Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Realize closed-loop recycling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Leaching and recycling method for metals in anode waste materials of lithium-ion batteries
ActiveCN104868190AWide range of applicationsImprove leaching rateWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingScrapMetal leaching
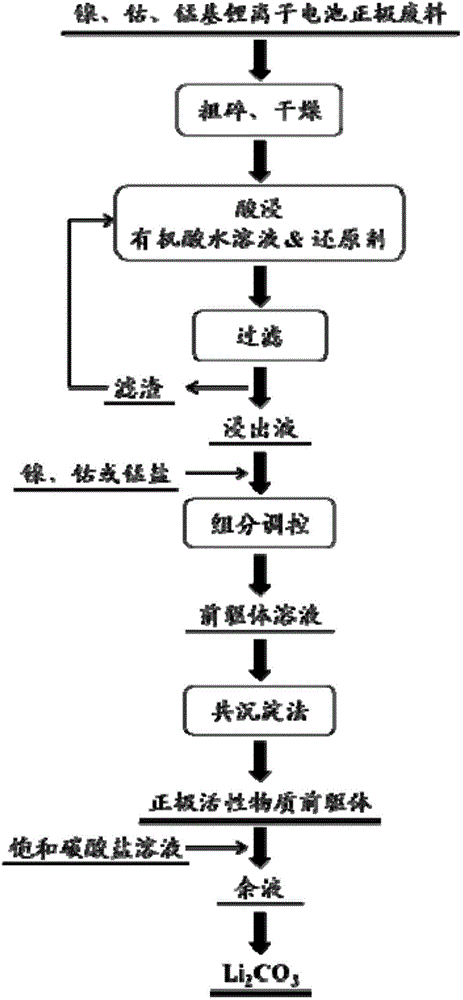
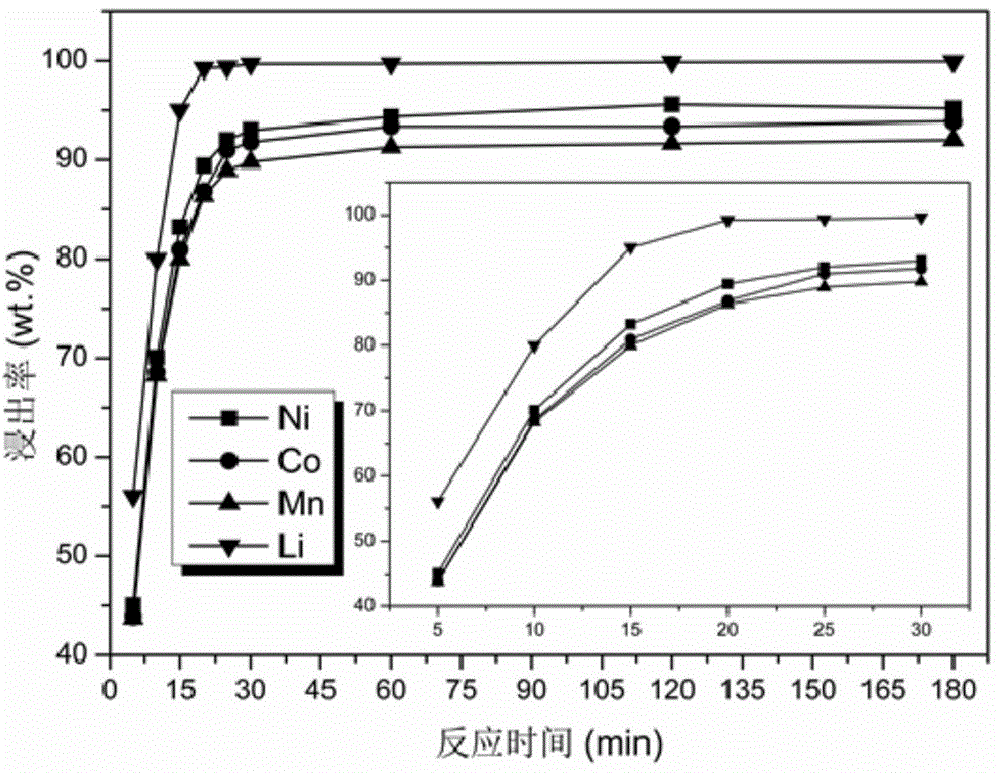
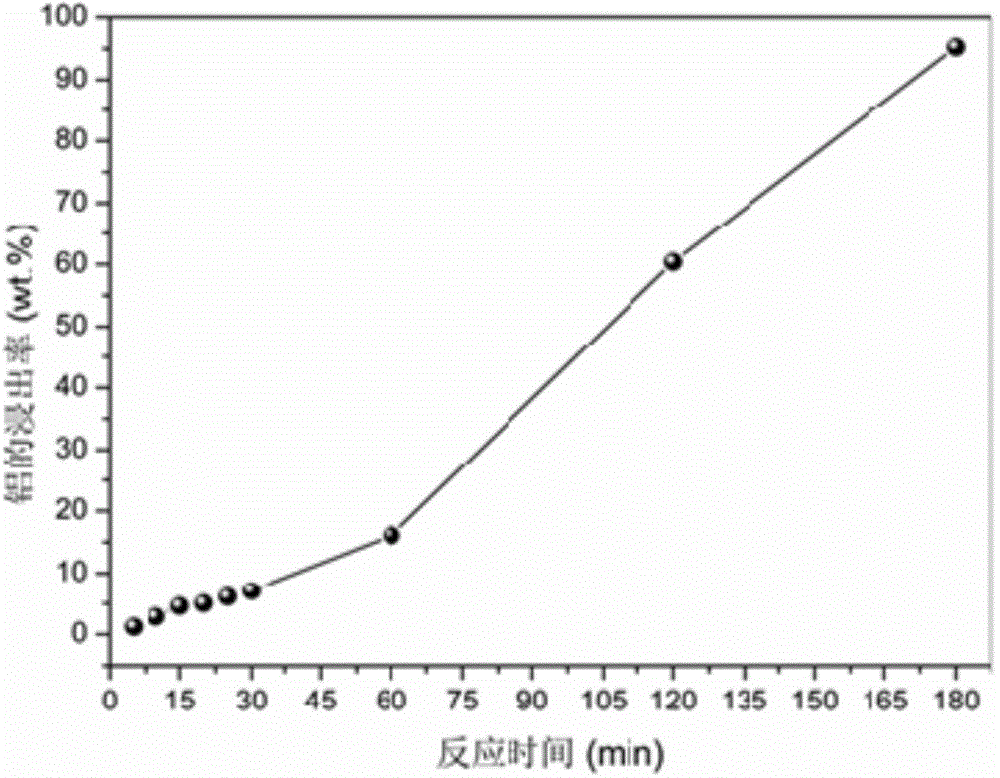
The invention provides a leaching and recycling method for metals in anode waste materials of lithium-ion batteries. The leaching method comprises the steps that: the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries react with organic acid solution containing a reducing agent; after reaction, solid-liquid separation is carried out and leaching solution and filter residues are obtained, so that the leaching of the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries is realized. Based on the leaching method, the invention provides a recycling method for the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries based on closed-loop circulation of metals. The leaching method for the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries has the advantages of high metal leaching rate, short leaching time, low processing cost and wide application range; secondary pollution and complex process for separating and purifying various metals in the leaching solution are avoided; according to the recycling method for the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries, the technological process is short and the closed-loop circulation of the metals is realized.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
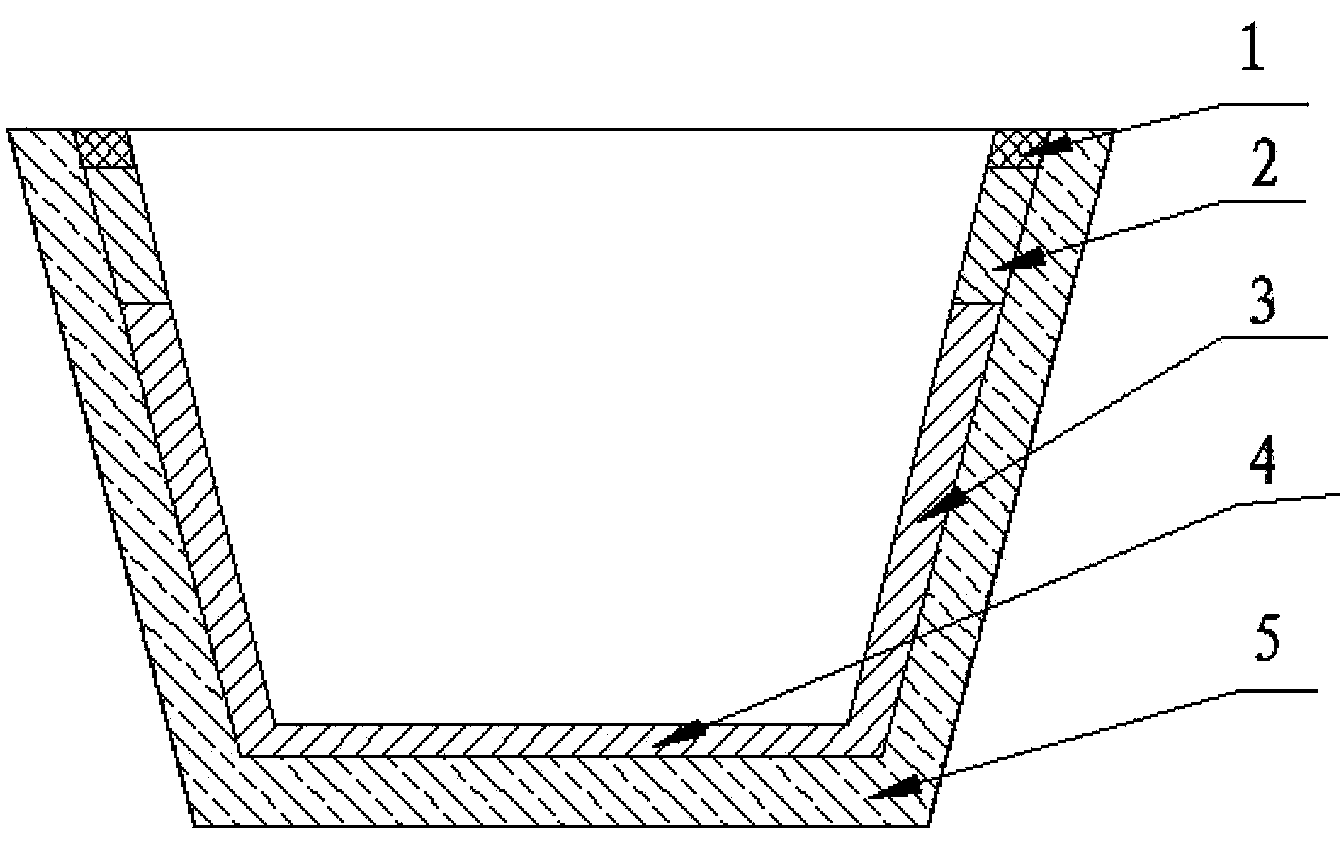
Classifying and recycling process for waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of steel tundish working linings as well as dry material and coating material for tundish
ActiveCN103319189AAchieving RecyclabilityMaximize regeneration valueSolid waste disposalBrickGranularity
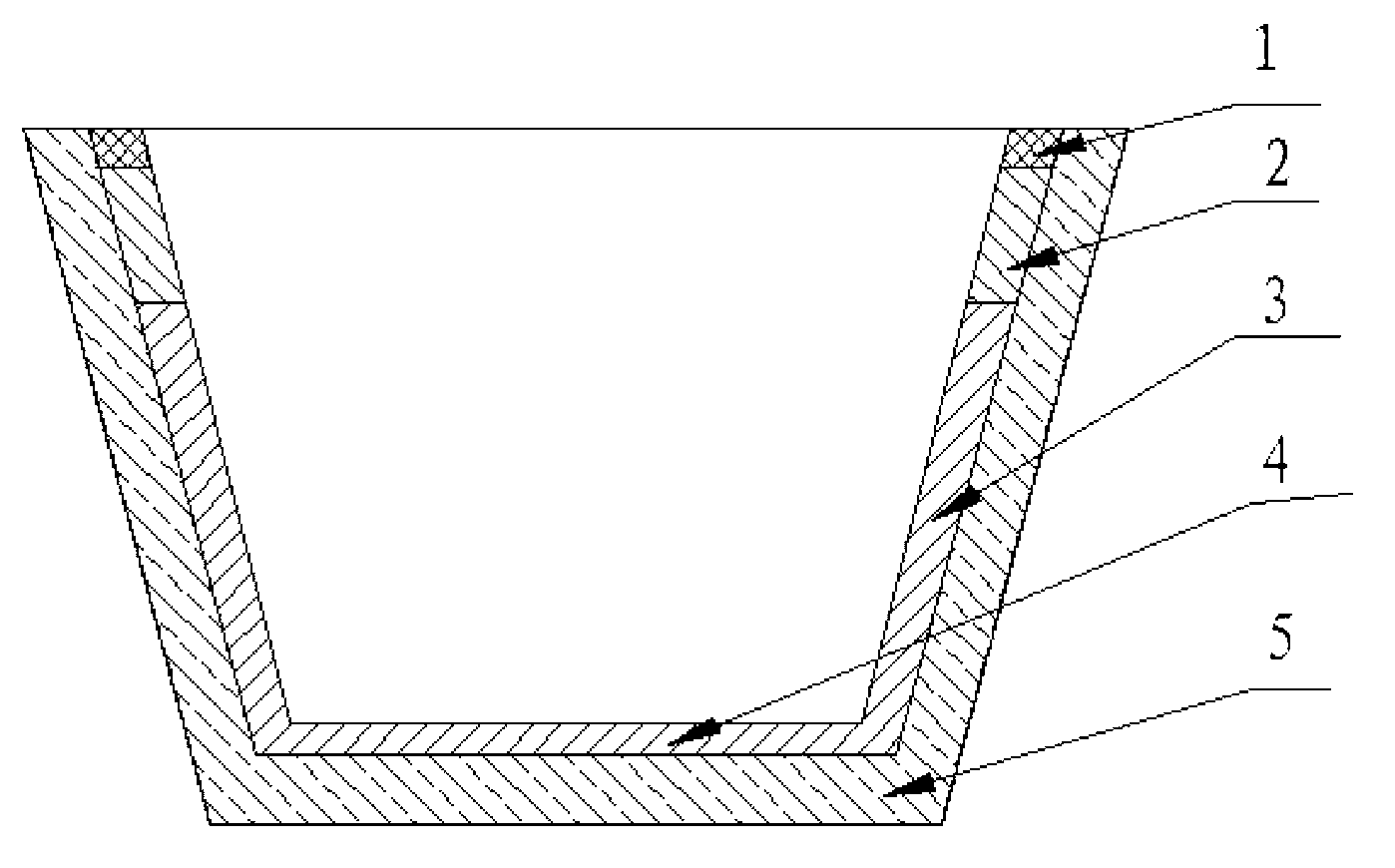
The invention relates to a classifying and recycling process for waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of steel tundish working linings as well as a dry material and a coating material for a tundish. The waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of the steel tundish working linings are subjected to recovery processing and are classified into reclaimed materials with three grain levels, i.e., the granularity is more than or equal to 3mm and less than 5mm, the granularity is more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm and the granularity is less than 1mm; the reclaimed materials with the granularity more than or equal to 3mm and less than 5mm and the granularity more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm are used as raw materials to prepare the dry material for the tundish, and the dry material is used for carrying out continuous casting on a slag line 2 and a tundish wall 3 and a tundish bottom 4 below the slag line 2 of the tundish working lining; the reclaimed materials with the granularity more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm and the granularity less than 1mm are used as raw materials to prepare the coating material for the tundish, and the coating material for the tundish is used for carrying out continuous costing on a tundish edge 1 above the slag line of the tundish working lining. The invention further provides a construction method for manufacturing the combined continuous casting tundish working lining by adopting the dry material and the coating material for the tundish. According to the classifying and recycling process, the dry material and the coating material for the tundish and the construction method, the classifying and recycling rate of the waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of the steel tundish working linings reaches 100 percent.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Process for extracting nickel and cobalt from laterite-nickel ore
