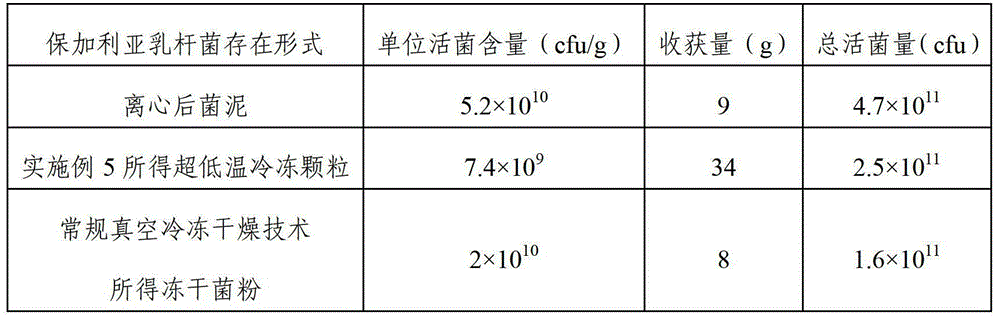
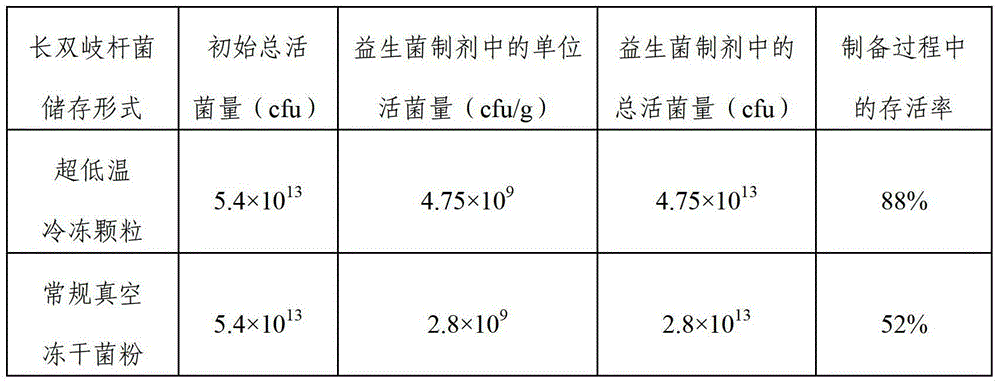
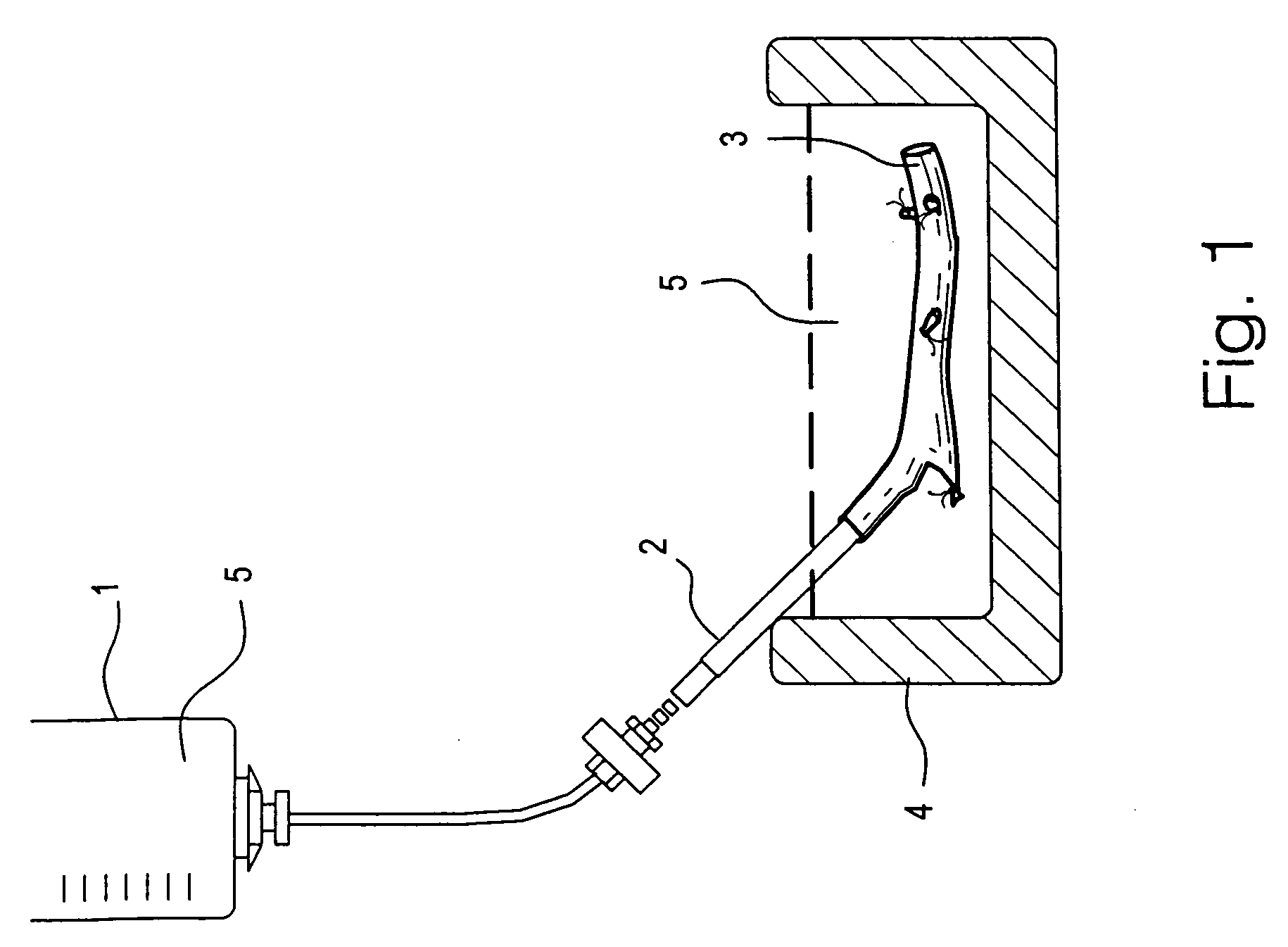
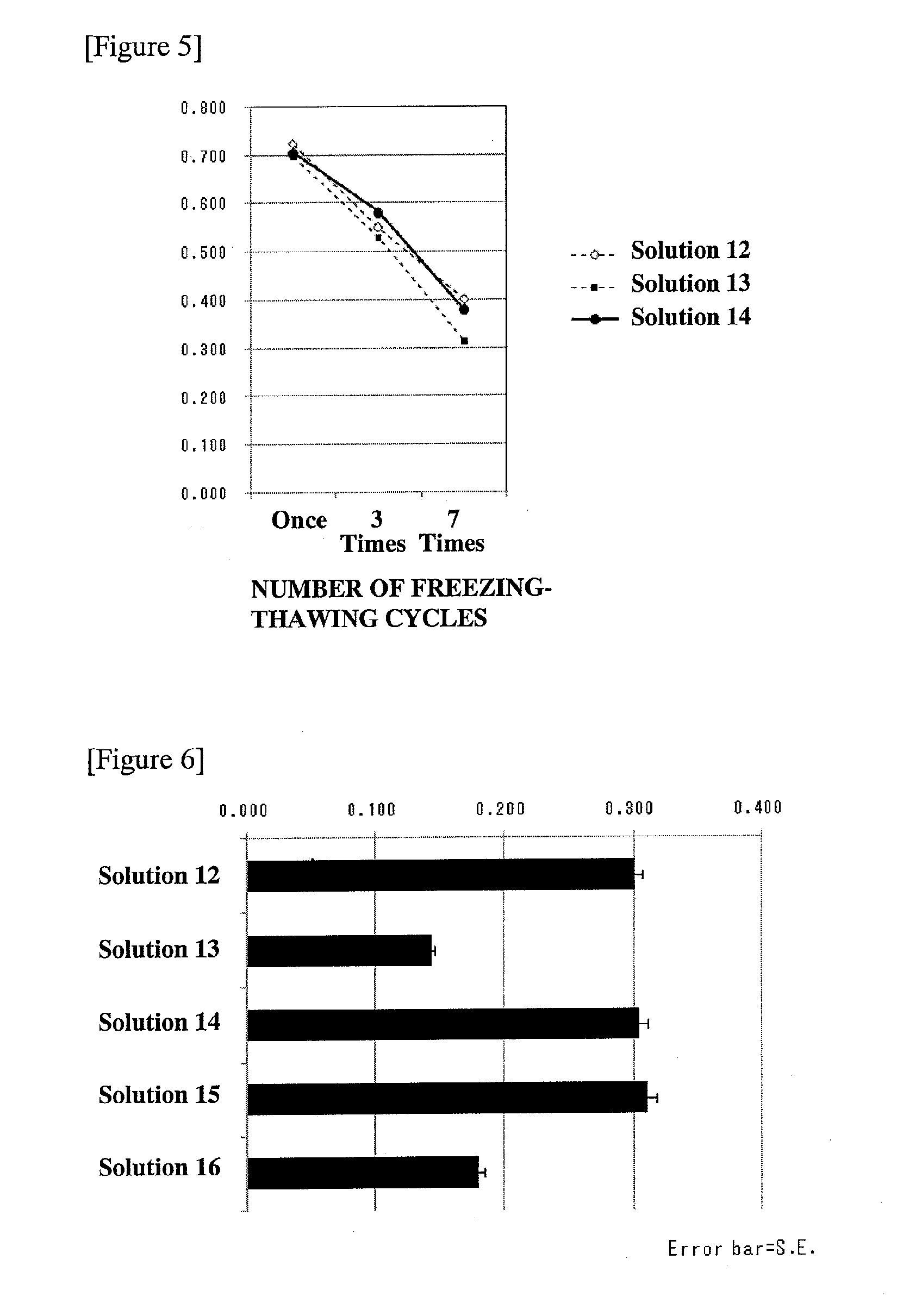
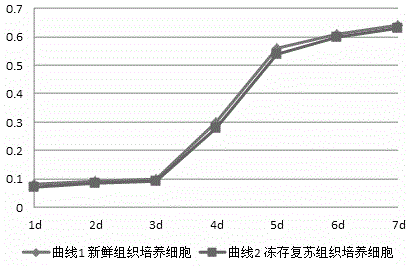
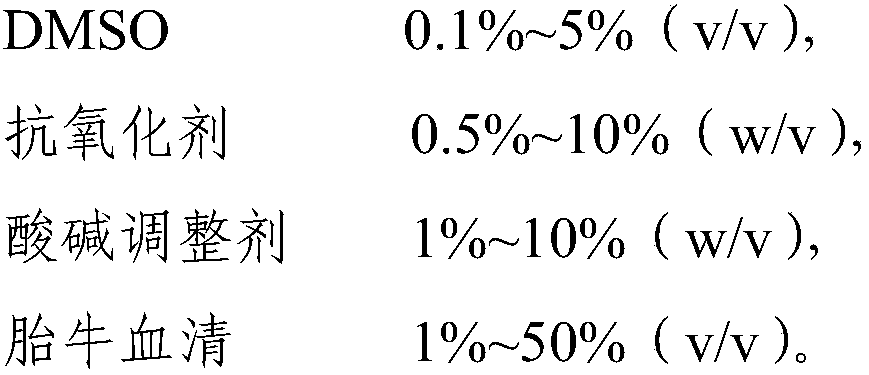Patents
Literature
608 results about "Cryoprotectant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cryoprotectant is a substance used to protect biological tissue from freezing damage (i.e. that due to ice formation). Arctic and Antarctic insects, fish and amphibians create cryoprotectants (antifreeze compounds and antifreeze proteins) in their bodies to minimize freezing damage during cold winter periods. Cryoprotectants are also used to preserve living materials in the study of biology and to preserve food products.
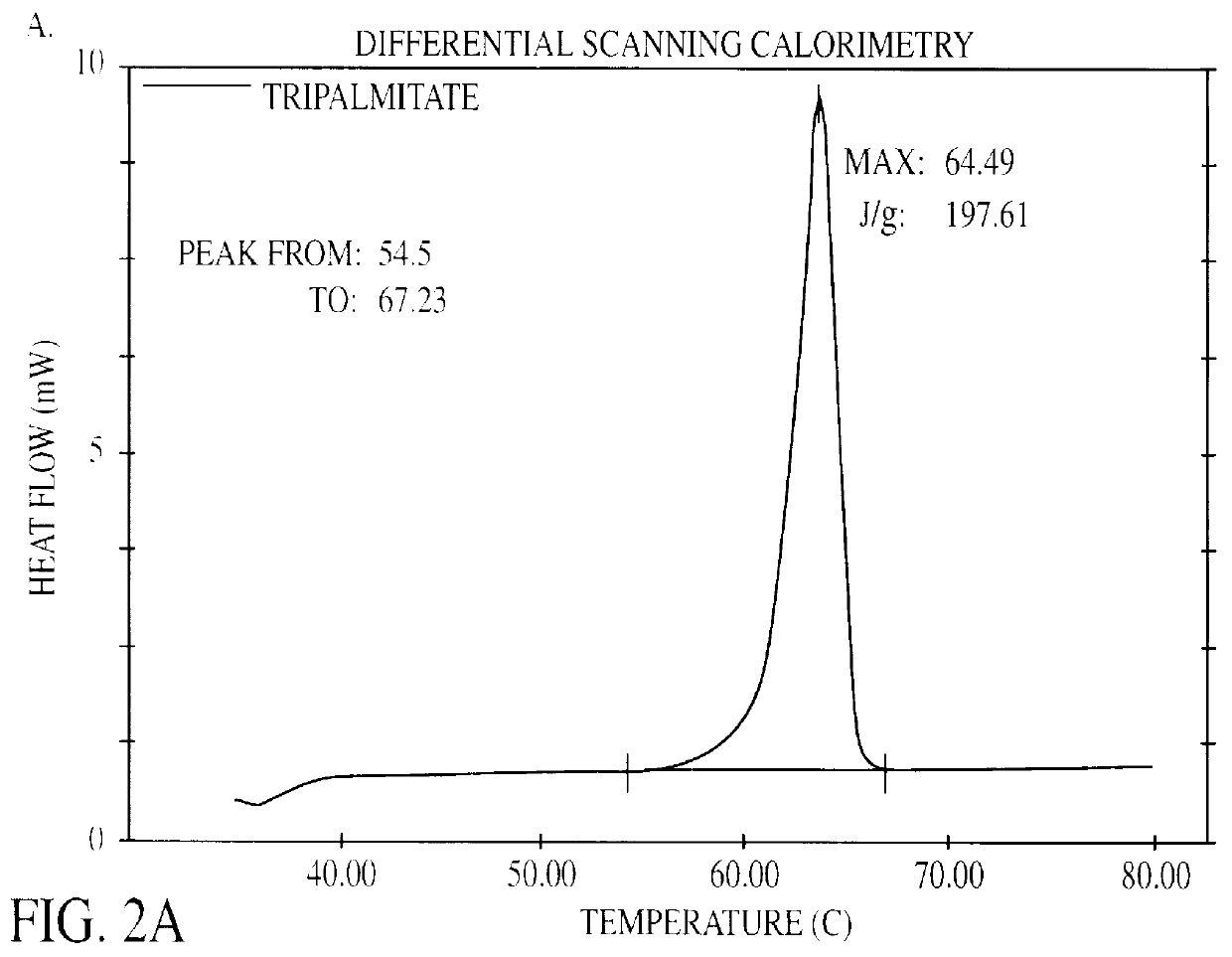
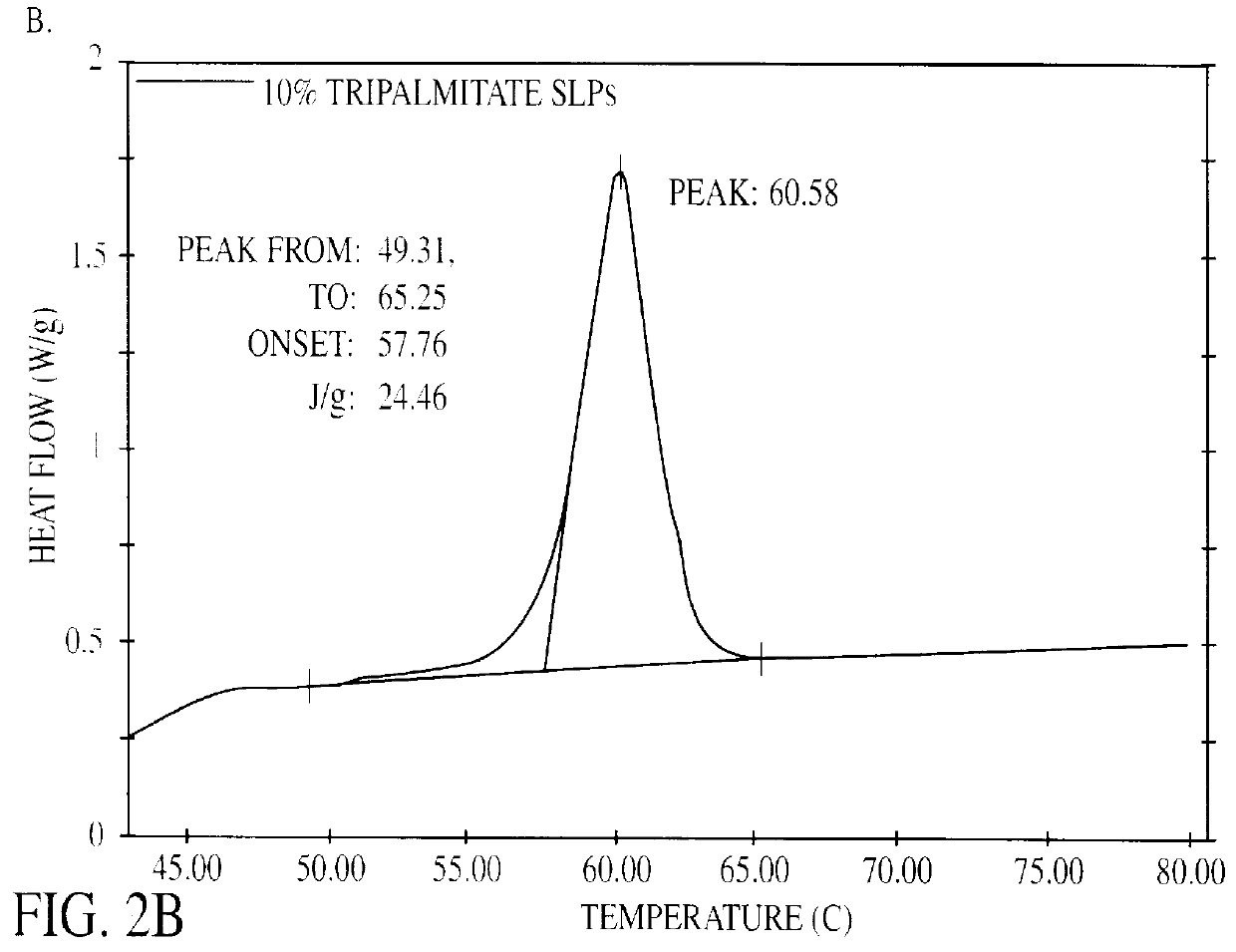
Solid lipid particles, particles of bioactive agents and methods for the manufacture and use thereof
InactiveUS6207178B1Suppresses decrease in specific surface areaImprove bioavailabilityBiocideCosmetic preparationsLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention is in the area of administration forms and delivery systems for drugs, vaccines and other biologically active agents. More specifically the invention is related to the preparation of suspensions of colloidal solid lipid particles (SLPs) of predominantly anisometrical shape with the lipid matrix being in a stable polymorphic modification and of suspensions of micron and submicron particles of bioactive agents (PBAs); as well as to the use of such suspensions or the lyophilizates thereof as delivery systems primarily for the parenteral administration of preferably poorly water-soluble bioactive substances, particularly drugs, and to their use in cosmetic, food and agricultural products. SLPs and PBAs are prepared by the following emulsification process: (1) A solid lipid or bioactive agent or a mixture of solid lipids or bioactive agents is melted. (2) Stabilizers are added either to the lipid or bioactive agent and to the aqueous phase or to the aqueous phase only depending on their physicochemical characteristics. Stabilizers may also be added or exchanged after homogenization. (3) Drugs or other bioactive substances to be incorporated into the SLPs may be melted together with the lipids if the physicochemical characteristics of the substance permit or may be dissolved, solubilized or dispersed in the lipid melt before homogenization. (4) The aqueous phase is heated to the temperature of the melt before mixing and may contain for example stabilizers, isotonicity agents, buffering substances, cryoprotectants and / or preservatives. (5) The molten lipid compounds and the bioactive agents are emulsified in an aqueous phase preferably by high-pressure homogenization.
