Patents
Literature
140 results about "Coordination number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
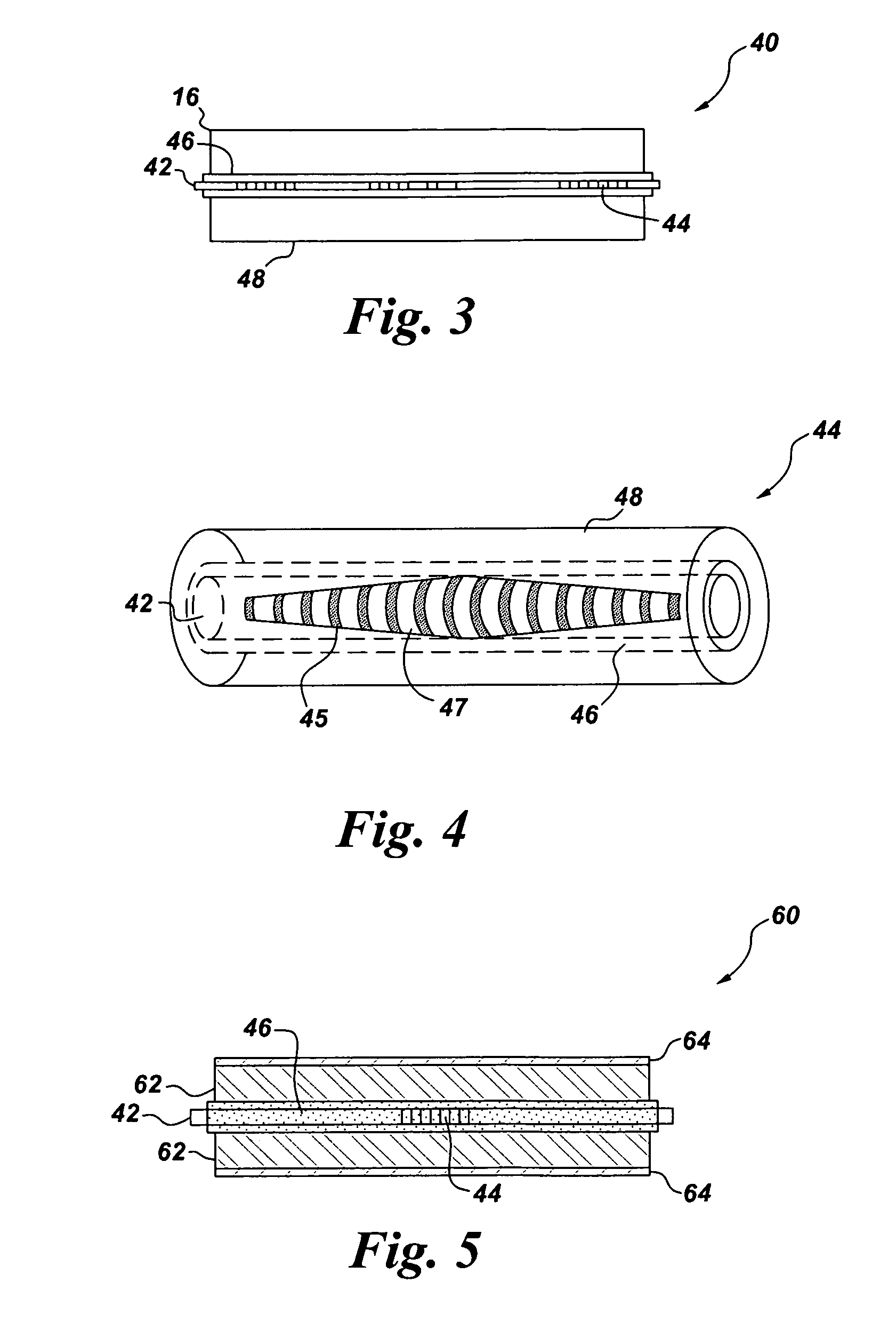
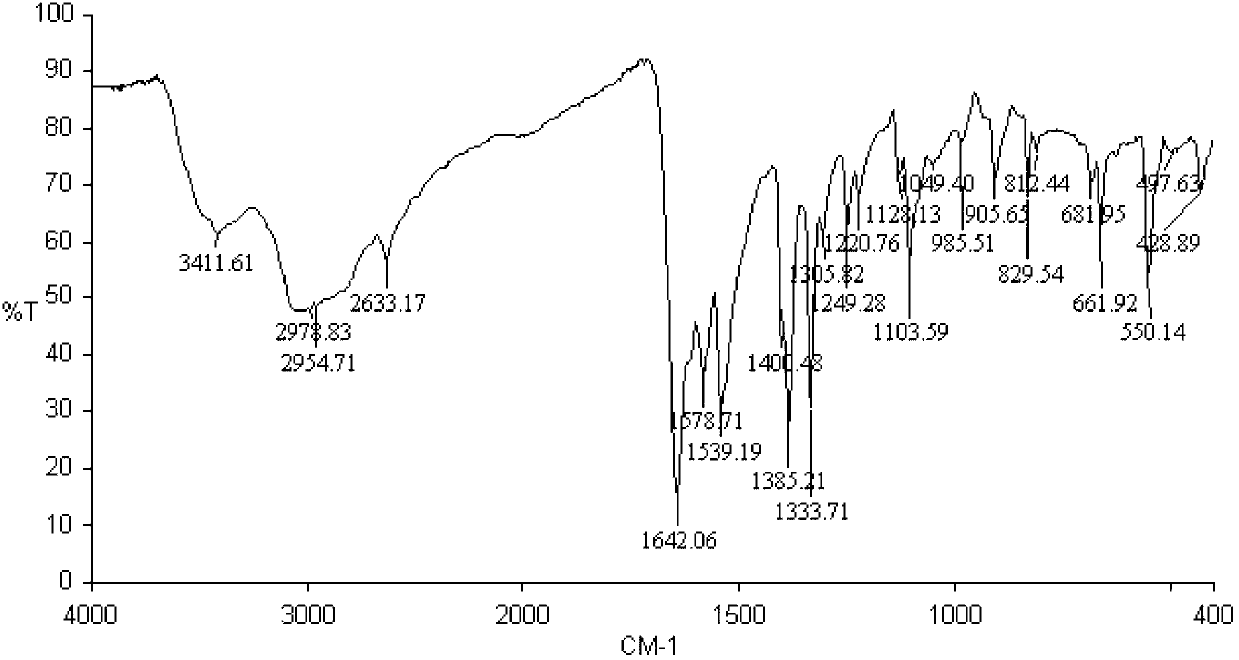
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion/molecule/atom is called a ligand. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules than for crystals.
Organometallic complex, organic EL element and organic EL display
InactiveUS20050244673A1Improve efficiencyExcellent lifetimeGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesRheniumNitrogen
An organic EL element includes an organometallic complex including a rhenium atom; one ligand which has a coordinated nitrogen atom and a coordinated oxygen atom, each coordinated with the rhenium atom, and has at least one π conjugation part; and the other ligand coordinated with the rhenium atom in such a way that the ligand saturates the coordination number of the rhenium atom and the charge of the whole organometallic complex is neutral.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Catalytic oxidation process
InactiveUS6447745B1Hydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst activation/preparationElemental compositionPartial oxidation
A process for the partial catalytic oxidation of a hydrocarbon containing feed comprising contacting the feed with an oxygen-containing gas in the presence of a catalyst retained within a reaction zone in a fixed arrangement, wherein the catalyst comprises at least one catalytically active metal selected from the group consisting of silver and Group VIII elements supported on a porous ceramic carrier. The porous ceramic carrier has a distribution of total pores wherein about 70% of the total pores (1) have a volume-to-surface area (V / S) ration that is within about 20% of the mean V / S value for the total pores and no pores have a V / S ration that is greater than twice the mean V / S value for the total pores; (2) have a pore-to-pore distance between neighboring pores that is within about 25% of the mean pore-to-pore distance between neighboring pores; and (3) have a pore throat area that is within about 50% of the mean pore throat are for the pores. Additionally, about 50% of the total pores have a coordination number between neighboring pores that is within about 25% of the mean coordination number between neighboring pores. Preferably, the oxidation process comprises a multistage, staged oxygen, catalytic partial oxidation process having fewer than or equal to about five stages and including a first stage preheat temperature of greater than about 550° C., and wherein the temperature of the product mixture in each stage following the first stage is at least about 700° C.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
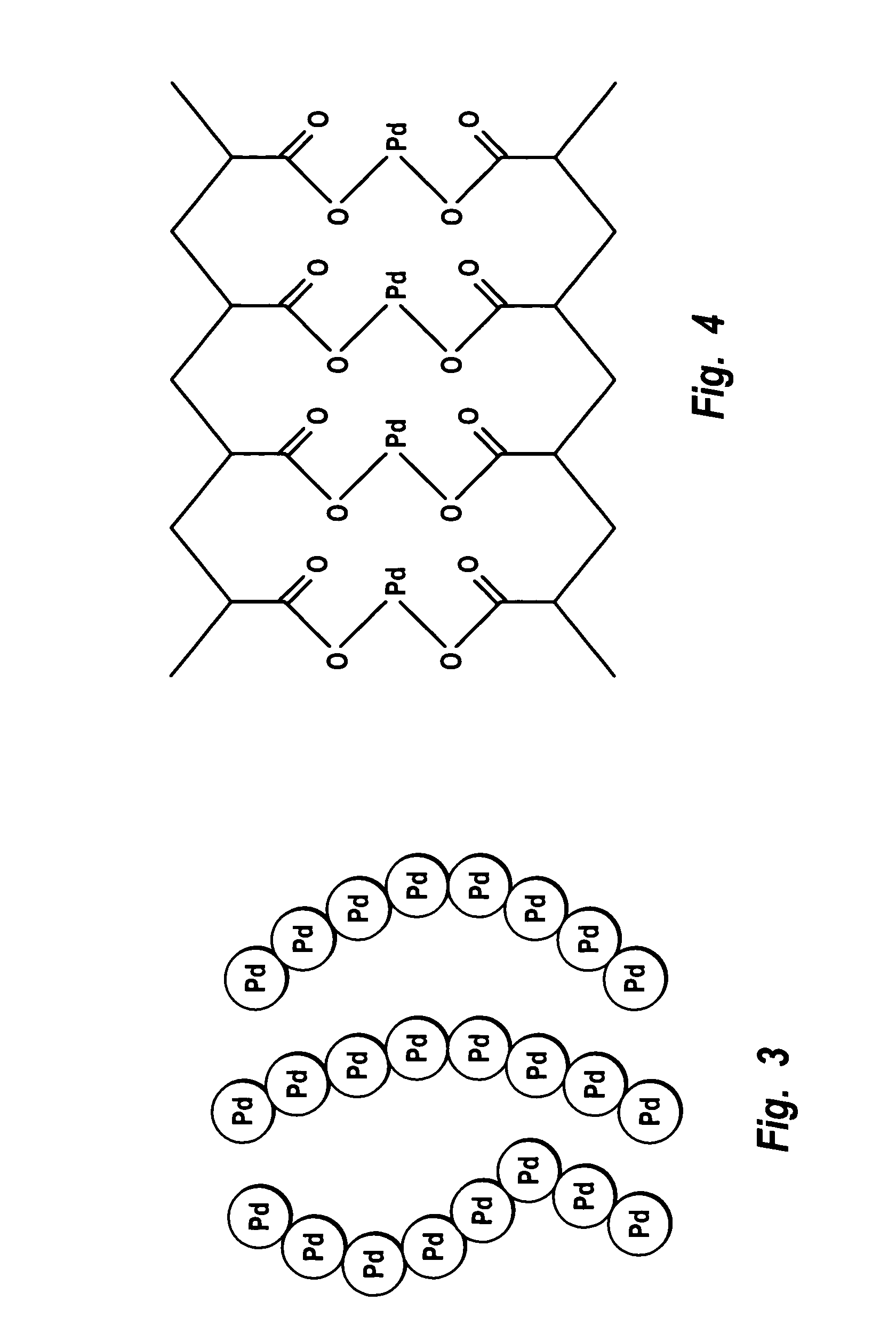
Supported catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for preparing such catalysts
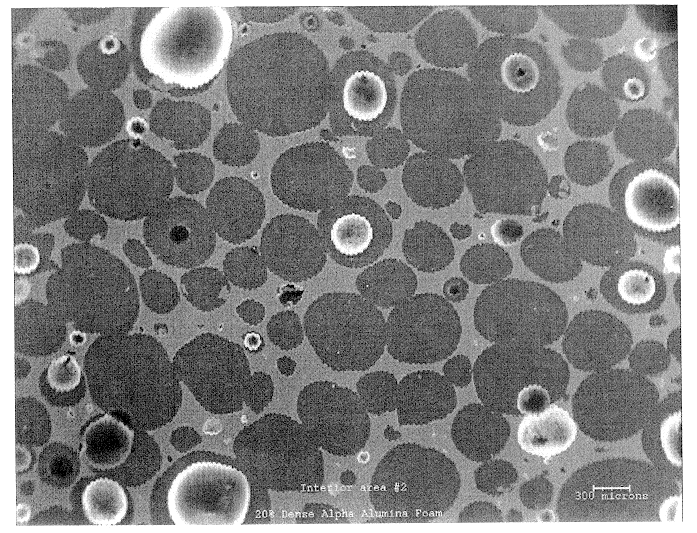
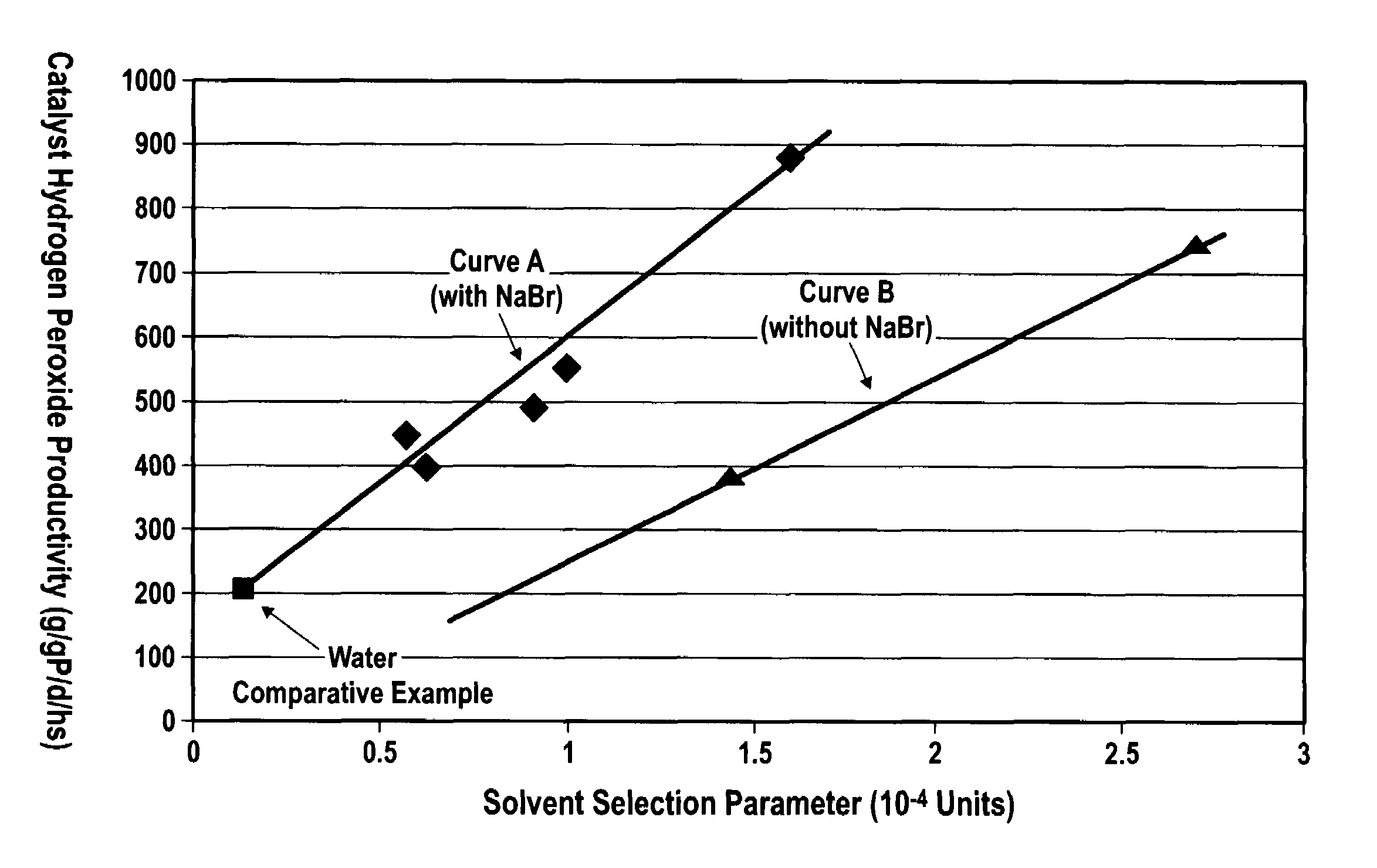
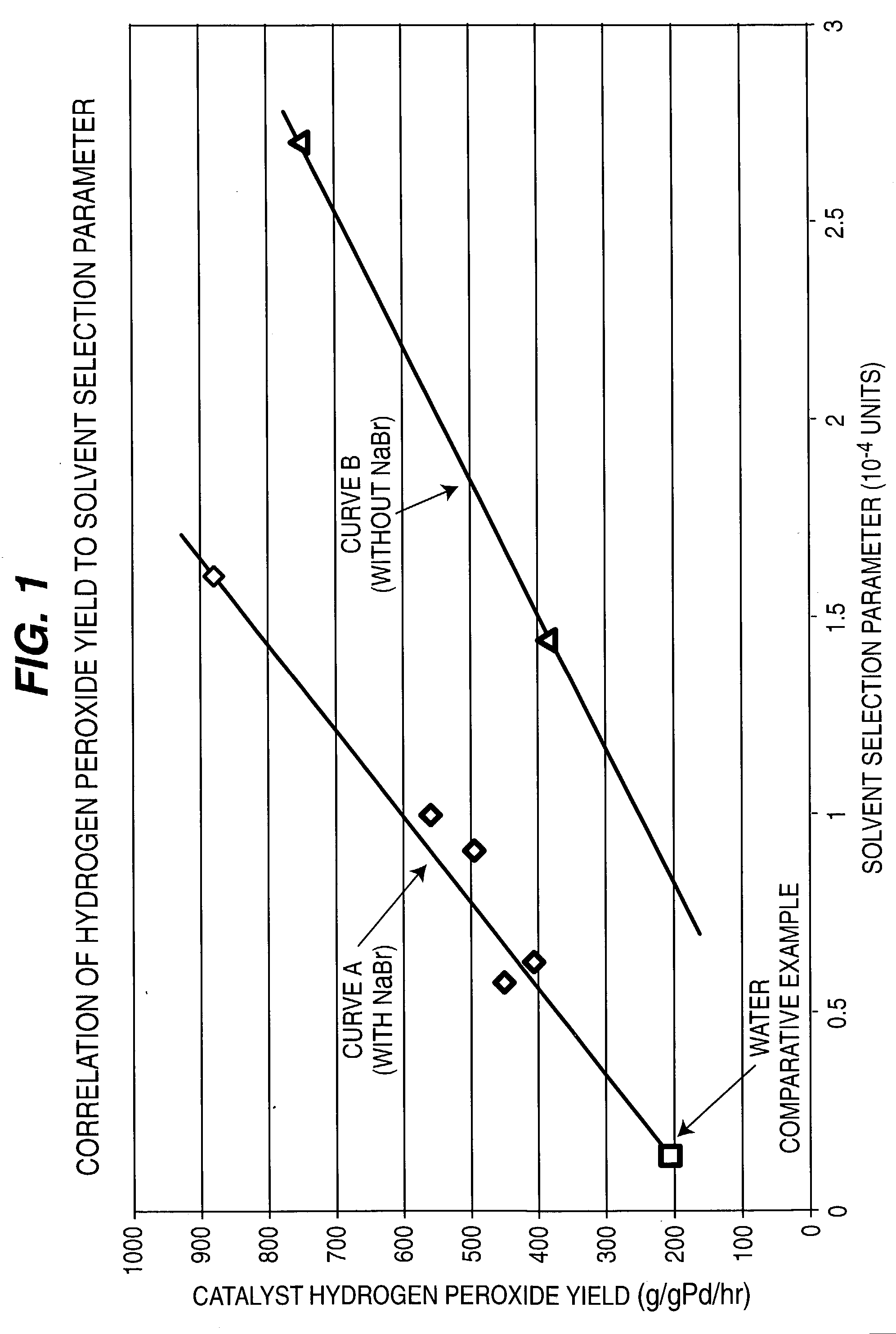
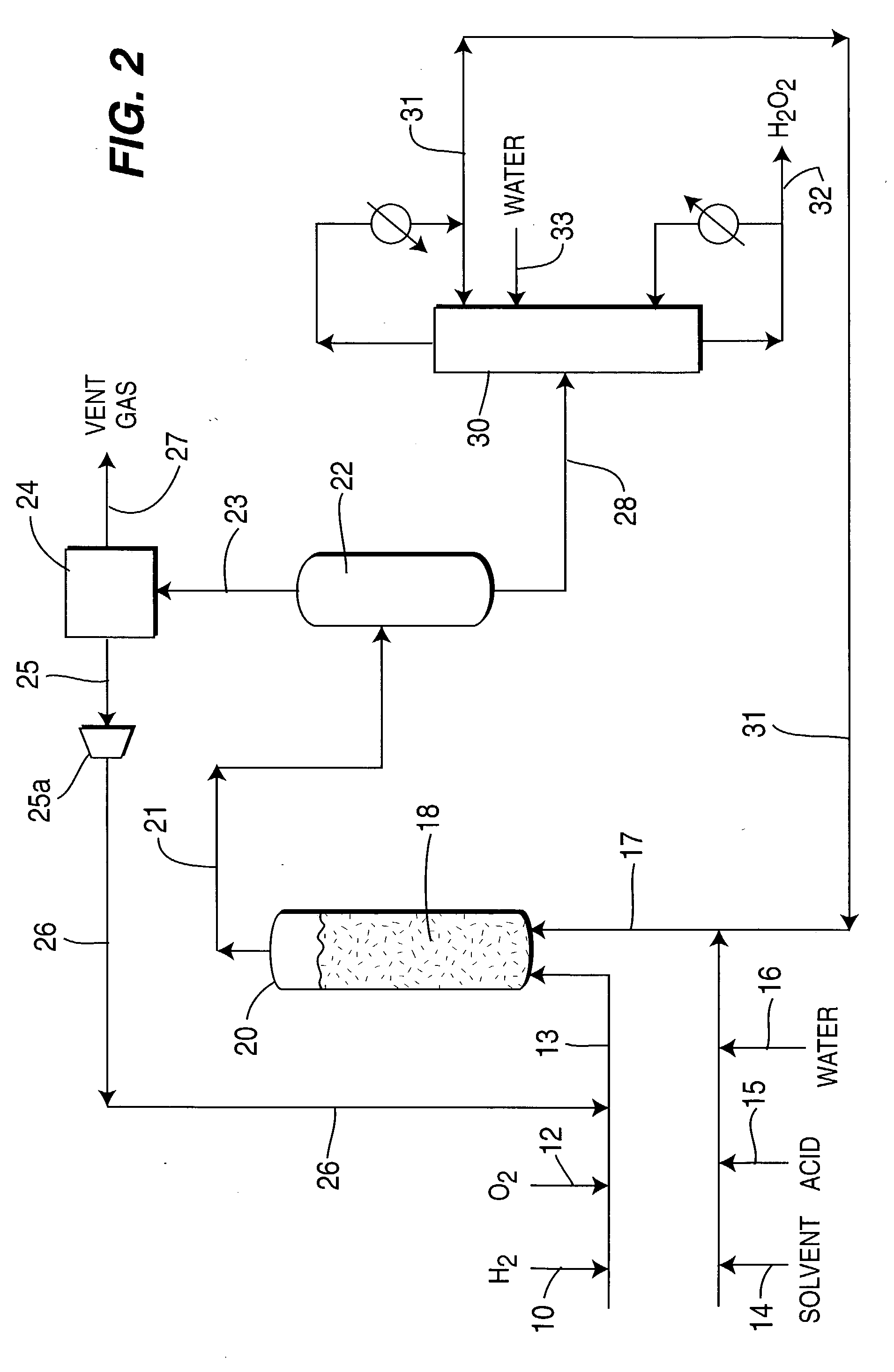
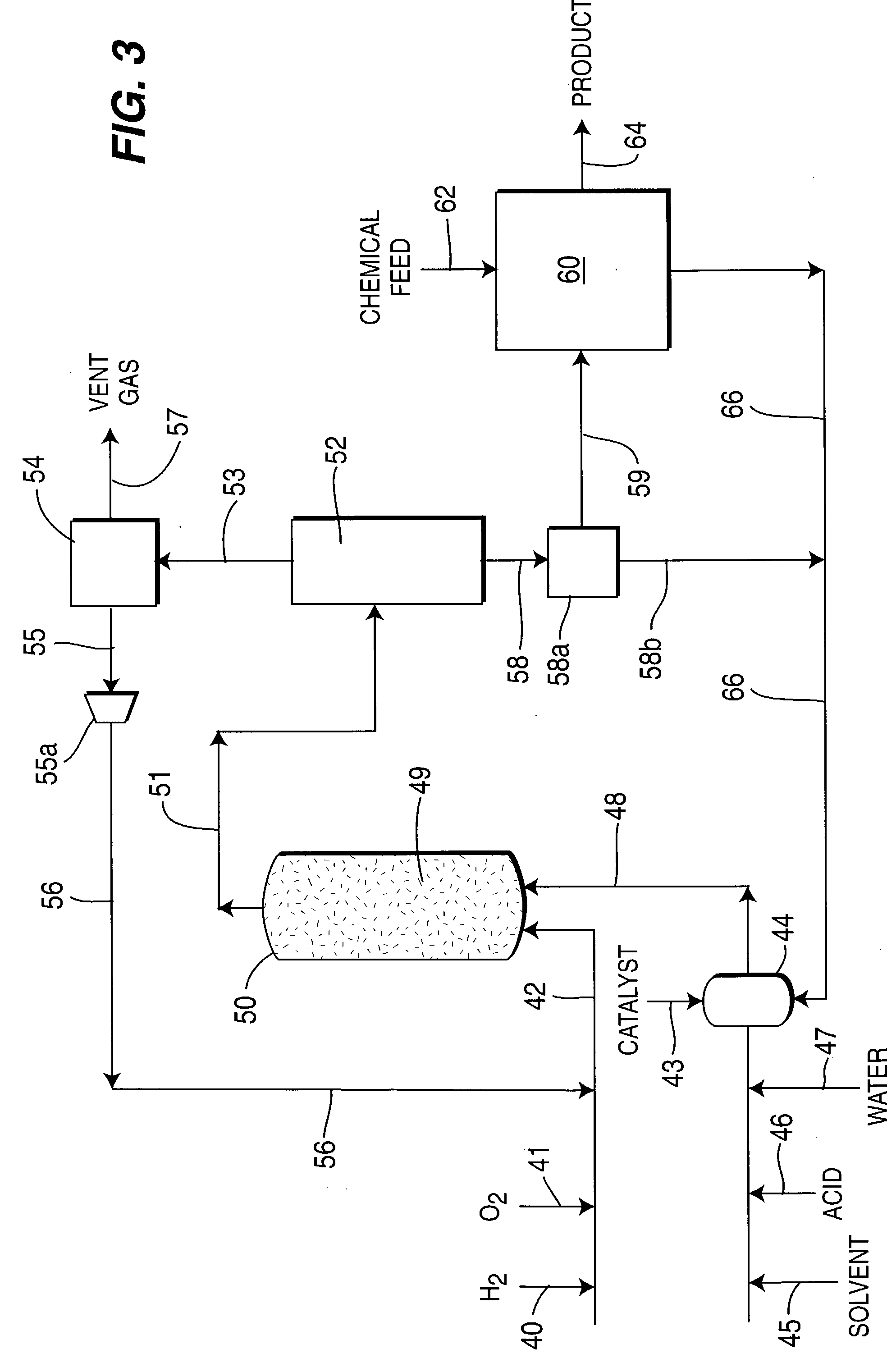
ActiveUS7011807B2Reduce molecular weightReduce the possibilityHydrogen peroxideHydrogenHydrogenOrganic fluid
