino acid and the derivative thereof. The snake venom cathelicidin antibacterial peptide consisting of the non-natural fully D-type amino acid and the derivative thereof have an obvious effect of suppressing growth of bacteria and fungus, in particular to an excellent effect of suppressing clinical drug-resistant bacteria, have the beneficial characteristics of simple structure, convenience in artificial synthesis and wide antibacterial spectrum system, have the obvious characteristics of capability of resisting degradation of various protease, long antibacterial activity retention time and no drug residue, and can be applied to prevention and treatment of human or animal infected diseases, clinical artificial biomaterials, food preservative and fruit and vegetable refreshment, feed additives and daily chemical supplies.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
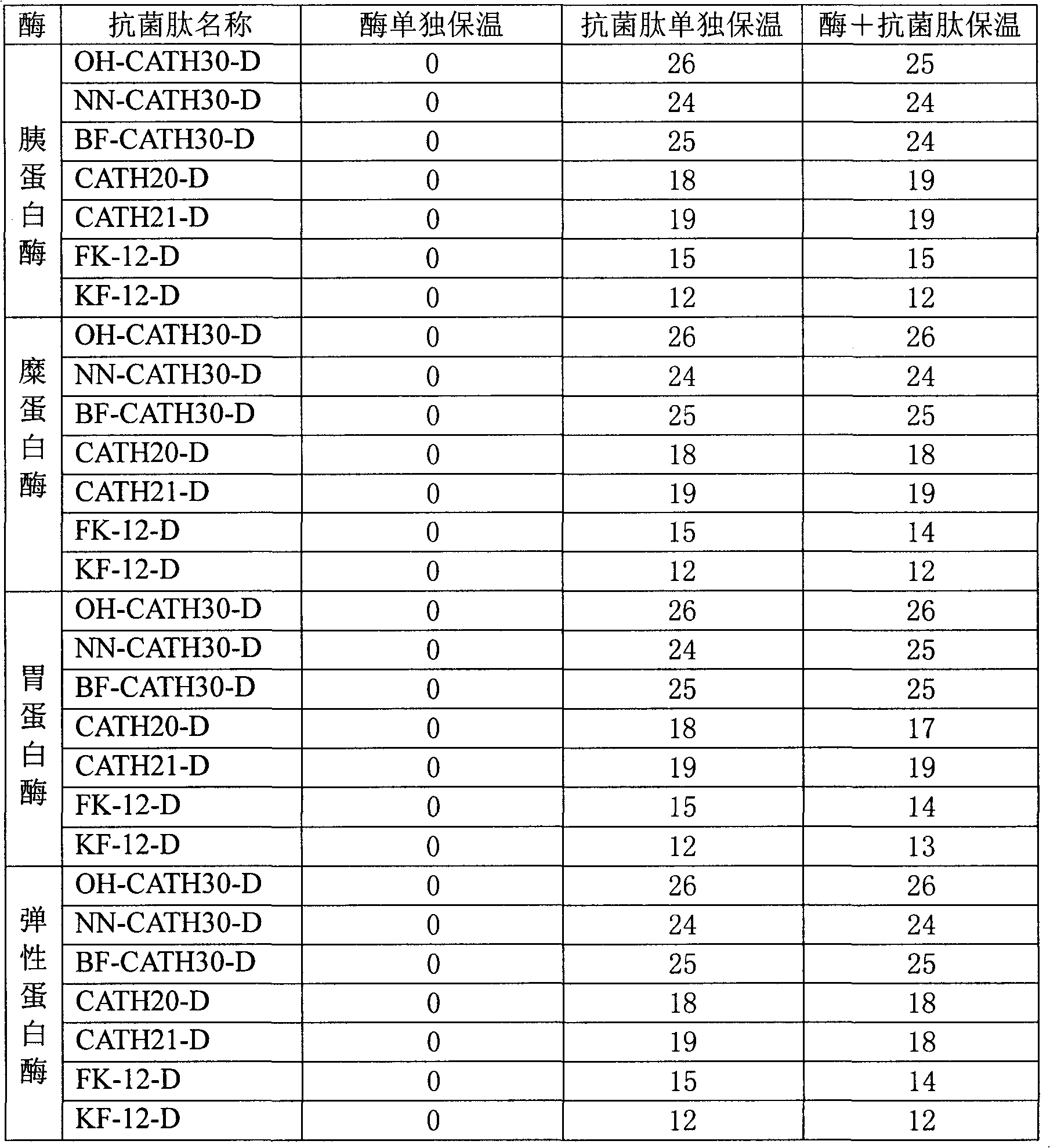
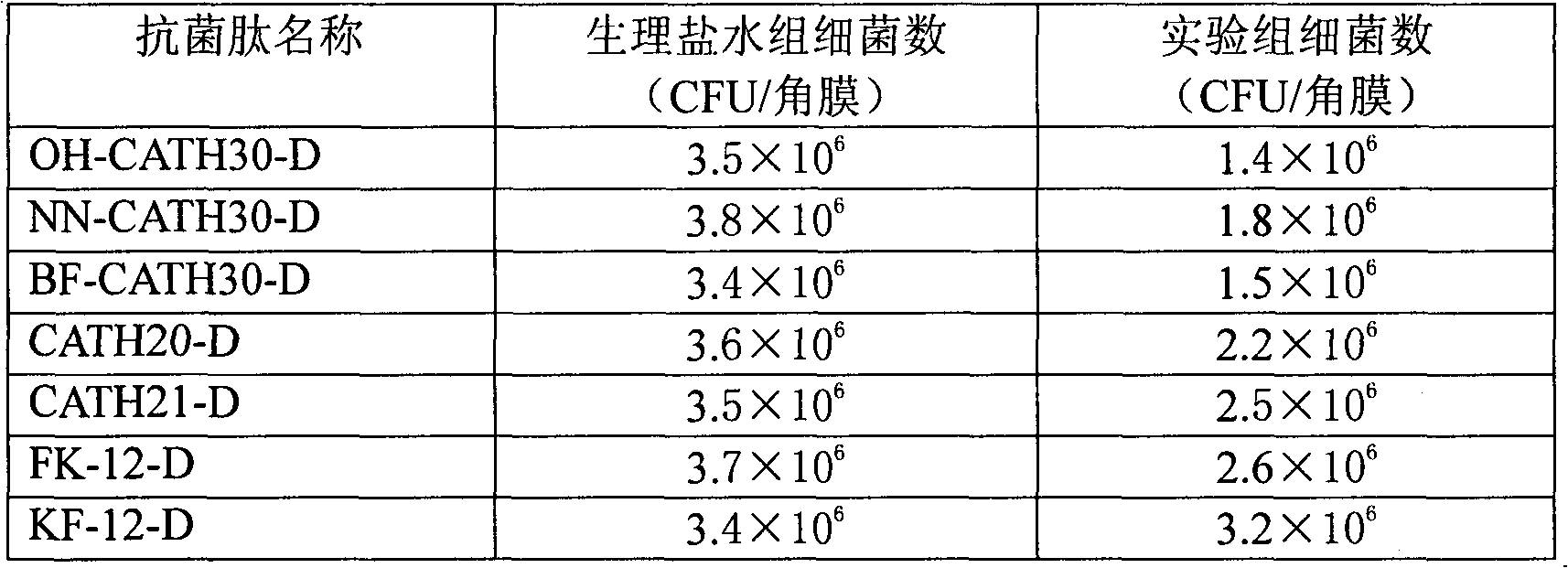
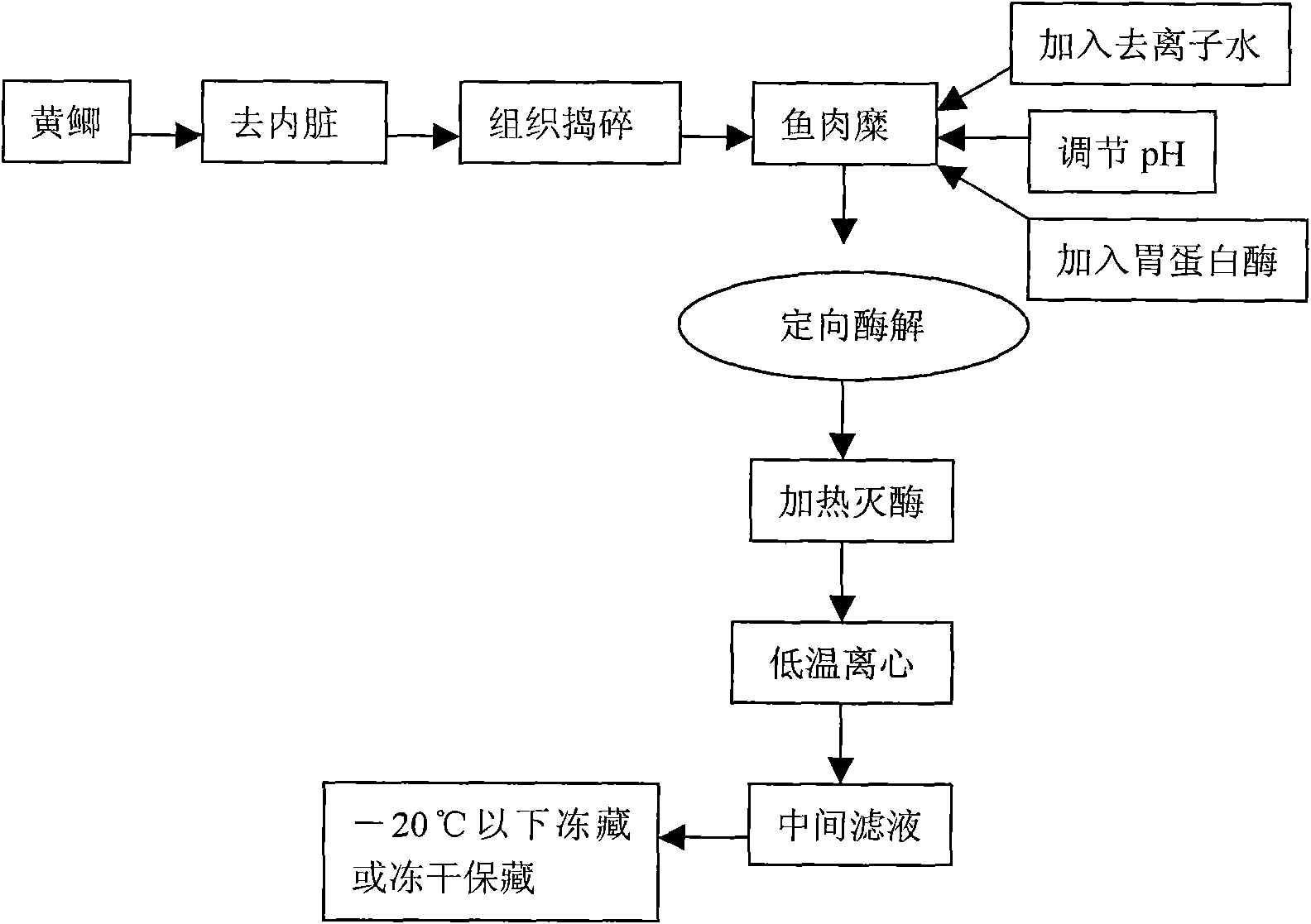
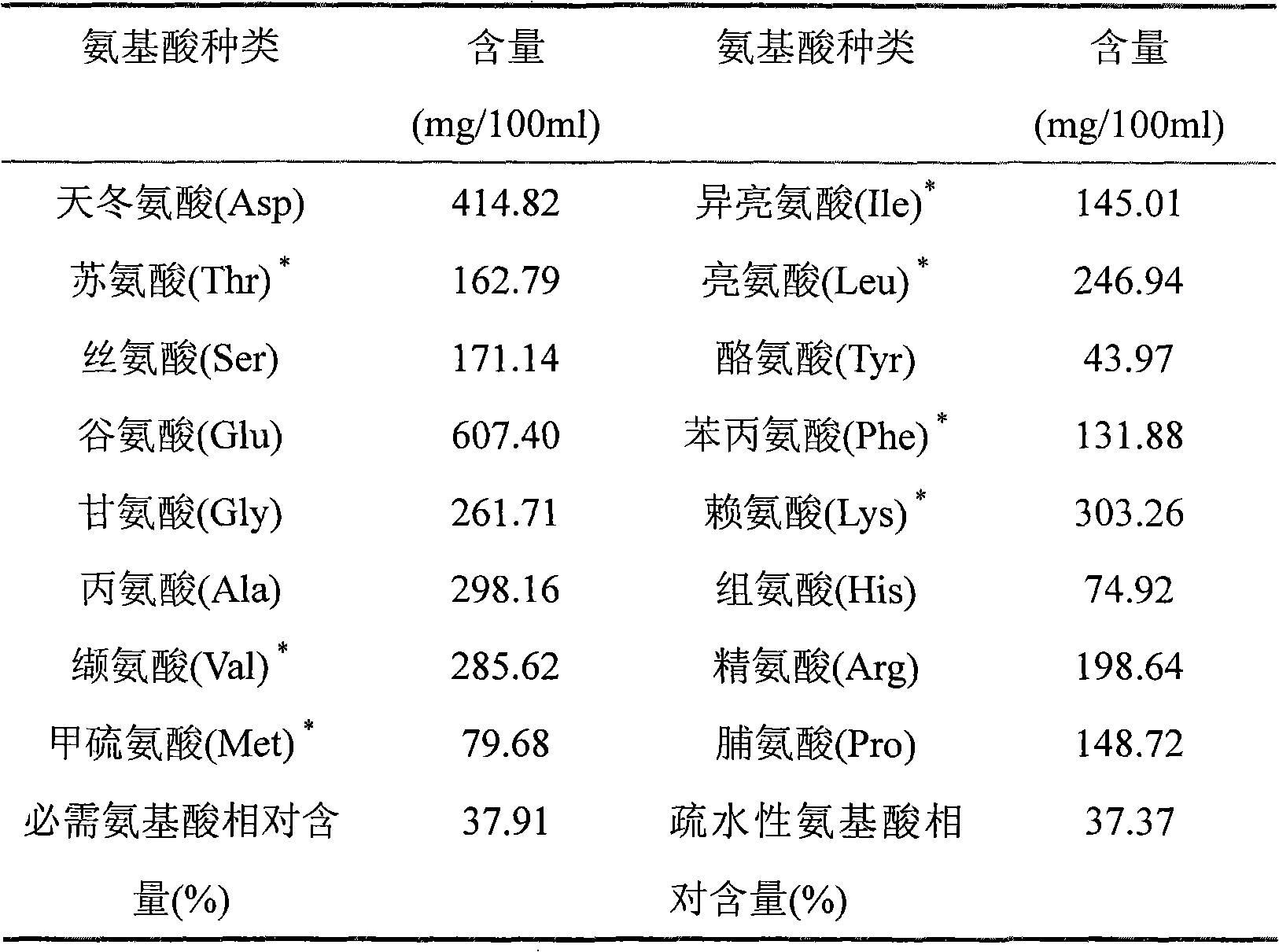
Method for preparing half-fin anchovy antibacterial peptides
The invention relates to a method for preparing half-fin anchovy antibacterial peptides, which comprises the following steps of: homogenating fish into fish paste, adding pepsin into the fish paste according to a ratio of 1,000-1,300U / g under the condition that the pH value