Patents
Literature
407 results about "Dram memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic random access memory (DRAM) is a type of memory that is typically used for data or program code that a computer processor needs to function.
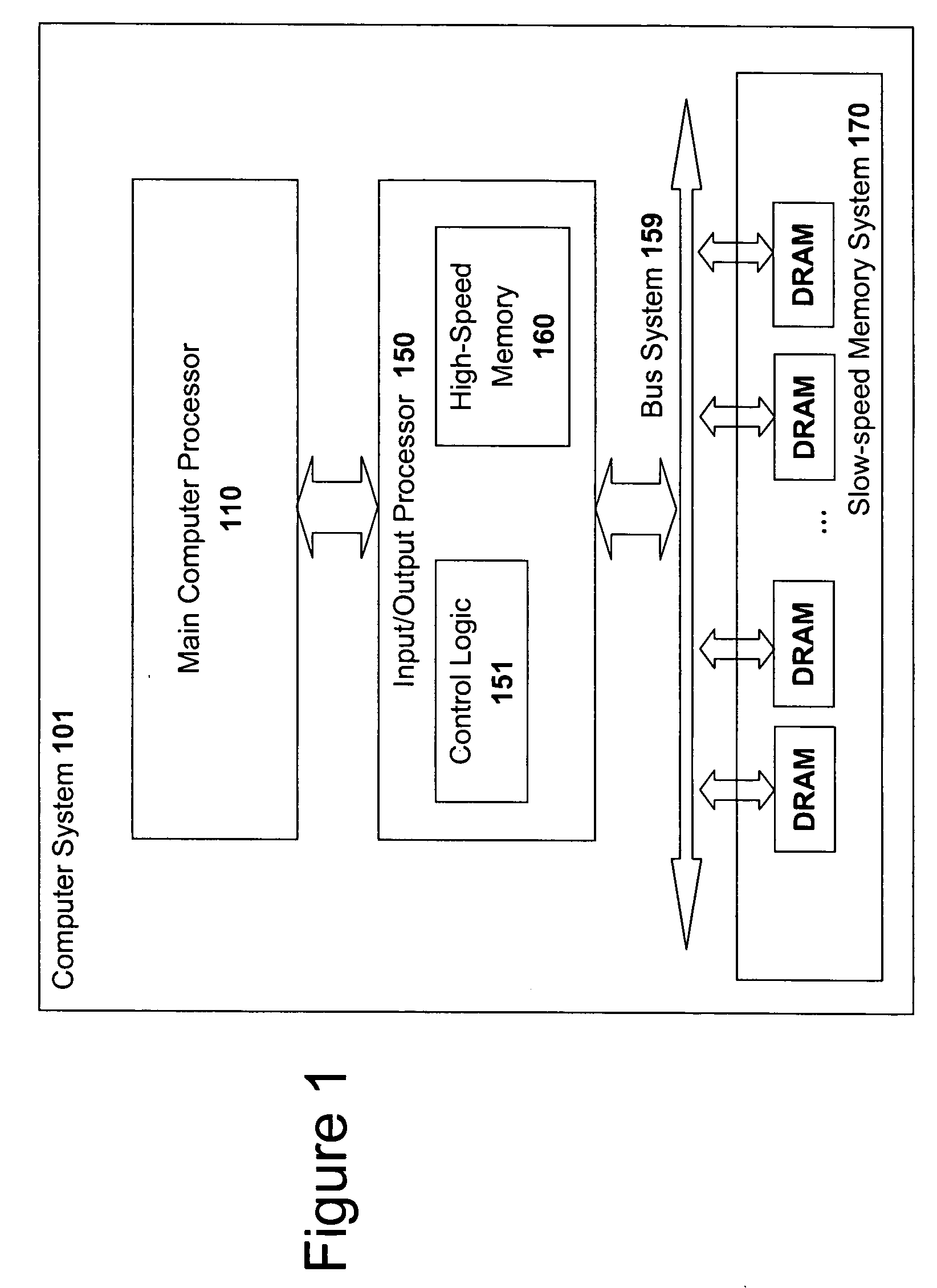
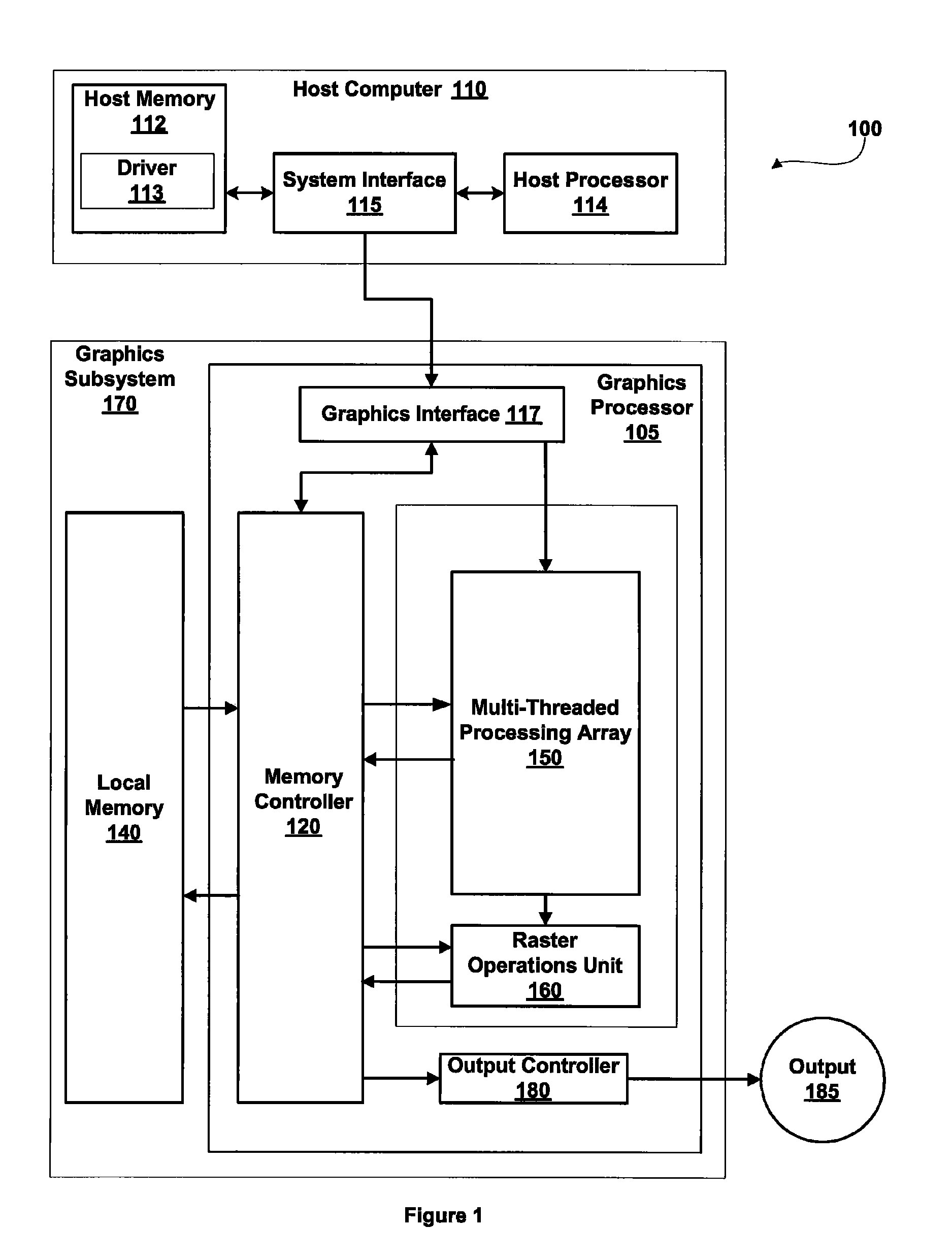
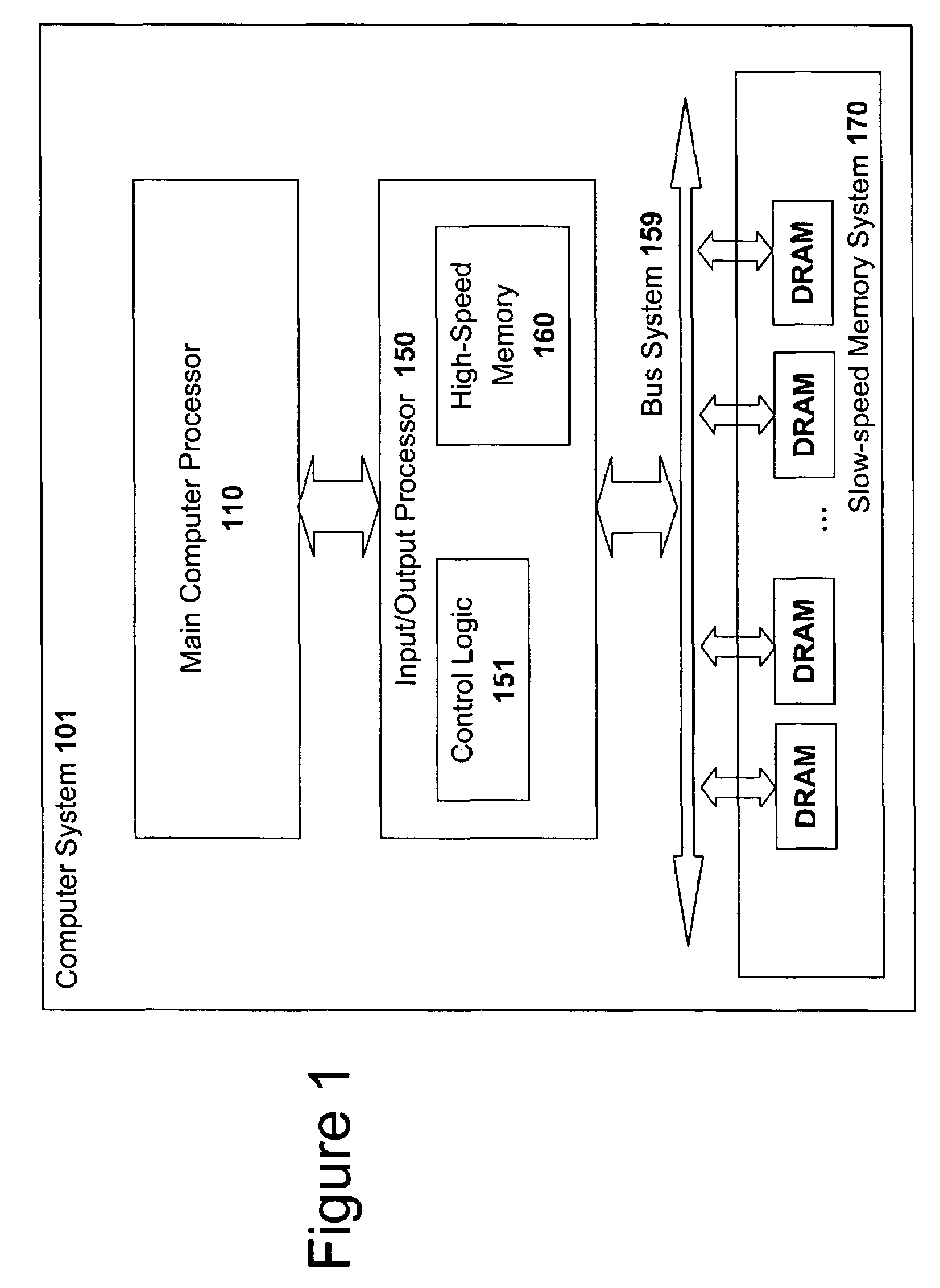
High speed memory control and I/O processor system
ActiveUS20050240745A1Easy to handleSimplify memory access taskMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh speed memoryTailored approach
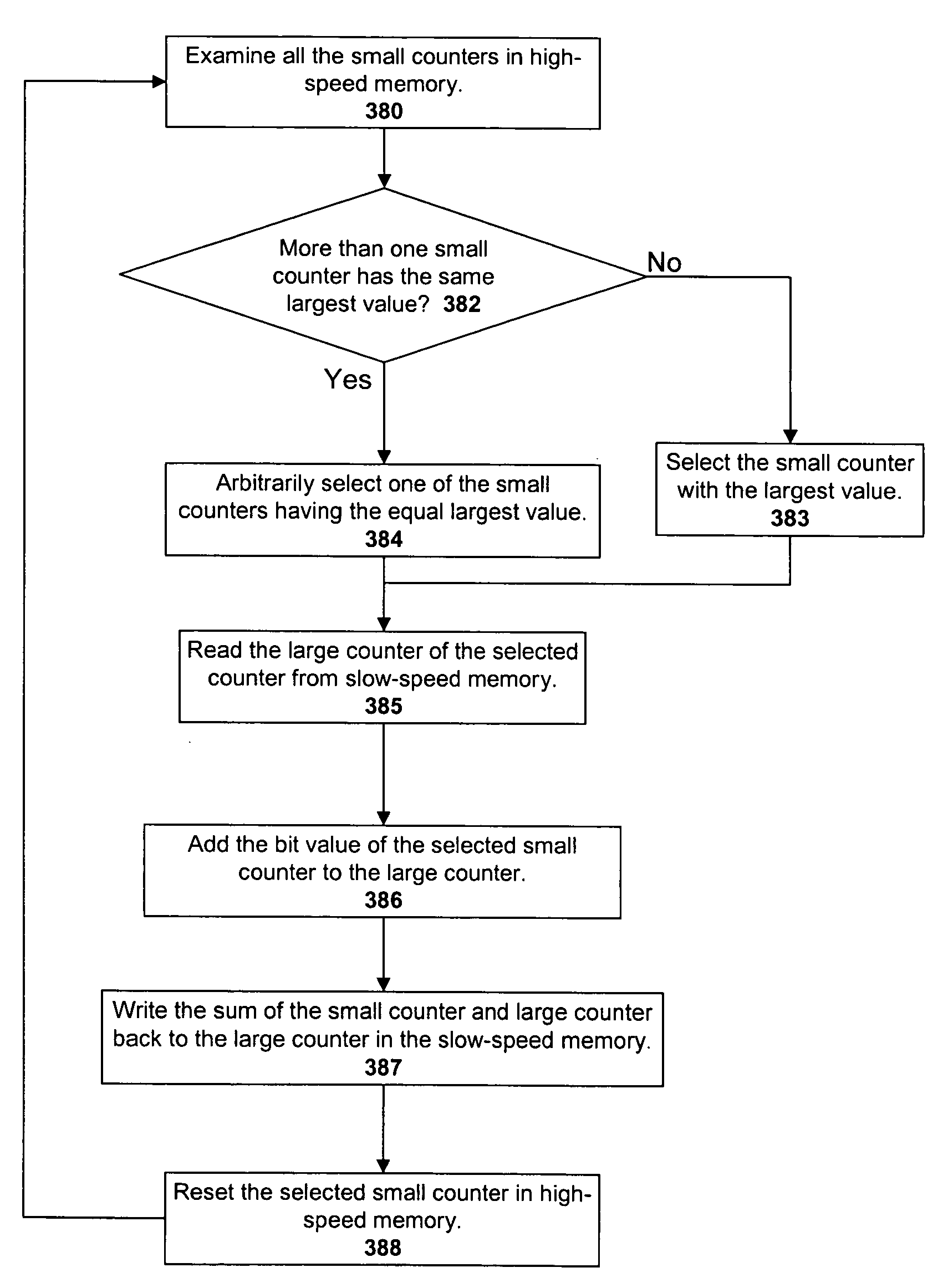
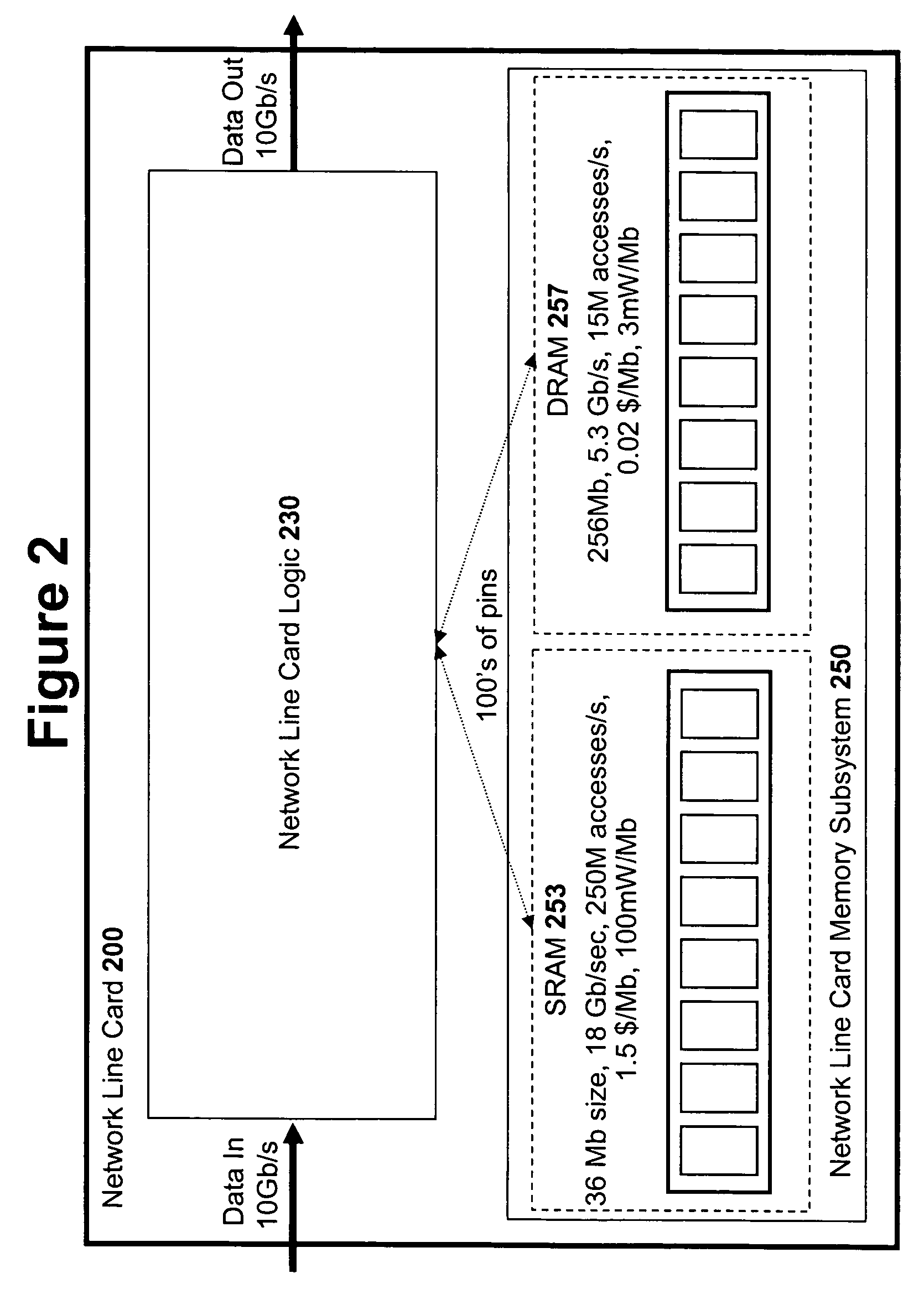
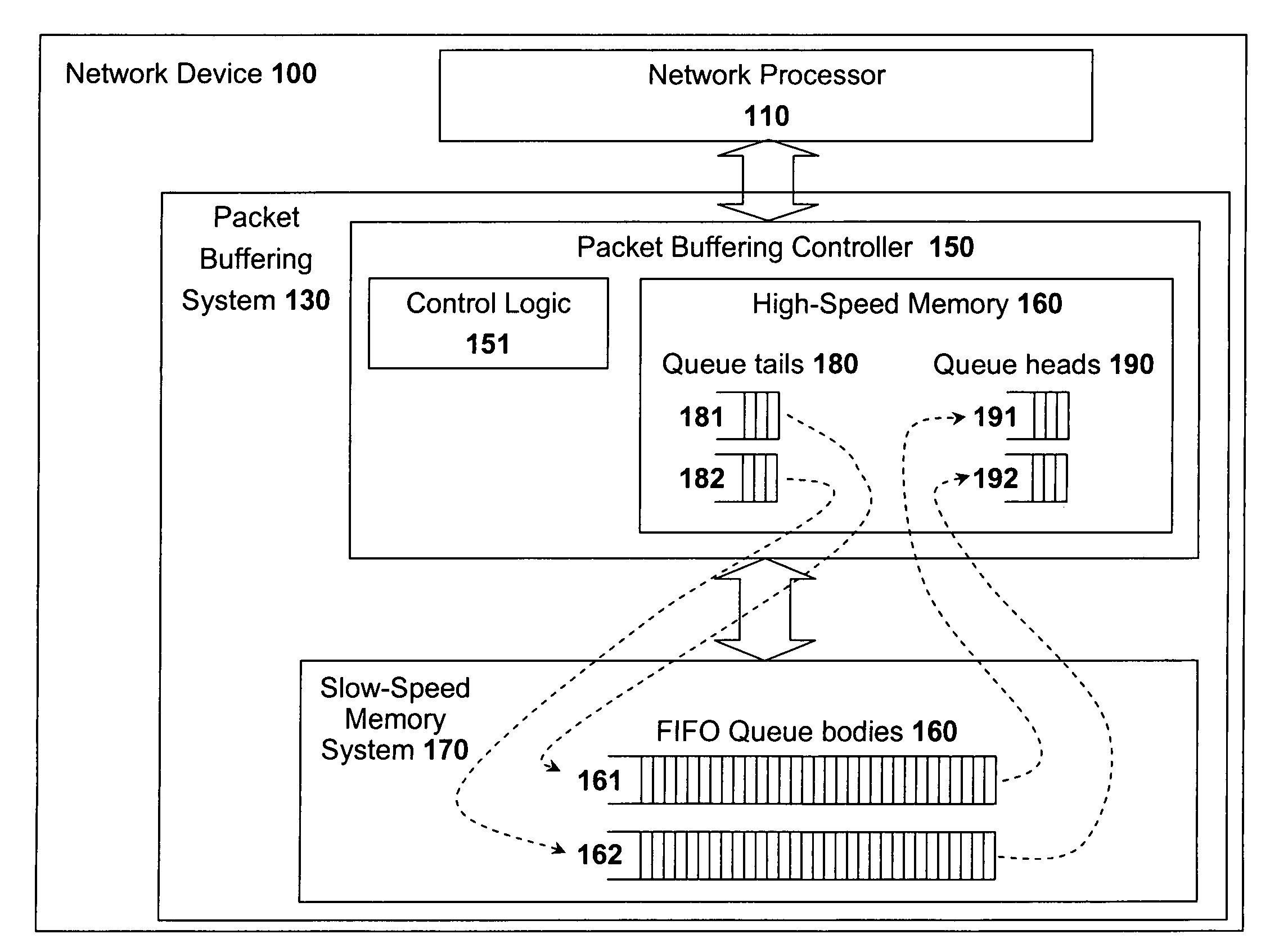
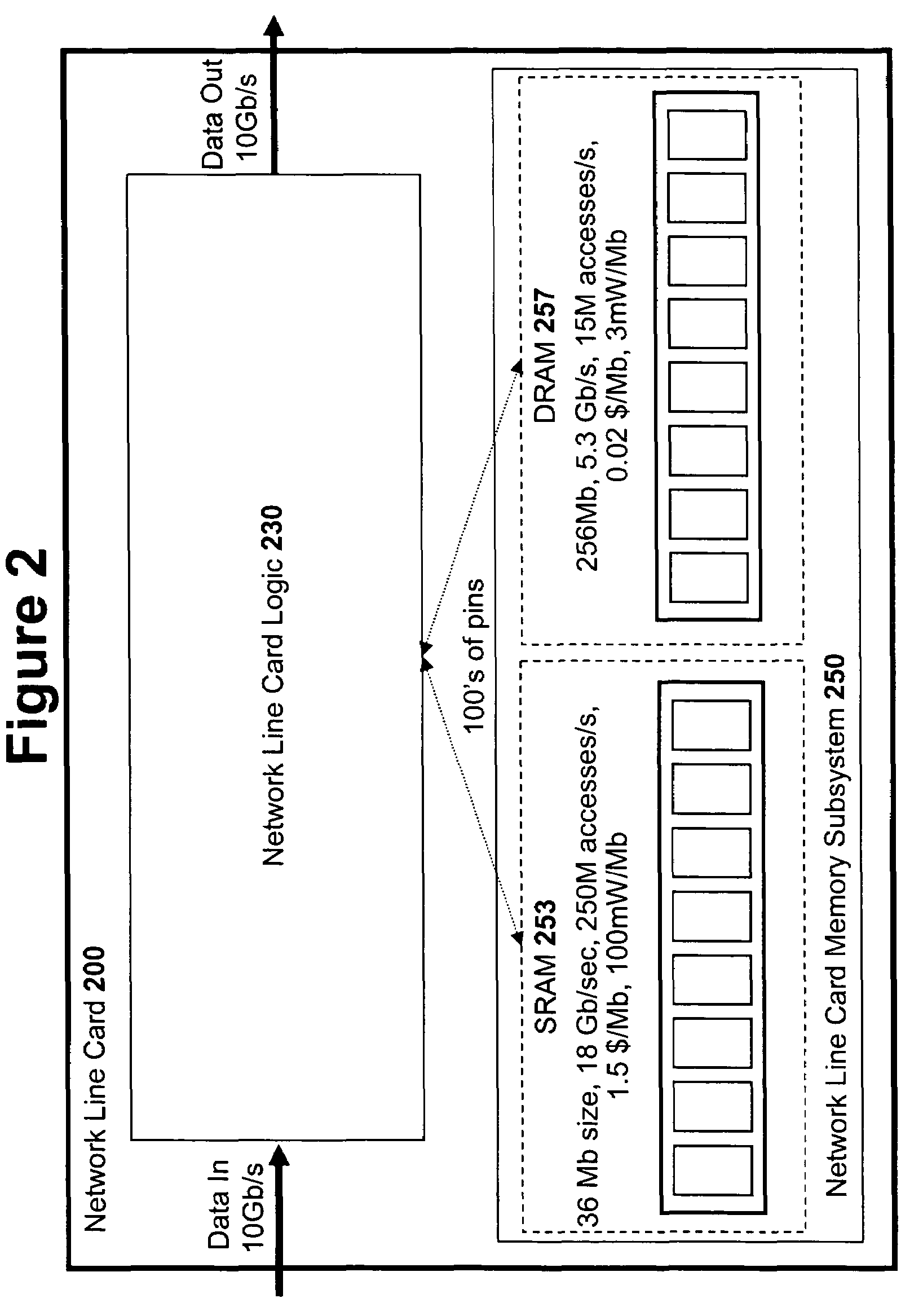