Owner:PHARMACIA AB
Freeze dried fecal microbiota for use in fecal microbial transplantation
The present invention provides freeze-dried compositions that include an extract of human feces and a cryoprotectant, and methods for making and using such compositions, including methods for replacing or supplementing or modifying a subject's colon microbiota, and methods for treating a disease, pathological condition, and / or iatrogenic condition of the colon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method for processing and preserving collagen-based tissues for transplantation
InactiveUS20060210960A1Minimize surface tension damageAugment selective preservationSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsOrganismBiology
A method for processing and preserving an acellular collagen-based tissue matrix for transplantation is disclosed. The method includes the steps of processing biological tissues with a stabilizing solution to reduce procurement damage, treatment with a processing solution to remove cells, treatment with a cryoprotectant solution followed by freezing, drying, storage and rehydration under conditions that preclude functionally significant damage and reconstitution with viable cells.
Owner:LIFECELL
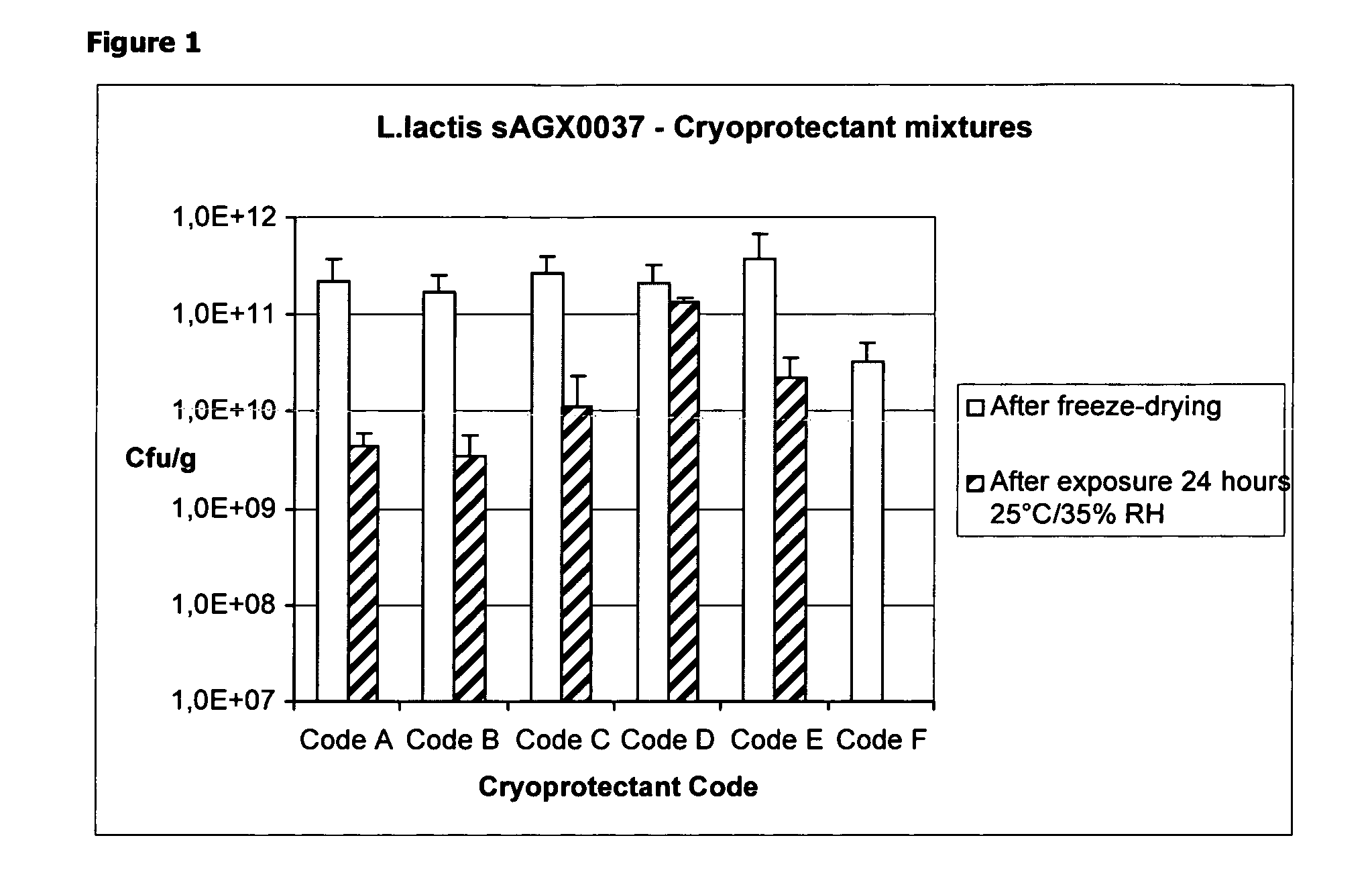
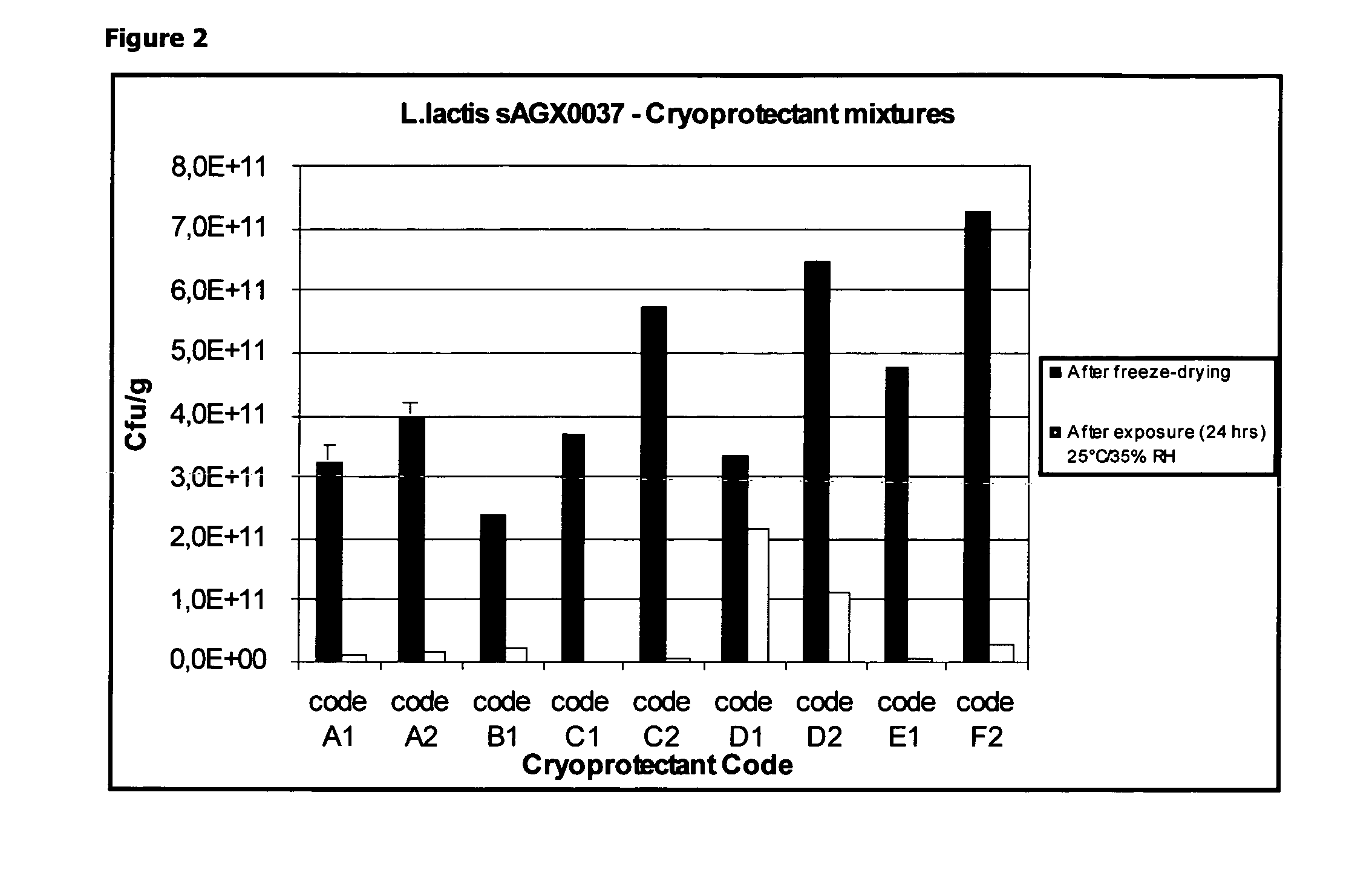
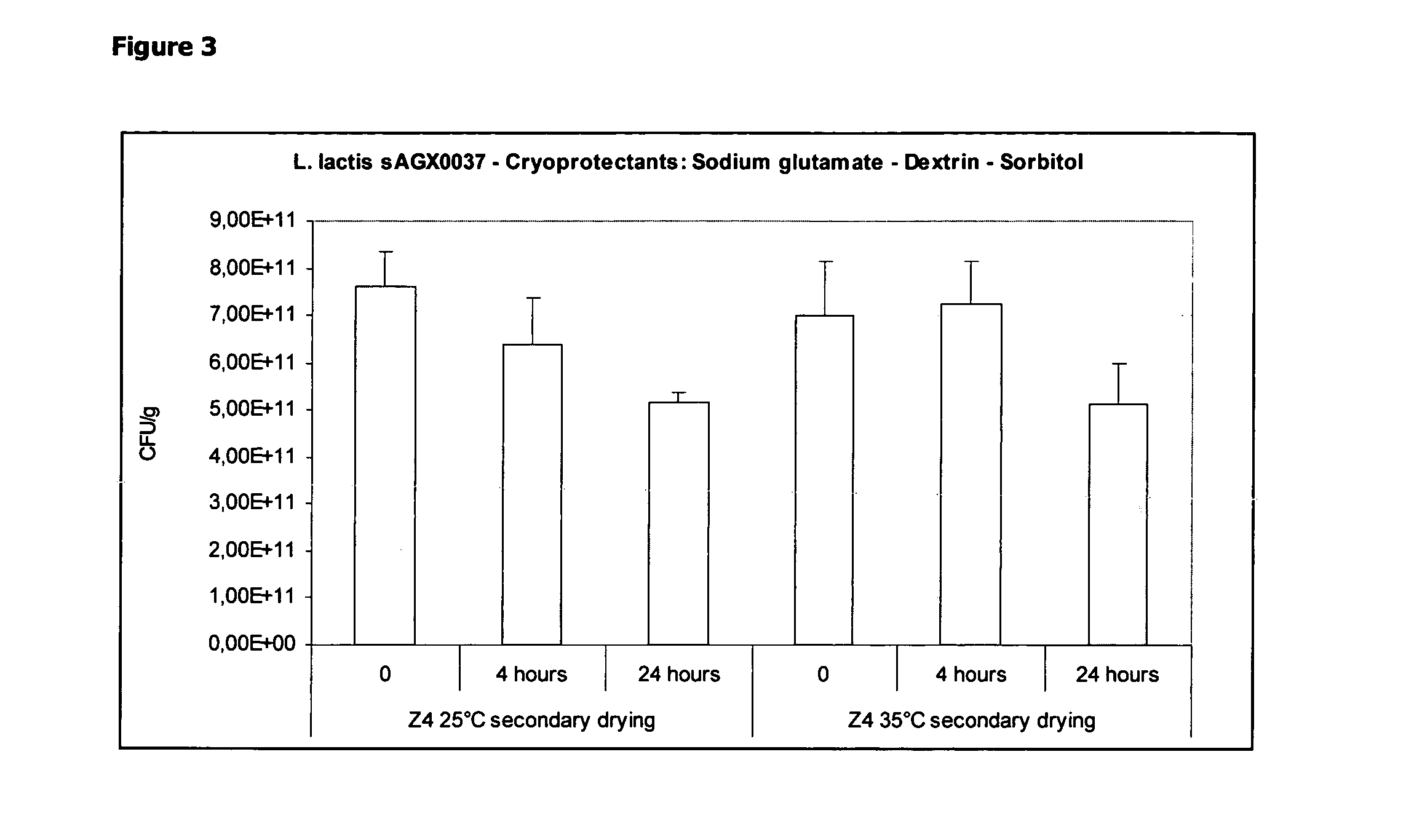
Cryoprotectants for freeze drying of lactic acid bacteria
ActiveUS20120039853A1Improve survivabilityImprove textureBiocideMilk preparationBacteroidesVaccination
The present invention comprises the discovery and development of an effective cryoprotectant composition, without containing skim milk or any other animal-derived compounds, to achieve long-term stability of freeze-dried lactic acid bacteria (LAB), at different temperatures, whereby the retention of viability of the freeze-dried LAB after 6 months of storage, preferably after 9 months of storage, more preferably after 12 months of storage is more than 50%. The invention is in the field of producing freeze dried bacteria, in particular Lactic acid bacteria. More in particular, the invention relates to the use of a novel combination of cryoprotectants for increasing the viability of bacteria after freeze drying, improving the texture of the lyofilized cake for easy grinding and improving the long term stability of the freeze dried bacteria at different temperature conditions. The invention further relates to such freeze dried bacteria for use in food industry or in human or animal health applications. More in particular, the invention relates to the increased viability and long-term storage of recombinant bacteria capable of expressing heterologous proteins or peptides and administered to humans or animals for therapeutic or vaccination purposes.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
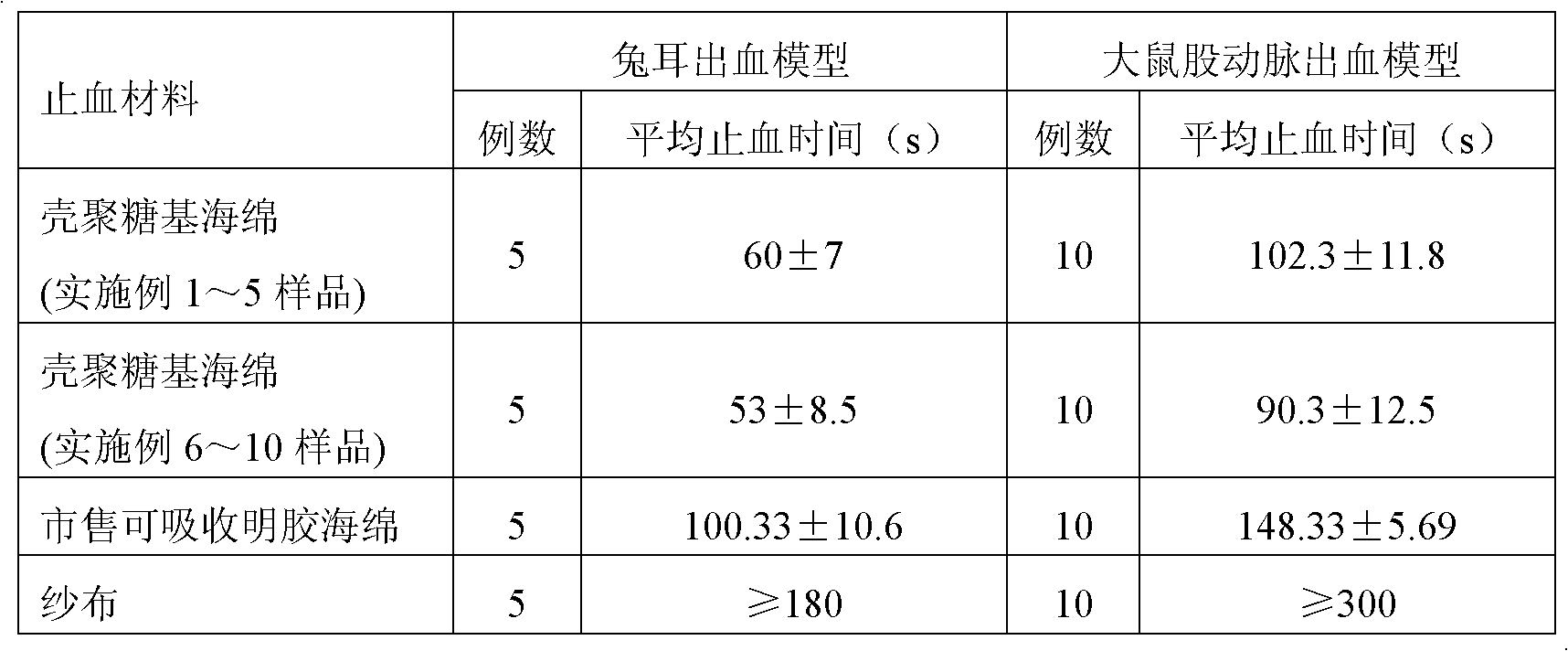
Chitosan-based styptic sponge and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102526795AImprove stabilityMaintain coagulation activityAbsorbent padsBandagesWound healingThrombin activity
The invention relates to chitosan-based styptic sponge with a thrombin immobilization effect, and the chitosan-based styptic sponge is a porous sponge made from chitosan with the thrombin immobilization effect and hemostatic. The preparation method of the chitosan-based styptic sponge provided by the invention comprises the following steps: immobilizing thrombin with chitosan or carboxymethyl chitosan, and adding other styptics, cryoprotectants and crosslinking agents to prepare the porous styptic sponge, wherein the weight ratio of the chitosan or carboxymethyl chitosan to the thrombin is 100:(0.1-20); pre-freezing, lyophilizing in vacuum, casting, cutting, encapsulating and sterilizing to prepare the chitosan-based styptic sponge. According to the chitosan-based styptic sponge, the thrombin is immobilized through the chitosan or carboxymethyl chitosan, so that the stability and procoagulant activity of the thrombin can be improved, and the property of the prepared chitosan-based styptic sponge is more stable, the procoagulant and wound healing effects are remarkably improved, and the chitosan-based styptic sponge can be widely applied to wound or surgery hemostasis.
Owner:WUHAN GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY
Composition for the preservation of viruses
InactiveUS7091030B2Easy to storeIncrease storage spaceBiocideGenetic material ingredientsBiologyVirus
This invention relates to a composition for the preservation of a virus, the composition including a virus, a lipid and a cryoprotectant.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Acellular dermal matrix and method of use thereof for grafting
InactiveUS8067149B2Reduce harmSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsMedicineAcellular Dermis
A method for processing and preserving an acellular collagen-based tissue matrix for transplantation is disclosed. The method includes the steps of processing biological tissues with a stabilizing solution to reduce procurement damage, treatment with a processing solution to remove cells, treatment with a cryoprotectant solution followed by freezing, drying, storage and rehydration under conditions that preclude functionally significant damage and reconstitution with viable cells.
Owner:LIFECELL
Cryopreservation medium for primate embryo stem cells and cryopreservation method
InactiveUS20050026133A1Easy to controlLow costArtificial cell constructsDead animal preservationPrimateMicrobiology
A cryopreservation medium and a cryopreservation method which make it possible to cryopreserve ES cells from primates simply with high viability are provided. A cryopreservation medium containing a cryoprotectant at a Concentration of from 12% (W / V) to 50% (W / V) and a cryopreservation method for primate embryonic stem cells, which comprises a step of suspending primate embryonic stem cells in the cryopreservation medium, and a refrigeration step of freezing the suspension of the primate embryonic stem cells in the cryopreservation medium by cooling it to −80° C. or below at a rate of from 0.5° C. to 10° C. per minute, and a preservation step of storing the frozen suspension of primate embryonic stem cells in the cryopreservation medium enable simple cryopreservation of primate embryonic stem cells with high viability.
Owner:ASAHI TECHNO GLASS CORP
Methods and apparatus for reducing protein content in sperm cell extenders
ActiveUS20070026378A1Reduced protein contentDead animal preservationGerm cellsCentrifugationLow density
The inventive technology relates to methods and apparatus for reducing protein content in sperm cell extenders and may include one or more of the following features: techniques for reducing protein content in a sperm cell extender; techniques for reducing protein content in a cryoprotectant-containing B fraction of a sperm cell extender; techniques for preparing sperm cell extenders that do not require clarification; techniques for preparing low density gradient sperm cell extenders suitable for centrifugation; techniques for reducing protein content between individual steps in preparing a sperm cell extender, and techniques for establishing novel values of reduced protein content in sperm cell extenders.