Supported reactive catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for their production are disclosed. The supported catalysts of the present invention are useful for the preparation of hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity in addition to other chemical conversion reactions. The supported catalyst comprises catalyst particles having top or outer layer of atoms in which at least a portion of the atoms exhibit a controlled coordination number of 2. The catalyst and methods may be used for the concurrent in situ and ex situ conversion of organic compounds. In addition, a process is provided for catalytically producing hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen feeds by contacting them with the catalysts of the invention and a suitable organic liquid solvent having a Solvent Selection Parameter (SSP) between 0.14×10−4 and 5.0×10−4.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Amido complex compound and preparation method and usage
InactiveCN101182006AFast separationImprove conversion efficiencyAmmonia compoundsTransformation efficiencyAmmonia
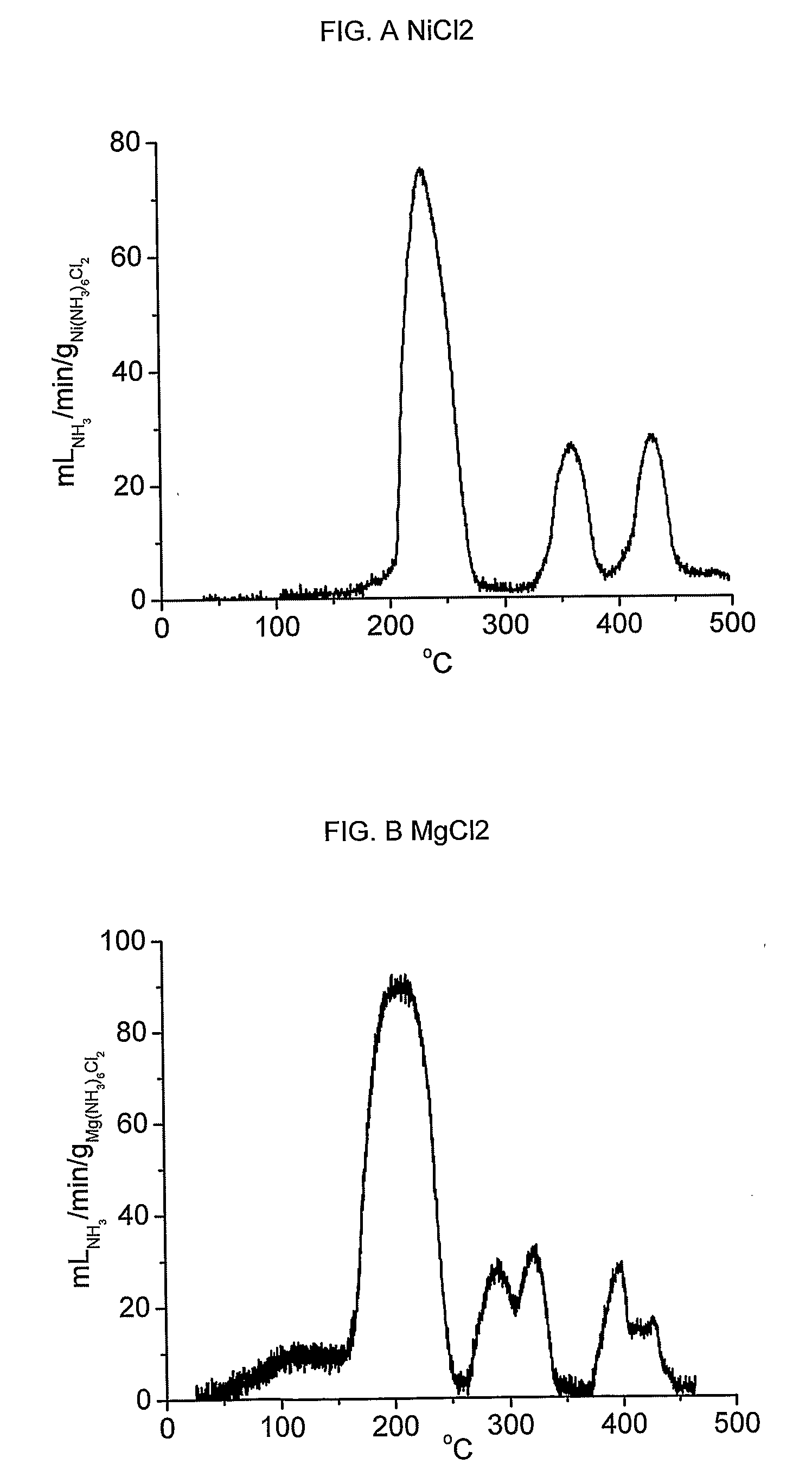
The invention discloses an amino complex compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The components of the amino complex compound are MX (NH3)n, wherein, M is one or a plurality of Li, Mg, Al, Ca, Sc, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Sr, Ba, Sn; X is one or a plurality of F, Cl, Br, NO3, SO4; m is determined according to chemical valence, which is less than or equal to 5 and more than or equal to 1; n is determined according to coordination number, which is less than or equal to 15 and more than or equal to 1. The amino complex compound is used as an absorbent of amino after deamination and realizes separation, purification, storage and transporting of ammonia gas through low-temperature ammonia absorption and high-temperature ammonia discharge. The ammonia in circulating gas used in a synthetic ammonia technique of the invention has fast separation speed and the ammonia content entering into a tower can be reduced below 0.1 percent, thus remarkably promoting the ammonia net value and improving the transformation efficiency of the synthetic ammonia technique; furthermore, the invention can be suitable for different ammonia synthesis systems, in particular to a low-pressure ammonia synthesis system and realize the solidification of the ammonia gas during storage and transporting processes; the ammonia storage quantity can reach 40 to 70wt percent with safety and high efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Use of an ammonia storage device in production of energy
An electric power generating unit comprising (i) an ammonia storage device in the form of a container comprising an ammonia absorbing and releasing salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals such as Li, K, Mg, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu or Zn, X is one or more anions selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, thiocyanate, sulphate, molybdate, phosphate, and chlorate ions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, Z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and n is the coordination number of 2 to 12. (ii) means for heating said container and ammonia absorbing and releasing salt for releasing ammonia gas and (iiia) a fuel cell for converting ammonia directly into electric power; or (iiib1) a reactor for dissociating ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen and (iiib2) a fuel cell for converting hydrogen into electric power.
