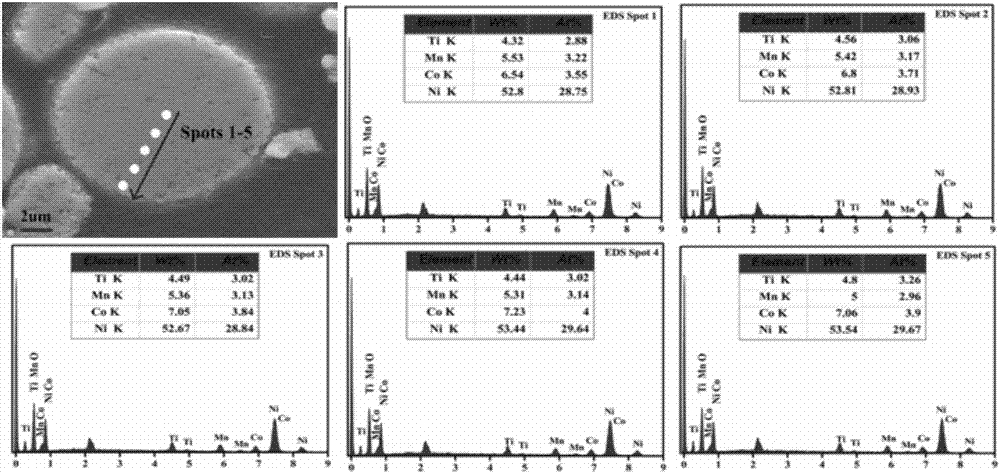
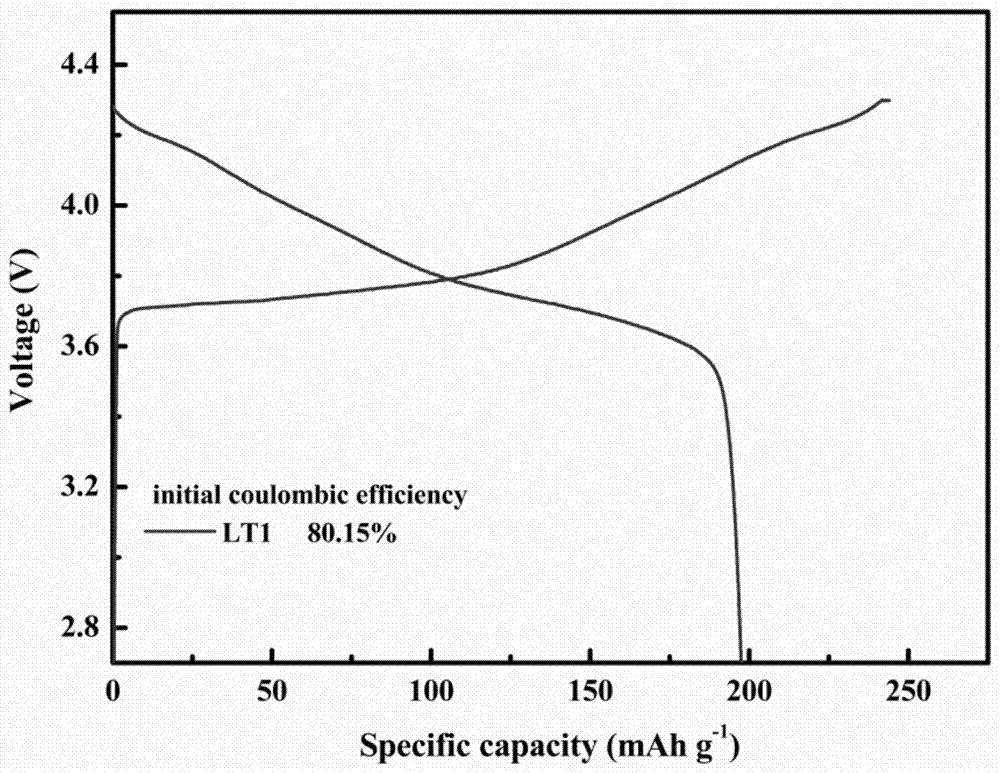
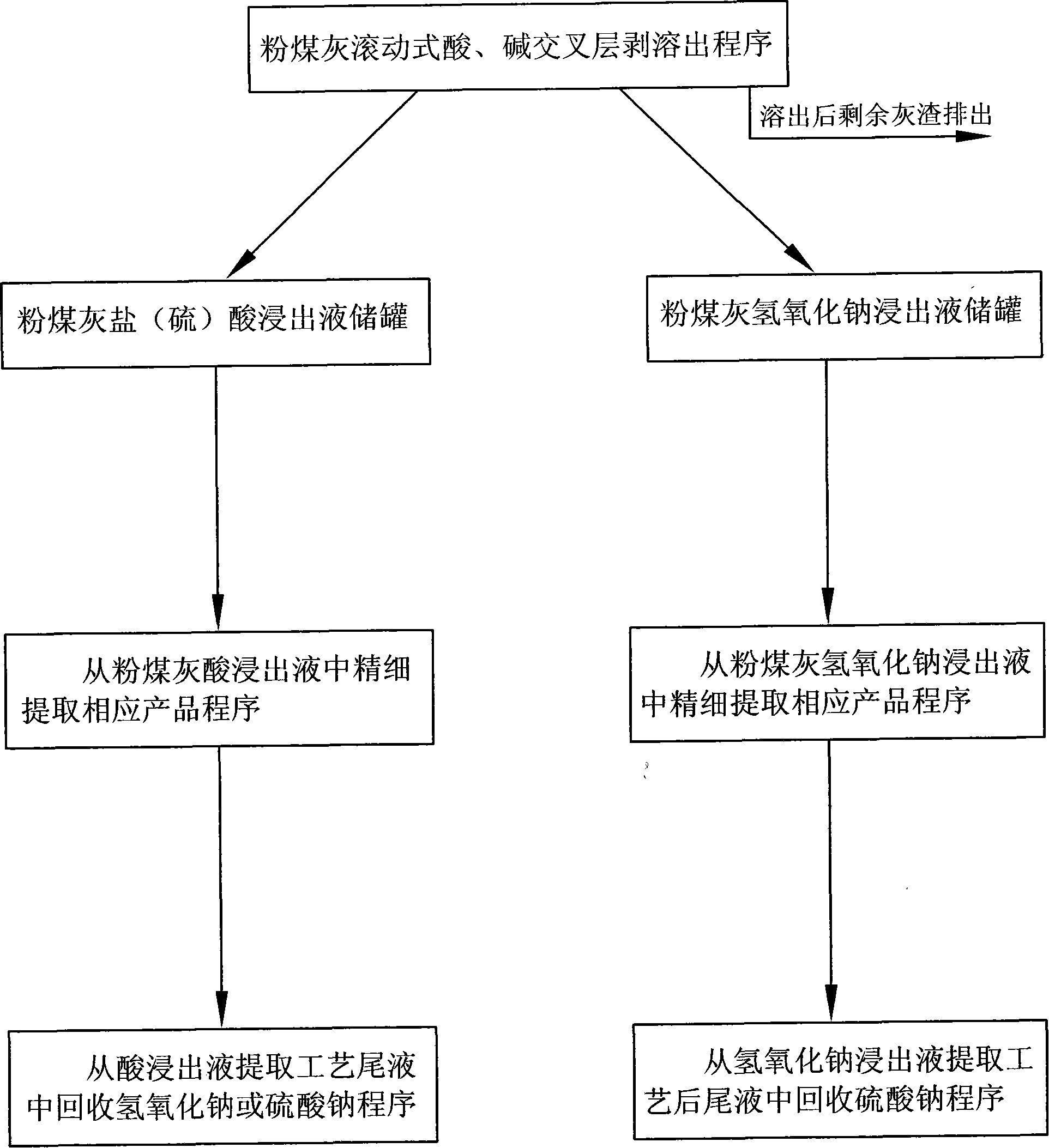
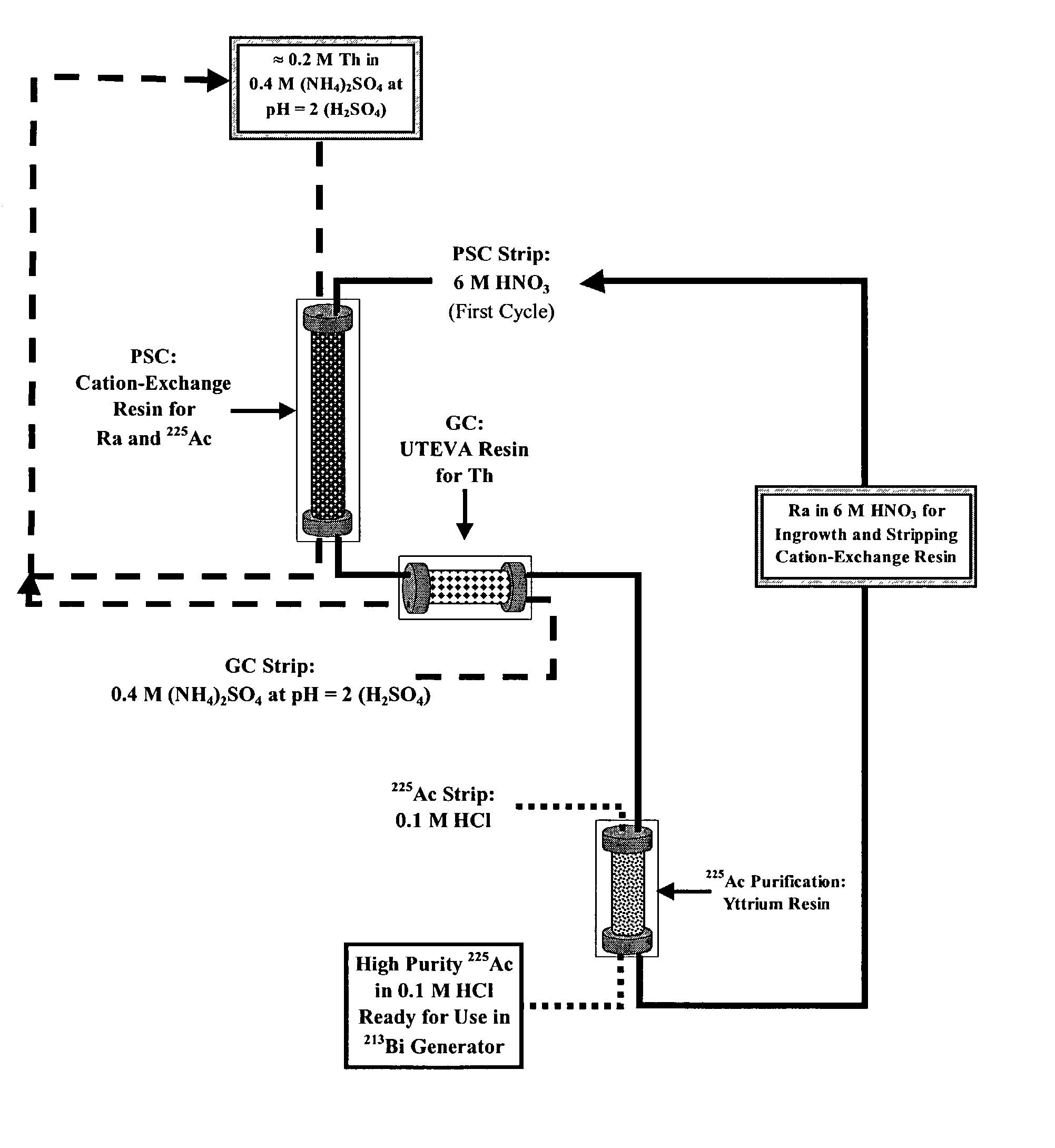
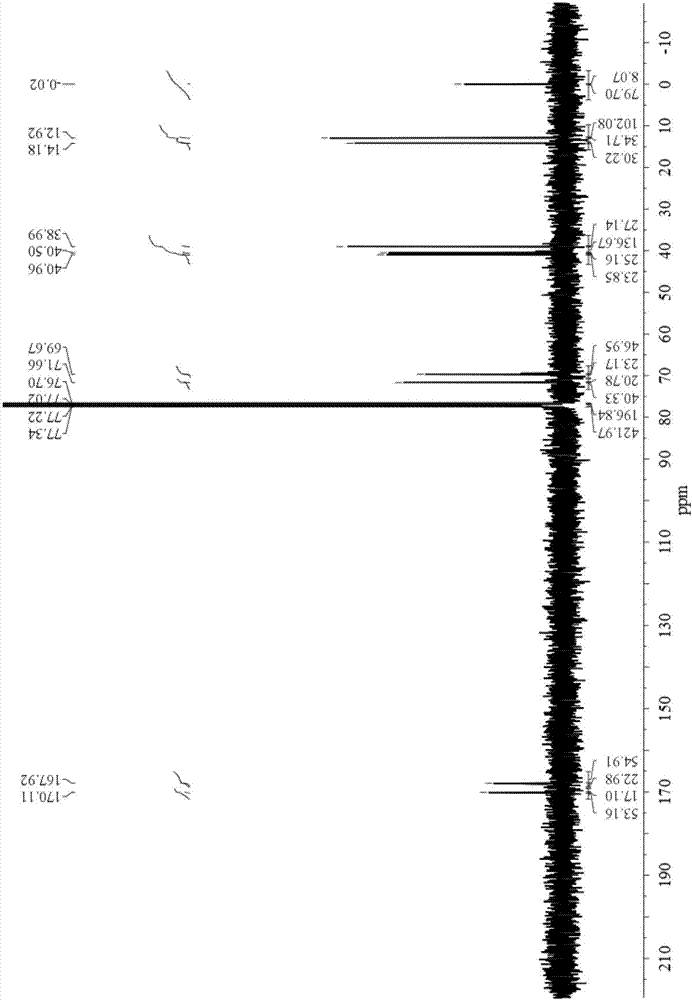
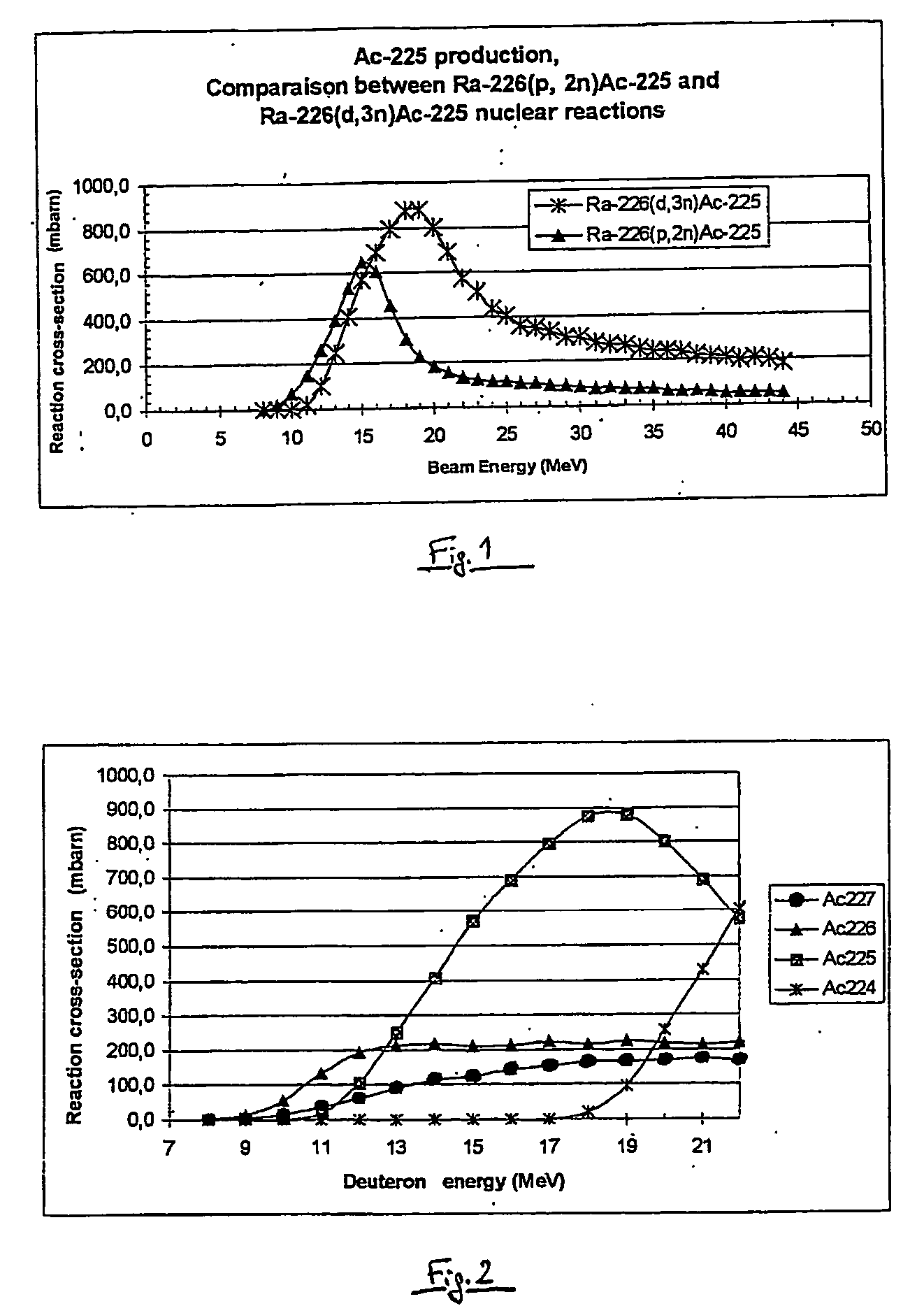
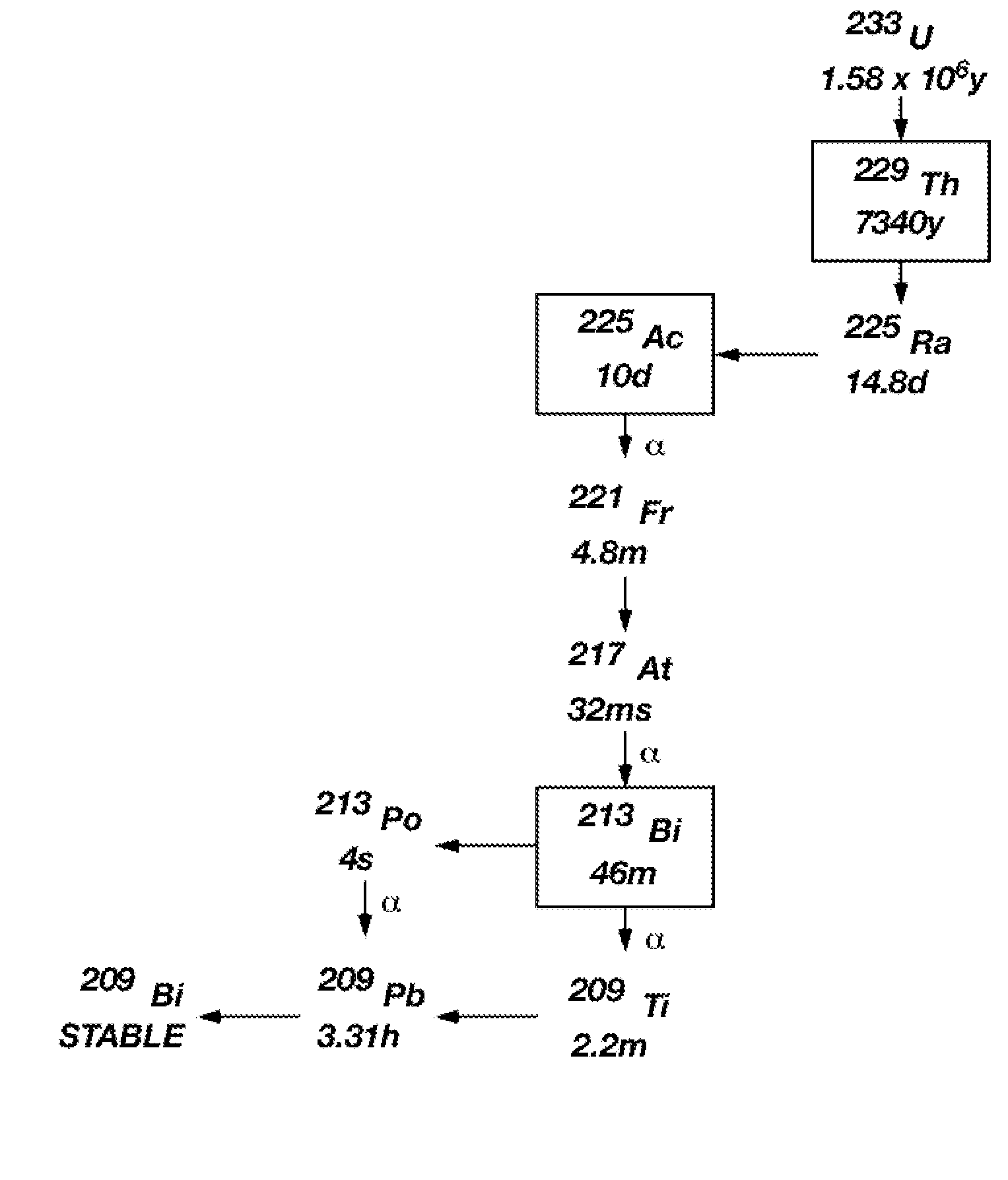
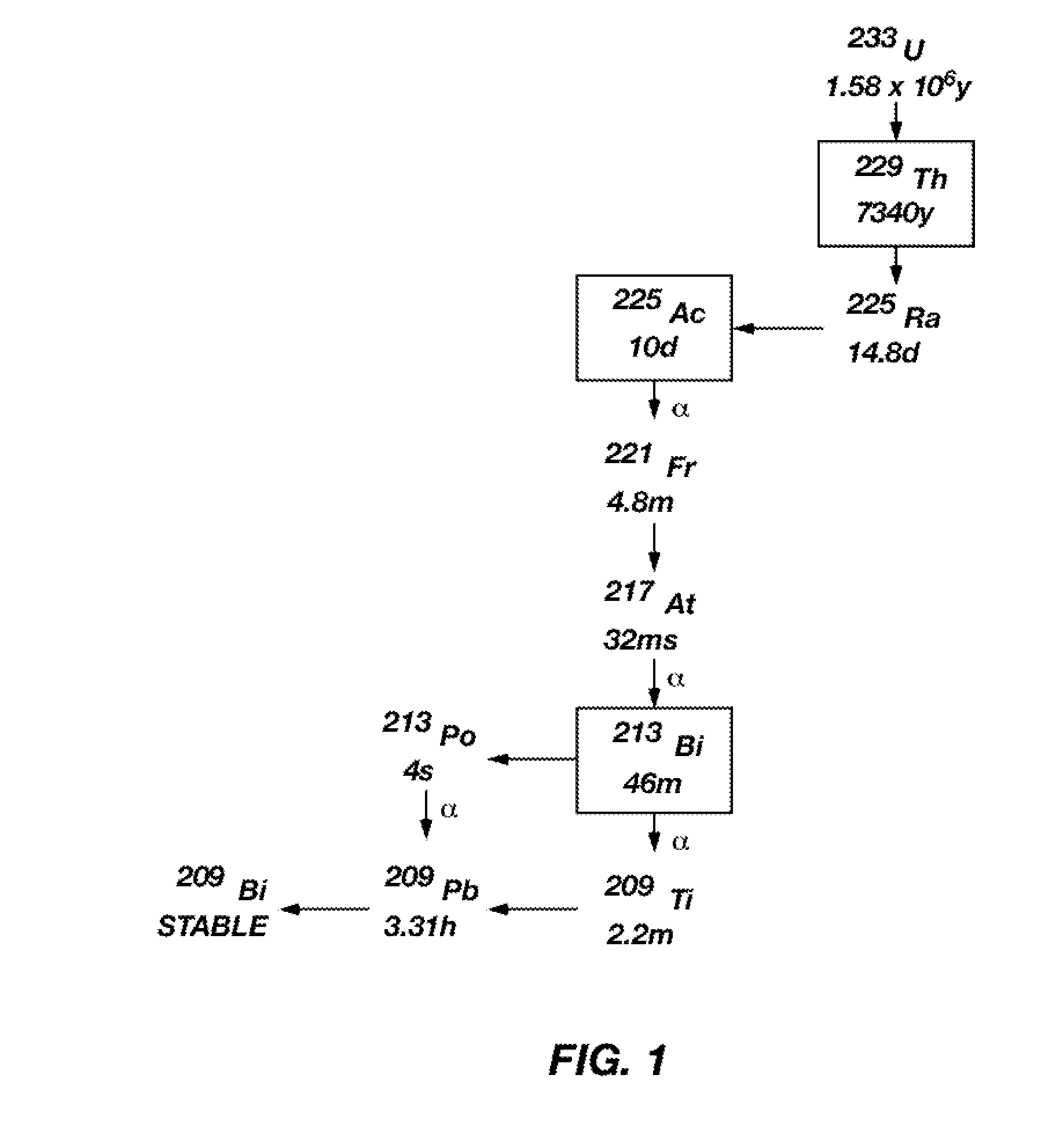
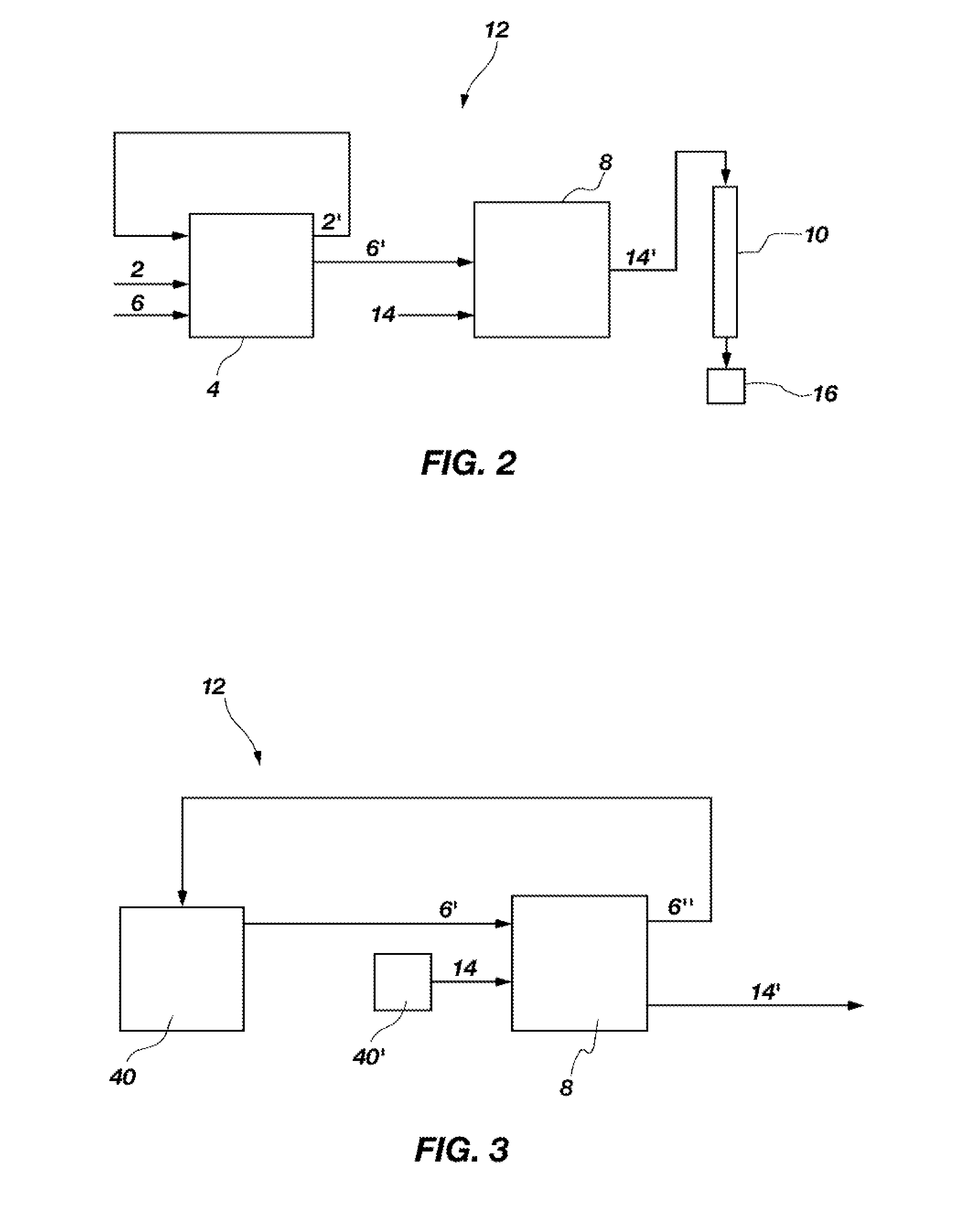
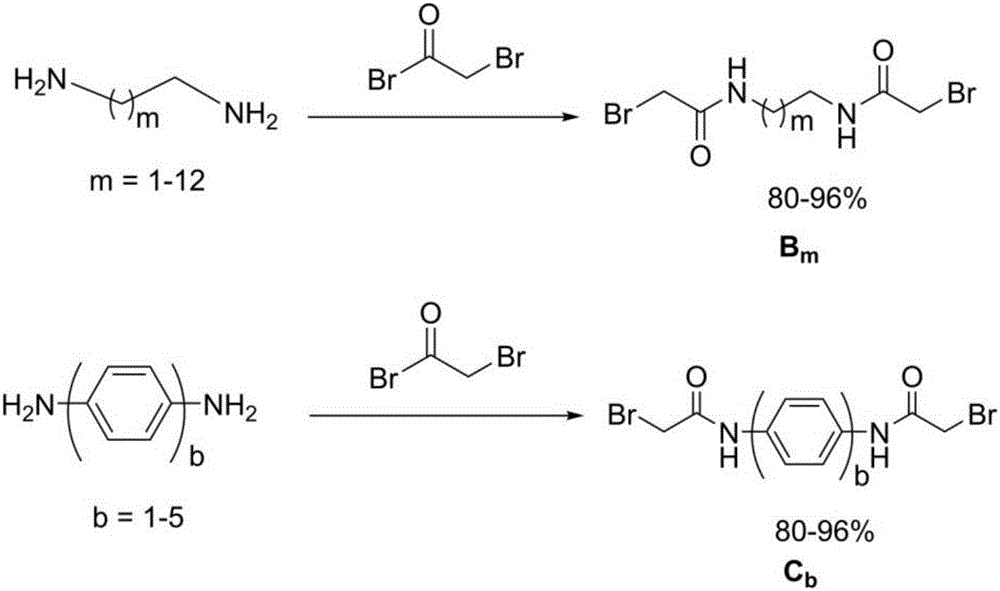
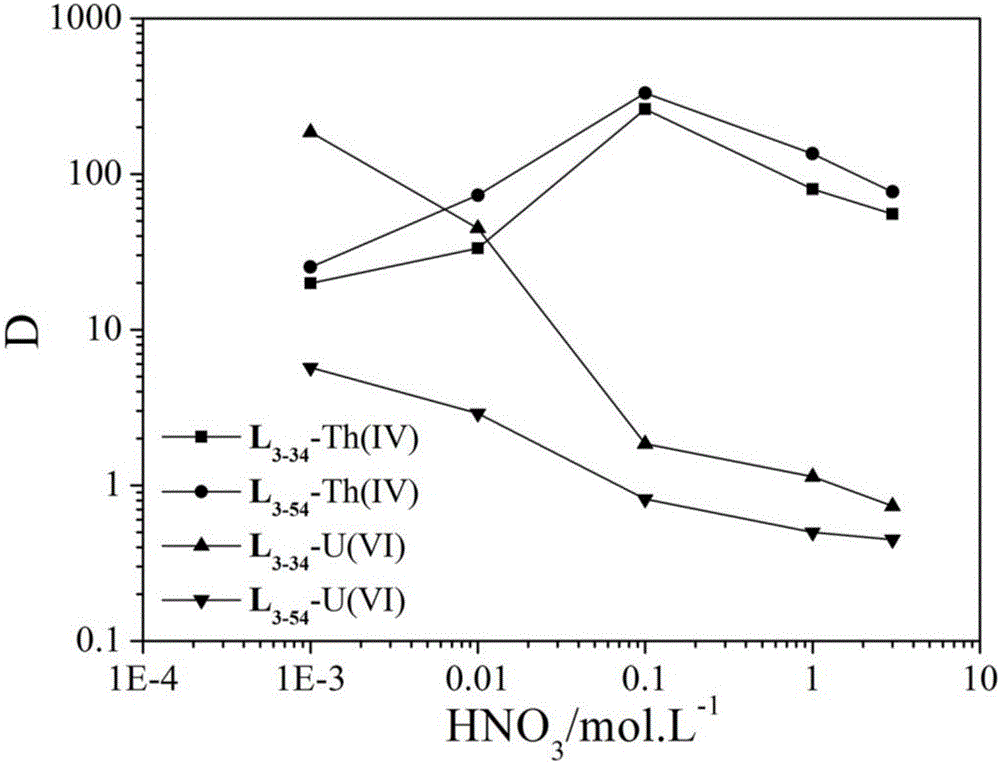
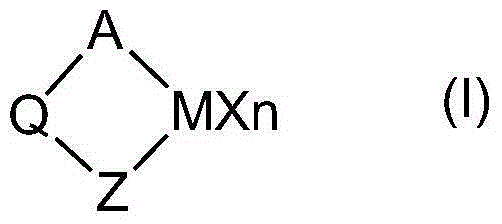Patents
Literature
51 results about "Actinium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
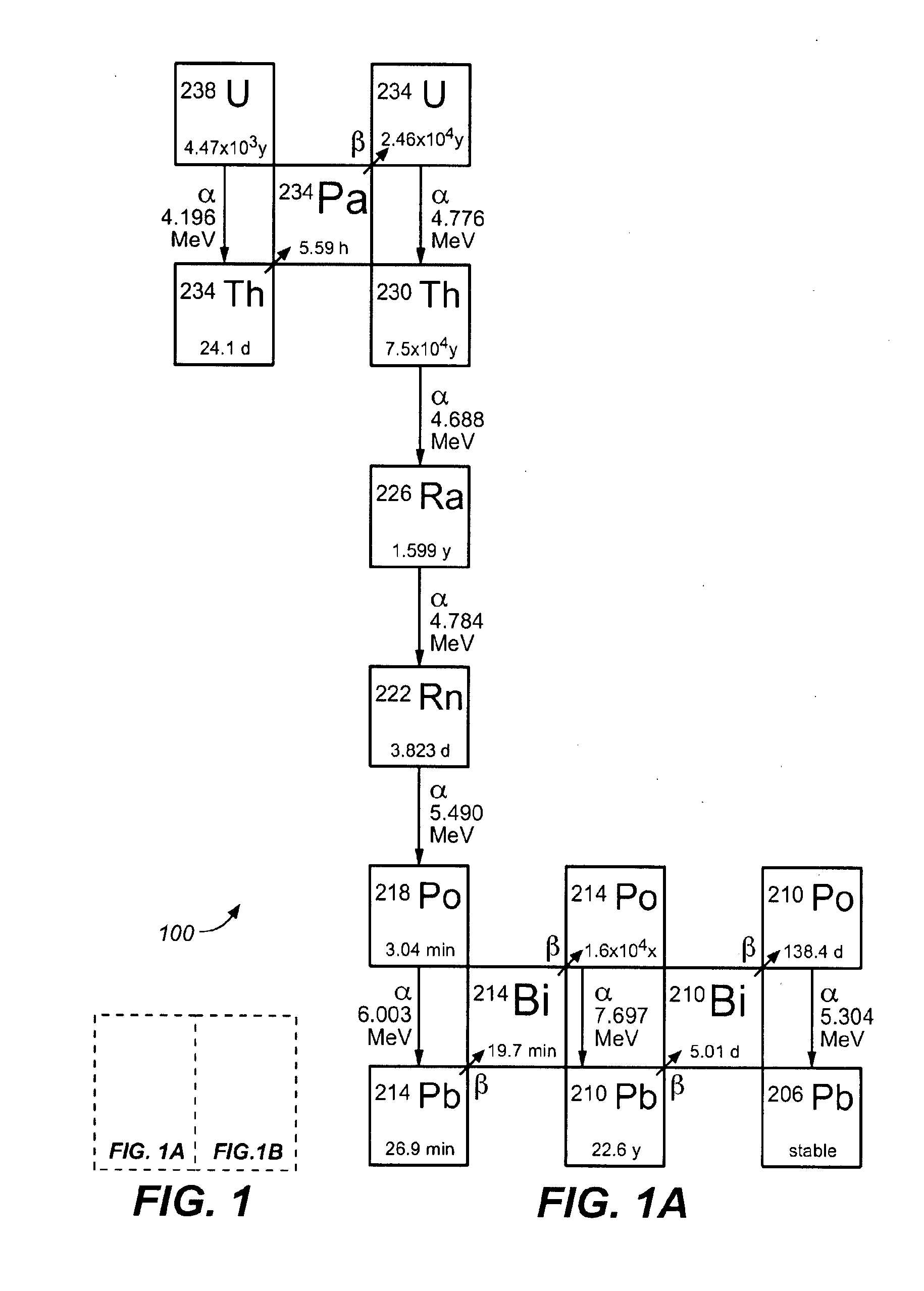
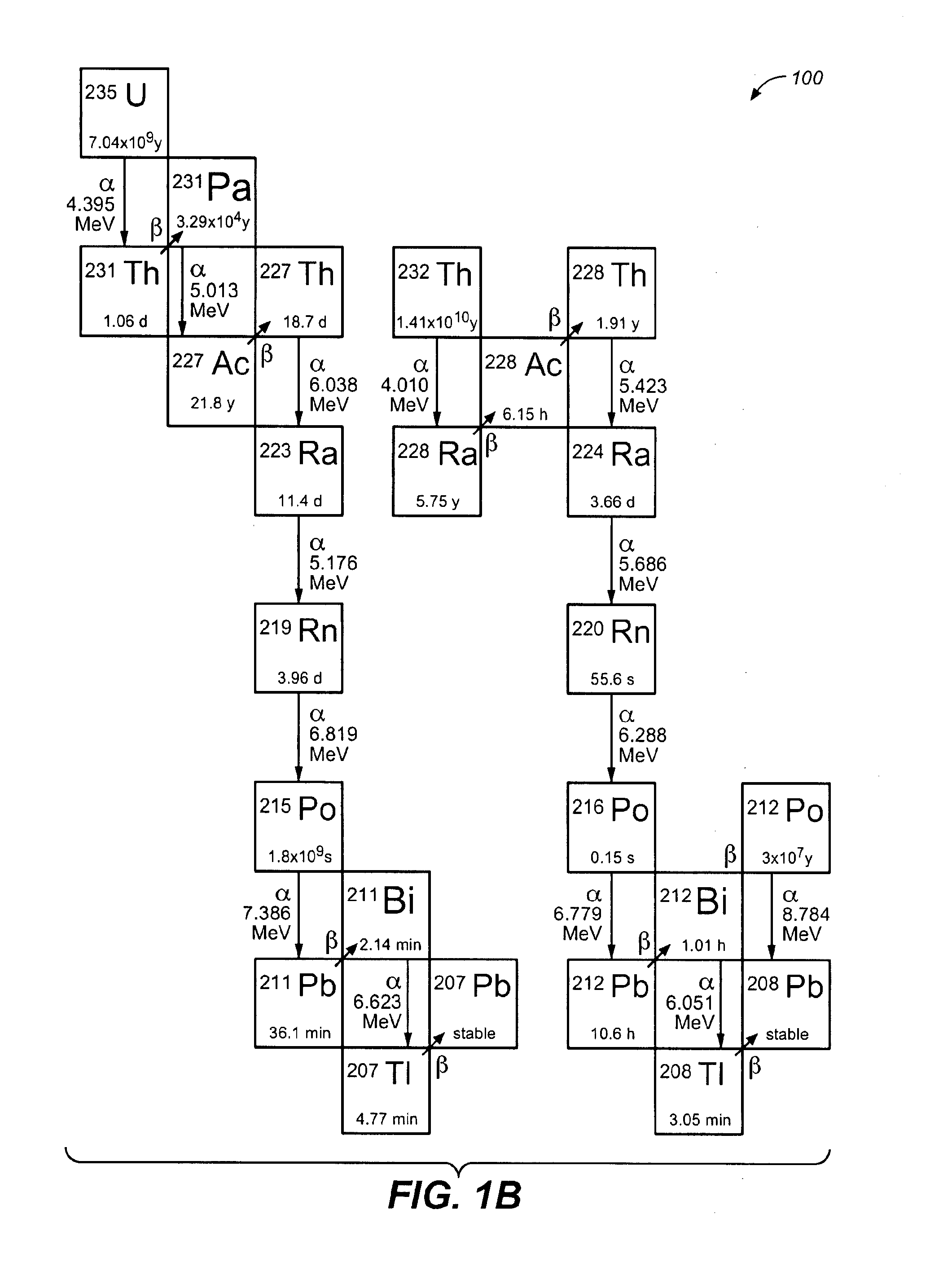
Actinium is a chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89. It was first isolated by French chemist André-Louis Debierne in 1899. Friedrich Oskar Giesel later independently isolated it in 1902 and, unaware that it was already known, gave it the name emanium. Actinium gave the name to the actinide series, a group of 15 similar elements between actinium and lawrencium in the periodic table. It is also sometimes considered the first of the 7th-period transition metals, although lawrencium is less commonly given that position. Together with polonium, radium, and radon, actinium was one of the first non-primordial radioactive elements to be isolated.
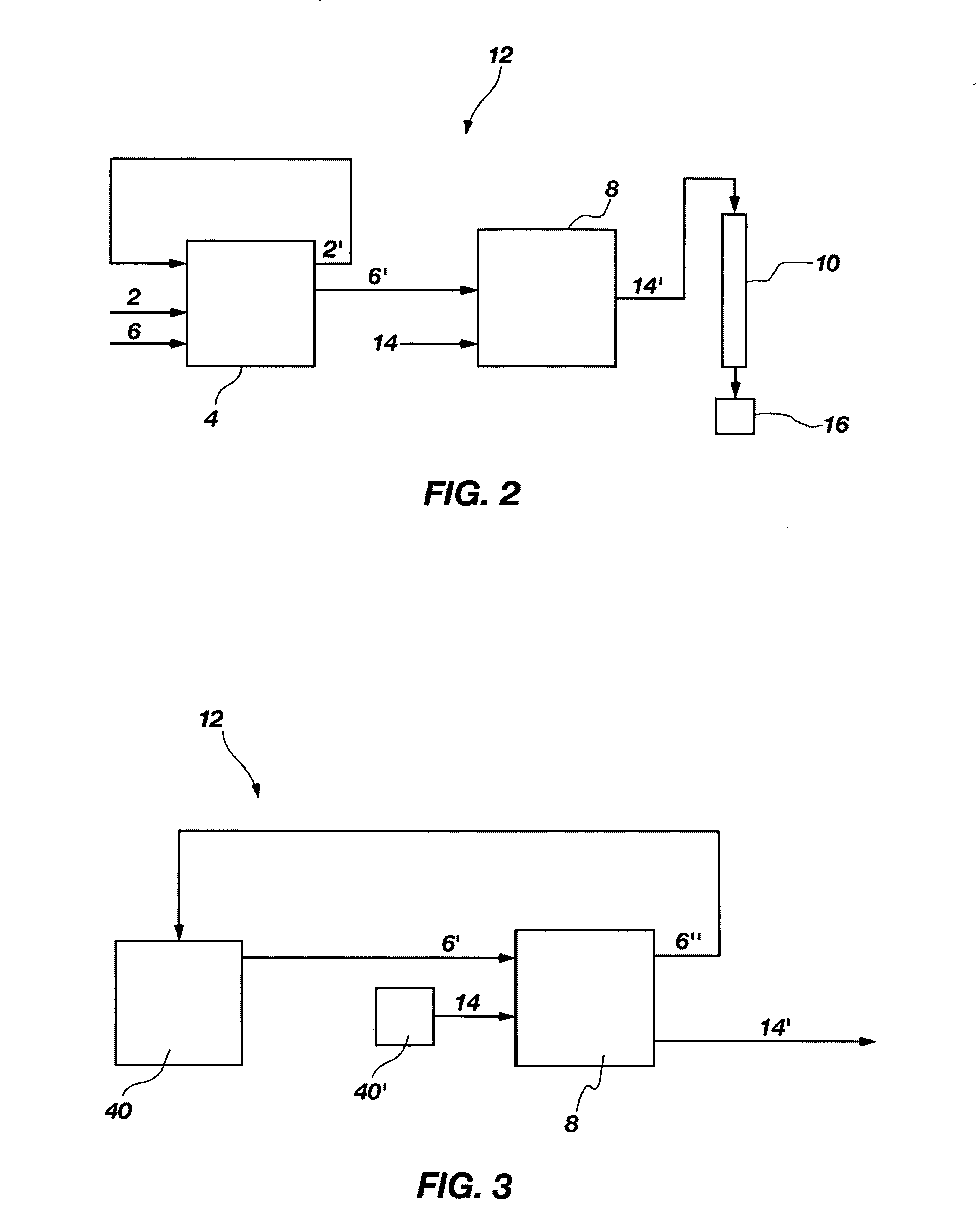
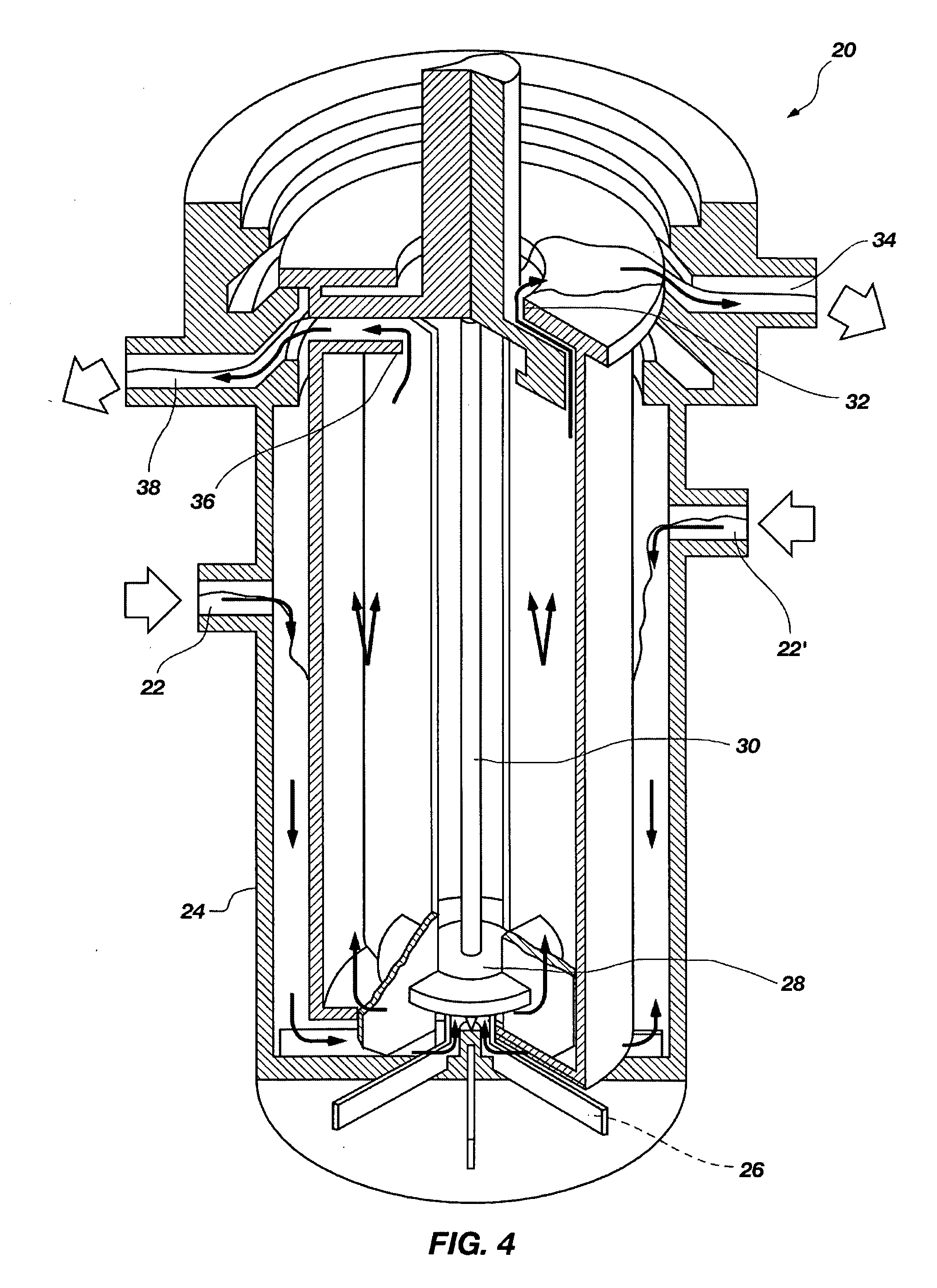
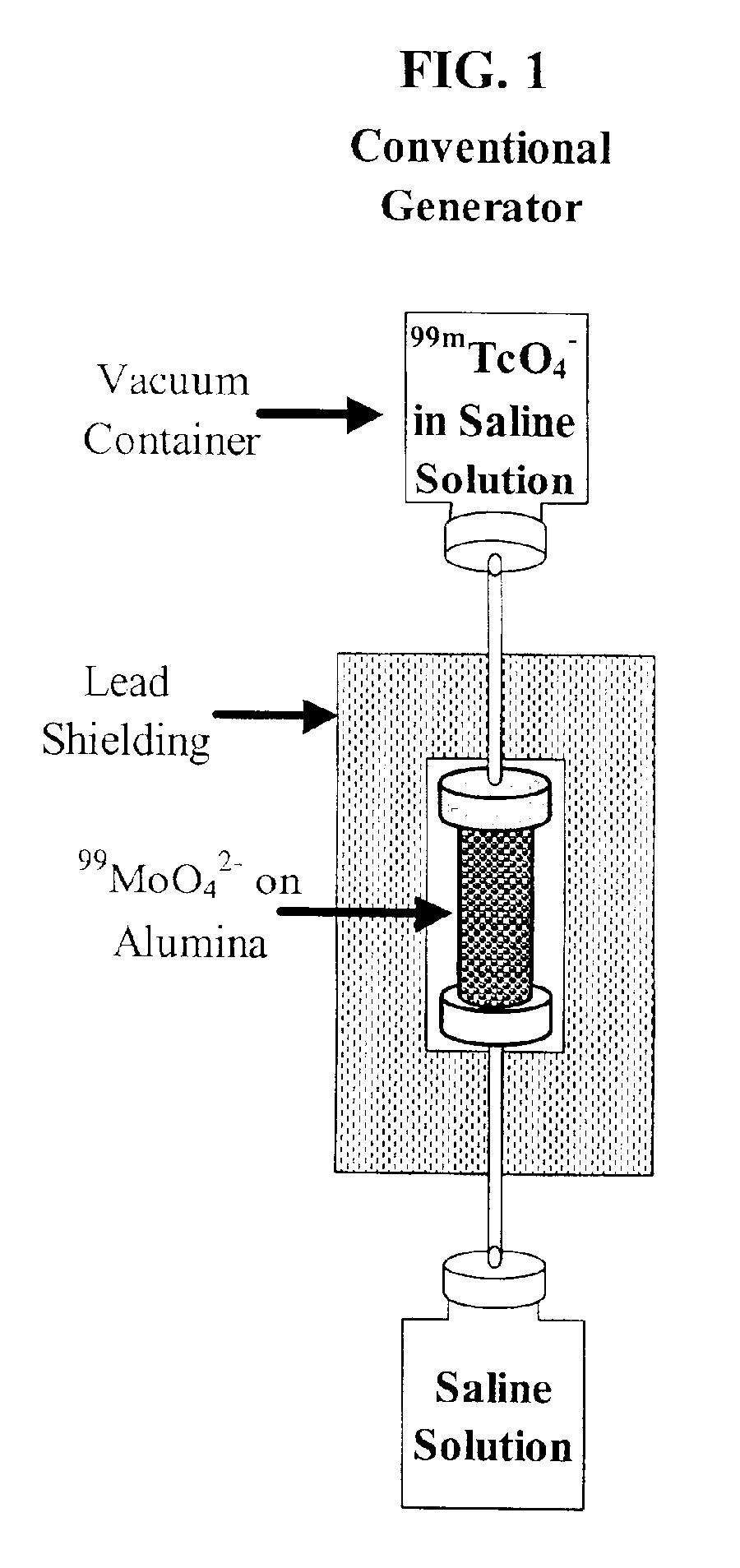
Process for radioisotope recovery and system for implementing same
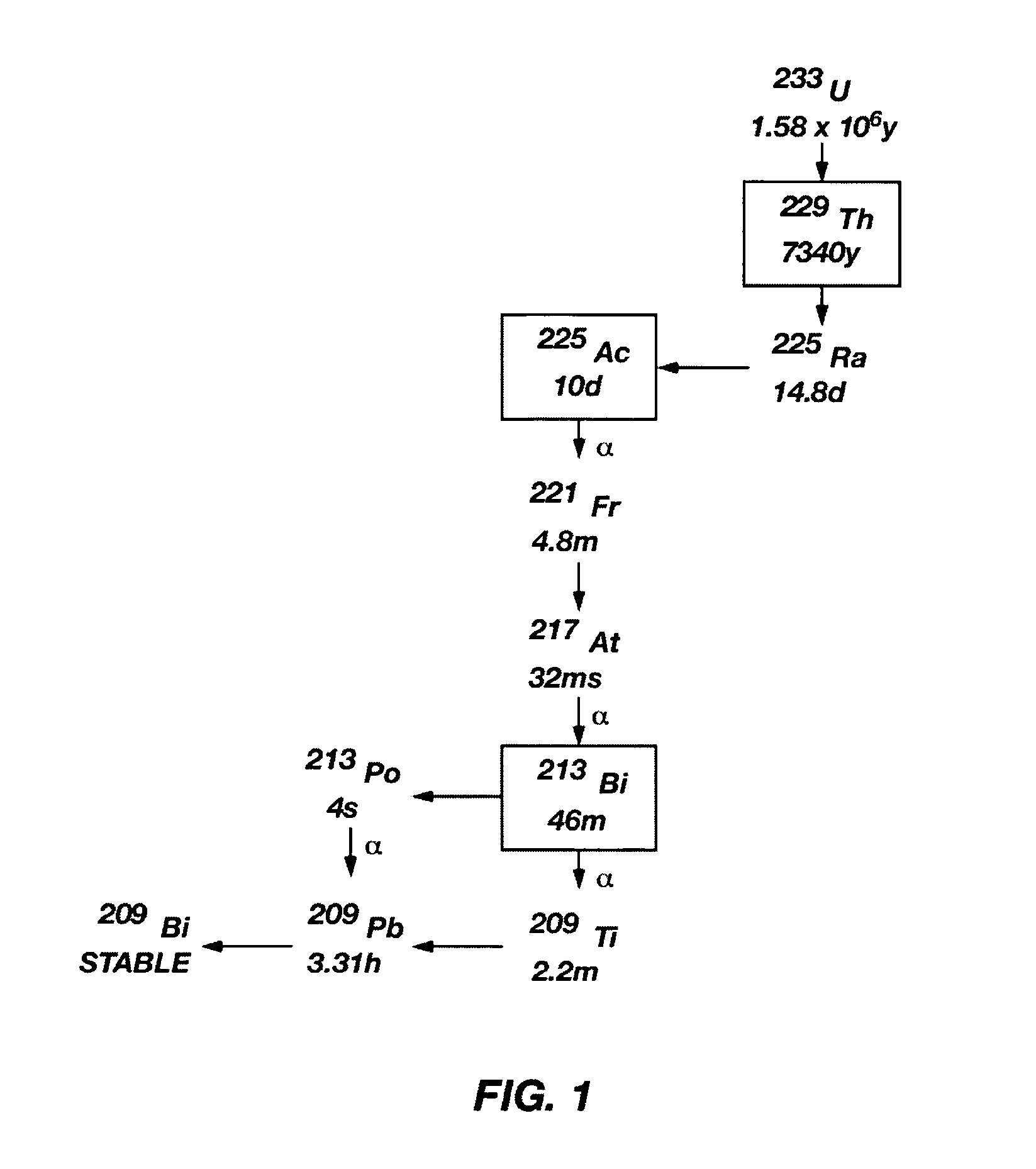
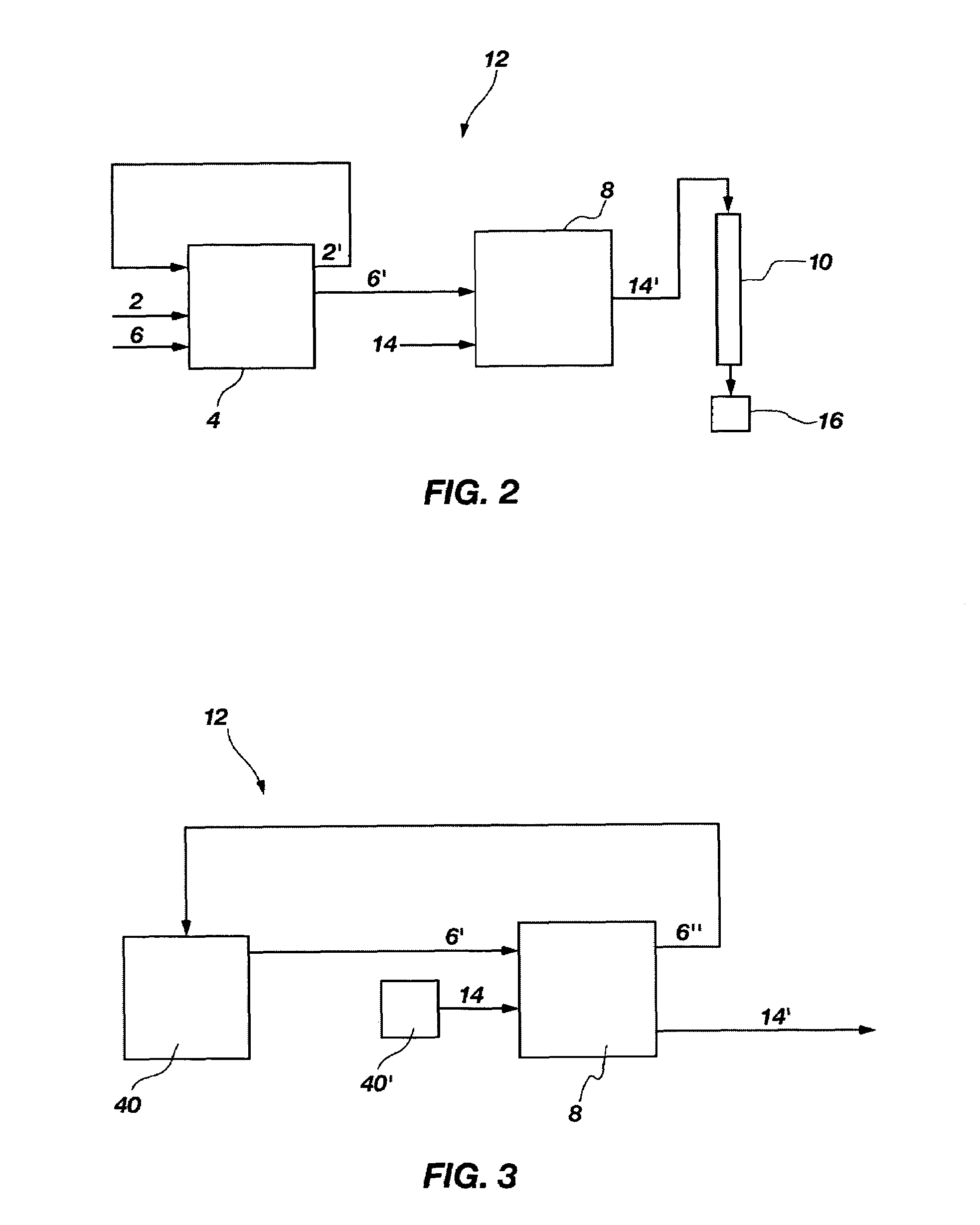
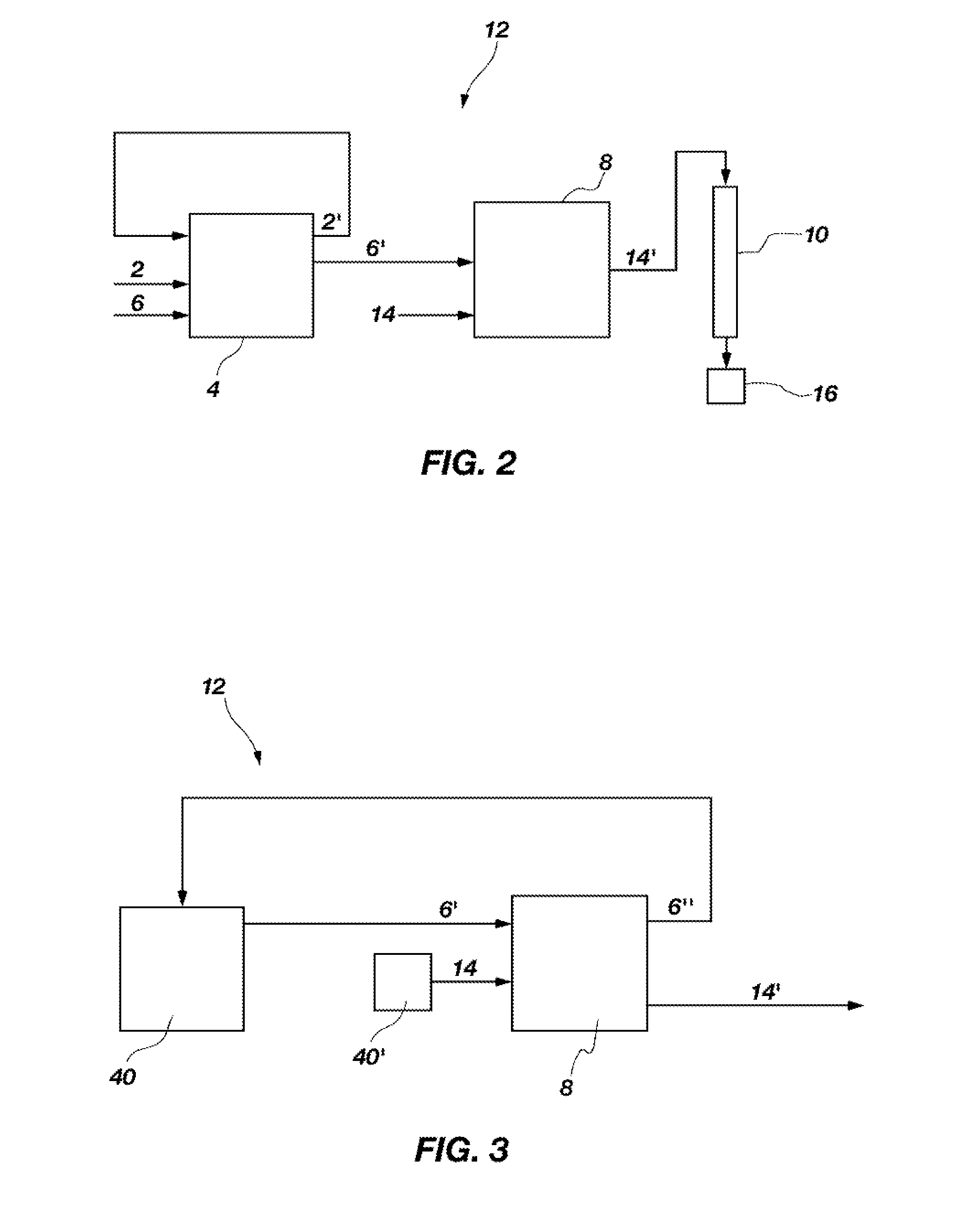
A method of recovering daughter isotopes from a radioisotope mixture. The method comprises providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one parent isotope. The at least one parent isotope is extracted into an organic phase, which comprises an extractant and a solvent. The organic phase is substantially continuously contacted with an aqueous phase to extract at least one daughter isotope into the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase is separated from the organic phase, such as by using an annular centrifugal contactor. The at least one daughter isotope is purified from the aqueous phase, such as by ion exchange chromatography or extraction chromatography. The at least one daughter isotope may include actinium-225, radium-225, bismuth-213, or mixtures thereof. A liquid-liquid extraction system for recovering at least one daughter isotope from a source material is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Separation of radium and rare earth elements from monazite
