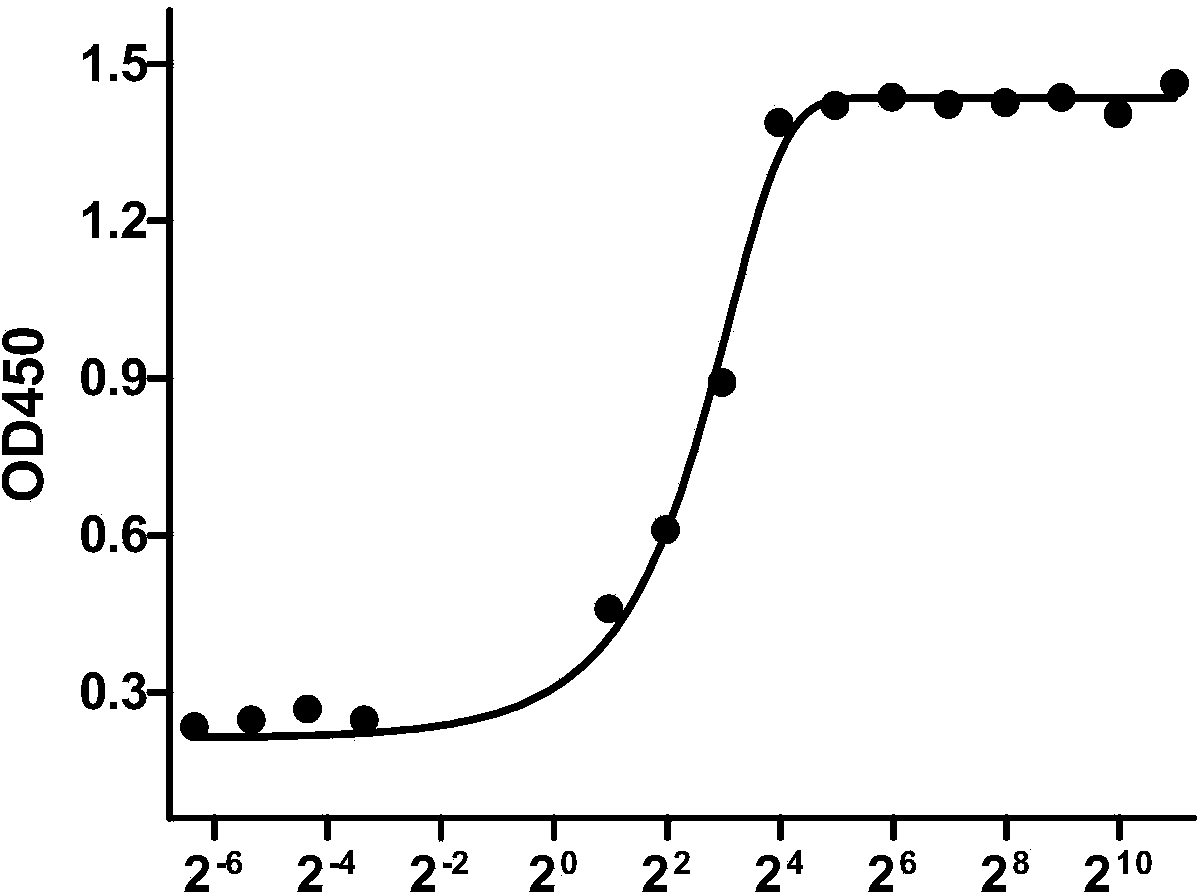
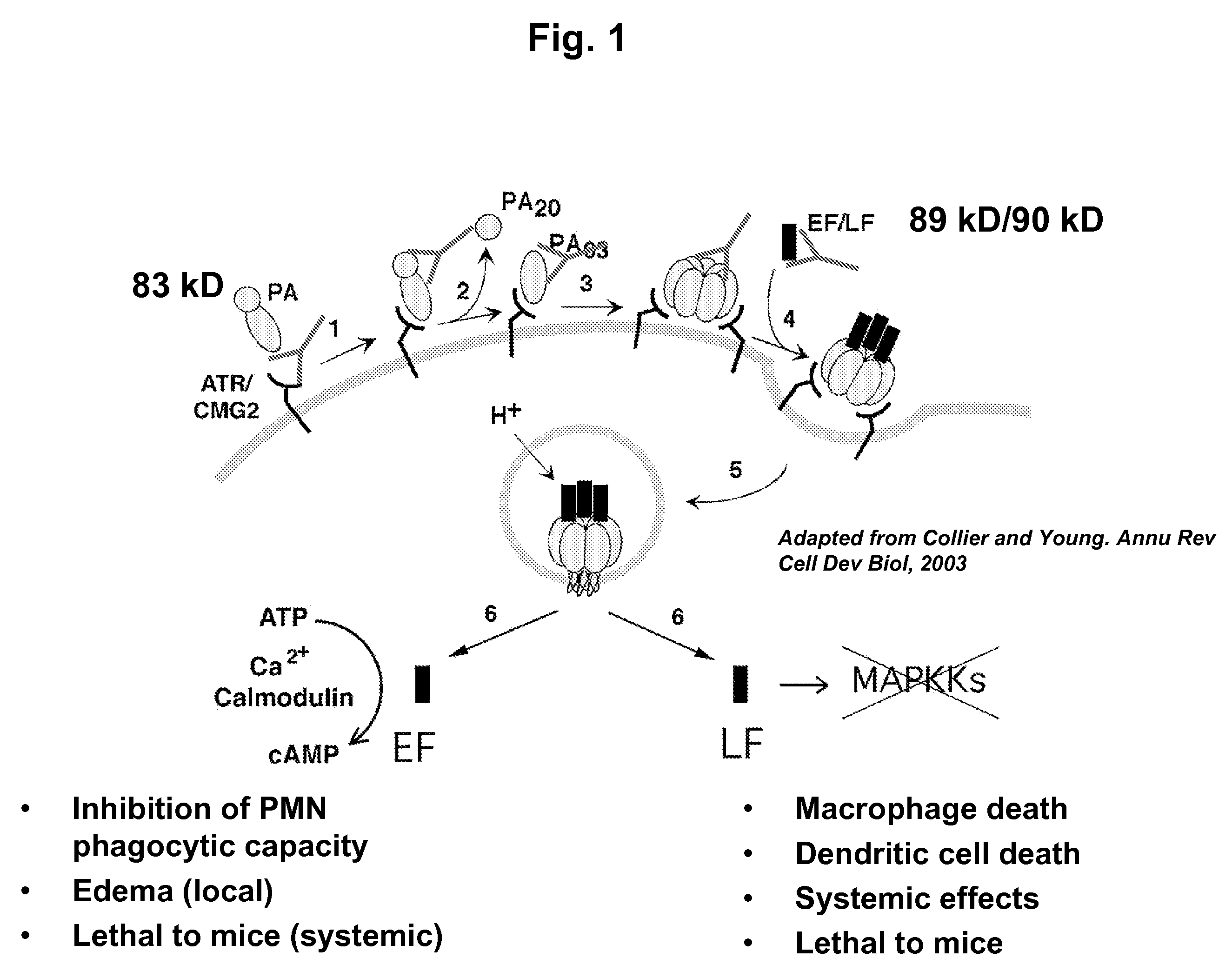
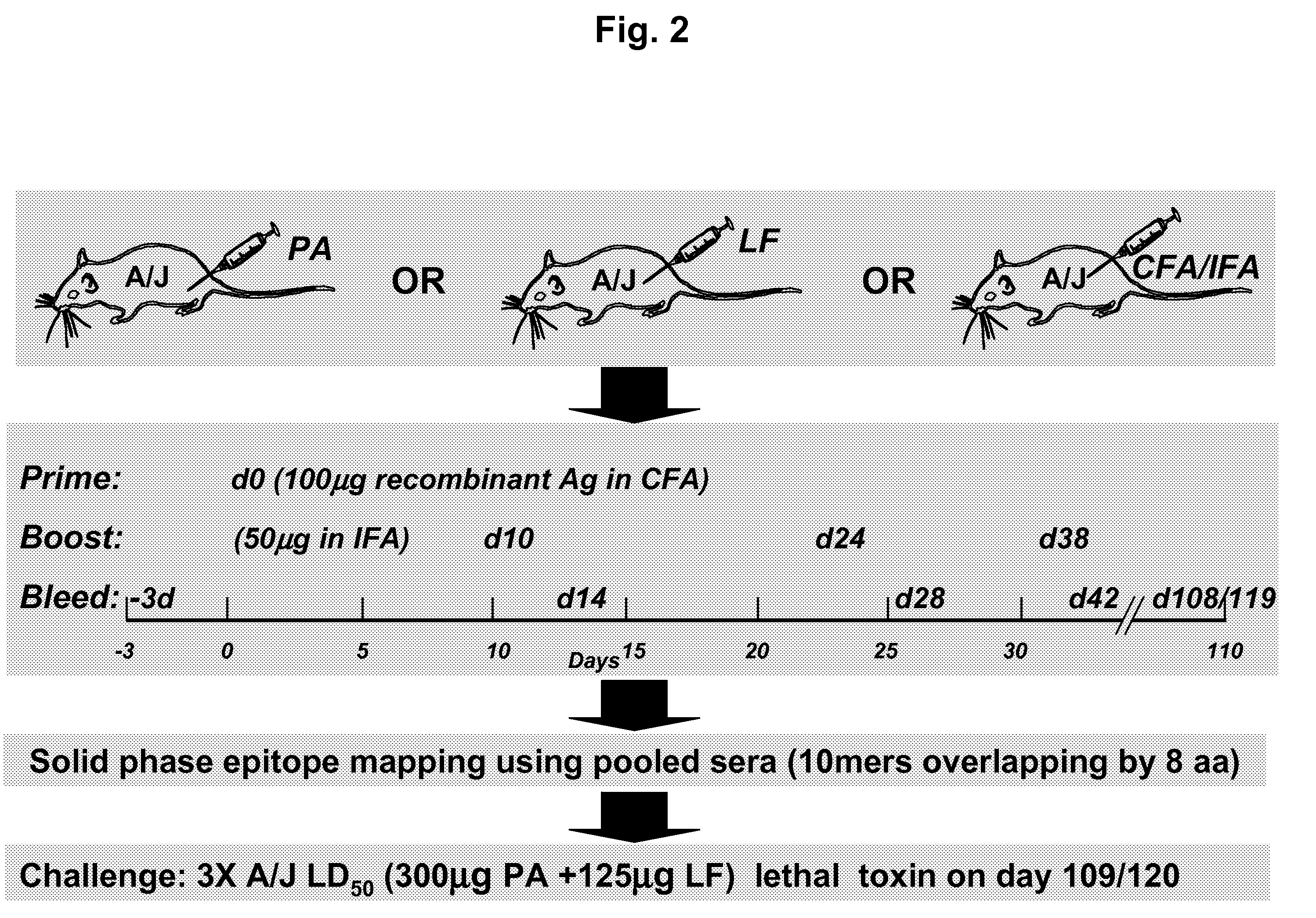
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Lethal factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
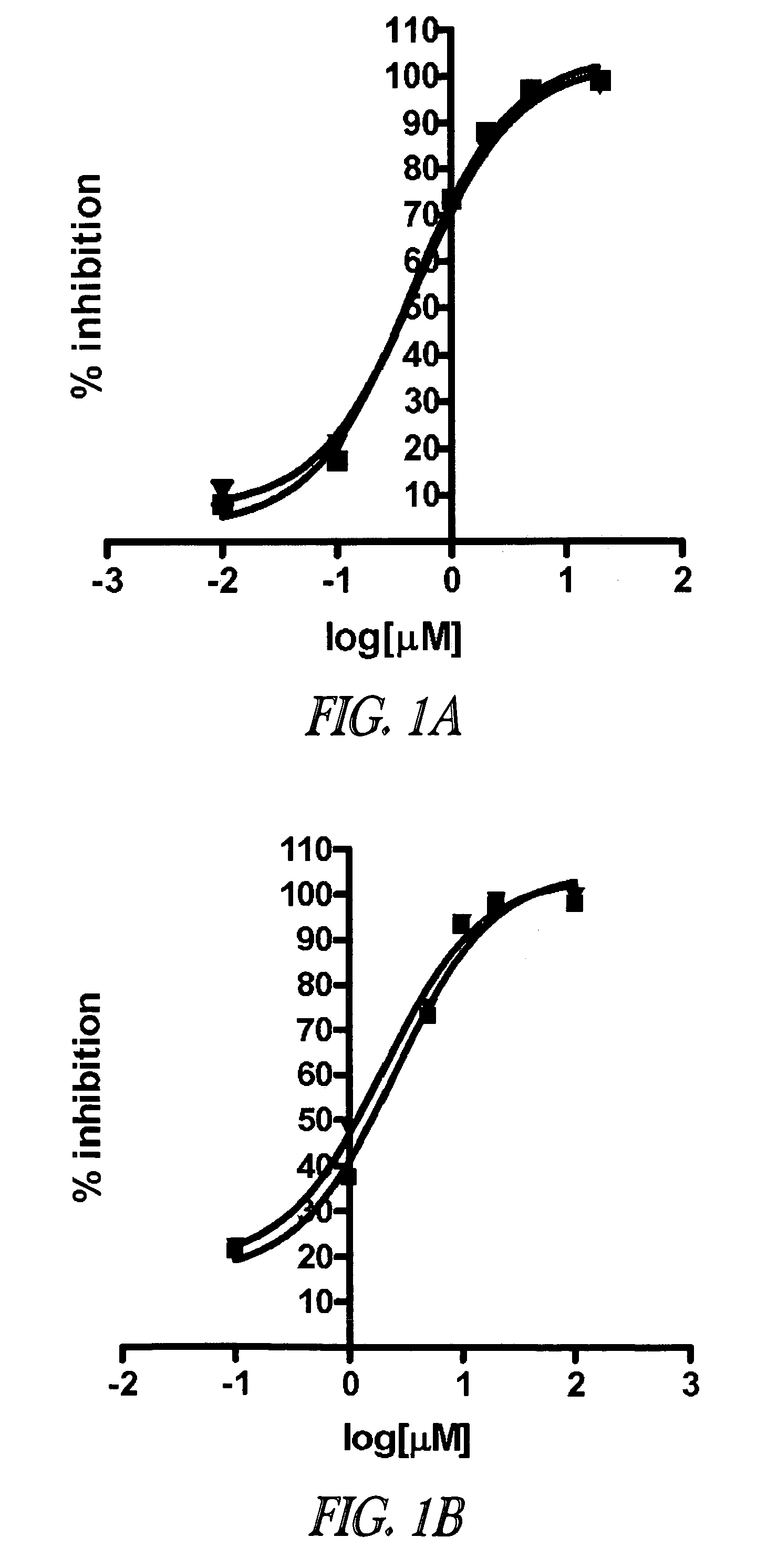
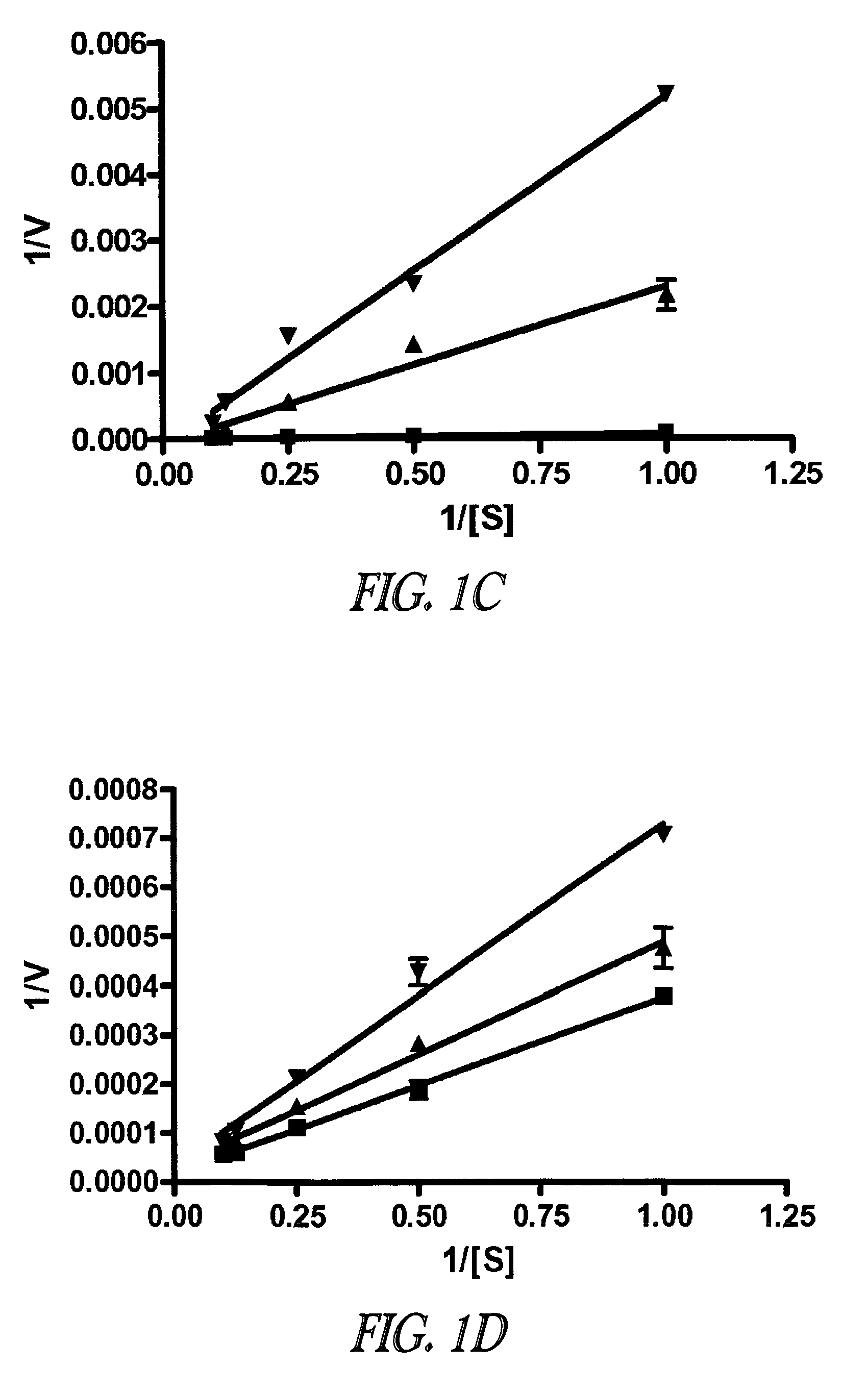
Inhibition of lethal factor protease activity from anthrax toxin
The present invention provides compounds that efficiently and specifically inhibit lethal factor (LF) protease activity of anthrax toxin.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INST
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against Bacillus anthracis infection
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based anthrax vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding Bacillus anthracis antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the B. anthracis antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. In certain embodiments, the coding regions are also modified so as to remove potential N-linked glycosylation sites. B. anthracis antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF), and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to B. anthracis in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Recombinant immunogenic compositions and methods for protecting against lethal infections from Bacillus anthracis
ActiveUS7201912B2Reduce in quantityLow costBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsProtective antigenFusion Protein Expression
Recombinant immunogenic compositions and methods for protecting against lethal infections from Bacillus anthracis having a variant of recombinant Bacillus anthracis protective antigen (rPA) and a variant of recombinant Bacillus anthracis lethal factor (rLF). These proteins may be expressed separately or as a fusion protein. The recombinant proteins are produced in an avirulent strain of Bacillus anthracis that overproduces the desired antigens. The compositions and methods induce the animal host to produce antibodies against a virulent strain of Bacillus anthracis.
Owner:EMERGENT BIODEFENSE OPERATIONS LANSING
Peptide biosensors for anthrax protease
InactiveUS7410769B2Increase speedImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProteinase activityProtease
The present invention provides a protease biosensor that can be used to detect the presence of the lethal factor protease from Bacillus anthracis, as well as methods for using the protease biosensor.