InactiveCN101338374ARealize closed loop recyclingImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementMetal chlorideSlurry
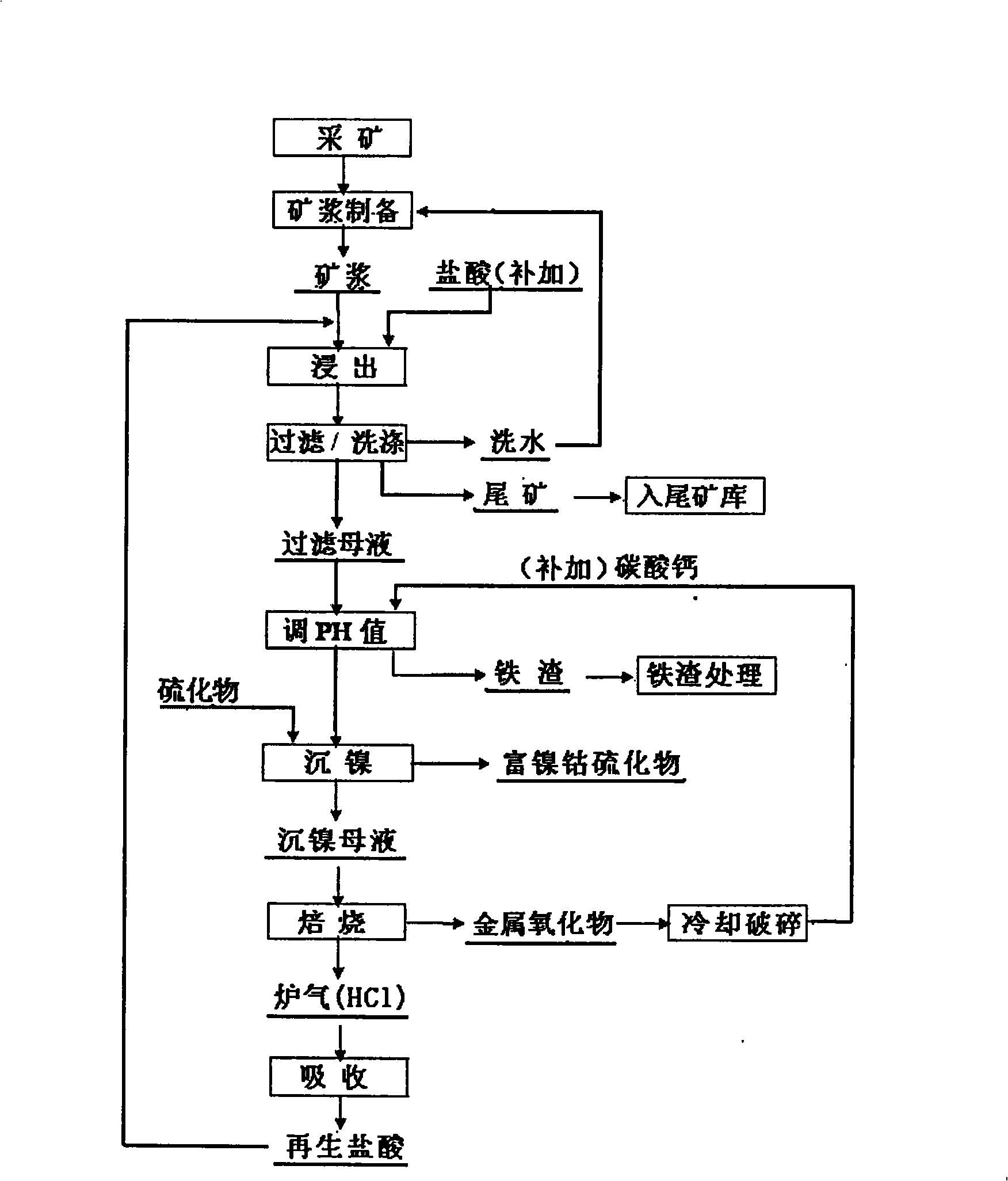
The invention discloses a method for extracting nickel and cobalt from a lateritic nickel ore which includes the steps of: (1) preparing the slurry of the ore: cracking the ores and preparing the slurry; (2) dipping the ores with muriatic acid: adding the muriatic acid in the slurry of the ore to carry out stirring and extraction under a normal pressure; (3) separating the solid and liquid; (4) neutralizing an extraction liquid; (4) sulfurizing and depositing the nickel; (6) regenerating the muriatic acid: the mother deposition liquid after nickel depositing is concentrated and roasted, the metal chloride in the mother liquid is hydrolyzed into chlorine hydride and metal oxide; the chlorine hydride after being absorbed by water obtains the regenerated muriatic acid and return to the working procedure of ore extraction; the metal oxide after being cracked and grinded returns to the working procedure of neutralizing. The method of the invention has a simple flow and an environment protective technique; the application range to resources is large; besides, the extraction speed is fast; the impurity removing capacity is high; the extraction rate of the nickel and cobalt is high; the method realizes the closed circulation of HCl and the comprehensive utilization of the resources.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag
ActiveCN103014333ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodDecomposition
The invention discloses a separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag, namely a method for separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing and extraction of valuable components. According to the invention, the uranium, thorium and rare earth are leached out by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; the secondary slag is subjected to beneficiation and alkaline decomposition by a beneficiation technology, and closed-loop circular recovery of uranium, thorium and rare earth is realized; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
Separation and recovery method of monazite slag
ActiveCN103014359ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium, rare earth and monazite concentrate and zircon concentrate from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing, extraction of valuable components and treatment of filter residue. According to the invention, the monazite slag is leached by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
A method for regenerating waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material
ActiveCN109065996AReduce acid consumptionShorten the leaching timeCell electrodesTransportation and packagingOxideOxalate
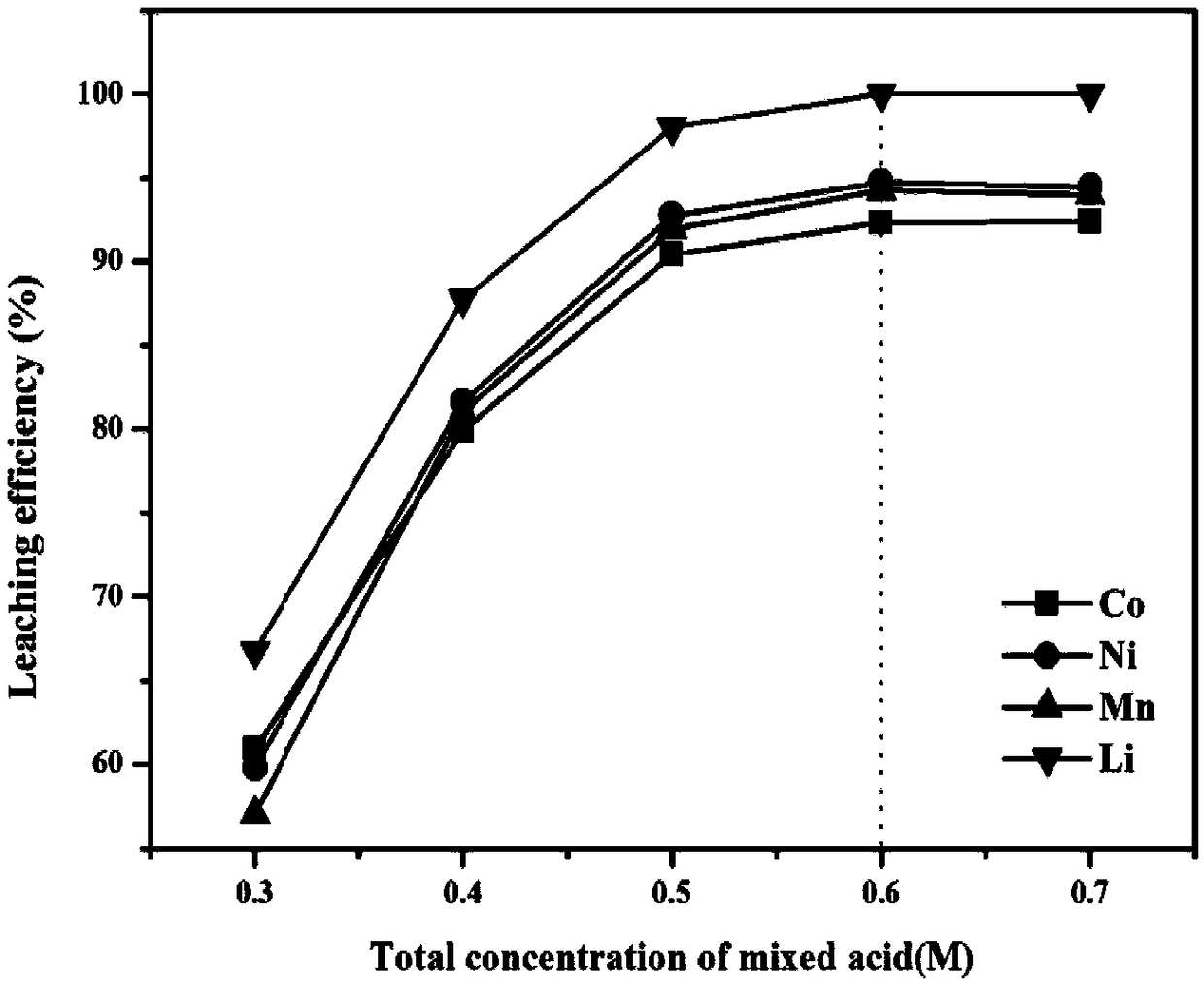
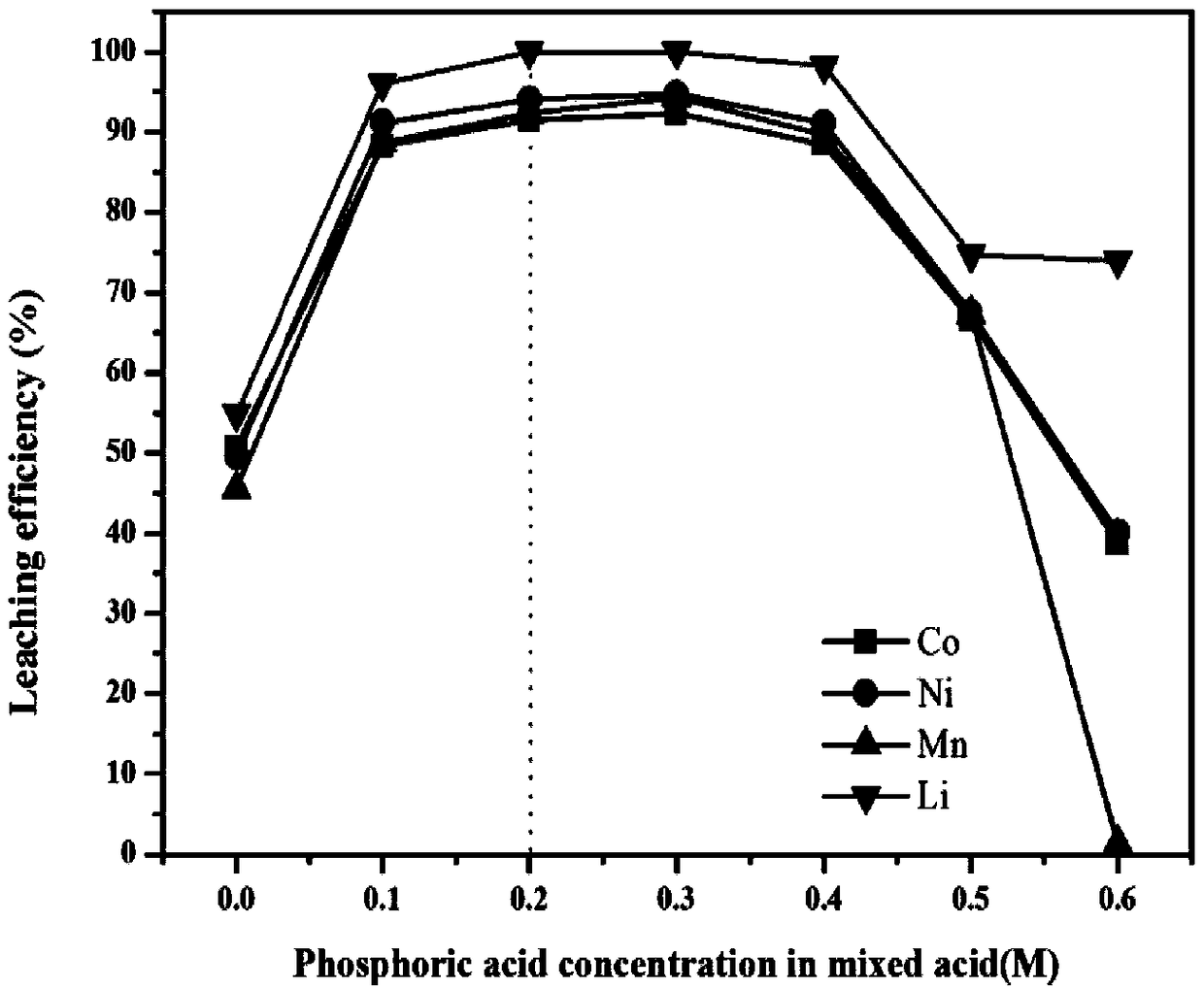
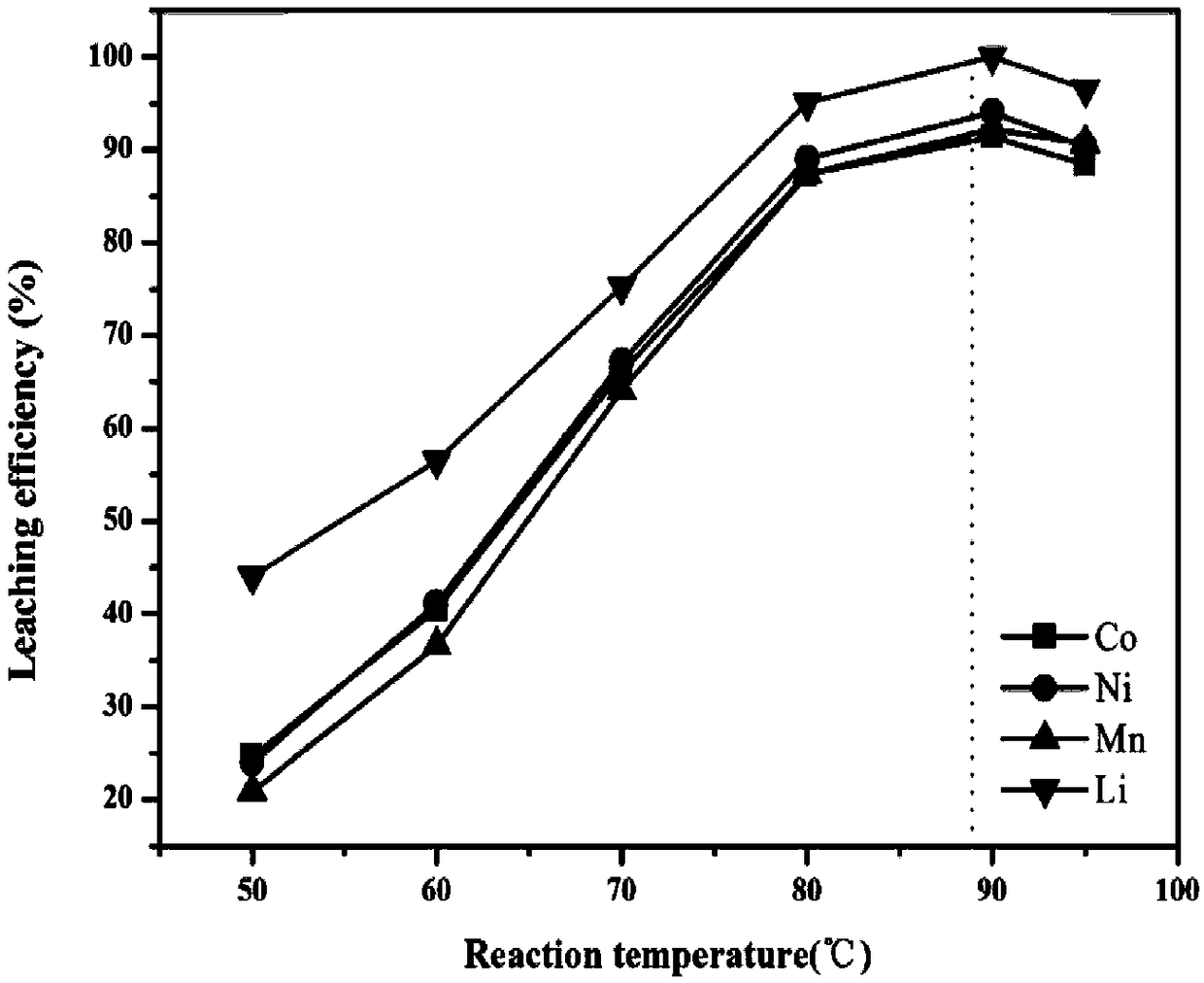