Owner:AMMINEX
Hydrotreating catalyst of catalytic cracking gasoline
InactiveUS20050261124A1High degreeHigh desulfurization activityInorganic chemistryCatalyst activation/preparationXANES SpectroscopyStructure analysis
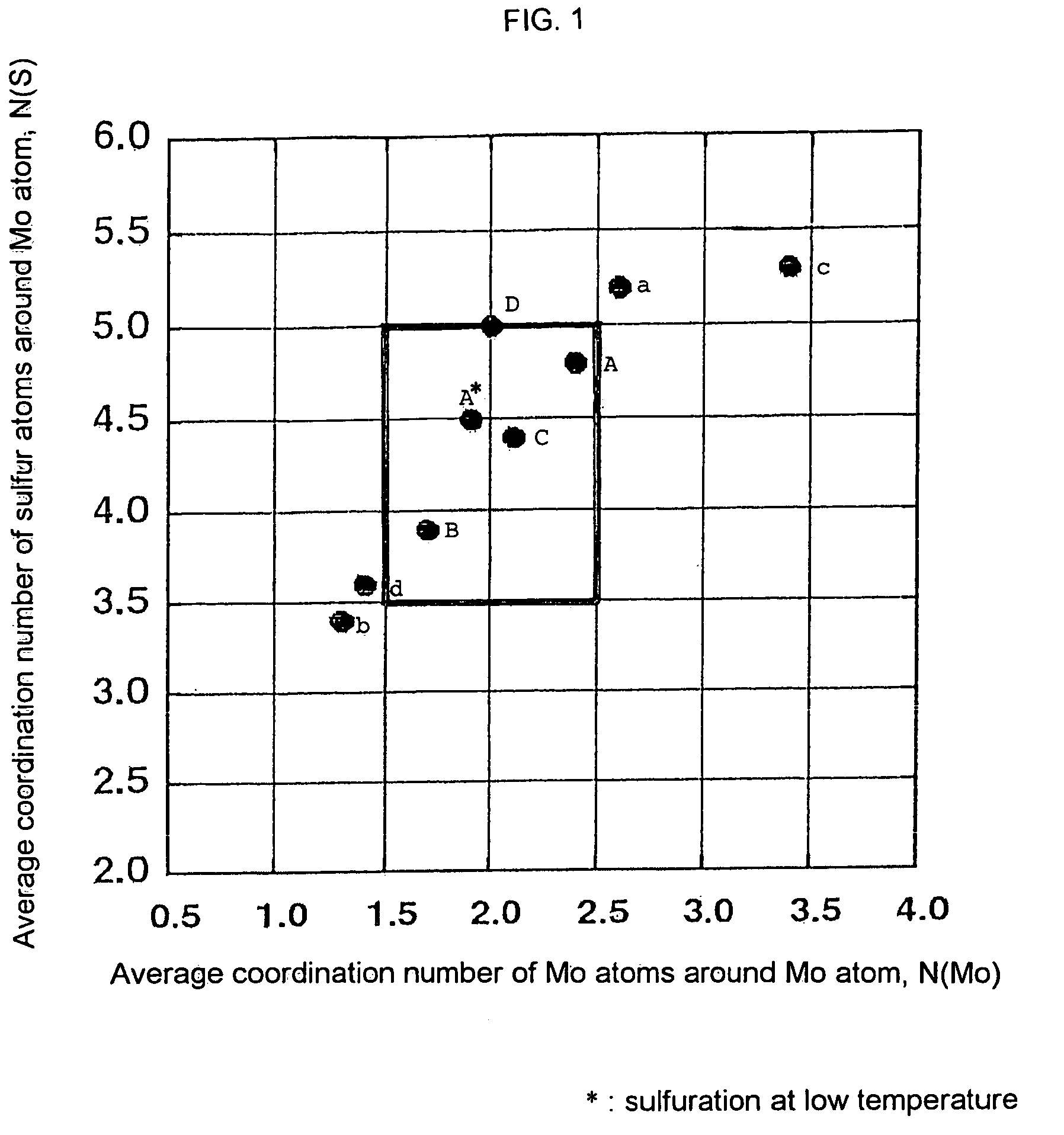
A hydrotreating catalyst comprising a Group 8 metal of the periodic table, molybdenum (Mo), phosphorus and sulfur, wherein the average coordination number [N(Mo)] of the molybdenum atoms around the molybdenum atom is from 1.5 to 2.5 and the average coordination number [N(S)] of the sulfur atoms around the molybdenum atom is from 3.5 to 5.0 when MoS2 structure in the catalyst is measured in accordance with extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Supported catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for preparing such catalysts
ActiveUS20050014635A1Reduce molecular weightReduce the possibilityHydrogen peroxideHydrogenHydrogenOrganic fluid
Supported reactive catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for their production are disclosed. The supported catalysts of the present invention are useful for the preparation of hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity in addition to other chemical conversion reactions. The supported catalyst comprises catalyst particles having top or outer layer of atoms in which at least a portion of the atoms exhibit a controlled coordination number of 2. The catalyst and methods may be used for the concurrent in situ and ex situ conversion of organic compounds. In addition, a process is provided for catalytically producing hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen feeds by contacting them with the catalysts of the invention and a suitable organic liquid solvent having a Solvent Selection Parameter (SSP) between 0.14×10−4 and 5.0×10−4.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Use Of An Ammonia Storage Device In Production Of Energy
InactiveUS20070207351A1Reactant parameters controlMagnesium halidesAlkaline earth metalAmmonia storage
An electric power generating unit comprising (i) an ammonia storage device in the form of a container comprising an ammonia absorbing and releasing salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals such as Li, K, Mg, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu or Zn, X is one or more anions selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, thiocyanate, sulphate, molybdate, phosphate, and chlorate ions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, Z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and n is the coordination number of 2 to 12. (ii) means for heating said container and ammonia absorbing and releasing salt for releasing ammonia gas and (iiia) a fuel cell for converting ammonia directly into electric power; or (iiib1) a reactor for dissociating ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen and (iiib2) a fuel cell for converting hydrogen into electric power is useful for large stationary energy producing facilities, but also for use for is useful for large stationary energy producing facilities, but also for use for small rechargeable and / or replaceable power supply units for micro-fabricated or miniaturized ammonia decomposition reactors for use in mobile units and portable devices may be used for large energy producing facilities, and by use of small rechargeable and / or replaceable ammonia storage decomposition reactors, it is also possible to provide energy for mobile units and portable devices.
Owner:AMMINEX
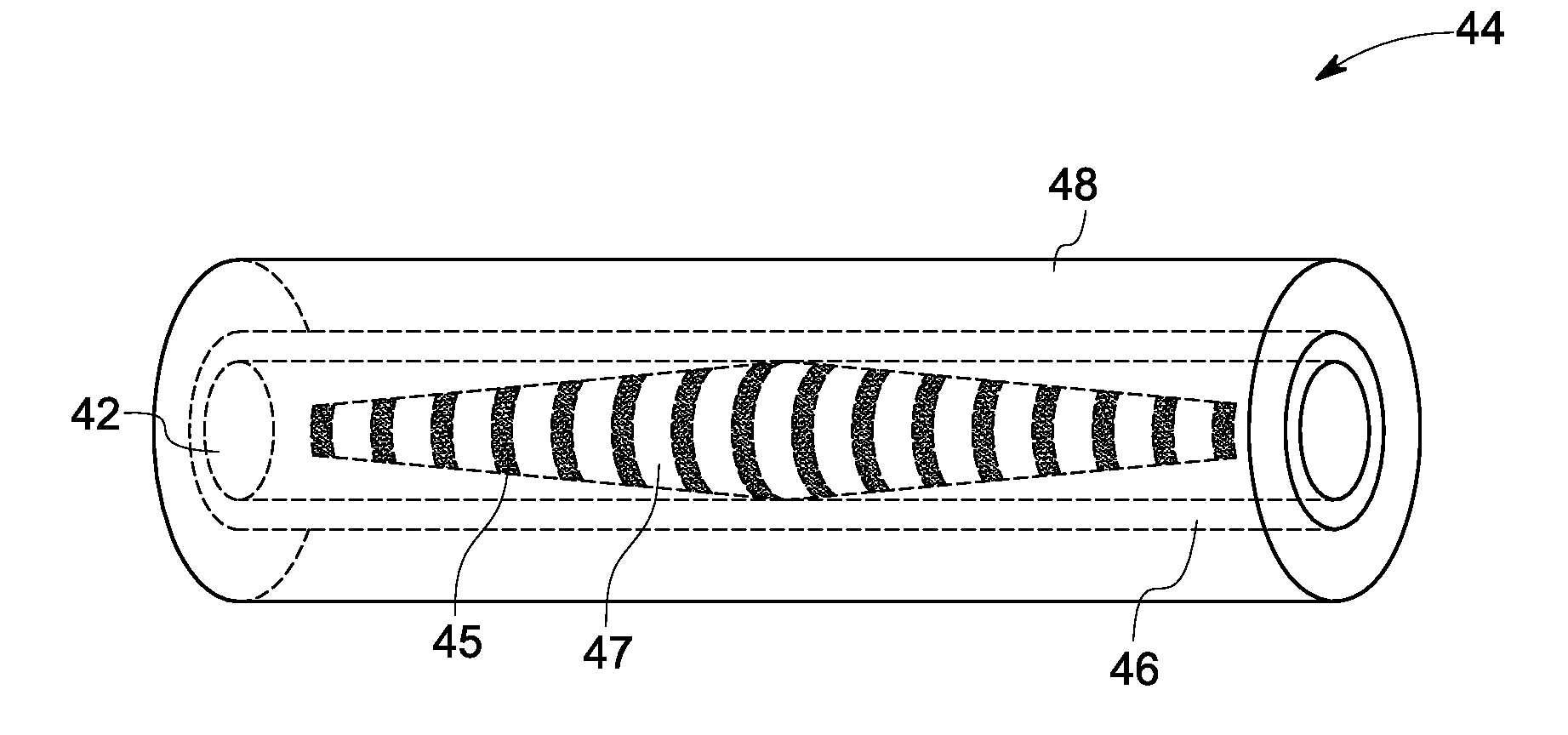
Intermediate precursor compositions used to make supported catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for preparing such compositions
ActiveUS20050014636A1Reduce molecular weightReduce the possibilityHydrogenMolecular sieve catalystsChemical reactionHydrogen
Intermediate precursor compositions for use in manufacturing supported reactive catalysts having a controlled coordination structure, and methods for manufacturing such precursor compositions are disclosed. The precursor compositions include a catalyst complex formed from catalyst atoms and a control agent that is applied to a substrate. Reduction of the catalyst complex yields supported reactive catalyst in which a preponderance of the top or outer layer of atoms of the catalyst particles exhibit a controlled coordination number of 2. The supported catalysts are useful for a variety of chemical reactions, including the preparation of hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20070228427A1Increasing oxygen coordination numberHigh dielectric constantTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricEngineering
HfO2 films and ZrO2 films are currently being developed for use as capacitor dielectric films in 85 nm technology node DRAM. However, these films will be difficult to use in 65 nm technology node or later DRAM, since they have a relative dielectric constant of only 20-25. The dielectric constant of such films may be increased by stabilizing their cubic phase. However, this results in an increase in the leakage current along the crystal grain boundaries, which makes it difficult to use these films as capacitor dielectric films. To overcome this problem, the present invention dopes a base material of HfO2 or ZrO2 with an oxide of an element having a large ion radius, such as Y or La, to increase the oxygen coordination number of the base material and thereby increase its relative dielectric constant to 30 or higher even when the base material is in its amorphous state. Thus, the present invention provides dielectric films that can be used to form DRAM capacitors that meet the 65 nm technology node or later.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
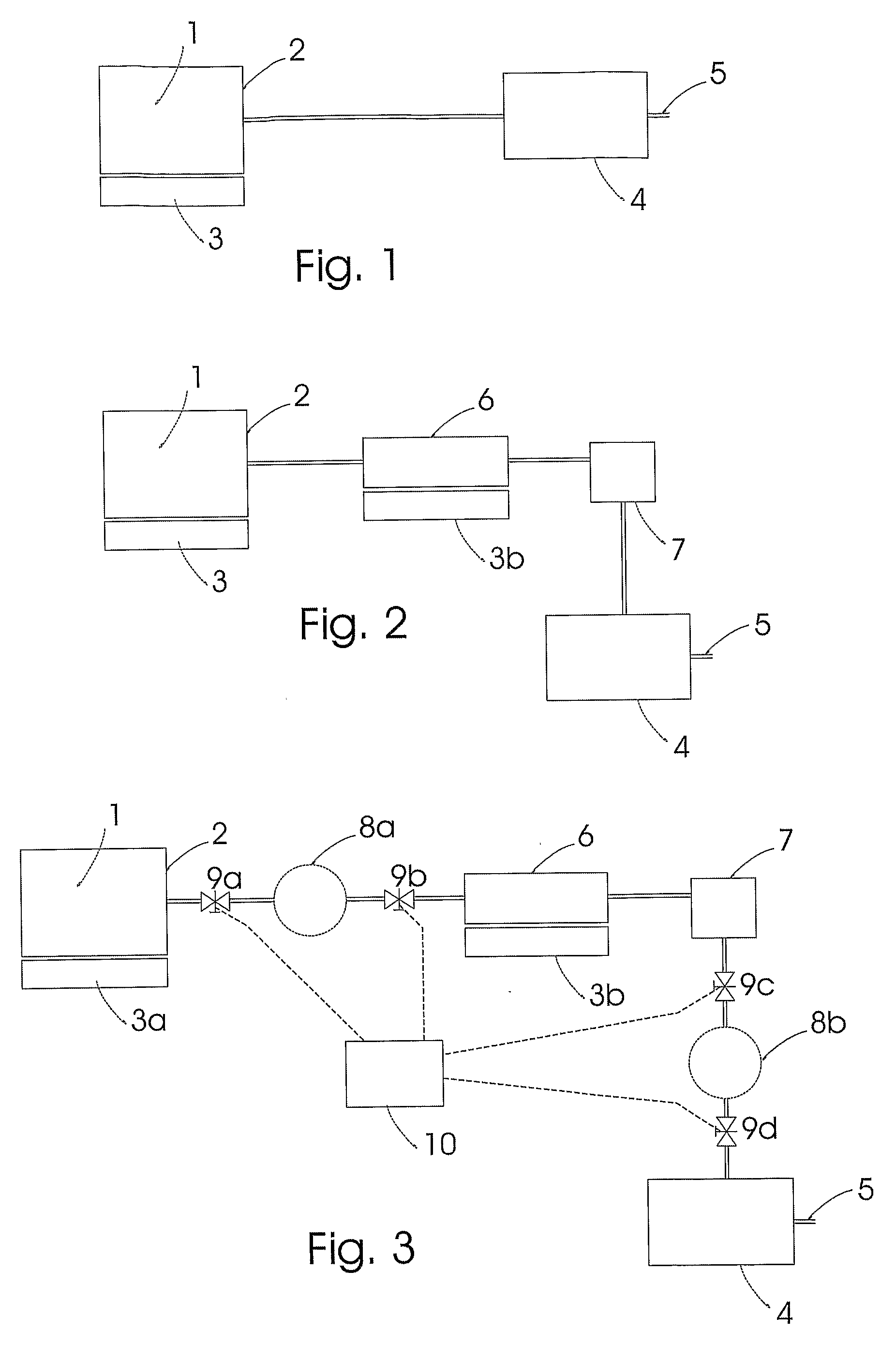
Method and device for safe and controlled delivery of ammonia from a solid ammonia storage medium
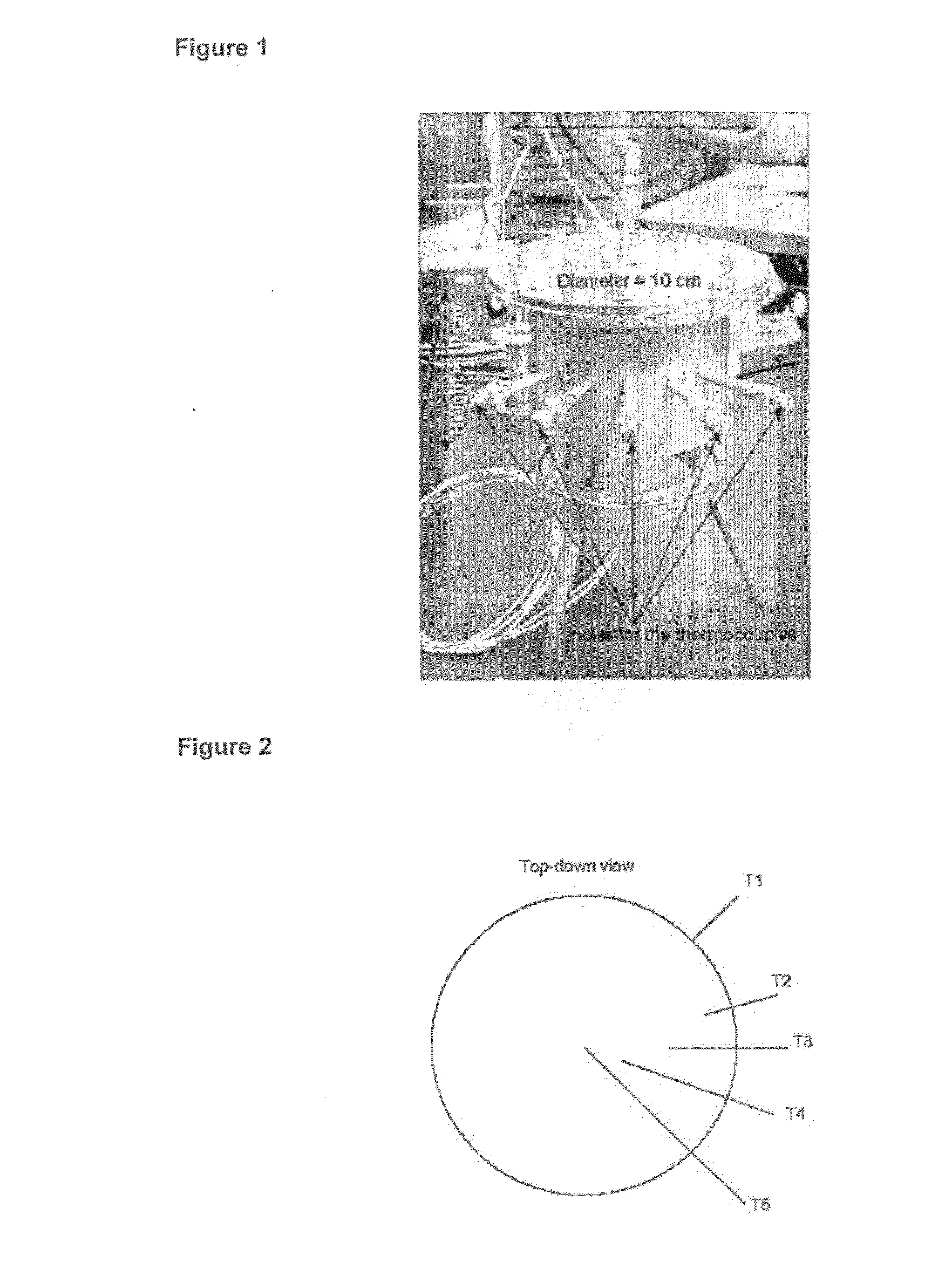
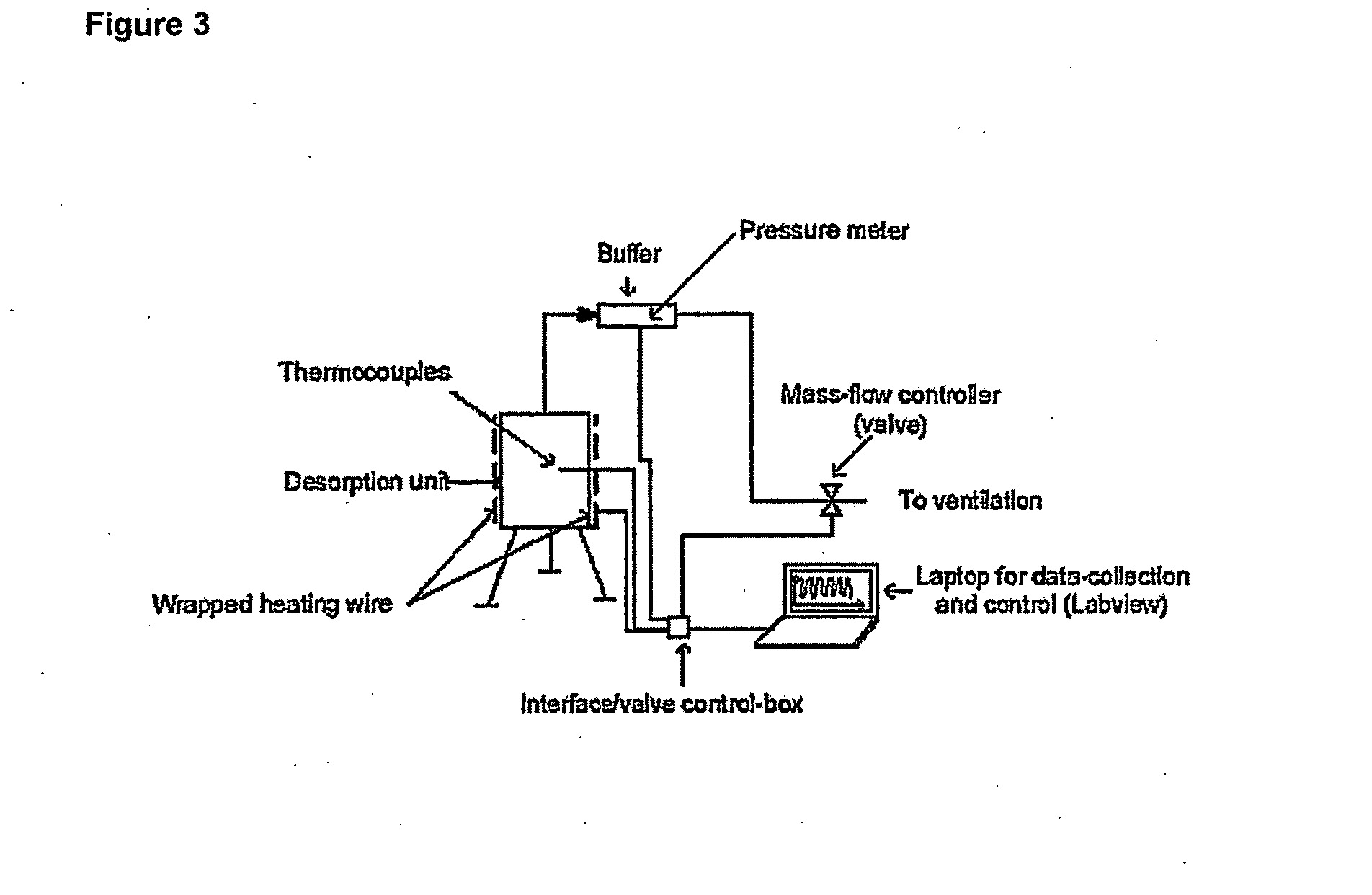
InactiveUS20100293927A1Facilitated releaseReduce the temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusGas phaseDesorption
Solid metal ammine complexes are applied for safe and high-density storage of ammonia to be released for use as reducing agent in selective catalytic reduction of NOx in exhaust gases. The compositional formula of the metal ammine complexes is M(NH3)nXz, where MZ+ represents one or more metal ions capable of binding ammonia, X represents one or more anions, n is the coordination number (from 2 to 12), and z the valency of the metal ion (and thus the total number of compensating anion charges). Ammonia is released by generating a reduced gas-phase pressure of ammonia inside the container, which is below the equilibrium desorption pressure of ammonia at the operating temperature of the storage material thus enabling the unit to be operated is a safe manner with lower operating temperature and pressure.
