Patents
Literature
3137results about "Ammonia preparation/separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
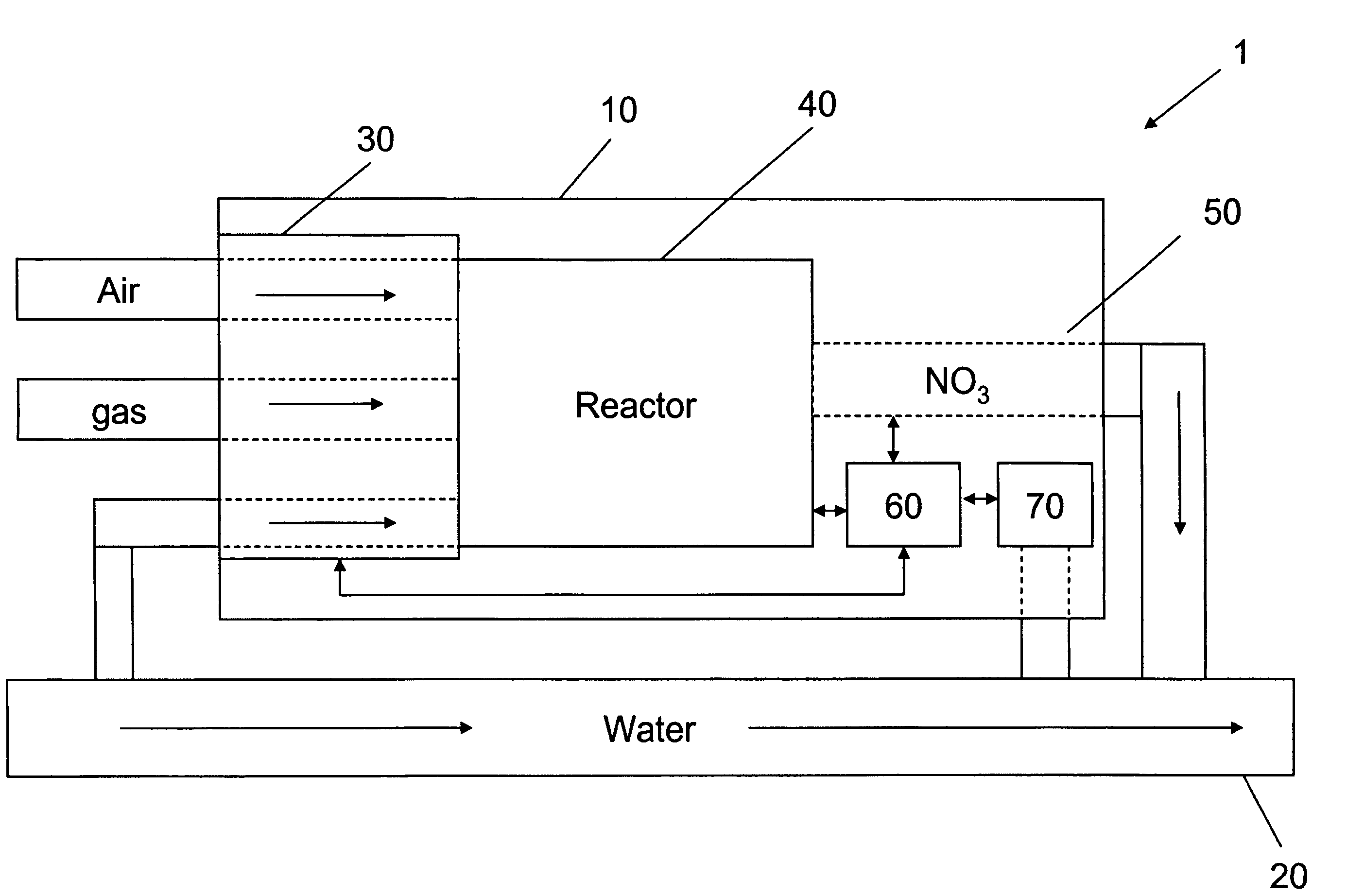
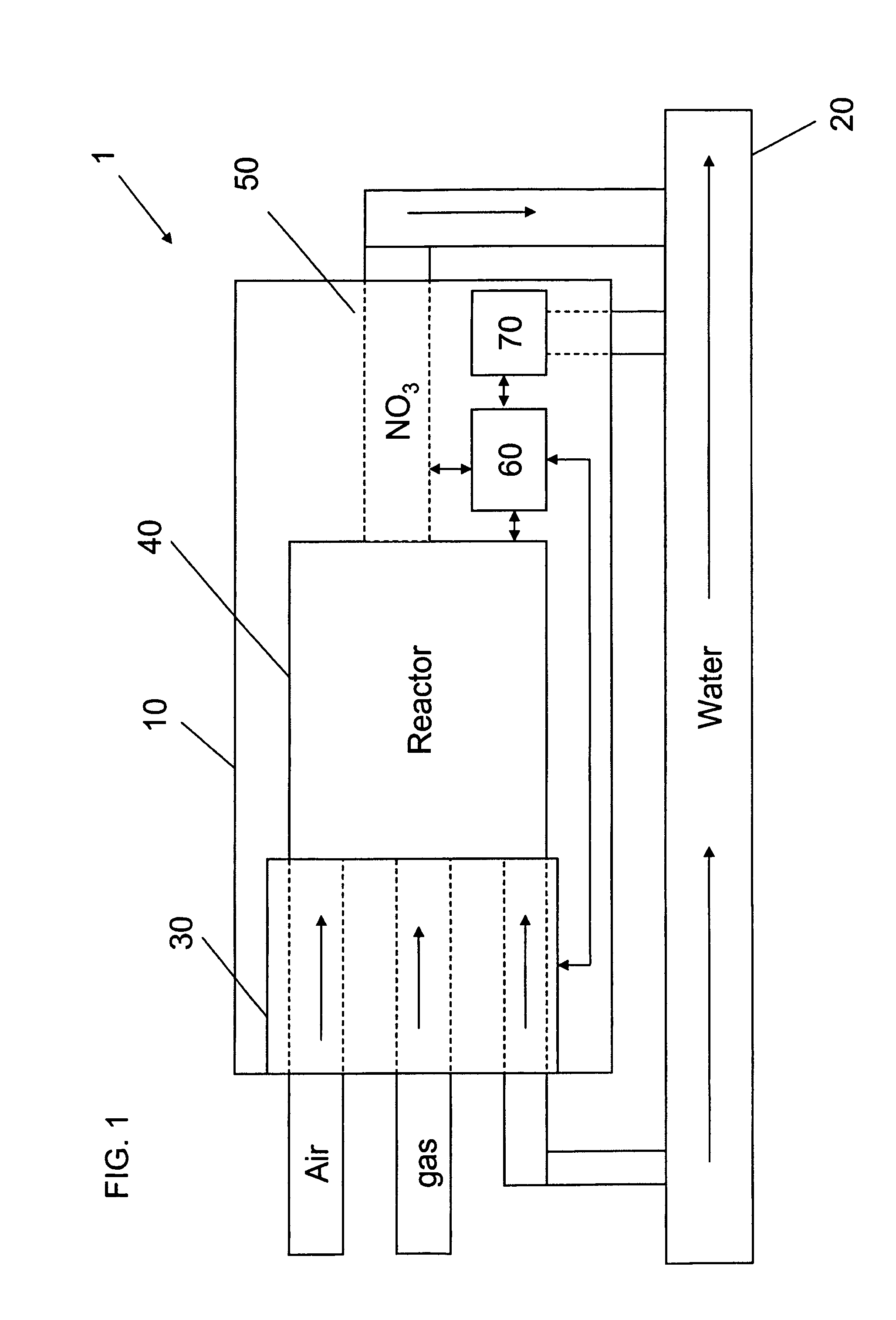
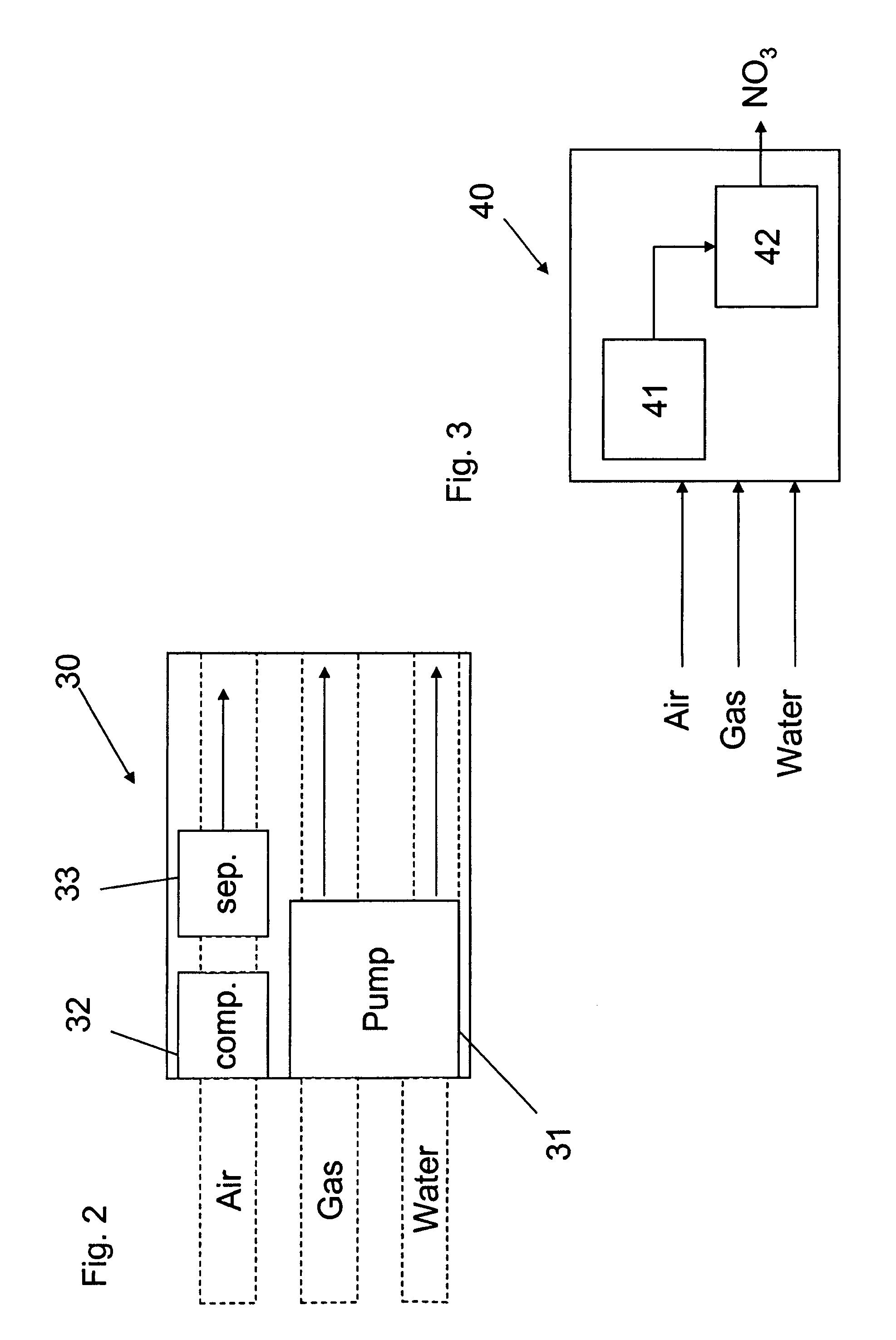
Apparatus for on-site production of nitrate ions
InactiveUS7514058B1Enhanced overall recoveryWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsMicrobial enhanced oil recoverySulfate-reducing bacteria
An apparatus and method produces nitrate ions on-site from water, natural gas and air extracted in proximity to the apparatus. The apparatus generates nitrate ions and brings the nitrate ions into contact with an aqueous system. Hydrogen sulfide present in the aqueous system is removed and the production of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) is eliminated by introducing into the system nitrate ions, whereby denitrifying microorganisms, using nitrate, outcompete the sulfate-reducing bacteria for the available carbon nutrients, thus preventing the SRB from producing hydrogen sulfide. Nitrate ions generated by the apparatus and added to the aqueous system which contains the denitrifying microorganisms can enhance oil recovery by means of microbial enhanced oil recovery mechanisms.
Owner:NITRA GEN LLC
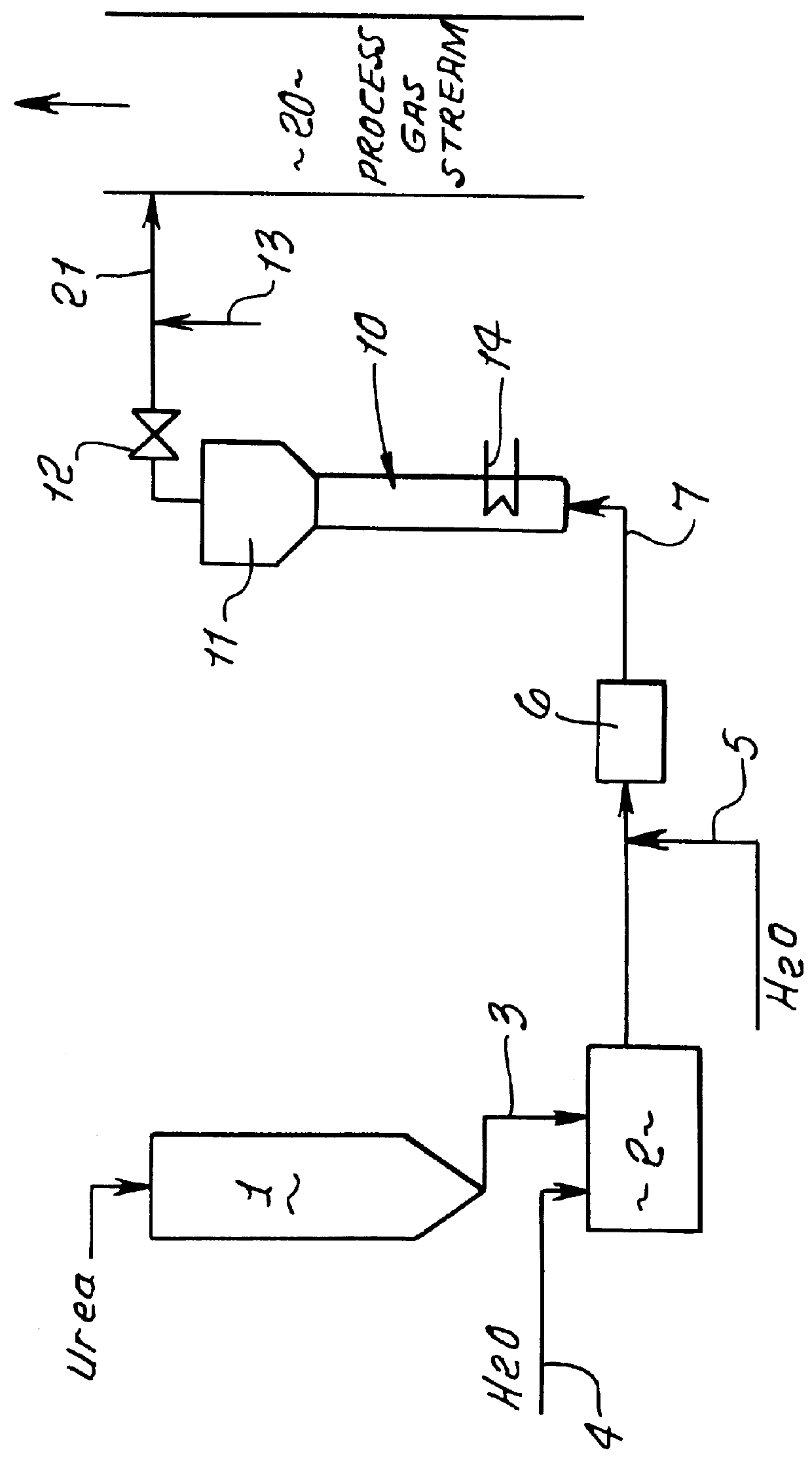
Methods for the production of ammonia from urea and/or biuret, and uses for NOx and/or particulate matter removal
InactiveUS6077491ARisk minimizationReduce amountNitrogen compoundsDispersed particle separationHydrolysisAmmonia
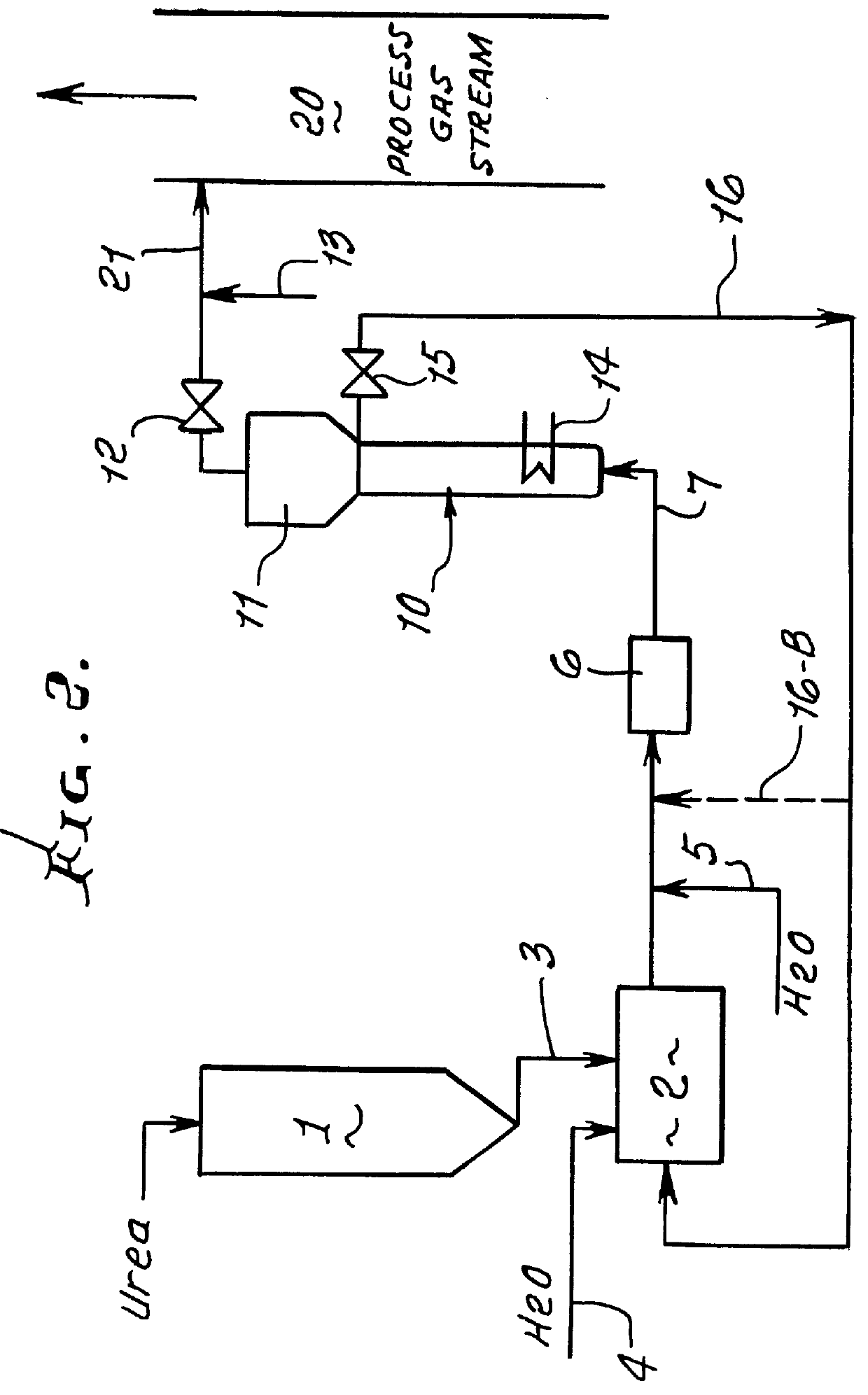
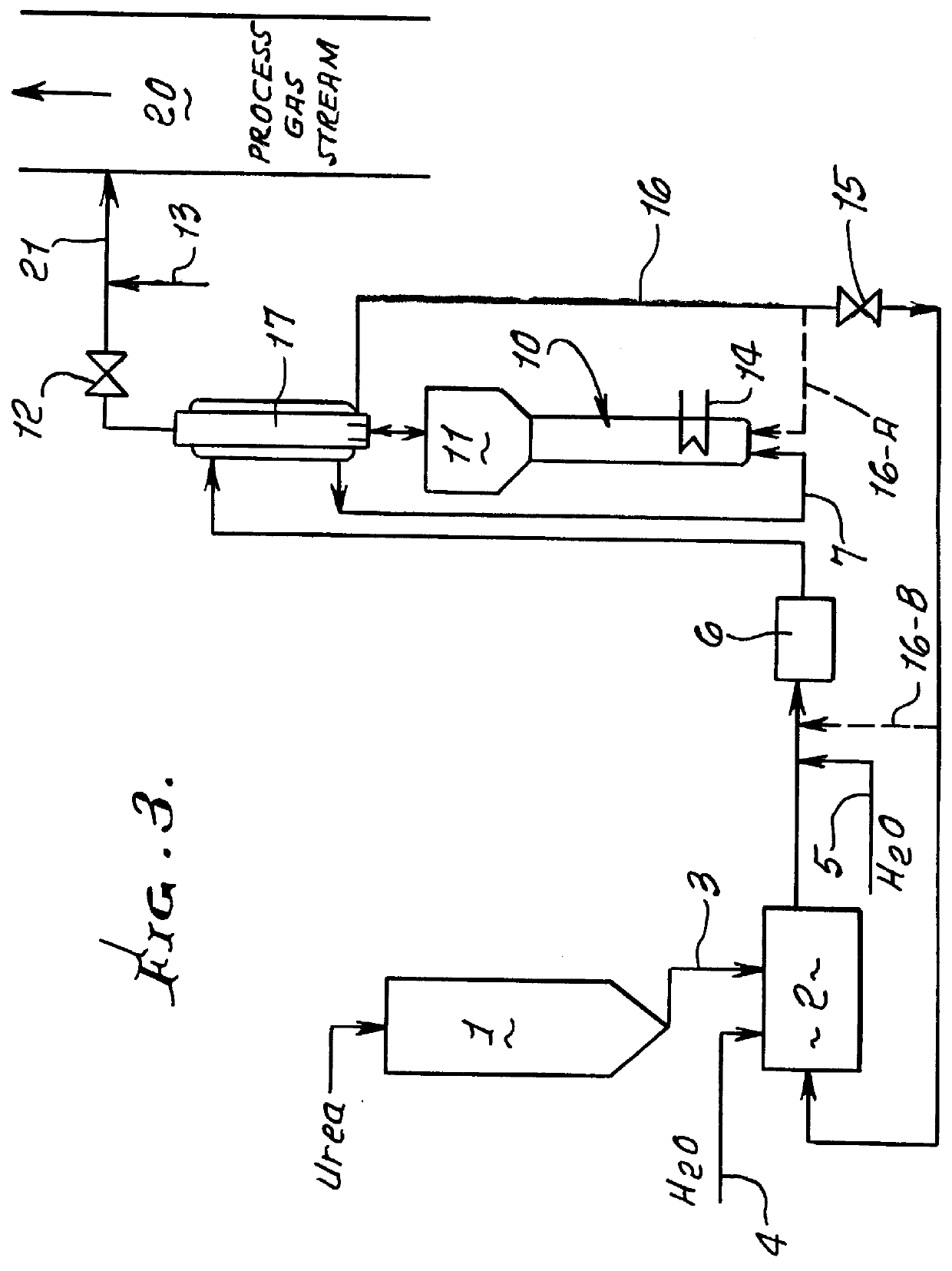
This patent describes technology for generating ammonia from urea. The method is based on the hydrolysis of an aqueous solution of urea and / or biuret by heating under pressure to form a mixture of ammonia, carbon dioxide and water. The gas mixtures produced are useful for supplying ammonia at controlled pressure and rate of flow for many industrial applications without the risks and hazards associated with the transportation and on-site storage of ammonia, thereby providing a significant safety advantage over present industrial practice.