The invention discloses a method for regenerating waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material of. The method comprises lixiviating the waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternarycathode material by using phosphoric acid- citric acid mixed acid solution to obtain a lixivium; adjusting the metal ion ratio of the lixivium by a nickel salt, a cobalt salt and a manganese salt, andthen adding the lixivium into an oxalic acid solution for coprecipitation reaction; pre-calcining the obtained precipitate to obtain nickel cobalt manganese oxide, and grinding and mixing the nickelcobalt manganese oxide with a lithium source, calcining a resultant object to obtain a regenerated lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material; The method adopts mixed acid lixiviating process, the acid consumption is small, the lixiviating time is short, the cost is low, the environmental impact is small, and the reducing agent is not needed, and the process is simple; The mixed acidlixivium is directly used for synthesizing ternary cathode materials, thereby avoiding the complicated process of separating and purifying various metals in the lixivium in the prior art, and realizing the closed-loop recycling utilization of metals.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
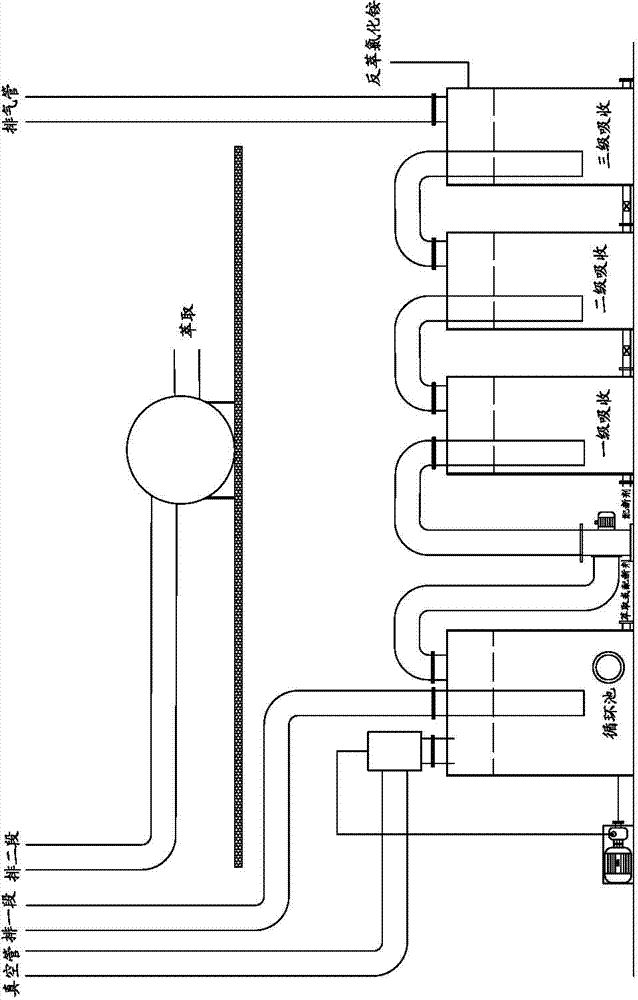
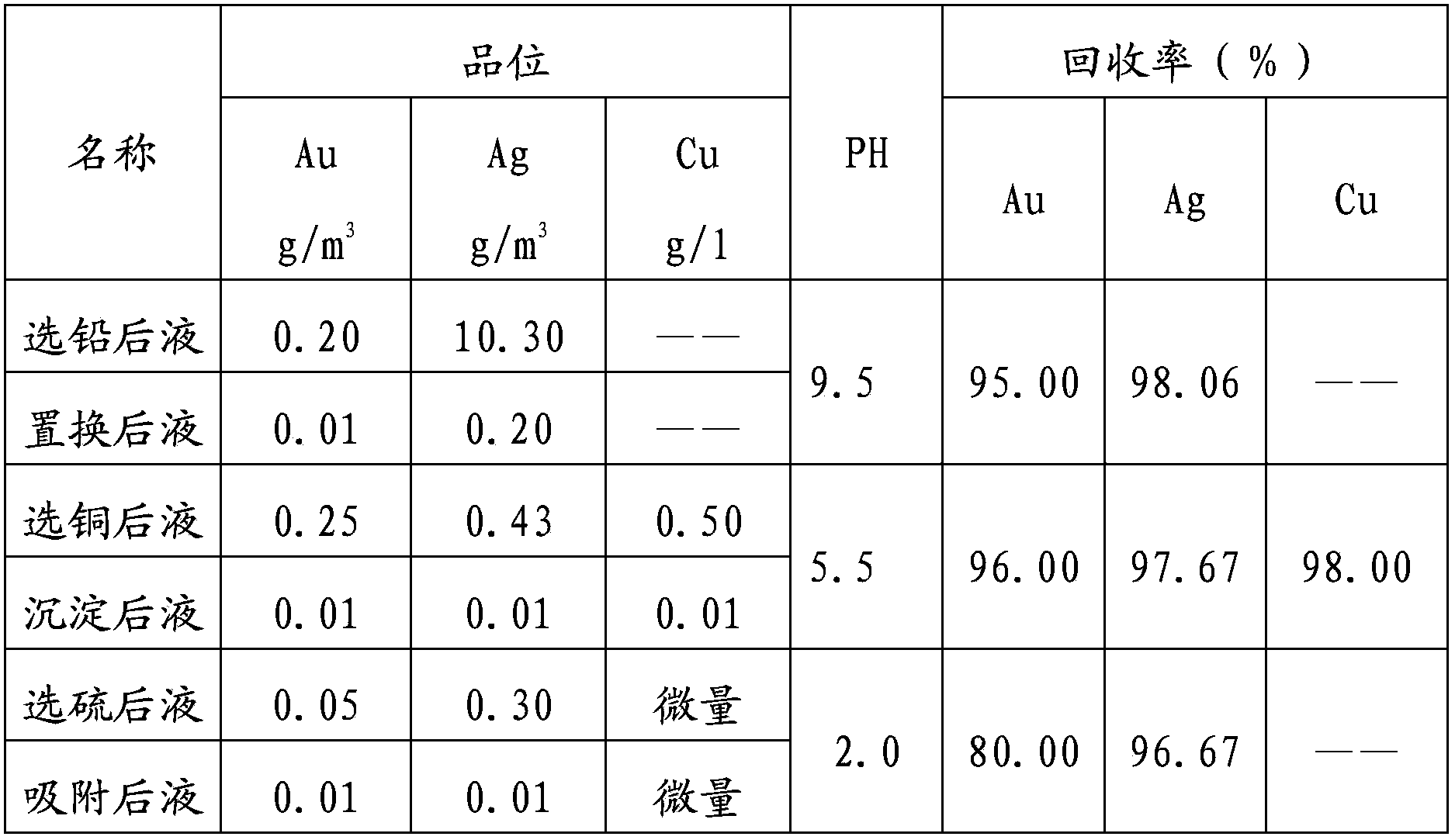
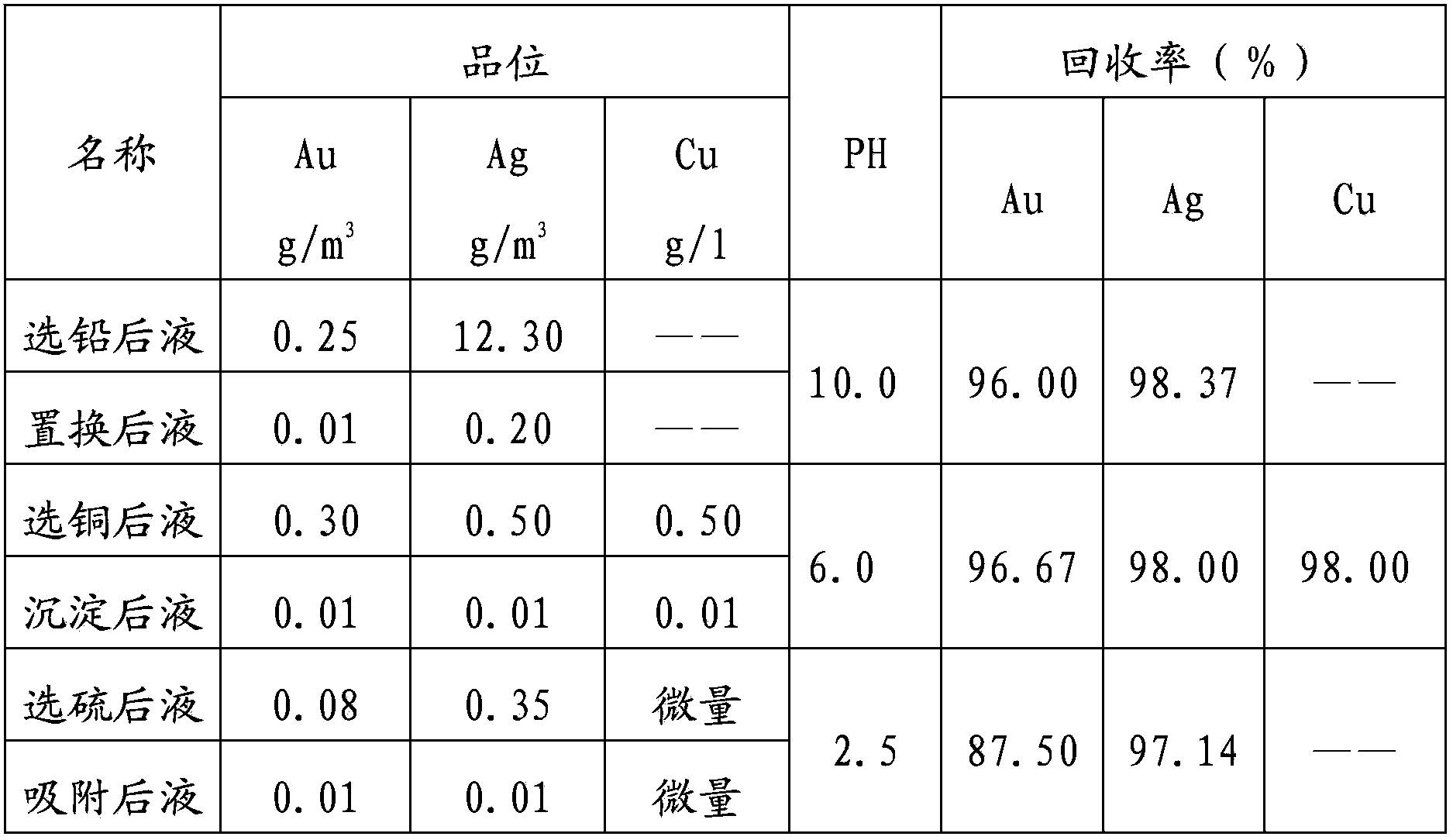
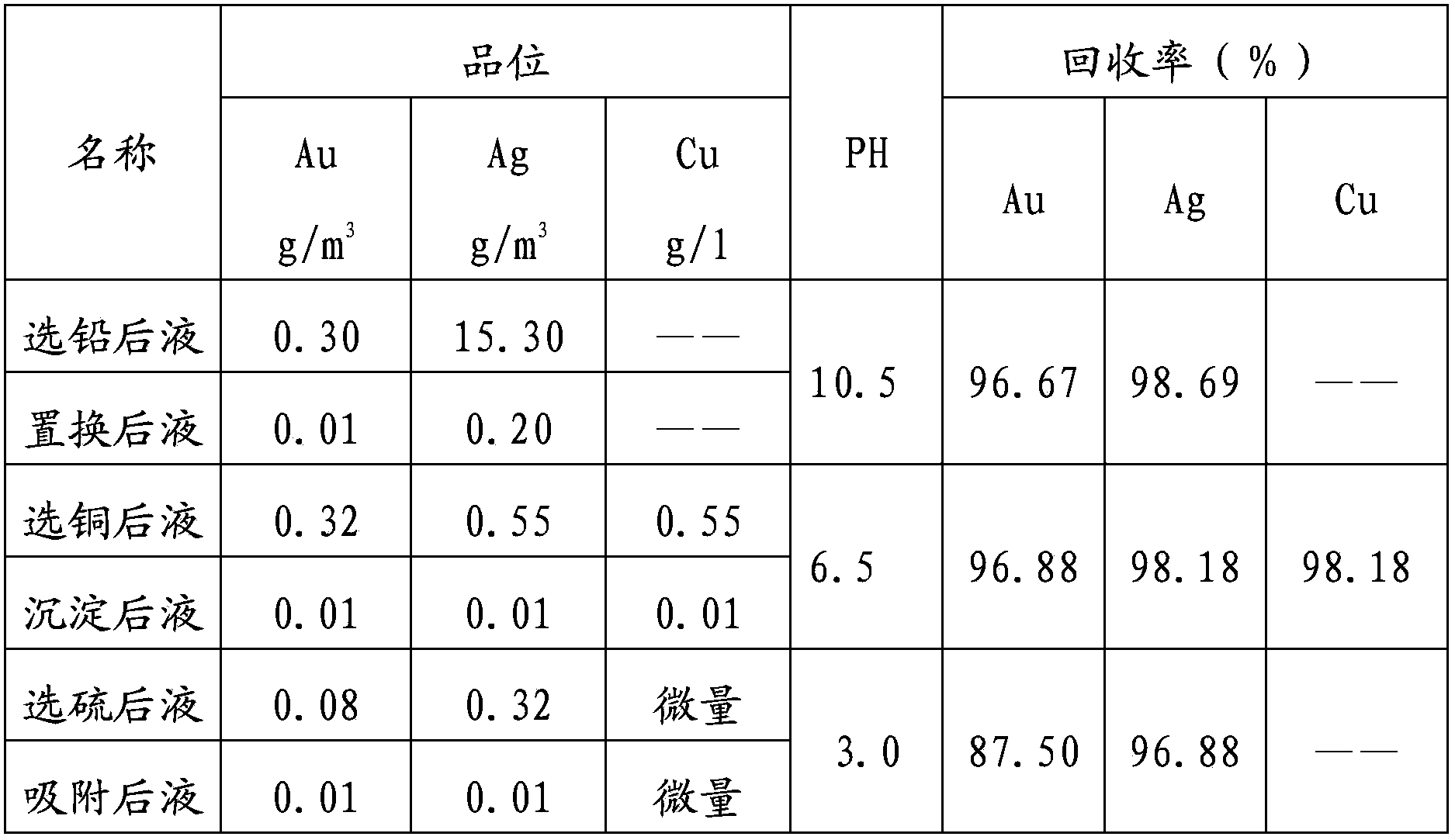
Method for recycling multiple elements of liquid after cyanided tailing flotation
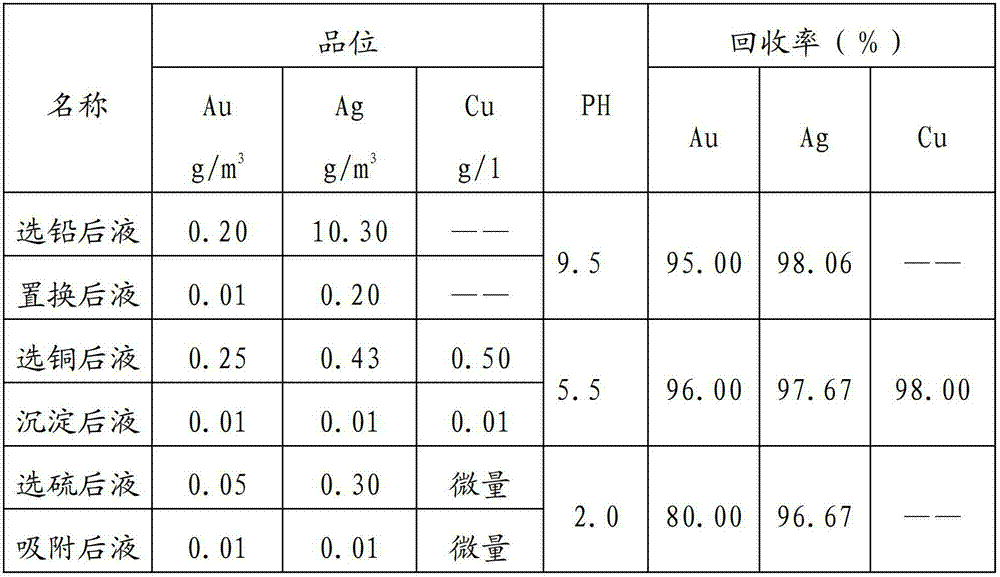
ActiveCN102784713AImprove efficiencyAchieving zero emissionsSolid separationActivated carbonWater treatment
The invention relates to a method for recycling multiple elements of liquid after cyanided tailing flotation, belonging to the technical field of gold smelting, cyanided tailing flotation of lead and copper concentrate, and waste water treatment of sulfur concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining lead concentrate through flotation; comprehensively recycling gold and silver from liquid after lead flotation; obtaining copper concentrate through flotation; comprehensively recycling gold, silver and copper from liquid after copper flotation; obtaining sulfur concentrate through flotation; recycling gold and silver through gold-loaded activated carbon desorption electrodeposition; and the like. By the method, the comprehensive utilization efficiency of resources is improved, closed loop recycle of the liquid in a flotation system is achieved, zero discharge of wastewater is achieved, pollution to the surrounding environment is reduced, and ultimately the economic efficiency of an enterprise is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG GUODA GOLD
Electroplating equipment
The invention discloses electroplating equipment, which consists of an electroplating groove, an anode, a cathode, an electroplating liquid, an automatic additive replenishing system, a circular filtering system, an electric heating system, a water bath circular heat supply center, an automatic purifying system and an electroplating rectifying power supply. The electroplating equipment is generally suitable for electroplating of super hard material products, and particularly relates to electroplating of wear-resistant composite layers and electroplating of diamond geological drill bits. Production process conditions have high stability and consistence; the electroplating liquid treatment period is prolonged effectively, closed-loop circular utilization of the electroplating liquid is realized, energy is saved, and the environment is protected; meanwhile, the working environment is improved greatly, and the physical and psychological health of employees is facilitated; and the product quality is more stable and is improved greatly, the product yield is increased by 13 percent, electricity is saved by 56.2 percent, and the product cost is reduced by 32.7 percent.
