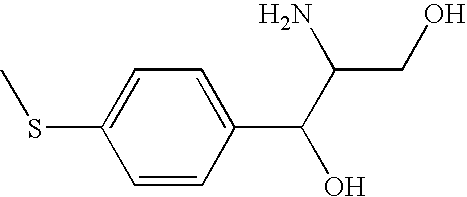
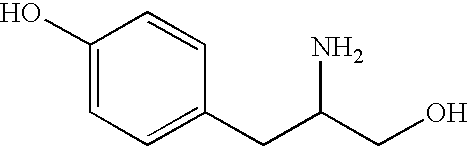
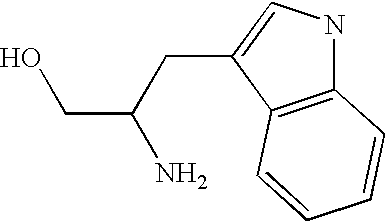
Patents
Literature
3299 results about "Negative charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
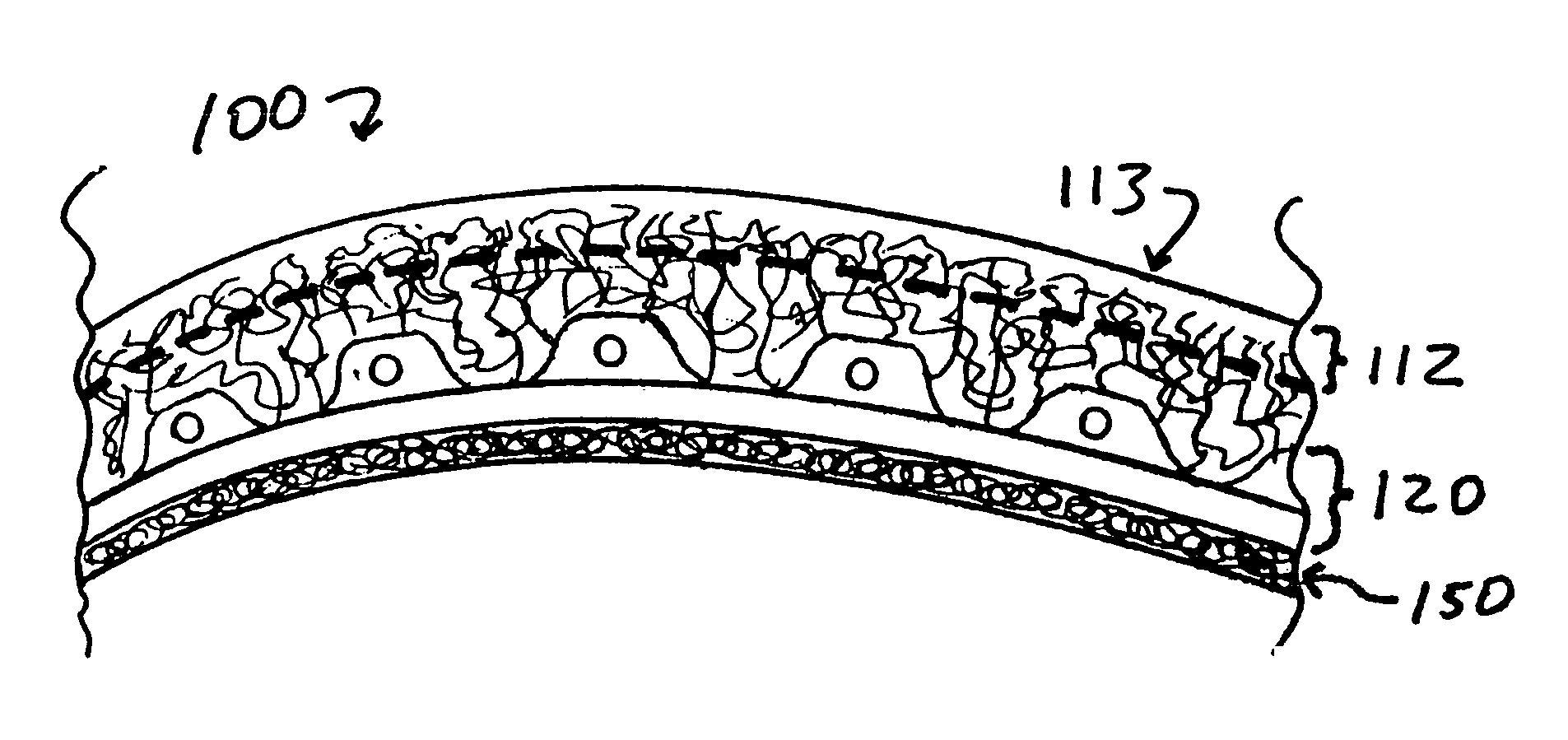
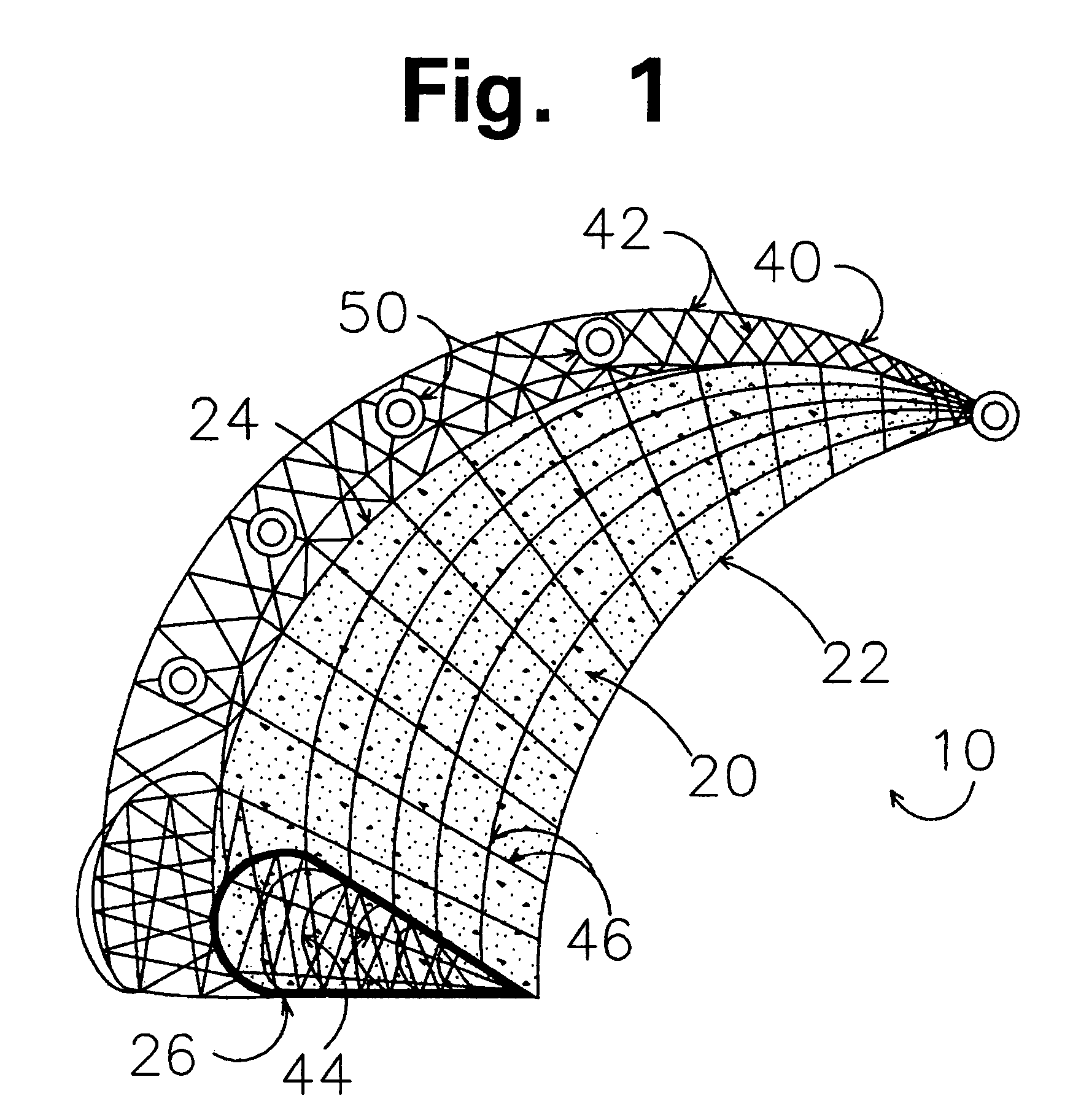
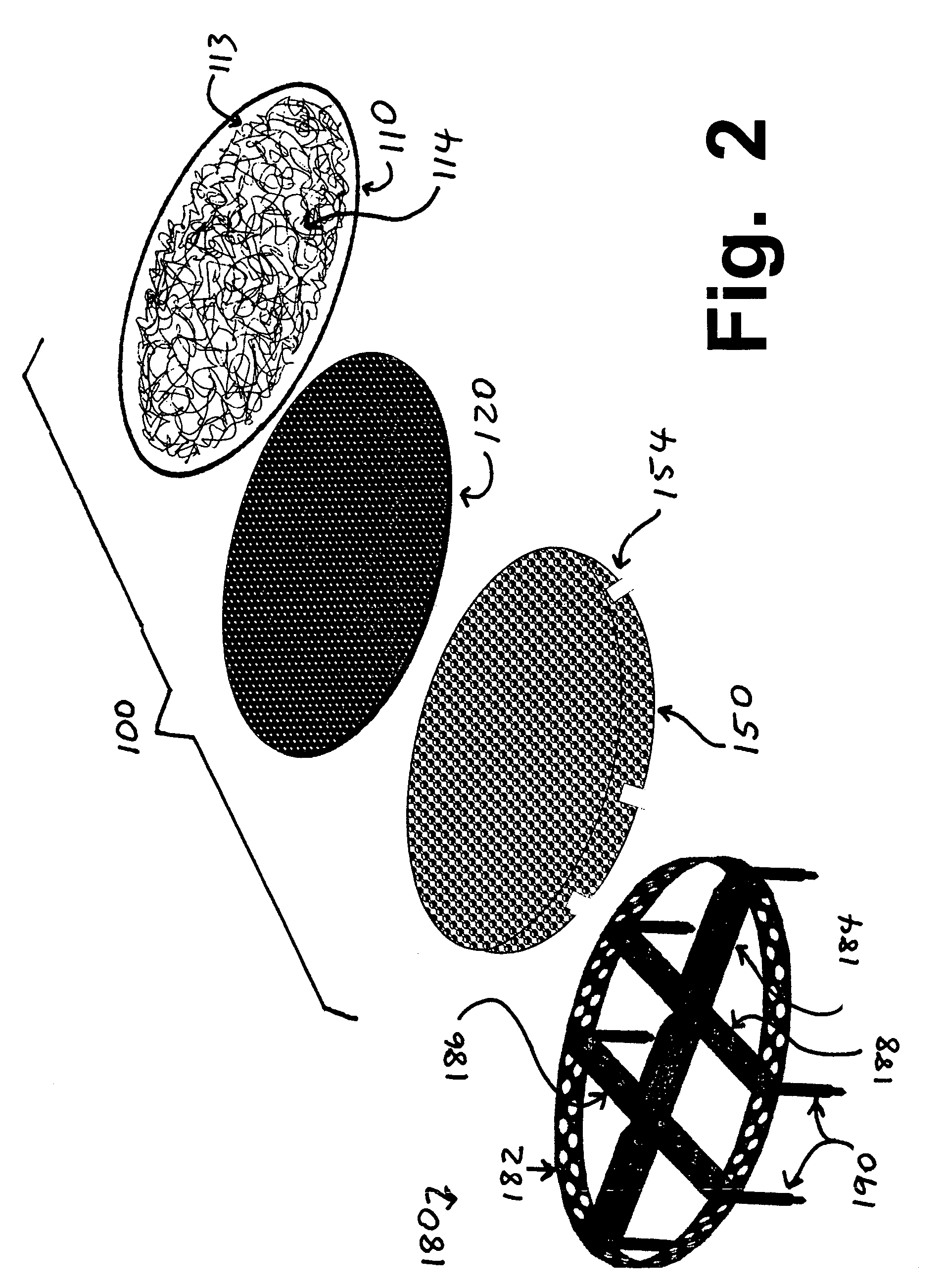
Implants for replacing cartilage, with negatively-charged hydrogel surfaces and flexible matrix reinforcement
ActiveUS9314339B2Strong and durableStrong and secure anchoringFinger jointsWrist jointsFiberChemical agent
A permanent non-resorbable implant allows surgical replacement of cartilage in articulating joints, using a hydrogel material (such as a synthetic polyacrylonitrile polymer) reinforced by a flexible fibrous matrix. Articulating hydrogel surface(s) are chemically treated to provide a negative electrical charge that emulates the negative charge of natural cartilage, and also can be treated with halogenating, cross-linking, or other chemical agents for greater strength. For meniscal-type implants, the reinforcing matrix can extend out from the peripheral rim of the hydrogel, to allow secure anchoring to soft tissue such as a joint capsule. For bone-anchored implants, a porous anchoring layer enables tissue ingrowth, and a non-planer perforated layer can provide a supportive interface between the hard anchoring material and the softer hydrogel material.