Owner:EC&C TECH INC A
Method and apparatus for producing ammonia (NH3)
InactiveUS6928807B2High activityNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesHydrolysisRapid thermal processing
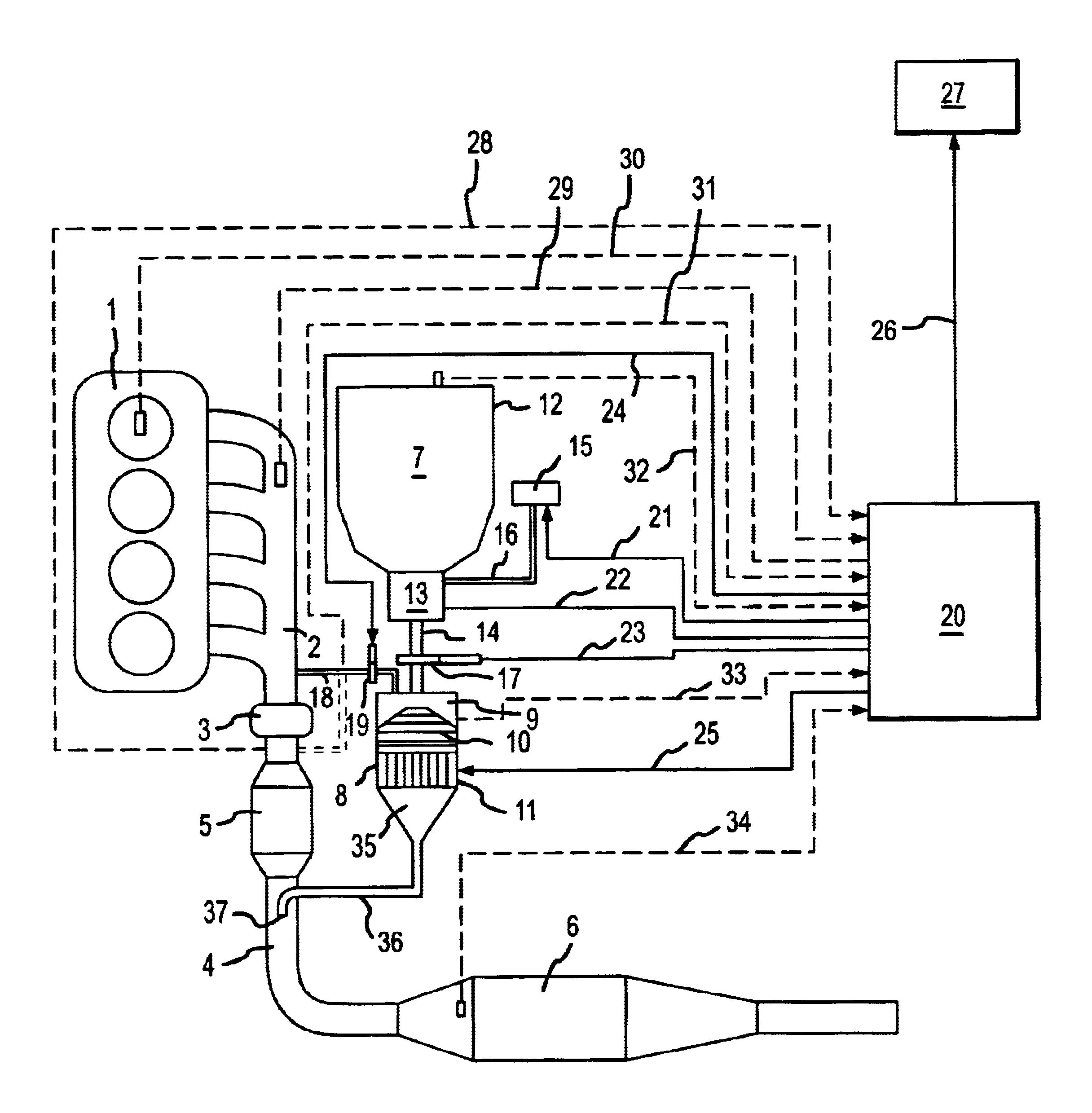
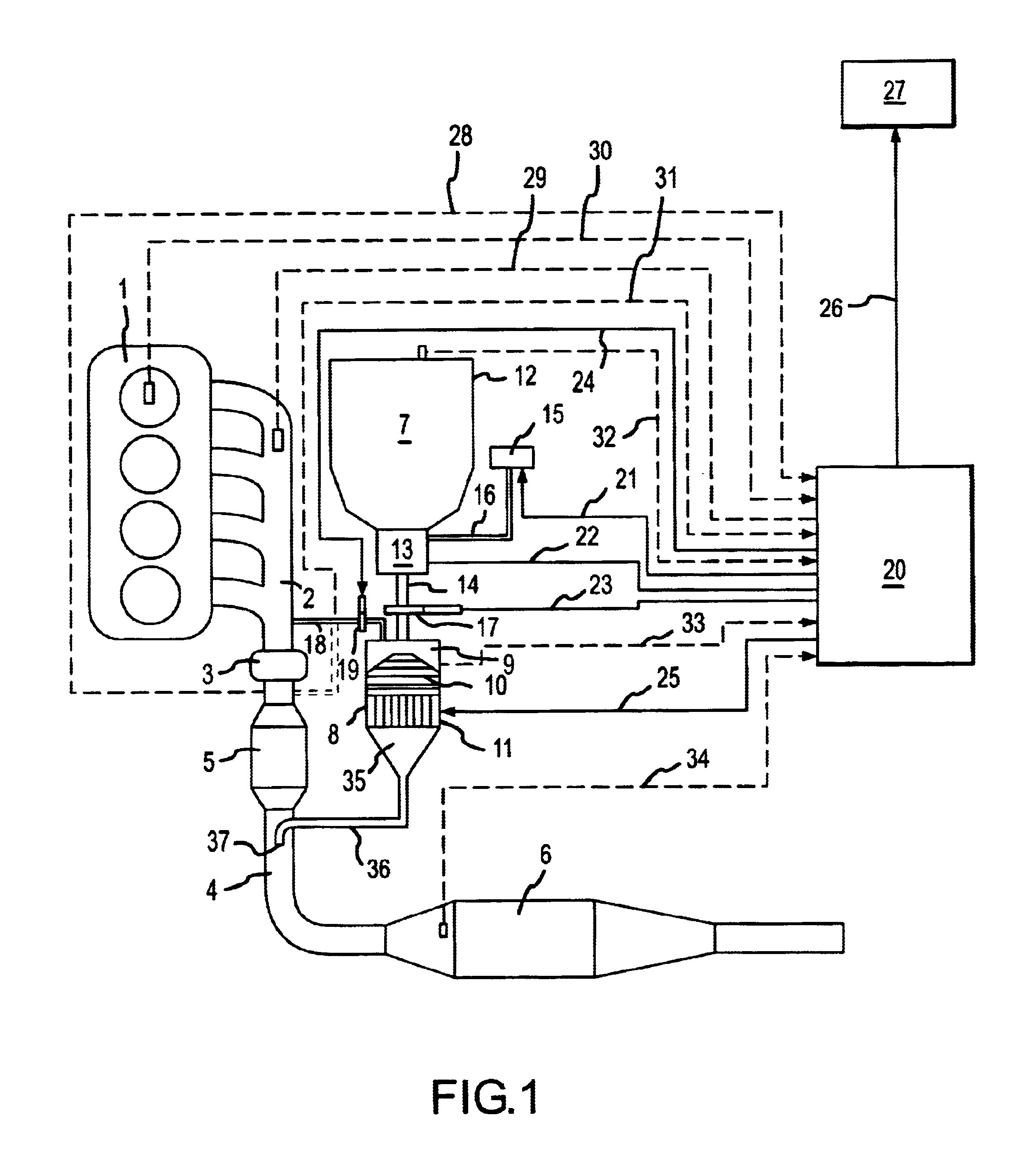
A method is provided for producing ammonia (NH3) and introducing the produced ammonia (NH3) into an exhaust gas stream as a reduction means for selectively catalytically reducing nitrogen oxides contained in the exhaust gas stream, which is an exhaust stream generated by the combustion process of a motor, a gas turbine, or a burner. The method comprises feeding dry urea from a supply container in a controlled amount to reactor and subjecting the dry urea in the reactor to a sufficiently rapid thermal treatment such that a gas mixture comprising the reaction products of ammonia (NH3) and isocyanic acid (HCNO) is created. Also, the method comprises immediately catalytically treating the thus produced gas mixture in the presence of water such that the isocyanic acid (HCNO) resulting from the rapid thermal treatment is converted, via quantitative hydrolysis treatment, into ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Owner:MAN NUTZFAHRZEUGE AG
Method and apparatus for purification of hydride gas streams
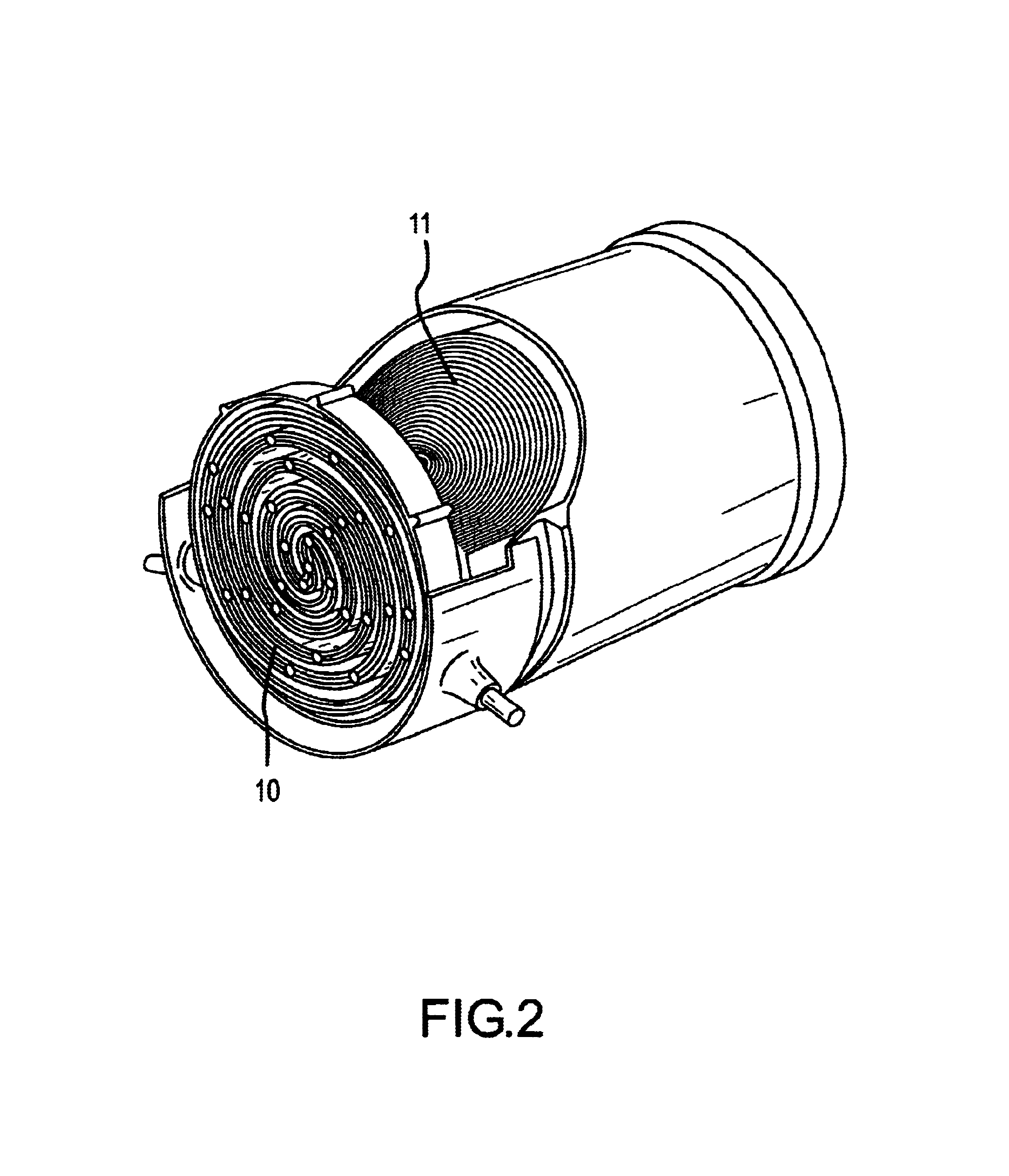
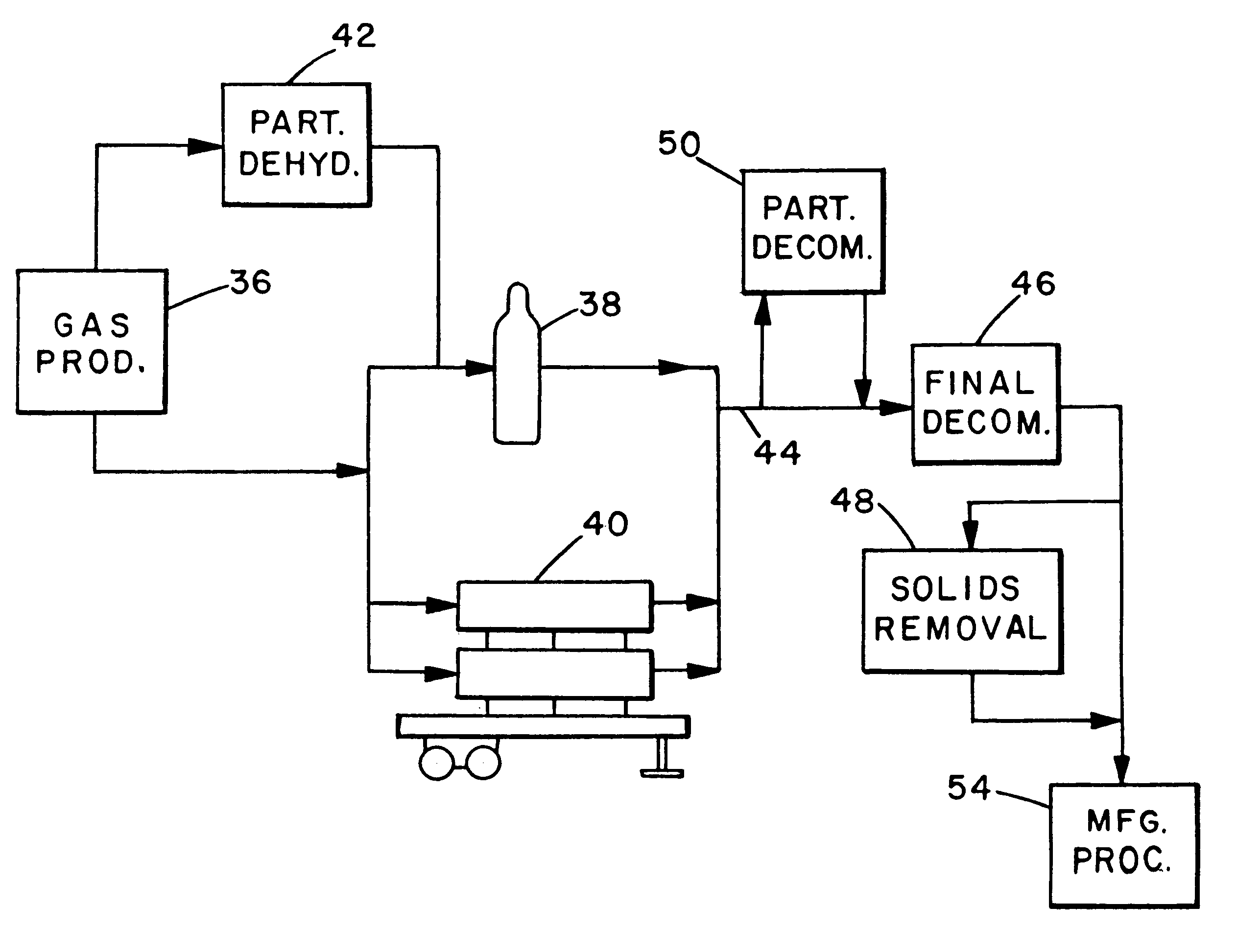
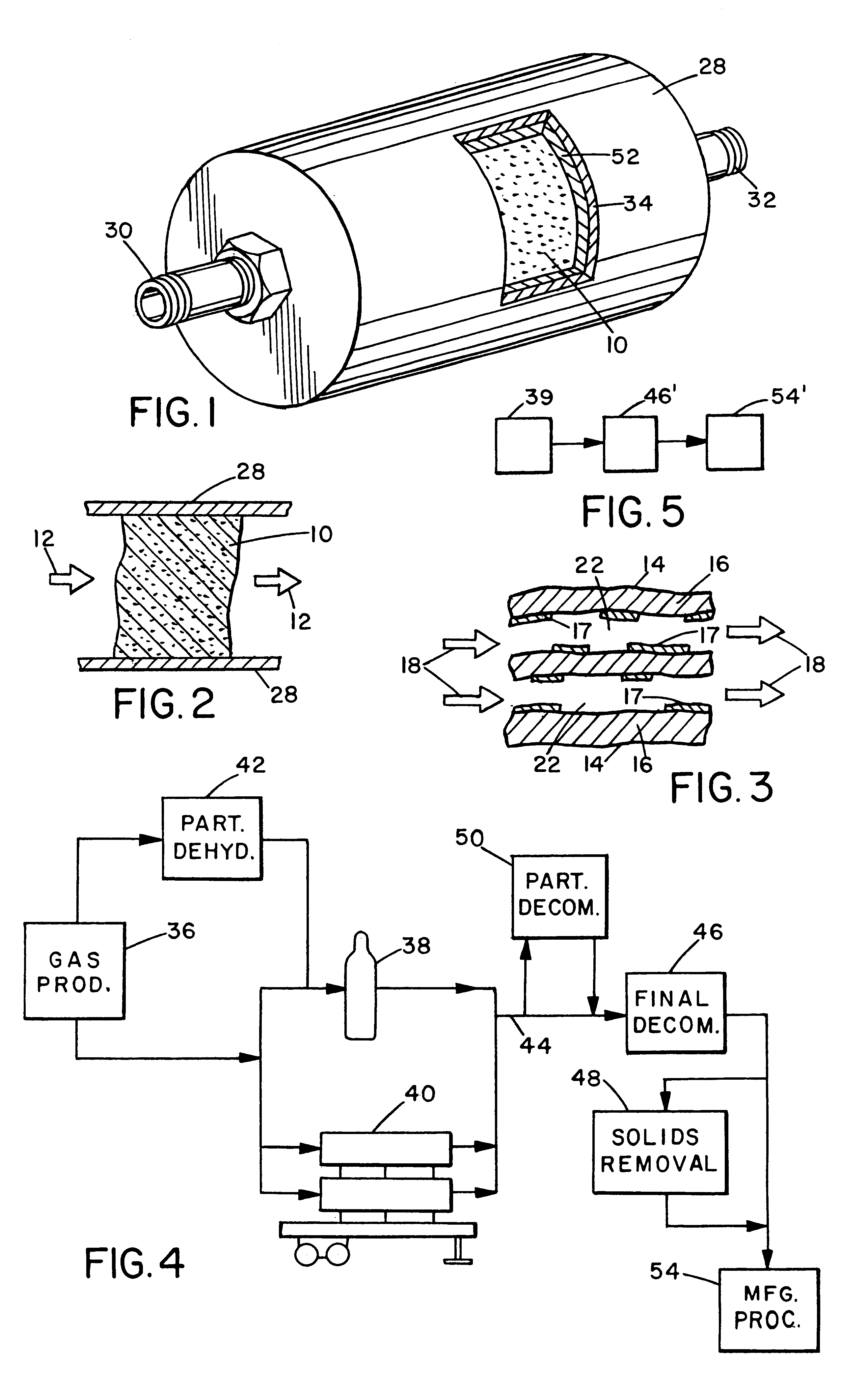
A process and apparatus for the decontamination of gaseous contaminants (especially oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor) from hydride gases (including their lower alkyl analogs) down to <=100 ppb contaminant concentration are described. The critical component is a high surface area metal oxide substrate with reduced metal active sites, which in various physical forms is capable of decontaminating such gases to <=100 ppb, <=50 ppb or <=10 ppb level without being detrimentally affected by the hydride gases. The surface area of the substrate will be >=100 m2 / g, and preferably 200-800 m2 / g. Oxides of various metals, especially manganese or molybdenum, can be used, and mixtures of integrated oxides, or one type of oxide coated on another, may be used. The substrate is preferably retained in a hydride-gas-resistant container which is installed in a gas supply line, such as to a gas- or vapor-deposition manufacturing unit. The invention provides final decontamination for hydride gas streams intended for gas- or vapor-deposition formation of high purity LED, laser (especially blue laser), electronic, optical or similar products, and can be used in combination with upstream preliminary decontamination process and / or upstream or downstream solid particulate removal units.
Owner:SAES PURE GAS
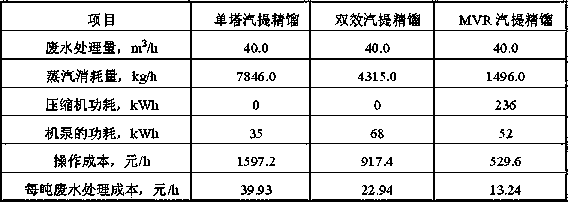
MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) vapor-stripping deamination system and application method thereof
InactiveCN103408086AIncrease pressureIncrease temperatureWater/sewage treatment by degassingAmmonia preparation/separationAxial-flow pumpWater discharge
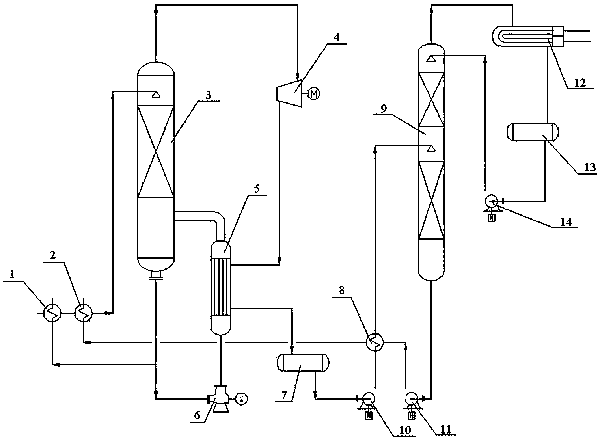
The invention relates to an MVR vapor-stripping deamination system. The MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) vapor-stripping deamination system comprises a vapor-stripping deamination tower, an ammonia water rectification tower and a condenser, wherein a high-ammonia-nitrogen sewage input pipe, a vapor input pipe I, a post-deamination waste water discharge port and an ammonia-containing vapor discharge port I are arranged on the vapor-stripping deamination tower; the vapor-stripping deamination tower is connected with a reboiler; the high-ammonia-nitrogen sewage input pipe is connected with waste water feed preheaters (II and I); the post-deamination waste water discharge port is connected with the waste water feed preheater I and an axial flow pump respectively; the ammonia-containing vapor discharge port I is connected with the reboiler through a mechanical vapor compressor; the reboiler is connected with a dilute ammonia water storage tank connected with the ammonia water rectification tower; a discharge port, an ammonia-containing vapor discharge port II and a vapor input pipe are arranged on the ammonia water rectification tower; the discharge port is connected with a rectification tower kettle discharge pump and the waste water feed preheater II; the ammonia-containing vapor discharge port II is connected with the condenser; a strong ammonia water discharge port is connected with a strong ammonia water storage tank connected with the ammonia water rectification tower. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses an application method of the MVR vapor-stripping deamination system. The MVR vapor-stripping deamination system has the advantages of less investment, high feasibility and high comprehensive utilization ration.