An input / output processor for speeding the input / output and memory access operations for a processor is presented. The key idea of an input / output processor is to functionally divide input / output and memory access operations tasks into a compute intensive part that is handled by the processor and an I / O or memory intensive part that is then handled by the input / output processor. An input / output processor is designed by analyzing common input / output and memory access patterns and implementing methods tailored to efficiently handle those commonly occurring patterns. One technique that an input / output processor may use is to divide memory tasks into high frequency or high-availability components and low frequency or low-availability components. After dividing a memory task in such a manner, the input / output processor then uses high-speed memory (such as SRAM) to store the high frequency and high-availability components and a slower-speed memory (such as commodity DRAM) to store the low frequency and low-availability components. Another technique used by the input / output processor is to allocate memory in such a manner that all memory bank conflicts are eliminated. By eliminating any possible memory bank conflicts, the maximum random access performance of DRAM memory technology can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
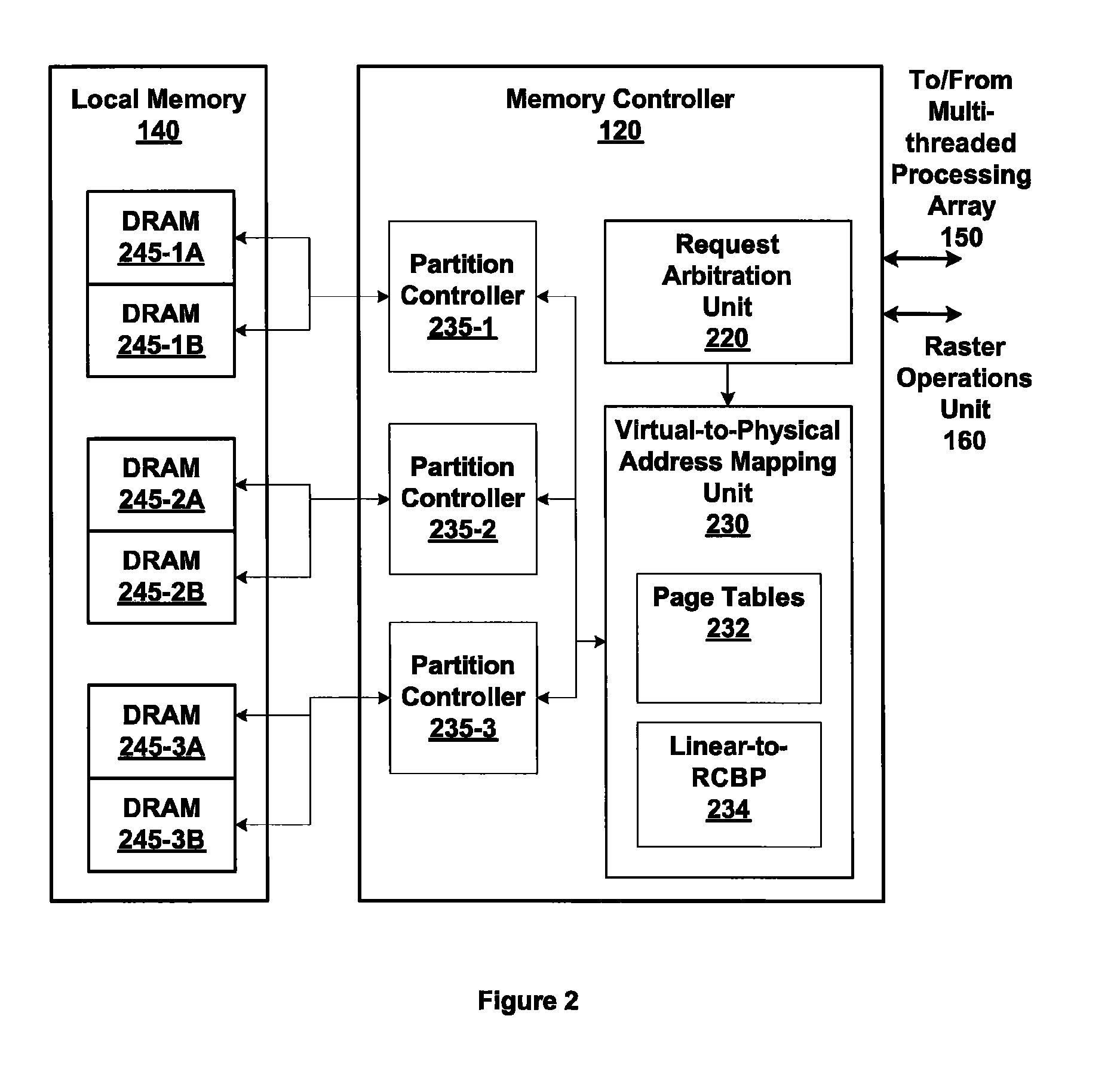
Memory addressing controlled by PTE fields
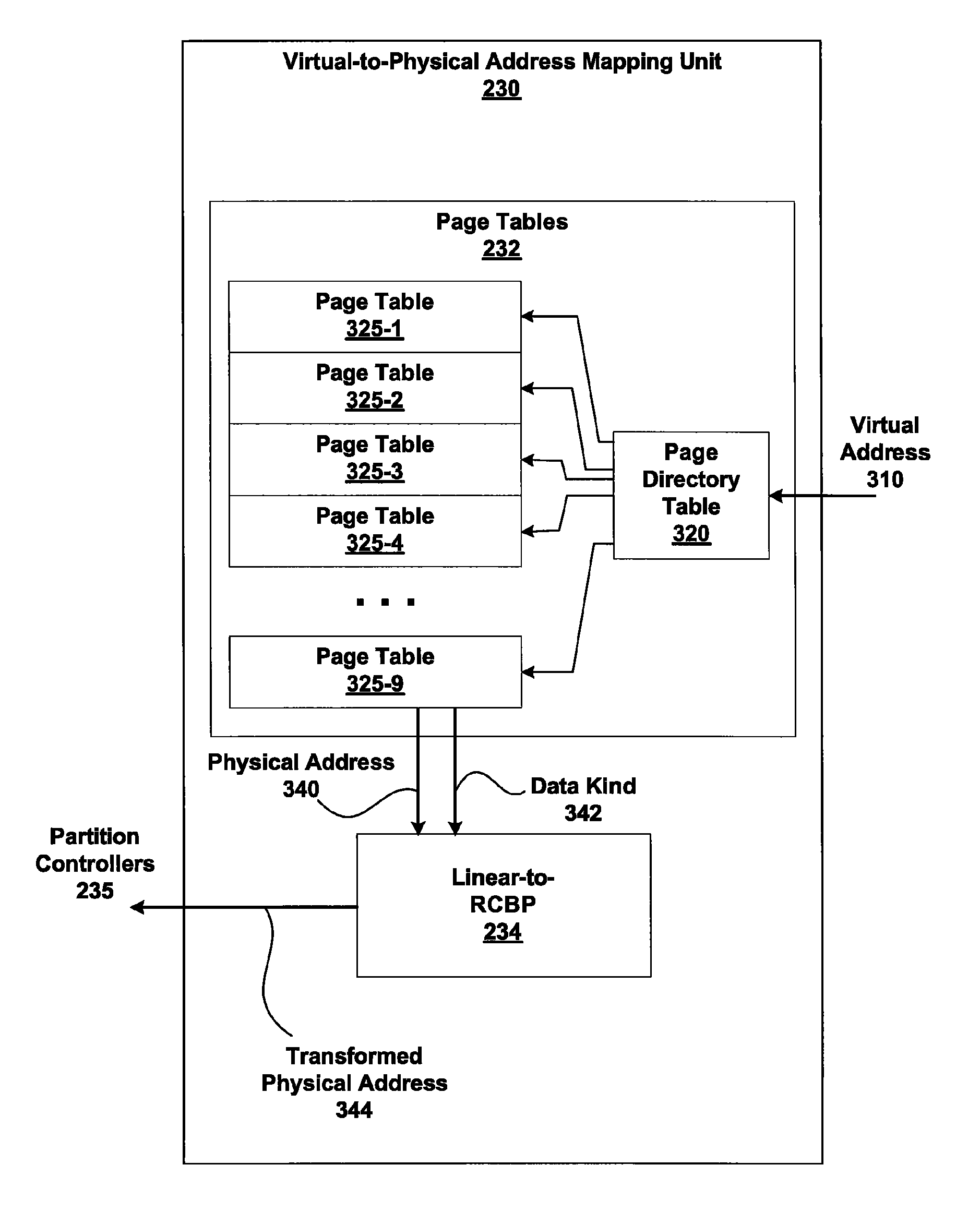
ActiveUS7805587B1Reduce accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMemory addressDram memory
Embodiments of the present invention enable virtual-to-physical memory address translation using optimized bank and partition interleave patterns to