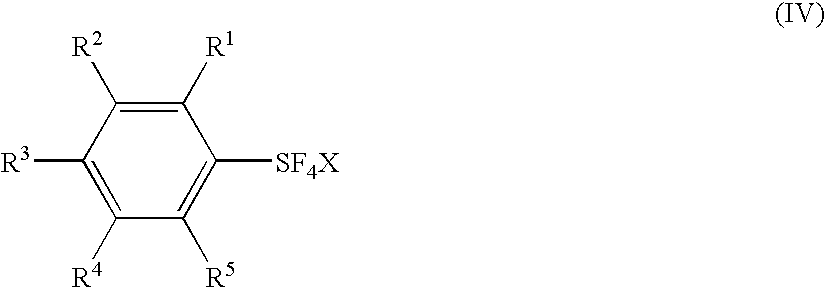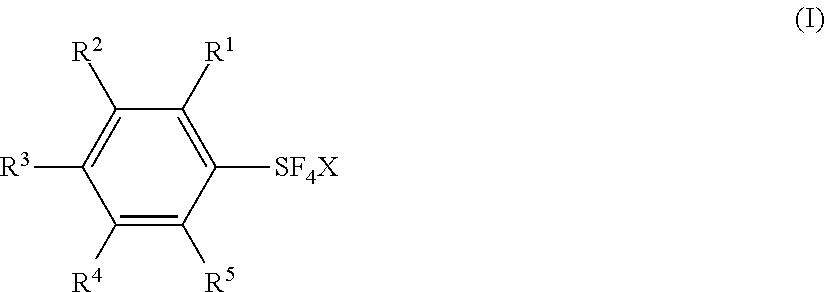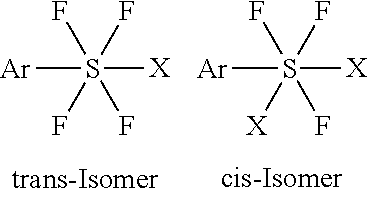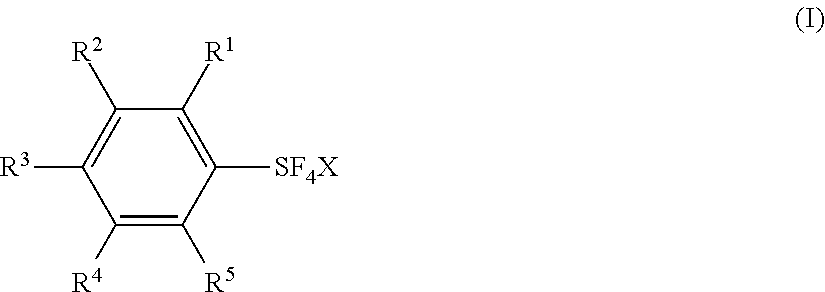Patents
Literature
417 results about "Tetrafluoride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with four fluorines in its formula.
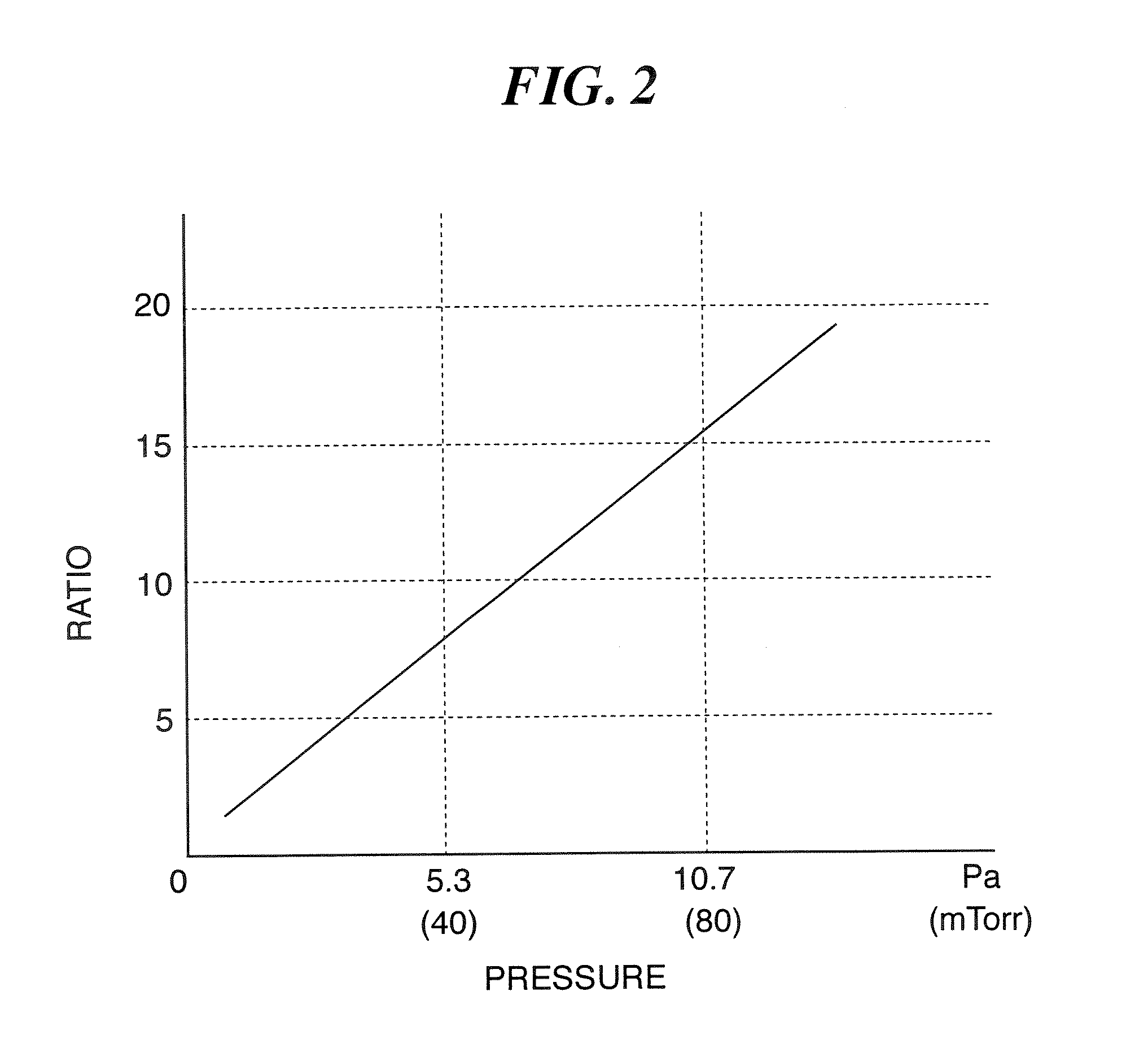
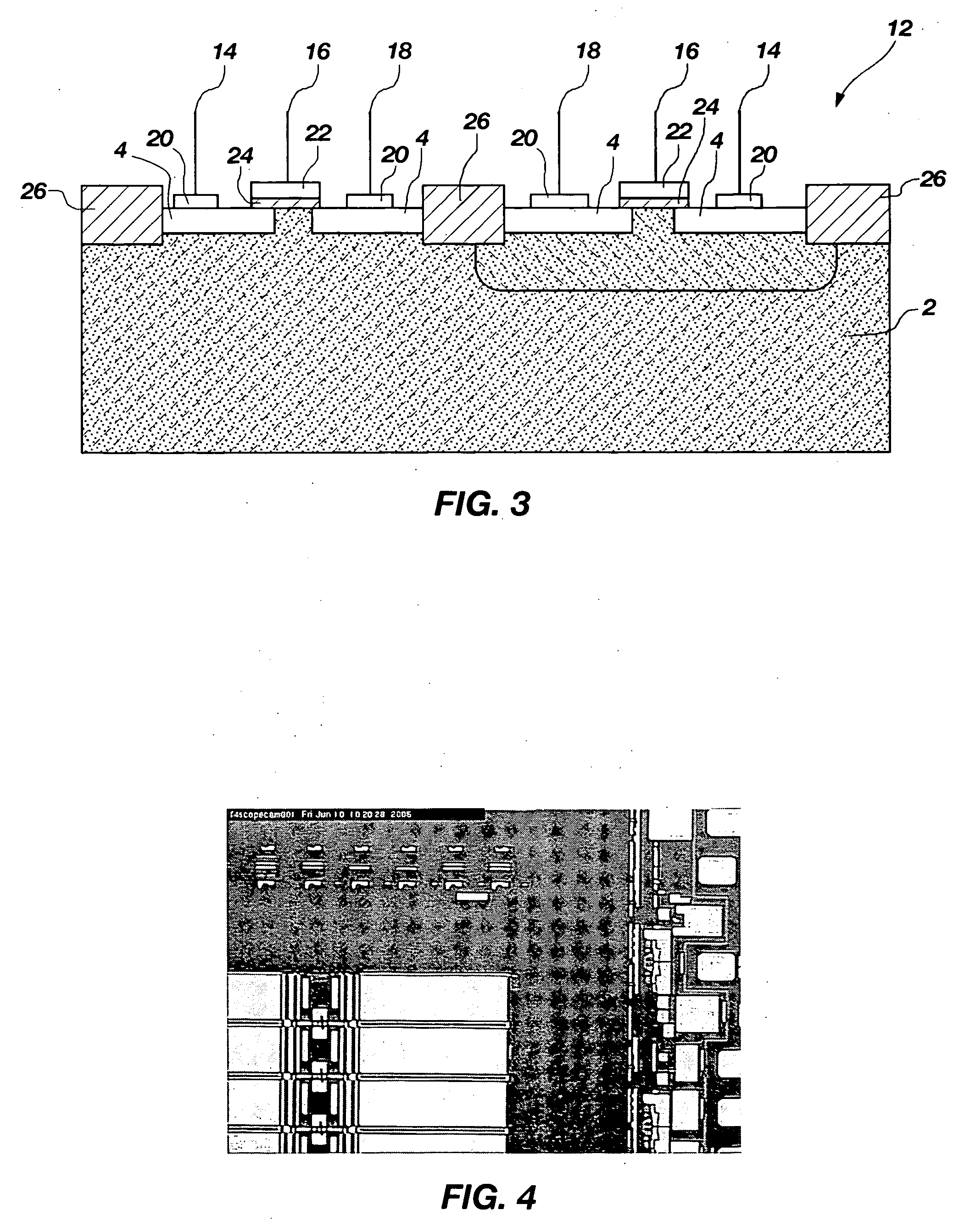
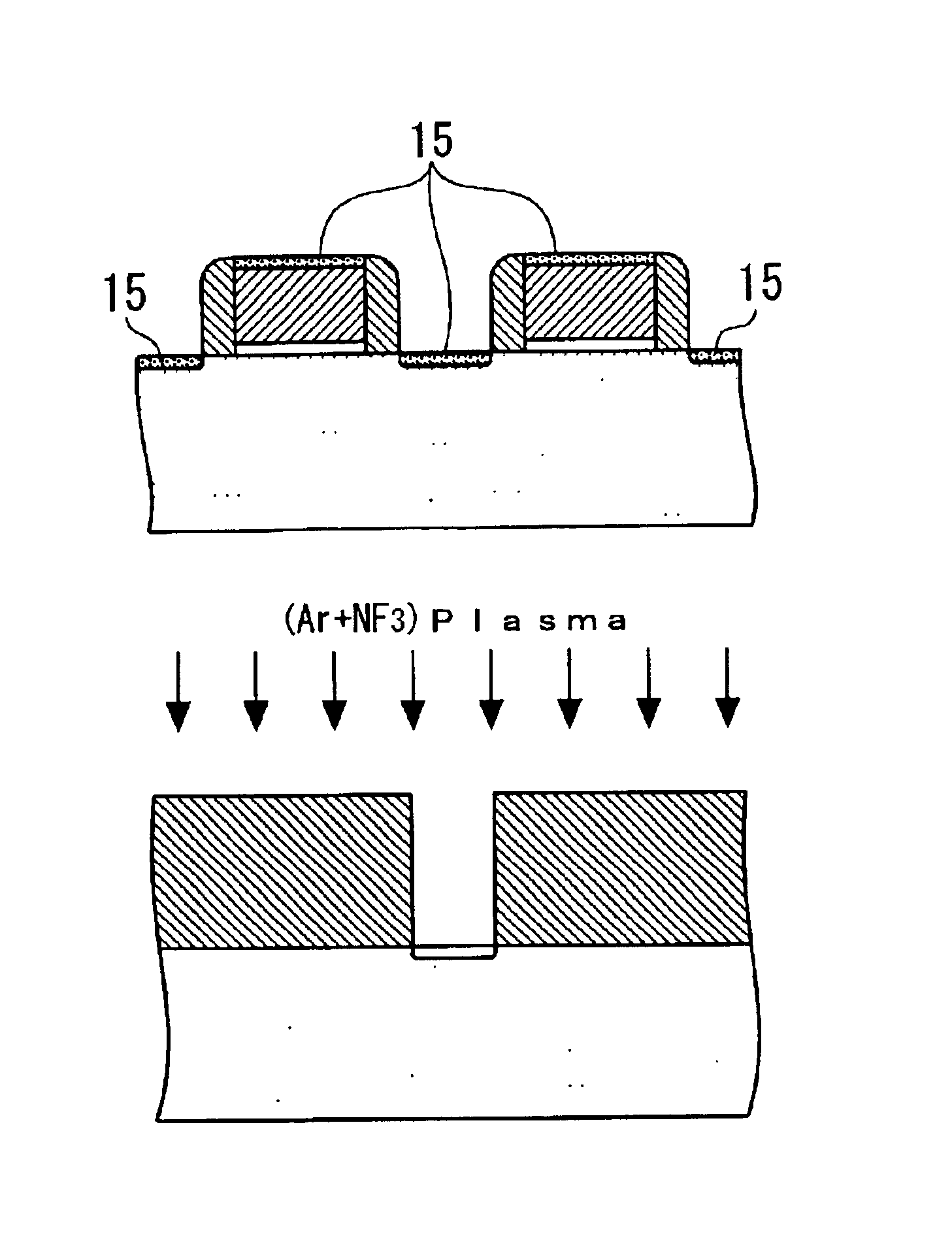
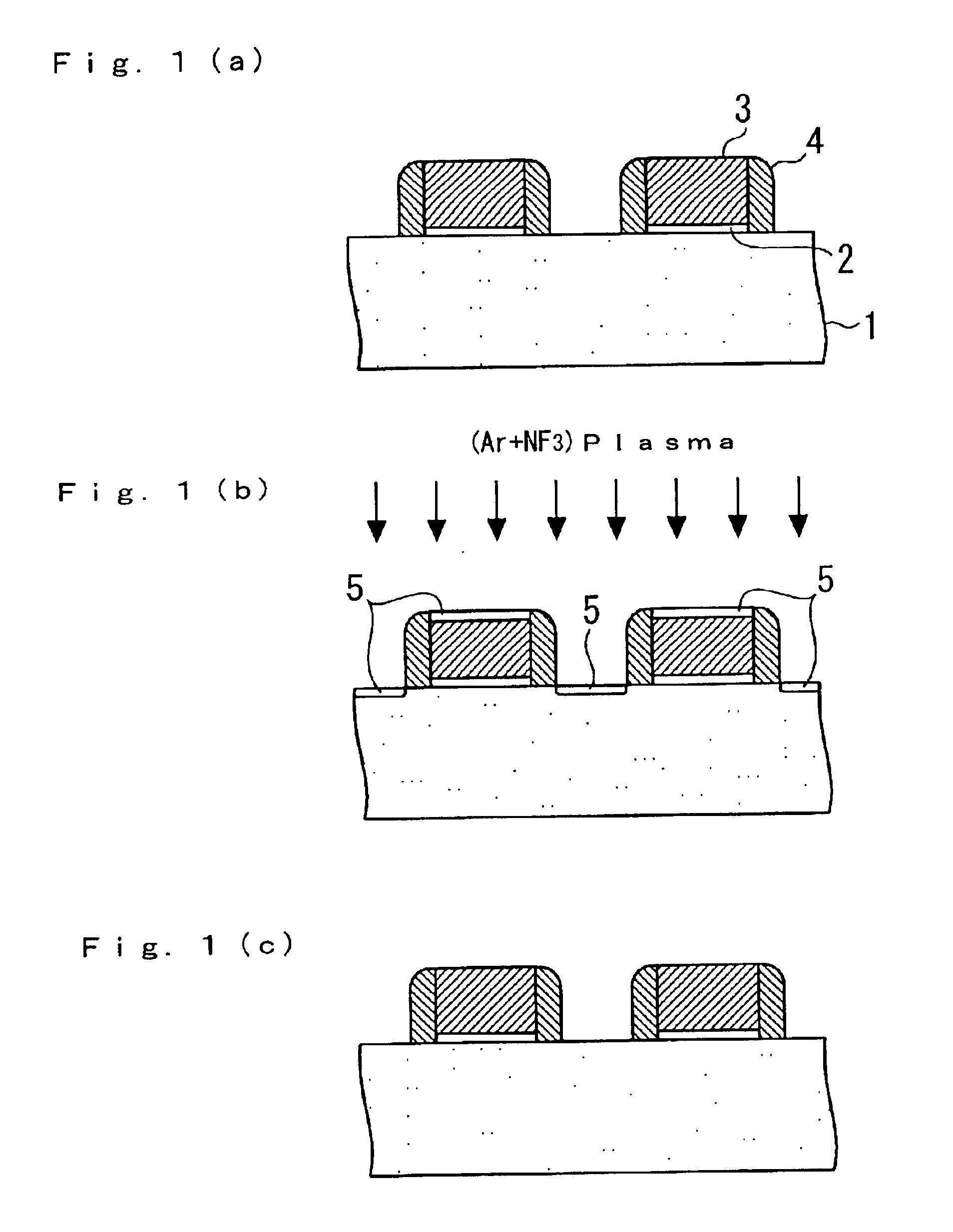
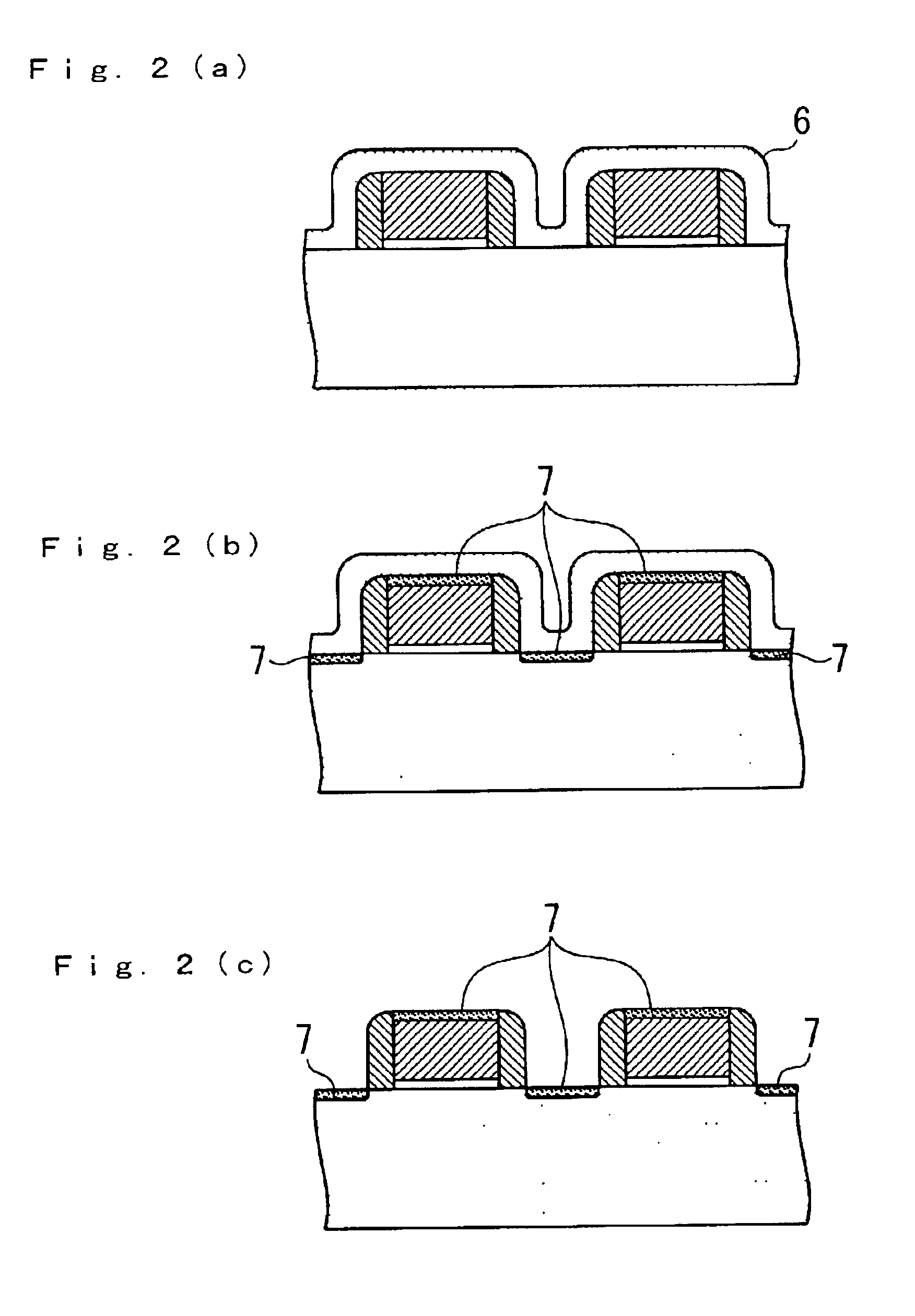
Method of cleaning etching apparatus
ActiveUS20060191555A1Clean interiorMaintain repeatabilityHollow article cleaningElectrostatic cleaningBoron trichlorideOxygen
To provide a cleaning method for an etching apparatus for a metal film that efficiently removes an etching residue deposited in an etching process chamber, assures the reproducibility of the etching performance, and keeps the etching process chamber in a low-dust-emission condition. Each time one workpiece with a metal film is etched (S1), the interior of the vacuum chamber is cleaned by replacing the workpiece with a dummy substrate (S2), performing a first step of plasma processing using oxygen (O2) and carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) to remove a carbon-based deposit pile (S3), and performing a second step of plasma processing using boron trichloride (BCl3) and chlorine (Cl2) to remove a residue that could not be removed by the first step and an etching residue of the metal film (S4).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
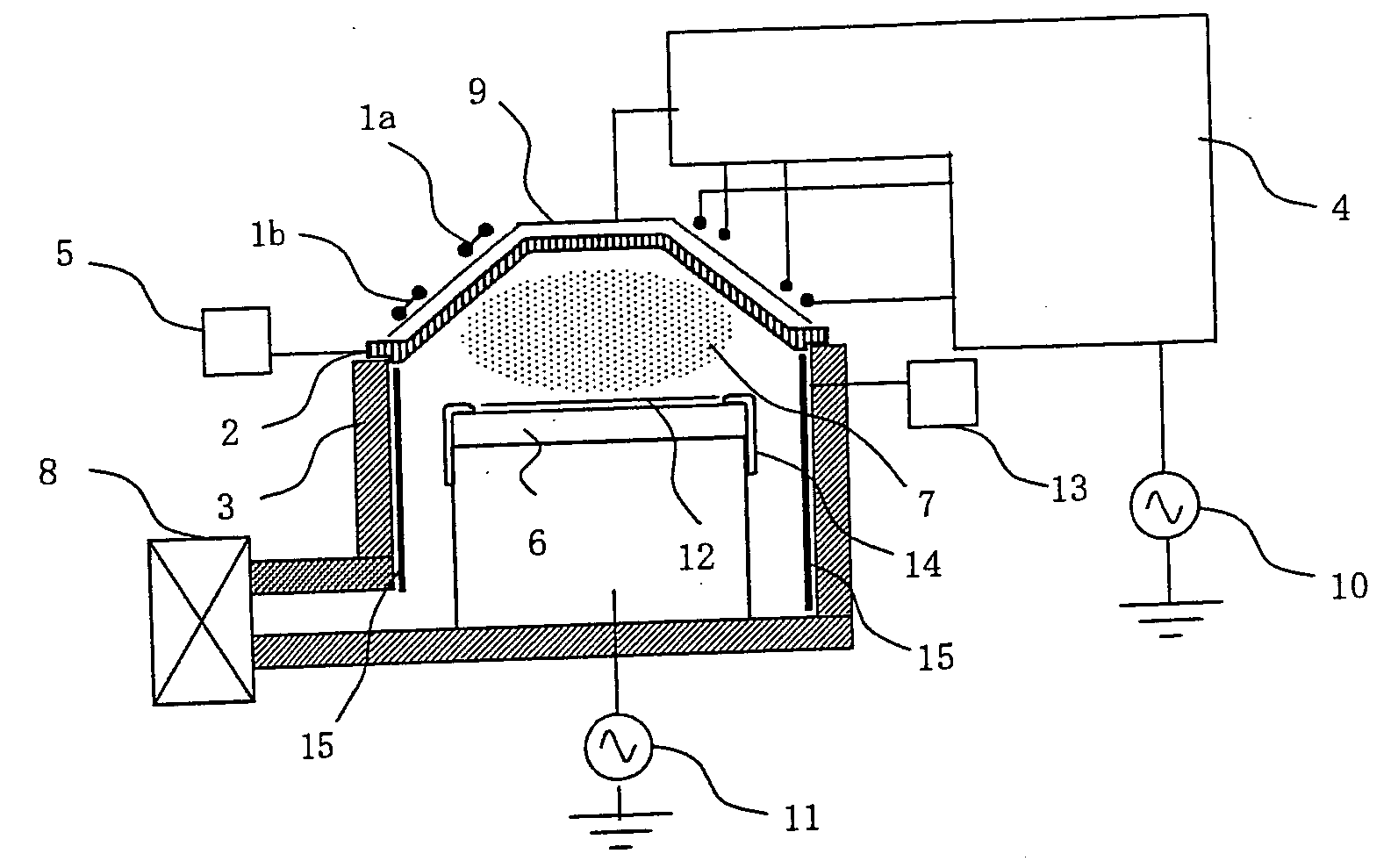
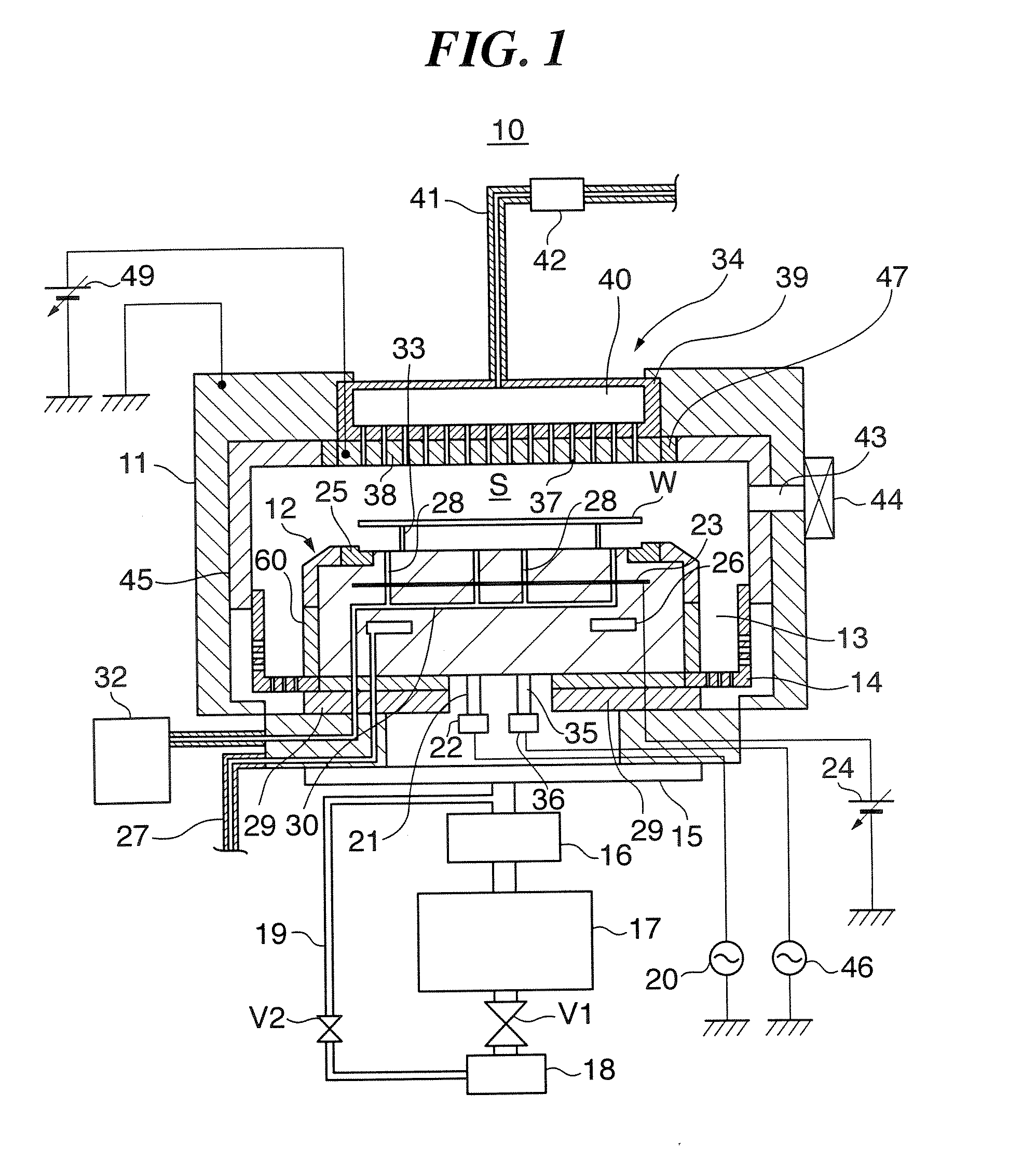
Method of cleaning substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber
ActiveUS20070186952A1Inhibition formationElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningElectricityReactive-ion etching
A method of cleaning a substrate processing chamber that enables formation of an oxide film on a surface of a processing chamber inside component to be prevented. A substrate processing chamber 11 has therein a processing space S into which a wafer W is transferred and carries out reactive ion etching on the wafer W in the processing space S. The substrate processing chamber 11 has an upper electrode plate 38 that comprises silicon and a lower surface of which is exposed to the processing space S. A dry cleaning is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using oxygen radicals produced from oxygen gas introduced into the processing space S. An oxide removal processing is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using fluorine ions and fluorine radicals produced from carbon tetrafluoride gas introduced into the processing space S.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Preparation method for ion liquid assisted hydrothermal synthesis of MoS2 microsphere
InactiveCN1994895AImprove performanceMild reaction conditionsMolybdenum sulfidesTetrafluoroborateMolybdate
The invention discloses a making method of MoS2 microball synthesized by ionic liquid auxiliary water, which comprises the following steps: dissolving molybdate in the deionized water to form 0.05-0.1m solution; adding thioacetamide or sulfourea as sulfur source with molar rate of thioacetamide or sulfourea and molybdate at 31-51; stirring evenly; adding 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazole tetrafluoride borate as ionic liquid with the bulk rate of ionic liquid and synthetic solution at 1300-1 50; stirring completely; transmitting solution into water heat reacting autoclave to react under 200-240 deg. c for 20-24h; cooling naturally; separating; washing; drying to obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Metal mask etching of silicon
