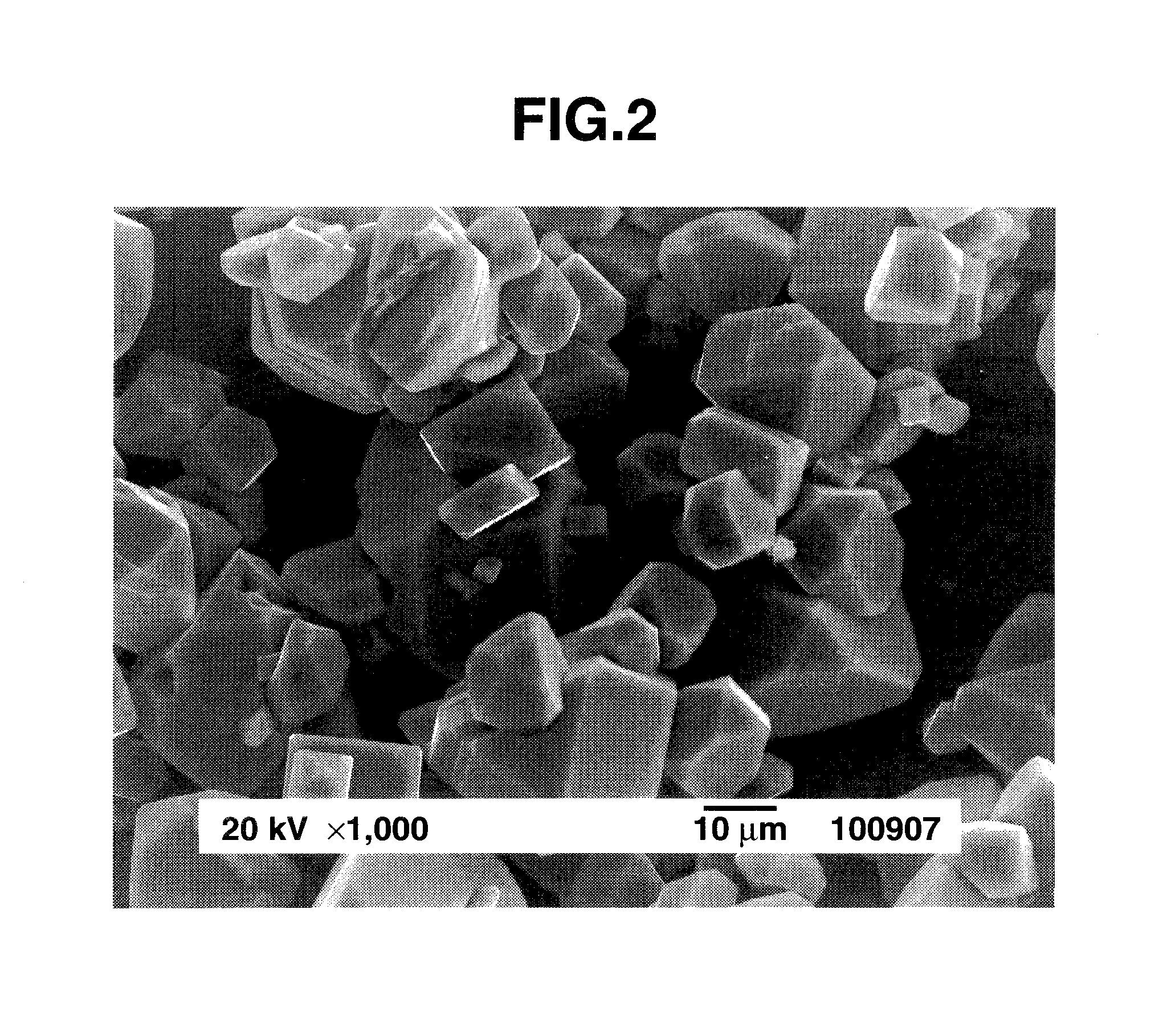
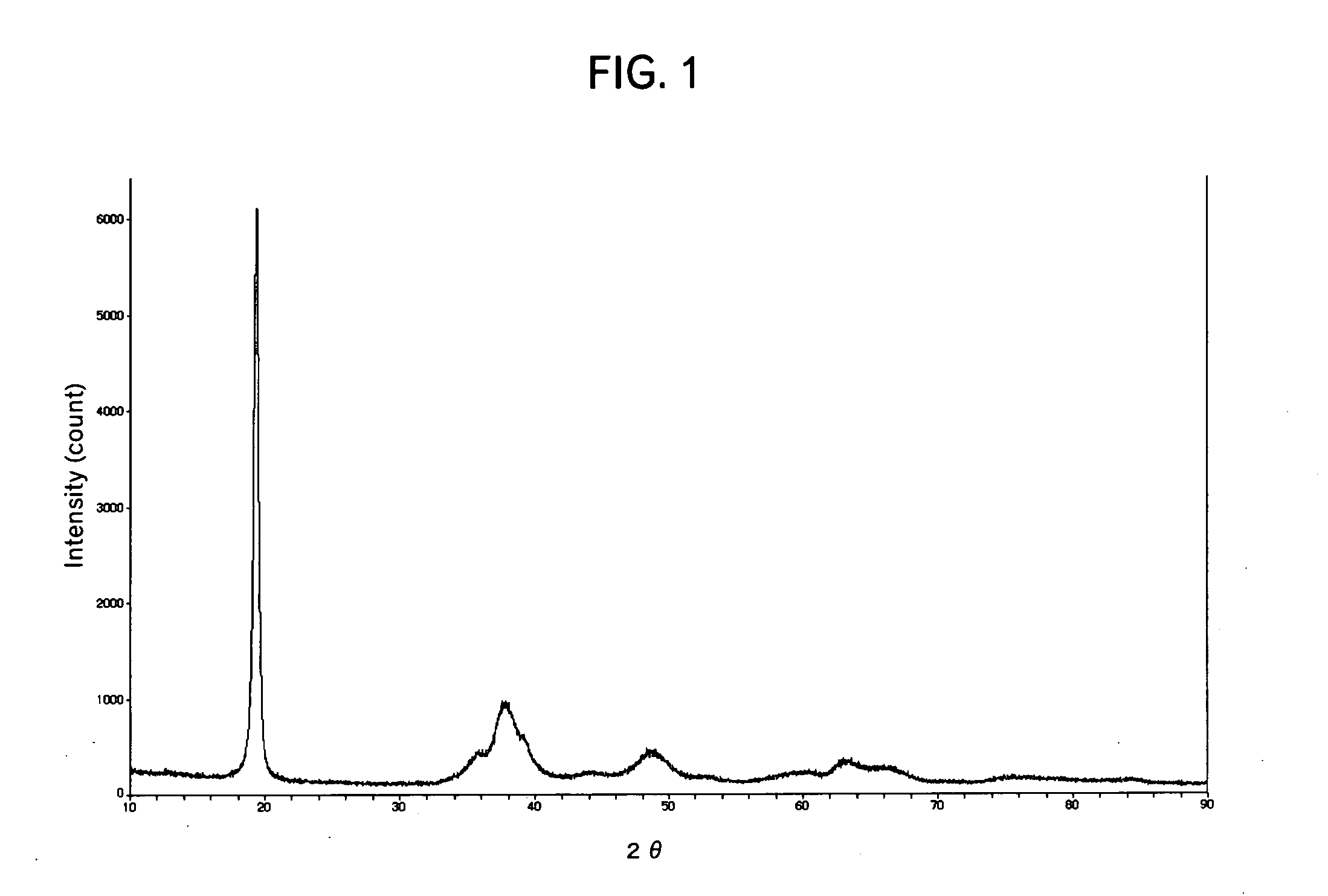
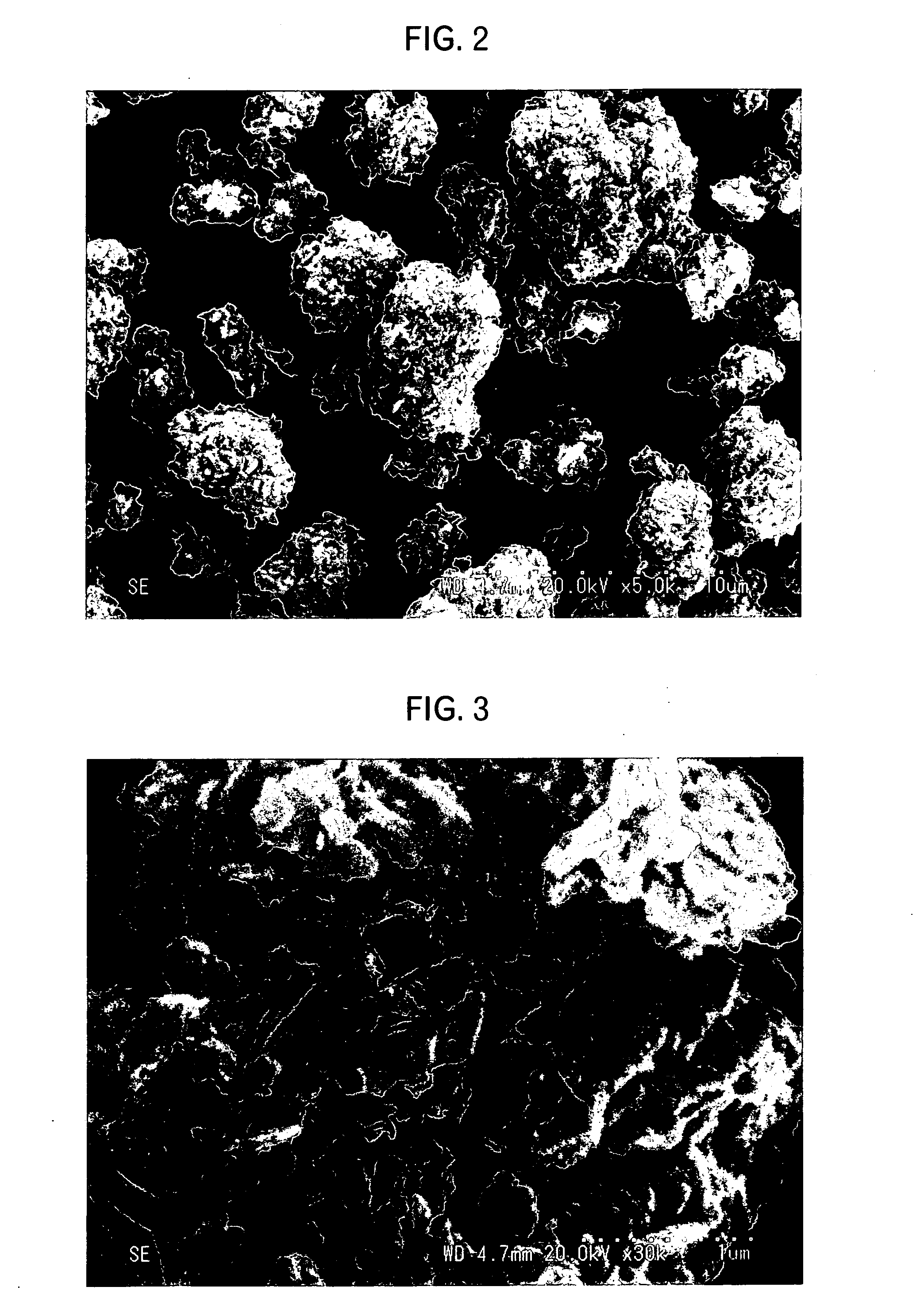
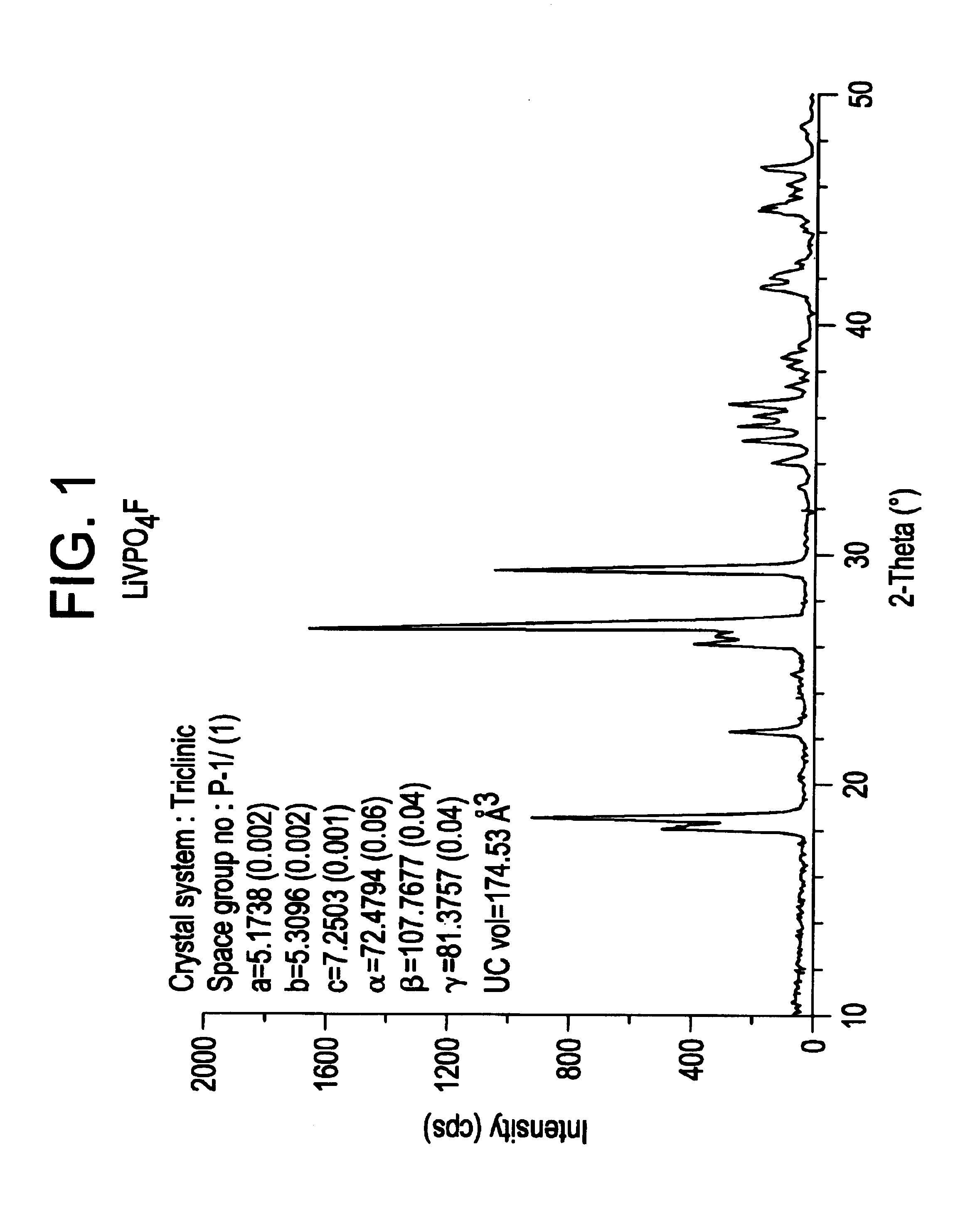
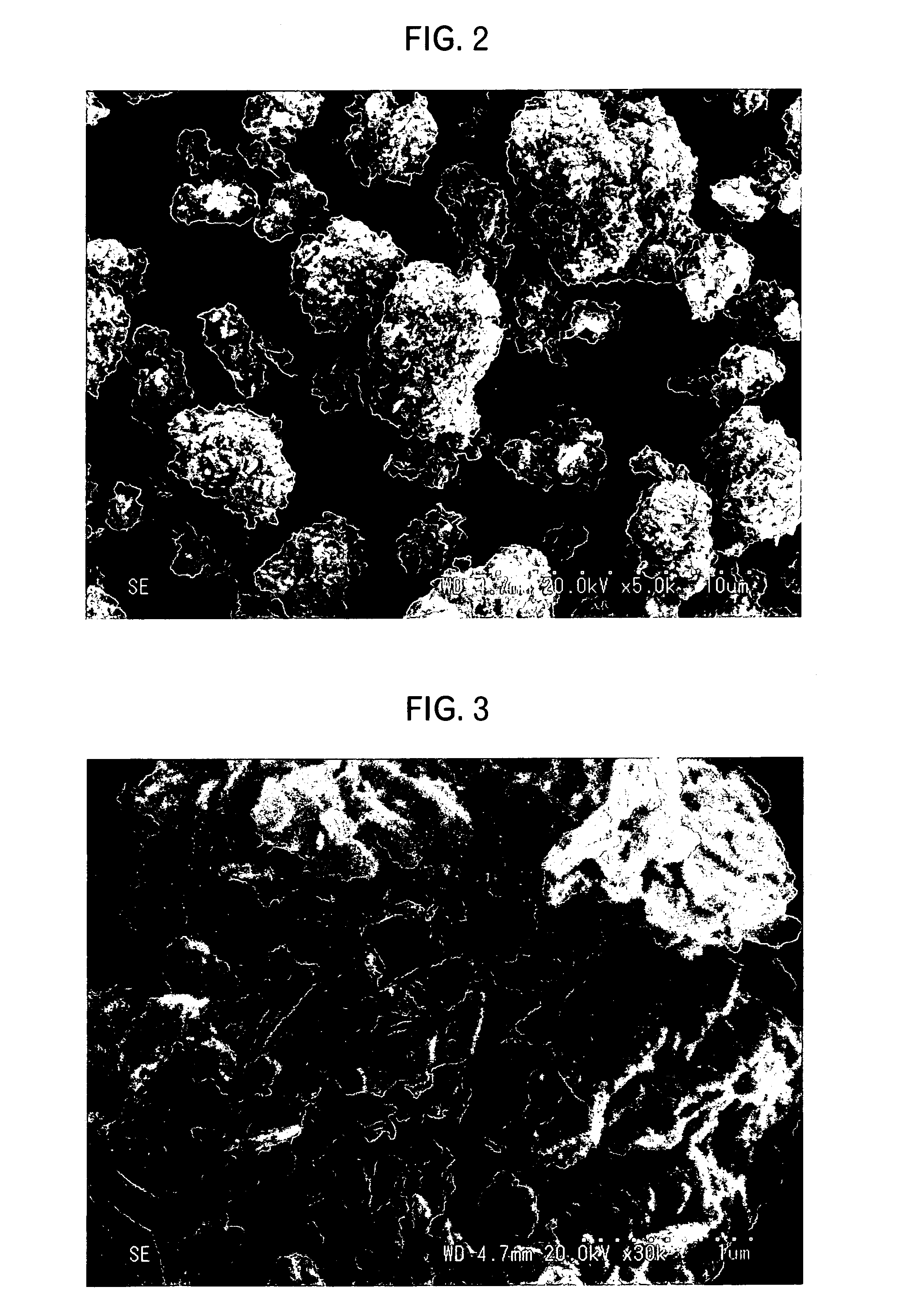
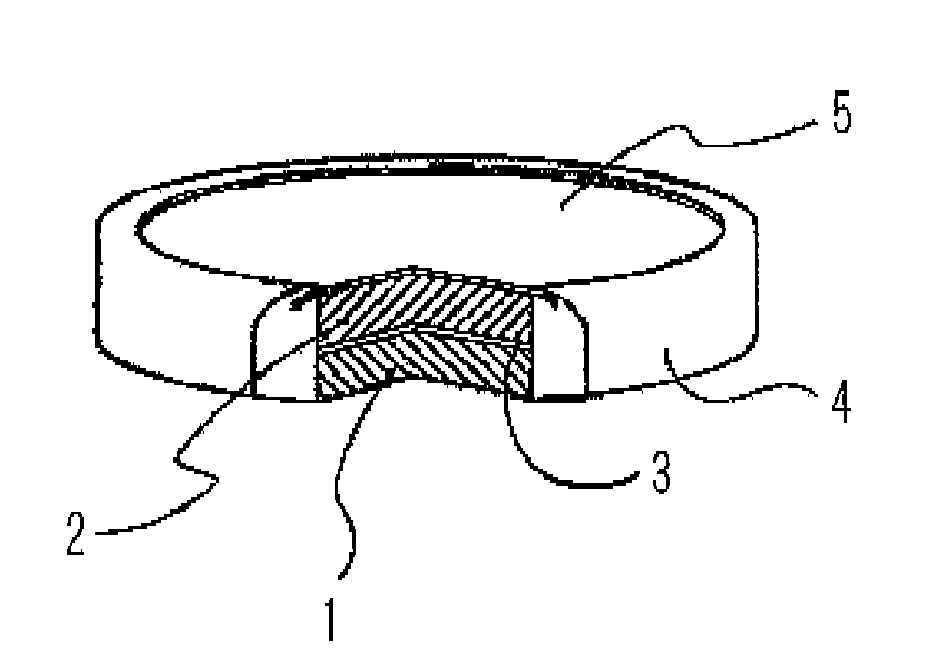
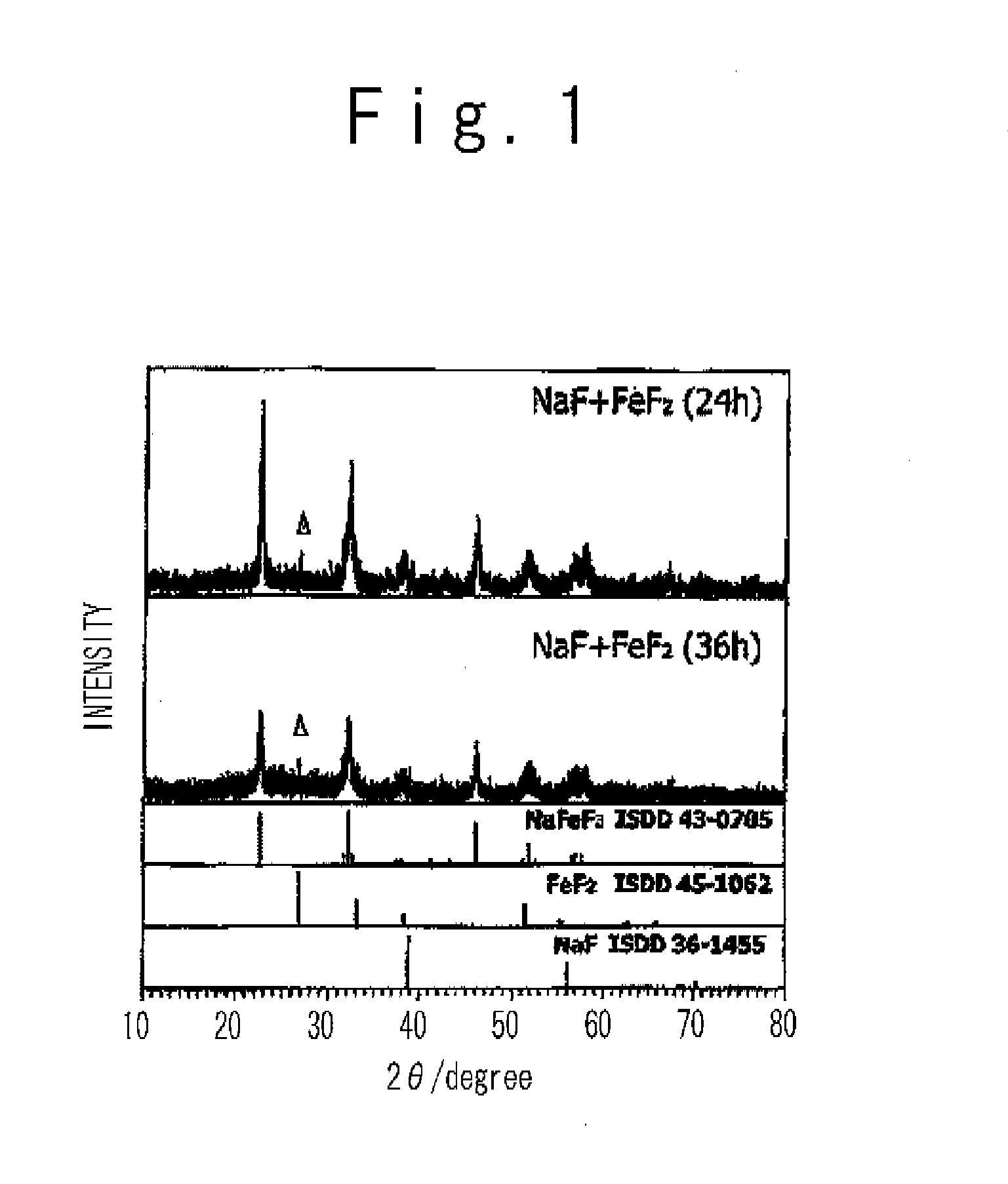
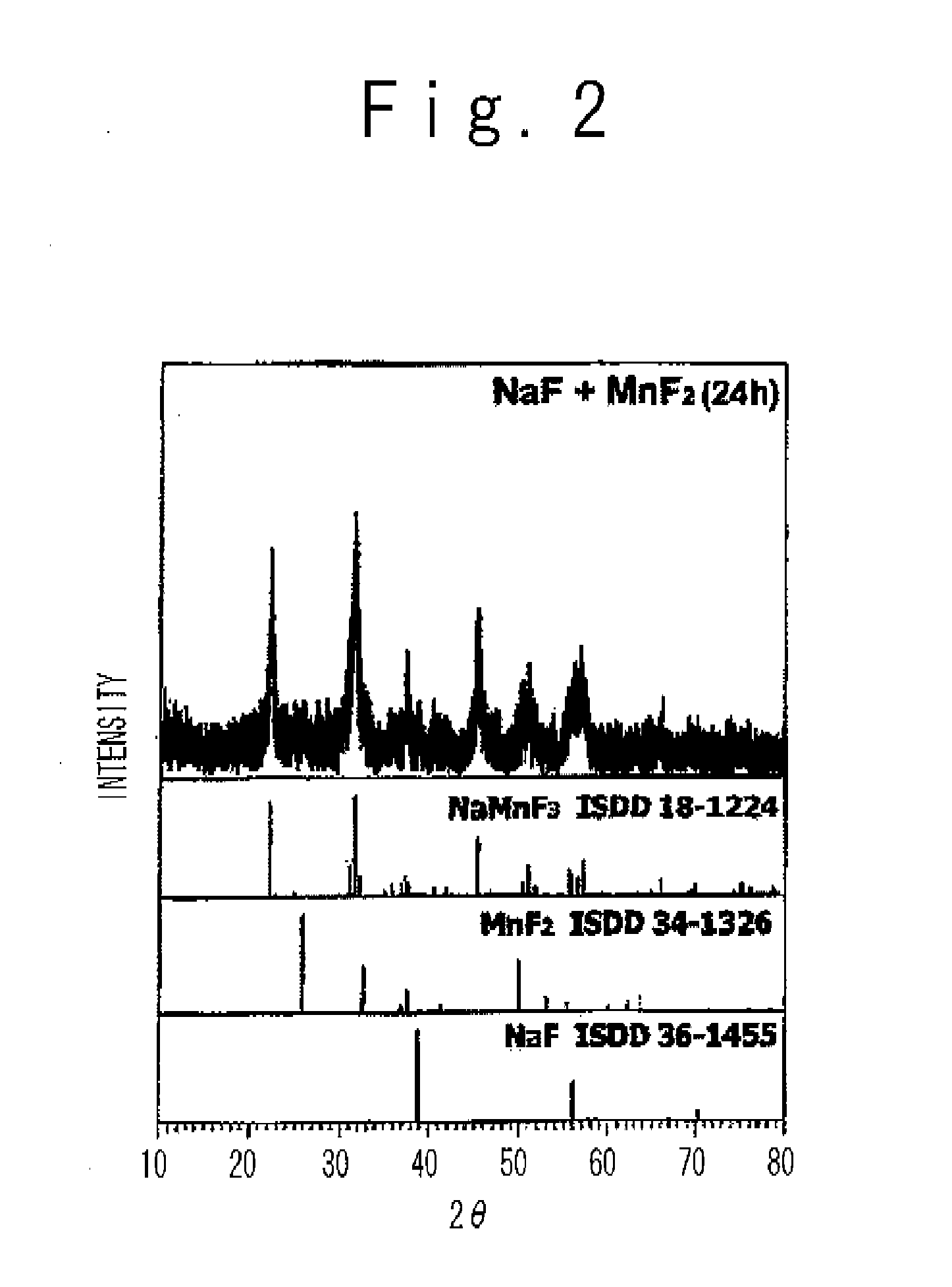
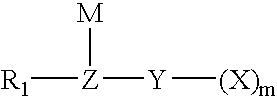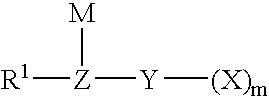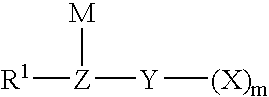Patents
Literature
295results about "Fluoride preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
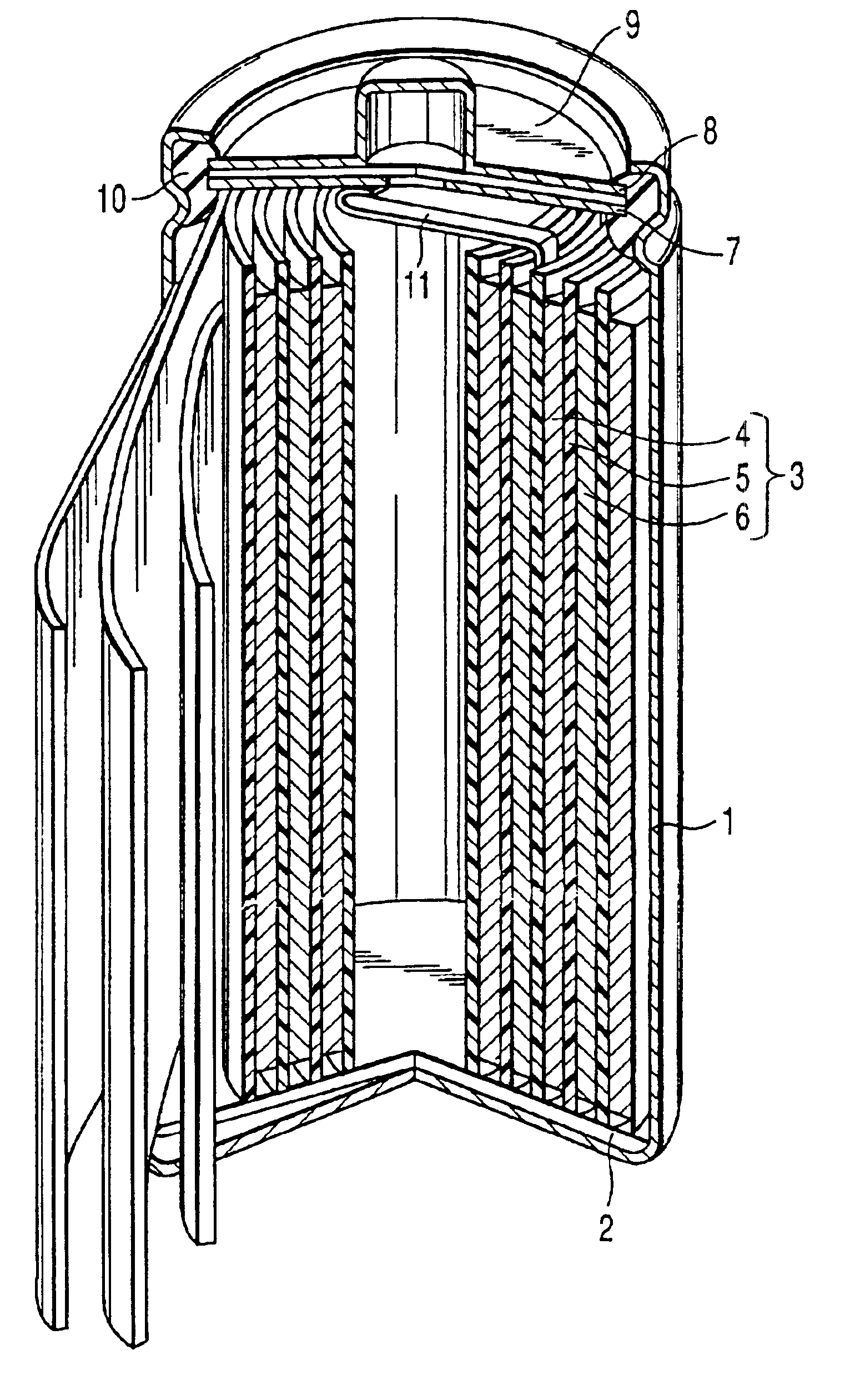