Owner:AMMINEX
Intermediate precursor compositions used to make supported catalysts having a controlled coordination structure and methods for preparing such compositions
InactiveUS7045479B2Reaction selectivity would be expected to be even further increasedReaction selectivity can be maximizedHydrogenMolecular sieve catalystsHydrogenChemical reaction
Intermediate precursor compositions for use in manufacturing supported reactive catalysts having a controlled coordination structure, and methods for manufacturing such precursor compositions are disclosed. The precursor compositions include a catalyst complex formed from catalyst atoms and a control agent that is applied to a substrate. Reduction of the catalyst complex yields supported reactive catalyst in which a preponderance of the top or outer layer of atoms of the catalyst particles exhibit a controlled coordination number of 2. The supported catalysts are useful for a variety of chemical reactions, including the preparation of hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Oxygen ion conducting materials
InactiveUS6916570B2Improve conductivityHigh activityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesDopantFuel cells
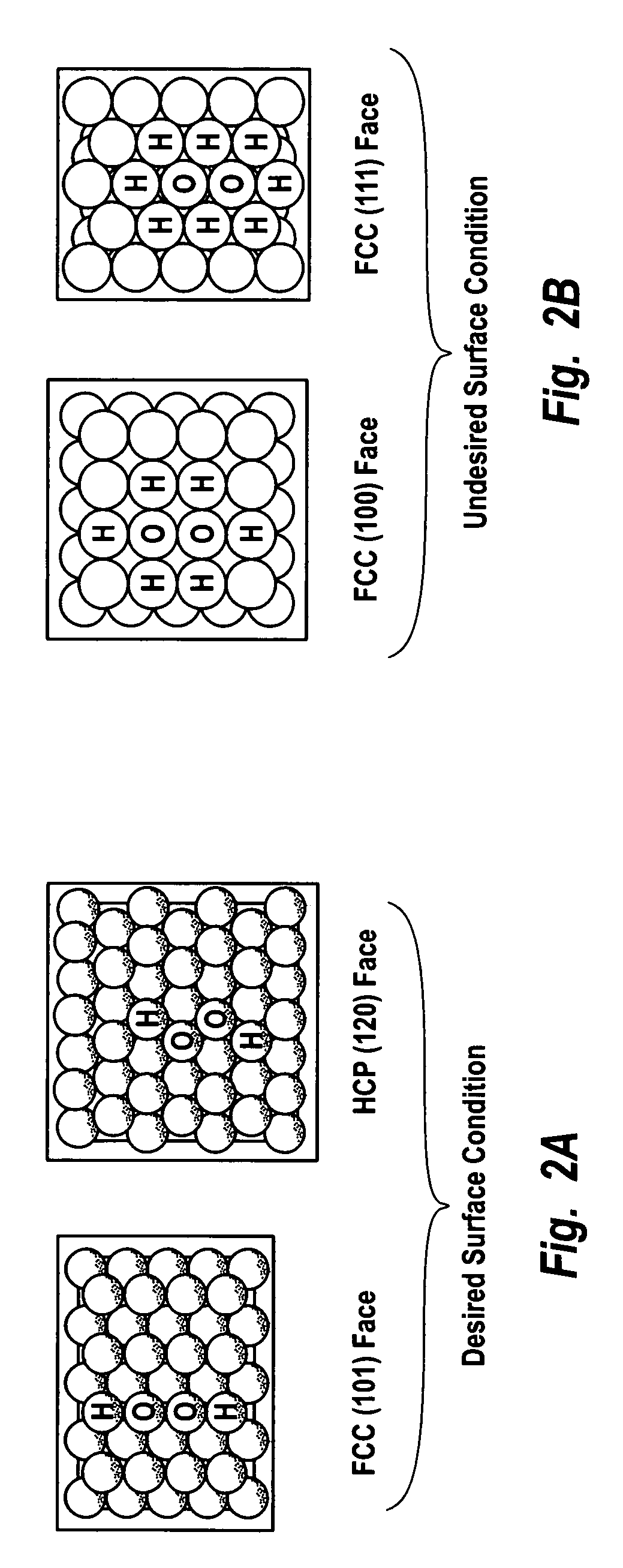
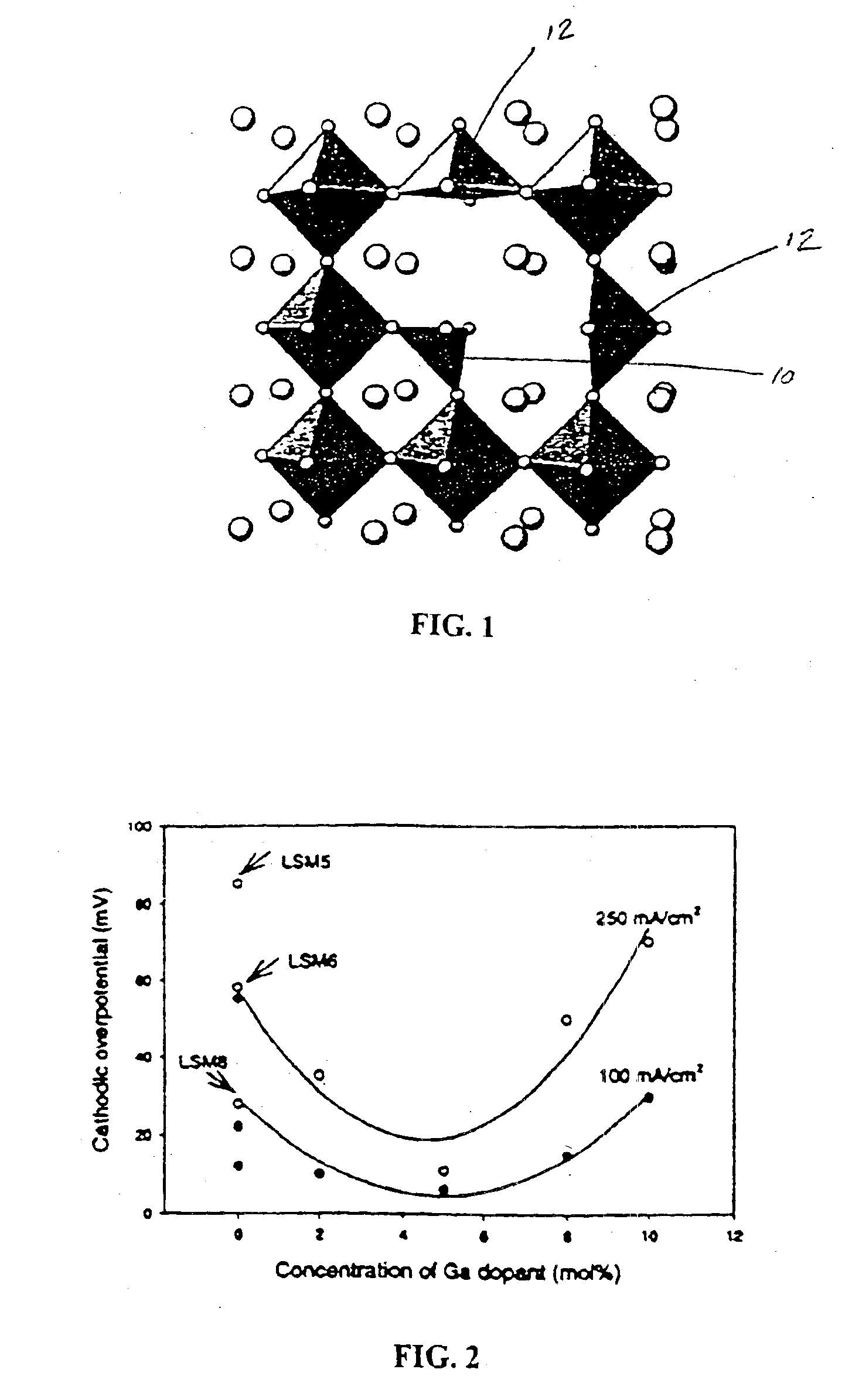
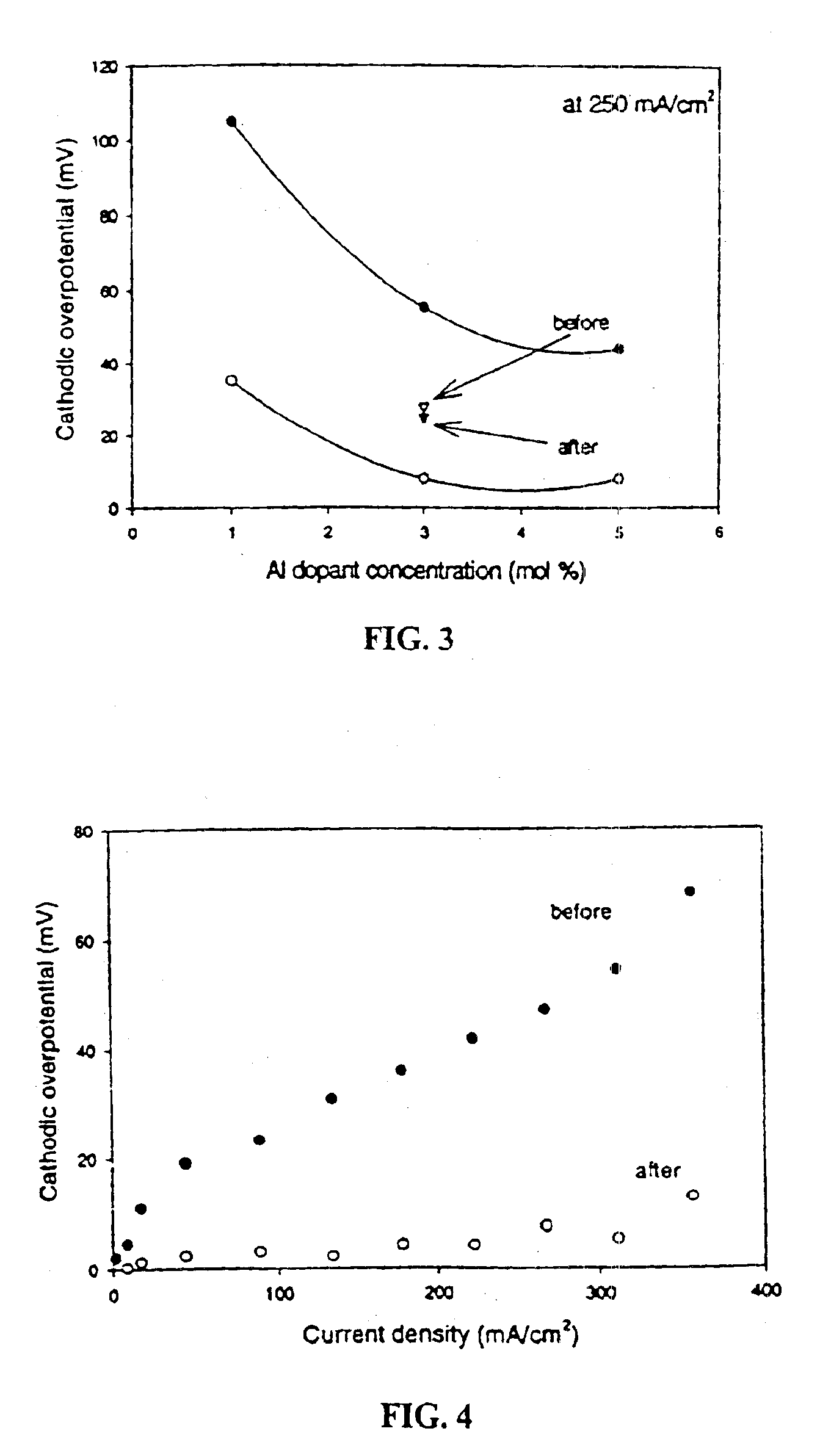
An oxygen ion conducting ceramic oxide that has applications in industry including fuel cells, oxygen pumps, oxygen sensors, and separation membranes. The material is based on the idea that substituting a dopant into the host perovskite lattice of (La,Sr)MnO3 that prefers a coordination number lower than 6 will induce oxygen ion vacancies to form in the lattice. Because the oxygen ion conductivity of (La,Sr)MnO3 is low over a very large temperature range, the material exhibits a high overpotential when used. The inclusion of oxygen vacancies into the lattice by doping the material has been found to maintain the desirable properties of (La,Sr)MnO3, while significantly decreasing the experimentally observed overpotential.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
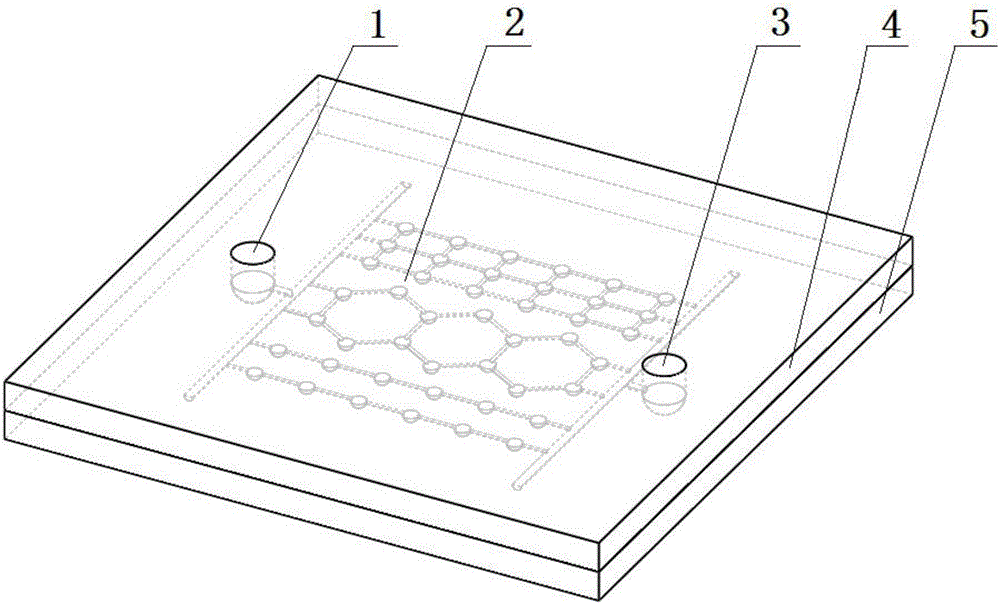
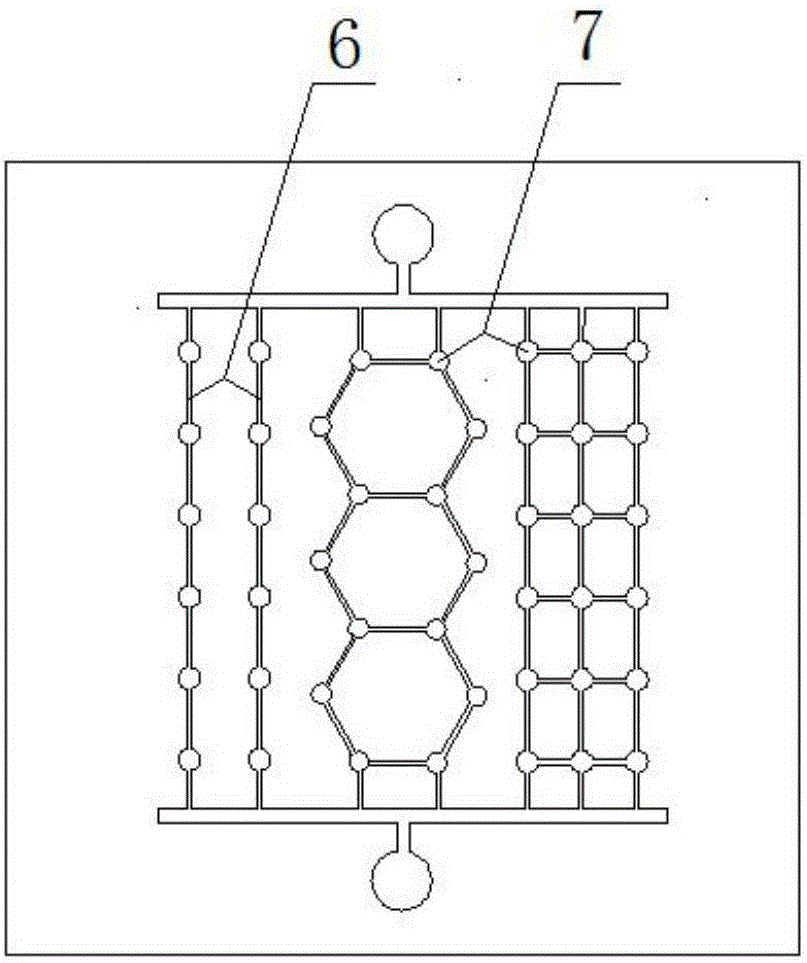
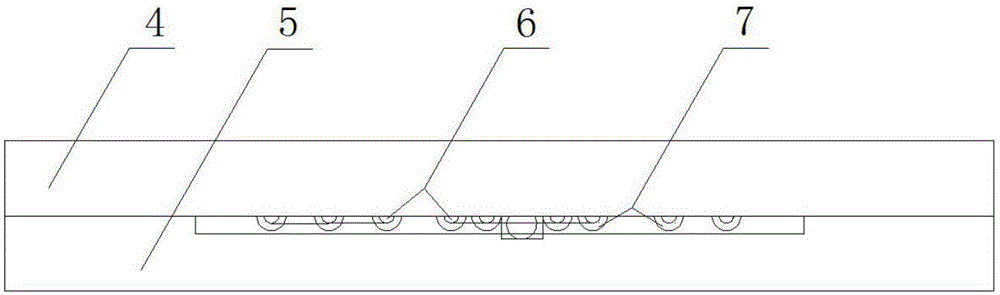
Visual micro-pore structure simulation physical model and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105869496AMeet the requirements of high temperature and high pressure experimentsEasy to observeEducational modelsEpoxyThroat
The invention mainly belongs to the technical field of oil and gas field microcosmic mechanism research and particularly relates to a visual micro-pore structure simulation physical model and a manufacturing method thereof. The simulation physical model comprises a primary board and a secondary board. The secondary board comprises an injection port and a recovery port. The primary board is formed by mixing epoxy resin and a curing agent. The secondary board is formed by processing planar optical glass. The primary board comprises a pore network structure which is composed of three parts. The front ends of the three parts of the pore network structure are connected with the injection port through a common throat, and the tail ends of the three parts of the pore network structures are connected with the recovery port through a common throat. By means of the method, the throat diameter, any throat-to-pore ratio and various coordination numbers under micrometer size can be achieved, and the manufactured physical model is good in transparency, high in visualization and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Solid ammonia storage and delivery material
InactiveUS20090280047A1Cobalt ammonia complexesNitrogen compoundsAlkaline earth metalAmmonia storage
A solid ammonia storage and delivery material A solid ammonia storage material comprising: an ammonia absorbing salt, wherein the ammonia absorbing salt is an ionic salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkaline earth metals, and / or one or more transition metals, such as Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and / or Zn, X is one or more anions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and ri is the coordination number of 2 to 12, wherein M is Mg provides a safe, light-weight and cheap compact storage for ammonia to be used in the automotive industry.
