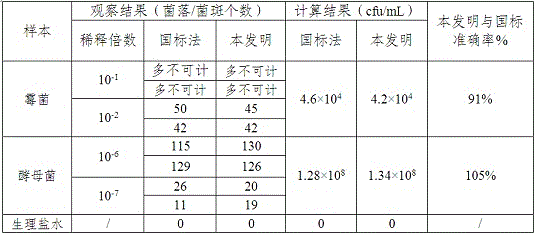
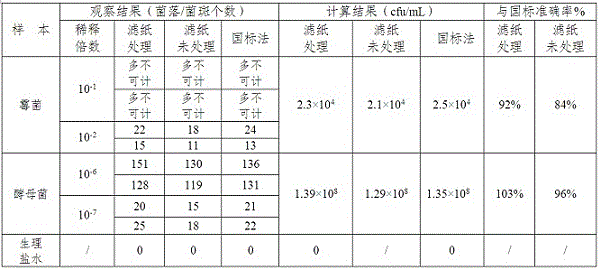
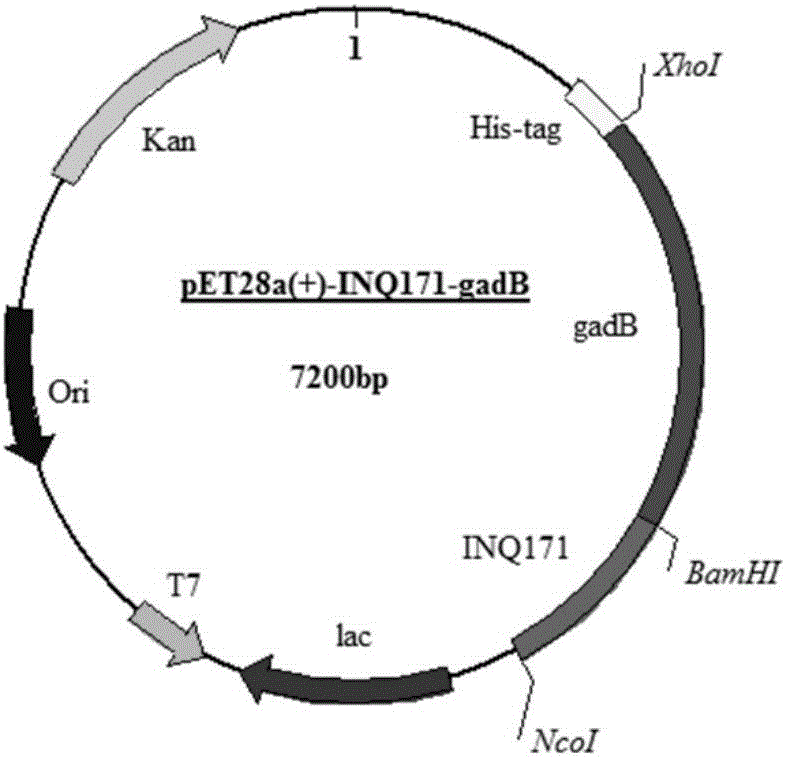
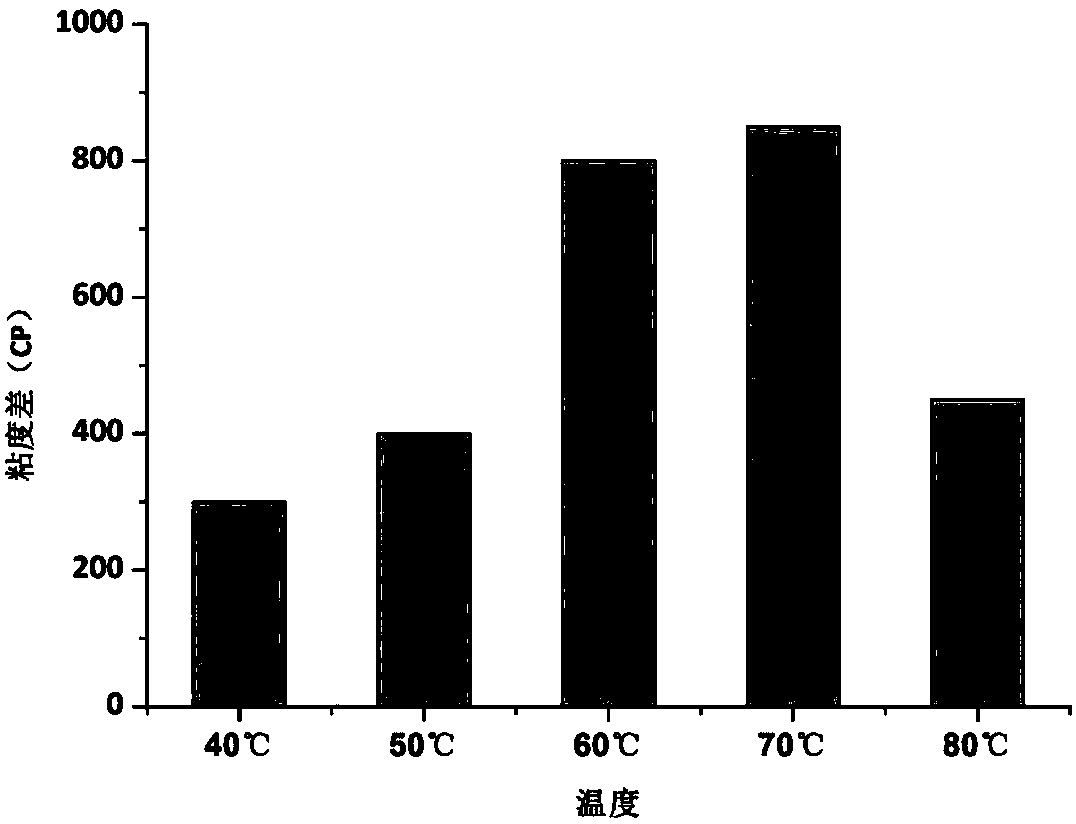
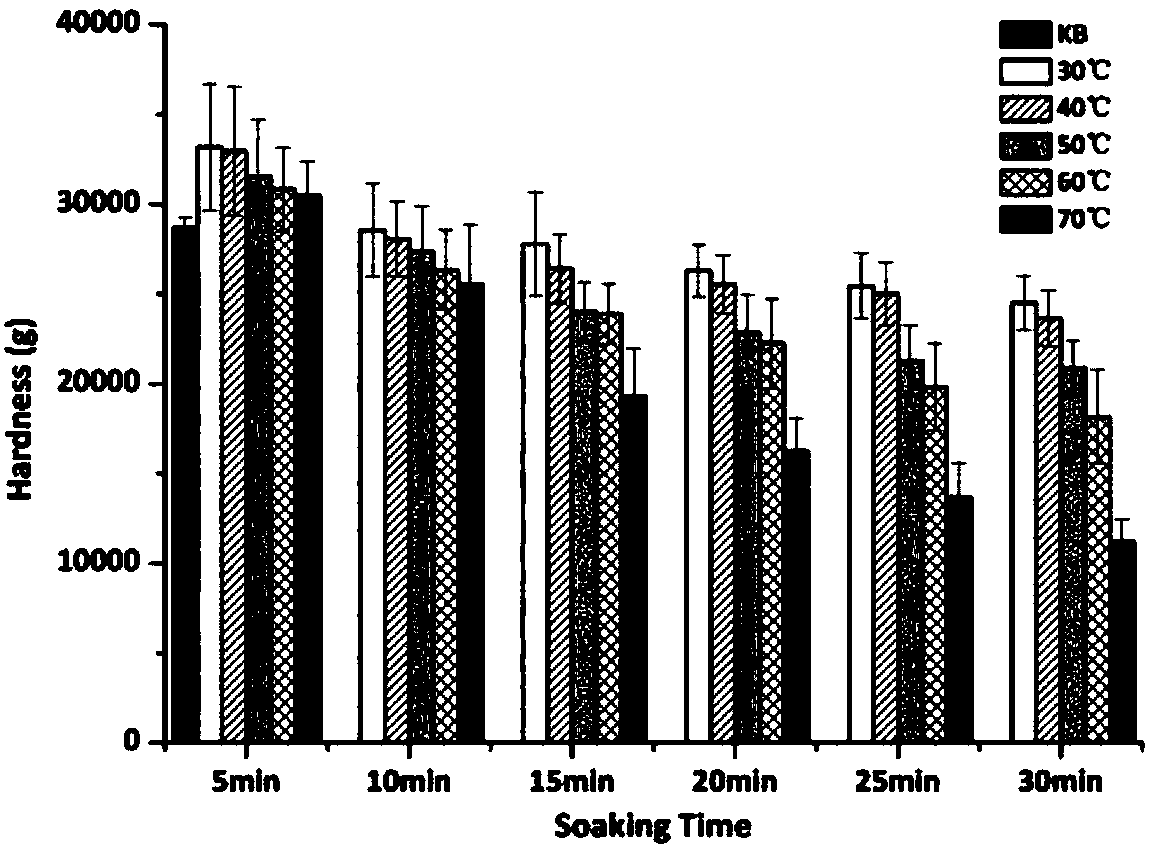
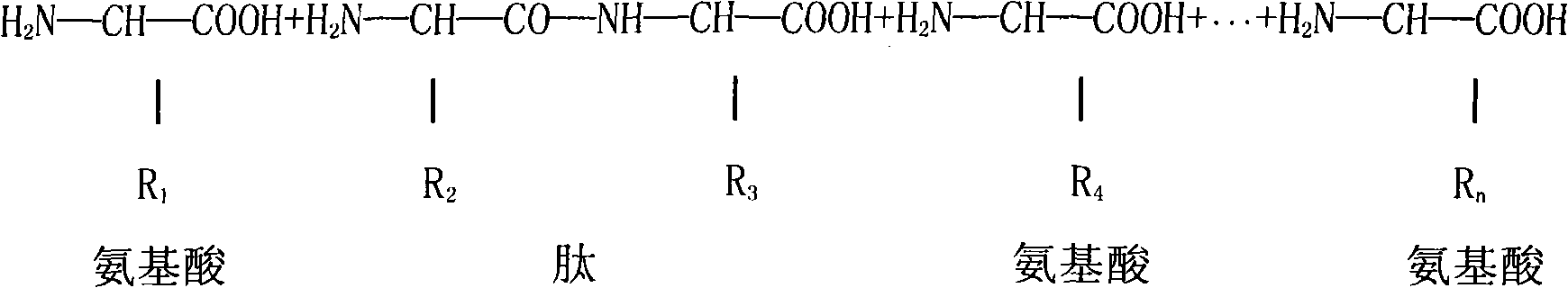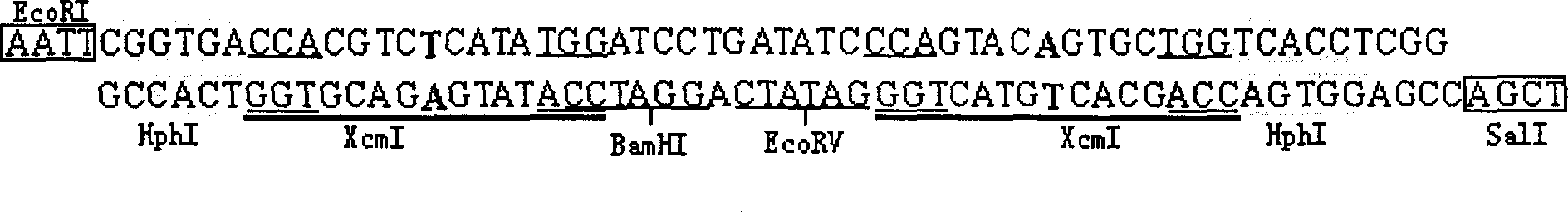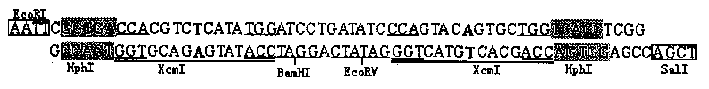Patents
Literature
111 results about "Endoenzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
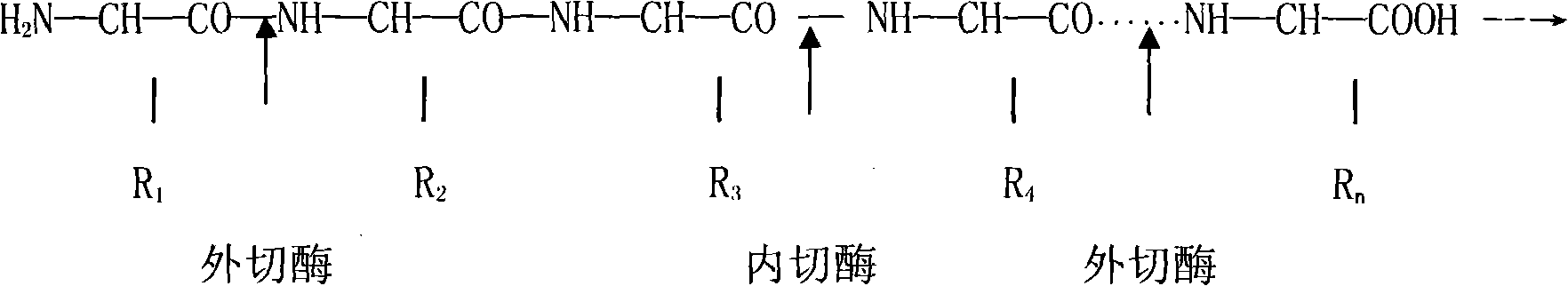
An endoenzyme, or intracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that functions within the cell in which it was produced. Because the majority of enzymes fall within this category, the term is used primarily to differentiate a specific enzyme from an exoenzyme. It is possible for a single enzyme to have both endoenzymatic and exoenzymatic functions; for example, glycolytic enzymes of Kreb's Cycle. In most cases the term endoenzyme refers to an enzyme that binds to a bond 'within the body' of a large molecule - usually a polymer. For example an endoamylase would break down large amylose molecules into shorter dextrin chains. On the other hand, an exoenzyme removes subunits from the polymer one at a time from one end; in effect it can only act at the end ponts of a polymer. An exoamylase would therefore remove one glucose molecule at a time from the end of an amylose molecule.