The present disclosure provides a method for etching trenches, contact vias, or similar features to a depth of 100 mum and greater while permitting control of the etch profile (the shape of the sidewalls surrounding the etched opening). The method requires the use of a metal-comprising masking material in combination with a fluorine-comprising plasma etchant. The byproduct produced by a combination of the metal with reactive fluorine species must be essentially non-volatile under etch process conditions, and sufficiently non-corrosive to features on the substrate being etched, that the substrate remains unharmed by the etch process. Although aluminum is a preferred metal for the metal-comprising mask, other metals can be used for the masking material, so long as they produce an essentially non-volatile, non-corrosive etch byproduct under etch process conditions. By way of example, and not by way of limitation, metallic materials recommended for the mask include aluminum, cadmium, copper, chromium, gallium, indium, iron, magnesium, manganese, nickel, and combinations thereof. In particular, aluminum in combination with copper or magnesium is particularly useful, where the copper or magnesium content is less than about 8% by weight, and other constituents total less than about 2% by weight. The plasma feed gas includes at least one fluorine-containing compound such as nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), carbon tetrafluoride (CF4), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), by way of example and not by way of limitation. Oxygen (O2), or an oxygen-comprising compound, or hydrogen bromide (HBr), or a combination thereof may be added to the plasma feed gases to help provide a protective layer over etched sidewalls, assisting in profile control of the etched feature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Mold for photocuring nano-imprint and its fabrication process
InactiveUS20070267764A1Improve reliabilityImprove robustnessNanoinformaticsFoundry mouldsCarbon monofluorideUltraviolet lights
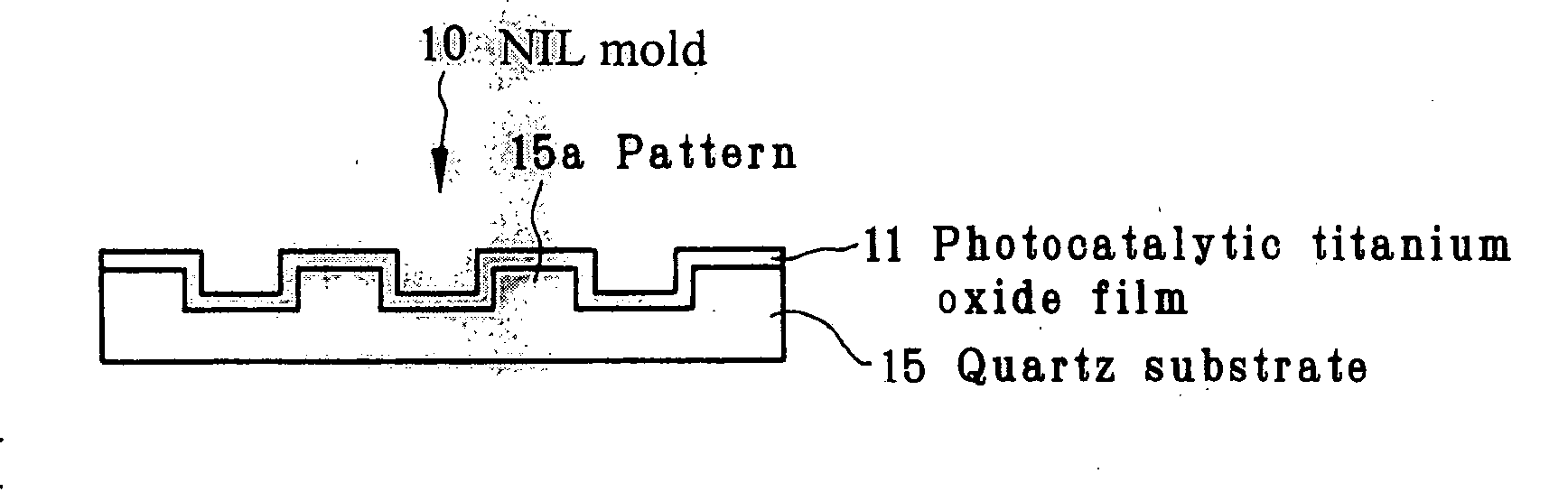
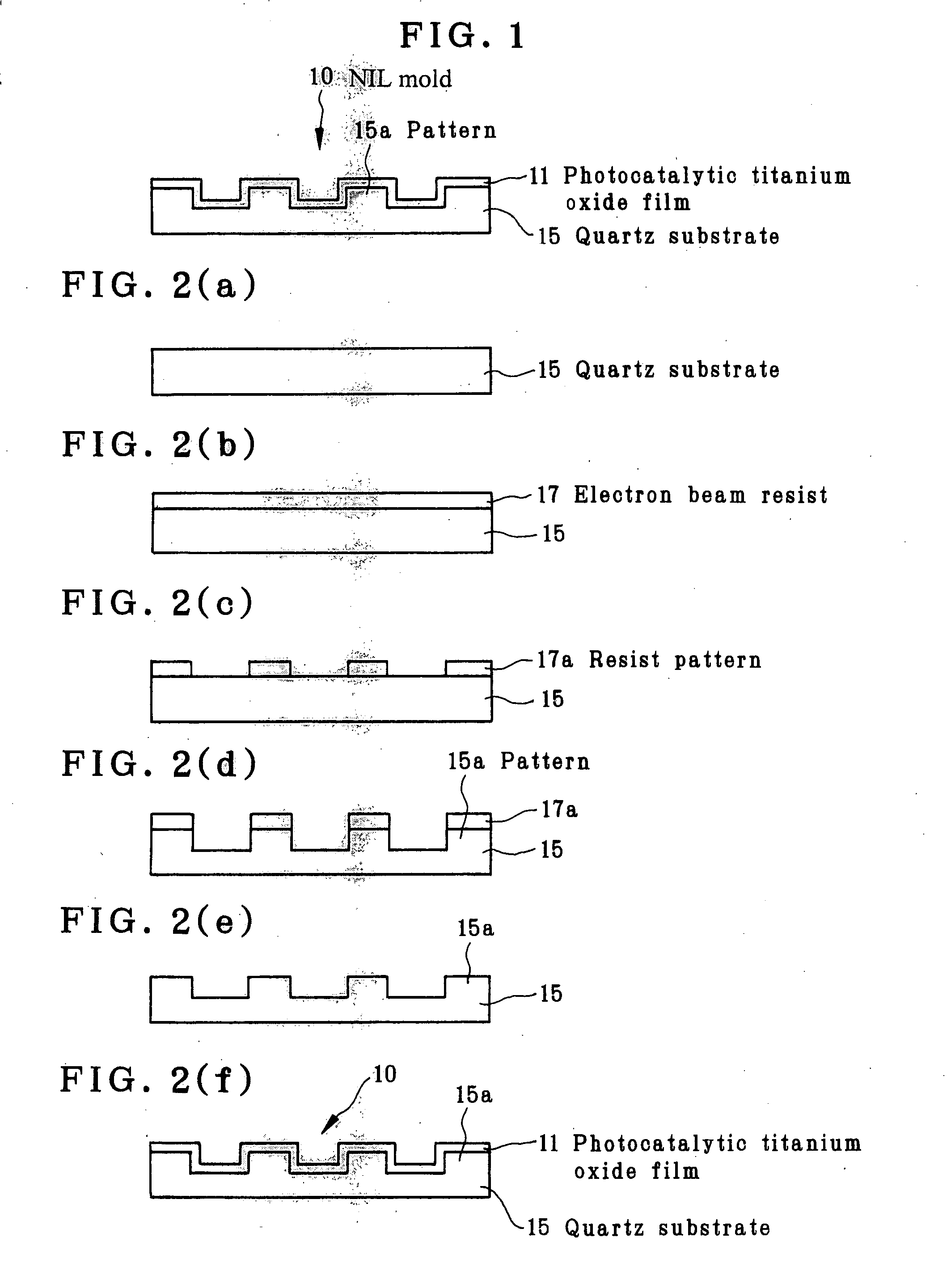
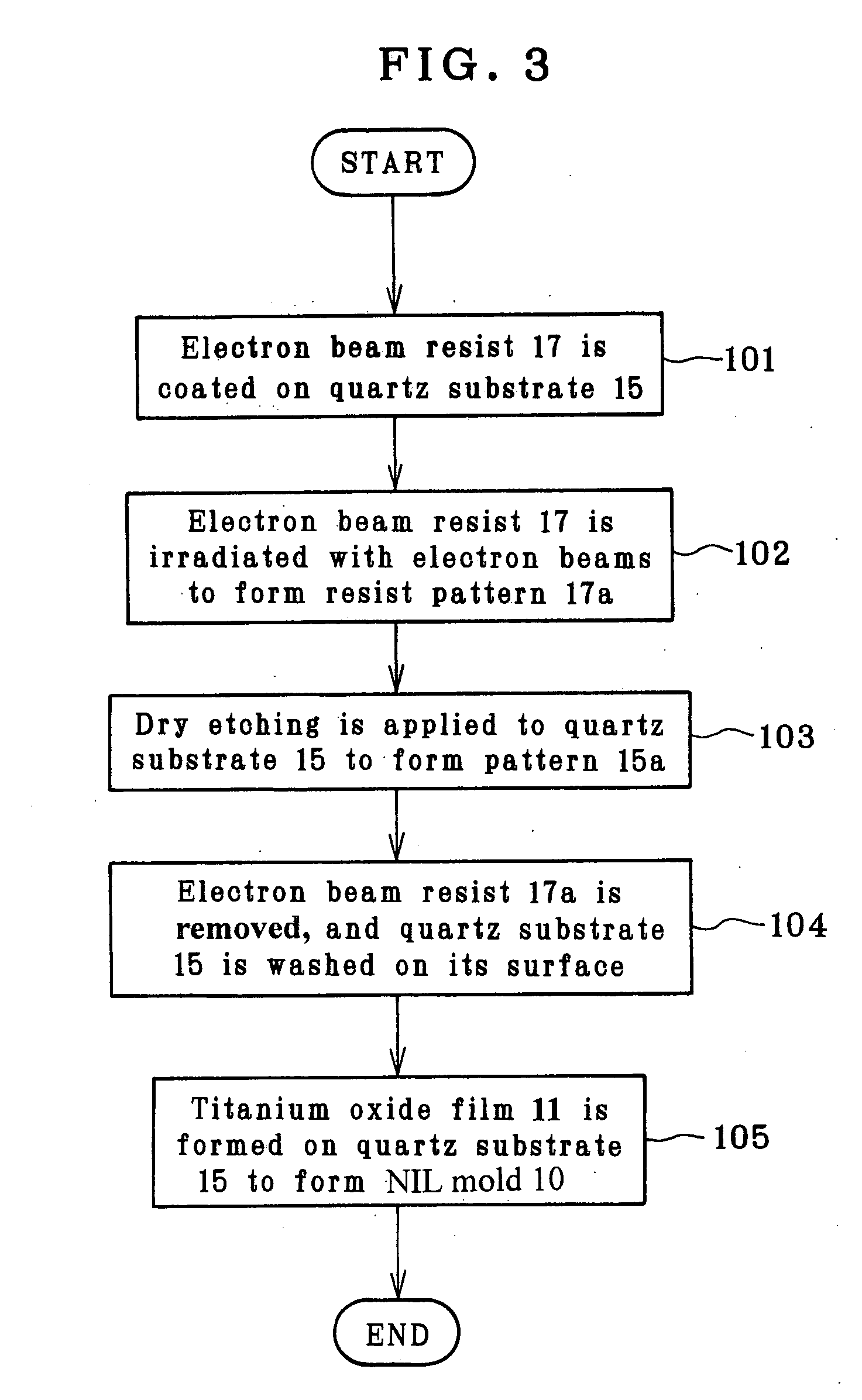
The invention relates to a mold that has an improved releasability for a photocured resin and an improved robustness. First, an electron beam resist 17 is coated on a quartz substrate 15 having the nature of being transmissive to ultraviolet light. A resist pattern 17a is formed by irradiation with electron beams. Thereafter, the quartz substrate is dry etched using etching gas such as carbon tetrafluoride to form a pattern 15a on the quartz substrate 15. A photocatalytic titanium oxide film 11 is formed as by sputtering on the surface of the quartz substrate 15 with the pattern 15a formed on it to fabricate an NIL mold 10.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
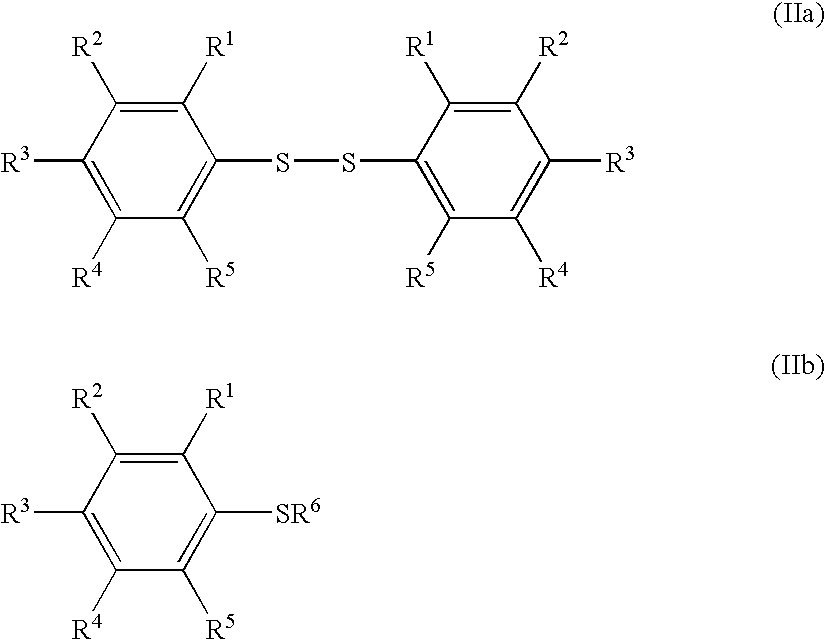
Process for producing arylsulfur pentafluorides
Novel processes for preparing arylsulfur pentafluorides are disclosed. Processes include reacting at least one aryl sulfur compound with a halogen and a fluoro salt to form an arylsulfur halotetrafluoride. The arylsulfur halotetrafluoride is reacted with a fluoride source to form a target arylsulfur pentafluoride.
Owner:UBE CORP
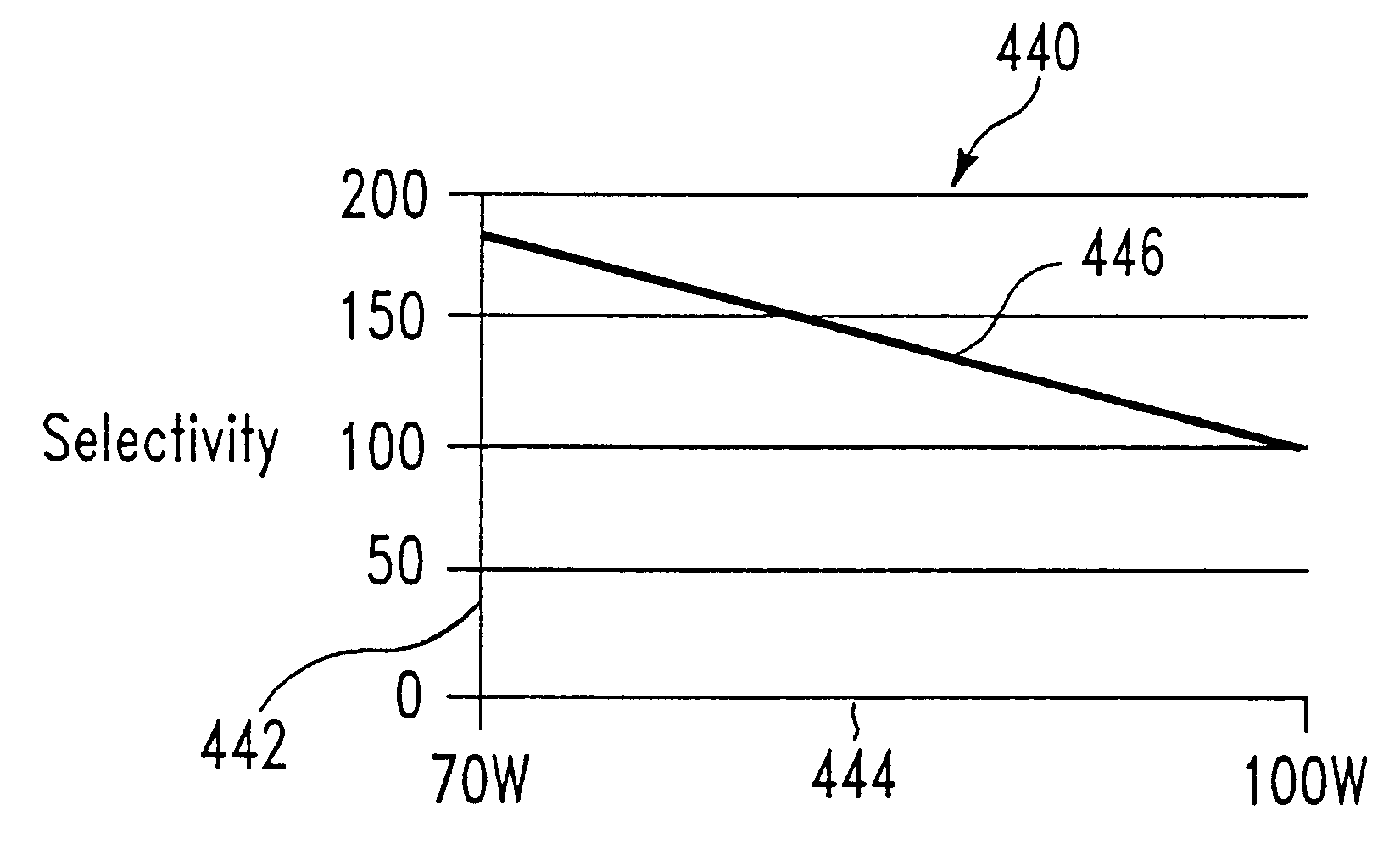
Method of etching tungsten or tungsten nitride electrode gates in semiconductor structures
InactiveUS6440870B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSulfur hexafluoride
