Patents
Literature
47 results about "Inhibitor protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
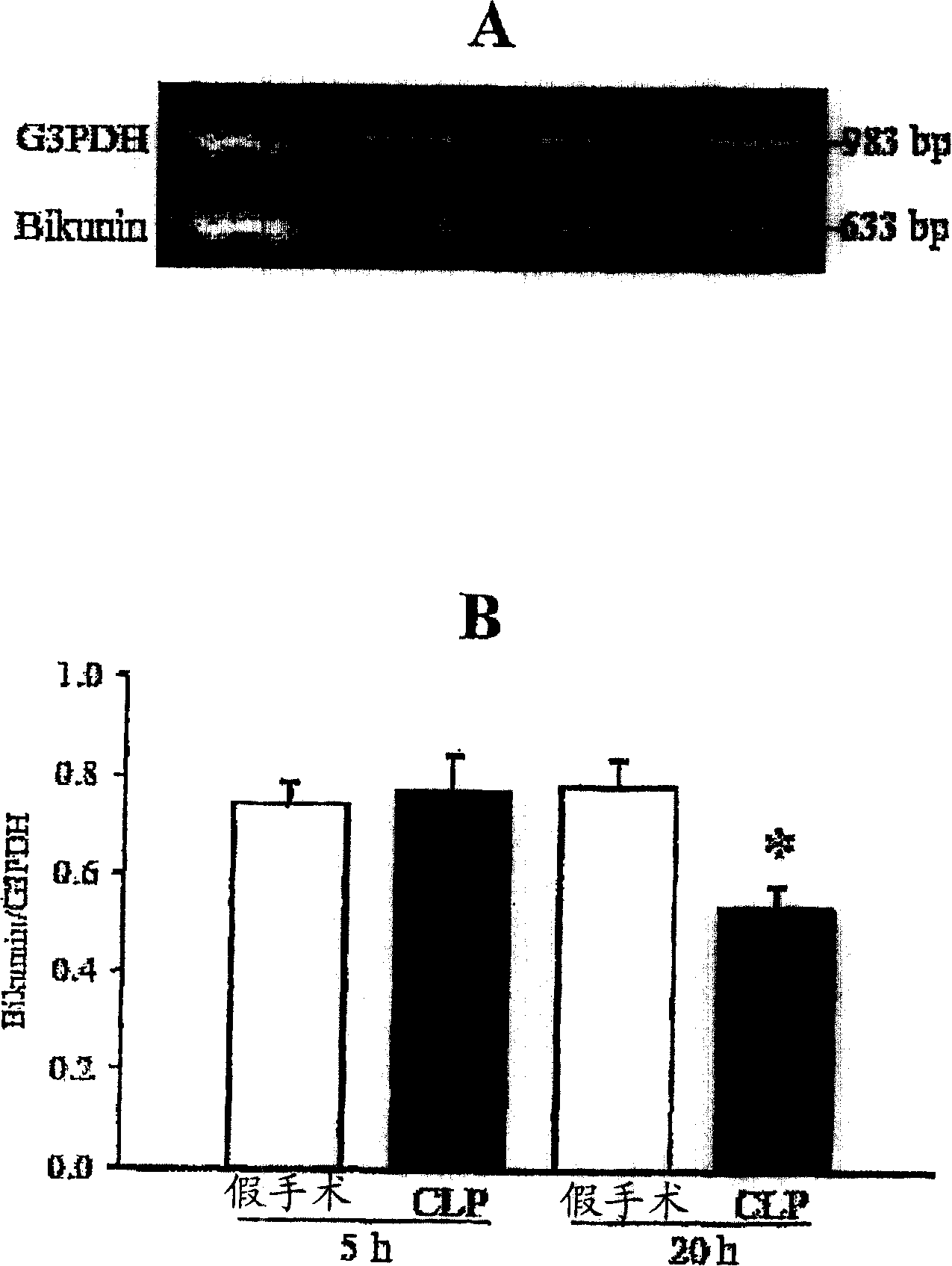
The inhibitor protein (IP) is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and protects the cell against rapid ATP hydrolysis during momentary ischaemia. In oxygen absence, the pH of the matrix drops. This causes IP to become protonated and change its conformation to one that can bind to the F1Fo synthetase and stops it thereby preventing it from moving in a backwards direction and hydrolyze ATP instead of make it. When oxygen is finally incorporated into the system, the pH rises and IP is deprotonated. IP dissociates from the F1Fo synthetase and allows it to resume its ATP synthesis.
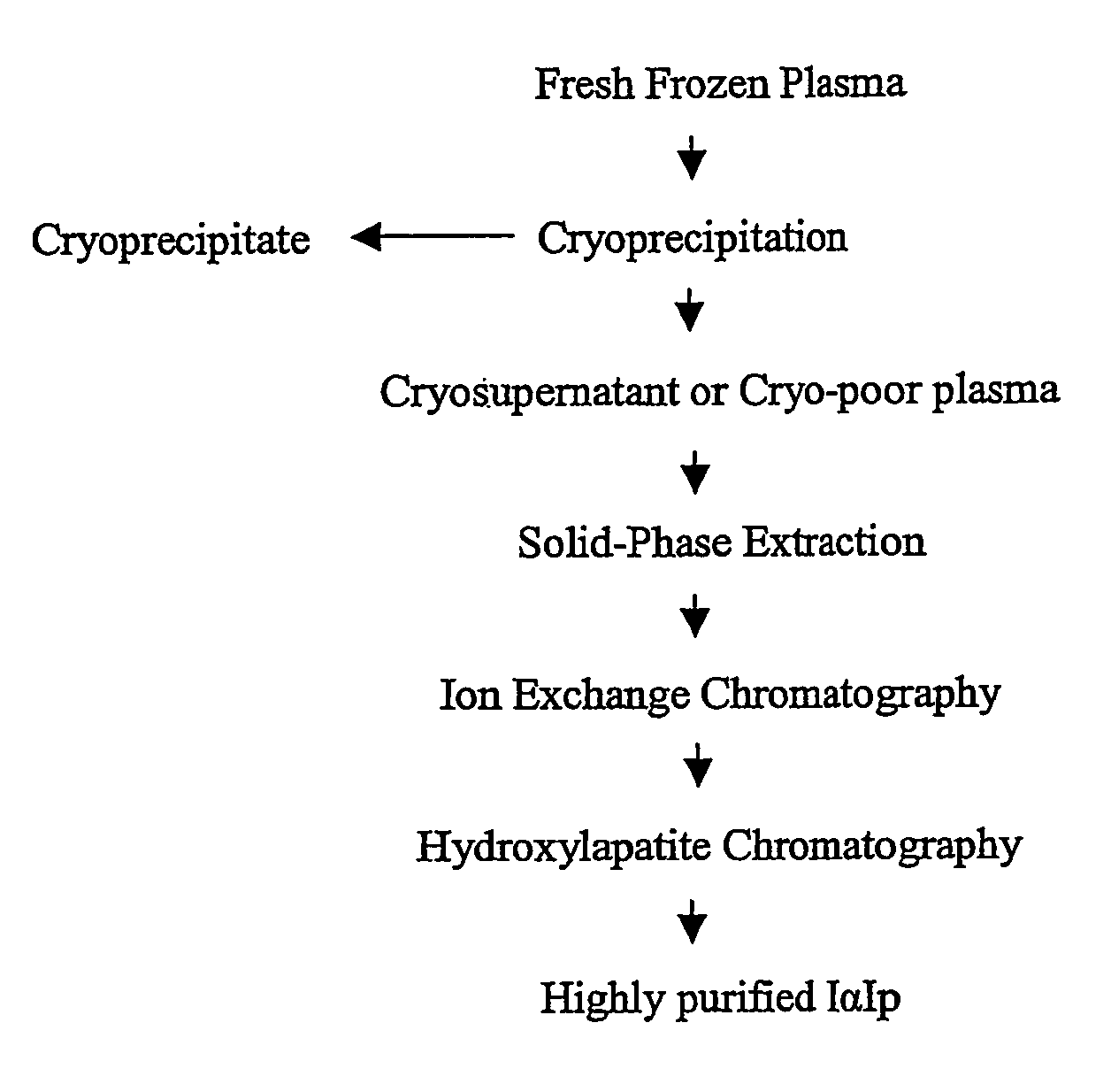
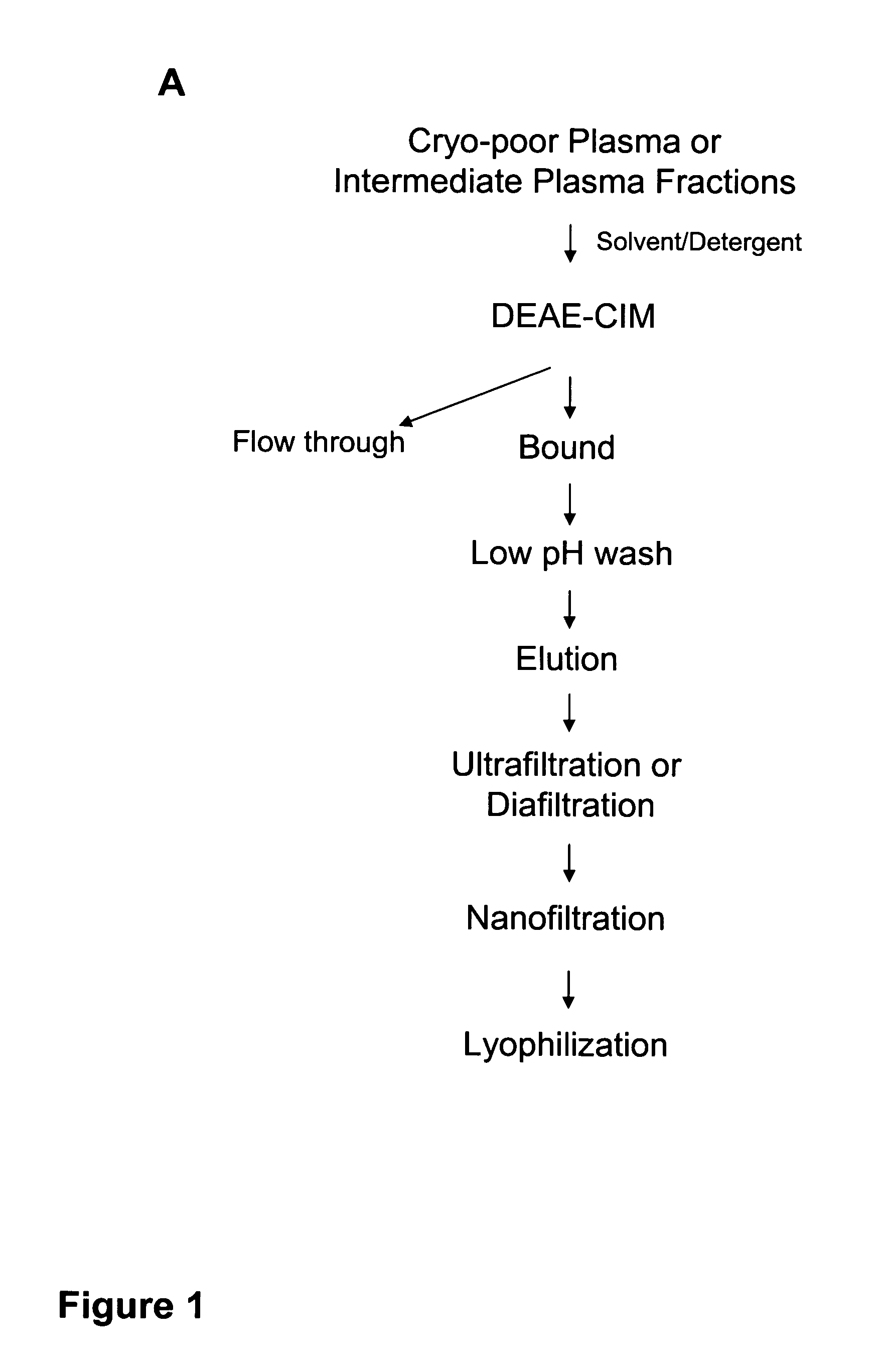
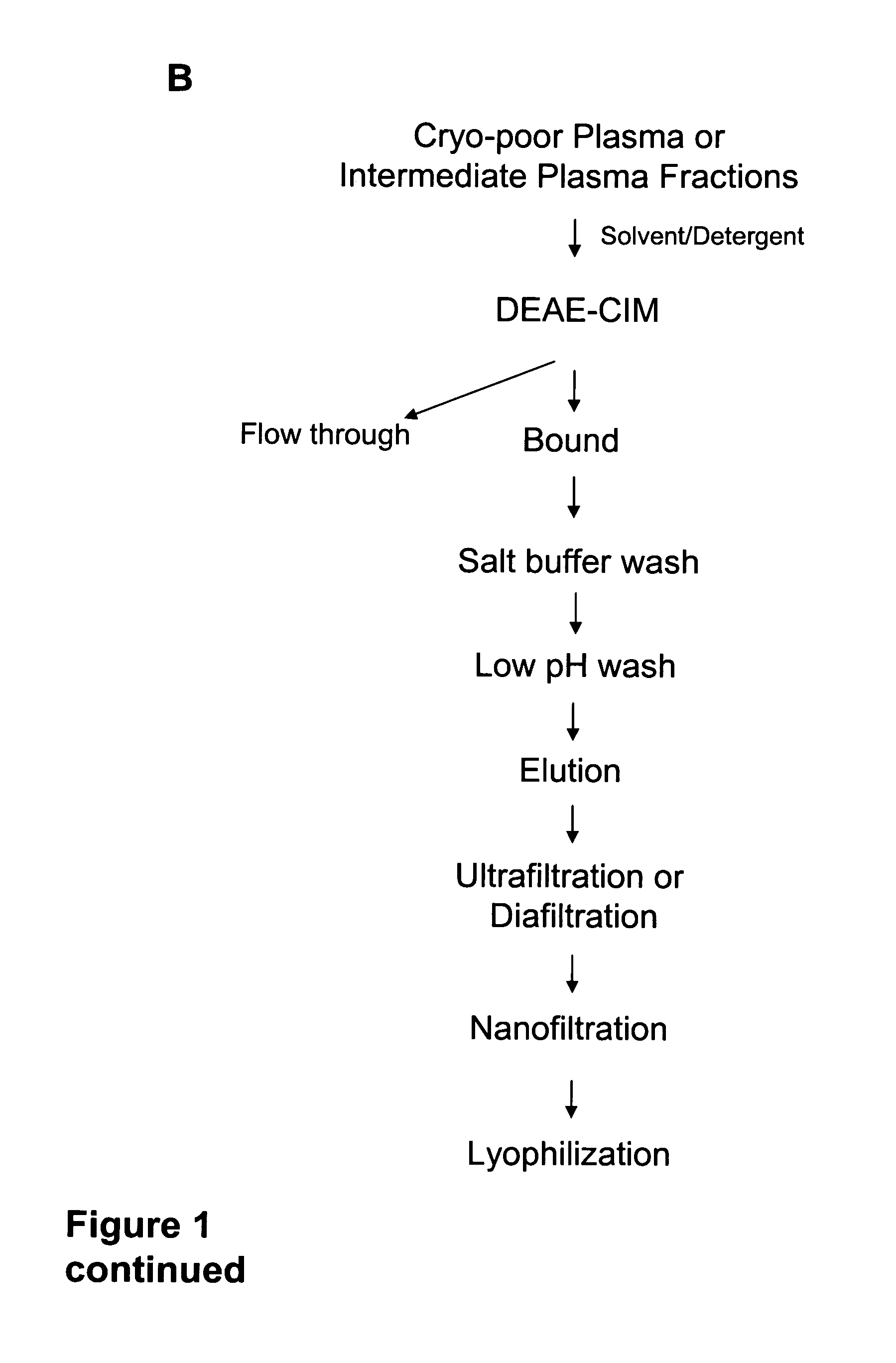
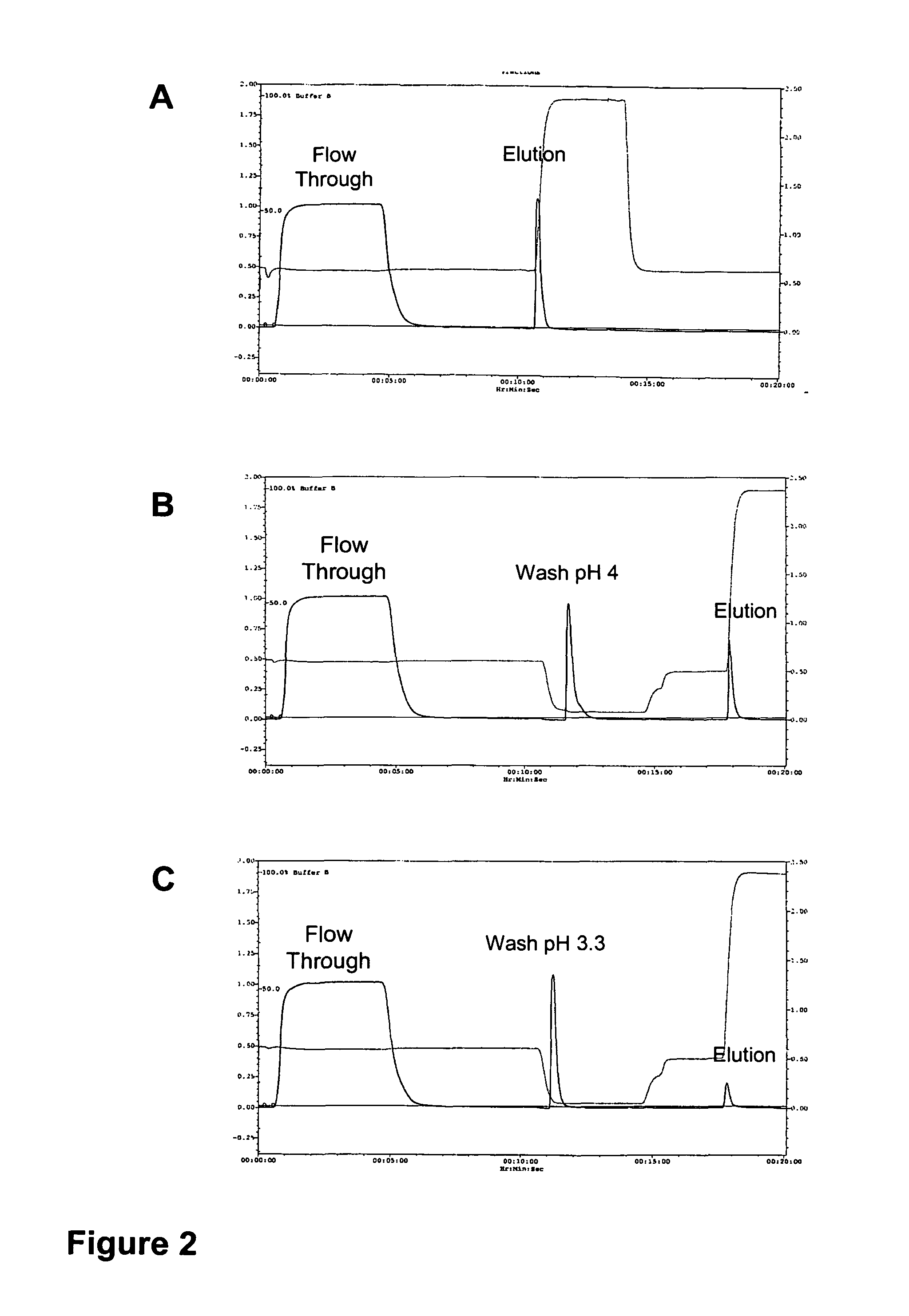
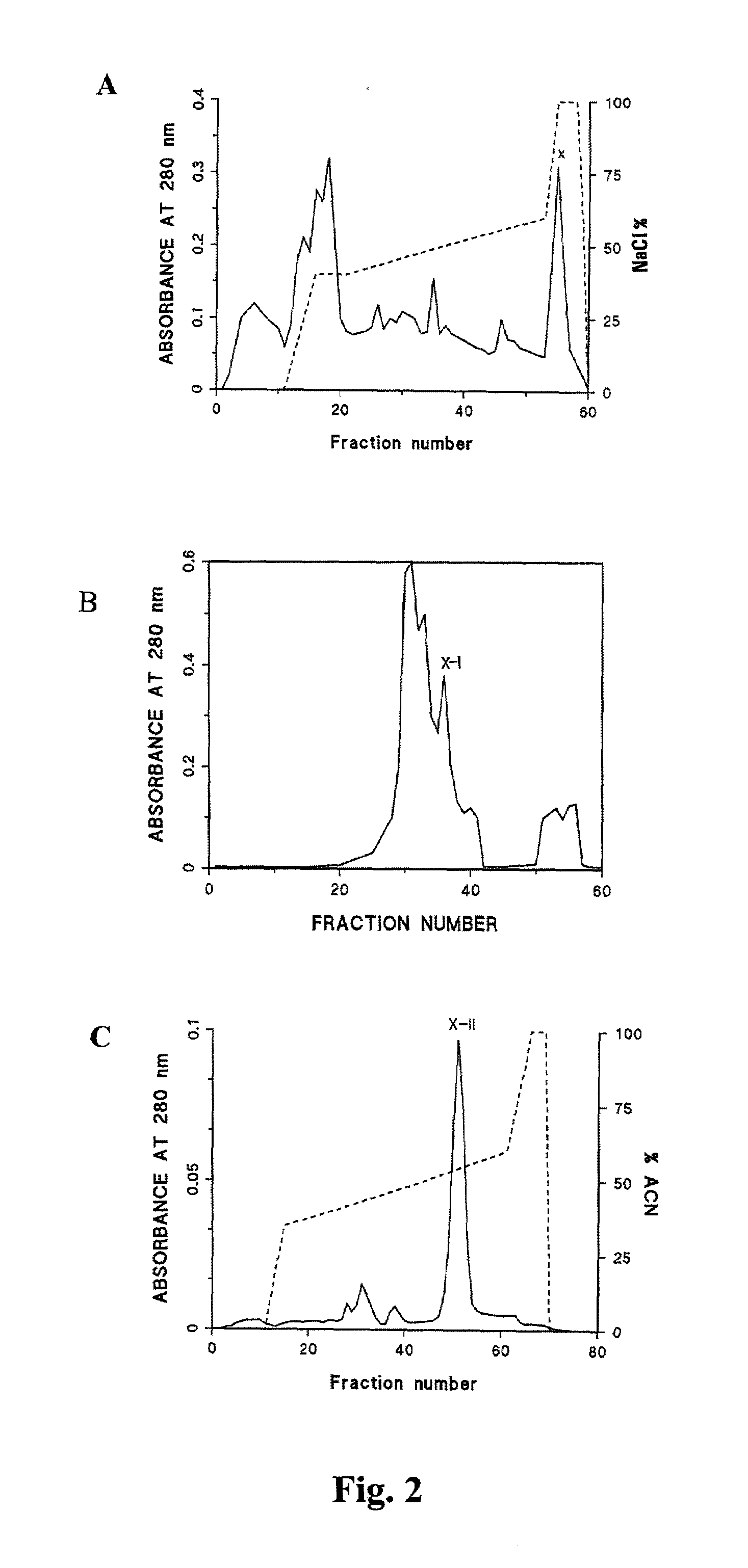
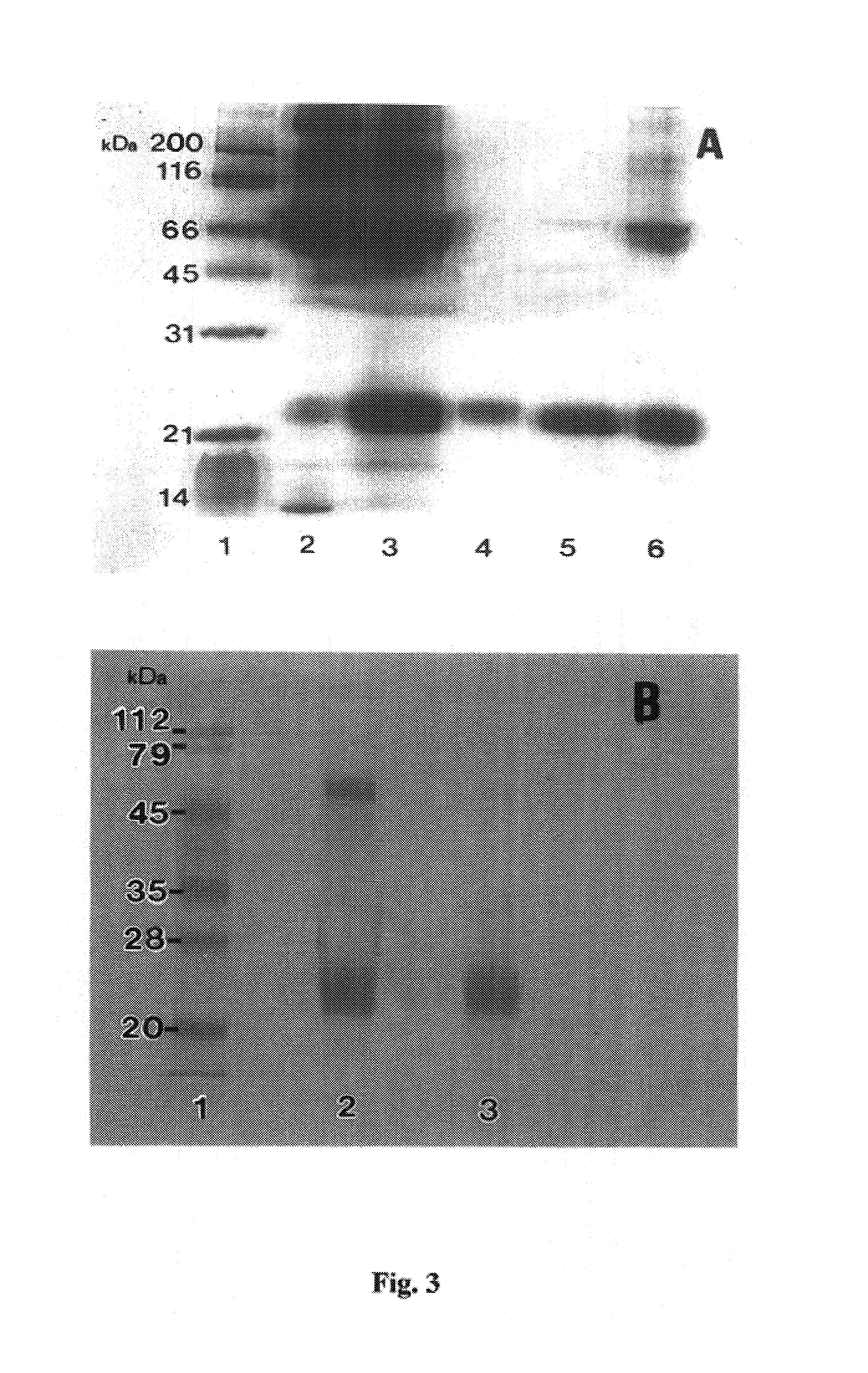
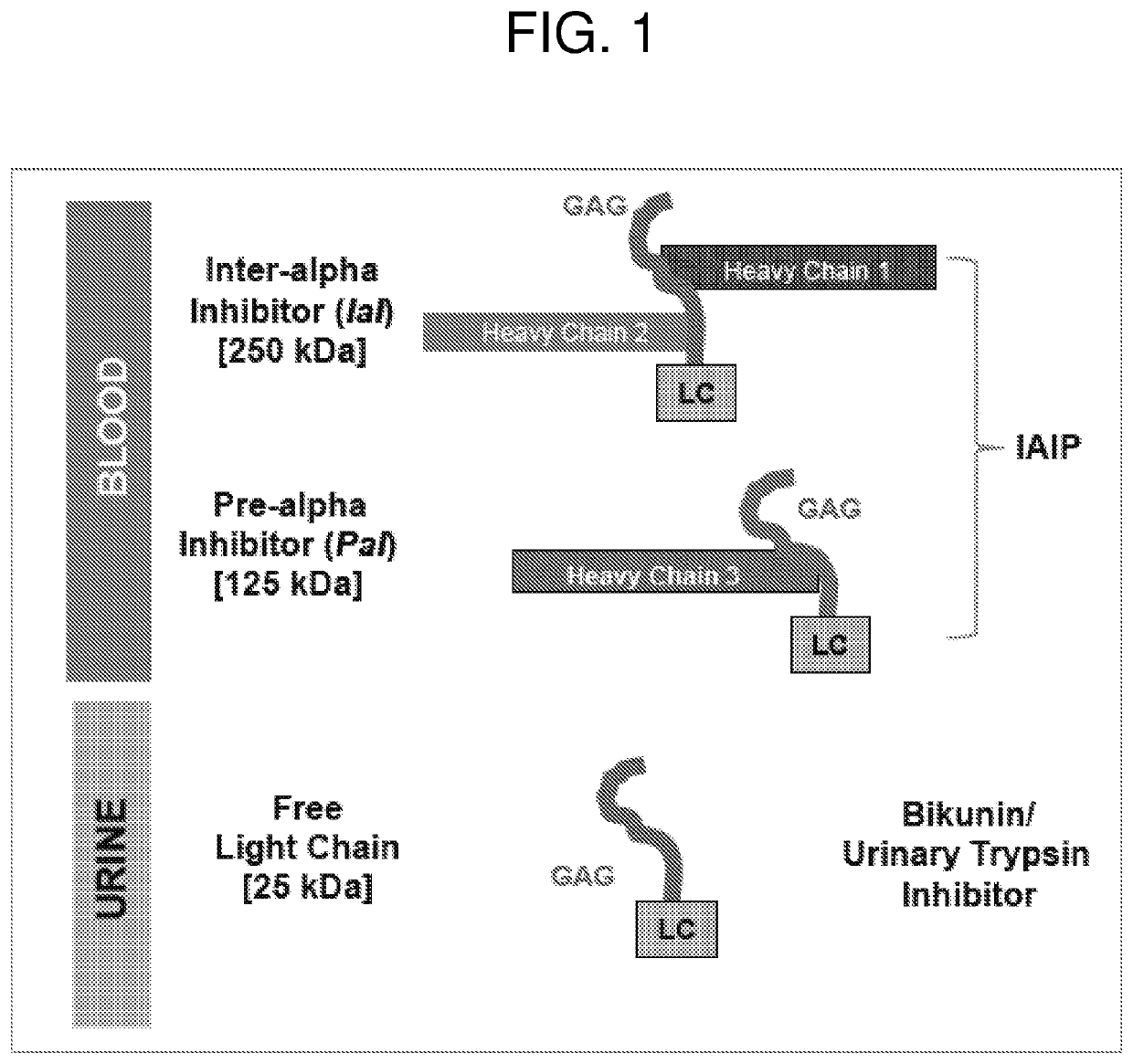
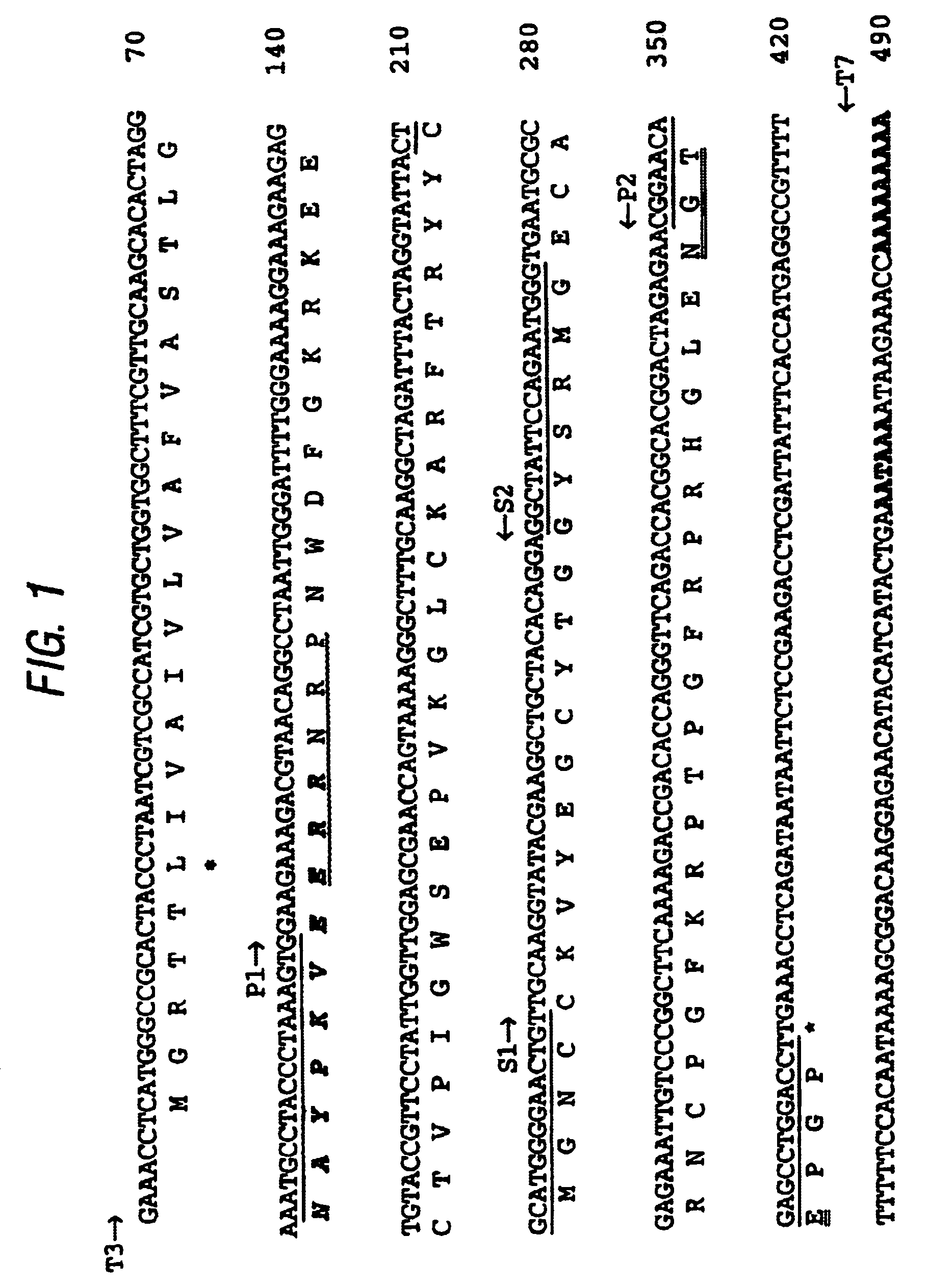
Preparation and composition of inter-alpha inhibitor proteins from human plasma for therapeutic use
ActiveUS7932365B2Reduce riskAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood plasmaRheumatoid arthritis
The invention relates to Inter-alpha inhibitor proteins (IαIp). The invention further relates to processes for purification of IαIp compositions and their use for treatment of human diseases such as sepsis and septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer and infectious diseases.