is 1.5-2.5, raising the temperature to 35-45DEG C, performing enzymolysis for 2 to 3 hours, heating enzymolysis liquid at the temperature of between 95 and 100DEG C for 5 to 15 minutes for killing enzyme, cooling to the temperature of between 3 and 5DEG C, centrifuging at a rate of 6,000 to 8,000r / min for 5 to 15 minutes, filtering, taking intermediate filtrate, and performing frozen storage or freeze-dried storage at -20DEG C at least. The antibacterial peptides is prepared from a pure natural low-value marine product, namely half-fin anchovy; the half-fin anchovy antibacterial peptides are rich in amino acid necessary for human bodies, and have stable physical and chemical properties; the antibacterial peptides prepared from food-derived protein through enzymolysis have high safety, good absorptivity and good antibacterial effect, and can serve as a nutritional and functional additive in foods or is developed into drug resistant bacteria antibiotics. The preparation method is simple, economic and easy to operate, can be carried out in a common laboratory, and is suitable for industrial expanded production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Reduction of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
InactiveUS20090263416A1Reduce resistanceReduce presenceAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiotechnology
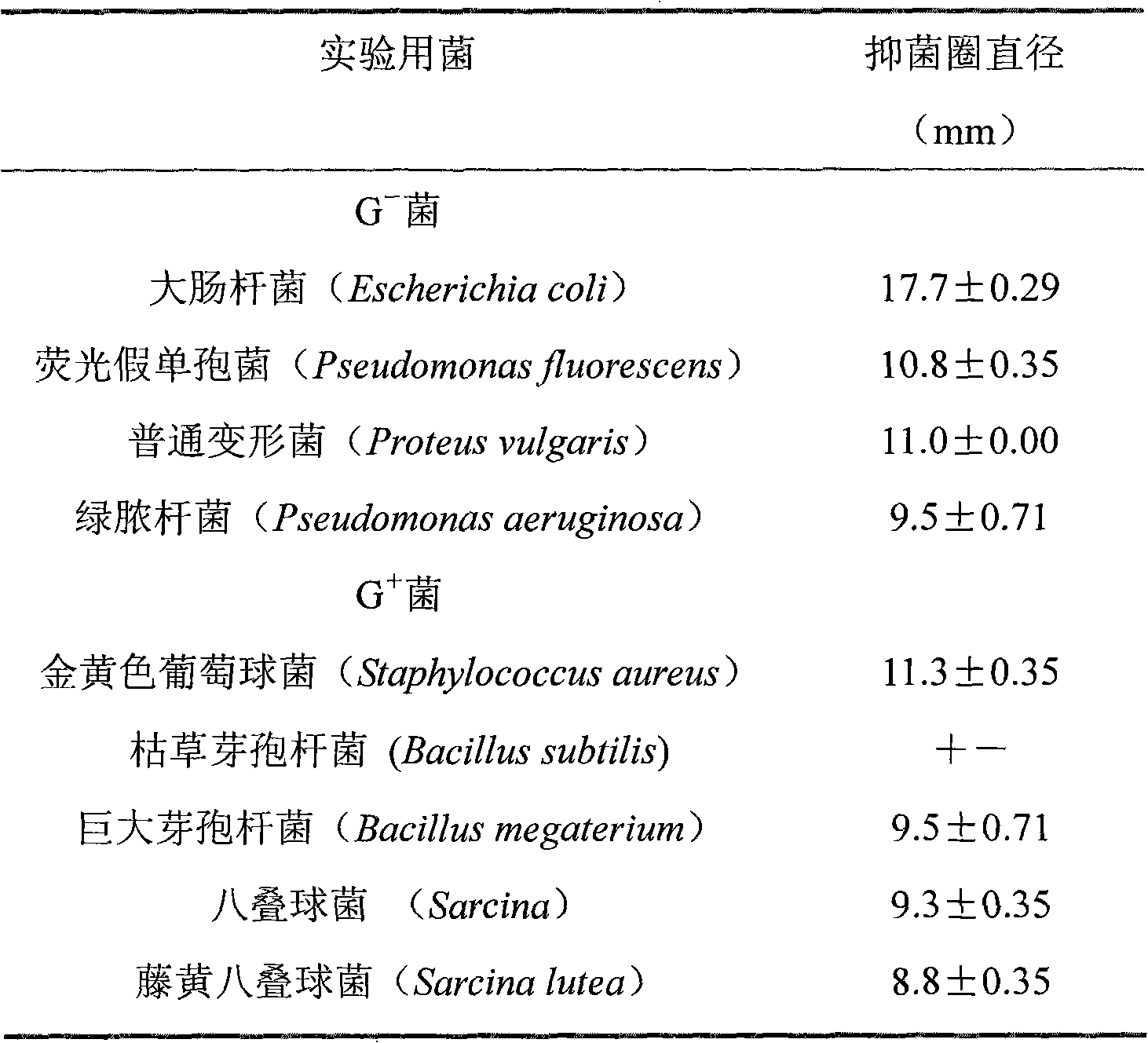
In one aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for reducing or eliminating antibiotic resistance in bacteria, comprising exposing the bacteria to a composition comprising a yeast cell wall preparation in an amount effective for reducing or eliminating resistance of the bacteria to at least one antibiotic. In one embodiment, the method comprises exposing the bacteria to the yeast cell wall preparation in an amount effective for eliminating a plasmid conferring resistance to the antibiotic, or for preventing transfer of the plasmid between bacteria. In another aspect, a method is provided for reducing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in an animal, comprising administering to the animal a composition comprising a yeast cell wall preparation in an amount effective for reducing or eliminating the presence of an antibiotic-resistant bacterial population in the animal.
Owner:ALLTECH CO LTD +1
Azaphilones compounds in marine fungus HK1-6 and application of azaphilones compounds as MRSA-resistant drug
ActiveCN108101878AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaSecondary metabolite
The invention relates to azaphilones compounds in marine fungus HK1-6 and an application of the azaphilones compounds as an MRSA-resistant drug, in particular to secondary metabolites 1-4 produced bymarine fungus Penicillium