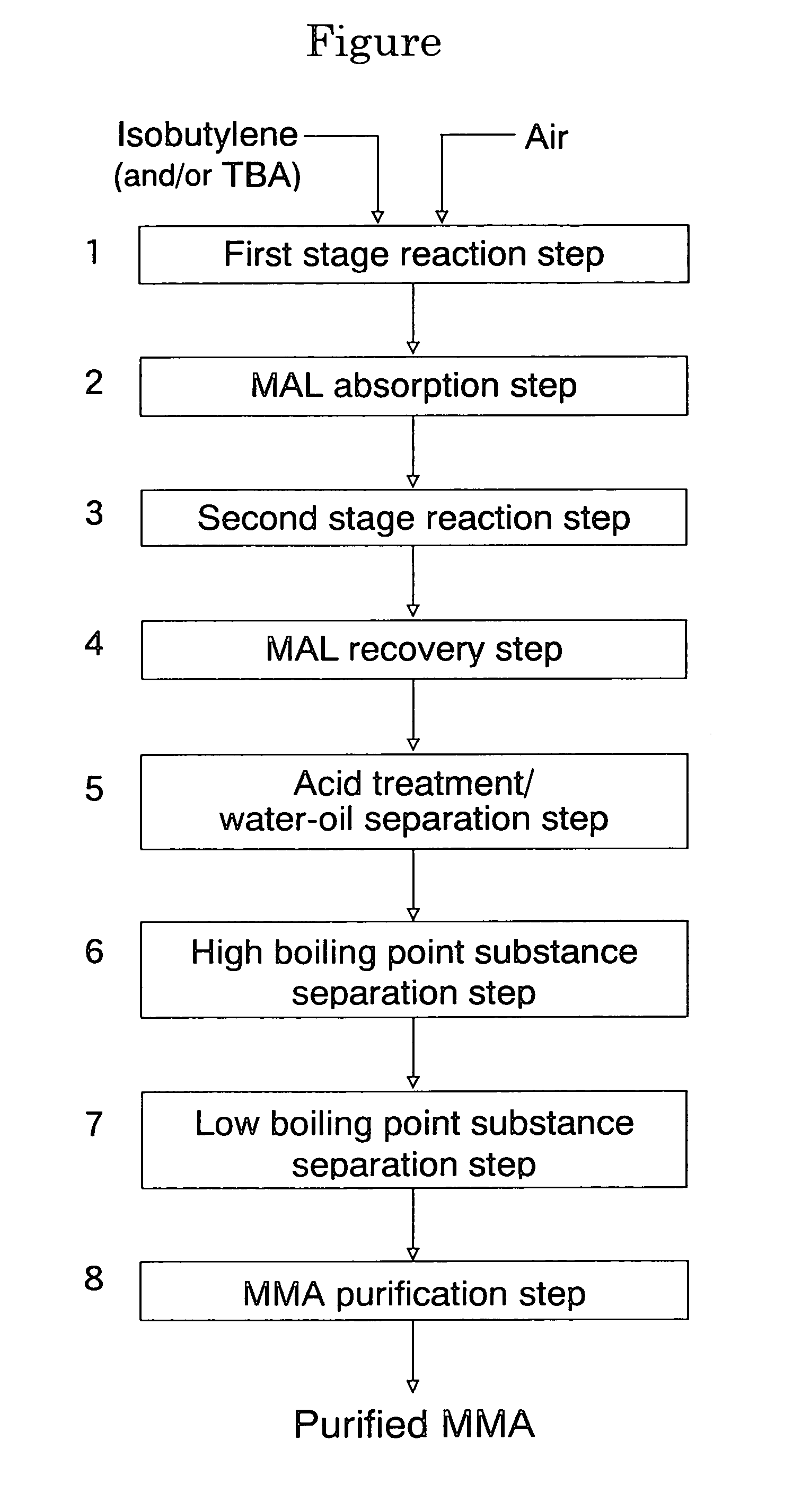
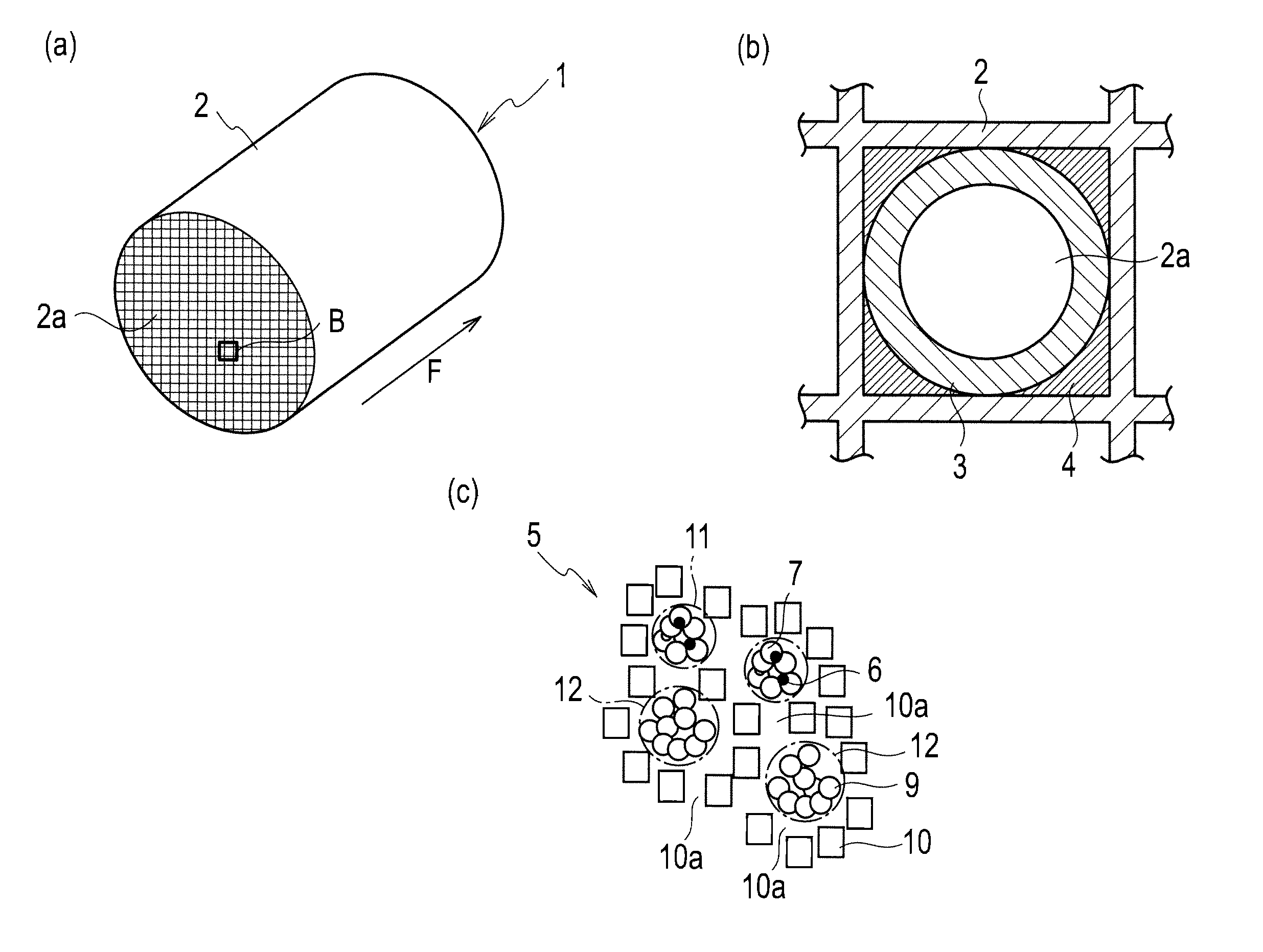
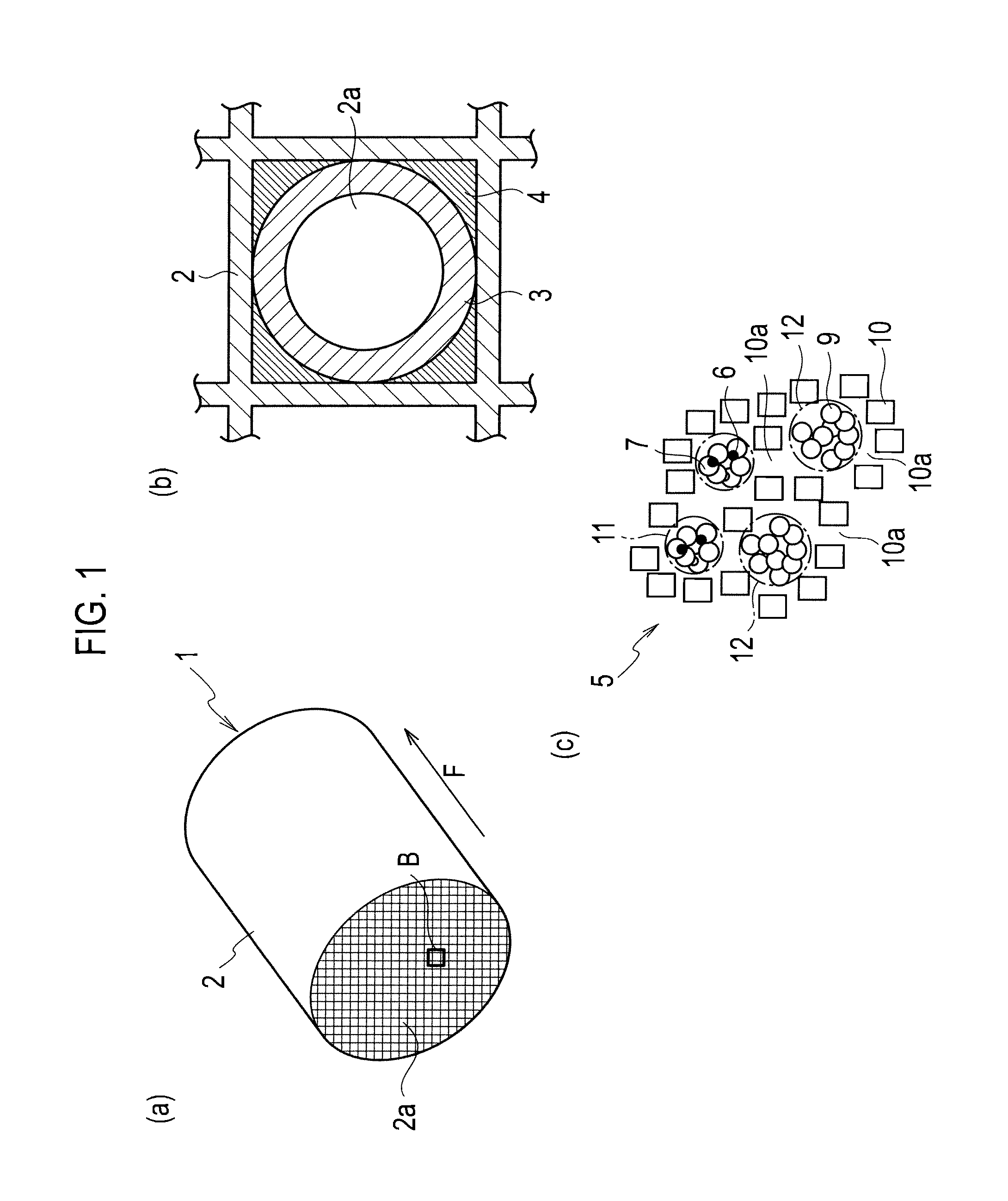
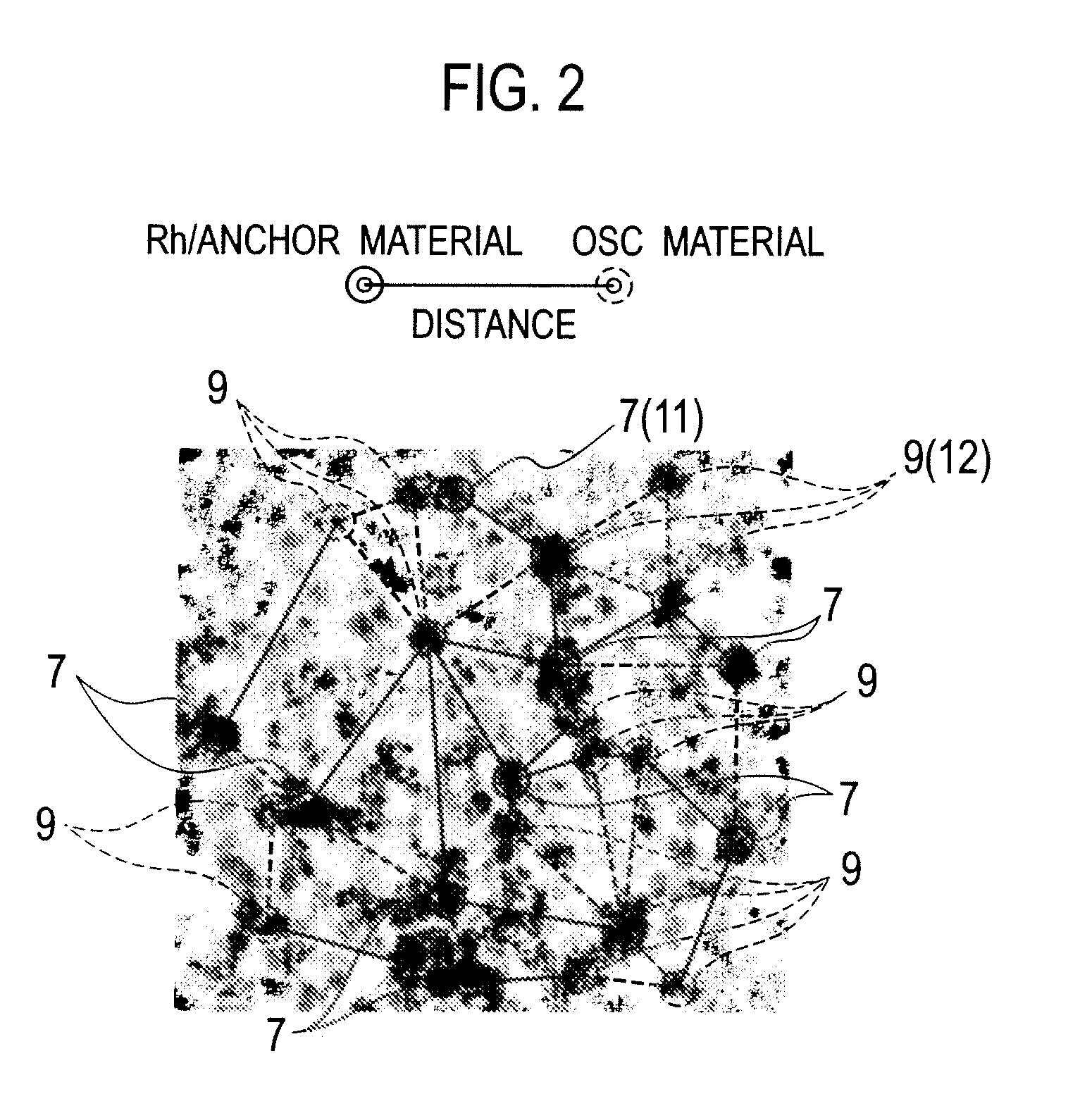
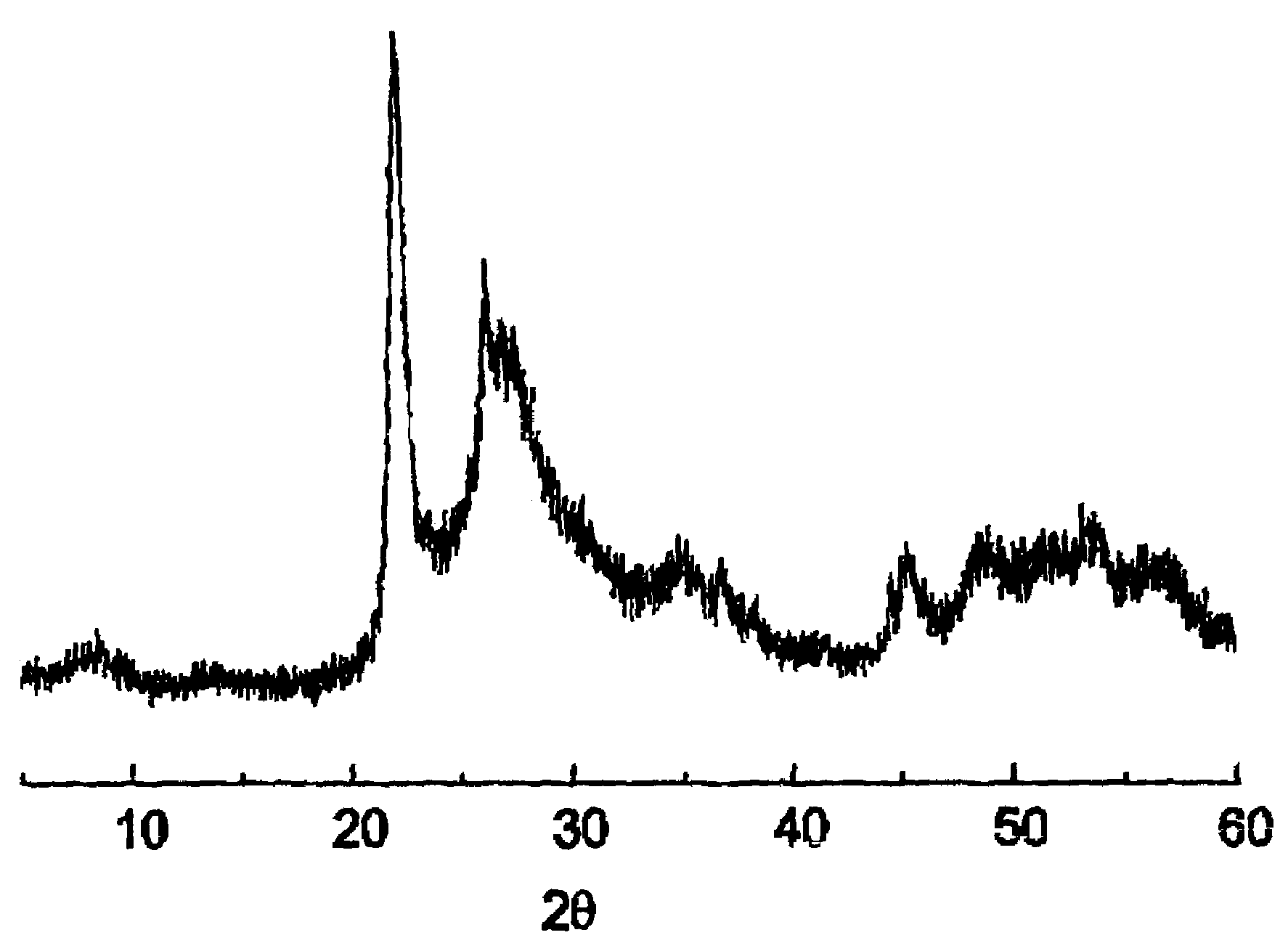
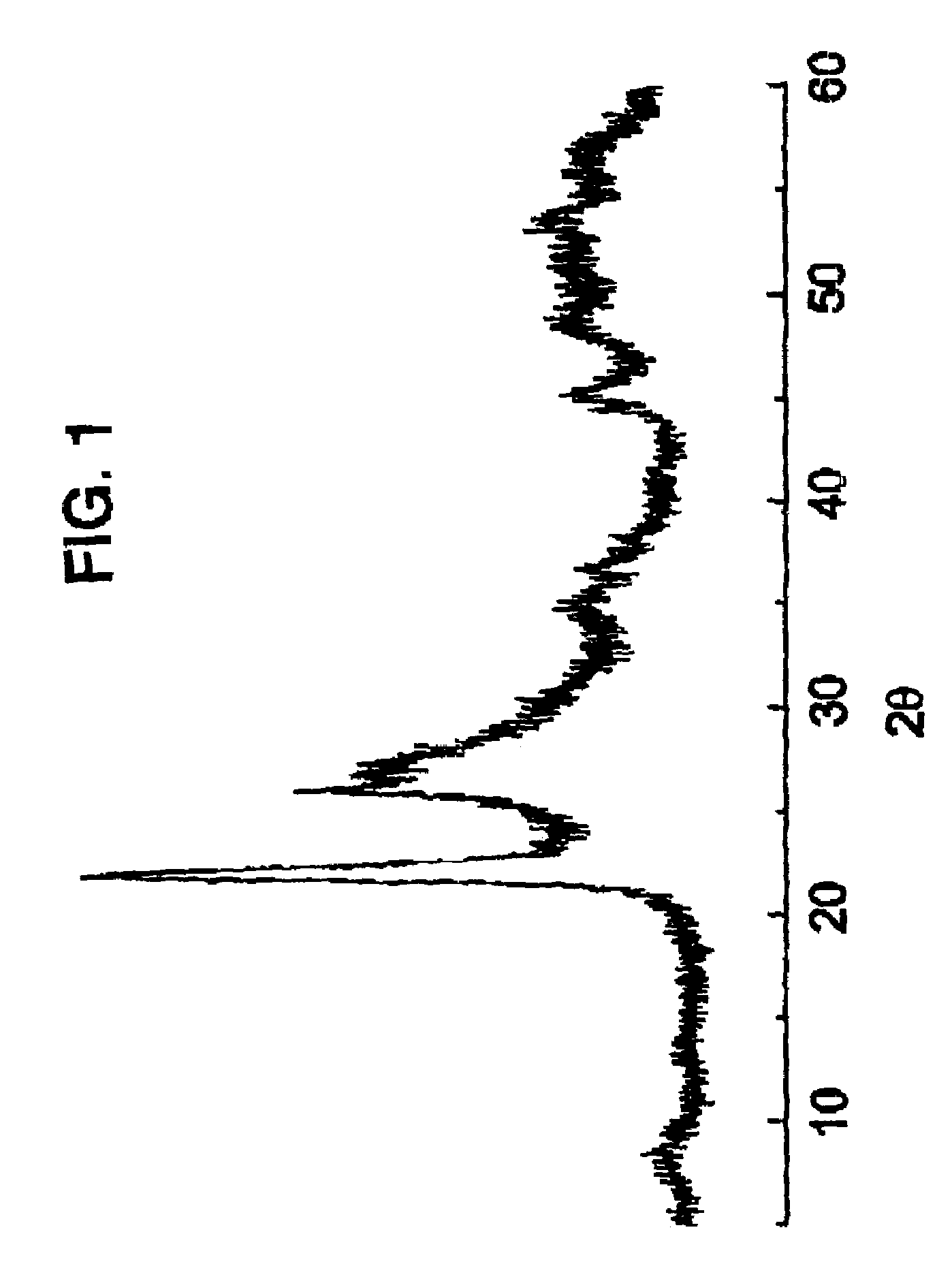
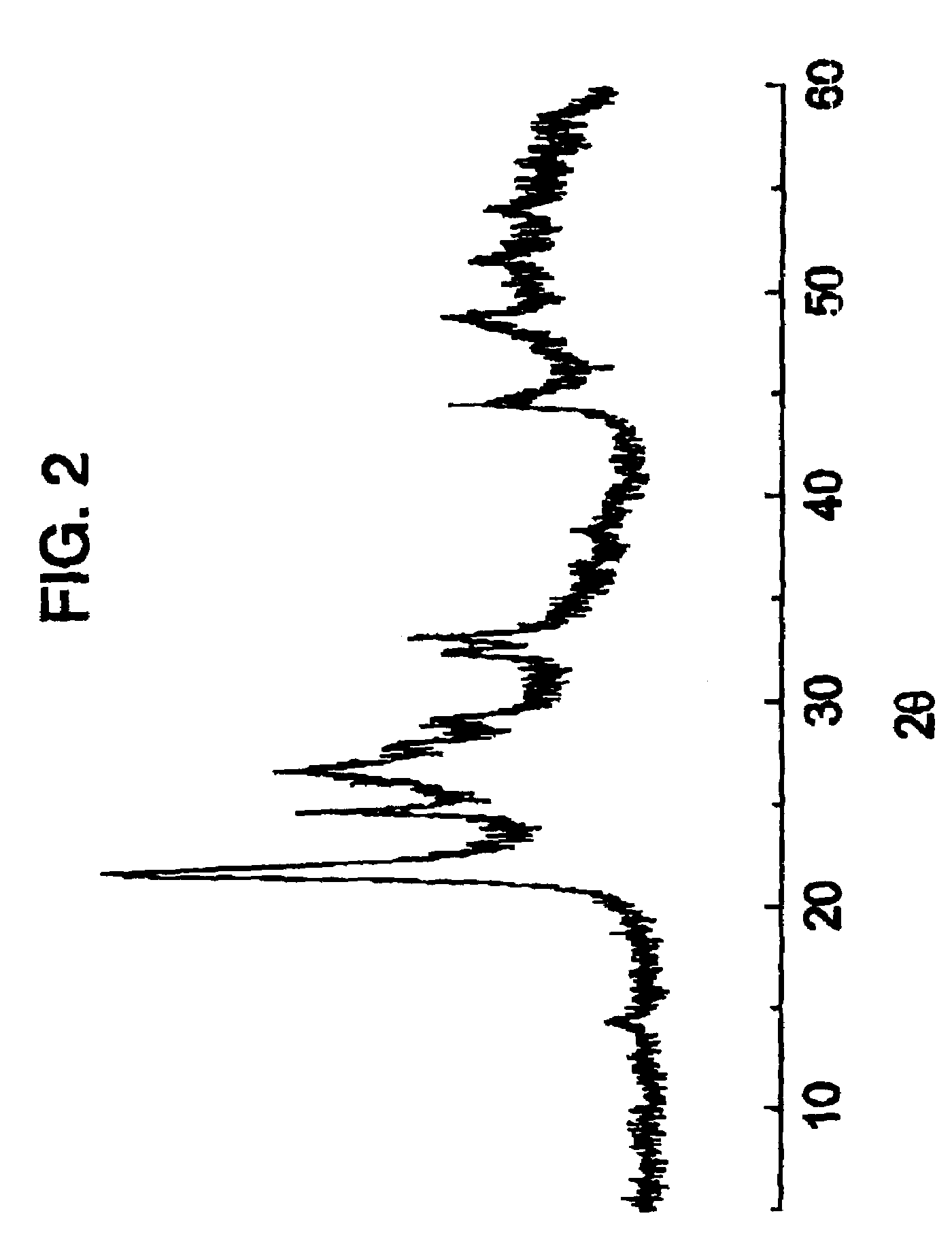
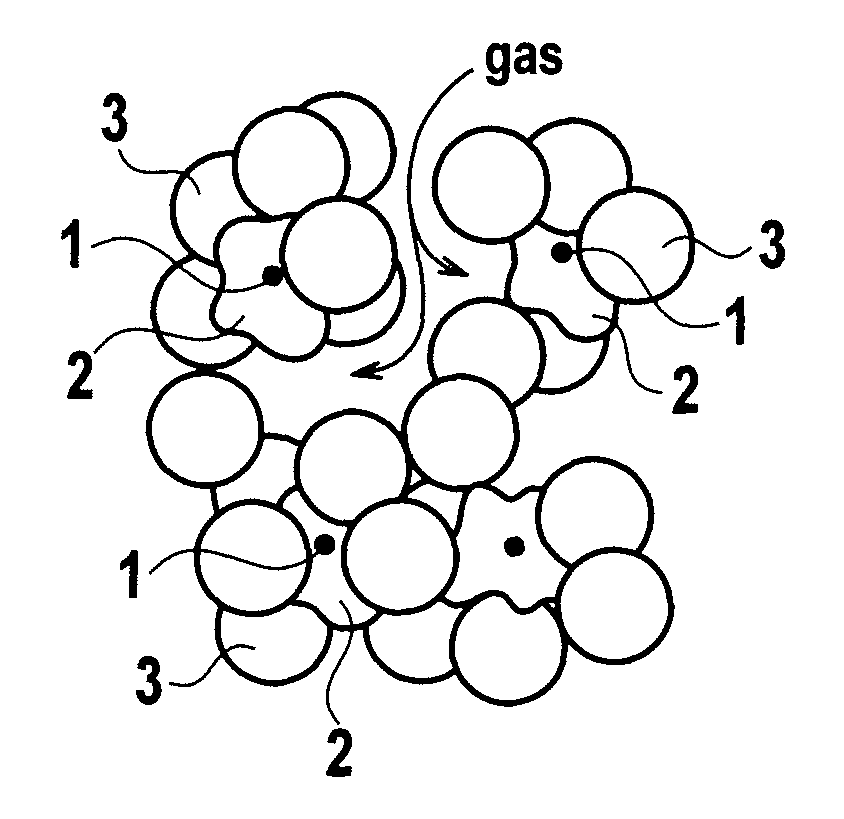
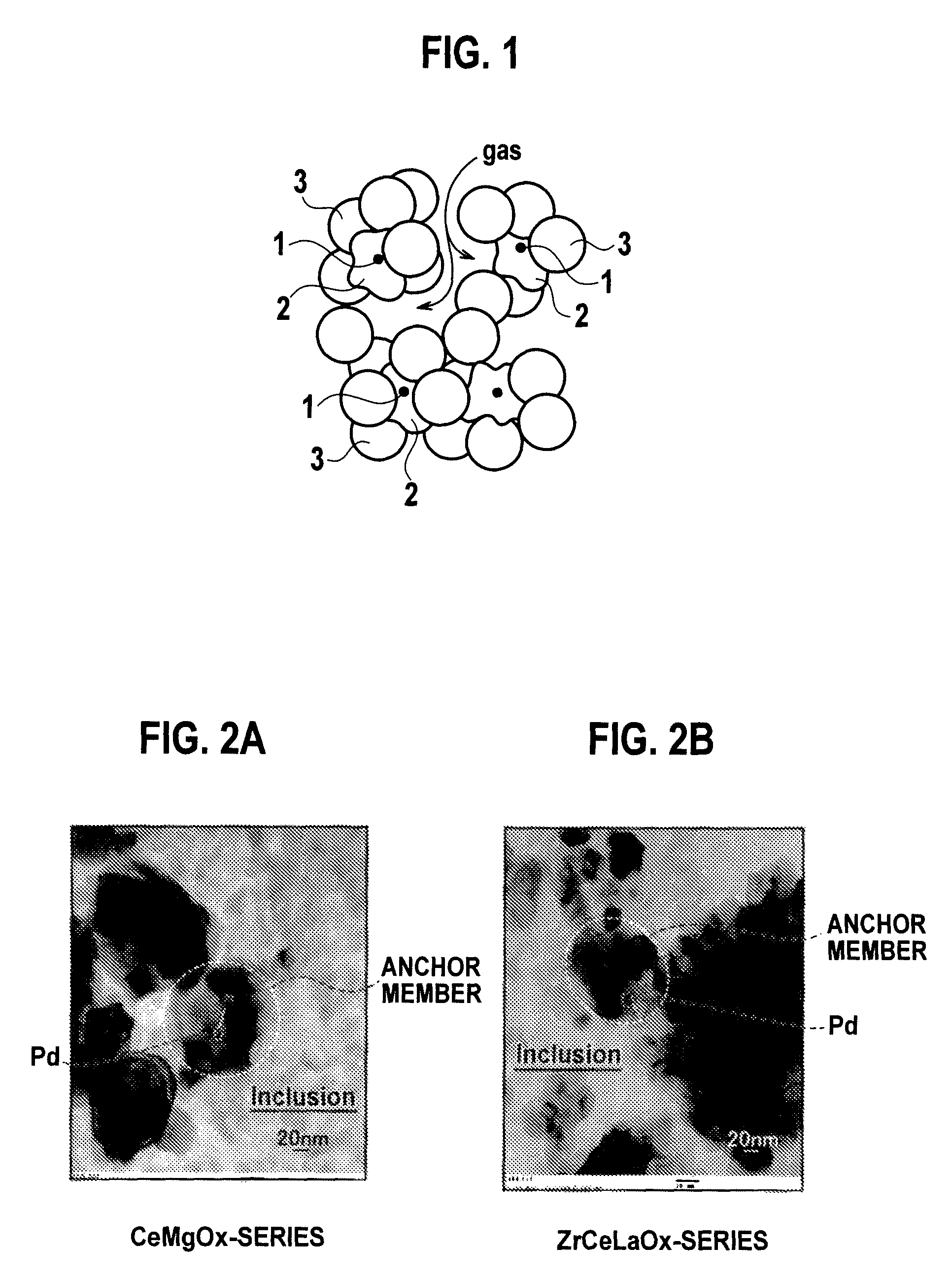
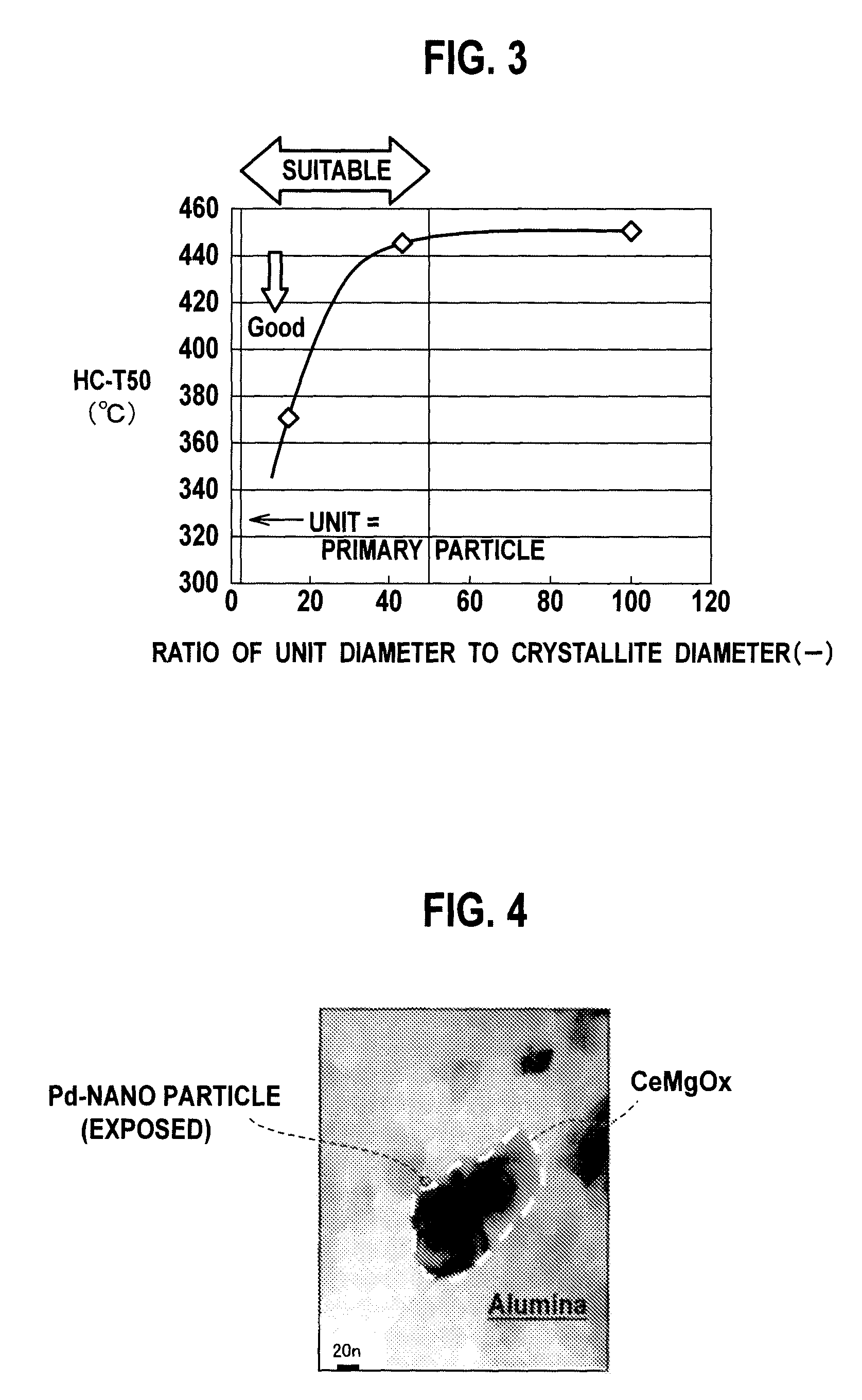
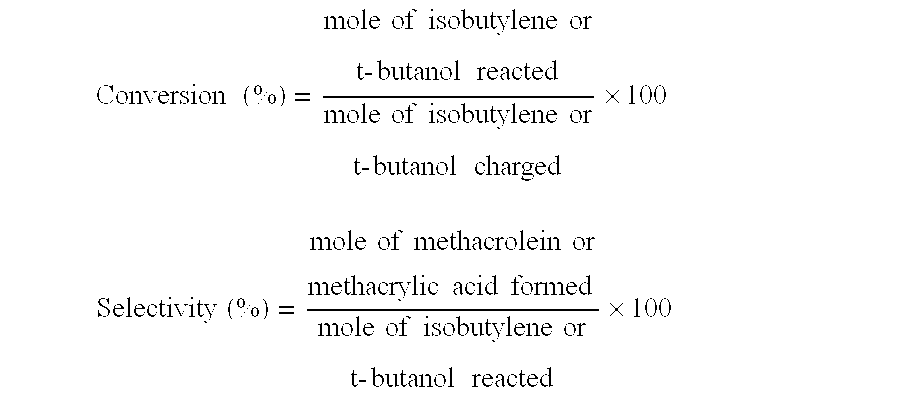Patents
Literature
9932results about "Heterogenous catalyst chemical elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
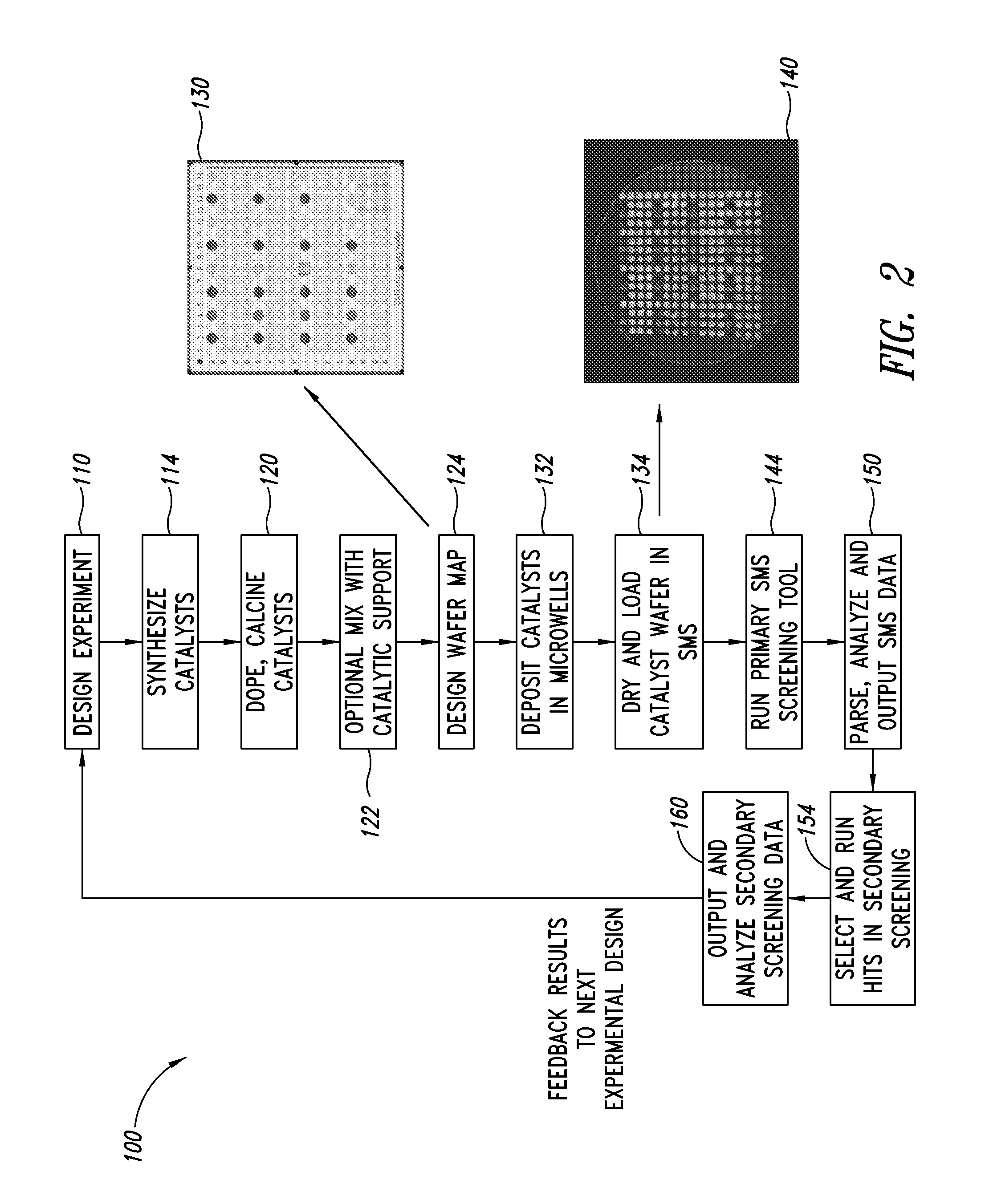
Tunable catalyst gas phase hydrogenation of carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20100121114A1High selectivityExcessive loss of activityOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPlatinumAcetic acid
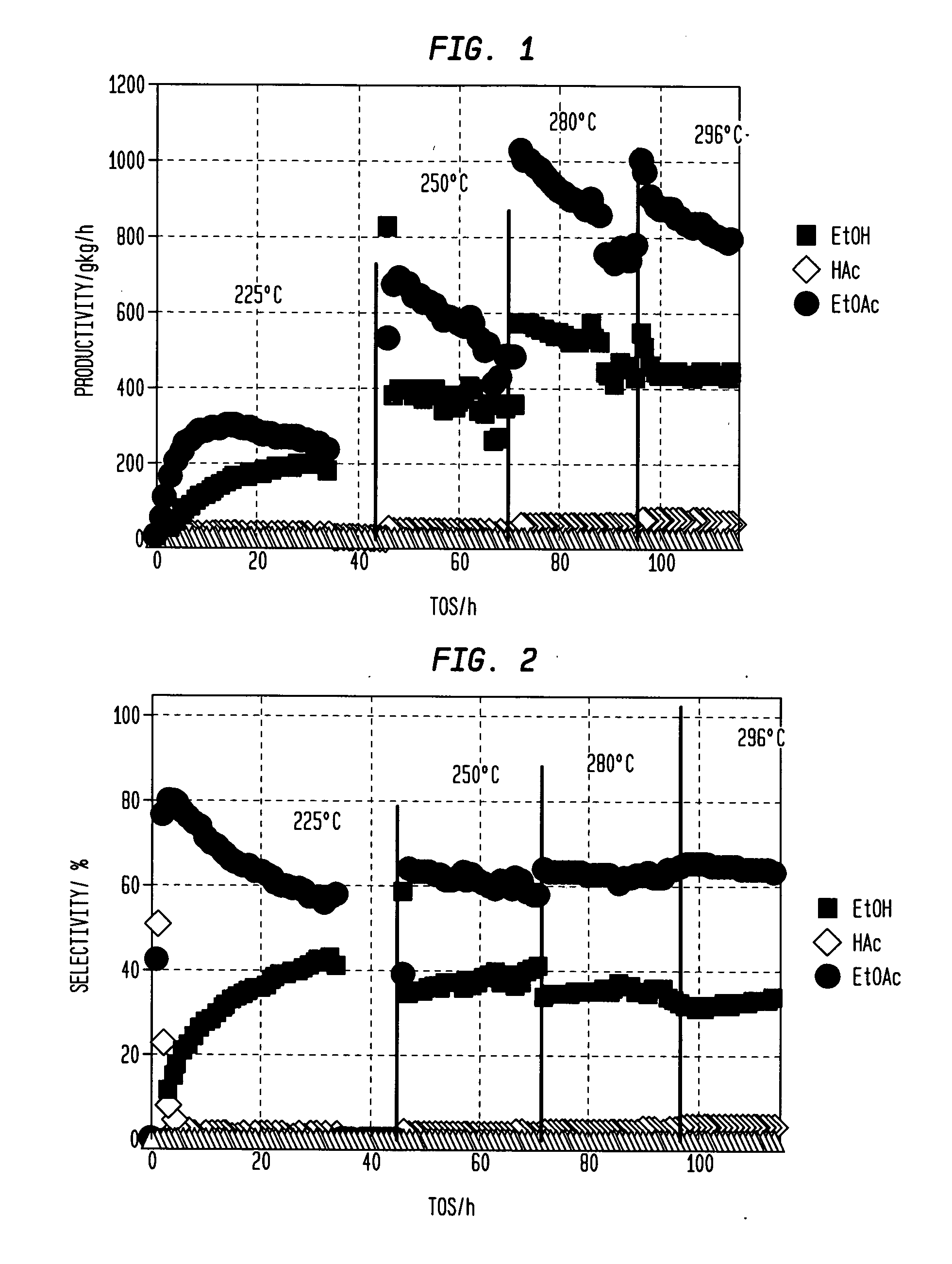
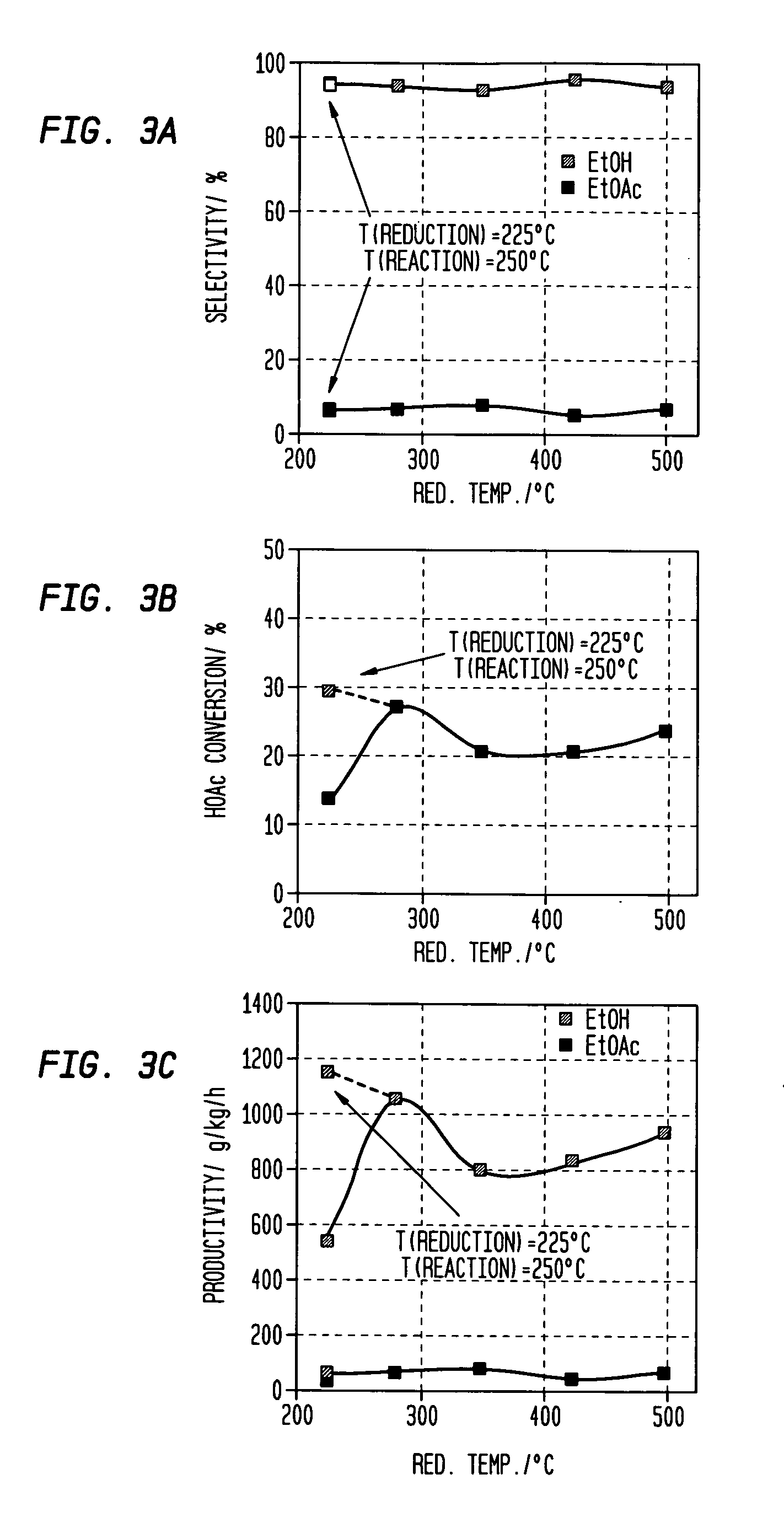
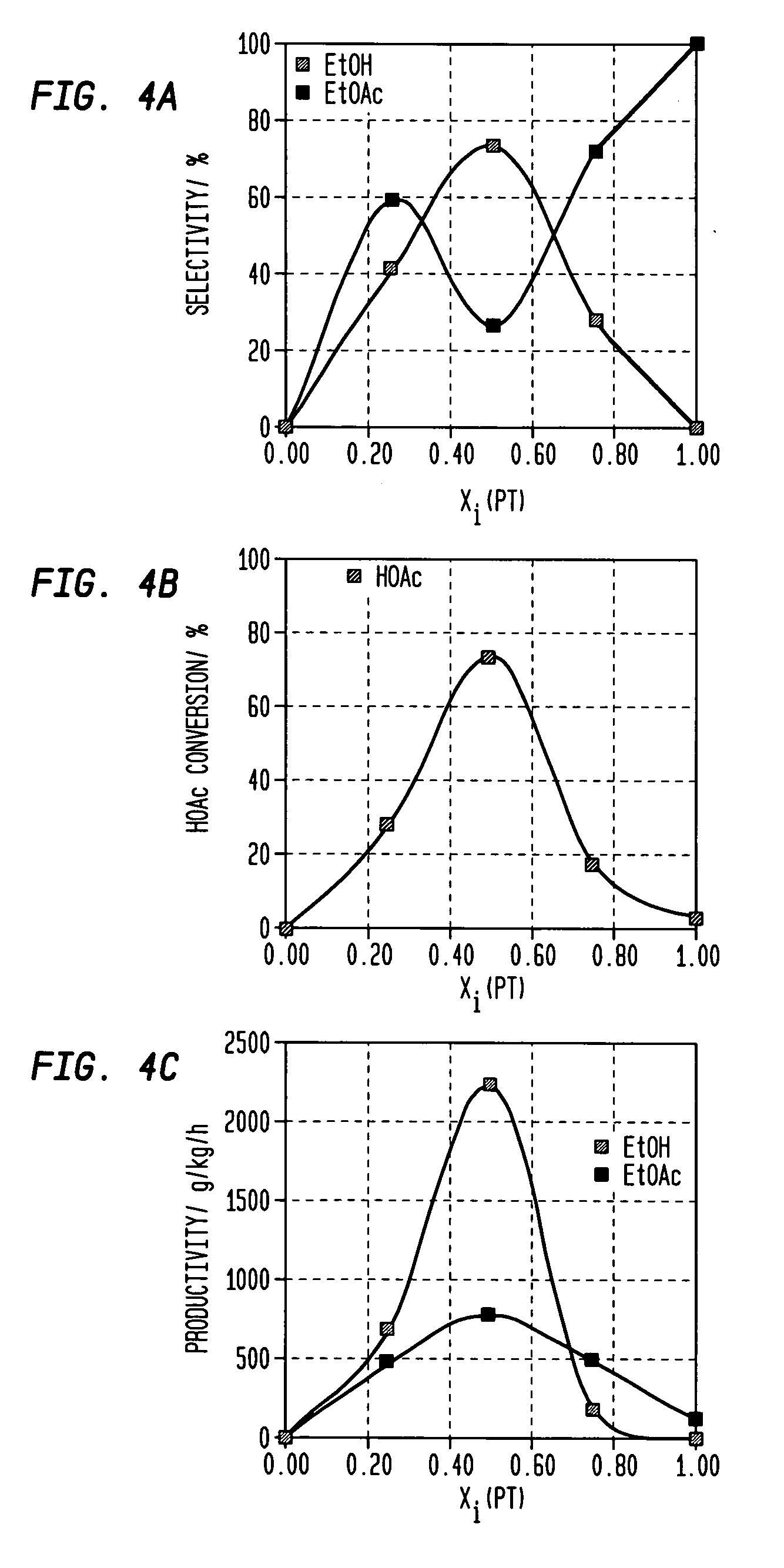
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid includes contacting a feed stream containing acetic acid and hydrogen at an elevated temperature with catalyst comprising platinum and tin on a high surface area silica promoted with calcium metasilicate. Selectivities to ethanol of over 85% are achieved at 280° C. with catalyst life in the hundreds of hours.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
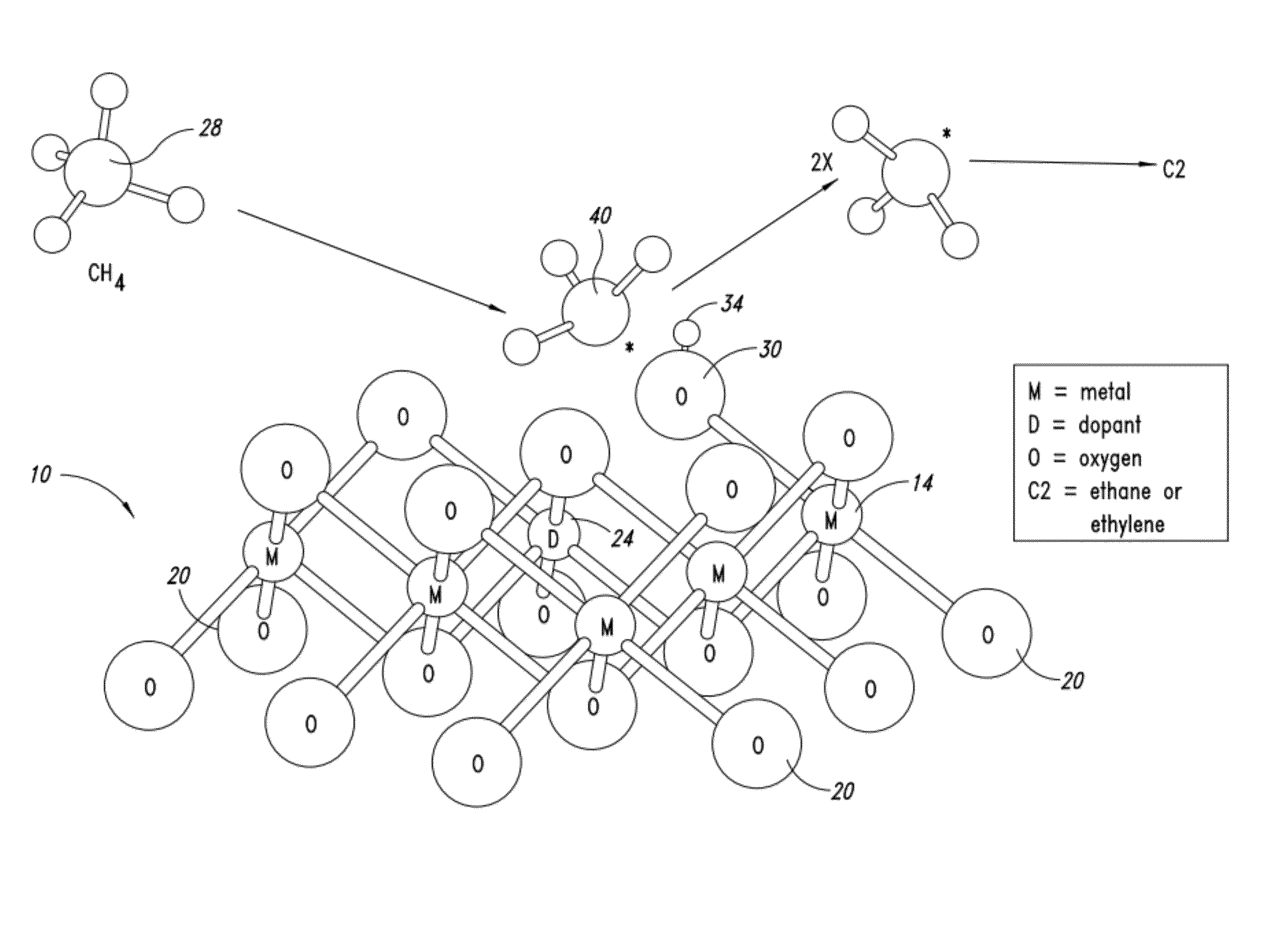
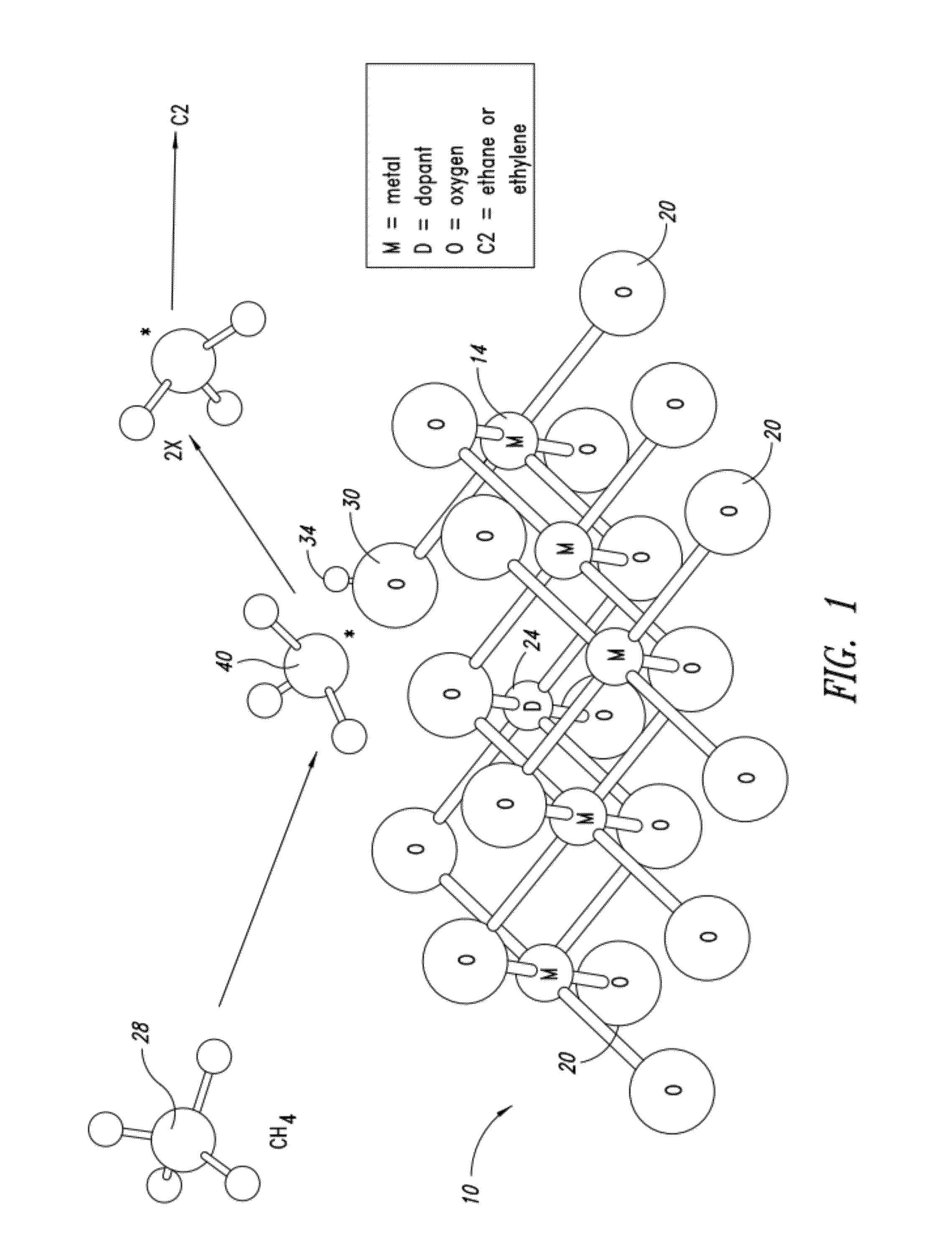
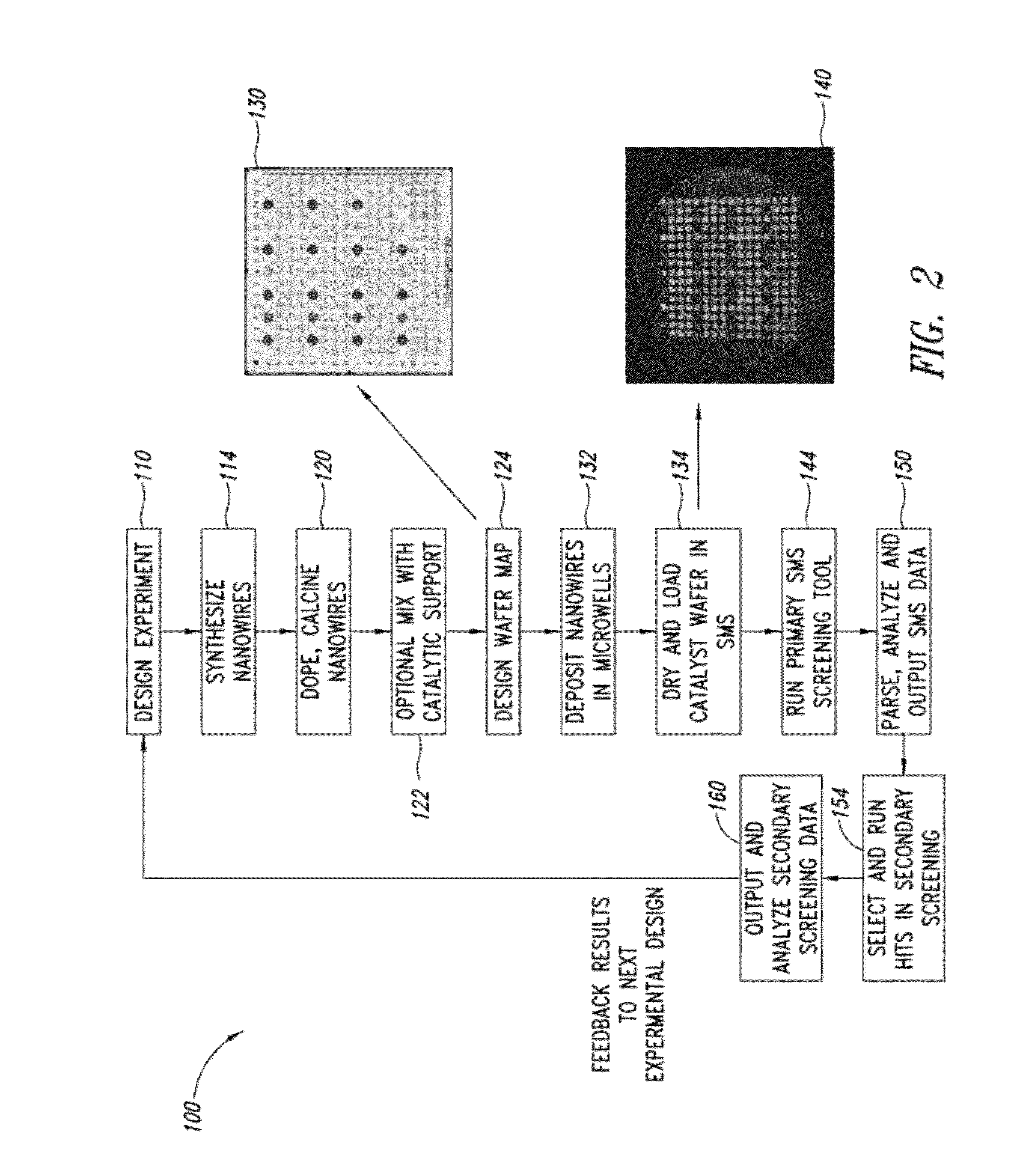
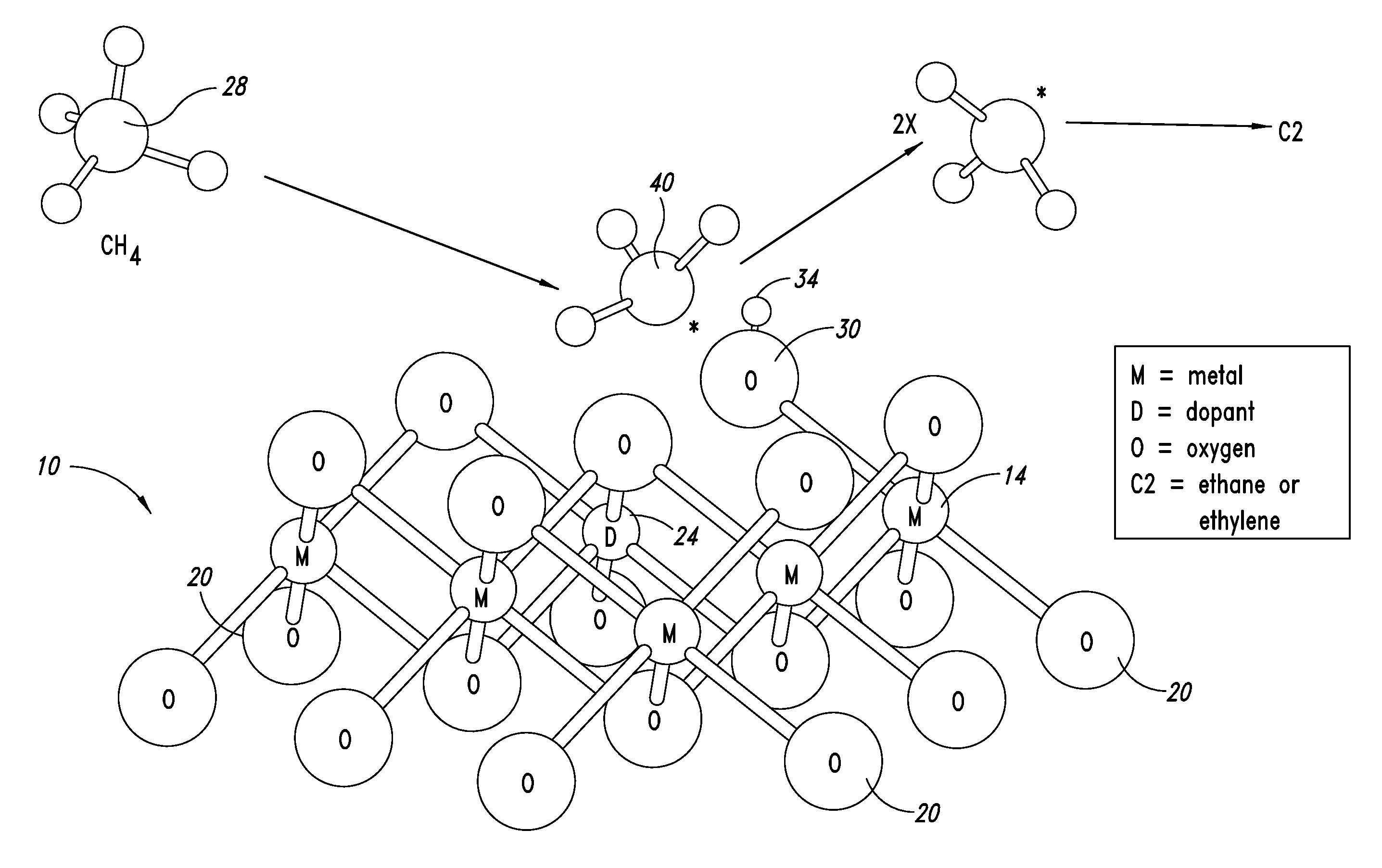
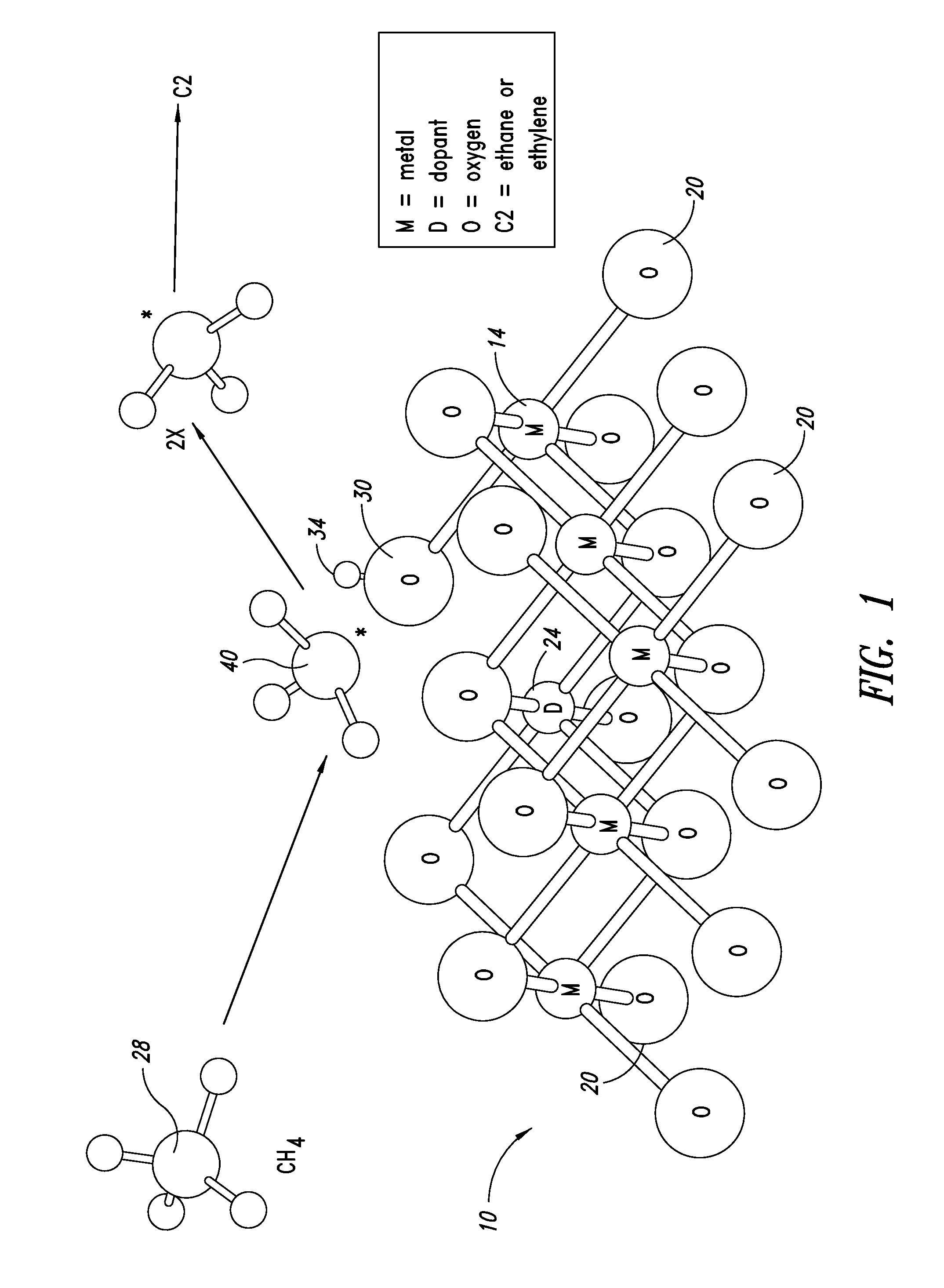
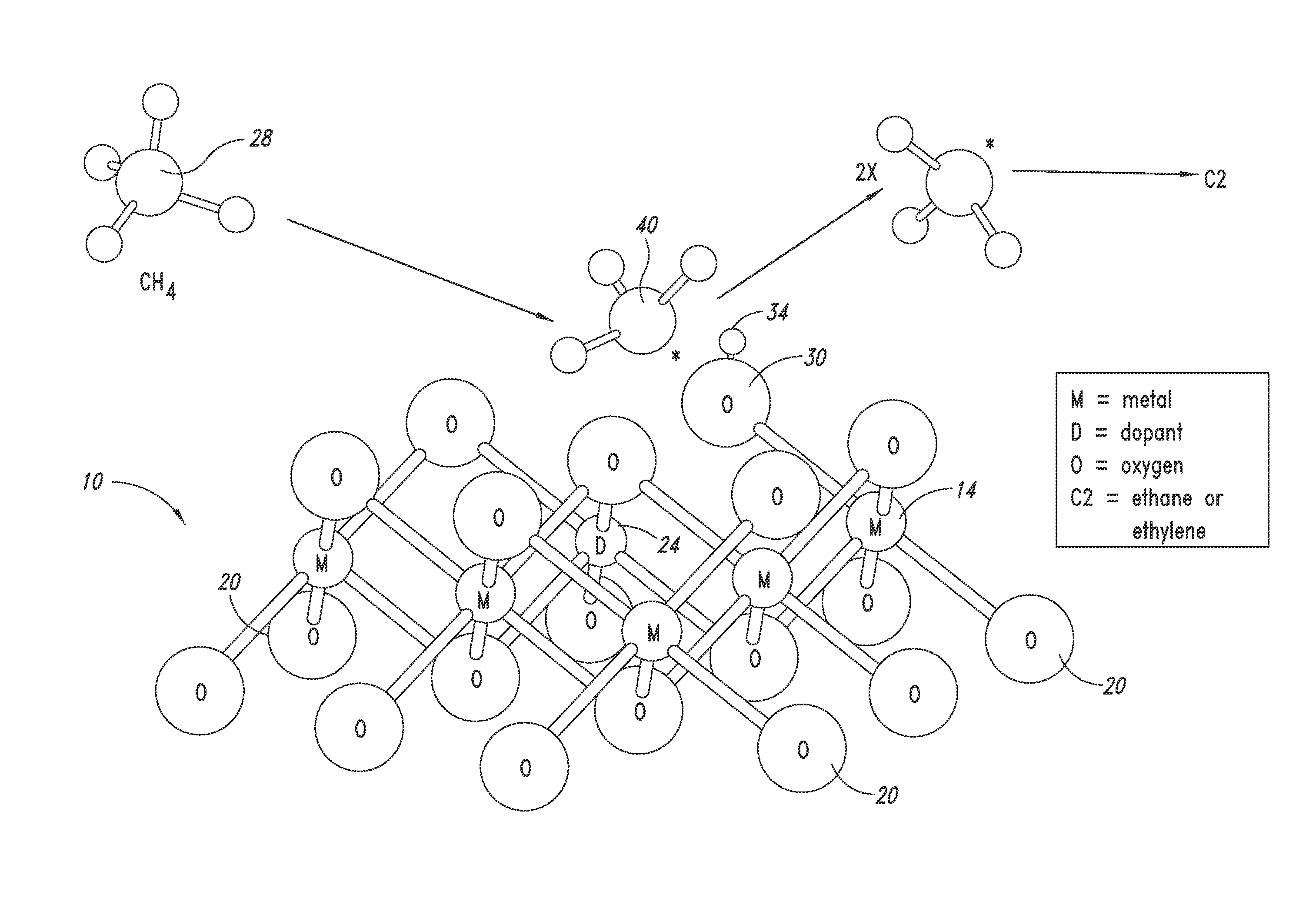
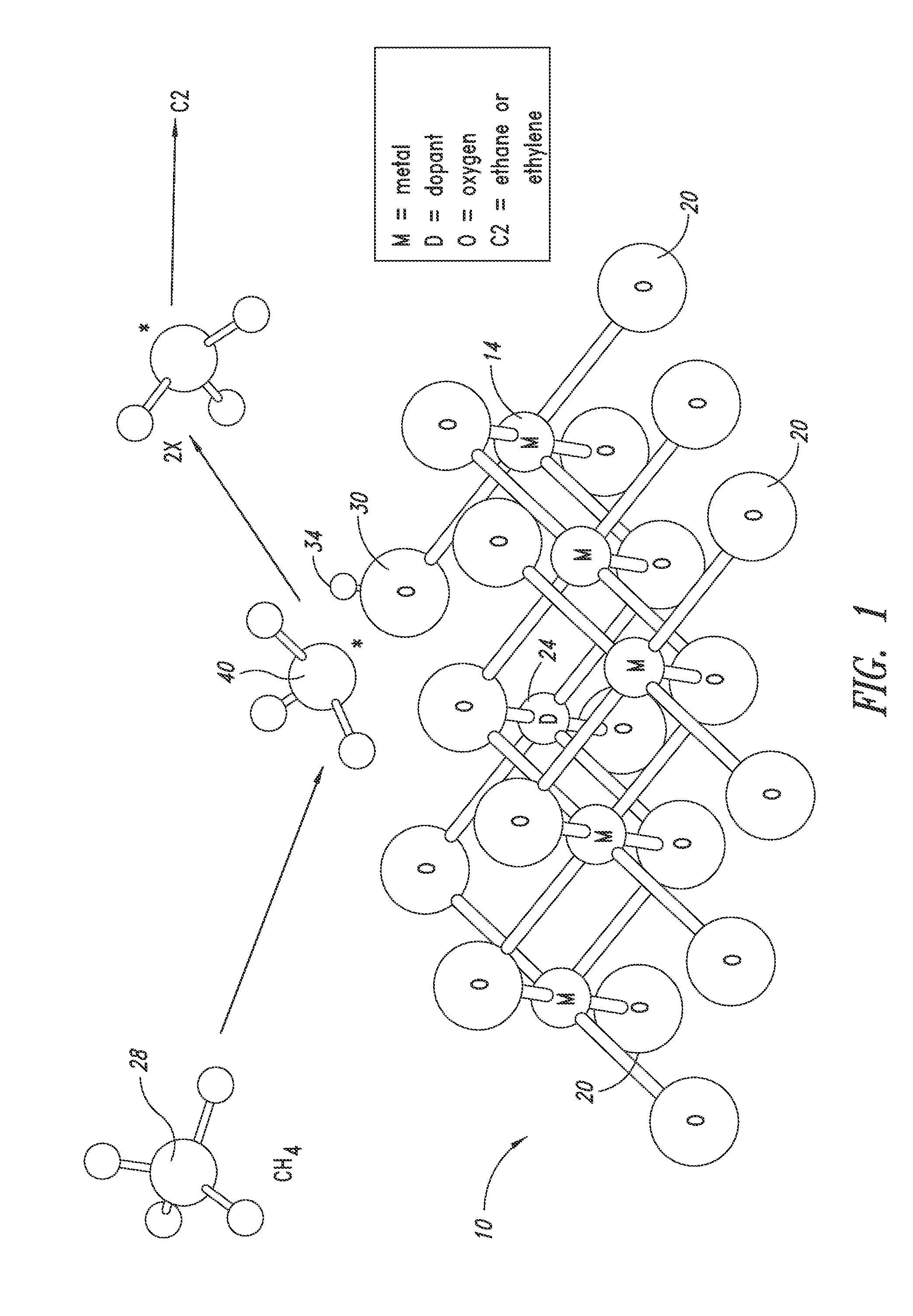
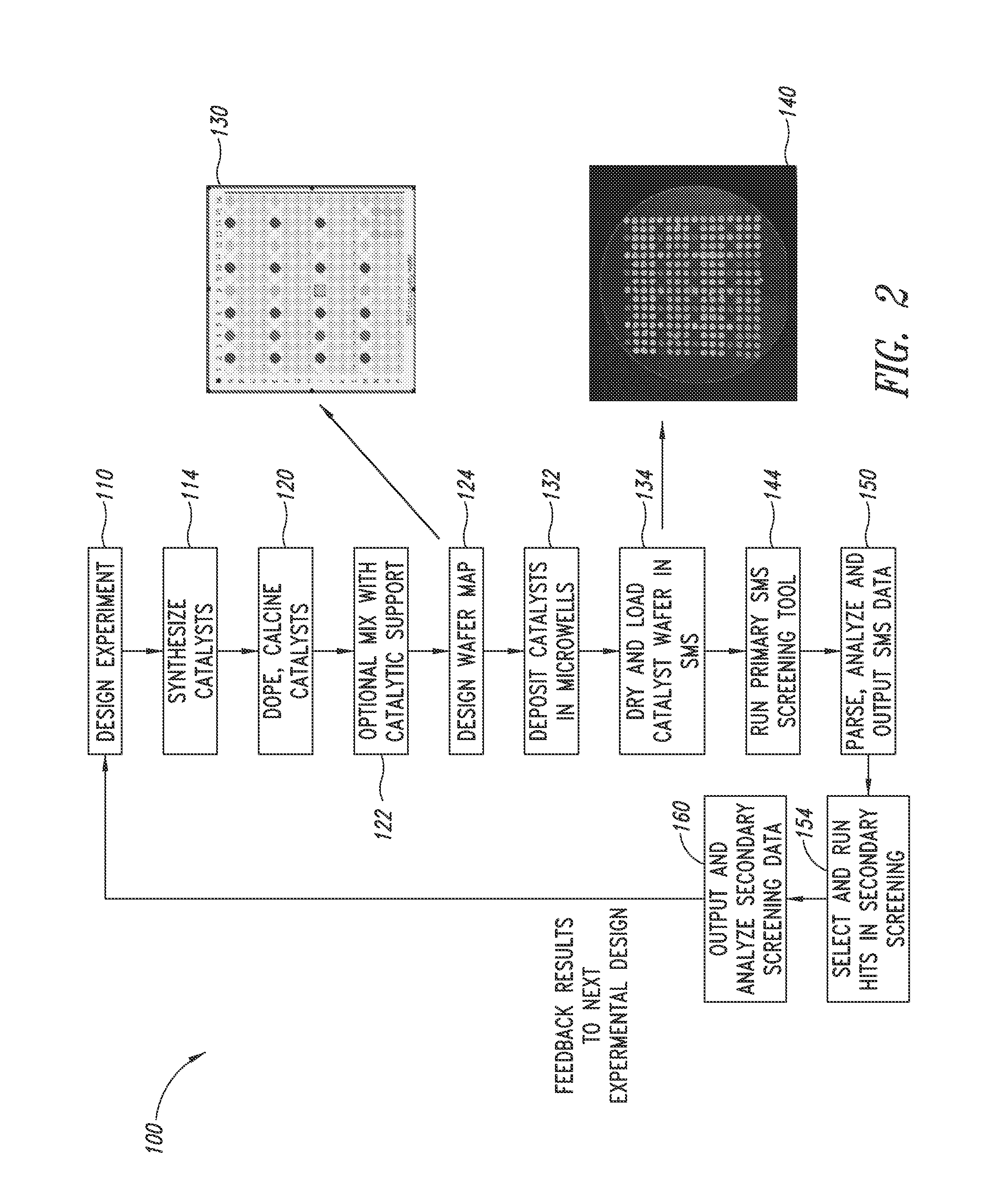
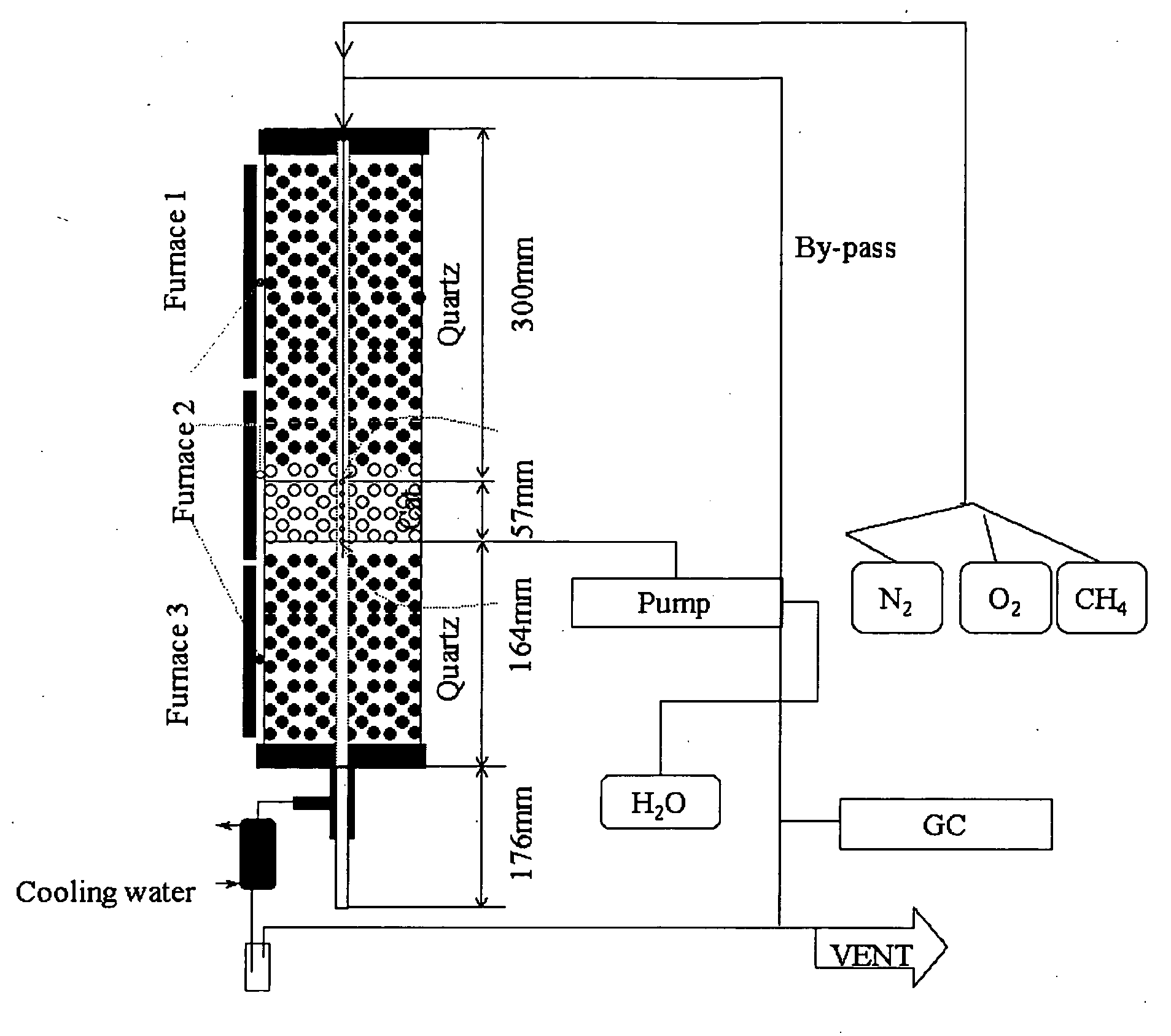
Nanowire catalysts
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Two stage process for hydrodesulfurizing distillates using bulk multimetallic catalyst
InactiveUS6929738B1Preparation by oxo-reaction and reductionOrganic compound preparationLiquid productHydrogen
