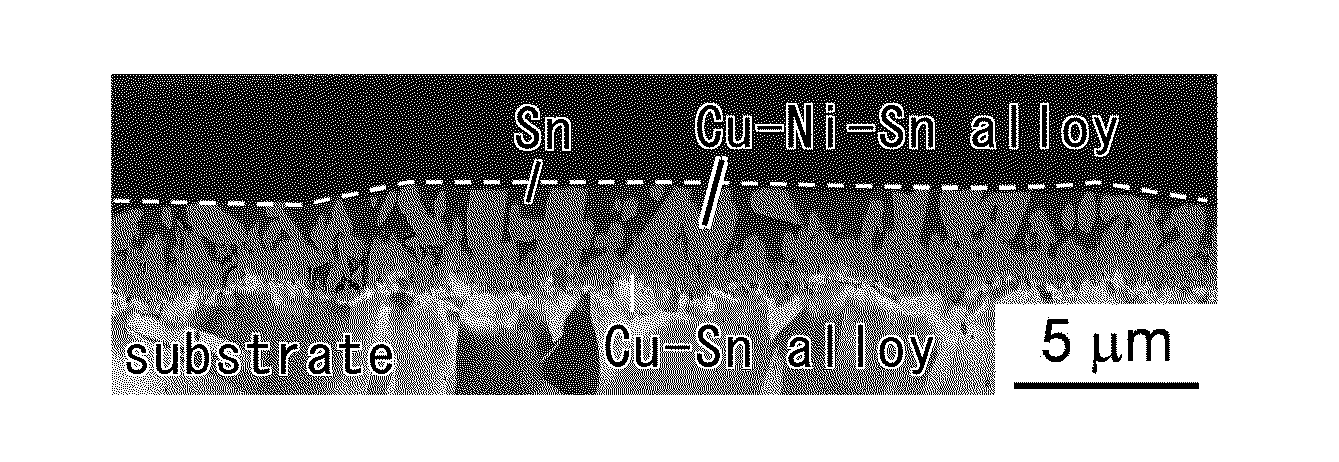Patents
Literature
83results about How to "Good solder wettability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
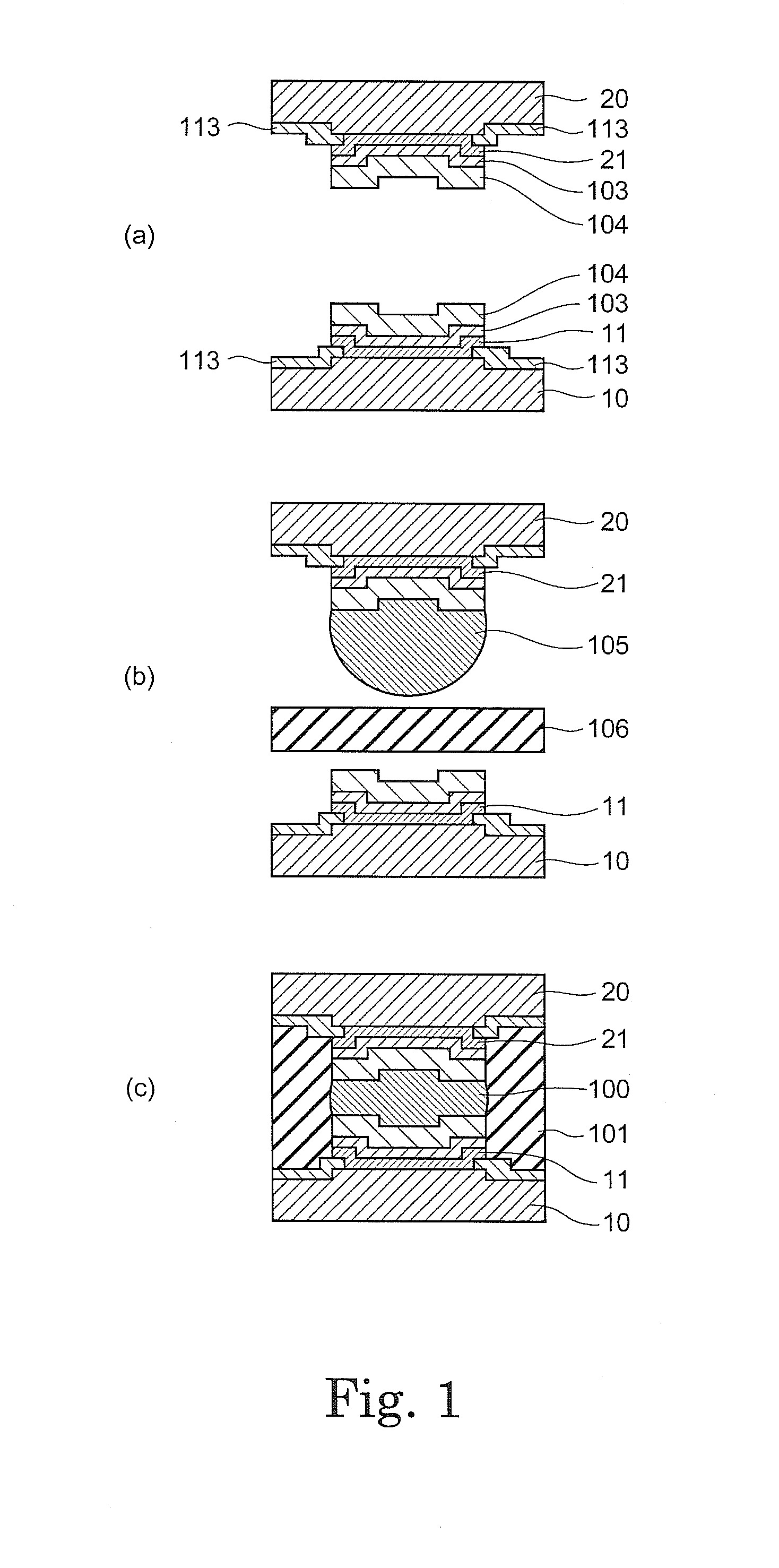
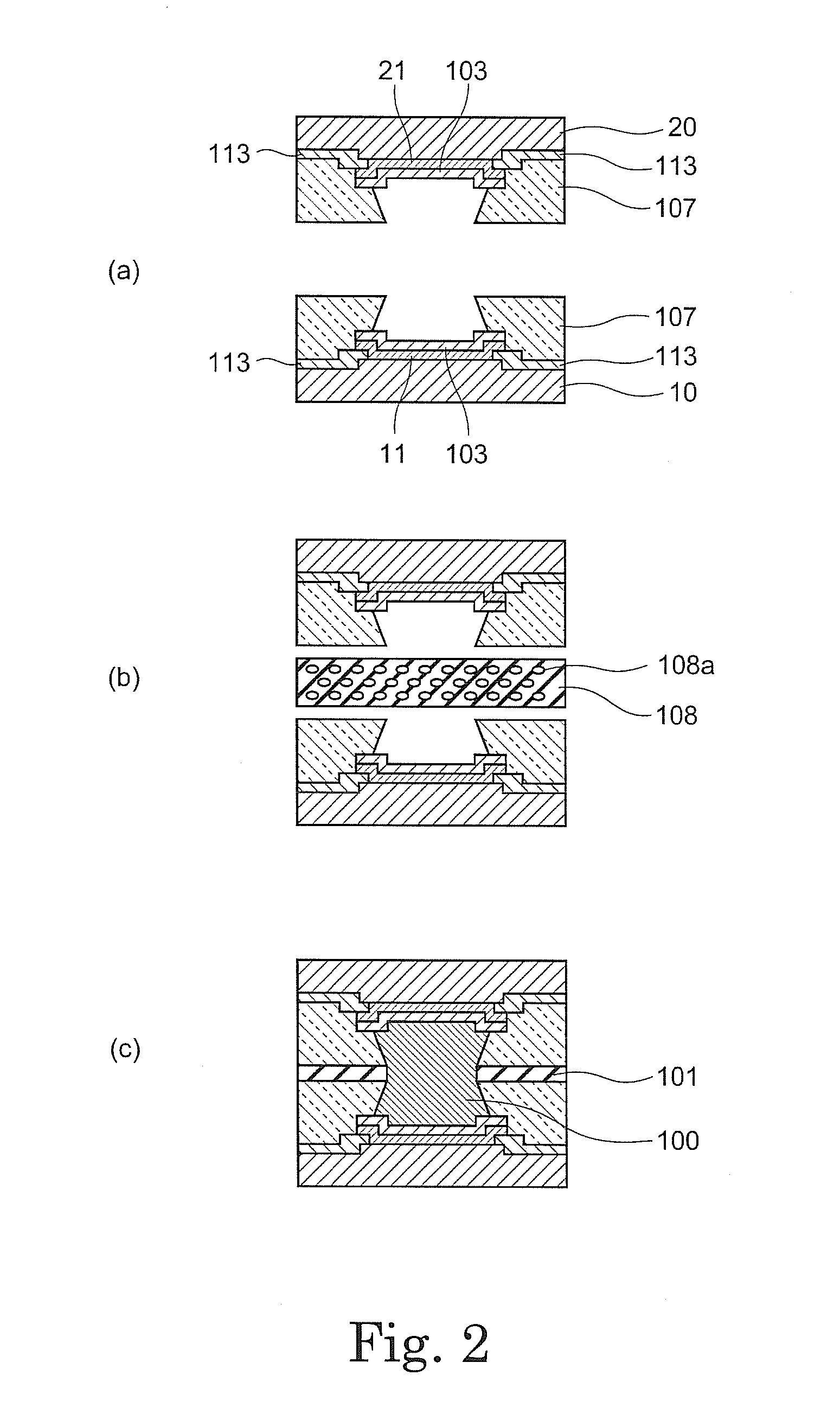
Solder material, method for manufacturing the same, joined body, method for manufacturing the same, power semiconductor module, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100193801A1Good solder wettabilityImprove wettabilityNon-insulated conductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsZincSemiconductor
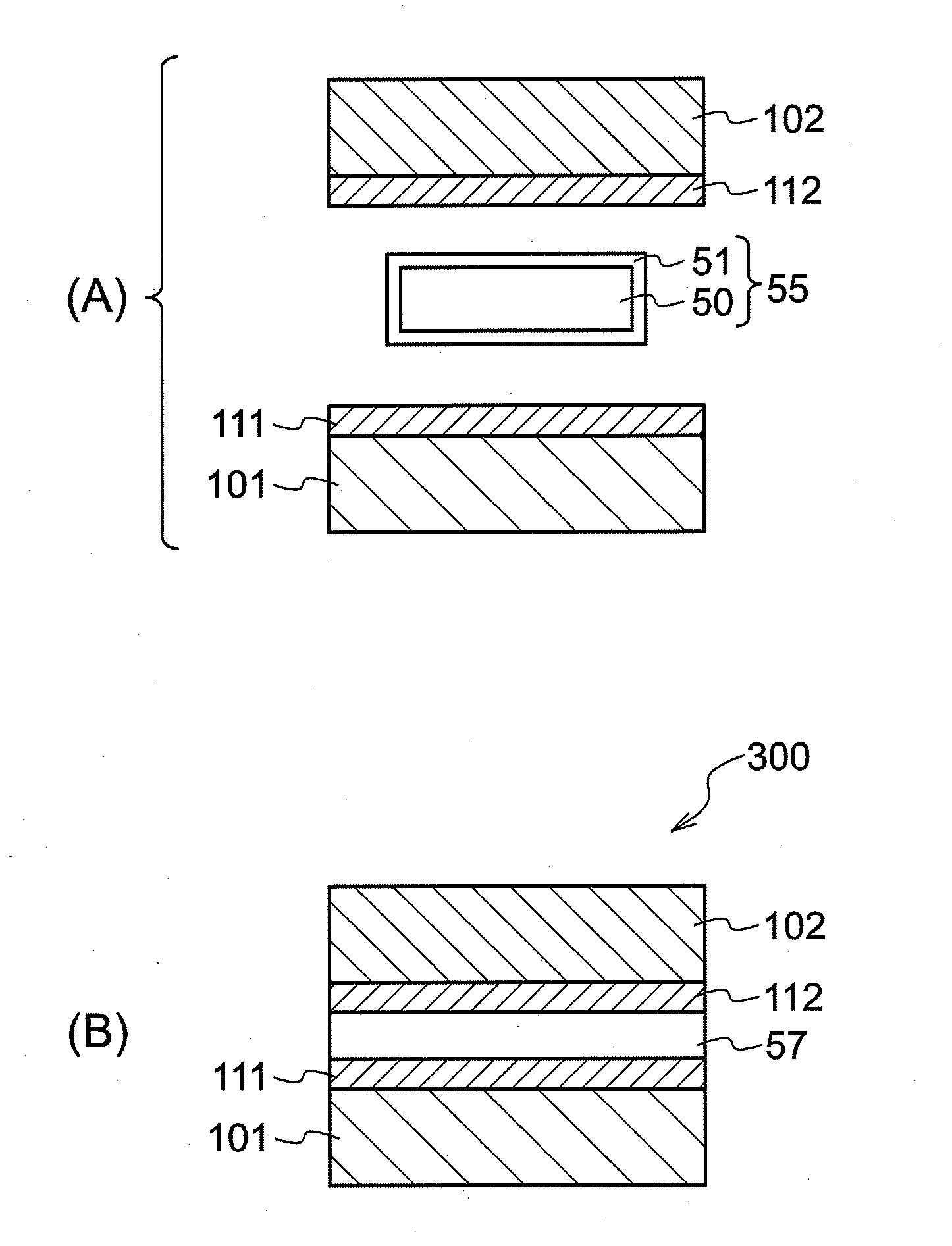
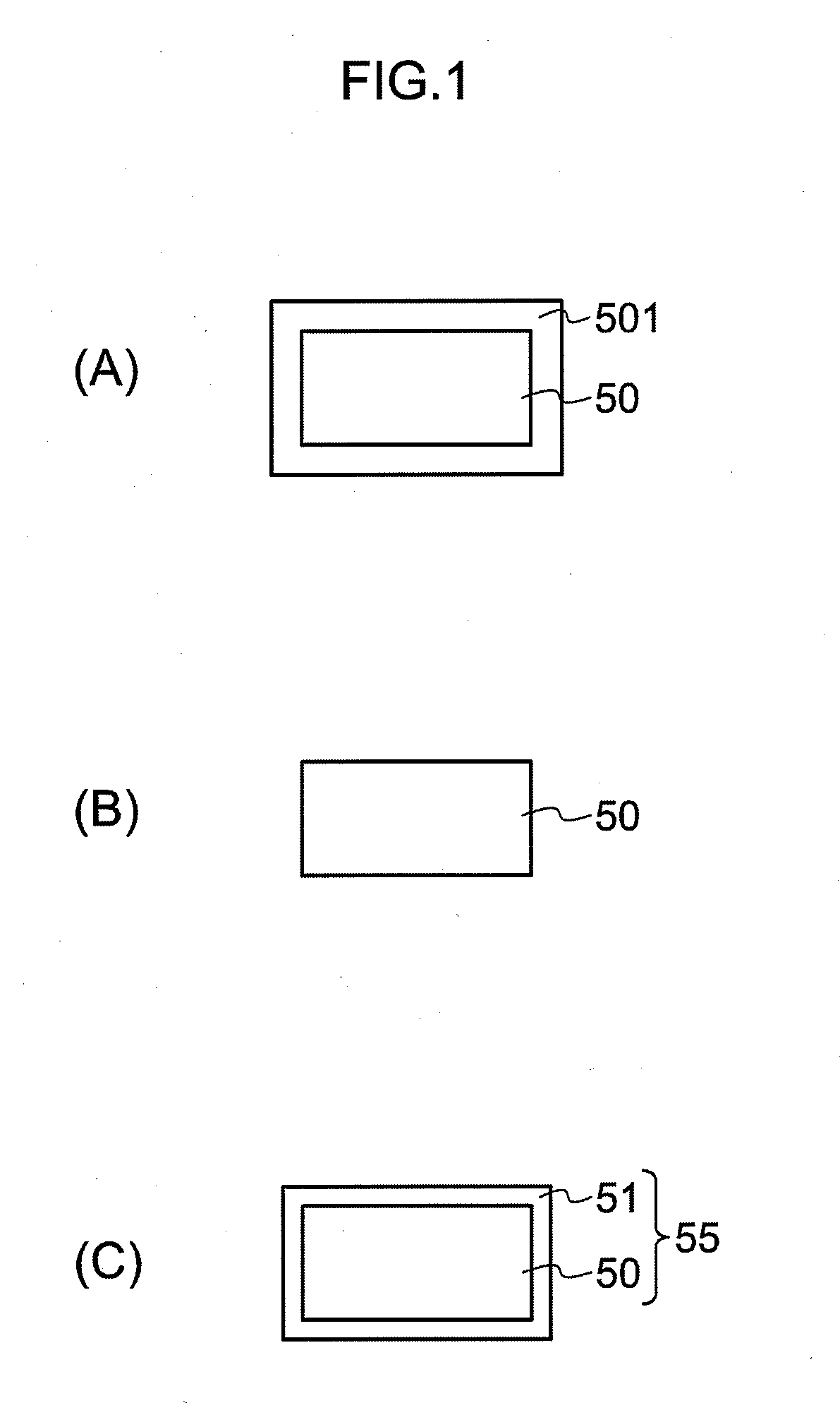
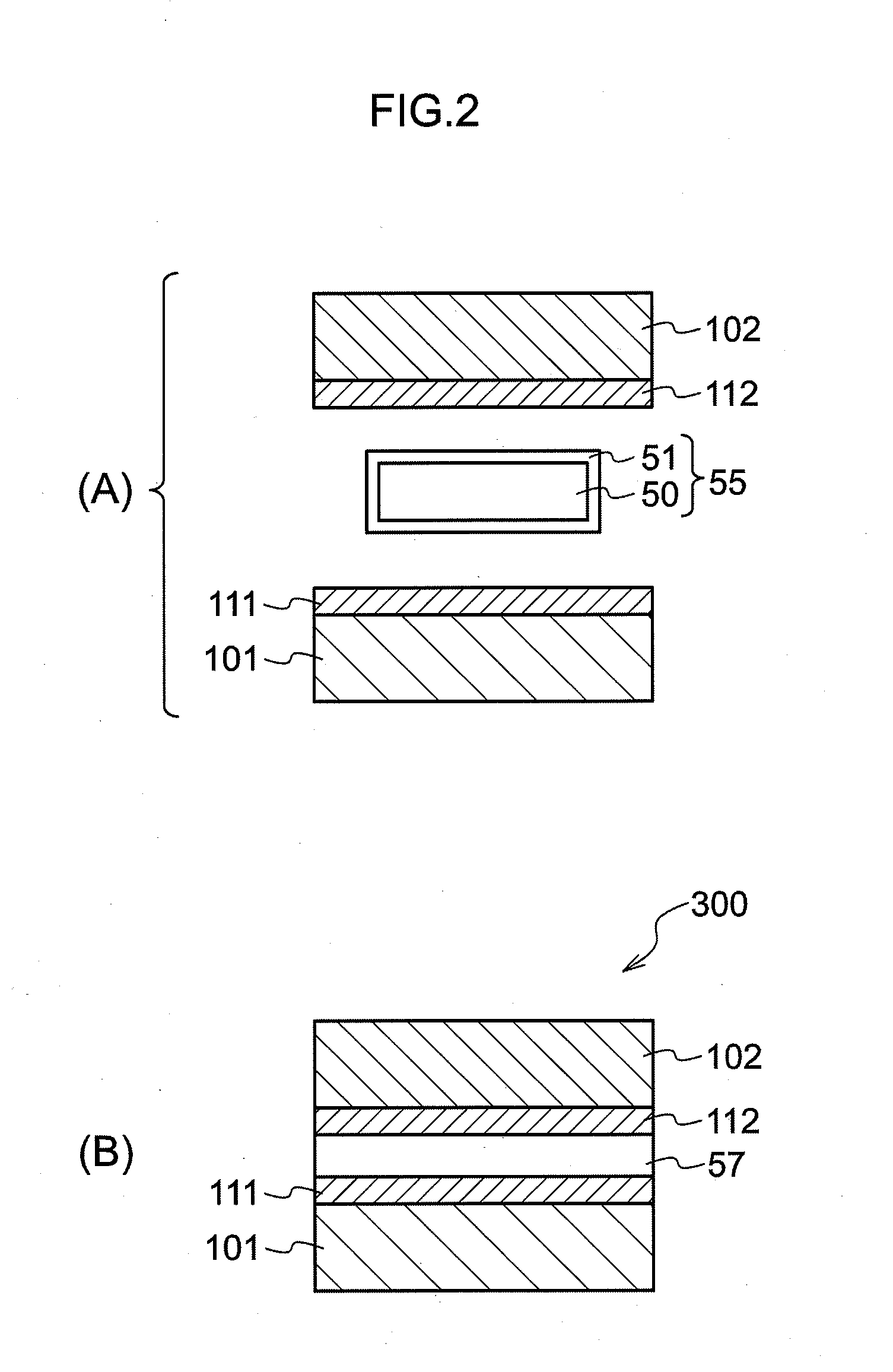
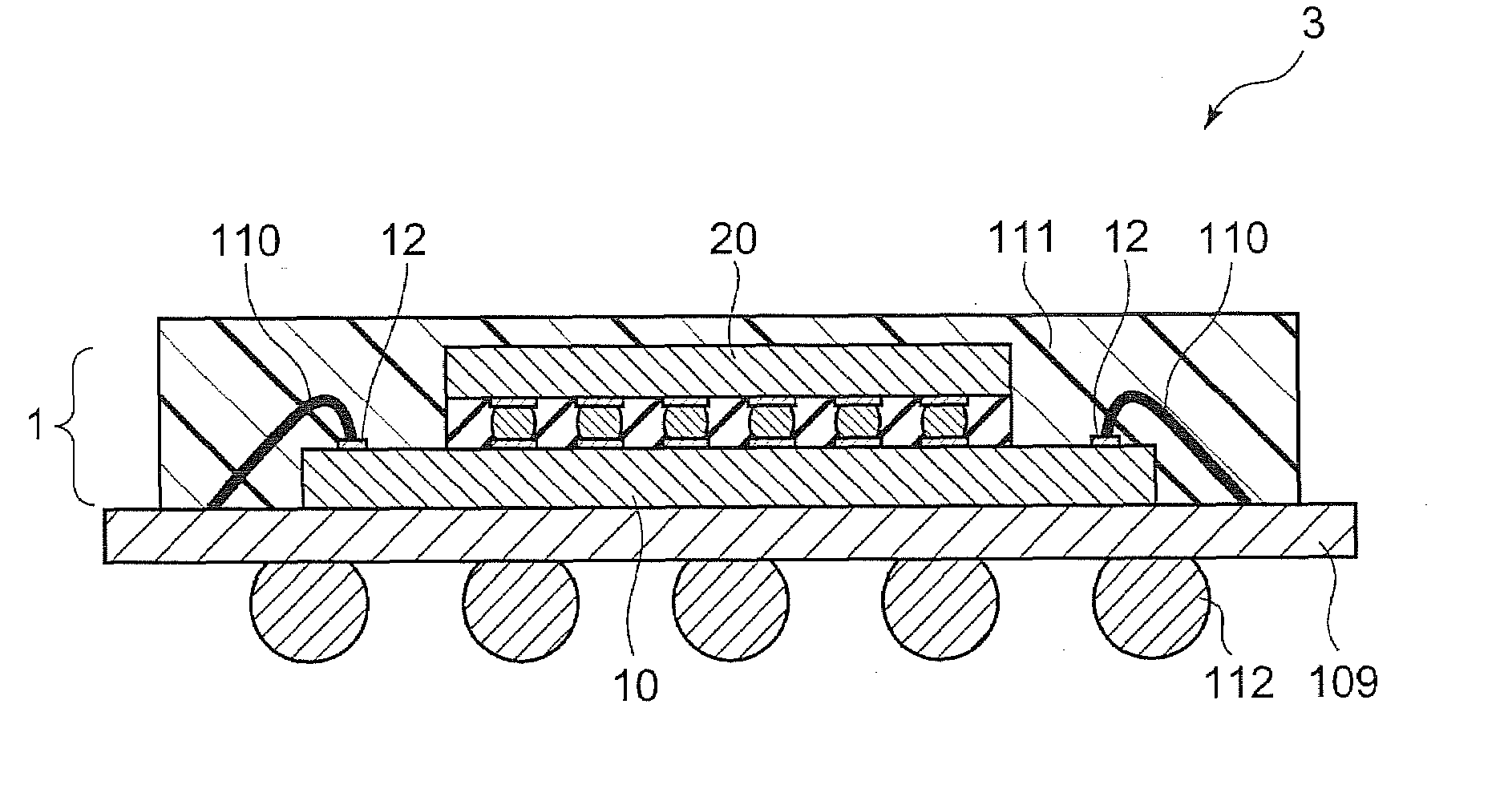
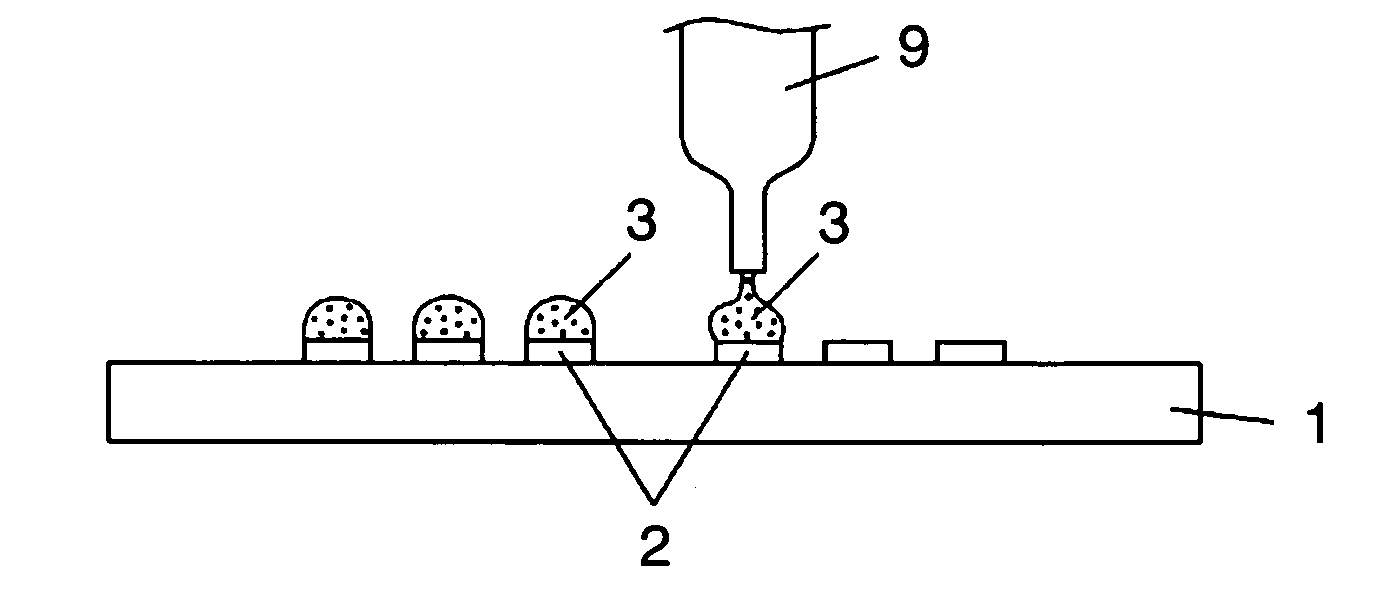
A zinc based solder material 55 of the present invention is prepared by providing on the surface of a zinc based material 50, from which an oxide film 501 has been removed or at which an oxide film 501 does not exist, with a coating layer 51 containing primarily a metal whose oxide is more easily reducible than the oxide film 501. In a joined body and a power semiconductor module of the present invention, the zinc based solder material 55 is used in the joining portion, and after joining, the coating layer 51 does not exist.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Adhesive tape and semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS20100078830A1Good ion migration resistanceGood solder wettabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsChIP-on-chipSemiconductor chip
The present invention relates to an adhesive tape for electrically connecting semiconductor chips in a chip-on-chip type semiconductor device. The adhesive tape comprising: (A) 10 to 50 wt % of film forming resin; (B) 30 to 80 wt % of curable resin; and (C) 1 to 20 wt % of curing agent having flux activity.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
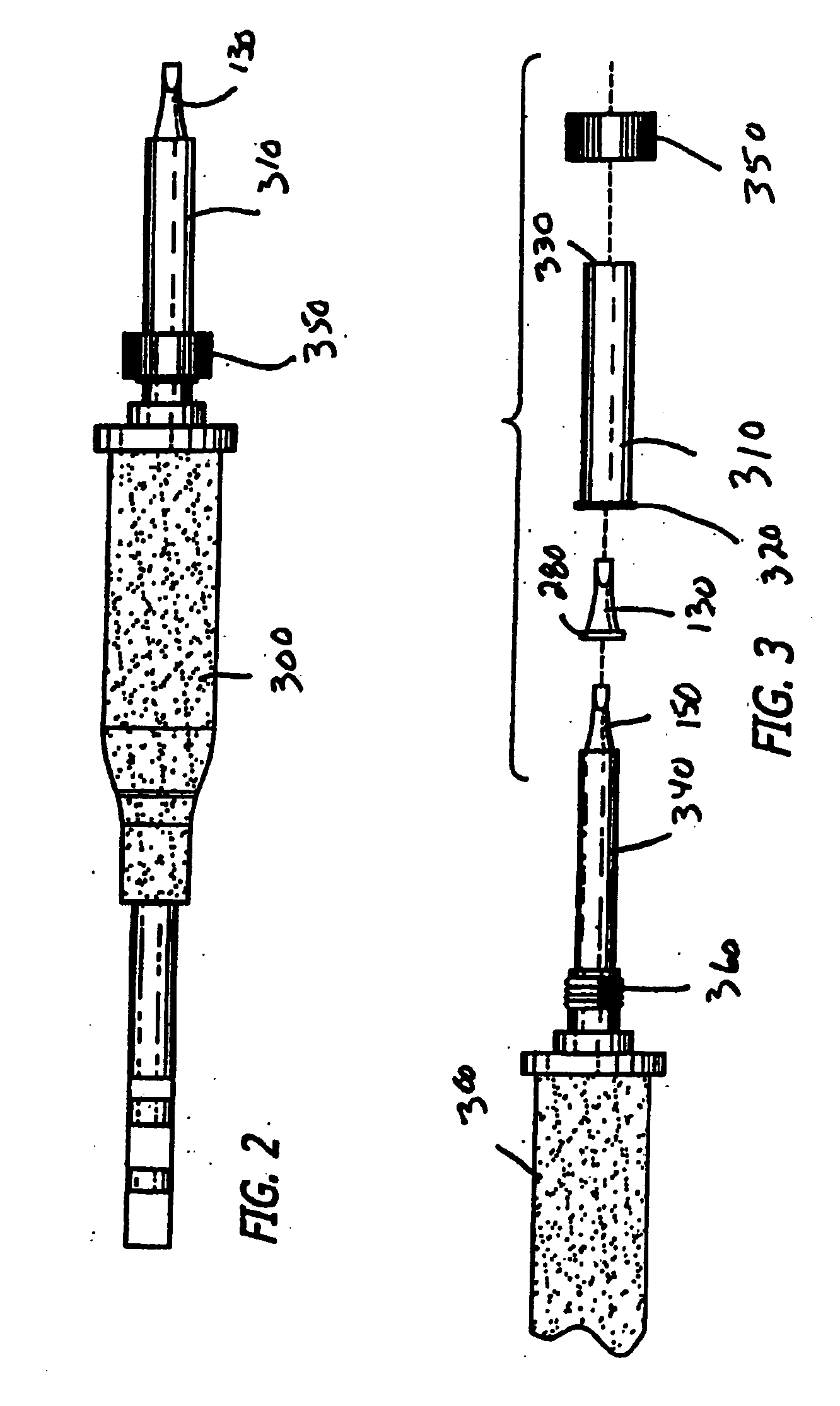
Soldering iron with replaceable tip
ActiveUS20060022018A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove the immunityHeating element shapesSoldering ironHeat conductingCoil spring
A soldering iron (and a desoldering iron) with a replaceable tip, which is releasably securable on the forward heat-conducting end of a soldering (or desoldering) iron heat assembly. The tip has a tapered heat conducting core in a tip cap. The face of the core can have a depression for mating engagement with a protrusion of the heat-conducting end. Also, the face can lie in the rear plane of the tip cap. An assembly which allows for the easy removal and application of a replacement tip can include a sleeve with tightening bolt, a coil spring sleeve, or a slotted compressible sleeve. The tip can thus be replaced after it has worn out, and the heat assembly unit need not be replaced until it has burnt out. Methods of manufacturing and using the tip are also disclosed.
