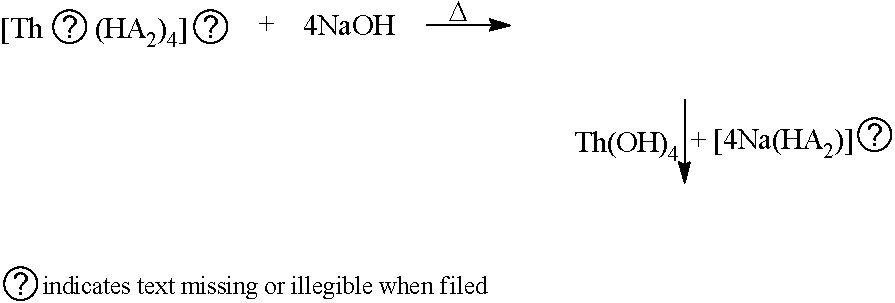
Patents
Literature
249 results about "Monazite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
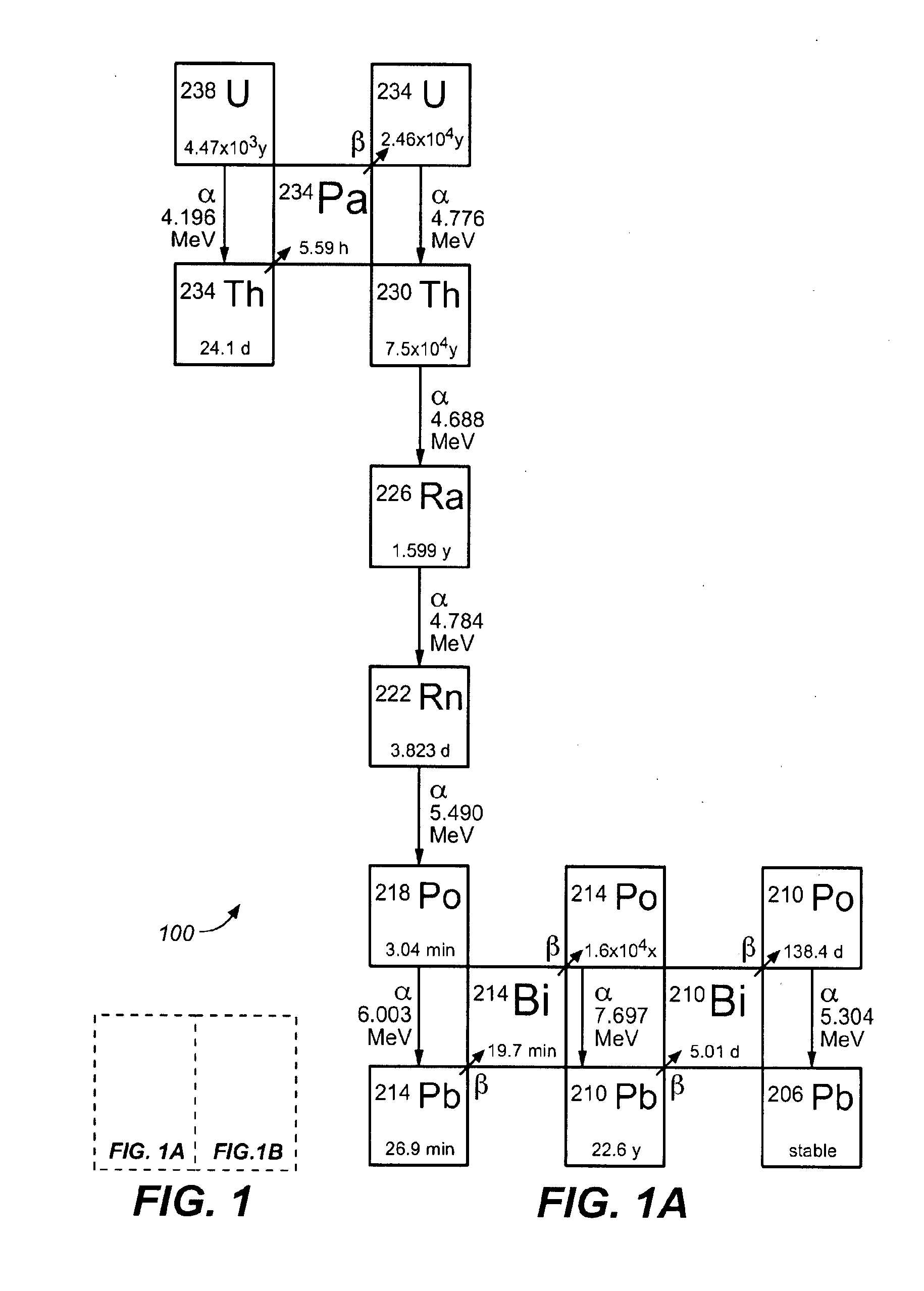
Monazite is a reddish-brown phosphate mineral containing rare-earth metals. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm³.
Monazite-based thermal barrier coatings
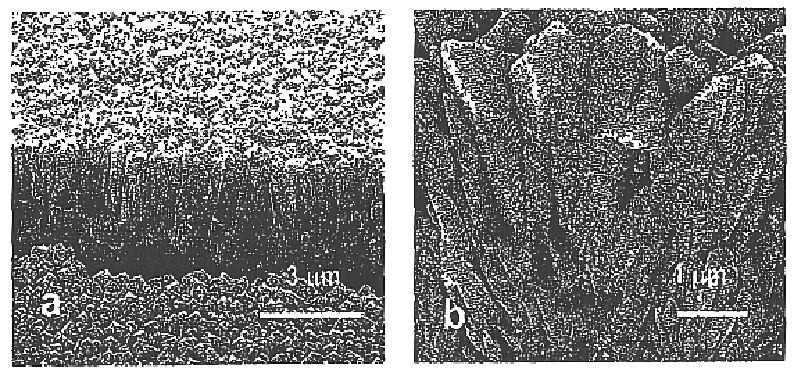
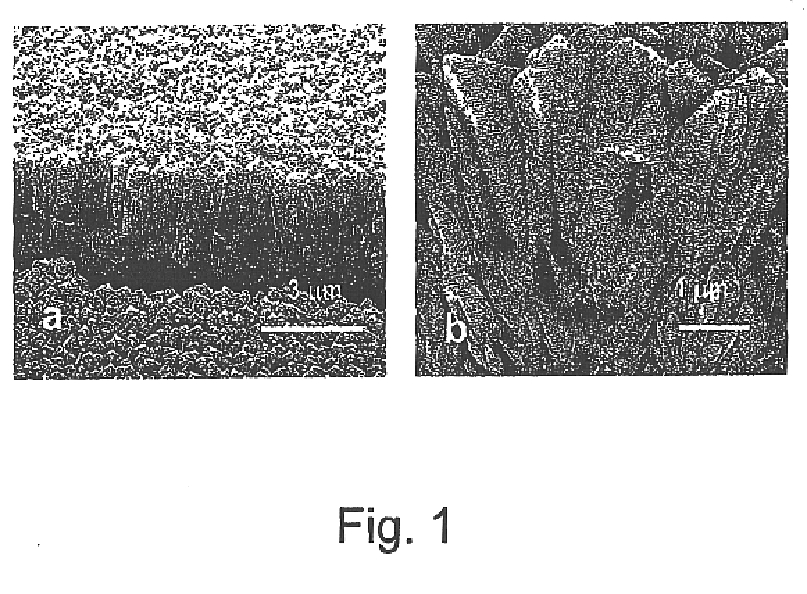
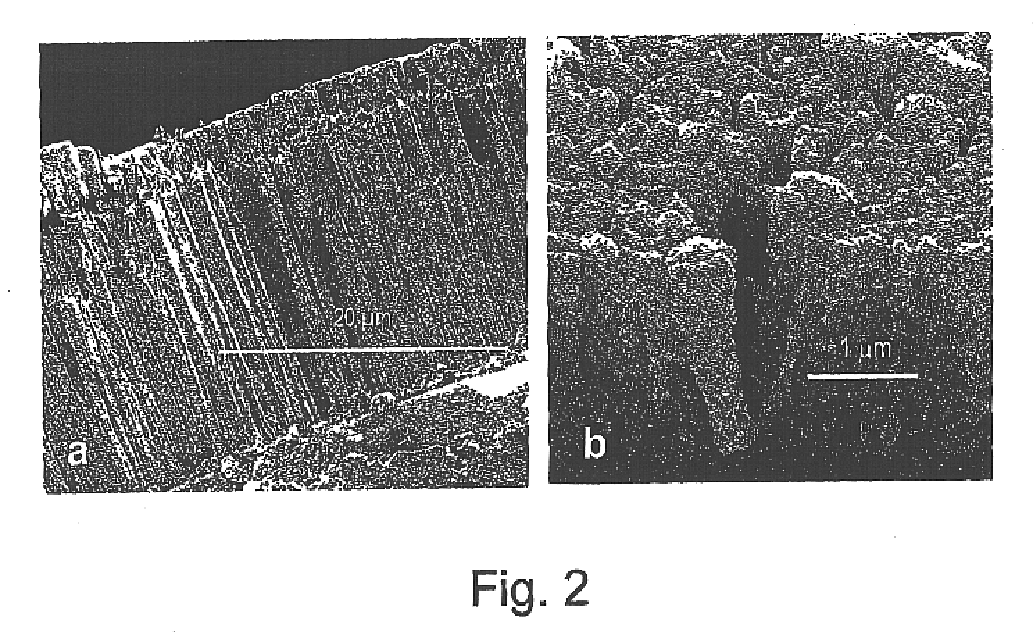
Monazites and xenotimes are rare-earth phosphates showing a combination of properties expected to be suitable for thermal barrier coatings. For example, lanthanum phosphate (La-monazite) can be used to form thermal barrier coatings to protect superalloy and ceramic parts exposed to high temperature and damage by sulfur, vanadium, phosphorus and other contaminants. The monazite or xenotime coatings can be applied using any of the common application methods including EB-PVD, laser ablation and plasma spraying. The stoichiometry of the coatings can be modulated according to the stoichiometry of specially prepared starting target (source) material. The most effective coatings appear to be largely crystalline and show a columnar structure with feather-like microstructure. For La-monazite, effective coatings between 10 and 500 micrometers in thickness can be deposited on substrates having temperatures between about 750° C. and about 950° C.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
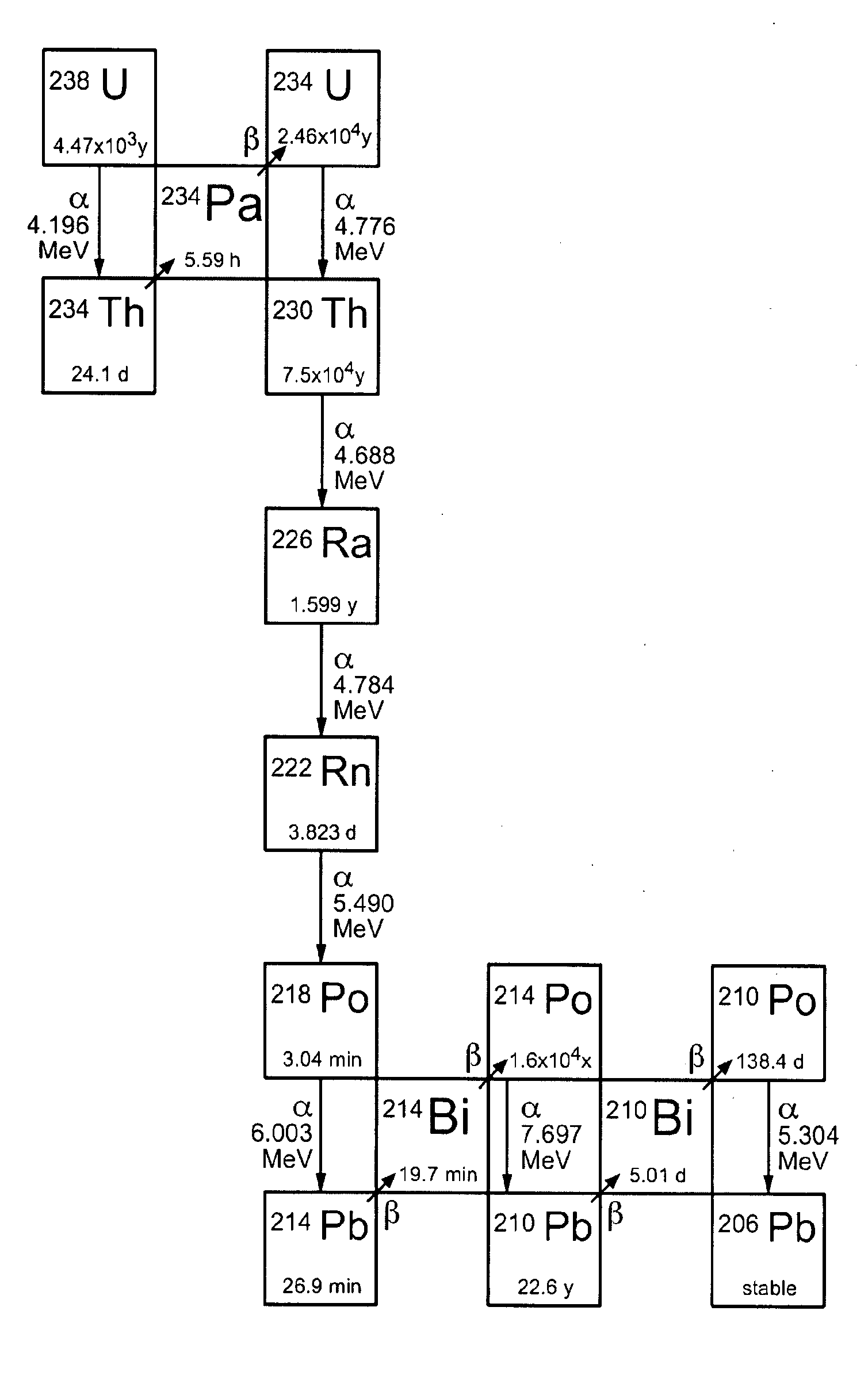
Separation of radium and rare earth elements from monazite
InactiveUS20100018347A1Efficiently recoversEfficient separationIon-exchange process apparatusAnion exchanger materialsRare-earth elementDecay product
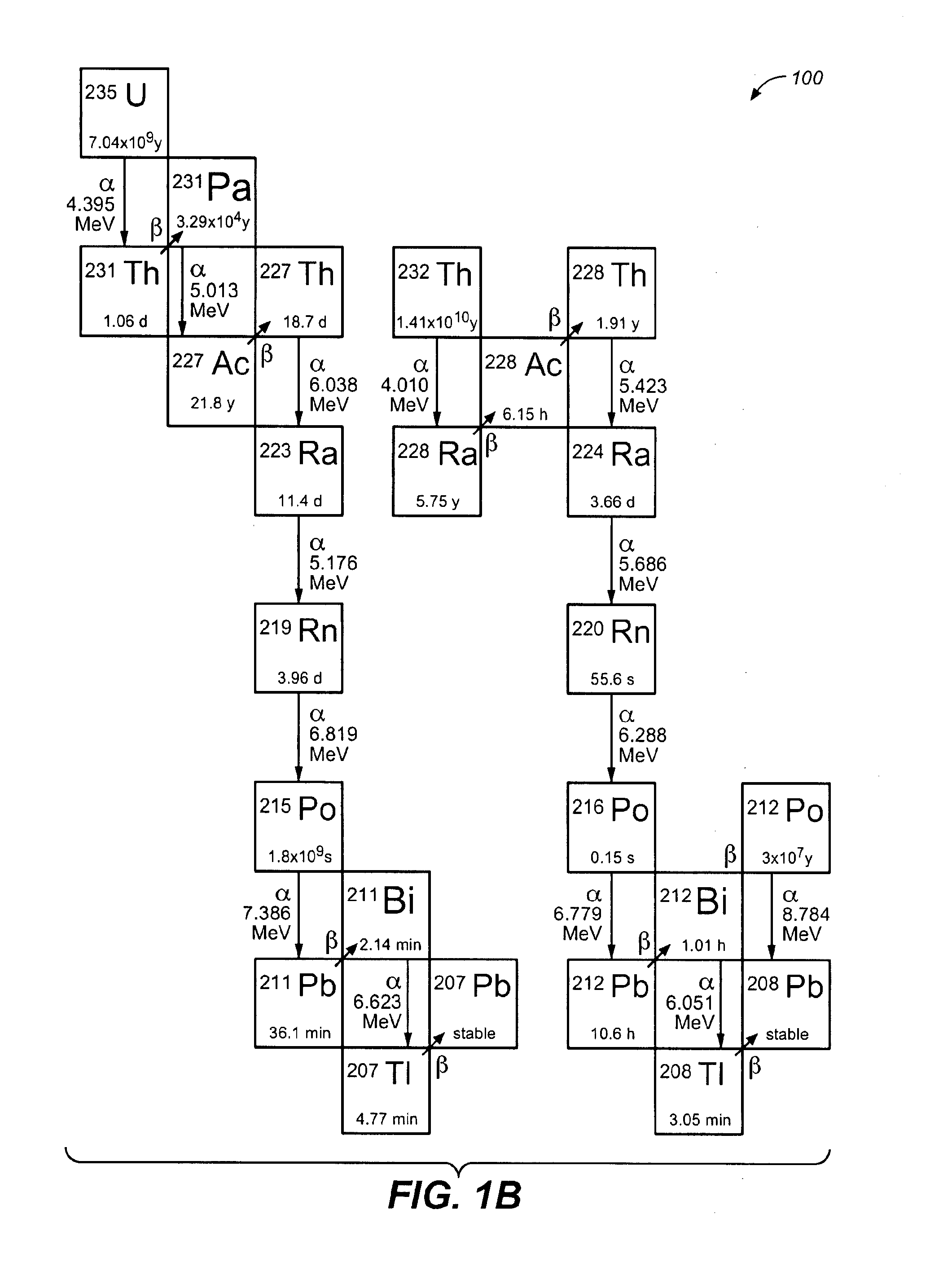
A method of chemically extracting radium-228, rare earth metals, thorium, the decay products of thorium, and phosphates from thorium-containing ores. The method involves breaking thorium-containing ore into fragments, wetting the fragments with a concentrated strong acid to make a slurry, heating the slurry, passing the heated solution through a first anion exchange column, retaining metals and radium-228 captured on the resin, allowing the radium-228 ions to decay to actinium-228, purifying the actinium-228 fraction, sending the actinium-228 fraction through a capture column, eluting the captured thorium-228 with acid, removing radium from the solution, retaining the radium-228 fraction for isomer in-growth, retaining decay products from the radium-228, separating the REEs from the process stream; and eluting and retaining the REEs.
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S +1
Thermal barrier coating system, components coated therewith and method for applying a thermal barrier coating system to components
A thermal barrier coating system on a base material includes a bond coat layer with a lower face in direct contact with the base material and an upper face, a first ceramic layer in direct contact with the upper face of the bond coating layer and a second ceramic layer disposed on an outermost surface of the coating system and configured to be exposed to hot gas. The first ceramic layer includes a layer, combination, mixture, alloy, blend or multilayer structure of at least one of yttria-stabilized zirconia with a yttria content in a range of 6-8 wt-%, YTaO4 doped zirconia, and titania doped zirconia. The second ceramic layer includes a layer, combination, mixture, alloy, blend or multilayer structure of at least one of YTaO4 doped zirconia, titania doped zirconia, scandia stabilized zirconia, ceria containing perovskite material, yttrium aluminium garnet material, Monazite material, and spinel material. A material of the second ceramic layer is different from a material of the first ceramic layer.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Multiple product separation method of sea beach placer
InactiveCN102614978AStrong magnetismImprove qualityHigh gradient magnetic separatorsWet separationMagnetic mediaEngineering