Owner:FORMAE
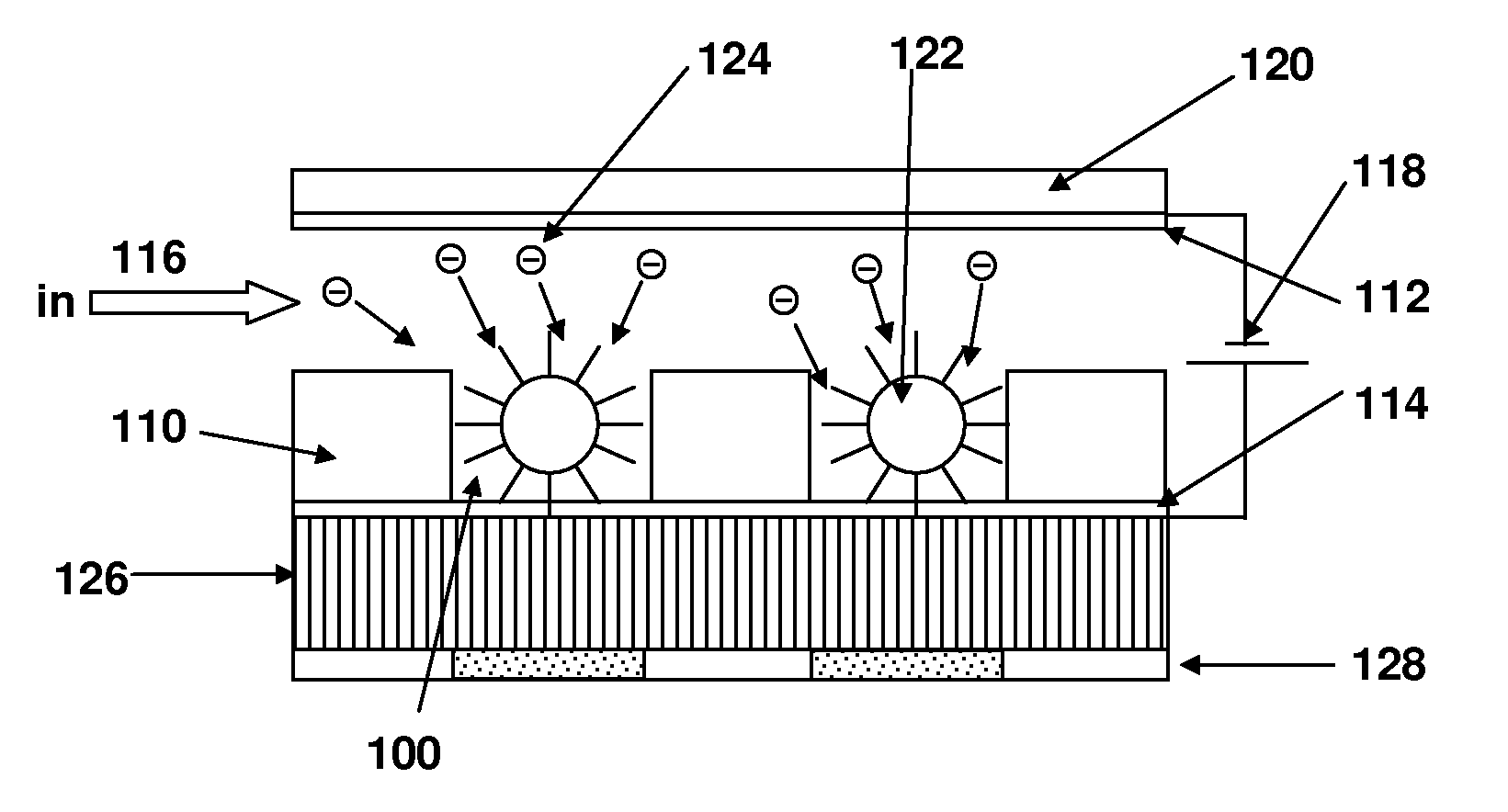
Method and Apparatus Using Electric Field for Improved Biological Assays
ActiveUS20090032401A1Avoid corrosionIncrease electric fieldElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPresent methodEngineering
Disclosed are a method and apparatus that use an electric field for improved biological assays. The electric field is applied across a device having wells, which receive reactants, which carry a charge. The device thus uses a controllable voltage source between the first and second electrodes, which is controllable to provide a positive charge and a negative charge to a given electrode. By controlled use of the electric field charged species in a fluid in a fluid channel are directed into or out of the well by an electric field between the electrodes. The present method involves the transport of fluids, as in a microfluidic device, and the electric field-induced movement of reactive species according to various assay procedures, such as DNA sequencing, synthesis or the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Organic electroluminescent device based upon emission of exciplexes or electroplexes, and a method for its fabrication
InactiveUS20050048310A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureLow efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceMaterials science
An organic electroluminescent device (1) based upon emission of exciplexes or electroplexes, the device basically including an anode (2), a cathode (3), a first layer (4), which comprises organic material for transporting positive charges (5), and a second layer (6), which comprises organic material for transporting negative charges (7), said organic material for transporting negative charges (7) and said organic material for transporting positive charges (5) being capable to form between them exciplexes or electroplexes.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
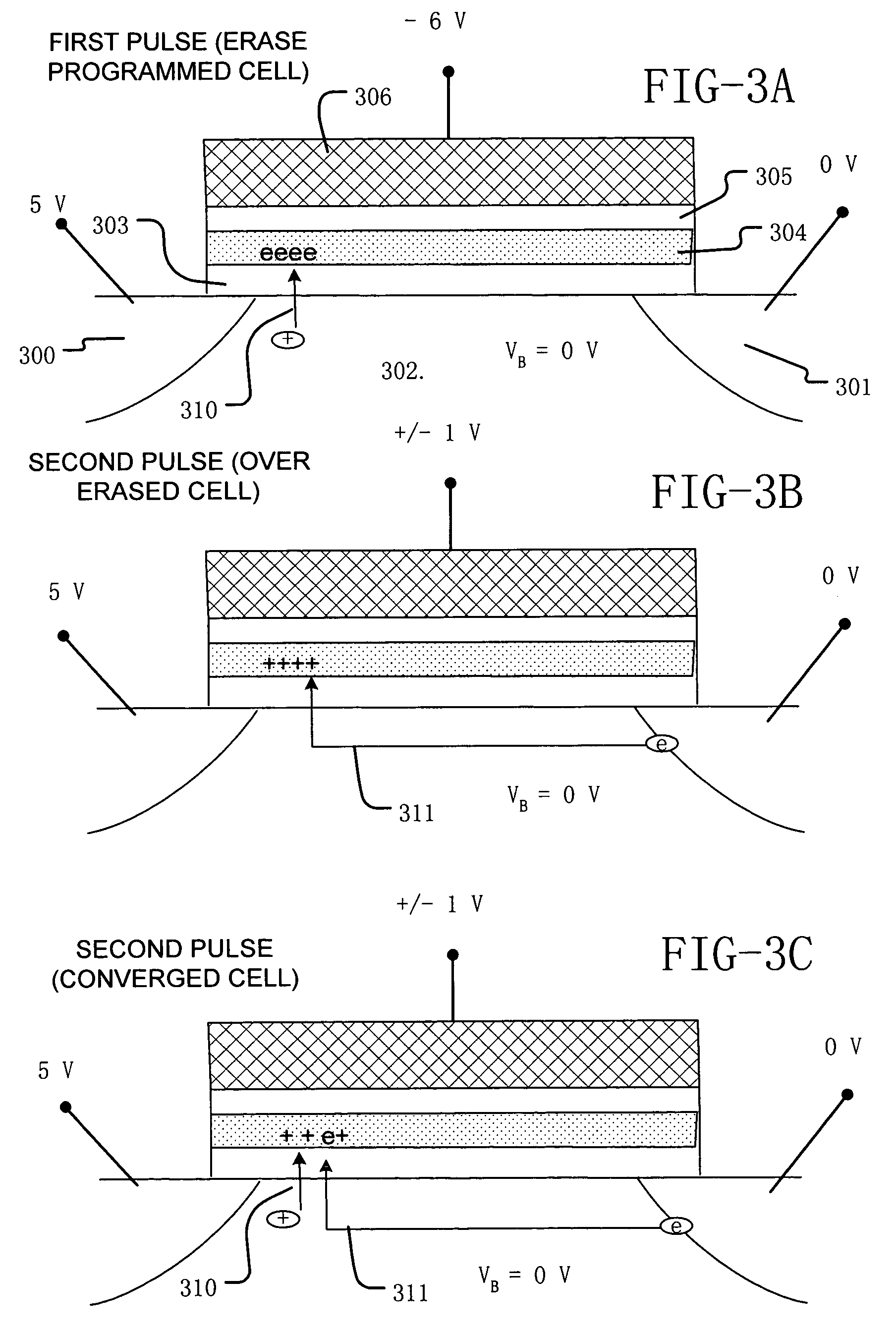
Operation scheme with charge balancing erase for charge trapping non-volatile memory
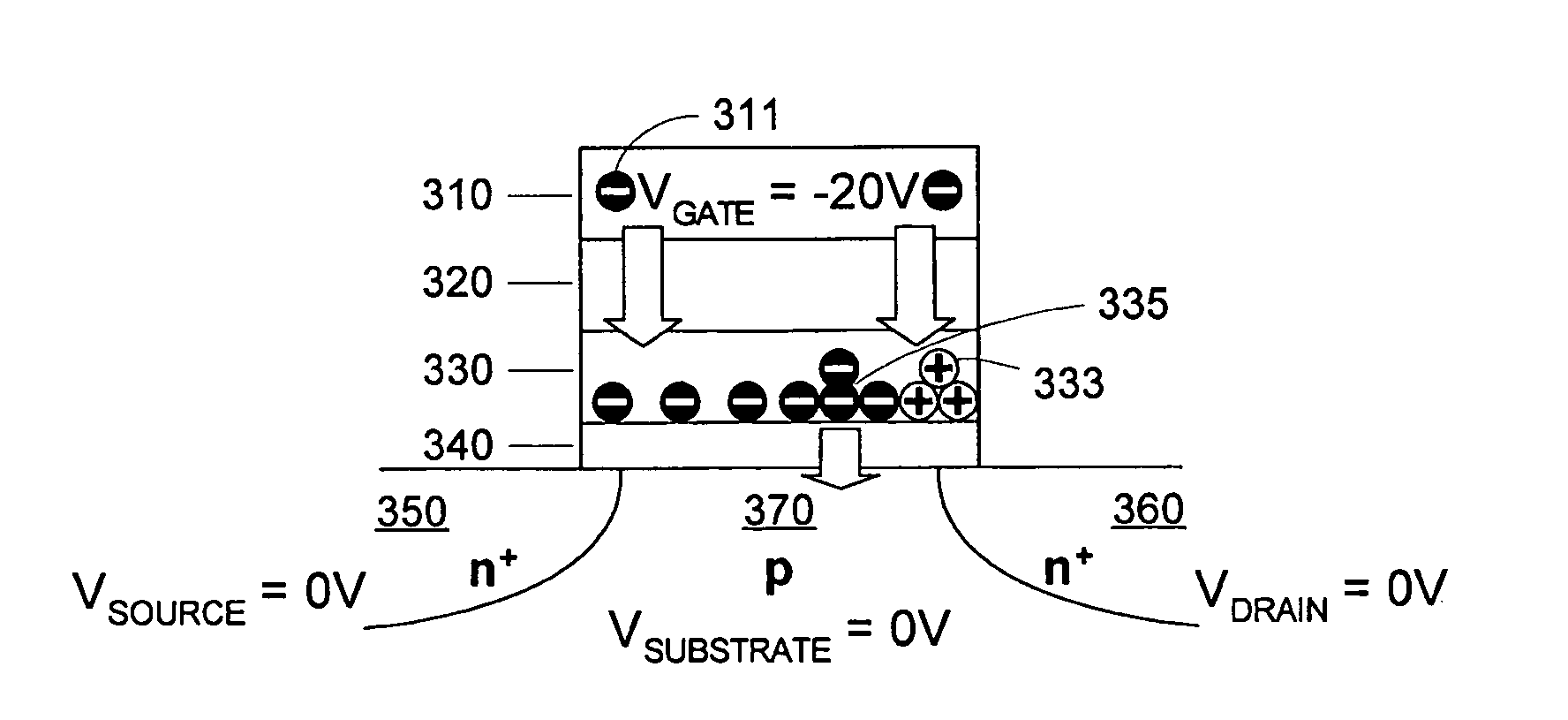
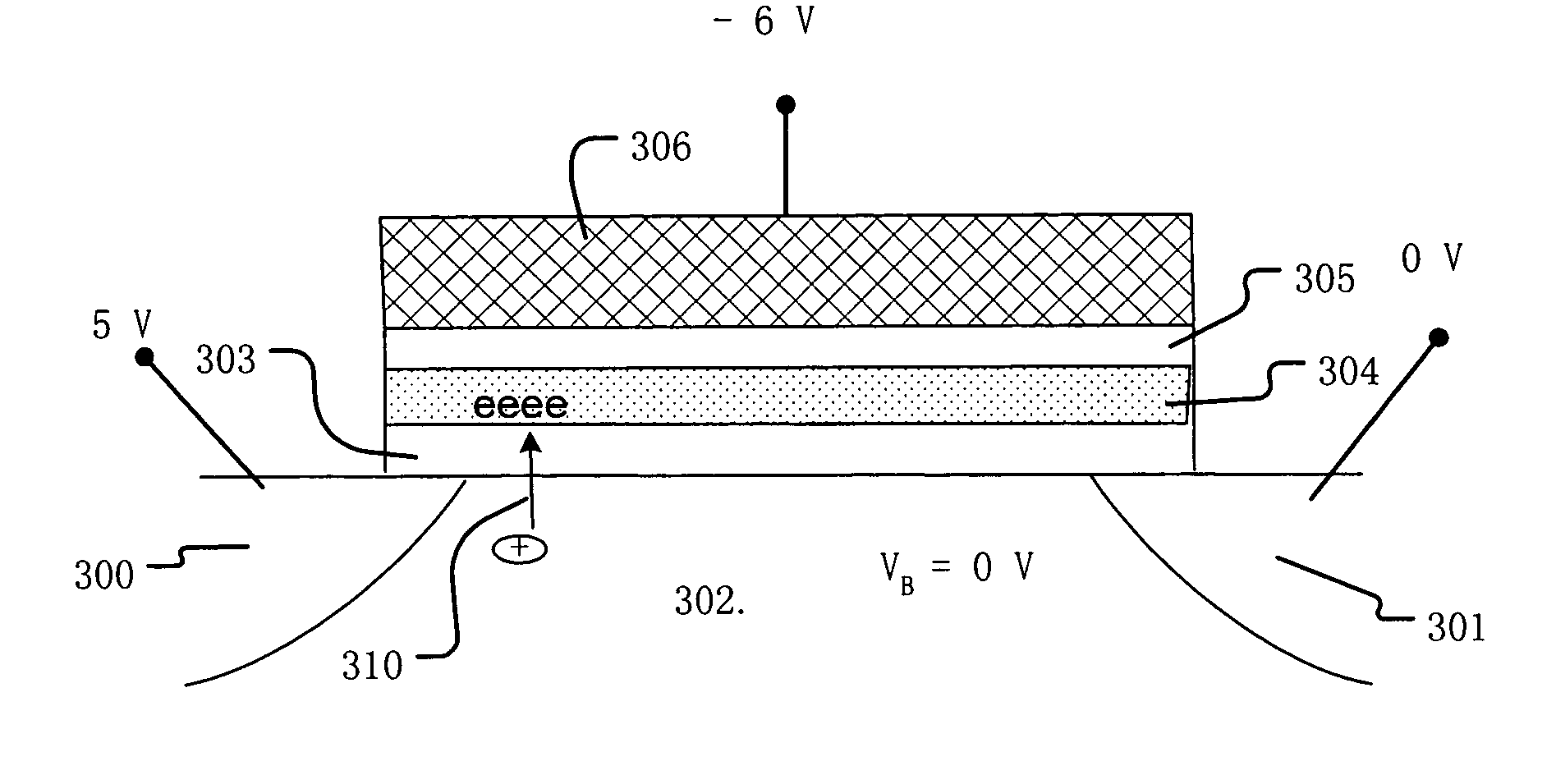
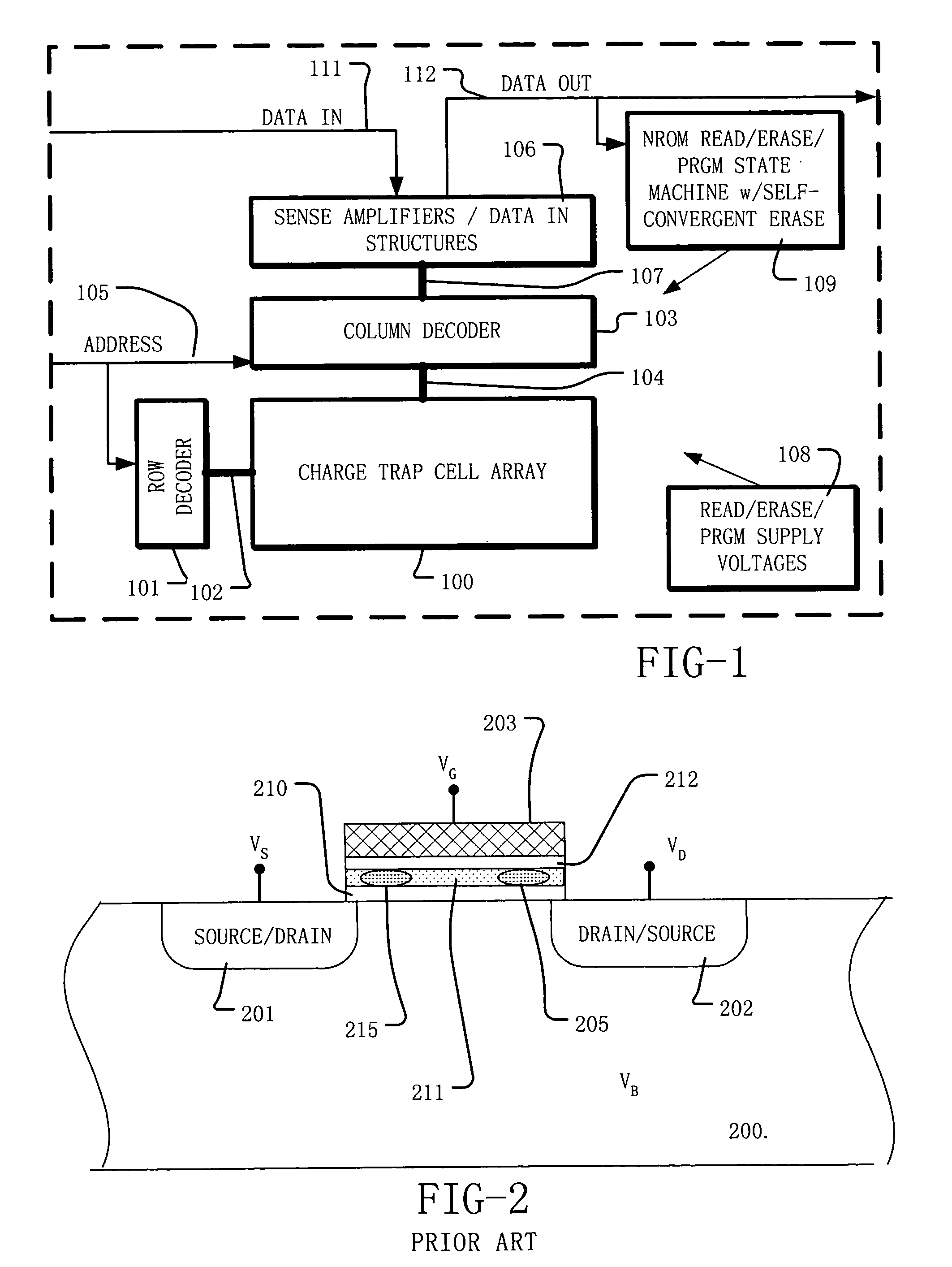
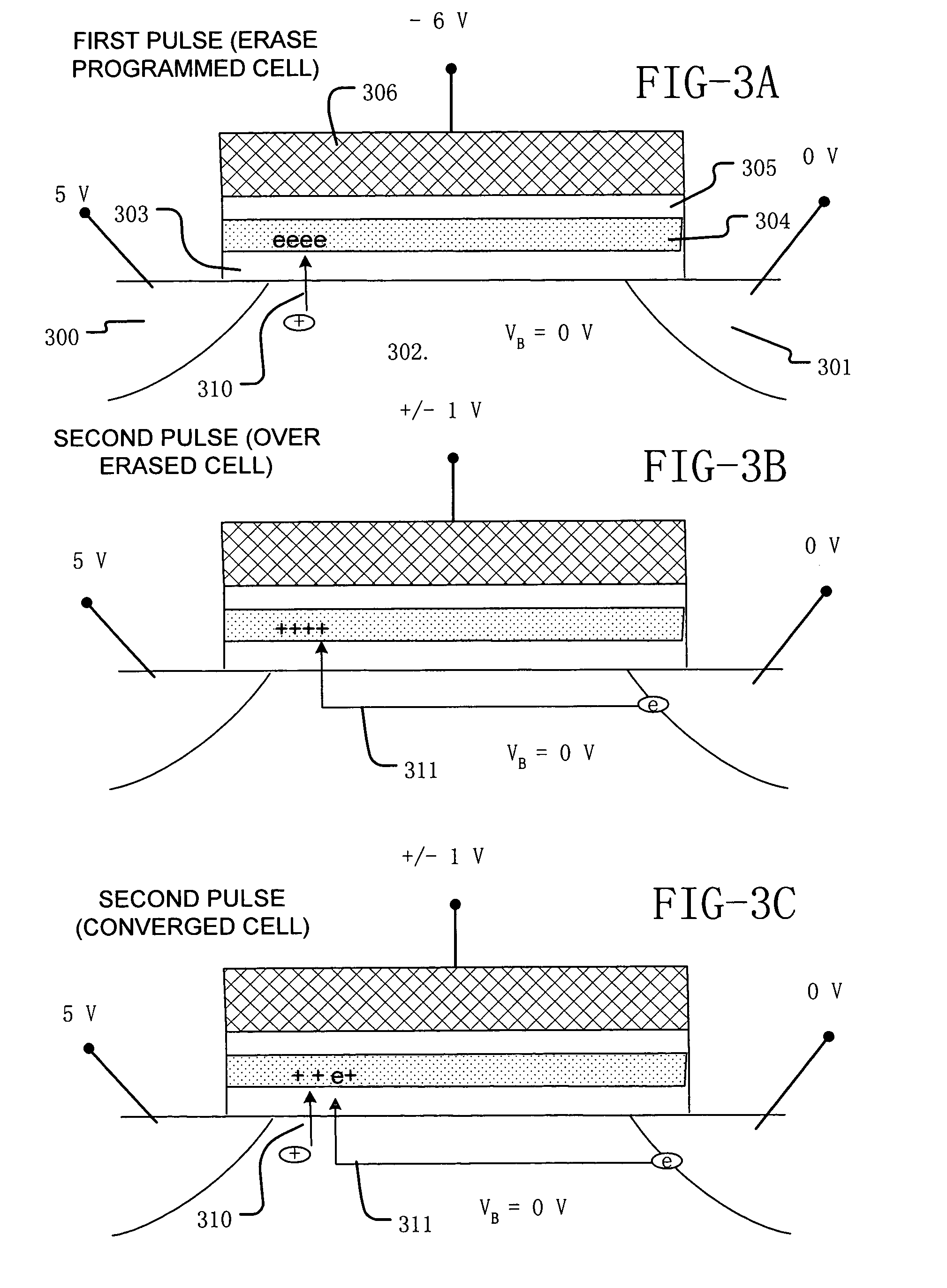
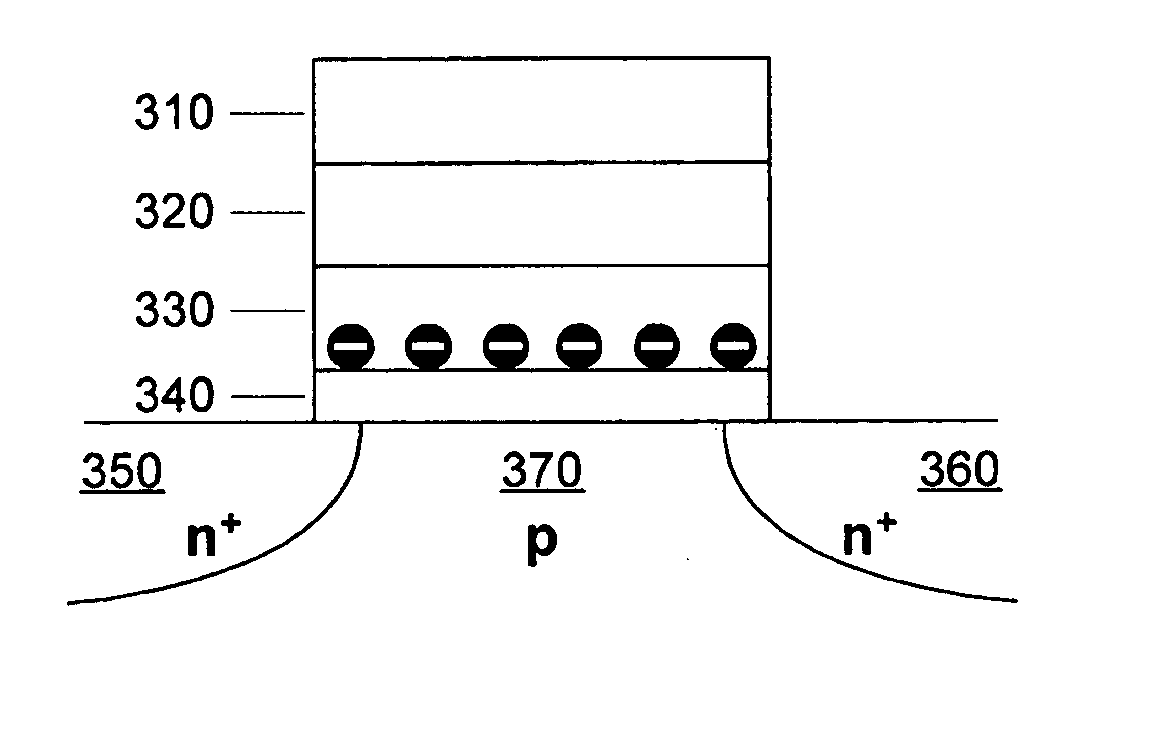
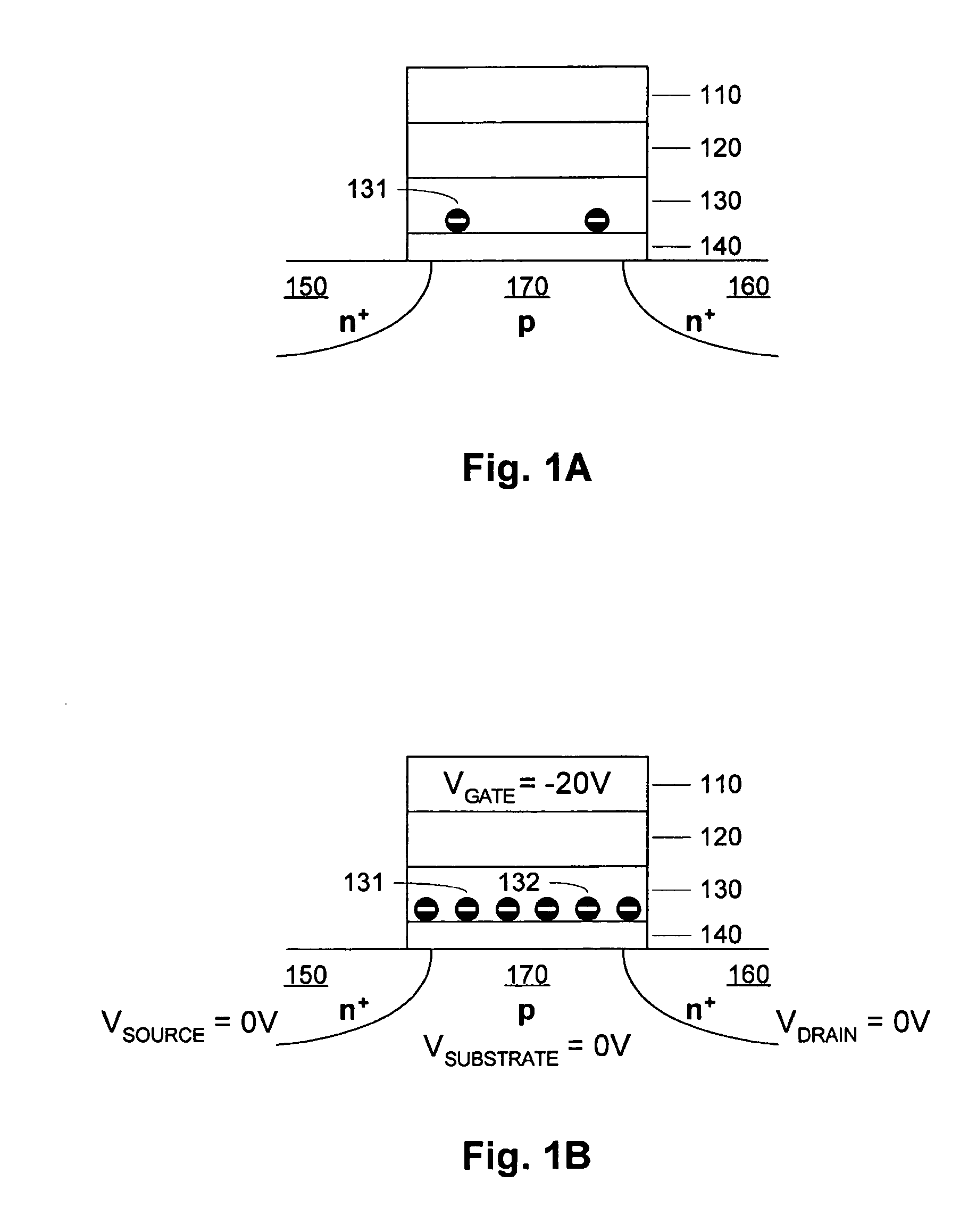
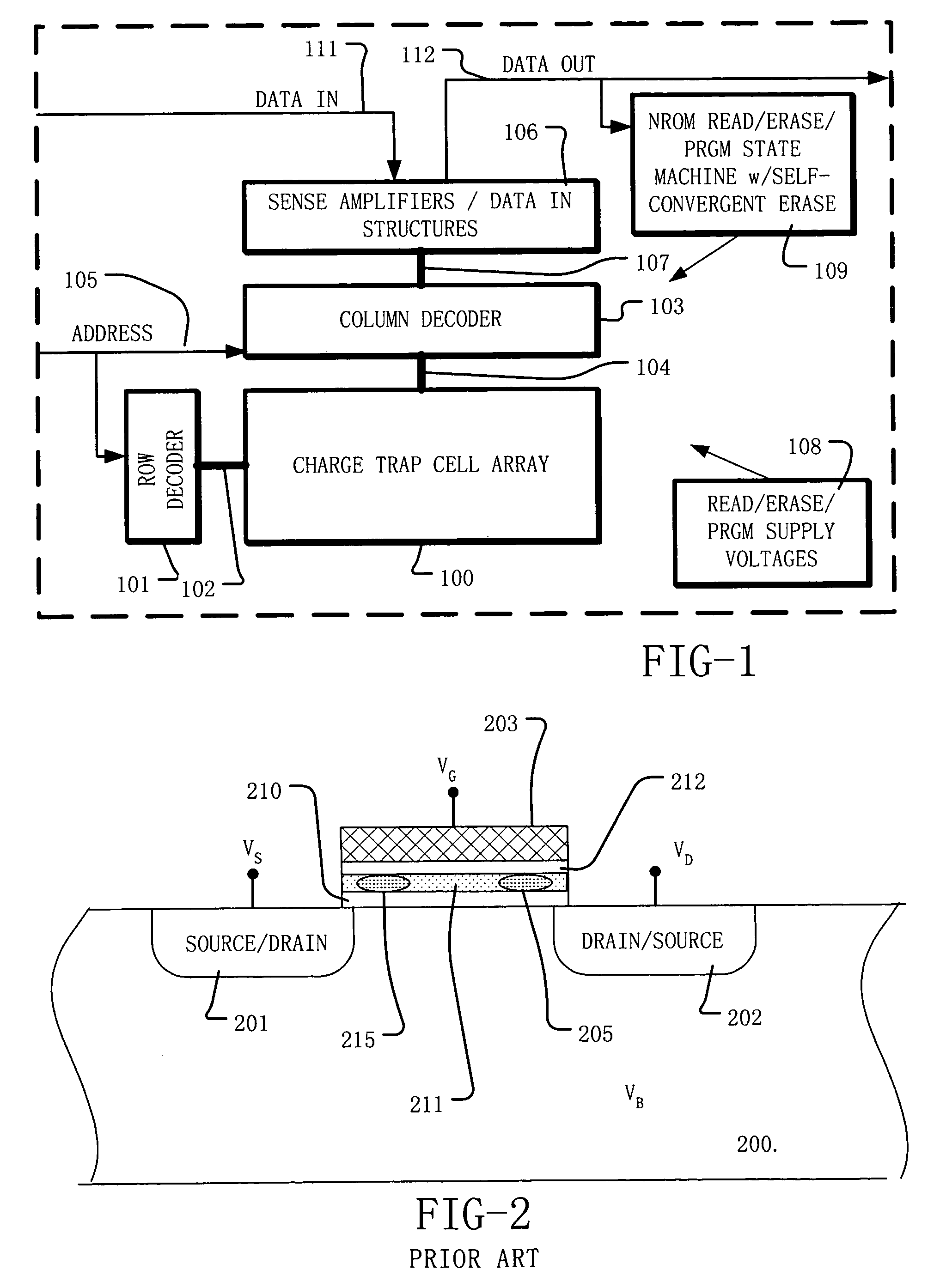
A method of operating a memory cell comprises applying a first procedure (typically erase) to establish a low threshold state including a first bias arrangement causing reduction in negative charge in the charge trapping structure, and a second bias arrangement tending to the induce balanced charge tunneling between the gate and the charge trapping structure and between the charge trapping structure in the channel. A second procedure (typically program) is used to establish a high threshold state in the memory cell, including a third bias arrangement that causes an increase in negative charge in the charge trapping structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Compositions and methods for drug delivery using pH sensitive molecules
Owner:ROCHE MADISON
Method and system for self-convergent erase in charge trapping memory cells
ActiveUS20050237813A1Reduce negative chargeNegatively chargedTransistorRead-only memoriesTrappingEngineering
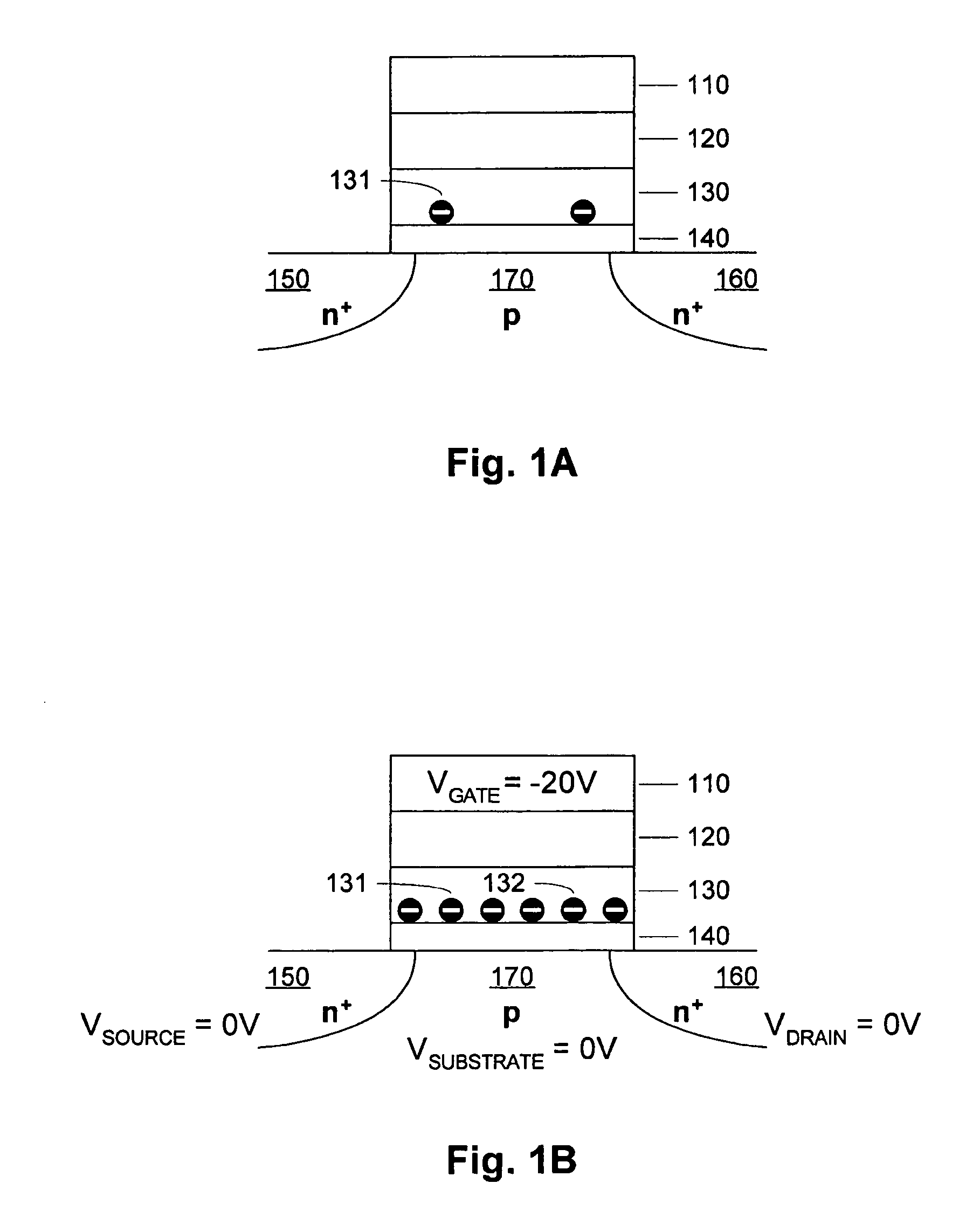
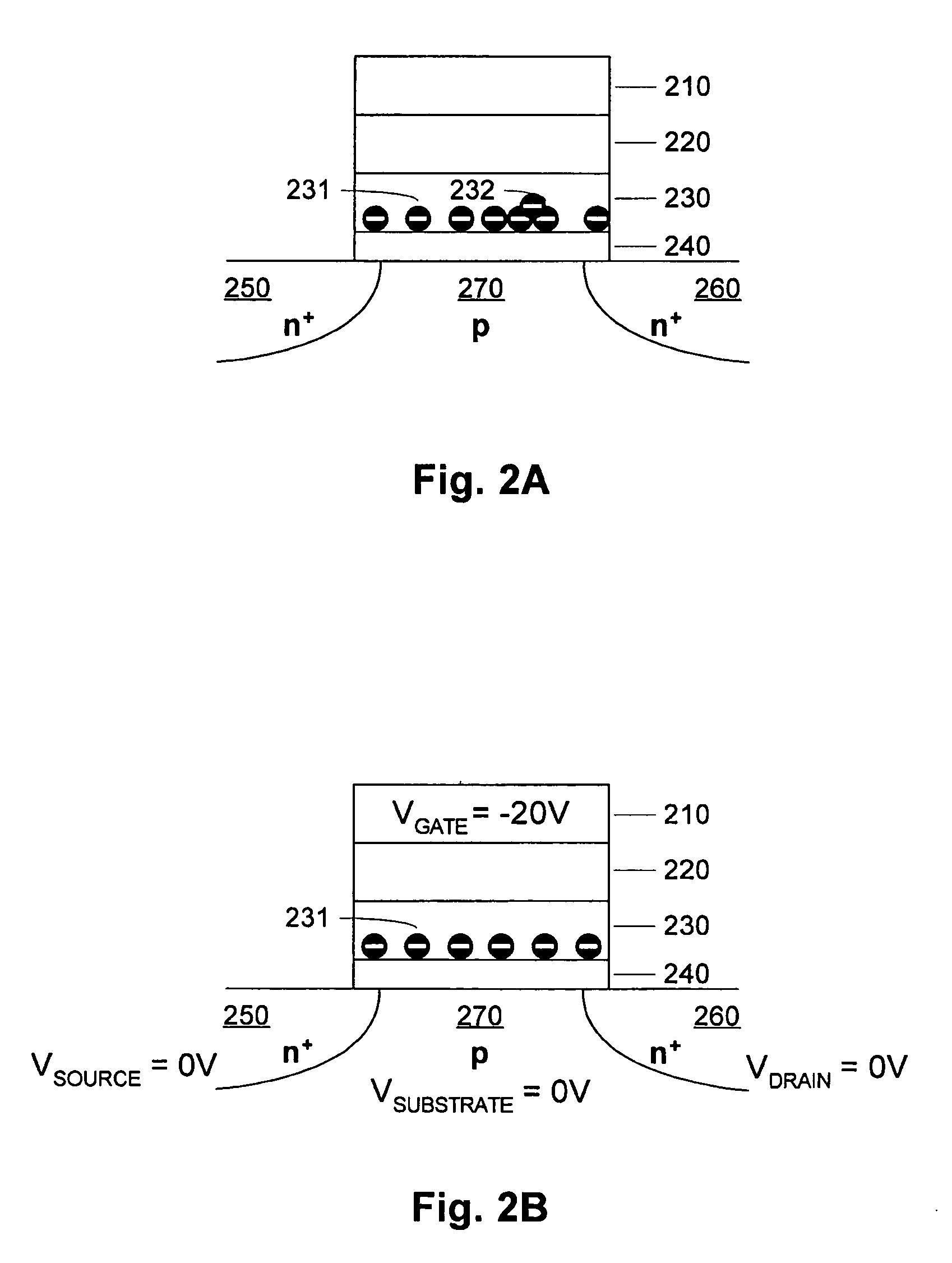
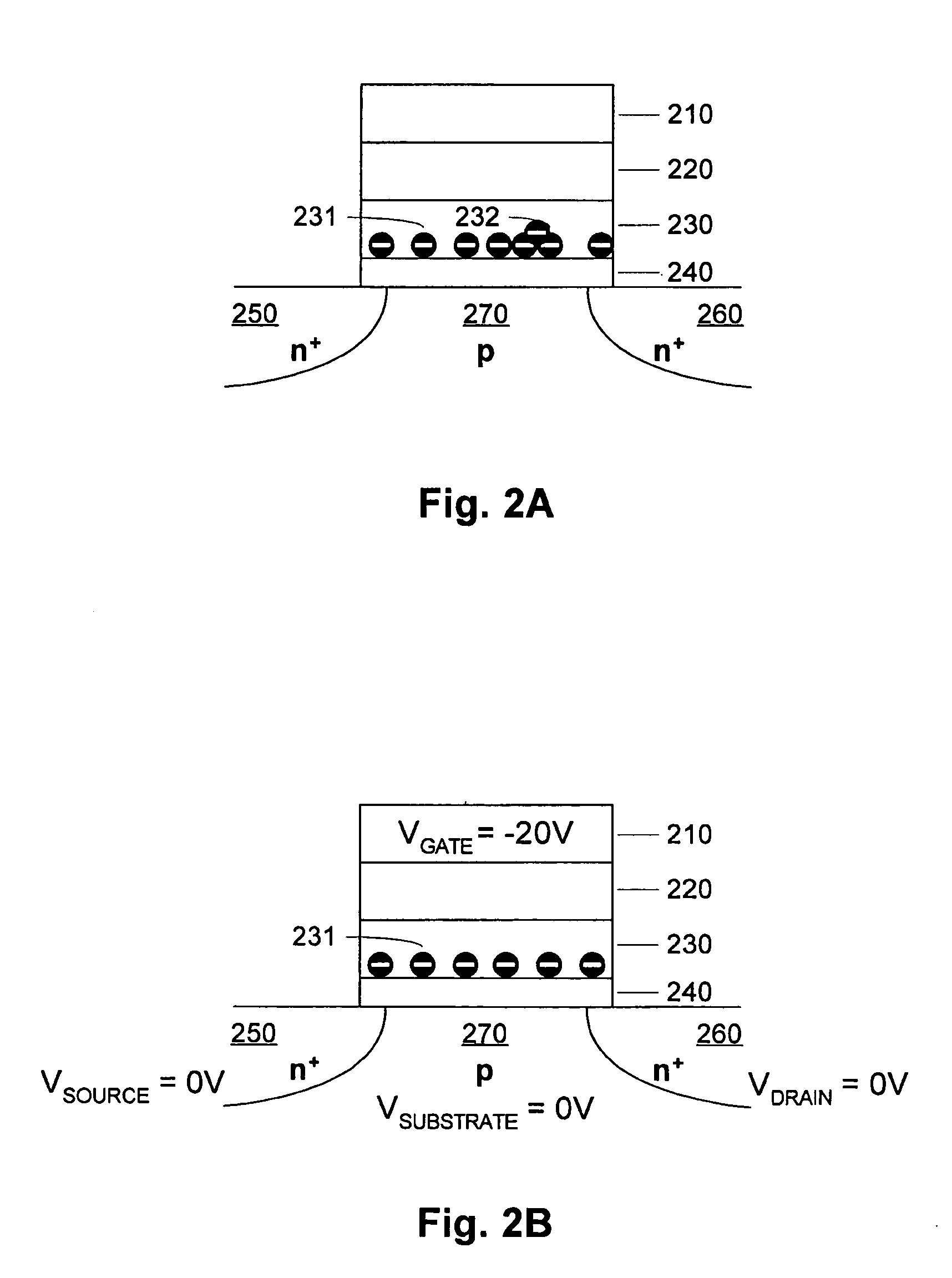
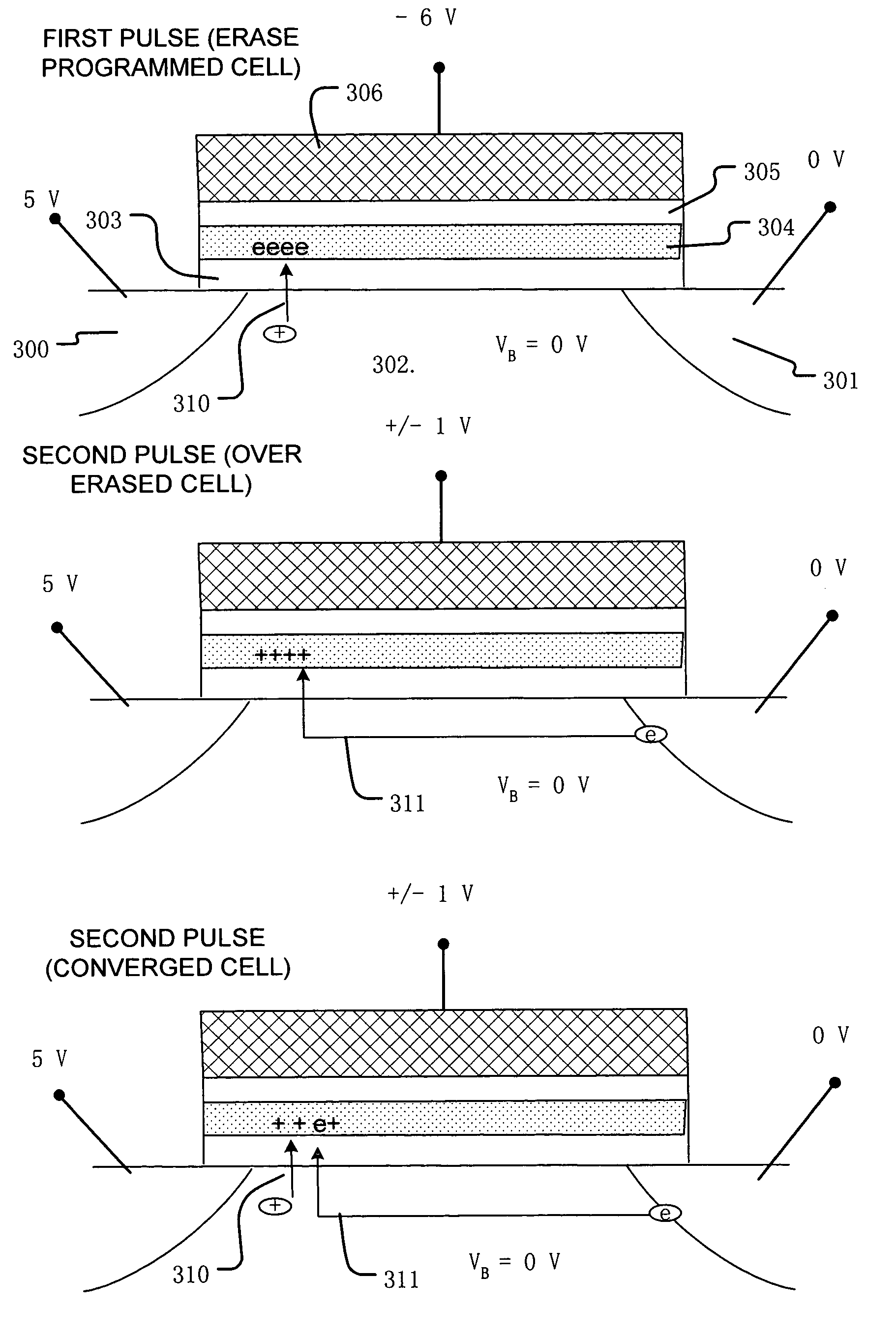
