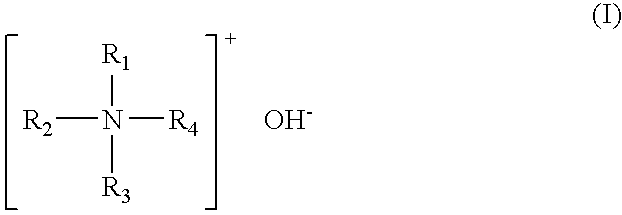Patents
Literature
5663 results about "Ammonium hydroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
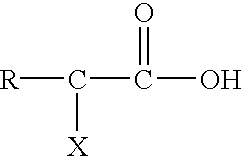
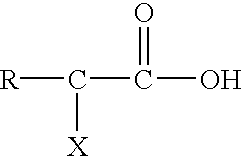
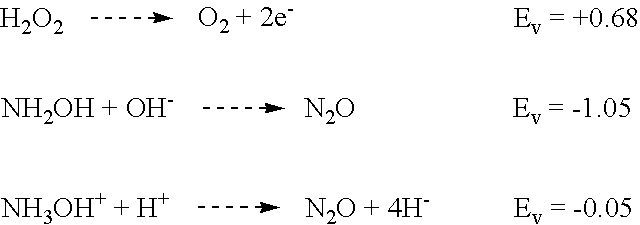
Ammonium hydroxide, also known as ammonia water, ammonia solution, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH₃(aq). Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an alkali with composition [NH₄⁺][OH⁻], it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH₄OH. The ions NH₄⁺ and OH⁻ do not account for a significant fraction of the total amount of ammonia except in extremely dilute solutions.
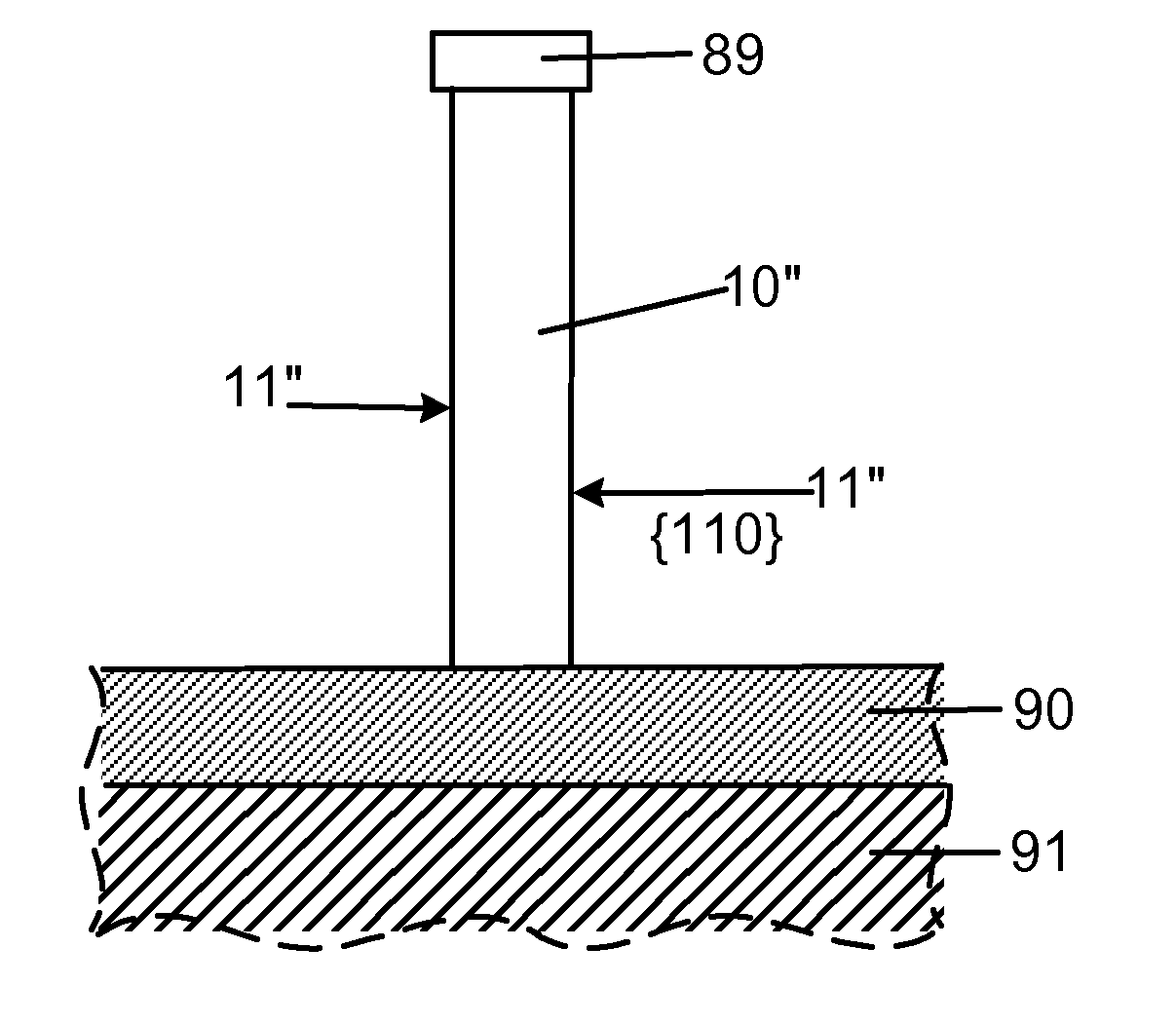
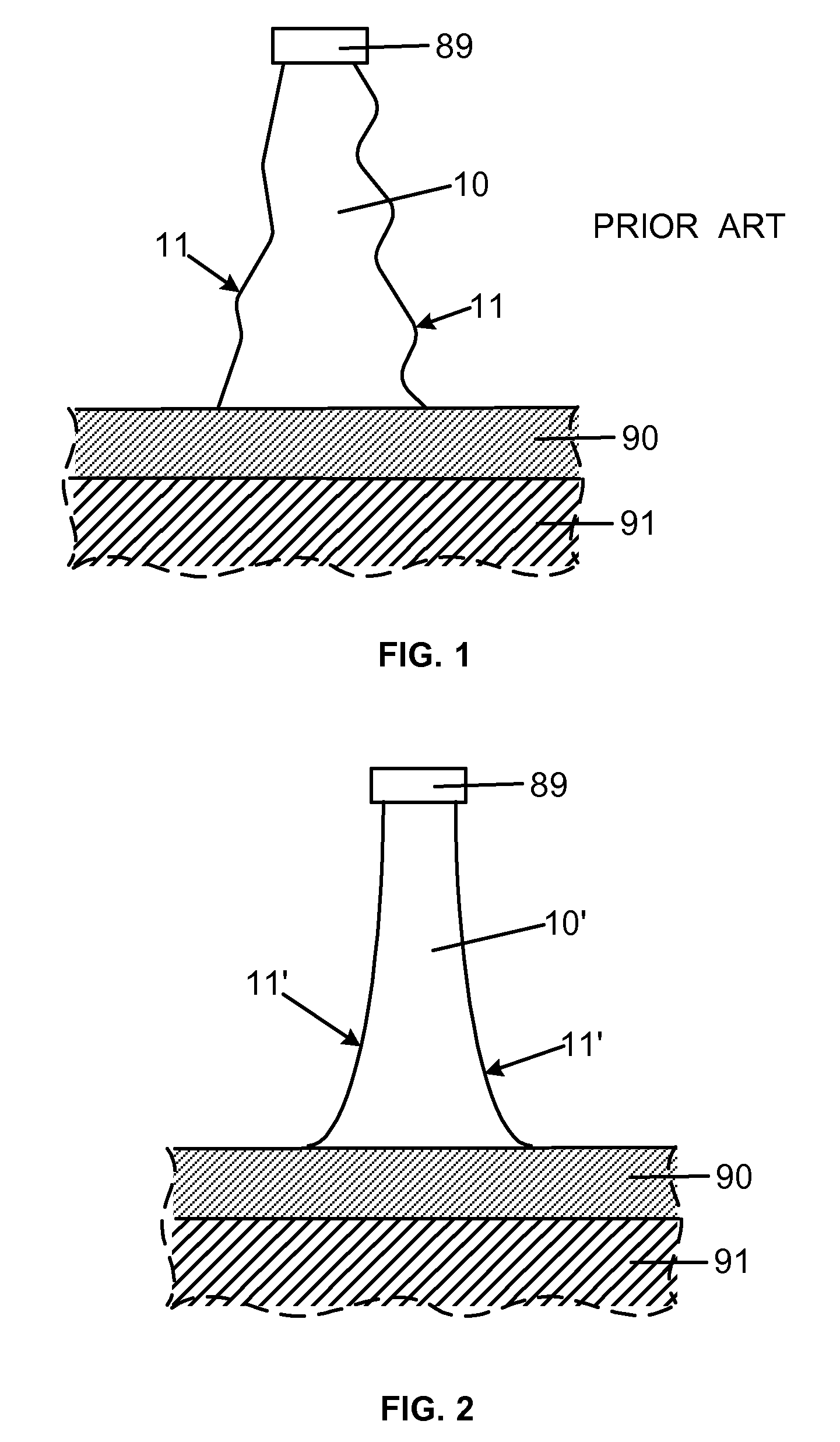
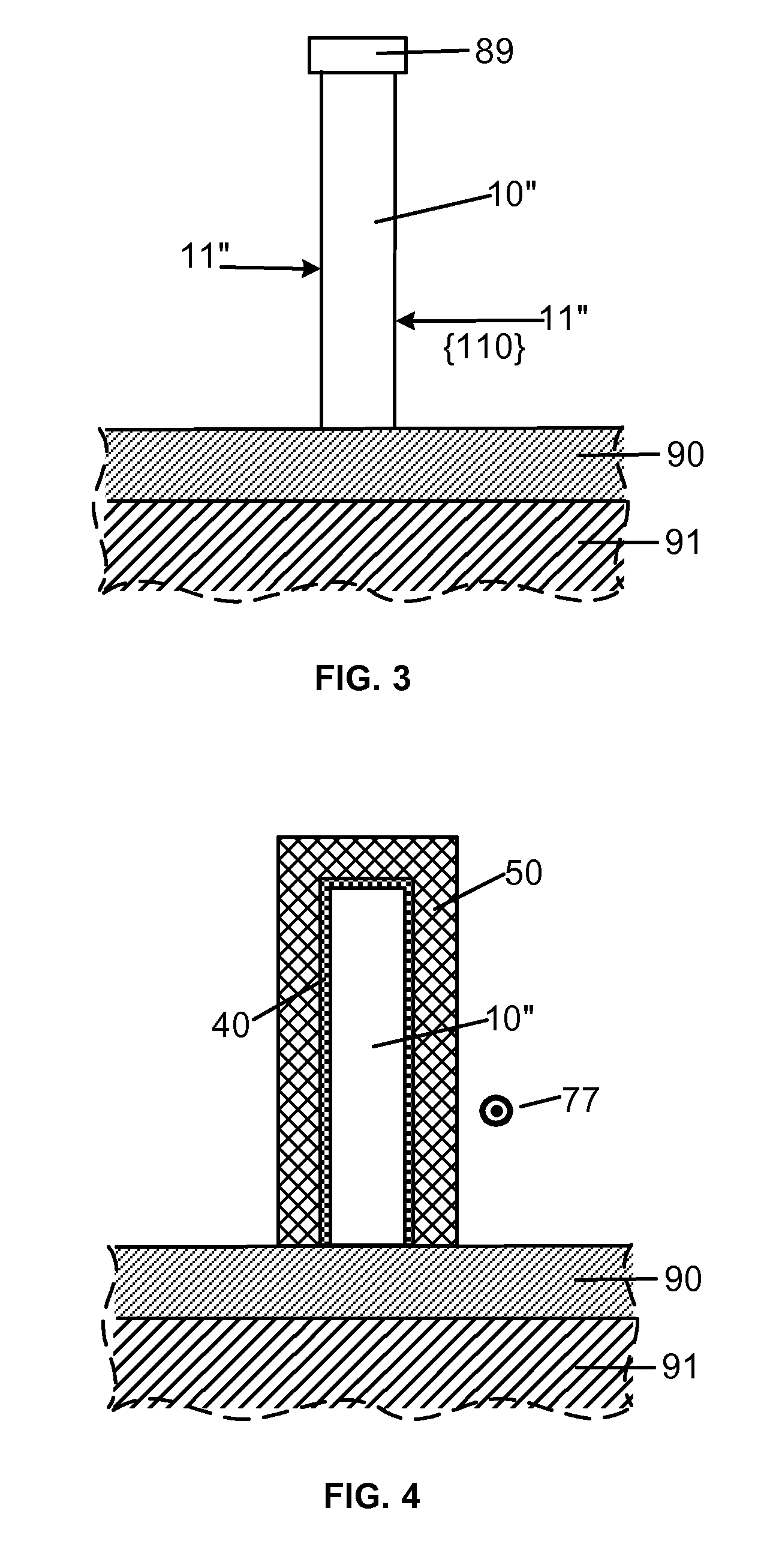
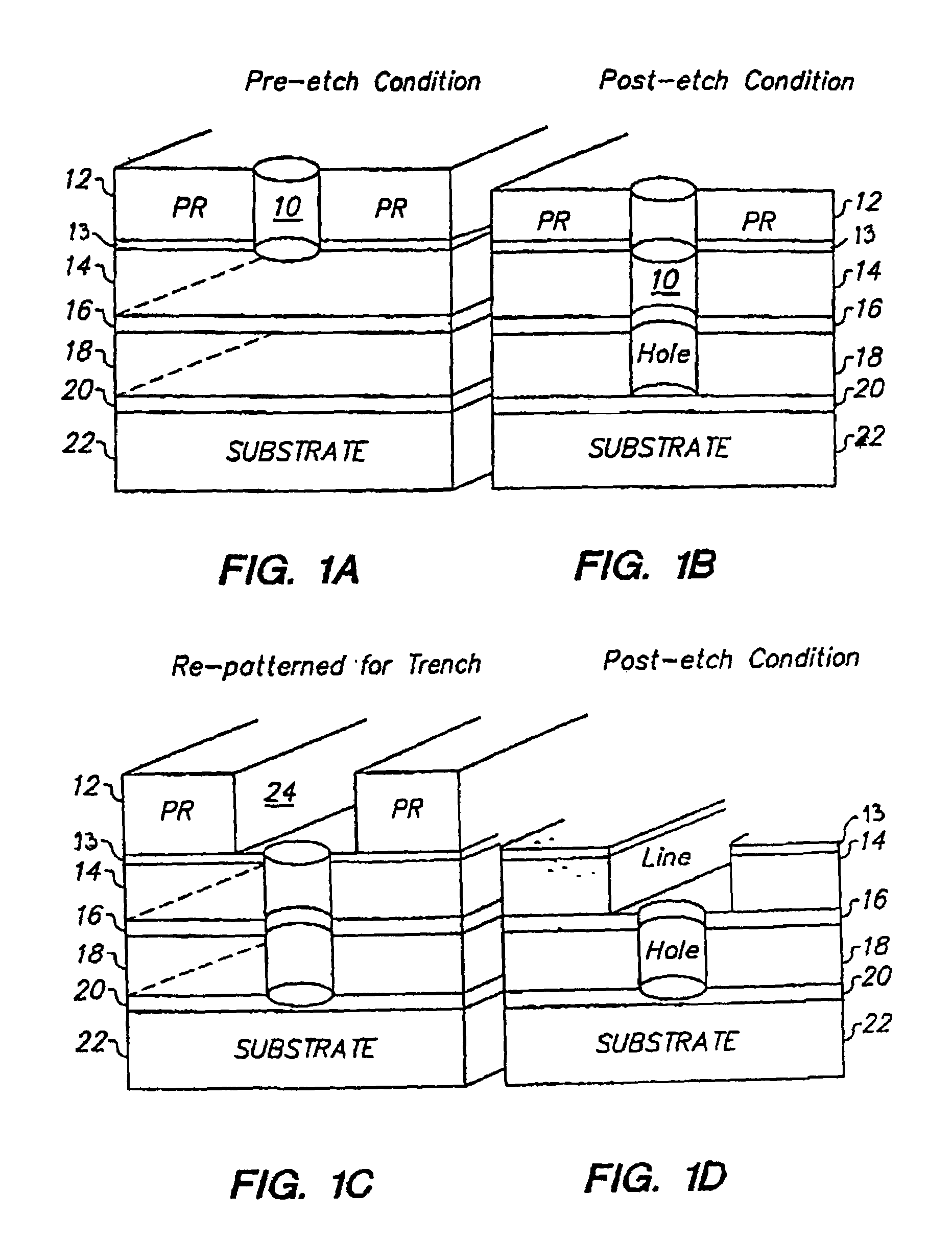
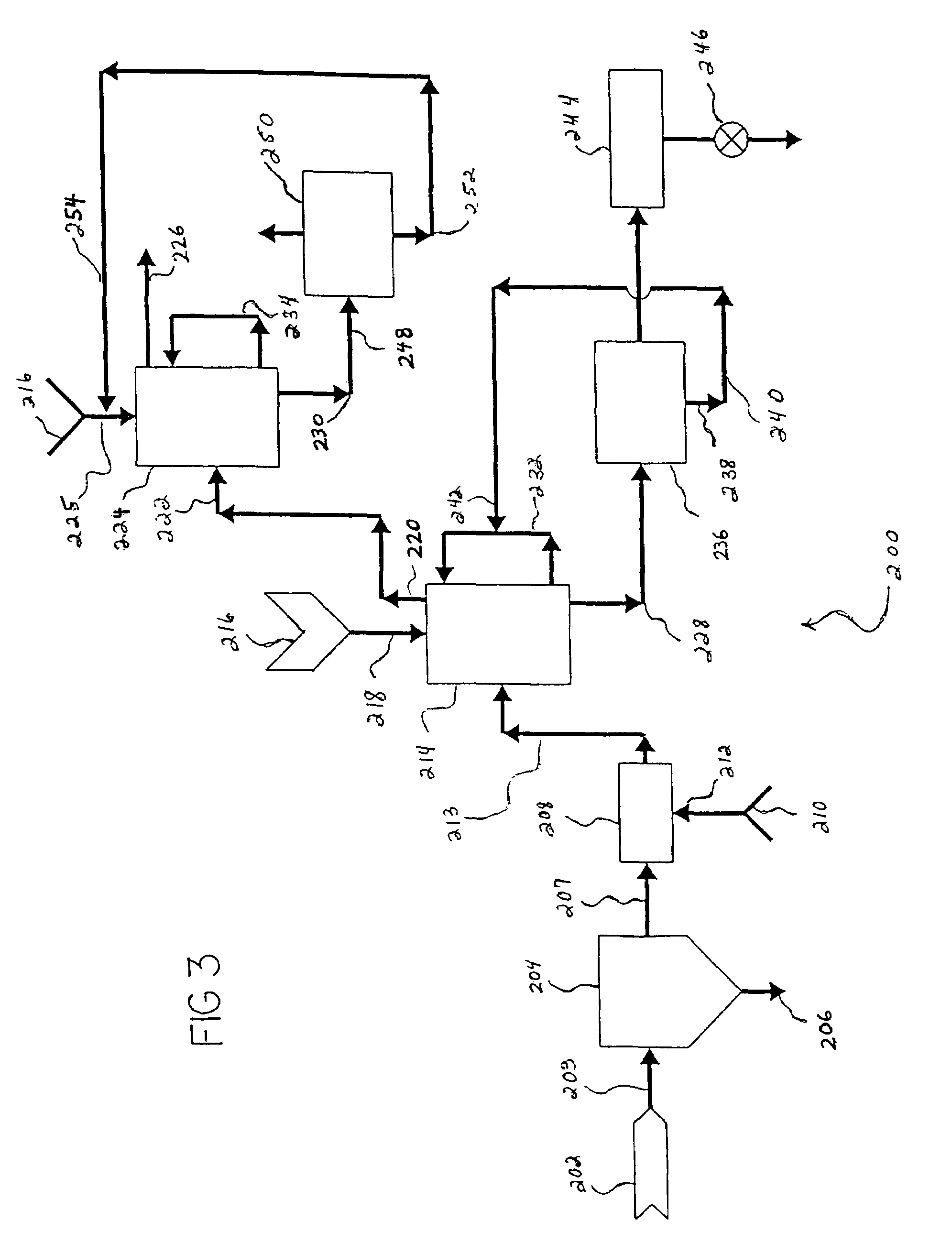
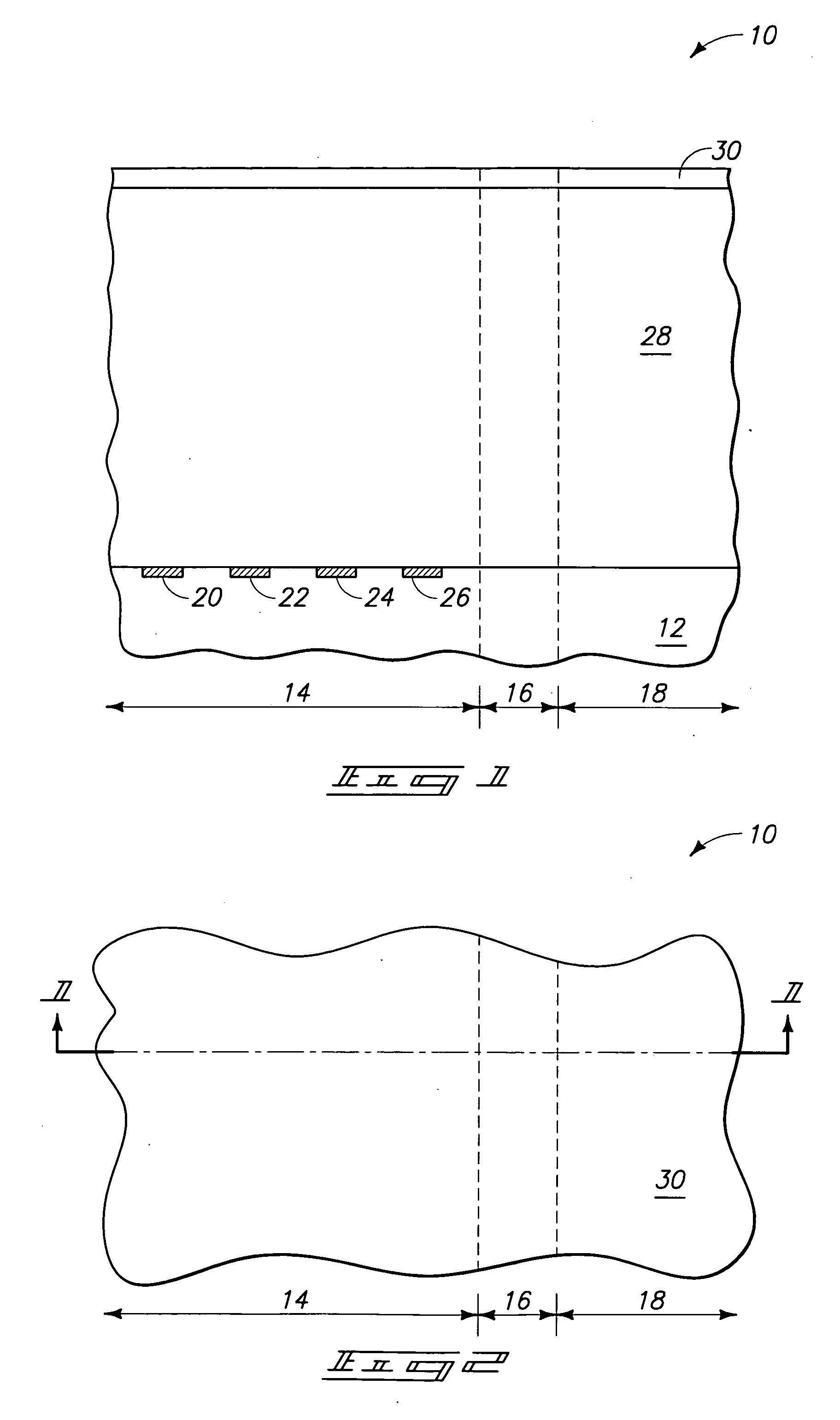
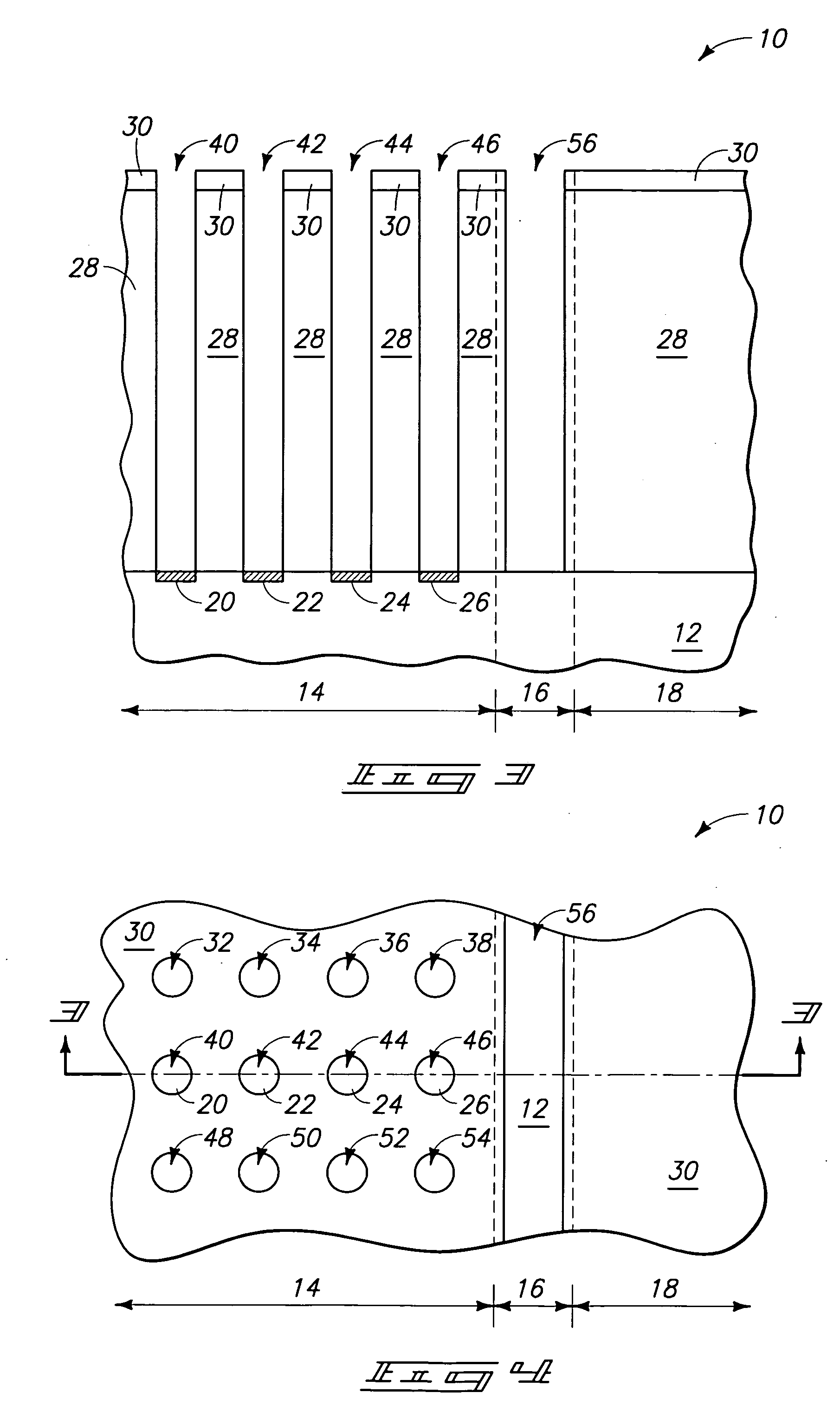
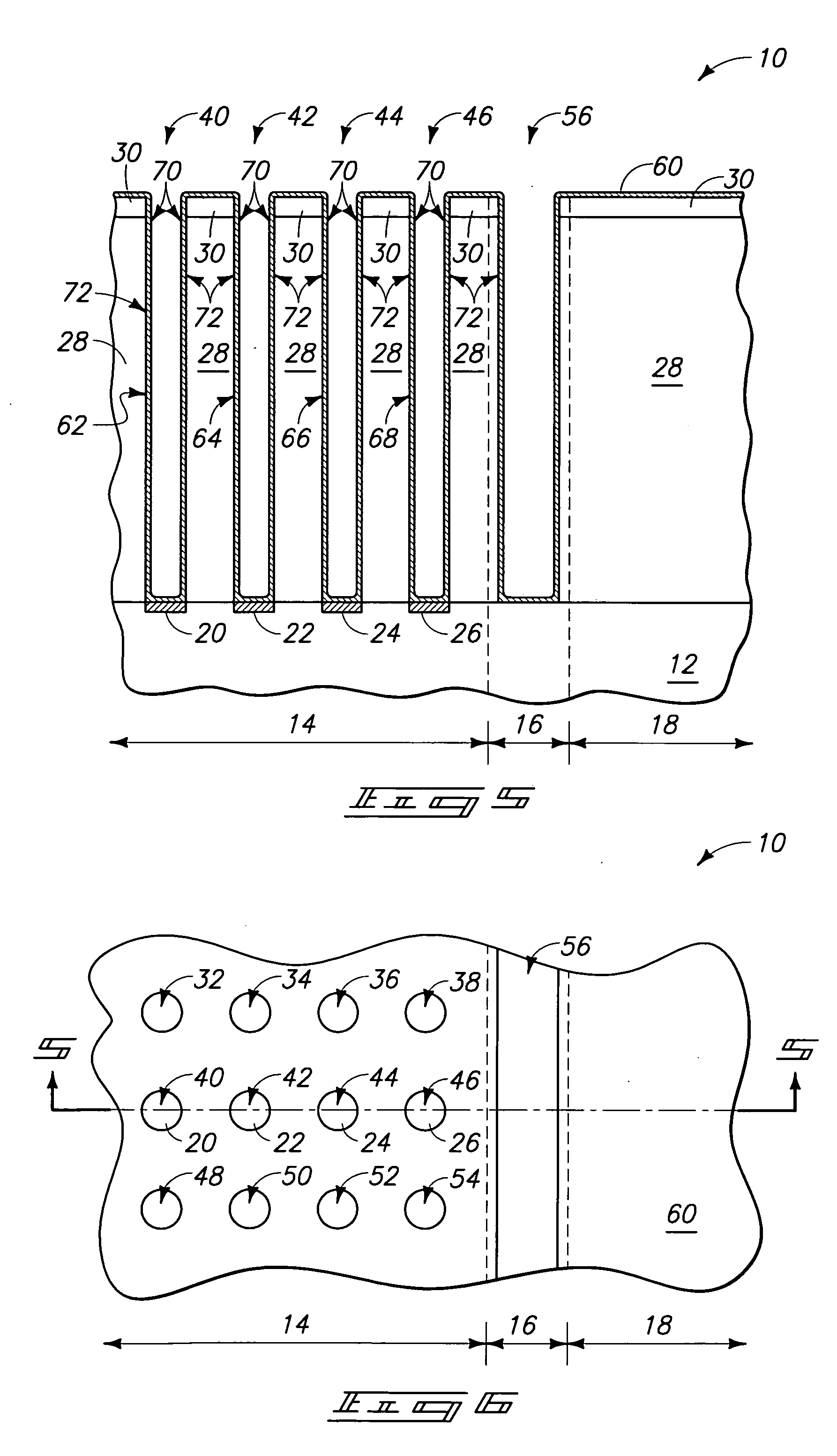
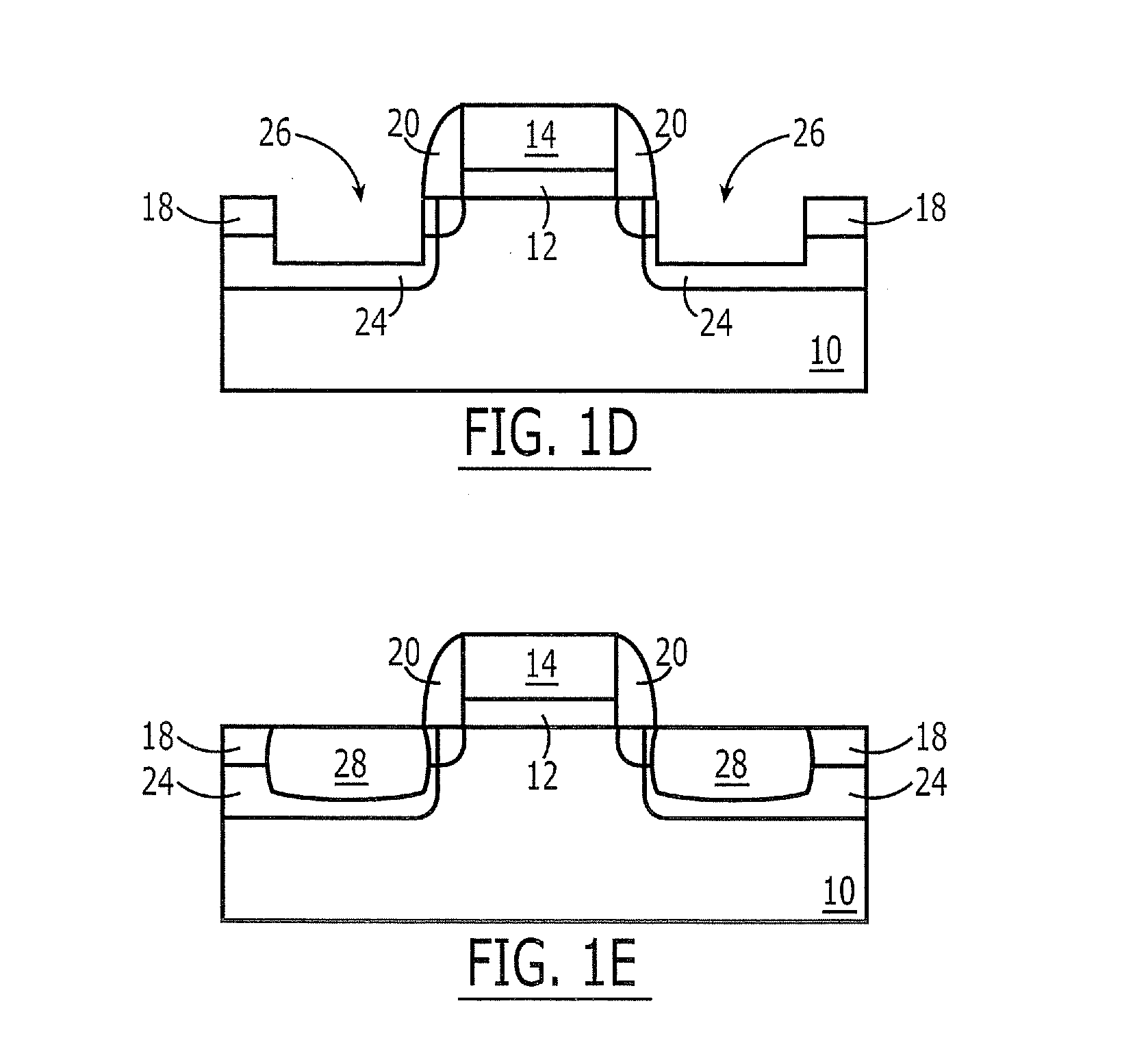
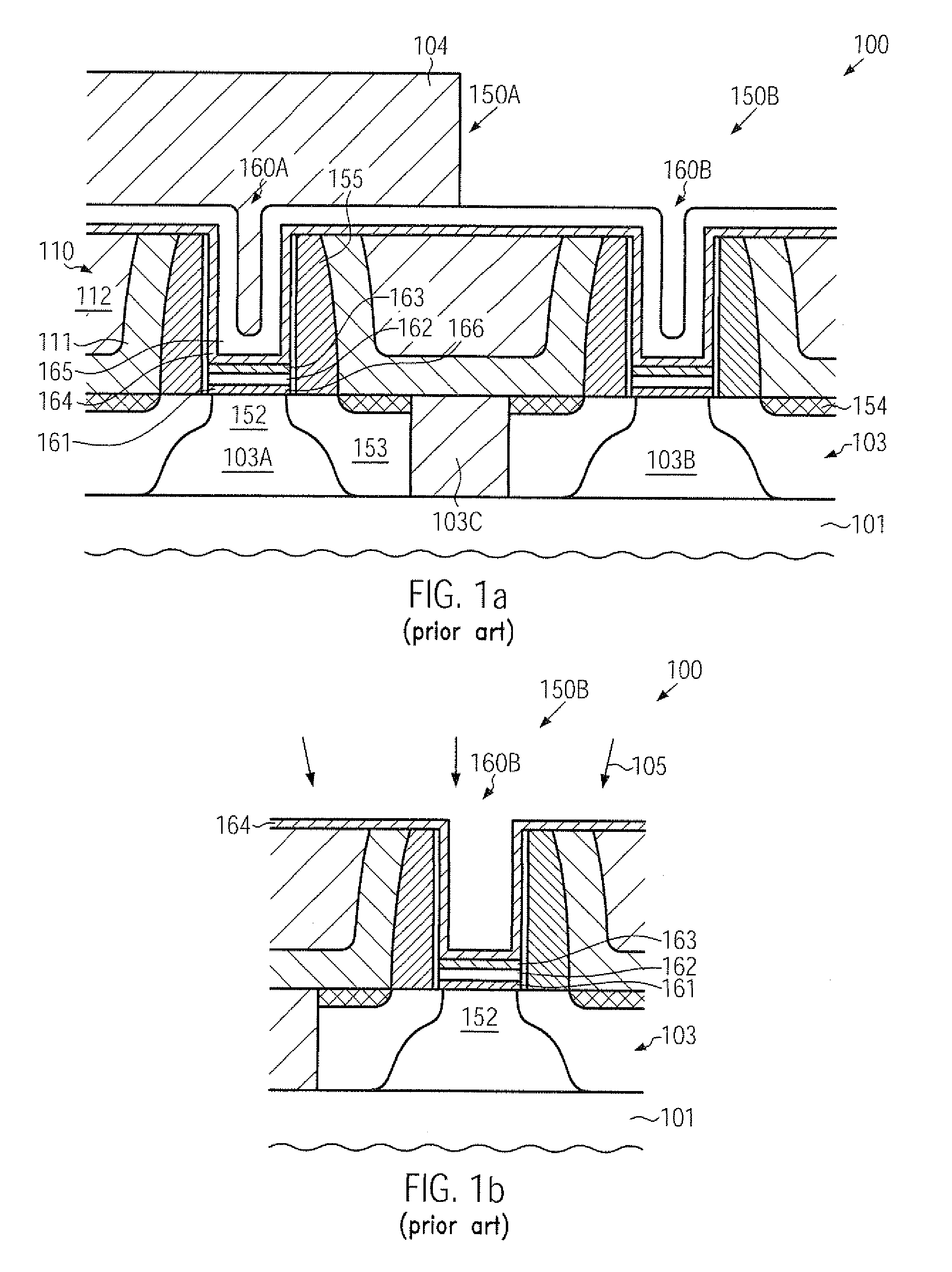
Smooth and vertical semiconductor fin structure
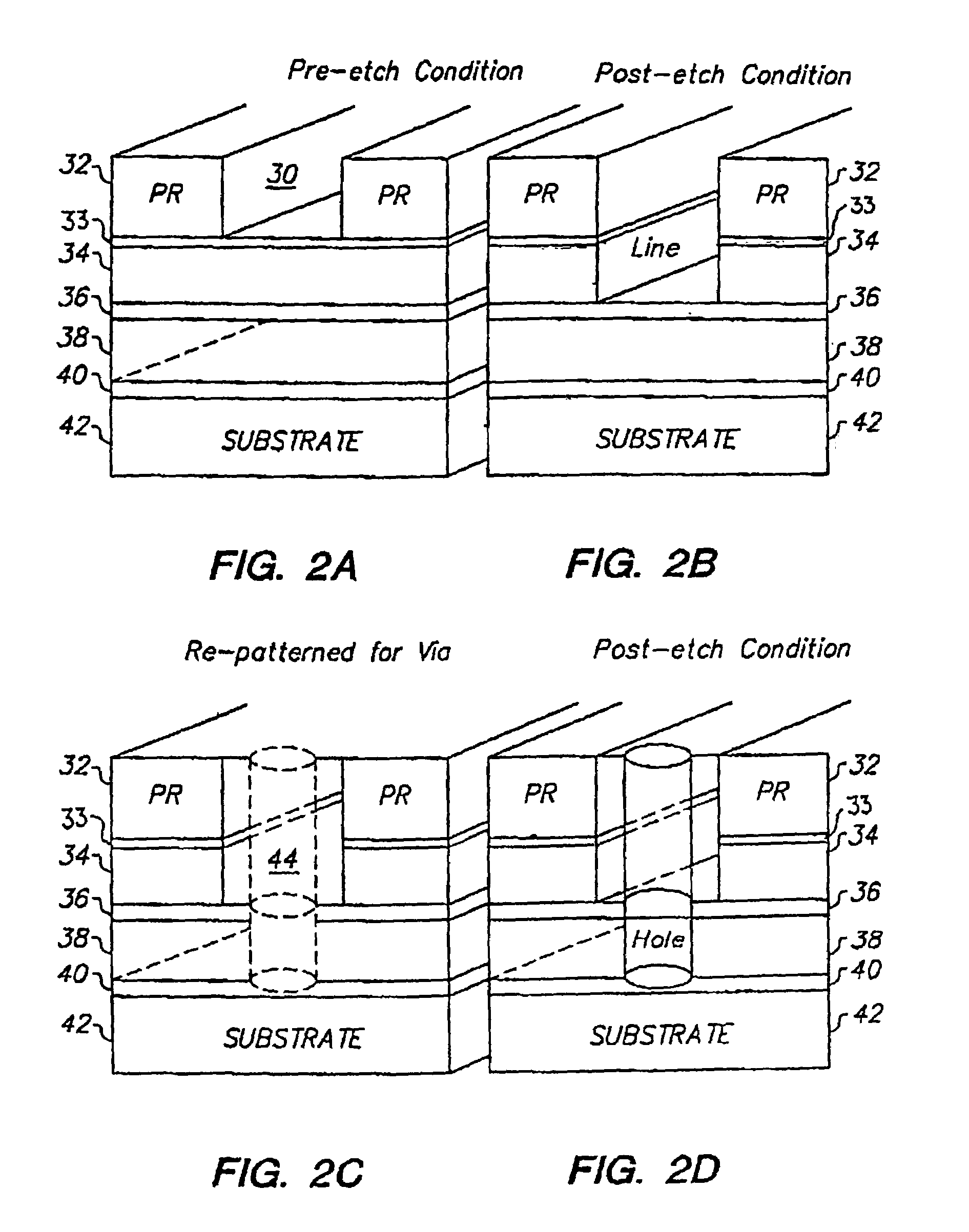
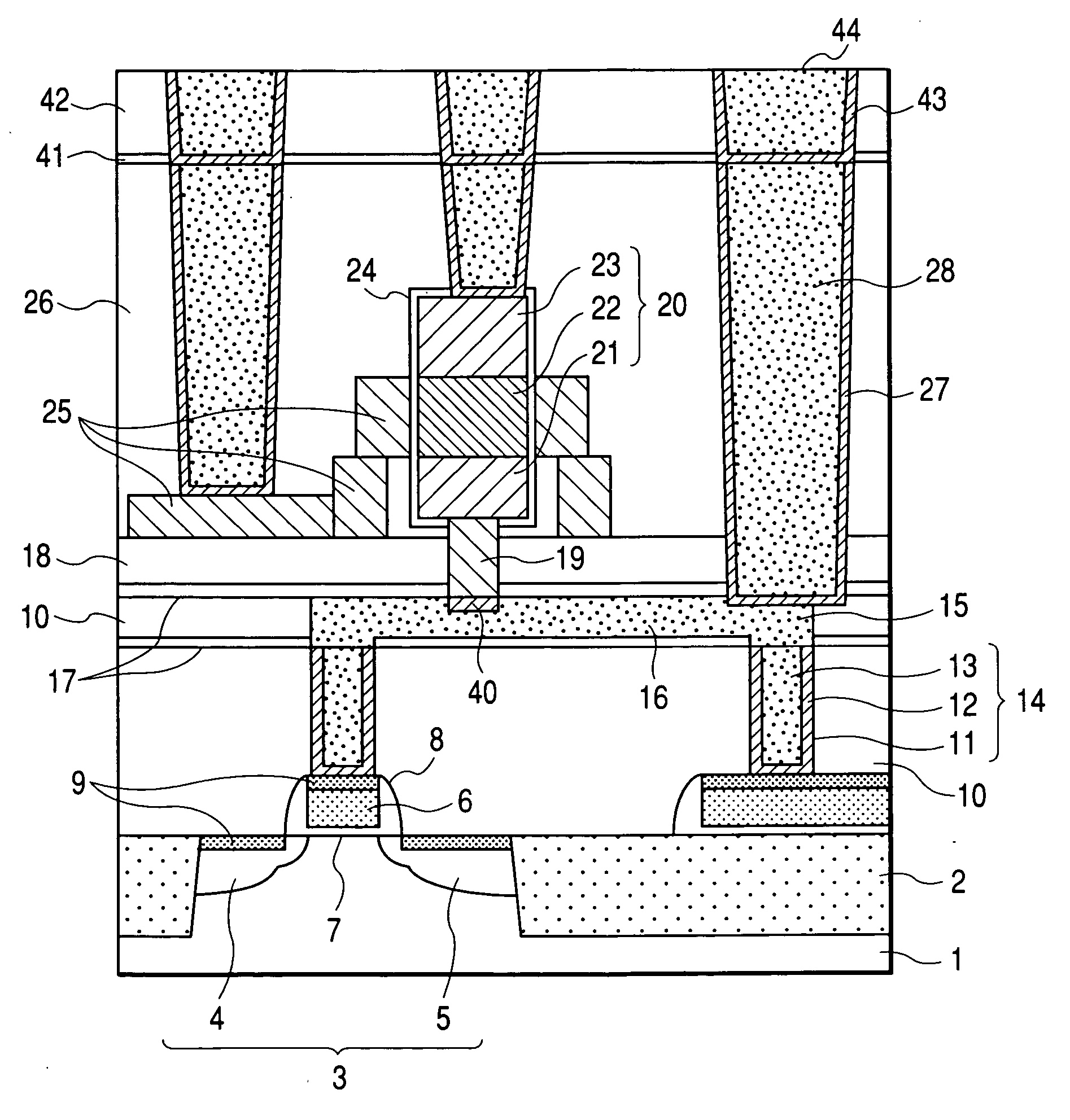
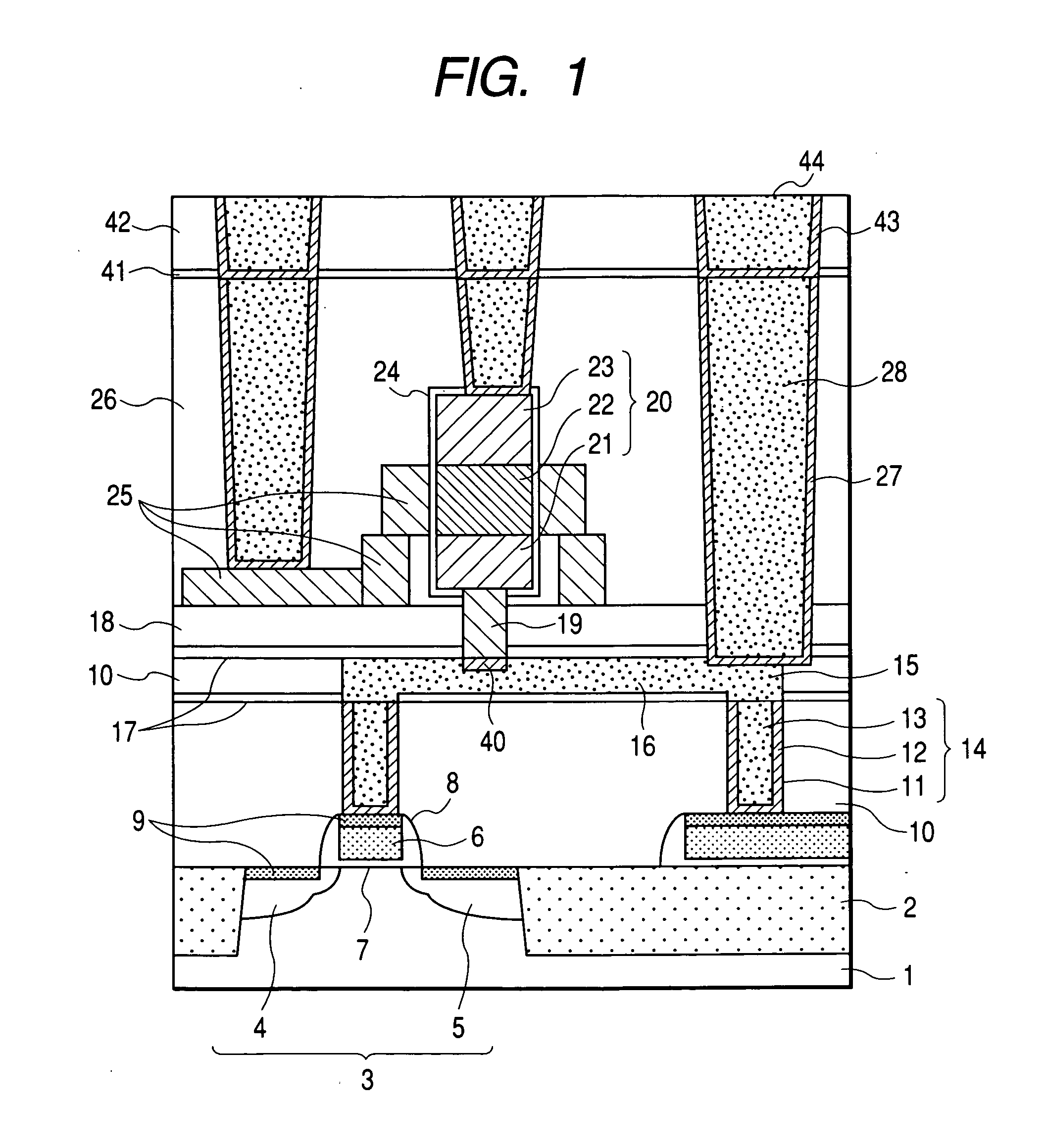
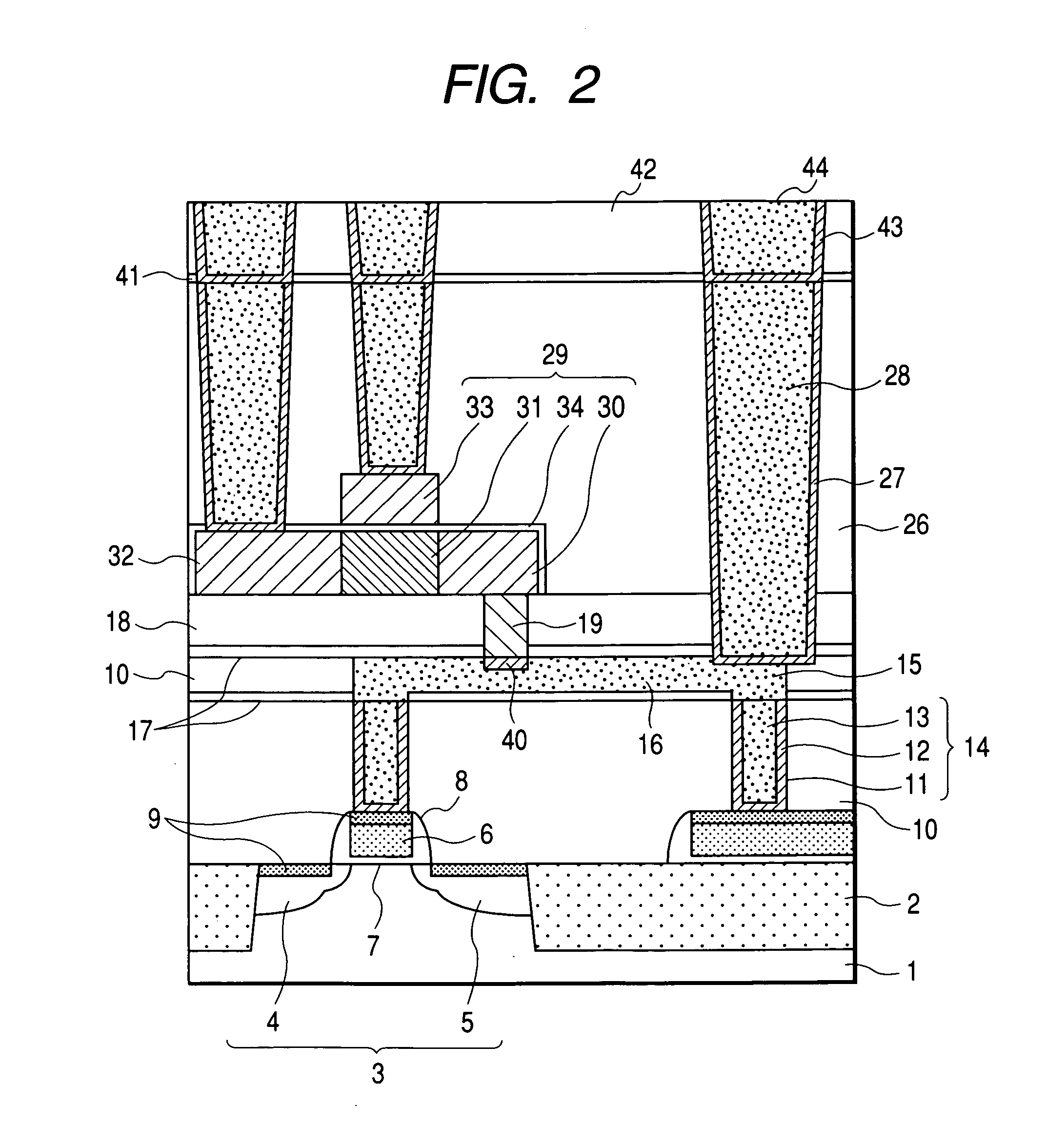
InactiveUS20100048027A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingCrystal orientation
A method for processing a semiconductor fin structure is disclosed. The method includes thermal annealing a fin structure in an ambient containing an isotope of hydrogen. Following the thermal annealing step, the fin structure is etched in a crystal-orientation dependent, self-limiting, manner. The crystal-orientation dependent etch may be selected to be an aqueous solution containing ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). The completed fin structure has smooth sidewalls and a uniform thickness profile. The fin structure sidewalls are {110} planes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
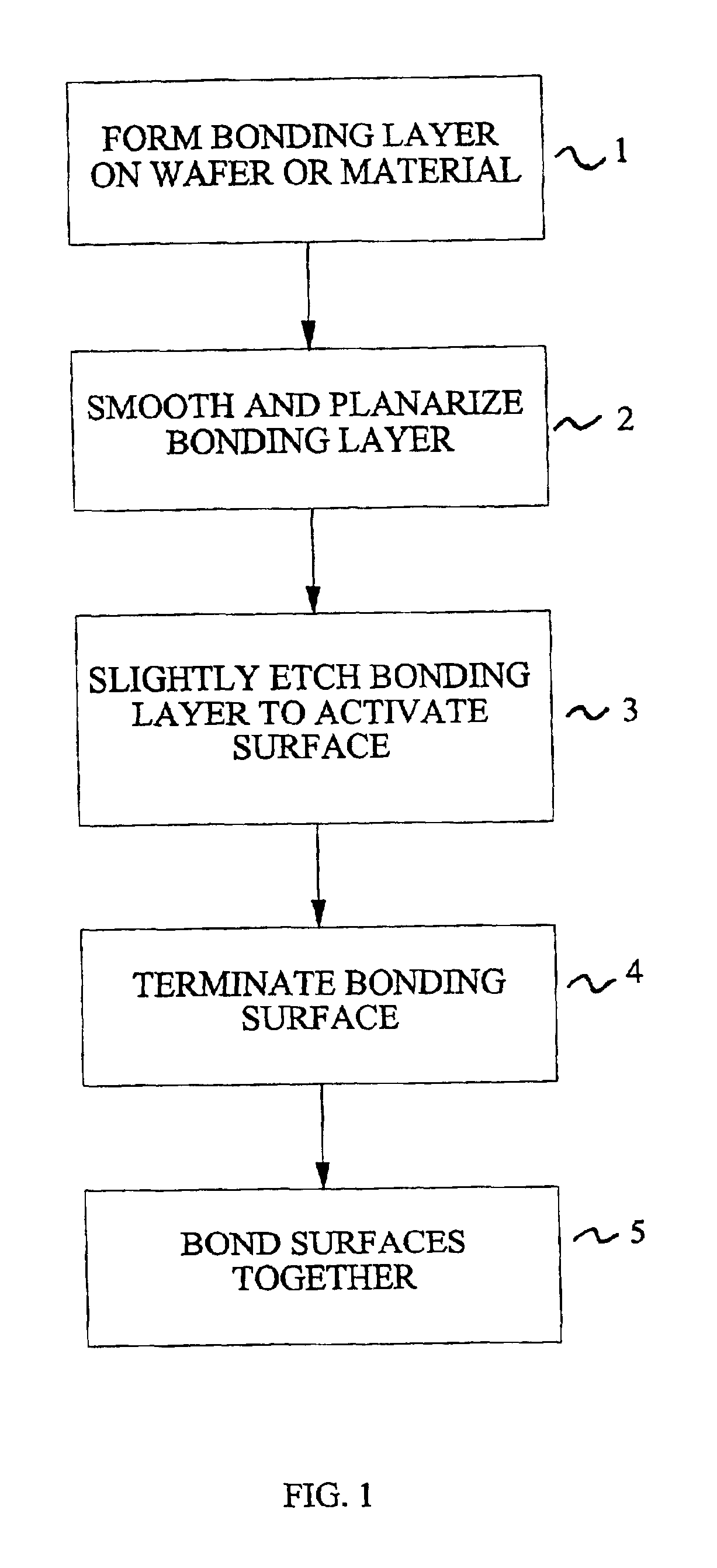
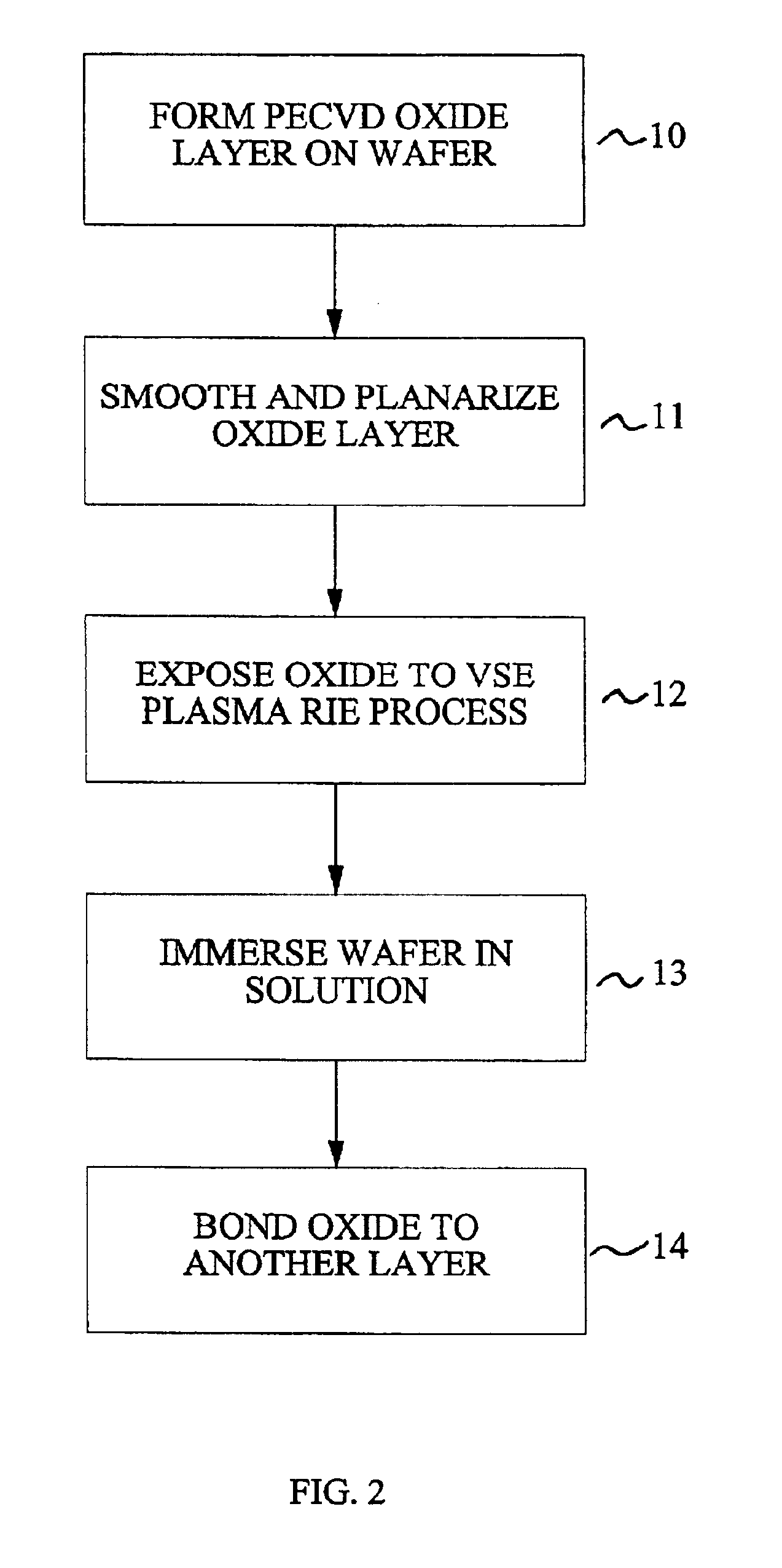
Method for low temperature bonding and bonded structure
InactiveUS6902987B1High bonding strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface cleaningBiological activation
A method for bonding at low or room temperature includes steps of surface cleaning and activation by cleaning or etching. One etching process the method may also include removing by-products of interface polymerization to prevent a reverse polymerization reaction to allow room temperature chemical bonding of materials such as silicon, silicon nitride and SiO2. The surfaces to be bonded are polished to a high degree of smoothness and planarity. VSE may use reactive ion etching or wet etching to slightly etch the surfaces being bonded. The surface roughness and planarity are not degraded and may be enhanced by the VSE process. The etched surfaces may be rinsed in solutions such as ammonium hydroxide or ammonium fluoride to promote the formation of desired bonding species on the surfaces.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
