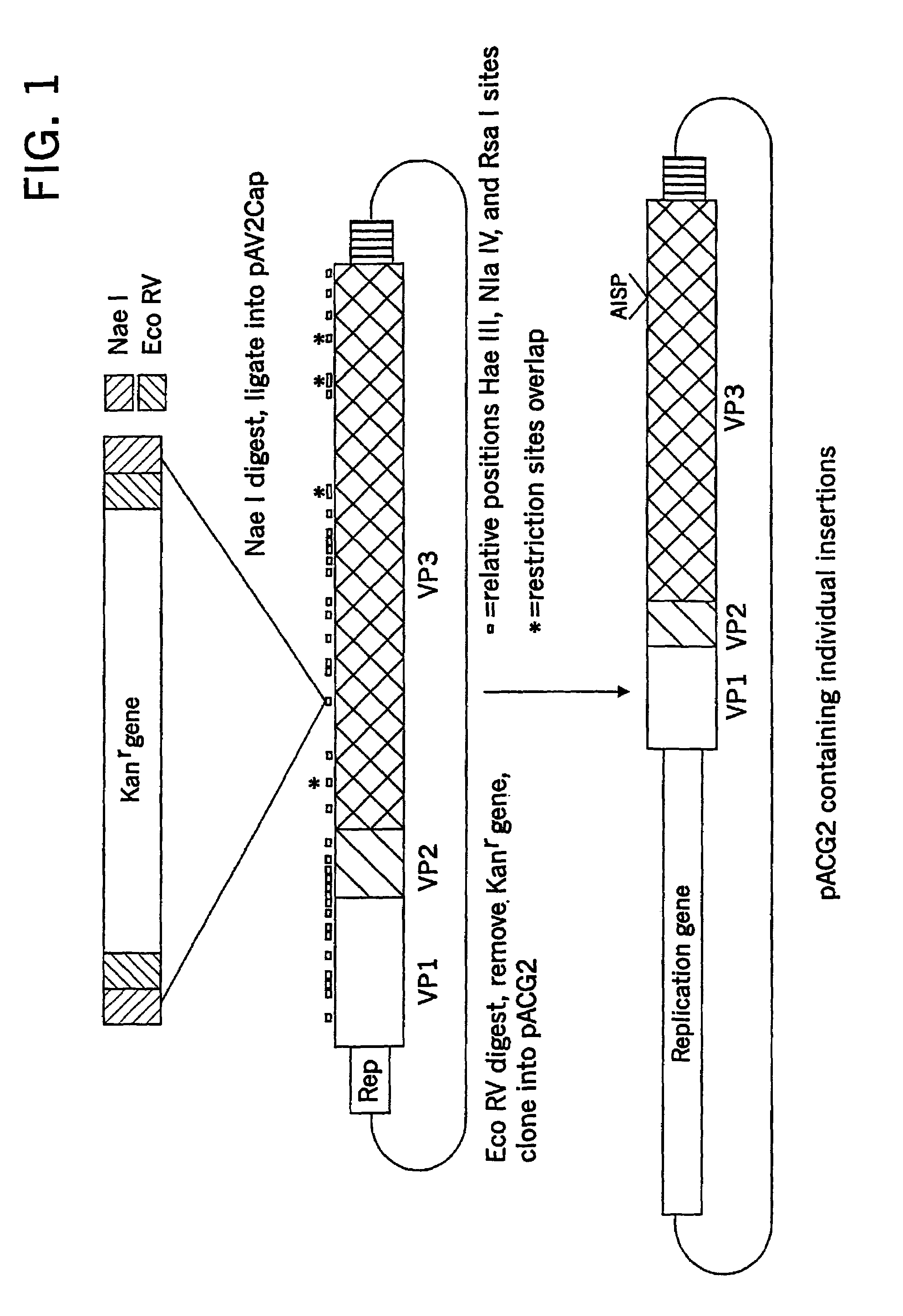
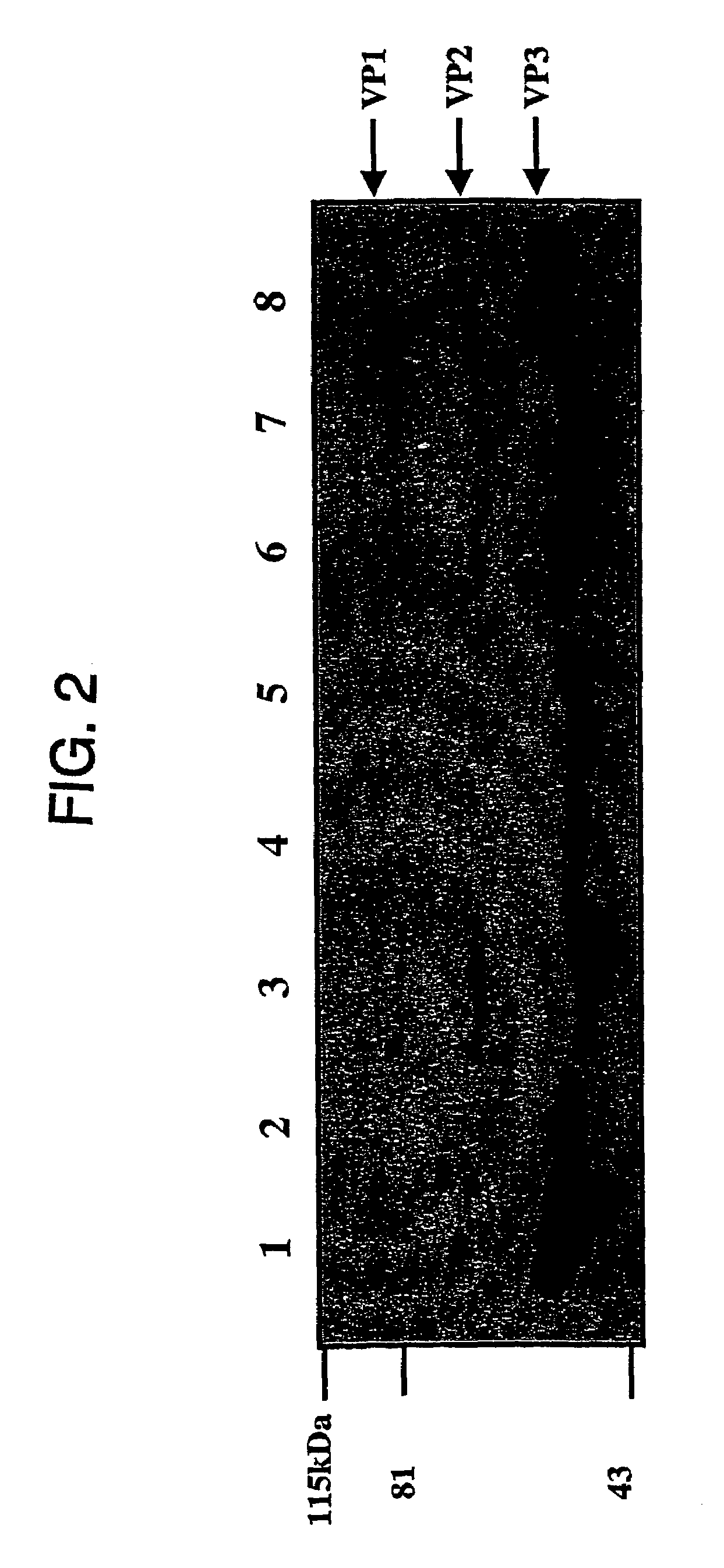
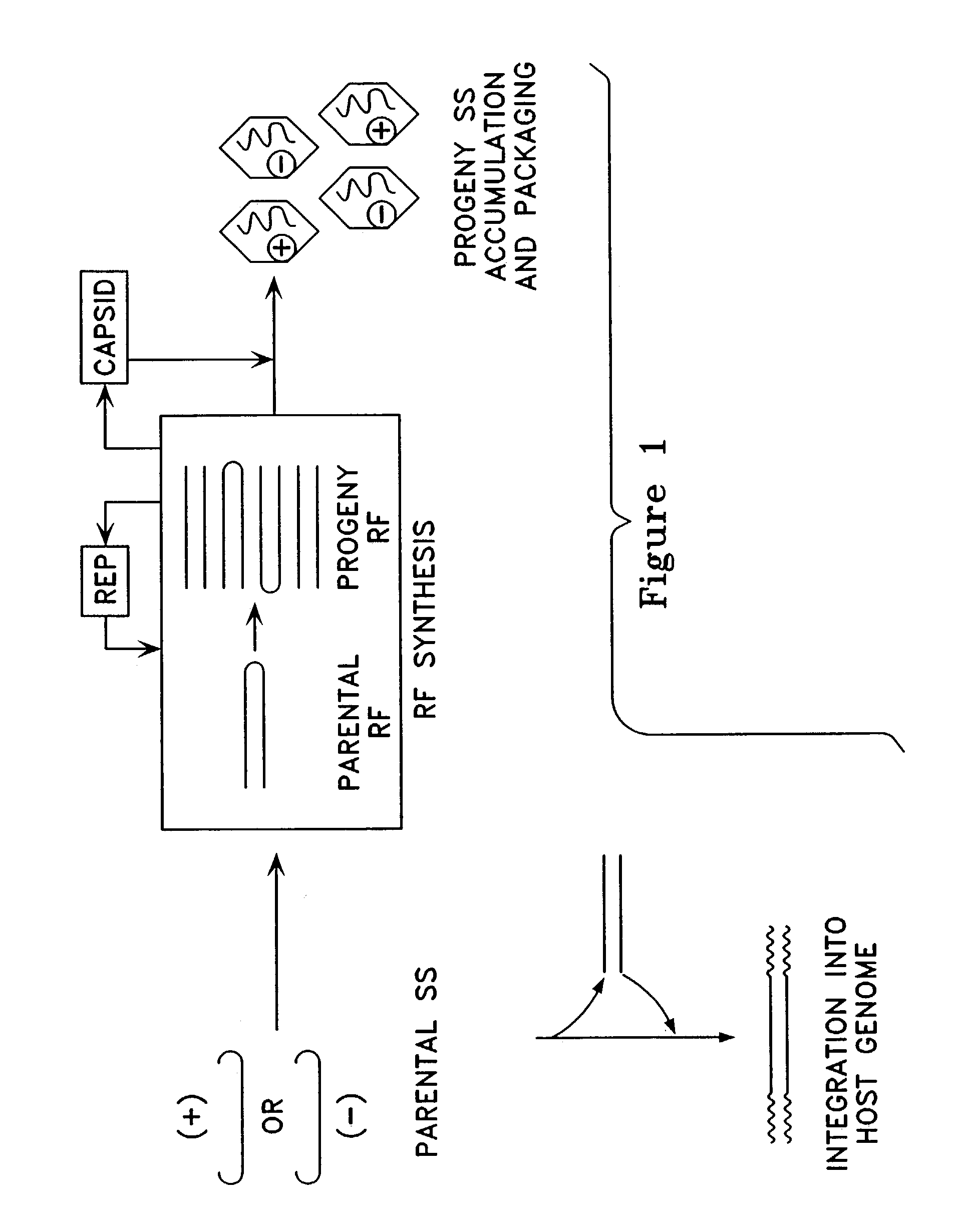
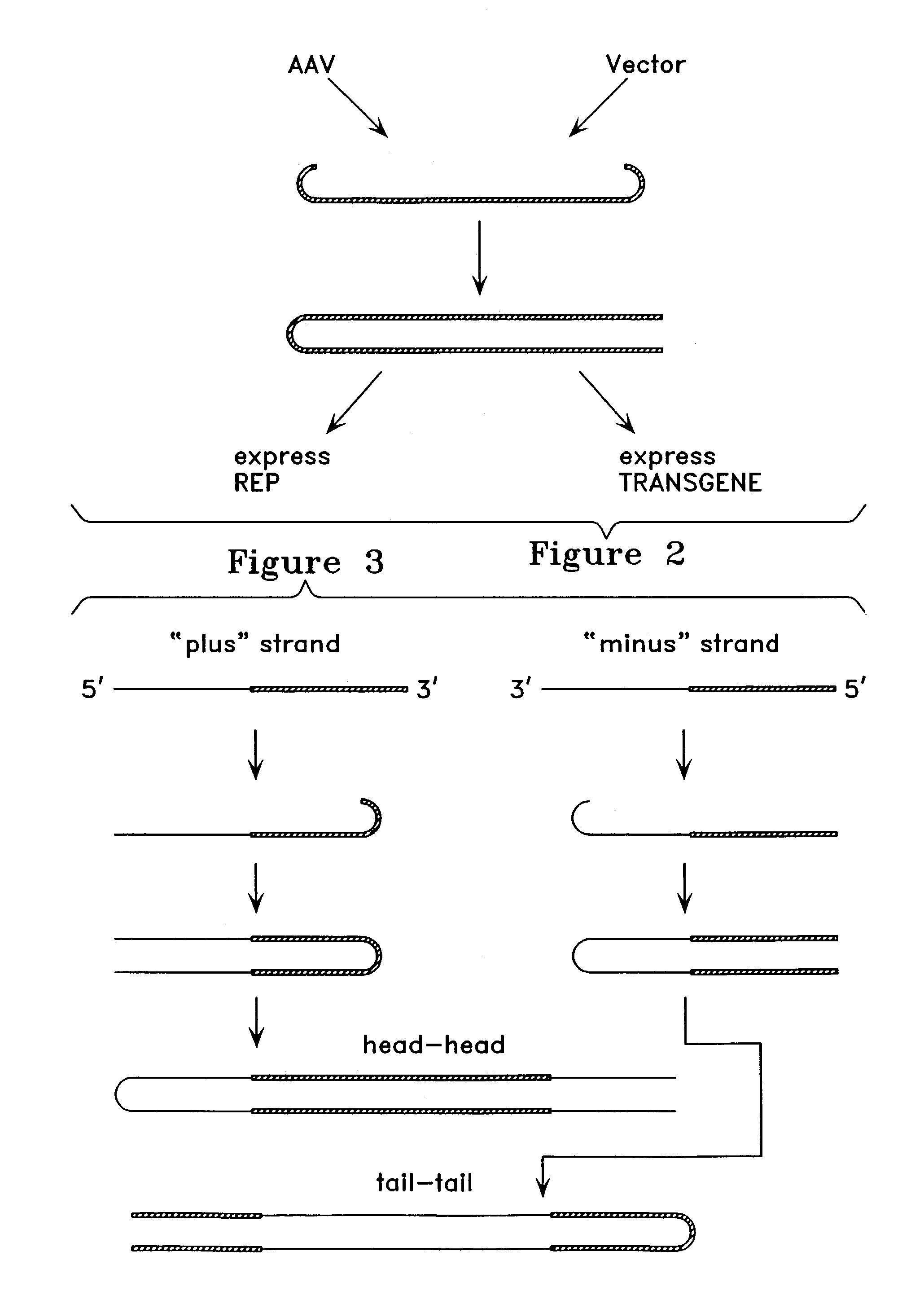
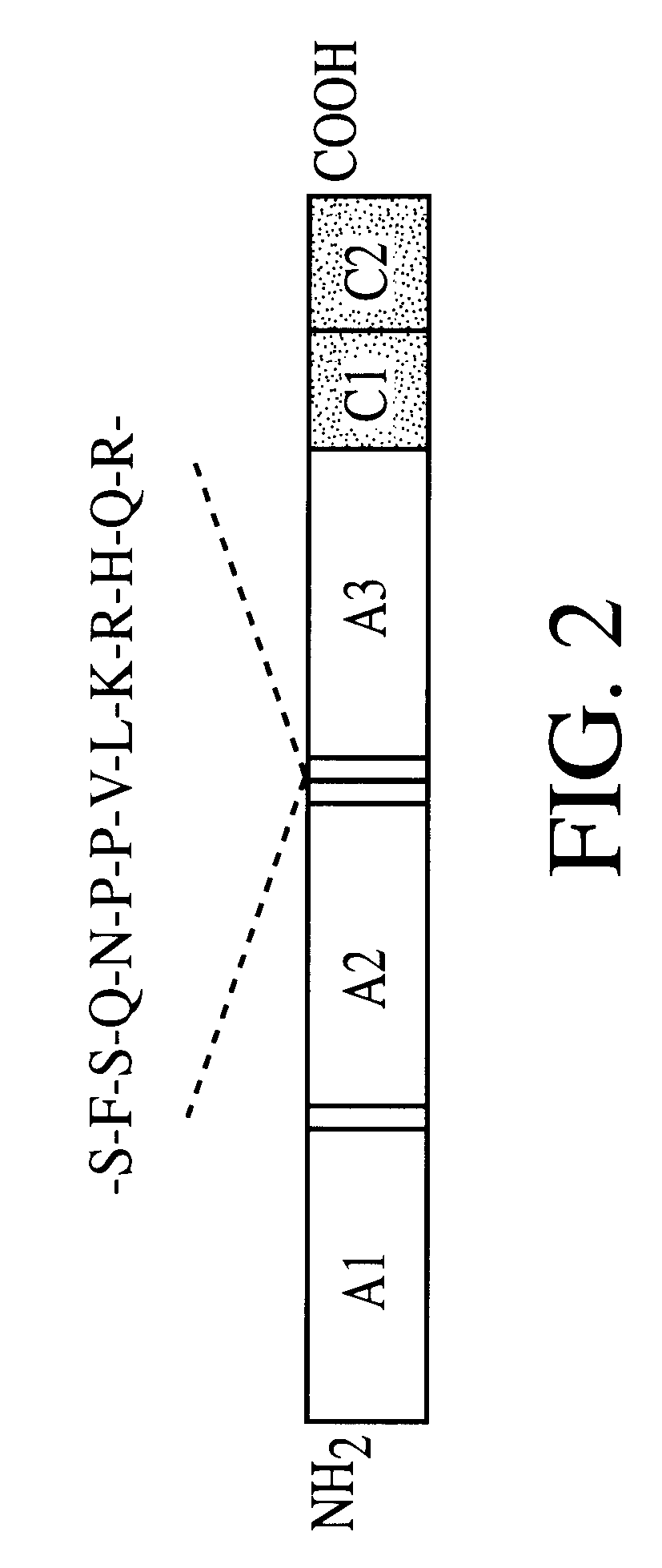
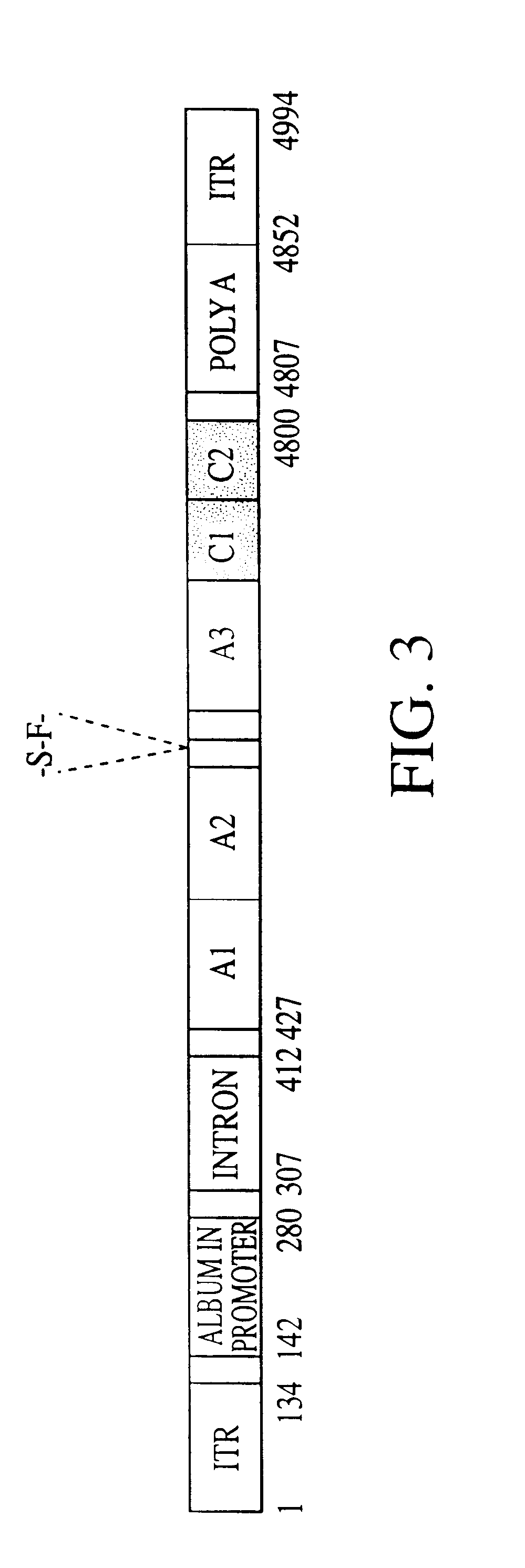
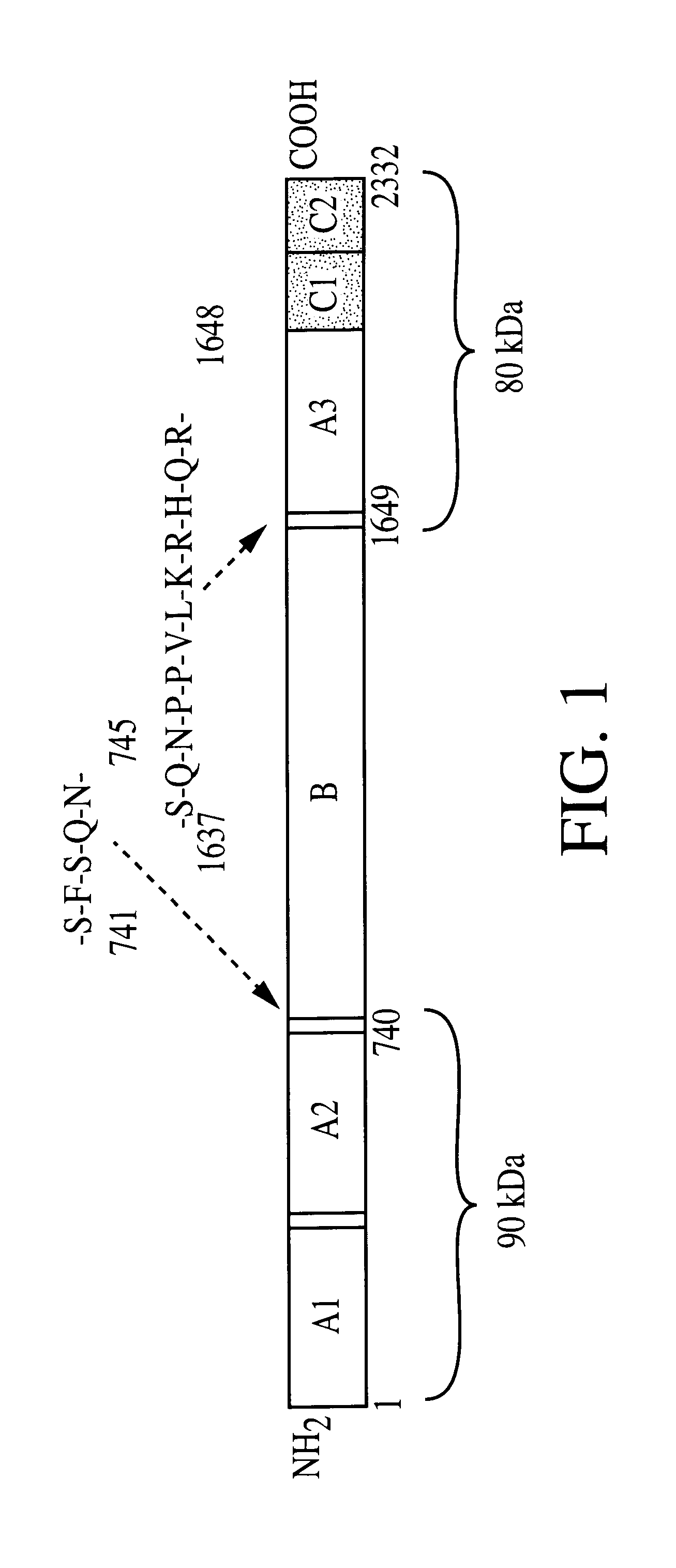
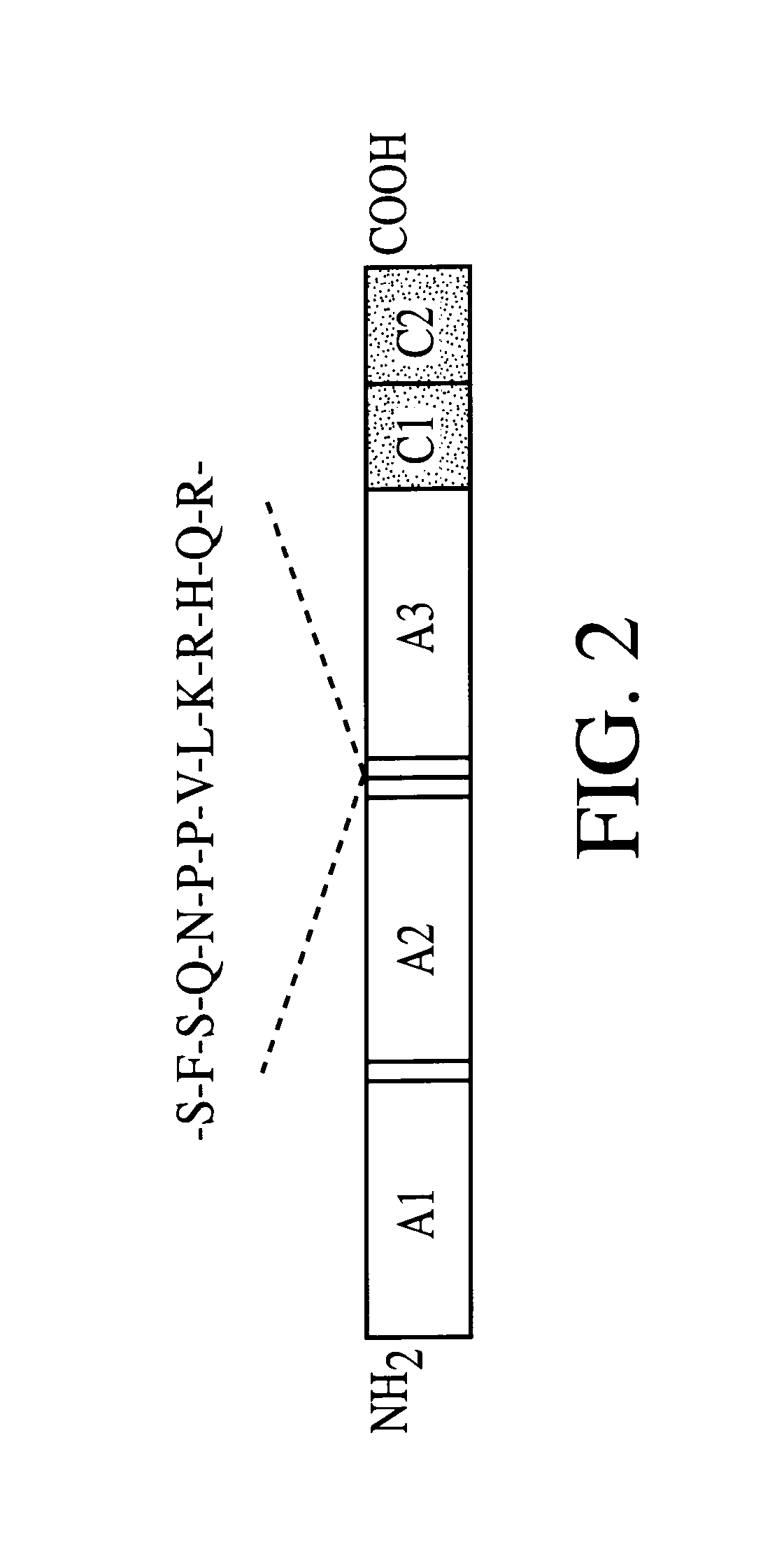
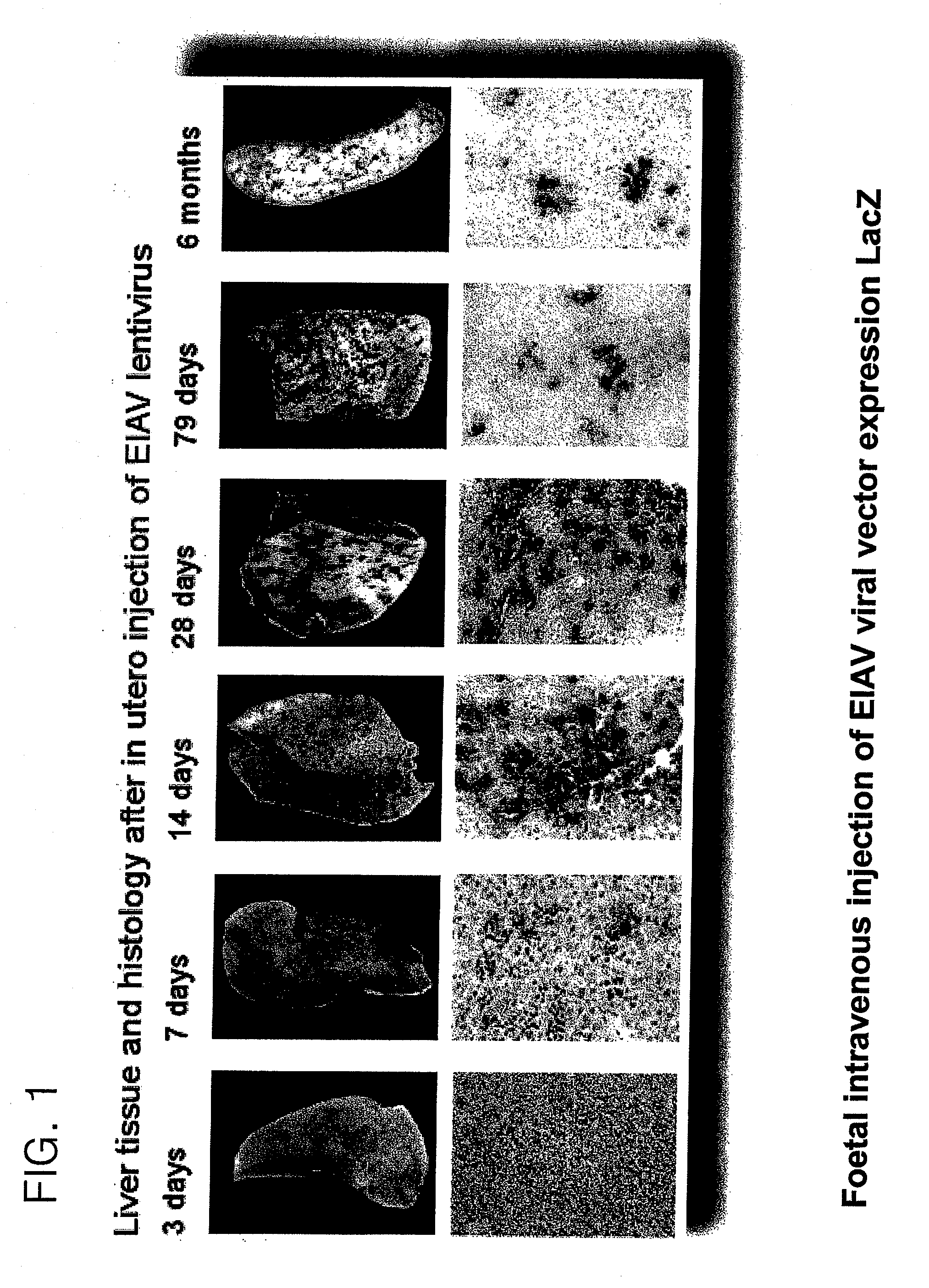
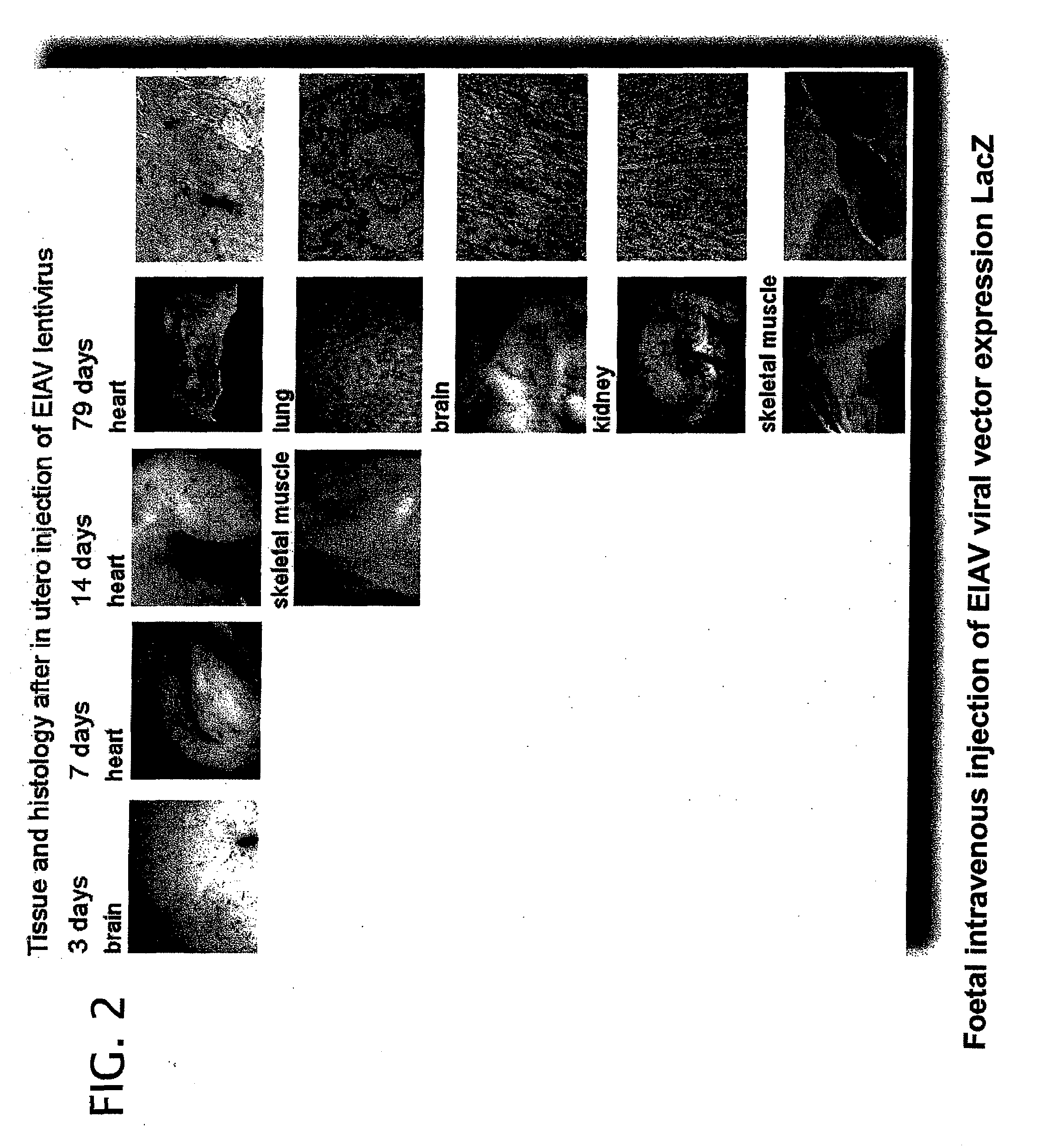