Efficient pig-feed complex enzyme preparation with enzyme protectant
InactiveCN102860438AImprove conversion rateFast growthAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnimal science
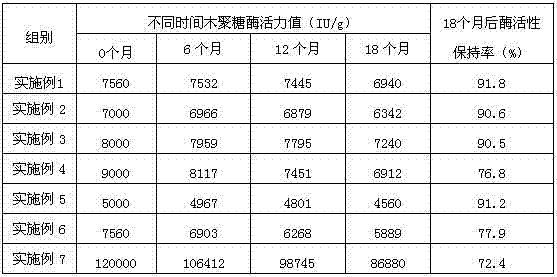
The invention provides an efficient pig-feed complex enzyme preparation with enzyme protectant. The efficient pig-feed complex enzyme preparation with enzyme protectant is capable of promoting absorption of nutrients in the feed by pigs to increase feed utilization rate by degrading antinutritional factors, such as beta-glucan, phytic acid and pectin, biomacromolecules and the like. By adding the protectant, inactivity rate in enzymes can be reduced, effective time can be prolonged, and the effects of the enzyme preparation are more evident and longer. The efficient pig-feed complex enzyme preparation with enzyme protectant is high in feed conversion rate, feed-to-grain ratio can be lowered by more than 19%, growth speed of pigs is increased by more than 23%, and enzyme activity is kept in 18 months and can be kept by more than 90%.
Owner:东莞市双胞胎饲料有限公司
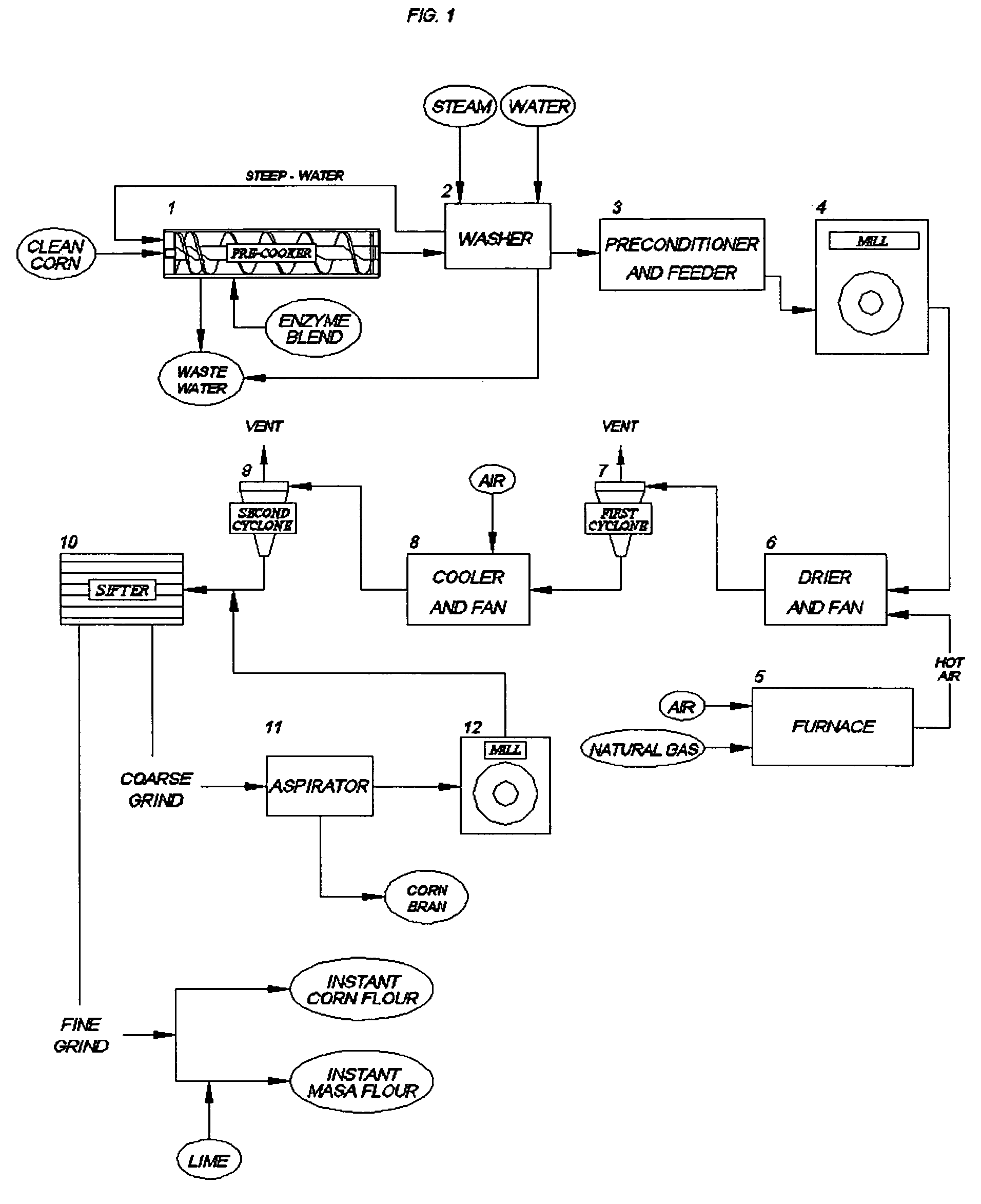
Continuous production of an instant corn flour for snack and tortilla, using a neutral enzymatic precooking
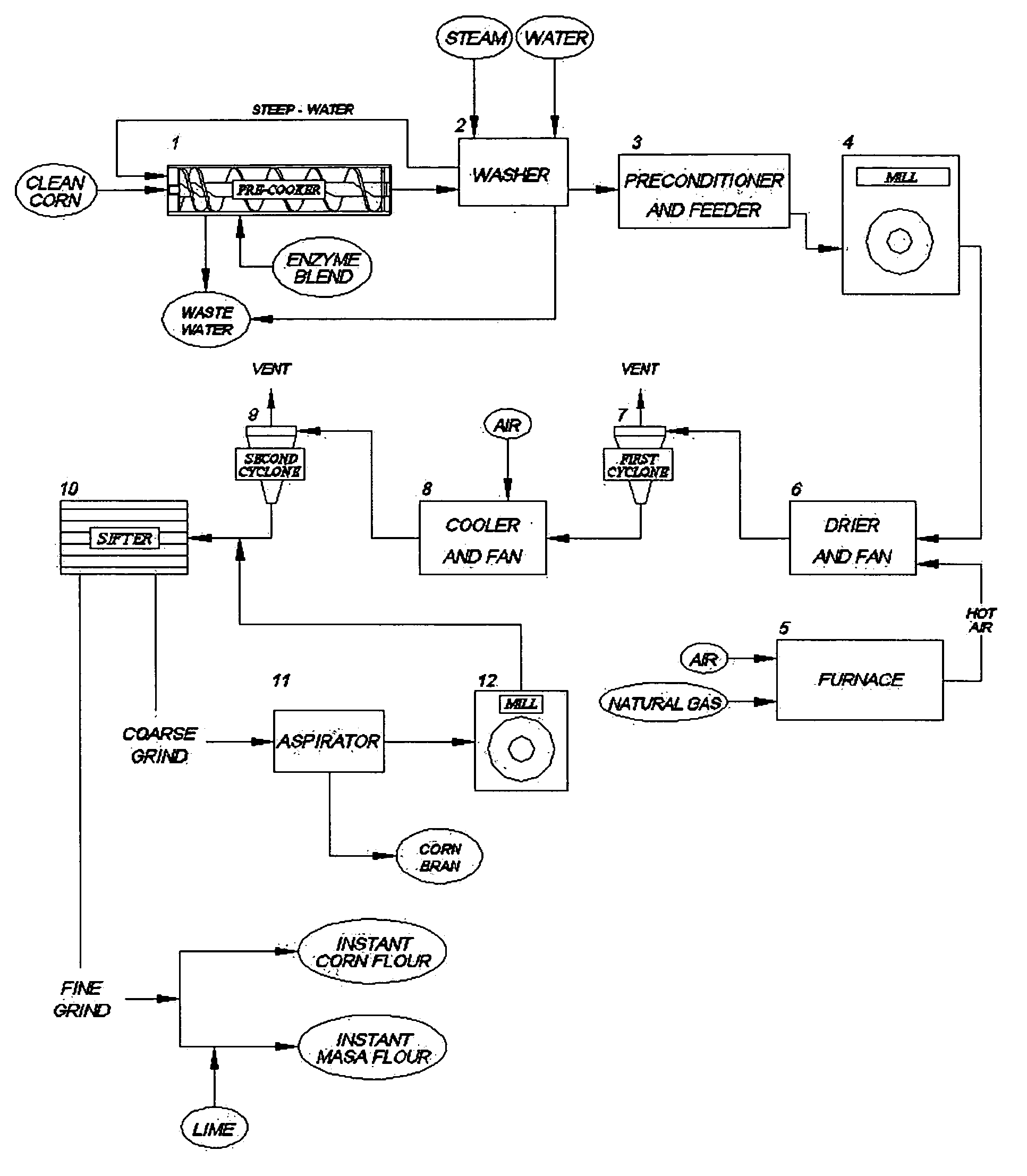