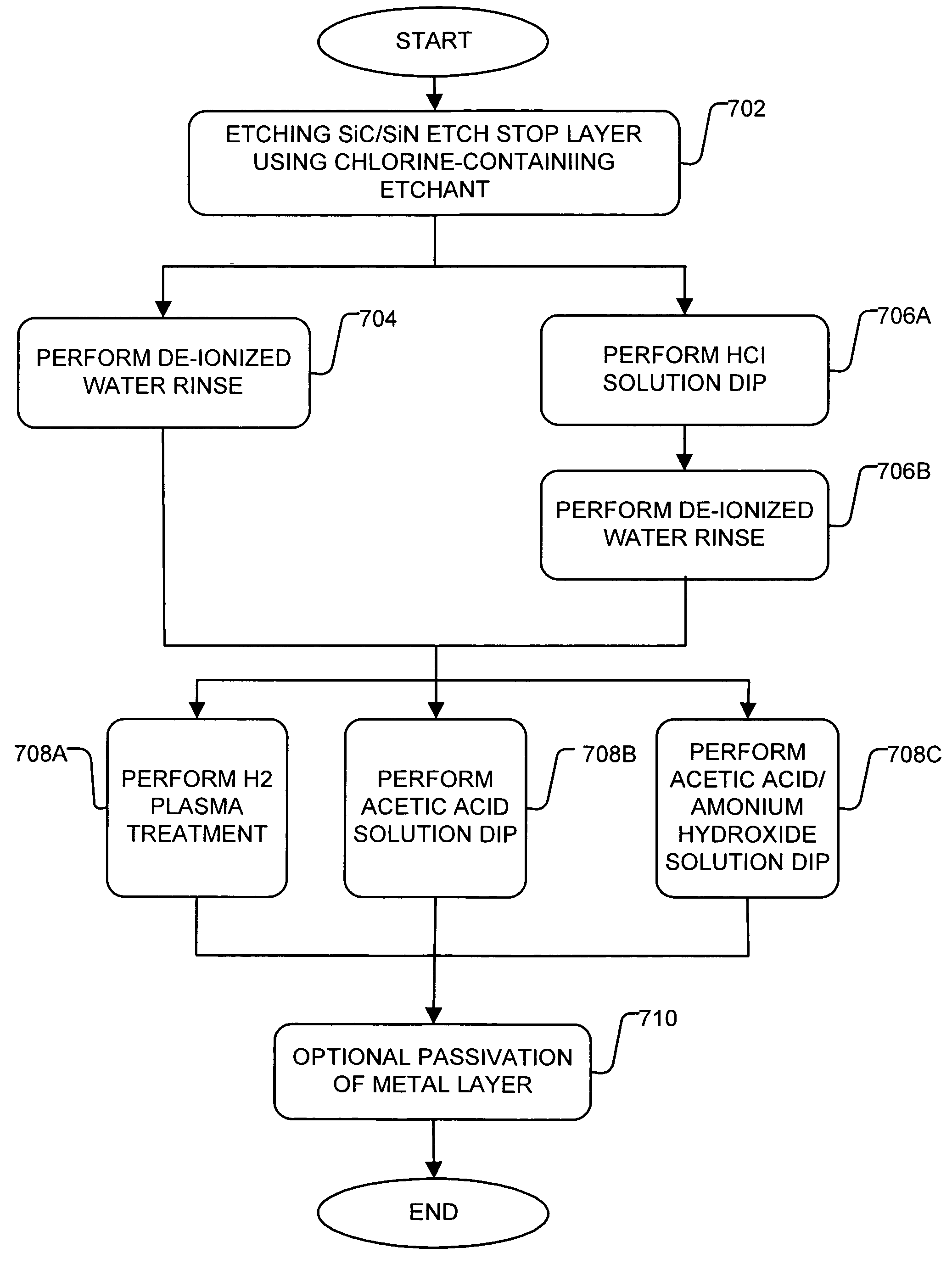
Treatment for corrosion in substrate processing
InactiveUS7084070B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningAcetic acidAmmonium hydroxide
A method for processing substrate to form a semiconductor device is disclosed. The substrate includes an etch stop layer disposed above a metal layer. The method includes etching through the etch stop layer down to the copper metal layer, using a plasma etch process that utilizes a chlorine-containing etchant source gas, thereby forming etch stop layer openings in the etch stop layer. The etch stop layer includes at least one of a SiN and SiC material. Thereafter, the method includes performing a wet treatment on the substrate using a solution that contains acetic acid (CH3COOH) or acetic acid / ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) to remove at least some of the copper oxides. Alternatively, the copper oxides may be removed using a H2 plasma. BTA passivation may be optionally performed on the substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050073051A1Minimize the possibilityEfficient removalTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh energyUltraviolet lights
A manufacturing process for a semiconductor integrated circuit device which prevents occurrence of reaction between metal wiring and a boron-doped silicon plug over it in heat treatment for a MOS transistor to be formed over them and reduces the possibility of rise in contact resistance. Metal boride is formed on an exposed metal surface in the bottom of an opening made in an interlayer insulating film over the metal wiring. In order to facilitate formation of such metal boride, metal oxide remaining on the metal surface is removed with an aqueous ammonia solution. The meal surface is irradiated with high energy ultraviolet light in order to remove organic matter remaining in the opening and facilitate removal of the metal oxide with the aqueous ammonia solution.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN101847763AImprove performanceLow priceWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAdhesiveCalcination
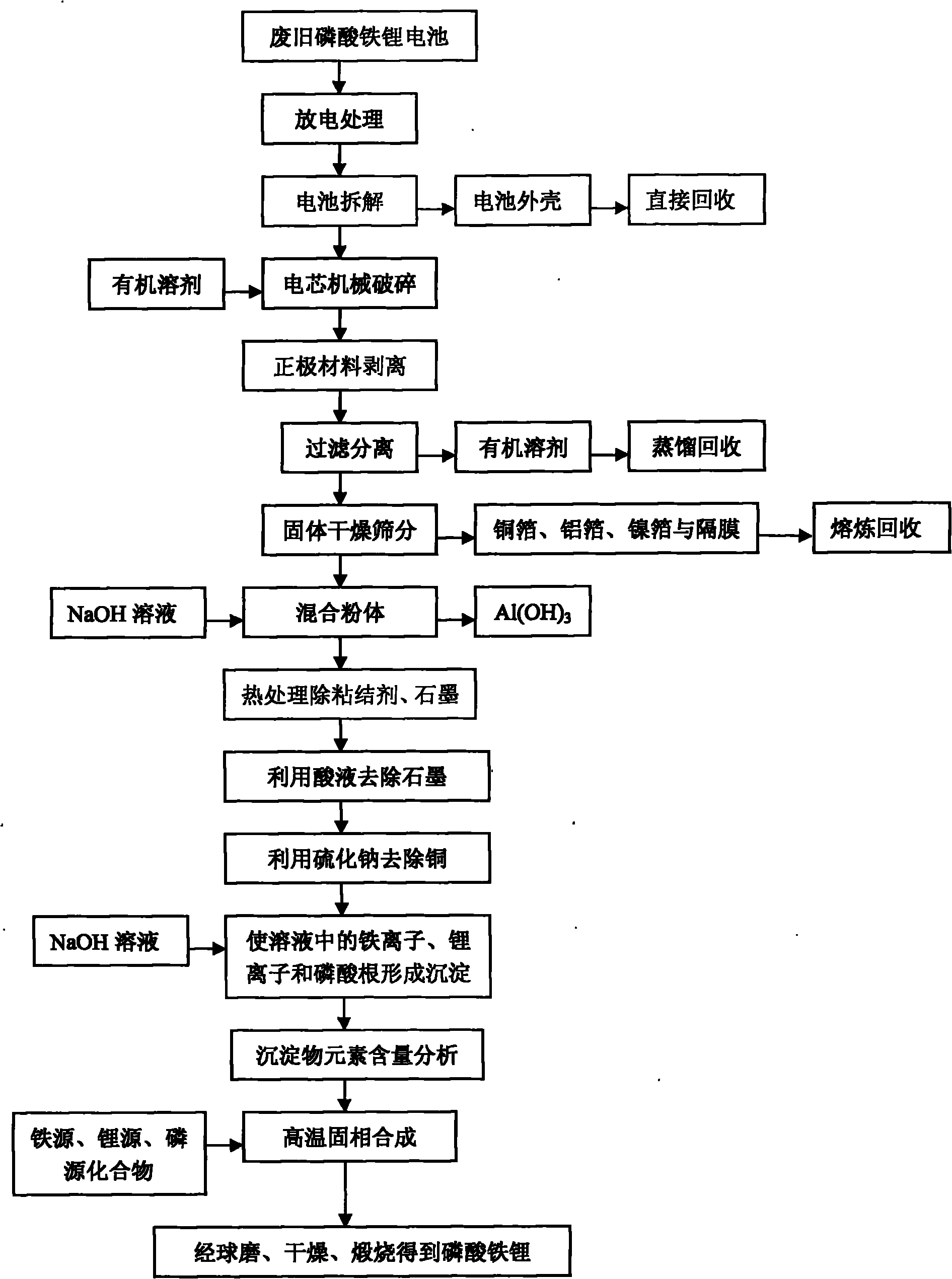
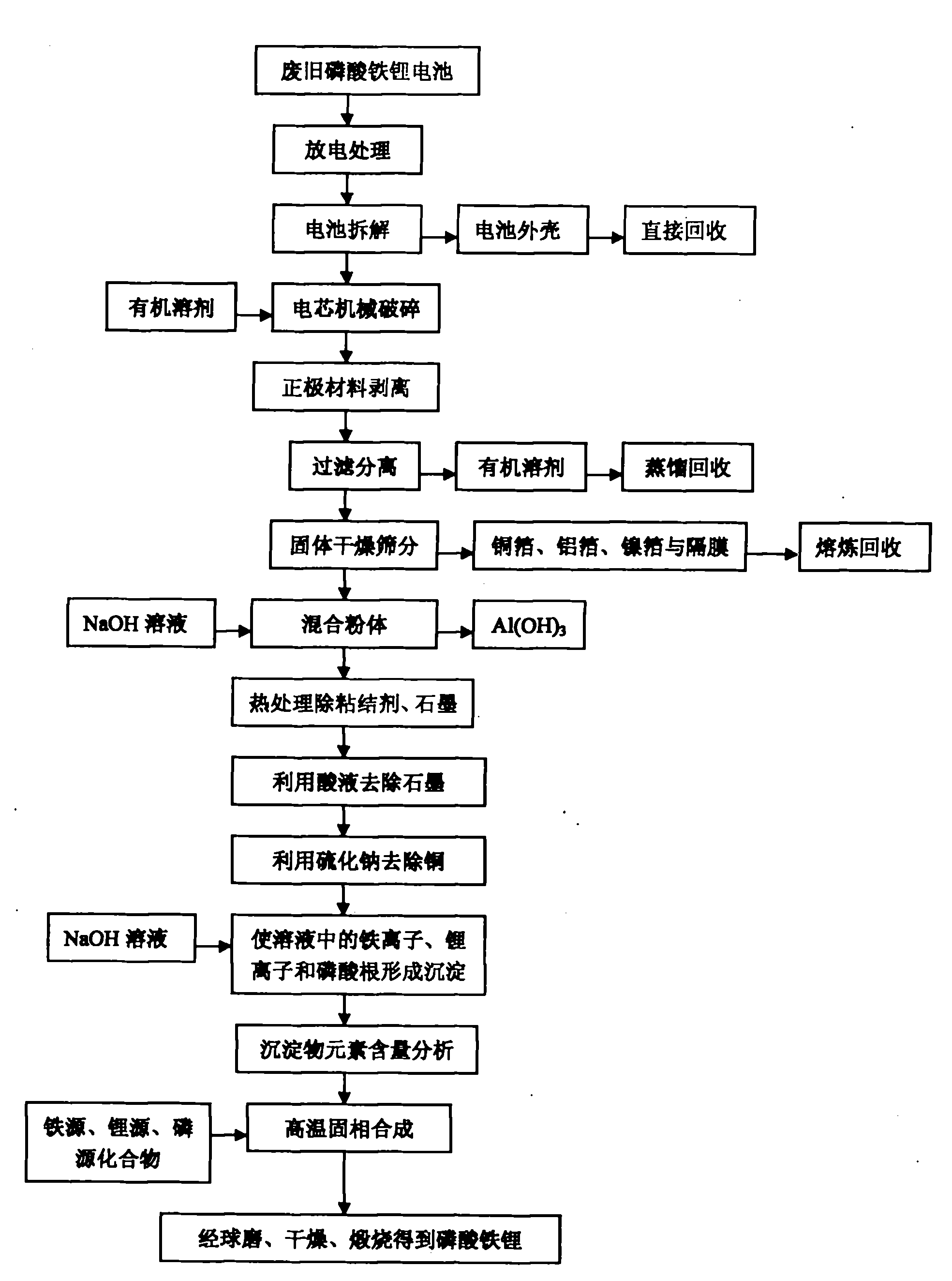
The invention provides a comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, which has simple and reasonable process, low recovering cost and high added value. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing an organic solvent to dissolve an adhesive on battery cell fragments, and realizing the separation of lithium iron phosphate material and clean aluminum and copper foils through screening, wherein the aluminum and copper foils are recovered by smelting; utilizing a NaOH solution to remove residual aluminum foil scraps in the lithium iron phosphate material, and removing graphite and remaining adhesive by heat treatment; after dissolving the lithium iron phosphate with acid, utilizing sodium