Owner:HAKKO CO LTD
Monolithic electronic component
ActiveUS20080128860A1Uniform coating thicknessMoisture resistance of the monolithic electronic component can be ensuredSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFixed capacitor dielectricEngineeringElectronic component
In a monolithic electronic component in which a resistive element is incorporated by forming a resistor film on a terminal electrode, a plating film can be formed on the terminal electrode having the resistor film via electroplating in an efficient manner and with a uniform film thickness. In order to form the terminal electrode, the resistor film is disposed directly on the surface of the component body, and a conductive resin film having a relatively low volume resistivity is disposed over the resistor film. The conductive resin film is preferably adapted to have a specific resistance of less than about 1×10−4 Ω·m, on which a plating film having a uniform film thickness can be formed efficiently via electroplating.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Paste For Soldering And Soldering Method Using The Same
ActiveUS20080048009A1Good solder wettabilityFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsSolder pasteMetal powder
It provides metal-powder-contained flux disposed between bumps and circuit electrodes when electronic parts are mounted by soldering, the metal powder comprises a core metal formed of metal such as tin and zinc and a surface metal covering surfaces of the core metal formed of noble metal such as gold and silver. Accordingly, metal powder will not remain as residue that is liable to cause migration after the reflow process, and it is possible to assure both soldering effect and insulation effect.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Soldering iron with replaceable tip cap
InactiveUS20050011876A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove the immunityHeating element shapesSoldering bitsConductive pasteHeat conducting
A soldering iron (and a desoldering iron) with a replaceable tip cap are herein disclosed. The replaceable tip cap is fitted on the forward heat-conducting core end of a soldering (or desoldering) iron heat assembly. Conductive paste, powder or a low melting temperature material such as solder, can be sandwiched between the tip cap and the forward end to improve heat conductivity therebetween. An assembly which allows for the easy removal and application of a replacement tip cap can include a sleeve with tightening bolt, a coil spring sleeve, or a slotted compressible sleeve. The tip cap can thus be replaced after it has worn out, and the heat assembly unit need not be replaced until it has burnt out.