Owner:肖云捷
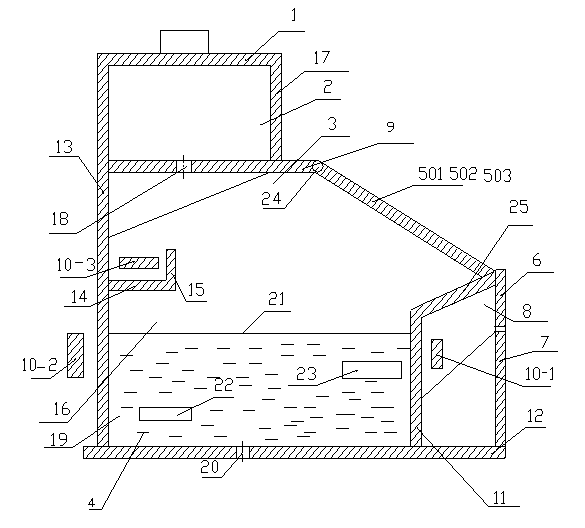
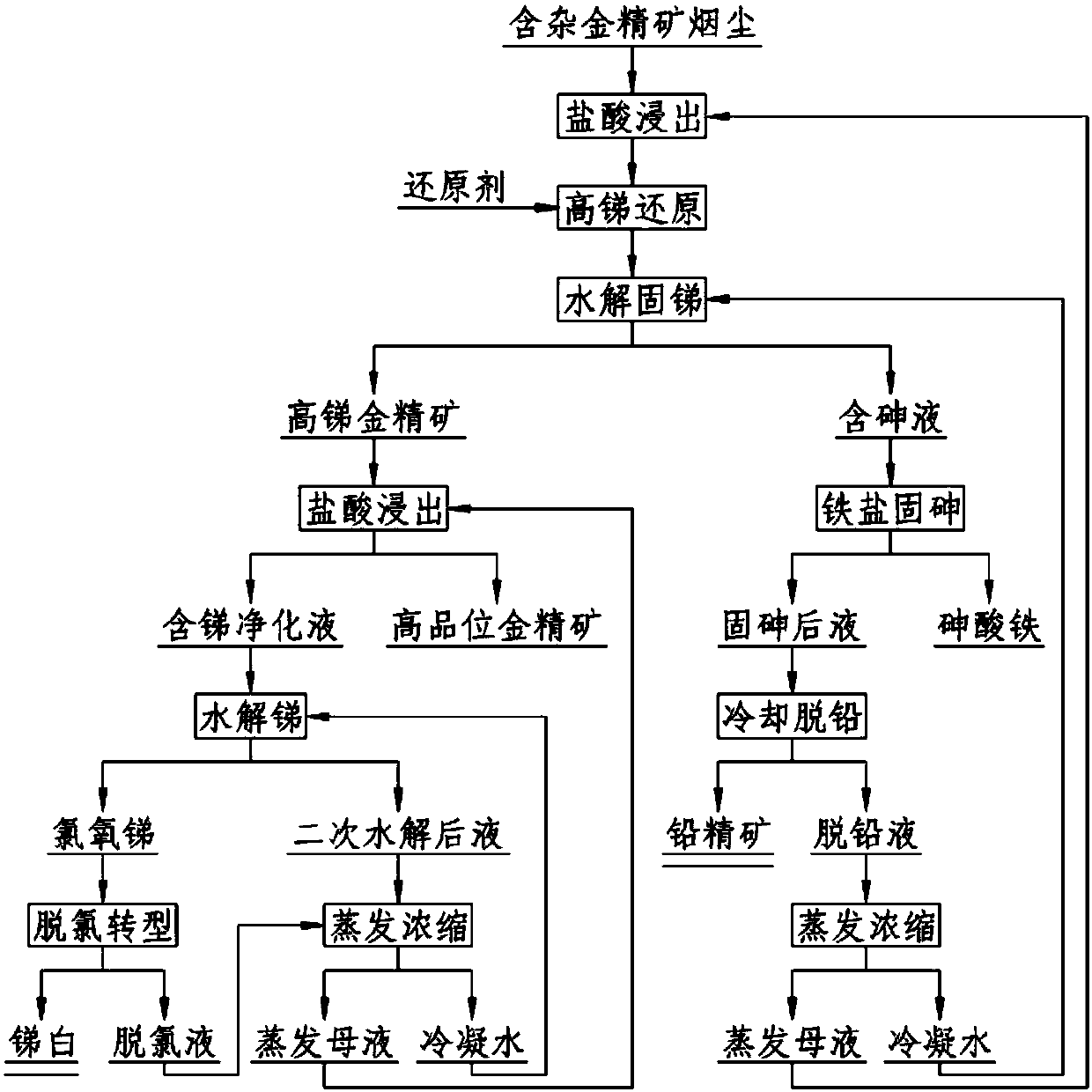
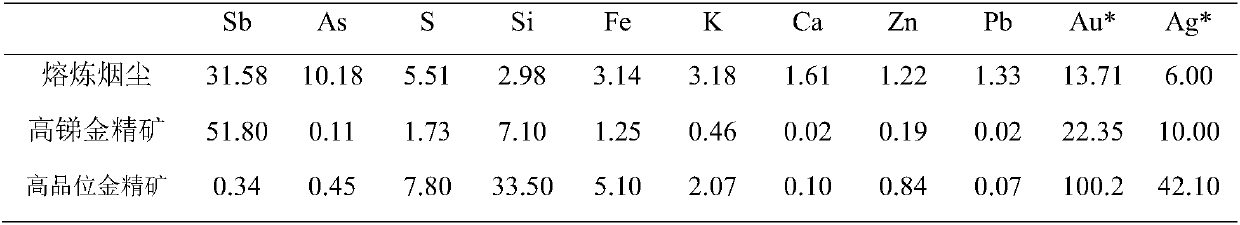
Comprehensive treatment method for smelting dust containing miscellaneous gold concentrate
ActiveCN108034831ASolve difficult industry problemsEasy to produceIron compoundsProcess efficiency improvementArsenatePregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a comprehensive treatment method for smelting dust containing miscellaneous gold concentrate and belongs to the technical field of precious metal pyrometallurgy. The comprehensive treatment method for the smelting dust containing the miscellaneous gold concentrate comprises the steps that firstly, the smelting dust is subjected to primary hydrochloric acid leaching, leachedslurry is subjected to high-price antimony reduction and hydrolysis antimony fixing, high-antimony gold concentrate and primarily-hydrolyzed liquid are obtained, secondary hydrochloric acid leachingis conducted on the high-antimony gold concentrate, high-grade gold concentrate with low impurities and secondary lixivium are obtained, high-grade oxychloride and secondarily-hydrolyzed liquid are obtained after hydrolysis is conducted on the secondary lixivium, dechlorinating transformation is conducted on the oxychloride, and then an antimony white terminal product is obtained; and a molysite arsenic fixing process is adopted for arsenic-containing liquid, and stable low-toxicity arsenic compound ferric arsenate and arsenic-removed liquid are obtained. By the adoption of the method, the smelting dust containing the miscellaneous gold concentrate is treated, the precise metal antimony can be effectively recovered, and the harmful element arsenate is fixed, so that the industrial problemthat arsenic and antimony dust is difficult to treat is solved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for closed cycle high-efficiency comprehensive recovery of multiple elements of gold concentrate
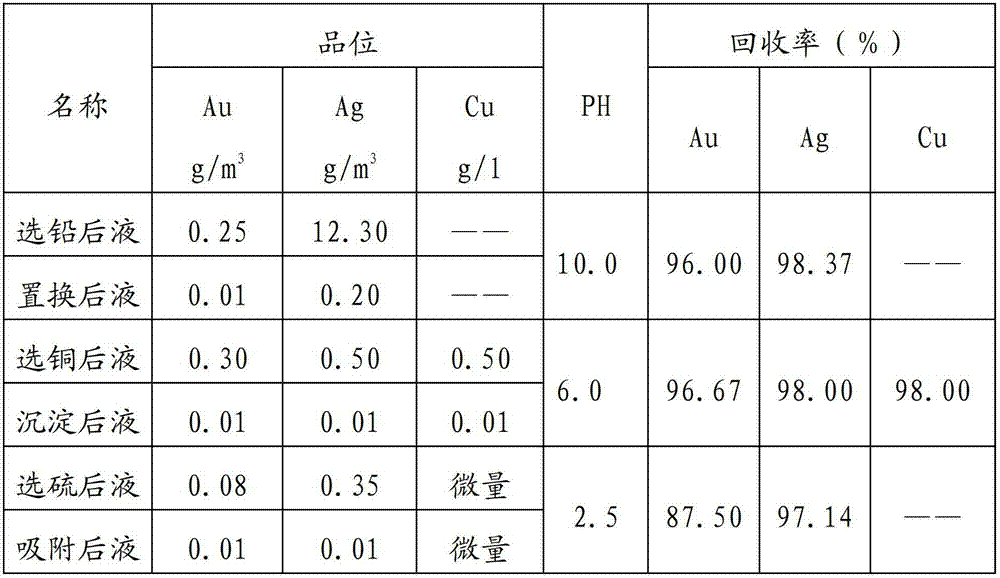
InactiveCN102828020AImprove leaching rateRealize closed loop recyclingSulfur compoundsProcess efficiency improvementActivated carbonSulfur
The invention relates to a method for recovery and recycle of multiple elements in a liquid obtained by cyanidation tailing flotation and belongs to the technical field of gold smelting and treatment on a waste liquid obtained by flotation of lead, copper concentrate and sulfur concentrate in cyanidation tailings. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out flotation to obtain lead concentrate, carrying out comprehensive recovery of gold and silver in a liquid obtained by lead flotation, carrying out flotation to obtain copper concentrate, carrying out comprehensive recovery of gold, silver and copper in a liquid obtained by copper flotation, carrying out flotation to obtain sulfur concentrate, and recovering gold and silver by gold-loaded activated carbon desorption eletrolysis. The method improves resource comprehensive utilization efficiency, realizes closed cycle utilization of a flotation system liquid, realizes zero discharge of waste water, reduces the pollution of the surrounding environment, and improves economic benefits of enterprises.
Owner:SHANDONG GUODA GOLD
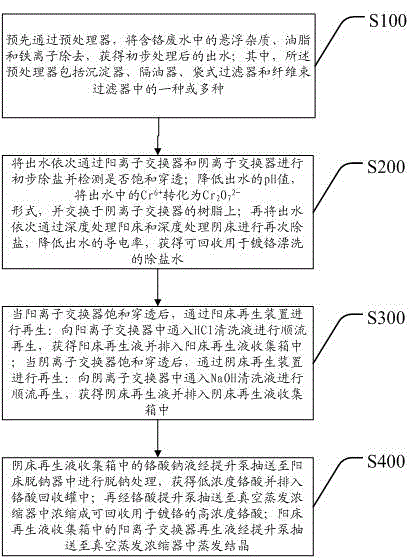
Electroplating chromium-containing wastewater treatment method and device
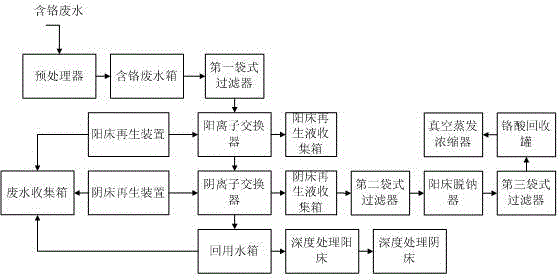
ActiveCN104909508ARealize closed loop recyclingReduce dosageGeneral water supply conservationWater contaminantsHigh concentrationImpurity
The invention discloses an electroplating chromium-containing wastewater treatment method and device. The treatment method comprises the following steps: (A) pre-removing impurities in chromium-containing wastewater by virtue of a pretreatment device, so as to acquire primarily treated effluent; (B) sequentially carrying out primary desalination on effluent by virtue of a cation exchanger and an anion exchanger, carrying out secondary desalination on effluent by virtue of an advanced treatment cation bed and an advanced treatment anion bed again, so as to obtain desalted water which can be recycled for chromium plating rinsing; (C) regenerating by virtue of a cation bed regeneration device when the cation exchanger is saturated and penetrated, and regenerating by virtue of an anion bed regeneration device when the anion exchanger is saturated and penetrated; and (D) carrying out sodium removal on anion bed regenerated liquid, and concentrating to form recyclable high-concentration chromic acid or carrying out evaporative crystallization. According to the electroplating chromium-containing wastewater treatment method, by virtue of a two-stage cation-anion bed system, the environmental pollution of hexavalent chromium is eliminated, and meanwhile, high-quality desalted water can be obtained and can be applied to production, so that the consumption of tap water and desalted water is saved, and the good economic benefit is achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINTAILONG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION GRP CO LTD
Method for separating valuable components of monazite slags
ActiveCN102925681ARealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating valuable components of monazite slags, and particularly relates to a method for separating valuable components of monazite slags into a liquid phase (a solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earth) and a solid phase (a filter residue containing useful minerals such as monazite, zirconite and rutile). The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of acid leaching, filter pressing and water scrubbing. According to the invention, monazite slags are subjected to low-acid and low-temperature leaching, and a liquid phase and a solid phase are separated easily; after secondary slags are subjected to mineral processing and alkaline decomposition by using a mineral processing process, the closed cycle collection of uranium, thorium and rare earths can be realized; meanwhile, an extract residue waste acid can be subjected to cyclic utilization, thereby reducing the wastewater discharge, reducing the consumption of sulfuric acids and new water and the wastewater treatment cost, and reducing the production cost; and the recovery rates of valuable elements such as uranium, thorium and rare earths can be greater than 97%, therefore, an effect of no radioactive wastewater and waste residue discharge in the whole process can be achieved.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
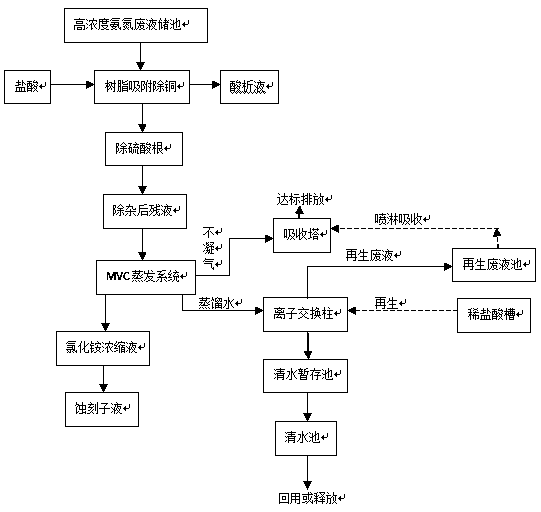
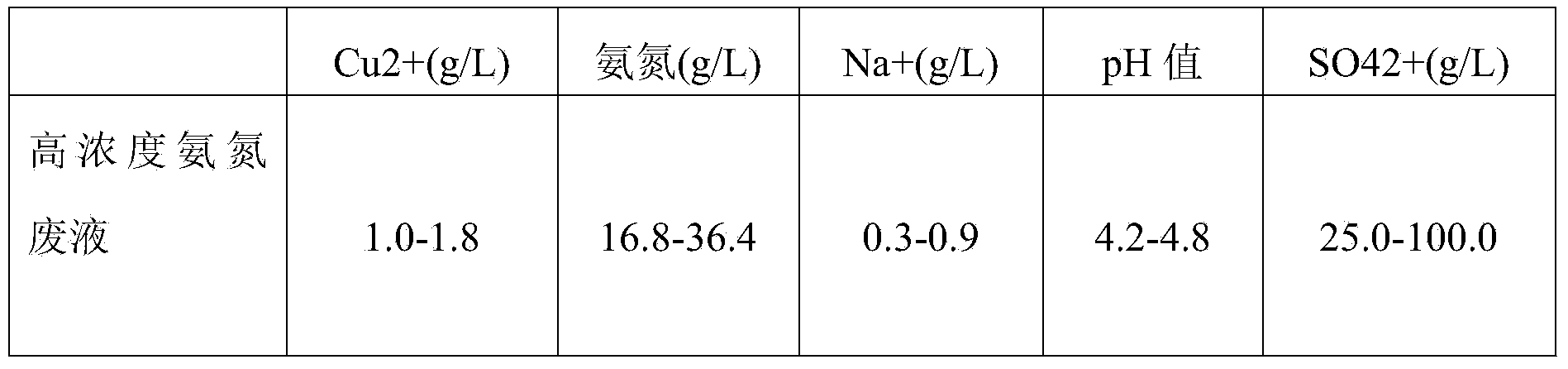
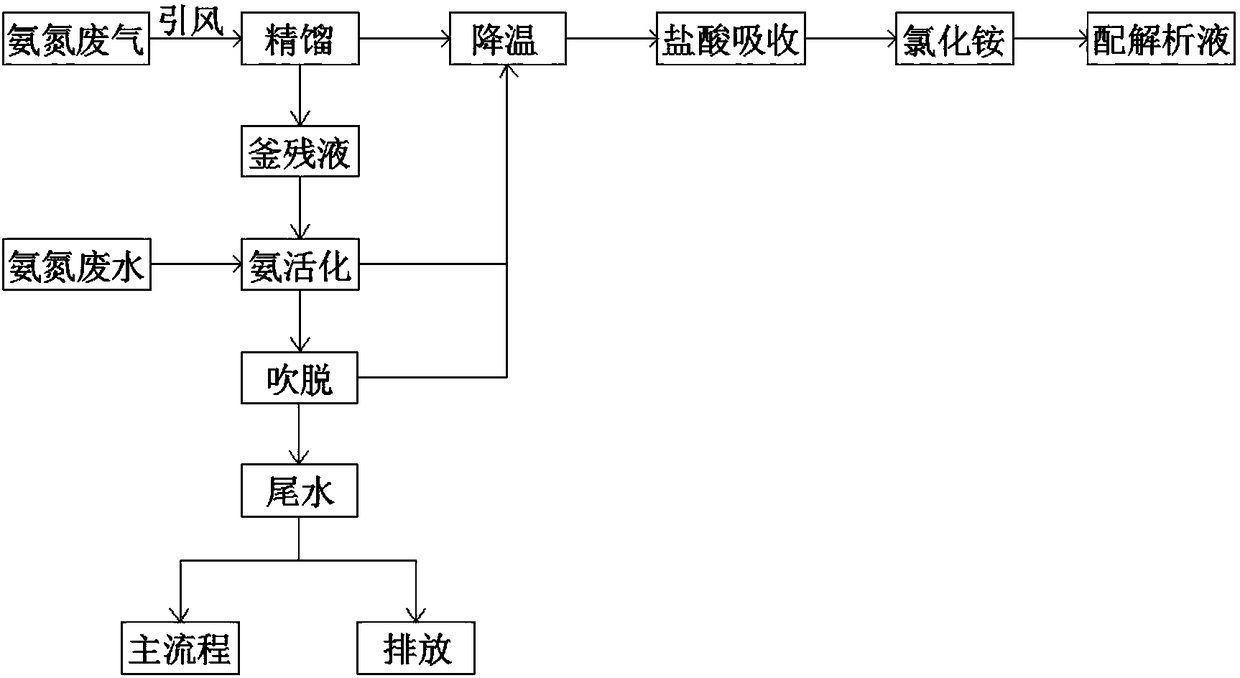
Resource utilization method of high-concentration ammonia nitrogen waste liquid
InactiveCN103819026AWill not cause secondary pollutionHigh copper removal rateWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processHigh concentrationLiquid waste
The invention discloses a resource utilization method of a high-concentration ammonia nitrogen waste liquid. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1, impurity removal: after copper in an etching liquid containing copper is recovered, an ion exchange technique is utilized to absorb and recover low-concentration copper ions in residual high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, and a regenerative copper chloride raw material is obtained after resin dissolving; and an appropriate amount of barium chloride is added in wastewater without copper so as to remove sulfate radical impurities introduced during a copper sulfate production process; and 2, blending: residual wastewater without copper is the high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, ammonium chloride concentration is adjusted with an addition method or through evaporation and concentration by a multi-effect evaporator, and then an auxiliary etching liquid is blended according to a corresponding formula and is reused for the circuit board industry. With the adoption of the method, not only is an environmental pollution problem caused by heavy metal ions and the high-concentration ammonia nitrogen waste liquid solved, but also the closed cyclic utilization of the etching liquid of the circuit board industry is achieved, the resource is saved, and the environment is protected.