sulphide to remove copper ions, and utilizing the NaOH solution or ammonia solution to allow iron, lithium and phosphorus ions in the solution to generate sediments; adding iron source, lithium source or phosphorus source compounds to adjust the molar ratio of iron, lithium and phosphorus; and finally adding a carbon source, and obtaining a lithium iron phosphate cathode material through ball milling and calcination in inert atmosphere. After the treatment of the steps, the recovery rate of valuable metals in the batteries is more than 95%, and the comprehensive recovery rate of the lithium iron phosphate cathode material is more than 90%.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Multi-component removal in flue gas by aqua ammonia
InactiveUS7255842B1Regeneration process is less-costlyIncrease load capacityGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsNitric oxideSlurry
A new method for the removal of environmental compounds from gaseous streams, in particular, flue gas streams. The new method involves first oxidizing some or all of the acid anhydrides contained in the gas stream such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O) to sulfur trioxide (SO3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The gas stream is subsequently treated with aqua ammonia or ammonium hydroxide which captures the compounds via chemical absorption through acid-base or neutralization reactions. The products of the reactions can be collected as slurries, dewatered, and dried for use as fertilizers, or once the slurries have been dewatered, used directly as fertilizers. The ammonium hydroxide can be regenerated and recycled for use via thermal decomposition of ammonium bicarbonate, one of the products formed. There are alternative embodiments which entail stoichiometric scrubbing of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides with subsequent separate scrubbing of carbon dioxide.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Post clean treatment
InactiveUS6546939B1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydroxylamineHydrazine compound
A composition for removal of chemical residues from metal or dielectric surfaces or for chemical mechanical polishing of a copper or aluminum surface is an aqueous solution with a pH between about 3.5 and about 7. The composition contains a monofunctional, difunctional or trifunctional organic acid and a buffering amount of a quaternary amine, ammonium hydroxide, hydroxylamine, hydroxylamine salt, hydrazine or hydrazine salt base. A method in accordance with the invention for removal of chemical residues from a metal or dielectric surface comprises contacting the metal or dielectric surface with the above composition for a time sufficient to remove the chemical residues. A method in accordance with the invention for chemical mechanical polishing of a copper or aluminum surface comprises applying the above composition to the copper or aluminum surface, and polishing the surface in the presence of the composition.