The invention discloses a multiple product separation method of a sea beach placer, which comprises the following steps: firstly, the roughing integrated concentrate is obtained through the spiral chute re-separation, then, the sectional fine separation of a SLon magnetic separator is adopted for replacing the electronic separation, the sectional section of magnetic separation and fine separation is adopted, meanwhile, high-pulsation fluid force fields and medium width magnetic media are assisted in the magnetic separation process for twice fine separation to separate high-quality titanium concentrate, and the titanium-containing grade TiO2 is greater than or equal to 47 percent; and tailings after ilmenite fine separation are subjected to twice fine separation of high-intensity and large-width magnetic media to respectively separate out monazite, and the final tailings are zircon sand, so the goal of effectively separating the ilmenite, the monazite and the zircon sand is reached. The sectional fine separation of the SLon magnetic separator is adopted for replacing the electronic separation, the problems in the electronic separation flow process are solved, and the separation method has the advantages that the ilmenite, the monazite and the zircon sand can be effectively separated, the production flow process is simple, the field operation implementation is easy, the environment pollution is avoided, and the production cost is low.
Owner:赣州金环磁选科技装备股份有限公司
Method for extracting high-purity uranium, thorium and mixed rare earths from excellent molten slag
ActiveCN104775026ASimple processEase of mass productionProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationRare earth
The invention discloses a method for extracting high-purity uranium, thorium and mixed rare earths from excellent molten slag, which comprises the following steps: acid pickling: adding urdite excellent molten slag into an acid solution, stirring at normal temperature for some time, clarifying, and carrying out siphoning on the supernate to obtain a solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earths; and (2) pressure filtration and water washing: adding the slurry subjected to supernate siphoning into a plate and frame filter press, carrying out pressure filtration until no solution flows out, merging the filtrate with the supernate in the step (1), washing the filter residue of the plate and frame filter press with water until the pH value of the filtrate is 2.0-3.0, and merging the water washing solution with the supernate in the step (1) to obtain a clarified water solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earths and a filter residue. The method is simple in technical process, only adopts liquid-liquid extraction and uses one organic extractant, and thus, can easily implement large-scale production. The chemical materials are common and are low in consumption. The method can effectively extract single uranium and thorium products and mixed rare earths from the urdite excellent molten slag, and the overall yield is up to 90% above. The method is environment-friendly, and has obvious social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:JIANGXI JIEQIU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
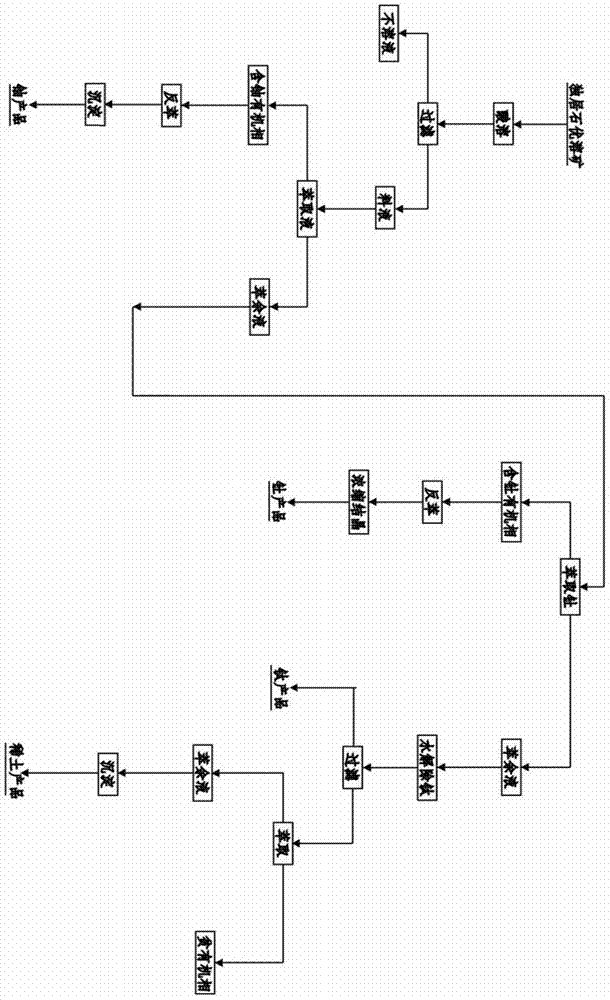
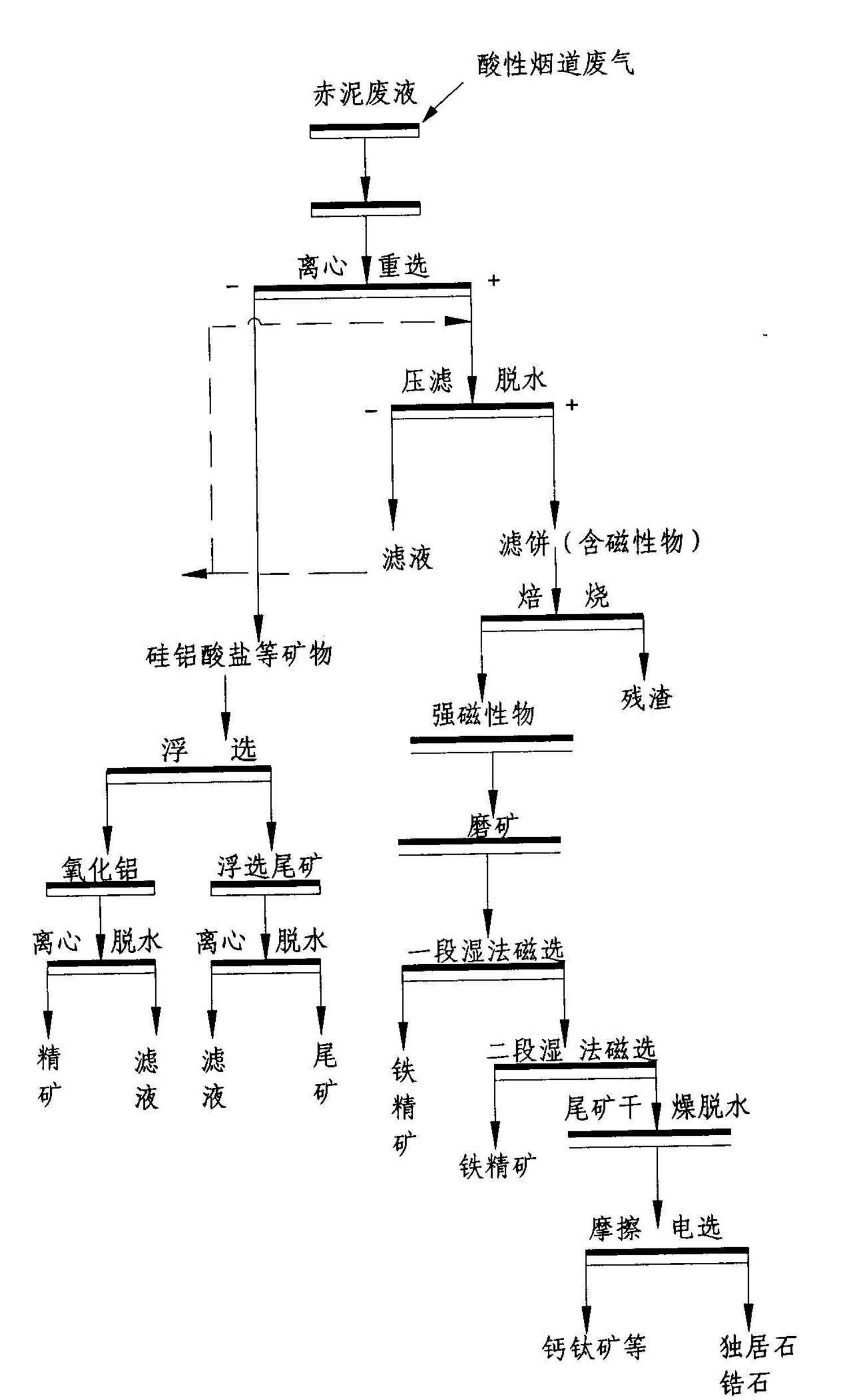
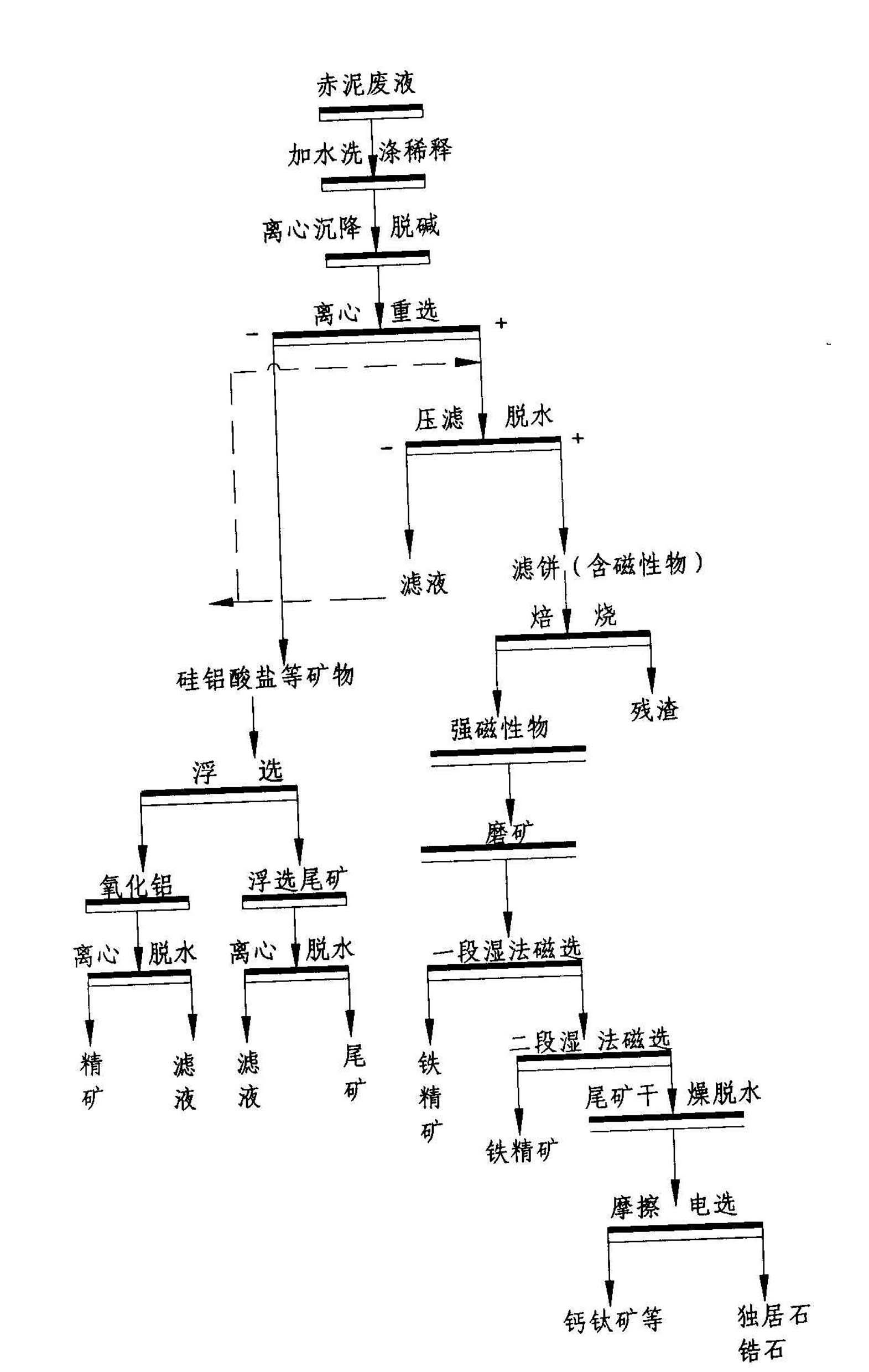
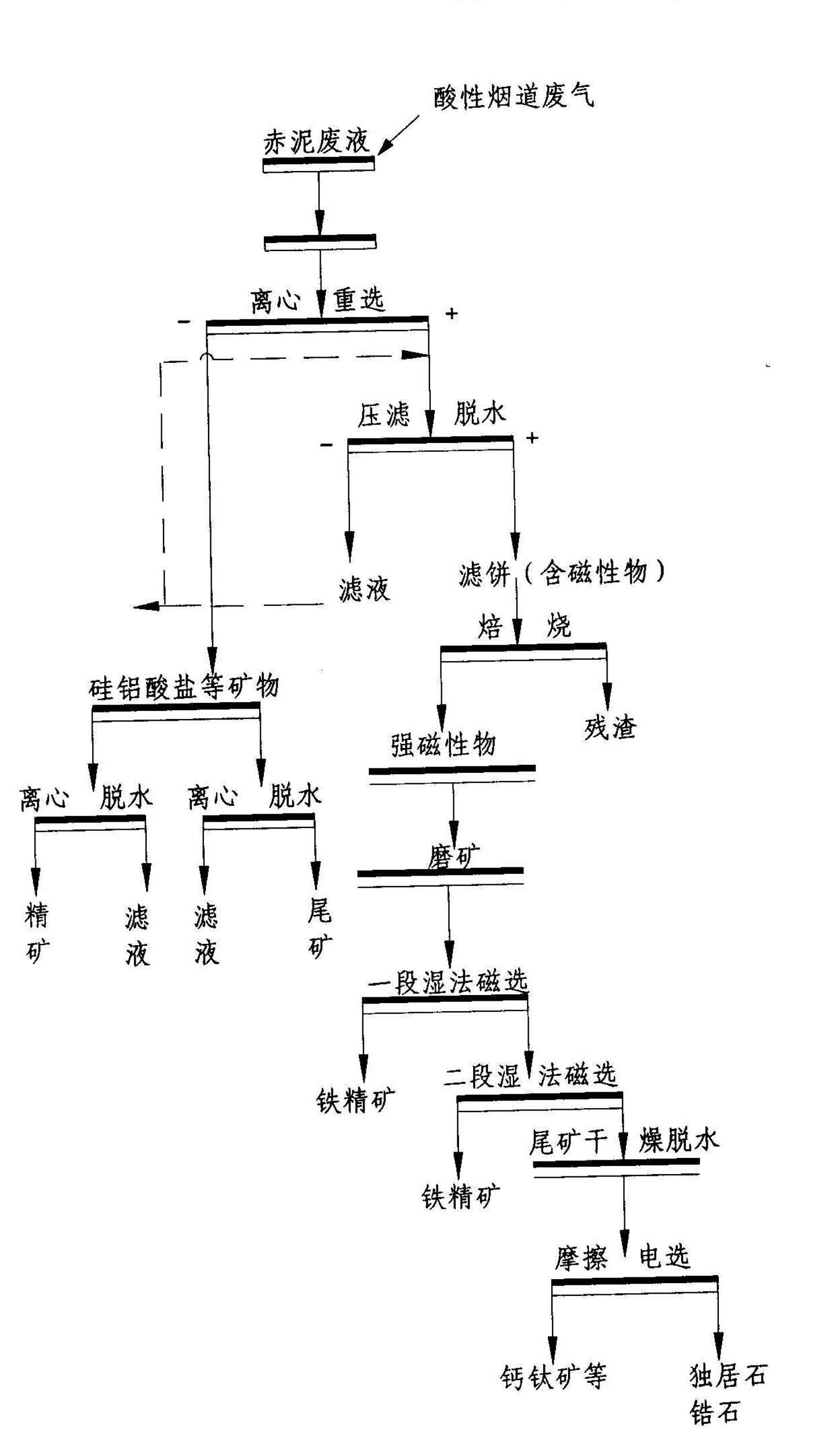
Red mud harmless comprehensive recycling technology suitable for Bayer process
The invention discloses a red mud harmless comprehensive recycling technology suitable for a Bayer process. The technology is mainly used for removing alkaline matters in the red mud and selecting a great quantity of iron minerals in the red mud through technical means while separating the radioactive minerals such as zircon, monazite and the like from the red mud at the same time; the separated red mud tailings are used as a large quantity of raw materials for cement processing, brick / tile firing, road building and the like, or used as mine filling materials and the like; the red mud minerals are turned into wealth and sufficiently used; large-scale resource utilization of red mud is realized; and a series of problems in resources and environment and potential safety hazard caused by red mud damming and stacking are fundamentally solved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
