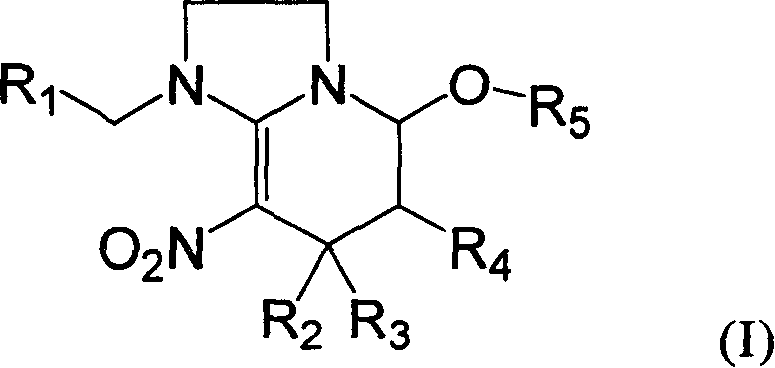
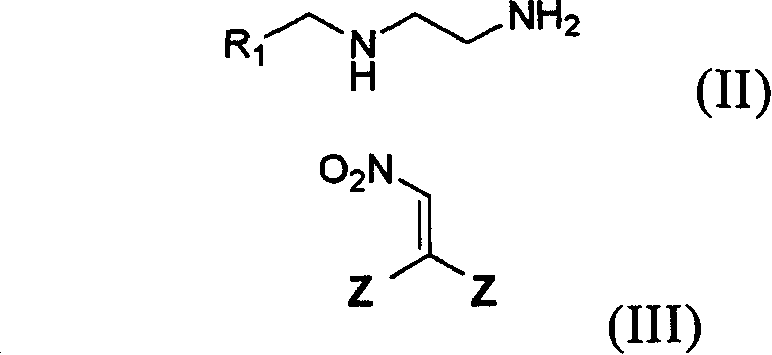
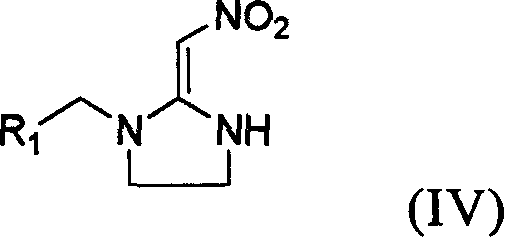
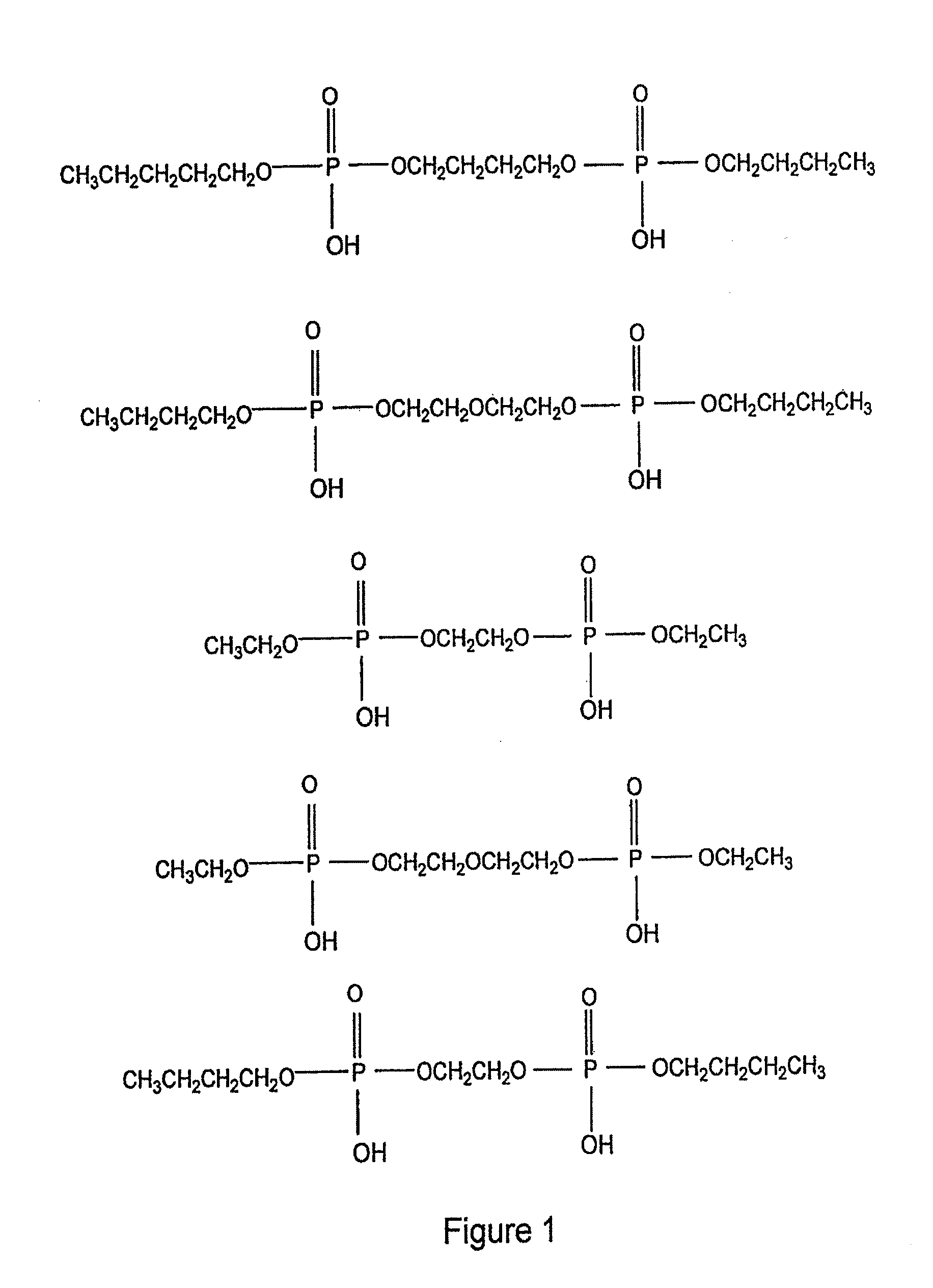
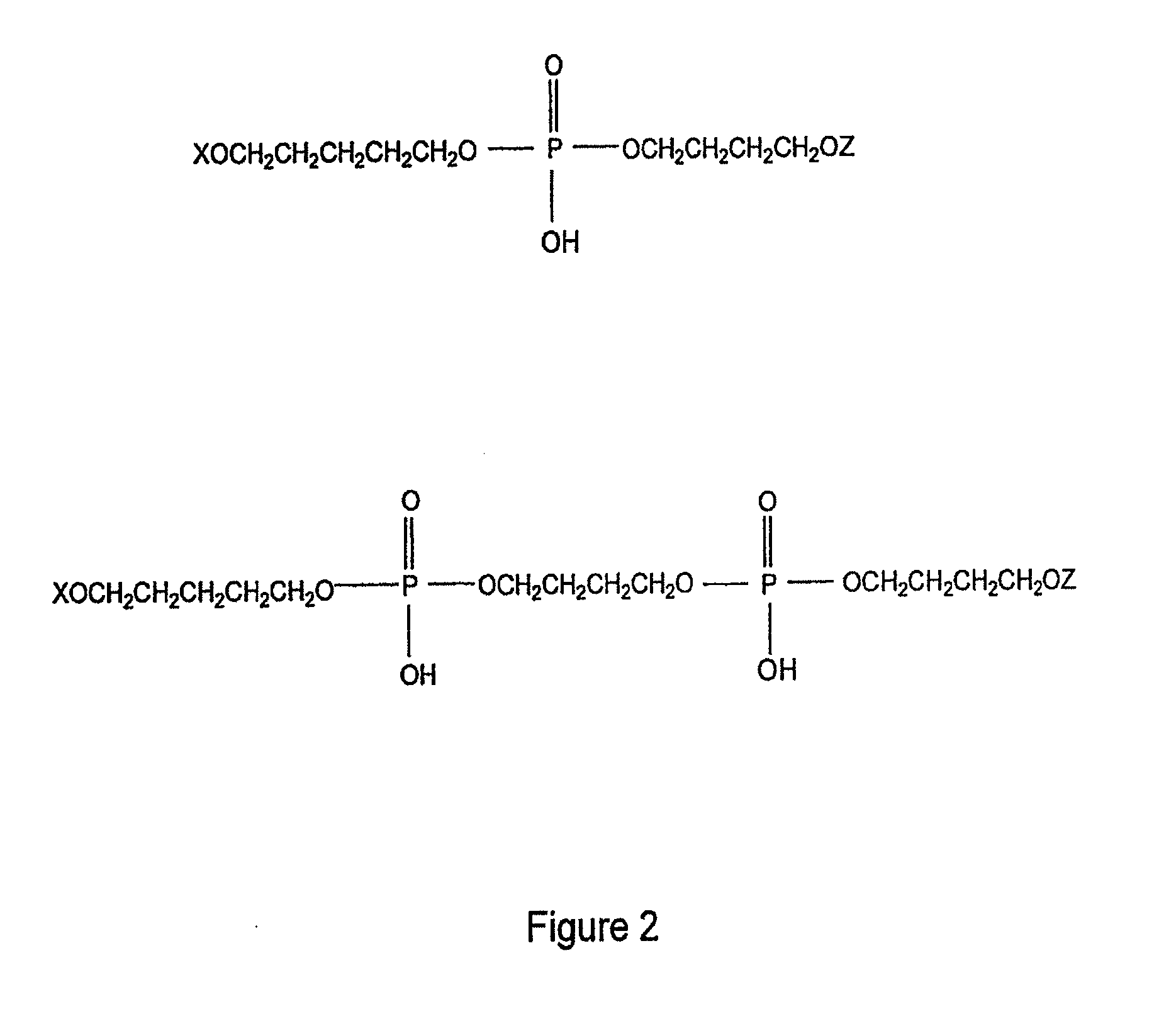
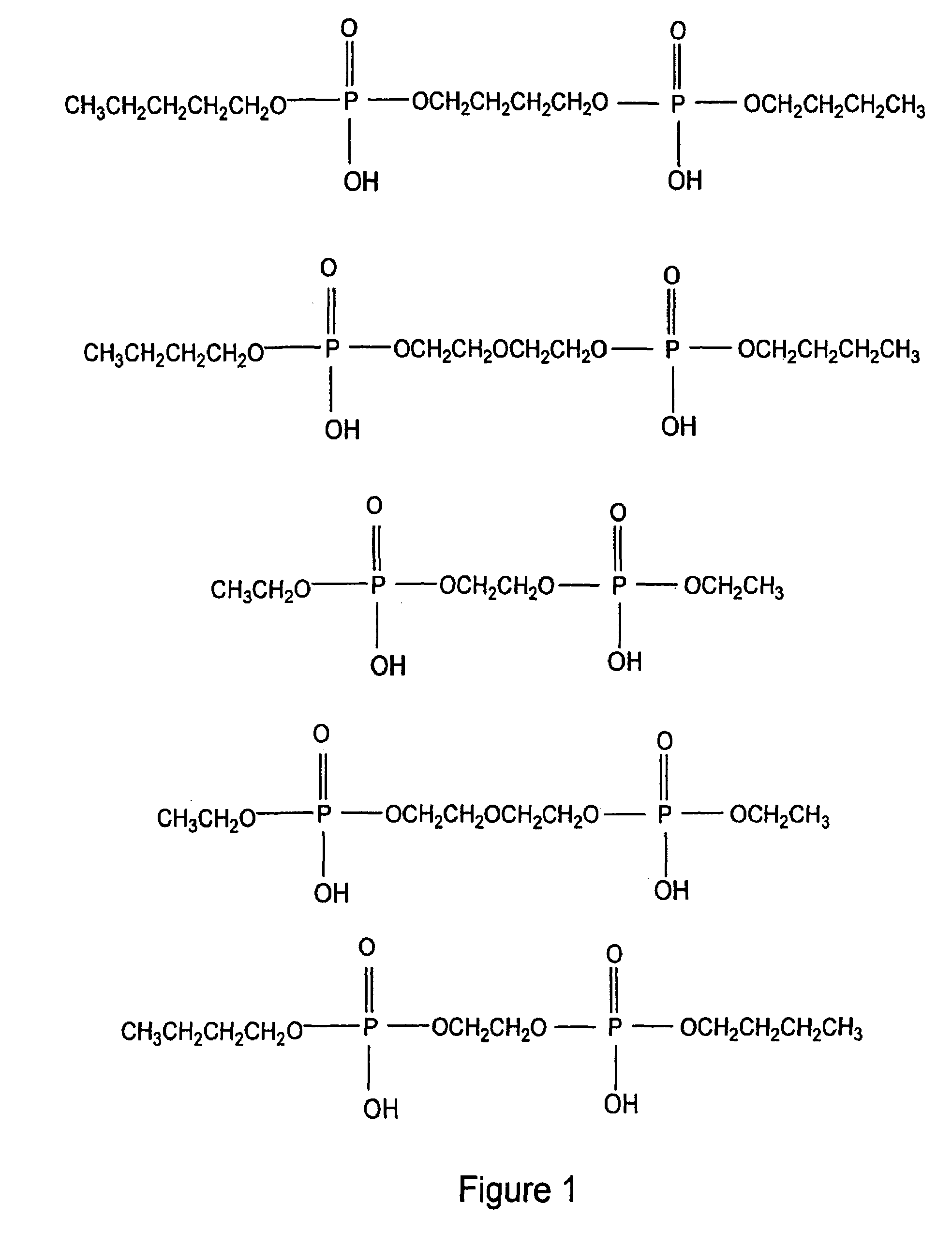
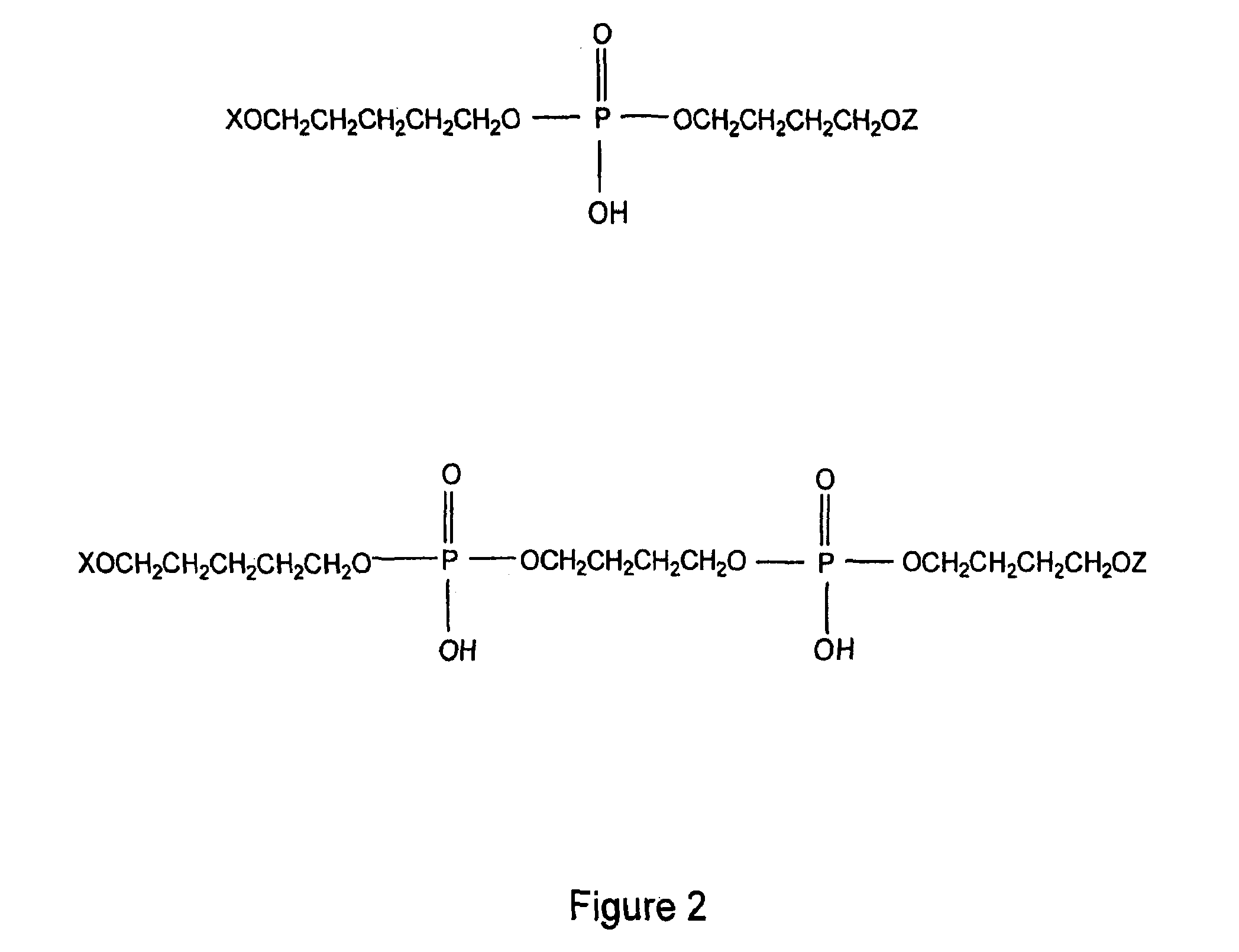
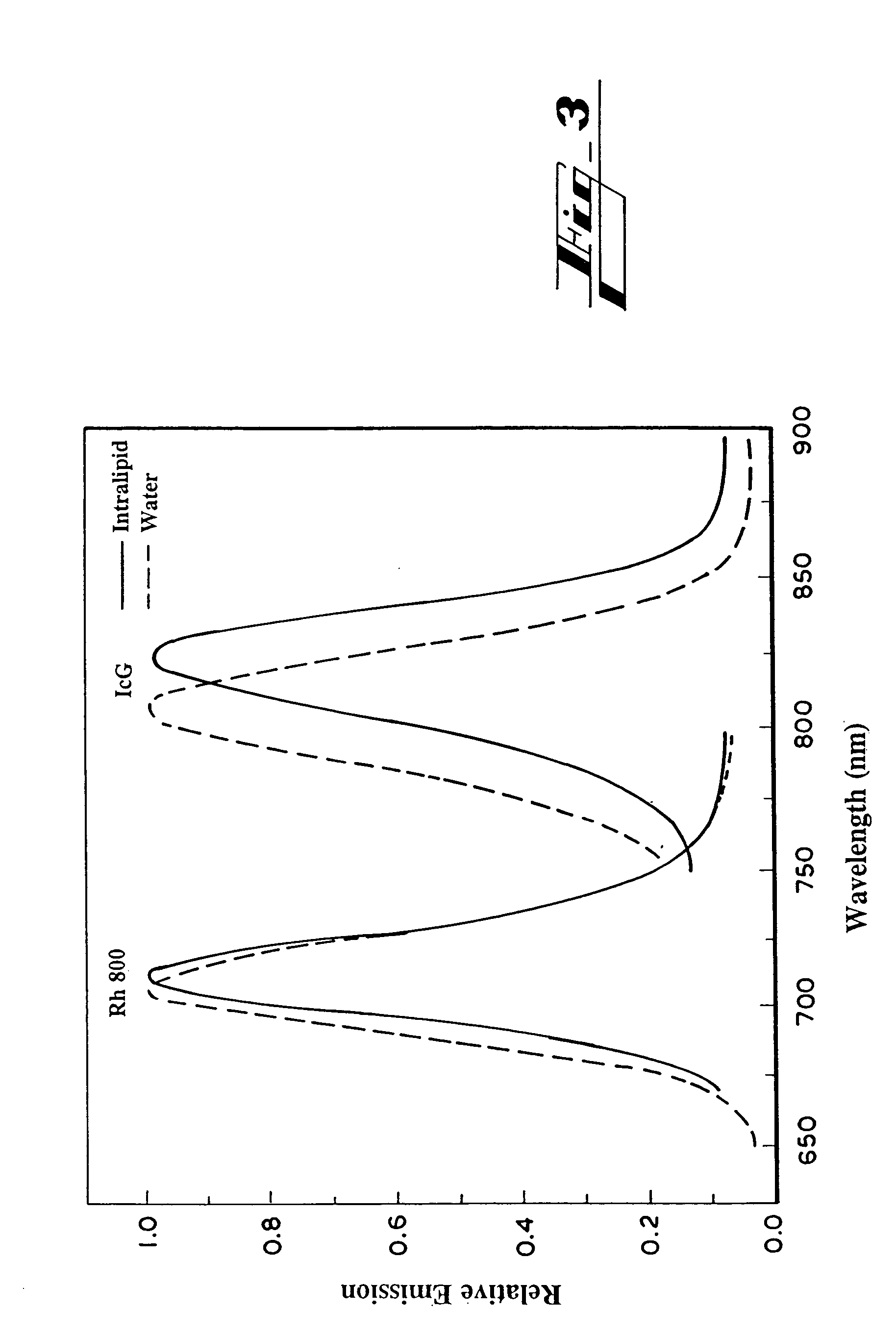