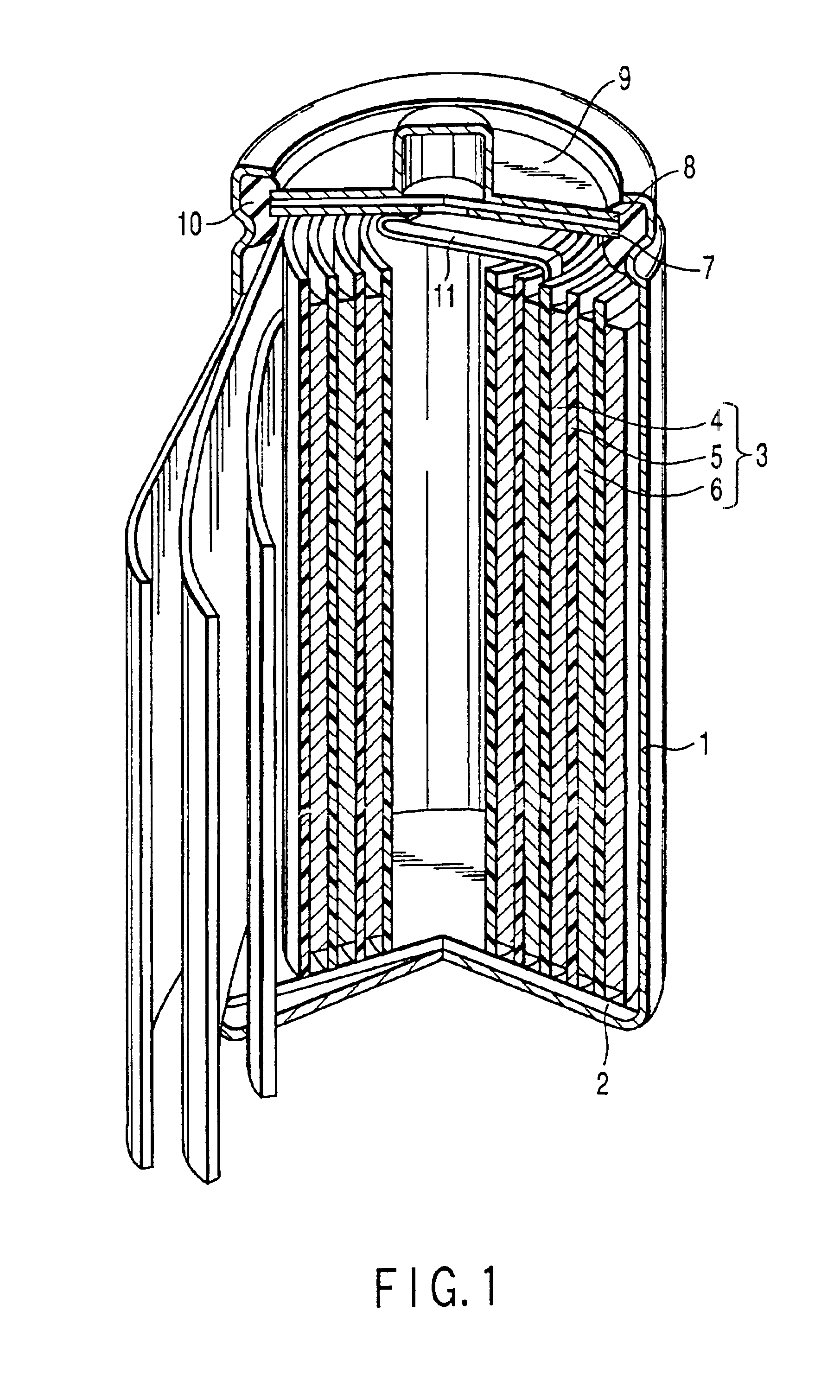
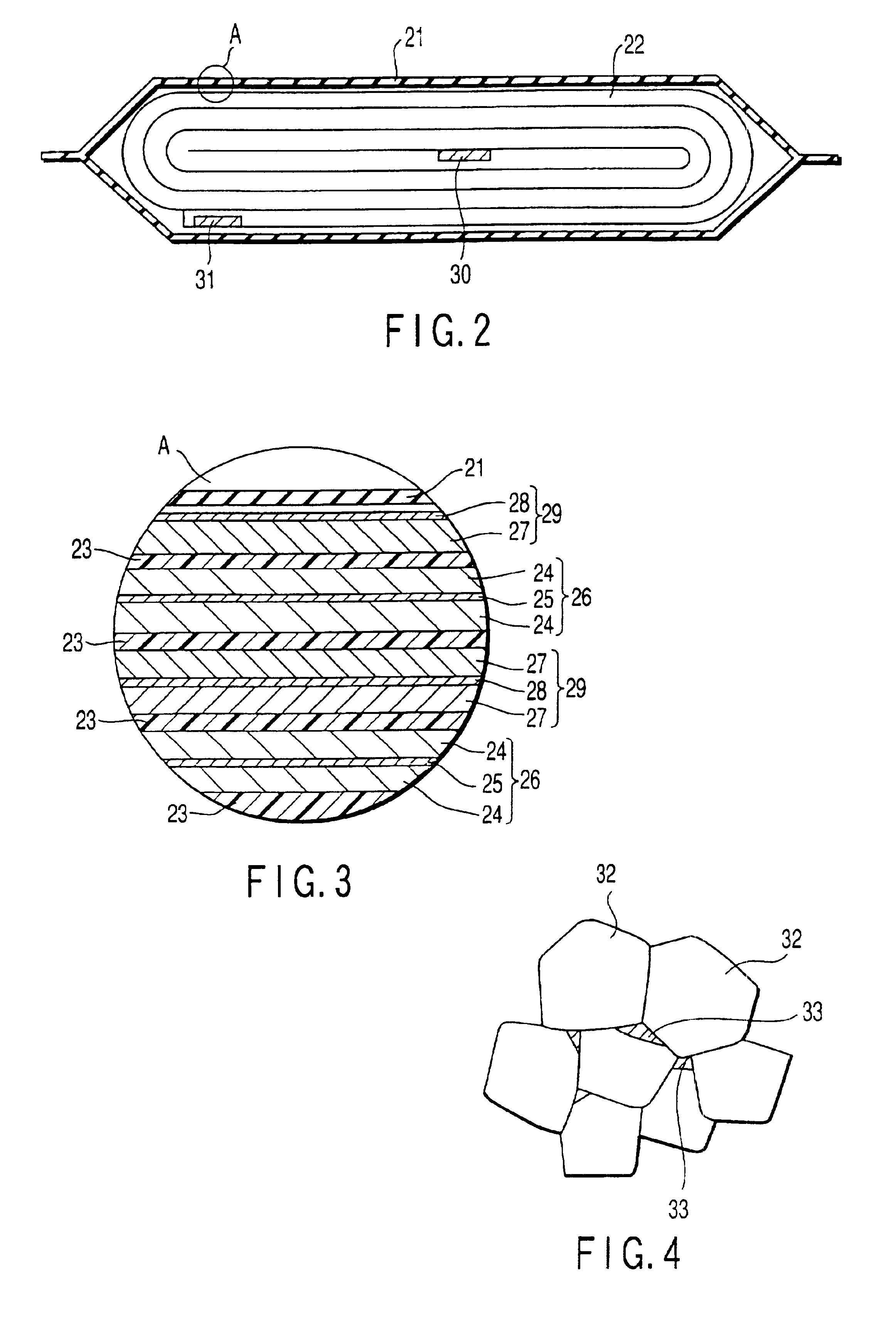
Medium rate and high rate batteries
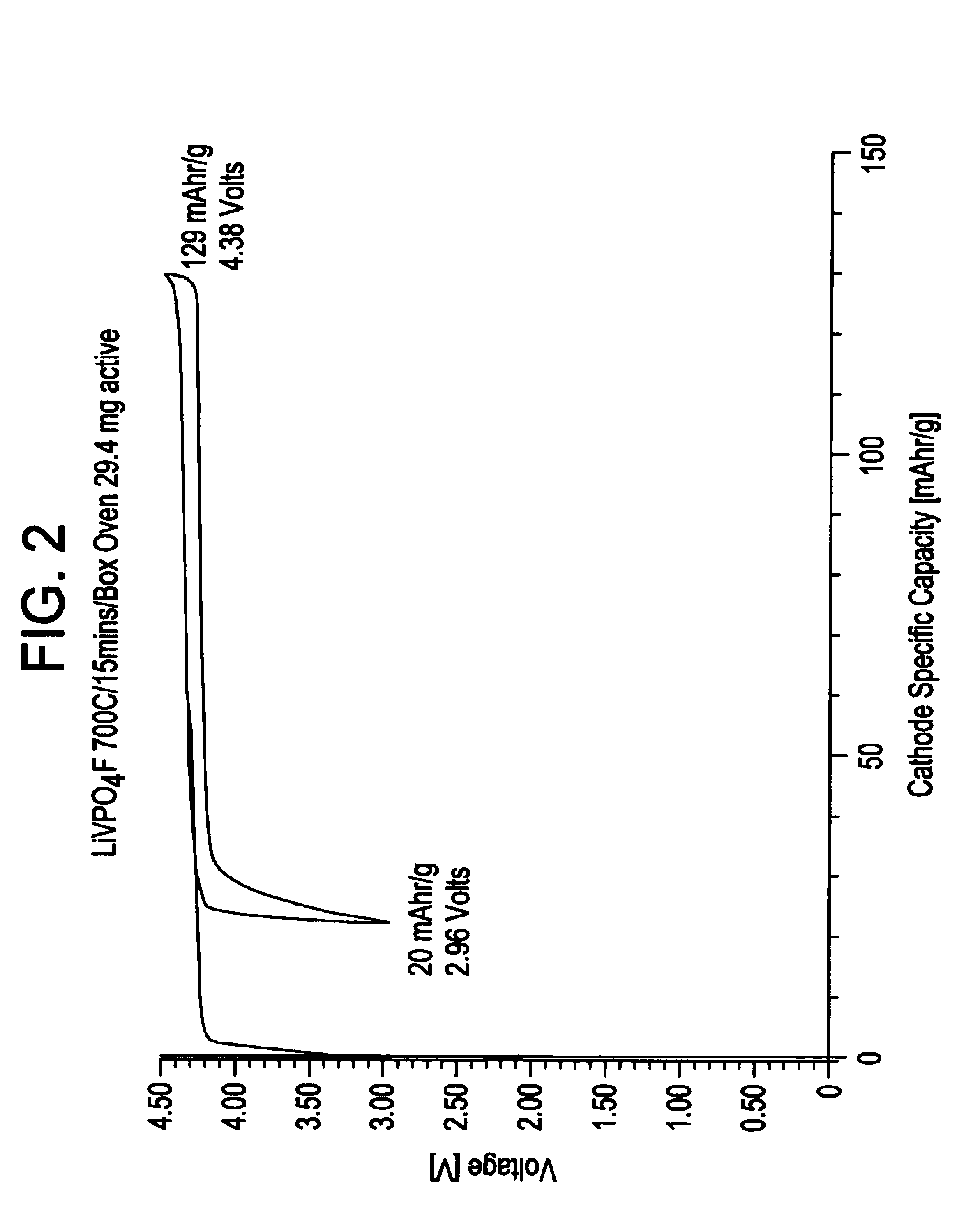
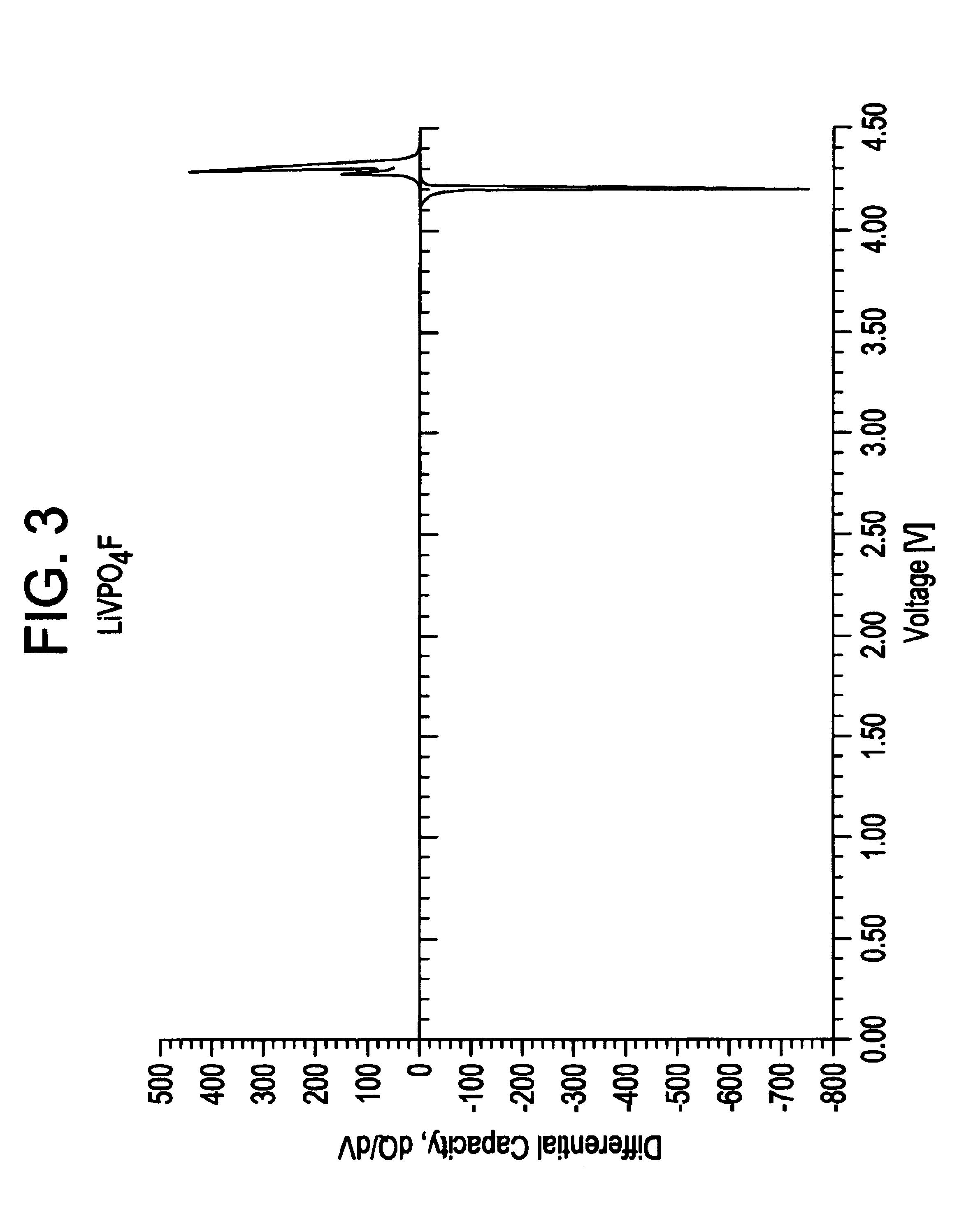
Improved submicron carbon fluoride has increased graphite content and can also have improved uniformity. The increased graphite content and / or uniformity can result in improved battery performance, for example with respect to specific capacity. Desirable battery structures provide for use with implantable medical devices. Suitable batteries can be used for high rate, medium rate, low rate or a combination of rate applications.