Owner:XY
Compositions, treatment systems and methods for improved cooling of lipid-rich tissue
Compositions and formulations for use with devices and systems that enable tissue cooling, such as cryotherapy applications, for alteration and reduction of adipose tissue are described. Aspects of the technology are further directed to methods, compositions and devices that provide protection of non-targeted cells (e.g., non-lipid-rich cells) from freeze damage during dermatological and related aesthetic procedures that require sustained exposure to cold temperatures. Further aspects of the technology include systems for enhancing sustained and / or replenishing release of cryoprotectant to a treatment site prior to and during cooling applications.
Owner:ZELTIQ AESTHETICS INC
Method for preparing exosome freeze-dried powder of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
The invention relates to the field of stem cells, discloses a method for preparing exosome freeze-dried powder of stem cells, and particularly relates to a method for preparing exosome freeze-dried powder of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. The method for preparing the exosome freeze-dried powder of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: mixing trehalose with exosomes of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells as a cryoprotectant; filtering and removing bacteria by virtue of a filter membrane; and firstly carrying out ultralow temperature pre-freezing, and then carrying out low-temperature freezing at a certain vacuum degree. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, safe and effective. An experiment proves that compared with a conventional preparation method of the freeze-dried powder, the morphologies and the activity of the exosomes of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can be well kept by the method for preparing the exosome freeze-dried powder of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells disclosed by the invention; and the method is suitable for long-term preservation and application of the exosomes of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Cocktail type cryoprotectant and application thereof
ActiveCN108207930AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityDead animal preservationHigh concentrationIce crystals
The invention relates to the field of biological medicines and in particular to cocktail type cryoprotectant and application thereof. The cocktail type cryoprotectant comprises the following components: 1-60% (w / v) of a polysaccharide, 1-50% (w / v) of an amino acid, 1-20% (w / v) of a polyhydric alcohol and 0-10% (w / v) of a hydroxyl-containing macromoleclar polymer. The polysaccharide, the amino acid, the polyhydric alcohol and the hydroxyl-containing macromoleclar polymer of the cryoprotectant are relatively low in toxicity with high concentrations, formation of intracellular ice crystals can beeffectively inhibited with the polysaccharide, the amino acid, the polyhydric alcohol and the hydroxyl-containing macromoleclar polymer of the proportions, cryopreserved cells can be alleviated fromdamage caused by low temperature environments, the survival rates of the cryopreserved cells after anabiosis culture can be increased, the toxicity of the cryopreserved cells can be greatly reduced, and thus the cocktail type cryoprotectant provided by the invention has very high security feasibility and application and popularization values.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration technology and applications thereof in probiotic preparation
ActiveCN103333840AHigh activityLow freezing pointBacteriaFood preparationBacterial strainRefrigeration
The invention discloses a probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration technology, a formula of a total-salt cryoprotectant which is suitable for the probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration technology, and probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration particles prepared by using the probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration technology. The probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration technology comprises following steps: (1) preparing a fermentation medium; (2) culturing probiotics; (3) centrifuging; (4) preparing the cryoprotectant; (5) adding the cryoprotectant; and (6) quick-freezing and moulding. The invention also provides a probiotic preparation prepared by using the probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration particles, and a preparation method of the probiotic preparation. The probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration particles are probiotic refrigerated bacterial strains which do not need to be dried and possesses advantages of fast refrigeration speed, high living bacterial rate and excellent rehydration performance. The probiotic ultralow temperature refrigeration particles contain water, can be dissolved in solutions more quickly, and are capable of preventing probiotic cells from damage caused by rehydration of normal low temperature refrigeration dried probiotic powder, and increasing the living bacterial rate of the probiotic preparation greatly.
Owner:THANKCOME BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method of cryopreservation of tissues by vitrification
InactiveUS7157222B2Direct effectEffective protectionMammal material medical ingredientsDead animal preservationVitrificationSmooth muscle
A method for vitrification of a tissue or organ includes immersing the tissue or organ in increasing concentrations of cryoprotectant solution at a temperature greater than −15° C. to a cryoprotectant concentration sufficient for vitrification; cooling the tissue or organ at an average rate of from 2.5–100° C. per minute to a temperature between −80° C. and the glass transition temperature; and further cooling the tissue or organ at an average rate less than 30° C. per minute to a temperature below the glass transition temperature to vitrify the tissue or organ. After the vitrified tissue or organ has been stored, the tissue or organ may be removed from vitrification by warming the tissue or organ at an average rate of from 20–40° C. per minute to a temperature between −80° C. and the glass transition temperature; further warming the tissue or organ at a rate greater than 80° C. per minute to a temperature above −75° C.; and reducing the concentration of the cryoprotectant. Tissues or organs treated in this manner exhibit near normal functions, for example, blood vessels exhibit near normal smooth muscle contractility and normal graft functions.