Owner:HAKKO CO LTD
Semiconductor device using multi-layer unleaded metal plating, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060071335A1Whisker resistance can be improvedSecure adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndiumDevice material
A semiconductor device comprises a semiconductor integrated circuit, an external connection terminal connecting the semiconductor integrated circuit to an external device, and a plurality of tin or tin-alloy plating layers formed on the external connection terminal as multiple unleaded metal plating layers. The multiple unleaded metal plating layers comprise a first layer made of a tin alloy and provided as an inner layer of the multiple unleaded metal plating layers, the tin alloy of the first layer containing as a second element one of bismuth, silver, copper, indium, and zinc, and a second layer made of either 100% tin or a tin alloy and provided as an outer surface layer of the multiple unleaded metal plating layers, the 100% tin or the tin alloy of the second layer having a percentage of tin content greater than that of the first layer.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
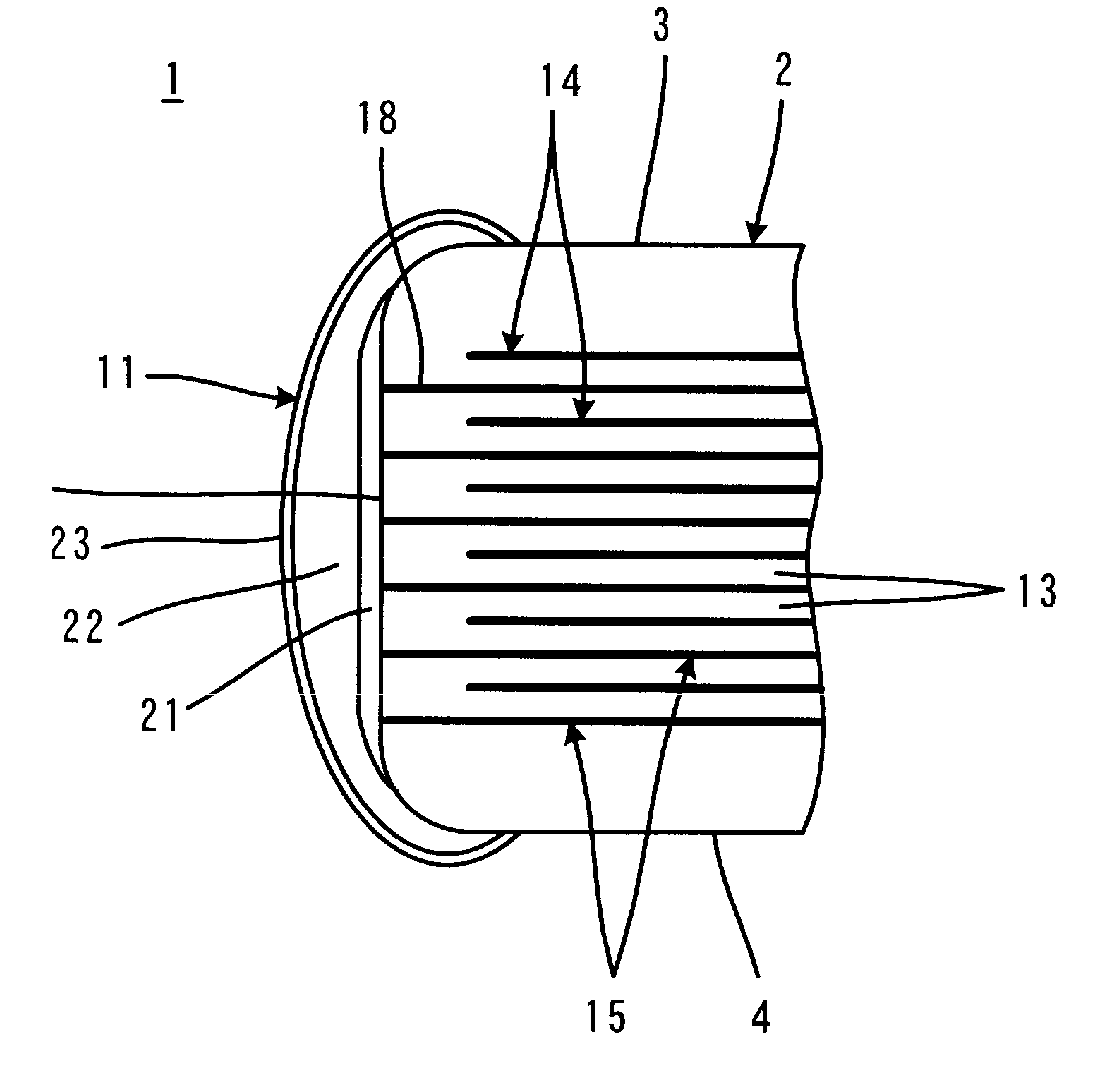
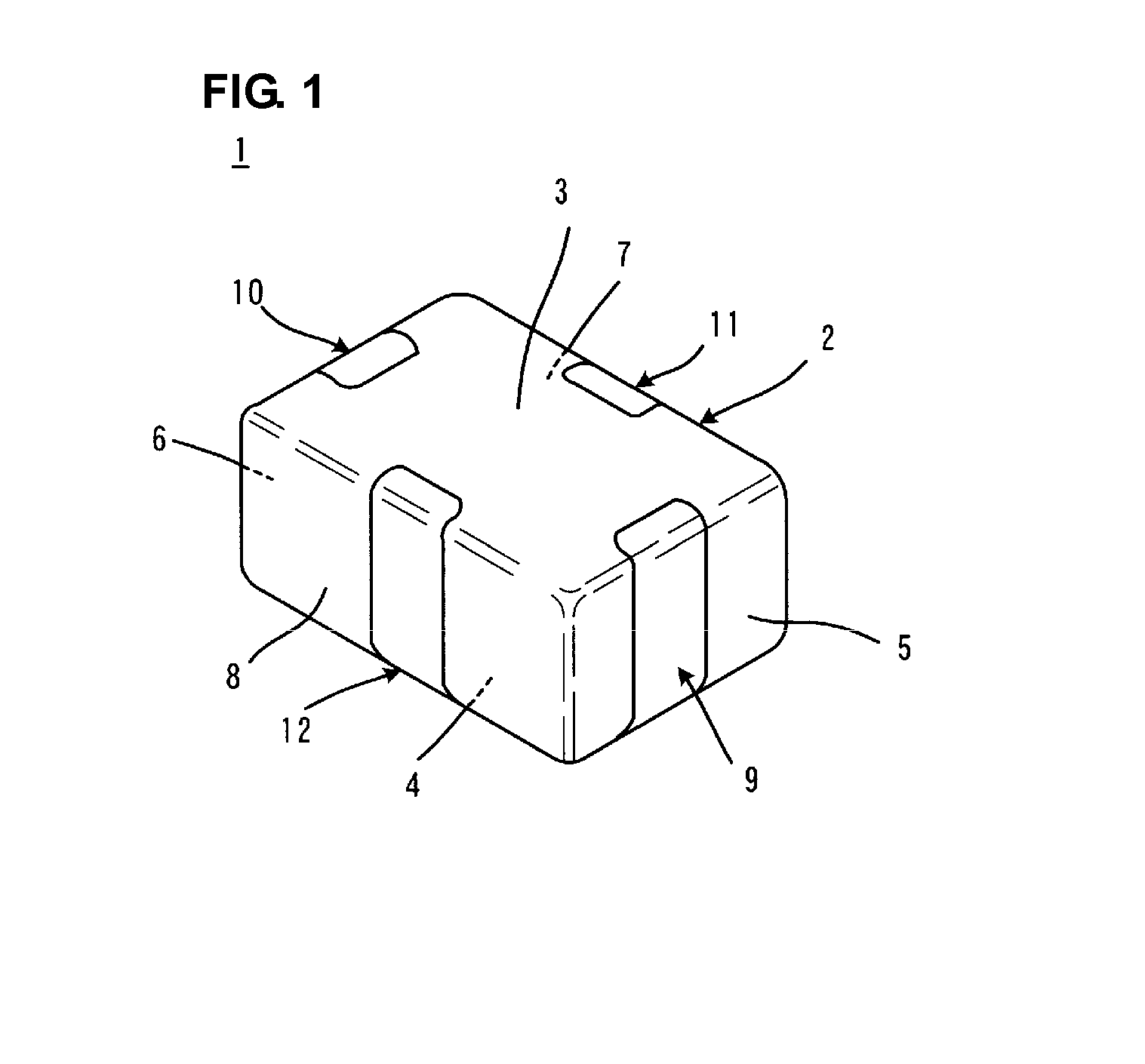
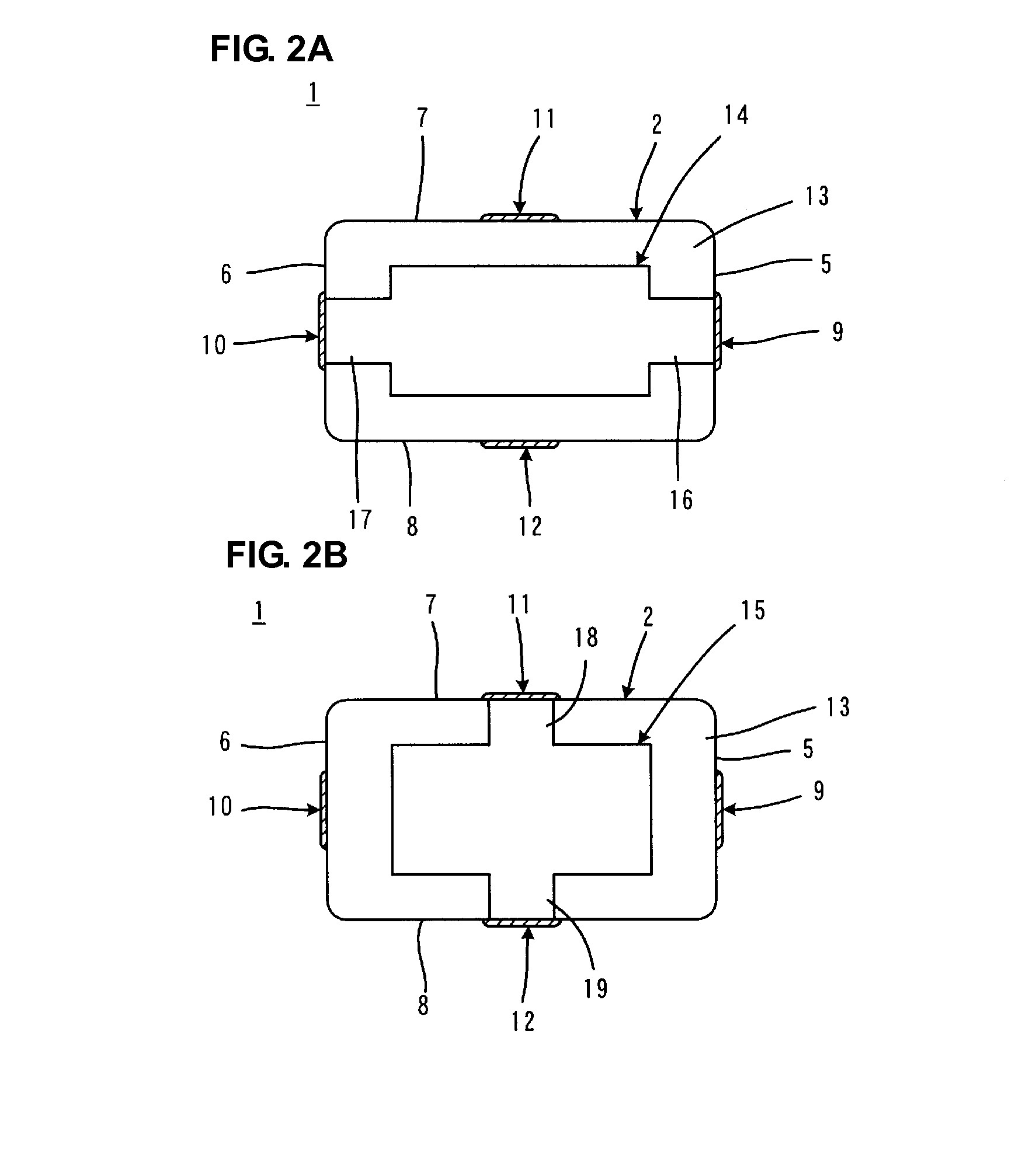
Electronic component
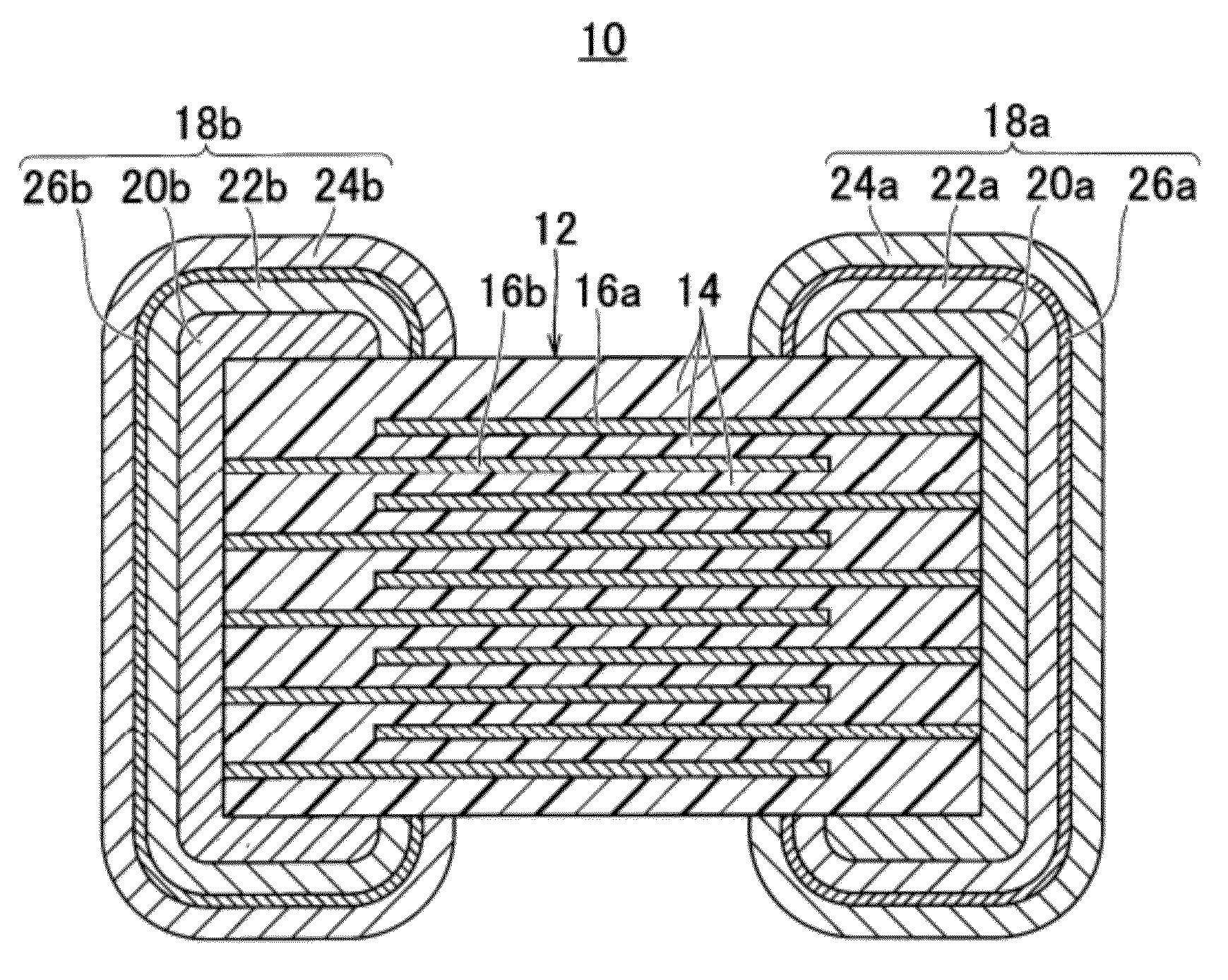
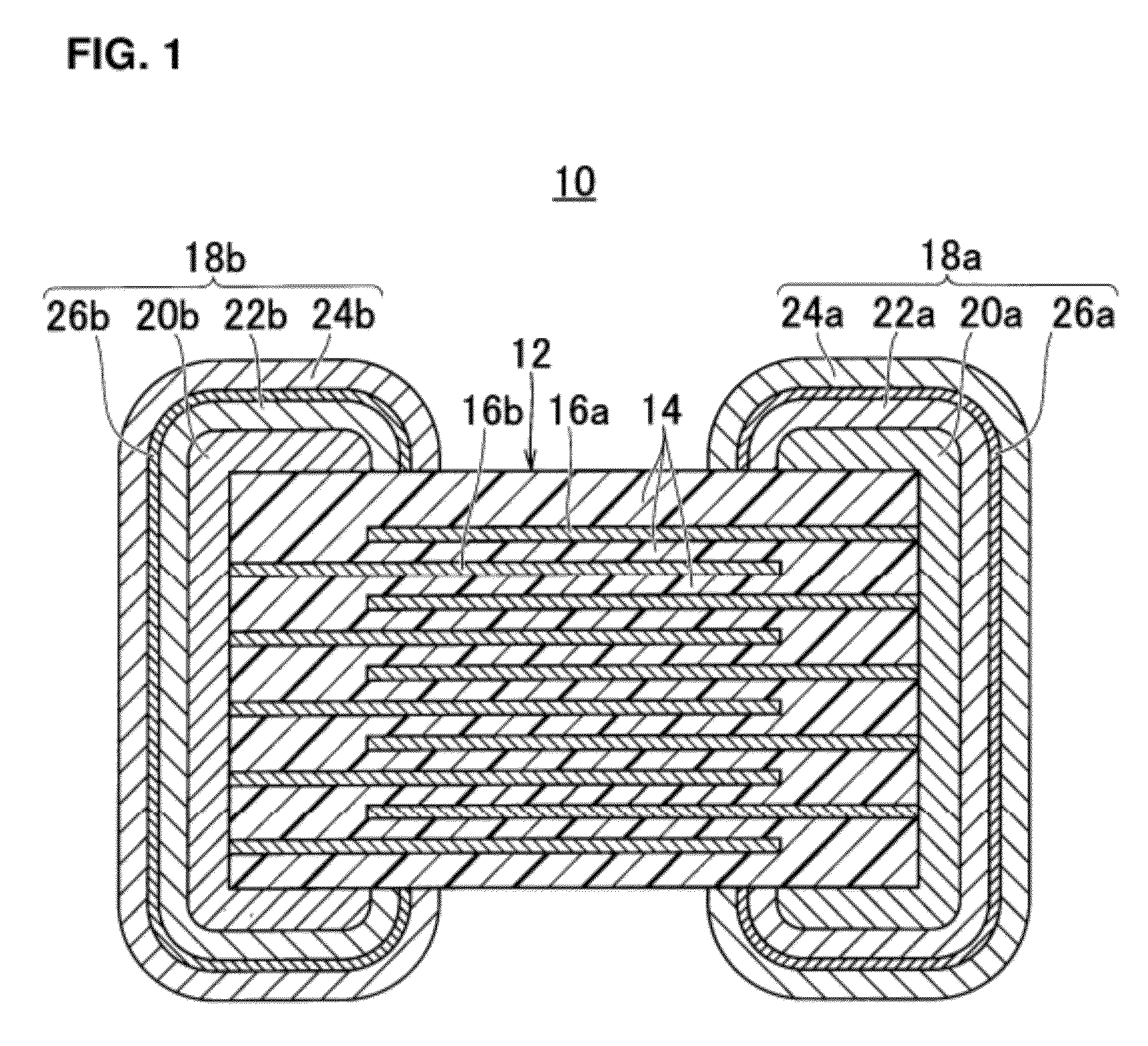
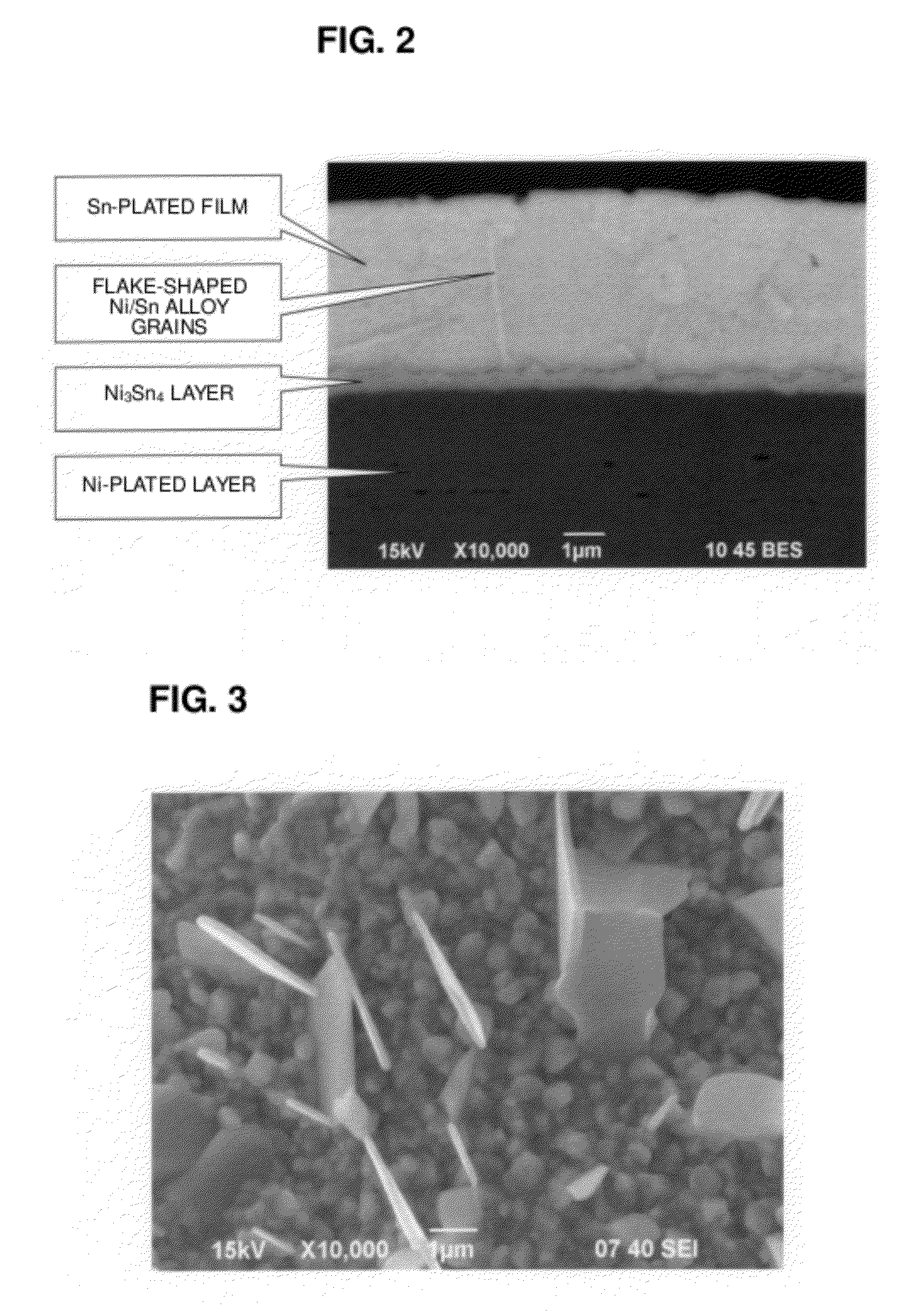
InactiveUS20120288724A1Growth be prevent and minimizeGood solder wettabilityStacked capacitorsFixed capacitor terminalsCrystalliteEngineering
An electronic component that prevents or minimizes whiskers or has good solder wettability includes a rectangular solid-shaped electronic component element and external electrodes of terminal electrodes provided at opposed end surfaces of the electronic component element. First plated films including Ni are provided on the surfaces of the external electrodes. Second plated films including Sn defining an outermost layer are arranged so as to cover the first plated films. The second plated films have a polycrystalline structure, and flake-shaped Sn—Ni alloy grains are provided at a Sn crystal grain boundary. Intermetallic compound layers including Ni3Sn4 are provided at interfaces between the first plated films and the second plated films.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