InactiveUS20100018347A1Efficiently recoversEfficient separationIon-exchange process apparatusAnion exchanger materialsRare-earth elementDecay product
A method of chemically extracting radium-228, rare earth metals, thorium, the decay products of thorium, and phosphates from thorium-containing ores. The method involves breaking thorium-containing ore into fragments, wetting the fragments with a concentrated strong acid to make a slurry, heating the slurry, passing the heated solution through a first anion exchange column, retaining metals and radium-228 captured on the resin, allowing the radium-228 ions to decay to actinium-228, purifying the actinium-228 fraction, sending the actinium-228 fraction through a capture column, eluting the captured thorium-228 with acid, removing radium from the solution, retaining the radium-228 fraction for isomer in-growth, retaining decay products from the radium-228, separating the REEs from the process stream; and eluting and retaining the REEs.
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S +1
Novel neodymium iron boron magnetic material
The invention discloses a novel neodymium iron boron magnetic material, which is characterized in that the general molecular formula of the neodymium iron boron magnetic material is RExNd(0.27-x)Fe0.72B0.01, wherein the RE is selected from at least one of lanthanide / actinium metals except neodymium, and x is the weight ratio of the RE and is about 0.027-0.108. For the novel neodymium iron boron magnetic material preferably selected in the invention, rare earth element cerium (Ce) replaces the partial neodymium (Nd), good magnetism and corrosion resistance can be still kept basically, and has remarkable cost and price advantages are realized.
Owner:麦格昆磁(天津)有限公司
Doped and coated dual-modified lithium/sodium layered metal oxide positive electrode material and one-step synthesis method therefor
ActiveCN107369826ASimple processImprove structural propertiesCell electrodesSecondary cellsSynthesis methodsLanthanide
