Patents
Literature
627results about How to "Improve integration density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
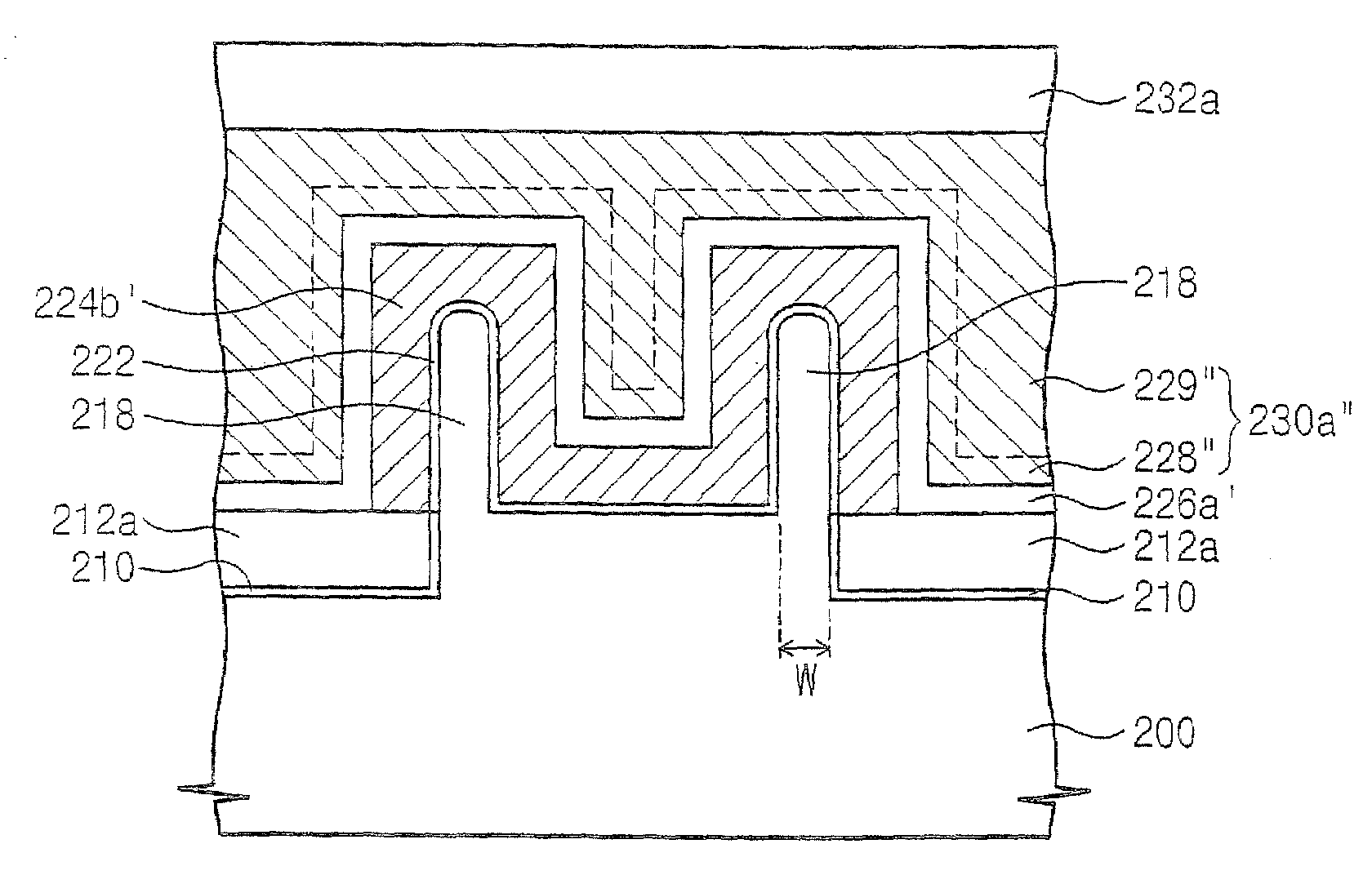
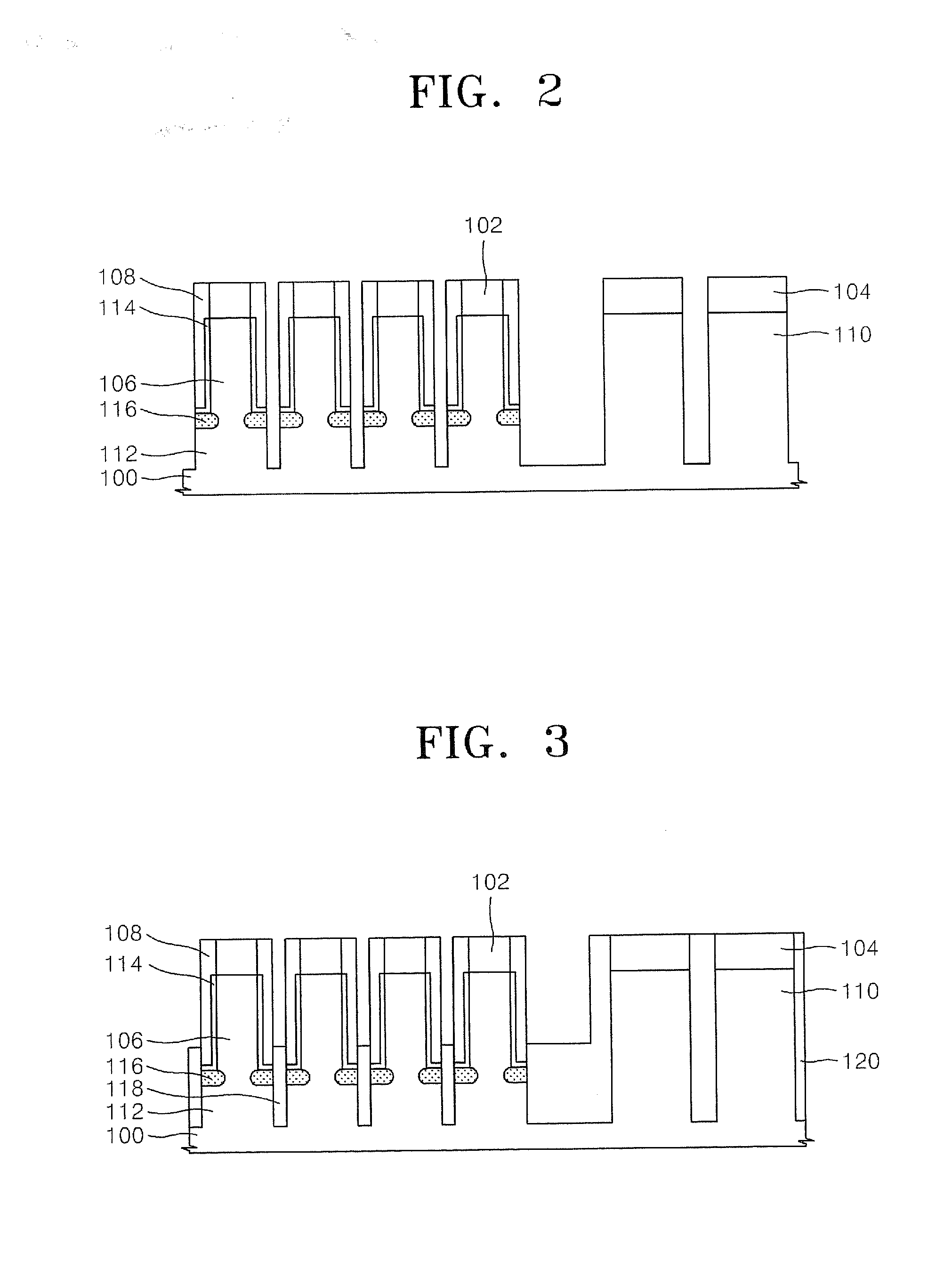
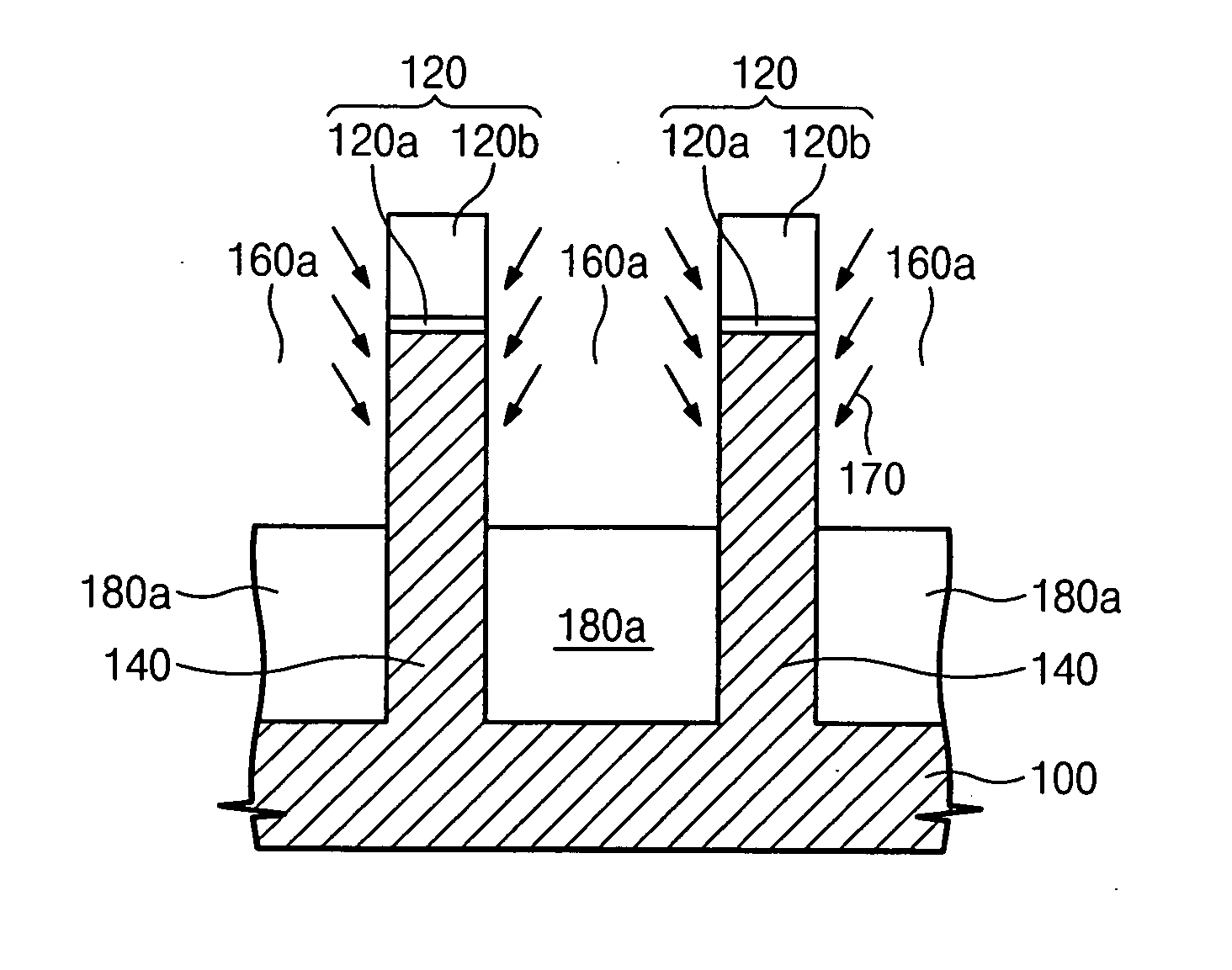
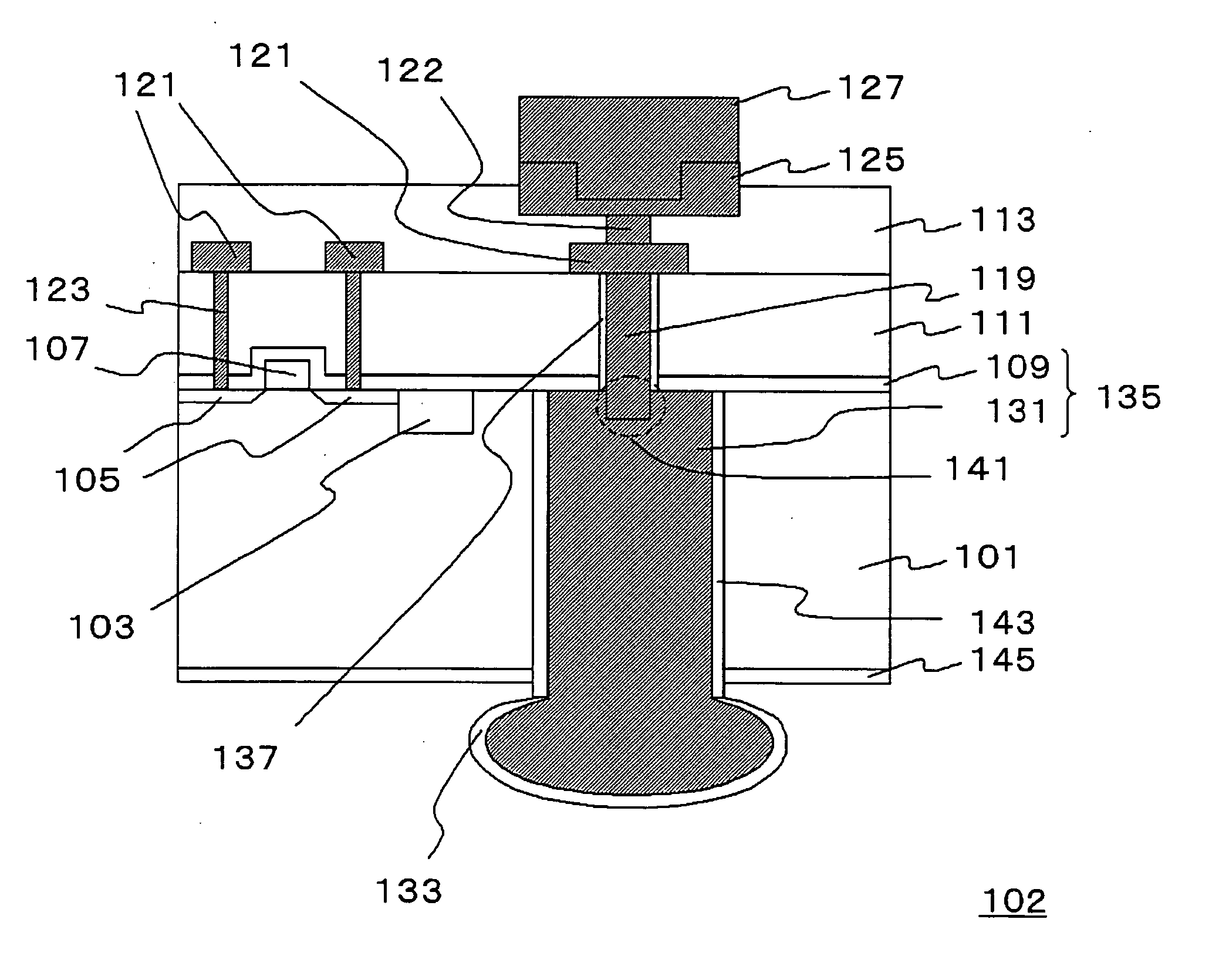
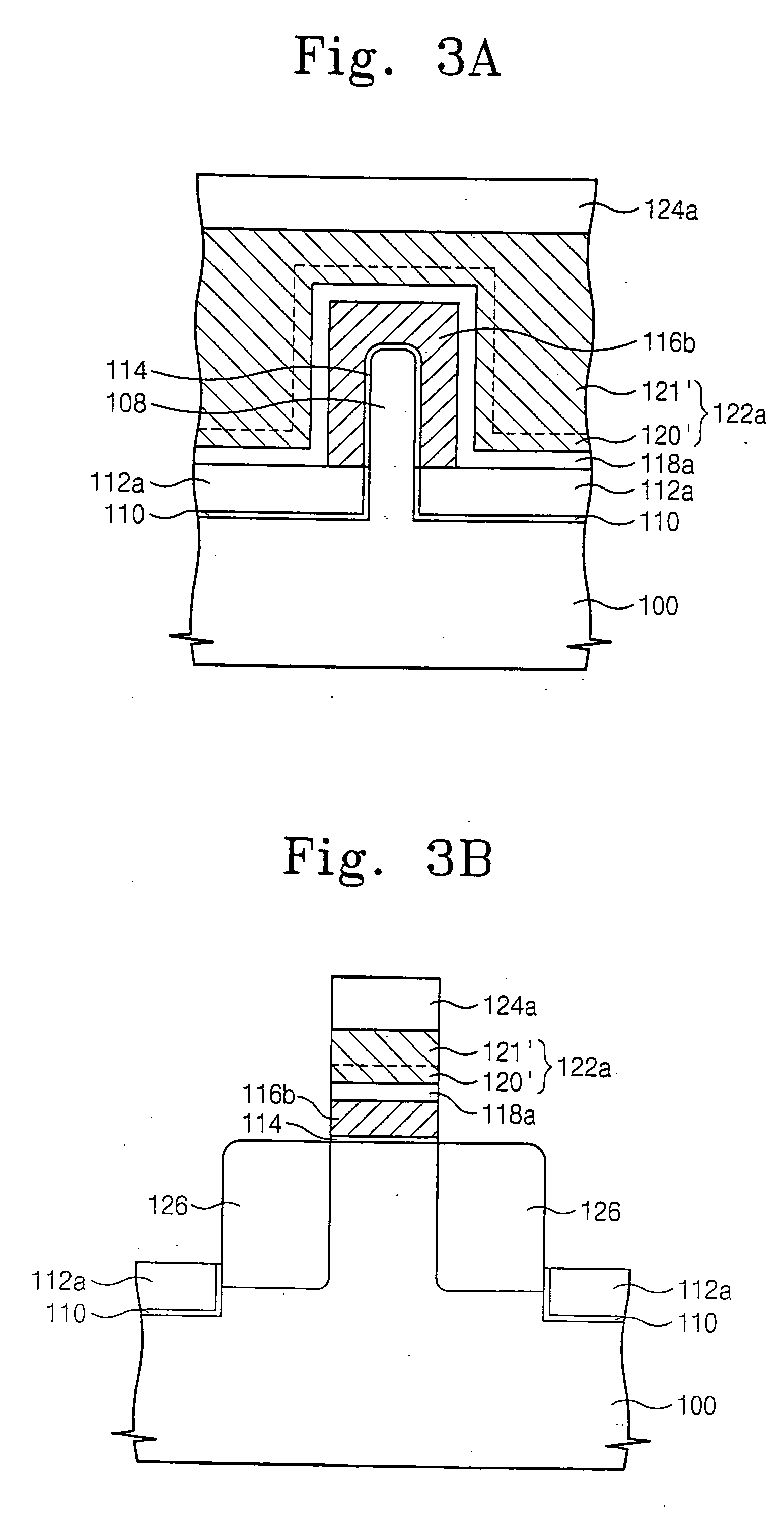
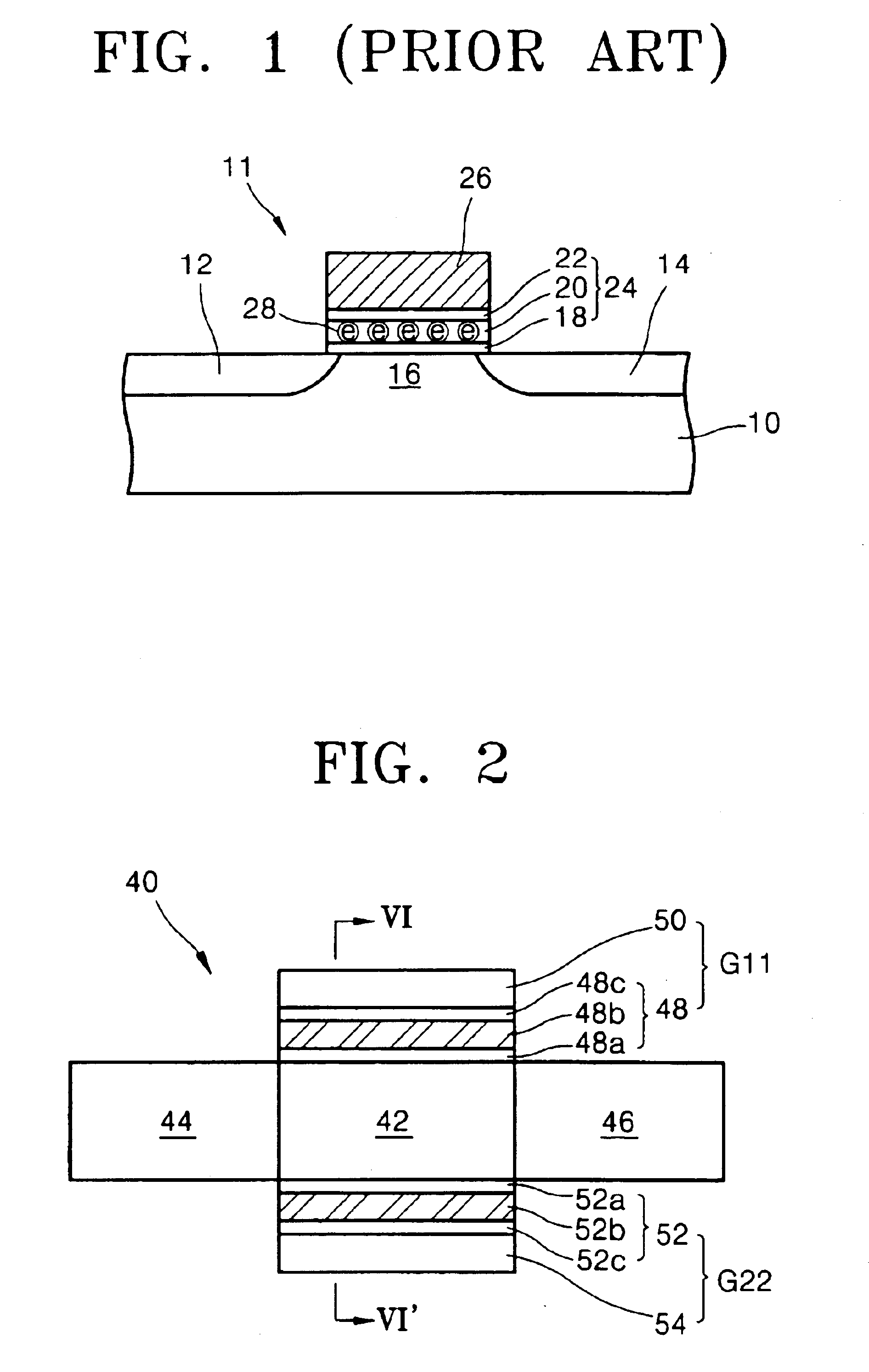
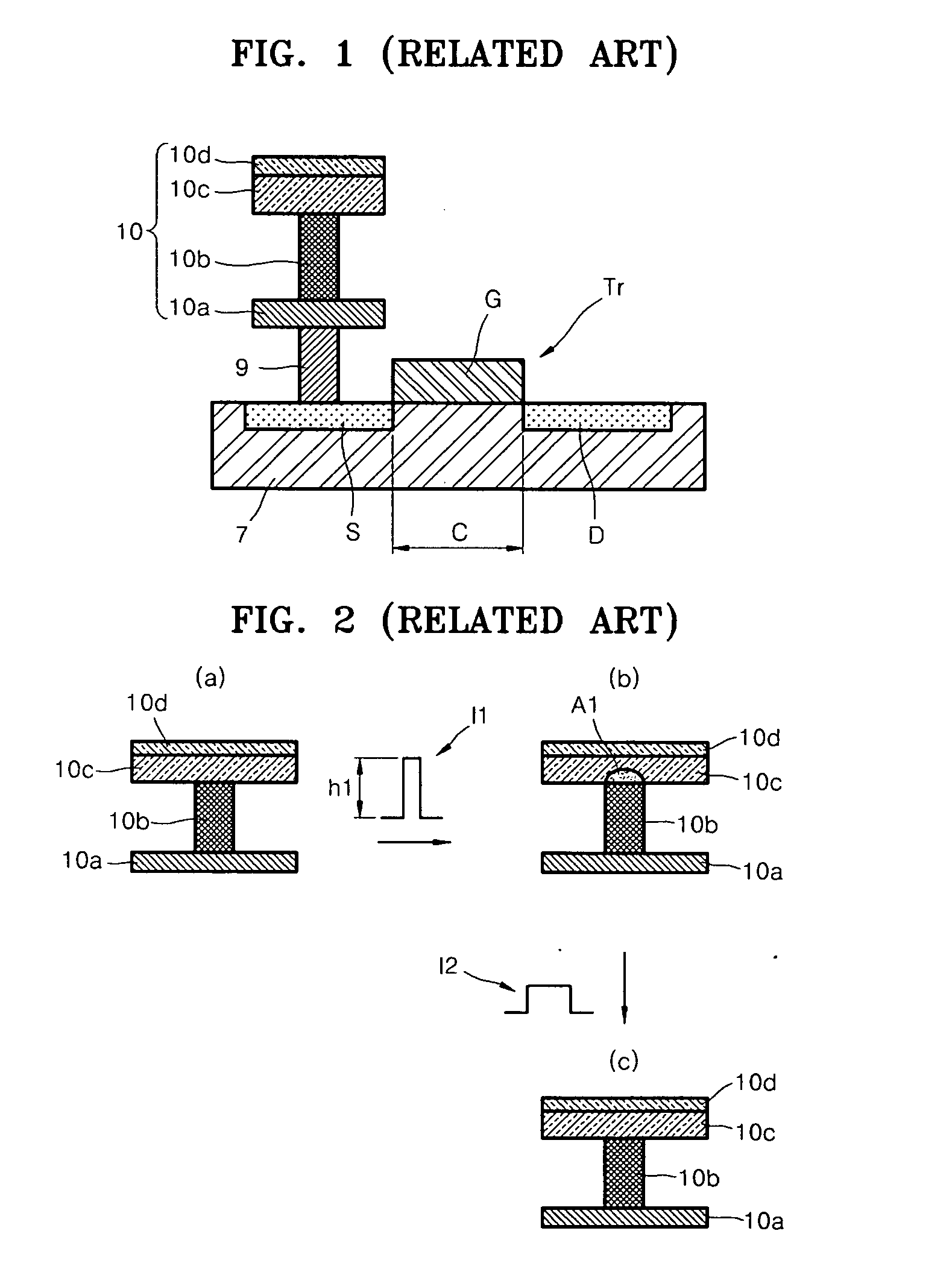
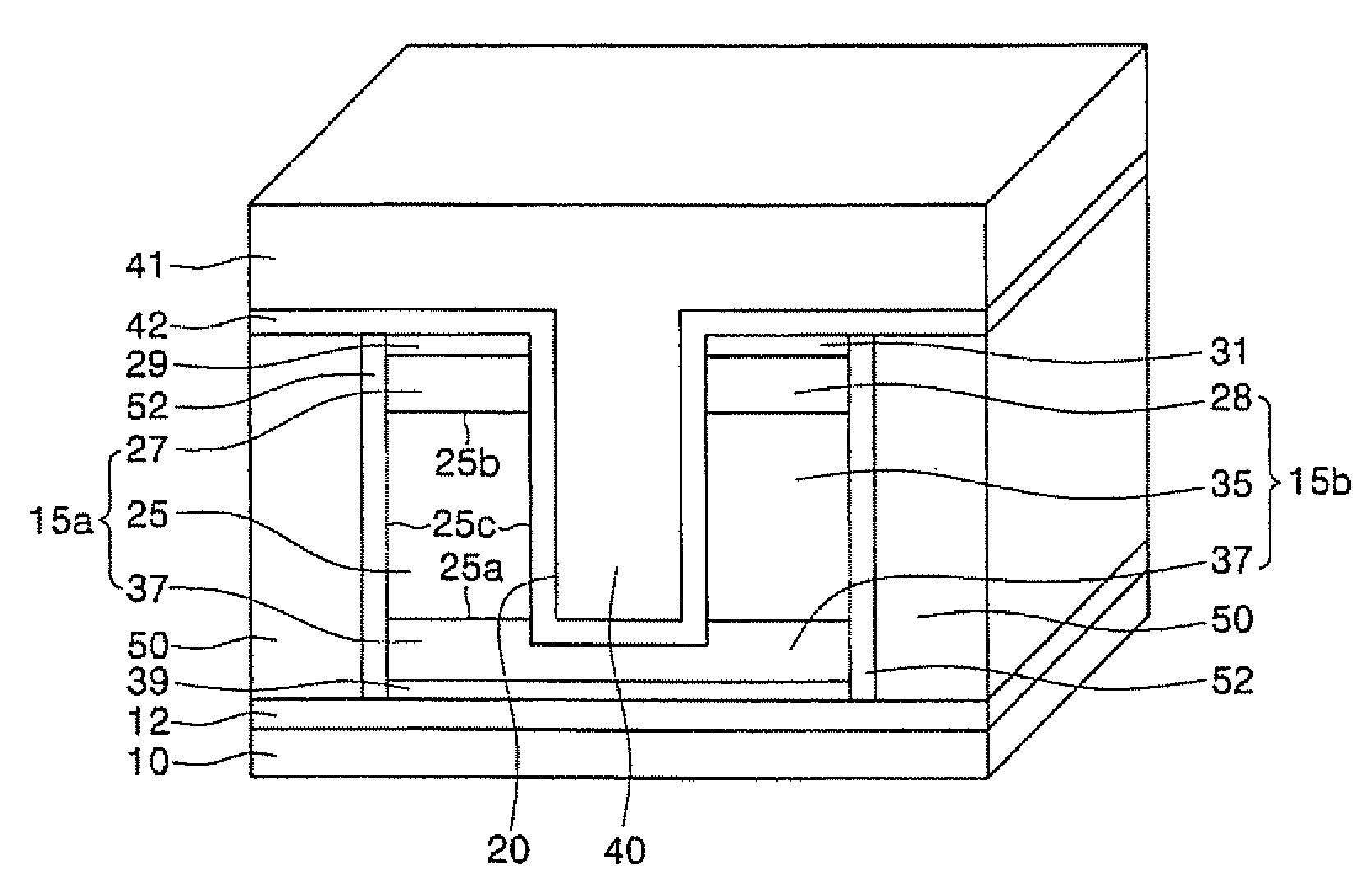
Methods of forming non-volatile memory cells including fin structures
InactiveUS7473611B2Low working voltageImprove integration densityTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerNon-volatile memory
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-volatile Memory Cells Including Fin Structures
InactiveUS20080303079A1Low working voltageImprove integration densityTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerNon-volatile memory
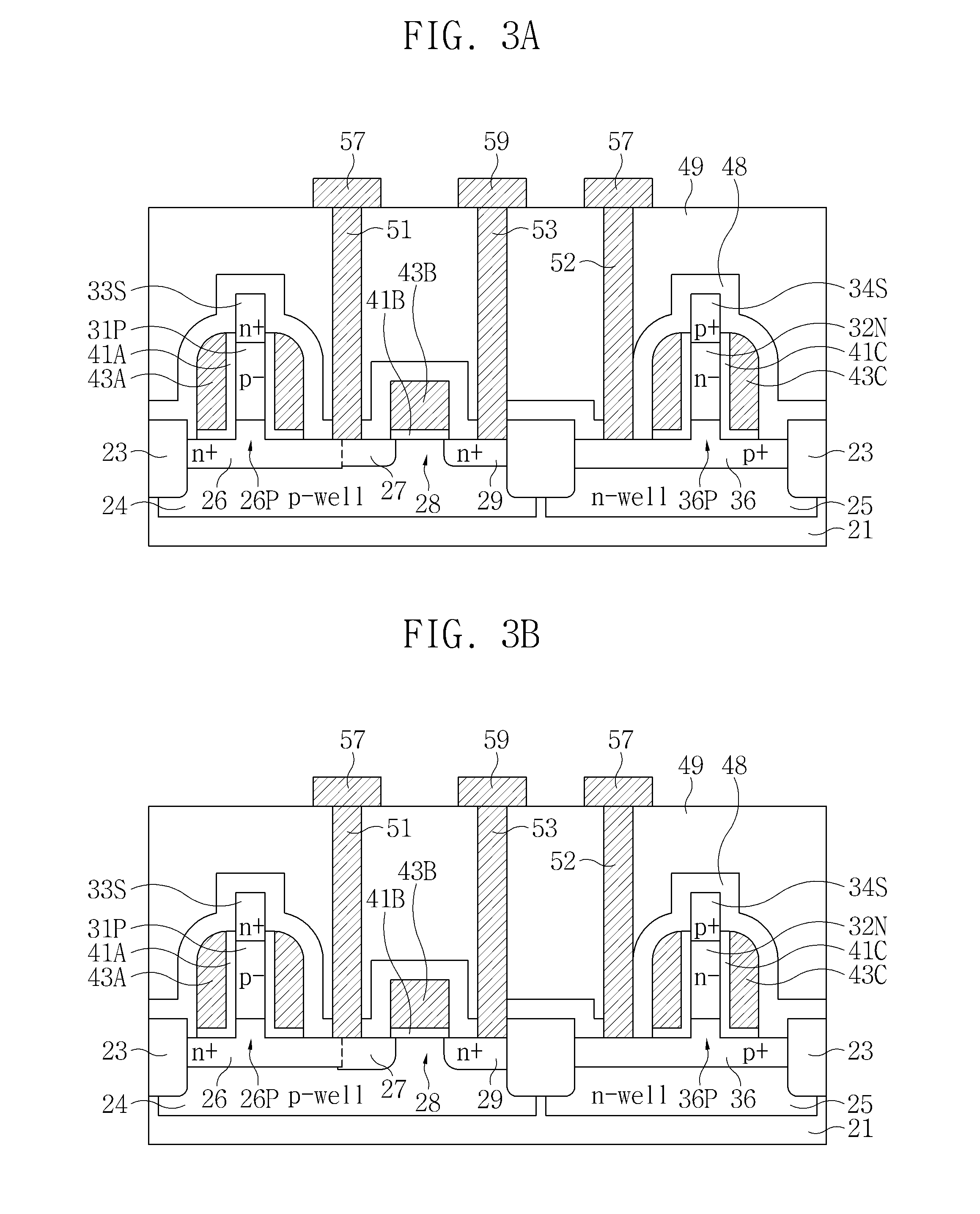
A method of forming a non-volatile memory device may include forming a fin protruding from a substrate, forming a tunnel insulating layer on portions of the fin, and forming a floating gate on the tunnel insulting layer so that the tunnel insulating layer is between the floating gate and the fin. A dielectric layer may be formed on the floating gate so that the floating gate is between the dielectric layer and the fin, and a control gate electrode may be formed on the dielectric layer so that the dielectric layer is between the control gate and the fin. Related devices are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated Circuit Semiconductor Device Including Stacked Level Transistors and Fabrication Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090108318A1Improve integration densityEasy to manufactureTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerInterconnection
An integrated circuit semiconductor device includes a first transistor formed at a lower substrate and configured with at least one of a vertical transistor and a planar transistor. A bonding insulation layer is formed on the first transistor, and an upper substrate is bonded on the bonding insulation layer. A second transistor configured with at least one of a vertical transistor and a planar transistor is formed at the upper substrate. The first transistor and the second transistor are connected by an interconnection layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-volatile memory devices and method for forming the same
ActiveUS20050227435A1Improve abilitiesHighly integratedTransistorNanoinformaticsEngineeringNon-volatile memory
According to a nonvolatile memory device having a multi gate structure and a method for forming the same of the present invention, a gate electrode is formed using a damascene process. Therefore, a charge storage layer, a tunneling insulating layer, a blocking insulating layer and a gate electrode layer are not attacked from etching in a process for forming the gate electrode, thereby forming a nonvolatile memory device having good reliability.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050221601A1Improve featuresSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device having a through electrode excellent in performance as for an electrode and manufacturing stability is provided. There is provided a through electrode composed of a conductive small diameter plug and a conductive large diameter plug on a semiconductor device. A cross sectional area of the small diameter plug is made larger than a cross sectional area and a diameter of a connection plug, and is made smaller than a cross sectional area and a diameter of the large diameter plug. In addition, a protruding portion formed in such a way that the small diameter plug is projected from the silicon substrate is put into an upper face of the large diameter plug. Further, an upper face of the small diameter plug is connected to a first interconnect.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device with stacked memory cell and method of manufacturing the stacked memory cell