Owner:TIANHUA INST OF CHEM MACHINERY & AUTOMATION
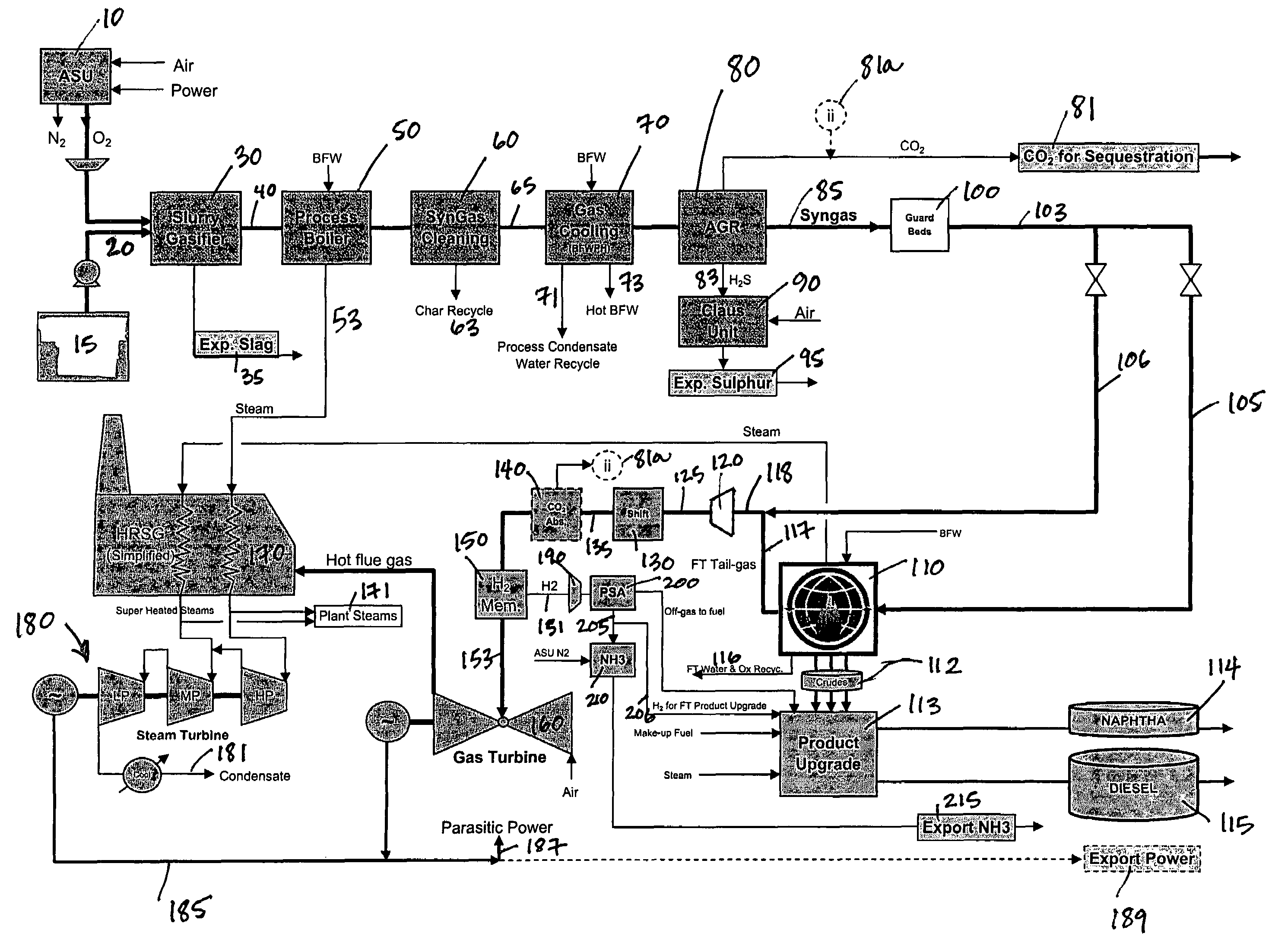
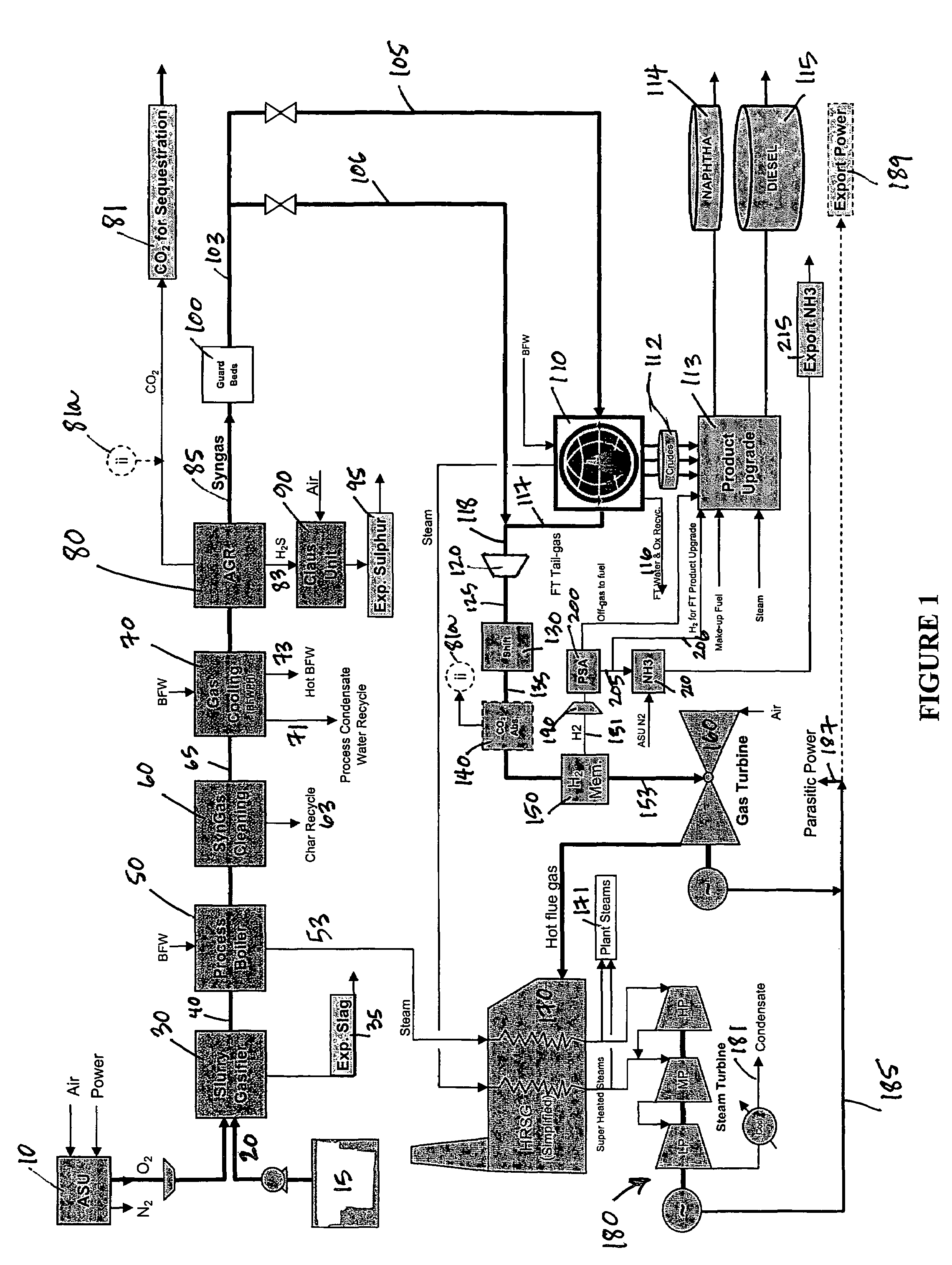
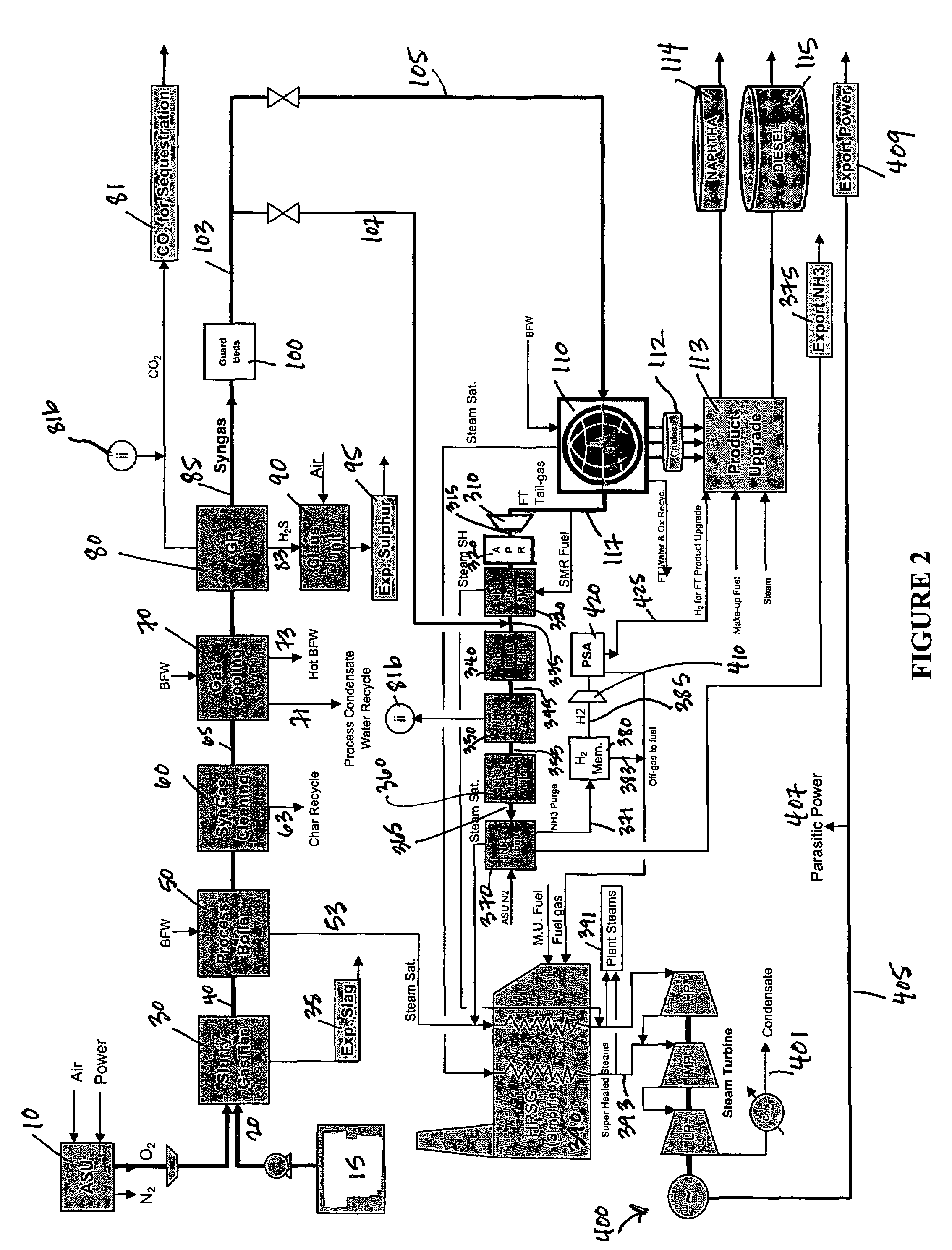
Process for the production of ammonia and Fischer-Tropsch liquids
InactiveUS7300642B1Combustible gas catalytic treatmentLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionAmmoniaElectric power
Owner:RES USA LLC
Combined plant
InactiveUS20120100062A1Obviates problemLower average energyNitrogen purification/separationHydrogen productionNitrogenNitrogen gas
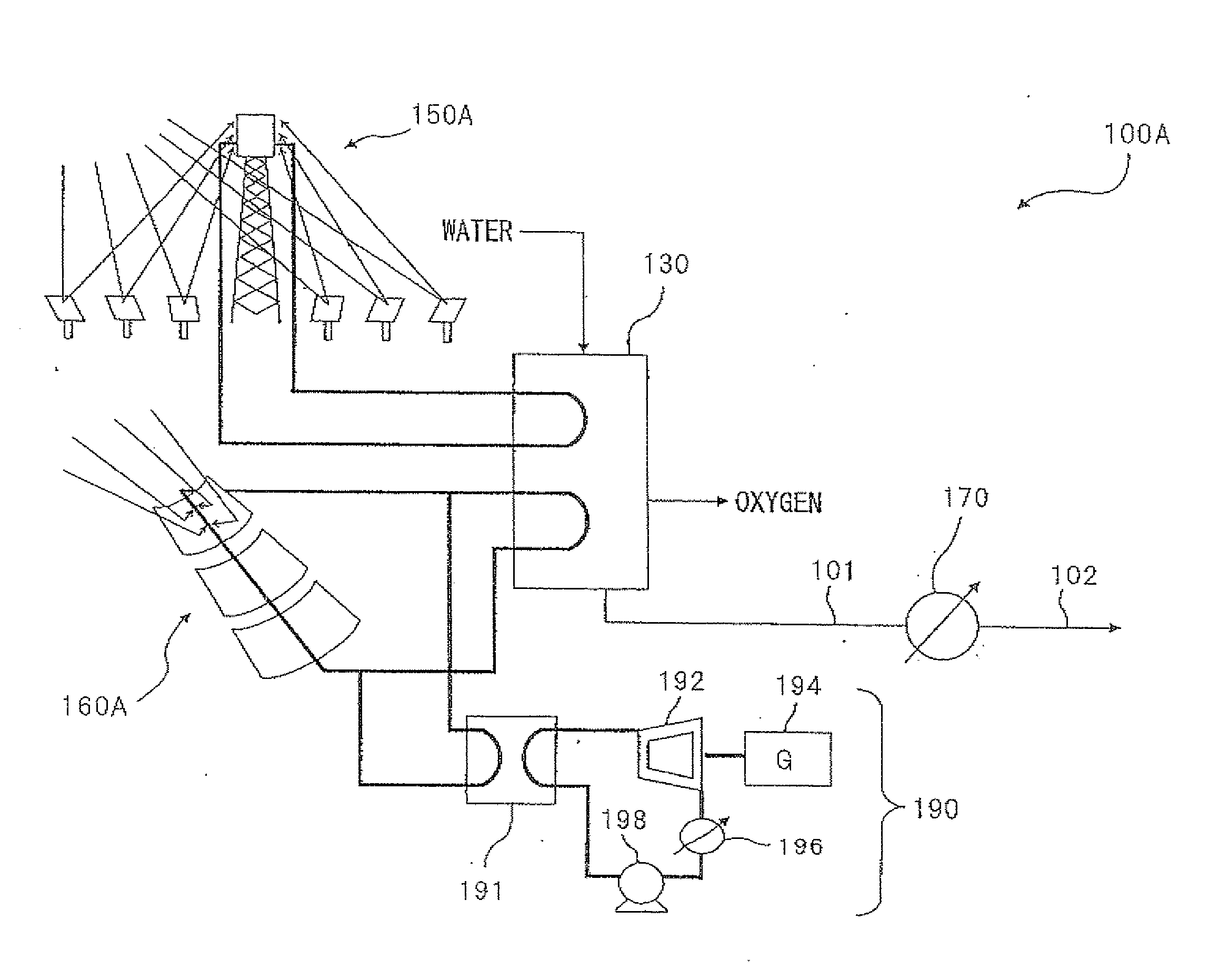
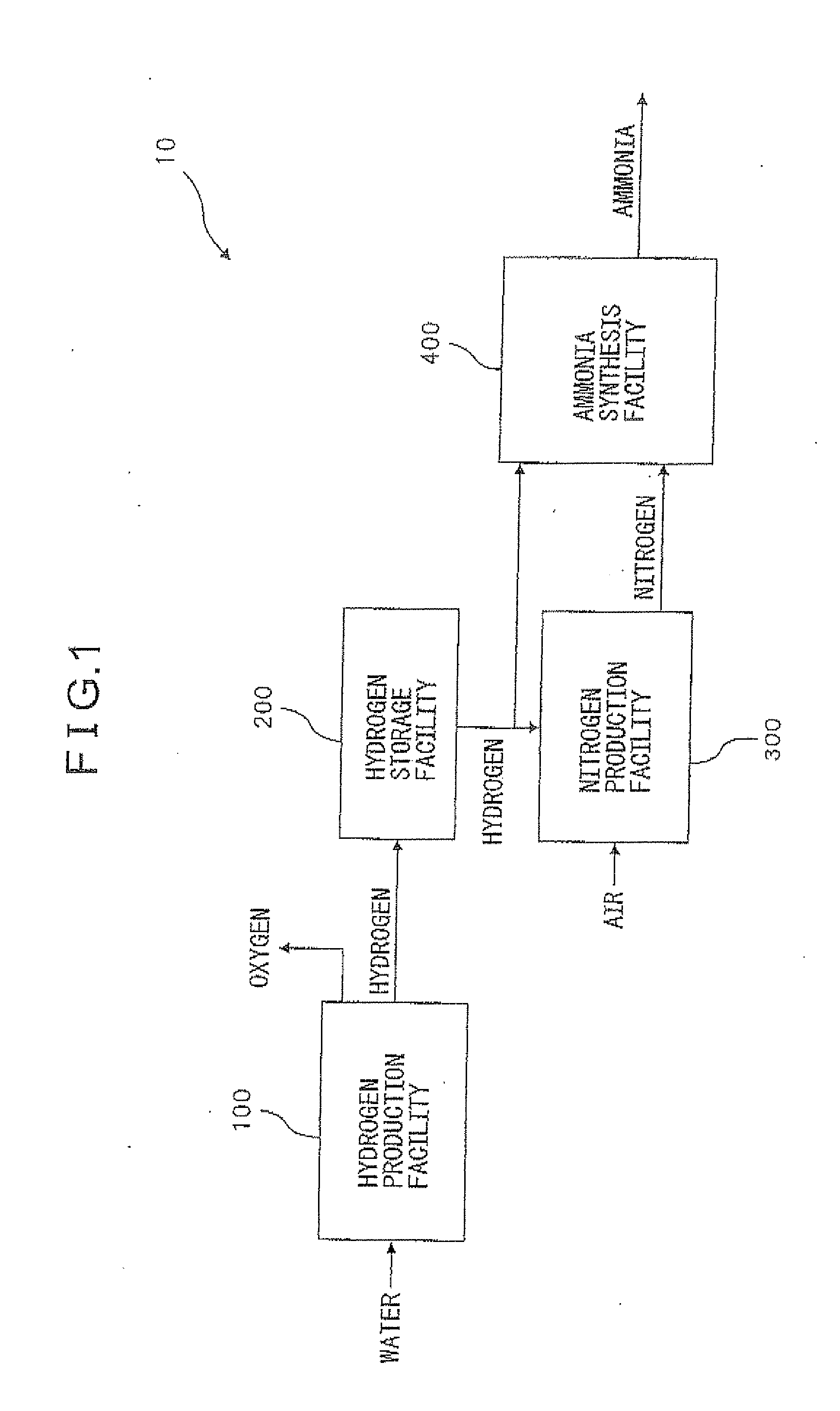
A combined plant is provided. The combined plant of continuously supplying hydrogen and nitrogen to an ammonia synthesis facility that continuously synthesizes ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen, the combined plant including: a hydrogen production facility for acquiring solar energy and producing hydrogen by utilizing a part of the acquired solar energy; a nitrogen production facility for producing nitrogen from air and supplying the nitrogen to the ammonia synthesis facility; and a hydrogen storage facility for storing the hydrogen produced by the hydrogen production facility and supplying the produced hydrogen to the ammonia synthesis facility.
Owner:NAKAMURA NORIHIKO +6
Method of preparing ceramic powders using chelate precursors
InactiveUS20070148065A1Oxide/hydroxide preparationStacked capacitorsBarium titanateAmmonium hydroxide
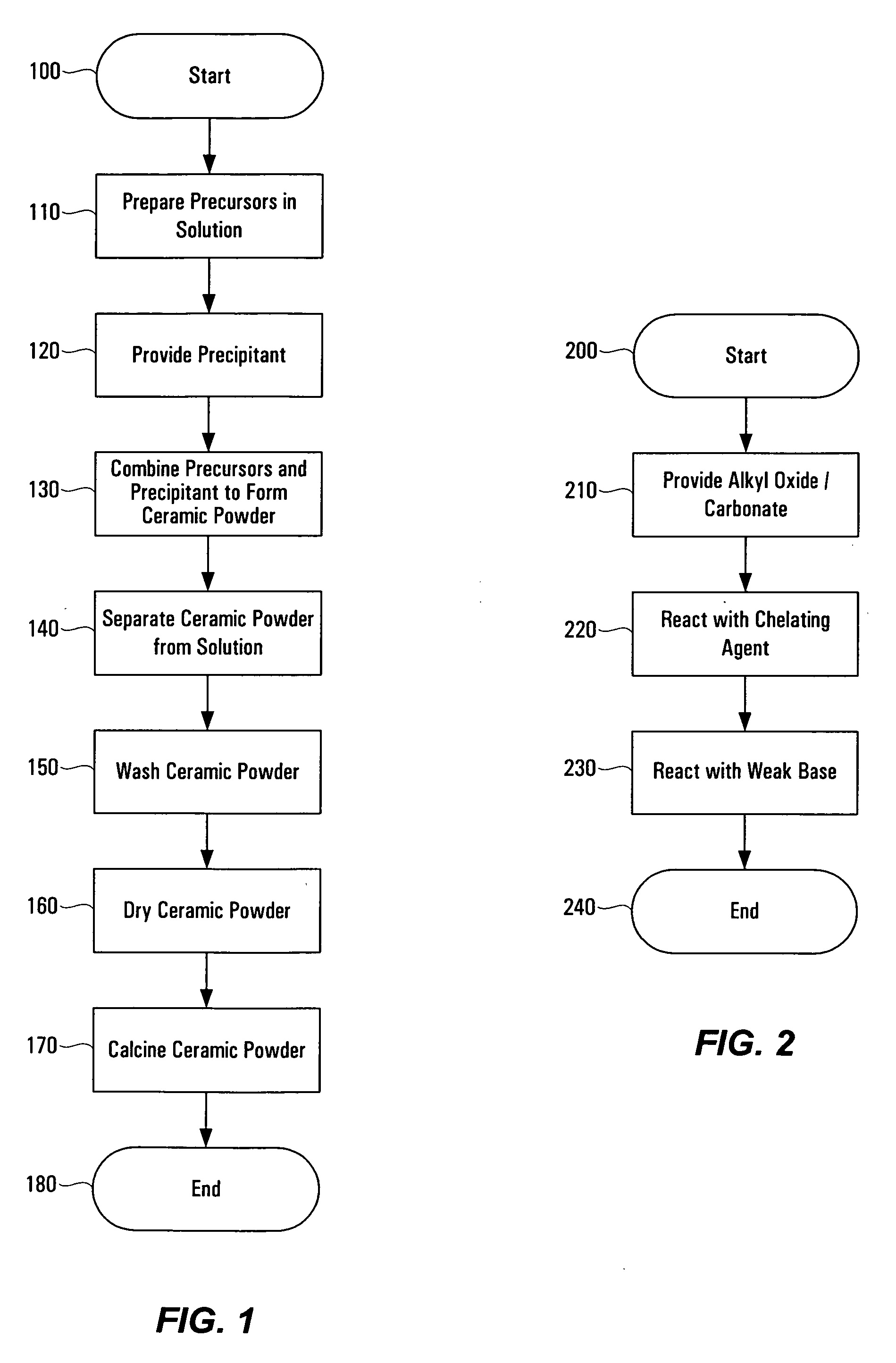
Wet-chemical methods involving the use of water-soluble hydrolytically stable metal-ion chelate precursors and the use of a nonmetal-ion-containing strong base can be used in a coprecipitation procedure for the preparation of ceramic powders. Examples of the precipitants used include tetraalkylammonium hydroxides. A composition-modified barium titanate is one of the ceramic powders that can be produced. Certain metal-ion chelates can be prepared from 2-hydroxypropanoic acid and ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:EESTOR
Urea based composition and system for same
InactiveUS20030219371A1Safe handlingLow degreeGas turbine plantsFused electrolyte fuel cellsNitrogenNitrogen gas
A method and apparatus for generating energy from a composition comprising urea and water are described. The method in one embodiment includes: (a) reacting the urea with water to form ammonia; and (b) oxidizing the ammonia formed in step (a) to form water and nitrogen generating energy. The apparatus in one embodiment contains: (a) a first container for providing the composition; (b) a second container for reacting the urea with water to form ammonia, wherein the second container is connected to the first container by means for delivering the composition from the first container to the second container; (c) a third container for providing ammonia, wherein the third container is connected to the second container by means for delivering ammonia from the third container to the second container; and (d) a fourth container for oxidizing ammonia to form water and nitrogen generating energy, wherein the fourth container is connected to the second container by means for delivering ammonia from the second container to the fourth container. The method and apparatus are used to generate energy for use in stationary and mobile applications.