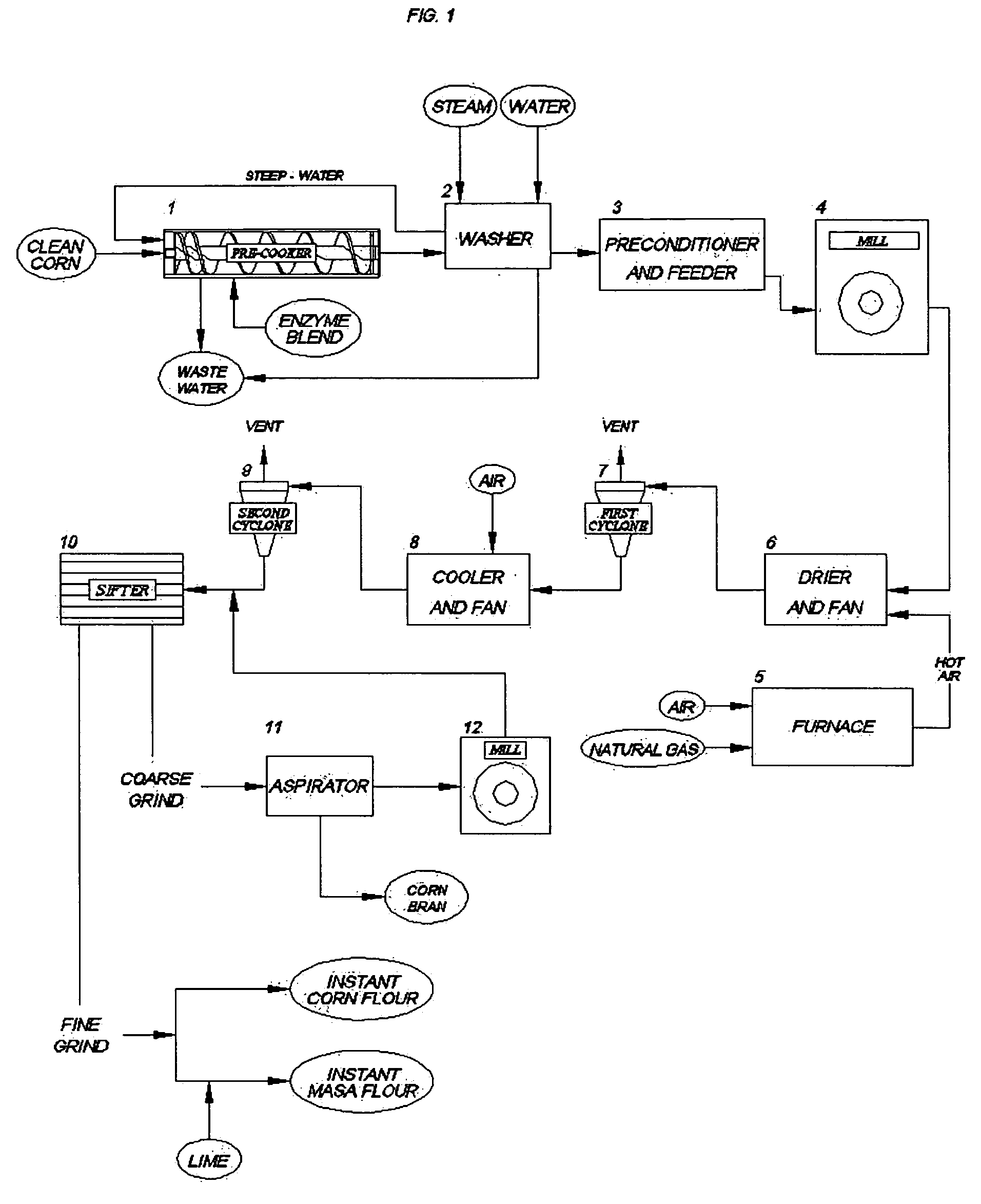
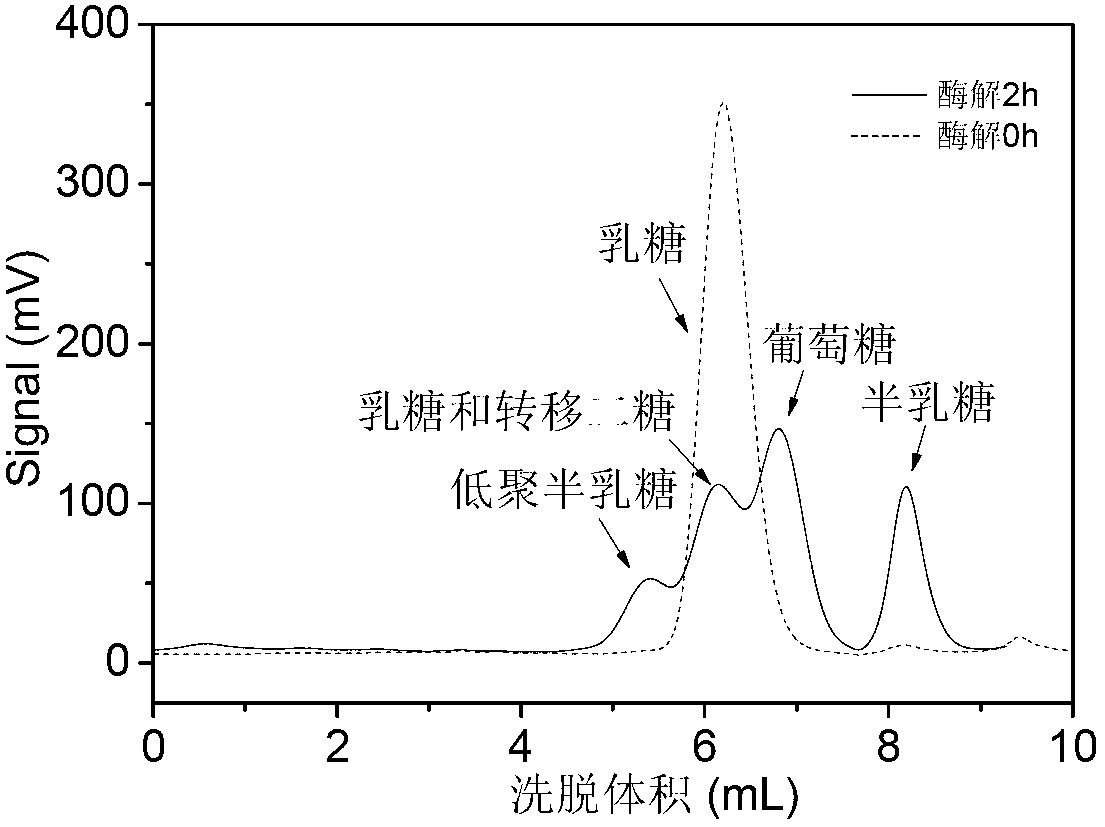
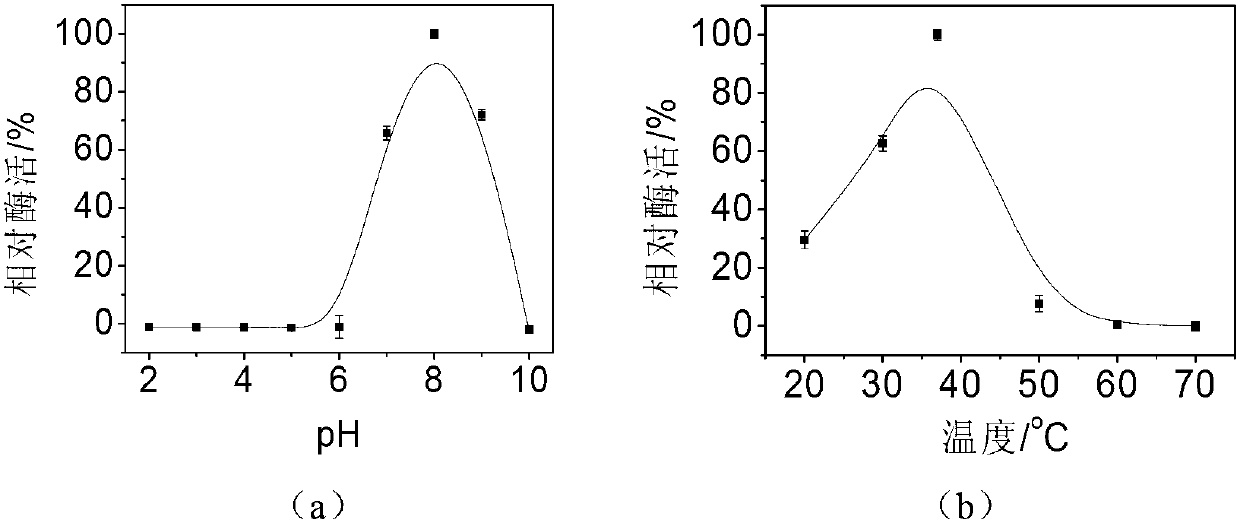
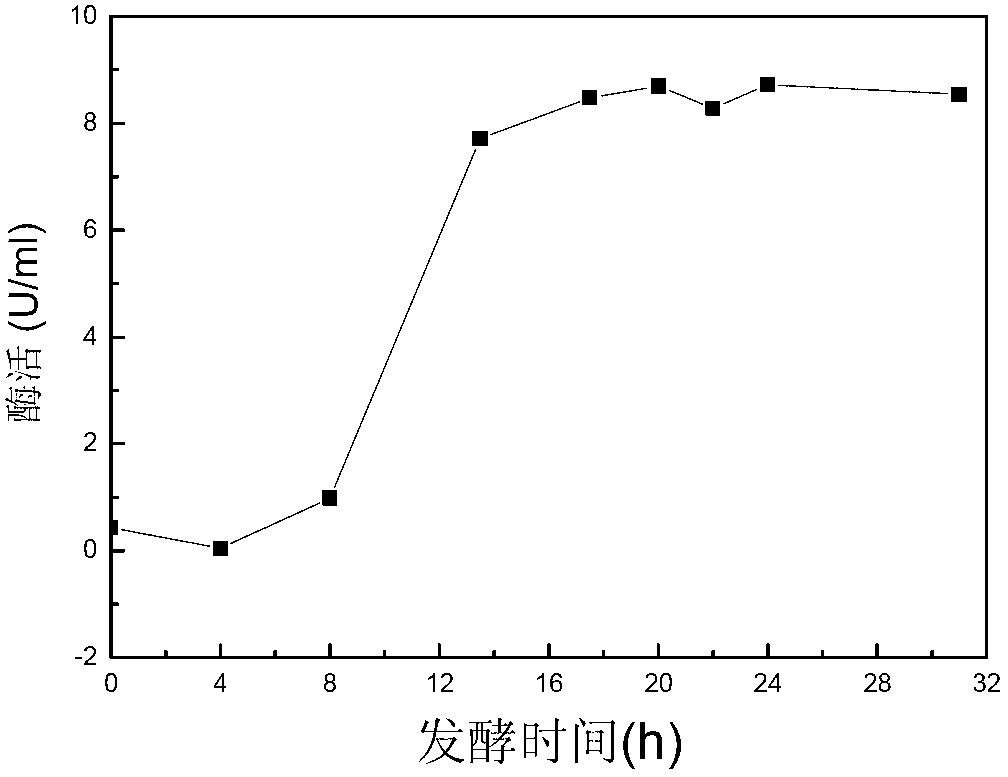
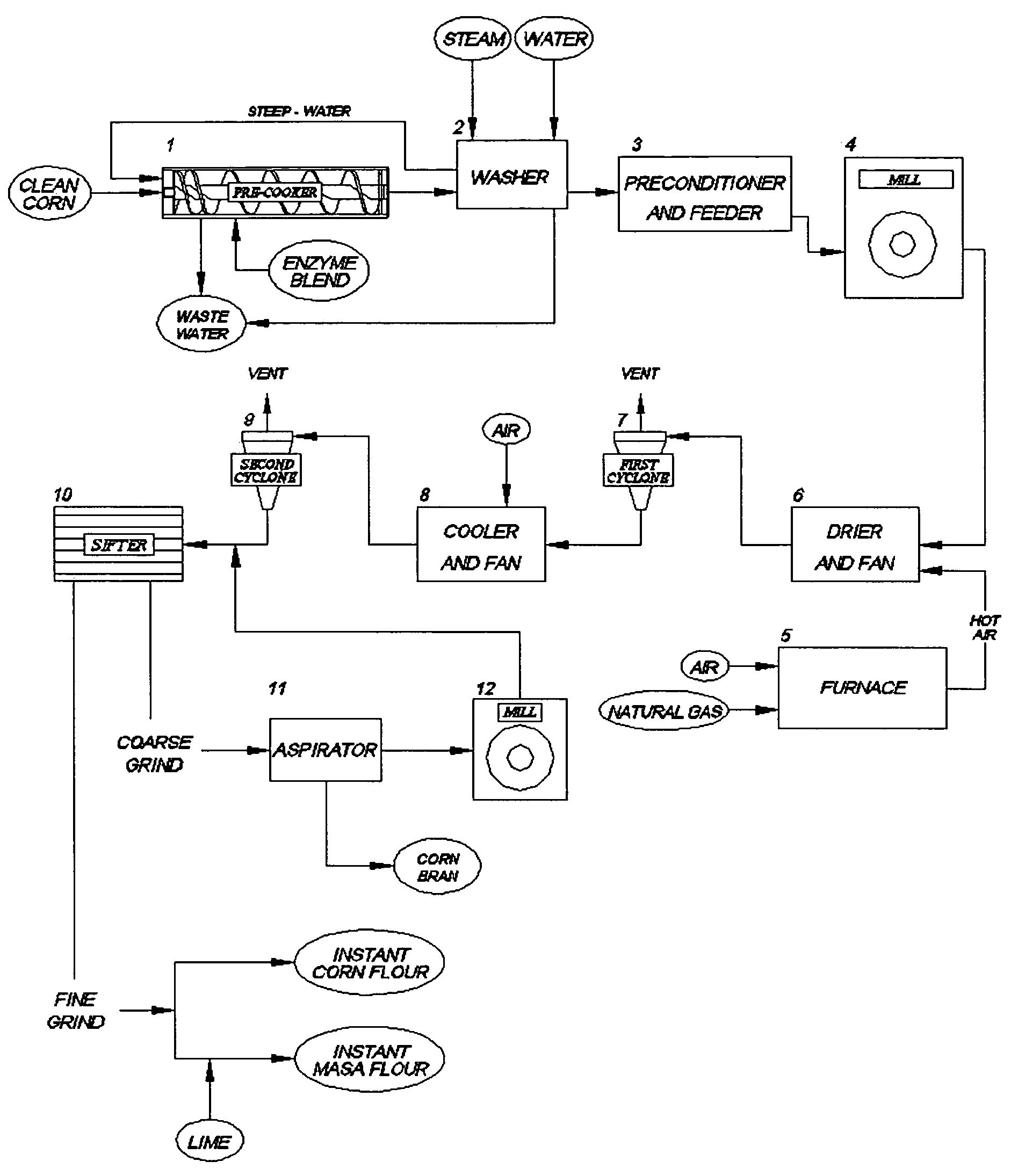
ActiveUS20060024407A1Reduced corn solid lossReduce gelatinizationDough treatmentTea extractionSnack foodXylanase
Precooked and partially-debranned corn flour is continuously produced by an enzymatic precooking using a commercial blend of xylanase, endoamylase and endoprotease as a processing aid. The low-temperature and neutral-pH precooking with an endoenzyme solution effected a partial bran hydrolysis while avoiding excessive pregelatinization, reduced washing and corn solid loss in wastewater. Moisture content is then stabilized, followed by milling and drying at a high-temperature and short-time to produce a controlled gelatinization and denaturation in the ground kernel, cooling and further drying the dried-ground particle. A fine particle size or flour is separated and recovered from the coarser particle which is also segregated to isolate a partially hydrolysed bran fraction for integral flour or animal feed diet, remilling and sieving the coarser particle to produce an instant corn flour for snack, and admixing the fine particle with lime to obtain a masa flour for tortilla and other corn foods.