The present invention relates to a method of etching tungsten or tungsten nitride in semiconductor structures, and particularly to the etching of gate electrodes which require precise control over the etching process. We have discovered a method of etching tungsten or tungsten nitride which permits precise etch profile control while providing excellent selectivity, of at least 175:1, for example, in favor of etching tungsten or tungsten nitride rather than an adjacent oxide layer. Typically, the oxide is selected from silicon oxide, silicon oxynitride, tantalum pentoxide, zirconium oxide, and combinations thereof. The method appears to be applicable to tungsten or tungsten nitride, whether deposited by physical vapor deposition (PVD) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In particular, an initial etch chemistry, used during the majority of the tungsten or tungsten nitride etching process (the main etch), employs the use of a plasma source gas where the chemically functional etchant species are generated from a combination of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen (N2), or in the alternative, from a combination of nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), chlorine (Cl2), and carbon tetrafluoride (CF4). Toward the end of the main etching process, a second chemistry is used in which the chemically functional etchant species are generated from Cl2 and O2. This final portion of the etch process may be referred to as an "overetch" process, since etching is carried out to at least the surface underlying the tungsten or tungsten nitride. However, this second etch chemistry may optionally be divided into two steps, where the plasma source gas oxygen content and plasma source power are increased in the second step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
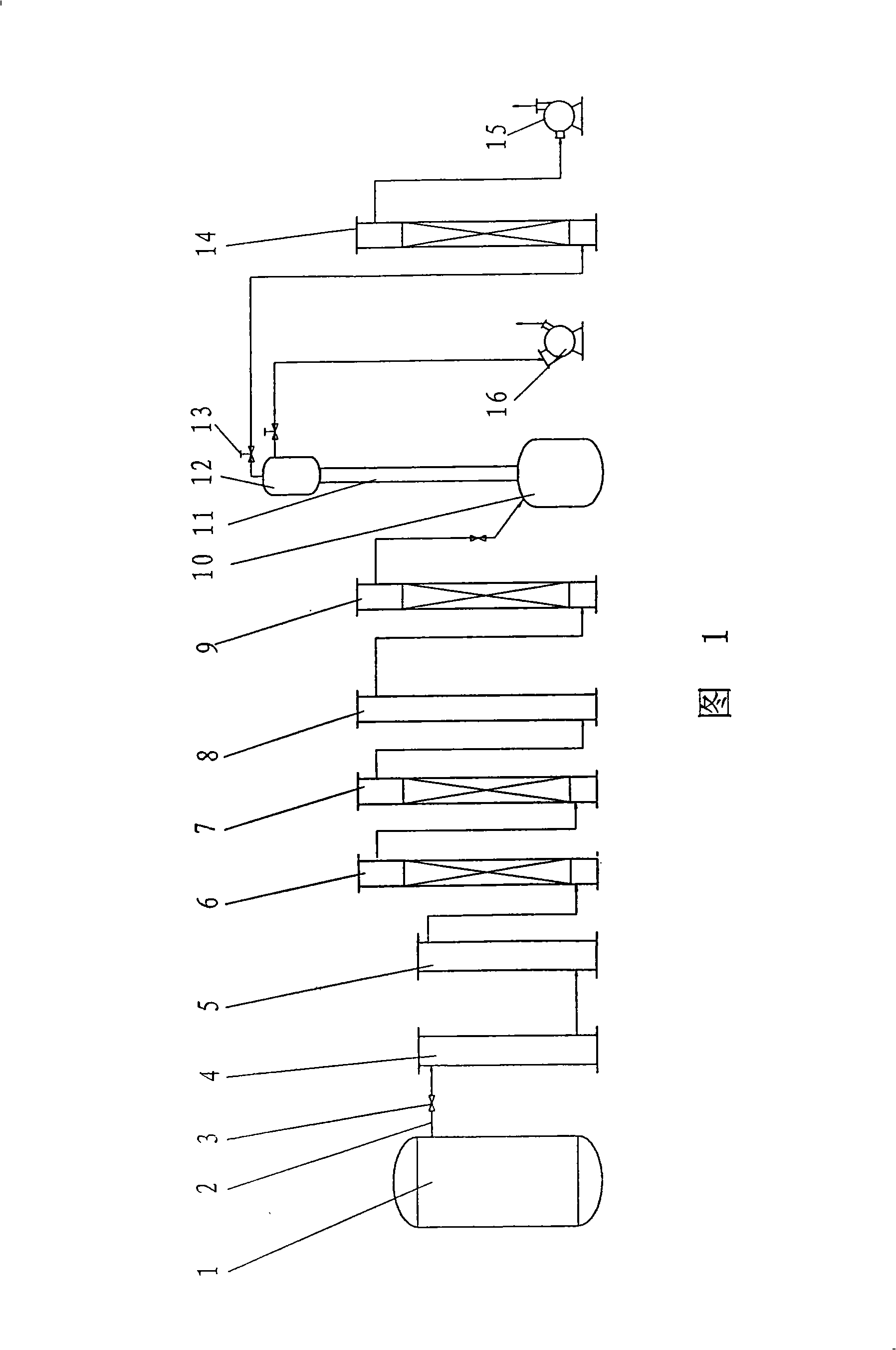
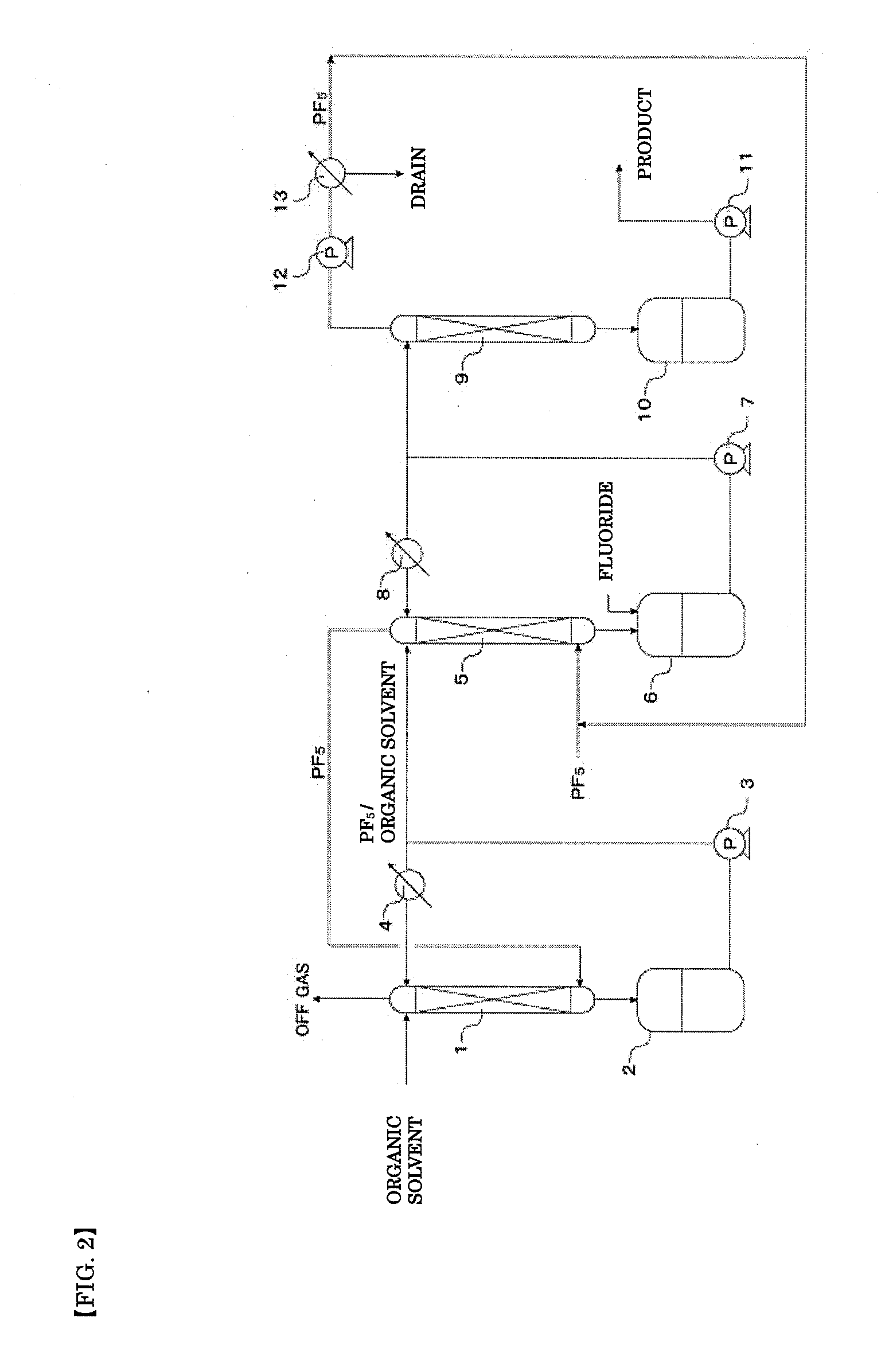
Method and apparatus for preparing high-pure carbon tetrafluoride gas
The invention discloses a method and equipment for producing highly purity carbon tetrafluoride gas; the method includes the steps: the fluorine gas and highly purity active carbon successively experience the chemical synthesis reaction, dedusting, water washing, alkaline washing, gas liquid separation, water removal, rectification, liquefaction and collection. The equipment includes a fluorine gas storage tank, a reaction kettle, a dust catcher, a water scrubber, an alkaline tower, a gas-liquid separator, an absorption column, a rectifying still, a rectifying column and a condenser. The carbon tetrafluoride gas produced with the method and equipment has high purity and the invention has the advantages of simple equipment, easy operation, convenient and safe operation, continuous production and so on.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
Method of photoresist strip for plasma doping process of semiconductor manufacturing
ActiveUS20070243700A1Sure easySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantHexafluoroethane
A method of forming an intermediate semiconductor device is disclosed that comprises providing a semiconductor substrate, forming a photoresist layer on the semiconductor substrate, implanting a dopant into the semiconductor substrate, and removing a dopant-containing layer from the photoresist layer. The dopant-containing layer includes dopant residuals and a carbon-rich crust and may be formed during implantation. The dopant-containing layer may be removed from the photoresist layer by exposing the dopant-containing layer to a water rinse, a chlorinated plasma or to a fluorinated plasma. The water rinse may include deionized water that is maintained at a temperature that ranges from approximately 25° C. to approximately 80° C. The fluorinated plasma may be formed from a gaseous precursor selected from the group consisting of nitrogen trifluoride, carbon tetrafluoride, trifluoromethane, hexafluoroethane, sulfur hexafluoride, and mixtures thereof. A method of forming an ultrashallow junction is also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Surface-treated powder and cosmetics containing same