Owner:惠州TCL环境科技有限公司
Method for recycling waste terylene fibers to obtain polyester raw materials as well as device system and microwave purifying equipment
ActiveCN104842473ASlow heat transferAvoid overheating and oxidationPlastic recyclingPolyesterMicrowave
The invention discloses a method for recycling waste terylene fibers. The method comprises the following steps of primarily crushing the waste terylene fibers to obtain staple fiber pompons; purifying and degrading on the staple fiber pompons by dense microwave fields with high-frequency rotation; performing vacuum pumping on water and oil; finally, grinding and crushing to obtain finely-ground terephthalate (BHET) polymer powder; meanwhile, the invention provides a device system and microwave purifying equipment for realizing the method. The method, the device system and the microwave purifying equipment disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the waste terylene fibers are recycled by adopting microwave purification degradation to obtain the BHET polymer powder which can be used as the polyester raw materials; an original recovery mode of obtaining bubble powder is thoroughly changed, and closed circulating recovery of the waste terylene fibers is realized; the method is green and environment-friendly, high in economy and resource-saving; the device system and the equipment provide hardware guarantee for realizing the method.
Owner:镇江宝利玛机械有限公司
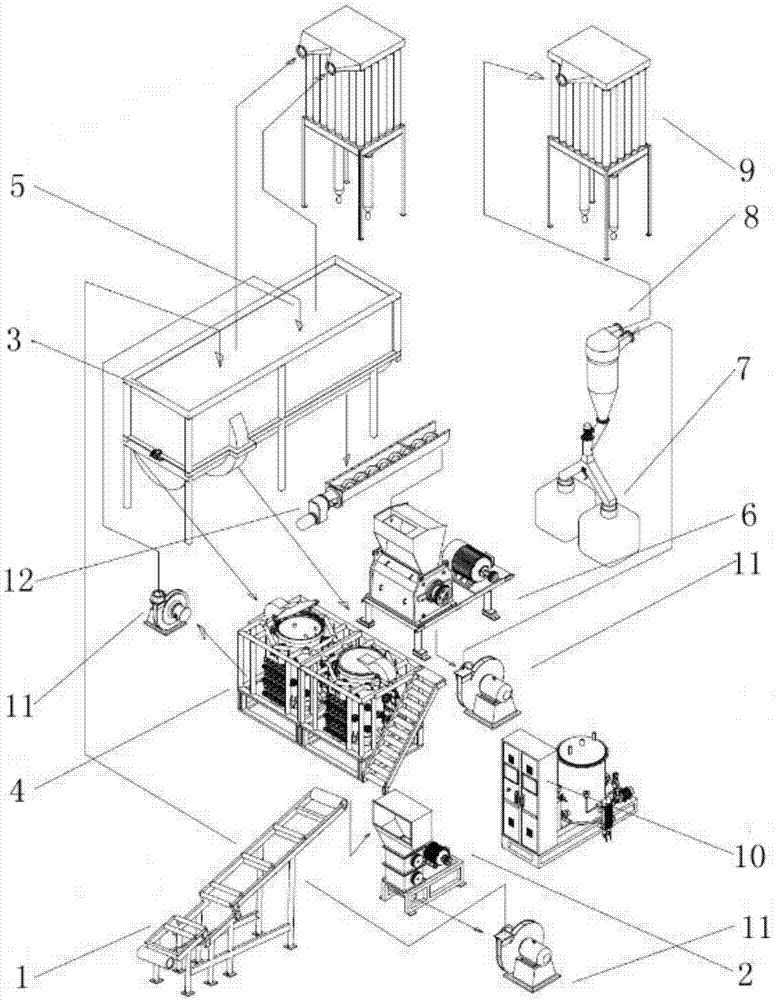
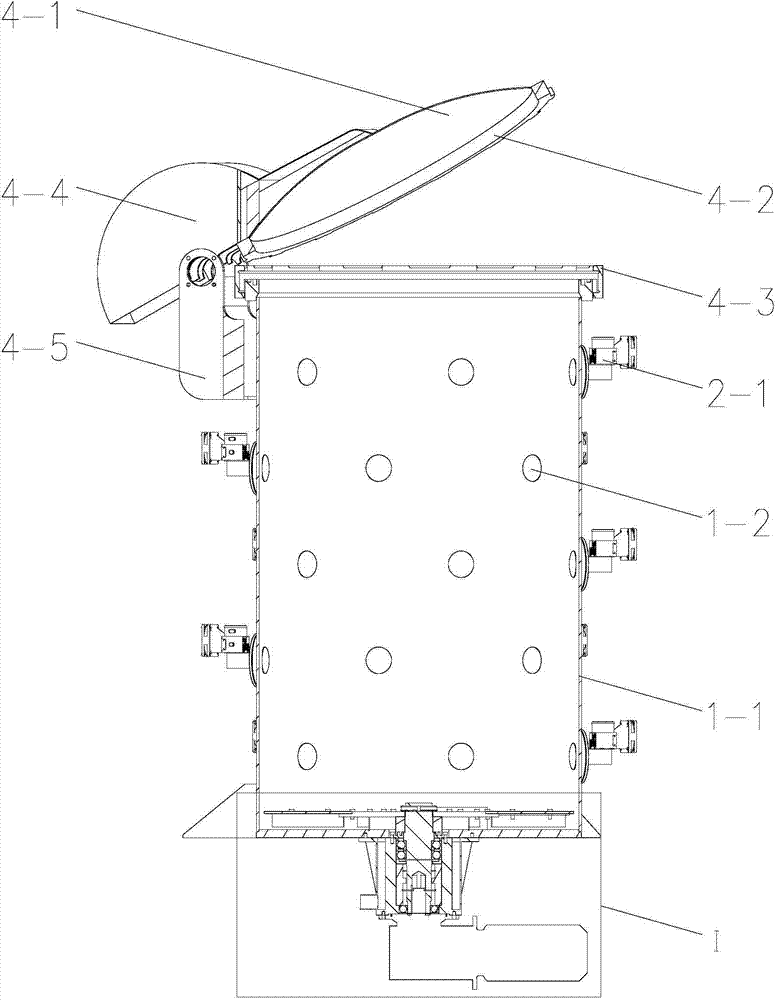
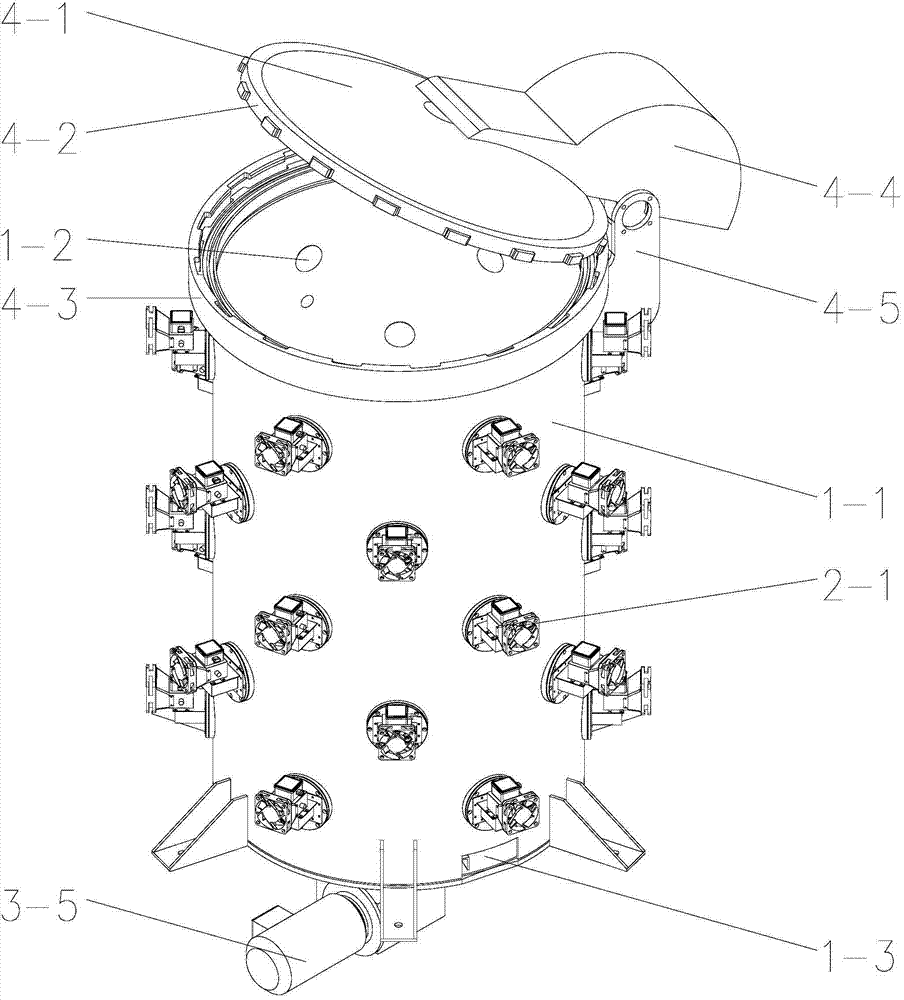
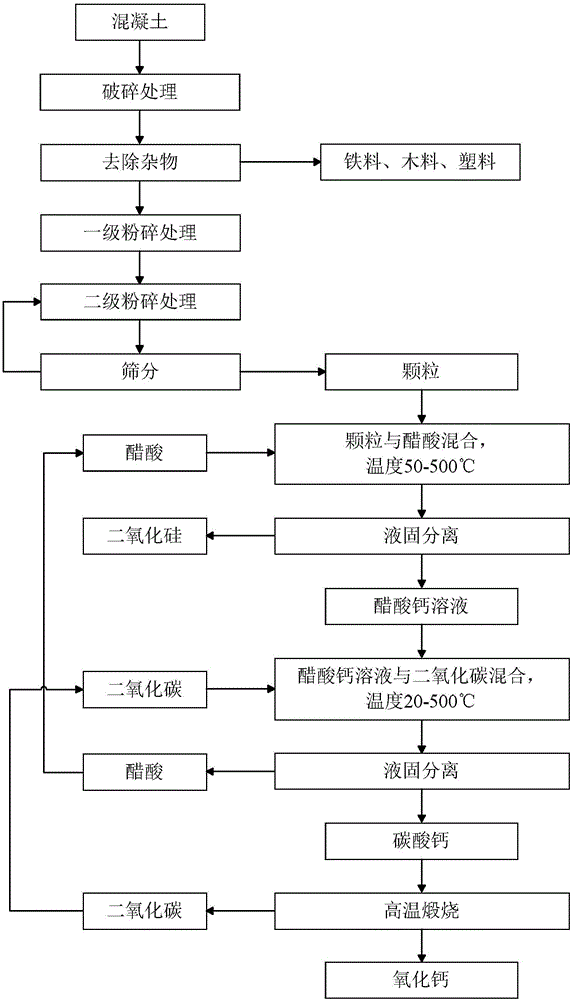
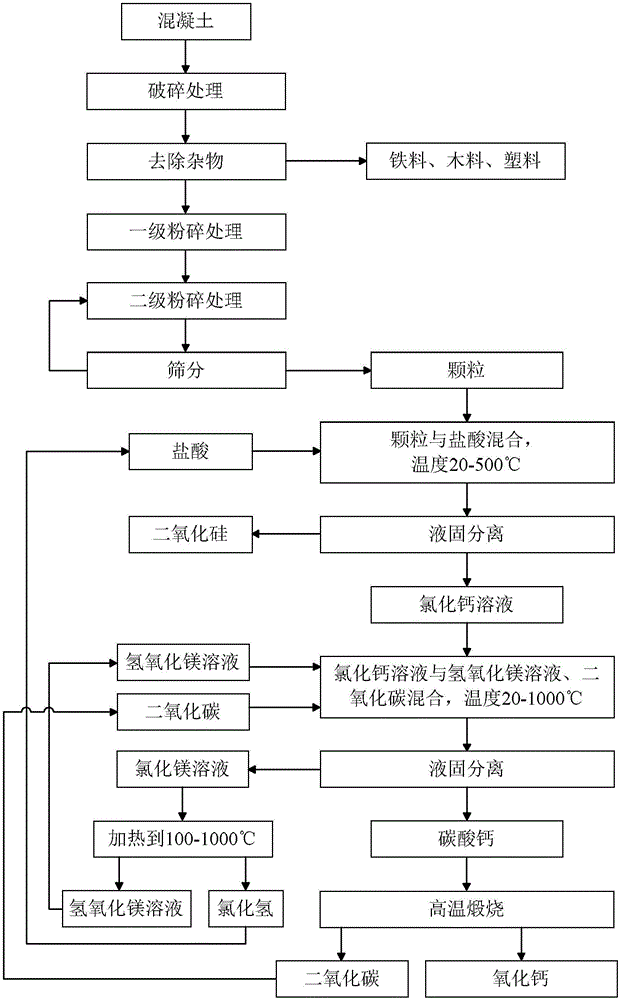
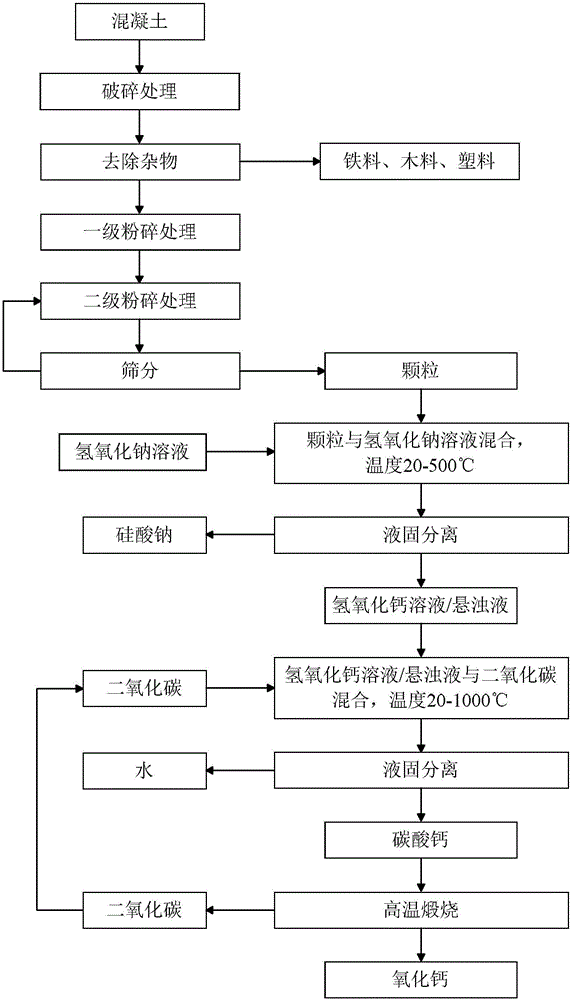
Building waste material utilization method
InactiveCN106348331AReduce miningEmission reductionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesSilicaPre treatmentMaterials science
The invention discloses a building waste material utilization method. The building waste material utilization method comprises the steps of pretreating building waste materials into particles with size in a preset size range; and obtaining calcium carbonate from the particles. According to the building waste material utilization method provided by the invention, the range of the usable building waste materials is wider, and useful compounds which have higher purity and facilitate wider application can be obtained.