The invention discloses a doped and coated dual-modified lithium / sodium layered metal oxide positive electrode material and a one-step synthesis method therefor. The ion-doped and interface-coated lithium / sodium layered metal oxide positive electrode material is synthesized by adopting a solvent-thermal treatment process / solid-phase ball milling process, wherein the doped ions are one or more than one kinds of F<->, Mg<2+>, Cu<2+>, Zn<2+>, Al<3+>, Fe<3+>, Cr<3+>, Ti<4+>, Zr<4+>, Mo<4+>, Sb<5+> and V<5+>; and the interface coating material is an ion compound which comprises lanthanide series or actinium series ions with radiuses greater than or equal to 1.016<angstrom>. By abandoning the idea that an ion-doped positive electrode material sample is prepared firstly and then interface coating is performed in the conventional process, the new method for the doped and coated dual-modified lithium / sodium layered metal oxide positive electrode material is developed through one-step synthesis, and the new method has the characteristic of simple process; and in addition, the electrochemical performance of the dual-modified positive electrode material is greatly improved, so that the positive electrode material can be used for a power battery and an energy storage secondary battery.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Coal ash roller type fine extractive technique
InactiveCN101200305ACompletely zero emissionsIron oxides/hydroxidesSolid waste disposalFerric hydroxideBrick
The invention relates to a powder coal ash rolling-type fine extraction method which can effectively peel and dissolve extractive, serially extract active silica, ferric hydroxide, iron oxide red, magnesium hydrate, calcium hydroxide, barium sulfate, lithium carbonate and lanthanide series and actinium series rare earth hydroxide with an enrichment amount >=0.01%, manganese, copper, zinc and gallium with an enrichment amount >=0.05%, and germanium dioxide, vanadium pentoxide, gold, silver, palladium and platinum metal with an enrichment amount >=0.0001% from the powder coal ash. The powder coal ash rolling-type fine extraction method has the advantages that the remainder ash of the powder coal ash after the treatment by the rolling-type fine extraction technique can be still comprehensively used for making brick and blending coagulation, thereby fully using the powder coal ash and realizing zero emission.
