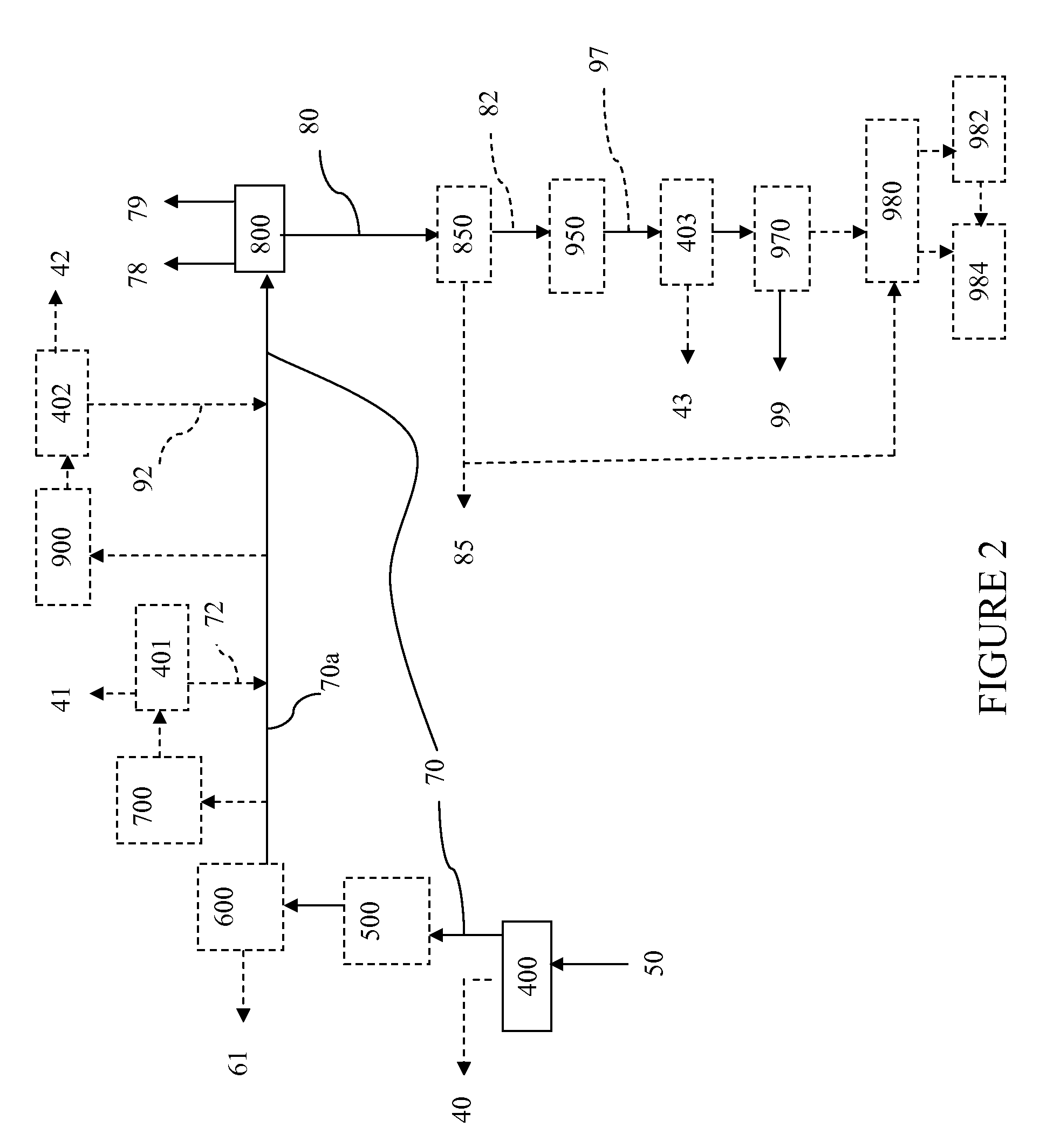
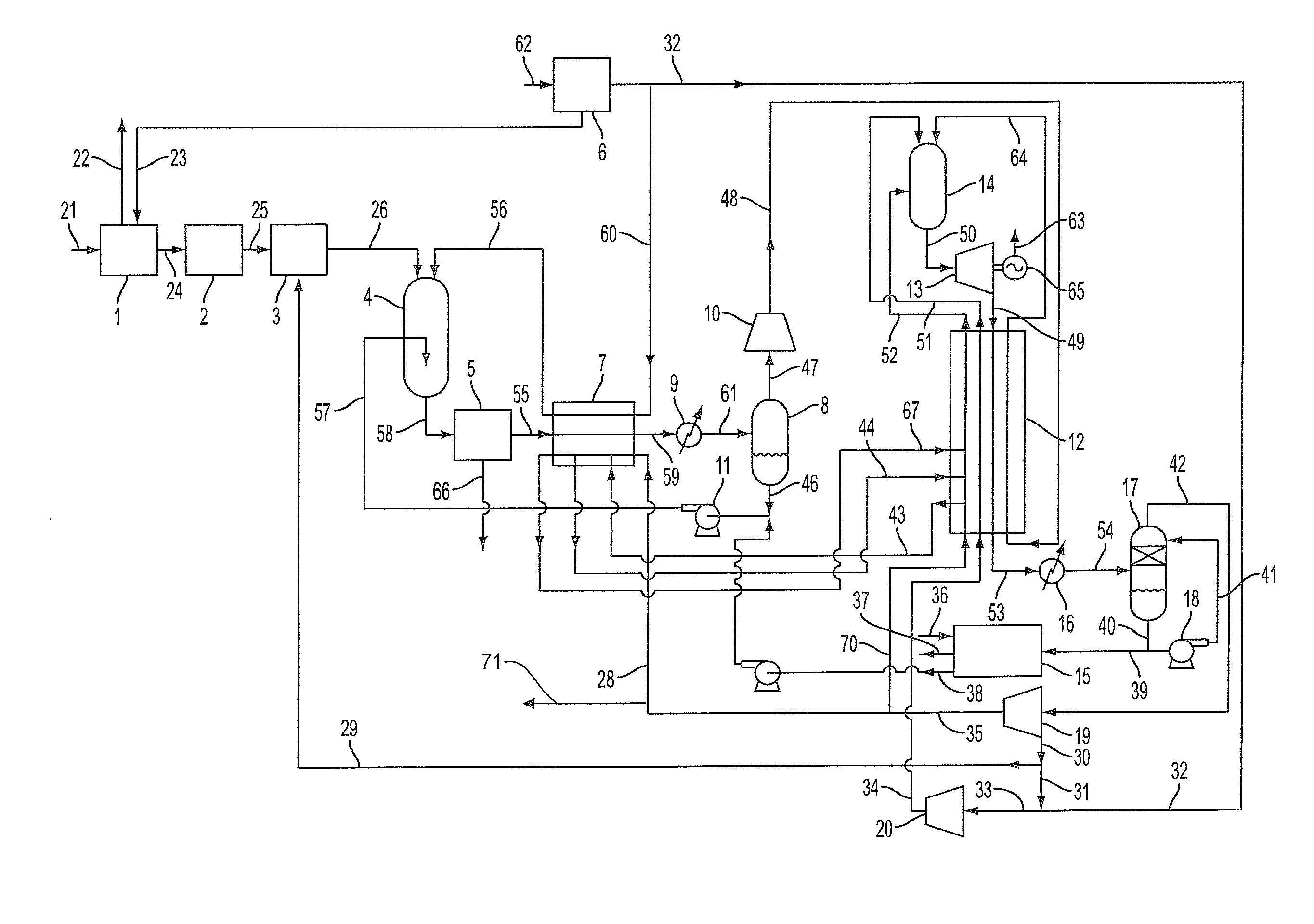
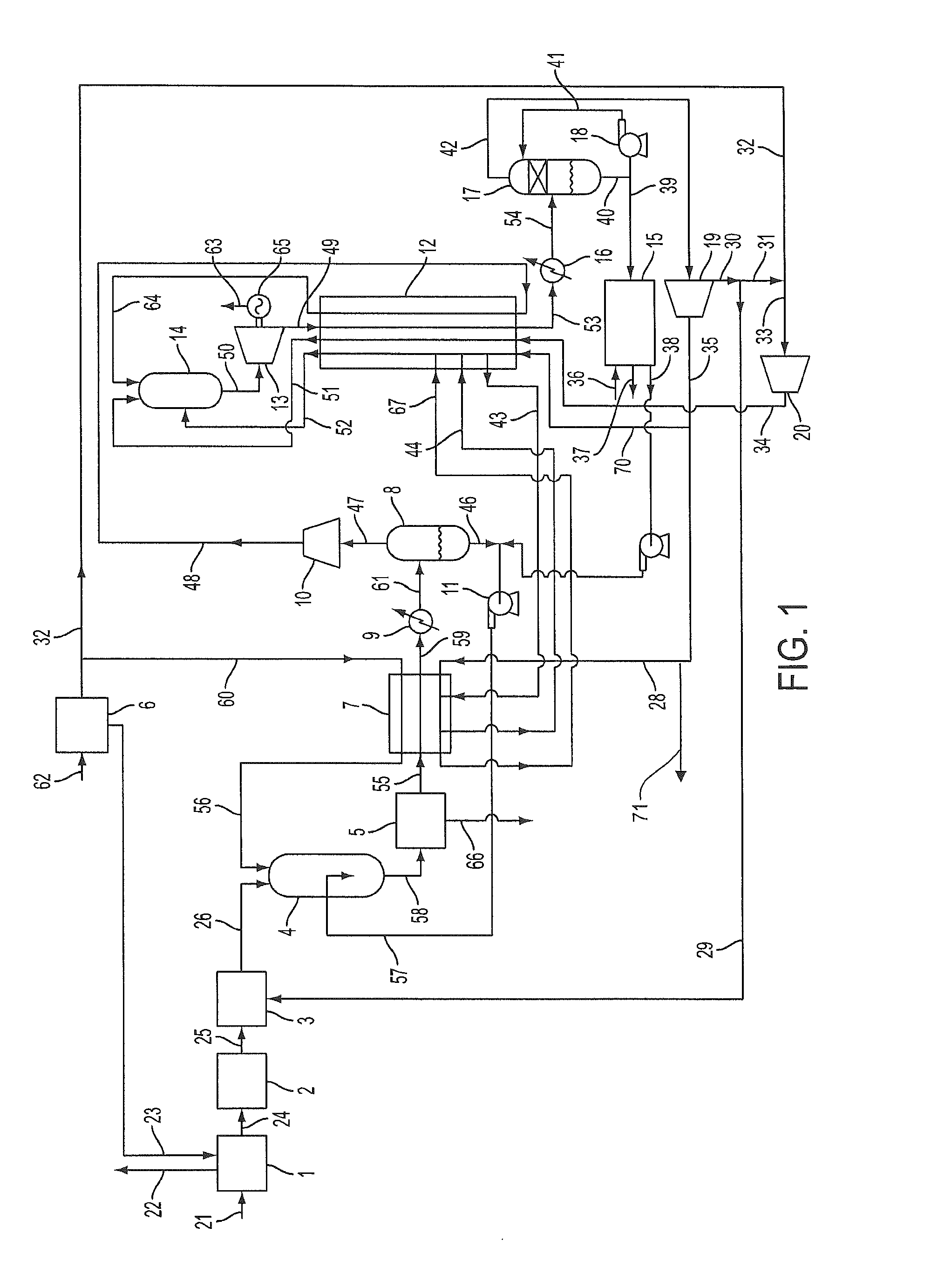
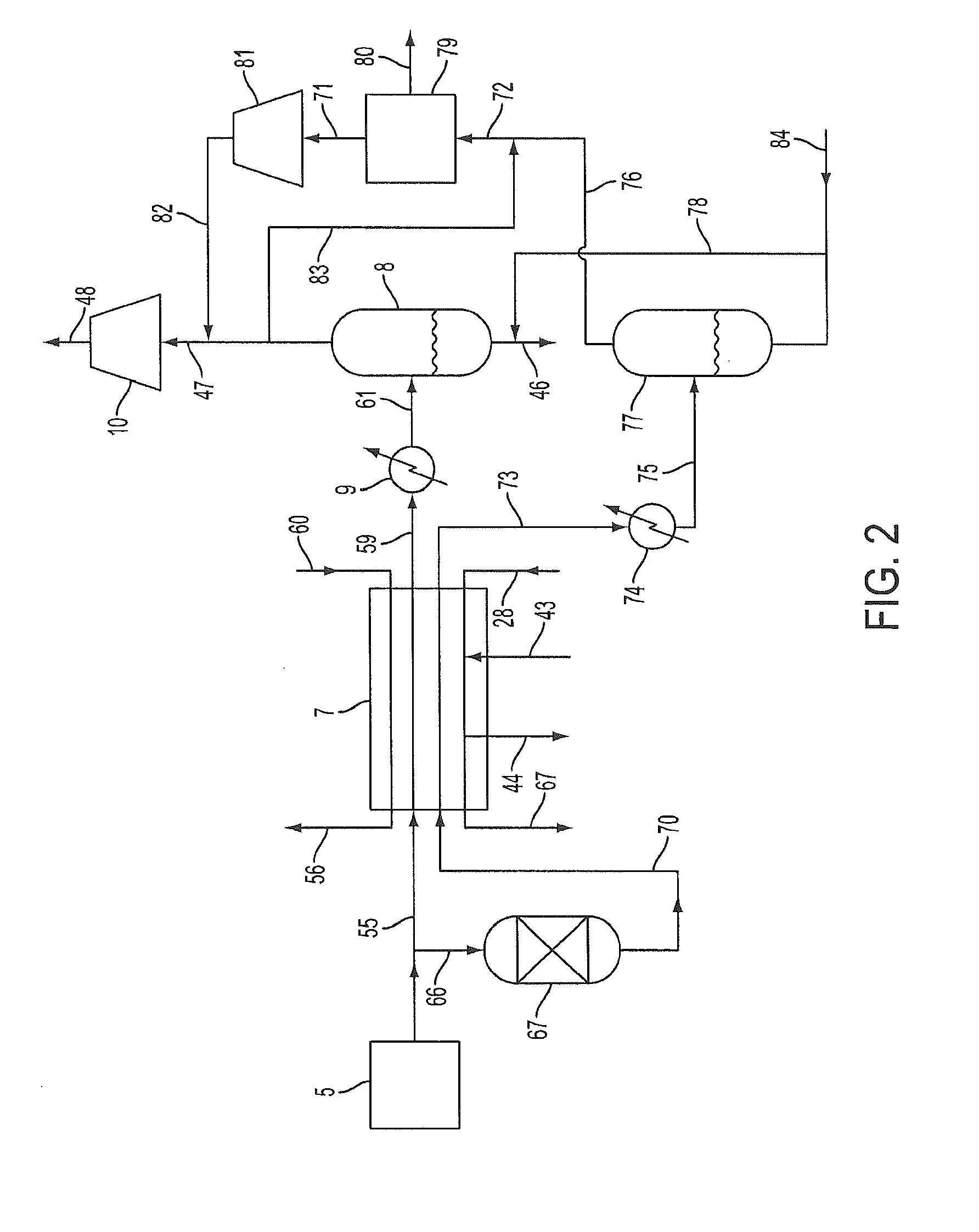
Patents
Literature
889results about "Combustible gas catalytic treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
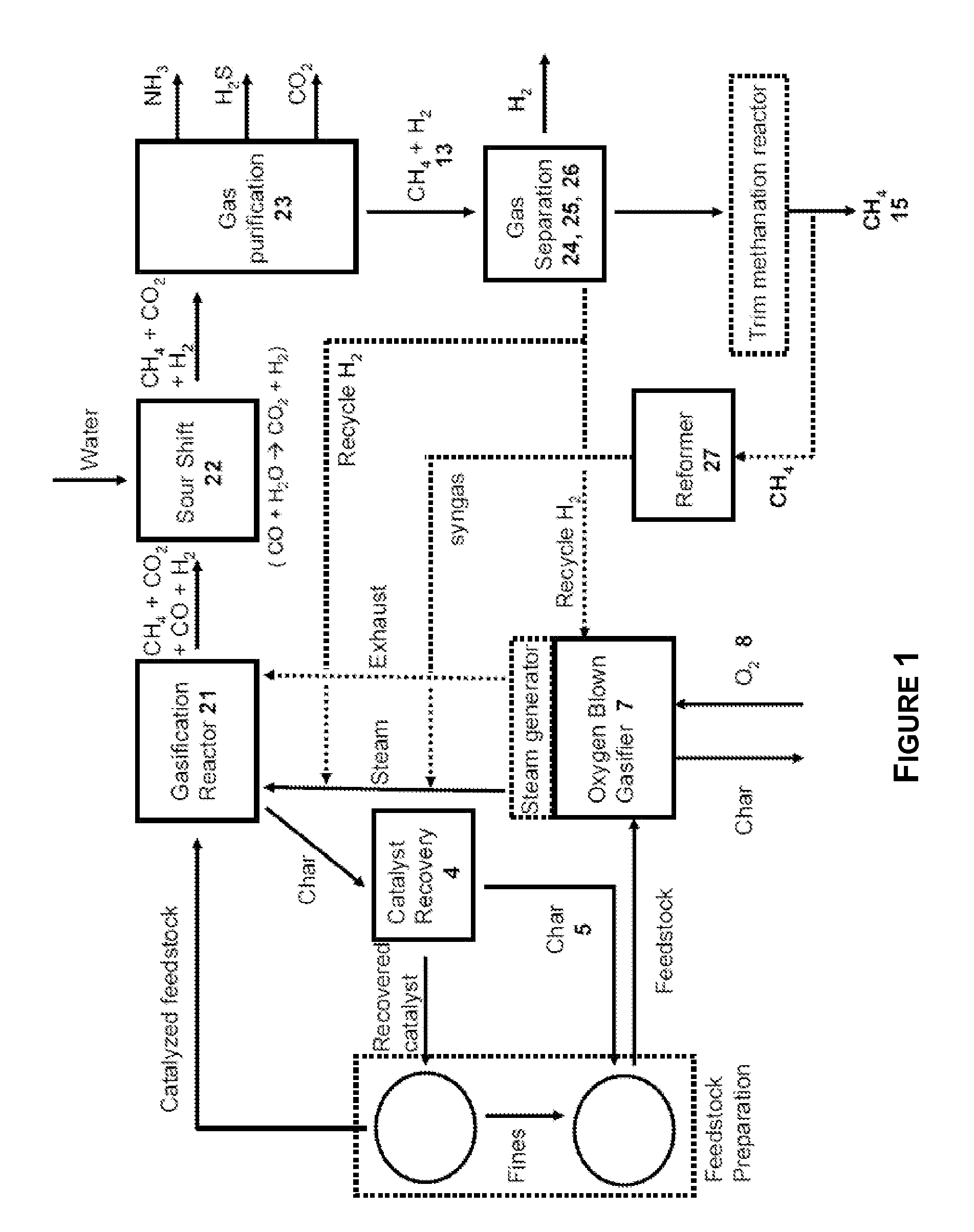
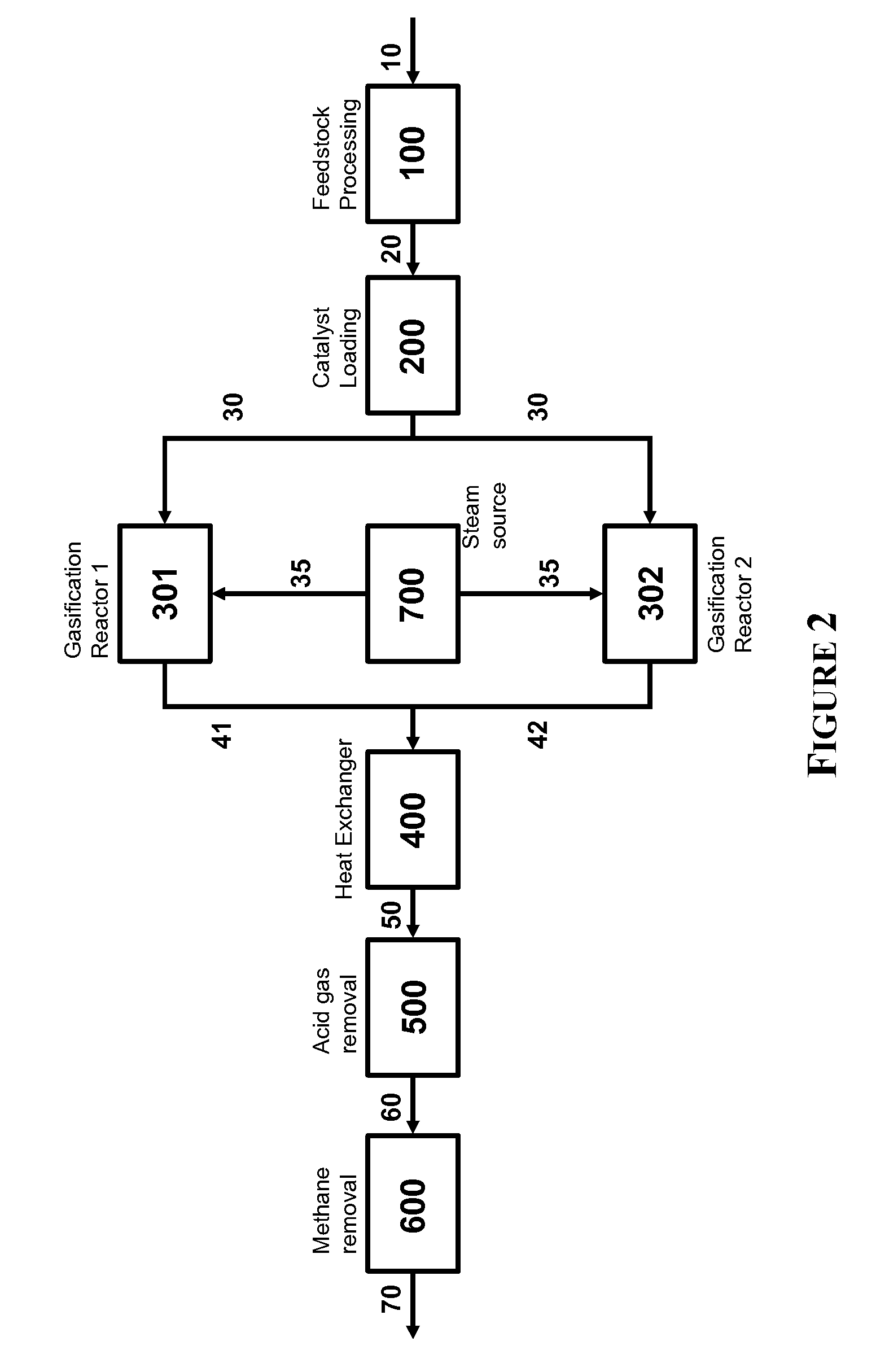
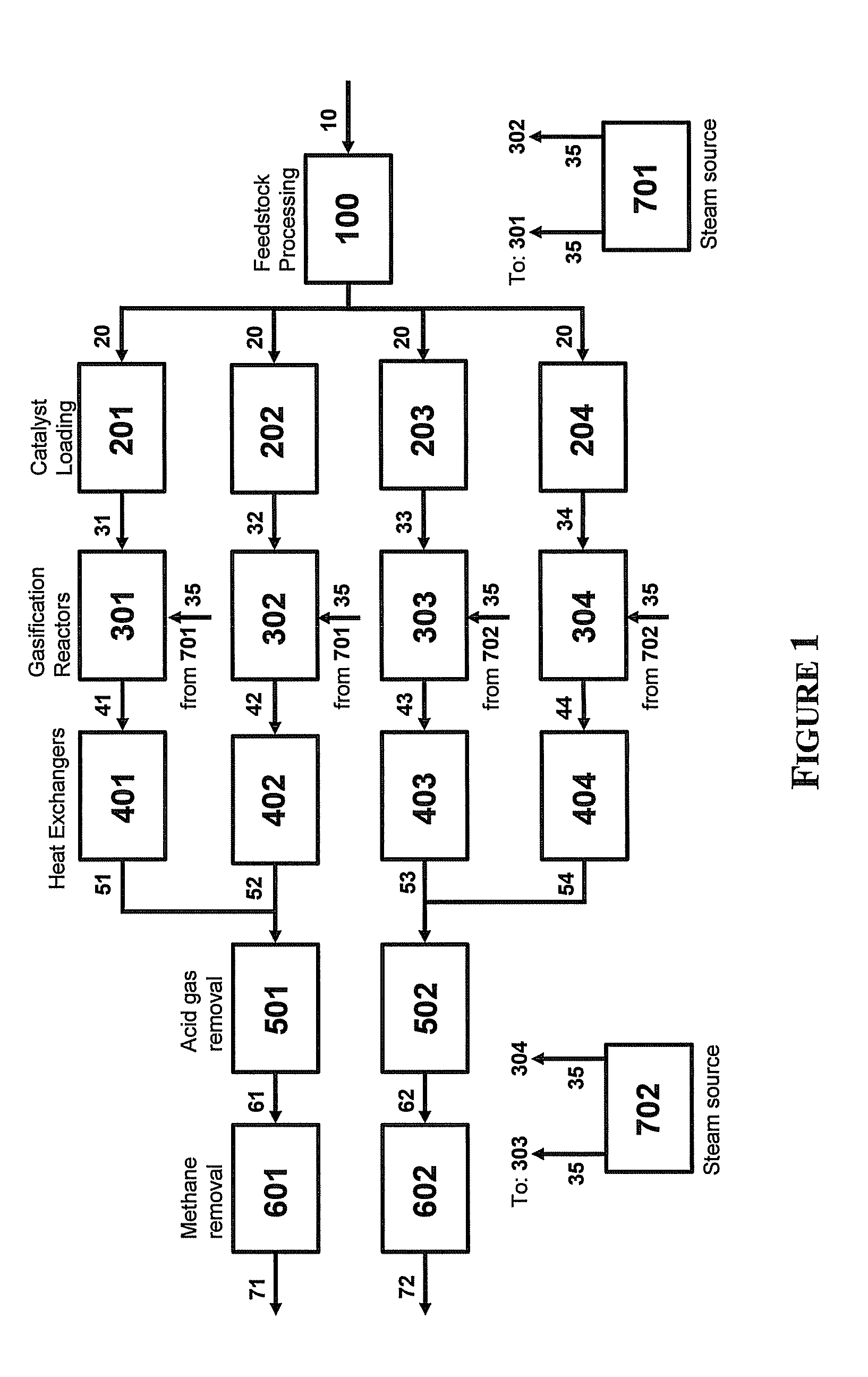
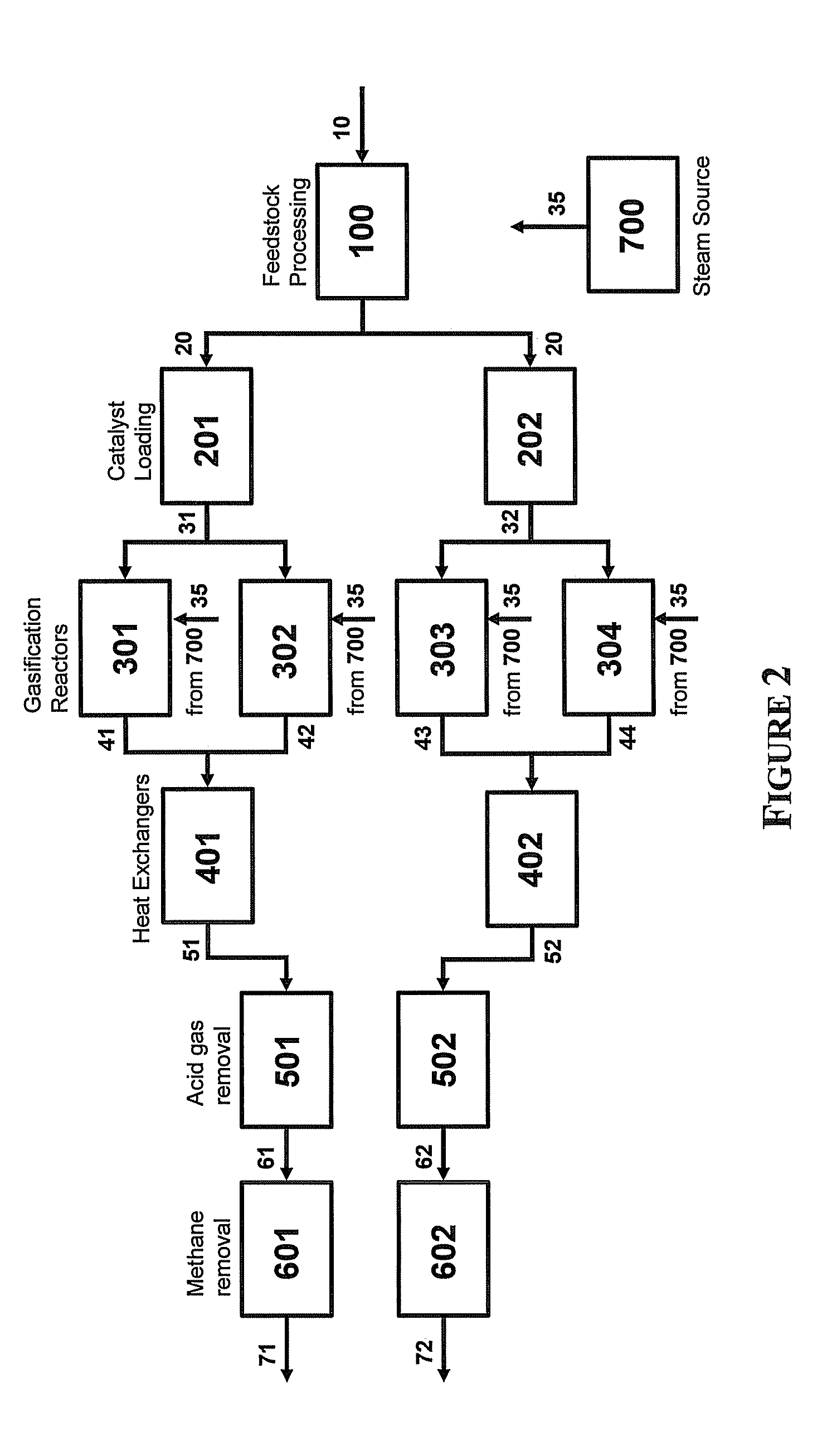
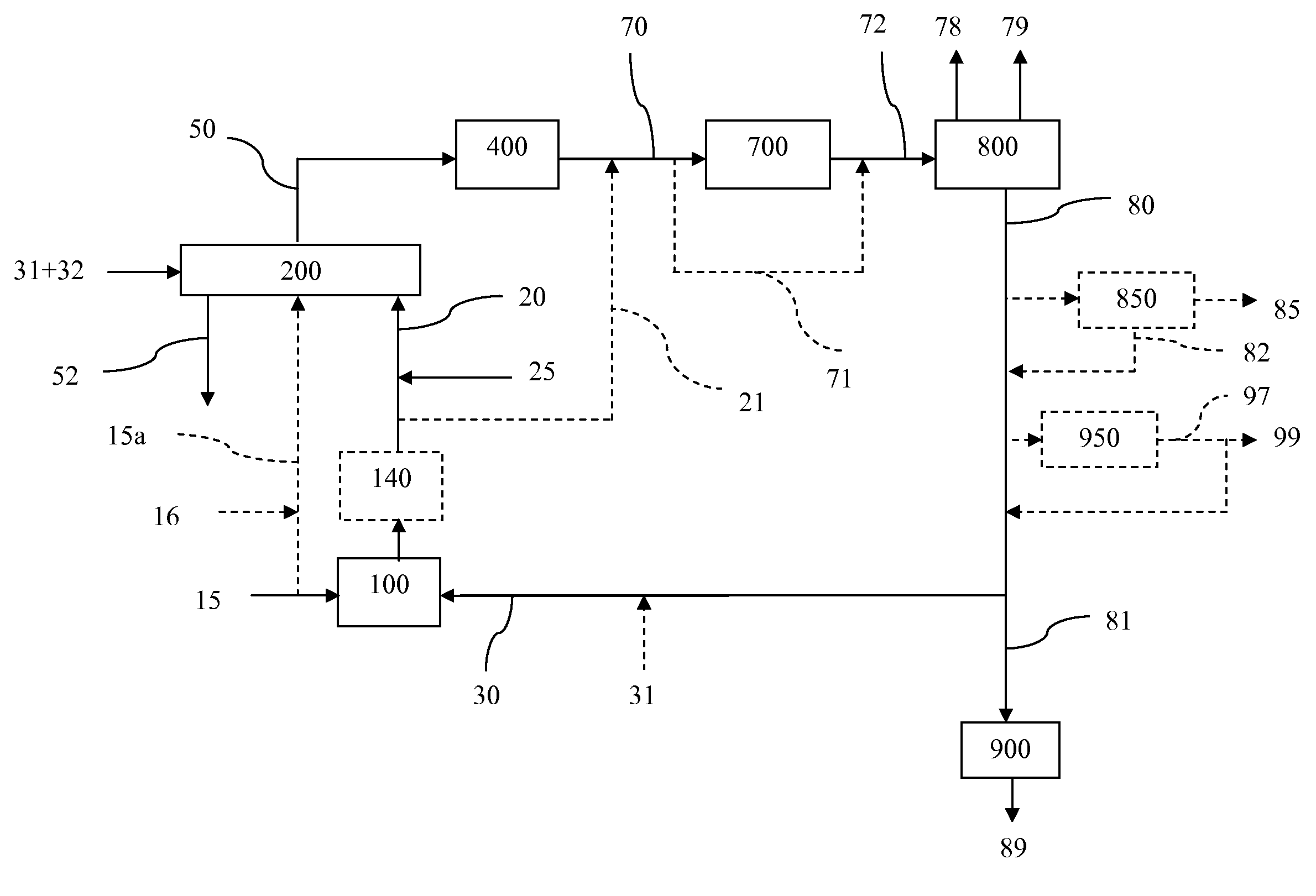
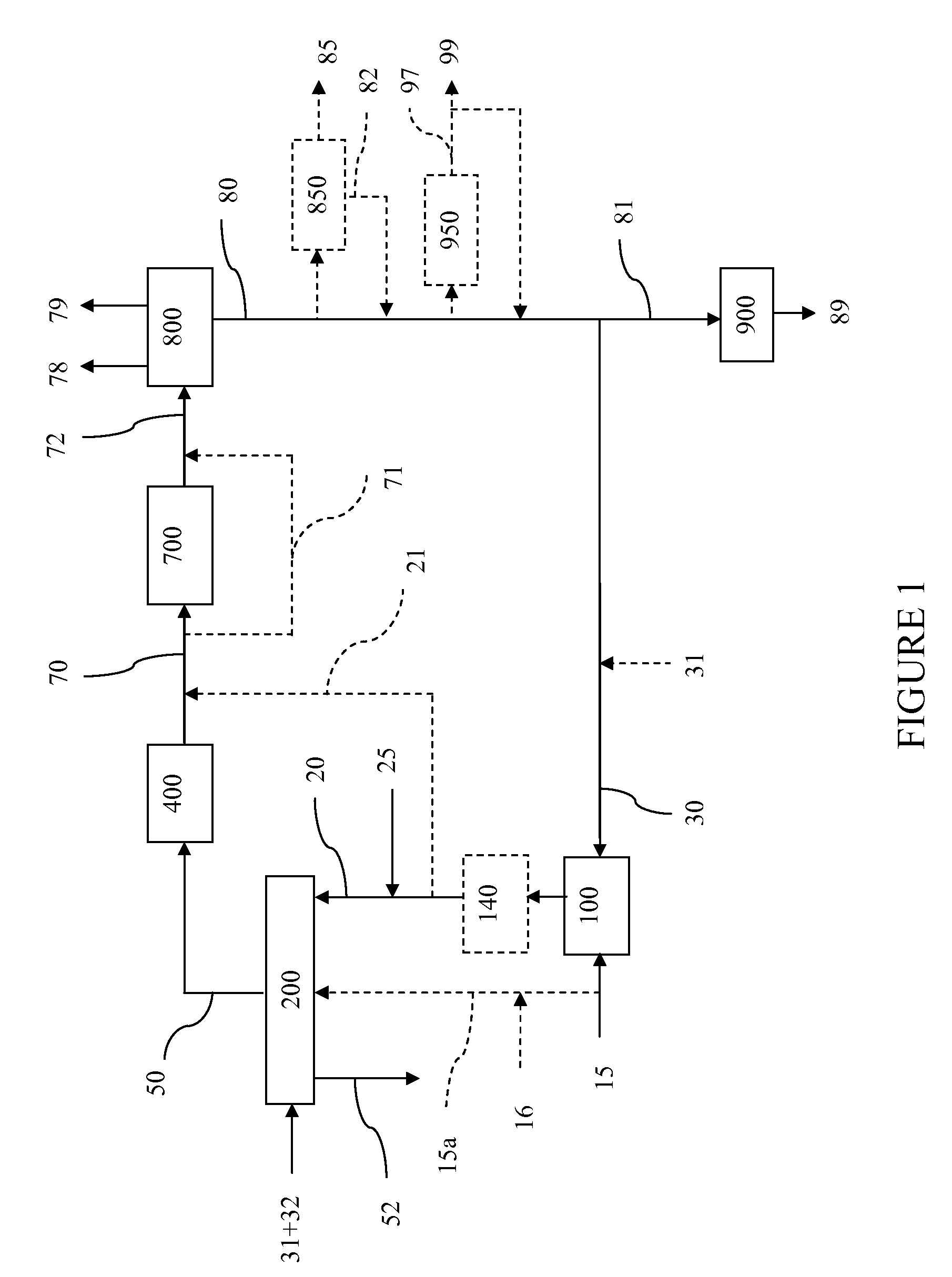
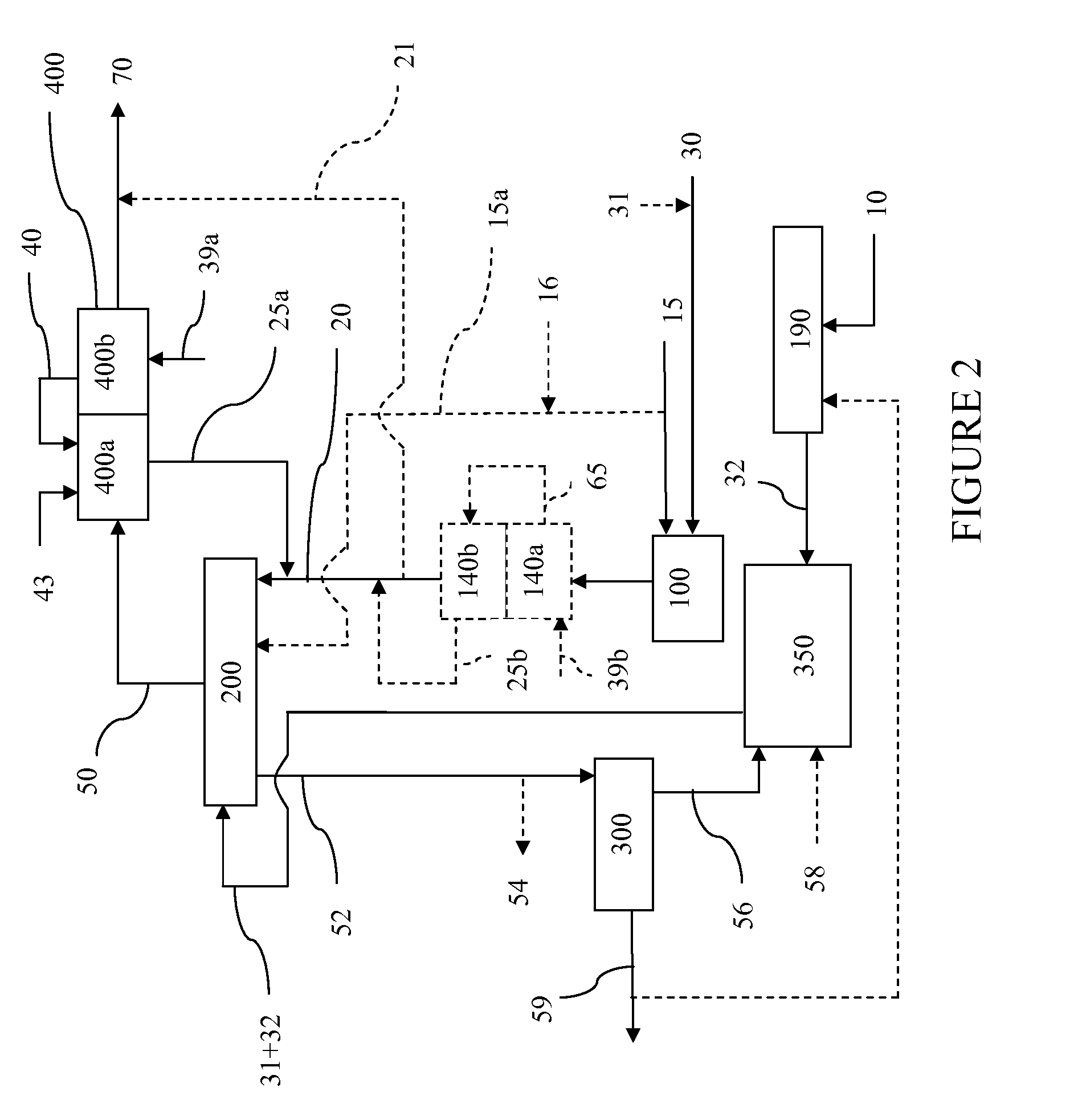
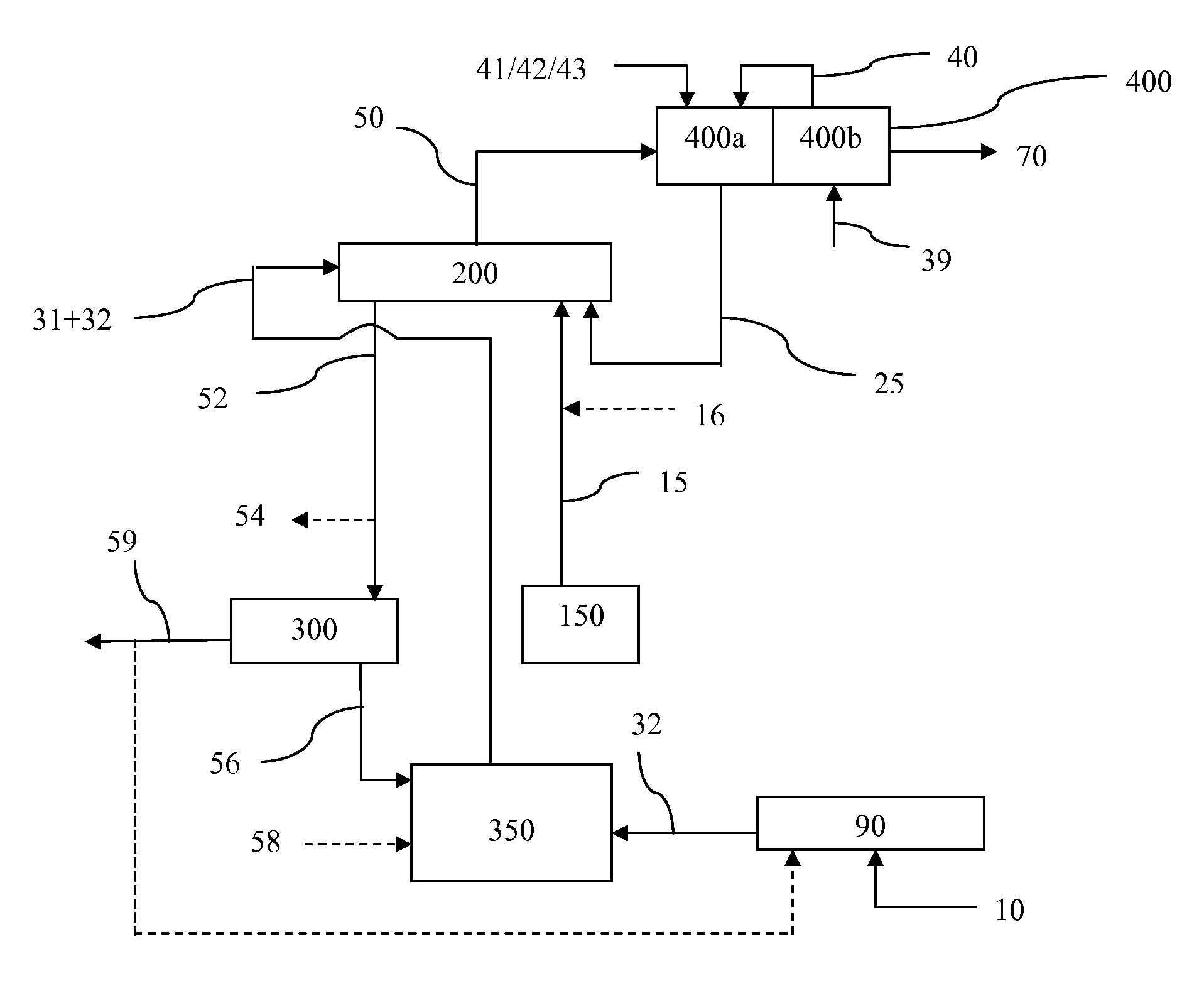
Processes for Gasification of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
The present invention relates to processes and continuous processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular, methane via the catalytic gasification of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam. In one aspect of the invention, the processes comprise at least partially combusting a first carbonaceous feedstock with an oxygen-rich gas stream in an oxygen-blown gasifier, under suitable temperature and pressure, to generate a first gas stream comprising hydrogen, carbon monoxide and superheated steam; and reacting a second carbonaceous feedstock and the first gas stream in a catalytic gasifier in the presence of a gasification catalyst under suitable temperature and pressure to form a second gas stream comprising a plurality of gaseous products comprising methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide. The processes can comprise using at least one catalytic methanator to convert carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the gaseous products to methane and in certain embodiments do not recycle carbon monoxide or hydrogen to the gasifier.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
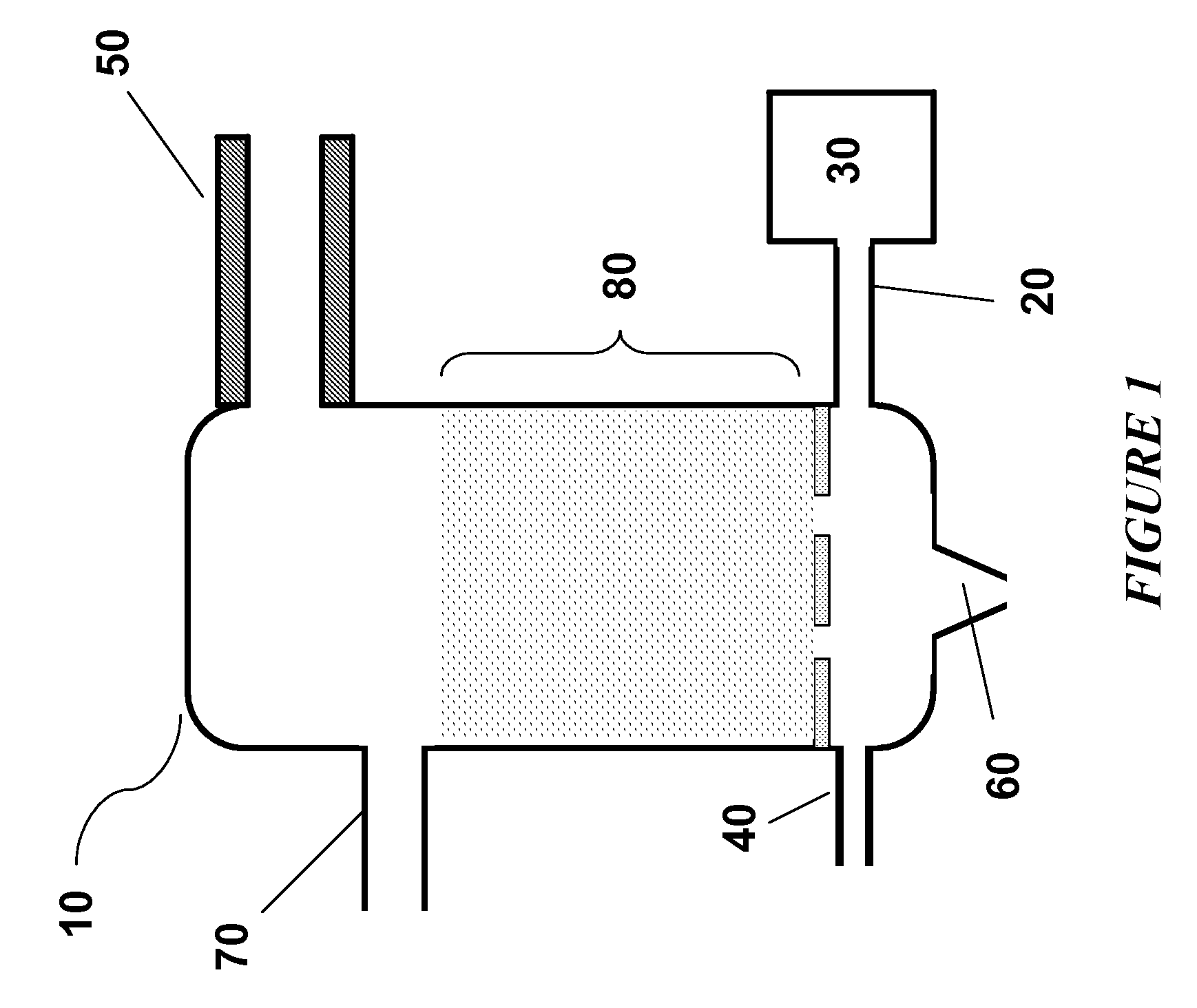
Steam Generating Slurry Gasifier for the Catalytic Gasification of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
Steam generating gasification reactors for providing high-pressure and high-temperature steam for catalytic gasification of a carbonaceous feedstock can be based on oxygen blown gasification reactors adapted for processing a slurry feedstock comprising at least 40% water. The exhaust from the slurry gasifier comprises at least steam, carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The slurry composition and the oxygen to fuel ratio can be varied to control the ratio of carbonaceous gases in the generator exhaust. By directing substantially all of exhaust gases produced from the slurry gasification reactor through the catalytic gasifier and subsequent gas separation and sequestration processes, a greatly higher energy efficiency and decreased carbon footprint can be realized.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Processes for Gasification of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular, methane via the catalytic gasification of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam and an oxygen-rich gas stream. The processes comprise using at least one catalytic methanator to convert carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the gaseous products to methane and do not recycle carbon monoxide or hydrogen to the catalytic gasifier.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