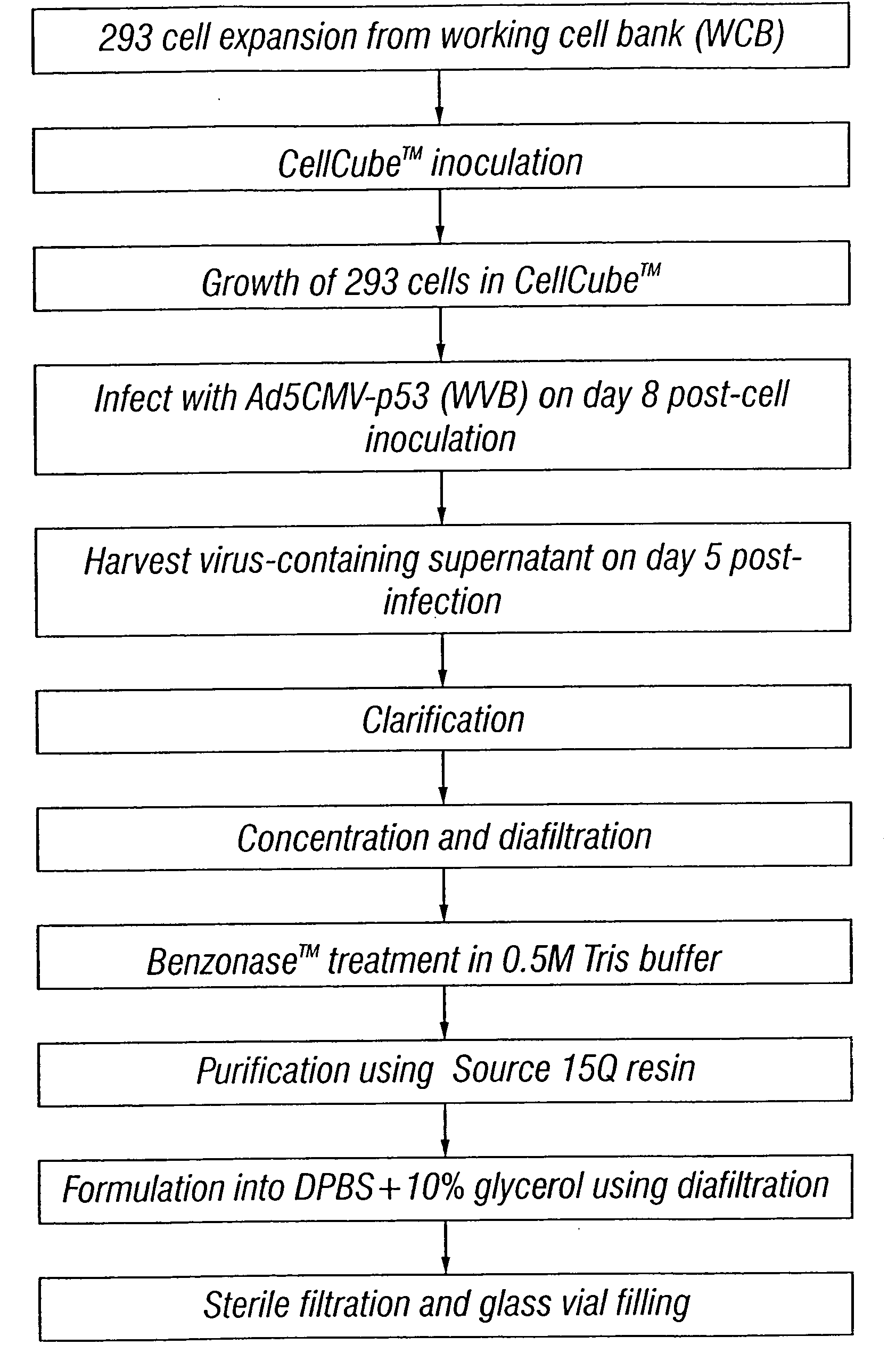
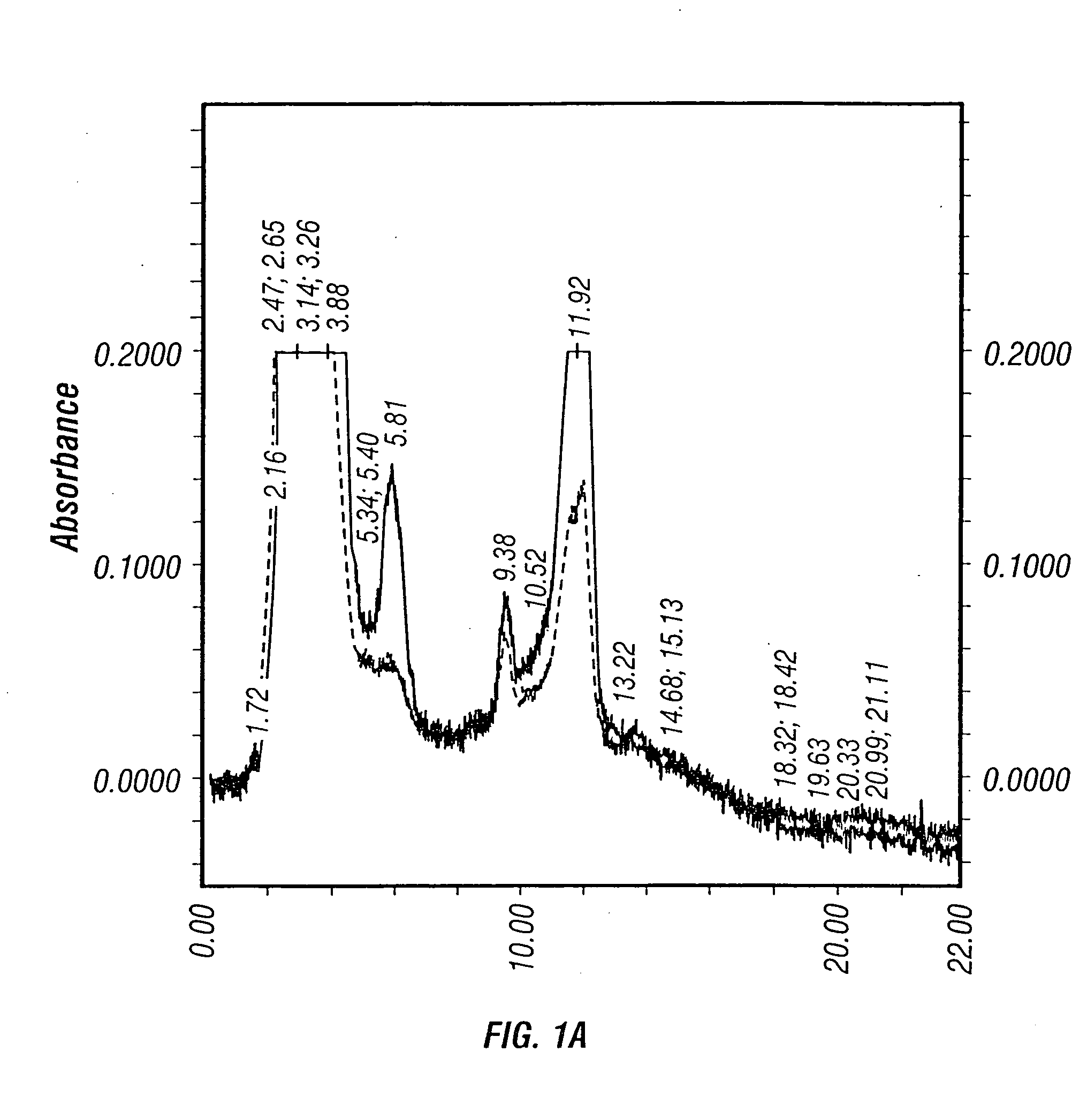
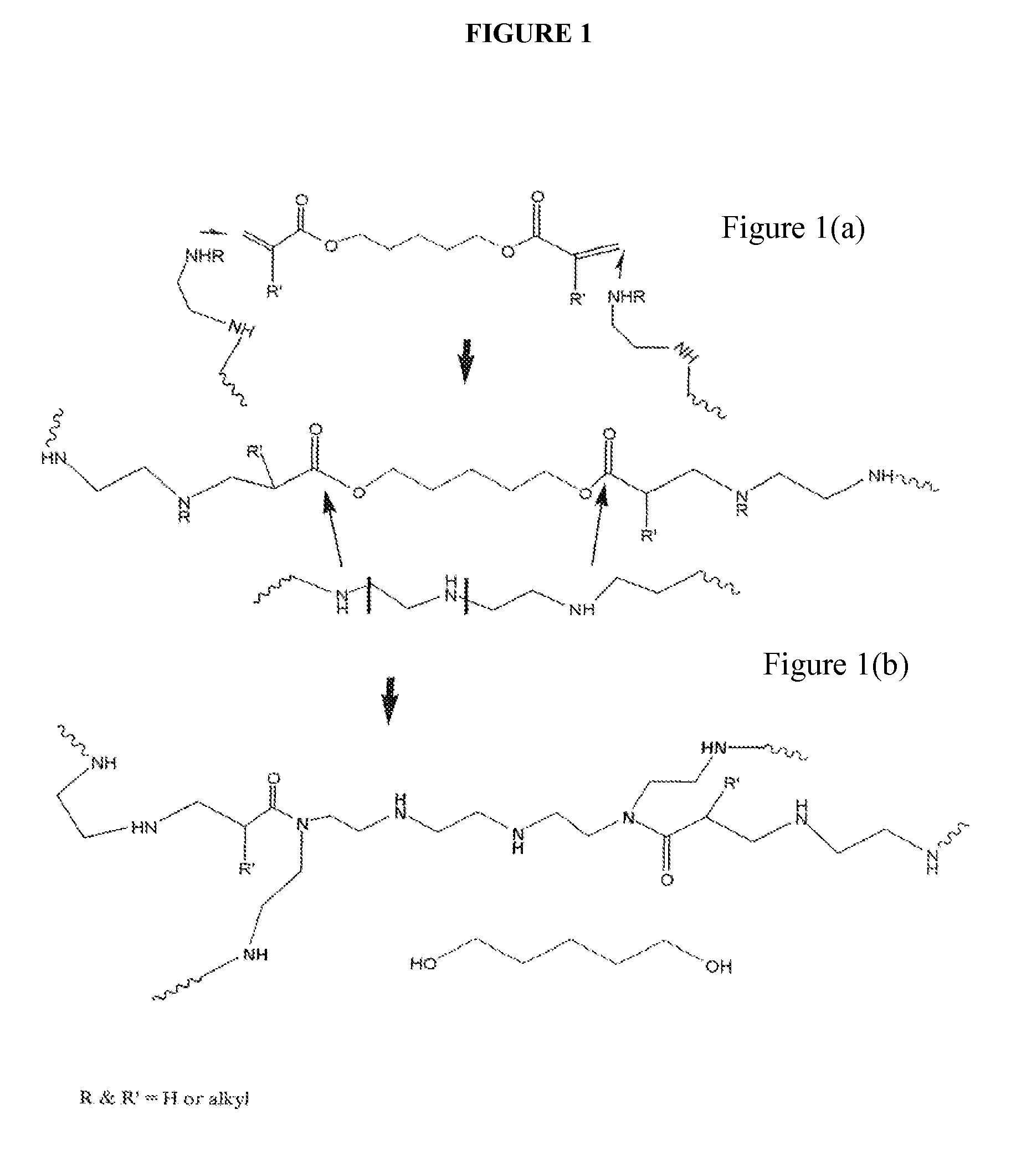
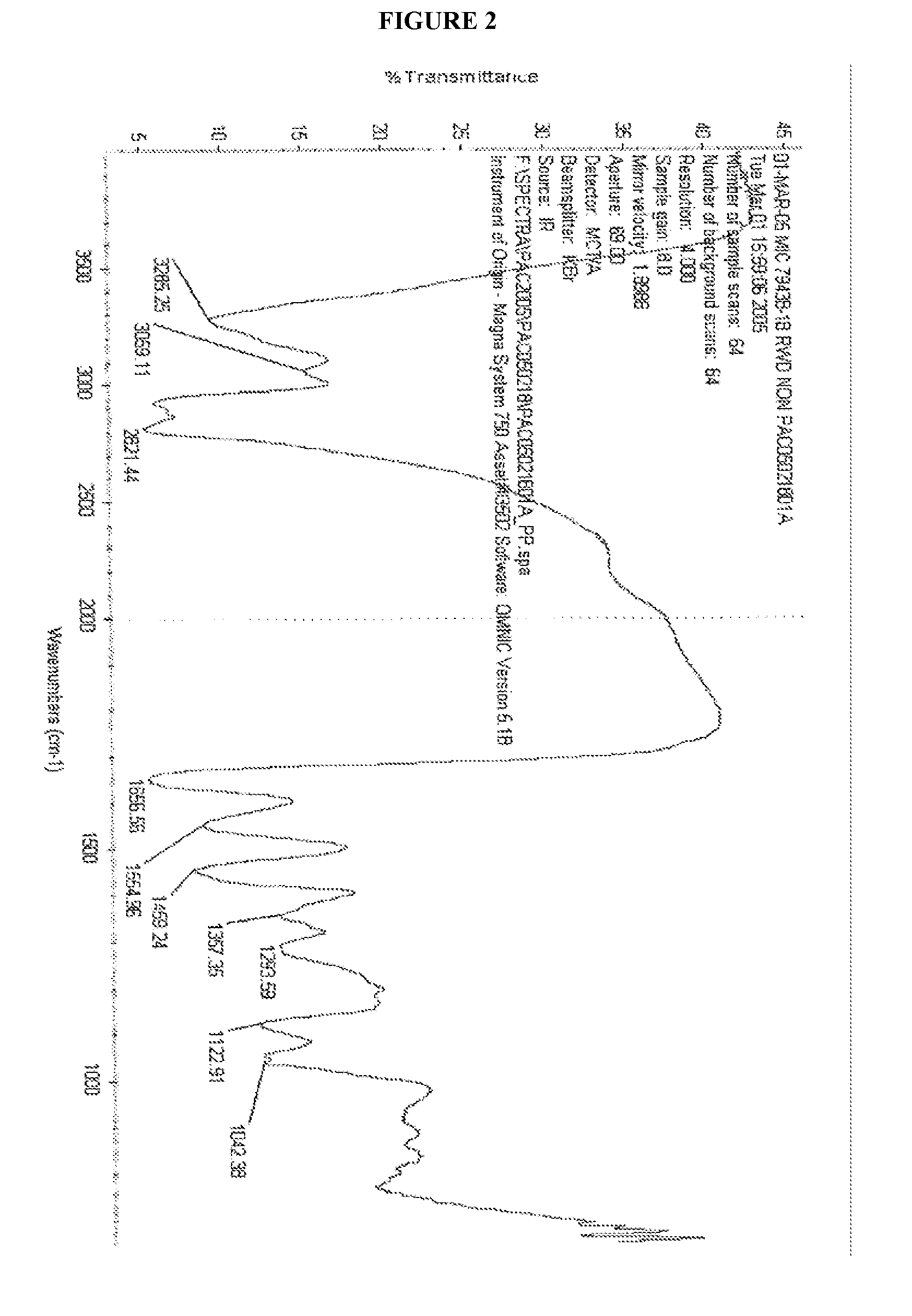
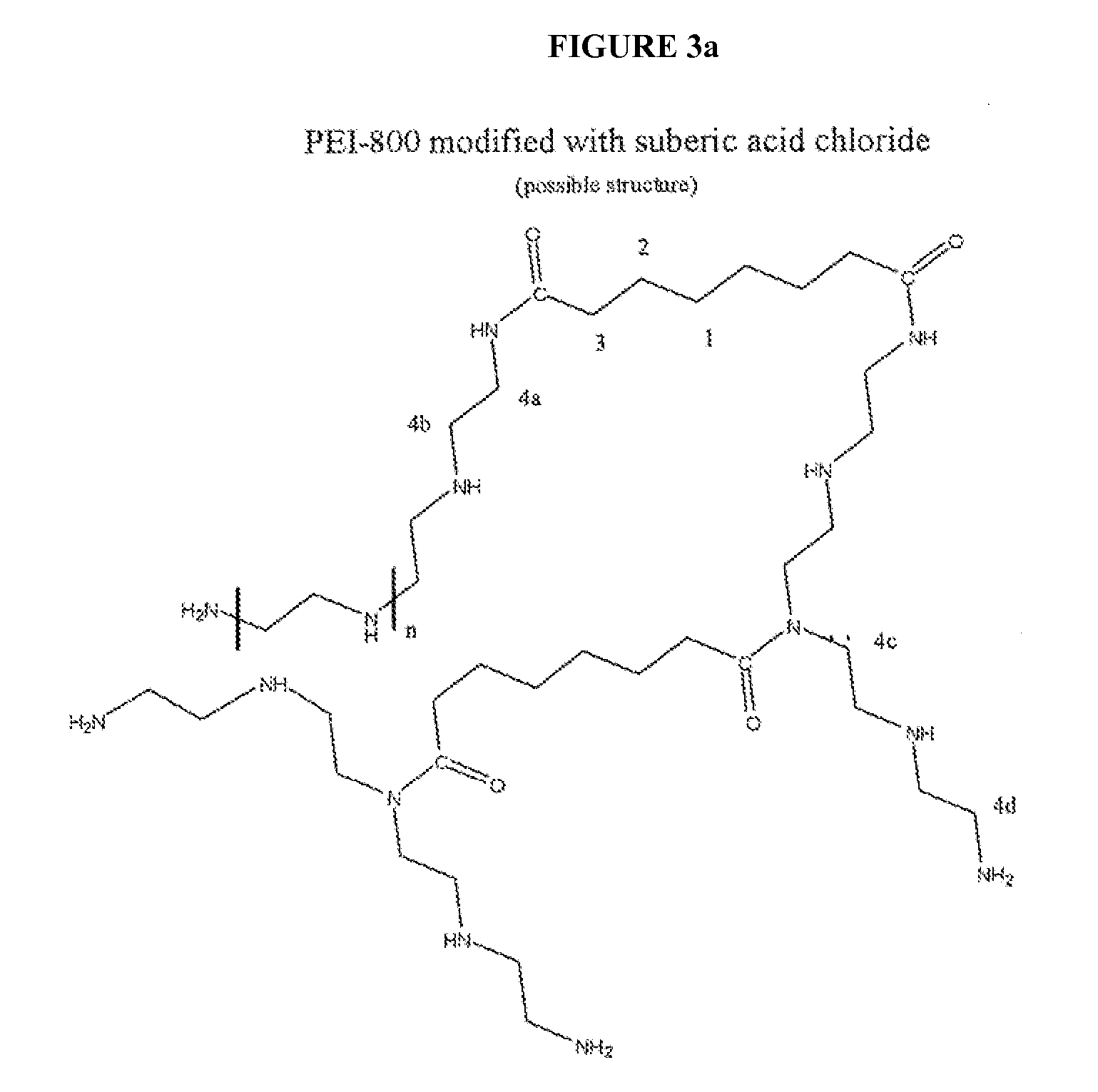
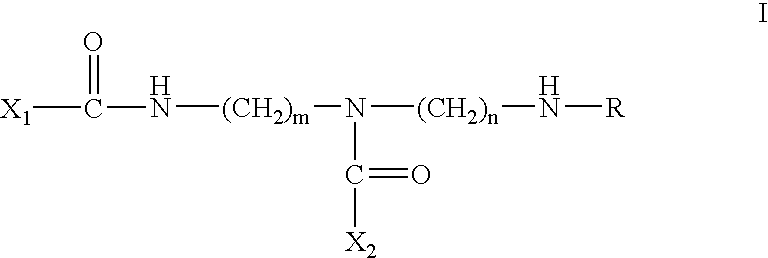
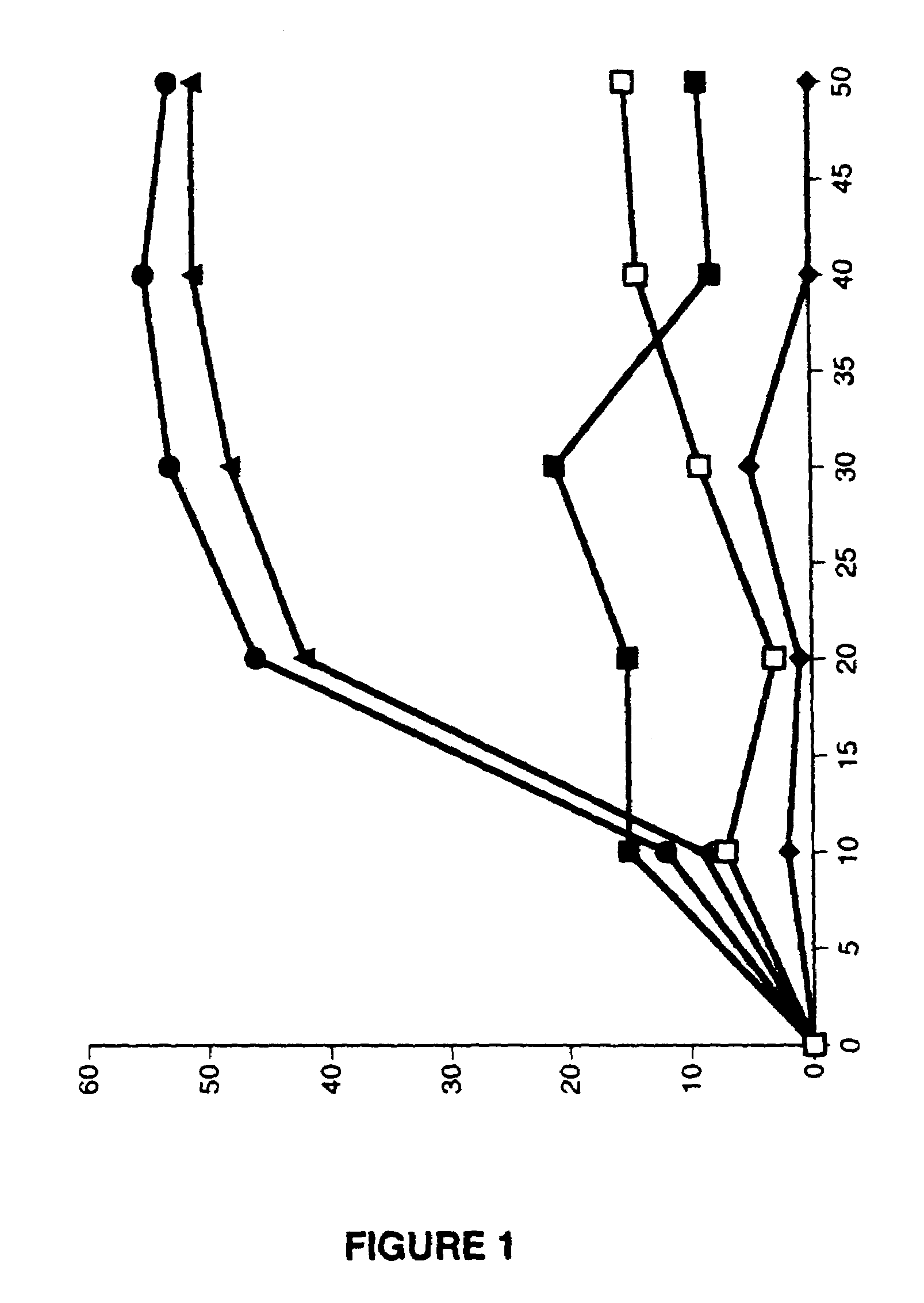
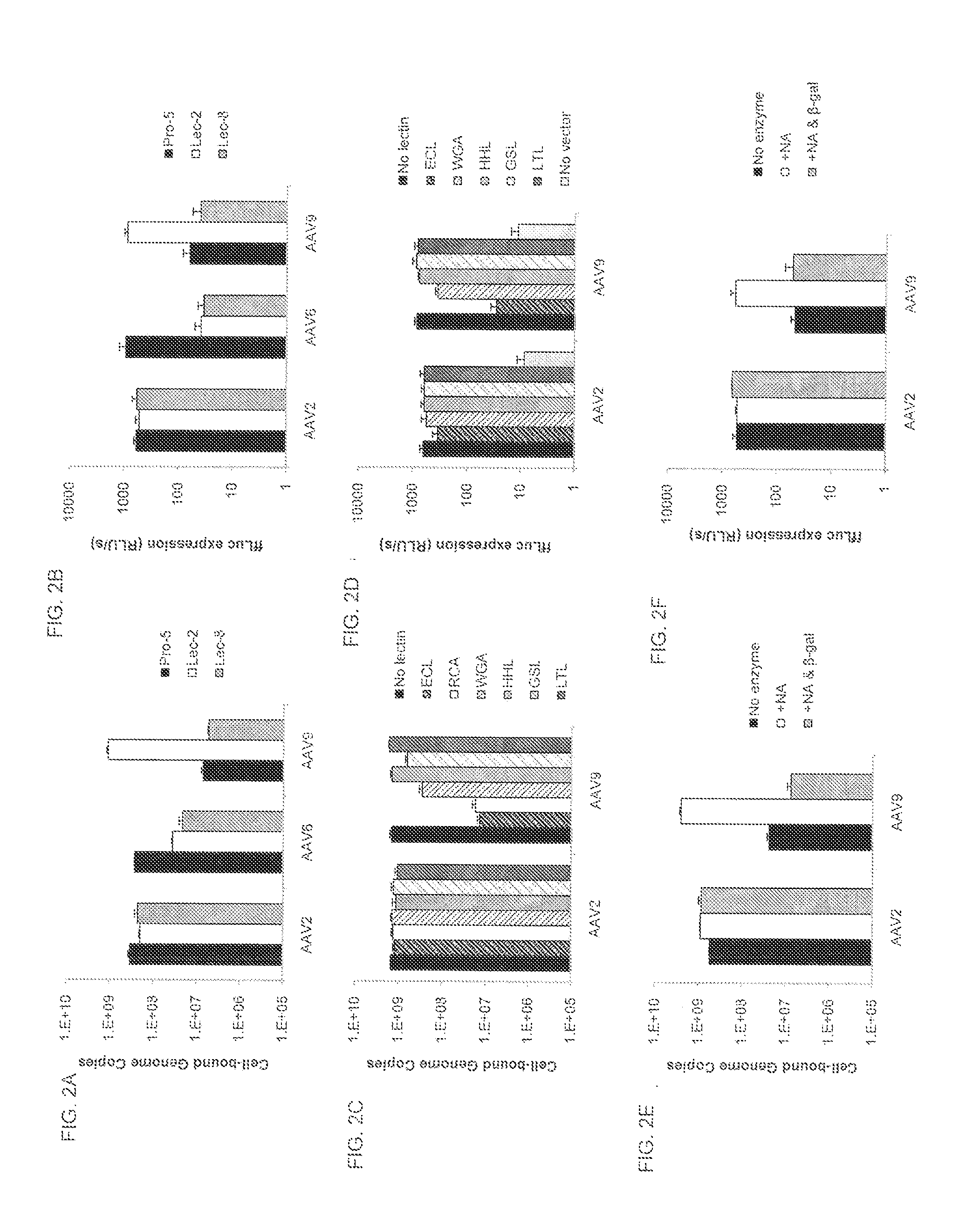Patents
Literature
2411 results about "Viral vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside a living organism (in vivo) or in cell culture (in vitro). Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect. Delivery of genes, or other genetic material, by a vector is termed transduction and the infected cells are described as transduced. Molecular biologists first harnessed this machinery in the 1970s. Paul Berg used a modified SV40 virus containing DNA from the bacteriophage λ to infect monkey kidney cells maintained in culture.
