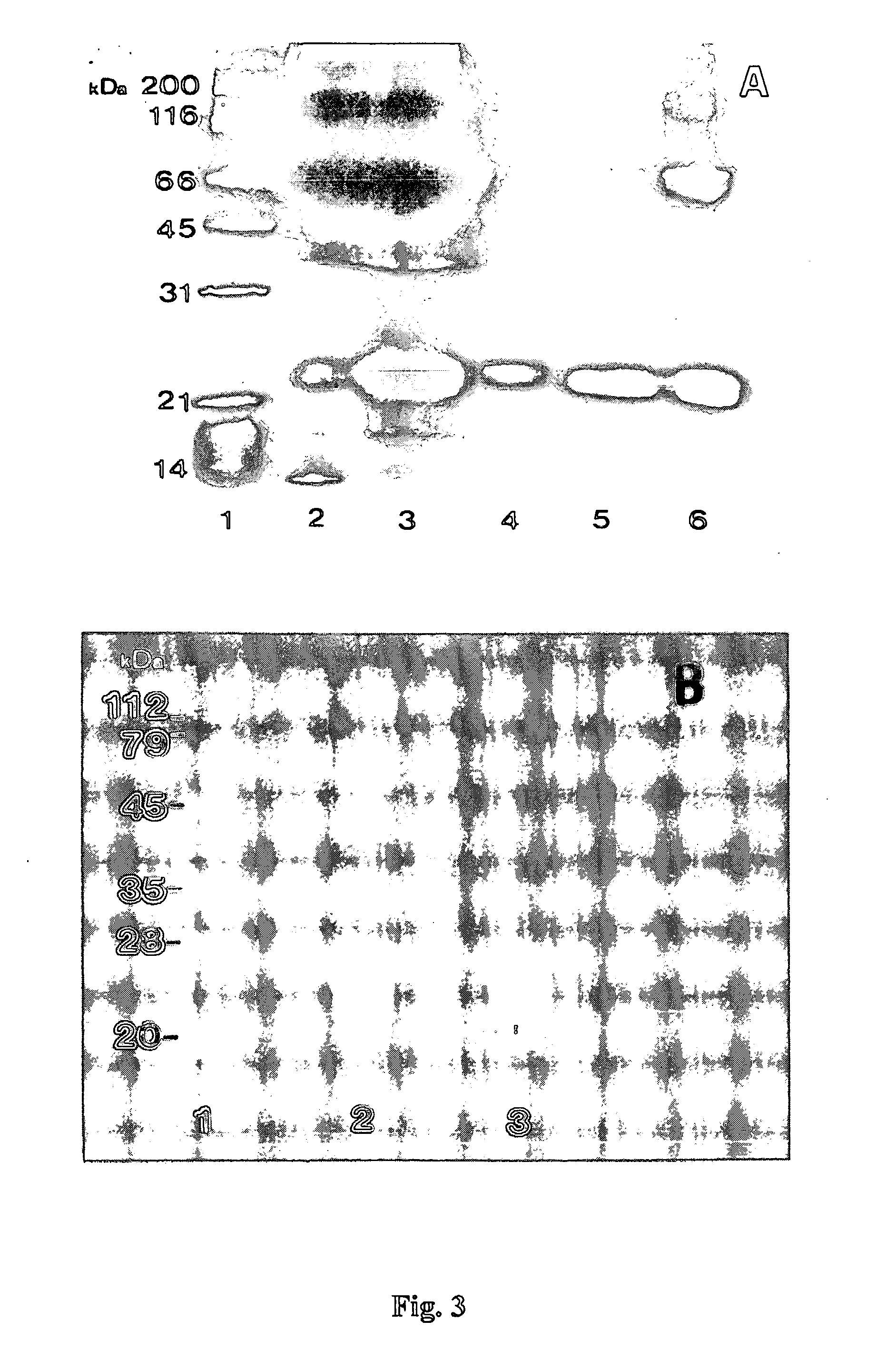
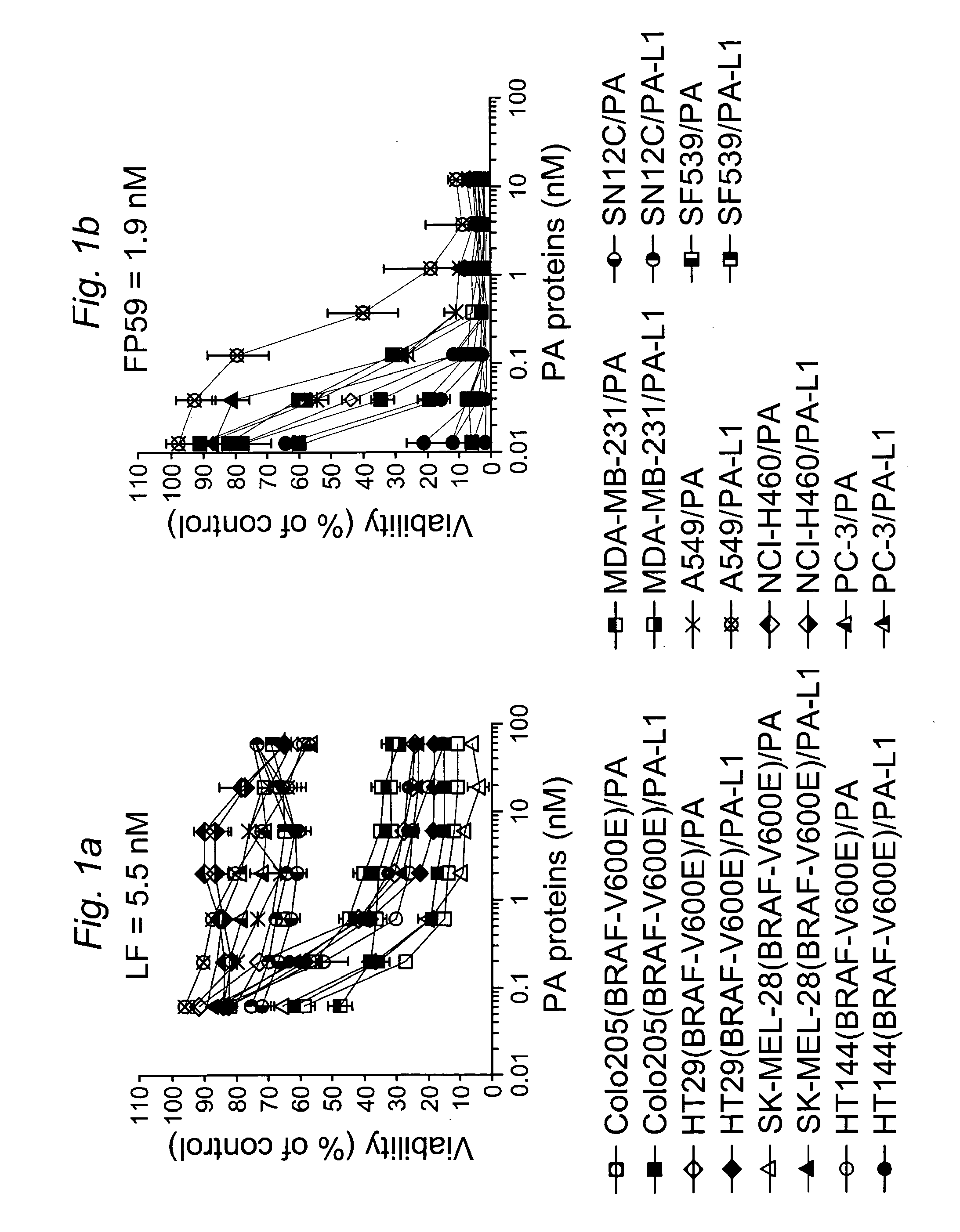
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Lethal toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Combination bacteriolytic therapy for the treatment of tumors
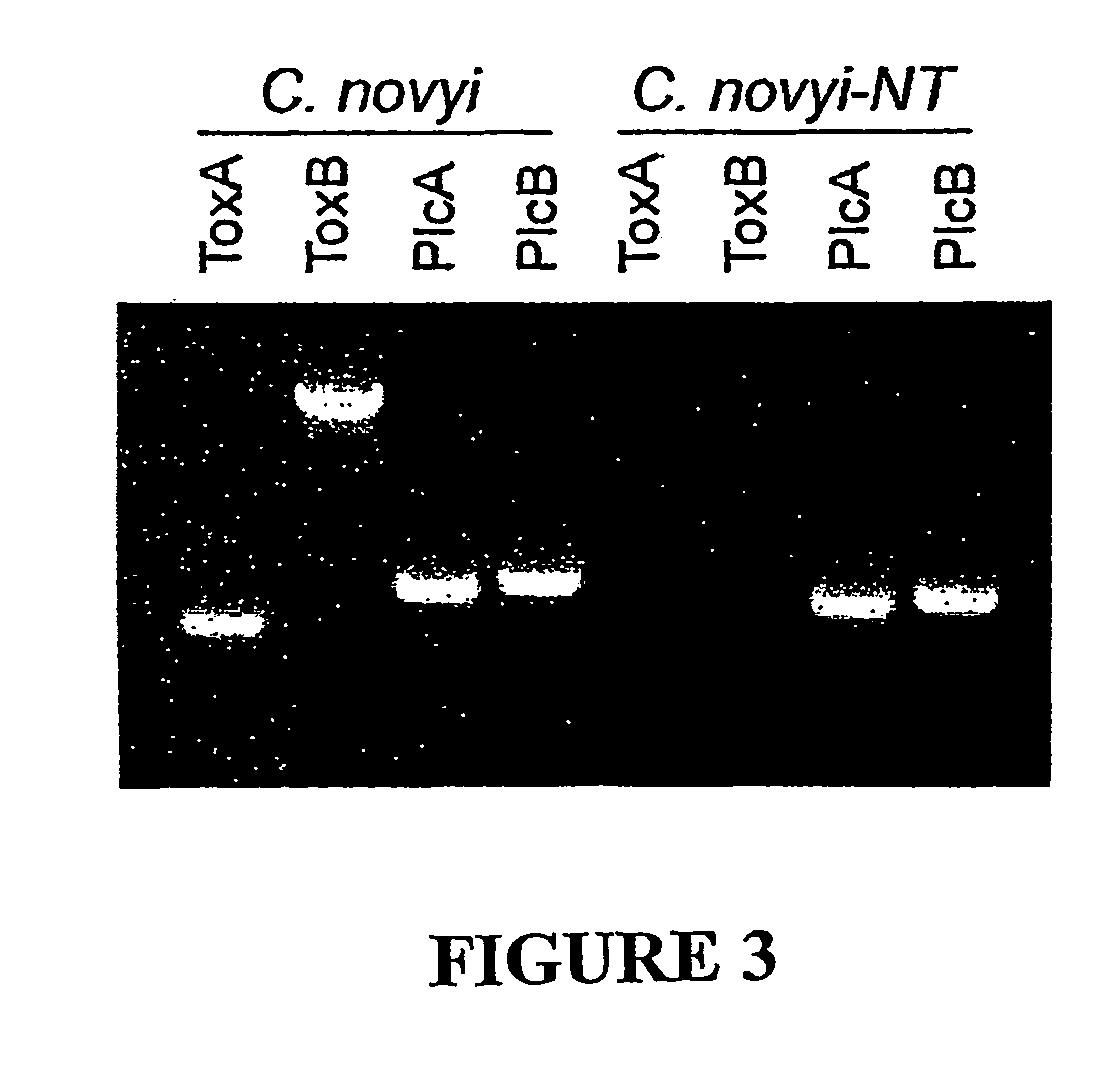
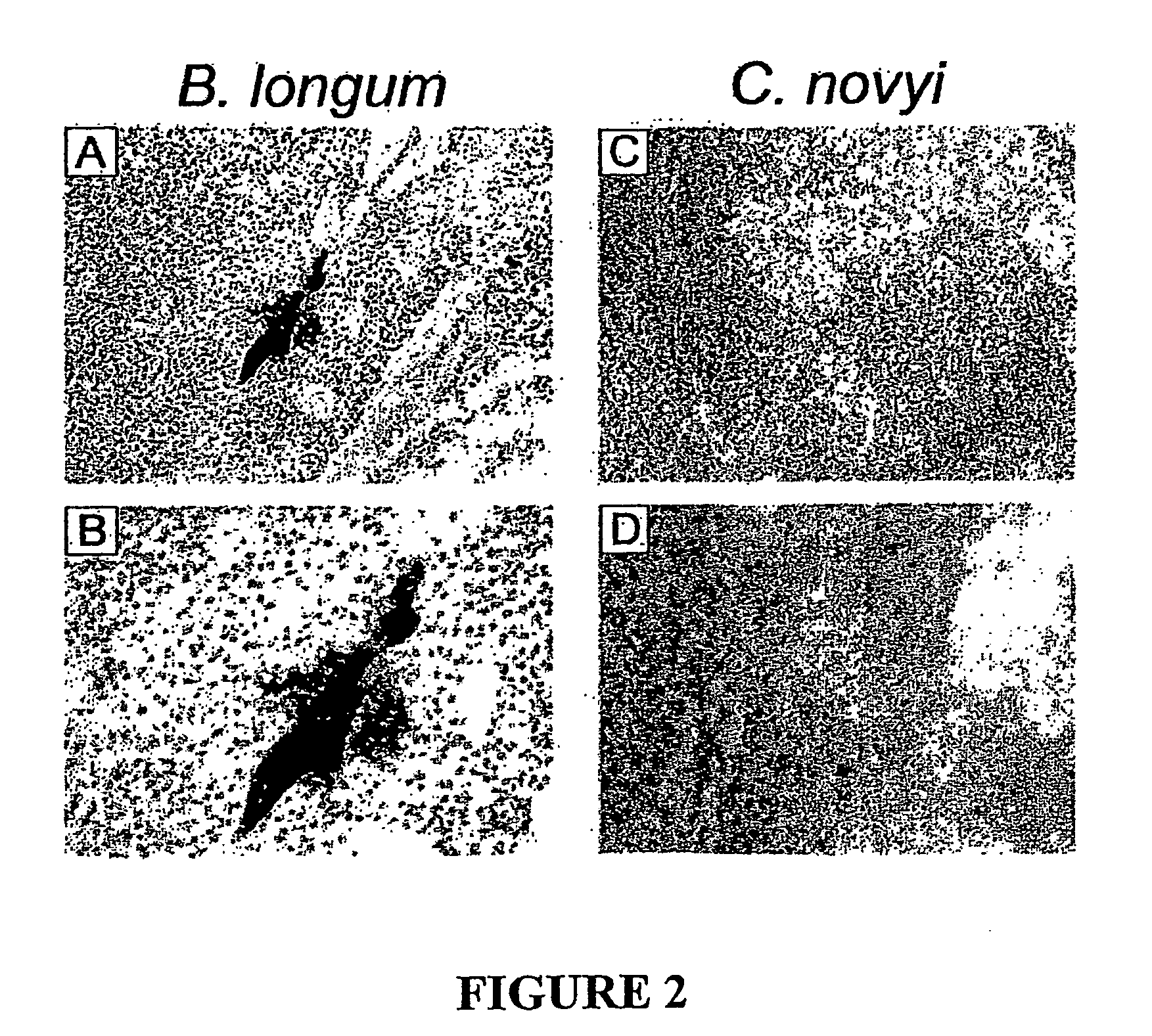
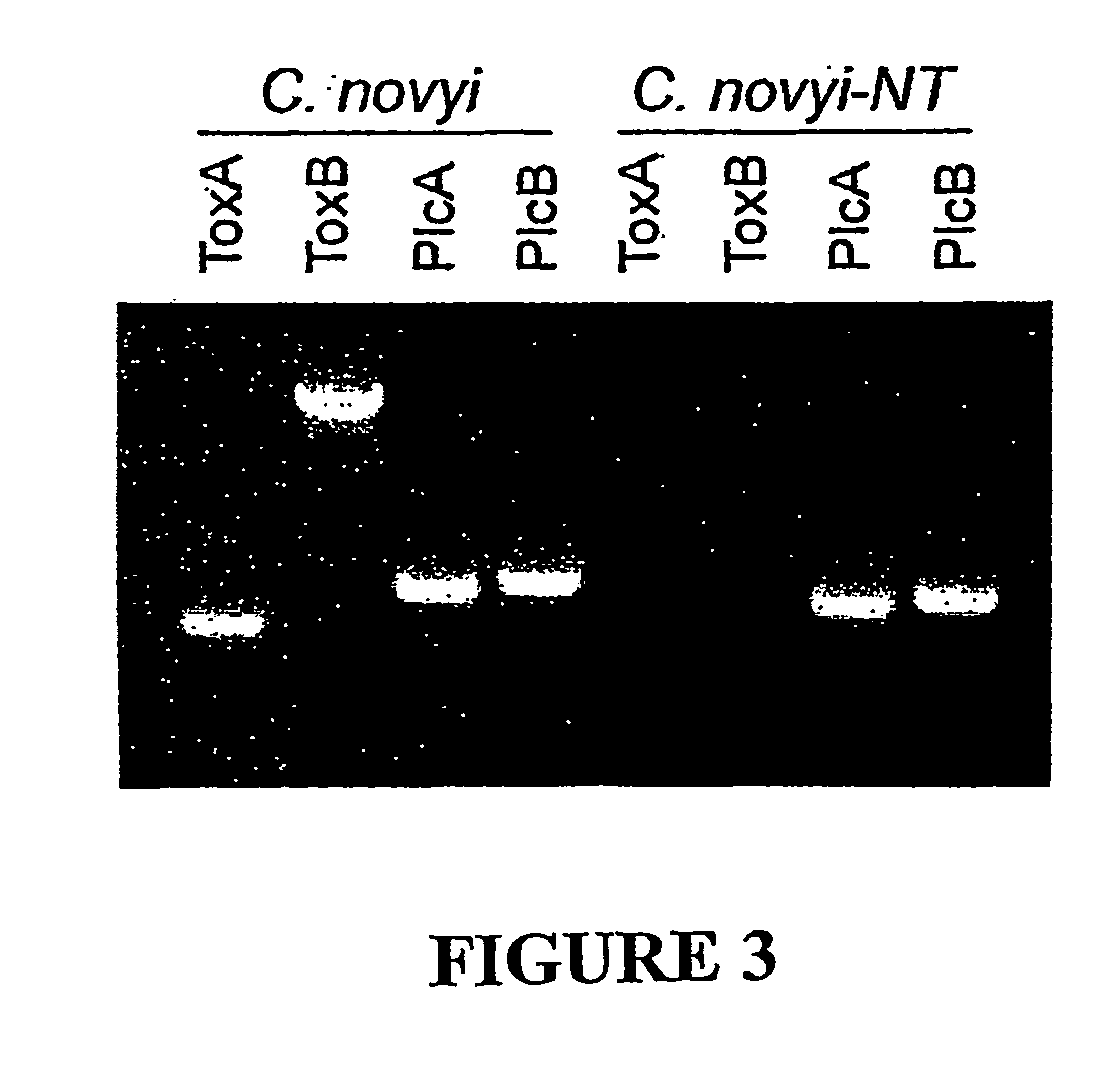
Current chemotherapeutic approaches for cancer are in part limited by the inability of drugs to destroy neoplastic cells within poorly vascularized compartments of tumors. We have here systematically assessed anaerobic bacteria for their capacity to grow expansively within avascutar compartments of transplanted tumors. Among 26 different strains tested, one (Clostridium novyi) appeared particularly promising. We created a strain of C. novyi devoid of its lethal toxin (C. novyi-NT) and showed that intravenously injected C. novyi-NT spores germinated within the avascular regions of tumors in mice and destroyed surrounding viable tumor cells. When C. novyi-NT spores were administered together with conventional chemotherapeutic drugs, extensive hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors often developed within 24 hours, resulting in significant and prolonged anti-tumor effects. This strategy, called combination bacteriolytic therapy (COBALT), has the potential to add a valuablle dimension to the treatment of cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Combination bacteriolytic therapy for the treatment of tumors
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High-level expression of tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc in Escherichia coli and application
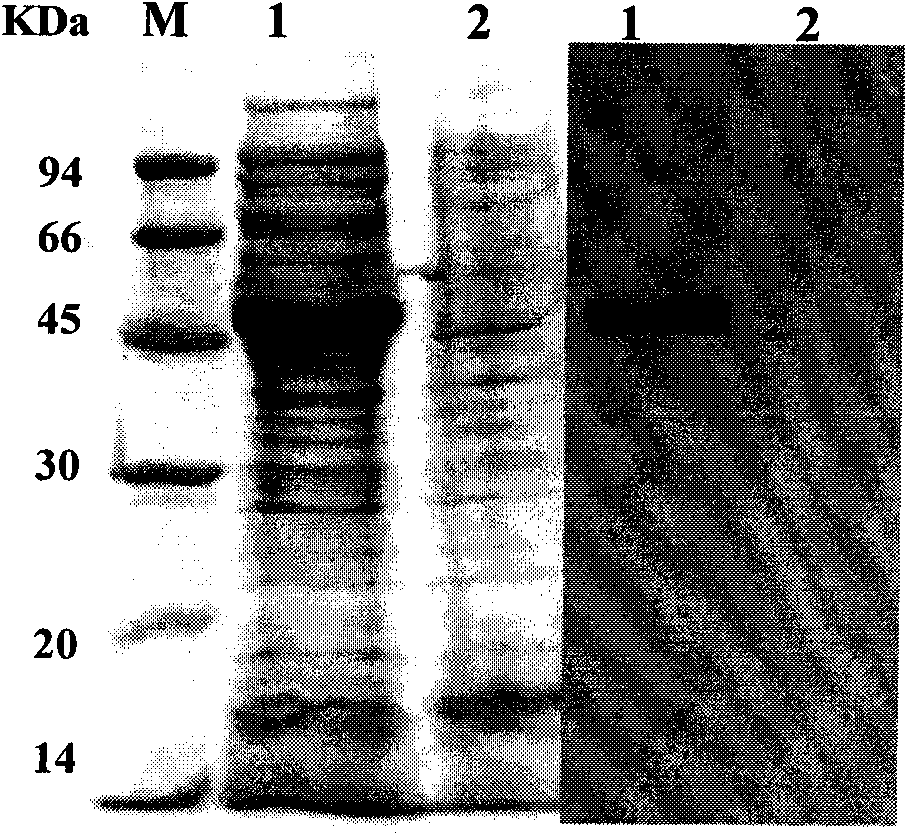
The invention relates to a method for a tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc to be subjected to high-level soluble expression in Escherichia coli through nucleotide sequence optimization. According to the sequencing result of a domestic C.Tetani virulent strain CMCC64008, the tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc sequence is analyzed and optimized, the optimized sequence is SEQ ID No.1 and the coded protein sequence is SEQ ID No.2. The synthesized Hc gene is linked into an expression vector pET32a(+) after undergoing double enzyme digestion, the recombinant Hc is subjected to high soluble expression in Escherichia coli and the target protein accounts for about 46% of the total protein in the supernatant undergoing bacteriociasis. After QFF column purification, phenyl hydrophobic column purification and SP column purification, the purity of the target protein can be more than 95% and the yield thereof is more than 300mg / L. The recombinant protein prepared by the method of the invention has good immunogenicity, can induce the mice to produce high-titre protective antibodies and can resist attack of high-dose lethal toxins. The method has extensive application prospect in large-scale high-level preparation of the tetanus toxin recombinant subunit vaccine Hc.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