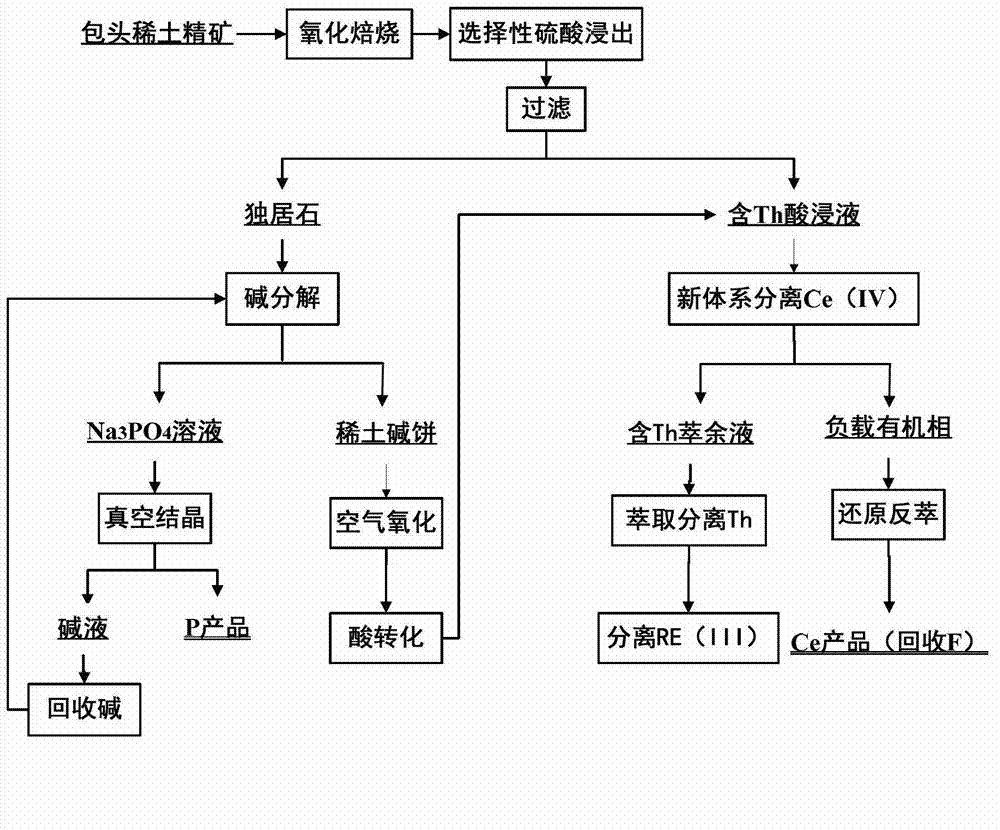
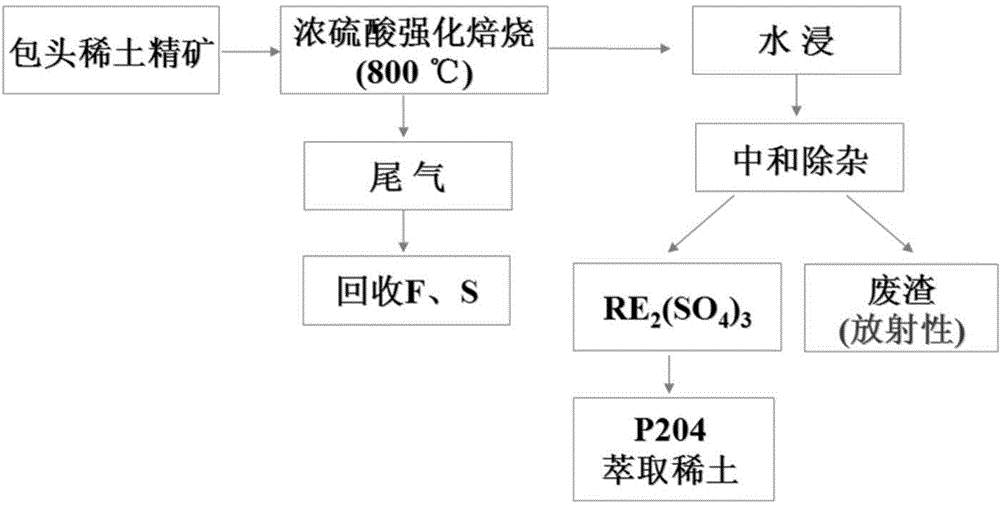
Technique for decomposing Baotou rare-earth ores
InactiveCN103045851AReduce stockpilesReduce processingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSodium phosphates
The invention relates to a technique for decomposing Baotou rare-earth ores. The invention solves the technical problems of environmental pollution and resource loss caused by the rare-earth ore separation technique in the prior art. The technique comprises the following steps: carrying out oxidizing roasting on mixed rare-earth concentrate; leaching the roasted ores with an H2SO4 solution to obtain a leach solution and urdite; extracting and separating Ce (IV), F and Th as well as single RE (III) from the sulfuric acid leach solution; and carrying out alkali conversion on the urdite to obtain a rare-earth alkali cake, carrying out size mixing, filtering, and crystallizing the alkaline solution to recover sodium phosphate, wherein the residual alkali liquor is used for cyclically leaching urdite slag. When being used for treating the mixed rare-earth concentrate, the technique provided by the invention can implement multi-step extraction of bastnaesite and urdite in the mixed ores. Besides, the invention is beneficial to further effectively recovering Th, F and P from baotite, thereby avoiding environmental pollution, enhancing the rare-earth yield, saving the cost and implementing clean production and comprehensive resource utilization in deed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
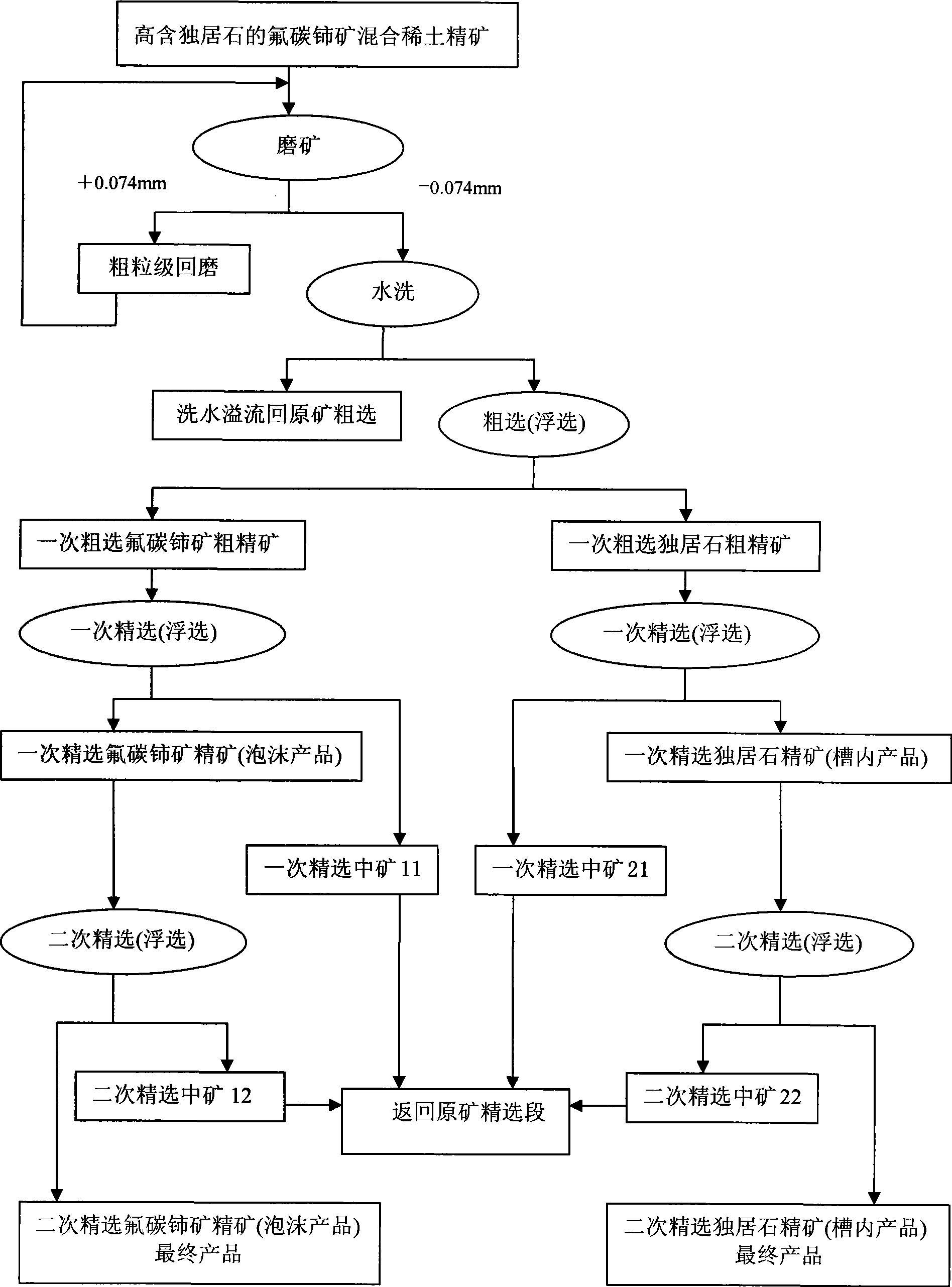
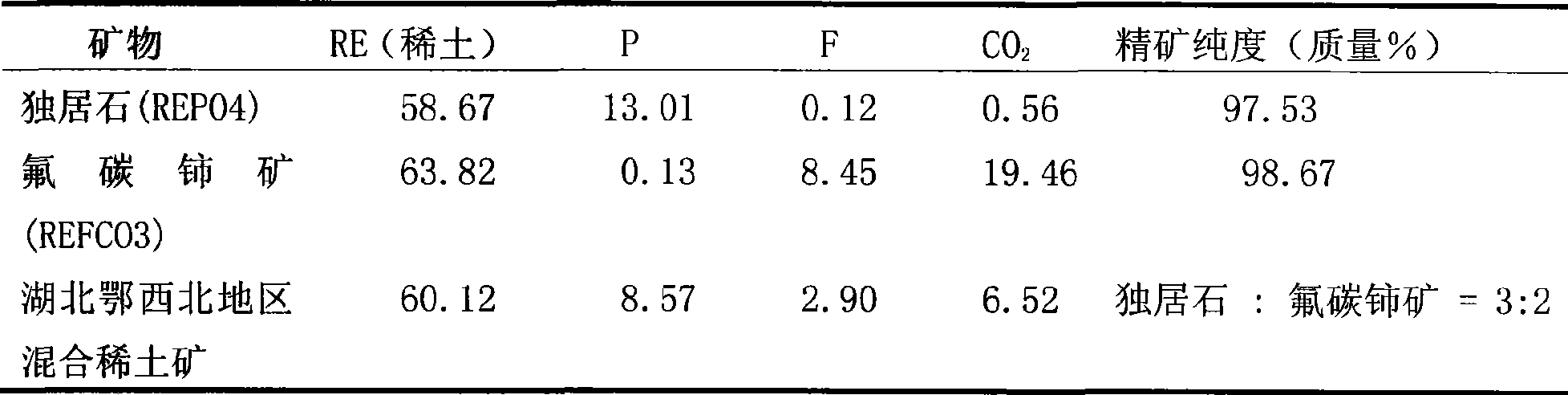
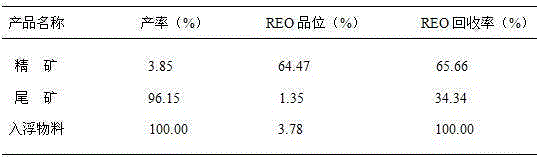
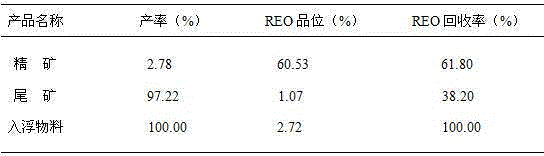
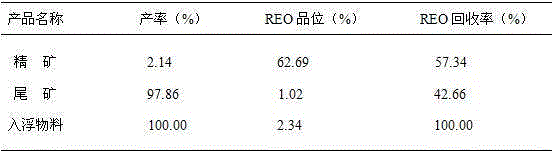
Floatation separation method for mengite and hamartite in misch metal ore concentrate
The invention relates to a method for the flotation separation of a collective rare earth ore, in particular to a method for the flotation separation of monazite and bastnaesite of a collective rare earth ore concentrate. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: an aluminium sulphate inhibitor, a hydroximic acid collecting agent and a frothing agent are used as floating agents, and bastnaesite collective rare earth ore concentrate with the high content of monazite is processed at a temperature ranging from 18 to 30 DEG C; first-stage roughing parisite rough concentrate and first-stage roughing monazite rough concentrate are obtained by first-stage separation and rougher flotation; the first-stage roughing parisite rough concentrate is processed by the operation of second-stage close sizing to obtain second-stage close sizing bastnaesite concentrate; the first-stage roughing monazite rough concentrate is also processed by the operations of size mixing and second-stage close sizing to obtain second-stage close sizing parisite concentrate; and the first-stage roughing monazite rough concentrate is processed by the operations of size mixing and second-stage close sizing to obtain second-stage close sizing monazite concentrate. High grade single monazite concentrate and single bastnaesite concentrate can be produced by the separation roughing and the flotation operation of the respective close sizing of the first-stage roughing parisite rough concentrate and the first-stage roughing monazite rough concentrate. The method has the advantages of simple process and low production cost, and can produce the high grade single monazite and the single bastnaesite.
Owner:武汉工大科技园发展有限公司
BiPO4 nanorod and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102872888AGood UV photocatalytic activitySave raw materialsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationUltraviolet lightsMonazite