Virus vectors and methods of making and administering the same
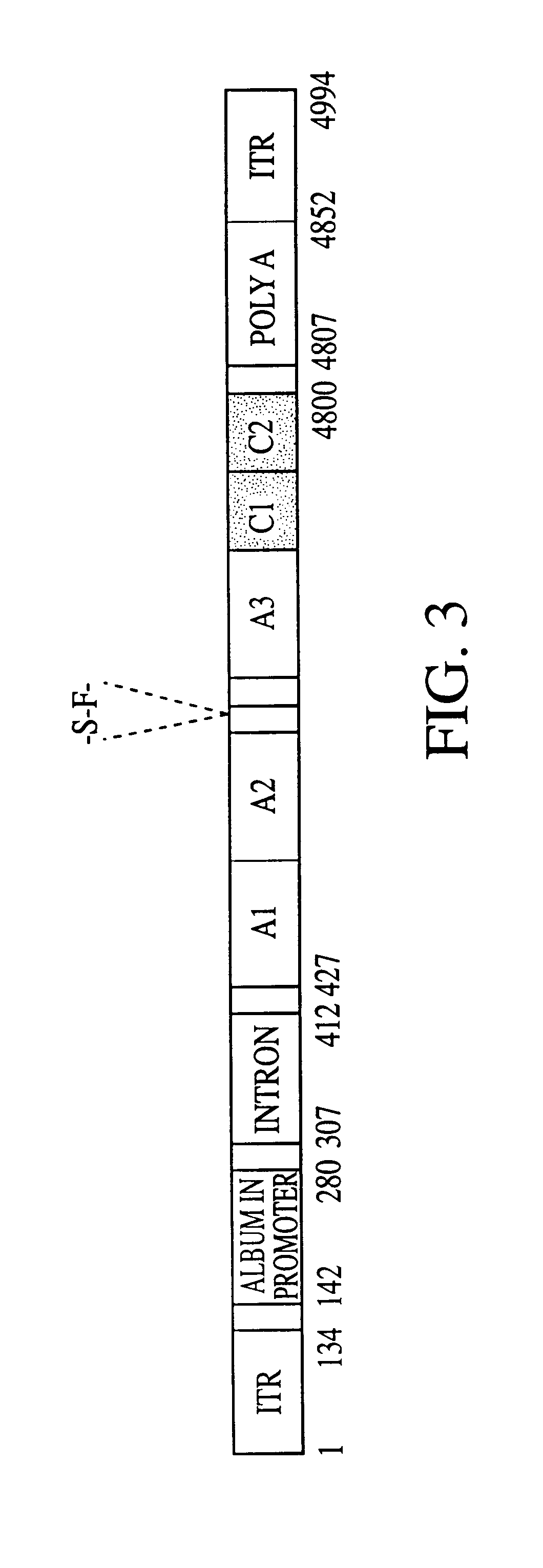
The present invention provides genetically-engineered parvovirus capsids and viruses designed to introduce a heterologous gene into a target cell. The parvoviruses of the invention provide a repertoire of vectors with altered antigenic properties, packaging capabilities, and / or cellular tropisms as compared with current AAV vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Metabolically activated recombinant viral vectors and methods for their preparation and use
Recombinant viral vectors, especially parvovirus vectors such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, capable of enhanced expression of heterologous sequences, and methods for their construction and use, are provided. The vectors have a structure, or are capable of rapidly adopting a structure, which involves intrastrand base pairing of at least one region in a heterologous sequence.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Methods and compounds for controlled release of recombinant parvovirus vectors
InactiveUS7201898B2Prevent relapseImproved pulmonary mechanicsSuture equipmentsAntibacterial agentsControlled releaseSupport matrix
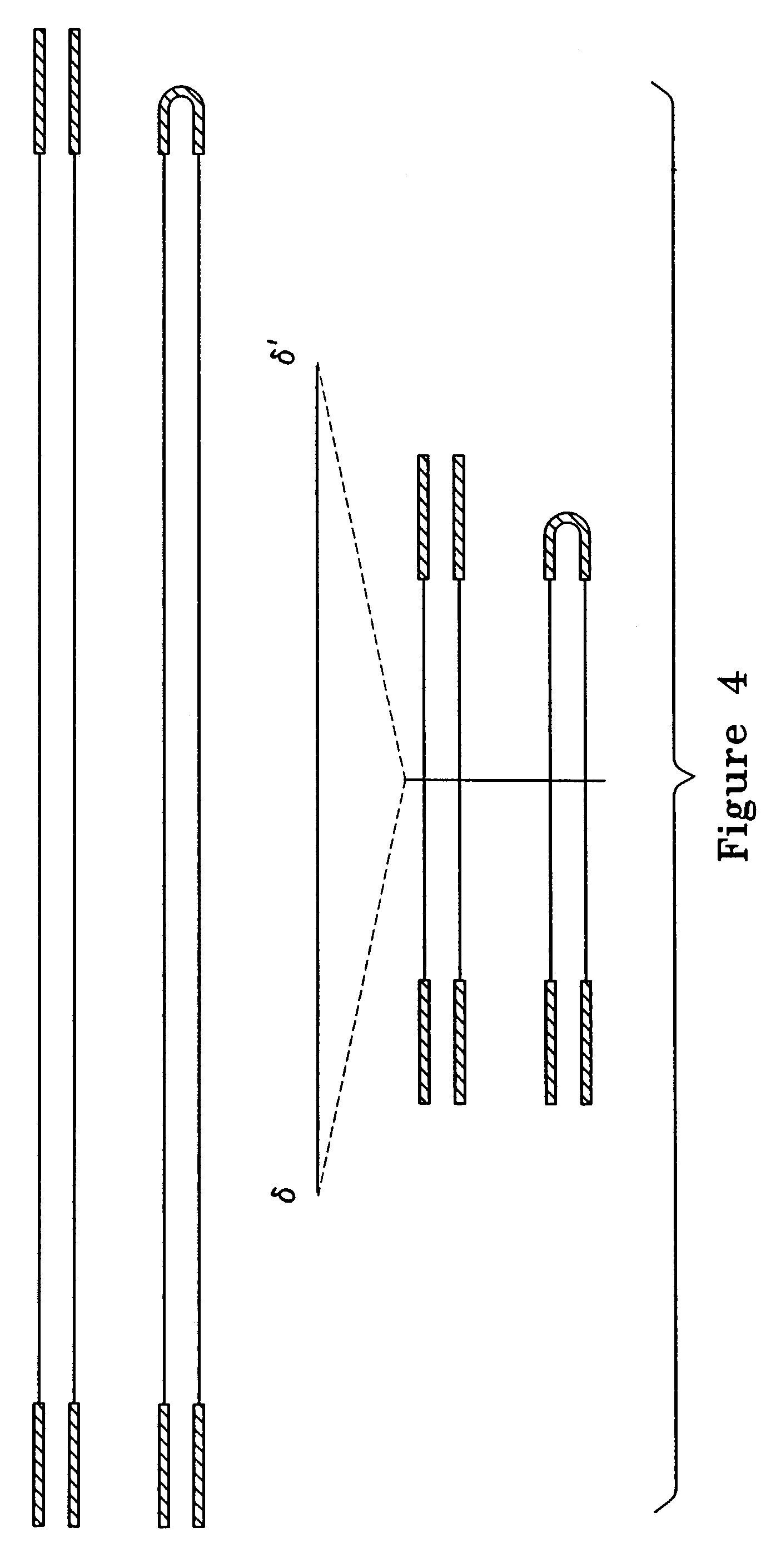
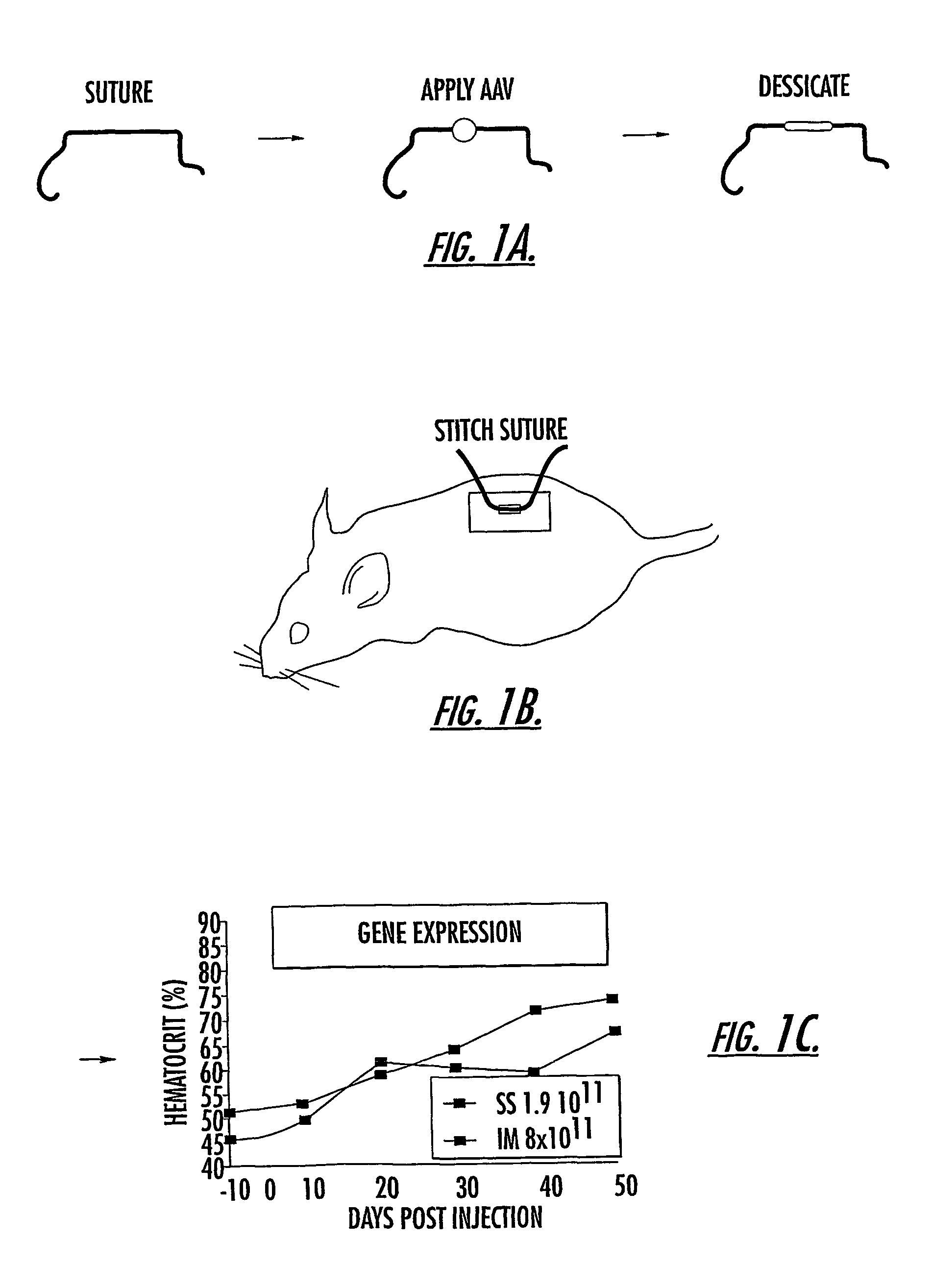
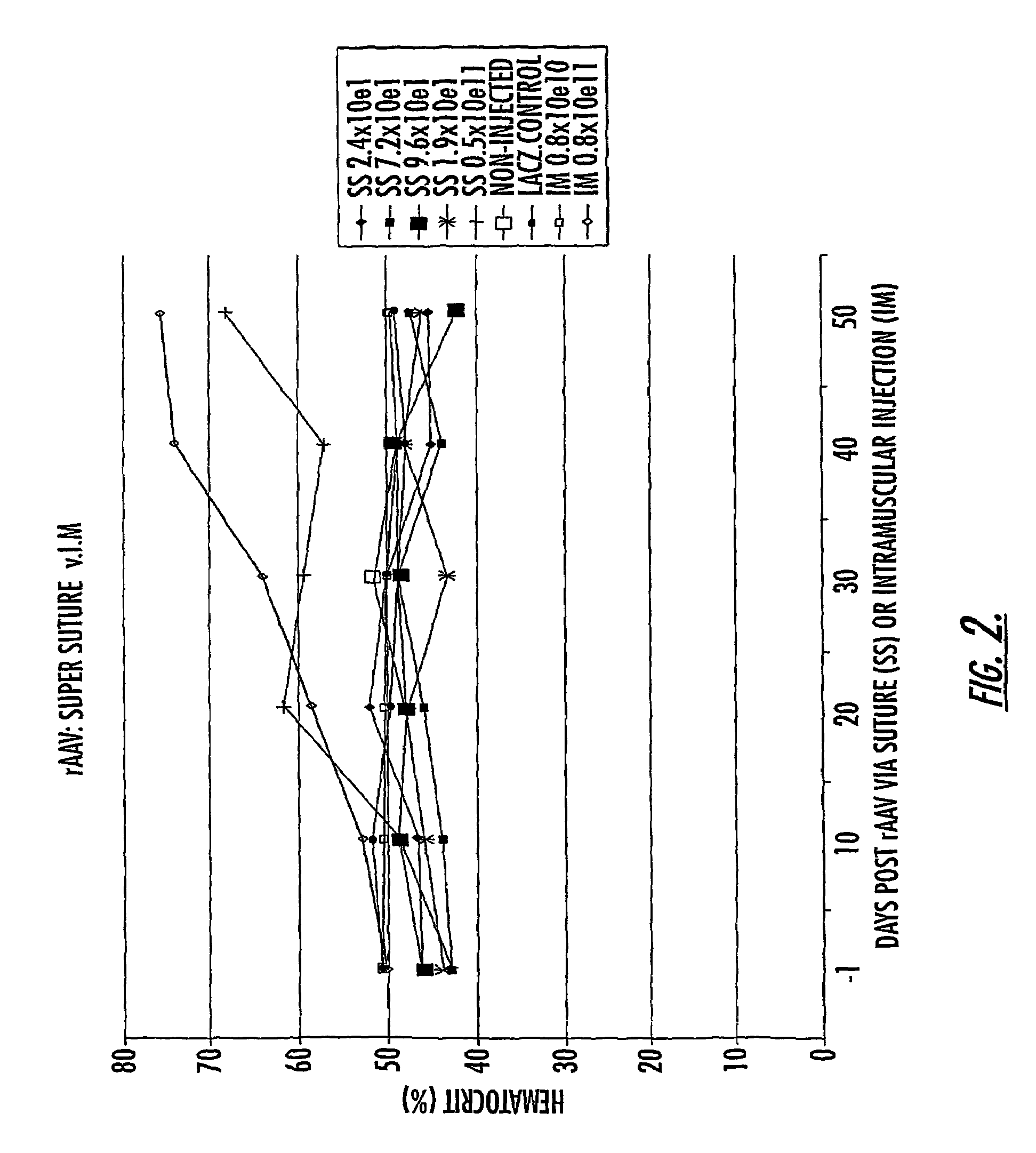
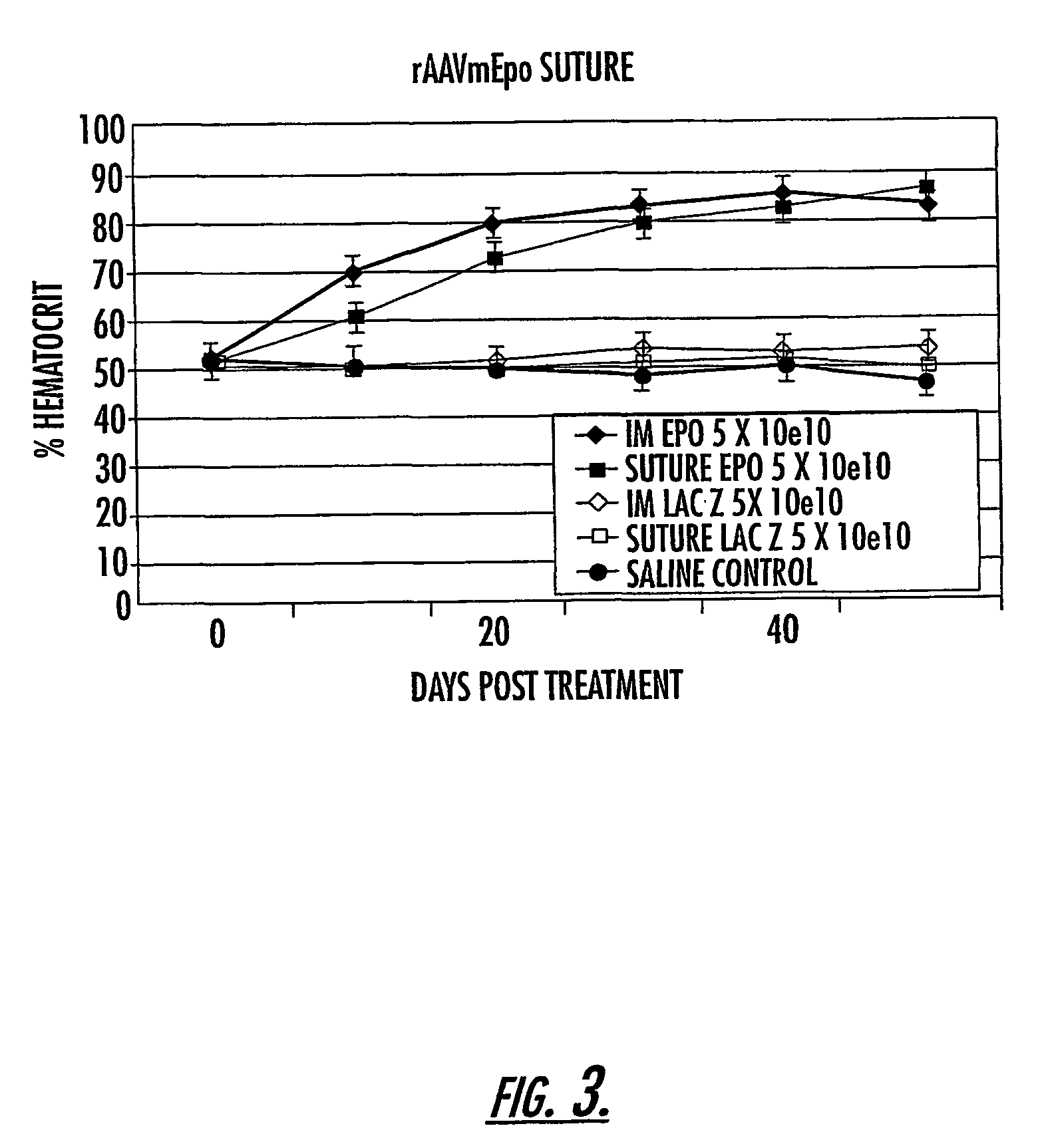
The invention uses recombinant parvoviruses, and particularly recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) to deliver genes and DNA sequences for gene therapy following manipulation of the therapeutic virus for packaging and transport. The invention delivers therapeutic viral vectors via rAAV affixed to support matrixes (i.e., sutures, surgically implantable materials, grafts, and the like).