High-level expression of tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc in Escherichia coli and application
The invention relates to a method for a tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc to be subjected to high-level soluble expression in Escherichia coli through nucleotide sequence optimization. According to the sequencing result of a domestic C.Tetani virulent strain CMCC64008, the tetanus toxin receptor binding domain Hc sequence is analyzed and optimized, the optimized sequence is SEQ ID No.1 and the coded protein sequence is SEQ ID No.2. The synthesized Hc gene is linked into an expression vector pET32a(+) after undergoing double enzyme digestion, the recombinant Hc is subjected to high soluble expression in Escherichia coli and the target protein accounts for about 46% of the total protein in the supernatant undergoing bacteriociasis. After QFF column purification, phenyl hydrophobic column purification and SP column purification, the purity of the target protein can be more than 95% and the yield thereof is more than 300mg / L. The recombinant protein prepared by the method of the invention has good immunogenicity, can induce the mice to produce high-titre protective antibodies and can resist attack of high-dose lethal toxins. The method has extensive application prospect in large-scale high-level preparation of the tetanus toxin recombinant subunit vaccine Hc.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Method for separating lethal toxin protein from cyanea nozakii nematocyst toxin
ActiveCN102174098ALittle loss of activityFast flowPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesChromatographic separationLethal dose
The invention relates to the technical field of marine organisms, in particular to a method for separating and purifying a cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein. The method comprises the following steps of: ultrasonically crushing cyanea nozakii nematocyst cells to extract a jellyfish crude toxin, dialyzing and desalting, and separating and purifying by affinity chromatographic separation and an anion exchange chromatographic technology in turn to obtain a jellyfish toxin protein with lethal activity, wherein through measurement, the molecular weight of the toxin protein is 30kDa, and the lethal dose 50 (LD50) of the toxin protein to 1g of zebra fish is 0.56mu g. The method has the characteristics that: the method is quick, simple and convenient and provides important guidance for obtainingthe cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein.