Owner:GRUMA S A B DE CV
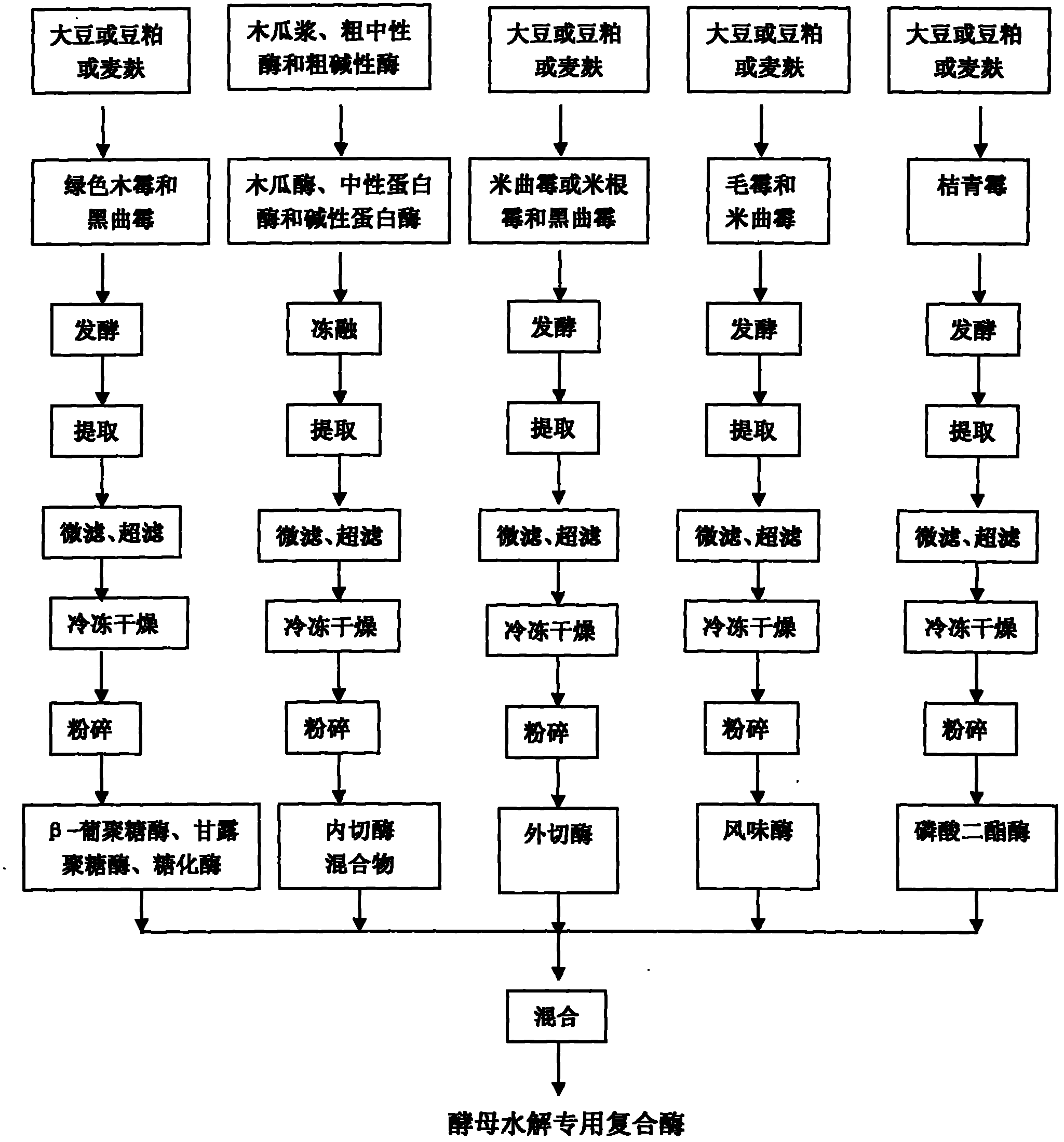
Special compound enzyme for yeast hydrolysis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102115734AEfficient releaseEffective structureEnzymesFood preparationPhosphodiesteraseGeneration rate
Owner:南宁庞博生物工程有限公司
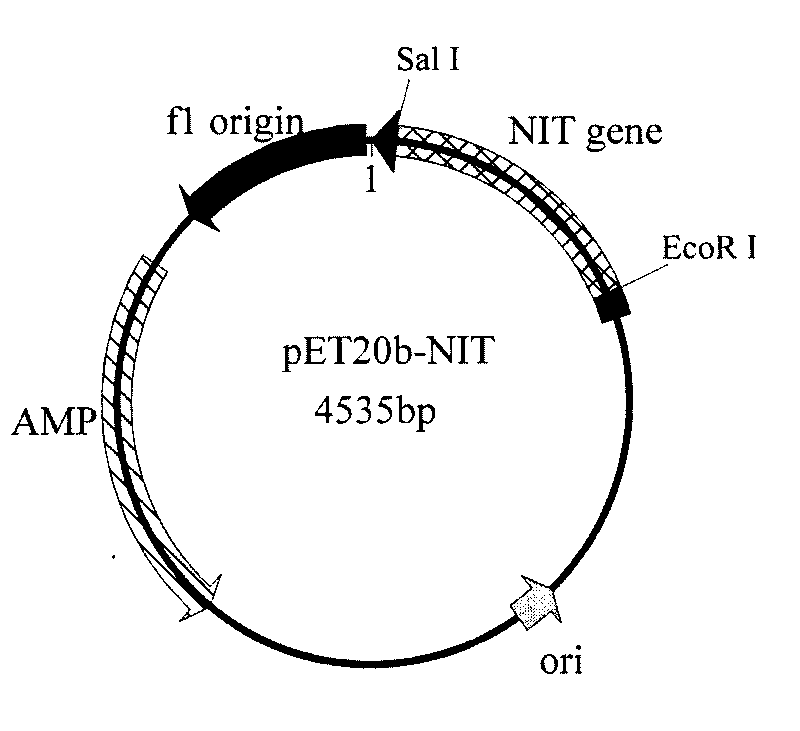
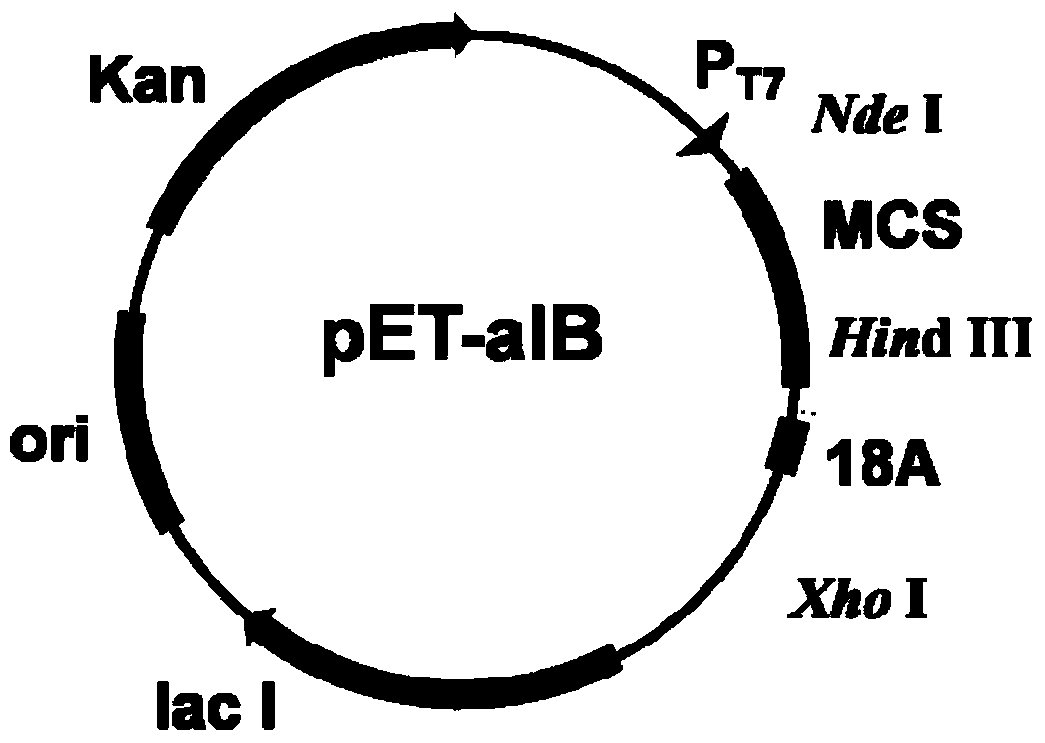
Nitrilase gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
The invention provides a nitrilase gene coding nitrilase, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a recombinant gene engineering bacteria obtained by converting the recombinant vector and application thereof in preparing recombinant nitrilase. The nitrilase gene can be connected with an expression vector for construction to obtain endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or secretion expression recombinant plasmid, and then the endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or the secretion expression recombinant plasmid is respectively and correspondingly converted to a colibacillus bacterial strain to obtain recombinant colibacillus; the recombinant colibacillus contains recombinant nitrilase and can recombine colibacillus into an enzyme resource for biological catalysis and conversion. The recombinant nitrilase serves as the enzyme for conversion, and racemisation mandelonitrile, acrylonitrile, iminodiacetonitrile or 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carbonitrile and the like serve as a substrate for converting to react and prepare corresponding R-mandelic acid, crylic acid, iminodiacetic acid or chiral 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane formic acid and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase and implementation method thereof
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase in the technical field of bioengineering and an implementation method thereof. A beta-glucosidase gene is cloned from Streptomyces griseorubens (Streptomyces griseorubens) JSD-1, and then is connected to an expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, and the recombinant expression vector is further introduced into escherichia coli and is induced to synthesize beta-glucosidase. The engineering bacteria provided by the invention overcomes the defects that the beta-glucosidase in the prior art is generally endoenzyme and the expression quantity is very low, and the like, the beta-glucosidase gene of the invention is expressed by genetically engineered bacteria to prepare beta-glucosidase, and a new method is provided for producing beta-glucosidase by industrial fermentation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for rapid construction of carrier for gene targeting recombination
InactiveCN1844401AReduce generationReliable fidelityVector-based foreign material introductionEndoenzymeGateway cloning
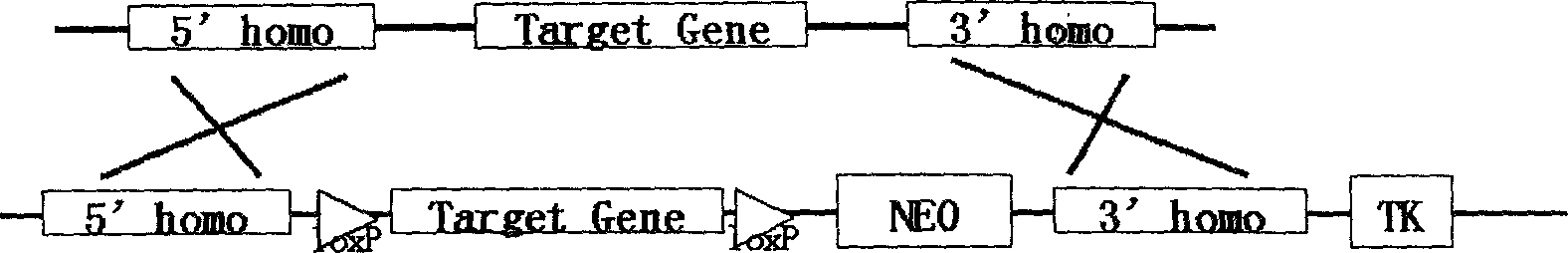
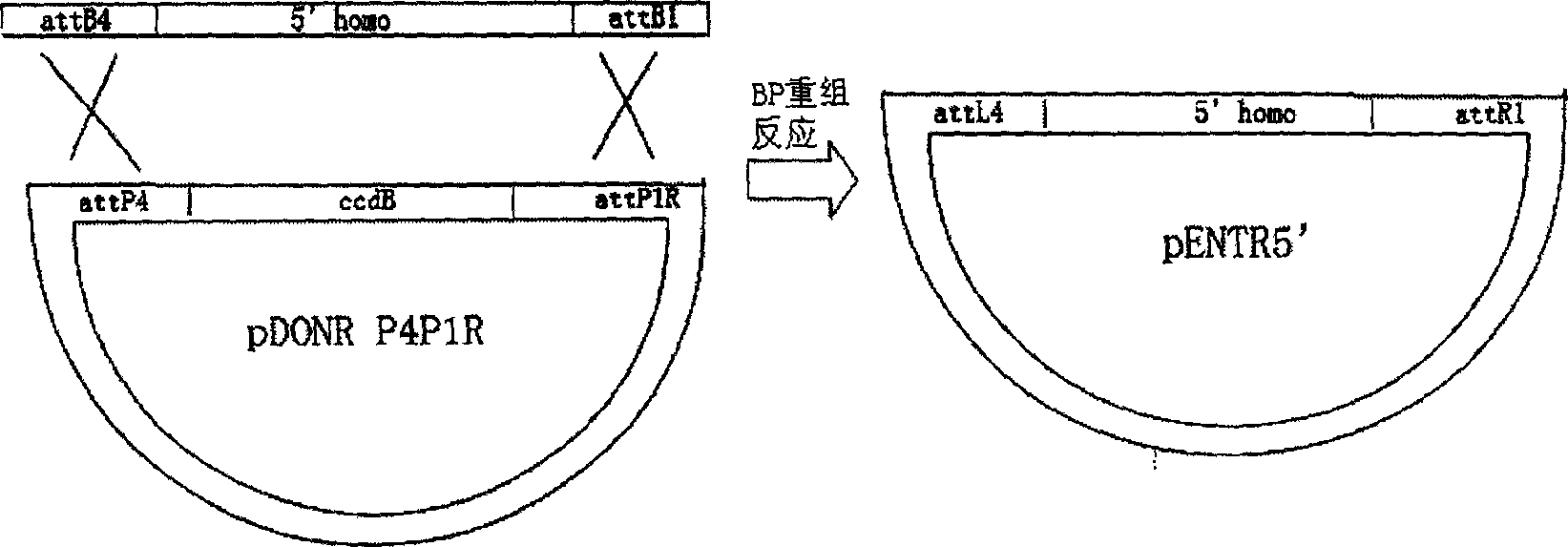
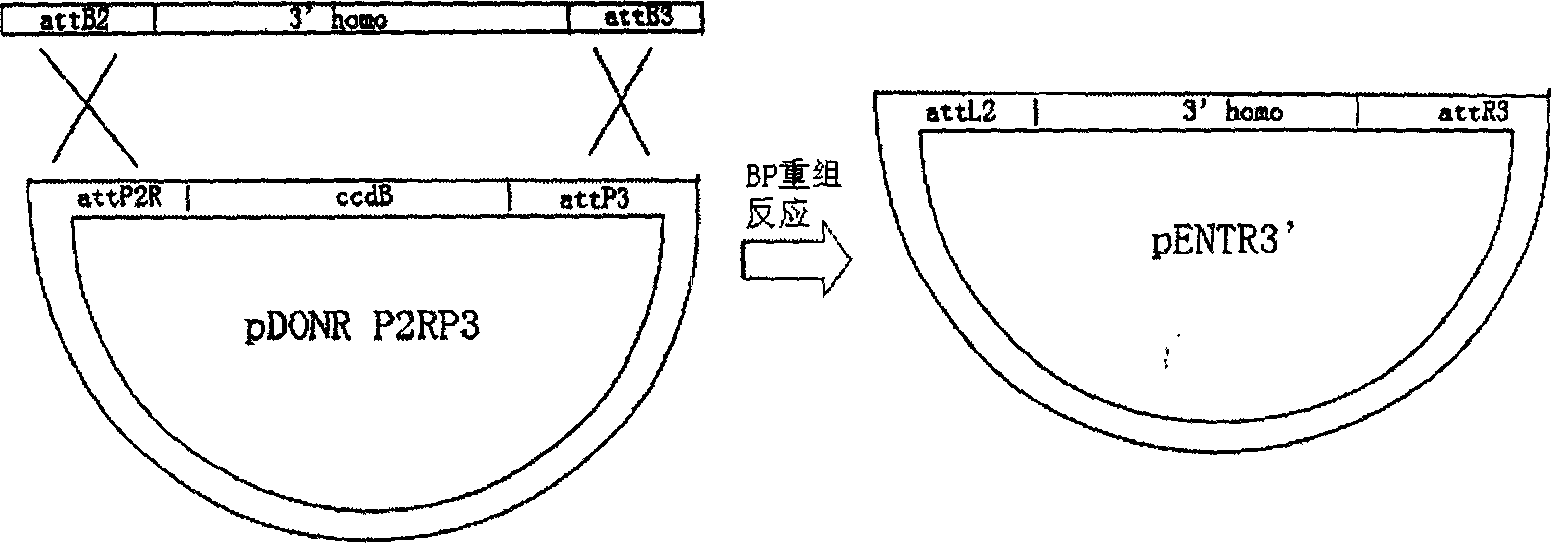
The invention discloses a method of rapid construct vector by aid of Gateway clone system used for gene-shooting-target recombination, Firstly, by using special designing PCR primer for PCR amplification to obtain 5' and 3' homologous arms that use in homologous recombination, insert the homologous arms in vector pDONRP4-P1R and pDONRP2R-P3 individually by BP recombination reaction; then, inserting the target fragment to intermediate vector pDONR loxP / MCS / loxP- FRT / NEO / FRT that we construct creativity; finally, after one hour fast LR recombination reaction of the 3 vectors showing above and pDEST R4-R3TK vector mixture, the 5' homologous arm, the intermediate fragment, 3' homologous arm and the TK subtractive screen selecting element will split joint according to the designing sequence, by transformation and purification, shoot target gene vector will obtained. The method has the advantage of rapid, flexible, timesaving and labor saving, and the method break-through the controlling of endoenzyme site distribution in traditional method. The method has significant in study of gene function.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for improving activity of nitrification function microbiology in activated sludge through directly feeding Fe ions
ActiveCN102502950AAvoid toxic effectsSolve training problemsSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeChemical agent
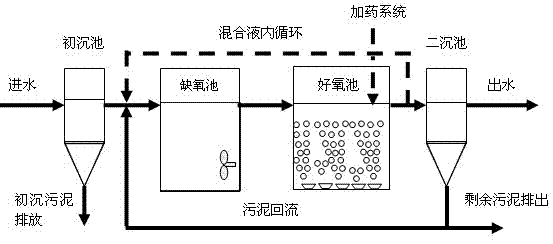
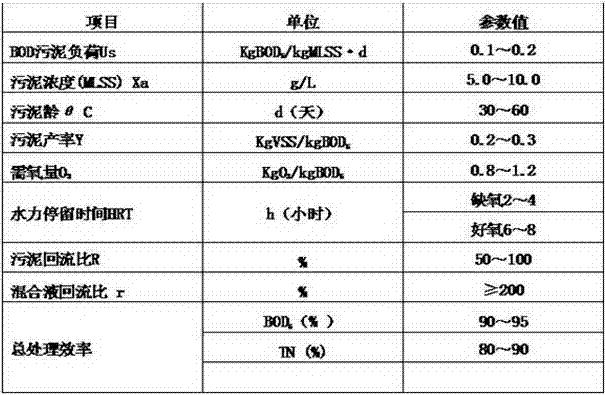