Owner:AMENDOLA STEVEN C
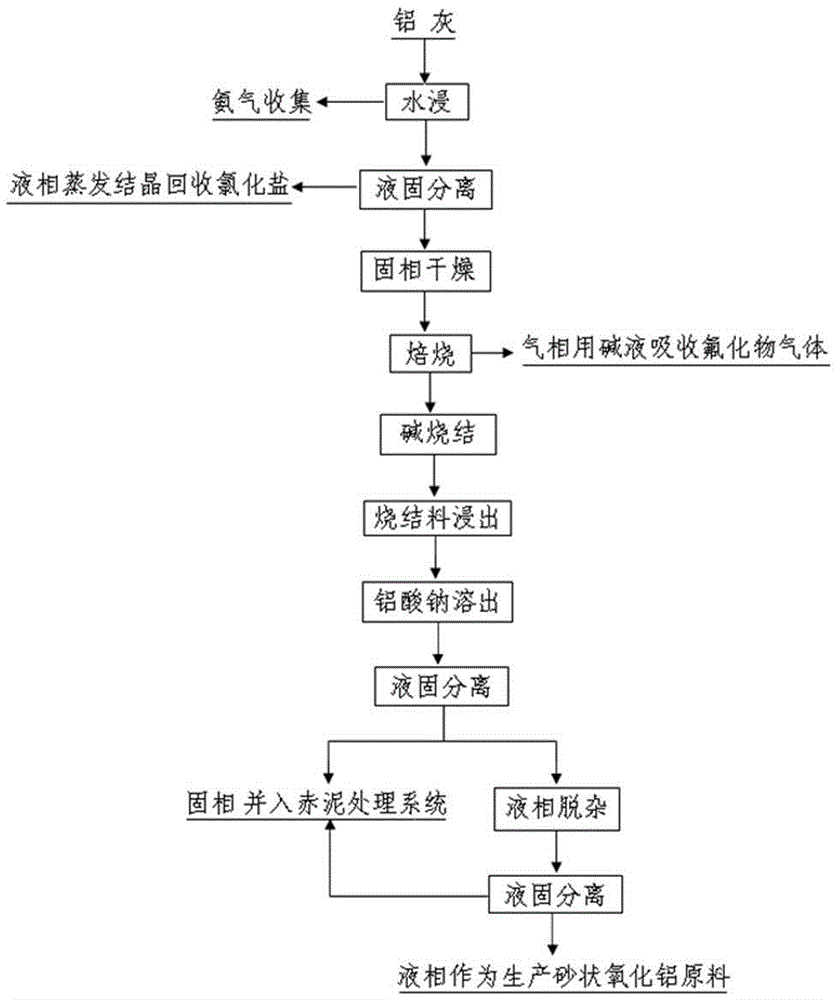
Comprehensive utilization method of aluminum ash
ActiveCN105347361AHarmlessAvoid pollutionAmmonium salt preparationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationAtmospheric dustAluminum industry
The invention belongs to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of waste resources from the aluminum industry and specifically discloses a comprehensive utilization method of aluminum ash. According to the comprehensive utilization method of aluminum ash, metallic aluminium is extracted from aluminum ash through an ore grinding method; the aluminum ash obtained after aluminium extraction undergoes catalytic deamination; the aluminum ash obtained after deamination is mixed with alkali and granulation forming is then carried out; and the granulation product is sintered and the sintered product is finally dissolved out. By the above method, useful components in the aluminum ash can be recovered to the maximum; ammonia gas which has been ignored for a long time is effectively recovered; components such as aluminium oxide, villiaumite and the like are recovered and utilized to the maximum; pollution of aluminum ash processing to the environment is avoided; atmospheric dust pollution is avoided; atmospheric pollution is also avoided due to ammonia gas recovery; pollution of aluminum ash stacking to underground water and soil is avoided due to extraction and recovery of fluoride salt; and environmental safety during the treating process is guaranteed.
Owner:湖南绿脉环保科技股份有限公司
Ammonia recovery process
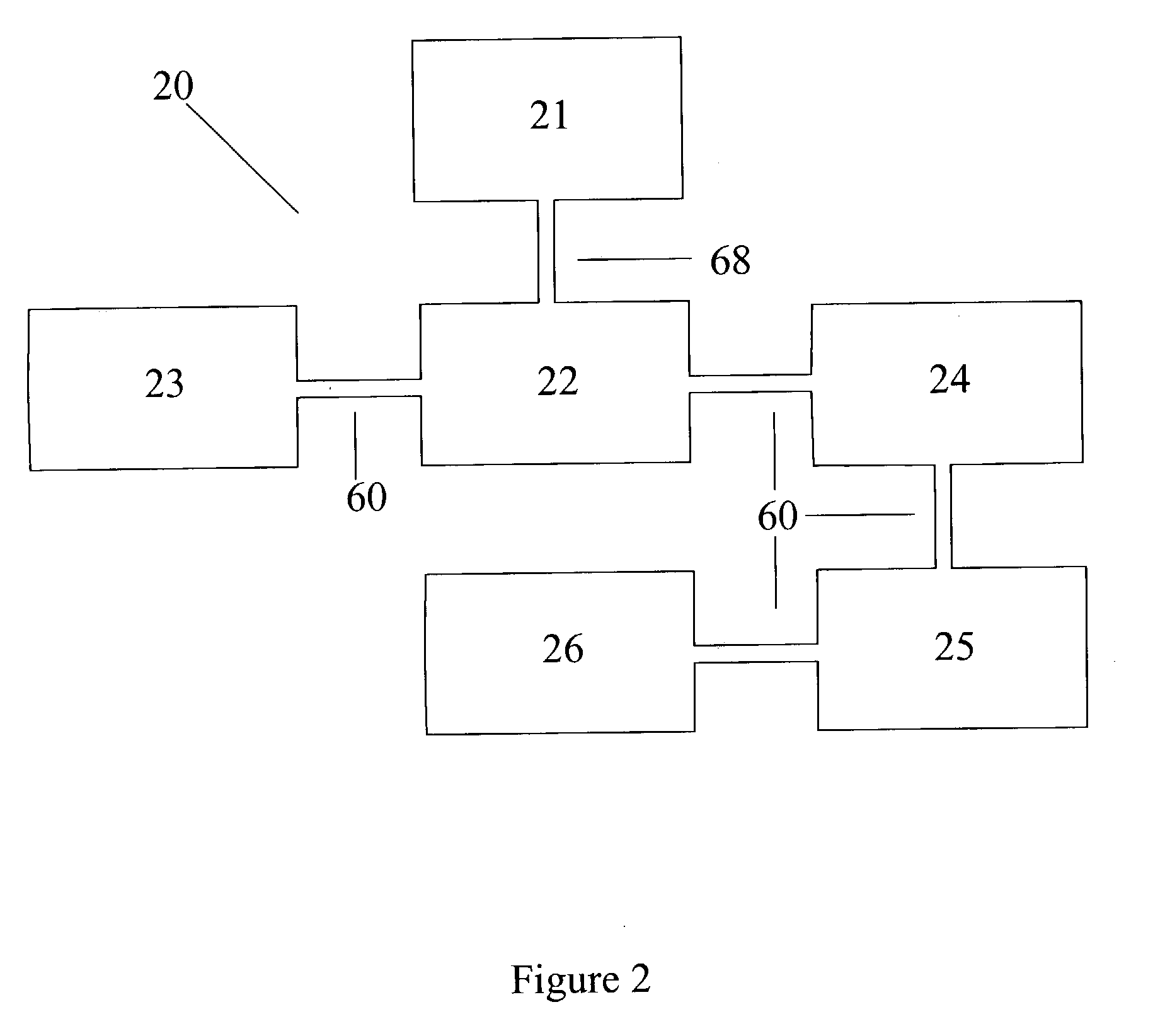
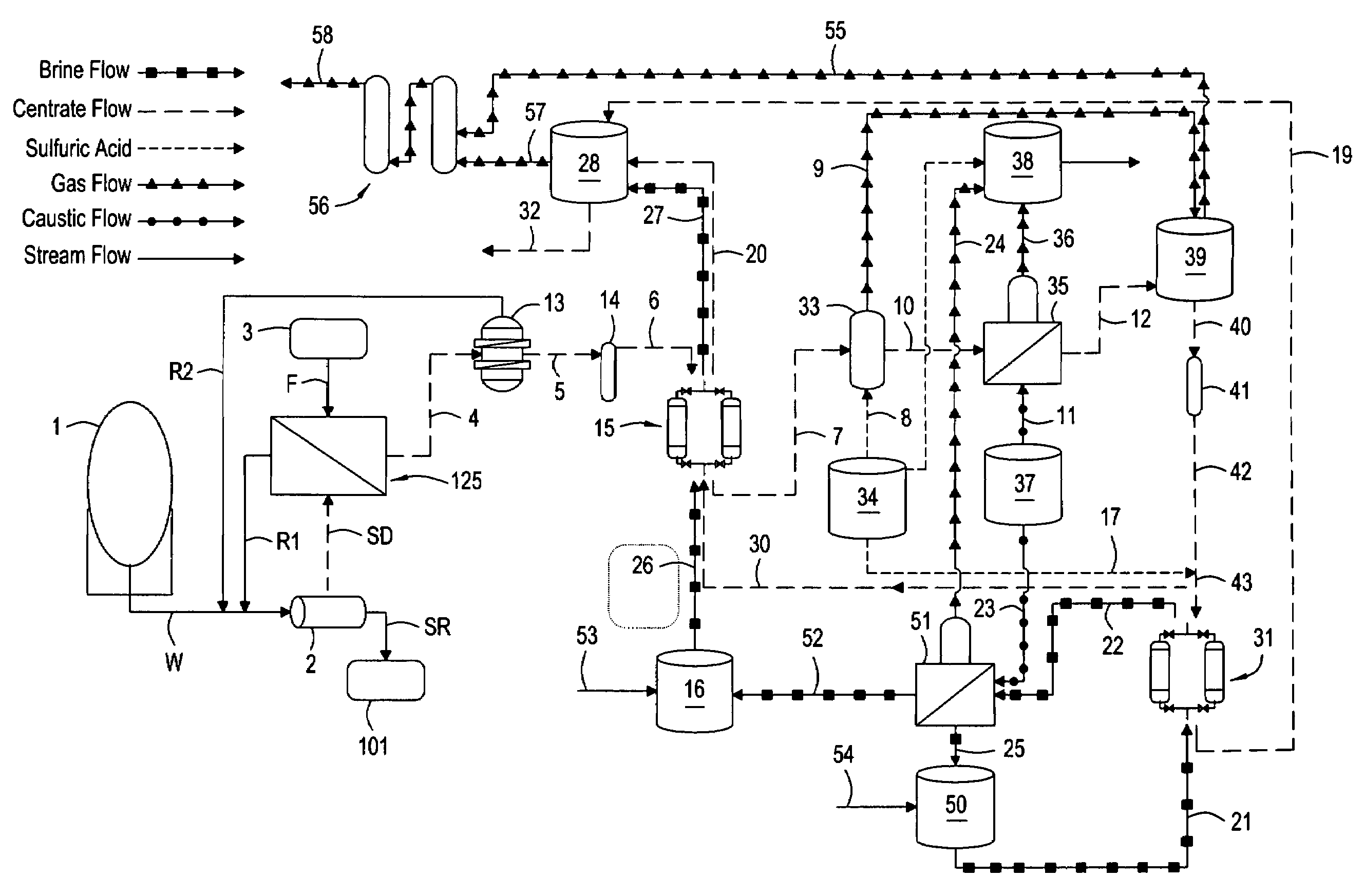
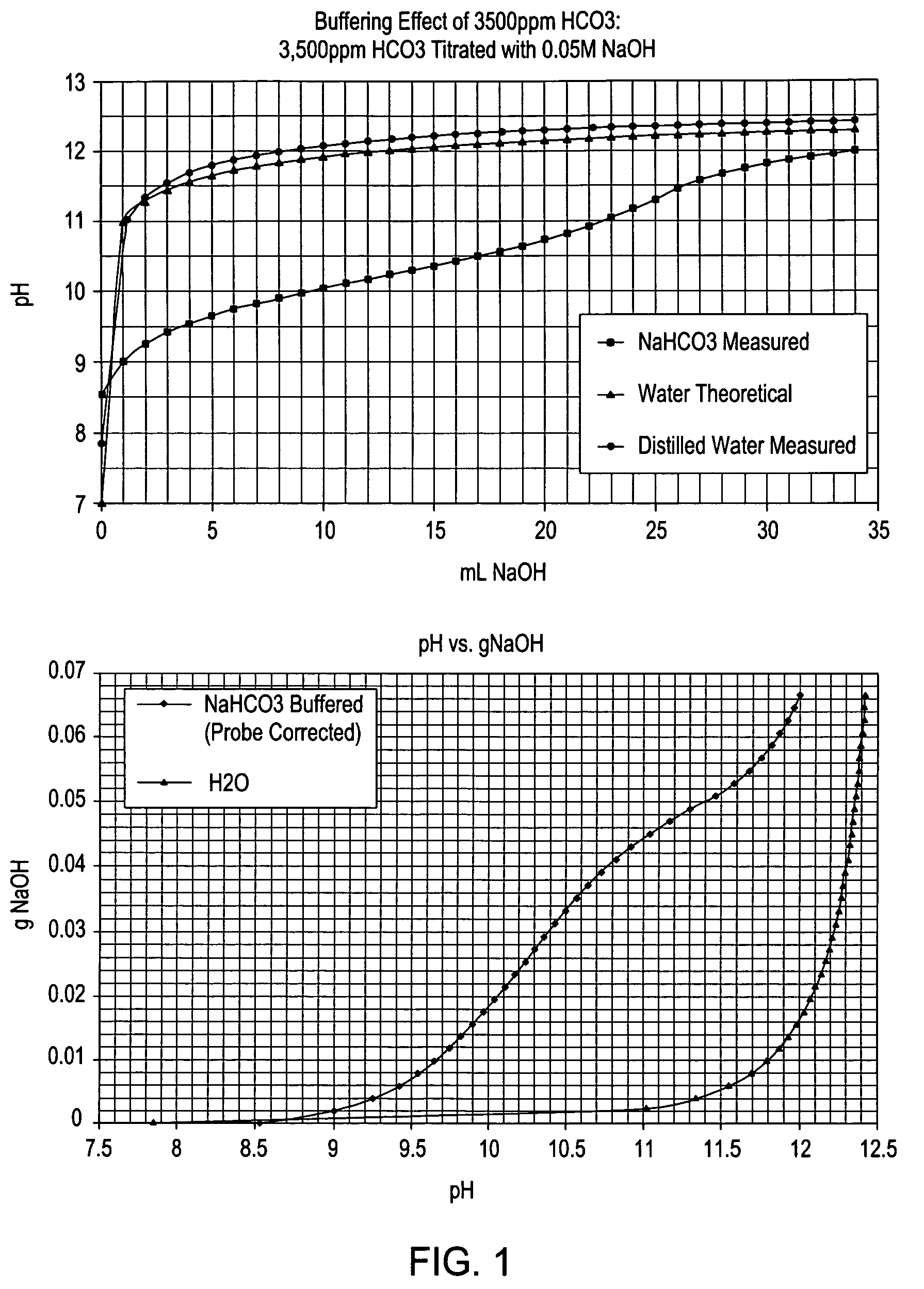
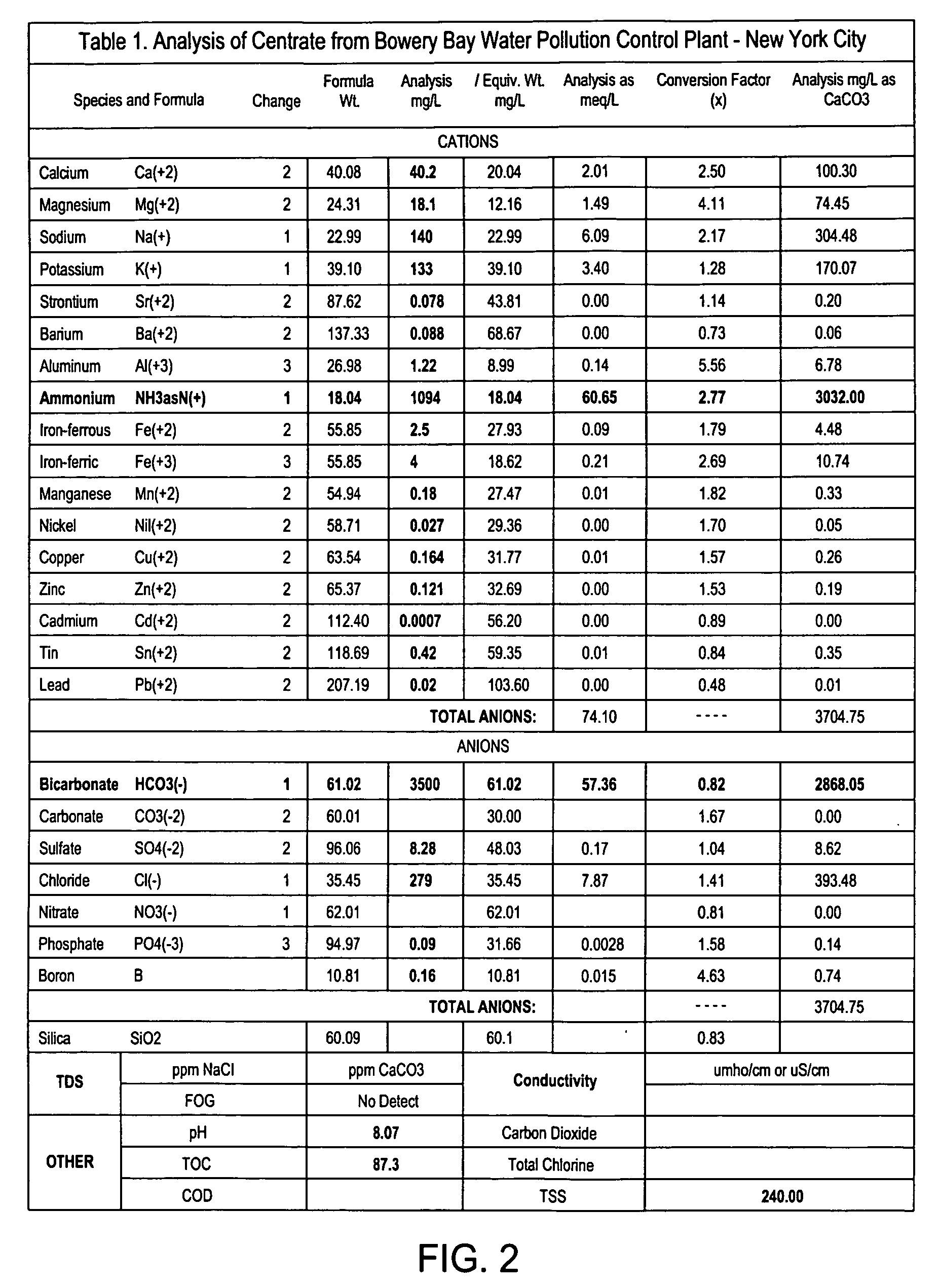
InactiveUS20080053909A1Effective and efficient ammonia recovery processEfficient and effective processIon-exchanger regenerationSolid sorbent liquid separationWaste streamAmmonia
Embodiments include a method and apparatus for cost-effective and efficient ammonia recovery from a waste stream. In some embodiments, ammonia is recovered after bicarbonate buffer removal from the waste stream via addition of an acid.
