Method for improving bacillus subtilis strain
A Bacillus subtilis and bacterial strain technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as the production limit of Bacillus subtilis extracellular enzymes, and achieve the effect of avoiding cannibalism and improving yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
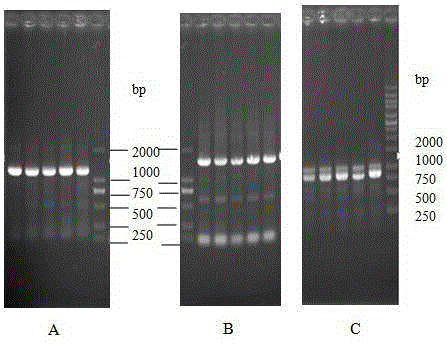
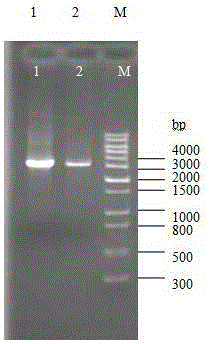
[0060] The method for transforming the Bacillus subtilis bacterial strain provided by the present invention, at first artificially constructing does not contain (knockout) sporulation lethal factor gene ( skf ) gene sequence, and then the constructed gene sequence without (knockout) sporulation lethal factor ( skf ) gene sequence to perform homologous recombination replacement in Bacillus subtilis to obtain a new knockout (excluding) sporulation lethal factor gene ( skf ) of the Bacillus subtilis strain, specifically comprising the following steps.
[0061] (1) The artificial construction does not contain (knockout) the sporulation lethal factor gene ( skf ) gene sequence
[0062] The gene without (knockout) sporulation lethal factor ( skf ) gene sequence, which consists of 3 parts of DNA fragments, which are skf Upstream partial sequence (fragment A), tetracycline resistance gene expression sequence (fragment B), skf The downstream partial sequence of the gene (...
Embodiment 2
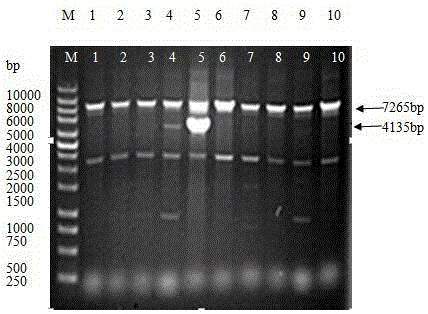
[0173] This example is mainly to test the applicability of the new Bacillus subtilis strain constructed in Example 1 (i.e. the No. 5 transformant strain), mainly including the number of viable bacteria and the determination of amylase activity after fermentation. The introduction is as follows.
[0174] Determination of Viable Bacteria
[0175] Transformant No. 5 obtained in Example 1 (the new constructed Bacillus subtilis strain) and the starting strain (Bacillus subtilis WB800) were cultured in shake flasks at 37°C and 220rpm, and 0.1 mL, were added to centrifuge tubes containing 0.9mL sterile water, vortexed, and serially diluted 10 times (10, 10 1 、10 2 、10 3 、10 4 、10 5 、10 6 、10 7 、10 8 、10 9 ).
[0176] Draw 0.1mL of the dilution, add it to the LB solid plate, and then spread the bacterial solution evenly with a coating rod, make 3 plates for each dilution, let it stand for 30 minutes, then place it upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C, an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com