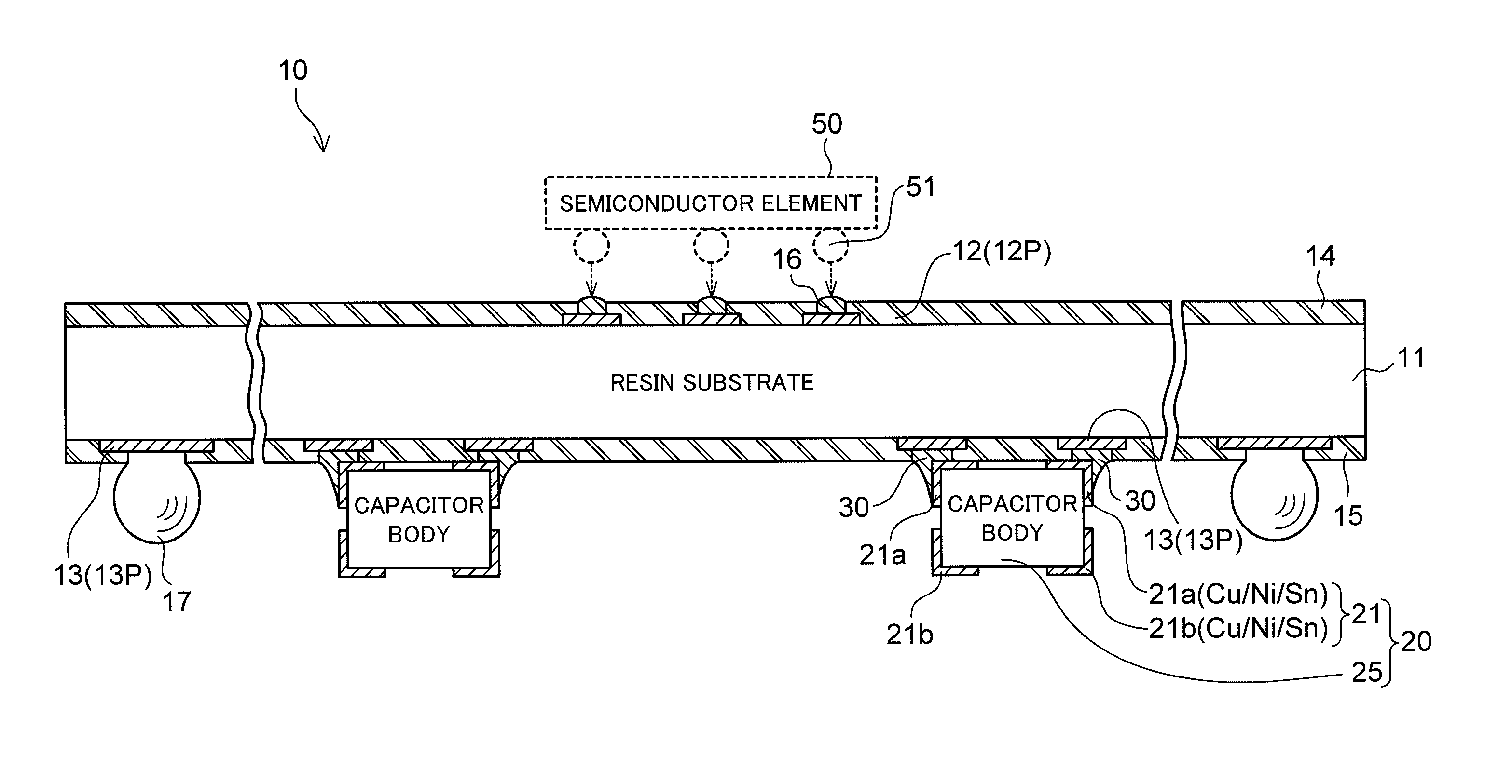
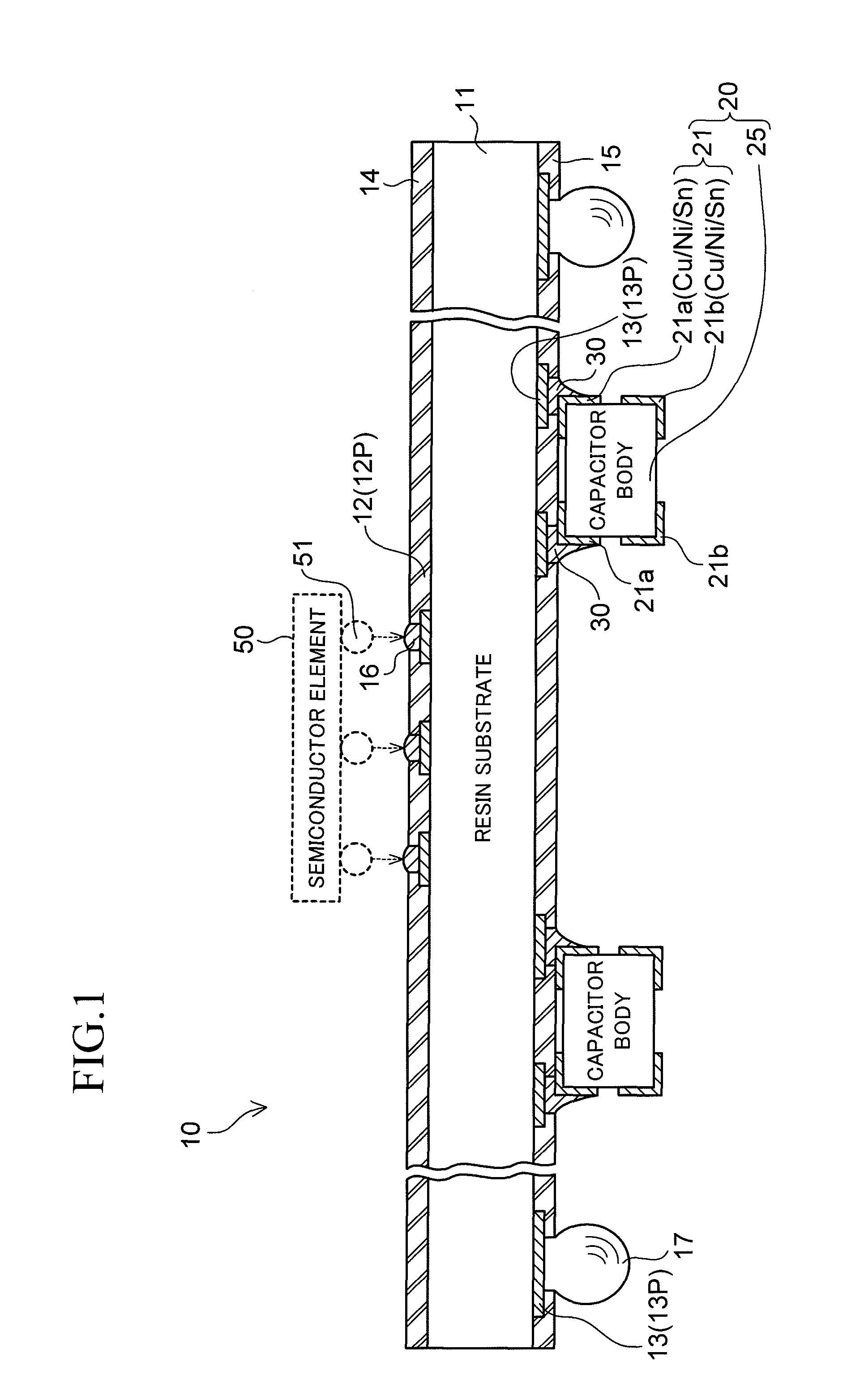
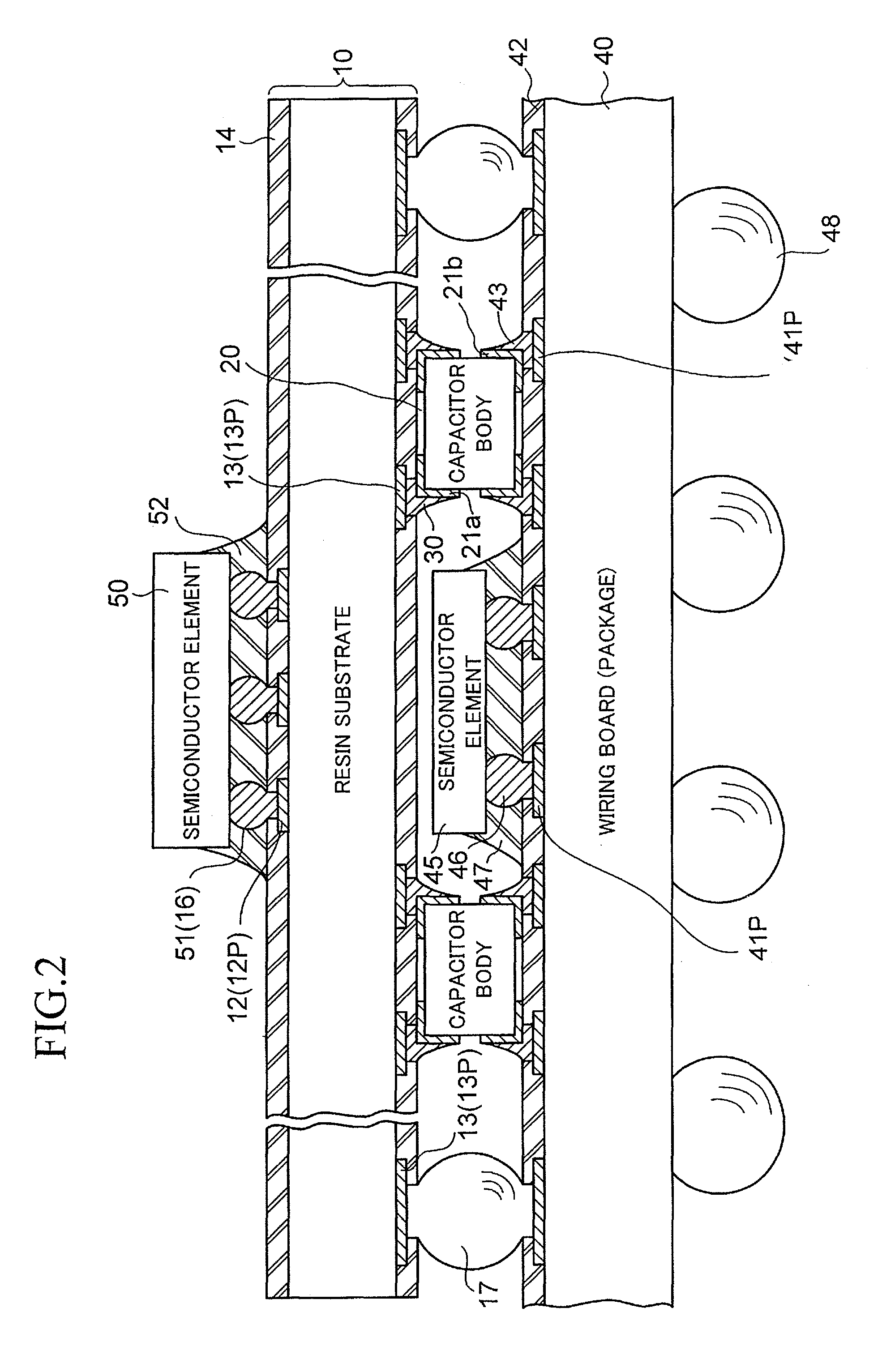
Chip component mounted wiring board
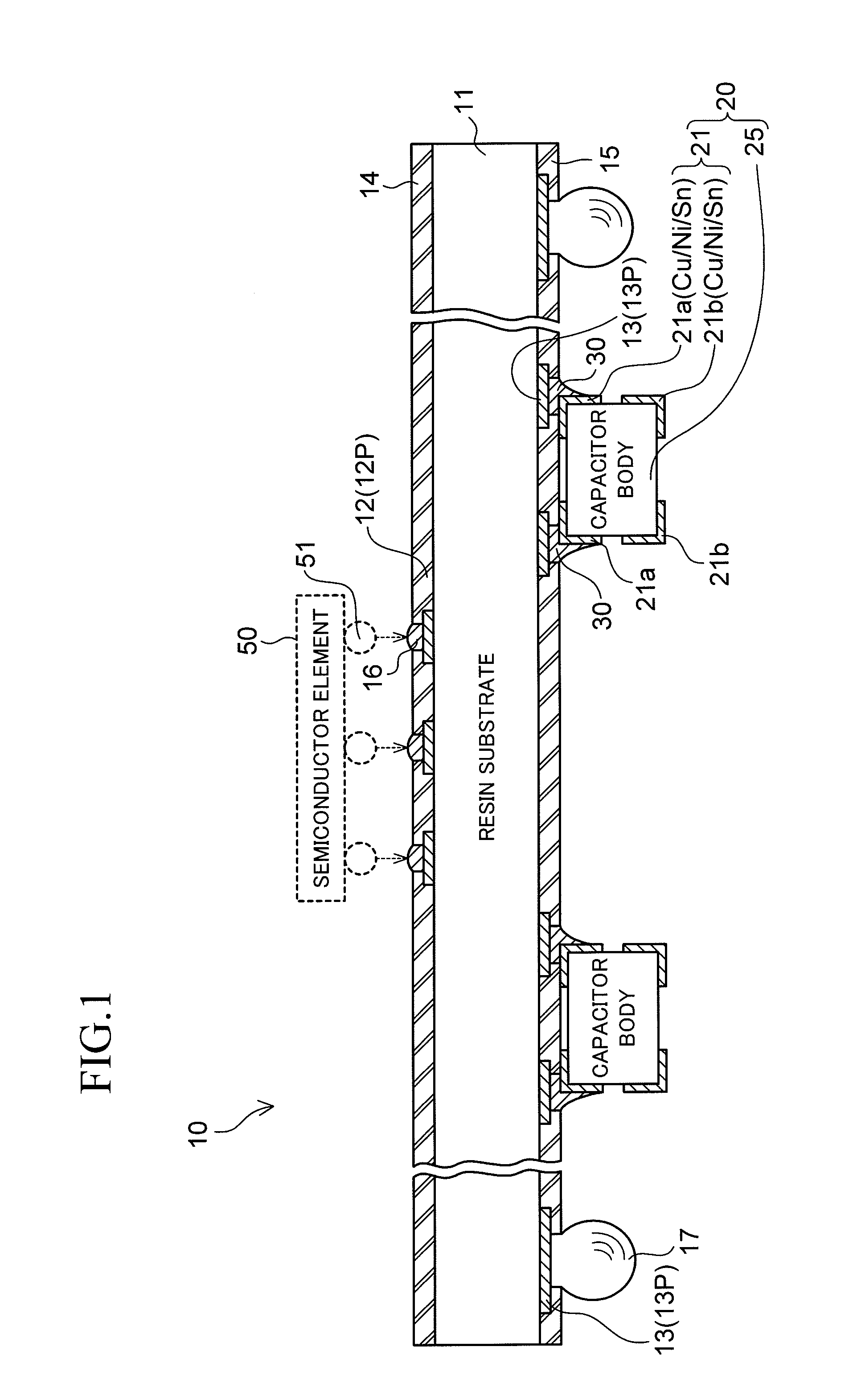
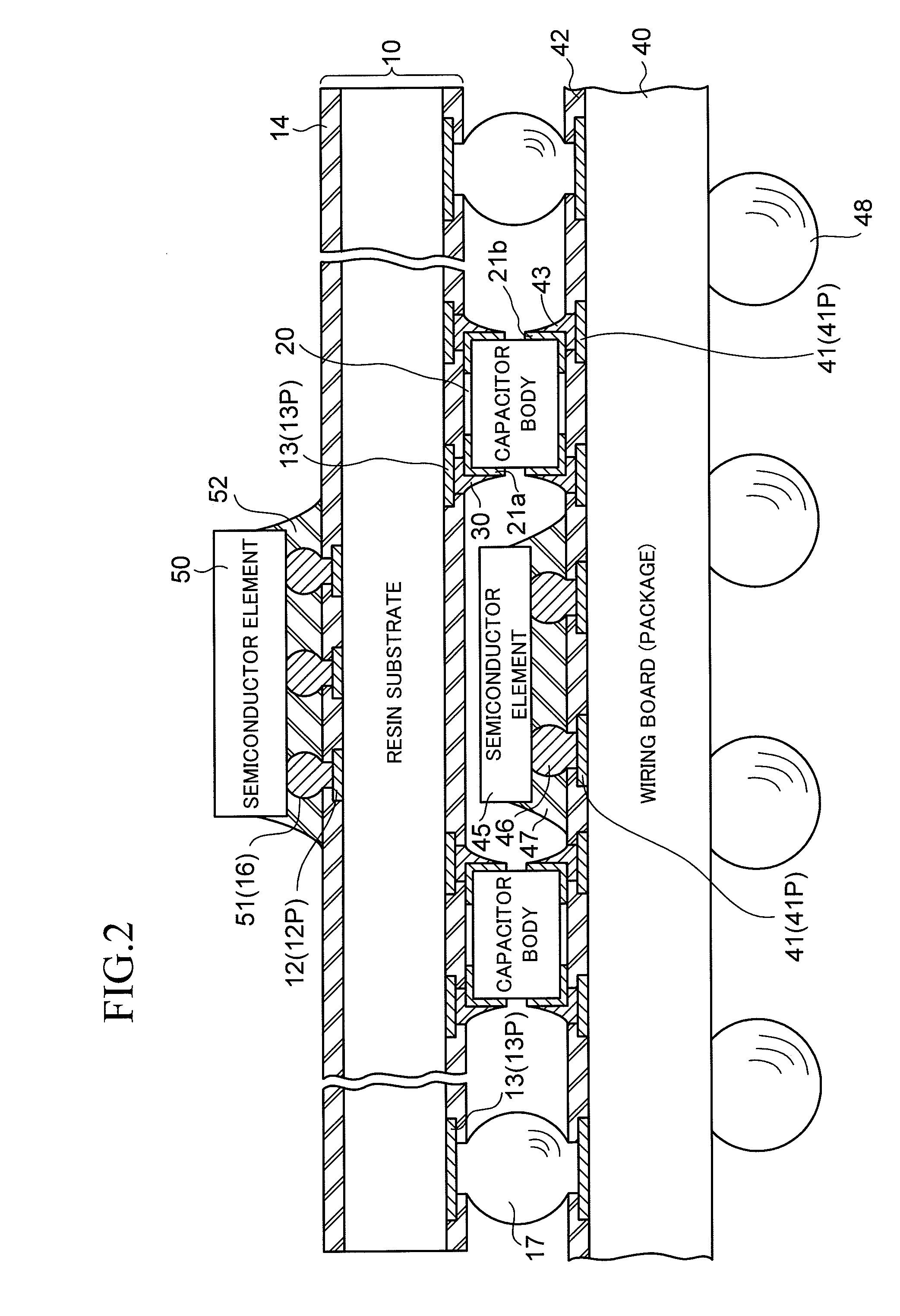
ActiveUS20100214751A1Good solder wettabilityElectrically conductive connectionsFinal product manufactureSurface mountingEngineering
A wiring board to be used with being mounted on a packaging board includes a chip component surface-mounted on a surface facing the packaging board. The chip component includes terminal electrodes at both end portions of the component body thereof. Each of the terminal electrodes is provided in a form in which a plated film (Sn) formed on the surface of the terminal electrode is separated into two portions, one portion being on the wiring board side, and another portion being on the packaging board side. In one aspect, each of the terminal electrodes of the chip component is separated into a portion on the wiring board side and a portion on the packaging board side, and the plated film (Sn) is formed on a surface of each of the separated portions of each of the terminal electrodes.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Solder resist ink composition
InactiveCN1364247AExcellent impregnationNo stickingPhotomechanical apparatusNon-metallic protective coating applicationResistAdditive ingredient
A solder resist ink composition for printed circuit boards which is suitable for forming, with satisfactory adhesion, a primer deposit layer, e.g., an Ni-Au deposit layer, having satisfactory wettability by a solder. The composition comprises a thermosetting ingredient, comprising as the main component (A) a photosensitive prepolymer having a carboxyl group and at least two ethylenically unsaturated bonds per molecule and having an acid value of 50 to 150 mg-KOH / g on a solid basis, (B) a photopolymerization initiator having a melting point of 100 DEG C or higher, (C) a diluent, and (D) an epoxy compound having two or more epoxy groups per molecule.