The invention provides a BiPO4 nanorod and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the BiPO4 nanorod includes the steps: adding Bi(NO3)3 5H2O and NaH2PO4 2H2O into deionized water for reaction so as to obtain precipitate, namely the BiPO4 nanorod. BiPO4 which is prepared by the method and of monoclinic-phase monazite and hexagonal mixed crystal structures has fine ultraviolet light catalytic activity, and MB (methylene blue) liquid phase degradation rate of the BiPO4 reaches degradation activity of BiPO4 prepared by a hydrothermal method; and the whole preparation method is low in raw material cost, simple in process, low in preparation temperature and suitable for industrialized mass production and has extremely high practical value and application prospect, and product cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag
ActiveCN103014333ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodDecomposition
The invention discloses a separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag, namely a method for separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing and extraction of valuable components. According to the invention, the uranium, thorium and rare earth are leached out by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; the secondary slag is subjected to beneficiation and alkaline decomposition by a beneficiation technology, and closed-loop circular recovery of uranium, thorium and rare earth is realized; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
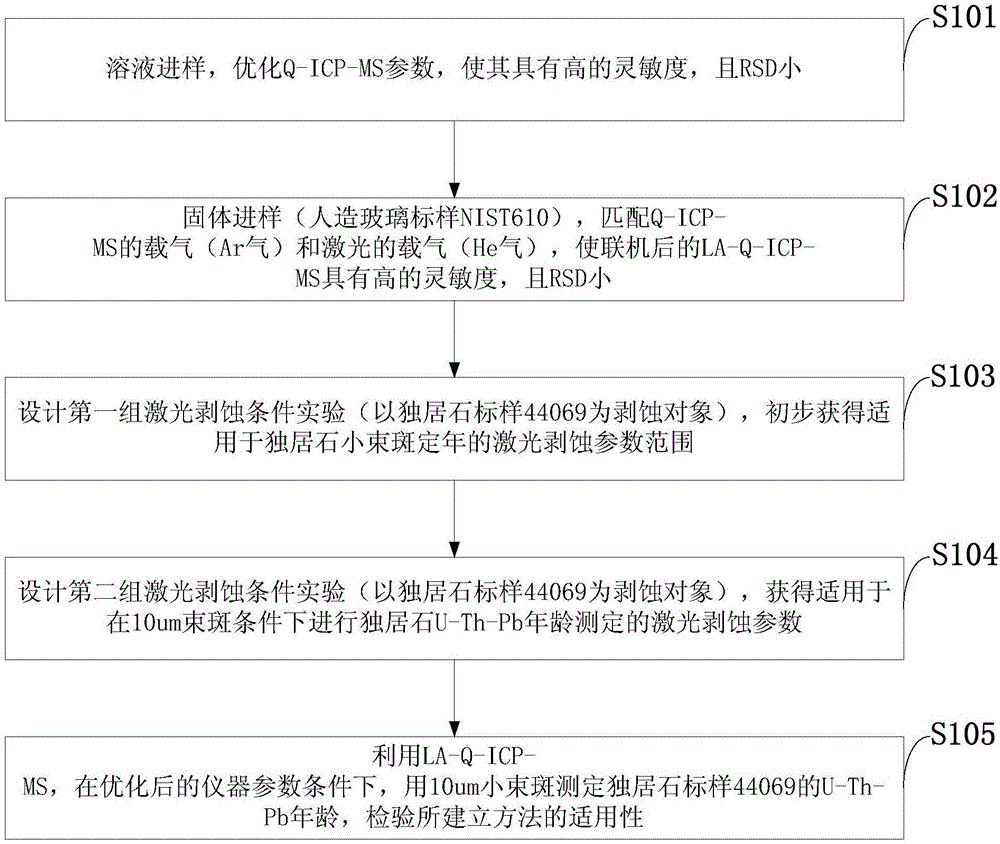
Monazite 10-micron small-beam-spot LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination method
ActiveCN106124606AIncreased Elemental Response StrengthGuarantee optimal detection statusMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRelative standard deviationMass analyzer
The invention discloses a monazite 10-micron small-beam-spot LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination method. The method includes the steps that a standard solution sample with the concentration of 1 ppb is directly led into a four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer, the instrument parameters are optimized, the response strength of <205>T1 is larger than 200,000 cps / ppb, the relative standard deviation is 1% to 2%, the double charges are smaller than 1.5%, and the yield of oxidation is smaller than 1%; an artificial glass NTSI 610 solid standard sample is led into the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in a laser ablation mode, carrier gas of a laser and carrier gas of the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer are matched, and counting of <238>U reaches the maximum; a monazite standard sample 44069 is led into the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in a laser ablation mode, the density of laser energy is 3 J / cm<2>, the impulse frequency is 4 Hz, and the age of monazite U-Th-Pb is determined through a 10-micron small laser beam spot. By means of the method, the space resolution ratio of monazite LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination is increased, and the testing requirement of monazite is met.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
Rare earth ore collecting agent and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a rare earth ore direct flotation collecting agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The collecting agent is formed by mixing octanohydroxamic acid, naphthalene formohydroxamic acid, salicyhydroxamic acid, fatty acid with the iodine value of 90-120 and Span-80. The prepared collecting agent is high in collecting capacity, small in use quantity, resistant to low temperature, low in cost and small in pollution, and can be used for mineral flotation of bastnaesite or xenotime or monazite.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Separation and recovery method of monazite slag
ActiveCN103014359ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium, rare earth and monazite concentrate and zircon concentrate from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing, extraction of valuable components and treatment of filter residue. According to the invention, the monazite slag is leached by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
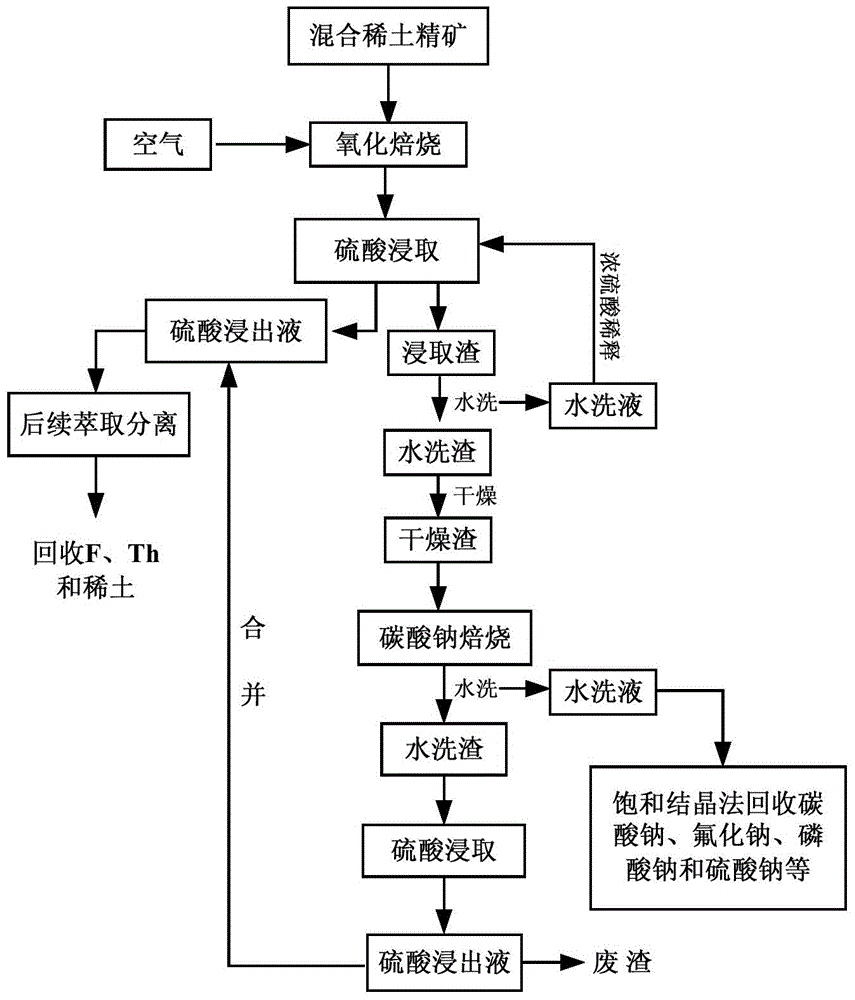
Cleaning smelting technology of bastnaesite and monazite mixed rare earth ore concentrate
InactiveCN104862502AEasy to recycleAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementRare earthMaterials science