A two stage hydrodesulfurizing process for producing low sulfur distillates. A distillate boiling range feedstock containing in excess of about 3,000 wppm sulfur is hydrodesulfurized in a first hydrodesulfurizing stage containing one or more reaction zones in the presence of hydrogen and a hydrodesulfurizing catalyst. The liquid product stream thereof is passed to a first separation stage wherein a vapor phase product stream and a liquid product stream are produced. The liquid product stream, which has a substantially lower sulfur and nitrogen content then the original feedstream is passed to a second hydrodesulfurizing stage also containing one or more reaction zones where it is reacted in the presence of hydrogen and a second hydrodesulfurizing catalyst at hydrodesulfurizing conditions. The catalyst in any one or more reaction zones is a bulk multimetallic catalyst comprised of at least one Group VIII non-noble metal and at least two Group VIB metals.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
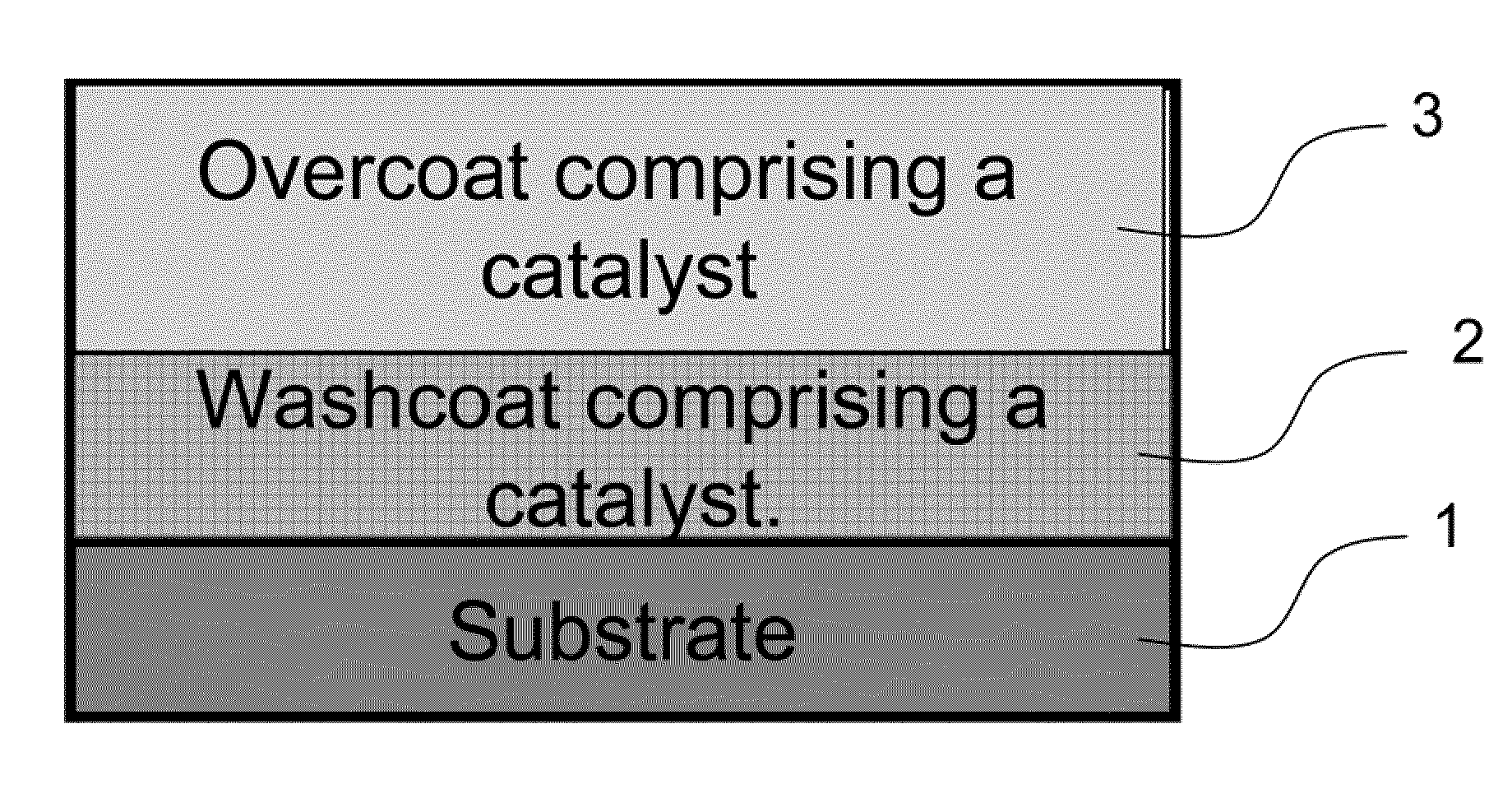
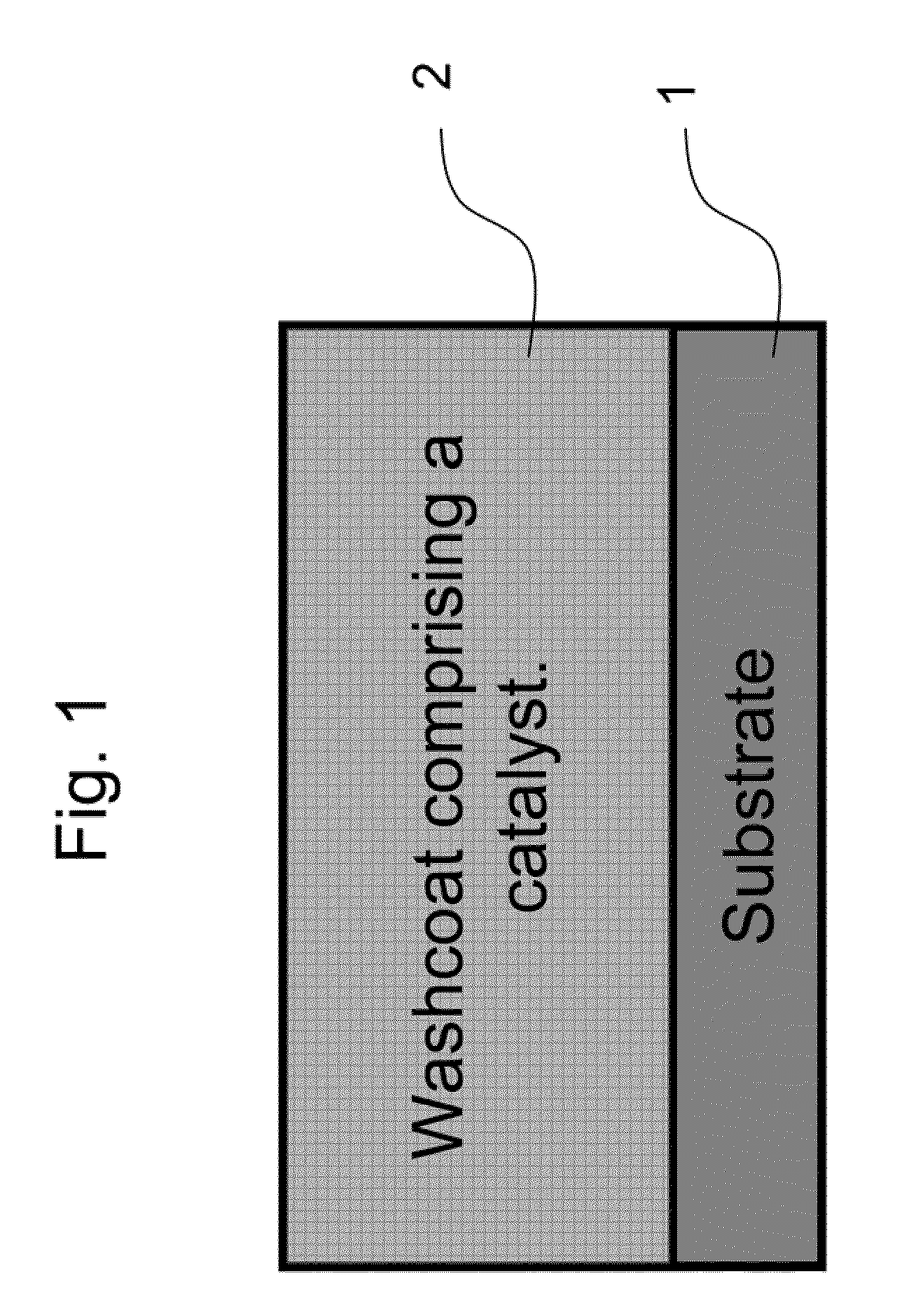
Zero platinum group metal catalysts
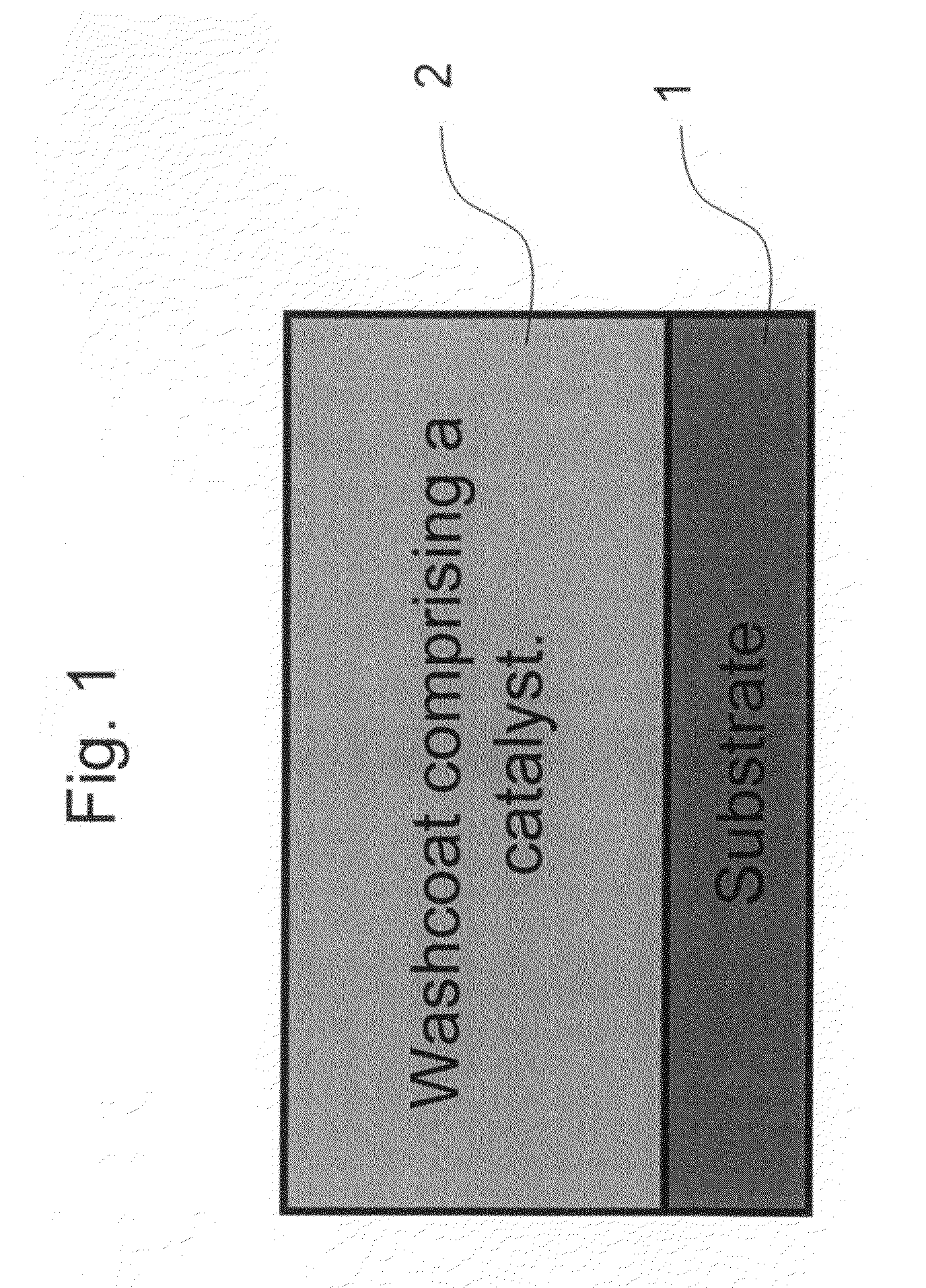
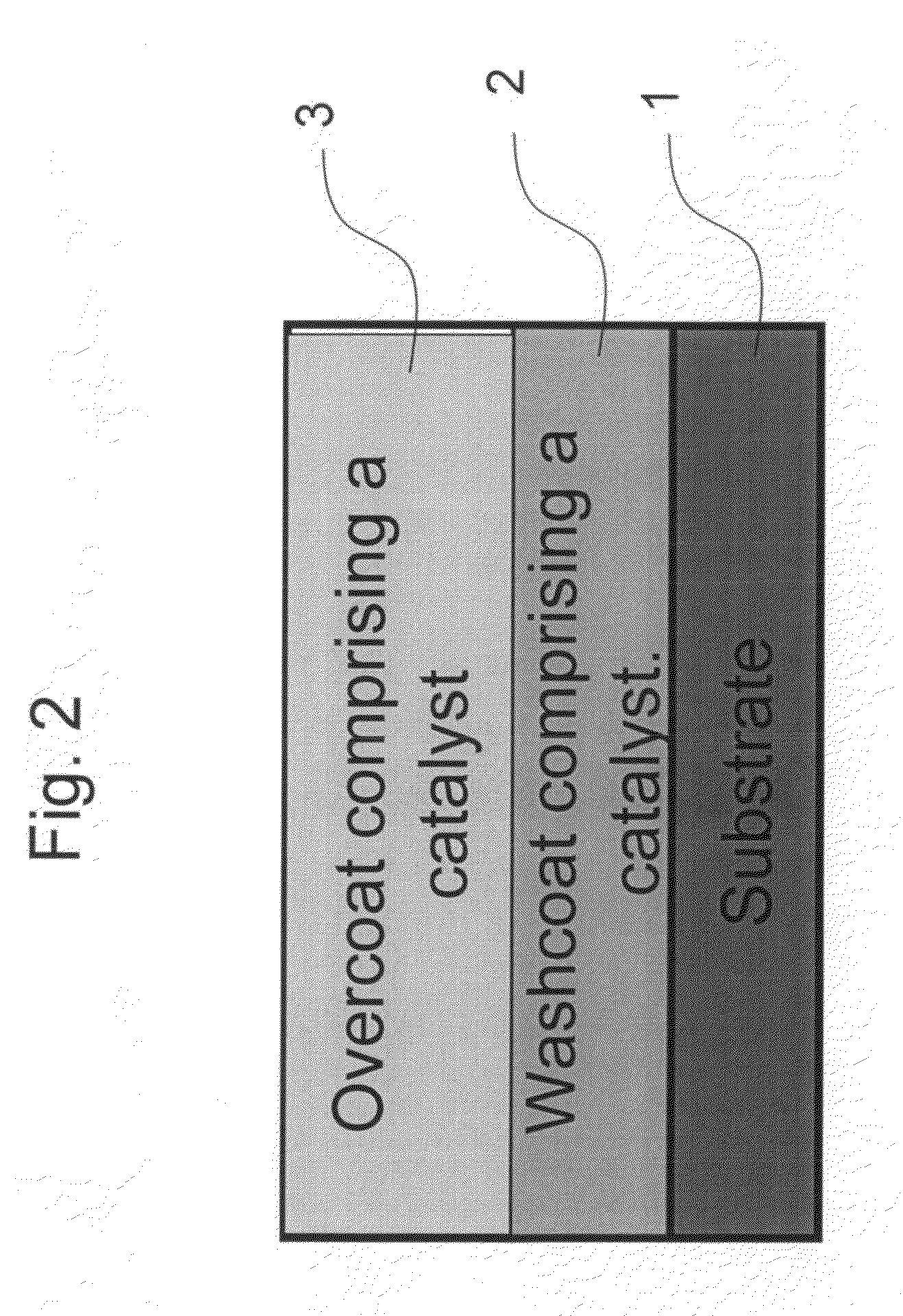
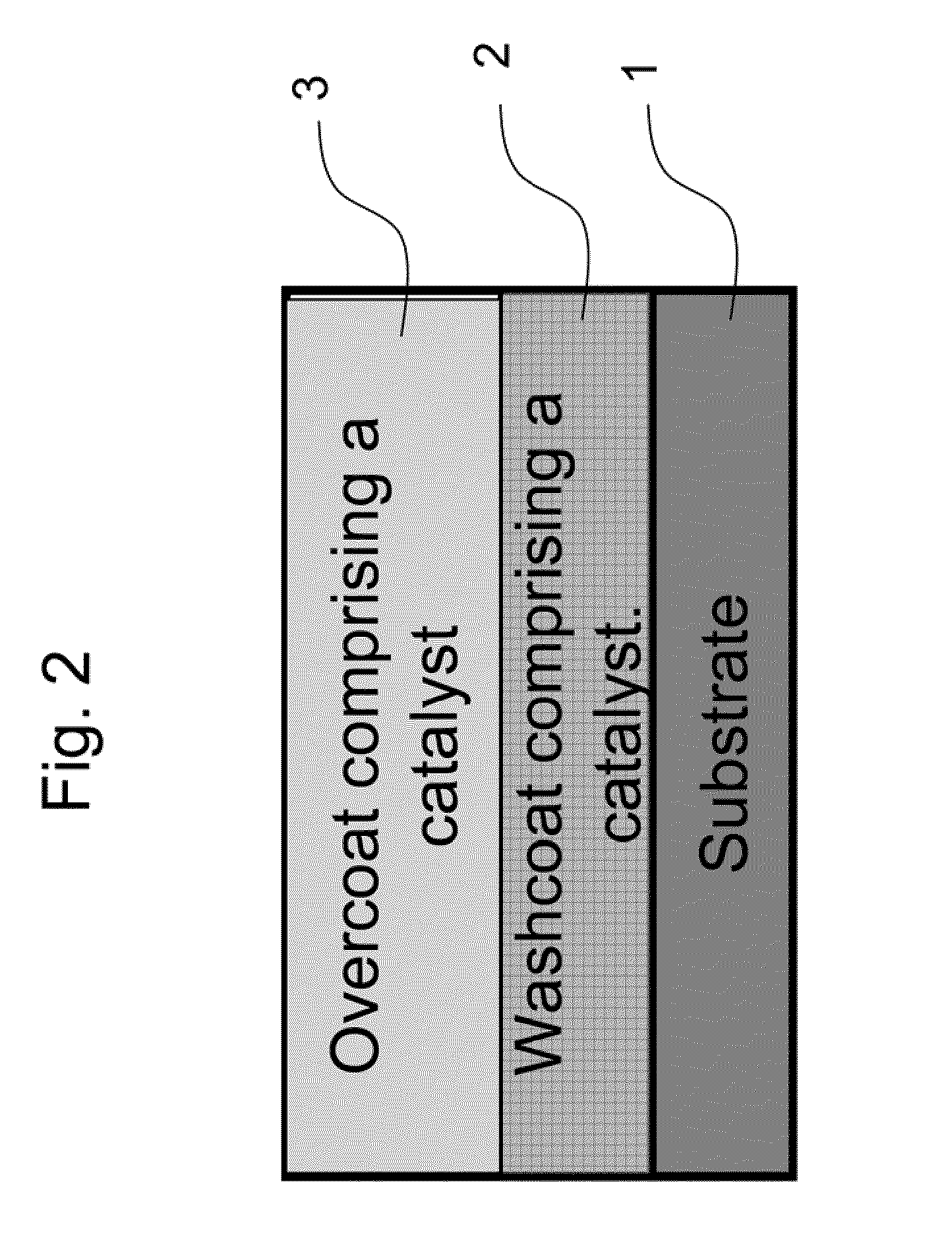
The present invention pertains to catalyst systems for nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon, and sulfur reactions that are free or substantially free of platinum group metals. The catalyst system of the present invention comprise a substrate and a washcoat, wherein the washcoat comprises at least one oxide solid, wherein the oxide solid comprises one or more selected from the group consisting of a carrier material oxide, a catalyst, and mixtures thereof. The catalyst system may optionally have an overcoat, wherein the overcoat comprises at least one oxide solid, wherein the oxide solid comprises one or more selected from the group consisting of a carrier material oxide, a catalyst, and mixtures thereof. The catalyst comprises one or more selected from the group consisting of a ZPGM transition metal catalyst, a mixed metal oxide catalyst, a zeolite catalysts, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Catalysts for petrochemical catalysis
ActiveUS20130023709A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsManganese oxides/hydroxidesDopantPetrochemical