Owner:TAIYO INK MFG
Ag electrode paste, solar battery cell, and process for producing the solar battery cell
ActiveCN101809758AAvoid it happening againLower resistanceNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPrinted circuitsSolar batteryAg electrode
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device, lead frame, and manufacturing method for the lead frame
InactiveUS20090008759A1Good solder wettabilityReduced strengthFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead frameUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a semiconductor device having an element covered with a resin mold and a metal lead protruding from the resin mold in which a lead-tip portion thereof is entirely covered by solder plating and in which a lead-tip end surface, which is not covered by solder plating, has an area less than half of a cross-sectional area of the metal lead, whereby solder wettability of the metal lead is improved and a bonding strength to a circuit board is also improved.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Monolithic electronic component
ActiveUS7605683B2Moisture resistance of the monolithic electronic component can be ensuredGood solder wettabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFixed capacitor dielectricEngineeringElectronic component
In a monolithic electronic component in which a resistive element is incorporated by forming a resistor film on a terminal electrode, a plating film can be formed on the terminal electrode having the resistor film via electroplating in an efficient manner and with a uniform film thickness. In order to form the terminal electrode, the resistor film is disposed directly on the surface of the component body, and a conductive resin film having a relatively low volume resistivity is disposed over the resistor film. The conductive resin film is preferably adapted to have a specific resistance of less than about 1×10−4 Ω·m, on which a plating film having a uniform film thickness can be formed efficiently via electroplating.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having excellent insertion/extraction performance
InactiveUS20140287262A1Reduce coefficient of frictionReduce contact resistanceConductive materialCoupling contact membersTinningSurface layer
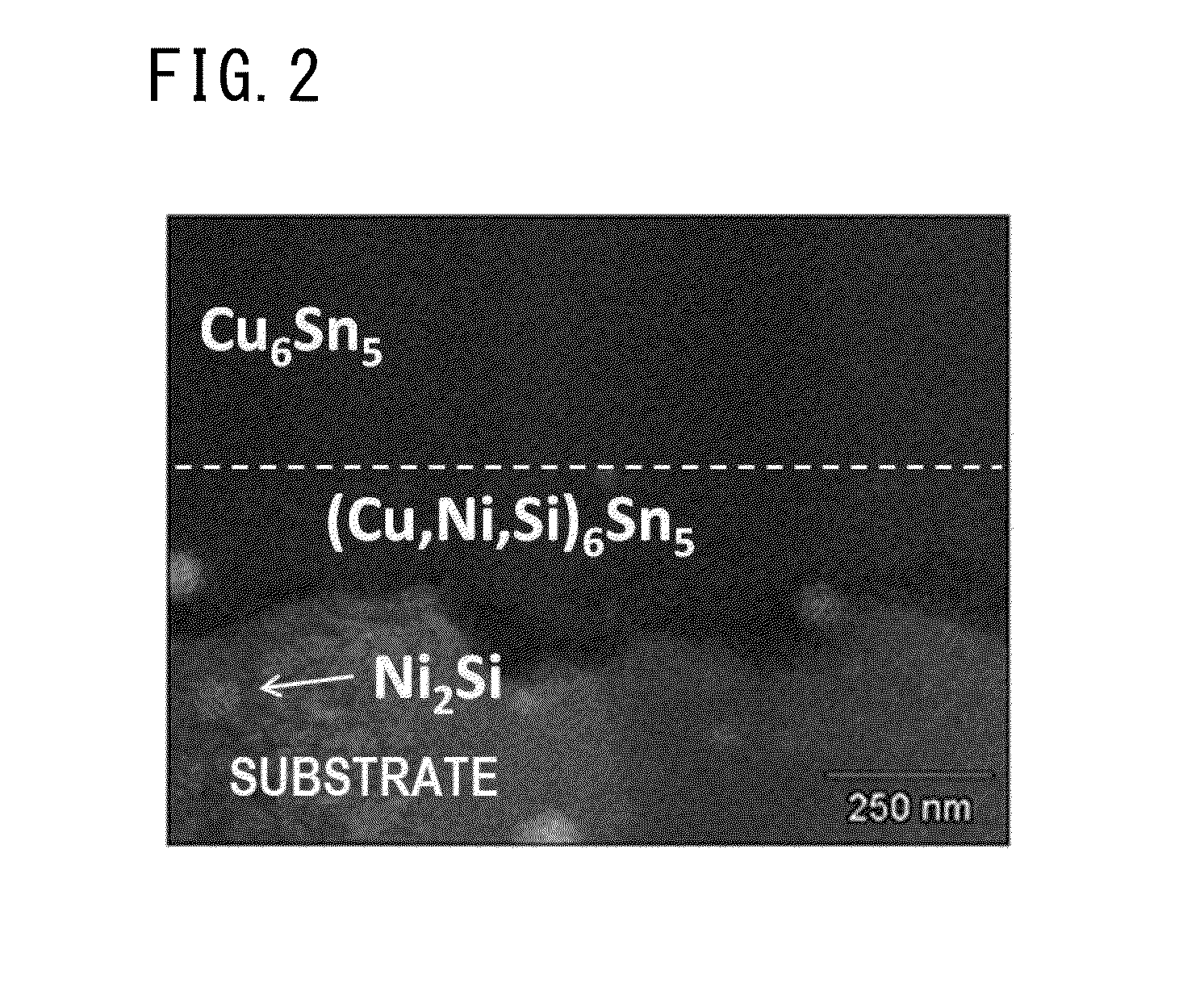
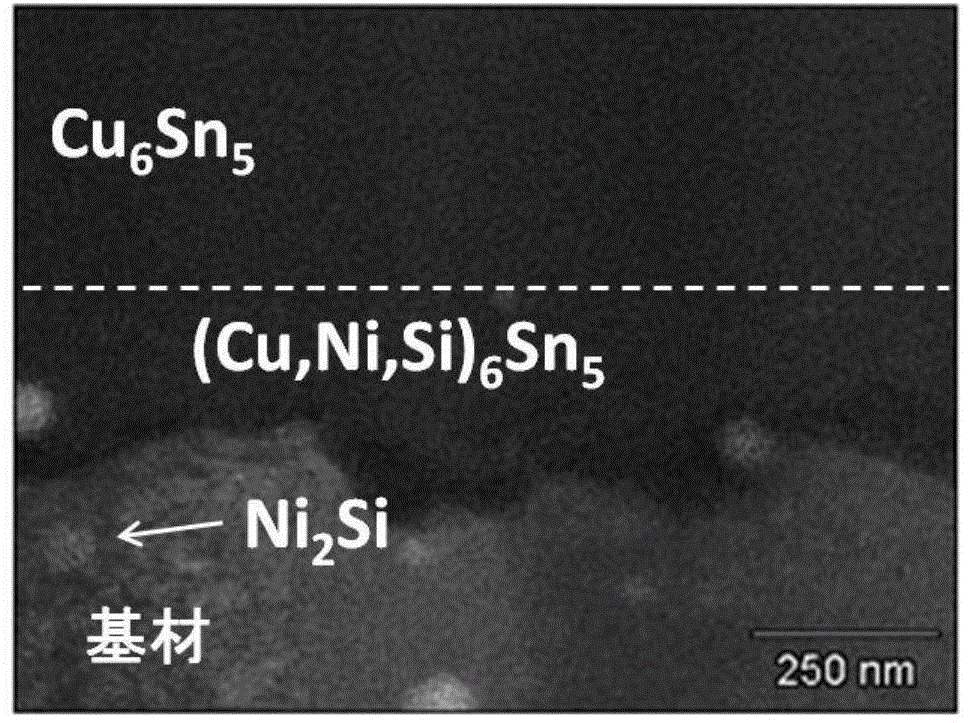
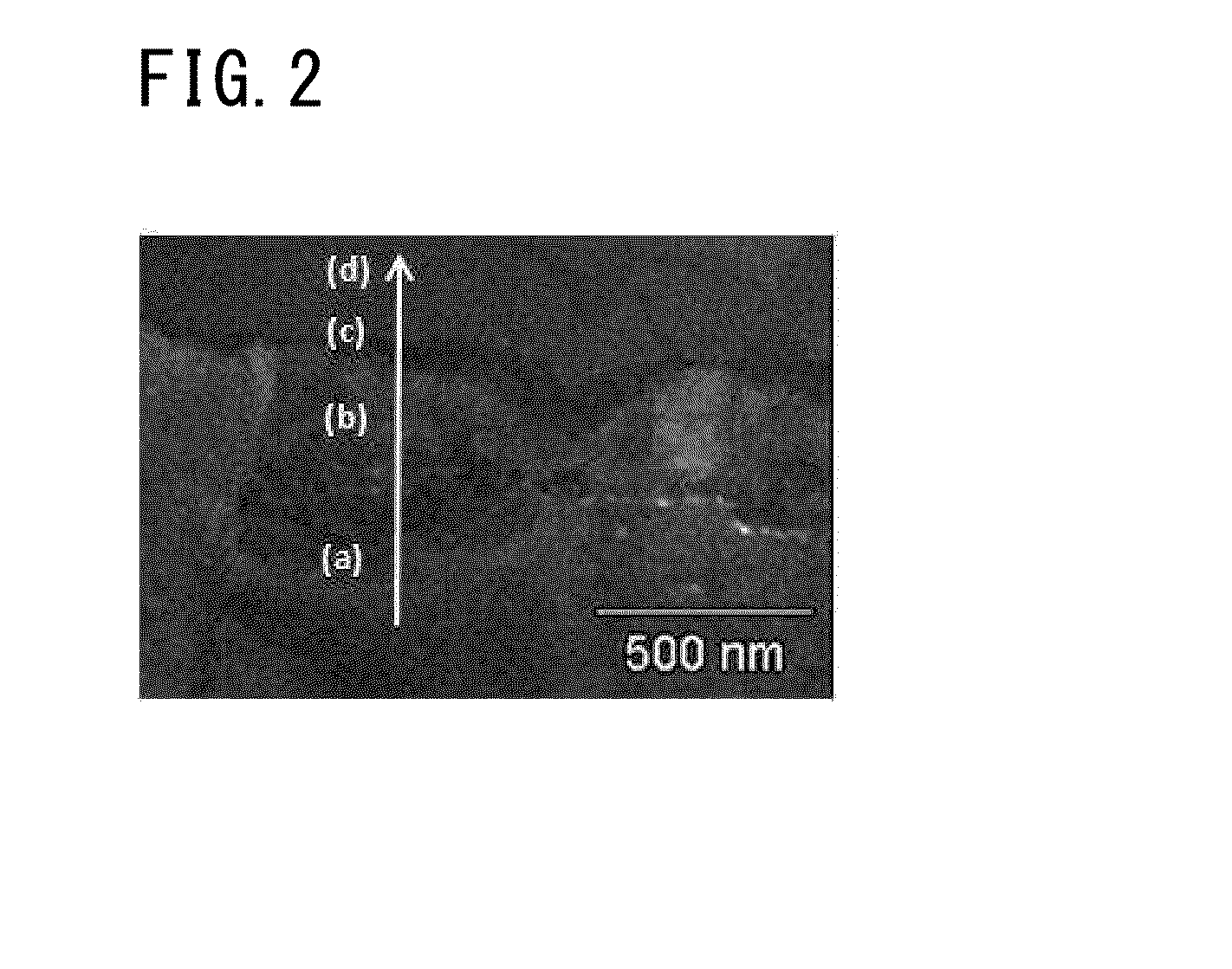
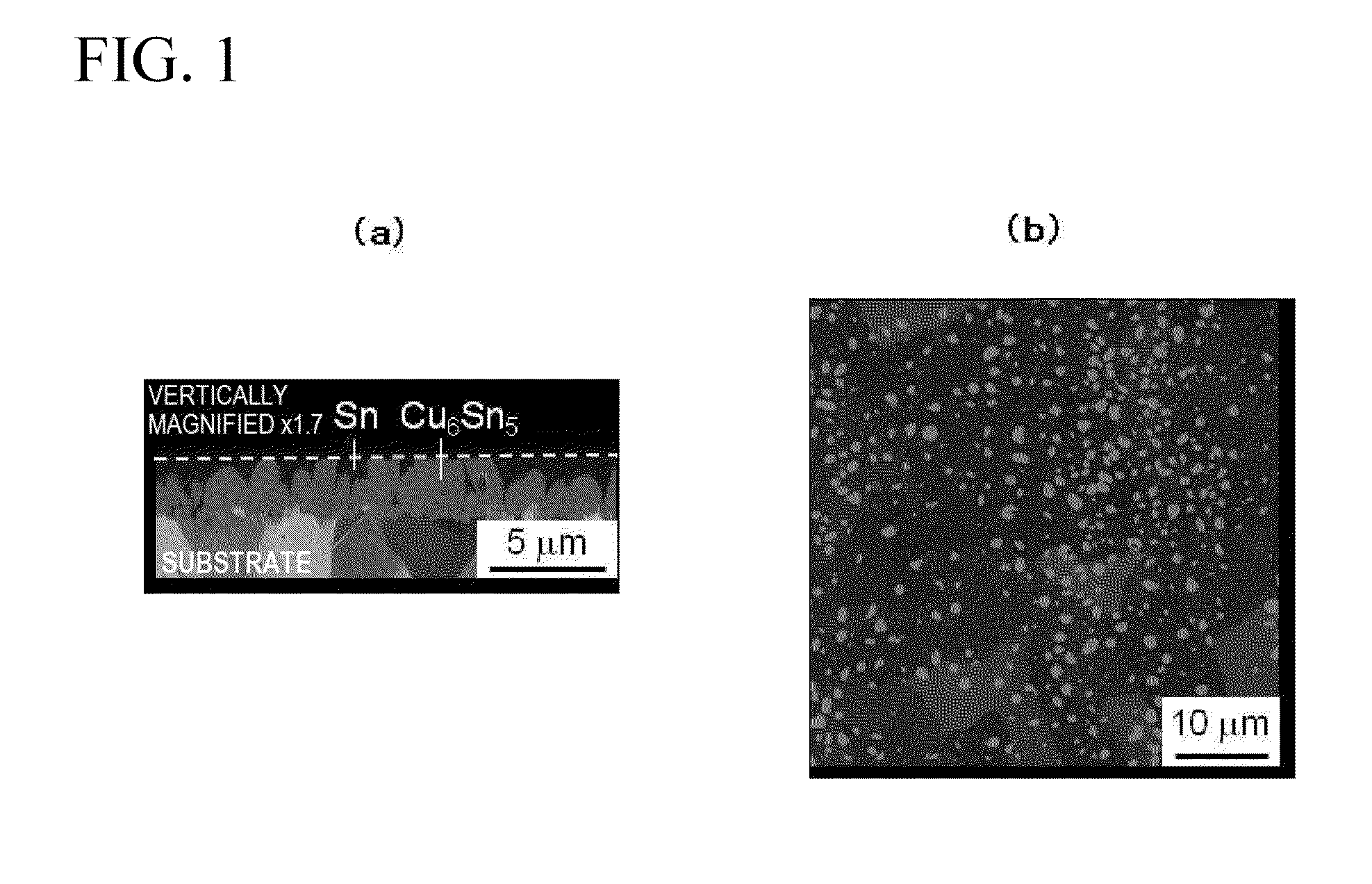
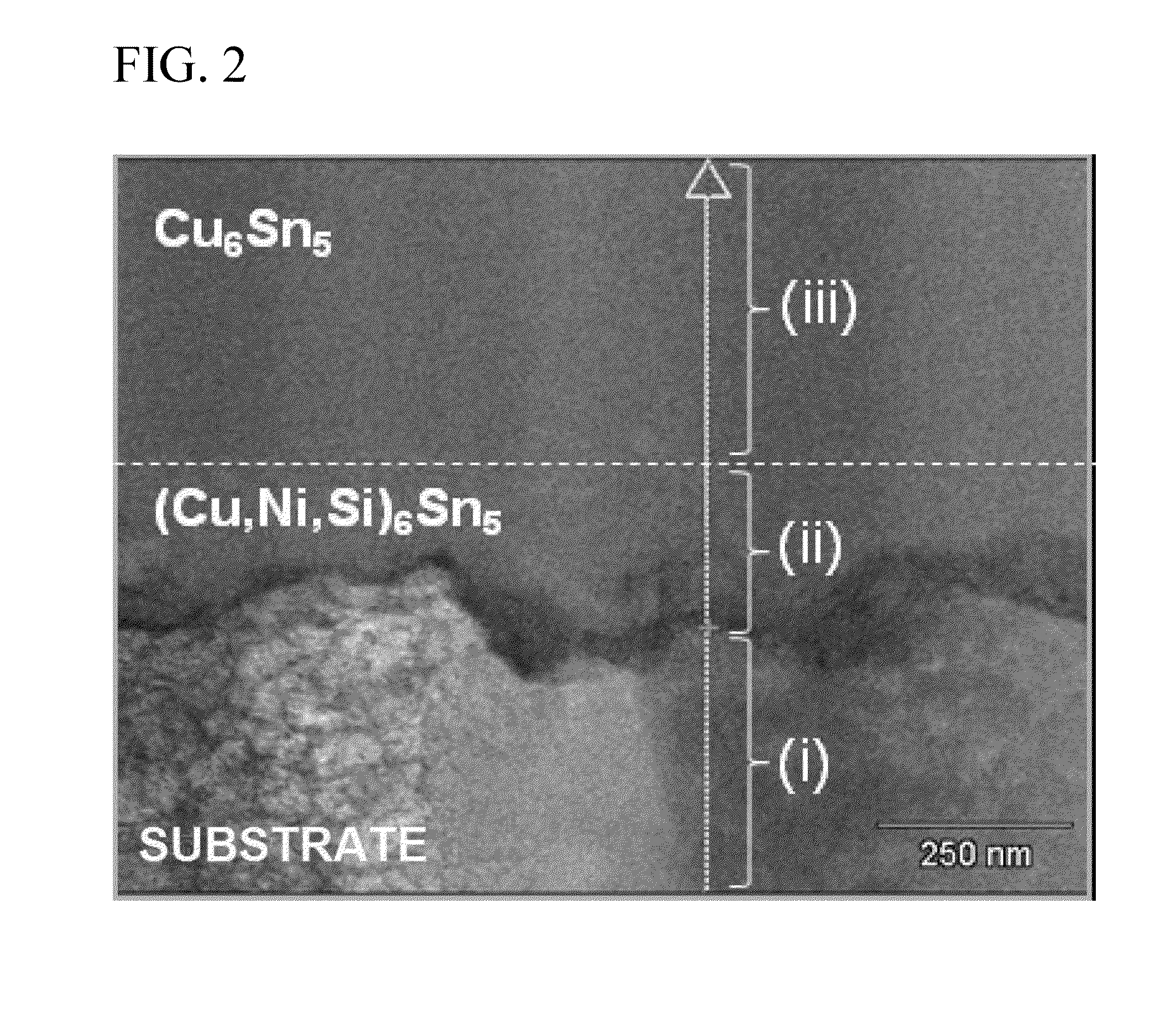
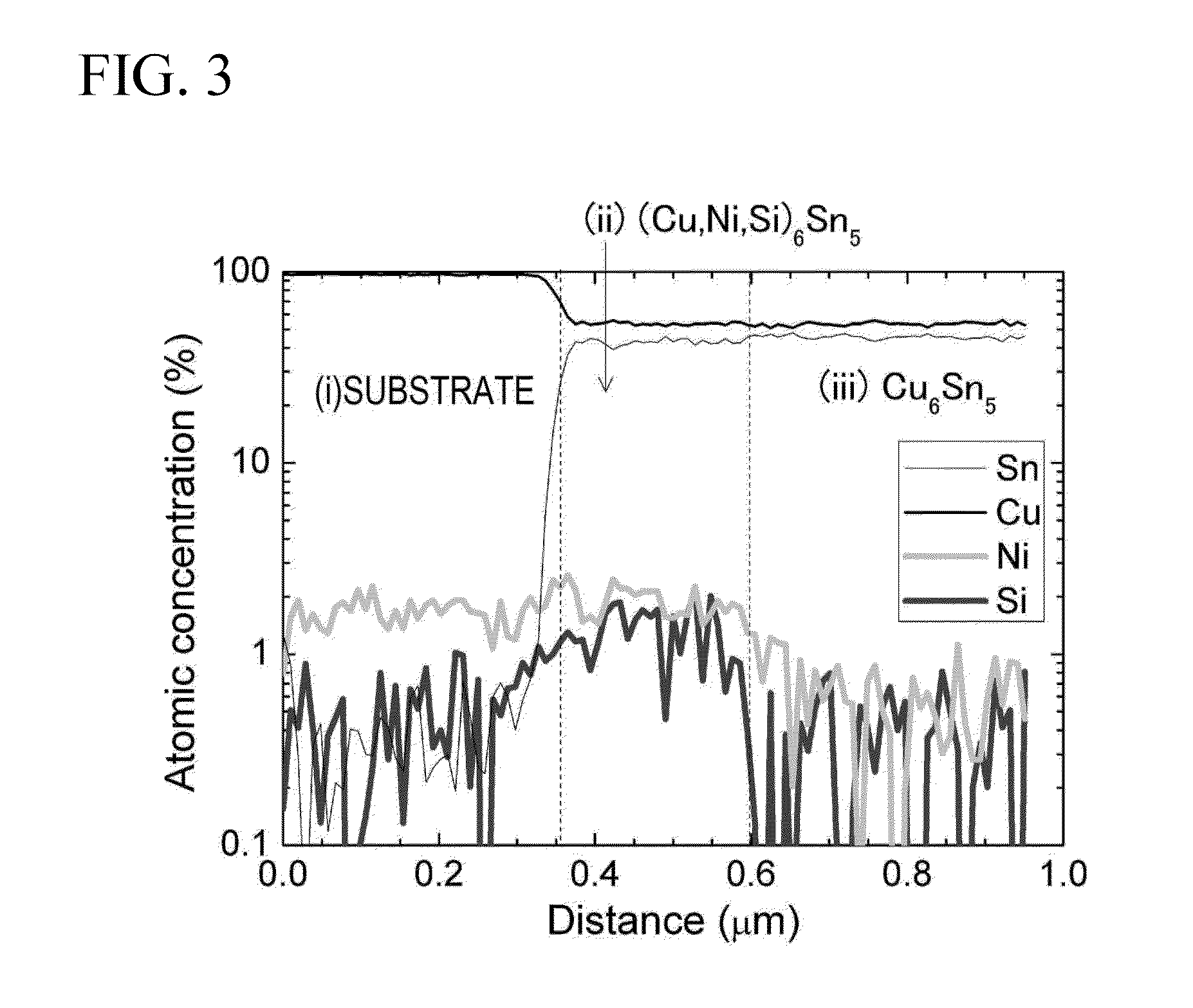
Tin-plated copper-alloy terminal material in which Sn-based surface layer is formed on a surface of a substrate made of Cu alloy, and a Cu—Sn alloy layer is formed between the Sn-based surface layer and the substrate; the Cu—Sn alloy layer contains Cu6Sn5 as major proportion and has a compound in which a part of Cu in the Cu6Sn5 is substituted by Ni and Si in the vicinity of a boundary face at the substrate side; an arithmetic average roughness Ra of the Cu—Sn alloy layer is 0.3 μm or more in at least one direction and an arithmetic average roughness Ra in all direction is 1.0 μm or less; an oil-sump depth Rvk of the Cu—Sn alloy layer is 0.5 μm or more; and an average thickness of the Sn-based surface layer is 0.4 μm or more and 1.0 μm or less and dynamic friction coefficient is 0.3 or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Method for plating electrodes of ceramic chip electronic components
InactiveUS6911138B2Extended service lifePrevent oxidationElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor devicesMalonic acidTin plating
A method for plating electrodes of ceramic chip electronic components includes performing electroplating in a plating bath. The plating bath contains tin (II) sulfamate, acting as a tin (II) salt; a complexing agent including at least one selected from the group consisting of citric acid, gluconic acid, pyrophosphoric acid, heptoic acid, malonic acid, malic acid, salts of these acids, and gluconic lactone; and a brightener including at least one surfactant having an HLB value of about 10 or more. The tin plating adhesion of the resulting ceramic chip electronic components can be limited to a certain level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Lead frame for semiconductor device
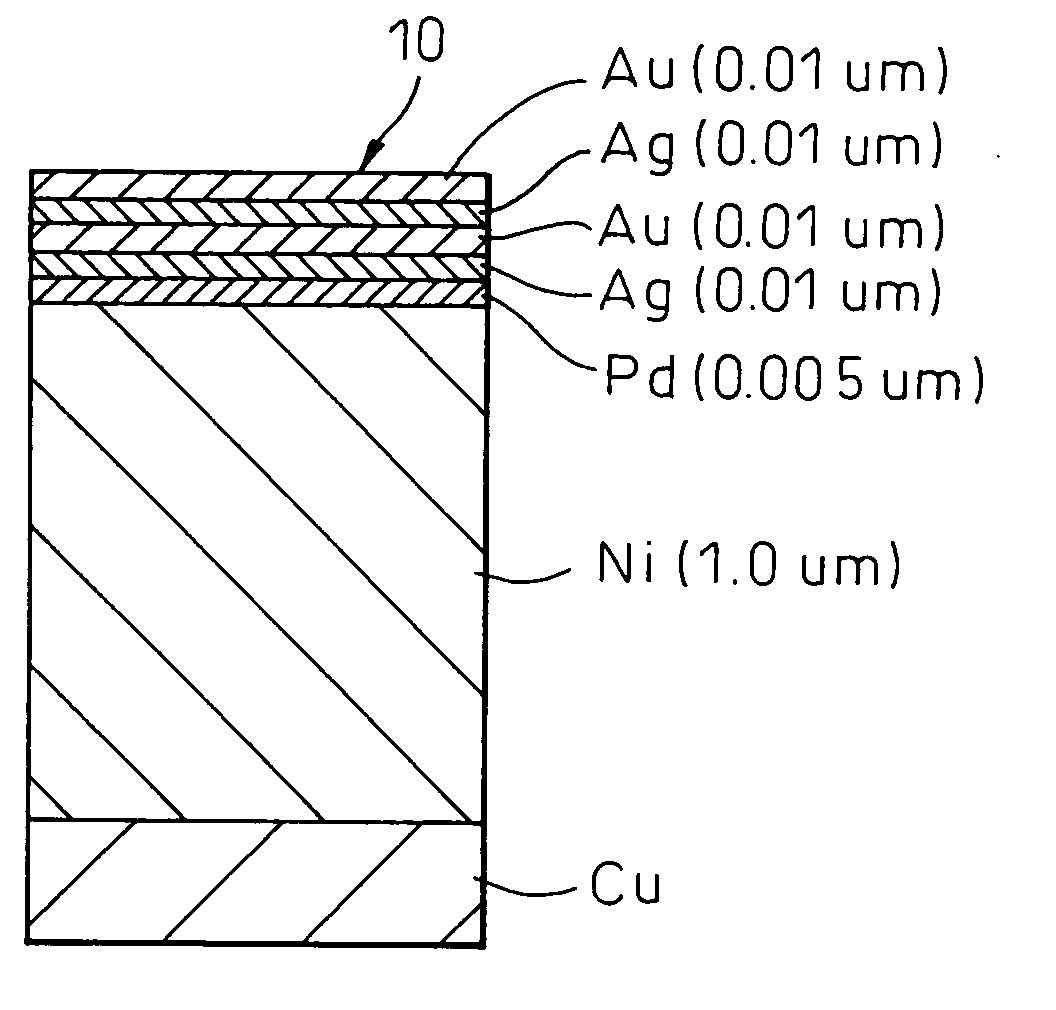
ActiveUS20060125073A1Good solder wettabilityImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
Lead frames of a Pd-PPF structure for use in a semiconductor device comprising inner leads and outer leads, wherein a whole surface of the substrate constituting the lead frame or at least the outer leads has a composite plated layer, and the composite plated layer comprises an underlayer consisting of an Ni-based plating layer deposited on the whole surface of the substrate constituting the lead frame or on at least the outer leads, a Pd— or Pd alloy-plating layer deposited at a thickness of 0.005 to 0.01 μm on an upper surface of the underlayer, and an Au-plating layer deposited at a thickness of 0.02 to 0.1 μm on an upper surface of the Pd— or Pd alloy-plating layer. When a semiconductor device is mounted on a packaging substrate by using a lead-free Sn—Zn-based solder or any other lead-free solder, the wettability between the lead frame and the lead-free Sn—Zn-based solder or any other lead-free solder is improved to thereby improve the packaging property of the semiconductor device.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Silver-Bismuth Powder,Conductive Paste and Conductive Film
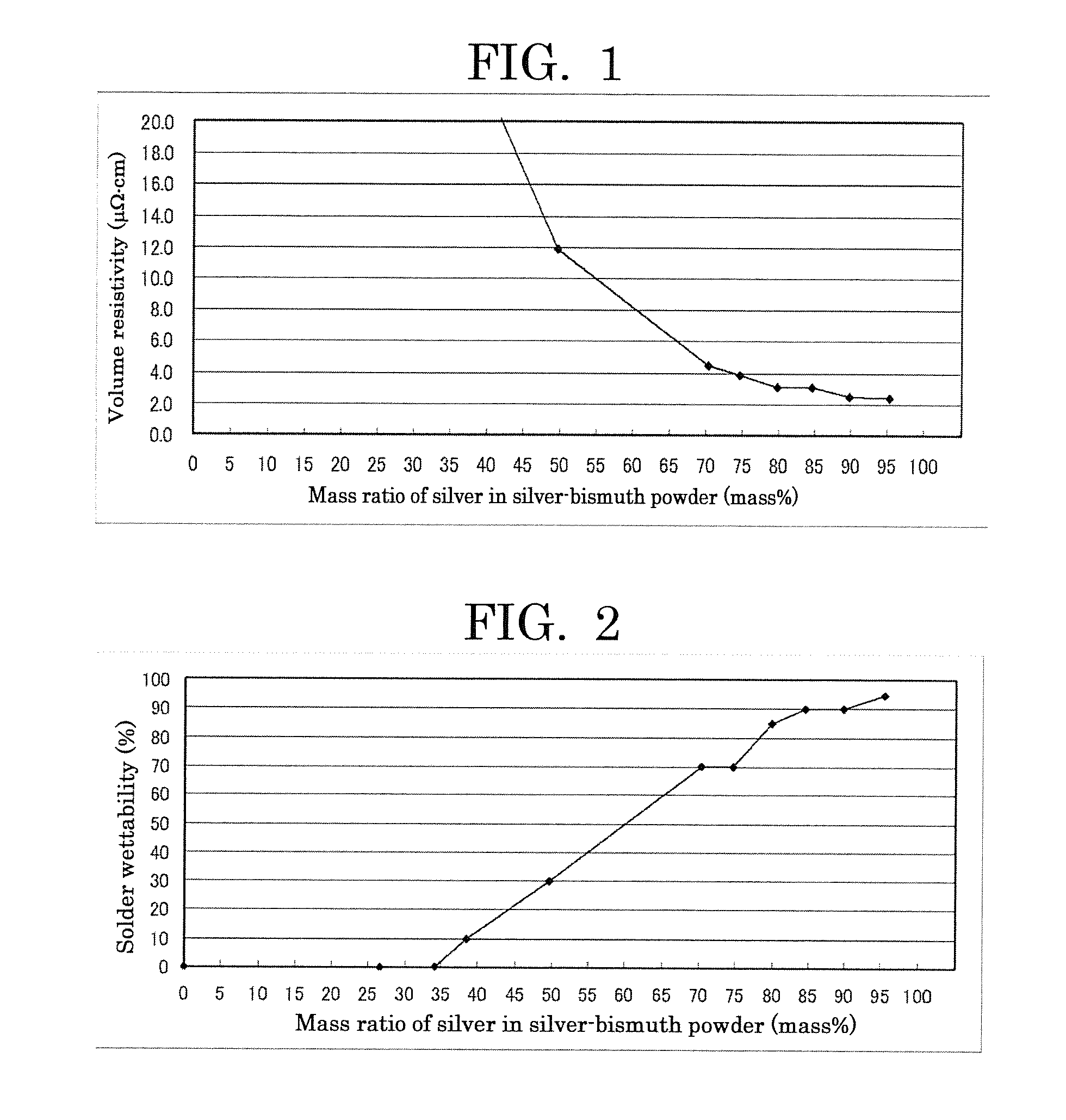