ActiveUS20090263660A1Easily dispersed uniformlyGood dispersionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolyesterDispersion stability
By coating the surface of a powder comprising a silicone resin and / or an organic powder with a specific hydrophilizing agent, such powder is hydrophilized. The hydrophilizing agent includes water-soluble polyoxyalkylene glycol derivatives. The organic powder is at least one selected from PMMA, nylon, polyester, polystyrene, cellulose, silicone elastomer powder, silicone rubber powder, benzoguanamine, styrenedivinylbenzene pinhole polymer, ethylene tetrafluoride, polyethylene powder, polypropylene powder, polyurethane powder, silk powder, metal soap powder, starch powder, N-acylated lysine, an organic pigment, and a composite of at least one of these organic powders described above with a metal oxide and / or a metal hydroxide. Such coated (treated) powder has extremely great dispersibility (ease of dispersion) and very good dispersion stability (long-term dispersion stability with lapse of time) in aqueous dispersion media, particularly under acidic and alkaline conditions, specifically at pH 3 through 13. Using the surface-treated powder, additionally, a dispersion with good dispersibility (ease of dispersion) and great dispersion stability, preferably for cosmetics can be provided. The use of the surface-treated powder, or the use of the dispersion can provide further a cosmetic excellent in dispersibility and dispersion stability and further in re-dispersibility and dispersion stability with lapse of time and smooth feeling as compared to the related art when selecting aqueous cosmetic as an agent form.
Owner:MIYOSHI KASEI
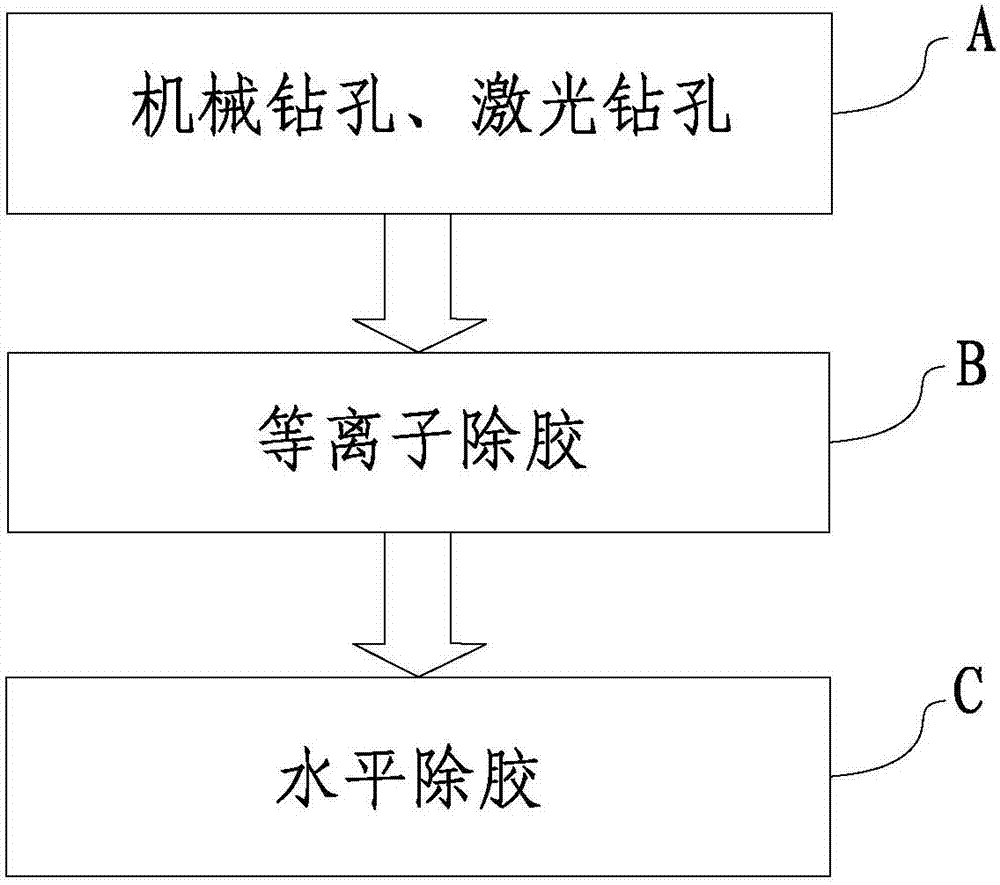
Adhesive-removal method for printed circuit board HDI (high density interconnection) product
ActiveCN102833952AEasy to cleanEfficient removalPrinted circuit manufactureCarbon monofluorideAdhesive
The invention relates to the technical field of the printed circuit board, in particular to an adhesive-removal method for a printed circuit board HDI (high density interconnection) product. The adhesive-removal method comprises the following steps of: A) mechanical drilling and laser drilling: carrying out mechanical drilling on an HDI product, and carrying out laser drilling on the HDI product to form a through hole and a blind hole; B) plasma adhesive removal: generating a plasma by oxygen and carbon tetrafluoride under the action of the nitrogen environment and an RF electric field, and enabling the plasma to react with resin on the walls of the through hole and the blind hole to generate carbon dioxide, hydrogen fluoride and water; and C) horizontal adhesive removal: processing the through hole and the blind hole by chemical potion in a horizontal adhesive removal method. Firstly, the blind hole and the through hole are subjected to the plasma adhesive removal, the generated carbon dioxide, hydrogen fluoride and water can be absorbed without residuals in the blind hole, and then the blind hole and the through hole are subjected to horizontal adhesive removal to effectively remove tiny residual adhesives on the bottom of the blind hole and clean the blind hole.