Owner:CELLOMICS
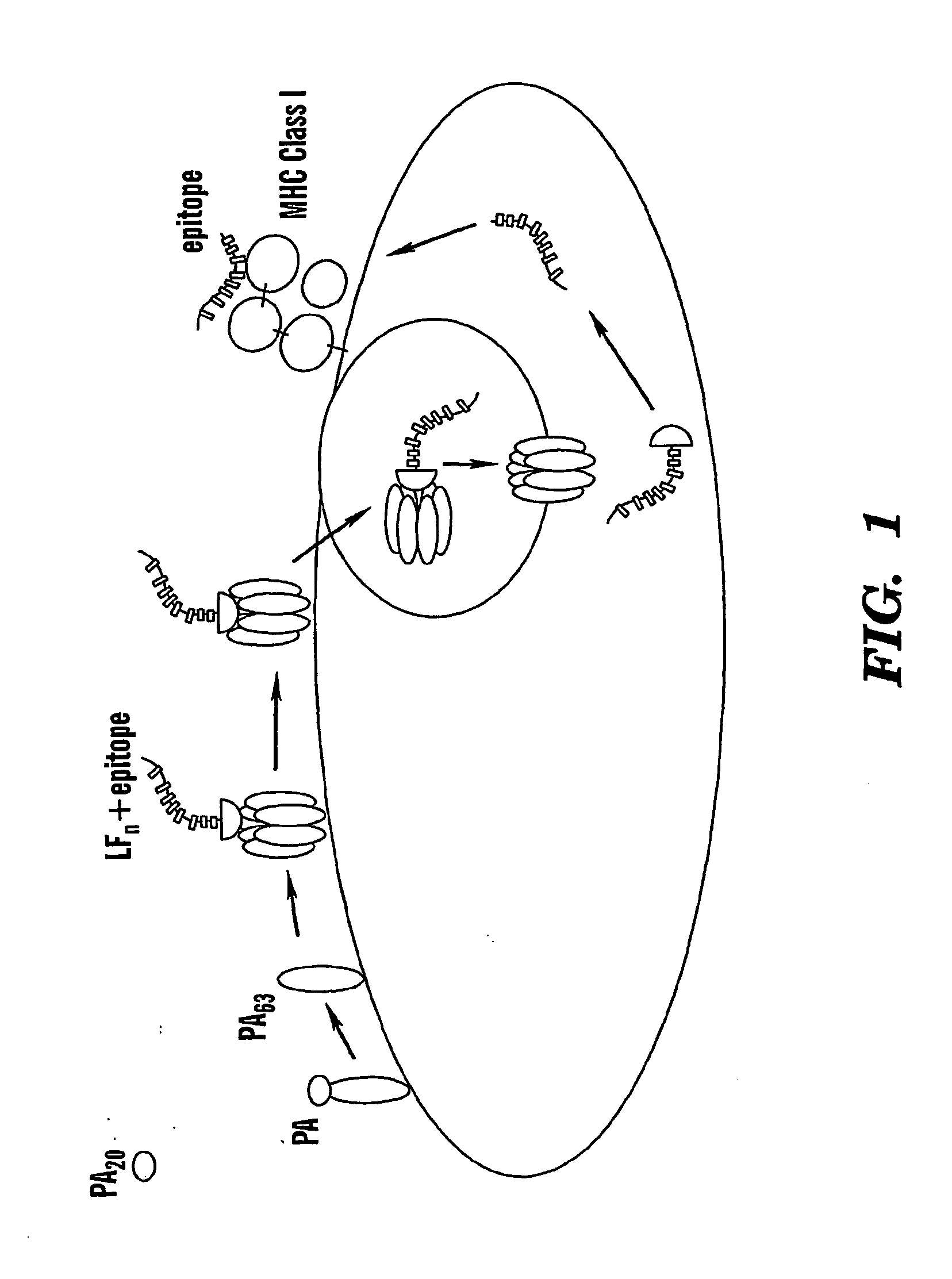
Methods of delivery of exogenous proteins to the cytosol and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050220807A1Effective immune responseEvaluated effectively and efficientlyAntibacterial agentsVirusesProtective antigenAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to a method for delivering exogenous proteins to the cytosol, by binding a target antigen (such as a protein) to a transport factor that contains a fragment of a bipartite protein exotoxin, but not the corresponding protective antigen. Preferably, the target antigen is fused to the transport factor. Preferred transport factors include the protective antigen binding domain of lethal factor (LFn) from B. anthracis, consisting of amino acids 1-255, preferably a fragment of at least 80 amino acids that shows at least 80% homology to LFn, and a fragment of about 105 amino acids from the carboxy portion that does not bind PA. The target antigen can include any molecule for which it would be desirable to elicit a CMI response, including viral antigens and tumor antigens.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
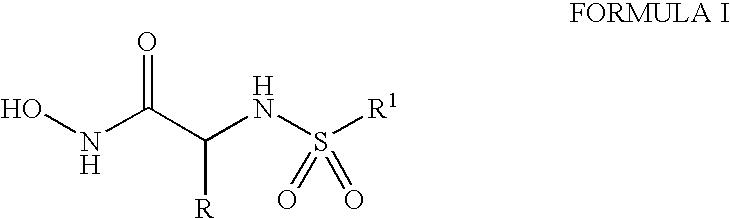
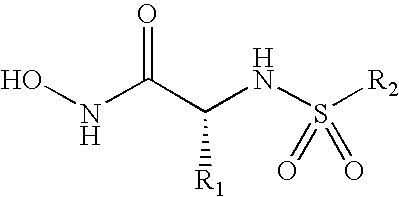
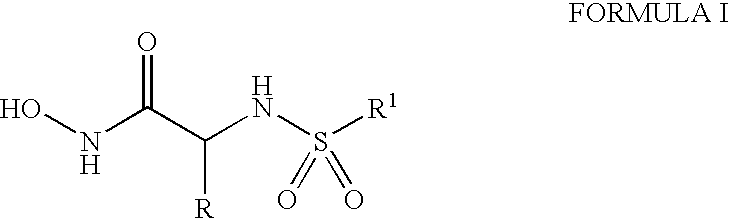
Compounds useful in the treatment of anthrax and inhibiting lethal factor
This invention relates to compounds of formula (I), and a method for treating anthrax or inhibiting lethal factor by administrating a composition containing a compound of formula (I) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. This invention further relates to the use of the compounds of formula (I) to treat other conditions related to an anthrax infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Inhibition of lethal factor protease activity from anthrax toxin
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INST
Pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting metal ion dependent enzymatic activity and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070027064A1High activityPrevent pathological NO activityBiocideSenses disorderFungal microorganismsCyclooxygenase
Methods for inhibiting metalloprotease activity; treating a pathological condition influenced by the action of MMP; treating a pathological condition influenced by cyclooxygenases, endonucleases, metallopepitidases and 5-epoxigenase; treating a pathological condition for which the presence of a metal ion is required; inhibiting the lethal factor produced by toxigenic strains of anthrax; inhibiting activities of fungi, bacteria or plants that utilize zinc-dependent methionine synthetase; inhibiting the activity of a zinc-dependent enzyme in prokaryotic systems; and inhibiting the activity of zinc-dependent enzymes; and compositions thereof, are disclosed.
Owner:APPELBAUM JERACHMIEL YORI
Inhibitors of lethal factor protease
The invention provides compounds that can efficiently and specifically inhibit bacterial toxins, such as inhibit the lethal factor (LF) protease activity of anthrax toxin and / or botulinum neurotoxin type A. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting proteases, such as lethal factor protease, as well as methods for treating bacterial infections, such as anthrax and botulinum.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Compositions and methods for production of immunoglobulins
Provided are oligonucleotides for isolating human antibody cDNAs from cells or cell lines, such as hybridomas. The invention also provides cDNAs that encode at least one provided CDR of a heavy chain or a light chain of a human monoclonal antibody that binds to B. anthracis protective antigen; and cDNAs that encode at least one provided CDR of a heavy chain or a light chain of a human monoclonal antibody that binds to B. anthracis lethal factor. The invention further provides expression vectors that contain one or more cDNAs isolated according to the methods of the invention, host cells expressing one or more inventive cDNAs, and transgenic plants and animals that express one or more inventive cDNAs. In certain embodiments of the invention the expression system is a plant-based expression system. The invention further provides antibody compositions comprising one or more antibodies produced by expressing a cDNA isolated according to the methods of the invention in a suitable expression system. Additionally encompassed in the invention are kits containing one or more of provided compositions, as well as methods of production and use of provided compositions.