Owner:GREATBATCH TECH ADVANCED RES LAB
Preparation of complex fluoride and complex fluoride phosphor
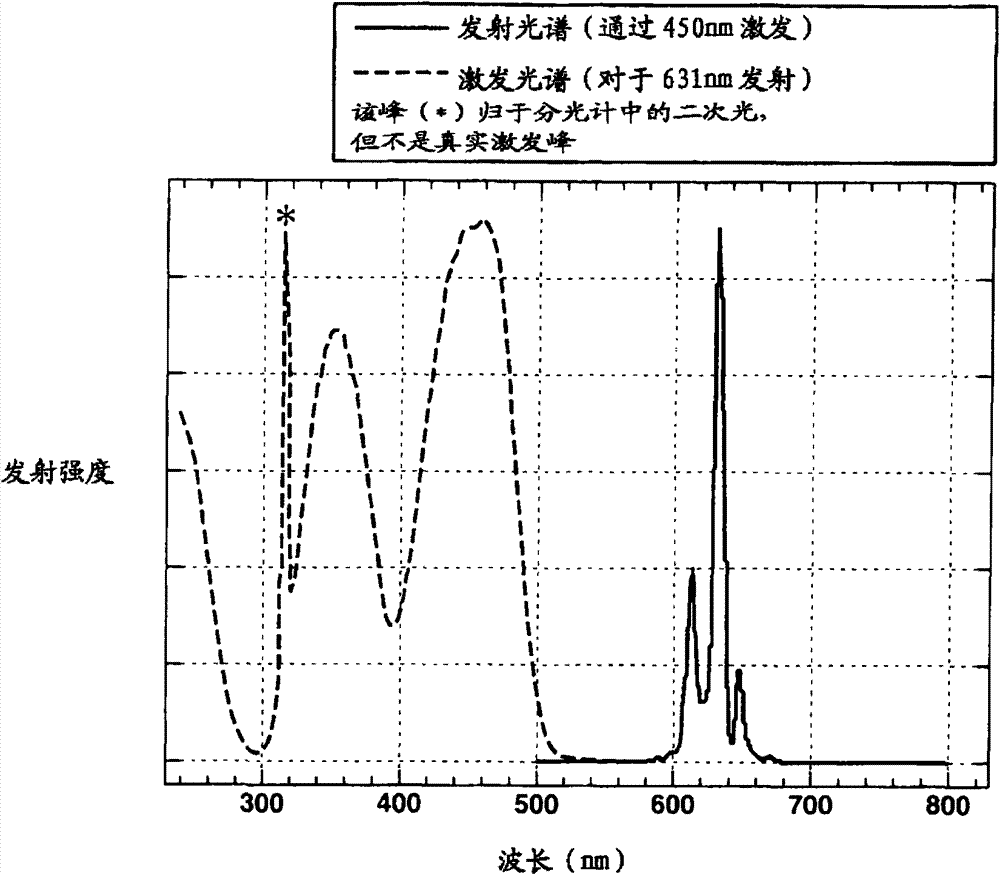
ActiveUS20120256125A1Uniform sizeSatisfactory emissive propertyTin compoundsSilicon halogen compoundsPhysical chemistryFluoride
A complex fluoride A2MF6 wherein M is a tetravalent element Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, Ge or Sn, A is an alkali metal Li, Na, K, Rb or Cs is prepared by providing a first solution containing a fluoride of M, providing a second solution containing a compound of A and / or the compound of A in solid form, mixing the first solution with the second solution and / or the solid for reacting the fluoride of M with the compound of A, and recovering the resulting solid product via solid-liquid separation.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Lithium-nickel-cobalt-maganese containing composite oxide, material for positive electrode active material for lithium secondary battery, and methods for producing these
ActiveUS20060083989A1Large capacityExcels in charge-discharge cycle durabilityElectrode rolling/calenderingFluoride preparationManganeseOxygen
Coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxide wherein primary particles are coagulated to form secondary particles are synthesized by allowing an aqueous solution of a nickel-cobalt-manganese salt, an aqueous solution of an alkali-metal hydroxide, and an ammonium-ion donor to react under specific conditions; and a lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese-containing composite oxide represented by a general formula, LipNixMn1-x-yCoyO2-qFq (where 0.98≦p≦1.07, 0.3≦x≦0.5, 0.1≦y≦0.38, and 0≦q≦0.05), which is a positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary cell having a wide usable voltage range, a charge-discharge cycle durability, a high capacity and high safety, is obtained by dry-blending coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese composite oxyhydroxide formed by making an oxidant to act on the coagulated particles with a lithium salt, and firing the mixture in an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Methods of making lithium metal cathode active materials
The invention provides a novel method for making lithium mixed metal materials in electrochemical cells. The lithium mixed metal materials comprise lithium and at least one other metal besides lithium. The invention involves the reaction of a metal compound, a phosphate compound, with a reducing agent to reduce the metal and form a metal phosphate. The invention also includes methods of making lithium metal oxides involving reaction of a lithium compound, a metal oxide with a reducing agent.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV
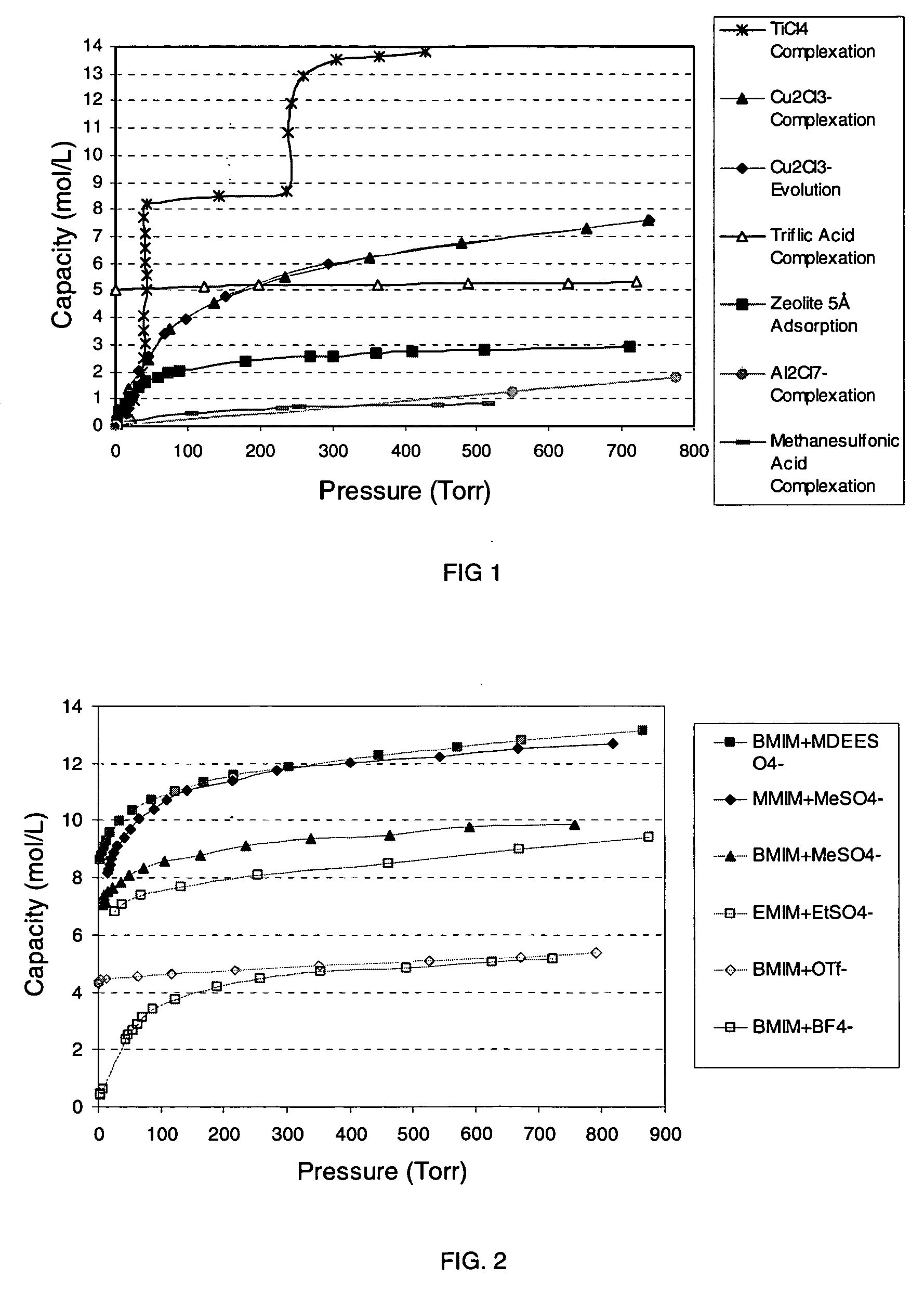
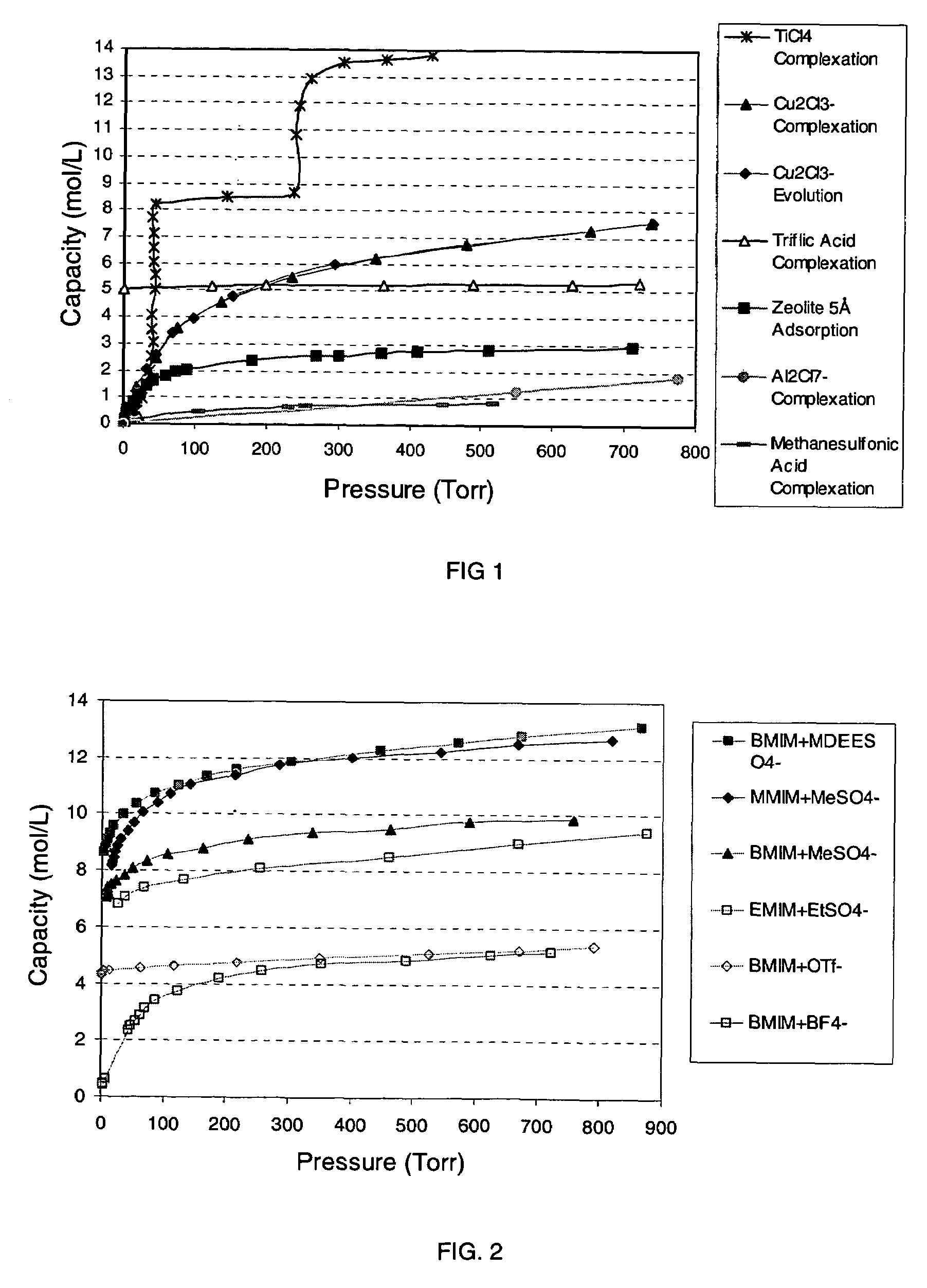
Ionic liquid based mixtures for gas storage and delivery
InactiveUS20060060817A1Oxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid degasificationChemical reactionIonic liquid