Metal oxide catalysts comprising various dopants are provided. The catalysts are useful as heterogenous catalysts in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2 hydrocarbons such as ethane and ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
Supported palladium-gold catalysts and preparation of vinyl acetate therewith
InactiveUS20100121100A1High activity selectivityImproves oxygen selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTungsten trioxidePalladium
Disclosed is a catalyst. The catalyst comprises palladium, gold, and a support comprising titanium dioxide and tungsten trioxide. The support preferably comprises from 75 wt % to 99 wt % of titanium dioxide and from 1 wt % to 25 wt % of tungsten trioxide. A method for preparing the catalyst is also disclosed. The method comprises impregnating the support with a palladium compound and a gold compound, calcining the impregnated support, and then reducing the calcined support. Further disclosed is a method for preparing vinyl acetate with the catalyst. The catalyst exhibits improved catalytic activity and selectivity.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ACETYLS
Zero Platinum Group Metal Catalysts
Owner:ECS HLDG +1
Multimetal oxide materials
Owner:BASF SE
Inorganic dopants, inks and related nanotechnology
InactiveUS6849109B2Facilitated DiffusionLower transition temperatureSelenium/tellurium compundsCell electrodesIndiumCerium
Ink compositions with modified properties result from using a powder size below 100 nanometers. Colored inks are illustrated. Nanoscale coated, uncoated, whisker inorganic fillers are included. The pigment nanopowders taught comprise one or more elements from the group actinium, aluminum, antimony, arsenic, barium, beryllium, bismuth, cadmuim, calcium, cerium, cesium, chalcogenide, cobalt, copper, dysprosium, erbium, europium, gadolinium, gallium, gold, hafnium, hydrogen, indium, iridium, iron, lanthanum, lithium, magnesium, manganese, mendelevium, mercury, molybdenum, neodymium, neptunium, nickel, niobium, nitrogen, oxygen, osmium, palladium, platinum, potassium, praseodymium, promethium, protactinium, rhenium, rubidium, scandium, silver, sodium, strontium, tantalum, terbium, thallium, thorium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Porous sintered body, method of manufacturing porous sintered body, and method of manufacturing exhaust gas purifying apparatus