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
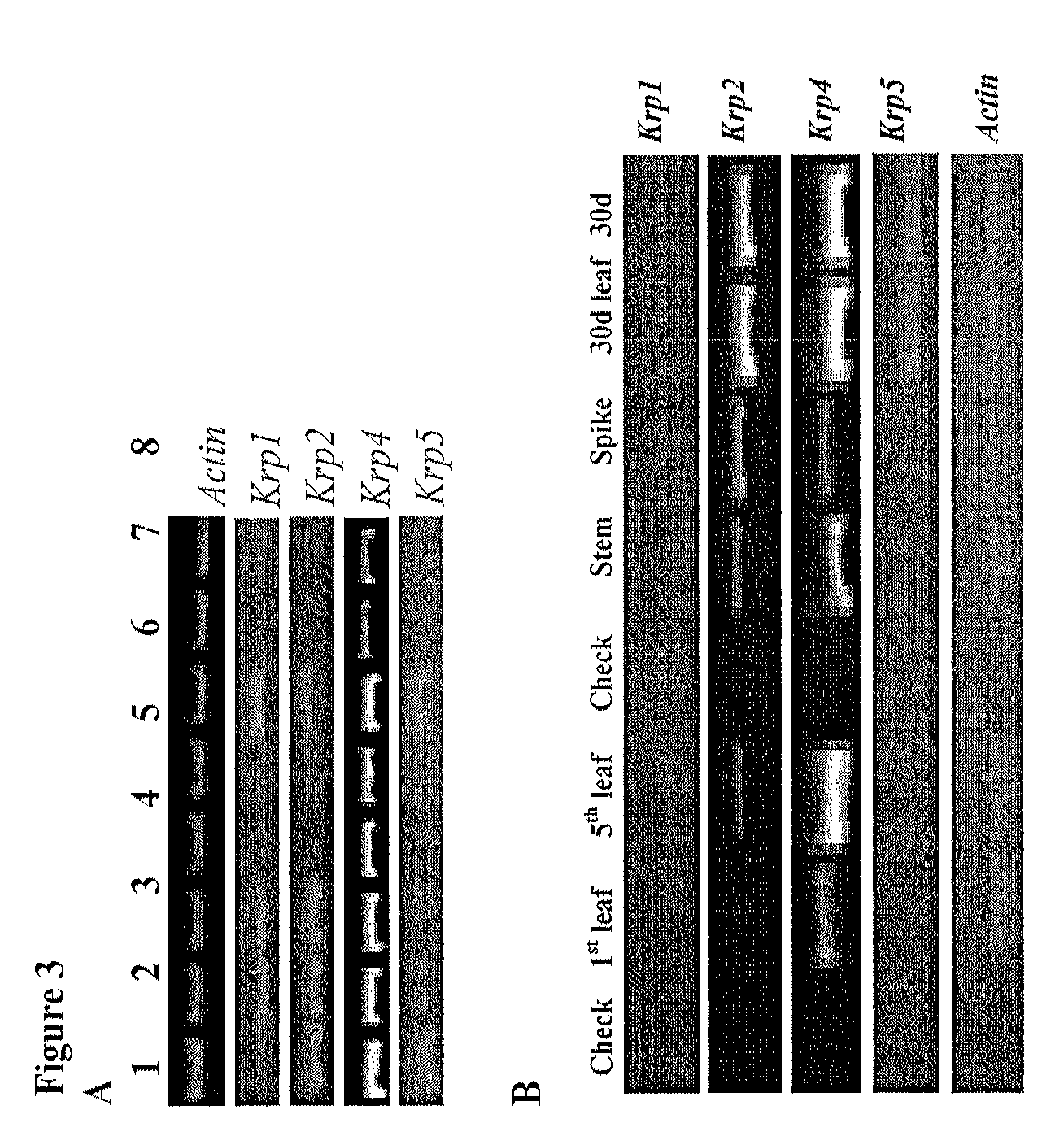
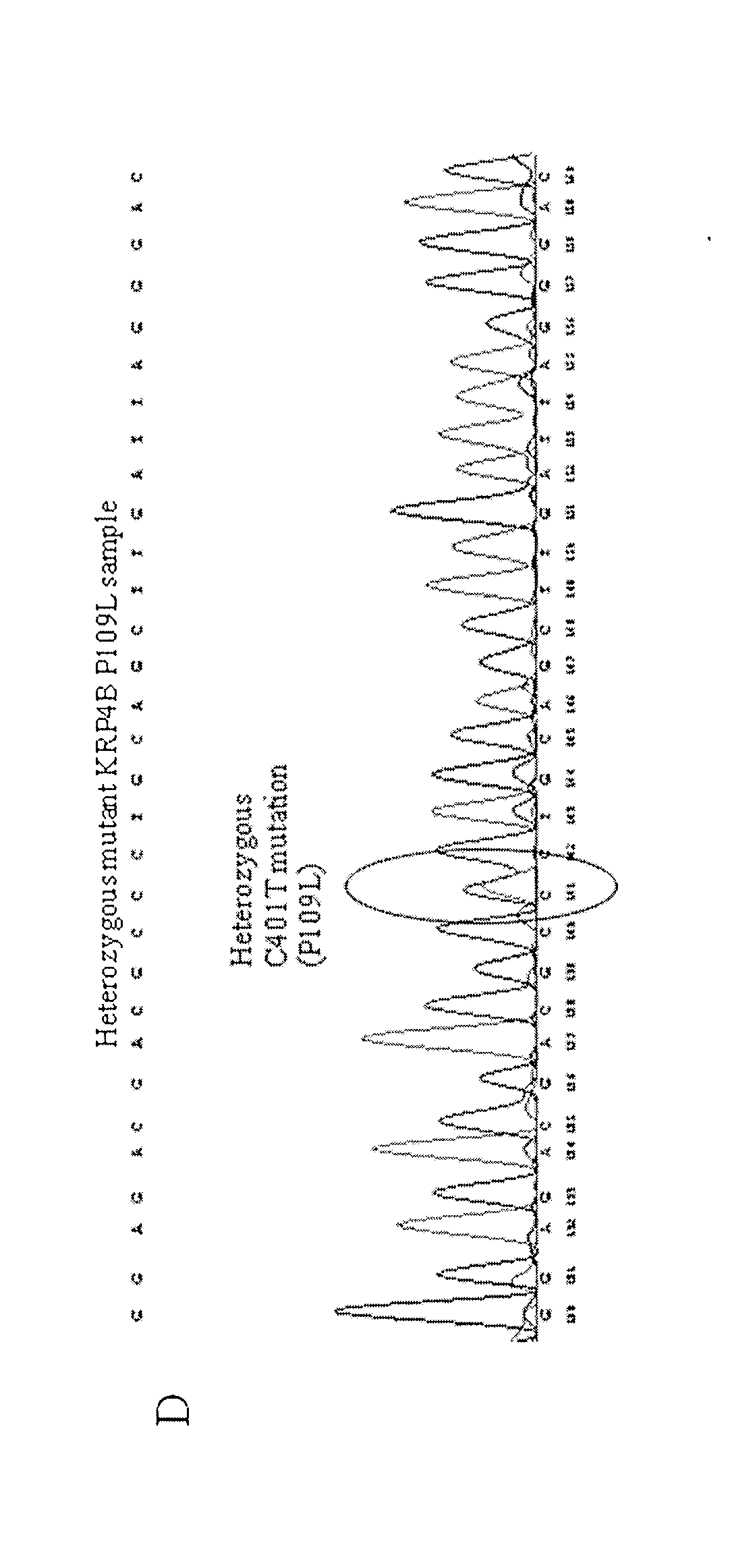
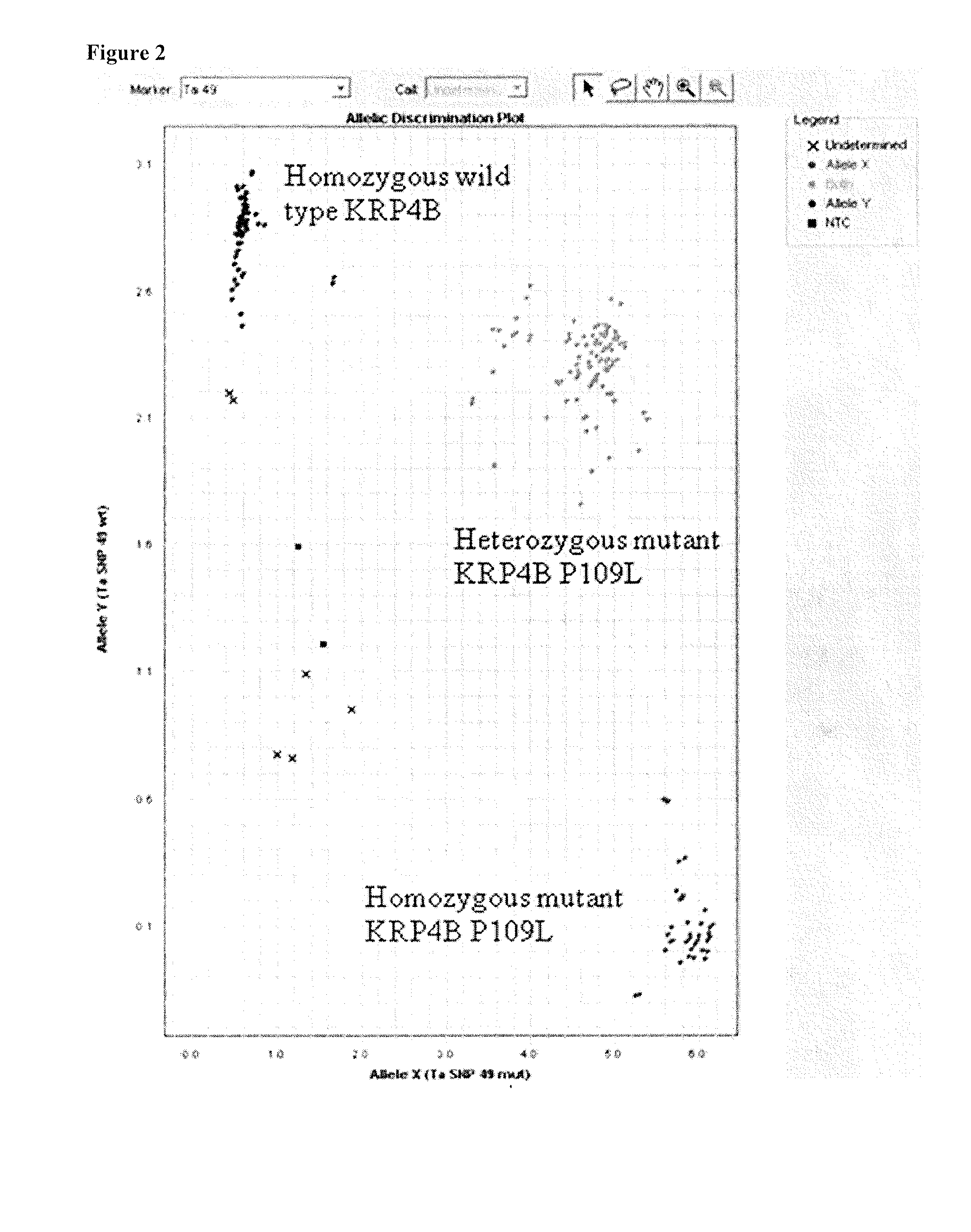
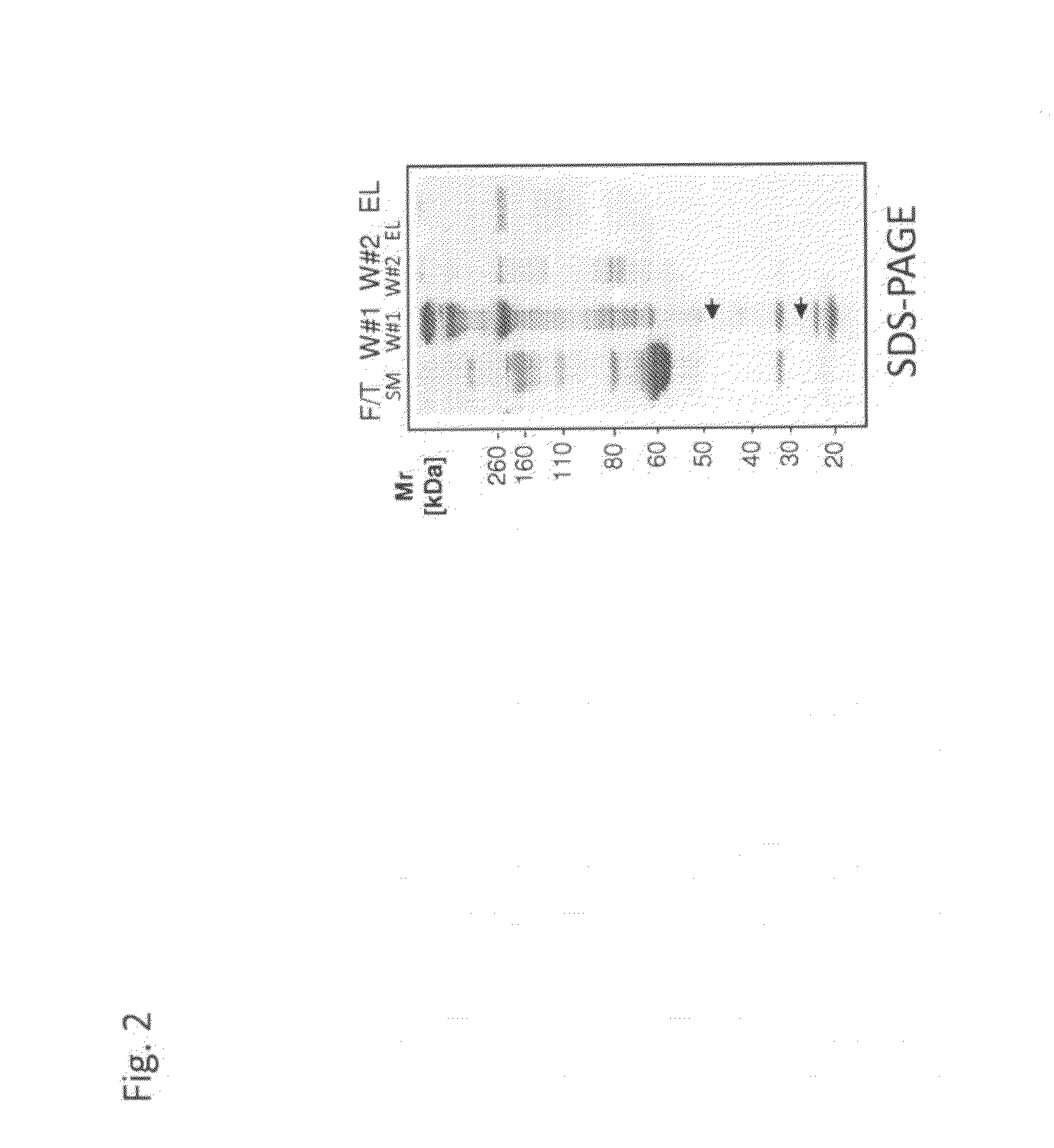
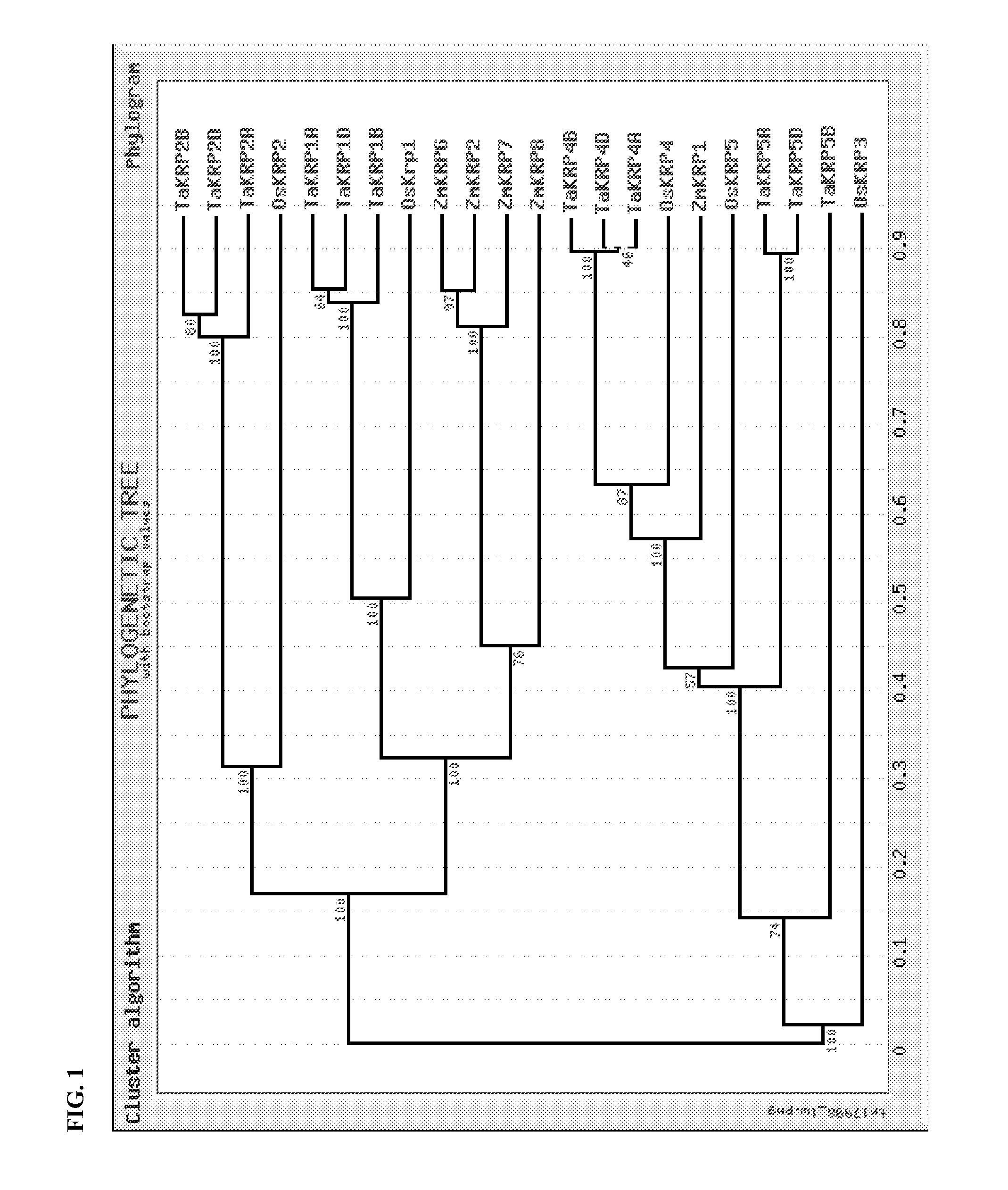
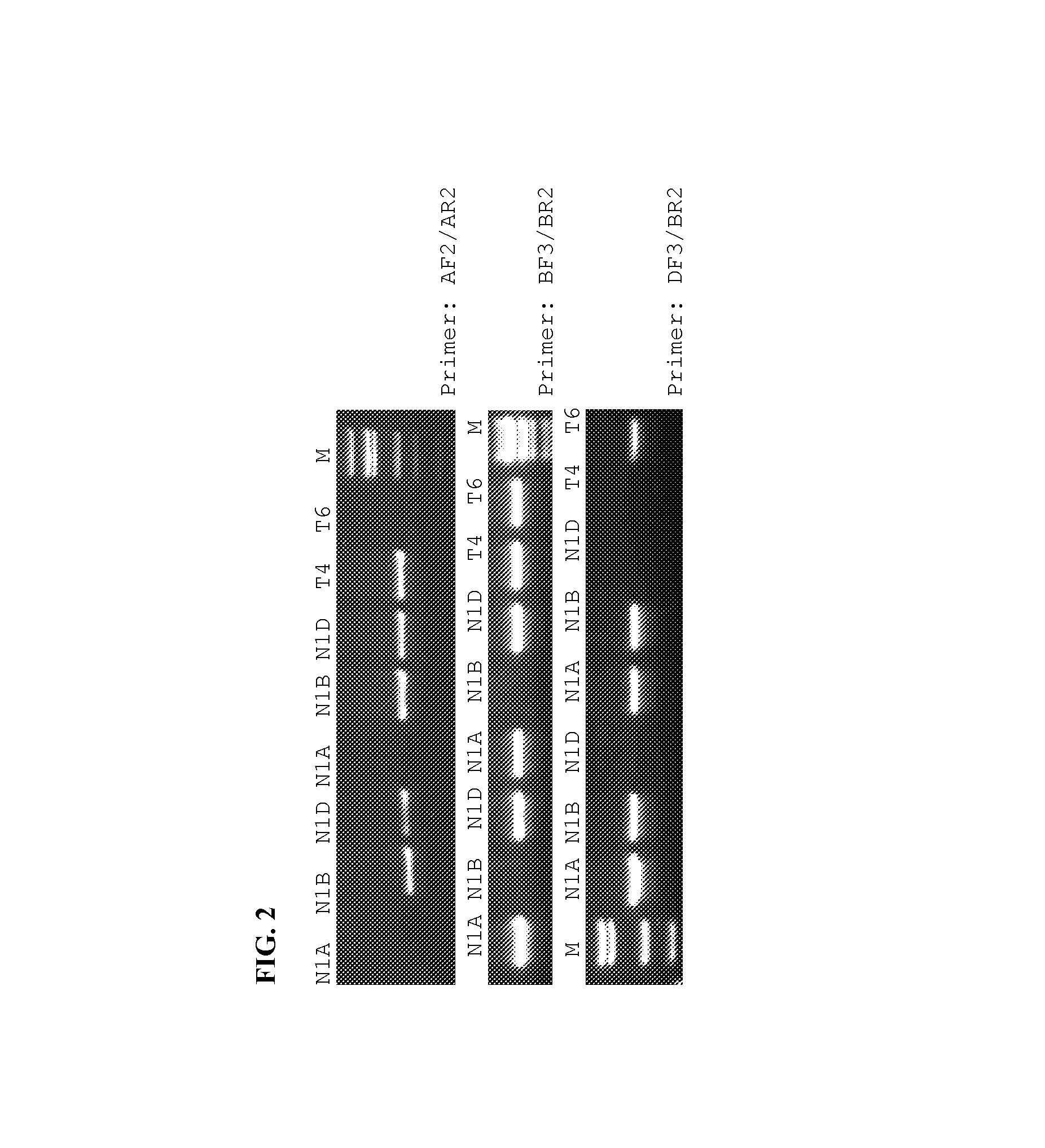
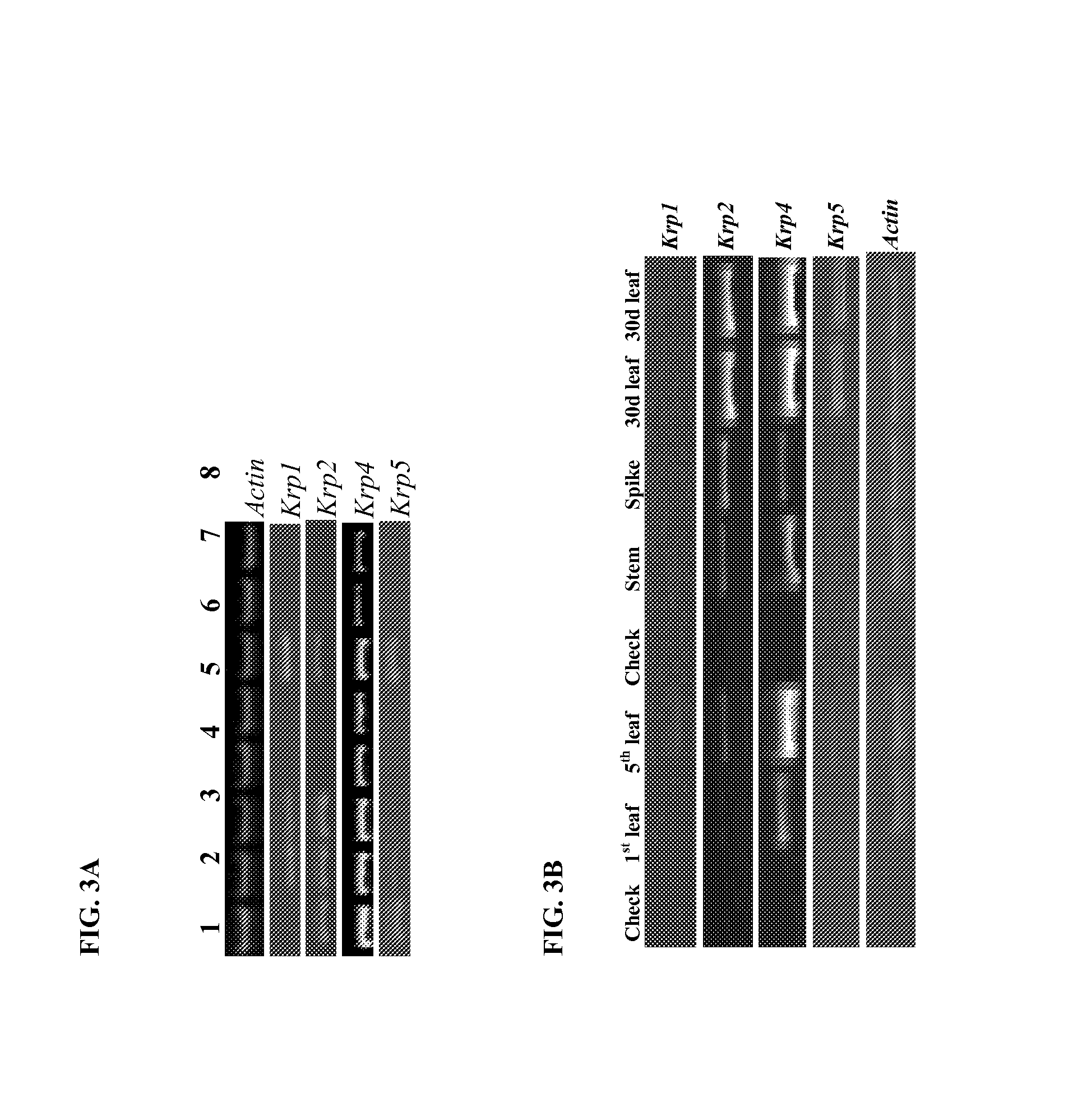
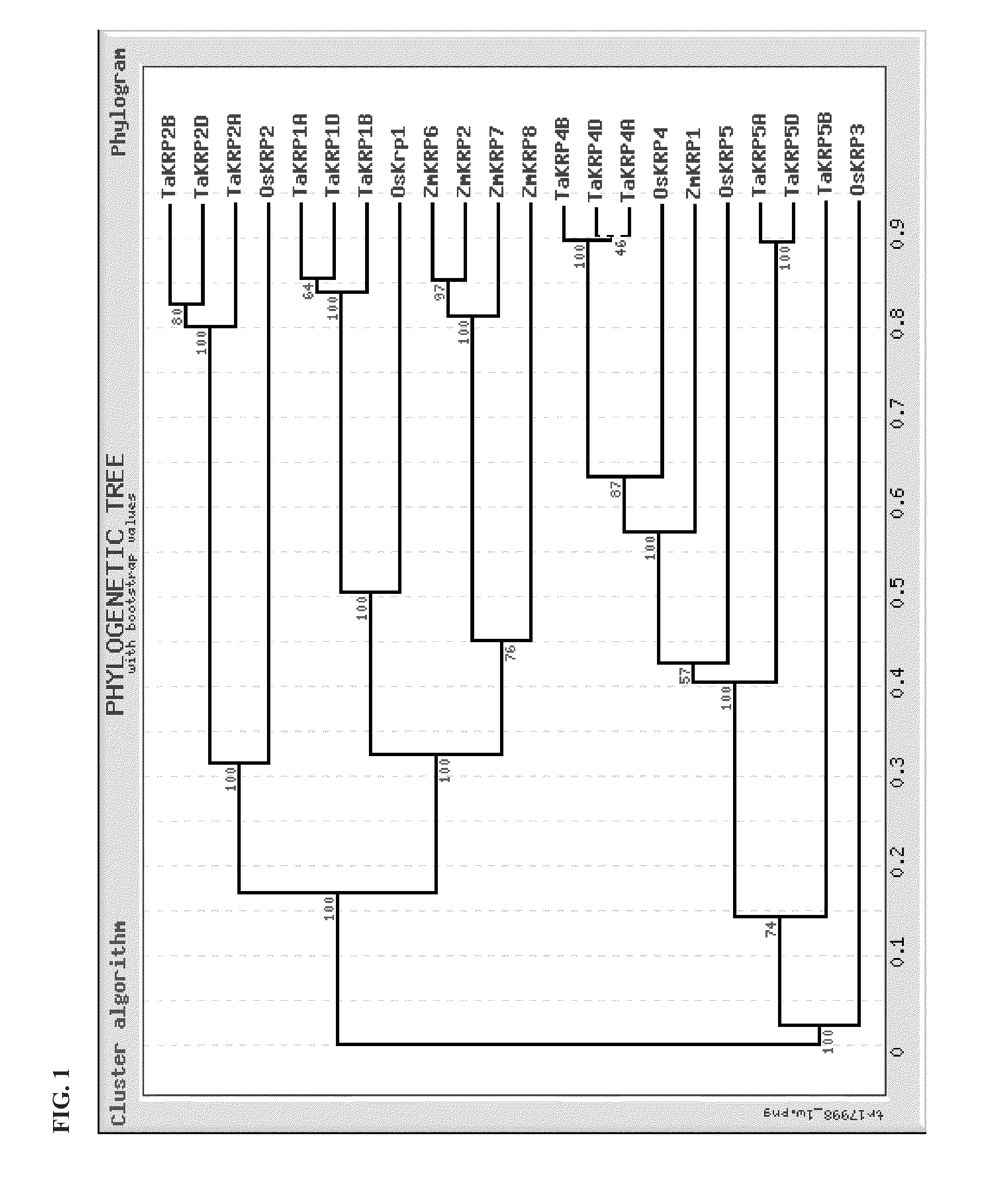
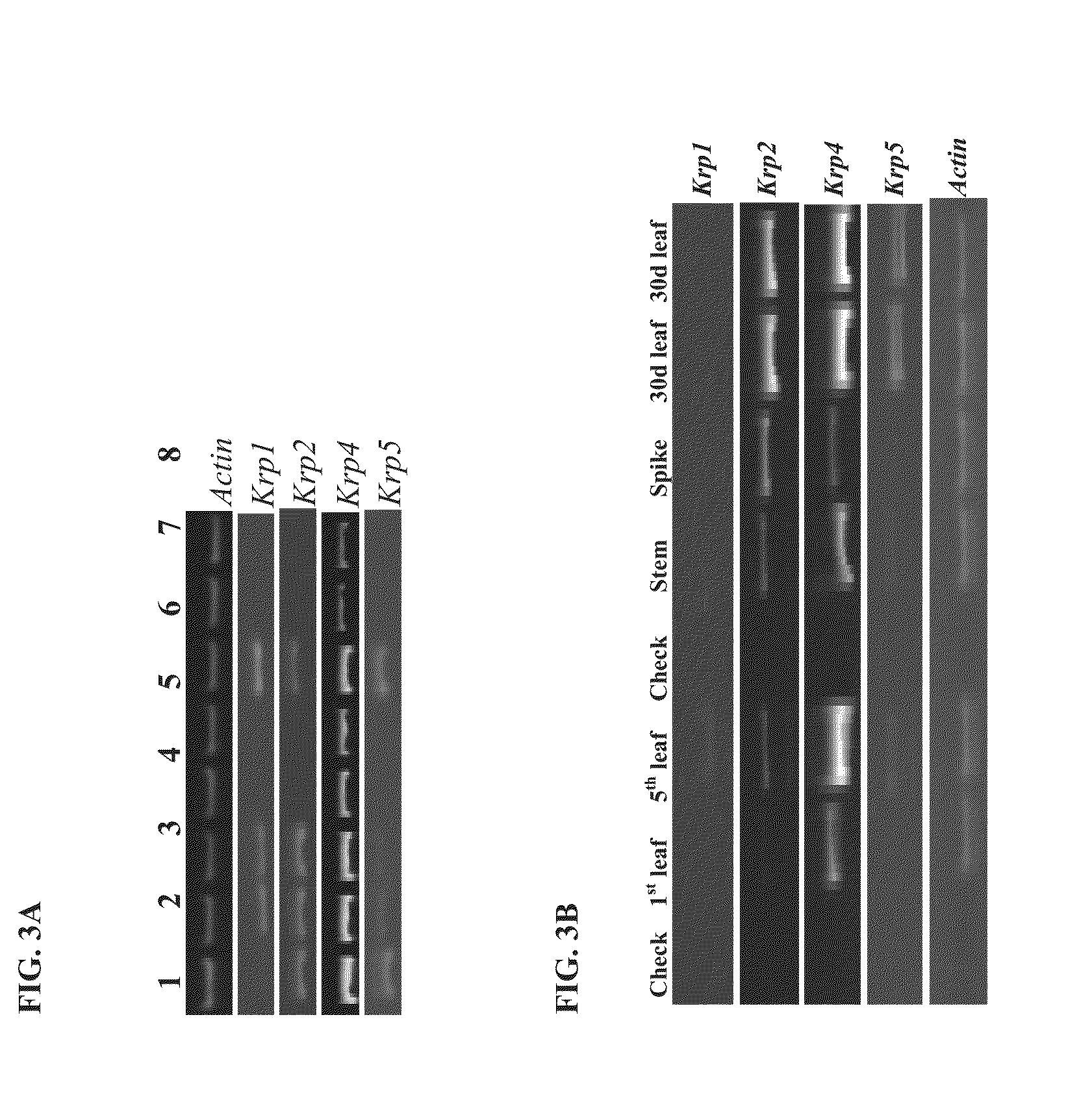
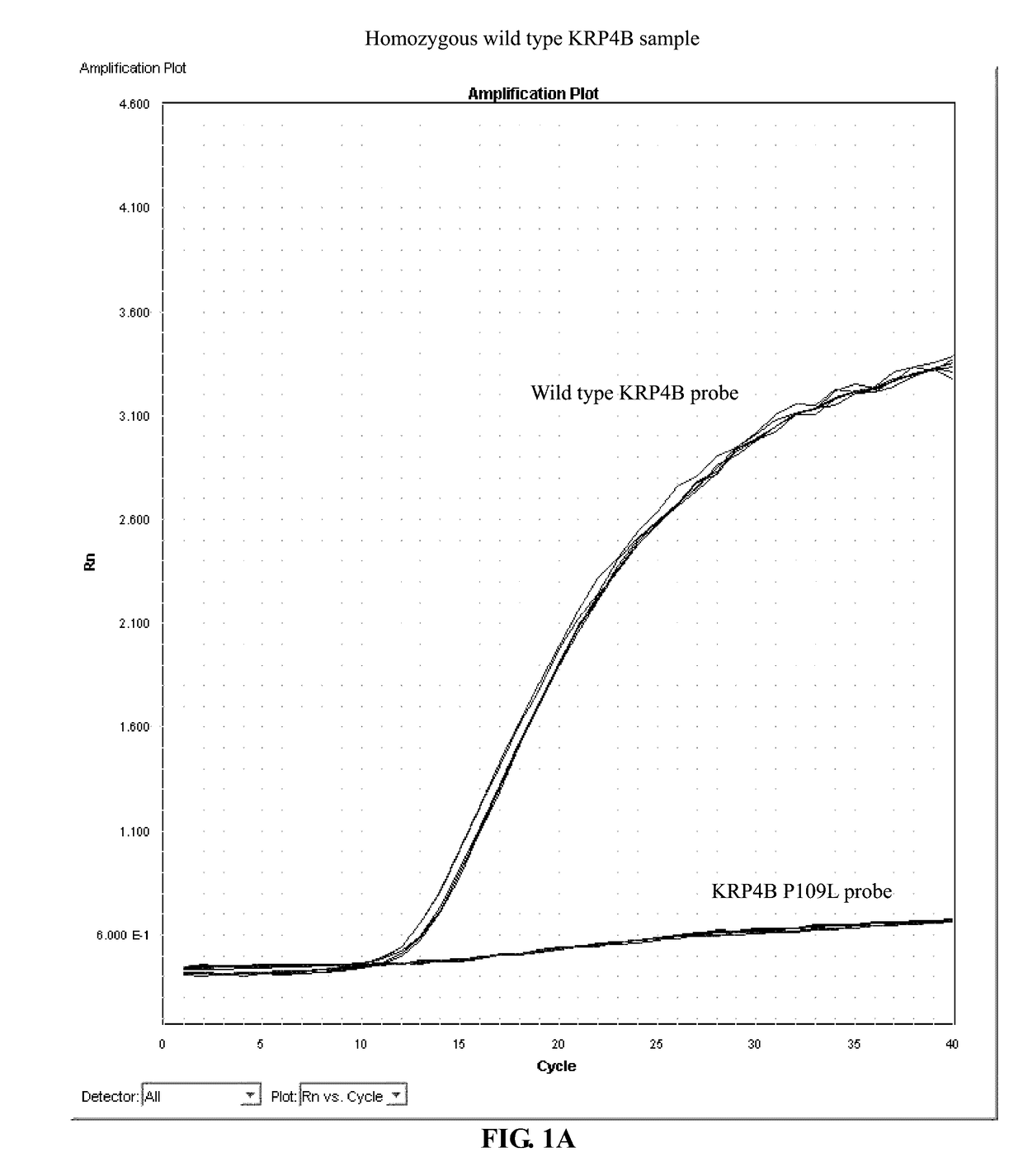
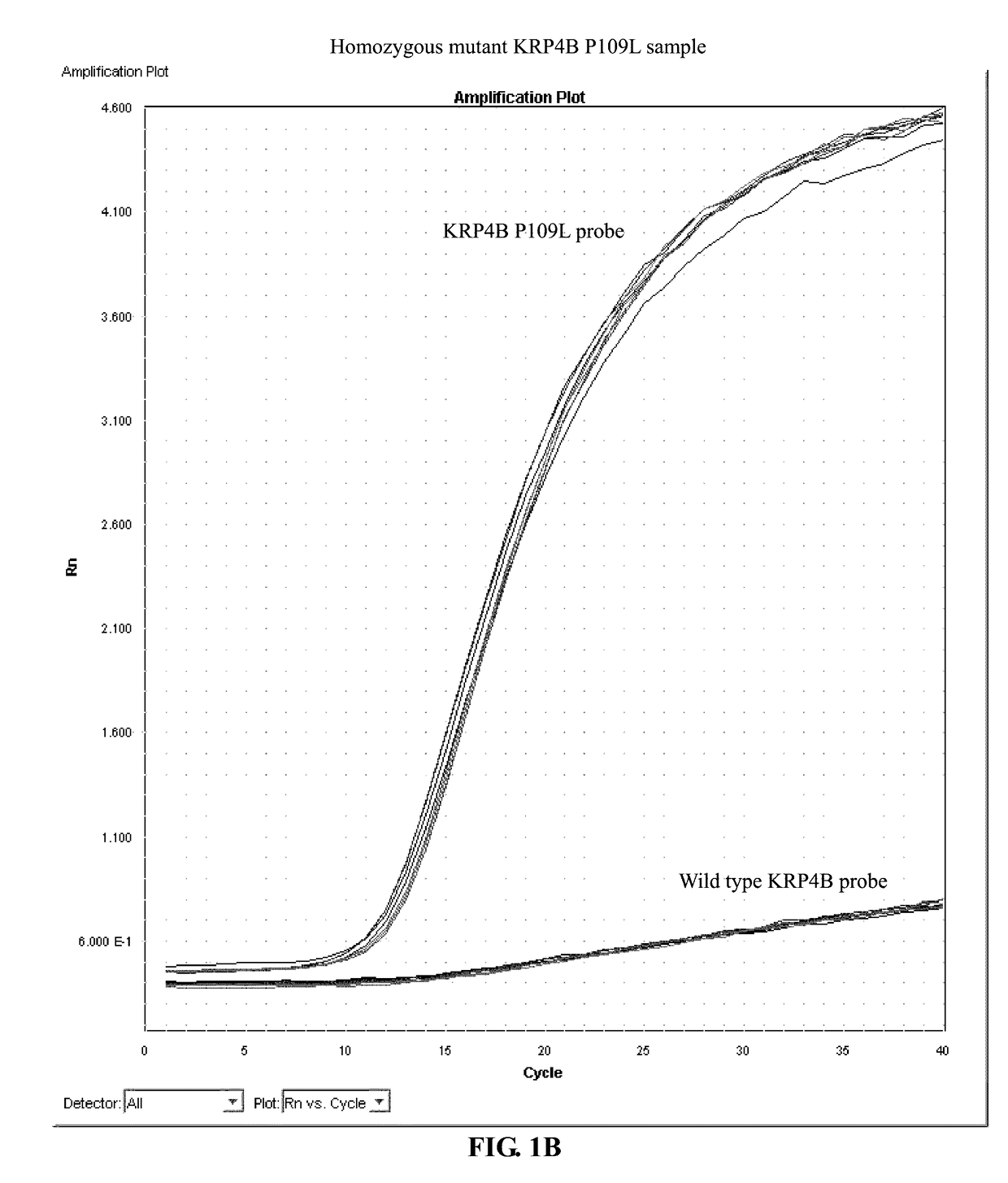
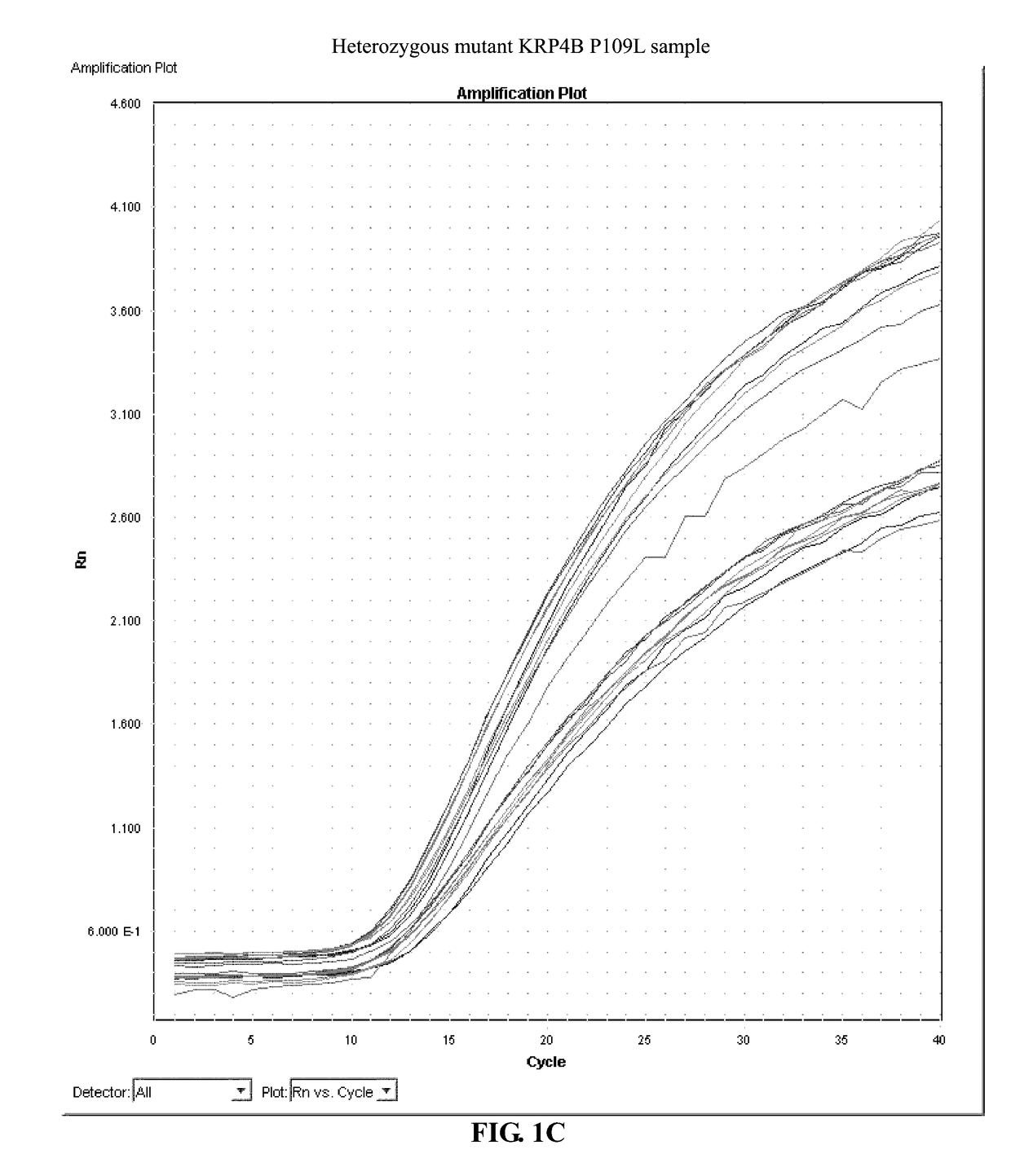
Identification and use of krp mutants in wheat
InactiveUS20120284813A1Improved agronomicImproved horticultural characteristicImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiotechnologyMutant
The invention provides a wheat cell, part, tissue culture or whole plant comprising at least one disrupted KRP gene of the present invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield of a wheat plant by utilizing the disrupted KRP genes of the present invention. Furthermore, methods of breeding wheat plants to produce new wheat plants having increased weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield are provided. The present invention provides isolated Kinase Inhibitor Protein (KIP) Related Protein (KRP) polynucleotide sequences and isolated KRP polypeptide sequences and methods of their use.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH +1
Preparation And Composition Of Inter-Alpha Inhibitor Proteins From Human Plasma For Therapeutic Use
ActiveUS20070297982A1Reducing risk of mortalityReduce riskAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood plasmaRheumatoid arthritis
The invention relates to Inter-alpha inhibitor proteins (IαIp). The invention further relates to processes for purification of IαIp compositions and their use for treatment of human diseases such as sepsis and septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer and infectious diseases.
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
Preparation and composition of inter-alpha inhibitor proteins from human plasma for therapeutic use
ActiveCN101160133AAvoid blockingReduce biological activityMammal material medical ingredientsDisease diagnosisBlood plasmaPyaemia
The present invention relates to an inner-alpha inhibitor protein (I alpha Ip). The invention also relates to a method for purifying the I alpha Ip composition and the usage for treating the human diseases such as pyaemia, septicemic shock, atrophic arthritis, cancer and infectious disease.