Owner:IBIO
Small molecules and a pharmacophore model for inhibition of anthrax lethal factor
InactiveUS20050251345A1Chemical structure searchMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityProtease
Disclosed herein is a pharmacophore model for inhibiting anthrax lethal factor protease activity which comprises a first aromatic center A, a second aromatic center B, a first polar center C, a second polar center D, a third polar center E, and a neutral linker F. In some embodiments, the distance between the first aromatic center A and the neutral linker F is about 4.7 to about 6.7 Å, preferably about 5.7 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between the neutral linker F and the second aromatic center B is about 3.4 to about 4.4 Å, preferably about 3.9 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between first aromatic center A and the first polar center C is about 5.5 to about 7.5 Å, preferably about 6.5 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between the first aromatic center A and the second polar center D is about 4.6 to about 6.6 Å, preferably about 5.6 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between the second aromatic center B and the second polar center D is about 3.6 to about 4.6 Å, preferably about 4.1 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between the second aromatic center B and the third polar center E is about 2.6 to about 3.6 Å, preferably about 3.1 Å. In some embodiments, the distance between the first polar center C and the third polar center E is about 15.6 to about 19.6 Å, preferably about 17.6 Å. Also disclosed are small molecules fitting the pharmacophore model and compositions and methods of using thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Anthrax lethal factor is a MAPK kinase protease
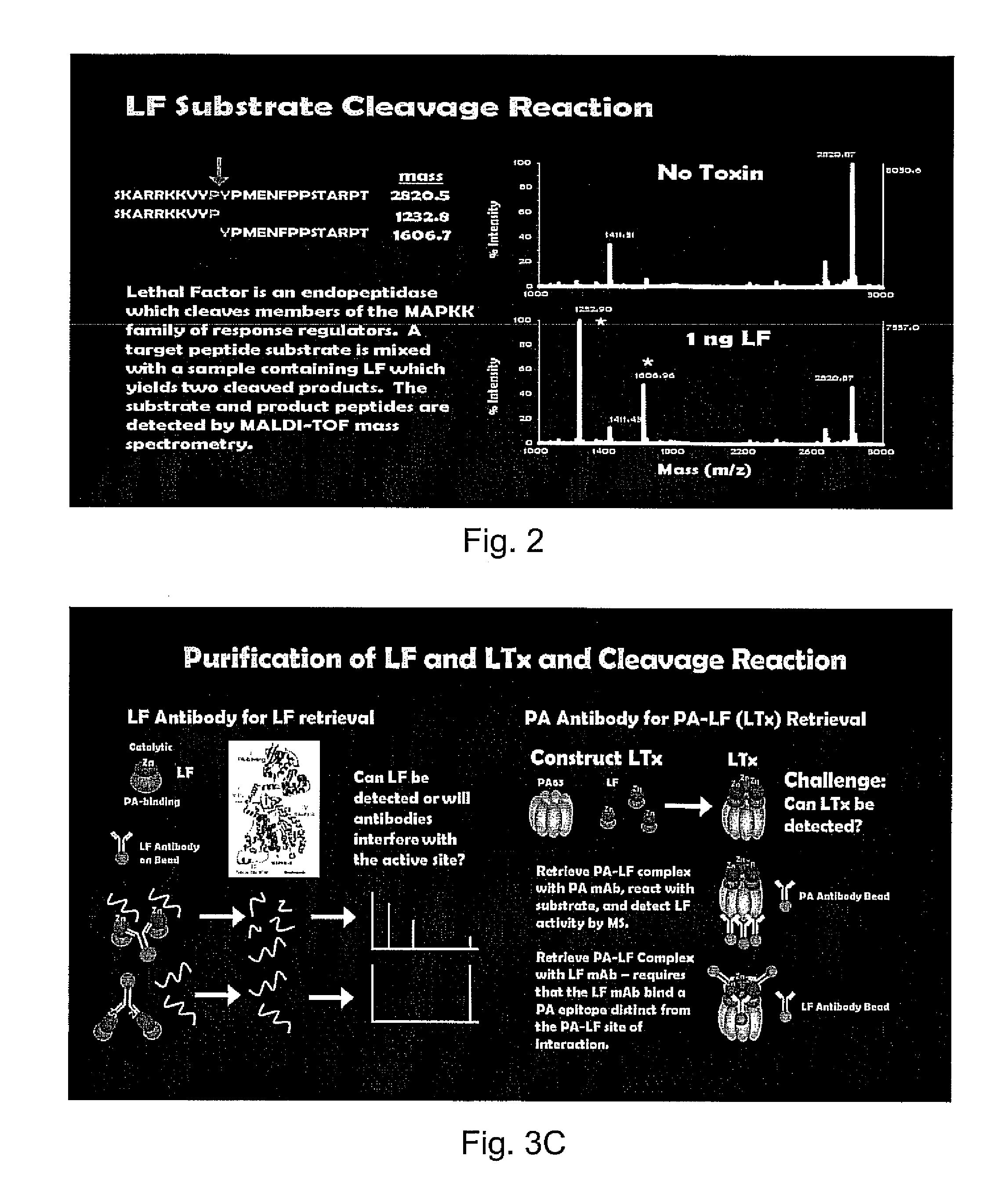
The present invention relates to in vitro and ex vivo methods of screening for modulators, homologues, and mimetics of lethal factor mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) protease activity, as well as methods of treating cancer by administering LF to transformed cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Mutated anthrax toxin protective antigen proteins that specifically target cells containing high amounts of cell-surface metalloproteinases or plasminogen activator receptors
InactiveUS20090142794A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCompound specificBinding site
The present invention provides methods of specifically targeting compounds to cells overexpressing matrix metalloproteinases, plasminogen activators, or plasminogen activator receptors, by administering a compound and a mutant protective antigen protein comprising a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator-recognized cleavage site in place of the native protective antigen furin-recognized cleavage site, wherein the mutant protective antigen is cleaved by a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator overexpressed by the cell, thereby translocating into the cell a compound comprising a lethal factor polypeptide comprising a protective antigen binding site.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for treating anthrax and inhibiting lethal factor
InactiveUS20100003276A1Unique and effective immune responseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCo administrationImmunology
This invention relates to a method of inhibiting lethal factor (LF) or for treating anthrax and other conditions related to anthrax infection comprising co-administration of an effective amount of an LF inhibitor and a vaccine to a patient in need of such treatment. Such co-administration unexpectedly provides an effective immune response.
