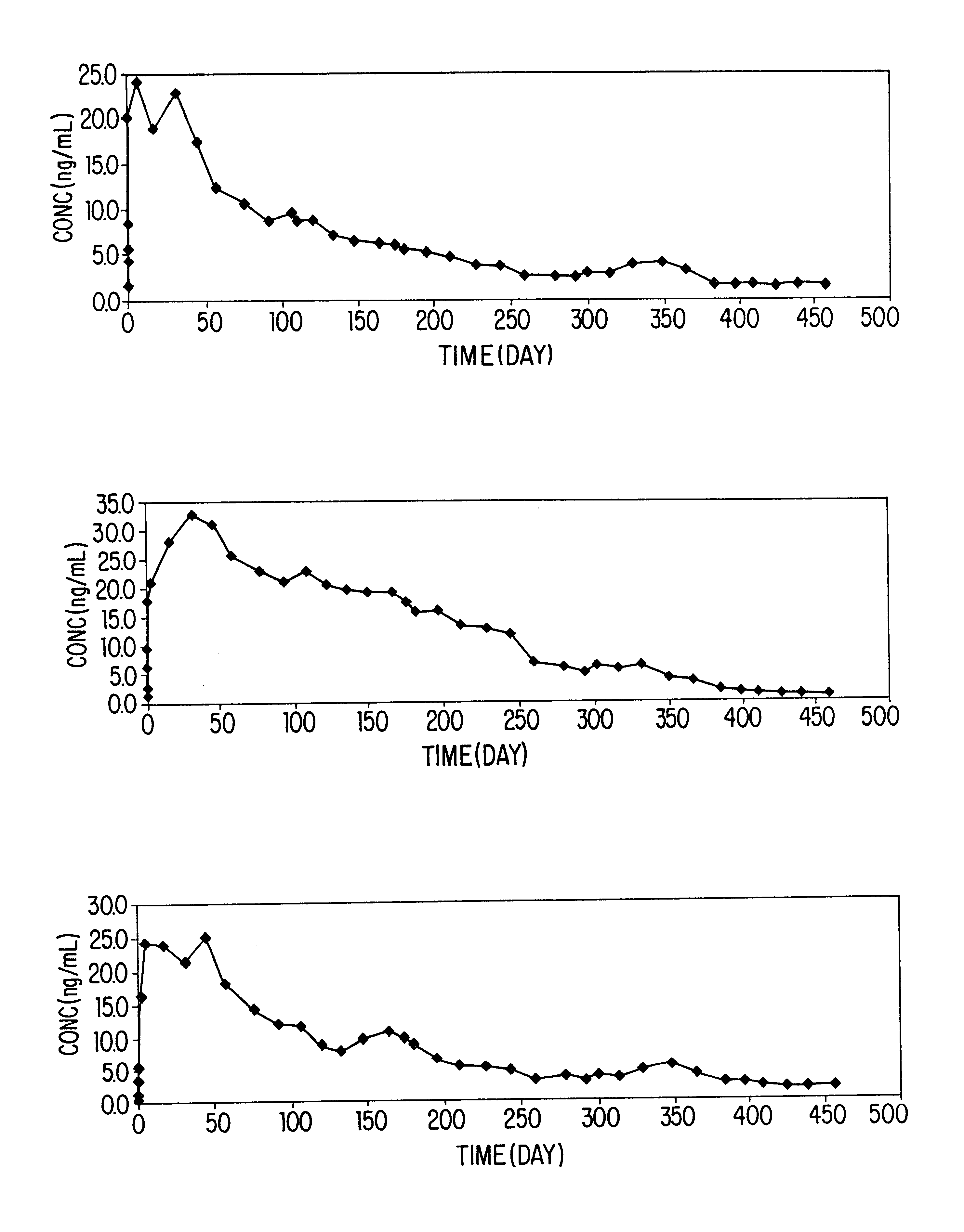
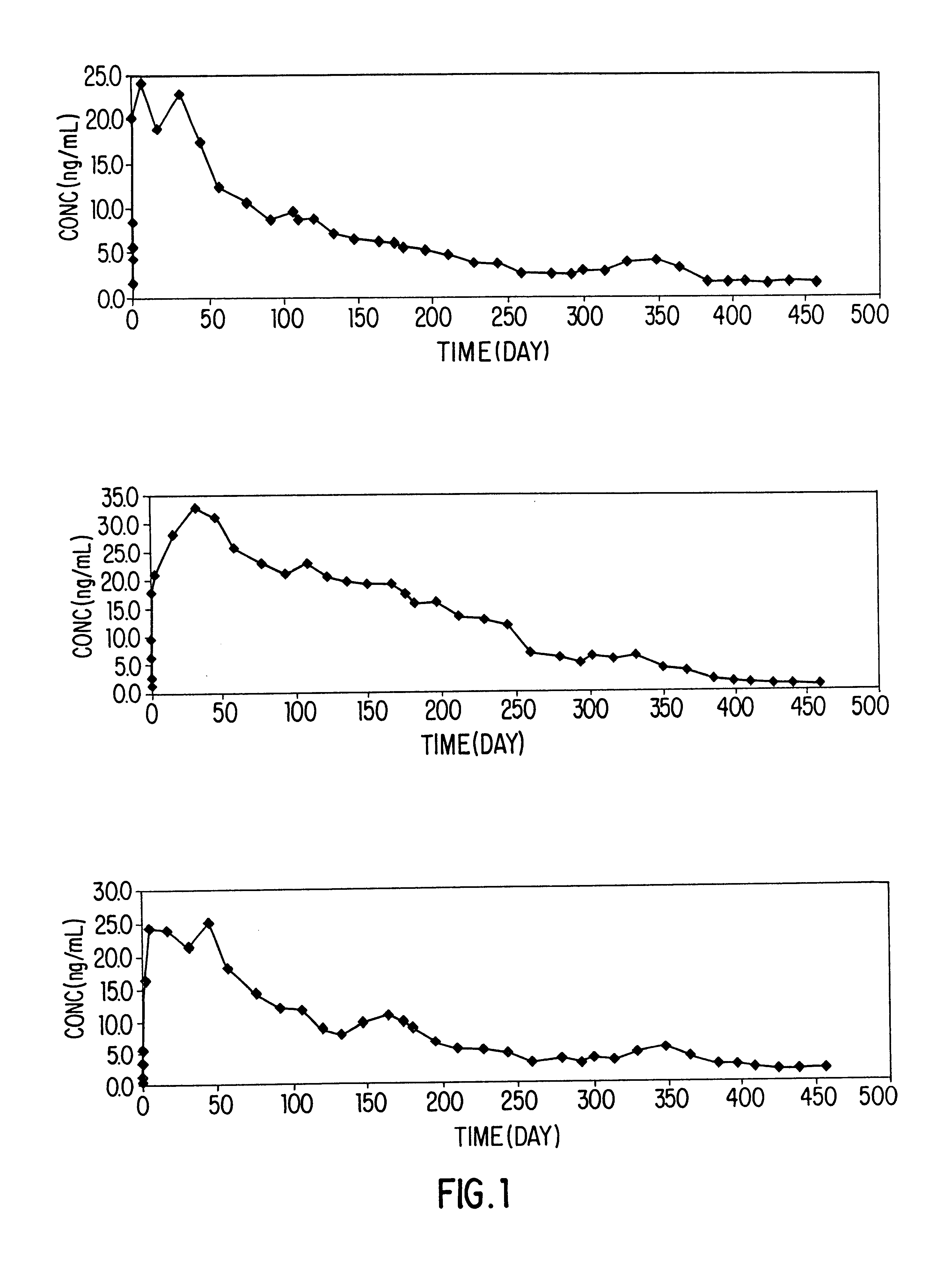
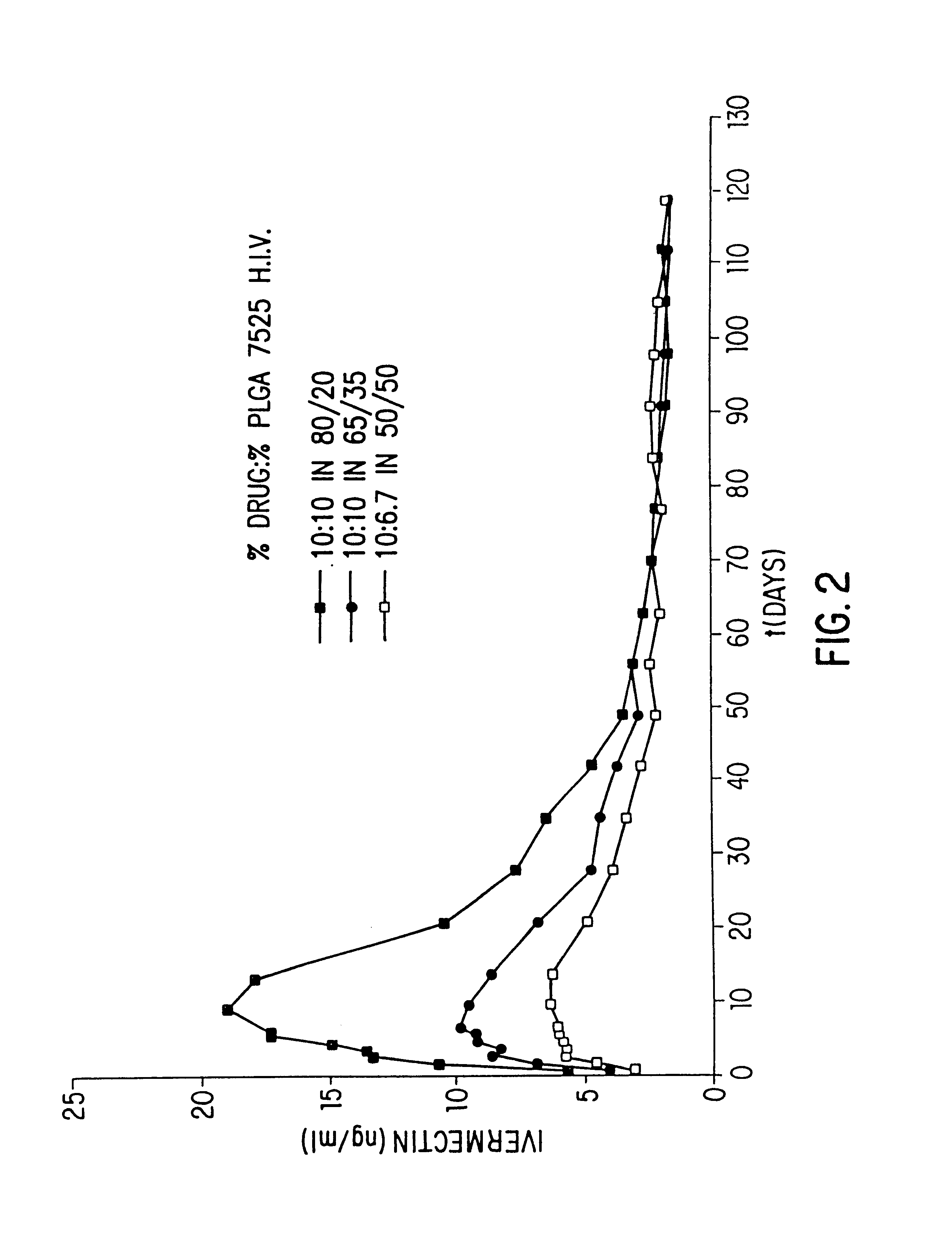
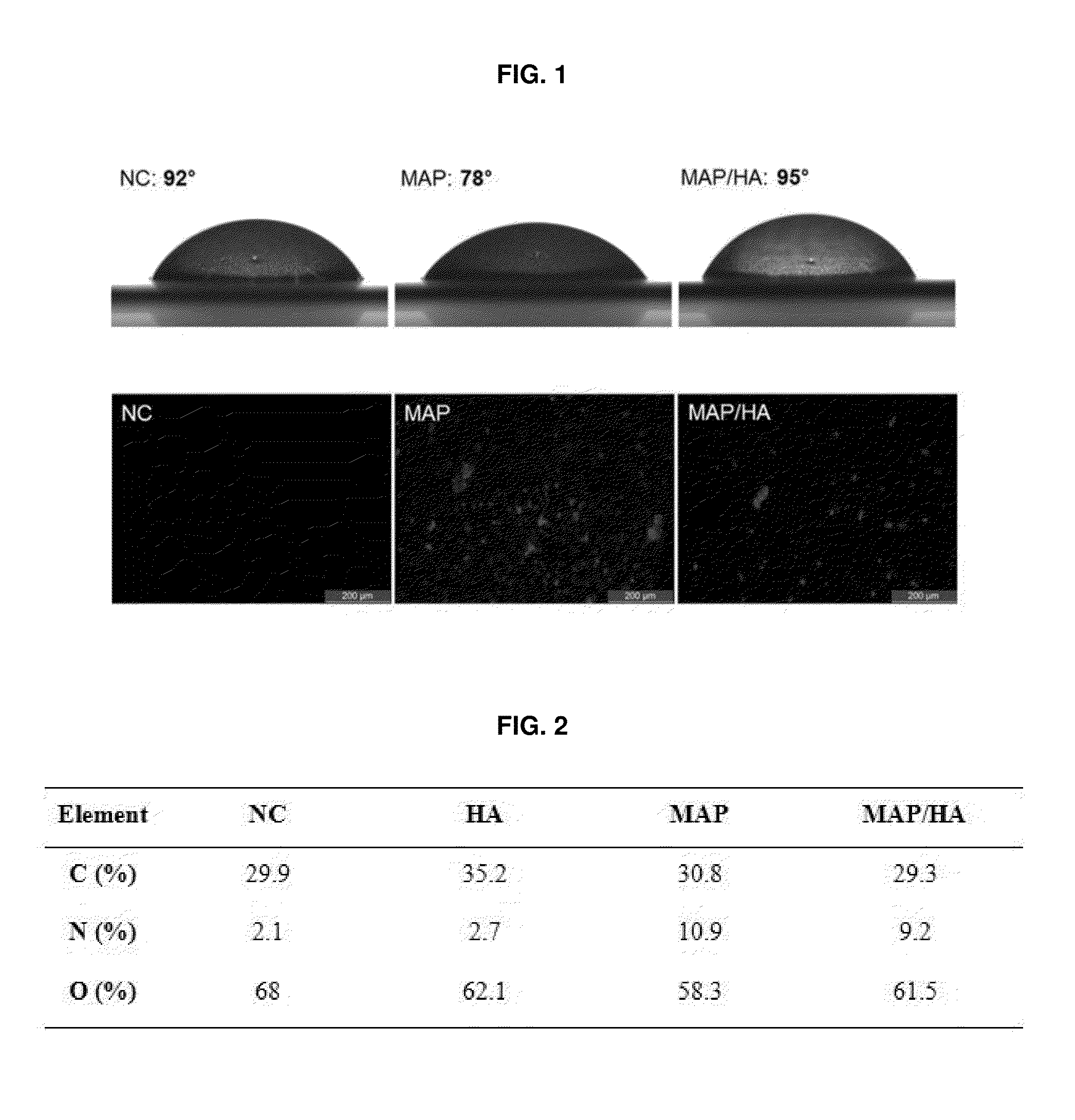
Patents
Literature
1136 results about "Bioactive substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physiologically active components of foods that may have an effect on health. (Source: International Dietetics and Nutrition Terminology (IDNT) Reference Manual, edition 4; ISBN #978-0-88091-467-3)
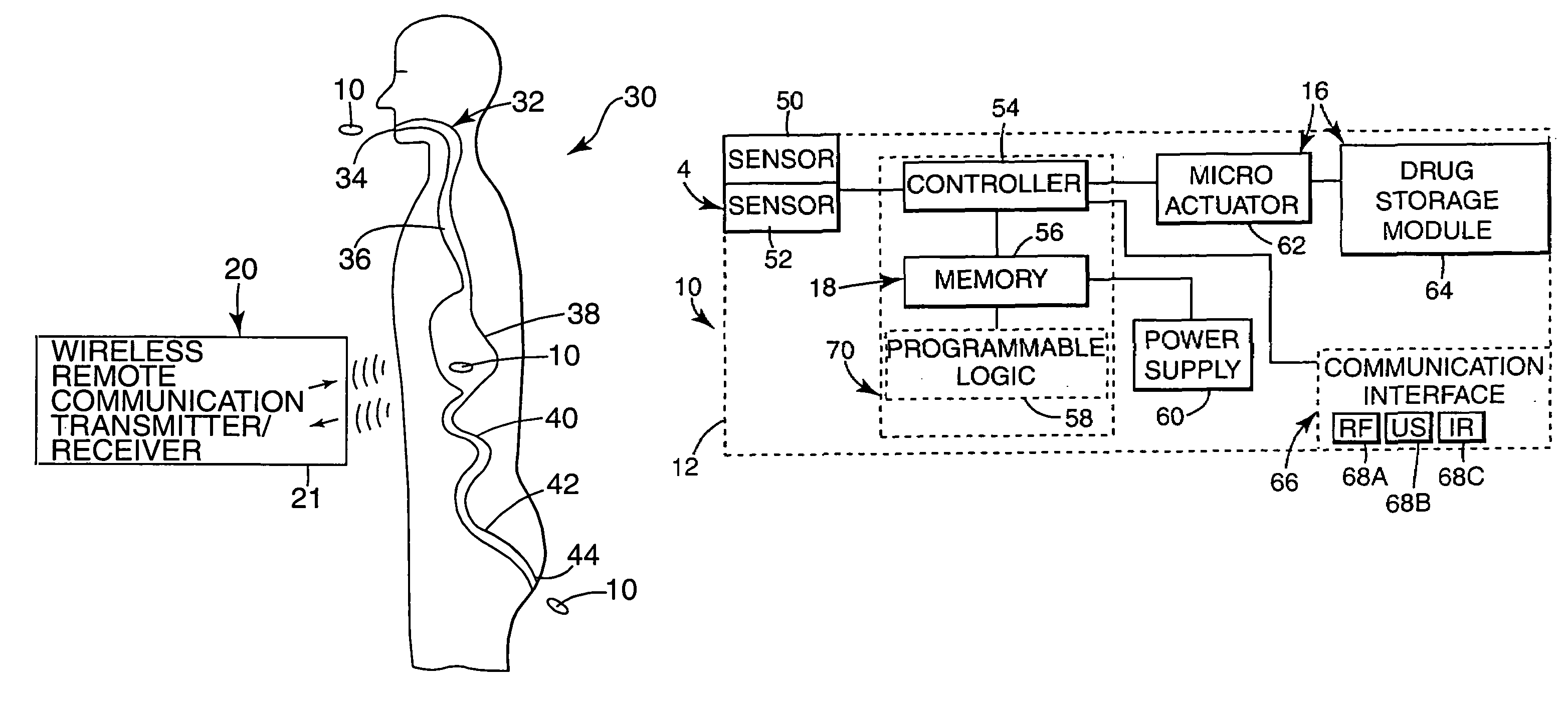
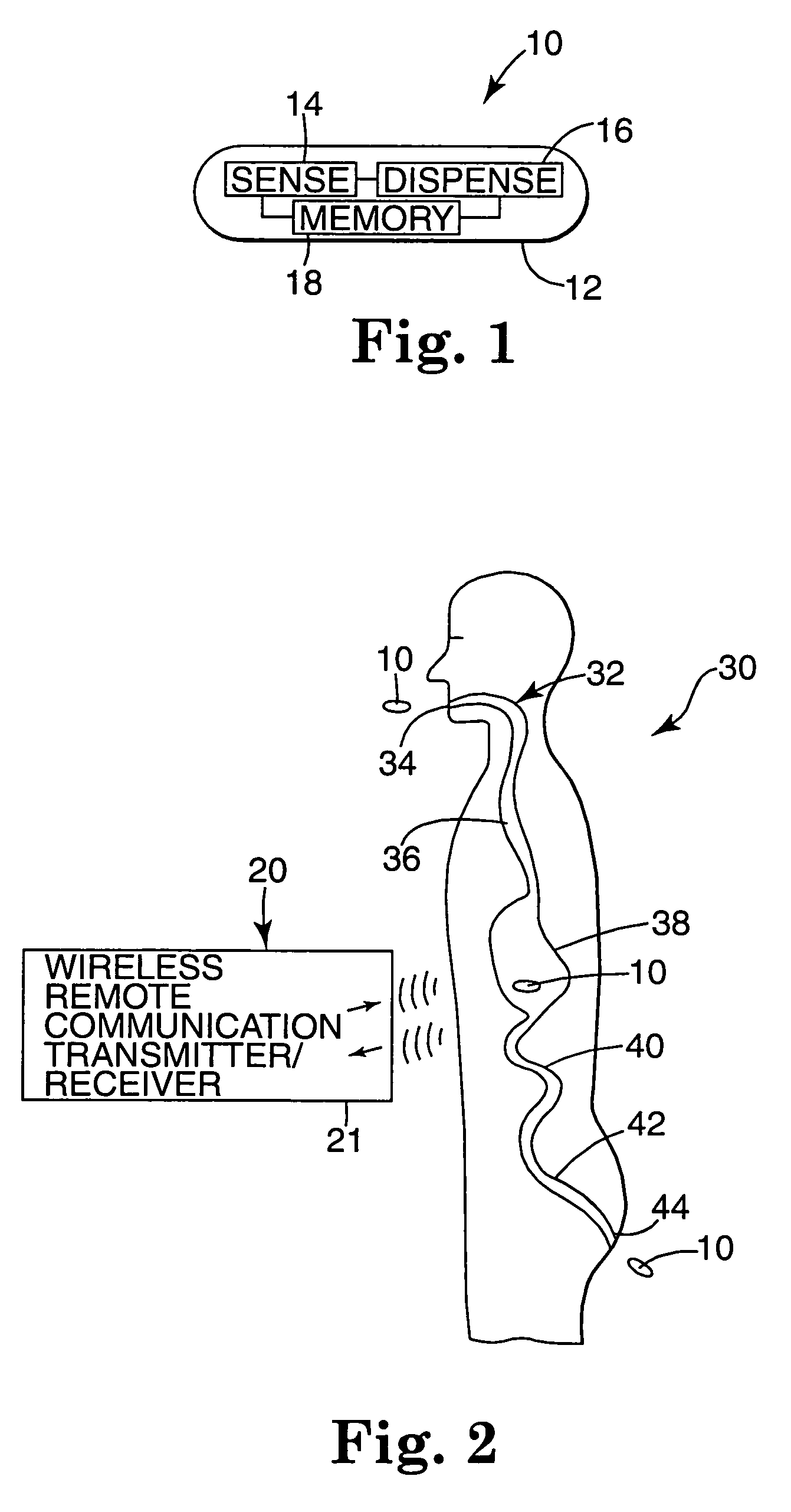
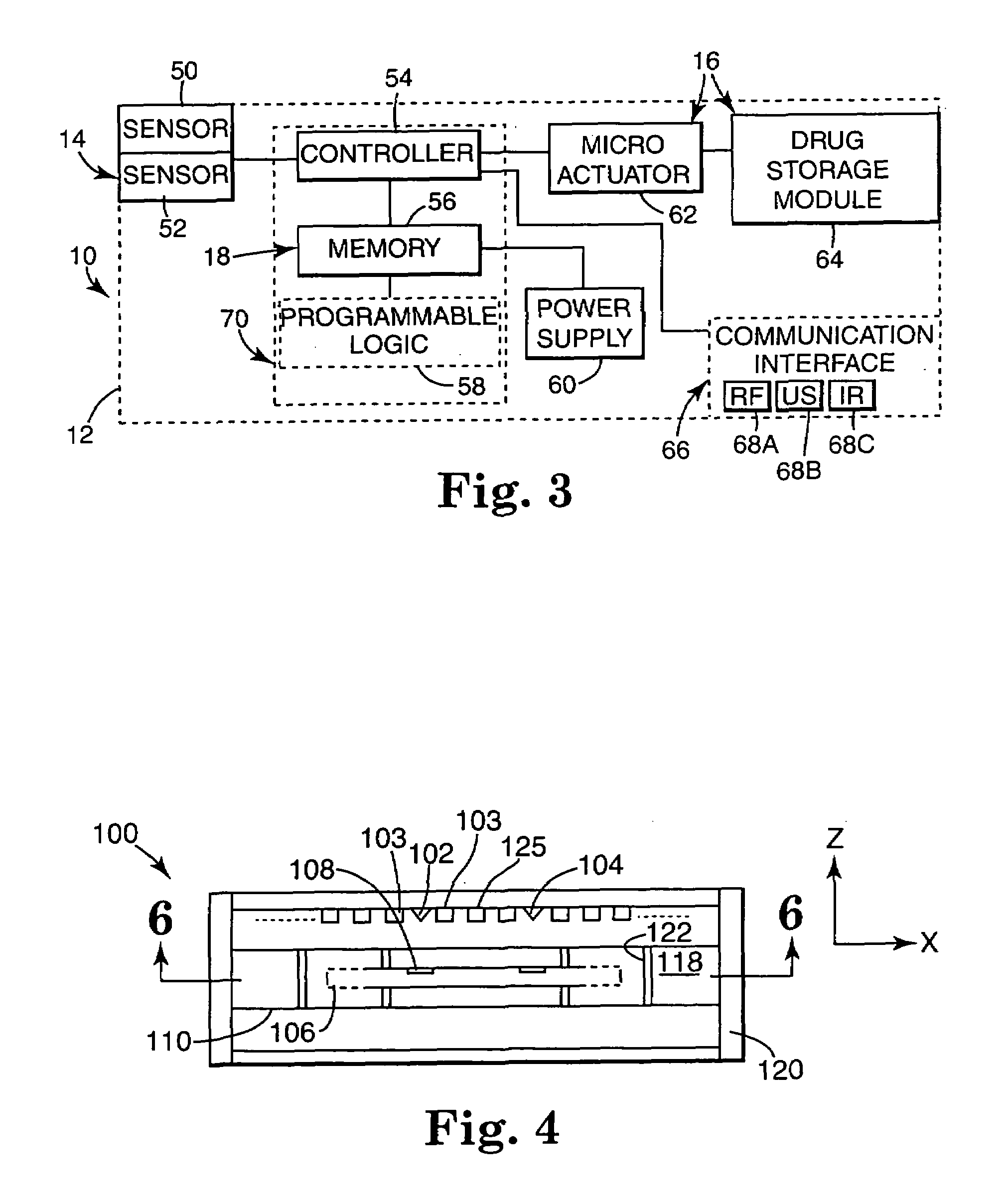
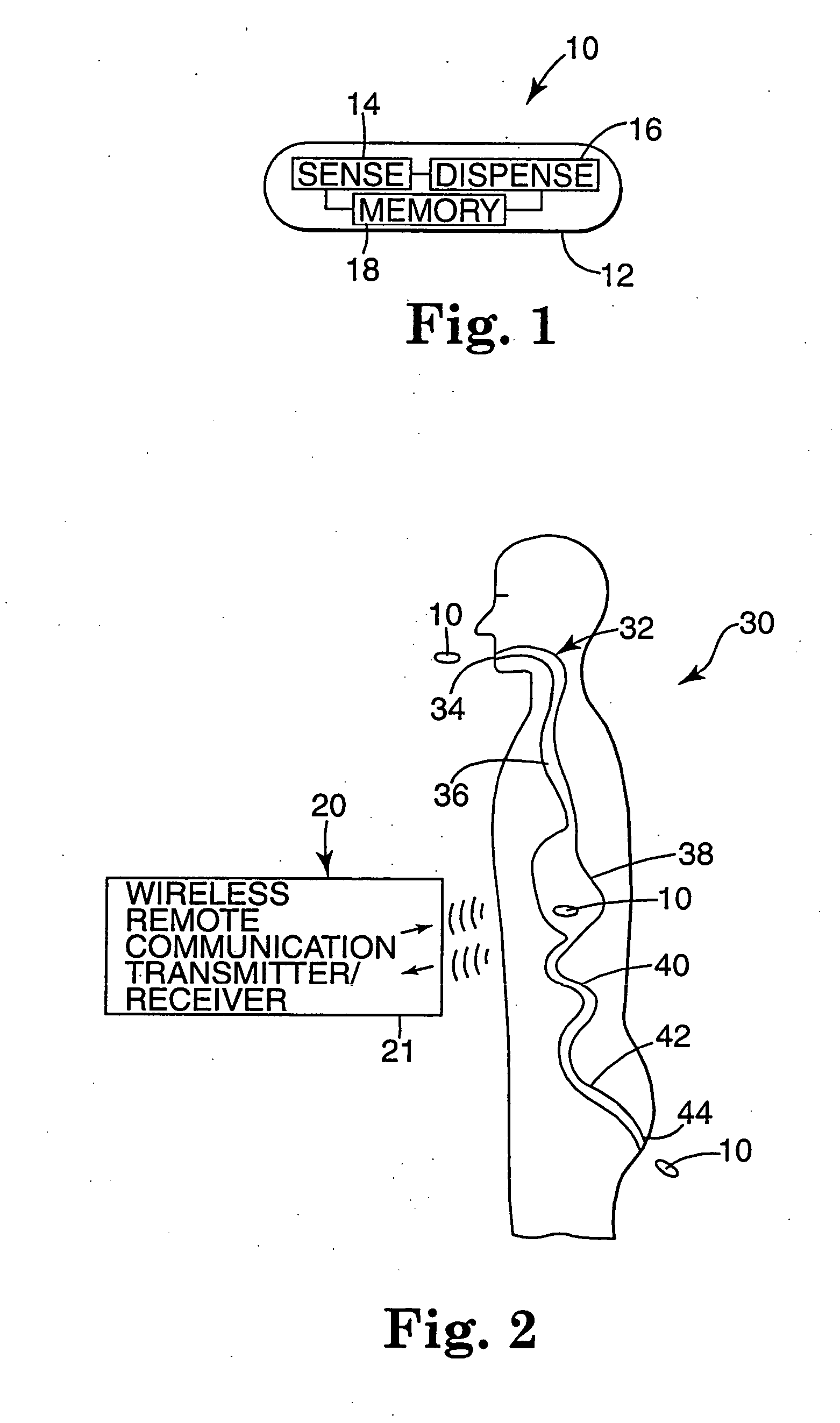
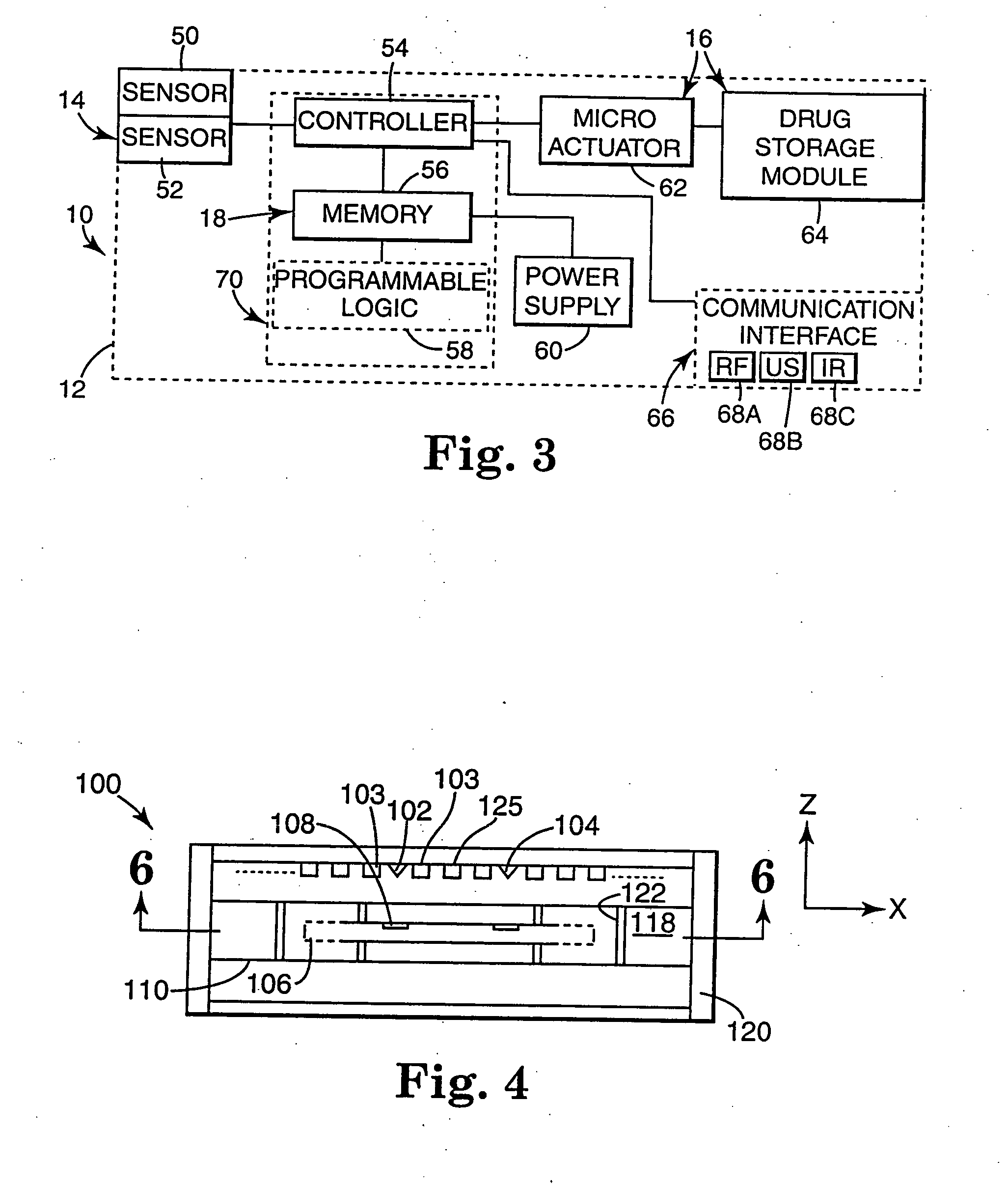
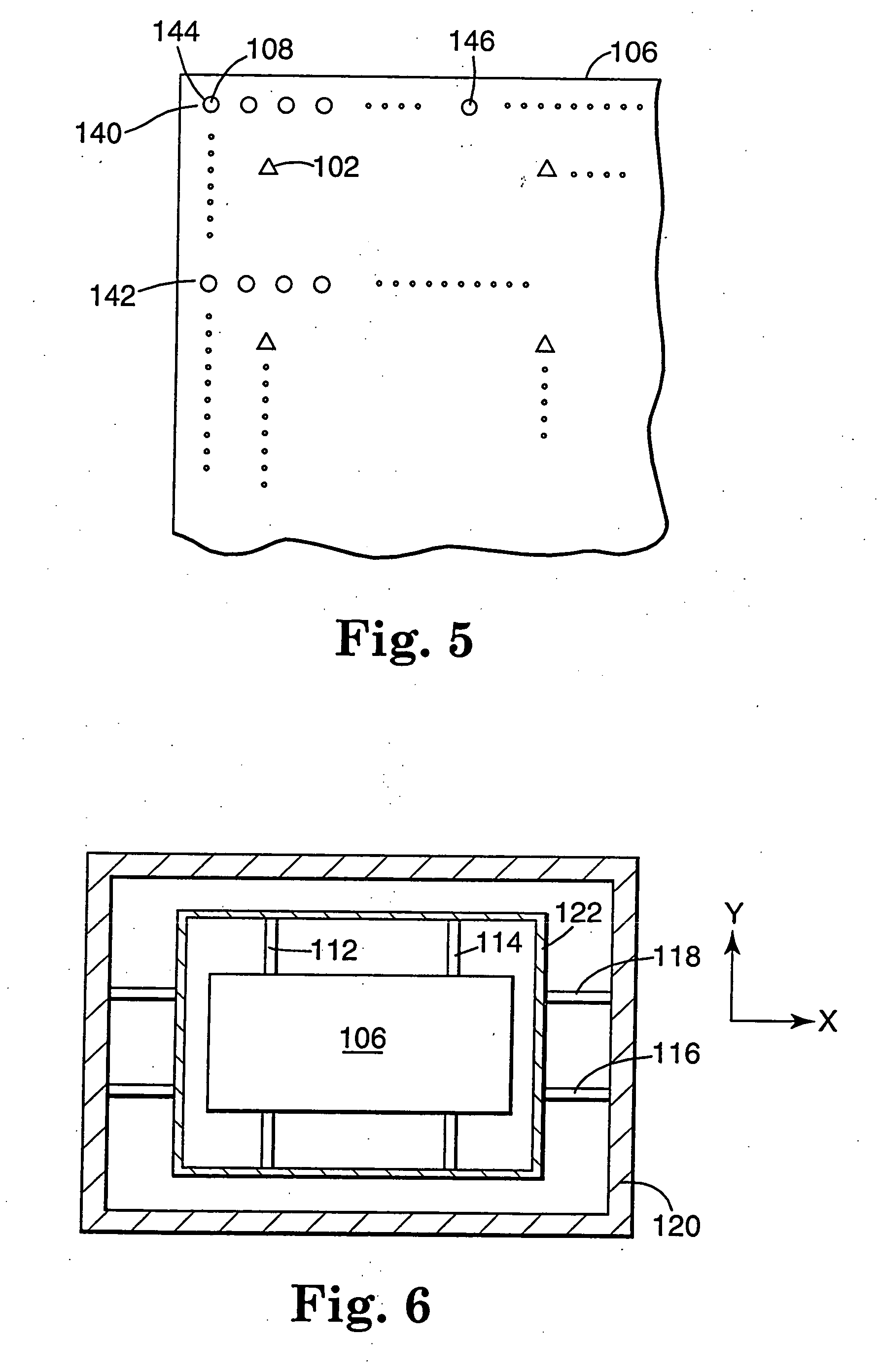
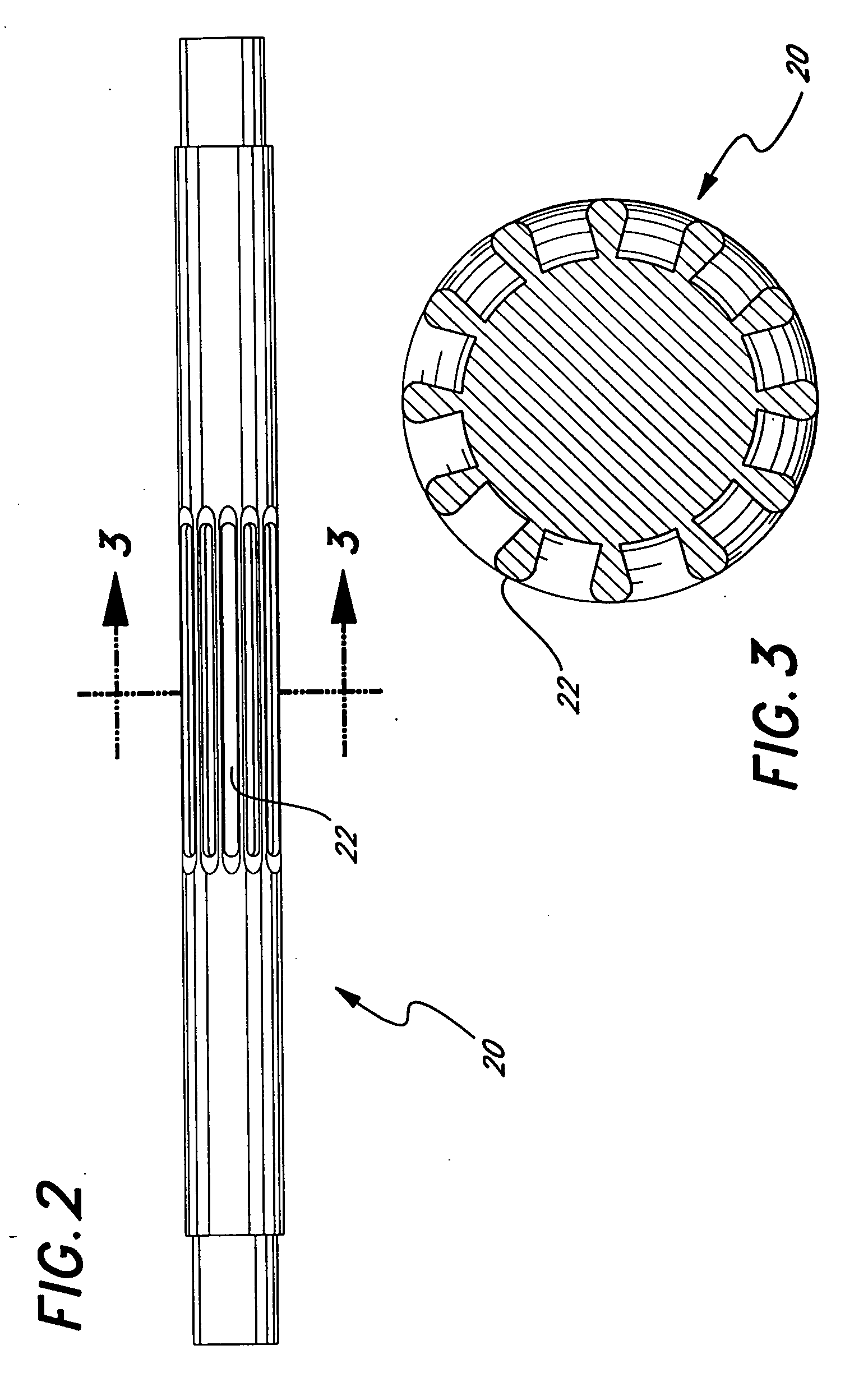
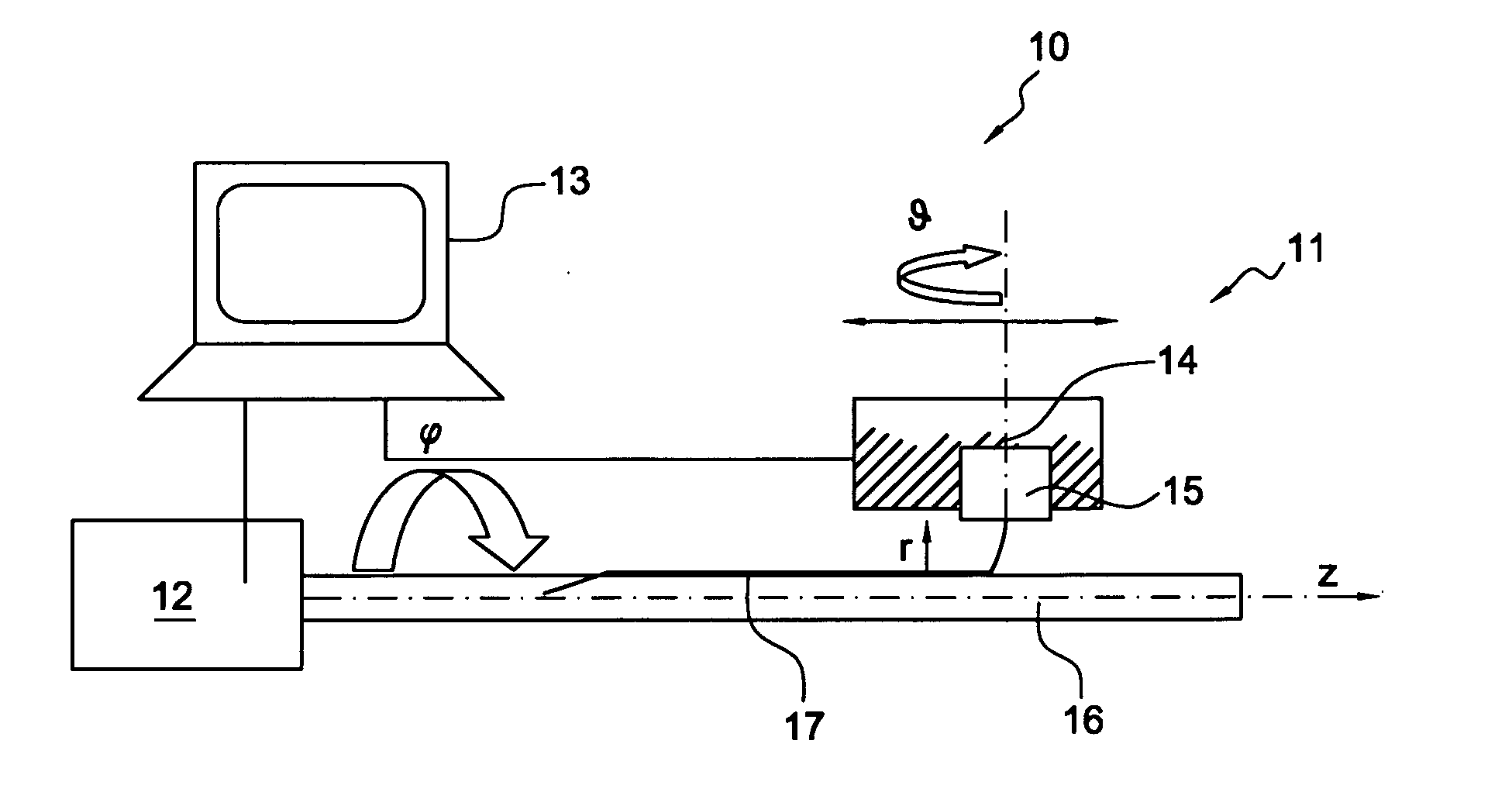
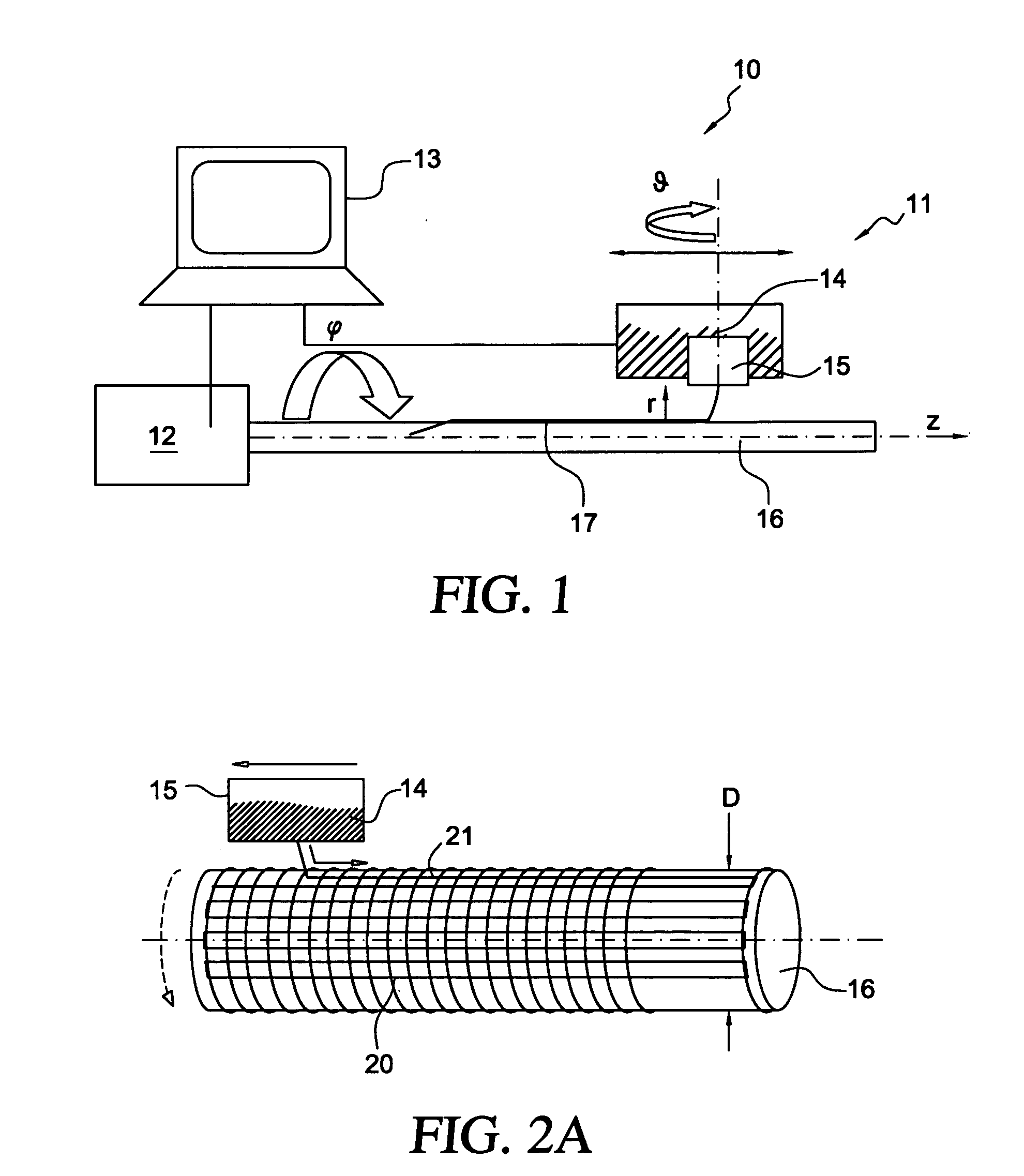
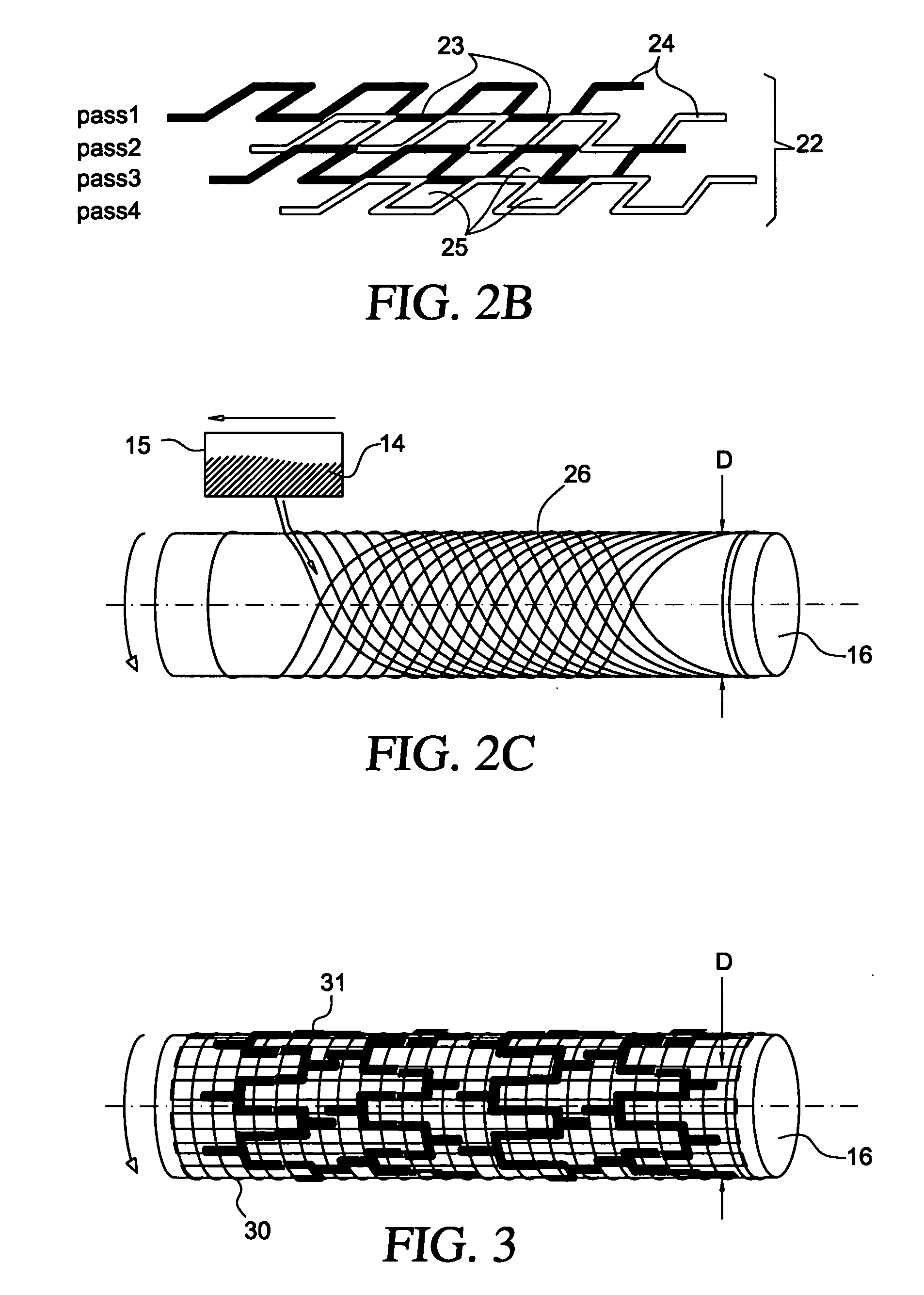
Internal drug dispenser capsule medical device
The present invention provides a swallowable internal drug medical device. The device includes a swallowable capsule. A sensing module is disposed in the capsule. A bioactive substance dispenser is disposed in the capsule. A memory and logic component is disposed in the capsule and in communication with the sensing module and the dispenser.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Internal drug dispenser capsule medical device
The present invention provides a swallowable internal drug medical device. The device includes a swallowable capsule. A sensing module is disposed in the capsule. A bioactive substance dispenser is disposed in the capsule. A memory and logic component is disposed in the capsule and in communication with the sensing module and the dispenser.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Eluting, implantable medical device
Owner:COOK INC
Solid lipid particles, particles of bioactive agents and methods for the manufacture and use thereof
InactiveUS6207178B1Suppresses decrease in specific surface areaImprove bioavailabilityBiocideCosmetic preparationsLipid formationLipid particle
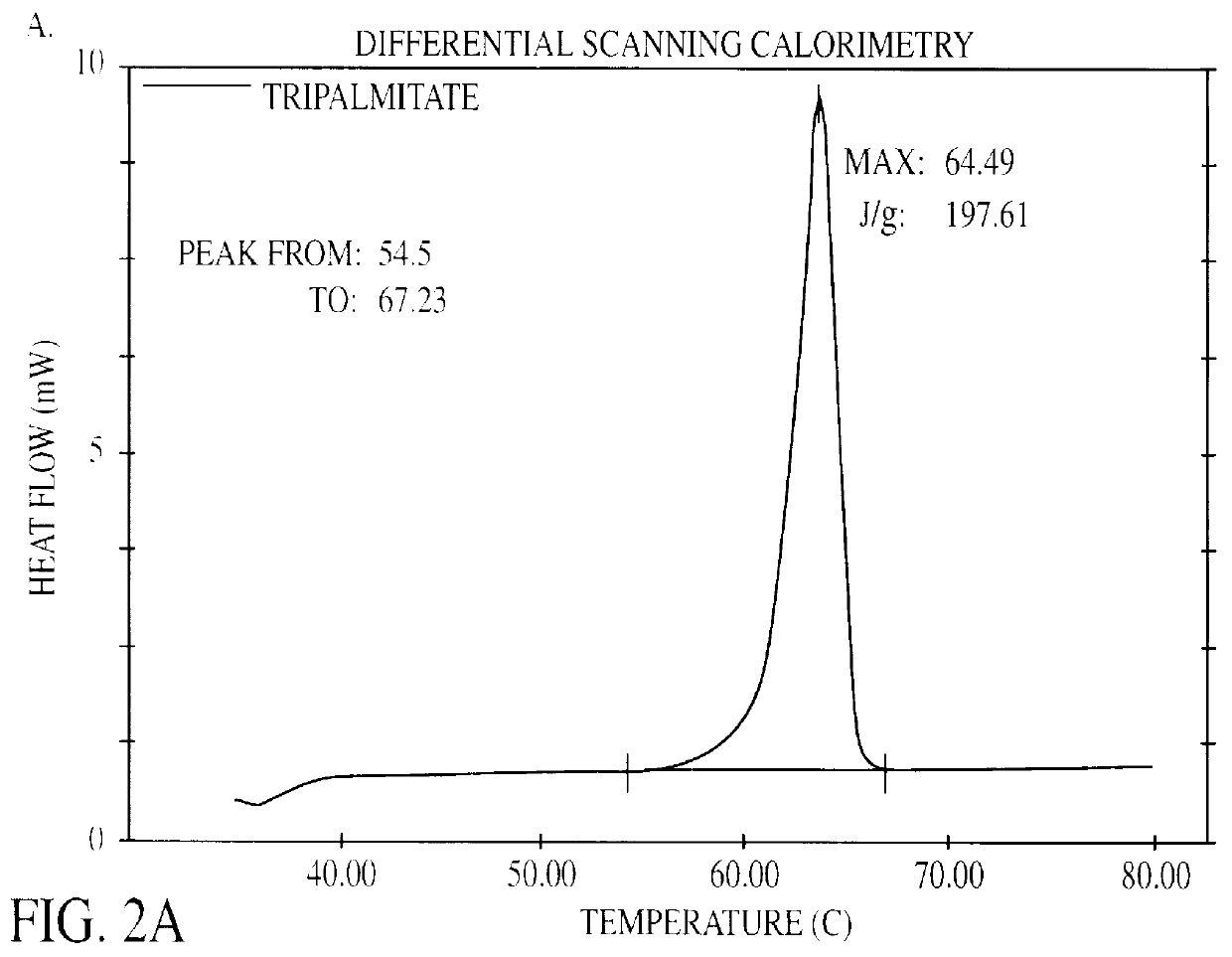
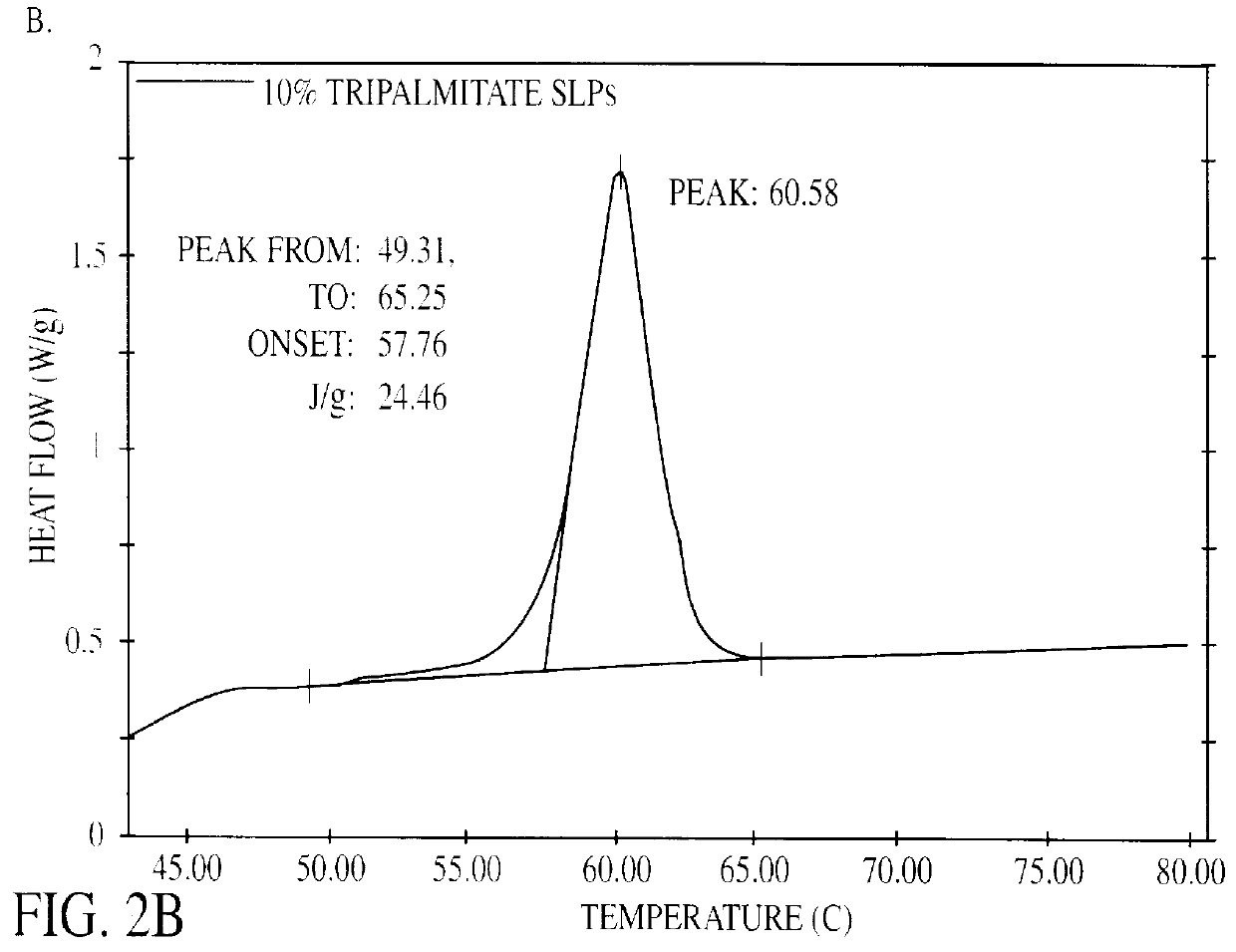