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
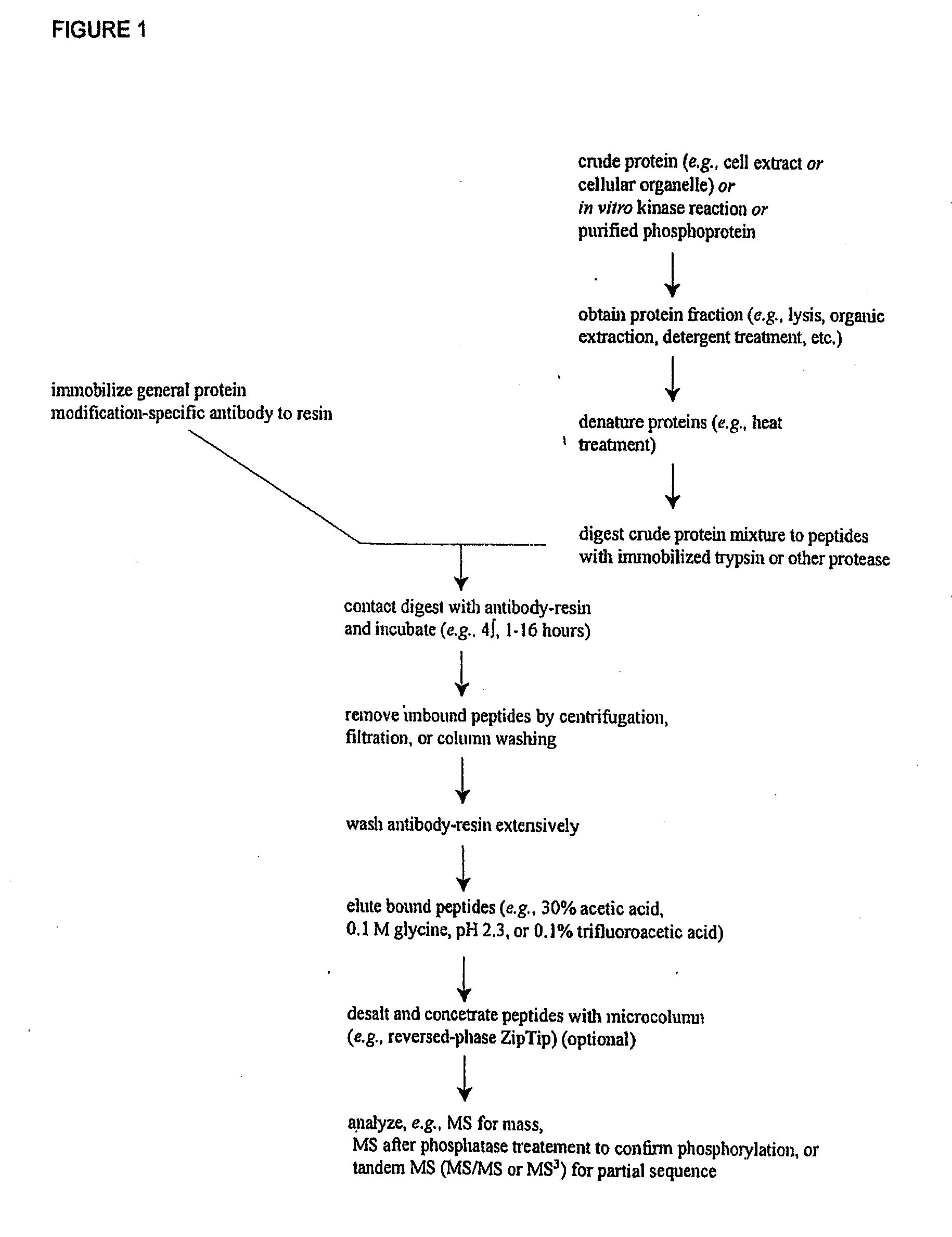
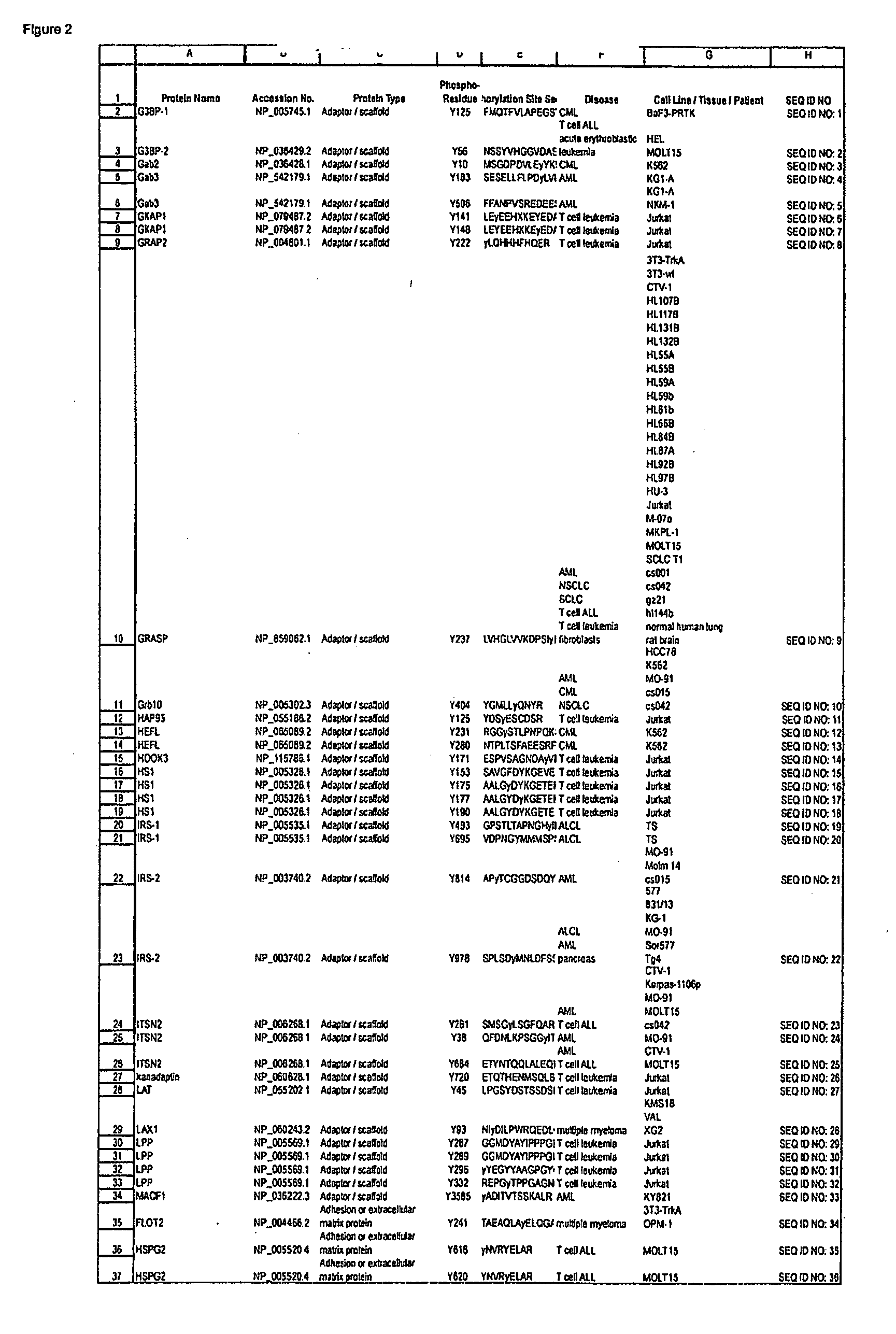
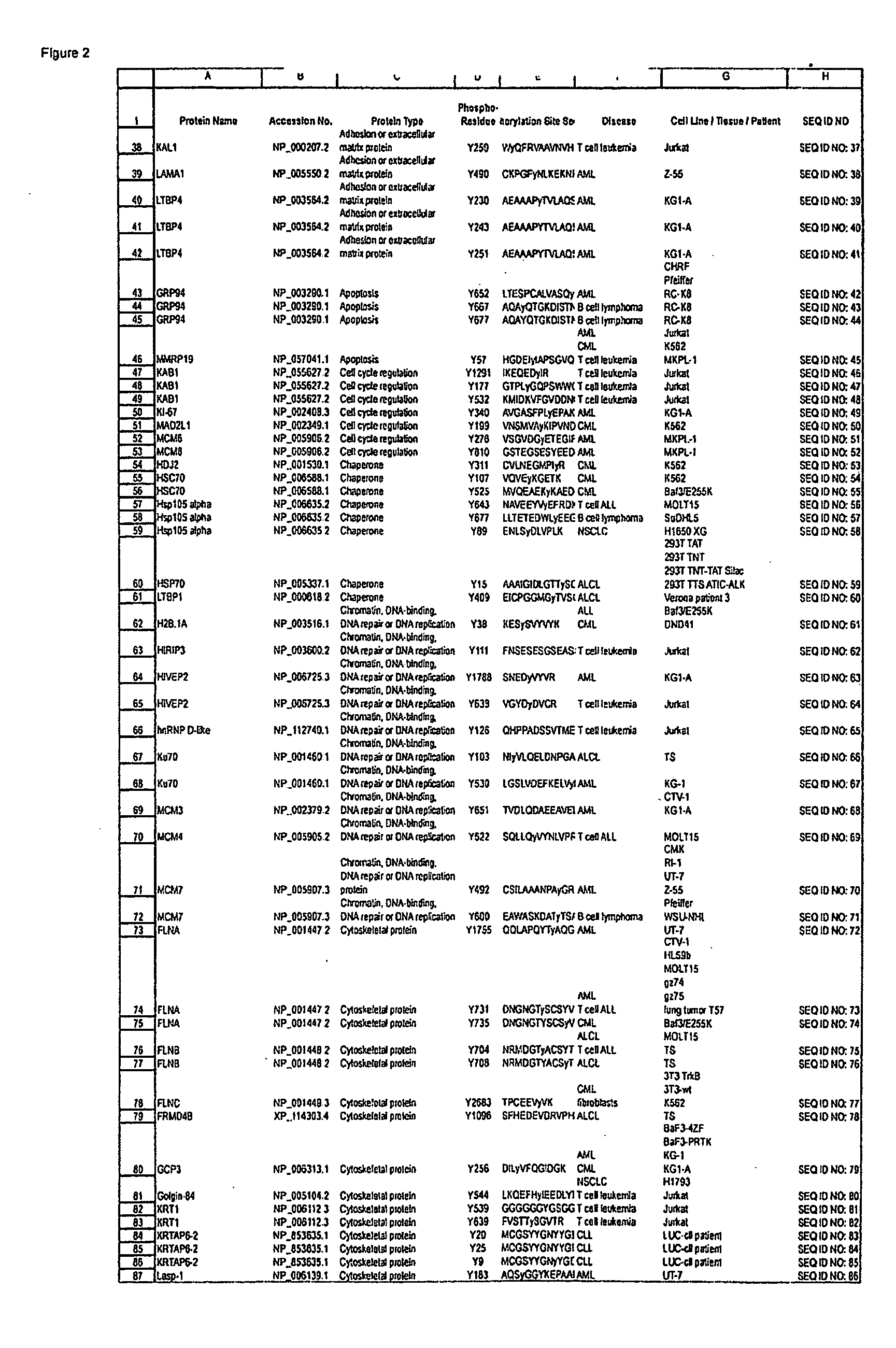
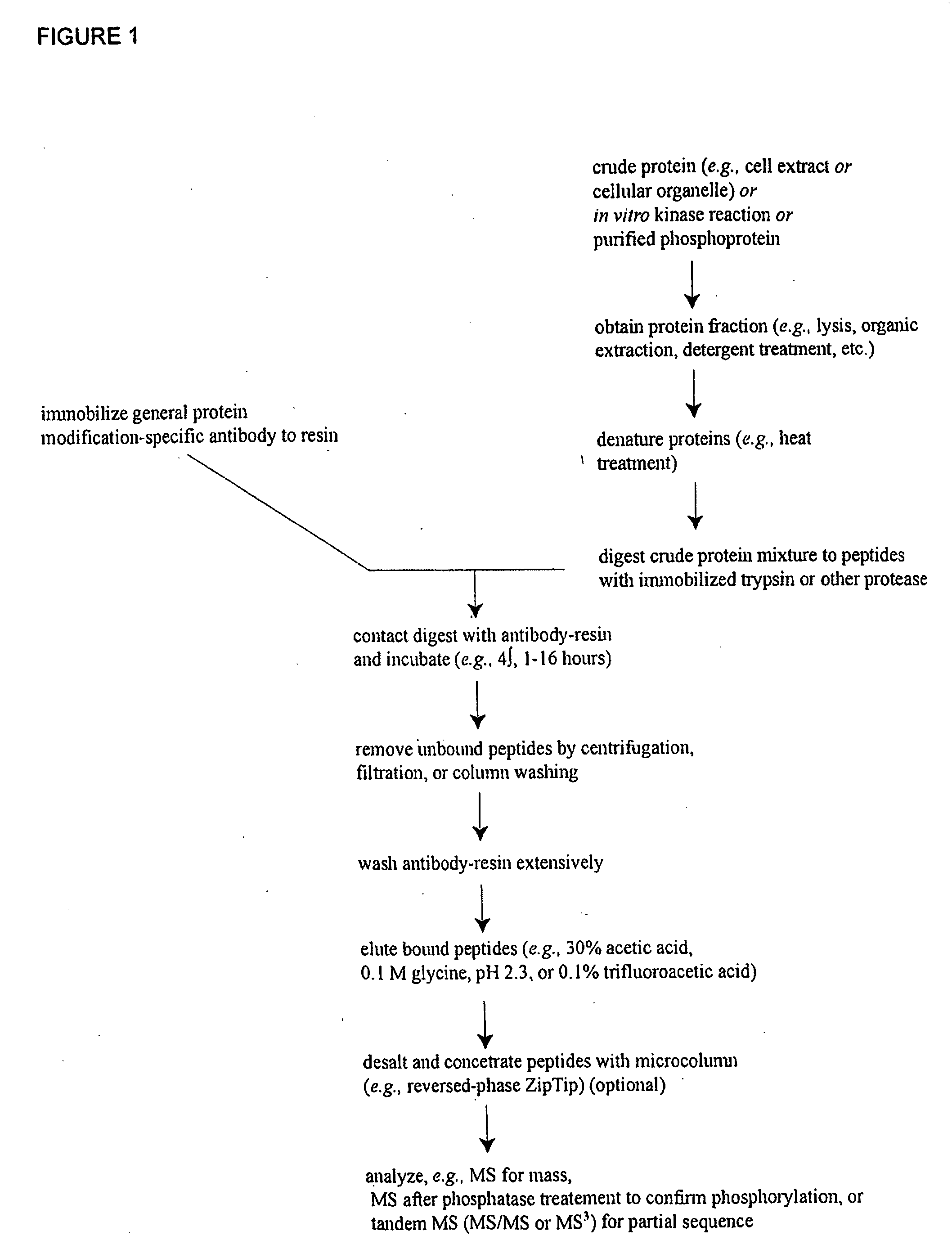
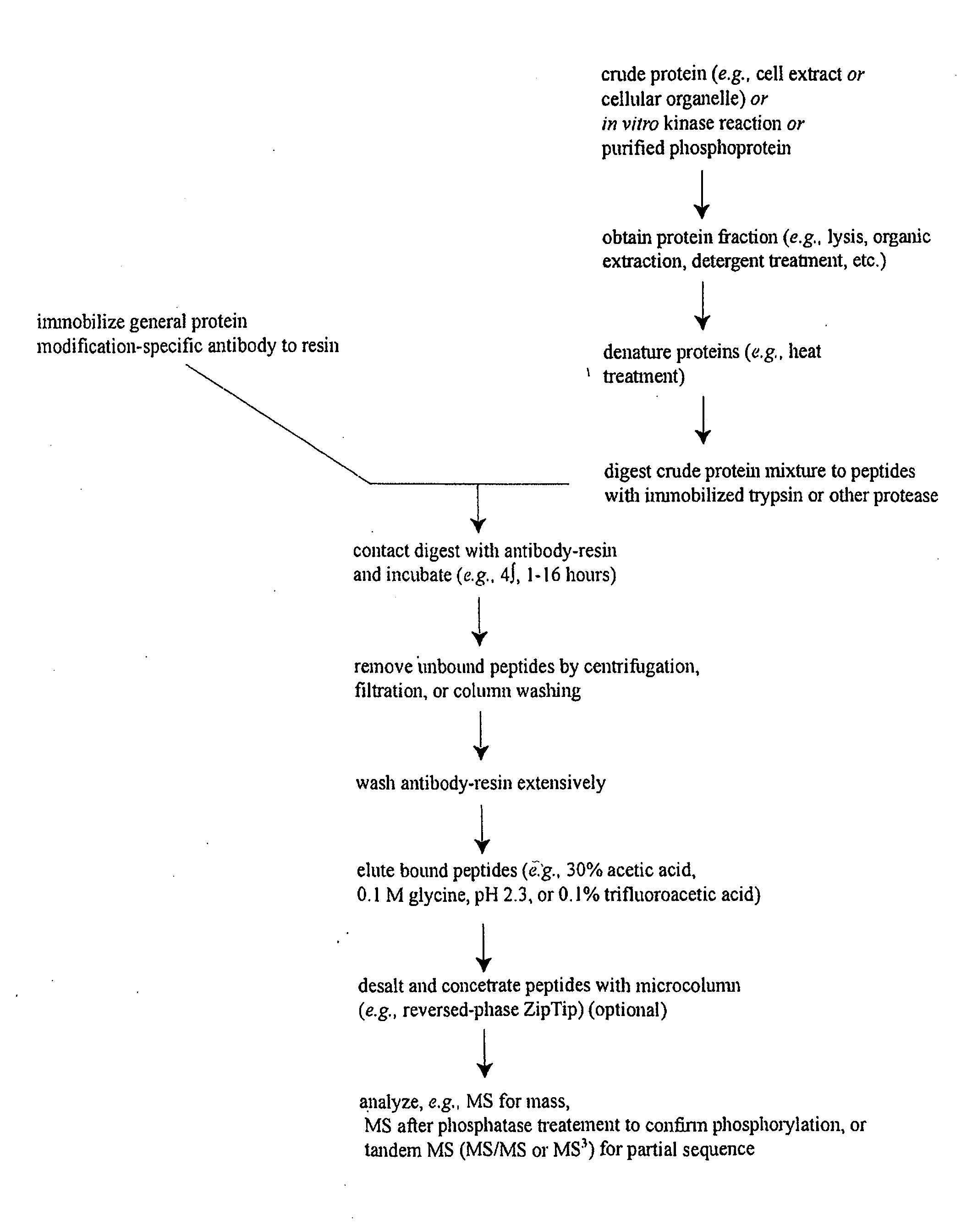
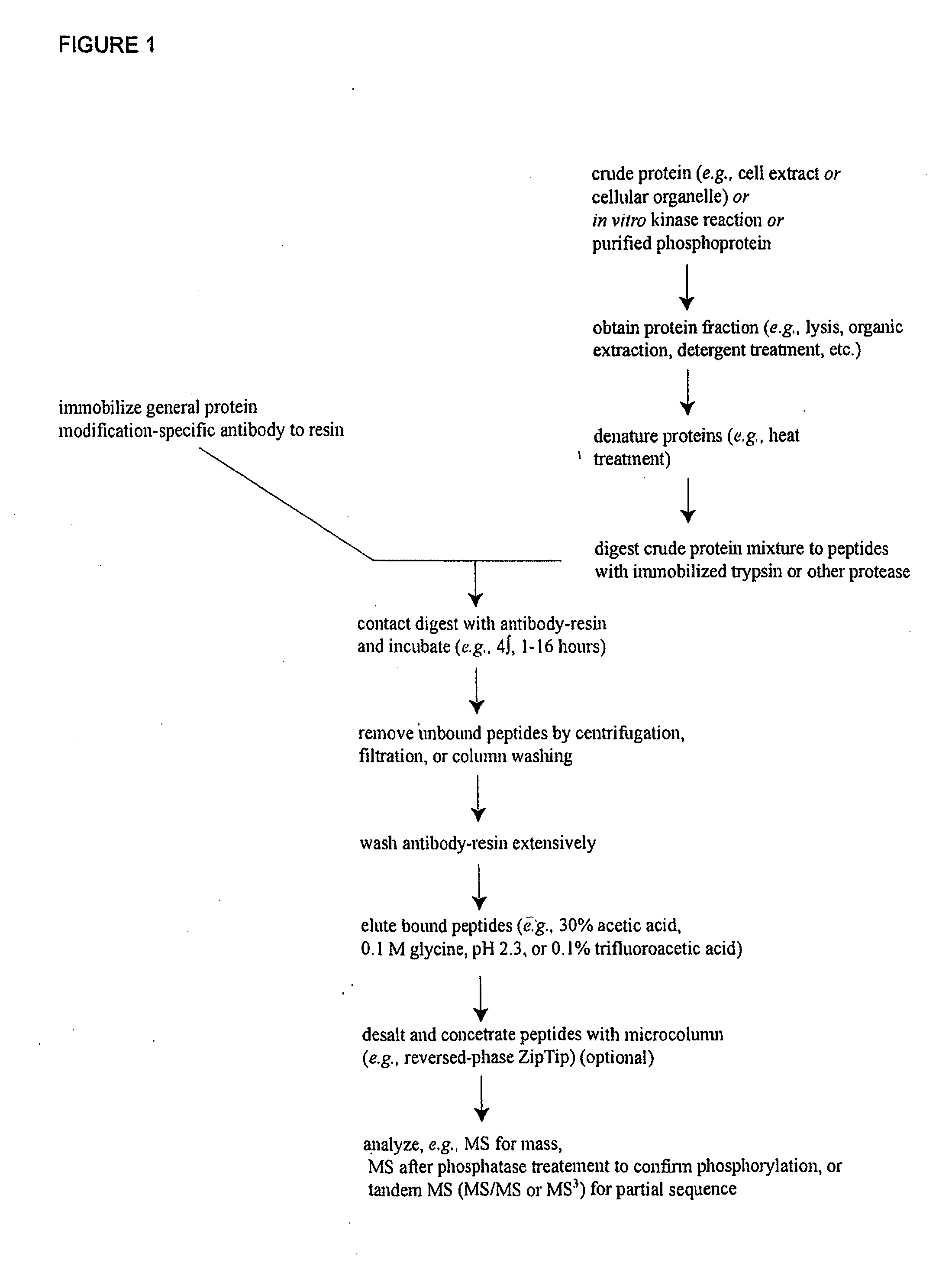
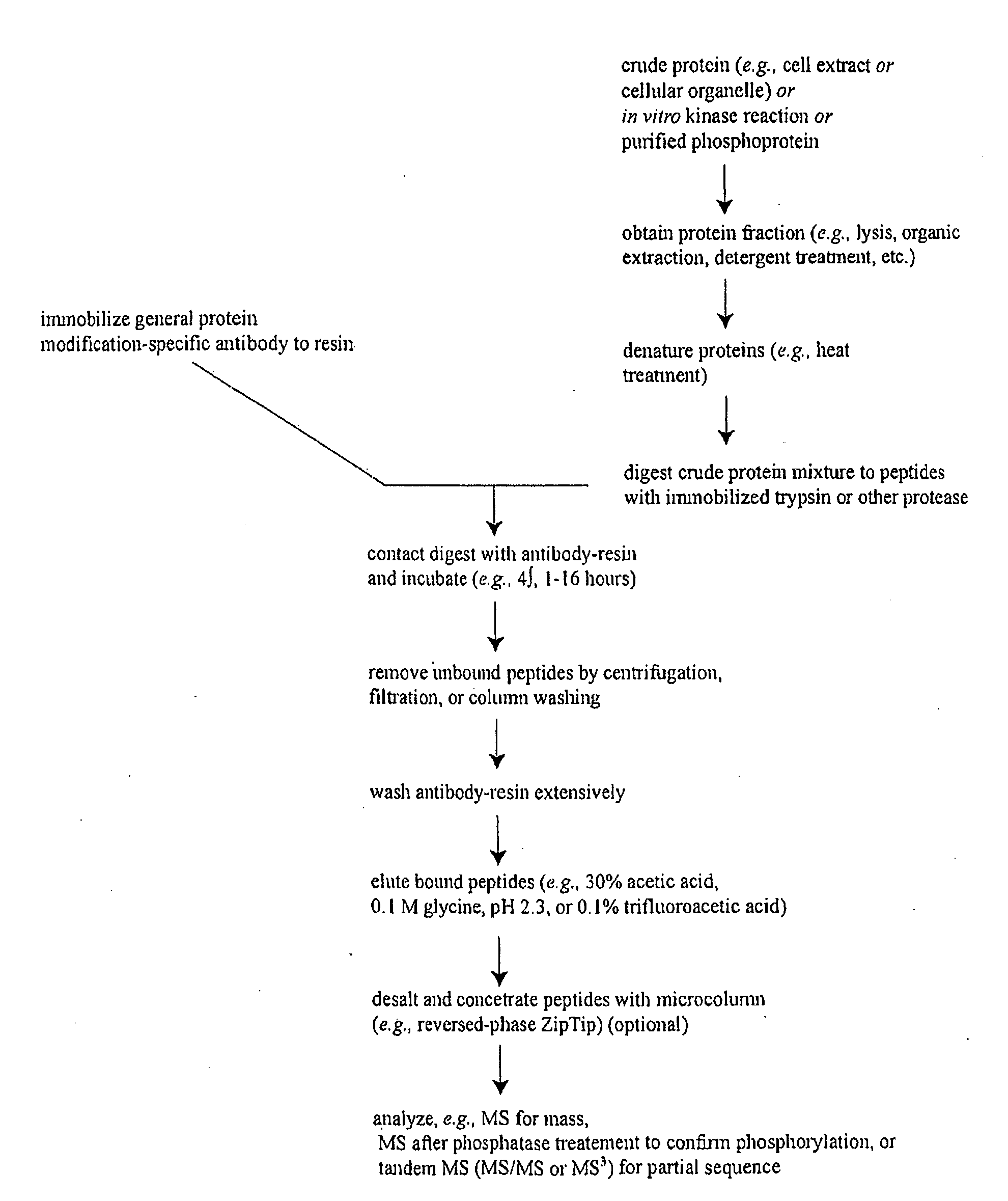
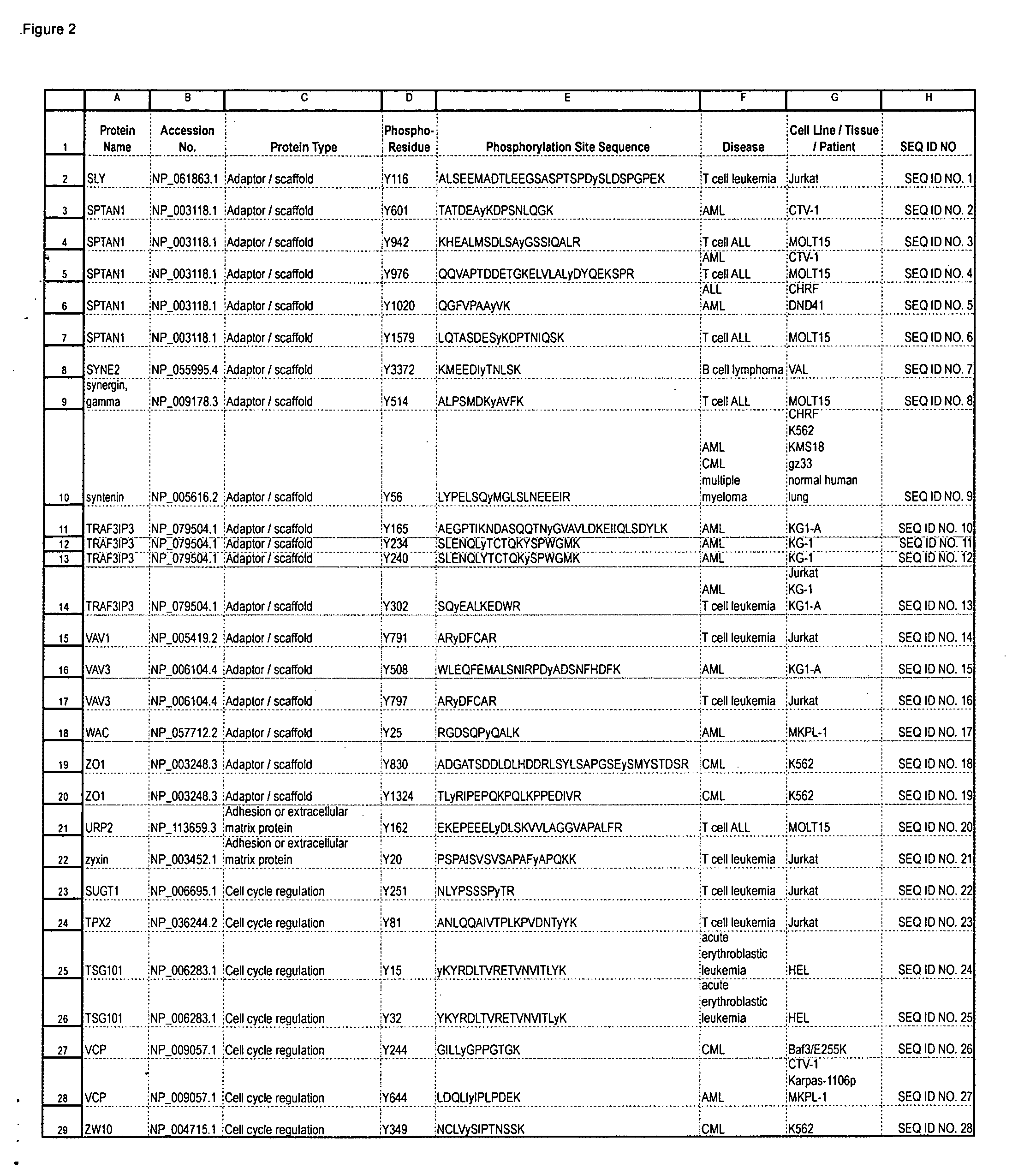
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100009463A1Animal cellsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsCell Surface ProteinsPhosphorylation
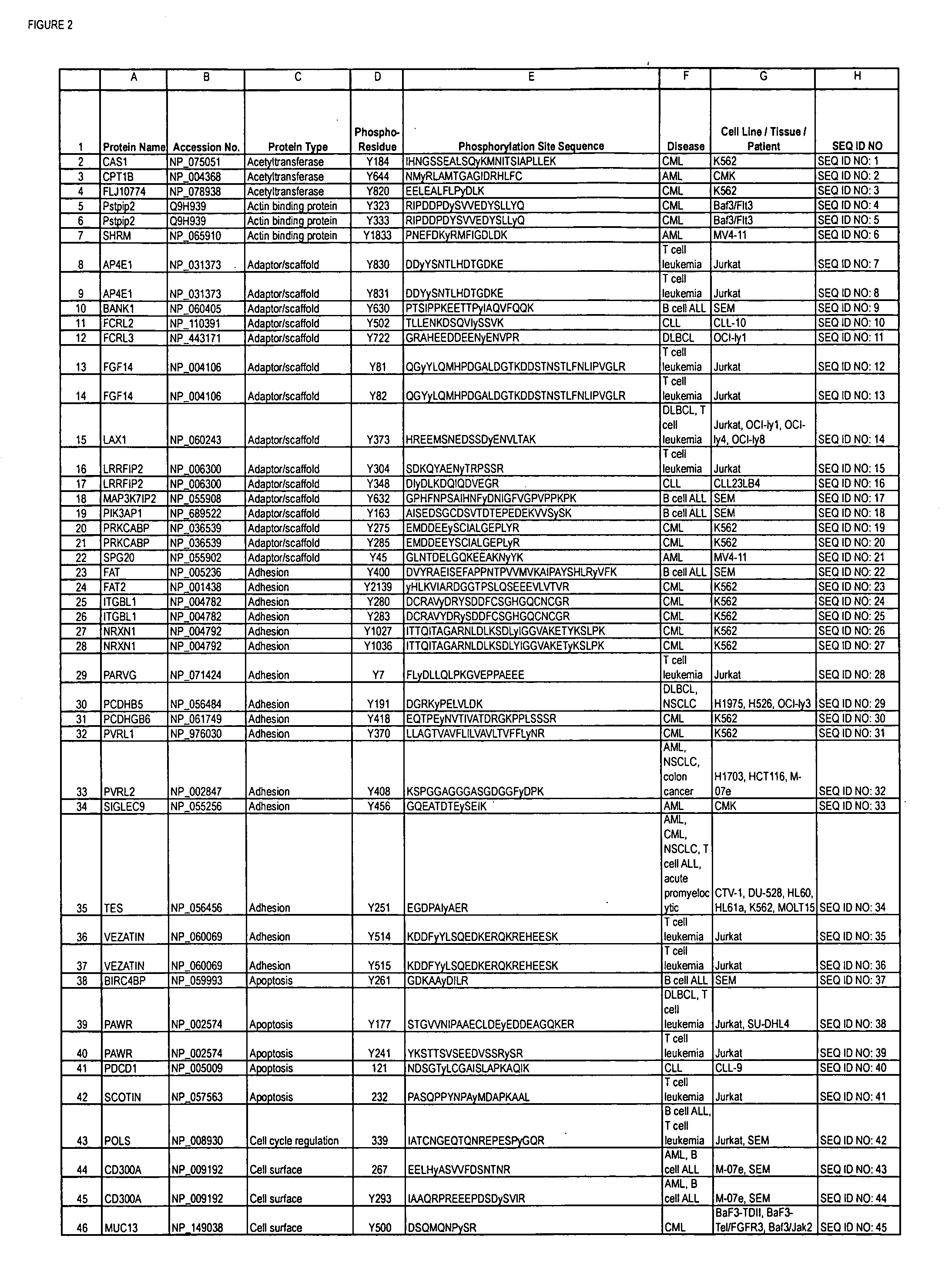
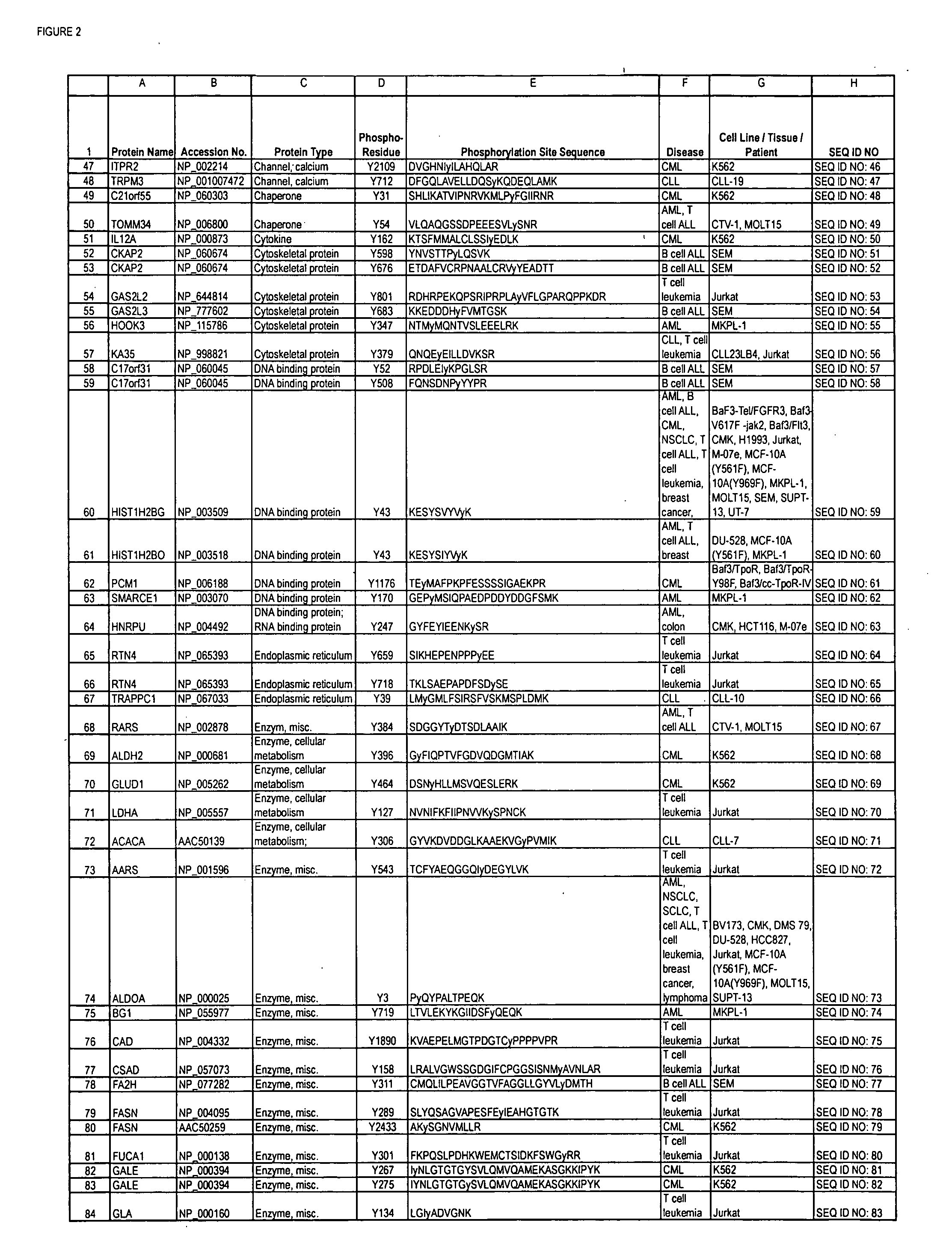
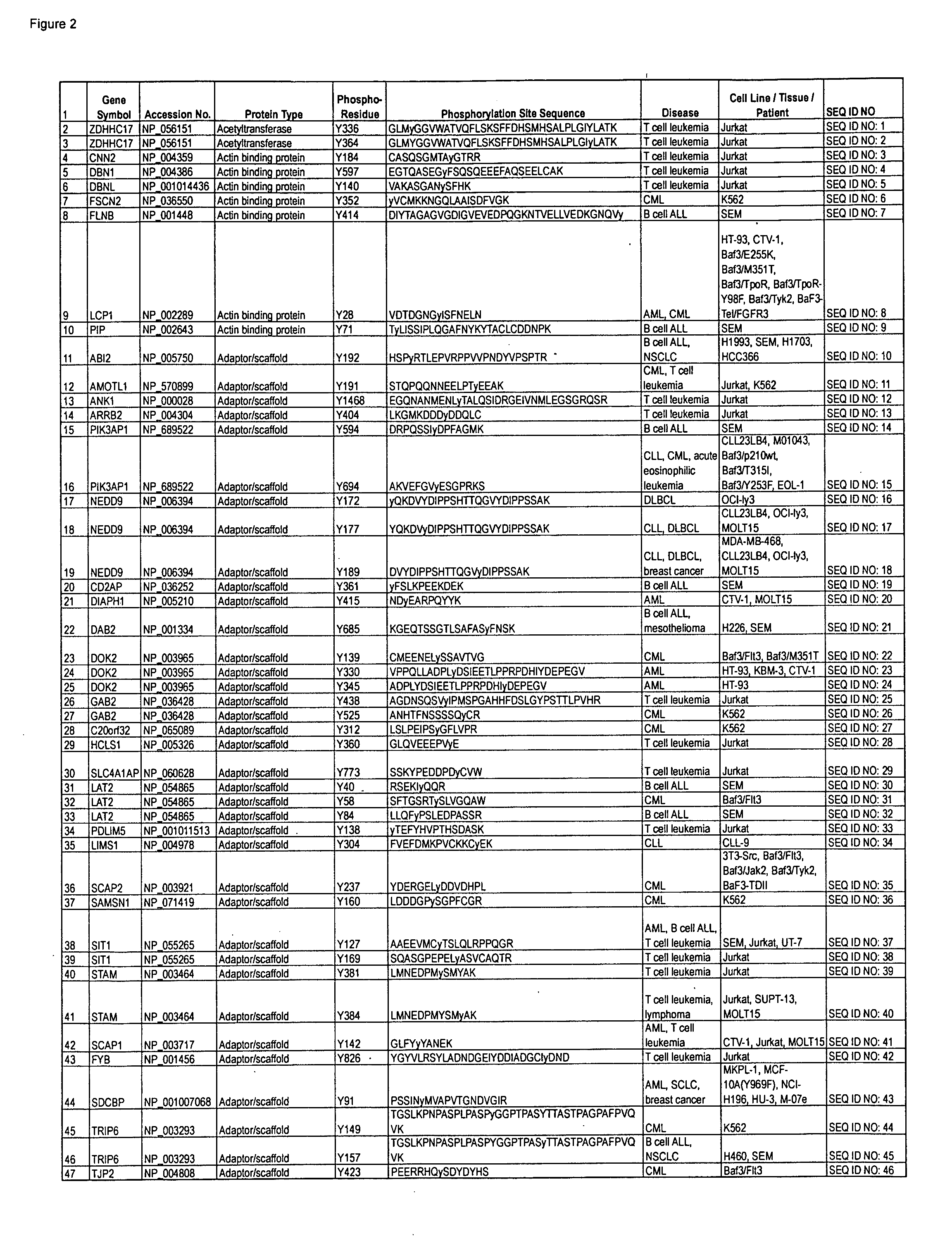
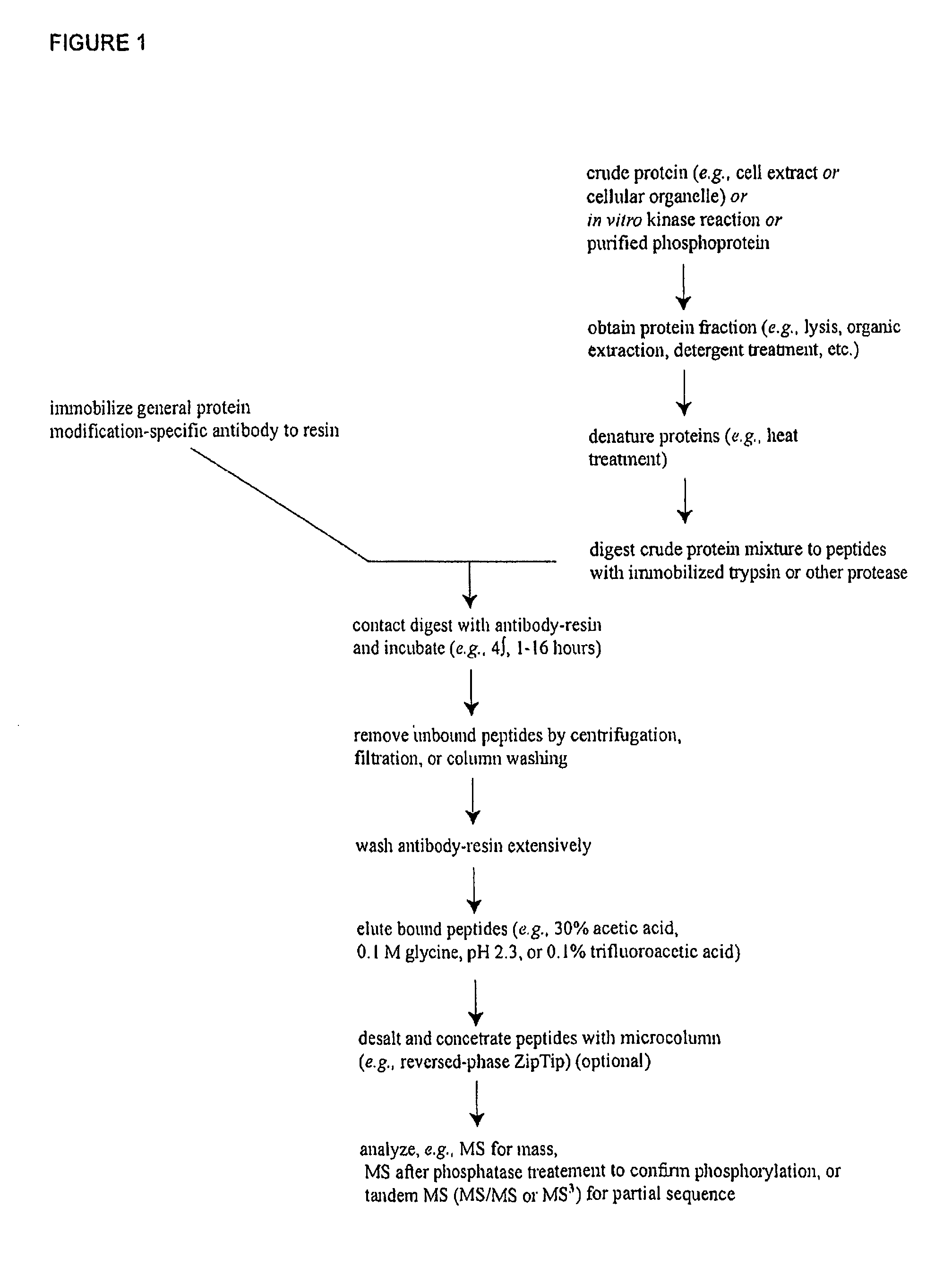
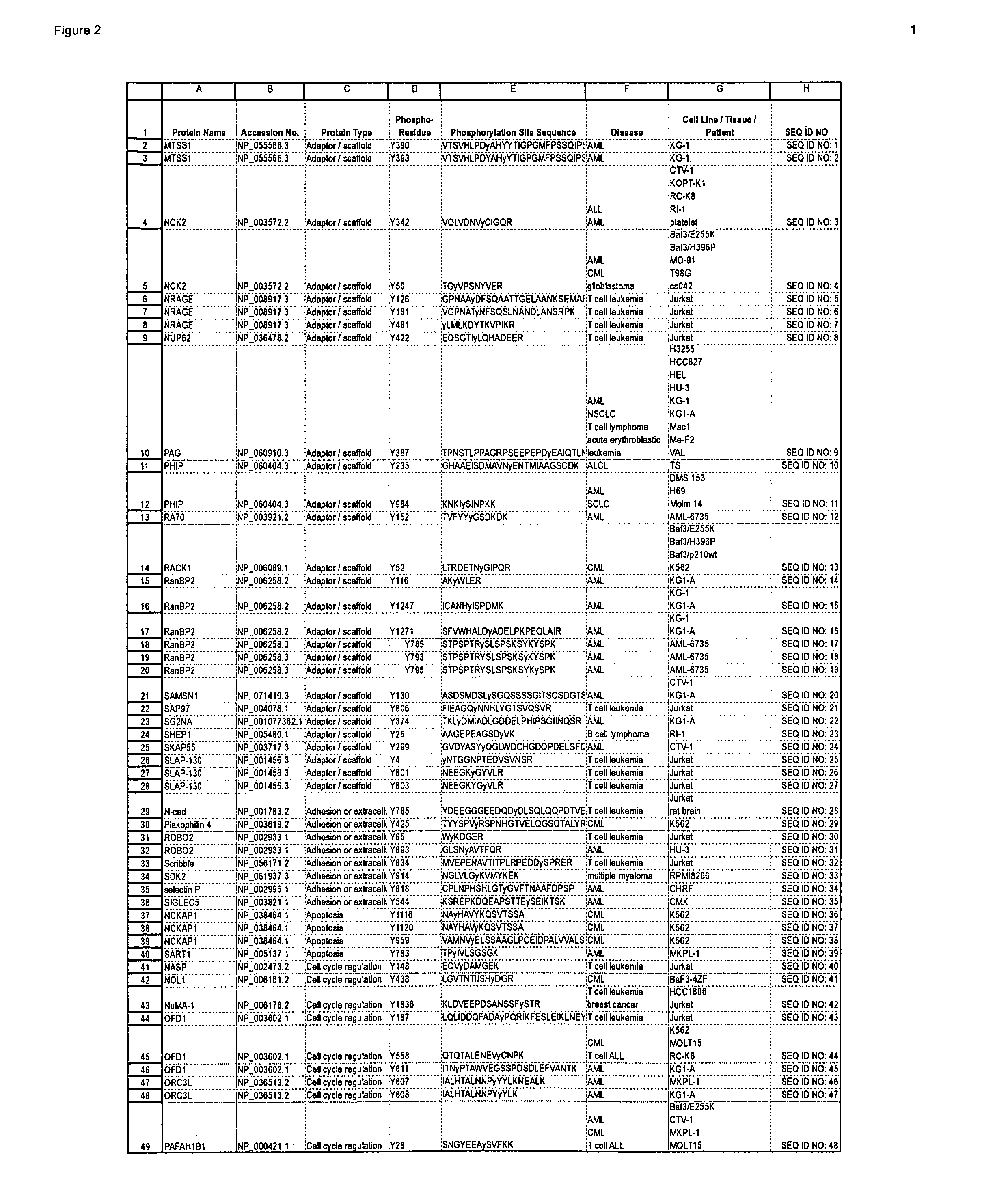
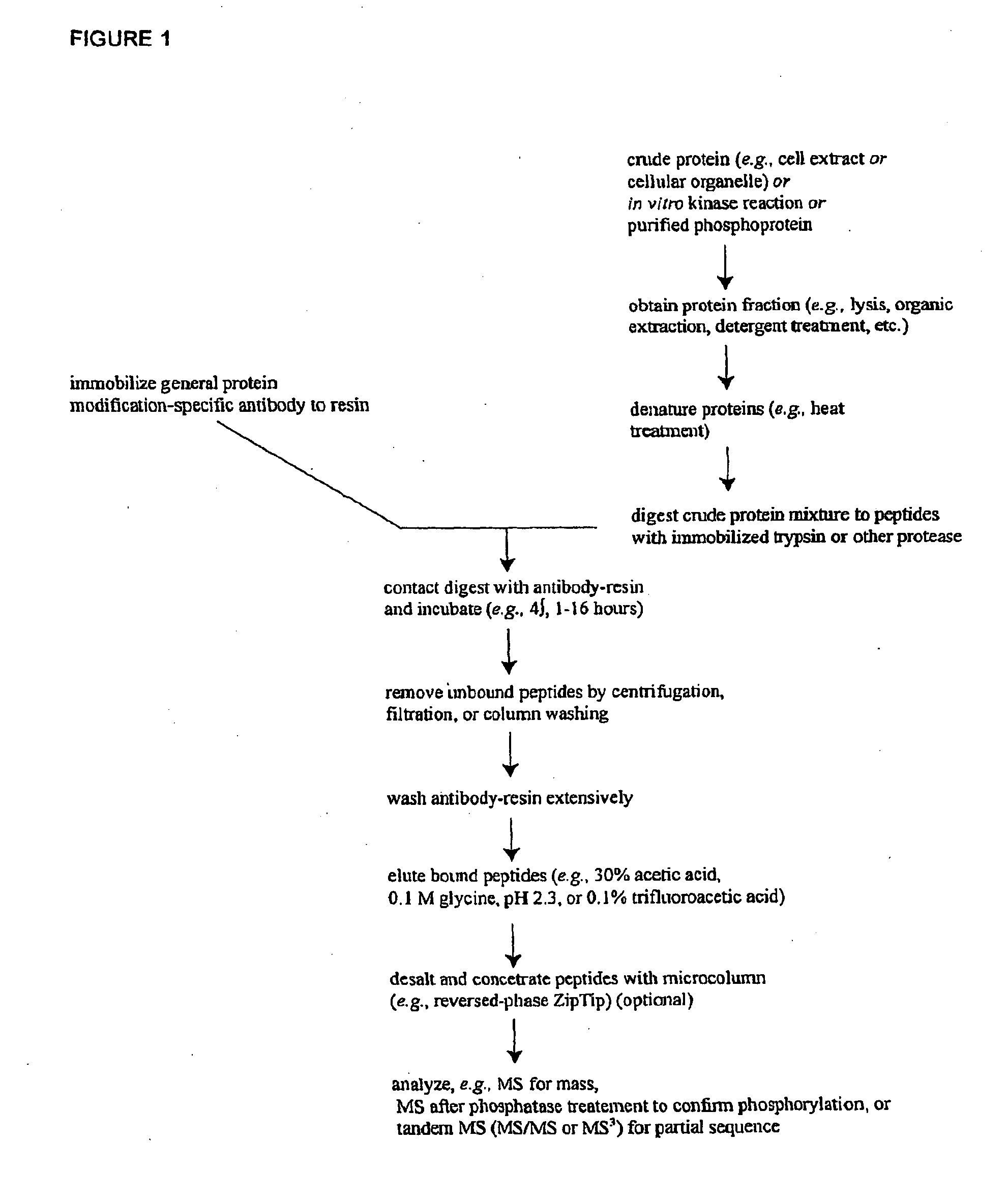
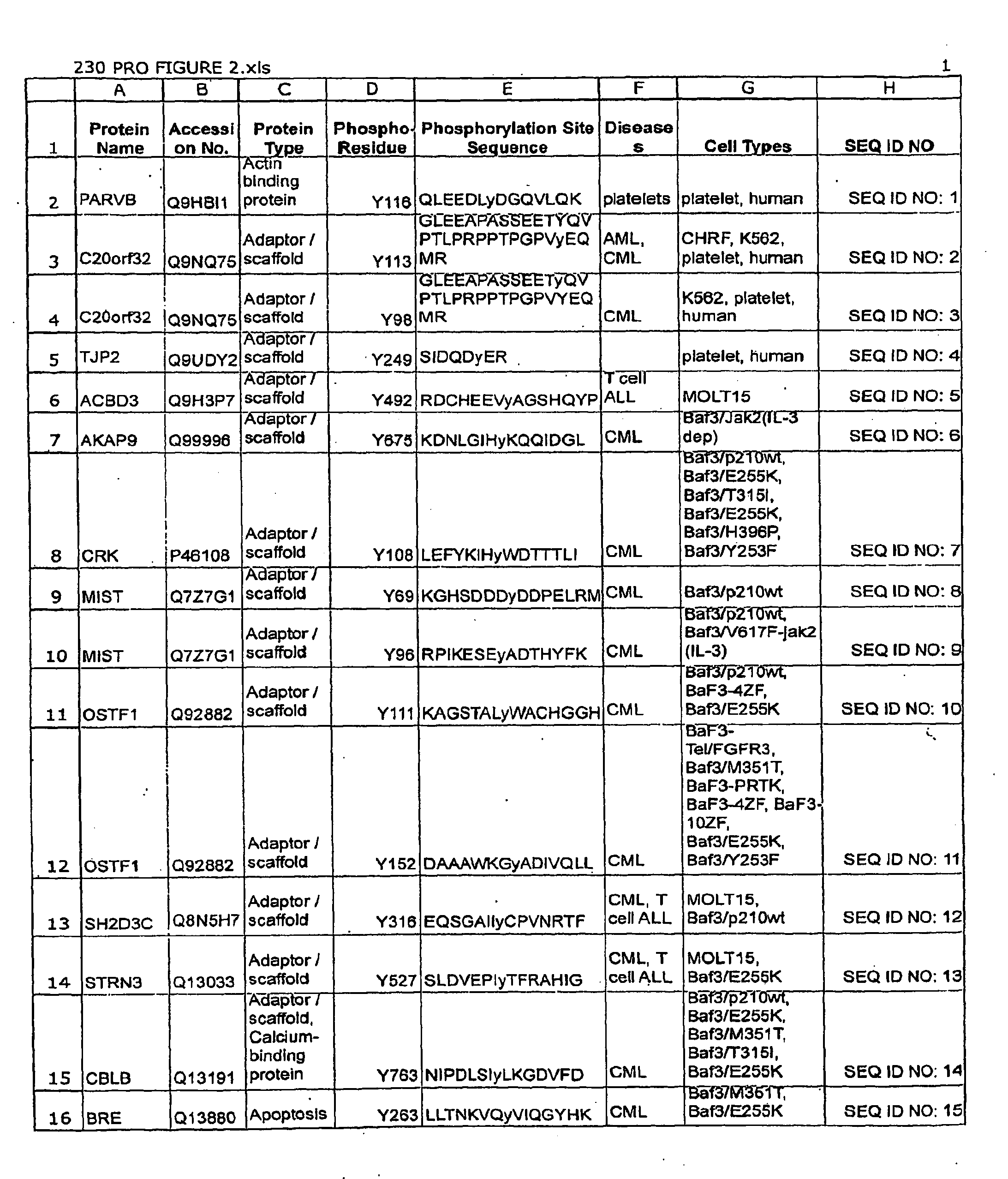
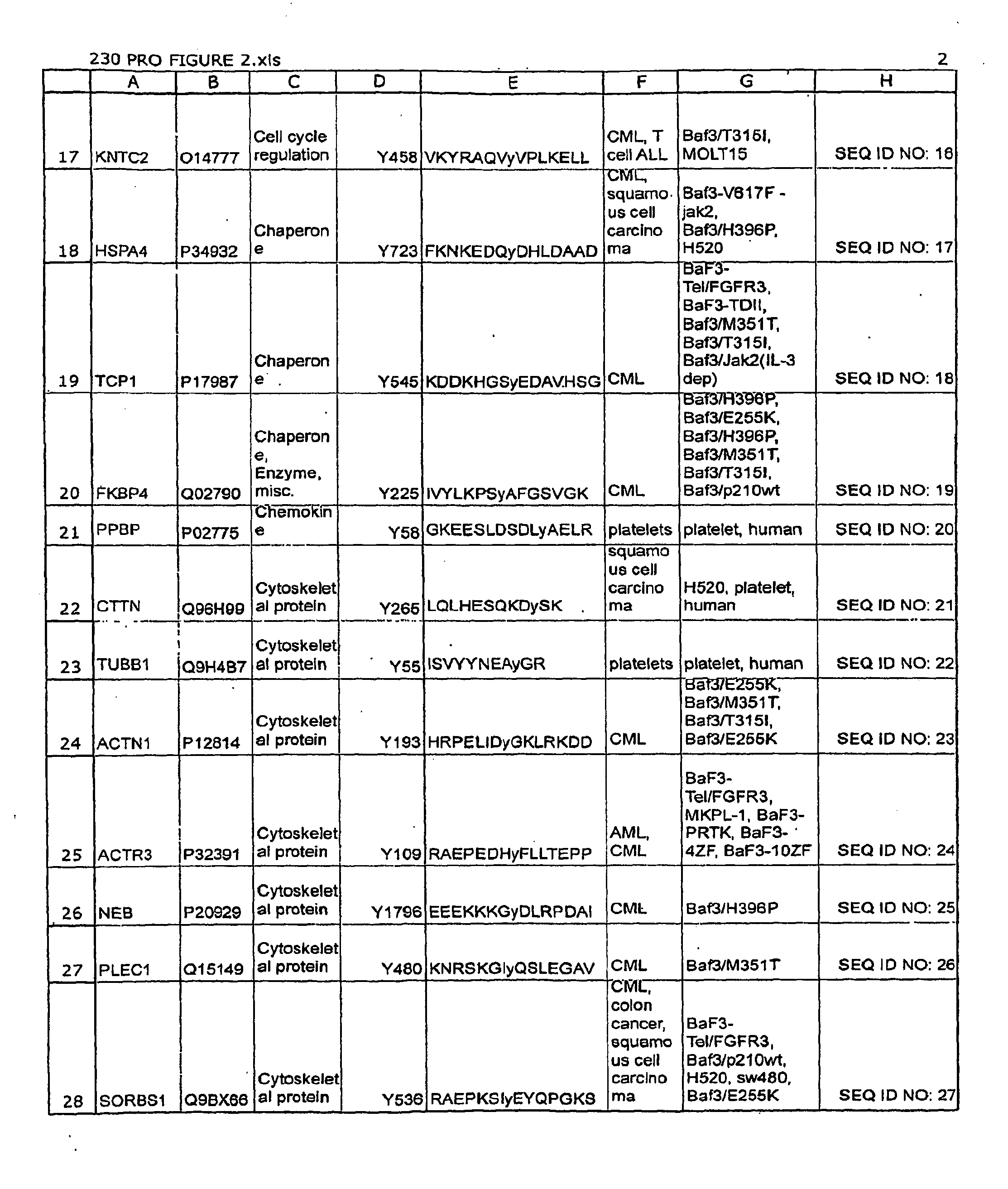
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Preparation and composition of inter-alpha proteins from blood
ActiveUS9139641B2Reduce riskReduce probabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyInhibitor protein
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
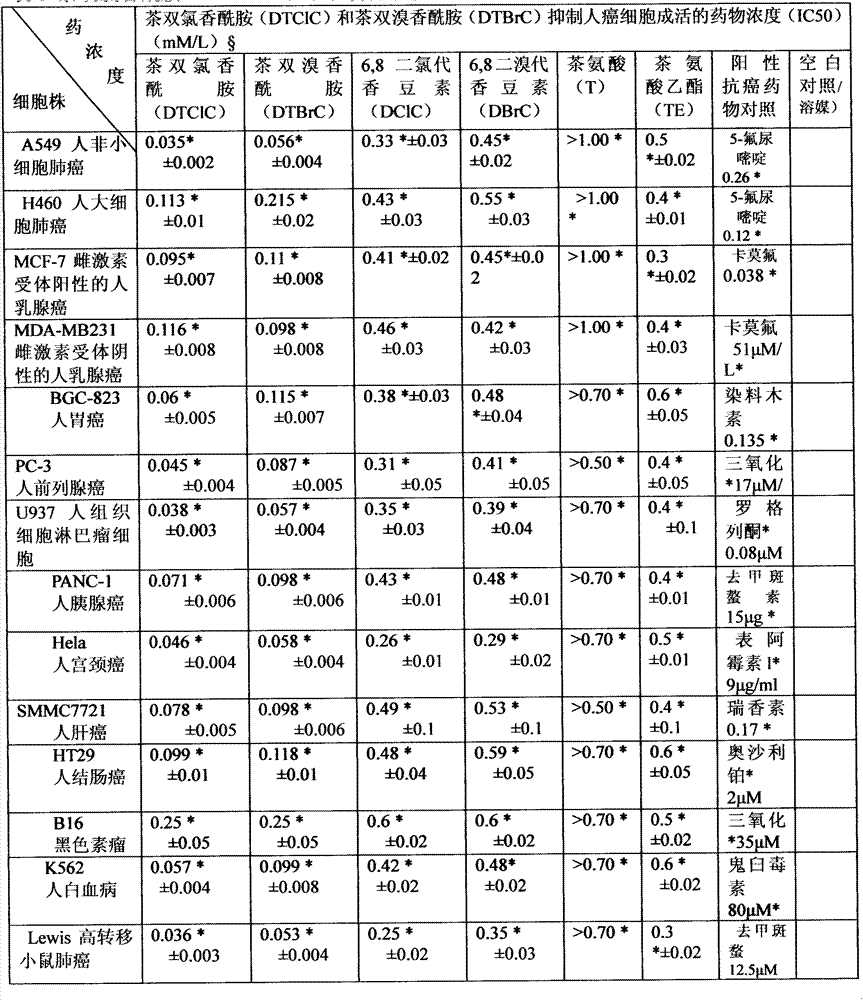
Applications of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide or like in preparation of products for prevention and treatment of diseases such as cancer
InactiveCN103110621AEfficient killingGood curative effectAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseLymphatic Spread
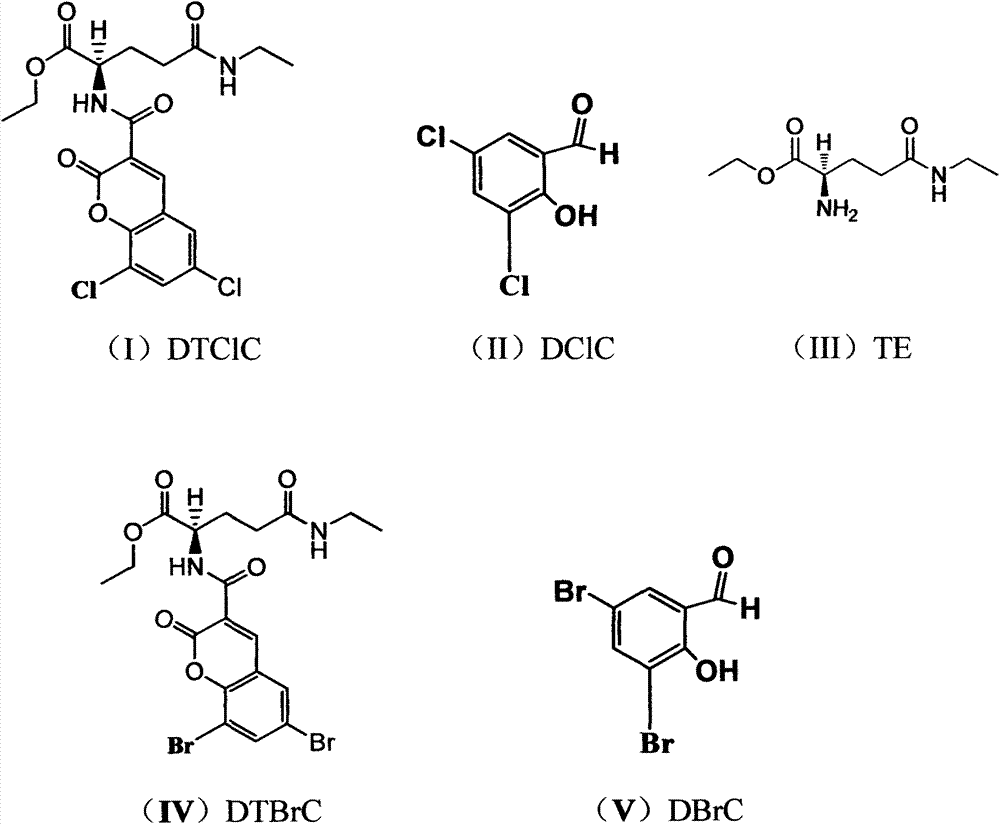
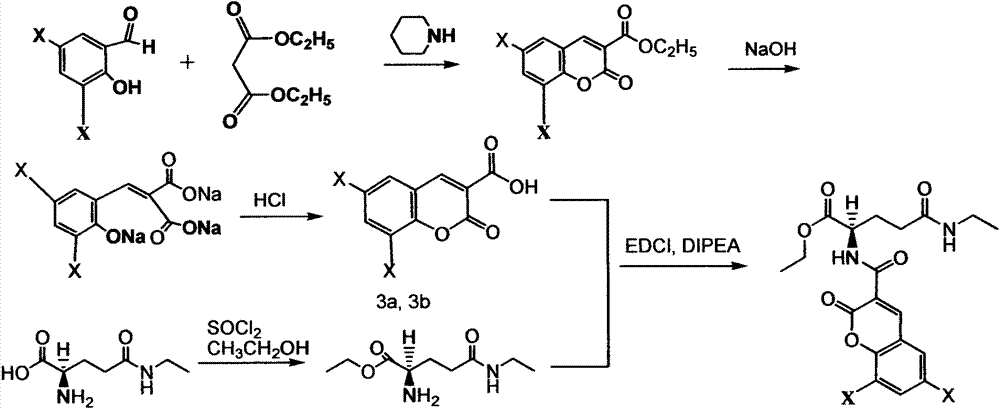
The invention relates to the technical field of medical treatment. The tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide are newly synthesized compounds which can inhibit growths and invasions of cancer cells such as lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, and melanoma, and can obviously inhibit the tumor growth and metastasis in the body, and the inhibition effect of the compound is better than that of an anticancer medicament; the mechanism of action involves a receptor which is closely related to down-regulation and inhibition of the growth, invasion and metastasis of a tumor, signal transduction and regulation protein and kinase levels and a binding of a nuclear factor and DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), and up-regulation of factors such as tumor suppressor proteins and cell cycle inhibitor proteins simultaneously; double tea chlorine carboxamide and double tea chlorine carboxamide can directly inhibit activities of histone deacetylase and histone methyltransferase EZH2(Enhancer Of Zeste Homolog 2) and the binding of the inflammatory factor NF-kB and DNA, and the activities of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide are better than that of the clinical anti-cancer medicament. The invention provides new applications of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide and intermediate compounds in preventing and treating the diseases such as cancers, inflammation, cardiovascular and immune deficiencies.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
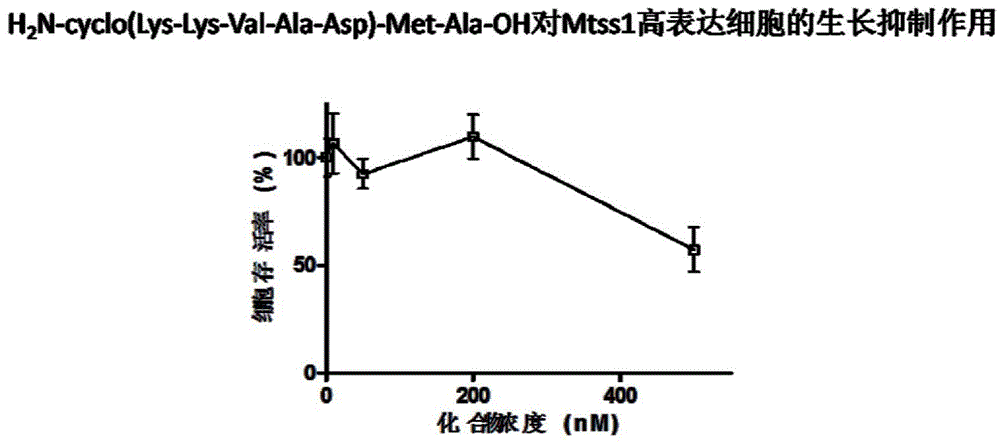
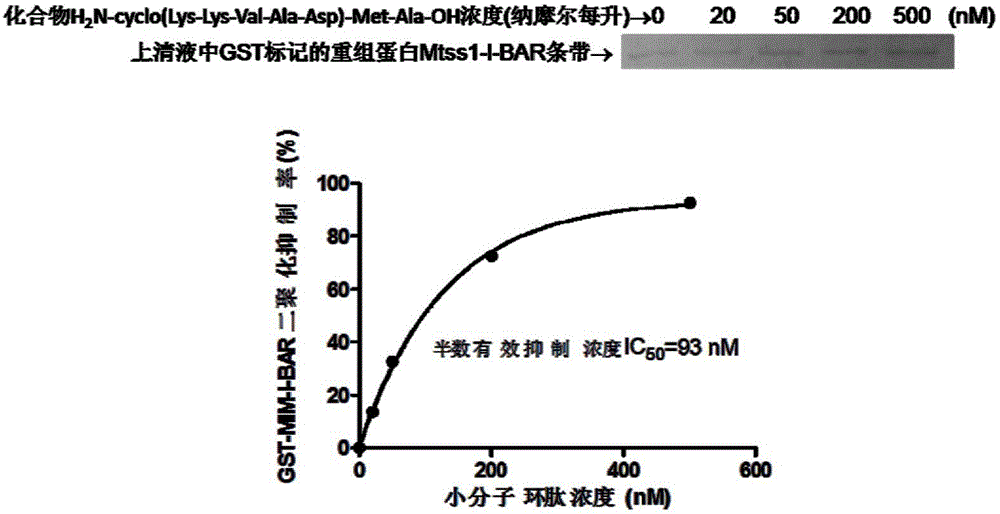
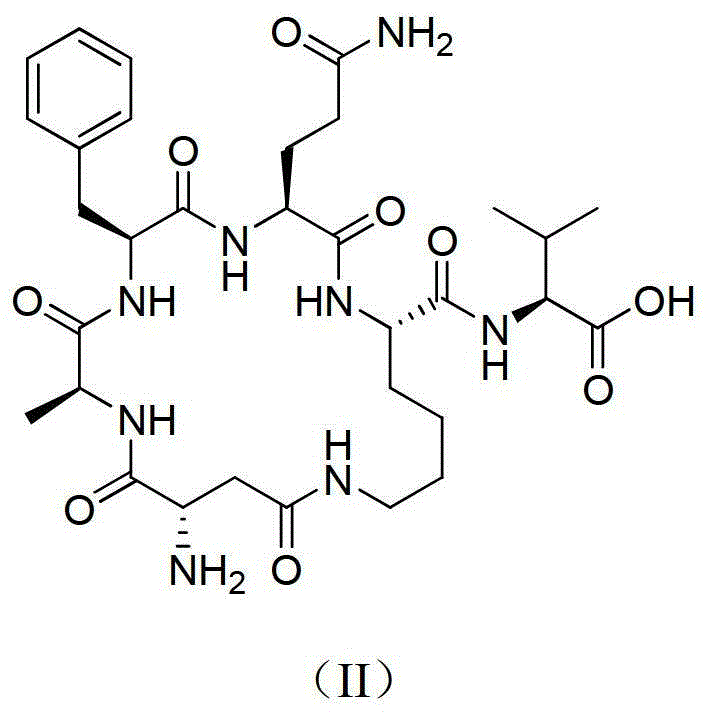
Metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103333227ASmall molecular weightImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclic peptideCell membrane
The invention provides metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, derivatives or salts thereof, a preparation method for the metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, the derivatives or salts thereof and an application of the metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, the derivatives or salts thereof in preparation of antitumor medicaments. The metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide is low in molecular weight, high in stability and very low in toxicity and can enter cells through cell membranes to inhibit endocytosis of tumor cells and interfere morphologic change of the cell membranes and conduction of relevant antitumor signals by inhibiting dimerization of Mtss1 protein, so that cell proliferation and growth caused by tumor stimulating factors such as epidermal growth factors EGF, platelet derived growth factor PDGF or sonic hedgehog (shh) factors are weakened, wherein the in-vitro inhibition activity of nanomole-scale inhibitor-protein can remarkably inhibit the endocytosis of the cells after the inhibitor-protein is directly added into cell culture fluid without being transfected or packaged by lipidosome.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
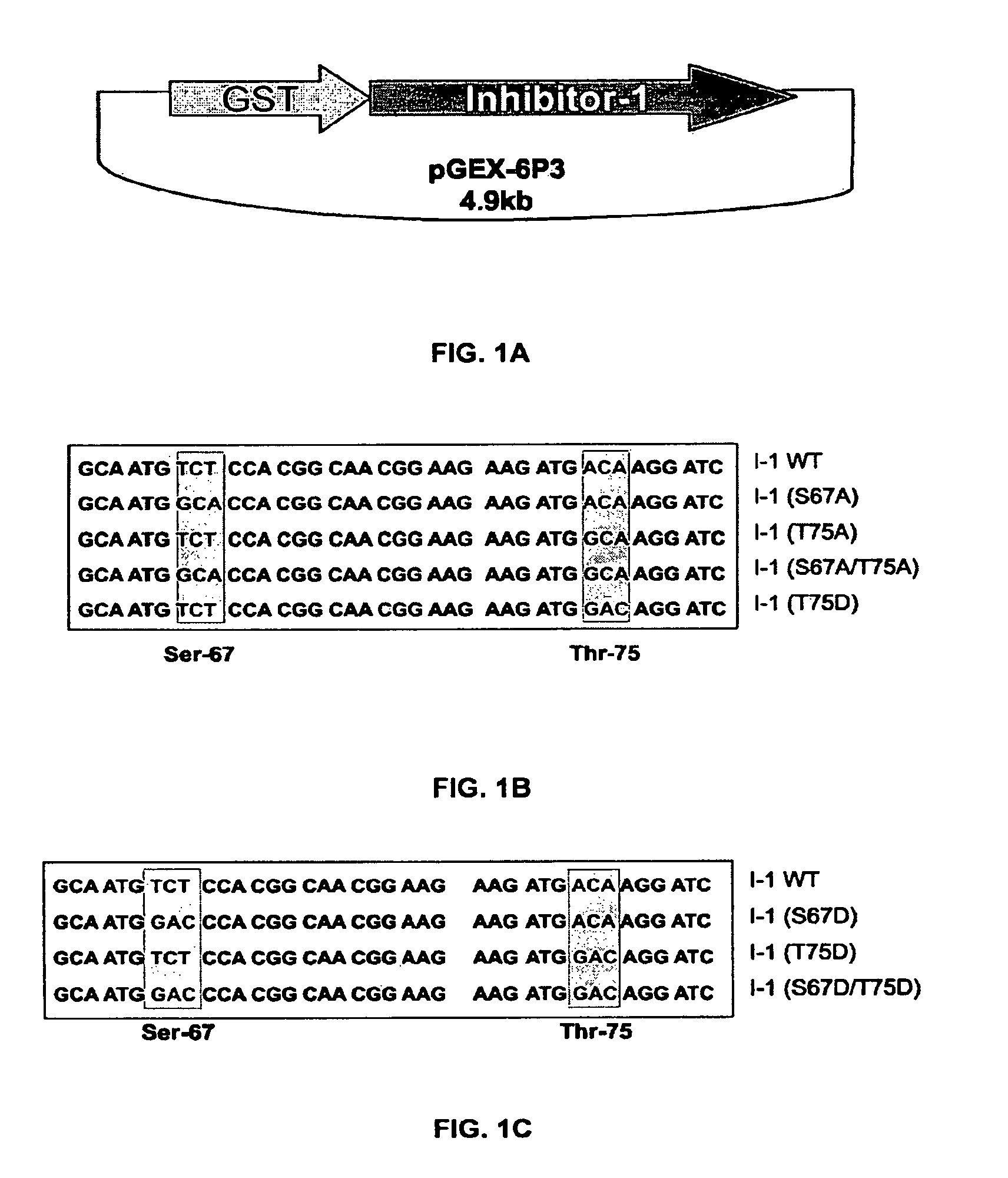