Owner:DUPONT AIR PRODS NANOMATERIALS
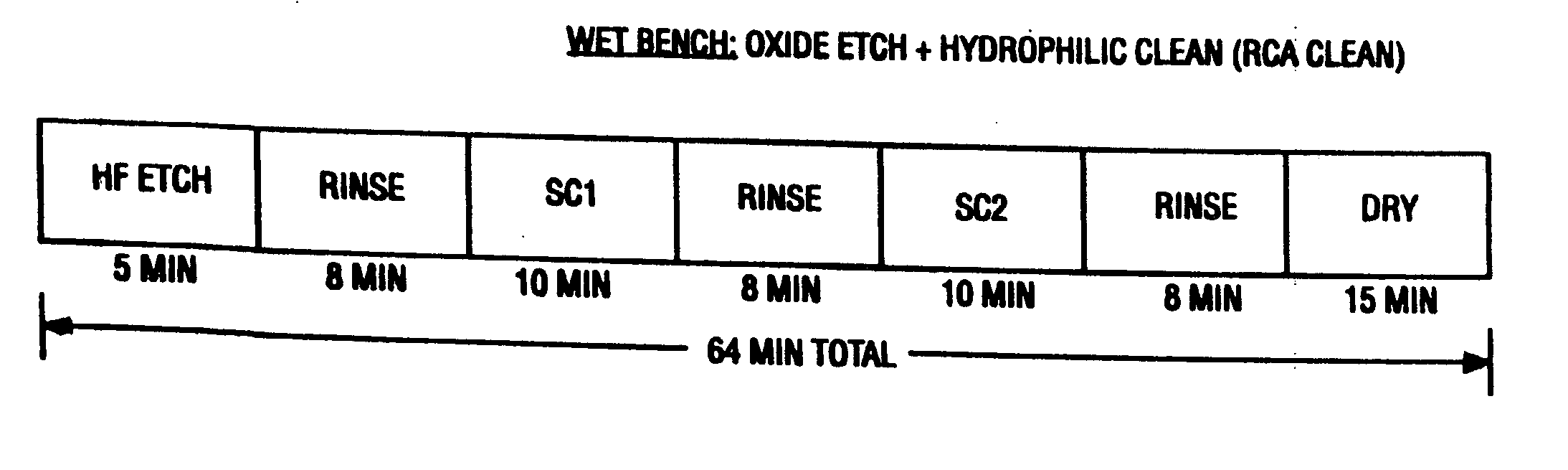
Method and apparatus for removing photoresist and post-etch residue from semiconductor substrates by in-situ generation of oxidizing species
InactiveUS6848455B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningAmmonium hydroxideAmount of substance
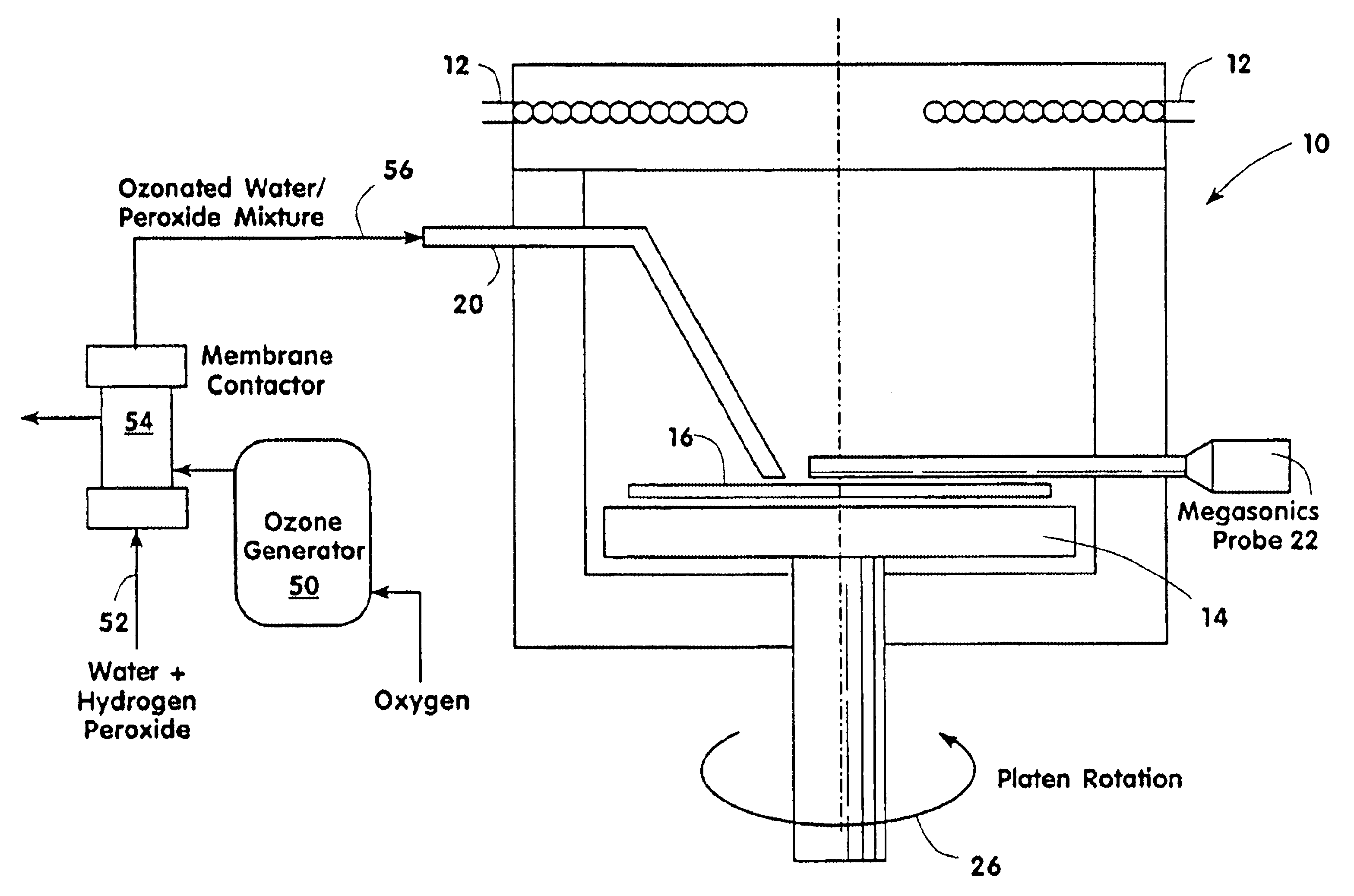
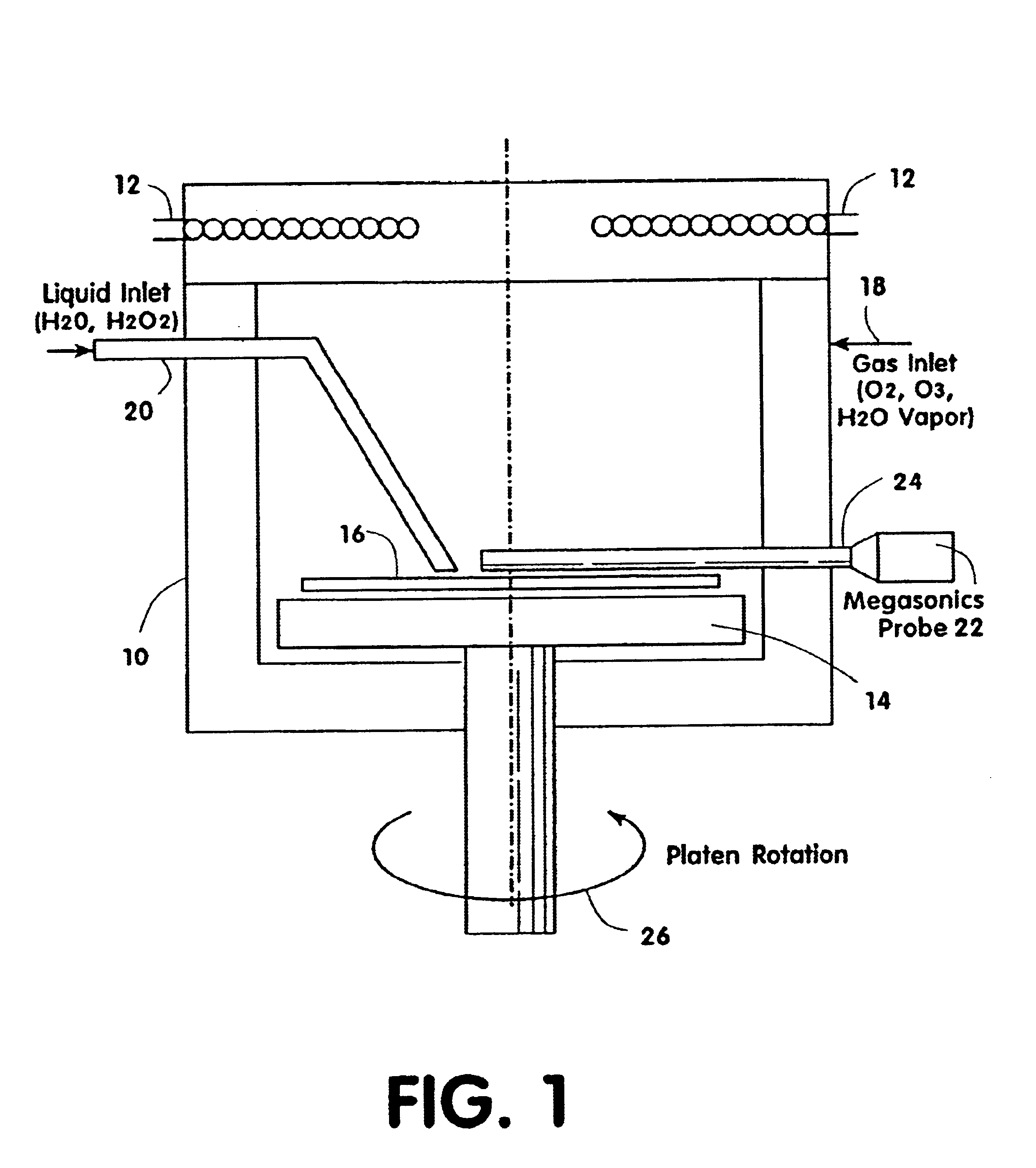
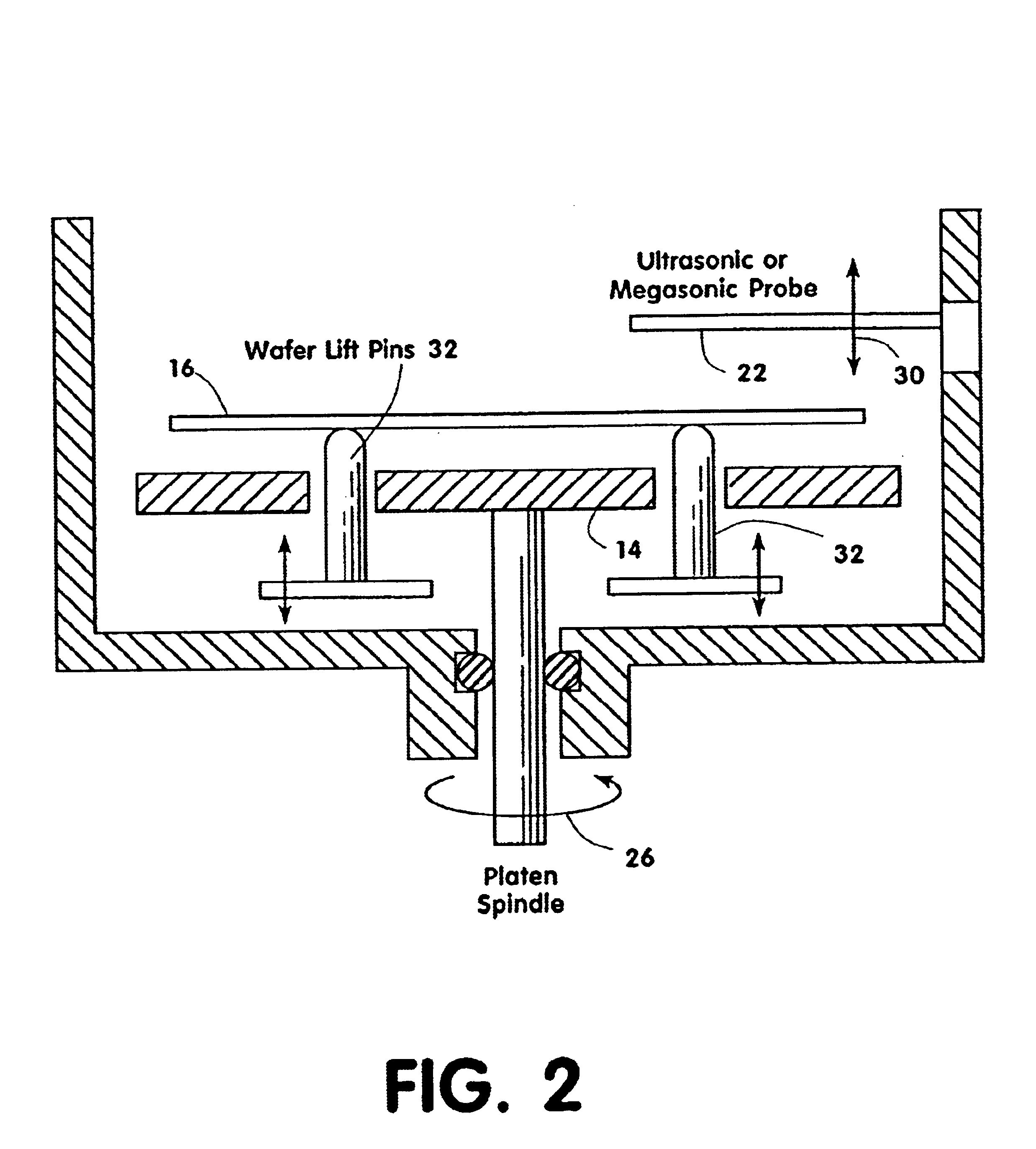
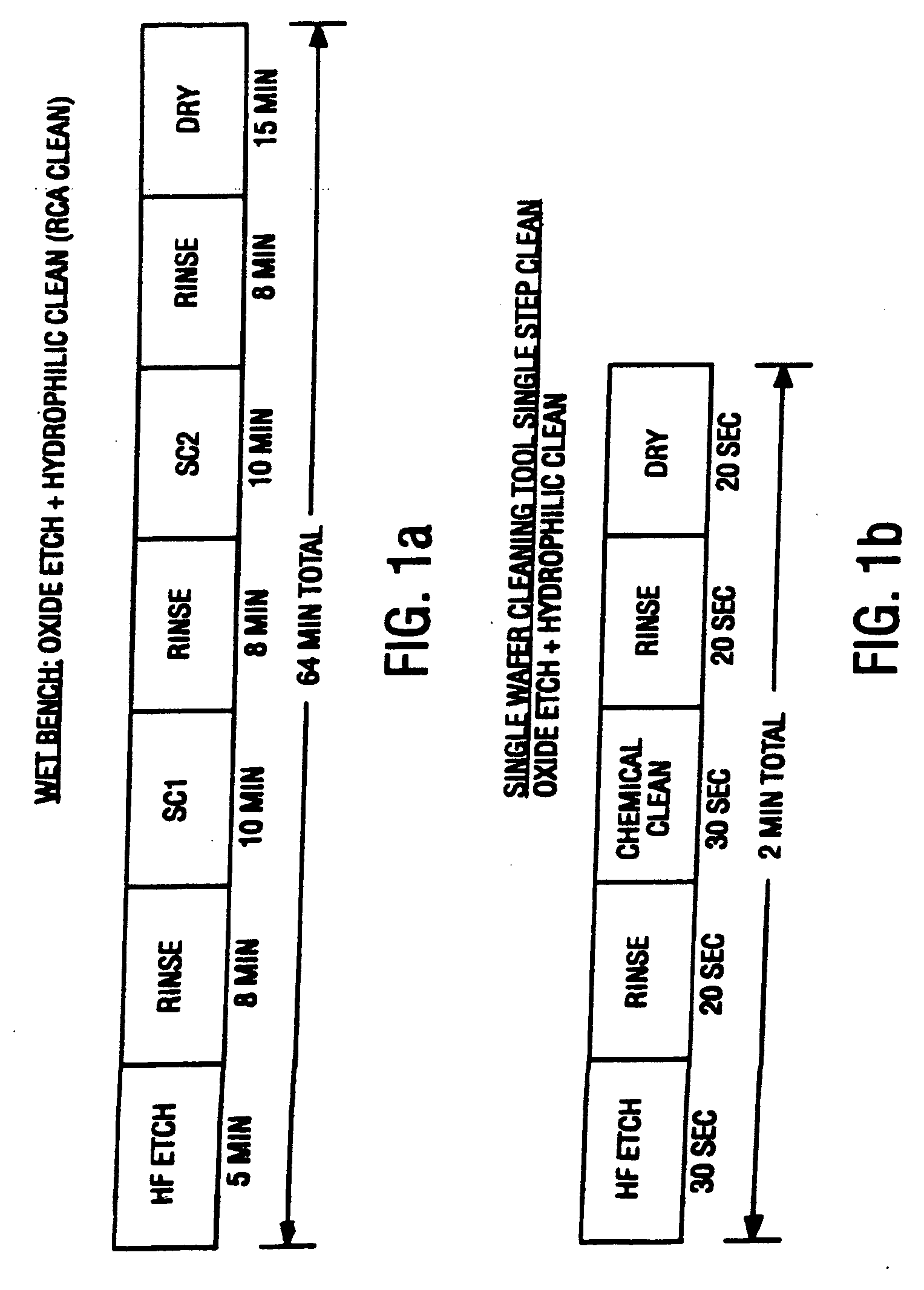
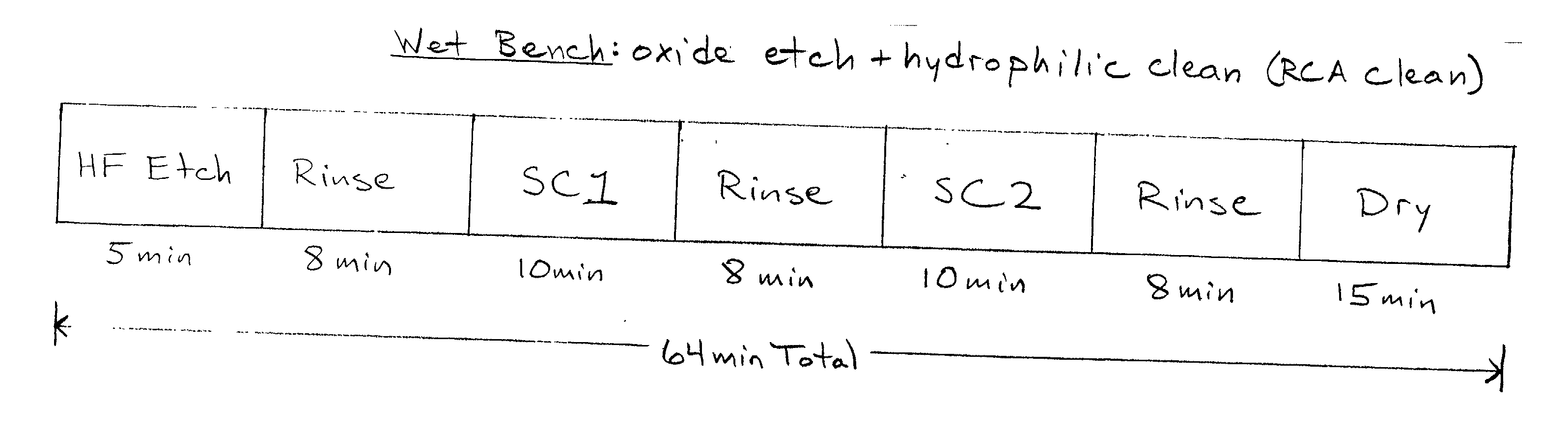
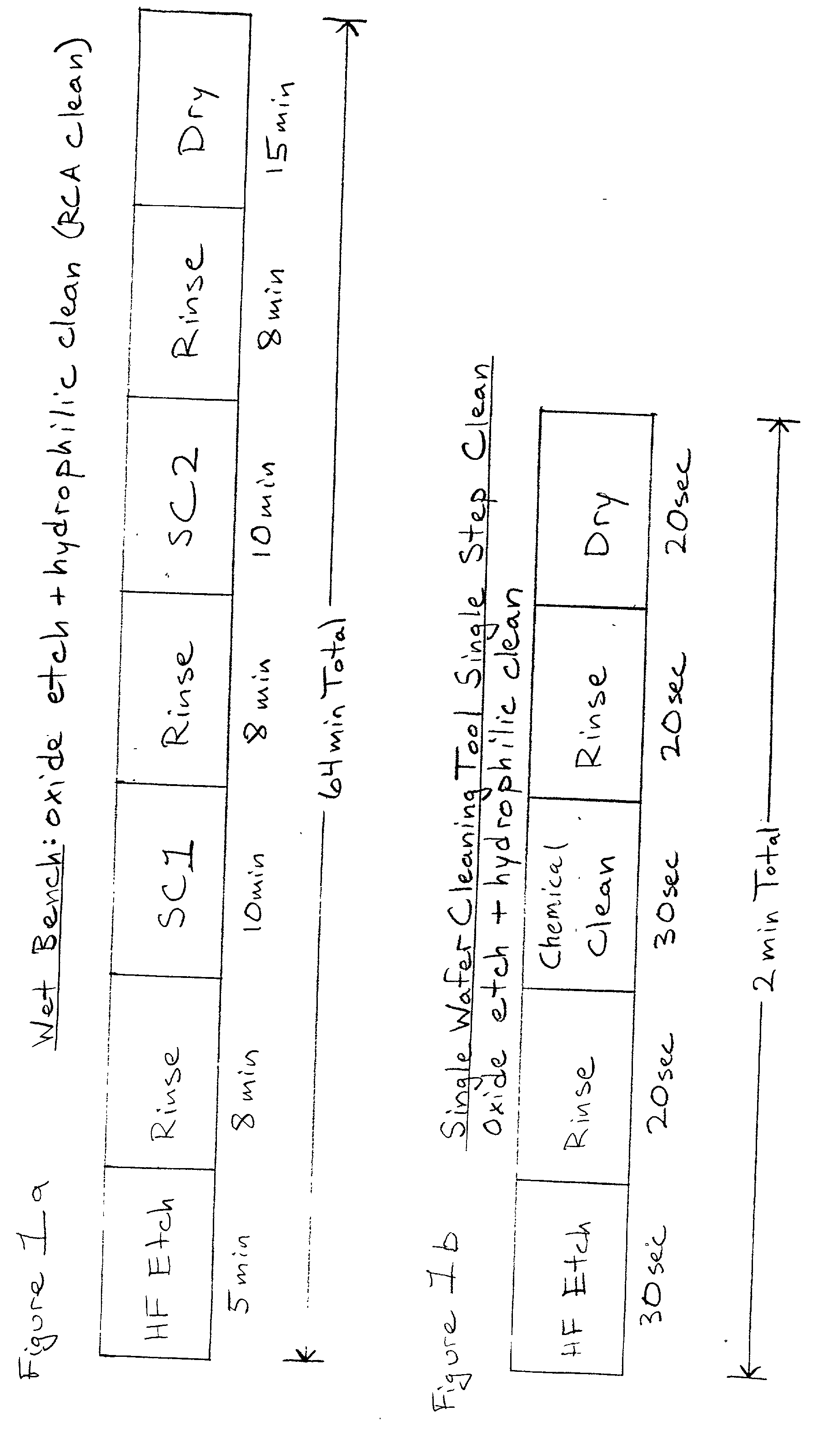
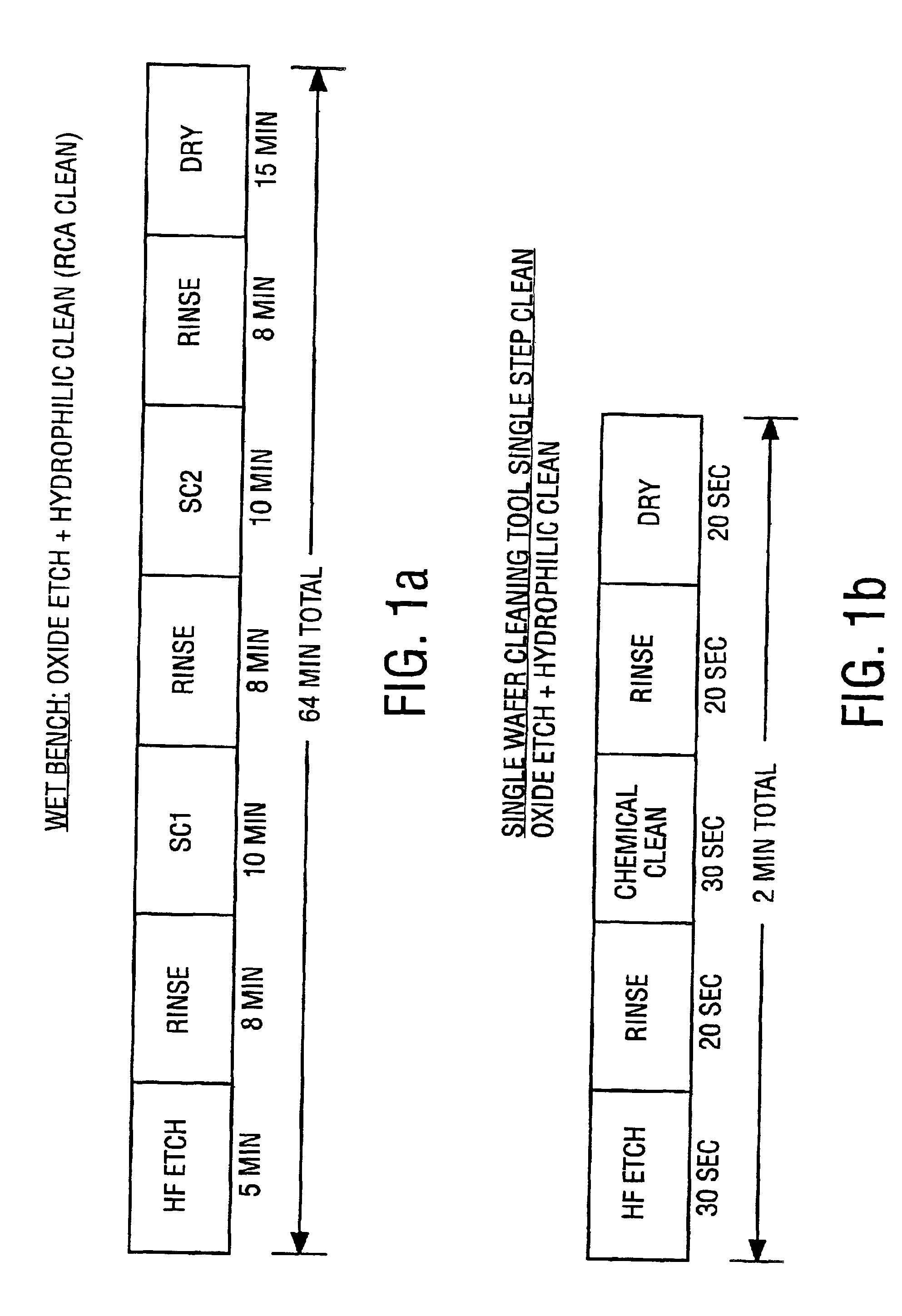
Contaminants are removed from a semiconductor wafer by the in-situ generation of oxidizing species. These active species are generated by the simultaneous application of ultra-violet radiation and chemicals containing oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide and dissolved ozone. Ultrasonic or megasonic agitation is employed to facilitate removal. Radicals are generated in-situ, thus generating them close to the semiconductor substrate. The process chamber has a means of introducing both gaseous and liquid reagents, through a gas inlet, and a liquid inlet. O2, O3, and H2O vapor gases are introduced through the gas inlet. H2O and H2O2 liquids are introduced through the liquid inlet. Other liquids such as ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), hydrochloric acid (HCI), hydrofluoric acid (HF), and the like, may be introduced to further constitute those elements of the traditional RCA clean. The chemicals are premixed in a desired ration and to a predetermined level of dilution prior to being introduced into the chamber. The chamber is equipped with megasonic or ultrasonic transducer probe(s), placed in close proximity to the substrate as the substrate rotates with the rotating platen.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Removal of cured silicone adhesive for reworking electronic components
InactiveUS20020000239A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsOrganic baseSolvent
Owner:IBM CORP
Stripping liquid for semiconductor device, and stripping method
A stripping liquid for a semiconductor device is provided that includes an aqueous solution containing a quaternary ammonium hydroxide, an oxidizing agent, an alkanolamine, and an alkali metal hydroxide. There is also provided a stripping method that includes a stripping liquid preparation step of preparing the stripping liquid and a stripping step of removing at least one deposit selected from the group consisting of a photoresist, an anti-reflection film, and an etching residue by means of the stripping liquid obtained in the stripping liquid preparation step.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and apparatus for producting negative and positive oxidative reductive potential (orp) water