A process and a memory architecture for operating a charge trapping memory cell is provided. The method for operating the memory cell includes establishing a high threshold state in the memory cell by injecting negative charge into the charge trapping structure to set a high state threshold. The method includes using a self-converging biasing procedure to establish a low threshold state for the memory cell by reducing the negative charge in the charge trapping structure to set the threshold voltage for the cell to a low threshold state. The negative charge is reduced in the memory cell by applying a bias procedure including at least one bias pulse. The bias pulse balances charge flow into and out of the charge trapping layer to achieve self-convergence on a desired threshold level. Thereby, an over-erase condition is avoided.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Operation scheme with charge balancing erase for charge trapping non-volatile memory
ActiveUS20050237815A1Improve enduranceImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesTrappingEngineering
A method of operating a memory cell comprises applying a first procedure (typically erase) to establish a low threshold state including a first bias arrangement causing reduction in negative charge in the charge trapping structure, and a second bias arrangement tending to the induce balanced charge tunneling between the gate and the charge trapping structure and between the charge trapping structure in the channel. A second procedure (typically program) is used to establish a high threshold state in the memory cell, including a third bias arrangement that causes an increase in negative charge in the charge trapping structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Compositions for prevention of adhesions and other barrier applications
ActiveUS20080032934A1Minimizing contaminationMinimizing infectionBiocideNervous disorderNucleotideMedicinal chemistry
A method has been developed of preventing or limiting formation of adhesions by administering to a site in need thereof, in the absence of or after bleeding or leakage of fluid has been substantially stopped, a self-assembling material which forms a barrier to formation of adhesions. In one embodiment, the self-assembling material comprises peptides having a sequence of amino acid residues conforming to one or more of Formulas I-IV: ((Xaa°′−Xaa+)x(Xaane1_Xaa−)y)n (I); ((Xaa′_Xaa)x(Xaa°e°−Xaa+)y)n (II); ((Xaa+−Xaa″e1)x(Xaa−Xaa″)y)n (III); and ((Xaa−XaaQe7)x(Xaa+Xaa1e″)y)n (IV), where Xaan′ represents an amino acid residue having a neutral charge; Xaa+ represents an amino acid residue having a positive charge; Xaa represents an amino acid residue having a negative charge; x and y are integers having a value of 1, 2 or 4, independently; and n is an integer having a value of 1-5. In another embodiment, the self assembling materials are peptidomimetics, nucleotidomimetics, di- and triblock copolymers, N-alkylacrylamides, or dendimers. These materials are also useful in a method for regeneration or repair of tissue or cells forming tissue.
Owner:ARCH BIOSURGERY
Method and system for self-convergent erase in charge trapping memory cells
A process and a memory architecture for operating a charge trapping memory cell is provided. The method for operating the memory cell includes establishing a high threshold state in the memory cell by injecting negative charge into the charge trapping structure to set a high state threshold. The method includes using a self-converging biasing procedure to establish a low threshold state for the memory cell by reducing the negative charge in the charge trapping structure to set the threshold voltage for the cell to a low threshold state. The negative charge is reduced in the memory cell by applying a bias procedure including at least one bias pulse. The bias pulse balances charge flow into and out of the charge trapping layer to achieve self-convergence on a desired threshold level. Thereby, an over-erase condition is avoided.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