The invention relates to a cleaning smelting technology of bastnaesite and monazite mixed rare earth ore concentrate. In the cleaning smelting technology, first, bastnaesite and monazite mixed rare earth ore concentrate is roasted; the roasted products are subjected to acid leaching, and a sulfuric acid leachate containing F<->, Ce <4+>, Th<4+> and trivalent rare earth and leached residues are obtained; the leached residues are washed to be neutral, are dried, and are roasted together with sodium carbonate; the roasted product is subjected to water washing, and a washing liquid and washed residues are obtained; the washed residues are subjected to acid leaching, a sulfuric acid leachate containing a few of F<->, Ce <4+>, Th<4+> and trivalent rare earth is obtained, the sulfuric acid leachates are mixed, Ce and F are recoveried, Th is separated, then grouping separation of trivalent rare earth is achieved further. Through the above flows, integrated and efficient recovery of rare earth oxide and valuable elements fluorine, phosphor and thorium in mixed rare earth ore concentrate can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
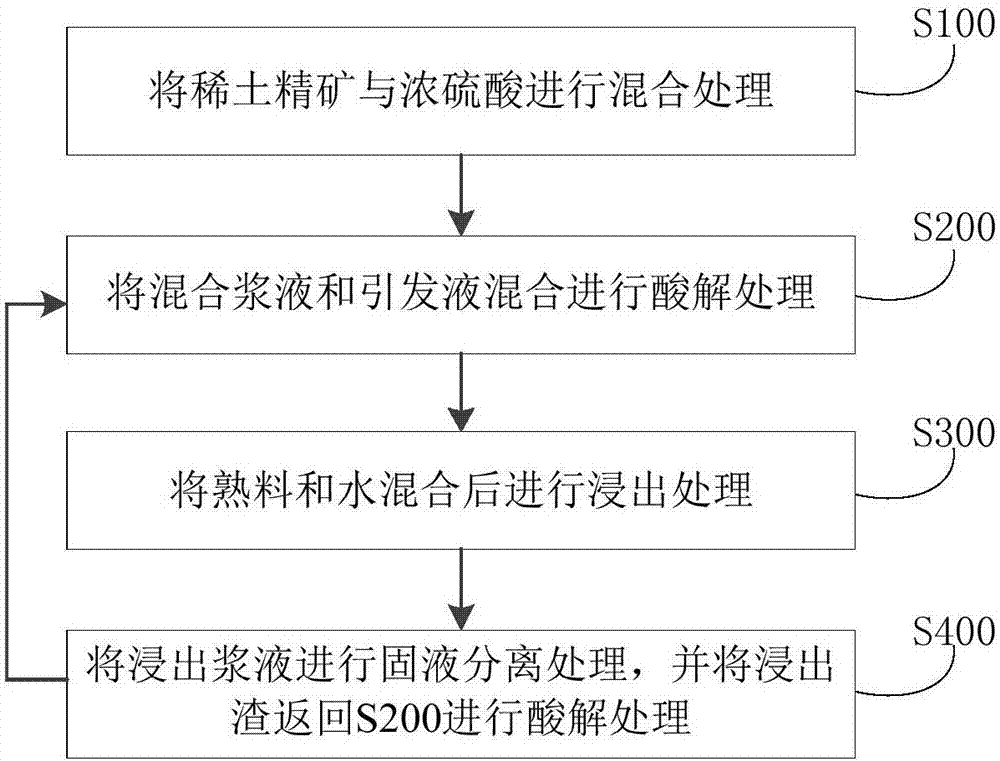
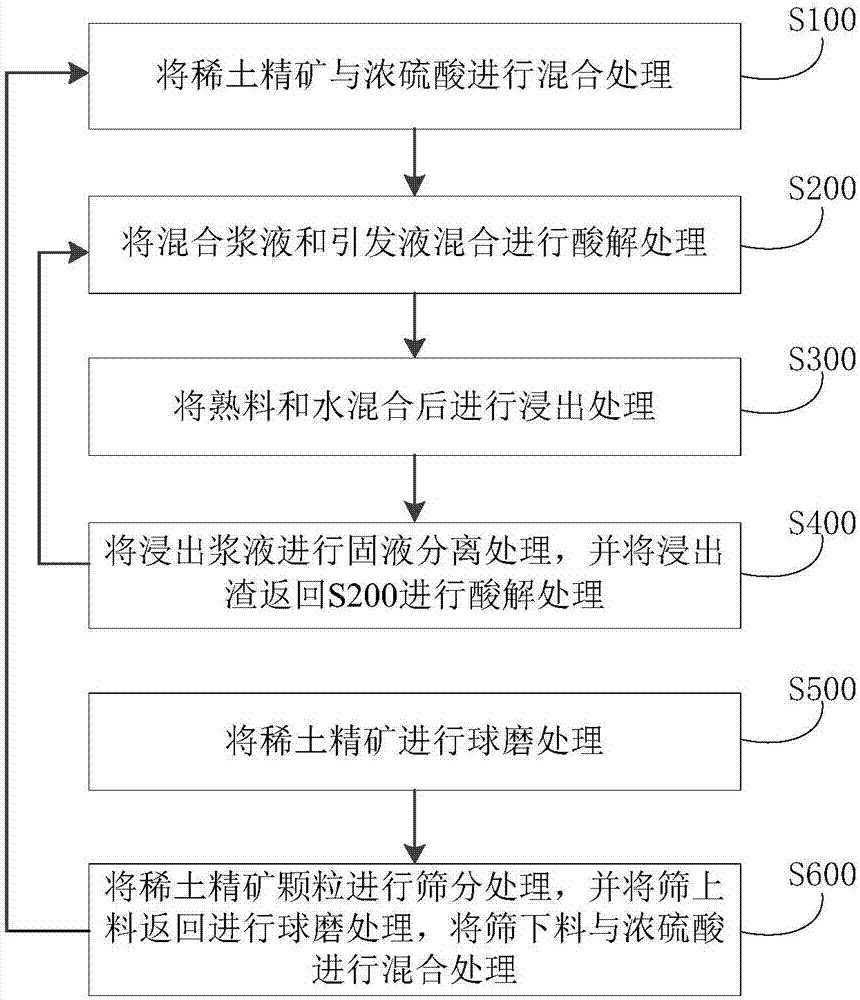
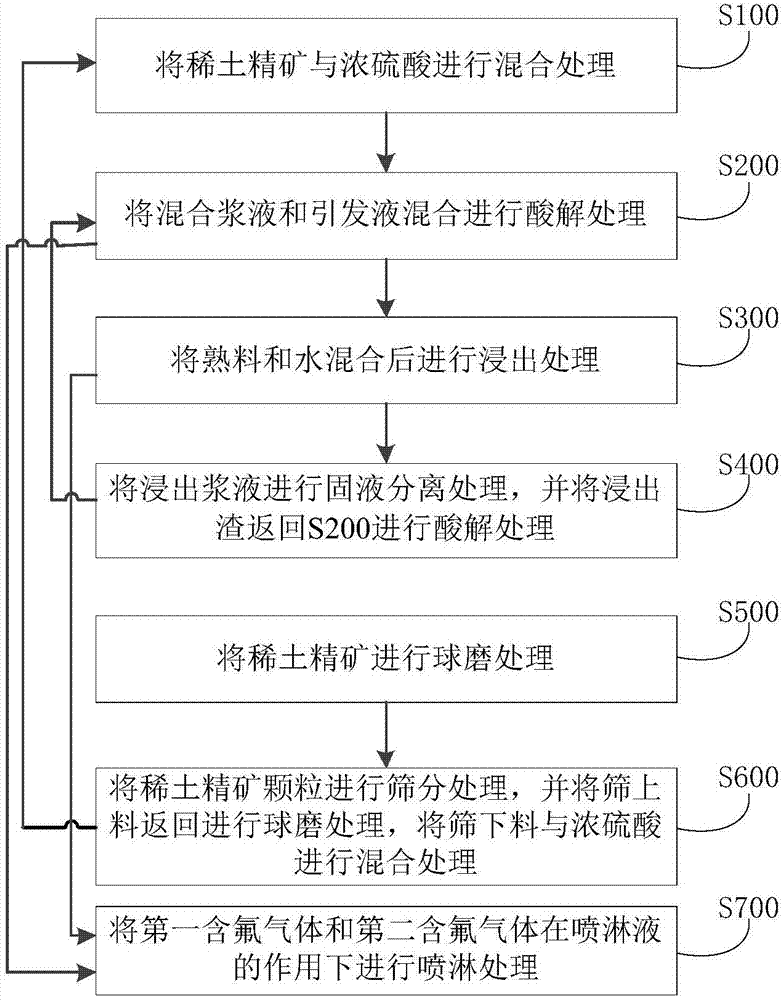
Method for processing rare earth ore concentrate
ActiveCN107475542AAchieve recyclingAvoid decompositionProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionRare earth
The invention discloses a method for processing rare earth ore concentrate. The method includes the steps that firstly, the rare earth ore concentrate and concentrated sulfuric acid are mixed so that mixed slurry and first fluorine-containing gas can be obtained; secondly, the mixed slurry and initiating liquid are mixed and subjected to acidolysis processing so that clinker and second fluorine-containing gas can be obtained; thirdly, the clinker and water are mixed and then subjected to leaching processing so that leached slurry can be obtained; and fourthly, the leached slurry is subjected to solid-liquid separation processing so that filtered fluid and leached residues can be obtained, and the leached residues are returned to the second step to be subjected to acidolysis processing. By means of the method, bastnaesite rare earth ore and mixed ore containing fluorine-containing rare earth ore and monazite can be processed, the energy consumption is low, and continuous production can be achieved; and meanwhile, thorium resources can be effectively recycled, the decomposition rate of the rare earth ore concentrate is remarkably increased, and the REO decomposition rate can reach 96%.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
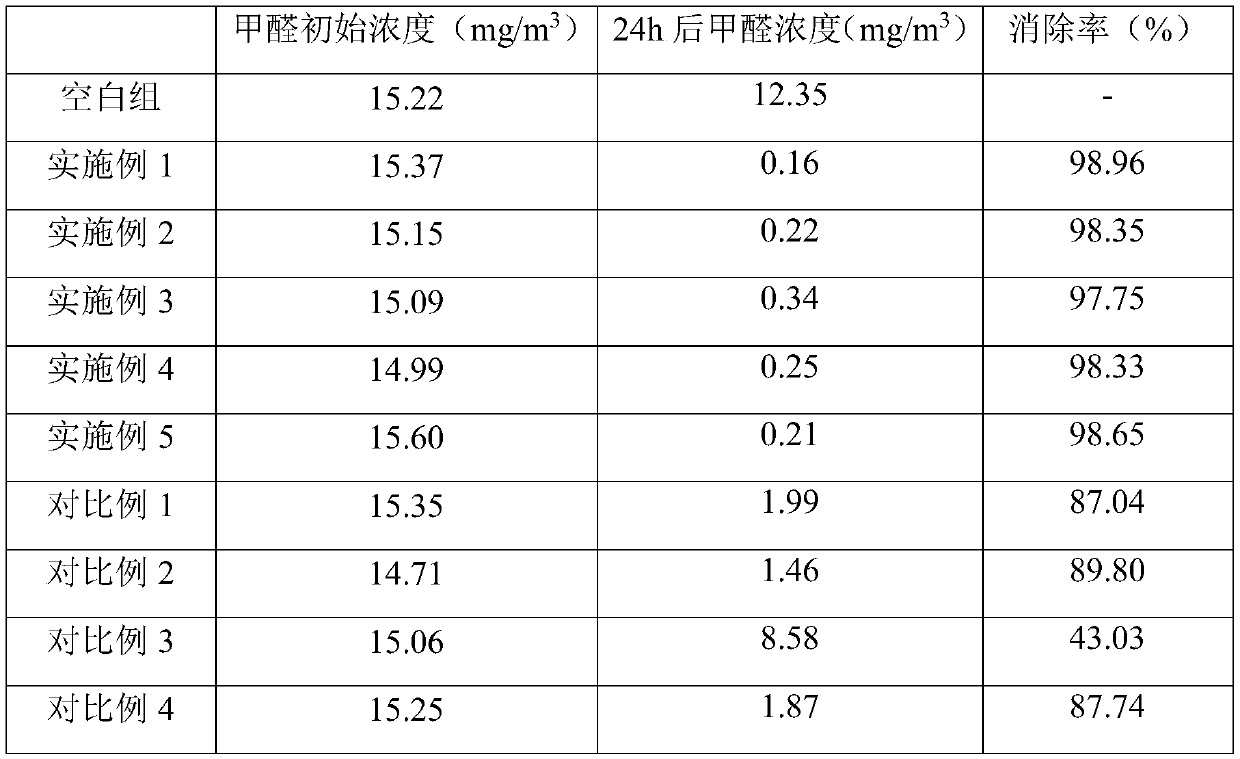
Plant negative oxygen ion air purifying agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109701387AIncrease concentrationReduce radiation effectsDispersed particle separationSolid solvent extractionManufacturing technologyOxygen ions
The invention relates to the technical field of air purification materials and manufacturing, and particularly provides a plant negative oxygen ion air purifying agent. The plant negative oxygen ion air purifying agent is prepared by mixing a pinus thunbergii extract, a cactus extract, tourmaline powder, monazite powder, nano titanium dioxide and a dispersing agent step by step. When the pinus thunbergii extract and the cactus extract are used during preparation, a plurality of modes such as superfine grinding, high-pressure homogenization, subcritical extraction, supercritical extraction andthe like are adopted to decompose macromolecular substances into micromolecular substances, so that the macromolecular substances have higher biological effects; then the tourmaline powder and the monazite powder are combined to rapidly induce the pinus thunbergii extract and the cactus extract to further release negative oxygen ions, and a larger effect is exerted on the aspect of air purification; meanwhile, the radiation effect of ore powder such as the tourmaline powder and the like can be reduced, so that the safety is higher; and on the other hand, the nano titanium dioxide can decomposeformaldehyde in the air, and the air can be purified fundamentally.