Owner:李文志 +1
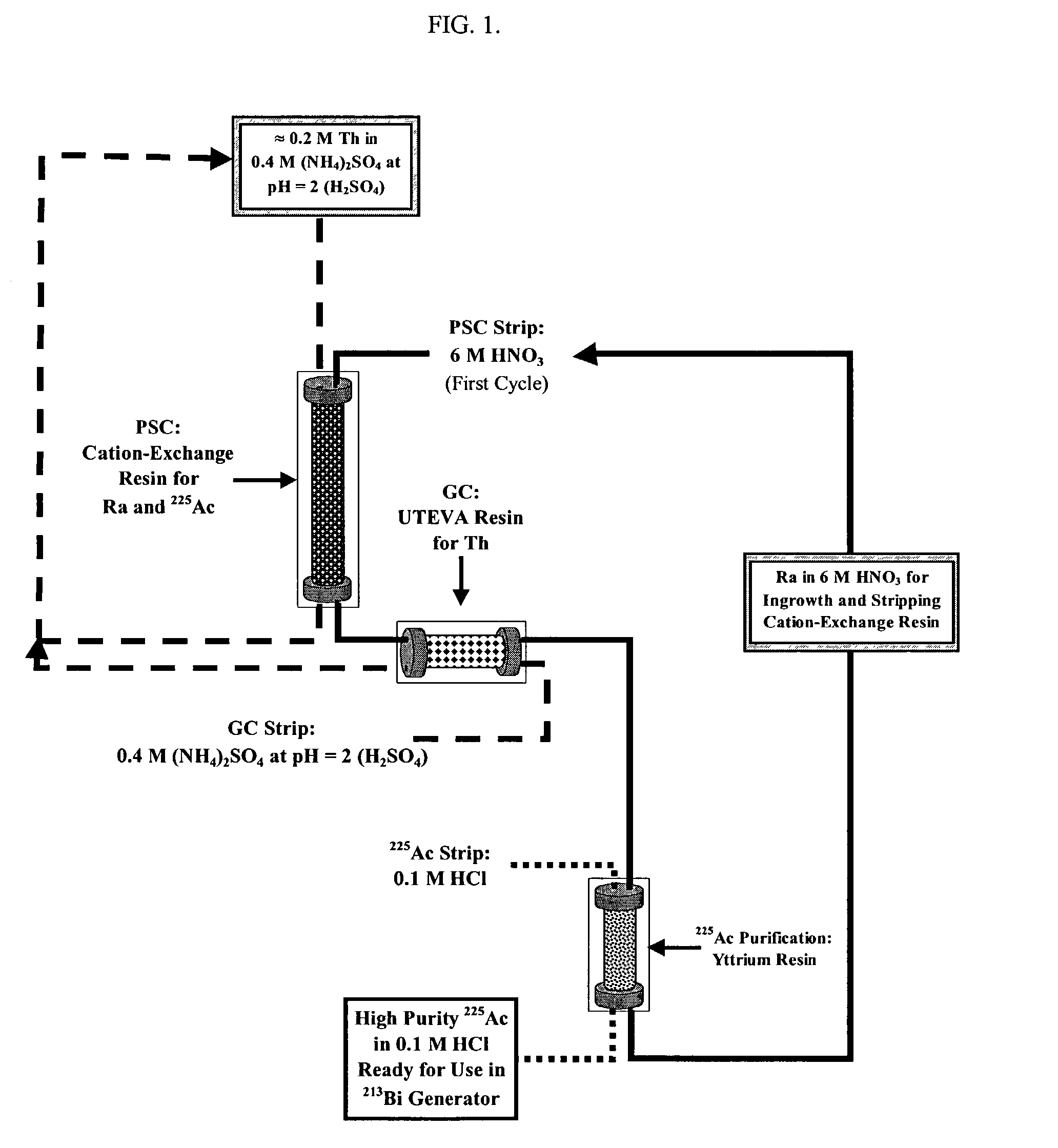
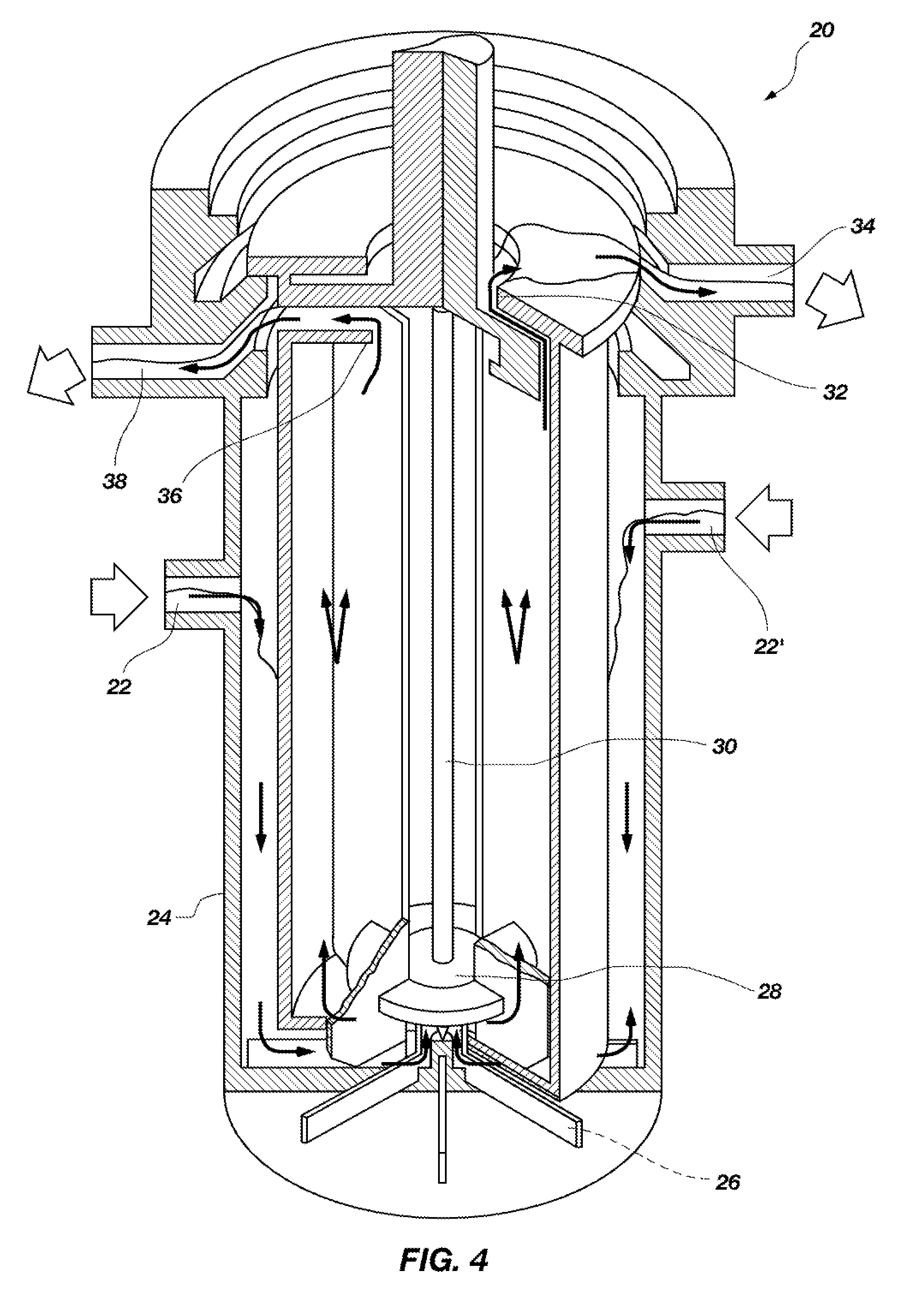
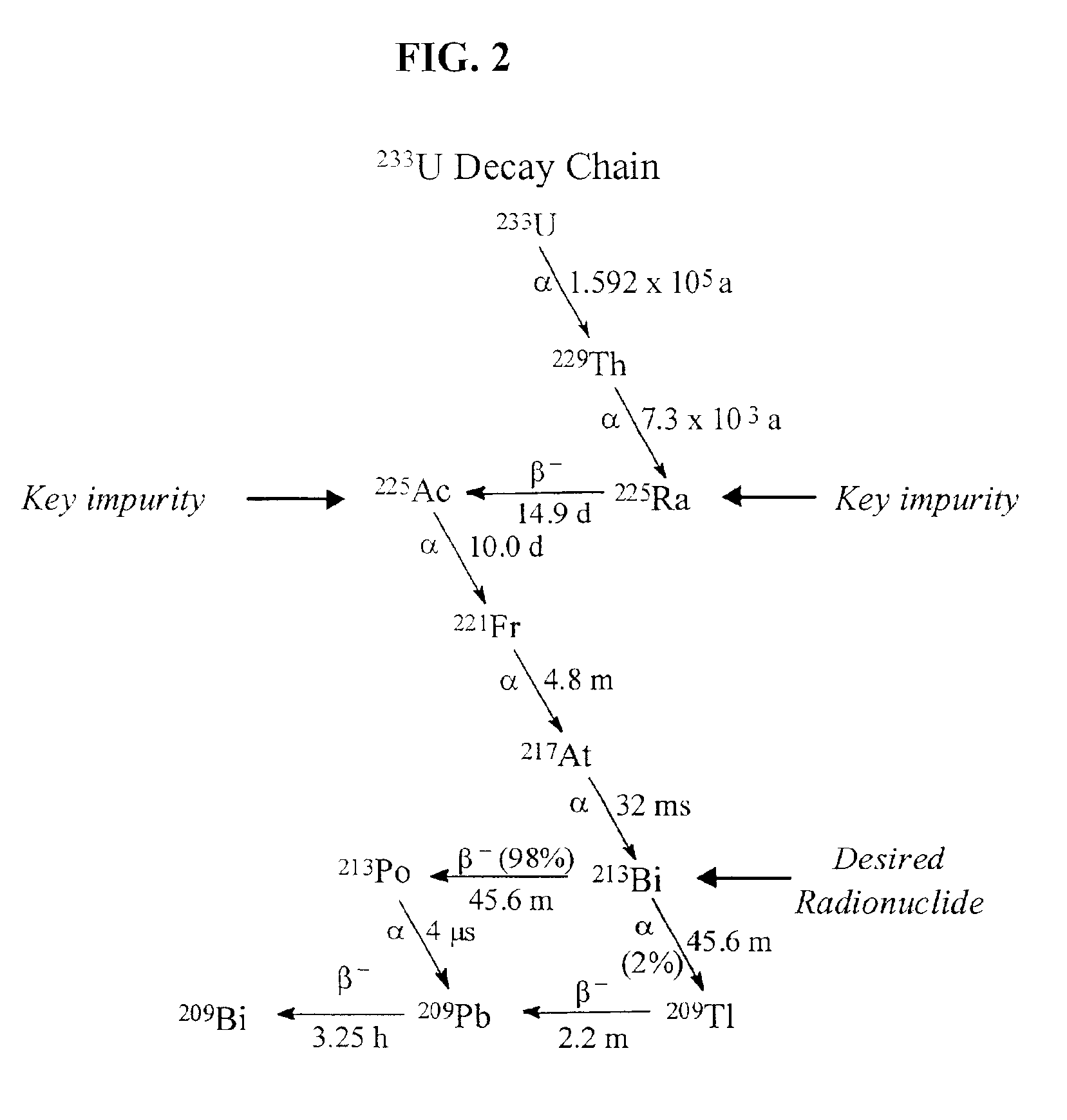
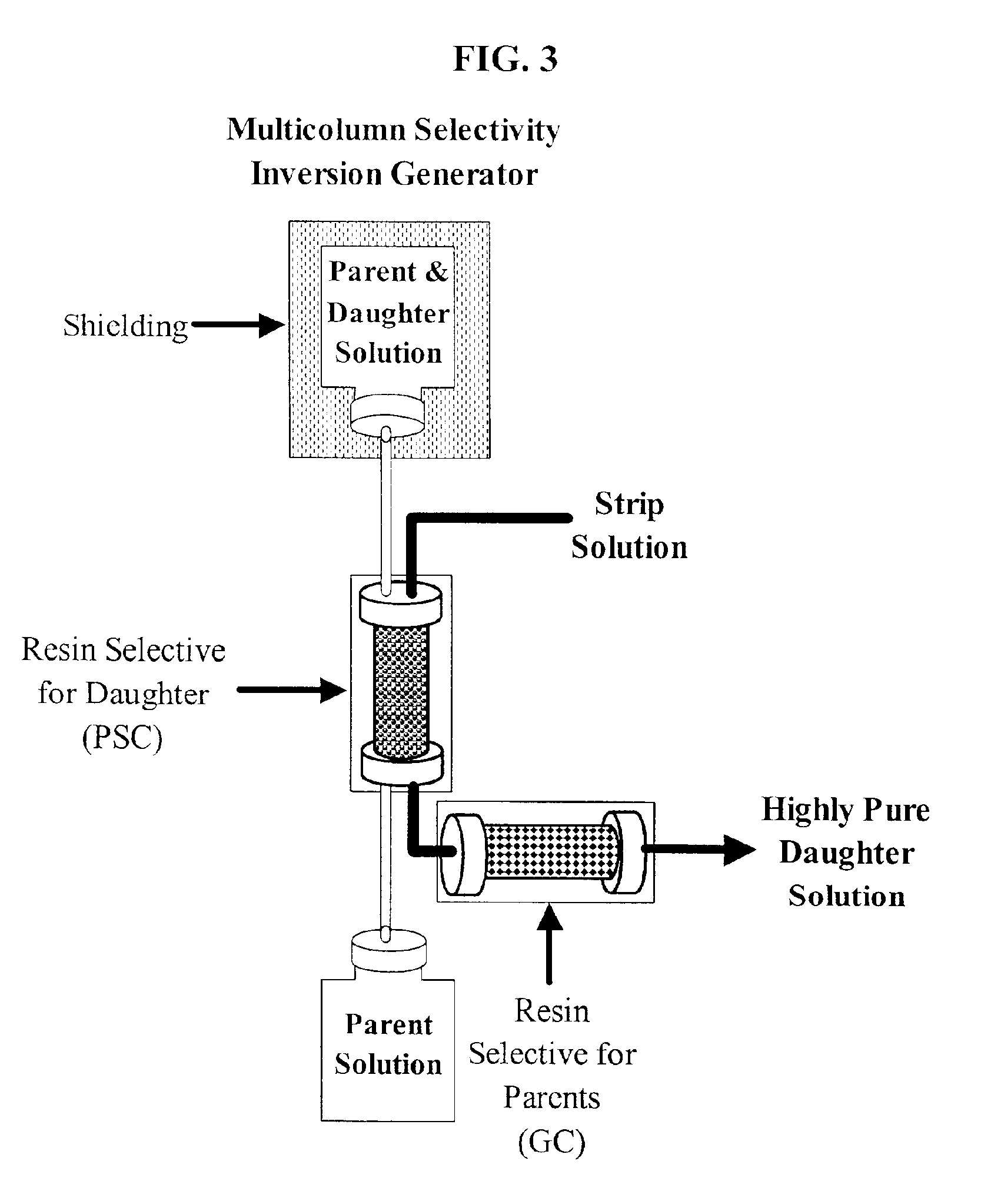
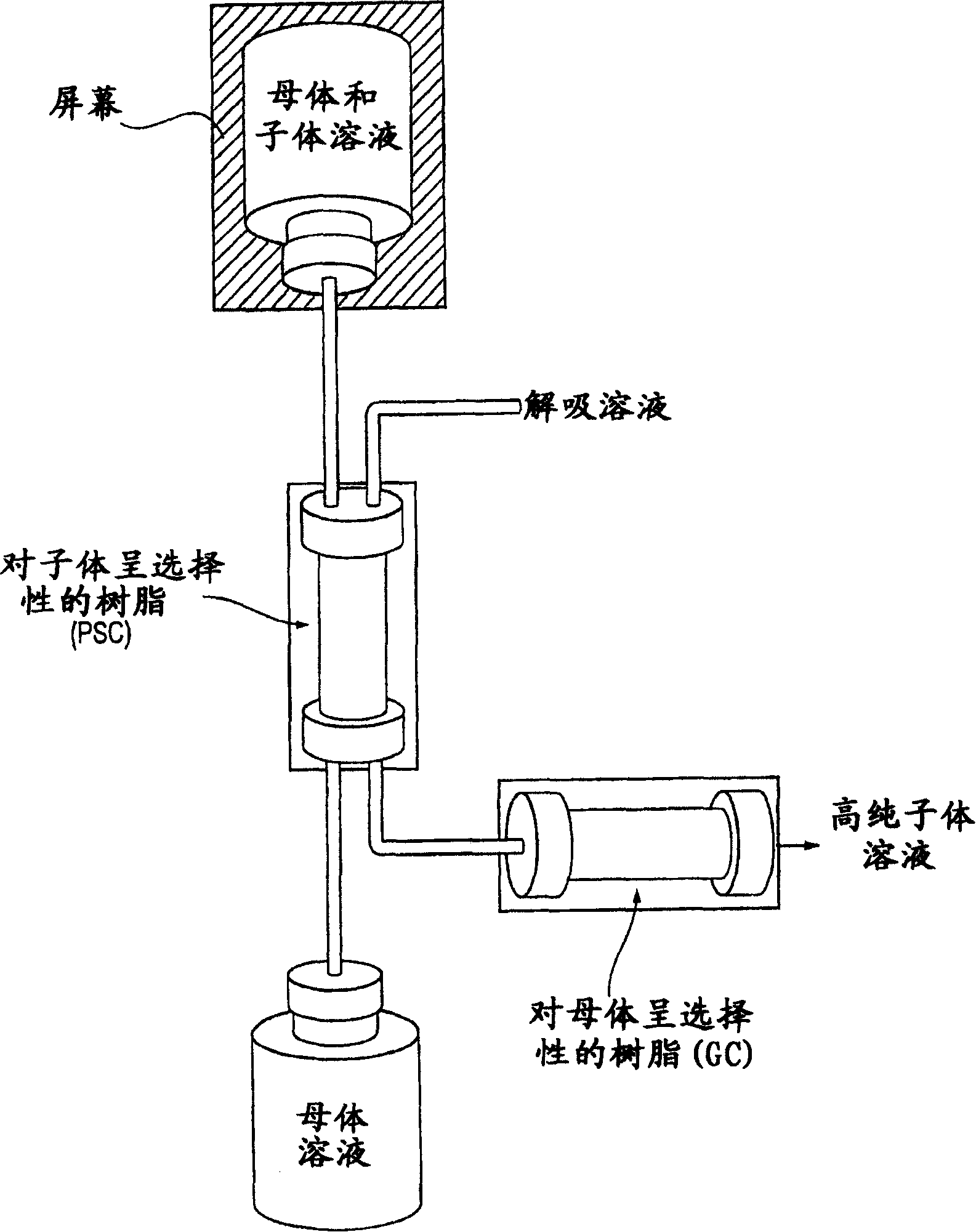
Multicolumn selectivity inversion generator for production of high purity actinium for use in therapeutic nuclear medicine
InactiveUS7087206B2Separation efficiency is highSmall volumeIsotope delivery systemsTransuranic element compoundsActiniumRadiation damage
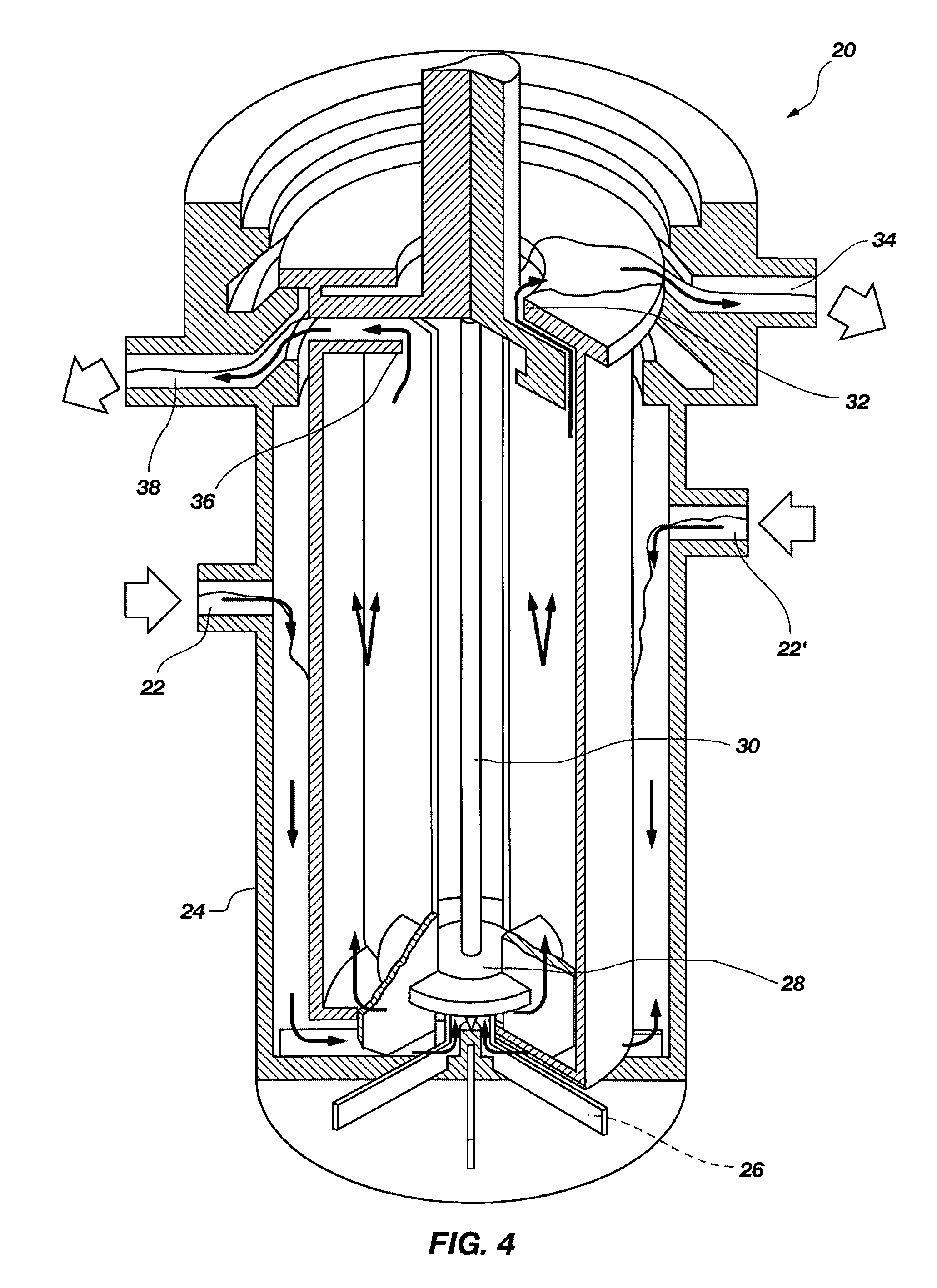
A multicolumn selectivity inversion generator separation method has been developed in which actinium ions, a desired daughter radionuclide, are selectively extracted from a solution of the thorium parent and daughter radionuclides by a primary separation column, stripped, and passed through a second guard column that retains any parent or other daughter interferents, while the desired daughter actinium ions and radium ions elute. This separation method minimizes the effects of radiation damage to the separation material and permits the reliable production of radionuclides of high chemical and radionuclidic purity for use in diagnostic or therapeutic nuclear medicine.