Owner:AMMINEX EMISSIONS TECH
Fiber Bragg grating and fabrication method
ActiveUS7574075B2Increase photosensitivityIncrease the number ofGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberGrating
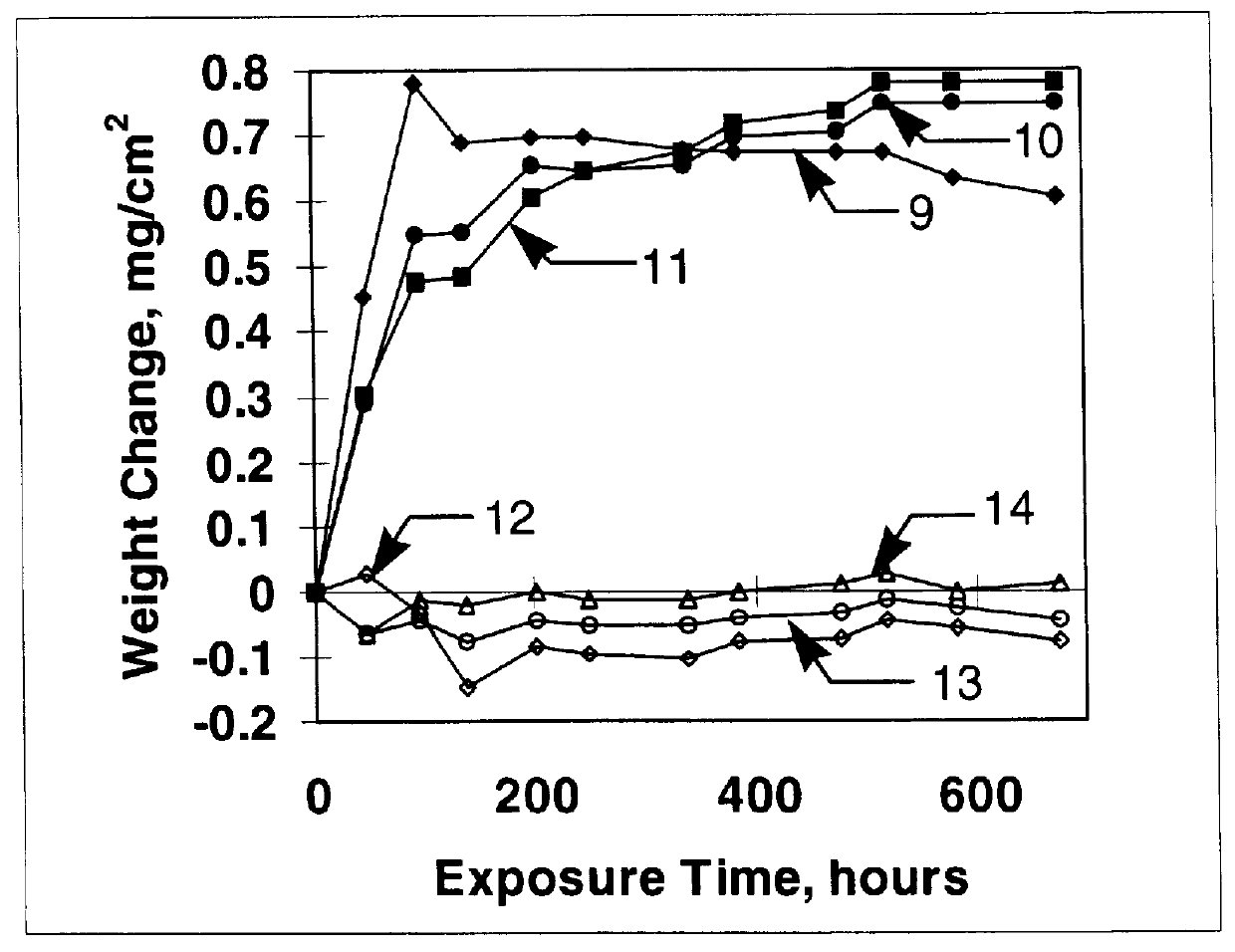
A method of fabrication of a thermally stabilized Type I fiber Bragg grating-based temperature sensing device includes doping a fiber core material with germanium or germanium oxide for enhancing photosensitivity, co-doping the fiber core material with fluorine or chorine or for increasing a mean coordination number; and ultraviolet laser inscribing a periodic or quasiperiodic modulated refractive index structure in the fiber core using a laser energy operating at less than 1000 milliJoules per square centimeter per pulse. The resulting sensor is operable for more than 1000 hours at temperatures up to at least 550 degrees Celsius.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Porous medium water saturation calculation method based on network simulation
InactiveCN102540265AAvoid errorsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentPressure curveCapillary pressure
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
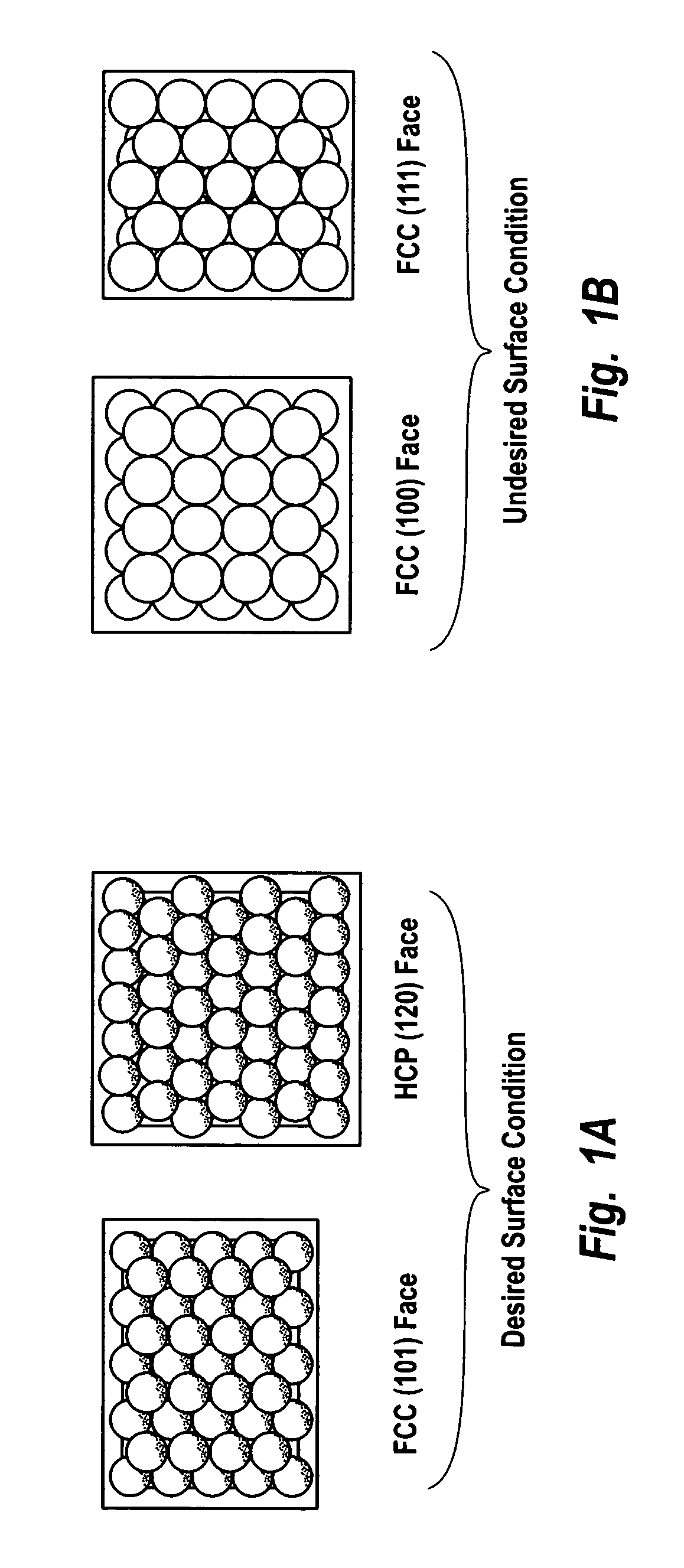
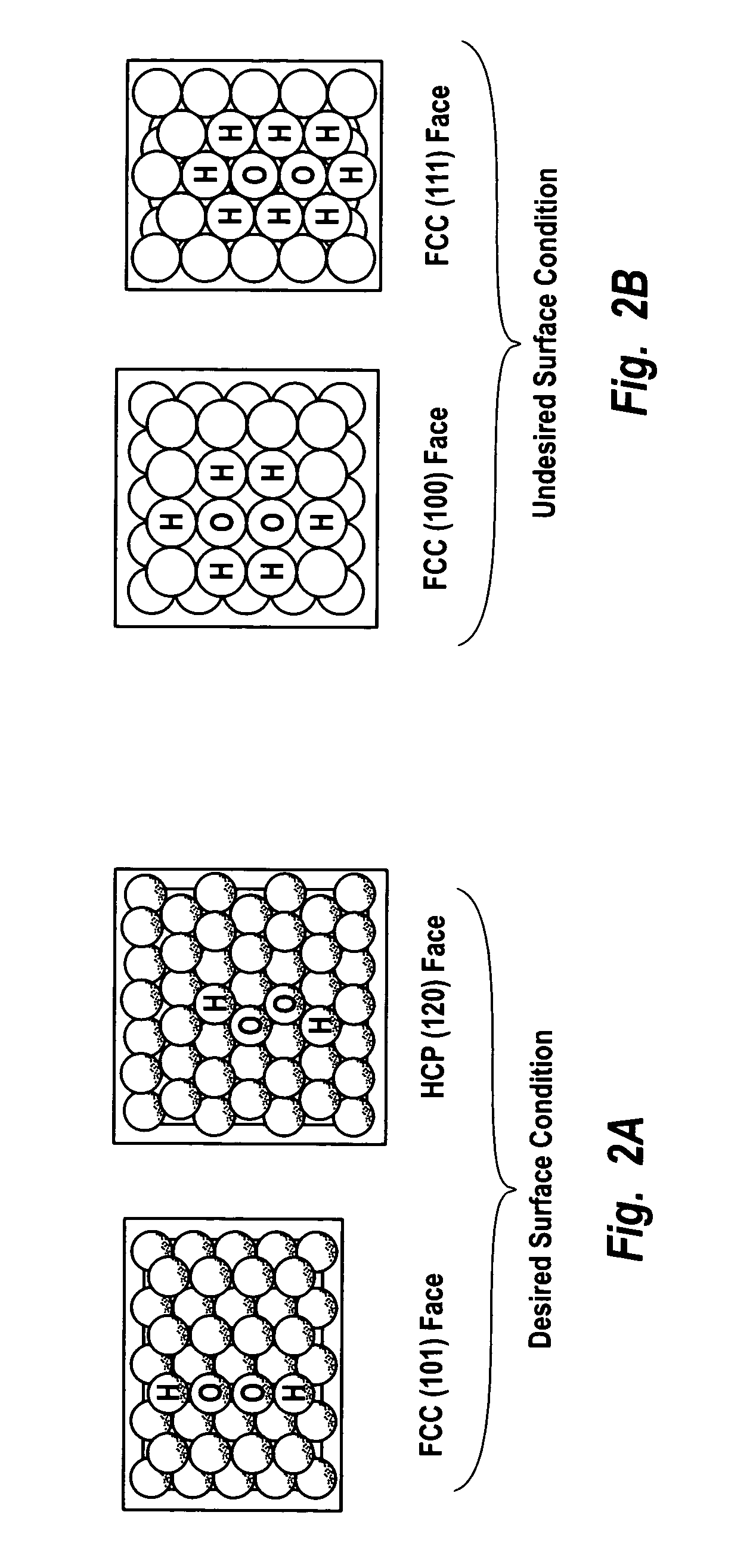
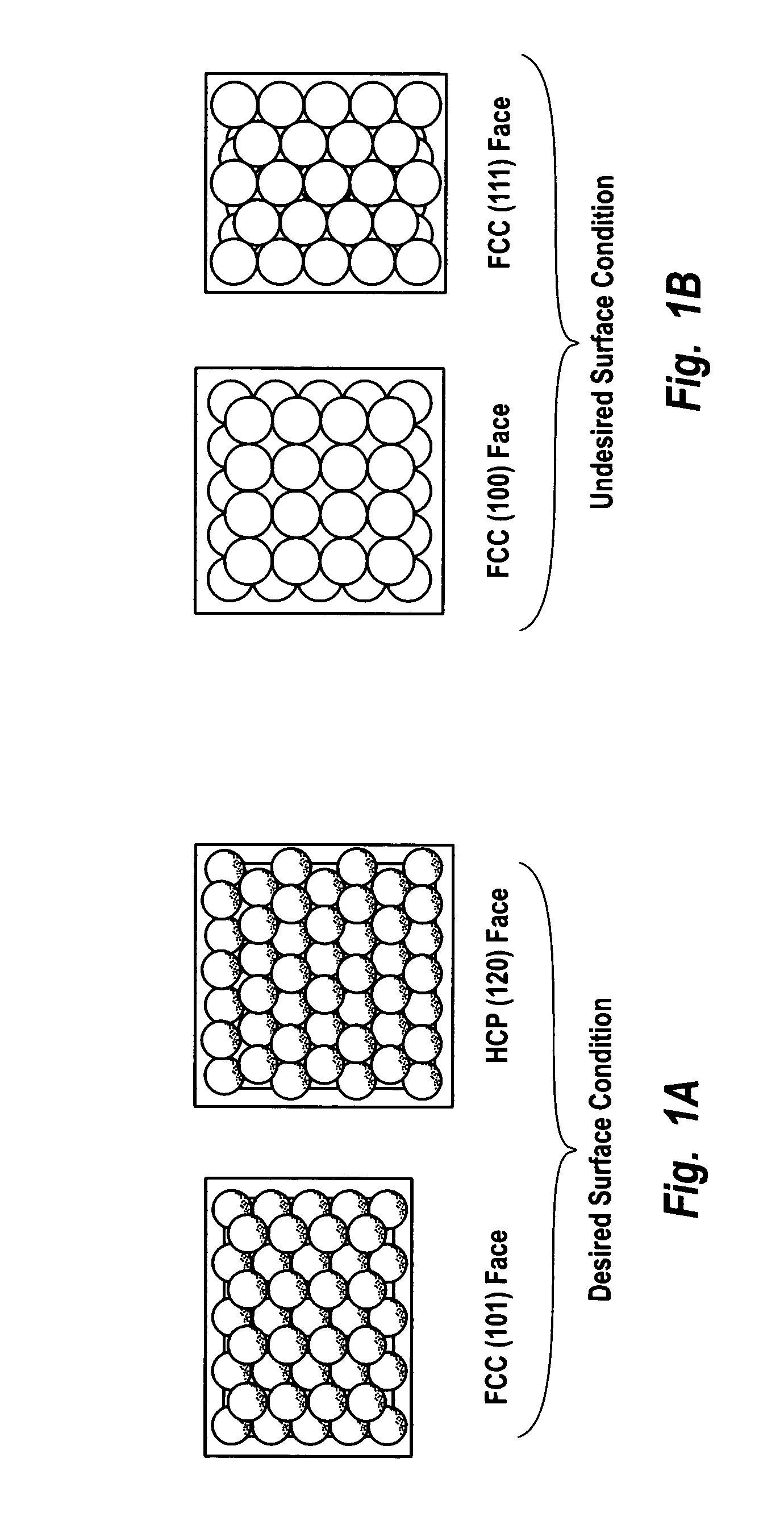
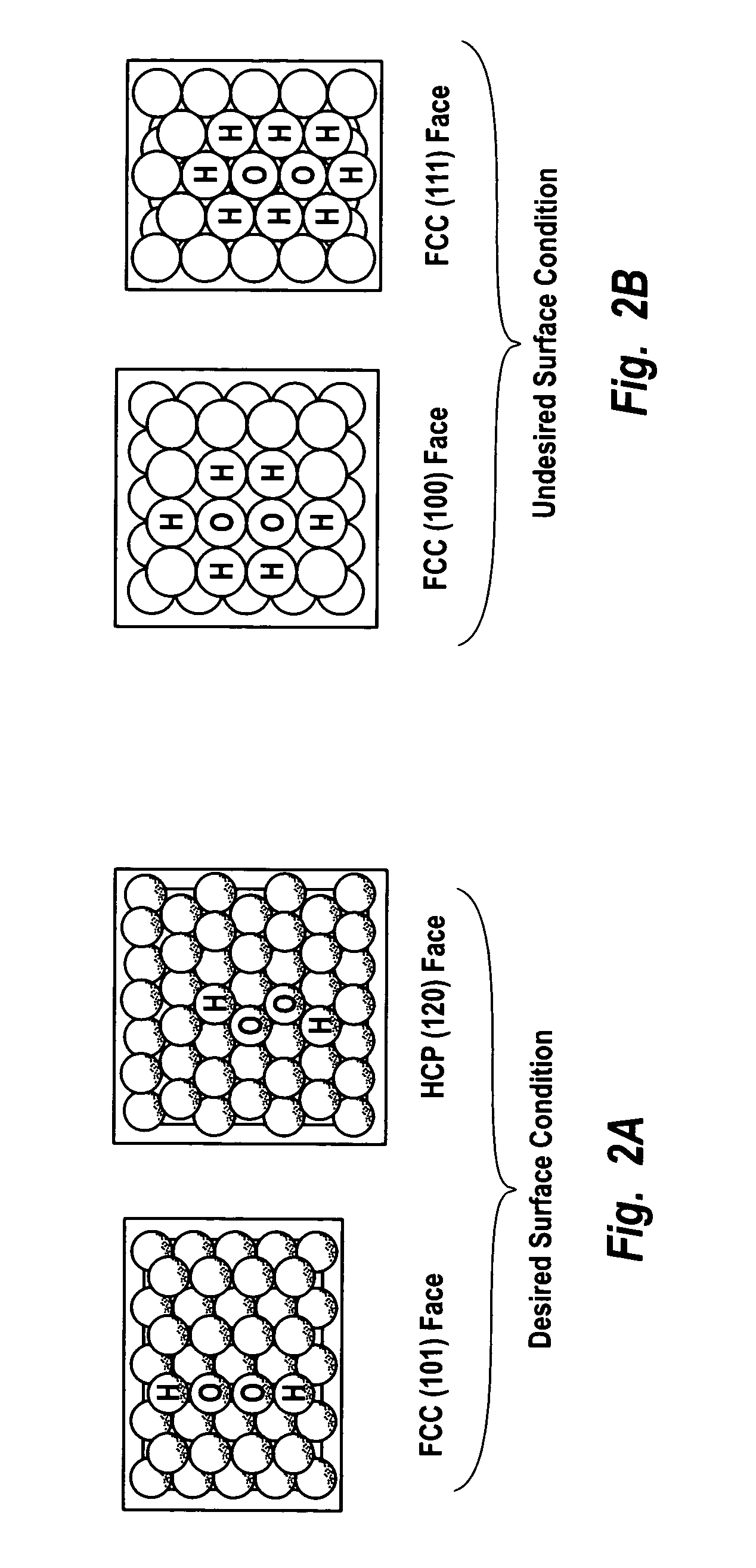
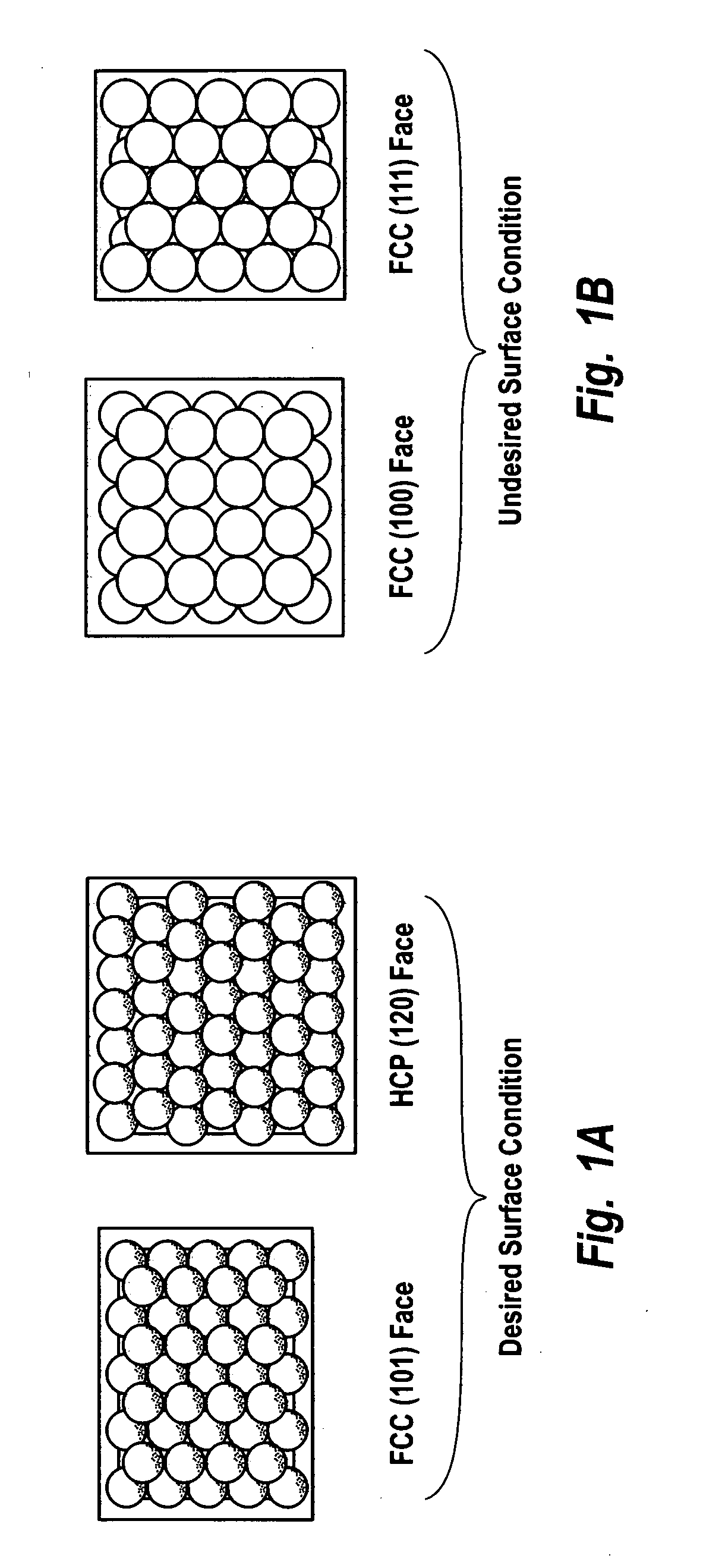
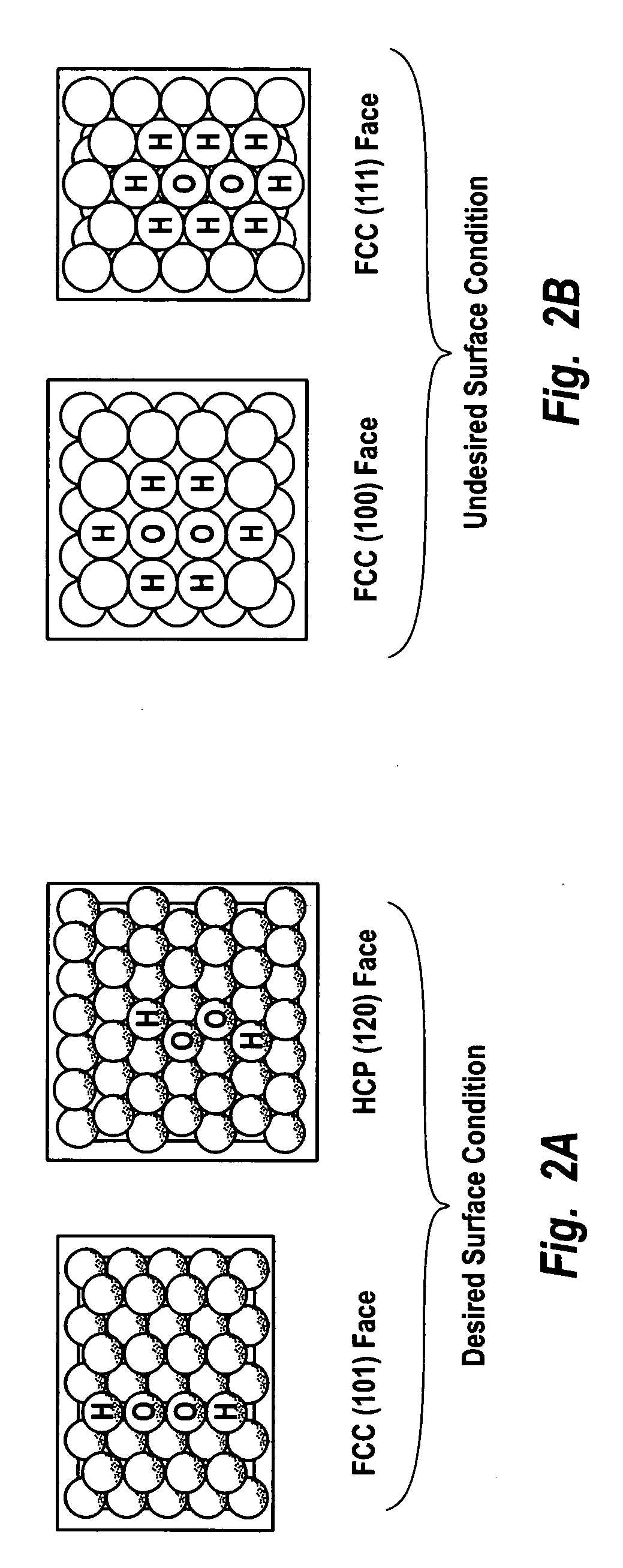
Hydrogen peroxide production using catalyst particles with controlled surface coordination number
InactiveUS20040018143A1Increase concentrationHigh yieldHydrogen peroxideCatalyst activation/preparationOrganic fluidNear neighbor
A process for catalytically producing hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen feeds by contacting them with a supported noble metal catalyst and a suitable organic liquid solvent having a Solvent Selection Parameter (SSP) between 0.14x10<-4 >and 5.0x10<-4 >at reaction condition of 0-100° C. temperature and 100-3,000 psig pressure. The catalyst comprises supported noble metal particles having an exposed crystal face atomic surface structure comprising atoms exhibiting a controlled coordination number of two (2). The nearest neighbors of each top-layer atom are two other top-layer atoms, also having a controlled coordination number of two (2).
Owner:HYDROCARBON TECH
Fiber bragg grating for high temperature sensing
ActiveUS20090074347A1Increase photosensitivityIncrease the number ofGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberGrating
A method of fiber core material band gap engineering for artificially modifying fiber material properties is provided. The method includes doping the fiber core material with one or more atoms for enhancing photosensitivity to the fiber material. The method also includes co-doping the fiber core material with one or more ions for enhancing an amorphous network crosslink mean coordination number. The method further includes thermally annealing the fiber core material for widening the band gap of the fiber core material.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method of Storing and Delivering Ammonia and the Use of Electromagnetic Radiation for Desorption of Ammonia from a Chemical Complex
InactiveUS20090313976A1High NOx ConversionMinimizing ammonia slipNitrous oxide captureCombination devicesDesorptionBiological activation
A method of storing and delivering ammonia and the use of electromagnetic radiation for desorption of ammonia from a chemical complex. Solid metal ammine complexes are applied for safe and high-density storage of ammonia to be released for use as reducing agent in selective catalytic reduction of NOx in exhaust gases. The compositional formula of the metal ammine complexes is M(NH3)nXz, where M2+ represents one or more metal ions capable of binding ammonia, X represents one or more anions, n is the coordination number (from 2 to 12), and z the valency of the metal ion (and thus the total number of compensating anion charges). Ammonia is released non-thermally by photon-activation using electromagnetic irradiation of the complex bond between ammonia coordinated to the metal ion
Owner:AMMINEX EMISSIONS TECH
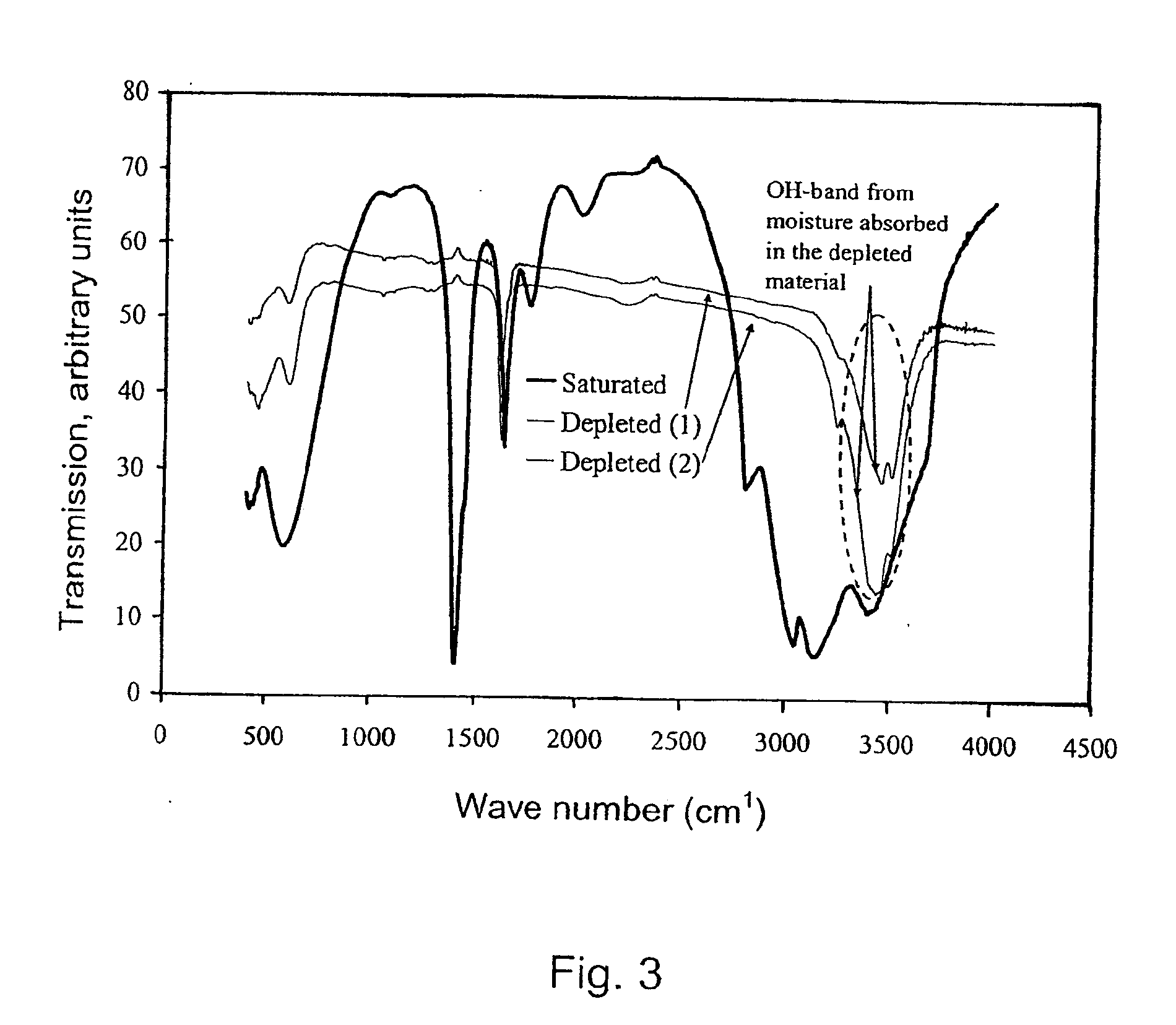
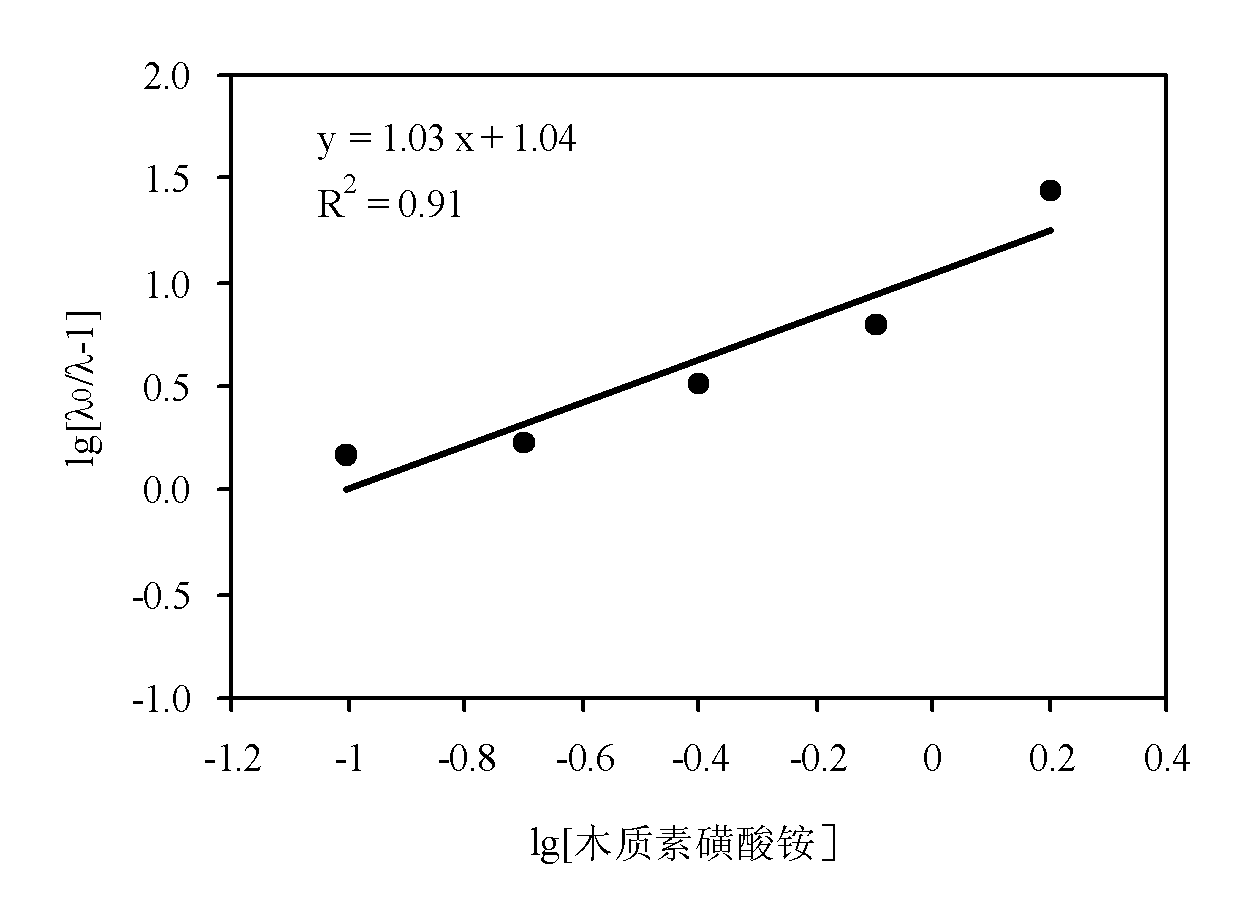
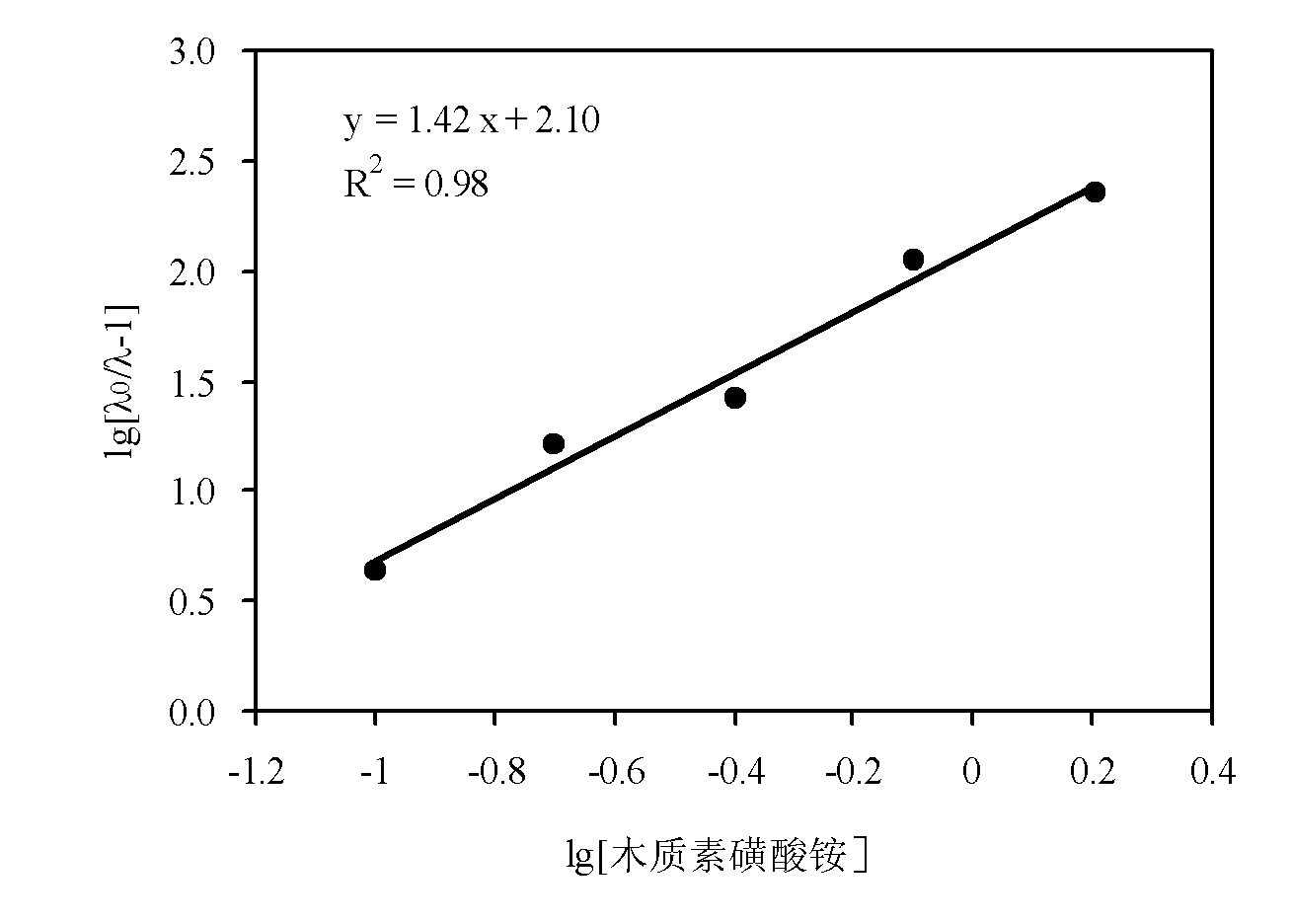
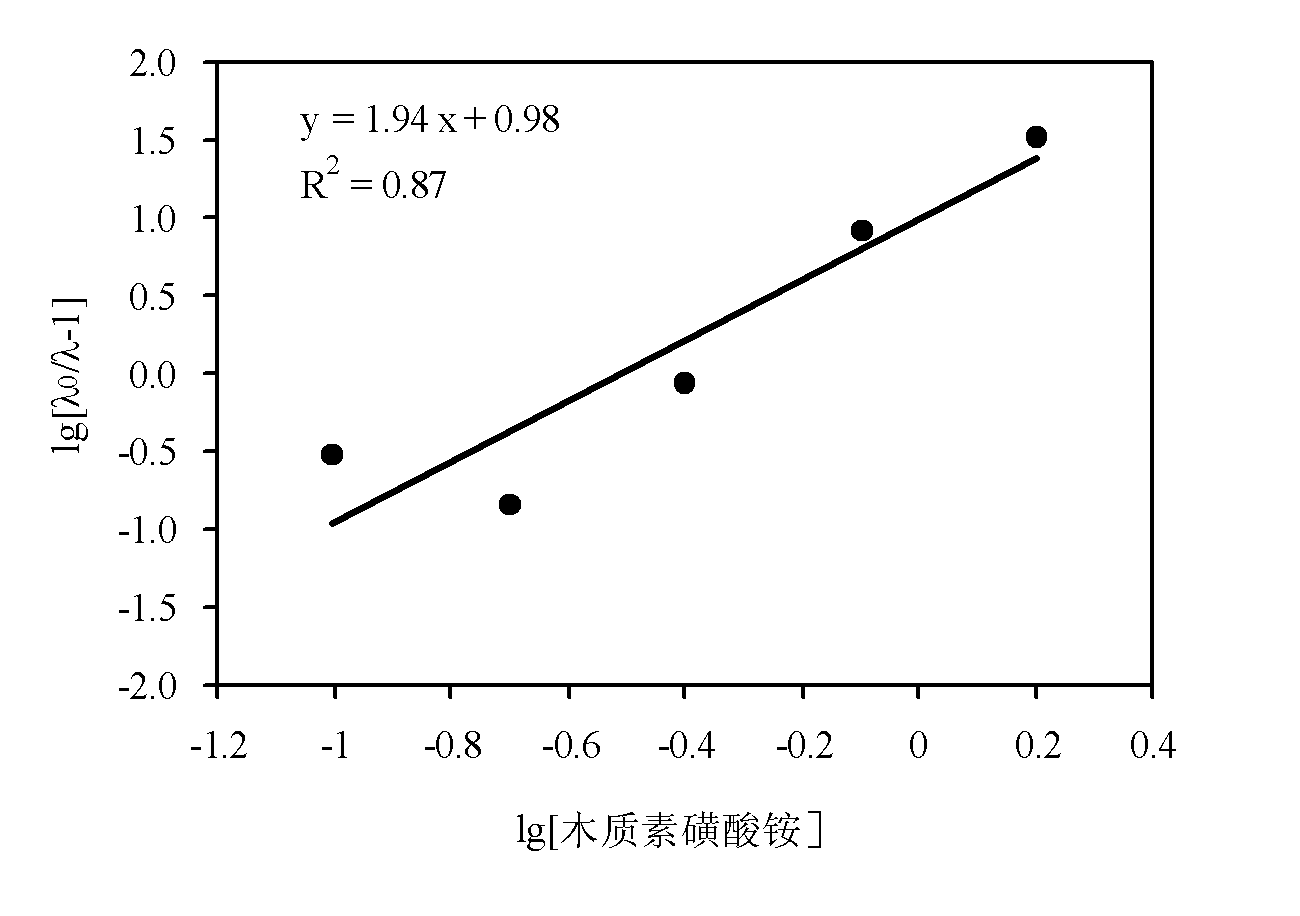