The present invention is in the area of administration forms and delivery systems for drugs, vaccines and other biologically active agents. More specifically the invention is related to the preparation of suspensions of colloidal solid lipid particles (SLPs) of predominantly anisometrical shape with the lipid matrix being in a stable polymorphic modification and of suspensions of micron and submicron particles of bioactive agents (PBAs); as well as to the use of such suspensions or the lyophilizates thereof as delivery systems primarily for the parenteral administration of preferably poorly water-soluble bioactive substances, particularly drugs, and to their use in cosmetic, food and agricultural products. SLPs and PBAs are prepared by the following emulsification process: (1) A solid lipid or bioactive agent or a mixture of solid lipids or bioactive agents is melted. (2) Stabilizers are added either to the lipid or bioactive agent and to the aqueous phase or to the aqueous phase only depending on their physicochemical characteristics. Stabilizers may also be added or exchanged after homogenization. (3) Drugs or other bioactive substances to be incorporated into the SLPs may be melted together with the lipids if the physicochemical characteristics of the substance permit or may be dissolved, solubilized or dispersed in the lipid melt before homogenization. (4) The aqueous phase is heated to the temperature of the melt before mixing and may contain for example stabilizers, isotonicity agents, buffering substances, cryoprotectants and / or preservatives. (5) The molten lipid compounds and the bioactive agents are emulsified in an aqueous phase preferably by high-pressure homogenization.
Owner:PHARMACIA AB
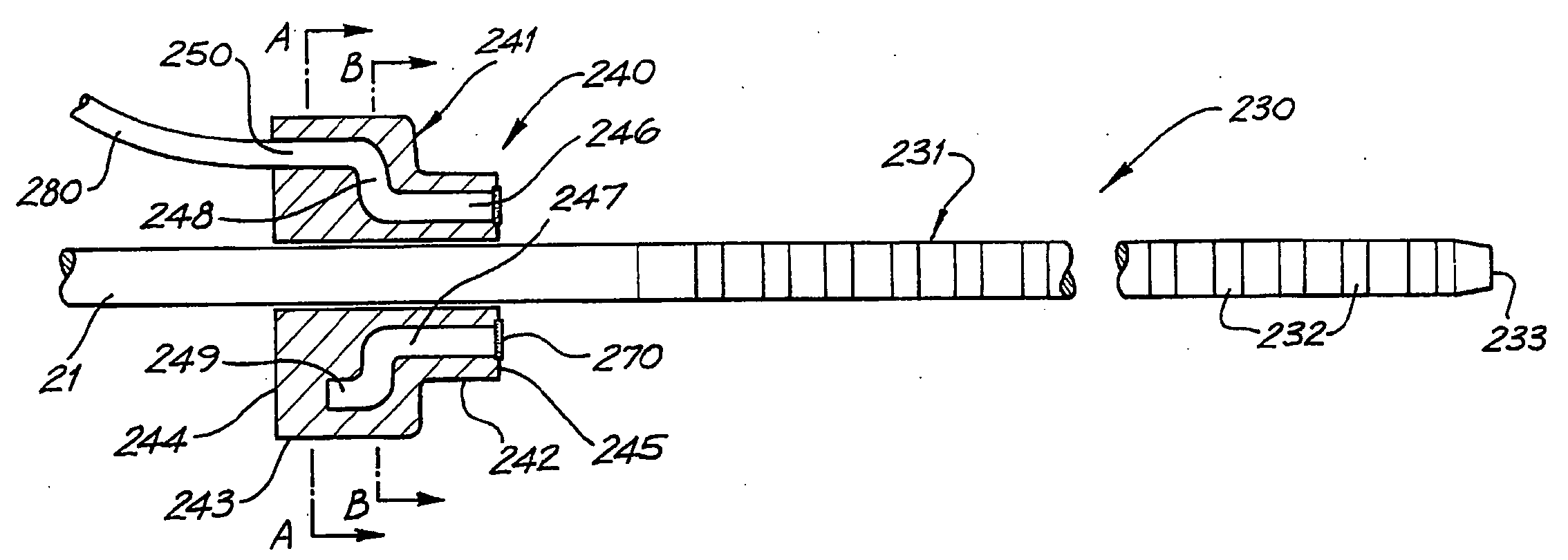
Cochlear implant drug delivery device
ActiveUS20060287689A1Small dimensionReduce frictionHead electrodesEar treatmentMedicineBiomedical engineering
Devices for the delivery of a bioactive substance to a cochlea and methods of delivery thereof. The devices include means to allow the release of the bioactive substance within a cochlea.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Bioactive prostheses with immunosuppressive, antistenotic and antithrombotic properties