improve memory bandwidth by distributing data accesses over multiple banks and multiple partitions. Each virtual page has a corresponding page table entry that specifies the physical address of the virtual page in linear physical address space. The page table entry also includes a data kind field that is used to guide and optimize the mapping process from the linear physical address space to the DRAM physical address space, which is used to directly access one or more DRAM. The DRAM physical address space includes a row, bank and column address. The data kind field is also used to optimize the starting partition number and partition interleave pattern that defines the organization of the selected physical page of memory within the DRAM memory system.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
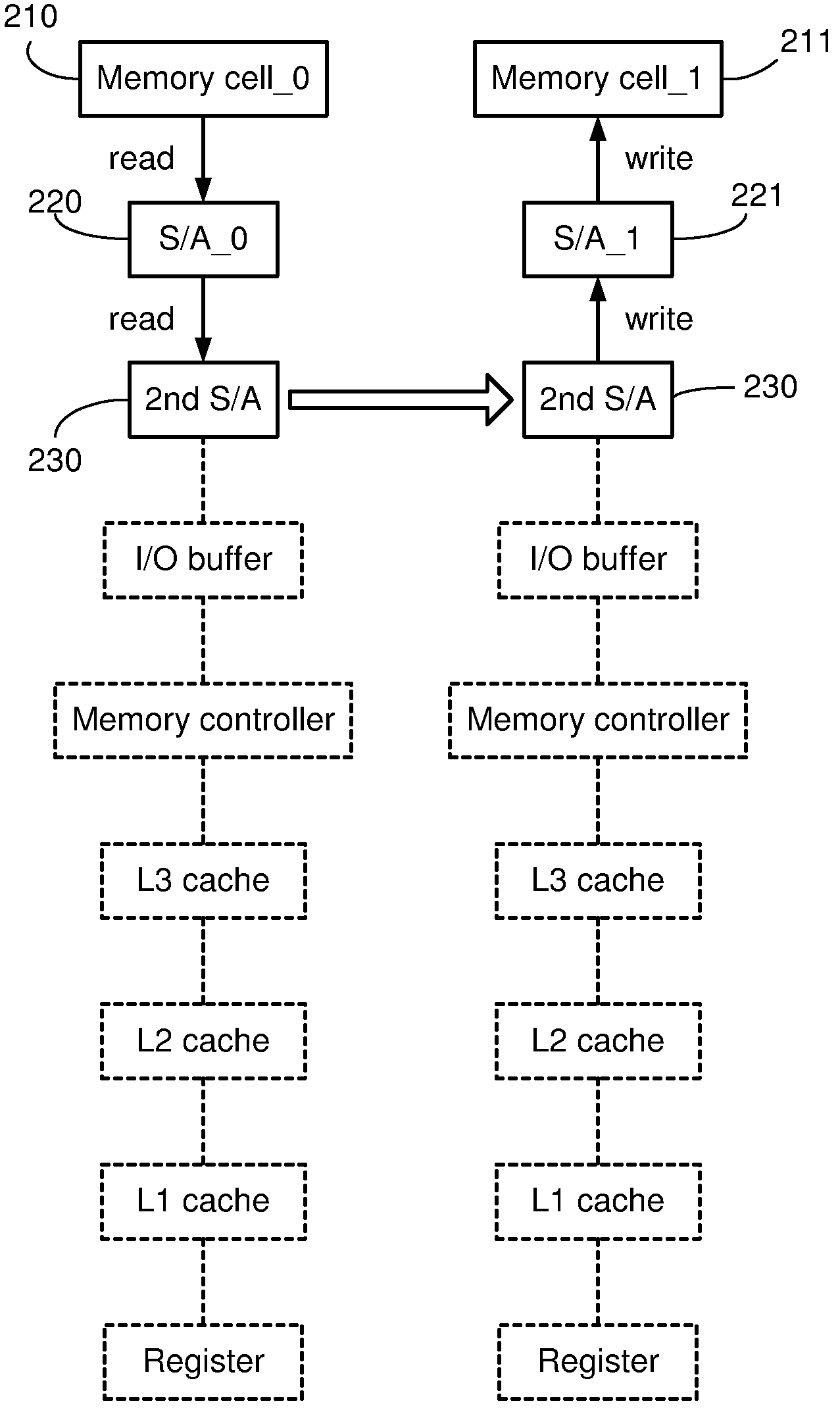
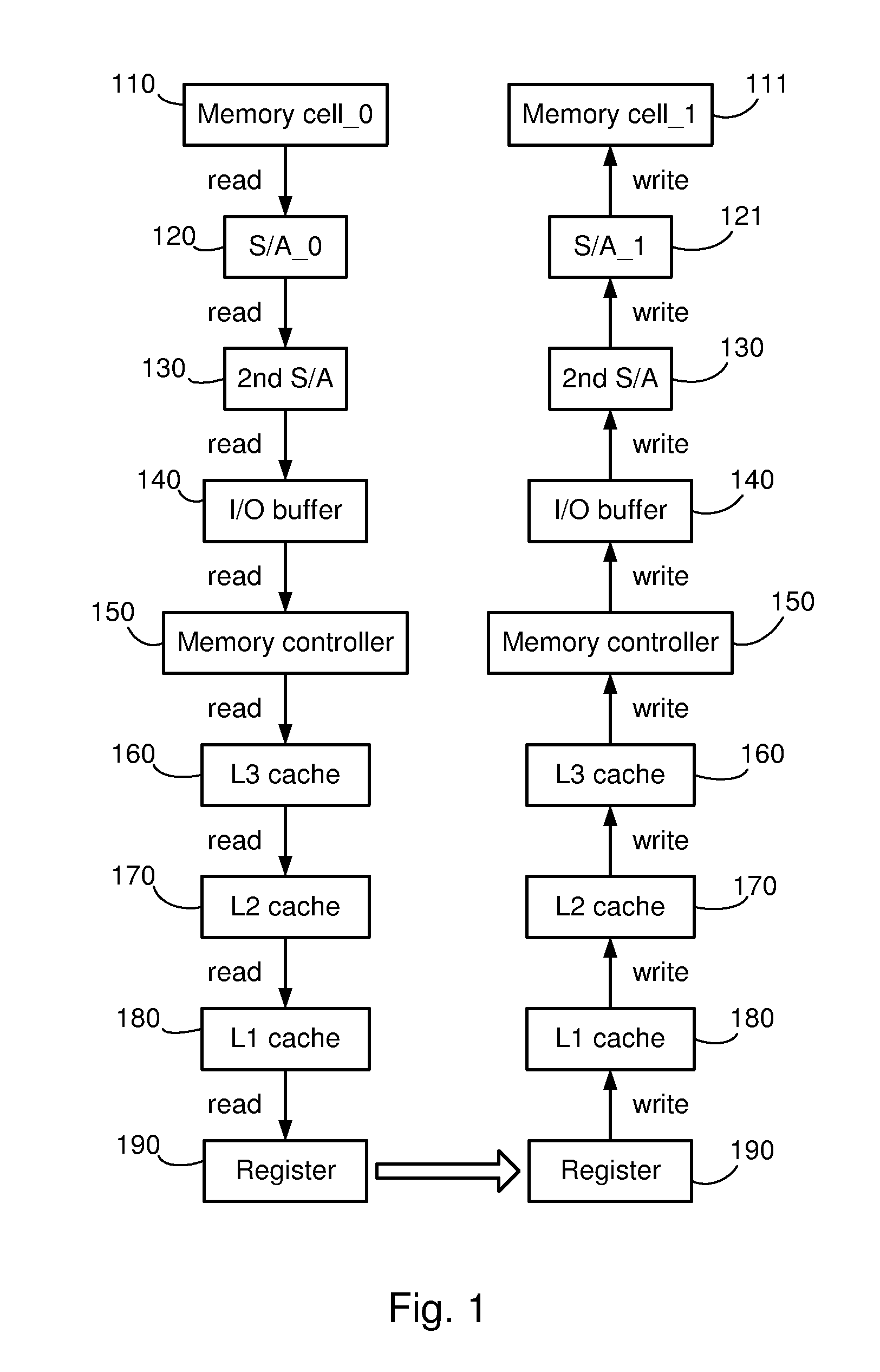
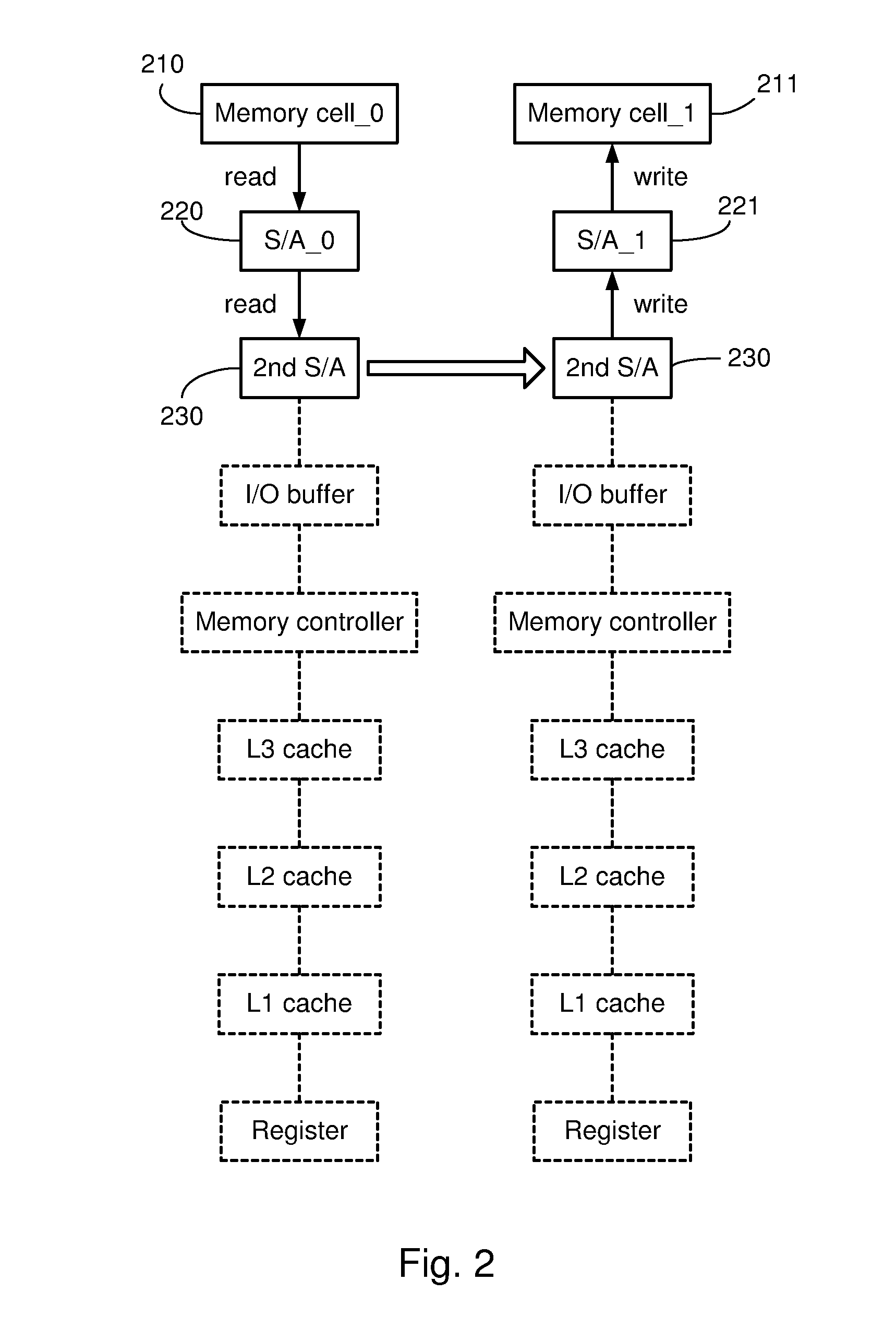
Systems and methods for data transfers between memory cells
Systems and methods for reducing the latency of data transfers between memory cells by enabling data to be transferred directly between sense amplifiers in the memory system. In one embodiment, a memory system uses a conventional DRAM memory structure having a pair of first-level sense amplifiers, a second-level sense amplifier and control logic for the sense amplifiers. Each of the sense amplifiers is configured to be selectively coupled to a data line. In a direct data transfer mode, the control logic generates control signals that cause the sense amplifiers to transfer data from a first one of the first-level sense amplifiers (a source sense