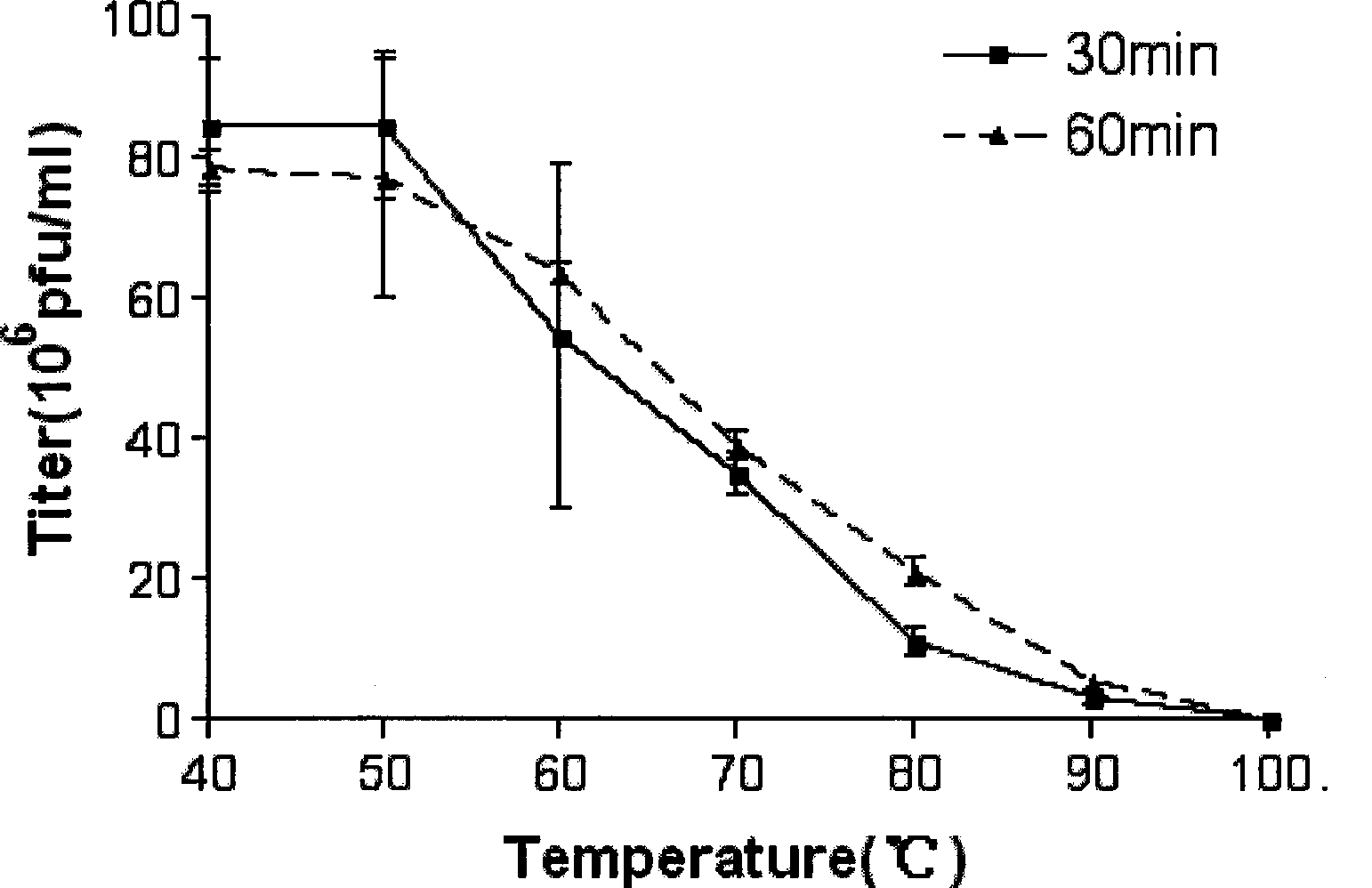
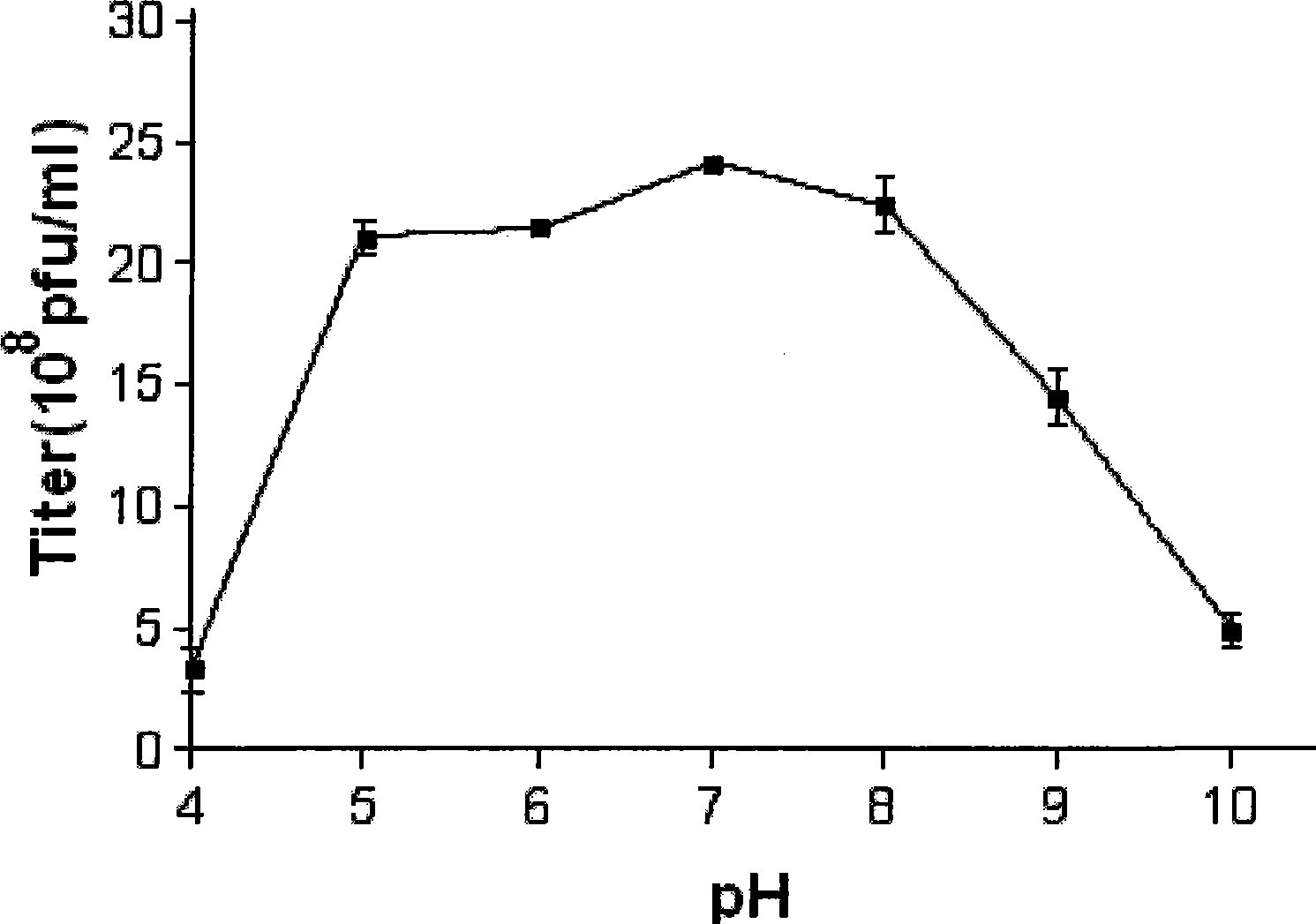
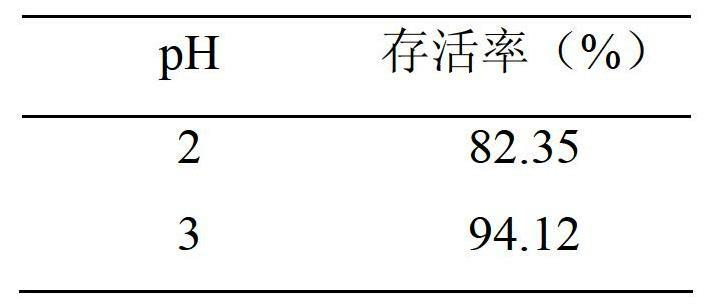
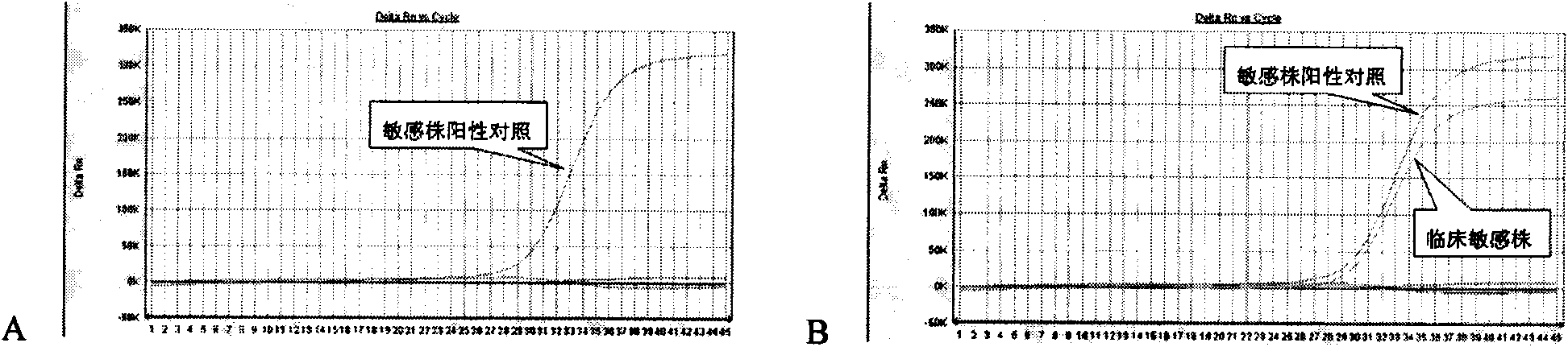
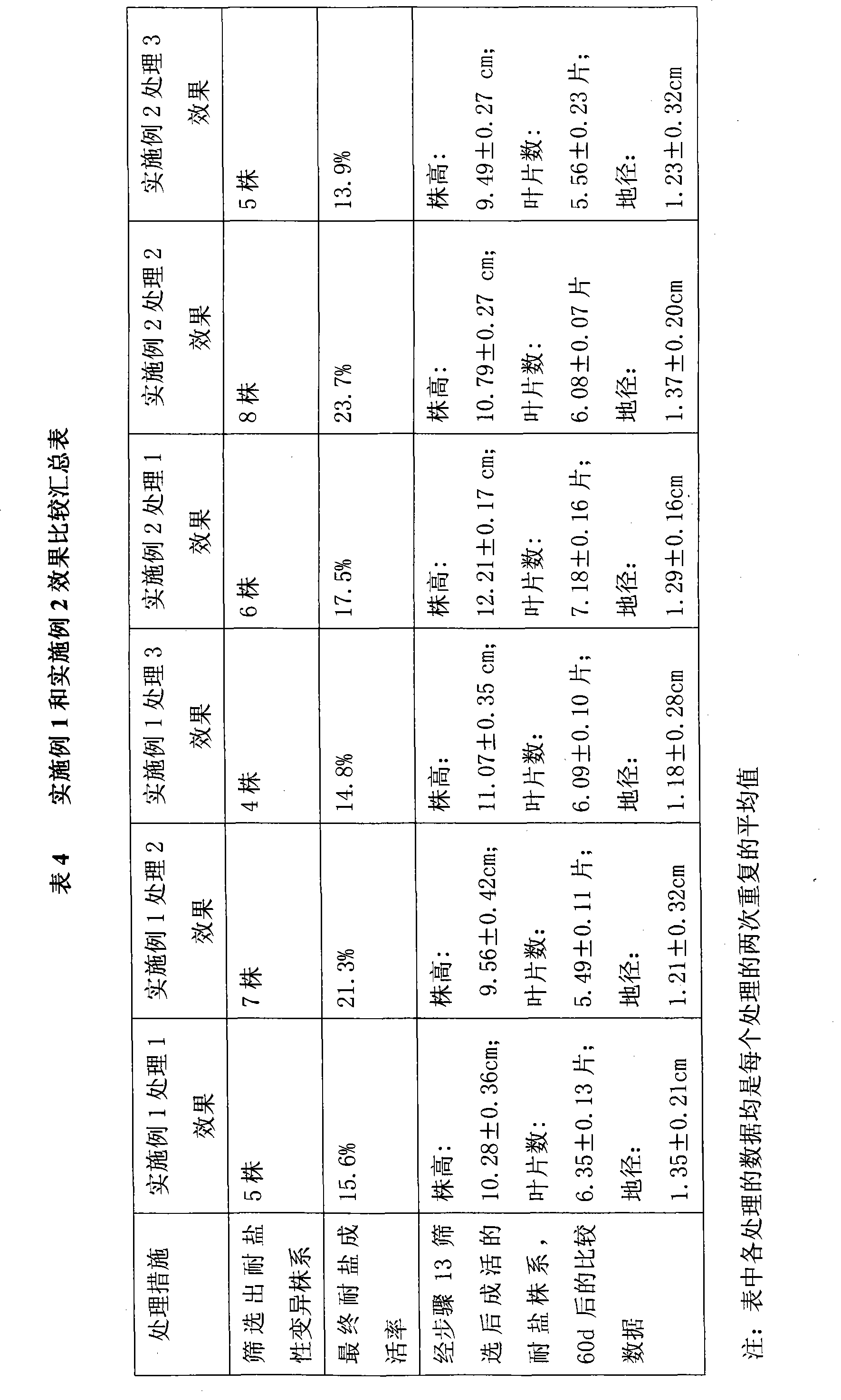
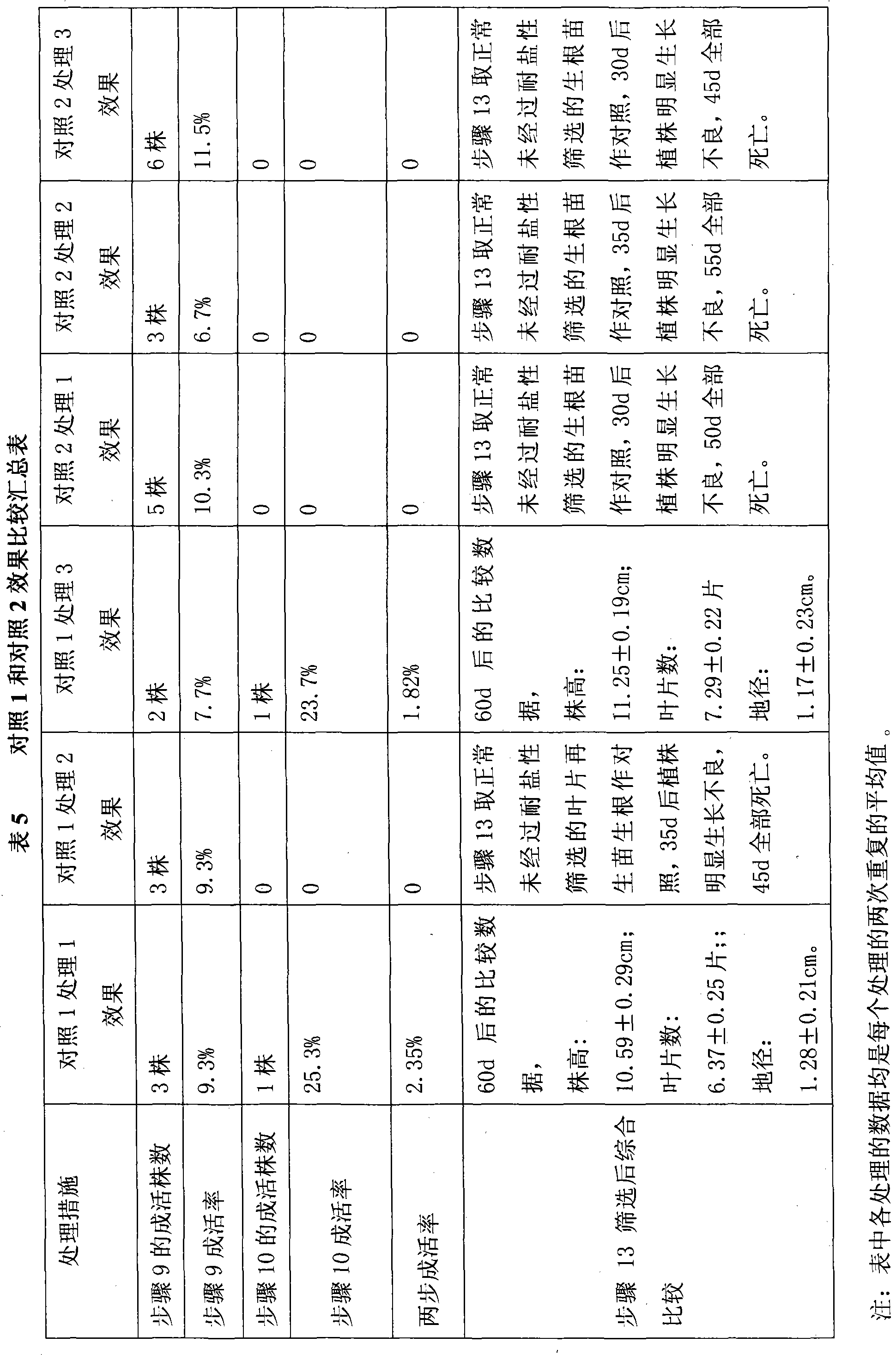
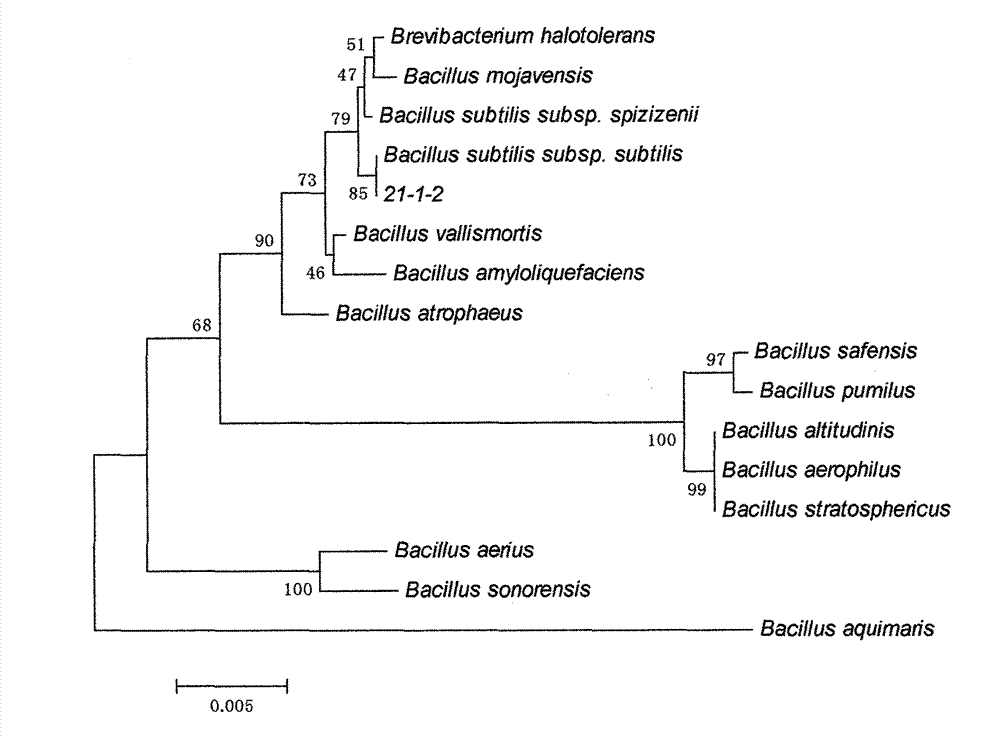
Patents
Literature
443 results about "Resistant strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resistant strain meaning, resistant strain definition | English Cobuild dictionary. resistant. 1 adj Someone who is resistantto something is opposed to it and wants to prevent it. Some people are very resistant to the idea of exercise. 2 adj If something is resistantto a particular thing, it is not harmed by it.