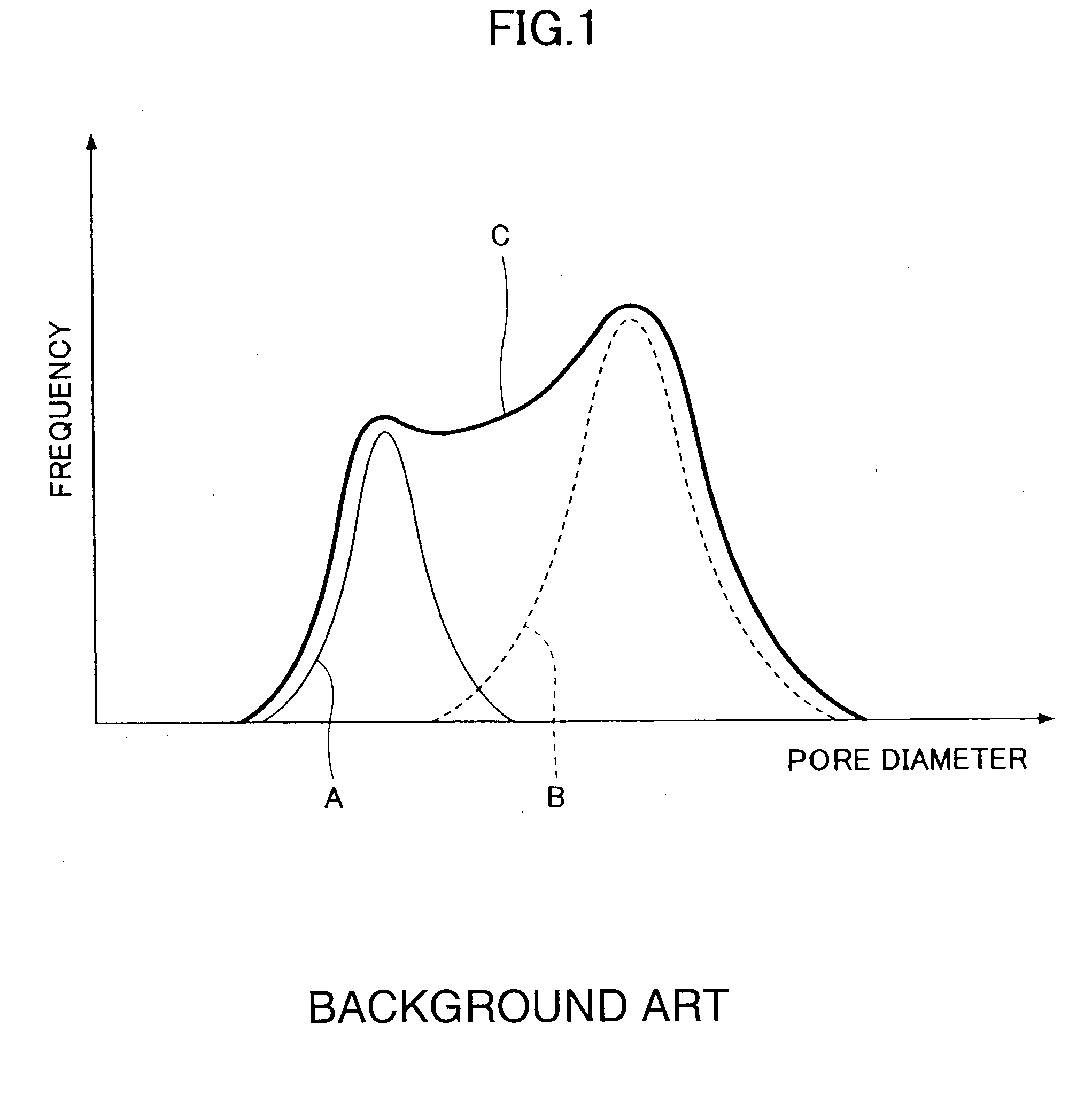
A method of manufacturing a porous sintered body includes mixing at least two groups of silicon carbide particles and a pore forming material having an average particle diameter Y μm to obtain a molding material. The at least two groups of silicon carbide particles have different average particle diameters and have a first group of silicon carbide particles whose blending quantity by weight in the molding material is greatest among the at least two groups of silicon carbide particles. The first group have an average particle diameter X μm. The relationships 15≦X, 0.5·X≦Z≦0.9·X, and 0.8·Z≦Y≦1.8·Z are satisfied, wherein Z μm is an average pore diameter of the porous sintered body no less than 10 μm and no greater than 20 μm.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
Oxide catalyst composition
InactiveUS7012039B2High selectivityLow selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationLanthanideMethacrolein
An oxide catalyst composition for use in producing methacrolein or a mixture of methacrolein and methacrylic acid, wherein the oxide catalyst composition is represented by the formula (Mo+W)l2BiaAbBcFedXeSbfOg, wherein: A is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Y and the elements of the lanthanoid series exclusive of Pm; B is at least one member selected from the group consisting of K, Rb and Cs; X is Co solely, or a mixture of Co and at least one member selected from the group consisting of Mg and Ni; and a, b, c, d, e, f and g are, respectively, the atomic ratios of Bi, A, B, Fe, X, Sb and O, relative to twelve atoms of the total of Mo and W, wherein the atomic ratios (a to f) of the elements and the relationship between the amounts of the elements are chosen so as to satisfy specific requirements.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Exhaust gas purifying catalyst and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8486853B2Increased durabilityImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesOther chemical processesExhaust fumesExhaust gas