Owner:FASSBENDER ALEXANDER G
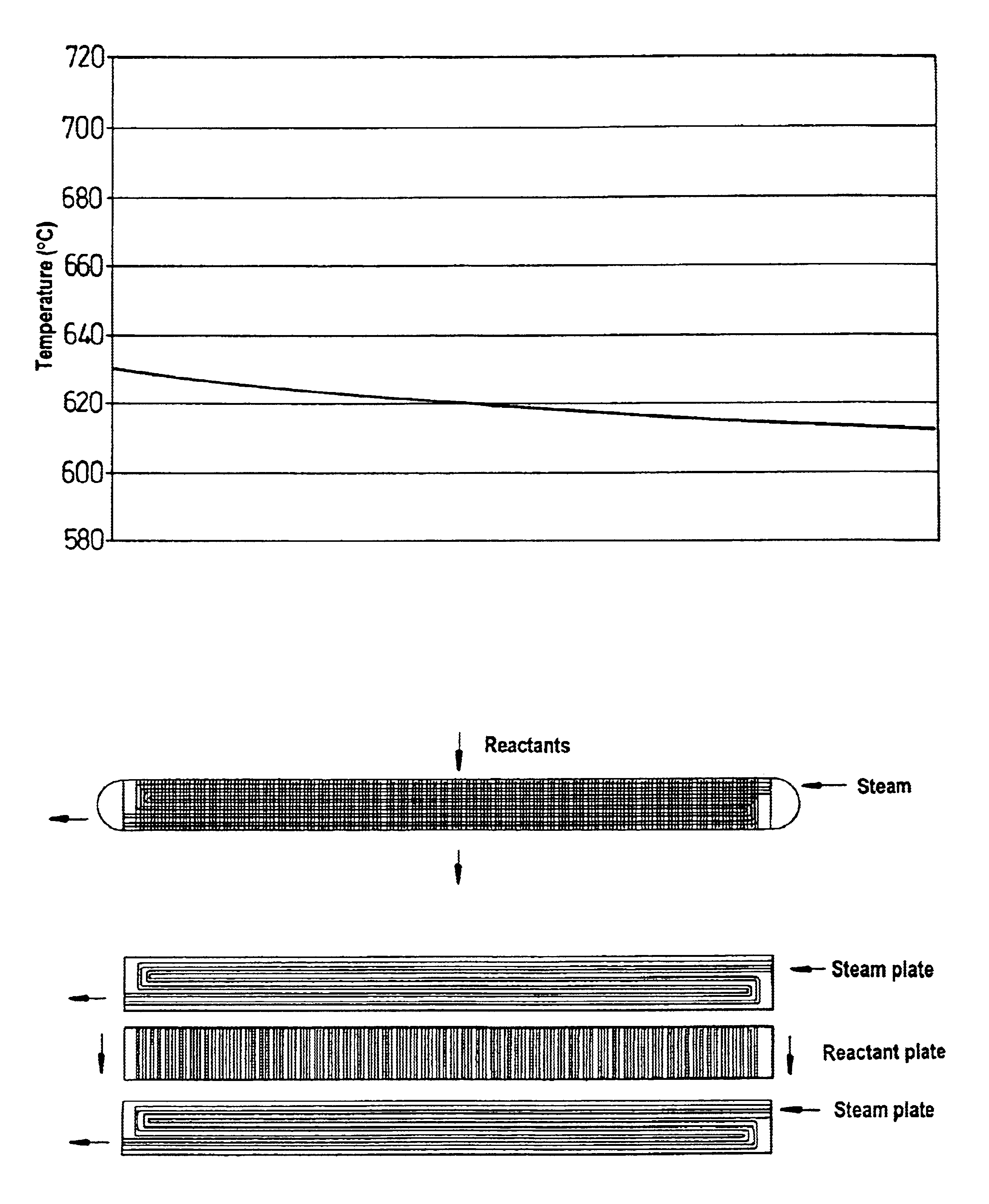
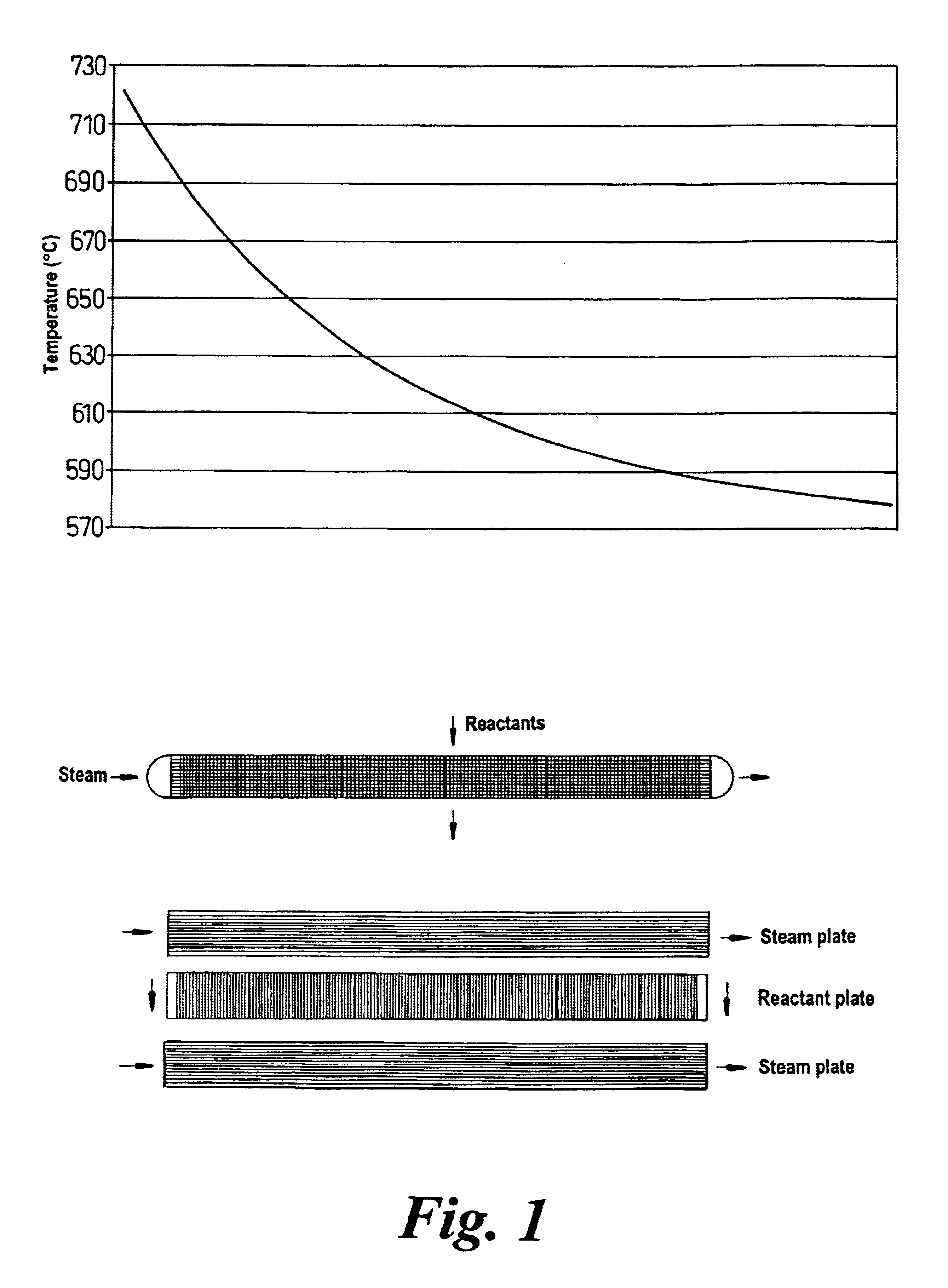
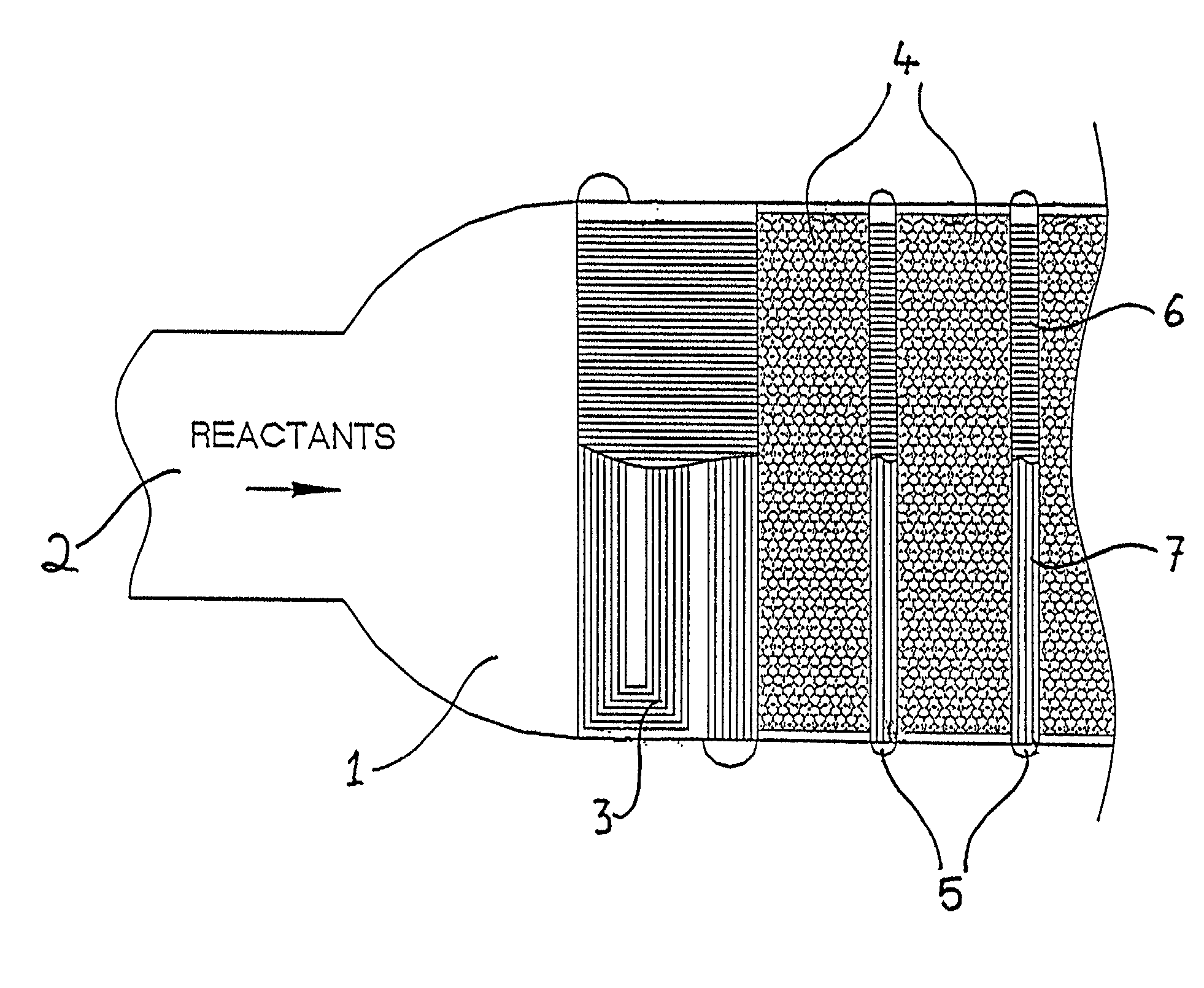
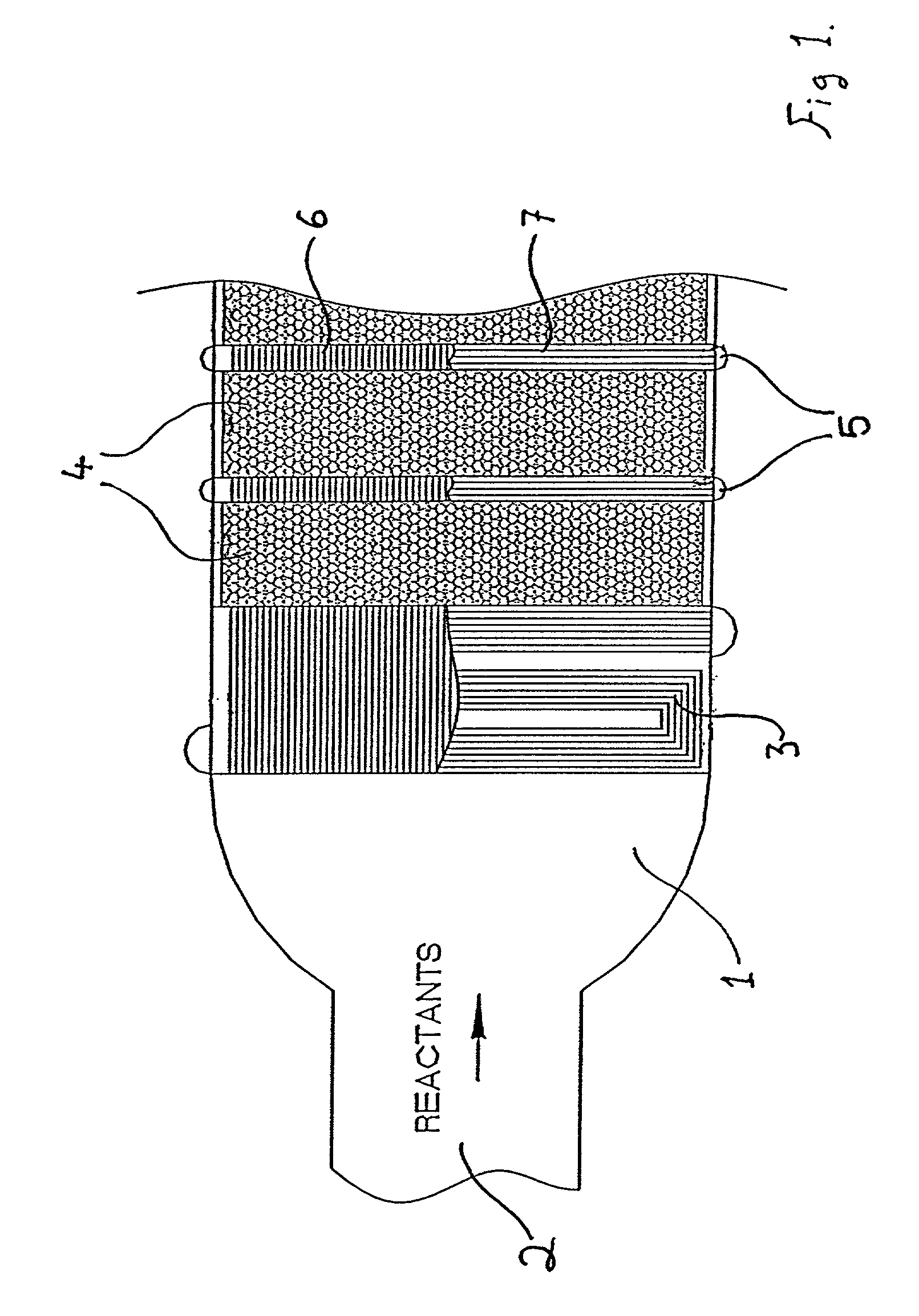
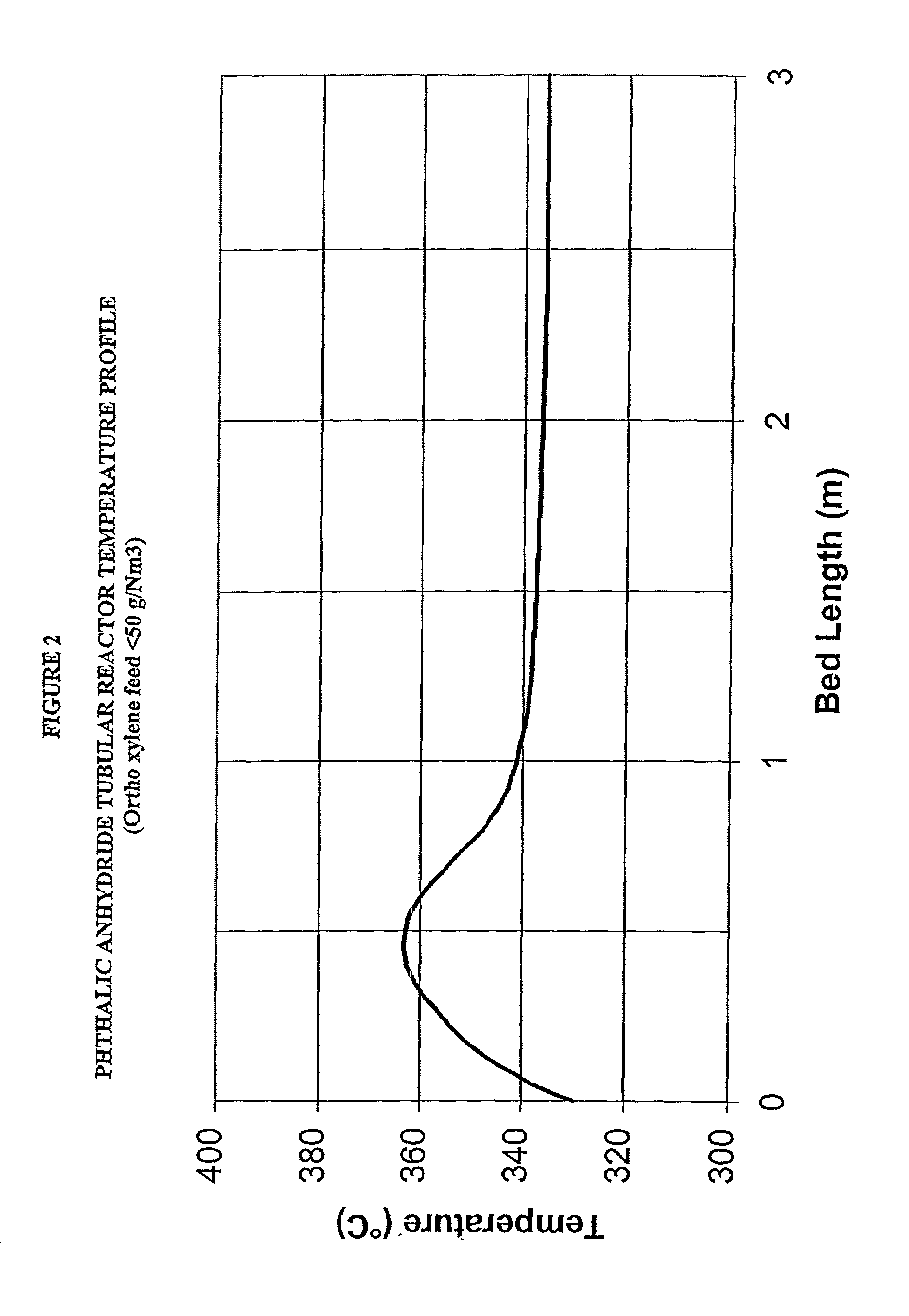
Chemical reactor
InactiveUS6921518B2Significant changeAvoid mixingLiquid surface applicatorsVapor condensationChemical reactorProcess engineering
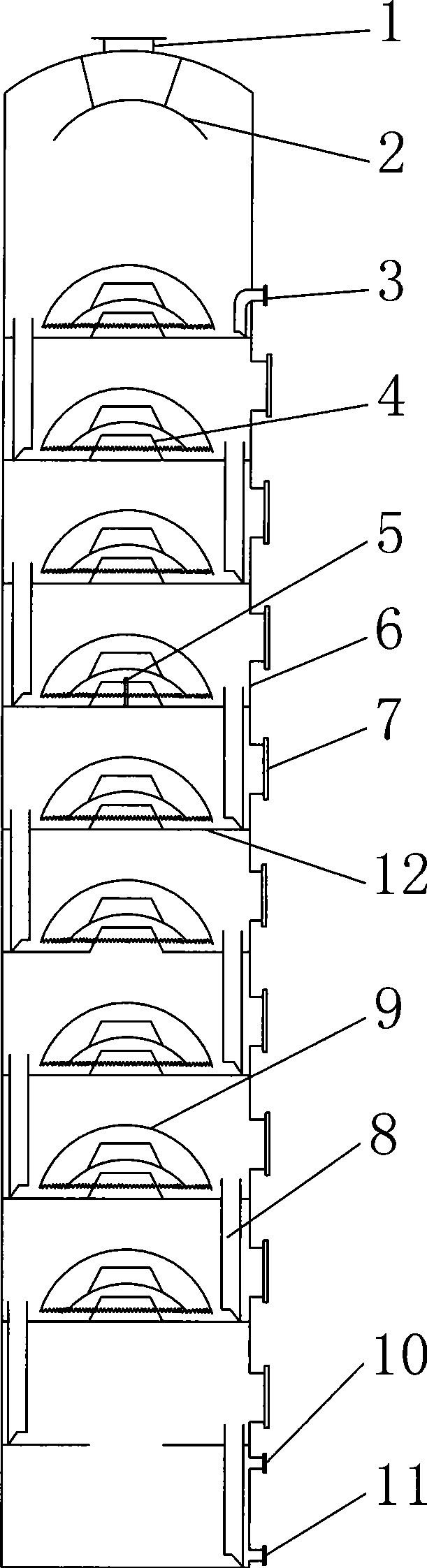
A reactor of the staged adiabatic reactor type, comprises at least one heat exchanger panel, preferably a printed circuit heat exchange (PCHE) panel, interposes between adiabatic beds of catalyst, wherein the facial area of the panels and the superficial facial area of the corresponding catalyst are substantially similar, and the panels include means defining discrete passages for handling of reactants and heat transfer media, wherein the means defining passages for heat transfer media provide for at least two differing flow path directions for the heat transfer media through the heat exchanger panel whereby the occurrence of temperature bias or differentials is reduced.
Owner:MEGGIT (UK) LTD
Method for harmless disposal and recycling of aluminum ash
ActiveCN105271327ATo achieve the purpose of comprehensive recycling of resourcesGreat social valueAmmonia preparation/separationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesMetallic aluminumSodium aluminate
The invention discloses a method for harmless disposal and recycling of aluminum ash. The method comprises steps of raw material water immersion nitrogen and chlorine removal, calcination fluorine removal, alkali fusion sintering, sintering material dissolving-out and purifying impurity removal. Aluminum ash generated in metal aluminum smelting process is employed as a raw material, after metal aluminum is recycled through secondary processing, nitrides are removed through water immersion, fluorides are removed through calcinations, alkali fusion sintering is carried out, the sintering materials are dissolved out, impurities are removed through a sodium aluminate solution, the processed aluminum ash is employed as a raw material for producing sand-shaped aluminum oxide. Ammonia gas generated in the aluminum ash harmless disposal process can be employed as an ammonium production raw material, a chlorination liquid generated can be employed as a chlorate production raw material, and silicon fluoride gas generated in the calcination process is absorbed by an aqueous solution. The method is simple and practical, environmental protection benefits are high, the production efficiency is high, the device investment is low, and energy consumption is low. Harmless and recycling disposal of hazardous wastes can be achieved. The obtained product can be applied in practical production.