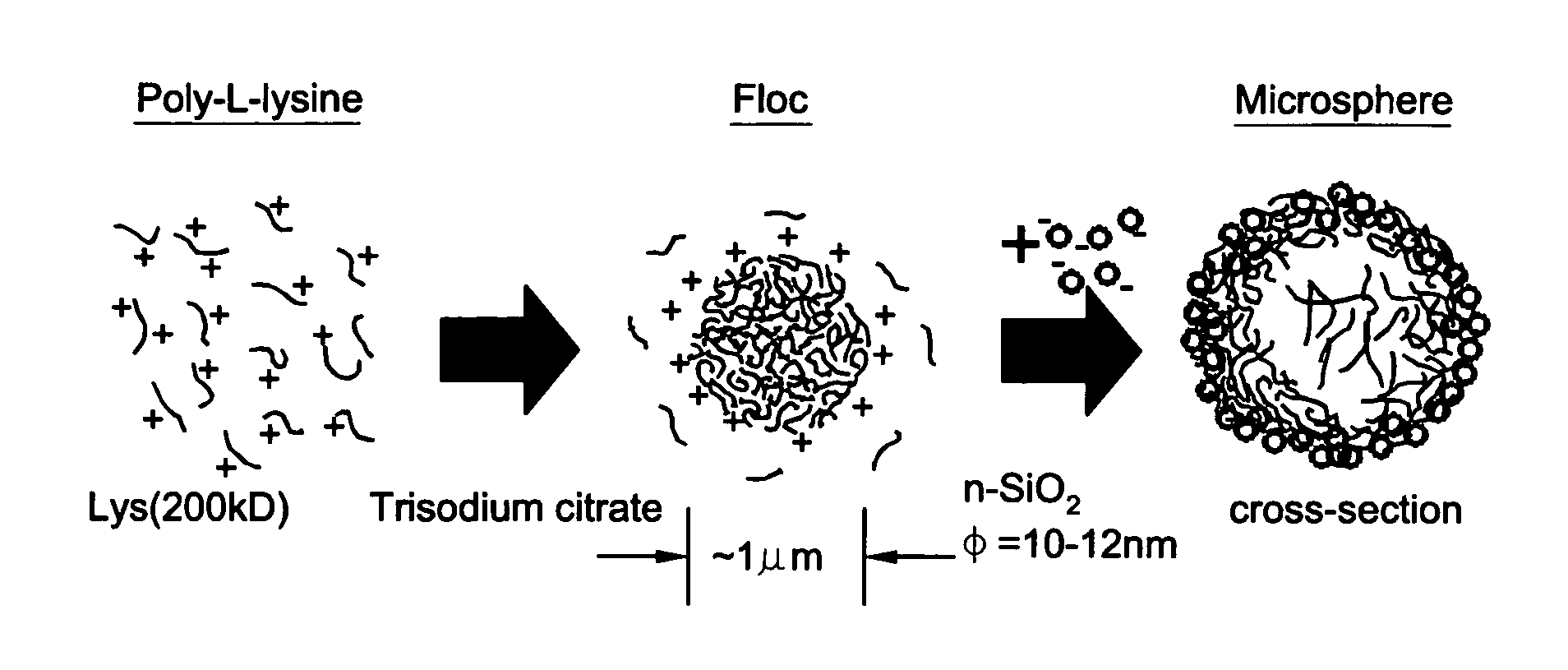
Method to fabricate microcapsules from polymers and charged nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050158390A1Economically and environmentally favorableRequirement for reaction conditionMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryPolyelectrolyteNanoparticle
A method for making hollow nanoparticles, comprises a) providing an amount of a polyelectrolyte having a charge, b) providing an amount of a counterion having a valence of at least 2, c) combining the polyelectrolyte and the counterion in a solution such that the polyelectrolyte self-assembles to form spherical aggregates, and d) adding nanoparticles to the solution such that nanoparticles arrange themselves around the spherical aggregates. The polyelectrolyte may have a positive or negative charge. The charge ratio R of total charge of the counterions to the total charge of the polyelectrolyte is greater than 1.0.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Supercharged proteins for cell penetration
InactiveUS20110112040A1Improved cell penetrationReduce biological activityMicrobiological testing/measurementSaccharide peptide ingredientsInfective disorderDisease cause
Compositions, systems and related methods for delivering a supercharged protein or a complex of a supercharged protein and therapeutic agent (e g, nucleic acid, peptide, small molecule) to cells are disclosed. Superpositively charged proteins may be associated with nucleic acids (which typically have a net negative charge) via electrostatic interactions. The systems and methods may involve altering the primary sequence of a protein in order to “supercharge” the protein (e g, to generate a superpositively-charged protein). The compositions may be used to treat proliferative diseases, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, inborn errors in metabolism, genetic diseases, etc.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
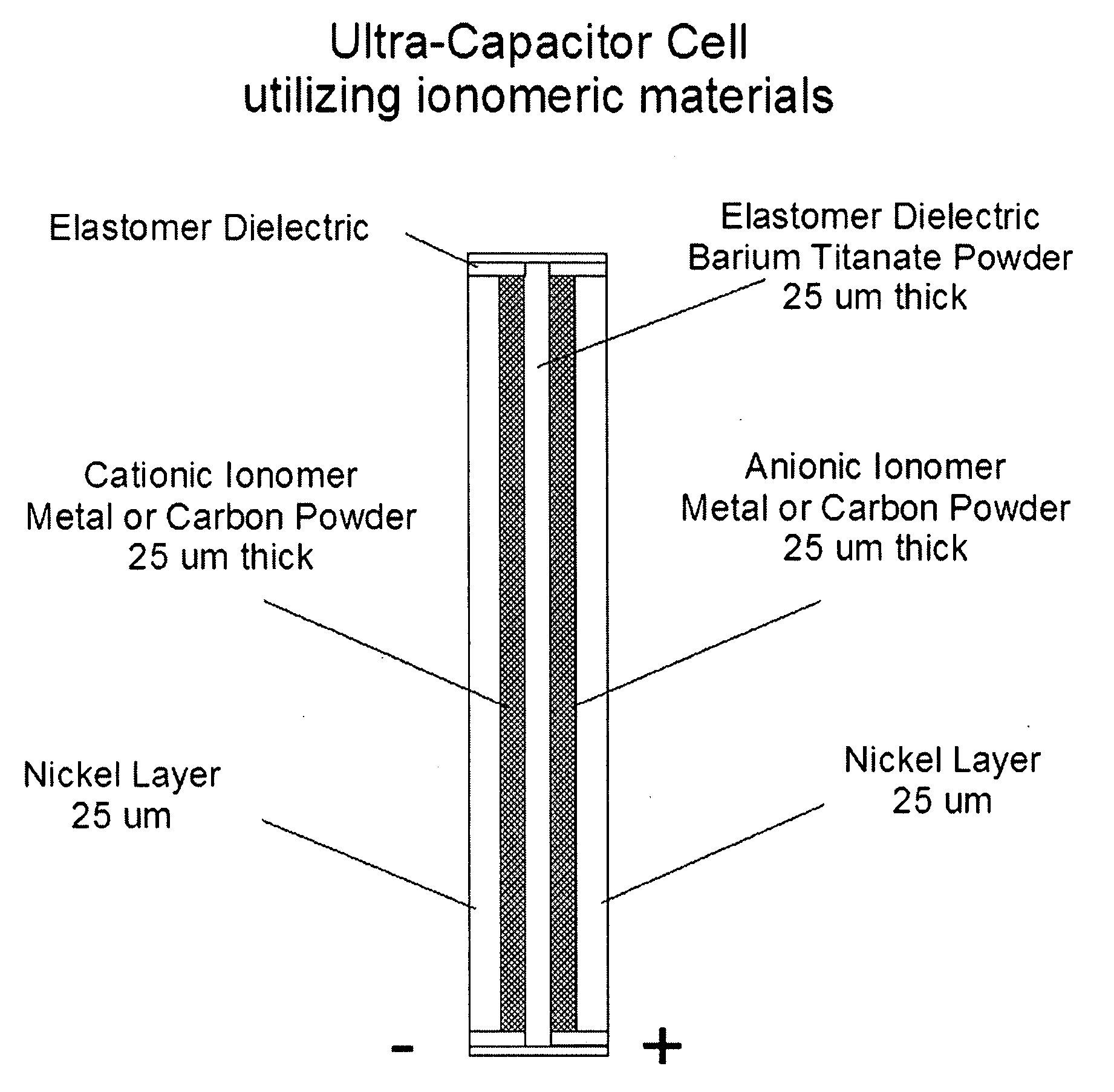
Nanoparticle ultracapacitor
InactiveUS20080316678A1Hybrid capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitancePolymer science
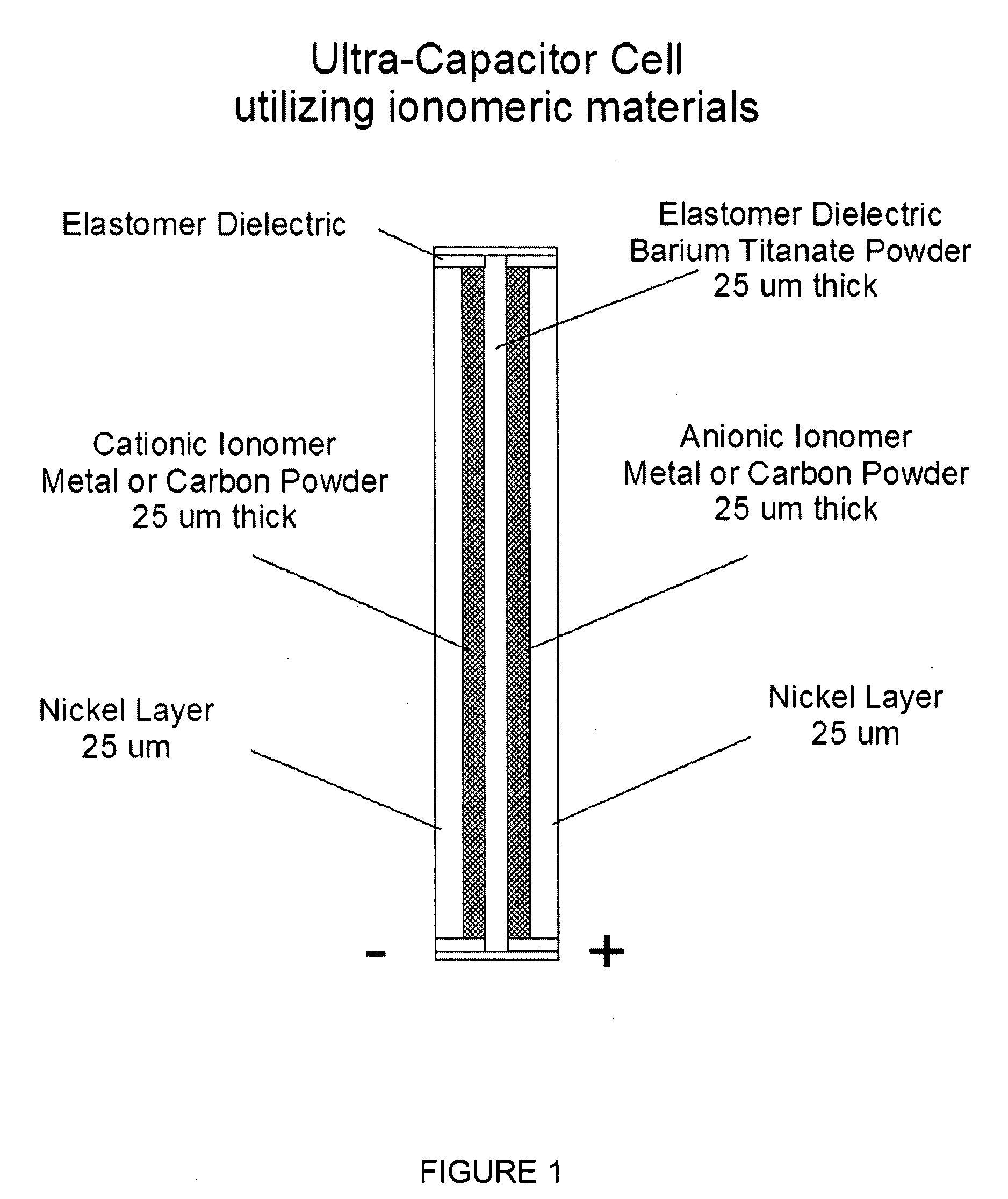
Particular aspects provide capacitors, and particularly ultracapacitors, comprising molecules suitable to substantially increasing the capacitance of the capacitor, and methods for making same Particular aspects provide ultracapacitors that include nanoparticles optionally coated with molecules, such as polymer electrolytes. Certain aspects provide an energy storage device or capacitor, comprising at least three layers sealed in a fluid-tight covering, wherein a first layer comprises at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of positive charge and at least one nanoparticle; a second dielectric layer comprising at least one insulative polymer; a third layer comprising at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of negative charge and at least one nanoparticle. In certain aspects, the electrolytic polymer of the first layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of positive charge, and wherein the electrolytic polymer of the third layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of negative charge.