ActiveUS20050121334A1Effective and efficient and economicalCellsWater treatment parameter controlParticulatesElectrolysis
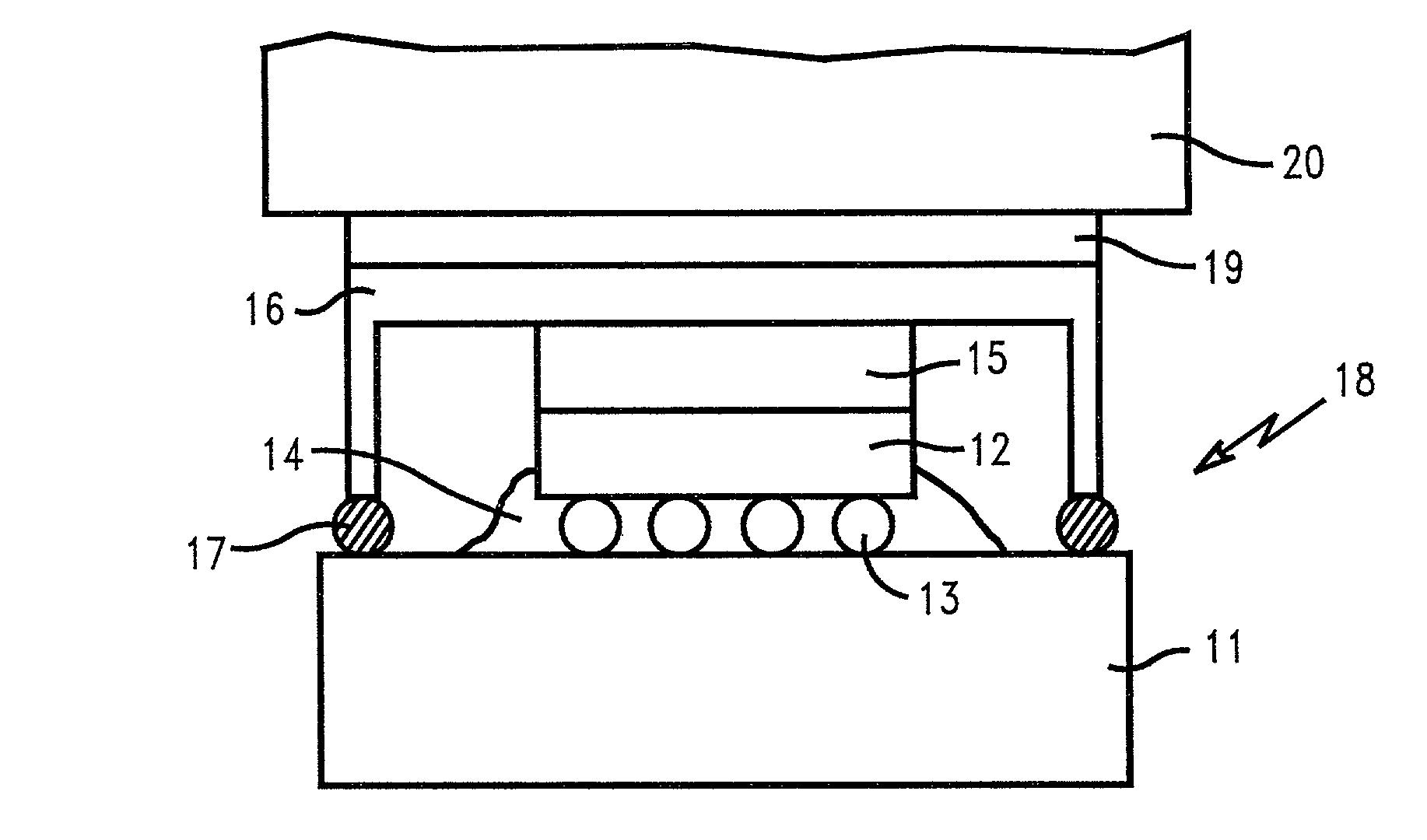
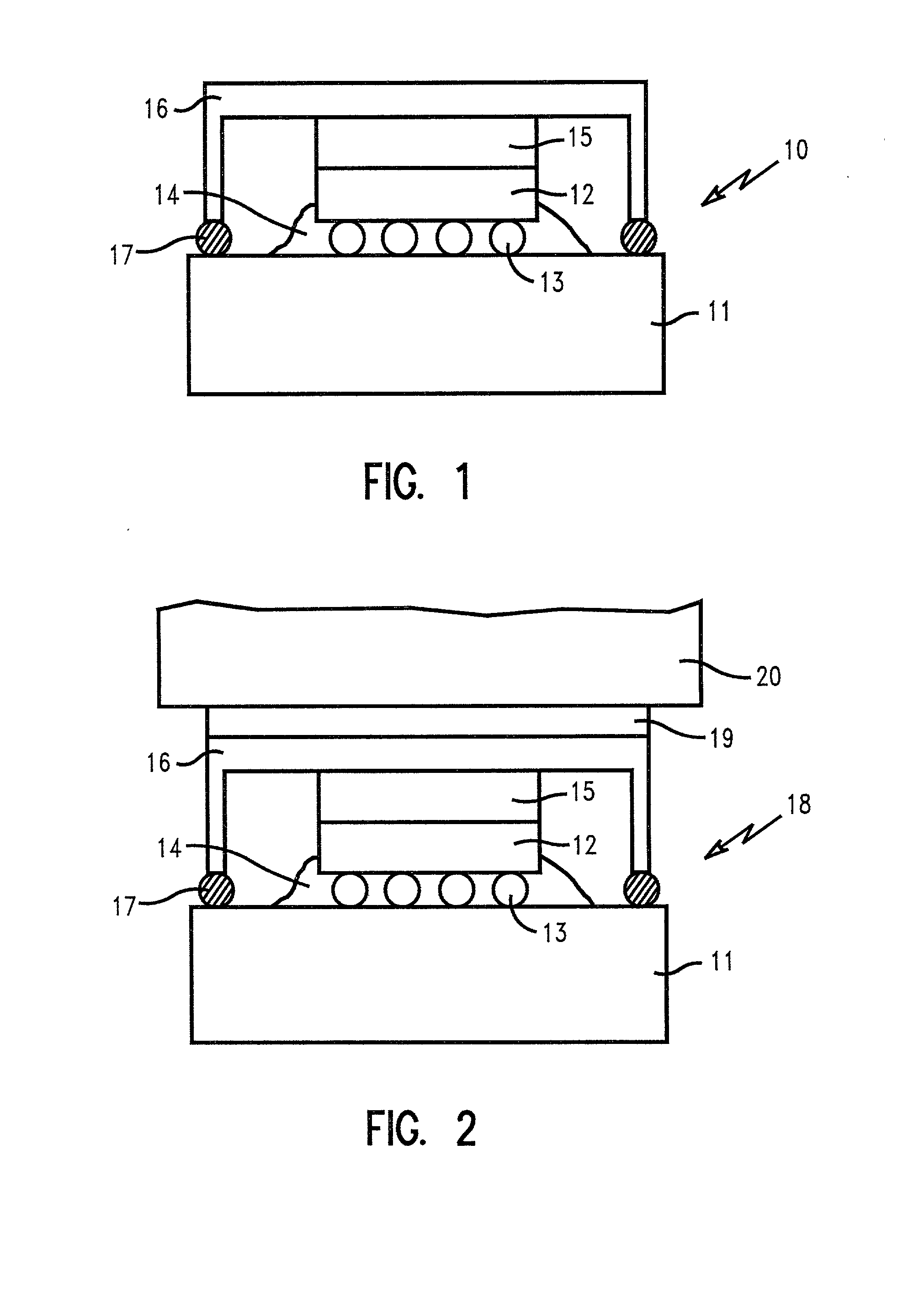
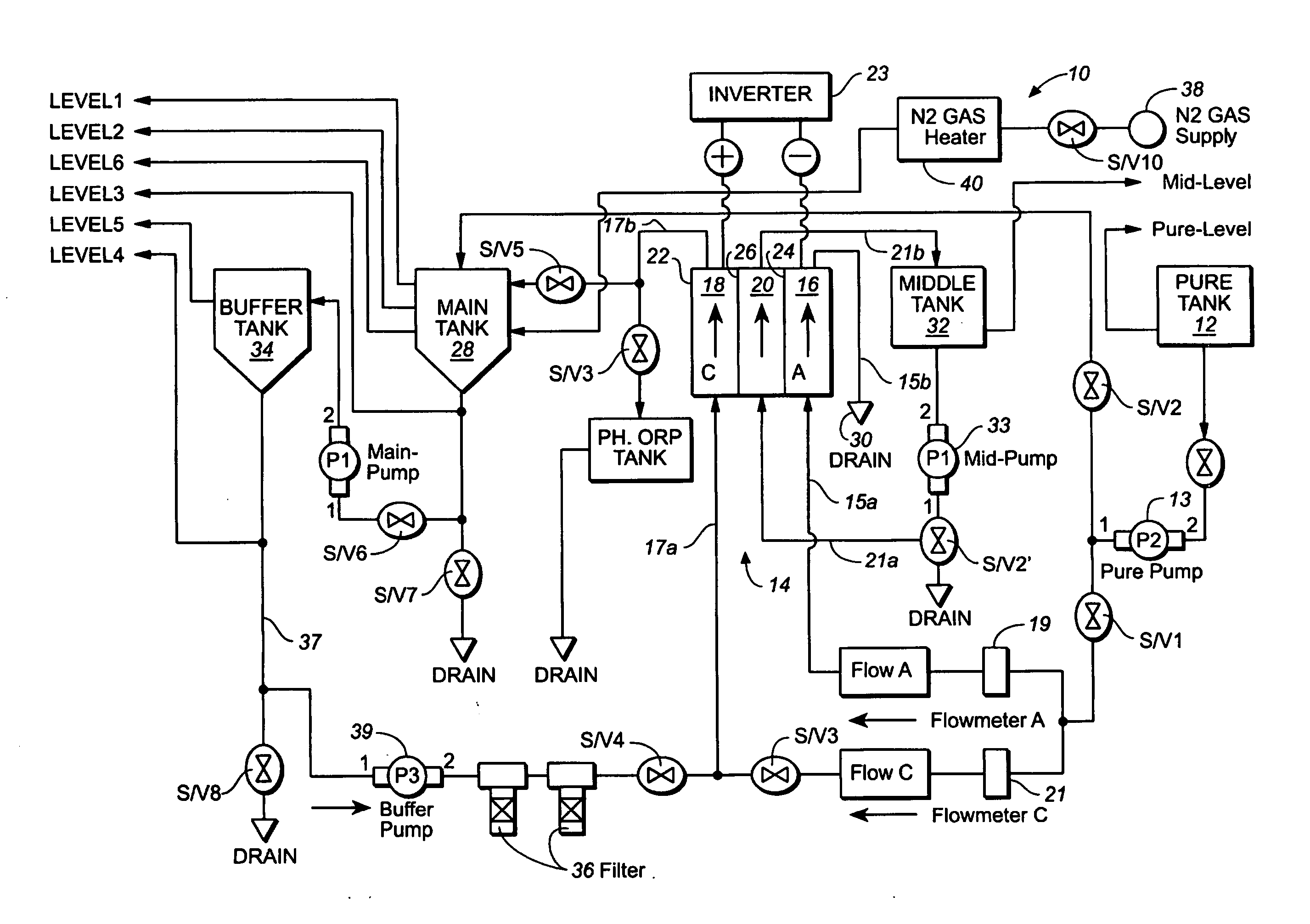
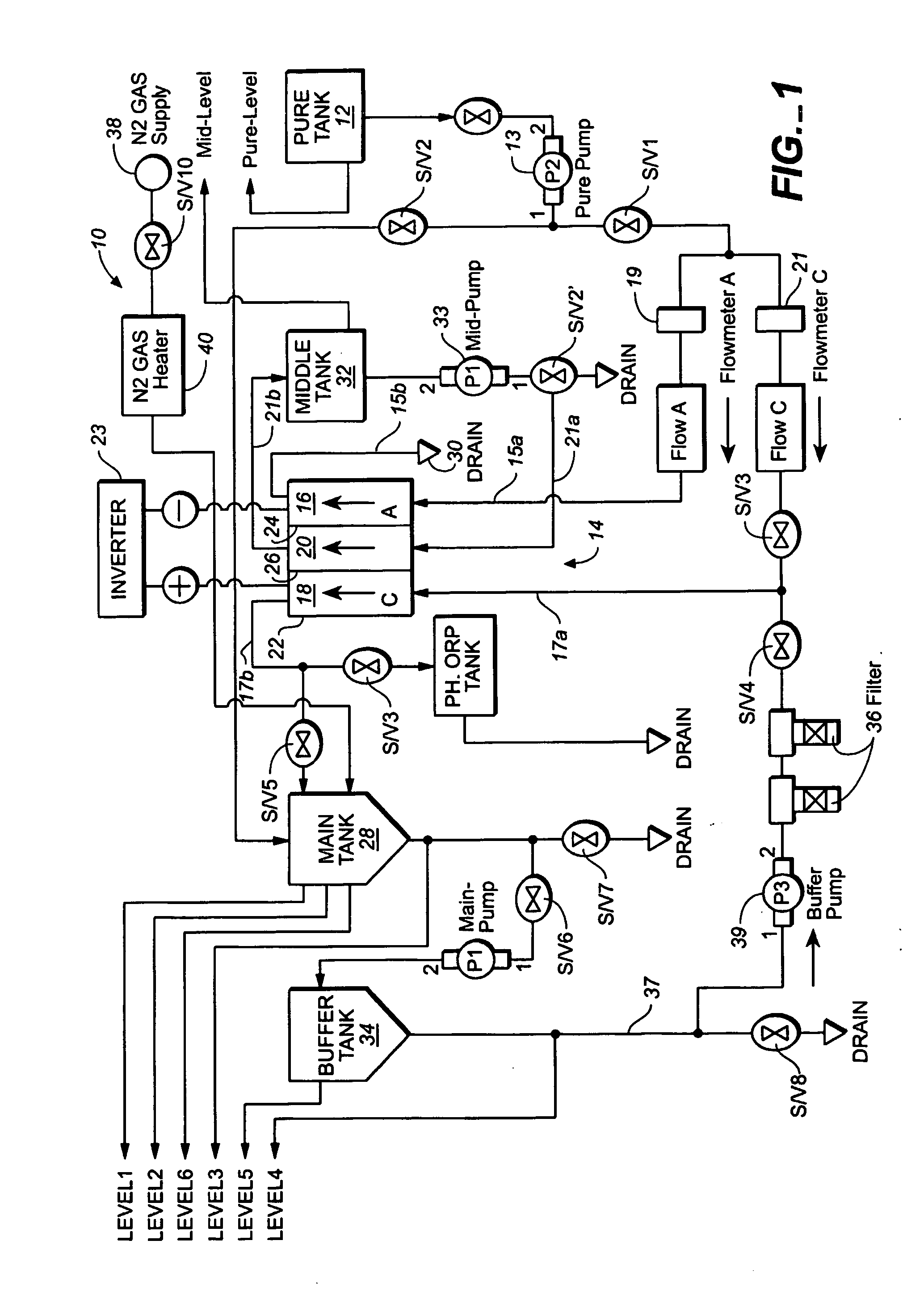
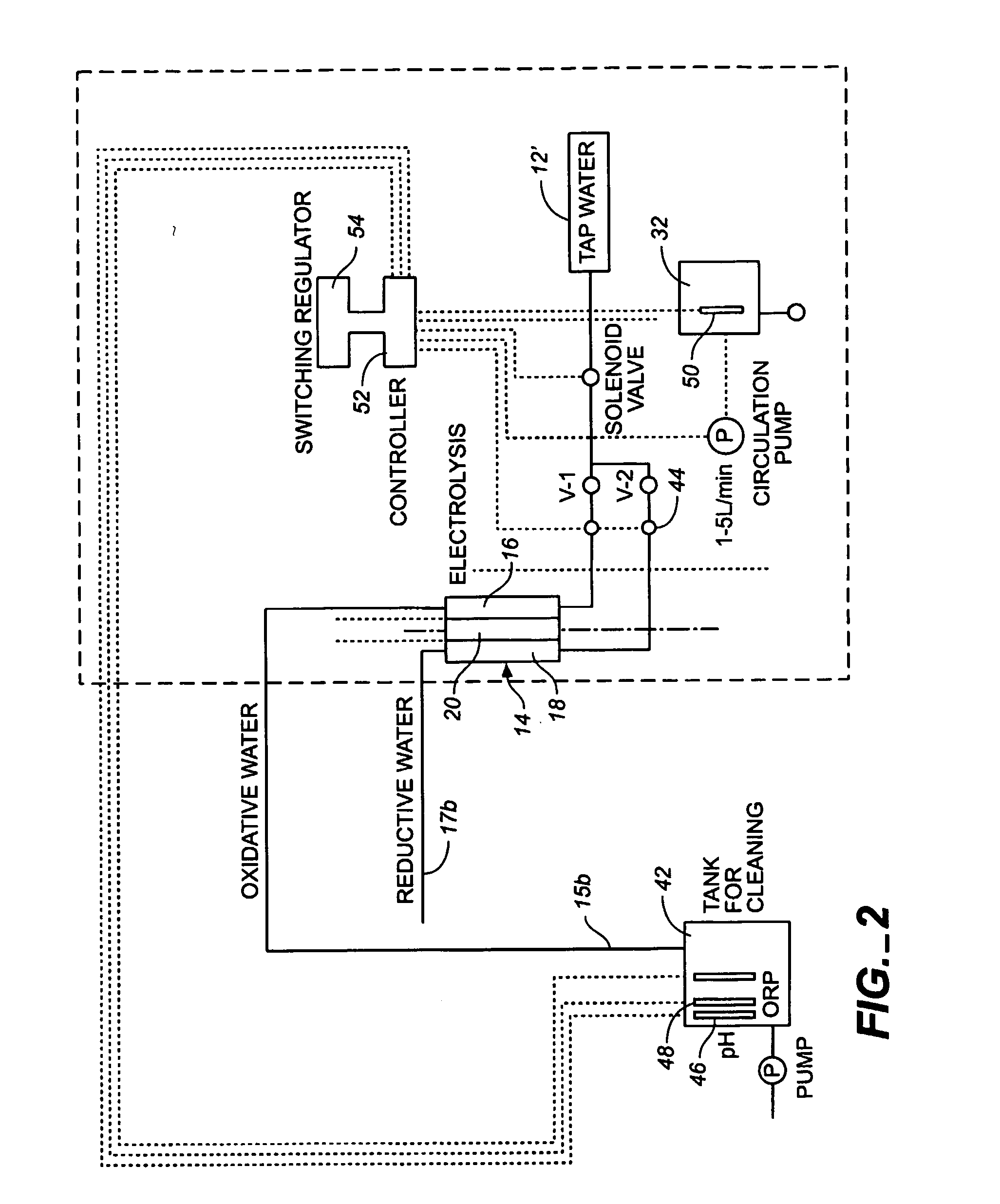
A method and apparatus for electrolytically producing oxidation reduction potential water from aqueous salt solutions for use in disinfection, sterilization, decontamination, wound cleansing. The apparatus includes an electrolysis unit having a three-compartment cell (22) comprising a cathode chamber (18), an anode chamber (16), and a saline solution chamber (20) interposed between the anode and cathod chambers. Two communicating (24, 26) membranes separate the three chambers. The center chamber includes a fluid flow inlet (21a) and outlet (21b) and contains insulative material that ensures direct voltage potential does not travel through the chamber. A supply of water flows through the cathode and anode chambers at the respective sides of the saline chamber. Saline solution flows through the center chamber, either by circulating a pre-prepared aqueous solution containing ionic species, or, alternatively, by circulating pure water or an aqueous solution of, e.g., aqueous hydrogen chloride and ammonium hydroxide, over particulate insulative material coated with a solid electrolyte. Electrical current is provided to the communicating membranes separating the chambers, thus causing an electrolytic reaction that produces both oxidative (positive) and reductive (negative) ORP water.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
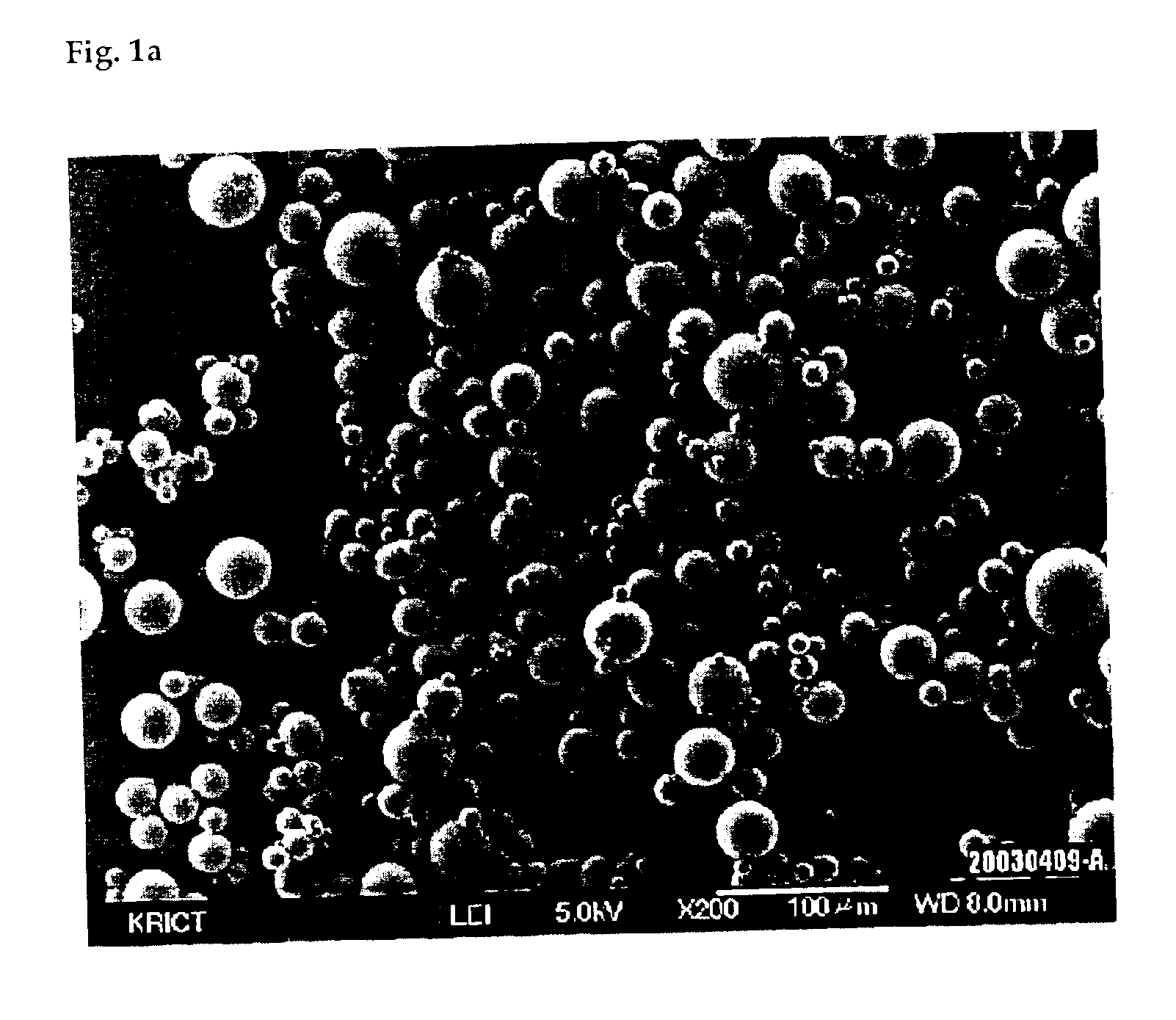
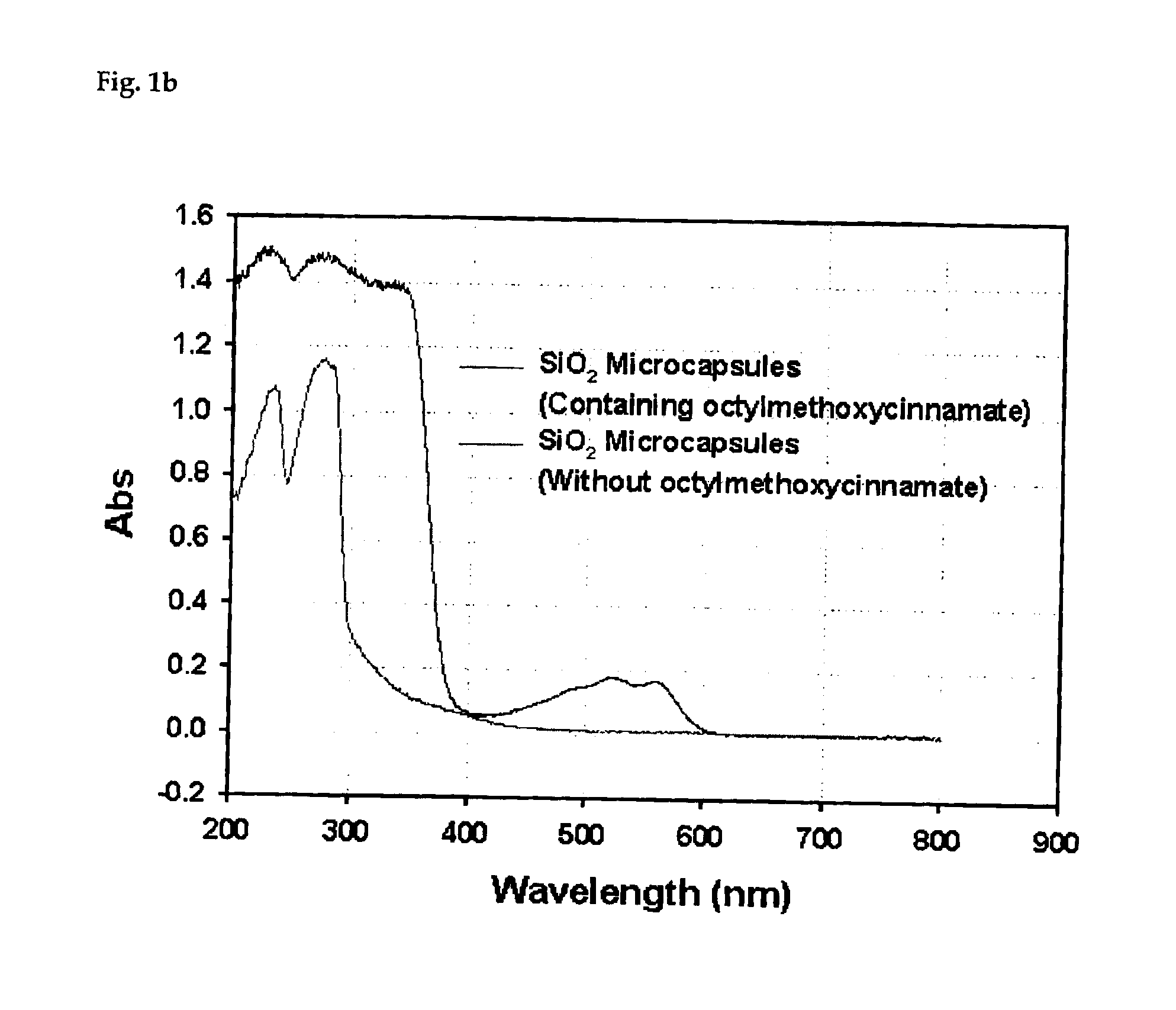
Process for preparing silica microcapsules
InactiveUS6855335B2Reduce environmental pollutionPowder deliveryGlass/slag layered productsAmmonium hydroxideSilica gel
The present invention relates to a process for preparing silica microcapsules and more particularly, to a process for preparing silica microcapsules comprising the steps of dissolving tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) into an aqueous solution containing a hydrolysis catalyst to control a degree of hydrolysis and contribute hydrophilicity or lipophilicity, adding a core material and an appropriate amount of aminopropyltrialkoxysilane(APS) as a gelling agent into the solution, and emulsifying and dispersing the resulting solution to a solution having a polarity opposite to that of the core material to microcapsulate by coating the core material with silica shell via a sol-gel reaction. The process for preparing microcapsules of the present invention reduces environmental pollution compared to conventional processes using an alkali gelling agent such as an ammonia solution, and are suitable for both organic or inorganic core materials having hydrophilic or lipophilic property.