InactiveUS6517858B1Reduce riskPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCoronary arteriesPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention relates to a bioactive implant comprising a substrate coated with a polymer layer with reactive functions, and a bioactive substance fixed on the implant by means of said reactive functions to enable progressive release on the implant site.Such implants are useful in the field of cardiology for example to prevent restenosis resulting from the fitting of stents in the coronary arteries.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
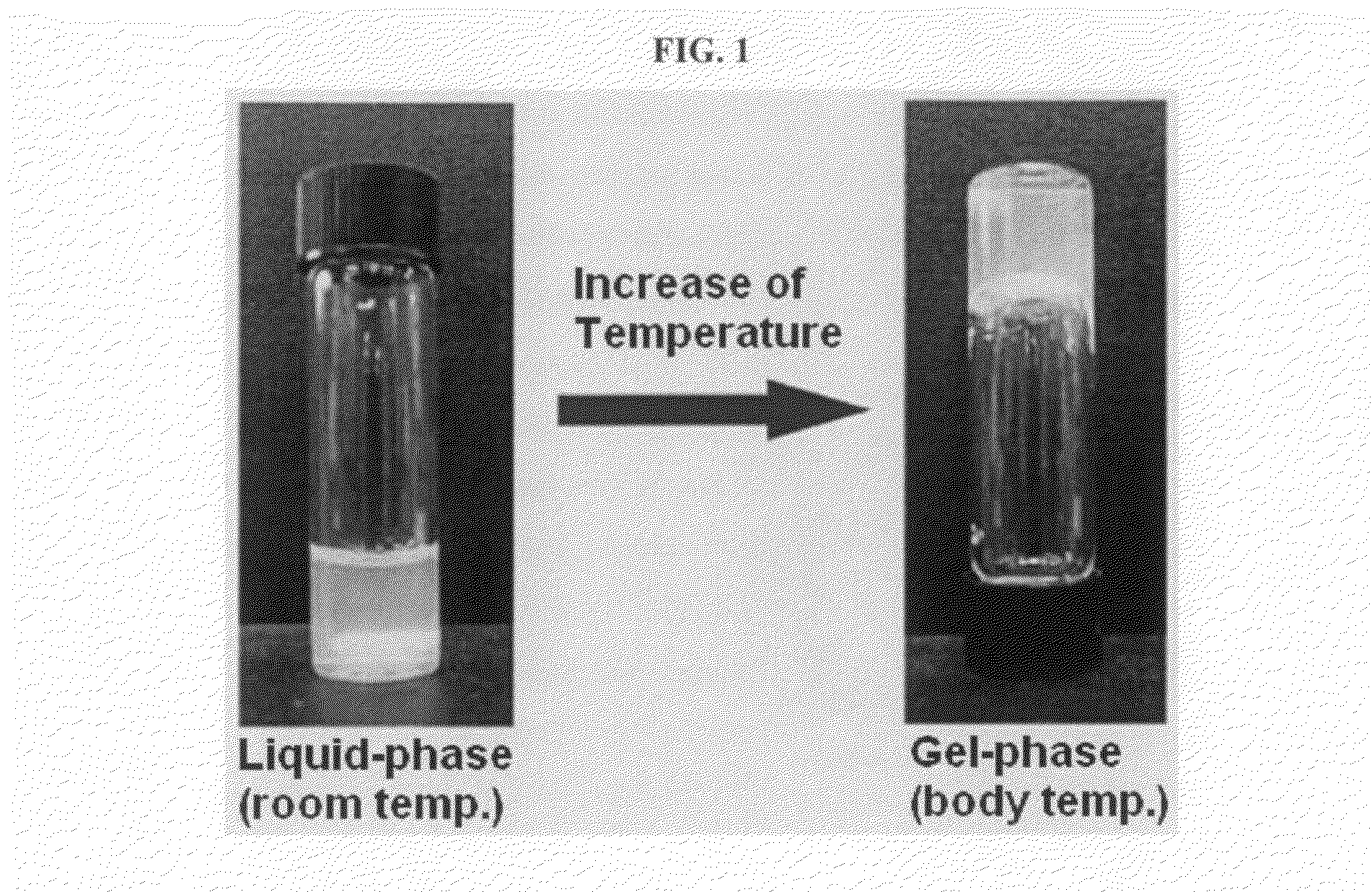
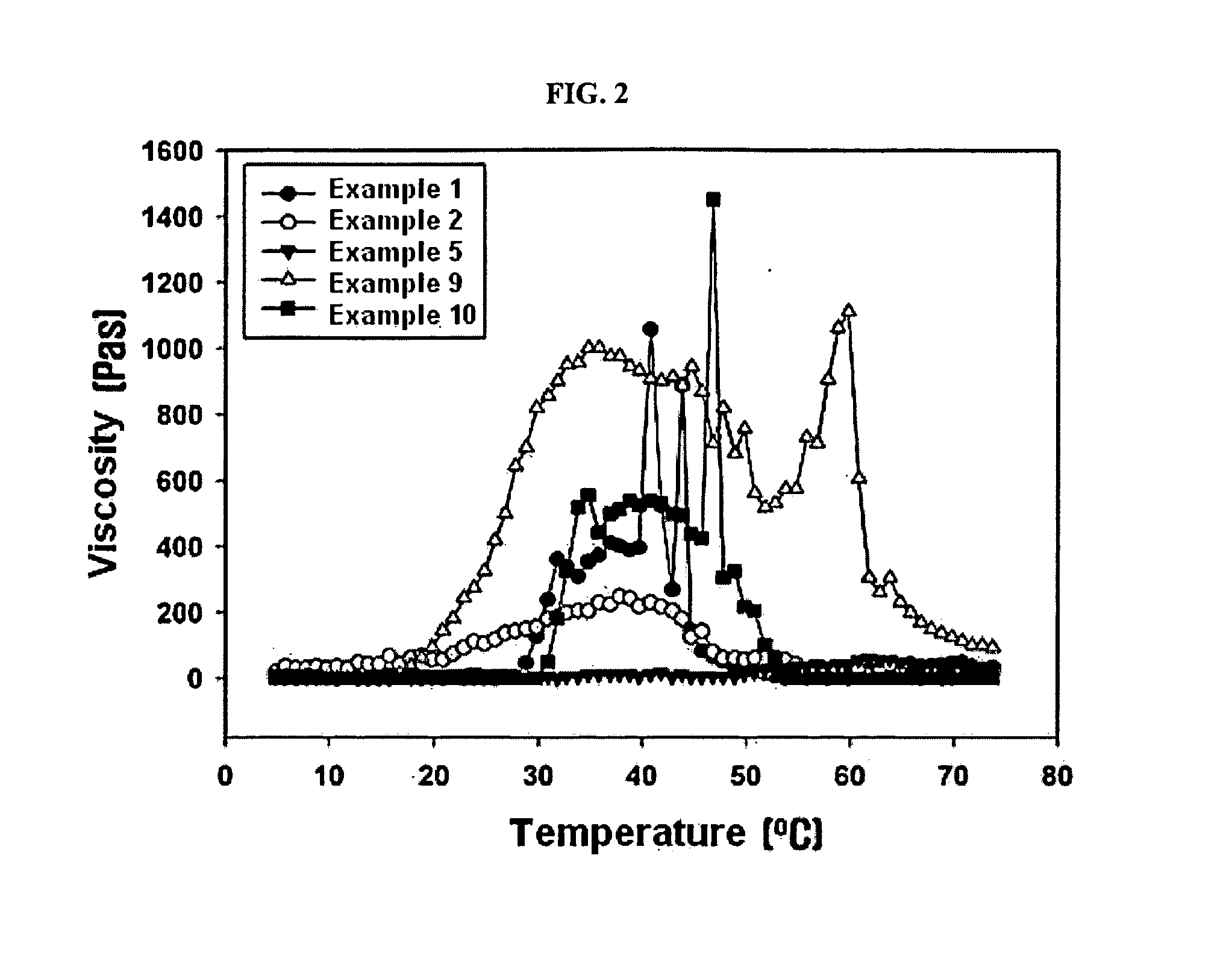
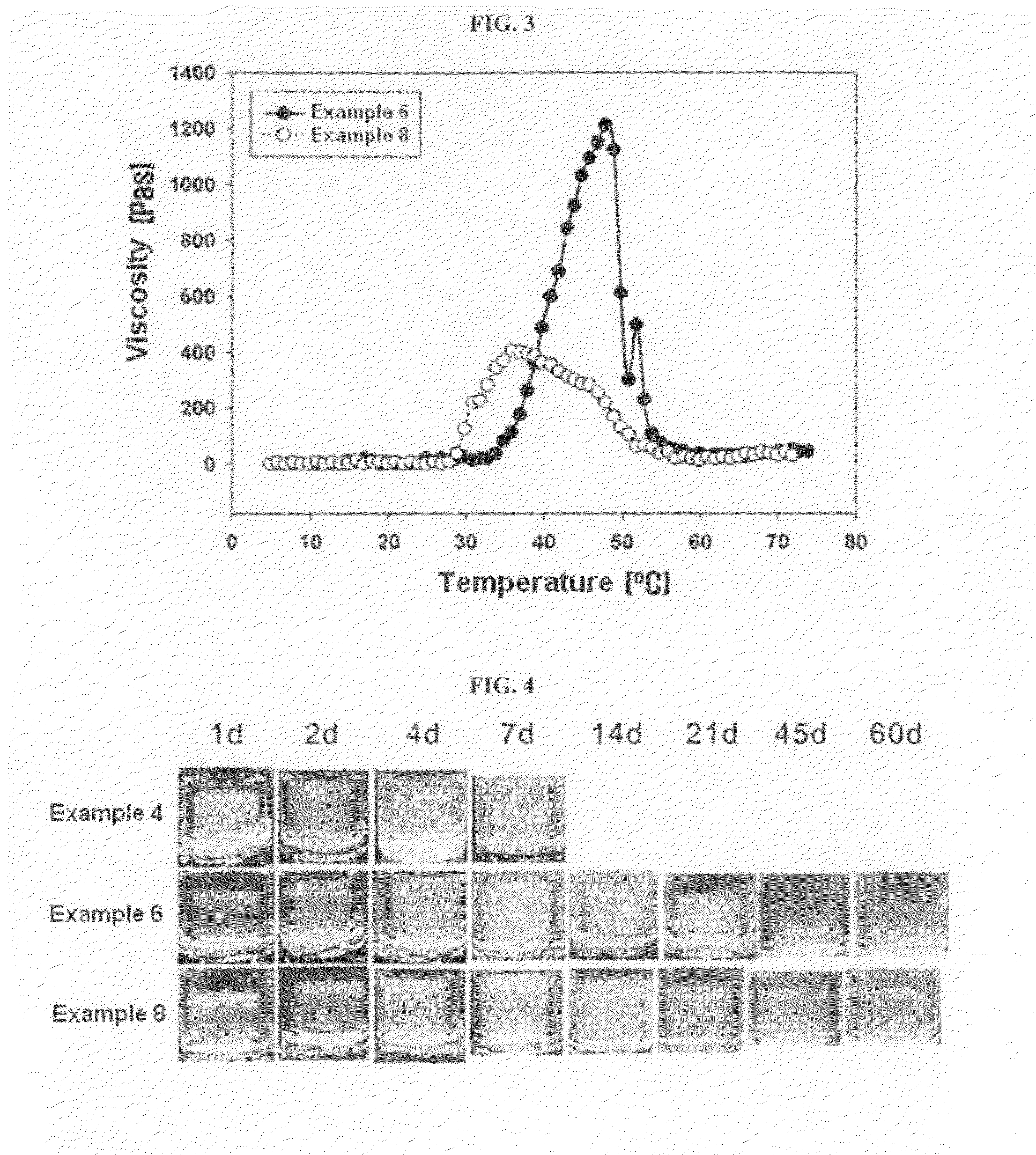
Biodegradable and Thermosensitive Poly(Organophosphazene) Hydrogel, Preparation Method Thereof and Use Thereof
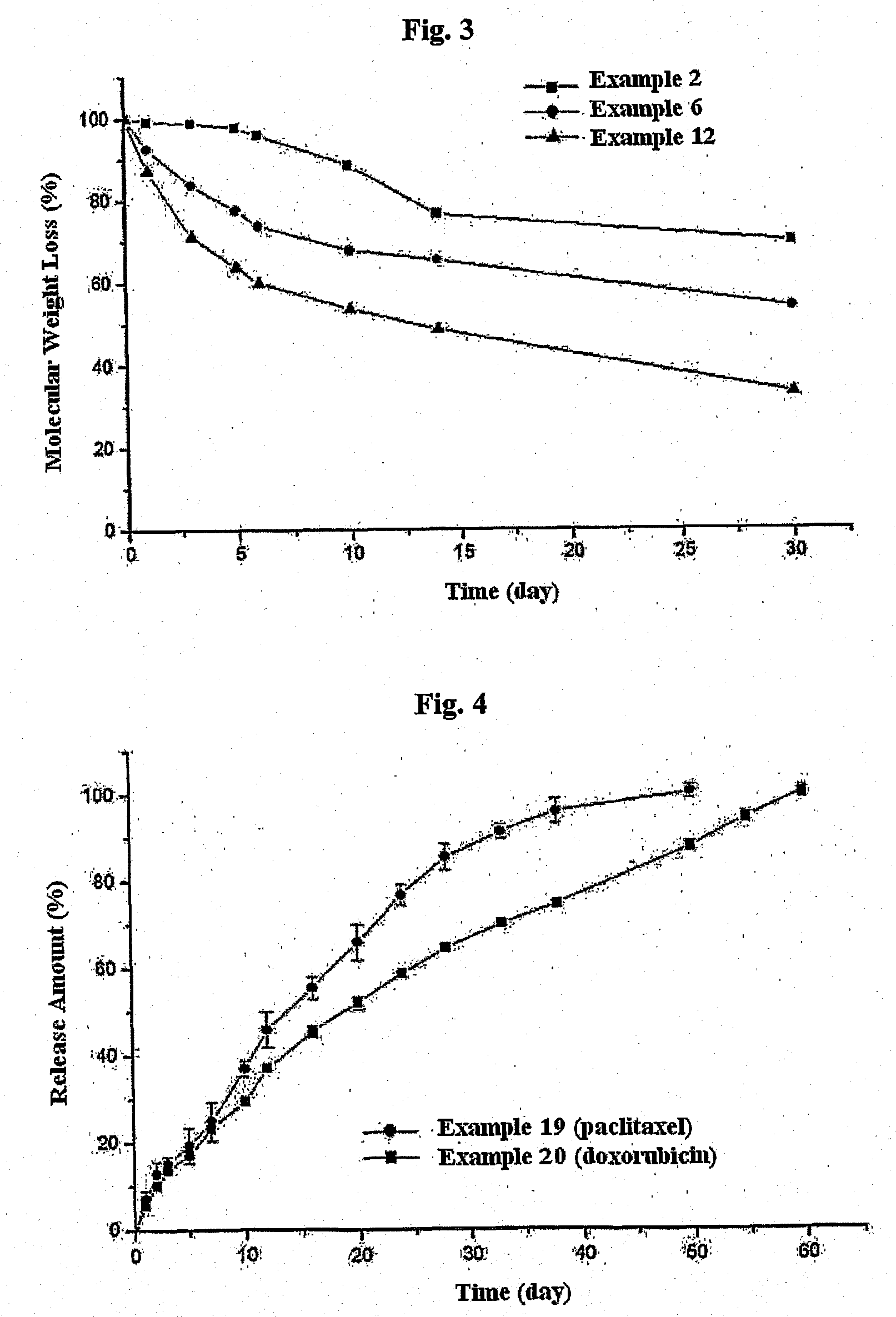
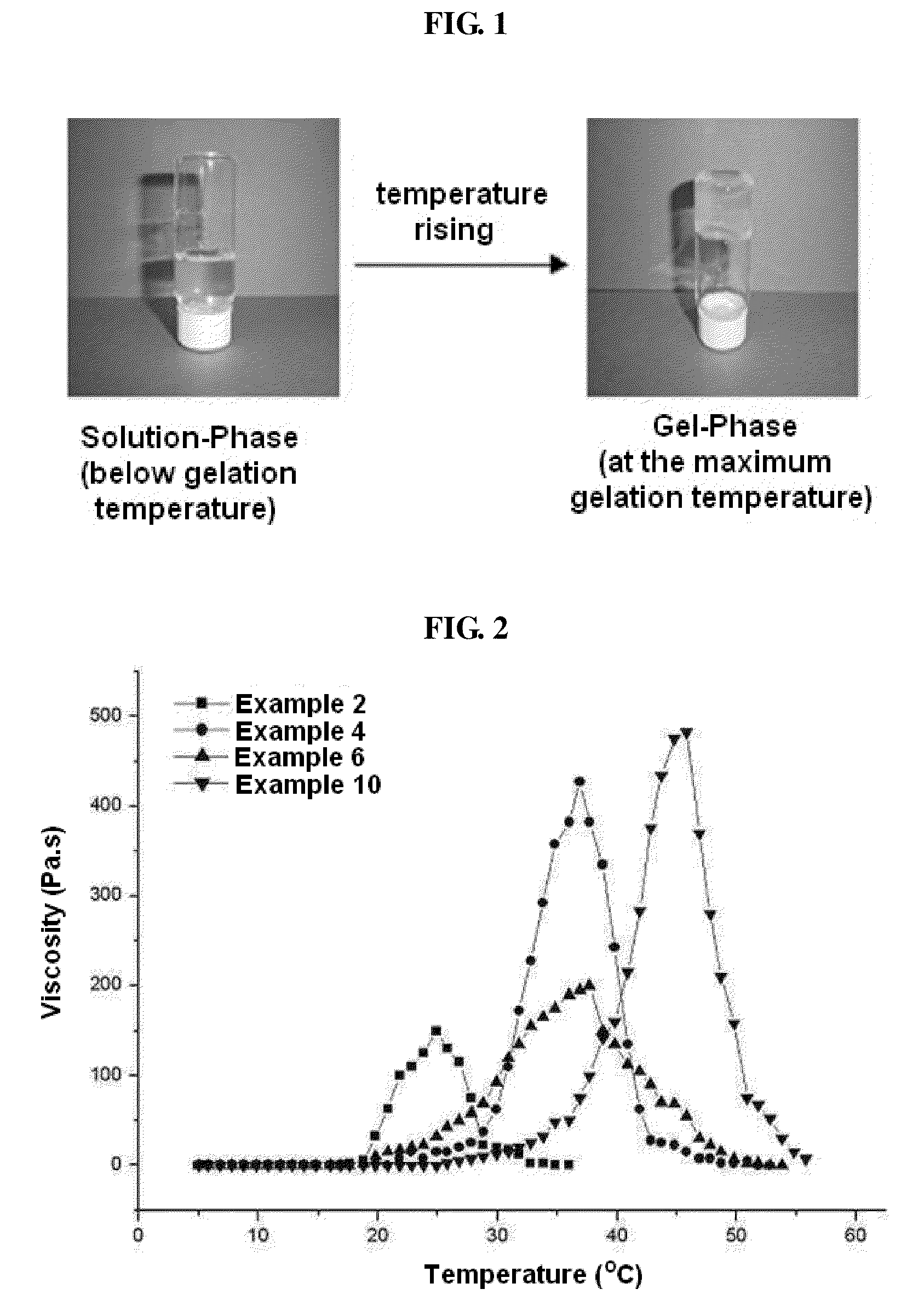
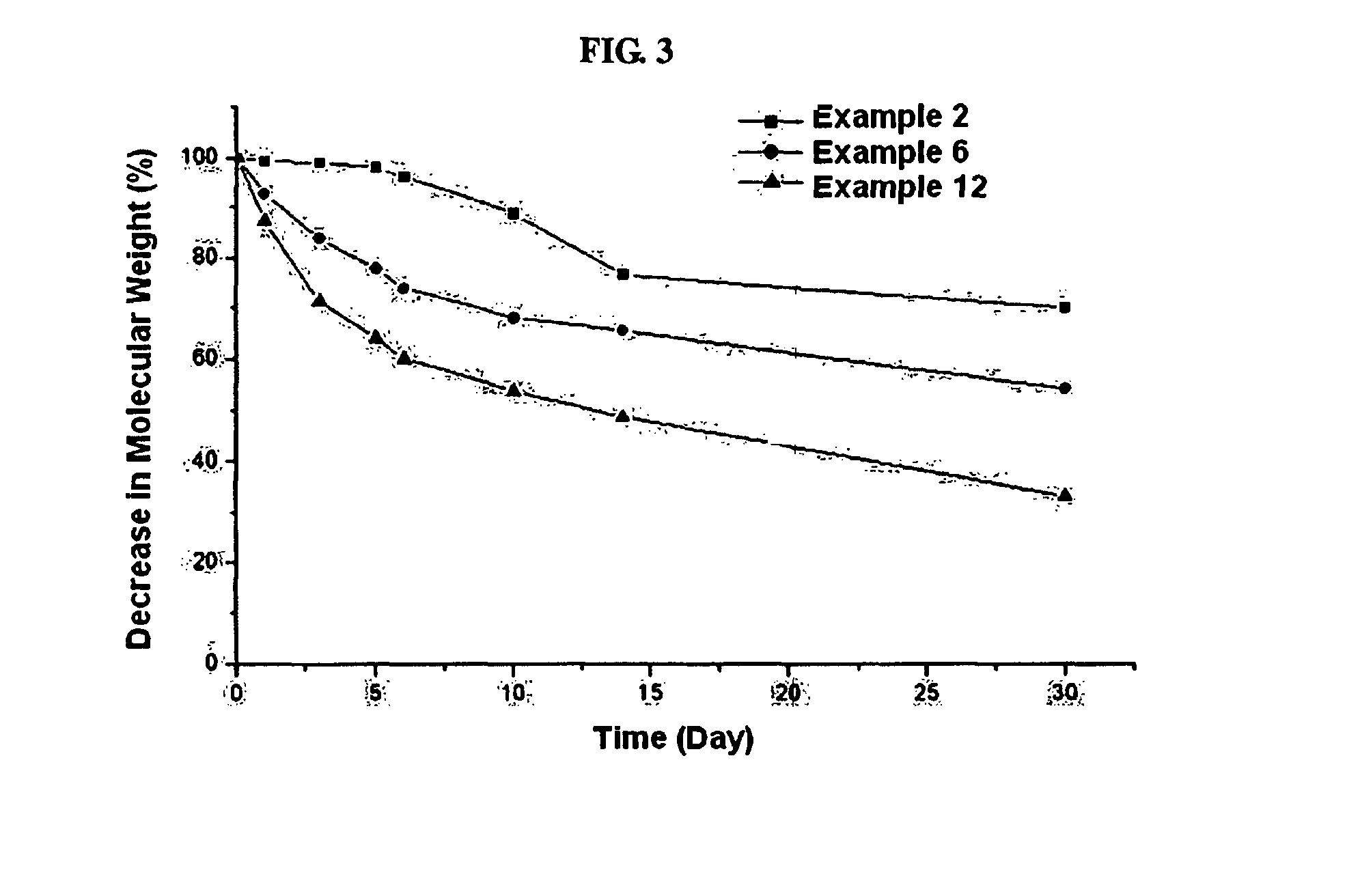
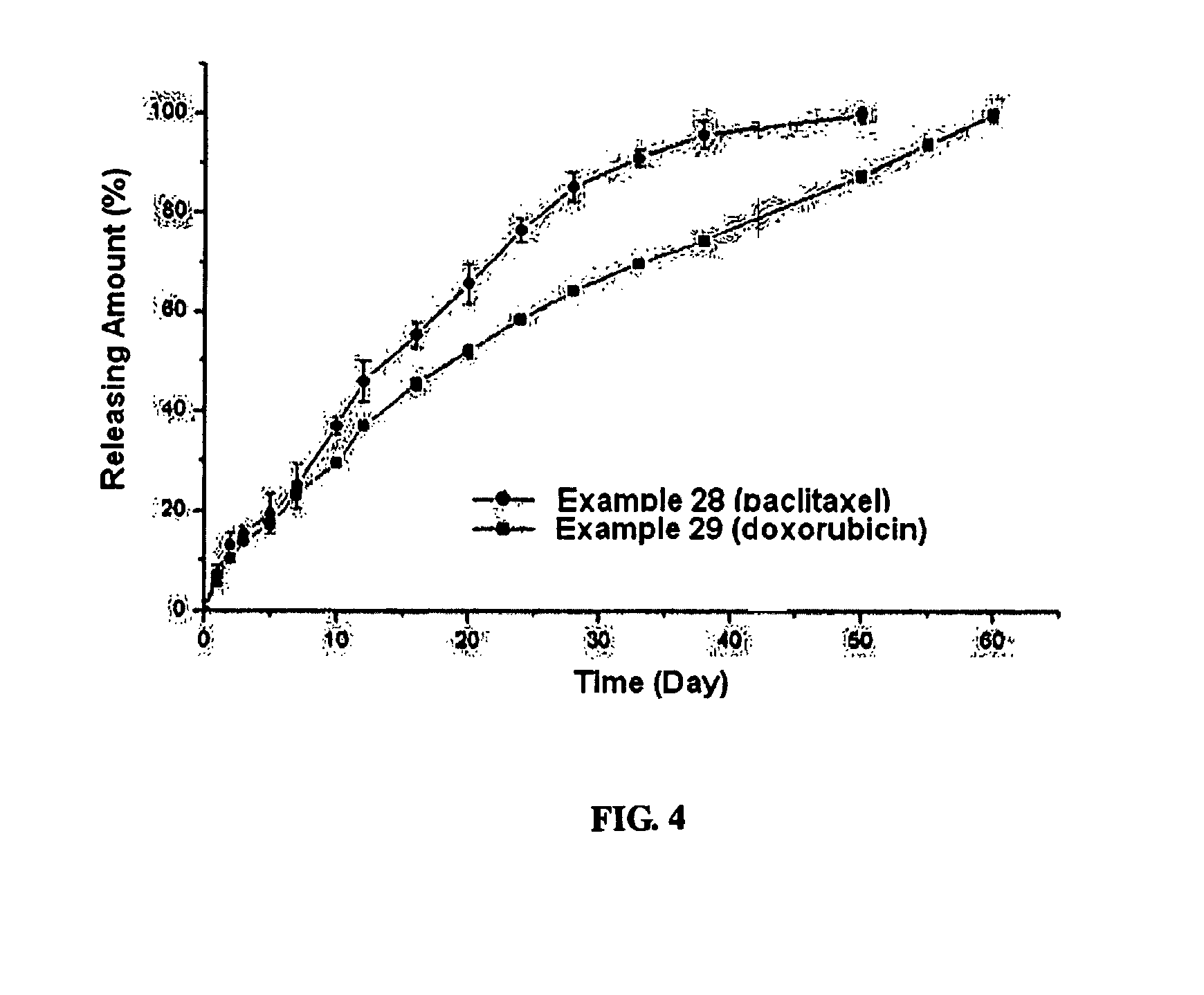
The present invention relates to a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) with a functional group, a preparation method thereof, and a use thereof for delivery of bioactive substances. According to the present invention, poly(organophosphazene) is a phosphagen-based polymer showing biodegradability, thermosensitivity, and sol-gel phase transition depending on temperature change, whereby when administered into a living body with bioactive substances such as drugs, the poly(organophosphazene) forms a gel-phase at body temperature to be capable of controlled release of the bioactive substances. Further, the poly(organophosphazene) has functional groups to chemically bind with bioactive substances through an ionic bond, covalent bond, or coordinate covalent bond to be capable of a sustained release of the bioactive substances due to its good binding property. Therefore, the poly(organophosphazene) is useful as a delivery material for bioactive substances.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Poly(organophosphazene) hydrogels for drug delivery, preparation method thereof and use thereof
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Controlled release of bioactive substances
InactiveUS6916490B1Improve bioavailabilityStimulate receptor-mediated endocytosisPowder deliveryBiocideControlled releaseMedicine