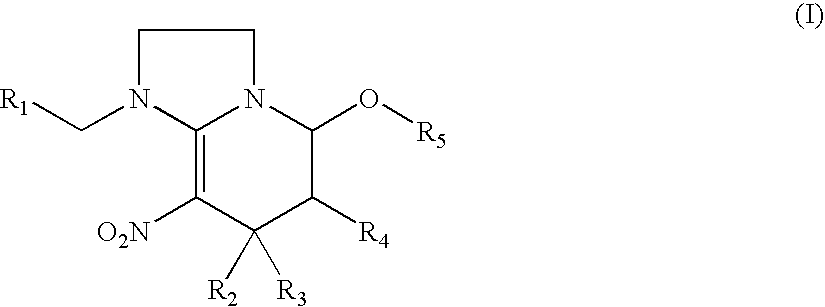
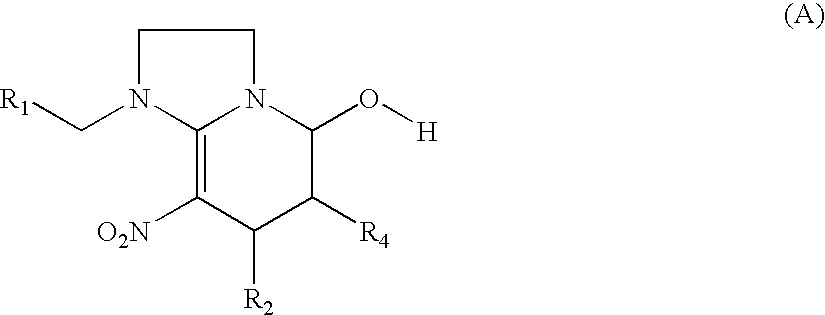
Preparation method and use of compound with high insecticidal activity
This invention relates to a kind of nitryl methylene ramification, and its preparation method and application. Anthelminthic activity test indicate: this ramification has very high insecticidal activity to thorn-suck type, scrape-suck type gnathite pest, such as aphid, leafhopper, planthoppers, thrips, aleyrodids and resistant strain, also possess prevention and cure action to rice water weevil, acarid cochineal spider, hygiene pest and termite.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
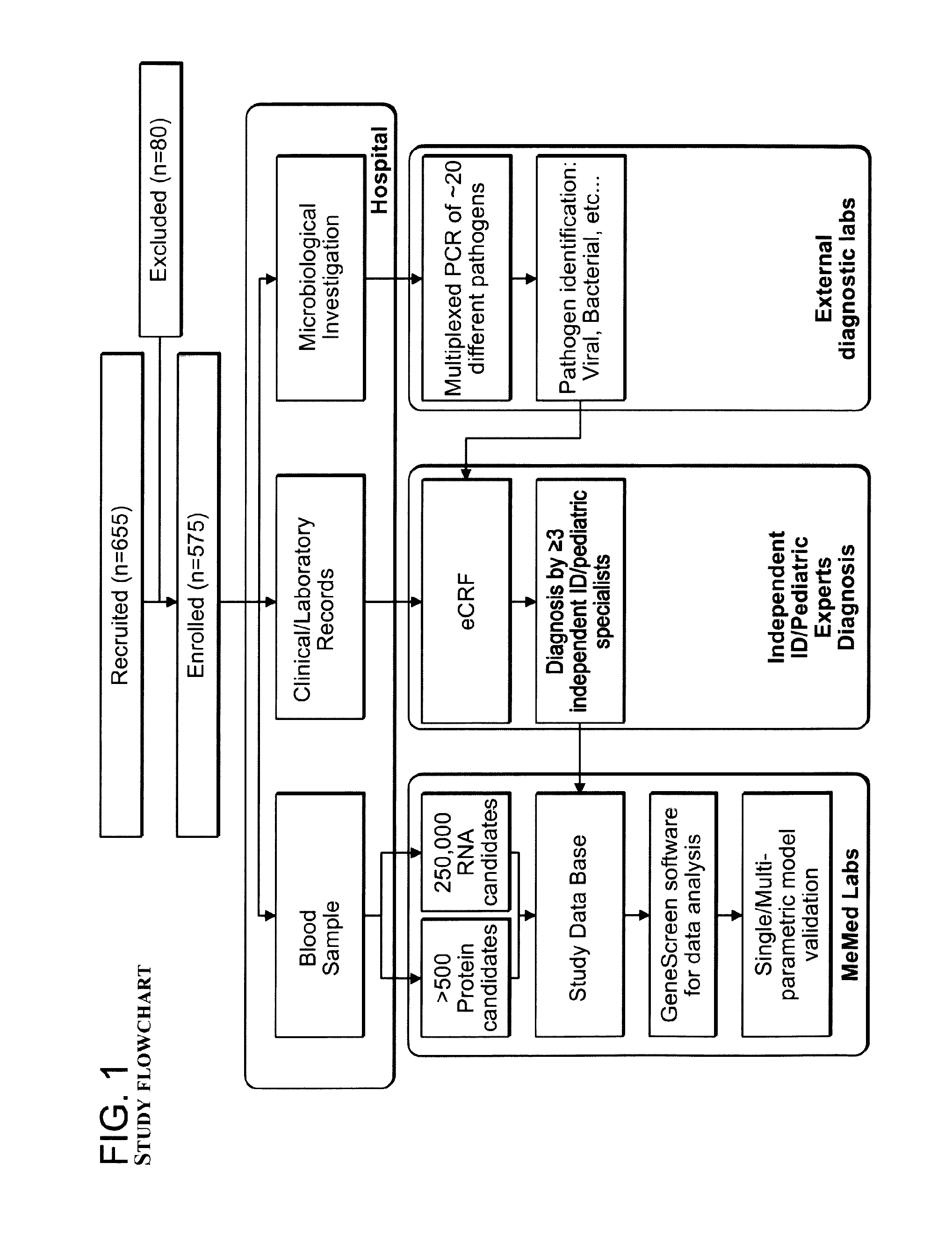
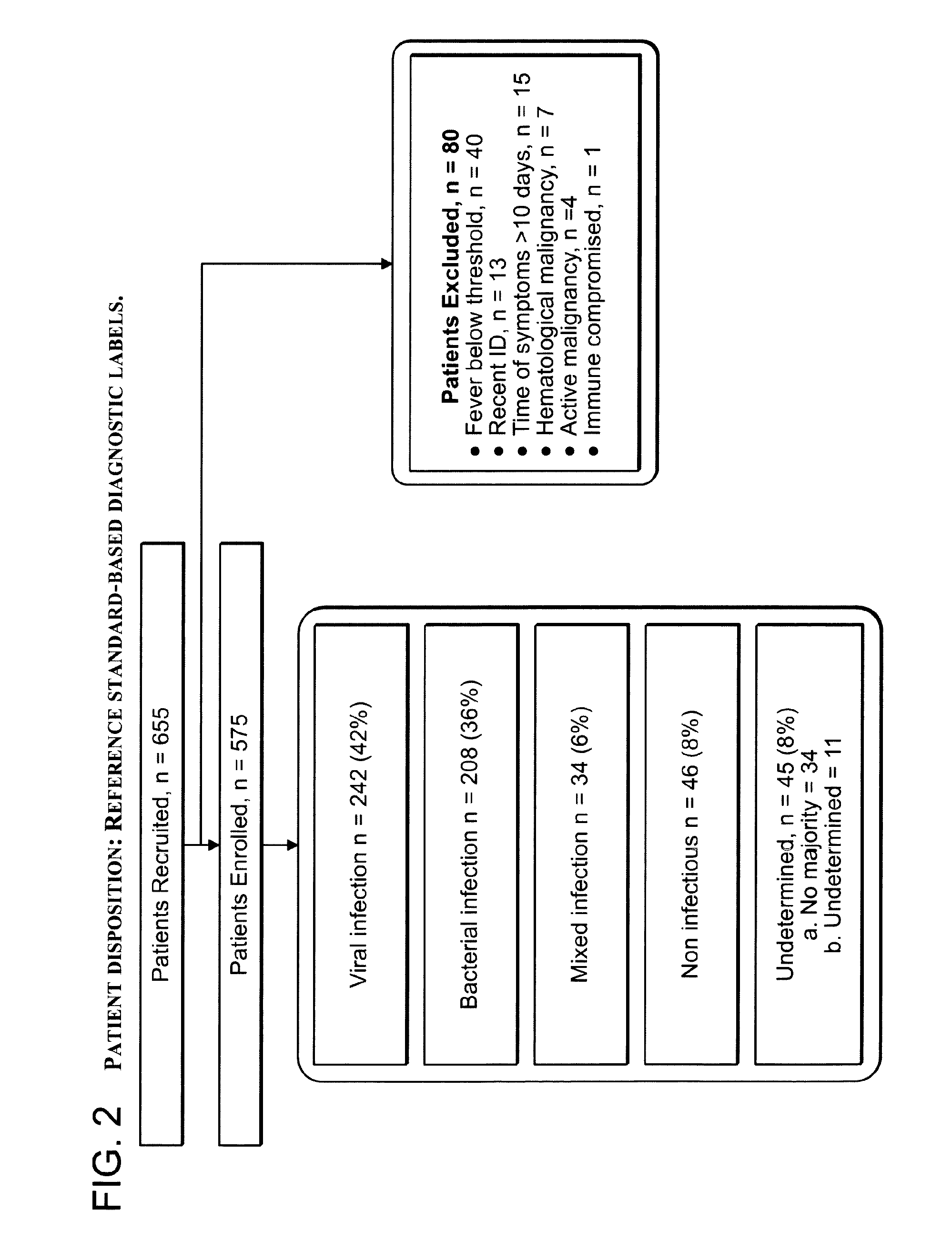
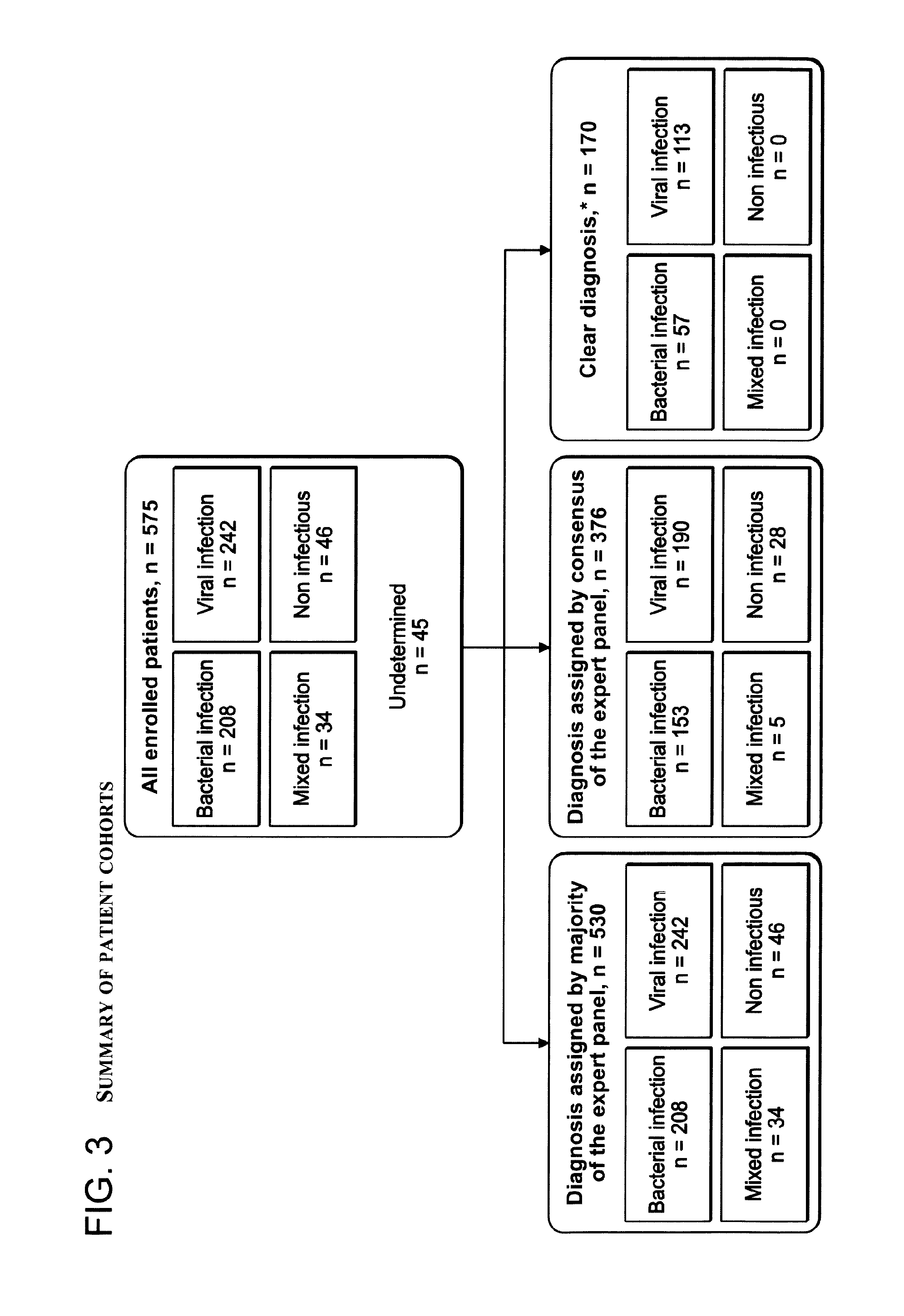
Signatures and determinants for diagnosing infections and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20150017630A1Prevent unnecessary antibiotic treatmentRapid diagnosisElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementPoint of careSide effect
Antibiotics (Abx) are the world's most misused drugs. Antibiotics misuse occurs when the drug is administered in case of a non-bacterial infection (such as a viral infection) for which it is ineffective. Overall, it is estimated that 40-70% of the worldwide Abx courses are mis-prescribed. The financial and health consequences of Abx over-prescription include the direct cost of the drugs, as well as the indirect costs of their side effects, which are estimated at >$15 billion annually. Furthermore, over-prescription directly causes the emergence of Abx-resistant strains of bacteria, which are recognized as one of the major threats to public health today. This generates an immediate need for reliable diagnostics to assist physicians in correct Abx prescription, especially at the point-of-care (POC) where most Abx are prescribed. Accordingly, some aspects of the present invention provide methods using biomarkers for rapidly detecting the source of infection and administrating the appropriate treatment.
Owner:MEMED DIAGNOSTICS
Bacillus belesei BMF 03 and use and fermentation method thereof
A marine-derived Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) BMF 03 having a deposit number of CCTCC NO: 2017374 is disclosed. BMF 03 strain and its aseptic fermentation broth have inhibitory effect onplant pathogenic fungi, including apple rot fungi, grape white rot fungi, mango anthracnose fungi and so on. The aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03 strain can be used as an active ingredient to prepare an antibacterial drug, and the bacteria is selected from the group consisting of Keratinobacteria, Bacillus subtilis and Ralstonia solanacearum. The invention also discloses a fermentation methodof aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03. The invention adopts a plate confrontation method and an Oxford cup method to screen a new marine bacterial strain BMF-03 with strong bacteriostatic effect andwide bacteriostatic spectrum, and adopts strain morphological observation, physiological and biochemical tests and 16S rDNA sequence analysis to determine the species relationship of excellent resistant strains. At that same time, the bacteriostatic substance produce by the strain, the sporulation fermentation medium and the shake flask fermentation conditions were also study, and the promoting effect of the strain fermentation broth and the solid fermentation product on the growth of the cucumber seedling was clarified, which laid a foundation for the application of the strain.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