A mixture and method for the storage and delivery of at least one gas are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a mixture for the storage and delivery of at least one gas comprising: an ionic liquid comprising an anion and a cation; and at least one gas that is disposed within and is reversibly chemically reacted with the ionic liquid. In another aspect, there is provided a method for delivering at least one gas from a mixture comprising an ionic liquid and at least one gas comprising: reacting the at least one gas and the ionic liquid to provide the mixture and separating the at least one gas from the mixture wherein the at least one gas after the separating step is substantially the same as the at least one gas prior to the reacting step.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Positive electrode active material and lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveUS6872491B2Eliminate cracksLarge dischargeFluoride preparationFinal product manufactureStructural formulaComposite oxide
The present invention provides a positive electrode active material containing a composite oxide having a composition represented by a structural formula (1) given below:Lix(Ni1-yMe1y)(O2-zXz)+A (1)
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
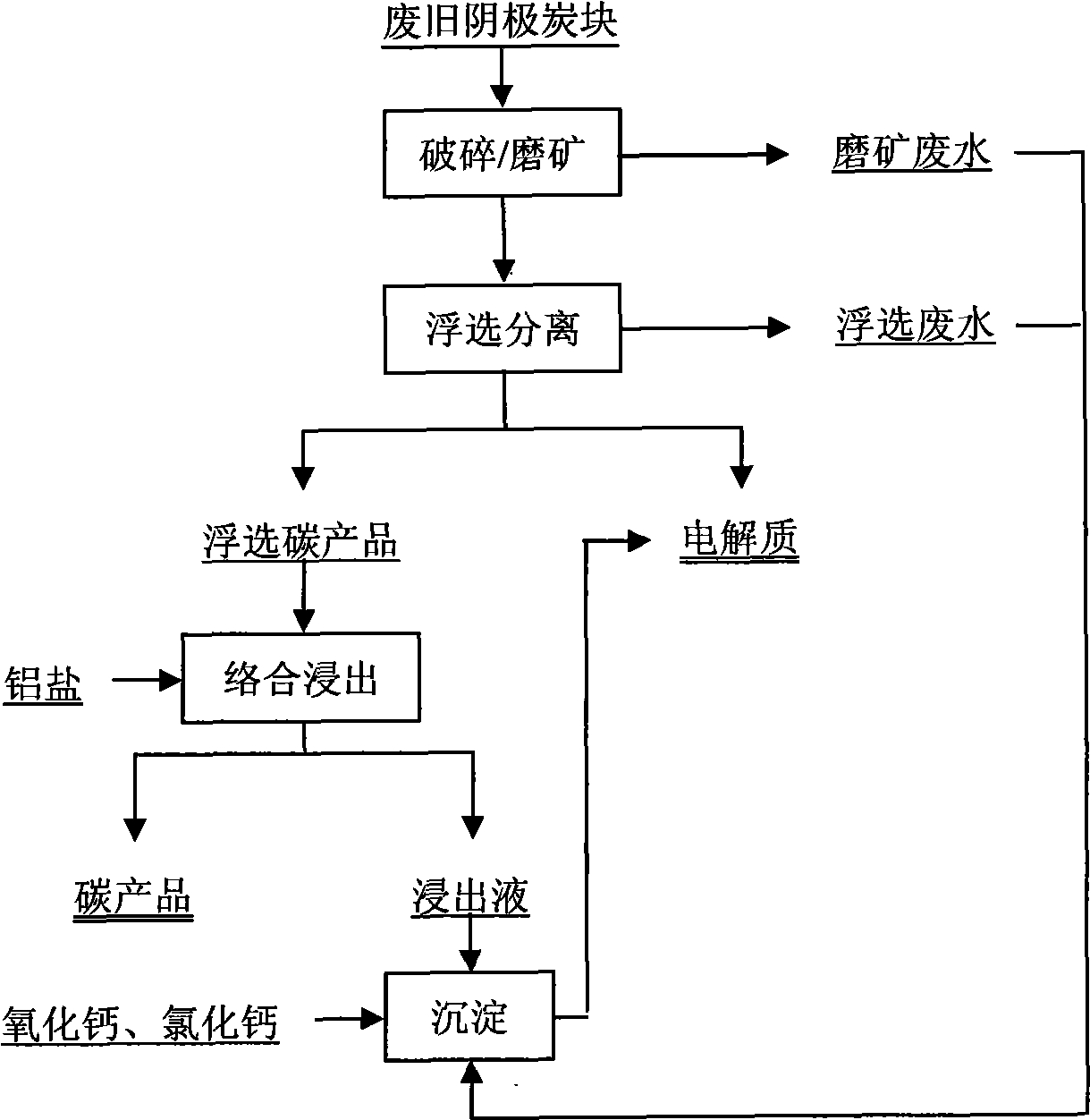
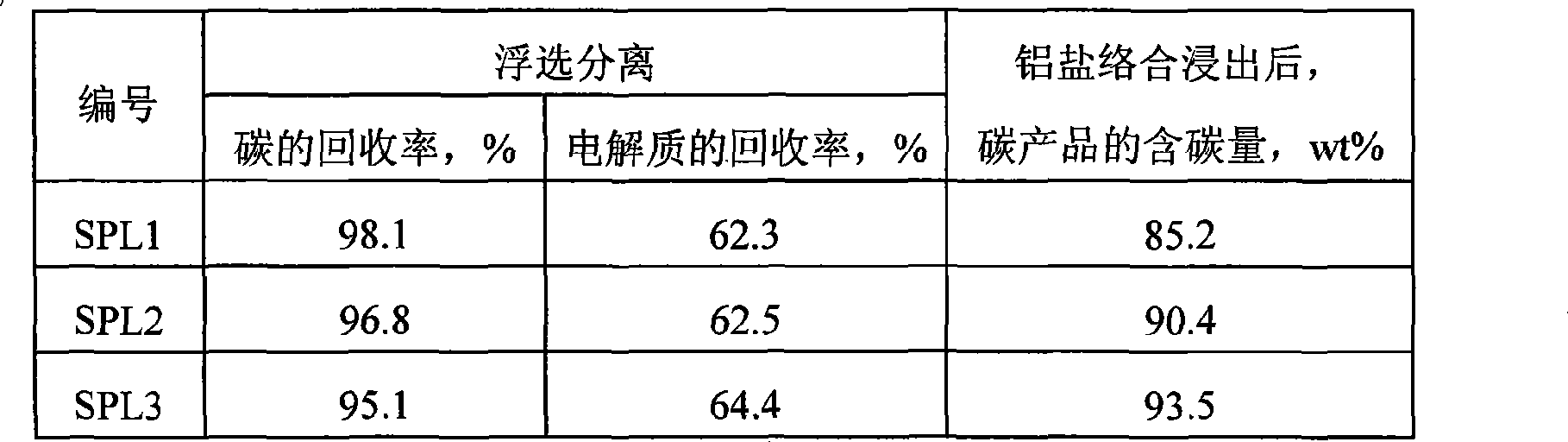
Method for electrolyzing waste and old cathode carbon block by comprehensive utilization of aluminum
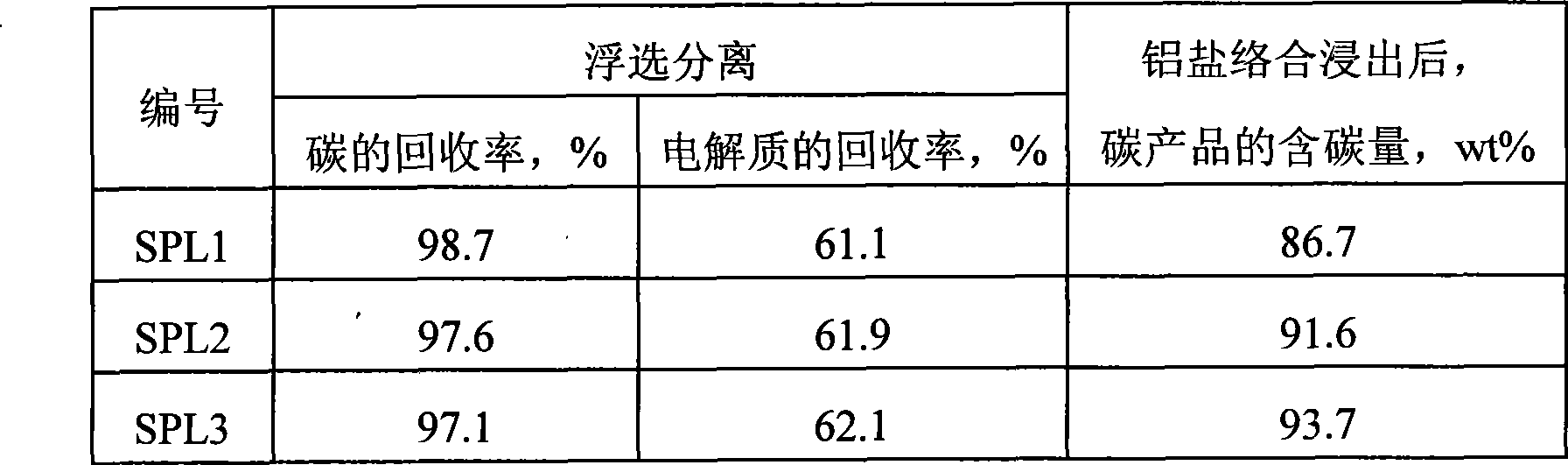
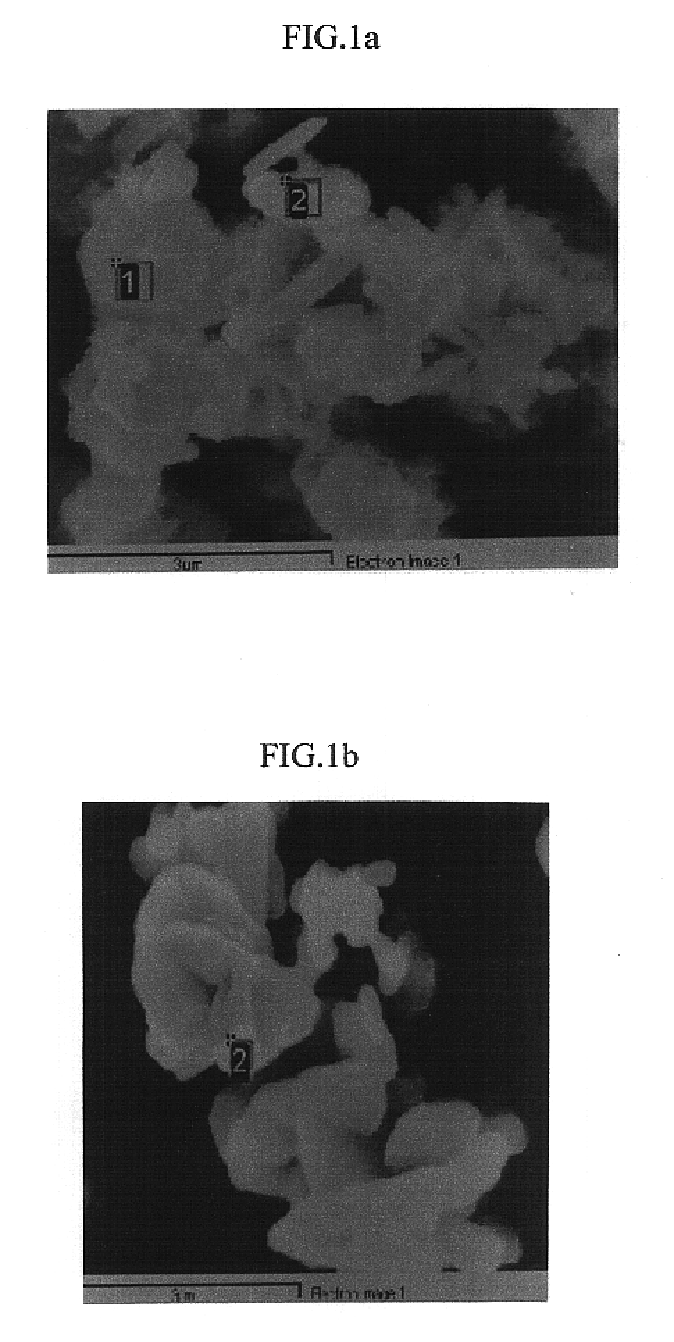
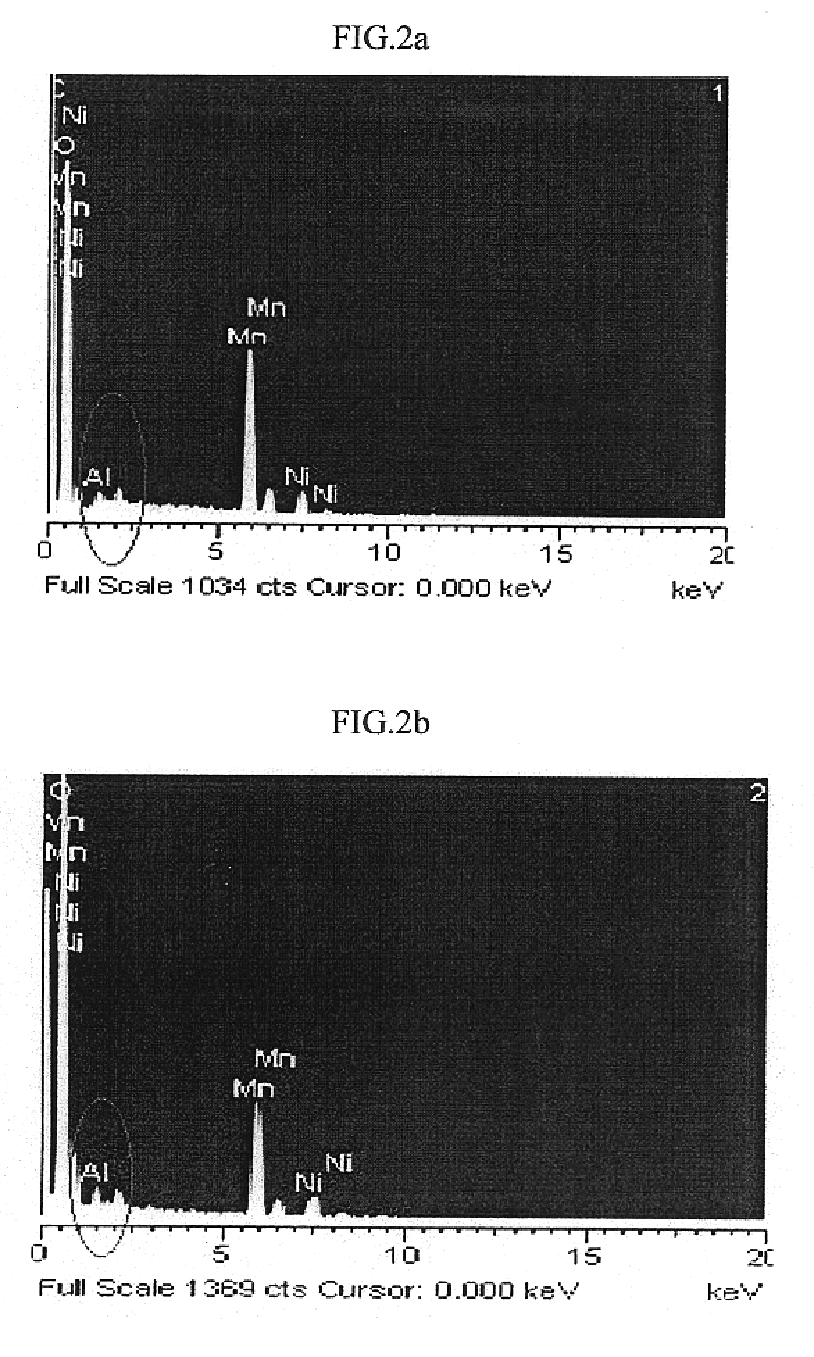
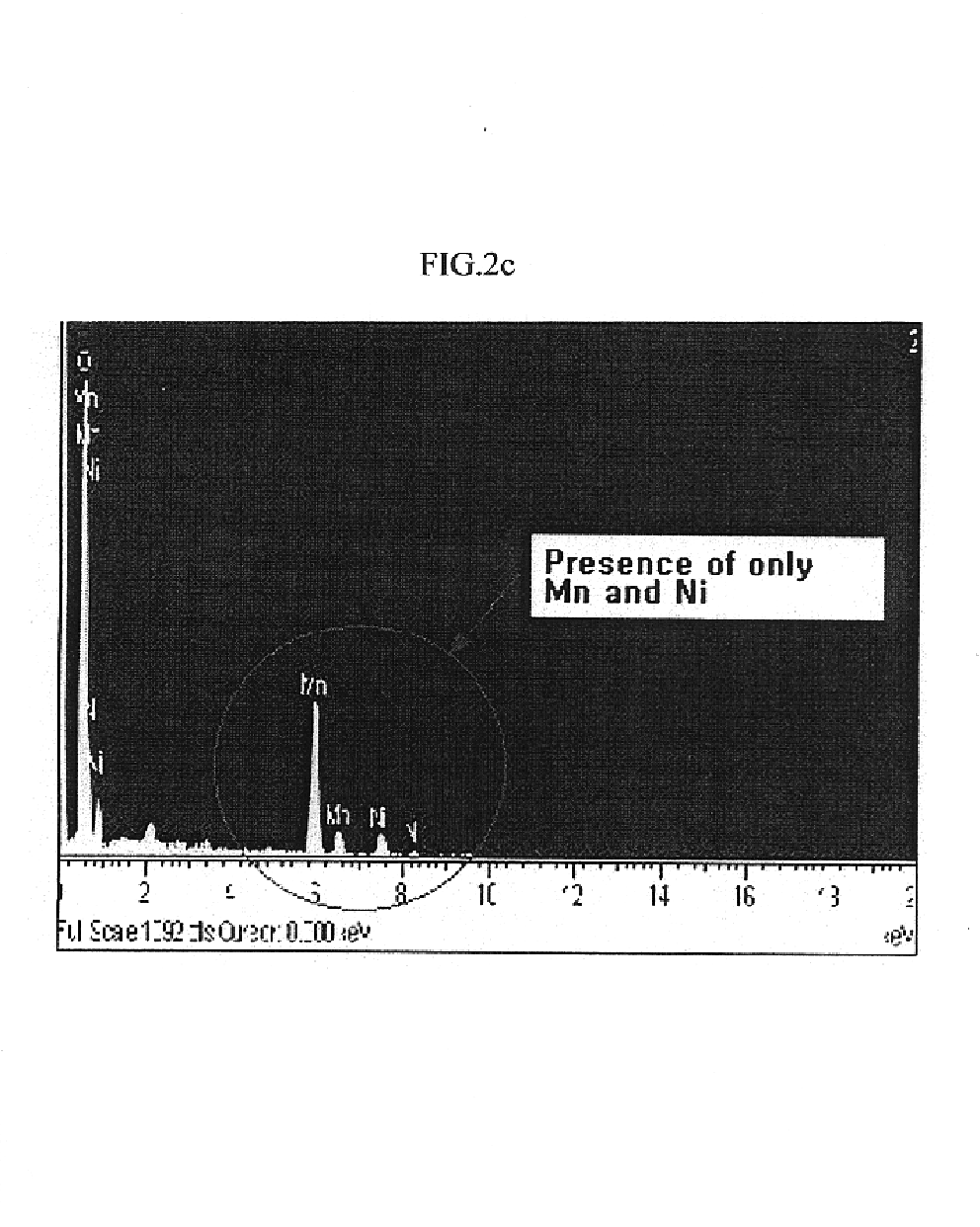
ActiveCN101480658ARealize flotation separationHigh carbon contentFluoride preparationWaste processingPregnant leach solutionHigh carbon
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively using aluminium to electrolyze a waste cathode carbon block, which belongs to the technical field of environment protection and comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding the waste cathode carbon block; adjusting the concentration and the PH value of ore slurry after the grinding, then using floatation equipment to carry out floatation treatment, and separating electrolyte and carbon which are contained in the waste cathode carbon block; using an aluminium salt solution to soak for extracting the electrolyte contained in a carbon product obtained from the floatation, and further improving the grade of a high-carbon product; mixing the grinding waste water, the floatation waste water and the soaking solution, and adding CaO and CaCl2 to precipitate and recover aluminium and fluothane in the mixture. The method for comprehensively using aluminium to electrolyze a waste cathode carbon block has simple operating condition, low energy consumption, high recovery ratio of valuable substances and good application prospect.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method of preparing positive active material for rechargeable lithium batteries
InactiveUS6949233B2Improved cycle life characteristicsHigh discharge rateElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphatesPhysical chemistryHeat treated
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross
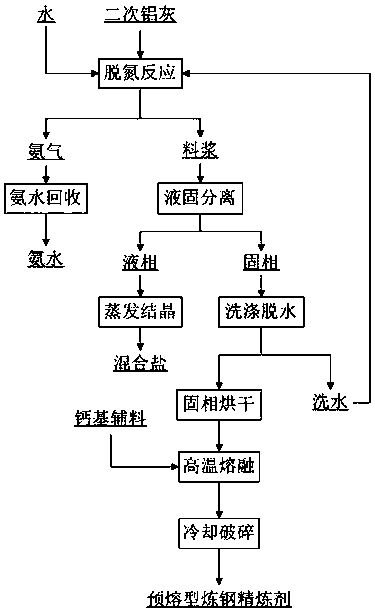