sp.HK1-6 or pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The compounds 1-4 show very high antibacterial activity for MRSA (such as S. aureus ATCC4330 and S. aureus ATCC33591) and VER (such as E. faecalis ATCC51299), MIC is smaller than or equal to 12.5 mu g / mL, the MIC of a compound 2 for E. faecalis ATCC51299 is one times higher than that of positive drug vancomycin, and the compounds have good prospects to be developed into drugs resisting drug-resistant bacteria, lead compounds of drugs and candidate drugs.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Fluorescent probe for carbapenem type antibioticbacteria and synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN106279178AHigh selectivityReduce usage costsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCarbamateSynthesis methods
The invention provides a structural general formula (shown in the description) of a fluorescent probe for carbapenem type antibiotic bacteria. In the structural general formula, X represents carbon atoms or sulfur atoms; when the X represents CH, R1 represents methyl and can be of the configuration S or R, or the X represents CH2 or S; Y represents oxygen atoms, sulfur atoms or linkers on a fluorophorearomatic nucleus and comprises 4-hydroxymethylbenzyl or 4-hydroxyl or sulfydrylbenzyl or carbamate linkers. The synthesis method of the fluorescent probe comprises the following steps that 1, a compound 2 is prepared; 2, intermediates 3 and 4 are prepared; 3, a compound 5 is prepared; 4, a compound 6 is prepared; 5, a compound 7 is prepared; 6, a compound 8 is prepared; 7, a compound 9 is prepared; 8, a compound 10 is prepared;9, a compound CPC-1, namely a fluorescent probe compound is prepared. The fluorescent probe can be applied to detection of carbapenemases and drug-resistant bacteria containing the carbapenemases and has the important significance on antibiotic abandoning or few antibiotics adopted in medical treatment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Micromolecular substance for improving sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics
ActiveCN102973542AIncreased sensitivityEffective infectionAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsResistant bacteriaMetabolite
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and particularly relates to a new function of micromolecular metabolin, namely glutamine. The micromolecule can improve the sensitivity of bacteria including drug-resistant bacteria to antibiotics so as to solve the problem of drug resistance of bacteria. The micromolecule provided by the invention has better effect and higher safety and operability compared with antibiotic which is applied to the medicament for resisting drug resistance of bacteria at present.