The invention provides a method for improving the activity of nitrification function microbiology in activated sludge through directly feeding Fe ions, which comprises a cultivation stage of the nitrification function microbiology and a long-time running activity maintenance stage. In a saprobiont denitrification system, ferric salt chemical agent with Fe <2+> or Fe<3+> is directly fed into an activated sludge mixture of an aerobic pond of a biology denitrification system, and basic compounds are also fed simultaneously; and in the long-time running activity maintenance stage of nitrificationfunction microbiology, the feeding amount of the ferric salt chemical agent with the Fe <2+> or the Fe<3+> is gradually reduced, and the fed ferric salt chemical agent with the Fe <2+> or the Fe<3+> is only used for replenishing loss amount of the Fe<3+> or the Fe <2+>. According to the method, the biochemical reaction metabolic activity of the nitrification function microbiology can be effectively improved, the breeding of the nitrification function microbiology and the secretion of endoenzyme of microbial cell are promoted, the applicability of saprobiont denitrification technology is improved, the bottleneck problems existing in the saprobiont denitrification system are solved, and the low temperature resistant capacity of the system is obviously improved.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) by using biotransformation method
ActiveCN105087699AShort productionIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiological activationDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses a method for preparing GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) by using a biotransformation method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of GABA. The method comprises the following steps: adopting lactobacillus brevis CGMCC NO.3414 as an original strain; carrying out enrichment culture and thallus collection; resuspending the thallus in a scientifically compounded buffer solution of a mixture of L-sodium glutamate and glutamic acid; adding Na2B4O7.10H2O or MgSO4 having relatively strong activation for the endoenzyme generated by the strain, so as to enable the activity of endoenzyme to be maximally given into play; catalyzing and converting the mixture of L-sodium glutamate and glutamic acid into GABA, wherein the content of GABA in the conversion solution is 45.74-202.18 g / L, the molar conversion rate of the substrate is 95.92-99.75%, and the thallus can be repeatedly used for 8 times. According to the method, the product quality and yield are improved, the environment is protected, the method is relatively good in economic and social benefits and applicable to scale production, and industrial popularization is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
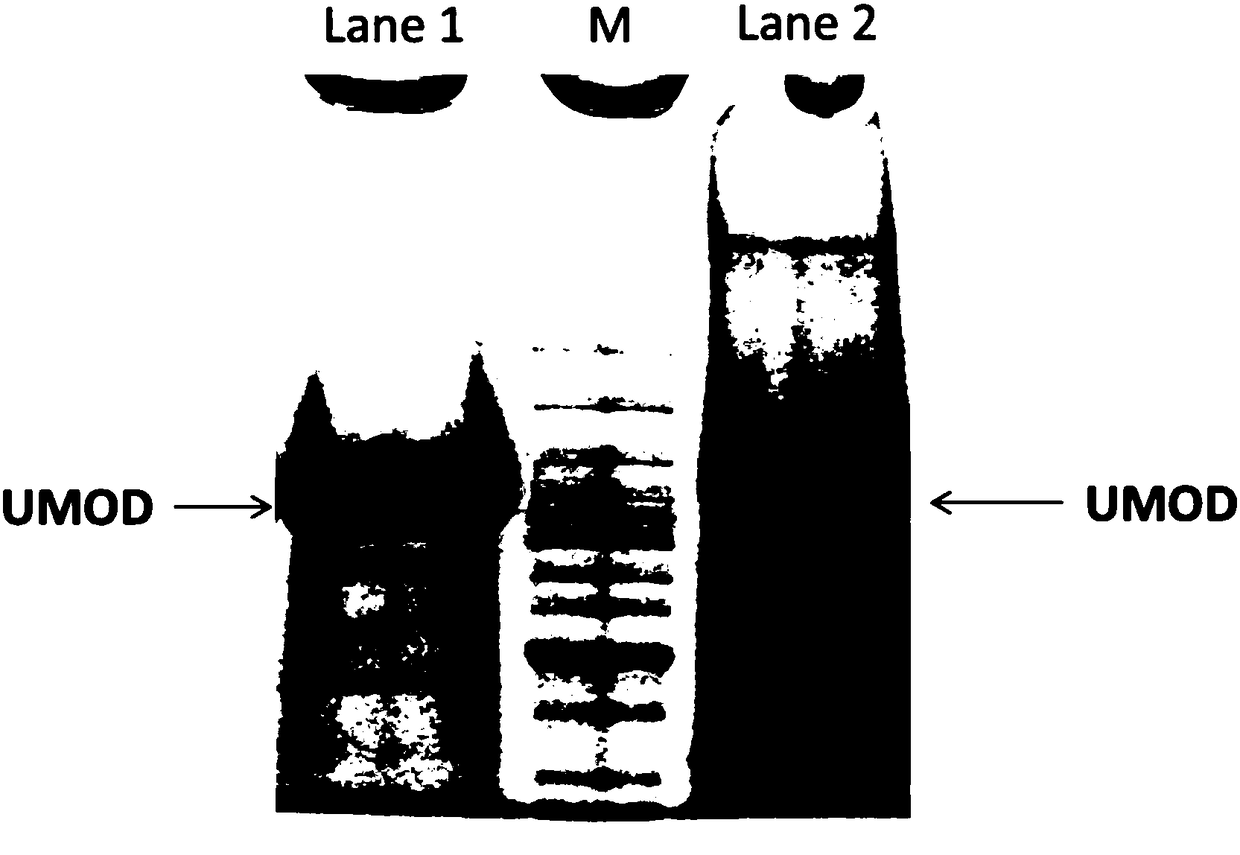
Preparation method of urinary protein and detection method for urinary proteome
PendingCN108333263AEasy to prepareImprove accuracy and repeatabilityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationChemistryMass spectrum analysis
The invention discloses a detection method for urinary proteome, which includes the steps of preparation of urinary protein, separation at protein or peptide level, and mass spectrum identification. The method of preparation of urinary protein includes steps of: 1) performing ultracentrifugation to a urine sample at normal temperature for a certain time and rejecting the supernatant and maintaining a precipitate; 2) adding a proper amount of resuspending buffer liquid to the precipitate in the step 1) to re-suspend the precipitate; 3) adding a reducing agent, which can break a disulfide bond,to the resuspension liquid and heating the resuspension liquid for 10-60 min at 37-80 DEG C; 4) adding a cleaning buffer solution to the solution in the step 3) and performing high-speed centrifugation for a certain time, and rejecting the supernatant and maintaining a precipitate; 5) re-dissolving the precipitate in the step 4) with a digestive buffer solution, and performing in-solution enzymolysis to proteins or performing protein separation through one-dimensional electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The method simplifies preparation process of urinary protein and improves accuracy and repeatability of detection. The method can be used for high-throughput quantitative deep detection of the urinary proteome.
Owner:北京松果天目健康管理有限公司
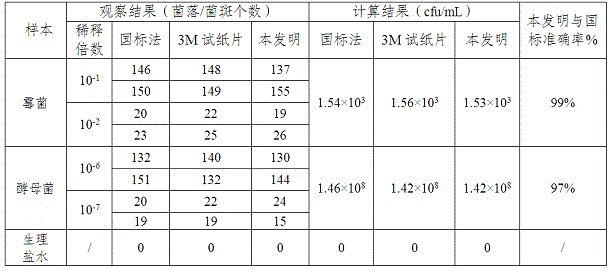
Detection vessel for rapidly detecting moulds and yeasts and preparation method
InactiveCN105483204AImprove breathabilityImprove adsorption capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementYeastMetabolite
The invention provides a detection vessel capable of rapidly culturing and detecting moulds and yeasts at the same time. A biochemical reaction characteristic of microorganisms is utilized, types and reaction conditions of endoenzymes of the microorganisms are determined as main bases for microorganism classification and identification, a microorganism specific enzyme chromogenic substrate is added into an isolation medium or a selective medium, and when target bacteria grow on the medium, the chromogenic substrate can be degraded by specific enzymes and metabolites in special colors can be generated to realize specific colors or forms of colonies, thereby implementing culturing and detection of the microorganisms in a sample. The detection vessel has the advantages of convenience in operation, low cost, labor saving, simple judgment result, reliable detection result, short detection time and the like, and can play an important role in microorganism detection, and accuracy of a detection result reaches 90 percent or over 90 percent of a national standard detection method.