InactiveCN107555447ARealize harmless treatmentTo achieve the purpose of "zero emission" utilizationChloride preparationFluoride preparationSlurryLiquid solid
The invention provides a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross and relates to a harmless and comprehensive utilization method of secondary aluminum dross produced in an aluminum dross treating process. The harmless and comprehensive utilization method is characterized in that slurry is prepared from the secondary aluminum dross produced in the aluminum dross treating process and water, a stirring deamination reaction is performed, and ammonia gas formed through the reaction is condensed or absorbed by water; slurry after the reaction is subjected to liquid-solid separation, separated liquid phase is subjected to evaporative crystallization, and a chlorate and fluoride salt mixture is obtained; separated solid phase is used for producing a calcium aluminate material. With adoption of the method, the aluminum dross can be treated harmlessly, useful components in the aluminum dross are recovered efficiently, the harmless secondary aluminum dross can replace high-alumina bauxite for preparing a calcium aluminate product, production cost is reduced greatly, zero-release utilization of the aluminum dross is realized, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, environmental protection is realized, and the method has wide applicability.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
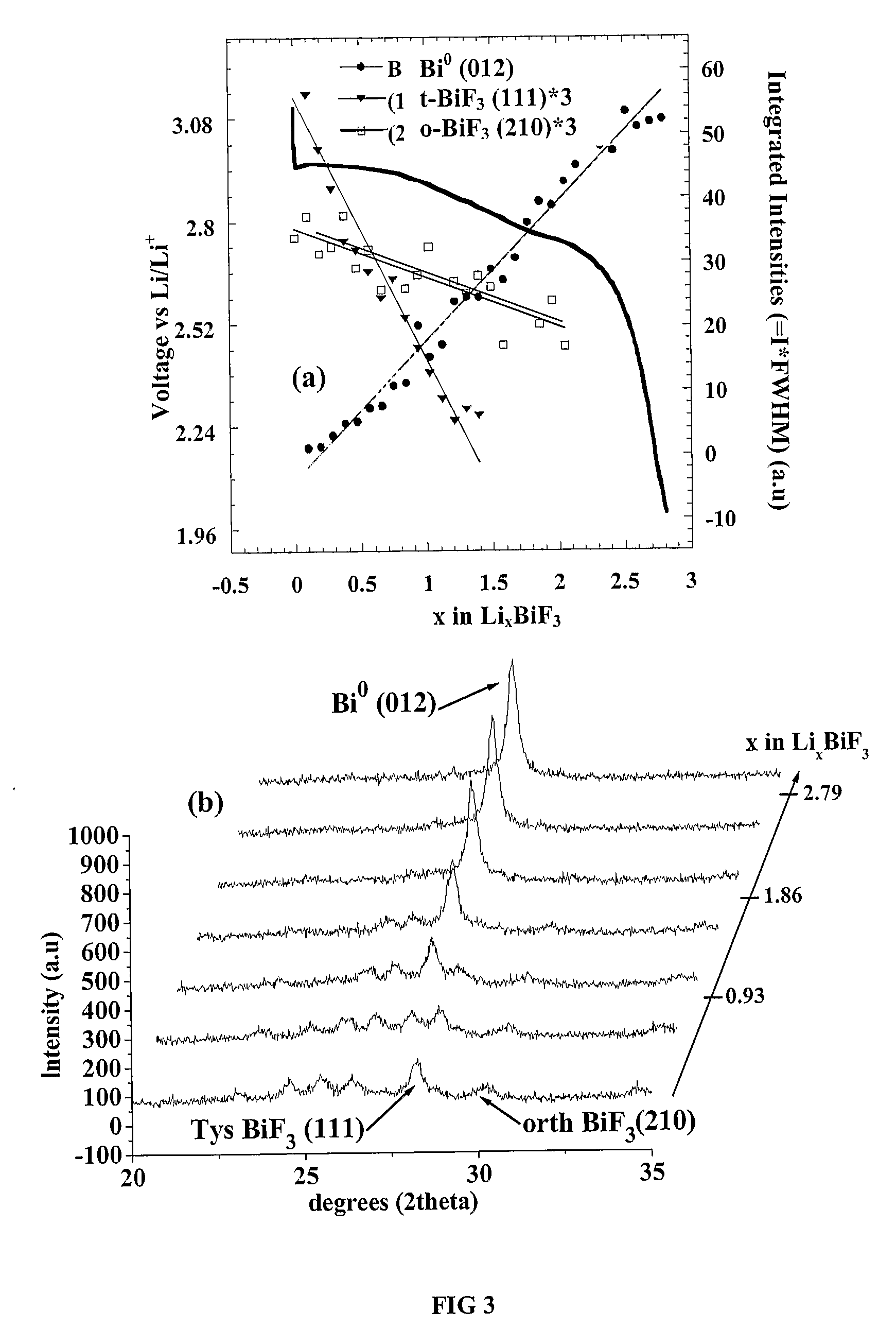
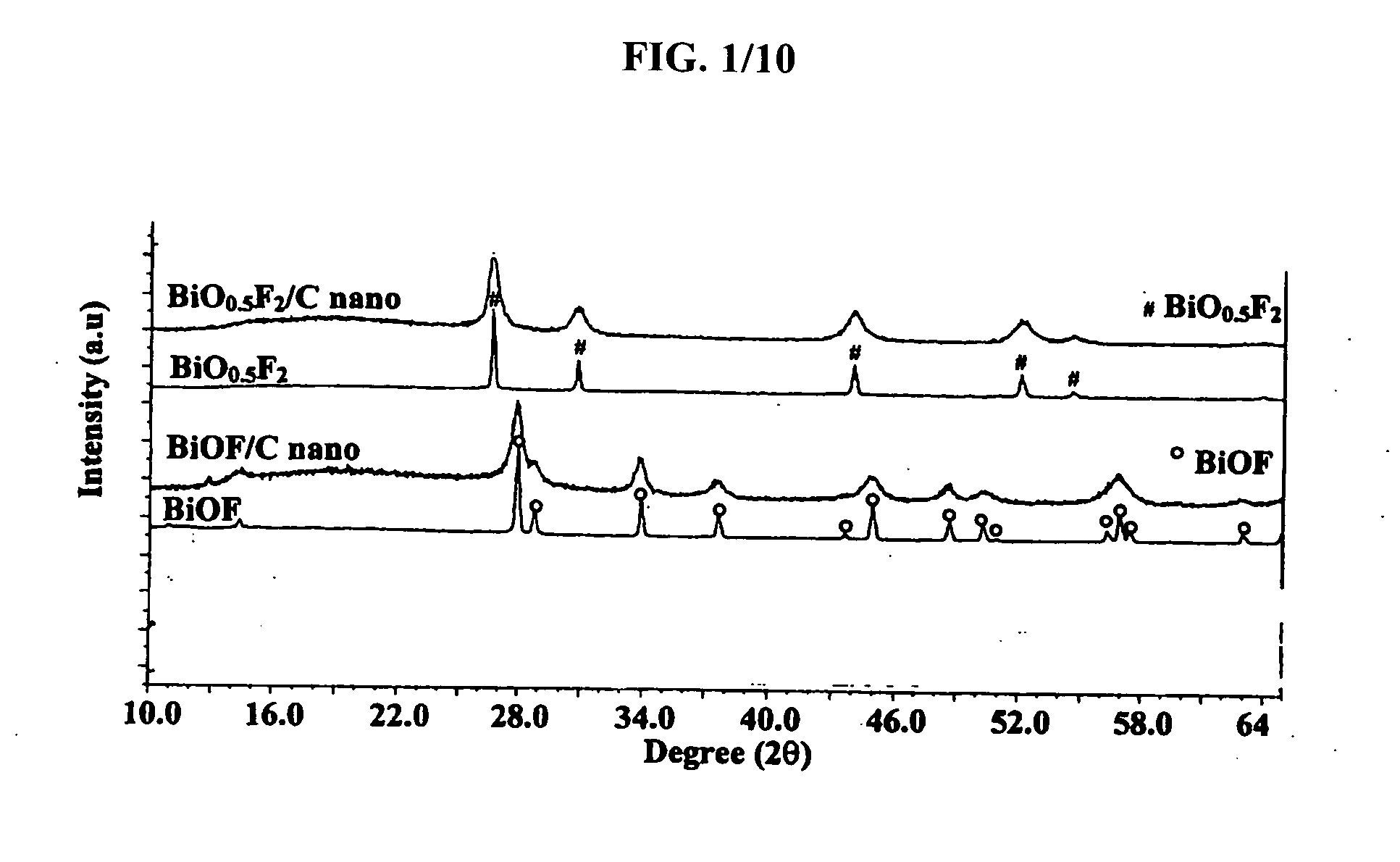
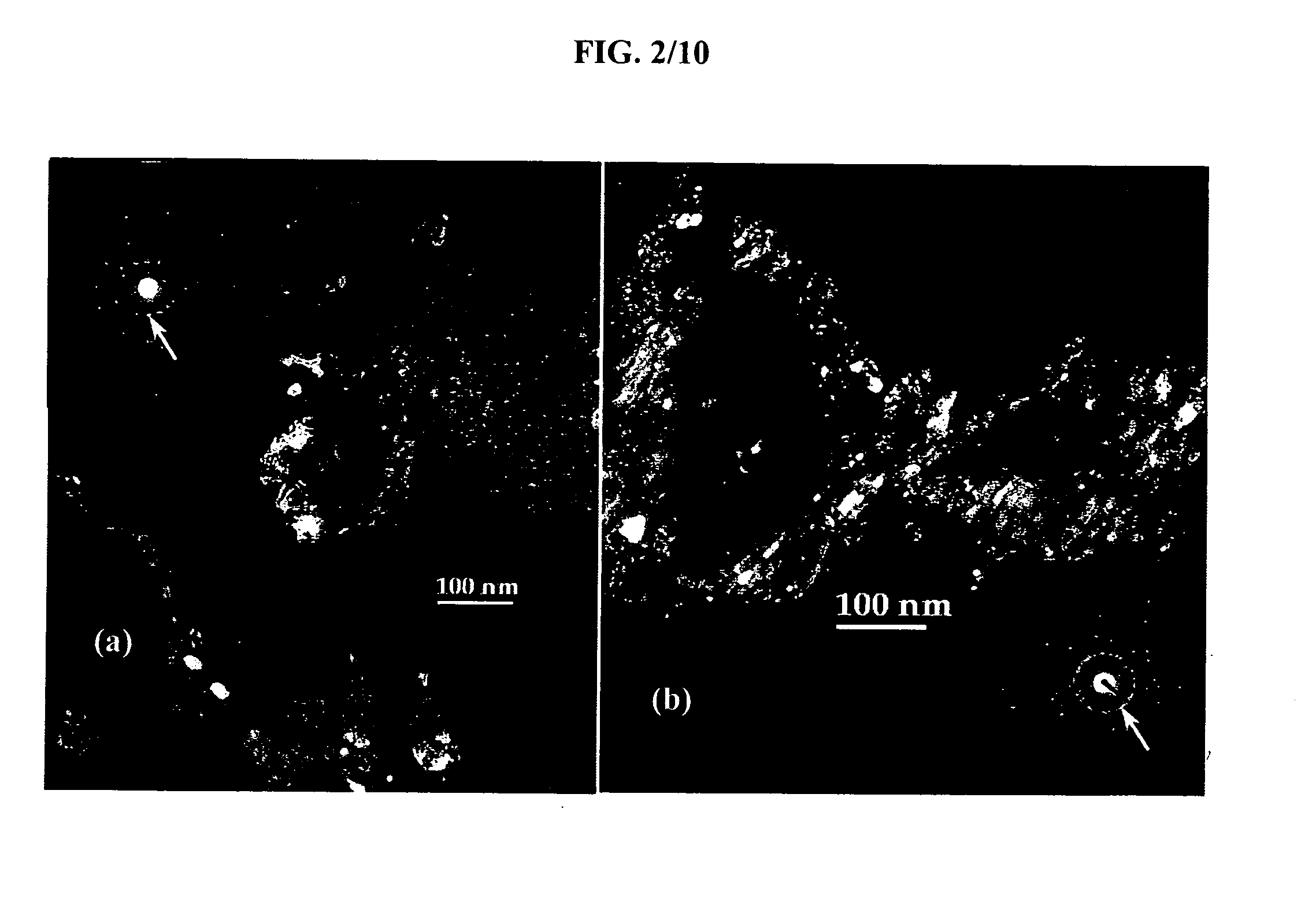
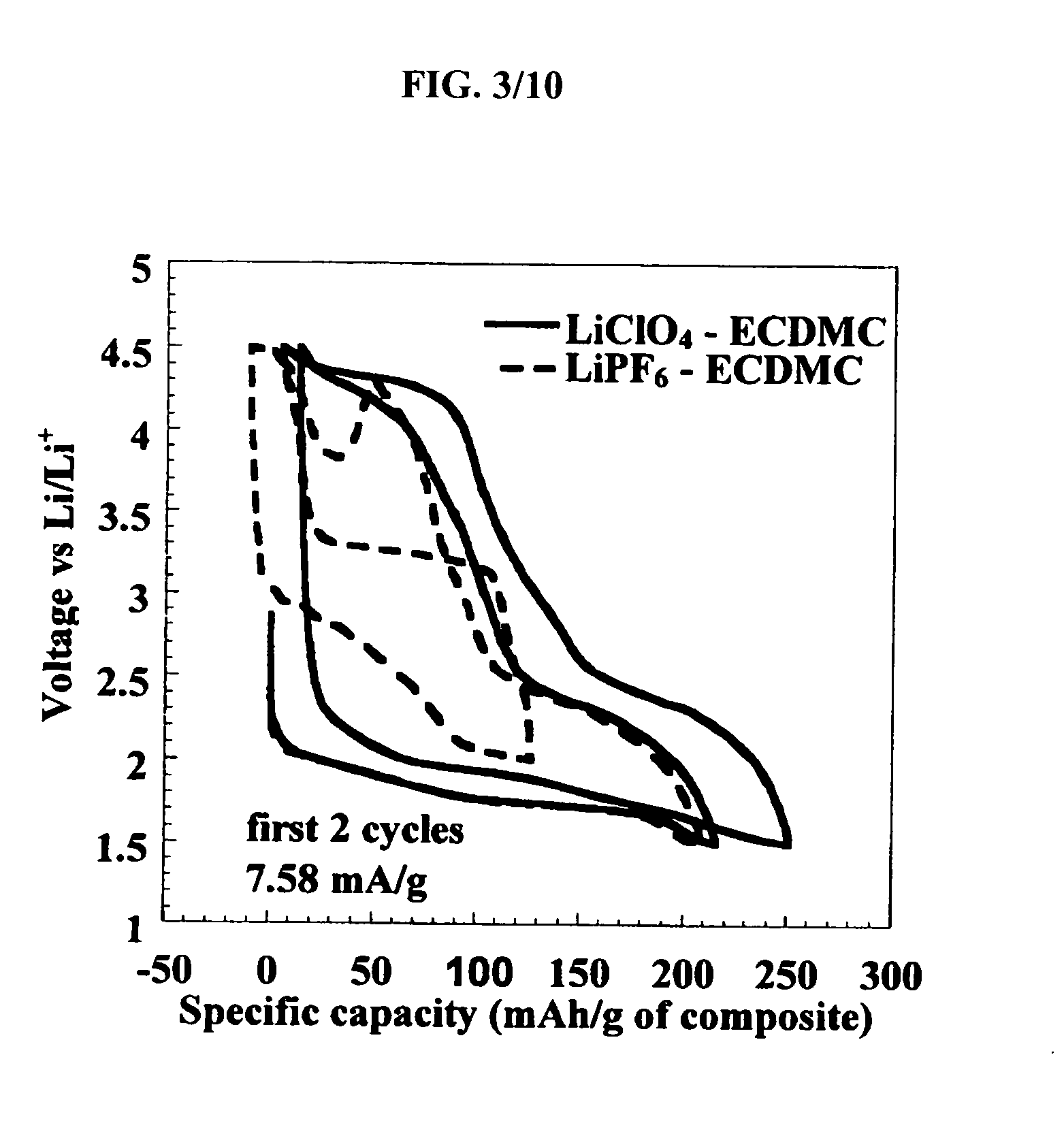
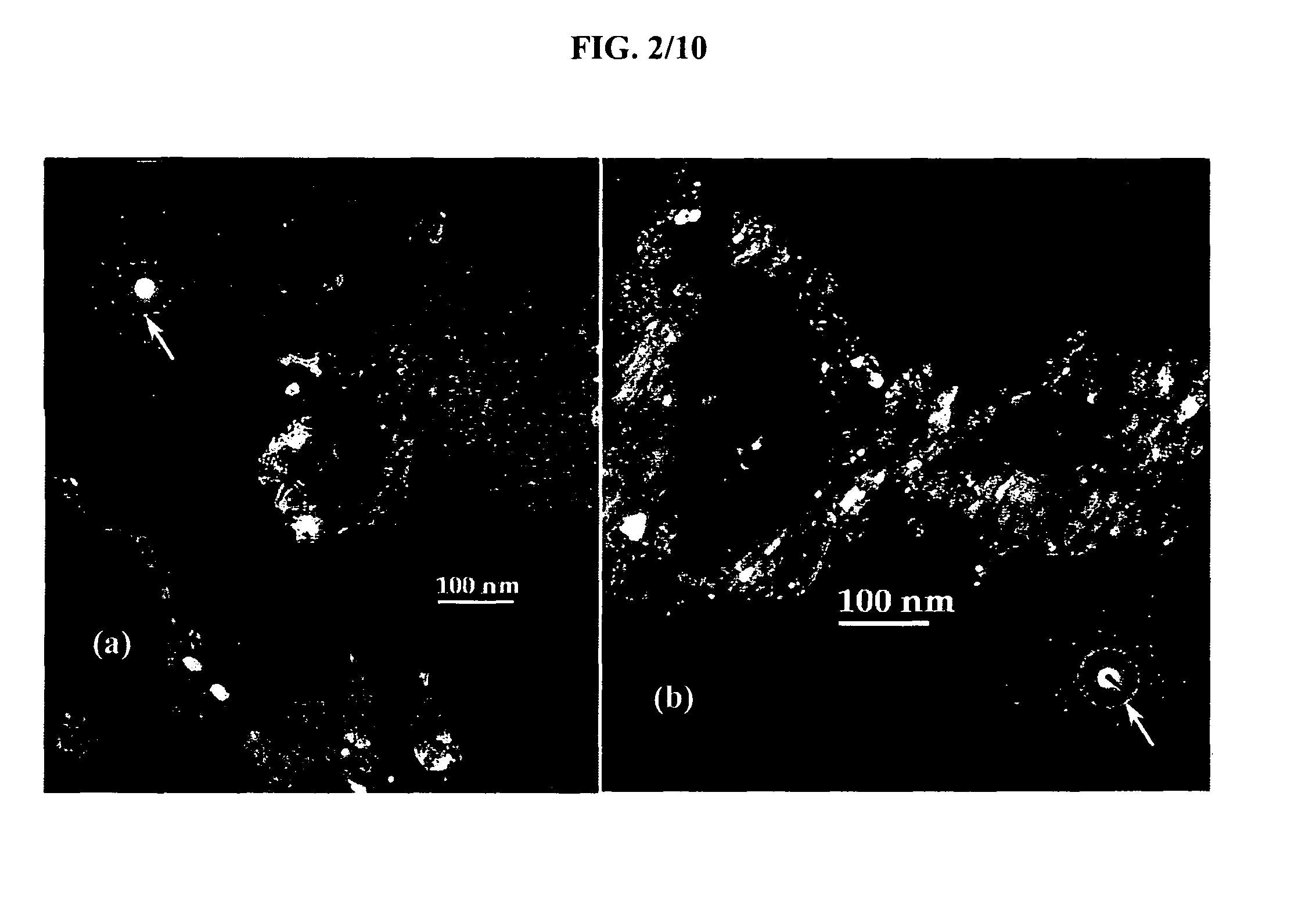
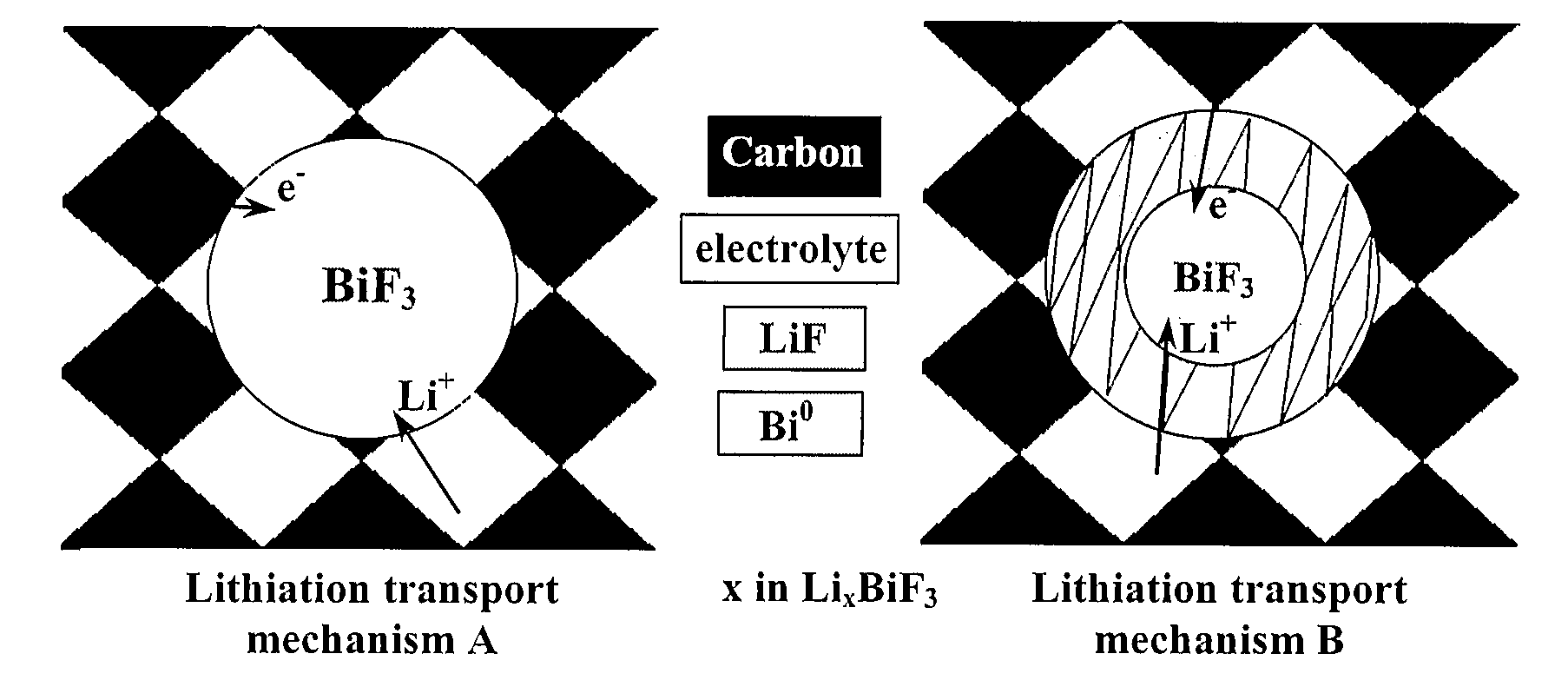
Bismuth Fluoride Based Nanocomposites as Electrode Materials
The present invention relates to primary and secondary electrochemical energy storage systems, particularly to such systems as battery cells, which use materials that take up and release ions as a means of storing and supplying electrical energy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Preparation of complex fluoride and complex fluoride phosphor
ActiveCN102732249AHigh yieldSatisfied with launch performanceTin compoundsFluoride preparationPhosphorFluoride
A complex fluoride A 2 MF 6 wherein M is a tetravalent element Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, Ge or Sn, A is an alkali metal Li, Na, K, Rb or Cs is prepared by providing a first solution containing a fluoride of M, providing a second solution containing a compound of A and / or the compound of A in solid form, mixing the first solution with the second solution and / or the solid for reacting the fluoride of M with the compound of A, and recovering the resulting solid product via solid-liquid separation.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Fluorosulfate-based electrode active materials and method of making the same
The invention provides an electrochemical cell which includes a first electrode and a second electrode which is a counter electrode to said first electrode, and an electrolyte material interposed there between. The first electrode includes a fluorosulfate-based compound.