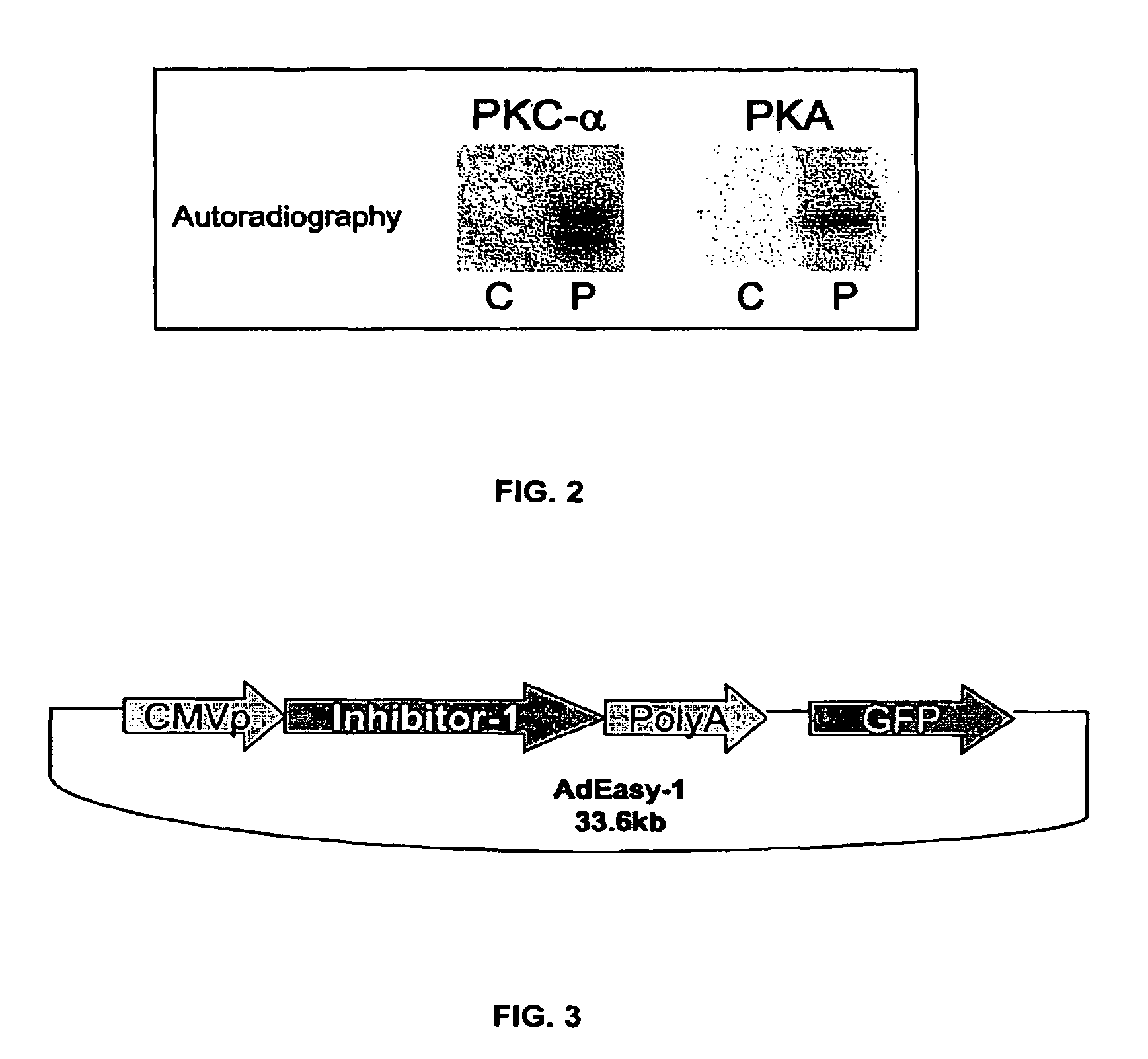
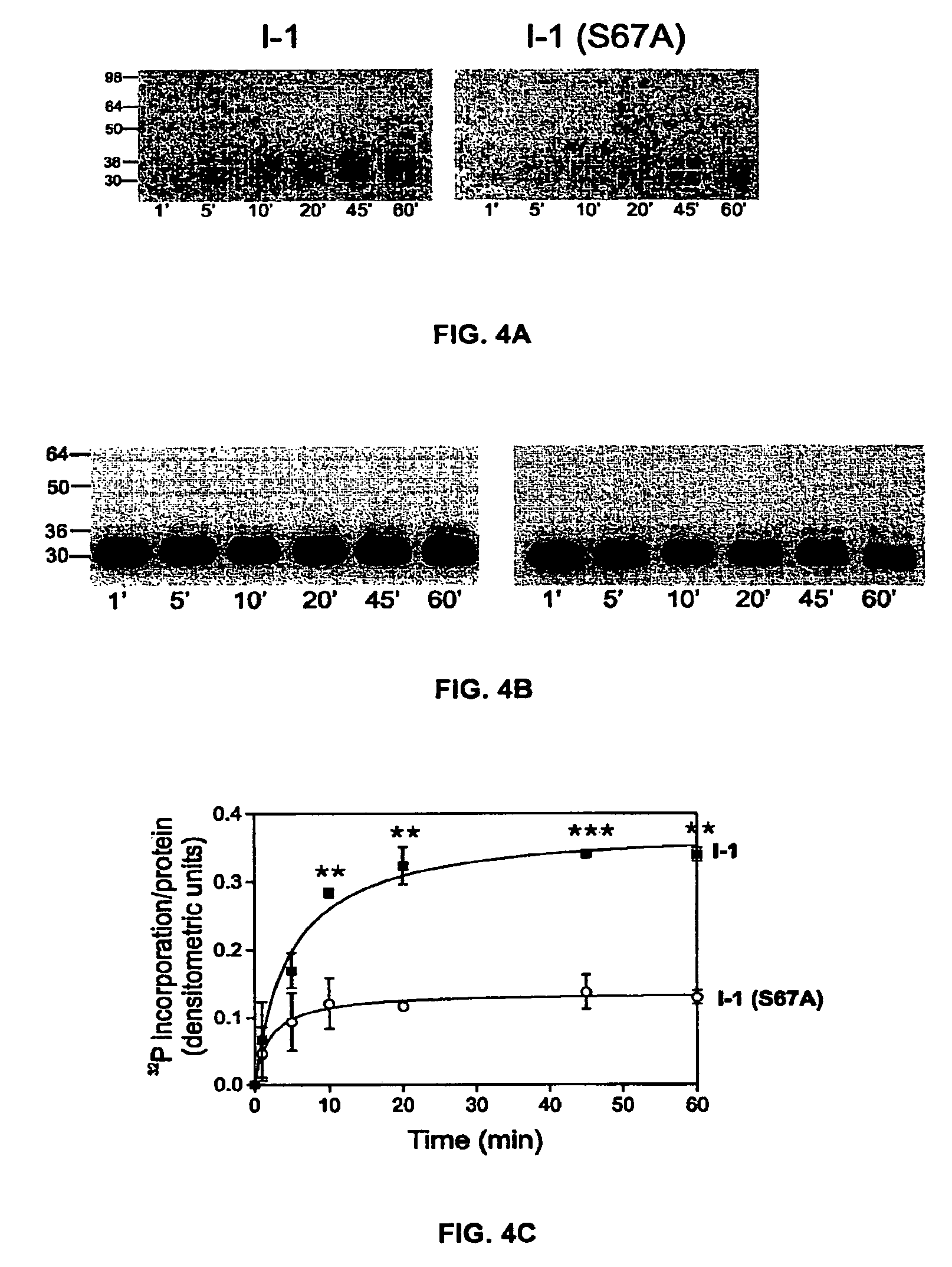
Phosphatase inhibitor protein-1 as a regulator of cardiac function
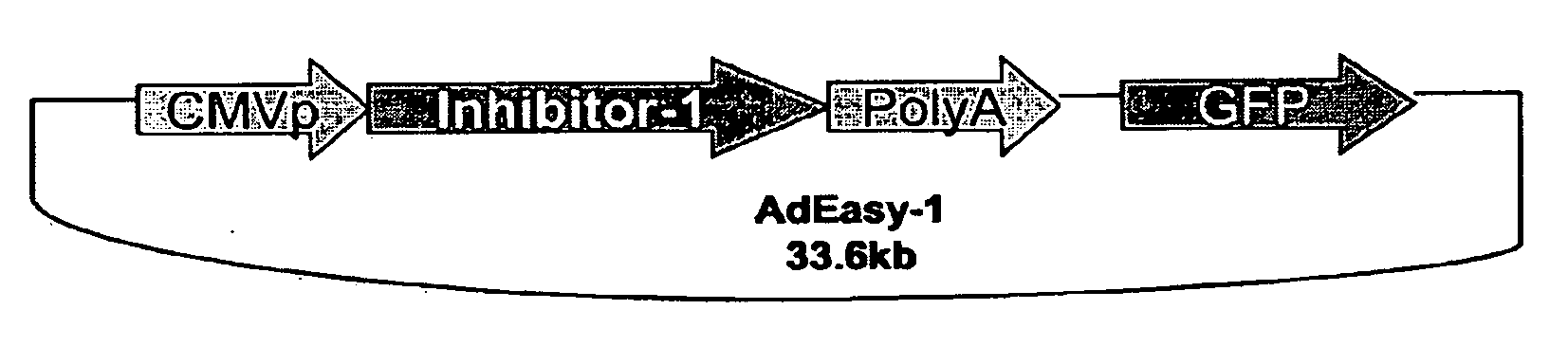
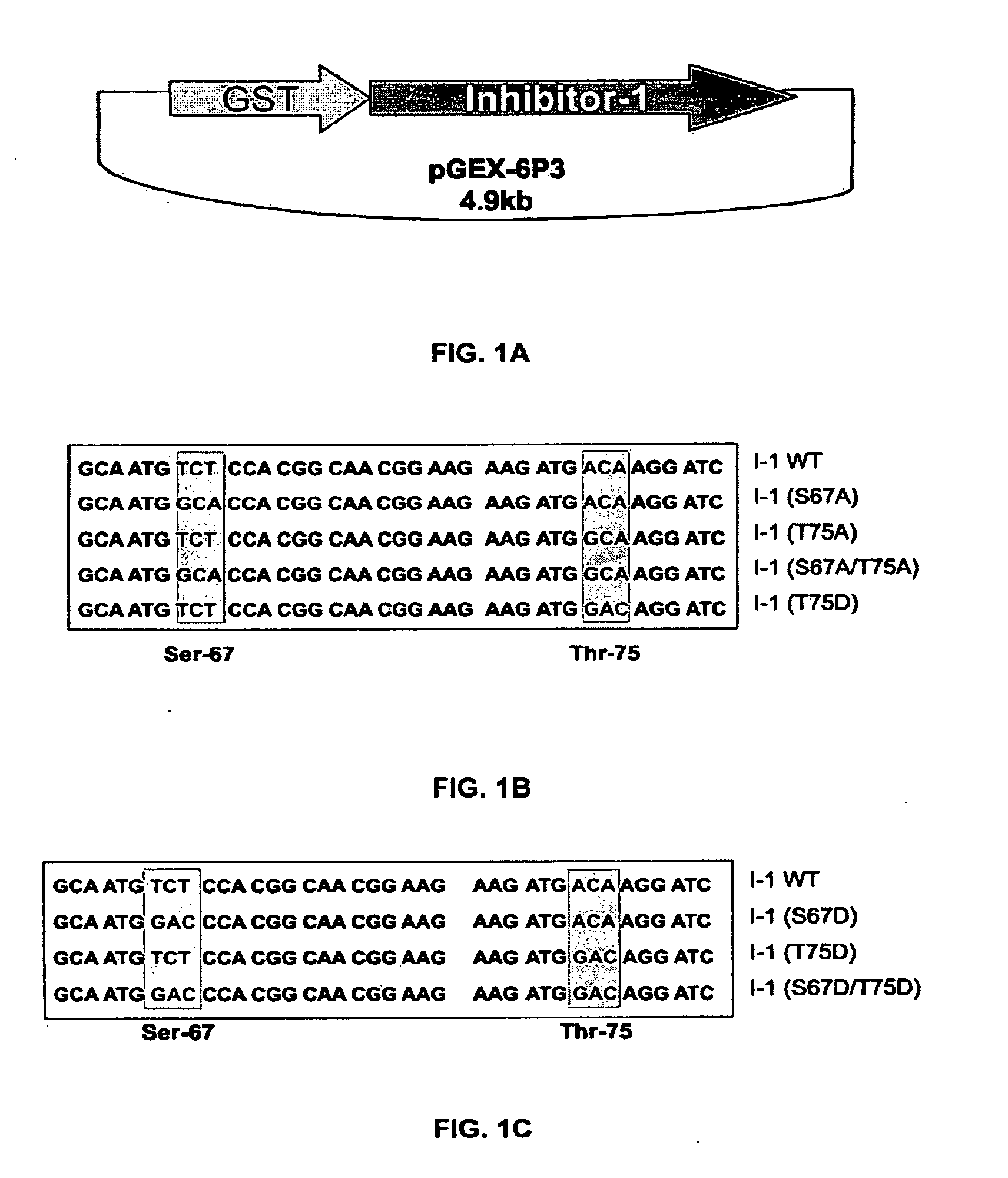
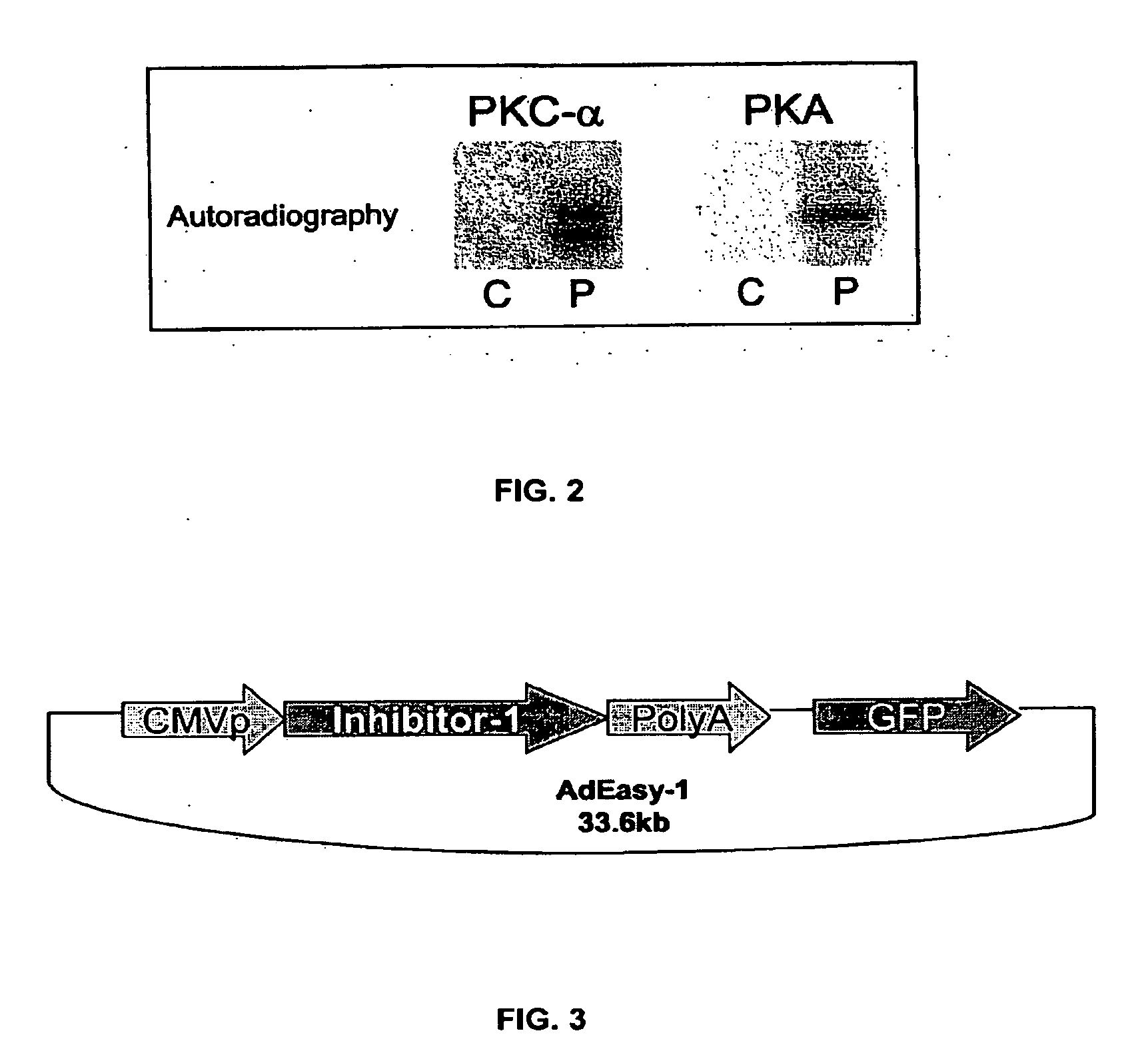
The present invention relates to novel nucleic acids which encode novel mutant forms of Inhibitor Protein-1 (1-1). In particular, the 1-1 mutant forms comprise altered phosphorylation sites of PKC-α. In addition, the present invention relates to methods of regulating cardiac contractility and function, and for treatment of cardio myopathy and heart failure, which employ the novel nucleic acids and polypeptides. Vectors comprising the novel nucleic acids, Antibodies to the novel proteins, and diagnostic and screening methods associated therewith, are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Identification and the use of krp mutants in plants
InactiveUS20140143900A1Weight increaseIncrease in sizeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant cell
The invention provides a plant cell, part, tissue culture or whole plant comprising at least one disrupted KRP gene of the present invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield of a plant by utilizing the disrupted KRP genes of the present invention. Furthermore, methods of breeding plants to produce new plants having increased weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield are provided. The present invention provides isolated Kinase Inhibitor Protein (KIP) Related Protein (KRP) polynucleotide sequences and isolated KRP polypeptide sequences and methods of their use. Exemplary plants include wheat, rice and soybean.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in leukemia signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090220991A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPhosphodiesteraseLipid kinases
The invention discloses nearly 480 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, acetyltransferases, actin binding proteins, adhesion proteins, apoptosis proteins, calcium-binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, cell surface proteins, channel proteins, chaperone proteins, contractile proteins, cytokine proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, G protein regulators and GTPase activating proteins, guanine nucleotide exchange factors, helicase