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method for the oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
InactiveUS7319179B2Organic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAlkaline earth metalDehydrogenation
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Zinc ferrite catalysts, method of preparing thereof and method of preparing 1,3-butadiene using thereof
ActiveCN101674883ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalystsButeneDehydrogenation
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Perovskite-type metal oxide compounds
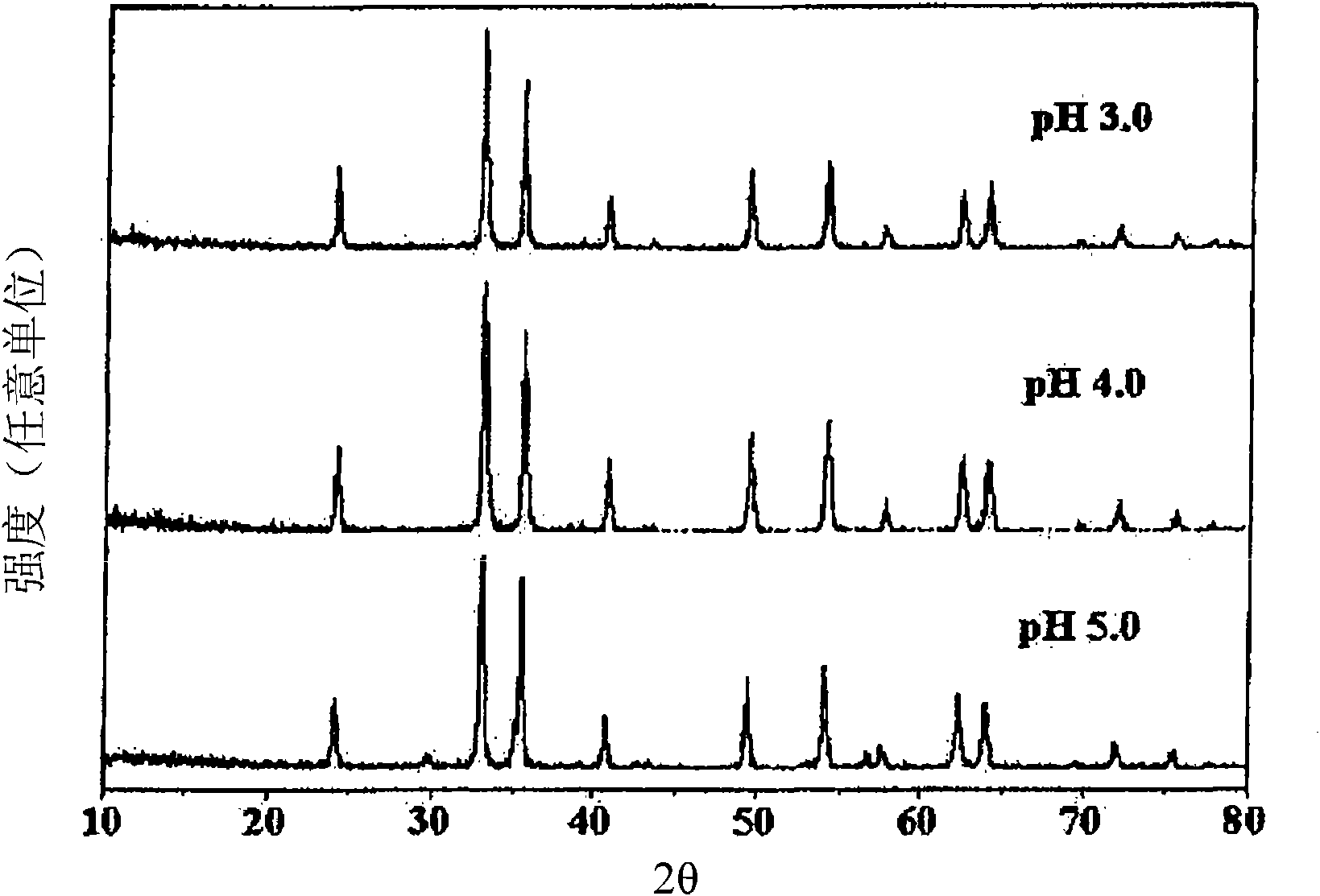
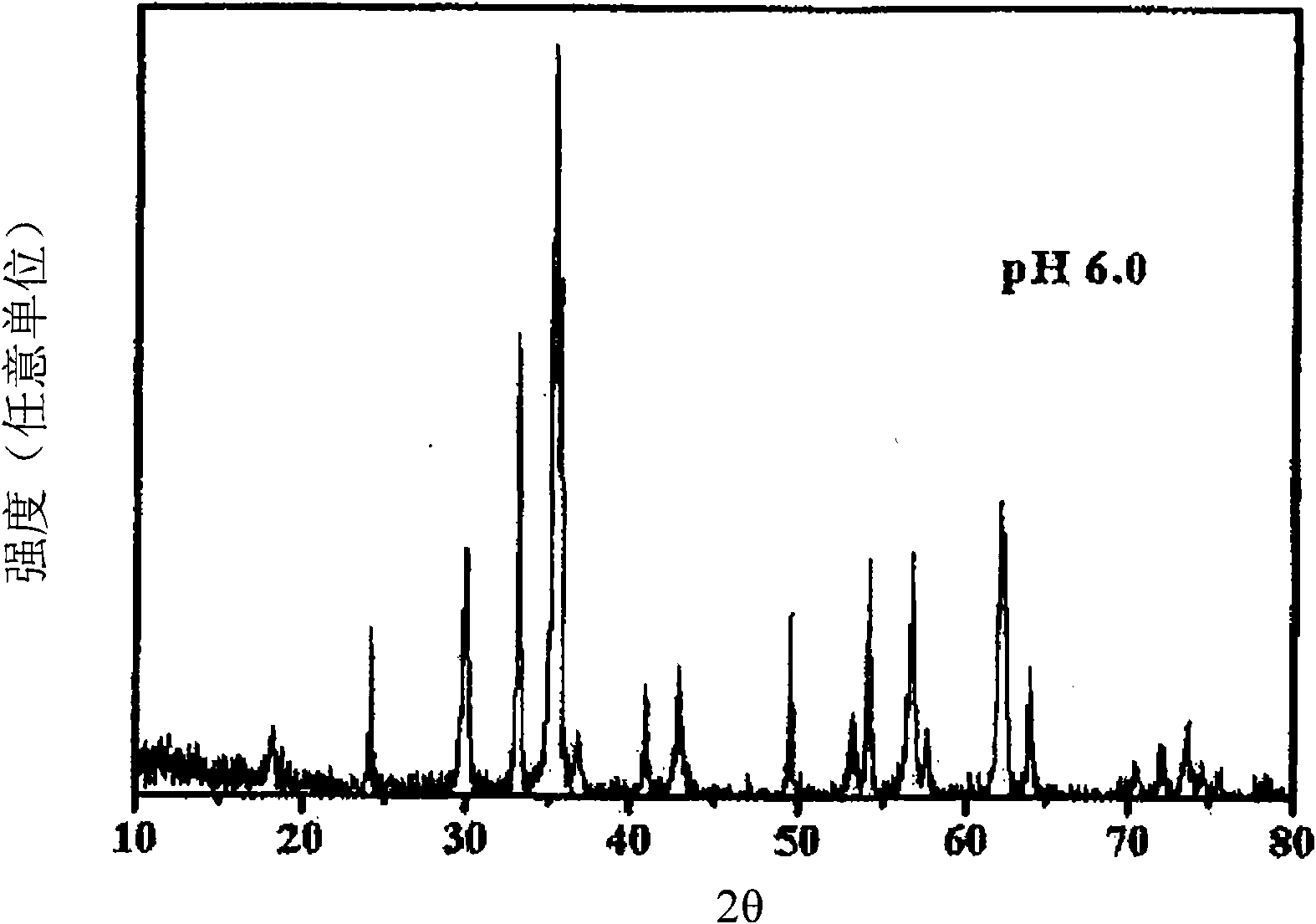
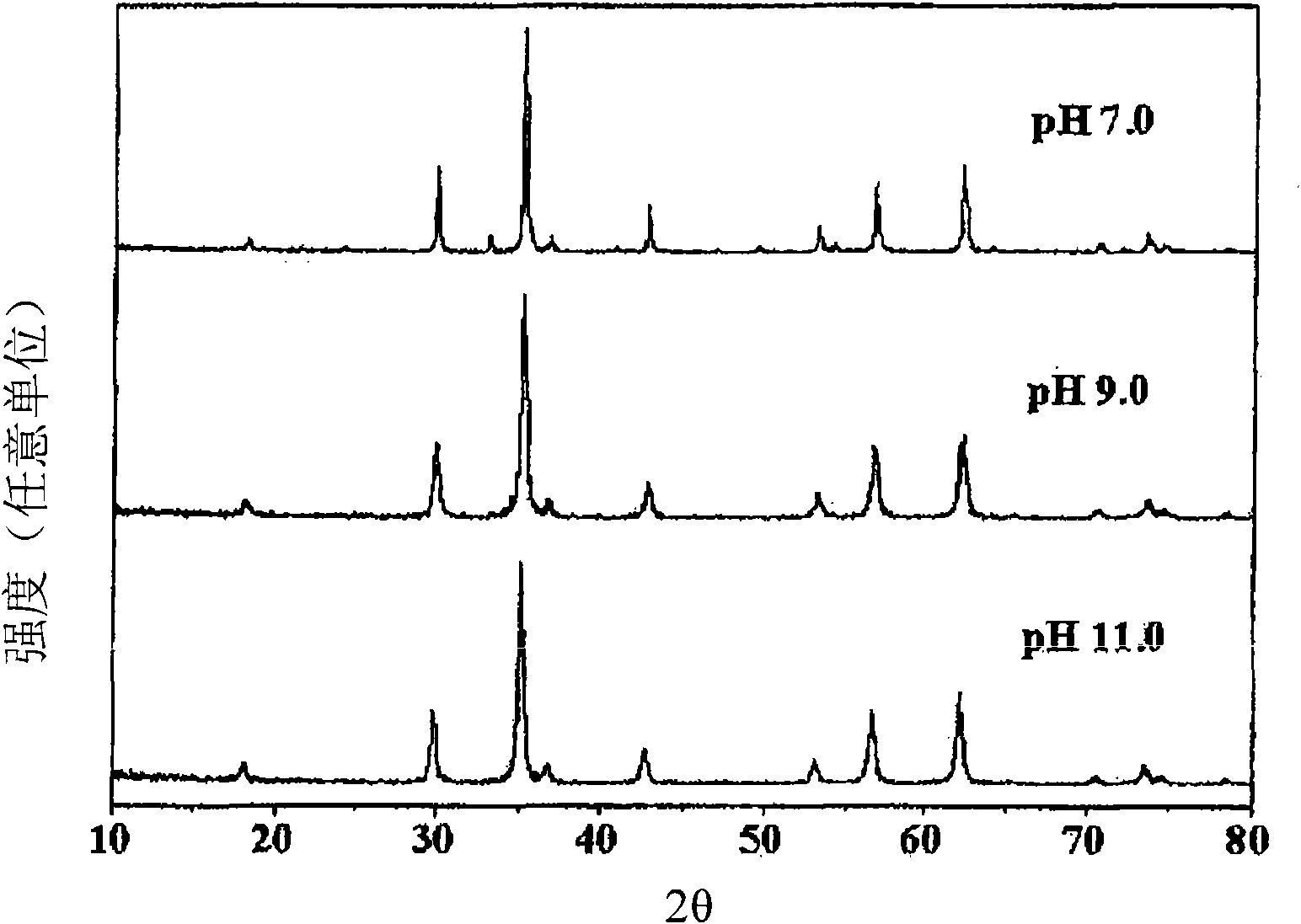
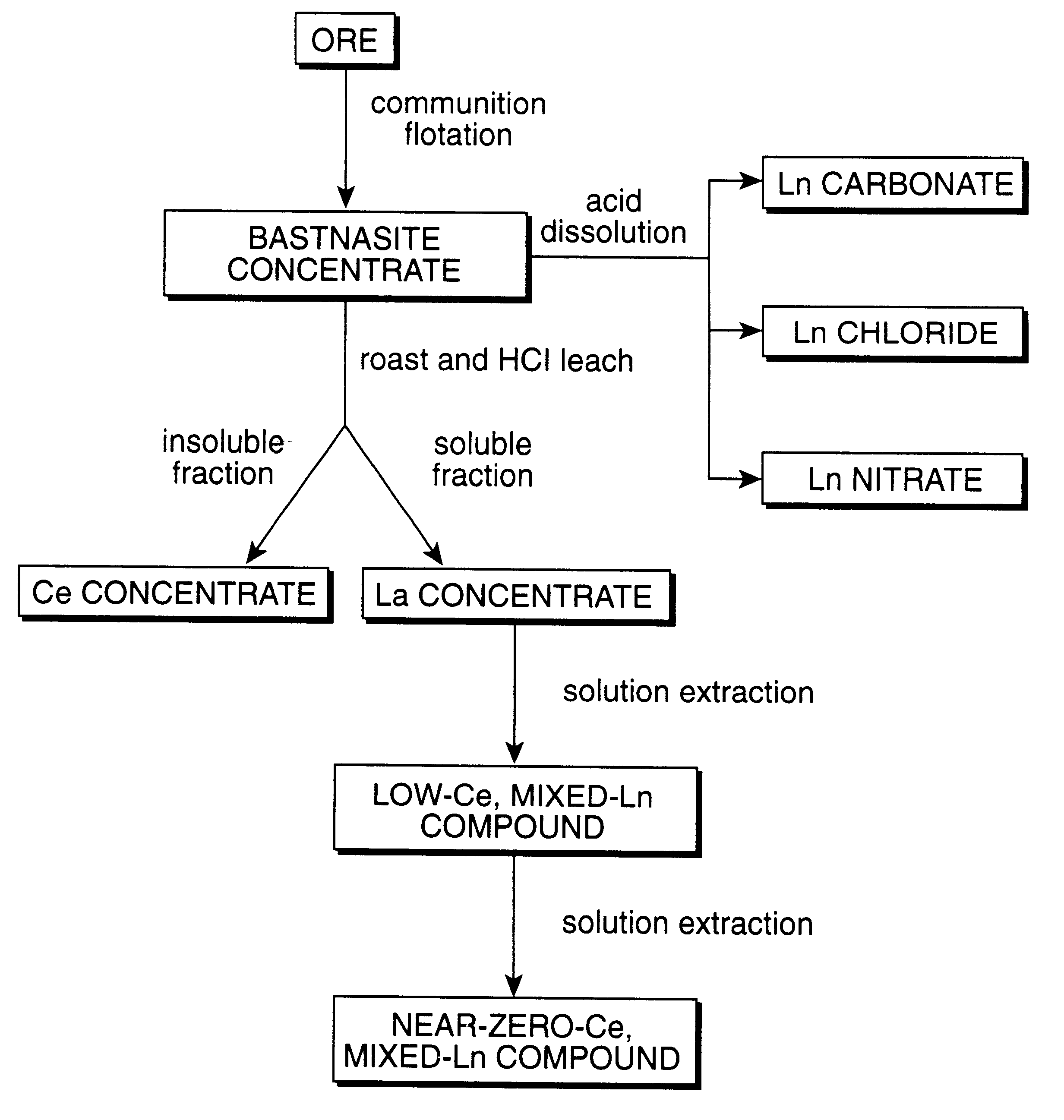
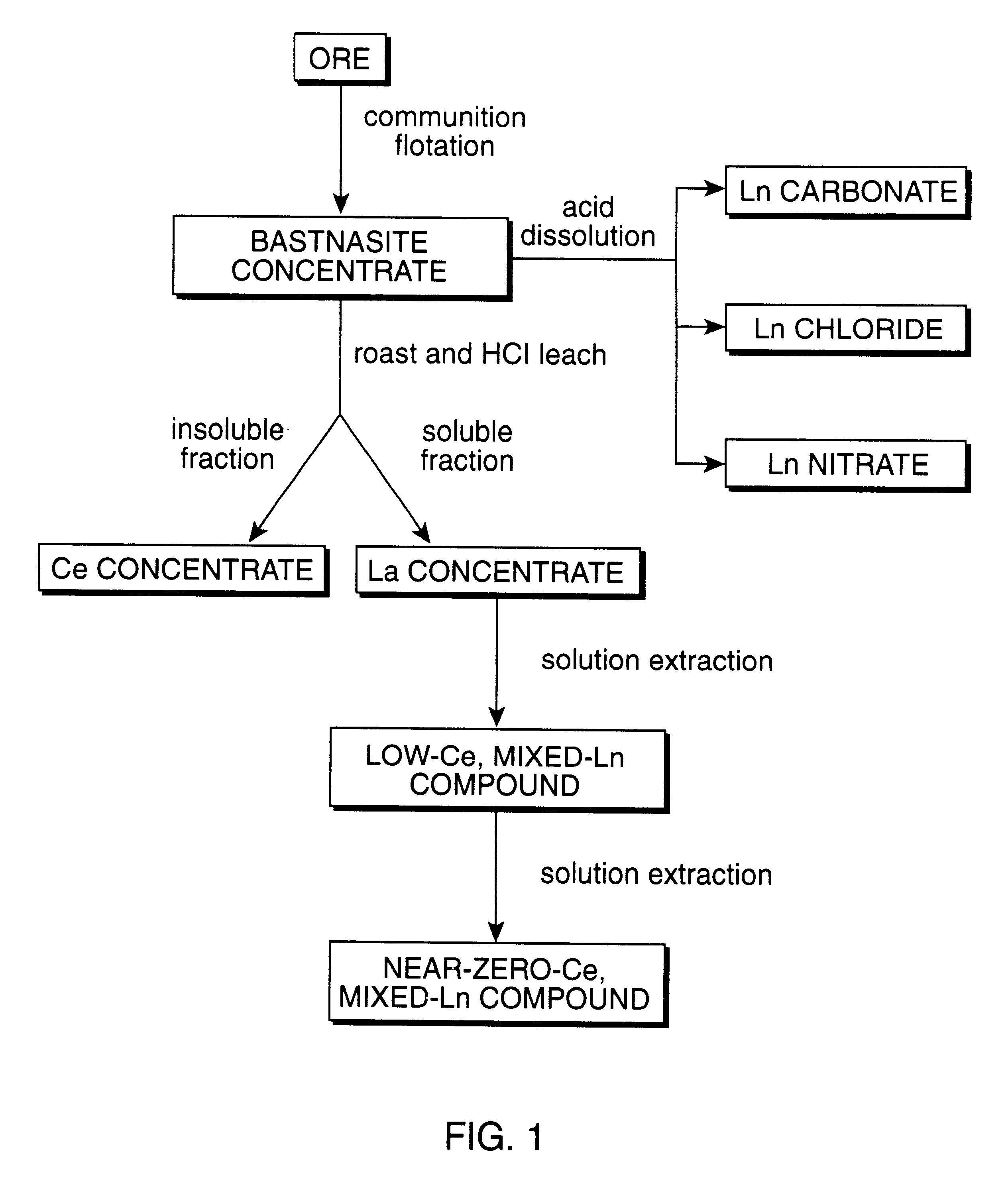
Perovskite-type catalyst consists essentially of a metal oxide composition is provided. The metal oxide composition is represented by the general formula A.sub.1-x B.sub.x MO.sub.3, in which A is a mixture of elements originally in the form of single phase mixed lanthanides collected from bastnasite; B is a divalent or monovalent cation; M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of elements of an atomic number of from 22 to 30, 40 to 51, and 73 to 80; and x is a number defined by 0.ltoreq.x<0.5.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Catalyst and method for converting natural gas to higher carbon compounds
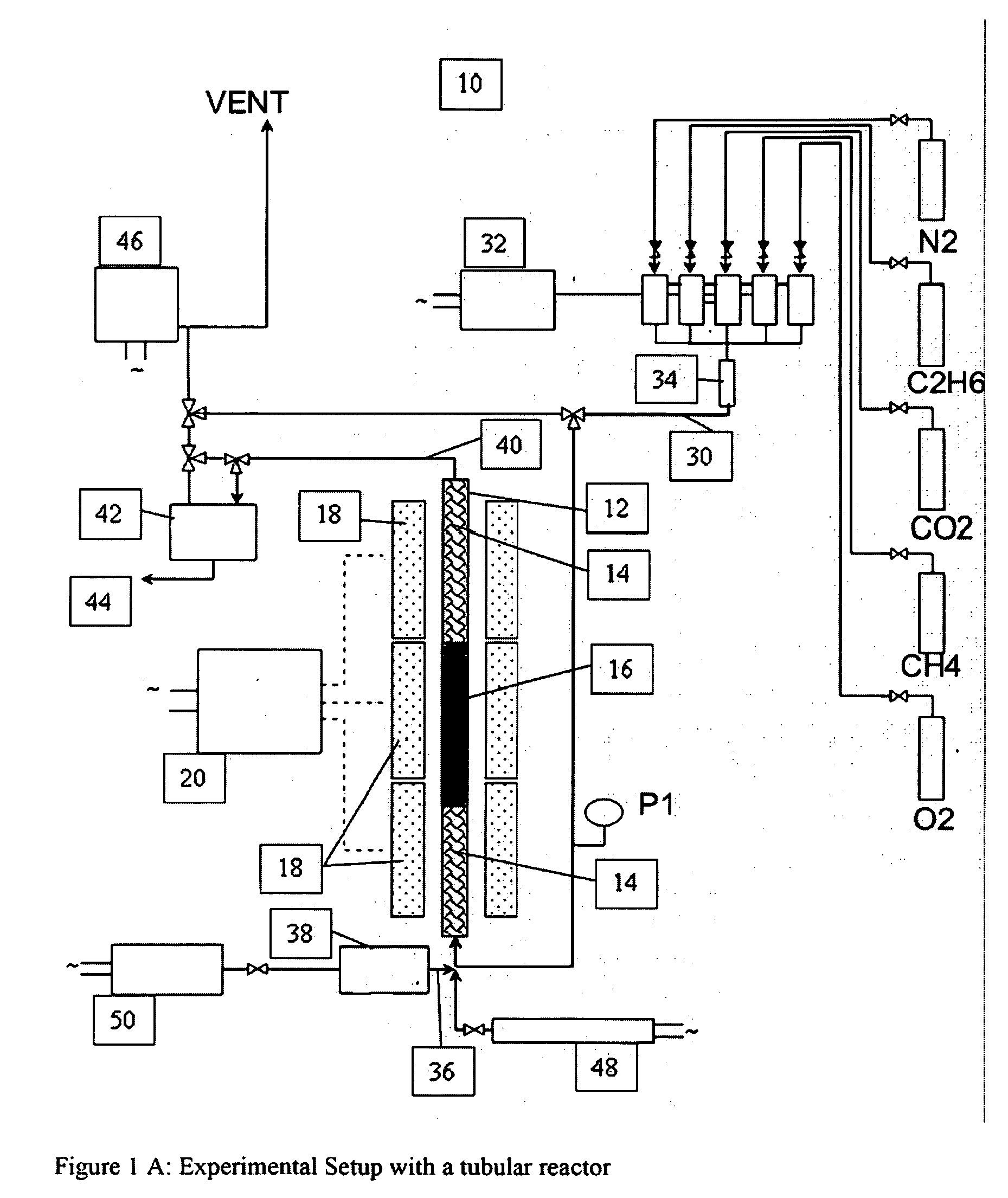
InactiveUS20080281136A1High conversion rate of methaneMaintain catalytic activityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationHigh rateHigh carbon
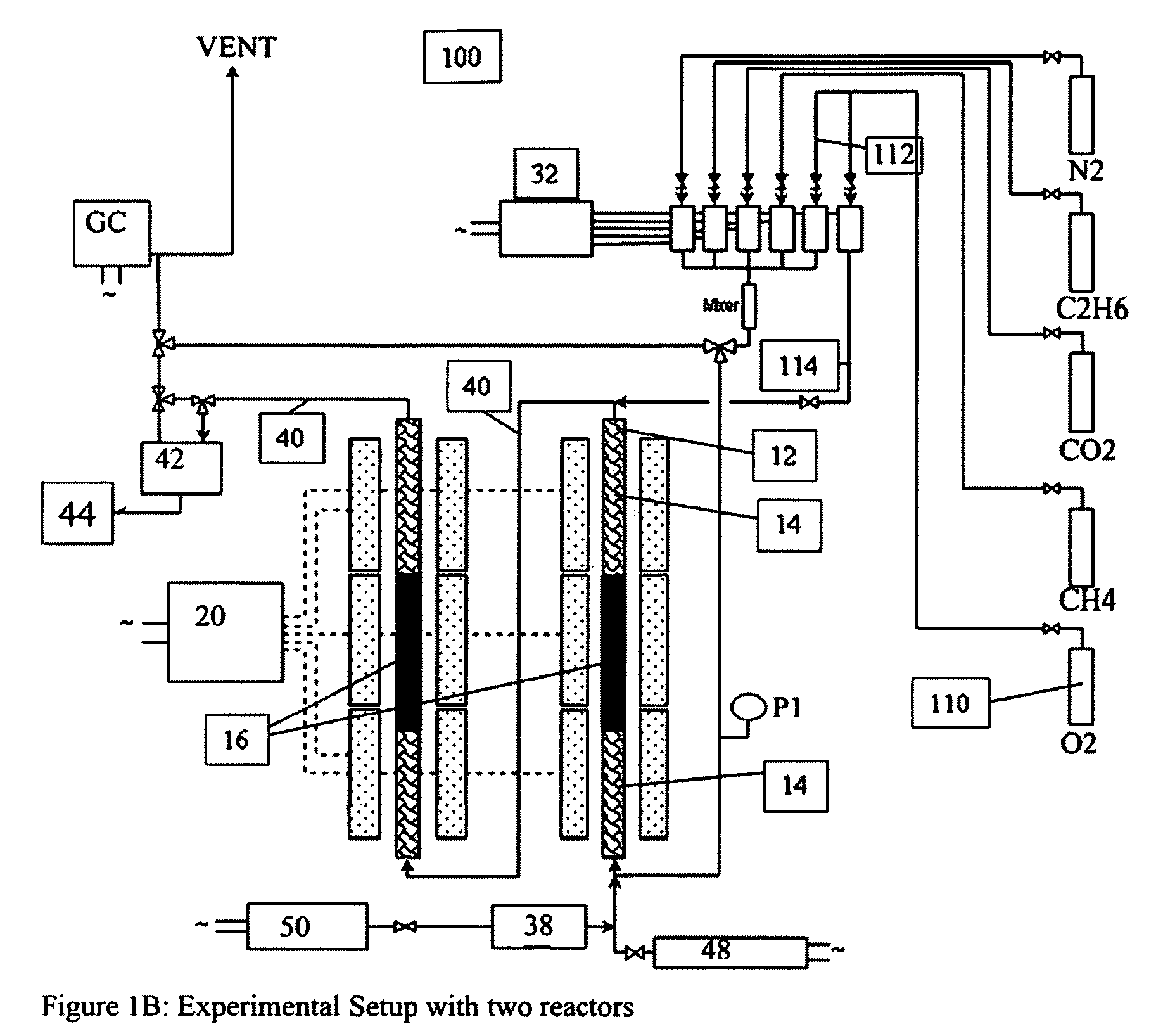
A catalyst composition and process facilitates the oxidative reforming of low molecular weight hydrocarbons, such as methane, to other hydrocarbons having 2 or more carbon atoms (“C2+ compounds”). Compositions having a formula comprising a metal, tungsten, manganese and oxygen effectively catalyze the oxidative reforming of methane with a