Owner:PG RES FOUND
Process for radioisotope recovery and system for implementing same
InactiveUS20060153760A1Sure easySolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsSource materialIon exchange
A method of recovering daughter isotopes from a radioisotope mixture. The method comprises providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one parent isotope. The at least one parent isotope is extracted into an organic phase, which comprises an extractant and a solvent. The organic phase is substantially continuously contacted with an aqueous phase to extract at least one daughter isotope into the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase is separated from the organic phase, such as by using an annular centrifugal contactor. The at least one daughter isotope is purified from the aqueous phase, such as by ion exchange chromatography or extraction chromatography. The at least one daughter isotope may include actinium-225, radium-225, bismuth-213, or mixtures thereof. A liquid-liquid extraction system for recovering at least one daughter isotope from a source material is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
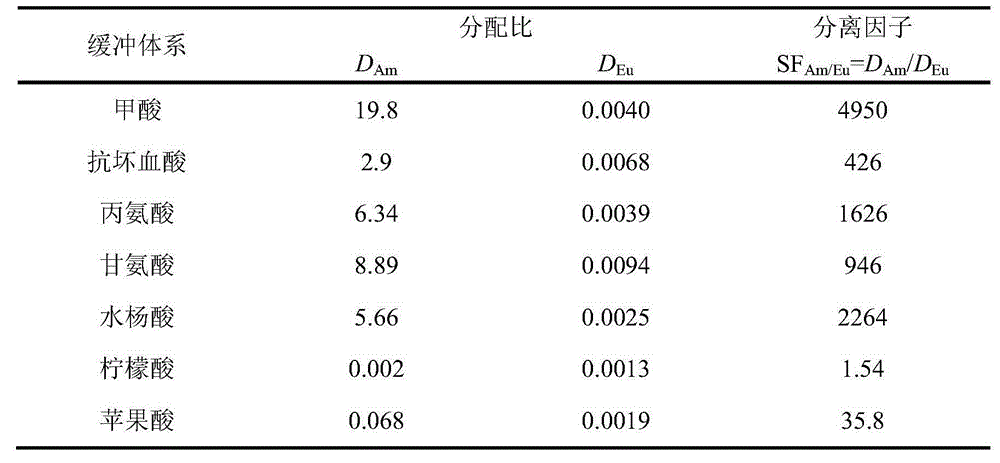
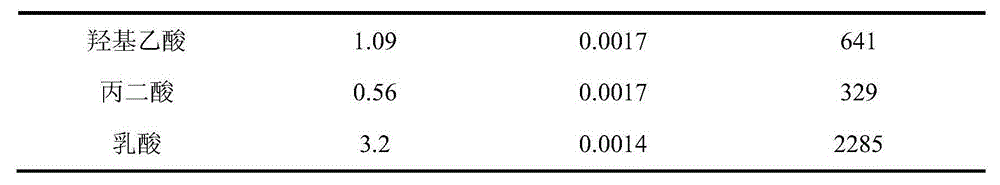
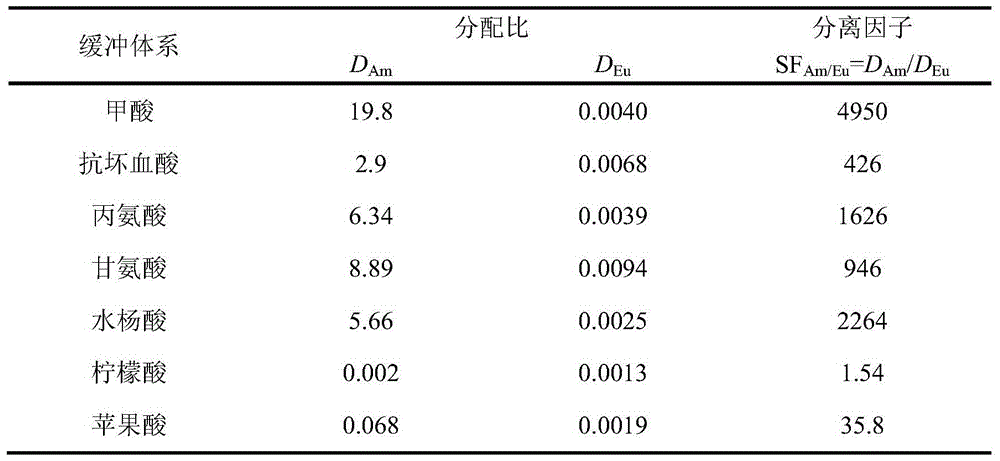
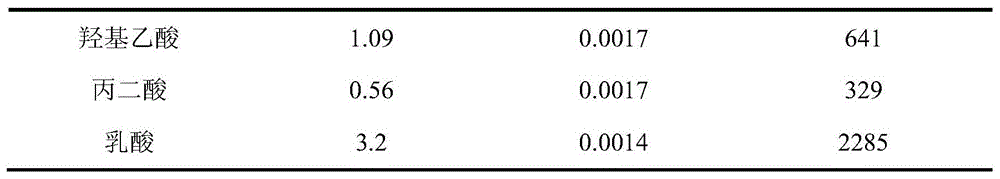
Method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ion
ActiveCN104894372AMaintain efficient extraction and separation performanceImprove stabilityProcess efficiency improvementPh regulationActinium
The invention relates to a method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions and belongs to the technical field of nuclear fuel circulation and waste liquid treatment. The method uses bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) dithiophosphinic acid as an extracting agent, uses long-chain alkane as a thinning agent and uses a weak acid buffer system to effectively stabilize the pH value of the water phase of an extraction system, pH regulation does not need to be performed to the system during extraction, trivalent actinium elements can be high-selectively extracted and separated out from the water phase, and most of trivalent lanthanum elements are remained in the water phase. The method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions has the advantages that the extraction and separation performance of trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions is high and stable and the prospect of application in the field of advanced nuclear circulation is better.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Efficient nuclear waste evolution sub-critical reactor core based on mixed energy spectrum
InactiveCN102623078AIncrease profitSimple structureRadioactive decontaminationLead bismuthLiquid state
The invention relates to an efficient nuclear waste evolution sub-critical reactor core based on a mixed energy spectrum, comprising an external neutron source area, an evolution area, a slowing-down layer area, a reflecting layer area and a shielding layer area from the center to the outside in sequence; and as the slowing-down layer area and the reflecting layer area are arranged on the periphery of the evolution area, a neutron is sufficiently slowed down and then is reflected back to the evolution area to form a mixed energy spectrum, and the mixed energy spectrum is utilized to carry out evolution to sub-actinium-series nuclide (MA) and long-life fission products (LLFP) simultaneously. According to the invention, the mixed energy spectrum is formed by reasonable reactor core structure arrangement, a transuranium nuclide (TRU) fuel area and an LLFP fuel area are respectively arranged according to the distribution conditions of fast neutrons and thermal neutrons, and the two fuel areas adopt a same fuel assembly form, so as to realize evolution of the MA and the LLFP simultaneously in a same evolution area and in a same reaction core; the reactor core structure is simple, the neutron utilization rate is high, the function of efficient nuclear waste evolution is realized, and a liquid state lead-bismuth alloy is adopted as a cooling agent to take fission energy generated in the evolution area out of the reactor core to realize the capacity.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bisdiglycolamide ligand and preparation method thereof and lanthanum serial/actinium serial separation and extraction system containing bisdiglycolamide ligand
InactiveCN106892835AImprove radiation stabilityImprove protectionOrganic chemistryLiquid solutions solvent extractionNitrilotriacetamideWater soluble
The invention discloses a bisdiglycolamide ligand and a preparation method thereof and a lanthanum serial / actinium serial separation and extraction system containing the bisdiglycine amide ligand. The extraction system is formed by mixing an organic phase and an aqueous phase in equal volume, wherein the organic phase contains 0.1-0.7mol / L N,N,N',N',N',N'-hexa n-octyl-nitrilotriacetamide [NTAamide (C8)] as an extraction agent, and the aqueous phase contains the 0.005-0.02mol / L bisdiglycine amide ligand as a masking agent. The N,N,N',N',N',N'-hexa n-octyl-nitrilotriacetamide [NTAamide] in the extraction system has a unique non-N-heterocyclic triangular structure, so that the irradiation-resistant stability of the extraction system can be greatly improved, secondary pollutants are not generated, and the environmental protection is facilitated; and the extraction system which takes the water soluble bisdiglycolamide ligand as the masking agent has the characteristic of more tending to be complex with lanthanum series, and the lanthanum series can be effectively masked in the aqueous phase, so that selective separation of actinium series and lanthanum series is realized.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fusion driving subcritical cladding of transmutation subordinate actinium series nuclide
ActiveCN103093836AEasy loadingEasy to disassembleNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorMetal alloyStructure of the Earth