The present invention contemplates in part coacervates in which a bioactive substance and delivery agent are encapsulated therein for controlled release. In certain embodiments, said bioactive substance and delivery agent are a viral vector and virus, respectively. Processes for preparing and using coacervates of the present invention are described.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Liquid polymeric compositions for controlled release of bioactive substances
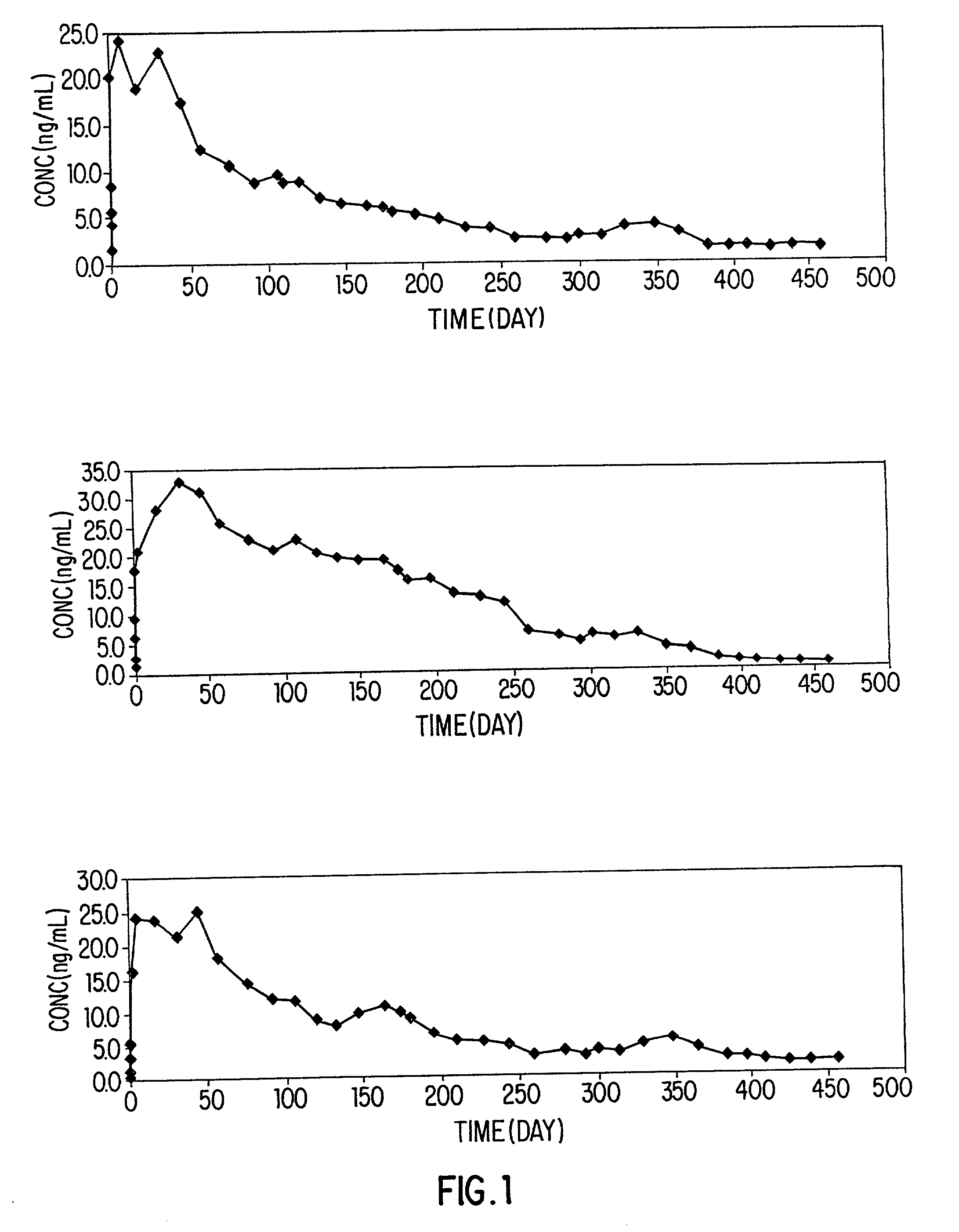
Controlled release of hydrophobic bioactive substances in vivo over an extended time period and without "bursts" of drug release is achieved using a liquid polymeric composition including a polymer such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer in a mixture of hydrophilic and lipophilic solvents.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
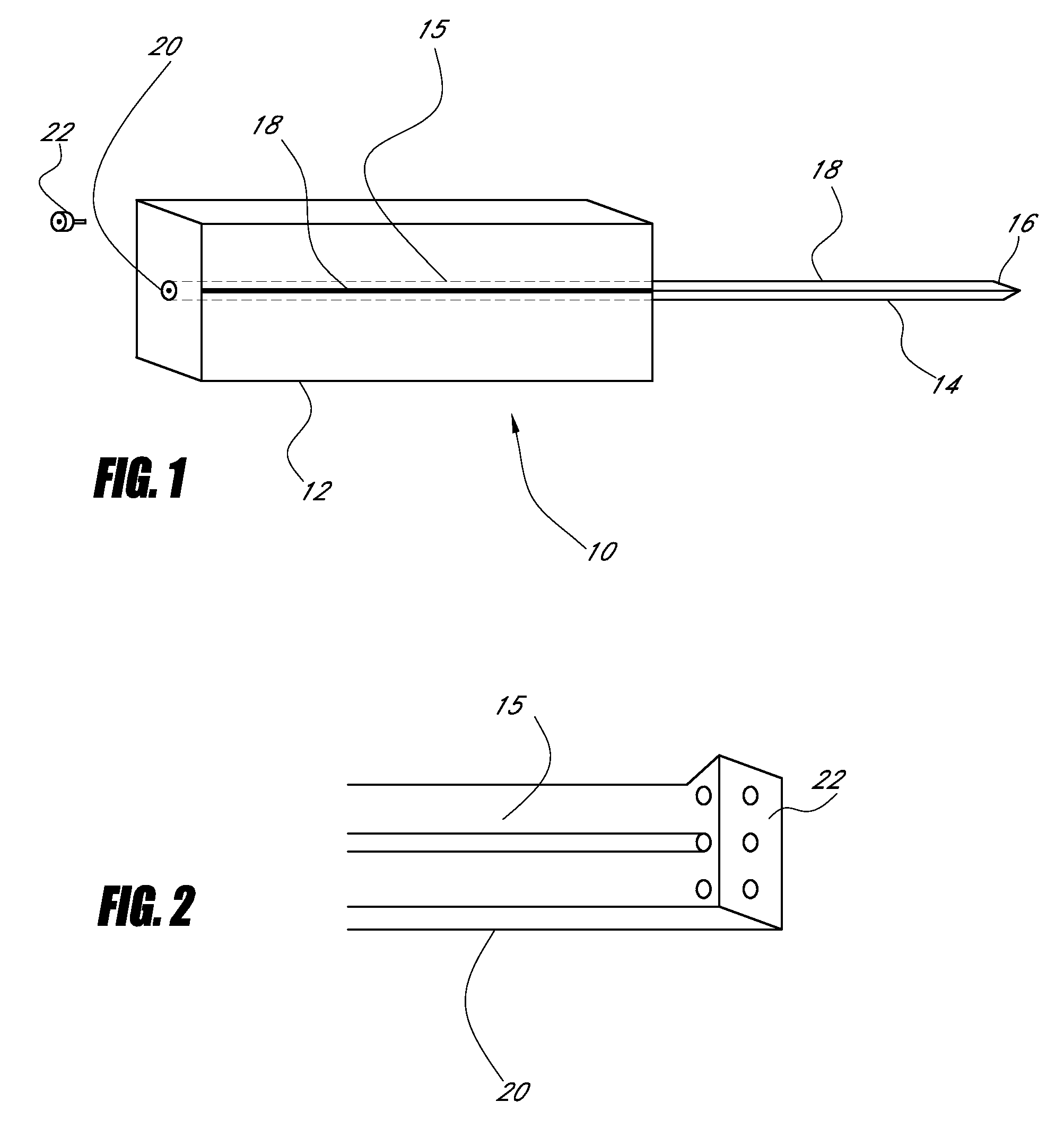
Device for cartilage repair
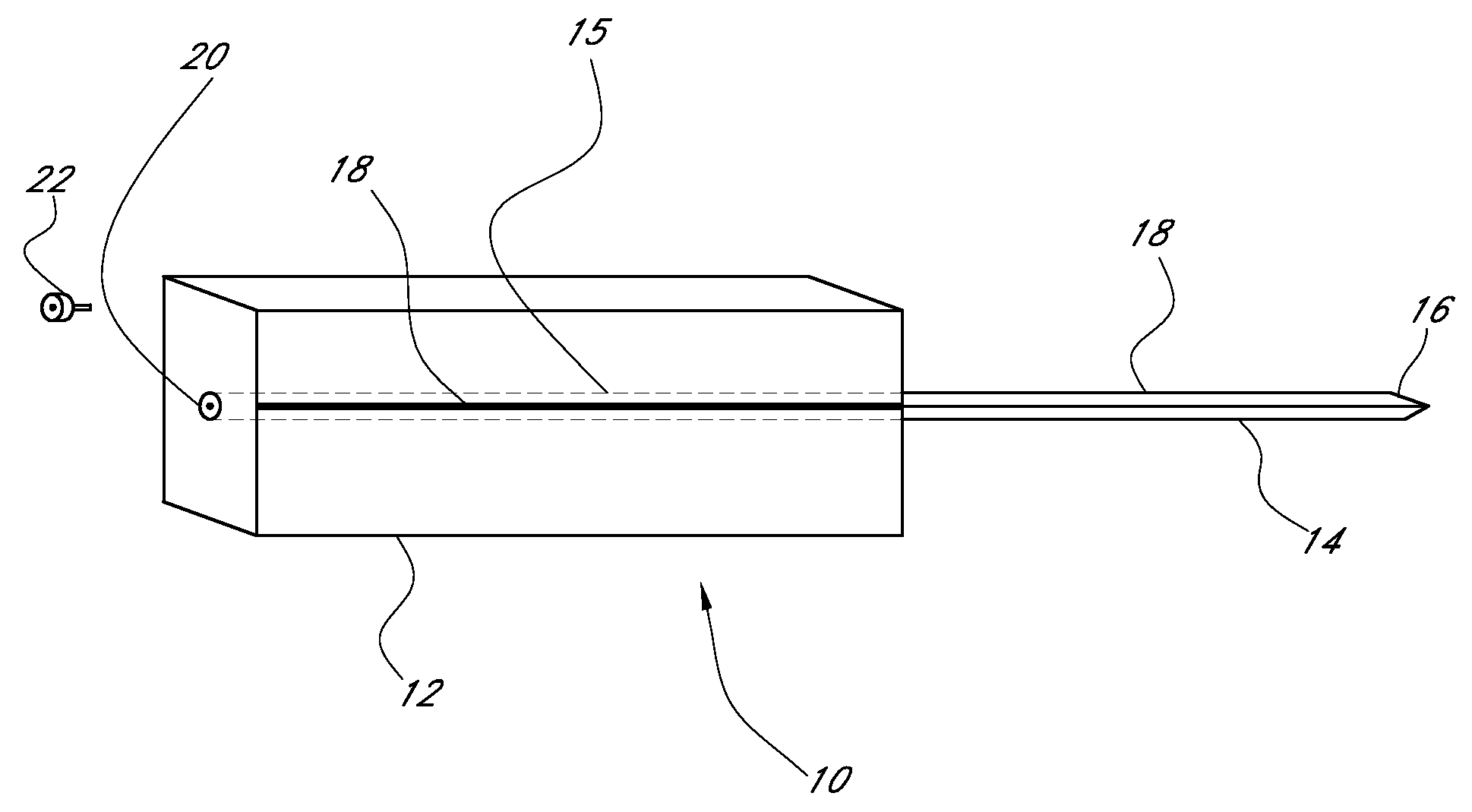
A surgical awl is disclosed for tissue repair. The surgical awl includes an internal lumen through which bioactive substances, such as platelet-rich plasma, may be delivered to a site of tissue or organ disease or dysfunction. In particular, the surgical awl is useful as a microfracture awl for cartilage repair augmented by delivery of platelet-rich plasma through the lumen of the device.
Owner:MISHRA ALLAN
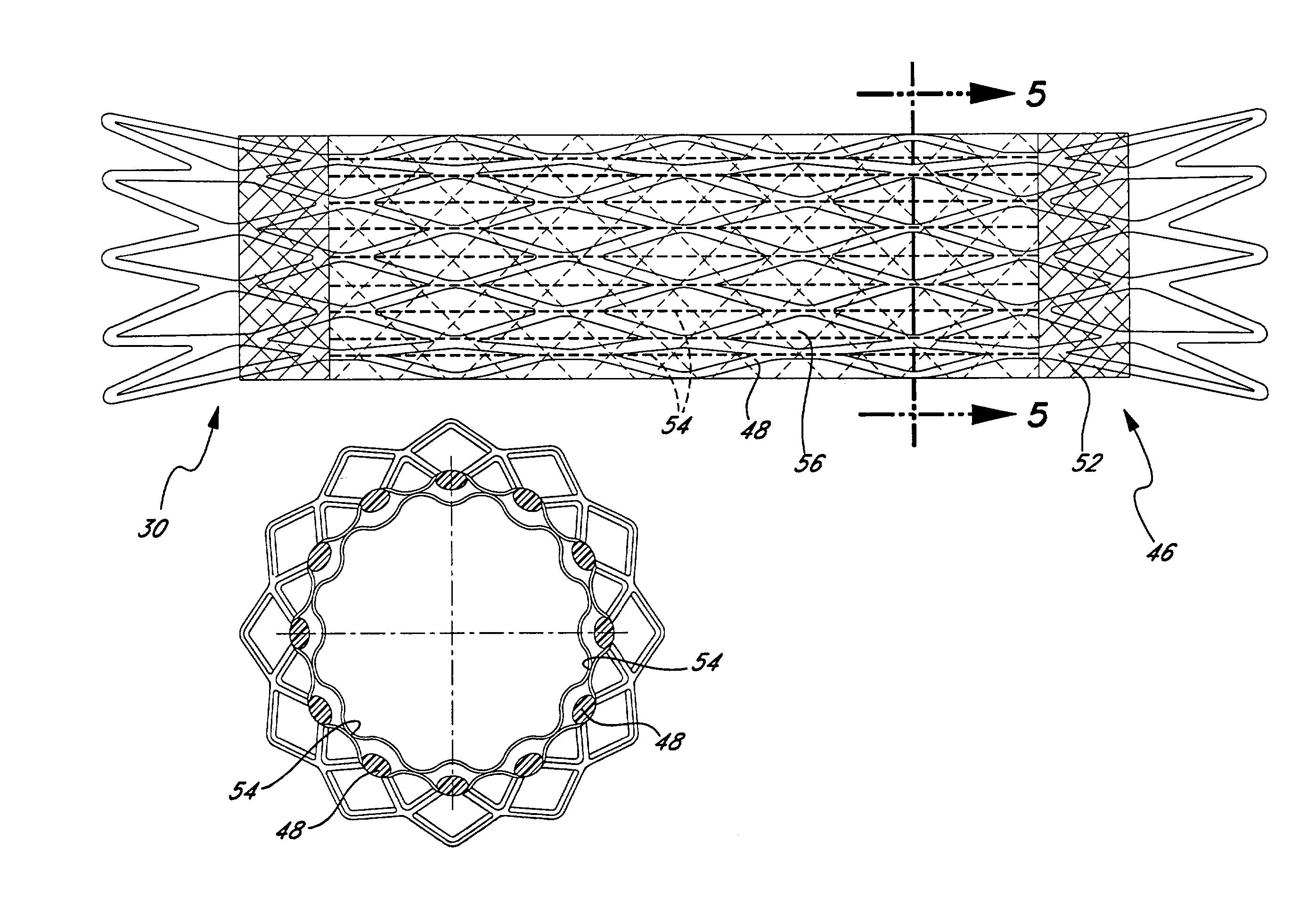
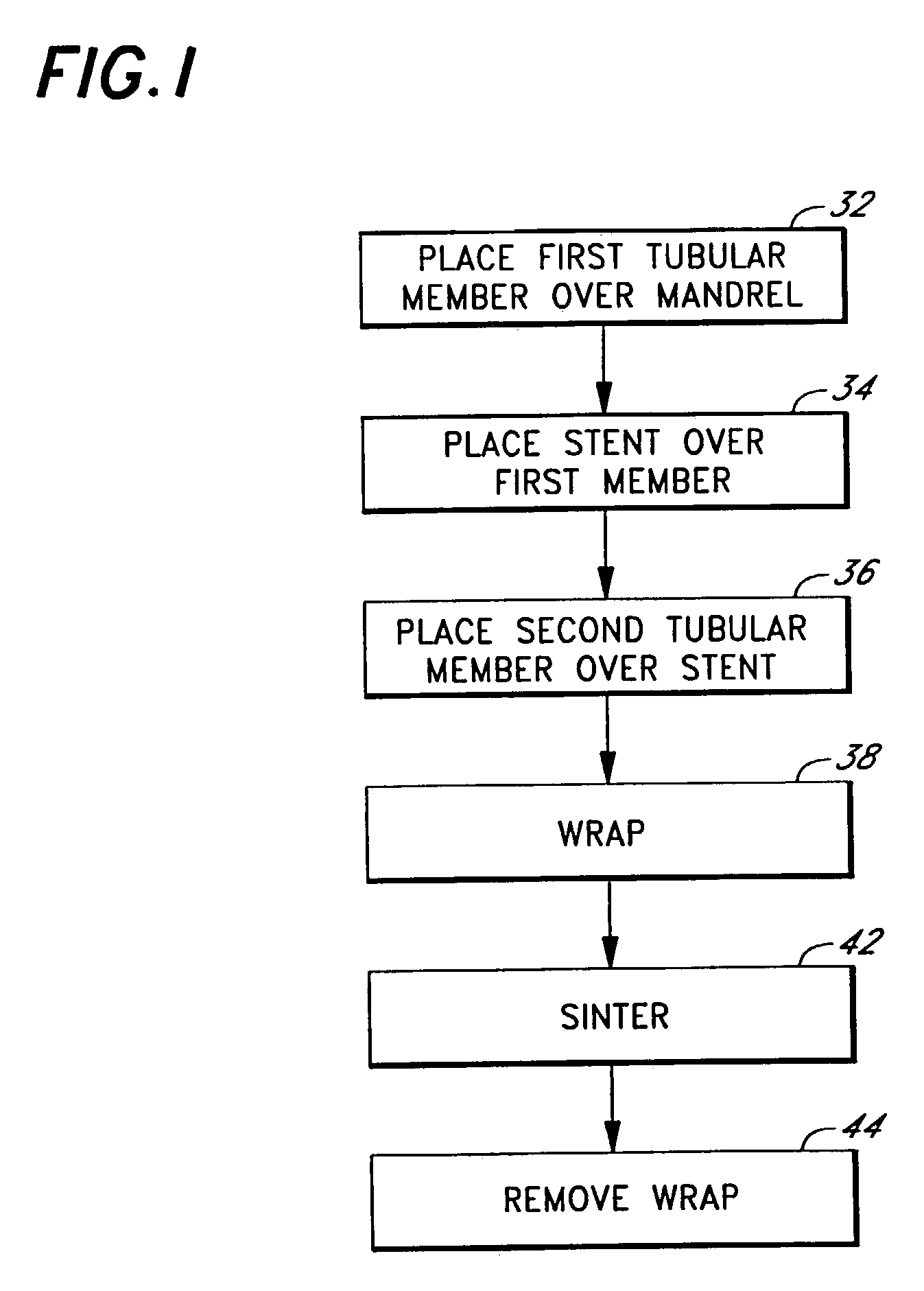
Selective adherence of stent-graft coverings
InactiveUS7004966B2Little strengthReduce inflation pressureStentsDomestic articlesStent graftingVascular device
An endoluminal vascular device having a plurality of predetermined boding locations between respective first and second covering members to selectively encapsulate a support member. Selective bonding between the first and second covering members results in unbonded slip pockets to accommodate movement of the support member. Such a configuration allows compression of the support member with minimal force and also promotes a low profile of the compressed device. Unbonded regions of the covering members also encourage enhanced cellular penetration for rapid healing and can be configured to hold bioactive substances that diffuse through the covering members.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