Owner:马建
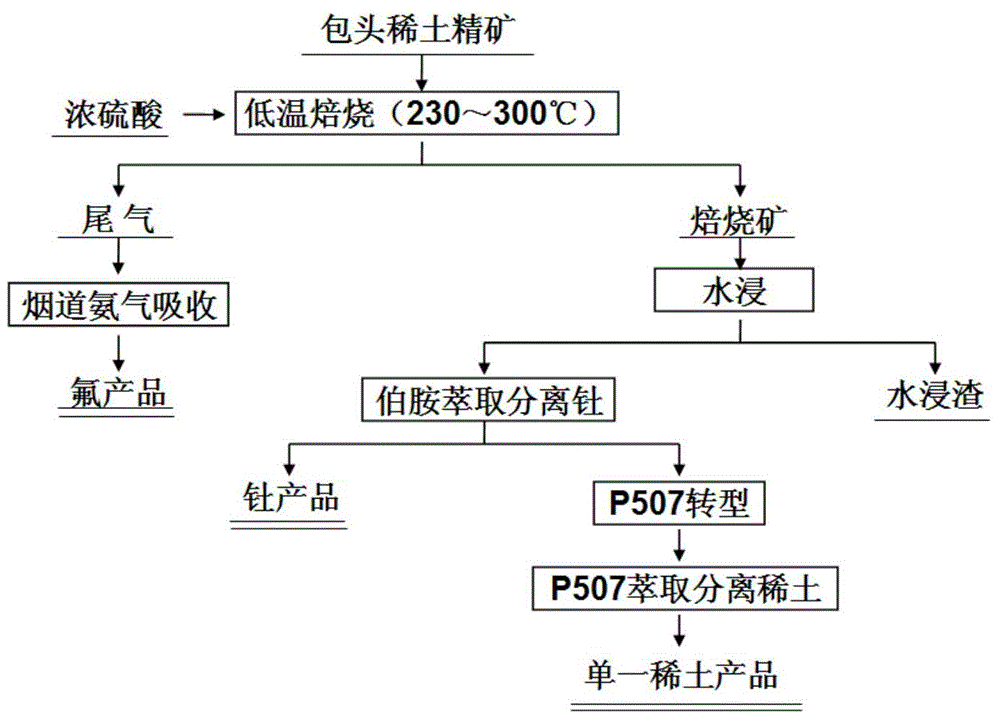
Monazite ore comprehensive utilization and recovery process
InactiveCN106367590ARealize comprehensive utilizationReduce pollutionProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionRare earth
The invention relates to a monazite ore comprehensive utilization and recovery process, wherein monazite and xenotime and other associate minerals are completely separated through mineral dressing, and alkali decomposition treatment, preferred dissolving, complete dissolving and extraction separation are used, such that the recovery rate of rare earth, uranium and thorium is improved, and the production of radioactive waste residue is reduced. According to the present invention, the comprehensive utilization of the radioactive waste residue is achieved, the amount of the radioactive waste residue is reduced, and the environmental pollution is avoided; during the mineral dressing process, the titanium-containing ilmenite and the monazite are separated, such that the problem that titanium enters the subsequent rare earth, uranium, thorium extraction process so as to easily cause the generation of the three-phase matter is avoided; and H2O2 is added during the preferred dissolving process of the hydrochloric acid, such that the recovery rate of the rare earth is easily increased, and the extraction separation pressure of the subsequent complete dissolving residue is reduced.
Owner:永州市湘江稀土有限责任公司
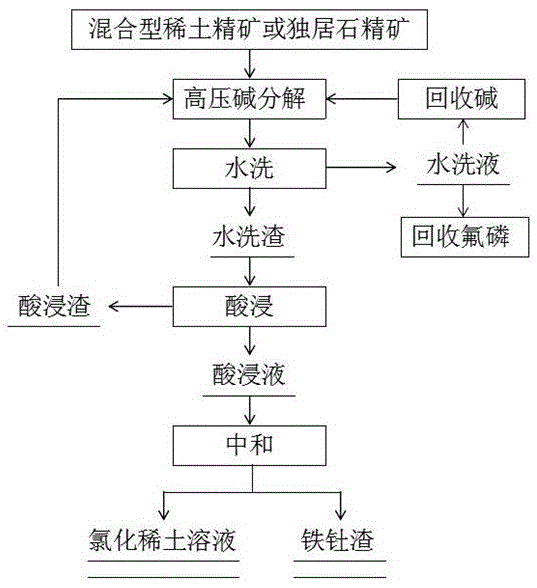
Method for preparing rare earth chloride from mixed rare earth concentrate or monazite concentrate
InactiveCN105543510AShort processAlkali decomposition temperature range is lowProcess efficiency improvementRare earthMonazite
The invention relates to a method for preparing rare earth chloride from mixed rare earth concentrate or monazite concentrate and belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy. According to the method, the rare earth chloride with the rare earth leaching rate reaching 94.87-99.26% is prepared by controlling the alkali decomposing temperature, the reaction time and the reaction pressure of the mixed rare earth concentrate or the monazite concentrate in the high-pressure alkali decomposing process. The method has the beneficial effects that the mineral decomposing rate is high under the high-pressure condition, the decomposing temperature is reduced, the reaction time is shortened, and energy conservation and environment friendliness are achieved; caustic soda can be recycled, so that cost is reduced; no three-waste pollution is generated, and various valuable elements are comprehensively recycled; and the technological process is short, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:李梅
Increase in the separation factor between americium and curium and/or between lanthanides in a liquid-liquid extraction operation
ActiveUS20120160061A1Improved separation factorEasy to separateNuclear energy generationNuclear elementsSeparation factorRare earth
A method using diglycolamide for increasing the separation factor between americium and curium and / or between lanthanides during an extraction operation. The operation comprising putting an acid aqueous phase, in which are found the americium, curium and / or lanthanides, in contact with an organic phase non-miscible with water, containing at least one extractant in an organic diluent. The aqueous and organic phases are then separated, and the diglycolamide is added to the aqueous phase. This method can be used for processing and recycling irradiated nuclear fuels, in particular for selectively recovering americium from high activity aqueous solutions such as raffinates stemming from the processing of irradiated nuclear fuels with a PUREX or COEX™ method; processing of rare earth ores of the monazite, xenotime or bastnaesite type, in order to facilitate separation of <<lightweight>> rare earths from <<heavy>> rare earths and of yttrium, or that of two rare earths with adjacent or close atomic numbers.
Owner:ORANO RECYCLAGE +1
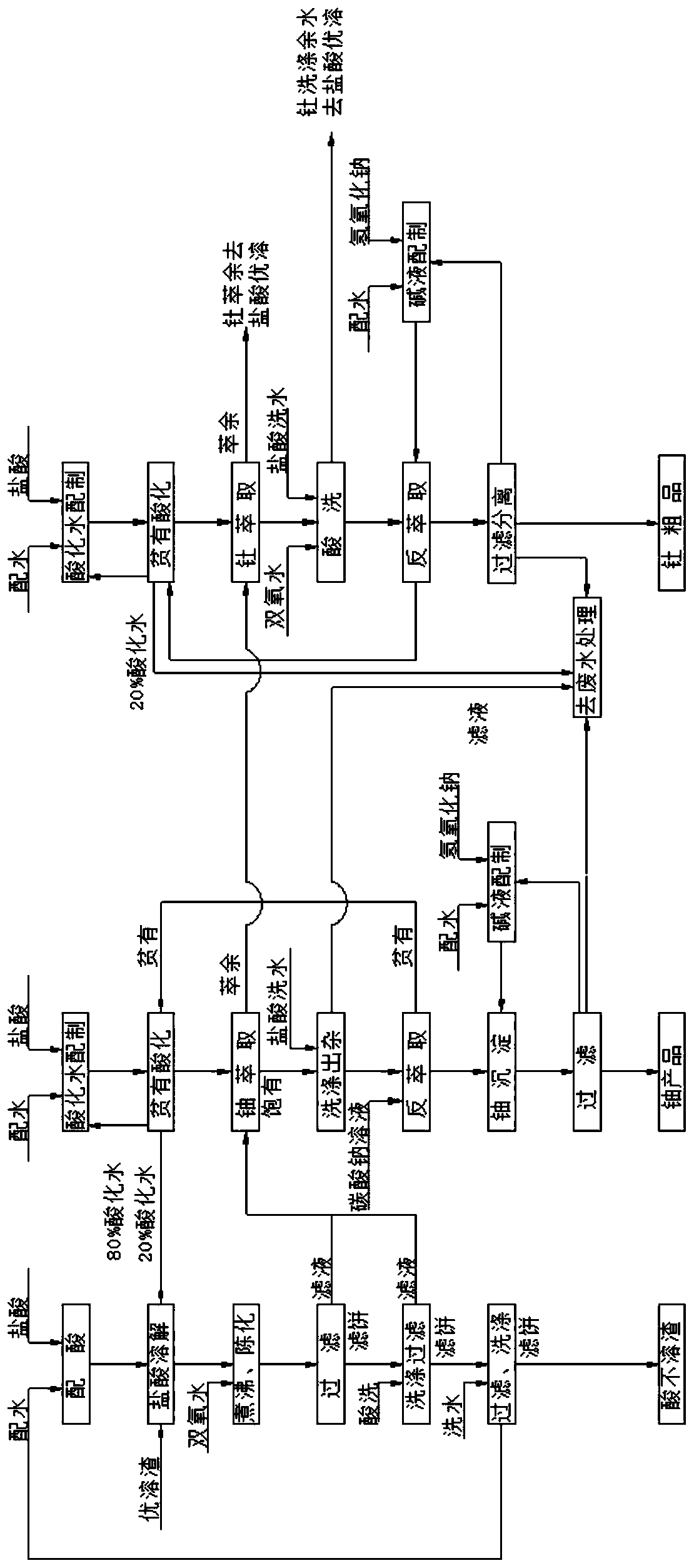
Method for smelting and separating uranium, thorium and rare earth from residual slag of processed monazite
ActiveCN111004920AReduce consumptionHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagWater chlorination
The invention provides a method for smelting and separating uranium, thorium and rare earth from residual slag of processed monazite. The residual slag of processed monazite is used as the raw material. The method comprises the following steps of performing hydrochloric acid complete dissolving, performing dissolving liquid aging, performing liquid-solid separation, extracting uranium by an amineextraction agent and performing extracting and enriching, extracting thorium from an acidic phosphorus-containing extraction agent and performing wastewater treatment. A raffinate phase obtained afterthorium extraction is returned to a monazite hydrochloric acid optimum solubilizing procedure to recover a rare earth chloride mixture, after extraction and separation, a single uranium product and athorium product are obtained through precipitation, and the recovery rate of resources such as uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 95%; and most of process water in the production processis directly returned to a system for cyclic utilization, a small amount of wastewater is recycled back to the system after comprehensive treatment, and zero drainage of the wastewater is realized. Bythe adoption of the technical scheme, the flow is simple and flexible, and large-scale production is achieved easily; the chemical material consumption is low, valuable resources such as rare earth,uranium and thorium can be efficiently recovered, and the resource recovery rate is increased; and the comprehensive treatment and environmental-friendly, efficient and clean production of the monazite resources are guaranteed.