Owner:YUNNAN WENSHAN ALUMINUM
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water
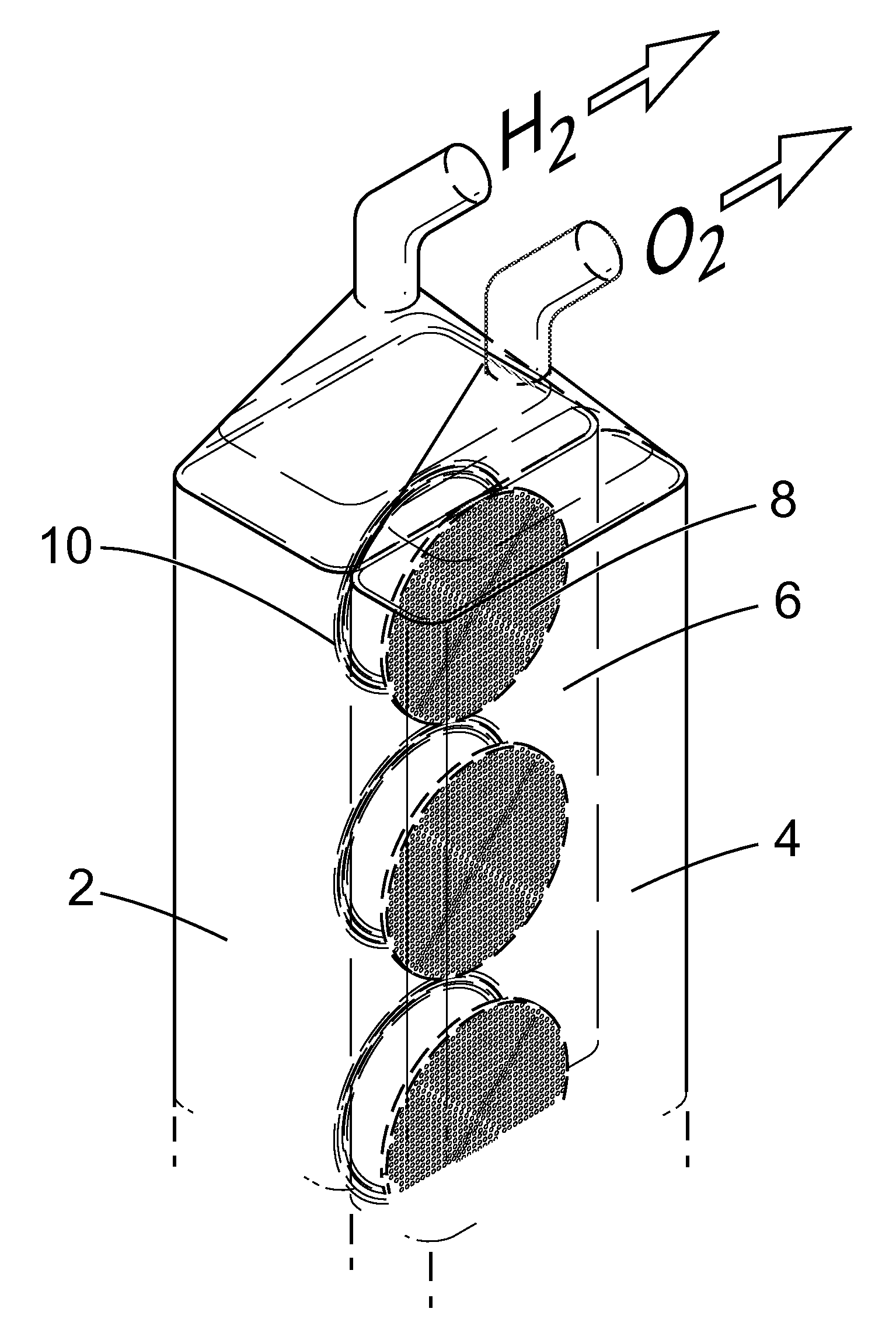
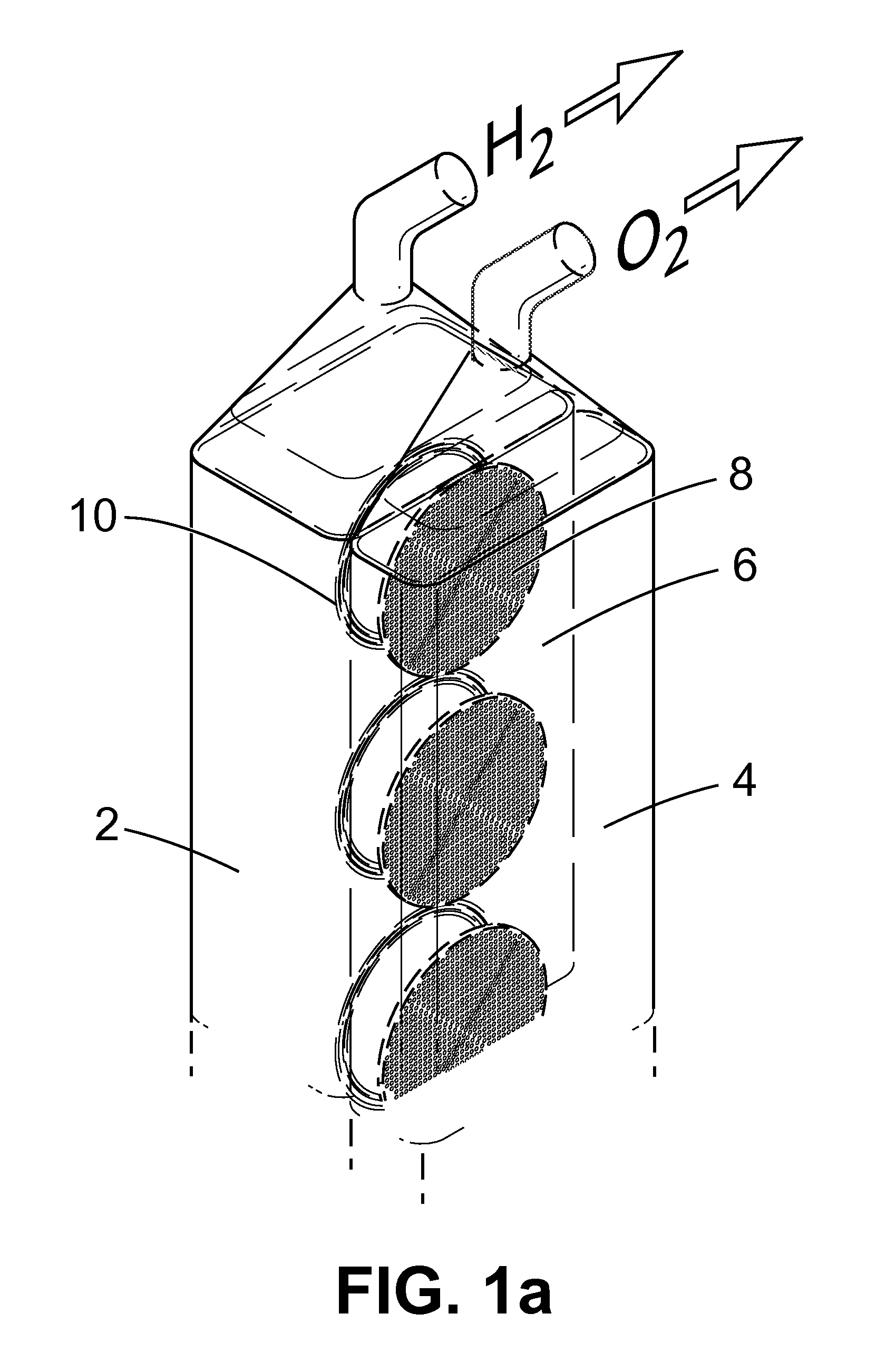
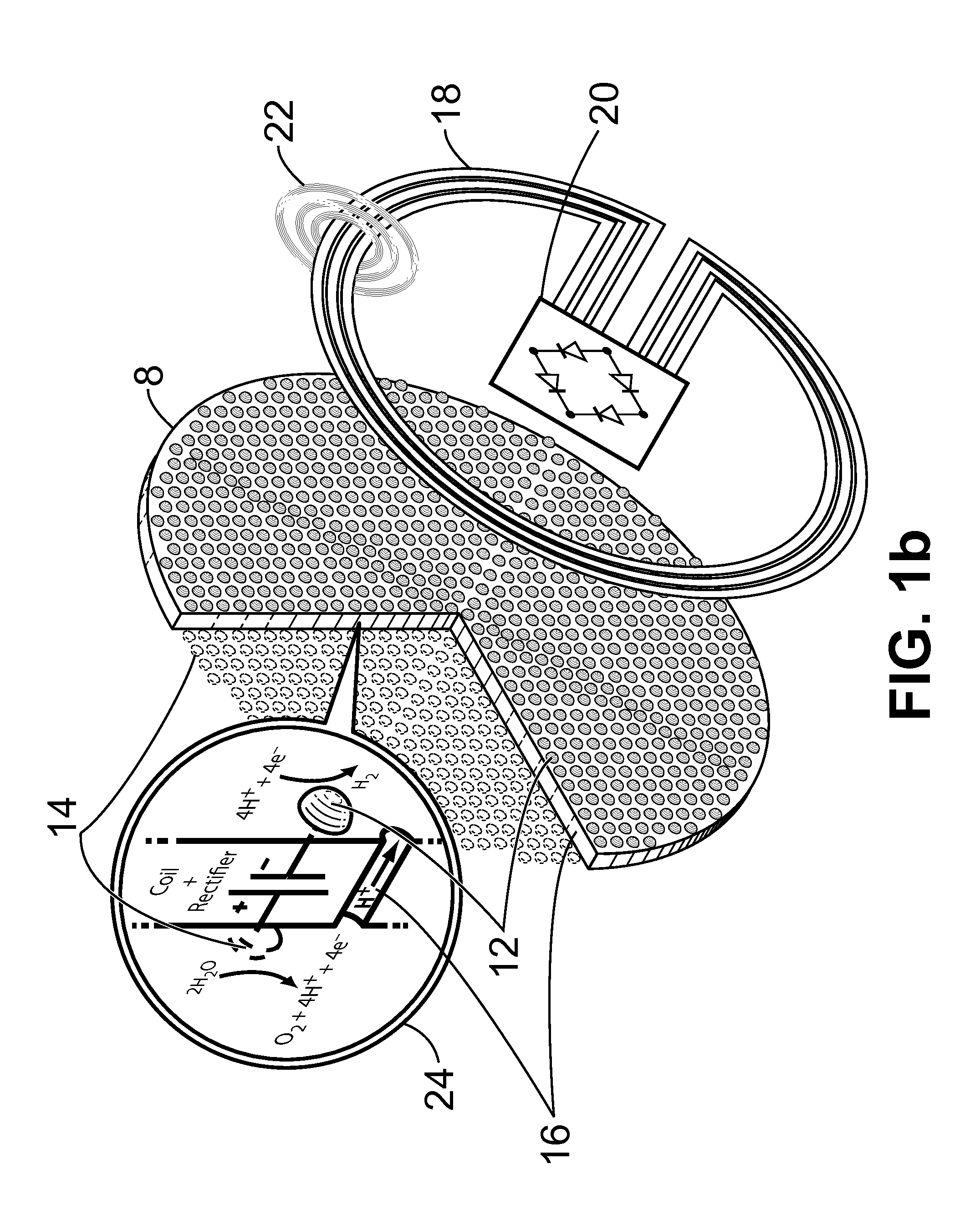
InactiveUS20120149789A1Reduce the amount requiredMaintain efficient productionPhotography auxillary processesHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrogenElectrolysed water
An apparatus for the electrolytic splitting of water into hydrogen and / or oxygen, the apparatus comprising: (i) at least one lithographically-patternable substrate having a surface; (ii) a plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes embedded in said surface; (iii) at least one counter electrode in proximity to but not on said surface; (iv) means for collecting evolved hydrogen and / or oxygen gas; (v) electrical powering means for applying a voltage across said plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes and said at least one counter electrode; and (vi) a container for holding an aqueous electrolyte and housing said plurality of microscaled catalytic electrodes and said at least one counter electrode. Electrolytic processes using the above electrolytic apparatus or functional mimics thereof are also described.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Catalyst supports, supported catalysts and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6159892AHigh internal void volumeImprove blockageMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFluid phaseOrganic chemistry
A supported catalyst comprising a carbon fibril aggregate and a catalytically effective amount of a catalyst supported therein, a process for performing a catalytic reaction in fluid phase using the supported catalyst and a process for making the supported catalyst are disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Catalyst for ammonia synthesis and ammonia decomposition
ActiveCN103977828AGood effectOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionMain group elementDecomposition
The invention relates to a catalyst for ammonia synthesis and ammonia decomposition, and contains nitrogen compounds of main group elements and correlative carriers and additives. As a novel catalytic material, the catalyst provided by the invention shows good catalytic activity in ammonia synthesis and ammonia decomposition reactions.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
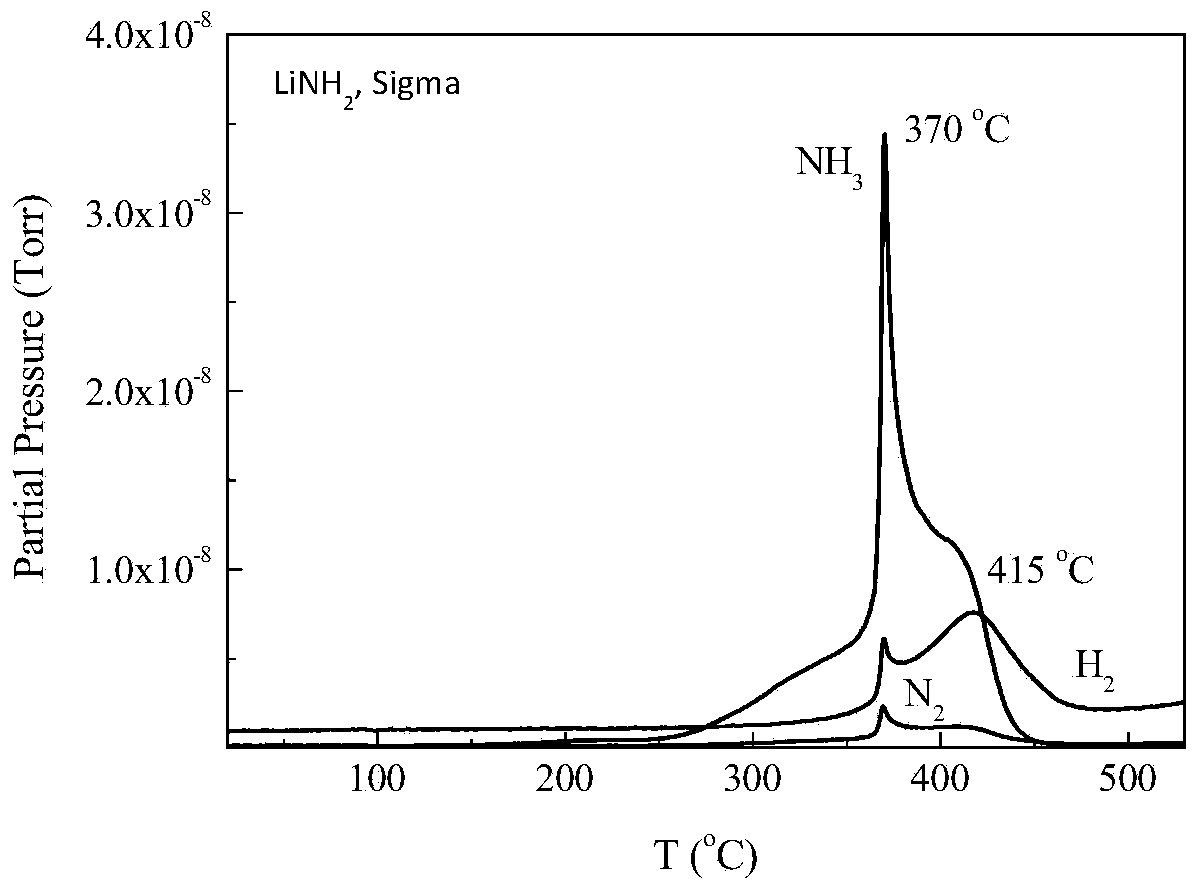
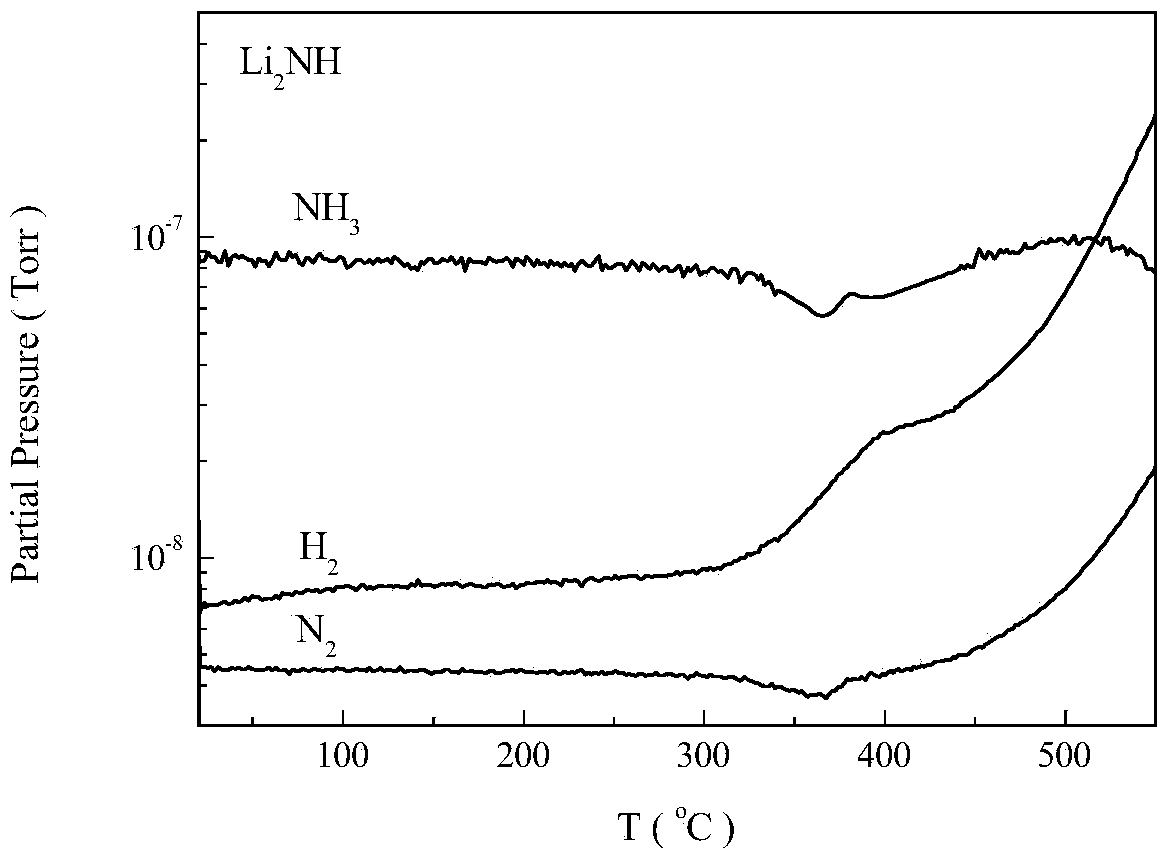
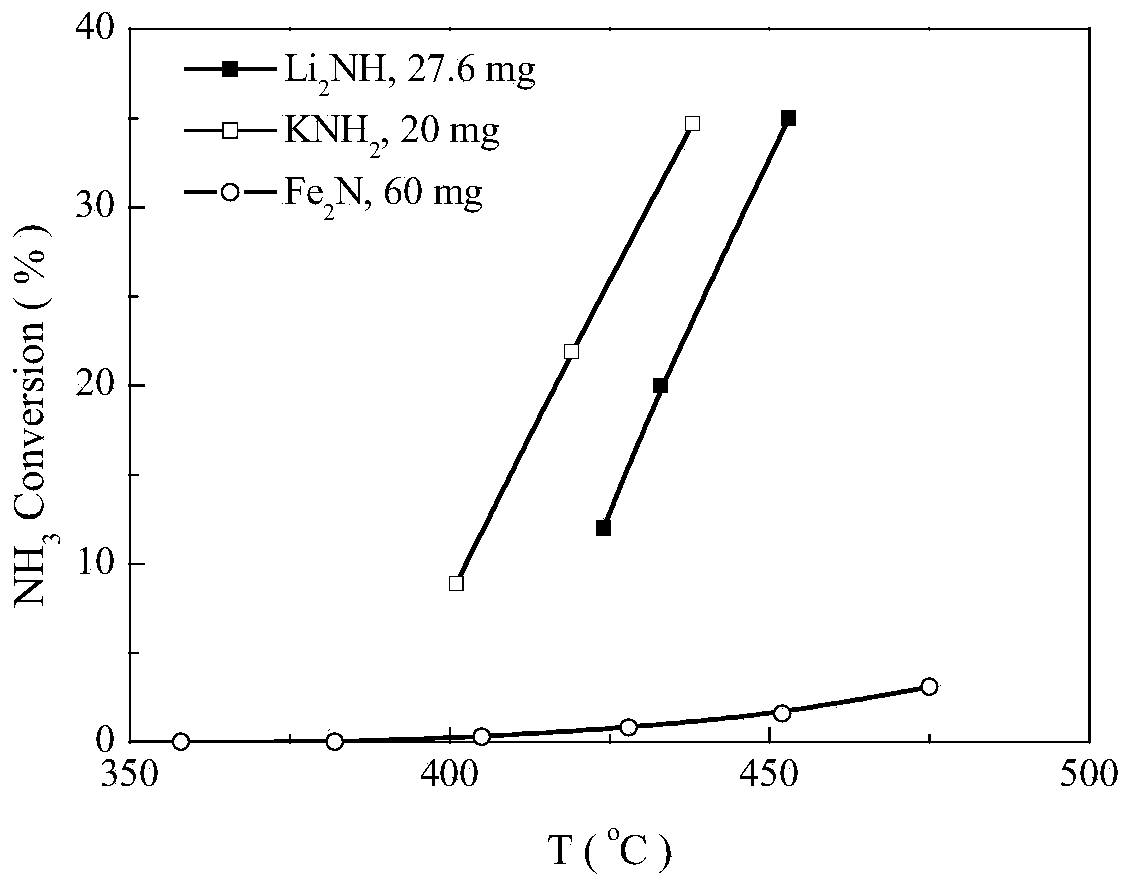
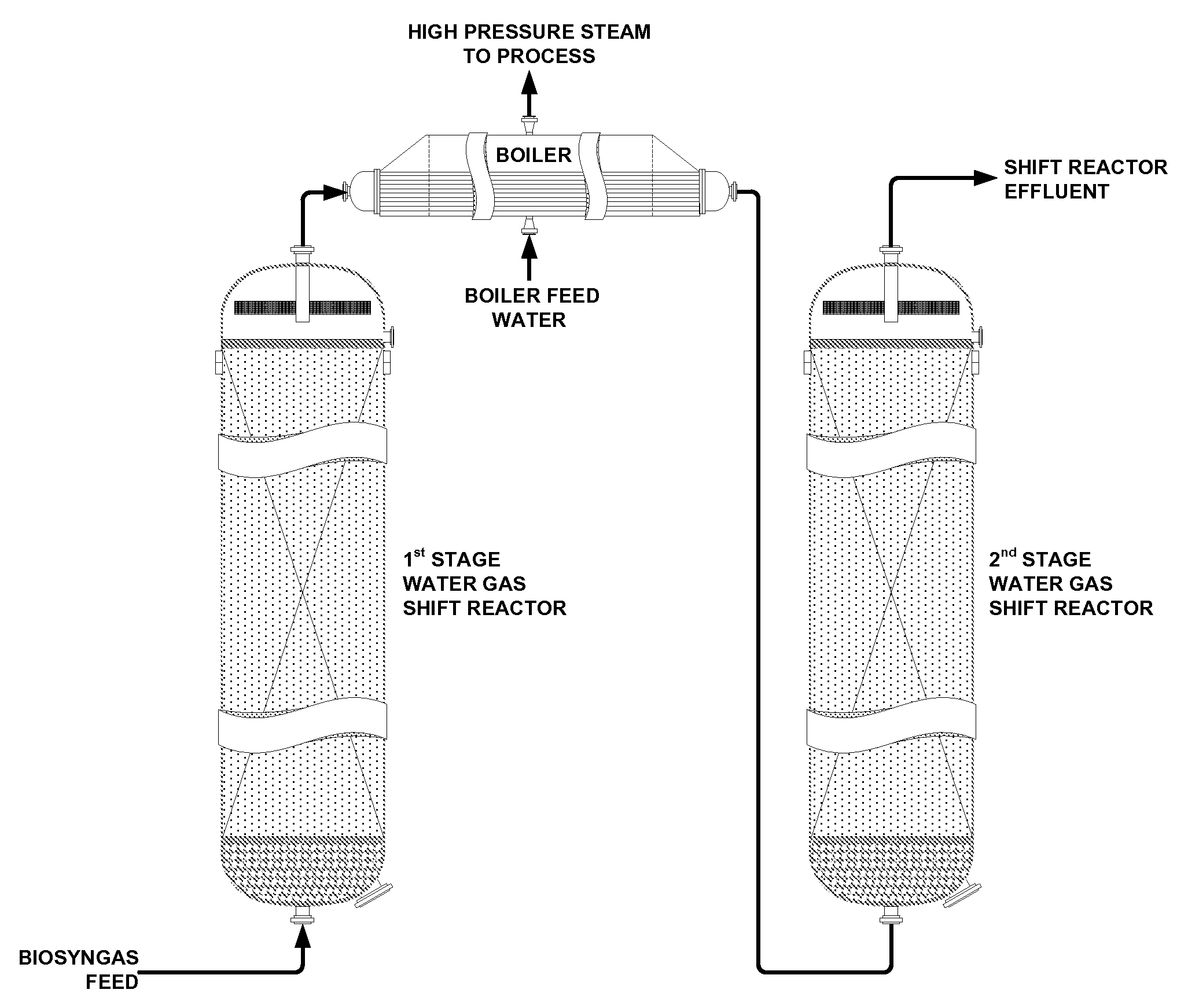
Process for producing ammonia from biomass
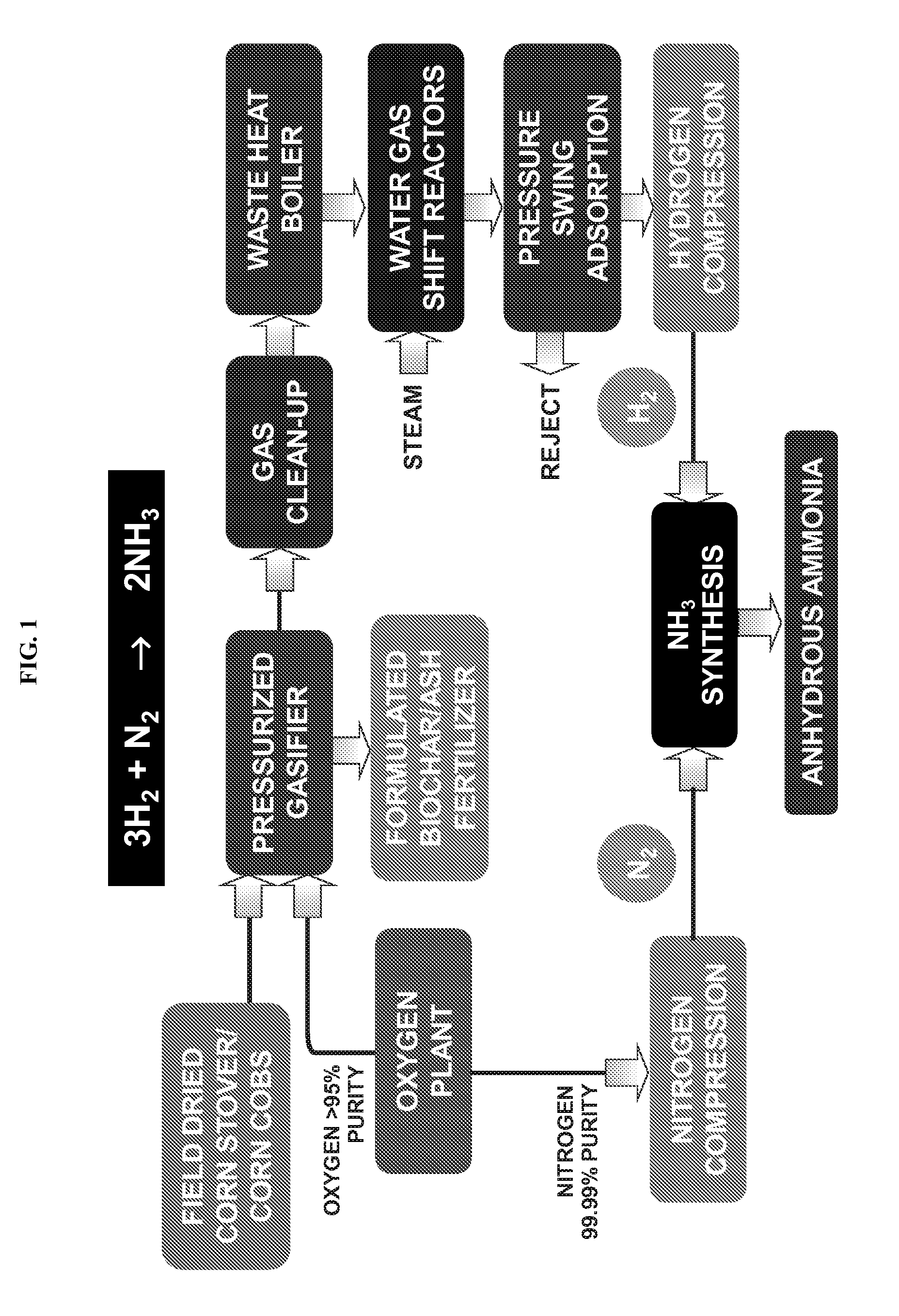
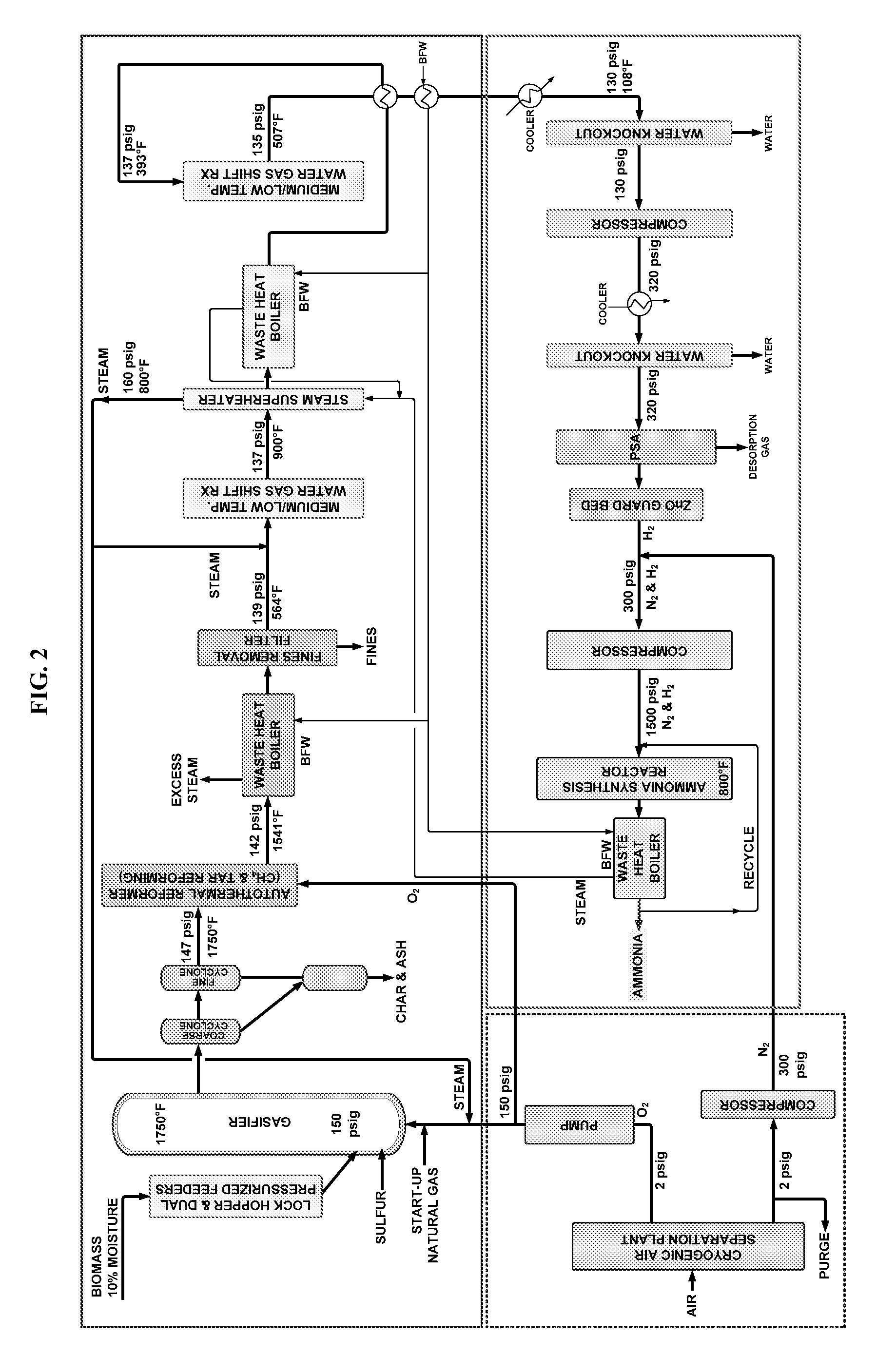
ActiveUS20100040527A1Methane significantly reduced.Eliminate all inertsProductsReagentsHydrogenActive component
This invention provides a process for making ammonia from biomass. The biomass may be first reacted with oxygen and steam to generate a biosyngas comprising hydrogen (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO) as the active components. The gasification step may be regulated to reduce the amount of methane in the biosyngas that may leave the gasifier.
Owner:SYNT
Method for recycling ammonia from low concentration ammonium chloride wastewater
The invention discloses a method for recovering ammonia from low-concentration ammonium chloride wastewater, which comprises the following steps that: an alkaline substance is added into the low-concentration ammonium chloride wastewater to prepare mixed slurry containing ammonia water and chloride salt; the mixed slurry is subjected to the separation and concentration of the ammonia water in an ammonia water distillation concentration tower to obtain ammonia vapor and a drained waste liquid; the ammonia vapor is conveyed to an ammonia water cooler for cooling treatment, and the ammonia water obtained by the cooling treatment is stored for standby; and the drained waste liquid is subjected to solid-liquid separation to obtain solid-phase residue and a waste liquid containing the chloride salt. The method evaporates the ammonia in the low-concentration ammonium chloride wastewater and concentrates the ammonia to an industrial grade concentration, and has the advantages of broad source of auxiliary materials, low cost, completely sealed technical process, and low energy consumption; and drained substances meet the requirement of no pollution and no nuisance.
Owner:包头市西骏环保科技有限公司
System for comprehensive utilization of three industrial wastes
InactiveCN101618292AAchieve energy saving and emission reductionReduce manufacturing costDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatmentElectric powerToxic industrial waste