Owner:HERMES JEFFERY D
Plasmids encoding therapeutic agents
InactiveUS7252993B2Easy constructionHighly versatilePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesER retentionENCODE
Plasmids encoding anti-HIV and anti-anthrax therapeutic agents are disclosed. Plasmid pWKK-500 encodes a fusion protein containing DP178 as a targeting moiety, the ricin A chain, an HIV protease cleavable linker, and a truncated ricin B chain. N-terminal extensions of the fusion protein include the maltose binding protein and a Factor Xa protease site. C-terminal extensions include a hydrophobic linker, an L domain motif peptide, a KDEL ER retention signal, another Factor Xa protease site, an out-of-frame buforin II coding sequence, the lacZα peptide, and a polyhistidine tag. More than twenty derivatives of plasmid pWKK-500 are described. Plasmids pWKK-700 and pWKK-800 are similar to pWKK-500 wherein the DP178-encoding sequence is substituted by RANTES- and SDF-1-encoding sequences, respectively. Plasmid pWKK-900 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the HIV protease cleavable linker is substituted by a lethal factor (LF) peptide-cleavable linker.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Anthrax compositions and methods of use and production
InactiveUS7794732B2Reducing debilitating effectEliminate the effects ofAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtective antigenImmunogenicity
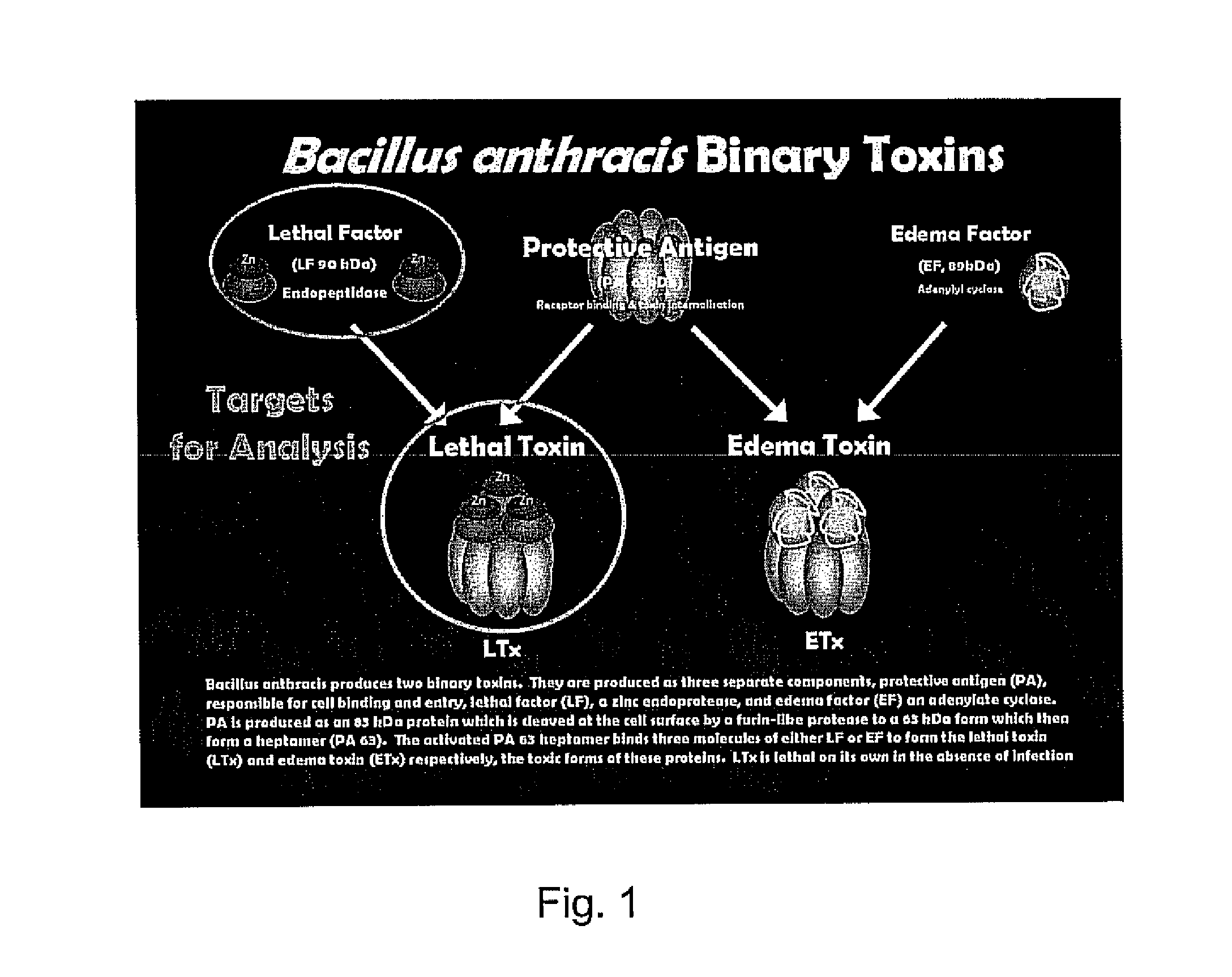
Compositions and methods effective for eliciting an immune response for preventing or reducing infection or improving clinical outcomes caused by Bacillus anthracis are provided. The compositions include a naturally occurring or synthetic protein, peptide, or protein fragment containing all or an active portion of an antigenic epitope associated with anthrax toxin proteins optionally combined with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The preferred antigenic epitopes correspond to immunogenic regions of protective antigen, lethal factor or edema factor, either individually or in combination. In addition, methods and compositions containing antibodies for reducing the effects of anthrax toxins are described. The methods involve administering to a human or animal the compositions described herein in a dosage sufficient to elicit an immune response or treat the anthrax infection.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Rapid immunoassay of anthrax protective antigen in vaccine cultures and bodily fluids by fluorescence polarization
The inventive subject matter relates to a competitive method for estimating the concentration in a sample of a Bacillus anthracis protein or antibody thereof selected from the group consisting of protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF) and edema factor (EF). The method may employ the use of Fluorescence Polarization, FLT or FRET. The competitive methods are capable of detecting a target protein within 5 minutes within the range of 0.1 to 10.0 nM. The methods provide for the rapid detection and quantitation of bacteria, bacterial antigen or antibody in culture media or broth of growing cultures of bacteria, including B. anthracis by fluorescent methods.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Plasmids encoding therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050202561A1Easy constructionHighly versatilePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesER retentionEukaryotic plasmids
Plasmids encoding anti-HIV and anti-anthrax therapeutic agents are disclosed. Plasmid pWKK-500 encodes a fusion protein containing DP178 as a targeting moiety, the ricin A chain, an HIV protease cleavable linker, and a truncated ricin B chain. N-terminal extensions of the fusion protein include the maltose binding protein and a Factor Xa protease site. C-terminal extensions include a hydrophobic linker, an L domain motif peptide, a KDEL ER retention signal, another Factor Xa protease site, an out-of-frame buforin II coding sequence, the lacZa peptide, and a polyhistidine tag. More than twenty derivatives of plasmid pWKK-500 are described. Plasmids pWKK-700 and pWKK-800 are similar to pWKK-500 wherein the DP178-encoding sequence is substituted by RANTES- and SDF-1-encoding sequences, respectively. Plasmid pWKK-900 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the HIV protease cleavable linker is substituted by a lethal factor (LF) peptide-cleavable linker. Plasmid pWKK-21 is similar to pWKK-500 wherein the highly truncated ricin B chain is substituted by a one-domain ricin B chain. Oligonucleotide cassettes encoding an HIV protease-cleavable peptide linker and a method of making modified plasmids encoding modified fusion proteins are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Inhibitors of lethal factor protease
The invention provides compounds that can efficiently and specifically inhibit bacterial toxins, such as inhibit the lethal factor (LF) protease activity of anthrax toxin and / or botulinum neurotoxin type A. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting proteases, such as lethal factor protease, as well as methods for treating bacterial infections, such as anthrax and botulinum.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Antibody of humanized anti-anthrax protective antigen PA and application thereof
InactiveCN103789270AImprove protectionStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAnthrax protective antigenBiology
The invention discloses an antibody of a humanized anti-anthrax protective antigen PA and an application thereof. According to the antibody, a heavy chain variable region has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4; a light chain variable region has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:4; a heavy chain constant region has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:6; and a light chain constant region has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:8. The antibody can be specifically combined with the anthrax protective antigen (PA) and can be used for preventing a lethal factor LF so as to play a protective role.