Owner:LIFELINE SCI
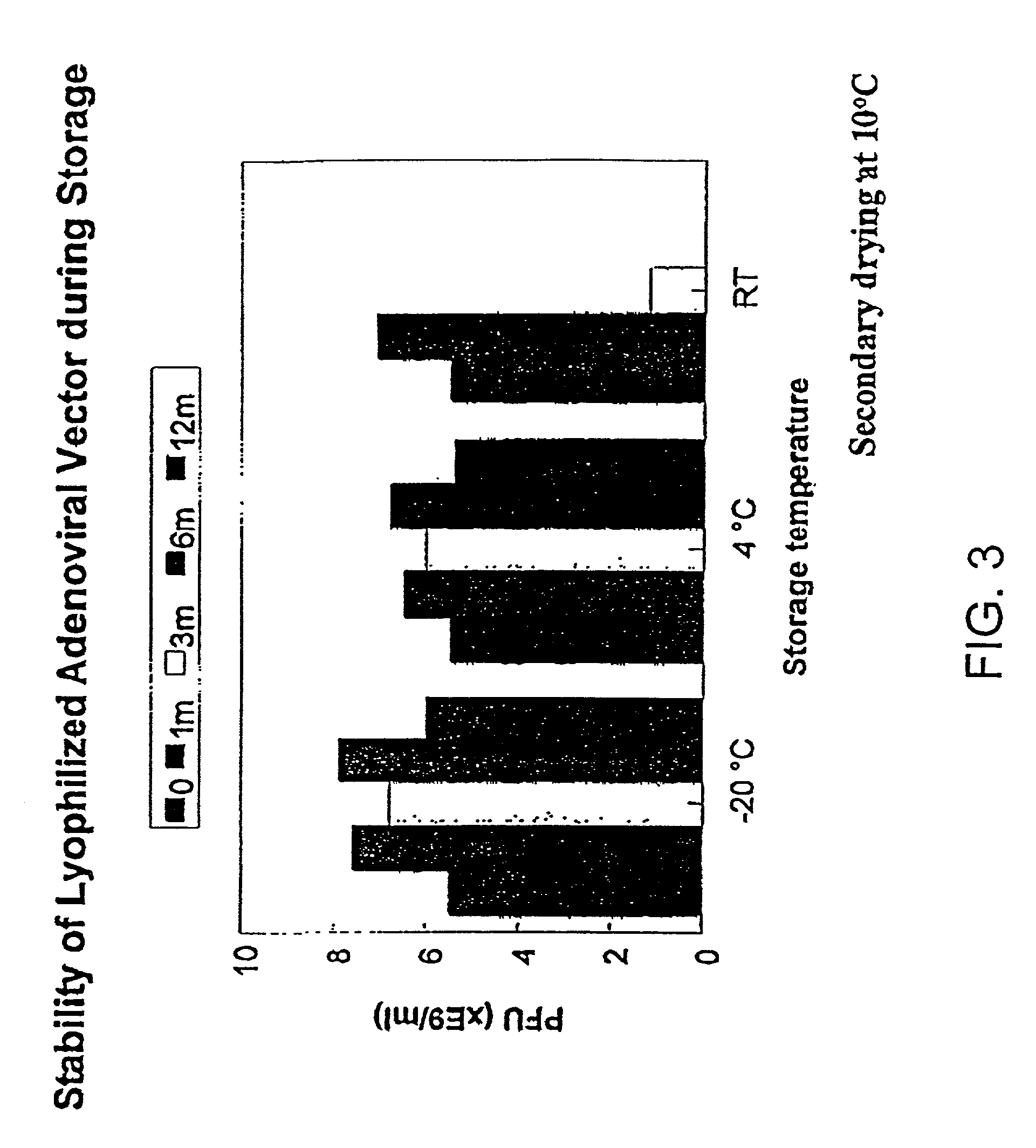
Formulation of adenovirus for gene therapy
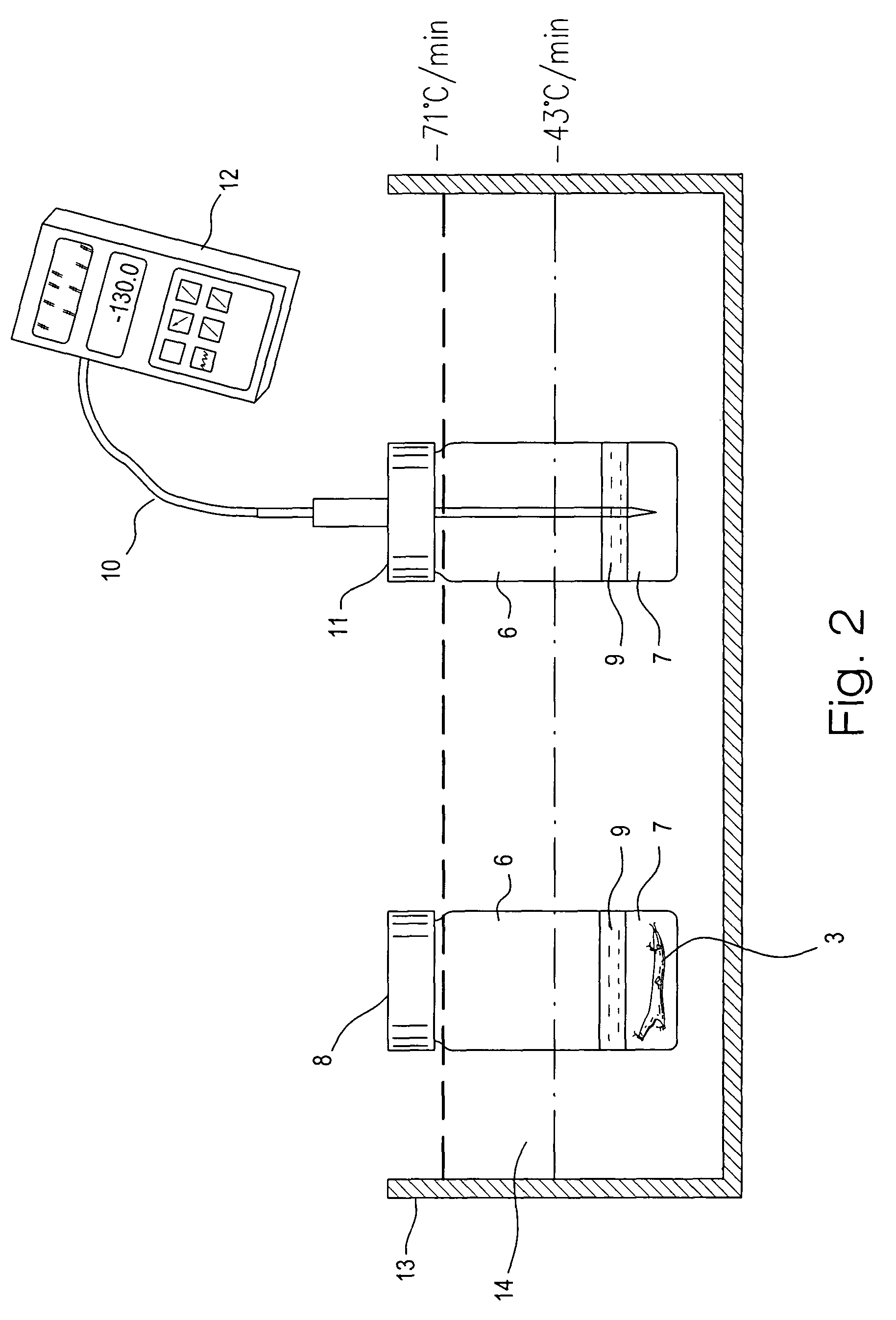
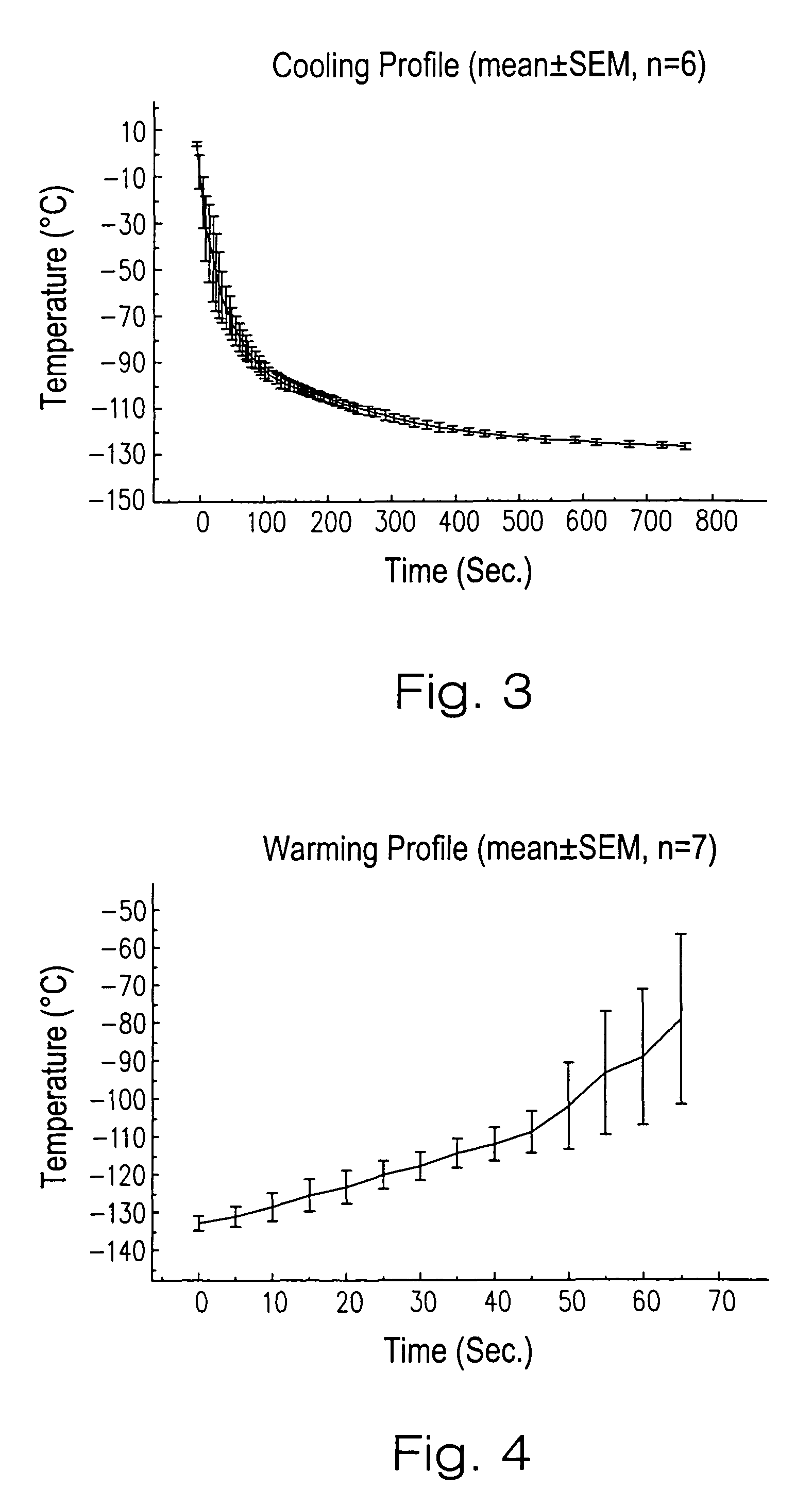
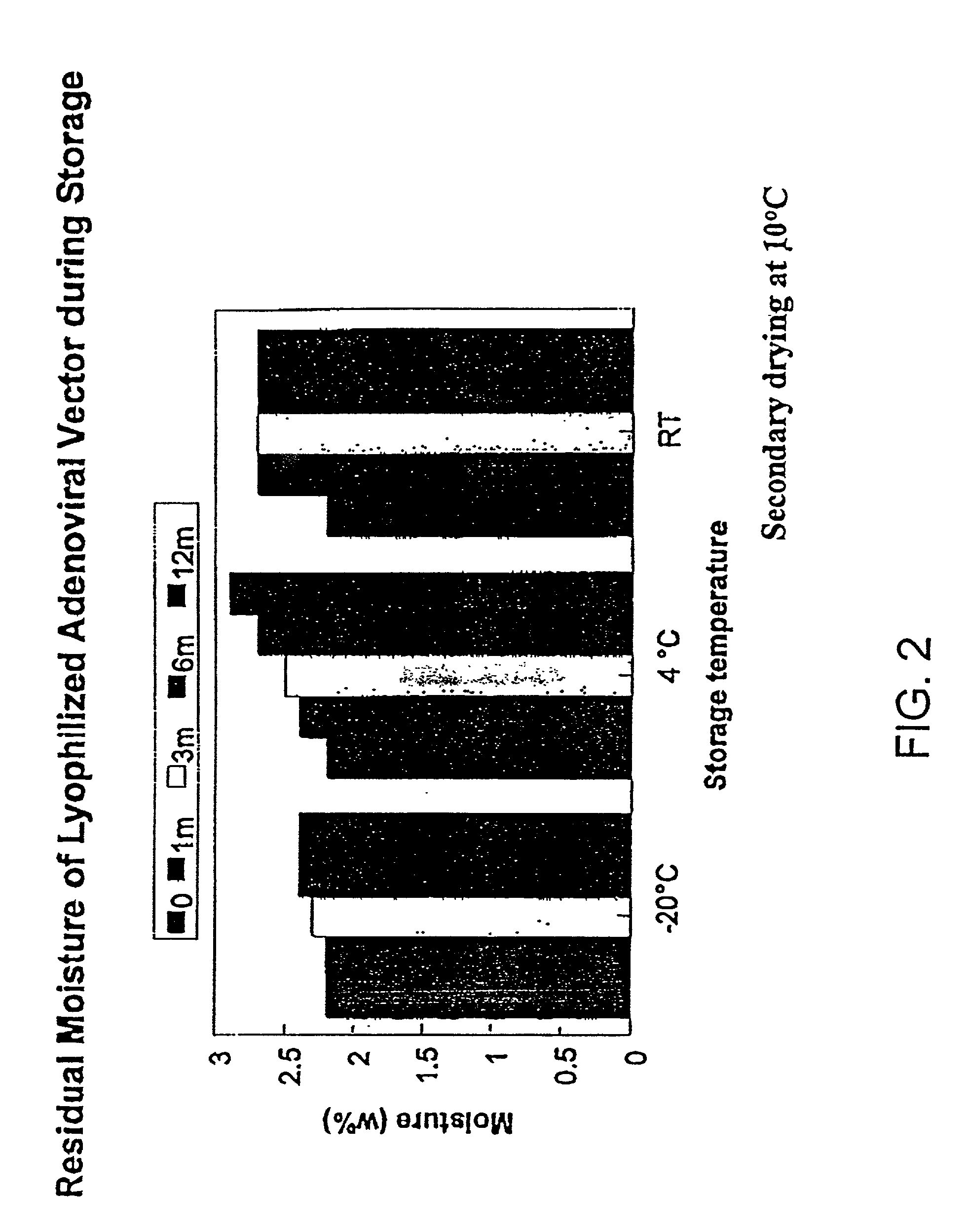
The present invention addresses the need to improve the long-term storage stability (i.e. infectivity) of vector formulations. In particular, it has been demonstrated that for adenovirus, the use of bulking agents, cryoprotectants and lyoprotectants imparts desired properties that allow both lyophilized and liquid adenovirus formulations to be stored at 4° C. for up to 6 months and retain an infectivity between 60–100% of the starting infectivity.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Frozen tilapia mossambica slice and its processing method
InactiveCN1935029AImprove water holding capacityReduce denaturationMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingFood preparationTilapiaAquatic product
The present invention discloses a kind of frozen tilapia mossambica fish fillets containing freezing protective agent trehalose and its processing method. Said processing method includes the following steps: making the tilapia mossambica fish undergo the processes of cleaning dressing, boning, skinning and filleting treatments, then adding protective agent to treat fish fillets, taking out said fish fillets, draining to remove excess solution and freezing below-18 deg.C so as to obtain the invented frozen tilapia mossambica fish fillets. The described protective agent is an aqueous solution containing trehalose, glycine and sodium chloride.
Owner:南宁中诺生物工程有限责任公司 +2
Preserved Viable Cartilage, Method for Its Preservation, and System and Devices Used Therefor
InactiveUS20080160496A1Good choiceFully testedBone implantDiagnosticsPreservation methodsBiomedical engineering
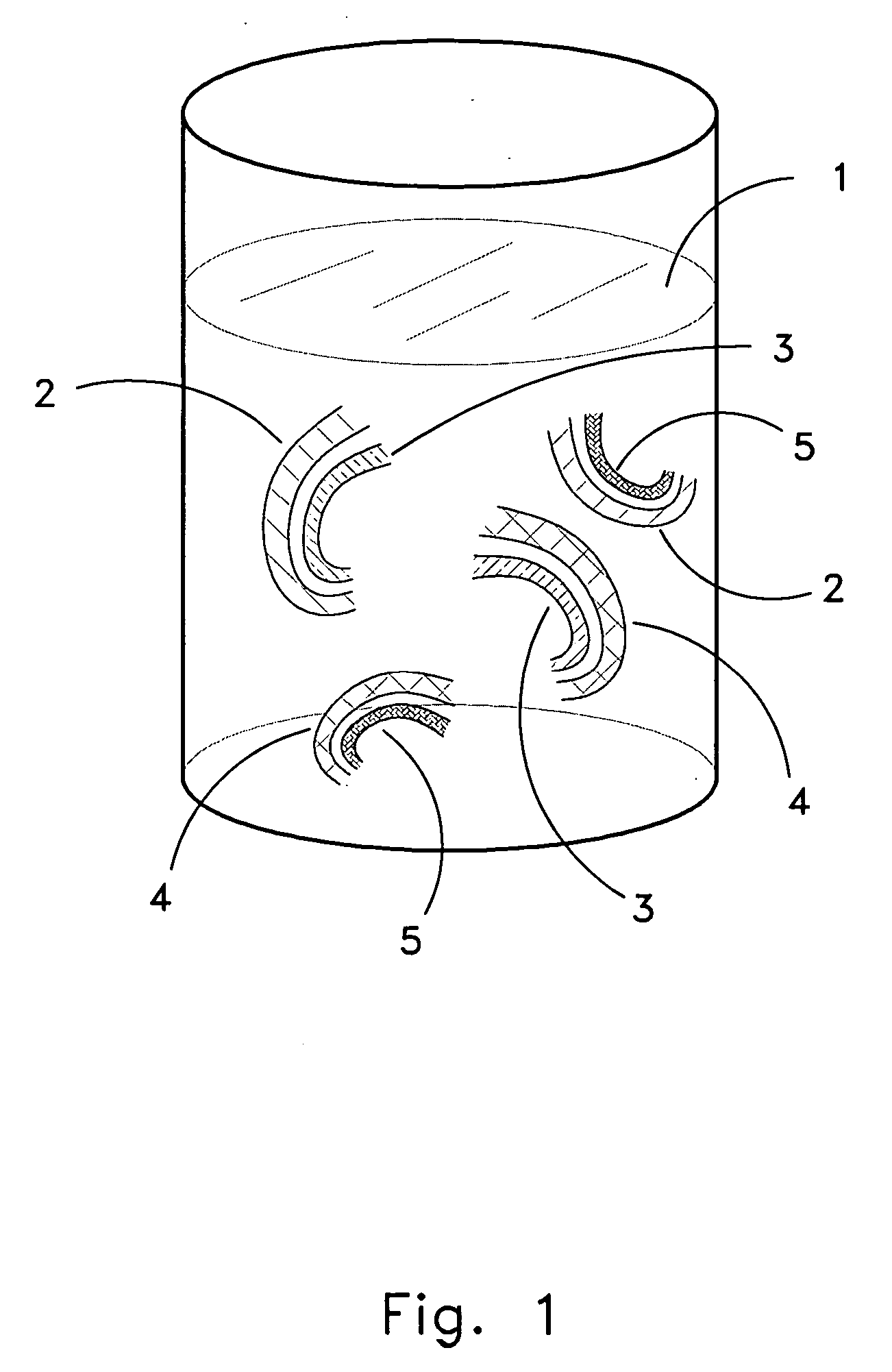
The present invention provides methods for providing cartilage-containing tissue for grafting, comprising providing excised cartilage-containing tissue; and treating said excised cartilage-containing and cryogenically preserving the treated cartilage-containing tissue under appropriate cryogenic preservation conditions so as to yield cryogenically preserved cartilage-containing tissue having at least 10% viable chondrocytes throughout the cartilage portion of the cartilage-containing tissue after preservation, as tested in a live / dead ratio assay. Treatment may comprise providing one or a plurality of incisions in said cartilage portion to a predetermined depth therein and / or introducing a cryoprotectant agent at least into said cartilage portion. The invention also provides viable cartilage obtainable by the methods of the invention, methods of grafting such preserved, viable cartilage containing tissue in a recipient, as well as apparatuses, vessels and systems for preparing a cartilage-containing tissue for cryogenic preservation and subsequent grafting in a recipient.