Owner:VALENCE TECH INC
Method for fluorinating a compound comprising a halosulphonyl or dihalophosphonyl group
The invention relates to a fluorination process for producing fluorinated compounds.The process consists in reacting a compound (I) corresponding to the formulawith an ionic fluoride of a monovalent cation. M represents H, an alkali metal, a quaternary phosphonium group or a quaternary ammonium group. Y represents SO2 and m is 1, or else Y is PO and m is 2. Z represents CR2, N or P. R1 represents an electron-withdrawing group which has a Hammet σP parameter of greater than 0.4. R2 represents a carbonaceous and / or electron-withdrawing group. X represents a halogen other than a fluorine.The fluorinated compounds obtained are of use in particular as electrolytes in lithium batteries.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Lithium-nickel-cobalt-maganese containing composite oxide, material for positive electrode active material for lithium secondary battery, and methods for producing these
ActiveUS7384706B2Large capacityExcels in charge-discharge cycle durabilityElectrode rolling/calenderingFluoride preparationManganeseCharge discharge
Coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxide wherein primary particles are coagulated to form secondary particles are synthesized by allowing an aqueous solution of a nickel-cobalt-manganese salt, an aqueous solution of an alkali-metal hydroxide, and an ammonium-ion donor to react under specific conditions; and a lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese-containing composite oxide represented by a general formula, LipNixMn1-x-yCoyO2-qFq (where 0.98≦p≦1.07, 0.3≦x≦0.5, 0.1≦y≦0.38, and 0≦q≦0.05), which is a positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary cell having a wide usable voltage range, a charge-discharge cycle durability, a high capacity and high safety, is obtained by dry-blending coagulated particles of nickel-cobalt-manganese composite oxyhydroxide formed by making an oxidant to act on the coagulated particles with a lithium salt, and firing the mixture in an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Cathode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20100035155A1Increase energy densityElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationMechanical millingFluoride
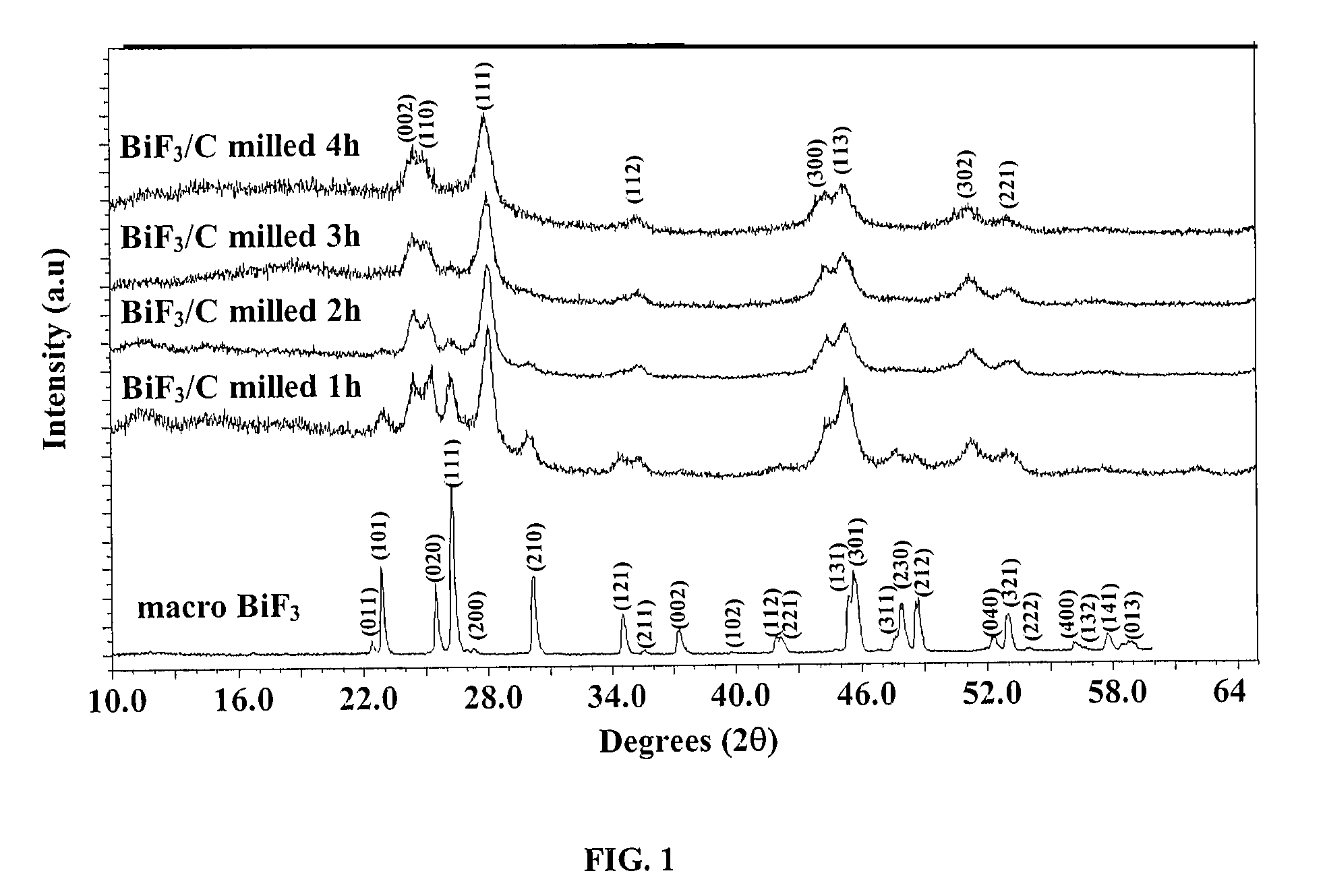
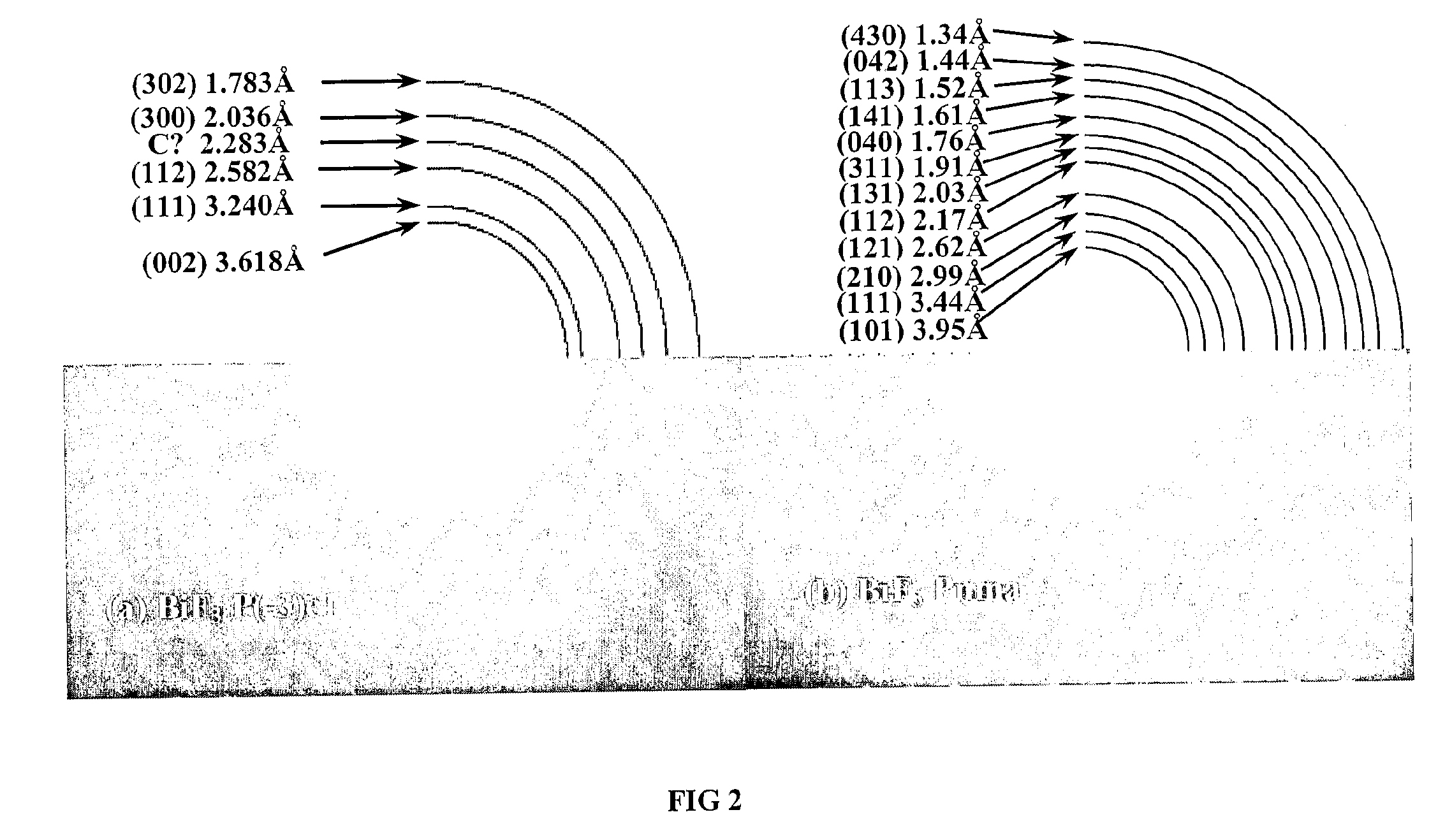
In a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, in order to adjust a cathode active material in which guest cation such as Na and Li is included, alkaline metal fluoride which is expressed by a general formula AF and transition metal fluoride which is expressed by a formula M′ F2 are subjected to a mechanical milling process to produce metal fluoride compound AM′ F3. The mechanical milling process desirably uses a planetary ball mill.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
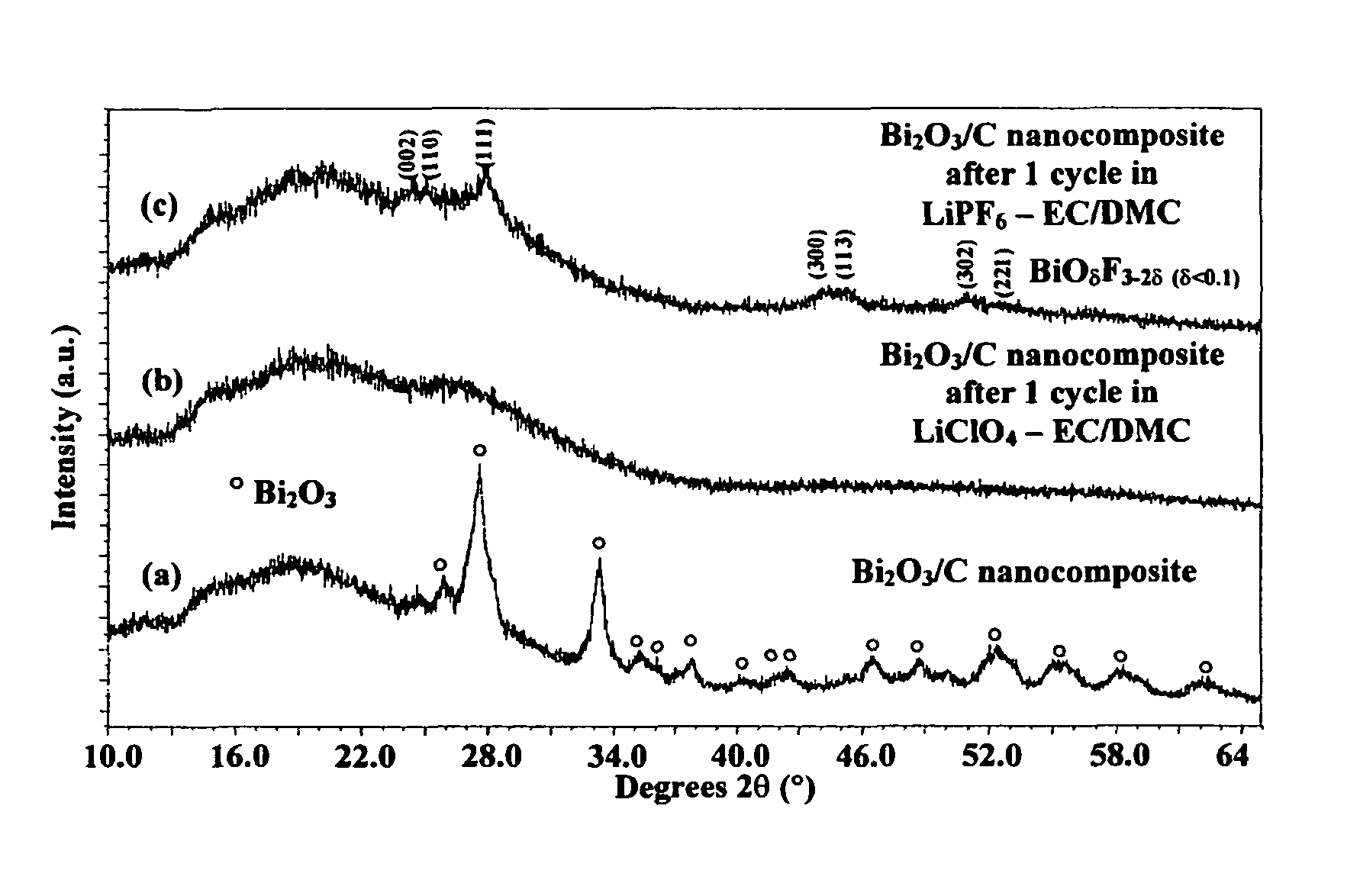
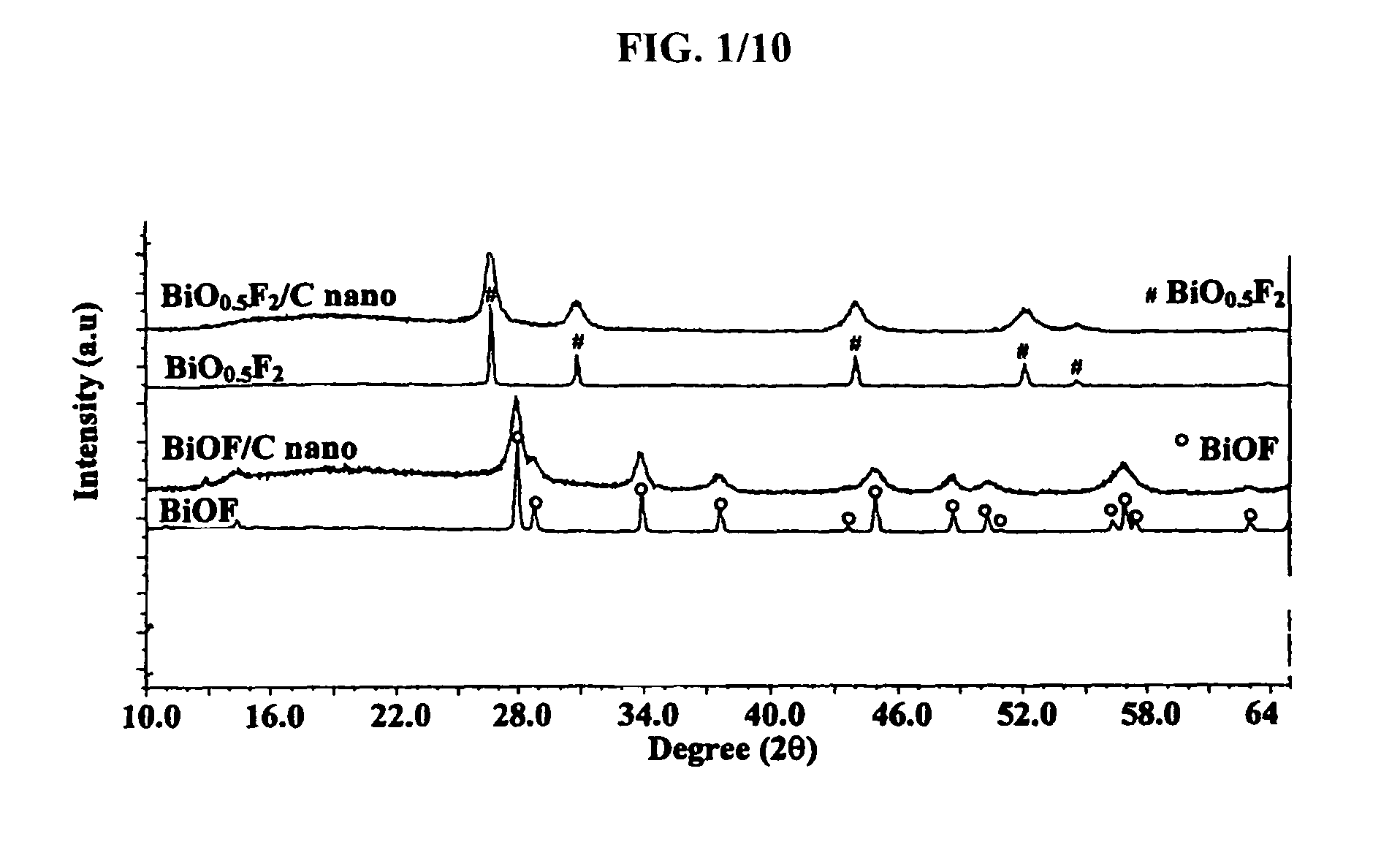
Bismuth oxyfluoride based nanocomposites as electrode materials
ActiveUS20070190414A1Simple materialMaterial nanotechnologyFluoride preparationNanometreNanocomposite
The present invention relates to bismuth oxyfluoride nanocomposites used as positive electrodes in primary and rechargeable electromechanical energy storage systems.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Nano-scale metal halide scintillation materials and methods for making same
Crystalline scintillator materials comprising nano-scale particles of metal halides are provided. The nano-scale particles are less than 100 nm in size. Methods are provided for preparing the particles. In these methods, ionic liquids are used in place of water to allow precipitation of the final product. In one method, the metal precursors and halide salts are dissolved in separate ionic liquids to form solutions, which are then combined to form the nano-crystalline end product. In the other methods, micro-emulsions are formed using ionic liquids to control particle size.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
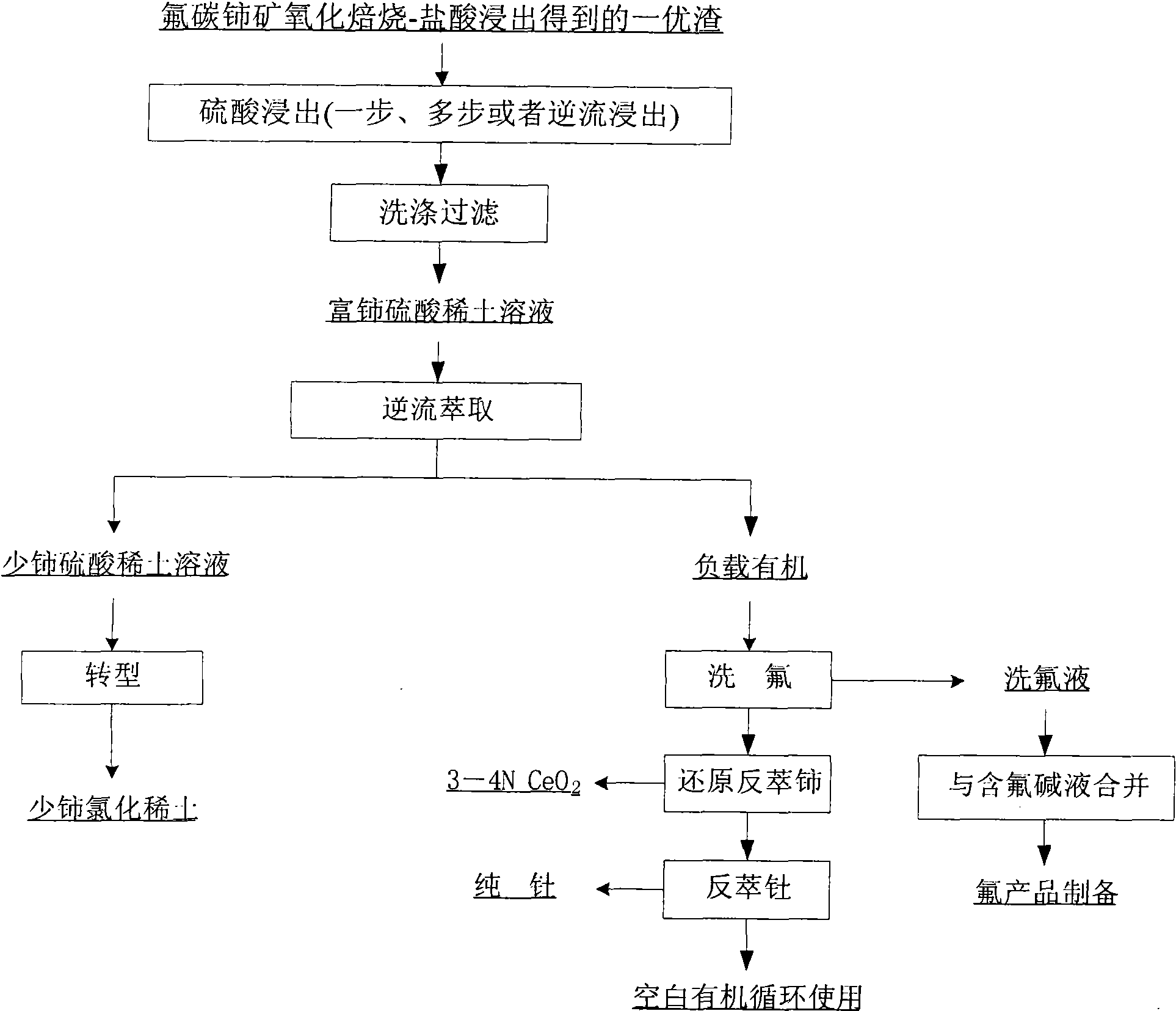
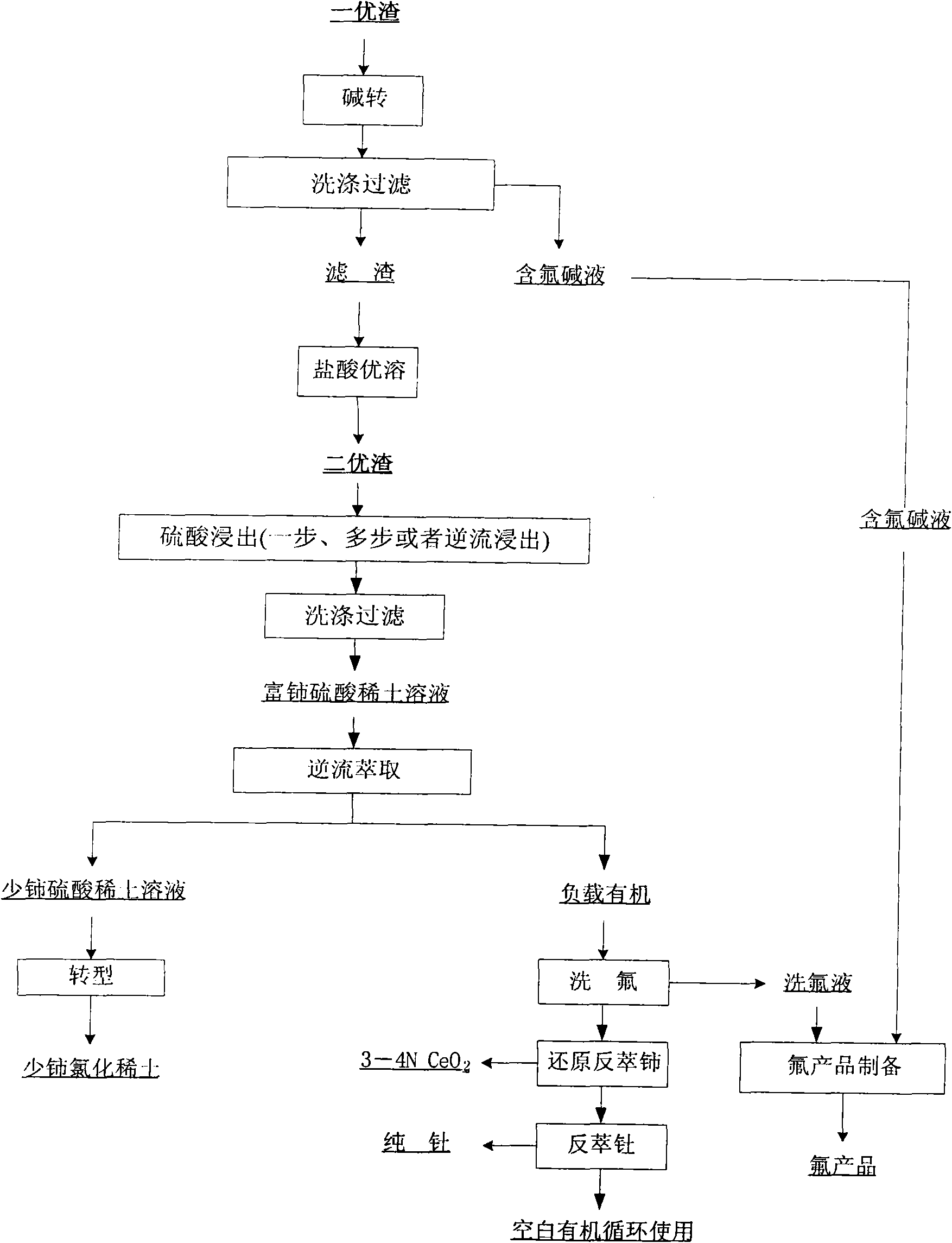
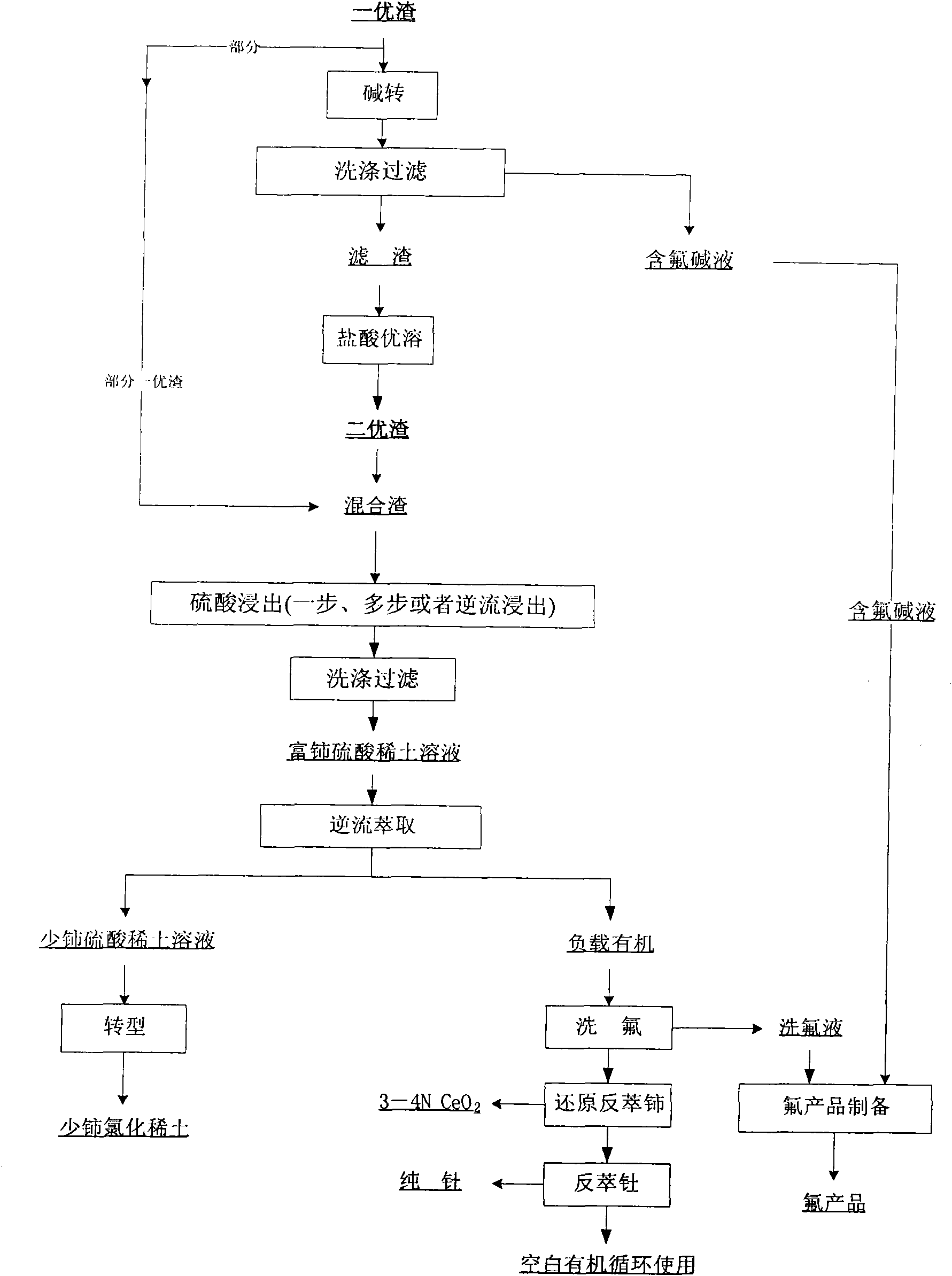
Hamartite smelting separation process
ActiveCN102146512AAchieve recyclingIncrease the added value of resourcesFluoride preparationProcess efficiency improvementFluoride productsSlag
The invention discloses a hamartite smelting separation process. First optimal slag or / and second optimal slag mainly containing cerium (IV), thorium (IV) and fluorine, obtained by oxidative roasted salt acid leaching of hamartite, is / are used as raw materials, and extraction and separation of rare earth are performed. The process comprises the following steps of: 1) leaching the first optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; or leaching the second optimal slag obtained by alkali conversion-hydrochloric acid dissolution of the first optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; or leaching the mixed slag of the first optimal slag and the second optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; 2) performing extraction separation on the sulfuric acid-rare earth solution obtained in the step 1) to obtain a rare earth compound,fluorine washing liquor, a pure cerium product and a thorium product; and 3) synthesizing a fluoride product by using the fluorine-containing alkali wastewater obtained by alkali conversion in the step 1) and the fluorine washing liquor obtained by the extraction separation in the step 2). The process has the advantages that: the recovery rate of the rare earth is obviously improved, the fluorineand the thorium (IV) are effectively reclaimed in a product form, the high-purity cerium product is obtained, reclamation of the rare earth and associated resources is realized, and the additional values of the resources are improved; and the process flow is simple, the consumption of acid and alkali is low, the production cost is low, and the process is environmentally-friendly.