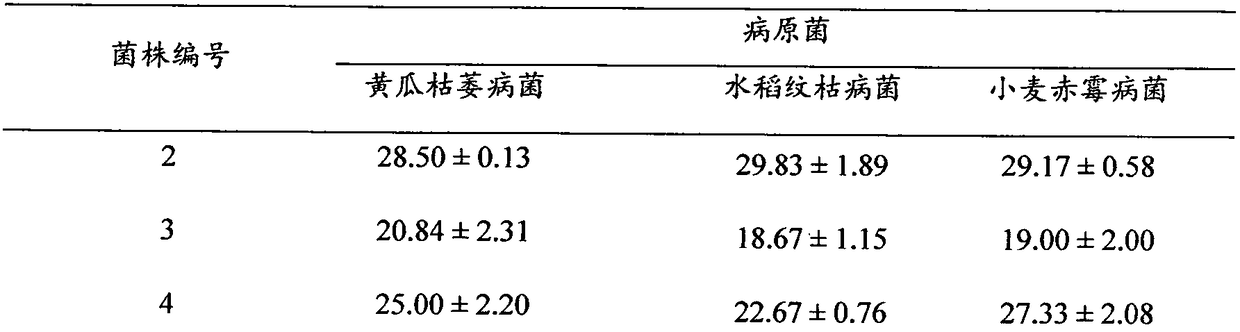
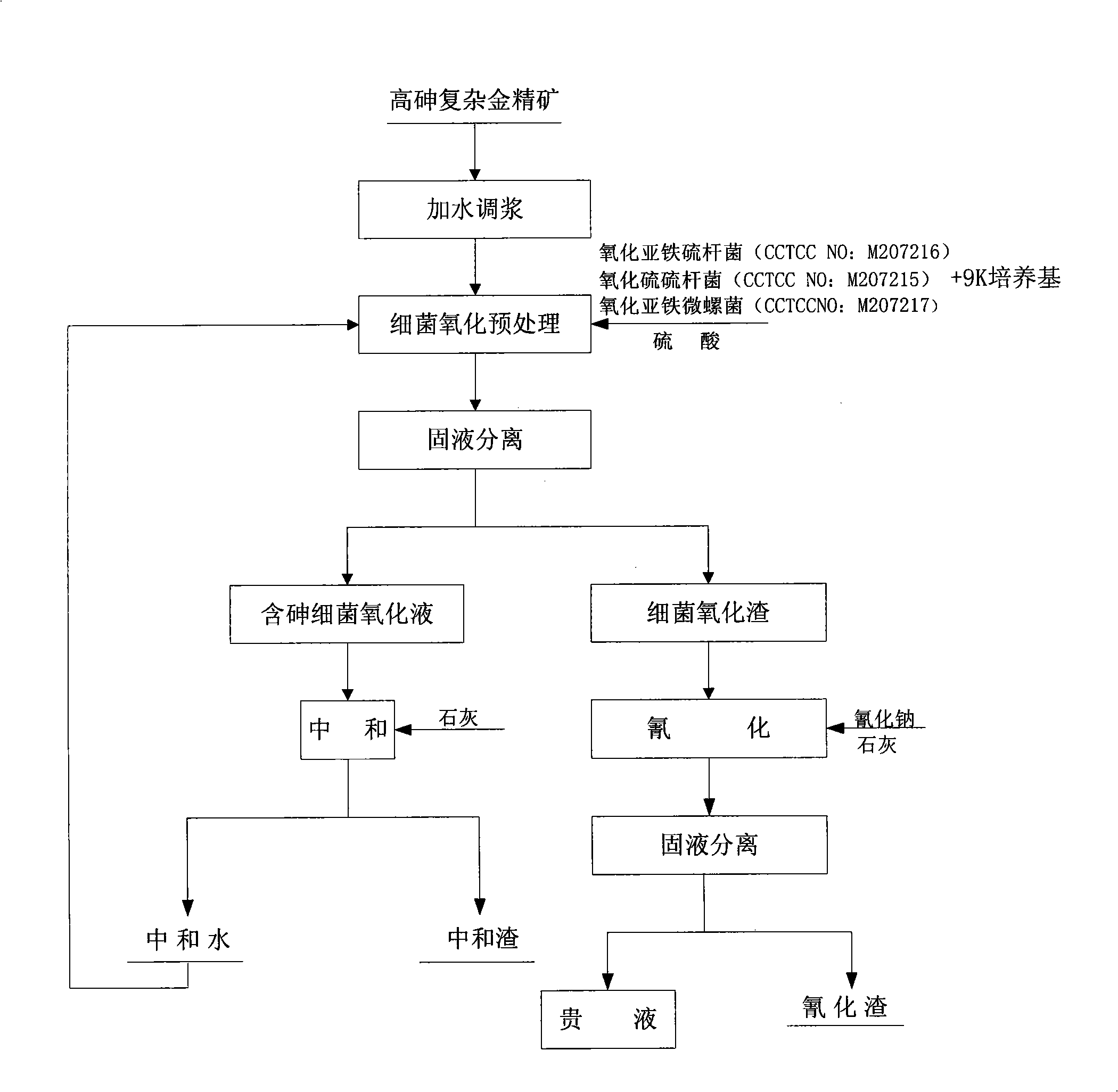
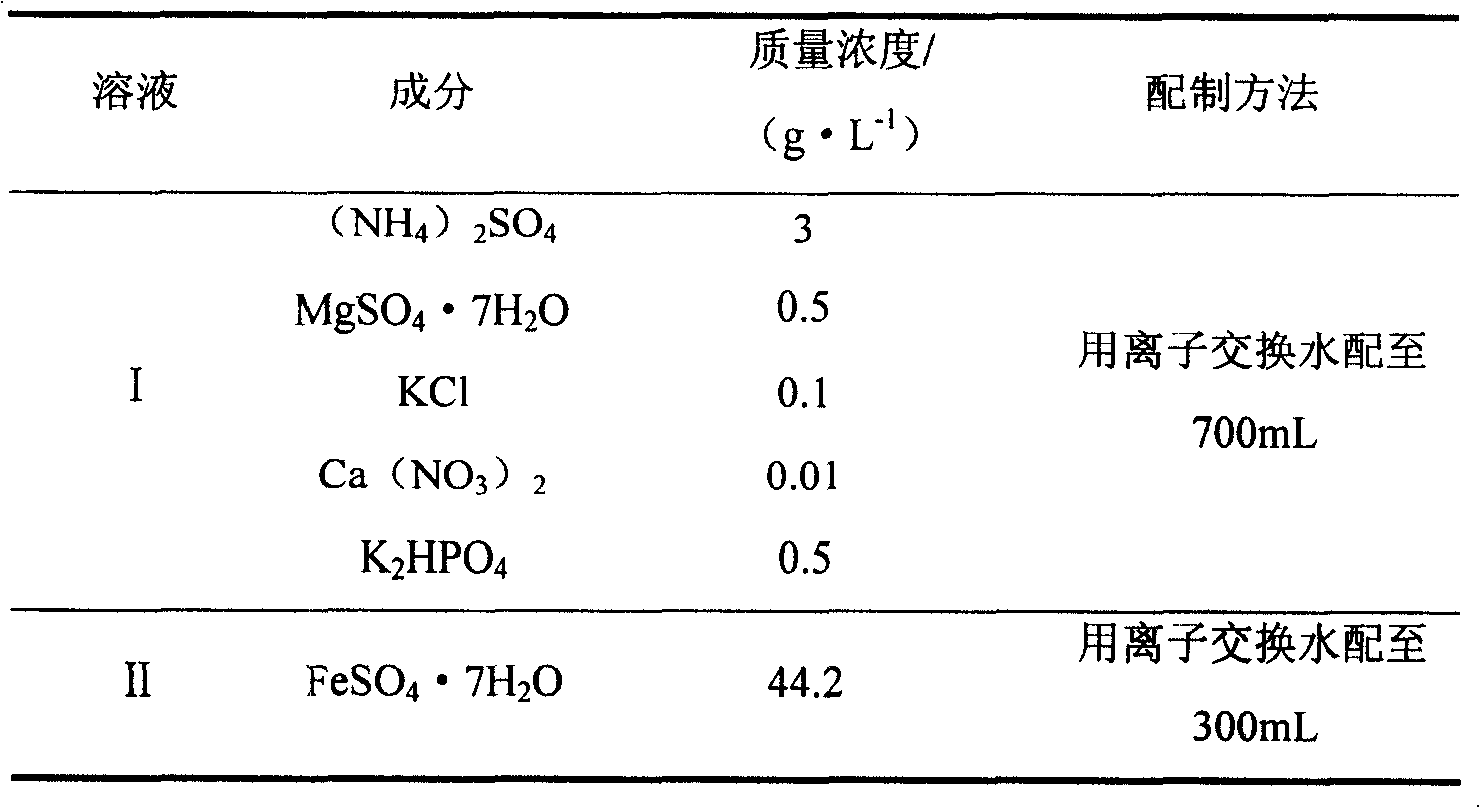
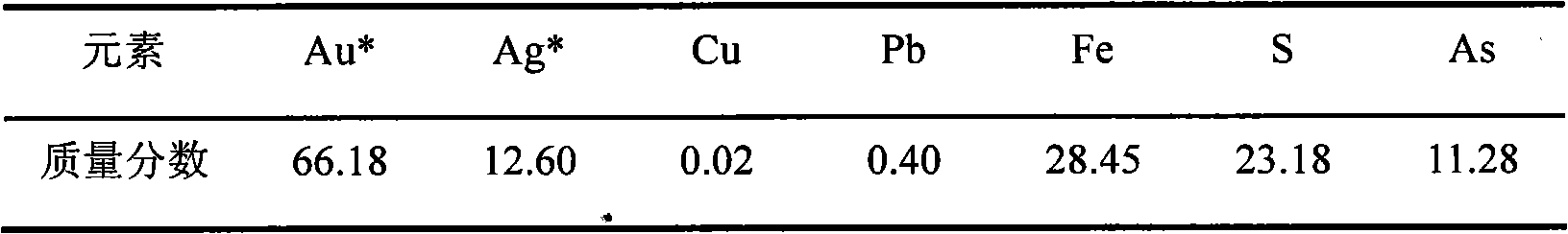
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
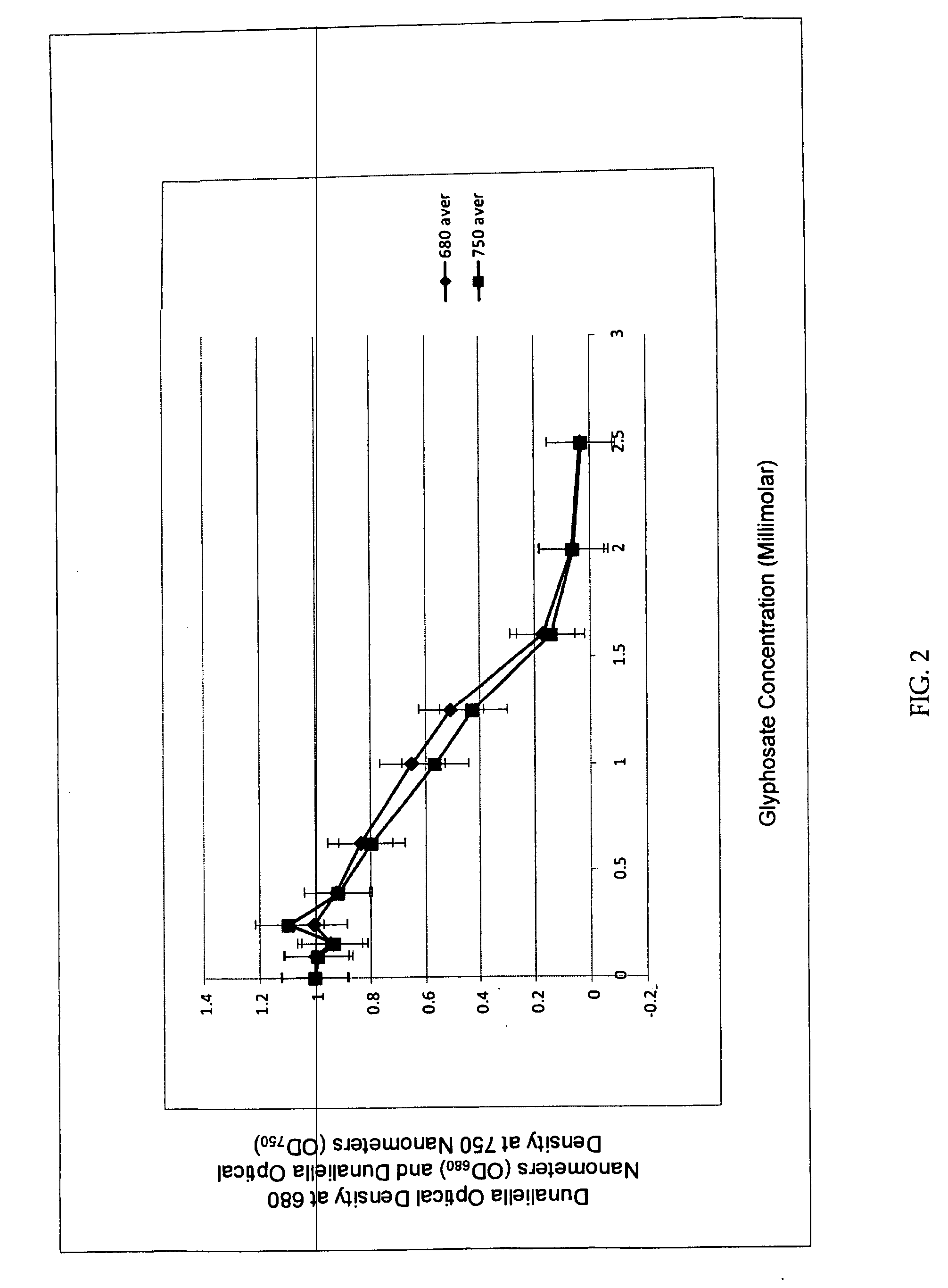
Glyphosate applications in aquaculture
Methods for controlling a density of algae growing in an aquatic environment are provided. Exemplary methods include applying an effective amount of glyphosate to a density of algae growing in an aquatic environment. The algae may include genus Nannochloropsis and / or Dunaliella. The algae may also include a glyphosate resistant strain of genus Nannochloropsis. The effective amount may result in an approximate concentration of between 0.1 millimolar to 0.3 millimolar glyphosate in the aquatic environment. Additionally, the aquatic environment may include seawater. The glyphosate may be applied to the aquatic environment before and / or after the aquatic environment is inoculated with algae. Alternative methods include applying an effective amount of glufosinate to a density of algae growing in an aquatic environment.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Antimicrobial and Antiviral Compounds and Methods for Their Use
The present invention provides protonated compounds having antiviral and antimicrobial activity. The invention also provides antimicrobial compositions comprising protonated compounds of the invention. The protonated compounds of the invention provide efficacious antimicrobial activity against resistant strains of bacteria and opportunistic fungi. The invention also provides antiviral compositions comprising compounds of the invention. Viruses that may be treated by compositions of the invention include, but are not limited to, HIV, HSV, CMV, HBV, HCV and influenza virus.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
Antimicrobial and antiviral compounds and methods for their use
The present invention provides protonated compounds having antiviral and antimicrobial activity. The invention also provides antimicrobial compositions comprising protonated compounds of the invention. The protonated compounds of the invention provide efficacious antimicrobial activity against resistant strains of bacteria and opportunistic fungi. The invention also provides antiviral compositions comprising compounds of the invention. Viruses that may be treated by compositions of the invention include, but are not limited to, HIV, HSV, CMV, HBV, HCV and influenza virus.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
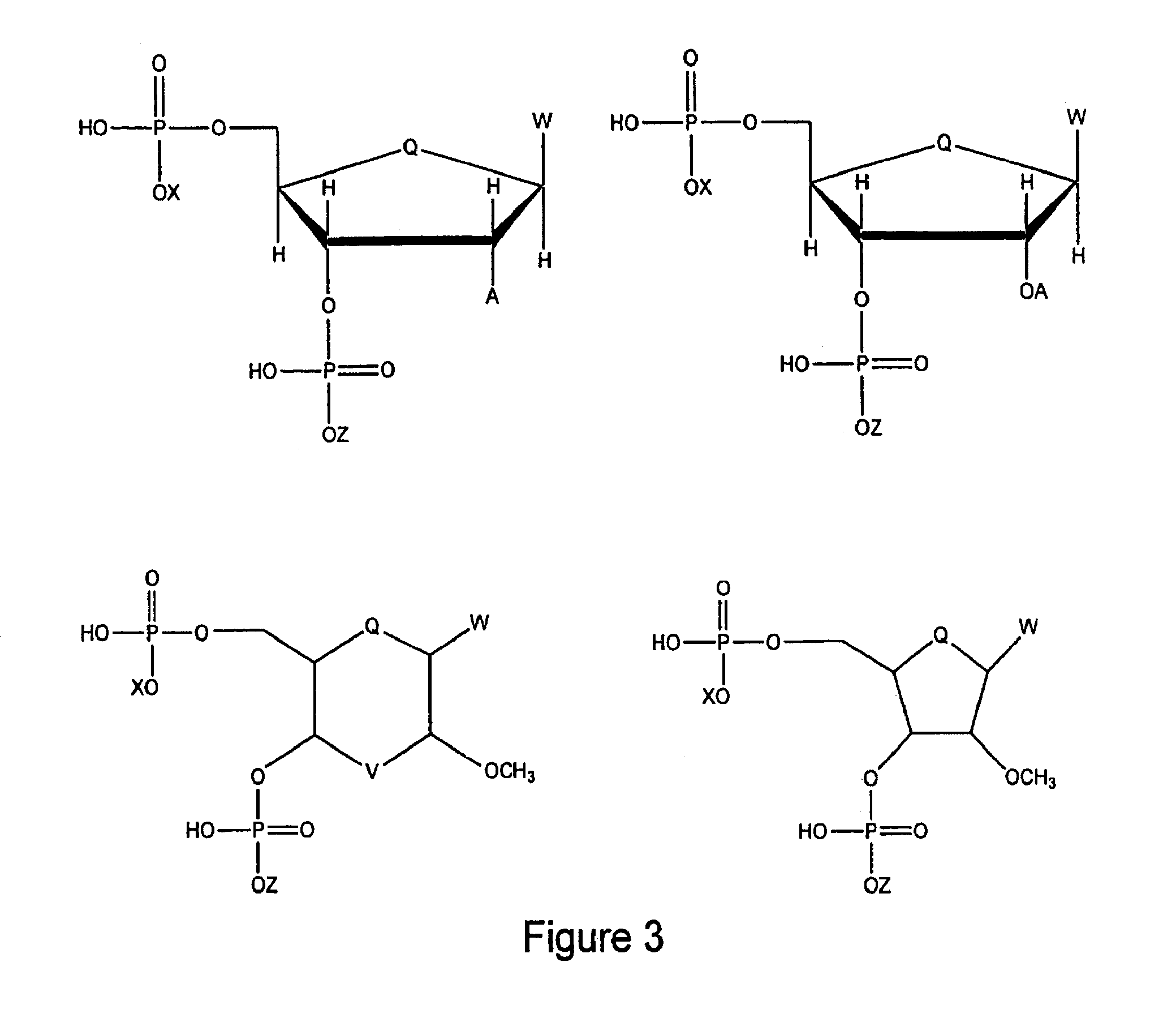
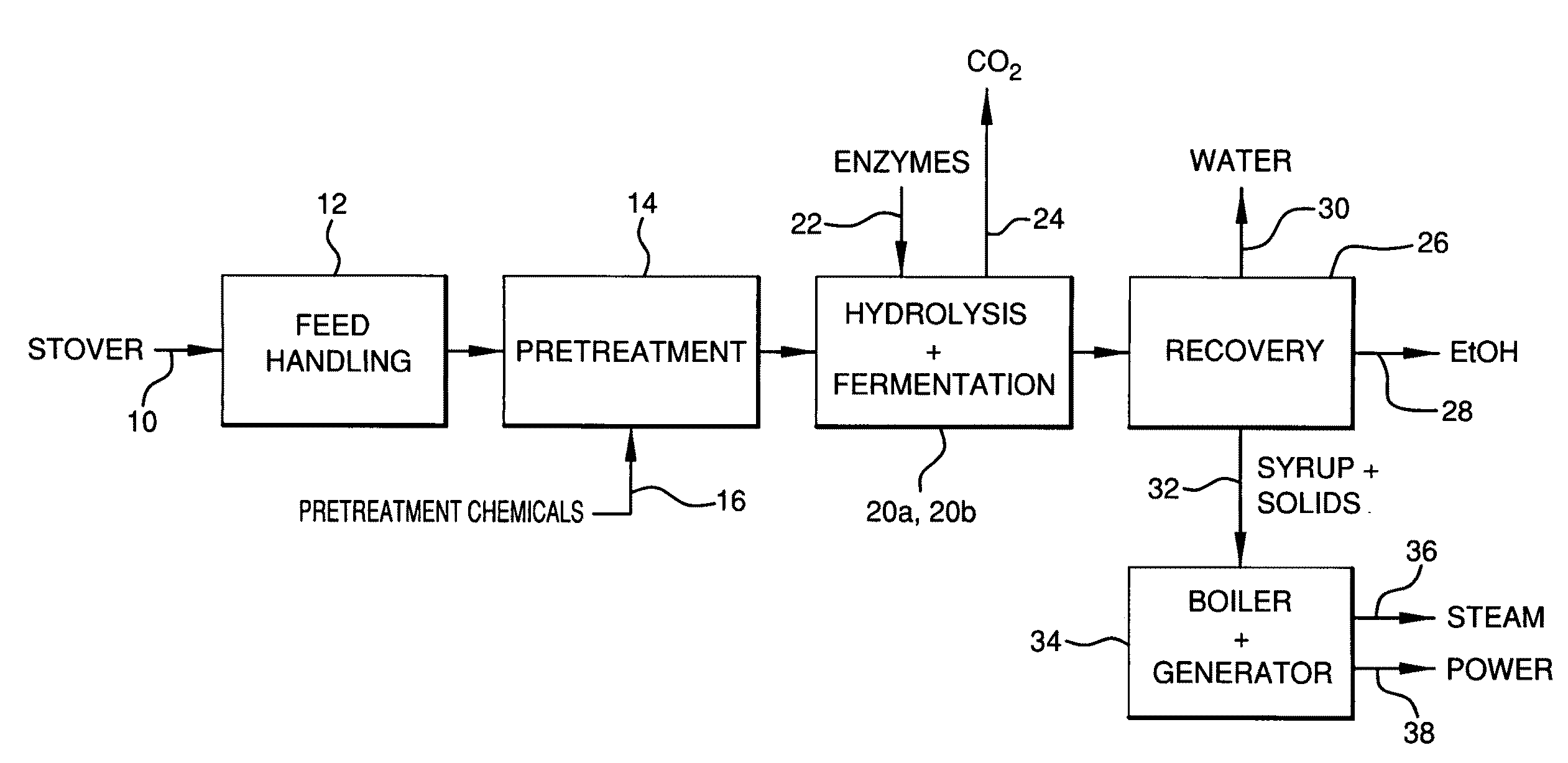
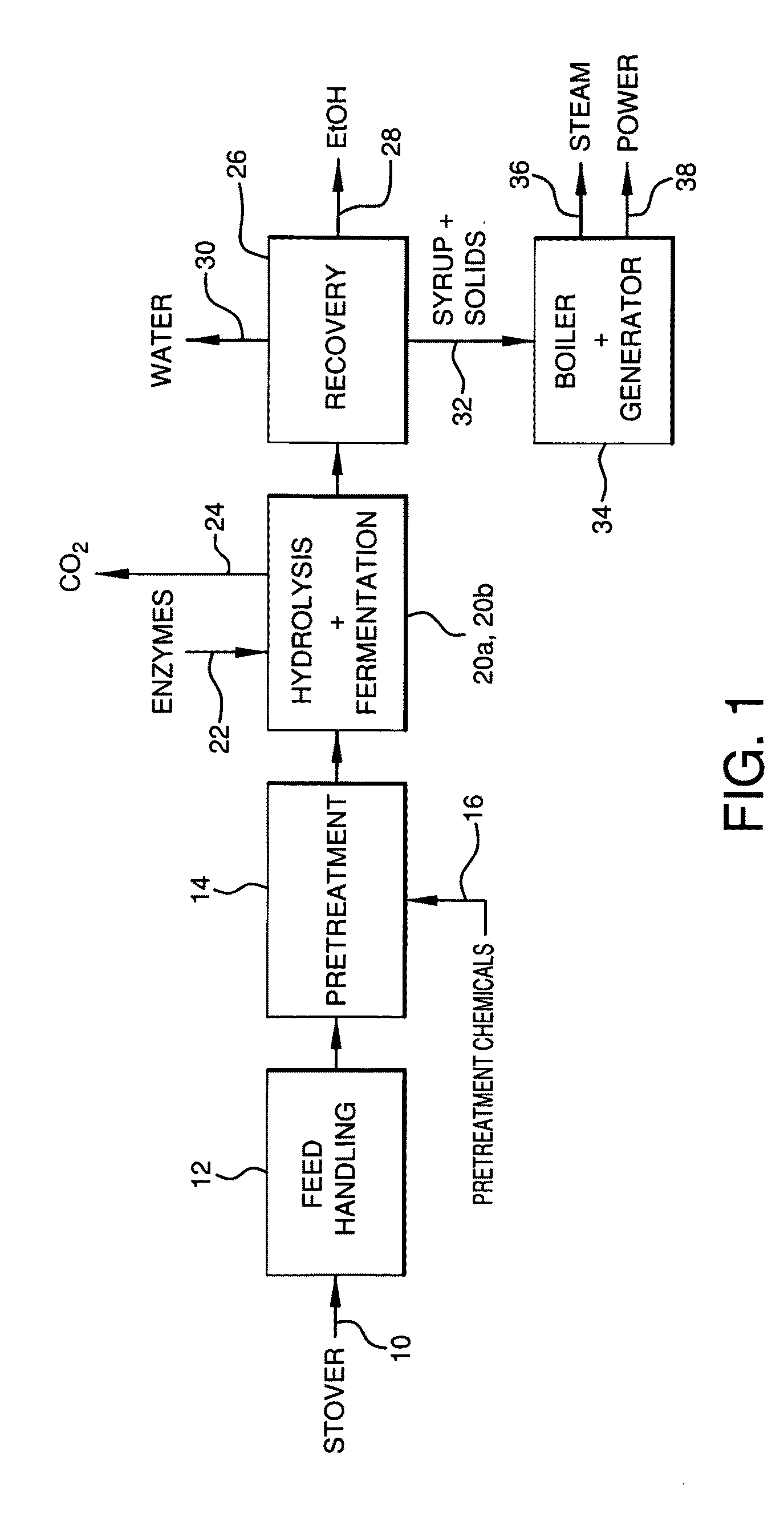
Ethanol resistant and furfural resistant strains of E. coli FBR5 for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20090053793A1Concentration maximizationHigh yieldBacteriaBiofuelsCelluloseResistant strain
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly and quantitatively calculating inherent drought resistance of plants