Owner:贵州勤邦食品安全科学技术有限公司
Method for preparing scallop hydrolyzed protein powder by using scallop scrap wastes
InactiveCN102835541AImprove utilization efficiencyDeliciousProtein composition from fishAnimal proteins working-upAdditive ingredientHydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for preparing scallop hydrolyzed protein powder, in particular to a method for preparing scallop hydrolyzed protein powder by using scallop scrap wastes, which belongs to the field of resource environment. The method uses the fresh or frozen scallop scrap wastes as a raw material and comprises the following steps: firstly, washing the raw material after the scallop scrap waste are washed or unfrozen, mashing into meat paste by a chopper mixer; secondly, grinding the mashed raw material into colloid homogenate by a colloid mill, and processing the homogenate by the ultrasonic waves; and thirdly, adding an exogenous enzyme to be conducted for enzymolysis, filtrating, sterilizing, condensing and drying a hydrolysate to obtain the scallop hydrolyzed protein powder. With the adoption of the ultrasonic waves, the lysate and endoenzyme can be effectively promoted to be released, and the use ratio of the exogenous enzyme can be improved; furthermore, the product has trophism and functionality; and meanwhile, the protein powder is fresh in taste, high in contents of protein and amino nitrogen and implements green and environmental protection, so that the protein powder can be served as an ingredient of the condiments including seafood soy sauce and seafood seasoning packet, and can be served as the raw material for health food and medicine deep processing.
Owner:大连格兰清水环境工程有限公司
Recombinant engineering bacterium with surface exhibiting and expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase as well as construction method and application of recombinant engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106754610AAvoid barrier effectImprove apparent vitalityFungiBacteriaGlutamate decarboxylaseGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to a recombinant engineering bacterium with the surface exhibiting and expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant engineering bacterium. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps of constructing ice nucleaiton protein-based recombinant engineering bacterium with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase, inoculating a glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacterium into a culture medium, carrying out shaking culture, adding IPTG or lactose to induce the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase, and collecting recombinant bacteria with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase, wherein the recombinant bacteria with the surface exhibiting glutamic acid decarboxylase is used for preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid from the substrate glutamic acid decarboxylation. According to the preparation method, a permeabilization treatment process required in whole-strain expression of conventionally expressed endoenzyme is avoided, recombinase is exhibited and expressed on the surface of the recombinant bacteria, and a substrate can be in contact with the recombinase to finish conversion without entering bacteria cells, so that the purpose of improving the expression activity of the recombinant bacteria is achieved. The preparation method is simple, convenient and low in cost, the operation is simple, and the expression activity of the recombinant bacteria can be efficiently improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
DNA sequence for constituting T carrier and the T carrier constituting process
InactiveCN1344795ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationDNA fragmentationEndoenzyme
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for preparing polysaccharide by using lucidum strain fermented laminaria leftover
InactiveCN101423855ARealize comprehensive utilizationAvoid the influence of physiological activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiltrationFungal mycelium
The invention relates to a method for preparing polysaccharide by using lucid ganoderma strain to ferment kelp waste, which comprises the following steps: using the kelp waste as a raw material, killing enzyme and centrifugating the raw material after the raw material is subjected to enzymolysis of cellulose; putting supernatant into a fermentation tank, inoculating deeply fermented lucid ganoderma strain, and quickly fermenting the lucid ganoderma strain under aerobic condition to obtain fermentation liquor and lucid ganoderma mycelium after the filtration; depositing the fermentation liquor by ethanol to obtain composition of kelp polysaccharide and lucid ganoderma polysaccharide; and drying the lucid ganoderma mycelium, and extracting the lucid ganoderma polysaccharide. The method combines enzyme treatment and fermentation of the lucid ganoderma strain to treat the kelp waste, shortens fermentation time, obtains lucid ganoderma endoenzyme and endoenzyme polysaccharide as well as kelp polysaccharide at the same time, has reasonable and effective preparing technology, originates a novel process route, realizes comprehensive utilization of the kelp waste, reduces production cost, improves economic effect, and reduces pollution to environment at the same time.
Owner:SHANDONG HOMEY AQUATIC DEV +1
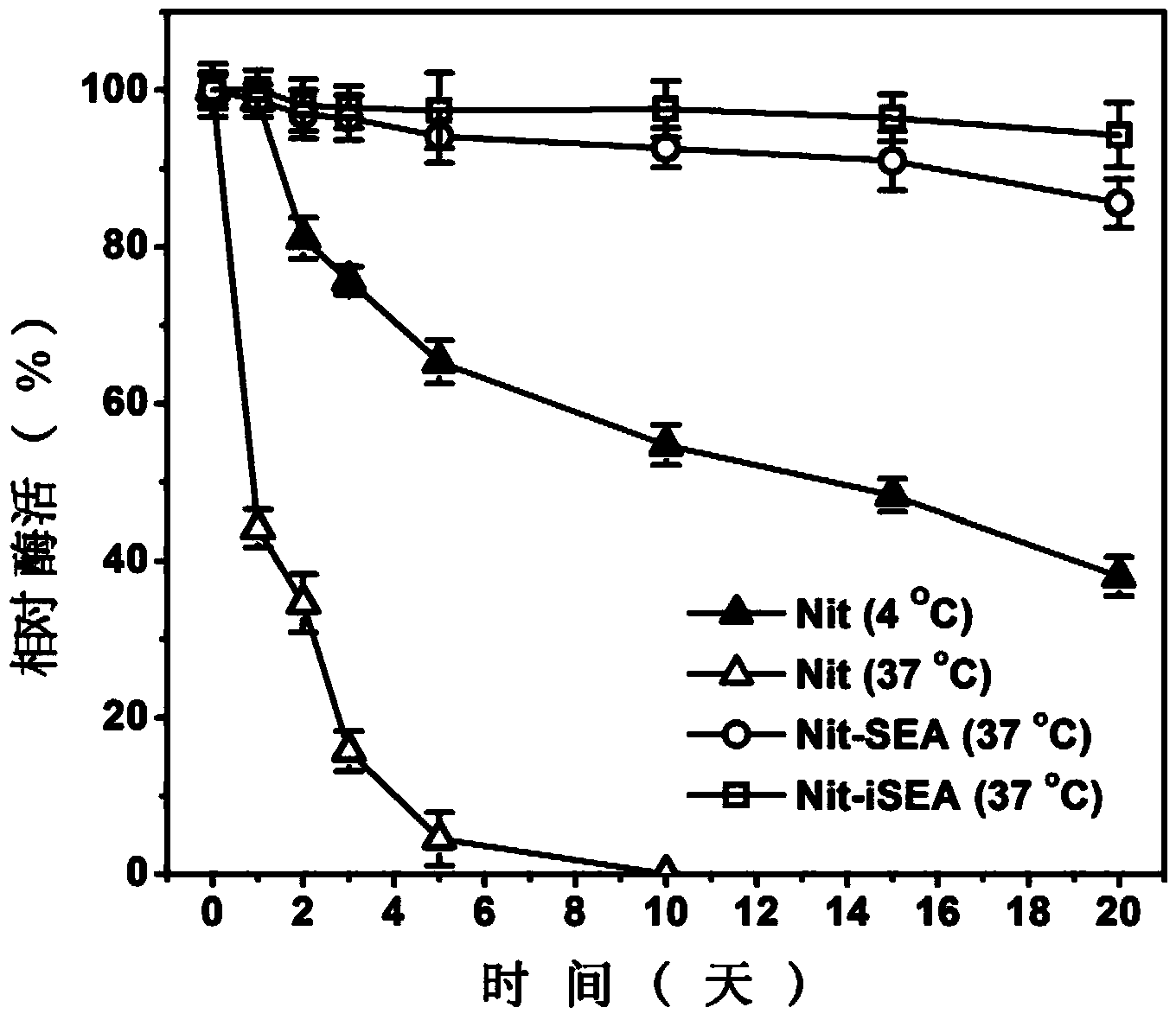
Self-aggregation short-peptide induction based immobilized nitrilase and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103757042AImprove mechanical stabilityHigh purityHydrolasesChemical industryFreeze-dryingEndoenzyme
The invention discloses a self-aggregation short-peptide induction based immobilized nitrilase and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) splicing connecting peptides and self-aggregation short peptides, so as to construct an expression vector; (2) connecting a nitrilase gene and the expression vector, and transforming into a recipient strain, so as to obtain an engineering strain; (3) carrying out induced expression on the engineering strain, carrying out wall breaking treatment on cells, and centrifuging and / or filtrating to obtain a precipitate, namely a nitrilase endoenzyme aggregate; (4) immobilizing the obtained nitrilase endoenzyme aggregate in alginate, thereby obtaining the immobilized nitrilase. According to the immobilized nitrilase aggregate obtained by the method, the particle diameter of the immobilized nitrilase is about 1mm. According to the immobilized nitrilase, particles can be subjected to freeze-drying preservation, and the enzyme activity is reserved to 90% when the immobilized nitrilase is preserved for 20 days at the temperature of 37 DEG C; the activity of the immobilized nitrilase is high, and the operating flow is simple.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
A preparation method of yeast-derived active polypeptide
The invention discloses a preparation method of active polypeptide derived from yeast. Mix yeast powder and water, add a mixed enzyme consisting of endoenzyme, exoenzyme, and flavor enzyme, and separate solid and liquid after enzymatic hydrolysis. The polysaccharide and nucleic acid impurities in the liquid phase components were removed by ethanol precipitation. The supernatant is filtered and separated by an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 5kDa to 10kDa, and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure and vacuum freeze-dried to obtain the active polypeptide. Through in vitro activity determination, the yeast-derived active polypeptide has blood pressure-lowering, anti-oxidation and blood-sugar-lowering activities.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Mutant Pul 324 of pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase and use thereof
ActiveCN102796751AReduce manufacturing costImprove stabilityEnzymesFermentationEscherichia coliPullulanase
The invention discloses a mutant Pul 324 of a pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase and a use thereof. Based on a modern enzyme engineering technology, an amino acid sequence of a pullulanibacillus naganoensis pullulanase is subjected to molecular modification. Through a PCR method, front 108 amino acid residues of a raw enzyme are deleted so that the mutant Pul 324 which can realize effective secretory expression in escherichia coli hosts is obtained. The mutant Pul 324 is inserted into pET-22b(+) so that a recombinant vector is constructed. The recombinant vector is introduced into an escherichia coli host for secretory expression of the mutant Pul 324. The mutant Pul 324 gene is smaller than a wild type gene and is conducive to plasmid stabilization. Compared with a raw enzyme, themutant Pul 324 can realize effective secretory expression in escherichia coli hosts, realize a fermentation supernatant enzyme activity improved by 24 times and realize an endoenzyme activity improved by 40%. The mutant Pul 324 can improve a pullulanase secretory expression level of a host. An expression product can improve starch hydrolysis efficiency.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus subtilis and alkali-resisting and salt-resisting oil field fracturing enzyme and application thereof