Owner:水母娘娘海洋生物科技有限公司
Novel therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060078551A1Good anti-inflammatory activityGood potencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipase inhibitorSnake bite venom
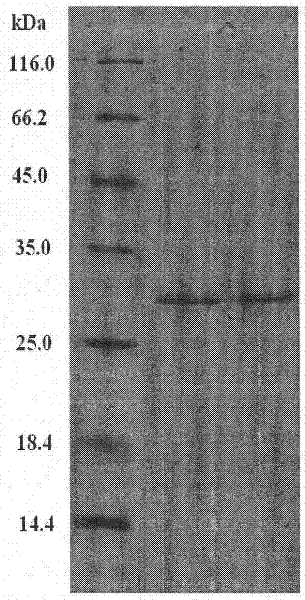
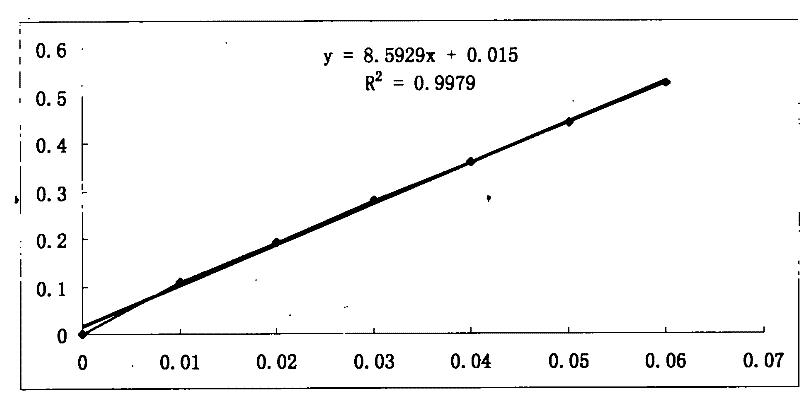
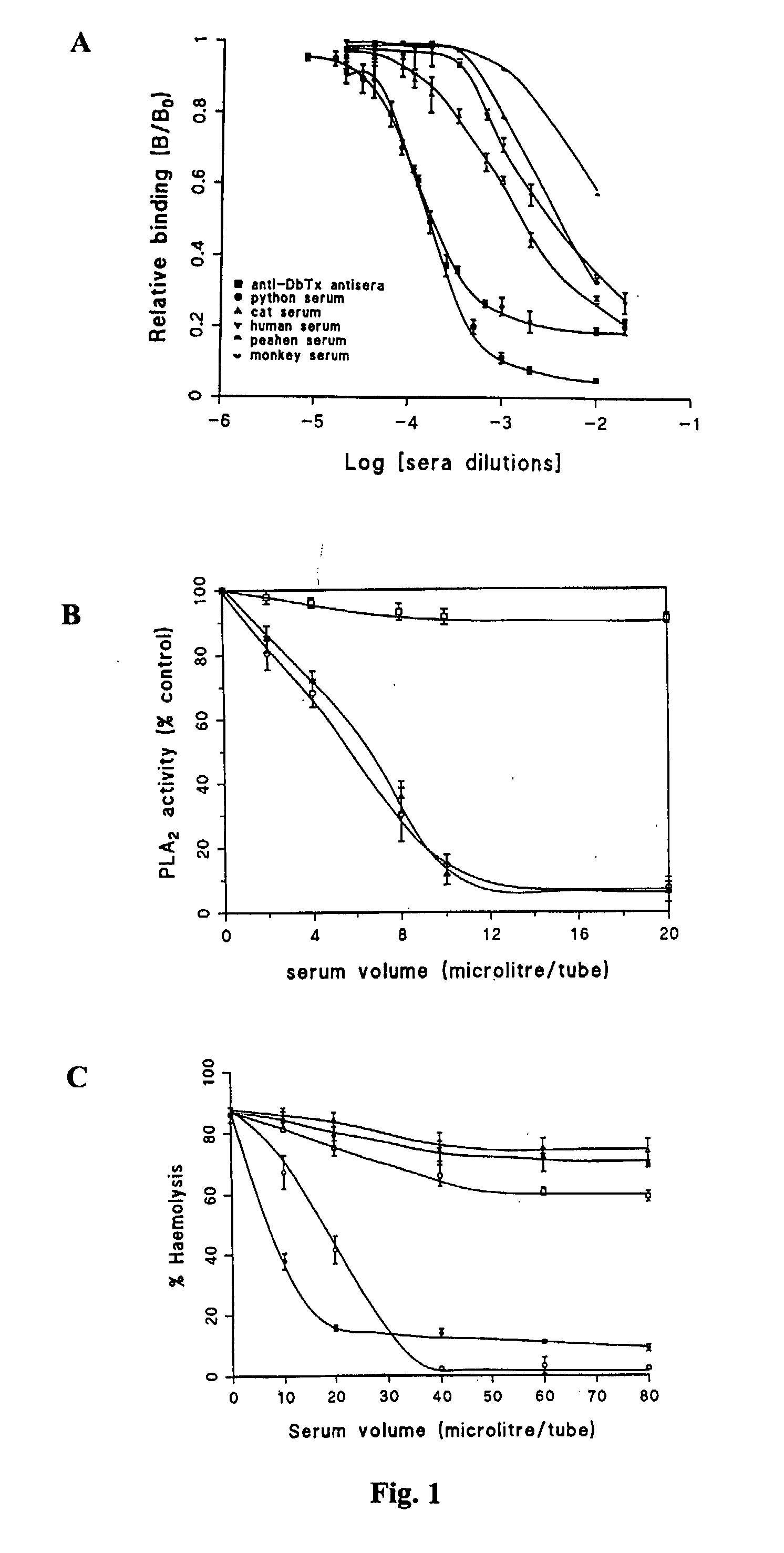
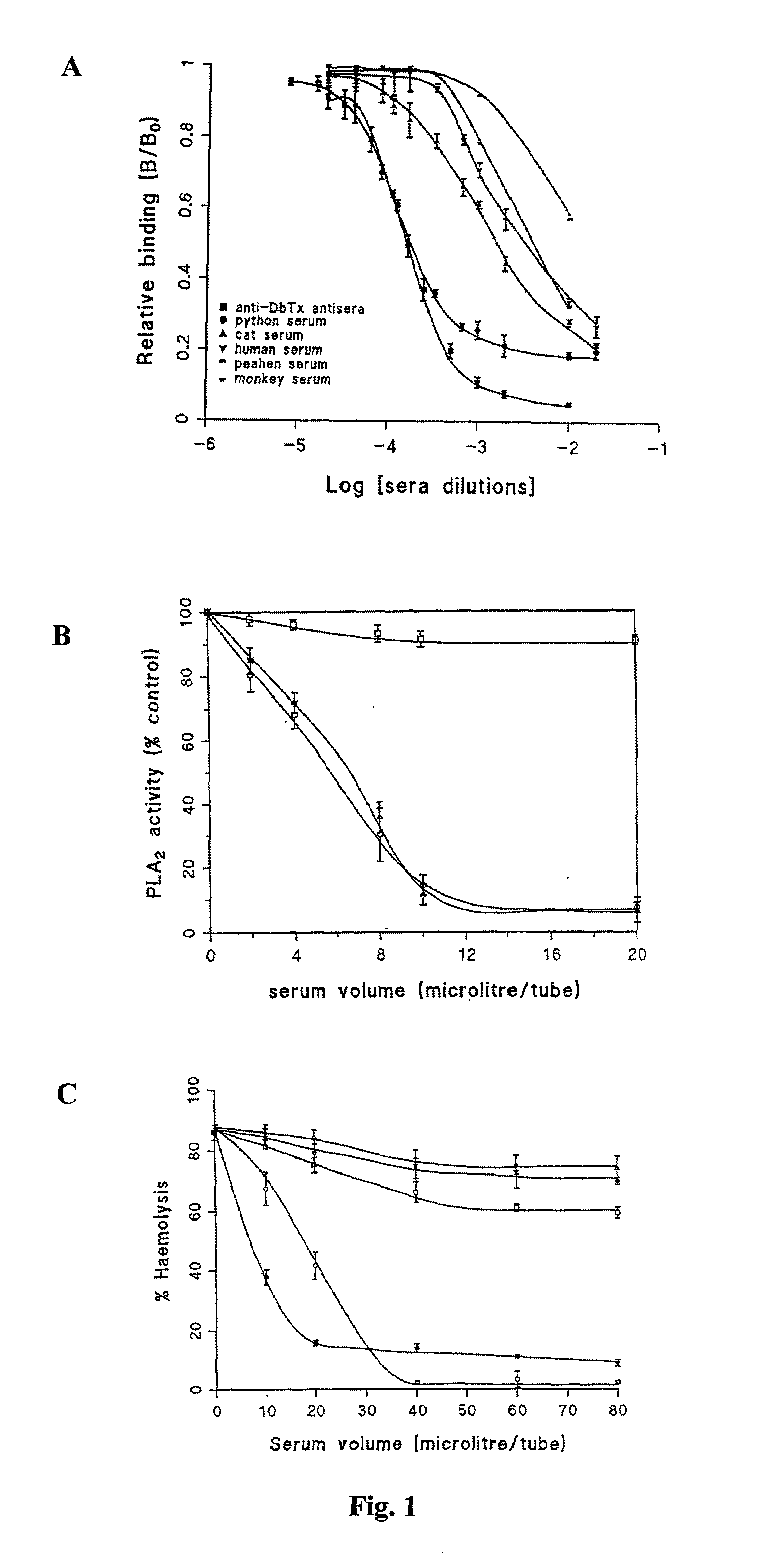
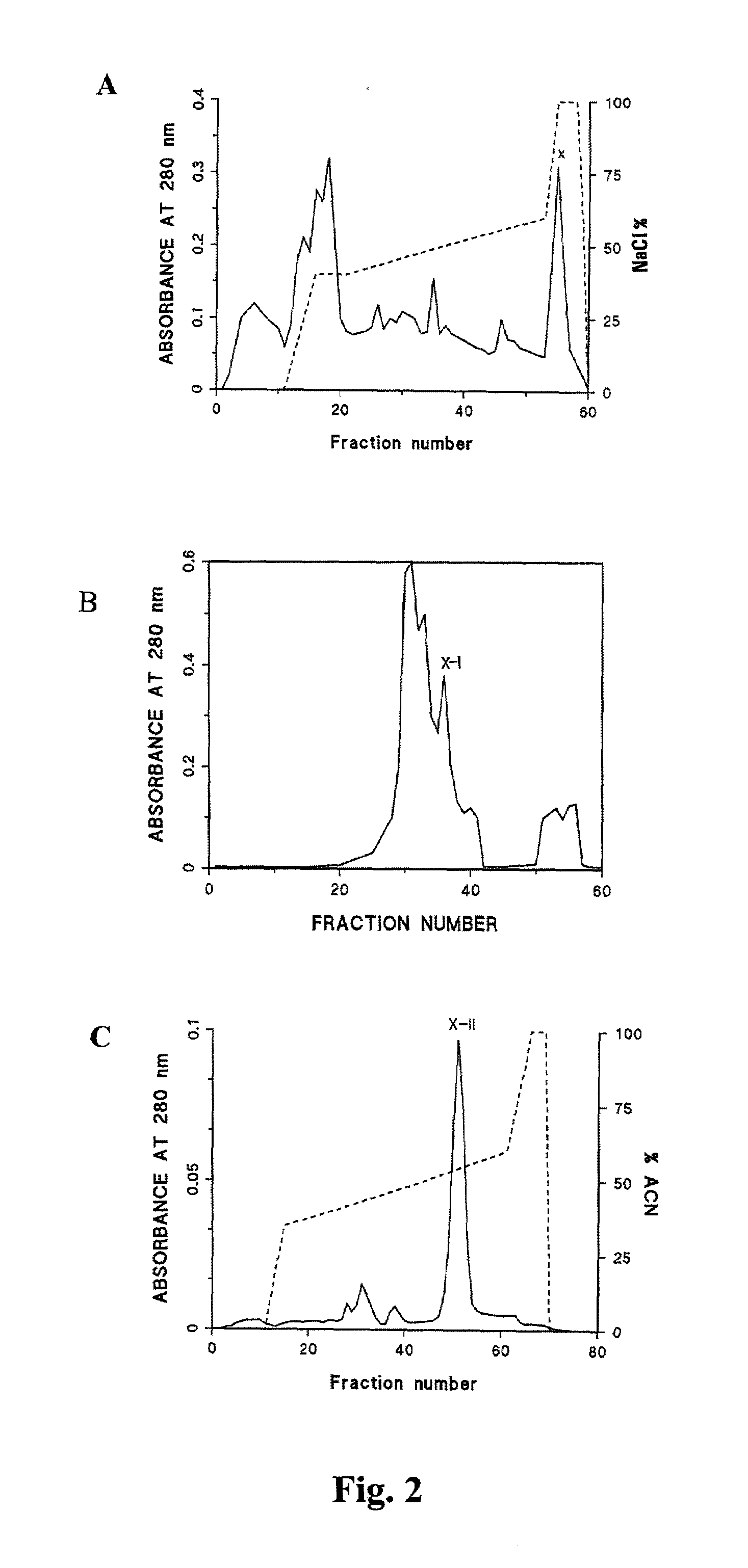
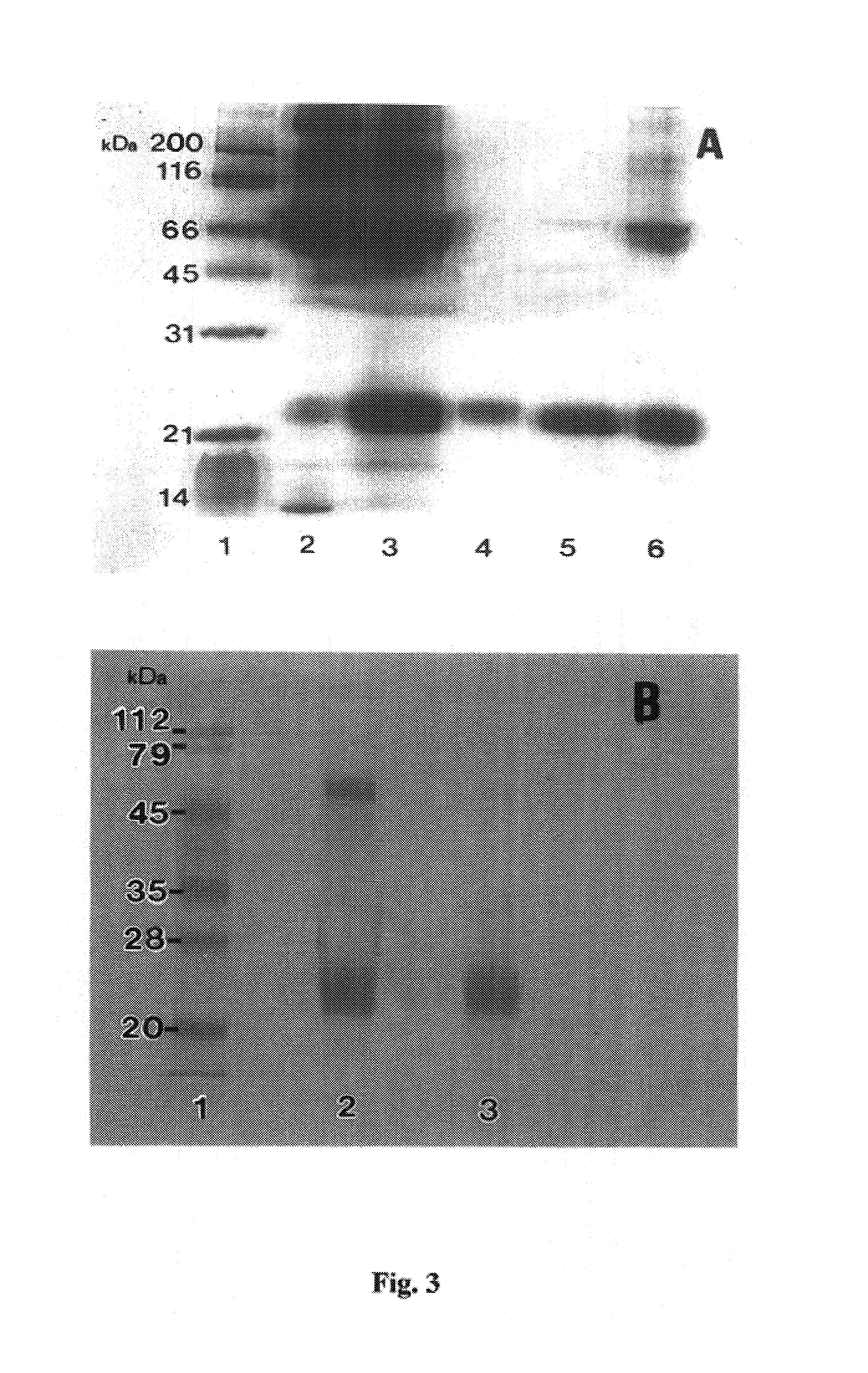
A phospholipase A2 inhibitor protein designated “Phospholipase Inhibitor from Python” (PIP)—formerly designated “Python Antitoxic Factor” (PAF)—is given by SEQ ID NO:2. The partial amino acid sequence for PIP was initially determined from the native protein purified from the blood serum of a non-venomous snake, Python reticulatus. The complete PIP polynucleotide sequence was obtained from a cDNA clone encoding PIP, given by SEQ ID NO:1, along with the full amino acid sequence deduced from it. Also disclosed is a recombinant protein PIP, which shows strong lethal toxin neutralizing activity similar to the native PIP, and has potent anti-inflammatory activity. Both the native and the functionally equivalent recombinant PIP are useful for the prevention or treatment of conditions such as snakebites, insect stings, and inflammatory diseases. Also, phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitory polypeptides designated P-0029, P-0009, and P-0006, the sequences of which are given as SEQ ID NO:10, SEQ ID NO:11, and SEQ ID NO:12, respectively, are disclosed. Those polypeptides, and their synthetic chemical analogues and polypeptide variants that inhibit PLA2 activity and alleviate inflammation, may also be used in the diagnosis, study, prevention, and treatment of PLA2-related human inflammatory diseases.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Human cancer therapy using engineered matrix metalloproteinase-activated anthrax lethal toxin that targets tumor vasculatuture
InactiveUS20100168012A1Good antitumor activityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsProtective antigenBinding site
The present invention provides methods for inhibiting tumor associated angiogenesis by administering a mutant protective antigen protein comprising a matrix metalloproteinase-recognized cleavage site in place of the native protective antigen furin-recognized site in combination with a lethal factor polypeptide comprising a protective antigen binding site. Upon cleavage of the mutant protective antigen by a matrix metalloproteinase, the lethal factor polypeptide is translocated into cancer and endothelial cells and inhibits tumor associated angiogenesis.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