In a semiconductor memory device and method, resistive-change memory cells are provided, each including a plurality of control transistors formed on different layers and variable resistance devices comprising a resistive-change memory. Each resistive-change memory cell includes a plurality of control transistors formed on different layers, and a variable resistance device formed of a resistive-change memory. In one example, the number of the control transistors is two. The semiconductor memory device includes a global bit line; a plurality of local bit lines connected to or disconnected from the global bit line via local bit line selection circuits which correspond to the local bit lines, respectively; and a plurality of resistive-change memory cell groups storing data while being connected to the local bit lines, respectively. Each of the resistive-change memory cells of each of the resistive-change memory cell groups comprises a plurality of control transistors formed on different layers, and a variable resistance device formed of a resistive-change memory. In addition, the semiconductor memory device has a hierarchical bit line structure that uses a global bit line and local bit lines. Accordingly, it is possible to increase both the integration density of the semiconductor memory device and the amount of current flowing through each of the resistive-change memory cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
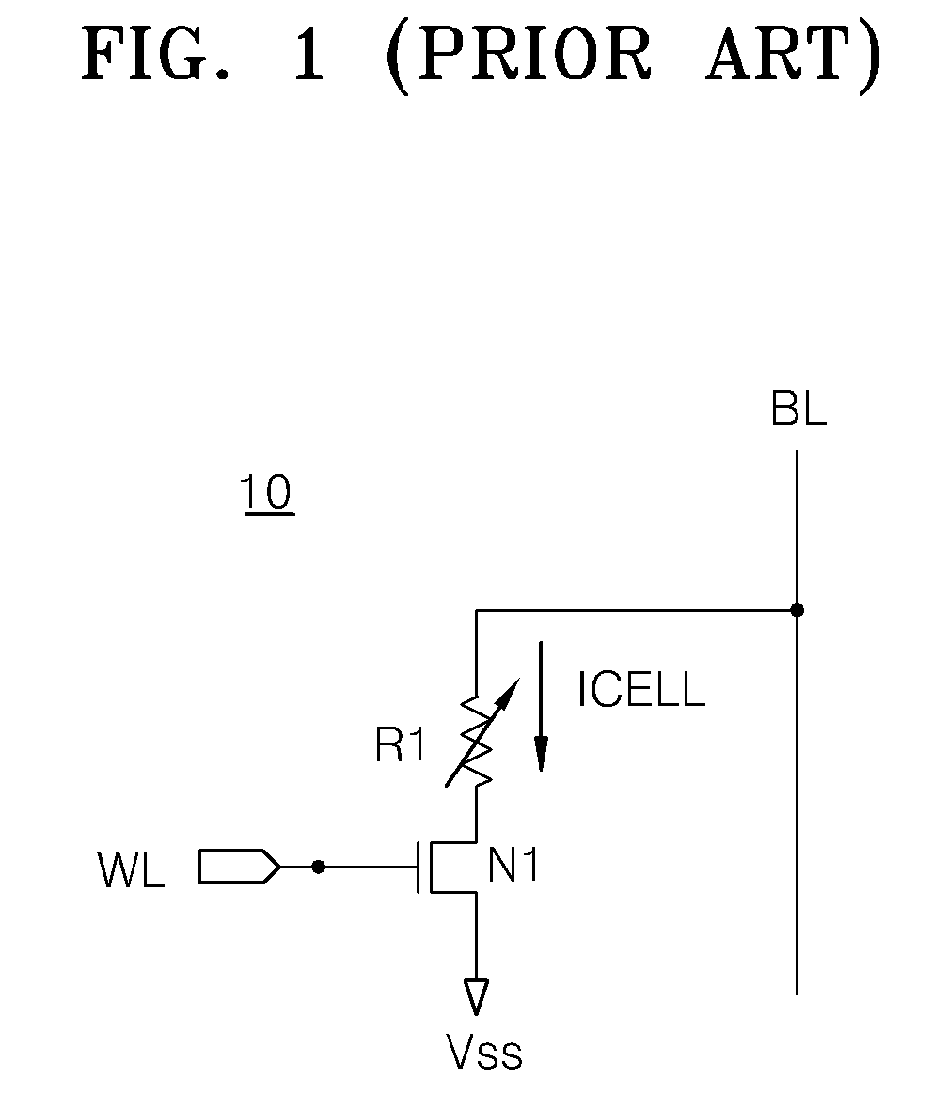
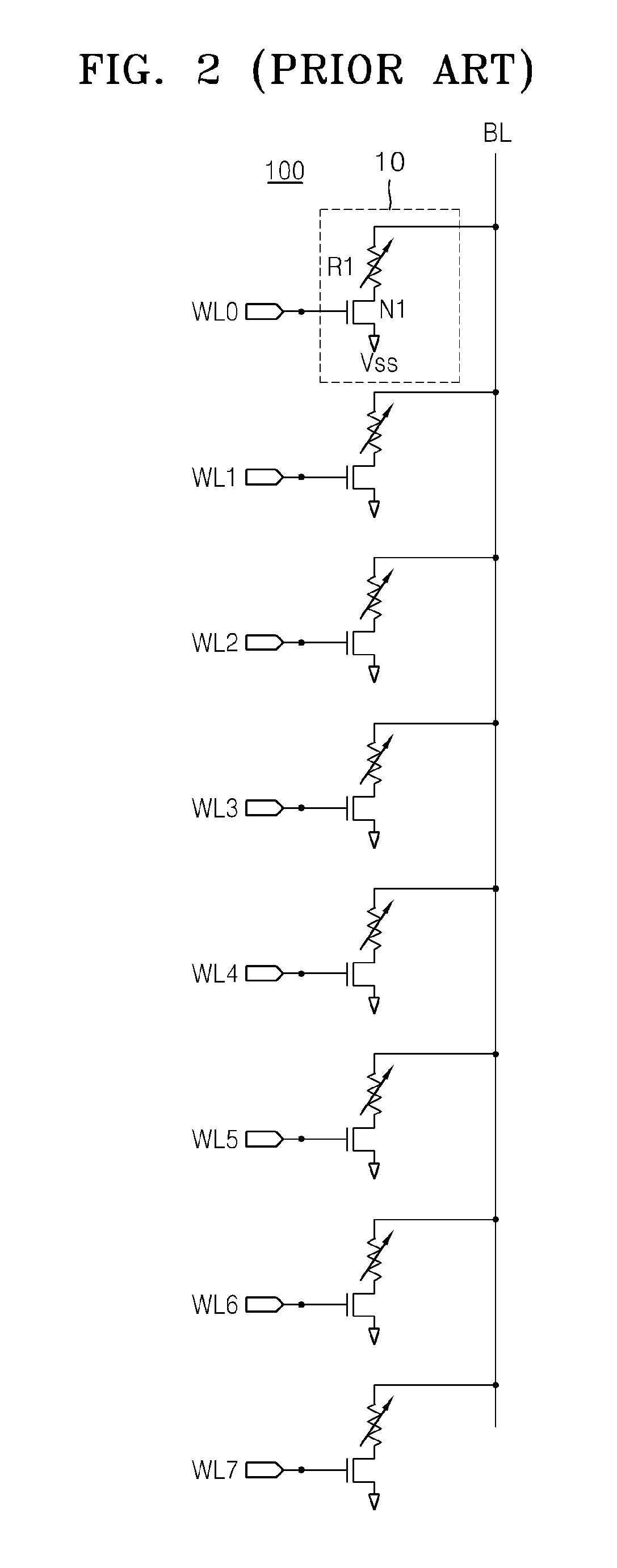
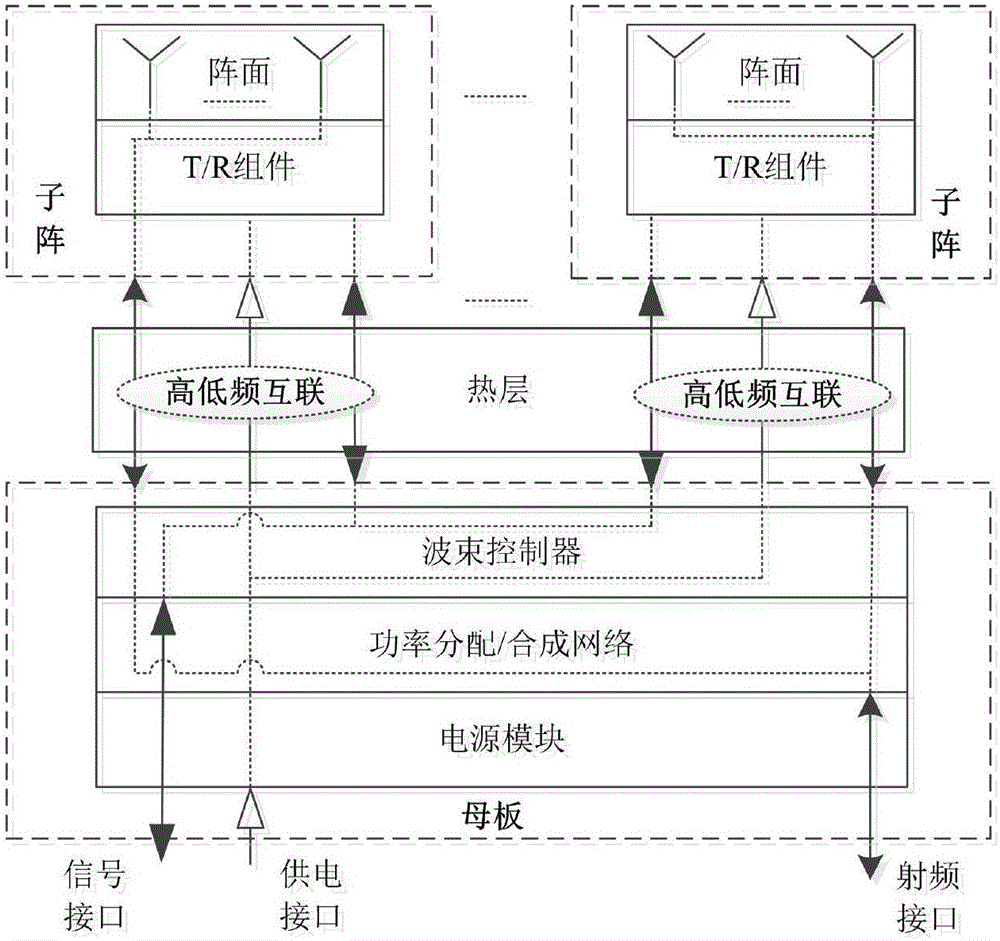
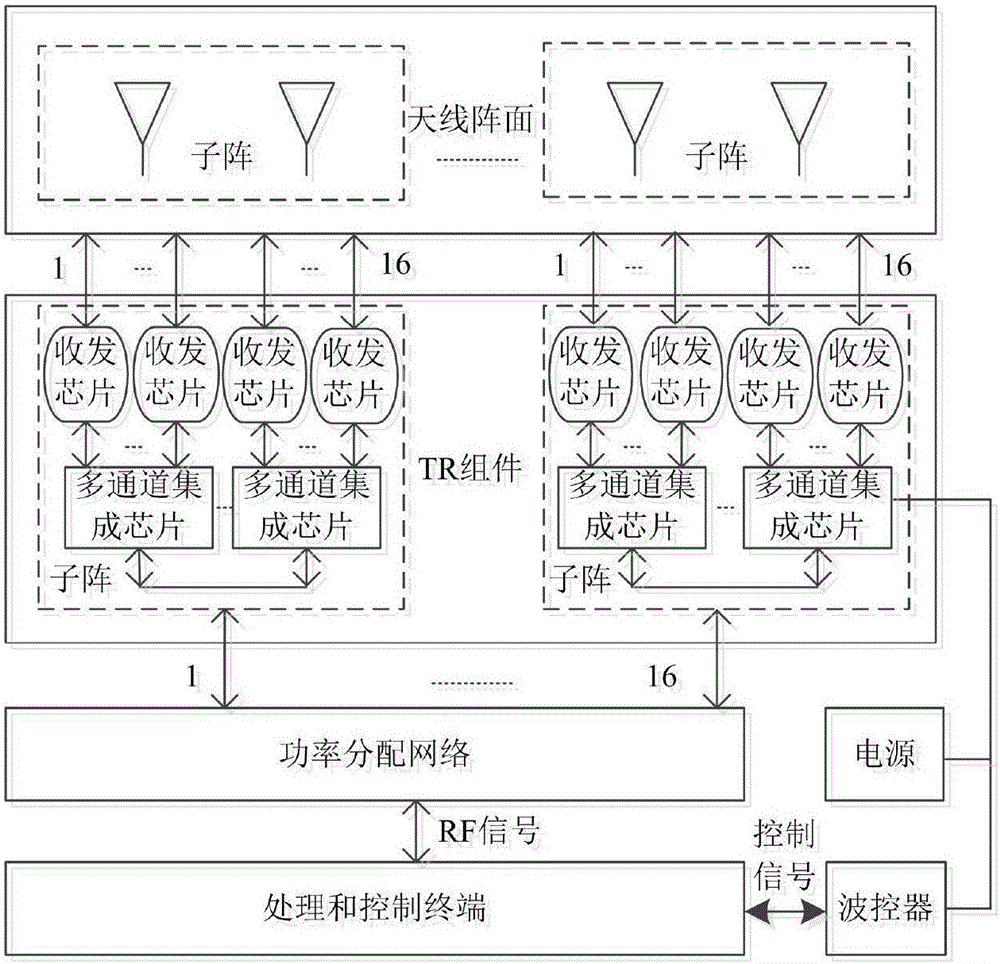
Ka-band tilt-structure active phased array antenna
InactiveCN105914476AHighly integratedImprove performanceAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationArray elementActive phase
The invention provides a Ka-band tilt-structure active phased array antenna, so as to provide an active phased array antenna which is high in integration density and can improve maintainability and interchangeability. According to the technical scheme, one path of RF signals transmitted by a transmitting signal processing terminal are transmitted to a power distribution / synthesis network (5) via a signal interface and a radio frequency interface to be divided into M paths of signals; according to information of an azimuth angle and a pitch angle of the phased array antenna provided by the transmitting signal processing terminal in real time, a beam controller (4) calculates and obtains beam pointing of the phased array antenna in real time through an FPGA; the beam pointing of the phased array antenna is converted into phase data needed by each array element under control of the beam controller (4); the data are transmitted to tilt-type TR assembly sub array modules in N channels respectively via a high and low-frequency interconnected multi-core high and low-frequency socket, and under control of the beam controller, M*N paths of signals are transmitted to an antenna array, and thus signal transmission is completed, and synchronous electric control scanning of beams transmitted by the phased array antenna is realized.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and its manufacture using automatic layout
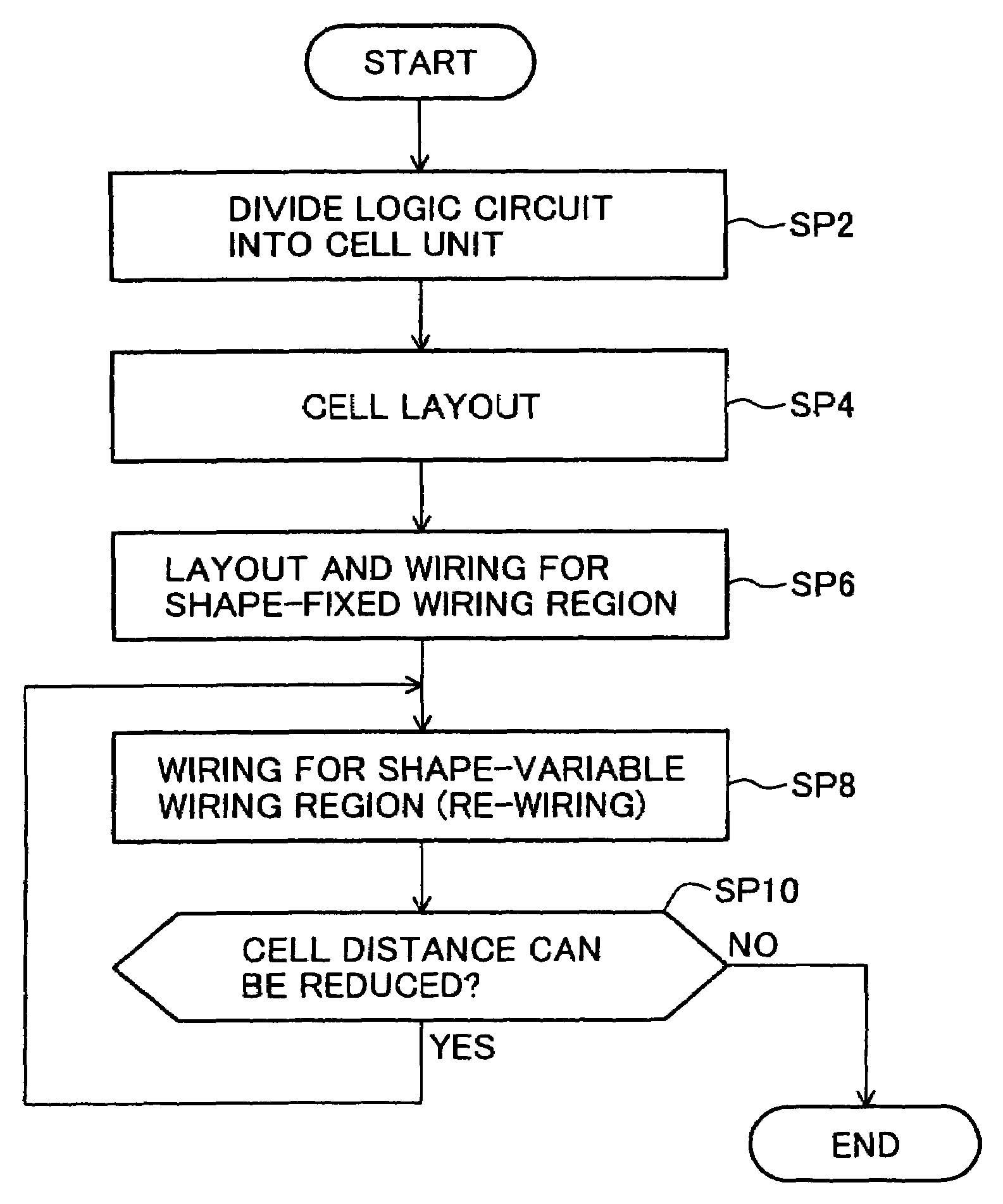
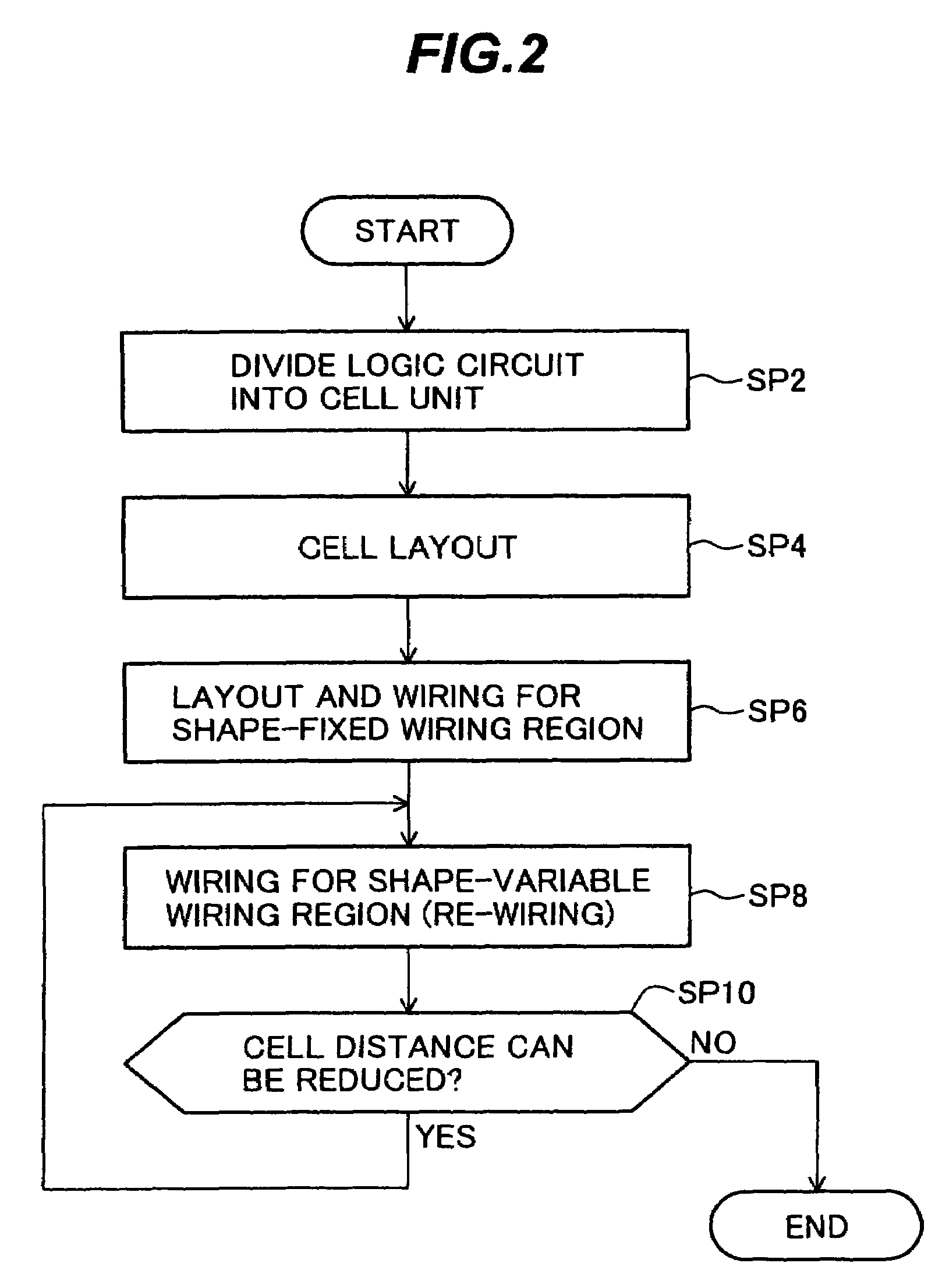