amplifier) to the second-level sense amplifier, and from there to a second one of the first-level sense amplifiers (a destination sense amplifier.) The structure of these sense amplifiers is conventional, and the operation of the system is enabled by modified control logic.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA ELECTRONICS COMPONENTS
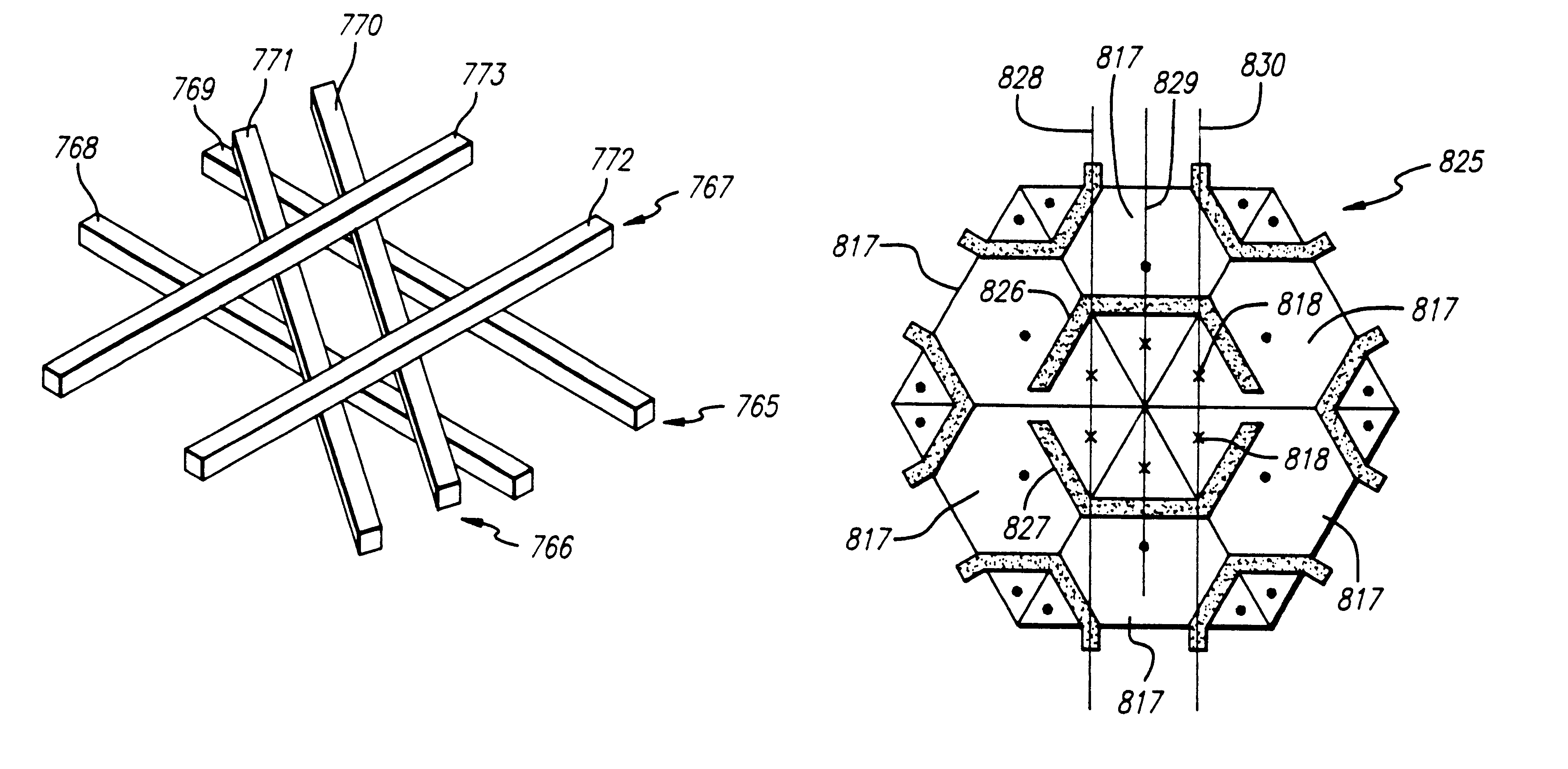
Hexagonal architecture
InactiveUS6407434B1Reduce total wirelength interconnect congestionReduce the numberTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
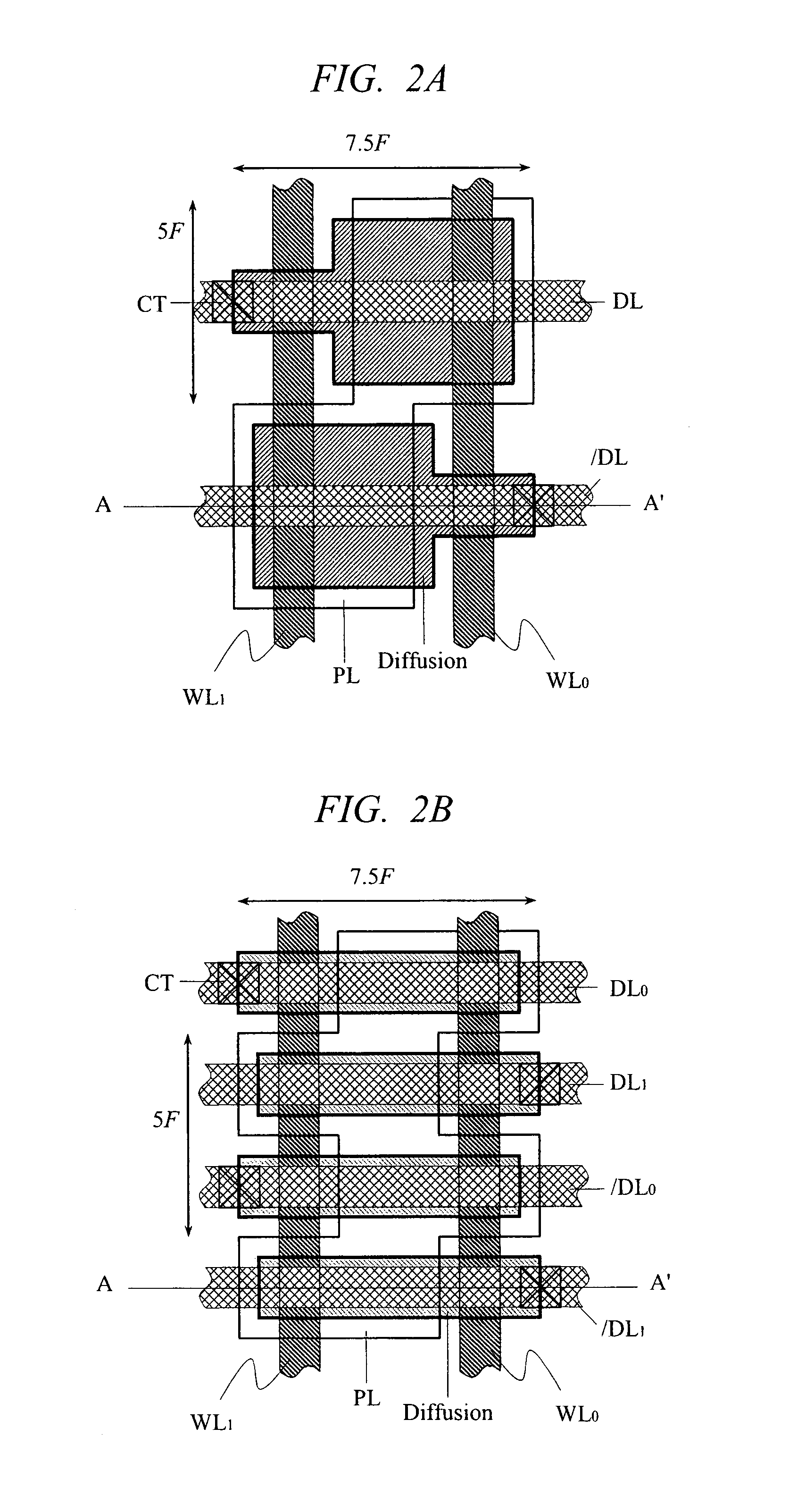
Several inventions are disclosed. A cell architecture using hexagonal shaped cells is disclosed. The architecture is not limited to hexagonal shaped cells. Cells may be defined by clusters of two or more hexagons, by triangles, by