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL THE UNIV OF
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS20070116690A1Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
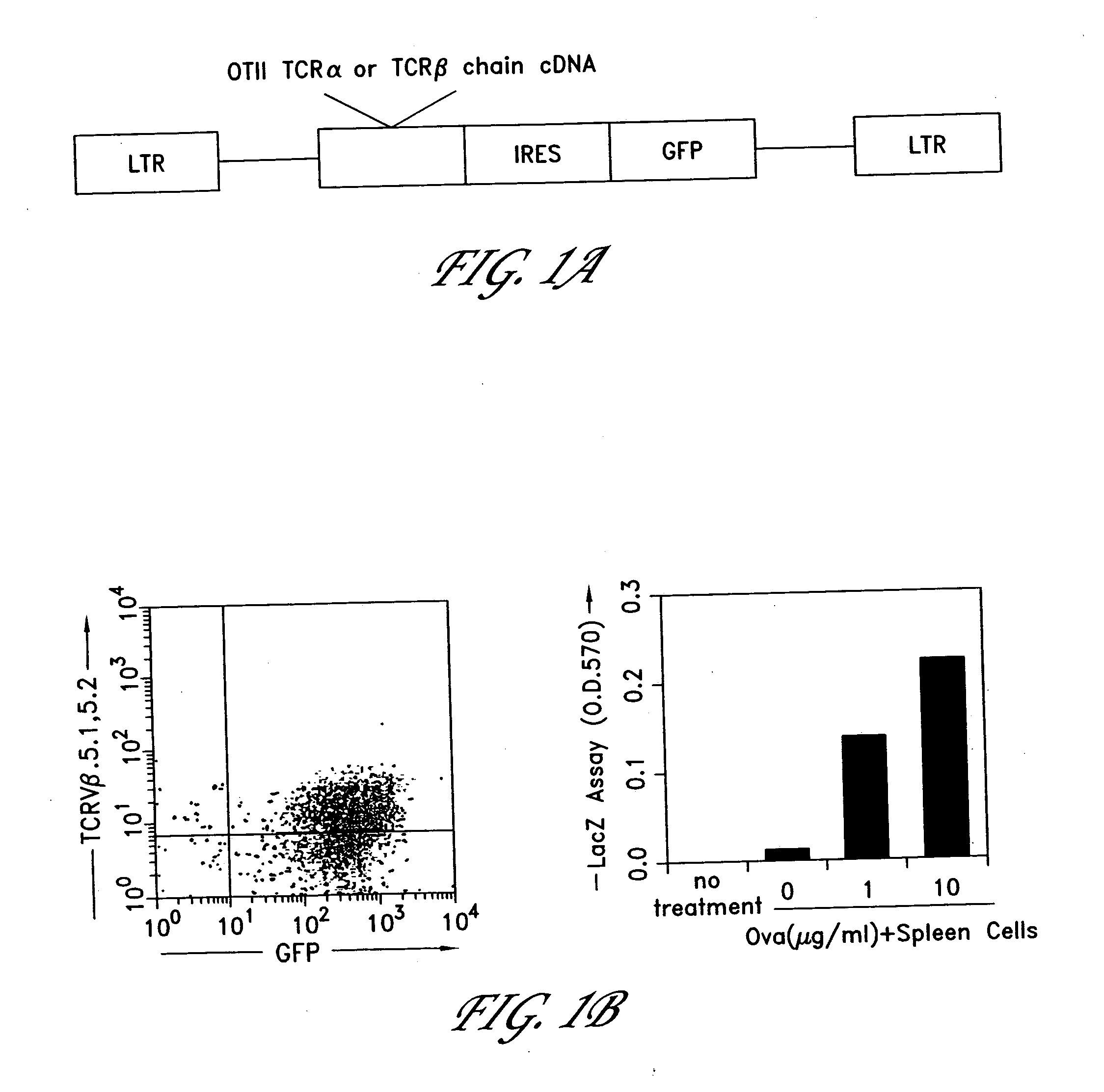
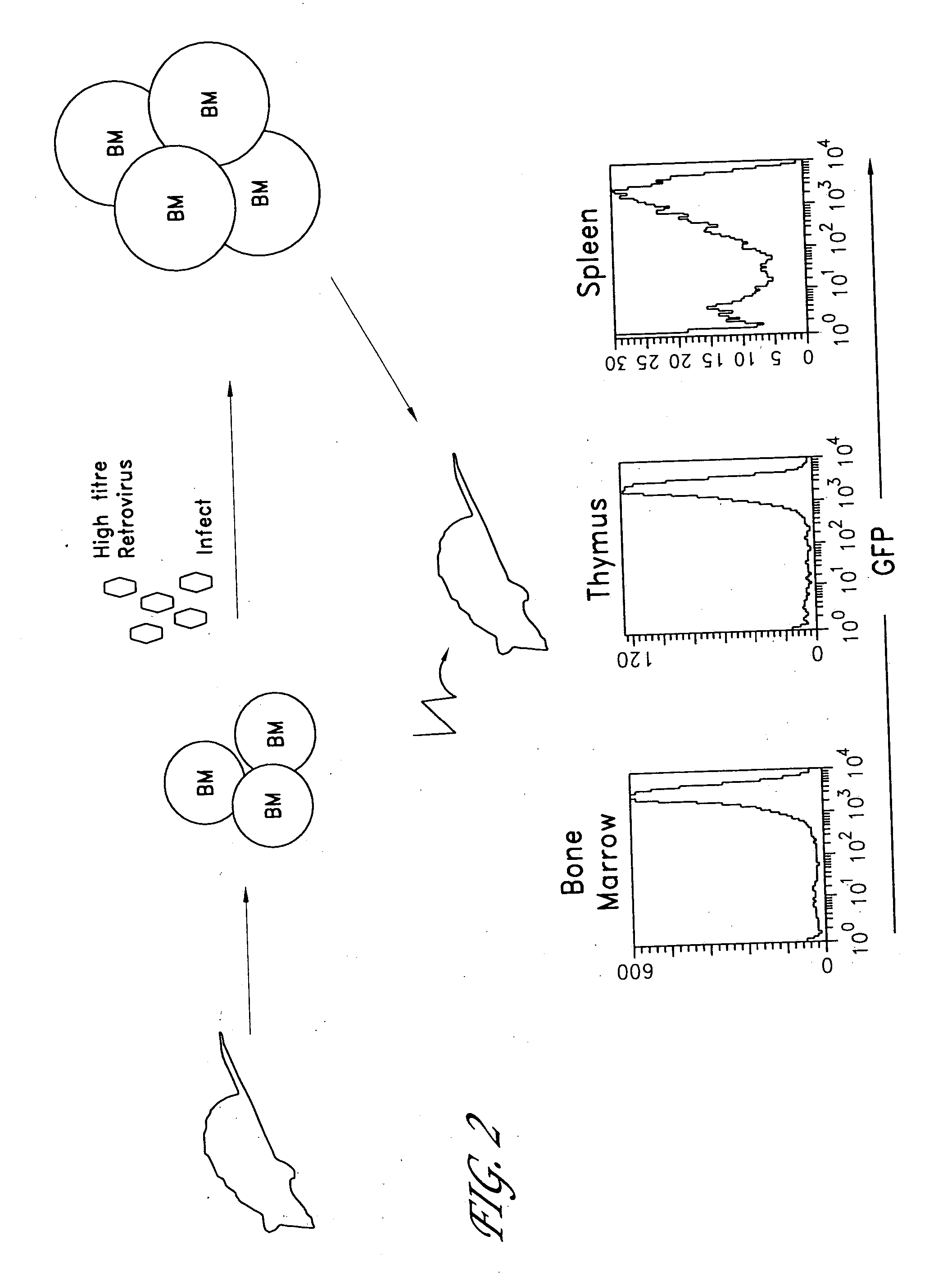
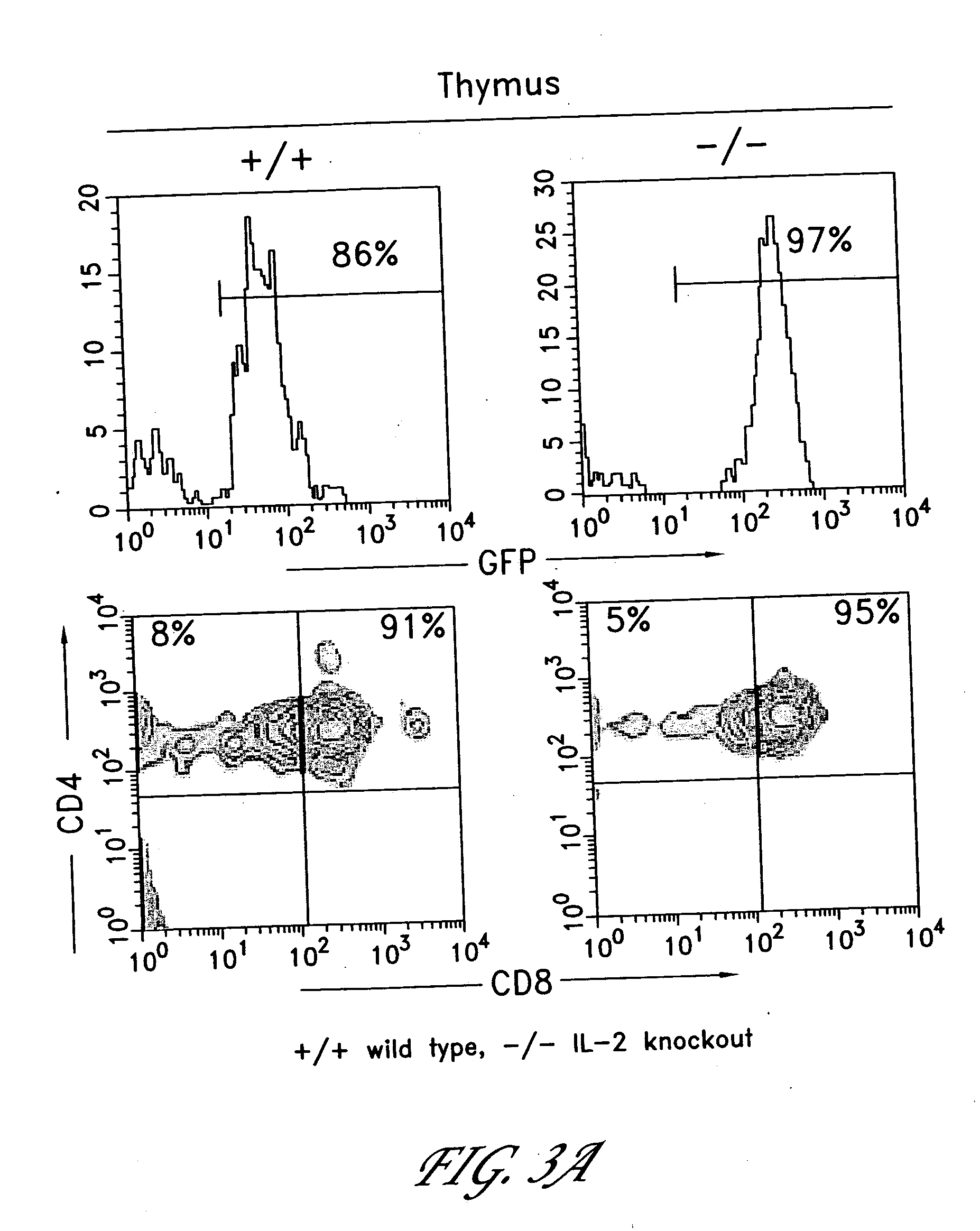
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Adeno-associated virus vectors for expression of factor VIII by target cells
InactiveUS6200560B1Easily transfectedConvenient platformBiocideFactor VIIHigh level expressionHuman cell
The present invention provides improved viral vectors useful for the expression of genes at high levels in human cells. In particular, the present invention provides recombinant adeno-associated vectors (AAV) suitable for gene therapy. These vectors are capable of delivering nucleic acid containing constructs which result in the production of full-length therapeutic levels of biologically active Factor VIII in the recipient individual in vivo. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such AAV vectors, as well as methods for making and using these constructs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Adeno-associated vectors for expression of factor VIII by target cells
InactiveUS6221349B1Easily transfectedConvenient platformBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh level expressionHuman cell
The present invention provides improved viral vectors useful for the expression of genes at high levels in human cells. In particular, the present invention provides adeno-associated vectors (AAV) suitable for gene therapy. These vectors are capable of delivering nucleic acid containing constructs which result in the production of full-length therapeutic levels of biologically active Factor VIII in the recipient individual in vivo. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such AAV vectors, as well as methods for making and using these constructs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Viral Vectors
InactiveUS20090017543A1Prevent reverse transcriptionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsViral vectorVirus
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Vector system
InactiveUS20070025970A1Eliminate the effects ofInhibition of activationBiocideFungiVector systemTyrosine hydroxylase
The present invention relates to retroviral vector genomes and to vector systems comprising such genomes. In particular the present invention relates to a retroviral vector genome comprising two or more NOIs operably linked by one or more Internal Ribosome Entry Site(s); a lentiviral vector genome comprising two or more NOIs suitable for treating a neurodegenerative disorder; and a lentiviral vector genome which encodes tyrosine hydroxylase, GTP-cyclohydrolase I and optionally Aromatic Amino Acid Dopa Decarboxylase.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Mammalian viral vectors and their uses
InactiveUS6255071B1Stable episomal maintenanceMaintain relatively stableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRetroviral provirusMammal
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the elucidation of mammalian gene function. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved mammalian complementation screening, functional inactivation of specific essential or non-essential mammalian genes, and identification of mammalian genes which are modulated in response to specific stimuli.In particular, the compositions of the present invention include, but are not limited to, replication-deficient retroviral vectors, libraries comprising such vectors, retroviral particles produced by such vectors in conjunction with retroviral packaging cell lines, integrated provirus sequences derived from the retroviral particles of the invention and circularized provirus sequences which have been excised from the integrated provirus sequences of the invention. The compositions of the present invention further include novel retroviral packaging cell lines.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Vectors
InactiveUS20060281180A1Stable long-term expressionEfficient expressionAntibacterial agentsFactor VIIGeneticsViral vector
Provided is a lentiviral vector capable of delivering a nucleotide of interest (NOI) to a desired target site and wherein the NOI encodes the Factor VIII and the Factor VIII is expressed following delivery of the NOI to the desired target site.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Transgenic organism
InactiveUS20090007284A1Efficient productionEfficiency advantageAnimal cellsVectorsNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
A method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a non-primate lentiviral expression vector comprising a nucleotide of interest (NOI). Also described is a method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a lentiviral expression vector comprising a NOI capable of generating an antisense oligonucleotide, a ribozyme, an siRNA, a short hairpin RNA, a micro-RNA or a group 1 intron. Also described is a viral vector comprising a first nucleotide sequence, wherein said first nucleotide sequence comprises: (a) a second nucleotide sequence comprising an aptazyme; and (b) a third nucleotide sequence capable of generating a polynucleotide; wherein (a) and (b) are operably linked and wherein the aptazyme is activatable to cleave a transcript of the first nucleotide sequence such that said polynucleotide is generated.
Owner:RADCLIFFE PHILIPPA +2
Method for the production and purification of adenoviral vectors
InactiveUS20080050770A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSerum igeUltracentrifuge
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Improved rAAv vectors
InactiveUS20060292117A1Efficient transductionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideSystemic lupus erythematosus
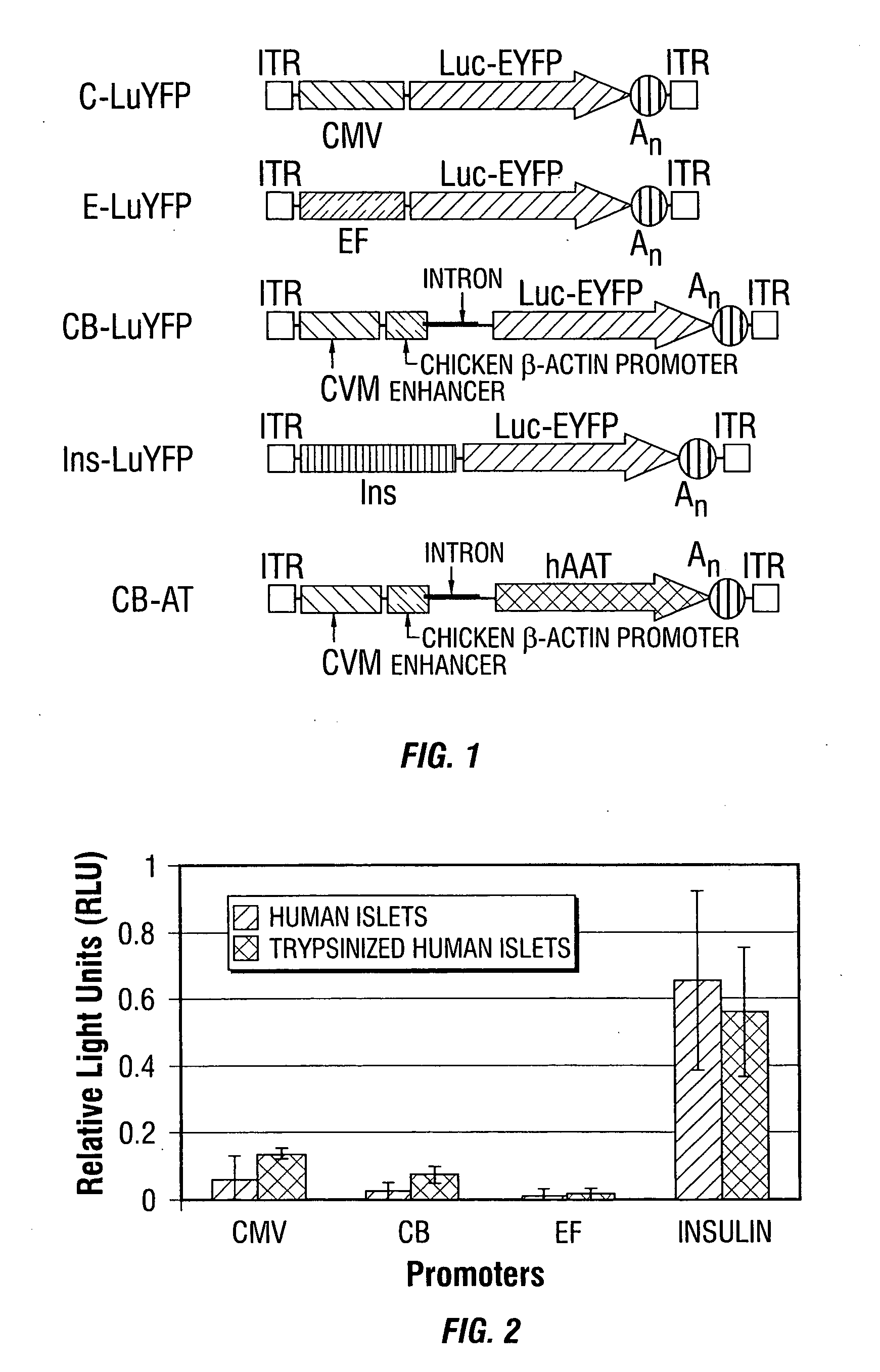
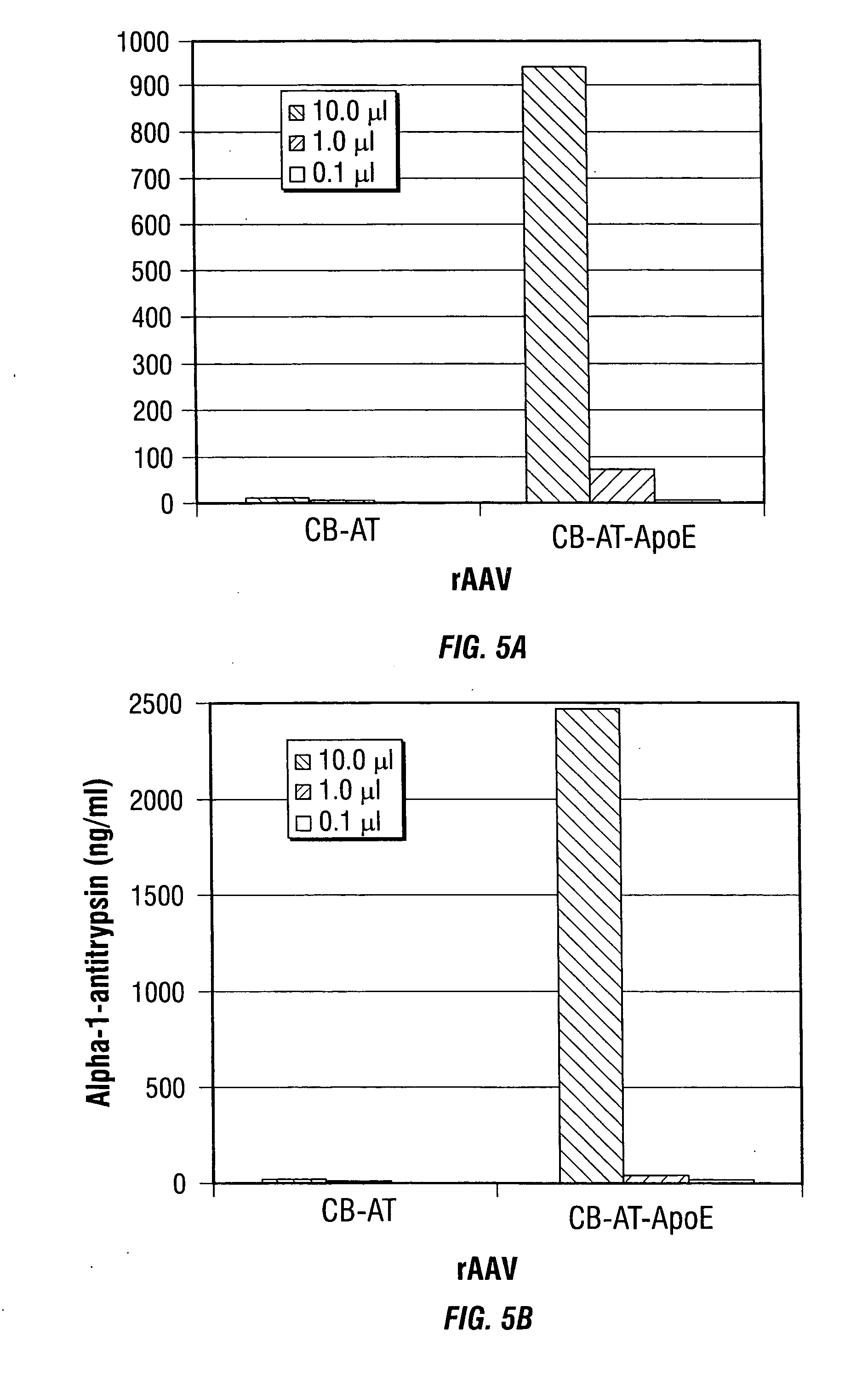
Disclosed are methods for the use of therapeutic polypeptide-encoding polynucleotides in the creation of transformed host cells and transgenic animals. In particular, the use of recombinant adeno-associated viral (rAAV) vector compositions that specifically target mammalian cells, such as pancreatic islets cells, that express low-density lipoprotein receptors on their cell surface. The disclosed vectors comprise one or more polynucleotide sequences that express one or more mammalian polypeptides having therapeutic efficacy in the amelioration, treatment and / or prevention of AAT- or cytokine polypeptide deficiencies, such as for example in diabetes and related diseases, as well as a variety of autoimmune disorders including, for example, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Retrovirus and viral vectors
InactiveUS6635472B1Prevent and attenuate diseaseEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesVirus-RetrovirusDna viral
This invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering, virus replication and gene transfer. More specifically, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors, wherein an ori derived from a DNA virus capable of replicating in vertebrate cells is inserted into the retrovirus, allowing the retrovirus following the reverse transcription to efficiently replicate as extrachromosomal or episomal DNA without the necessity of integration into the host cell chromosome. Additionally, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors replicating episomally without aid of an ori and related elements. Also, this invention encompasses preventive, therapeutic, and diagnostic applications employing said constructs, viruses and vectors.