InactiveUS7053424B2Improve integration densityEliminate spaceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit device has: a semiconductor substrate defining a plurality of rows, each row including areas for a sequence of cells; a plurality of active regions disposed in each of the rows constituting semiconductor elements of associated cells; and a wiring region of stripe shape elongated along a direction of row, defined on the semiconductor substrate outside of the active regions in each row, and including wirings belonging to the associated cells, each wiring region having height in a direction crossing the row direction, the wiring region having locally different height.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and its manufacture using automatic layout
InactiveUS7228510B2Improve integration densityEliminate spaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit device has: a semiconductor substrate defining a plurality of rows, each row including areas for a sequence of cells; a plurality of active regions disposed in each of the rows constituting semiconductor elements of associated cells; and a wiring region of stripe shape elongated along a direction of row, defined on the semiconductor substrate outside of the active regions in each row, and including wirings belonging to the associated cells, each wiring region having height in a direction crossing the row direction, the wiring region having locally different height.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Method for making a front and back conductive substrate
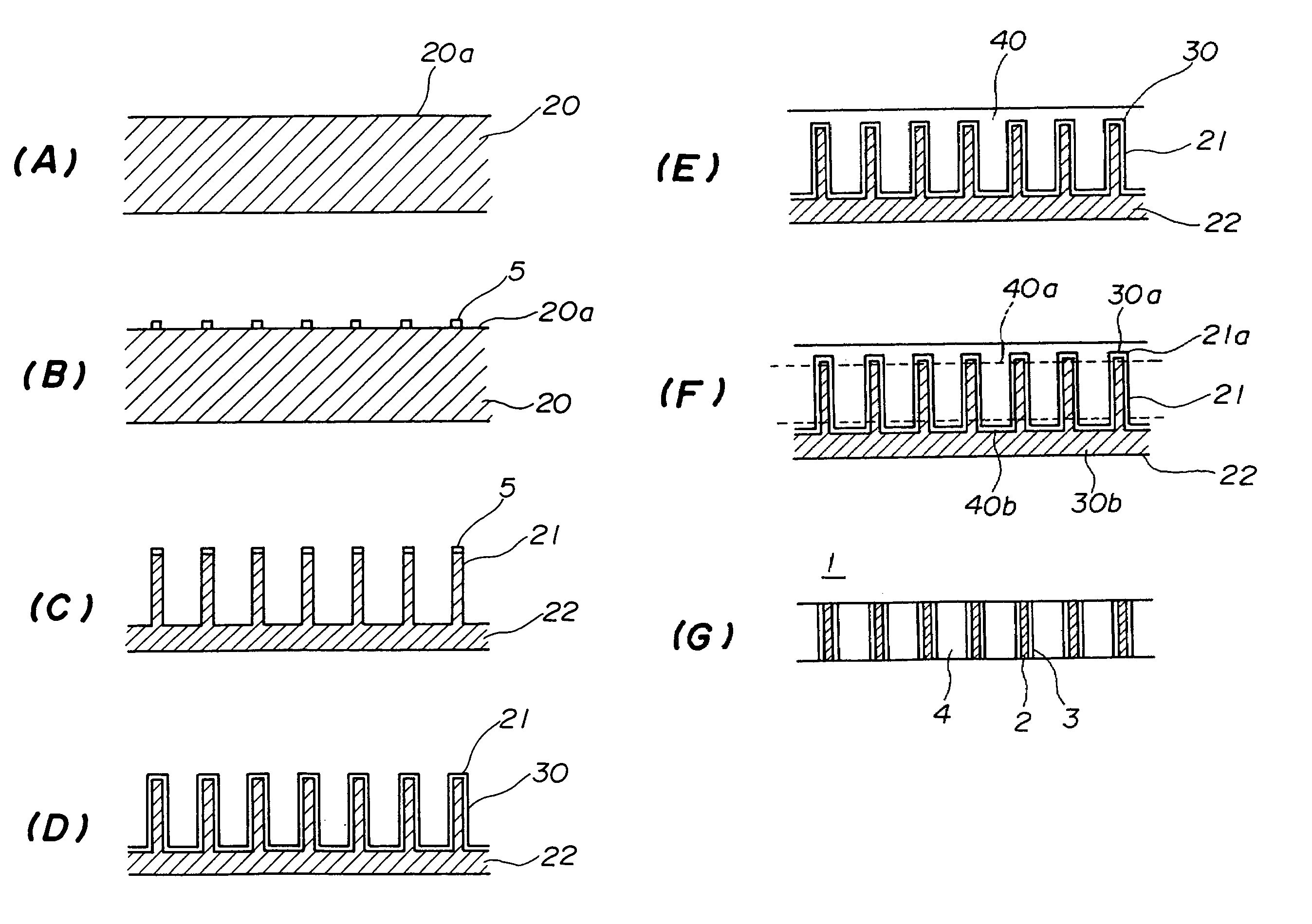
InactiveUS7222420B2Improve integration densityPrinted circuit assemblingContact member manufacturingEngineeringElectrically conductive
A front-and-back electrically conductive substrate includes a plurality of posts composed of a material that can be anisotropically etched and having an electrically conductive portion that has at least a first surface and a second surface that communicate with each other, and an insulative substrate that supports the plurality of posts.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
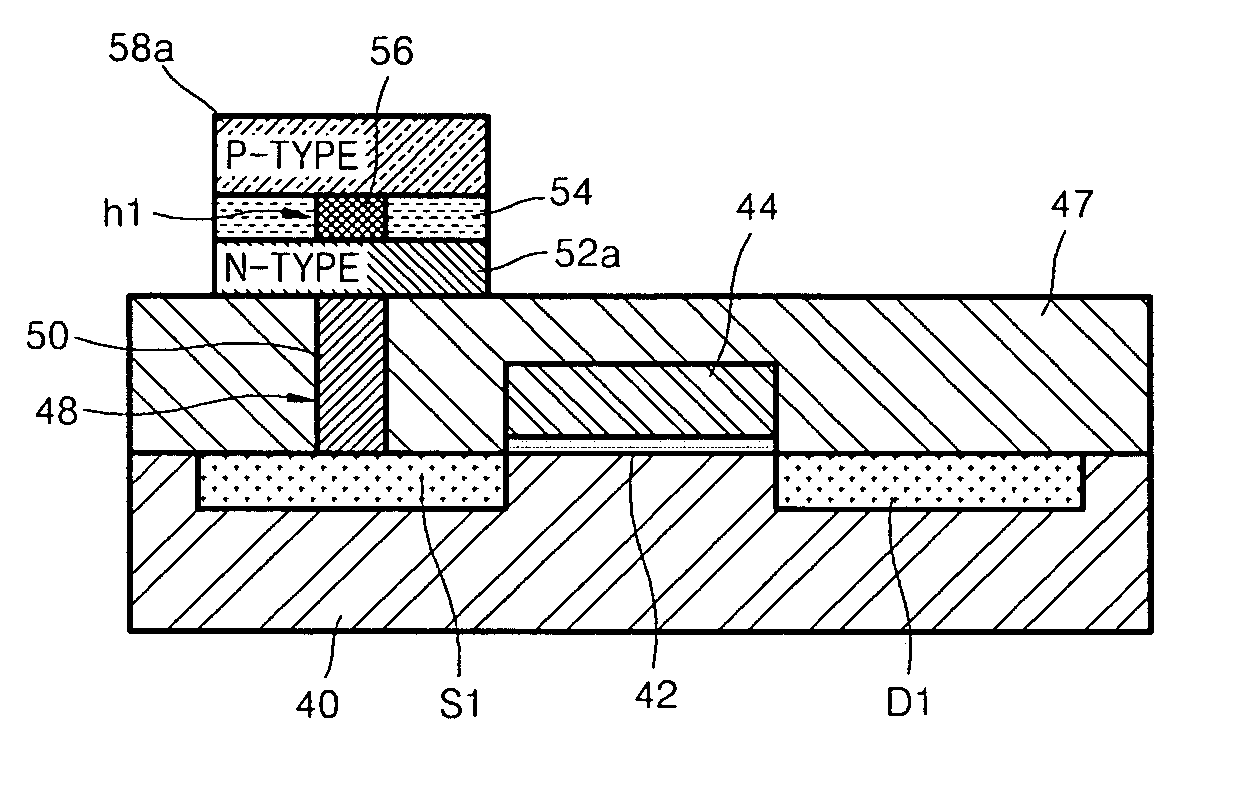
Semiconductor devices having vertical device and non-vertical device and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20120319201A1Improve integration densityReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
In a semiconductor device, a vertical transistor comprises: a first diffusion region on a substrate; a channel region on the first diffusion region and extending in a vertical direction; a second diffusion region on the channel region; and a gate electrode at a sidewall of, and insulated from, the channel region. A horizontal transistor is positioned on the substrate, the horizontal transistor comprising: a first diffusion region and a second diffusion region on the substrate and spaced apart from each other; a channel region on the substrate between the first diffusion region and the second diffusion region; and a gate electrode on the channel region and isolated from the channel region. A portion of a gate electrode of the vertical transistor and a portion of the gate electrode of the horizontal transistor are at a same vertical position in the vertical direction relative to the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20160049423A1Improve integration densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDevice materialIsolation layer