Trace metal element Chelation fertilizer in lignin and application thereof
InactiveCN101941860AStrong chelating abilityGood fertilizer effectFertilizer mixturesStability parameterTrace metal
The invention provides a trace metal element chelation fertilizer in lignin and application thereof. The trace metal element chelation fertilizer in the lignin is a mixture of lignosulfonate and metal element chelates and shows the following physical-chemical characteristics of: 1, appearance: white powder; and 2, stability parameters of chelate: the average coordination number x is between 0.9 and 1.95 and the stability constant 1gK is between 0.6 and 2.10; and 3, the metallic chelation rate is 10 to 13.55 percent. The lignosulfonate-metal element chelation fertilizer is prepared by performing oxidative modification reaction on paper-making waste liquid lignosulfonate and metal elements such as iron, zinc and copper which serve as raw materials, and the chelation property of lignin ammonium is quantitatively described by measuring the stability of the chelates of lignin ammonium-Fe and lignin ammonium-Zn. The industrial lignin and the metal elements form the 'lignin-metal elements' chelates, and the obtained chelates are dried to form solid products or the obtained chelates after proper concentration can be mixed with other kinds of fertilizers to prepare various compound fertilizers.
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG +1
Method for extracting copper from scrap copper through wet process
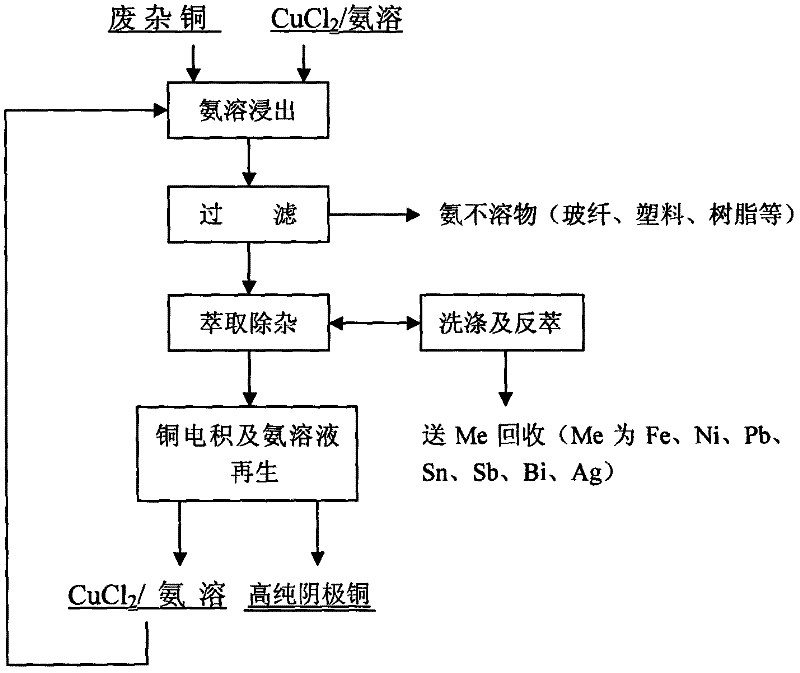
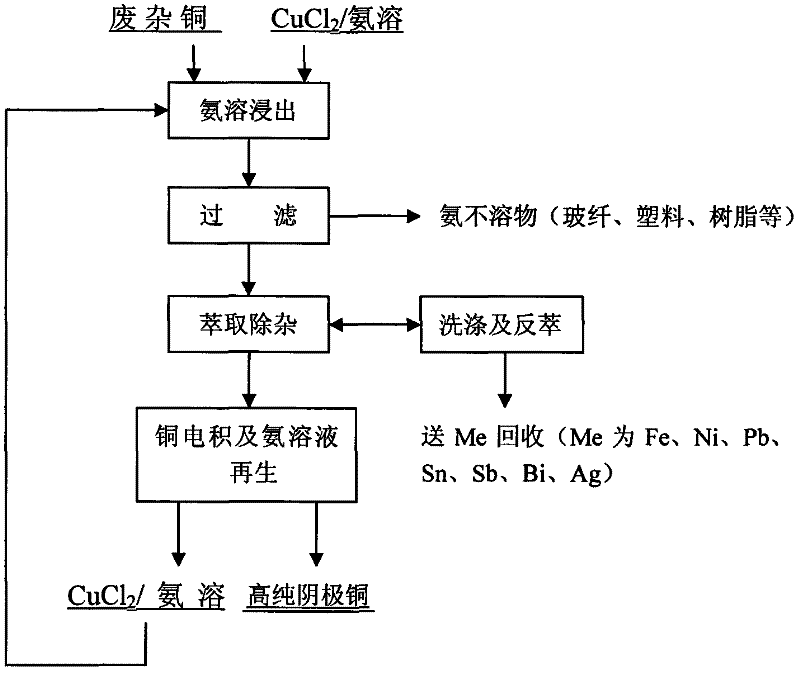
InactiveCN102443703ALower specific resistanceReduce concentration overpotentialPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper from scrap copper through a wet process. The method comprises the steps of: A) ammonia dissolving leaching: putting scrap copper in a multicomponent solution of ammonia, an ammonia salt, a monovalent chloride, and a divalent copper chloride to form an appropriate electric potential, and reacting the scrap copper with ammonia complex ions so as to be dissolved in the multicomponent solution and generate stable monovalent copper complex ions, filtering out most of metal element impurities Fe, Ni, Al, Sn and Pb from the scrap copper, leaving a small amount of impurities to undergo an oxidation reaction and react with ammonia molecules to generate complex ions of different coordination numbers and exist in the solution; B) extraction for impurity removing: extracting impurities Ag, Fe, Ni, Zn, Bi, Cr, Mn, Sb, Pb, and Sn into an organic phase, and keeping the monovalent copper complex ions in the solution; C) diaphragm electrolytic deposition for preparing high-purity cathode copper: carrying out electrolytic deposition of copper in the cathode chamber of a negative ion membrane electrolyzer, thus obtaining a well crystallized negative copper plate. The method of the invention is characterized by environmental protection and low energy consumption, and can generate high-purity copper directly.
Owner:周毅舟
Stabilized two-phase-glass diffusion barrier
InactiveUS6071622ALiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingGlass/slag layered productsSolubilityDissolution
An article with a corrosion-resistant diffusion barrier is provided to resist the attack of corrosion agents, during service at high temperature (>600 DEG C.). More specifically, a diffusion barrier containing a stabilized two-phase glass is provided. The stabilized two-phase glass comprises glass-forming oxides, other oxides with low cation coordination numbers and stabilizing agents wherein the glass-forming oxides block ionic transport by virtue of their network formation on the atomic scale and the stabilizing agents improve the stability of the diffusion barrier and compatibility with the substrate. The diffusion barrier covers some portion of the substrate that is optionally augmented by a base layer or a sealant layer. Being impervious and having low-solubility in corrosive environments, the diffusion barrier stops corrosive agents from reaching the substrate. When applied over aluminide coatings, it effectively improves the potency of the aluminides and prevents their rapid dissolution into the corrosive environment. The diffusion barrier can be applied by a process that evenly coats intricate geometries and does not harm substrate properties.