high rate of conversion and selectivity. Controlling feed gas flow and catalyst bed temperature controls the exothermic OCM reaction, avoiding runaway reactions or coking. A single or multiple reactor system can be utilized for the oxidative reforming reactions. Using two reactors in series, catalyst embodiments produced favorable yields of C2+ compounds, in the presence or absence of a distributed oxygen feed, and with or without interstage effluent cooling. Removal of desirable end products from the reactor effluent, followed by recycling of the residual effluent, increases the conversion to, and ultimate yield of desirable end product.
Owner:HRD CORP
Ammonia slip catalyst
ActiveUS20150037233A1Increases CO and HC oxidative potentialReduced footprintCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsAmmoniaPalladium
Provided is an ammonia slip catalyst article having supported palladium in a top or upstream layer for oxidation of carbon monoxide and / or hydrocarbons, an SCR catalyst either in the top layer or in a separate lower or downstream layer, and an ammonia oxidation catalyst in a bottom layer. Also provided are methods for treating an exhaust gas using the catalyst article, wherein the treatment involves reducing the concentrations of ammonia and optionally carbon monoxide and / or hydrocarbons in the exhaust gas.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Combined cracking and selective hydrogen combustion for catalytic cracking
A catalyst system and process for combined cracking and selective hydrogen combustion of hydrocarbons are disclosed. The catalyst system contains at least one solid acid component and at least one metal-based component which consists of (a) oxygen and / or sulfur and (b) a metal combination selected from the group consisting of: i) at least one metal from Group 3 and at least one metal from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; ii) at least one metal from Groups 5-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements, and at least one metal from at least one of Groups 1, 2, and 4 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; iii) at least one metal from Groups 1 