Analysis method for lethal toxicity of environmental pollutants to caenorhabditis eleganses
The invention provides an analysis method for lethal toxicity of environmental pollutants to caenorhabditis eleganses. The analysis method comprises the following steps: diluting synchronized caenorhabditis elegans culture solutions to obtain a caenorhabditis elegans sample solution; diluting an environmental-pollutant stock solution into n environmental-pollutant sample solutions according to a geometric concentration gradient; adding the caenorhabditis elegans sample solution into transparent micropores, correspondingly adding the environmental-pollutant sample solutions with different concentrations, adopting the transparent micropores without adding the environmental-pollutant sample solution as a blank control, and after culture for t0 hours, acquiring the number of normalized survival caenorhabditis eleganses and calculating normalized lethallty rate; and calculating median lethal concentration of the environmental pollutants by curve fitting. According to the analysis method provided by the invention, the lethal toxicity of the environmental pollutants to the caenorhabditis eleganses can be accurately calculated out, more statistic significance is achieved, and more scientific theoretical support can be provided for evaluating the safety problem of the environmental pollutants to the ecological system and the human health.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
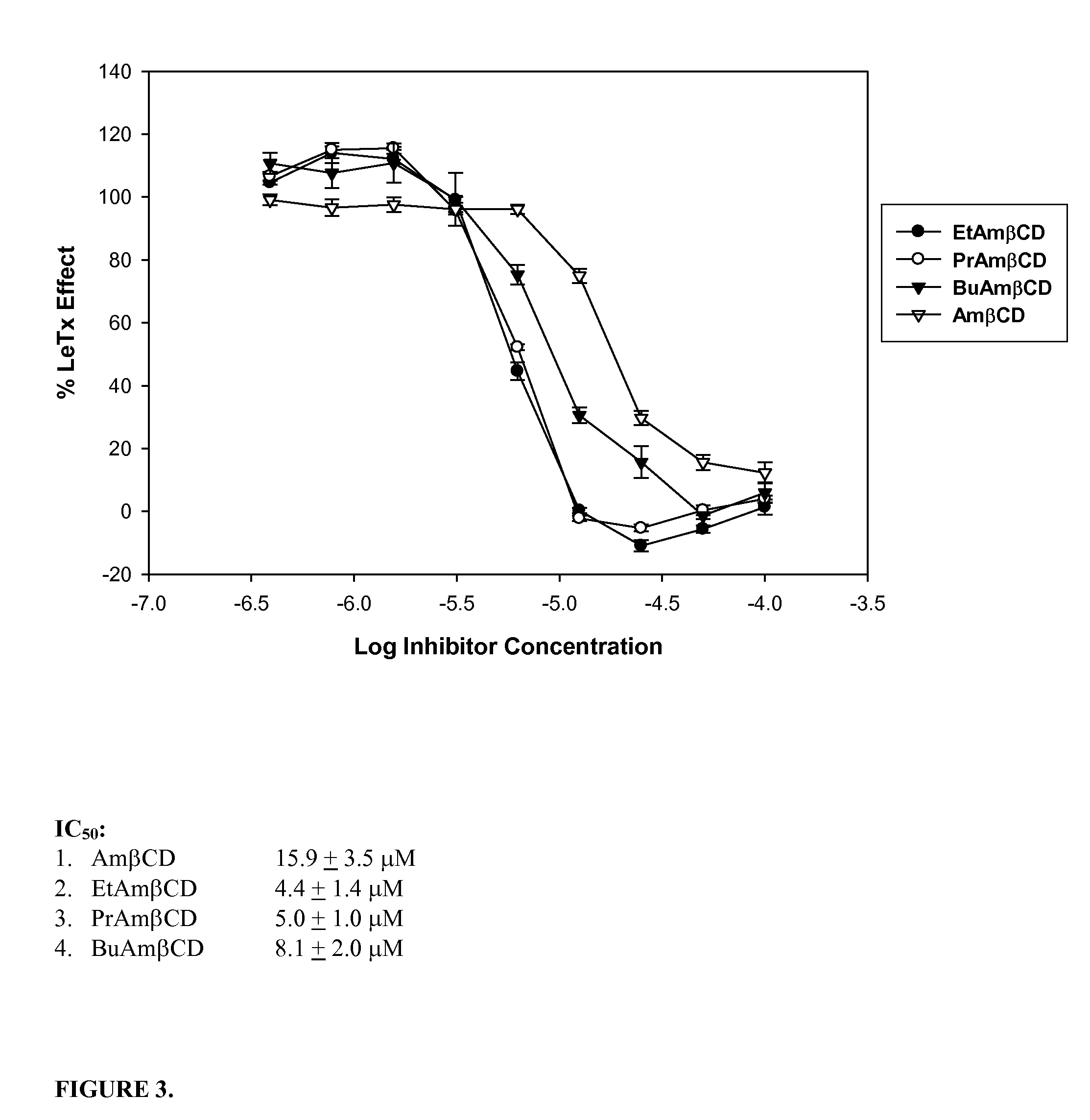
B-cyclodextrin derivatives and their use against anthrax lethal toxin
The invention provides low molecular weight compounds that block the pore formed by protective antigen and inhibit anthrax toxin action. Structures of the compounds are derivatives of β-cyclodextrin. Per-substituted alkylamino derivatives displayed inhibitory activity, and they were protective against anthrax lethal toxin action at low micromolar concentrations. Also, the addition of one of the alkylamino derivatives to the bilayer lipid membrane with multiple PA channels caused a significant decrease in membrane conductance. Thus, the invention also provides methods for protection against anthrax toxicity.