proteins, immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, inhibitor proteins, protein kinases, lipid kinases, ligases, lipid binding proteins, methytransferases, motor proteins, oxidoreductases, phosphotases, phosphodiesterases, phospholipases, proteases, receptor proteins, trascription factors, transferases, translation / transporter proteins, and ubiquitin conjugating system proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Expression and applications of novel non-restriction endonuclease in escherichia coli
The invention utilizes the property that nonspecific endonuclease from Anabaena sp. is provided with natural inhibitor protein to change the original expression way of the nonspecific endonuclease, i.e. to change secretory expression into endoenzyme high efficient expression. The invention adopts a strong promoter to largely express in cells in a way of inclusion bodies with no activity; wherein, the moment when the endonuclease is expressed, the natural inhibitor protein is expressed together so as to eliminate the strong toxicity that farthing activated nuclease imposes on the cells; protein engineering technology is used for replacing a non-activated central amino acid, thus reducing the possibility of forming multimer in renaturation, improving efficiency, and furthermore, raising the output in terms of improving the expression efficiency and the renaturation efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAILANG BIOTECHOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
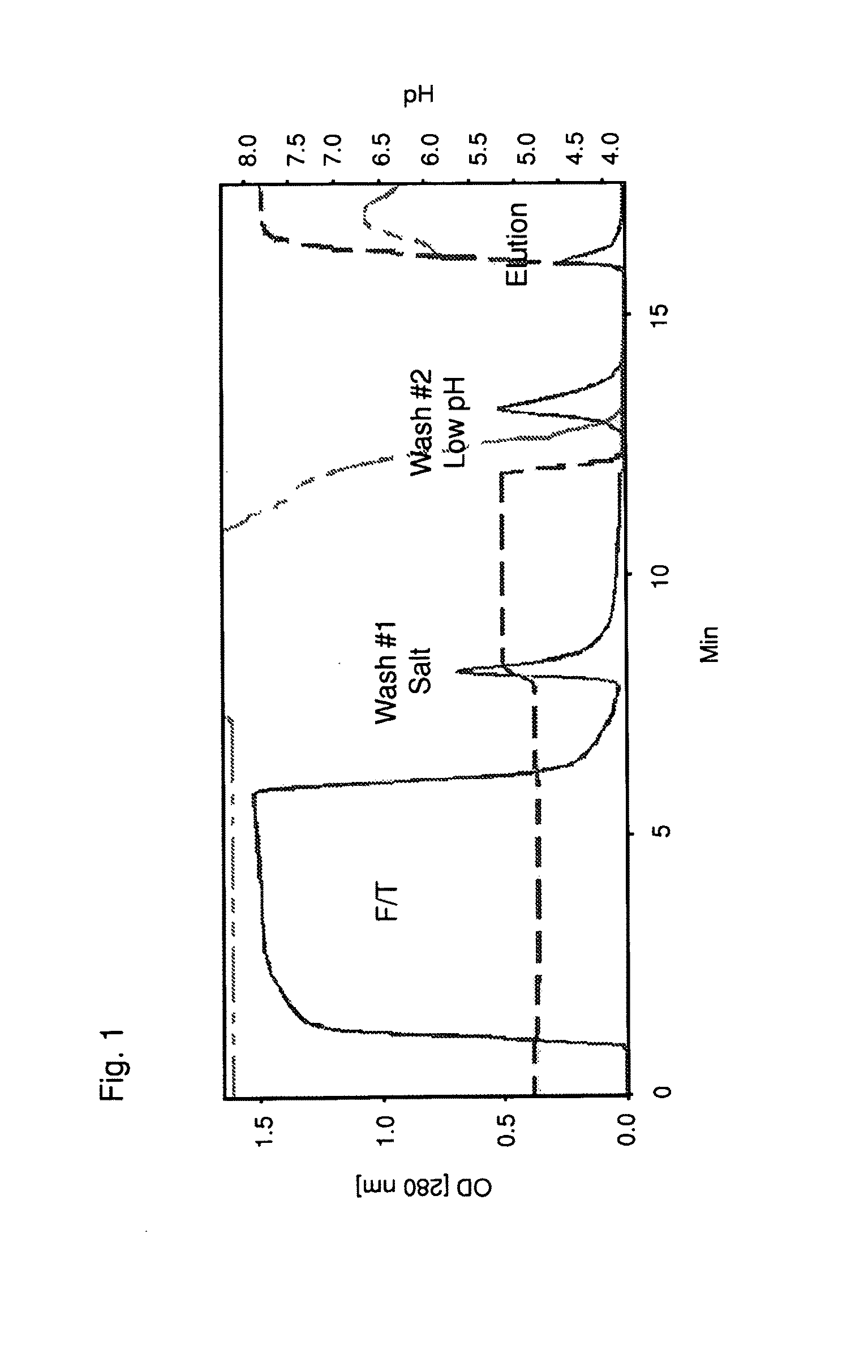
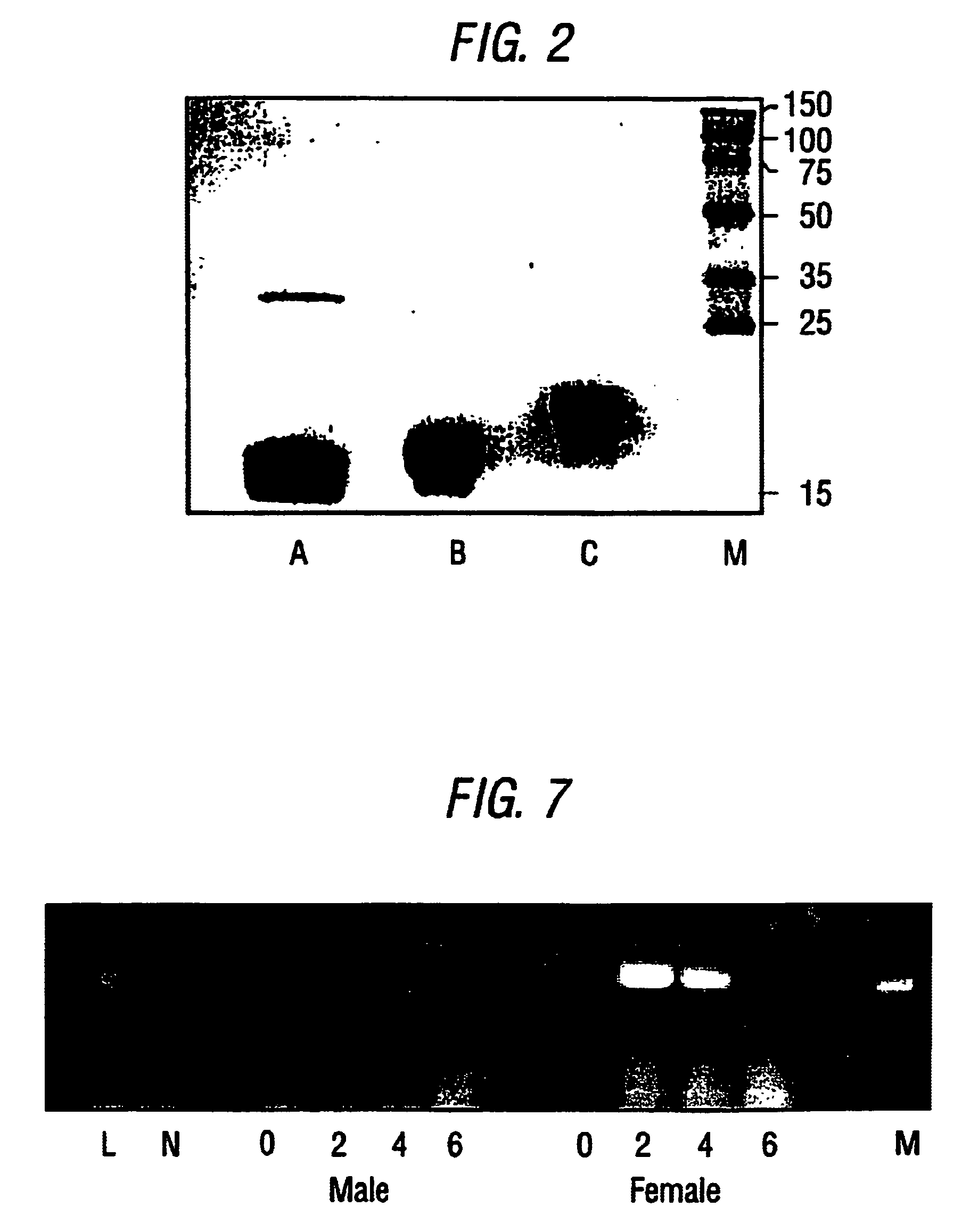
Methods for isolating blood products from an inter-alpha inhibitor protein-depleted blood product material
InactiveUS20150361127A1Maximize efficiencyImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsIon-exchanger regenerationBlood componentWhole blood product
Described is a method for isolating multiple blood products from a single starting material. Isolation of multiple blood products from a single starting material maximizes the efficiency of blood product isolation. In the present invention, one or more blood products are isolated from a blood product material previously depleted of inter-alpha inhibitor protein (lαlp). This method provides new paths for increasing the efficiency of isolating blood components and providing pharmaceutically acceptable forms of those components.