Owner:ANALYTICAL SERVICES & MATERIALS
Fiber Bragg grating for high temperature sensing
ActiveUS7499605B1Increase photosensitivityIncreased band gapGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberGrating
A method of fiber core material band gap engineering for artificially modifying fiber material properties is provided. The method includes doping the fiber core material with one or more atoms for enhancing photosensitivity to the fiber material. The method also includes co-doping the fiber core material with one or more ions for enhancing an amorphous network crosslink mean coordination number. The method further includes thermally annealing the fiber core material for widening the band gap of the fiber core material.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Dielectric ceramic composite and electronic device
InactiveCN1432548AAccelerated life is not improvedInhibition of segregationAlkaline earth titanatesFixed capacitor dielectricRare-earth elementCapacitance
A dielectric ceramic composition, comprising a main component including barium titanate, a fourth subcomponent including an oxide of R1 (note that R1 is at least one kind selected from a first element group composed of rare-earth elements having a effective ionic radius of less than 108pm when having a coordination number of nine), and a fifth subcomponent including an oxide of R2 (note that R2 is at least one kind selected from a second element group composed of rare-earth elements having a effective ionic radius of 108pm to 113pm when having a coordination number of nine). According to the composition, a dielectric ceramic composition having excellent reducing resisting property at firing, excellent temperature. dependence of capacitance after firing, and improved accelerated lifetime of insulation resistance can be provided.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS7728376B2High dielectric constantIncrease semaphoreTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricEngineering
HfO2 films and ZrO2 films are currently being developed for use as capacitor dielectric films in 85 nm technology node DRAM. However, these films will be difficult to use in 65 nm technology node or later DRAM, since they have a relative dielectric constant of only 20-25. The dielectric constant of such films may be increased by stabilizing their cubic phase. However, this results in an increase in the leakage current along the crystal grain boundaries, which makes it difficult to use these films as capacitor dielectric films. To overcome this problem, the present invention dopes a base material of HfO2 or ZrO2 with an oxide of an element having a large ion radius, such as Y or La, to increase the oxygen coordination number of the base material and thereby increase its relative dielectric constant to 30 or higher even when the base material is in its amorphous state. Thus, the present invention provides dielectric films that can be used to form DRAM capacitors that meet the 65 nm technology node or later.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Anionic type gold complex and application thereof
InactiveCN102731536AImprove stabilitySafe and reliableLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingGold organic compoundsChemical platingChemical compound
The invention belongs to the field of anionic type gold complex, and specifically provides an anionic type gold complex and an application thereof. The complex is characterized in that: a complex anion [AualphaLm]<-phi> formed by gold and a ligand contanining no free cyanogen (also known as complexing agent) L is adopted as a core component. Phi is the negative charge number of the complex anion [AualphaLm]<-phi>. The general chemical formula of a corresponding gold compound is Mr[AualphaLm]q.bH2O. L represents the ligand containing no free cyanogens, m represents a coordination number, M and r respectively represents an anion and a number thereof, b represents the number of crystal water, and alpha, m and phi are positive integers which are not 0. With a coordination reaction of a material containing gold and a material containing the ligand L, the compound can be prepared. The compound can be applied in fields such as electroplating and chemical plating.