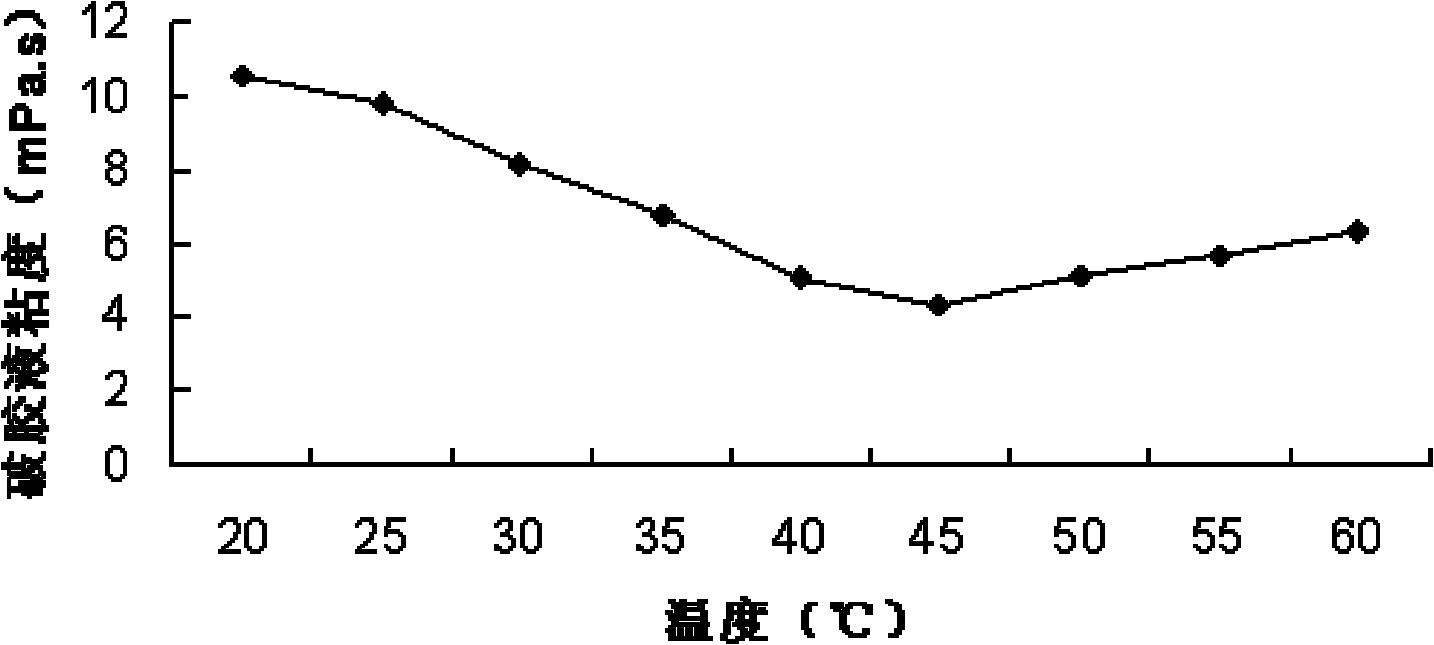
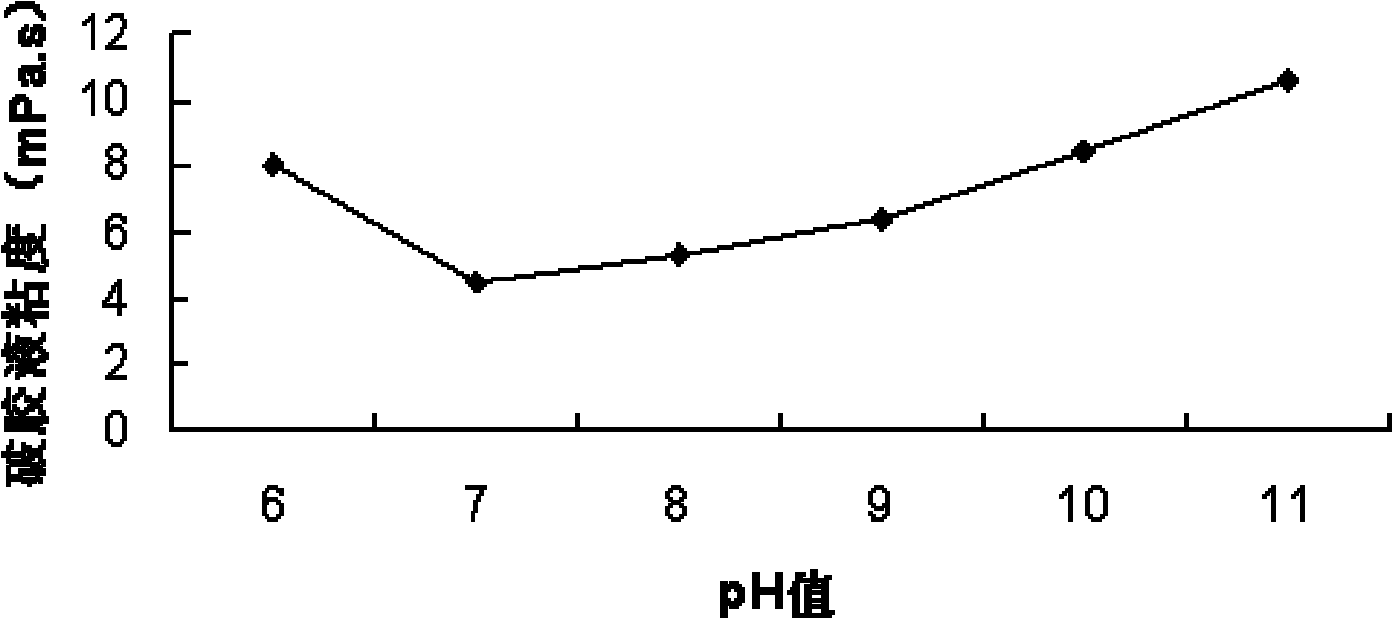
ActiveCN101838620AMeet the needs of fracturing engineeringEfficient gel breaking abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFracturing fluidFood flavor
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis and alkali-resisting and salt-resisting oil field fracturing enzyme and application thereof. A method for preparing the enzyme comprises the steps of: separating the bacillus subtilis BIT09L1 from a deep sea; culturing the bacillus subtilis in a culture medium taking konjak flavor powder and the like as carbon sources; and separating and purifying obtained fermentation liquor to obtain b mannogalactan. The enzyme has 6.0 to 10.0 of tolerance pH value, and 15 to 60 DEG C of temperature. The enzyme can keep the activity over 80 percent at the temperature and in the pH range. The prepared biological enzyme preparation is preserved at the temperature of between 4 and 8 DEG C, and has over 18 months of service life on storage racks. The enzyme has the advantages of simple process, readily available raw materials, easy purification of products, low cost and less pollution. The enzyme preparation has alkali resistance and salt resistance, particularly has high-efficient capacity of breaking the guar gum or modified guar gum of the fracturing fluid for oil fields, has no incompatibility with most chemical agents in the fracturing fluid, and meets the requirements of oil field fracturing engineering.
Owner:DALIAN BITEOMICS INC
Generation bacterium of heat-stable phytase
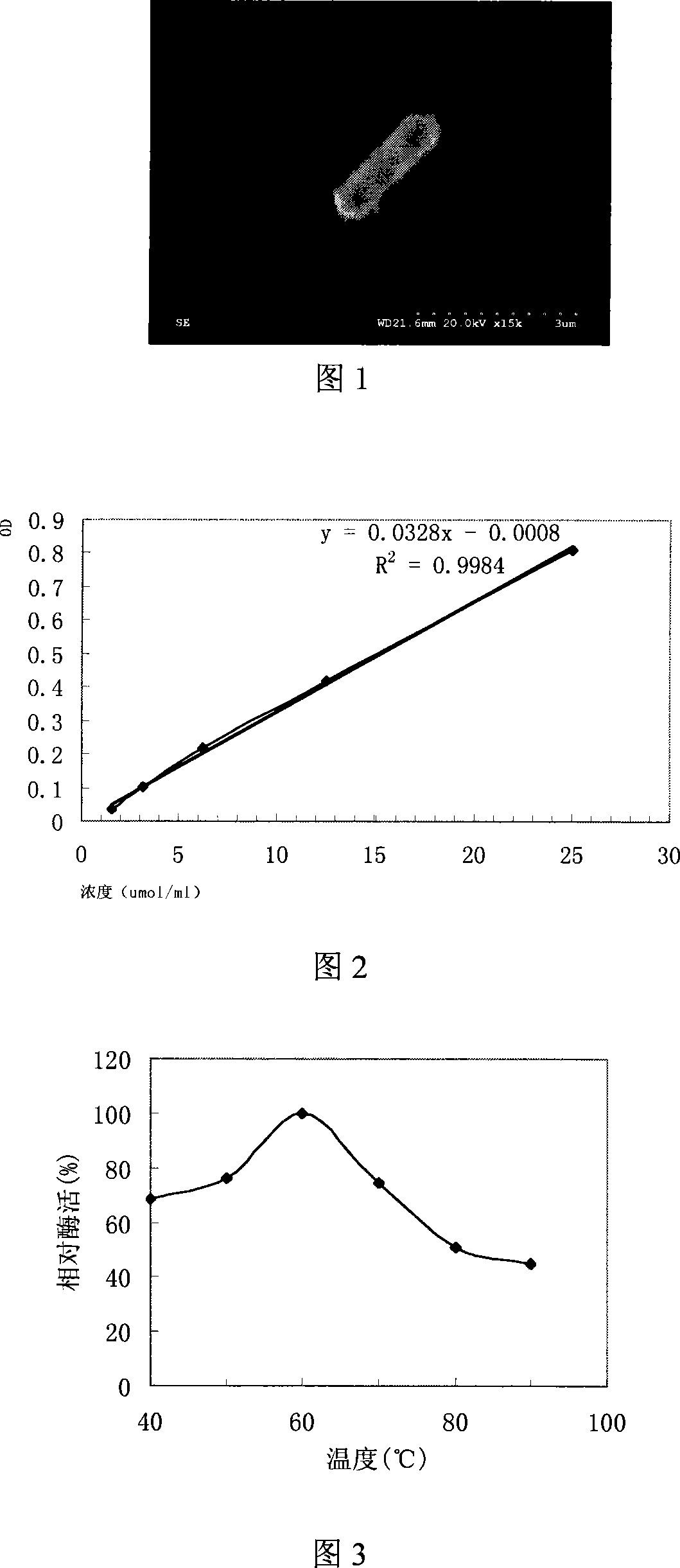
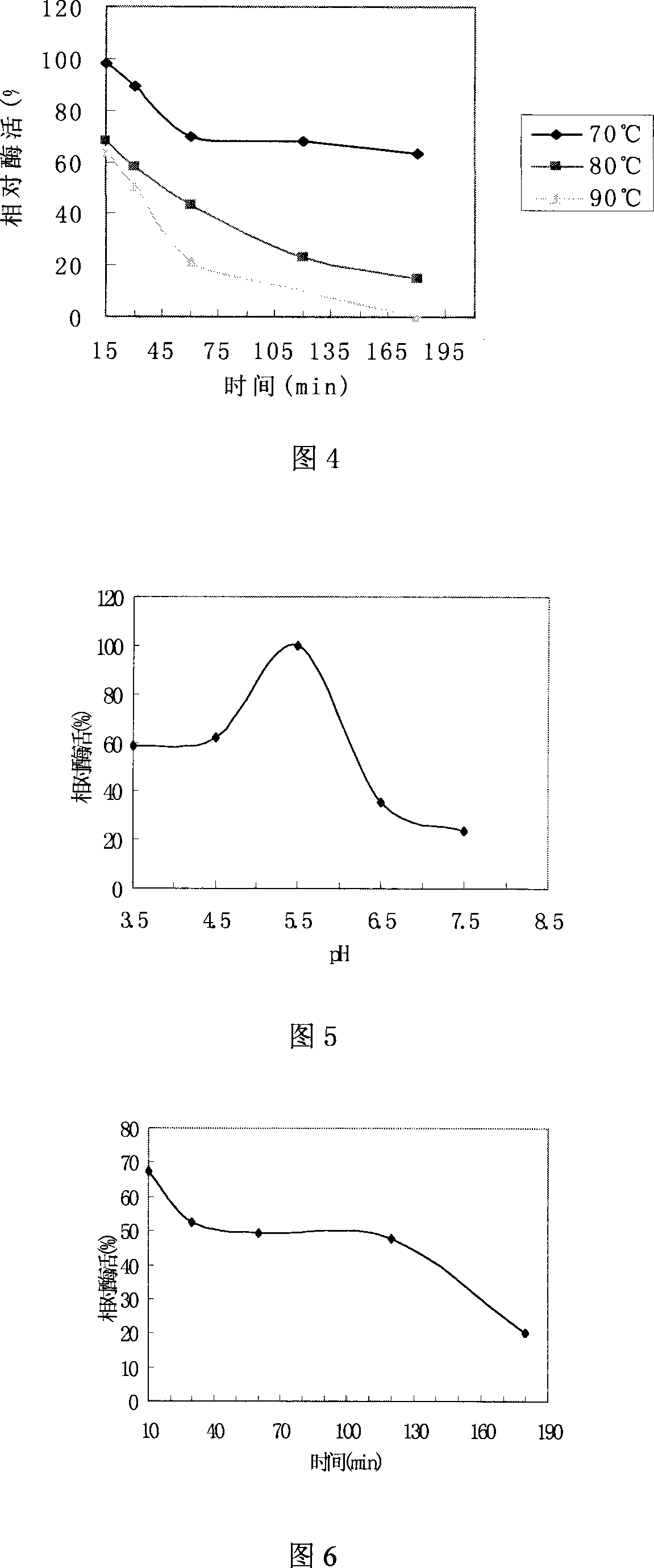
The invention relates to producing strains of a thermostable phytase. The classified nomenclature of the strains is bacillus subtilis with a preservation number of CGMCC No.2076. The phytase produced by the strains of the invention has a most suitable pH of about 5.5, when the pH is 2.2, the activity of remaining enzyme is 47.7 percent after the enzyme liquid is kept at room temperature for 2hr; the most suitable temperature is 60 DEG C, when the temperature is within the scope of 55 DEG C -65 DEG C, the activity of the enzyme changes little; if the enzyme is respectively kept for heat preservation at 70 DEG C for 60min, 120min and 180min, the activity of the remaining enzyme is 70 percent, 68 percent and 63 percent respectively; if the phytase is respectively kept for heat preservation at 80 DEG C for 60min, 120min and 180min, the activity of the remaining enzyme is 43 percent, 23 percent and 15 percent respectively; if the enzyme is respectively kept for heat preservation at 90 DEG C for 60min and 120min, loss of the activity of the enzyme is obvious with the activity of the remaining enzyme of 21 percent and 10 percent respectively; therefore, the enzyme has good temperature resistance. The strains of the invention not only meets the requirements of high temperature sterilization in feed process industry, but also meets the requirement of short-time of high temperature (73 DEG C-95 DEG C) in the granulation technique of grain feed. The thermostable phytase produced by the strains can be used as feed additive with excellent effect when is applied to actual production.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Expression and applications of novel non-restriction endonuclease in escherichia coli
The invention utilizes the property that nonspecific endonuclease from Anabaena sp. is provided with natural inhibitor protein to change the original expression way of the nonspecific endonuclease, i.e. to change secretory expression into endoenzyme high efficient expression. The invention adopts a strong promoter to largely express in cells in a way of inclusion bodies with no activity; wherein, the moment when the endonuclease is expressed, the natural inhibitor protein is expressed together so as to eliminate the strong toxicity that farthing activated nuclease imposes on the cells; protein engineering technology is used for replacing a non-activated central amino acid, thus reducing the possibility of forming multimer in renaturation, improving efficiency, and furthermore, raising the output in terms of improving the expression efficiency and the renaturation efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAILANG BIOTECHOLOGY
Engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104232555AStable enzymatic propertiesAchieve periplasmic space expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionProtein target
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase in the field of the genetic engineering and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria. The genome DNA of the streptomyces griseorubens is taken as a template, and PCR amplification is performed on the template and a primer containing an enzyme digestion site and a polyhistidine label so that the nucleotide sequence coding the manganese peroxidase can be obtained; next, the gene sequence obtained by amplification is connected to an expression vector, and then the obtained connection product is transferred into an escherichia coli expressed strain, and finally, the over-expressed recombinant strain of the manganese peroxidase is obtained. The engineering bacteria based on the manganese peroxidase are used for overcoming the shortage of seriously restricted application range and application effect because the manganese peroxidase mostly is an endoenzyme in vivo and is low in expression amount, and in-vitro mass expression and synthesis of the manganese peroxidase are realized by use of a genetic engineering method; besides, the purity of the purified manganese peroxidase is also guaranteed while the protein activity is improved by use of the method of adding the polyhistidine label to the C end of the expressed recombinant protein; in addition, the periplasmic space expression of the target protein is realized by use of a vector signal peptide and the activity of the manganese peroxidase is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Aspergillus niger and application in production of isomaltose hypgather
ActiveCN104877911ASimple nutritional requirementsThe cultivation method is simpleFungiMicroorganism based processesAlgluceraseIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention discloses an aspergillus niger which is classified and named aspergillus niger M1 with the preservation number being CCTCC NO: M2014421. The preservation date is September 23nd, 2014, and the preservation department is China Center for Type Culture Collection. Alpha-glucosidase produced by the aspergillus niger M1 strain is endoenzyme, and the aspergillus niger M1 strain can produce isomaltose hypgather containing more than 65% of active trisaccharide (IG+P+IG3) under the condition of high temperature. The required reaction time of preparing IMO-500 type isomaltose hypgather containing 35% of active trisaccharide is only half of the reaction time of preparing the isomaltose hypgather containing more than 65% of active trisaccharide. The alpha-glucosidase produced by the strain has advantages of excellent temperature characteristic, short glucoside conversion time, high content of the active trisaccharide in the product and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI NANNING ZHITIAN BIOTECH
Scorpion peptide for treating arrhythmia and its preparing process and application
InactiveCN1379042AObvious antiarrhythmic effectIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationSolubilityEscherichia coli
An anti-arrhythmia scorpion peptide whose amino acid sequence is disclosed is prepared through designing PCR upstream primer containing enteric kinase cut site, using the PCR to amplify anti-arrhythmia peptide gene fragment through limited enzymatic cut of endoenzyme, clonining to pGX-5x-1 expression carrier, transferring to colibacillus BL21 to obtain recombinant colibacillus BL21 (pGEX / BmK1M); after inducing by IPTG, through purifying by glutathion transferase affinity chromatographic column, expressing the resultant fusion protein by enteric kinase and desalting to obtain the said peptide.Its advantages are high anti-arrhythmia activity, high solubility and high output.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for preparing galactooligosaccharide by use of permeable cell beta-galactosidase