A three-dimensional semiconductor device may include a substrate including a cell array region, a word line contact region, and a peripheral circuit region, gate electrodes stacked on the substrate to extend from the cell array region to the word line contact region, a channel hole penetrating the gate electrodes on the cell array region and exposing an active region of the substrate, a dummy hole penetrating the gate electrodes on the word line contact region and exposing a device isolation layer provided on the substrate, and a semiconductor pattern provided in the channel hole but not in the dummy hole.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting device
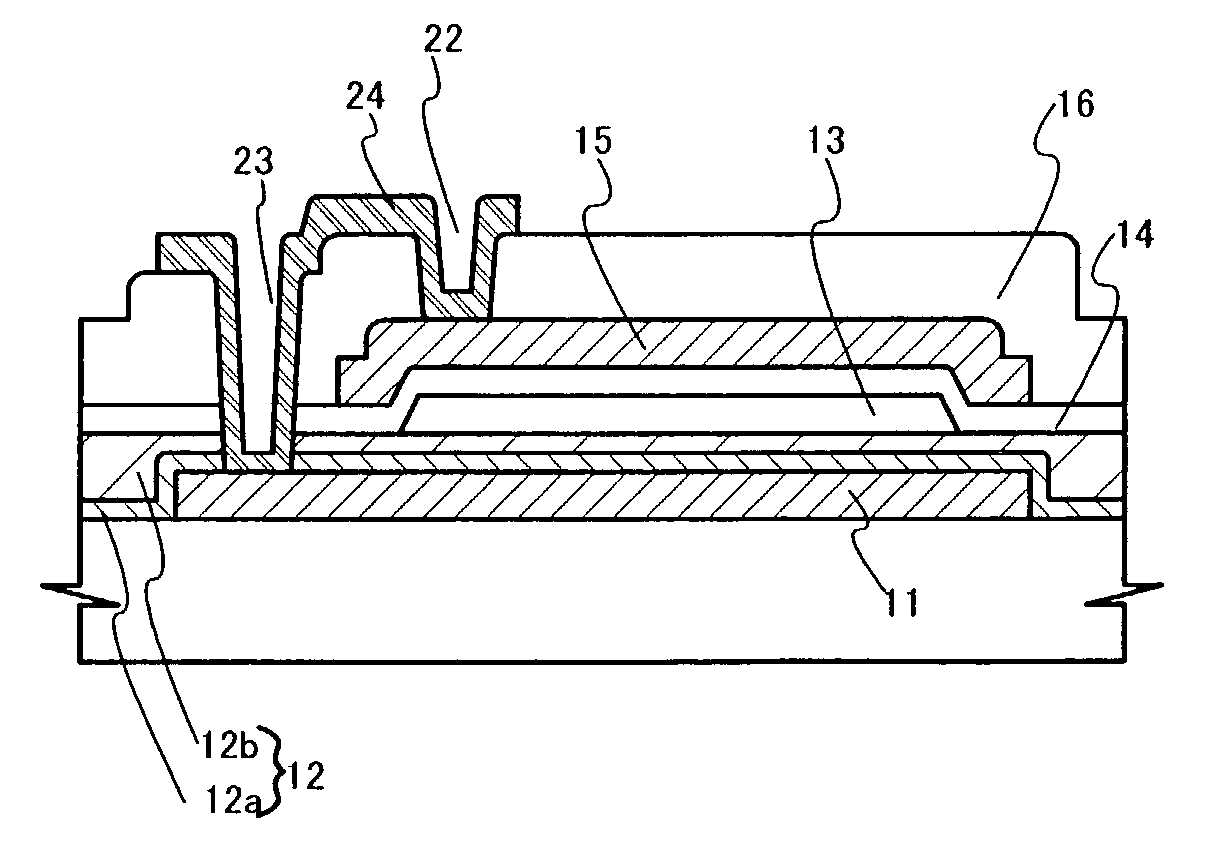
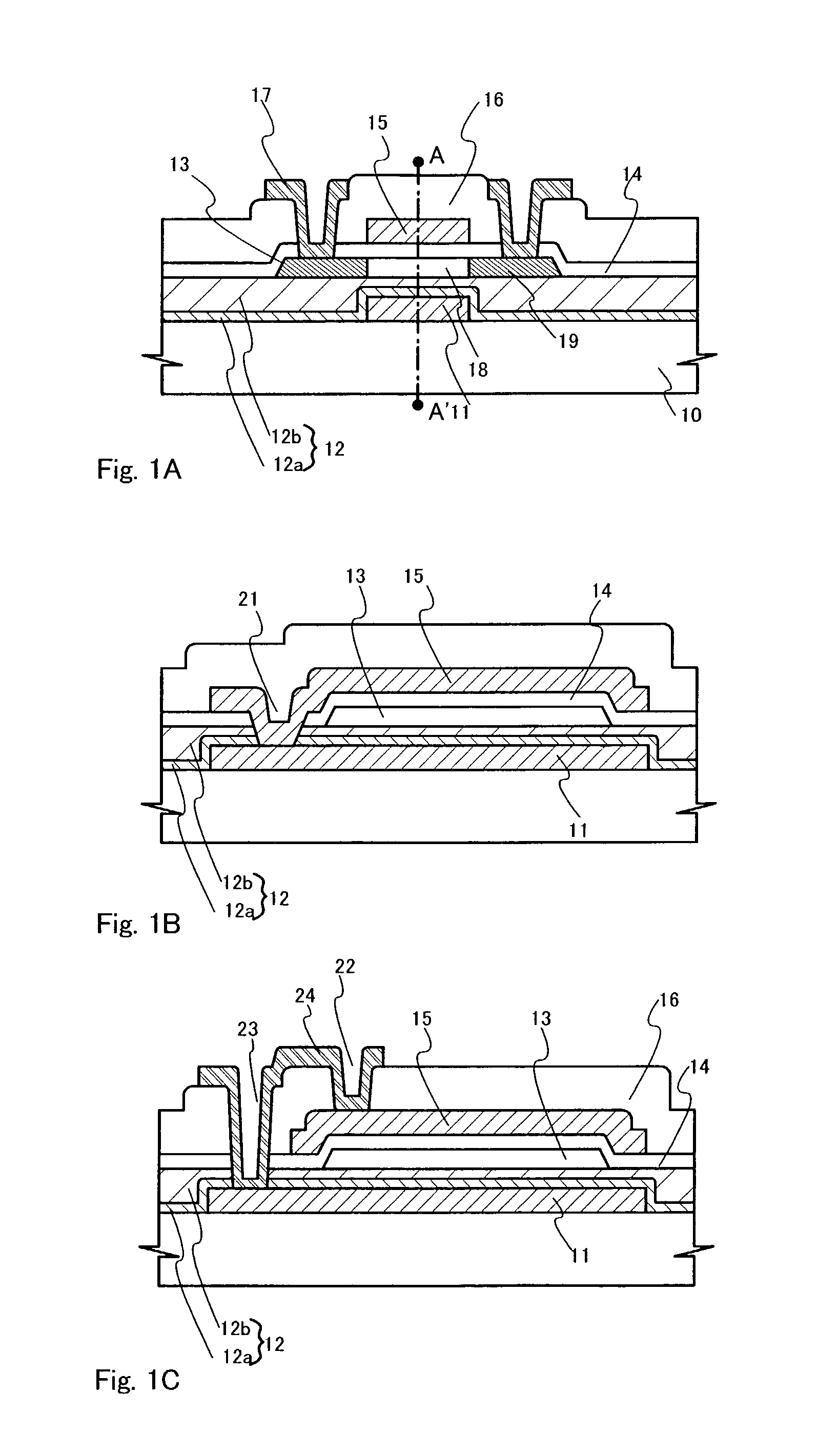
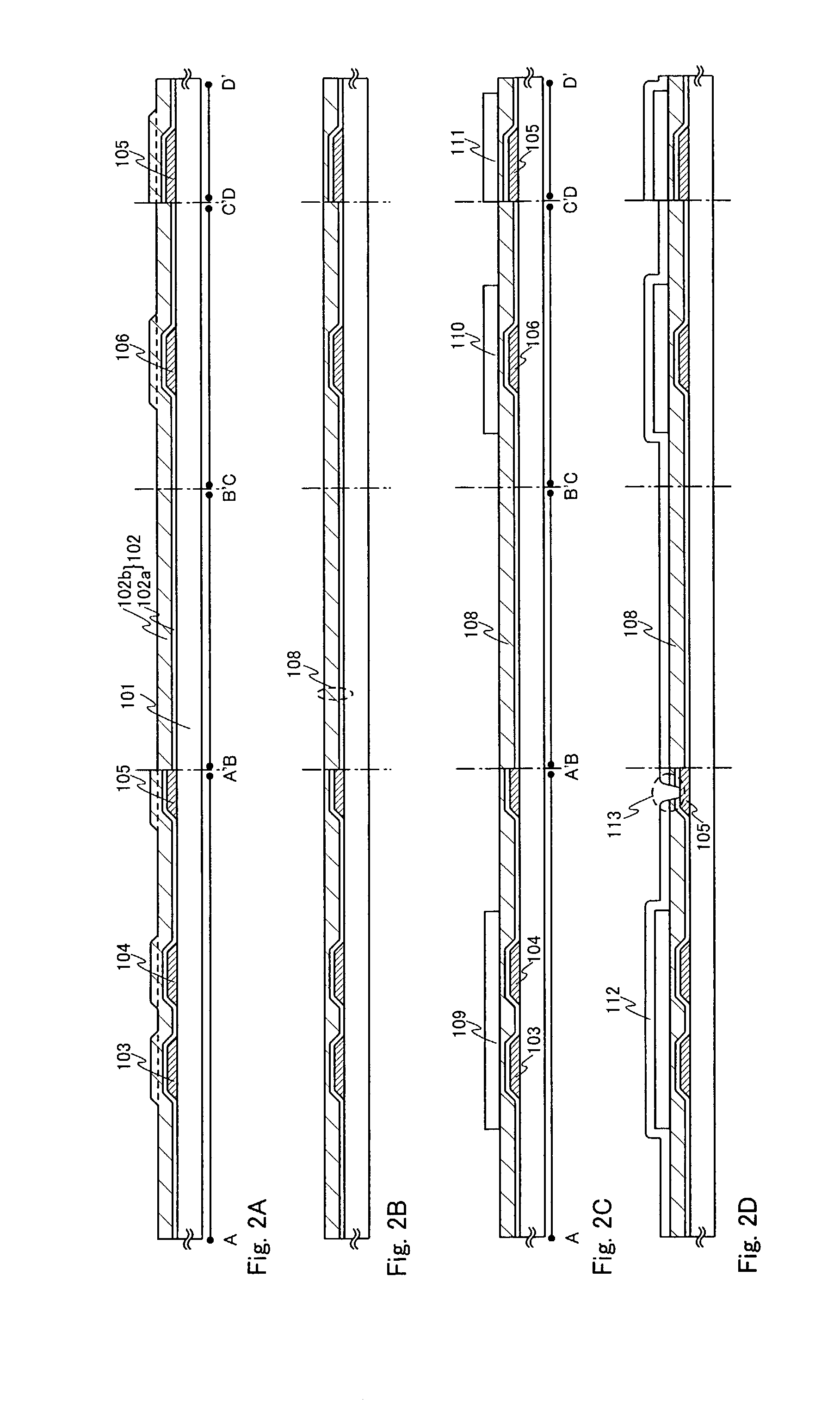
InactiveUS20030025166A1Suppress irregularityInhibit currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitLight emitting device
An object of the invention is to provide a technique for improving the characteristics of a TFT and realizing an optimum structure of the TFT for the driving conditions of a pixel section and a driving circuit by a small number of photo masks. Therefore, a light emitting device has a semiconductor film, a first electrode and a first insulating film nipped between the semiconductor film and the first electrode. Further, the light emitting device has a second electrode and a second insulating film nipped between the semiconductor film and the second electrode. The first and second electrodes are overlapped with each other through a channel forming area arranged in the semiconductor film. In the case of a TFT in which a reduction in off-electric current is considered important in comparison with an increase in on-electric current, a constant voltage (common voltage) is applied to the first electrode at any time. In the case of a TFT in which the increase in on-electric current is considered important in comparison with the reduction in off-electric current, the same voltage is applied to the first and second electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
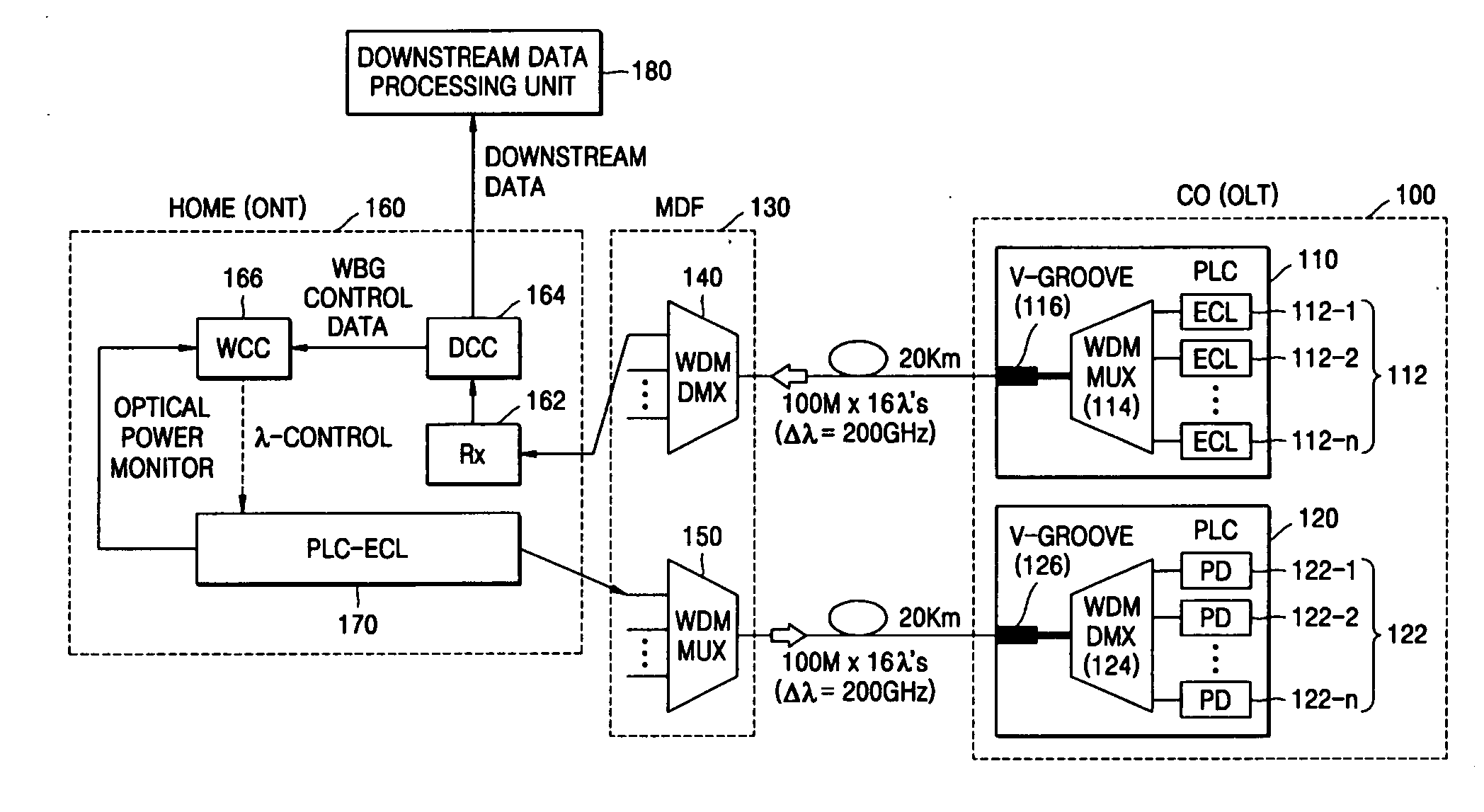
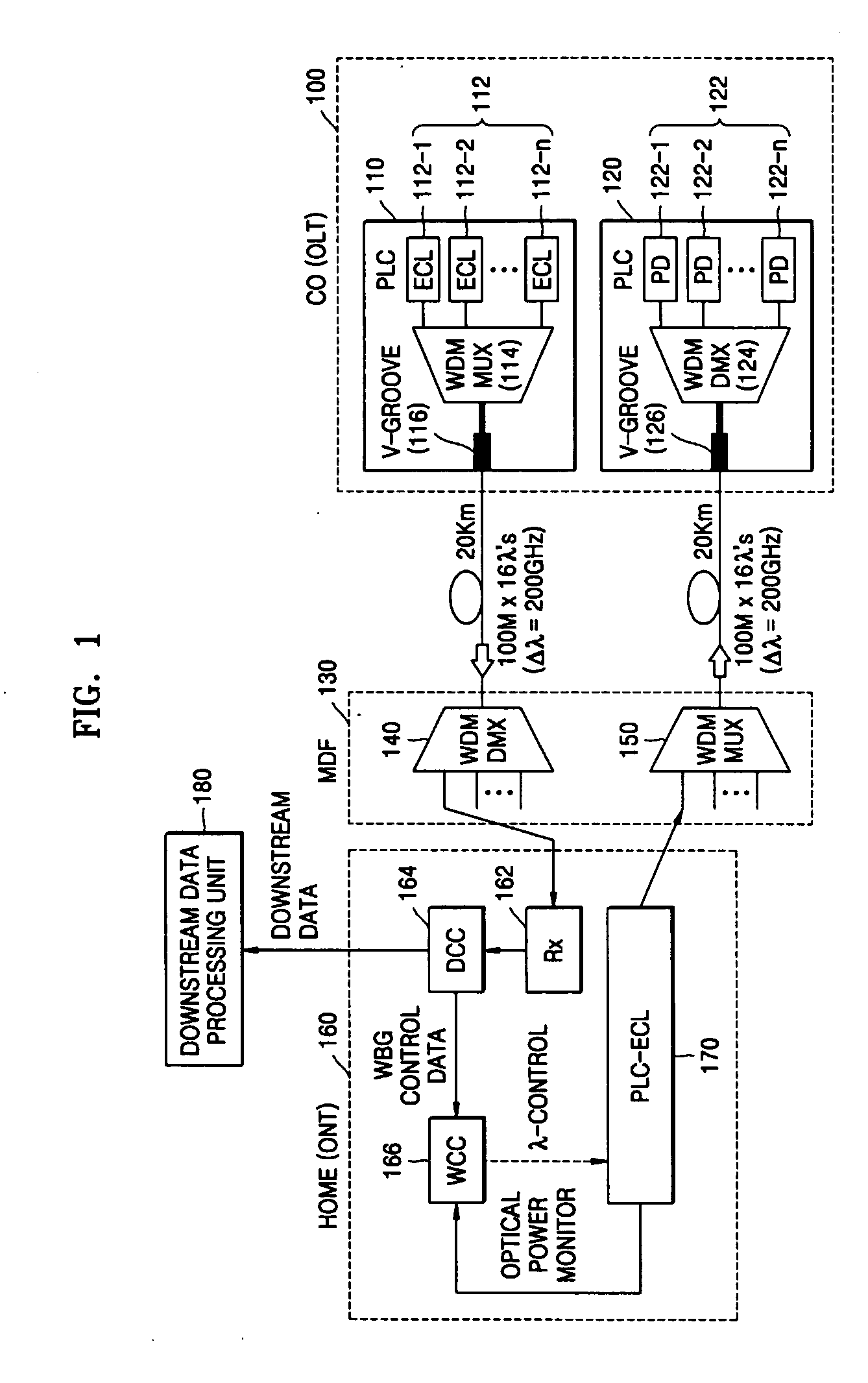
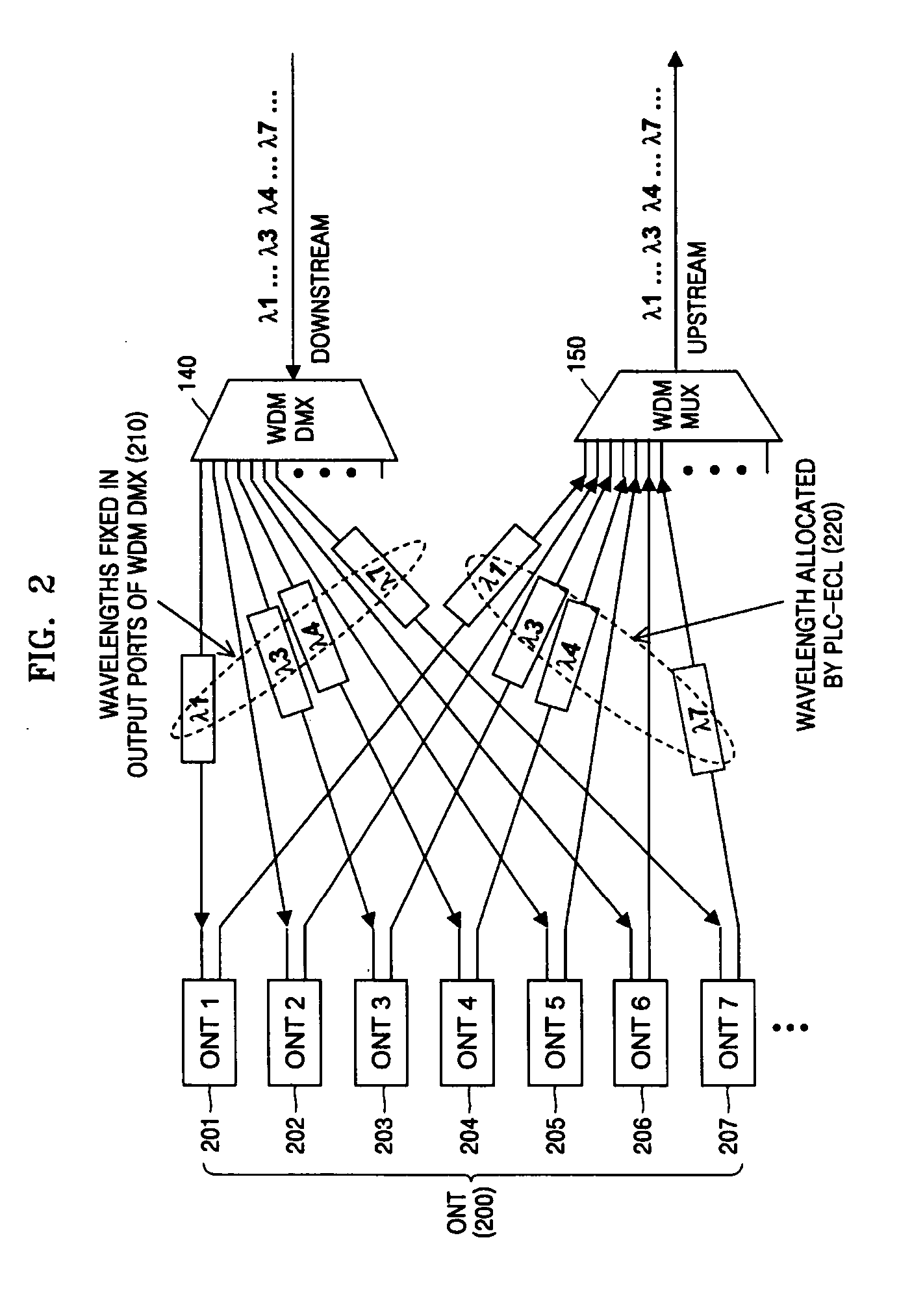
WDM-PON system based on wavelength-tunable external cavity laser light source
InactiveUS20050123300A1Easy to mass produceLow priceWavelength-division multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserLength wave
Provided is a WDM-PON system based on a wavelength-tunable ECL. A method of controlling an upstream optical wavelength of an ONT in WDM-PON system, the method comprises: determining upstream optical wavelength information of the ONT corresponding to a downstream optical wavelength predetermined to the ONT newly installed by being connected to a network; in an OLT, loading the determined upstream optical wavelength information onto the downstream optical wavelength assigned to the ONT and transmitting the loaded upstream optical wavelength information to the ONT; in the ONT, generating an upstream optical wavelength based on the upstream optical wavelength information transmitted by being loaded on the downstream optical wavelength from the OLT; and in the ONT, loading upstream data onto the generated upstream optical wavelength and transmitting the loaded upstream data to the OLT.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
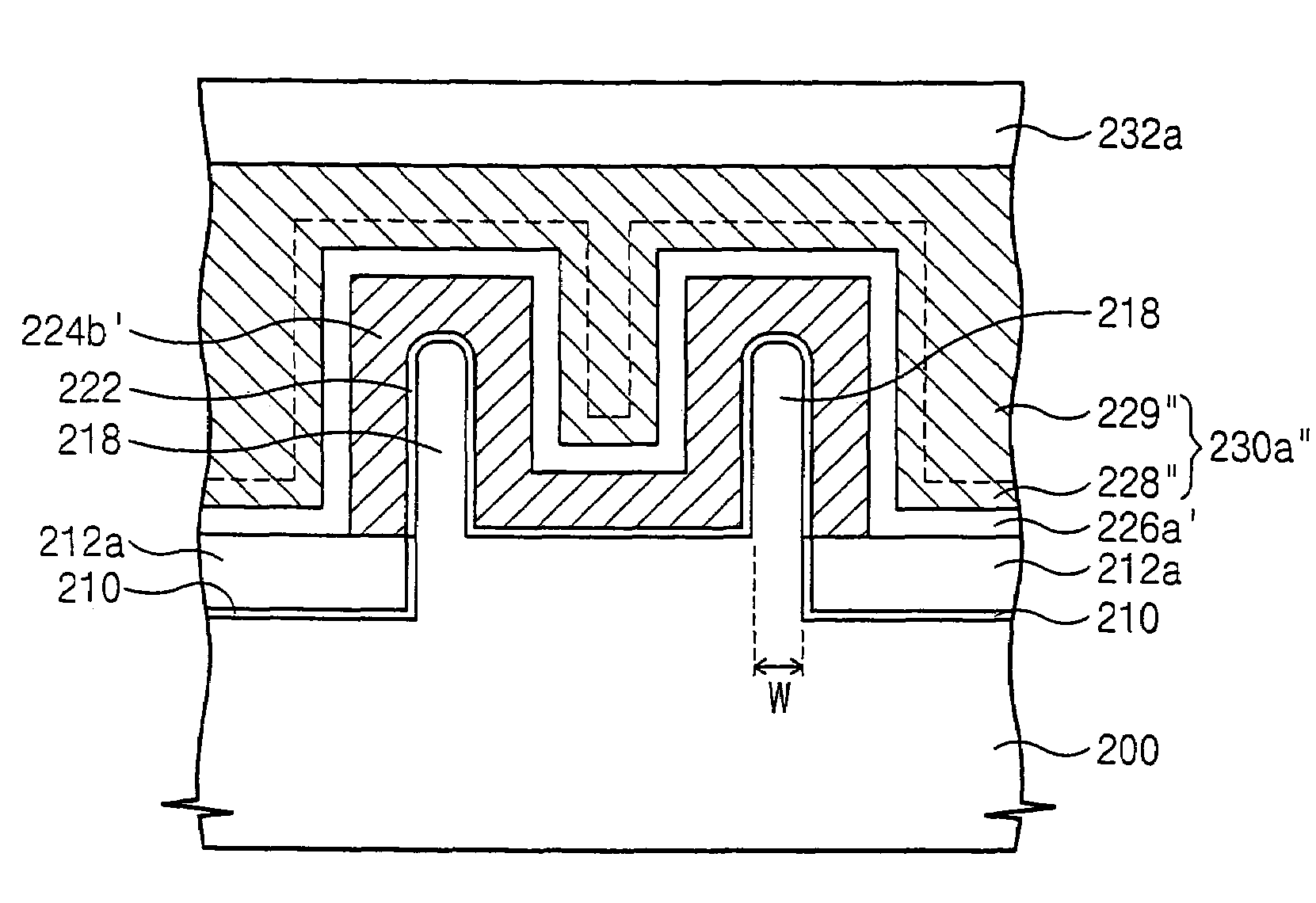
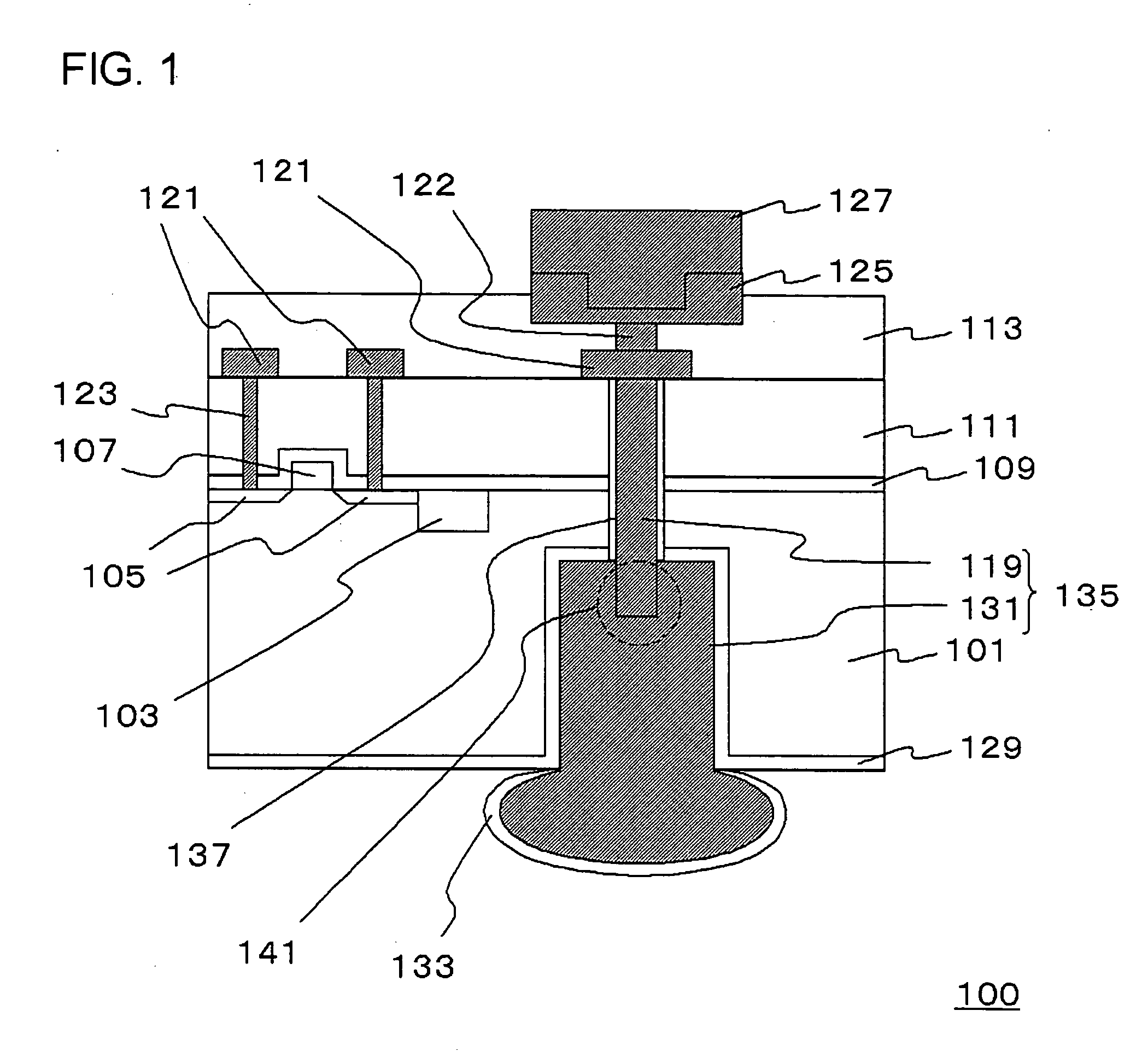
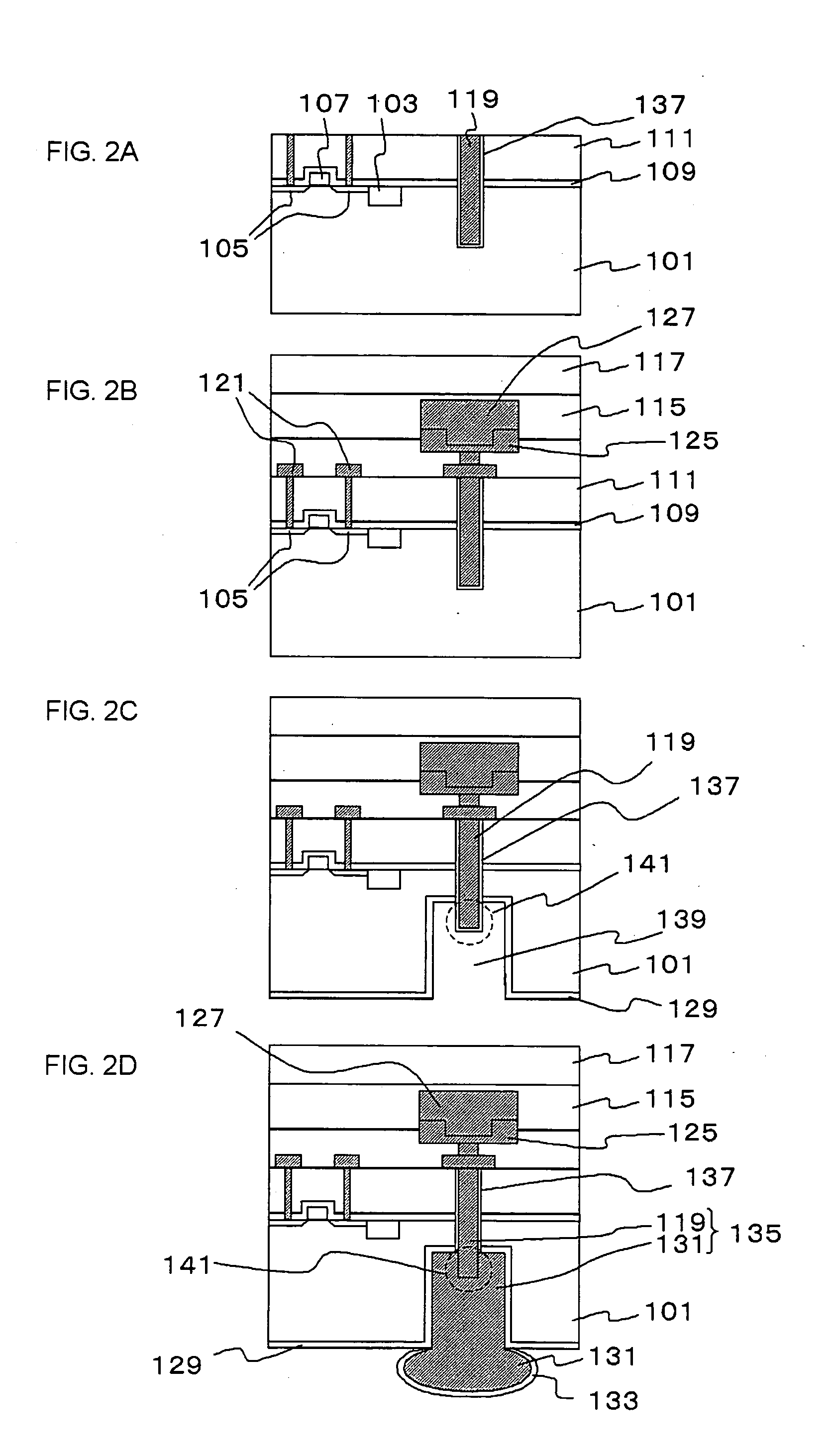
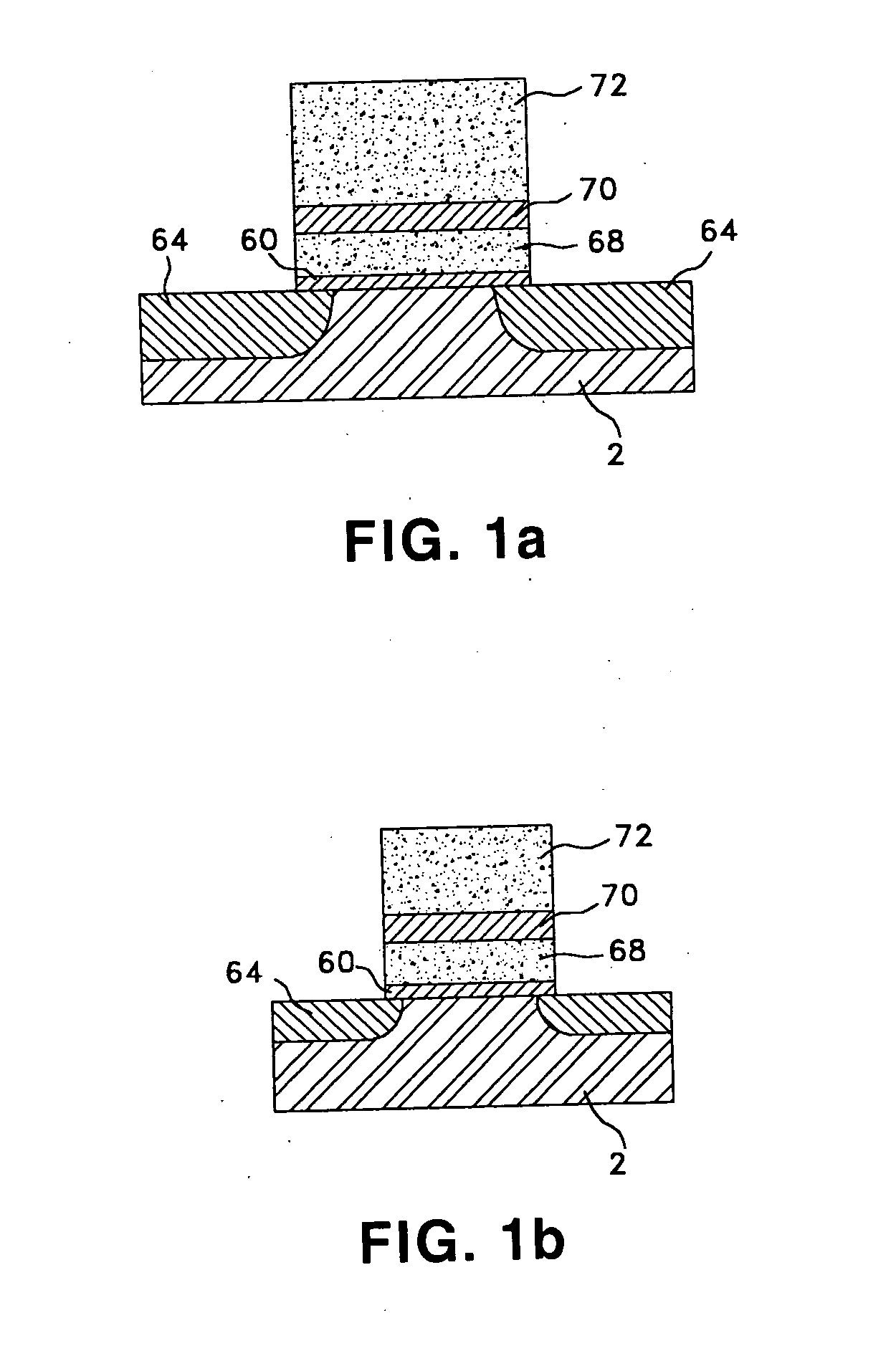
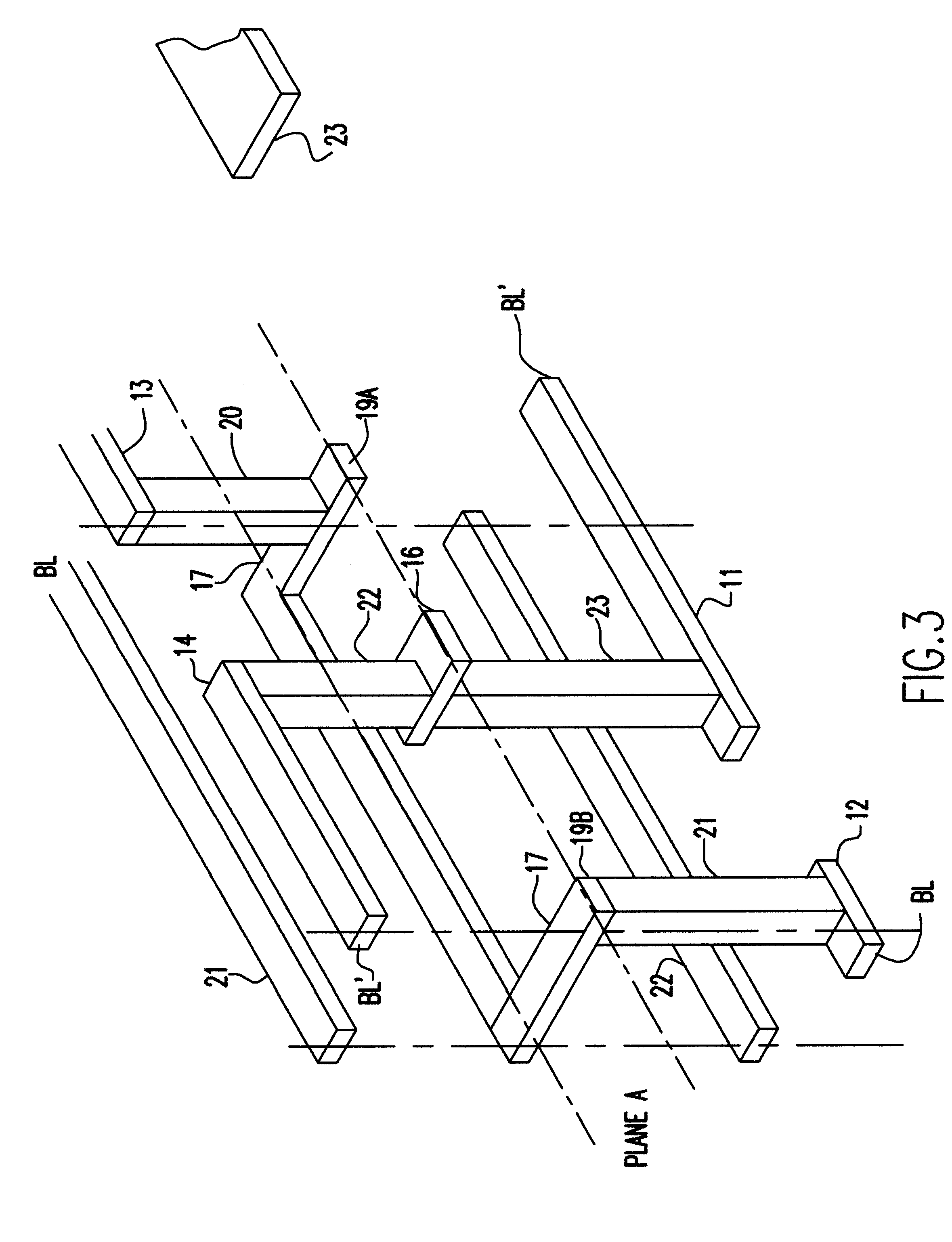
Methods of forming non-volatile memory cells including fin structures and related devices
InactiveUS20050266638A1Increase currentLow working voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerNon-volatile memory