Poly(organophosphazene) containing degradation controllable ionic group, preparation method thereof and use thereof
InactiveUS20140031289A1Control releaseExcellent in bearing the drugsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorous compound active ingredientsControlled releaseBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention relates to a thermosensitive phosphazene-based polymer having a degradation controllable ionic group, a use thereof, and a use thereof as a material for delivering bioactive substances. The phosphazene-based polymer according to the present invention has the thermosensitivity of showing the temperature-dependent sol-gel phase transition. Thus, it forms a gel phase at the body temperature when it is injected into the body to make it easy to control the release of bioactive substances such as drugs, and has the functional groups capable of making chemical bonds such as ionic bond, covalent bond, coordinate bond, etc. with drugs and thus is excellent in bearing the drugs. Since it can control the degradation rate depending on the kind of ionic group, it can selectively control the release time depending on the characteristics of drugs. Furthermore, it has an excellent biocompatibility and thus is very useful as a material for delivery of bioactive substances such as drugs, etc.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Multi-layered polymerizing hydrogels for tissue regeneration
A multi-layered tissue construct includes: a first layer comprising a first hydrogel; and a second layer comprising a second hydrogel, wherein the first layer is connected to the second layer at a first transition zone and wherein at least one of the first layer and the second layer further comprises a component selected from the group consisting of cells and a bioactive substance. Another multi-layered tissue construct includes: a first layer comprising a first hydrogel; a second layer comprising cells of a first type, wherein the second layer is disposed on the first layer; and a third layer comprising a second hydrogel and optionally cells of the first type encapsulated in the second hydrogel, wherein the third layer is disposed on the second layer. Methods for producing these multi-layered tissue constructs are also disclosed.