Owner:东莞市若美电子科技有限公司
Friction material
A friction material, including a fibrous reinforcement, a friction modifier, a lubricant and a binder, comprising a water-repellent fluoropolymer incorporated therein. The further incorporation of an alkaline metal salt makes it possible to render the matrix more hydrophilic and hence reduce creep noise. The foregoing fluoropolymer is one selected from the group consisting of ethylene tetrafluoride polymer, tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene copolymer and polyvinylidene fluoride or a combination thereof.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE IND CO LTD
Method for preparing titanium dioxide/mesoporous carbon composite photocatalyst by electron beam irradiation
InactiveCN101829555AImprove photocatalytic performanceEasy to operateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationRadiation chemistryMesoporous carbon
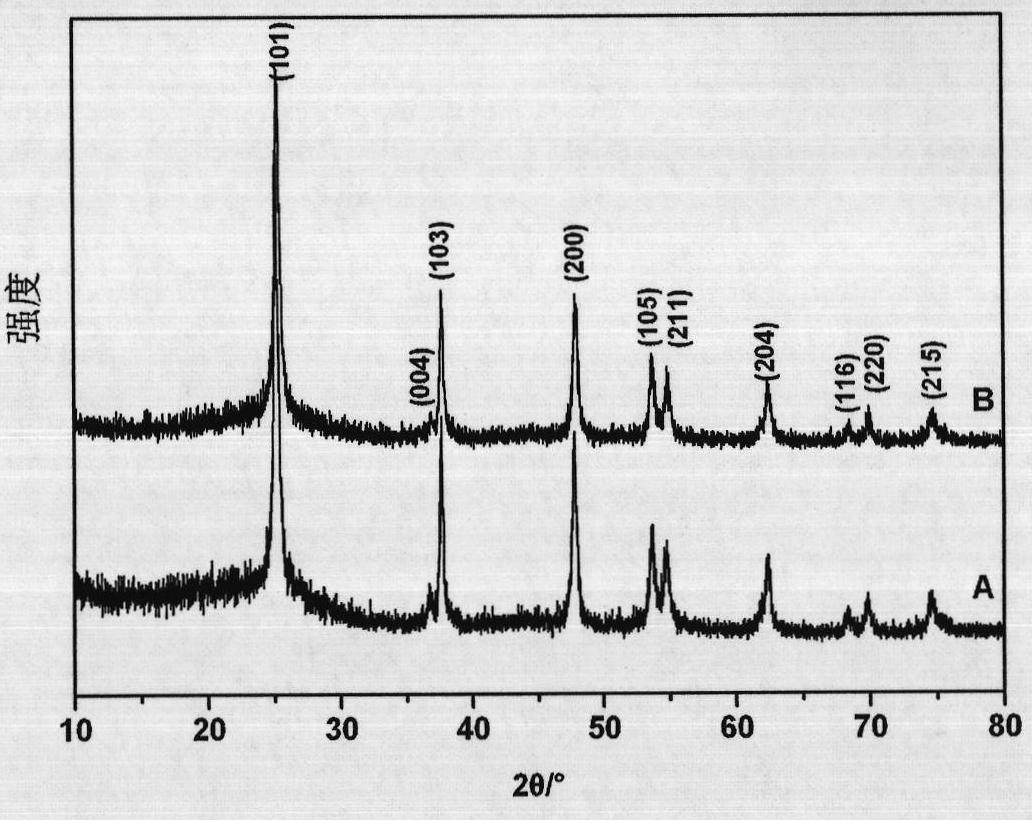
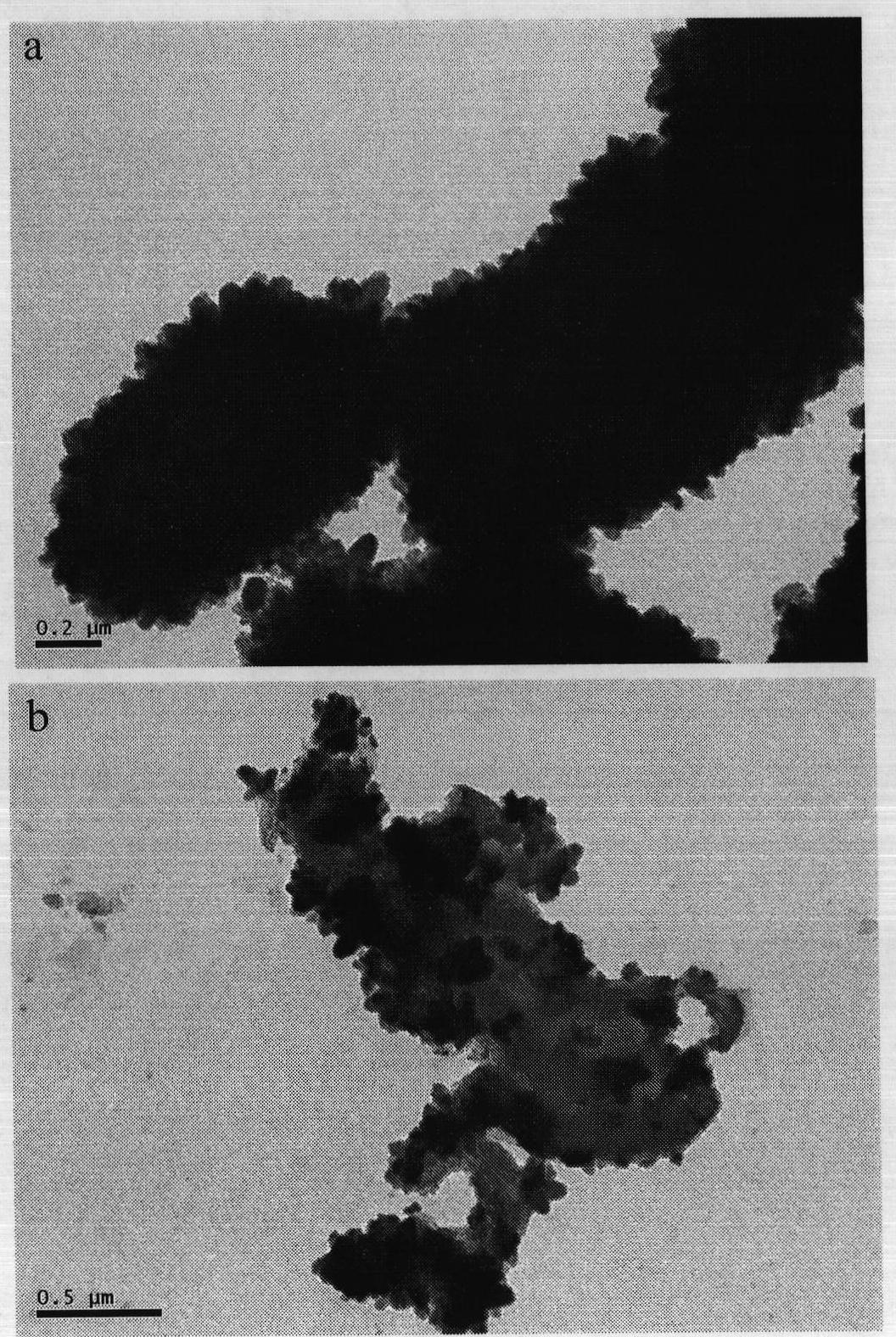
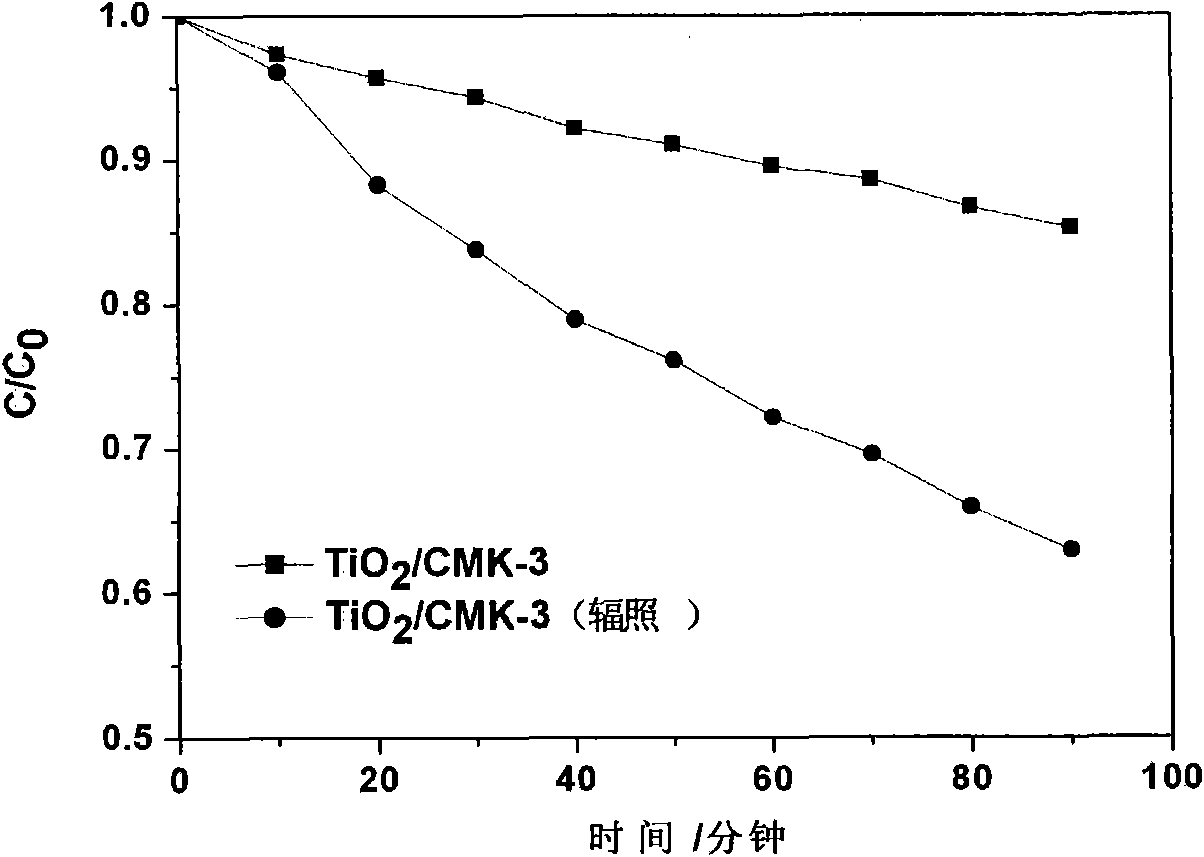
The invention relates to a method for preparing titanium dioxide / mesoporous carbon composite photocatalyst by electron beam irradiation, belonging to the technical field of radiation chemistry and photocatalyst preparation technology. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps of: firstly, adding mesoporous carbon CMK-3 into TiF4 solution, uniformly mixing by ultrasound, pouring the solution into a self encapsulation, irradiating under an 2.5MeV and 40mA electronic accelerator with the irradiation dose of 140-700Kgy, wherein the mass ratio of the mesoporous carbon and the carbon tetrafluoride is 0.17, i.e. CMK-3: TiF4=0.17; secondly, putting the solution after irradiation into an oven to react for 20h under the temperature of 60 DEG C; and thirdly, washing and drying to finally obtain obtaining TiO2 / CMK-3 composite photocatalyst. A product has favorable the photocatalysis performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method of photoresist strip for plasma doping process of semiconductor manufacturing
ActiveUS7737010B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHexafluoroethaneDopant
A method of forming an intermediate semiconductor device is disclosed that comprises providing a semiconductor substrate, forming a photoresist layer on the semiconductor substrate, implanting a dopant into the semiconductor substrate, and removing a dopant-containing layer from the photoresist layer. The dopant-containing layer includes dopant residuals and a carbon-rich crust and may be formed during implantation. The dopant-containing layer may be removed from the photoresist layer by exposing the dopant-containing layer to a water rinse, a chlorinated plasma or to a fluorinated plasma. The water rinse may include deionized water that is maintained at a temperature that ranges from approximately 25° C. to approximately 80° C. The fluorinated plasma may be formed from a gaseous precursor selected from the group consisting of nitrogen trifluoride, carbon tetrafluoride, trifluoromethane, hexafluoroethane, sulfur hexafluoride, and mixtures thereof. A method of forming an ultrashallow junction is also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for producing semiconductor device
InactiveCN101051610AEliminate dentsSimplify the etch processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPolysilicon gateSemiconductor
When etching ONO laminated construction of SONOS parts, the method uses mixed gas of carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) and fluoroform (CHF3) as main etching gas instead of mixed gas of HBr and C2F6, and uses CHF3 as over etching gas instead of mixed gas of CH2F2 / SF6. Using mixed gas of CF4 and CHF3 accomplishes main etching and over etching step for one time so as to simplify etching technique. Based on good etching selectivity and suitable etching speed, the method controls and buffers effect for etching ONO laminated construction by plasma of etching gas. In procedure for etching wafer thin oxidizing layer of grid electrode, the method is capable of controlling etching depth accurately, stopping etching at oxidation surface at low layer of ONO. Moreover, the method eliminates concave phenomena at sidewall and root part of polysilicon gate caused by transversal etching.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Device and method for machining large-area plane optical element