ActiveUS20160040271A1Good solder wettabilityLow resistivityTransportation and packagingConductive materialConductive pasteMass ratio
To provide a silver-bismuth powder, which includes: silver; and bismuth, wherein a mass ratio (silver:bismuth) of the silver to the bismuth is 95:5 to 40:60, wherein a cumulative 50% point of particle diameter (D50) of the silver-bismuth powder in a volume-based particle size distribution thereof as measured by a laser diffraction particle size distribution analysis is 0.1 μm to 10 μm, and wherein an oxygen content of the silver-bismuth powder is 5.5% by mass or less.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Electronic component
ActiveUS20100071949A1Good solder wettabilityIncrease contact areaFixed capacitor electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptoelectronicsElectronic component
An electronic component has an element body, and a plurality of external electrodes formed on one principal face of the element body. Each external electrode has a first electrode layer joined to the one principal face of the element body, and a second electrode layer joined as laid on an inside region inside an edge of the first electrode layer. An apical surface of the second electrode layer is planar. A joint portion in the second electrode layer to the first electrode layer is rounded.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal and method for producing the same
ActiveCN103531933ALower coefficient of dynamic frictionLow pluggabilityConductive materialCoupling contact membersTinningSurface layer
The invention provides a tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal and a method for producing the same with an excellent insertion / extraction performance and has an object of reducing dynamic friction coefficient to 0.3 or less with an excellent electrical-connection characteristic. A Cusn alloy layer / a NiSn alloy layer / a Ni or Ni alloy layer are formed between a Sn-based surface layer and a substrate made of Cu or Cu alloy; the Cusn alloy layer is a compound-alloy layer containing Cu 6 Sn 5 as a major proportion and a part of Cu in the Cu 6 Sn 5 is displaced by Ni; the Nisn alloy layer is a compound-alloy layer containing Ni 3 Sn 4 as a major proportion and a part of Ni in the Ni 3 Sn 4 is displaced by Cu; an average interval S of point peaks of the Cusn alloy layer is not less than 0.8 [mu]m and not more than 2.0 [mu]m; an average thickness of the Sn-based surface layer is not less than 0.2 [mu]m and not more than 0.6 [mu]m; an exposed-area rate of the CuSn alloy layer exposed at a surface of the Sn-based surface layer is not less than 1% and not more than 40%; an average of equivalent-circle diameter of the exposed portions of the Cusn alloy layer exposed at the surface of the Sn-based surface layer is not less than 0.1 [mu]m and not more than 1.5 [mu]m; and dynamic friction coefficient is not more than 0.3.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Electrolytic capacitor
InactiveUS20090316337A1Improve solderabilityScarcely deteriorated in solder wettabilitySolid electrolytic capacitorsLiquid electrolytic capacitorsElectrolytic capacitorNickel
To provide an electrolytic capacitor having lead wires excellent in weldability with a boss member made of aluminum, excellent in solder wettability, and less whisker. The lead wires have a nickel plating layer in a thickness of 0.3 to 5.0 μm, a palladium plating layer in a thickness of 0.01 to 0.10 μm, and a gold plating layer in a thickness of 0.002 to 0.030 μm.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +2
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20130196171A1Reduction factorReduce contact resistanceCoupling contact membersDomestic articlesSurface layerArea ratio
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having: a substrate made of Cu or Cu alloy; an Sn-based surface layer formed on a surface of the substrate; and a Cu—Ni—Sn alloy layer including Ni formed between the Sn-based surface layer and the substrate, in which the Cu—Ni—Sn alloy layer is made of: fine Cu—Ni—Sn alloy particles; and coarse Cu—Ni—Sn alloy particles, an average thickness of the Sn-based surface layer is not less than 0.2 μm and not more than 0.6 μm, an area ratio of the Cu—Ni—Sn alloy layer exposed at a surface of the Sn-based surface layer is not less than 10% and not more than 40%, and a coefficient of kinetic friction of the tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal is not more than 0.3.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having excellent insertion/extraction performance
InactiveCN104078782ALower coefficient of dynamic frictionLow pluggabilityConductive materialCoupling contact membersTinningSurface layer
To provide tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having an excellent insertion / extraction performance by reducing dynamic friction coefficient to 0.3 or less with bringing out an excellent electrical-connection characteristic. Tin-plated copper-alloy terminal material in which an Sn-based surface layer is formed on a surface of a substrate made of Cu alloy, and a Cu-Sn alloy layer is formed between the Sn-based surface layer and the substrate; the Cu-Sn alloy layer contains Cu 6 Sn 5 as a major proportion and has a compound in which a part of Cu in the Cu 6 Sn 5 is substituted by Ni and Si in the vicinity of a boundary face at the substrate side; an arithmetic average roughness Ra of the Cu-Sn alloy layer is 0.3 [mu]m or more in at least one direction and an arithmetic average roughness Ra in all direction is 1.0 [mu]m or less; an oil-sump depth Rvk of the Cu-Sn alloy layer is 0.5 [mu]m or more; and an average thickness of the Sn-based surface layer is 0.4 [mu]m or more and 1.0 [mu]m or less and dynamic friction coefficient is 0.3 or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Copper alloy sheet and process for producing copper alloy sheet