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
Identification and use of KRP mutants in wheat
InactiveUS9062323B2Improved agronomic and horticultural characteristicIncrease the number ofClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesMutantKinase
The invention provides a wheat cell, part, tissue culture or whole plant comprising at least one disrupted KRP gene of the present invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield of a wheat plant by utilizing the disrupted KRP genes of the present invention. Furthermore, methods of breeding wheat plants to produce new wheat plants having increased weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield are provided. The present invention provides isolated Kinase Inhibitor Protein (KIP) Related Protein (KRP) polynucleotide sequences and isolated KRP polypeptide sequences and methods of their use.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH +1
Phosphatase Inhibitor Protein-1 As A Regulator of Cardiac Function
ActiveUS20090203596A1Lowering of time constant for relaxationAccelerating calcium signal decayOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMyopathyPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to novel nucleic acids which encode novel mutant forms of Inhibitor Protein-1 (1-1). In particular, the 1-1 mutant forms comprise altered phosphorylation sites of PKC-α. In addition, the present invention relates to methods of regulating cardiac contractility and function, and for treatment of cardio myopathy and heart failure, which employ the novel nucleic acids and polypeptides. Vectors comprising the novel nucleic acids, Antibodies to the novel proteins, and diagnostic and screening methods associated therewith, are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Novel therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using the same
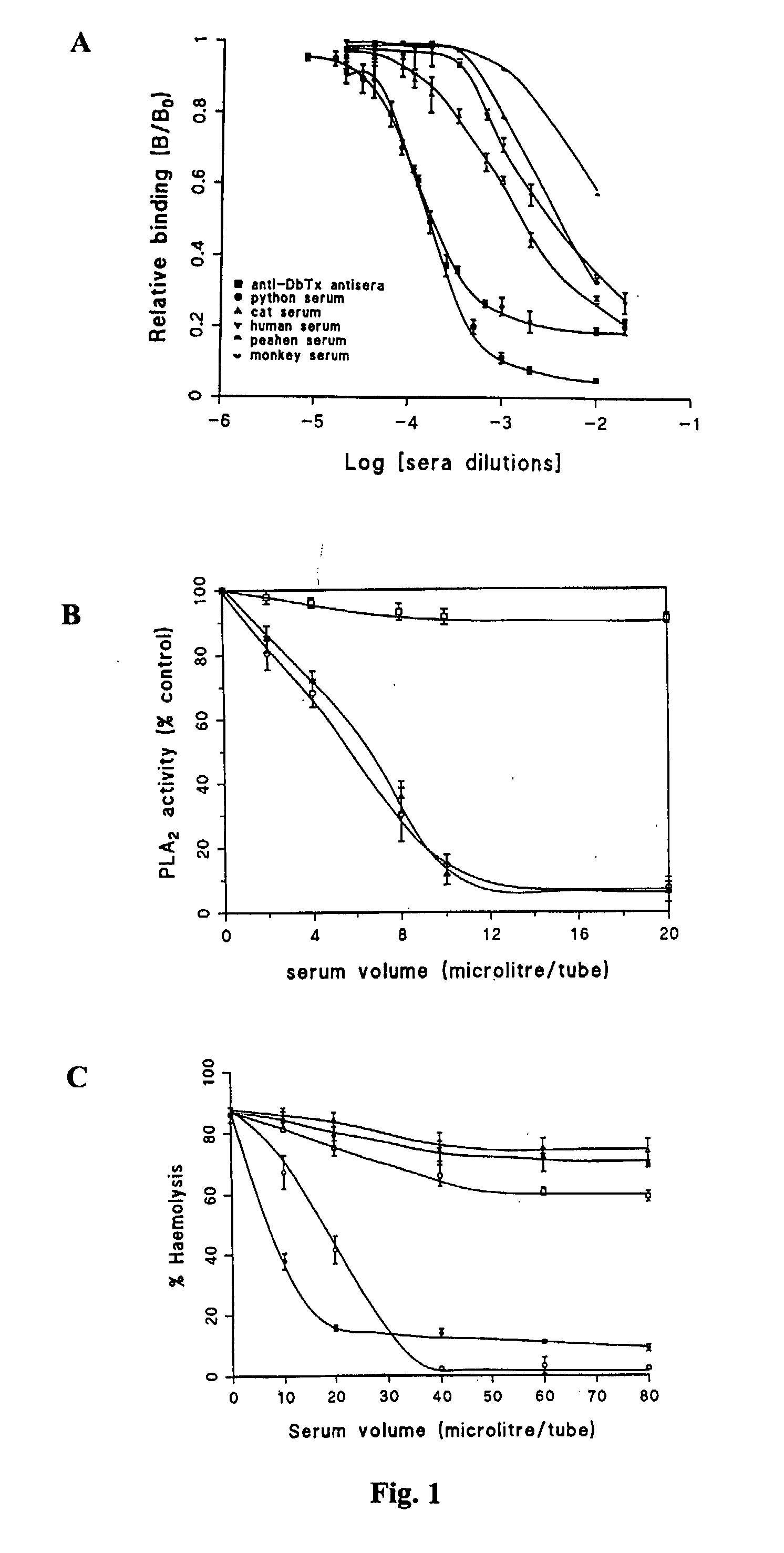
InactiveUS20060078551A1Good anti-inflammatory activityGood potencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipase inhibitorSnake bite venom
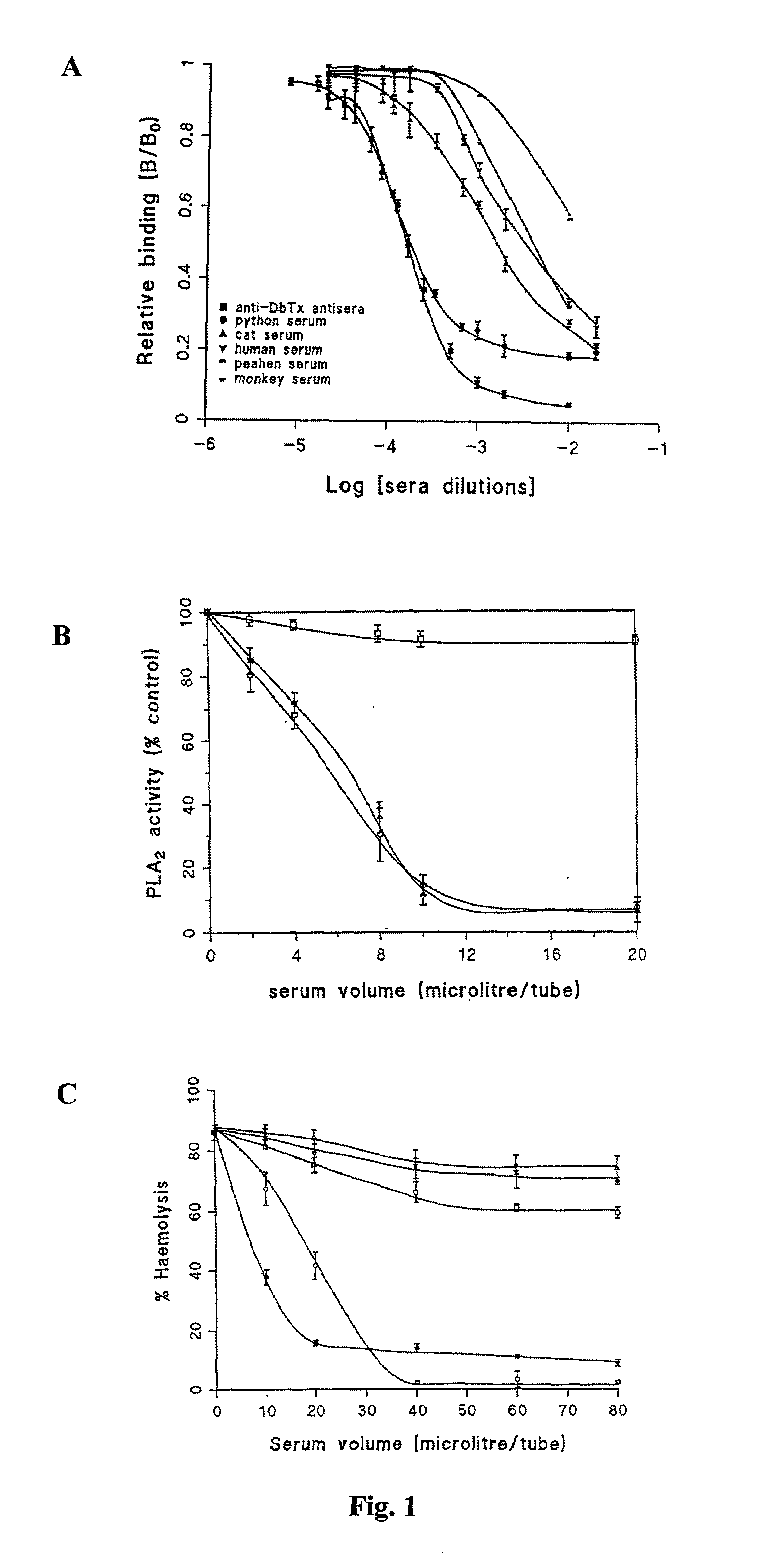
A phospholipase A2 inhibitor protein designated “Phospholipase Inhibitor from Python” (PIP)—formerly designated “Python Antitoxic Factor” (PAF)—is given by SEQ ID NO:2. The partial amino acid sequence for PIP was initially determined from the native protein purified from the blood serum of a non-venomous snake, Python reticulatus. The complete PIP polynucleotide sequence was obtained from a cDNA clone encoding PIP, given by SEQ ID NO:1, along with the full amino acid sequence deduced from it. Also disclosed is a recombinant protein PIP, which shows strong lethal toxin neutralizing activity similar to the native PIP, and has potent anti-inflammatory activity. Both the native and the functionally equivalent recombinant PIP are useful for the prevention or treatment of conditions such as snakebites, insect stings, and inflammatory diseases. Also, phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitory polypeptides designated P-0029, P-0009, and P-0006, the sequences of which are given as SEQ ID NO:10, SEQ ID NO:11, and SEQ ID NO:12, respectively, are disclosed. Those polypeptides, and their synthetic chemical analogues and polypeptide variants that inhibit PLA2 activity and alleviate inflammation, may also be used in the diagnosis, study, prevention, and treatment of PLA2-related human inflammatory diseases.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Human telomerase active inhibitor protein and use thereof
InactiveCN1670032APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTelomeraseNucleotide
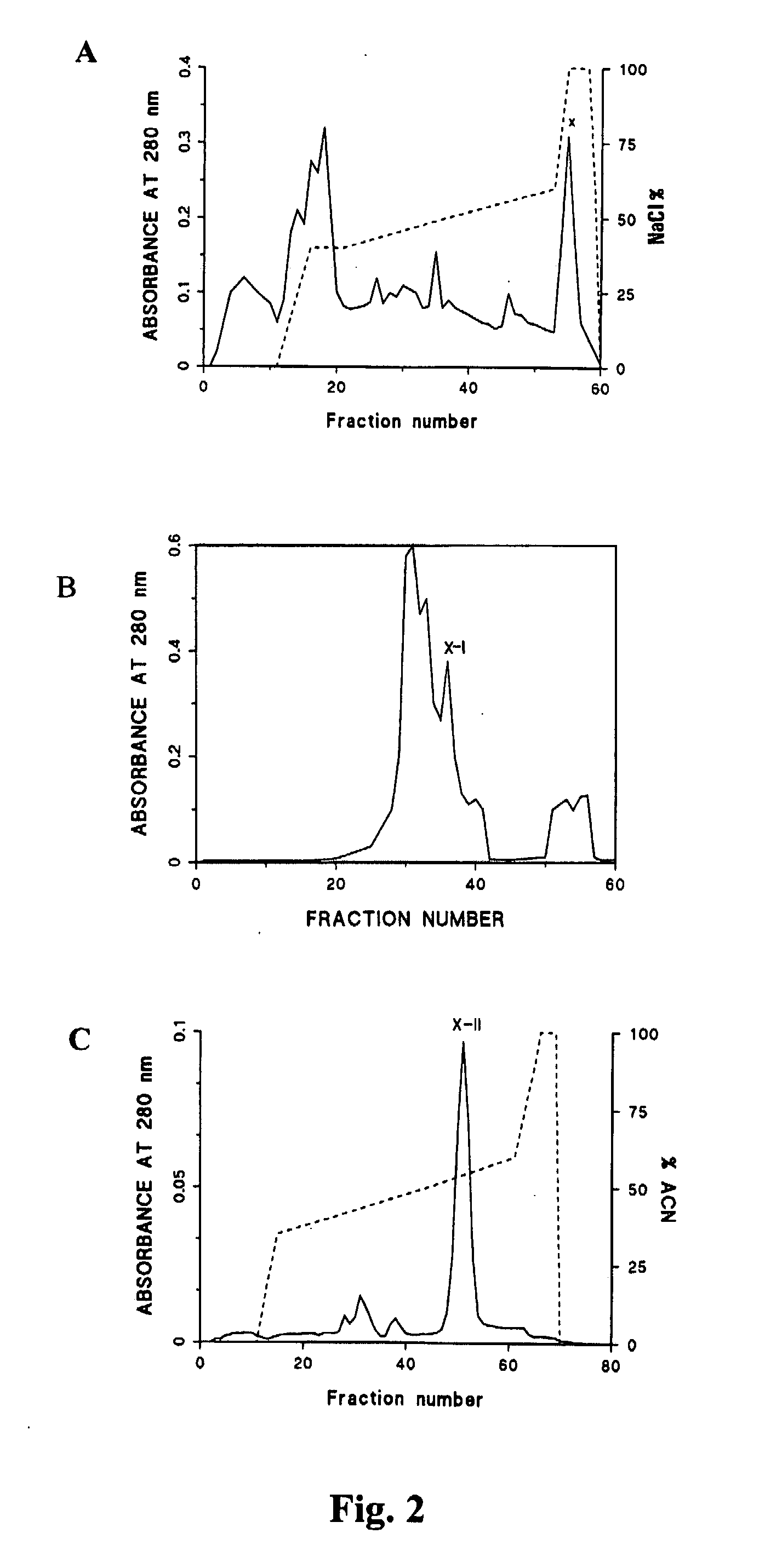
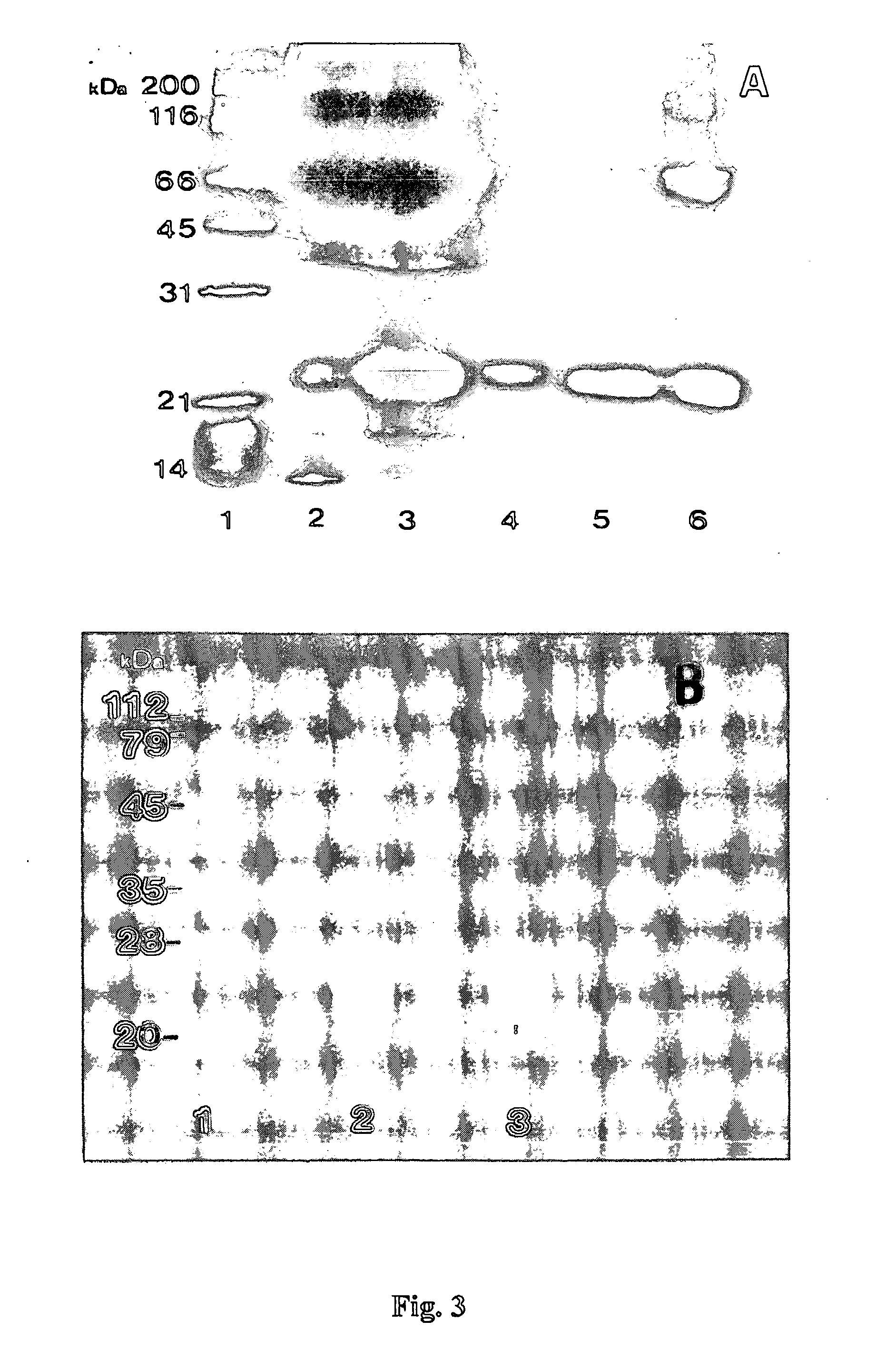
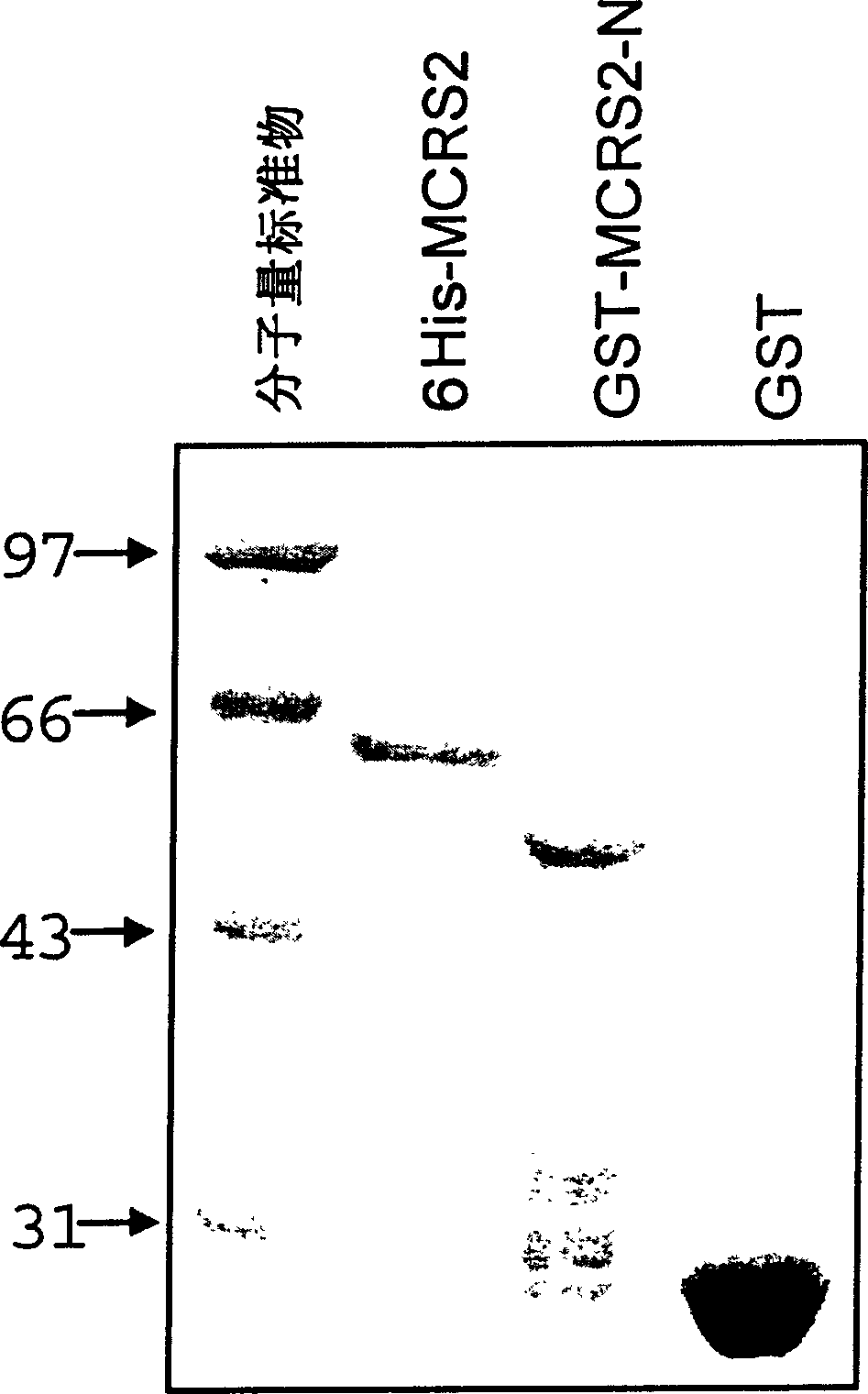
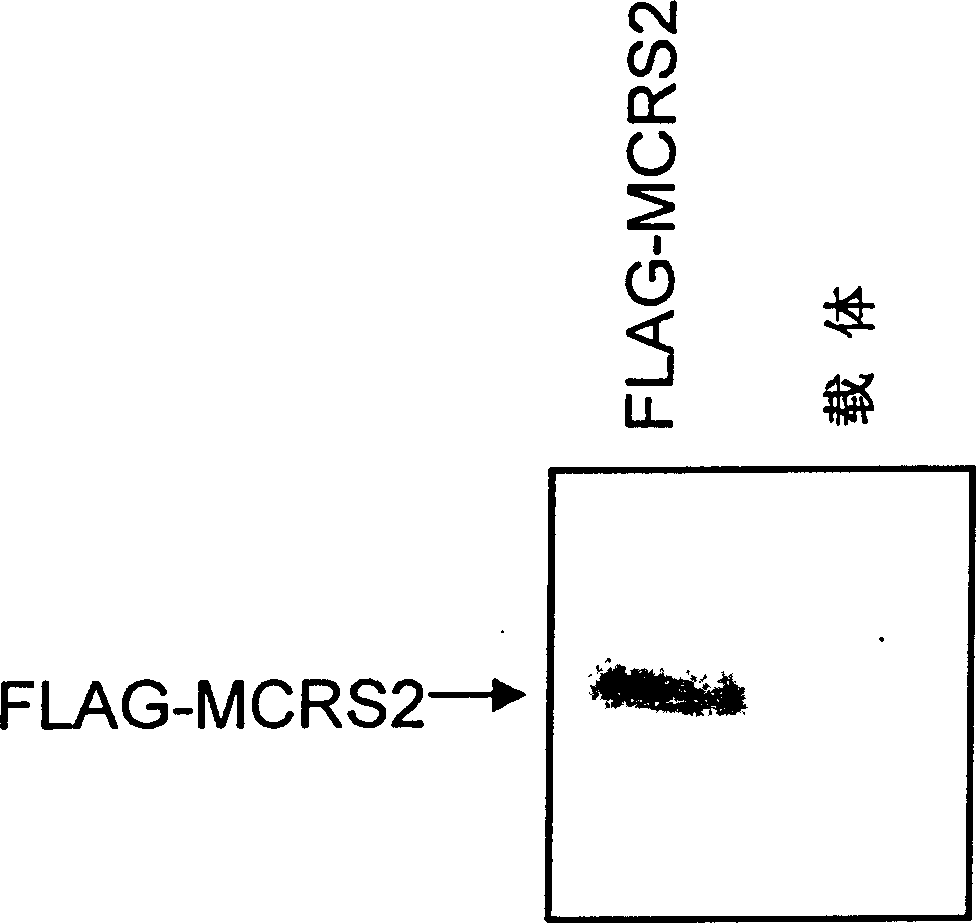
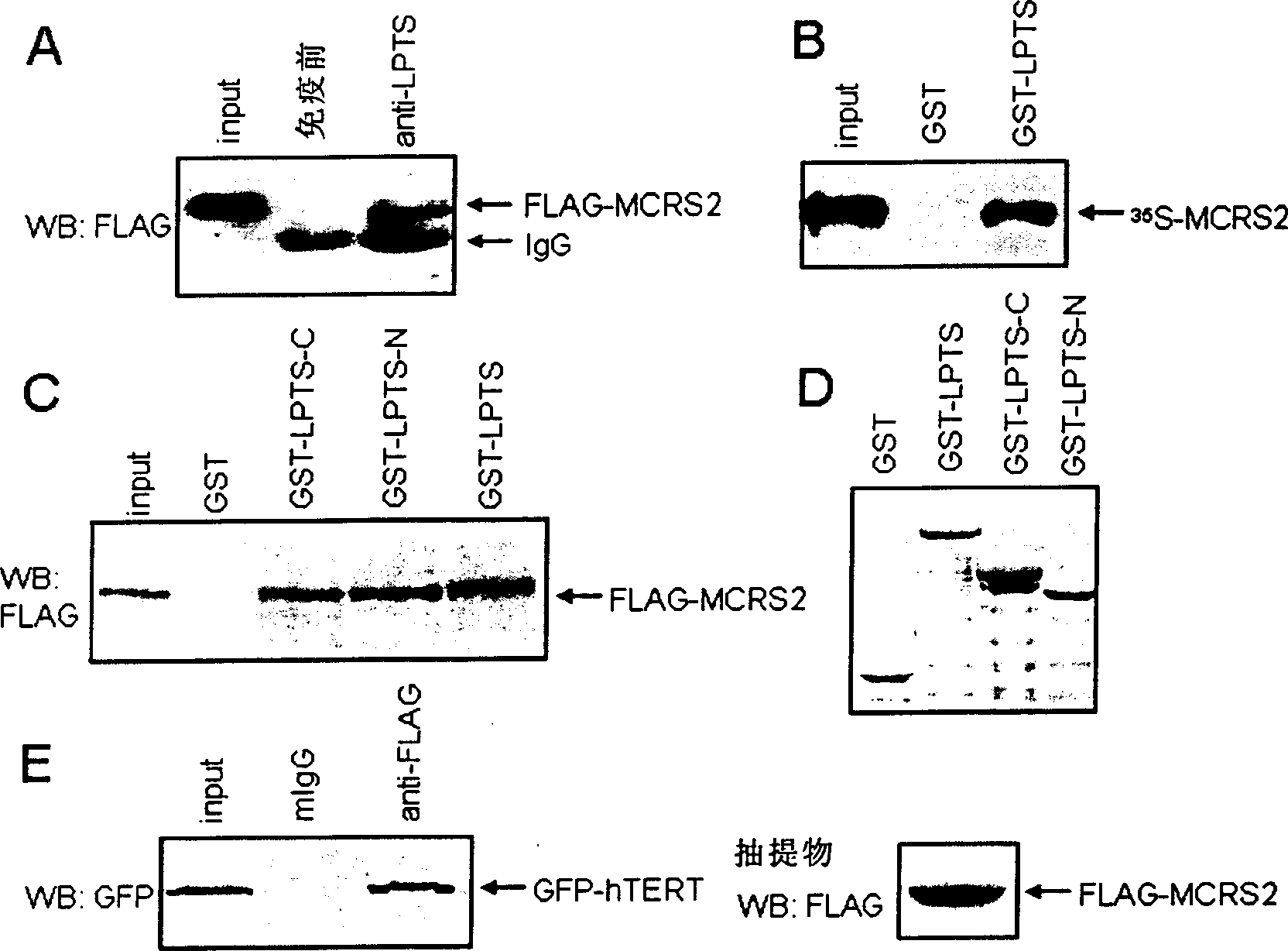
The invention provides a new telomerase inhibition of active protein- MCRS2 protein, polynucleotides of coded MCRS2 protein and the method produced by recombination technology. The invention also discloses the application of MCRS2 protein and its coded sequence that the MCRS2 protein has the capacity of making the chromosome telomeric of liver cancer cells short and inhibiting telomerase activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
ActiveUS7999080B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCell Surface ProteinsSignalling pathways
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Identification and use of krp mutants in wheat
InactiveUS20160002656A1Improved agronomic and horticultural characteristicIncrease the number ofClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyMutant
The invention provides a wheat cell, part, tissue culture or whole plant comprising at least one disrupted KRP gene of the present invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield of a wheat plant by utilizing the disrupted KRP genes of the present invention. Furthermore, methods of breeding wheat plants to produce new wheat plants having increased weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield are provided. The present invention provides isolated Kinase Inhibitor Protein (KIP) Related Protein (KRP) polynucleotide sequences and isolated KRP polypeptide sequences and methods of their use.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
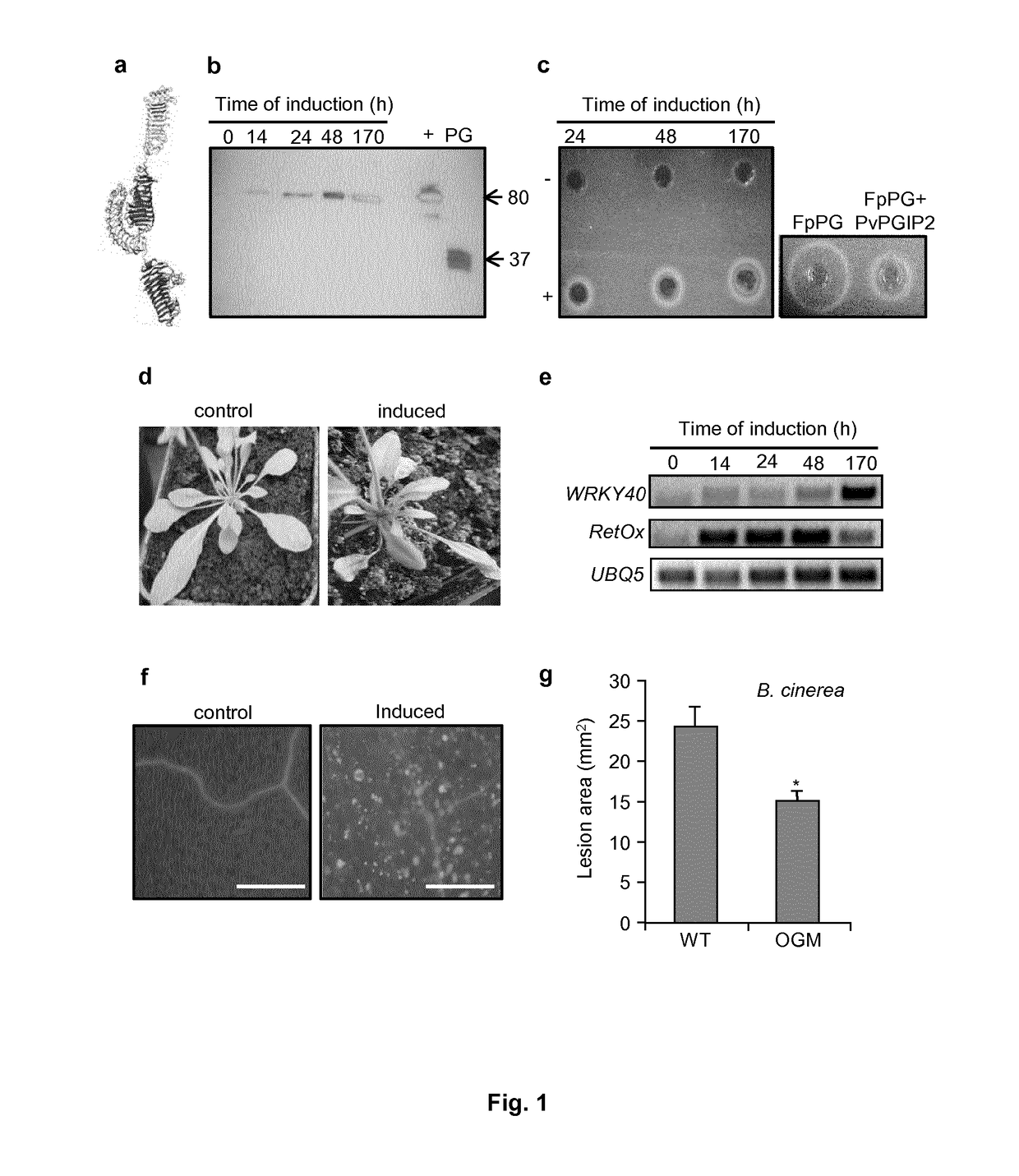
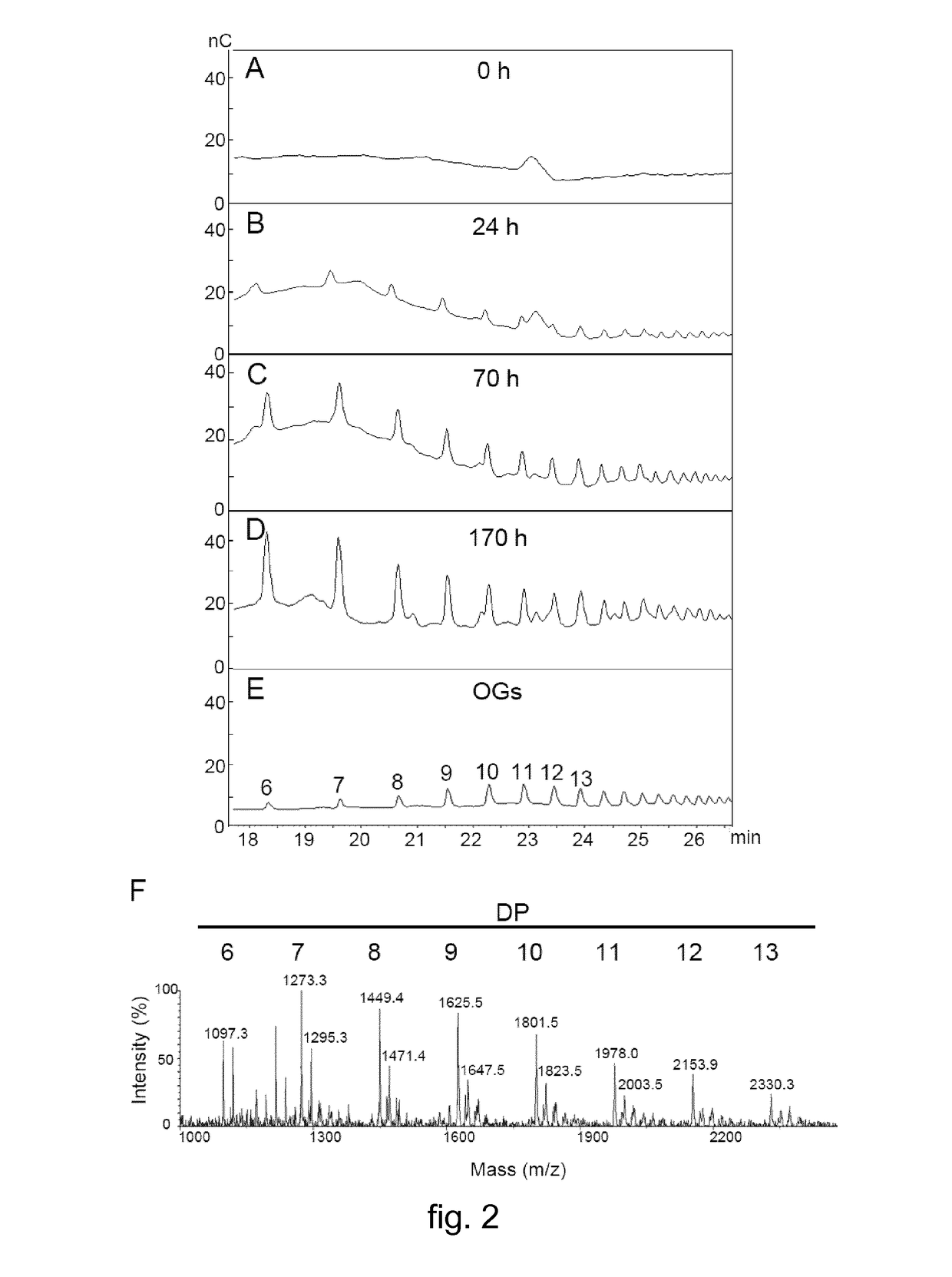
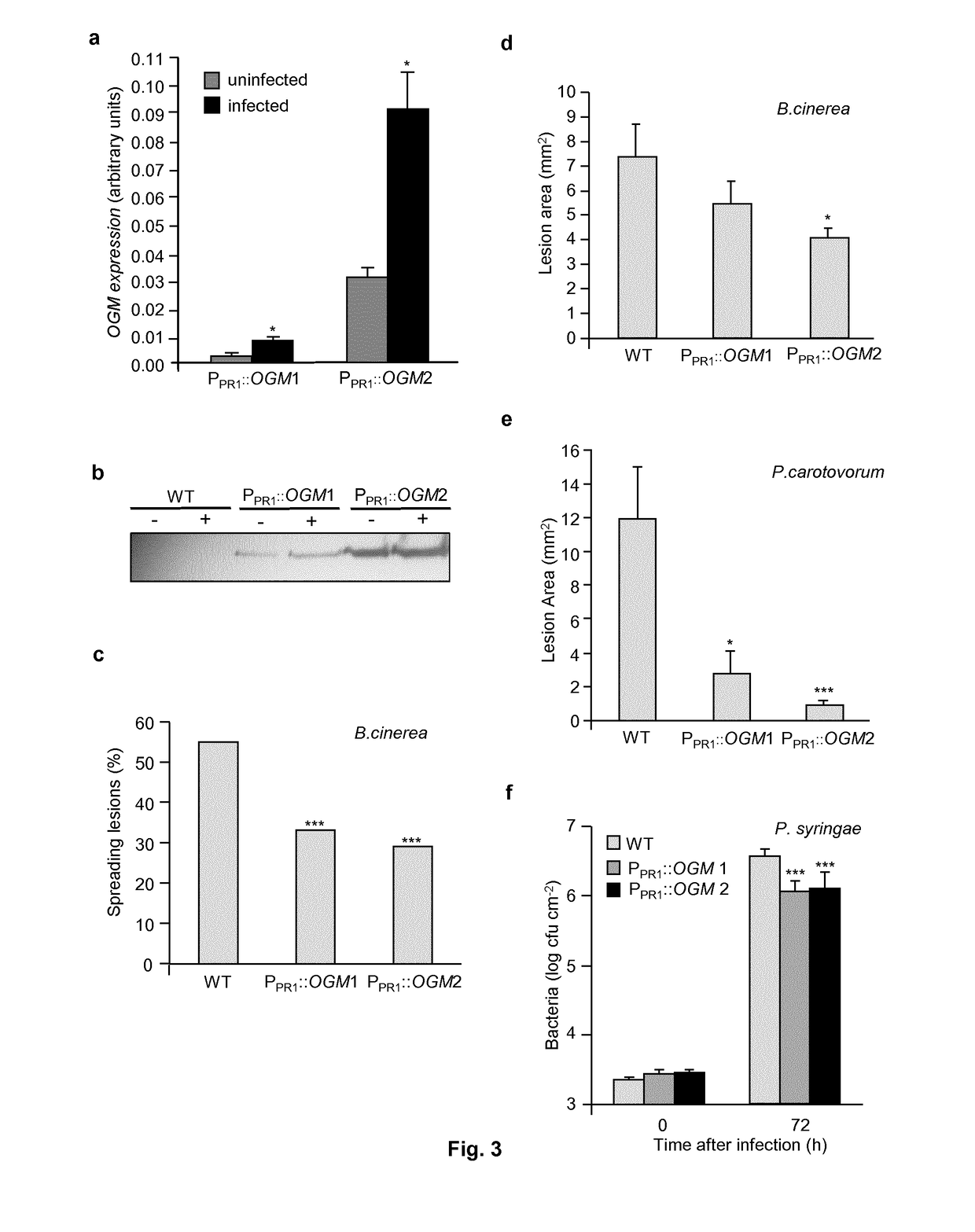
Fusion protein and transgenic plant expressing said protein
ActiveUS20180002705A1Increase resistanceProvide protectionBiocideDepsipeptidesPentagalacturonic acidPlant tissue
The present invention concerns a nucleic acid molecule capable of expressing, in at least one plant tissue, a chimeric protein comprising a polygalacturonase (PG) of fungal, bacterial or insect origin and a plant polygalacturonase inhibitor protein (PGIP) plant capable of inhibiting said PG. The present invention also relates to transgenic plants that express said chimeric protein.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Leukemia Signaling Pathways