Owner:TANGREDI PATRICIA
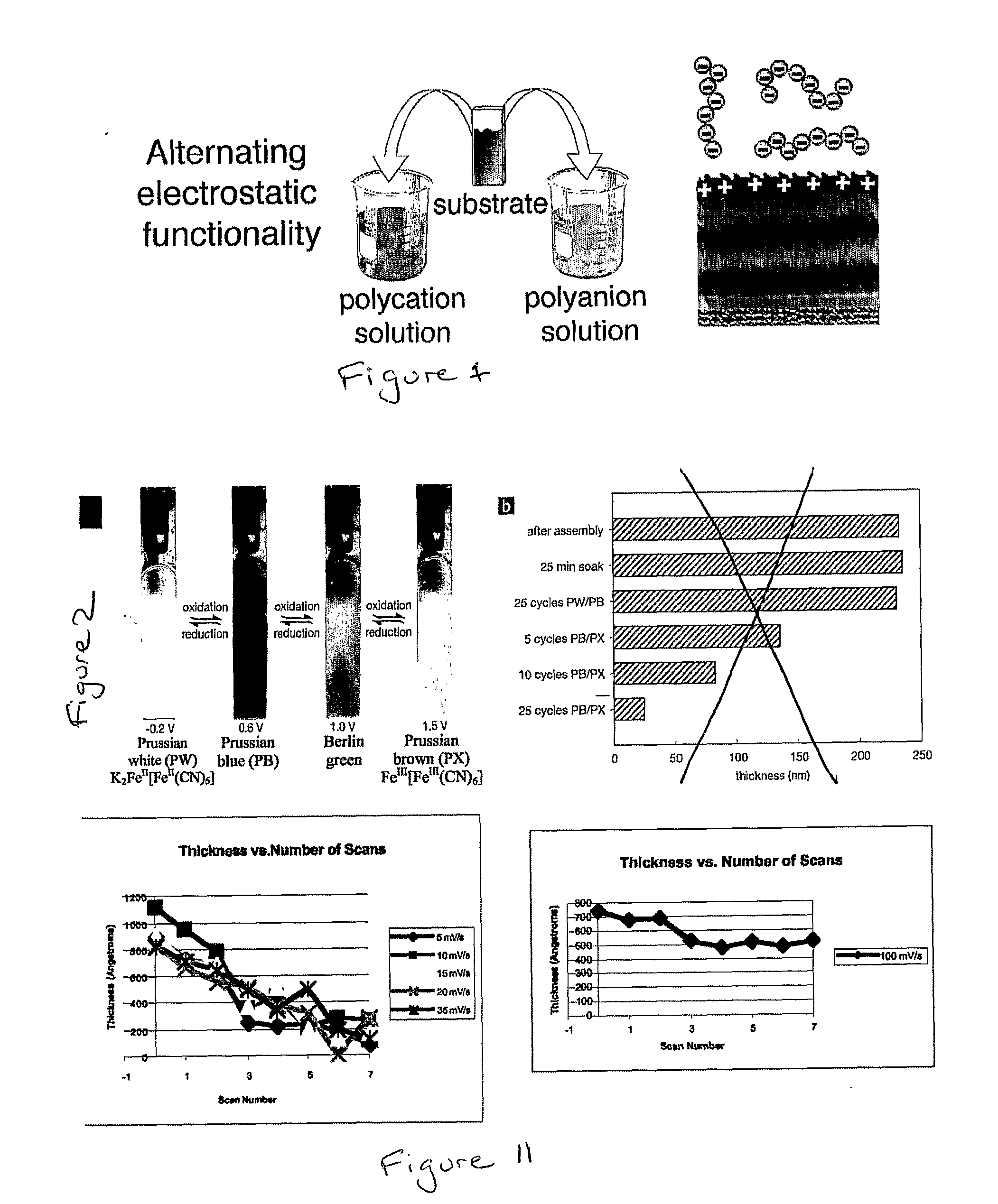
Electronically-Degradable Layer-by-Layer Thin Films
A decomposable thin film comprising a plurality of alternating layers of net positive and negative charge. At least a portion of the positive layers, the negative layers, or both, comprise a polyelectrolyte.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus using electric field for improved biological assays
ActiveUS8277628B2Quality improvementEfficient removalElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPresent methodEngineering
Disclosed are a method and apparatus that use an electric field for improved biological assays. The electric field is applied across a device having wells, which receive reactants, which carry a charge. The device thus uses a controllable voltage source between the first and second electrodes, which is controllable to provide a positive charge and a negative charge to a given electrode. By controlled use of the electric field charged species in a fluid in a fluid channel are directed into or out of the well by an electric field between the electrodes. The present method involves the transport of fluids, as in a microfluidic device, and the electric field-induced movement of reactive species according to various assay procedures, such as DNA sequencing, synthesis or the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for preparing fibrilia carboxylation cellulose nanowhiskers
The invention provides a method for preparing fibrilia carboxylation cellulose nanowhiskers, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: soaking fibrilia powder in sodium hydroxide for processing, then processing the fibrilia powder by a former treating agent and taking out the fibrilia powder to be dried in a vacuum oven to obtain preprocessed fibrilia powder; and placing the preprocessed fibrilia powder in a TEMPO oxidation system for catalytic oxidation to obtain a stable cellulose nanowhiskers suspending liquid after mechanical processing and freeze drying the suspending liquid to obtain the fibrilia carboxylation cellulose nanowhiskers having grain diameters of 3-10 nm. According to the invention, fibrilia carboxylation and nano fibrillation are realized and surfaces of prepared nanocrystalline celluloses have carboxyl functional groups, thus the surfaces generate negative charges, electrostatic repulsion among the negative charges can avoid the reunion of nanoparticles, so that the nanocrystalline celluloses can be well dispersed in water and the obtained nanocrystalline celluloses have excellent uniformity of grain sizes.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
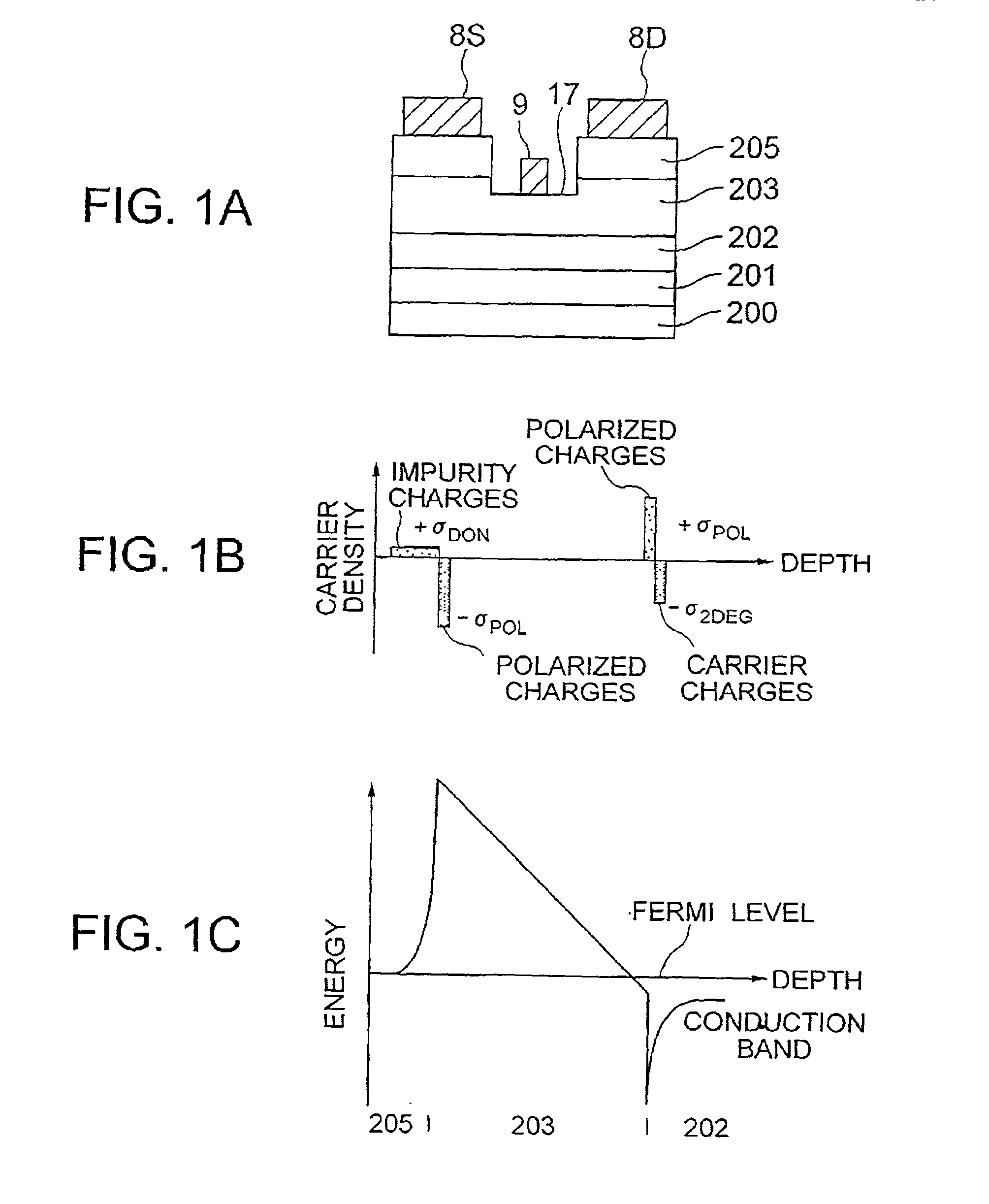
Hetero-junction field effect transistor having an intermediate layer
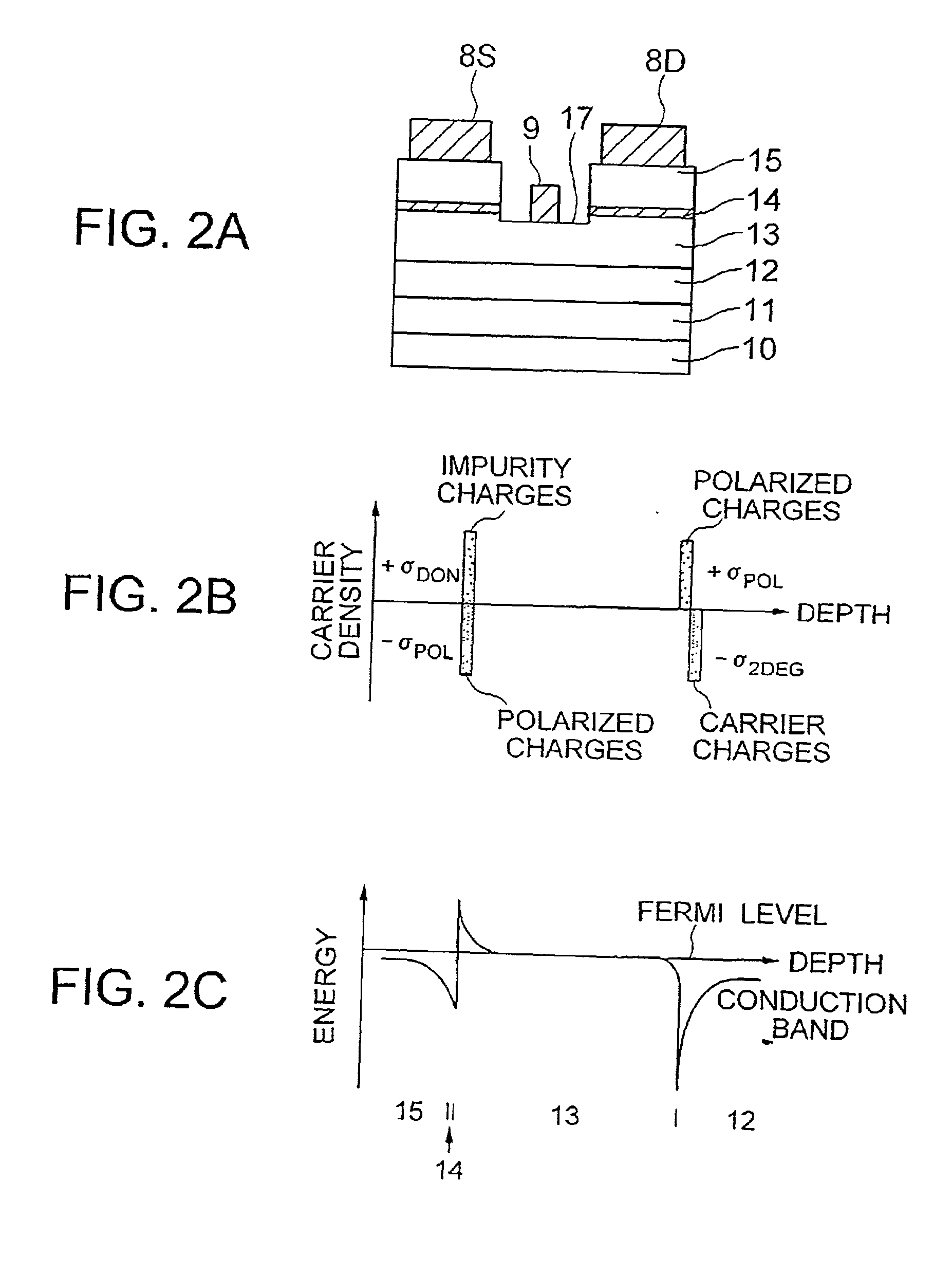
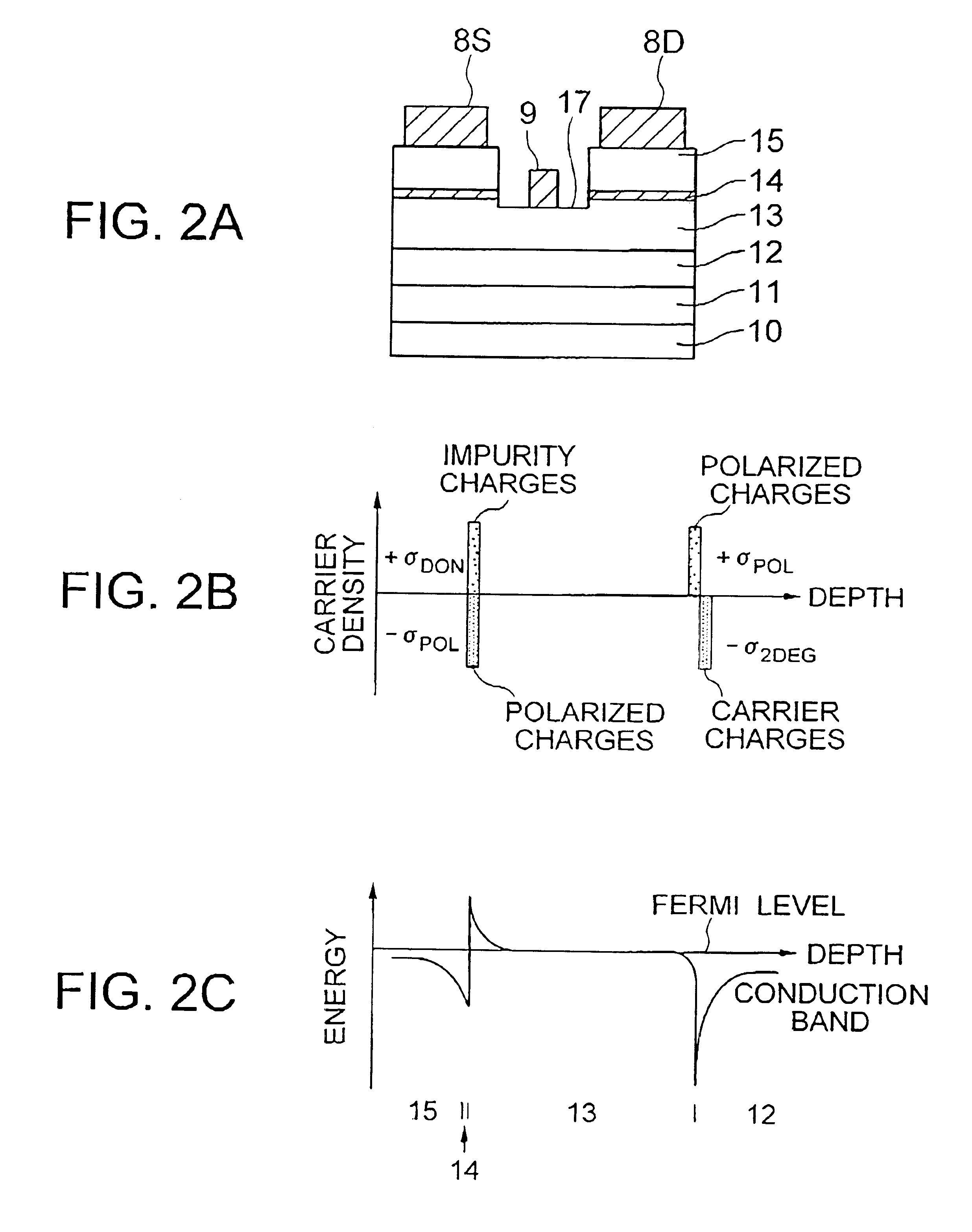
InactiveUS20010040247A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurityElectron
A hetero-junction FET has an intermediate layer including n-type-impurity doped layer between an electron supply layer and an n-type cap layer. The intermediate layer cancels the polarized negative charge generated between the electron supply layer and the n-type cap layer by ionized positive charge, thereby reducing the barrier against the electrons and source / drain resistance.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Photoconductor on active pixel image sensor
InactiveUS20040036010A1Low costMass productionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor materialsSpectral response
A MOS or CMOS based photoconductor on active pixel image sensor. Thin layers of semi-conductor material, doped to PIN or NIP photoconducting layers, located above MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits produce an array of layered photodiodes. Positive and negative charges produced in the layered photodiodes are collected and stored as electrical charges in the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits. The present invention also provides additional MOS or CMOS circuits for reading out the charges and for converting the charges into images. With the layered photodiode of each pixel fabricated as continuous layers of charge generating material on top of the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits, extremely small pixels are possible with almost 100 percent packing factors. MOS and CMOS fabrication techniques permit sensor fabrication at very low costs. In preferred embodiments all of the sensor circuits are incorporated on or in a single crystalline substrate along with the sensor pixel circuits. Techniques are disclosed for tailoring the spectral response of the sensor for particular applications.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Coatings for use on medical devices