Owner:湖南中核金原新材料有限责任公司
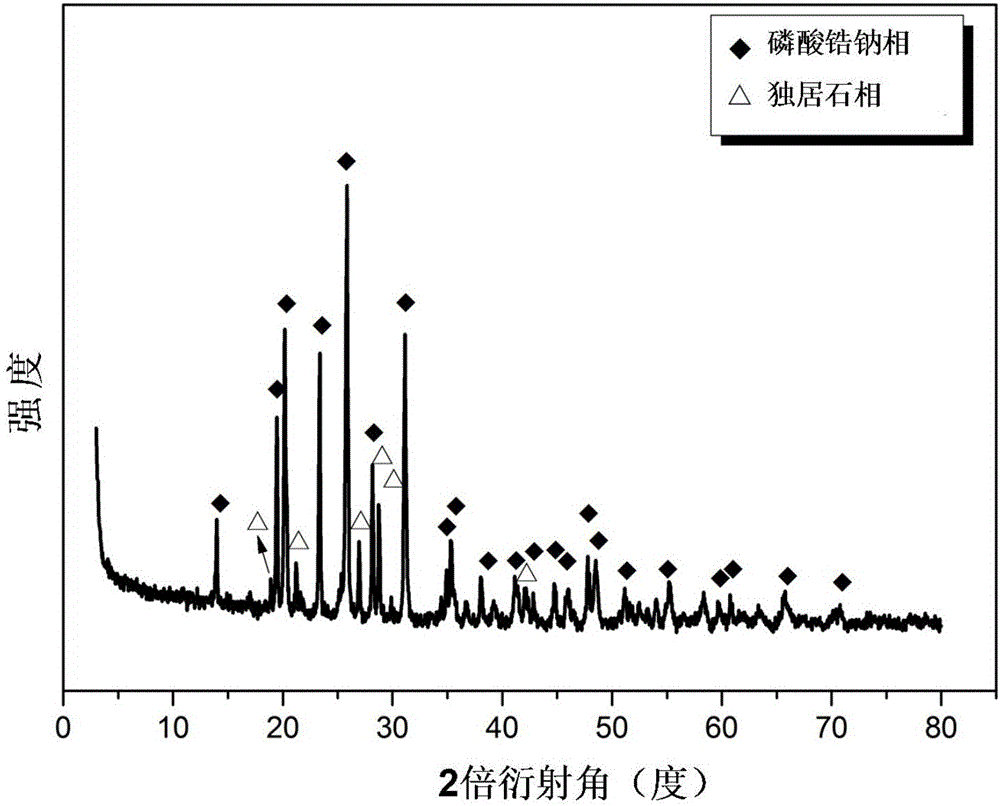
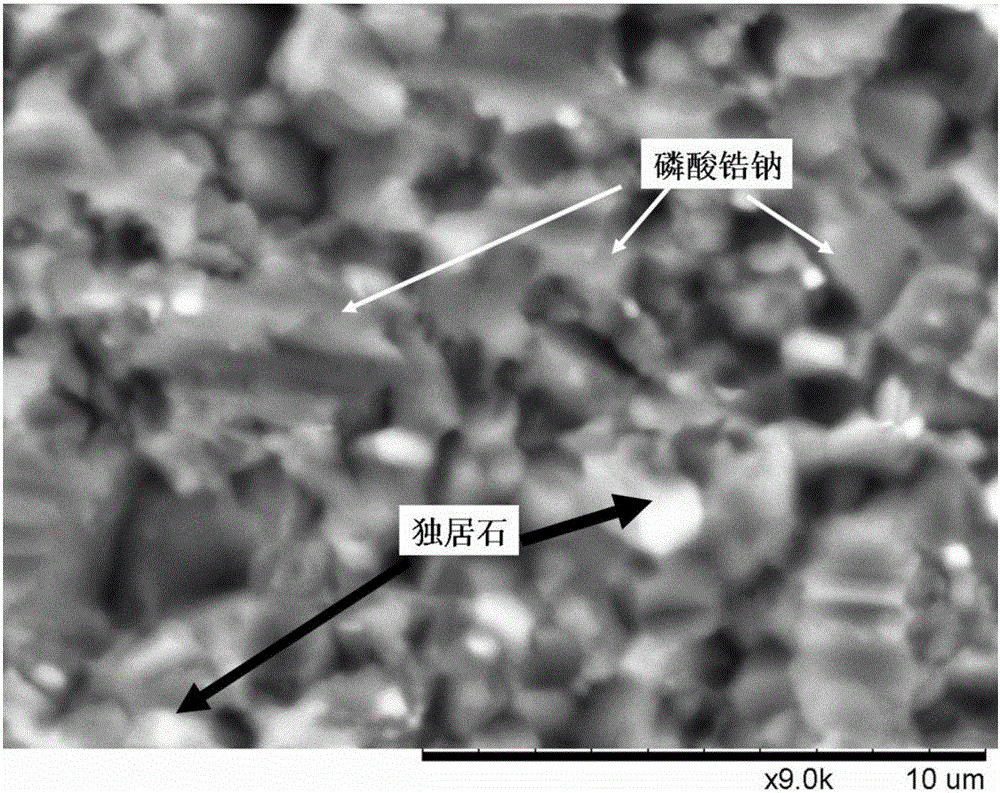
Zirconium sodium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic solidified body and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105777101AEfficient curingGood chemical stabilityRadioactive decontaminationSodium phosphatesRadioactive waste
The invention discloses a zirconium sodium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic solidified body and a preparation method thereof. The solidified body is prepared by taking the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of P2O5, 10-35 parts of Fe2O3, 1-4 parts of B2O3, 3.5-14 parts of CeO2, 6-32 parts of ZrO2 and 1.5-8 parts of Na2CO3 and carrying out mixing, pre-sintering and ball-milling, thus obtaining substrate raw material powder; and then mixing 45-100 parts of substrate raw material powder and 0-55 parts of high-level radioactive wastes or simulated high-level radioactive wastes by weight and carrying out ball-milling, forming under pressure and sintering, thus preparing the solidified body. The zirconium sodium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic solidified body has high occlusion capacity toward the high-level radioactive wastes, high volume reduction ratio and good stability; and the preparation process is simple, is easily applied to engineering and can be widely used for solidified disposal of the high-level radioactive wastes.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Slurry shield cutter head washing system
ActiveCN103867211AEasy to useAvoid blockingWelding/cutting media/materialsTunnelsManganeseEngineering
The invention relates to a slurry shield cutter head washing system. The slurry shield cutter head washing system comprises a water pump and spray nozzles, wherein the spray nozzles are distributed and installed on a slurry shield cutter head, the spray nozzles consist of middle spray nozzles and peripheral spray nozzles, the middle spray nozzles are installed at the side part of a fishtail cutter frame, the peripheral spray nozzles are distributed on the outer surface of a cutter arm of the slurry shield cutter head, the nozzle orifices of the peripheral spray nozzles face to the outer side of the slurry shield cutter head, U-shaped sheaths are arranged at the upper parts of the peripheral spray nozzles, the sheaths are welded on the slurry shield cutter head and the sheaths are welded with the slurry shield cutter head through high-wear-resistance electrodes, wherein the coating of the high-wear-resistance electrode is made of the following raw materials by weight percentage: 2-5 percent of vanadium iron nitride, 2-5 percent of chromium iron nitride, 2-5 percent of ferromanganese iron nitride, 5-10 percent of ferrotitanium, 5-10 percent of tungsten carbide, 5-10 percent of titanium carbide, 1-5 percent of cobalt carbide, 5-10 percent of ferrotungsten, 10-25 percent of metal manganese, 5-10 percent of ferroboron, 1-5 percent of monazite powder, 2-5 percent of nitrocellulose and balance of metal iron.
Owner:中铁十四局集团装备有限公司
Monazite ballast separation and recovery method
ActiveUS20150307958A1The fermentation process is simpleEasy to separateRare earth metal compoundsProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodSlag
The invention relates to a separation and recovery method for radioactive waste slag and specifically relates to a separation and recovery method for monazite slag. The separation and recovery method comprises the following steps: acid leaching, pressure filtration, water washing, extraction of valuable components and treatment of filtration slag. The separation and recovery method provided by the invention performs low-acid and low-temperature leaching on monazite slag, so that a liquid phase and a solid phase are easy to separate; after an ore dressing process is adopted for performing ore dressing and alkali decomposition on secondary slag, closed-loop circulation and recovery of uranium, thorium and rare earth is realized; and simultaneously, extraction raffinate waste acid is recycled, so that the emission of waste water is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and fresh water and the treatment cost of the waste water are reduced, the production cost is reduced, the recovery rate of the valuable elements, namely the uranium, the thorium and the rare earth is more than 97%, and the whole process has no emission of the radioactive waste water and waste slag.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
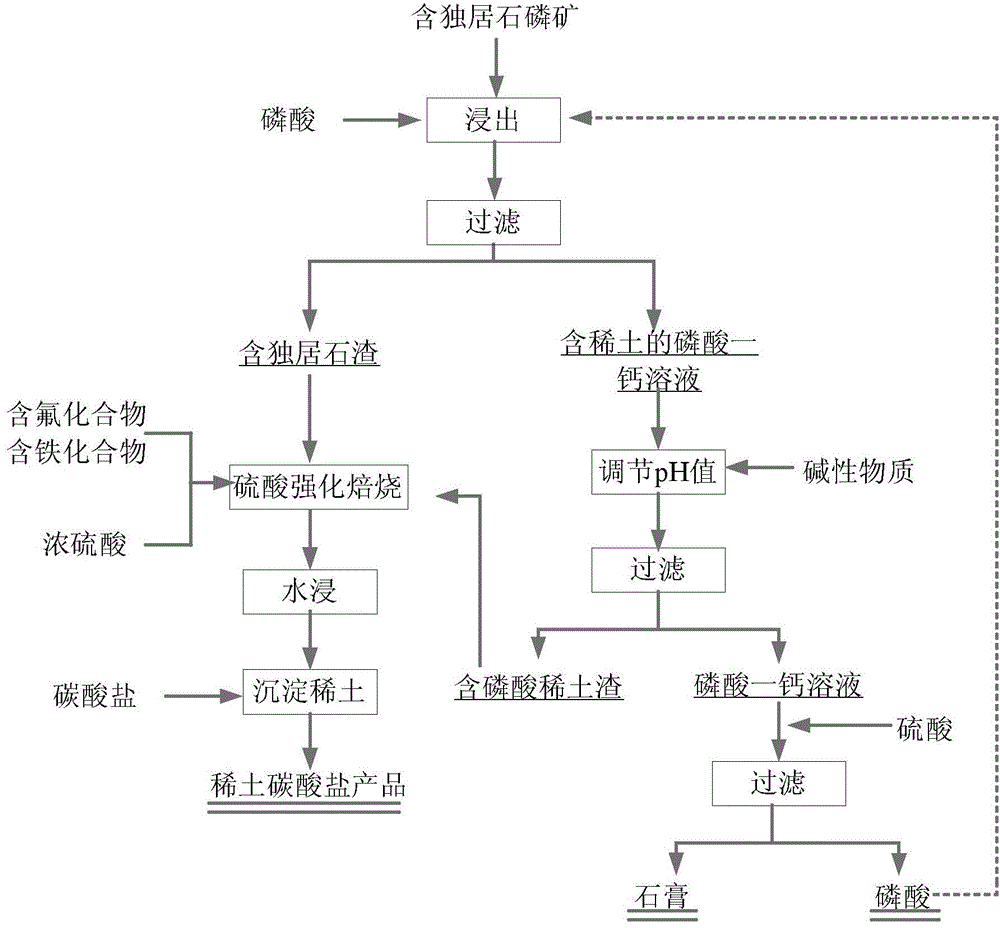
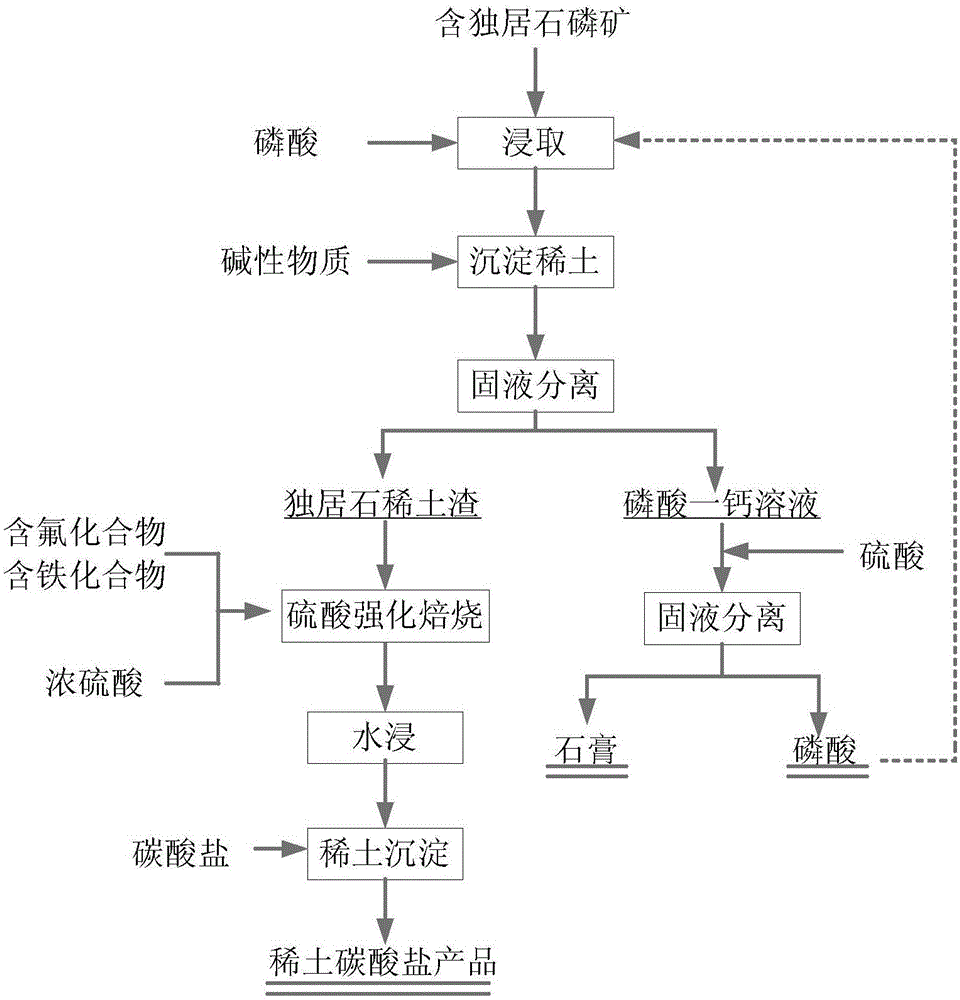
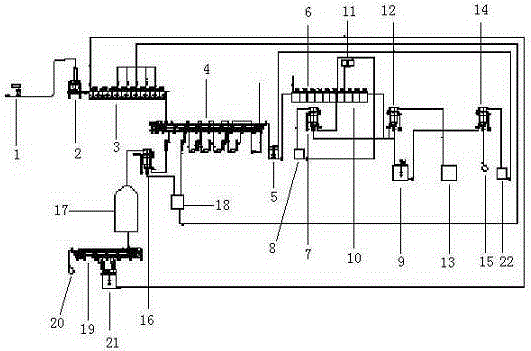
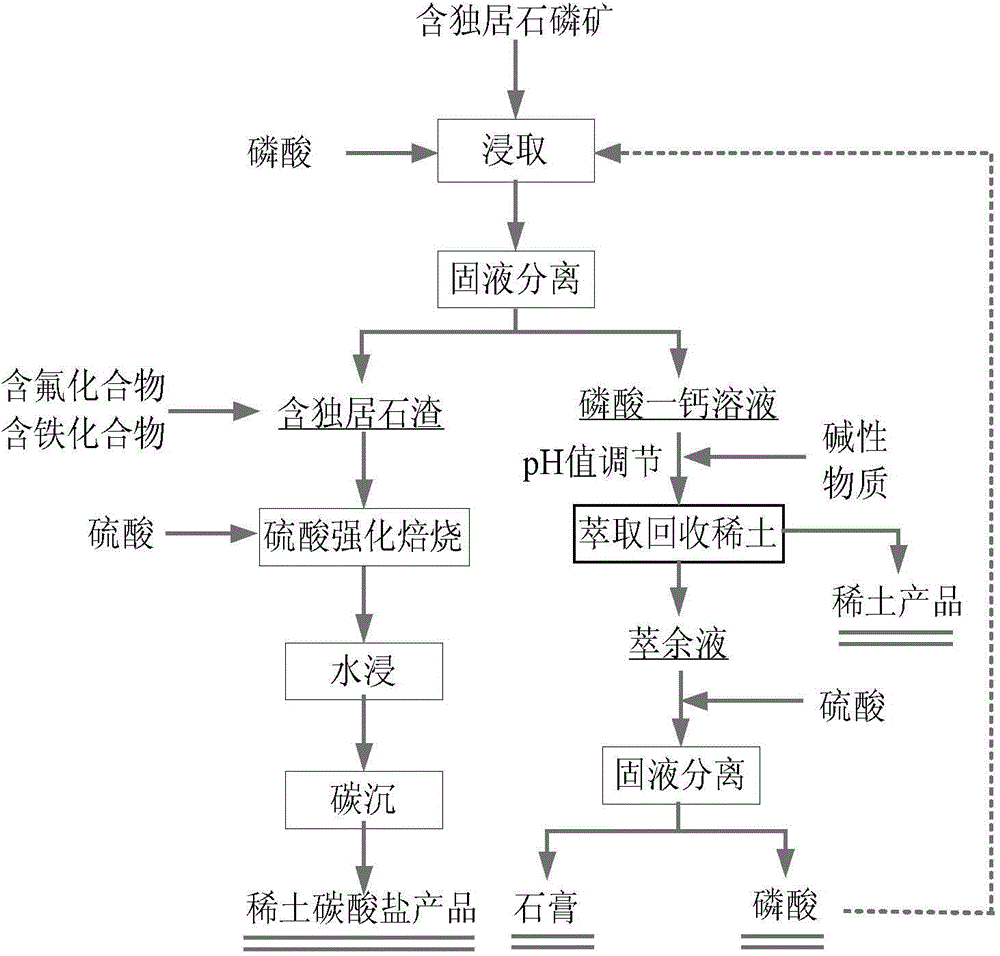
Method for comprehensively recycling phosphorus and rare earth from rare earth phosphorite containing monazite
ActiveCN105331812AHigh recovery rateEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementRaw phosphate material treatmentSolubilitySlag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recycling phosphorus and rare earth from rare earth phosphorite containing monazite. The method includes the following steps that rare earth phosphorite containing monazite is obtained from phosphoric acid in a leaching manner, and a monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth and slag containing monazite are obtained through filtration; the monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth is processed through a precipitation method, dissolved rare earth precipitates, a monocalcium phosphate solution and rare earth slag containing phosphoric acid are obtained through filtration, and the rare earth slag containing phosphoric acid and slag containing monazite are mixed to form mixed slag; and phosphorus in the monocalcium phosphate solution is recycled, and rare earth in the mixed slag is recycled. Acid leaching is conducted by adding phosphoric acid, phosphorus in rare earth phosphorite containing monazite forms monocalcium phosphate high in solubility, and therefore monazite existing in a precipitation manner and phosphorus can be separated. Then, the monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth is processed through the precipitation method, and rare earth and phosphorus elements in phosphorite can be effectively separated. Rare earth and phosphorus are effectively separated through two times of separation steps, and therefore the rare earth recycling rate is increased.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
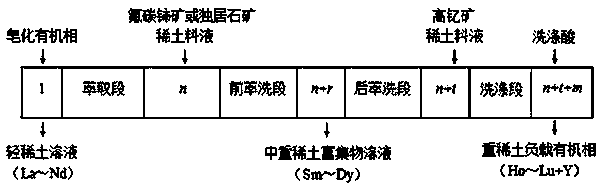
Method for grouping and separating light rare earth ore and high-yttrium ore by two-inlet and three-outlet fractional extraction
InactiveCN104388710AReduce consumptionReduce investmentProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementMonazite
The invention discloses a method for grouping and separating light rare earth ore and high-yttrium ore by two-inlet and three-outlet fractional extraction. Two rare earth feed inlets and three rare earth product solution outlets are formed in a fractional extraction system, and a third outlet is formed in an extraction segment. P507 is taken as an extraction agent for simultaneously treating rare earth chloride solutions of two types of rare earth ore, namely the light rare earth ore (bastnasite or monazite rare earth ore) and the high-yttrium ore so as to obtain three products, namely a light rare earth element 'La-Nd' product, a heavy rare earth element 'Ho-Lu+Y' product and a medium-heavy rare earth element 'Sm-Dy' enrichment. Compared with an existing corresponding rare earth fractional extraction process, by grouping and separating the light rare earth ore and the high-yttrium ore by two-feed inlet and three-outlet fractional extraction of -Nd / Sm-Dy / Ho-, the consumption of a saponification alkali is reduced by 17%-86%, the consumption of a washing acid is reduced by 20%-89%, the number of stages of an extraction tank is reduced by 41%-49%, the separation cost of rare earth is significantly reduced, and the green degree of the process is obviously improved.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method for separating valuable components of monazite slags