Owner:长沙铂鲨环保设备有限公司
Method for forecasting pore medium transverse wave velocity which varies with pressure
ActiveCN103576196AEasy to analyzeEasy to identifySeismic signal processingShear modulusWeight coefficient
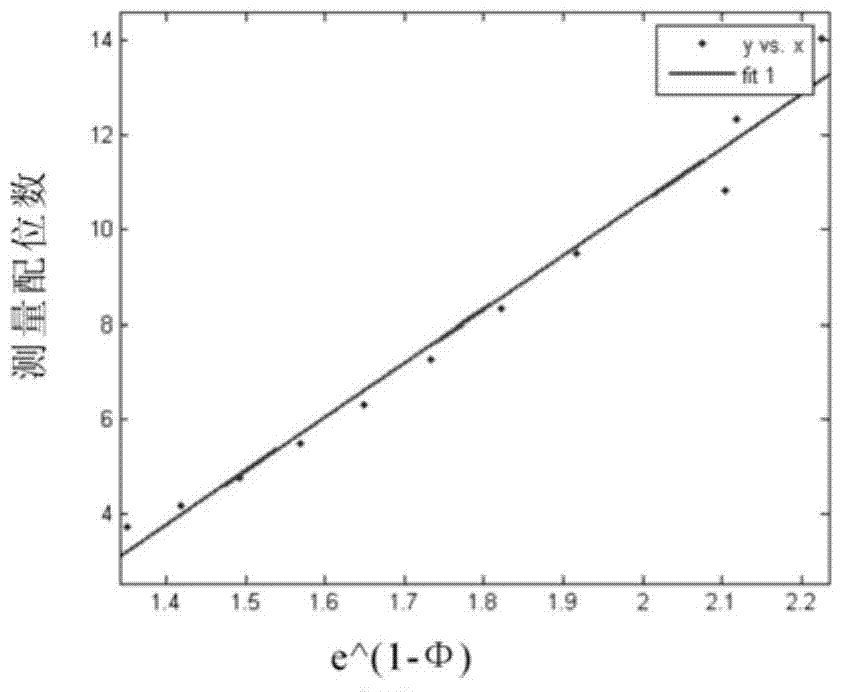
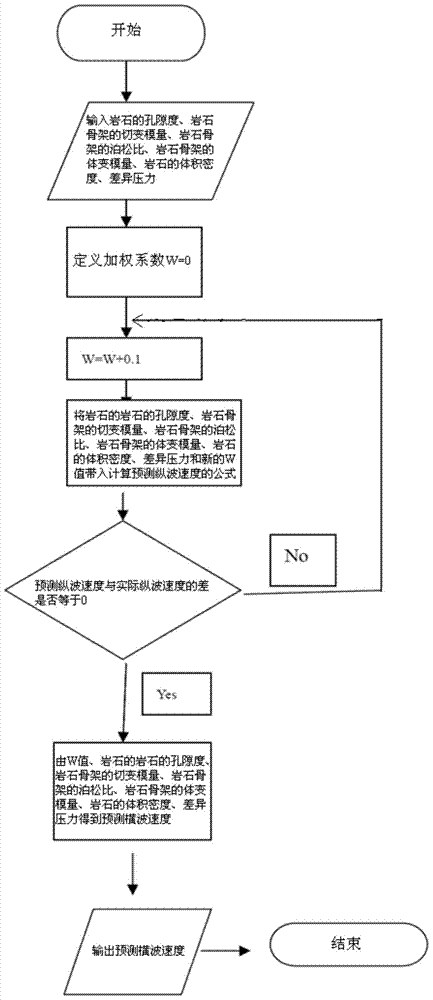
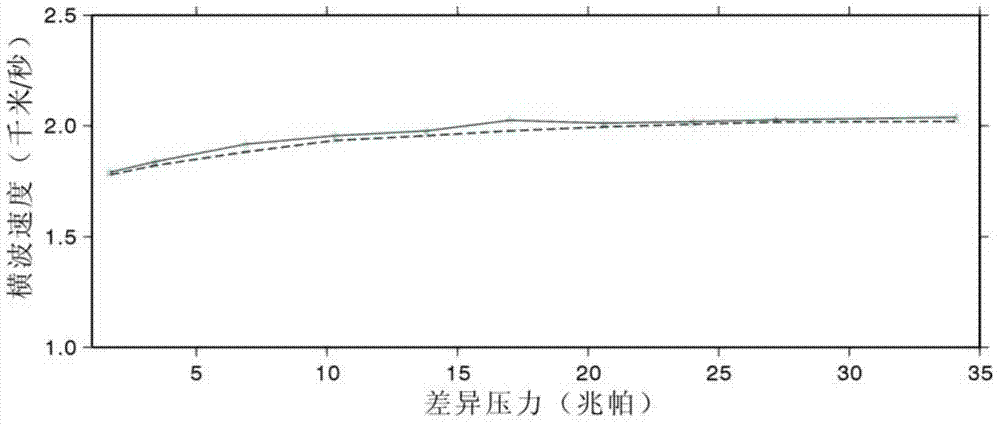
Provided is a method for forecasting a pore medium transverse wave velocity which varies with pressure. The method comprises the steps that measuring coordination numbers are matched and weighed to obtain a coordination number Cp, the coordination number Cp is substituted into a Digby formula considering pressure variation to obtain a Kdry, the coordination number Cp is substituted into a Mindlin formula considering pressure variation to obtain a mudry, and the Kdry and the mudry are substituted into a deformation formula of a Gassmann equation to calculate a forecasted longitudinal wave speed to obtain a weighting coefficient W; the weighting coefficient W is substituted into a formula (2) to obtain the coordination number Cp, after the Cp is obtained, the Cp value is substituted into a formula (8) to obtain the shear modulus mudry of dry rock, then the mudry is substituted into the deformation formula of the Gassmann equation to calculate a forecasted transverse wave speed, a four-dimensional AVO model, an elastic impedance model and the like can be established according to the transverse wave speed which varies with pressure, and therefore the property of oil and gas reservoir with pressure variation on a reservoir stratum in the developing stage can be forecasted. The forecasted transverse wave velocity varying with the pressure can more accord with actual reservoir stratum variation situations.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
Fiber bragg grating and fabrication method
ActiveUS20090169150A1Increase photosensitivityIncrease the number ofGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberGrating
A method of fabrication of a thermally stabilized Type I fiber Bragg grating-based temperature sensing device includes doping a fiber core material with germanium or germanium oxide for enhancing photosensitivity, co-doping the fiber core material with fluorine or chorine or for increasing a mean coordination number; and ultraviolet laser inscribing a periodic or quasiperiodic modulated refractive index structure in the fiber core using a laser energy operating at less than 1000 milliJoules per square centimeter per pulse. The resulting sensor is operable for more than 1000 hours at temperatures up to at least 550 degrees Celsius.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Dual-medium reservoir rock water saturation calculating method based on percolation network simulation
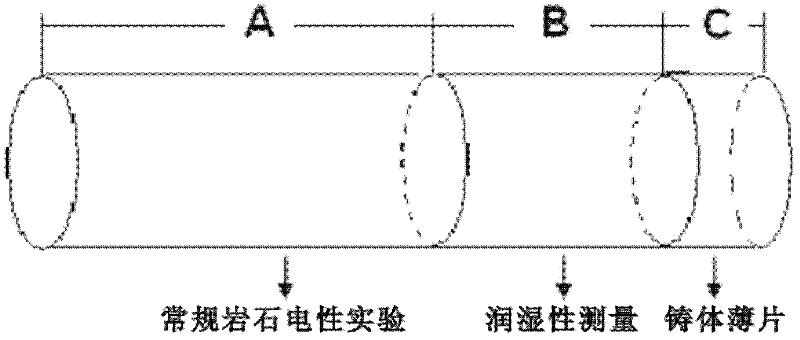
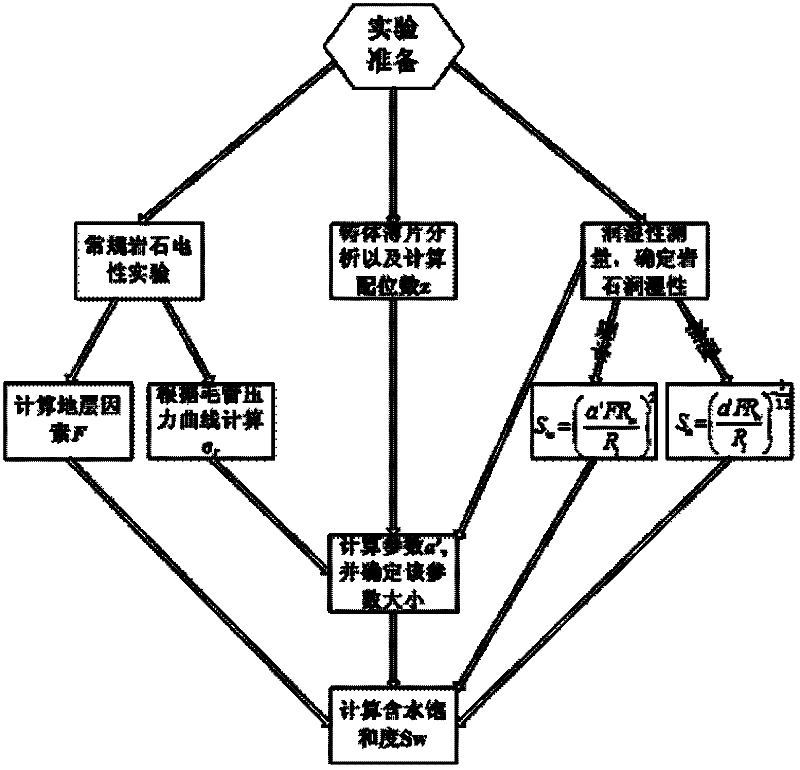
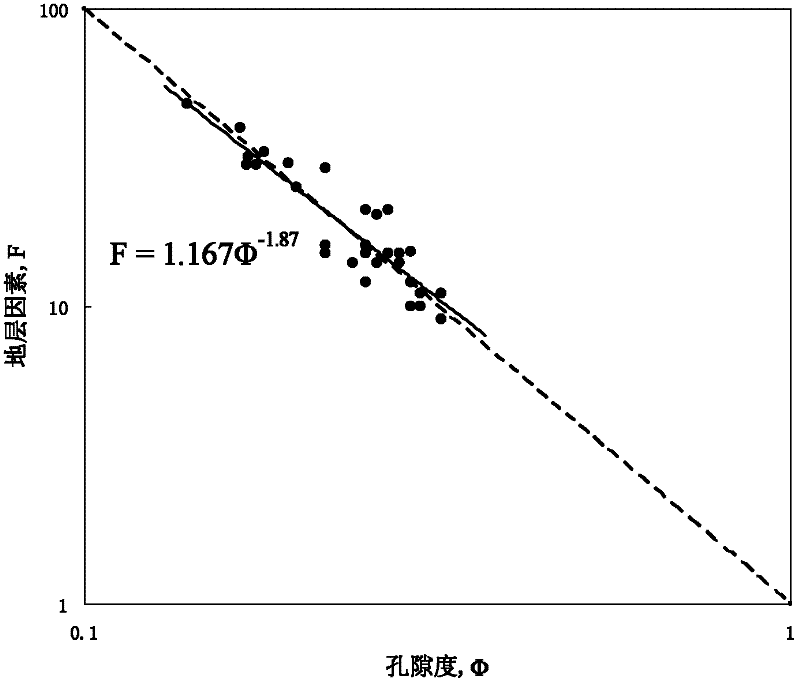
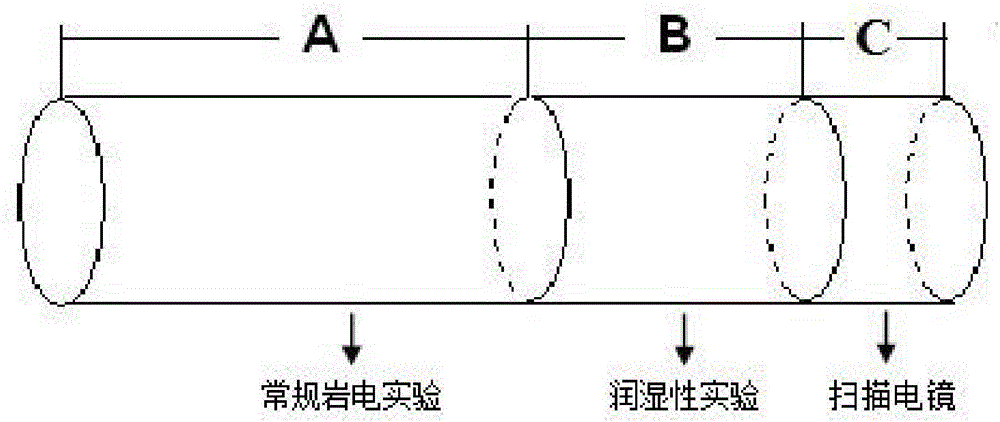
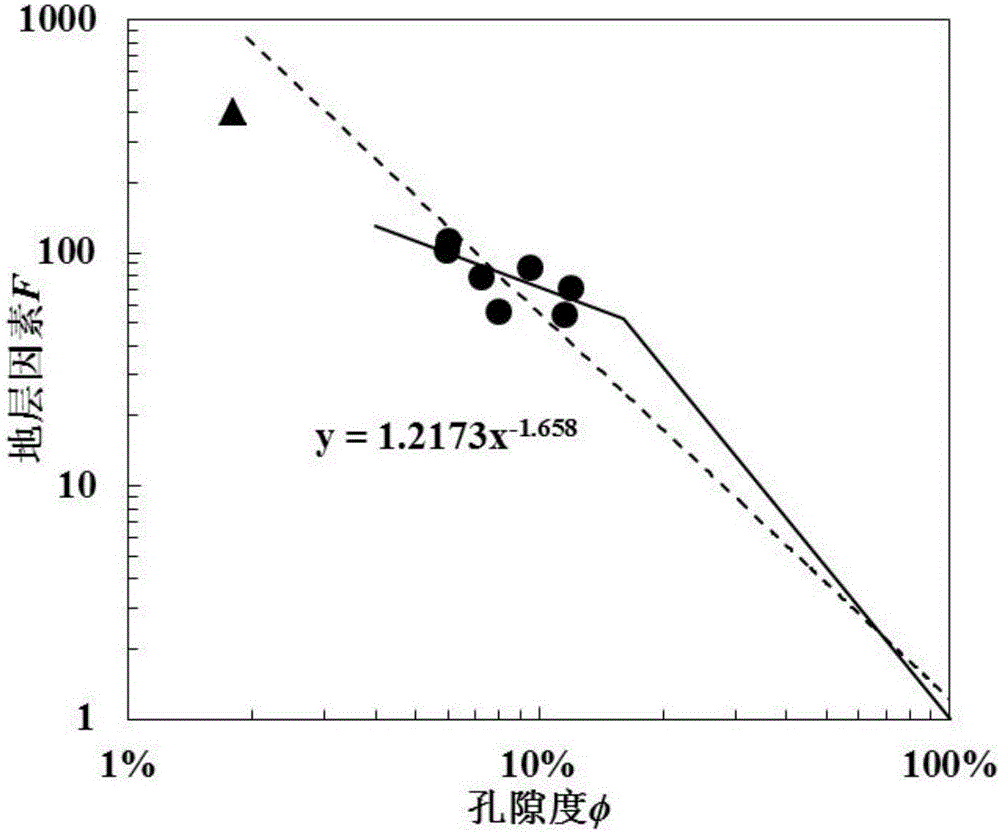
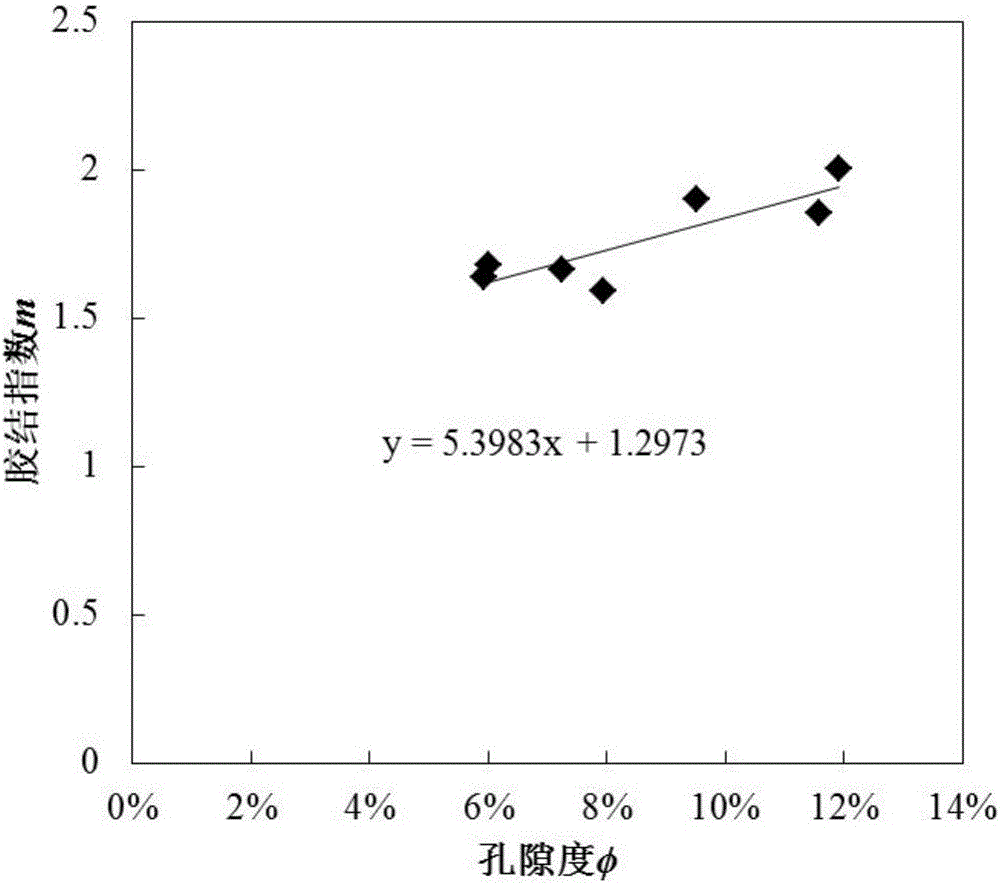
The invention discloses a dual-medium reservoir rock water saturation calculating method based on percolation network simulation. The method comprises the steps that (1) a rock sample is cut into a segment A, a segment B and a segment C, the segment A is subjected to a rock-electric test and a nuclear magnetic resonance test, the segment B is subjected to wettability measurement, and the segment C is subjected to a scanning electron microscope test; (2) the function relationship between the formation factor F and the porosity phi is fit; (3) constants C1 and C2 are calculated, and C1 and C2 reflect pore throat features and resistivity properties of dual-medium reservoir matrix pores; (4) the pore throat radius variable coefficient sigma of a rock dissolved pore system is worked out; (5) a dual-medium percolation network model is established, and by means of a trial-and-error method, the coordination number z of the dissolved pore system is determined through network simulation; and (6) the value of B' is determined, and the dual-medium reservoir rock water saturation S<w> is obtained. According to the method, an explanation method of logging through the electric field vector geophysical method is perfected, and the defects of theoretical knowledge of reservoir rock electrical properties and rock water saturation calculating methods are overcome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com