ActiveCN104007093ARapid Quantification of Drought ResistanceHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldArbitrary Fluorescence Unit
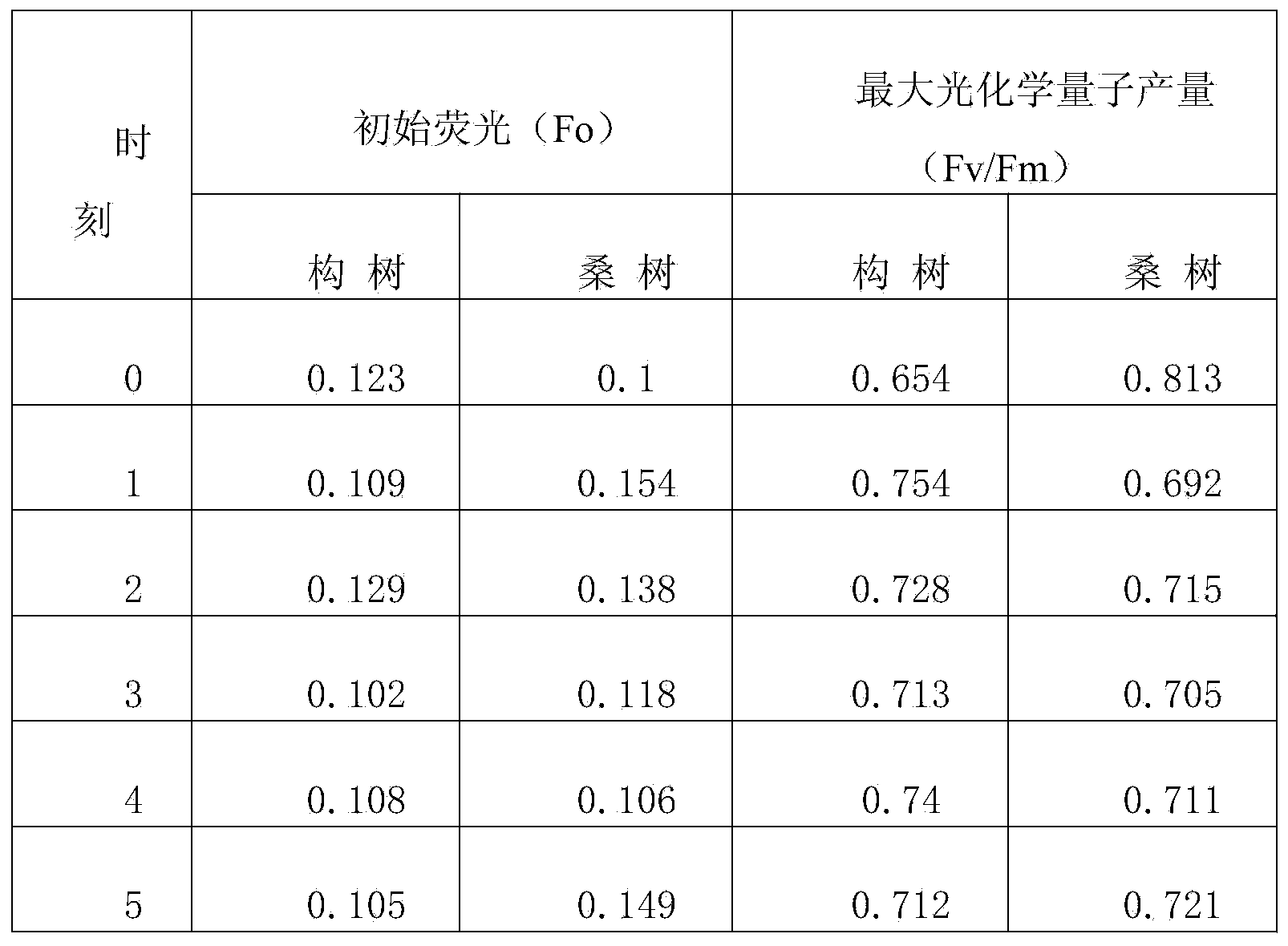
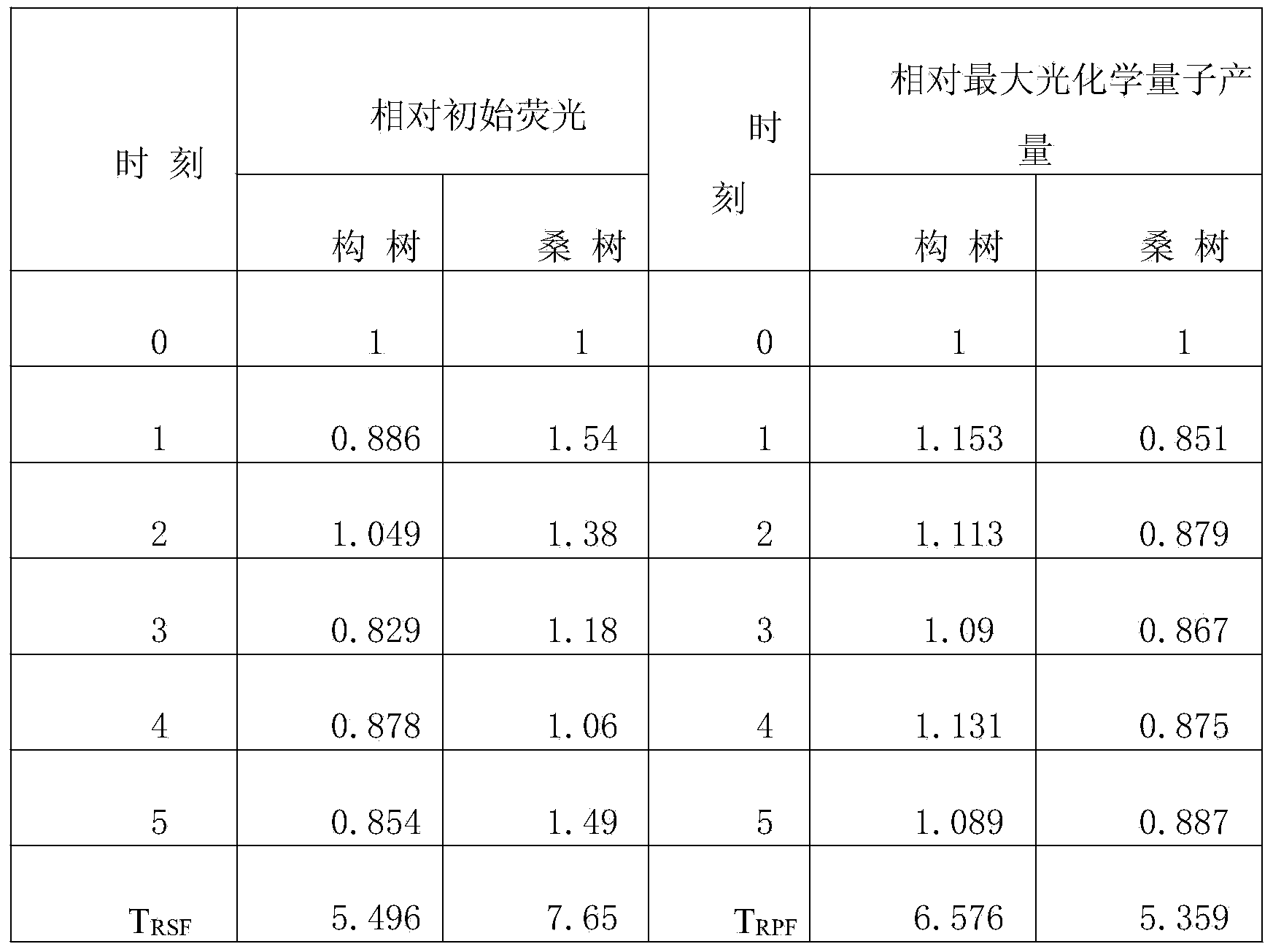
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and quantitatively calculating inherent drought resistance of plants. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning to-be-measured plant leaves, soaking the plant leaves in water, taking out the leaves after 30 minutes, and absorbing water on the surface; measuring minimal fluorescence (Fo) and PSII maximum photochemical quantum yield (Fv / Fm) of the leaves during 0 level fluorescence by using an IMAGING-PAM modulation type chlorophyll fluorescence spectrometer, and repeating for three times; then allowing the leaves to lose water, and repeating the operation every an hour; taking the measurement result during waterlogged 0 hour as reference, calculating relative Fo and relative Fv / Fm at each measurement moment, and respectively adding to obtain the accumulated relative Fo (TRSF) and accumulated relative Fv / Fm (TRPF) in the previous five hours after waterlogging; and comparing the numerical values of the TRSF and TRPF, and quantifying the inherent drought resistance of different plants. The method has the advantages of high accuracy, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high speed and the like and can be used for breeding drought-resistant strains.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
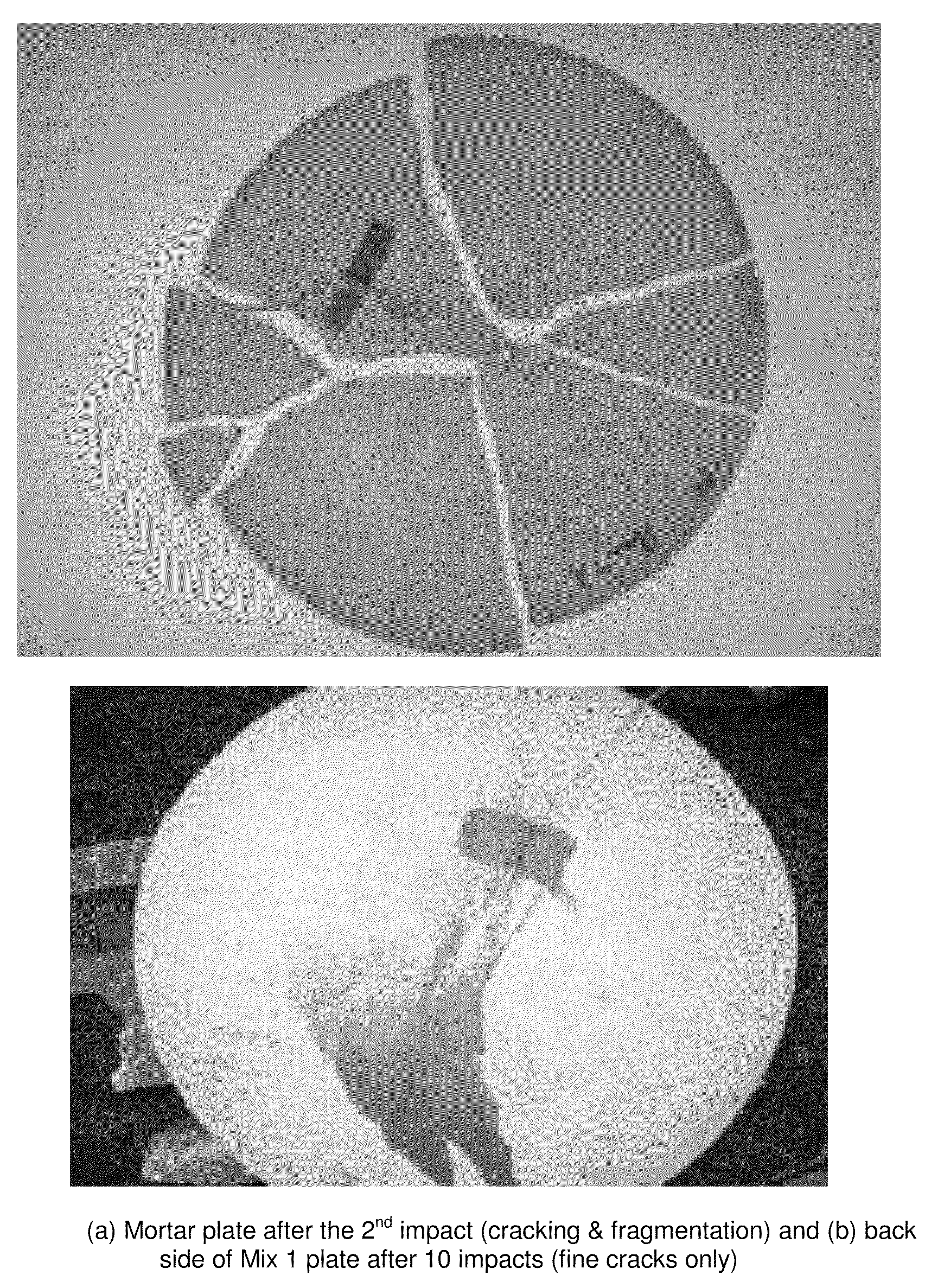
Impact resistant strain hardening brittle matrix composite for protective structures
InactiveUS20090075076A1Good tensile strain capacitySuppress localized brittle fractureSolid waste managementLayered productsResistant strainEngineered cementitious composite
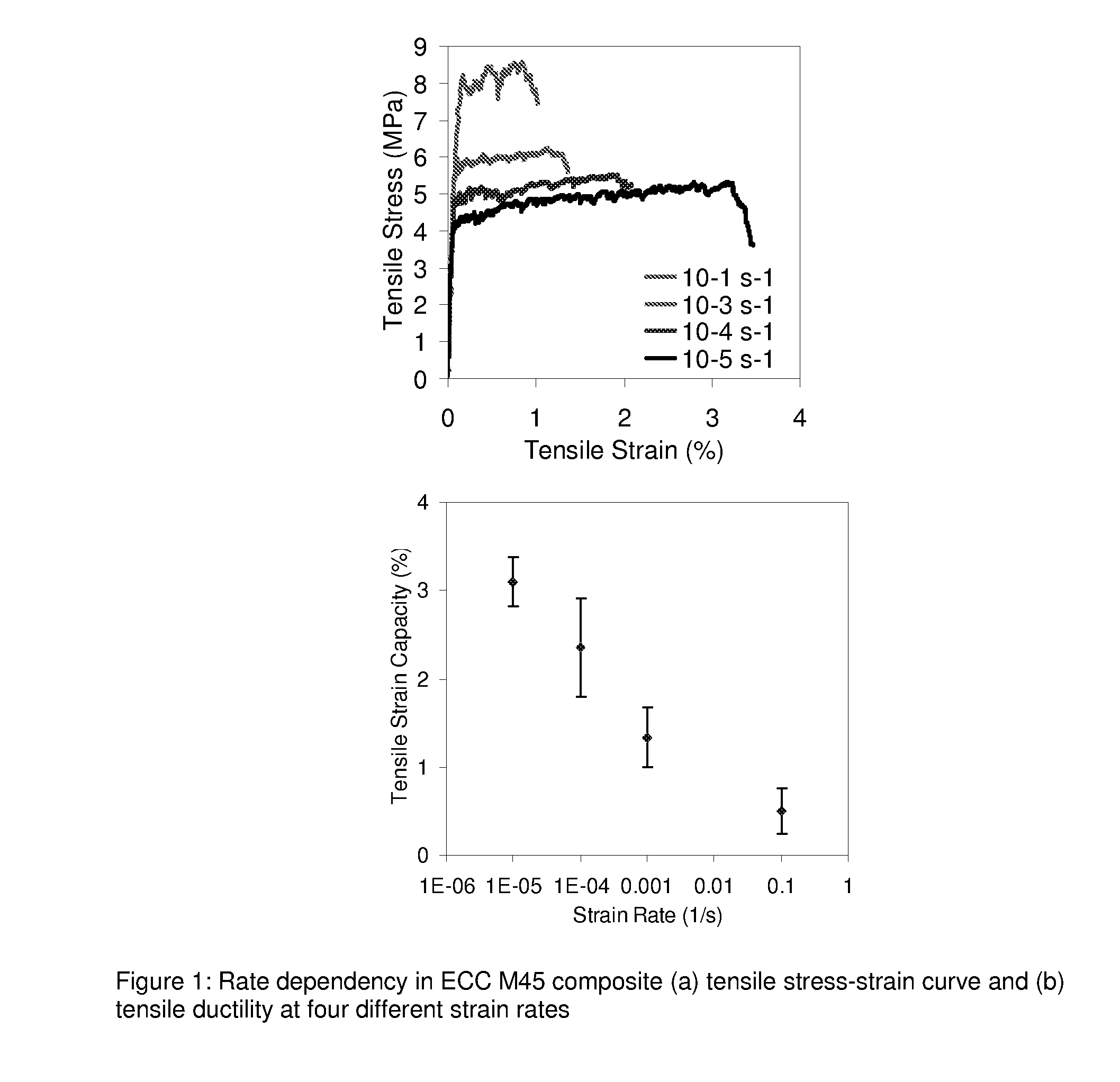
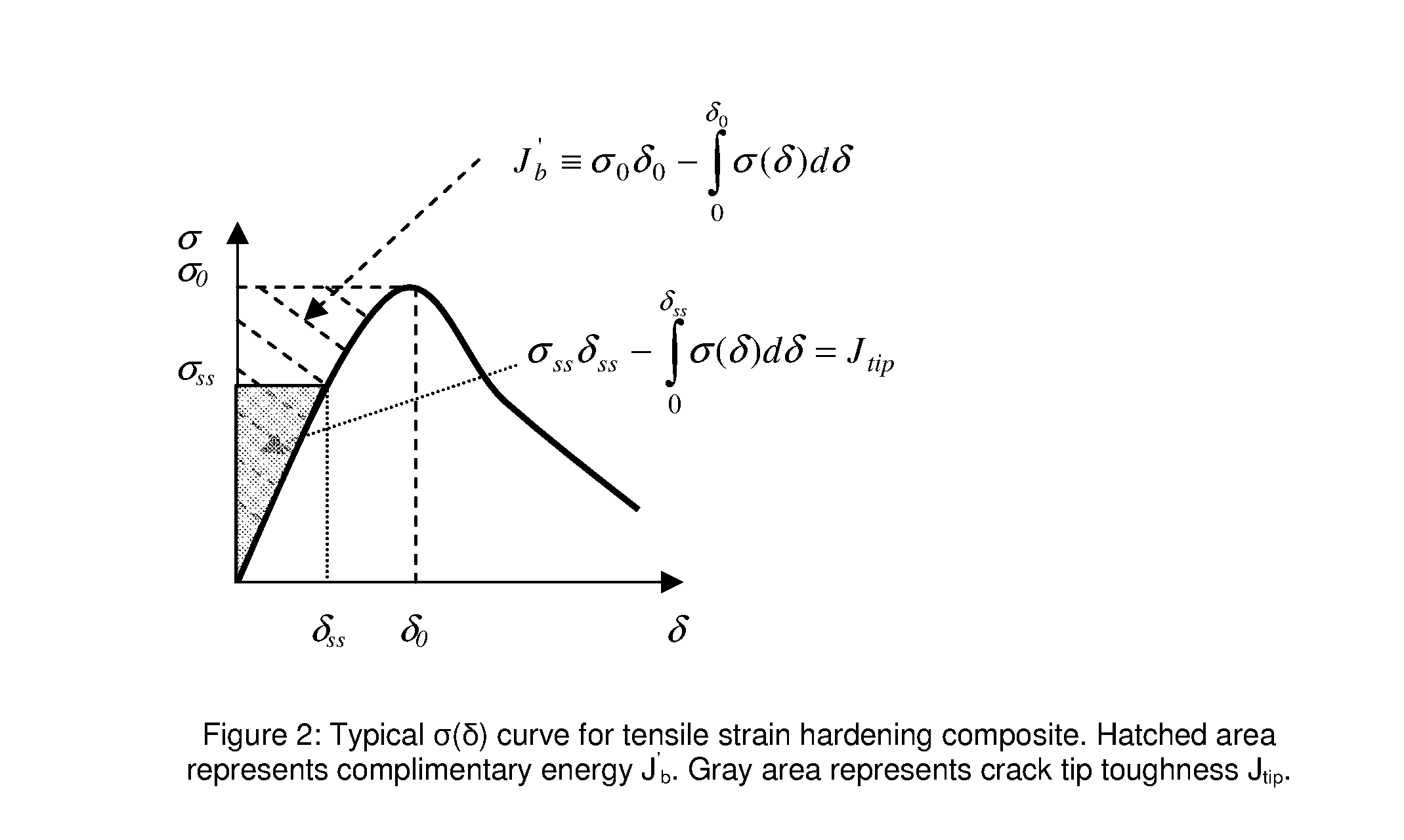
An extremely ductile fiber reinforced brittle matrix composite is of great value to protective structures that may be subjected to dynamic and / or impact loading. Infrastructures such as homes, buildings, and bridges may experience such loads due to hurricane lifted objects, bombs, and other projectiles. Compared to normal concrete and fiber reinforced concrete, the invented composite has substantially improved tensile strain capacity with strain hardening behavior, several hundred times higher than that of conventional concrete and fiber reinforced concrete even when subjected to impact loading. The brittle matrix may be a hydraulic cement or an inorganic polymer. In an exemplary embodiment of the teachings, the composites are prepared by incorporating pozzolanic admixtures, lightweight filler, and fine aggregates in Engineered Cementitious Composite fresh mixture, to form the resulting mixtures, then placing the resulting mixtures into molds, and curing the resulting mixtures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Salmonella enteritidis phage LPSE28 and application of salmonella enteritidis phage to food
ActiveCN108546685AStock solution titer is highStrong bacteriostasisMilk preservationMicroorganism based processesBacteriophageResistant strain