The invention discloses a device and a method for machining a large-area plane optical element, and relates to a device and a method for machining a plane optical element. With the adoption of the device and the method, the problems that the prior plasma polishing device is high in cost, and the polishing method is low in efficiency are solved. Two external electrodes and two isolating plates are opposite in pairs to form a closed structure; an internal electrode is located at the two external electrodes; two plasma generating cavities are formed among the two external electrodes, the two isolating plates and the internal electrode; and a helium tank, a carbon tetrafluoride bottle and an oxygen bottle are communicated with two first through holes through a flow controller. The method for machining the large-area plane optical element comprises the steps of adding cooling water to the electrodes, preheating the flow controller, controlling gas flow of helium and the carbon tetrafluoride by the flow controller, placing a workpiece to be machined on the electrodes on a working table so as to enable the workpiece to be machined to rotate counterclockwise, gradually increasing power on a radio frequency power source, controlling discharge of the stable plasma, turning off the radio frequency power source and a valve, and taking out the workpiece to be machined. The device and the method can be used for machining the large-area plane optical element.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Cosmetics
InactiveUS20050169867A1Satisfactory hydrophilic propertyGood dispersibilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsDispersion stabilityPolystyrene
Owner:MIYOSHI KASEI
Tech. for etching capable of controlling grid structural length
InactiveCN1787176AAvoid deformationIntegrity guaranteedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingThree stage
The invention relates to an etching process able to control the length of a grid structure, using hard mask to raise the selection ratio of etching polycrystalline silicon layer, and adopting three-stage etching (first primary etching / second primary etching / over etching) in the polycrystalline silicon layer etching process; the first primary etching gas contains carbon tetrafluoride to reinforce the whole patternized hard mask and high molecular film deposit on the side walls of the polycrystalline silicon layer to convert the high molecular film deposit into high molecular film combination; the high molecular film combination can effectively resist the side corrosion of halides to the polycrystalline silicon layer to make the horizontal width of the polycrystalline silicon layer unable to be reduced, and the patternized hard mask can better resist the corrosion of the etching gas to hold the pattern, thus solving the problem of generating initial creepage.
Owner:GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
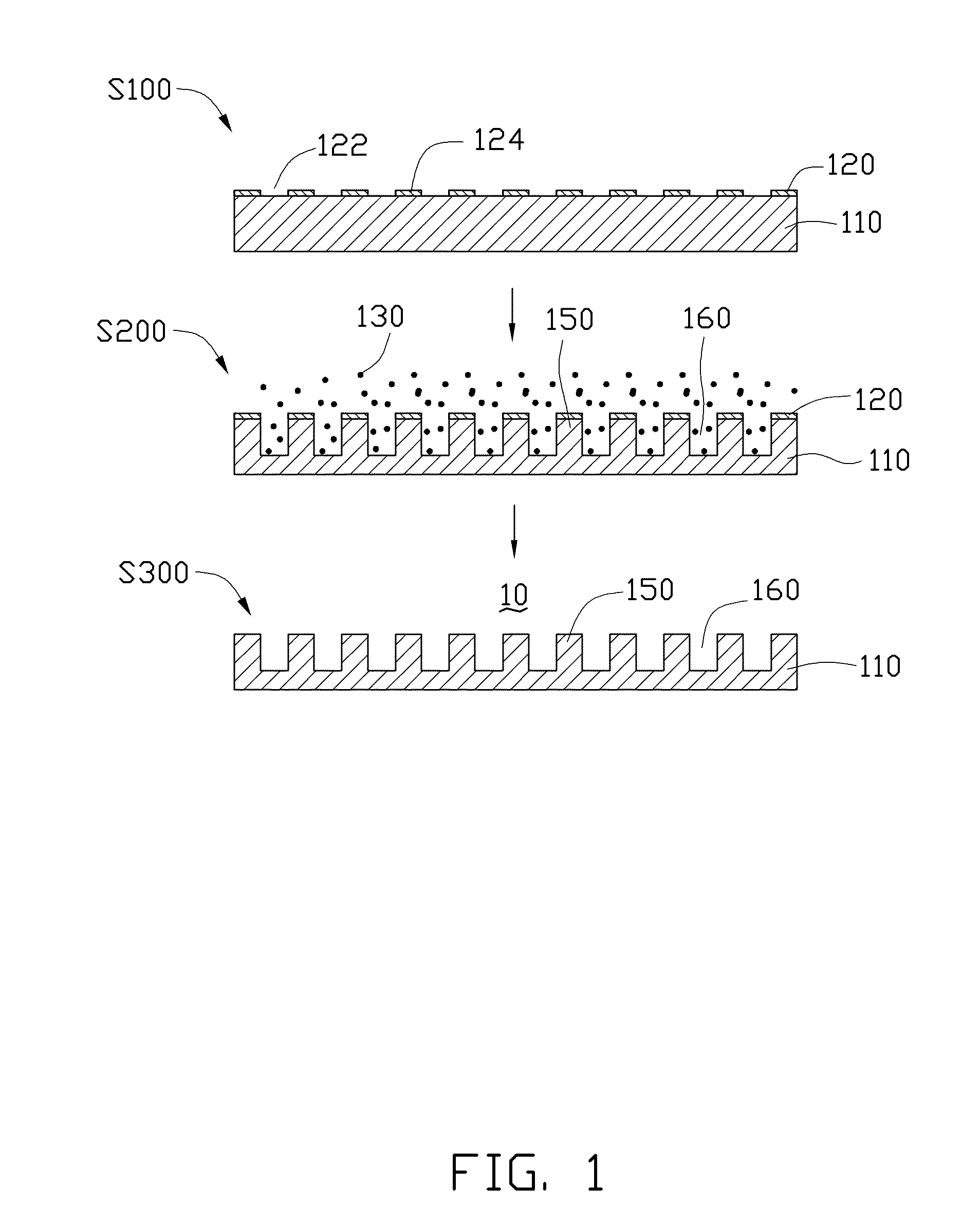
Manufacturing method of grating
The disclosure relates to a method for making a grating. The method includes the following steps. First, a substrate is provided. Second, a photoresist film is formed on a surface of the substrate. Third, a nano-pattern is formed on the photoresist film by nano-imprint lithography. Fourth, the photoresist film is etched to form a patterned photoresist layer. Fifth, a mask layer is covered on the patterned photoresist layer and the surface of the substrate exposed to the patterned photoresist layer. Sixth, the patterned photoresist layer and the mask layer thereon are removed to form a patterned mask layer. Seventh, the substrate is etched through the patterned mask layer by reactive ion etching, wherein etching gases includes carbon tetrafluoride (CF4), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and argon (Ar2). Finally, the patterned mask layer is removed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Binder composition for positive electrodes
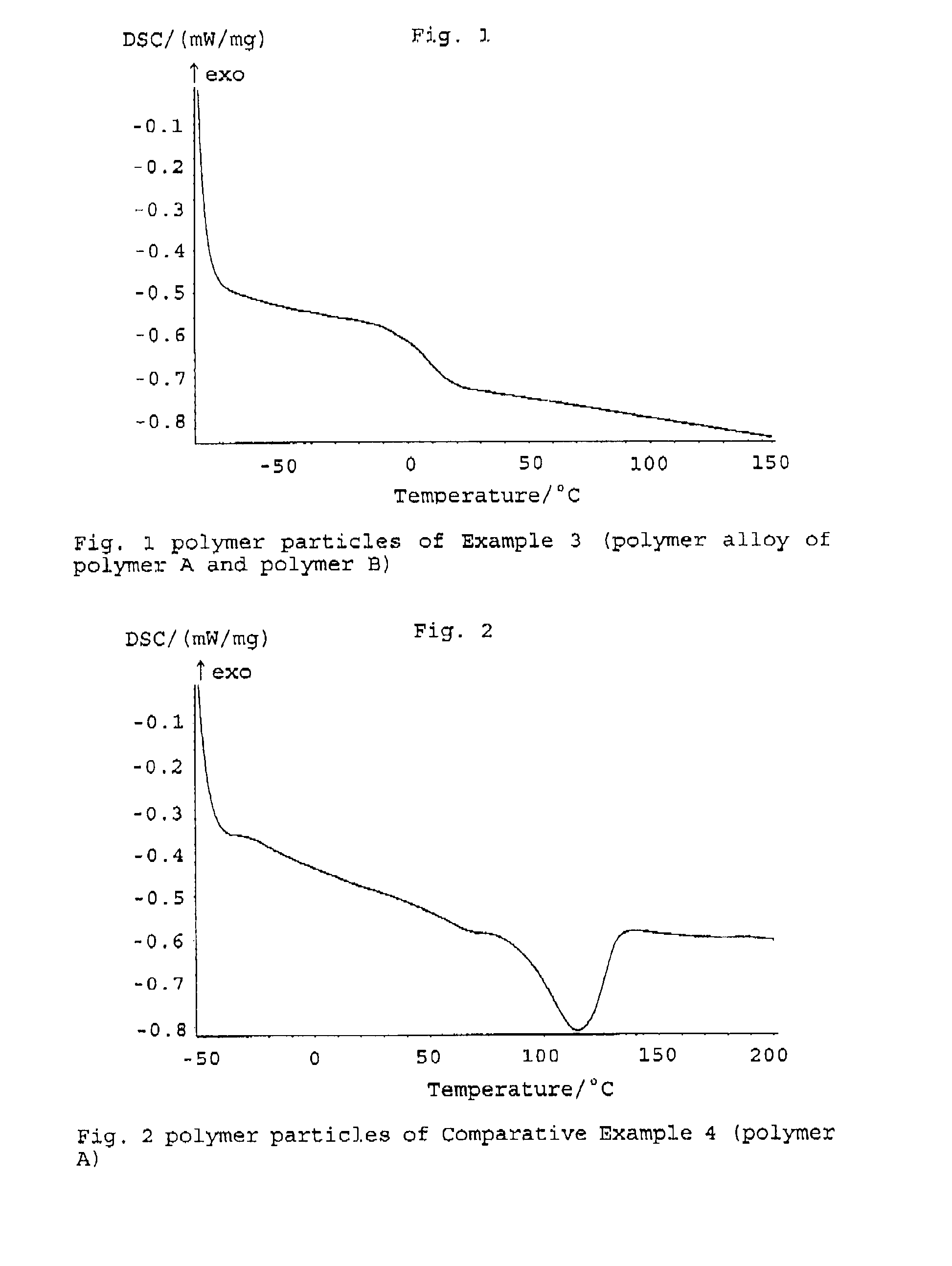
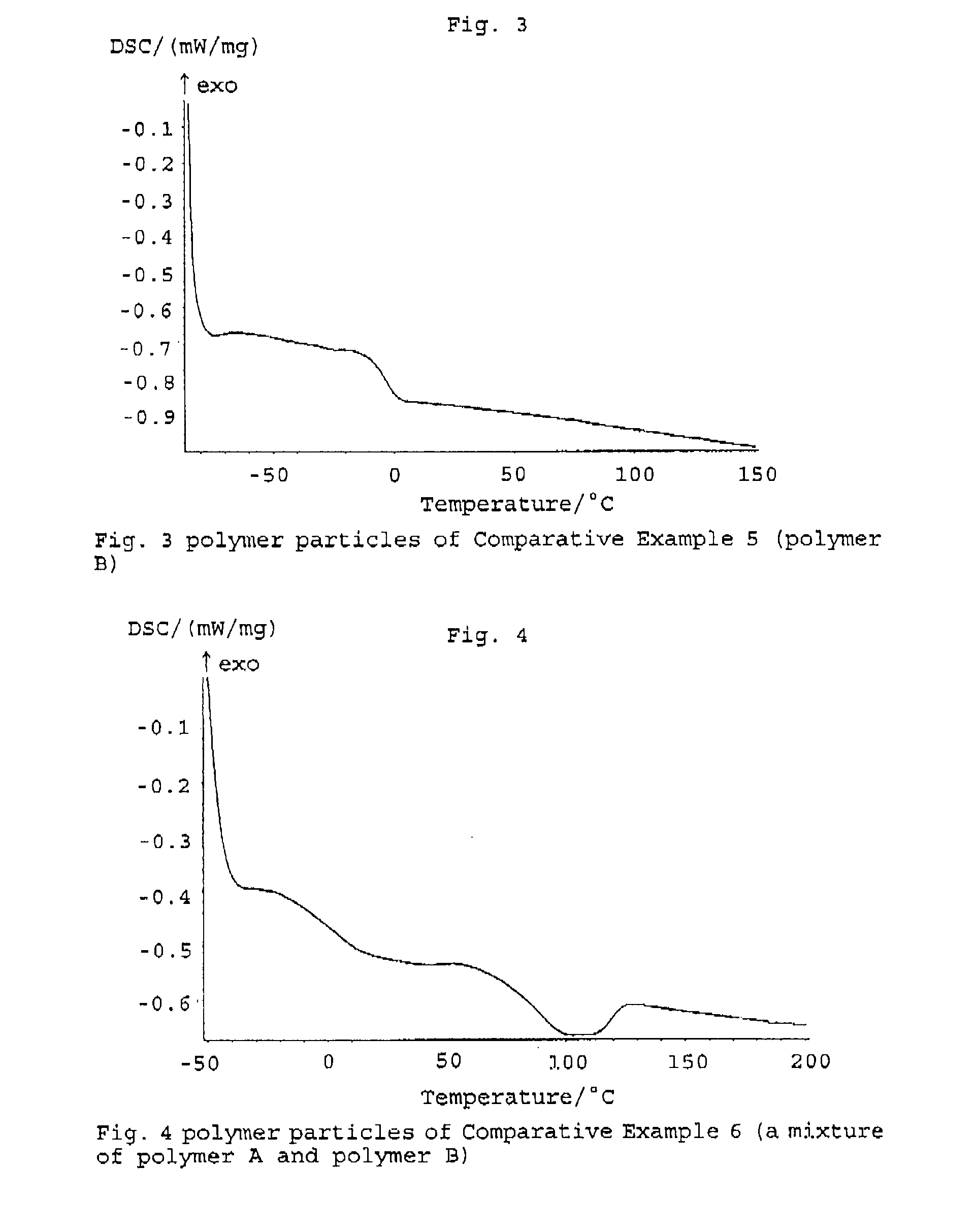
ActiveUS20120309892A1Positive electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesPolymer sciencePolymer alloy
A binder composition for the positive electrode of an electric storage device. The composition contains polymer alloy particles composed of: a polymer (A) having a recurring unit derived from vinylidene fluoride, ethylene tetrafluoride, propylene hexafluoride, or mixtures thereof; a polymer (B) having a recurring unit derived from an unsaturated carboxylic acid ester; and water. The average diameter of the polymer alloy particles is 50 to 400 nm. The polymer alloy particles are synthesized by absorbing a monomer (b) to the polymer (A) and polymerizing the monomer (b) to synthesize the polymer (B). The monomer (b) is an unsaturated carboxylic acid ester, or a mixture of an unsaturated carboxylic acid ester and one or more of the following monomers: an α,β-unsaturated nitrile compound, an unsaturated carboxylic acid, a conjugated diene compound, styrene, α-methylstyrene, p-methylstyrene, vinyltoluene, chlorostyrene, divinylbenzene, a carboxylic vinyl ester, and an acid anhydride of an ethylenically unsaturated dicarboxylic acid.
Owner:ENEOS MATERIALS CORP