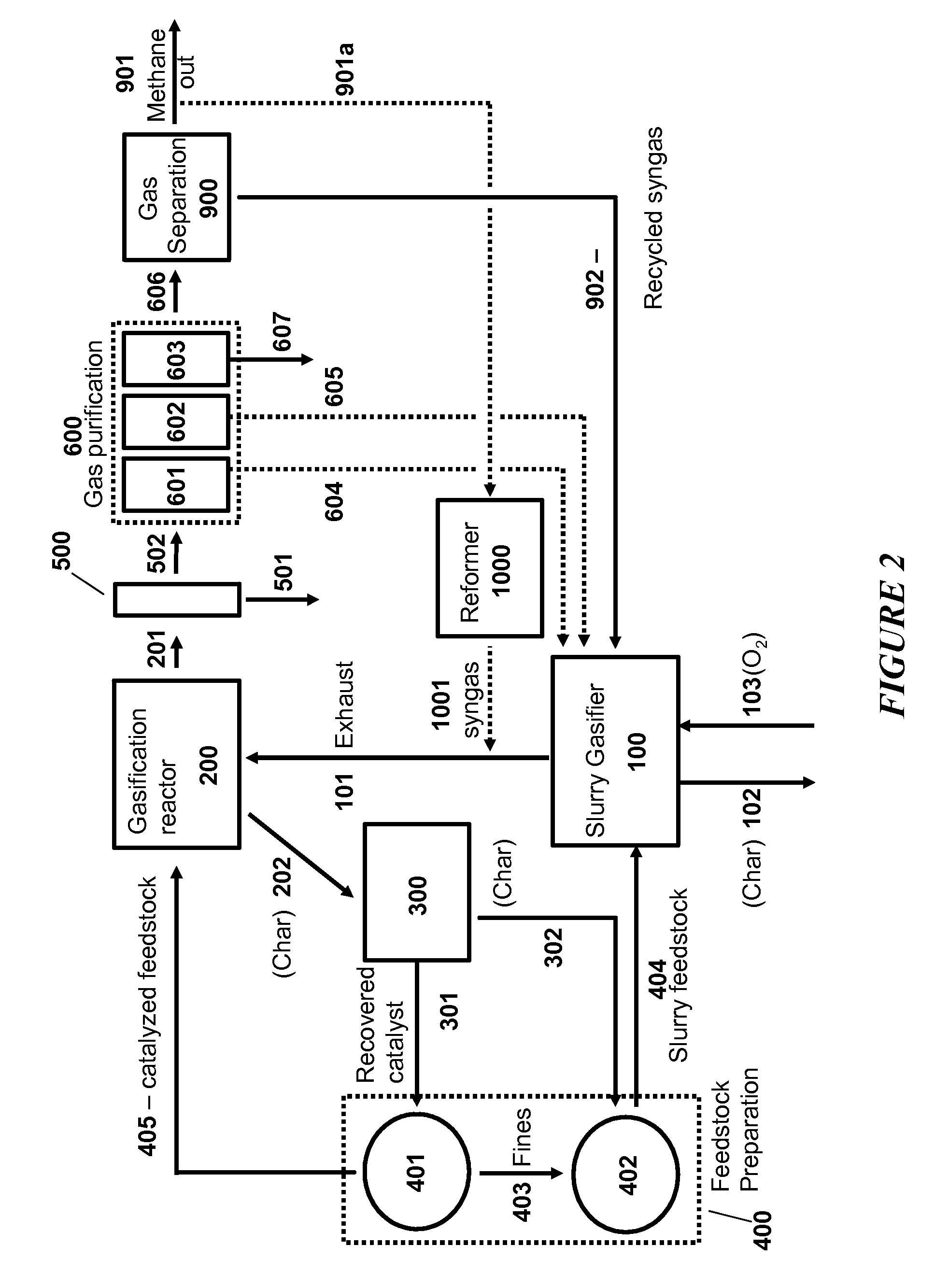
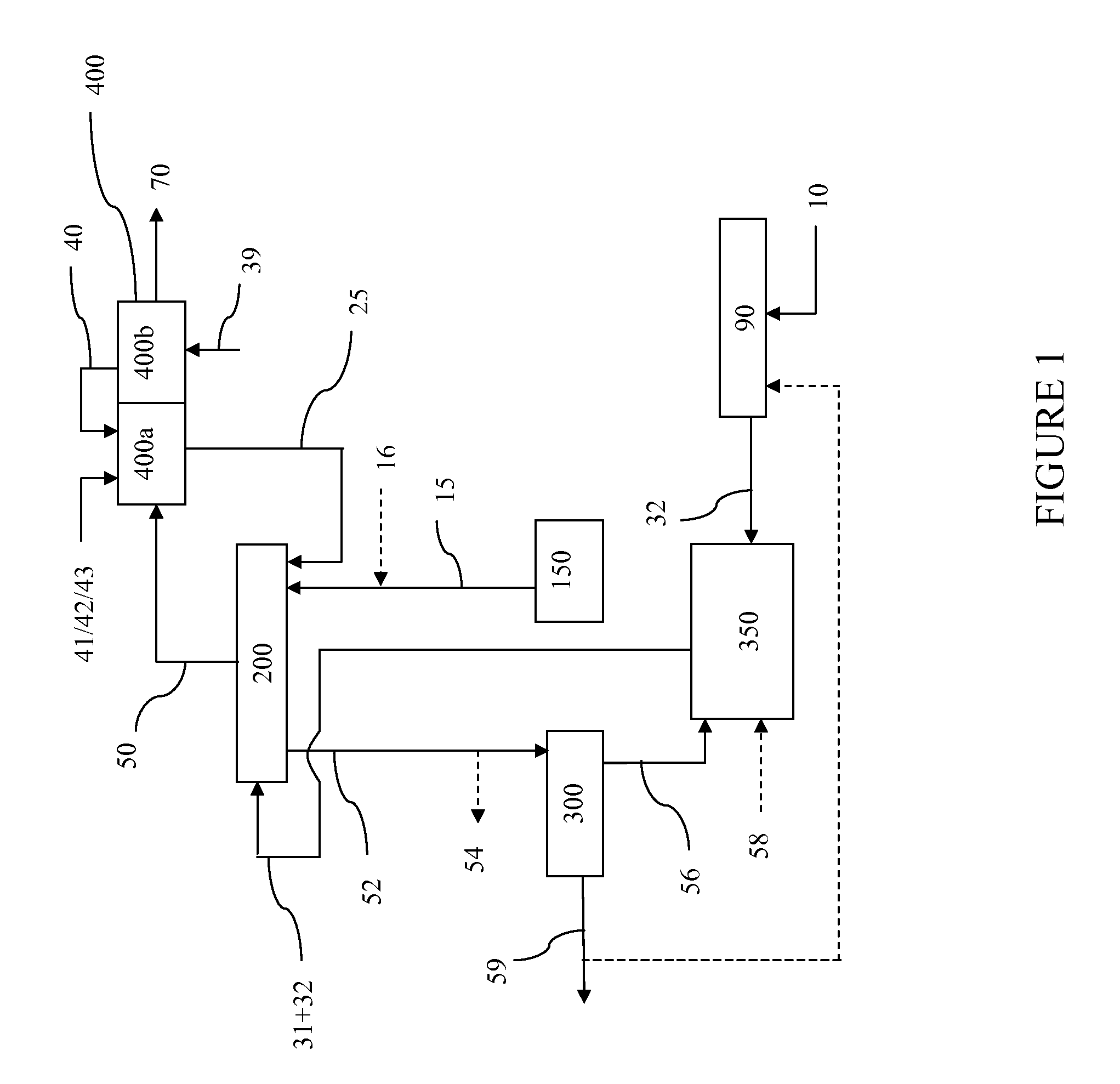
Processes for Making Synthesis Gas and Syngas-Derived Products
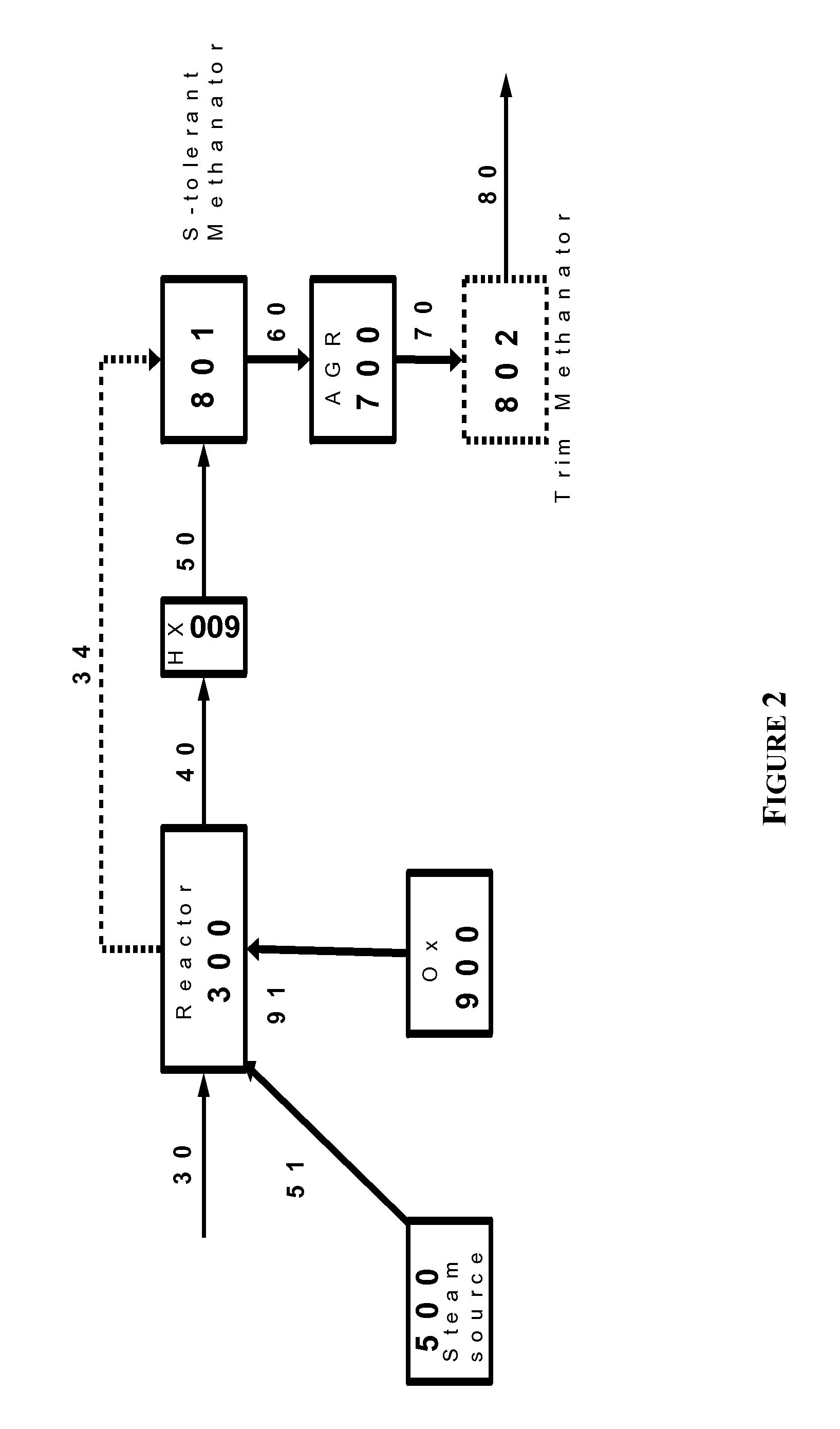
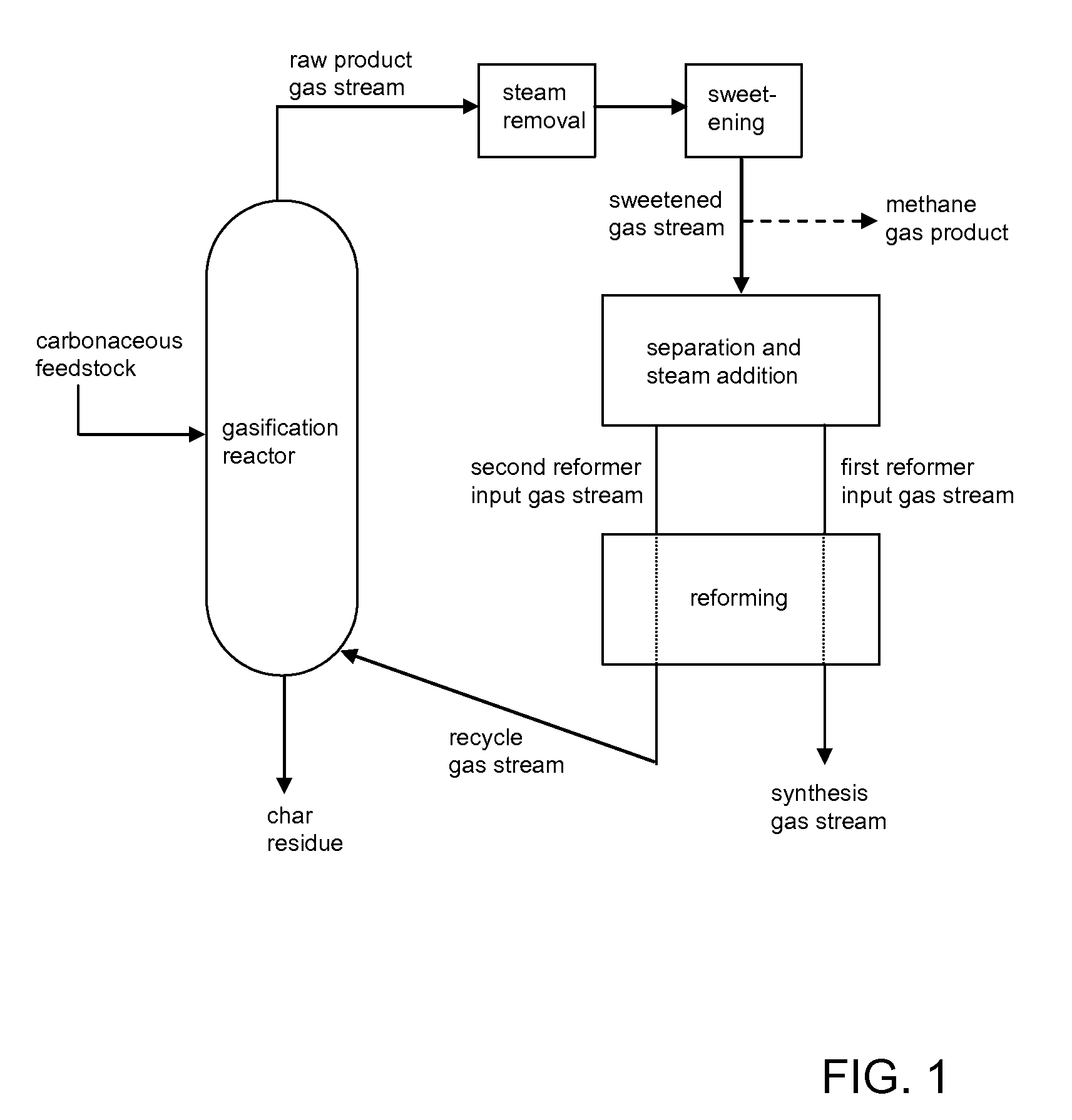
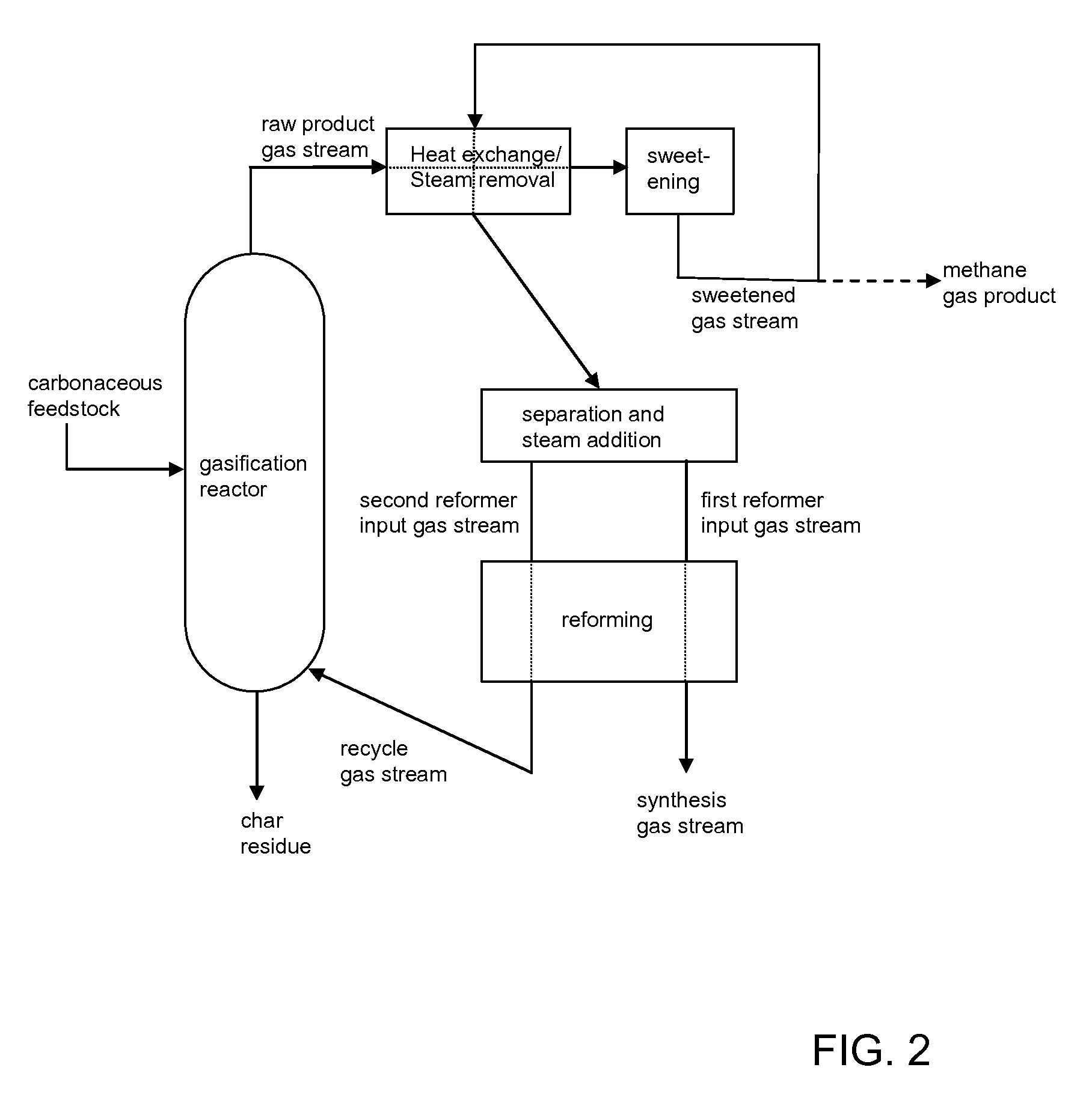
The present invention provides processes for making synthesis gas and processes for making syngas-derived products. For example, one aspect of the present invention provides a process for making a synthesis gas stream comprising hydrogen and carbon monoxide, the process comprising (a) providing a carbonaceous feedstock; (b) reacting the carbonaceous feedstock in a gasification reactor in the presence of steam and a gasification catalyst under suitable temperature and pressure to form a raw product gas stream comprising a plurality of gases comprising methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide; (c) removing steam from and sweetening the raw product gas stream to form a sweetened gas stream; (d) separating and adding steam to the sweetened gas stream to form a first reformer input gas stream having a first steam / methane ratio; and a second reformer input stream having a second steam / methane ratio, in which the first steam / methane ratio is smaller than the second steam / methane ratio; (e) reforming the second reformer input stream to form a recycle gas stream comprising steam, carbon monoxide and hydrogen; (f) introducing the recycle gas stream to the gasification reactor; and (g) reforming the first reformer input stream to form the synthesis gas stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
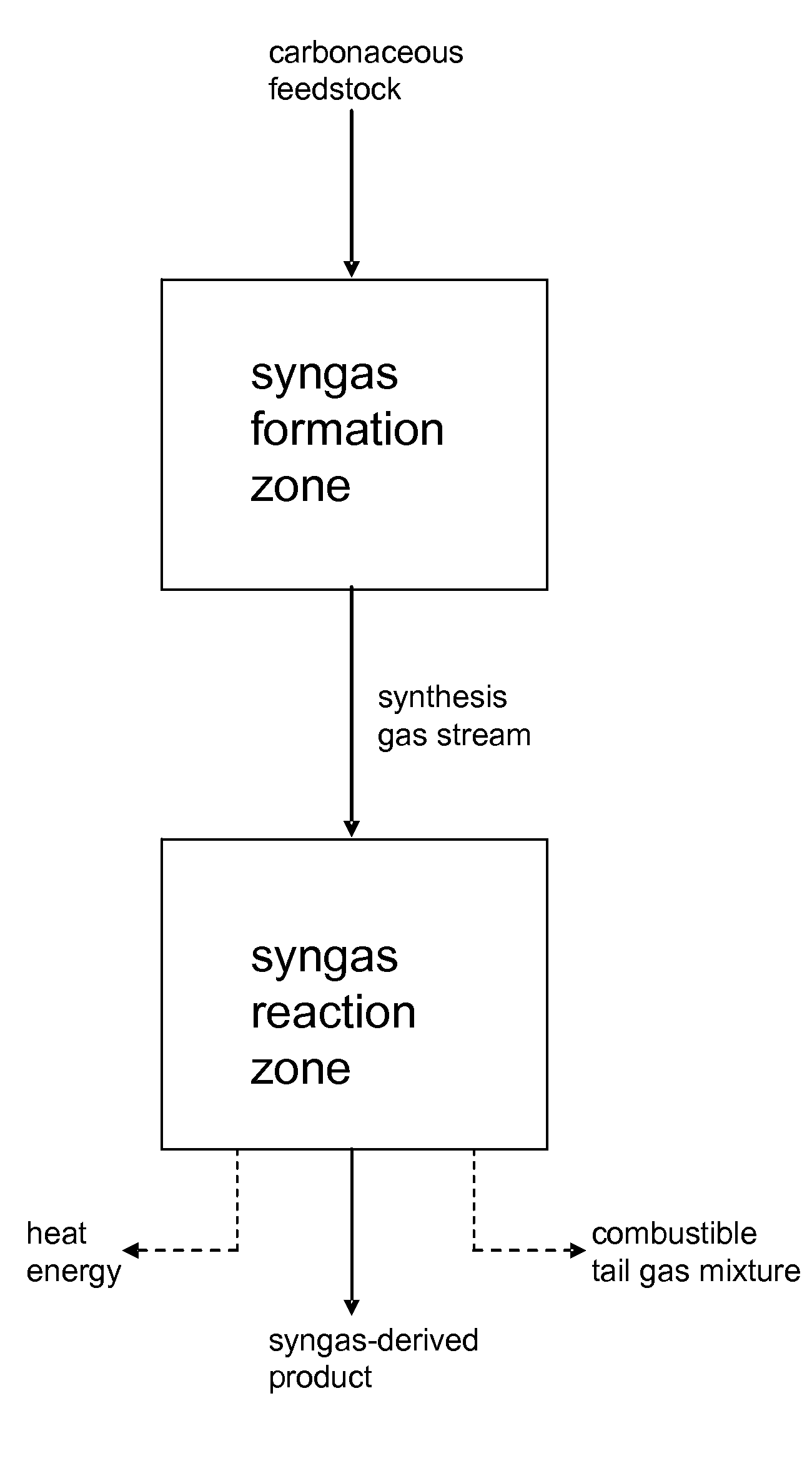
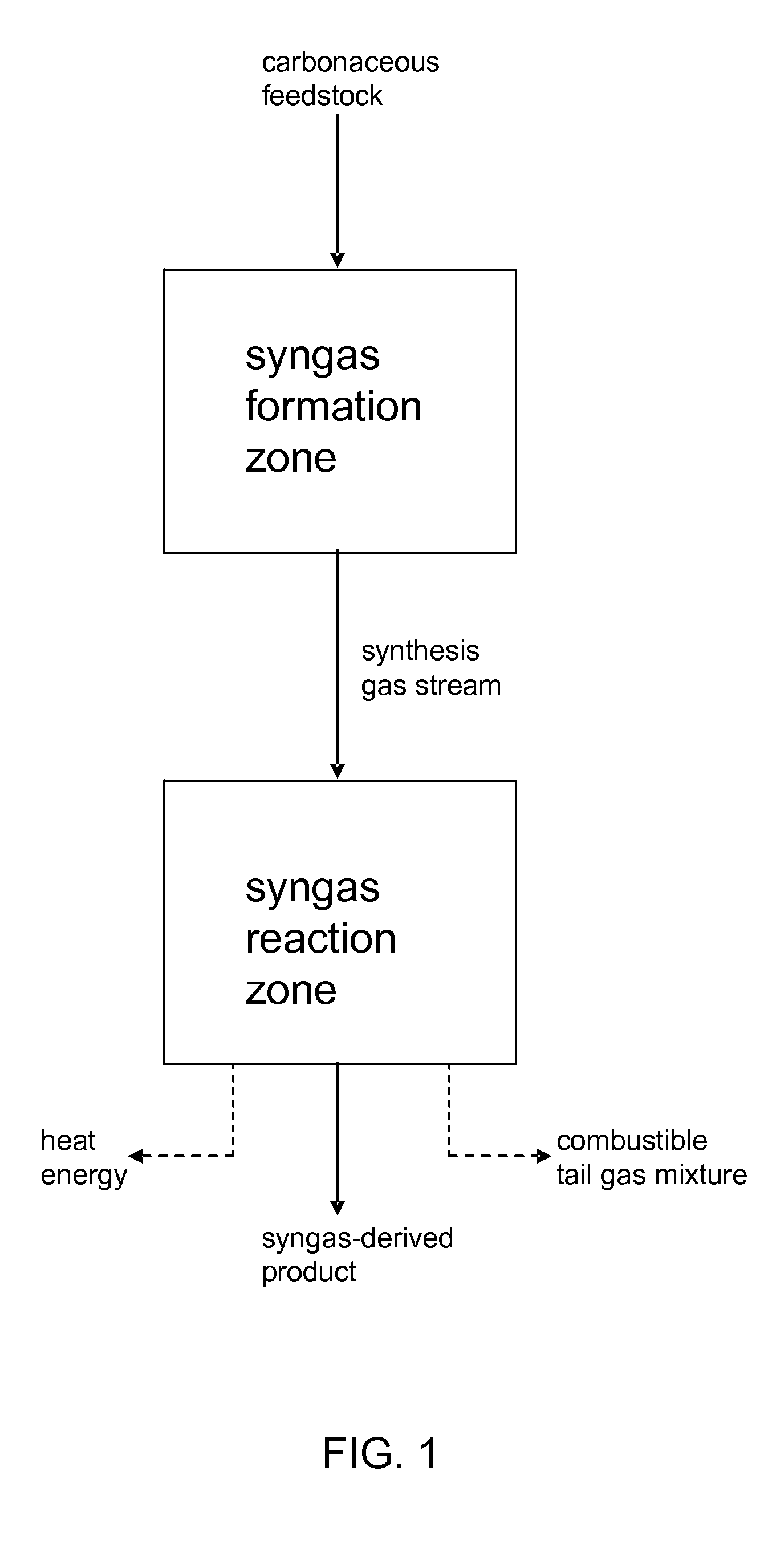
Processes for Making Syngas-Derived Products
The present invention provides processes for making syngas-derived products. For example, one aspect of the present invention provides a process for making a syngas-derived product, the process comprising (a) providing a carbonaceous feedstock; (b) converting the carbonaceous feedstock in a syngas formation zone at least in part to a synthesis gas stream comprising hydrogen and carbon monoxide; (c) conveying the synthesis gas stream to a syngas reaction zone; (d) reacting the synthesis gas stream in the syngas reaction zone to form the syngas-derived product and heat energy, a combustible tail gas mixture, or both; (e) recovering the syngas-derived product; and (f) recovering the heat energy formed from the reaction of the synthesis gas stream, burning the combustible tail gas mixture to form heat energy, or both.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
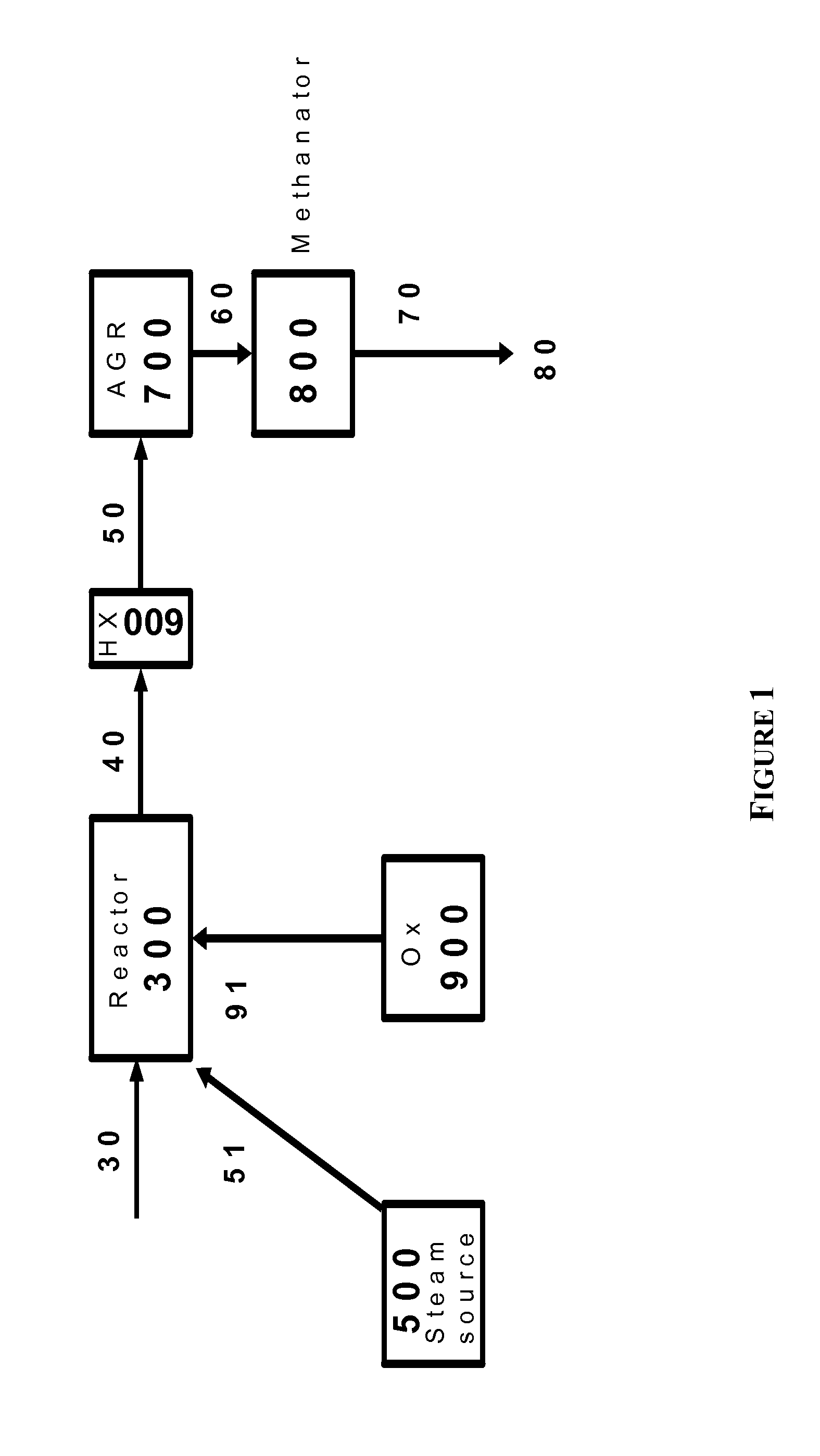
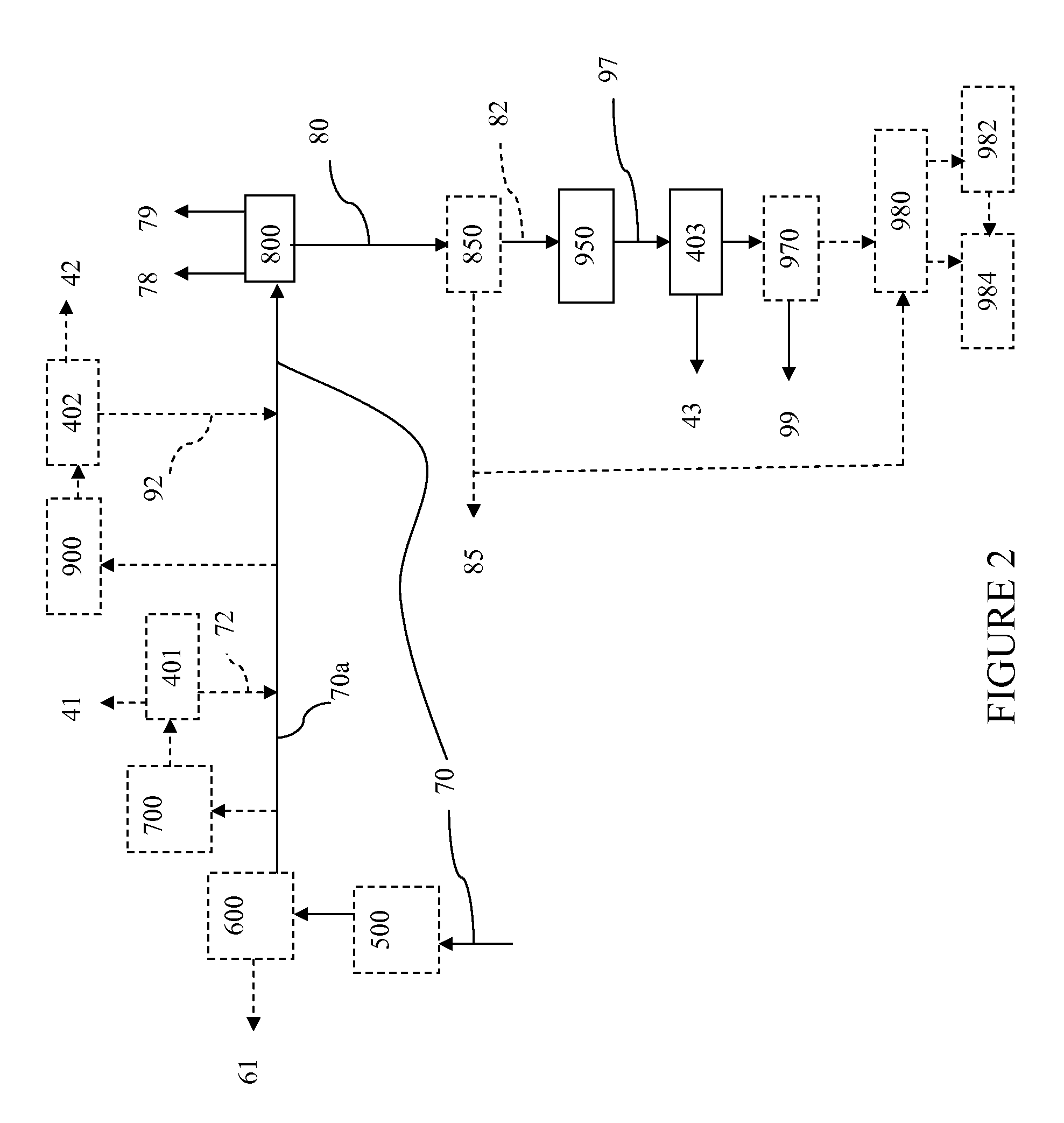
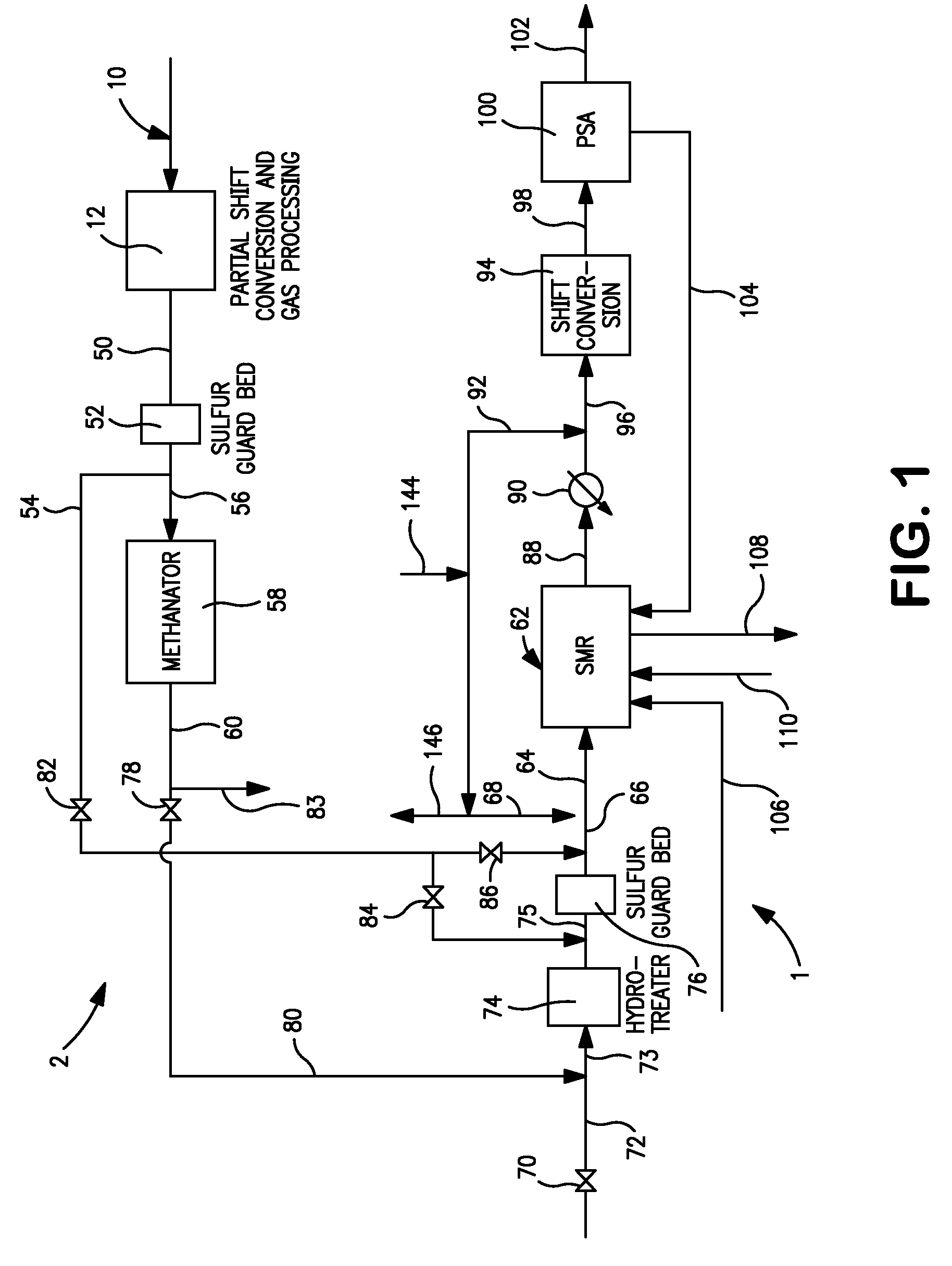
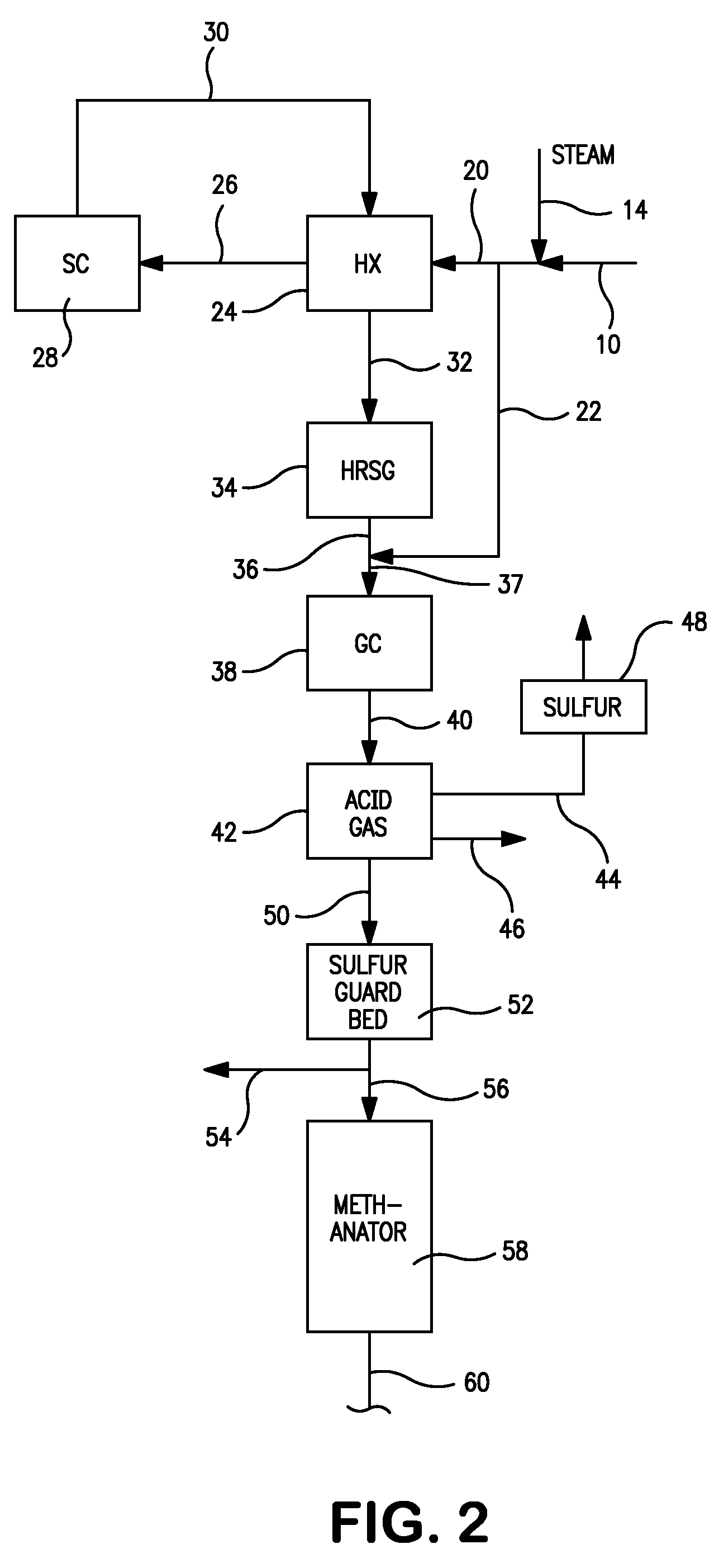
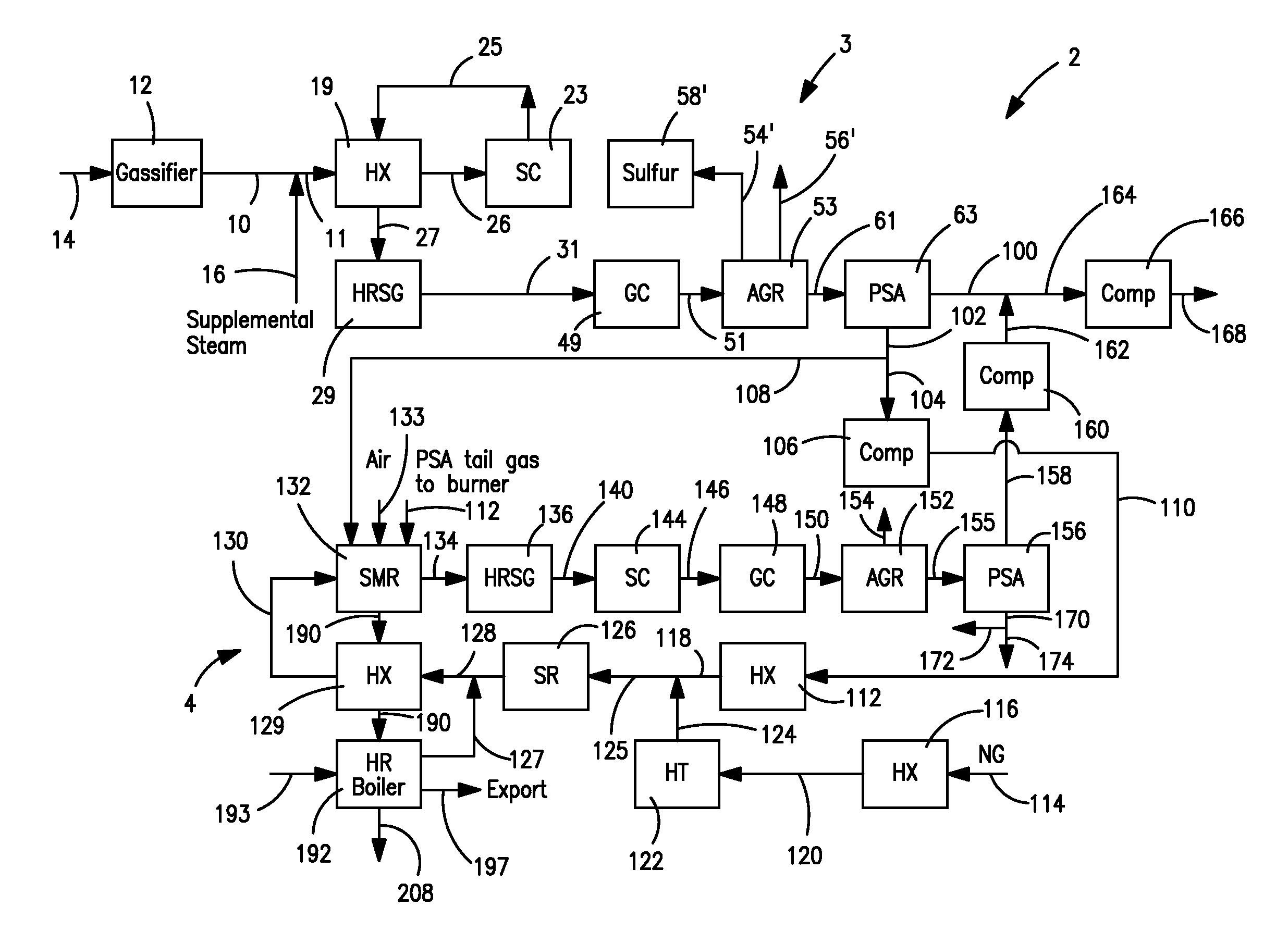
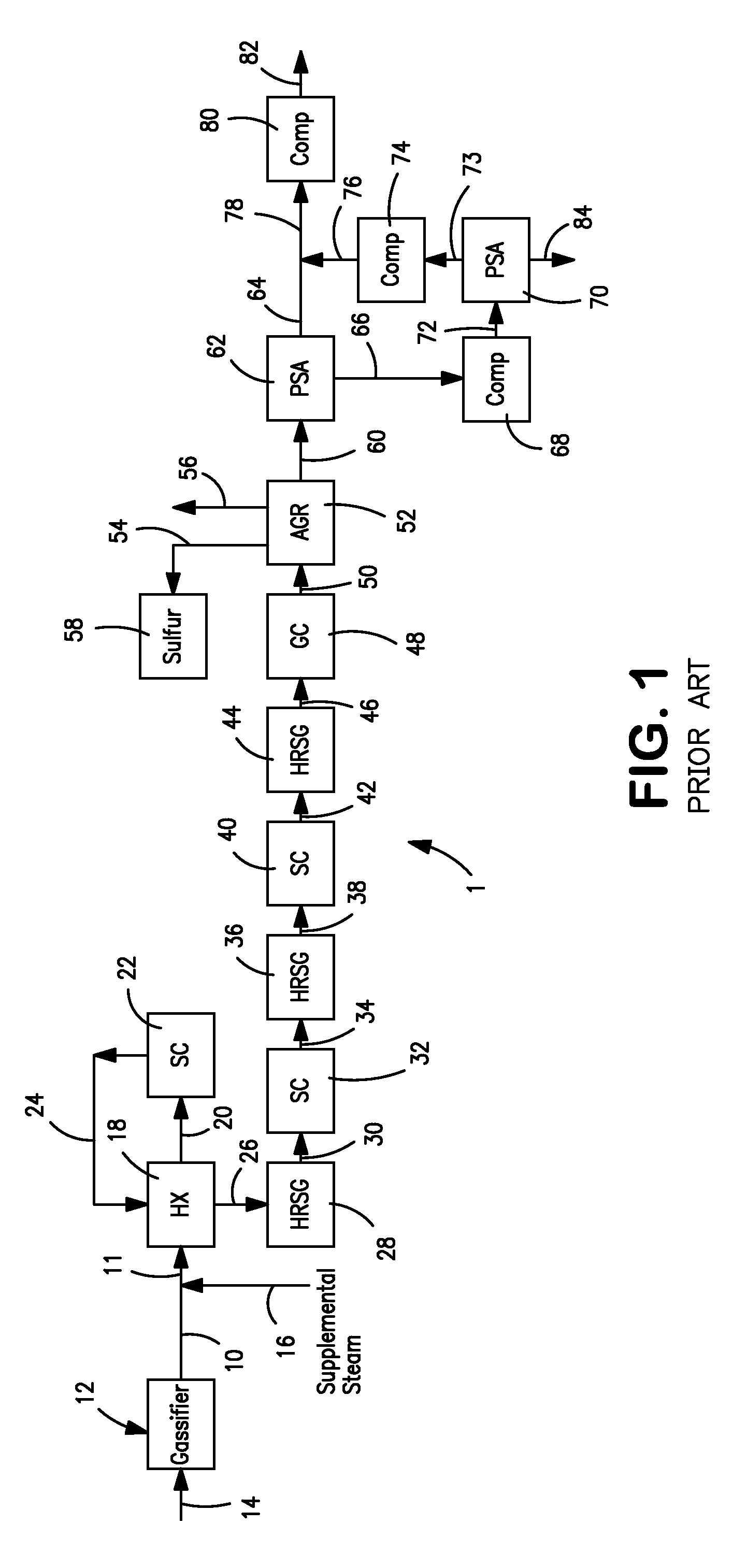
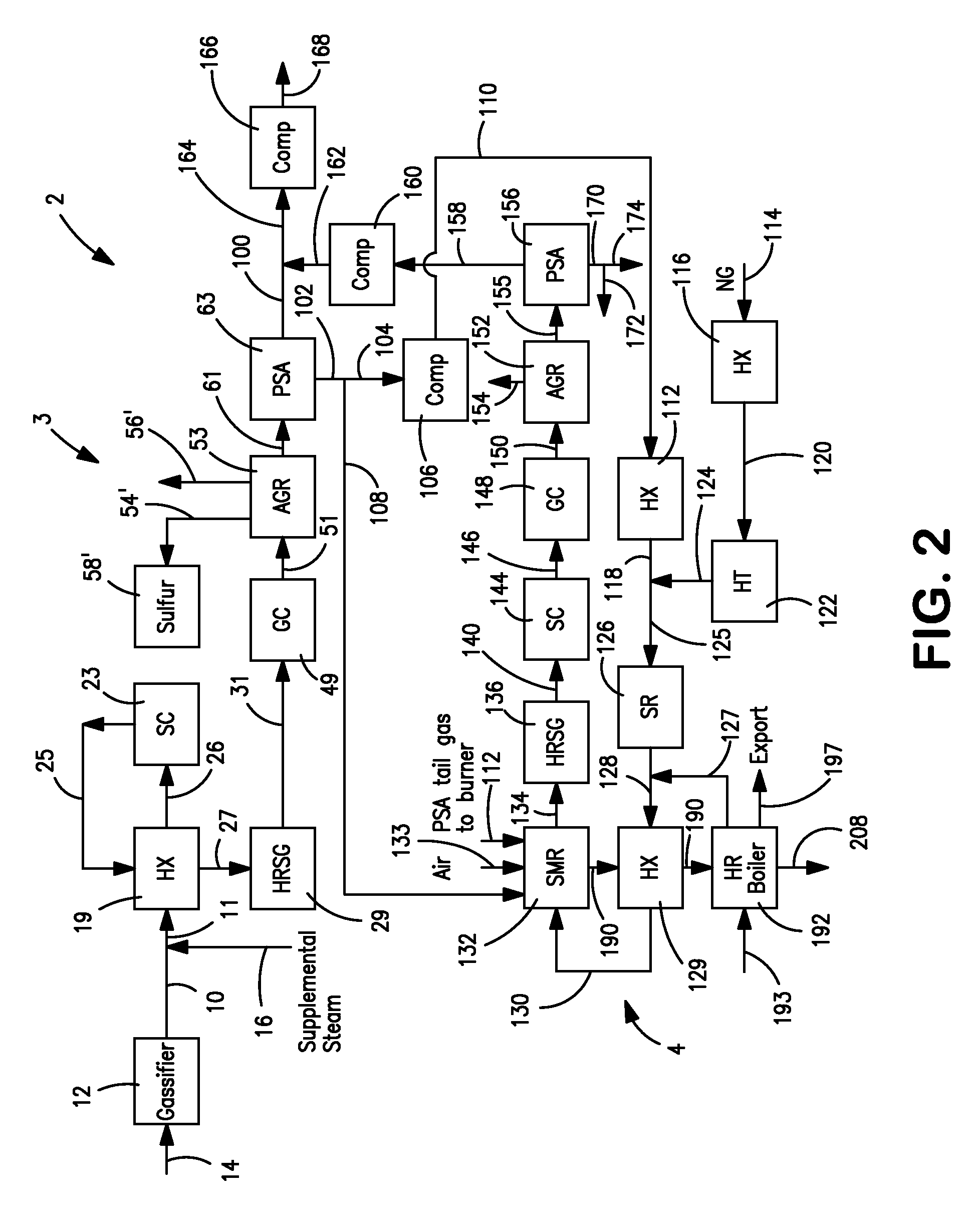
Sour Shift Process for the Removal of Carbon Monoxide from a Gas Stream
ActiveUS20090246120A1Hydrogen separation using liquid contactCombustible gas catalytic treatmentChemistryAirflow
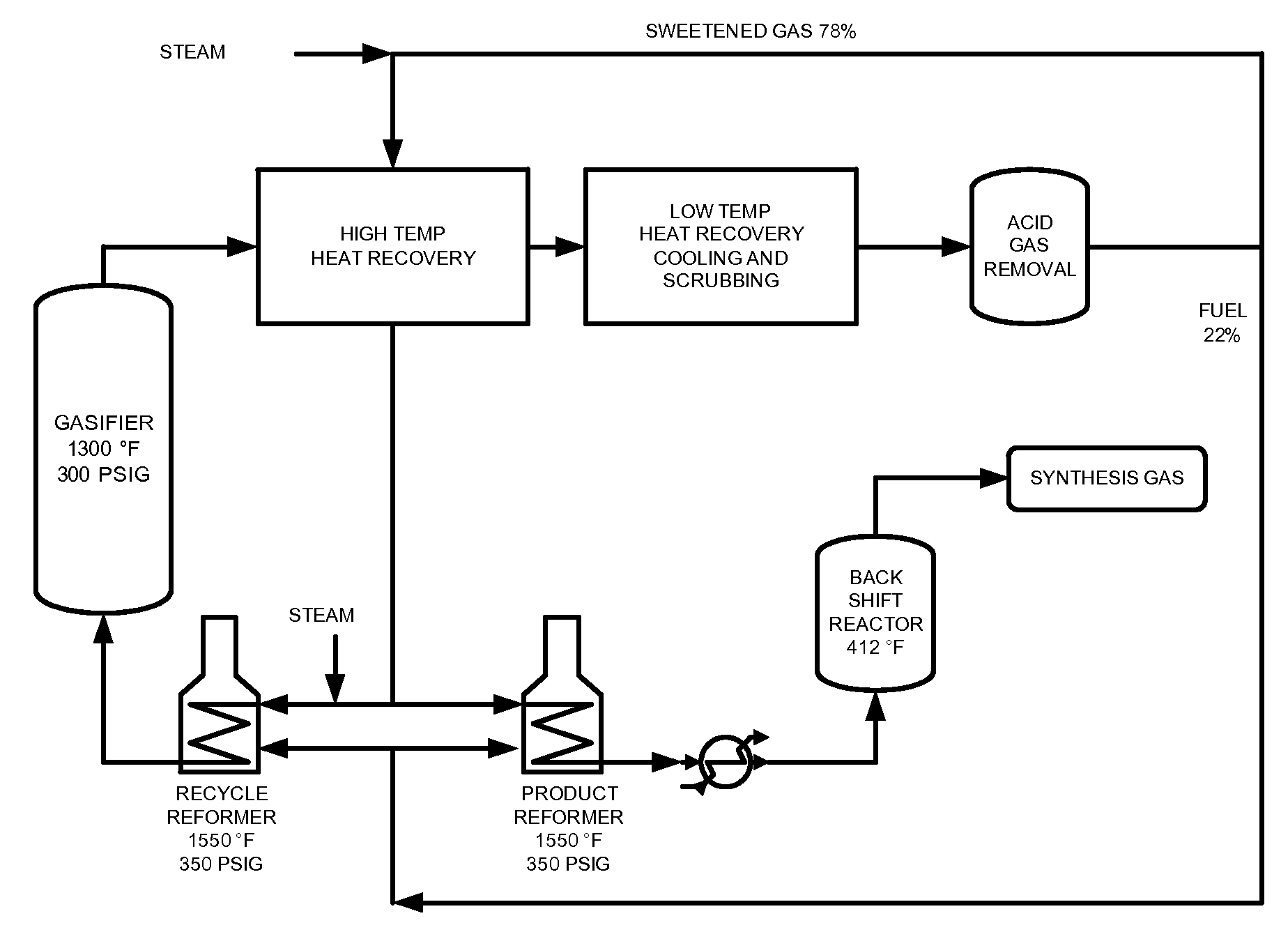