A fusion driving subcritical cladding of transmutation subordinate actinium series nuclide is formed by a plurality of same independent small modules. The whole shape of each small module is D-shaped. Each small module comprises an inner cladding, an outer cladding and a D-shaped plasma body cavity which is formed in each small module. The inner cladding is in a cylindrical shape. The inner cladding successively comprises an inner shield, an inner reflecting layer, an inner first wall and an inner scraping layer from inside to outside along the radial direction. The whole shape of the outer cladding is also D-shaped. The outer cladding successively comprises an outer scraping layer, an outer first wall, a transmutation area, a tritium breeding blanket, an outer reflecting layer and an outer shielding layer from inside to outside along the radial direction. A plurality of transmutation fuel subassemblies are horizontally arranged in the transmutation area along the first wall. By the adoption of the modularized design, fuel is convenient to load and unload. By the adoption of the horizontal arrangement of the transmutation fuel subassemblies in the transmutation area, the filling rate of the transmutation area is improved to enable the structure of the transmutation cladding to be more compact. Metal alloy fuel is adopted by the fuel in the transmutation fuel subassemblies, and a hard energy spectrum is obtained to benefit metal alloy (MA) to carry out the direct and effective transmutation through fission reactions.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for solidifying actinium series nuclide by pyrochlore type rare earth zirconate
ActiveCN102779561AEasy disposalImprove efficiencyRadioactive decontaminationWaste processingDeep geological repository
The invention discloses a method for solidifying actinium series nuclide by pyrochlore type rare earth zirconate and belongs to the technical field of radioactive nuclear waste processing. The method includes adopting rare earth nitrate, zirconium nitrate or zirconium oxynitrate, actinium series nuclide raw materials and a little fluxing agent as raw materials, grinding and mixing the raw materials and directly placing the raw materials in a sintering furnace to conduct sintering under certain temperature to obtain a pyrochlore type rare earth zirconate solidified body containing actinium series nuclide. Therefore, radioactive nuclide can be solidified in lattices of the rare earth zirconate to facilitate deep geology processing. The whole solidification process does not require complex high-energy-consumption dangerous steps of repeated grinding, piece pressing, long-time high-temperature sintering, sol gel preprocessing, piece pressing, long-time high-temperature sintering and the like. The method is energy-saving, high in efficiency and good in safety and reduces consumption.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
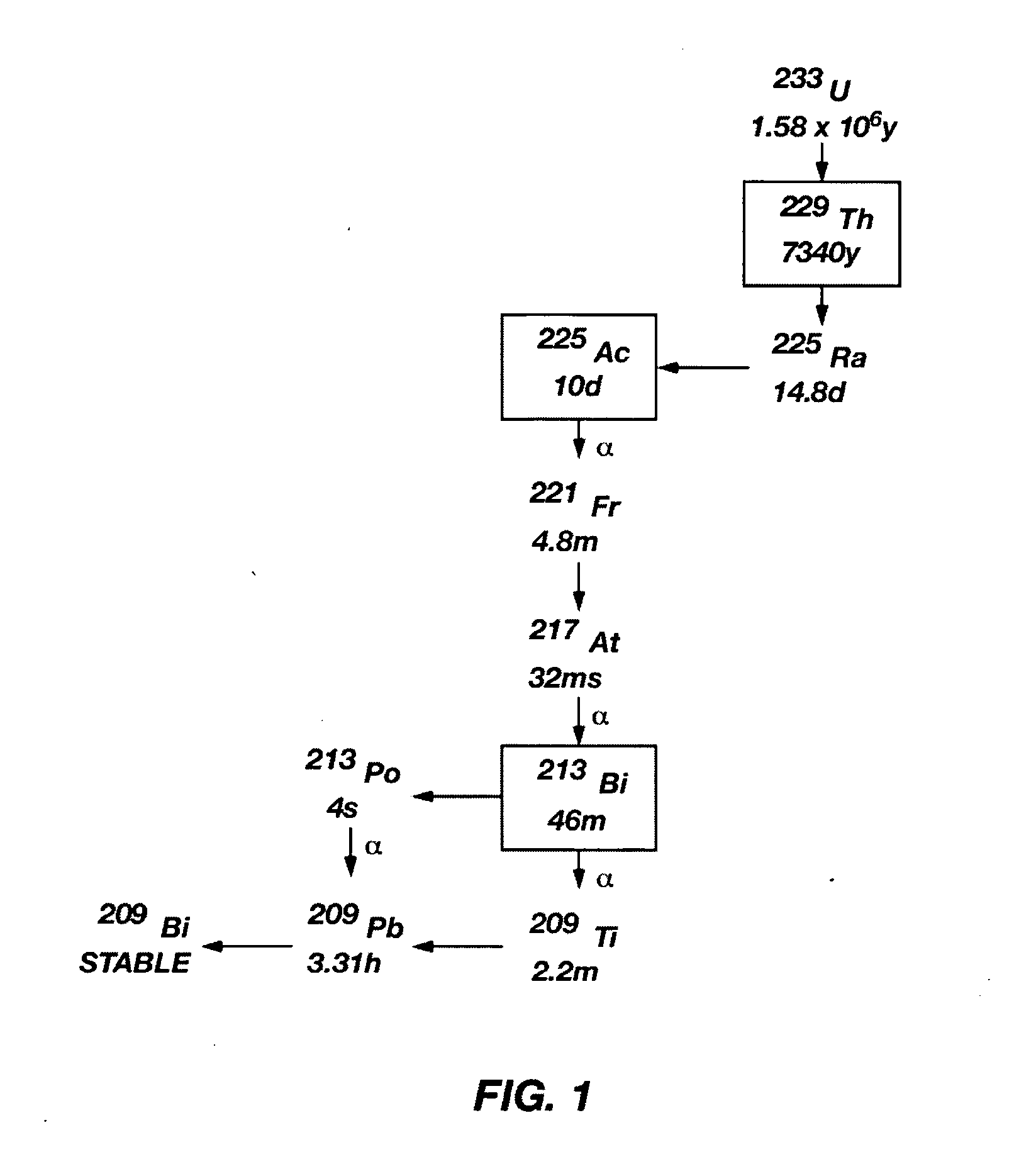
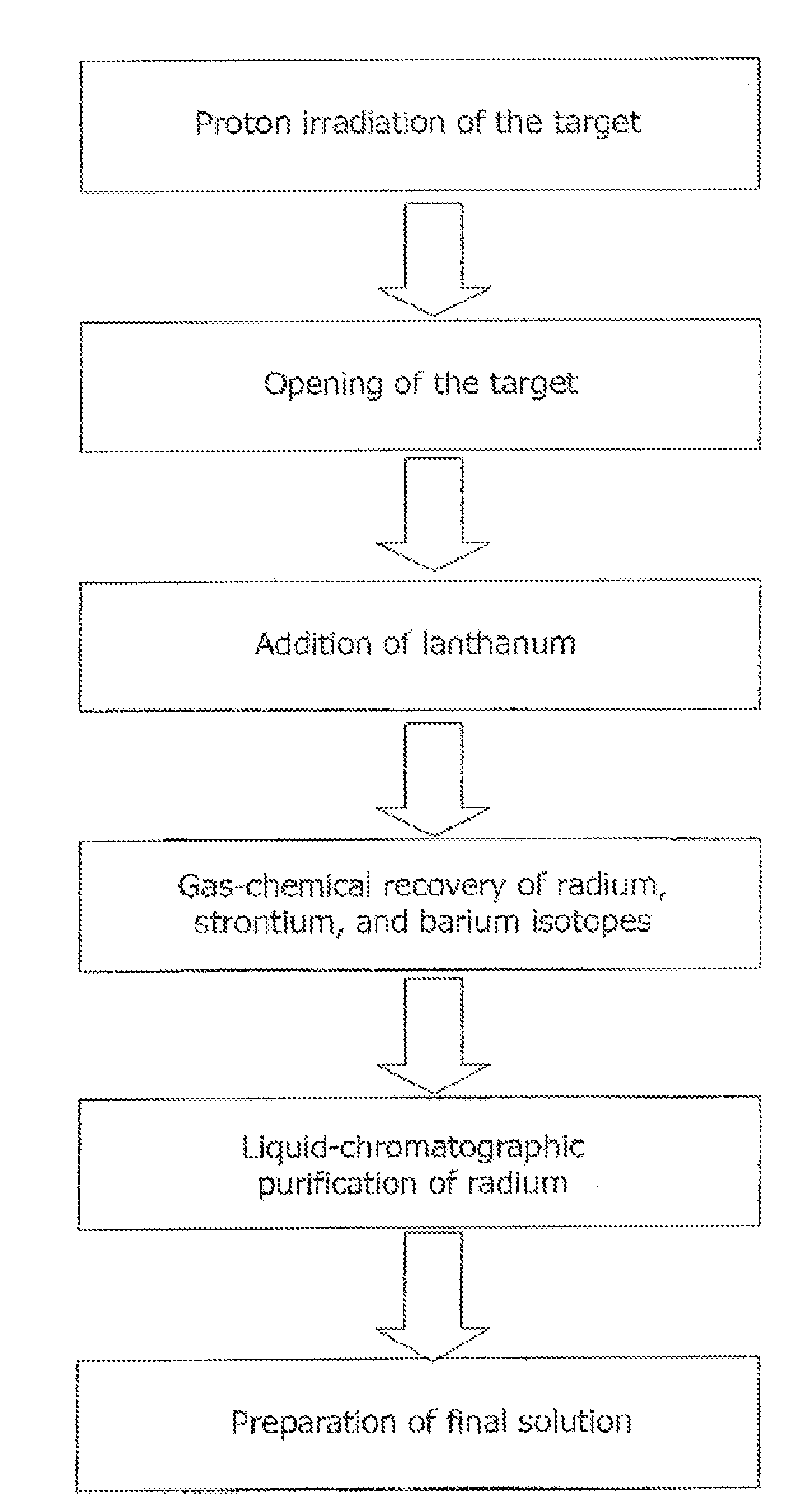
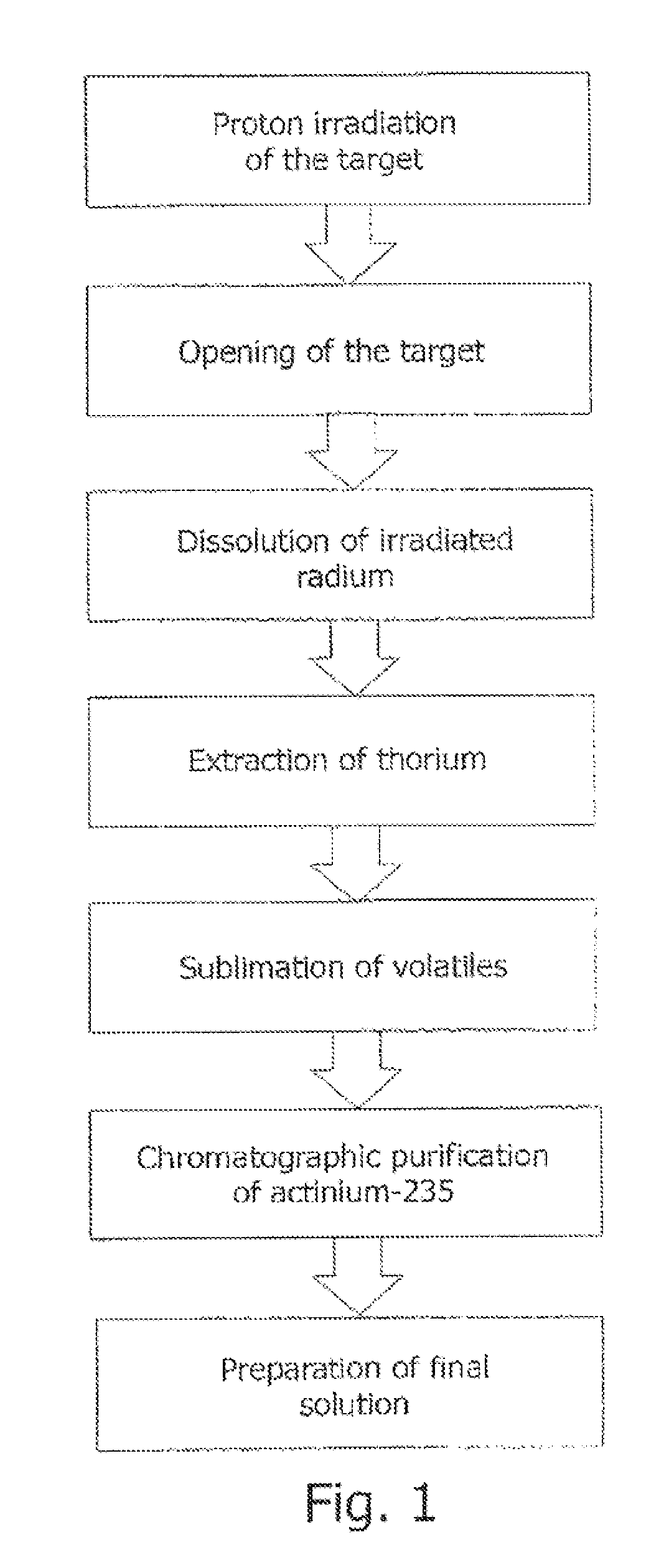
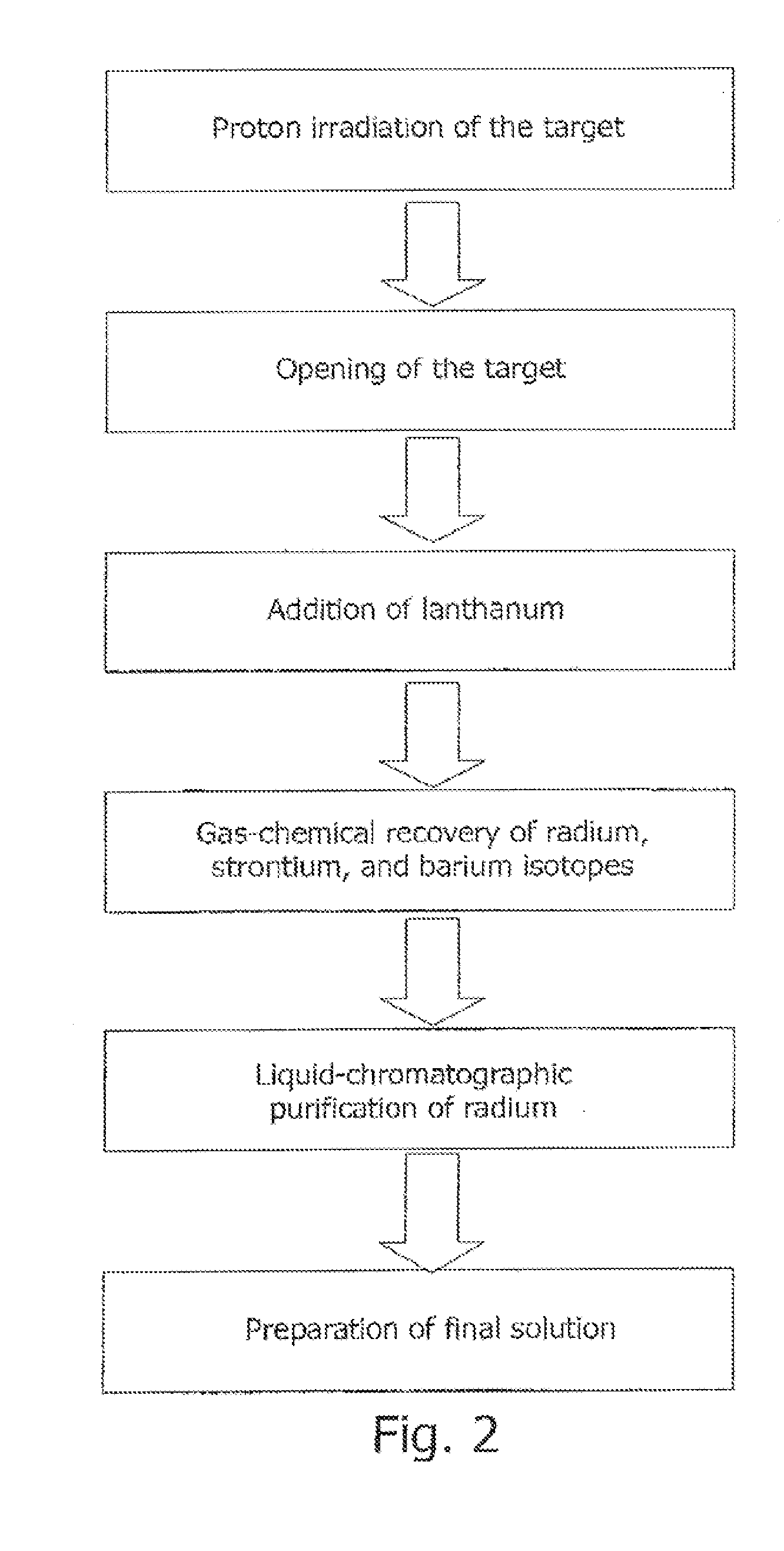
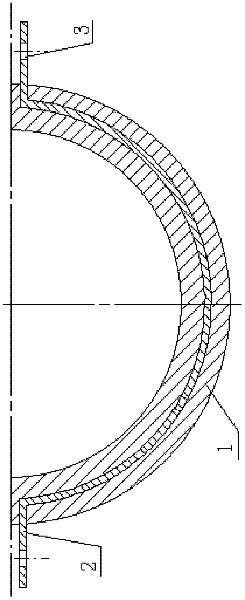
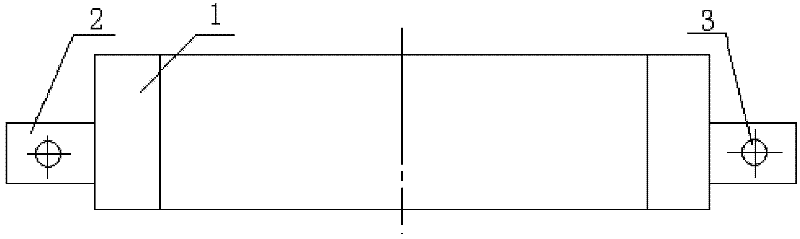
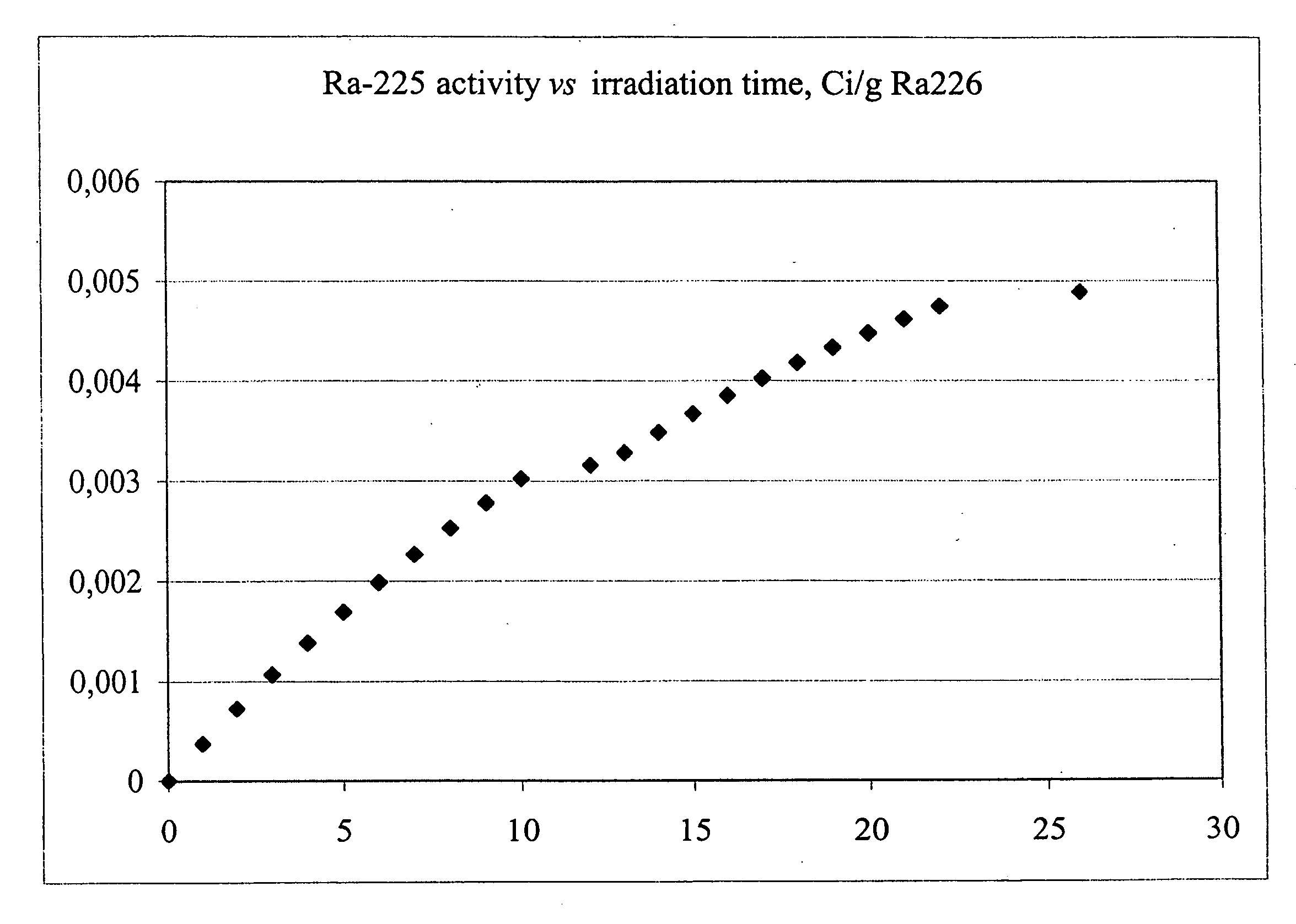
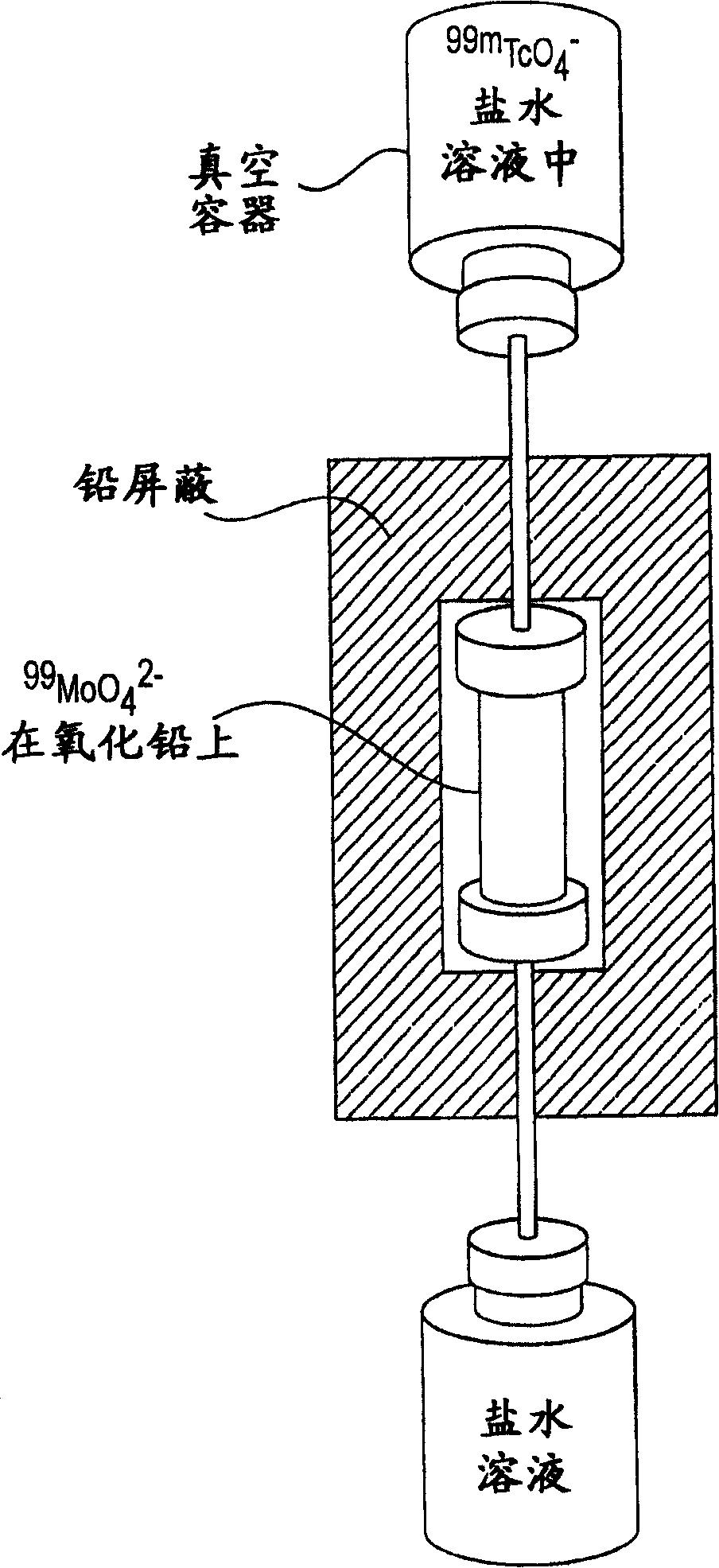
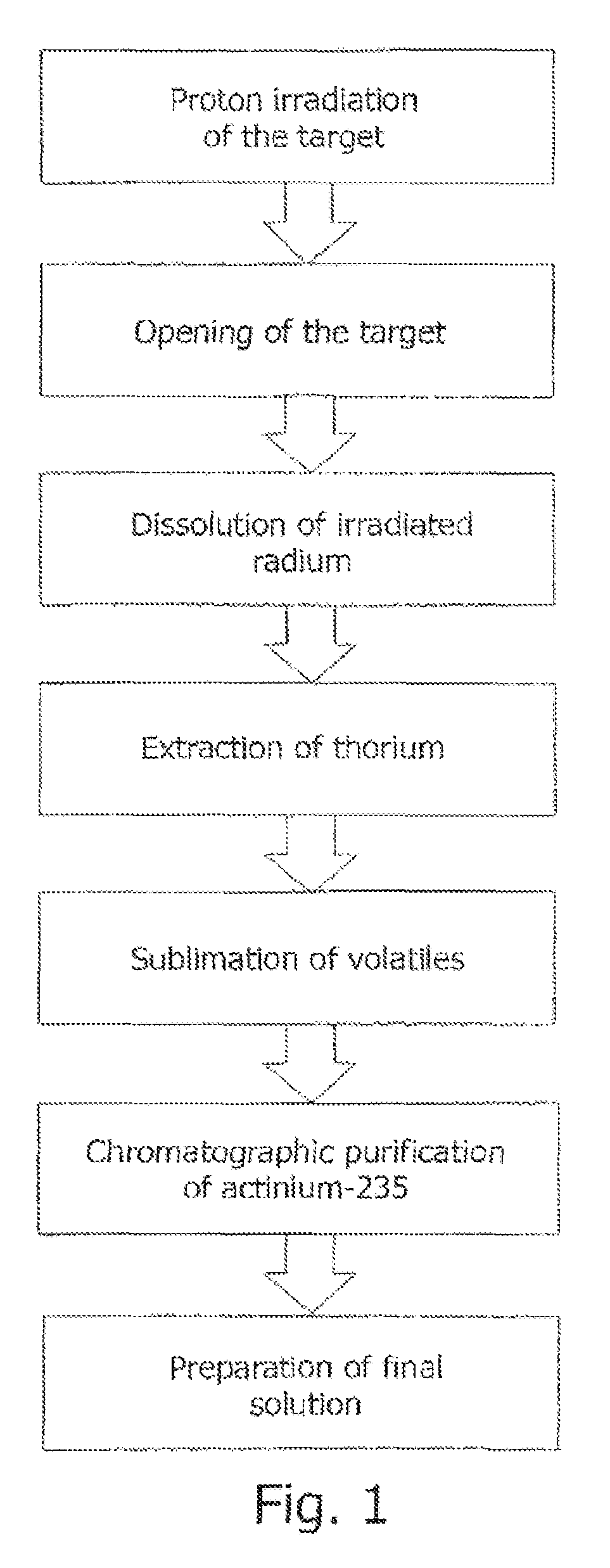
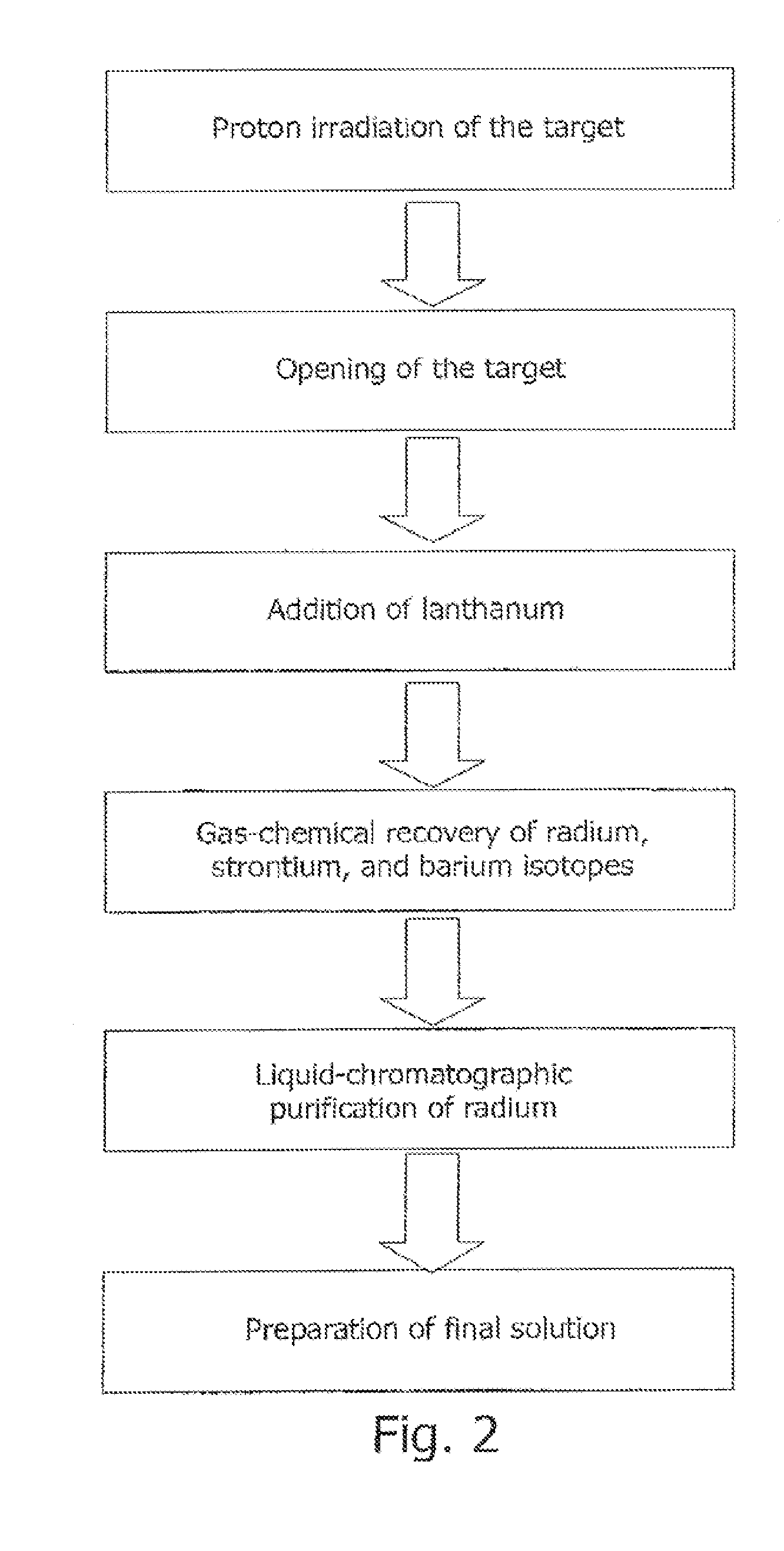
Method for producing actinium-225 and isotopes of radium and target for implementing same
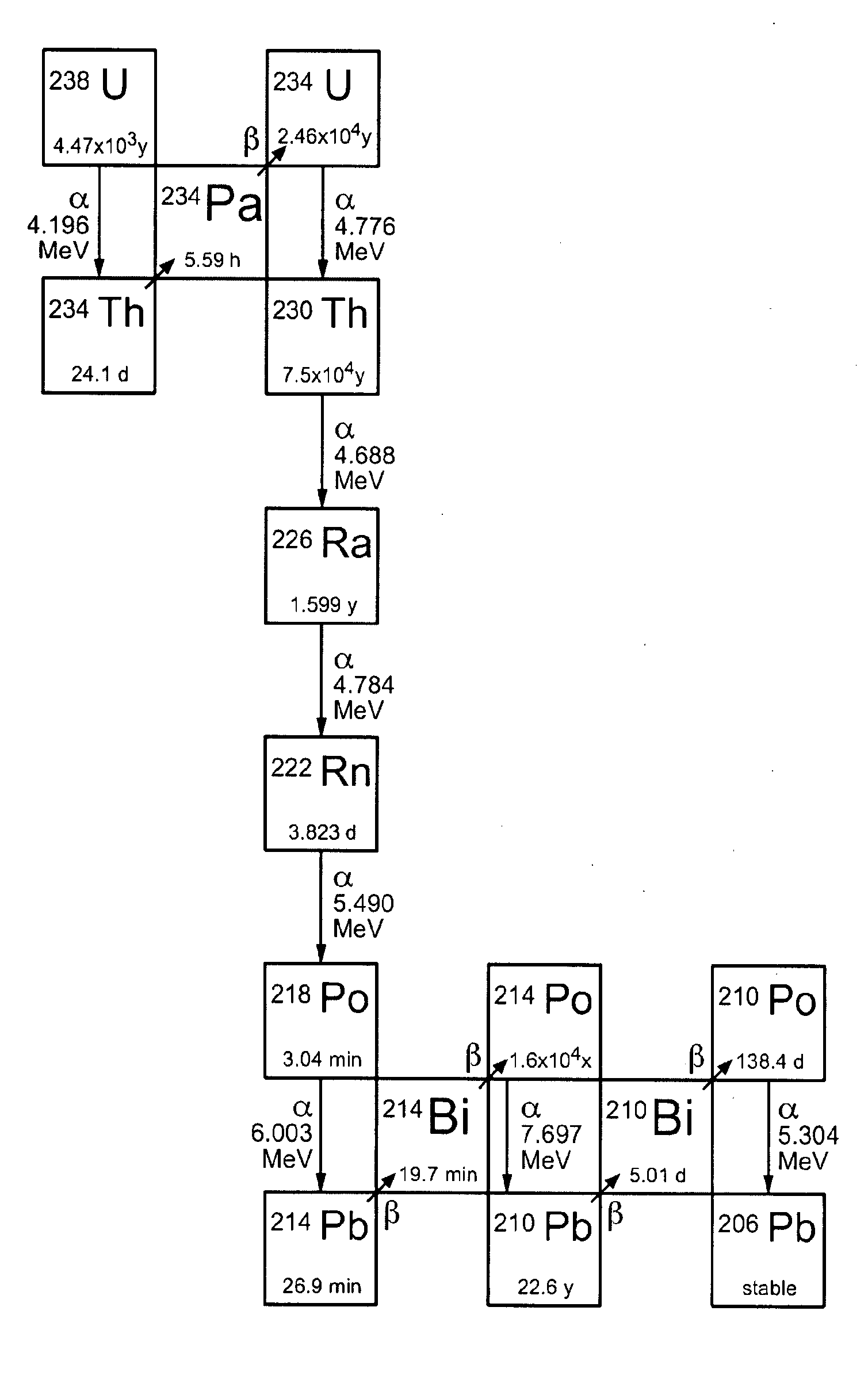
The invention relates to the field of nuclear technology and radiochemistry, more specifically to the production and isolation of radionuclides for medical purposes. The method for producing actinium-225 and isotopes of radium comprises irradiating a solid block of metallic thorium of a thickness of 2 to 30 mm, which is contained within a hermetically sealed casing made of a material which does not react with thorium, with a flow of accelerated charged particles with high intensity. The irradiated metallic thorium is removed from the casing and is either heated with the addition of lanthanum and the distillation of radium or is dissolved in nitric acid with the recovery of actinium-225 by extraction. A target for implementing this method consists of blocks of metallic thorium of a thickness of 2 to 30 mm, which are contained within a hermetically scaled casing made of different materials which do not react with thorium.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIJSKOJ AKADI NAUK INSTITUT JADERNYKH ISSLEDOVANIJ RAN IJAI RAN
Aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for sea mud in Bohai Sea Gulf
The invention relates to an aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for sea mud in the Bohai Sea Gulf. The aluminum alloy sacrificial anode is compounded from nine elements and comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 2.0-5.5 percent of Zinc, 0.01-0.05 percent of indium, 0.01-0.08 percent of tin, 4-8 percent of magnesium, 0.12-0.32 percent of lanthanum, 0.12-0.32 percent of actinium, 0.03-0.04 percent of cerium, less than or equal to 0.05 percent of silicon serving as an impurity element and the balance of aluminum. Most of added lanthanum, actinium and cerium elements exist in a phase segregation state, are mainly centralized on grain boundaries, are also distributed in crystals, are used for forming binary or polynary compounds such as aluminum-rich rare-earth phases such as LaAl4, CeAl4 and the like, and are used for forming intermetallic compounds with aluminum. The aluminum alloy sacrificial anode is suitable for sacrificial anode protection of the sea mud environment of the Bohai Sea Gulf, and has high adaptability to sea mud with high porosity ratio, large temperature range change and high corrosion, the characteristics of high current efficiency and long service life and the advantages of good protecting effect, long service life, saving in anode materials and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Production of actinium-227 and thorium-228 from radium-226 to supply alpha-emitting isotopes radium-223, thorium-227, radium-224, bismuth-212
InactiveUS20140226774A1Region can be greatHigh affinitySpecific isotope recoveryConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadium-224Actinium
An actinium-227 production device having a plurality of metallic or ceramic caplets, each enclosing a radium-226 compound in redundantly nested sealed cylinders. The radium-226 compound is compacted into a disk and diluted with heat transporting ceramic materials. A thermal neutron shield including spectrum shaping materials to protect actinium-227 produced from exposure to thermal neutrons is included along with a strong neutron absorber to shape the neutron spectrum such that radium-226 nuclei are exposed to neutrons in the higher epithermal energy groups upon entry into the target with an energy of between 20 eV and 1 KeV.
Owner:THORENCO MEDICAL ISOTOPES
Method for producing actinium-225
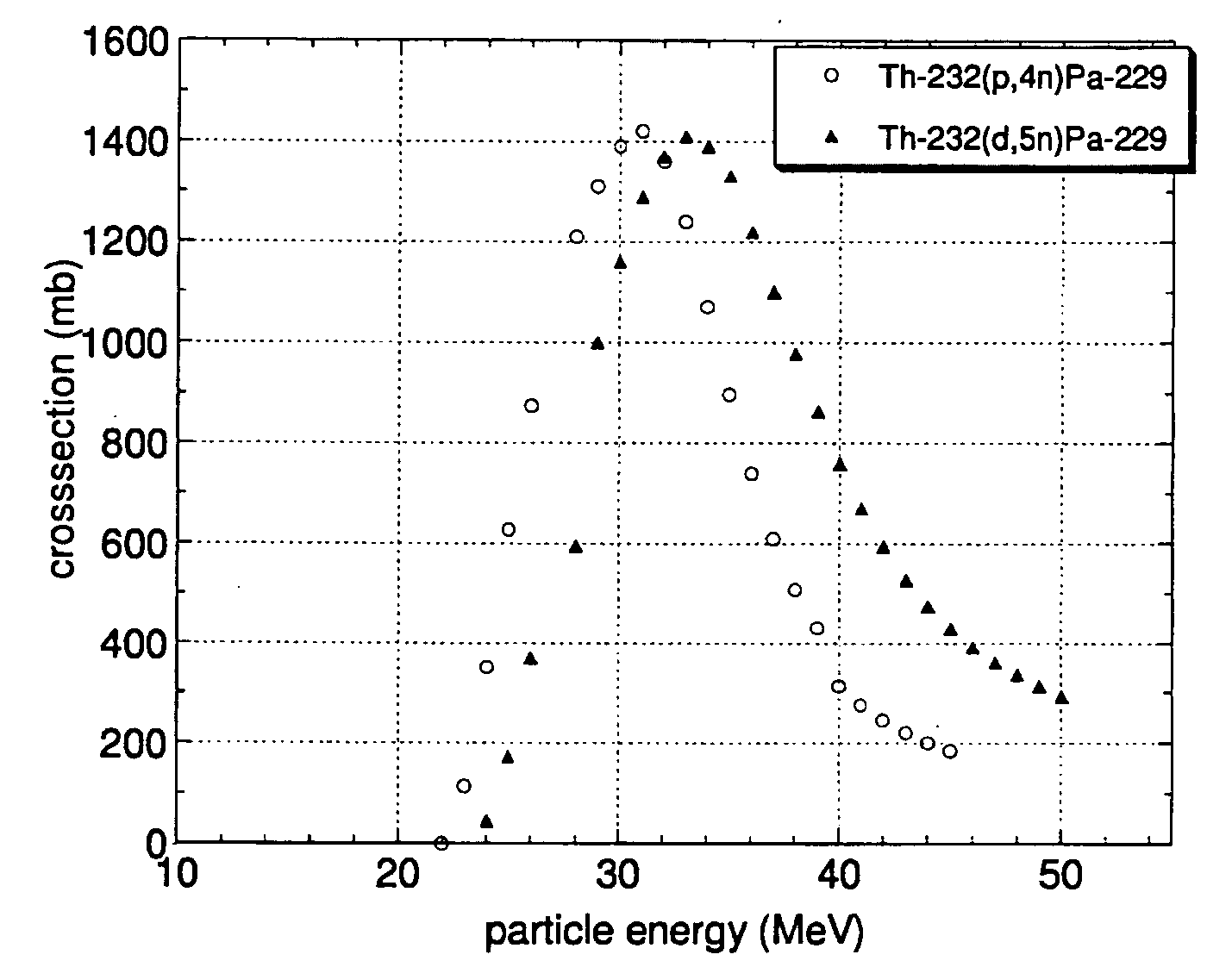
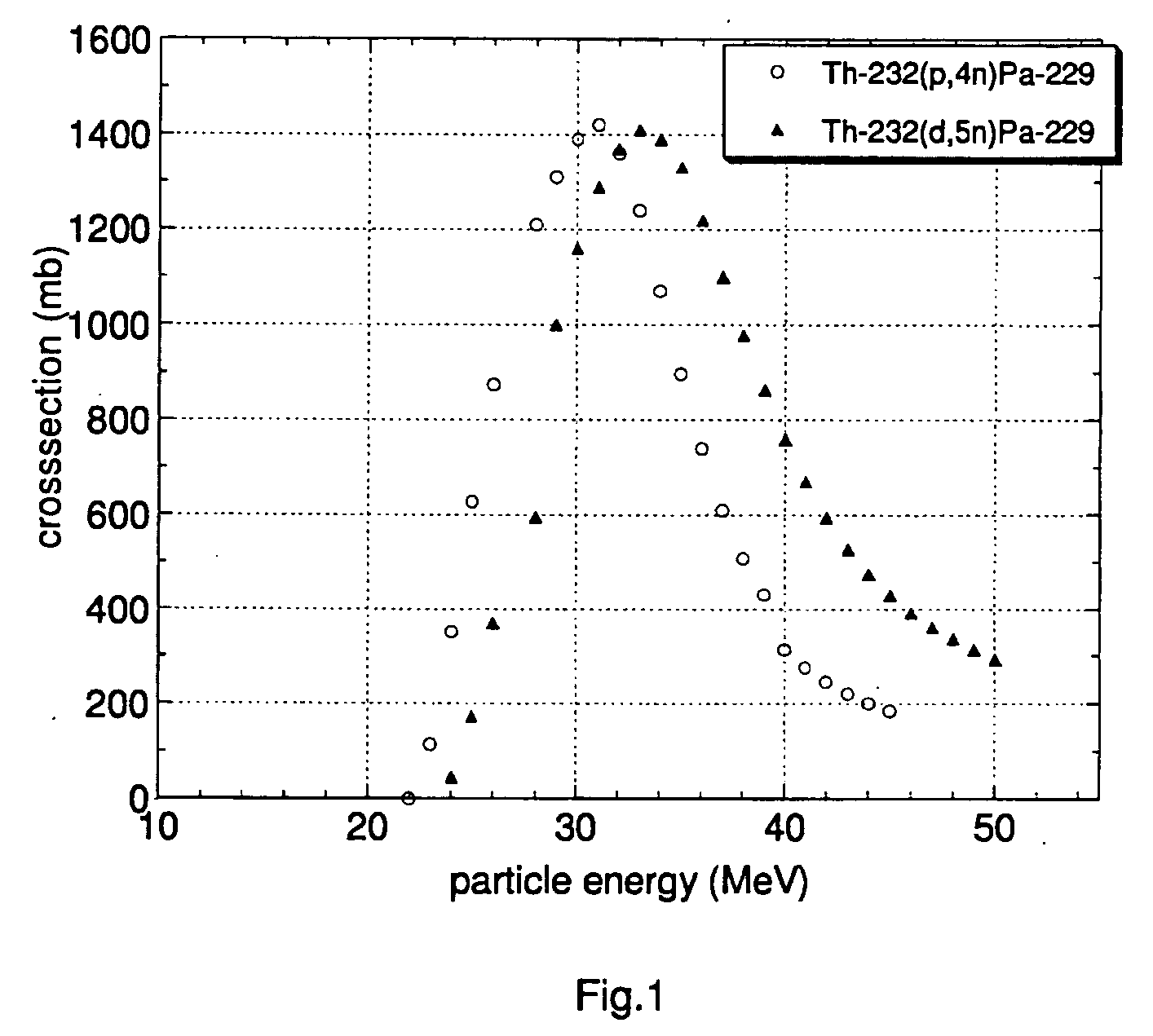
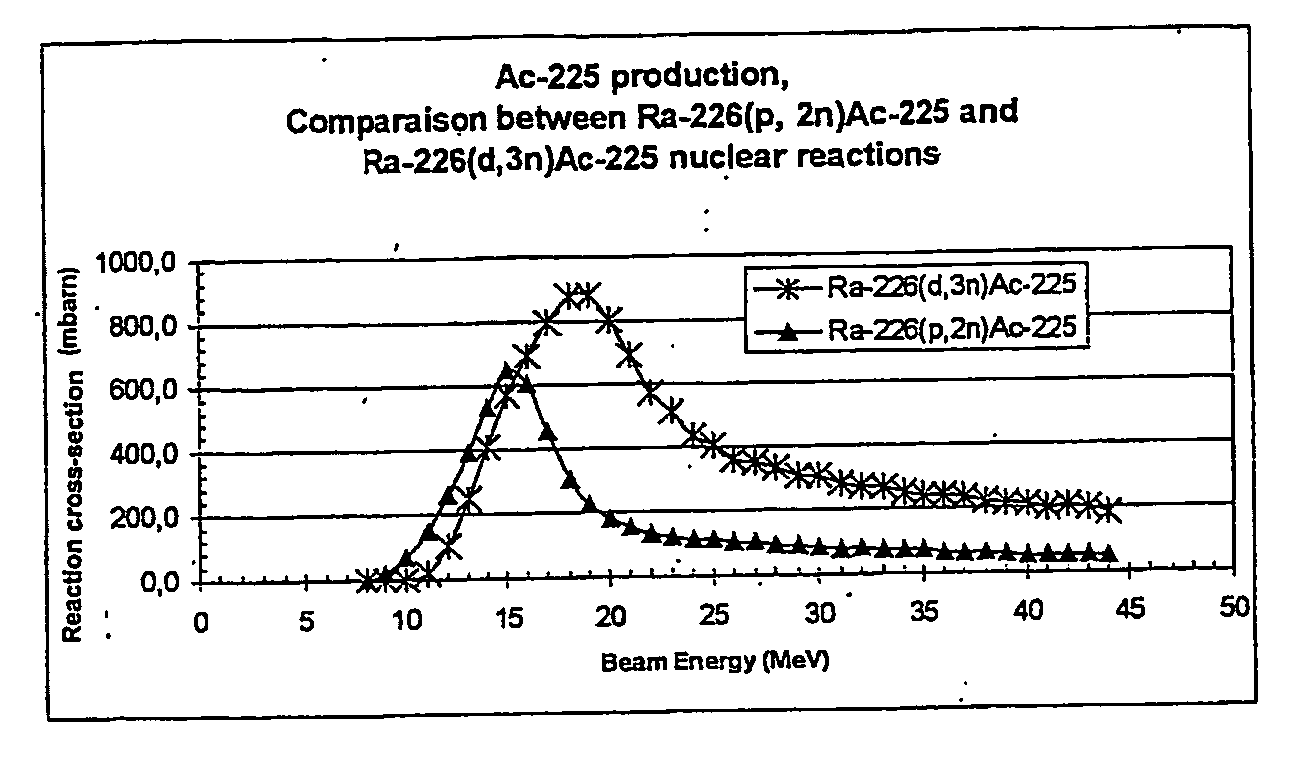
InactiveUS20060072698A1Simplify preparationSimple handlingConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsActiniumCyclotron
A method for producing Ac-225 is presented, wherein Ac-225 is produced by bombardment of Th-232 with hydrogen isotope nuclei accelerated in a cyclotron. The method, which allows production of Ac-225 at high yields and purity levels, is particularly interesting for the supply or Ac-225 or of the daughter Bi-213 for medical applications.