Owner:UNITECH CO LTD (JP)
Method for removing photoresist
InactiveUS20050176259A1Improve corrosion resistanceEfficient strippingDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmmonium hydroxideCopper
Disclosed is a method for stripping a photoresist comprising: (I) providing a photoresist pattern on a substrate where the substrate has at least a copper (Cu) wiring and a low-dielectric layer thereon, and selectively etching the low-dielectric layer by using the photoresist pattern as a mask; (II) contacting the substrate after the step (I), with ozone water and / or aqueous hydrogen peroxide; and (III) contacting the substrate after the step (II), with a photoresist stripping solution that contains at least a quaternary ammonium hydroxide. The present invention provides a method for stripping a photoresist that enables to strip effectively photoresist films and etching residues after etching step even in a process not including an O2 plasma ashing treatment in micropatterning of a substrate having at least Cu wiring and a low-dielectric layer thereon, as in a dual damascene forming process, and, in addition, the method of the invention does not have any negative influence on the dielectric constant of the low-dielectric layer, and ensures an excellent anti-corrosivity.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Compositions for processing of semiconductor substrates
InactiveUS20060166847A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationDevice materialAmmonium hydroxide
Compositions useful in semiconductor manufacturing for surface preparation and / or cleaning of wafer substrates such as semiconductor device precursor structures. The compositions can be employed for processing of wafers that have, or are intended to be further processed to include, copper metallization, e.g., in operations such as surface preparation, pre-plating cleaning, post-etching cleaning, and post-chemical mechanical polishing cleaning of semiconductor wafers. The compositions contain (i) alkanolamine, (ii) quaternary ammonium hydroxide and (iii) a complexing agent, and are storage-stable, as well as non-darkening and degradation-resistant in exposure to oxygen.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Process for preparing high density spherical nickel-cobalt lithium manganate as anode material of lithium ion cell
InactiveCN1622371AWell mixedImprove performanceElectrode manufacturing processesLithium compoundsNickel saltManganate
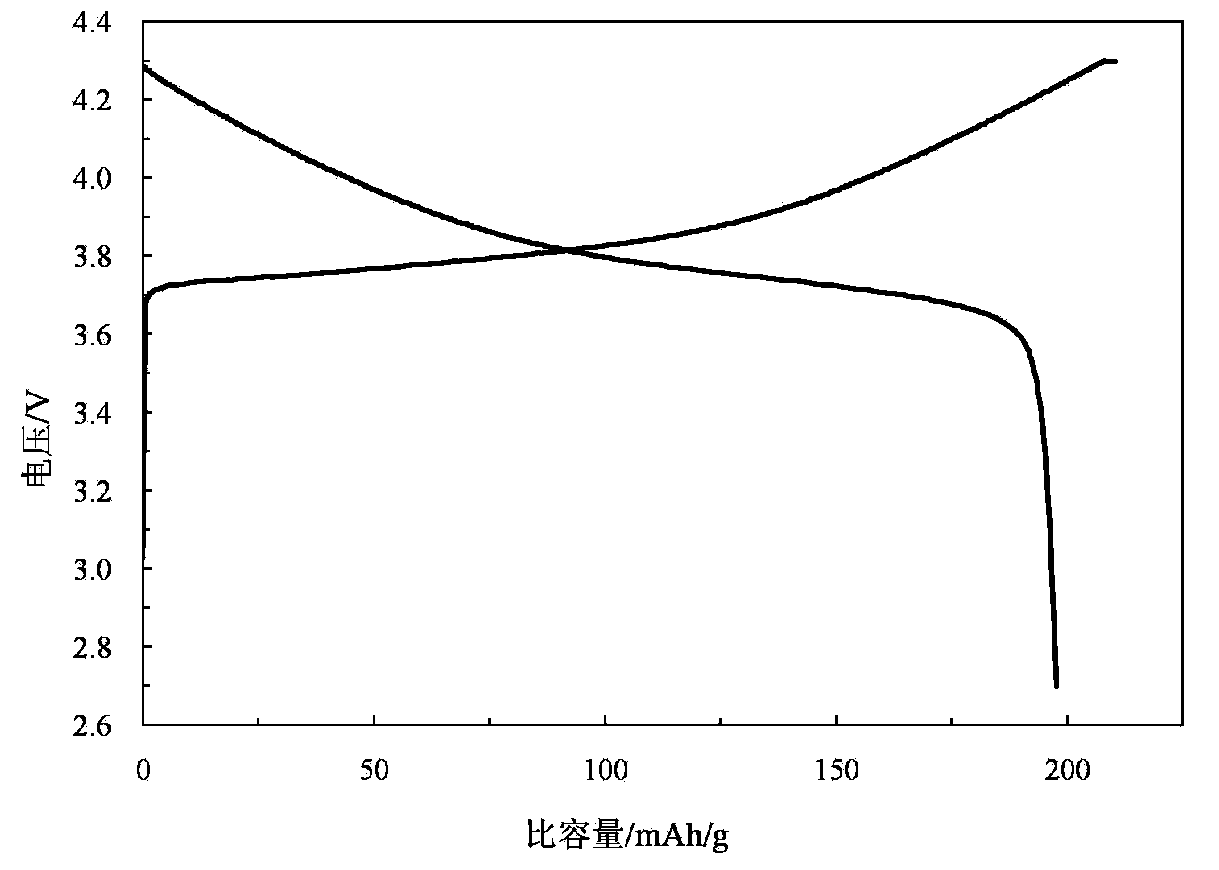
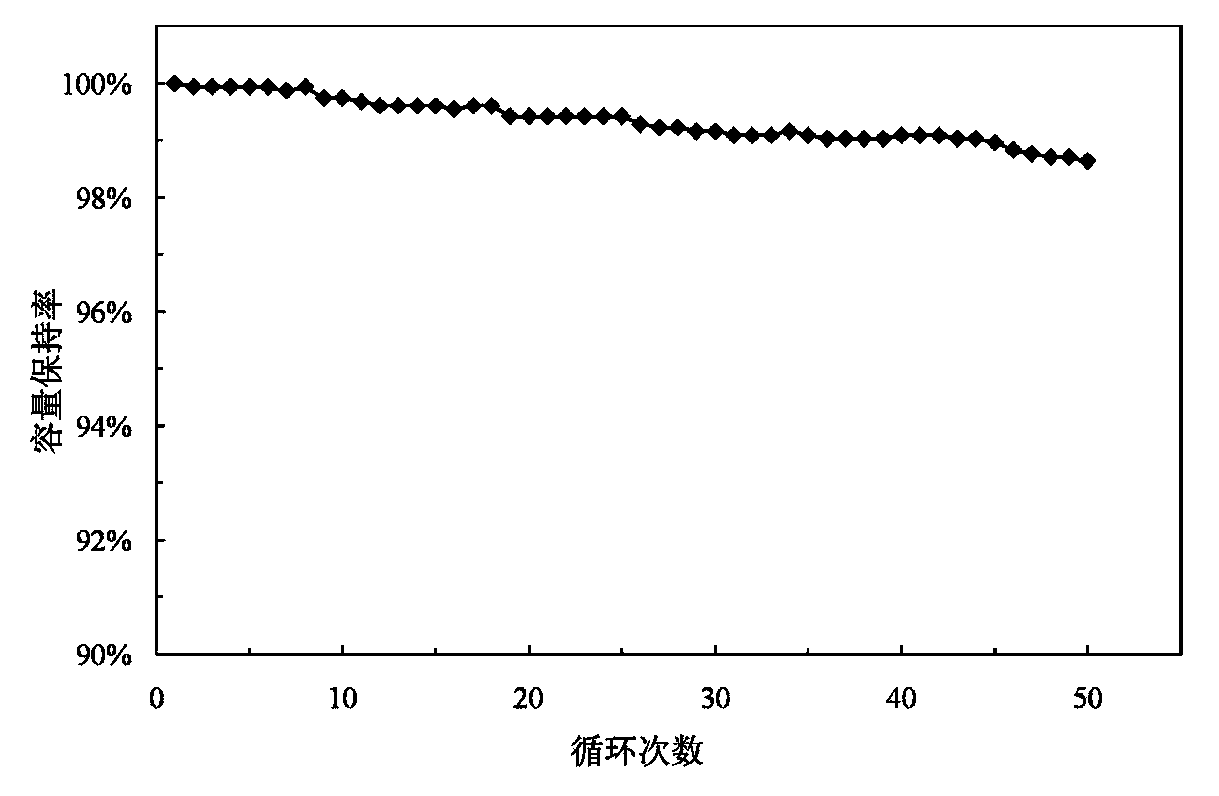
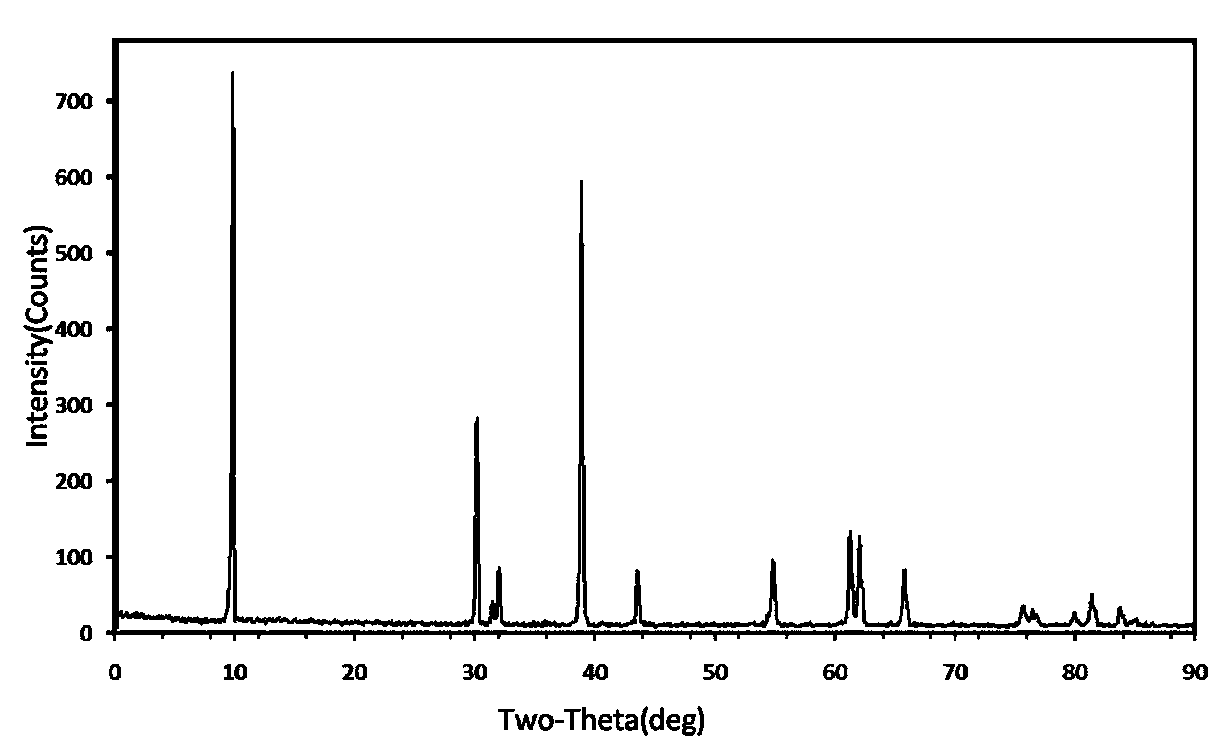
The present invention relates to energy source material technology, and is preparation process of high density spherical lithium nickel-cobalt-manganate as positive electrode material for lithium ion cell. The preparation process includes the reaction of nickel salt, cobalt salt, manganese salt, ammonium hydroxide and ammonian in water solution to synthesize spherical or spheroid precursor Ni1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3 (OTHER)2, washing, drying and mixing with lithium carbonate; and high temperature treatment in the air at 750-950 deg.c for 8-48 hr to obtain spherical lithium nickel-cobalt-manganate. The spherical lithium nickel-cobalt-manganate has great bulk density reaching 2.25-2.50 g / cu cm after vibration densifying, average grain size of 3-7 microns, and reversible specific capacity up to 172-185 mA.hr / g.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods of forming semiconductor constructions and capacitors
InactiveUS20070048976A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTetramethylammonium hydroxideOxygen compound
The invention includes methods in which silicon is removed from titanium-containing container structures with an etching composition having a phosphorus-and-oxygen-containing compound therein. The etching composition can, for example, include one or both of ammonium hydroxide and tetra-methyl ammonium hydroxide. The invention also includes methods in which titanium-containing whiskers are removed from between titanium-containing capacitor electrodes. Such removal can be, for example, accomplished with an etch utilizing one or more of hydrofluoric acid, ammonium fluoride, nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method of forming a minute resist pattern
InactiveUS6933100B2Excellent in residual film thicknessReduce processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsResistQuinone
A method of forming a minute resist pattern wherein a positive-working photoresist composition containing 3 to 15 parts by weight of a quinone diazide group-containing photosensitizer relative to 100 parts by weight of alkali-soluble novolak resin is developed by an aqueous organic or inorganic alkali solution having a lower alkali concentration than that of the conventional one as the developer. The preferable example of the organic alkali materials in the developer is quaternary ammonium hydroxide, and the preferable example of the inorganic alkali materials in the developer is alkali metal hydroxide. The concentrations of the quaternary ammonium hydroxide and the alkali metal hydroxide in the developing solution are 2.2% by weight or less and 0.4% by weight or less respectively. Using such developing solution, high sensitivity, a high film retention rate, high resolution, low process dependency of dimension accuracy, and a formation of excellent pattern profile can be achieved.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
Cleaning method and solution for cleaning a wafer in a single wafer process
InactiveUS20060054181A1Improve processing efficiencyMinimize processing timeInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsCleaning methodsContamination
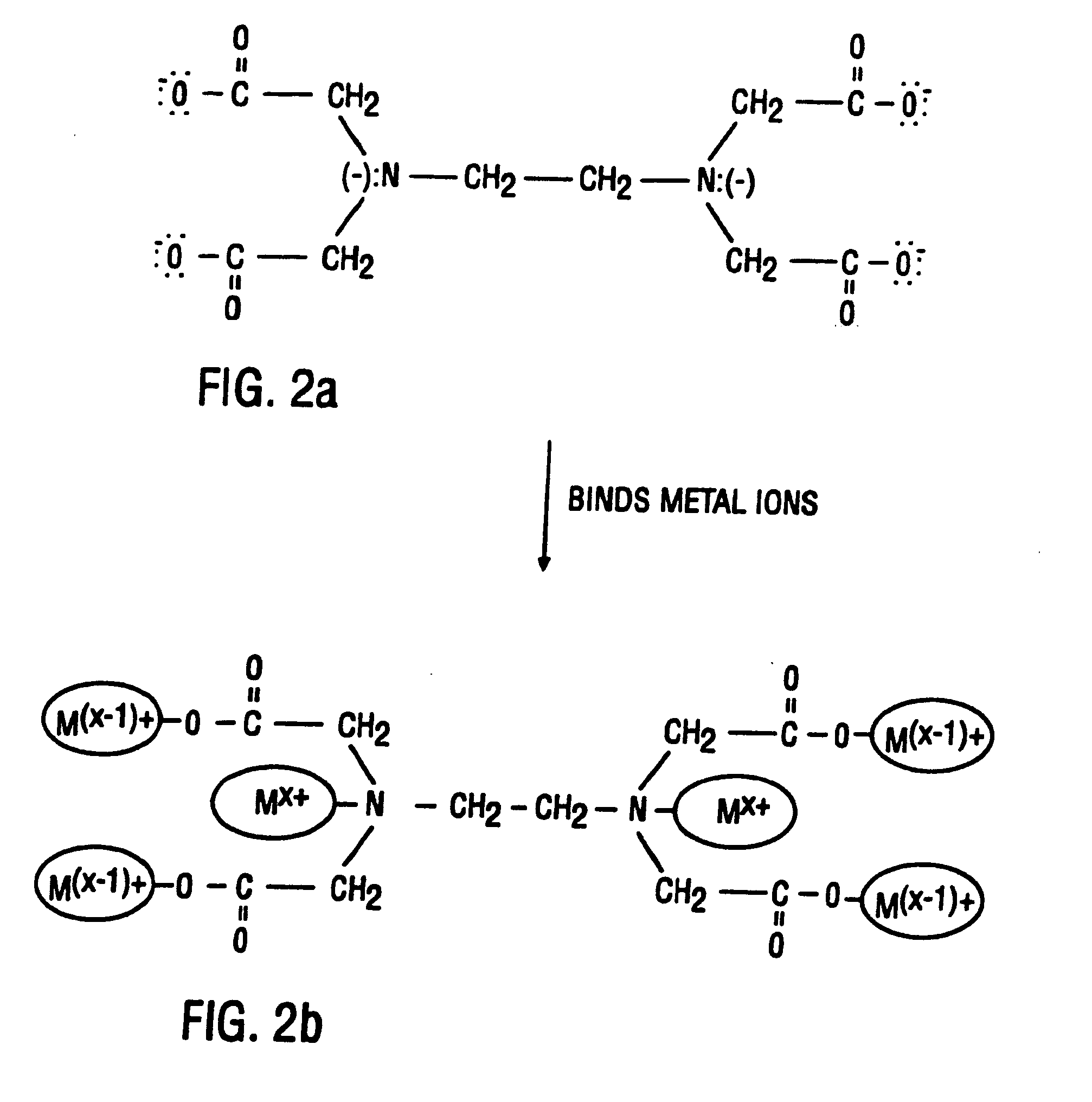
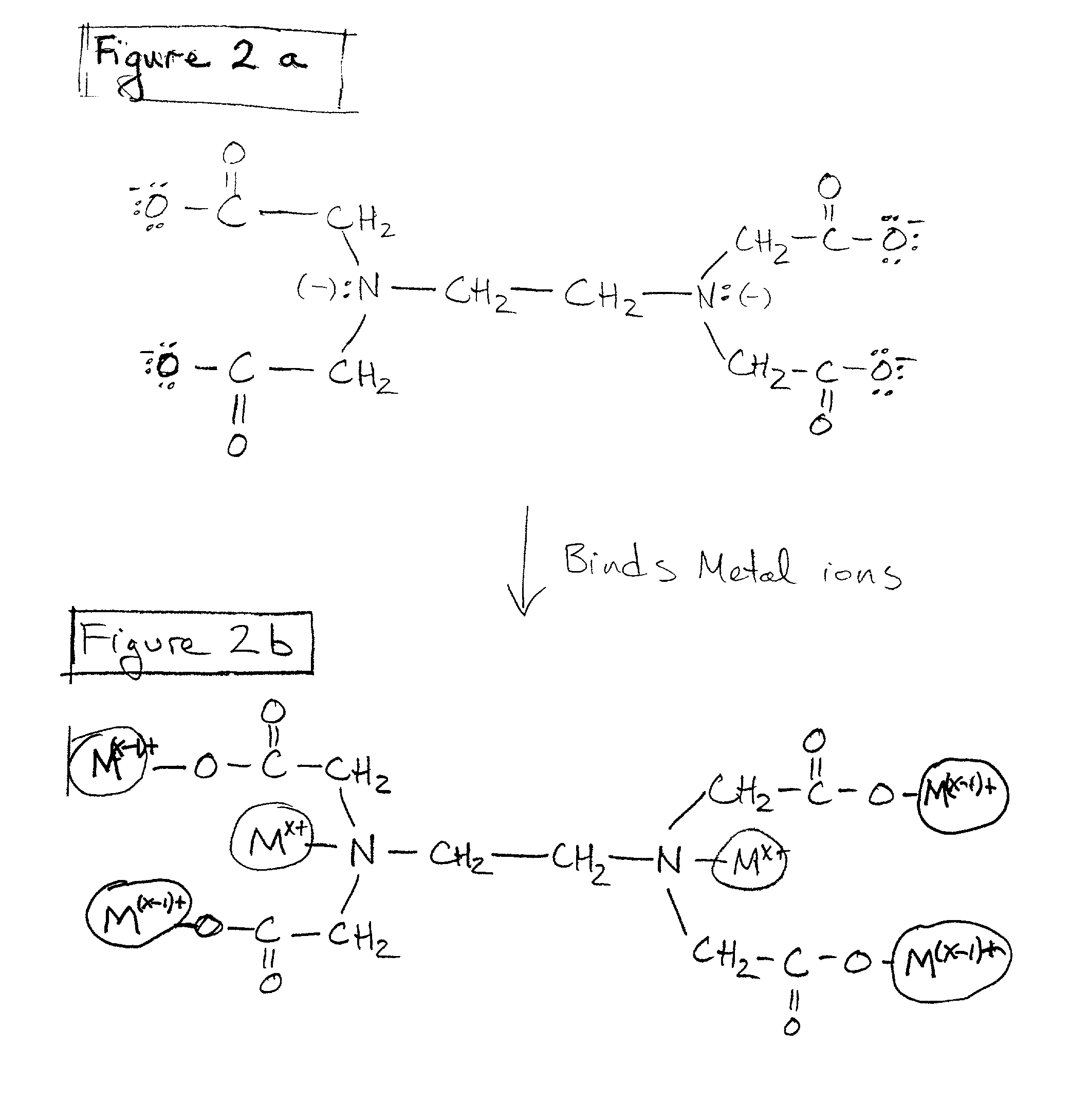
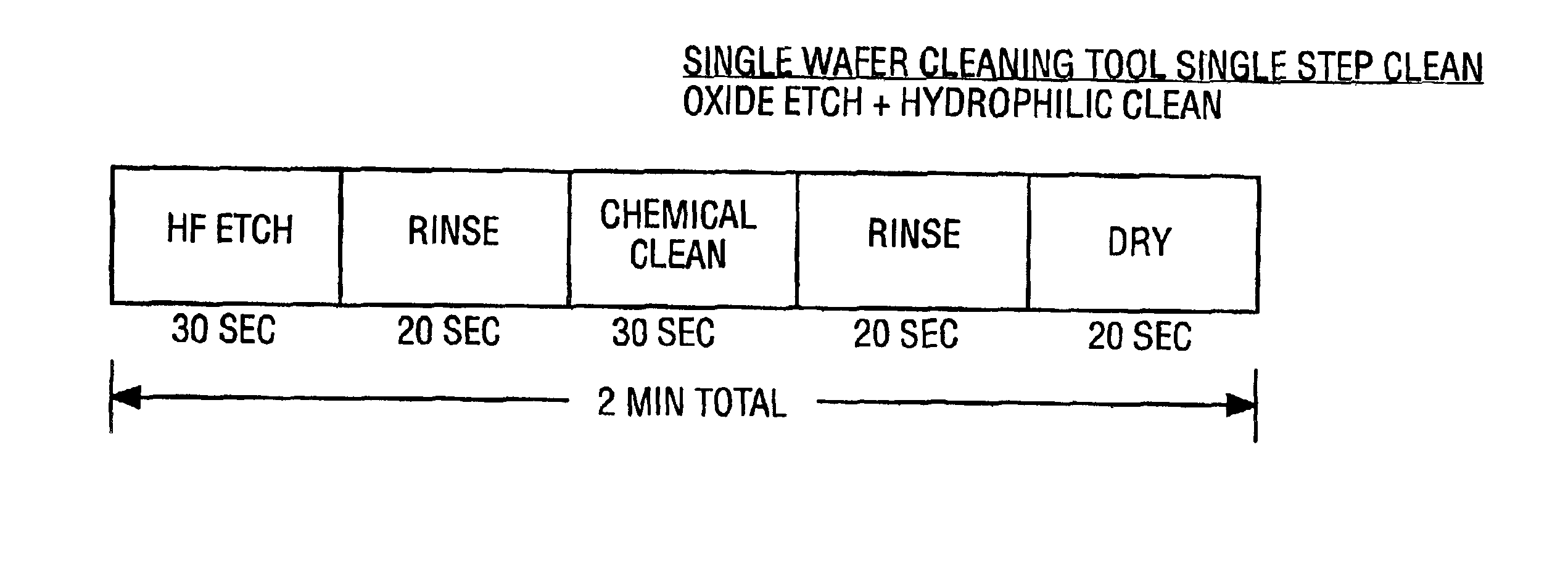
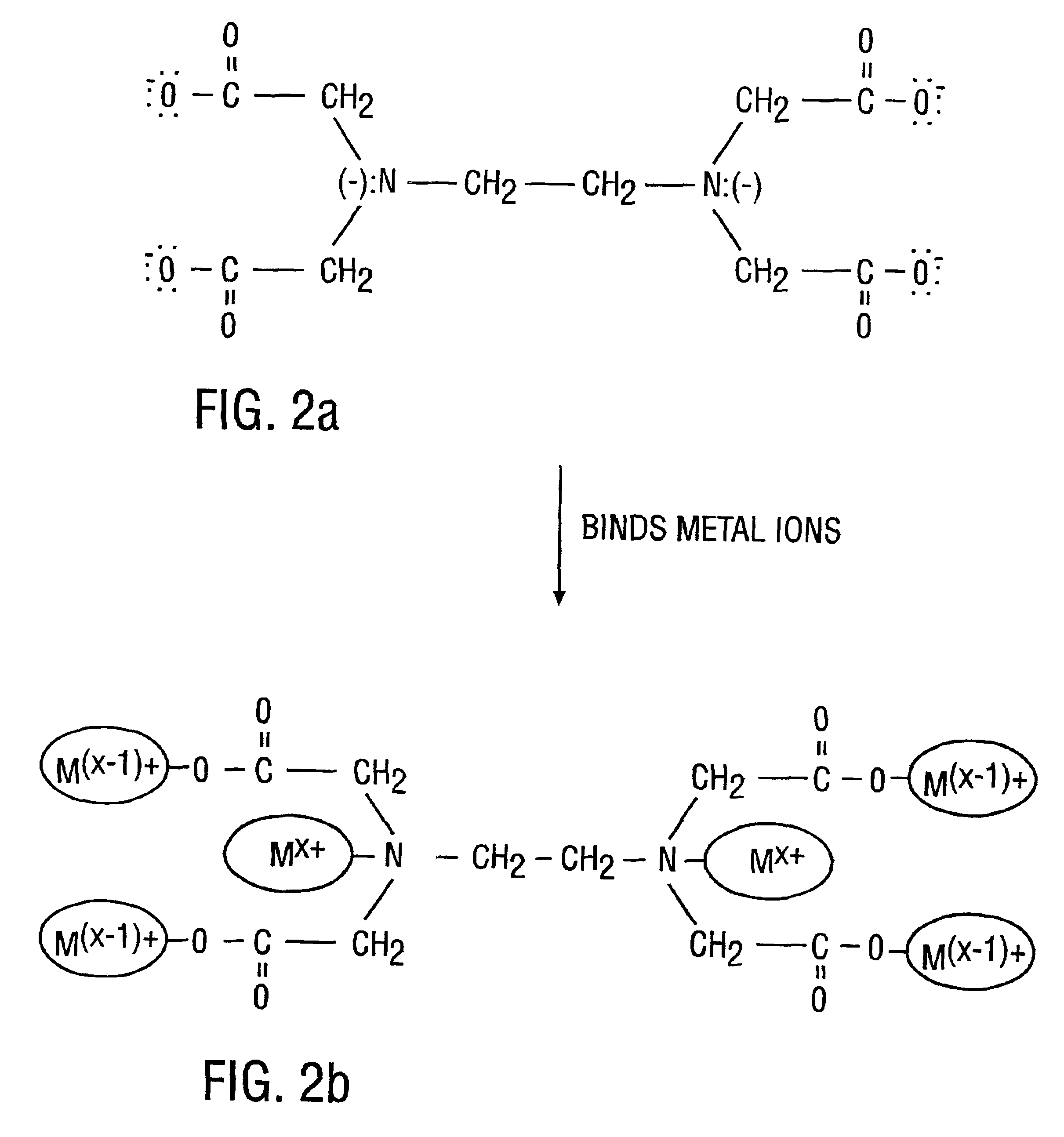
The present invention is a method of use of a novel cleaning solution in a single wafer cleaning process. According to the present invention the method involves using a cleaning solution in a single wafer mode and the cleaning solution comprises at least ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), water (H2O) and a chelating agent. In an embodiment of the present invention the cleaning solution also contains a surfactant. Moreover, the present invention also teaches a method of combining an ammonia hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide, and chelating agent step with a short HF step in a fashion that minimizes process time in a way that the entire method removes aluminum and iron contamination efficiently without etching too much oxide. The single wafer cleaning processes may also be used to increase the yield of high-grade reclaimed wafers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and method for point-of-use treatment of effluent gas streams
InactiveUS20040213721A1Highly efficient mannerReduce foaming in the scrubbing systemProcess control/regulationHydrogenSilanesChlorofluorocarbon
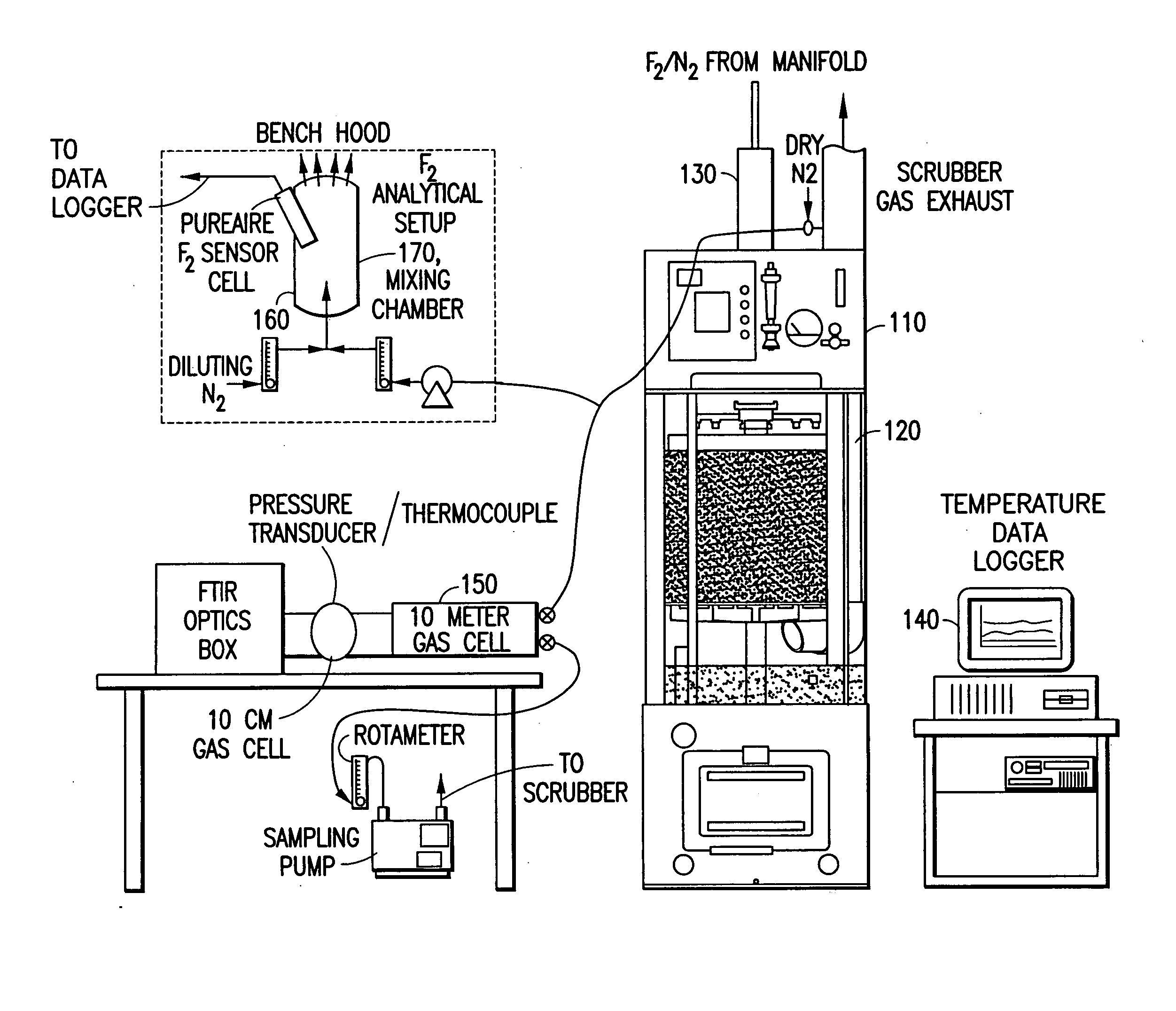
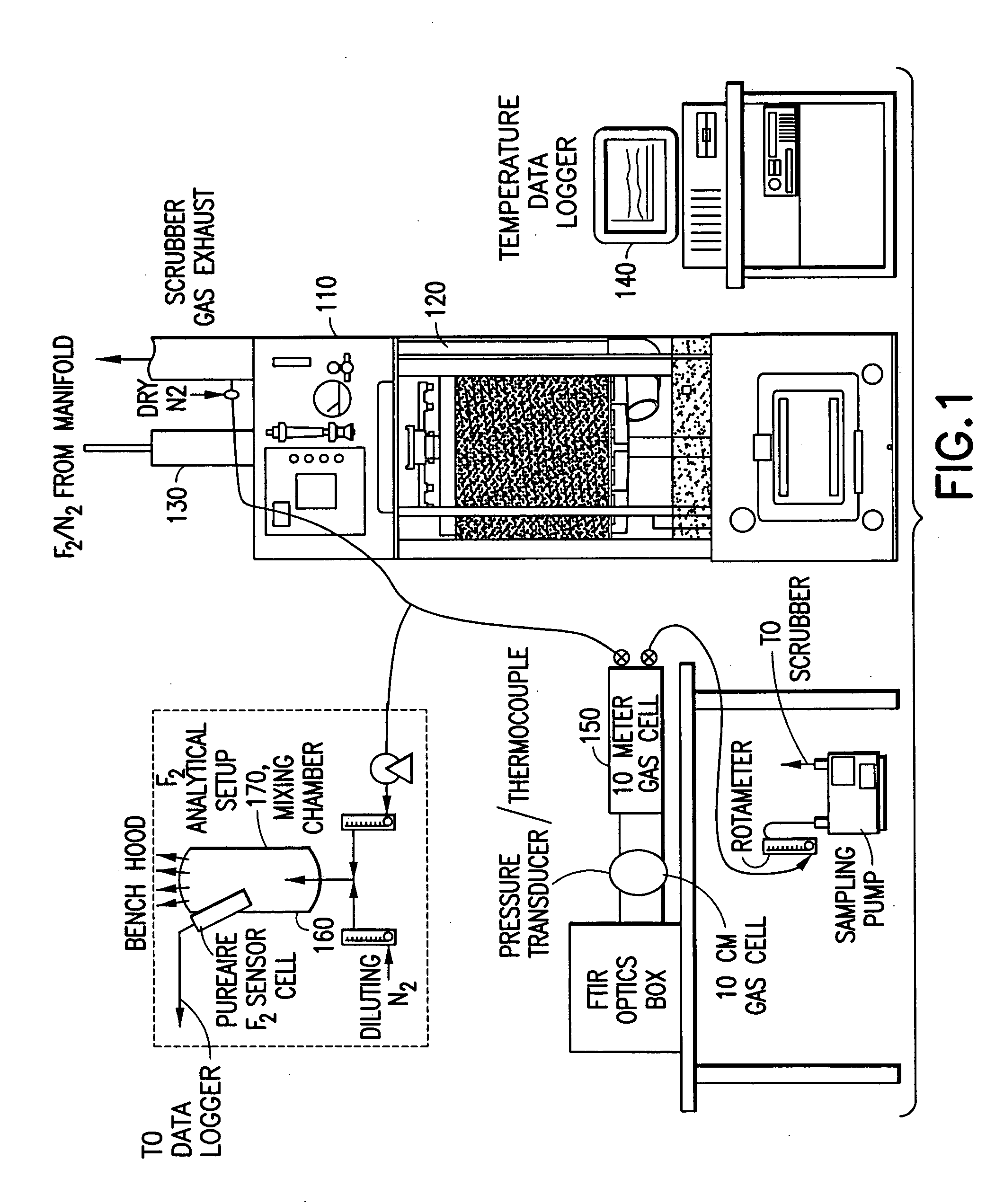