Processes for the catalytic conversion of a carbonaceous composition into a gas stream comprising methane are provided, where a sour shift reaction is used to remove carbon monoxide gas stream produced by the gasification process. The incorporation of the sour shift reaction provides an efficient and cost-effective means of eliminating carbon monoxide from the gas stream. In addition, the sour shift reaction also generates additional hydrogen, thus increasing the amount of hydrogen produced from the gasification process.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
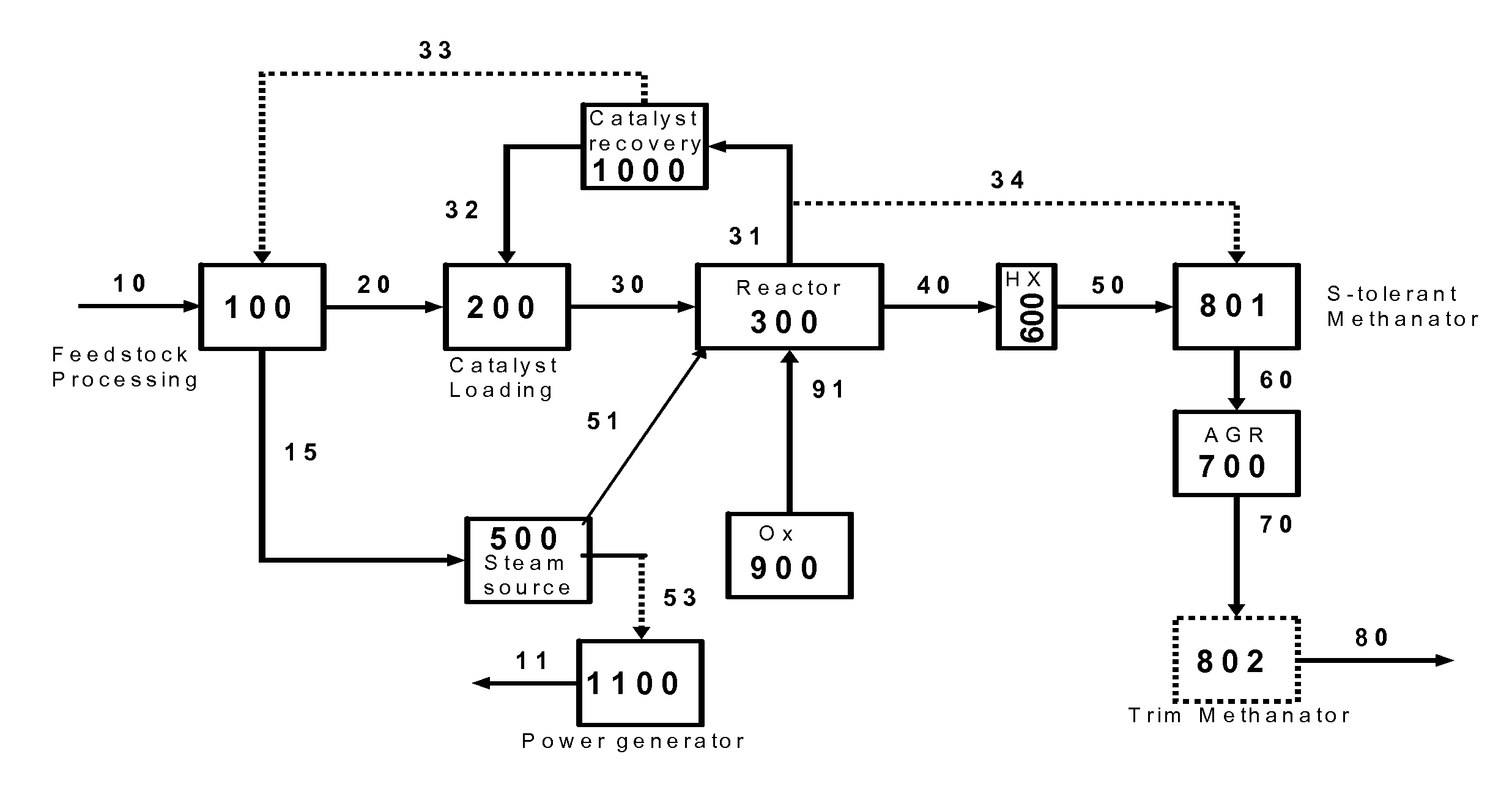
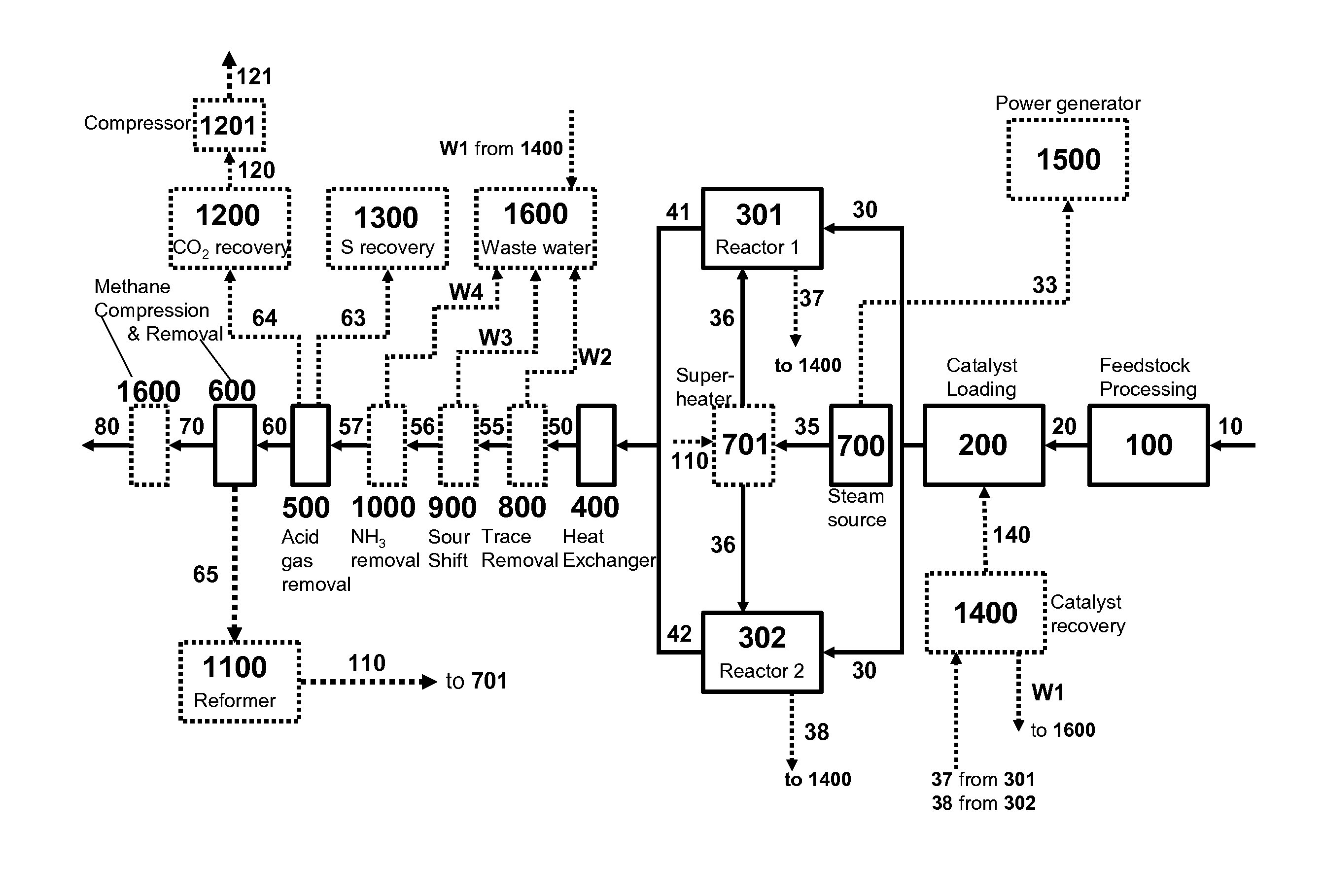
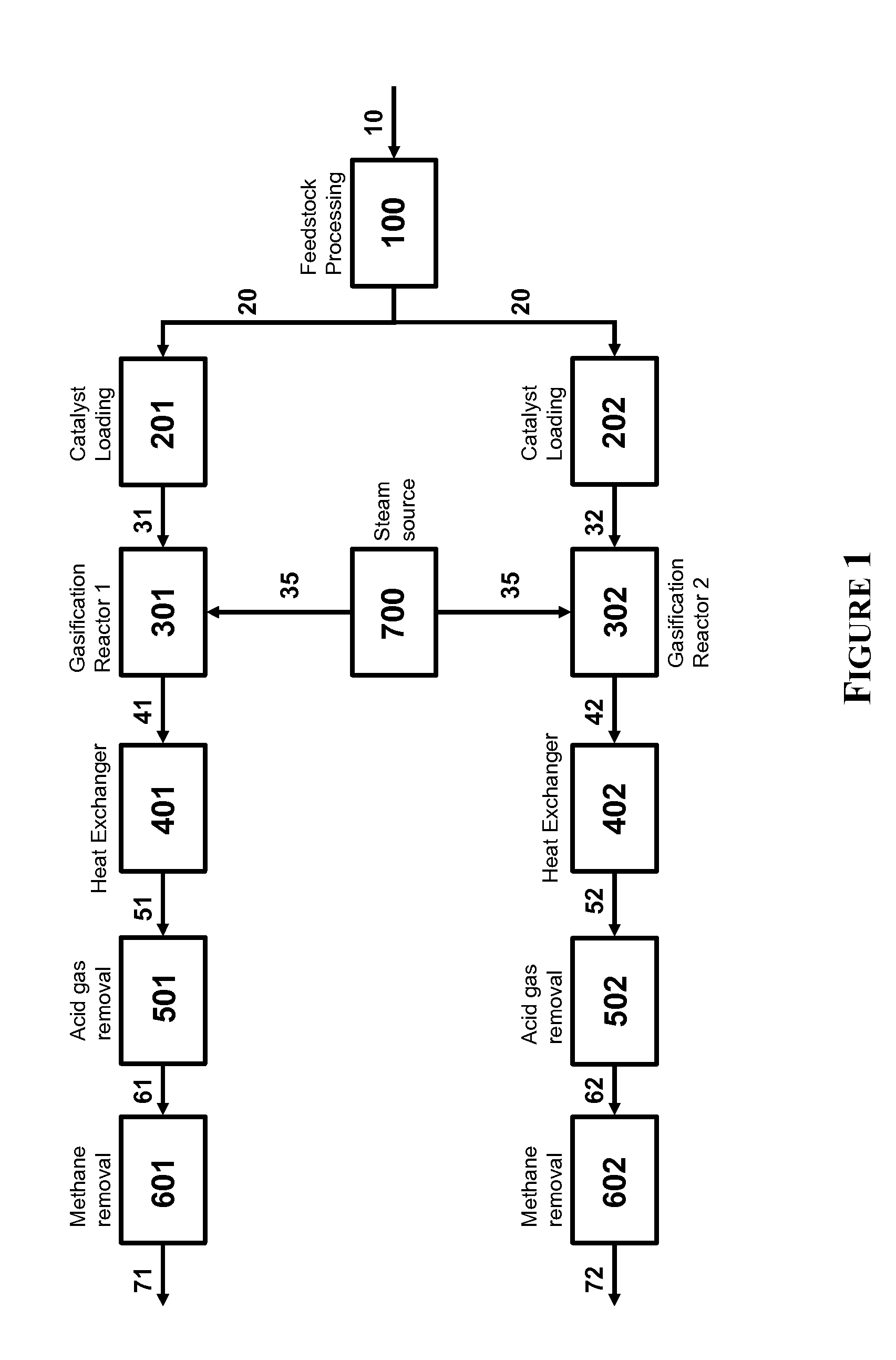
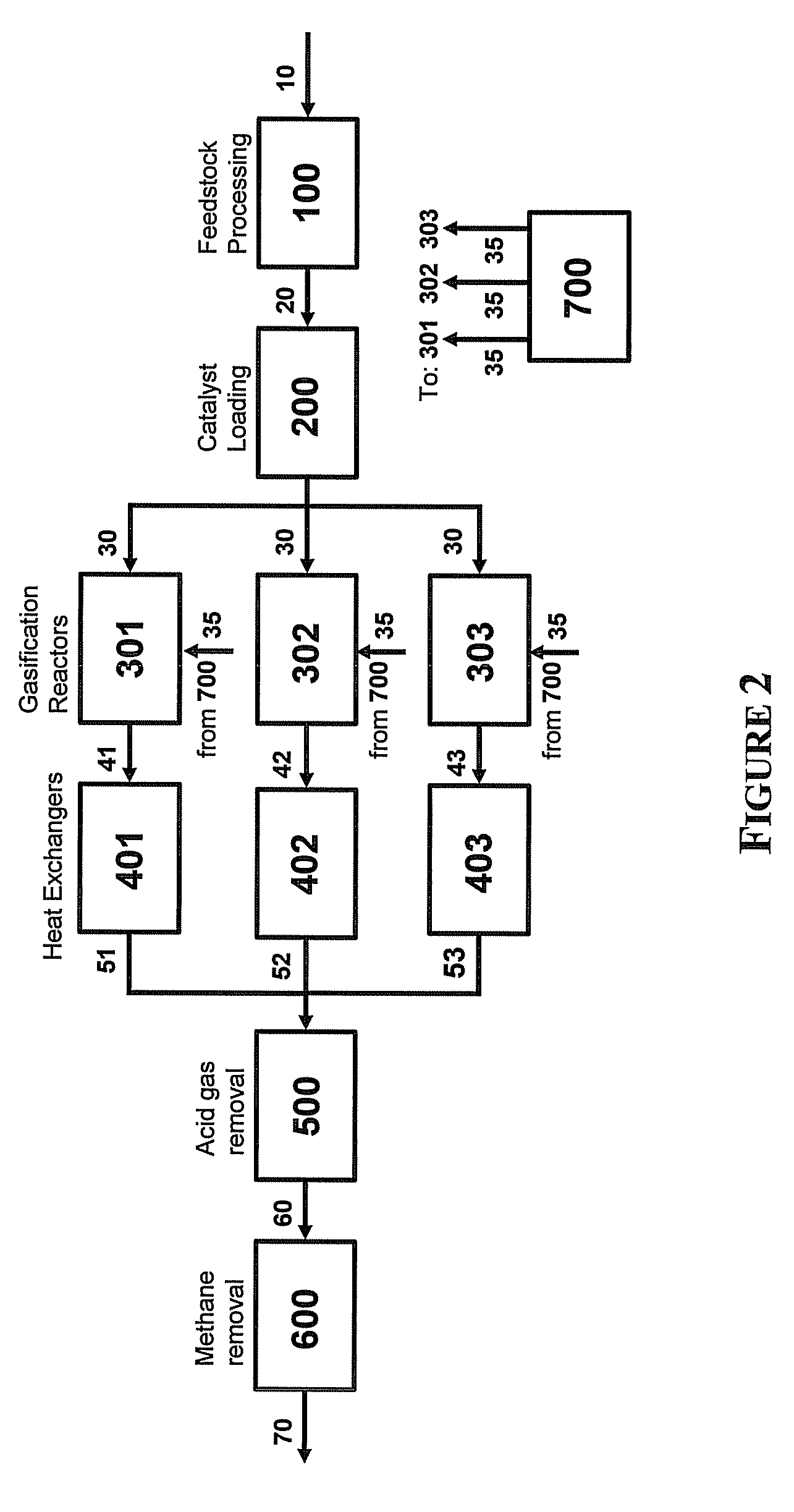
Two-Train Catalytic Gasification Systems
InactiveUS20090324458A1Reduce moisture contentGasifier mechanical detailsCombustible gas catalytic treatmentUnit operationAmmonia
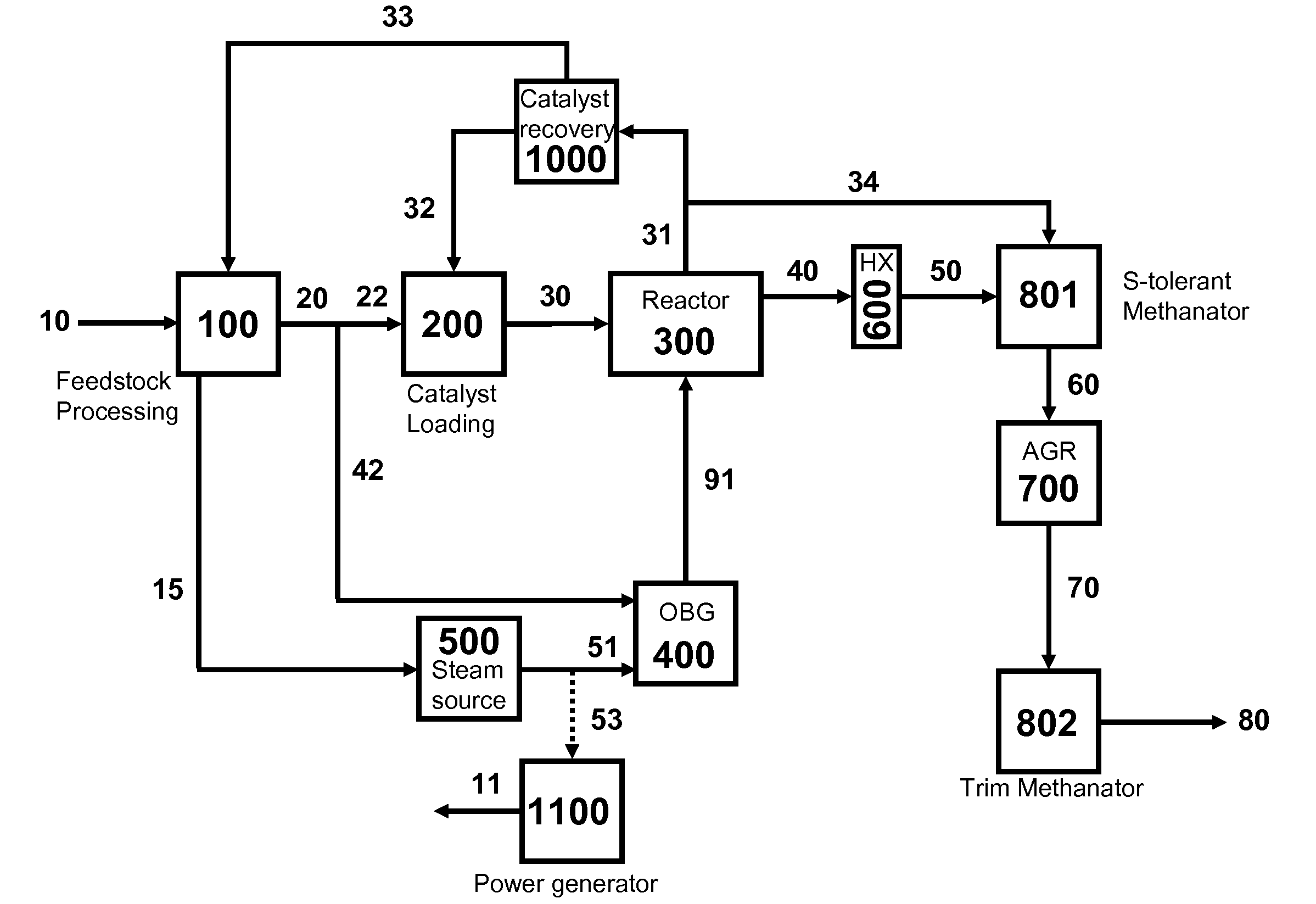
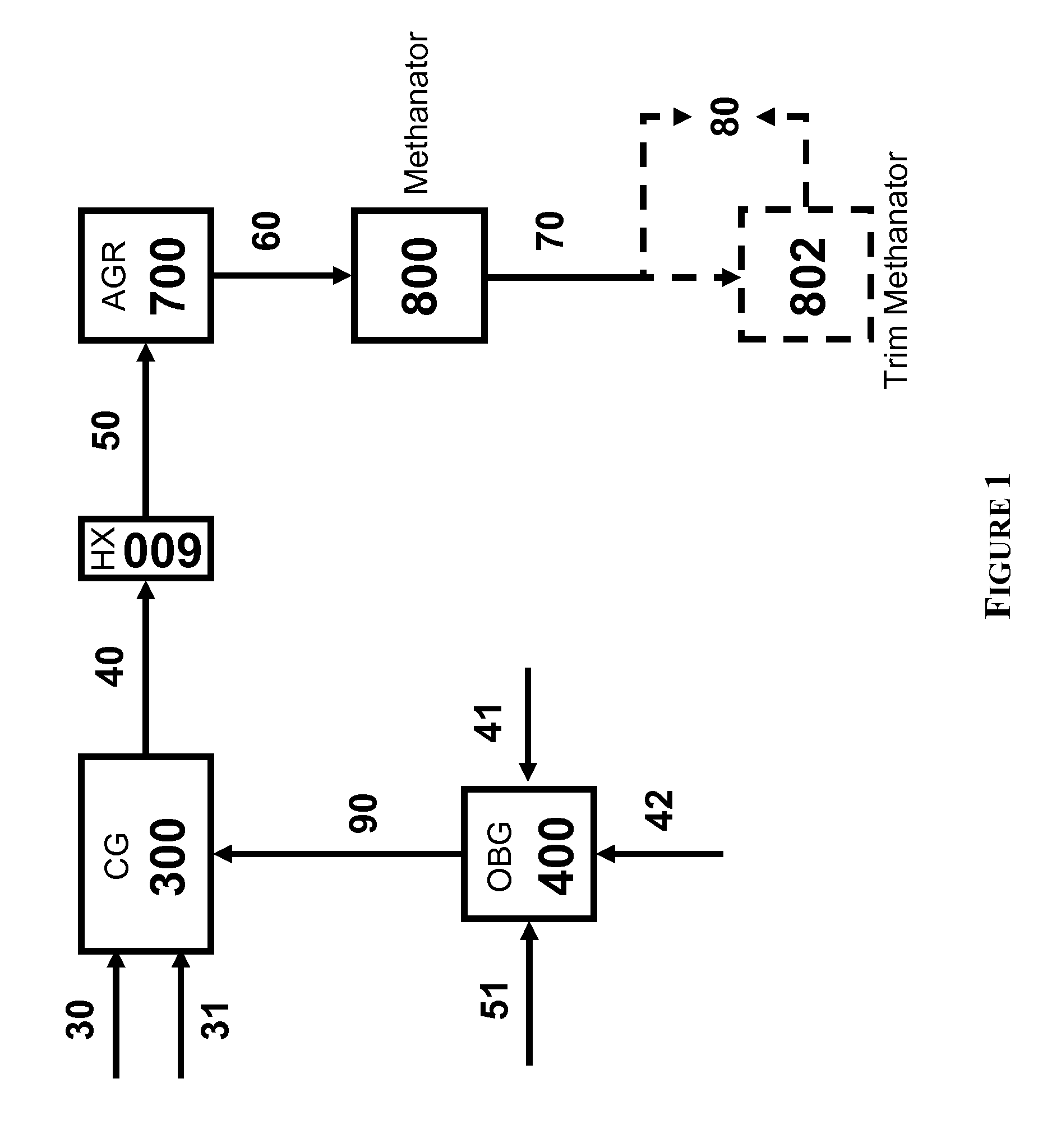
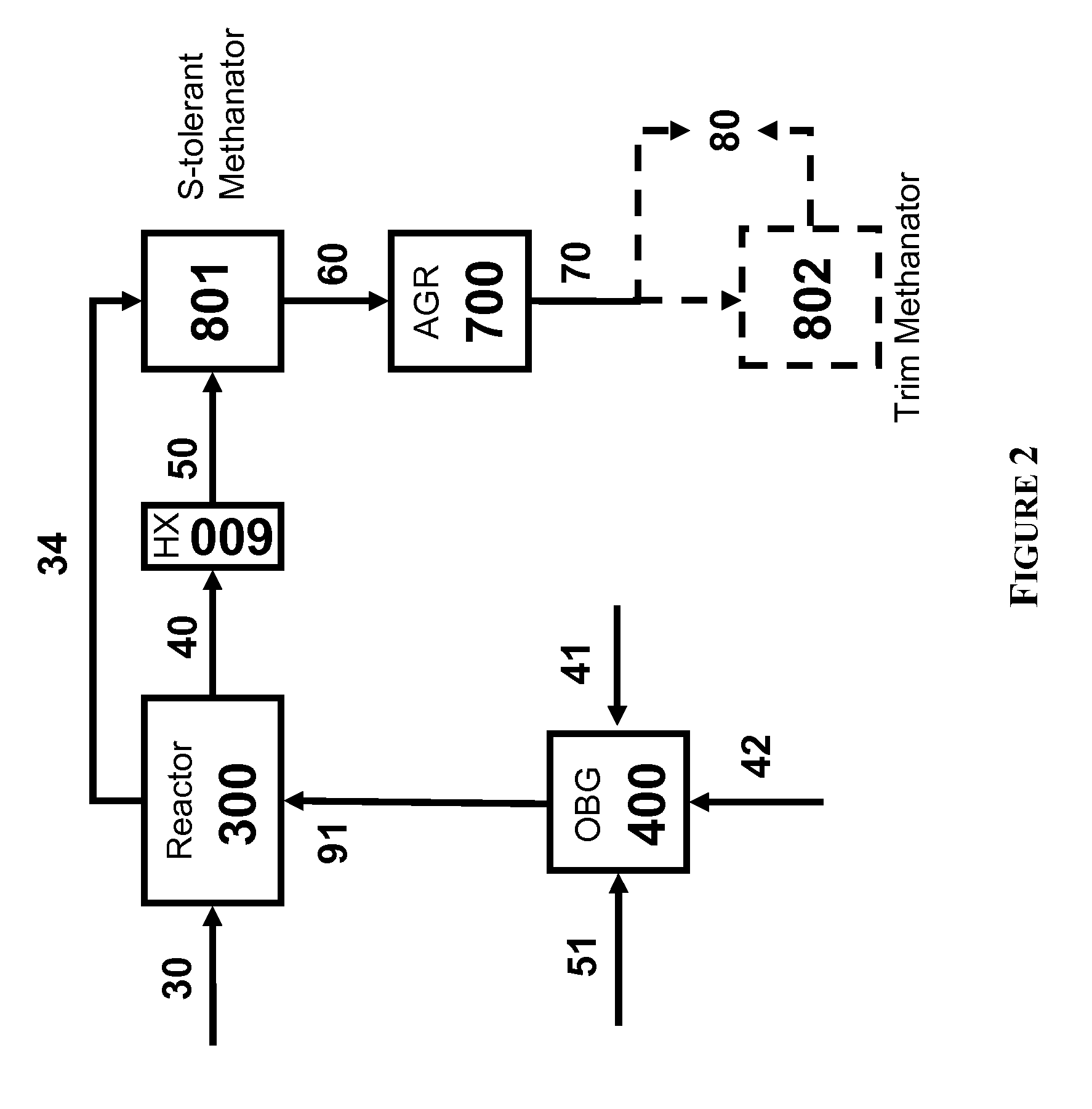
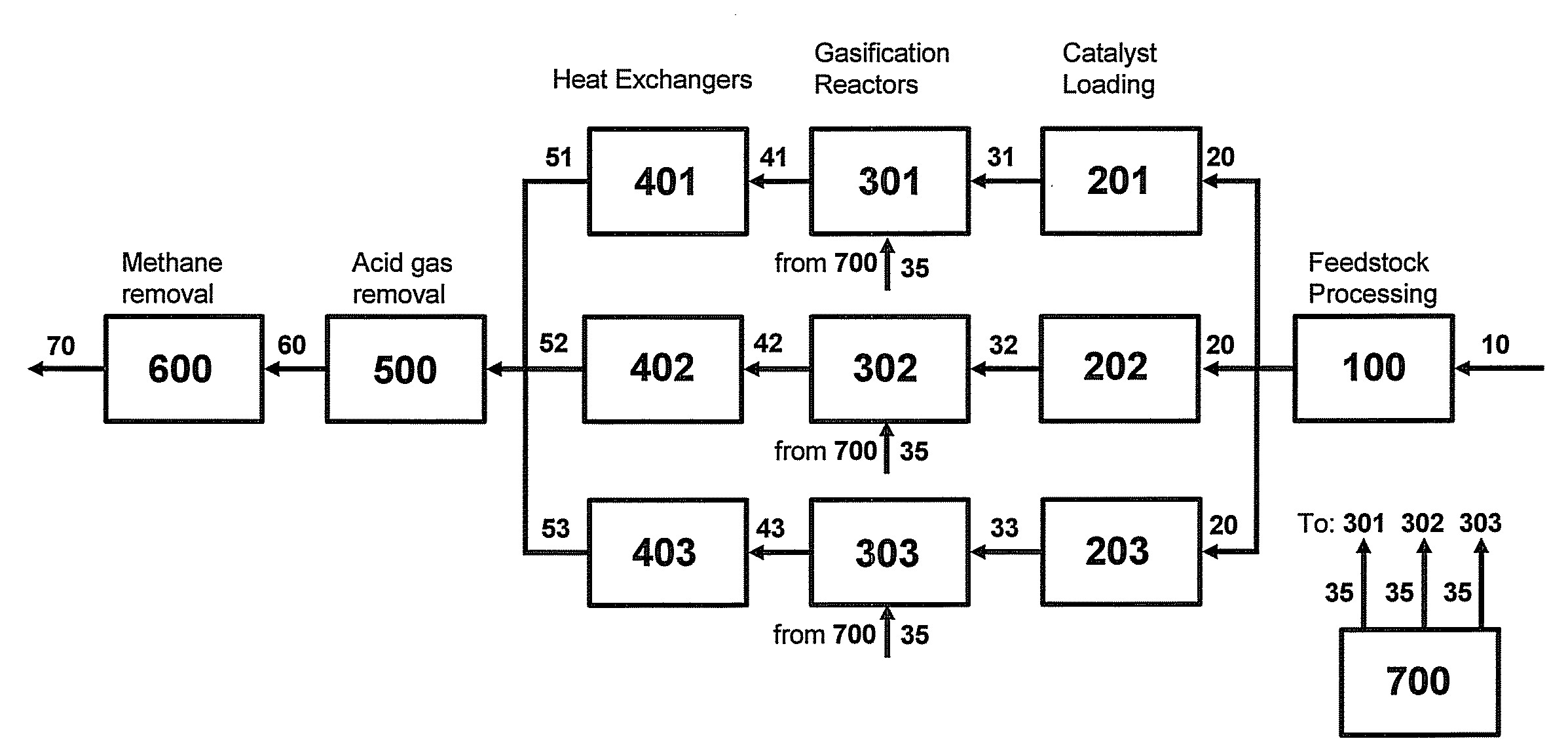
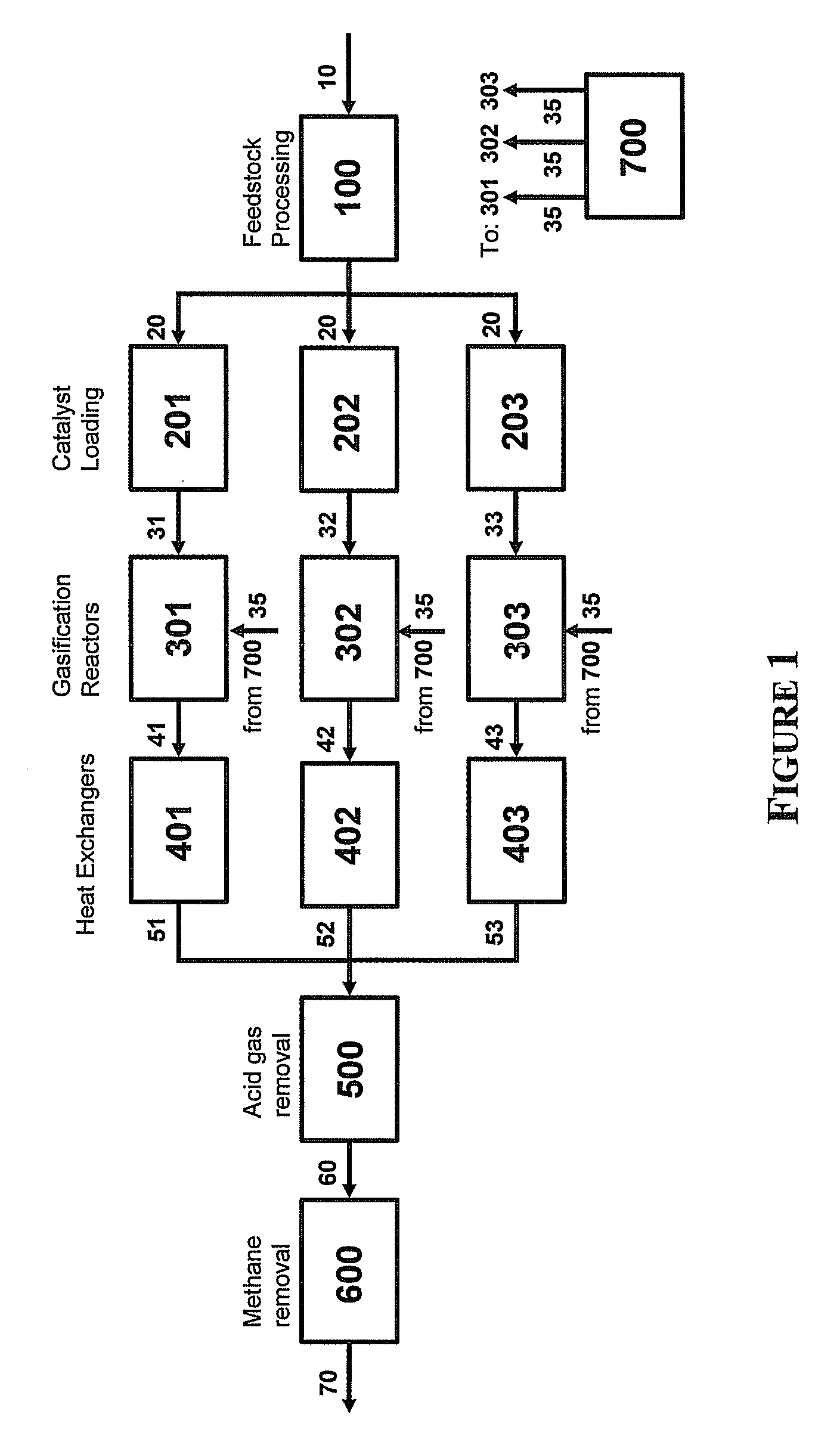
Systems for converting a carbonaceous feedstock into a plurality of gaseous products are described. The systems include, among other units, two separate gasification reactors to convert a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of an alkali metal catalyst into the plurality of gaseous products including at least methane. Each of the gasification reactors may be supplied with the feedstock from a single or separate catalyst loading and / or feedstock preparation unit operations. Similarly, the hot gas streams from each gasification reactor may be purified via their combination at a heat exchanger, acid gas removal, or methane removal unit operations. Product purification may comprise trace contaminant removal units, ammonia removal and recovery units, and sour shift units.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
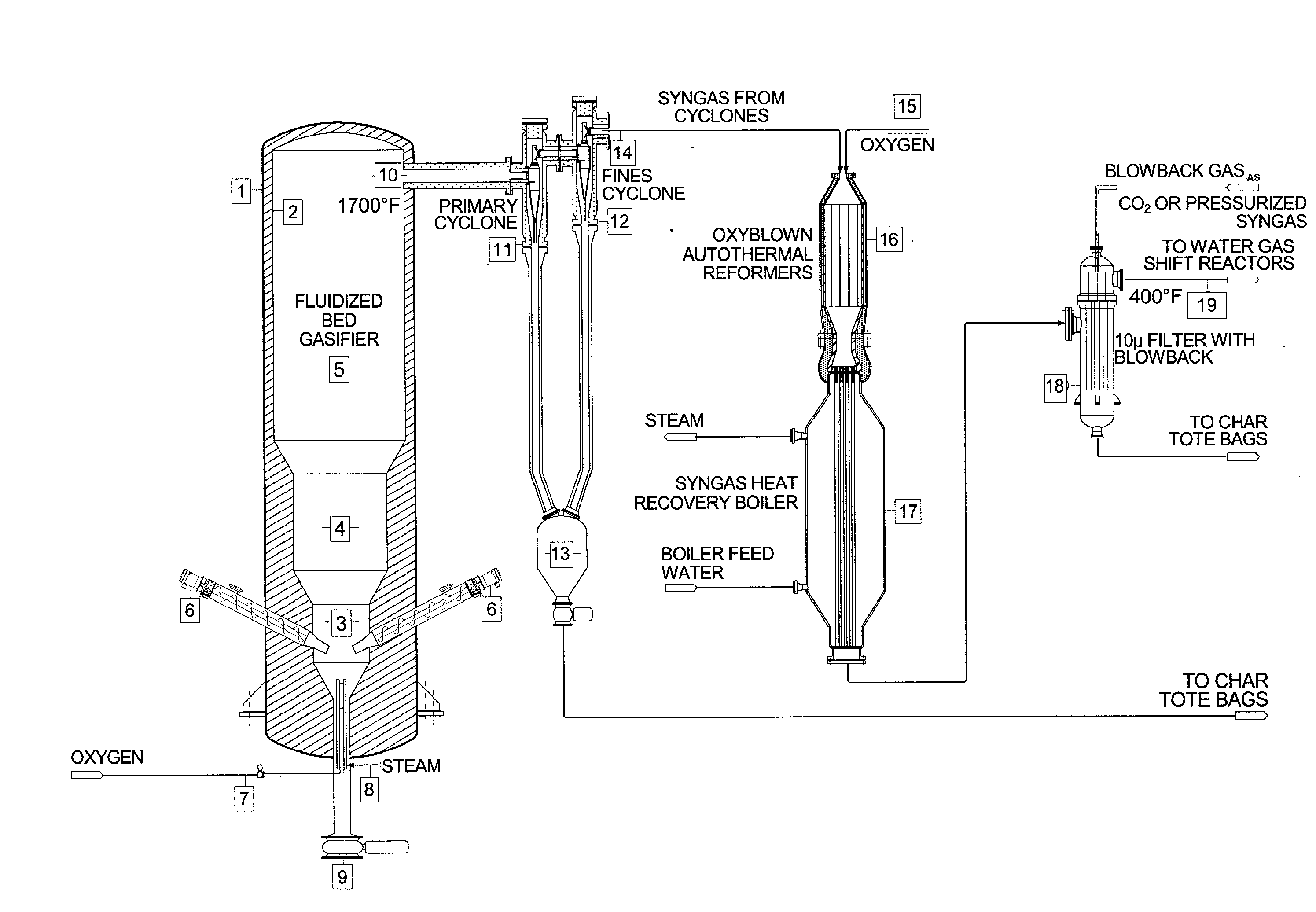
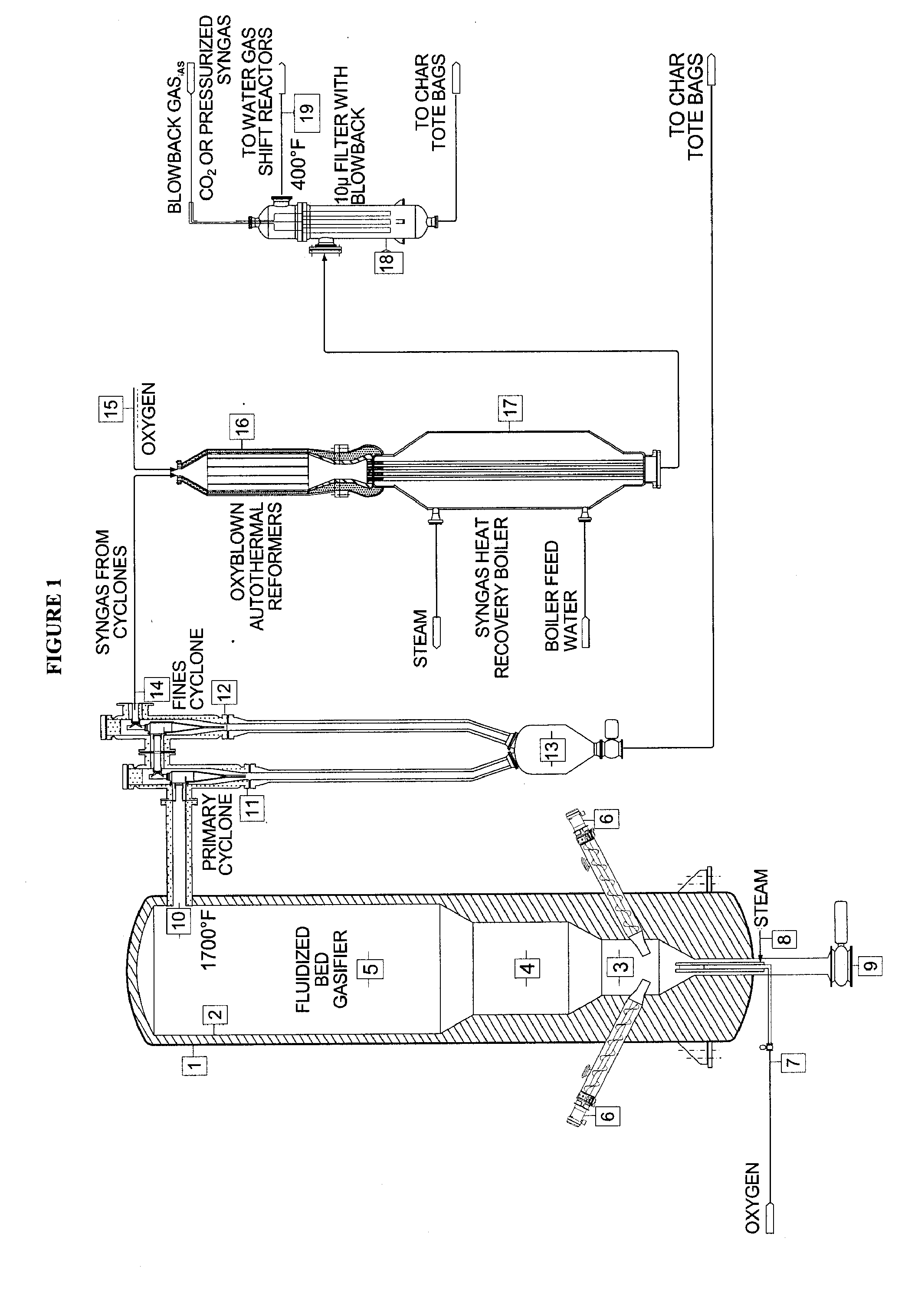
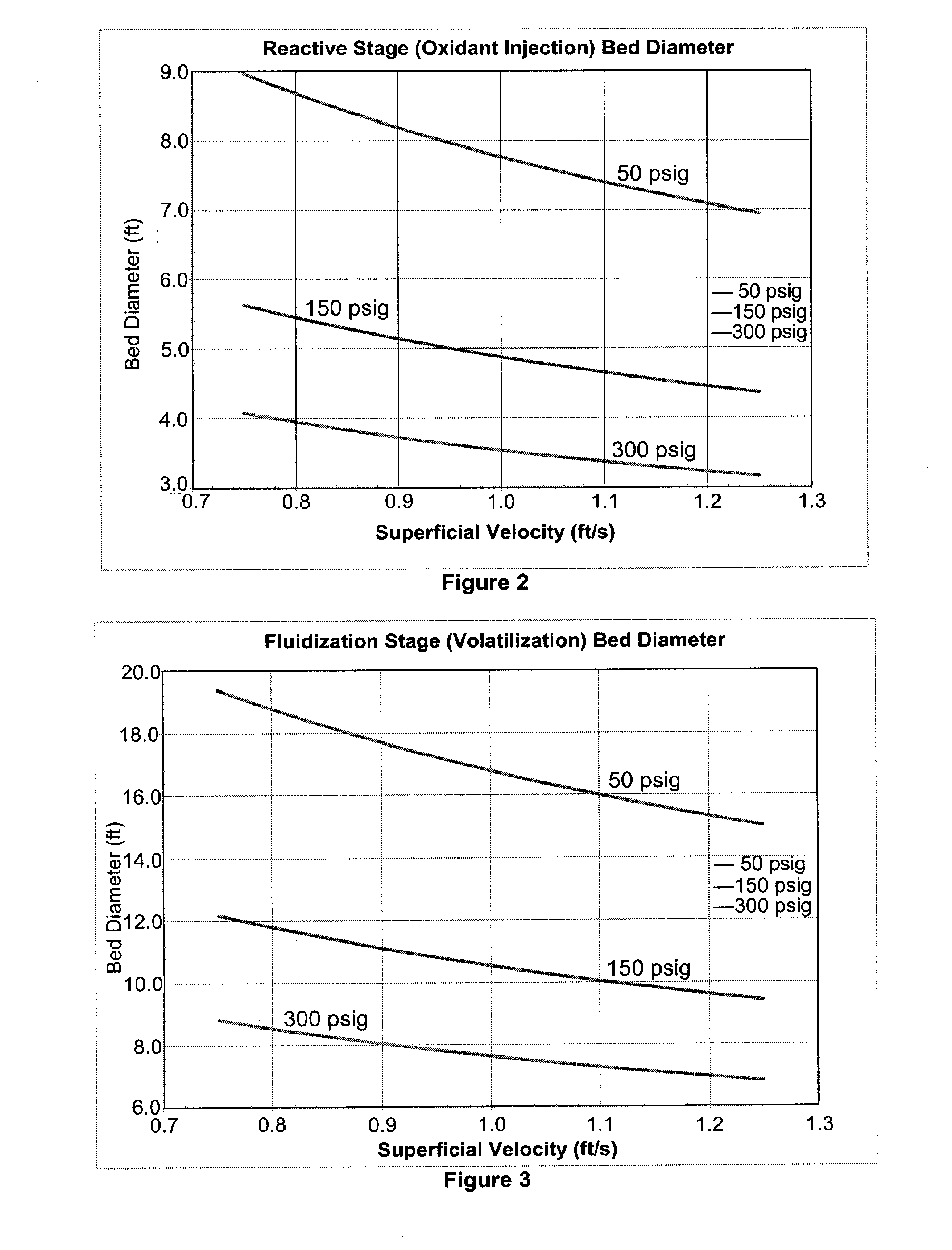
Method for converting biomass into synthesis gas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier followed by an oxyblown autothermal reformer to reduce methane and tars
InactiveUS20100040510A1Lower Level RequirementsGasifier mechanical detailsCombustible gas catalytic treatmentSyngasFluidized bed gasifier
The invention provides systems and methods for converting biomass into syngas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier to eliminate or reduce the formation of methane, volatiles such as BTX, and tars. The gasifier may include a reactive stage that may receive a biomass feed through a feed line and oxygen through an oxygen feed line. The gasifier may also include a fluidized bed section that may be configured to receive the reaction products from the first stage, mix them and perform fluidized bed activity. A gasifier may also have a disengagement section that may be configured to separate fluidized media and particulate matter from syngas product. A gasification system may also include oxyblown catalytic autothermal reactor and a cryogenic air separation unit.
Owner:SYNT
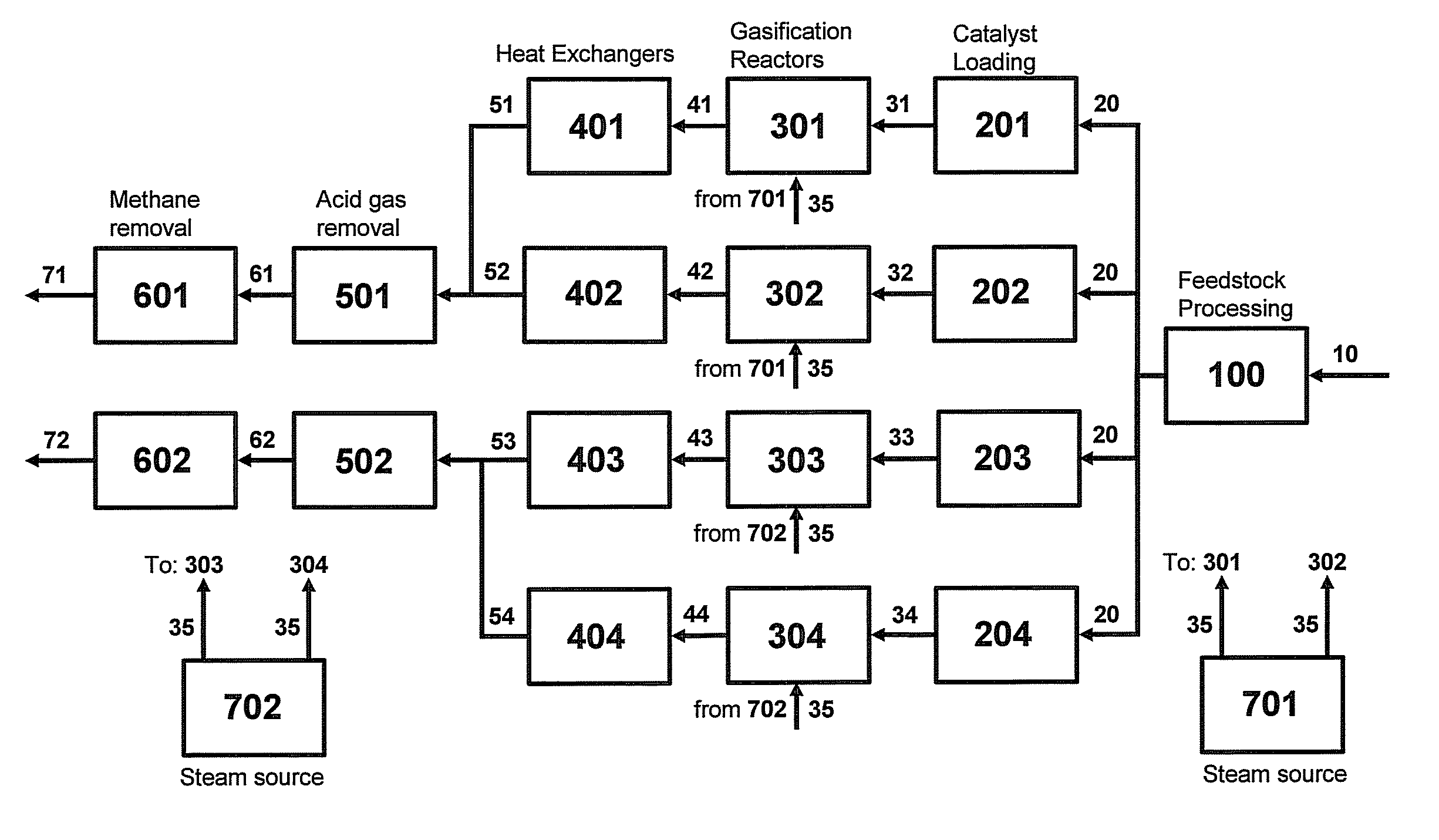
Four-Train Catalytic Gasification Systems
InactiveUS20090324460A1Reduce moisture contentHydrogen separation at low temperatureHydrogen separation using liquid contactUnit operationAmmonia