High-temperature enhanced upconversion fluorescence type nanocrystal for temperature sensing and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to high-temperature enhanced upconversion fluorescence type nanocrystal for temperature sensing. The high-temperature enhanced upconversion fluorescence type nanocrystal for temperature sensing refers to hexagonal phase sodium yttrium tetrafluoride spherical or rod-shaped nanocrystal with the average diameter or length of 15-50nm, and rare earth Yb<3+> and Tm<3+> are co-doped into the nanocrystal. The nanometer powder is heated from room temperature to a temperature of 220 DEG C, the crystal structure and the surface structure are kept invariable, the index of the upconversion fluorescence intensity under laser excitation of 980nm is enhanced in an exponent manner along with the temperature, and the nanocrystal can be repeatedly used after temperature reduction. According to relation analysis between a fluorescence intensity ratio in ground state transition from Tm<3+> thermal coupling energy levels <3>F3 and <3>H4 and the temperature, temperature measurement can be performed.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Brazing or soldering material and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS6183883B1Good solder wettabilityEnhanced solder connectionVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesCopper fluorideVacuum chamber
Brazing or soldering materials which effectively improve the wettability of the brazing alloy or solder without using flux and a method of manufacturing such materials are provided. A metallic base is placed on turntable inside a vacuum chamber. A copper target is affixed to a sputtering electrode above the metallic base. Air is removed from the vacuum chamber through a vacuum outlet to increase the vacuum therein to a specific pressure, and carbon tetrafluoride and argon are introduced from a gas inlet to control the sputter pressure. Thereafter, turntable is rotated while a high frequency voltage is applied between the target and the metallic base to form a halide layer, such as a layer of copper fluoride, on a surface of metallic base.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
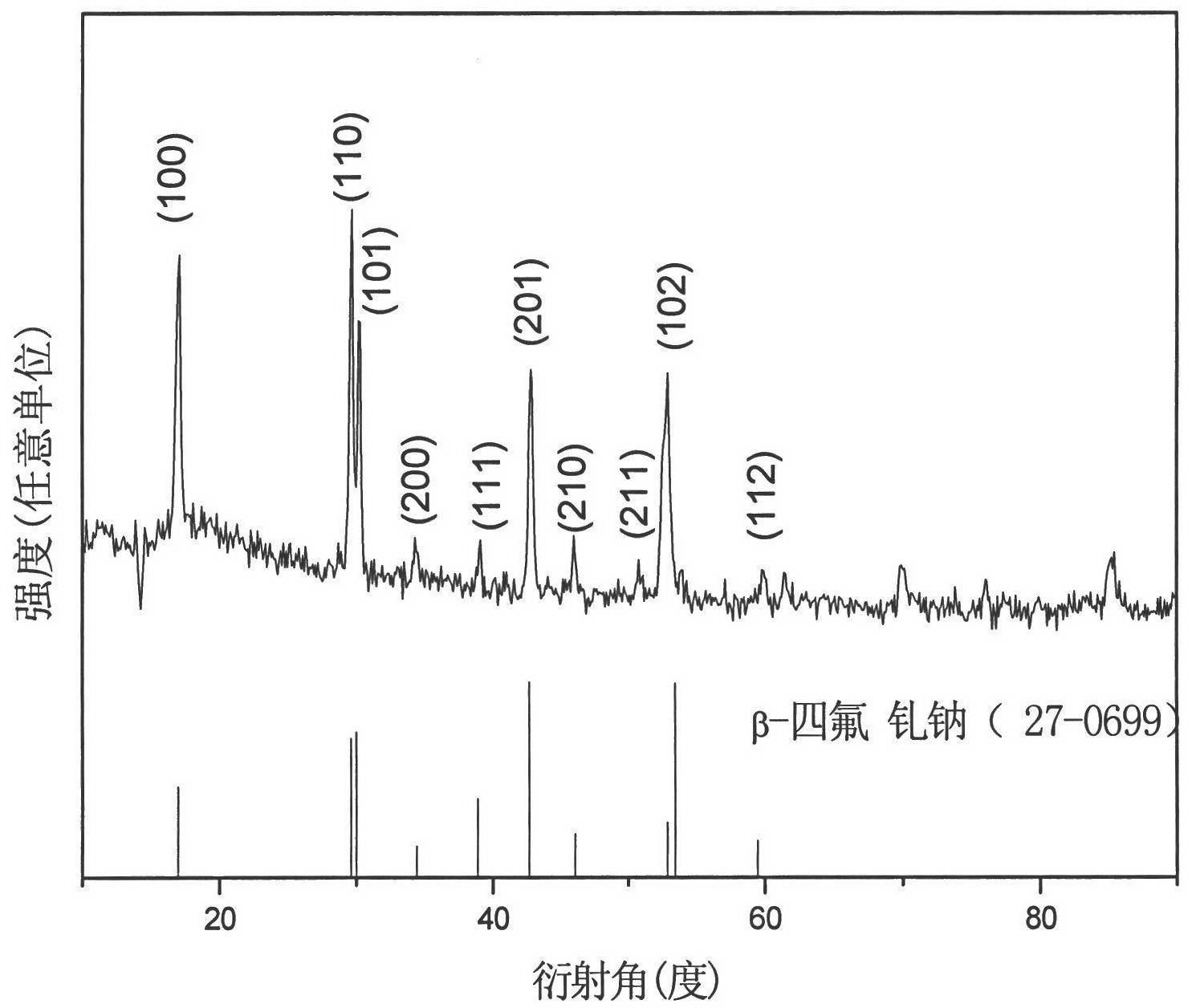
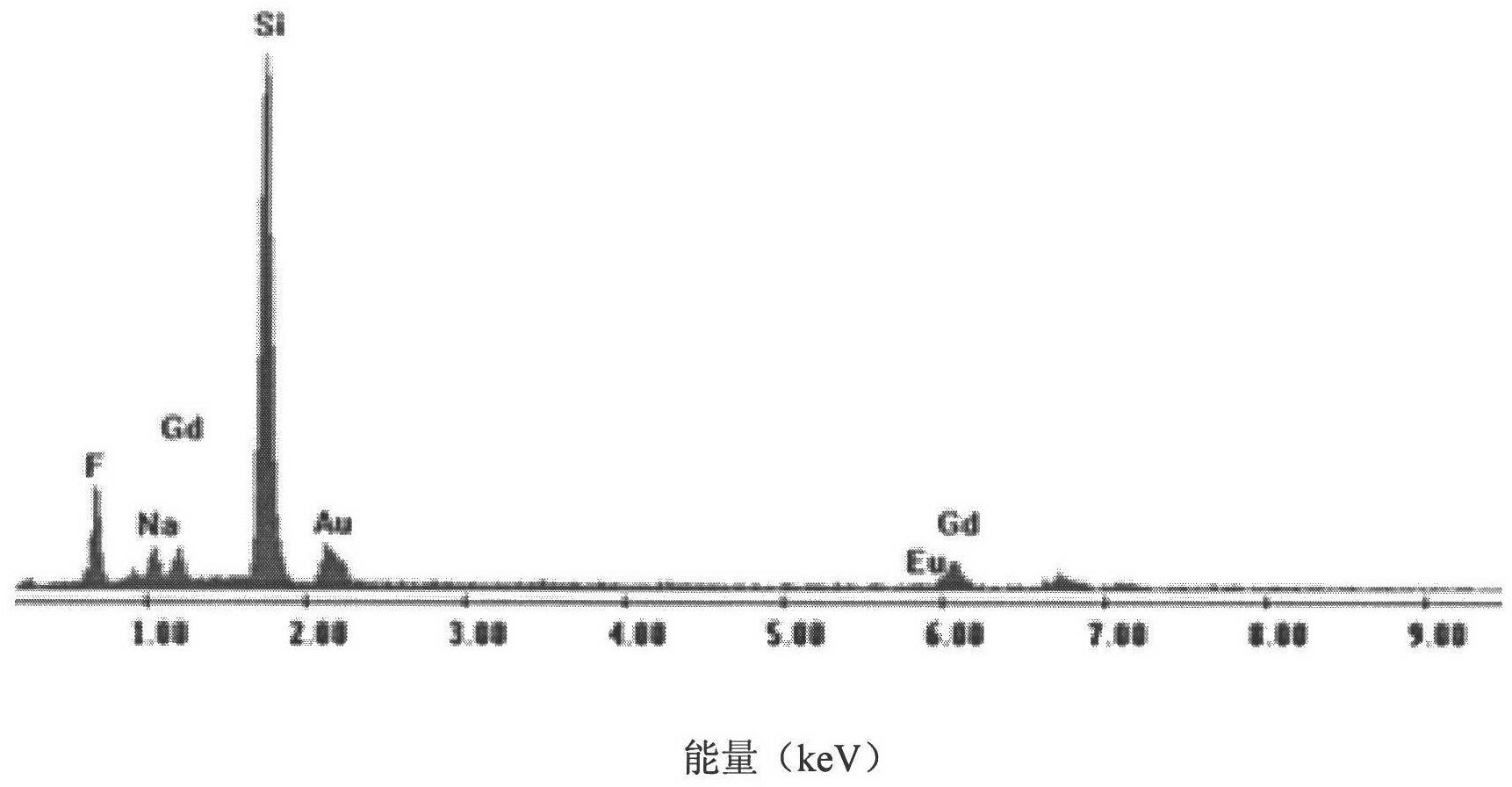
Europium ion-doped sodium gadolinium tetrafluoride luminescent nanorod and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a method for preparing rare earth ion europium-doped sodium gadolinium tetrafluoride (NaGdF4:Eu3+) luminescent nanorods and a method thereof, belonging to the technical field of preparation of rare earth doped luminescent materials. The present invention comprises the following steps: (1) mixing compound rare earth ions and sodium lauryl sulfate in proportion, and then adding fluoride to form a mixed solution; (2) carrying out hydrothermal reaction on the mixed solution at a certain temperature and time, Obtain the NaGdF4:Eu3+luminescent nanorods. The method has a simple synthesis process and is easy to produce in batches, and the prepared NaGdF4:Eu3+ nanorods have good red luminescent properties. The invention uses rare earth metal oxides as raw materials and sodium lauryl sulfate as a surfactant, and the whole reaction is carried out in an aqueous solution without any organic solvent, which is economical and environmentally friendly, has strong practicability, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
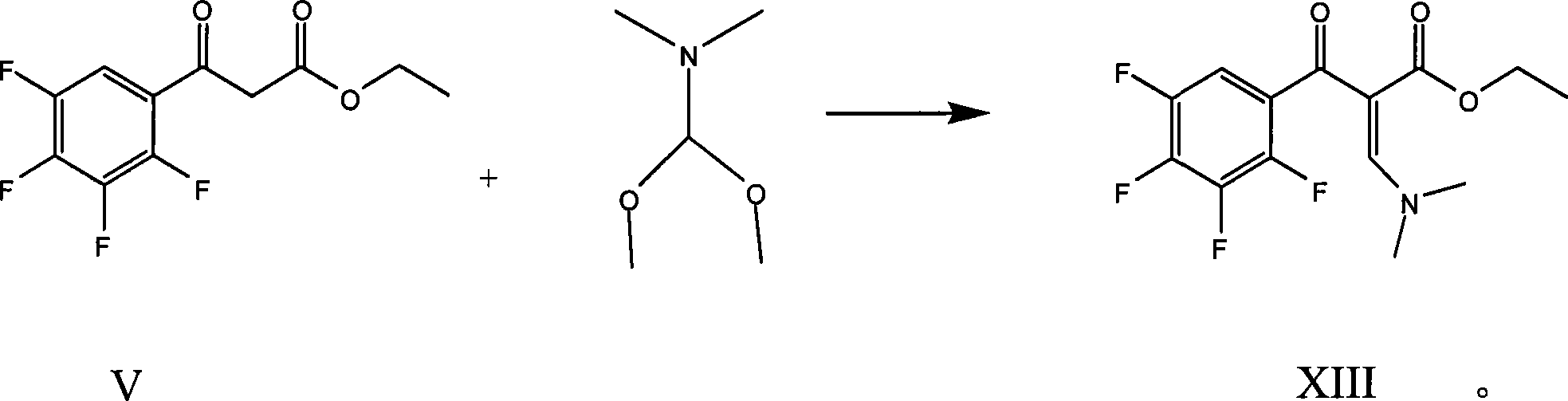
Preparation process of lavo-ofloxacin and ofloxacin
InactiveCN101519361AReduce generationIncrease production levelsOrganic compound preparationAntiinfectivesPotassium fluorideReaction temperature
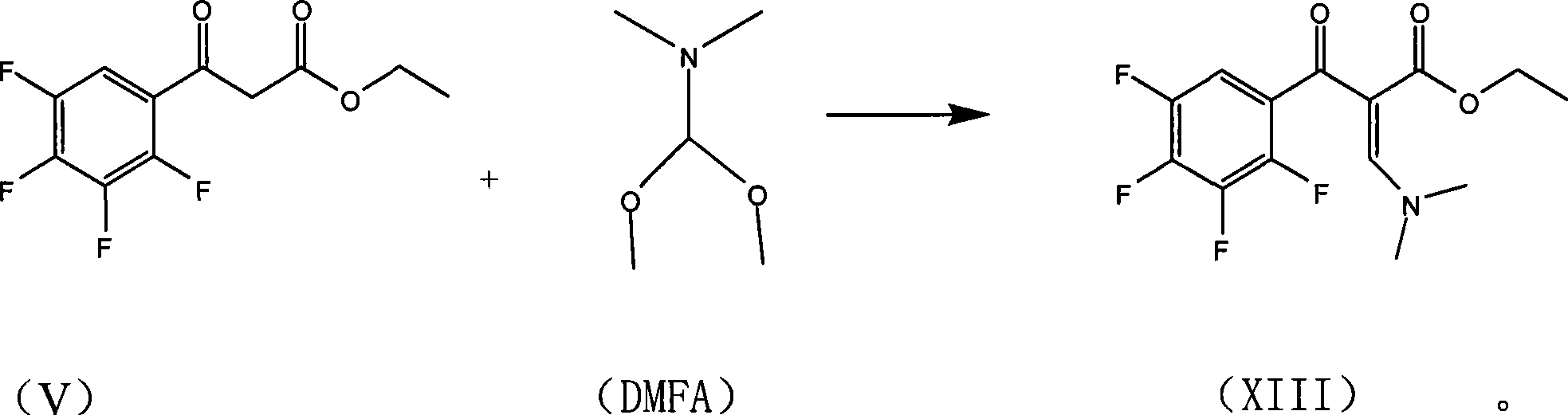
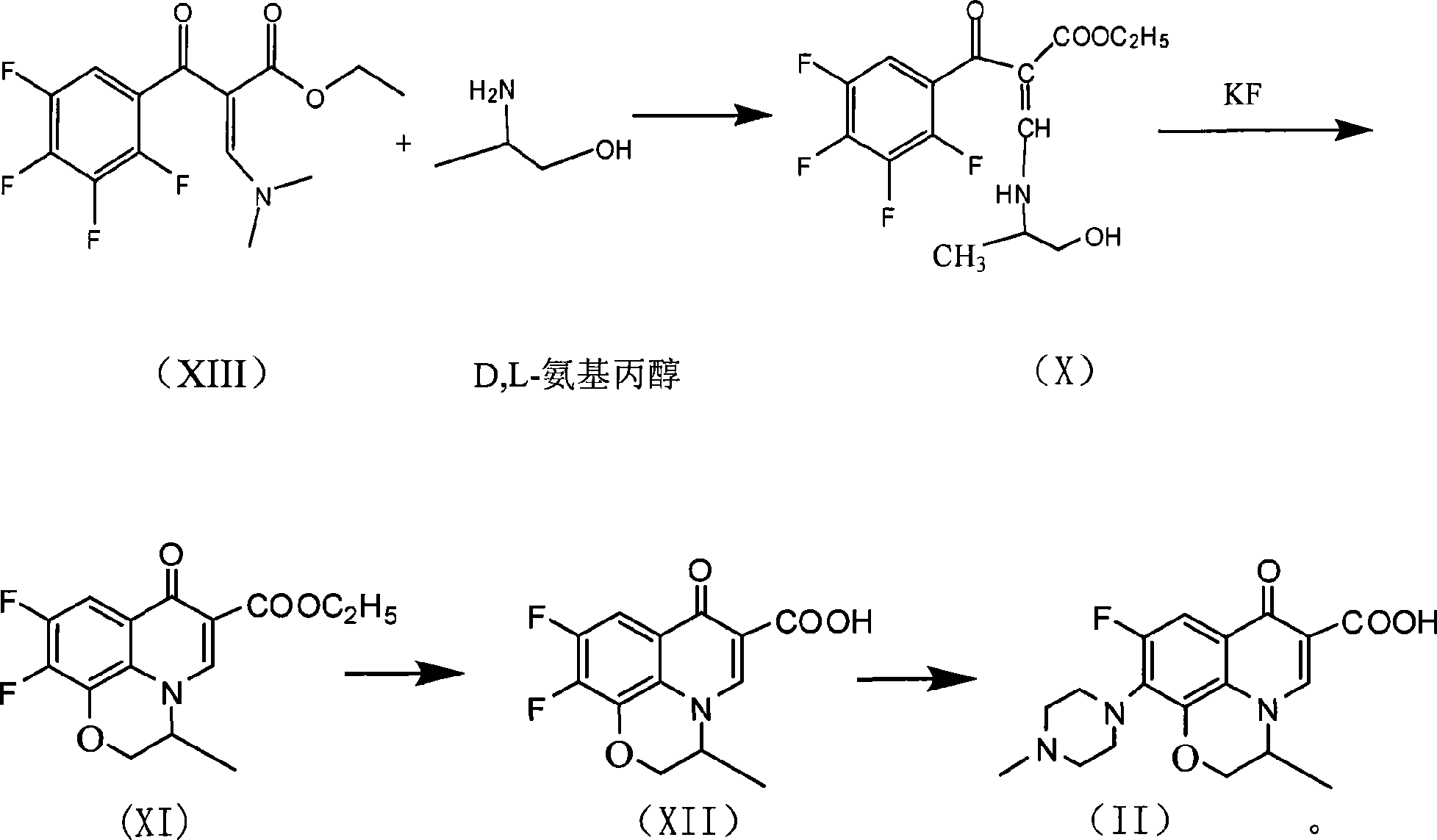
The invention relates to a preparation process of lavo-ofloxacin and ofloxacin which are anti-infectious medicaments, belonging to the synthetic process with tetrafluorobenzoic aid as raw material. The preparation method is characterized in that (2, 3, 4, 5-phenyl tetrafluoride formyl) ethyl acetate and DMFA react for 1.0-1.5h in toluene at 50-55 DEG C with the existence of acylating catalyst; the reaction product is washed by water, and an aqueous layer is separated; at 30-35 DEG C, L-amino propanol is dripped in an oil layer to carry out replacement reaction for 1.5-2.0h; toluene is decompressed, recovered and dried proper quantity of DMF is added to the oil layer for diluting; the diluted oil layer is dripped into back-flow DMF with the existence of anhydrous potassium fluoride to carry out back-flow reaction for 6h; DMF is recovered, water is added for centrifugation, acid is added to the obtained solid to be hydrolyzed to prepare lavo-perfluorocarboxylic acid, the lavo-perfluorocarboxylic acid reacts with N-methyl piperazine in DMSO at 90-110 DEG C by taking triethylamine as an acid-binding agent, and the lavo-ofloxacin is obtained after the fine purification of the product of reaction. The process improves the reaction condition of (2, 3, 4, 5-phenyl tetrafluoride formyl) ethyl acetate and DMFA, lowers the reaction temperature, shortens the reaction time and improves the reaction yield of lavo-fluoro ester serving as a reaction intermediate by 20 percent.
Owner:HENAN TOPFOND PHARMA
Balance strut for wind tunnel hot jet interference test