Owner:INNOVATIVE BIOLOGICS
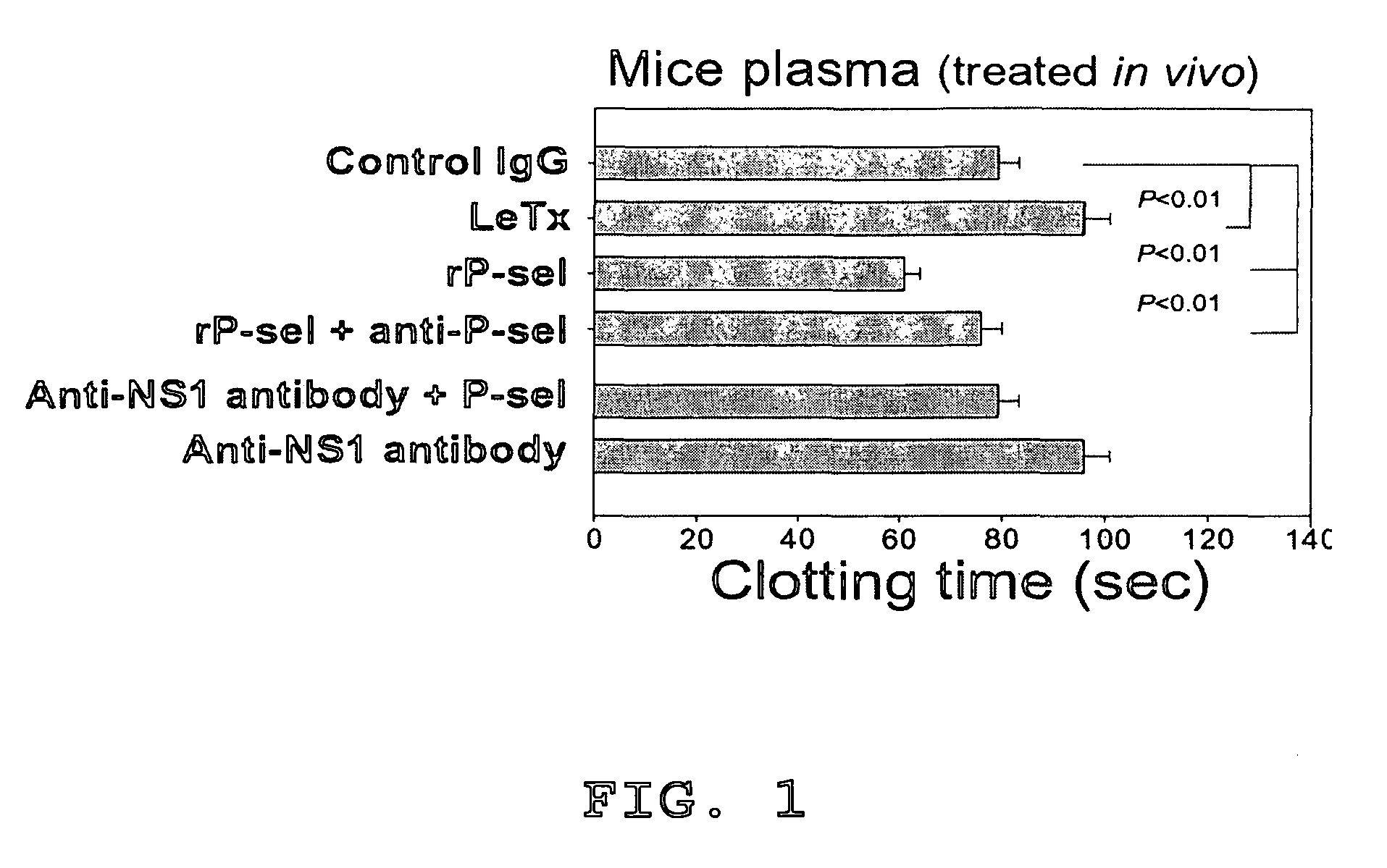
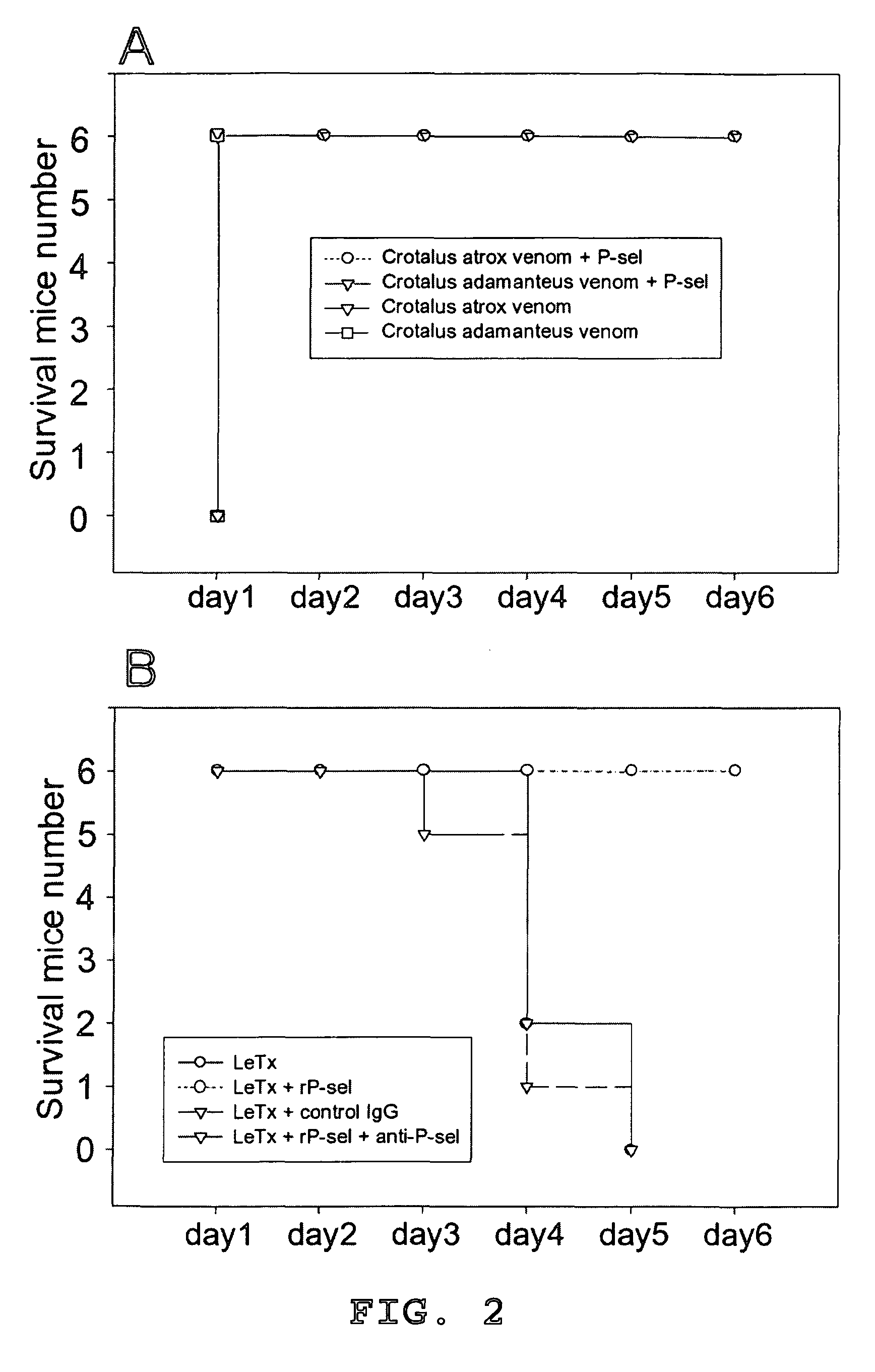
Methods of reducing hypoxic stress in a mammal by administering soluble P-selectin
ActiveUS8377887B1Stabilize blood pressureReduce stressNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSoluble P-SelectinMammal
The present invention provides a use of soluble P-selectin in treating systemic hemorrhagic conditions, stabilizing blood pressure, and protecting hypoxic / ischemic tissues. Also provided is a use of anthrax lethal toxin in treating thrombotic conditions.
Owner:CHANG HSIN HOU +1
Therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using same
InactiveUS7094575B2Good potencyGood anti-inflammatory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticPhospholipase inhibitorSaxitoxin
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Detection of anthrax pathogenicity factors
ActiveUS8663926B2Gentle and rapid separationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProper treatmentRapid identification
One major problem in diagnosis methods presently available for anthrax is that these methods require several days to produce a result. The only existing treatment for anthrax requires administration soon after infection at a time when patients are exhibiting only mild flu-like symptoms. Thus, a patient may be days beyond the time when treatment would be effective by the time a diagnosis is made. The present invention reduces diagnosis time to as little as four hours providing same day identification of anthrax radically increasing the odds of delivering proper treatment and patient recovery. The rapid identification of anthrax lethal factor activity exhibited by the instant invention is also amenable to in vivo screening protocols for the discovery and development of anthrax vaccines and lethal factor inhibitors. The instant invention isolates and concentrates lethal factor and lethal toxin from nearly any biological sample. By capitalizing on the endopeptidase activity of lethal factor the present invention amplifies output signals producing reliable detection of picomolar concentrations of lethal factor. The instant invention involves novel purification and detection techniques and substrates for rapid, reproducible, and quantitative measurements of anthrax lethal factor in biological samples.
Owner:CDC THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES CENTS FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Serologic correlates of protection against Bacillus anthracis infection
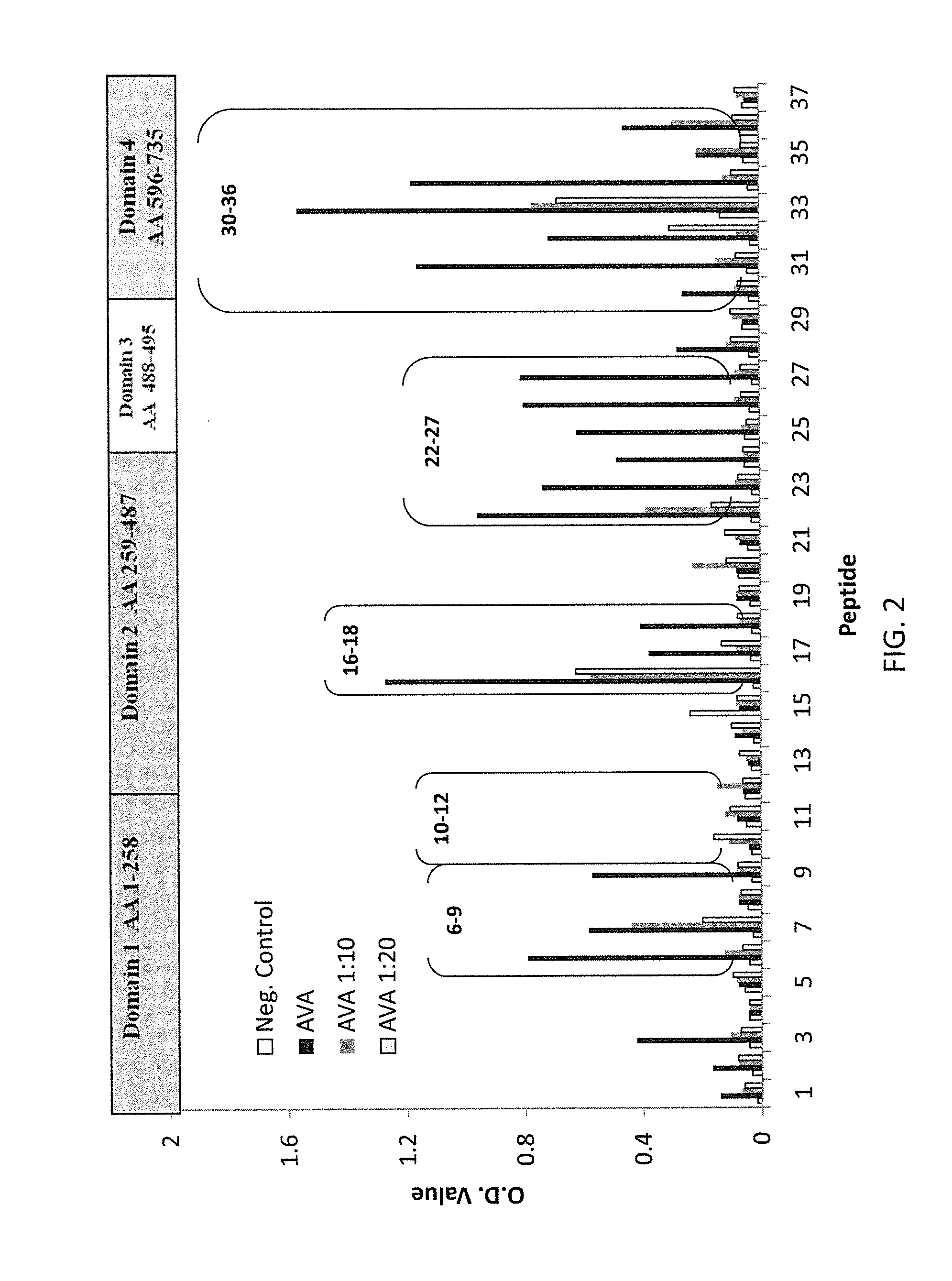
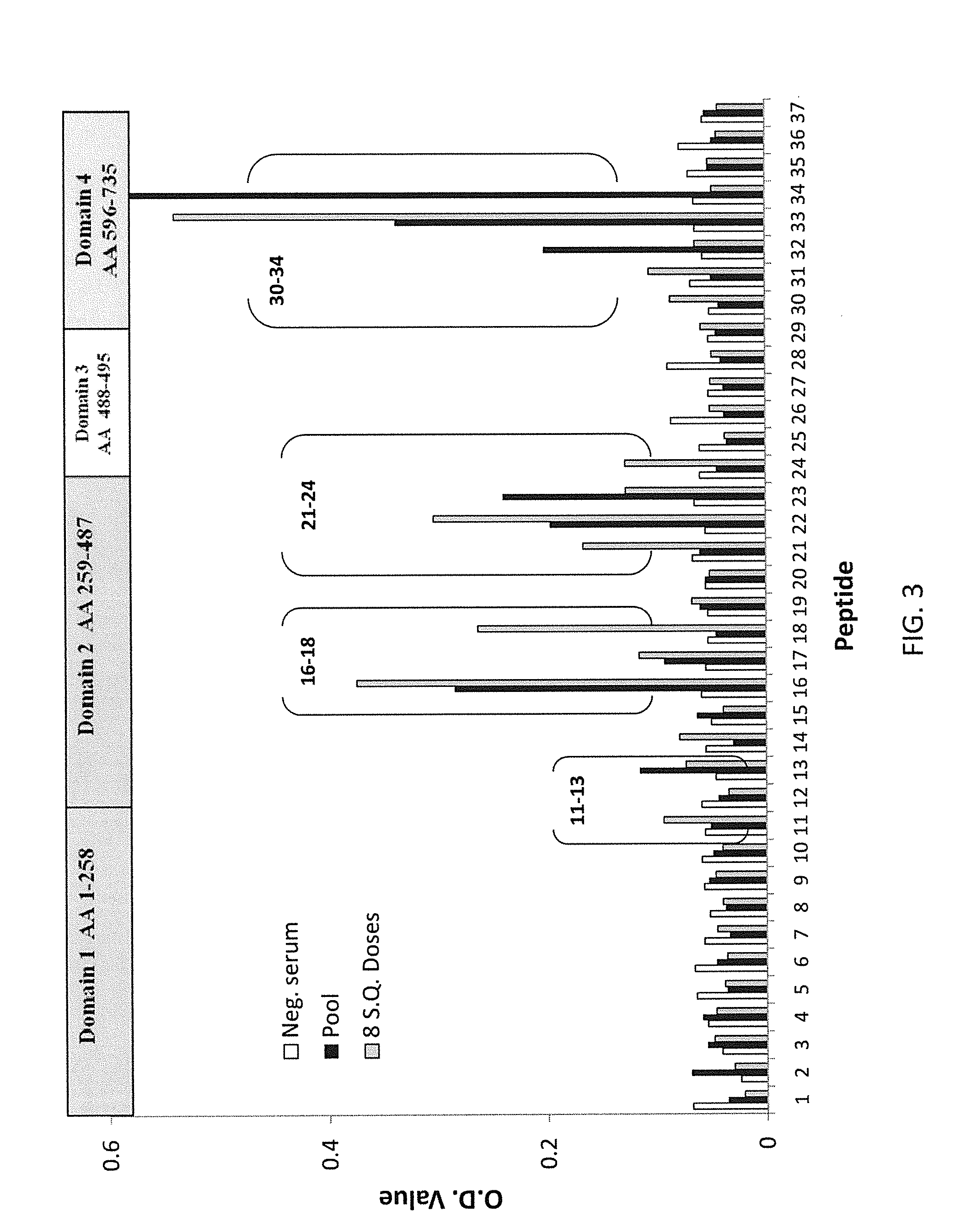
Regions of B. anthracis protective antigen are provided representing sequences recognized by antibodies in subjects that have vaccine induced lethal toxin neutralizing anti-PA IgG responses. The recognition of these PA regions enhances the utility of anti-PA IgG reactivity as an immune correlate of protection against anthrax in a subject and increases predictive probability of survival. Also provided are vaccines that include at least one of these PA regions that when administered to a subject improve the predictive value of vaccine induced anti-PA IgG and TNA responses as immune correlates of protection against inhalation anthrax.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
B-cyclodextrin derivatives and their use against anthrax lethal toxin
InactiveUS20060247208A1Reduced effectivenessEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntigenLipid formation