and 2, at least one metal from Group 3, and at least one metal from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements; and iv) two or more metals from Groups 4-15 of the Periodic Table of the Elements, wherein the at least one of oxygen and sulfur is chemically bound both within and between the metals and, optionally, (3) at least one of at least one support, at least one filler and at least one binder. The process is such that the yield of hydrogen is less than the yield of hydrogen when contacting the hydrocarbons with the solid acid component alone. Further the emissions of NOx from the regeneration cycle of the catalyst system are reduced.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalysts for petrochemical catalysis
Metal oxide catalysts comprising various dopants are provided. The catalysts are useful as heterogenous catalysts in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2 hydrocarbons such as ethane and ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Catalyst and method for converting low molecular weight paraffinic hydrocarbons into alkenes and organic compounds with carbon numbers of 2 or more
InactiveUS20070083073A1Reduce the amount requiredPromotes oxidative couplingHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCarbon numberOxygen
A catalyst and process for formation of hydrocarbons having carbon numbers of two or greater, the result of both oxidative coupling of methane (“OCM”), and other reforming reactions of OCM end products. An OCM catalyst has a structure represented by formula ABTiO3, wherein A is samarium or tin, B is barium; the reforming catalysts a composition represented by formula XYZ, wherein X is a metal from Group IA, Group IIA or Group VIIIA, or not present, Y a metal from Group VA, Group VIA, Group VIIA or Group VIIIA, Z chosen from oxygen, silica, silicalite and alumina. The inventive catalyst comprises an OCM catalyst and a reforming catalyst blended together; when used in a reactor effects an increased yield of hydrocarbons having a carbon number greater than 2 (in excess of 27%-30%, first pass rate of methane conversion about 50%) than occurs under OCM conditions alone.