The invention discloses a balance strut for a wind tunnel hot jet interference test. The balance strut comprises a strut body, a gas circuit module, a water cooling module, a debugging nozzle and a test nozzle. The strut body is used for installing a balance and a model; the gas circuit module is used for carrying out jet gas intake; the water cooling module is used for cooling the strut, so as toreduce the influence of the high temperature of jet gas on the measurement of the balance. The jet gas intake adopts the mixed gas of carbon tetrafluoride and nitrogen, and the specific heat ratio ofthe mixed gas is adjusted by changing the ratio of the two gases. Before the test, only the debugging nozzle is installed to adjust the total temperature and total pressure of the jet; and the debugging nozzle is taken down during the test, the test nozzle and the model are installed, and the wind tunnel test is performed according to the debugging state. The balance strut for the wind tunnel hotjet interference test provided by the invention is applicable to a wind tunnel hot jet test in a thin atmospheric environment and can measure the influence of jet interferences on the model aerodynamic force.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所
Fluorination Processes with Arylsulfur Halotetrafluorides
InactiveUS20110160488A1Improve stabilityPrevent degradationOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationTrifluorideCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6864183B2Excellent electrical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSulfur hexafluorideMetal silicide
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
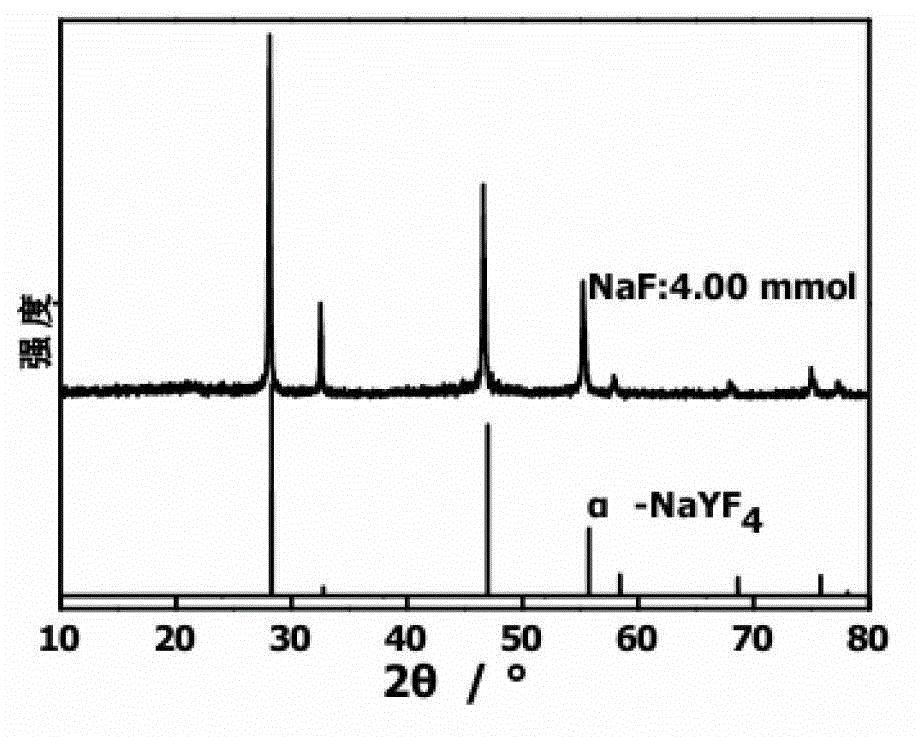
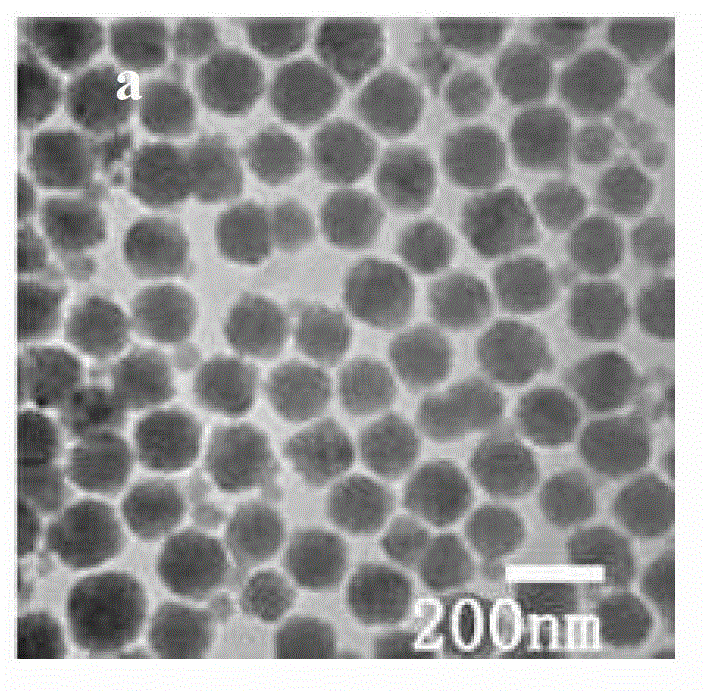
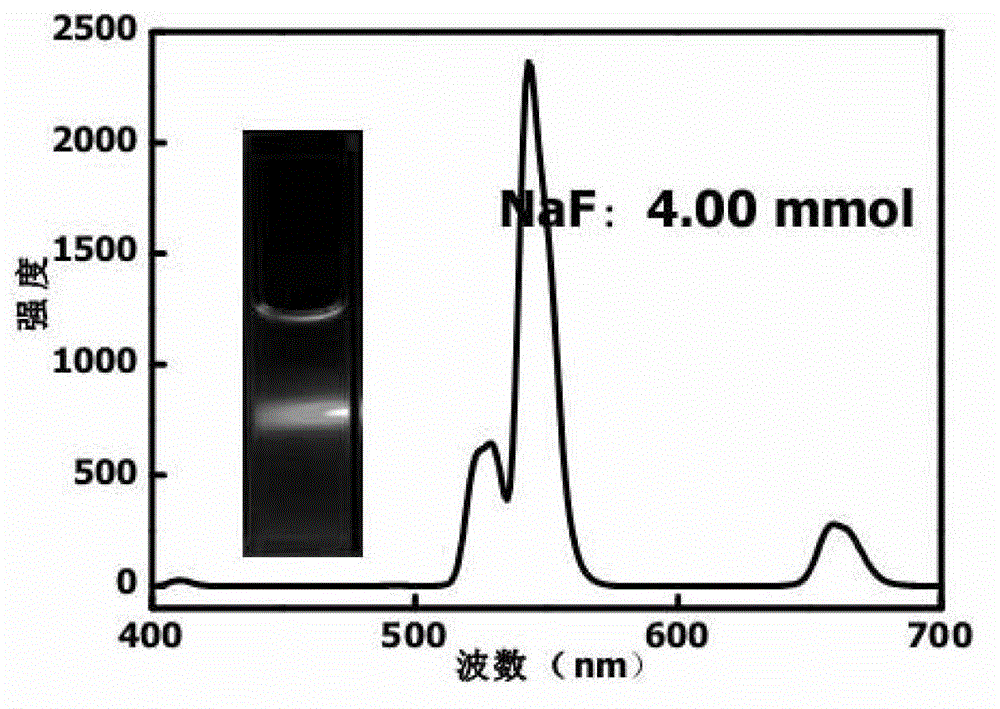
In-water-phase monodisperse sodium yttrium tetrafluoride multi-color luminescent nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102942933AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityLuminescent compositionsBiocompatibility TestingErbium doping
The invention discloses an in-water-phase monodisperse sodium yttrium tetrafluoride ytterbium-and-erbium-doped multi-color upconversion luminescent nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of multifunctional application-oriented inorganic advanced nano materials. According to the method, a product is synthesized in one step through a hydrothermal method, and a sodium yttrium tetrafluoride nanoparticle capable of emitting light of different colors can be obtained by regulating the amount of NaF; and the particle which is uniform in size and is in morphology of cubic phases or hexagonal phases can be obtained through simple condition change. The sodium yttrium tetrafluoride multi-color luminescent nanoparticle can stably exist in water for long time, has excellent biocompatibility and can be directly used in hydrophilic systems of biosensors, cell imaging, magnetic resonance imaging, disease diagnosis and treatment and the like. The cost of raw materials is low, less pollution is caused to the environment, and the method is simple, so that the sodium yttrium tetrafluoride multi-color luminescent nanoparticle has wide application prospects in the field of biology and the fields such as thin-film materials, luminescent devices, anti-counterfeiting materials and the like. It is worth mentioning that the material has been successfully used in the field of cell imaging.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Processes for producing phosphorus tetrafluoride and phosphate hexafluoride
InactiveUS20110286905A1High purityPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesPhosphatePhotochemistry
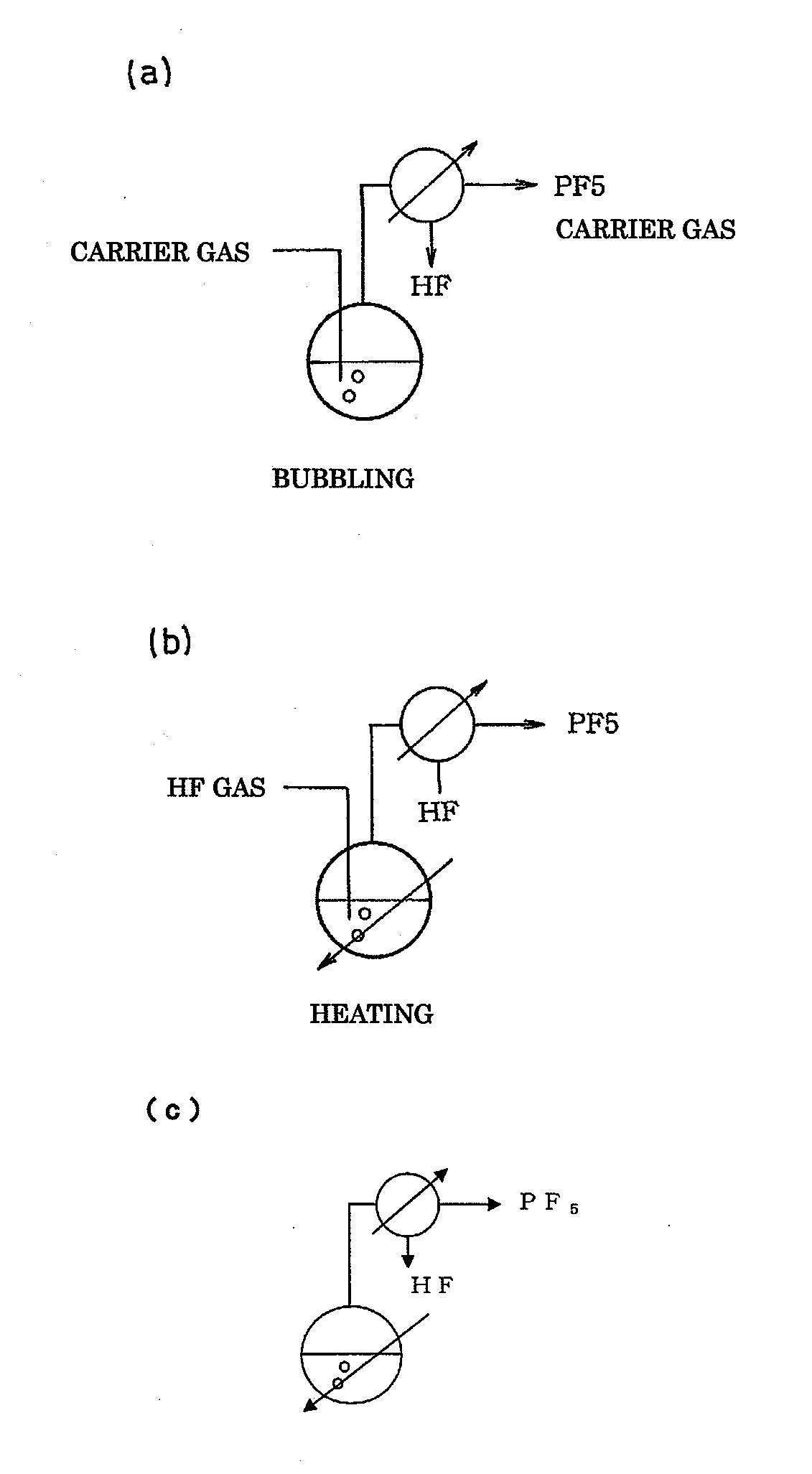
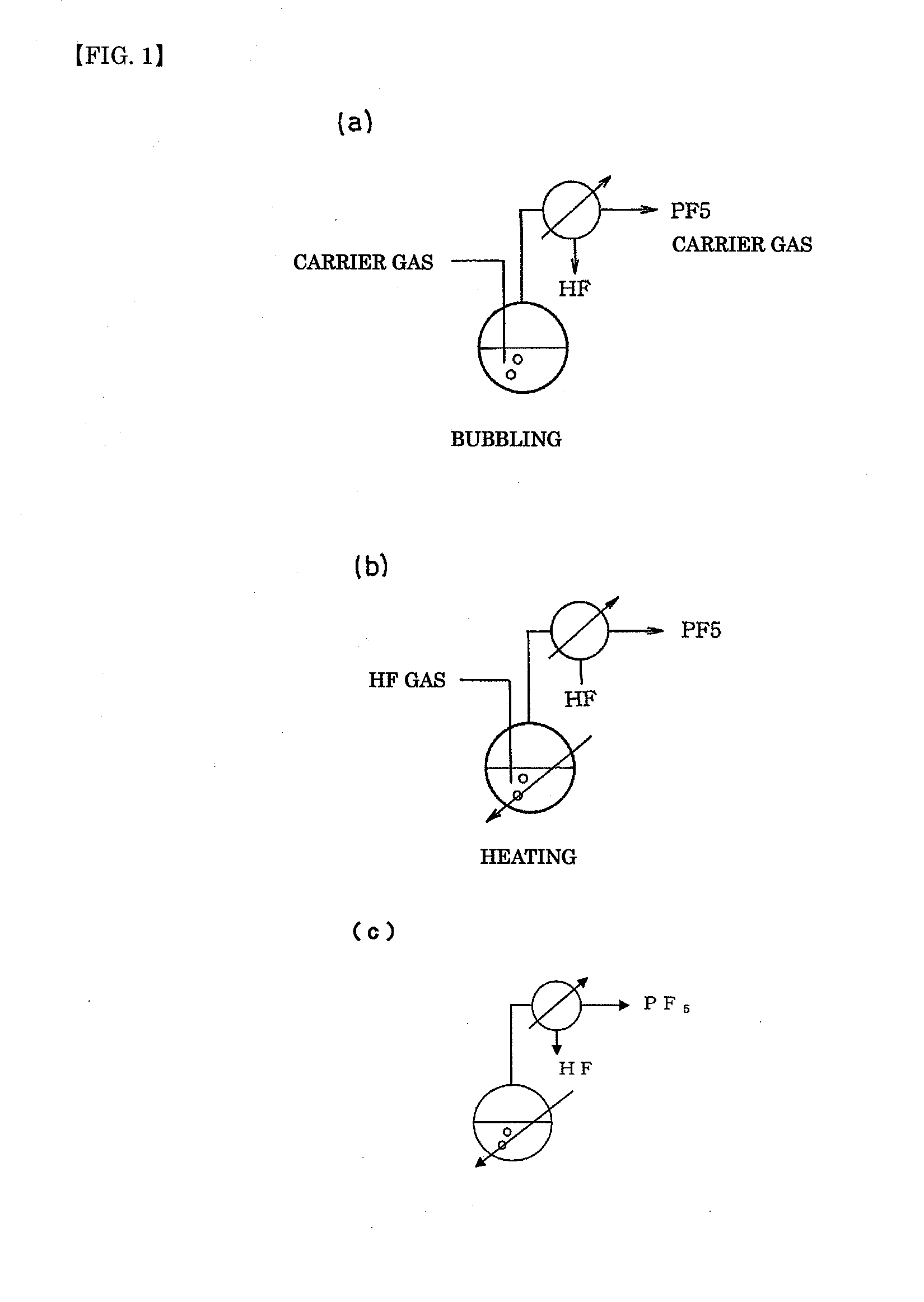
An object the invention is to provide a phosphorus pentafluoride producing process wherein phosphorus pentafluoride is separated / extracted from a pentavalent phosphorus compound or a solution thereof, or a composition obtained by allowing the pentavalent phosphorus compound or the solution thereof to react with hydrogen fluoride, thereby producing phosphorus pentafluoride; and a phosphate hexafluoride producing process wherein the resultant phosphorus pentafluoride is used as raw material to produce a phosphate hexafluoride high in purity. The present invention relates to a process for producing phosphorus pentafluoride, wherein a carrier gas is brought into contact with either of the following one: a pentavalent phosphorus compound, a solution thereof, or a solution in which a composition obtained by allowing the pentavalent phosphorus compound or the solution thereof to react with hydrogen fluoride is dissolved, thereby a phosphorus pentafluoride is extracted into the career gas.
Owner:STELLA CHEMIFA CORP
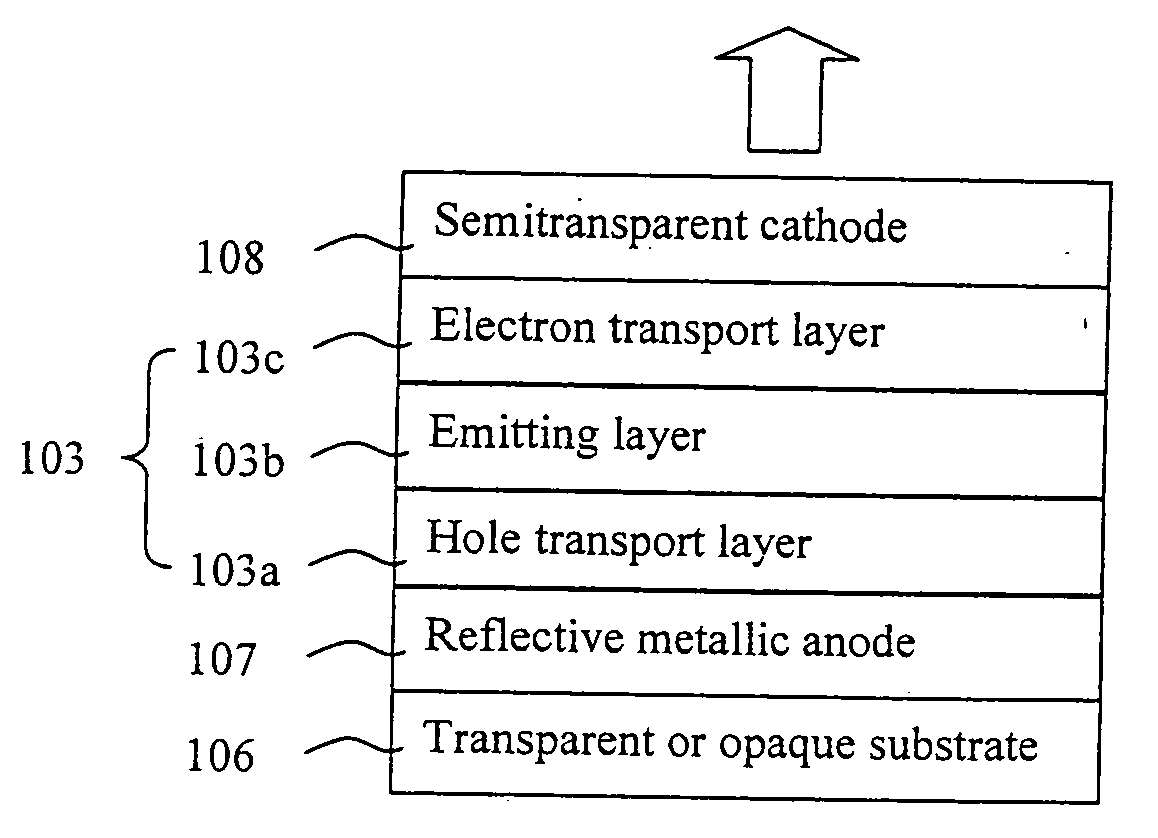
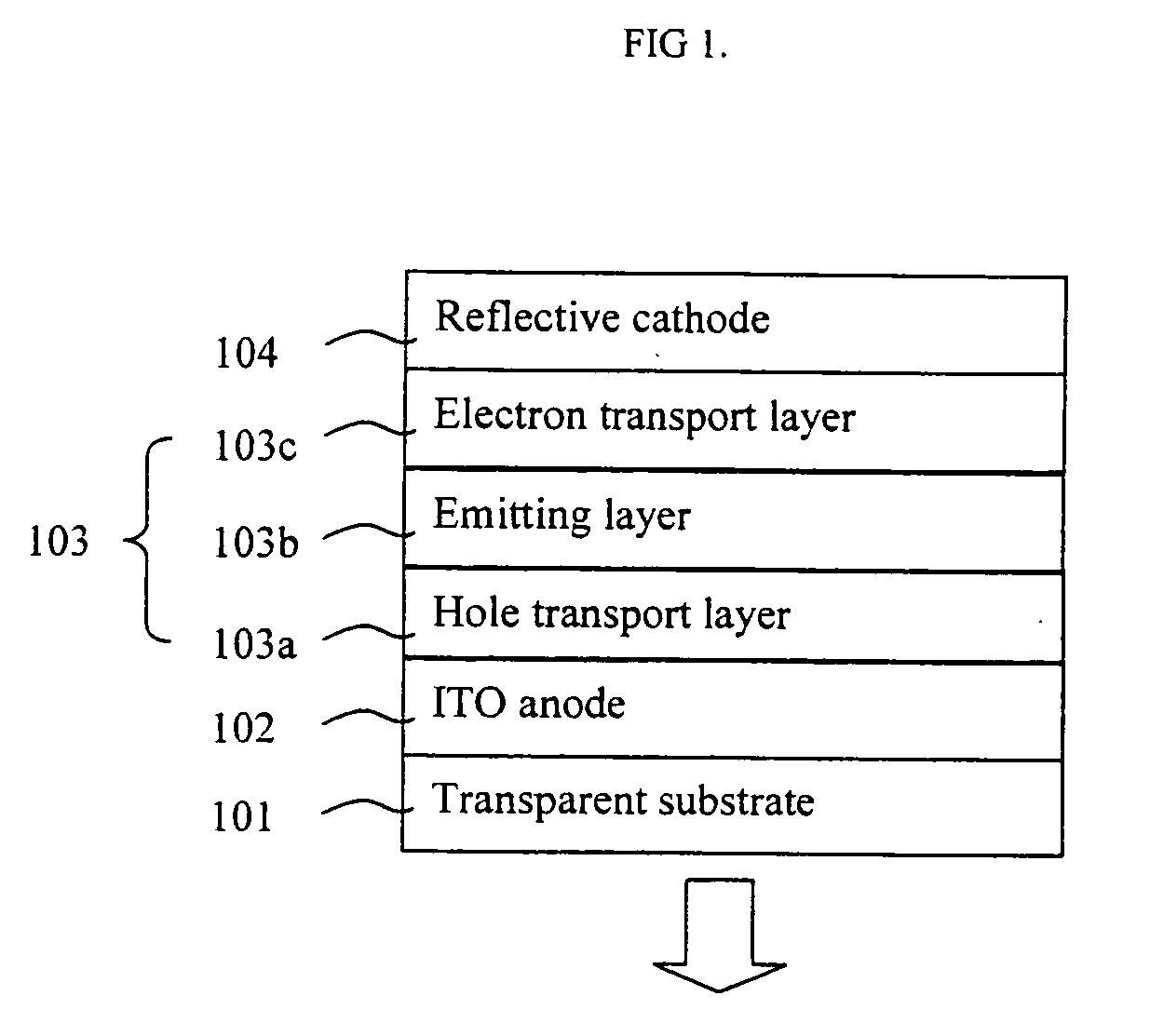
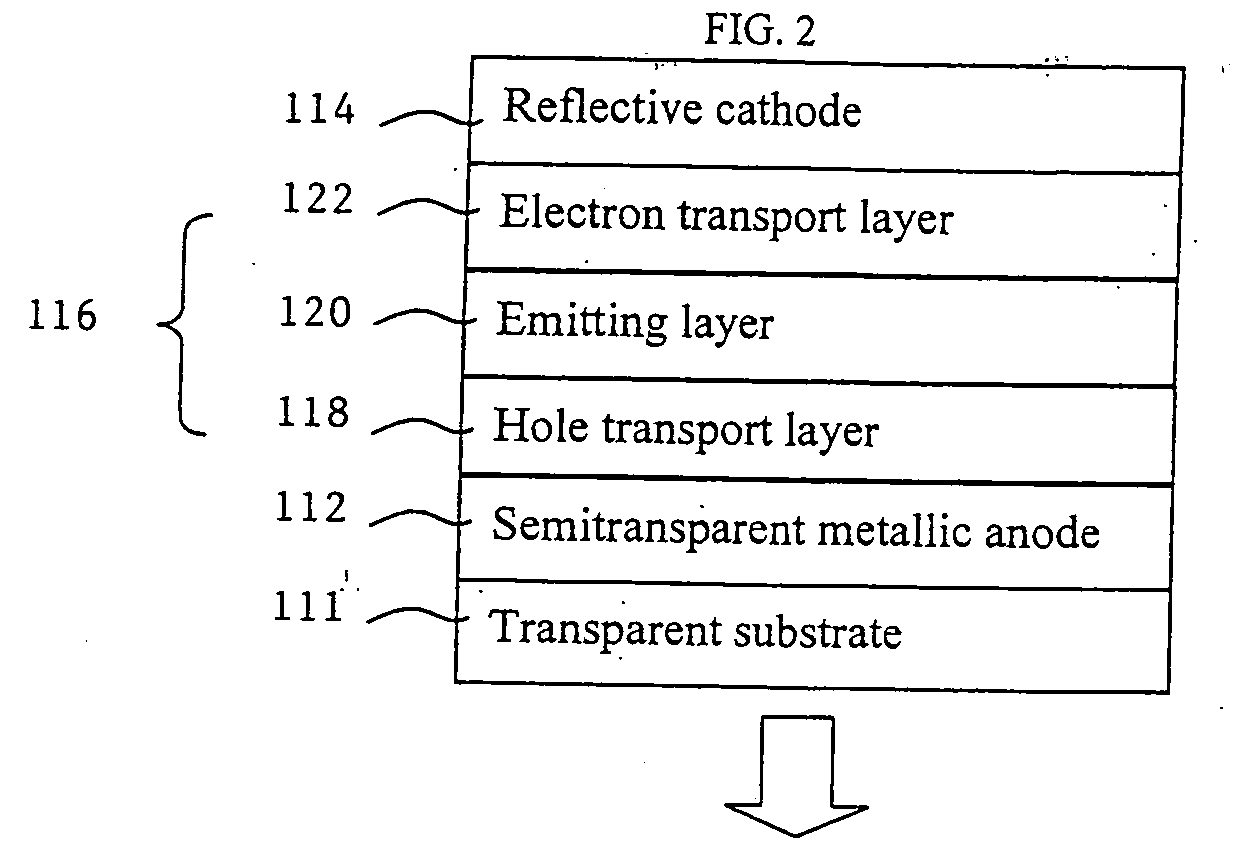
Metallic anode treated by carbon tetrafluoride plasma for organic light emitting device
InactiveUS20070046183A1Improve abilitiesEasy to makeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOrganic light emitting deviceCarbon plasma
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com