Owner:EURON COMMUNITY EC
Actinium radioisotope products of enhanced purity
InactiveUS7736610B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsTransuranic element compoundsIsotopes of actiniumManganese
A product includes actinium-225 (225Ac) and less than about 1 microgram (μg) of iron (Fe) per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225. The product may have a radioisotopic purity of greater than about 99.99 atomic percent (at %) actinium-225 and daughter isotopes of actinium-225, and may be formed by a method that includes providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one of uranium-233 (233U) and thorium-229 (229Th), extracting the at least one of uranium-233 and thorium-229 into an organic phase, substantially continuously contacting the organic phase with an aqueous phase, substantially continuously extracting actinium-225 into the aqueous phase, and purifying the actinium-225 from the aqueous phase. In some embodiments, the product may include less than about 1 nanogram (ng) of iron per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225, and may include less than about 1 microgram (μg) each of magnesium (Mg), Chromium (Cr), and manganese (Mn) per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
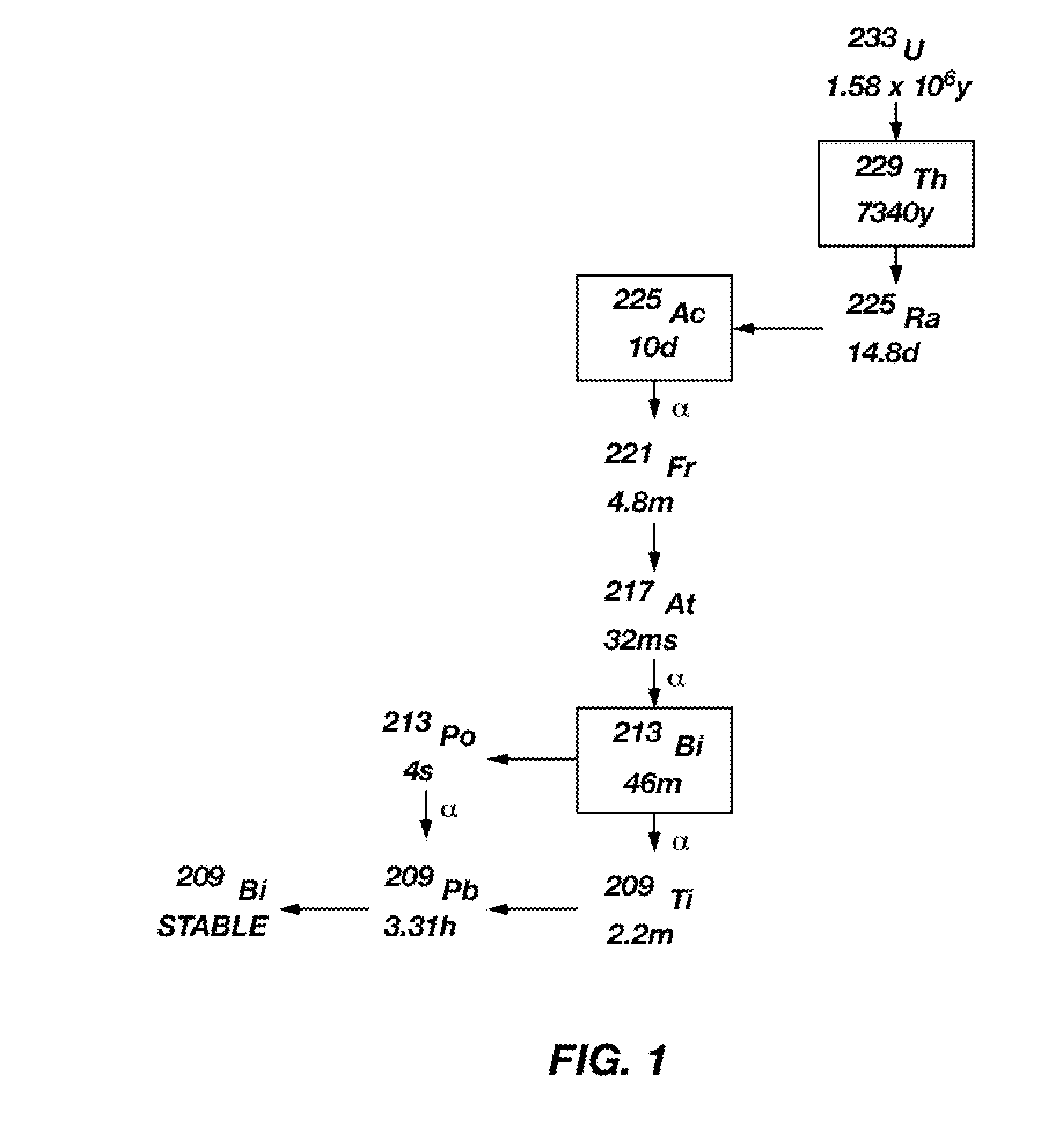
Method of producing radium-225 and decay products thereof
InactiveUS20070092051A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesDecay productActinium
Provided herein are methods of producing radium-225 and actinium-225 from an activated radium-226 source. Irradiation of the radium-226 by neutrons with energy effective to drive the reaction 226Ra (n,2n) 225Ra produces abundant radium-225 which decays to its daughter radionuclide actinium-225. Also provided is a system for supplying radiotherapeutic bismuth-213 in situ to a subject in need of radiotherapy using the actinium-225 produced by this method in a generator device effective to generate bismuth-213.
Owner:ADELMAN STUART LEE
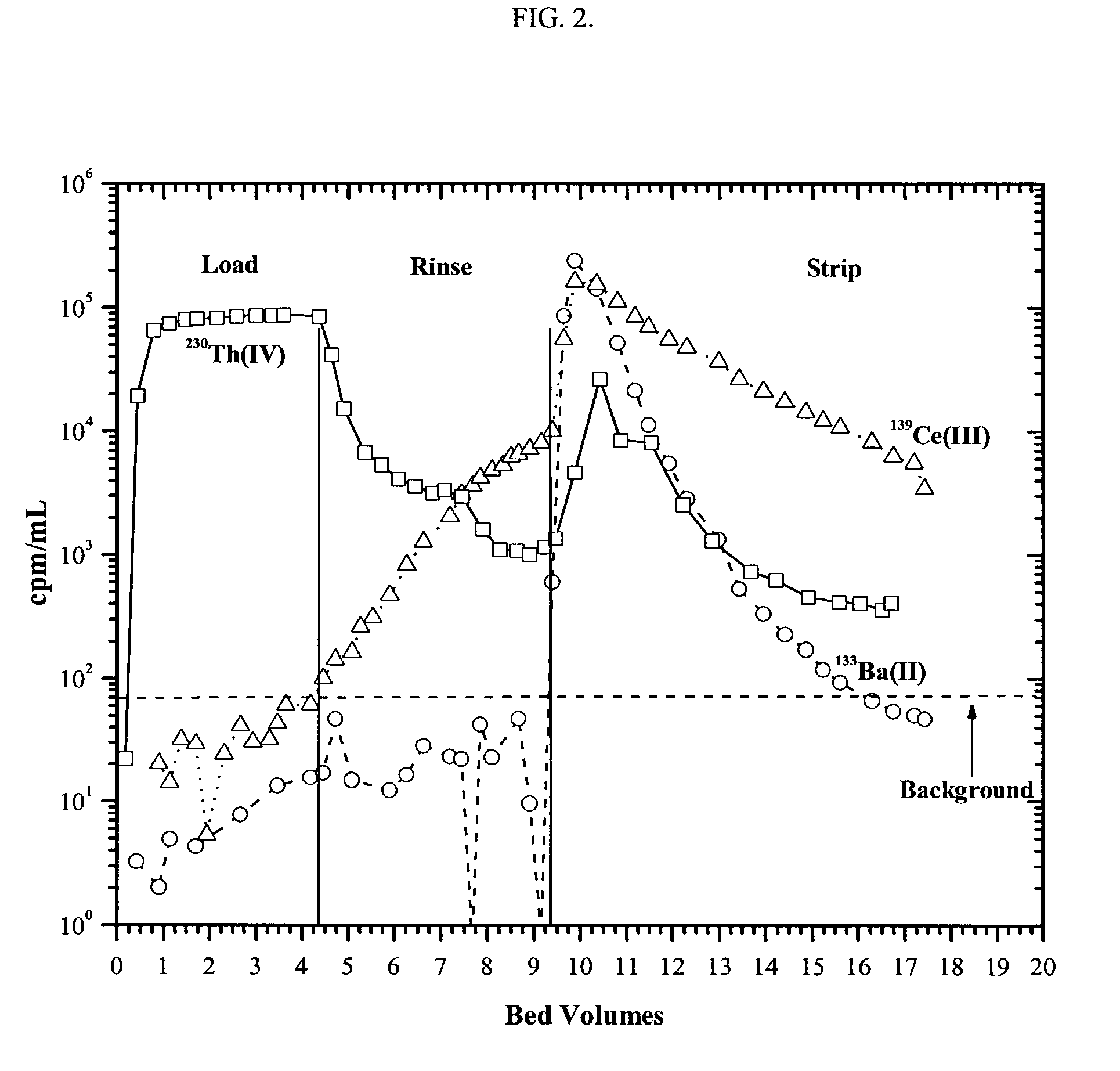
Production of ultrapure bismuth-213 for use in therapeutic nuclear medicine
InactiveUS6852296B2Separation efficiency is highSmall volumeCation exchanger materialsIsotope delivery systemsActiniumRadiation damage
A multicolumn selectivity inversion generator has been developed in which bismuth-213 is selectively extracted from an HCl solution of the actinium-225 parent (and its radiogenic descendents) by a primary separation column containing a separation medium containing a neutral oxygenated organophosphorus extractant. After rinsing with dilute HCl, the bismuth-213 is stripped with a buffered NaCl solution. The stripped solution is passed through a cation-exchange resin guard column that retains the actinium-225 and radium-225 contaminants while the bismuth-213 elutes. This generator method minimizes the unpredictable effects of radiation damage to the support material and permits the reliable production of bismuth-213 of high chemical and radionuclidic purity.
Owner:PG RES FOUND
Heteroatom-containing Pi-ligand metallocene complex, preparation method thereof, catalyst system thereof and application of catalyst system
The invention relates to a heteroatom-containing Pi-ligand metallocene complex, a preparation method thereof, a catalyst system thereof and an application of the catalyst system. The metallocene complex has a chemical structure shown as a following chemical formula (I):, wherein, M is the third, fourth, fifth or sixth transition metal element in periodic table of elements, which comprises lanthanide and actinium series elements; X, equal to or different from each other, are selected from the group consisting of the hydrogen element, halogen, alkyl R, alkyloxy OR, mercapto SR, carboxyl OCOR, amidogen NR2, phosphino PR2, -OR.O- and OSO2CF3; n is an integer from 1 to 4, n is not equal to zero; the product of electrical numbers of n and X is equal to the charge number by reducing 2 of the central metal atom M; Q is divalent free radical; A is a Pi-ligand, and has a structure shown as the chemical formula (II):, and Z is the Pi-ligand, and Z is equal to A, or Z has the chemical structure shown as the following chemical formula.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Multicolumn selectivity inversion generator for production of high purity actinium for use in therapeutic nuclear medicine
InactiveCN1658938AGood chromatographic performanceChemically pureIsotope delivery systemsSolid sorbent liquid separationActiniumAqueous solution
Disclosed is a process for producing a solution of a daughter radionuclide that is substantially free of impurities by contacting an aqueous parent-daughter radionuclide solution with a first separation medium, eg. Chromatographic column. The product solution of the desired daughter radionuclide is then contacted with a second separation medium to produce a pure daughter radionuclide solution.
Owner:PG RES FOUND
One-Step Labeling of Antibodies to High Specific Activity with Actinium-225
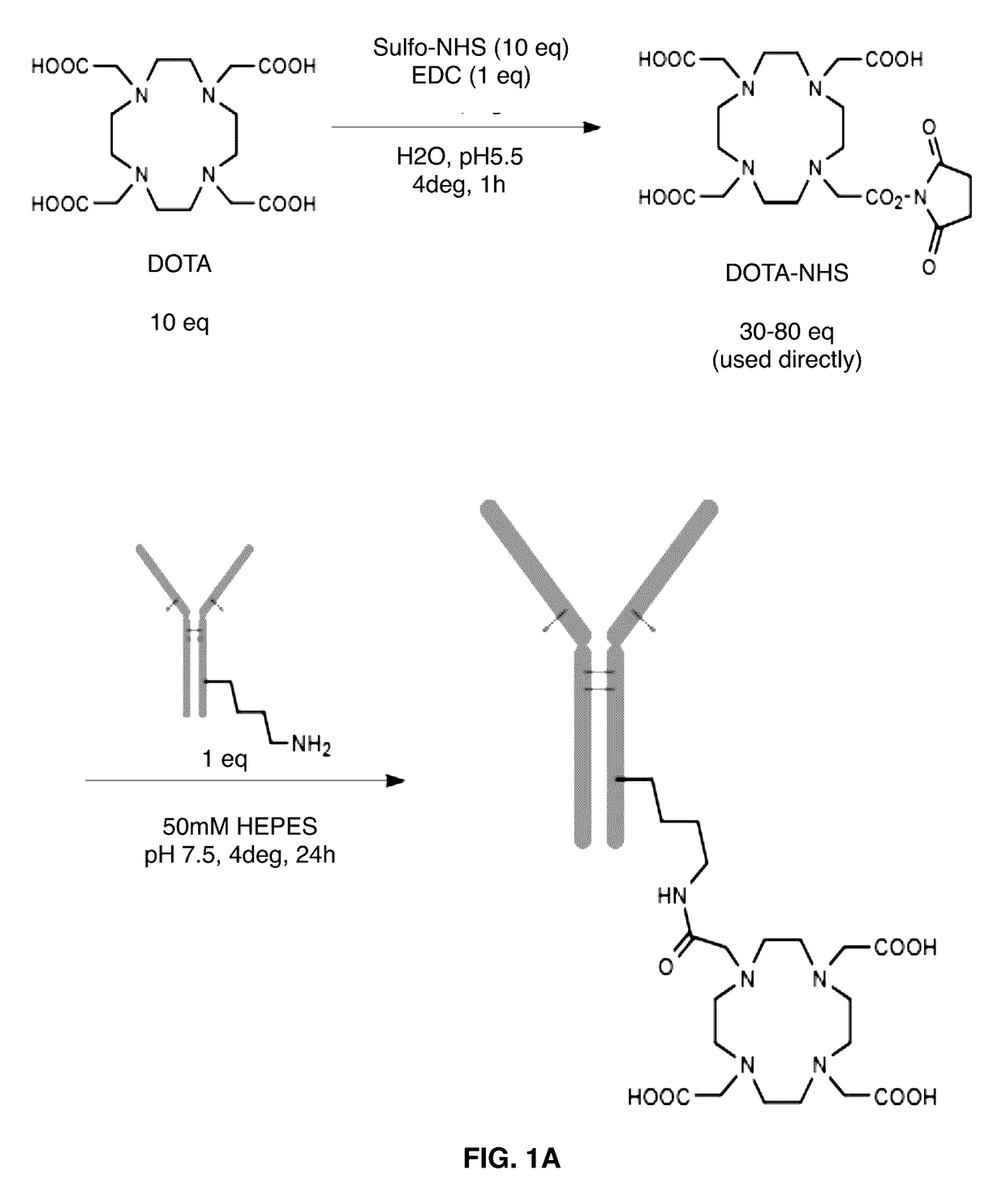
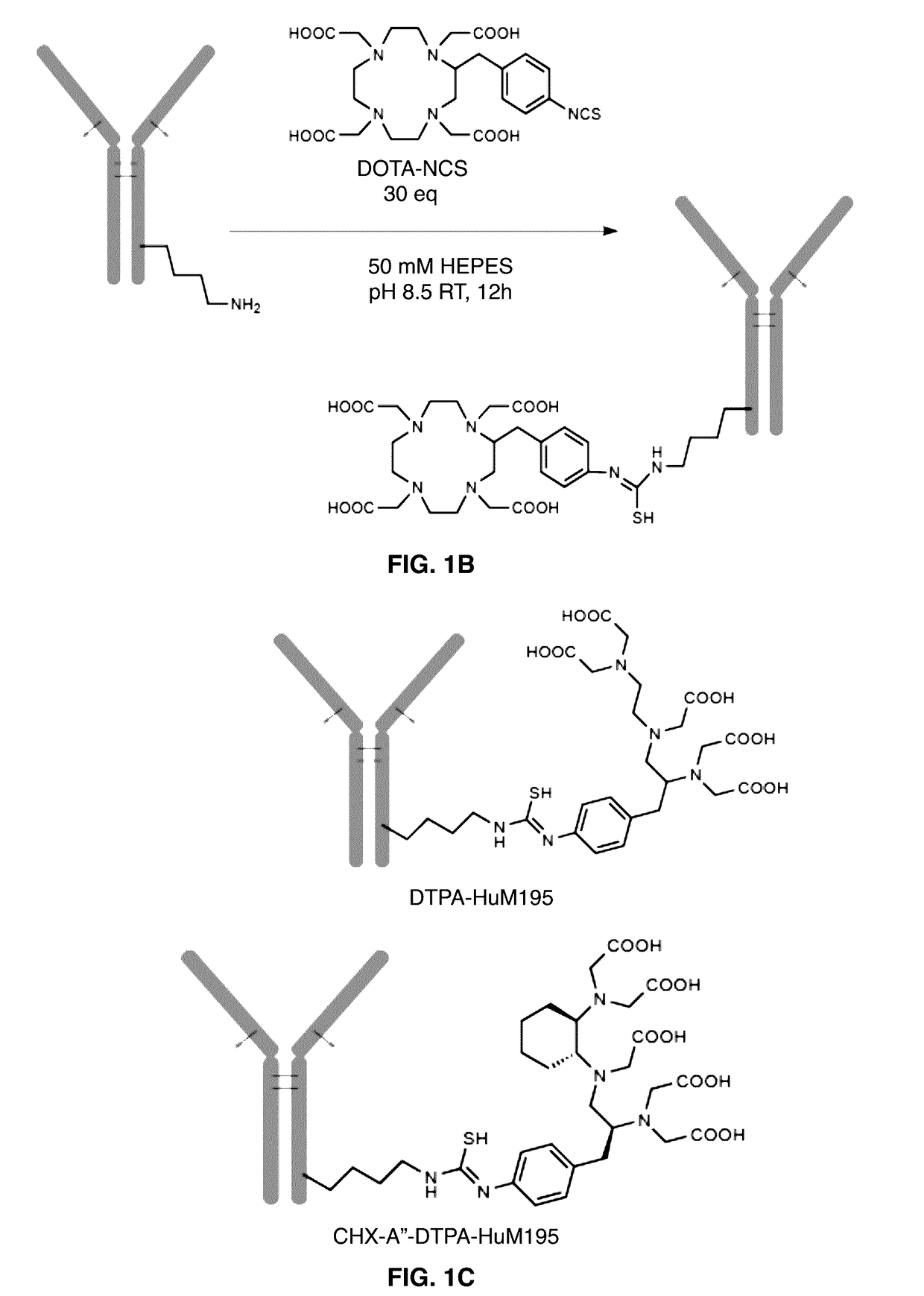
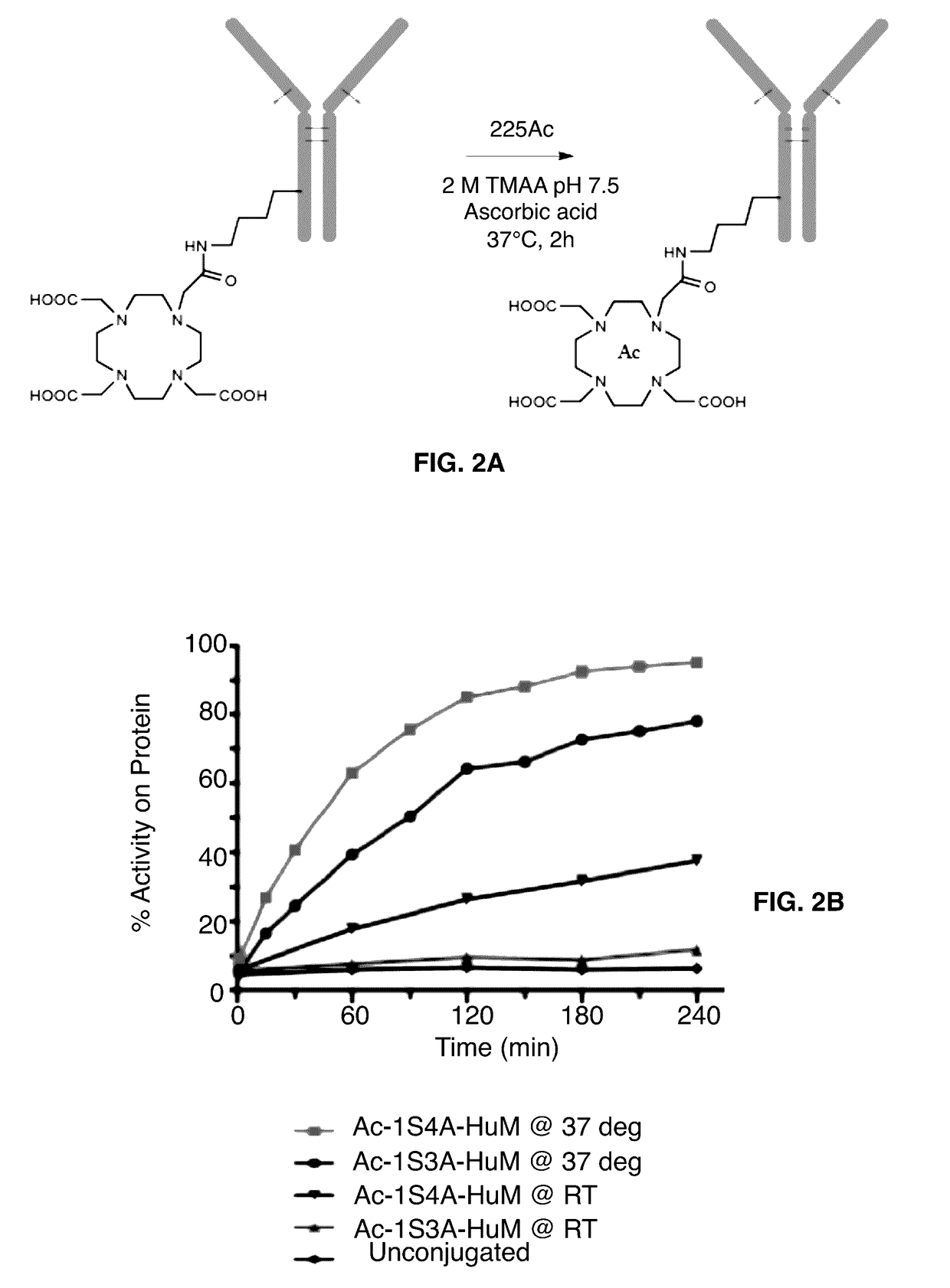
ActiveUS20170112951A1Increasing radiochemicalHigh radiochemical yieldRadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMonoclonal antibodyActinium
Provided herein is a one-step method for chelating actinium-225 to a construct comprising a chelator linked to a bio-molecule, such as, an antibody or monoclonal antibody, via a bifunctional ligand in, for example, a 3-arm configuration. Also provided are methods for increasing the radiochemical yield of an actinium-225-chelant-biomolecule complex and for producing a high specific activity actinium-225 complex. The chelation is performed at a physiological temperature, about 37° C. Also provided are high specific activity actinium-225 complexes, that is, actinium-225 chelated to the chelator-biomolecule construct and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. Further provided are methods of treating a neoplastic disease or disorder with the actinium-225 complexes.