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
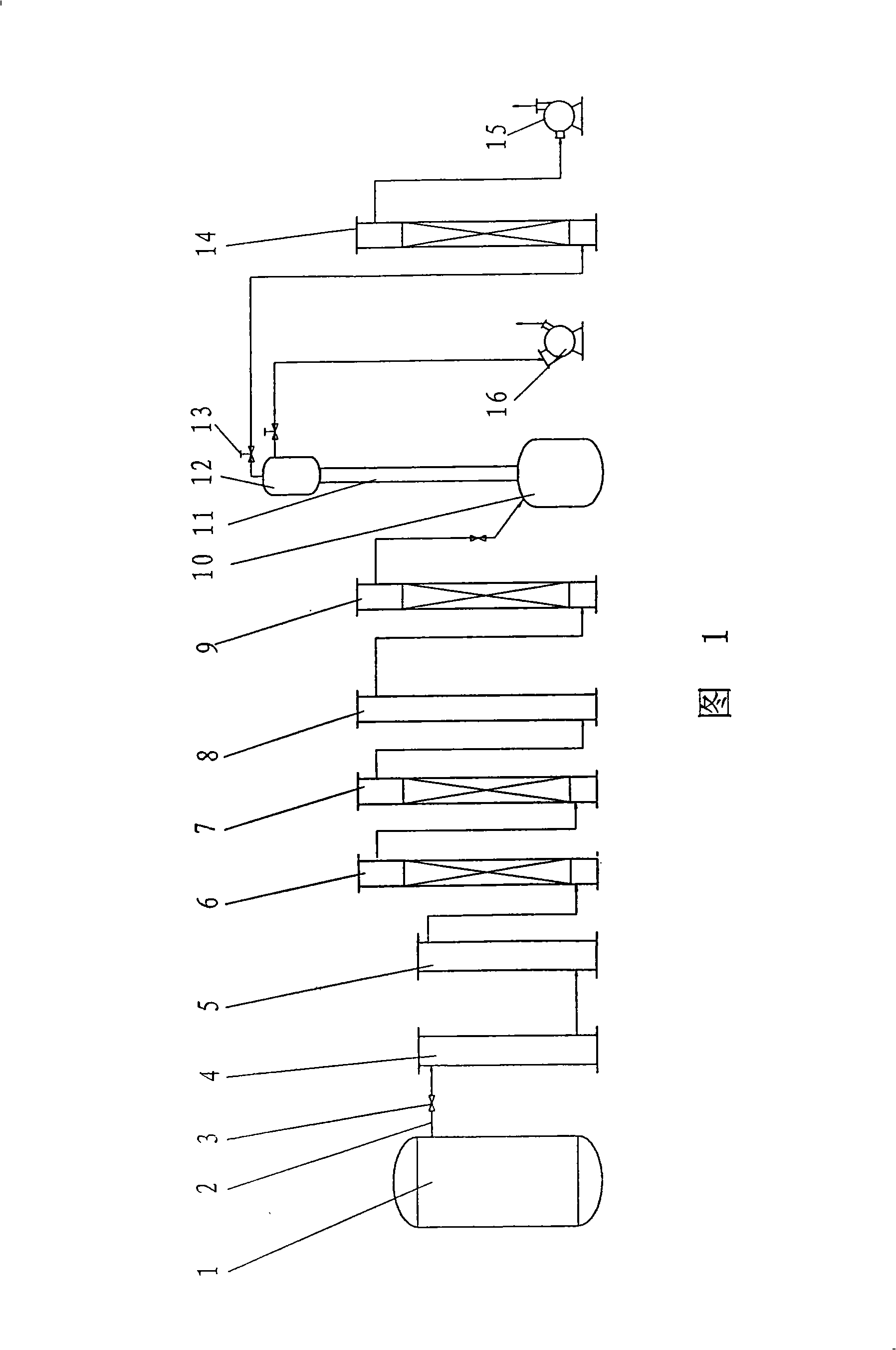
Method and apparatus for preparing high-pure carbon tetrafluoride gas
The invention discloses a method and equipment for producing highly purity carbon tetrafluoride gas; the method includes the steps: the fluorine gas and highly purity active carbon successively experience the chemical synthesis reaction, dedusting, water washing, alkaline washing, gas liquid separation, water removal, rectification, liquefaction and collection. The equipment includes a fluorine gas storage tank, a reaction kettle, a dust catcher, a water scrubber, an alkaline tower, a gas-liquid separator, an absorption column, a rectifying still, a rectifying column and a condenser. The carbon tetrafluoride gas produced with the method and equipment has high purity and the invention has the advantages of simple equipment, easy operation, convenient and safe operation, continuous production and so on.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
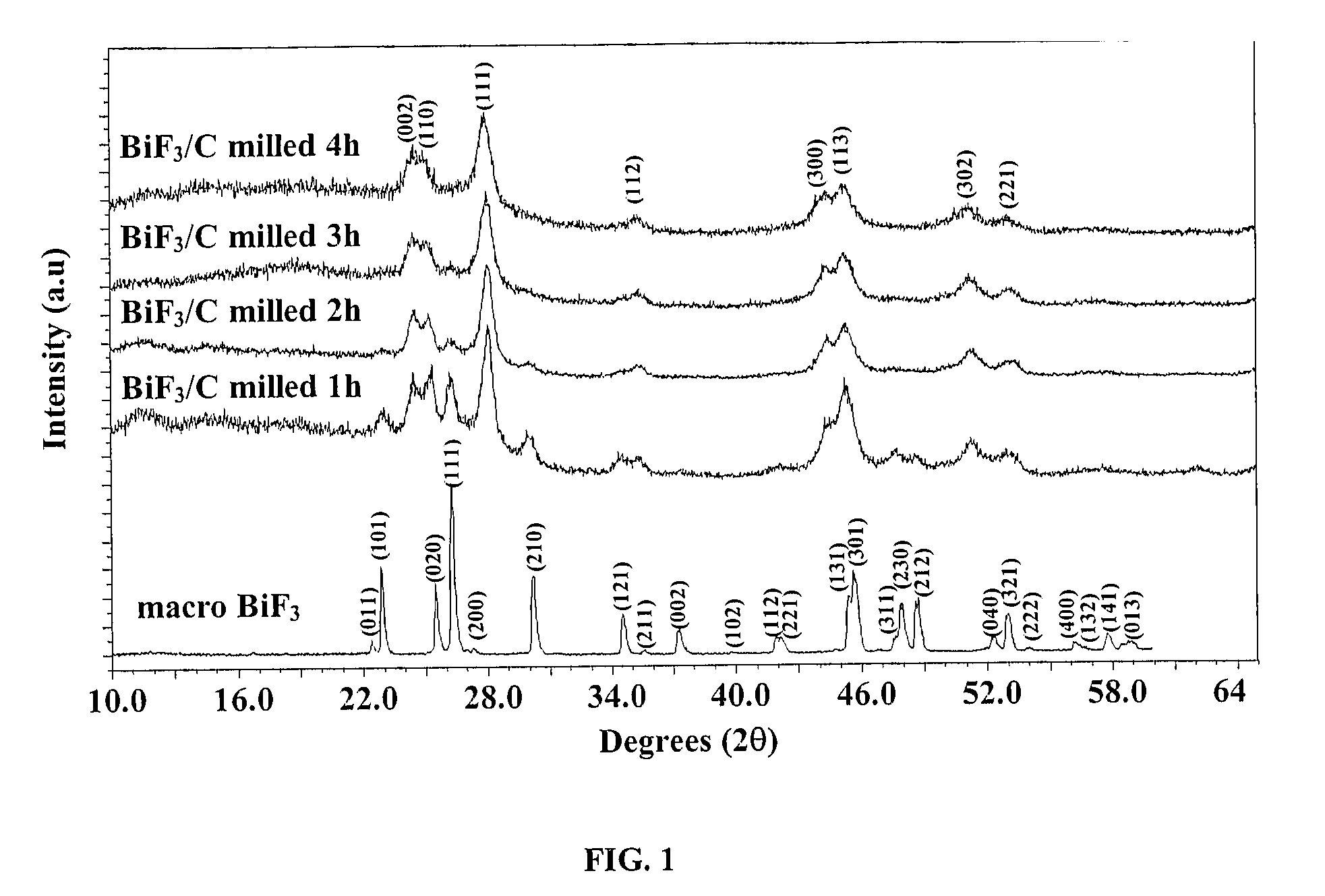
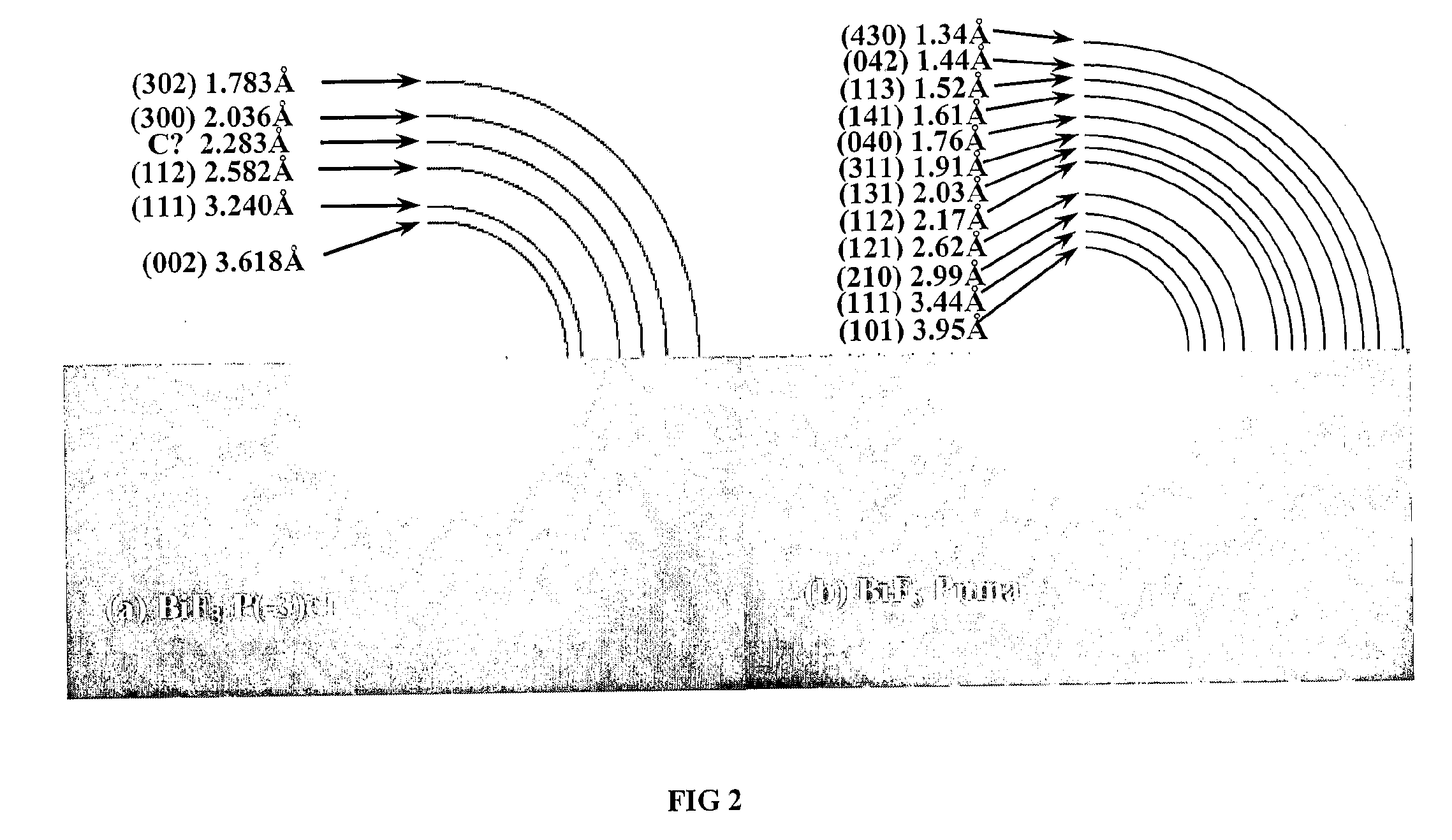
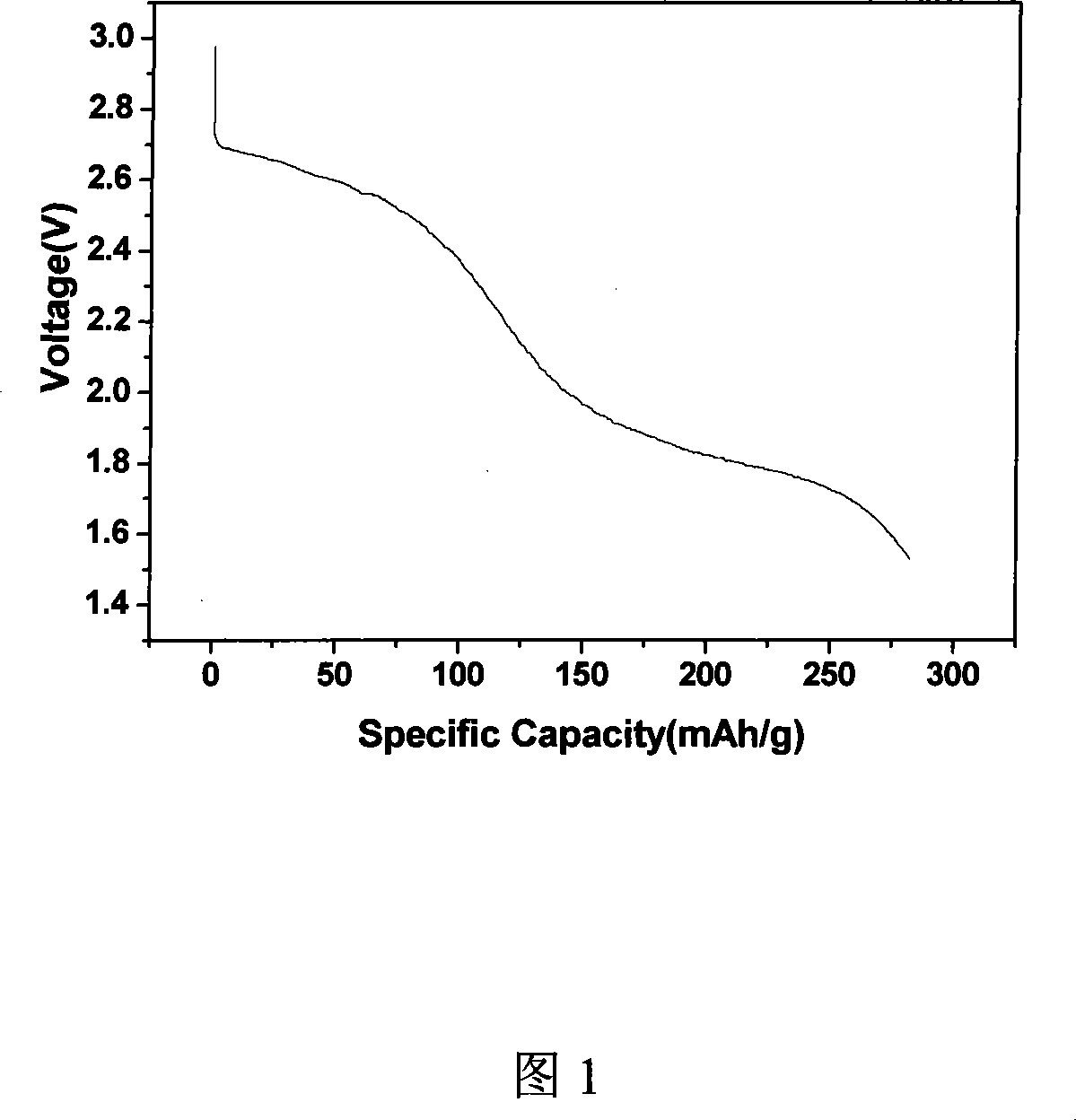
Method for producing bismuth trifluoride anode material of Li secondary battery
InactiveCN101212050ACrystallization rulesHigh purityElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationSurface-active agentsSolvent
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a fluoride bismuth anode material in a lithium ion secondary battery, which comprises the following steps: 1) the bismuth salt is stirred for 1-10 hours until the bismuth salt is dissolved in the acetum solution of 5-45 per cent under the temperature of 0-50 DEG C, and then the solution of bismuth salt and the acetum is obtained; 2) surface active agent is added into the solution of bismuth salt and the acetum, and then the mixing solution of bismuth salt is obtained; 3) the soluble fluoride salt or the HF is dissolved in the 1-30 per cent ethanol water, and then the mixing solution of ethanol and fluoride is obtained; 4) the mixing solution of ethanol and fluoride obtained is dropped into the solution of bismuth salt and the acetum under a temperature of 0-45 DEG C, and a deposition of BiF3 is obtained; 5) the deposition of the BiF3 is filtered, washed and dried in the vacuum for 8-48 hours under the temperature of 45-100 DEG C to obtain the product of BiF3. The invention has the following beneficial effects: firstly, the acetic acid is used as solvent of Bi<3+> and the F<-> is directly added into the solvent. The BiF3 is prepared using the method of liquid phase deposition together. The obtained product has a high purity. The grain diameter can be controlled through adding surface active agent and controlling the time and the temperature of the deposition reaction. The solvent can be used repeatedly. Secondly, the product manufactured according to the method has the advantages of high purity, orderly grain crystal, good dispersivilty and good performance of discharging, and therefore the method is a novel, simple and high field manufacturing method for BiF3.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Process for producing lithium-containing composite oxide for positive electrode for lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20060210879A1Large volume capacity densityImprove securityElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationPowder mixtureAlkaline earth metal
A lithium-containing composite oxide for a positive electrode for a lithium secondary battery is prepared by formulating a powder mixture by impregnating an N element source powder having an average particle size (D50) ranging from 2 to 20 μm with an aqueous solution of a carboxylic acid having a total of two or more carboxylic acid groups or carboxylic acid groups and hydroxyl groups in its molecule, and optionally, containing an M element, or its salt, and then drying the material obtained; and firing the N element powder material in admixture with a lithium source, optionally, an M element source and a fluorine source, at a temperature ranging from 700° C. to 1050° C. in an oxygen-containing atmosphere, thereby obtaining a lithium-containing composite oxide having the formula LipNxMyOzFa, wherein N is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Co, Mn and Ni, M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Sn, Zn, Al, alkaline earth metal elements, and transition metal elements other than N, 0.9≦p≦1.1, 0.97≦x≦1.00, 0<y≦0.03, 1.9≦z≦2.1, x+y=1 and 0≦a≦0.02).