Owner:YUANCHU TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag
ActiveCN103014333BRealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodDecomposition
The invention discloses a separation and recovery method of uranium, thorium and rare earth in monazite slag, namely a method for separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing and extraction of valuable components. According to the invention, the uranium, thorium and rare earth are leached out by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; the secondary slag is subjected to beneficiation and alkaline decomposition by a beneficiation technology, and closed-loop circular recovery of uranium, thorium and rare earth is realized; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
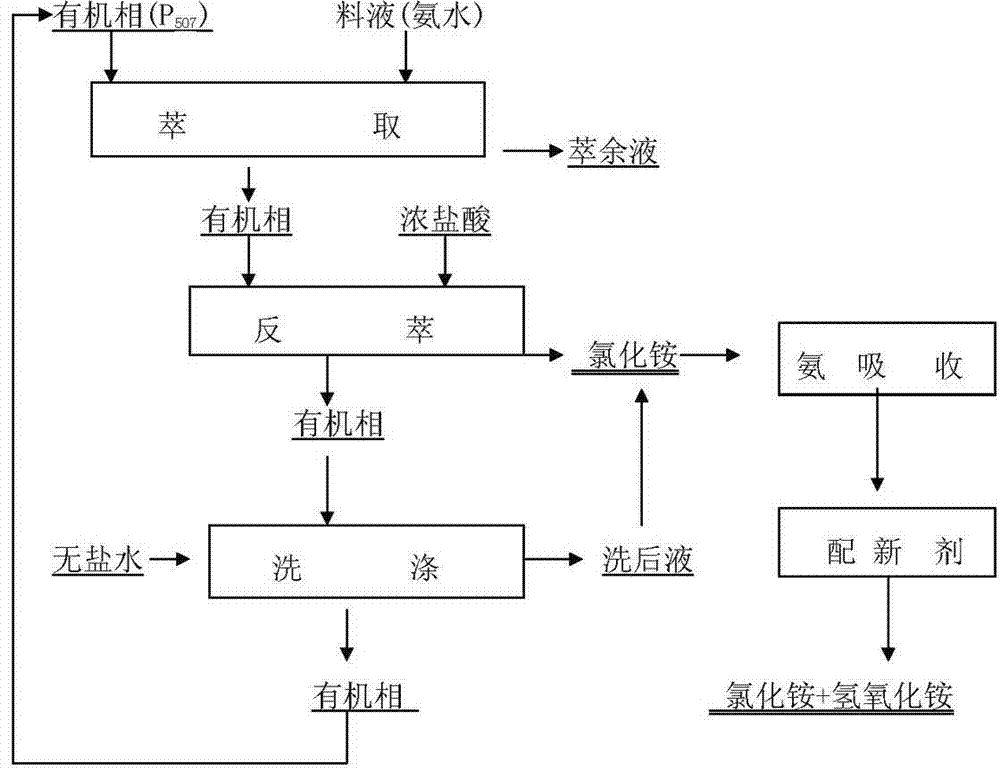
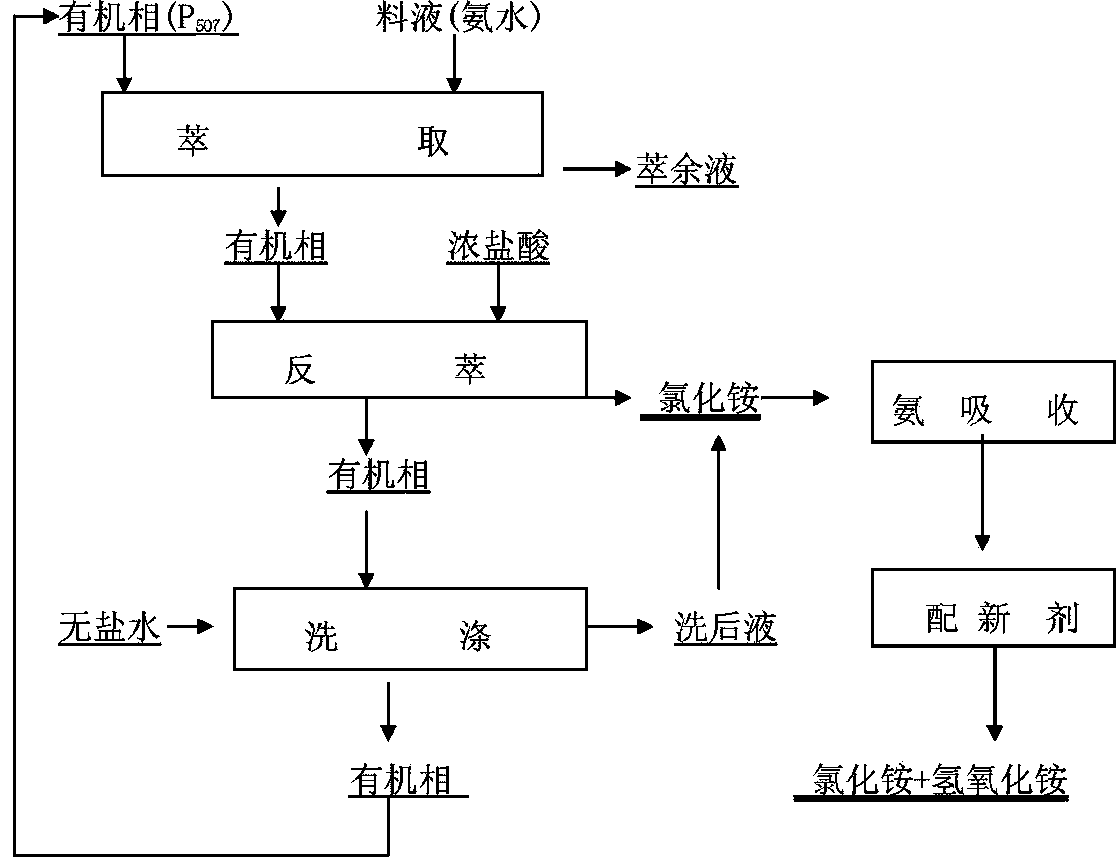
Method for treating ammonia nitrogen in tungsten smelting by using extraction absorption
ActiveCN102923805ARealize closed loop recyclingWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationLiquid waterSalt free
The invention discloses a method for treating ammonia nitrogen in tungsten smelting by using extraction absorption. According to the method, the recovery rate of the ammonia nitrogen is further improved, and the working environment is improved and the production cost is decreased. Primary extraction: organic phase extractants are added to weak aqua ammonia recycled by evaporation to perform extraction to obtain ammonium ions NH4+, and free water and hydroxide ions in ammonia water enter extraction residual liquid water phases; secondary extraction: industrial concentrated hydrochloric acids are added in extracted organic phases, heavy phases after reverse extraction are ammonium chloride at the bottom; light phases containing P507 organic phases enter a next circle for extraction after washing; an reverse extraction solution of an ammonium chloride solution is subjected to ammonia absorption; ammonia water with a concentration of 110g / l returns to a tungsten smelting departure and transfer procedure to serve as an analyzing agent; and final washing: salt-free water is added to organic phases after reverse extraction, organic phase residual ammonium chloride is guaranteed to be discharged as far as possible, an after-washing solution is an ammonium chloride solution, the ammonium chloride solution and the reverse extraction of the last step are subjected to ammonia absorption, and an organic phase extraction agent P507 after washing enters a next circle for usage. The method further improves the ammonia nitrogen recovery rate, the work environment is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN TUNGSTEN
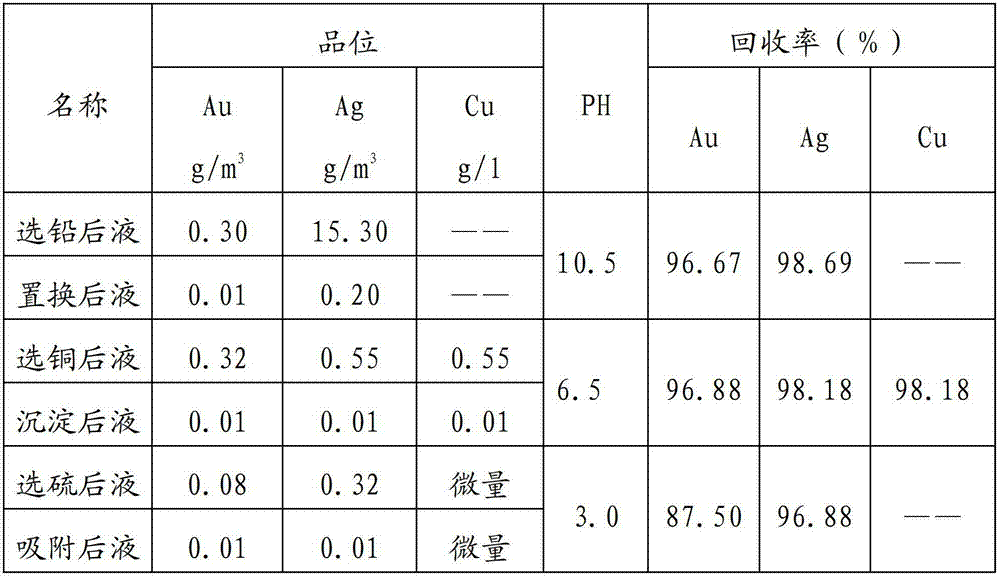
Method for recycling multiple elements of liquid after cyanided tailing flotation
ActiveCN102784713BImprove utilization efficiencyRealize closed loop recyclingSolid separationActivated carbonSulfur
The invention relates to a method for recycling multiple elements of liquid after cyanided tailing flotation, belonging to the technical field of gold smelting, cyanided tailing flotation of lead and copper concentrate, and waste water treatment of sulfur concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining lead concentrate through flotation; comprehensively recycling gold and silver from liquid after lead flotation; obtaining copper concentrate through flotation; comprehensively recycling gold, silver and copper from liquid after copper flotation; obtaining sulfur concentrate through flotation; recycling gold and silver through gold-loaded activated carbon desorption electrodeposition; and the like. By the method, the comprehensive utilization efficiency of resources is improved, closed loop recycle of the liquid in a flotation system is achieved, zero discharge of wastewater is achieved, pollution to the surrounding environment is reduced, and ultimately the economic efficiency of an enterprise is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG GUODA GOLD
Ammonia recycling method and system in APT production process
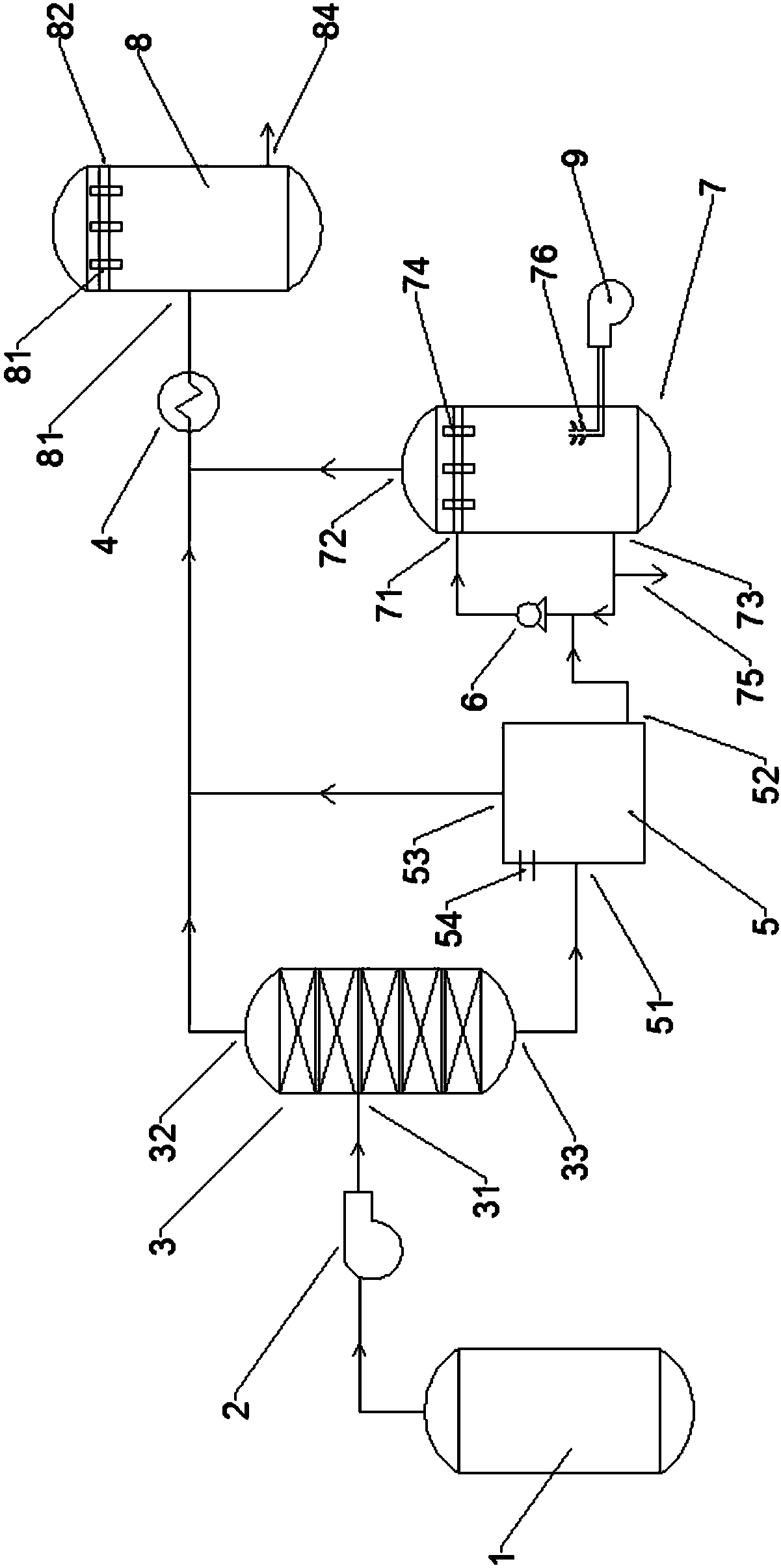
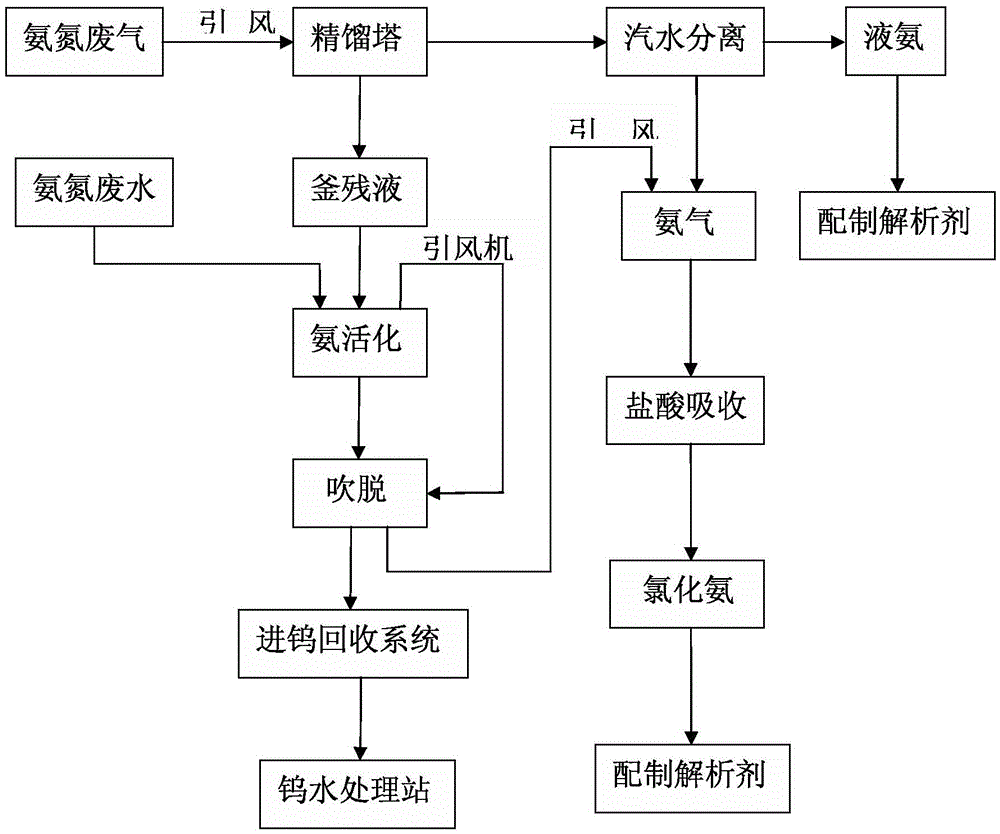
PendingCN108371869AFully contactedImprove absorption efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsDesorptionIon exchange
The invention provides an ammonia recycling method and a system in APT production process. The ammonia recycling method comprises following steps: 1, APT crystallization steam is discharged using a centrifugation blower fan, is introduced into a rectifying tower for rectification and condensation of ammonia tail gas to remove most water, and is introduced into a heat exchanger; 2, a three stage solution obtained via ion exchange is directly used for preparing a desorption agent, the rest ammonia nitrogen wastewater is pumped into a stirring tank, an alkali is added for ammonia activation, andgenerated ammonia tail gas is introduced into the heat exchanger; wastewater obtained via ammonia activation is pumped into an air stripping tower, and ammonia tail gas obtained via air stripping is introduced into the heat exchanger; when the ammonia-nitrogen value of obtained air stripping wastewater is detected to be qualified, discharging through a branch pipe is carried out, otherwise, the wastewater is pumped into the air stripping tower for air stripping; and 3, the temperature of the ammonia tail gas is reduced to be lower than 45 DEG C after treatment using the heat exchanger, the ammonia tail gas is introduced into a hydrochloric acid absorbing tower for circulating absorption, and an obtained solution is sent back to the main treatment stream directly for preparation of the desorption agent. The ammonia recycling method and the system are used for comprehensive treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater waste gas obtained in tungsten smelting, waste is changed into valuables,the method flow is simple, operation is convenient, the method is easy to control, and cost is low.