Systems to convert a carbonaceous feedstock into a plurality of gaseous products are described. The systems include, among other units, four separate gasification reactors for the gasification of a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of an alkali metal catalyst into the plurality of gaseous products including at least methane. Each of the gasification reactors may be supplied with the feedstock from a single or separate catalyst loading and / or feedstock preparation unit operations. Similarly, the hot gas streams from each gasification reactor may be purified via their combination at a heat exchanger, acid gas removal, or methane removal unit operations. Product purification may comprise trace contaminant removal units, ammonia removal and recovery units, and sour shift units.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
ActiveUS20110088896A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processMethane
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or methane reforming, involving combined capture and recycle of carbon dioxide from both processes.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from gas mixtures
ActiveUS7618606B2Good repeatabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCombustible gas catalytic treatmentCo2 removalSorbent
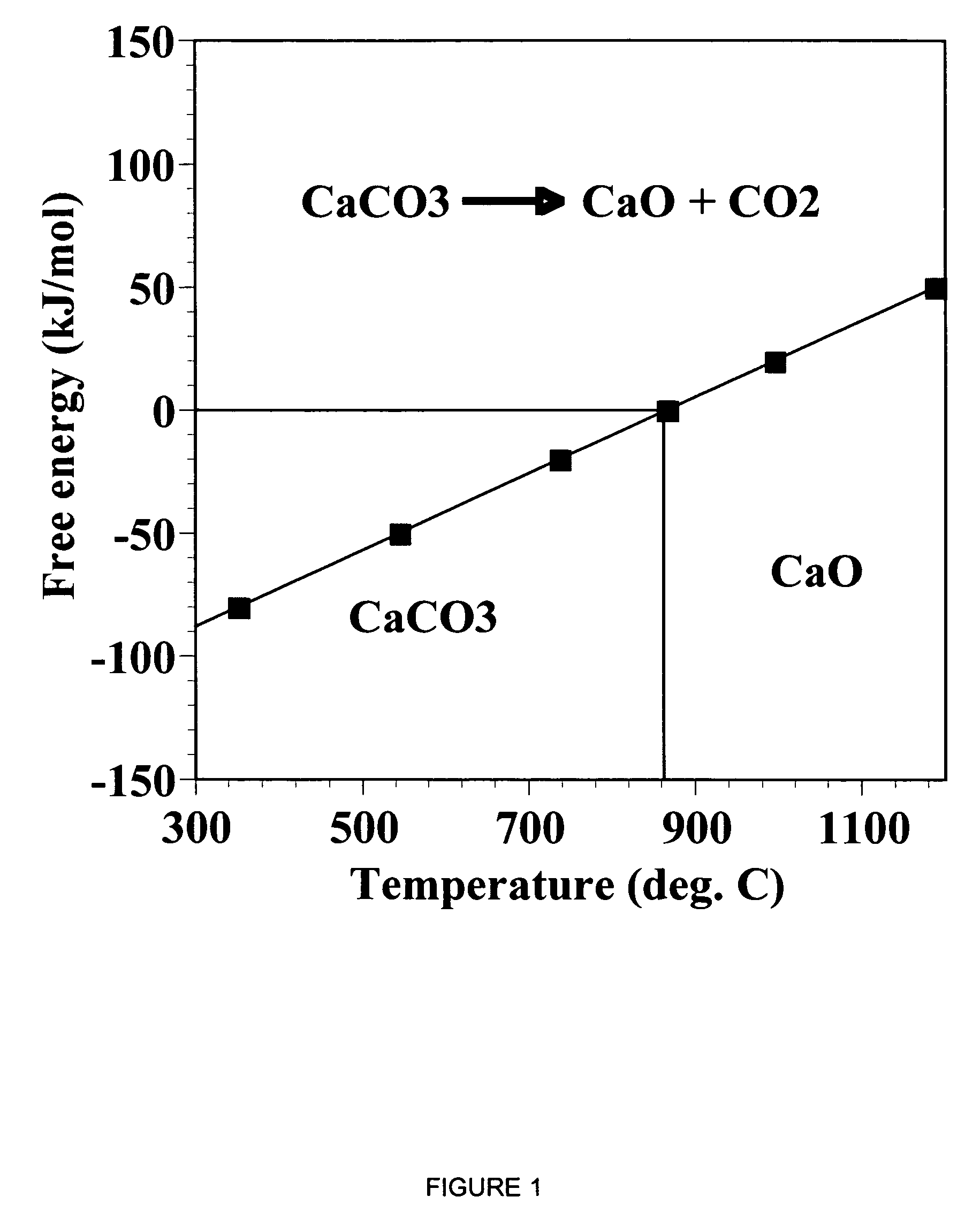
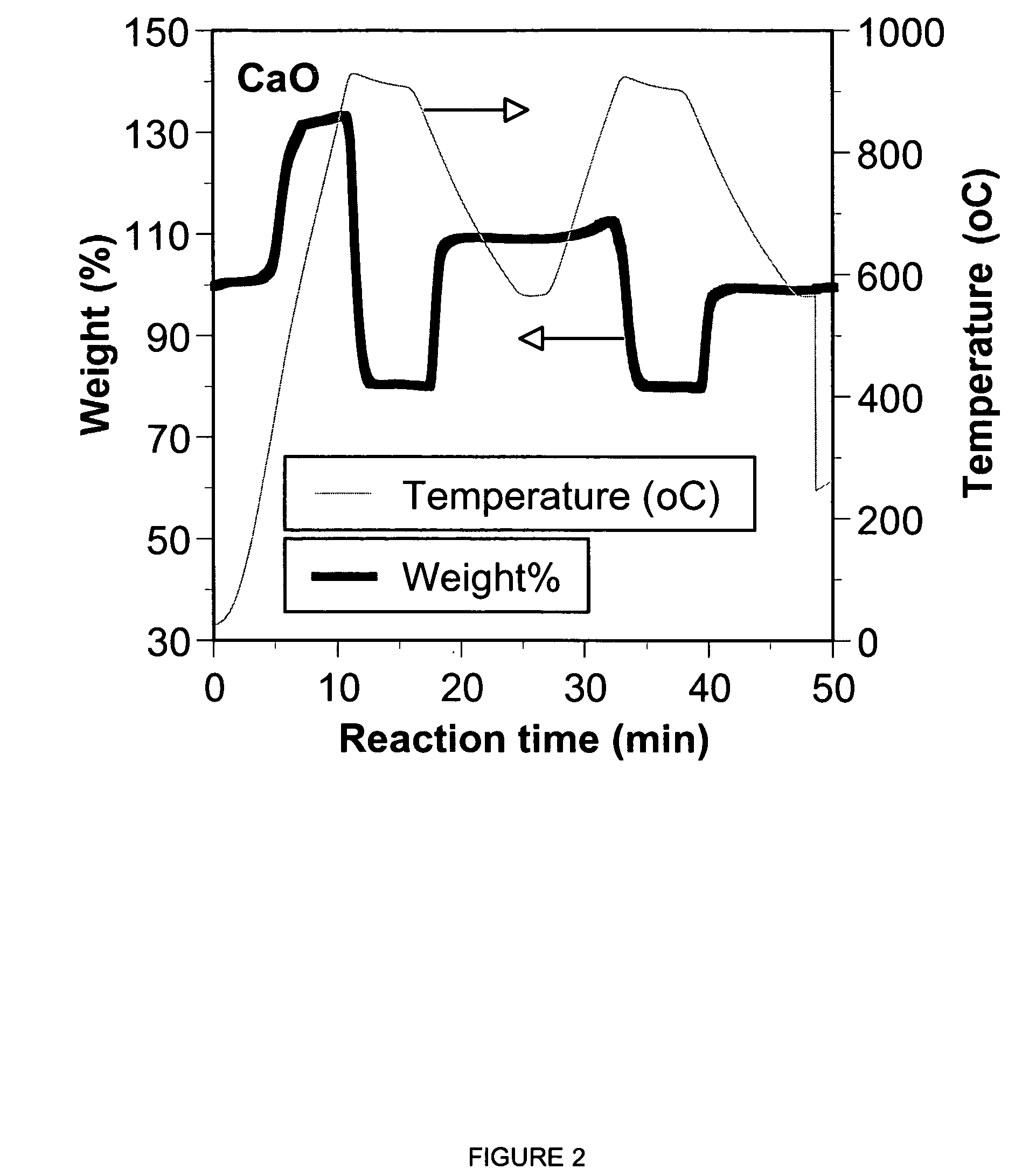
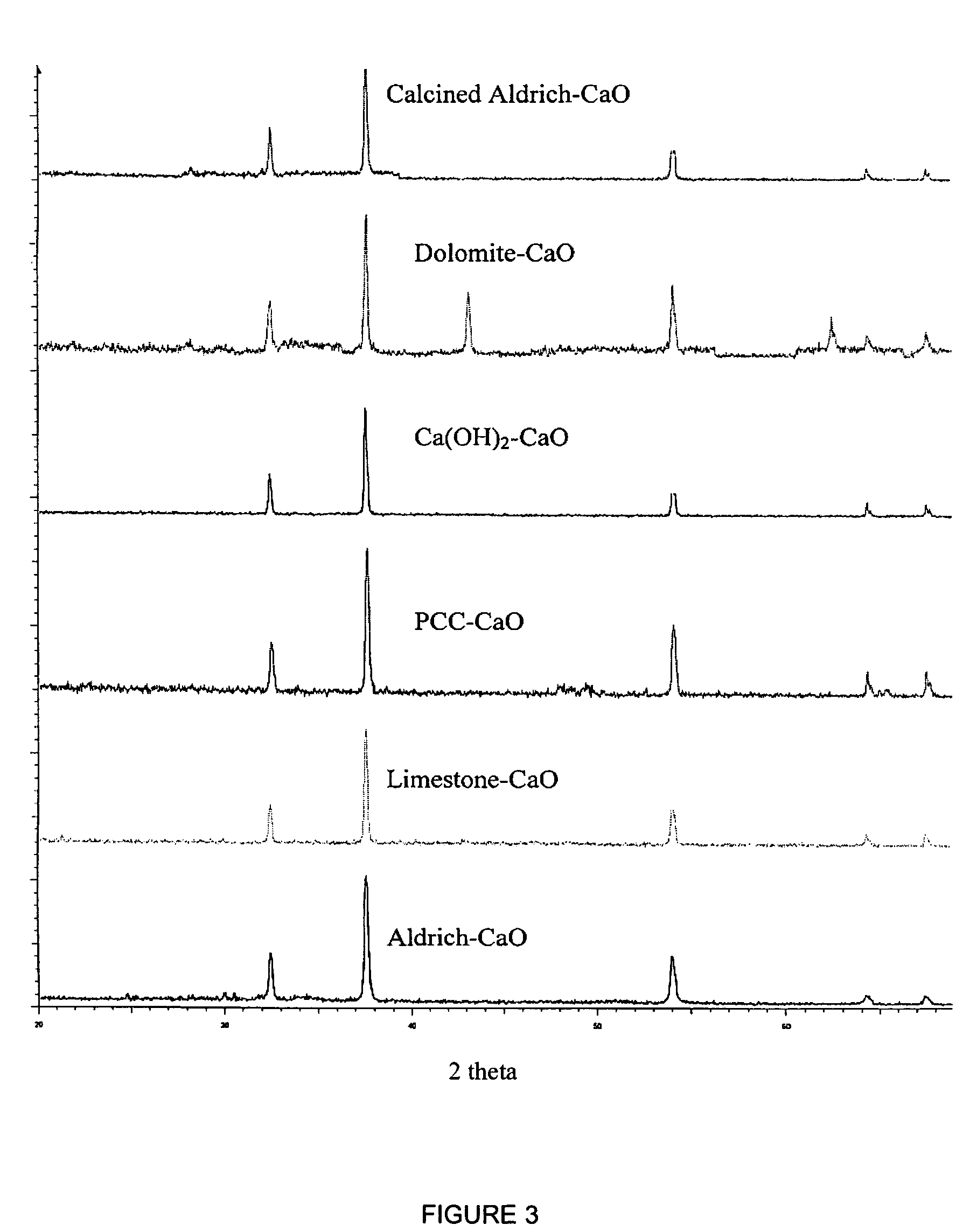
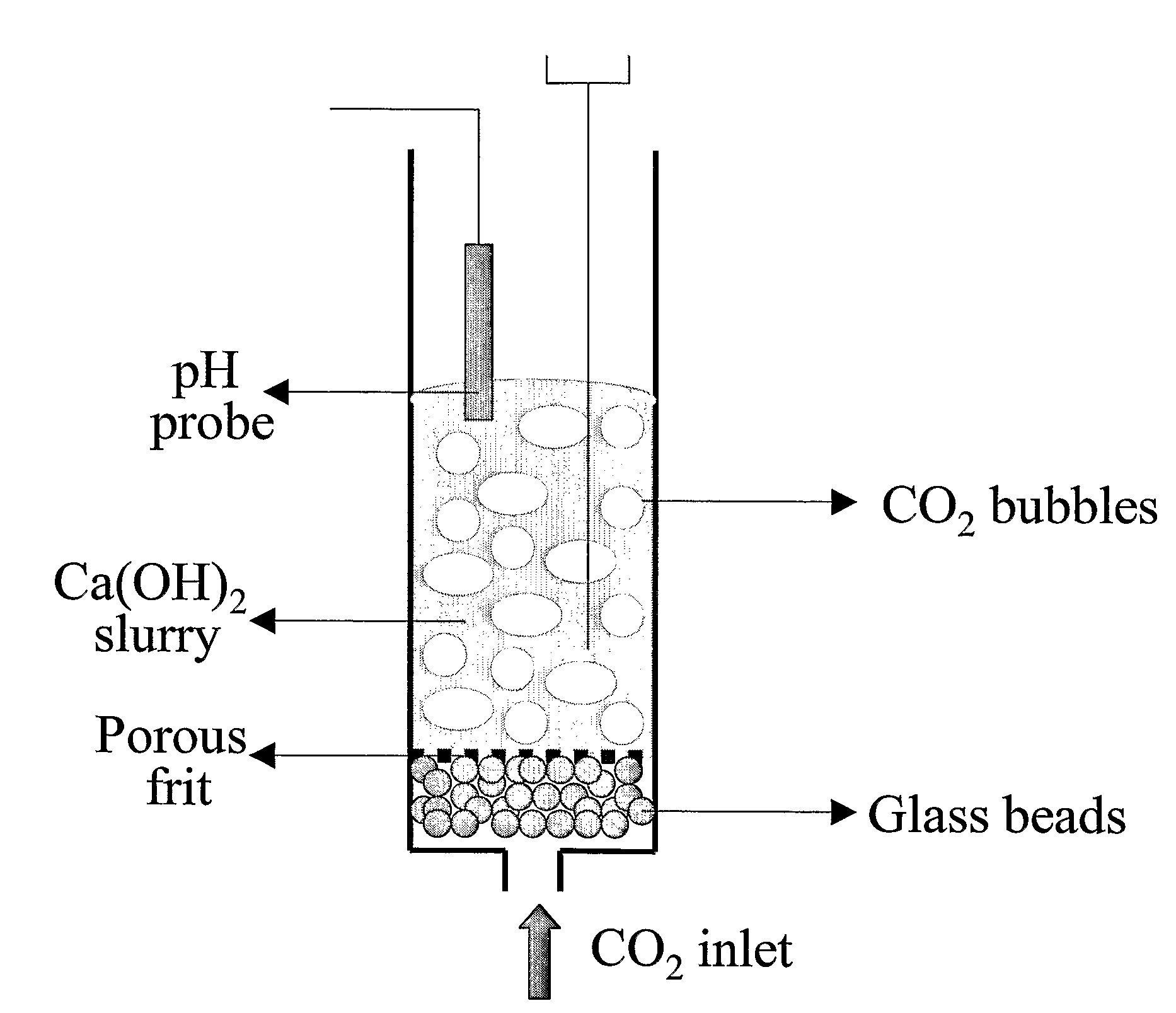
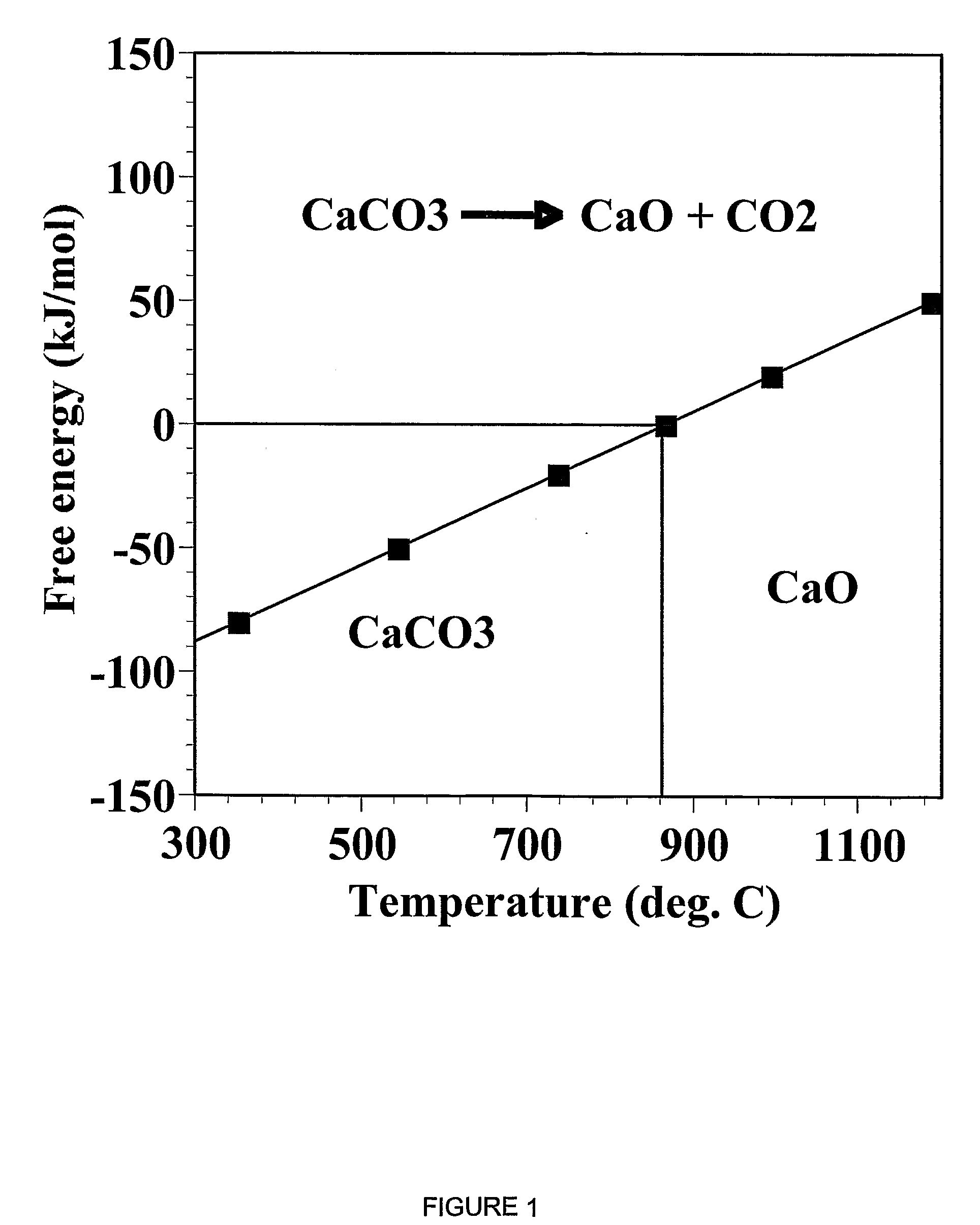
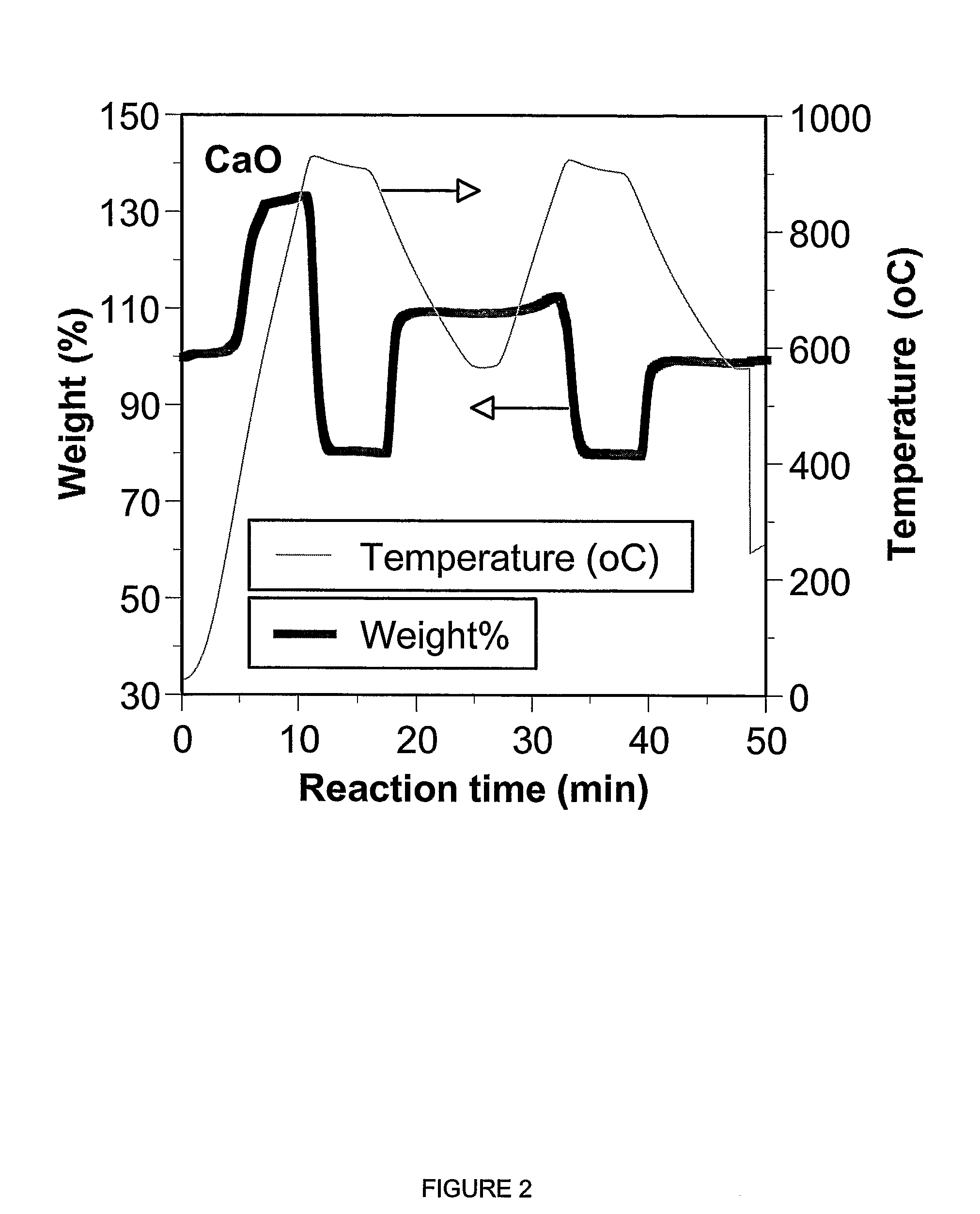
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide from a multicomponent gas mixture. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases by its reaction with metal oxides. The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate. Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Three-Train Catalytic Gasification Systems
InactiveUS20090324459A1Reduce moisture contentCombustible gas catalytic treatmentGaseous fuelsUnit operationAmmonia
Systems to convert a carbonaceous feedstock into a plurality of gaseous products are described. The systems include, among other units, three separate gasification reactors for the gasification of a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of an alkali metal catalyst into the plurality of gaseous products including at least methane. Each of the gasification reactors may be supplied with the feedstock from a single or separate catalyst loading and / or feedstock preparation unit operations. Similarly, the hot gas streams from each gasification reactor may be purified via their combination at a heat exchanger, acid gas removal or methane removal unit operations. Product purification may comprise trace contaminant removal units, ammonia removal and recovery units, and sour shift units.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Separation of Carbon Dioxide (Co2) From Gas Mixtures By Calcium Based Reaction Separation (Cars-Co2) Process
InactiveUS20080233029A1Good repeatabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCombustible gas catalytic treatmentSorbentTransformation ratio