Owner:HRD CORP
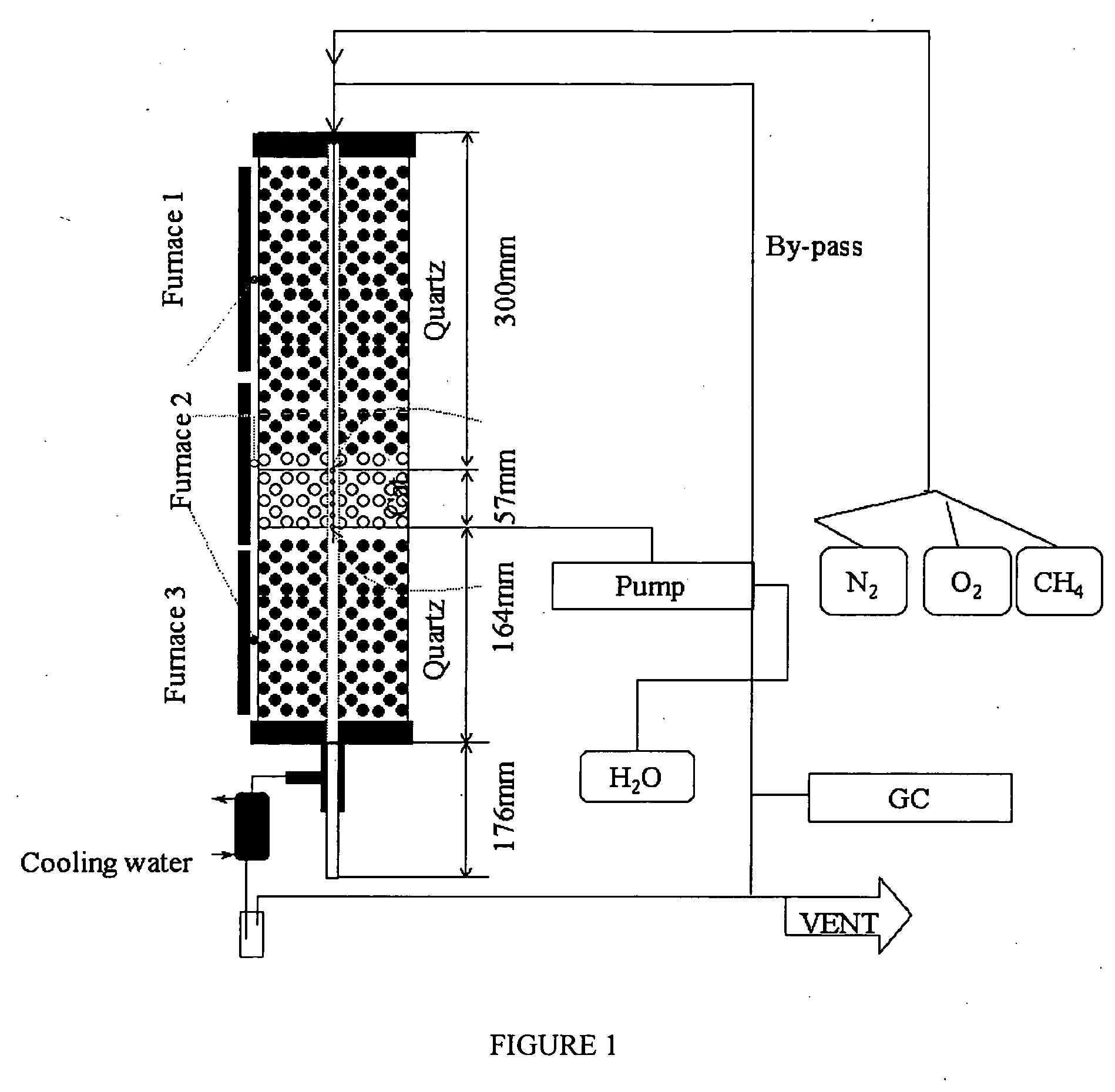
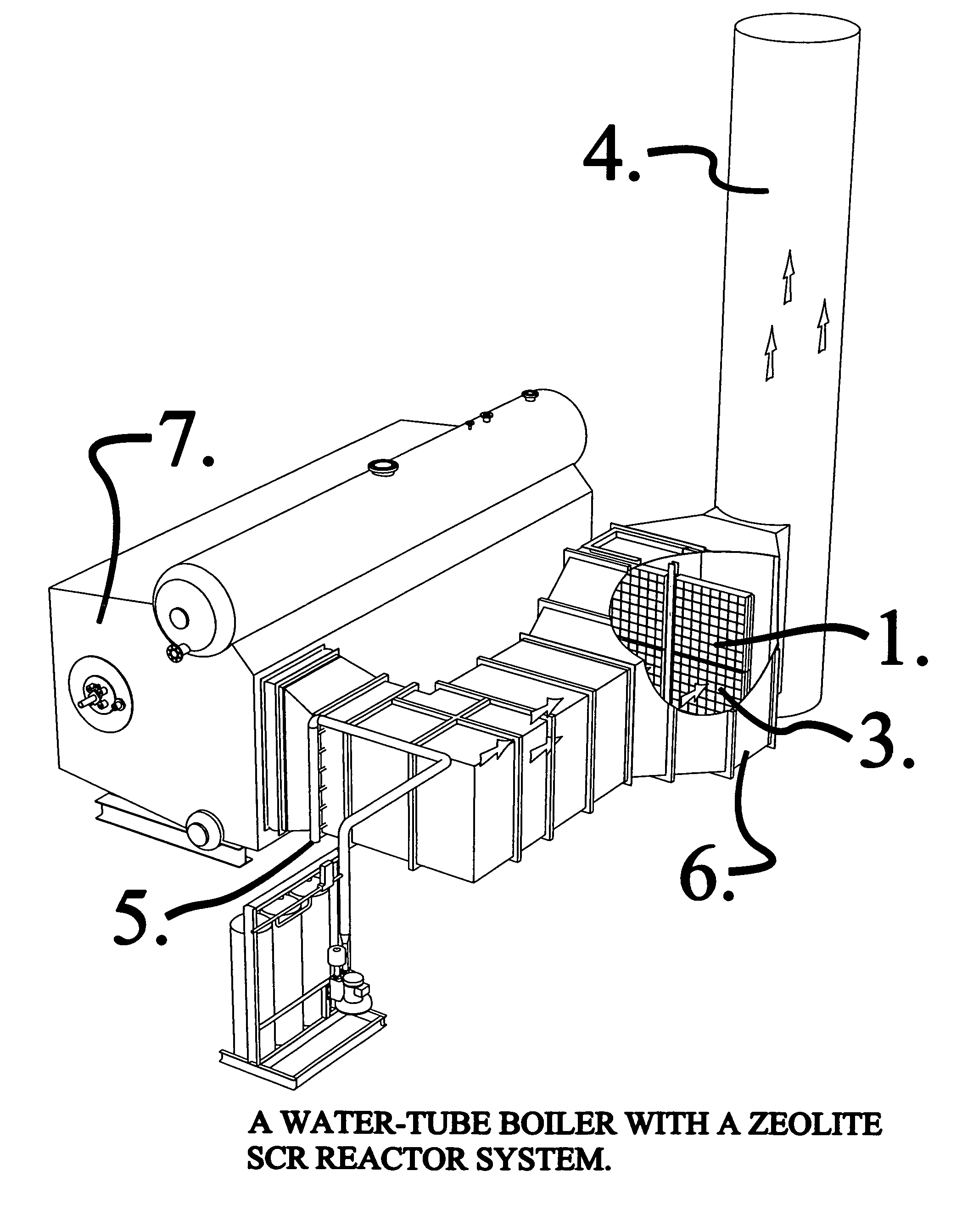
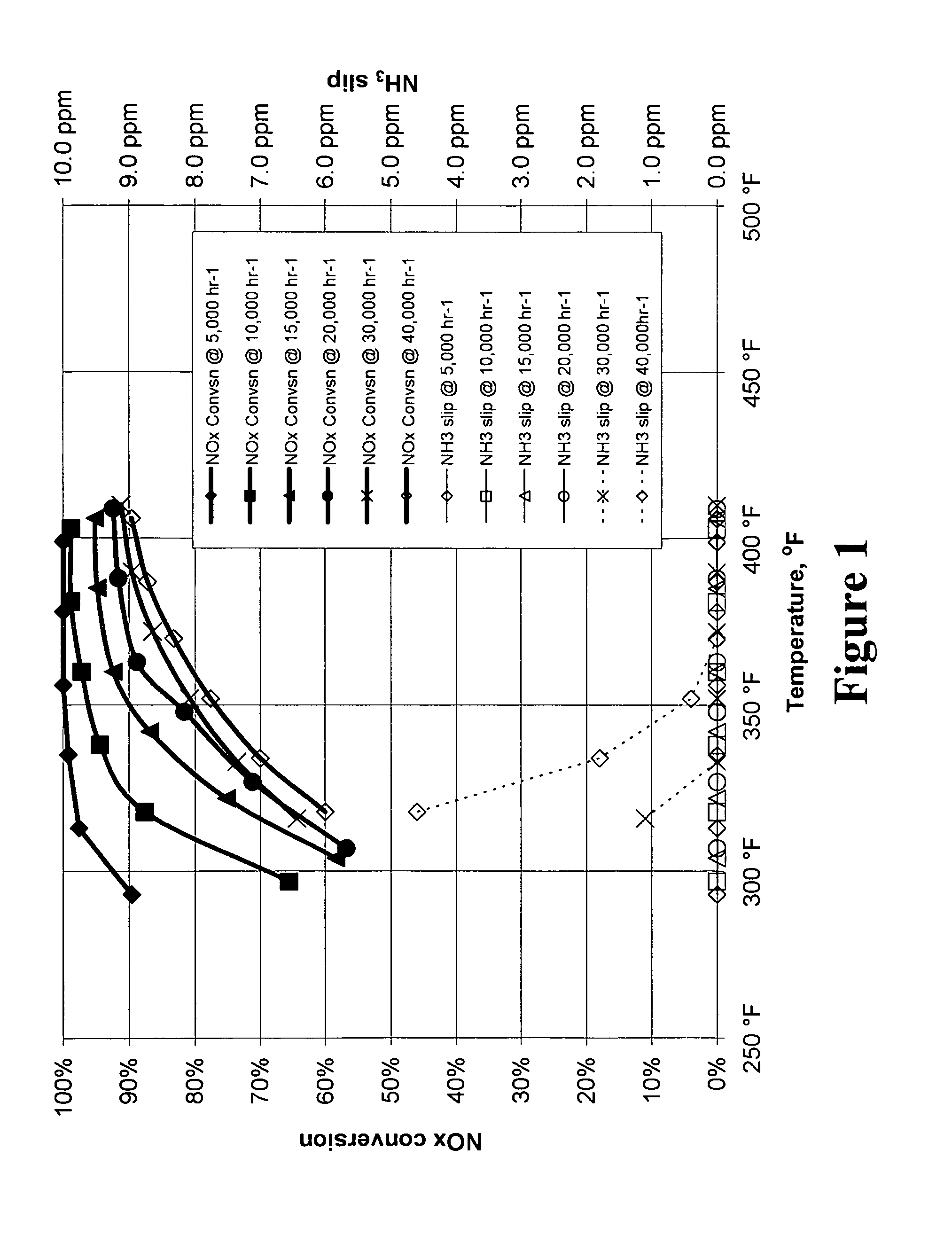
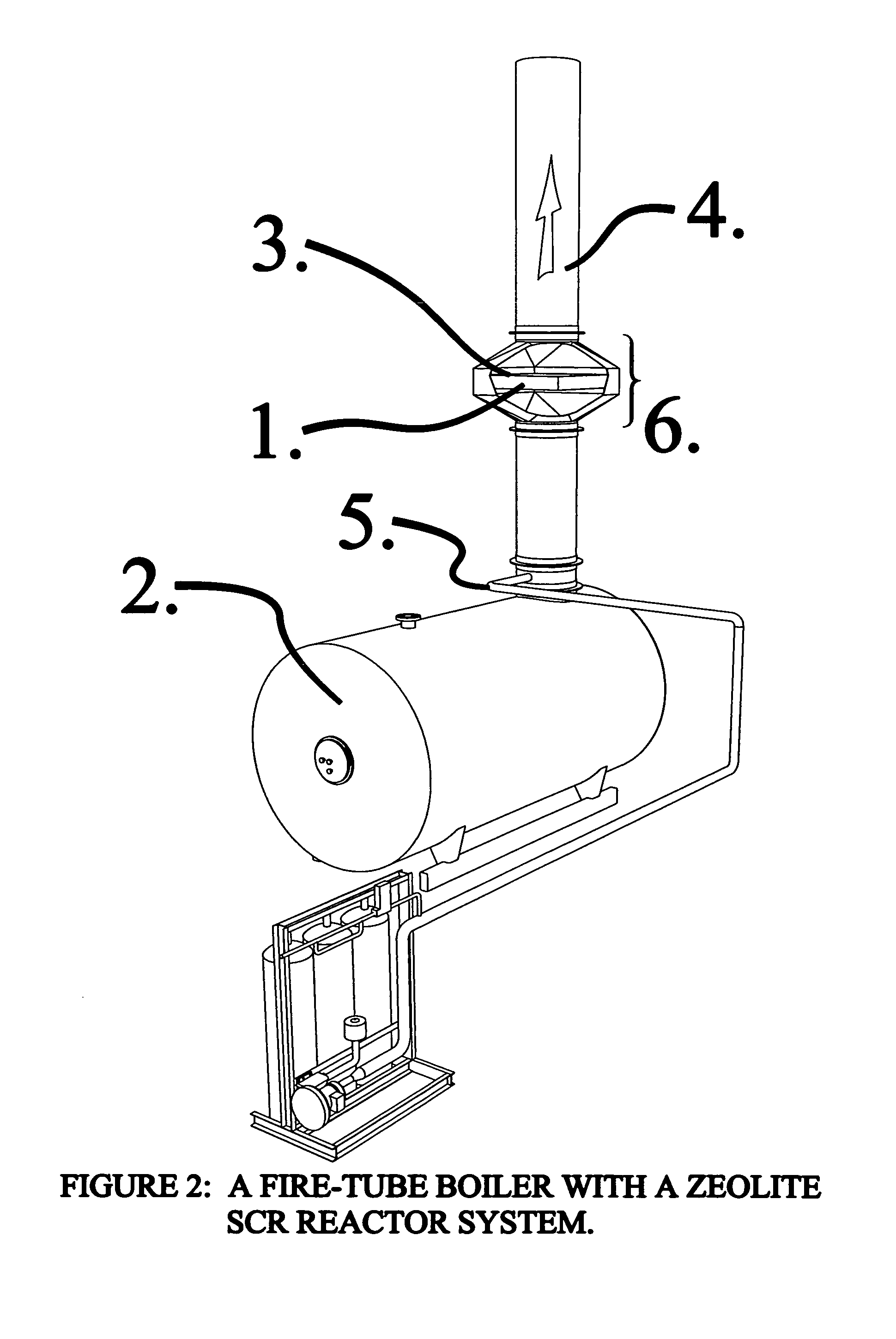
Reactor system for reducing NOx emissions from boilers
ActiveUS7943097B2Low costEasy maintenanceCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsCombustorReactor system
A zeolite based SCR catalyst for NOx reduction using a reducing agent for treating exhaust streams from industrial and commercial boilers is provided. The reactor system has a zeolite based catalyst arranged in catalyst cassettes in a modular fashion where the reactor containing the zeolite based SCR catalyst cassettes is placed in a perpendicular direction to the exhaust exiting the industrial and / or commercial boiler. The catalyst selectively reduces nitrogen oxides to nitrogen with a reducing agent at low to medium temperatures. The reactor results in high NOx conversions and very low ammonia slip and is active for a wide range of boiler firing conditions. Boilers with low NOx and / or ultra low NOx burners can be replaced with a standard conventional burner for overall emissions reduction performance, efficiency improvements and energy savings. Boilers with low NOx and ultra low NOx burners can also be fitted with this zeolite based SCR catalyst reactor for additional NOx reductions and energy savings.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Inorganic material that has metal nanoparticles that are trapped in a mesostructured matrix
An inorganic material that consists of at least two elementary spherical particles, each of said spherical particles comprising metal nanoparticles that are between 1 and 300 nm in size and a mesostructured matrix with an oxide base of at least one element X that is selected from the group that consists of aluminum, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, gallium, germanium, tin, antimony, lead, vanadium, iron, manganese, hafnium, niobium, tantalum, yttrium, cerium, gadolinium, europium and neodymium is described, whereby said matrix has a pore size of between 1.5 and 30 nm and has amorphous walls with a thickness of between 1 and 30 nm, said elementary spherical particles having a maximum diameter of 10 μm. Said material can also contain zeolitic nanocrystals that are trapped within said mesostructured matrix.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Exhaust gas purifying catalyst and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:RENAULT SA
Removal of particulates from the exhaust gas of internal combustion engines operated with a predominantly stoichiometric air/fuel mixture
ActiveUS20090087365A1Sufficient thermal aging stabilityImproved thermal cycling stabilityCombination devicesOrganic chemistryExternal combustion engineEngineering
The exhaust gas of internal combustion engines operated with a predominantly stoichiometric air / fuel mixture contains, as well as the gaseous hydrocarbon (HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) pollutants, also ultrafine particulates. The introduction of the EU-5 exhaust gas standard in Europe in 2010 will for the first time impose a legal limit to these particulate emissions for gasoline vehicles. Future exhaust gas cleaning concepts for these vehicles must include devices for removing these particulates.A catalytically active particulate filter, an exhaust gas cleaning system and a process for cleaning the exhaust gases of predominantly stoichiometrically operated internal combustion engines are presented, which are suitable, as well as the gaseous CO, HC and NOx pollutants, also for removing particulates from the exhaust gas. The particulate filter comprises a filter body and a catalytically active coating consisting of two layers. Both layers contain alumina. The first layer contains palladium. The second layer contains rhodium. The latter is disposed above the first layer.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Catalyst and method for converting natural gas to higher carbon compounds
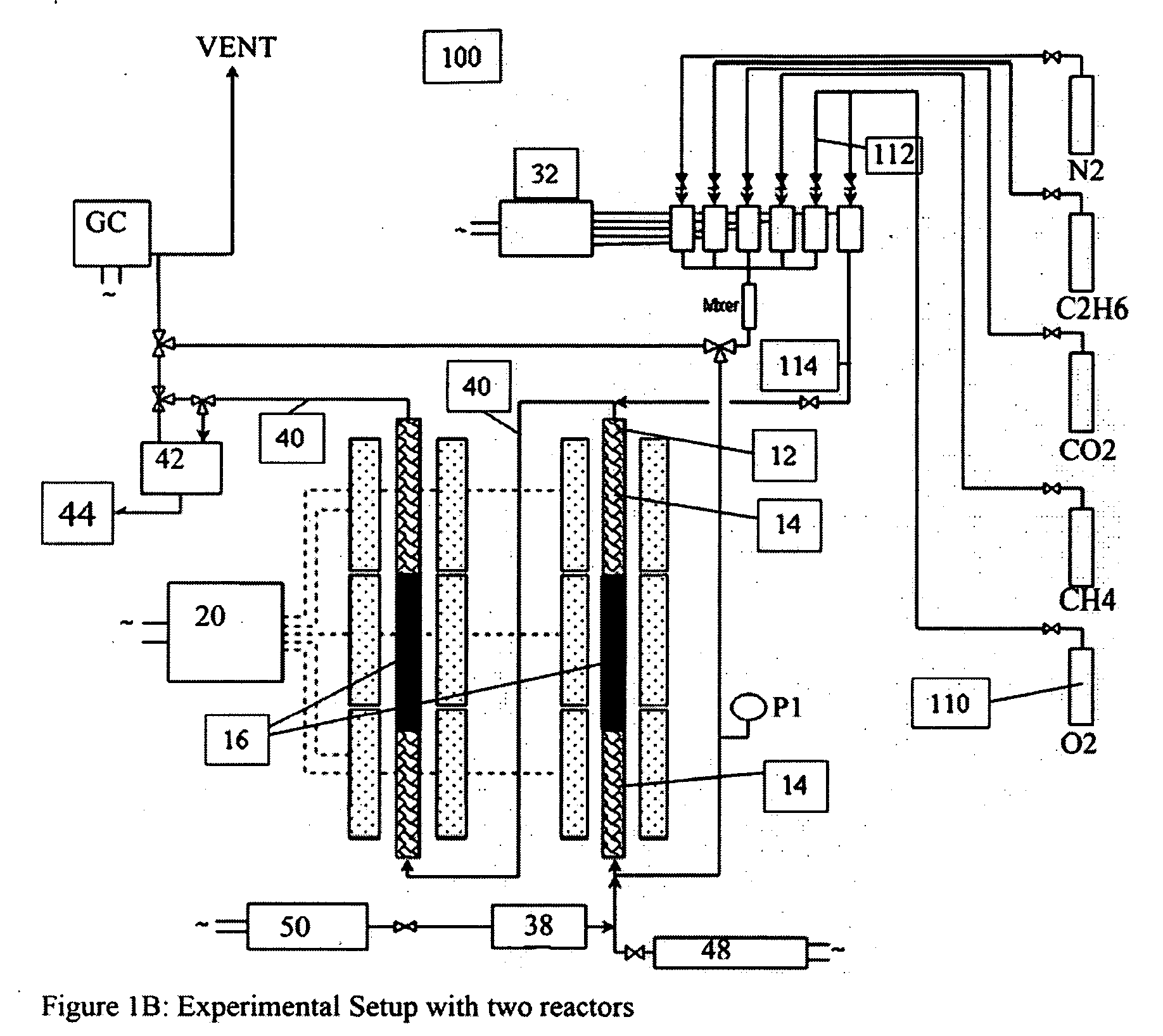
InactiveUS8129305B2Eventual catalyst deactivation is delayed or avoidedMaintain catalytic activityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationHigh rateHigh carbon
A catalyst composition and process facilitates the oxidative reforming of low molecular weight hydrocarbons, such as methane, to other hydrocarbons having 2 or more carbon atoms (“C2+ compounds”). Compositions having a formula comprising a metal, tungsten, manganese and oxygen effectively catalyze the oxidative reforming of methane with a high rate of conversion and selectivity. Controlling feed gas flow and catalyst bed temperature controls the exothermic OCM reaction, avoiding runaway reactions or coking. A single or multiple reactor system can be utilized for the oxidative reforming reactions. Using two reactors in series, catalyst embodiments produced favorable yields of C2+ compounds, in the presence or absence of a distributed oxygen feed, and with or without interstage effluent cooling. Removal of desirable end products from the reactor effluent, followed by recycling of the residual effluent, increases the conversion to, and ultimate yield of desirable end product.
Owner:HRD CORP
Production process for catalyst
InactiveUS20060205978A1Efficiently and uniformlyHigh strengthOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsParticulates
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Inorganic material that has metal nanoparticles that are trapped in a mesostructured matrix
An inorganic material that consists of at least two elementary spherical particles, each of said spherical particles comprising metal nanoparticles that are between 1 and 300 nm in size and a mesostructured matrix with an oxide base of at least one element X that is selected from the group that consists of aluminum, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, gallium, germanium, tin, antimony, lead, vanadium, iron, manganese, hafnium, niobium, tantalum, yttrium, cerium, gadolinium, europium and neodymium is described, whereby said matrix has a pore size of between 1.5 and 30 nm and has amorphous walls with a thickness of between 1 and 30 nm, said elementary spherical particles having a maximum diameter of 10 μm. Said material can also contain zeolitic nanocrystals that are trapped within said mesostructured matrix.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Hydrogen transport membranes
InactiveUS6899744B2Increase ratingsThickness minimizationSemi-permeable membranesMembranesSupport matrixNiobium
Composite hydrogen transport membranes, which are used for extraction of hydrogen from gas mixtures are provided. Methods are described for supporting metals and metal alloys which have high hydrogen permeability, but which are either too thin to be self supporting, too weak to resist differential pressures across the membrane, or which become embrittled by hydrogen. Support materials are chosen to be lattice matched to the metals and metal alloys. Preferred metals with high permeability for hydrogen include vanadium, niobium, tantalum, zirconium, palladium, and alloys thereof. Hydrogen-permeable membranes include those in which the pores of a porous support matrix are blocked by hydrogen-permeable metals and metal alloys, those in which the pores of a porous metal matrix are blocked with materials which make the membrane impervious to gases other than hydrogen, and cermets fabricated by sintering powders of metals with powders of lattice-matched ceramic.
Owner:ELTRON RES
Popular searches
Oxygen compounds preparation by reduction Biofuels Hydroxy compound preparation Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compounds Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Bulk chemical production Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensation Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Aluminium oxides/hydroxides Tungsten oxides/hydroxides
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com