ActiveCN102925681ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating valuable components of monazite slags, and particularly relates to a method for separating valuable components of monazite slags into a liquid phase (a solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earth) and a solid phase (a filter residue containing useful minerals such as monazite, zirconite and rutile). The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of acid leaching, filter pressing and water scrubbing. According to the invention, monazite slags are subjected to low-acid and low-temperature leaching, and a liquid phase and a solid phase are separated easily; after secondary slags are subjected to mineral processing and alkaline decomposition by using a mineral processing process, the closed cycle collection of uranium, thorium and rare earths can be realized; meanwhile, an extract residue waste acid can be subjected to cyclic utilization, thereby reducing the wastewater discharge, reducing the consumption of sulfuric acids and new water and the wastewater treatment cost, and reducing the production cost; and the recovery rates of valuable elements such as uranium, thorium and rare earths can be greater than 97%, therefore, an effect of no radioactive wastewater and waste residue discharge in the whole process can be achieved.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
Production method and device for extracting rare earth from monazite ores
InactiveCN105200230AReduce consumptionReduce the introductionProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationRadioactive agent
The invention relates to a method and a device for extracting rare earth, in particular to a production method and device for extracting the rare earth from monazite ores. The production operation stability is guaranteed by means of a caustic decomposition procedure, a washing procedure, a chlorination procedure, a phosphorus base liquor fine filtration and crystallization procedure as well as a special JQL reactor and a full-automatic metering system; by the aid of the JQL reactor as caustic decomposition equipment, fully-enclosed continuous and automatic operation is realized, heat energy consumption and alkali consumption are reduced, the labor intensity of workers is reduced, wastewater emission is avoided in a production process, the production efficiency is high, the rare earth yield is increased, and the worker bodies are prevented from radiation injury caused by radioactive substances. The clean, automatic, and fully-enclosed continuous production operation mode is realized by the aid of equipment, the utilization rate of the equipment is increased greatly, and the operation cost of the equipment is reduced.
Owner:包头市锦园化工科技有限公司
Method for comprehensive recovery of phosphor and rare earth from monazite-containing phosphate rock
ActiveCN105441674AHigh recovery rateReduce dosageProcess efficiency improvementPhosphorus preparationDecompositionSlag
The present invention discloses a method for comprehensive recovery of phosphor and rare earth from monazite-containing phosphate rock. The method comprises the following steps: a rare-earth-containing monocalcium phosphate solution and monazite-containing slag are obtained by leaching of the monazite-containing phosphate rock with phosphoric acid and solid-liquid separation; an extractant organic solution is added into the rare-earth-containing monocalcium phosphate solution for extraction and recovery of the rare earth in the monocalcium phosphate solution, and a monocalcium-phosphate-containing extraction raffinate is obtained; the rare earth in the monazite-containing slag is recovered, and the phosphor in the monocalcium-phosphate-containing extraction raffinate is recovered. According to the method, on the basis of the characteristics that decomposition conditions of the monazite-containing phosphate rock are harsher than that of phosphate rock due to the structural features of monazite and other rare-earth minerals which are difficult to decompose, the phosphoric acid is used for leaching treatment of the monazite-containing phosphate rock to dissolve the phosphate rock to produce monocalcium phosphate (Ca (H2PO4) 2) to entering the liquid phase, so that phosphorite and the monazite are separated. By respective recovery of the rare earth in the monocalcium phosphate solution and the rare earth in the monazite-containing solid slag, the rare earth recovery rate is improved.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent and its preparation method
InactiveCN103495407AHigh viscosityNot easy to disintegrateOther chemical processesSodium metasilicateHazardous substance
A bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent is prepared from the following raw materials: by weight, 80-90 parts of mao bamboo, 3-4 parts of polyethylene glycol, 40-45 parts of tourmaline powder, 35-40 parts of monazite powder, 5-7 parts of sodium metasilicate, 12-14 parts of potassium fluosilicate, 8-10 parts of modified attapulgite and a moderate amount of water. According to the bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent, the used tourmaline powder can generate negative ions and far infrared ray, at the same time, the oxidized metals therein can desulfurize, so that the bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent is beneficial to human body; also the monazite powder and the sodium metasilicate are used to fast and effectively desulfurize; in addition, the polyethylene glycol is added to increase the viscosity of the activated carbon, so that the bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent is not easy to collapse. The bamboo-based modified activated carbon desulfurization adsorbent produces no harmful substances, is simple in technology and wide in application range.
Owner:ANHUI PHOENIX INT CO LTD
Separation method for rare earth elements in monazite
InactiveCN108034816AHigh rate of returnReduce dosageProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementSlag
The invention discloses a separation method for rare earth elements in monazite. The method comprises the following steps that monazite and a rare earth ore are mixed and ground into ore powder at first, the particle size of the ore powder is -80 microns, batch open-circuit grinding is adopted at first, then simulation-closed-circuit grinding is adopted, and a method adopted for grinding comprisesthe substeps that after selected crude ore is ground for a certain time, products with the particle sizes being equal to or greater than -70 microns are screened out, oversize products are reground,water is added during regrinding according to the oversize product weight and the ore grinding concentration during crude ore grinding, and ore powder is washed after the content of ore powder with the particle size being -50 microns reaches 80% or above; and monazite slag (in kg) is added into a sulfuric acid solution (in L) with the concentration being 0.25-0.5 mol / L according to the proportionof the monazite slag to acid being 1:1-15, a mixture is heated to 40-100 DEG C, stirring is conducted for 5-8 h, cooling, still standing and clarification are conducted for 4-8 h, and a solution containing valuable elements of uranium, thorium and rare earth is obtained through siphoning of a supernatant.
Owner:宁波市鄞州智伴信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com