The invention provides a system for comprehensive utilization of three industrial wastes, mainly relating to the field of energy conservation and emission reduction, in particular to the comprehensive utilization of the three industrial wastes; to realize the objective of energy conservation and emission reduction required by the recycle economy, a system technology targeted at comprehensive utilization of the three industrial wastes of factories is adopted; in the invention, the reactor in the nuclear plant, the boiler in the coal-fired power plant and other types of supercritical boilers are utilized to provide a new cooling and turbine drive mode to solve the issue of industrial discharge of greenhouse gas and other polluting gases; in addition, collected emissions are utilized to produce nuclear fuel, compound chemical fertilizer or feedstuff and other chemical raw materials; moreover, to realize recycling of resources and sustainable utilization of energy, the original three wastes are innovatively applied to nuclear electric power generation. The system is characterized by comprising 10 major links and the beneficial effect thereof lies in utilizing new methods to realize energy conservation and emission reduction and production cost in the late stage of production can be reduced.
Owner:李元胜
Poly-generation technique for using coal gas and coke oven gas as raw materials
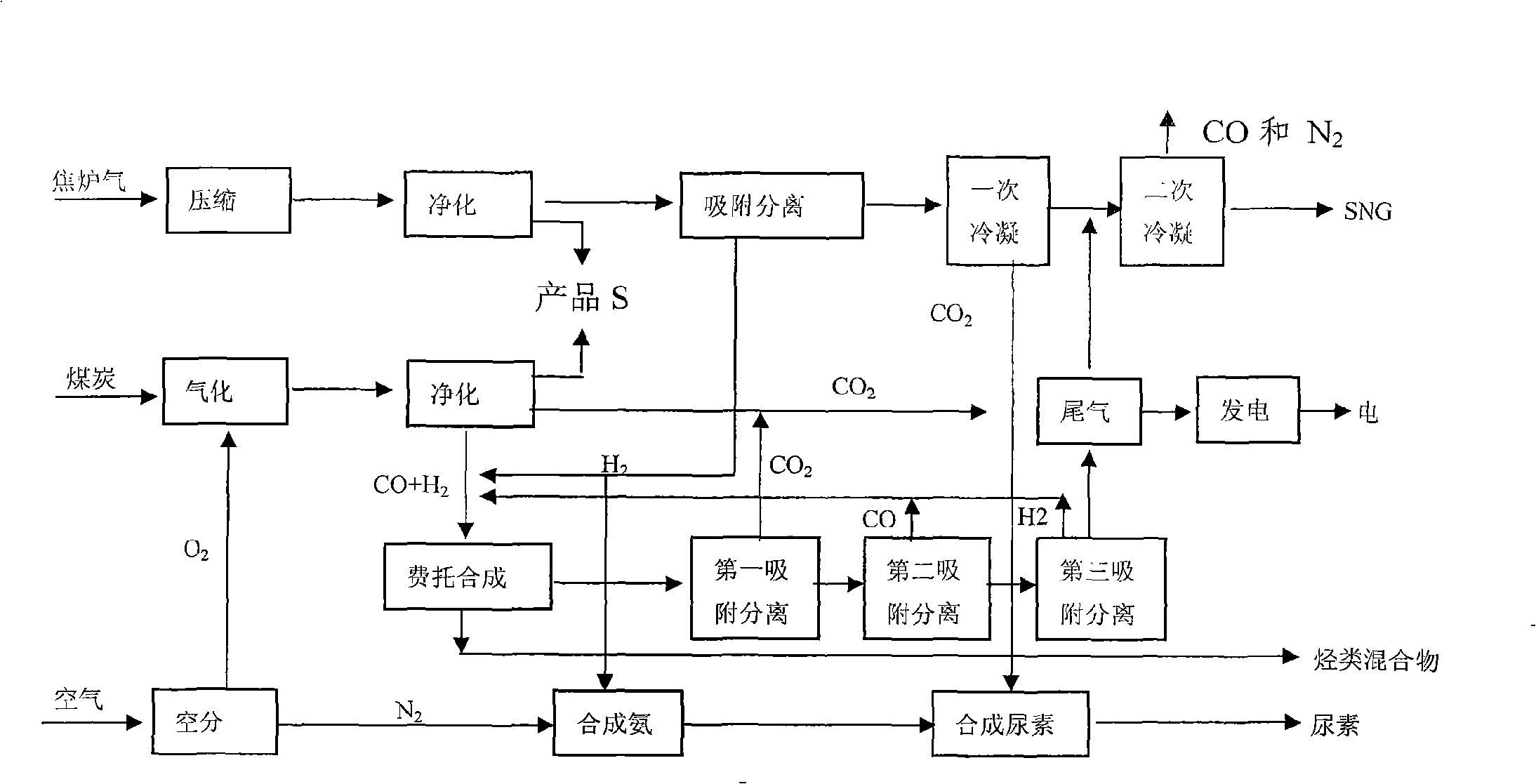
ActiveCN101538483ANo conversionNo transform operationUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon mixturesDesorption
The invention relates to a poly-generation technique for using coal gas and coke oven gas as raw materials. The poly-generation technique comprises the following steps of: carrying out mixing on part of H2 prepared by purified water gas and coke oven gas through pressure swing adsorption and tail gas obtained by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, carrying out Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and obtaining hydrocarbon mixture and tail gas. The CO2 separated from tail gas separate by first pressure swing adsorption enters a urea synthesis unit for reaction, the CO and the hydrogen respectively obtained by separation of second pressure swing adsorption and third pressure swing adsorption of the residual tail gas are circulated back to a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis unit for reaction; and the residual gases can be used for generating power or obtaining SNG by secondary condensation. The coke oven gas enters pressure swing adsorption after being purified and desulphurized so as to separate H2; wherein one part of H2 is used as supplementation of H2 needed by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and the other part of H2 is mixed with N2 for ammonia synthesis so as to obtain synthetic ammonia; and the synthetic ammonia is mixed with CO2 obtained by the first condensation and CO2 separated from the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis for urea synthesis so as to obtain urea. The CO2 separated from the first condensation of desorption gas by pressure swing adsorption of the coke oven gas is used for urea synthesis; and the residual gases is treated by the second condensation to obtain SNG and mixed gas of CO and N2. The invention has no emission of greenhouse gases, uses richness in carbon and deficiency in hydrogen of the coal gas and the richness in hydrogen and deficiency in carbon of the coke oven gas to carry out complementation, realizes modulation of product structure by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and improves the economical efficiency of the process of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.
Owner:中科潞安能源技术有限公司
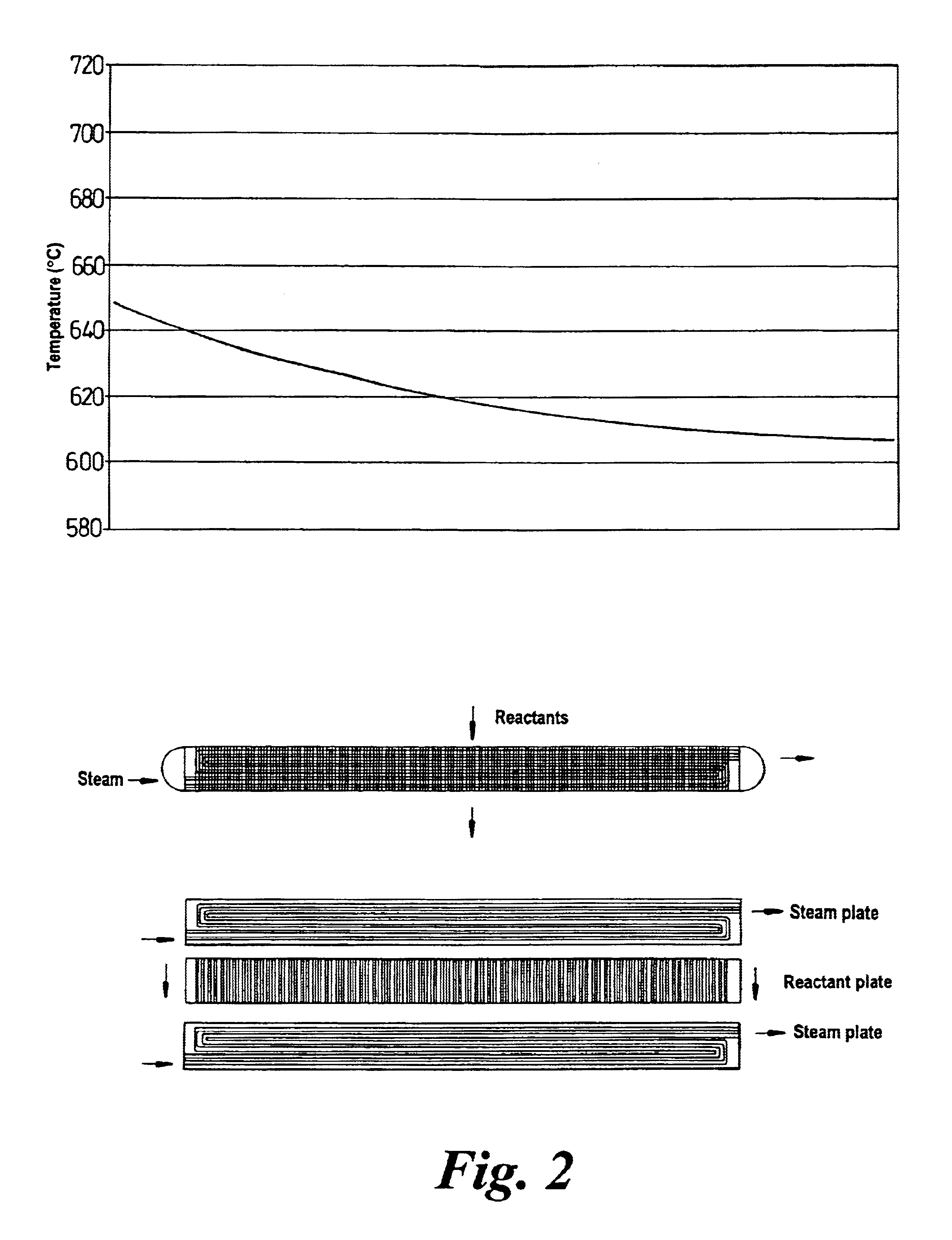
Chemical reactor
InactiveUS7033553B2Tight controlReduce backmixingPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesWorking fluidChemical reactor
A reactor comprises a reaction zone, optionally containing a catalyst bed, and heat exchange means inoperative contact with the reaction zone, e.g. embedded in a catalyst bed, and arranged so as to received reactants for heat exchange purposes, wherein the heat exchange means is formed from a plurality of superposed metal plates wherein fluid flow channels have been formed, according t a pre-determined pattern, the channel-bearing plates being aligned during superposition to define discrete heat exchange pathways respectively for reactant and working fluids, and the said plates are diffusion bonded together.