Owner:中国人民解放军南京军区军事医学研究所 +1
Compounds useful in the treatment of anthrax and inhibiting lethal factor
This invention relates to compounds of formula (I), and a method for treating anthrax or inhibiting lethal factor by administrating a composition containing a compound of formula (I) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. This invention further relates to the use of the compounds of formula (I) to treat other conditions related to an anthrax infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Human cancer therapy using engineered matrix metalloproteinase-activated anthrax lethal toxin that targets tumor vasculatuture
InactiveUS20100168012A1Good antitumor activityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsProtective antigenBinding site
The present invention provides methods for inhibiting tumor associated angiogenesis by administering a mutant protective antigen protein comprising a matrix metalloproteinase-recognized cleavage site in place of the native protective antigen furin-recognized site in combination with a lethal factor polypeptide comprising a protective antigen binding site. Upon cleavage of the mutant protective antigen by a matrix metalloproteinase, the lethal factor polypeptide is translocated into cancer and endothelial cells and inhibits tumor associated angiogenesis.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
Anthrax compositions and methods of use and production
InactiveUS20100172926A1Reducing and preventing effectReducing debilitating effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtective antigenADAMTS Proteins
Compositions and methods effective for eliciting an immune response for preventing or reducing infection or improving clinical outcomes caused by Bacillus anthracis are provided. The compositions include a naturally occurring or synthetic protein, peptide, or protein fragment containing all or an active portion of an antigenic epitope associated with anthrax toxin proteins optionally combined with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The preferred antigenic epitopes correspond to immunogenic regions of protective antigen, lethal factor or edema factor, either individually or in combination. In addition, methods and compositions containing antibodies for reducing the effects of anthrax toxins are described. The methods involve administering to a human or animal the compositions described herein in a dosage sufficient to elicit an immune response or treat the anthrax infection.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
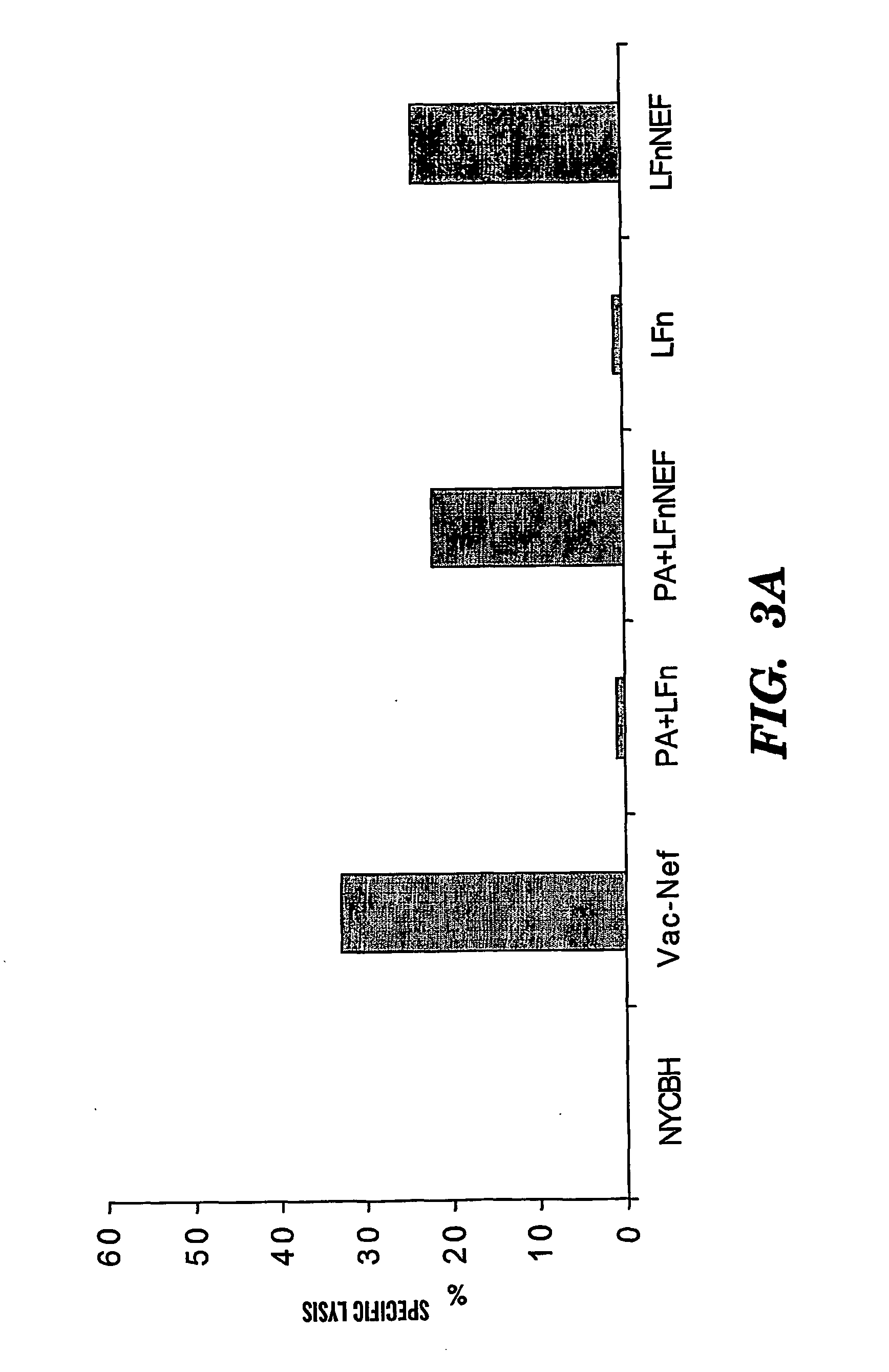
Methods and compositions for promoting a cell-mediated immune response
ActiveUS9968666B2Good curative effectEasy to displayAntibacterial agentsPeptide librariesProtective antigenBacterial exotoxin
The present invention is directed to a method for promoting or stimulating a cell-mediated immune response to an antigen, by administering a target antigen (such as a protein) with a transport factor that contains a fragment of a bipartite protein exotoxin, but not the corresponding protective antigen. Preferred transport factors include the protective antigen binding domain of lethal factor (LFn) from B. anthracis, consisting of amino acids 1-255, preferably a fragment of at least 80 amino acids that shows at least 80% homology to LFn, and a fragment of about 105 amino acids from the carboxy portion that does not bind PA. The target antigen can include any molecule for which it would be desirable to elicit a CMI response, including viral antigens and tumor antigens.
Owner:VACCINE TECH
Method for improving bacillus subtilis strain
ActiveCN105177049AIncrease exoenzyme productionAvoid cannibalismBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technologies, and particularly relates to a method for improving bacillus subtilis strains. The method includes the steps of manually constructing a gene sequence not containing spore production lethal factor genes, electric shock conversion, sieving verifying and others. In the prior art, although part of basic research is already implemented on the spore production lethal factor genes (skf), whether the yield of endogenous enzymes can be increased through deleting the spore production lethal factor genes is still not determined, and meanwhile for different microorganism strains, after the spore production lethal factor genes are deleted, whether improvements on the fermentation capacity of the strains are the same lacks more research. With the detailed bacillus subtilis strains being examples, new strains lacking spore production lethal factor genes (skf) are successfully constructed, when the strains are concretely used for fermenting and producing amylase, determination results show that the enzyme activity of the constructed new strains is improved well, and good application prospects are achieved.
Owner:河南新仰韶生物科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for diagnostic assays for measuring cell mediated immune response
InactiveCN102549425ARapid productionImprove stabilityPeptide librariesDisease diagnosisCytosolCell mediated immunity
Described are compositions and methods for detecting or monitoring the ability of an individual to mount a cell mediated immune response to a target antigen. Methods rely in part upon the physical association, e.g., by fusion, of a Lethal Factor (LF) polypeptide with a target antigen. The LF polypeptide moiety, including, for example, an LFn polypeptide moiety, serves as a transport factor to deliver target antigens, including full length target polypeptides, to the cytosol of an intact, living immune cell from an individual. Measurement of a cytokine response by the immune cell from the individual provides a read out of a cell mediated immune response. The methods and compositions described provide diagnostic as well as prognostic information and can guide the direction of therapy.