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from a multicomponent gas mixture to provide a gaseous stream depleted in CO2 compared to the inlet CO2 concentration in the stream. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases (such as flue gas / fuel gas) by its reaction with metal oxides (such as calcium oxide). The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 (CaRS—CO2) process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide (CaO) in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCOa). Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent and the evolution of a concentrated stream of CO2. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This carbonation-calcination cycle forms the basis of the CaRS—CO2 process. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, developed by a process detailed elsewhere, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Integrated hydromethanation combined cycle process
InactiveUS20110062721A1Easy to understandCombustible gas catalytic treatmentHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHydrogenCombustible gas
The present invention relates to an integrated process for preparing combustible gaseous products via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, a hydromethanation catalyst and optionally oxygen, and generating electrical power from those combustible gaseous products as well as a hydrogen and / or methane by-product stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
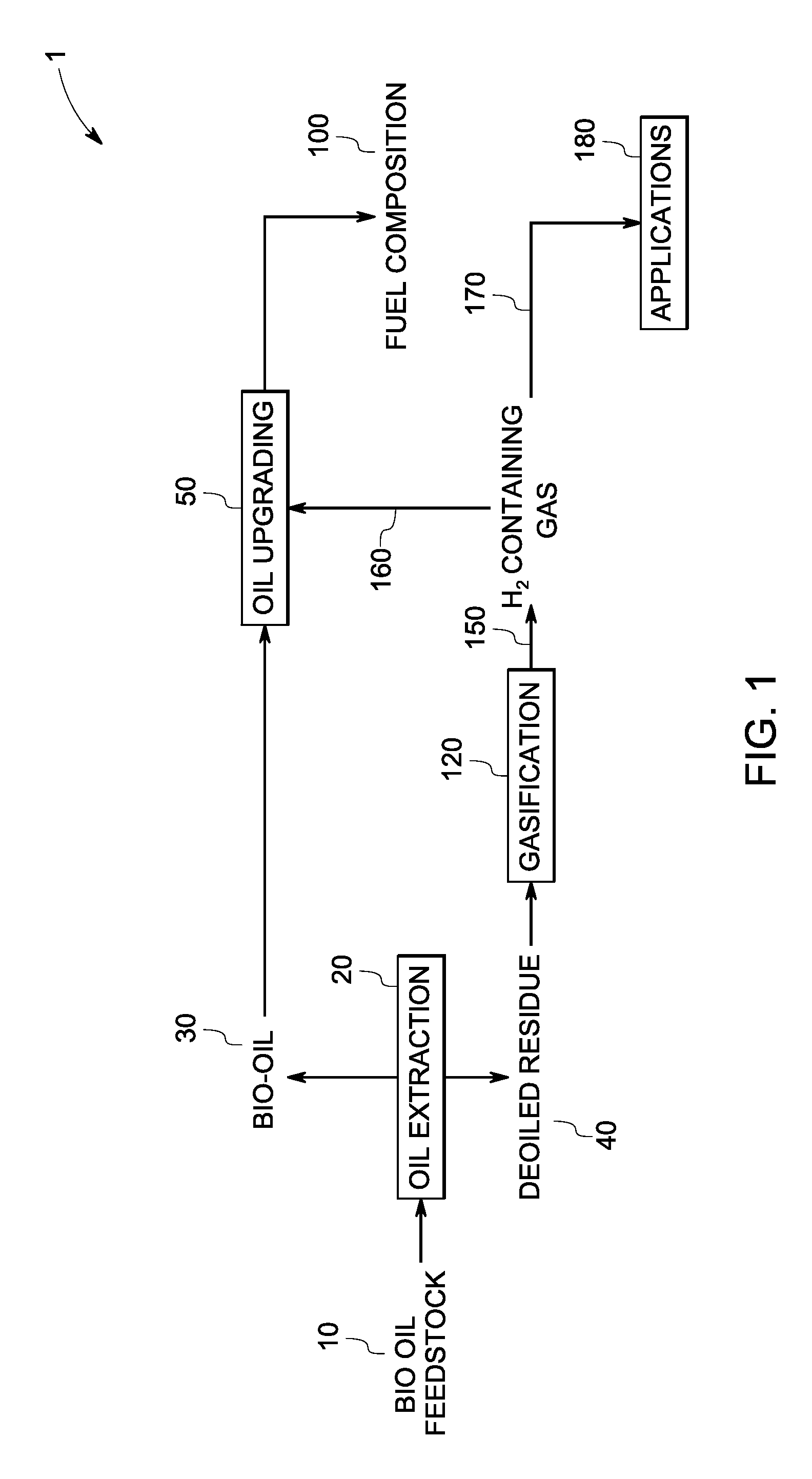
Integrated system and method for producing fuel composition from biomass
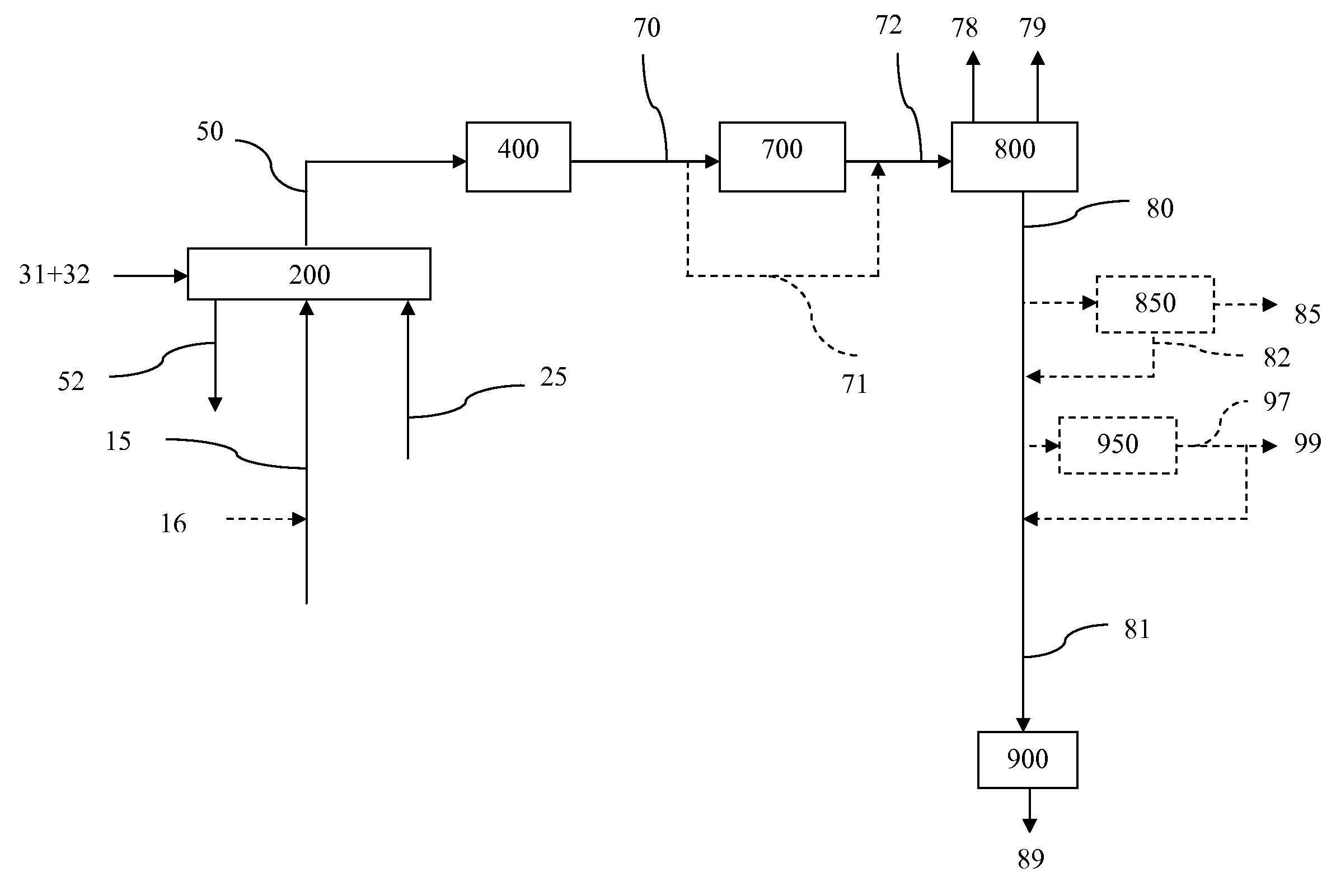
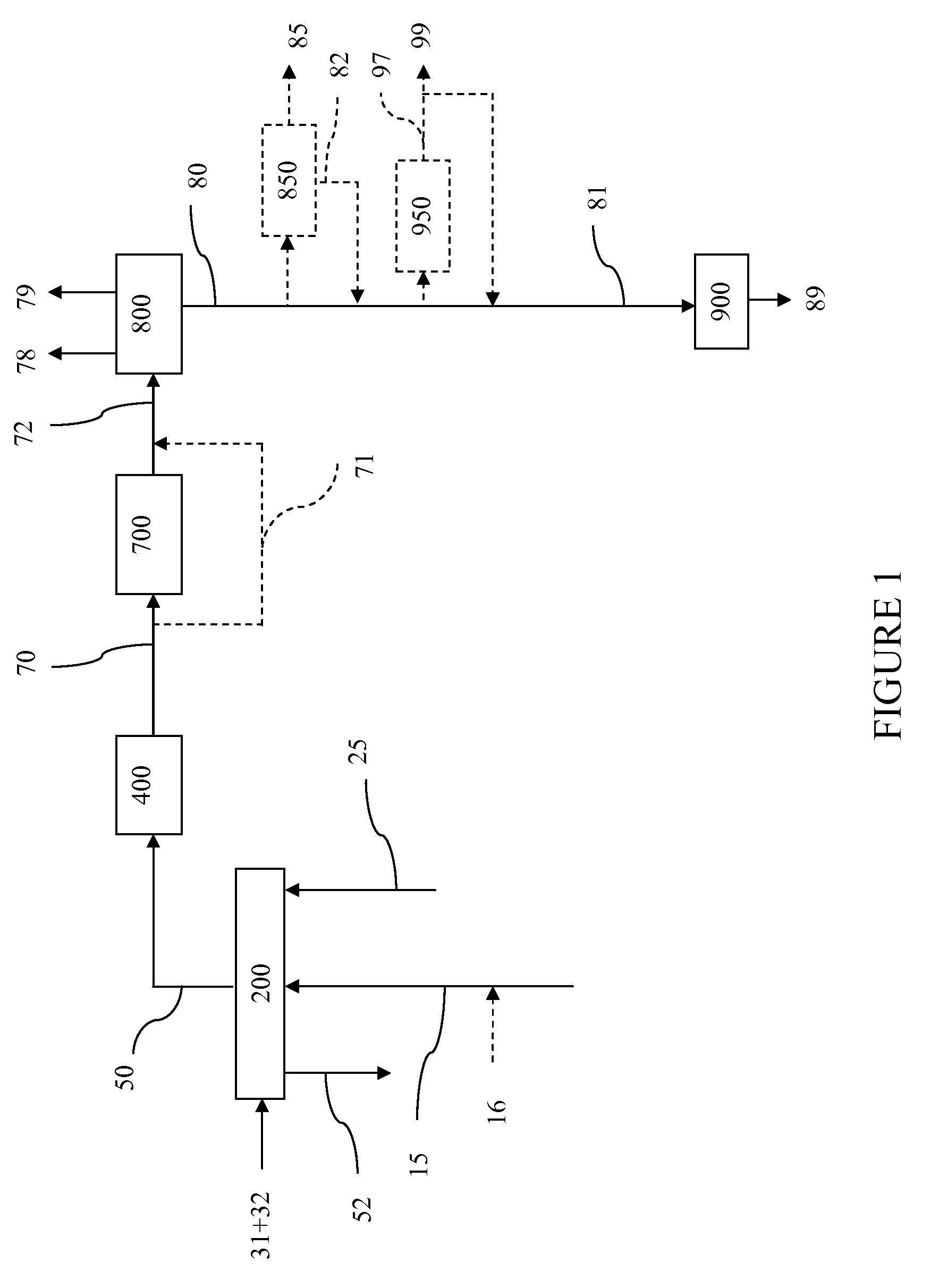
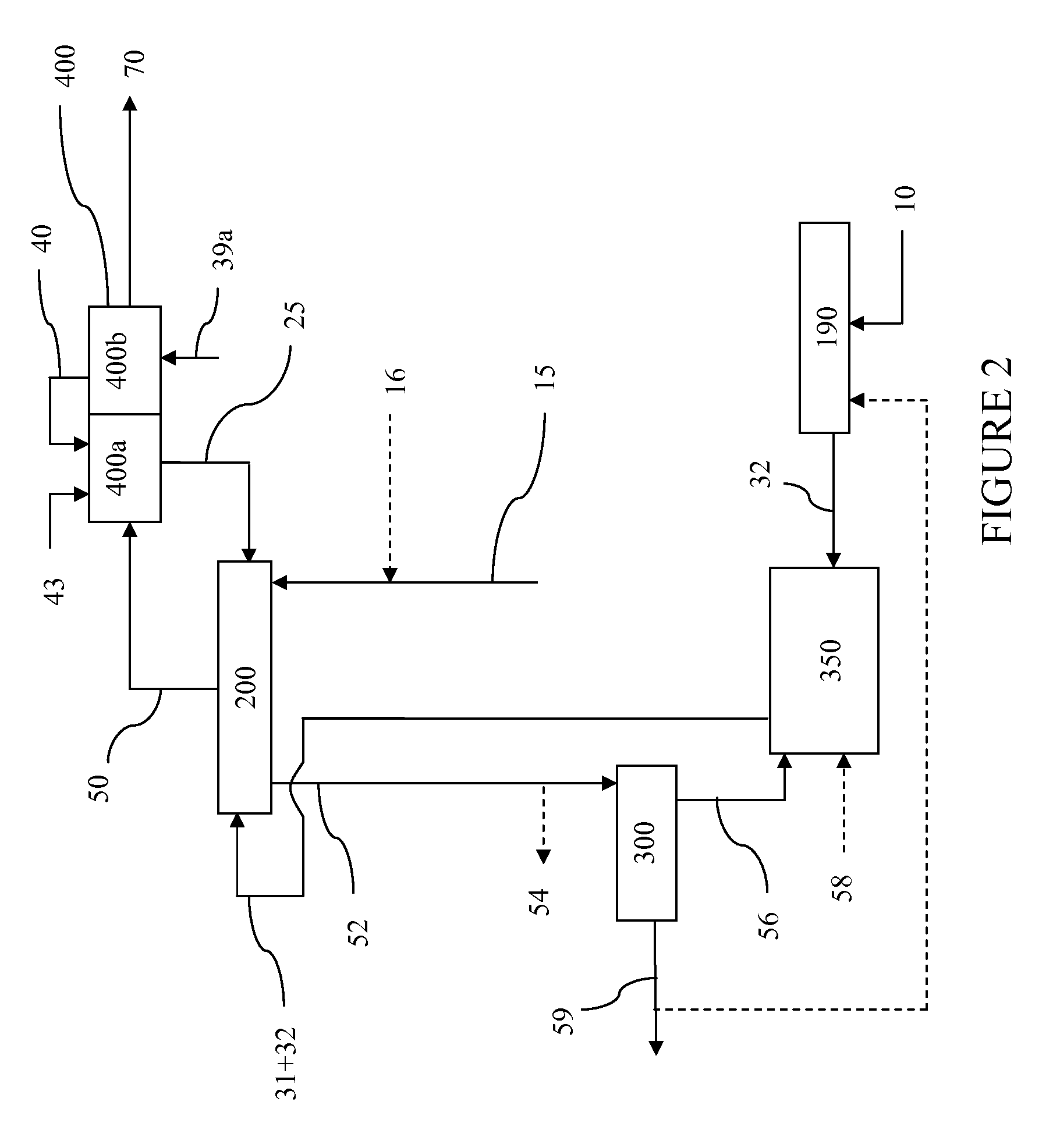
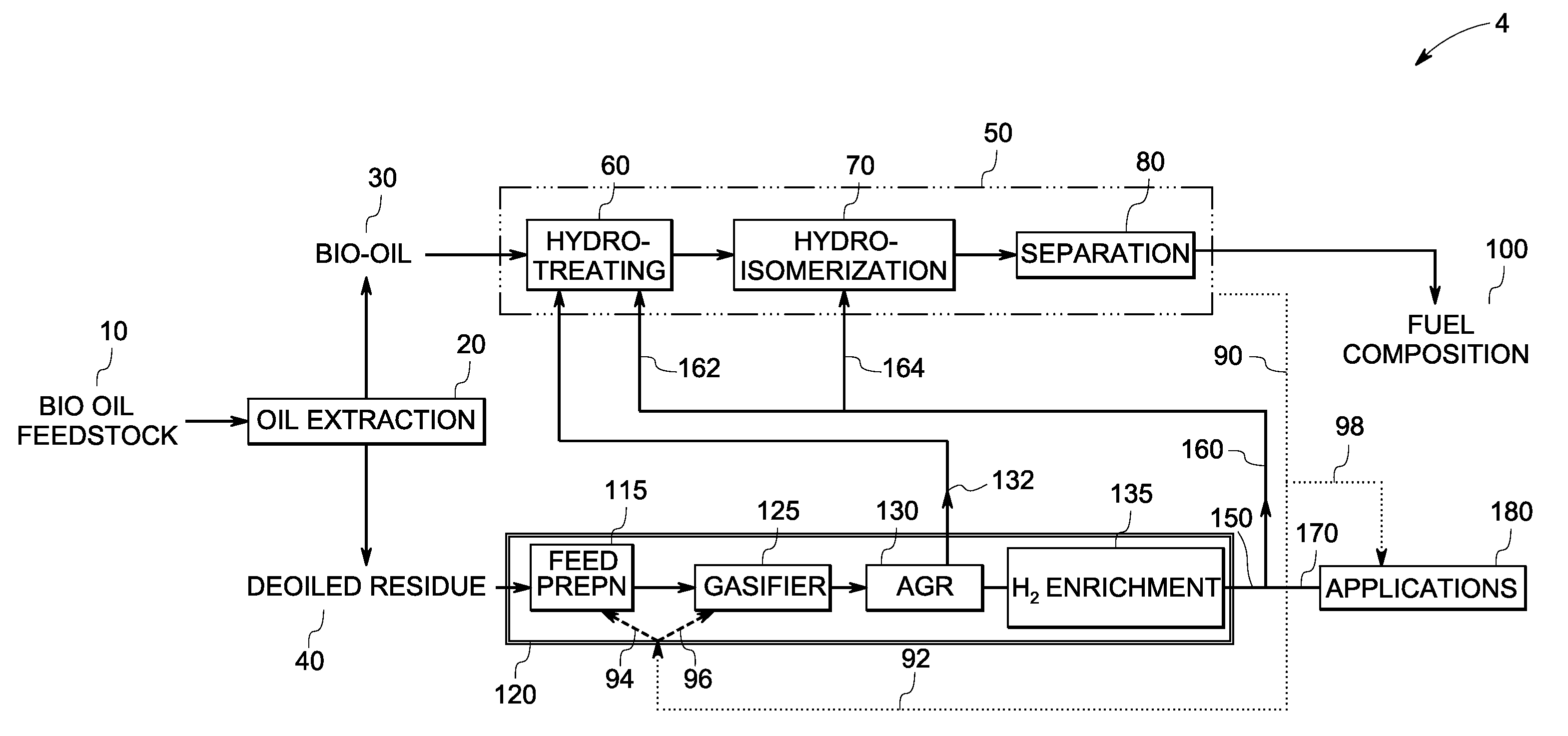
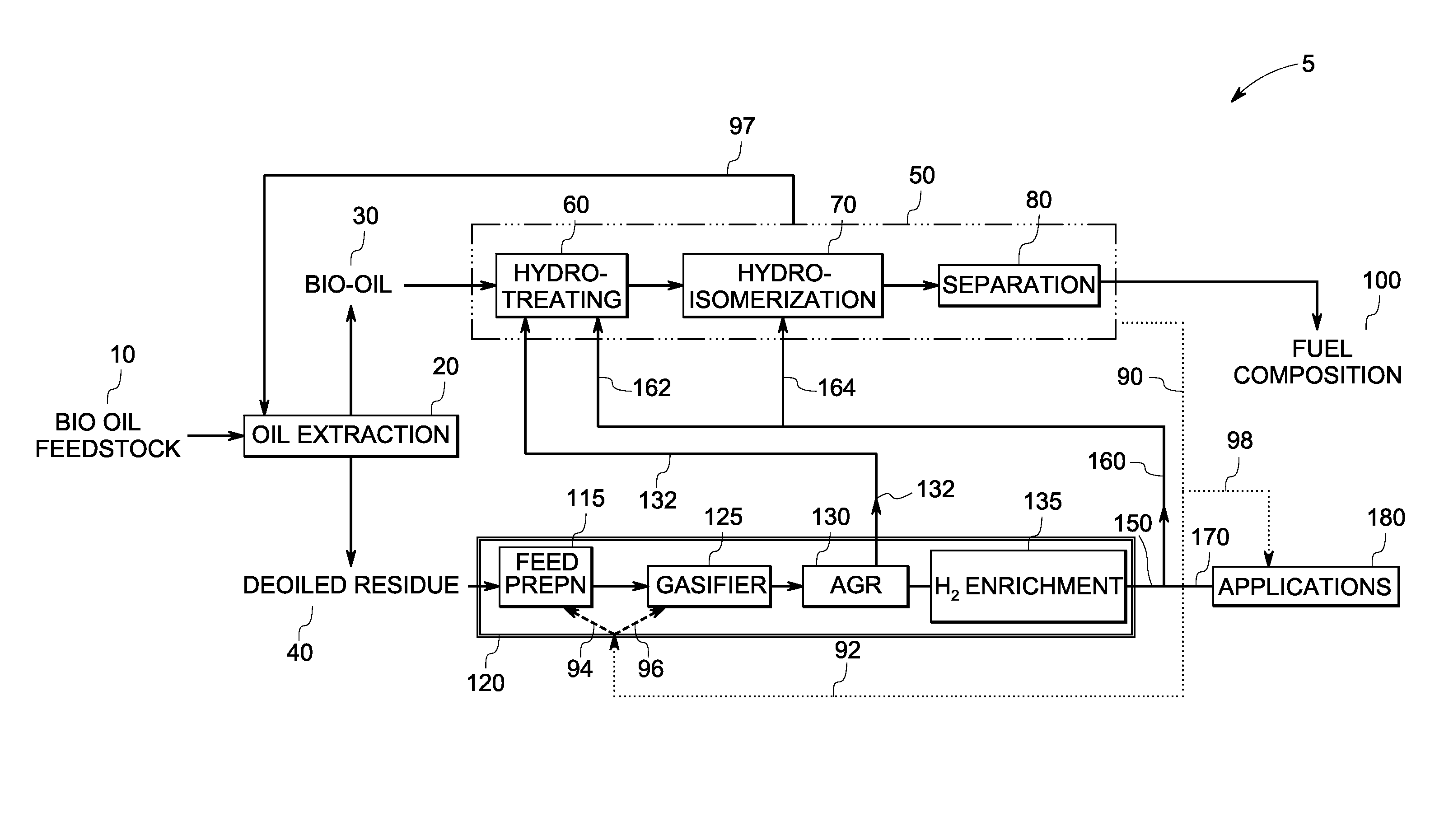
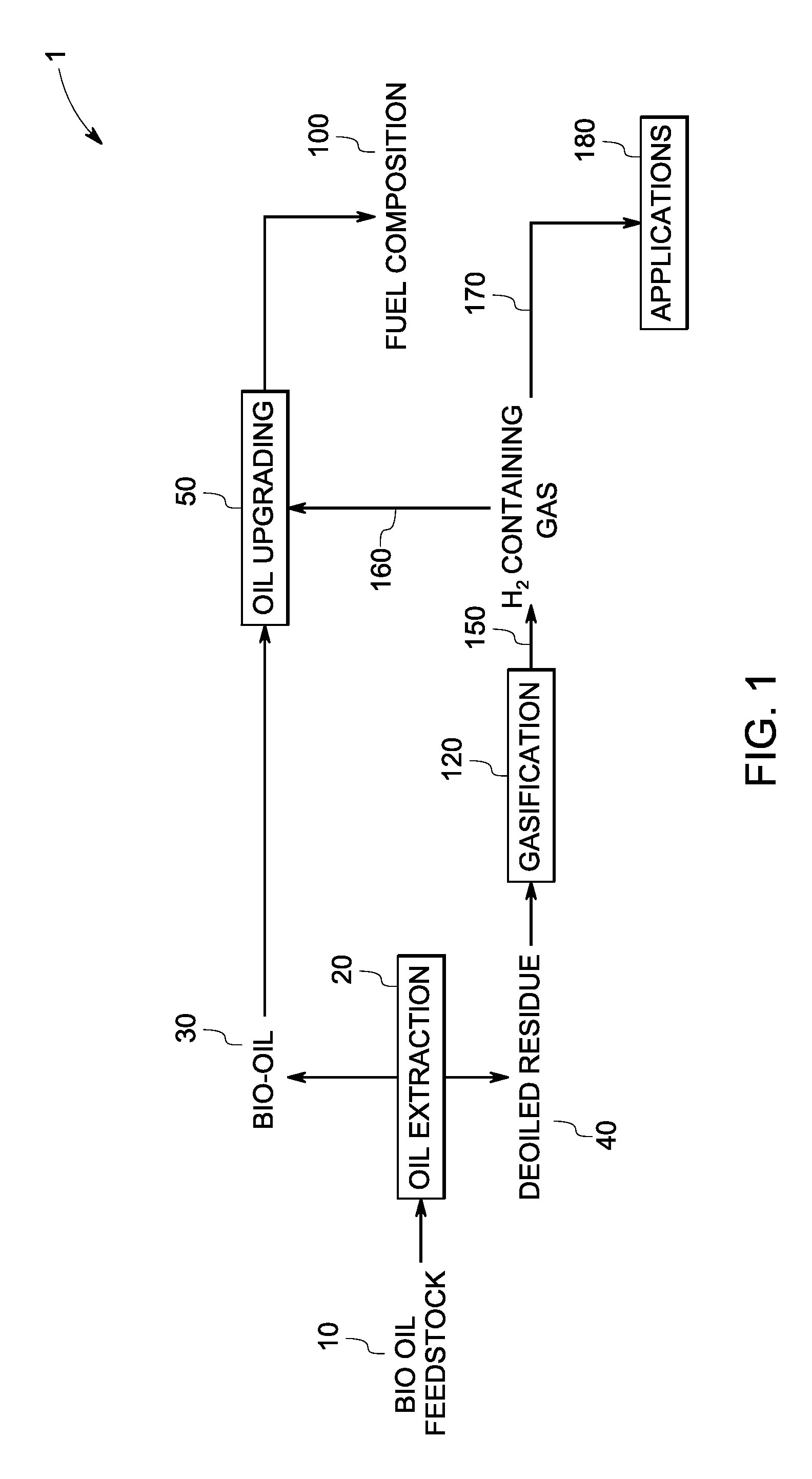
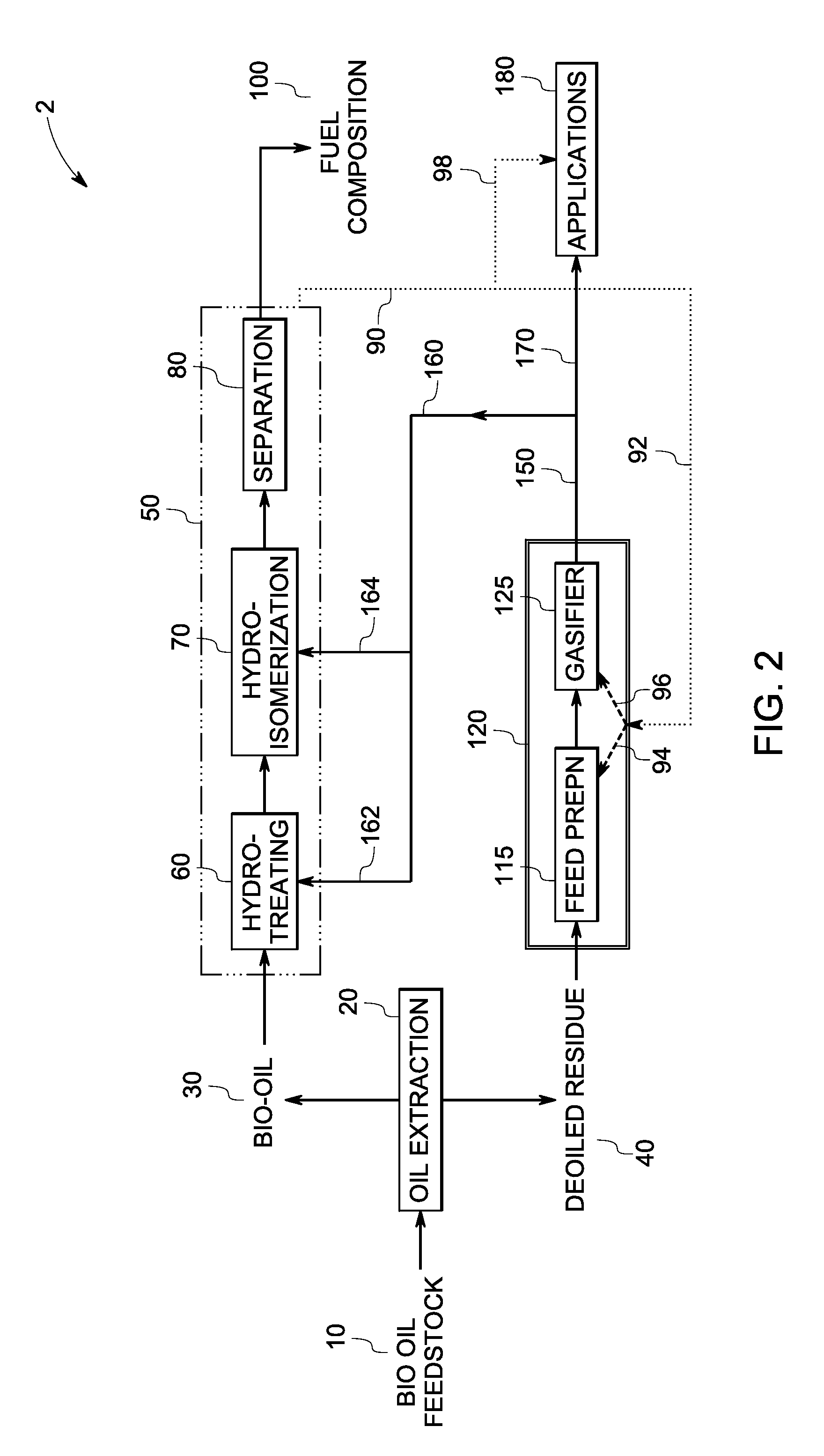
InactiveUS7888540B2Reduce formationHydrocarbon by isomerisationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentHydrogenTar
A method of producing a fuel composition from a bio-oil feedstock is provided, wherein the bio-oil feedstock is subjected to a step of oil extraction to produce a bio-oil and deoiled residue. At least a portion of the deoiled residue is gasified to produce a hydrogen-containing gas. The bio-oil is subjected to an upgrading process to ultimately produce a fuel composition. At least a part of the hydrogen-containing gas produced in the gasification of deoiled residue is used in the upgrading process of producing a fuel composition. The upgrading process, which can involve hydro-treating, hydroisomerization and at least one separation step, produces light hydrocarbons in addition to the product fuel composition. The light hydrocarbons can be used in the gasification operation, e.g., to reduce tar formation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
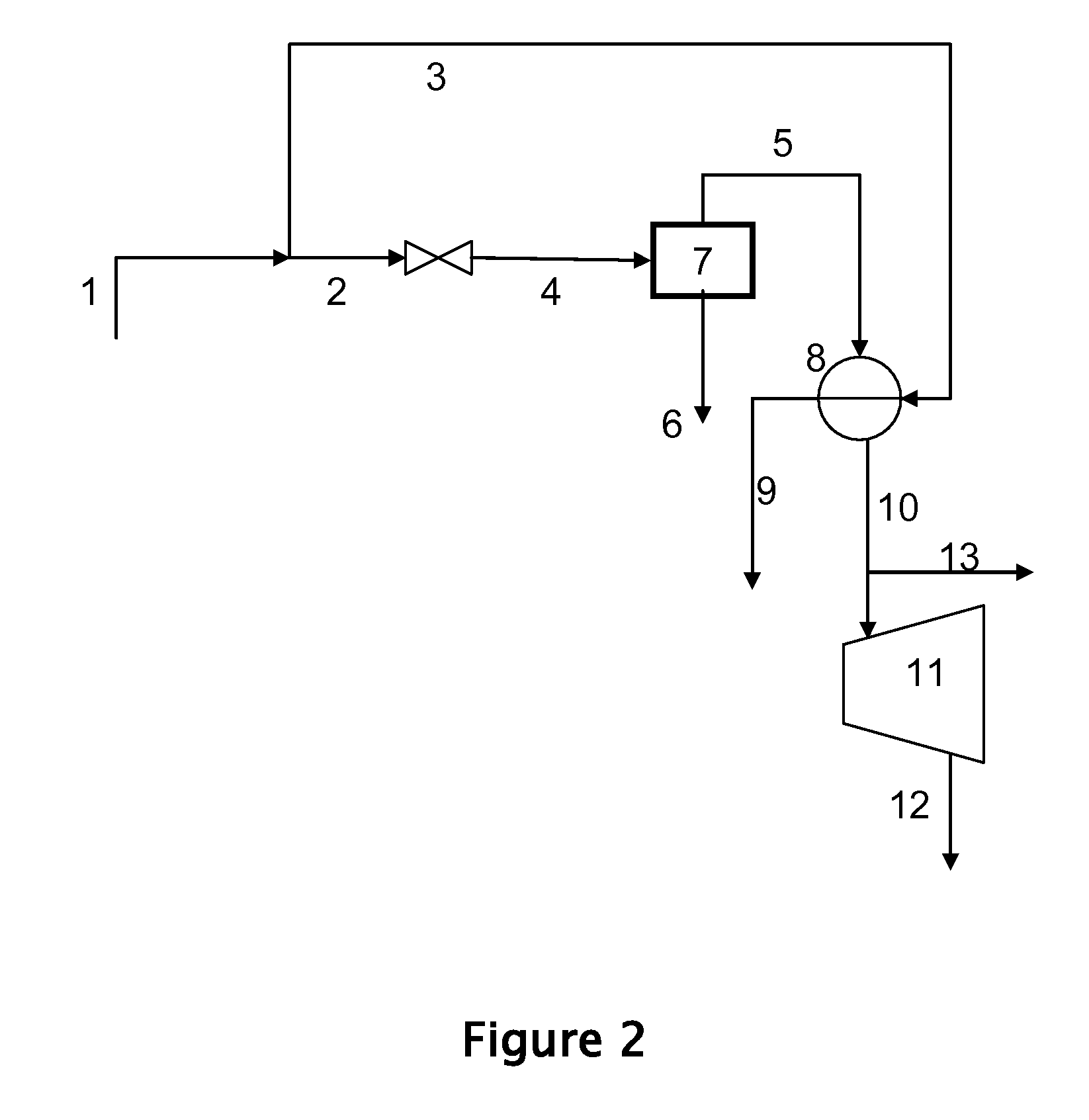
Process for superheated steam
InactiveUS20070245736A1Chemical industryCombustible gas catalytic treatmentElectricityPartial oxidation