A method of forming a non-volatile memory device may include forming a fin protruding from a substrate, forming a tunnel insulating layer on portions of the fin, and forming a floating gate on the tunnel insulting layer so that the tunnel insulating layer is between the floating gate and the fin. A dielectric layer may be formed on the floating gate so that the floating gate is between the dielectric layer and the fin, and a control gate electrode may be formed on the dielectric layer so that the dielectric layer is between the control gate and the fin. Related devices are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
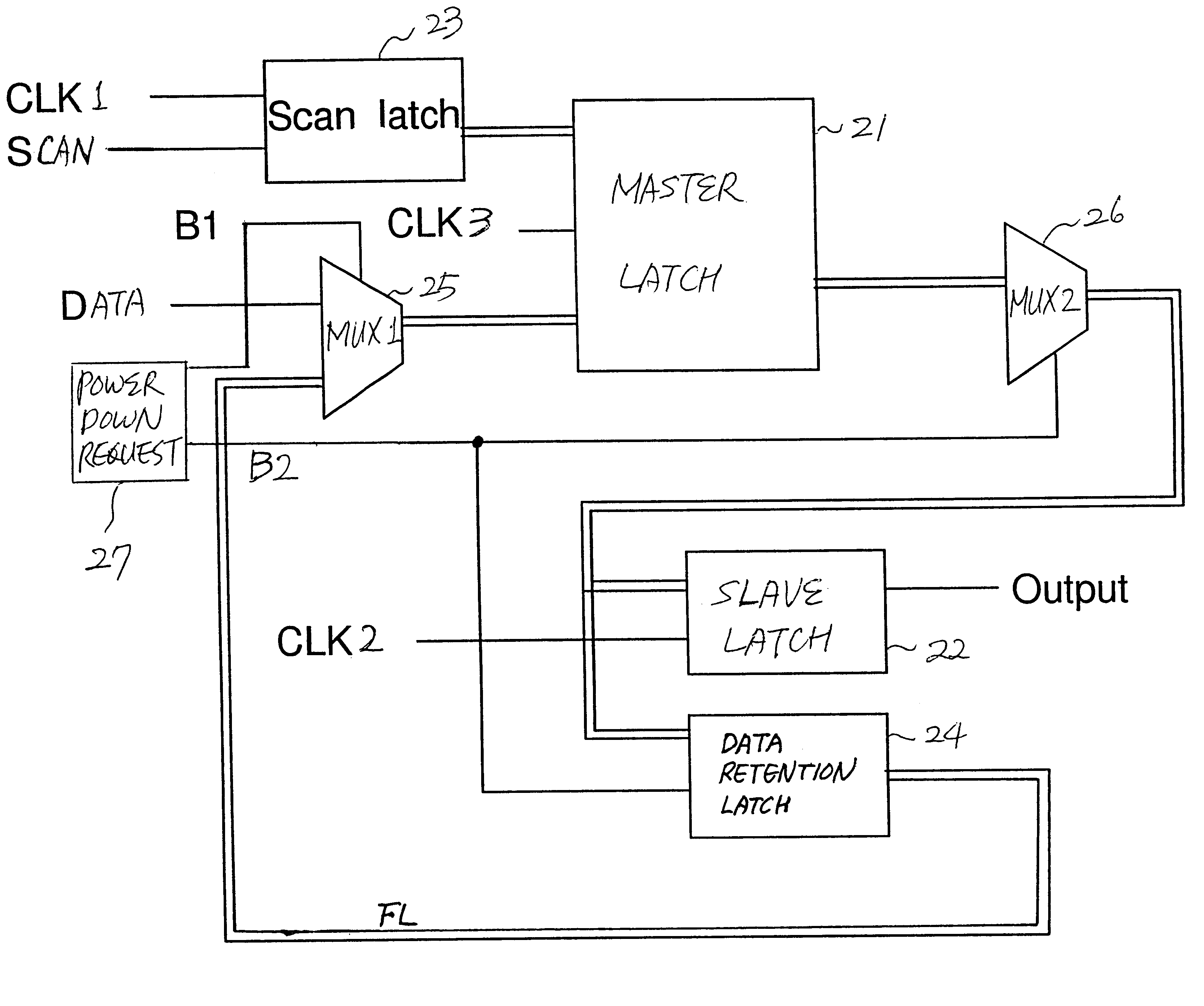
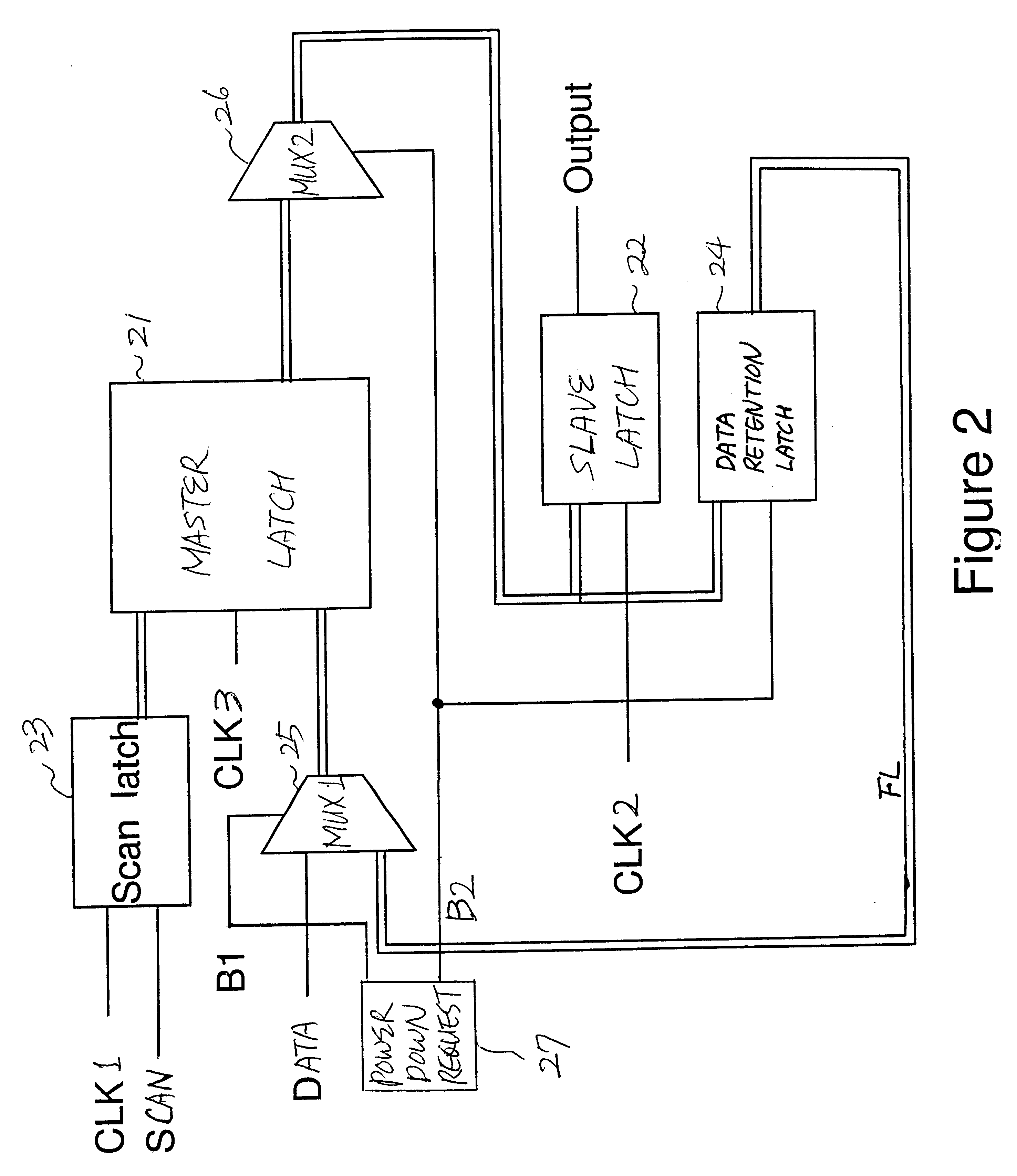
Data retention registers
InactiveUS6437623B1Performance of was minimizedSimple designDigital circuit testingElectric pulse generatorControl signalProcessor register
A data retention system has master-slave latches for holding data in an active mode; a data retention latch for preserving data read from the master latch in a sleep mode, which is connected to the master latch in parallel with the slave latch; a first multiplexer for receiving data externally provided and feedback data from the data retention latch, and selectively outputting either the data externally provided or the feedback data to the master latch in response to a first control signal; and a second multiplexer for transferring output data of the master latch to the slave latch and the data retention latch in response to a second control signal, wherein power for the data retention latch remains turned on in the sleep mode, while power for the data retention system except for the data retention latch is turned off. The data retention latch may include gate transistors controlled by the second control signal and a data holding unit having transistors for holding data transferred through the gate transistors, wherein the gate transistors and the transistors in the data holding unit have a high-threshold voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Stack-type semiconductor package, method of forming the same and electronic system including the same
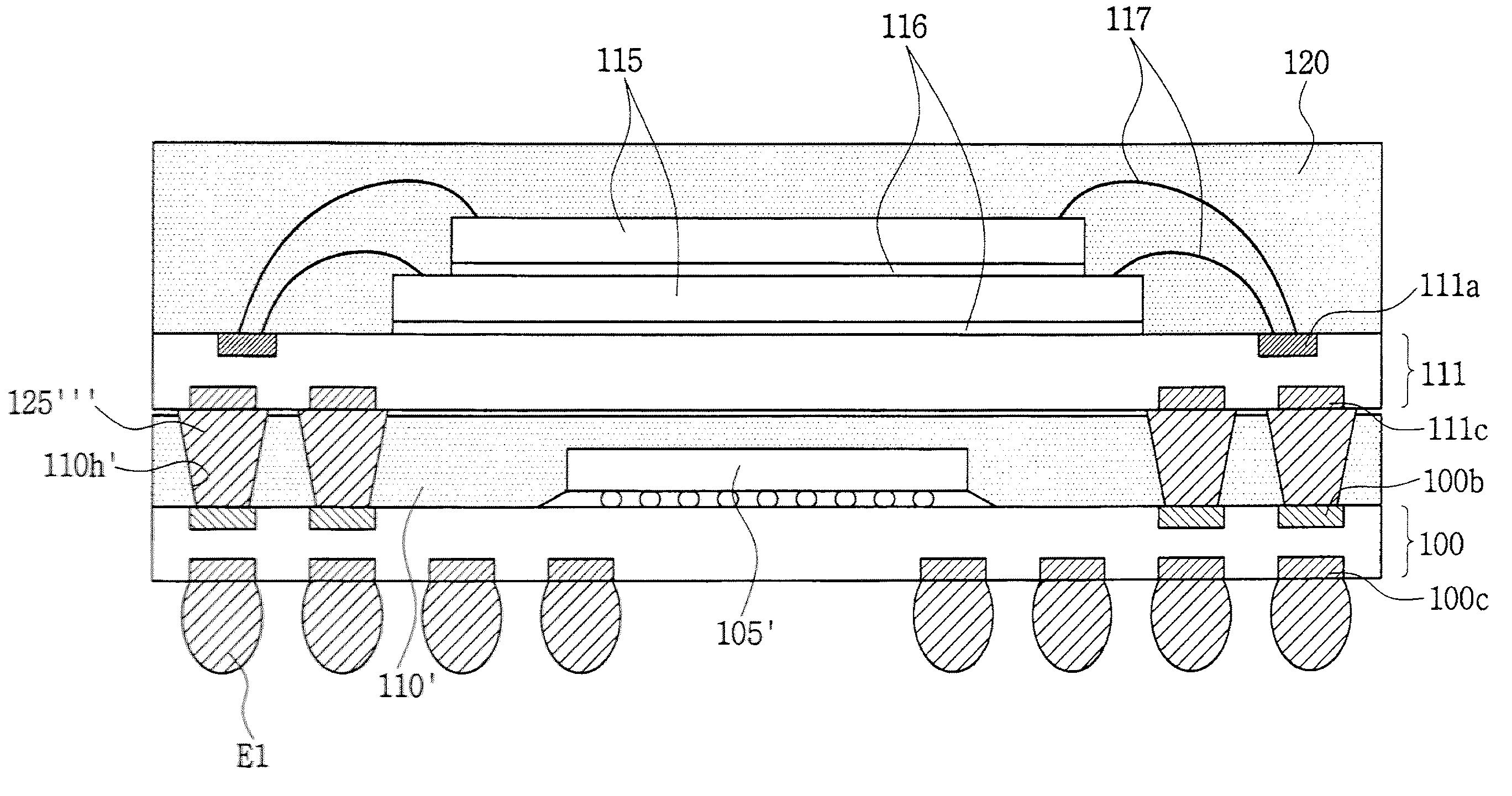
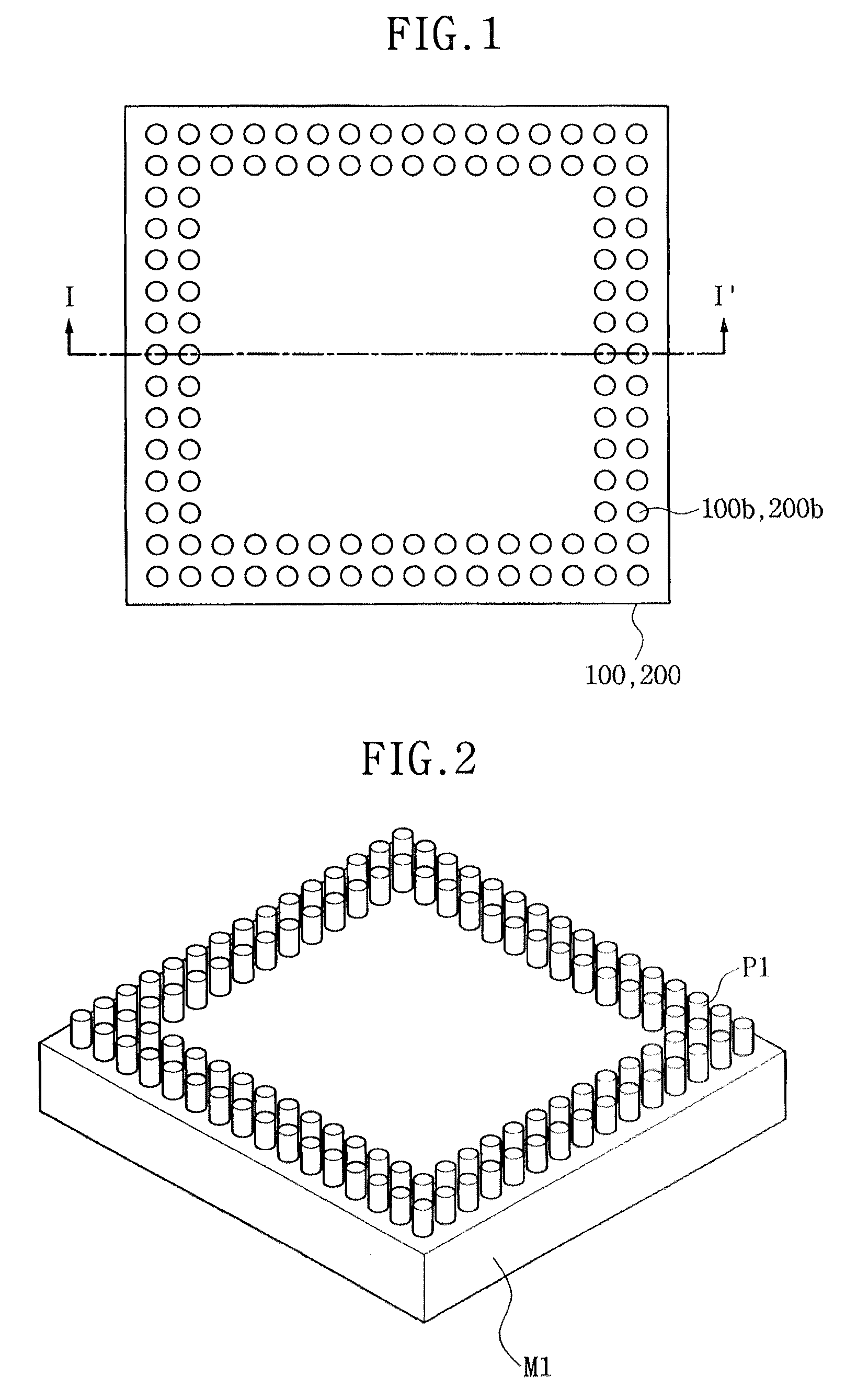
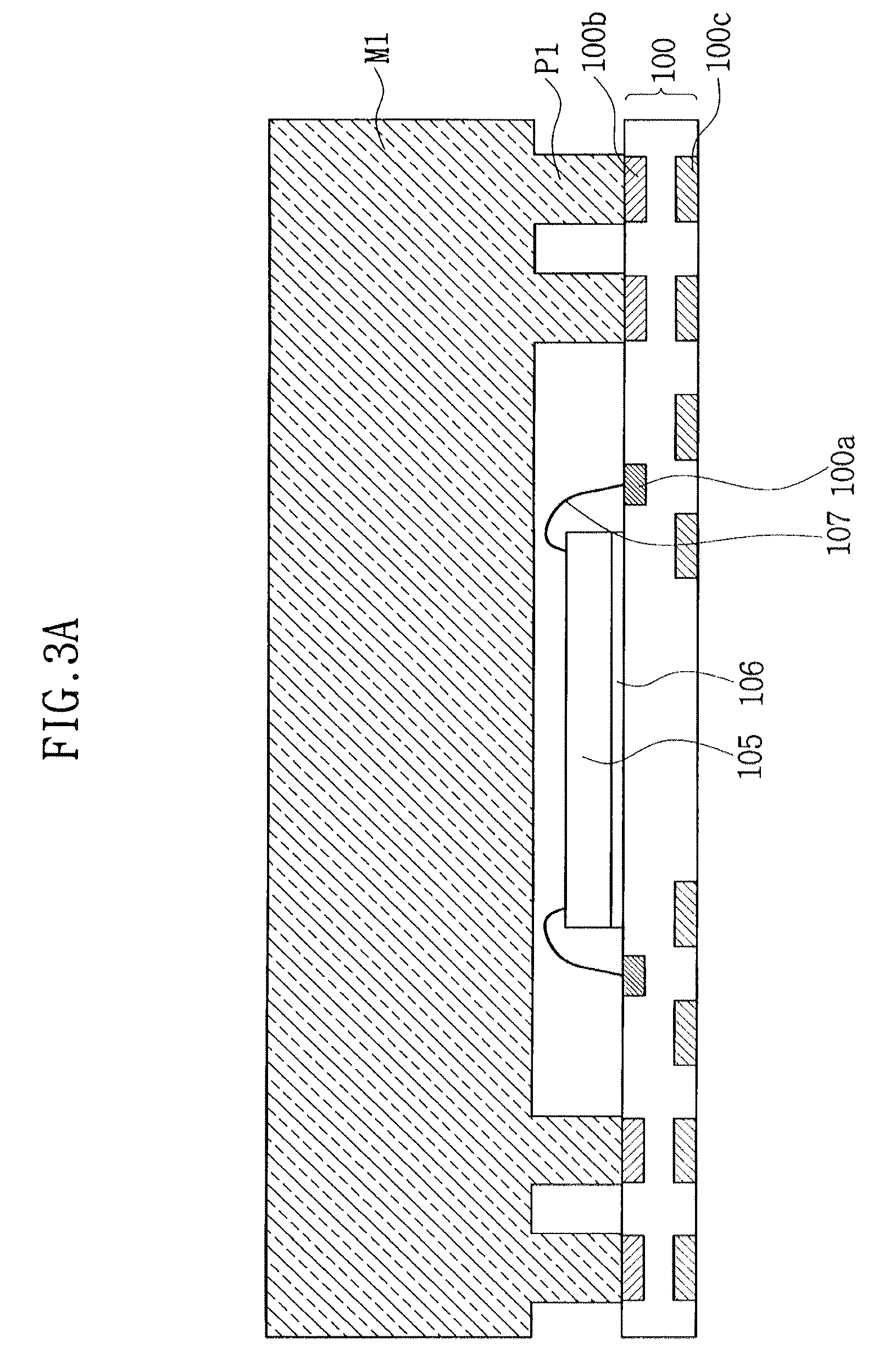
ActiveUS7851259B2Improve integration densityPreventing a bridge defectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorElectronic systems
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
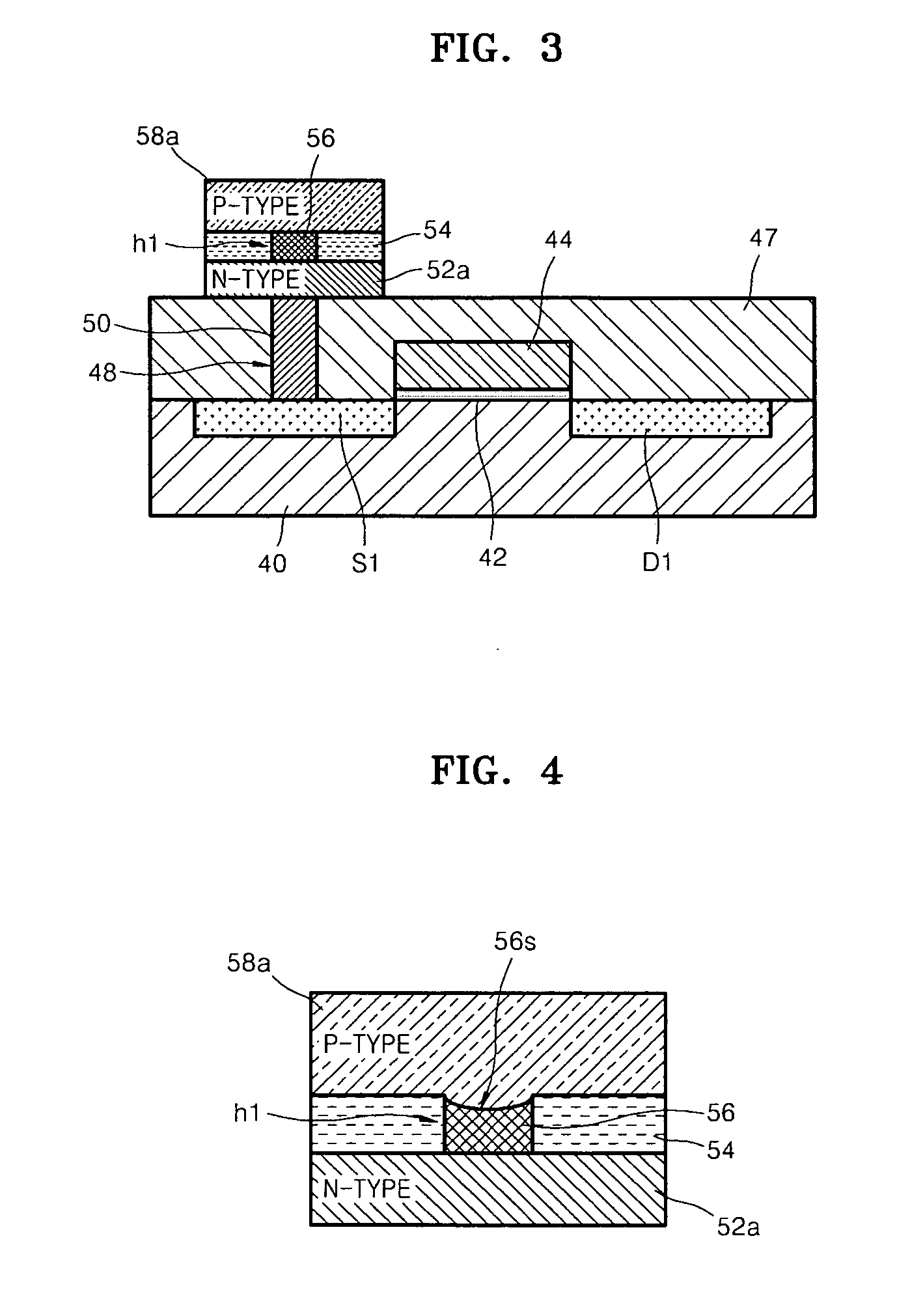
SONOS memory device having side gate stacks and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6946703B2Improve integration densityHigh density storageTransistorNanoinformaticsGate stackSilicon oxide
In a silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) memory device and a method of manufacturing the same, a SONOS memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, an insulating layer deposited on the semiconductor substrate, an active layer formed on a predetermined region of the insulating layer and divided into a source region, a drain region, and a channel region, a first side gate stack formed at a first side of the channel region, and a second side gate stack formed at a second side of the channel region opposite the first side of the channel region. In the SONOS memory device, at least two bits of data may be stored in each SONOS memory device, thereby allowing the integration density of the semiconductor memory device to be increased without increasing an area thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Double-gate flash memory device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20050145926A1Improve featuresImprove integration densityTransistorNanoinformaticsFloating body effectEngineering