InactiveCN102994589AAvoid extraction and purification processEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesEnzymesGalactooligosaccharideToxic chemical
The invention relates to a method for preparing galactooligosaccharide by use of permeable cell beta-galactosidase, which comprises the following steps of: adding permeable cell beta-galactosidase into a lactose solution, wherein the concentration of the lactose solution is 100-500g / L, and the addition amount of permeable cell beta-galactosidase is 200-1,500mg per gram of lactose; reacting for 2-15 hours at 30-45 DEG C; and performing centrifugal separation, wherein the obtained supernate is a galactooligosaccharide solution. By preparing galactooligosaccharide by use of permeable cell beta-galactosidase, the extraction and purification processes of endoenzyme are avoided, the technological operation is simplified, and the production cost is reduced. Kluyveromyces lactis is processed by absolute ethyl alcohol to prepare a permeable cell, toxic chemical reagents such as chloroform and the like are not introduced, the food safety problem is avoided, and the permeable cell can be widely applied to the food industry. Moreover, the permeable cell can be used repeatedly, thus the production cost of galactooligosaccharide can be obviously reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Continuous production of an instant corn flour for snack and tortilla, using a neutral enzymatic precooking
ActiveUS7459174B2Reduced corn solid lossPartial hydrolysis of insoluble bran layersDough treatmentTea extractionSnack foodXylanase
Precooked and partially-debranned corn flour is continuously produced by an enzymatic precooking using a commercial blend of xylanase, endoamylase and endoprotease as a processing aid. The low-temperature and neutral-pH precooking with an endoenzyme solution effected a partial bran hydrolysis while avoiding excessive pregelatinization, reduced washing and corn solid loss in wastewater. Moisture content is then stabilized, followed by milling and drying at a high-temperature and short-time to produce a controlled gelatinization and denaturation in the ground kernel, cooling and further drying the dried-ground particle. A fine particle size or flour is separated and recovered from the coarser particle which is also segregated to isolate a partially hydrolysed bran fraction for integral flour or animal feed diet, remilling and sieving the coarser particle to produce an instant corn flour for snack, and admixing the fine particle with lime to obtain a masa flour for tortilla and other corn foods.
Owner:GRUMA S A B DE CV
Enzyme and receptor modulation
InactiveUS20140088159A1Extended stayHydrolysed effectivelyBiocideOrganic chemistryGlycineIntracellular
Covalent conjugates of an α,α-disubstituted glycine ester and a modulator of the activity of a target intracellular enzyme or receptor, wherein the ester group of the conjugate is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to the corresponding acid and the α,α-disubstituted glycine ester is conjugated to the modulator at a position remote from the binding interface between the inhibitor and the target enzyme or receptor pass into cells and the active acid hydrolysis product accumulates within the cells.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Process for preparing T vector
InactiveCN1142279CQuality improvementImprove cloning efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionEndoenzymeT vector
A process for preparing T vector by using endoenzyme to digest the pre-T vector features that the single- or dual-chain oligo-DNA as the competitive substrate of exoenzyme, whose mole concentration is at least 10 times higher than that of pre-T vector, is added to the over-digestive system used to prepare said T vector in the condition of no excessive increasement of total DNA concentration to suppress the influence of exoenzyme activity on T vector, so obtaining excellent T vector with stable quality.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
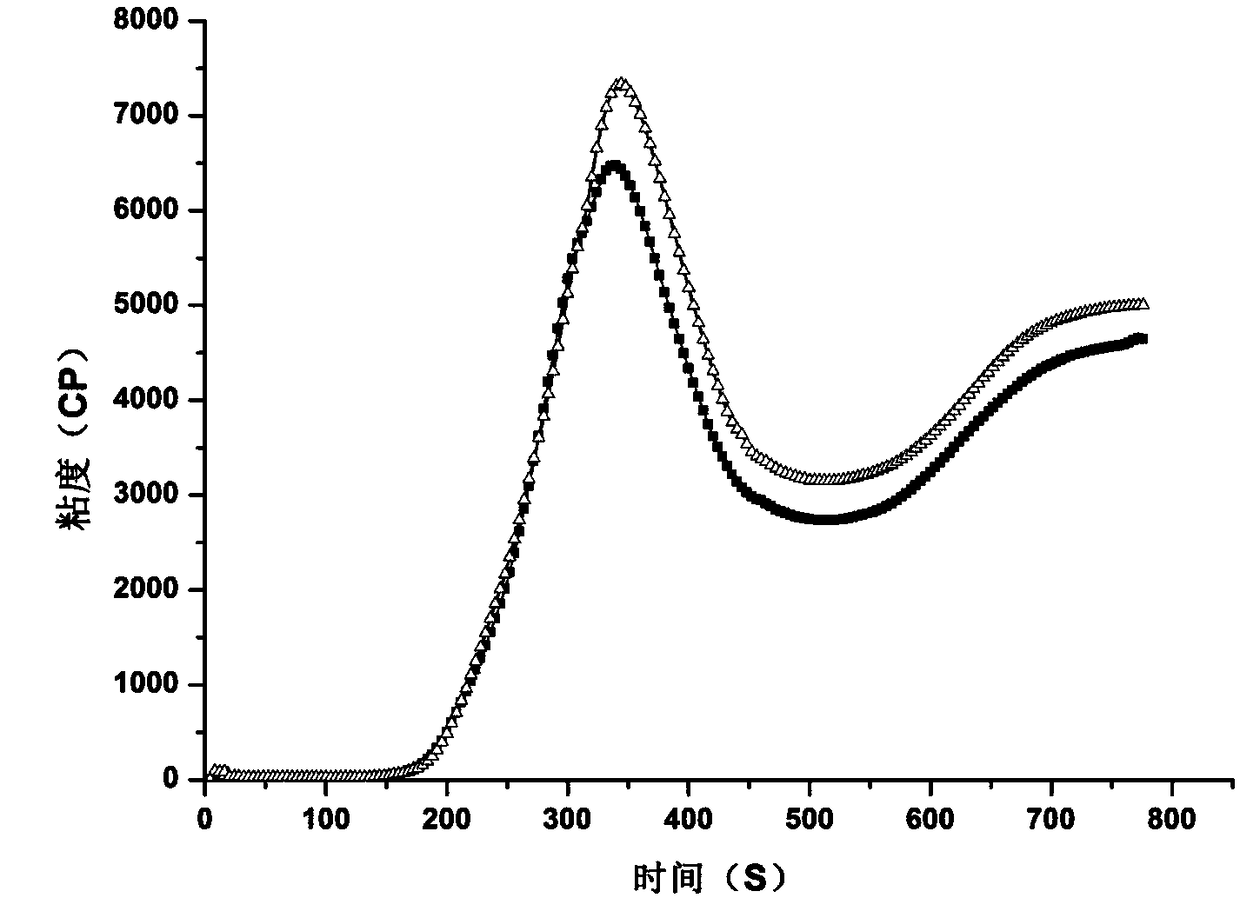
Method for fast judging enzyme activity in grain and predicting enzyme adaptation temperature
ActiveCN108398356AQuality understandingImprove the efficiency of quality analysisTesting starch susbtancesFlow propertiesOperabilityContent determination
The invention discloses a method for fast judging the enzyme activity in grain and predicting the enzyme adaptation temperature, and relates to the technical field of grain quality evaluation and determination method. The method mainly comprises the following steps of (1) pretreatment; (2) moisture content determination and sample weighting; (3) fast viscosity analysis instrument temperature procedure setting; (4) feature viscosity determination on blank sample and enzyme inhibitor adding samples; (5) enzyme activity judgment according to the obtained comparison feature spectrogram; (6) judgment of most proper temperature of enzyme in the grain through the differences of enzyme activities at different temperatures. The invention provides the novel method for determining the enzyme activityand enzyme adaptation temperature in the grain. The method has the characteristics that the operation is simple and convenient; high speed and high accuracy are realized; the repeated performance isgood; the cost is low; the time is saved. The grain quality analysis efficiency can be favorably improved; the quality determination operability can be favorably improved; the labor and material wasteis avoided; the theoretical guidance is provided for grain processing, storage and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Beta-Galactosidase-producing Klebsiella and application thereof
InactiveCN106479925AHigh hydrolase activityStrong transglycosidic activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroscopic observationMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to Beta-galactosidase-producing Klebsiella and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganism separation and cultivation. The Beta-galactosidase-producing Klebsiella of the invention is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 23 September, 2016 under CGMCC No. 13035. The Beta-galactosidase-producing Klebsiella is subjected to plate culture with a screening plate medium at 37 DEG C for 24 h, and then a colony is circular with a diameter of 2-5 mm, is raised in the middle, has smooth and vicious surface and is difficult to pick; after staining by gram staining, Gram-negative Brevibacterium is observed under a microscope and no spores are produced. The Beta-galactosidase-producing Klebsiella of the invention may produce Beta-galactosidase; the produced Beta-galactosidase is endoenzyme; the produced Beta-galactosidase has hydrolytic activity and transglycosidation activity. The Beta-galactosidase-producing Klebsiella of the invention is constantly capable of producing Beta-galactosidase after more than 10 generations of continuous passage.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Targeted multifunctional nanoparticles and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109350750AAccurate importGuaranteed Particle SizePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSide effectMultifunctional nanoparticles
The invention relates to targeted multifunctional nanoparticles and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. The targeted multifunctional nanoparticles are prepared by an ultrasonic double-emulsification method, covalent binding is carried out by branching PEI and PLGA, PLGA nanoparticles which have negative charge originally are modified into kation nanoparticles with positive charge, plasmids can be adsorbed effectively, it ensures that the plasmid cannot drop due to physical effect in a circulation system, and after the plasmid enters cells, the possibility that the plasmid is degraded by endoenzyme is also reduced. The nanoparticles further contain IR780 which can target tumor cell mitochondria, meanwhile, by strong fluorescent light and photosensitizer characteristics of IR780, the nanoparticles become a great fluorescent and photoacoustic imaging medium, and thus, tumors can be convenient to observe. The nanoparticles can carry drug to facilitate combination with transgenic therapy, tumor cells are killed favorably, and furthermore, toxic and side effects of chemotherapy drugs can further be reduced. The preparation method of the targeted multifunctional nanoparticles is simple, is easy to operate, and is suitable for expanded production.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com