Disclosed is a process for the preparation of superheated of steam by transferring heat from at least a fraction of a high pressure steam to a lower pressure steam to produce a superheated, lower pressure steam. The high pressure steam can be generated by recovering heat from a heat producing chemical process such as, for example, the partial oxidation of carbonaceous materials. The lower pressure steam can be generated by reducing the pressure of a portion of the high pressure steam or by recovering heat from one or more chemical processes. The superheated, lower pressure steam may used to generate electricity in a steam turbine, operate a steam turbine drive, or as a heat source. Also disclosed is a process for driving a steam turbine using superheated steam produced by the process of the invention.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Integrated hydromethanation combined cycle process
InactiveUS20110062722A1Increase the amount of carbonIncrease volumeCombustible gas catalytic treatmentHydrogen/synthetic gas productionChemistryElectric energy
The present invention relates to an integrated process for preparing combustible gaseous products via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, a hydromethanation catalyst and optionally oxygen, and generating electrical power from those combustible gaseous products.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
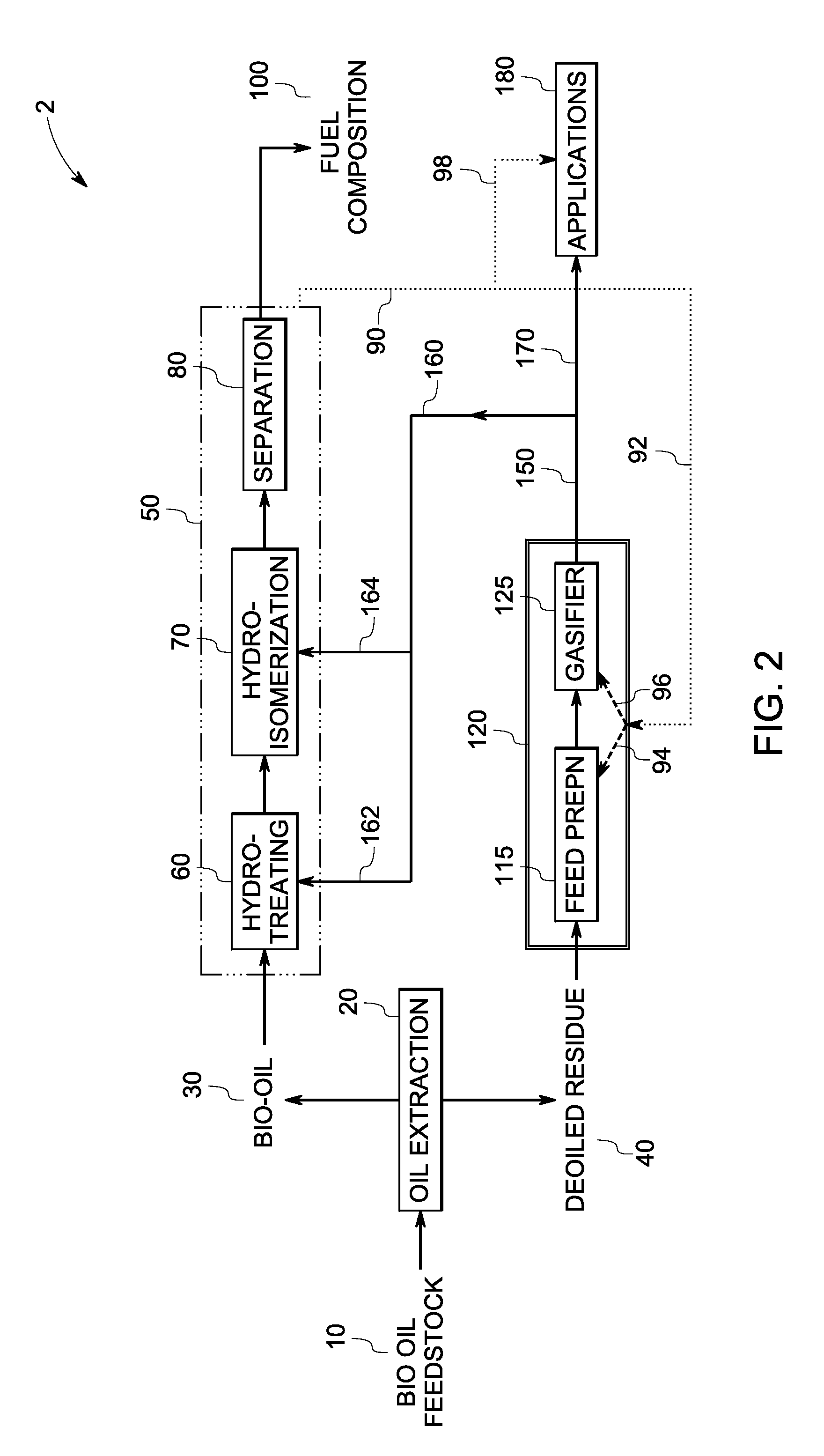
Integrated system and method for producing fuel composition from biomass
InactiveUS20090259082A1Reduce formationHydrocarbon by isomerisationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentThermodynamicsProcess engineering
A method of producing a fuel composition from a bio-oil feedstock is provided, wherein the bio-oil feedstock is subjected to a step of oil extraction to produce a bio-oil and deoiled residue. At least a portion of the deoiled residue is gasified to produce a hydrogen-containing gas. The bio-oil is subjected to an upgrading process to ultimately produce a fuel composition. At least a part of the hydrogen-containing gas produced in the gasification of deoiled residue is used in the upgrading process of producing a fuel composition. The upgrading process, which can involve hydro-treating, hydroisomerization and at least one separation step, produces light hydrocarbons in addition to the product fuel composition. The light hydrocarbons can be used in the gasification operation, e.g., to reduce tar formation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Processes For Hydromethanation Of A Carbonaceous Feedstock
ActiveUS20100292350A1Increase oxygenIncrease the amount of carbonOrganic compound preparationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentPhysical chemistryProcess engineering
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular methane, via the catalytic hydromethanation of a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of steam, syngas and an oxygen-rich gas stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Partial oxidation reaction with closed cycle quench
ActiveUS8776532B2Prevent metal dustingReaction is slowSolidificationLiquefactionPartial oxidationCombustor