Owner:江西铜鼓有色冶金化工有限责任公司
Method for preparing regenerated polyester by closed-loop recovery of waste polyester with typical green and low-carbon characteristics
ActiveCN114031756AEnable chemical recyclingRealize closed loop recyclingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPlastic recyclingPolymer scienceDepolymerization
The invention discloses a method for preparing regenerated polyester by closed-loop recovery of waste polyester with typical green and low-carbon characteristics. The method comprises the steps: selecting a specific depolymerization catalyst to depolymerize waste polyester under a microwave condition; removing a polyol solvent from the depolymerized product, and purifying to remove byproducts to obtain a depolymerized monomer; and mixing the depolymerized monomer with dibasic acid, polyol, a polymerization catalyst and a chain extender, carrying out esterification reaction, adding a stabilizer and a catalyst, and carrying out polycondensation to obtain the regenerated polyester. According to the method, the depolymerization temperature is low, the efficiency is high, the dosage of the polyol solvent is small, and the content of the byproducts is extremely low; meanwhile, the depolymerization catalyst does not need to be separated, co-esterification of the regenerated polyester can be directly carried out, and no adverse effect is caused on the performance of the prepared regenerated polyester. The method provided by the invention can realize closed-loop recovery of waste polyester.
Owner:NAT POLYMER MATERIALS IND INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
A process for recovering ammonia from tungsten smelting ammonia nitrogen wastewater waste gas
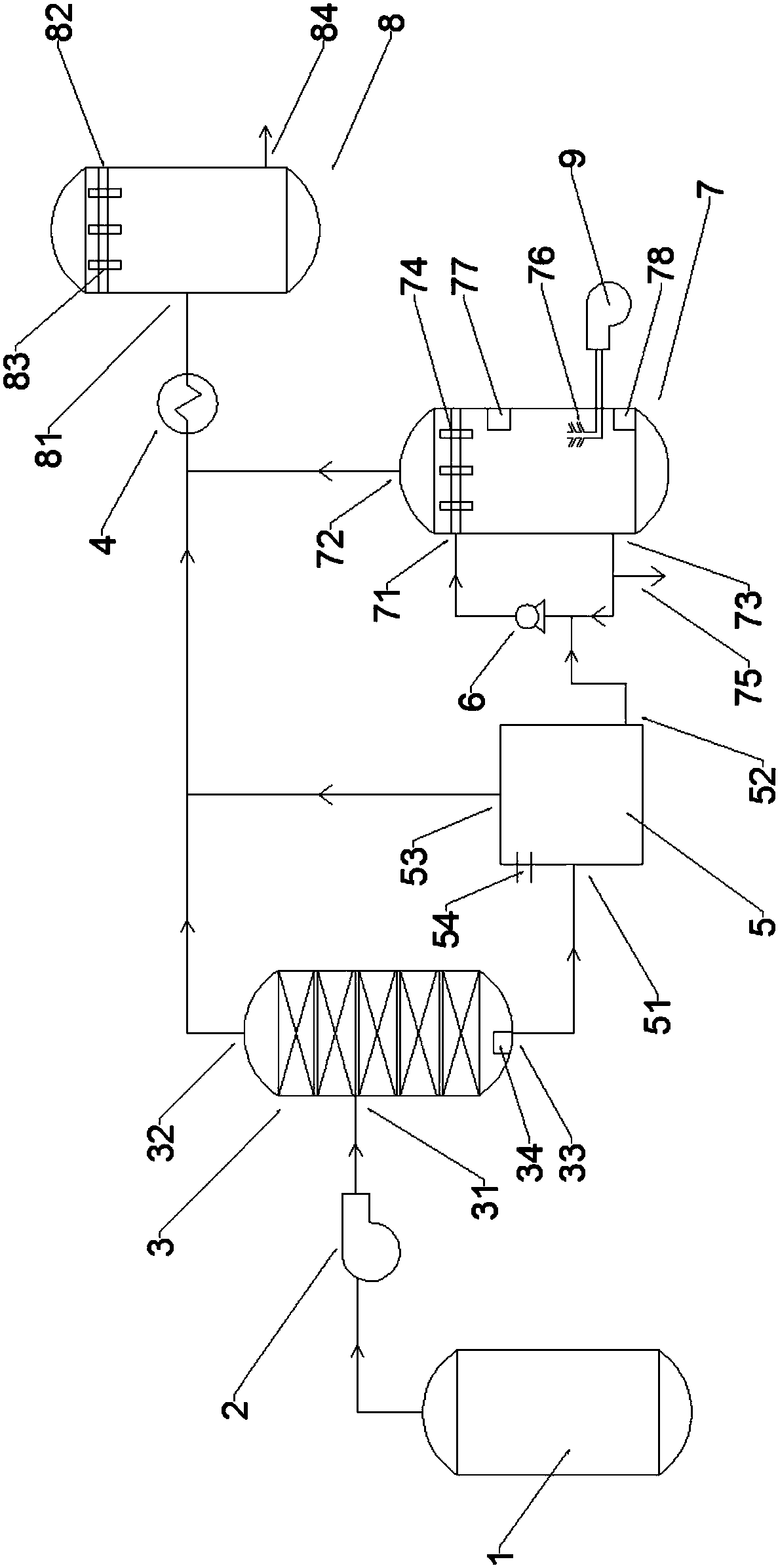
ActiveCN104310426BRealize closed loop recyclingPlay the role of turning waste into treasureAmmonia preparation/separationAmmonium paratungstateTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a process of recovering ammonia from ammonia-nitrogen wastewater and exhaust gas of tungsten metallurgy. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps: introducing ammonium paratungstate crystal steam and ammonia tail gas into a rectifying tower by virtue of an induced draft fan, maintaining the temperature in a range of 90-95 DEG C and condensing and recovering ammonia by using a steam separator; pumping kettle raffinate and ammonia-nitrogen wastewater which are generated after rectifying the ammonia-nitrogen wastewater into a stirring tank, adding sodium hydroxide for ammonia activation, and adjusting the pH value to 10-11; after ammonia activation, pumping to an air stripping tower, and meanwhile, introducing ammonia wastewater generated by ammonia activation into the air stripping tower, adding sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 10-11.5, and controlling the temperature at 45-90 DEG C and carrying out air stripping for 2 hours; feeding ammonia gas generated in the air-stripping process and ammonia gas which is not condensed by the steam separator into a hydrochloric acid spray tower for circular adsorption to generate ammonium chloride and returning to the main process to prepare an analytical solution. The process provided by the invention is simple in process flow, stable in treatment effect, less in equipment investment, free from secondary pollution and low in treatment cost.
Owner:CNMC GUANGXI PGMA
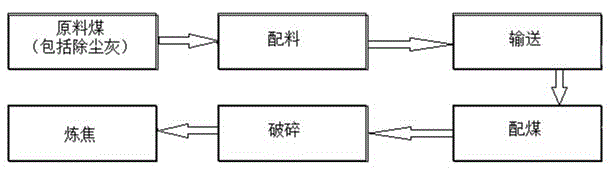
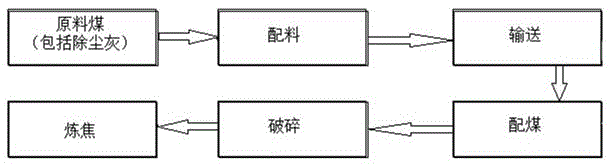
Blending method of dry coke quenching dust-removal ash in coal blending process
The invention discloses a blending method of dry coke quenching dust-removal ash in a coal blending process. The blending method comprises the following steps: transporting dust-removal ash generated by dry coke quenching every day to a coal storage yard through an ash discharge opening, arranging the dust-removal ash near low-sulfur coking coal of which the content of sulfur is less than 0.4% and low-ash meager lean coal of which the content of ash is less than 8.5% which can be blended for separately storing; according to the blending ratio required by the blending instruction of a forklift in a coal blending workshop, fully and uniformly blending the dry coke quenching dust-removal ash, low-sulfur coking coal and the low-ash meager lean coal at a weight ratio of 1:5:5 to form novel mixed dust-removal ash; conveying the mixed dust-removal ash to a coal blending bin, blending the mixed dust-removal ash and 1 / 3 coking coal, gas coal, coking coal and meager lean coal at a weight ratio of 7: 3 and rich coal to form into-the-furnace coal, crushing the into-the-furnace coal, adding water and conveying to the coal storage bin for coking coal production to replace partial meager lean coal for return blending and coking, wherein the mixed dust-removal ash, the 1 / 3 coking coal, the gas coal, the coking coal and meager lean coal at a weight ratio of 7:3 and the rich coal respectively account for 15%, 32%, 15%, 21% and 17% of the into-the-furnace coal in weight ratio. The process is convenient to operate and has the characteristic of high flexibility.
Owner:山东泰山焦化有限公司
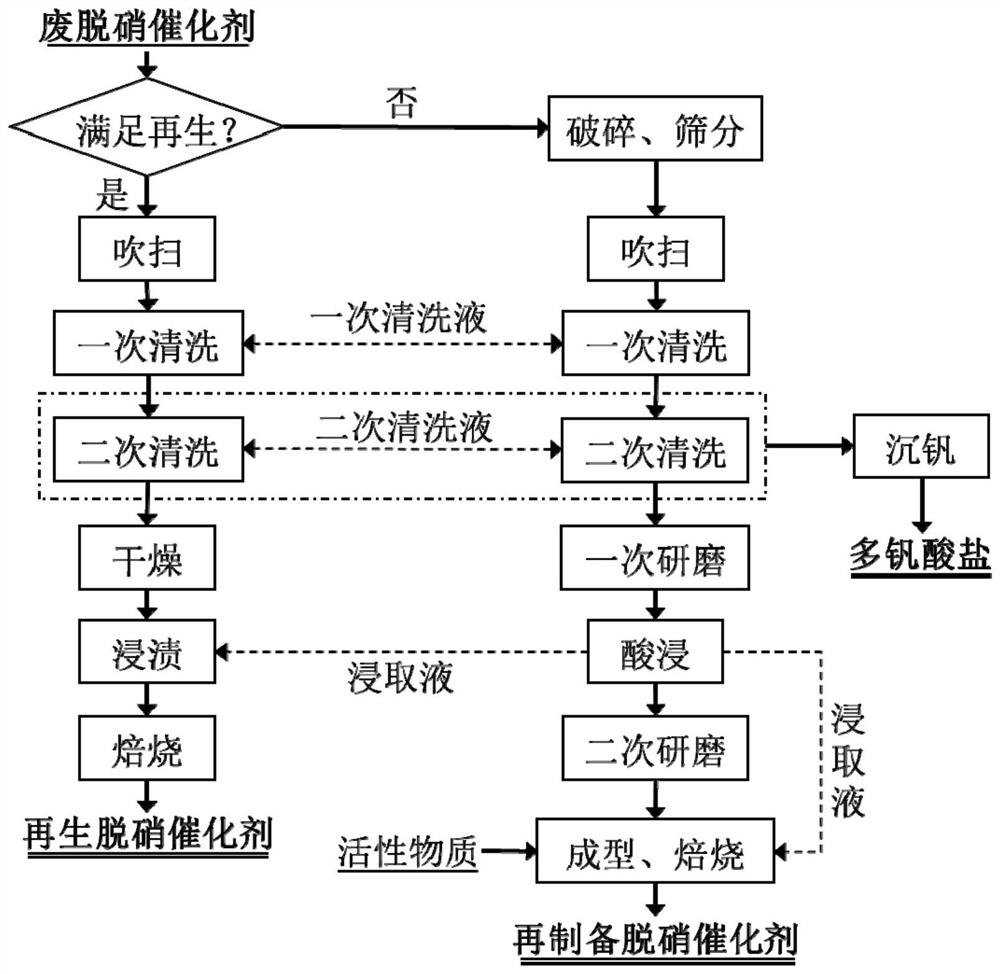
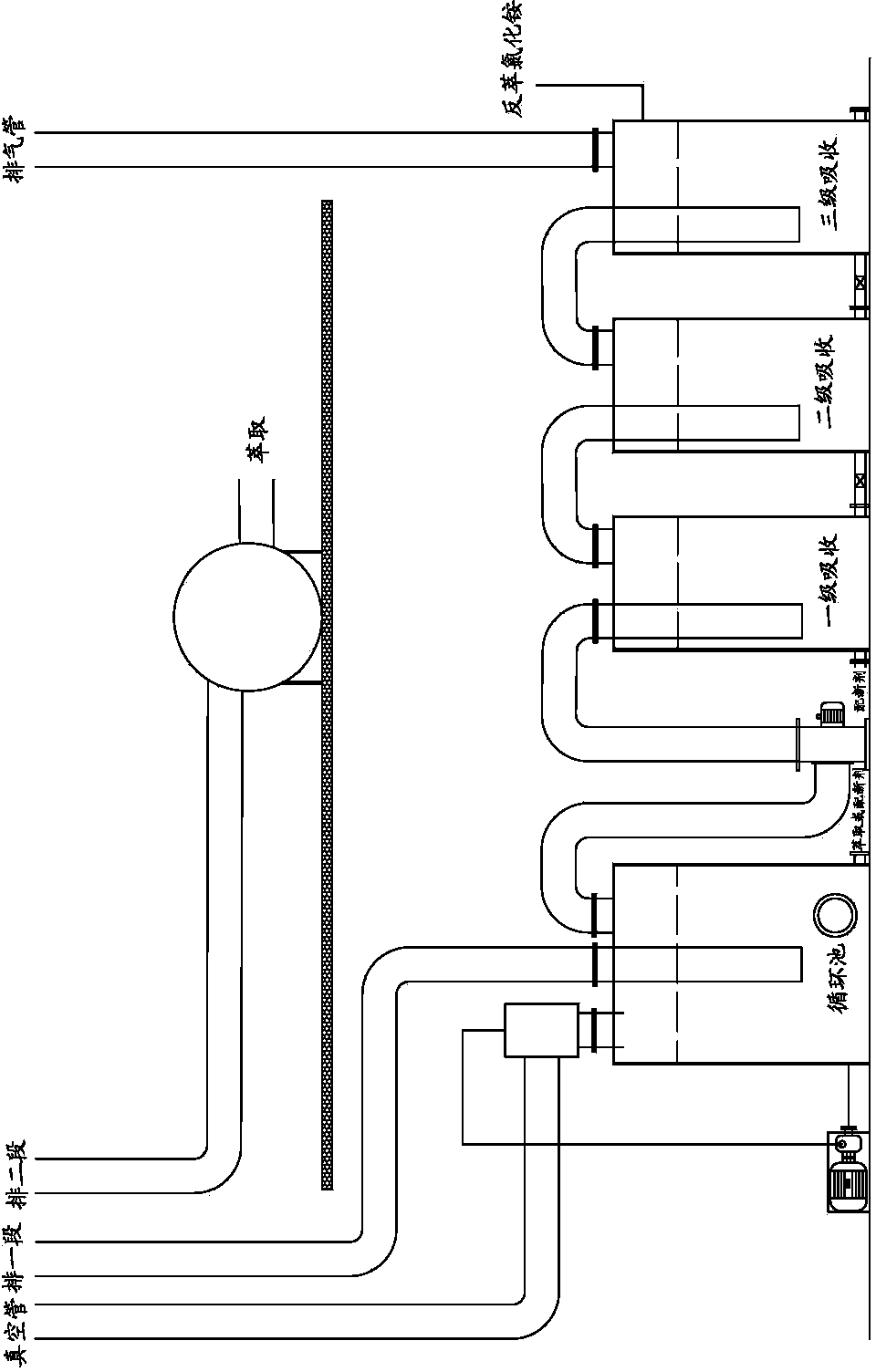
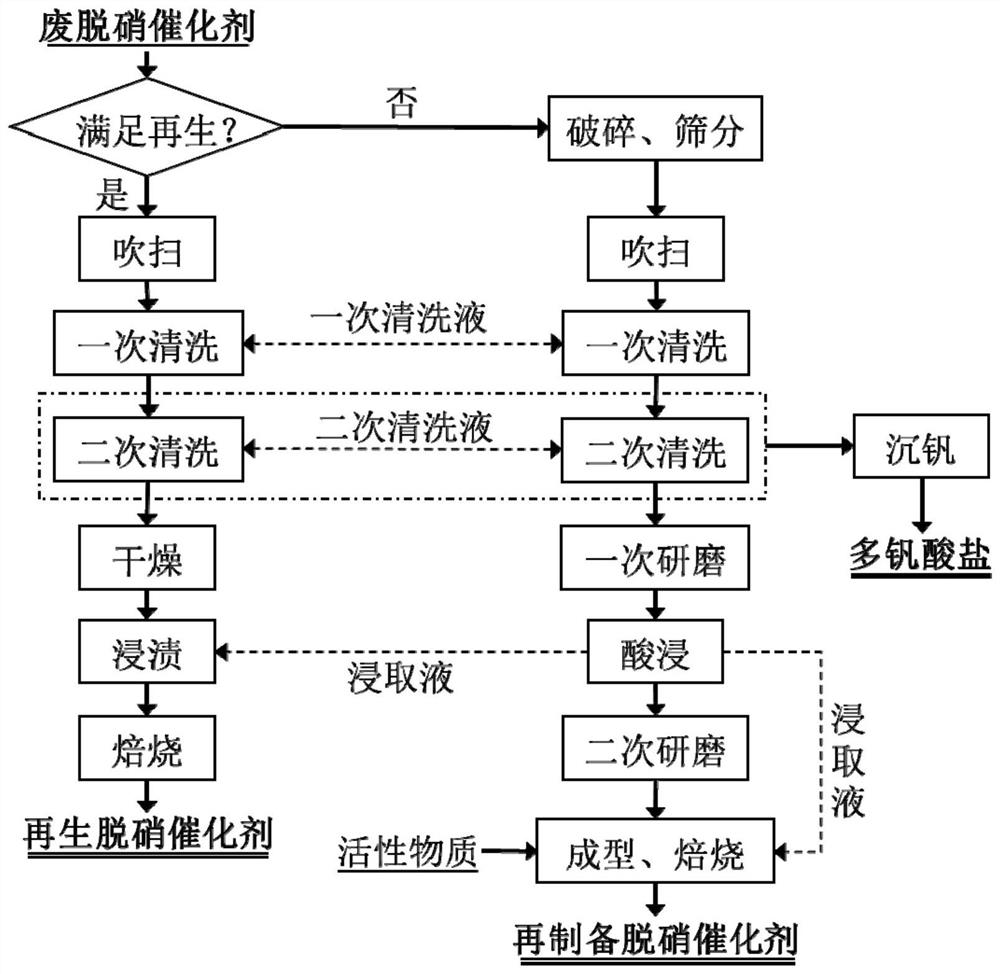
Green cyclic utilization method of honeycomb type denitration catalyst
ActiveCN112427050AAchieve recyclingRealize closed-loop recyclingDispersed particle separationCatalyst regeneration/reactivationPtru catalystFlue gas
The invention relates to a green cyclic utilization method of a honeycomb type denitration catalyst, and belongs to the field of flue gas denitration and material cyclic utilization. A regeneration process route and a repreparation process route are set, and a regeneration production line and a repreparation production line are arranged in parallel; a regeneration process or a repreparation process is selected according to the performance of the waste honeycomb type denitration catalyst for green cyclic utilization; and the selection basis of the regeneration process and the repreparation process is as follows: if the axial compressive strength and the radial compressive strength of the waste honeycomb type denitration catalyst are respectively greater than or equal to 1.0 MPa and greaterthan or equal to 0.2 MPa, and the specific surface area is greater than or equal to 40.0 m<2> / g, the regeneration process route is selected, and otherwise, the repreparation process route is selected.According to the green cyclic utilization method of the honeycomb type denitration catalyst, regeneration and repreparation processes are combined, valuable components in the waste denitration catalyst are fully utilized, the use amount of water is greatly reduced, and closed-loop cyclic utilization of the denitration catalyst can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Coke CDQ Dust Removal Ash Mixing Method in Coal Blending Process
Owner:山东泰山焦化有限公司
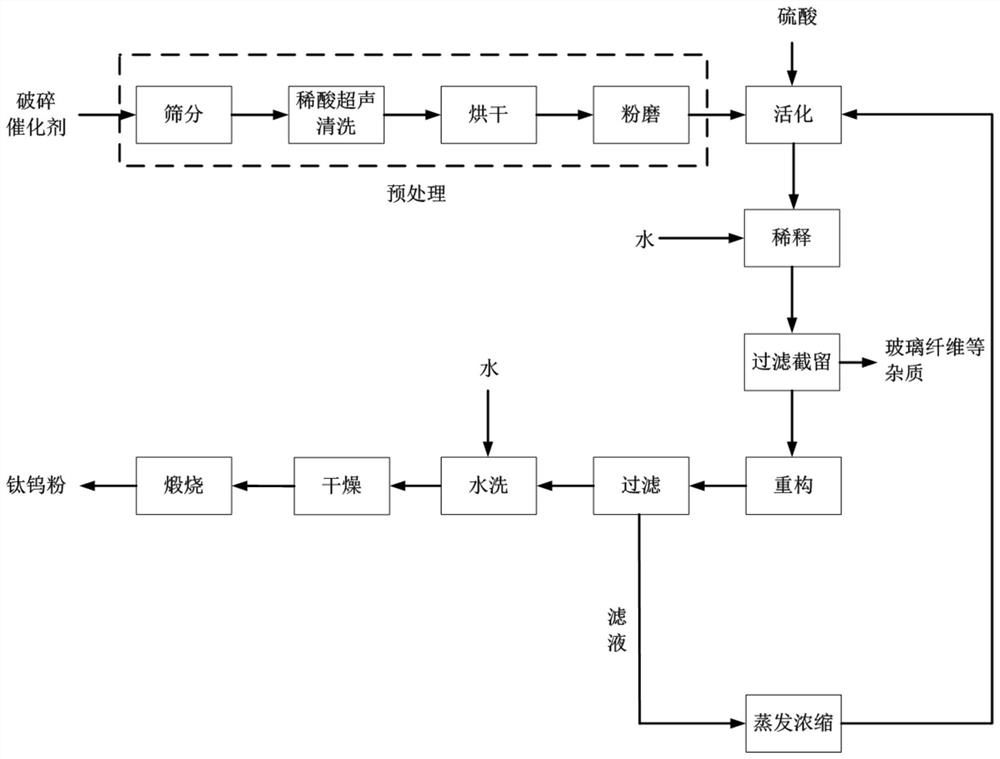
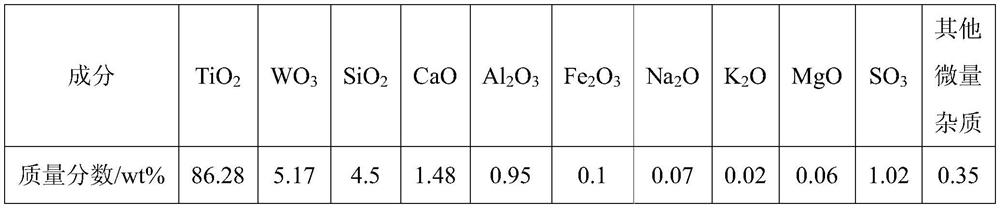
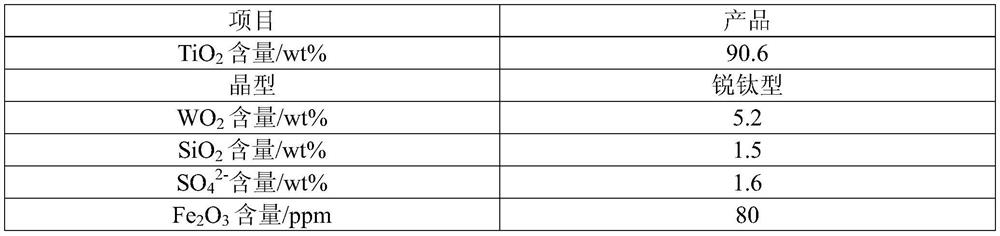
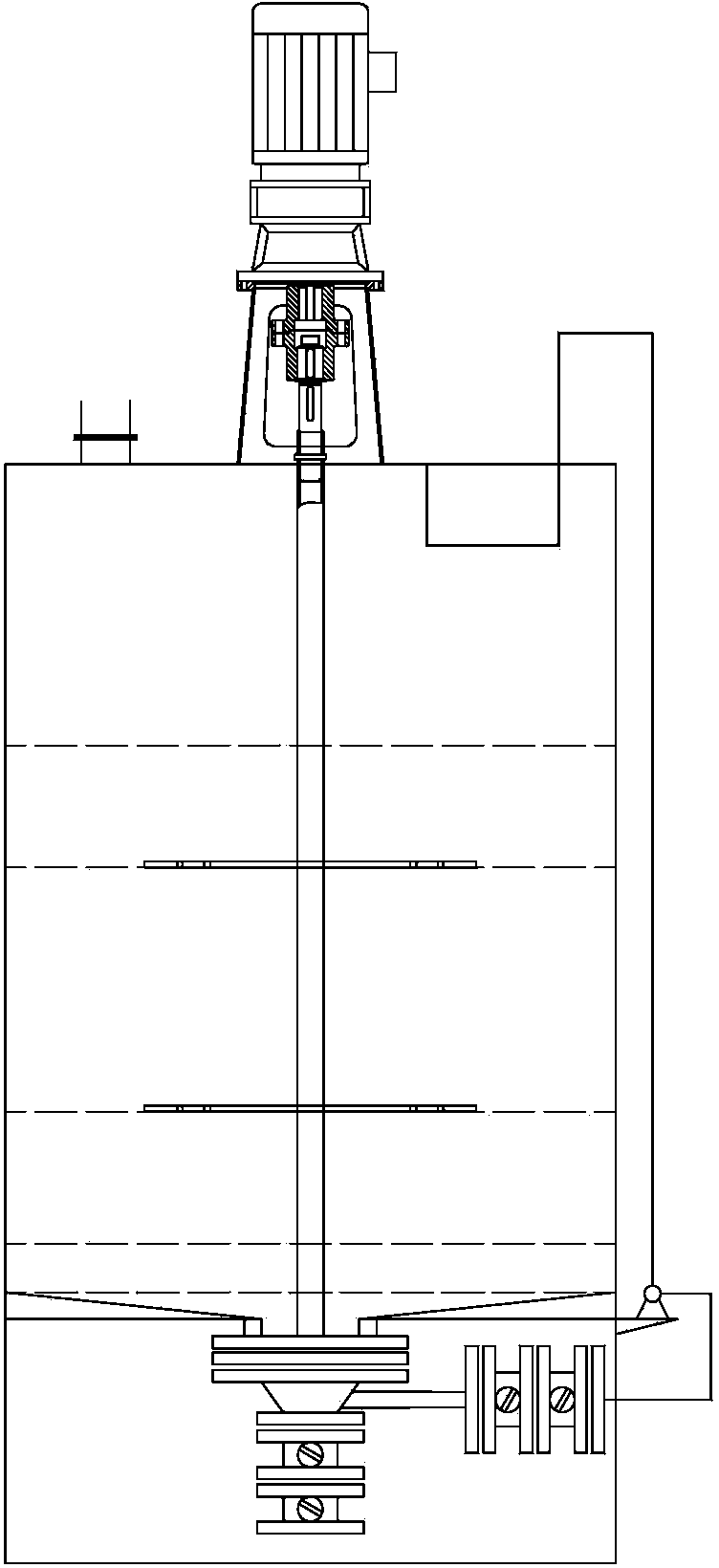
A method and application of recovering and preparing titanium-tungsten powder from waste scr denitrification catalyst
The invention relates to a method for preparing titanium tungsten powder by recycling waste SCR denitration catalyst. The method comprises the following steps that the waste SCR denitration catalyst is pretreated so as to obtain pretreated waste catalyst powder; activated treatment is carried on the pretreated waste catalyst powder by using sulfuric acid, and after the waste catalyst powder is cooled and diluted, crude activated slurry is obtained; glass fibers are removed in the crude activated slurry to obtain purified and activated slurry; the activated slurry is heated and purified to obtain a reconstructed slurry; the reconstructed slurry is filtered so as to obtain a solid-phase product and a filtrate; and solid-phase products are sequentially washed, dried and calcined to obtain titanium-tungsten powder products. According to the method, the waste SCR denitration catalyst is converted into the titanium tungsten powder, and the whole process is simple in process, so that the process complexity caused by the step of extracting Ti and W metal components step by step is avoided, the cost is high, the recovery rate of Ti and W exceeds 97%, and the obtained titanium tungsten powder products meet the requirements of industry indexes can completely replace fresh titanium tungsten powder, and are used for production of the SCR catalyst.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Classifying and recycling process for waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of steel tundish working linings as well as dry material and coating material for tundish