Owner:SCHEINBERG DAVID A +3
Method for producing actinium-225
InactiveUS20060198772A1Easy to carryAvoid introducingTransuranic element compoundsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsIncident energyActinium
A method for producing Ac-225 is presented, wherein Ac-225 is produced by bombardment of Ra-226 with deuterons accelerated in a cyclotron. The deuterons preferably have an incident energy of between 15 and 22 MeV. The method, which allows production of Ac-225 at high yields and purity levels, is particularly interesting in view of Bi-213 generation.
Owner:EURO COMMUNITY AS REPRESENTED BY THE EURO COMMISSION THE
Actinium radioisotope products of enhanced purity
InactiveUS20060213329A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsTransuranic element compoundsIsotopes of actiniumManganese
A product includes actinium-225 (225Ac) and less than about 1 microgram (μg) of iron (Fe) per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225. The product may have a radioisotopic purity of greater than about 99.99 atomic percent (at %) actinium-225 and daughter isotopes of actinium-225, and may be formed by a method that includes providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one of uranium-233 (233U) and thorium-229 (229Th), extracting the at least one of uranium-233 and thorium-229 into an organic phase, substantially continuously contacting the organic phase with an aqueous phase, substantially continuously extracting actinium-225 into the aqueous phase, and purifying the actinium-225 from the aqueous phase. In some embodiments, the product may include less than about 1 nanogram (ng) of iron per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225, and may include less than about 1 microgram (μg) each of magnesium (Mg), Chromium (Cr), and manganese (Mn) per millicurie (mCi) of actinium-225.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
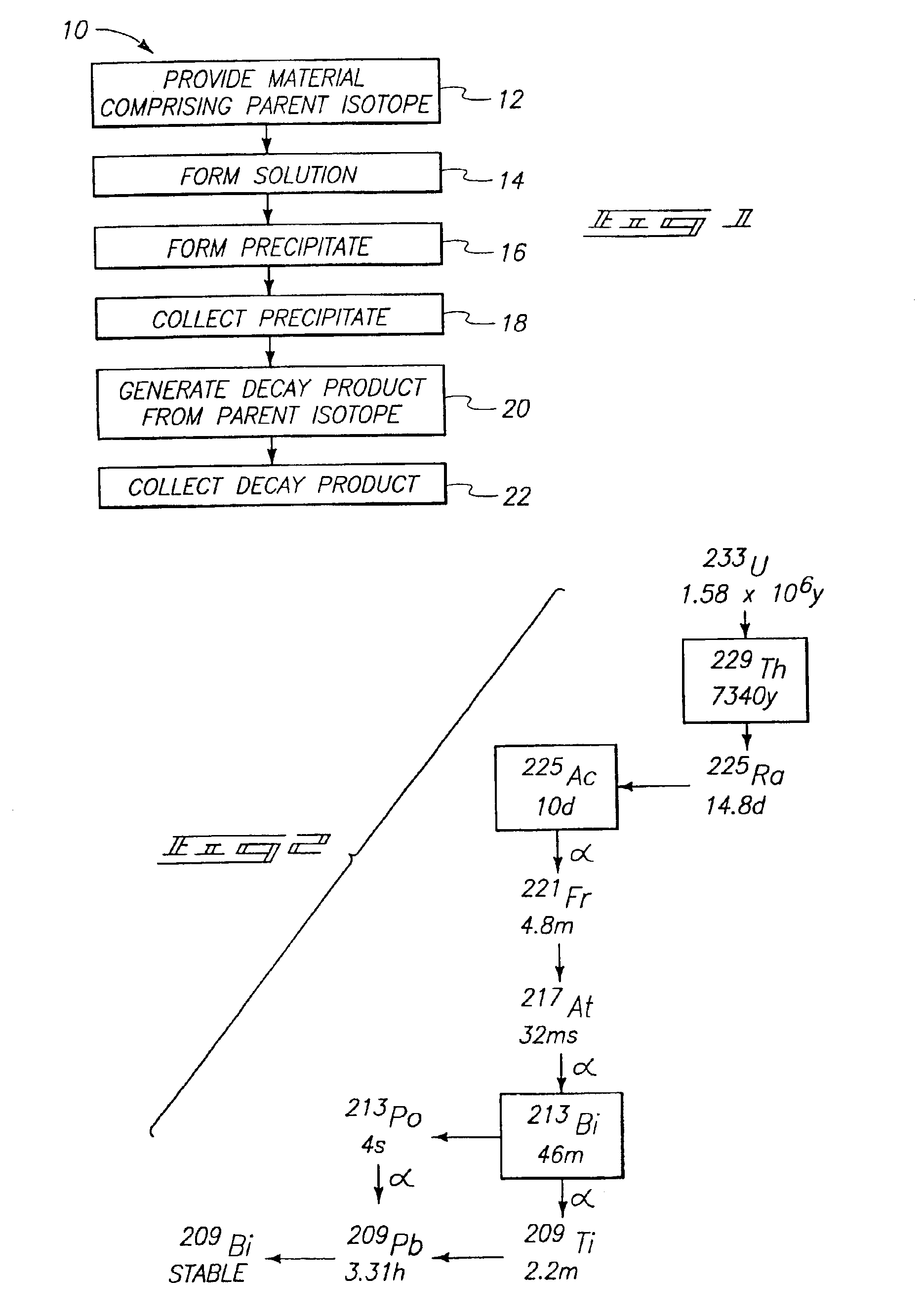
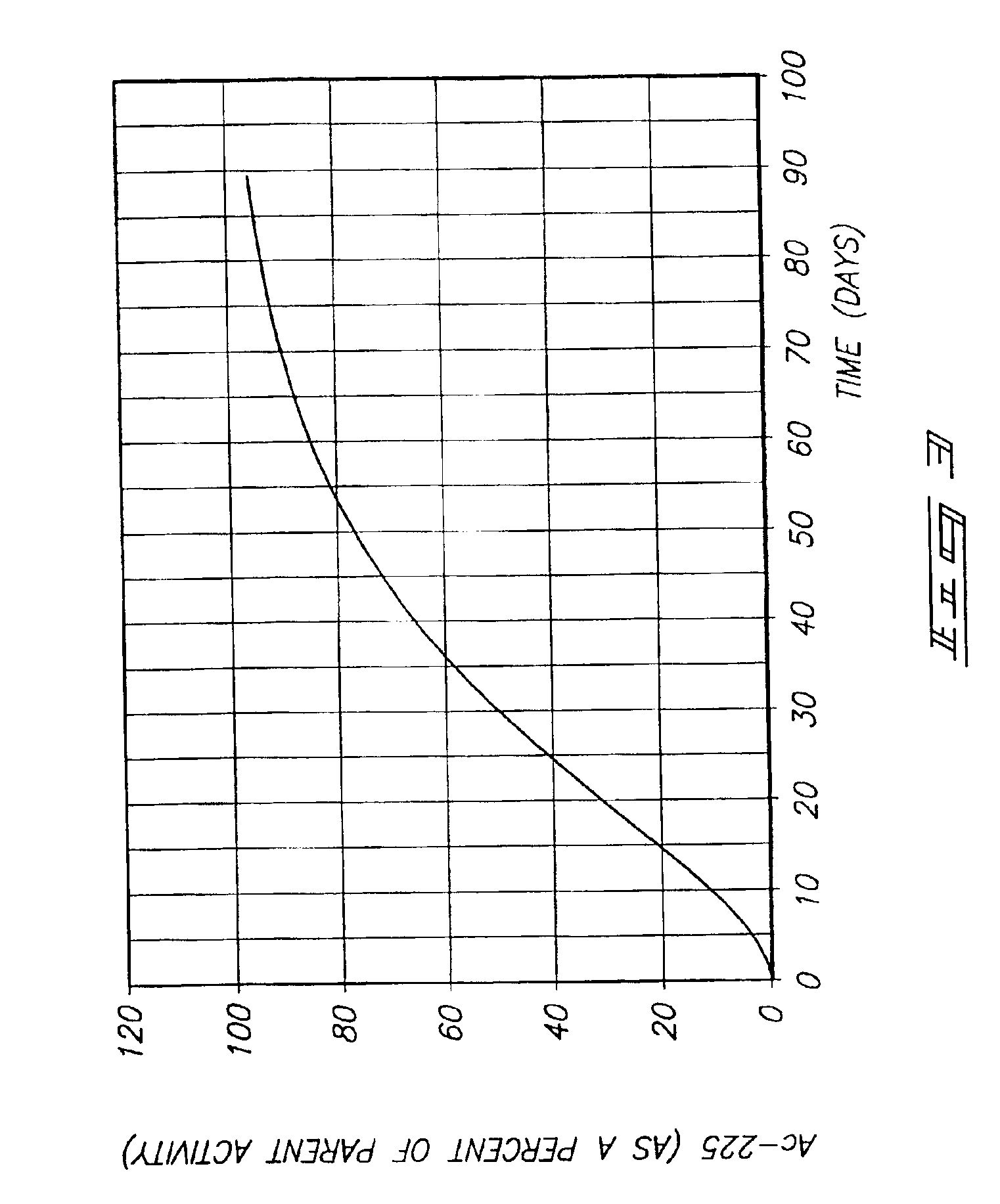
Process for recovery of daughter isotopes from a source material
The invention includes a method of separating isotopes from a mixture containing at least two isotopes in a solution. A first isotope is precipitated and is collected from the solution. A daughter isotope is generated and collected from the first isotope. The invention includes a method of producing an actinium-225 / bismuth-213 product from a material containing thorium-229 and thorium-232. A solution is formed containing nitric acid and the material and iodate is added to form a thorium iodate precipitate. A supernatant is separated from the thorium iodate precipitate and a second volume of nitric acid is added to the precipitate. The precipitate is stored and a decay product comprising actinium-225 and bismuth-213 is generated in the second volume of nitric acid which is then separated from the thorium iodate precipitate, filtered, and treated using at least one chromatographic procedure. The invention also includes a system for producing an actinium-225 / bismuth-213 product.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
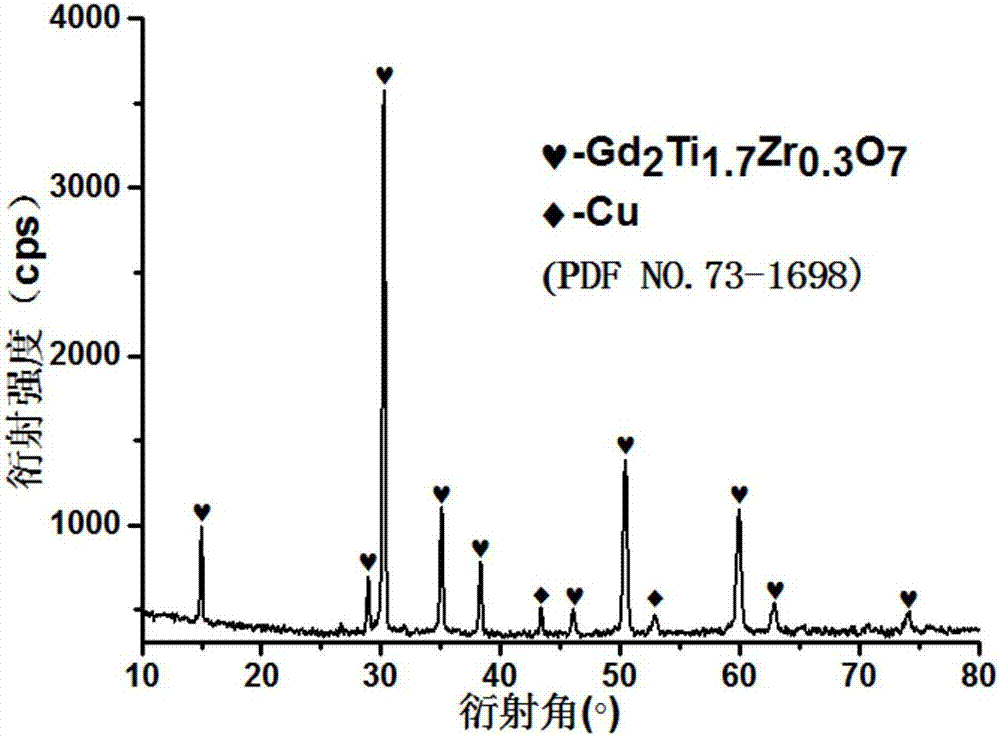
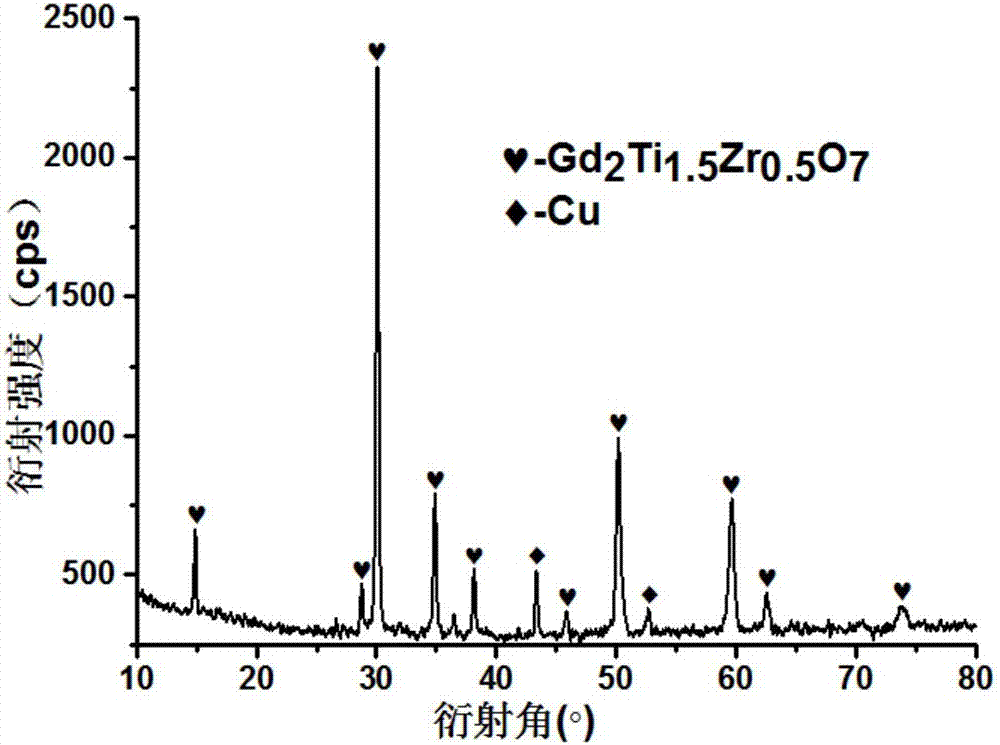
Self-propagating preparation method for Gd<2>Ti<2-x>Zr<x>O<7> pyrochlore
InactiveCN106986377ARaise the reaction temperatureHigh purityTitanatesSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesisReaction temperature
The invention discloses a self-propagating preparation method for Gd<2>Ti<2-x>Zr<x>O<7> pyrochlore. The self-propagating preparation method is characterized by including acquiring Ti, TiO<2>, ZrO<2>, Gd<2>O<3> and CuO powder to be used as raw materials according to certain proportions; carrying out dry ball milling, uniform mixing and drying on the raw materials and compressing the raw materials to obtain blanks; placing the blanks in self-propagating quasi-isostatic pressure devices, igniting the blanks by the aid of ignition devices to carry out reaction and applying pressures after combustion is completed to obtain the Gd<2>Ti<2-x>Zr<x>O<7> pyrochlore. The self-propagating preparation method has the advantages that self-propagating high-temperature synthesis is combined with fast densification processes, and accordingly pyrochlore-type man-made rock densification solidified bodies which are high in thermal stability and chemical stability and excellent in anti-irradiation property can be synthesized in a few minutes; the self-propagating preparation method is high in synthesis speed, production efficiency, reaction temperature and product purity, low in energy consumption and applicable to long-term safety solidification treatment and disposal on nuclide of actinium series in high-level radioactive waste, processes are simple, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
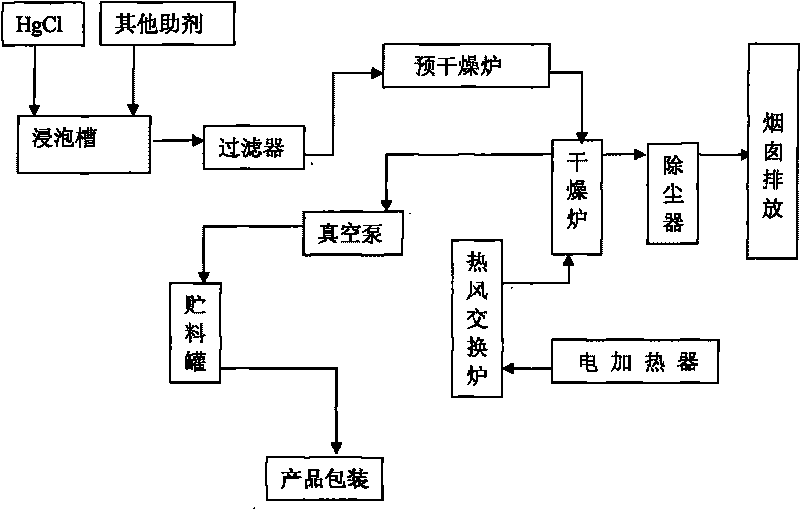
Chloroethylene catalyst converted and synthesized by fluidized bed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101703942AReduce generationLess investmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionActivated carbonAlkaline earth metal
The invention provides chloroethylene catalyst converted and synthesized by a fluidized bed, adopts activated carbon as carriers to adsorb mercuric chloride, and comprises the formula as follows: 11.0-12.0% of mercuiric chloride, 5-12% of rare earth chloride assistant A, 8-20% of alkaline earth chloride assistant B, 10-15% of assistant C and the balance activated carbon, wherein the purity of the mercuiric chloride is more than or equal to 99.5%; the rare earth chloride assistant A is composed of chlorides of lanthanide series metal and actinium series metal; the alkaline earth chloride assistant B is composed of BaCl2-CaCl2; and the assistant C consists of KCl-HCl solution. The catalyst provided by the invention has 11.0-12.0% of HgCl2, compared with traditional mercuric chloride catalyst, the temperature difference between the initial area and the end area of the whole reaction zone is effectively controlled to be no more than 2 DEG C, thus improving catalytic conversion efficiency, reducing generation of harmful adverse reaction, lowering investment on fixed assets, reducing occupied area of equipment, enhancing the technology level of the automatic equipment of the whole technique. The method is suitable for manufacturers for producing chloroethylene by fluidized catalytic conversion beds.
Owner:贵阳白云银星化工有限公司
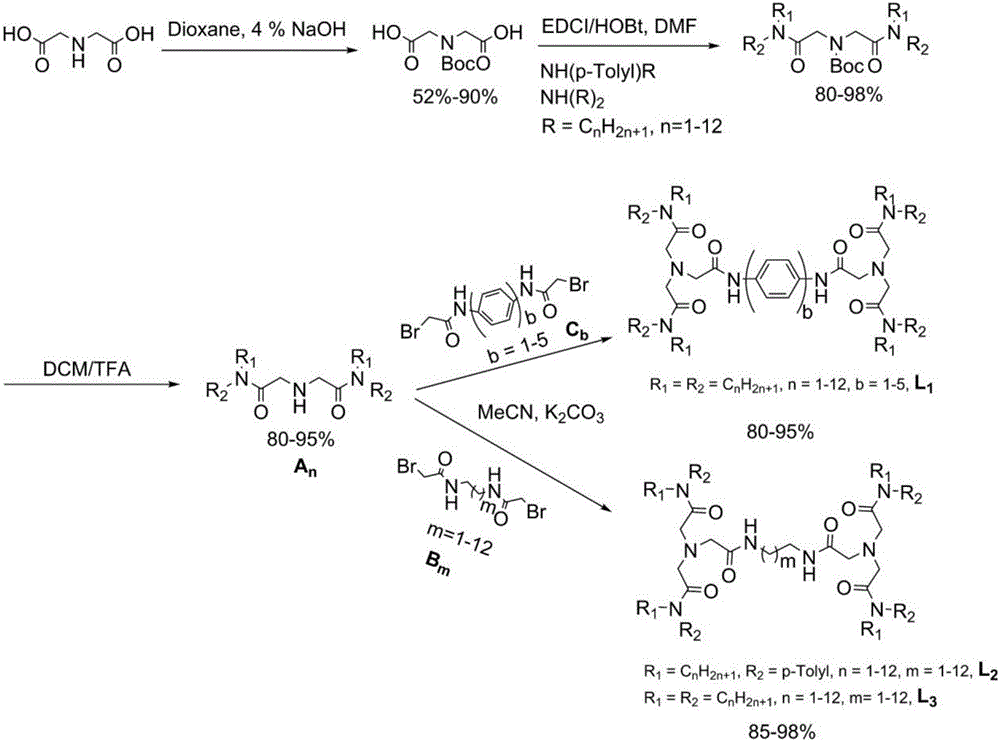
Preparation and application of novel bitriamide organic compounds
InactiveCN106631879AAchieve separationImplement Pu(IV)Carbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationActiniumRadioactive waste
The invention belongs to the field of radioactive waste treatment and discloses CHON-element-containing amide organic compounds which can be applied to uranium [U(VI)] / thorium[Th(IV)] separation, plutonium[Pu(IV)] / uranium[U(VI)] separation, lanthanum[Ln(III)] / actinium[Ac(III)] separation and fission fragment element technetium [Tc(VII)] separation. The amide organic compounds have the advantages that the amide organic compounds are synthesized rapidly, simply and conveniently at multiple steps, target product yields are all 80-99%, and economy and high efficiency are achieved. The amide organic compounds contain symmetric bitriamide groups, comprise symmetric double-tripod structures and control extraction power for Th(IV) and U(VI) by changing lengths of carbon chains of bitriamide; immiscibility of the amide organic compounds with water is enhanced through regulating carbon chains of alkyl groups (R) on amide nitrogen atoms, so that the amide organic compounds are soluble in aromatic, alkyl and halogen-containing solvents, and are applied to a liquid-liquid extraction process; the amide organic compounds can be used for achieving Th(IV) / U(VI) separation under a high-acidity condition without three-phase forming, are capable of achieving Pu(IV) / U(VI) separation under the equal conditions because Th(IV) and Pu(IV) are similar in chemical properties, are also capable of achieving Ln(III)] / Ac(III) separation, and are high in Re(VII) distribution ratio.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for producing actinium-225 and isotopes of radium and target for implementing same
ActiveUS9058908B2Specific isotope recoveryConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear technologyActinium
The invention relates to the field of nuclear technology and radiochemistry, more specifically to the production and isolation of radionuclides for medical purposes. The method for producing actinium-225 and isotopes of radium comprises irradiating a solid block of metallic thorium of a thickness of 2 to 30 mm, which is contained within a hermetically sealed casing made of a material which does not react with thorium, with a flow of accelerated charged particles with high intensity. The irradiated metallic thorium is removed from the casing and is either heated with the addition of lanthanum and the distillation of radium or is dissolved in nitric acid with the recovery of actinium-225 by extraction. A target for implementing this method consists of blocks of metallic thorium of a thickness of 2 to 30 mm, which are contained within a hermetically scaled casing made of different materials which do not react with thorium.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIJSKOJ AKADI NAUK INSTITUT JADERNYKH ISSLEDOVANIJ RAN IJAI RAN
A method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanide and trivalent actinide ions
ActiveCN104894372BMaintain efficient extraction and separation performanceImprove stabilityProcess efficiency improvementAlkanePh regulation
The invention relates to a method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions and belongs to the technical field of nuclear fuel circulation and waste liquid treatment. The method uses bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) dithiophosphinic acid as an extracting agent, uses long-chain alkane as a thinning agent and uses a weak acid buffer system to effectively stabilize the pH value of the water phase of an extraction system, pH regulation does not need to be performed to the system during extraction, trivalent actinium elements can be high-selectively extracted and separated out from the water phase, and most of trivalent lanthanum elements are remained in the water phase. The method for extracting and separating trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions has the advantages that the extraction and separation performance of trivalent lanthanum and trivalent actinium ions is high and stable and the prospect of application in the field of advanced nuclear circulation is better.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com