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Ionic liquid based mixtures for gas storage and delivery
A mixture and method for the storage and delivery of at least one gas are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a mixture for the storage and delivery of at least one gas comprising: an ionic liquid comprising an anion and a cation; and at least one gas that is disposed within and is reversibly chemically reacted with the ionic liquid. In another aspect, there is provided a method for delivering at least one gas from a mixture comprising an ionic liquid and at least one gas comprising: reacting the at least one gas and the ionic liquid to provide the mixture and separating the at least one gas from the mixture wherein the at least one gas after the separating step is substantially the same as the at least one gas prior to the reacting step.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Bismuth oxyfluoride based nanocomposites as electrode materials
The present invention relates to bismuth oxyfluoride nanocomposites used as positive electrodes in primary and rechargeable electromechanical energy storage systems.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
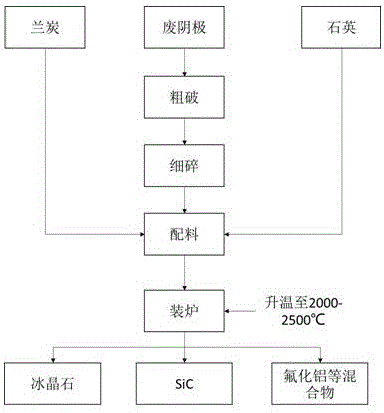
Method for treating spent cathodes of spent potlinings of aluminum electrolysis cells
InactiveCN106517209ARealize comprehensive utilizationReduce the cost of electrolytic productionFluoride preparationCarbon compoundsElectrolysisCyanide
The invention relates to a method for resource utilization of solid wastes of aluminum electrolysis cells, in particular to a method for treating spent cathodes of spent potlinings of aluminum electrolysis cells. The method includes adding a carbon material and quartz sand into the spent cathodes of the spent potlinings of the aluminum electrolysis cells, conducting high-temperature carbothermic reduction in a high-temperature reacting furnace to obtain SiC, enabling cryolite to form melts to sink, making the melts and the generated SiC to undergo solid-liquid separation, and subjecting a fluoride salt to furnace gas evaporation prior to gas-solid separation from the generated SiC so as to obtain SiC; collecting the sunk cryolite melts and conducting condensation recovery so as to obtain cryolite; collecting evaporated furnace gas and cooling so as to obtain the fluoride salt. The method has the advantages that the SiC is prepared through a high-temperature carbothermic reduction method, fluoride and electrolytes are recovered, the electrolytes are reused for the aluminum electrolysis industry, and cyanide in the spent potlinings is decomposed and removed, so that comprehensive resource utilization of the spent potlinings of the aluminum electrolysis cells is achieved and electrolysis production cost is reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Optically transparent nanocomposite materials
InactiveUS7094361B2Well formedReadily fiberizableMaterial nanotechnologyChloride preparationFluorescenceSolid solution
Optically transparent composite materials in which solid solution inorganic nanoparticles are dispersed in a host matrix inert thereto, wherein the nanoparticles are doped with one or more active ions at a level up to about 60 mole % and consist of particles having a dispersed particle size between about 1 and about 100 nm, and the composite material with the nanoparticles dispersed therein is optically transparent to wavelengths at which excitation, fluorescence or luminescence of the active ions occur. Luminescent devices incorporating the composite materials are also disclosed.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Crystalline filters for ultraviolet light sensors
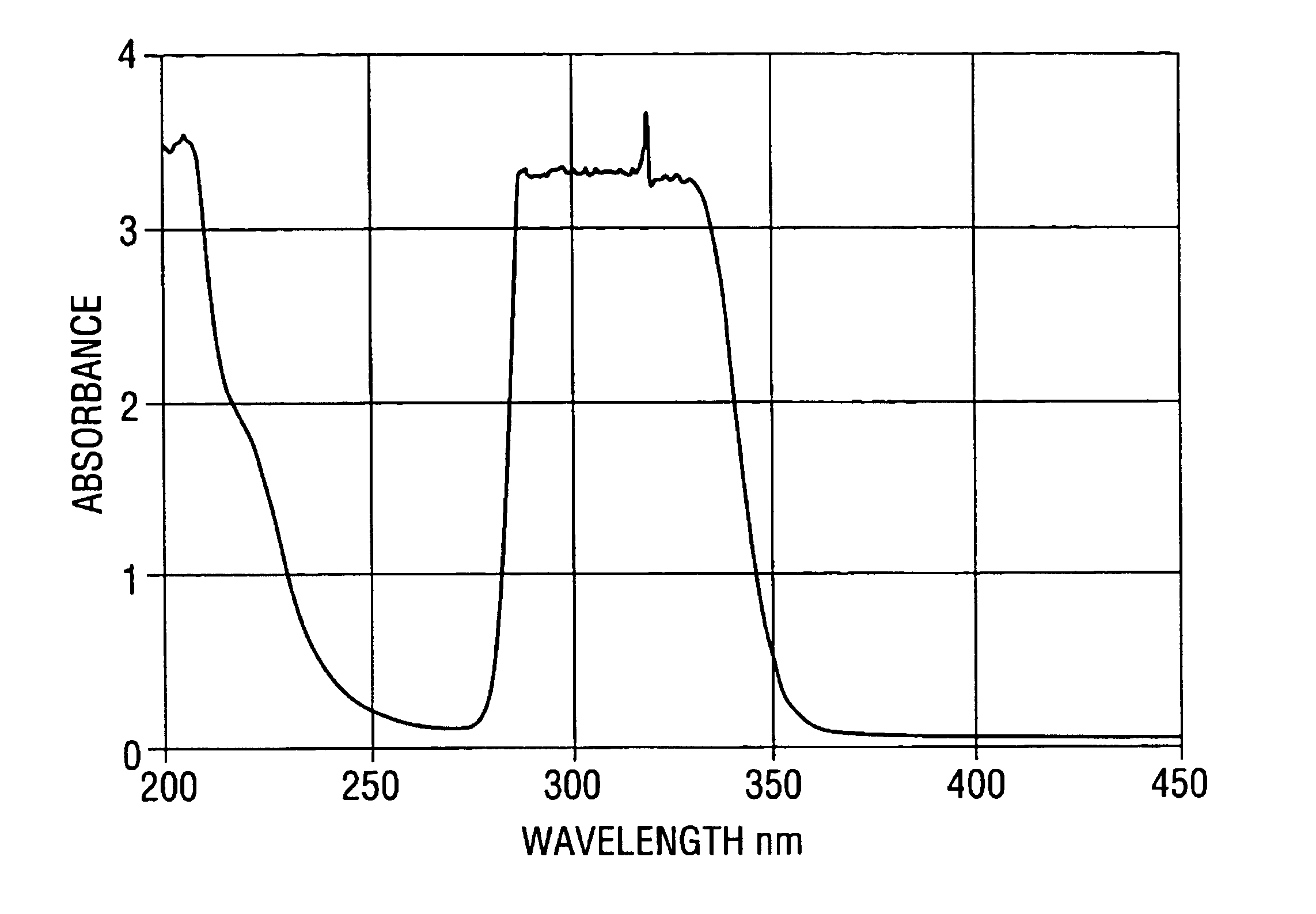
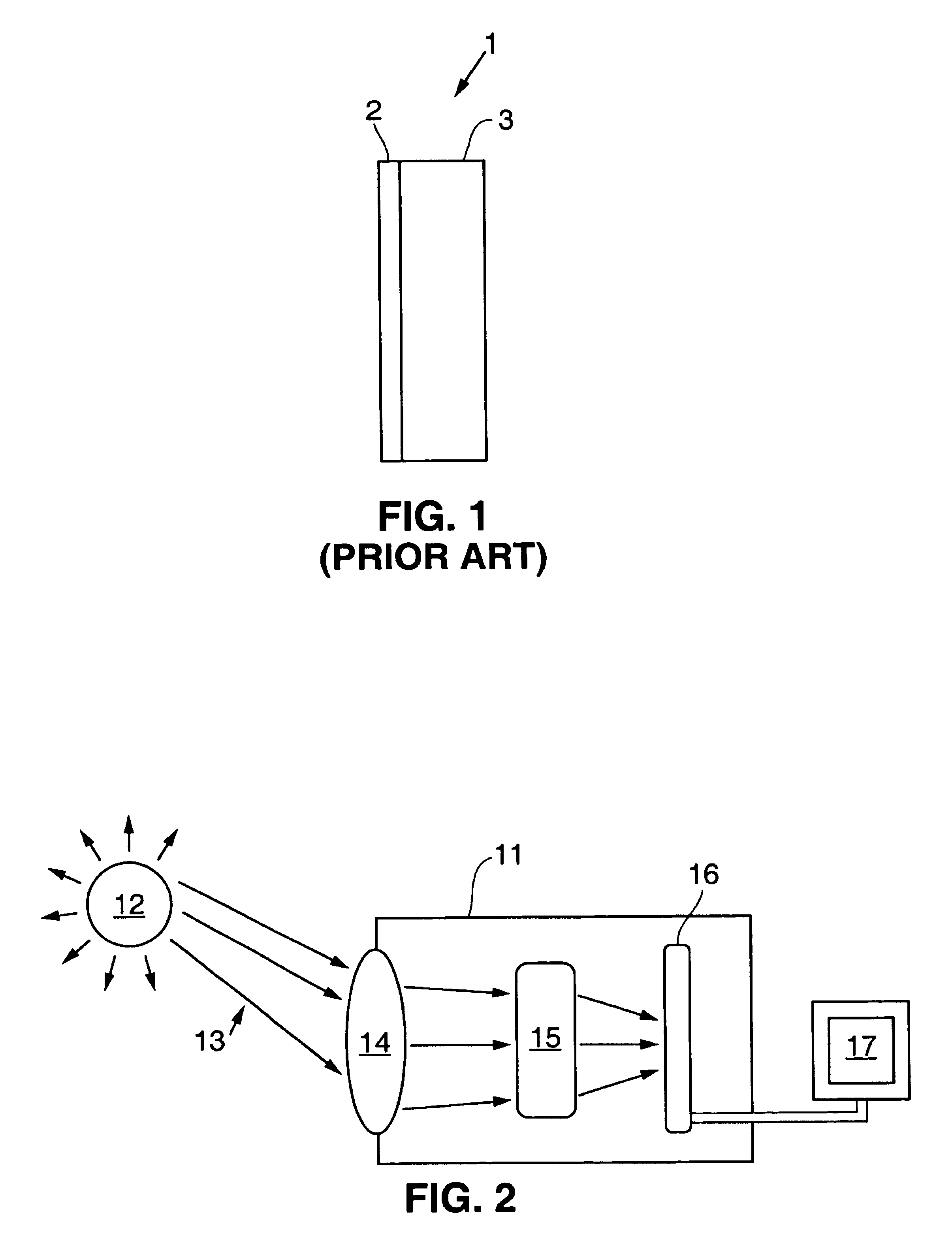
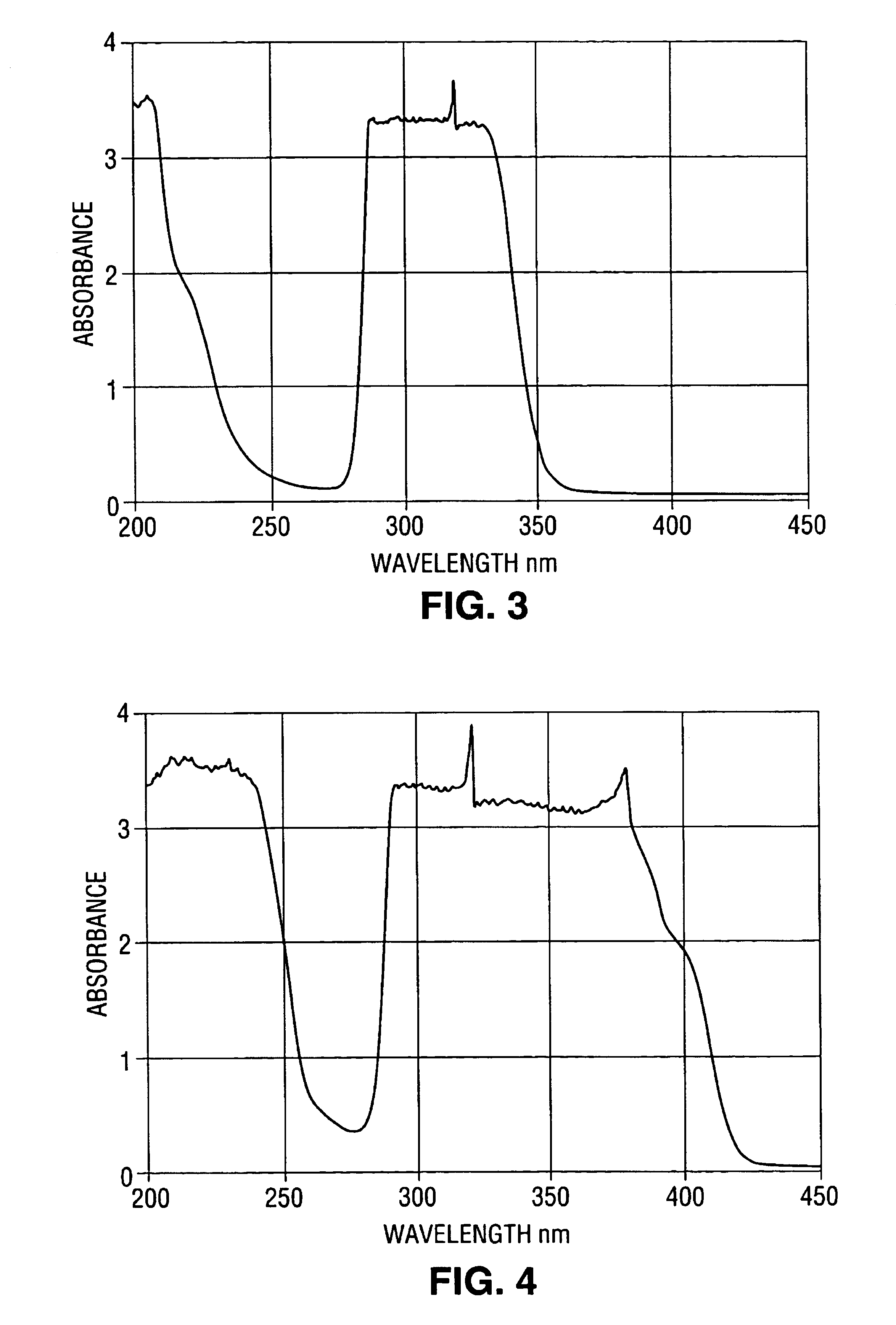
A crystal filter and a method of making a crystal filter capable of transmitting radiation within a particular pass band is disclosed. The crystal filter is particularly appropriate for a UV detection system, where the pass band is between about 200 to about 350 nm. A UV detection system incorporating the crystal filter is also described. One embodiment of crystal filter is formed from a single-crystal transparent host, such as a fluoride host, codoped with lanthanide or actinide fluorides and lanthanide or actinide nitrides, oxides, borides, carbides or hydroxides. Filter crystals according to the present invention can be grown by various crystal growth methods, including Czochralski and Bridgeman crystal growth methods.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method of preparing high purity cerium trifluoride micro powder
A process for preparing the superfine particles of high-purity cerium trifluoride includes proportionally mixing Cyanex 923 with diluent chosen from hexane, pentane, octane, etc to obtain composite extractant, extracting the Ce and F contained RE sulfate solution, washing and back extracting by strip liquid chosen from hydrogen peroxide, hydrazine hydrate, hydroxyamine hydrochloride, etc. Its purity is 99.9-99.999%.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bismuth fluoride based nanocomposites as electrode materials
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Positive electrode material for lithium secondary cell and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060222951A1High cycle durabilityImprove securityElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationLithiumHigh pressure
A positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery for high voltage high capacity use exhibiting high cycle durability and high safety. The positive electrode material is composed of particles having a composition represented by the general formula: LiaCObMgcAdOeFf (A is the group 6 transition element or the group 14 element, 0.90≦a≦1.10, 0.97≦b≦1.00, 0.0001≦c>0.03, 0.0001≦d≦0.03, 1.98≦e≦2.02, 0≦f≦0.02 and 0.0001≦c+d≦0.03), and magnesium, the element A and fluorine exist uniformly in the vicinity of the surfaces of the particles.
Owner:AGC SEIMI CHEM CO LTD
Particulate positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary cell
InactiveUS7018741B2High dischargeImprove securityFluoride preparationPositive electrodesParticulatesHigh temperature storage
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com