A system for abating undesired component(s) from a gas stream containing same, such as halocompounds, acid gases, silanes, ammonia, etc., by scrubbing of the effluent gas stream with an aqueous scrubbing medium. Halocompounds, such as fluorine, fluorides, perfluorocarbons, and chlorofluorocarbons, may be scrubbed in the presence of a reducing agent, e.g., sodium thiosulfate, ammonium hydroxide, or potassium iodide. In one embodiment, the scrubbing system includes a first acid gas scrubbing unit operated in cocurrent gas / liquid flow, and a second "polishing" unit operated in countercurrent gas / liquid flow, to achieve high removal efficiency with low consumption of water. The scrubbing system may utilize removable insert beds of packing material, packaged in a foraminous containment structure. The abatement system of the invention has particular utility in the treatment of semiconductor manufacturing process effluents.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
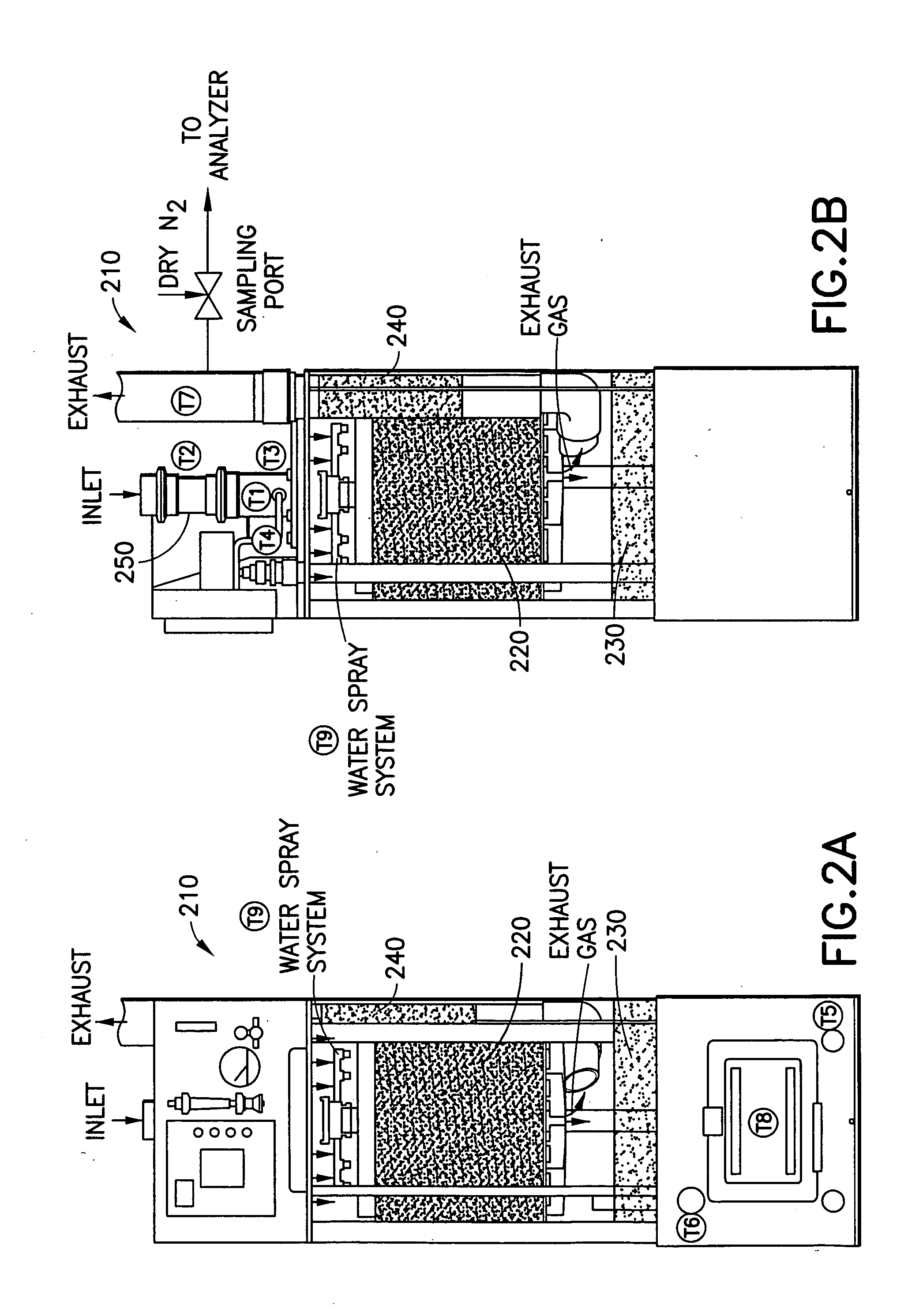
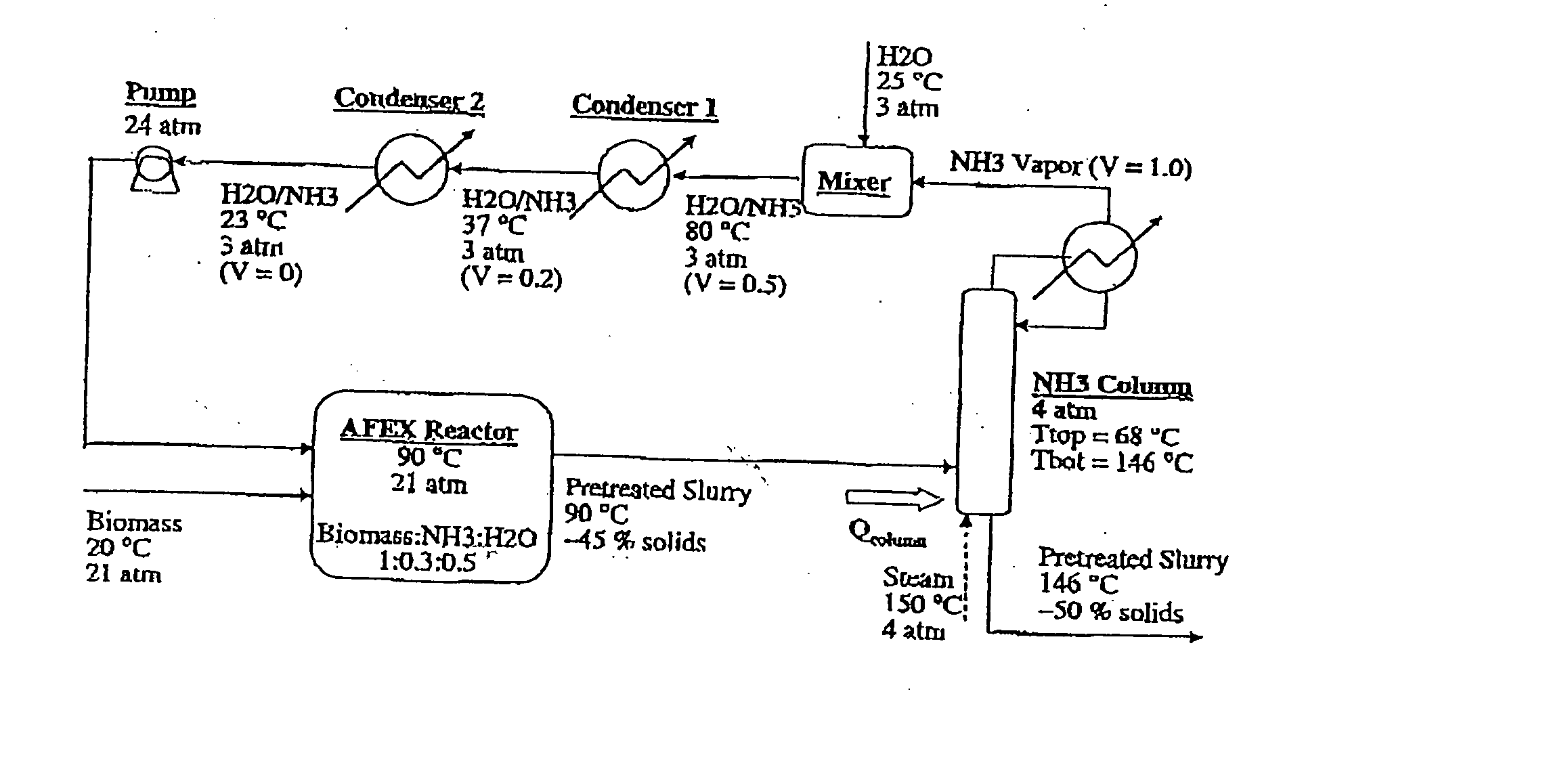
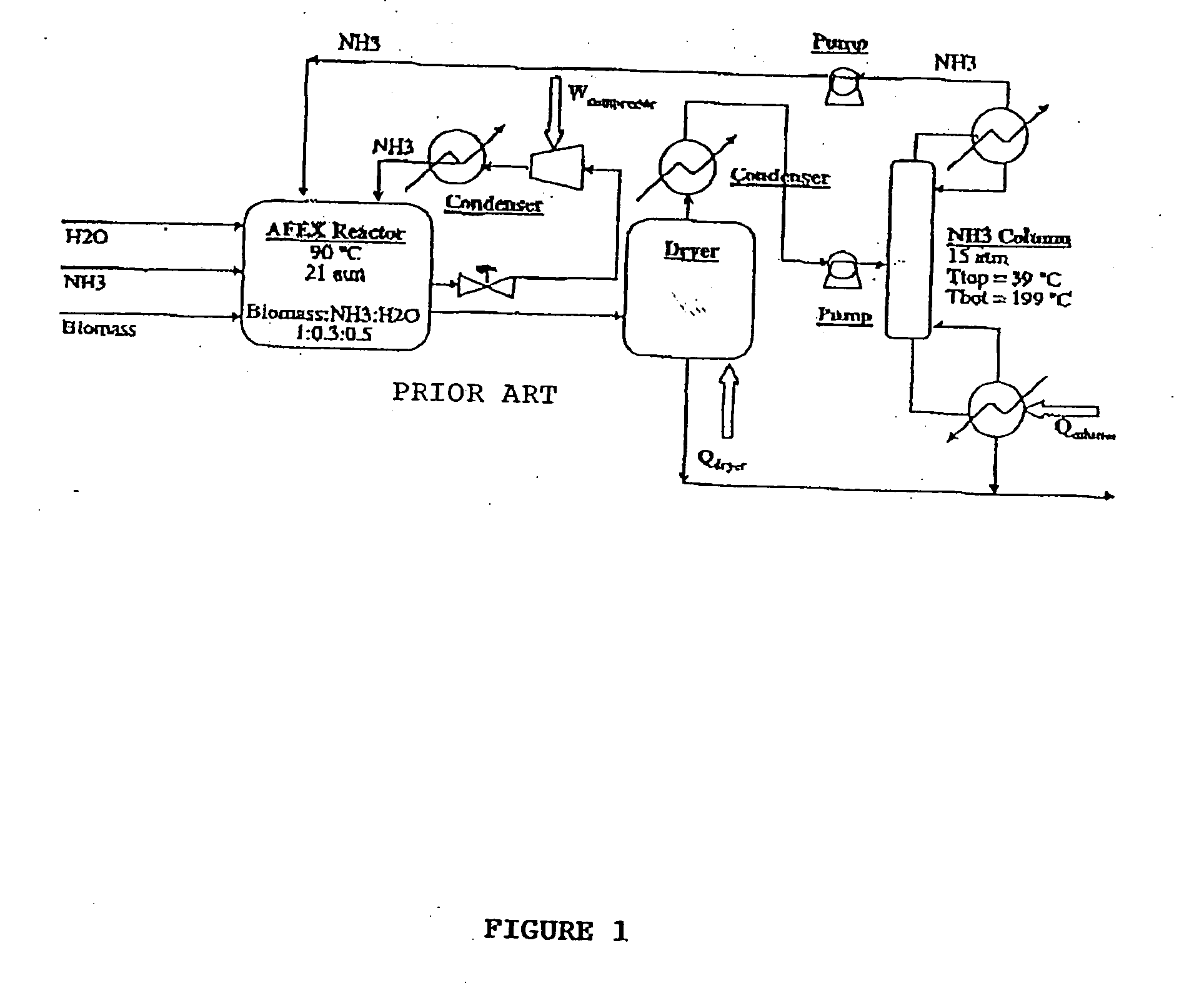
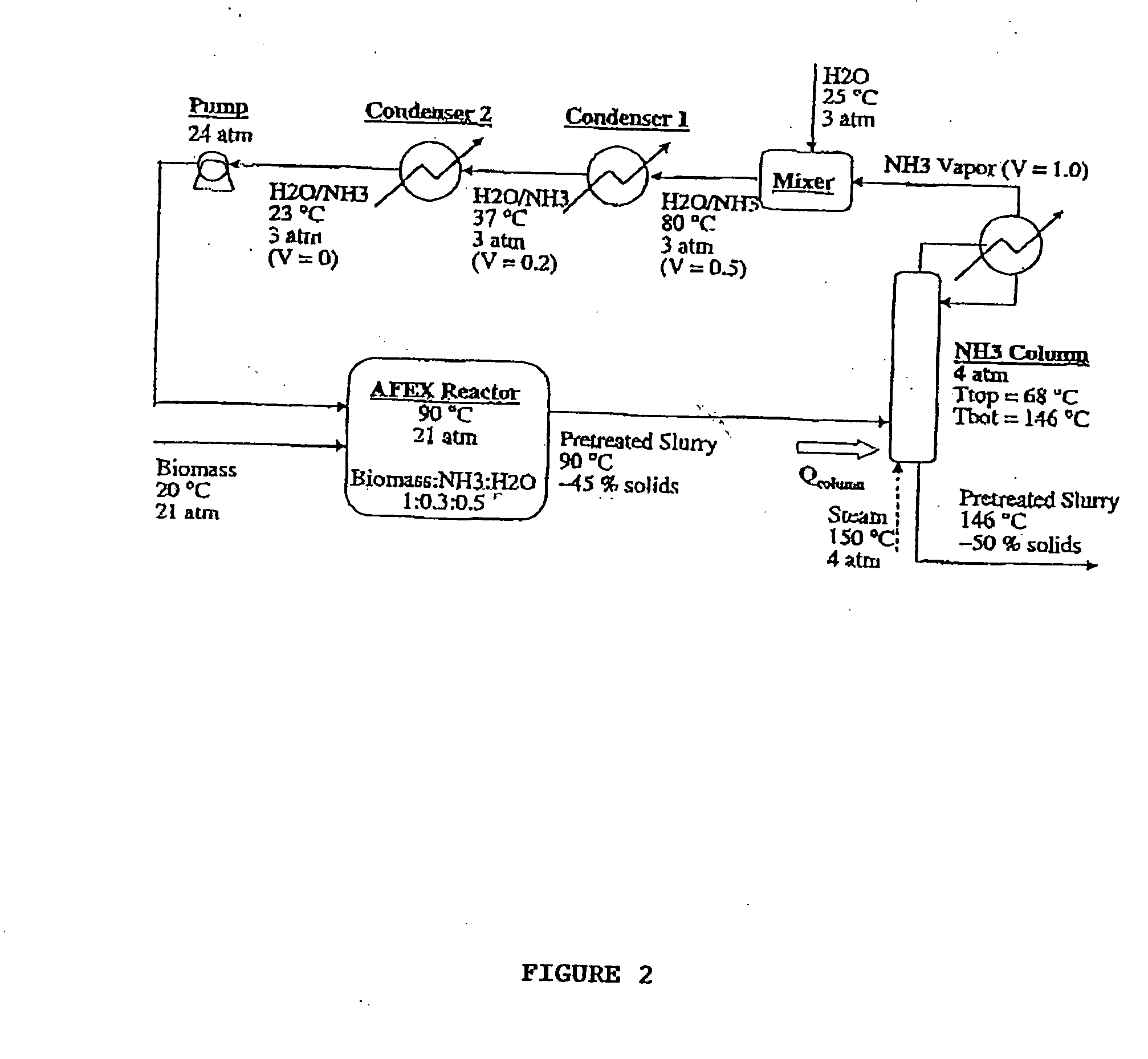
Process for the treatment of lignocellulosic biomass
ActiveUS20080008783A1Lower the volumeIncreasing fractionBiofuelsAnimal feeding stuffCelluloseEnergy source
A process for the treatment of biomass to render structural carbohydrates more accessible and / or digestible using concentrated ammonium hydroxide with or without anhydrous ammonia addition, is described. The process preferably uses steam to strip ammonia from the biomass for recycling. The process yields of monosaccharides from the structural carbohydrates are good, particularly as measured by the enzymatic hydrolysis of the structural carbohydrates. The monosaccharides are used as animal feeds and energy sources for ethanol production.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Water soluble package and liquid contents thereof
InactiveUS6451750B2AvoidanceDissolve fastInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydrogen ion bindingHydrogen
A water soluble package formed from a copolymeric polyvinyl alcohol film, wherein the comonomer comprises a carboxylate function, the package containing a substantially non-aqueous liquid composition which comprises: at least one ionic ingredient with an exchangeable hydrogen ion; and a molar excess (with respect to the amount of exchangeable hydrogen ions in the at least one ionic ingredient) of a stabilizing compound effective for combining with the exchangeable hydrogen ions to hinder the formation of lactones within the film, but can be as low as 95 mole % if the stabilizing compound comprises an inorganic base and / or ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Cleaning method and solution for cleaning a wafer in a single wafer process
InactiveUS20020102852A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAmmonium hydroxideCleaning methods
The present invention is a novel cleaning method and a solution for use in a single wafer cleaning process. According to the present invention the cleaning solution comprises ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), water (H2O) and a chelating agent. In an embodiment of the present invention the cleaning solution also contains a surfactant. And still yet another embodiment of the present invention the cleaning solution also comprises a dissolved gas such as H2. In a particular embodiment of the present invention, this solution is used by spraying or dispensing it on a spinning wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Water soluble package and liquid contents therof
InactiveUS20020013243A1AvoidanceDissolve fastNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydrogen ion bindingHydrogen
A water soluble package formed from a copolymeric polyvinyl alcohol film, wherein the comonomer comprises a carboxylate function, the package containing a substantially non-aqueous liquid composition which comprises: at least one ionic ingredient with an exchangeable hydrogen ion; and a molar excess (with respect to the amount of exchangeable hydrogen ions in the at least one ionic ingredient) of a stabilizing compound effective for combining with the exchangeable hydrogen ions to hinder the formation of lactones within the film, but can be as low as 95 mole % if the stabilizing compound comprises an inorganic base and / or ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Cleaning method and solution for cleaning a wafer in a single wafer process
InactiveUS6927176B2Improve processing efficiencyMinimize timeInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAmmonium hydroxideCleaning methods
The present invention is a novel cleaning method and a solution for use in a single wafer cleaning process. According to the present invention the cleaning solution comprises ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), water (H2O) and a chelating agent. In an embodiment of the present invention the cleaning solution also contains a surfactant. And still yet another embodiment of the present invention the cleaning solution also comprises a dissolved gas such as H2. In a particular embodiment of the present invention, this solution is used by spraying or dispensing it on a spinning wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
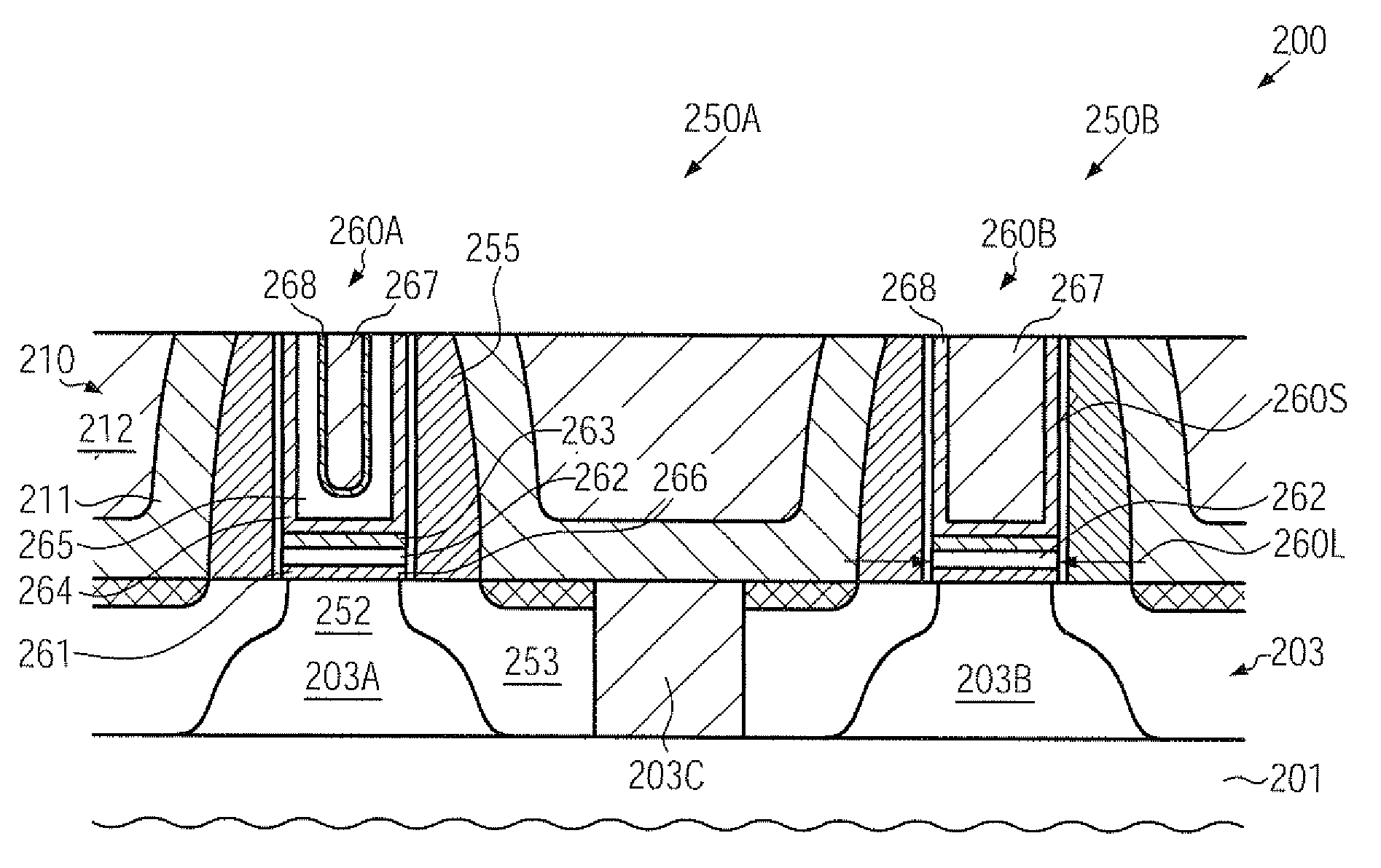
Methods of Forming Field Effect Transistors Having Silicon-Germanium Source and Drain Regions
InactiveUS20080124874A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn situ dopingAmmonium hydroxide
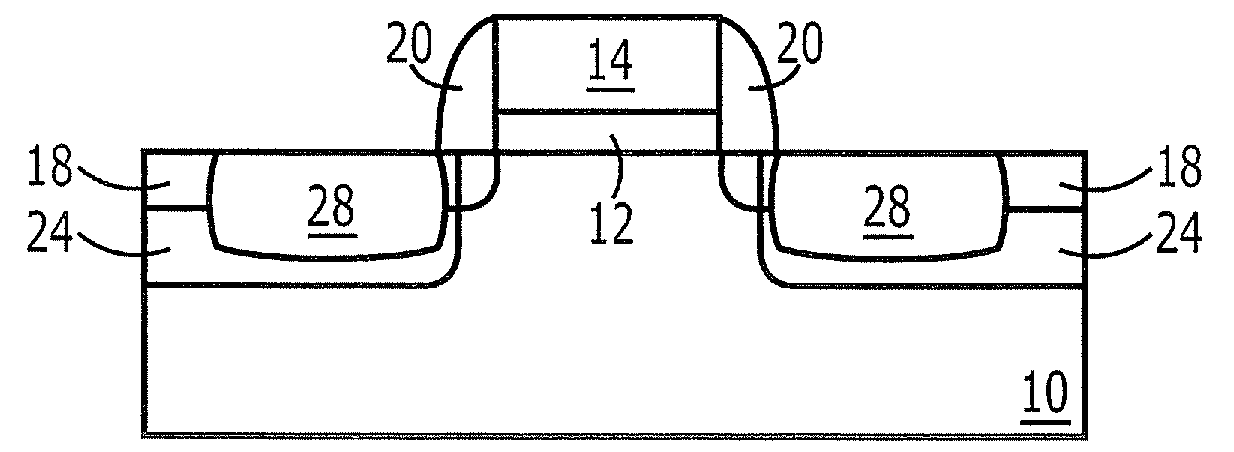
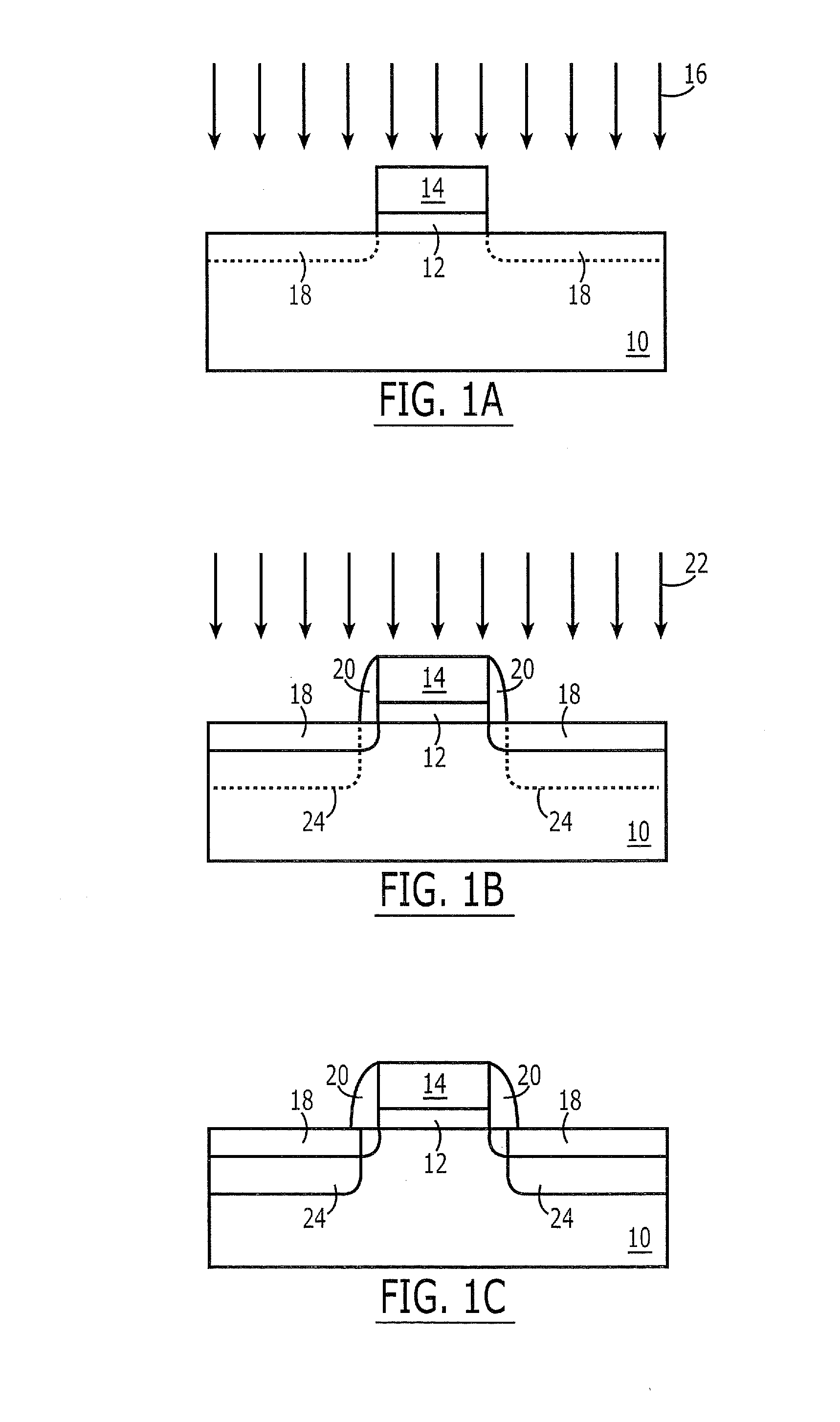
Methods of forming field effect transistors include forming an insulated gate electrode on a non-SiGe semiconductor substrate and then selectively etching the semiconductor substrate to define source and drain region trenches on opposite sides of the insulated gate electrode. A step is performed to remove native oxide layers from sidewalls of the source and drain region trenches. The removal of the native oxide is followed by recessing the sidewalls of the source and drain region trenches by selectively wet etching the sidewalls of the source and drain region trenches. This step of wet etching the sidewalls of the source and drain region trenches may include exposing the sidewalls to a cleaning solution including ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). A step is then performed to epitaxially grow SiGe source and drain regions in the source and drain region trenches. This step of epitaxially growing SiGe source and drain regions may include epitaxially growing in-situ doped SiGe source and drain regions of first conductivity type in the source and drain region trenches.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
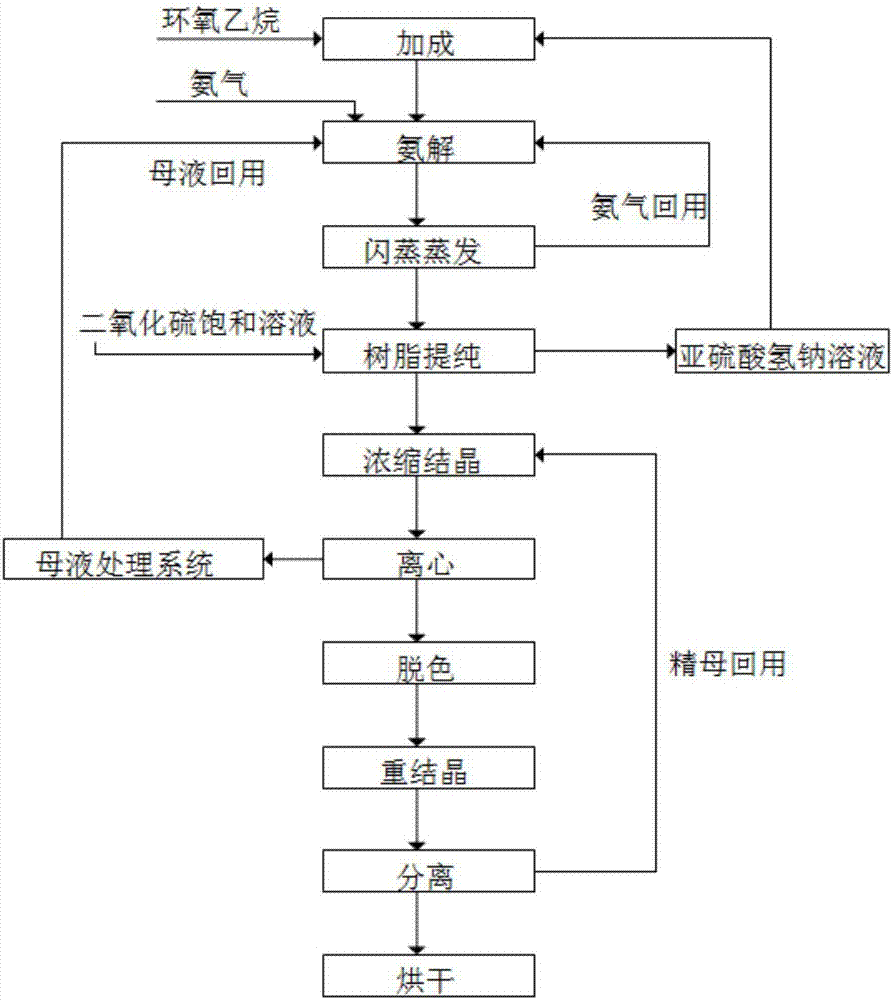
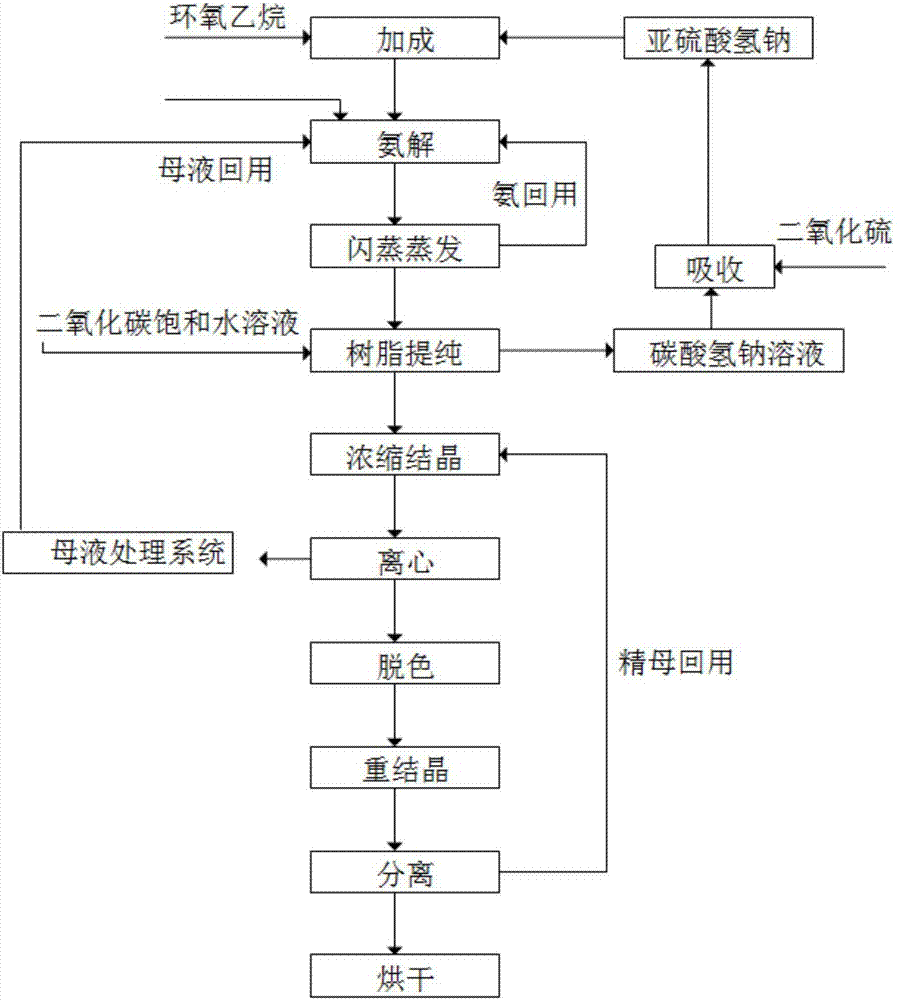
Method for cyclically producing taurine at high yield