Owner:MEGGIT (UK) LTD
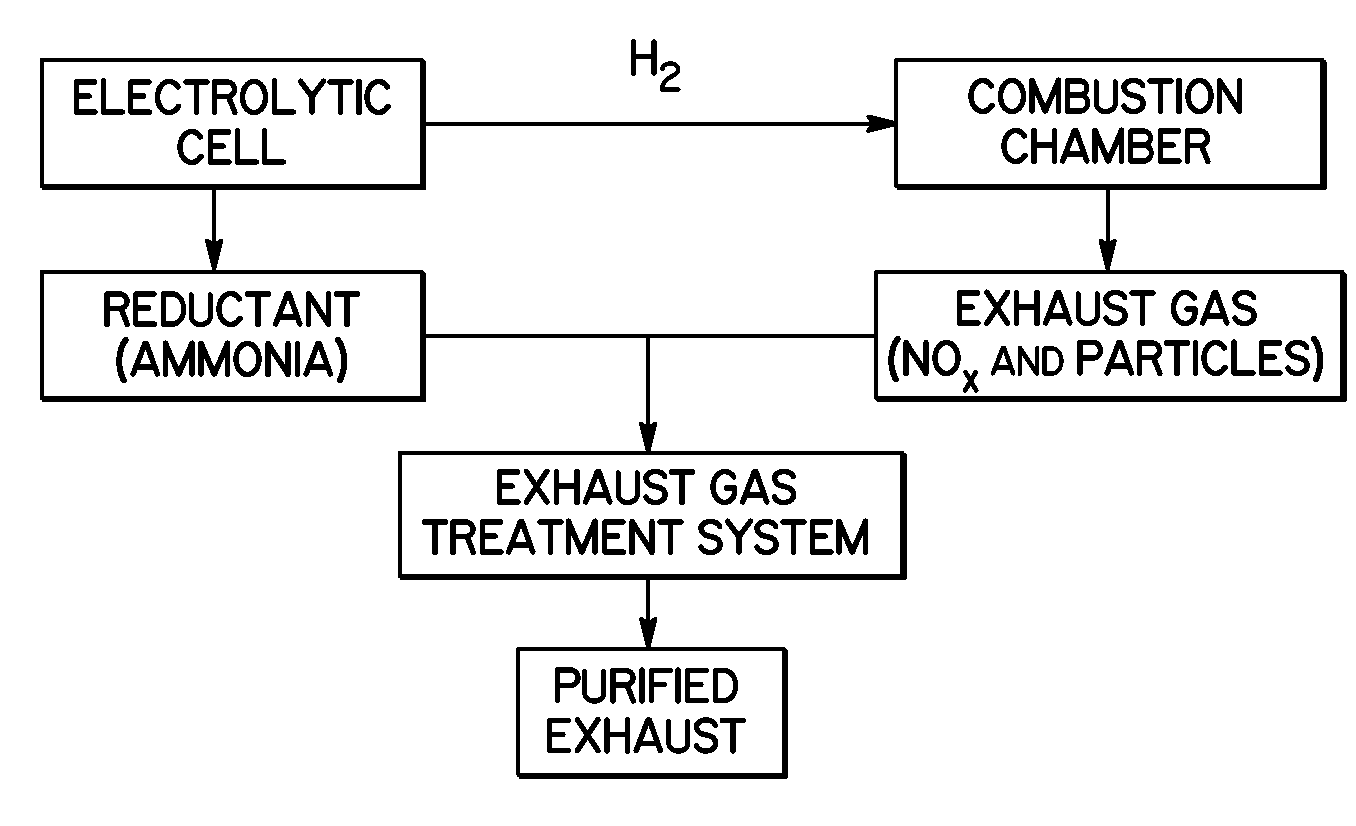
Selective Catalytic Reduction Via Electrolysis of Urea
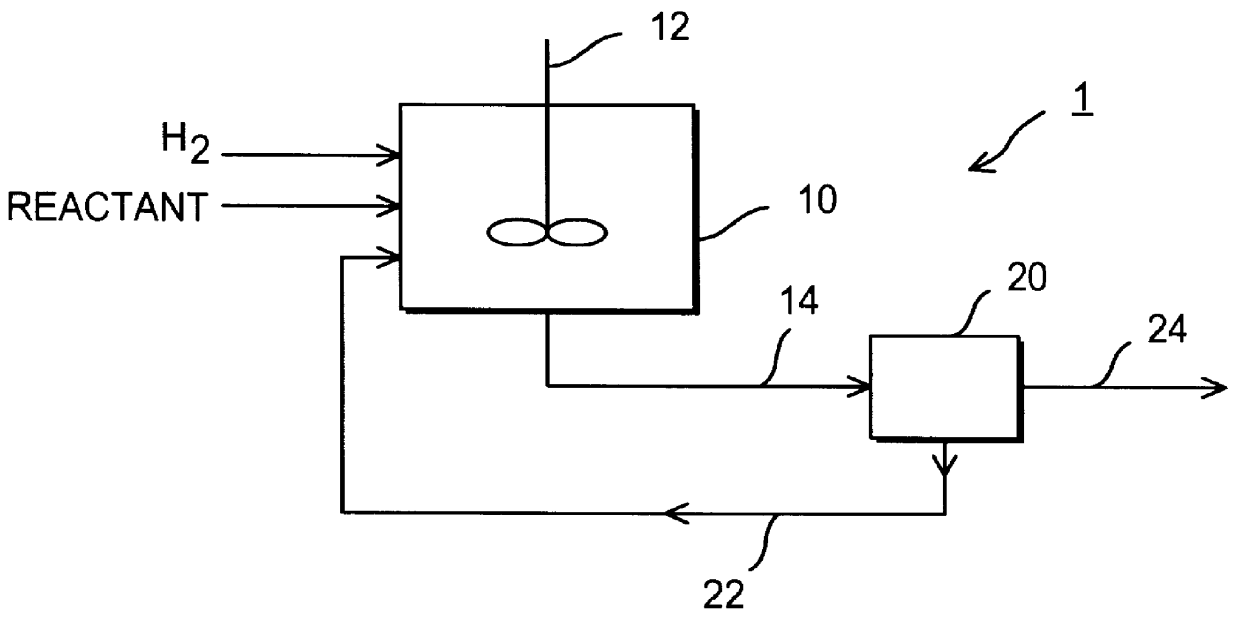
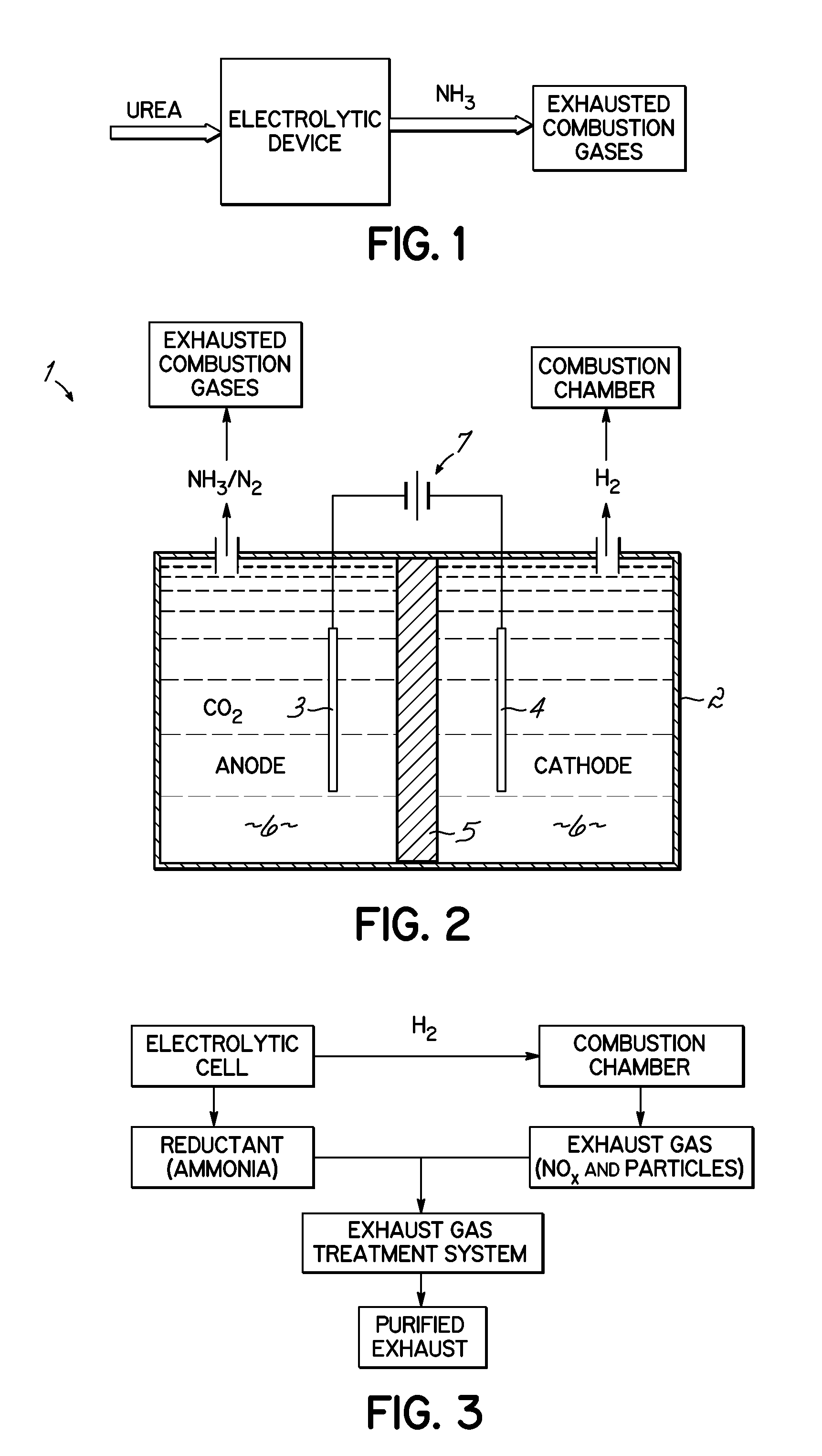
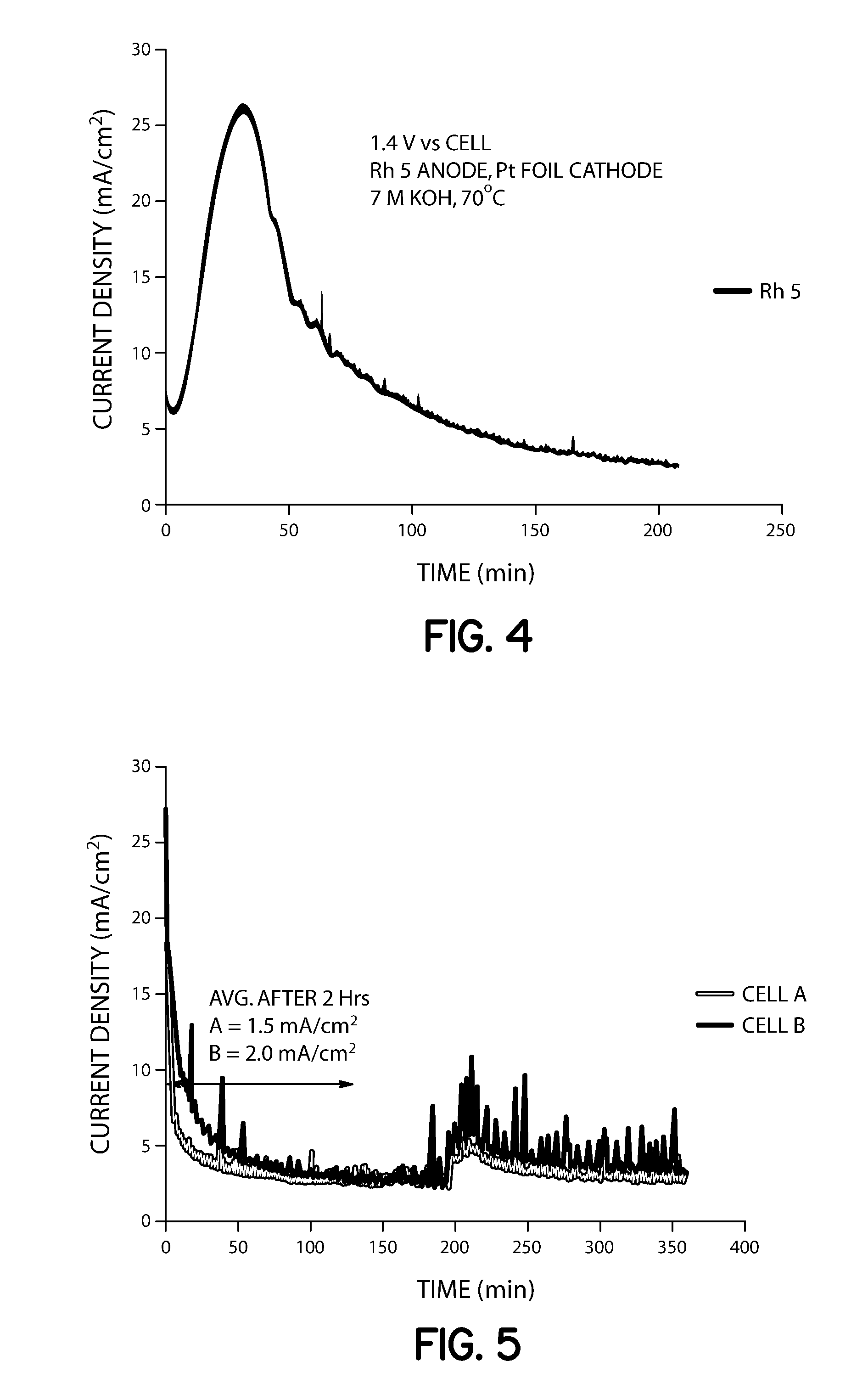
A method for producing ammonia suitable for use as a reductant in a combustion exhaust gas treatment system is provided that includes the electrolytic hydrolysis of urea under mild conditions. The ammonia generator, which includes an electrolysis apparatus including an electrolytic flow cell, an alkaline electrolyte composition, and a recirculation system, may be operatively coupled to an exhaust gas treatment system to provide an apparatus for reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx) and / or particulate in exhaust gases.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross
InactiveCN107555447ARealize harmless treatmentTo achieve the purpose of "zero emission" utilizationChloride preparationFluoride preparationSlurryLiquid solid
The invention provides a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross and relates to a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross produced in an aluminum dross treating process. The harmless and comprehensive utilization method is characterized in that slurry is prepared from the secondary aluminum dross produced in the aluminum dross treating process and water, a stirring deamination reaction is performed, and ammonia gas formed through the reaction is condensed or absorbed by water; slurry after the reaction is subjected to liquid-solid separation, separated liquid phase is subjected to evaporative crystallization, and a chlorate and fluoride salt mixture is obtained; separated solid phase is used for producing a calcium aluminate material. With adoption of the method, the aluminum dross can be treated harmlessly, useful components in the aluminum dross are recovered efficiently, the harmless secondary aluminum dross can replace high-alumina bauxite for preparing a calcium aluminate product, production cost is reduced greatly, zero-release utilization of the aluminum dross is realized, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, environmental protection is realized, and the method has wide applicability.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
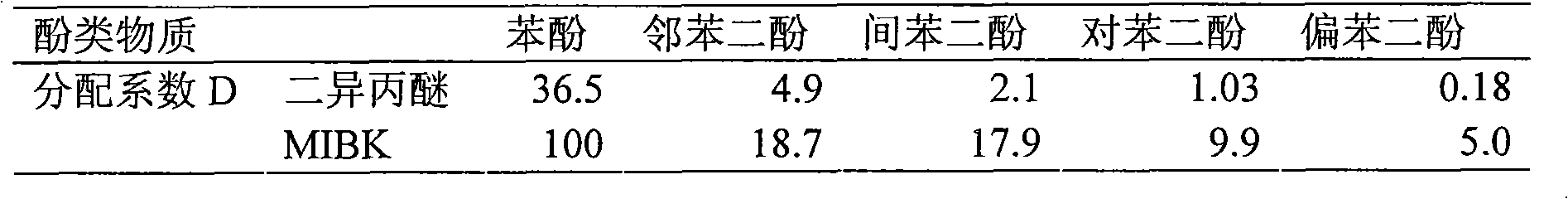
Method for treating gasified waste water containing high-concentration phenol and ammonia
InactiveCN101665309AEasy extractionImprove extraction efficiencyOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHigh concentrationThree level
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Use of an ammonia storage device in production of energy
An electric power generating unit comprising (i) an ammonia storage device in the form of a container comprising an ammonia absorbing and releasing salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals such as Li, K, Mg, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu or Zn, X is one or more anions selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, thiocyanate, sulphate, molybdate, phosphate, and chlorate ions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, Z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and n is the coordination number of 2 to 12. (ii) means for heating said container and ammonia absorbing and releasing salt for releasing ammonia gas and (iiia) a fuel cell for converting ammonia directly into electric power; or (iiib1) a reactor for dissociating ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen and (iiib2) a fuel cell for converting hydrogen into electric power.
Owner:AMMINEX
Organics and nutrient recovery from anaerobic digester residues
Sludge from an anaerobic digester is treated to recover one or more of fibers, or solids or liquids with a high nutrient content. The solids or liquids can be used as a fertilizer. The fibers can be used in a plant growing medium. Solids are separated from liquids in the sludge and dried. The solids may be dried to produce a flake or pellet. Ammonia in the liquids is recovered and used to produce a concentrated acidic ammonium salt solution. This solution may be mixed with the solids to produce a nitrogen enhanced solid. The fibers and solids or liquids can also be used in combination to produce an enhanced plant growing medium. A device and process for removing ammonia from a liquid can be used in the system or separately.
Owner:ANAERGIA
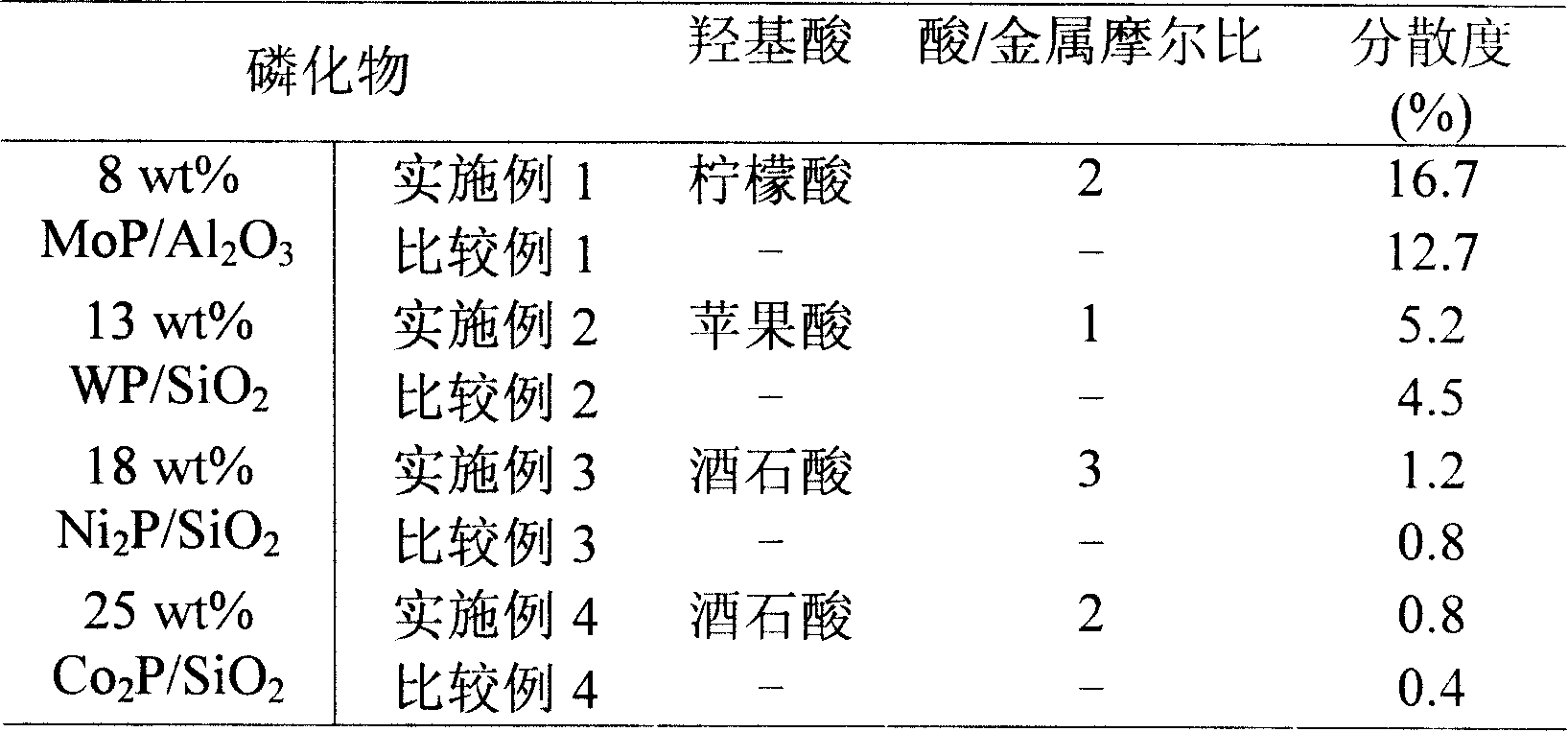
Process for preparing high dispersion supported type transition metal phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN101168132AIncreased dispersionReduce reunionPhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen preparationPhosphateActive component
The invention relates to a catalyst of supported metal phosphide, in particular to a process for preparing the catalyst of high dispersive supported metal phosphide. The catalyst is composed of two parts of active components and a carrier which can be represented by AP / Z or B2P / Z, wherein the A of the active components is Mo or W, the B of the active components is Ni or Co, and the Z of the carrier is Al2O3 or SiO2. The operation steps of the catalyst are that transient metal salt and mammonium dihydrogen phosphate are dissolved in deionized water according to the stoichiometric ratio of targeted phosphide, and simultaneously moderate hydroxy acid as chelating agent is added to get the impregnating solution for preparing supported transition metal phosphide. The porous carrier is immersed in the impregnating solution, and is rested, the procedure gains temperature and returns after the impregnating solution is dried, roasted and under the atmosphere of hydrogen gas, and finally the supported transition metal phosphide is made. The supported transition metal phosphide prepared by the preparation method has the advantages of high dispersion, simple and convenient operation, low cost, no pollution, good repeatability and easiness of large scale preparation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
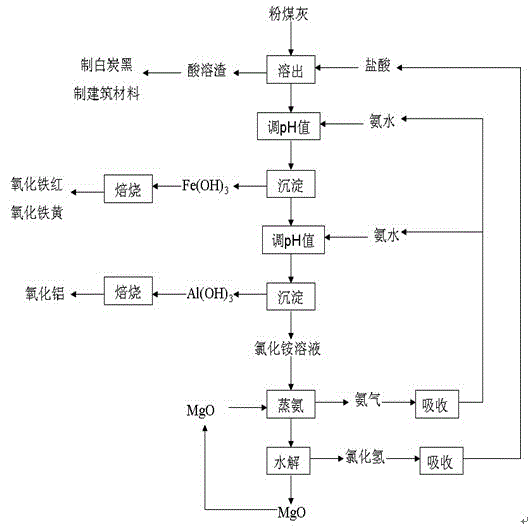
Method for processing fly ash used for circulating fluidized bed
ActiveCN104445212ASolve environmental pollutionHarm reductionChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideSilicaAluminium hydroxideHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for processing fly ash used for a circulating fluidized bed, which comprises the following steps: dissolving fly ash from the circulating fluidized bed out by hydrochloric acid, filtering to obtain filter residue and a leaching liquid; adjusting pH value of the leaching liquid to 1.5-3.5 by ammoniacal liquor, deposing, filtering to obtain the filter residue and a filtrate, washing filter residue, drying to obtain a compound of iron; adjusting the pH value of the filtrate after extracting iron to 3.8-5.2 by the ammoniacal liquor, deposing, filtering to obtain the filter residue and the filtrate, washing filter residue, drying to obtain aluminium hydroxide, further calcining to obtain metallurgy alumina; adding magnesium oxide in an ammonium chloride solution after extracting aluminium and performing ammonia distilling and hydrolysis reactions to obtain hydrogen chloride gas, ammonia gas and magnesium oxide. According to the invention, stepwise extraction of useful elements such as aluminium, silicon and iron in fly ash can be realized, cycle utilization of the materials can be realized, process is simple, cost is low, and the method opens new approach for high value utilization of fly ash from the circulating fluidized bed.
Owner:GUIYANG AL-MG DESIGN & RES INST
Compact reactor
InactiveUS7022294B2Avoid lostIncrease the number ofPhysical/chemical process catalystsStationary tubular conduit assembliesReaction zoneProcess engineering
A reactor comprises a plurality of reaction zones divided by heat exchanger panels but in fluid communication via the panels, the reaction zones being arranged in a spiral configuration whereby the reaction zones form a flow path for reactants that extends between a central part of the reactor and an outer peripheral part thereof.
Owner:MEGGIT (UK) LTD
Methods and systems for zero discharge water treatment
ActiveUS20100172819A1Treatment involving filtrationDialysis systemsParticulatesWater treatment system
Methods and systems for a zero discharge waste water treatment system are provided. The system includes a filtration train including filter media having successively smaller diameter filtration elements, a reverse osmosis apparatus including a pump and a membrane coupled in flow communication with said filtration train, a vapor compressor coupled in flow communication with said reverse osmosis apparatus, and a spray dryer coupled in flow communication with said vapor compressor, said spray dryer configured to separate moisture in a brine solution from particulate suspended in the brine solution.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com