The present disclosure relates to a power production system that is adapted to achieve high efficiency power production with complete carbon capture when using a solid or liquid hydrocarbon or carbonaceous fuel. More particularly, the solid or liquid fuel first is partially oxidized in a partial oxidation reactor. The resulting partially oxidized stream that comprises a fuel gas is quenched, filtered, cooled, and then directed to a combustor of a power production system as the combustion fuel. The partially oxidized stream is combined with a compressed recycle CO2 stream and oxygen. The combustion stream is expanded across a turbine to produce power and passed through a recuperator heat exchanger. The expanded and cooled exhaust stream is scrubbed to provide the recycle CO2 stream, which is compressed and passed through the recuperator heat exchanger and the POX heat exchanger in a manner useful to provide increased efficiency to the combined systems.
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
Processes for Hydromethanation of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
ActiveUS20100287835A1Increase the amount of carbonIncrease volumeHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrogen separationMethanationOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular methane, via the hydromethanation of a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of steam, syngas, a hydromethanation catalyst and an oxygen-rich gas stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
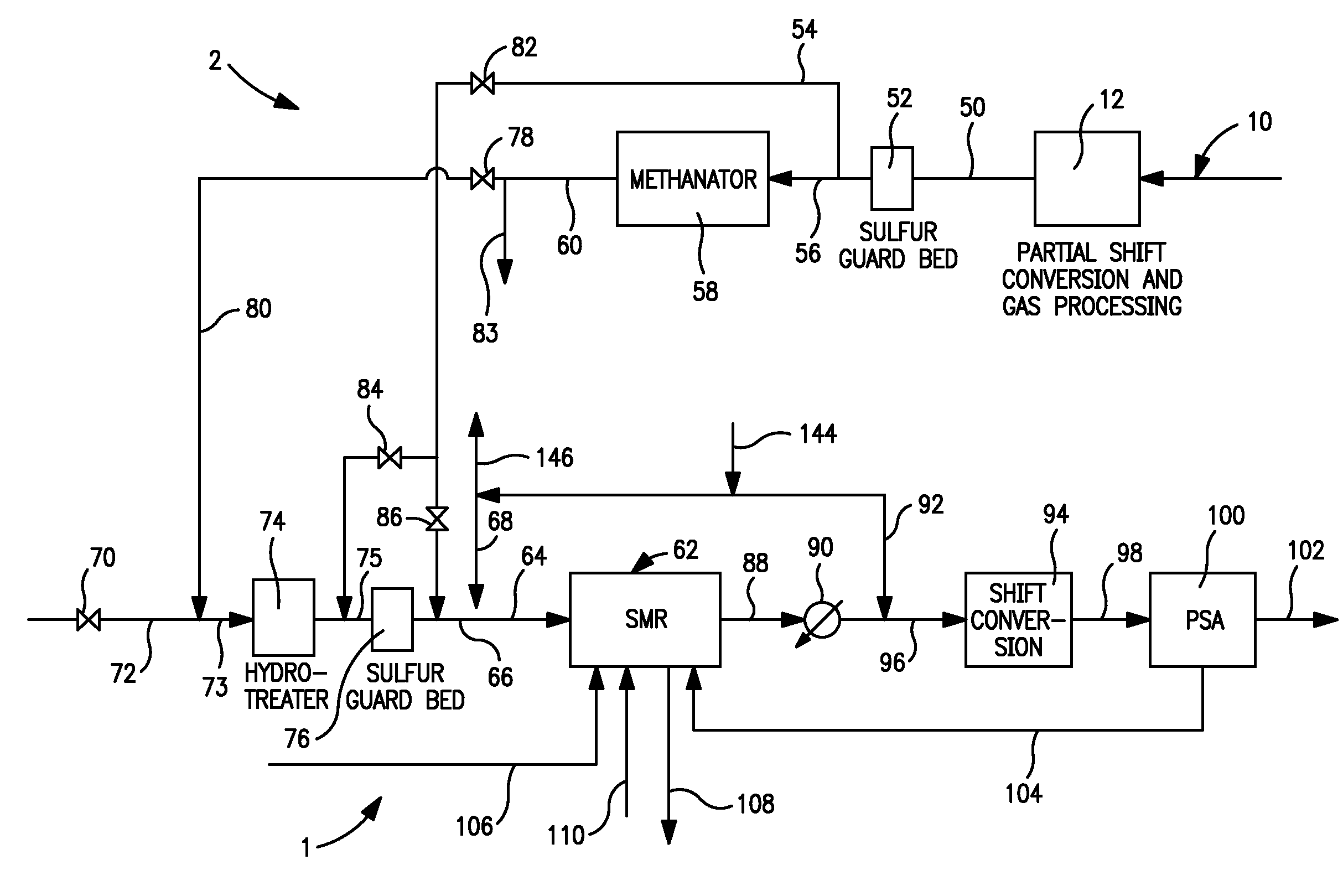
Hydrogen production method
ActiveUS7931888B2Maximize productionSteam flow rate essentially constantHydrogenCombustible gas catalytic treatmentMethane reformerMethane
A method of producing a hydrogen product stream in which a steam stream is reacted with a hydrocarbon containing stream within a steam methane reformer. The resulting product stream is subjected to a water gas shift reaction and then to pressure swing adsorption to produce the hydrogen product stream. The hydrocarbon stream is alternatively formed from a first type of feed stream made up of natural gas, refinery off-gas, naphtha or synthetic natural gas or combinations thereof and a second type that is additionally made up of a hydrogen and carbon monoxide containing gas. During use of both of the types of feed streams, the flow rate of the steam stream is not substantially changed and reformer exit temperatures of both the reactant and the flue gas side are held essentially constant.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
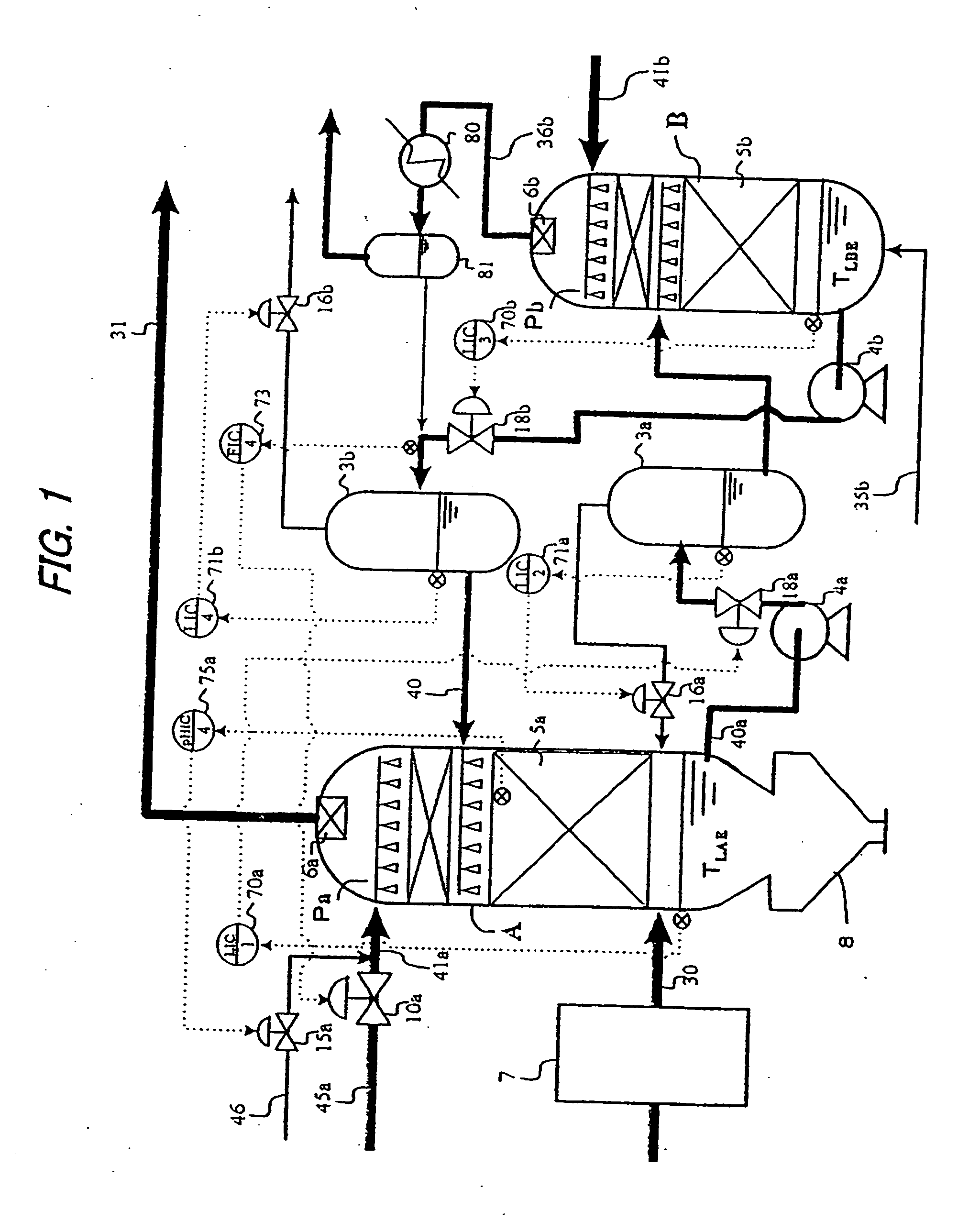
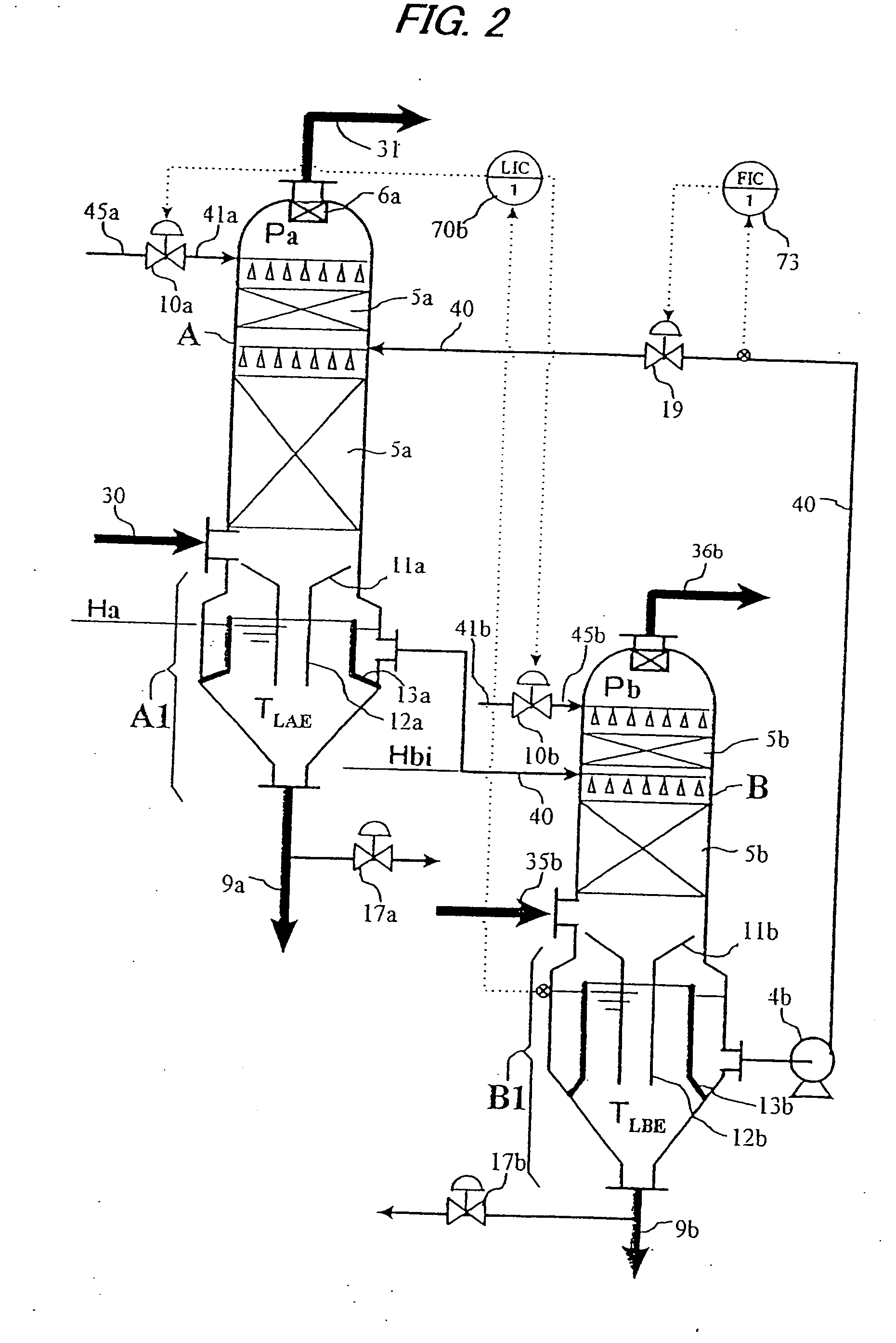
Acid gas scrubbing apparatus and method
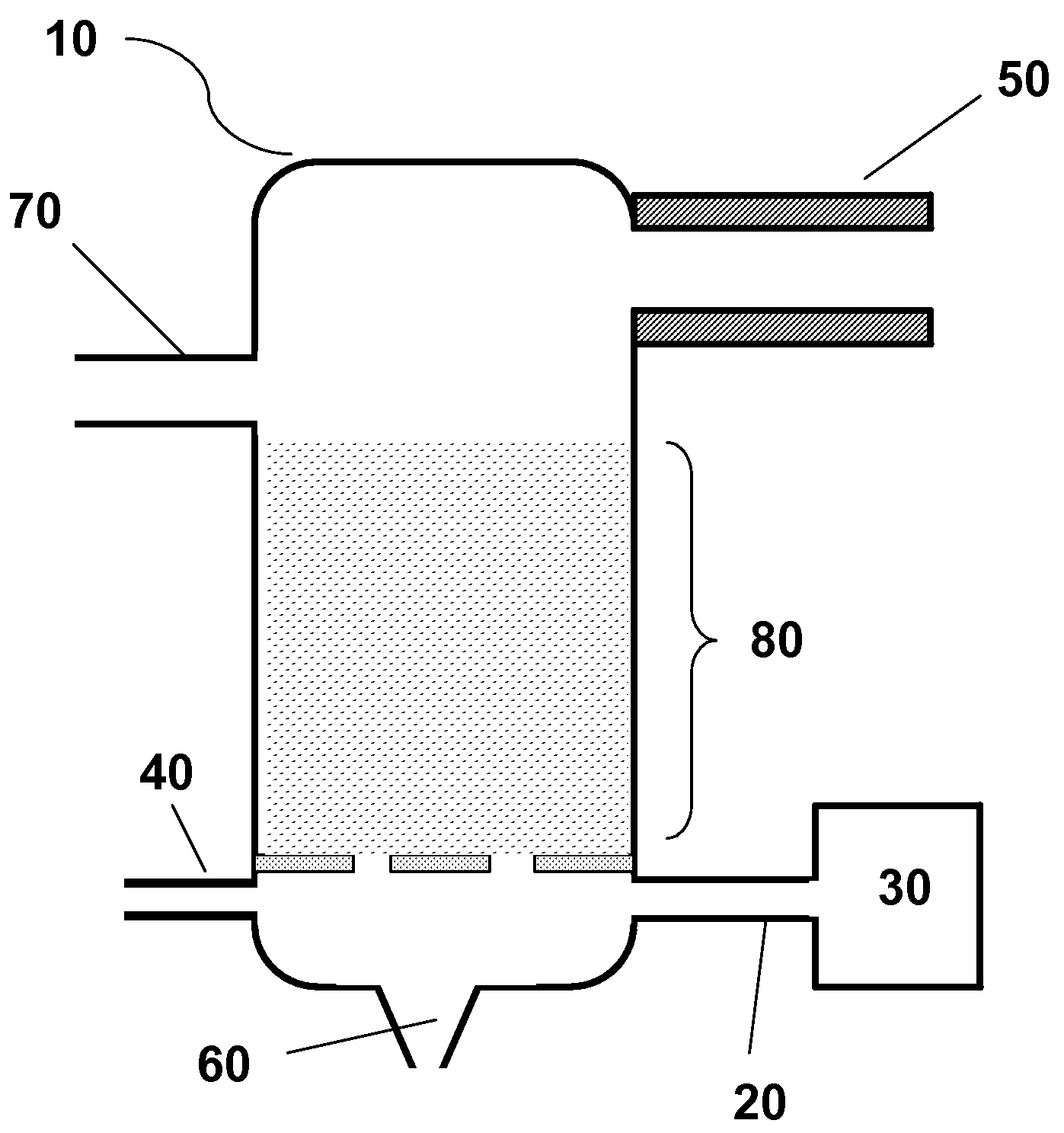
InactiveUS20050132883A1Improve energy efficiencyImprove acid gas removal capabilityUsing liquid separation agentCombustible gas catalytic treatmentScrubberCarbon dioxide
An acid gas scrubbing apparatus and method brings a gas, to be scrubbed, containing carbon dioxide into contact with a gas scrubbing liquid containing alkaline agent and cooled, and acid gases in the gas are removed. A gas scrubber removes acid gases in a gas, to be scrubbed, containing carbon dioxide by bringing the gas to be scrubbed into contact with a gas scrubbing liquid containing alkaline agent. A scrubbing liquid regenerator regenerates and cools the gas scrubbing liquid by bringing the gas scrubbing liquid into contact with a regenerating gas having components different from the gas scrubbing liquid and the gas to be scrubbed. A circulating device is provided between the gas scrubber and the scrubbing liquid regenerator for circulating the scrubbing liquid.