Owner:RUBICON LABS
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6716823B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideMalariaNon invasive
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, influenza M2, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, rabies glycoprotein, HBV surface antigen, HIV gp 120, HIV gp 160, human carcinoembryonic antigen, malaria CSP, malaria SSP, malaria MSP, malaria pfg, and mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP; and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The animal's cells can be epidermal cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector. The animal can be a vertebrate, e.g., a mammal, such as human, a cow, a horse, a dog, a cat, a goat, a sheep or a pig; or fowl such as turkey, chicken or duck. The vector can be one or more of a viral vector, including viral coat, e.g., with some or all viral genes deleted therefrom, bacterial, protozoan, transposon, retrotransposon, and DNA vector, e.g., a recombinant vector; for instance, an adenovirus, such as an adenovirus defective in its E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 region(s). The method can encompass applying a delivery device including the vector to the skin of the animal, as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can have all viral genes deleted therefrom. The vector can induce a therapeutic and / or an anti-tumor effect in the animal, e.g., by expressing an oncogene, a tumor-suppressor gene, or a tumor-associated gene. Immunological products generated by the expression, e.g., antibodies, cells from the methods, and the expression products, are likewise useful in in vitro and ex vivo applications, and such immunological and expression products and cells and applications are disclosed and claimed. Methods for expressing a gene product in vivo and products therefor and therefrom including mucosal and / or intranasal administration of an adenovirus, advantageously an E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 defective or deleted adenovirus, such as a human adenovirus or canine adenovirus, are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Duplexed parvovirus vectors
InactiveUS7465583B2High transduction efficiencyRapid onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral vector
The present invention provides duplexed parvovirus vector genomes that are capable under appropriate conditions of forming a double-stranded molecule by intrastrand base-pairing. Also provided are duplexed parvovirus particles comprising the vector genome. Further disclosed are templates and methods for producing the duplexed vector genomes and duplexed parvovirus particles of the invention. Methods of administering these reagents to a cell or subject are also described. Preferably, the parvovirus capsid is an AAV capsid. It is further preferred that the vector genome comprises AAV terminal repeat sequences.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
AAV2 vectors and methods
InactiveUS6962815B2Easy to adaptSuitable for mass productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsViral vectorCapsid
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
AAV vectors produced in insect cells
ActiveUS8163543B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideViral vector
The present invention relates to the production of adeno-associated viral vectors in insect cells. The insect cells therefore comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins, whereby the initiation codon for translation of the AAV VP1 capsid protein is a non-ATG, suboptimal initiation codon. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one AAV inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence; a third nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep52 or a Rep40 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell; and, a fourth nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep78 or a Rep68 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell. The invention further relates to adeno-associated viral vectors with an altered ratio of the viral capsid proteins that provides improved infectivity of the viral particles.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Efficient and stable in vivo gene transfer to cardiomyocytes using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS7078387B1The process is stable and efficientBiocideSugar derivativesCoronary sinusAdeno associate virus
This invention relates to the use of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors to transduce cardiomyocytes in vivo by infusing the rAAV into a coronary artery or coronary sinus. rAAV infection is not associated with detectable myocardial inflammation or myocyte necrosis. Thus, rAAV is a useful vector for the stable expression of therapeutic genes in the myocardium and can be used to deliver genes for inducing angiogenesis, inhibiting angiogenesis, stimulating cell proliferation, inhibiting cell proliferation and / or treating or ameliorating other cardiovascular conditions.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
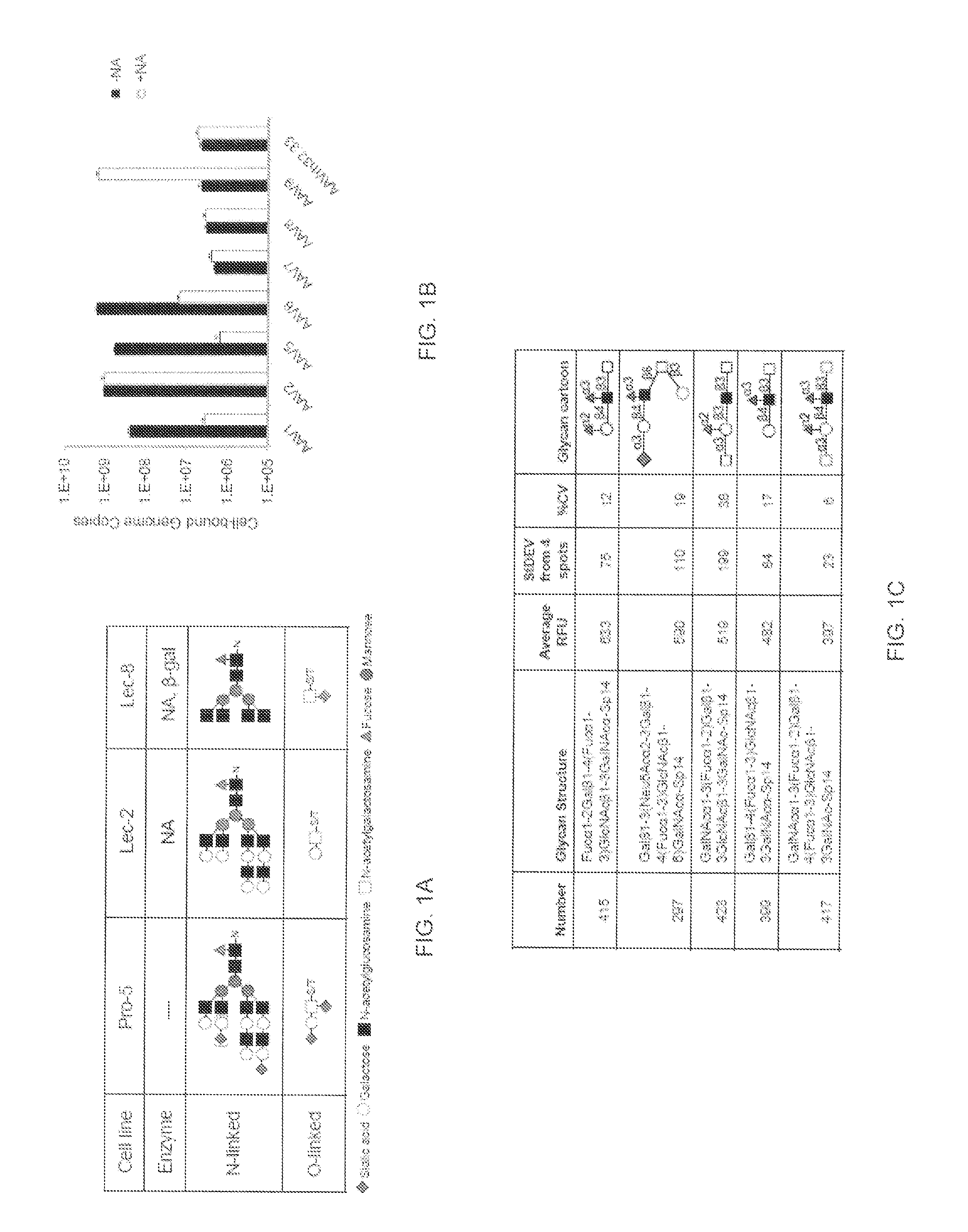
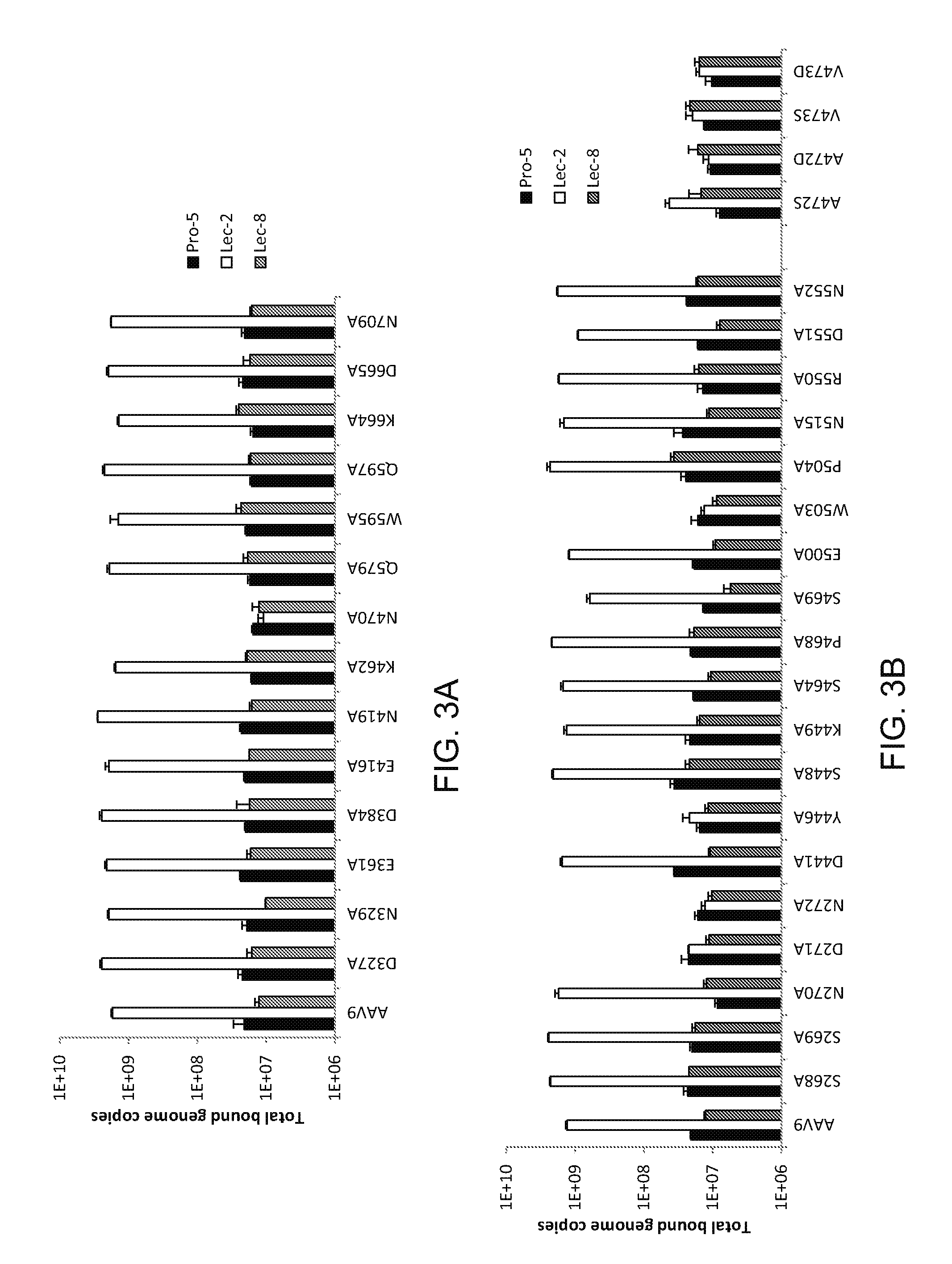
Compositions and Methods for Altering Tissue Specificity and Improving AAV9-Mediated Gene Transfer
ActiveUS20130323226A1Improve efficiencyImprove usabilityOrganic active ingredientsVectorsViral vectorFhit gene
A method of altering the targeting and / or cellular uptake efficiency of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector having a capsid containing an AAV9 cell surface binding domain is described. The method involves modifying a clade F cell surface receptor which comprises a glycan having a terminal sialic acid residue and a penultimate β-galactose residue. The modification may involve retargeting the vector by temporarily functionally ablate AAV9 binding in a subset of cells, thereby redirecting the vector to another subset of cells. Alternatively, the modification may involve increasing cellular update efficiency by treating the cells with a neuraminidase to expose cell surface β-galactose. Also provided are compositions containing the AAV9 vector and a neuraminidase. Also provided is a method for purifying AAV9 using β-galactose linked to solid support. Also provided are mutant vectors which have been modified to alter their targeting specificity, including mutant AAV9 in which the galactose binding domain is mutated and AAV in which an AAV9 galactose binding domain is engineered.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
CHEMICALLY MODIFIED POLYCATION POLYMER FOR siRNA DELIVERY
InactiveUS20070231392A1Reduced gene expressionReduce expressionPowder deliverySpecial deliveryIonic polymerizationIn vivo
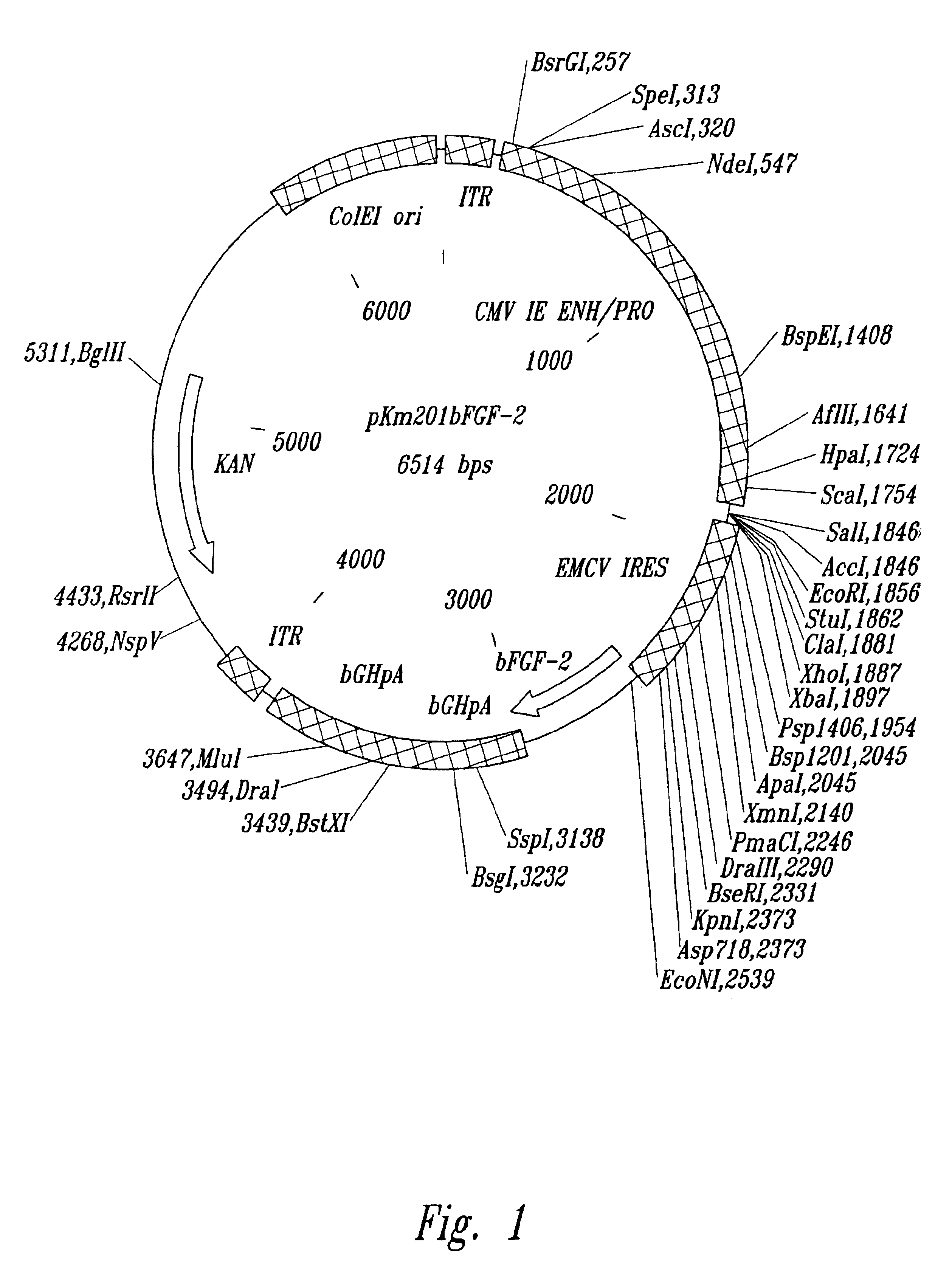
The present invention provides a unique non-viral carrier for nucleic acid delivery in vitro and in vivo, and methods of using thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
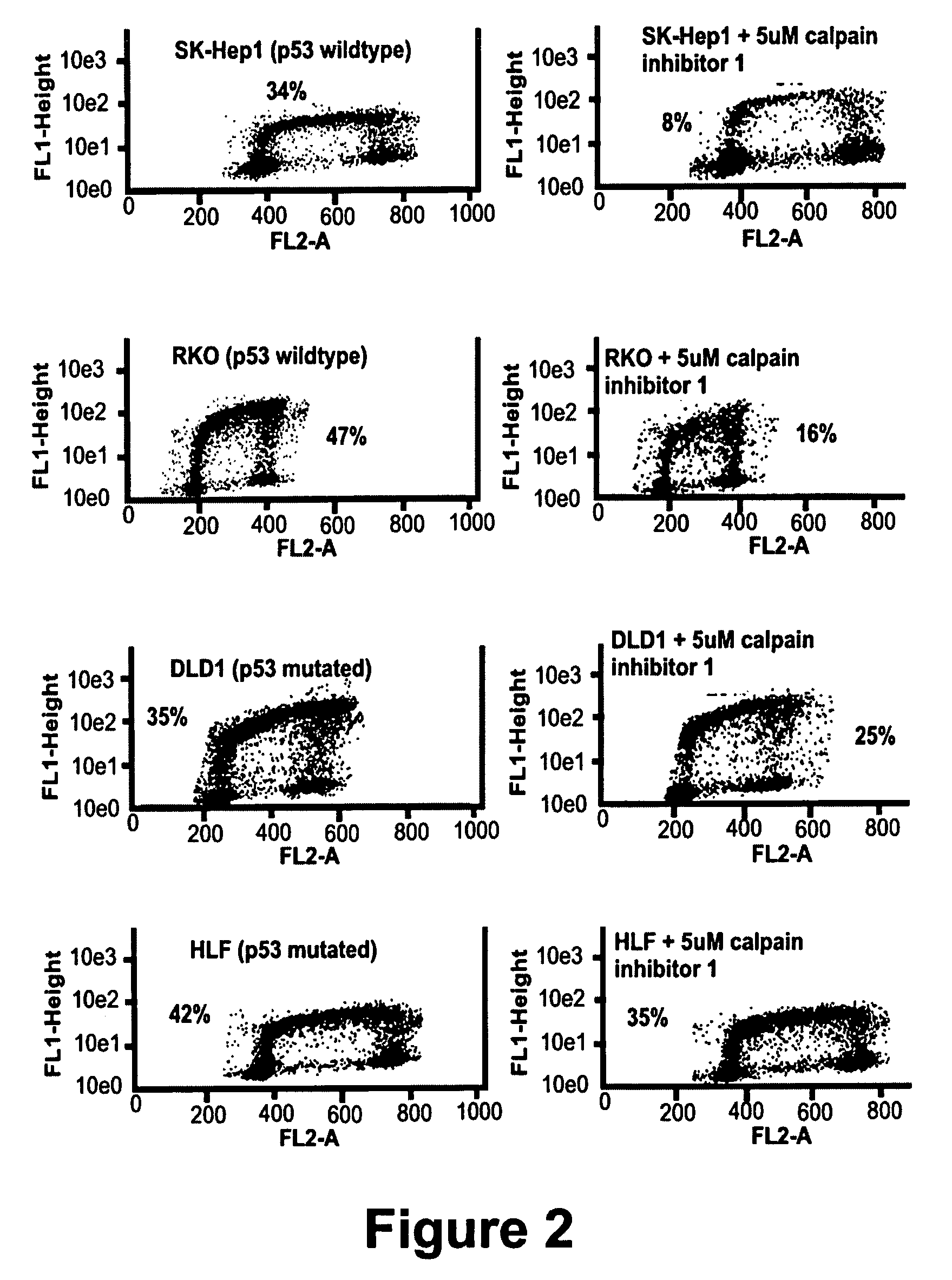
Calpain inhibitors and their applications
InactiveUS7001770B1Enhance p53-mediated apoptosisIncrease infectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationCo administrationApoptosis
The present invention provides a method to enhance apoptosis in a cell by the administration of p53 in combination with a calpain inhibitor. The present invention provides a method of increasing the infectivity of a cell to a viral vector by treatment of the cell with a calpain inhibitor. the present invention further provides a method of enhancing transciption of a therapeutic transgene from the CMV promoter. The present invention also provides a method of suppress the in vivo CTL response to viral vectors by the use of calpain inhibitors. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical formulations of p53 and a calpain inhibitor in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention provides a method of ablating neoplastic cells in a mammalian organism in vivo by the co-administration of a calpain inhibitor and p53. The present invention also provides a method of ablating neoplastic cells in a population of normal cells contaminated by said neoplastic cells ex vivo by the administration of a recombinant adenovirus in combination with a calpain inhibitor to said population.