The invention provides low molecular weight compounds that block the pore formed by protective antigen and inhibit anthrax toxin action. Structures of the compounds are derivatives of β-cyclodextrin. Per-substituted alkylamino derivates displayed inhibitory activity, and they were protective against anthrax lethal toxin action at low micromolar concentrations. Also, the addition of one of the alkylamino derivatives to the bilayer lipid membrane with multiple PA channels caused a significant decrease in membrane conductance. Thus, the invention also provides methods for protection against anthrax toxicity.
Owner:INNOVATIVE BIOLOGICS
Protective antigen mutant of Bacillus anthracis
InactiveCN101434960AAvoid cytotoxicityDepsipeptidesGenetic engineeringProtective antigenMutated protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism genetic engineering and particularly relates to a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen mutant and encoding protein thereof. The sequence of the mutant gene and the amino acid sequence of the encoding mutant protein are shown in SEQ ID NO of 1 in the sequence table. Through the verification of biology, the mutant protein has complete privation of cytotoxicity, and can inhibit the cytotoxicity of wild lethal toxin.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods of reducing hypoxic stress in a mammal by administering soluble p-selectin
ActiveUS20130045924A1Reduce stressNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSoluble P-SelectinMammal
The present invention provides a use of soluble P-selectin in treating systemic hemorrhagic conditions, stabilizing blood pressure, and protecting hypoxic / ischemic tissues. Also provided is a use of anthrax lethal toxin in treating thrombotic conditions.
Owner:CHANG HSIN HOU +1
Engineered anthrax lethal toxin for targeted delivery
ActiveUS9730993B2Superior delivery resultImprove target specificityBacterial antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesHeterologousProtective antigen
The present invention provides methods and systems for targeted delivery of a compound to a target cell that over-expresses two different proteinases. Specifically, two different modified protective antigen proteins, each comprising a cleavage site recognized by a distinct proteinase in place of the native proteinase cleavage site recognized by furin, are administered in combination with a compound that contains a protective antigen binding site. Upon cleavage by the two proteinases the two modified protective antigen proteins form a hetero-oligomer, allowing the compound to bind to the hetero-oligomer and subsequently to be translocated into the target cell.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Domain II Mutants Of Anthrax Lethal Factor
InactiveUS20080124362A1Avoid interactionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMutantImmunogenicity
A series of mutants of Anthrax lethal factor (LF) are disclosed which define a conformational epitope or region of the molecule that interacts with the LF target, the MEK enzyme. Such mutants or variants, and nucleic acids encoding them are disclosed. The knowledge of such binding, separate from recognition of MEK by the protease active site of LF, serves as the basis for novel screening assays for discovery of inhibitors of this additional form of LF-MEK binding which is necessary for ultimate proteolysis and toxicity. The nontoxic LF mutants are useful as immunogenic compositions for generating antibodies and a state of immunity specific for the LF component of a B. arithracis infection or exposure otherwise to the anthrax lethal toxin.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST
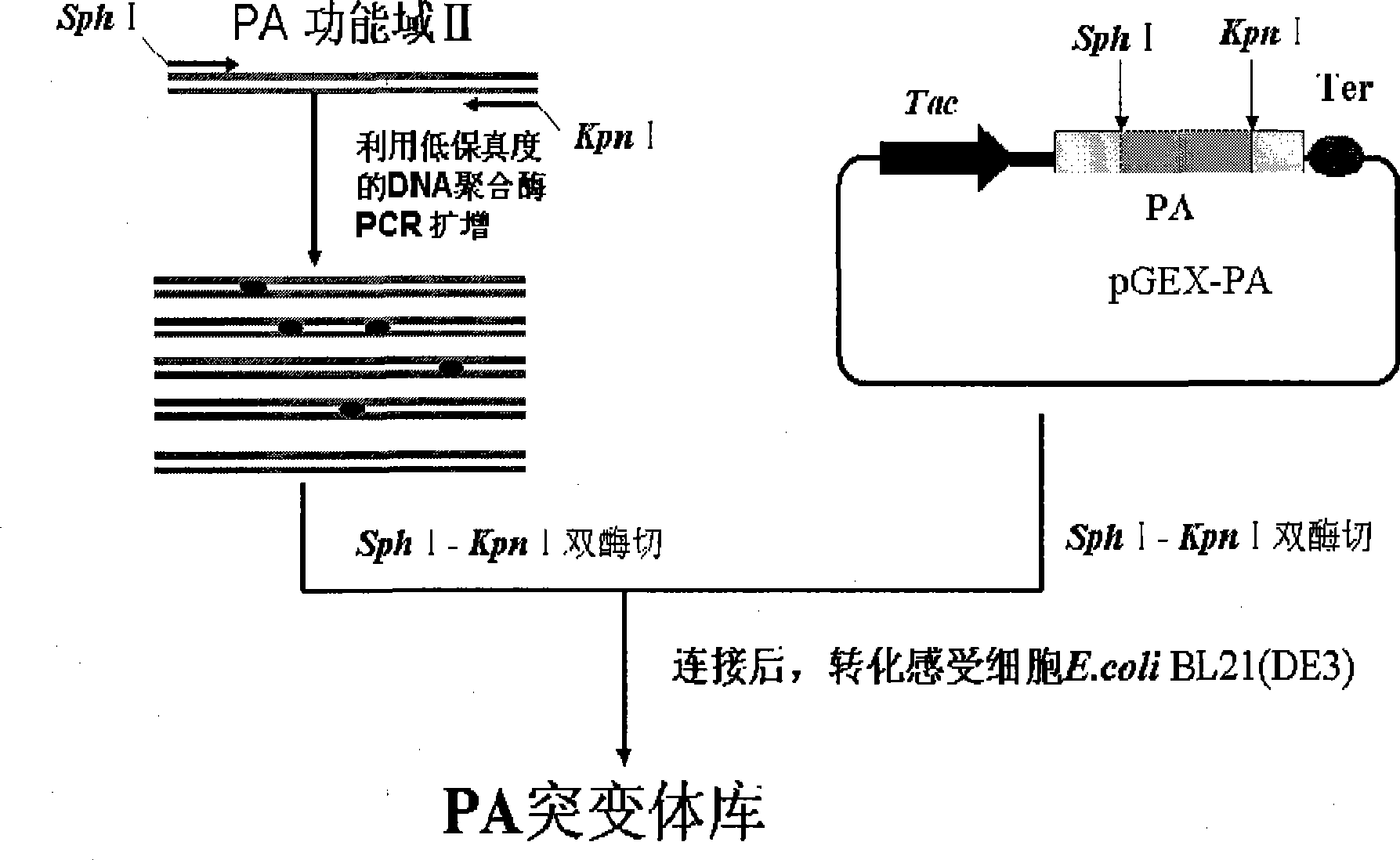
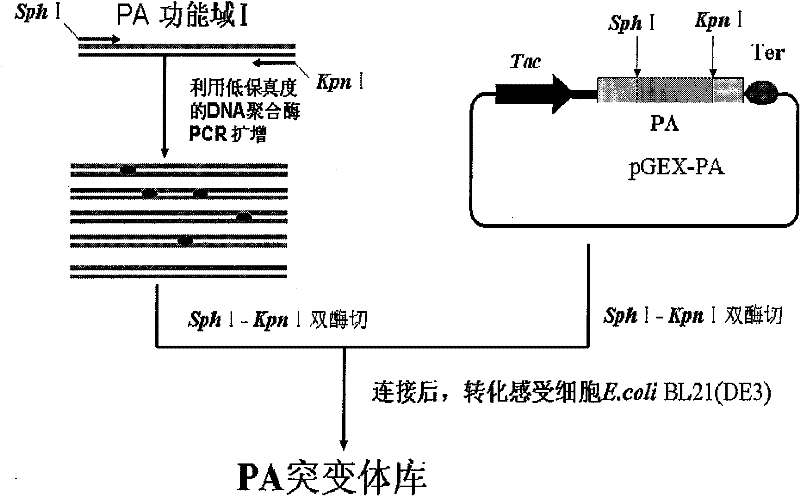
Application of dominant suppressing mutant F427D as anthrax bacillus toxin inhibitor and vaccine
InactiveCN101392232BImproving immunogenicityNo risk of latent infectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenEscherichia coli
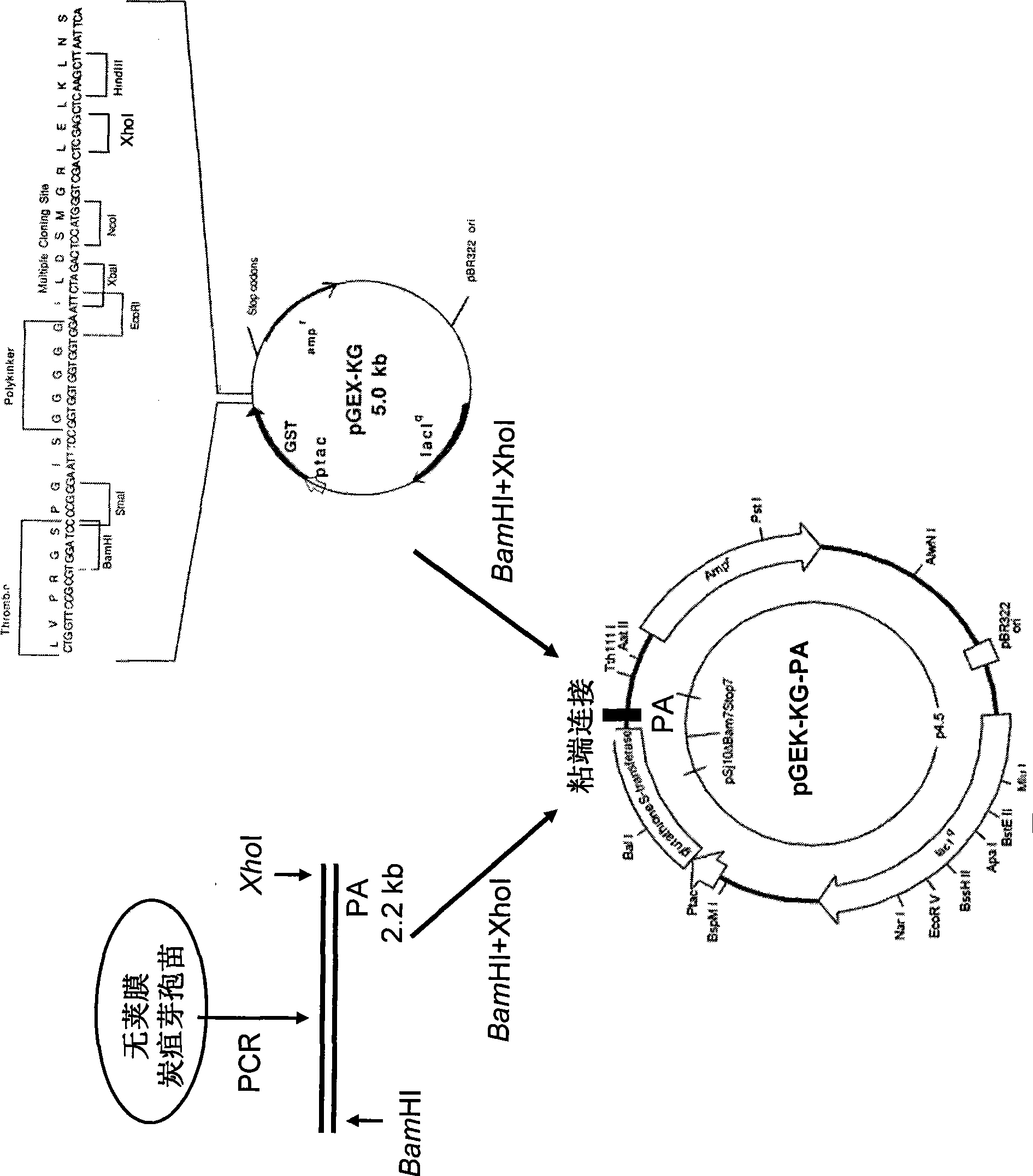
The invention relates to the technical fields of animal bacteriology and zoonosis science, particularly to an application of a dominant inhibitory mutant F427D as an inhibitor of Bacillus anthracis toxin and an application of vaccine thereof. The invention, through cloning of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin gene, expression and purification of proteins, site-directed saturation mutagenesis of genes and the like, obtains protective antigen (namely the dominant inhibitory mutant F427D) of the Bacillus anthracis, the mutant is successfully cloned into pronucleus expression carrier pGEX-KG and composes recomposed plasmid pGEX-KG-PA (F427D). Escherichia coli containing the recomposed plasmid is nominated as Escherichia coli DH5Alpha / pGEX-KG-PA (F427D) and collected in the China Center for TypeCulture Collection with a collection number of CCTCC-M208158. The invention further discloses the method for preparing the antigen protein, the preparation of anthrax toxin inhibitor and subunit vaccine by using the antigen protein and the application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
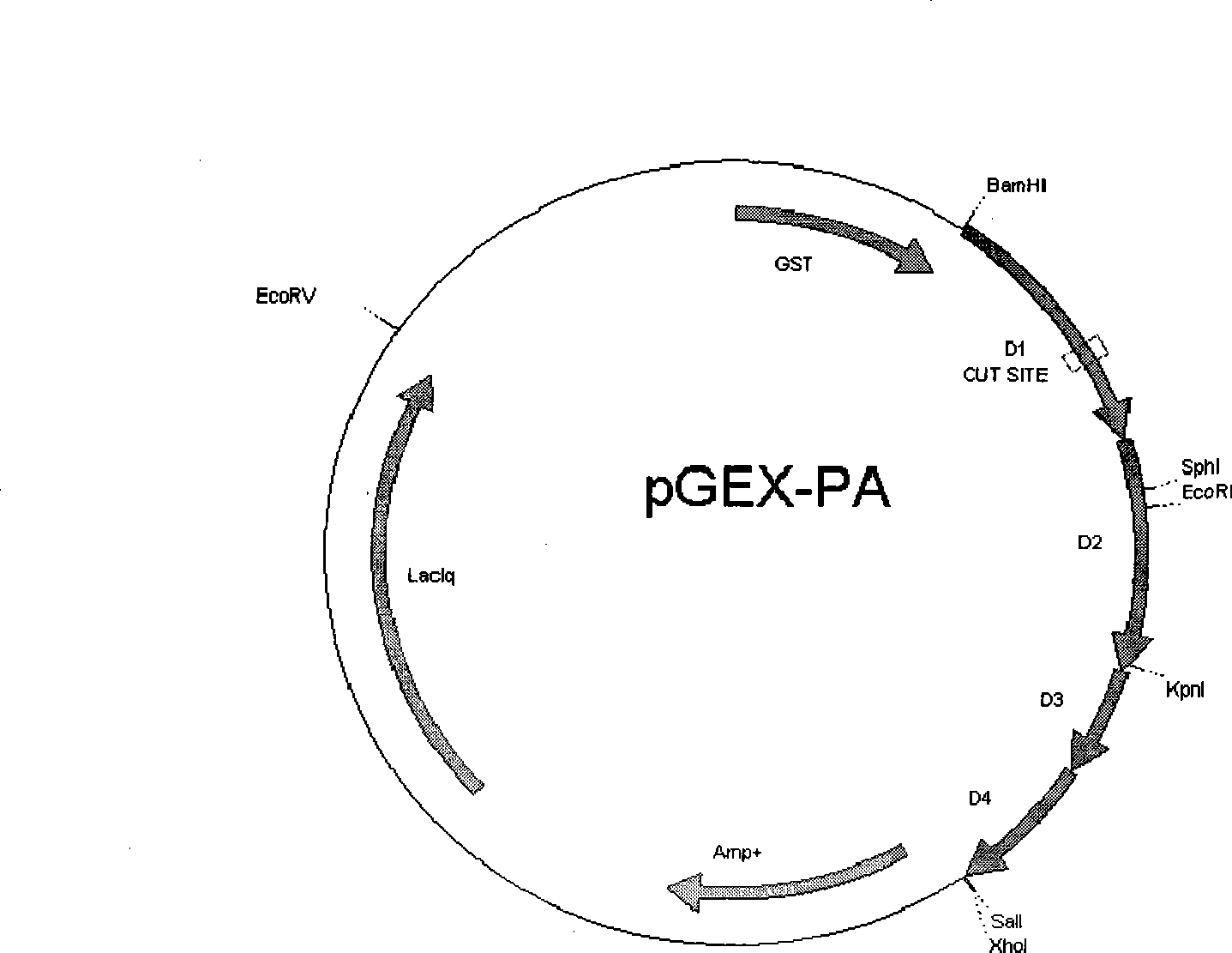
Novel usage of soluble P-lectin and anthrax lethal toxin
InactiveCN1565619AGood coagulationGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderDiseaseWhole body
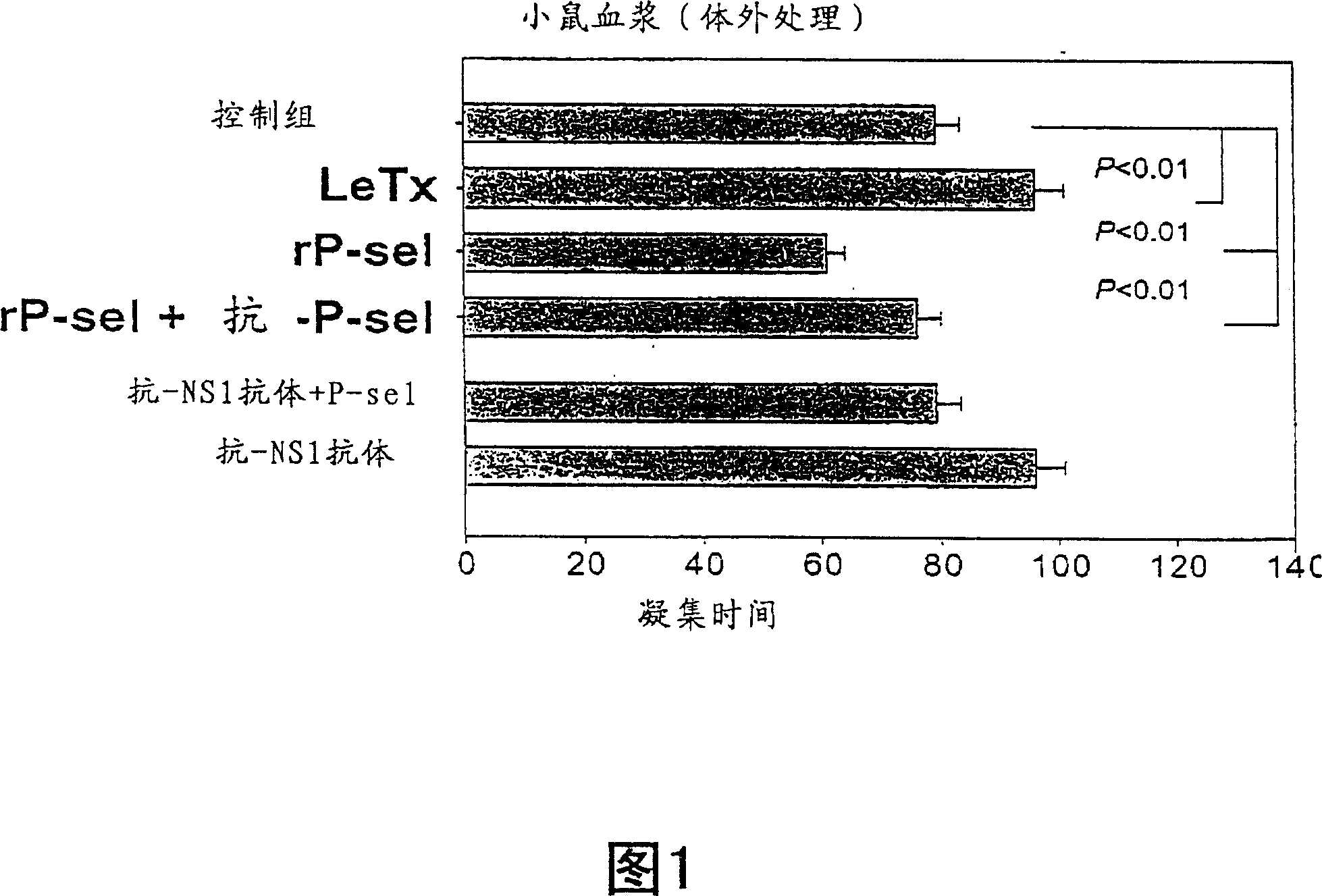
The invention relates to the use of soluble P-lectine in preparing medicament for treating whole body haemorrhage diseases, and the use of an anthracnose lethiferous toxin in preparing medicament for treating antithrombotic diseases.
Owner:张新侯
Methods for inhibiting cellular uptake of the anthrax lethal toxin (LT) protein complex
InactiveUS20170071950A1Intuitive effectReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsBiological material analysisGenes mutationLRP5
The present invention identifies compounds that disrupt the interaction between anthrax proteins and LRP5 / 6 receptors, resulting in a reduction in anthrax toxicity. The compounds act to disrupt the intracellular transport of toxin complexes into a target cell. The present invention also provides methods for testing the effect of compounds on Wnt activity, through the use of in vitro experiments involving cells that have in at least one gene mutation involved in the Wnt pathway.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
A bivalent anthrax vaccine
ActiveCN105749265BGood immune protectionImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMutated proteinReceptor
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Use of soluble P-selectin and anthrax lethal toxin
InactiveUS20050059582A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsSoluble E-SelectinSoluble P-Selectin
The present invention provides a use of soluble P-selectin in treating systemic hemorrhagic conditions, stabilizing blood pressure, and protecting hypoxic / ischemic tissues. Also provided is a use of anthrax lethal toxin in treating thrombotic conditions.