The conventional flash memory device is fabricated by the MOS processing technology on a bulk substrate and has a similar configuration to an MOS device. While the conventional CMOS device has a superior scaling down characteristic, the scaling down characteristic of a flash memory device is poor due to the inability to reduce the thickness below 7 nm or 8 nm for the tunneling oxide film where the charges in the channel are tunneled into the floating electrode through the tunneling oxide. In order to resolve this problem, the present invention, instead of a SOI wafer, uses a cheaper bulk silicon wafer with lower defect density. A wall shape Fin active region where the channel and the source / drain are formed is connected to the bulk silicon substrate by which floating body effect and heat conduction problem are resolved. a flash memory device is fabricated by forming a tunneling oxide film on side surfaces of the Fin active and a floating (storage) electrode where the charges could be stored. The above structure has a superior scaling down characteristic and enhanced memory performance due to a double-gate flash memory device structure.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Semiconductor device comprising through-electrode interconnect
ActiveUS7541677B2Improve integration densitySuitable for miniaturizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSilicon
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090278208A1Highly integratedReduce impurityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:CHANG DONG RYUL
Microwave multi-chip packaging structure using silicon through hole and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102723306AReduce lossIncrease packing densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSystem in package
The invention provides a microwave multi-chip packaging structure using a silicon through hole and a manufacture method thereof. The method uses a temperature safety valve (TSV) to achieve two-sided integrated system-stage packaging structure, when a monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC) chip needs integrating, a user does not need embed a substrate before wiring, and performance, reliability and rate of finished products of the packaging structure are improved. Simultaneously, processes such as injection, corrosion, release and high temperature annealing in a manufacture process can be used before integration of the MMIC, and components needing special processes can be assembled and integrated in advance on the other side of the substrate. Therefore, the substrate comprising active and passive devices, micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), photoelectric devices and the like can be conveniently manufactured in a large scale before integration of the MMIC, and the manufacture method is simple in process, reduces cost, and is advanced and reliable at present.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Front-and-back electrically conductive substrate
InactiveUS7579553B2Improve integration densityPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrically conductiveAnisotropy
A front-and-back electrically conductive substrate includes a plurality of posts composed of a material that can be anisotropically etched and having an electrically conductive portion that has at least a first surface and a second surface that communicate with each other, and an insulative substrate that supports the plurality of posts.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
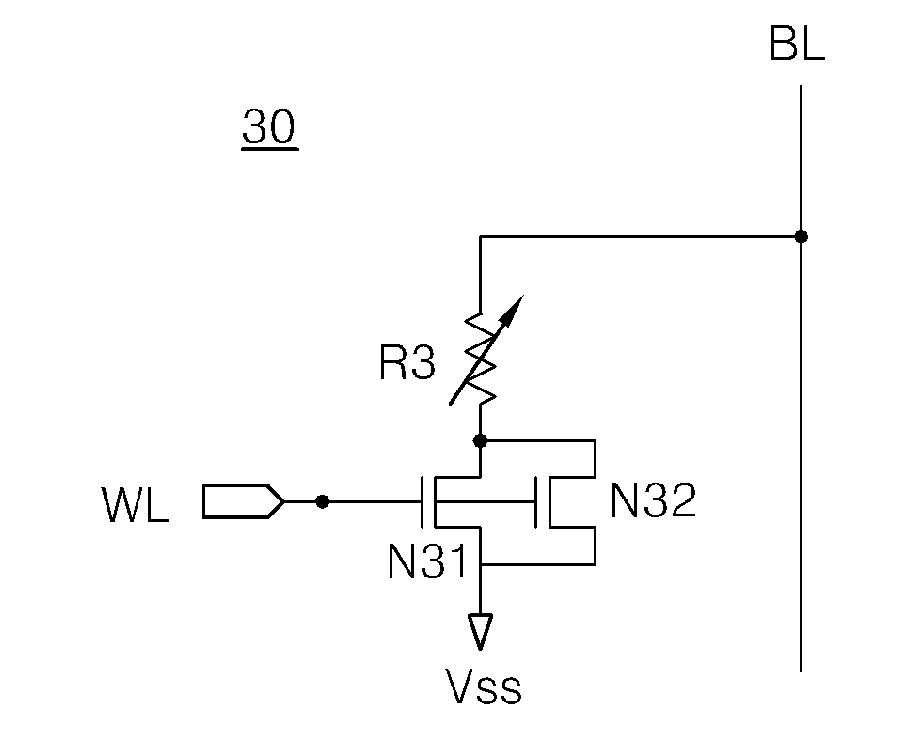
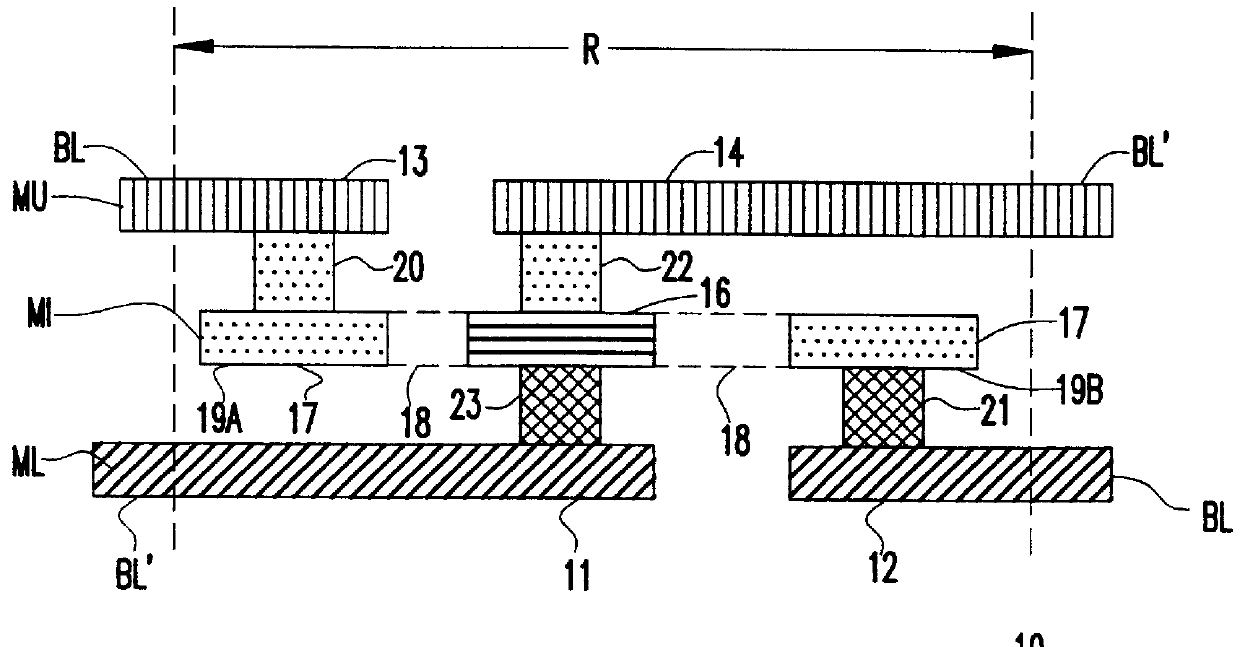
Method for simultaneously forming a storage-capacitor electrode and interconnect