ActiveCN103319189BMaximize recycling rateMaximize regeneration valueSolid waste disposalBrickGranularity
The invention relates to a classifying and recycling process for waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of steel tundish working linings as well as a dry material and a coating material for a tundish. The waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of the steel tundish working linings are subjected to recovery processing and are classified into reclaimed materials with three grain levels, i.e., the granularity is more than or equal to 3mm and less than 5mm, the granularity is more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm and the granularity is less than 1mm; the reclaimed materials with the granularity more than or equal to 3mm and less than 5mm and the granularity more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm are used as raw materials to prepare the dry material for the tundish, and the dry material is used for carrying out continuous casting on a slag line 2 and a tundish wall 3 and a tundish bottom 4 below the slag line 2 of the tundish working lining; the reclaimed materials with the granularity more than or equal to 1mm and less than 3mm and the granularity less than 1mm are used as raw materials to prepare the coating material for the tundish, and the coating material for the tundish is used for carrying out continuous costing on a tundish edge 1 above the slag line of the tundish working lining. The invention further provides a construction method for manufacturing the combined continuous casting tundish working lining by adopting the dry material and the coating material for the tundish. According to the classifying and recycling process, the dry material and the coating material for the tundish and the construction method, the classifying and recycling rate of the waste magnesia carbon bricks produced after use of the steel tundish working linings reaches 100 percent.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Treatment method of tailings after separation and recovery of monazite slag
ActiveCN103014358BRealize closed loop recyclingEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionSlag
The invention discloses a treatment method of tailings after the separation and recovery of monazite slag, namely a treatment method of tailings after separating and recovering valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth from monazite slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acid leaching, filter pressing, washing and treatment of filter residue. According to the invention, the tailings are leached out by weak acid at a low temperature, and the liquid phase and solid phase are easy to separate; the secondary slag is subjected to beneficiation and alkaline decomposition by a beneficiation technology, and closed-loop circular recovery of uranium, thorium and rare earth is realized; and meanwhile, the waste acid of residual liquid is circularly used, the discharge of wastewater is reduced, the consumption of sulfuric acid and new water as well as the wastewater treatment cost are reduced, the production cost is lowered, the recovery rate of the valuable elements uranium, thorium and rare earth is greater than 97%, and the discharge of radioactive wastewater and waste residue is avoided in the whole technology.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
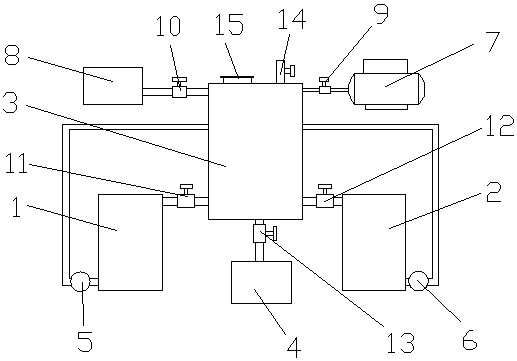
Method and device for recycling hot-dip copper waste liquid
InactiveCN113772845AReduce processing costsGood workmanshipCellsIron oxides/hydroxidesFerric hydroxideCopper plating
The invention relates to a method and a device for recycling a hot-dip copper waste liquid. The method comprises the following steps: feeding a waste liquid in a plating solution tank into an oxidation tank, adding hydrogen peroxide into the oxidation tank, adding compressed air into the oxidation tank, stirring 4-6 times to recover the pressure of a gas part at the upper portion of the oxidation tank to normal pressure, adding copper oxide into the oxidation tank, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 3.5-4, keeping for 8-10 hours, draining back the clear liquid in the oxidation tank to the plating solution tank, and after the residual turbid liquid in the oxidation tank is stirred for 8-10 minutes, making the turbid liquid flow into a turbid liquid recycling tank; and after the turbid liquid is subjected to solid-liquid separation, pumping the liquid into the plating solution tank to be reused, and recovering and storing the solid after being dried or air-dried. According to the invention, a copper plating enterprise can remove excessive ferrous ions in a waste liquid on site in a copper plating place by using simple equipment, a convenient process and low cost, copper ions in the waste liquid are recycled, and the ferrous ions are finally converted into a chemical raw material ferric hydroxide, so that closed-loop recycling is realized, high sewage treatment cost is saved for the enterprise, and considerable profits can be earned for enterprises due to cost difference.
Owner:周雪阳
Method for treating ammonia nitrogen in tungsten smelting by using extraction absorption
ActiveCN102923805BRealize closed loop recyclingWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationLiquid waterSalt free
The invention discloses a method for treating ammonia nitrogen in tungsten smelting by using extraction absorption. According to the method, the recovery rate of the ammonia nitrogen is further improved, and the working environment is improved and the production cost is decreased. Primary extraction: organic phase extractants are added to weak aqua ammonia recycled by evaporation to perform extraction to obtain ammonium ions NH4+, and free water and hydroxide ions in ammonia water enter extraction residual liquid water phases; secondary extraction: industrial concentrated hydrochloric acids are added in extracted organic phases, heavy phases after reverse extraction are ammonium chloride at the bottom; light phases containing P507 organic phases enter a next circle for extraction after washing; an reverse extraction solution of an ammonium chloride solution is subjected to ammonia absorption; ammonia water with a concentration of 110g / l returns to a tungsten smelting departure and transfer procedure to serve as an analyzing agent; and final washing: salt-free water is added to organic phases after reverse extraction, organic phase residual ammonium chloride is guaranteed to be discharged as far as possible, an after-washing solution is an ammonium chloride solution, the ammonium chloride solution and the reverse extraction of the last step are subjected to ammonia absorption, and an organic phase extraction agent P507 after washing enters a next circle for usage. The method further improves the ammonia nitrogen recovery rate, the work environment is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN TUNGSTEN
A method for green recycling of honeycomb denitrification catalyst
ActiveCN112427050BAchieve recyclingRealize closed-loop recyclingDispersed particle separationCatalyst regeneration/reactivationPtru catalystFlue gas
The invention relates to a green recycling method for a honeycomb denitrification catalyst, which belongs to the field of flue gas denitrification and material recycling. Two process routes of regeneration and re-preparation are set up, and the regeneration production line and the re-preparation production line are arranged side by side; the regeneration process or the re-preparation process is selected according to the performance of the waste honeycomb denitrification catalyst for green recycling; the regeneration process and the re-preparation process The basis for selection is: the axial and radial compressive strengths of spent honeycomb denitration catalysts are ≥1.0 and ≥0.2MPa respectively, and the specific surface area is ≥40.0m 2 / g, the regeneration process route is selected; otherwise, the re-production process route is selected. The green recycling method of honeycomb denitrification catalyst provided by the present invention combines regeneration and re-preparation process, fully utilizes the valuable components in the spent denitrification catalyst, and greatly saves the amount of water, which can realize the closed loop of denitrification catalyst recycle.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com