InactiveUS20060212106A1Improve medical device deployment accuracyPrevent slippingStentsBalloon catheterMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
A medical device at least a portion of which has a degradable coating, the coating degrading in an aqueous environment, and to methods of making and using the same. The coating may be a layer-by-layer coating, the first layer comprising a material having a positive charge and the second layer comprising a material having a negative charge.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
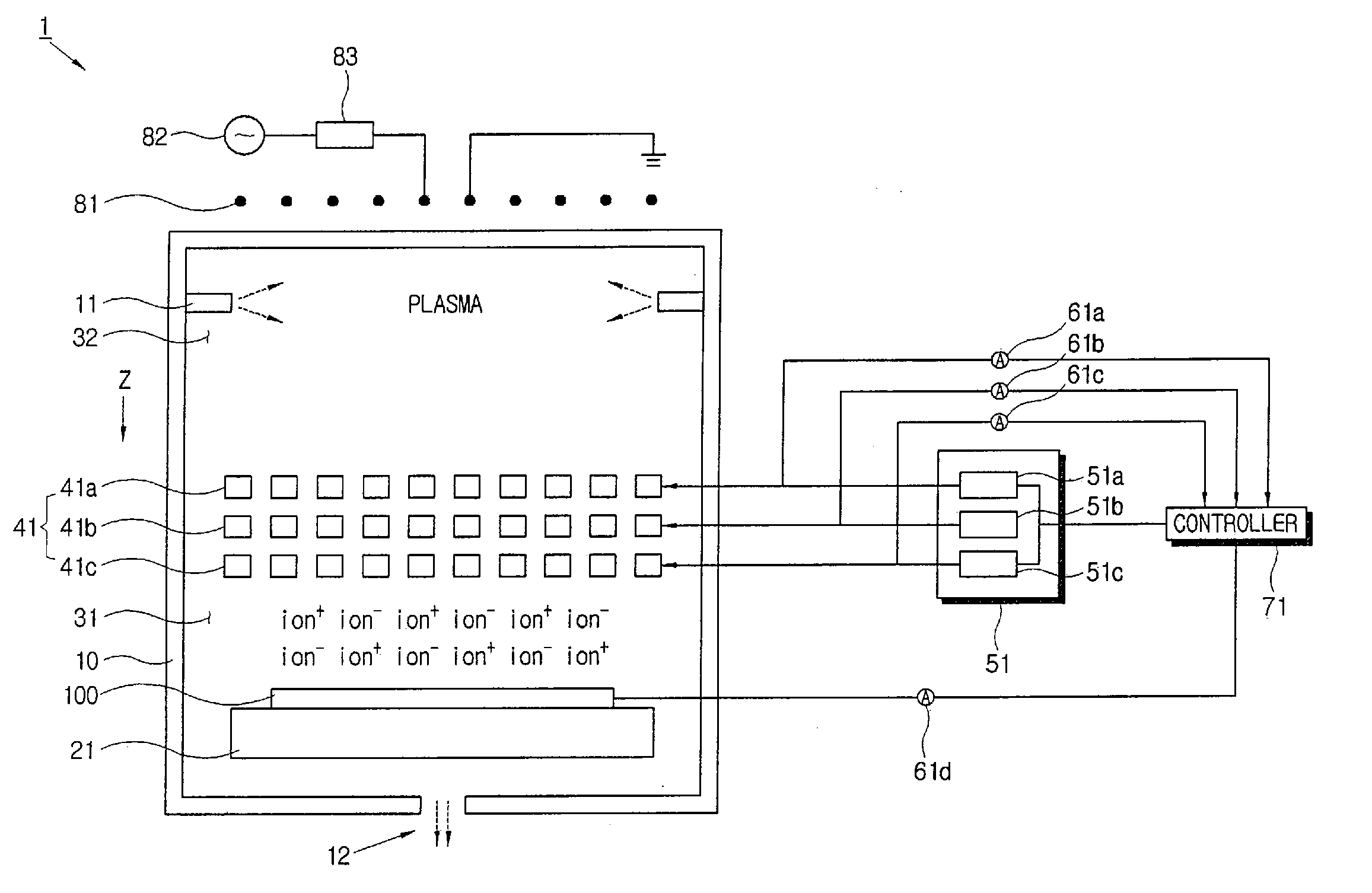
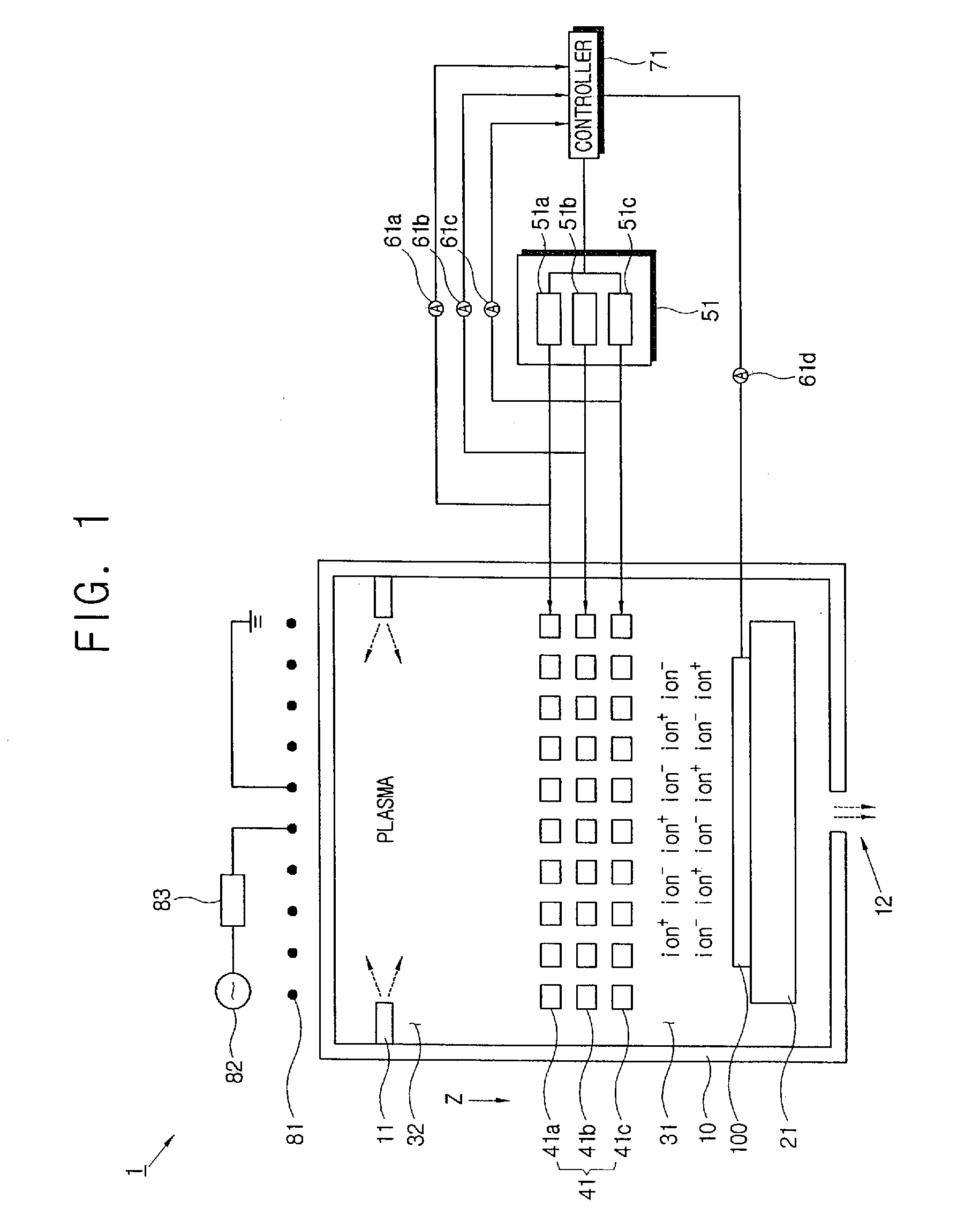
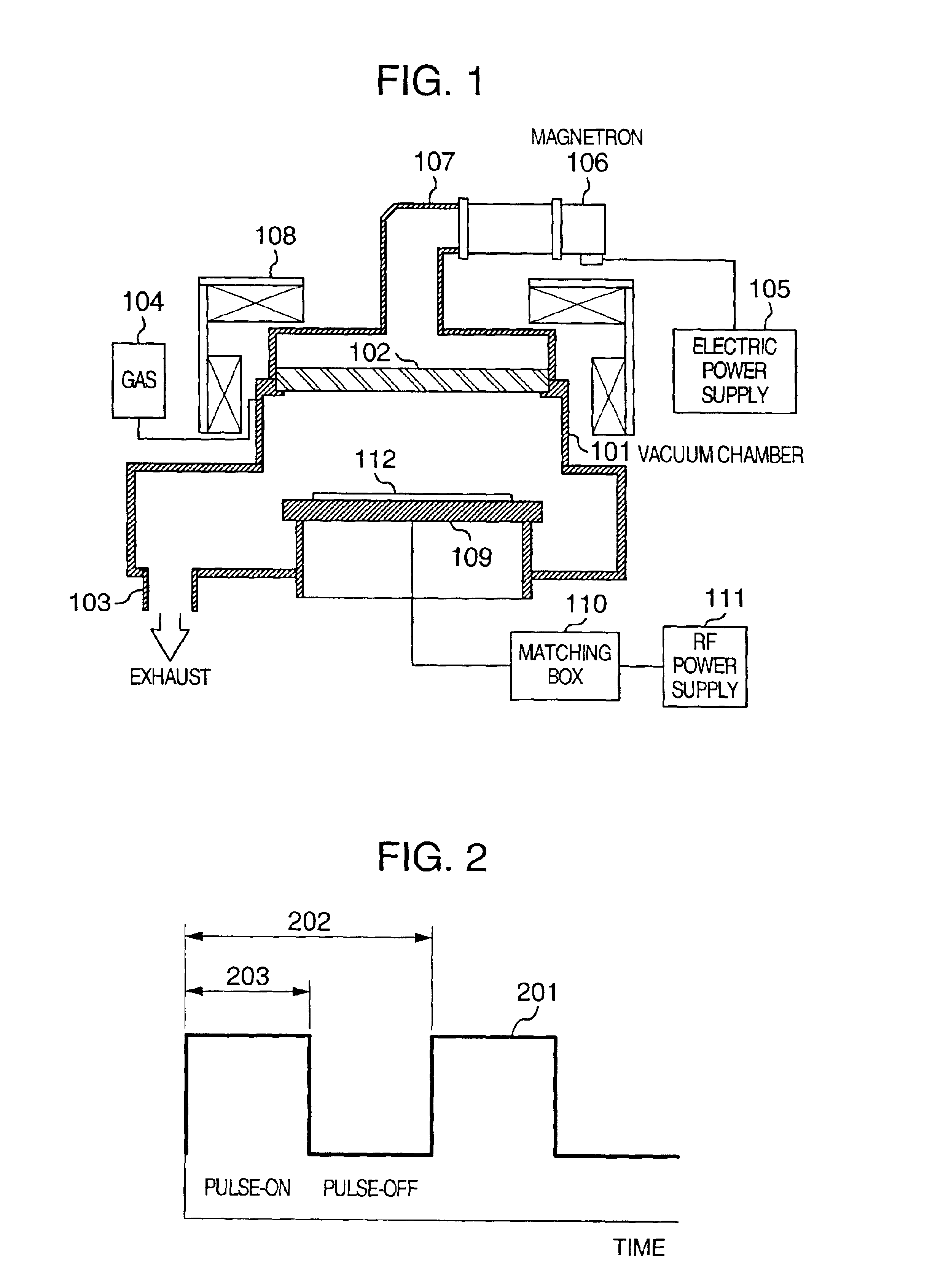
Apparatus to treat a substrate and method thereof
InactiveUS20070068624A1Avoid accumulationSimple structureElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVacuum chamberElectric power
An apparatus to treat a substrate including a vacuum chamber having a plasma space where plasma is generated and a treating space where a substrate is treated, an extract electrode disposed between the plasma space and the treating space, a power supply to provide power to the extract electrode, and a controller to control the power supply so that a cation beam and a negative charge beam are alternately extracted from a plasma in the plasma space to the treating space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Deoxyribonucleic acid measuring apparatus and method of measuring deoxyribonucleic acid
InactiveUS7838226B2Optimize immobilization densityEfficient executionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyDeoxyribonucleic acid probeField effect
With an insulated gate field effect transistor in which deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) probes are immobilized on a gold electrode, extension reaction on the gold electrode is performed with DNA polymerase to directly measure an increased amount of a phosphate group caused by the extension reaction, that is, negative charge, by means of a current change between a source and a drain of the insulated gate field effect transistor. Thus, presence / absence of hybridization of target DNAs with the DNA probes, and presence / absence of the extension reaction are detected. Optimum immobilization density of the DNA probes on the gold electrode is set at 4×1012 molecules / cm2. To reduce surface potential fluctuation caused by external variation (influences of foreign substances), which is a problem when using the gold electrode in a solution, a high-frequency voltage equal to or above 1 kHz is applied between the gold electrode and a reference electrode by a power source.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
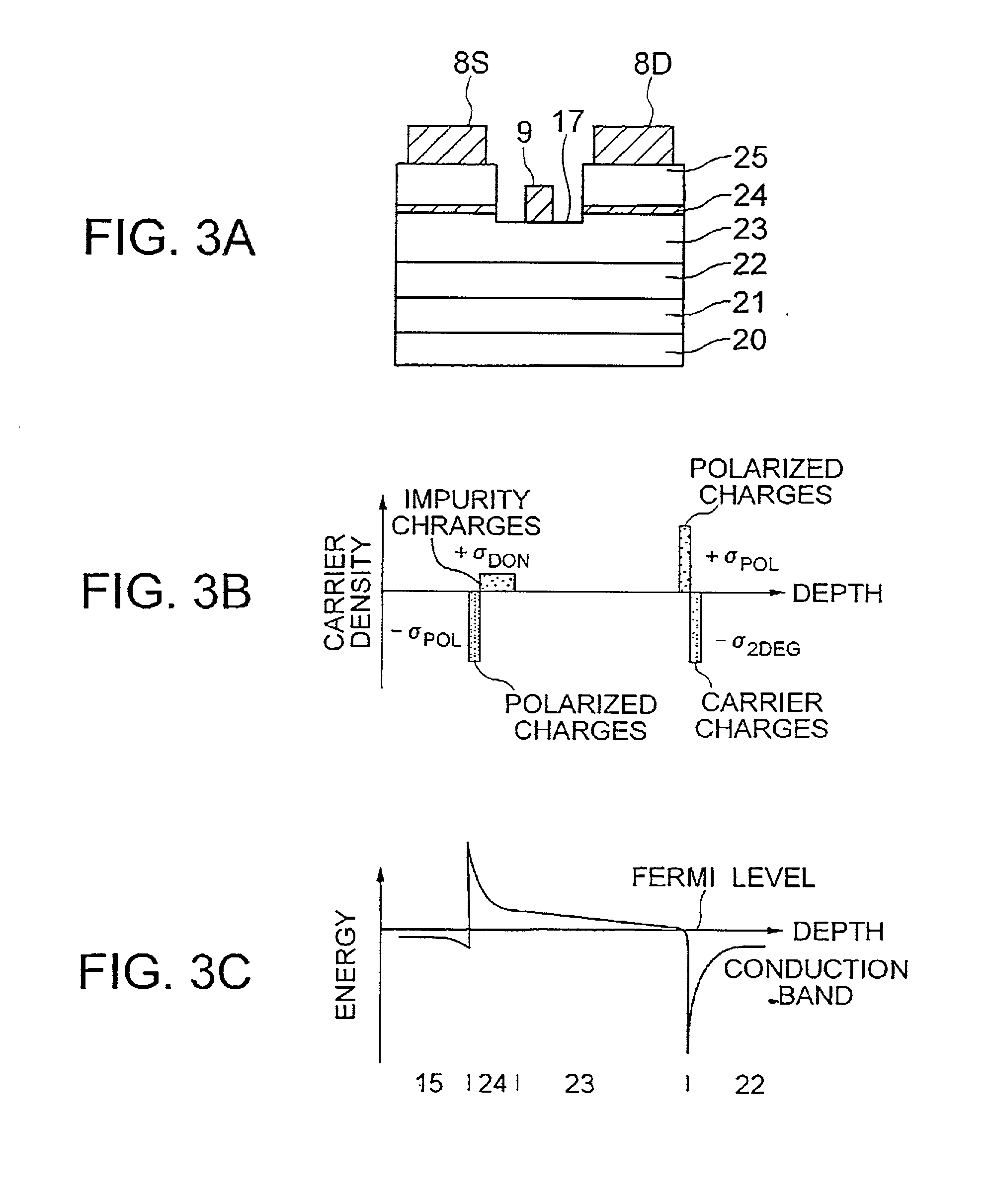
Hetero-junction field effect transistor having an intermediate layer
InactiveUS6552373B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronImpurity
A hetero-junction FET has an intermediate layer including n-type-impurity doped layer between an electron supply layer and an n-type cap layer. The intermediate layer cancels the polarized negative charge generated between the electron supply layer and the n-type cap layer by ionized positive charge, thereby reducing the barrier against the electrons and source / drain resistance.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
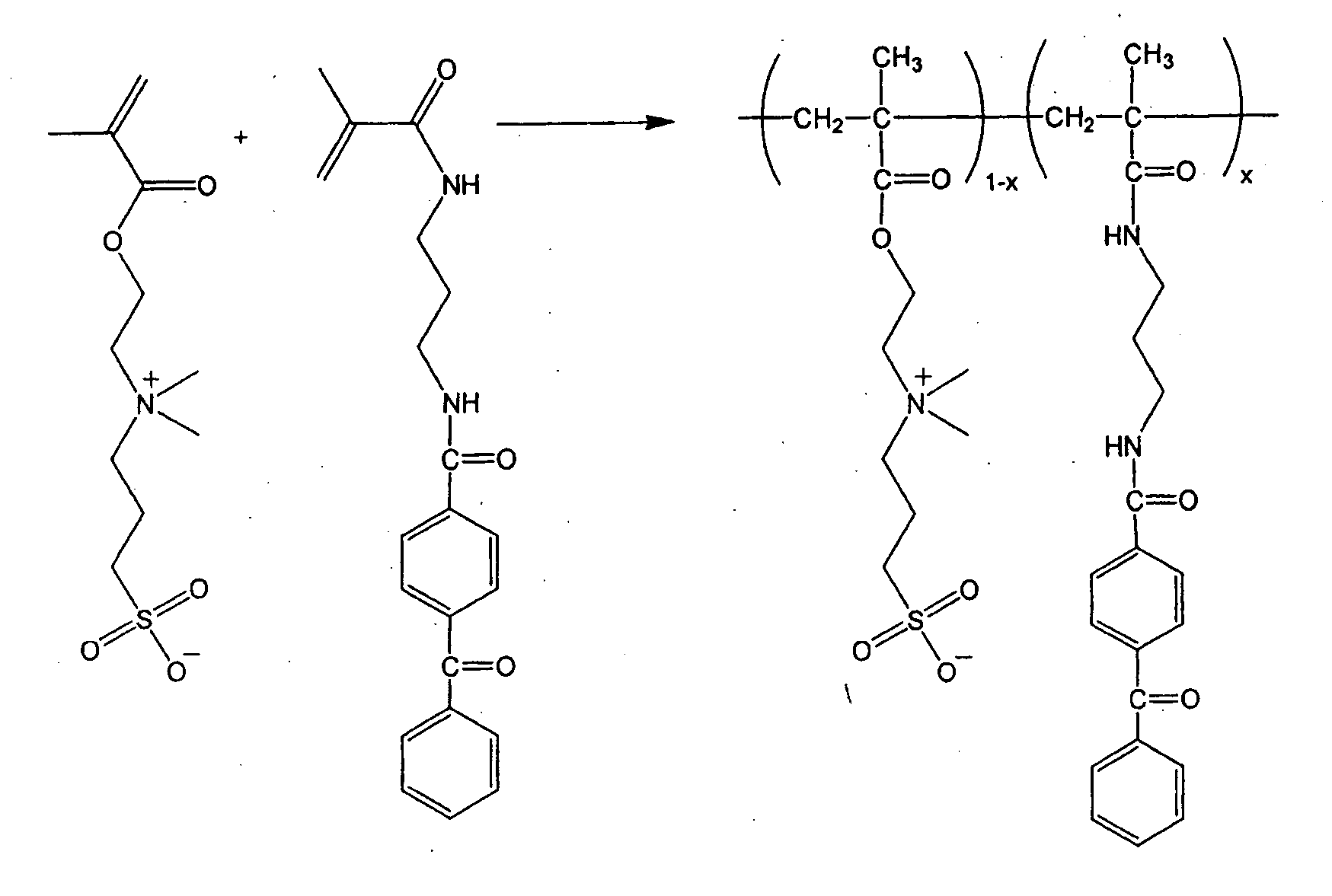
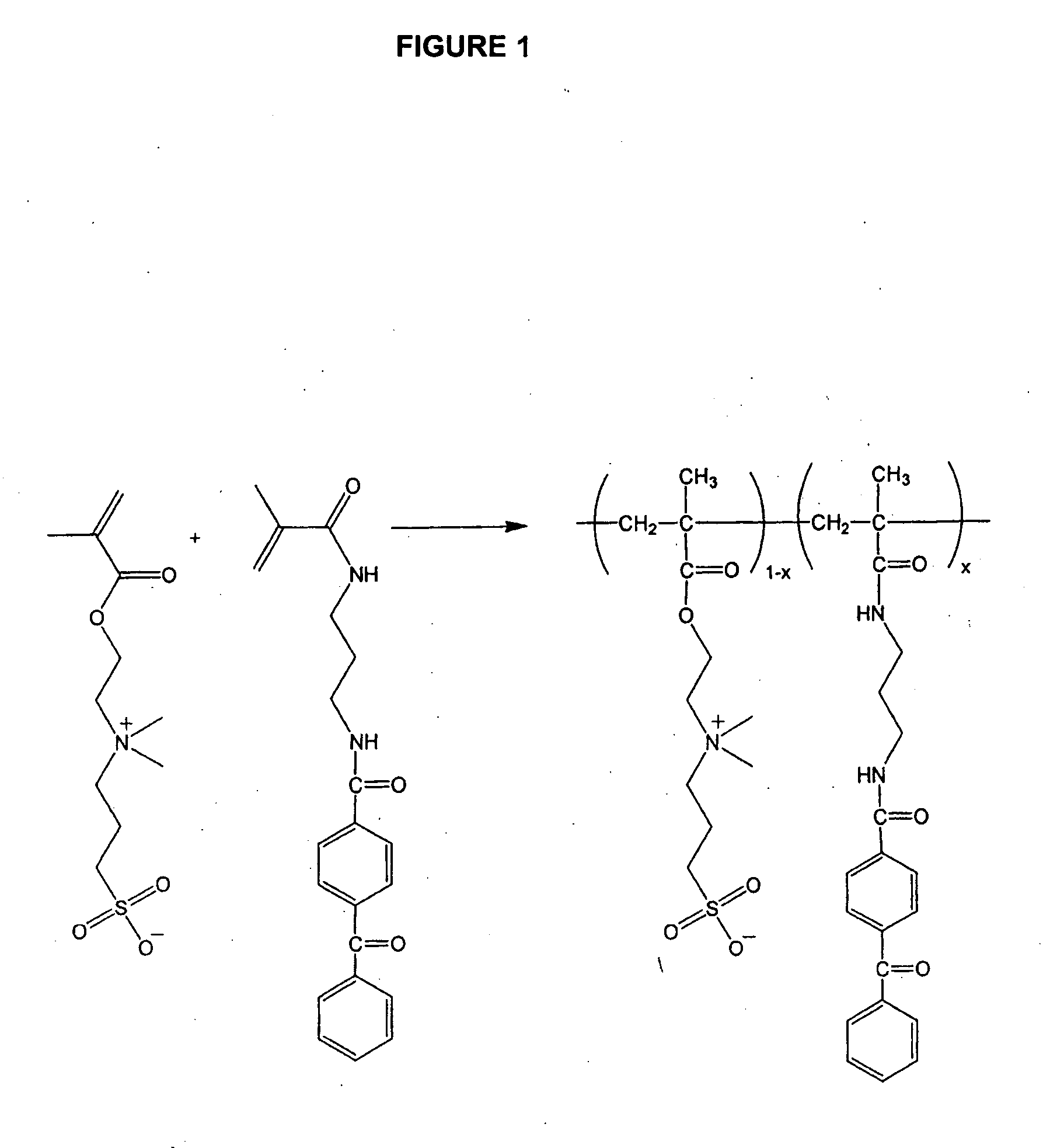
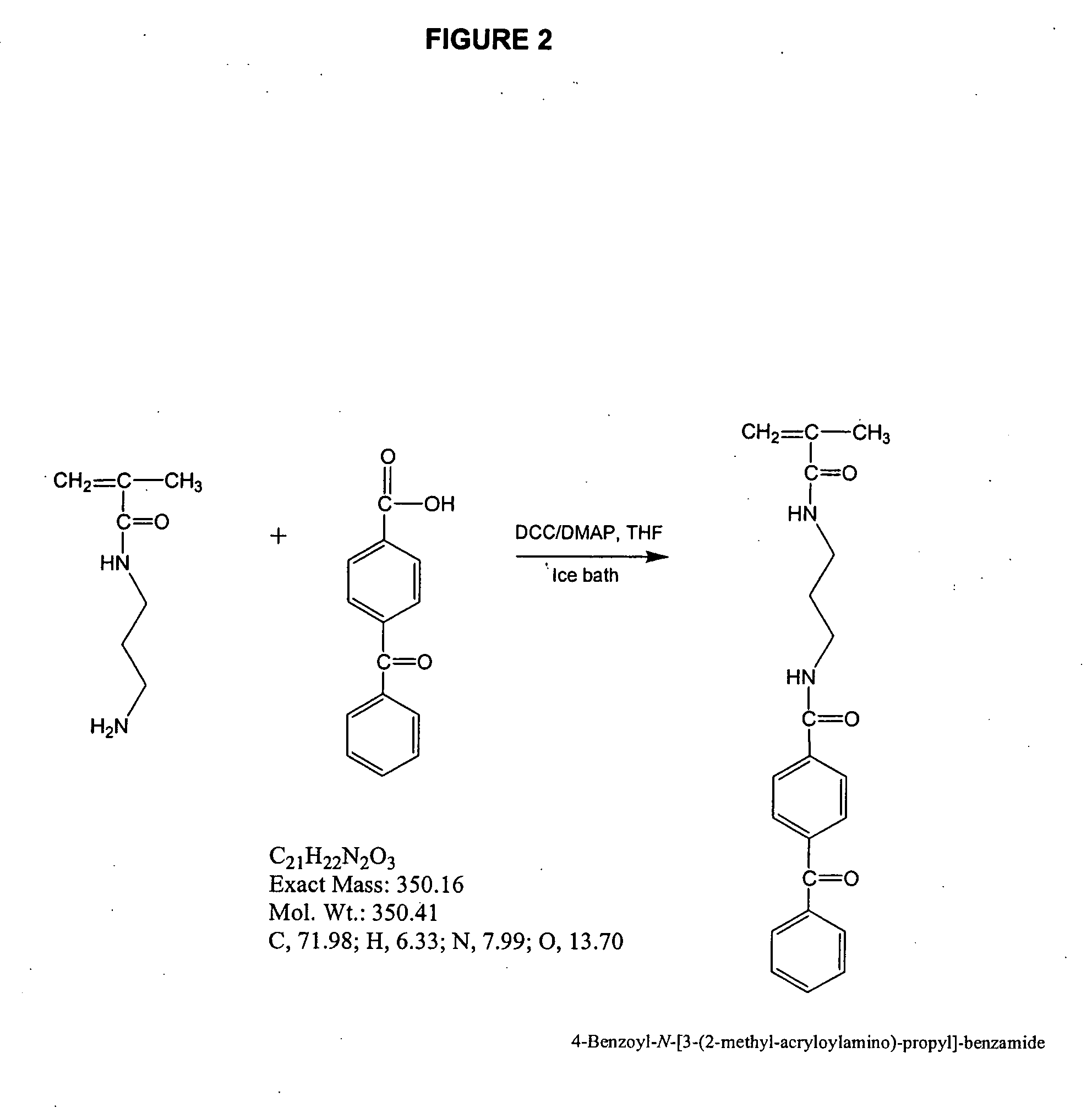
Zwitterionic polymers
InactiveUS20060183863A1Improve utilizationImprove versatilitySolid sorbent liquid separationCross-linkLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