Owner:GUANGDONG LITAI PHARM CO LTD
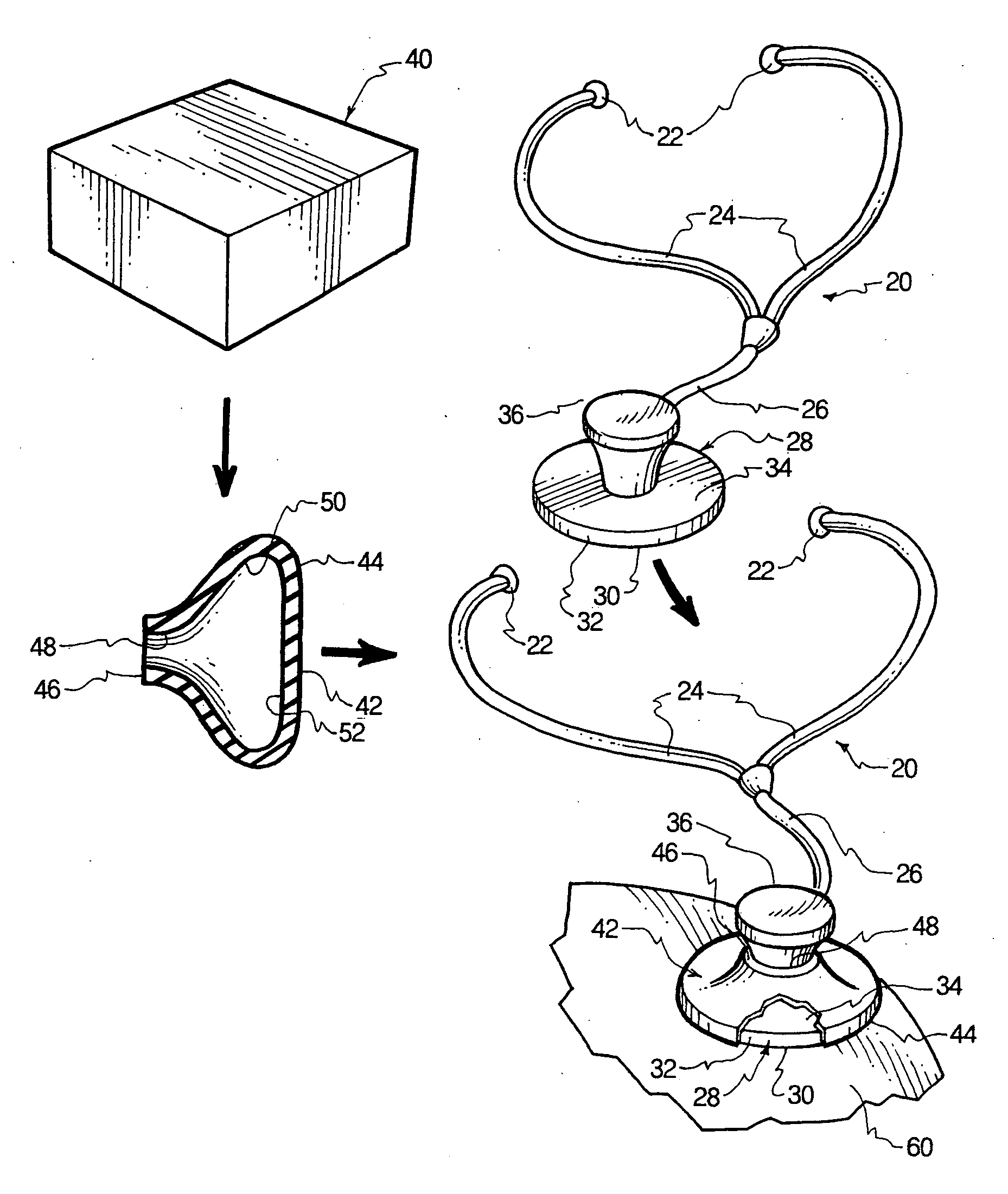
Alleviating stethoscopically-caused contamination
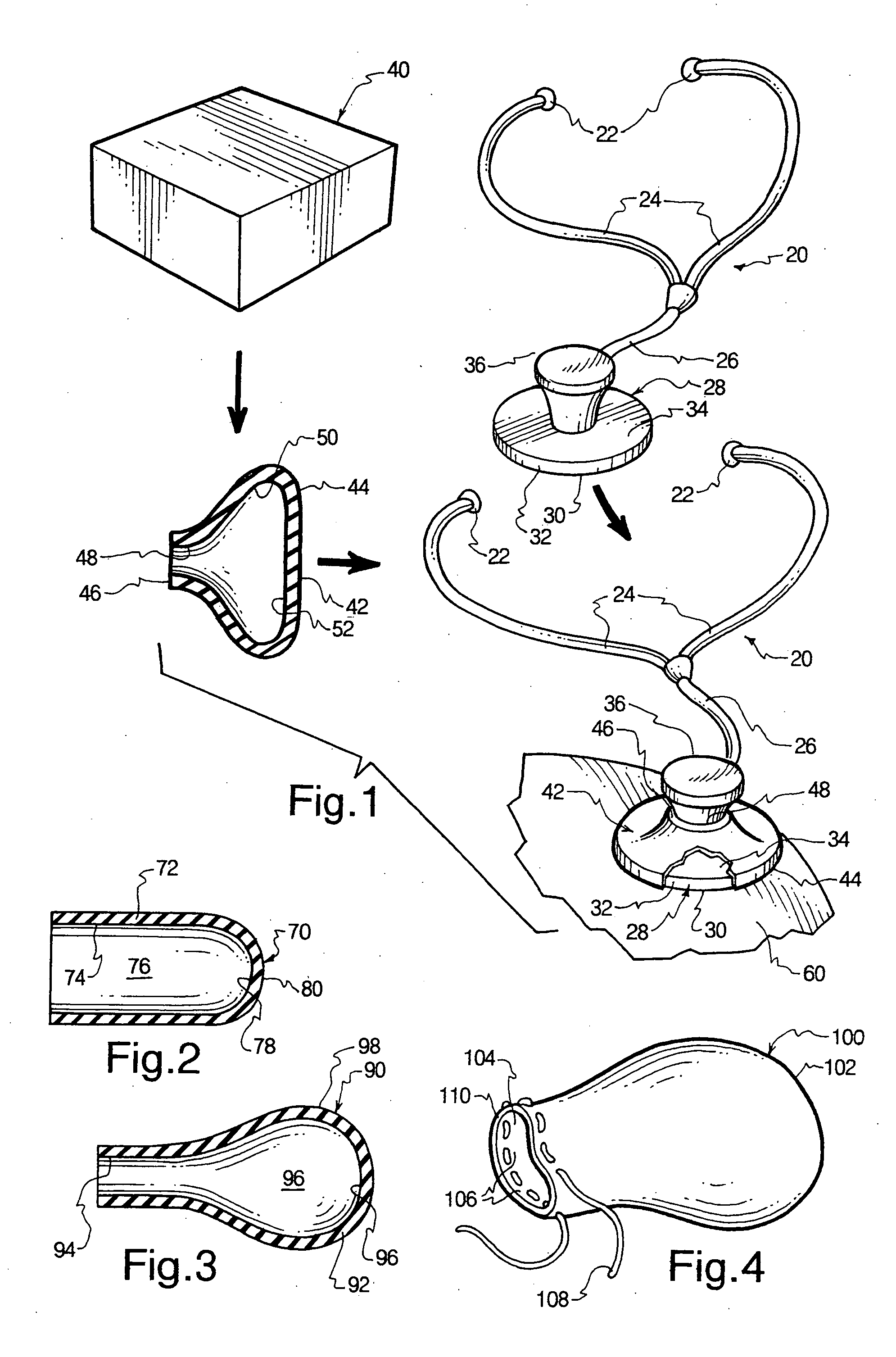
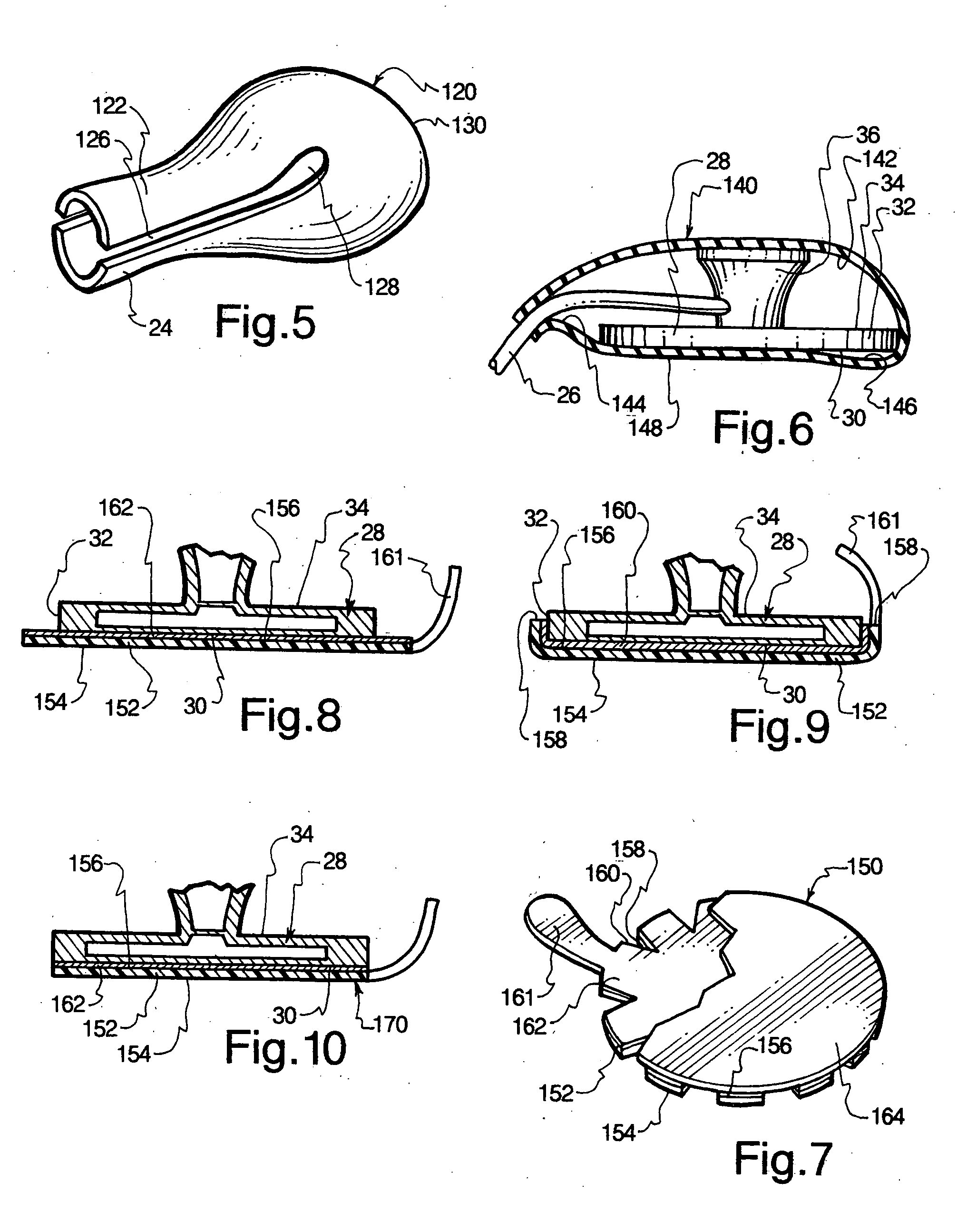
InactiveUS20060076184A1High quality patient dataAlleviating cross bacterialStethoscopeSurgical drapesResistant bacteriaContinuous use
Disposable sterile coverings impervious to bacteria and viruses, and related methods, are disclosed, the coverings temporarily insulating the operative base surface of the diaphragm of a traditional high quality, repeat use stethoscope. Each covering is discarded after a single use, thereby preventing cross bacterial and viral infections, including those caused by highly resistant bacteria, between patients on which the same stethoscope is successively used.
Owner:ROBINSON JEFFREY L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com