The invention discloses a salmonella enteritidis phage LPSE28, with the preservation number of CCTCC NO. 2018120. The salmonella enteritidis phage adopts a wide-spectrum type and can perform pyrolysison a drug-resistant strain of salmonella. Through verification, the salmonella enteritidis phage belongs to caudovirales myoviridaeT4-like viruses, and is called after LPSE28. The pH value of the phage LPSE28 is between 4 and 12, and the titer of the phage is stable at 40-60 DEG C. The invention also discloses application of the salmonella enteritidis phage LPSE28 to food. By utilization of the phage provided by the invention, salmonella enteritidis in food, particularly liquid eggs and milk systems can be effectively controlled, and compared with an antibiotic and a chemical preservative, the phage LPSE28 has the characteristics of high specificity, no residues and safety.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Acid-producing bacillus cereus and application thereof
ActiveCN102517238AIncrease payLower feed to meat ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMass ratioBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a strain called acid-producing bacillus cereus, which is collected in the China center for type culture collection, with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2011352, on October 16th, 2011. The strain can be used for preparing micro-ecological preparations. During application, acid-producing bacillus cereus powder can be used as an individual effective component to be mixed with corn starch to prepare the micro-ecological preparations, or is mixed with at least one other effective component or strain powder and corn starch to prepare composite micro-ecological preparations. The invention further provides a composite micro-ecological preparation M3 which is prepared by three high-temperature-resistant strains including bacillus subtilis N9-1-35, clostridium butyricum Cb-2, the acid-producing bacillus cereus and corn starch according to the mass ratio of 1:2:2:5, wherein the viable counts of the strain powder are larger than or equal to 1.0X109cfu / g, 5.0X108cfu / g and 5.0X108cfu / g respectively.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
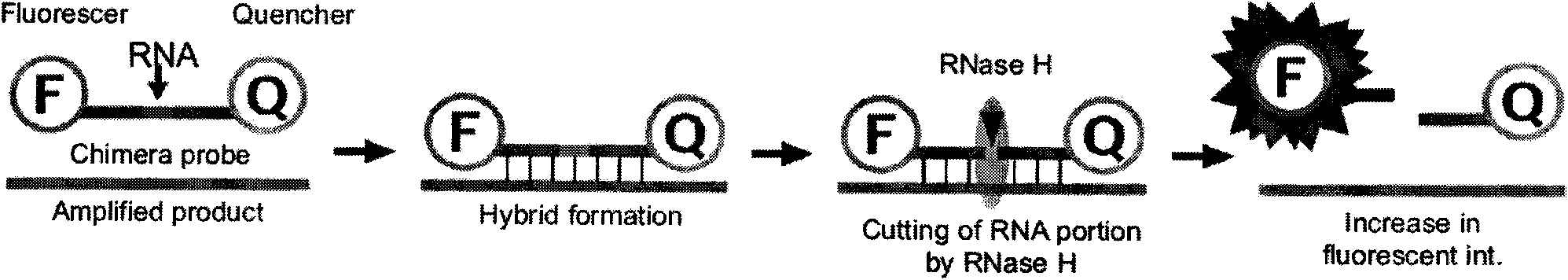
Staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit
ActiveCN102399877AGuaranteed credibilityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMethicillin resistance geneStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention relates to the field of microorganism detection, in particular to a staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit. The invention has the technical scheme of amplifying and detecting a highly conservative specific nucleic acid sequence nuc gene in the staphylococcus aureus gene by using the polymerase chain reaction and molecular beacon and fluorescent probe technologies and simultaneously amplifying and detecting the drug resistant nucleic acid sequence mecA gene to judge whether the strain is a methicillin resistant strain of staphylococcus aureus. The invention also provides PCR amplification primers of the nuc gene and the mecA gene and the sequence of the probe. The kit is applicable to the rapid detection of the staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain in a clinical specimen of a suspect staphylococcus aureus infector and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, stability, timeliness, convenience for operation and the like.