Owner:BIOMET INC
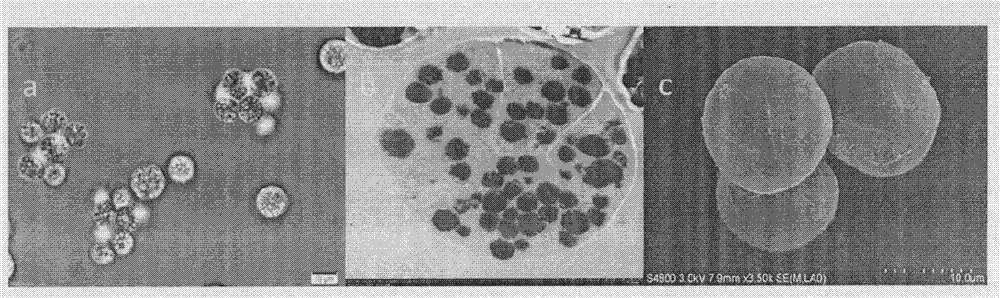
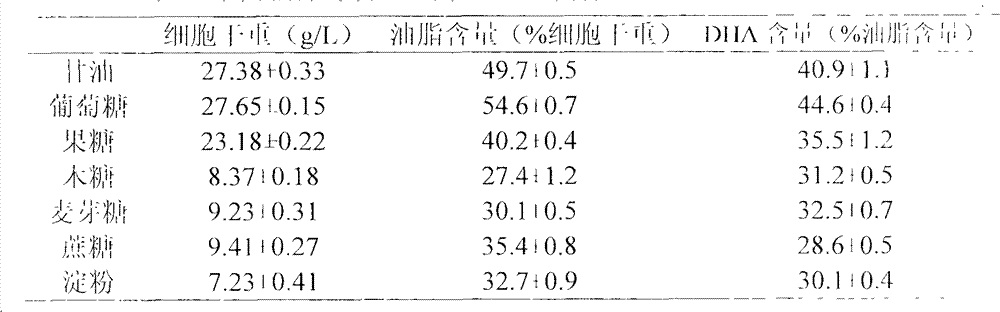
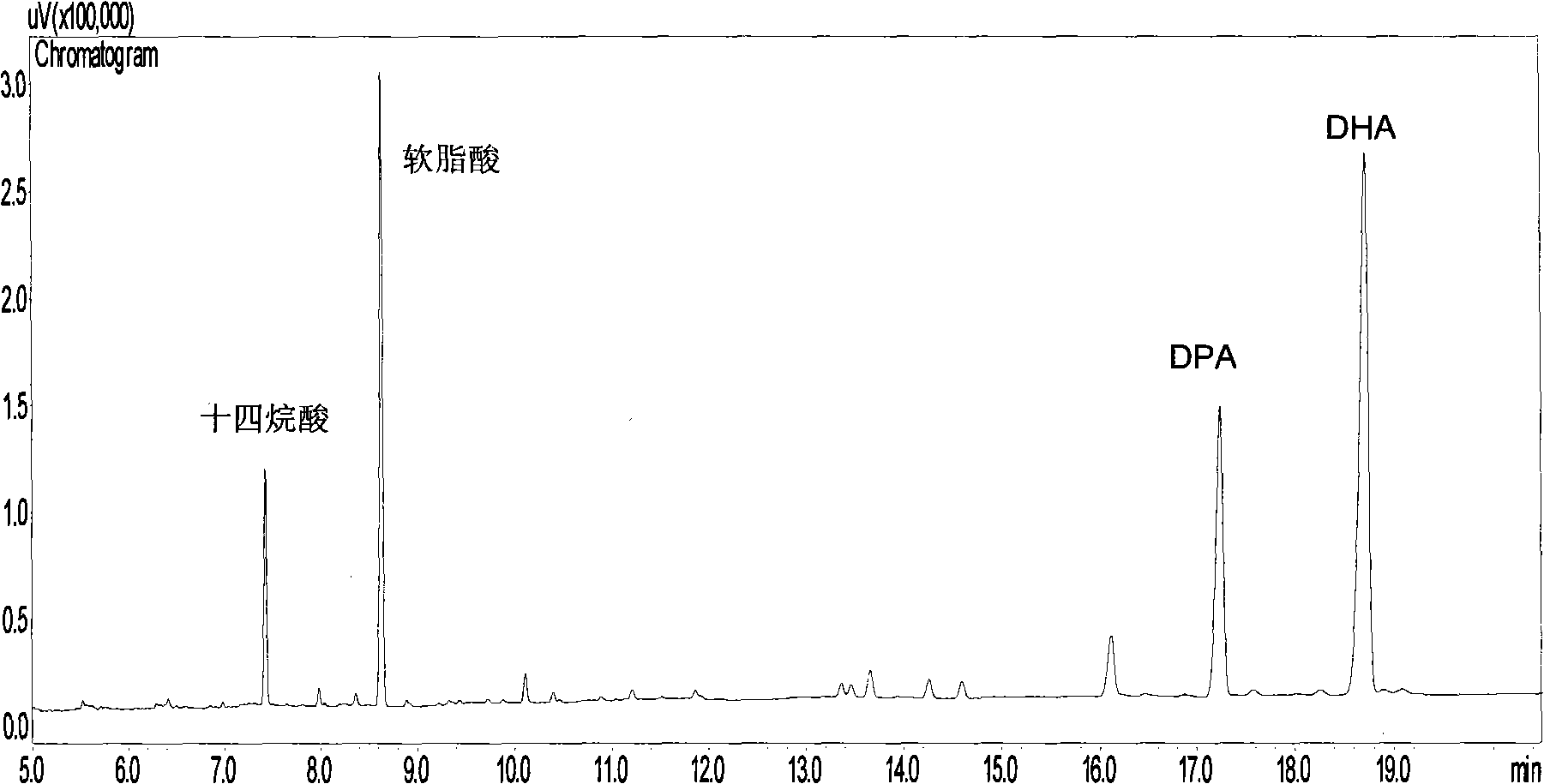
Schizochytrium limacinum and method or fermenting and producing DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) grease utilizing high density of schizochytrium limacinum
ActiveCN102888348AIncrease productionHigh price advantageFungiMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneAstaxanthin
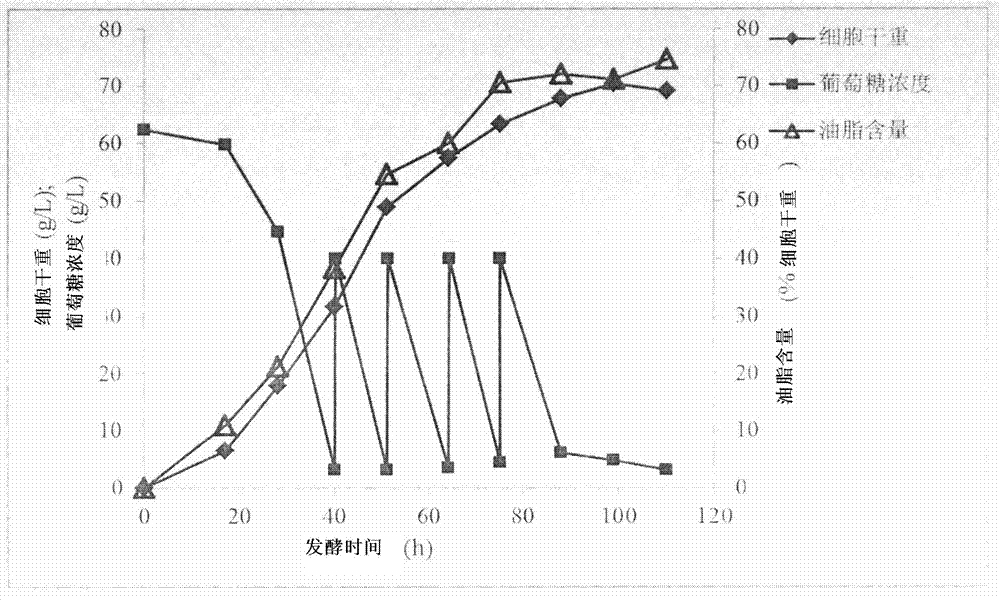
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fermentation engineering, and discloses schizochytrium limacinum (Aurantiochytrium sp.SD116). The schizochytrium limacinum is stored in China Microbial Culture Collection Administration Committee General Microbial Center with a number of CGMCC No: 6208), and a method for fermenting and producing DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) grease utilizing high density of the schizochytrium limacinum. According to the schizochytrium limacinum and the method disclosed by the invention, a bacterial strain fermenting condition is optimized based on element supply and a fermenting control angle, a carbohydrate supplementation operation is carried out, therefore, high-density fermentation is achieved, dry cell weight finally reaches 70.43g / L, grease content reaches 50.1g / L, DHA occupies more than 35% of total content of fatty acid; moreover, bioactive substances such as beta-carotene, astaxanthin and squalene are contained. The complete set of technology is convenient to operate; higher biomass liveweight and DHA content can be obtained; fermenting cost can be reduced; and the method is suitable for industrial fermenting production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Schizochytrium sp. and method for producing DHA lipa by using same
ActiveCN101575584AIncrease biomassHigh in DHABacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveSchizochytrium sp.
The invention discloses a Schizochytrium sp., which has a category name of Schizochytrium sp., is preserved in Common Microorganisms Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms and has a preservation number of CCTCC No.209059. The invention also discloses a method for producing DHA lipa by using the Schizochytrium sp. The method optimizes a strain fermentation medium from the perspectives of osmotic pressure and element supply and combines a fed-batch strategy to achieve high-density fermentation of microalgae, thus the final dry cell weight reaches 70 grams per liter, the lipa content reaches 31.5 grams per liter, and the DHA accounts for more than 35 percent of the total fatty acid content. All indexes of the DHA essential oil obtained by the method accord with the standard of food additives, and the DHA essential oil contains a bioactive substance of squalene. The method has the advantages of simple entire process, convenient operation, and high biomass and DHA content, reduces the fermentation cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Liquid polymeric compositions for controlled release of bioactive substances
Controlled release of hydrophobic bioactive substances in vivo over an extended time period and without "bursts" of drug release is achieved using a liquid polymeric composition including a polymer such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer in a mixture of hydrophilic and lipophilic solvents.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Formulations for topical delivery of bioactive substances and methods for their use
ActiveUS7241456B2Efficient deliveryNon-irritating to the skinBiocideCosmetic preparationsHigh concentrationIrritation
The invention relates to topical delivery of bioactive agents. More particularly, the invention relates to anhydrous formulations for percutaneous absorption. The invention provides formulations that allow efficient topical delivery of high concentrations of bioactive substances for percutaneous absorption. The formulations according to the invention are generally non-irritating to the skin.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN IMPORTERS
Surface immobilization of various functional biomolecules using mussel adhesive protein
The present invention relates to technology of immobilizing or coating various functional bioactive substances on various surfaces without physical chemical treatment using mussel adhesive protein. More specifically, the present invention relates to a functional scaffold for tissue engineering comprising artificial extracellular matrix, manufactured by coating various functional bioactive substances on the surface of nanofiber and metal scaffold using mussel adhesive protein, and a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Selective adherence of stent-graft coverings