ActiveCN107056659AReduce productionEfficient recyclingPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationAfter treatmentHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for cyclically producing taurine at a high yield. The method includes the following steps that S1, ethylene oxide reacts with a sodium hydrogen sulfite solution to generate sodium hydroxyethyl sulfonate; S2, sodium hydroxyethyl sulfonate obtained in S1 is subjected to an ammonolysis reaction in ammonium hydroxide, flashing is carried out after the reaction is completed, and ammonia gas is recycled; S3, taurine-containing feed liquid of reaction liquid obtained after flashing in S2 is collected through an acid cation exchange resin column, the resin column is regenerated with a sulfur dioxide or carbon dioxide water solution after being inactivated, and eluant obtained during regeneration can be directly reused or reused after being treated with sulfur dioxide; S4, the feed liquid collected in S3 is subjected to after-treatment, and taurine is obtained. The method has the advantages that the generation amount of waste liquid in the whole process is small, part of substances are effectively and cyclically utilized in the process, the cost is reduced, the yield of taurine can reach 90% or above, meanwhile, the production process is relatively simple, and large-scale production is easy.
Owner:QIANGJIANG YONGAN PHARMA
Work function adjustment in high-k metal gate electrode structures by selectively removing a barrier layer
ActiveUS20100301427A1Degree of improvementImprove uniformityTransistorSolid-state devicesTantalum nitrideWork function
In a replacement gate approach in sophisticated semiconductor devices, a tantalum nitride etch stop material may be efficiently removed on the basis of a wet chemical etch recipe using ammonium hydroxide. Consequently, a further work function adjusting material may be formed with superior uniformity, while the efficiency of the subsequent adjusting of the work function may also be increased. Thus, superior uniformity, i.e., less pronounced transistor variability, may be accomplished on the basis of a replacement gate approach in which the work function of the gate electrodes of P-channel transistors and N-channel transistors is adjusted after completing the basic transistor configuration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
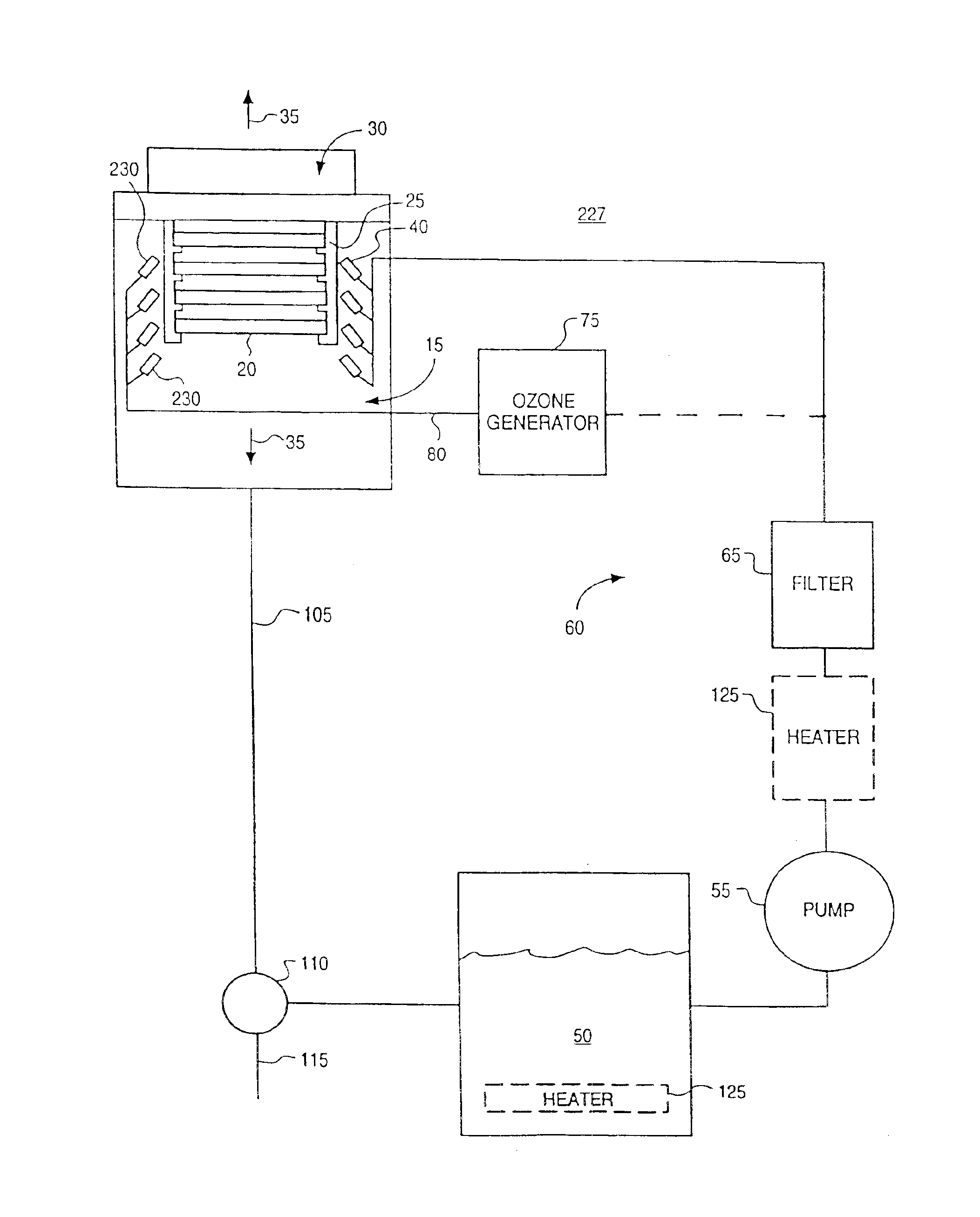
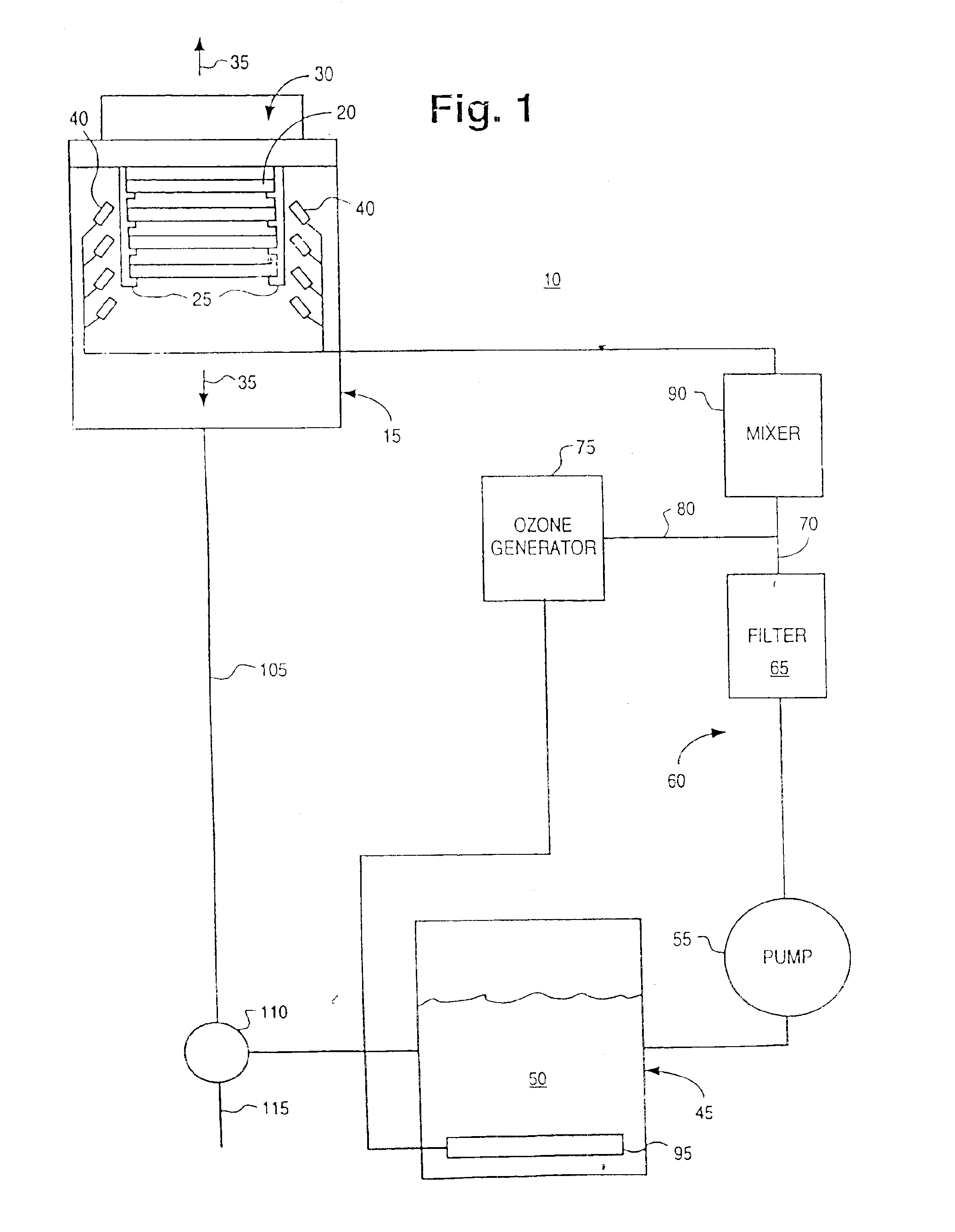
Process and apparatus for treating a workpiece such as a semiconductor wafer
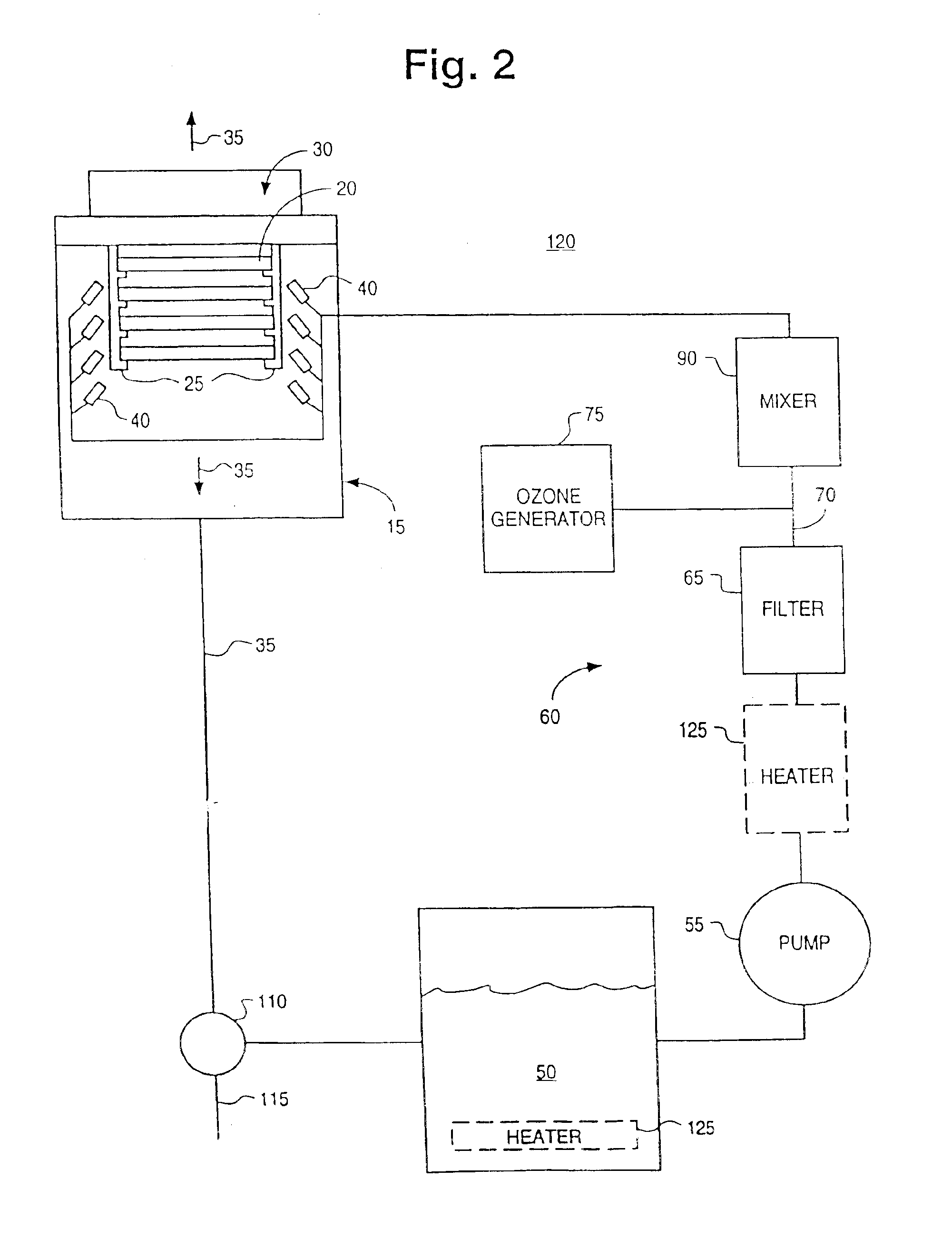
InactiveUS6869487B1Reduce pollutionProcessing speedPrinted circuit assemblingLighting and heating apparatusOzone generatorCompound (substance)
A novel chemistry, system and application technique reduces contamination of semiconductor wafers and similar substrates and enhances and expedites processing. A stream of liquid chemical is applied to the workpiece surface. Ozone is delivered either into the liquid process stream or into the process environment. The ozone is preferably generated by a high capacity ozone generator. The chemical stream is provided in the form of a liquid or vapor. A boundary layer liquid or vapor forms on the workpiece surface. The thickness of the boundary layer is controlled. The chemical stream may include ammonium hydroxide for simultaneous particle and organic removal, another chemical to raise the pH of the solution, or other chemical additives designed to accomplish one or more specific cleaning steps.
Owner:OEM GRP LLC
Rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103855384AEase of industrial productionImprove charge and discharge efficiencyCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesNickel salt
The invention relates to a rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material and a preparation method of the rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material. The chemical general formula of the material is as follows: LiNiaCo<1-a-b>MnbRxO2 / M, wherein a is more than 0 and less than 1, b is more than 0 and less than 1, (1-a-b) is more than 0 and less than 1, x is more than 0.005 and less than 0.1, R is one or more of rare-earth lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium and samarium, and M is a composite cladding layer of oxide of aluminum, titanium or magnesium and carbon. The soluble metal nickel salt, cobalt salt, manganese salt and rare-earth compound are mixed to prepare a mixed salt solution, the mixed salt solution is reacted with a mixed alkaline solution prepared by mixing NaOH and ammonium hydroxide, after the reaction solution is filtered, washed and dried, the obtained product is uniformly mixed with lithium salt powder to be ball milled, then the mixture is calcined at the high temperature and coated with the composite cladding layer of the aluminum, titanium or magnesium oxide and carbon, and finally the calcined mixture is calcined at a constant temperature to obtain the rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material. After doping the rare earth, the metal oxide and carbon composite cladding layer, which are cheap and easy to obtain, are adopted, so that the cycling performance and the rate performance can be improved, and the charging-discharging efficiency of the material also can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDARUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Compositions containing chromium, oxygen, and at least two modifier metals selected the group consisting of gold, silver, and palladium, their preparation, and their use as catalysts and catalyst precursors
InactiveUS20080207962A1Preparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offNitrateAmmonium hydroxide
A catalyst composition is disclosed that includes chromium, oxygen, and at least two of gold, silver, and palladium as essential constituent elements. The amount of modifier metals (gold, silver, and / or palladium) in the composition is from about 0.05 atom % to about 10 atom % based on the total amount of chromium and modifier metals. Also disclosed is a process for changing the fluorine distribution (i.e., content and / or arrangement) in a hydrocarbon or halogenated hydrocarbon in the presence of the catalyst composition; and methods for preparing said catalyst composition. One preparation method involves (a) co-precipitating a solid by adding ammonium hydroxide (aqueous ammonia) to an aqueous solution of soluble salts of modifier metals and a soluble chromium salt that contains at least three moles of nitrate per mole of chromium in the solution and has a modifier metal content of from about 0.05 atom % to about 10 atom % of the total content of modifier metals and chromium in the solution to form an aqueous mixture containing co-precipitated solid; (b) drying the co-precipitated solid formed in (a); and (c) calcining the dried solid formed in (b) in an atmosphere containing at least 10% oxygen by volume. Another preparation method involves (a) impregnating solid chromium oxide with a solution of a soluble modifier metal salts; (b) drying the impregnated chromium oxide prepared in (a); and optionally; (c) calcining the dried solid. Yet another preparation method involves mixing multiple compositions, each comprising chromium, oxygen, and at least one modifier metal.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com