Owner:福州泰普生物科学有限公司
Methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, including antimicrobial-resistant strains thereof, using gallium compounds
InactiveUS20080241275A1Effect be exertReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePresent methodInfectious Disorder
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, by systemically administering to a patient a compound containing gallium. The extracellular microorganisms targeted by the present methods include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), E. coli O157:H7, fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella typhi, and the like. Furthermore, in the present methods, gallium compounds can be co-administered with one or more conventional antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases with reduced risks of creating multi-drug resistant pathogens. The methods of the present invention is also applicable to those microorganisms, such as ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, complete eradication of which so far has been difficult to achieve.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of reducing insect resistant pests in transgenic crops
The present invention discloses Resistance Management (RM) practices that are critical to safeguard Bacillus thuringiensis as a natural resource and sustain genetically modified corn expressing Bt toxins as a suitable method for ECB and WCRW management. A useful tool in developing RM strategies is to develop laboratory selected colonies that exhibit high levels of resistance to a particular toxin. The availability of selected strains allows determination of the genetic expression of resistance (i.e., dominant vs. recessive, autosomal vs. sex-linked) and whether or not the resistance mechanism is specific for a given toxin. In addition, the availability of resistant strains will allow estimation of the particular resistance allele frequency in the field, and provides a tool to identify the biochemical and physiological basis of resistance and a means to develop molecular probes to monitor the evolution of resistance in the field.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Penicillium griseofulvum, antibacterial active compound generated thereby and application
ActiveCN103255061AHigh antibacterial activityProcess is easy to controlAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyPenicillium griseofulvum
The invention provides a?Penicillium griseofulvum?CPCC400528, the preservation number of which is CGMCC NO.5752. The Penicillium griseofulvum CPCC400528 can be fermented to generate an antibacterial active compound with a molecular formula of C7H6O4 and a structure shown as formula (I). The compound has a good growth inhibition effect on a variety of Gram positive pathogenic bacteria and Gram negative pathogenic bacteria. With the increase of concentration, the inhibition effect is gradually enhanced. Also, the compound has a good inhibition effect on a plurality of drug resistant strains. The Penicillium griseofulvum strain provided in the invention is easy to ferment and culture and has a high yield. The preparation process of the active compound is simple and is easy to control. The prepared compound has obvious antibacterial activity, lays the foundation for research and development of new antibacterial drugs, and has very broad market prospects.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods and compositions comprising monitoring devices
InactiveUS20050031536A1Sensitive highEasy to manageDrug and medicationsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionRegimenInfectious agent
Methods and compositions for the detection and monitoring of drug therapy are provided. In particular, efficient and sensitive methods for the detection of drug ingestion are provided for determining whether individuals are complying with prescribed therapeutic regimens, and for providing a mechanism for identifying drug-resistant strains of infectious agents. The claimed methods and compositions involve the application of transdermal devices containing detection mechanisms for receiving and recording signals generated by the ingestion of a labeled drug. Such devices are attached to the skin for the duration of drug therapy and compliance is determined either by direct reading, or by remote monitoring whereby signals are transmitted from the device and received at an external site such as a healthcare facility.
Owner:GRYCZYNSKI ZYGMUNT +3
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
Novel topical formulations of flucytosine and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090068287A1Promote resultsLimited systemic exposureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSide effectWhole body
The invention relates to topical formulations and methods of use of flucytosine which demonstrate a clear advantage over currently available therapeutic regimens for the treatment and maintenance of fungal infections, particularly vulvovaginal candidiasis. The invention provides compositions which solve the long-standing need for antimicrobial agents which treat effectively resistant strains of Candida spp., especially C. albicans, C. glabrata, and C. tropicalis, and which pose limited risk of side effects, adverse reactions, or the development of resistant pathogens. The invention provides novel topical formulations of flucytosine designed to allow the active drug to act at the local application area, but which inhibit or moderate transdermal or transmucosal absorption of the drug, thus limiting systemic exposure.
Owner:CAMARGO PHARMA SERVICES
Fumigant containing natural plant essential oil
InactiveCN101731319ANot easy to produceBroad spectrumFruit and vegetables preservationFungicideResistant strain
The invention provides a fumigant containing natural plant essential oil, which comprises the following main components: 5 to 30 parts of plant essential oil compound, 0.2 to 2 parts of fungicide, 3 to 10 parts of oxidant, 20 to 40 parts of combustible agent, 2 to 15 parts of flame retardant and 0.1 to 2 parts of coloring agent. The fumigant has the advantages of wide sterilization spectrum, strong sterilization capability, insusceptibility to producing resistant strains after long-term use, safety, wide use range, capability of being applied to the storage and preservation of various agricultural products, low cost, convenient operation, low investment and easy production. The fumigant has the bacteriostatic effect that the fumigant has preservative fresh-keeping effect on various fruits and vegetables, and after the fumigant is ignited in hermetic space, the whole space can be full of generated smoke in full contact with the surfaces of fruits and vegetables so as to effectively resist the infection of pathogenic fungi and kill pathogens.
Owner:NAT ENG AN TECH RES CENT FOR PRESERVATION OF AGRI PROD TIANJIN
Shigella flexneri phage strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101519651AAvoid pollutionAvoid it happening againAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyFood additive
The invention relates to a phage strain and application thereof. The preserving number of the phage strain is CCTCC NO: M209029; and the strain has strong cracking function for Shigella flexneri. After the phage strain is purified, amplified and cultured, the phage strain can be used for inhibiting the Shigella flexneri. The phage strain has the following advantages: because the Shigella flexneri with drug resistance can be killed by adopting the specificity of the phage strain to crack the Shigella flexneri, simultaneously the evolution of the Shigella flexneri and the generation of drug-resistant strains can be prevented; because the phage strain has an aqueous phase, flushing liquor or leacheate for sterilizing environments or apparatuses can be easily prepared by the prior method; and because the phage strain can specifically crack the Shigella flexneri and has no toxic and side effects, the phage strain can be used as a food additive to prevent the Shigella flexneri from polluting food, and used as a medicament for treating the diseases caused by the Shigella flexneri.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Lactobacillus brevis, freeze-dried powder of Lactobacillus brevis and application of freeze-dried powder
InactiveCN102660477AImprove performanceBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEscherichia coliIntestinal structure
The invention discloses Lactobacillus brevis, freeze-dried powder of the Lactobacillus brevis and application of the freeze-dried powder, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The name of the Lactobacillus brevis is Lactobacillus brevis ZLB004; the collection number is CGMCC No.5760; and the Lactobacillus brevis is an acid-resistant, cholate-resistant, and high-temperature-resistant strain with a good antibacterial property. The bacterial powder of the Lactobacillus brevis is obtained by the following steps of: performing fermentation culture on the Lactobacillus brevis, centrifuging, adding bacterial mud into a cryoprotectant, and freeze-drying. The bacterial powder of the Lactobacillus brevis, which serves as an animal feed additive, can improve the daily gain of growingpigs, reduce the feed-weight ratio, increase the content of viable lactic acid bacteria in intestines and reduce the content of Escherichia coli, and has the effects of reducing animal stress and promoting the health of organisms.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Anti-infective agents useful against multidrug-resistant strains of bacteria
The invention relates to novel methods for using macrolide anti-infective agents. The macrolide anti-infective agents demonstrate antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant strains of bacteria and, in particular, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Methods for inhibiting the activity of multi-drug resistant bacterial organisms and methods for treating a bacterial infection caused by such organisms are described herein.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Preparation method and use of compounds having high insecticidal activities
InactiveUS20090111847A1High insecticidal activityLow costBiocideOrganic chemistryArthropod mouthpartsLeafhopper
The present invention discloses a kind of nitromethylene derivatives as well as their preparation method and their uses. The insecticidal activity tests show that the nitromethylene derivatives of the present invention not only show high insecticidal activities against insects with piercing-sucking type or scratching type mouthparts, such as aphid, leafhopper, plant hopper, thrips and white fly and their resistant strains, but also show high insecticidal activities against Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus, carmine spider mite, and they can also be used to prevent sanitary pest, and white ant.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phage-derived compositions for improved mycobacterial therapy
InactiveUS20170136102A1Lower Level RequirementsShort durationPeptide/protein ingredientsCarbohydrate active ingredientsMedicineBacteriophage
Methods and compositions for the treatment of mycobacteria infections, particularly antibiotic resistant strains. Of particular use in treating tuberculosis infections, including dormant or difficult to treat forms.
Owner:BACTOCLEAR HLDG PTE LTD
Enhancers for microbiological disinfection
InactiveUS6881731B1Increase powerEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideDisinfectantOrganic dye
Simple carboxylic acids, in particular dicarboxylic acids such as citric acid shows an unexpected ability to enhance the antimicrobial power of a wide range of disinfectant and / or antibiotic agents. As little as 1% citrate greatly enhances the ability of antibiotics to kill or inhibit a wide range of bacterial species including antibiotic resistant strains. Citrate alone is effective in preventing bacterial growth in platelet concentrates and in red blood cell suspensions. Effective concentrations of citrate cause little if any damage to blood cells. Besides enhancing the power of antibiotics citrate also enhances the antimicrobial properties of disinfectant organic dyes such as crystal violet and methylene blue. In addition citrate enhances the antimicrobial properties of polyphenols of plant origin. Iodine-based disinfectants are also enhanced without enhancing protein denaturation.
Owner:SHANBROM TECH
Method for detecting resistant mutant of mycoplasma pneumoniae
InactiveCN102002522AQuick checkoutSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceResistant strainThermal cycler
The invention belongs to the fields of biology and medicines and particularly relates to a method for detecting a resistant mutant of mycoplasma pneumoniae. By adopting Real-time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and a cycling probe technology for distinguishing the difference of monobases and searching a specific primer aiming at the mycoplasma pneumoniae in an upstream and a downstream sequence of 2063 bit / 2064 bit of the mycoplasma pneumoniae 23SrRNA gene, specific cycling probes aiming at mutation-free sensitive strains, 2063-bit mutant drug-resistant strains and 2064-bit mutant drug-resistant strains can be respectively designed according to the difference of the bases at the 2063 bit / 2064 bit of the mutation-free sensitive strains and mutant drug-resistant 23SrRNA gene of the mycoplasma pneumoniae; the PCR amplification can be carried out by using the specific primer of the mycoplasma pneumoniae; and the fluorescence intensity change can be read by a Real-time PCR thermal cycler in real time to determine the mutant types of samples to be detected. The invention can correctly distinguish the mutation-free sensitive strains from the mutant drug-resistant strains of clinical separation strains of the mycoplasma pneumoniae. The specificity is 100 percent and the sensitivity can reach 102copy / PCR reaction.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
China rose salt-resistance strain vitro quick-screening method
InactiveCN101422132AImprove salt toleranceGood repeatabilityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsSalt resistanceAgricultural science
The invention discloses an excised quick screening method for the salt-resistant strains of a China rose, which belongs to the field of agriculture biotechnology. The invention consists of 13 steps of the selecting and sterilizing of an initial explant, sprout inducing, propagation culture, the continuous subculture of propagated seedlings, the direct regeneration of vanes, the indirection regeneration of vanes, physical mutagenesis, mutagenesis resuming and culturing, the excised quick screening of the salt-resistant strains, the quick propagation and re-screening of the salt-resistant strains, resuming and culturing and seedling strengthening, rootage and transplanting. In the invention, the callus or the directly regenerated adventitious bud of the vane of the China rose is used as a processing material to mainly research the four key procedures of the excised screening technology, the subculture propagation, the seedling strengthening and the rootage culturing of the salt-resistant strains; the method has good repetitiveness, can effectively eliminate false positive strains, and obtain the salt-resistant strains with stable heredity; and the average total surviving rate of the salt-resistant screening thereof achieves about 18 percent which is improved by about 16 percent than comparison 1 and is improved about 18 percent than comparison 2; and the salt-resistant screening efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & DETECTION TECH YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus subtilis and application of same in resisting aspergillus
InactiveCN102965306AImprove the level of prevention and controlPromote export tradeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesActinomyces flaveolus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and an application of the same in resisting aspergillus. The bacillus subtilis has antagonistic action in aspergillus flavus. A method for screening the bacillus subtilis which has antagonistic action in the aspergillus flavus from soil comprises the following steps: a, bacteria isolating; b, aspergillus culturing and spore liquid preparing; c, aspergillus-resistant strain screening; and d, aspergillus-resistant strain rescreening. Through aflatoxin panel screening tests and toxin production aspergillus flavus antagonistic tests, aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains in the peanut cultivation fields and storage warehouses are screened. A method for reasonably and effectively screening the aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains is established, so that the appropriate required aflatoxin inhibition strains are obtained. The bacillus subtilis is applied to the easy aflatoxin contamination stages which are before and after harvesting crops of peanuts and the like and during storage periods and the like, the aflatoxin prevention and control levels of the crops of export peanuts and the like can be improved, export risks are lowered, and the export trade of the crops and products thereof are promoted.
Owner:中华人民共和国潍坊出入境检验检疫局
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com