Zwitterionic polymers bearing positive and negative charges are readily prepared from easily accessible precursors. The polymers show enhanced binding affinities for analytes under high salt conditions, compared to similar polymers bearing a charge of a single polarity. The polymers can also include an energy absorbing moiety for use in matrix assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry. The polymer can also include a photo-curable group, which can be used to form cross-links within the bulk polymer or between the polymer and a surface functionalized with a polymerizable moiety. The polymers are incorporated into devices of use for the analysis, capture, separation, or purification of an analyte. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention provides a substrate coated with a polymer of the invention, the substrate being adapted for use as a probe for a mass spectrometer.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for anion-exchange adsorption and anion-exchangers
InactiveUS6702943B1Reduced ligand contentSolve insufficient capacityIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic anion exchangersHydrogenDesorption
A method for the removal of a substance carrying a negative charge and being present in an aqueous liquid (I). The method comprises the steps of: (i) contacting the liquid with a matrix carrying a plurality of ligands comprising a positively charged structure and a hydrophobic structure, and (ii) desorbing the substance. The characterizing feature is that (I) each of said ligands together with a spacer has the formula: -SP-[Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] where (A) [Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] represents a ligand a) Ar is an aromatic ring, b) R1 is [(L)nR'1]m where n and m are integers selected amongst zero or 1; L is amino nitrogen, ether oxygen or thioether sulphur; R'1 is a linker selected among 1) hydrocarbon groups; 2) -C(=NH)-; c) R2-4 are selected among hydrogen and alkyls; (B) SP is a spacer providing a carbon or a heteroatom directly attached to Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (C)-represents that SP replaces a hydrogen in (Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (D)-represents binding to the matrix; and (II) desorption. There is also described (a) anion-exchangers having high breakthrough capacities, (b) a screening method and (c) a desalting protocol.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Plasma processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6777037B2Suppress charging damageImprove accuracyElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringGate oxide
A plasma processing method and apparatus are provided for processing the surface of a semiconductor device or the like through the effect of plasma. A pulsed plasma discharge is performed by switching on and off the high frequency electric power for generating the plasma with a specified off period of the plasma generation, to control an inflow amount of positive and negative charges to sparse and dense portions of device patterns and suppress an electric potential on a gate oxide film. Thereby, a highly accurate etching process with no charging damage can be carried out.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for backside surface passivation of solar cells and solar cells with such passivation
InactiveUS20050022863A1Easy to manufactureSimple and cheap to manufacturePV power plantsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsAlloy
The present invention provides a method for dielectric passivating the surface of a solar cell by accumulation of negative fixed charges of a first type at the interface between semiconductor material and a passivating material. According to the invention the passivating material comprises an oxide system, for example a binary oxide system, comprising Al2O3 and at least one metal oxide or metalloid oxide which enhances the tetrahedral structure of Al2O3, for example, an (Al2O3)x(TiO2)1-x alloy. In this way it is possible to combine the desirable properties from at least two different oxides, while eliminating the undesirable properties of each individual material. The oxide system can be deposited onto the semiconductor surface by means of a sol-gel method, comprising the steps of formation of the metal oxide and / or metalloid oxide sol and the aluminum solution and then carefully mixing these together under stirring and ultrasonic treatment. Thin films of the oxide system can then be deposited onto the semiconductor surface by means of spin coating followed by a temperature treatment.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
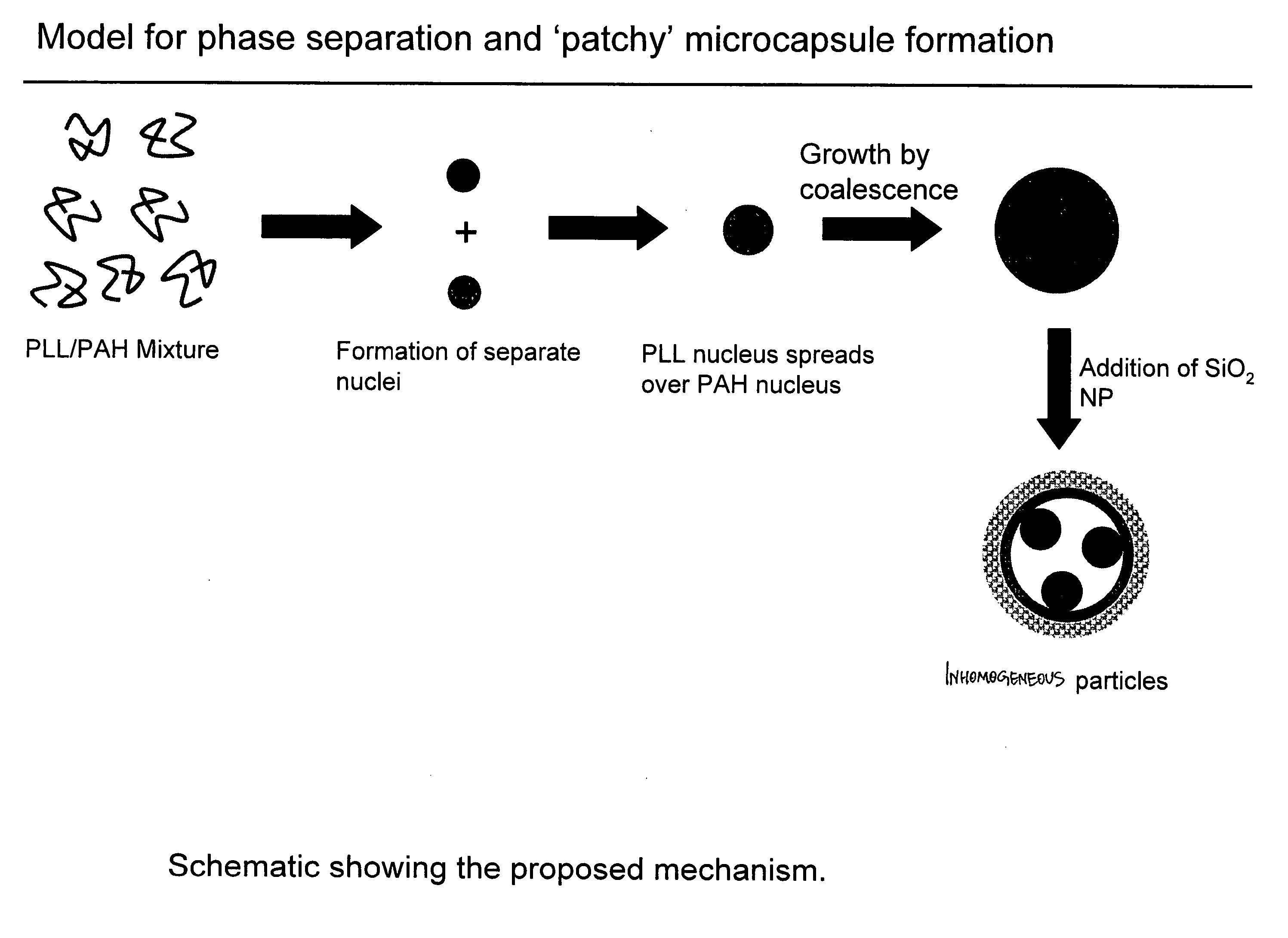