ActiveCN106460097AExcellent resistance to stress corrosion crackingExcellent stress relaxation propertiesStress relaxationStress corrosion cracking
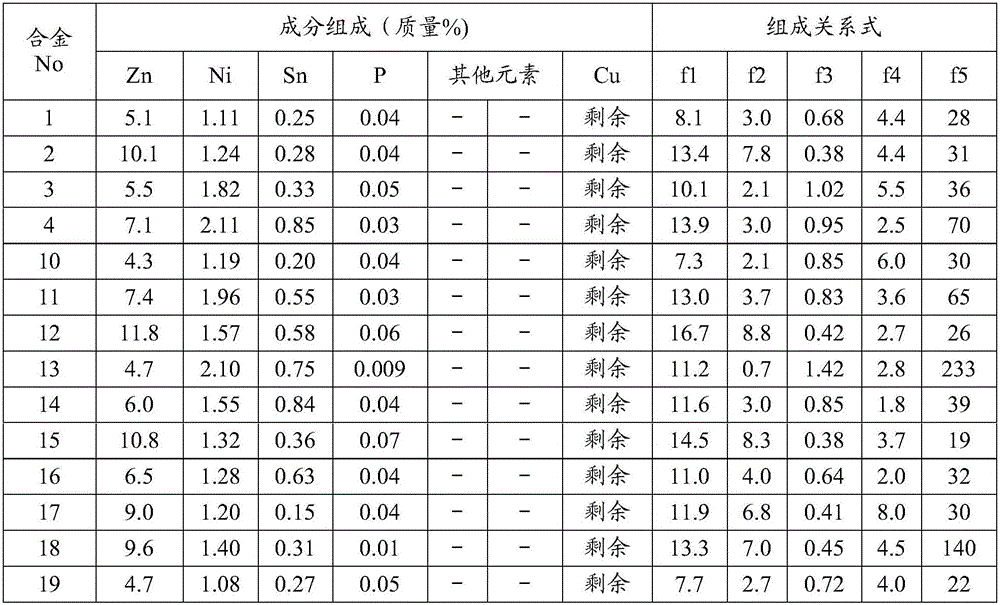
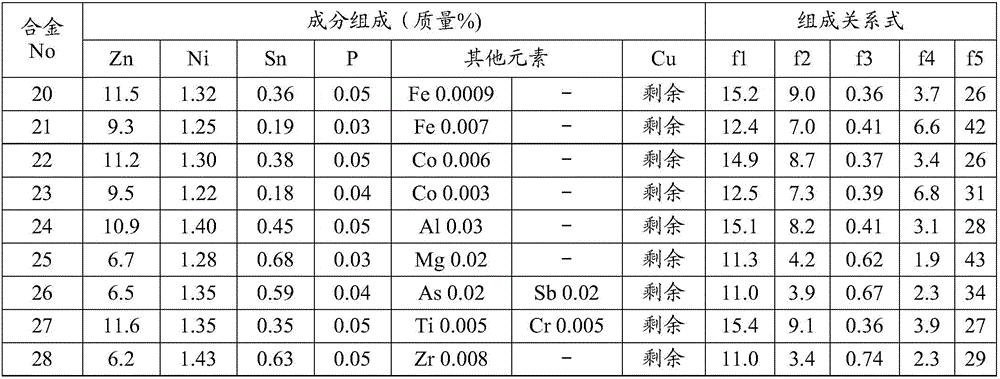
Provided is a copper alloy sheet which is excellent in terms of resistance to stress corrosion cracking, stress relaxation property, tensile strength, proof stress, electrical conductivity, bendability, and solder wettability. The copper alloy sheet contains 4-14 mass% Zn, 0.1-1 mass% Sn, 0.005-0.08 mass% P, and 1.0-2.4 mass% Ni, with the remainder comprising Cu and unavoidable impurities, and satisfies the relational expressions 7<=[Zn]+3*[Sn]+2*[Ni]<=18, 0<=[Zn]-0.3*[Sn]-1.8*[Ni]<=11, 0.3<=(3*[Ni]+0.5*[Sn]) / [Zn]<=1.6, 1.8<=[Ni] / [Sn]<=10, and 16<=[Ni] / [P]<=250. The copper alloy sheet has an average crystal grain diameter of 2-9 [mu]m and contains circular or elliptic precipitates which have an average grain diameter of 3-75 nm or in which precipitate grains each having a grain diameter of 3-75 nm account for 70% by number or more of all the circular or elliptic precipitates. The copper alloy sheet has an electrical conductivity of 24% IACS or greater and a degree of stress relaxation, measured at 150 DEG C for 1,000 hours as an index to resistance to stress relaxation, of 25% or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having excellent insertion/extraction performance
InactiveUS20150056466A1Reduction factorReduce contact resistanceCoupling contact membersSolid state diffusion coatingTinningSurface layer
A tin-plated copper-alloy terminal material wherein: a Sn-based surface layer formed on a surface of a substrate made of Cu alloy, and a Cu—Sn alloy layer / a Ni—Sn alloy layer / a Ni or Ni alloy layer are formed in sequence from the Sn-based surface layer between the Sn-based surface layer and the substrate; the Cu—Sn alloy layer is a compound-alloy layer containing Cu6Sn5 as a main component and a part of Cu in the Cu6Sn5 is displaced by Ni; the Ni—Sn alloy layer is a compound-alloy layer containing Ni3Sn4 as a main component and a part of Ni in the Ni3Sn4 is displaced by Cu; an arithmetic average roughness Ra of the Cu—Sn alloy layer is 0.3 μm or more in at least one direction and arithmetic average roughness Ra in all directions is 1.0 μm or less; an oil-sump depth Rvk of the Cu—Sn alloy layer is 0.5 μm or more.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal having excellent insertion/extraction performance
ActiveUS20140170436A1Reduce coefficient of frictionReduce contact resistanceConductive materialCoupling contact membersTinningSurface layer
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal in which: a Sn-based surface layer is formed on a surface of a substrate made of Cu alloy, and a Cu—Sn alloy layer is formed between the Sn-based surface layer and the substrate; the Cu—Sn alloy layer is an alloy layer containing Cu6Sn5 as a major proportion and having a compound in which a part of Cu in the Cu6Sn5 is substituted by Ni and Si in the vicinity of a boundary face at the substrate side; an average thickness of the Sn-based surface layer is 0.2 μm or more and 0.6 μm or less; an oil-sump depth Rvk of the Cu—Sn alloy layer is 0.2 μm or more; an area rate of the Cu—Sn alloy layer exposed at a surface of the Sn-based surface layer is 10% or more and 40% or less; and dynamic friction coefficient is 0.3 or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Tin-plated copper-alloy material for terminal and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8940404B2Reduction factorReduce contact resistanceElectrically conductive connectionsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingTinningSurface layer
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Halogenless soldering flux for tin and bismuth low-temperature solder wire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102922179AIncreased welding activityImprove solder wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaInsulation resistanceRosin
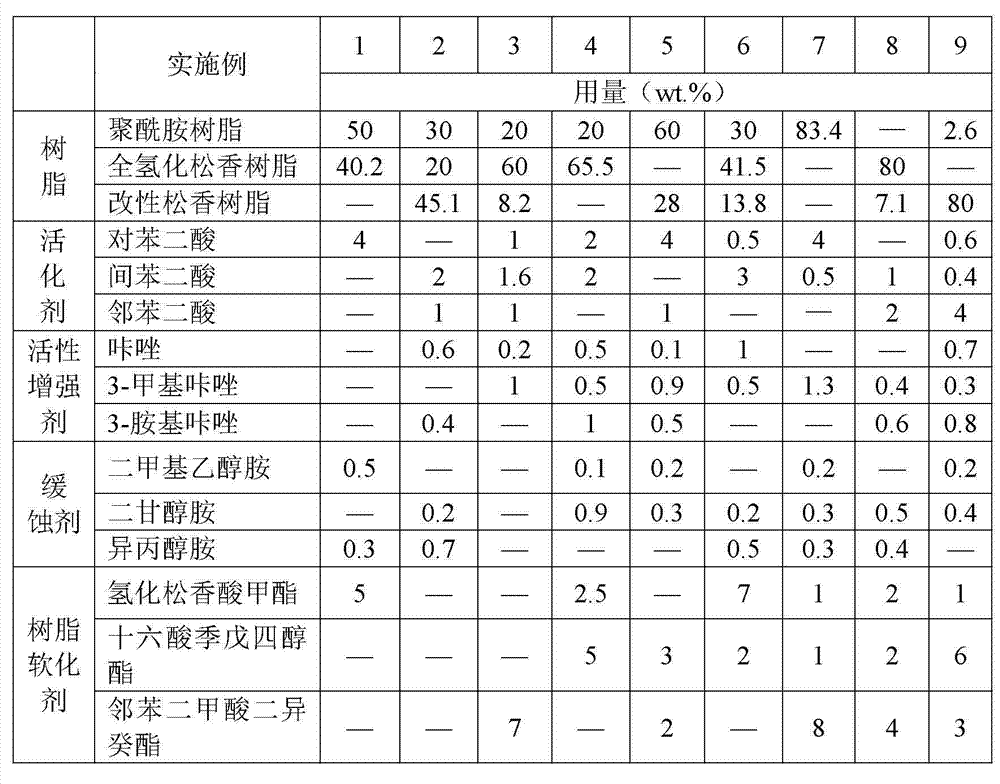
The invention discloses a halogenless soldering flux for a tin and bismuth low-temperature solder wire, which comprises the following components in percentage by total weight: 3-5 percent of benzene acid activating agent, 1-2 percent of carbazole active strengthening agent, 0.5-1.0 percent of alcohol amine inhibitor, 5-10 percent of resin softening agent and the balance of resin, wherein the resin is at least one of polyamide resin, fully-hydrogenated rosin resin and modified rosin resin. The halogenless soldering flux has the beneficial effects that the benzene acid activating agent and the carbazole active strengthening agent are mutually matched, so that the welding activity is greatly improved, a metal oxide film is effectively removed, and the welding wettability is improved; meanwhile, the alcohol amine inhibitor is adopted for preventing the secondary oxidation of a pad, components are not corroded after the completion of welding, the insulation resistance is high, and residues after welding are prevented from blackening; with the adoption of the resin softening agent, the residues are not only stable, but also cool and transparent in appearance; and the tin and bismuth low-temperature welding requirements in the electronic industry can be met.