Owner:SU QINGQUAN +4
Production of liquid fuels by a concatenation of processes for treatment of a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS7214720B2Maximize conversion of carbonReduce and to upgrade naphthaThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaKerosene
The invention relates to an installation and a process for the production of liquid fuels starting from a solid feedstock that contains the organic material in which:a) the solid feedstock is subjected to a gasification stage so as to convert said feedstock into synthesis gas,b) the synthesis gas is subjected to a purification treatment,c) the purified synthesis gas is subjected to a conversion stage that comprises the implementation of a Fischer-Tropsch-type synthesis so as to convert said synthesis gas into a liquid effluent and a gaseous effluent,d) the liquid effluent is fractionated so as to obtain a gaseous fraction, a naphtha fraction, a kerosene fraction and a gas oil fraction, ande) at least a portion of the naphtha fraction is recycled in gasification stage a).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Integrated Hydromethanation Fuel Cell Power Generation
The present invention relates to processes and apparatuses for generating electrical power from certain non-gaseous carbonaceous feedstocks through the integration of catalytic hydromethanation technology with fuel cell technology.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
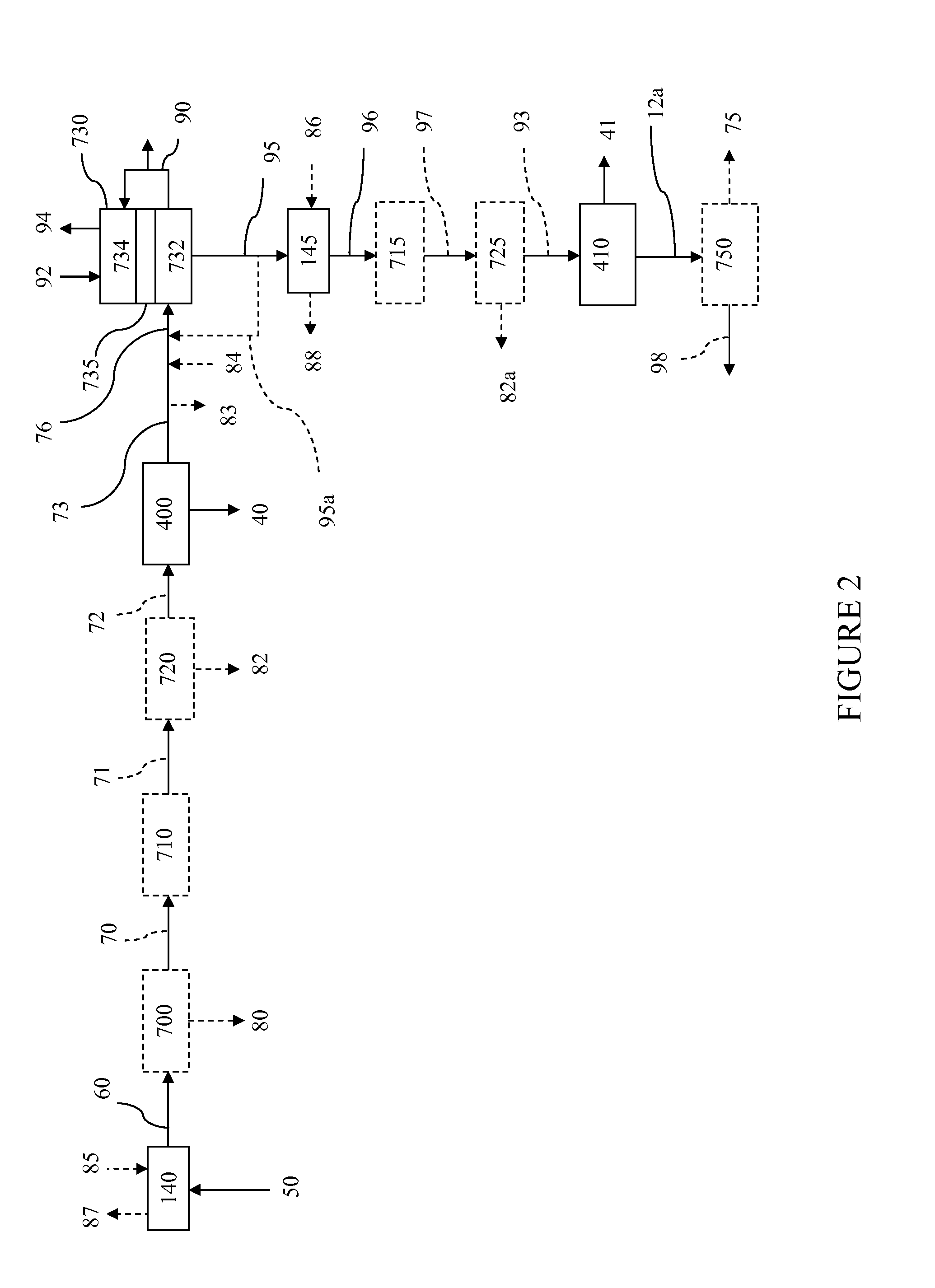
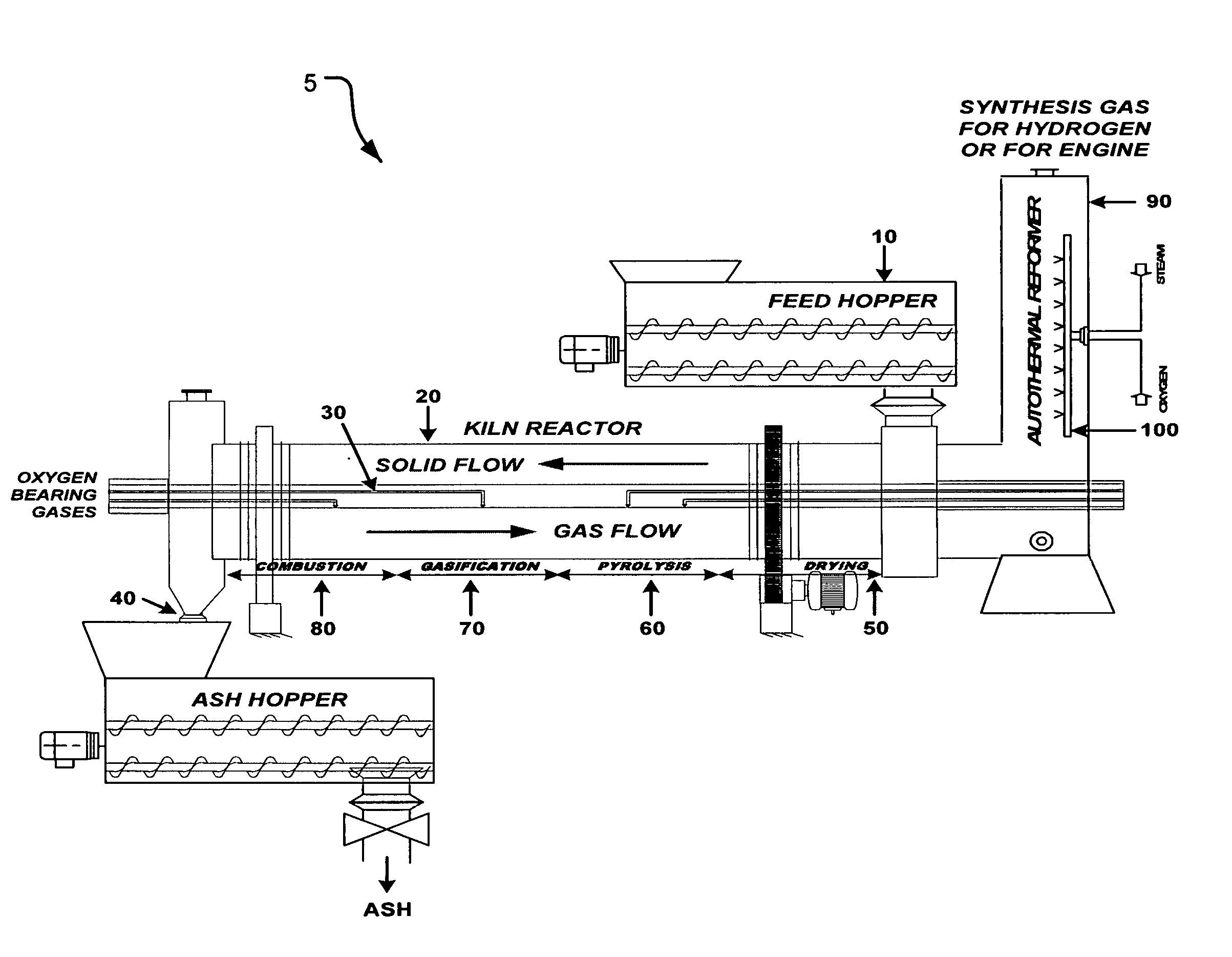
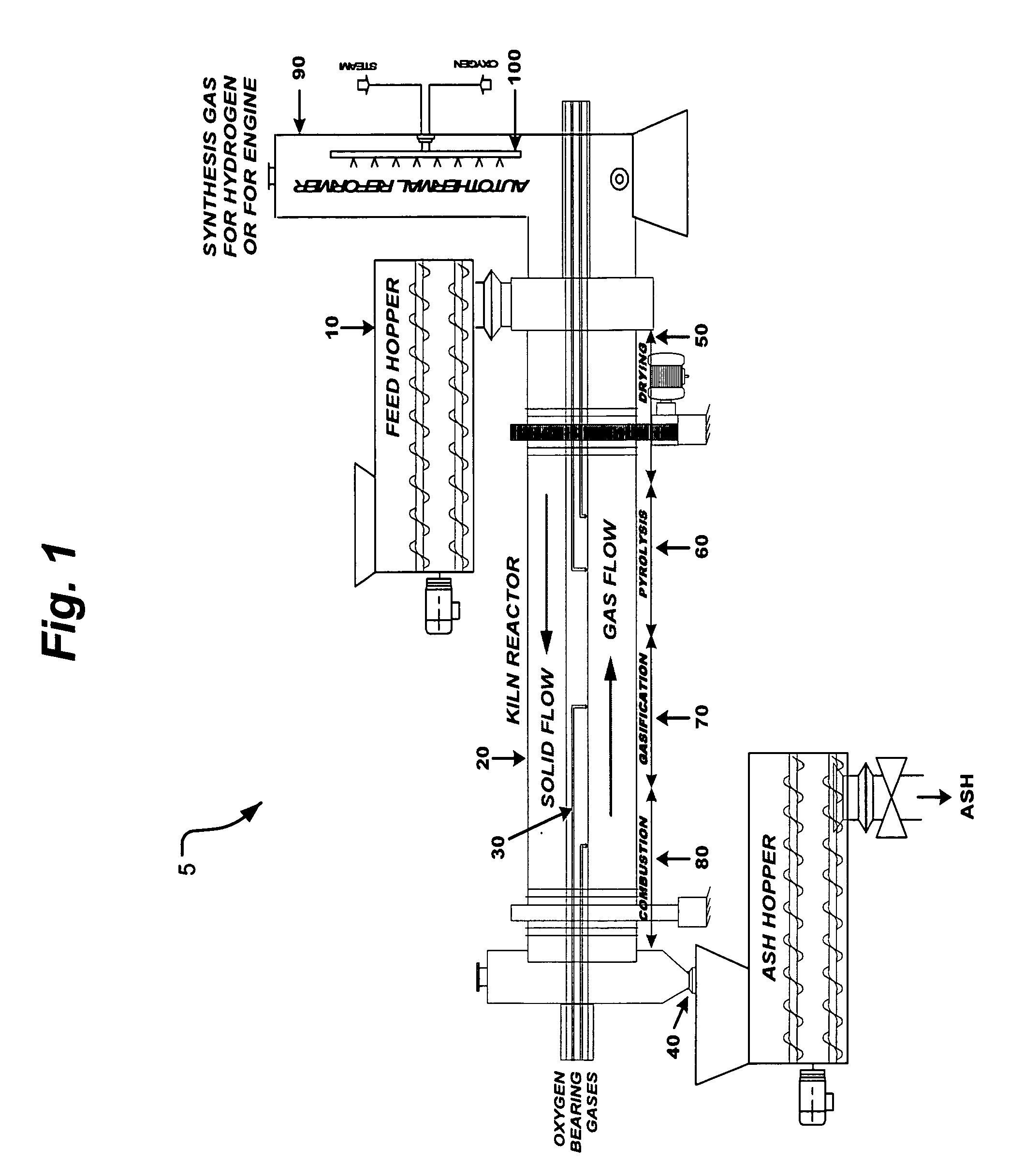
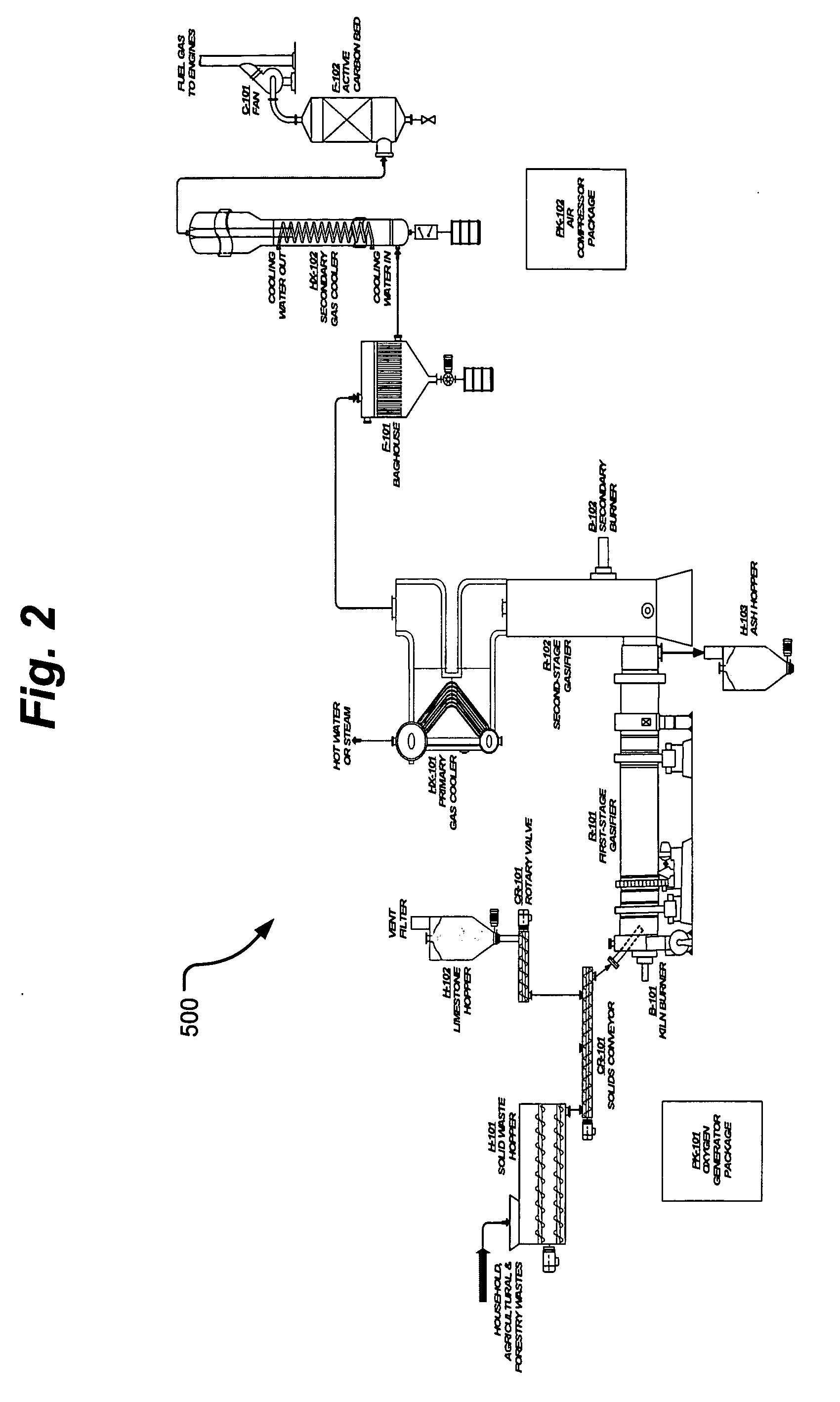
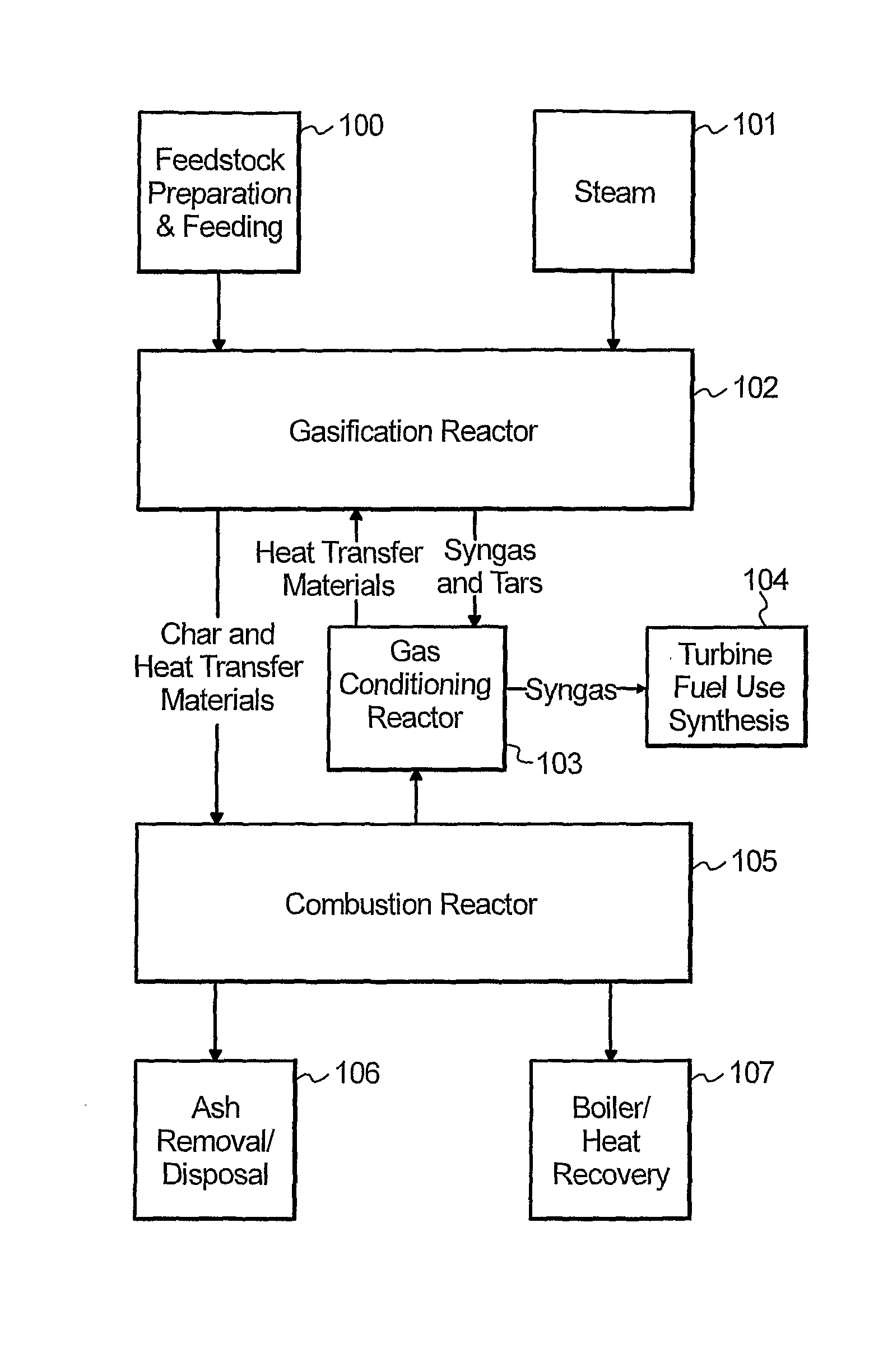
Process and apparatus for biomass gasification
InactiveUS20050095183A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationGasifier mechanical detailsForming gasTar
A waste-to-synthesis gas system including: a first gasifier for receiving biomass; a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the first gasifier in a countercurrent direction to the biomass flow and to define a plurality of reaction regions including a drying region, a pyrolysis region, a gasification region and a combustion region; and, a second gasifier for receiving gases from the plurality of regions of the first gasifier and a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the second gasifier in a concurrent direction to the flow of gases from the first gasifier. As a result, no carbon chars, oils or tars are expected to be present in the synthesis gas produced.
Owner:BIOMASS ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Hydrogen production method and facility
ActiveUS7985399B2High trafficHydrogen separation using solid contactHydrogen separation using liquid contactSyngasHydrocarbon
A hydrogen production method and facility in which a synthesis gas stream produced by the gasification of a carbonaceous substance is processed within a synthesis gas processing unit in which the carbon monoxide content is reacted with steam to produce additional hydrogen that is removed by a pressure swing adsorption unit. The tail gas from the pressure swing adsorption unit is further reformed with the addition of a hydrocarbon containing stream in a steam methane reforming system, further shifted to produce further additional hydrogen. The further hydrogen is then separated in another pressure swing adsorption unit.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Process and System for Gasification with In-Situ Tar Removal
ActiveUS20080244976A1Simplifying downstream heat recoveryIncreased hydrogenCombustible gas catalytic treatmentCombustible gas thermal treatmentHeat carrierTar
The present invention relates to a process and system for gasifying biomass or other carbonaceous feedstocks in an indirectly heated gasifier and provides a method for the elimination of condensable organic materials (tars) from the resulting product gas with an integrated tar removal step. More specifically, this tar removal step utilizes the circulating heat carrier to crack the organics and produce additional product gas. As a benefit of the above process, and because the heat carrier circulates through alternating steam and oxidizing zones in the process, deactivation of the cracking reactions is eliminated.
Owner:TAYLOR BIOMASS ENERGY
Gasifier fluidization
InactiveUS20130109765A1Gasifier mechanical detailsCombustible gas catalytic treatmentProduct gasProcess engineering
A method of producing synthesis gas by introducing a feed material to be gasified into a gasification apparatus comprising at least one fluidized component operable as a fluidized bed, wherein the gasification apparatus is configured to convert at least a portion of the feed material into a gasifier product gas comprising synthesis gas; and maintaining fluidization of the at least one fluidized component by introducing a fluidization gas thereto, wherein the fluidization gas comprises at least one component other than steam. A system for producing synthesis gas is also provided.
Owner:RES USA LLC
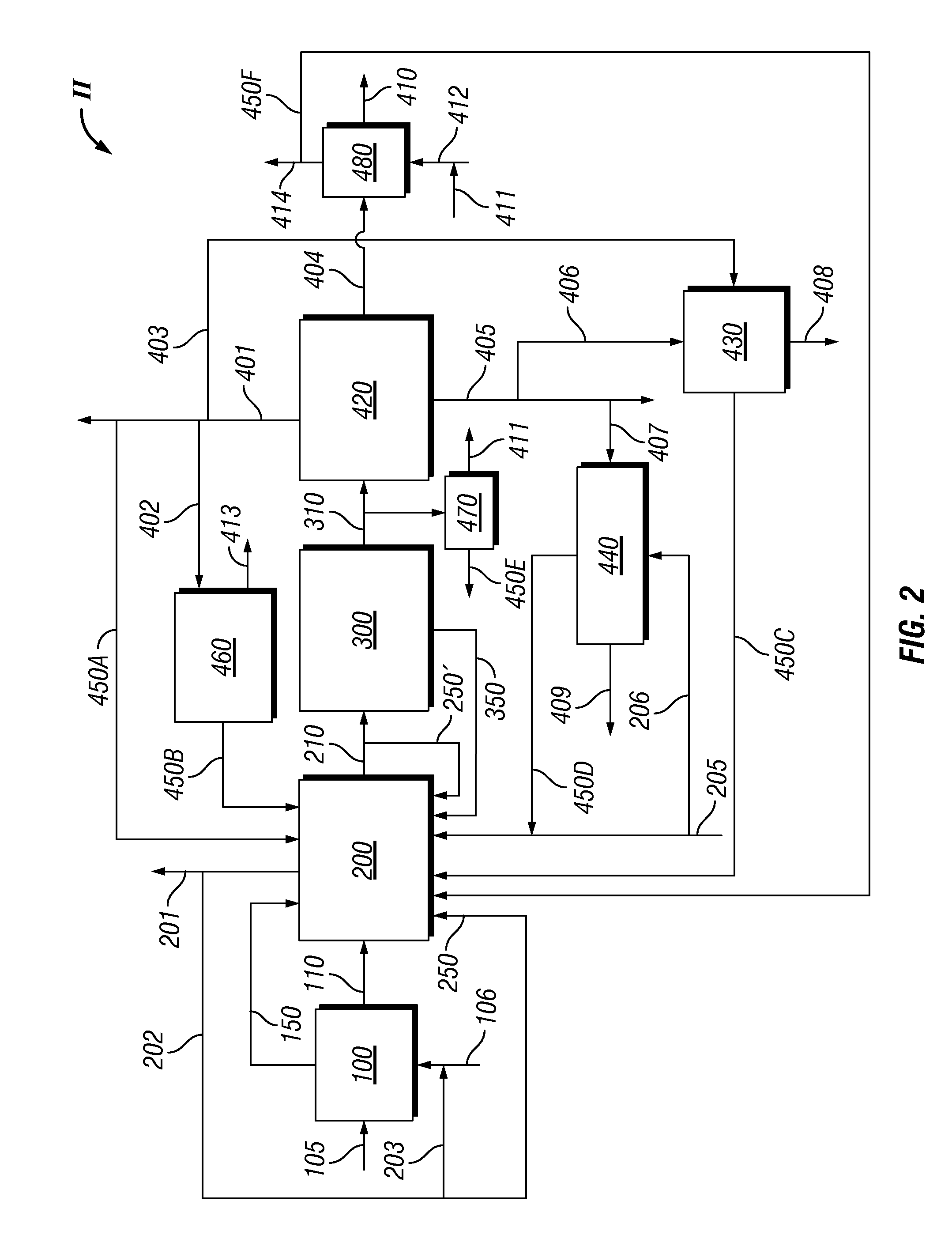
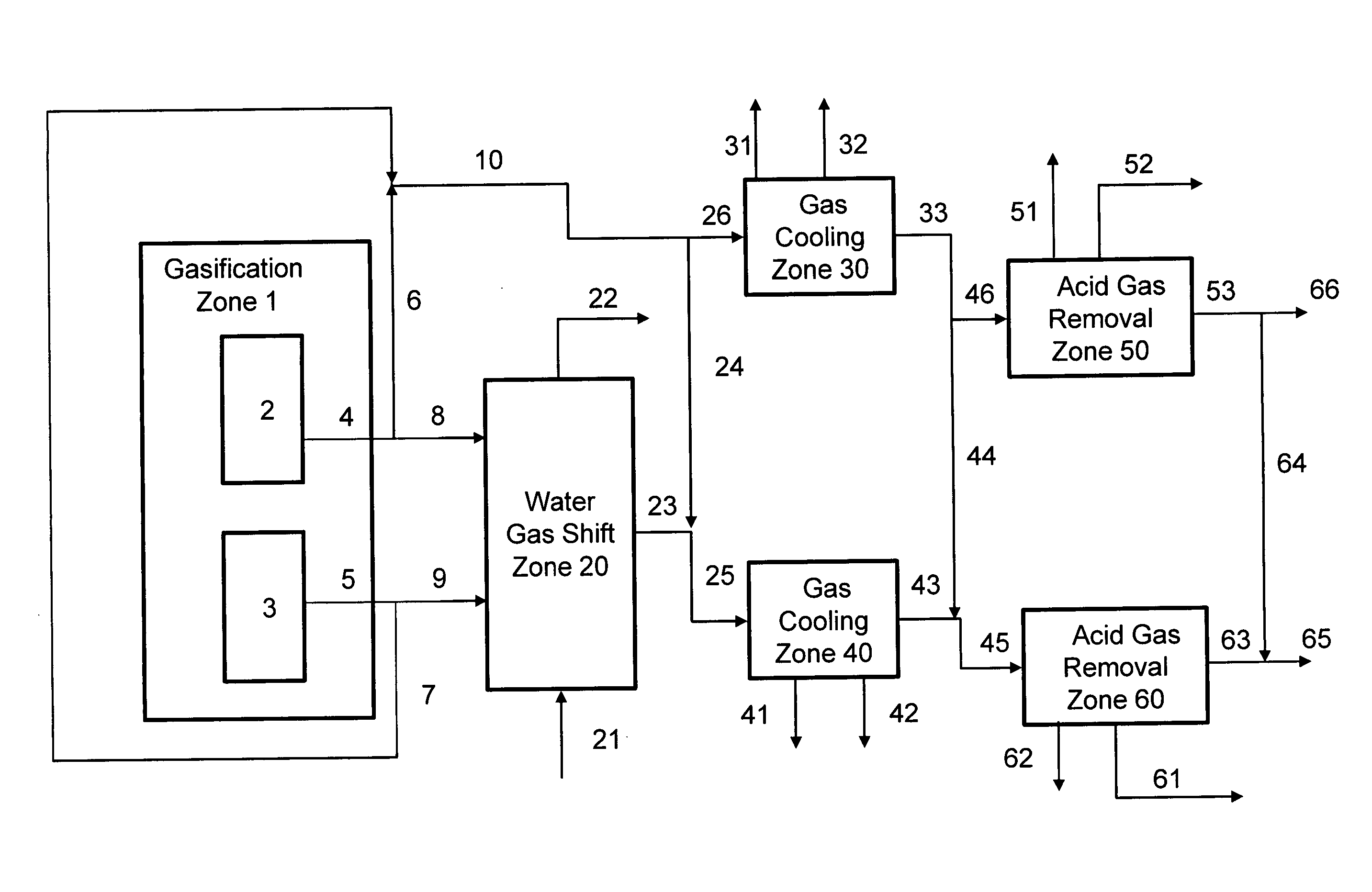
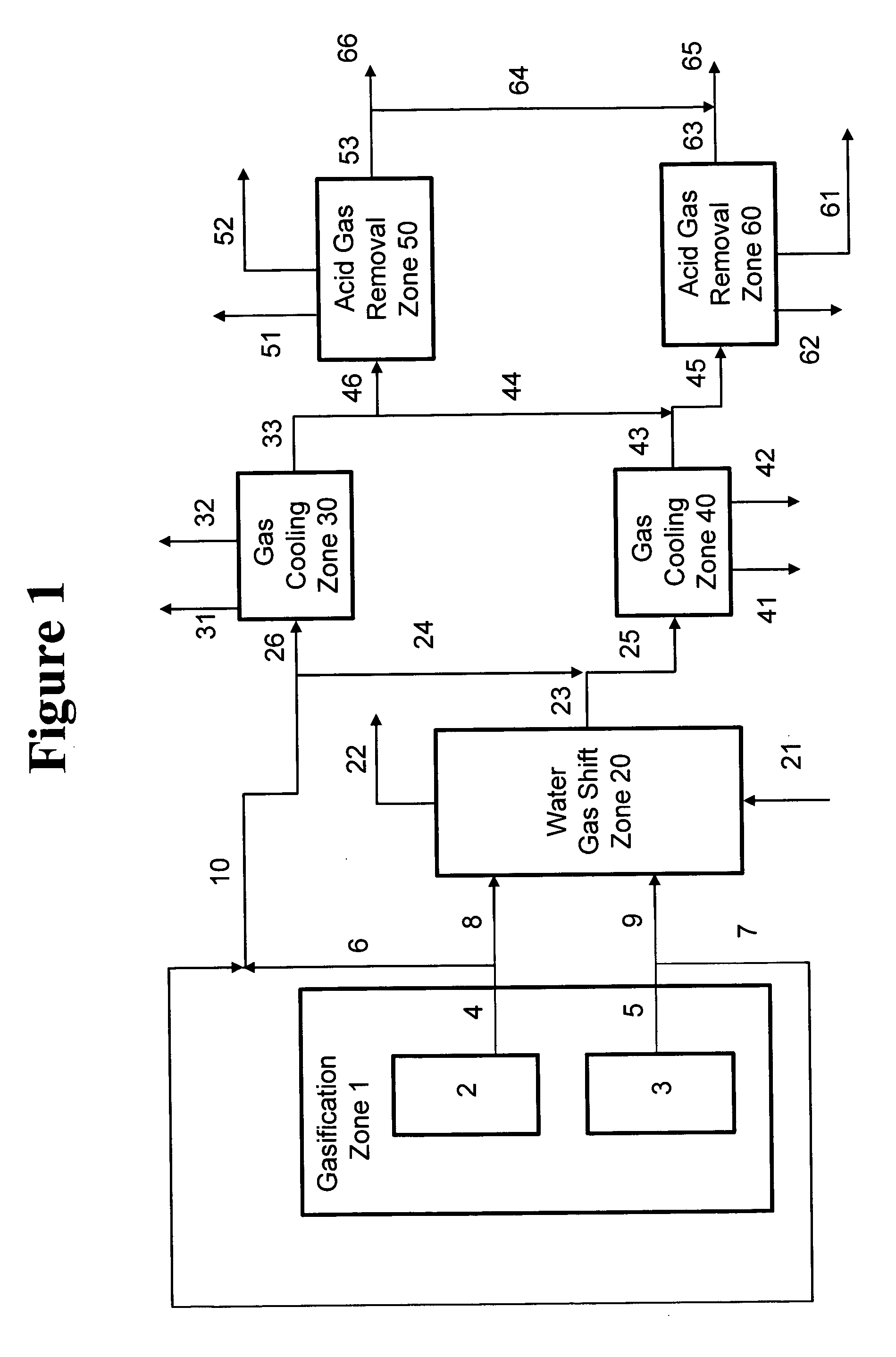
Process for producing variable syngas compositions
Disclosed is a process for the production of a variable syngas composition by gasification. Two or more raw syngas streams are produced in a gasification zone having at least 2 gasifiers and a portion the raw syngas is passed to a common water gas shift reaction zone to produce at least one shifted syngas stream having an enriched hydrogen content and at least one unshifted syngas stream. The shifted and the unshifted syngas streams are mixed downstream of the water gas shift zone in varying proportions produce blended and unblended synthesis gas streams in a volume and / or composition that may vary over time in response to at least one downstream syngas requirement. The process is useful for supplying syngas from multiple gasifiers for the variable coproduction of electrical power and chemicals across periods of peak and off-peak power demand.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com