InactiveUS20060155369A1Little strengthReduce inflation pressureStentsDomestic articlesMedicineStent grafting
An endoluminal prosthesis including a first polymer member bonded to a second polymer member to selectively encapsulate a stent. Selective bonding between the first and second polymer members results in unbonded regions or pockets that accommodate movement of the stent, permitting compression of the prosthesis using minimal force and enabling collapse of the prosthesis to a low profile. The pockets are believed to encourage enhanced cellular penetration for rapid healing and may contain bioactive substances.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
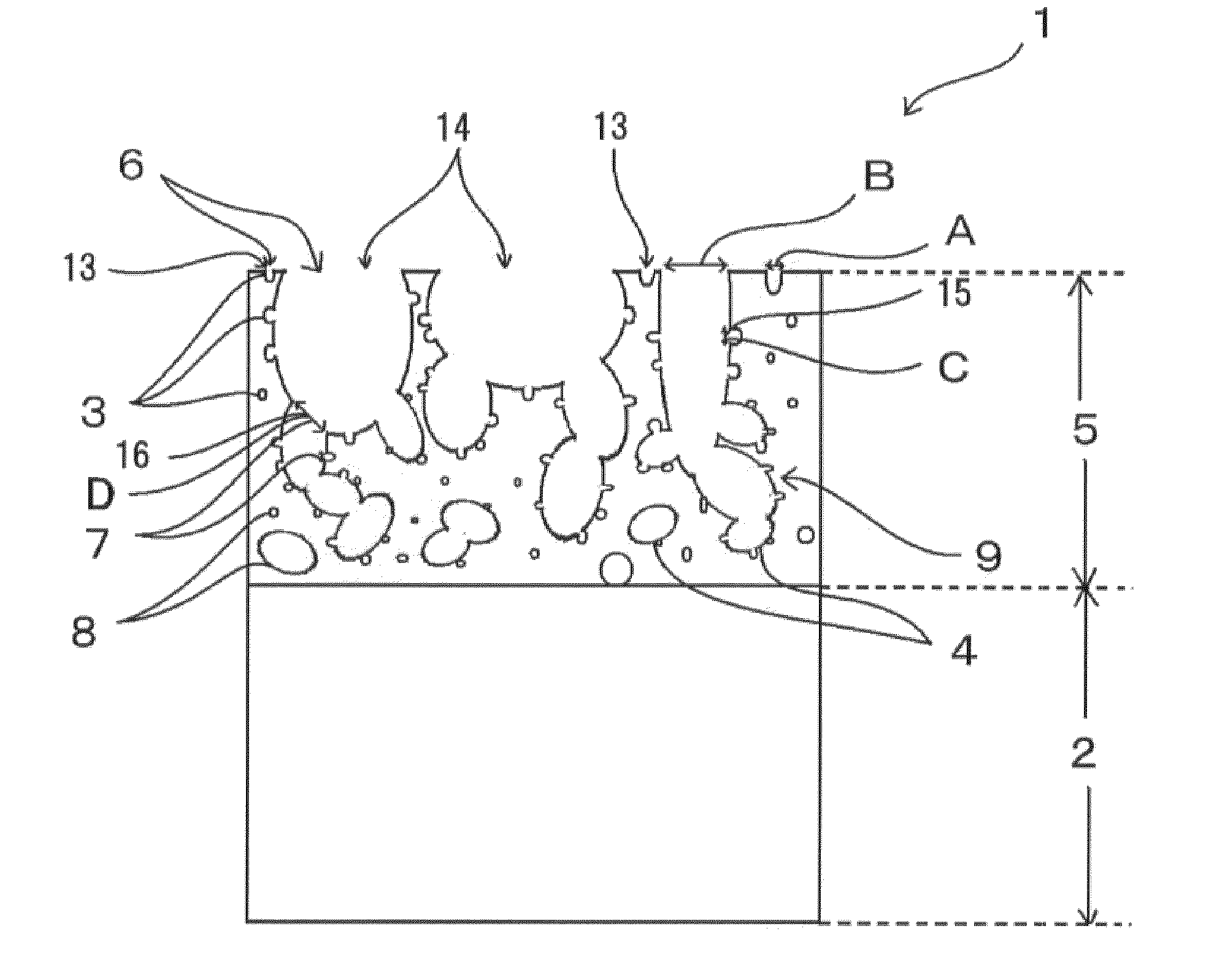
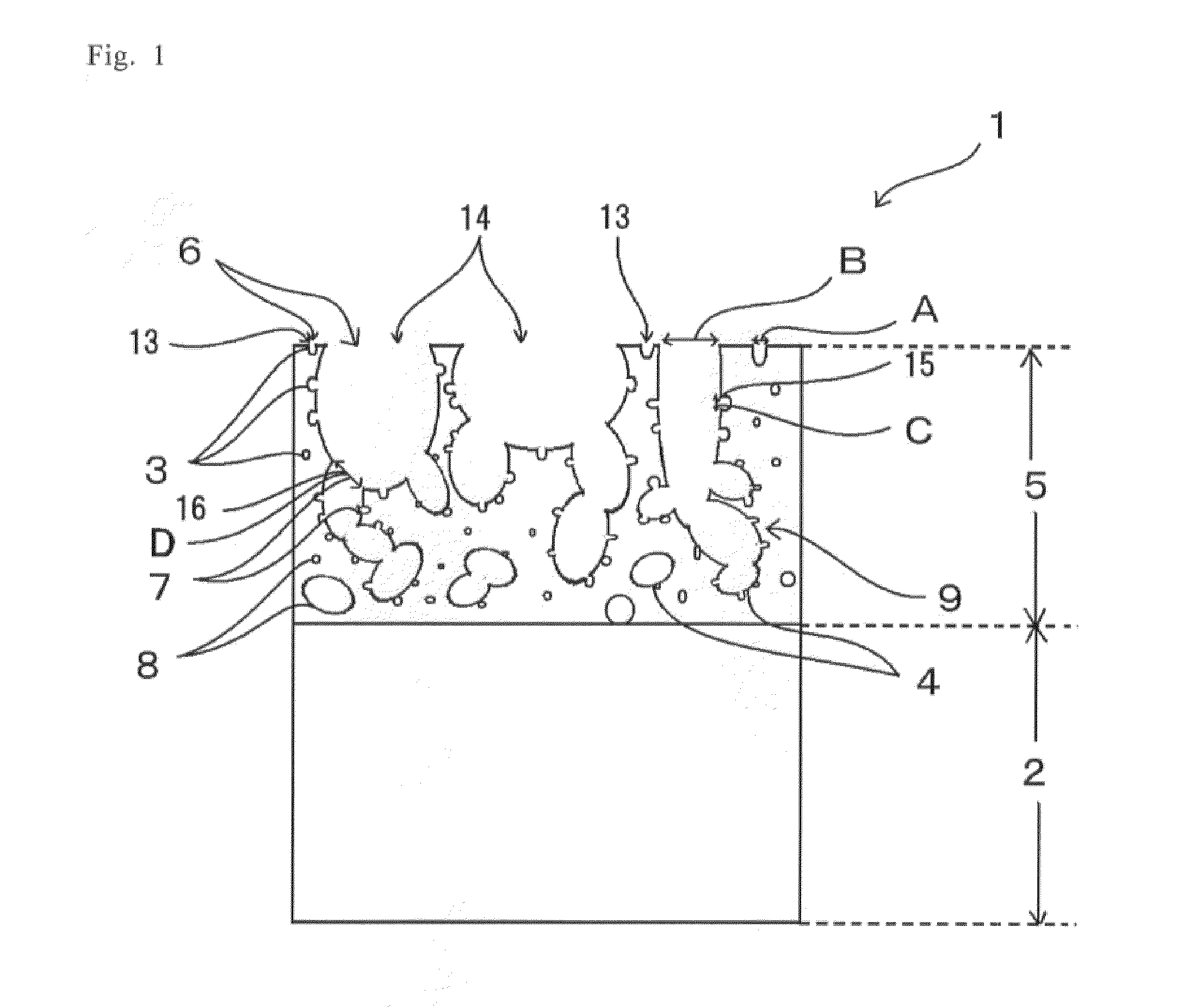
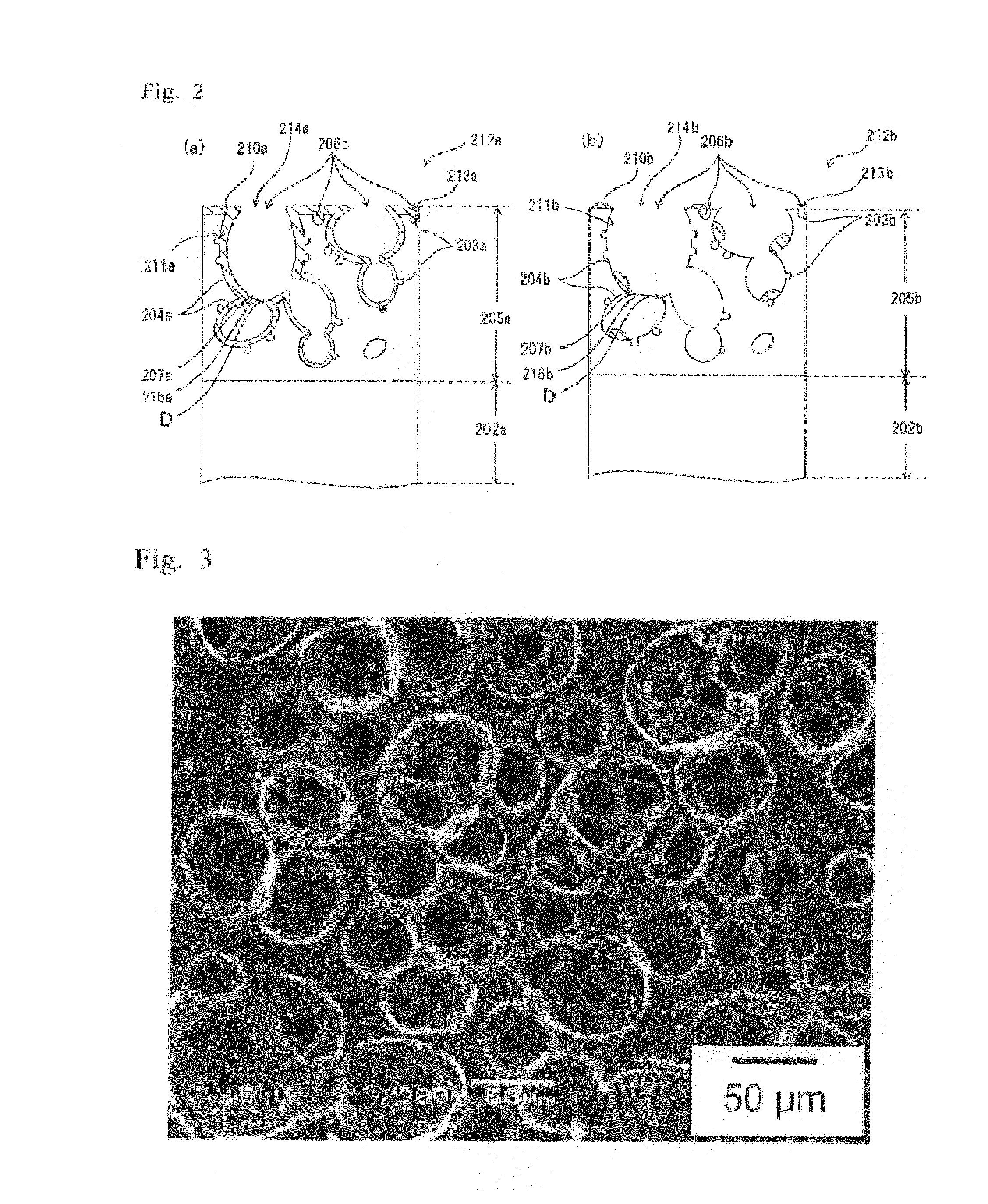
Article with foamed surface, implant and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20110022181A1Appropriate strengthHigh strengthSemi-permeable membranesBone implantMaterials scienceBioactive substance
The objection of this invention is to provide an article with a foamed surface having a porous structure in the surface of a plastic base, an implant and a method of producing them. The article has a body and a superficial layer formed in a surface of the body, the layer including small-diameter and large-diameter pores, wherein part of the small-diameter and large-diameter pores are open pores which are open at the surface of the layer; the open pores have small open pores with an average diameter of 5 μm or less and large open pores with an average diameter from 10 to 200 μm; and the large open pores have an inner wall with passages connected with the small-diameter large-diameter pores. The implant is the article itself or the article with a bioactive substance in the layer thereof. The method provides an example of producing the article and implant.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Controlled delivery system for bioactive substances
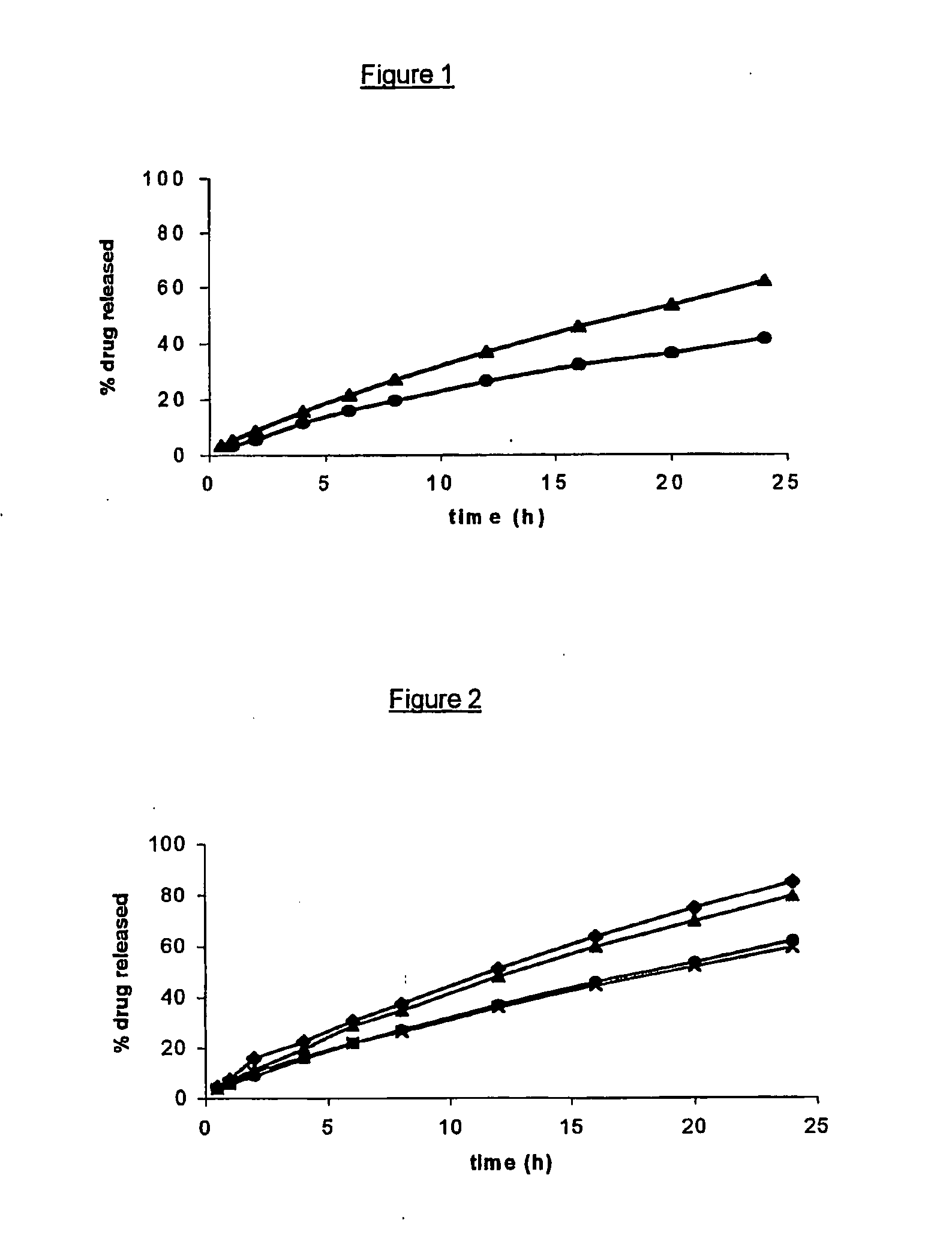
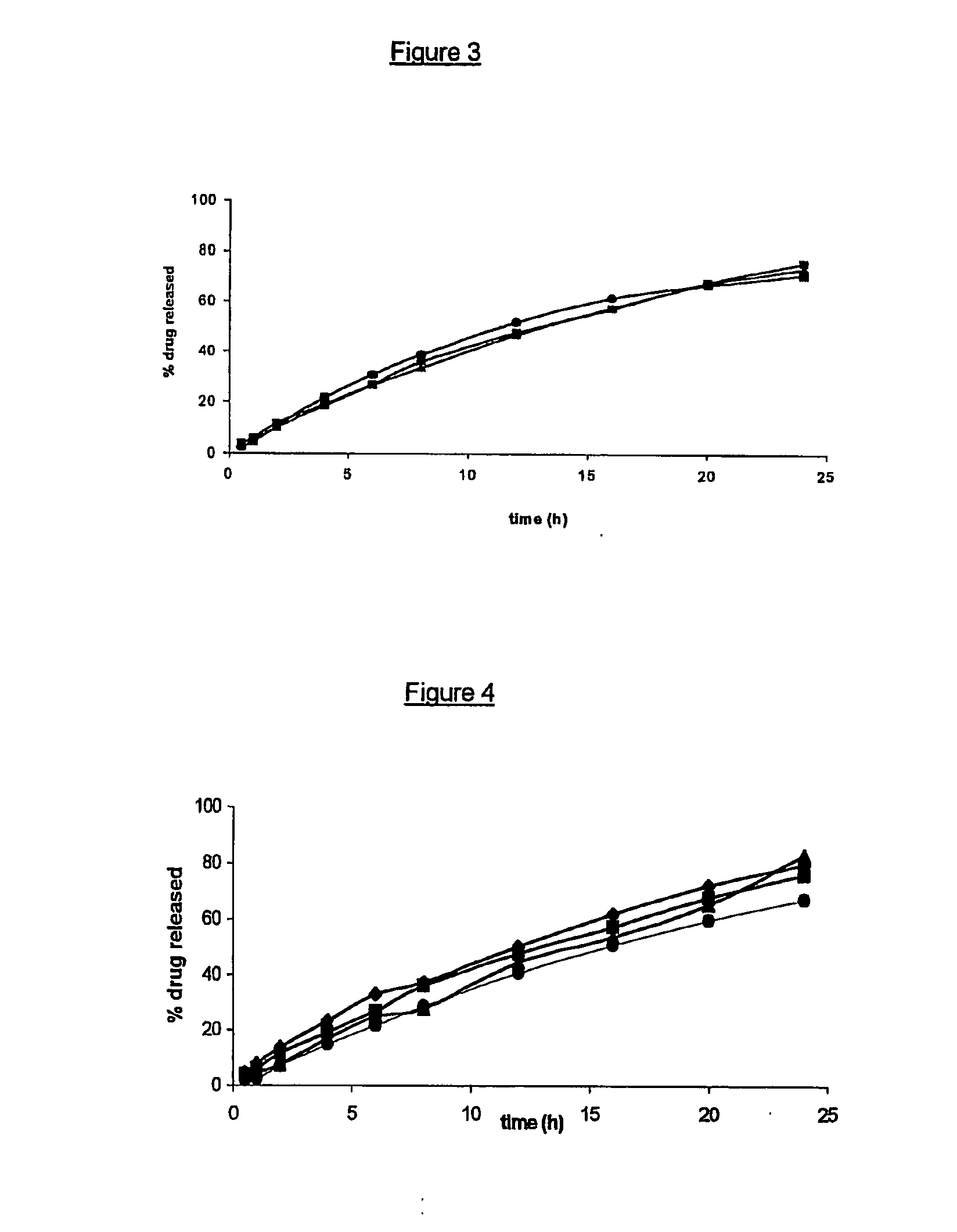
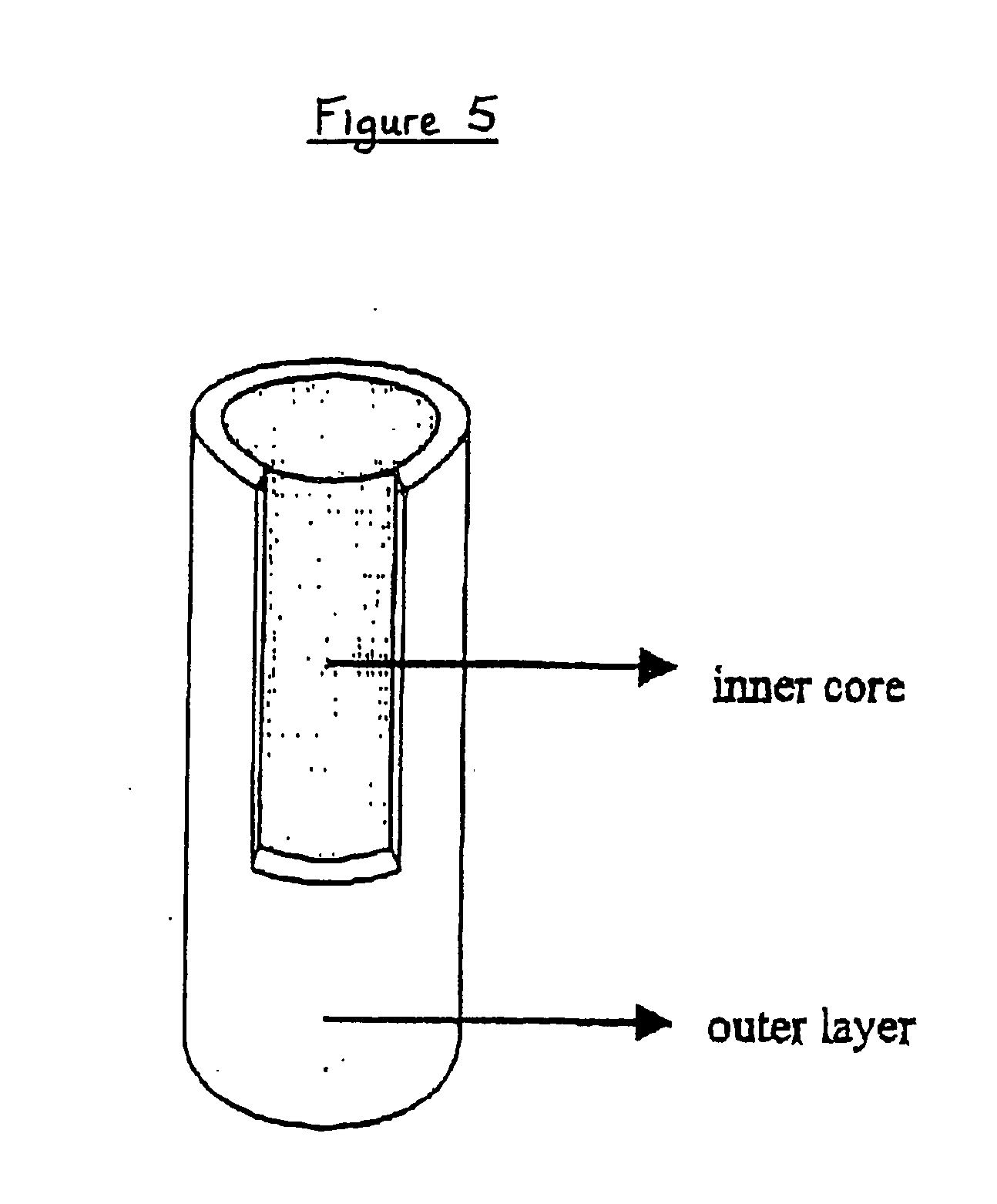
A biologically active composite solid shaped article comprising: (a) an outer layer, and (b) an inner core filling the said outer layer and comprising: at least a biologically active ingredient, and an excipient comprising at least a hydrophilic cellulose polymer and an amphiphilic material in the form of a blend with the said hydrophilic cellulose polymer, the weight ratio of the hydrophilic cellulose polymer to the amphiphilic material being from 0.2:1 to 0.6:1, provides improved sustained release of the biologically active ingredient.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Non sweet binder for savory food product
The present invention relates to non sweet food binder composition. Particularly, the food binder composition can be used in the preparation of savory snack bars, savory nutritional bars, or in savory food products used as snack or meal replacement, containing varied levels of protein, fiber, minerals, vitamins and other bioactive substances or nutritional supplements.
Owner:NELLSON NUTRACEUTICAL
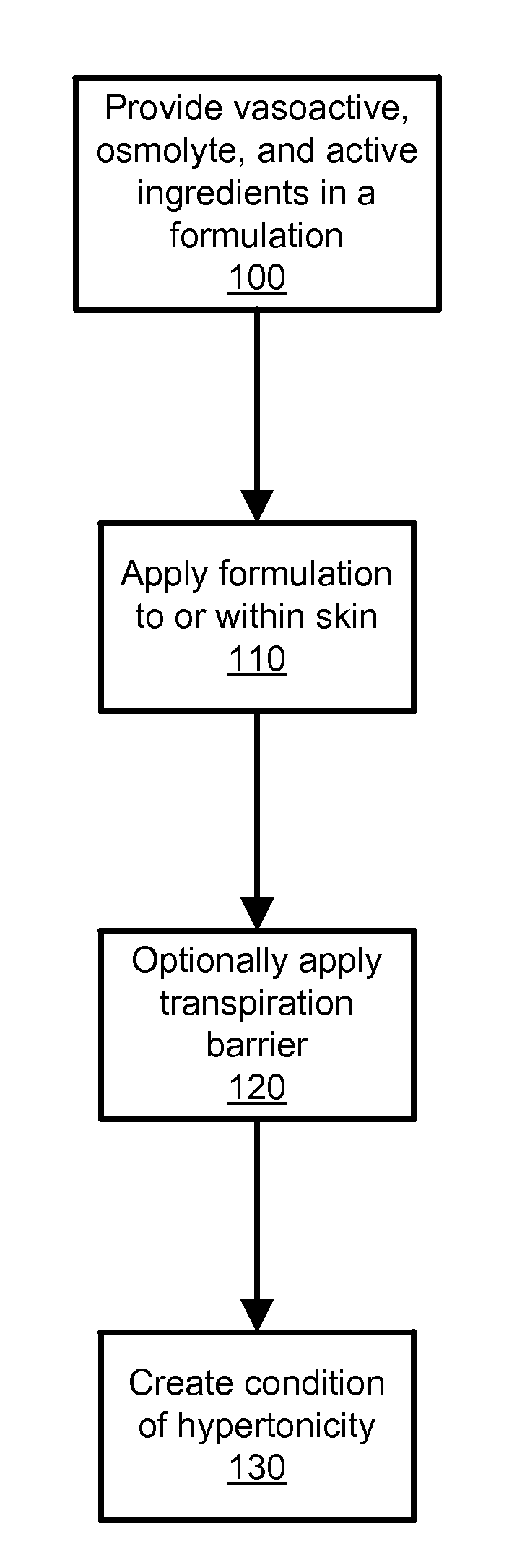
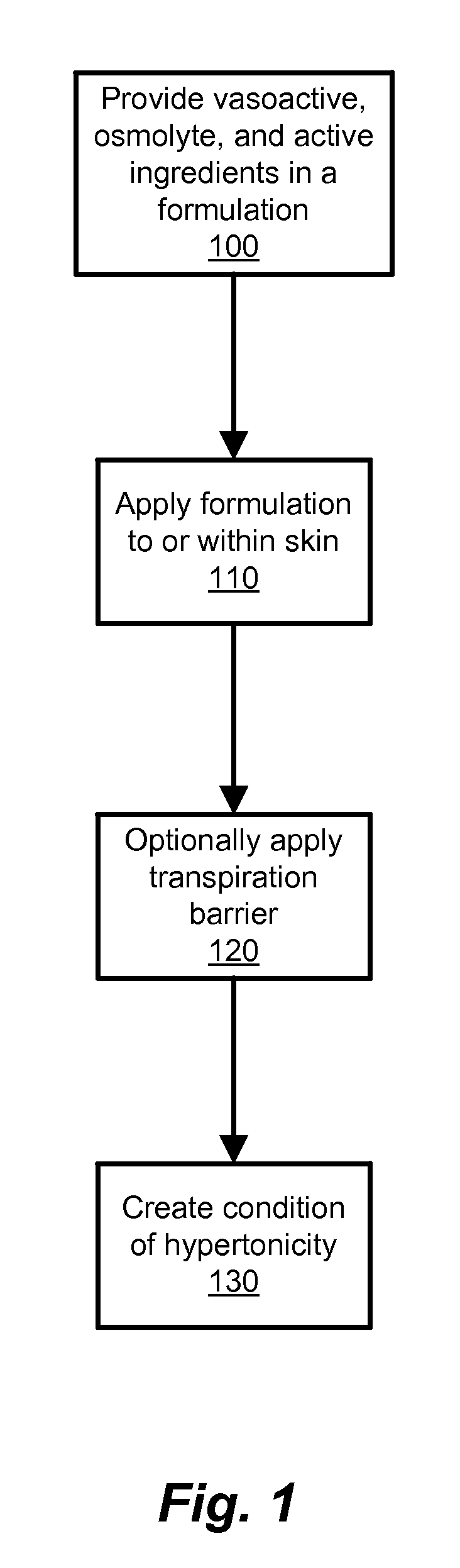
Transdermal Drug Delivery using an Osmolyte and Vasoactive Agent
ActiveUS20100076035A1Increase blood flowImprove permeabilityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsOtic AgentsActive agent
Owner:BIOCHEMICS +1
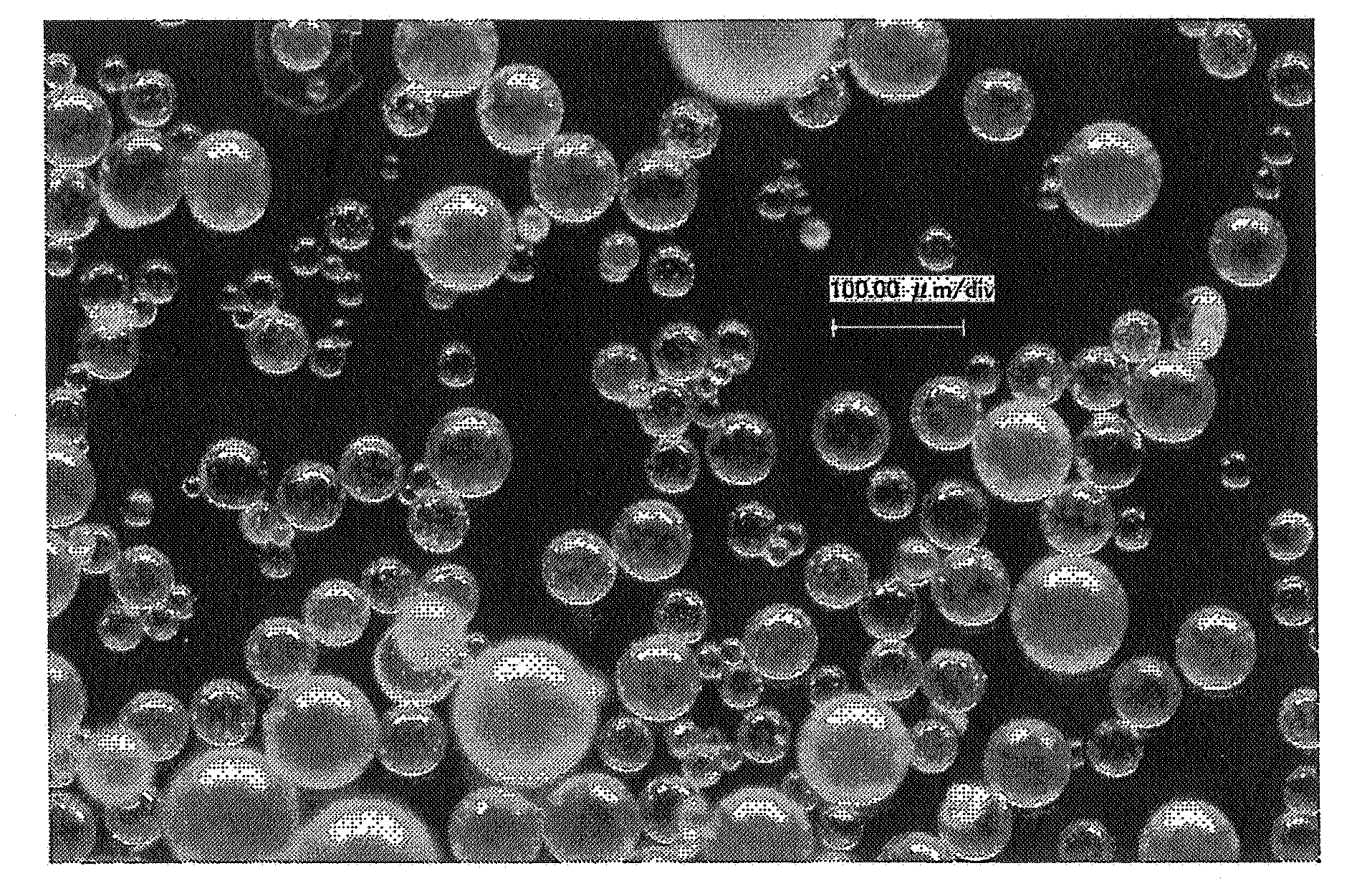
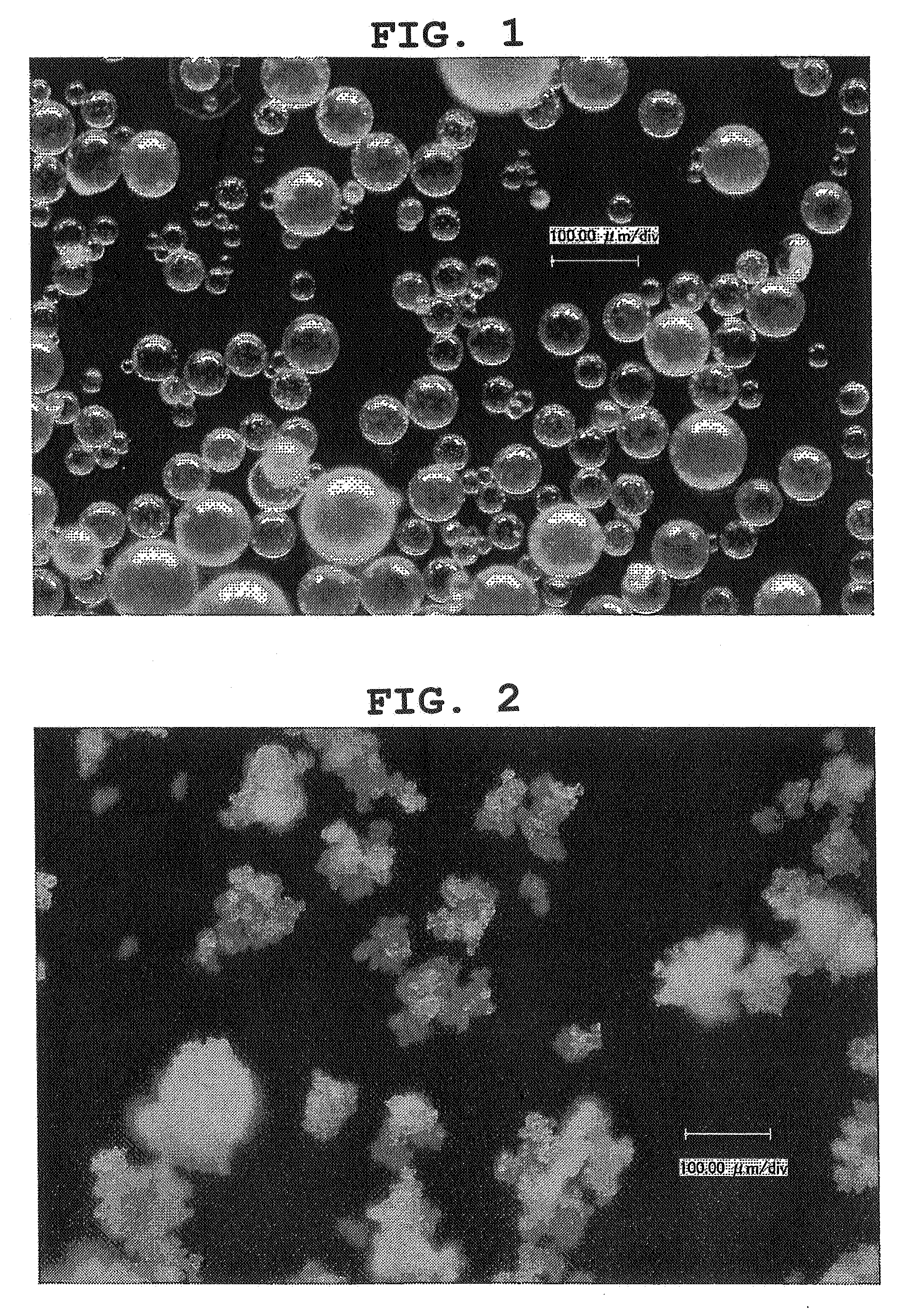
Particulate composition comprising bioactive substance and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20080102131A1High recovery rateAmeliorating issue of low recovery rateBiocidePowder deliverySolubilityParticulates
The present invention provides a particulate composition wherein an oil component (A) comprising a water-insoluble bioactive substance is poly-dispersed while forming a domain in a matrix comprising of a water-soluble excipient based on a water-soluble polymer, and wherein the sphericity of the particulate composition is not less than 0.9 and a method of producing the same. The particulate composition simultaneously has excellent water solubility, workability, tabletability and heat-resistance. It also provides a food, food with nutrient function claims, food for specified health uses, nutritional supplement, nutritional product, animal drug, drink, feed, pet food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical product, therapeutic drug, prophylactic drug and the like, which contain the particulate composition.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method and device for the delivery of a substance including a covering