Owner:CORE DYNAMICS
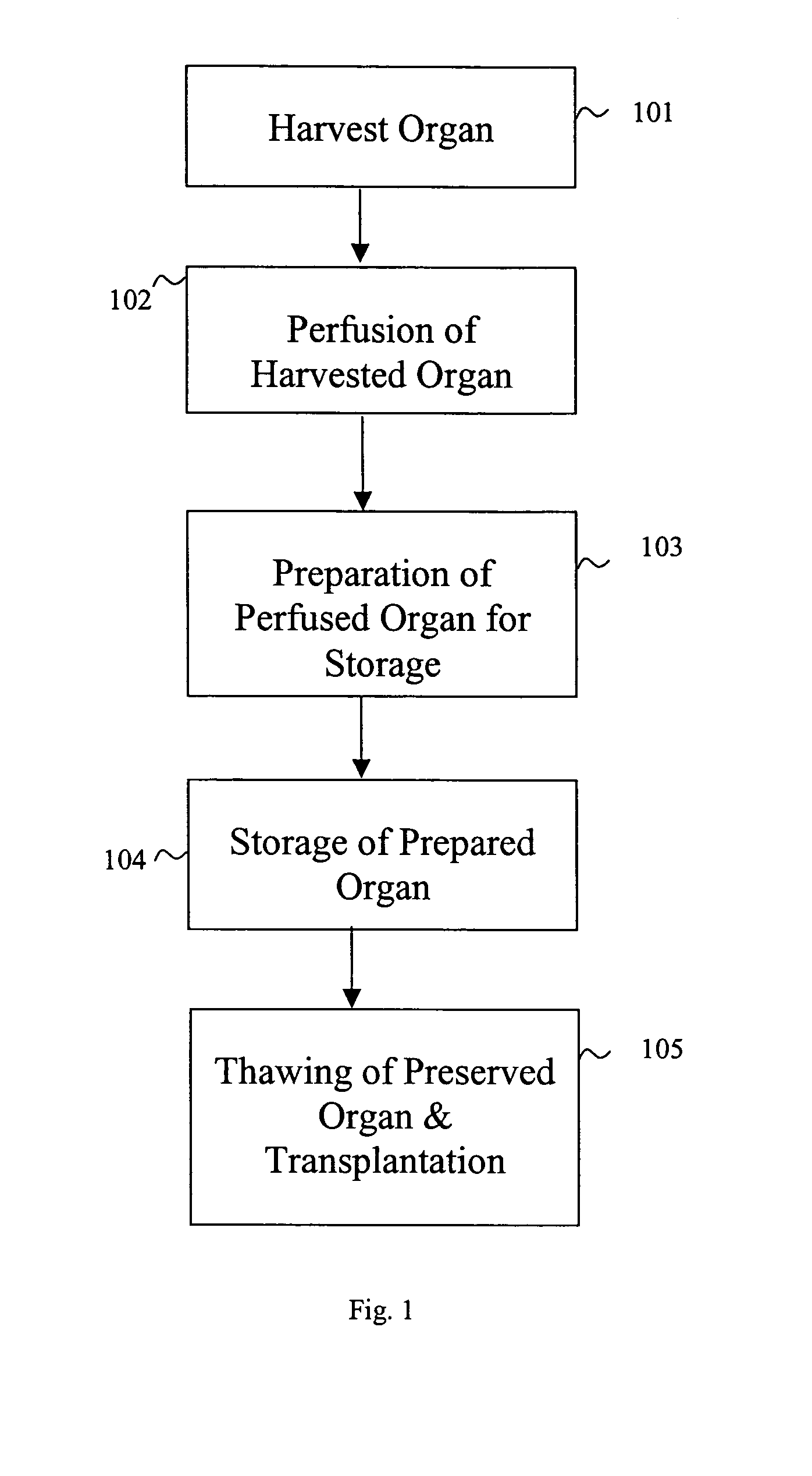
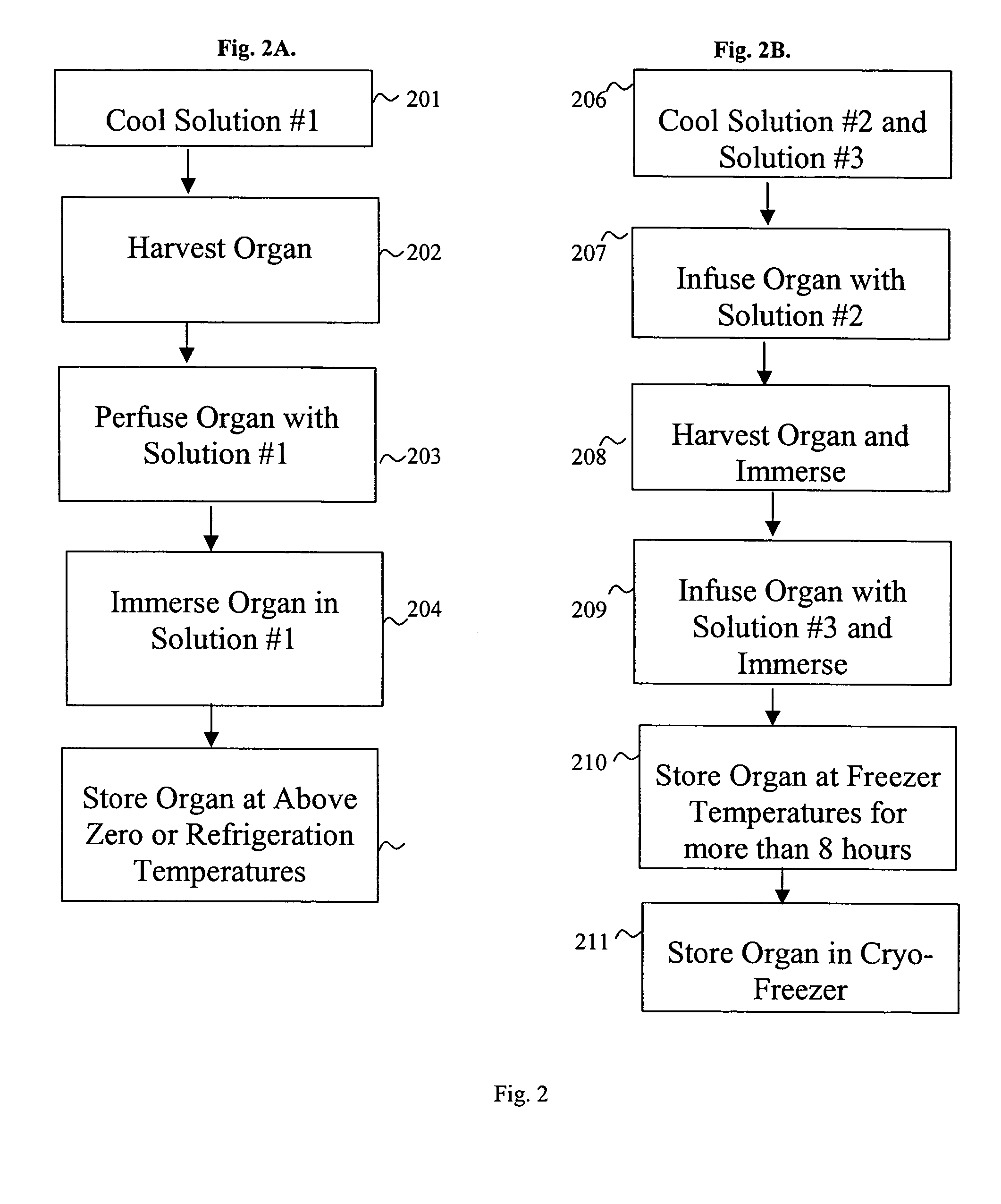
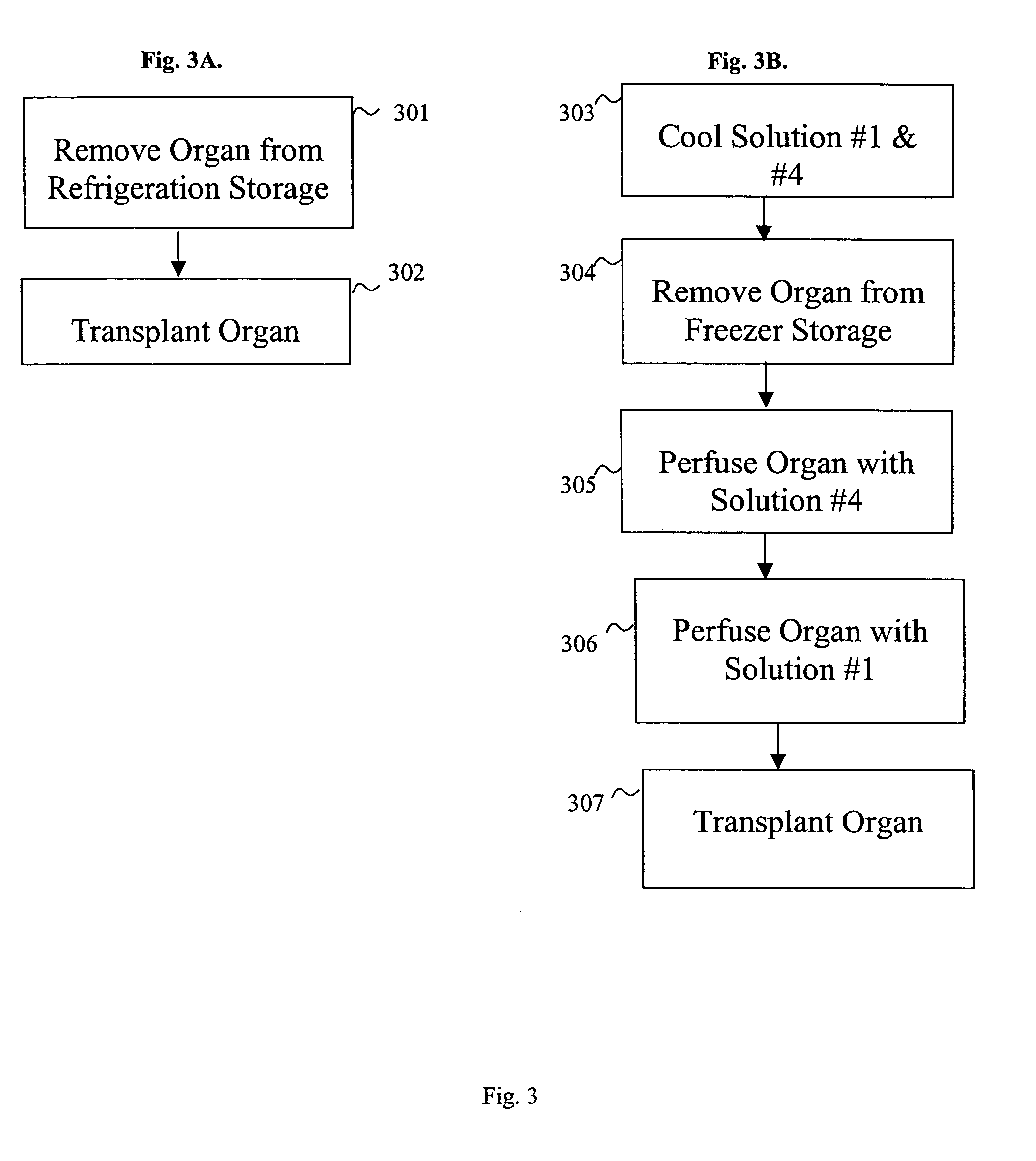
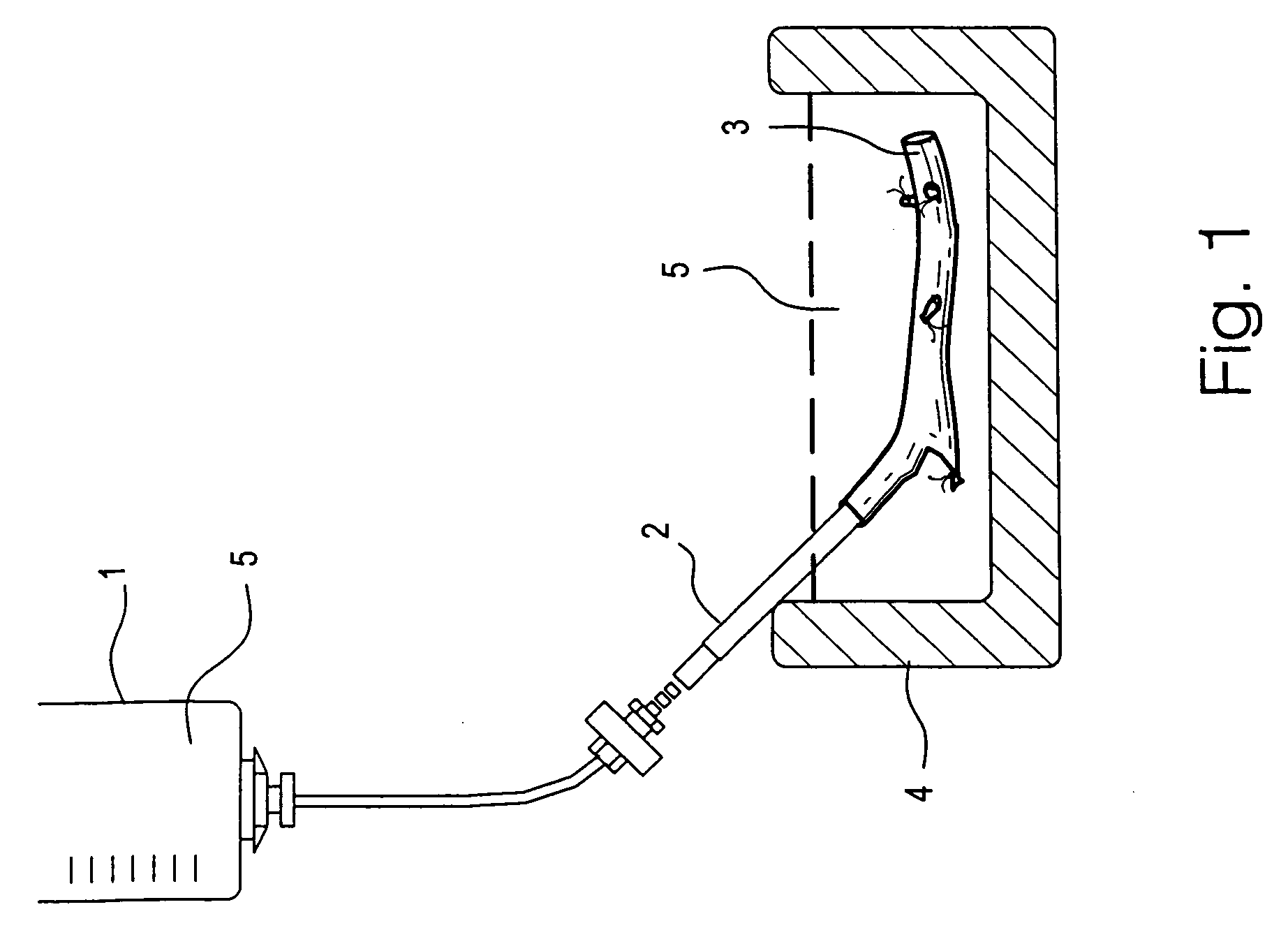
Methods and solutions for storing donor organs
InactiveUS7029839B2Reduction of interstitial edemaDead animal preservationTissue culturePolyethylene glycolPotassium
Owner:HUMAN BIOSYST
Method of cryopreservation of tissues by vitrification
InactiveUS20050100876A1Faster rateDirect protective effectMammal material medical ingredientsDead animal preservationVitrificationSmooth muscle
A method for vitrification of a tissue or organ includes immersing the tissue or organ in increasing concentrations of cryoprotectant solution at a temperature greater than −15° C. to a cryoprotectant concentration sufficient for vitrification; cooling the tissue or organ at an average rate of from 2.5-100° C. per minute to a temperature between −80° C. and the glass transition temperature; and further cooling the tissue or organ at an average rate less than 30° C. per minute to a temperature below the glass transition temperature to vitrify the tissue or organ. After the vitrified tissue or organ has been stored, the tissue or organ may be removed from vitrification by warming the tissue or organ at an average rate of from 20-40° C. per minute to a temperature between −80° C. and the glass transition temperature; further warming the tissue or organ at a rate greater than 80° C. per minute to a temperature above −75° C.; and reducing the concentration of the cryoprotectant. Tissues or organs treated in this manner exhibit near normal functions, for example, blood vessels exhibit near normal smooth muscle contractility and normal graft functions.