Owner:CANJI
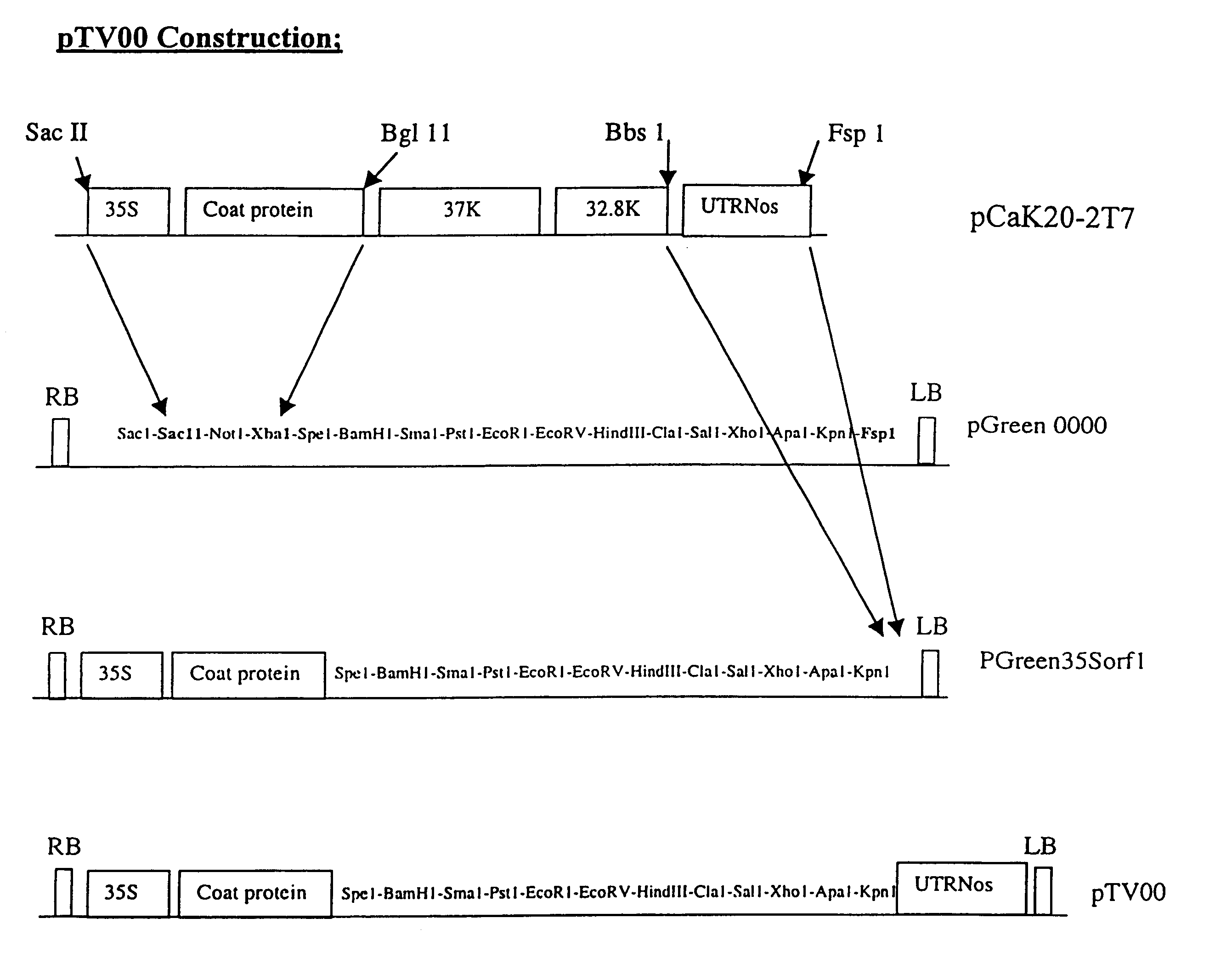
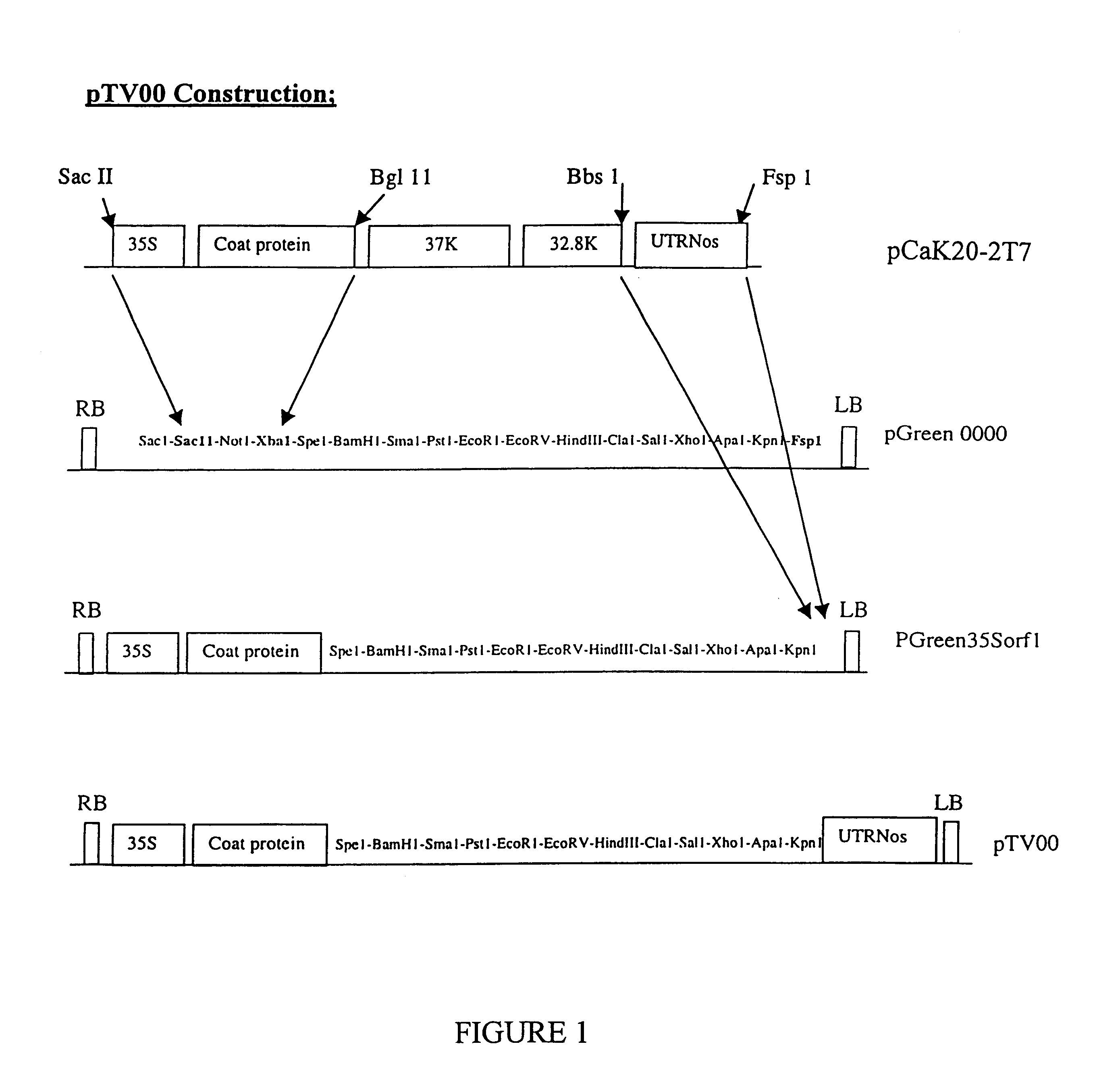
Recombinant plant viral vectors
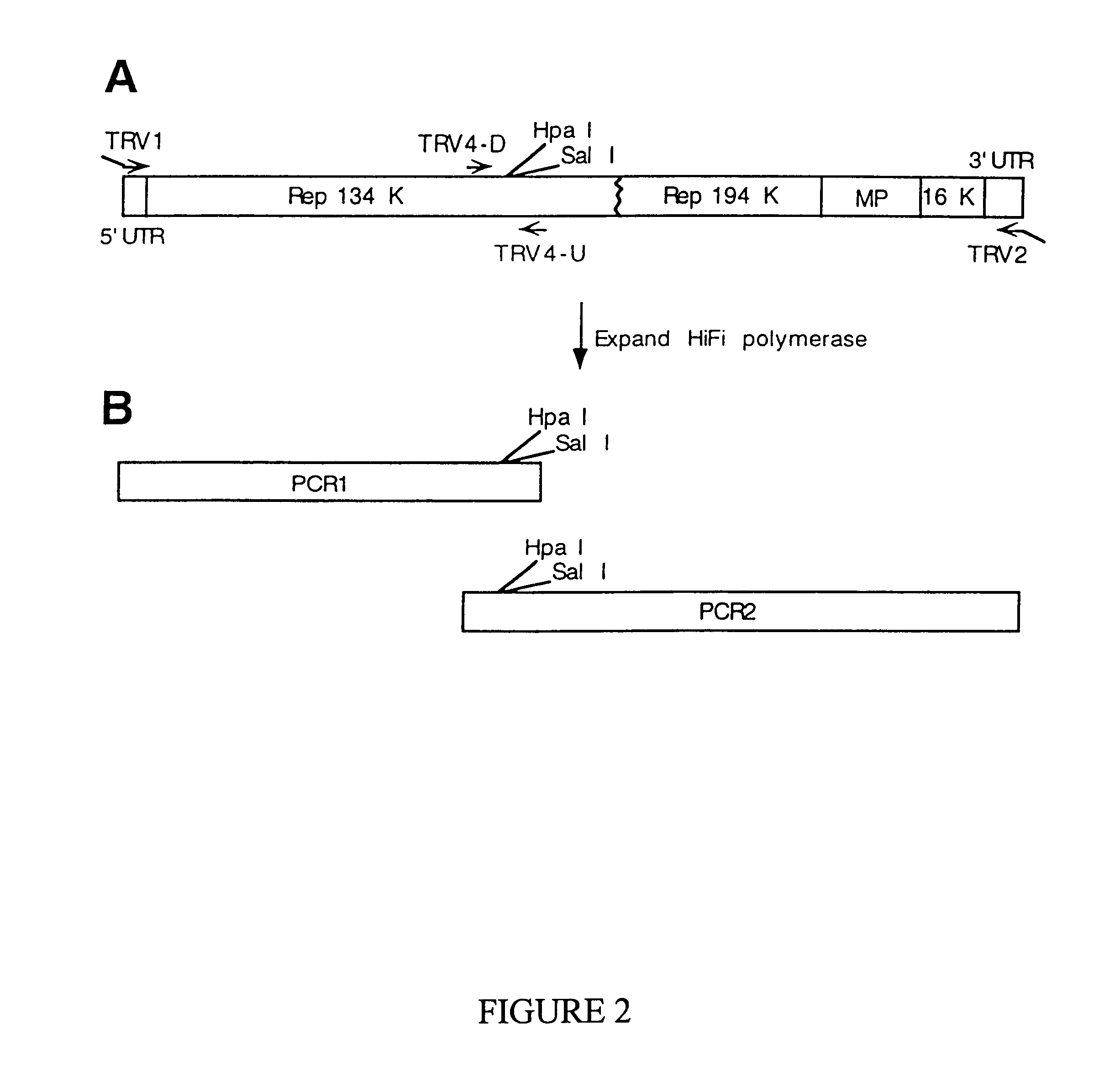
Disclosed are nucleic acid vectors which comprise: (a) a transfer nucleotide sequence comprising (i) a plant active promoter, operably linked to (ii) a recombinant tobacco rattle virus (TRV) cDNA (preferably derived from TRV RNA2) which includes at least cis acting elements permitting replication of the cDNA; a subgenomic promoter operably linked to a sequence encoding a TRV coat protein; and a heterologous nucleotide sequence which is foreign to the virus;(b) border sequences which permit the transfer of the transfer nucleotide sequence into a plant genome. Such vectors may be used as expression vectors or for achieving viral induced gene silencing (VIGS) of a target gene, wherein the heterologous nucleotide sequence is a targeting sequence which corresponding to that gene. Example vectors include pTV00 and vectors which are derived from PTV00 and have the characteristics thereof. Also disclosed are associated processes, methods, viruses or viral particle, kits, host cells and plant tissues.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Episomal reprogramming with chemicals
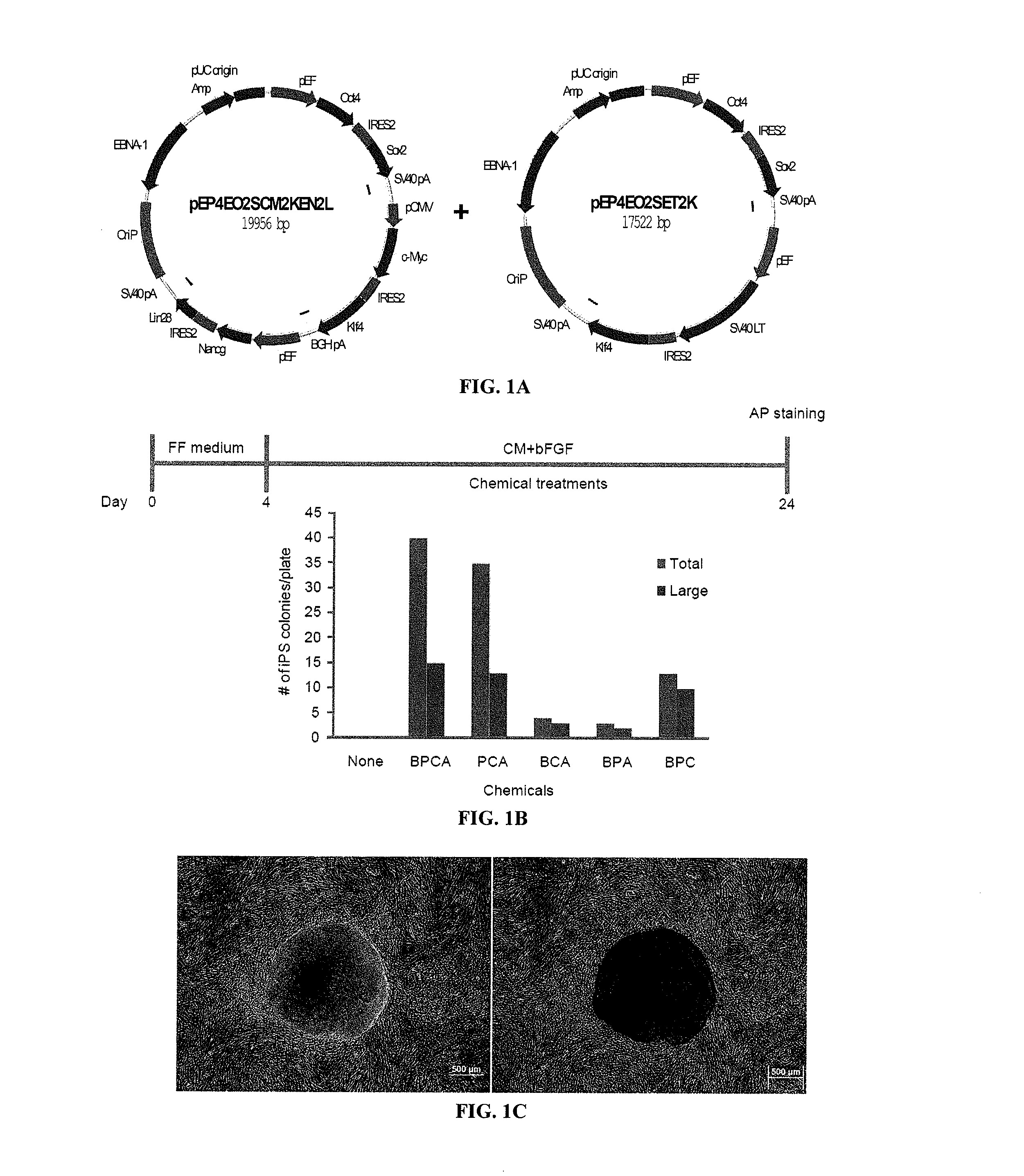
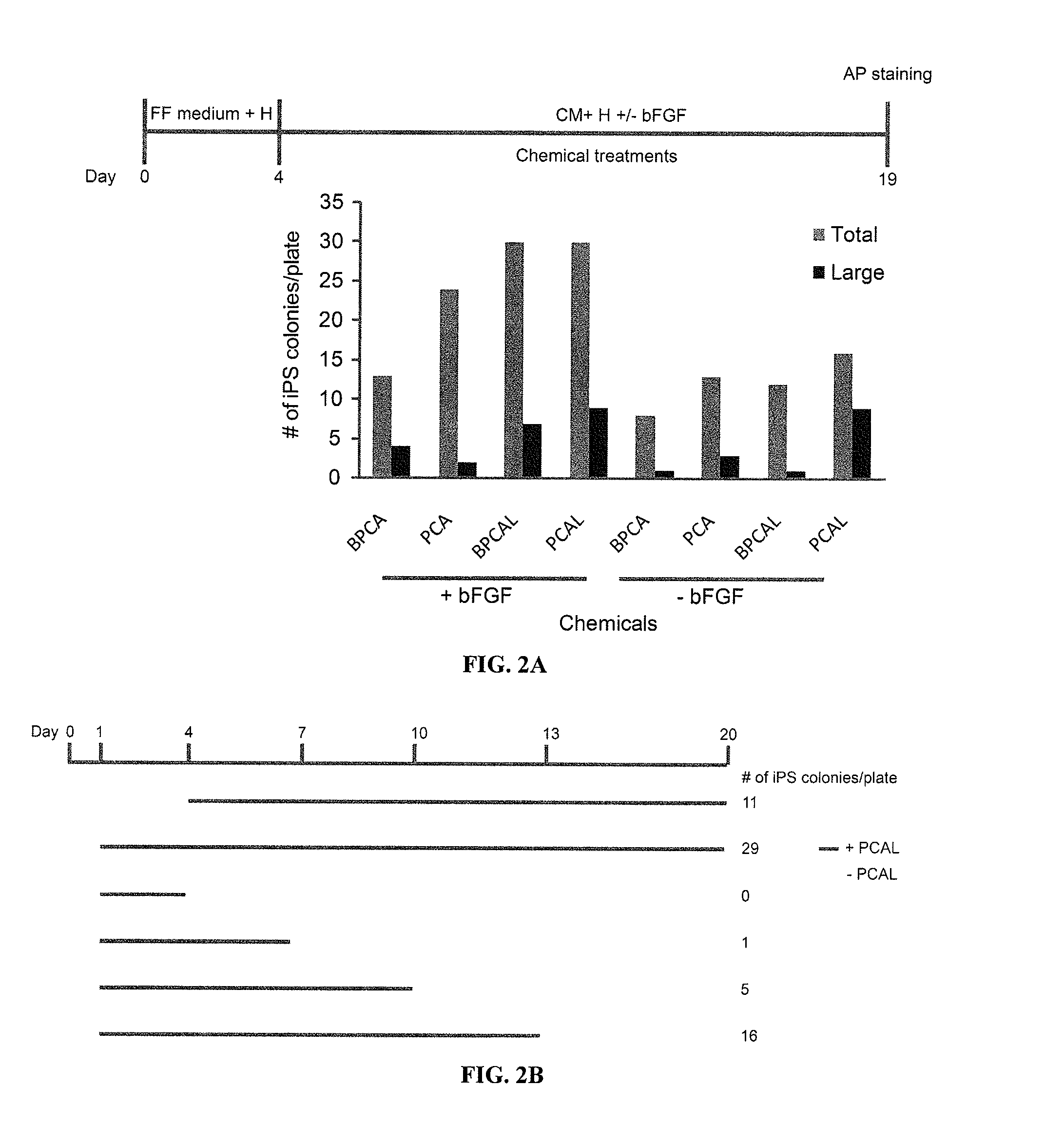
ActiveUS20110104125A1Easy to adaptHigh reprogramming efficiencyBiocideNervous disorderVector elementViral vector
Methods and composition of induction of pluripotent stem cells are disclosed. For example, in certain aspects methods for generating essentially vector-free induced pluripotent stem cells with cell signaling regulators are described. Furthermore, certain aspects of the invention provide novel compositions comprising induced pluripotent stem cells essentially free of exogenous retroviral vector elements in the presence of a medium comprising signaling inhibitors. In certain aspects, feeder-free episomal reprogramming methods may be provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Use of recombinant gene delivery vectors for treating or preventing diseases of the eye
Gene delivery vectors, such as, for example, recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors, and methods of using such vectors are provided for use in treating or preventing diseases of the eye.