InactiveUS6124199AImprove integration densityLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBit lineDram memory
A DRAM memory cell array includes a wiring layer formed at a storage-capacitor level of the cell for establishing a flipped connection of complementary bit lines, or for connecting support circuits in a DRAM cell array. The wiring layer includes a lower capacitor electrode and upper capacitor electrode which are formed simultaneously with respective plates of a storage capacitor. Both capacitor electrodes may be used to form distinct interconnections within a DRAM cell array.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
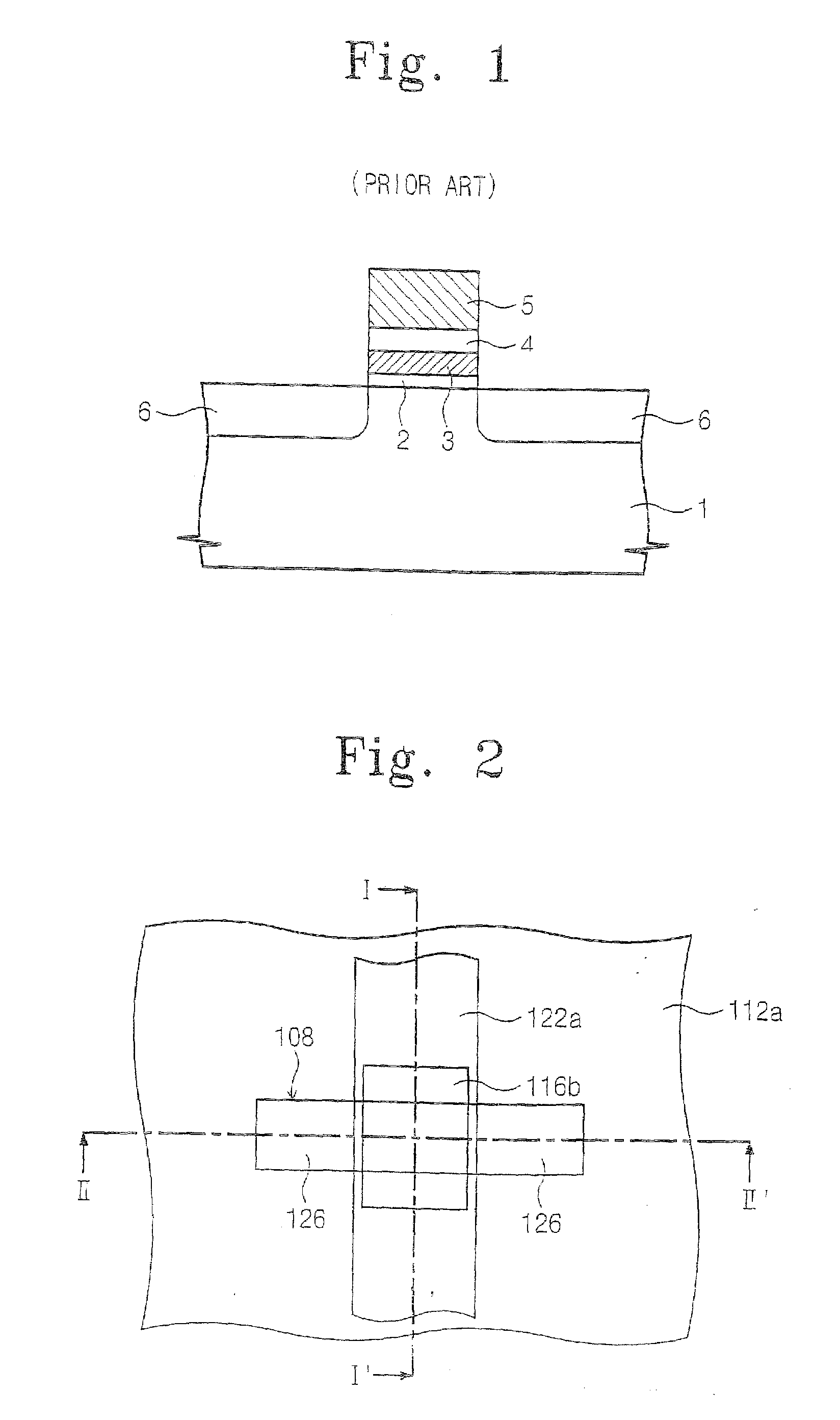
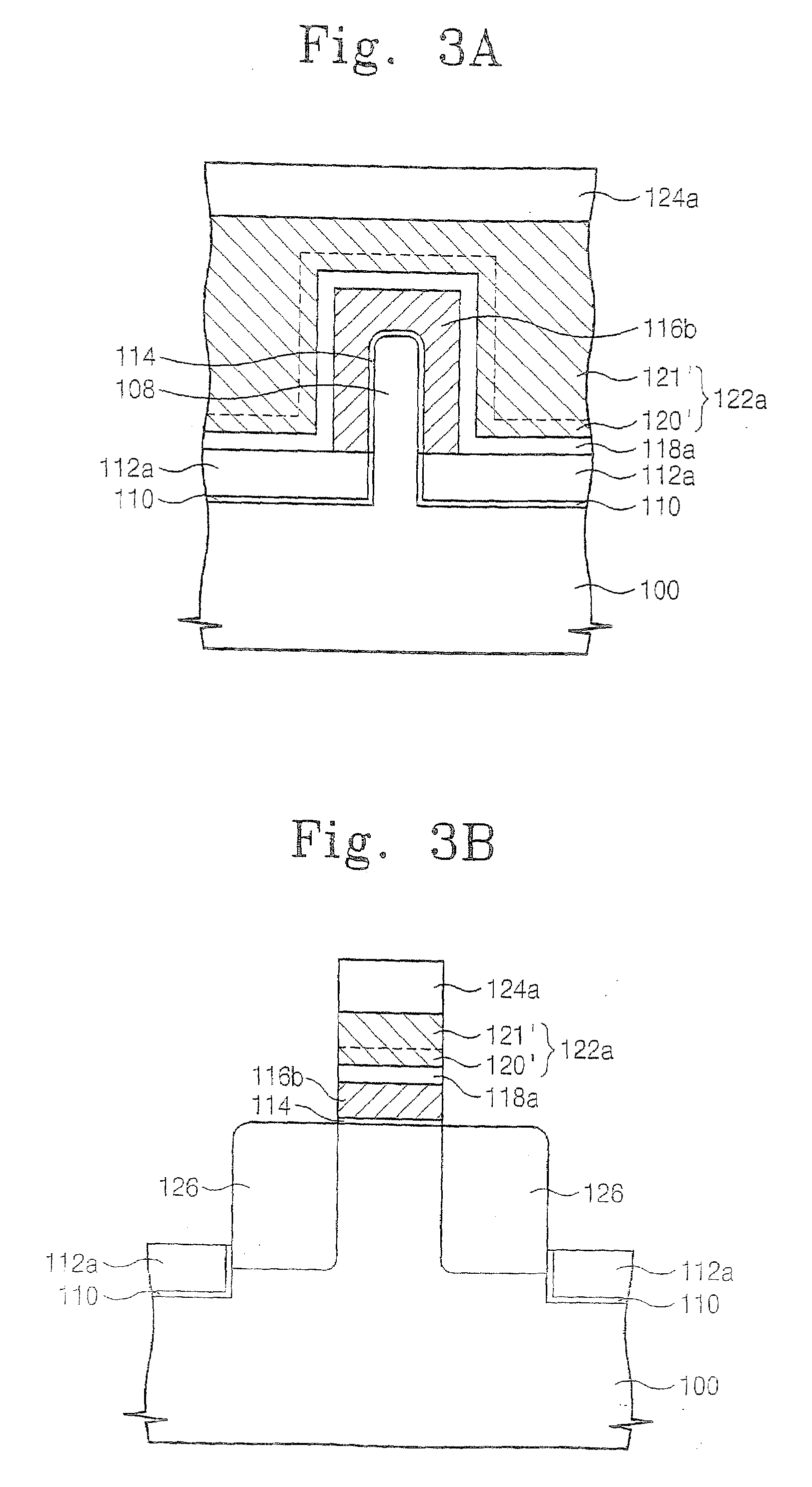
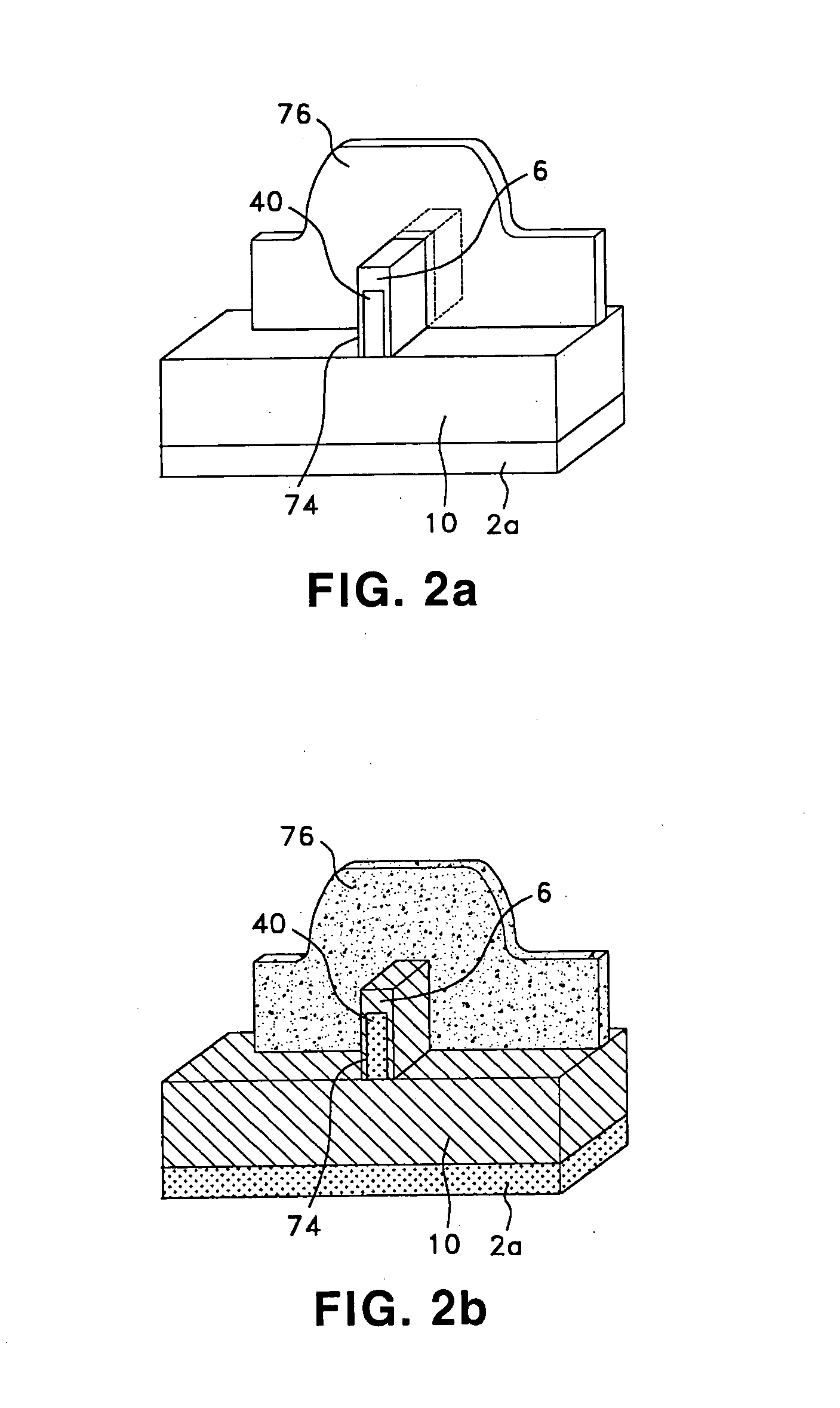
Storage node, phase change memory device and methods of operating and fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070108488A1Improve integration densityReduce the amount of solutionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermoelectric materialsPhase-change memory
A storage node, a phase change memory device, and methods of operating and fabricating the same are provided. The storage node may include a lower electrode, a phase change layer on the lower electrode and an upper electrode on the phase change layer, and the lower electrode and the upper electrode may be composed of thermoelectric materials having a melting point higher than that of the phase change layer, and having different conductivity types. An upper surface of the lower electrode may have a recessed shape, and a lower electrode contact layer may be provided between the lower electrode and the phase change layer. A thickness of the phase change layer may be about 100 nm or less, and the lower electrode may be composed of an n-type thermoelectric material, and the upper electrode may be composed of a p-type thermoelectric material, or they may be composed on the contrary to the above. Seeback coefficients of the lower electrode, the phase change layer, and the upper electrode may be different from each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
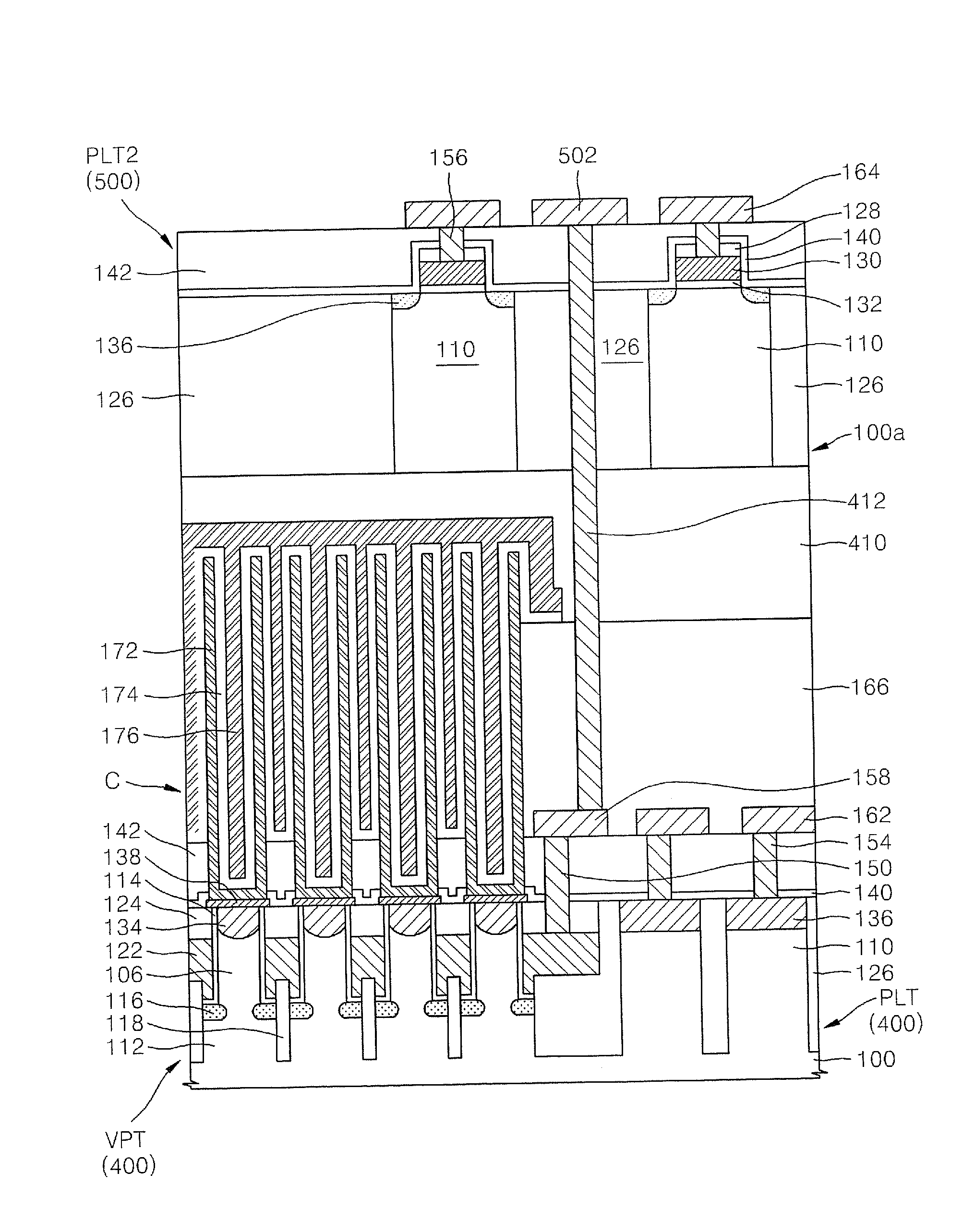
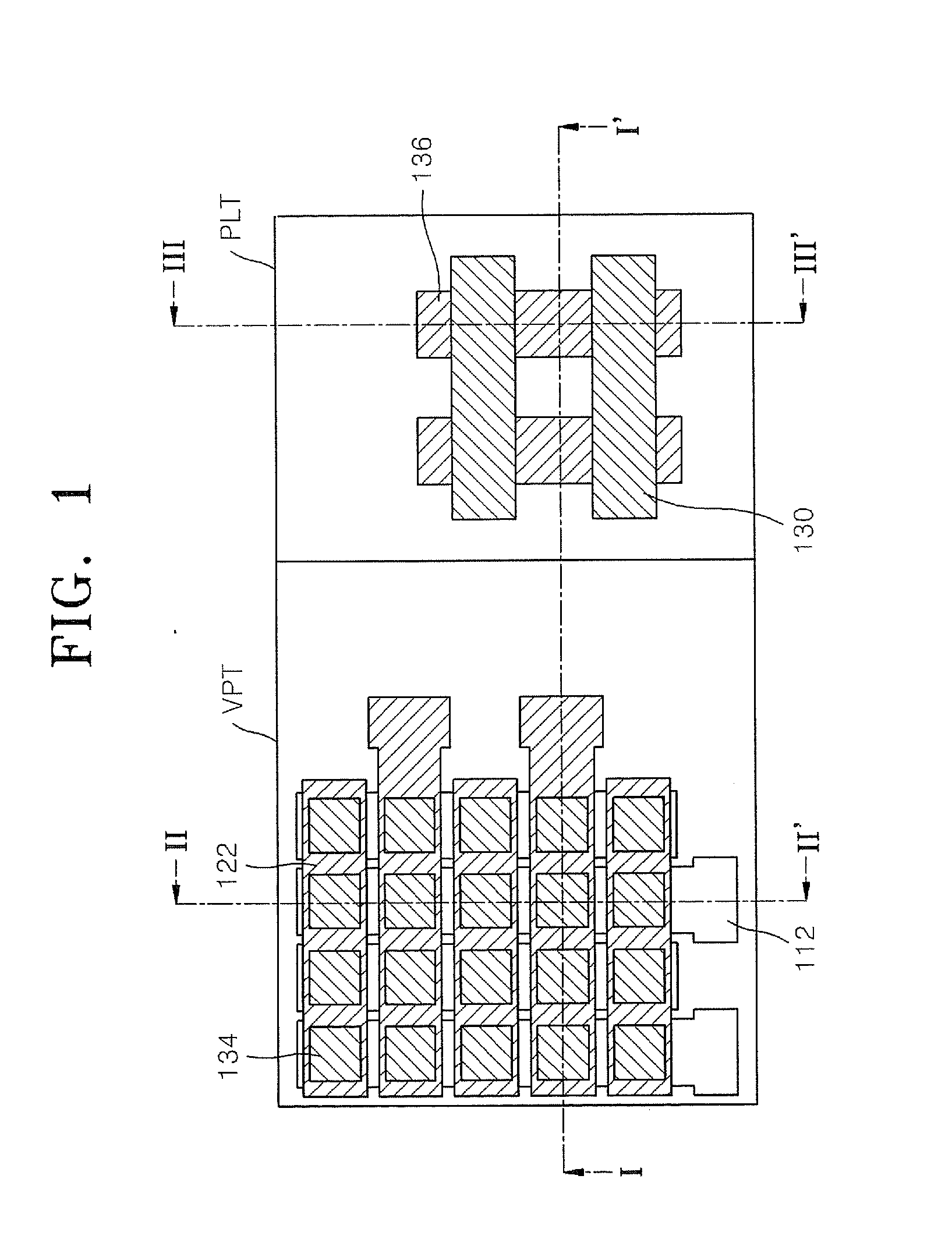
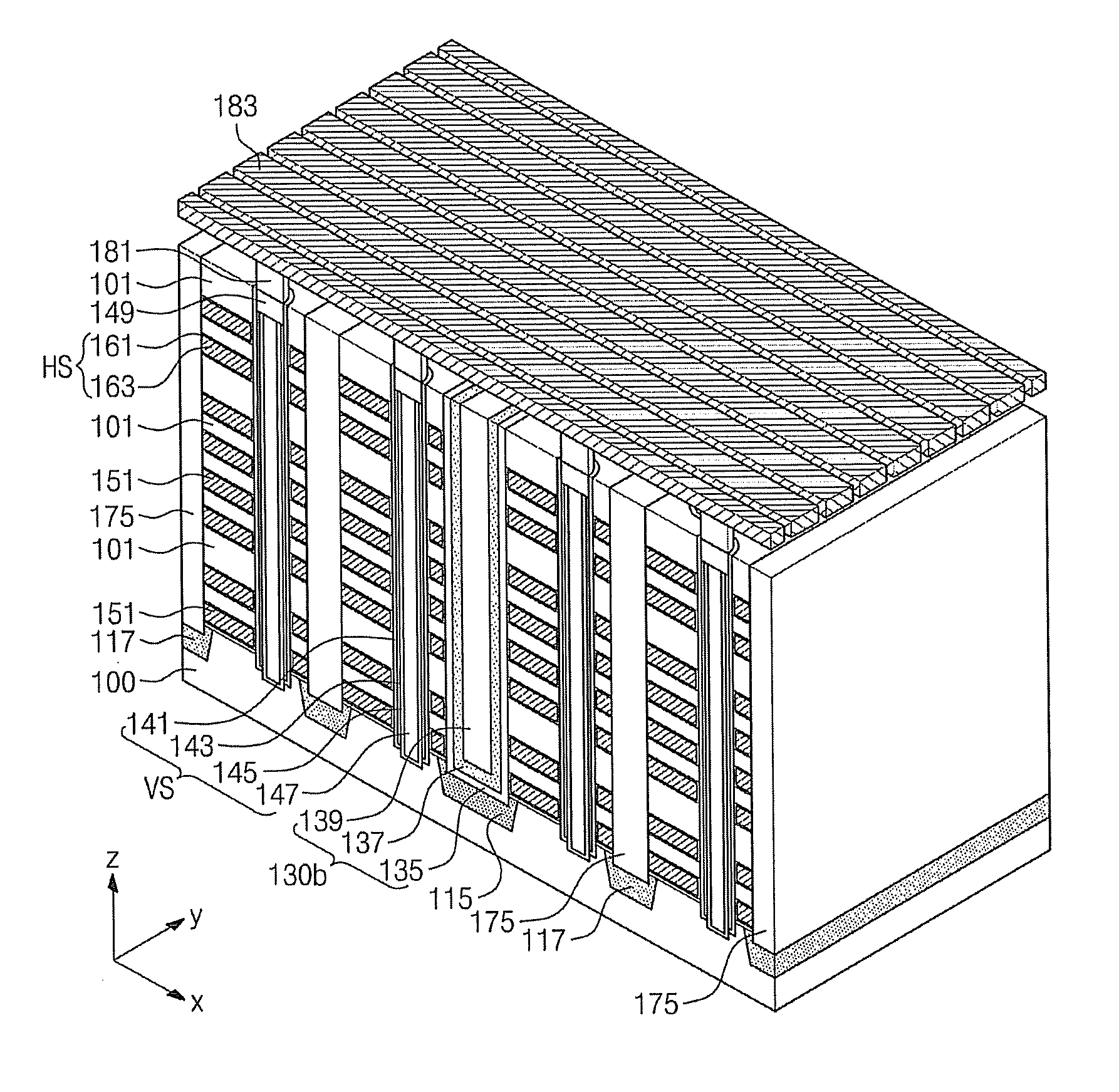
Methods of fabricating three-dimensional semiconductor memory devices
ActiveUS20120295409A1Improve integration densityImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Methods of fabricating three-dimensional semiconductor memory devices including forming a plate stack structure with insulating layers and sacrificial layers stacked alternatingly on a substrate, forming first and second trenches separating the plate stack structure into a plurality of mold structures, the first trench being between the second trenches, forming first vertical insulating separators in the first and second trenches, forming semiconductor patterns penetrating the mold structure and being spaced apart from the first and second trenches, removing the first vertical insulating separator from the second trench to expose the sacrificial layers, removing the sacrificial layers exposed by the second trench to form recess regions partially exposing the semiconductor patterns and the first vertical insulating separator, and forming conductive patterns in the recess regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods of forming multi-level cell of semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20100093130A1Improve integration densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
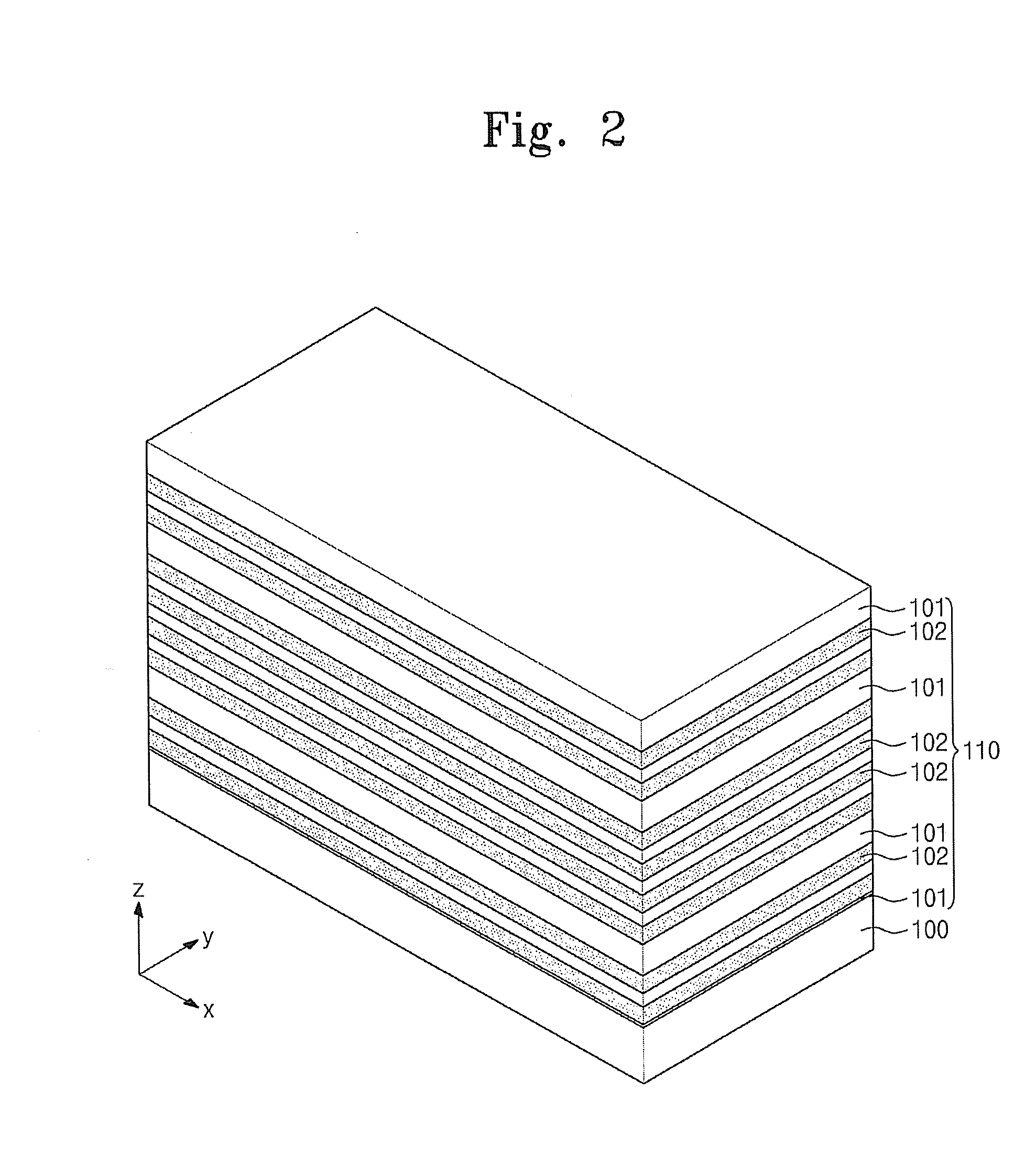
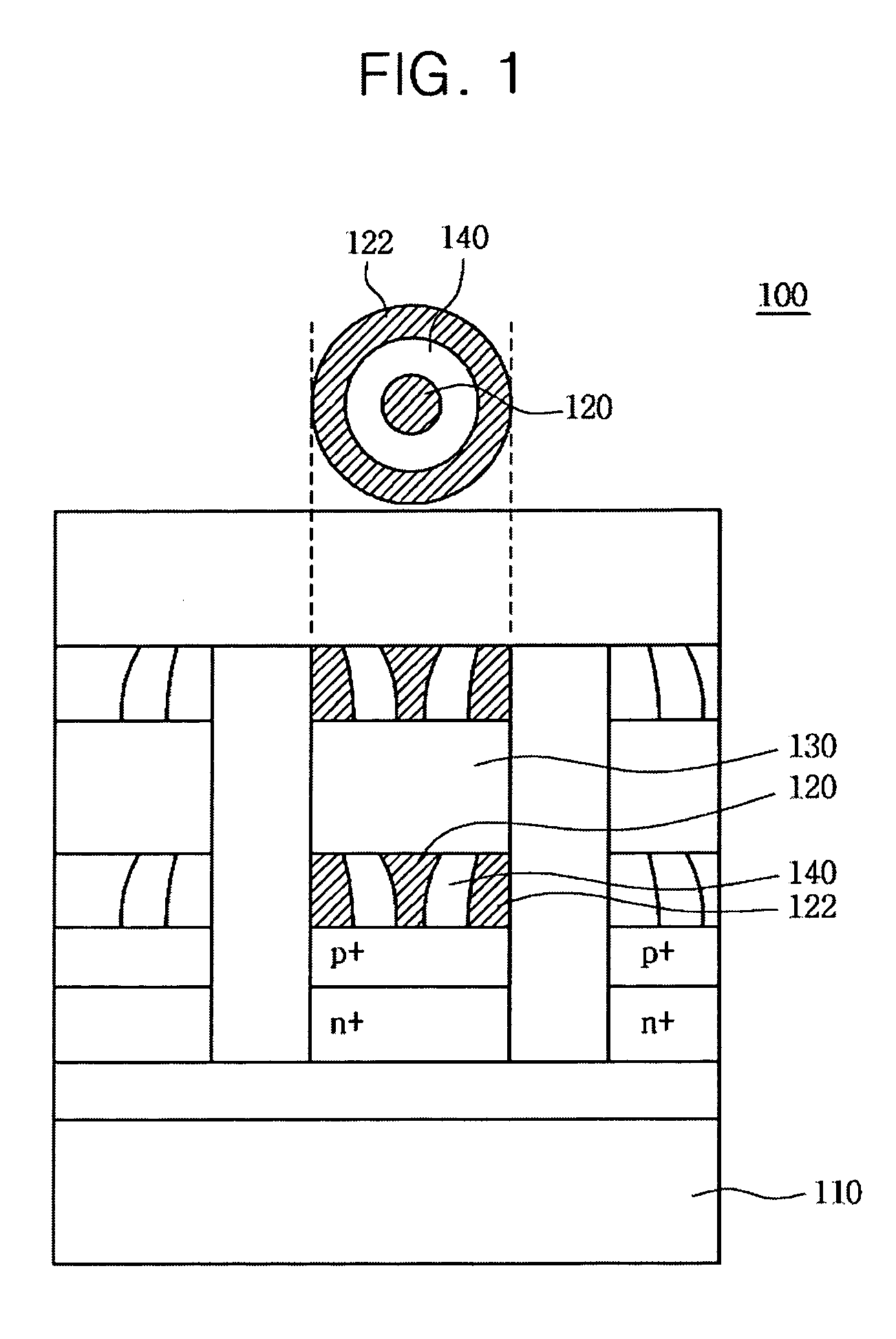
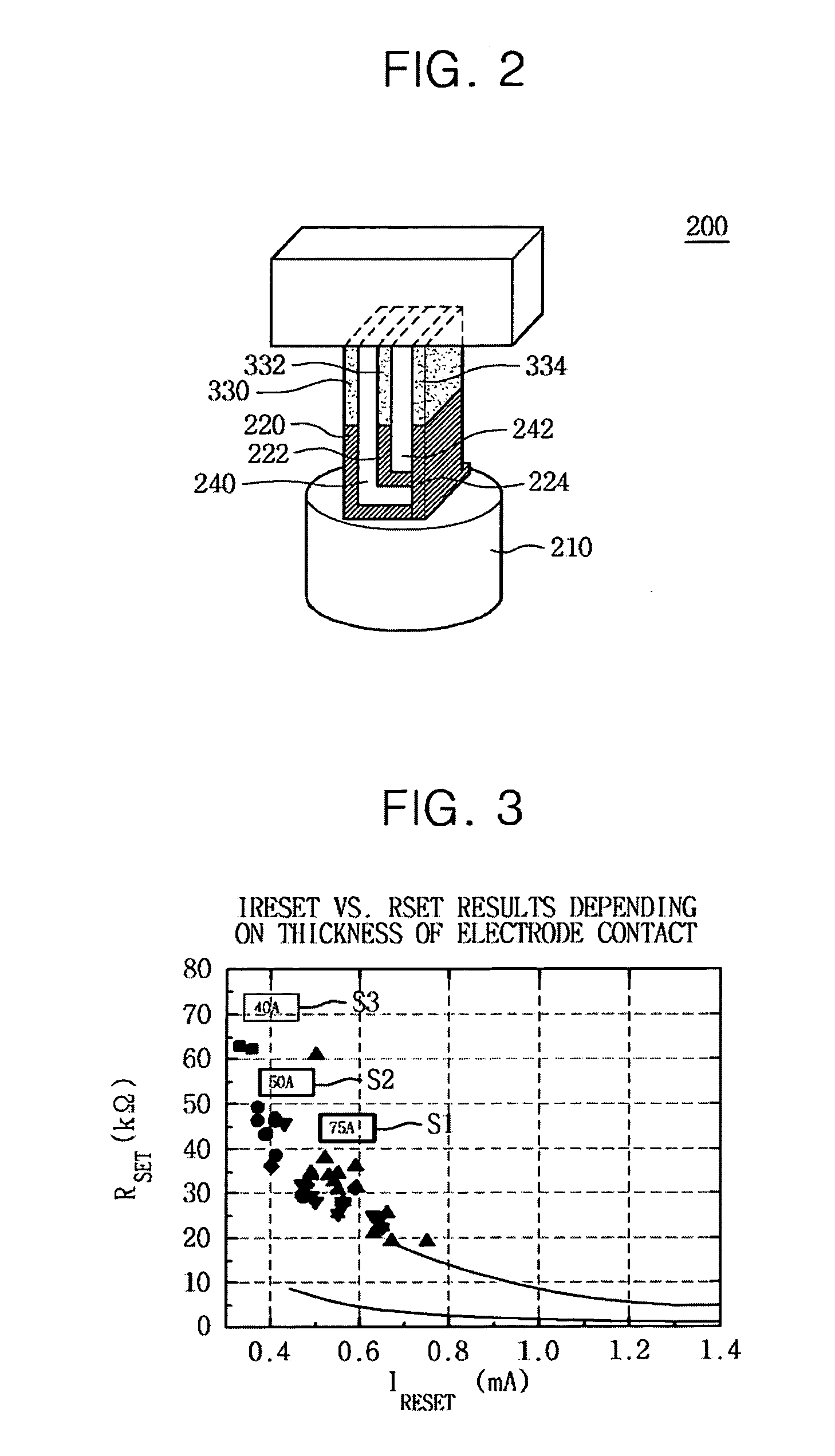