Owner:昆山成利焊锡制造有限公司
Printed wiring board, electronic component mounting method, and electronic apparatus
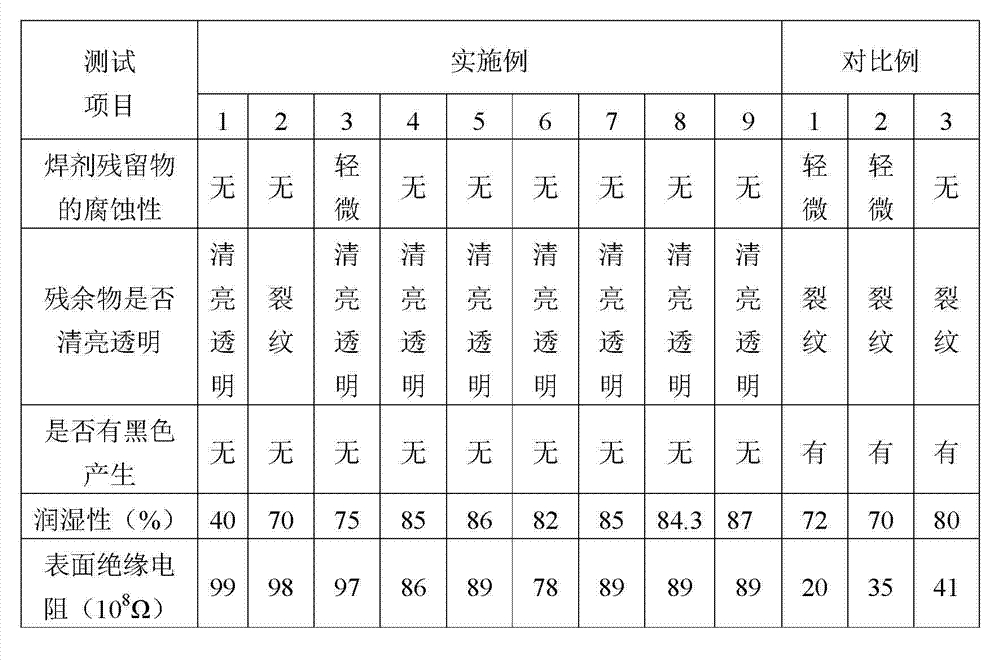
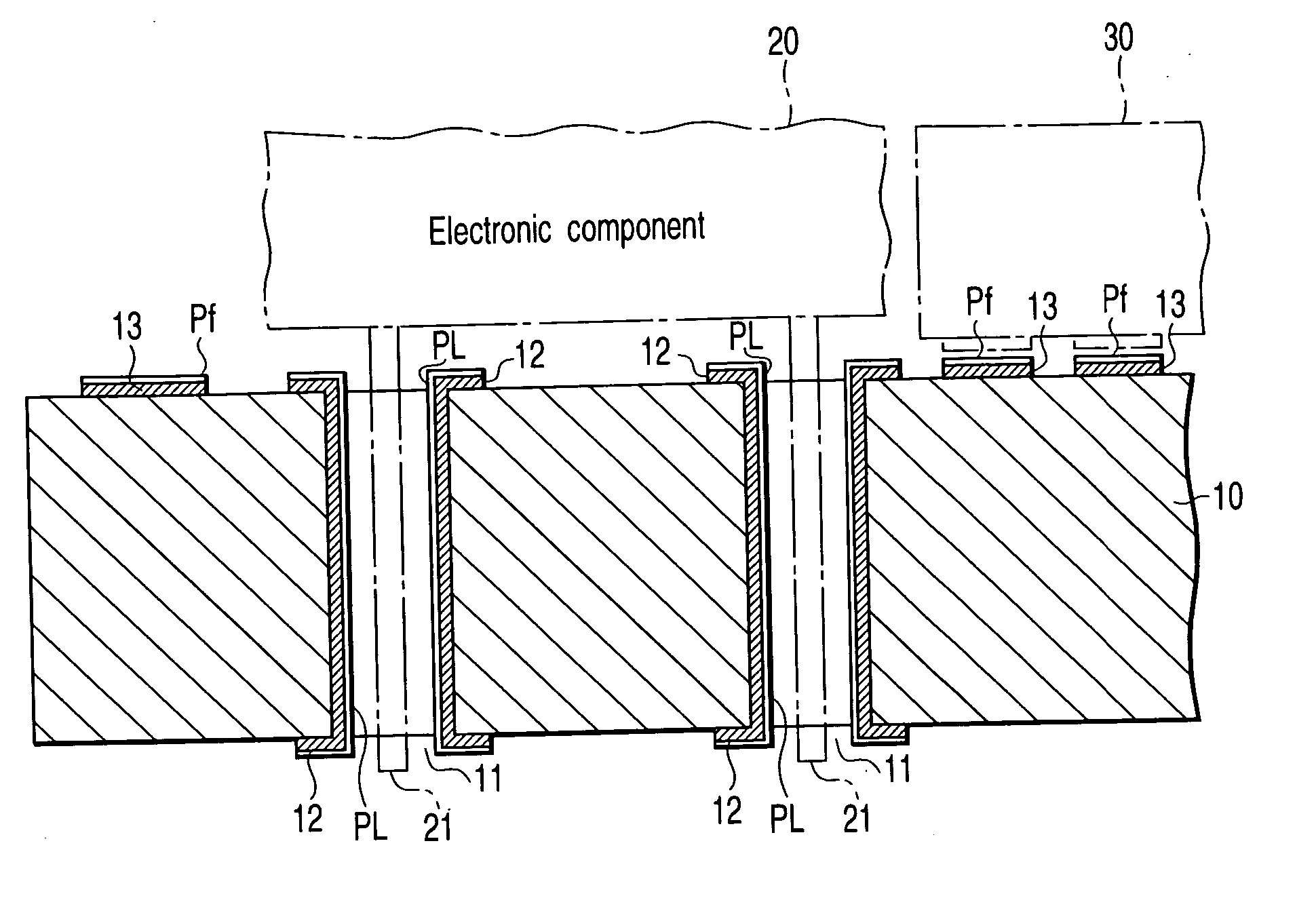
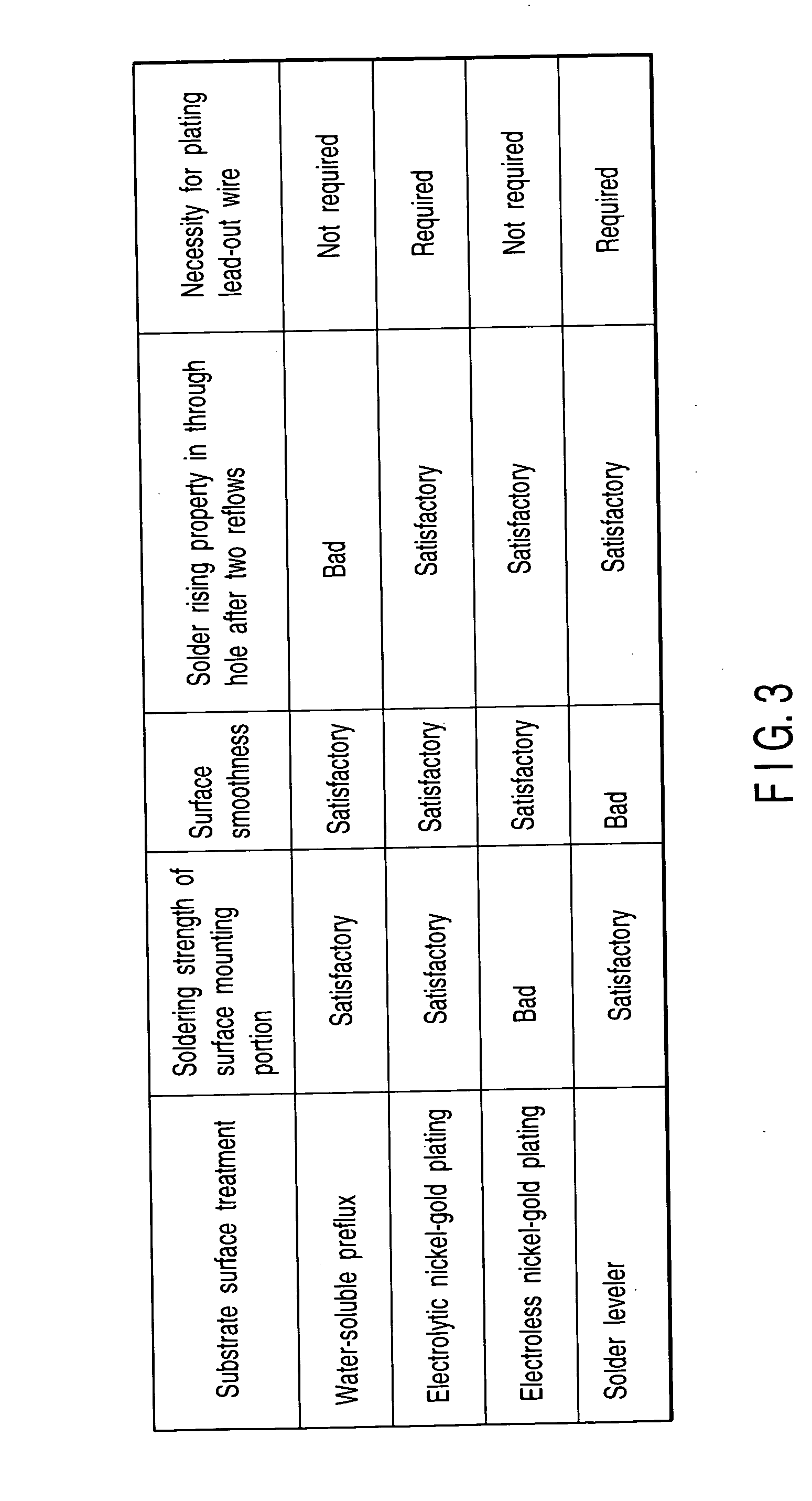
InactiveUS20050000730A1Good solder wettabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureWater solubleEngineering
A printed wiring board comprises a pad on which a surface mounting component is mounted, and a through hole into which a lead wire of an electronic component provided with the lead wire is inserted, and a surface treatment is performed to apply nickel-gold plating to the through hole to coat the pad with a water-soluble preflux.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor Device
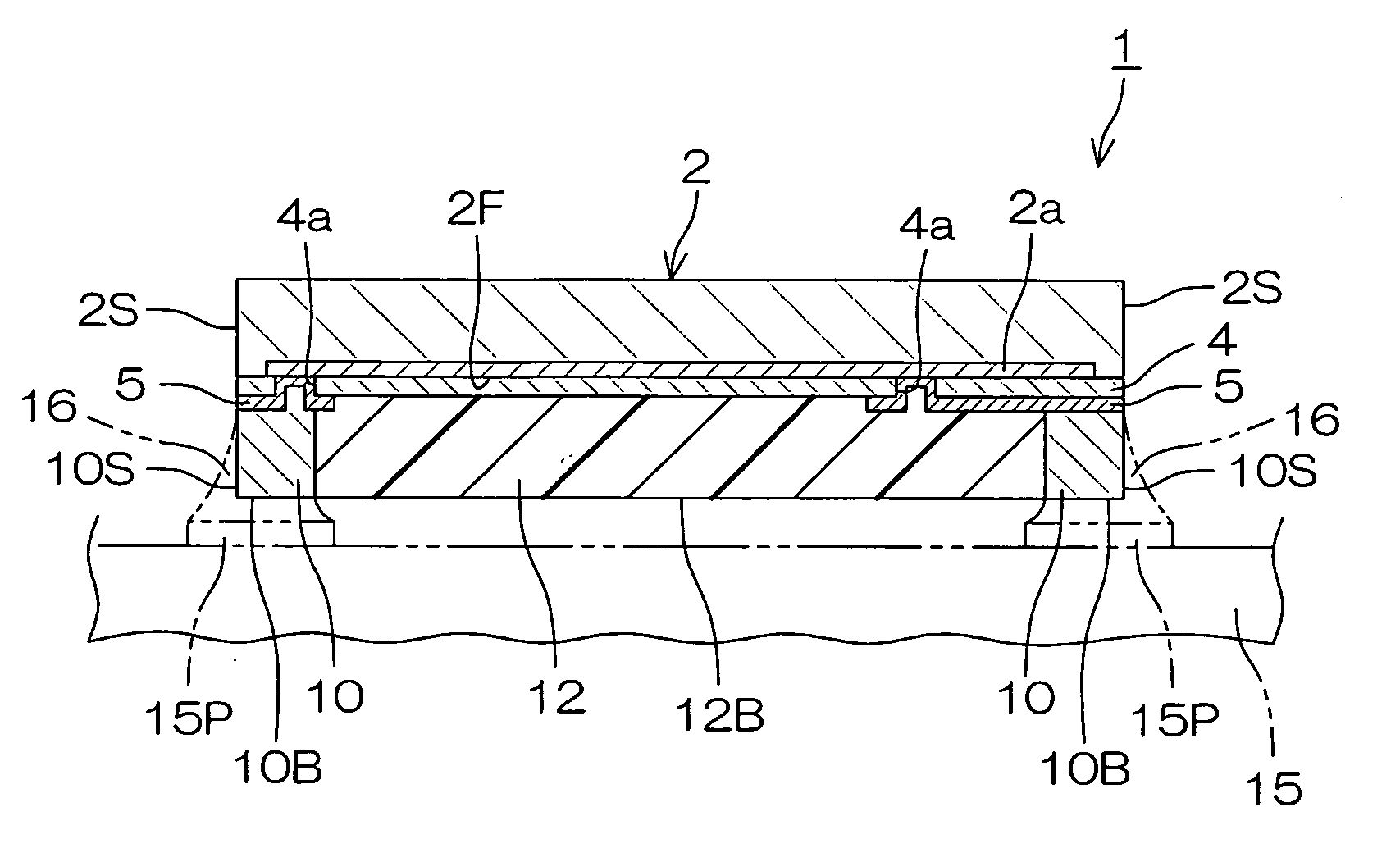
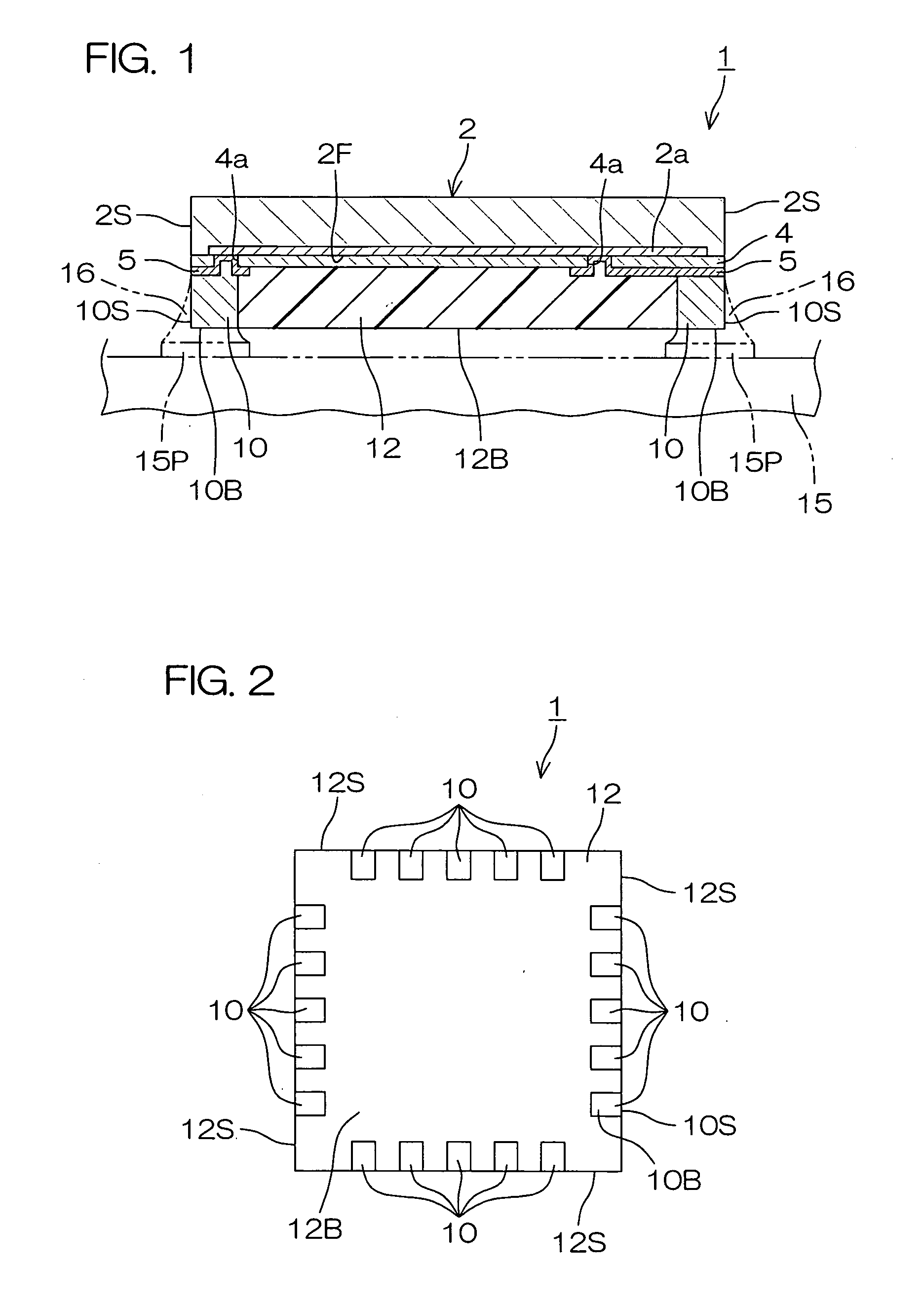
InactiveUS20070284735A1Easy to checkGood solder wettabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipElectrical connection
A semiconductor device (1, 1A, 21, 31, 41, 51) provided with a first semiconductor chip (3) having a first functional surface (3F) formed with a first functional element (3a), a protective resin layer (12) provided on the first functional surface, and an external connection terminal (10, 19, 52) provided on a peripheral portion of the first functional surface for external electrical connection, the external connection terminal having a bottom surface (10B, 19BB) exposed from a bottom surface (12B) of the protective resin layer facing away from the first functional surface and a side surface (10S, 19BS) exposed from a side surface (12S) of the protective resin layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
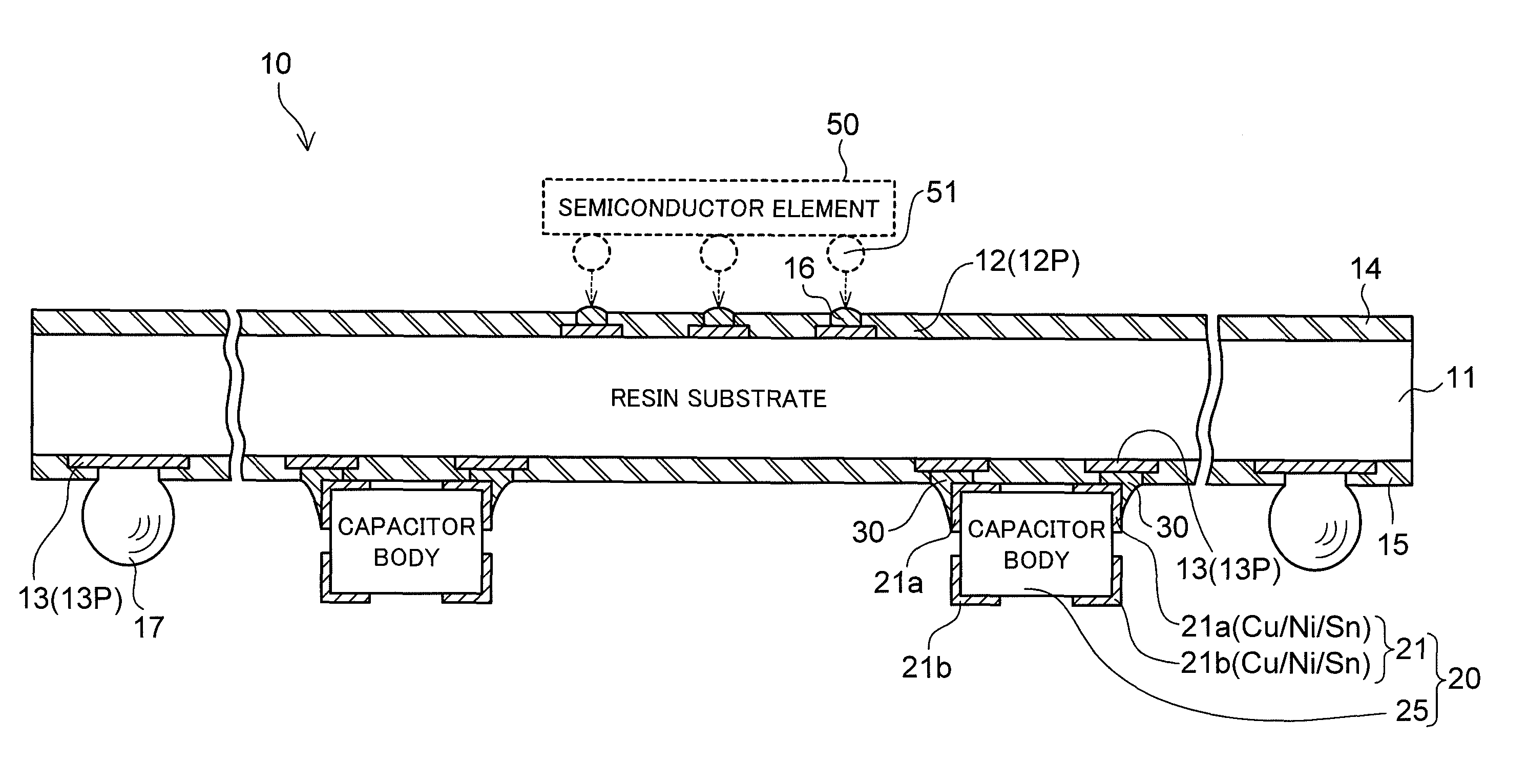
Chip component mounted wiring board
ActiveUS8331101B2Good solder wettabilityElectrically conductive connectionsFinal product manufactureSurface mountingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A wiring board to be used with being mounted on a packaging board includes a chip component surface-mounted on a surface facing the packaging board. The chip component includes terminal electrodes at both end portions of the component body thereof. Each of the terminal electrodes is provided in a form in which a plated film (Sn) formed on the surface of the terminal electrode is separated into two portions, one portion being on the wiring board side, and another portion being on the packaging board side. In one aspect, each of the terminal electrodes of the chip component is separated into a portion on the wiring board side and a portion on the packaging board side, and the plated film (Sn) is formed on a surface of each of the separated portions of each of the terminal electrodes.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com