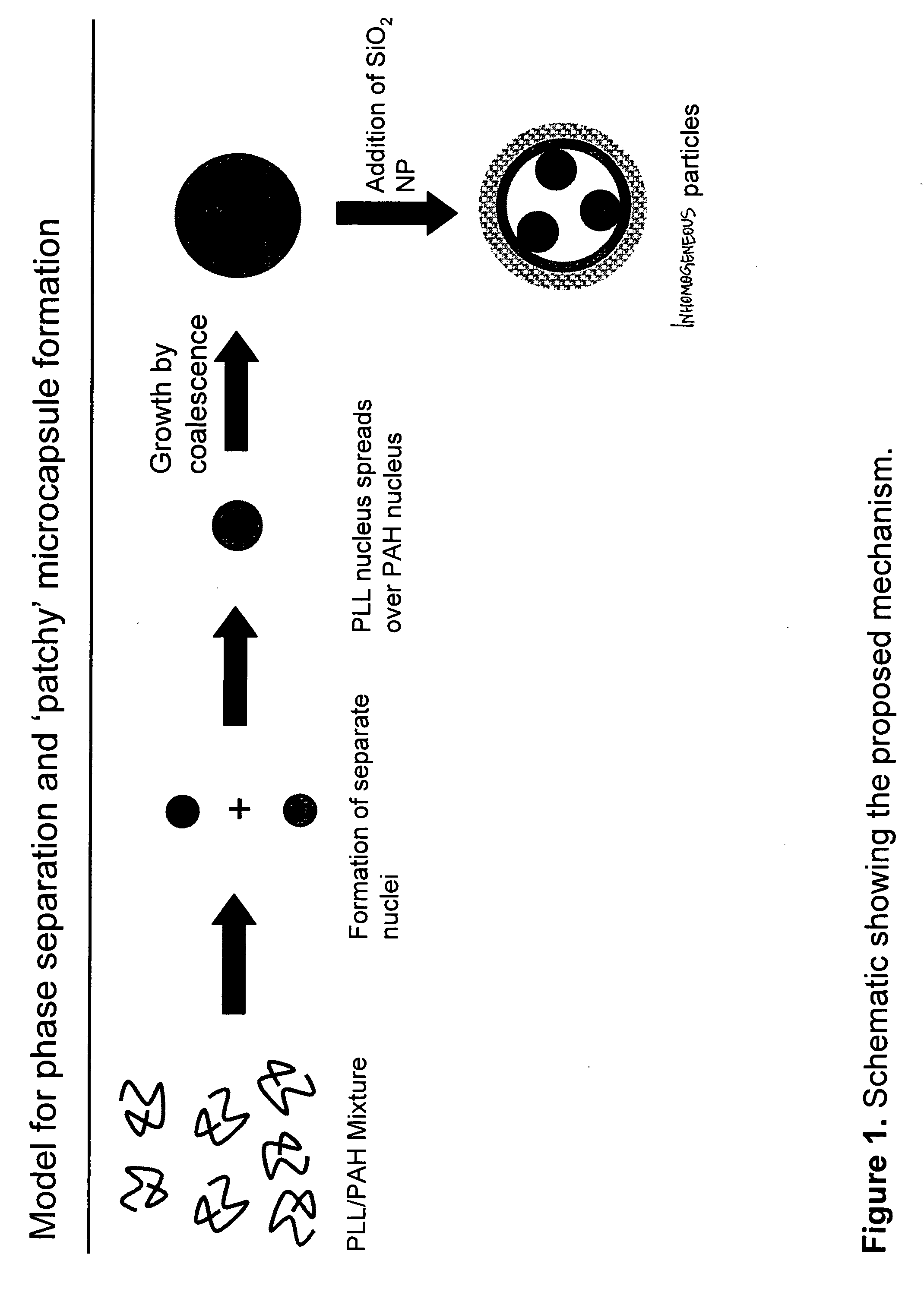
Method to fabricate inhomogeneous particles
InactiveUS20060159921A1Economically and environmentally favorableMinimize uncontrolled aggregationPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyPolyelectrolyteNanoparticle
A method for making inhomogeneous microparticles comprises a) providing an amount of each of at least two polyelectrolytes having a charge, b) providing an amount of a counterion having a valence of at least 2, c) combining the polyelectrolytes and the counterion in a solution such that the polyelectrolyte self-assembles to form inhomogeneous aggregates, and d) adding nanoparticles to the solution such that nanoparticles arrange themselves around the inhomogeneous aggregates to form inhomogeneous particles. The polyelectrolyte may have a positive or negative charge. The charge ratio R of total charge of the counterions to the total charge of the polyelectrolyte may be greater than 1.0.
Owner:RICE UNIV
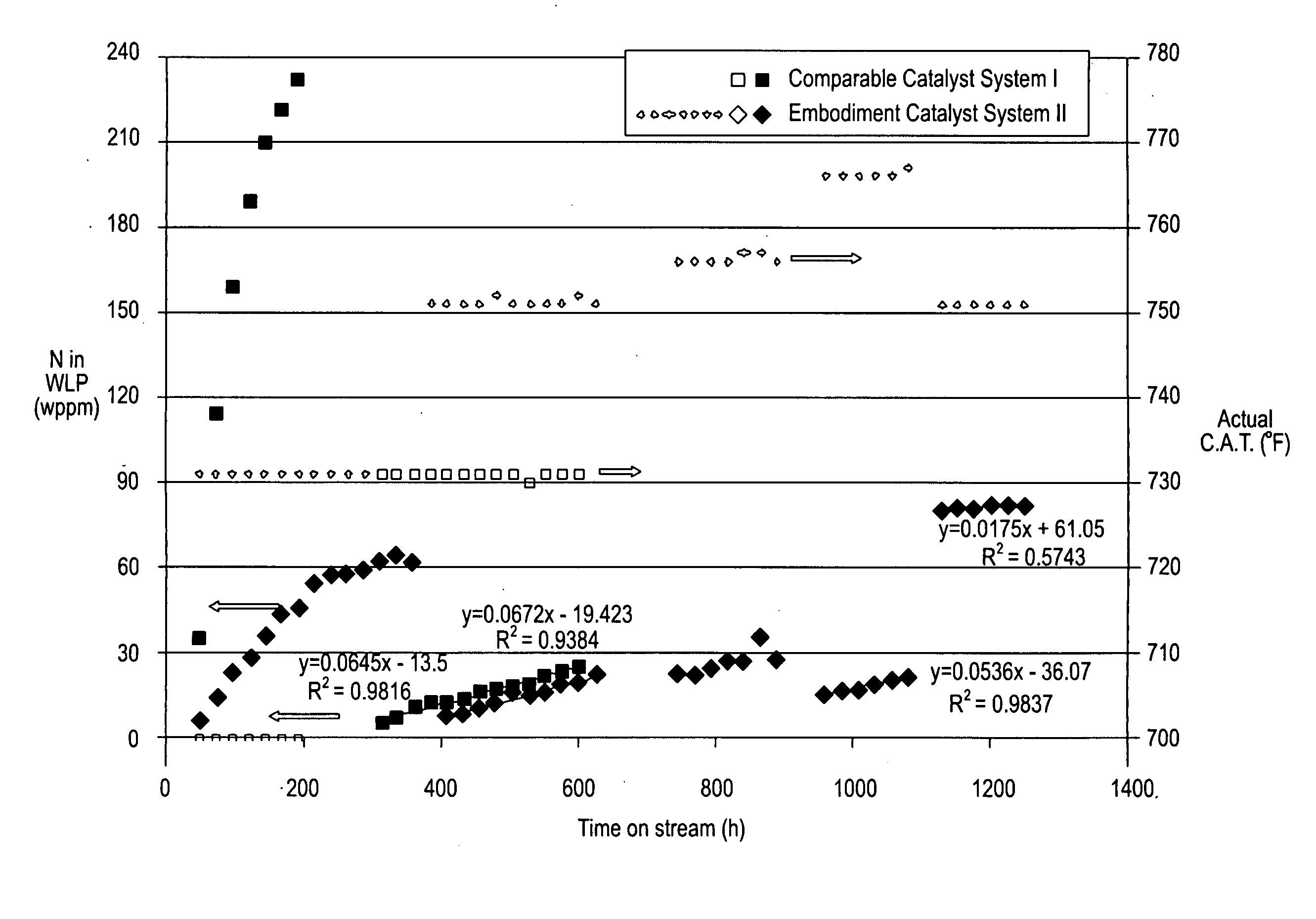
Hydroconversion Processes Employing Multi-Metallic Catalysts and Method for Making Thereof
ActiveUS20090107883A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCelluloseDiluent
A catalyst precursor composition and methods for making such catalyst precursor is disclosed. In one embodiment, the catalyst precursor is of the general formula Av[(MP)(OH)x(L)ny]z(MVIBO4), wherein MP is selected from Group VIII, Group IIB, Group IIA, Group IVA and combinations thereof; L is one or more oxygen-containing ligands, and L has a neutral or negative charge n<=0, MVIB is at least a Group VIB metal having an oxidation state of +6; MP:MVIB has an atomic ratio between 100:1 and 1:100; v−2+P*z−x*z+n*y*z=0; and 0≦y≦−P / n; 0≦x≦P; 0≦v≦2; 0≦z. In one embodiment, the catalyst precursor further comprises a cellulose-containing material. In another embodiment, the catalyst precursor further comprises at least a diluent (binder). In one embodiment, the diluent is a magnesium aluminosilicate clay.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Iontophoretic device and method of delivery of active agents to biological interface
InactiveUS20070083185A1Increase loadImproved release characteristicElectrotherapyMedical devicesActive agentElectrolyte composition
An iontophoresis device includes an active electrode element operable to provide an electrical potential; an electrolyte reservoir comprising an electrolyte composition; an inner active agent reservoir comprising a gel matrix and distributed in said gel matrix, a first positively charged active agent; an inner ion selective membrane deposed between said electrolyte reservoir and said inner active agent reservoir; and an outermost ion selective membrane having an outer surface, the outer surface being against the biological interface, wherein, the gel matrix comprises a hydrophilic polycarboxylated polymer having net negative charges.
Owner:TITI ELLEBEAU INC
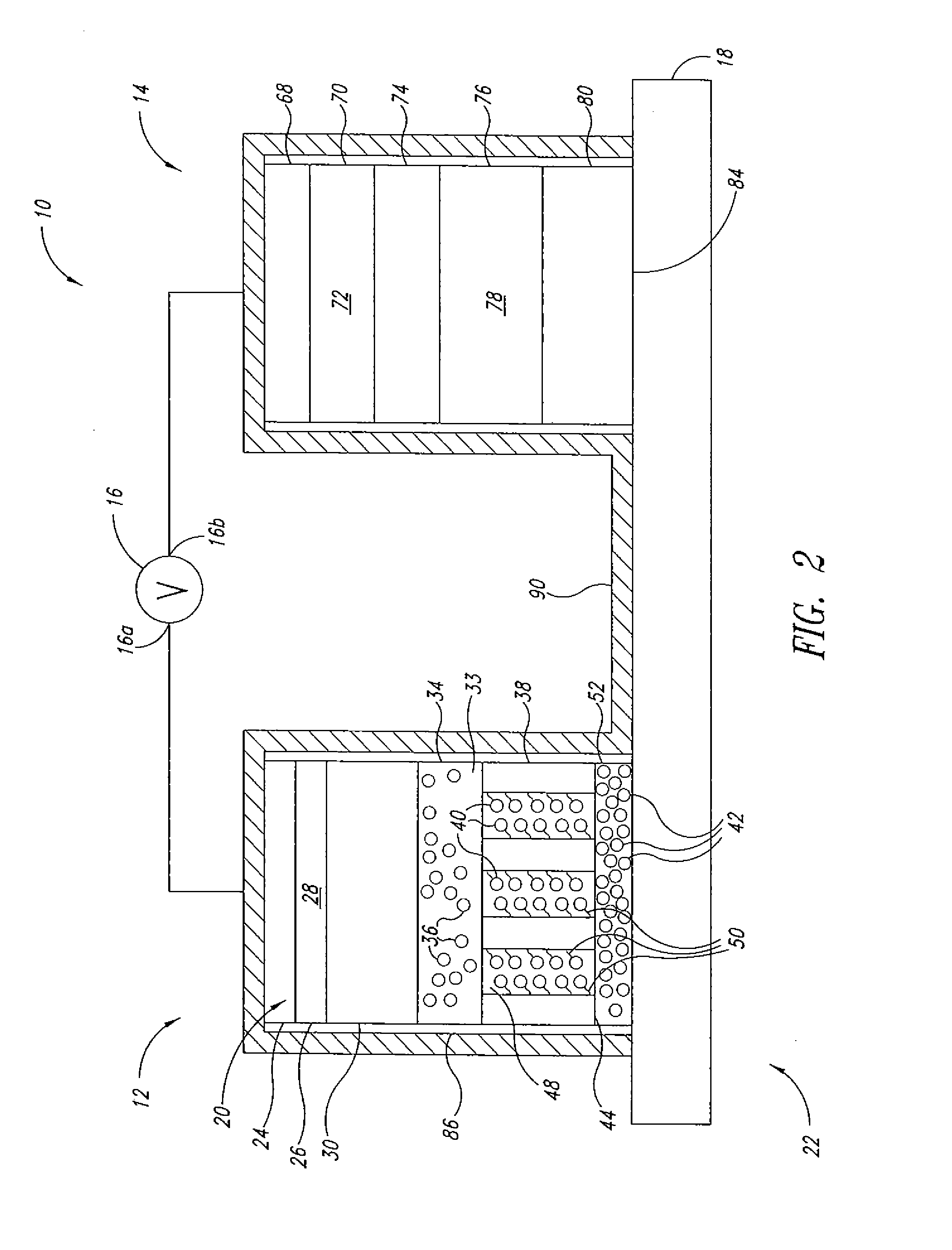
Electrophoretic display device and method for driving the same
An electrophoretic display device includes a pair of substrates arranged with a predetermined gap maintained therebetween, a dispersing fluid disposed between the pair of substrates, a plurality of charged particles mixed in the dispersing fluid, at least a pair of display electrodes arranged on one of the substrates and defining a pixel, and a guard electrode arranged in a border between adjacent pixels. The guard electrode limits the movement of the charged particles to within a single pixel when the guard electrode is biased at a potential higher than (lower than) each of the display electrodes of the two adjacent pixels with the border arranged therebetween if the particles are positively (negatively) charged.
Owner:CANON KK
Nano-coatings for articles
A nano-coating comprises multiple alternating layers of a first layer comprising a first nanoparticle having an aspect ratio greater than or equal to 10 and having a positive or negative charge, and a second layer comprising a second nanoparticle having an aspect ratio greater than or equal to 10 and having a positive or negative charge opposite that of the first nanoparticle, wherein the nano-coating is disposed on a surface of a substrate. An article comprising the nano-coating, and a method of forming the nano-coating, are each disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com