Owner:LIFELINE SCI
Use of polymeric excipients for lyophilization or freezing of particles
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Non-viable keratinocyte cell composition or lysate for promoting wound healing
Cultures of keratinocyte cells are provided which are free from nonautologous fibroblasts and organ extracts, and which have a high speed of cell amplification for a minimum seeding density. The cultures can be cryopreserved in a buffered isotonic medium containing serum and a cryoprotectant. The cultures are produced by a process that does not involve the use of a feeder layer and organ extracts. A culture medium which can be used contains Medium 199, serum, epidermal growth factor, cholera toxin and / or hydrocortisone, and optionally insulin. A substance for wound healing and for cosmetic applications is derived from cultured human keratinocytes. A non-viable total keratinocyte lysate for use in promoting wound healing is produced by growing keratinocyte cells on a support, detaching the cells from the support, and lysing the detached cells to obtain the lysate which may be frozen and lyophilized. The cells may be grown without using a support to produce the lysate, or to produce a non-viable keratinocyte cell culture lyophilisate or spray dried non-viable keratinocyte cell composition for use in healing wounds.
Owner:CELLTRAN LTD
Acoustic blood separation processes and devices
ActiveUS20170049949A1Improved fluid dynamicsEasy to separateOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesLipid formationUltrasonic sensor
Acoustophoretic devices are disclosed. The devices include a flow chamber, an ultrasonic transducer, a reflector, an inlet, a filtrate outlet, a concentrate outlet, and optionally a lipid collection trap. The ultrasonic transducer and reflector create a multi-dimensional acoustic standing wave in the flow chamber that traps and separates red blood cells and / or lipids from blood. Concentrated red blood cells can be recovered via the concentrate outlet, the lipids can be recovered via the lipid collection trap, and the remaining blood can be recovered via the filtrate outlet. Methods for separating blood components (e.g., red blood cells, lipids, platelets, white blood cells) from blood are also disclosed. The red blood cells can undergo washing with a solvent to remove undesired admixtures. Cryoprotectants can be added or removed from the blood.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
Method of cryopreserving cells
InactiveUS20060063141A1Maximum recoveryDead animal preservationBiological testingMathematical modelCryopreserved Cell
A non-linear cooling cryopreservation method for improving cryopreservation protocols for cells that involves producing a simulation of cellular responses to a range of cooling parameters; determining optimal cooling parameters required to minimize cryoinjury to the cells using simulation of cellular responses and experimental results; and incorporating optimal parameters into the protocol. The simulation is based on mathematical models of cellular parameters. A non-linear cooling cryopreservation protocol for cryopreserving stem cells is also disclosed that does not require cryoprotectants.
Owner:MCGANN LOCKSLEY EARL +2
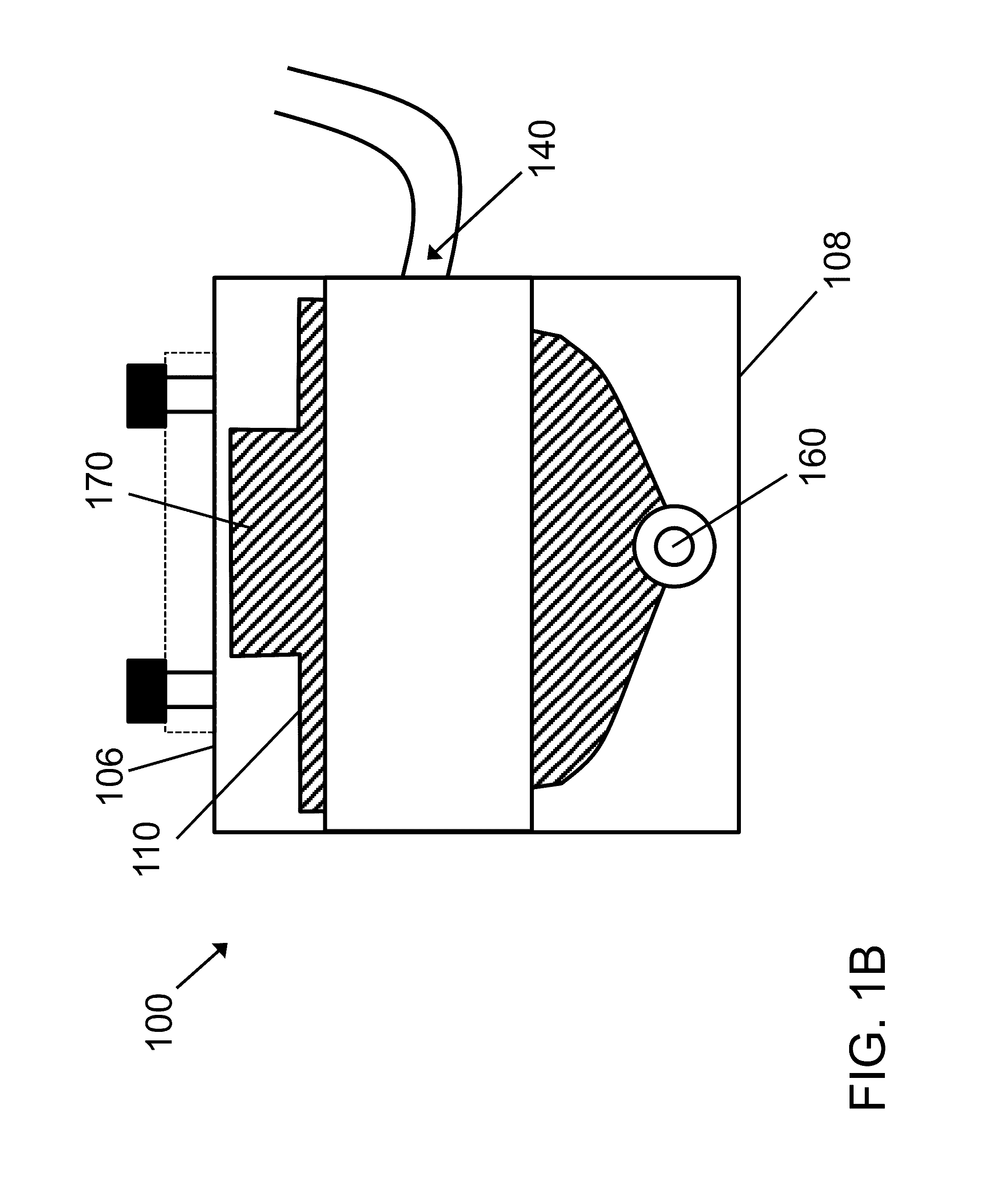
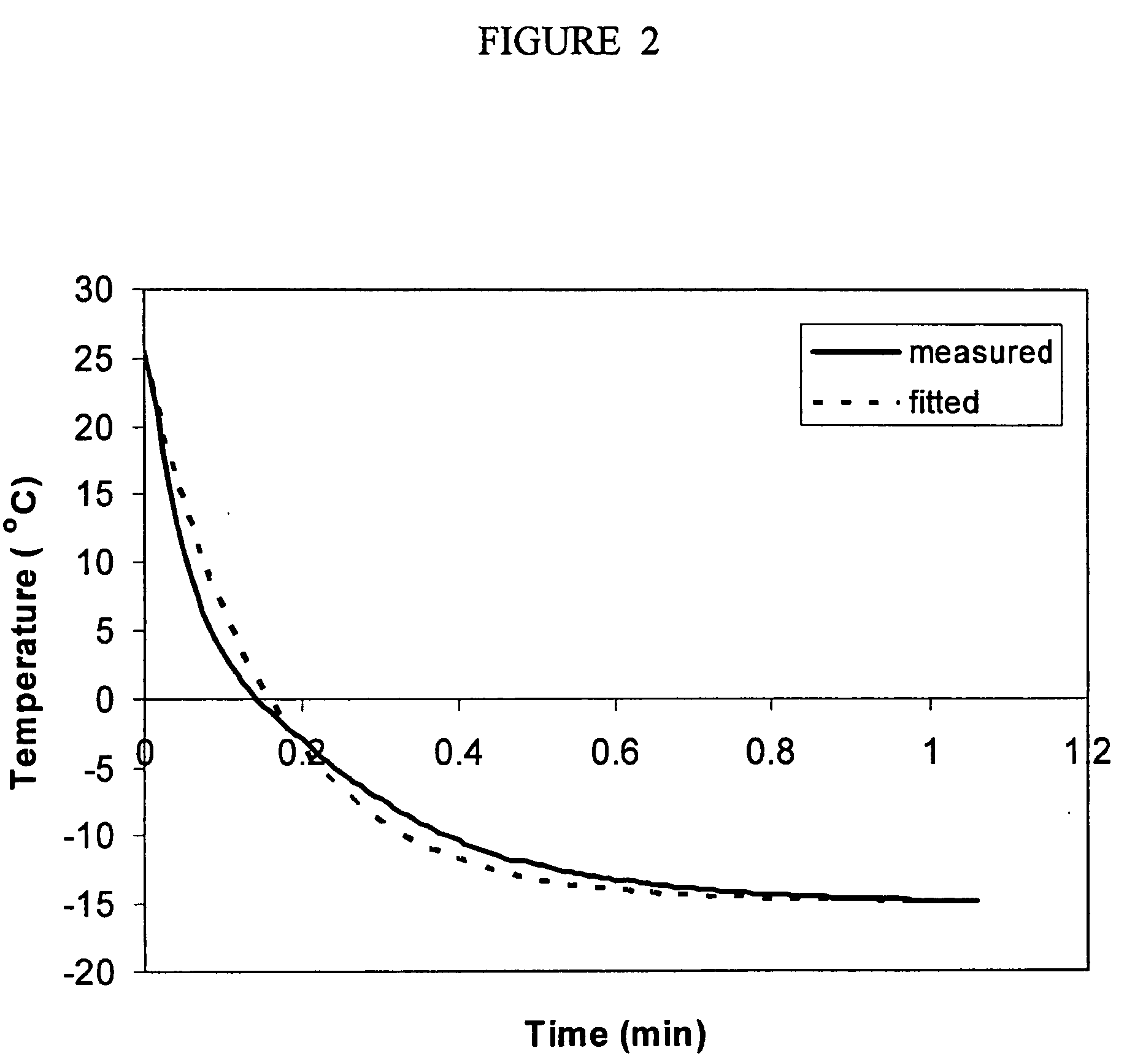
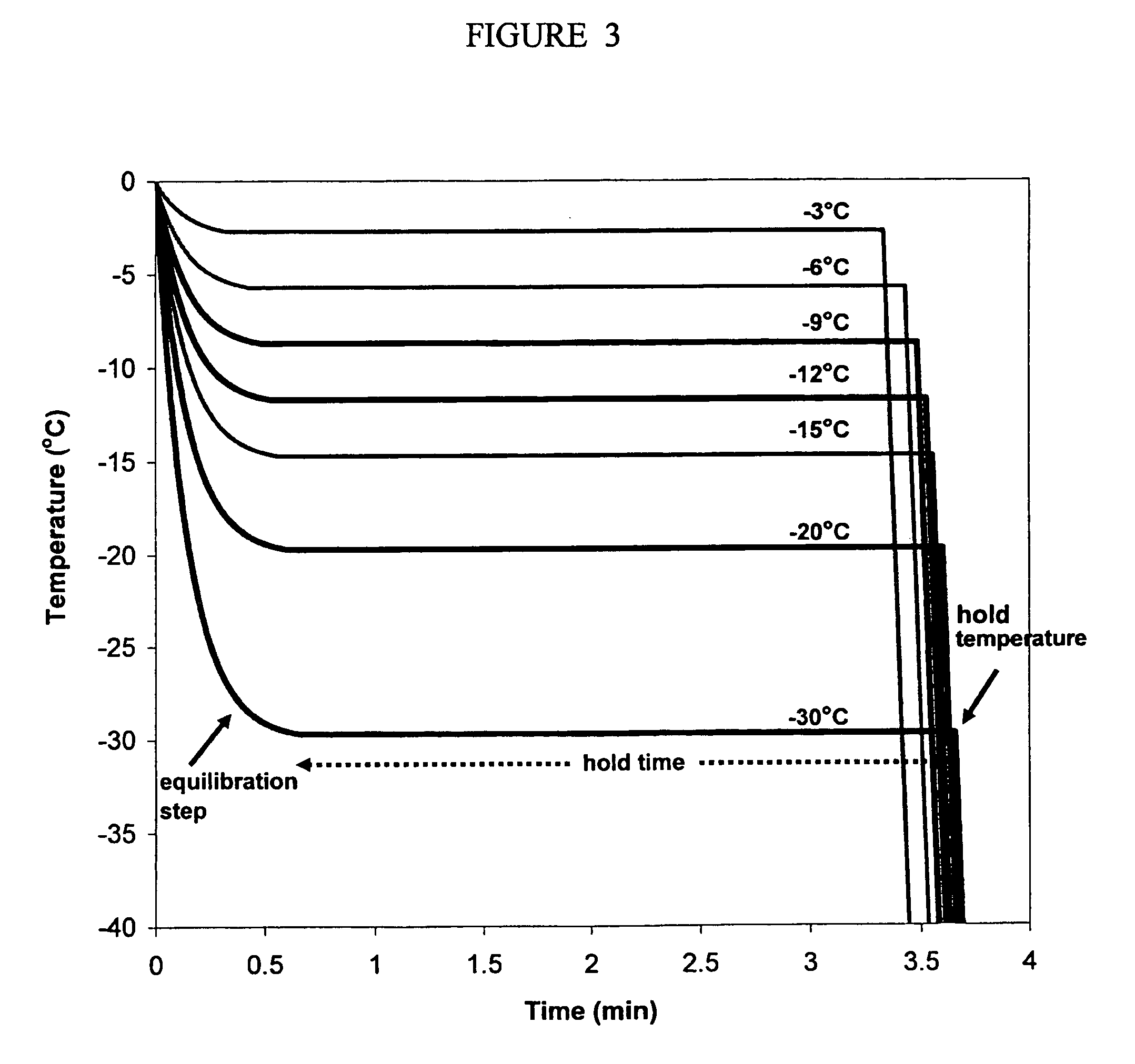
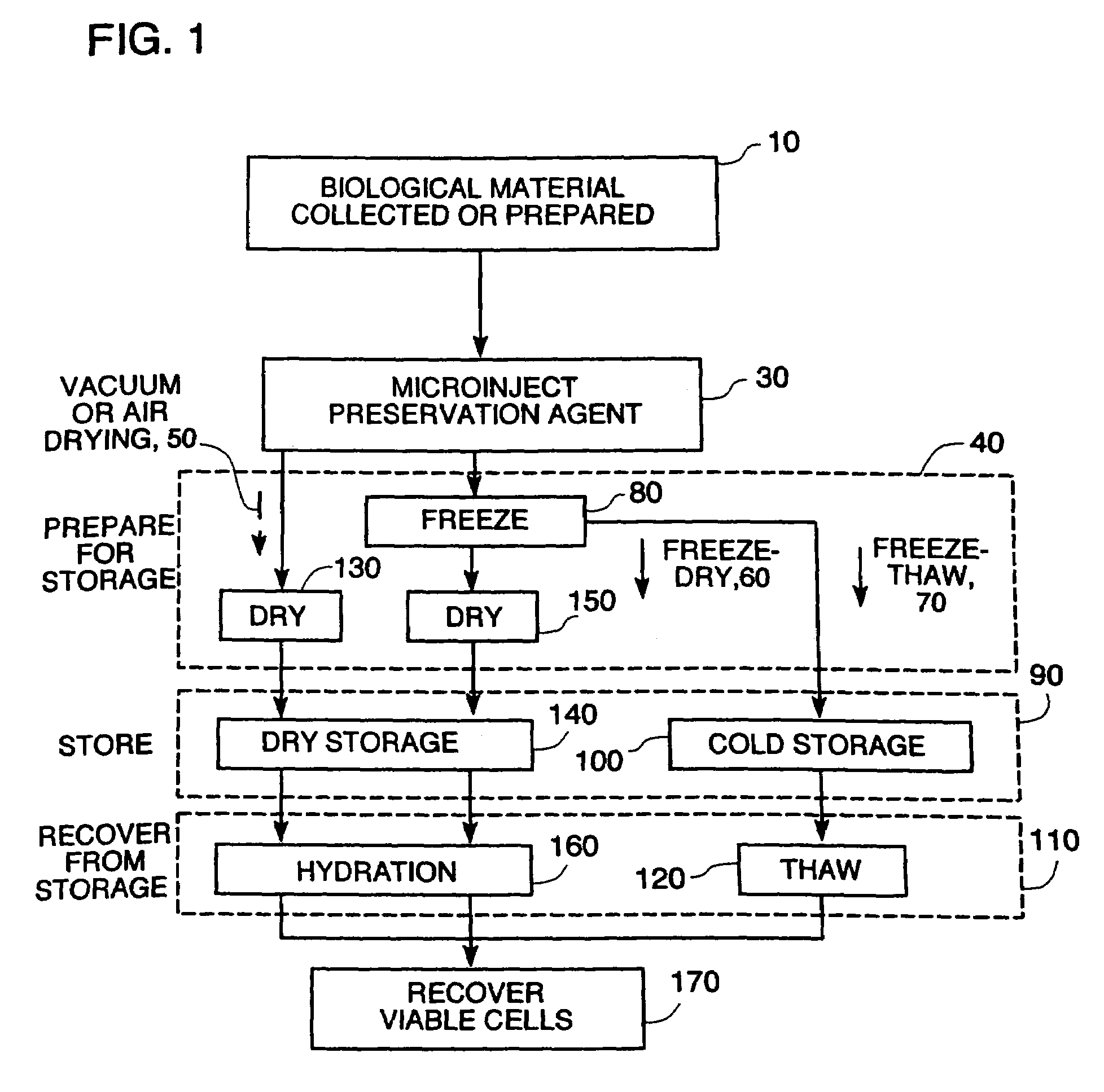
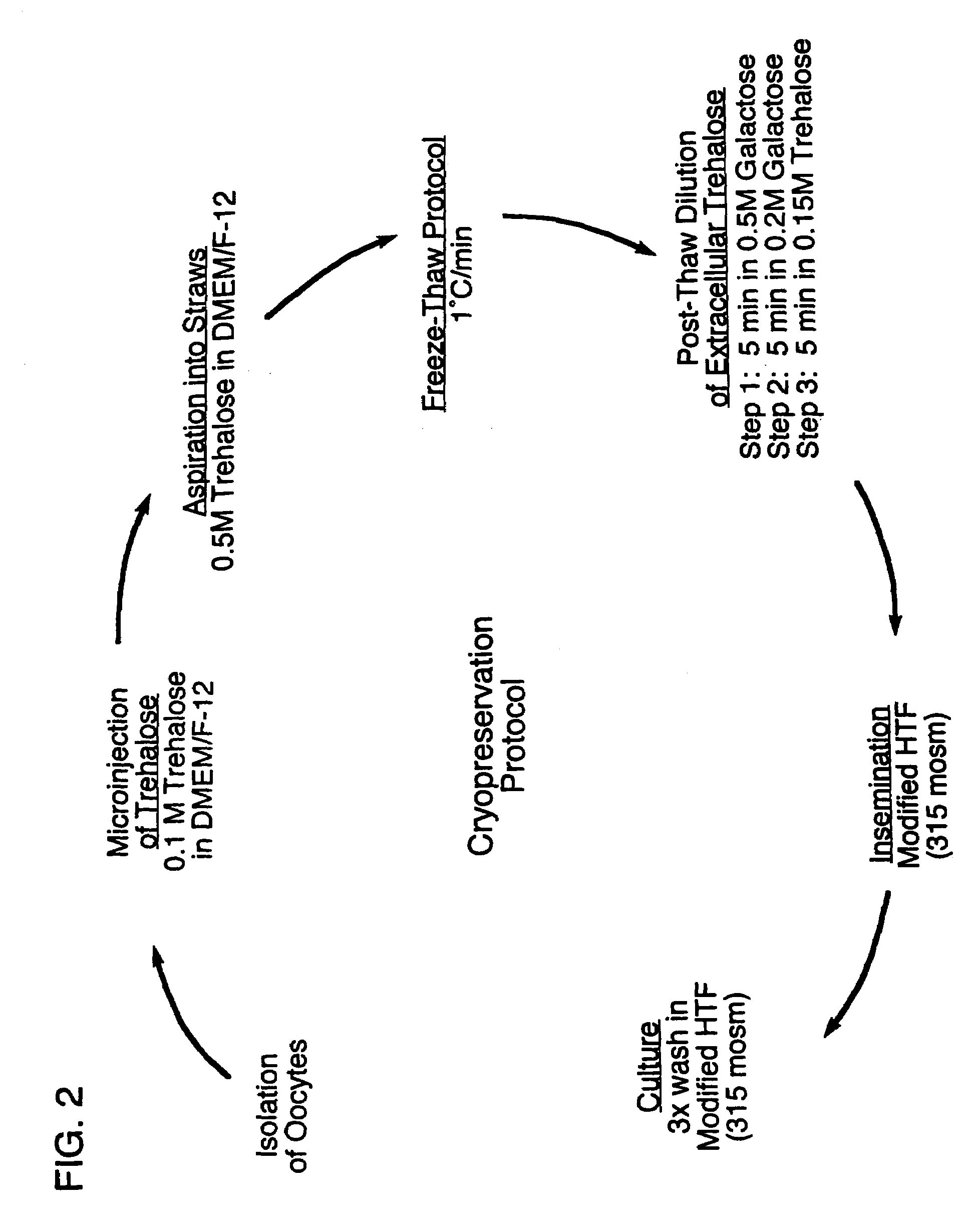
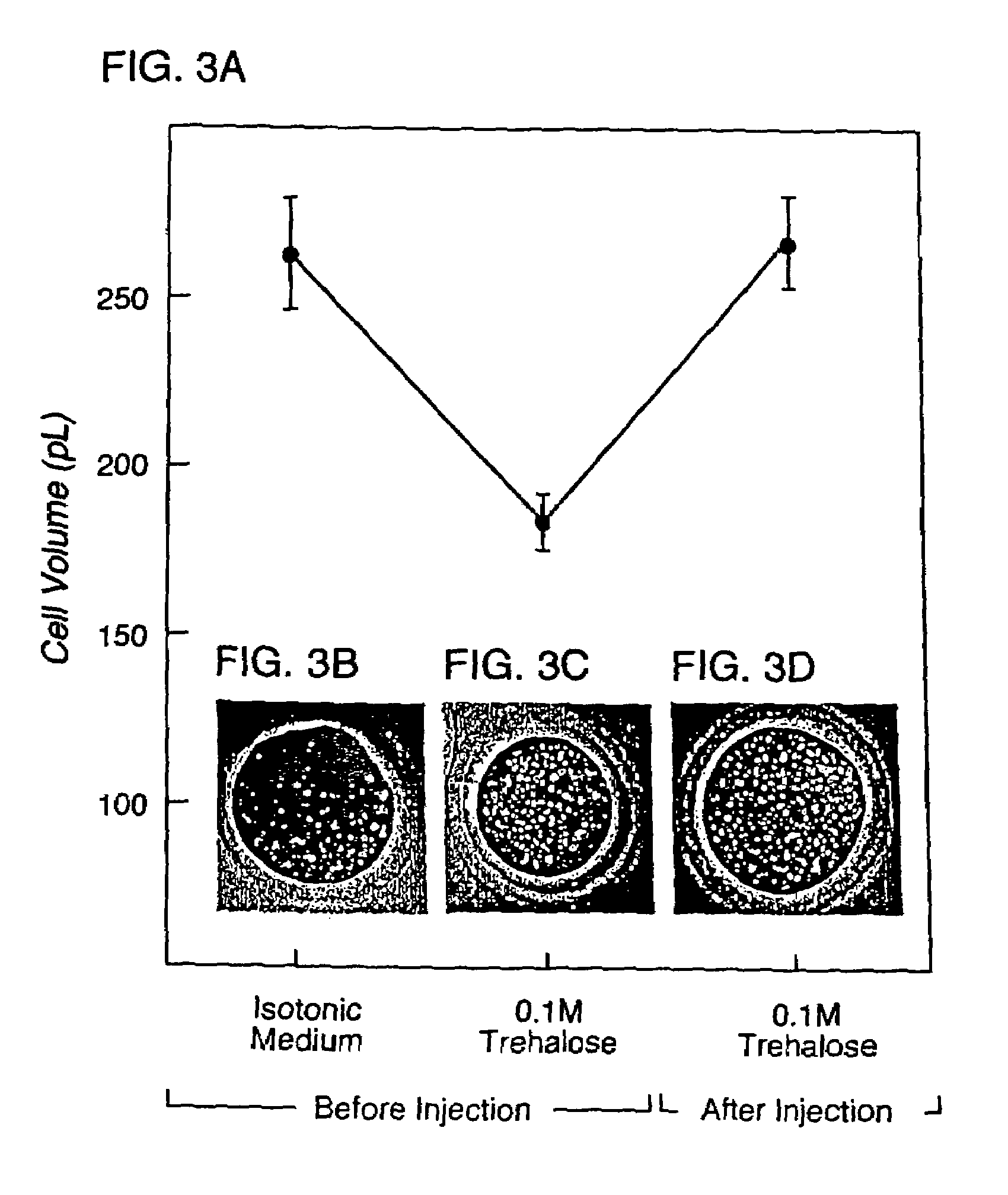
Microinjection of cryoprotectants for preservation of cells
A preservation method for biological material having cell membranes includes microinjecting the cells with sugar; preparing the cells for storage; storing the biological material; and recovering the stored biological material from storage. The invention also features a method of culturing a cell in vitro using a hypertonic medium. Carbohydrate sugars such as trehalose, sucrose, fructose, dextran, and raffinose, may be used as bio-protective agents or in the culture medium.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cell preservation method
InactiveUS20120149108A1High viability rateIncrease chanceAnimal cellsDead animal preservationMagnesium saltsSodium salt