Owner:CHIRON CORP +1
CHEMICALLY MODIFIED POLYCATION POLYMER FOR siRNA DELIVERY
InactiveUS20080112916A1Reduced gene expressionReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryIn vivoViral vector
The present invention provides a unique non-viral carrier for nucleic acid delivery in vitro and in vivo, and methods of using thereof.
Owner:WAGNER ERNST +3
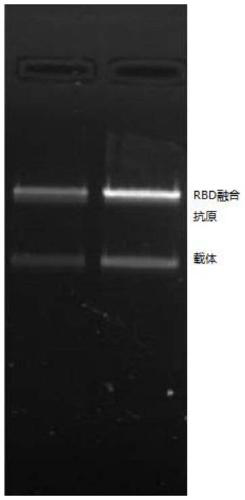
SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111217917AEnter to helpImproving immunogenicityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntigenDisease
The invention relates to a preparation method for a vaccine capable of treating and / or preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 diseases. The core antigen of the vaccine comprises the RBD (receptor binding zone) fusion protein of the SARS-CoV-2, and a vaccine form comprises an RBD fusion protein subunit vaccine, an RBD fusion protein mRNA vaccine or an RBD fusion protein adenovirus vector vaccine. The above vaccine immunizes an organism, and immune reaction for treating and / or preventing the SARS-CoV-2 infection can be generated so as to be used for treating and / or preventing COVID-19. The invention also relates to an RBD fusion gene, the RBD fusion protein, a carrier, a cell, a preparation method, a treatment method or a pharmacy purpose of the SARS-CoV-2.
Owner:CANSINO BIOLOGICS INC
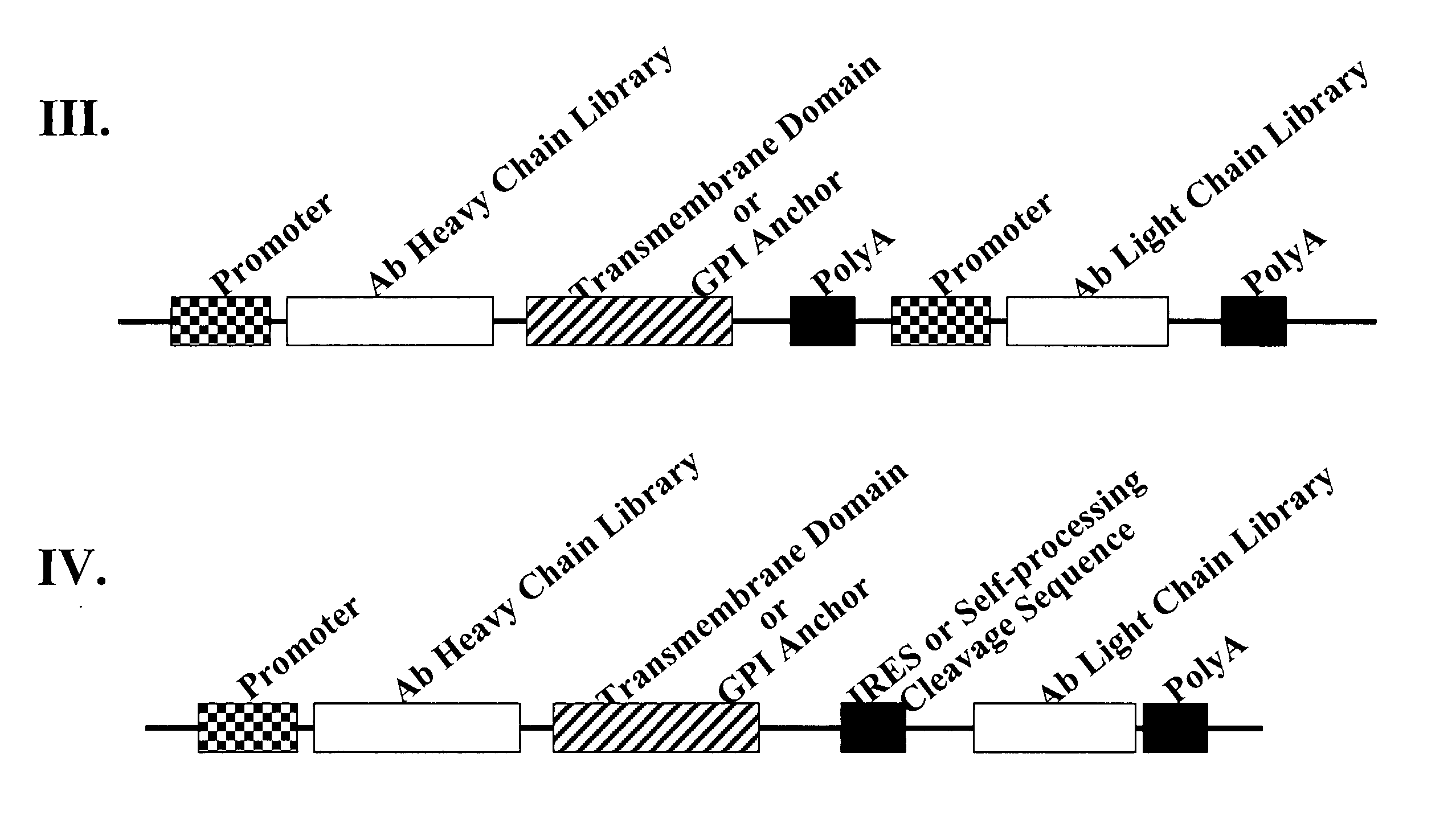
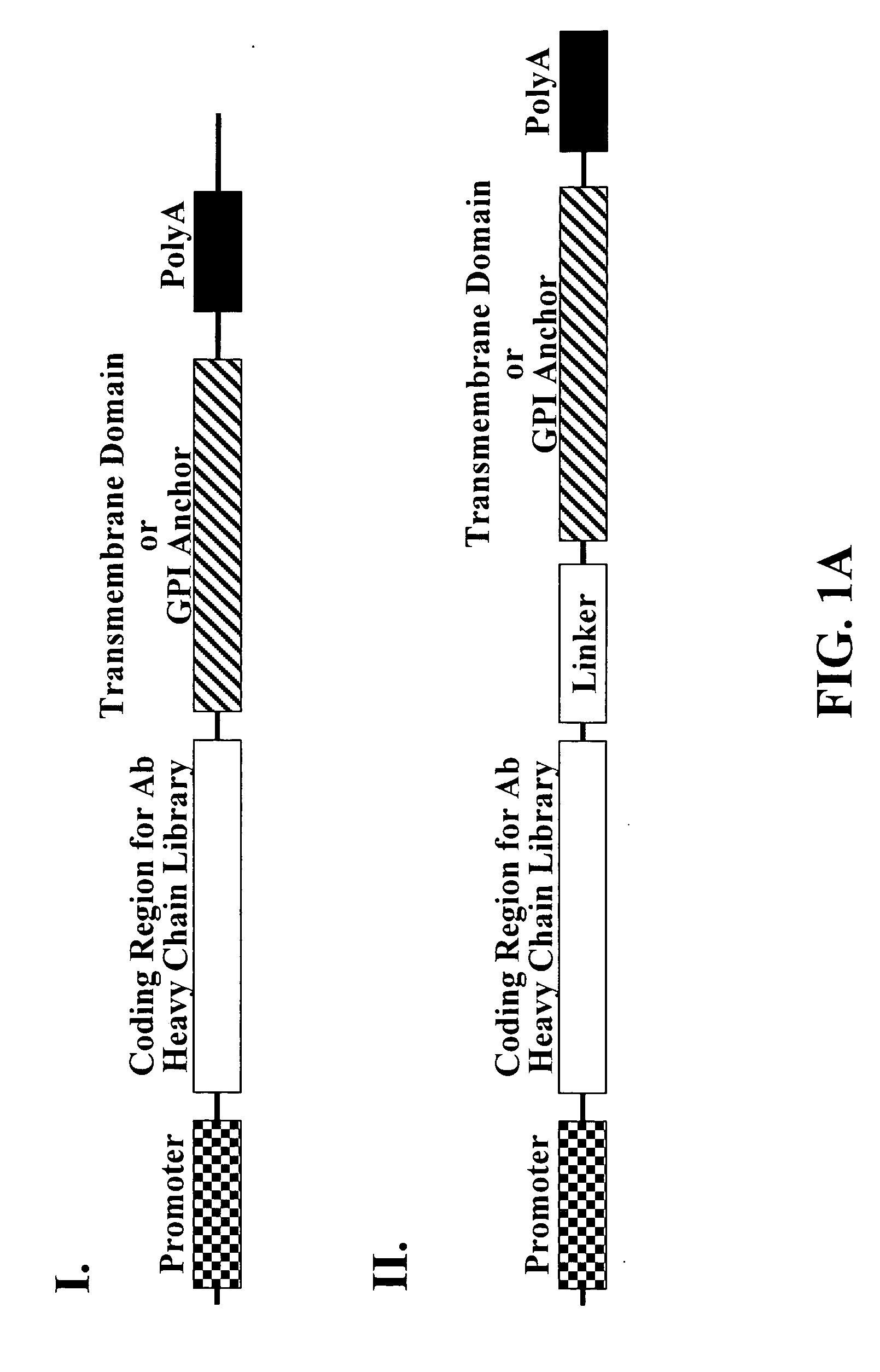
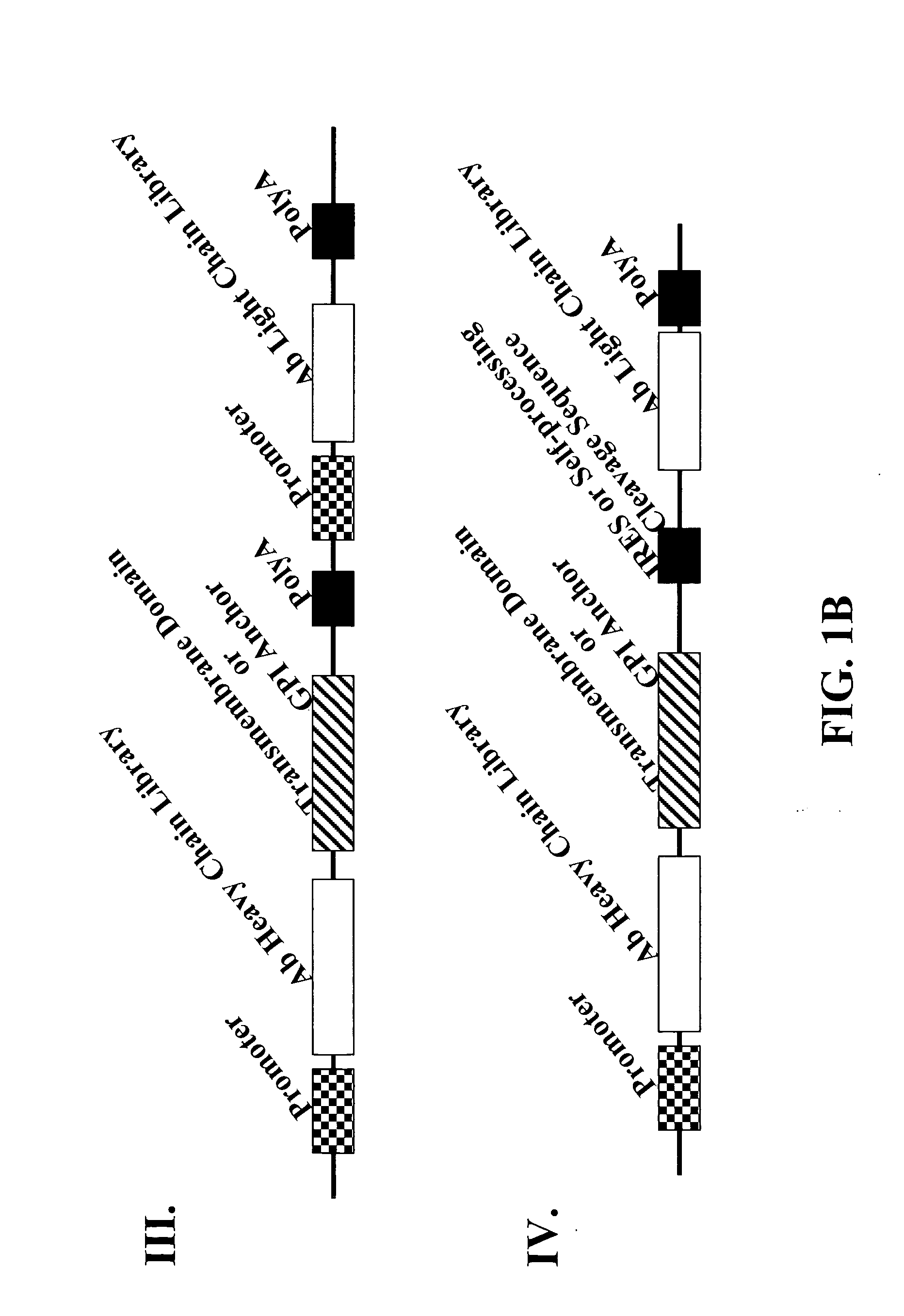
Cell display of antibody libraries
ActiveUS20070111260A1Altered bindingReduced antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicityPeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsCell membrane
The present invention relates to a viral vector encoding for a library of antibodies or antibody fragments that are displayed on the cell membrane when expressed in a cell. The present invention provides cells comprising the viral vector nucleic acids and methods of screening the libraries for antibodies or antibody fragments with desired characteristics.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
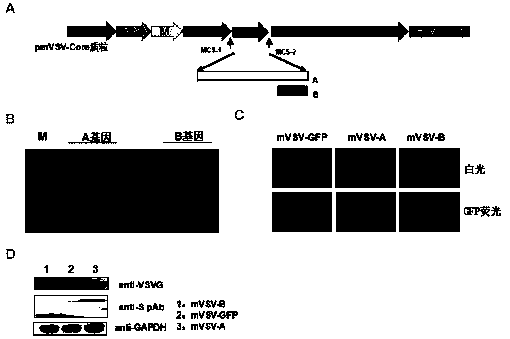
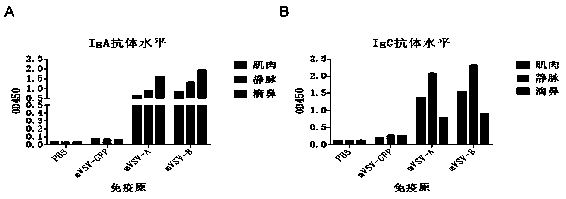
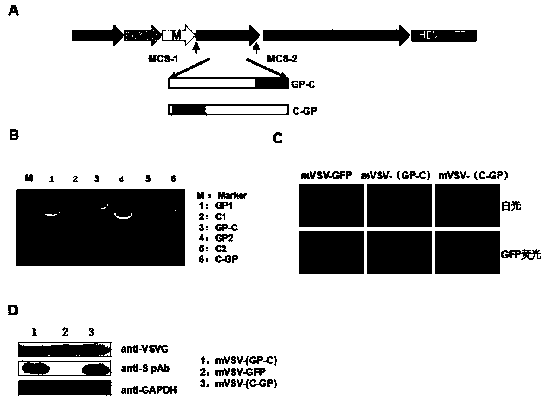
mVSV virus vector and virus vector vaccine, and COVID-19 vaccine based on mVSV mediation
ActiveCN111088283AEnhance immune responseStrong immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseHeterologousReceptor
The invention provides an mVSV virus vector, i.e., attenuated mVSV obtained after multiple modification mutations occur to an M protein amino acid site of a wild Indiana strain VSV, and an optimized heterologous antigen gene is preferentially integrated to a double cloning site area of an mVSV packaging core plasmid pmVSV-Core at the same time. The mVSV virus vector vaccine comprises a heterologous antigen gene which fuses or embeds a target virus between G and L genes of an mVSV vector envelope, wherein the antigen gene comprises an enveloped and embedded antigen gene encoding the target virus, an embedded combination antigen gene or a fused antigen gene; the mVSV virus vector is embedded or fused with a dominant antigen of spike protein S of an SARS-CoV-2 pathogen; the dominant antigen is preferably selected from a receptor binding domain of spike protein S, namely RBD; and a COVID-19 vaccine based on mVSV mediation is formed. The vaccine has good prevention or treatment effect on COVID-19 infected people.
Owner:FANTASIA BIOPHARMA ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vectors
InactiveUS20020141980A1Efficient deliveryEfficient expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseConvection-Enhanced Delivery
Methods of delivering viral vectors, particularly recombinant AAV virions, to the CNS are provided. Also provided are methods of treating Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com