ActiveUS7316665B2Increase gene expressionEnhance immune responseSurgeryMicroneedlesBiomedical engineeringBioactive substance
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Microfluidic technology for one-step continuous preparation of calcium alginate microgel
ActiveCN107930542AFast shippingMaintain biological activityLaboratory glasswaresGel preparationOil phaseWater in oil emulsion
The invention relates to a microflow droplet technology-based method for one-step continuous preparation of multi-chamber calcium alginate microgel for immobilization of bioactive substances. The method realizes high-throughput continuous production of a microgel material. The method comprises forming a parallel and stable flow field through different hydrogel prepolymer solutions in a microfluidic channel, pouring the hydrogel prepolymer solutions for forming different chambers of the microgel into a microfluidic chip to form water phase solutions of multiple phase parallel fluids, mixing thewater phase solutions and an immiscible fluid (oil phase) through a T-shaped channel or a fluid focusing design to obtain water-in-oil emulsion drops and then alginic acid in the drops is linked immediately so that multi-chamber microgel is prepared, and cleaning the emulsion drops on the microfluidic chip so that the microgel is fast conveyed into a water phase. The method realizes one-step preparation of the calcium alginate microgel immobilized with bioactive substances and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUA NOVA BIOTECH LTD
Porous membranes for medical implants and methods of manufacture
Owner:ABBOTT LAB VASCULAR ENTERPRISE
Alginate-based-polycationic microcapsule and applications thereof in embedding bioactive substance
InactiveCN106860422AImprove stabilityNo swellingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrocapsulesBiocompatibility TestingHydrogel microspheres
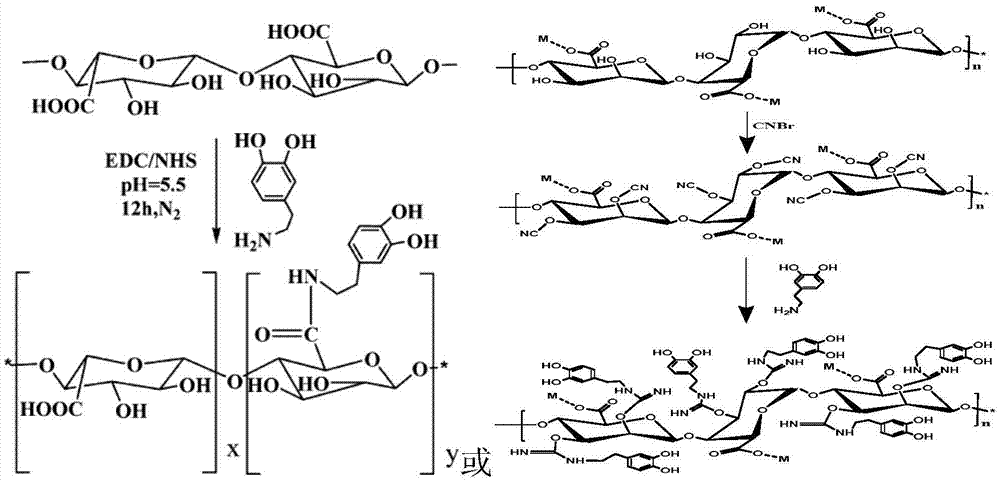
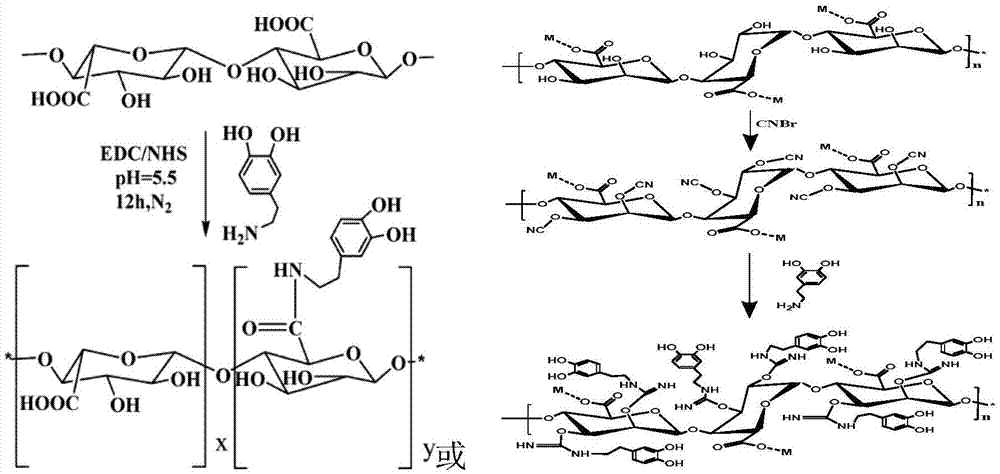
The invention relates to an alginate-polycationic microcapsule product used for embedding bioactive substance, in particular to an alginate-polycationic microcapsule subjected to graft modification of dopamine. According to the alginate-polycationic microcapsule subjected to graft modification of dopamine, dopamine molecules are in covalent bonding to sodium alginate molecules, the obtained molecules are used for preparing a hydrogel microsphere carrier, the embedded hydrogel microsphere carrier further has film formation reaction with polycations, and thus the dopamine-based alginate / polycationic microcapsule is prepared. The microcapsule has good stability, and does not swell or break in the body fluid environment. The product is mainly used for embedding the bioactive substance, the microcapsule film has the excellent biocompatibility while having the good film strength, and the integrity of the microcapsule film when taken as the histocyte transplantation carrier, the cell carrier of the in-vitro bioartificial liver system, the cell carrier in the cell culture process and the like in the application process is guaranteed.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Porous membranes for medical implants and methods of manufacture
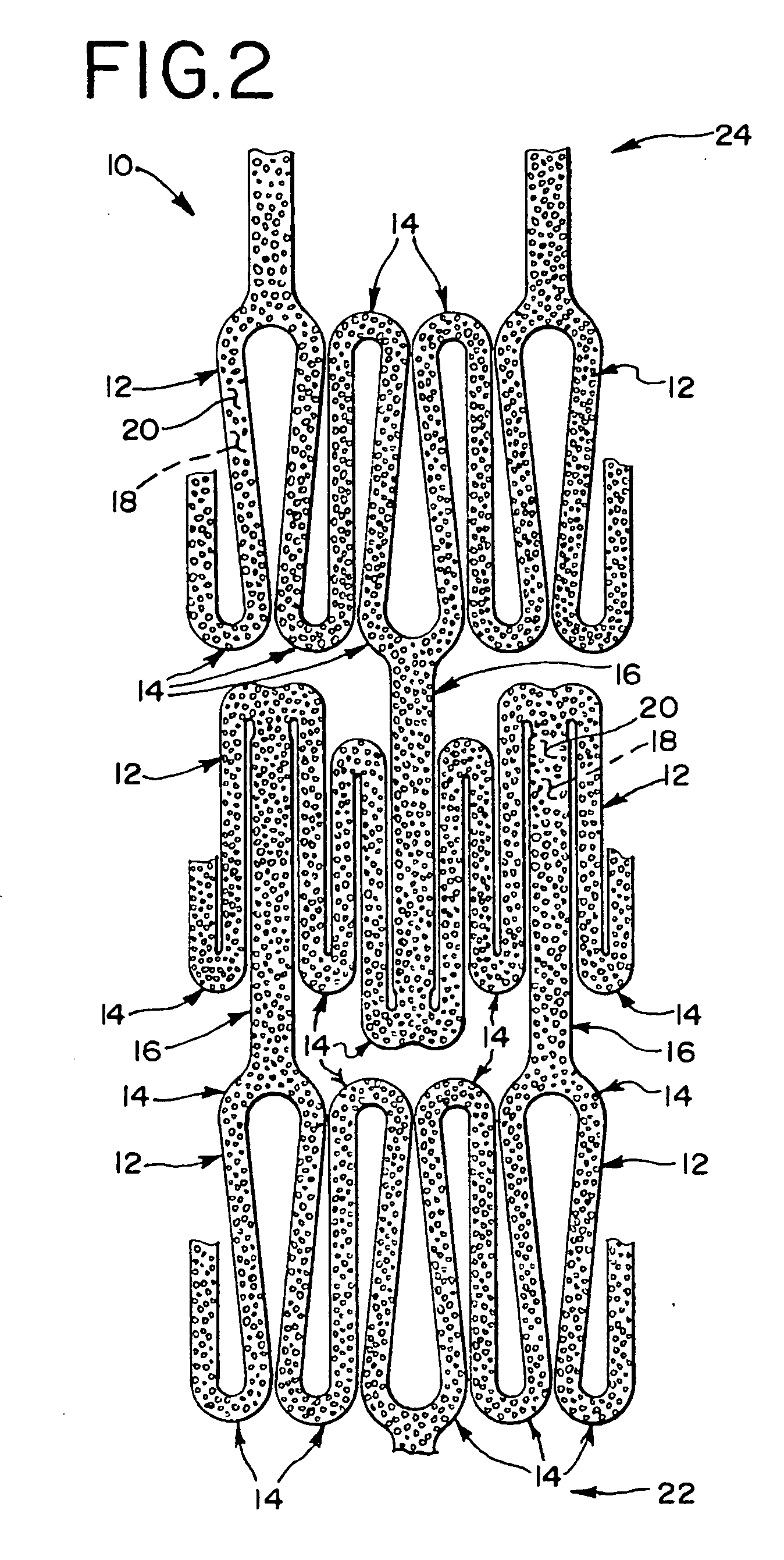
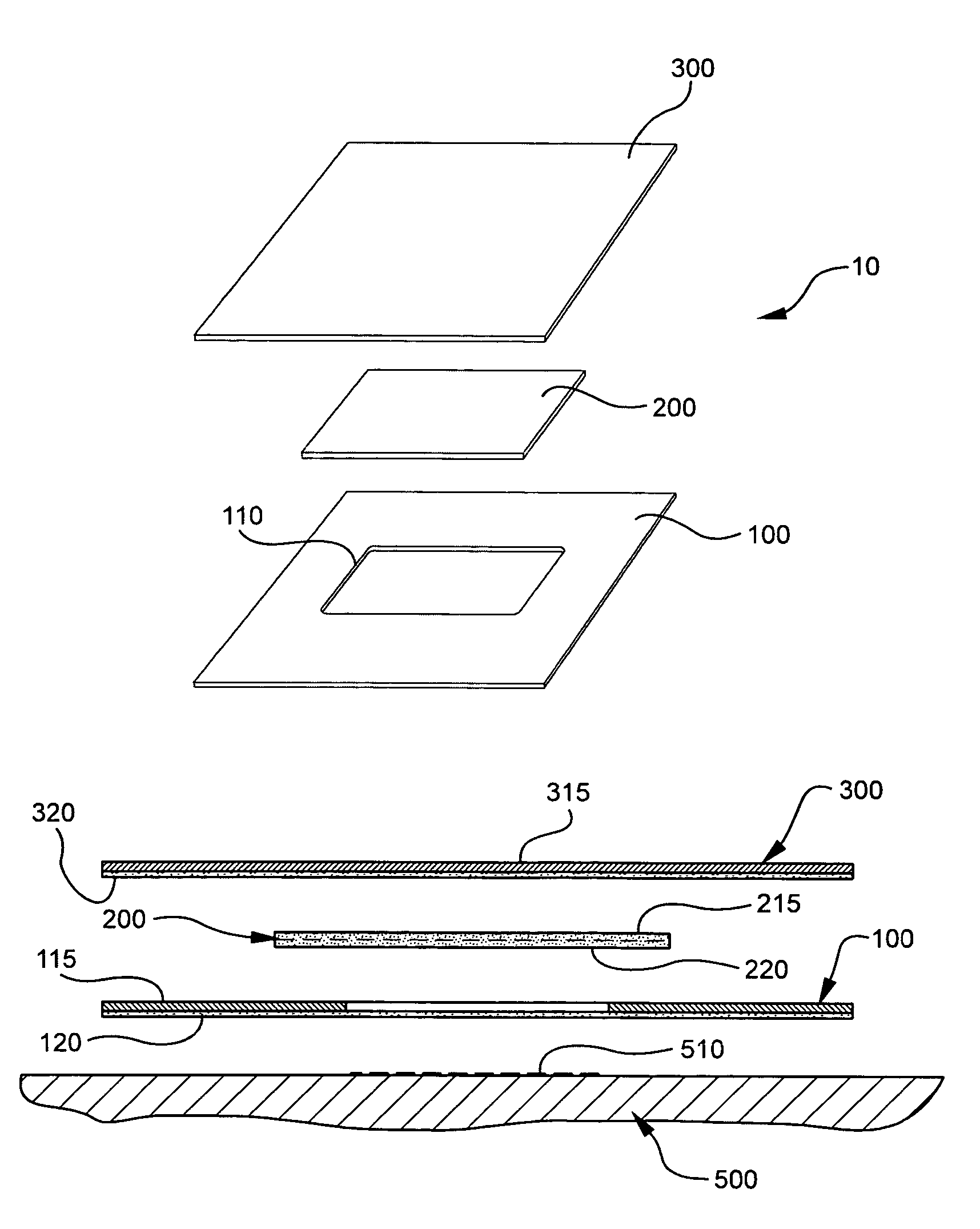
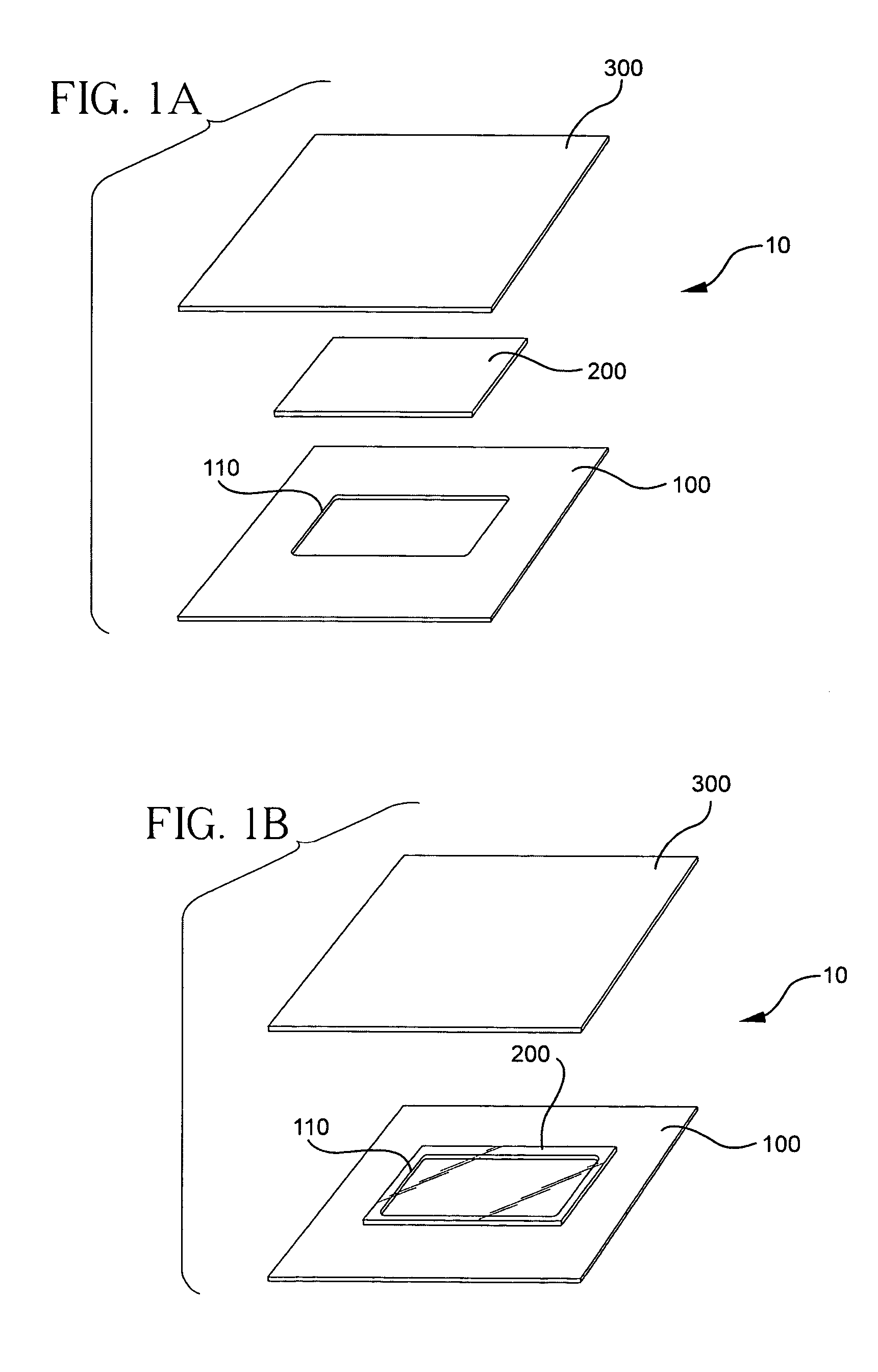
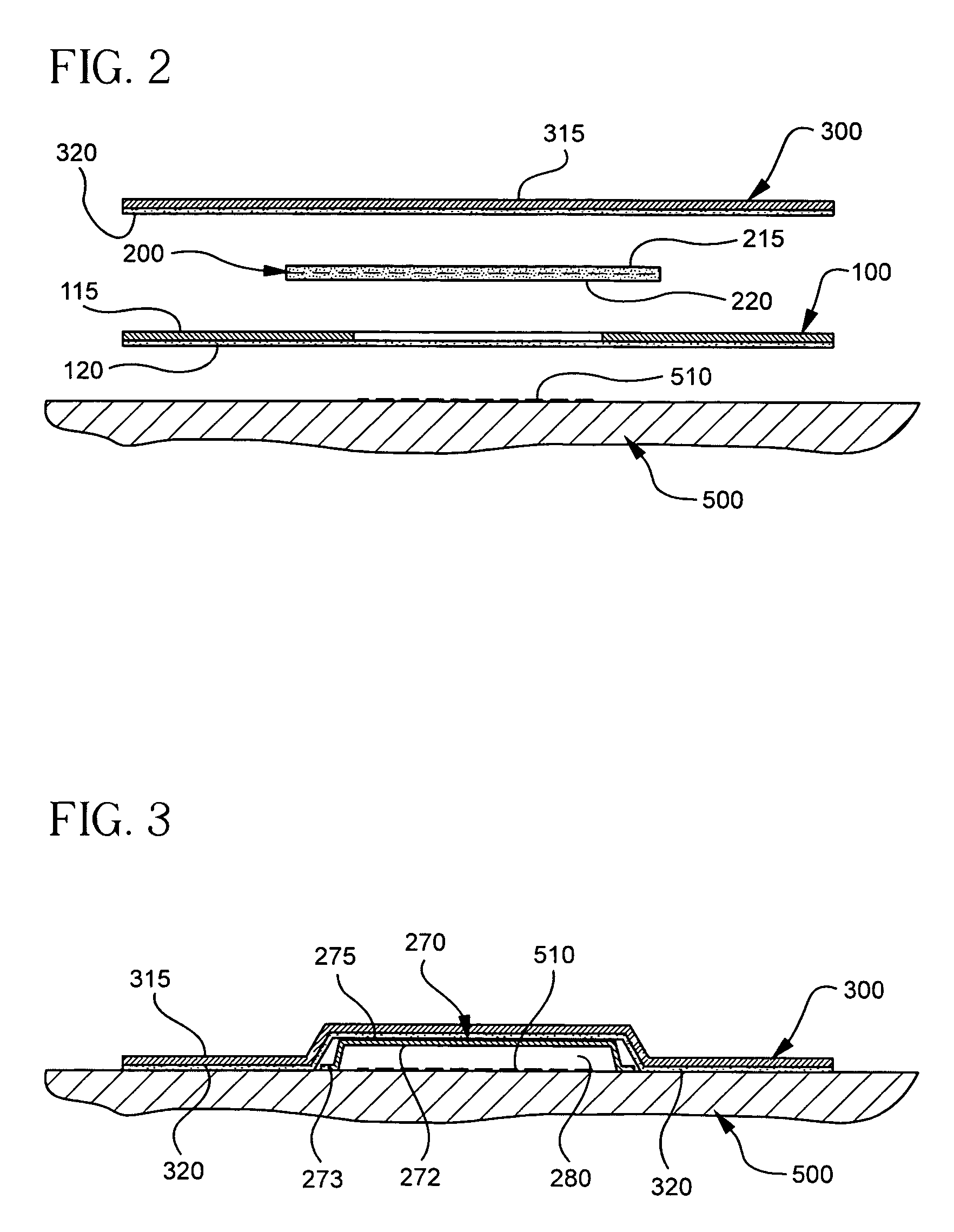
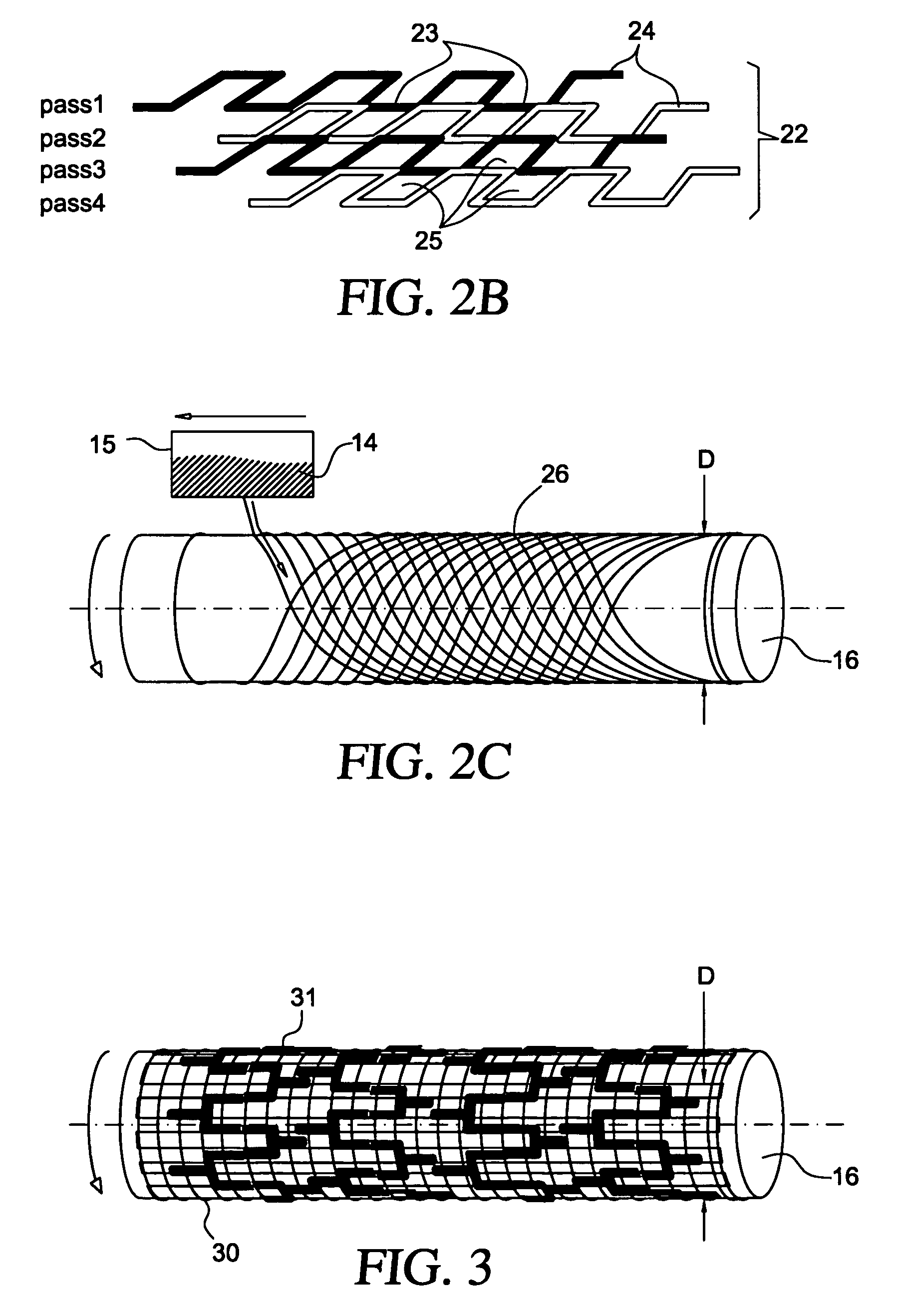
The present invention involves porous polymer membranes, suitable for use in medical implants, having controlled pore sizes, pore densities and mechanical properties. Methods of manufacturing such porous membranes are described in which a continuous fiber of polymer is extruded through a reciprocating extrusion head and deposited onto a substrate in a predetermined pattern. When cured, the polymeric material forms a stable, porous membrane suitable for a variety of applications, including reducing emboli release during and after stent delivery, and providing a source for release of bioactive substances to a vessel or organ and surrounding tissue.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB VASCULAR ENTERPRISE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com