A method for cryopreservation of cells characterized by the use of a solution containing, as essential components, a sodium salt, a potassium salt, a saccharide, a cryoprotectant, and a hydrogencarbonate salt and / or a carbonate salt, the solution further optionally containing a component selected from the group consisting of proteins, magnesium salts, and calcium salts. According to the present invention, a method for cryopreservation of cells capable of maintaining a high viability rate after thawing, and a cryopreservation solution used in the cryopreservation are provided. In addition, by using the method for cryopreservation, the cells can be preserved in a state of maintaining a high viability rate even after thawing, and also maintaining their physiological functions; further, a cell washing step after freezing and thawing is unnecessary, thereby making it very useful in the fundamental researches of cells and the application studies on the medical treatment.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Method for preparing freeze-dried microbial agent of kluyveromyces marxianus and application of freeze-dried microbial agent
ActiveCN107034149ASimple ingredientsLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesFruit juiceFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a method for preparing a freeze-dried microbial agent of kluyveromyces marxianus and application of the freeze-dried microbial agent. The freeze-dried microbial agent is prepared by the aid of high-density fermentation culture and freeze-drying technologies. The kluyveromyces marxianus is preserved in the Common Microorganism Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, called as CGMCC for short, on April 27th, 2010, the preservation number of the kluyveromyces marxianus is CGMCC NO.3781, and the strain number is A3. The method and the application have the advantages that the viable cell number of high-density culture solution of the kluyveromyces marxianus can reach 3.2*10<8> cfu / mL at least and is higher than culture results of YEPD (yeast peptone dextrose) culture media by 1.1 order of magnitude at least; zymocyte solution is centrifuged, then bacterial sludge is collected and is added into cryoprotectant solution, the freeze-dried microbial agent can be prepared by the aid of the vacuum freeze-drying technologies, protectants for the freeze-dried microbial agent comprise maltose and skimmed milk powder, and the freeze-dried viable bacterium rate can reach 75% at least; the freeze-dried microbial agent is high in bacterium content, long in storage time, convenient to use and free of pollution, is environmentally friendly and can be used for fermenting milk beer and cheese and making whey wine, fruit vinegar, fruit juice and the like, processes for preparing the freeze-dried microbial agent are simple, and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TIANRUN BIOTECH
Cryopreservation protection liquid for Wharton jelly tissues of human umbilical cord and preparation and application of cryopreservation protection liquid
The invention relates to cryopreservation protection liquid for Wharton jelly tissues of a human umbilical cord. The cryopreservation protection liquid comprises 5-10 percent of a permeable cryoprotectant, 1-5 percent of a non-permeable cryoprotectant, 10-20 percent of a knockout serum replacement and 70-80 percent of a serum-free basal culture medium. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the cryopreservation protection liquid. The preparation method specifically comprises the steps of (1) precooling the serum-free basal culture medium, the non-permeable cryoprotectant and the knockout serum replacement, mixing and uniformly shaking; (2) adding the permeable cryoprotectant; and (3) performing refrigeration under a temperature condition of 2-6 DEG C for more than 30min. The invention also discloses a cryopreservation method for the Wharton jelly tissues of the human umbilical cord by the cryopreservation protection liquid. The cryopreservation method comprises the following steps of (1) pretreating the umbilical cord; (2) peeling off the Wharton jelly tissues; and (3) cryopreserving the Wharton jelly tissues of the human umbilical cord. The cryopreservation protection liquid and the cryopreservation method which are used for treating the Wharton jelly tissues of the human umbilical cord have the advantages that injury to umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a cryopreservation process can be alleviated, so that the activity and the clinical use safety of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are guaranteed.