Provided is a method of forming a semiconductor memory cell in which in order to store two bits or more data in a memory cell, three or more bottom electrode contacts (BECs) and phase-change materials (GST) have a parallel structure on a single contact plug (CP) and set resistances are changed depending on thicknesses (S), lengths (L) or resistivities (ρ) of the three or more bottom electrode contacts, so that a reset resistance and three different set resistances enable data other than in set and reset states to be stored. Also, a method of forming a memory cell in which three or more phase-change materials (GST) have a parallel structure on a single bottom electrode contact, and the phase-change materials have different set resistances depending on composition ratio or type, so that four or more different resistances can be implemented is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
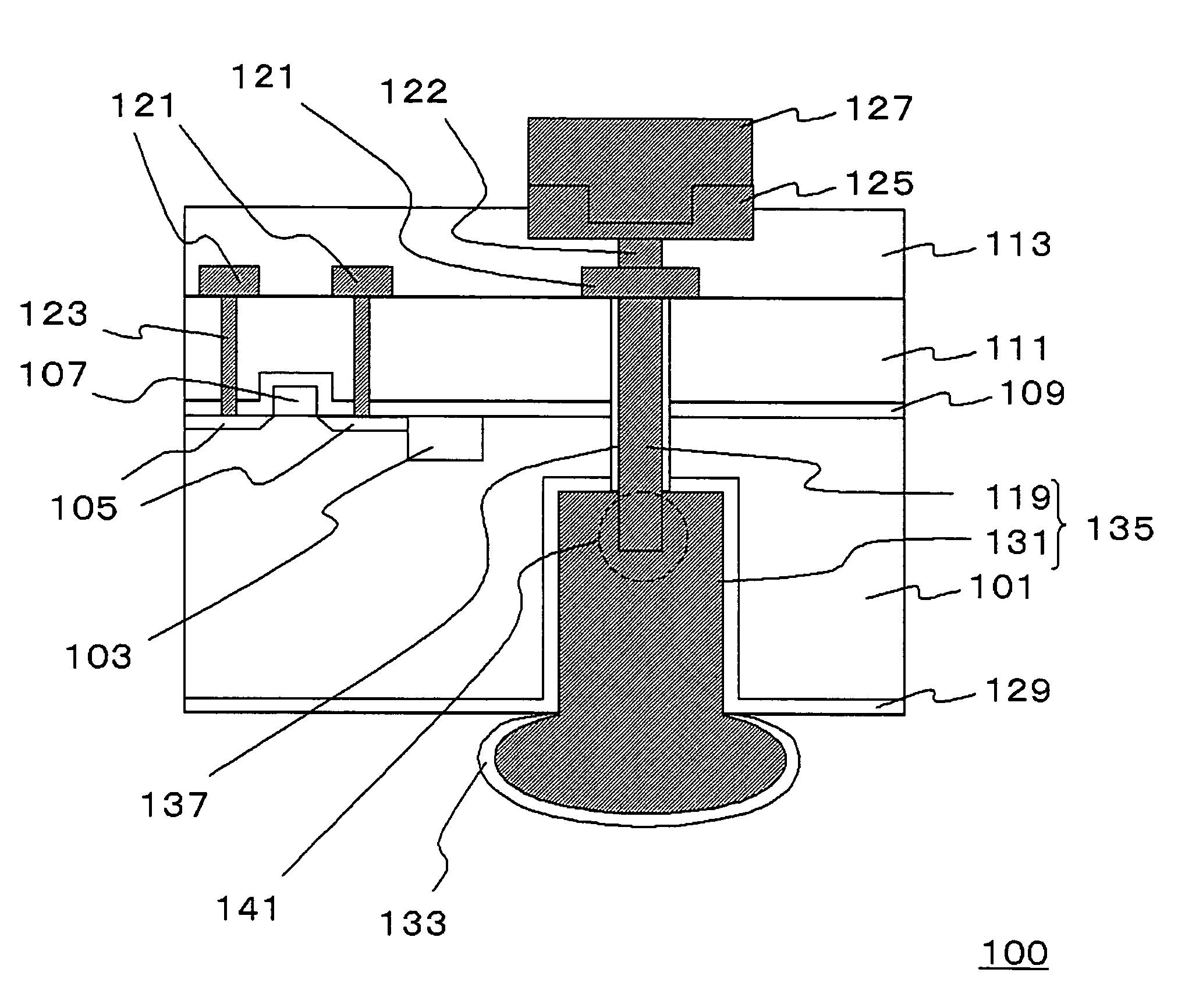
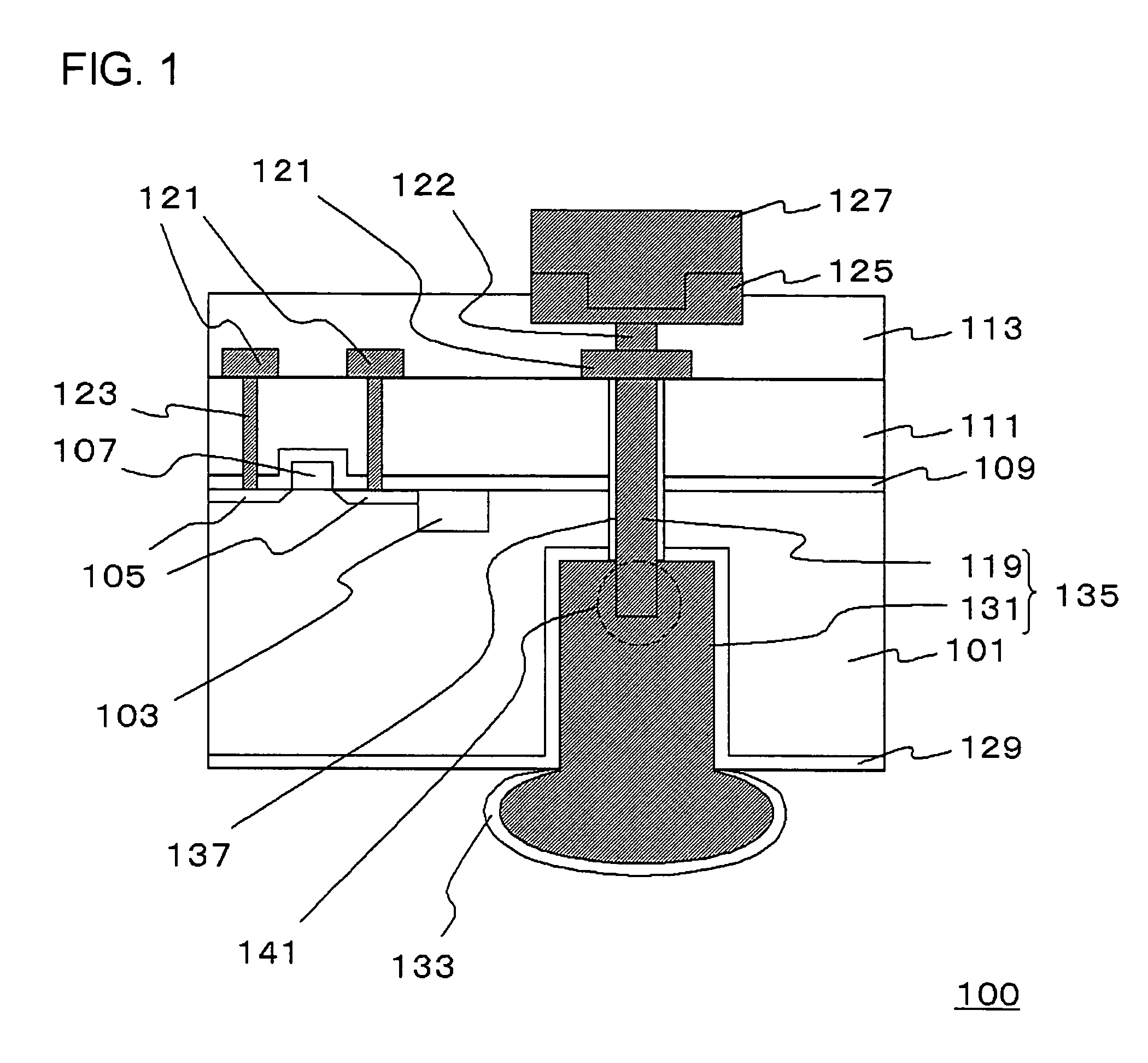
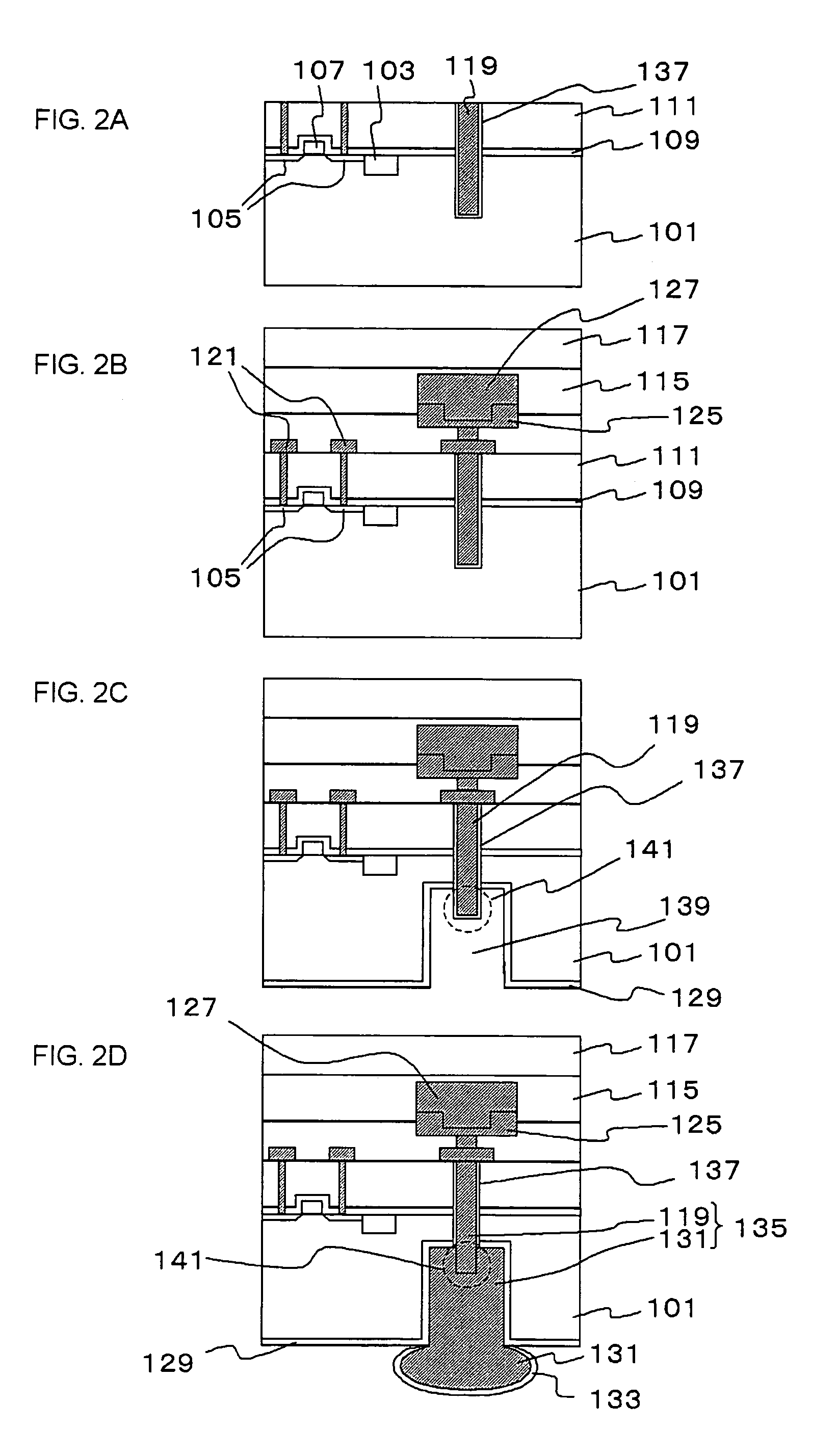
Single Transistor Floating-Body DRAM Devices Having Vertical Channel Transistor Structures and Methods of Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20060249770A1Improve integration densityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringVertical channel
Single transistor floating-body DRAM devices have a vertical channel transistor structure. The DRAM devices include a substrate, and first and second floating bodies disposed on the substrate and isolated from each other. A source region and a drain region are disposed under and above each of the first and second floating bodies. A gate electrode is disposed between the first and second floating bodies. Methods of fabricating the single transistor floating-body DRAM devices are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated circuits and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20110298551A1Improve integration densityReduce componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInductorVaricap
A three-dimensional integrated circuit includes a semiconductor substrate where the substrate has an opening extending through a first surface and a second surface of the substrate and where the first surface and the second surface are opposite surfaces of the substrate. A conductive material substantially fills the opening of the substrate to form a conductive through-substrate-via (TSV). An active circuit is disposed on the first surface of the substrate, an inductor is disposed on the second surface of the substrate and the TSV is electrically coupled to the active circuit and the inductor. The three-dimensional integrated circuit may include a varactor formed from a dielectric layer formed in the opening of the substrate such that the conductive material is disposed adjacent the dielectric layer and an impurity implanted region disposed surrounding the TSV such that the dielectric layer is formed between the impurity implanted region and the TSV.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Storage-capacitor electrode and interconnect
InactiveUS6429474B1Improve integration densityLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBit lineDram memory
A DRAM memory cell array includes a wiring layer formed at a storage-capacitor level of the cell for establishing a flipped connection of complementary bit lines, or for connecting support circuits in a DRAM cell array. The wiring layer includes a lower capacitor electrode and upper capacitor electrode which are formed simultaneously with respective plates of a storage capacitor. Both capacitor electrodes may be used to form distinct interconnections within a DRAM cell array.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com