Owner:CHANG HSIN HOU +1
Method for separating lethal toxin protein from cyanea nozakii nematocyst toxin
ActiveCN102174098BLittle loss of activityFast flowAnimals/human peptidesChromatographic separationLethal dose
The invention relates to the technical field of marine organisms, in particular to a method for separating and purifying a cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein. The method comprises the following steps of: ultrasonically crushing cyanea nozakii nematocyst cells to extract a jellyfish crude toxin, dialyzing and desalting, and separating and purifying by affinity chromatographic separation and an anion exchange chromatographic technology in turn to obtain a jellyfish toxin protein with lethal activity, wherein through measurement, the molecular weight of the toxin protein is 30kDa, and the lethal dose 50 (LD50) of the toxin protein to 1g of zebra fish is 0.56mu g. The method has the characteristics that: the method is quick, simple and convenient and provides important guidance for obtainingthe cyanea nozakii lethal toxin protein.
Owner:水母娘娘海洋生物科技有限公司
Serologic correlates of protection against bacillis anthracis infection
InactiveUS20140004139A1Easy to understandBacterial antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisProtective antigenInhalation anthrax
Regions of B. anthracis protective antigen are provided representing sequences recognized by antibodies in subjects that have vaccine induced lethal toxin neutralizing anti-PA IgG responses. The recognition of these PA regions enhances the utility of anti-PA IgG reactivity as an immune correlate of protection against anthrax in a subject and increases predictive probability of survival. Also provided are vaccines that include at least one of these PA regions that when administered to a subject improve the predictive value of vaccine induced anti-PA IgG and TNA responses as immune correlates of protection against inhalation anthrax.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Application of dominant suppressing mutant F427D as anthrax bacillus toxin inhibitor and vaccine
InactiveCN101392232AImproving immunogenicityNo risk of latent infectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention relates to the technical fields of animal bacteriology and zoonosis science, particularly to an application of a dominant inhibitory mutant F427D as an inhibitor of Bacillus anthracis toxin and an application of vaccine thereof. The invention, through cloning of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin gene, expression and purification of proteins, site-directed saturation mutagenesis of genes and the like, obtains protective antigen (namely the dominant inhibitory mutant F427D) of the Bacillus anthracis, the mutant is successfully cloned into pronucleus expression carrier pGEX-KG and composes recomposed plasmid pGEX-KG-PA (F427D). Escherichia coli containing the recomposed plasmid is nominated as Escherichia coli DH5Alpha / pGEX-KG-PA (F427D) and collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection with a collection number of CCTCC-M208158. The invention further discloses the method for preparing the antigen protein, the preparation of anthrax toxin inhibitor and subunit vaccine by using the antigen protein and the application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Novel usage of soluble P-lectin and anthrax lethal toxin
InactiveCN1323713CGood coagulationGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderDiseaseP-selectin
The invention relates to the use of soluble P-lectine in preparing medicament for treating whole body haemorrhage diseases, and the use of an anthracnose lethiferous toxin in preparing medicament for treating antithrombotic diseases.
Owner:张新侯
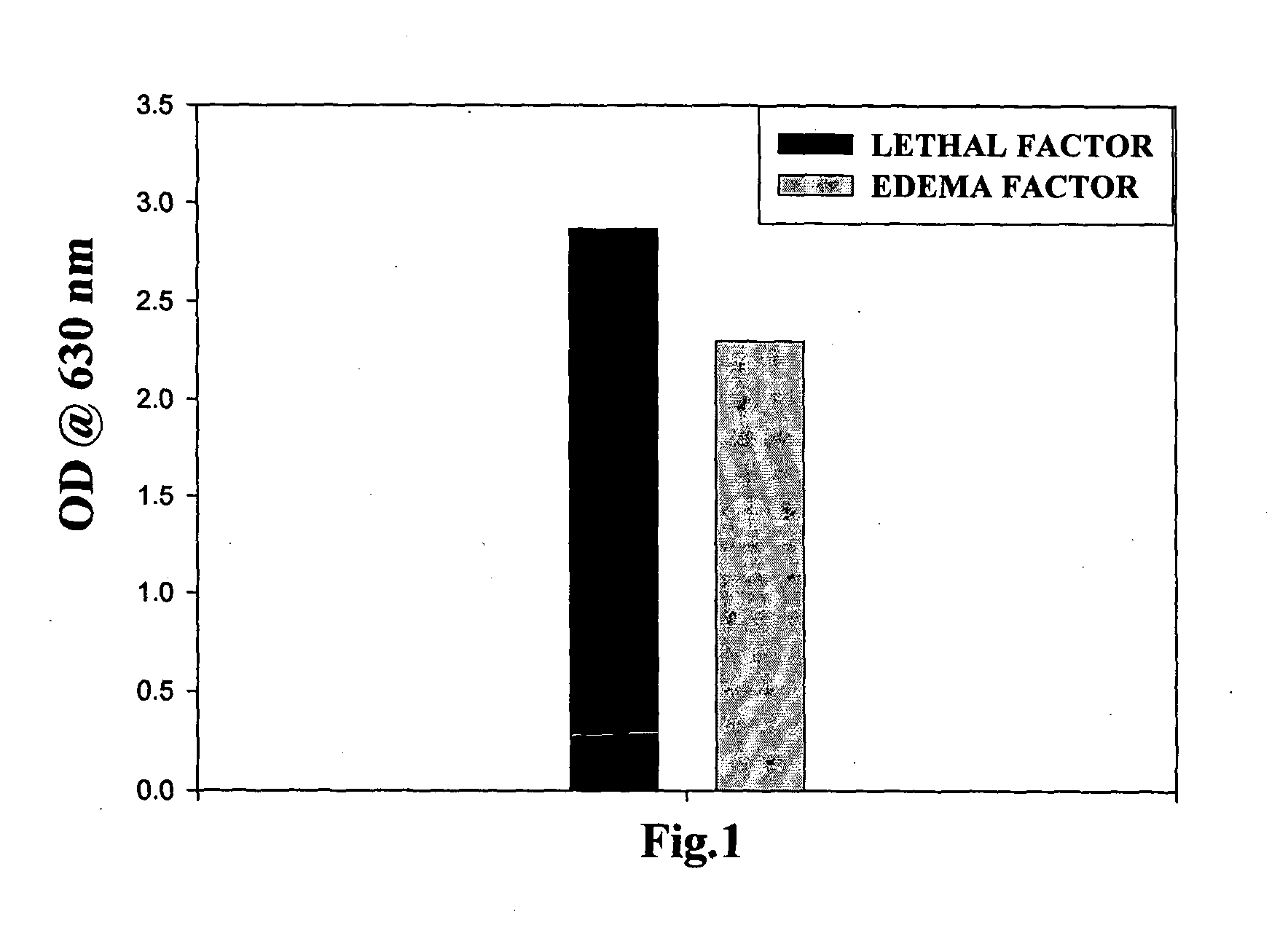
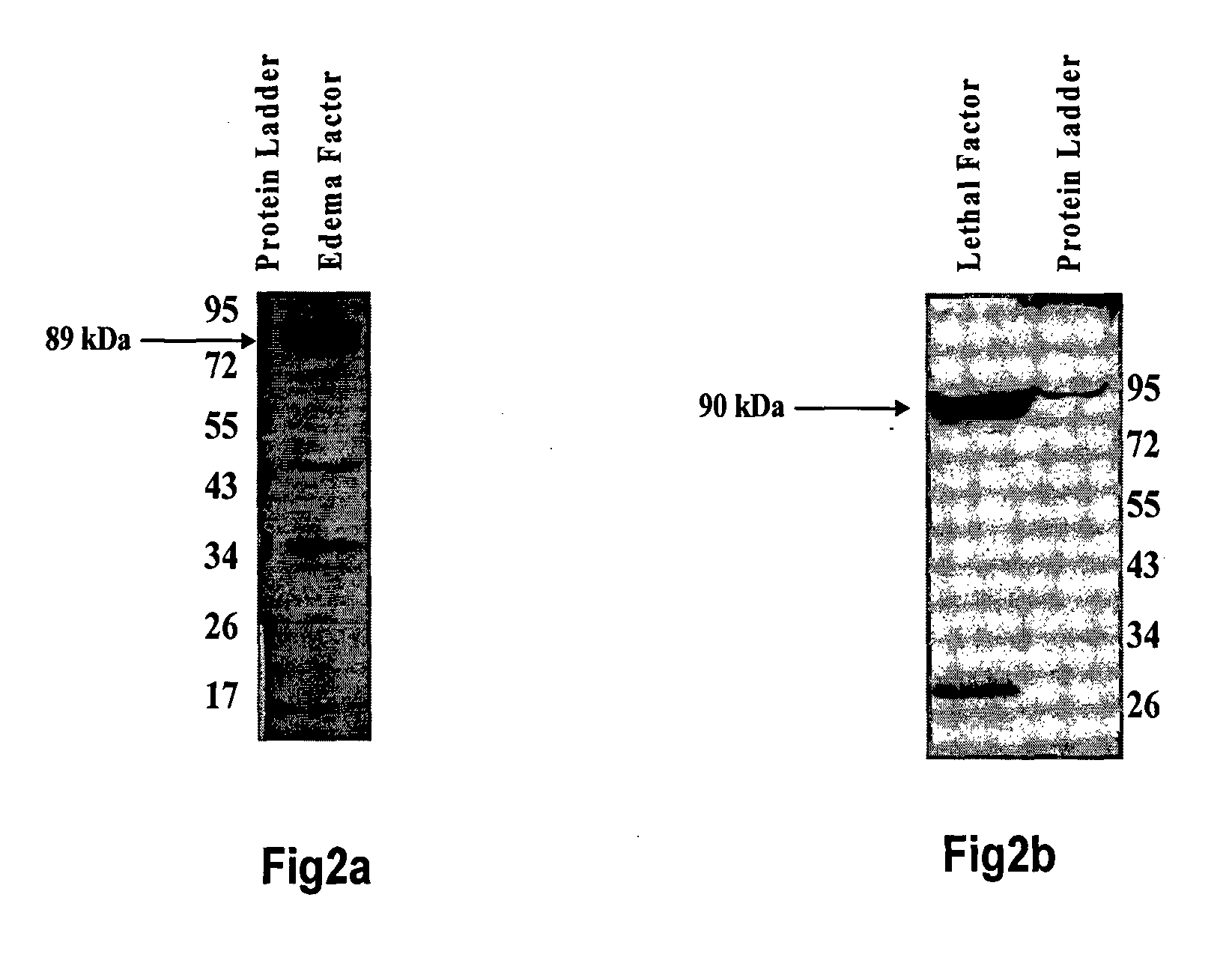
Bispecific monoclonal antibody capable of cross reacting with lethal factor (LF) and edema factor (EF), and neutralizing edema toxin (ET) as well as lethal toxin (LT) of bacillus anthracis
InactiveUS20130017201A1Avoid probabilityAntibacterial agentsHybrid immunoglobulinsAnthrax diseaseBispecific monoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody (mAb) having capabilities of binding with lethal factor (LF) as well as edema factor (EF), and neutralizing lethal toxin (LT) as well as edema toxin (ET) of B. anthracis. It also relates to process for preparation of said mAb, and to pharmaceutical preparations, anthrax diagnostic tool, in-vivo diagnostic imaging tool comprising said mAb. It also relates to genetically modified mAb, and method for prophylaxis against anthrax disease comprising administration of mAb or genetically modified mAb of present invention.
Owner:BHATNAGAR RAKESH
Protective antigen mutant of Bacillus anthracis
InactiveCN101434960BAvoid cytotoxicityDepsipeptidesFermentationProtective antigenAgricultural science
The present invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism genetic engineering and particularly relates to a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen mutant and encoding protein thereof. The sequence of the mutant gene and the amino acid sequence of the encoding mutant protein are shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table. Through the verification of biology, the mutant protein has complete privation of cytotoxicity, and can inhibit the cytotoxicity of wild lethal toxin.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Anti-anthrax lethal factor chimeric monoclonal antibody, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101892198AHigh affinityImprove featuresAntibacterial agentsHybrid immunoglobulinsMonoclonal antibodyToxin
The invention discloses an anti-anthrax lethal factor human-rat chimeric neutral monoclonal antibody, which can, as proved by in vitro experiment and animal experiment, effectively neutralize anthrax lethal toxin and be used for the preparation of antibody medicine for the treatment of human anthrax infection.
Owner:曹伯良 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com