Owner:VACCINE TECH
Therapeutic immunization in HIV infected subjects to augment antiretroviral treatment
InactiveUS20130115237A1Stimulate immune responseEnhanced inhibitory effectBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAntigenVirus
The present invention generally relates to HIV compositions and methods of use. One aspect of the present invention relates to a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an antigen preparation, the antigen preparation comprising an HIV polypeptide or fragment thereof and a Bacillus anthracis lethal factor (LF) polypeptide, such as a LFn polypeptide. In some embodiments, the LF polypeptide can be fused or otherwise associated with the HIV polypeptide. Other aspect of the present invention relate to use of vaccine comprising a HIV polypeptide and a Bacillus anthracis lethal factor (LF) polypeptide in methods to enhance efficacy traditional antiretroviral therapy.
Owner:VACCINE TECH
Detection of anthrax pathogenicity factors
ActiveUS8663926B2Gentle and rapid separationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProper treatmentRapid identification
One major problem in diagnosis methods presently available for anthrax is that these methods require several days to produce a result. The only existing treatment for anthrax requires administration soon after infection at a time when patients are exhibiting only mild flu-like symptoms. Thus, a patient may be days beyond the time when treatment would be effective by the time a diagnosis is made. The present invention reduces diagnosis time to as little as four hours providing same day identification of anthrax radically increasing the odds of delivering proper treatment and patient recovery. The rapid identification of anthrax lethal factor activity exhibited by the instant invention is also amenable to in vivo screening protocols for the discovery and development of anthrax vaccines and lethal factor inhibitors. The instant invention isolates and concentrates lethal factor and lethal toxin from nearly any biological sample. By capitalizing on the endopeptidase activity of lethal factor the present invention amplifies output signals producing reliable detection of picomolar concentrations of lethal factor. The instant invention involves novel purification and detection techniques and substrates for rapid, reproducible, and quantitative measurements of anthrax lethal factor in biological samples.
Owner:CDC THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES CENTS FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Mutated anthrax toxin protective antigen proteins that specifically target cells containing high amounts of cell-surface metalloproteinases or plasminogen activator receptors
InactiveUS7468352B1Bacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound specificBinding site
The present invention provides methods of specifically targeting compounds to cells overexpressing matrix metalloproteinases, plasminogen activators, or plasminogen activator receptors, by administering a compound and a mutant protective antigen protein comprising a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator-recognized cleavage site in place of the native protective antigen furin-recognized cleavage site, wherein the mutant protective antigen is cleaved by a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator overexpressed by the cell, thereby translocating into the cell a compound comprising a lethal factor polypeptide comprising a protective antigen binding site.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA A REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Bifunctional antibiotics for targeting rRNA and resistance-causing enzymes and for inhibition of anthrax lethal factor
InactiveUS7635685B2Highly potent and effective antibioticEffective treatmentBiocideSugar derivativesAntibiotic resistanceMedicine
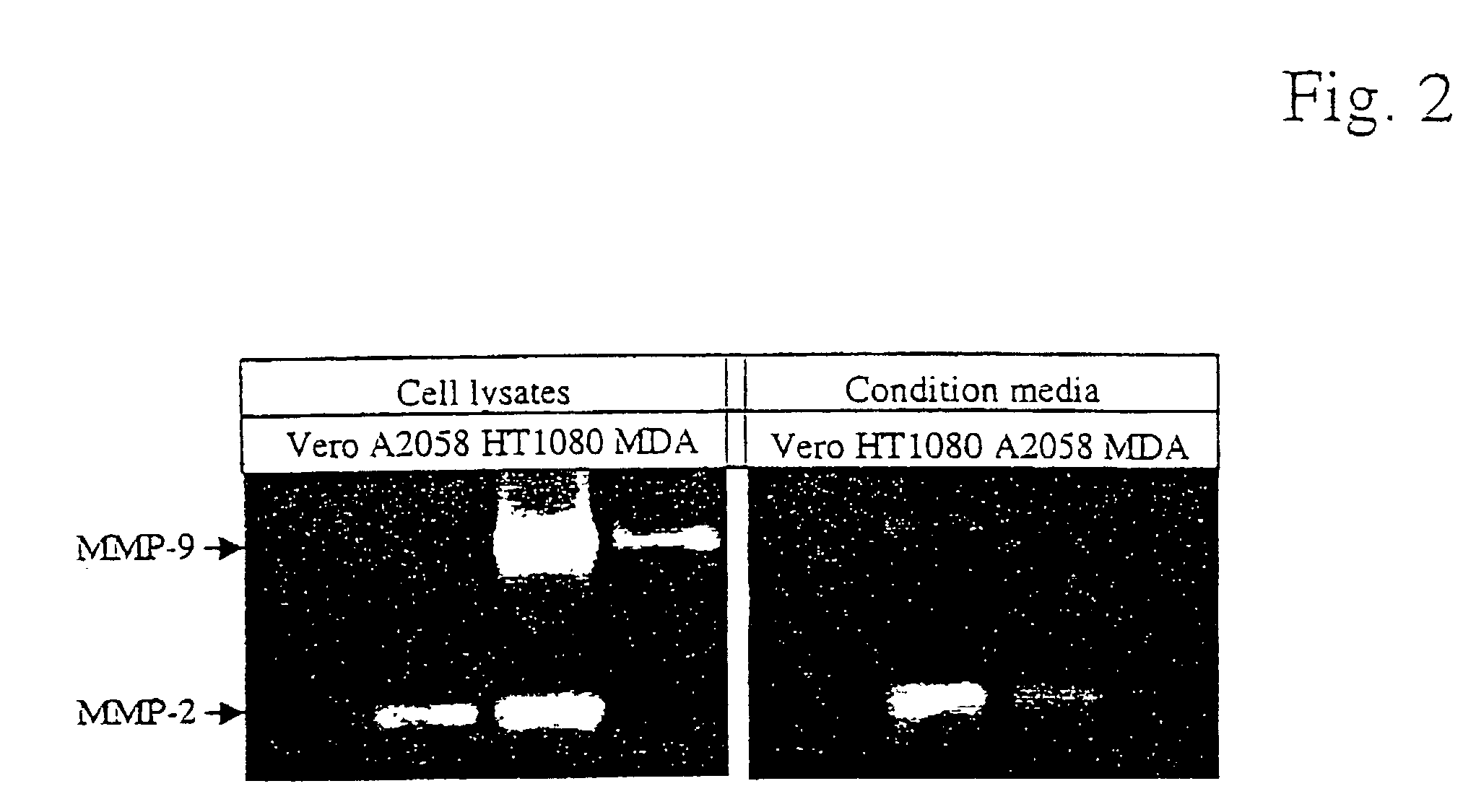
A novel group of aminoglycosides which share some structural features of currently available aminoglycosides with regard to the backbone, while also having significant structural differences, is disclosed. The similarity enables these aminoglycosides to be highly potent and effective antibiotics, while the significant differences enable these aminoglycosides to reduce or even block antibiotic resistance. The aminoglycosides of the present invention are suitable for inhibition of antrax lethal factor, hence are suitable for use as a cure for anthrax.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com