The invention discloses nearly 123 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: protein kinases, adaptor / scaffold proteins, phosphatase / phospholipases, G proteins / GTPase activating proteins / guanine nucleotide exchange factors, cellular metabolism enzymes, DNA binding proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, proteases, RNA binding proteins, transcription proteins, translation initiation complex proteins, transferases, ubiquitin conjugating system proteins, vesicle proteins, actin binding proteins, apoptosis proteins, chemokine proteins, enzyme proteins extra cellular matrix proteins, helicases, hydrolases, immunoglobin superfamily proteins, inhibitor proteins, isomerases, ligases, lipid binding proteins, methyltransferases, motor proteins, receptor proteins, and chaperone proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using same
InactiveUS7094575B2Good potencyGood anti-inflammatory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticPhospholipase inhibitorSaxitoxin
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
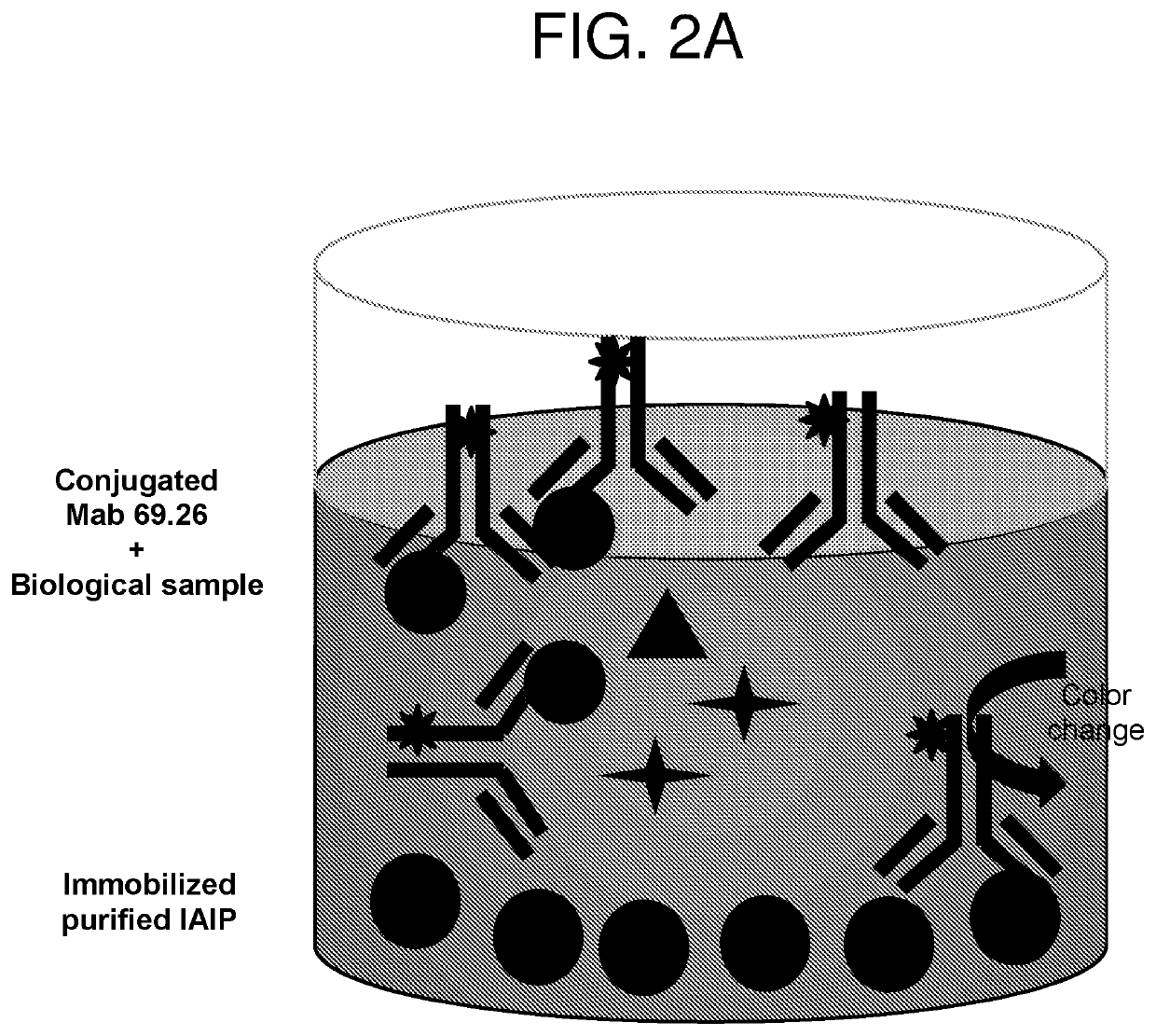
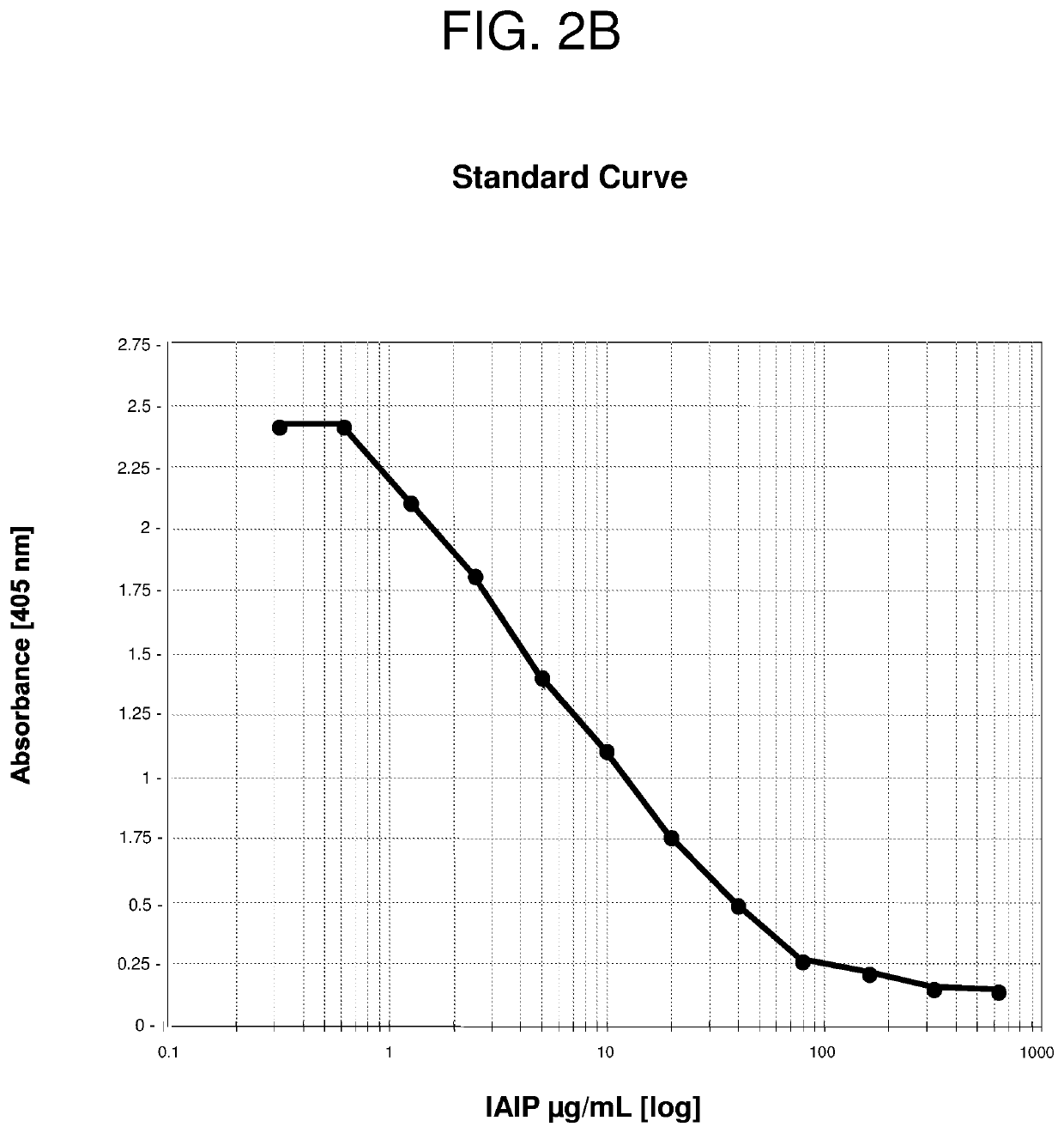
Methods for quantifying inter-alpha inhibitor proteins
InactiveUS20200057077A1Reducing and ameliorating disorderReducing and ameliorating and symptomPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAssayCell biology
Described herein are methods for quantifying lAIP levels in a sample (e.g., from a subject) using lAIP ligand-based assays. Also disclosed are methods for measuring lAIP-IAIP ligand complexes, and methods of evaluating, monitoring, and treating subjects using the aforementioned lAIP quantification methods.
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
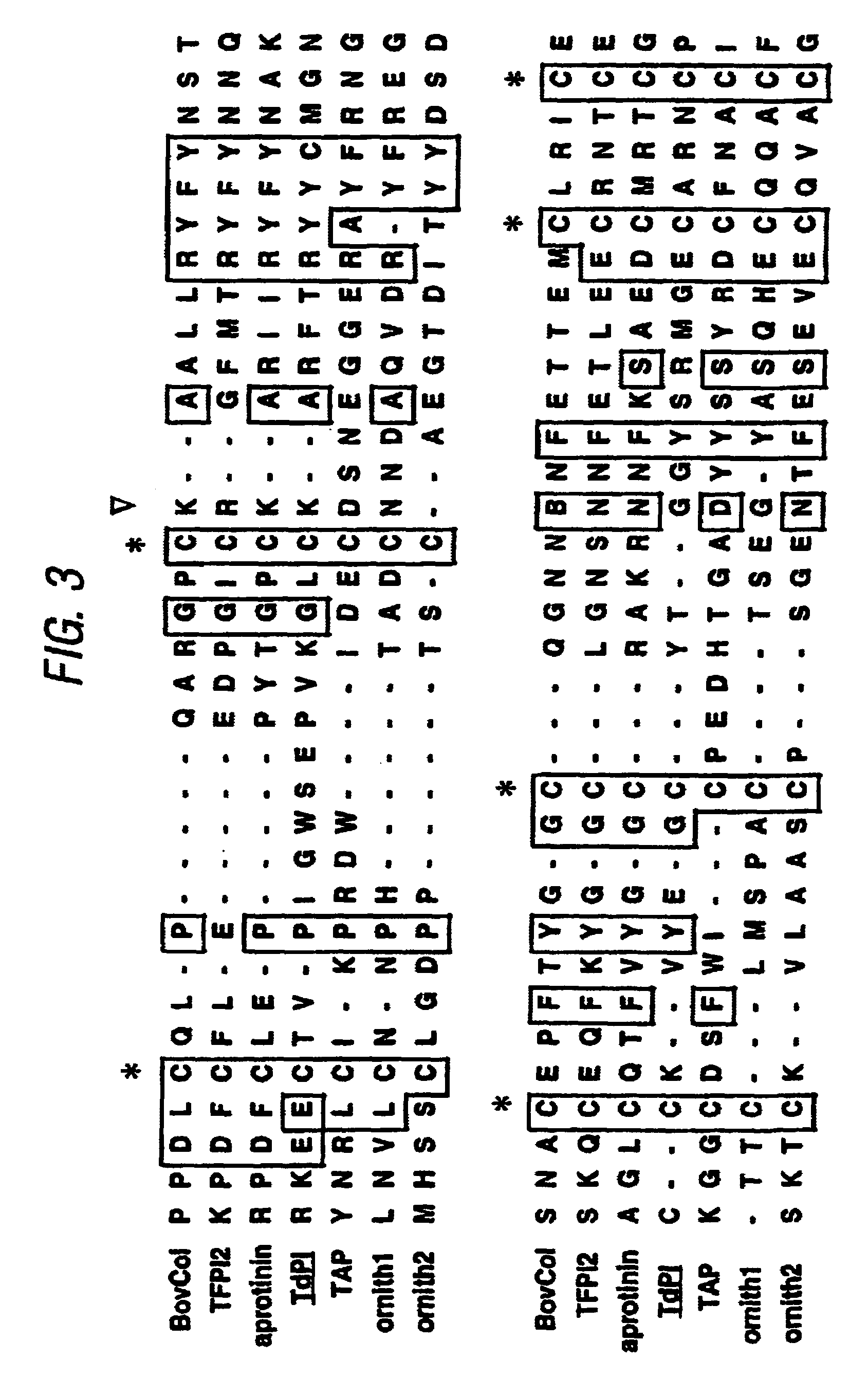
Tryptase inhibitor proteins derived from blood-feeding anthropod ectoparasites
InactiveUS6987168B1Improve efficiencyReduce releaseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntipyreticDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to novel protease inhibitor proteins that have been identified in ticks. These proteins may be used as components of vaccines, as inhibitors of mast cell tryptase, in detection of mast cells and in the isolation and purification of mast cell tryptase. The invention also relates to the control of diseases and injury caused by parasites in animals and humans and to the use of the proteins of the invention in the treatment of certain diseases and allergies.
Owner:EVOLUTEC LTD
Methods for treating pulmonary disease using inter-[alpha] inhibitor proteins
PendingCN109789193AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPre-alpha-inhibitorARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention features methods for treating or preventing pulmonary diseases, including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and pneumonia, in a subject in need thereof that involve administering to the subject inter-[alpha] inhibitor proteins (l[alpha]lps), including, e.g., inter-alpha inhibitor (l[alpha]l) and / or pre-alpha inhibitor (P[alpha]l).
Owner:POROTHERA BIOLOGY
Telomerase expression repressor proteins and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20050176629A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTelomeraseMinimal promoter
Telomerase repressor proteins and nucleic acid compositions encoding the same are provided. The subject repressor proteins bind to a repressor site in the TERT minimal promoter, e.g., a Site C site, and thereby inhibit TERT expression. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting or enhancing, TERT expression. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including therapeutic and therapeutic agent screening applications.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Identification and the use of krp mutants in plants
InactiveUS20170142919A1Weight increaseIncrease in sizeClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPlant cell
The invention provides a plant cell, part, tissue culture or whole plant comprising at least one disrupted KRP gene of the present invention. The present invention also provides methods of increasing weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield of a plant by utilizing the disrupted KRP genes of the present invention. Furthermore, methods of breeding plants to produce new plants having increased weight, size, and / or number of one or more organs, and / or yield are provided. The present invention provides isolated Kinase inhibitor Protein (KIP) Related Protein (KRP) polynucleotide sequences and isolated KRP polypeptide sequences and methods of their use. Exemplary plants include wheat, rice and soy bean.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH INC
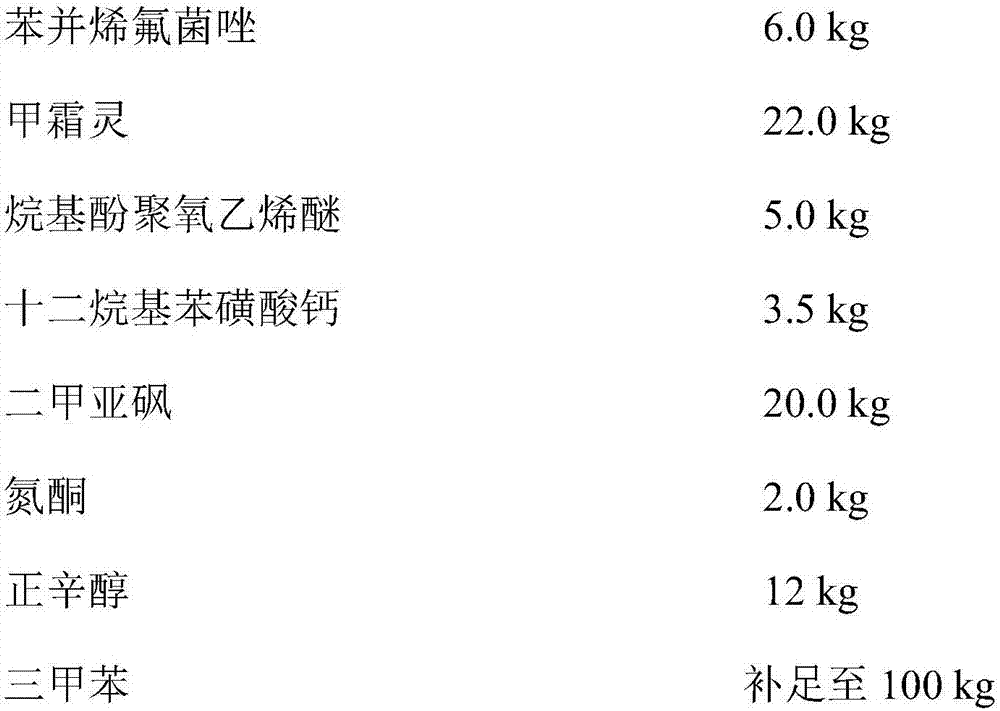
Pesticide composition containing benzovindiflupyr and benzamide fungicides
InactiveCN107156136AGood treatment effectImprove the eradication effectBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseBenzovindiflupyr
The invention discloses a pesticide composition containing benzovindiflupyr and benzamide fungicides. The pesticide composition is compounded from the following components (100% in total): an active component benzovindiflupyr, an active component (II) and other components including an aid and a solvent, wherein the active component (II) is any one of metalaxyl, benalaxyl and oxadixyl. The pesticide composition is applied to foliar spraying and is used for preventing and treating diseases of crops of rice, wheat, corns, tobaccos, tomatoes, potatoes, chili, oilseed rape, watermelons, longans and litchi. The pesticide composition has the advantages that the work efficiency is high, the labor intensity is low, the water is saved, the protein synthesis is inhibited, the pesticide effect is ultra-long, the resistance is delayed, and the labor and cost are saved.
Owner:广西南宁黑泥巴农业科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com