Owner:重庆市红汇脐血干细胞中心有限公司
Methods for the Cryopreservation of Mammalian Cells
ActiveUS20090305224A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove survivabilityDead animal preservationTissue cultureMammalSlow freezing
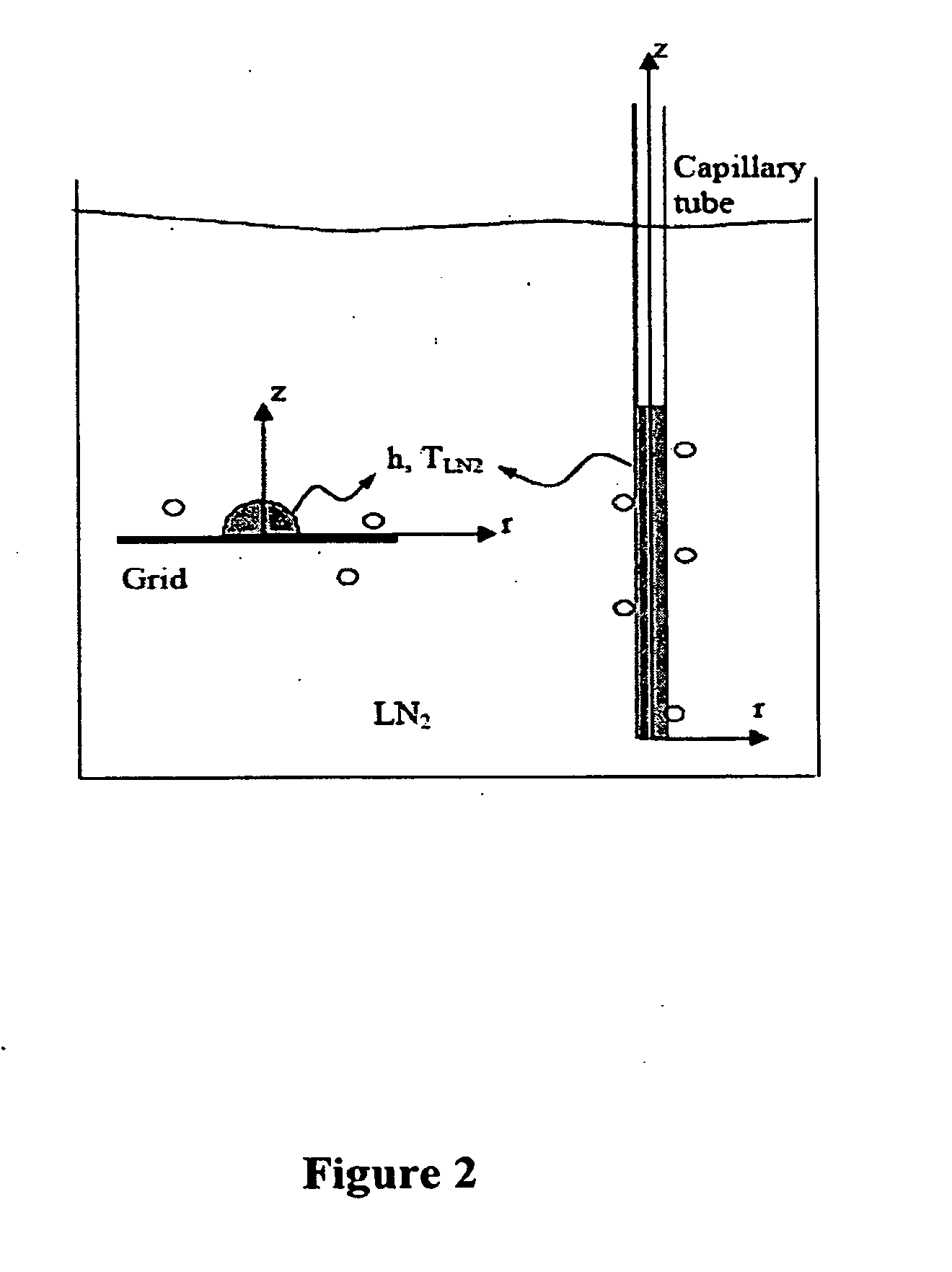
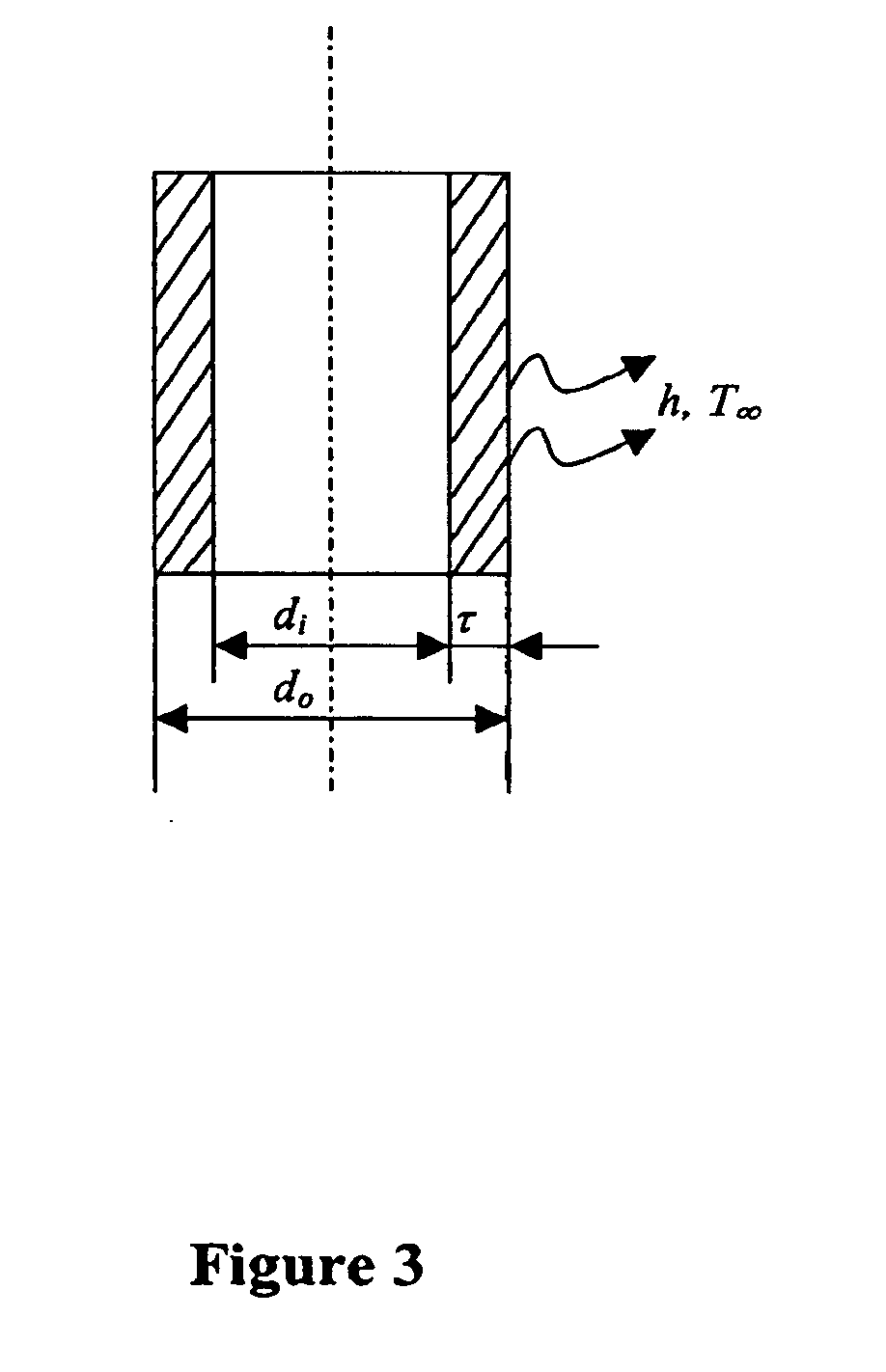
The present invention features novel methods for the cryopreservation of mammalian cell that combine the advantages of the slow-freezing and vitrification approaches while avoiding their shortcomings. Generally, the methods include the use of a capillary tube made of a thermally conductive wall material and a thin wall such that the ratio of the thermal conductivity of the wall material to the wall thickness is at least 1,000-500,000. The solution is then exposed to temperatures equal to or less than −80° C. and the vitrification solution containing the mammalian cells is cooled at a rate equal to or greater than 30,000-100,000,000° C. / minute. The exposure of the capillary tube with a thermally conductive and thin wall allows for vitrification of the solution in the absence of ice formation. Cryoprotectants can also be added to the vitrification solution to further prevent ice formation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
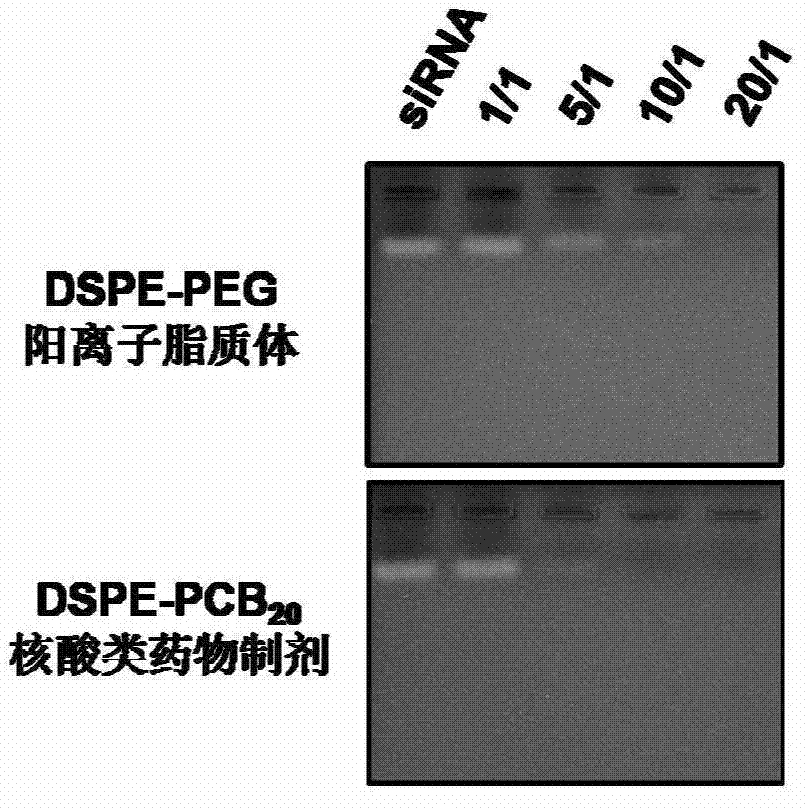
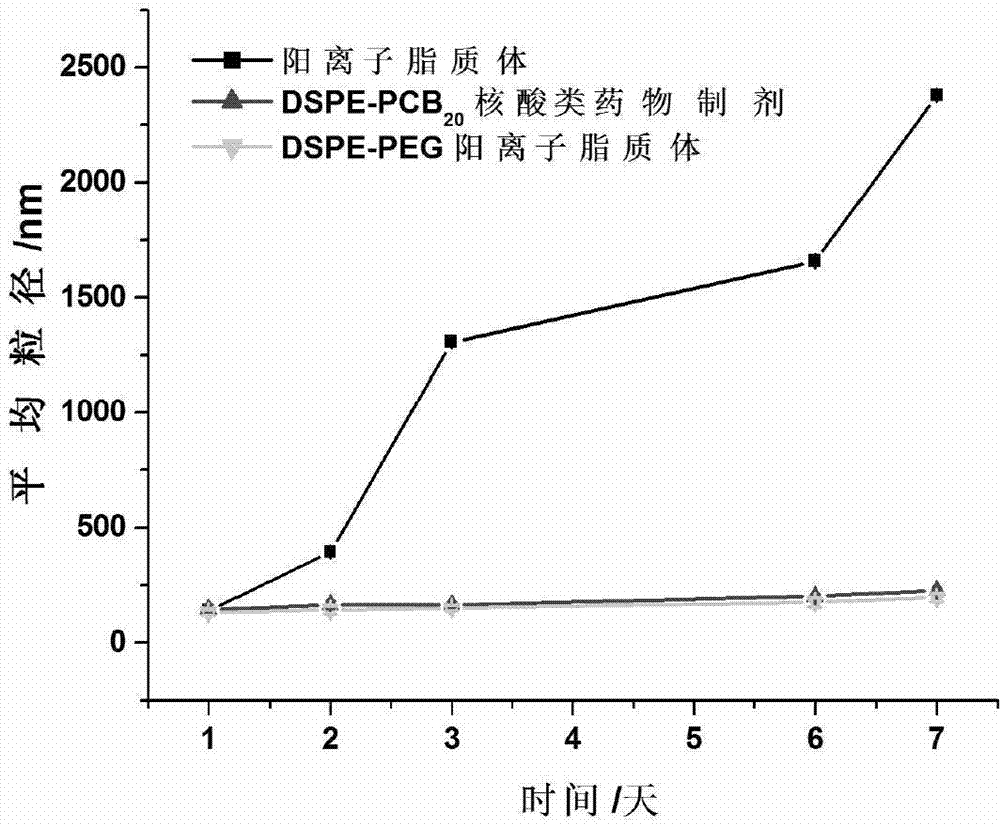
Novel cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
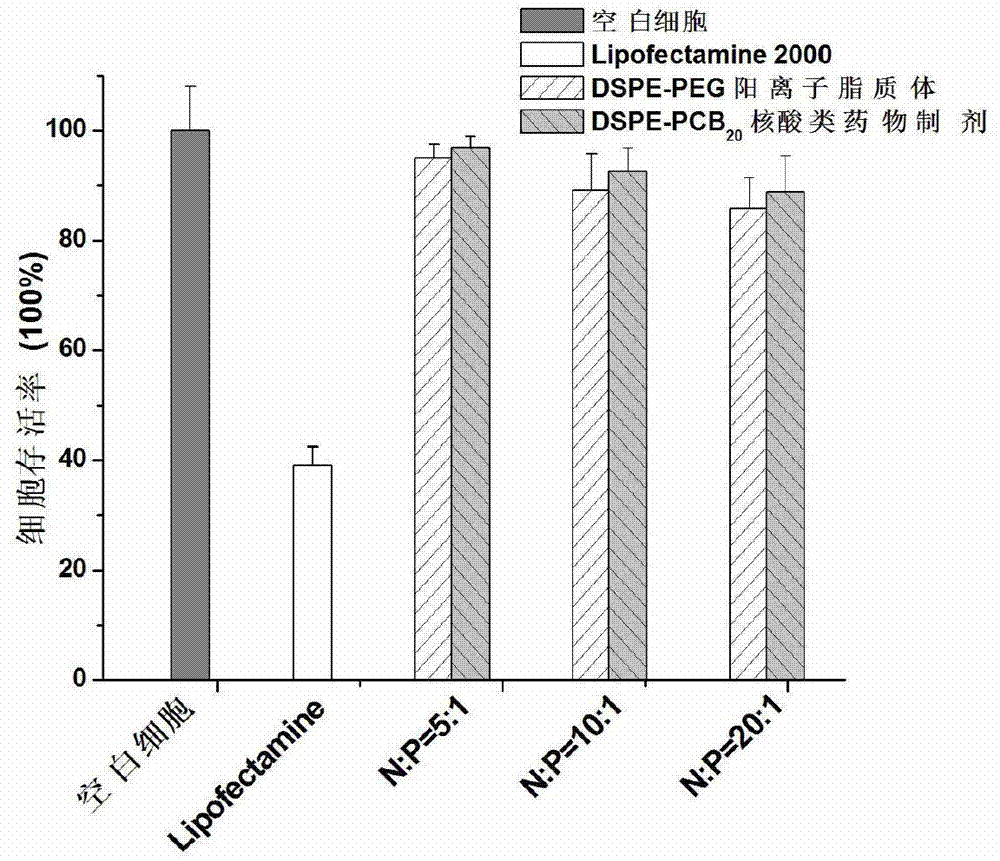
ActiveCN103194489APromote escapeIncrease serum stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticBetaineLipid molecule
The invention discloses a novel cationic liposome, a cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation having the same as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The cationic liposome comprises cationic lipid, assisted lipo, polycarboxyl betaine lipid molecule and a freezing protective agent. The cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation comprises cationic liposome modified by neutral lipid of polycarboxyl betaine and nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation working solution. According to the cationic liposome, the defects of high toxicity, bad blood stability and low transfection efficiency are overcome and the pharmaceutical effects of the nucleic acid drugs are effectively improved; and at the same time, as the preparation is undisturbed by blood serum during the use, the operations in the experiment and the treatment are simplified.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
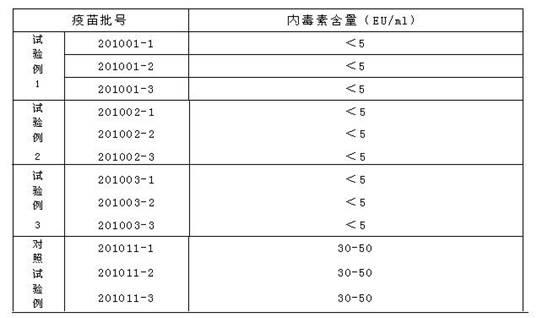
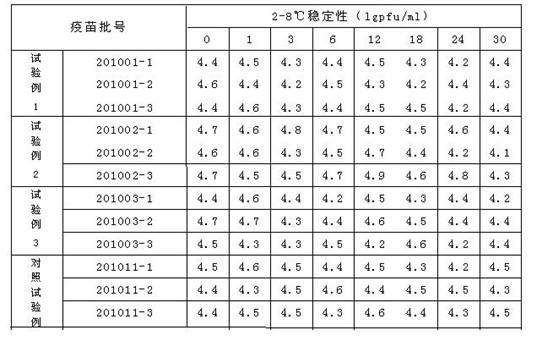
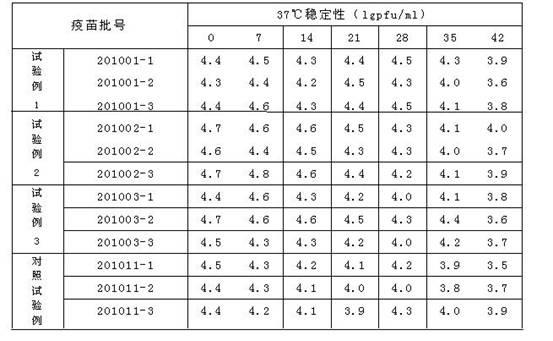
Vaccine cryoprotectant without composition of gelatin and human albumin
ActiveCN102657870ALow costLow endotoxin contentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsMonosodium glutamateSucrose
The invention discloses a vaccine cryoprotectant without composition of gelatin and human albumin. The vaccine cryoprotectant comprises dextran (40), cane sugar, lactose, mannitol, glycine, arginine, sodium glutamate, urea and 199 synthetic medium. The invention does not contain ingredients of animal origin and the content of endotoxin of vaccine is greatly decreased, thus irritation and harm to a human body are greatly decreased and the vaccine has better safety and stability. Meantime, the cryoprotectant disclosed by the invention does not contain expensive raw materials such as trehalose and the like, thus the cryoprotectant has the advantage of low cost and is more applicable to industrialization.
Owner:CHANGCHUN KEYGEN BIOLOGICAL PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com