parallelograms, and by other polygons enabling a variety of cell shapes to be accommodated. Polydirectional non-orthogonal three layer metal routing is disclosed. The architecture may be combined with the tri-directional routing for a particularly advantageous design. In the tri-directional routing arraingement, electrical conductors for interconnecting terminals of microelectronic cells of an integrated circuit preferrably extend in three directions that are angularly displaced from each other by 60°. The conductors that extend in the three directions are preferrably formed in three different layers. A method of minimizing wire length in a semiconductor device is disclosed. A method of minimizing intermetal capacitance in a semiconductor device is disclosed. A novel device called a "tri-ister" is disclosed. Triangular devices are disclosed, including triangular NAND gates, triangular AND gates, and triangular OR gates. A triangular op amp and triode are disclosed. A triangular sense amplifier is disclosed. A DRAM memory array and an SRAM memory array, based upon triangular or parallelogram shaped cells, are disclosed, including a method of interconnecting such arrays. A programmable variable drive transistor is disclosed. CAD algorithms and methods are disclosed for designing and making semiconductor devices, which are particularly applicable to the disclosed architecture and tri-directional three metal layer routing.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
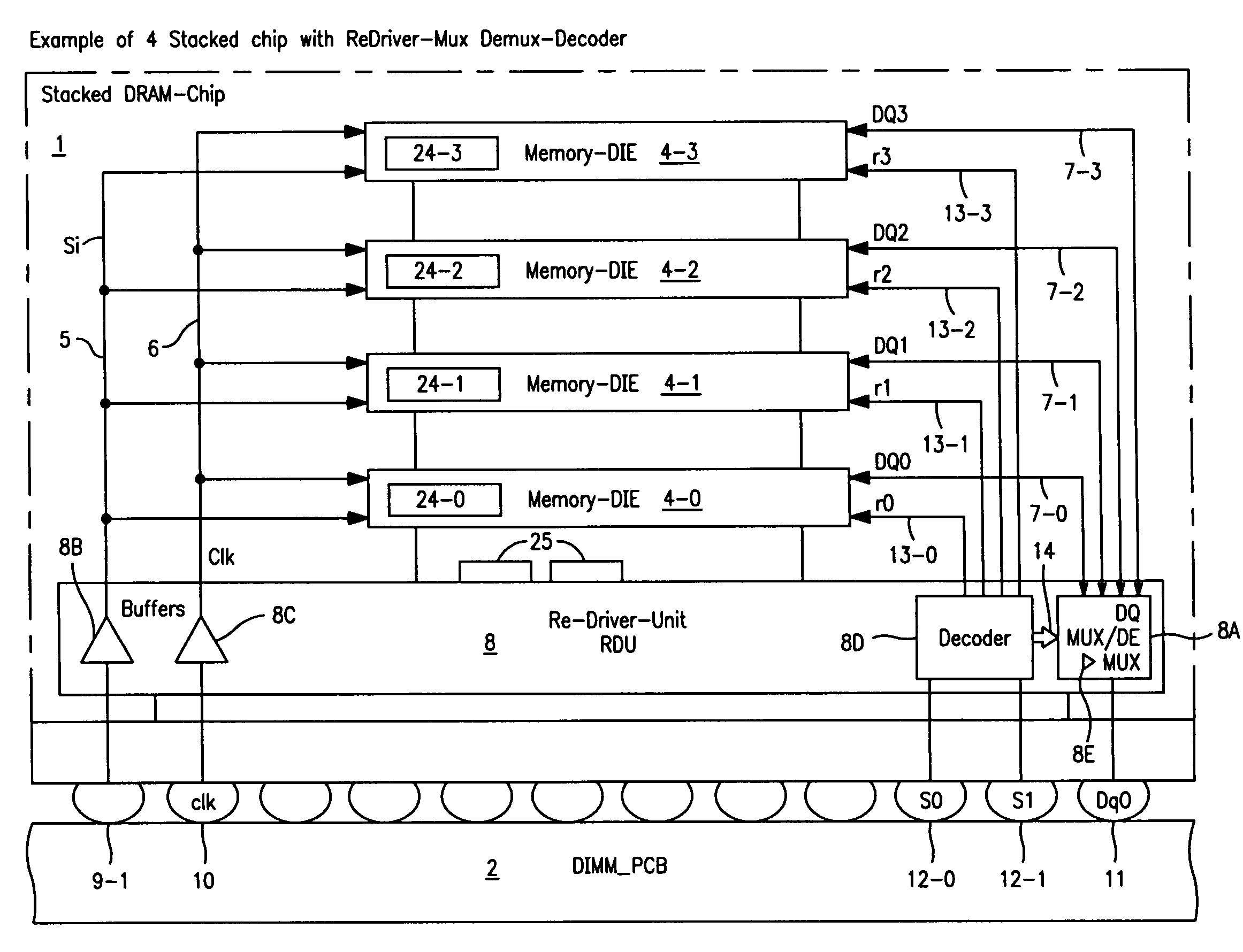
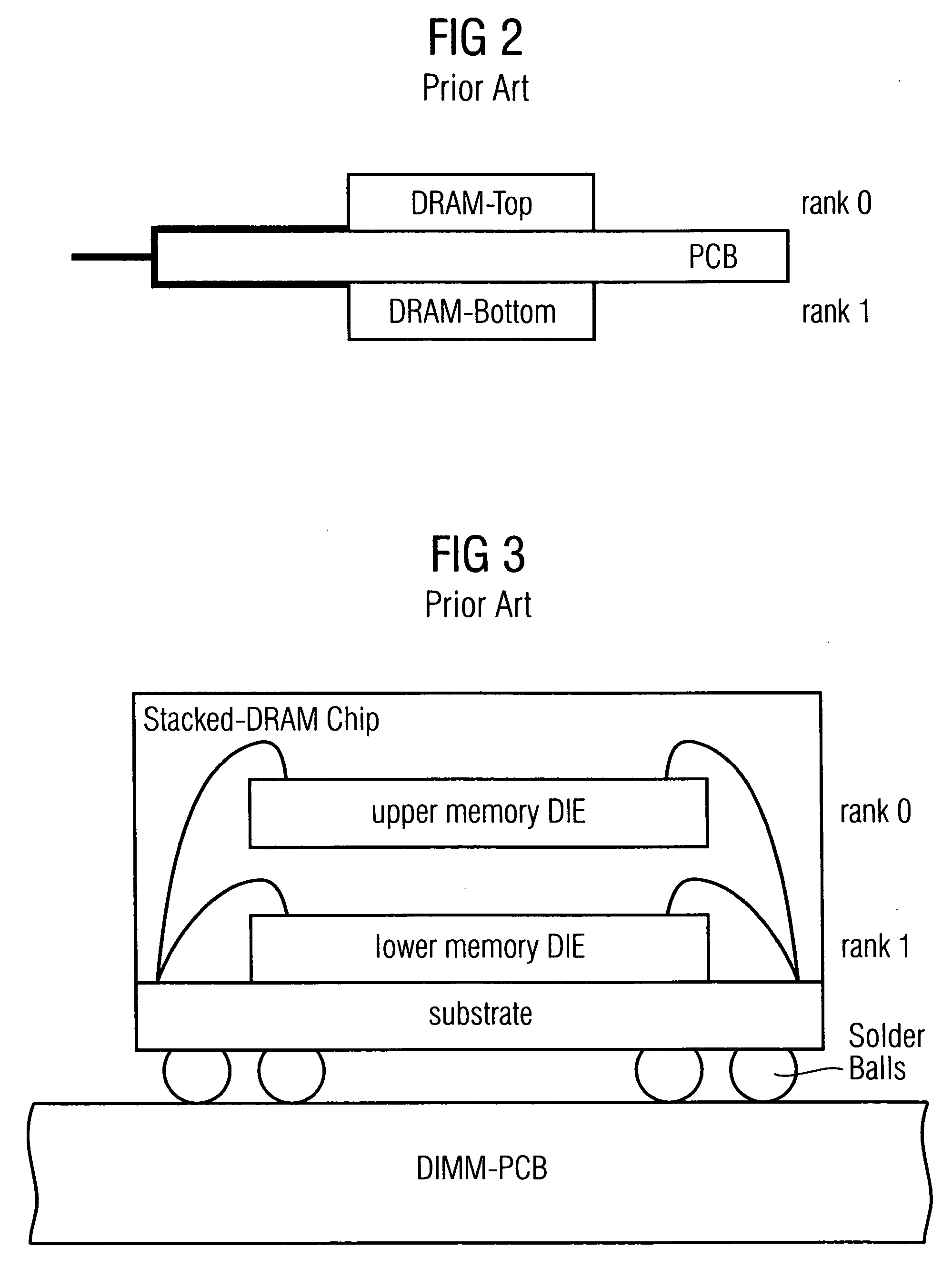
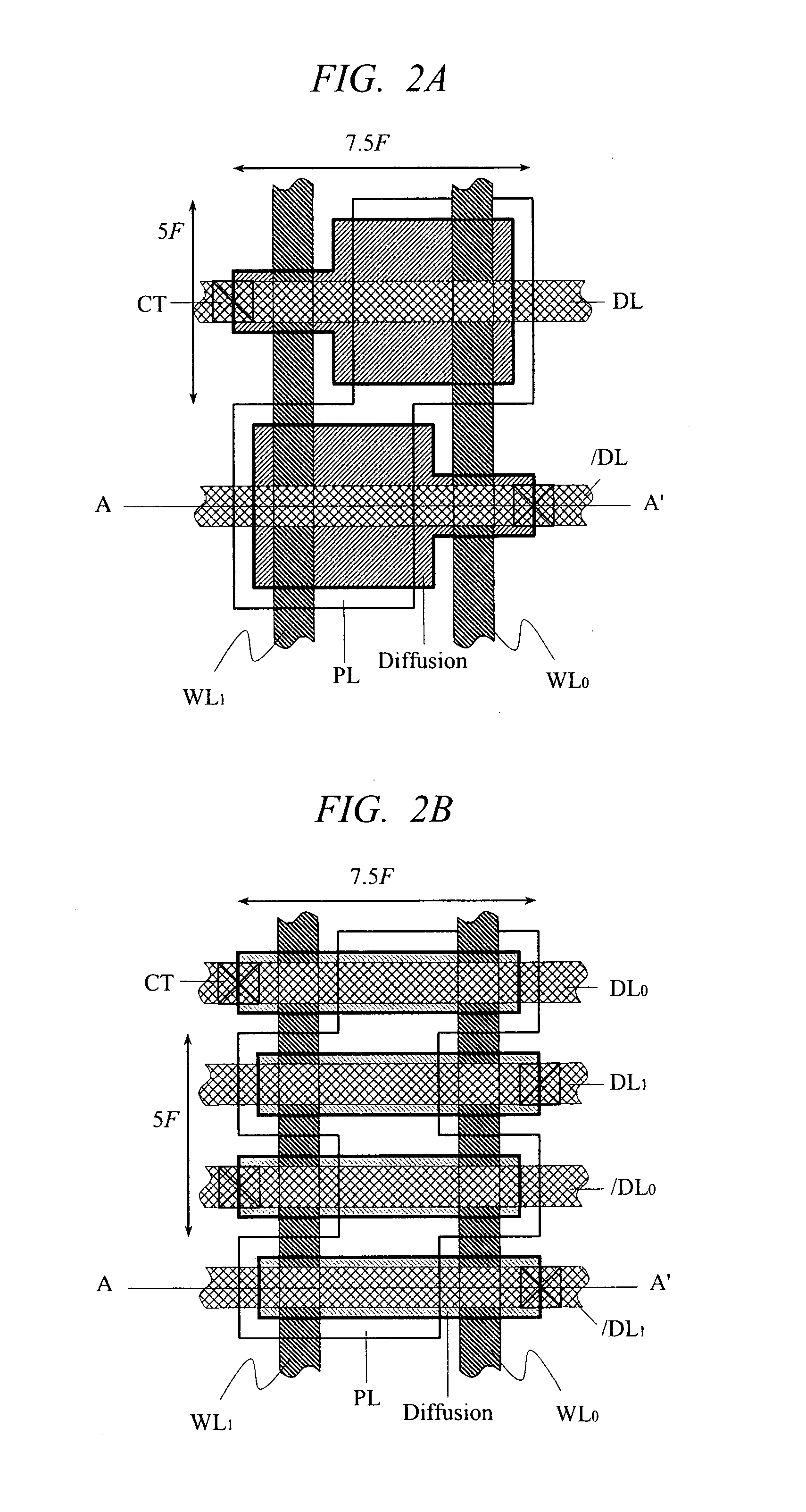
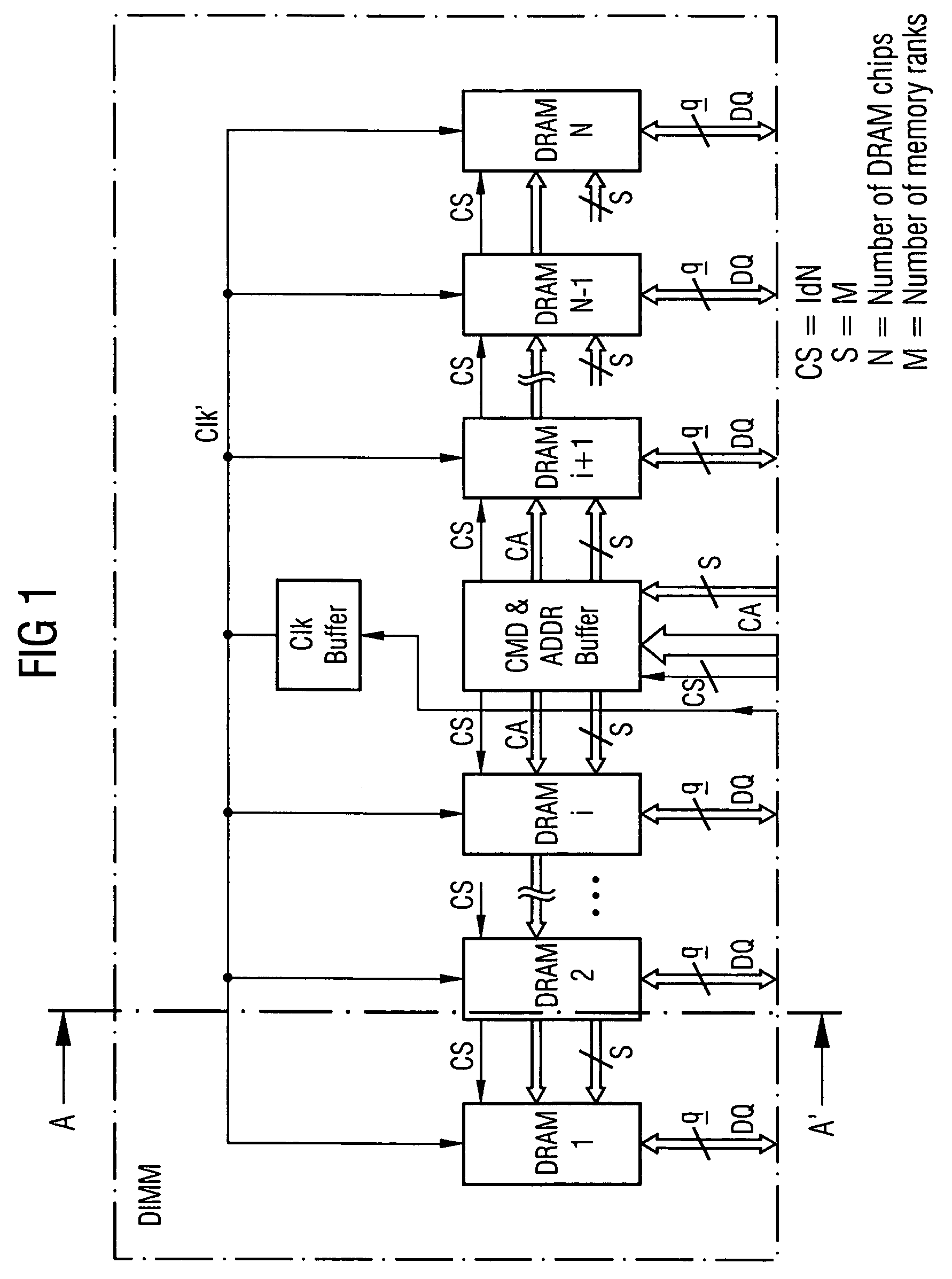
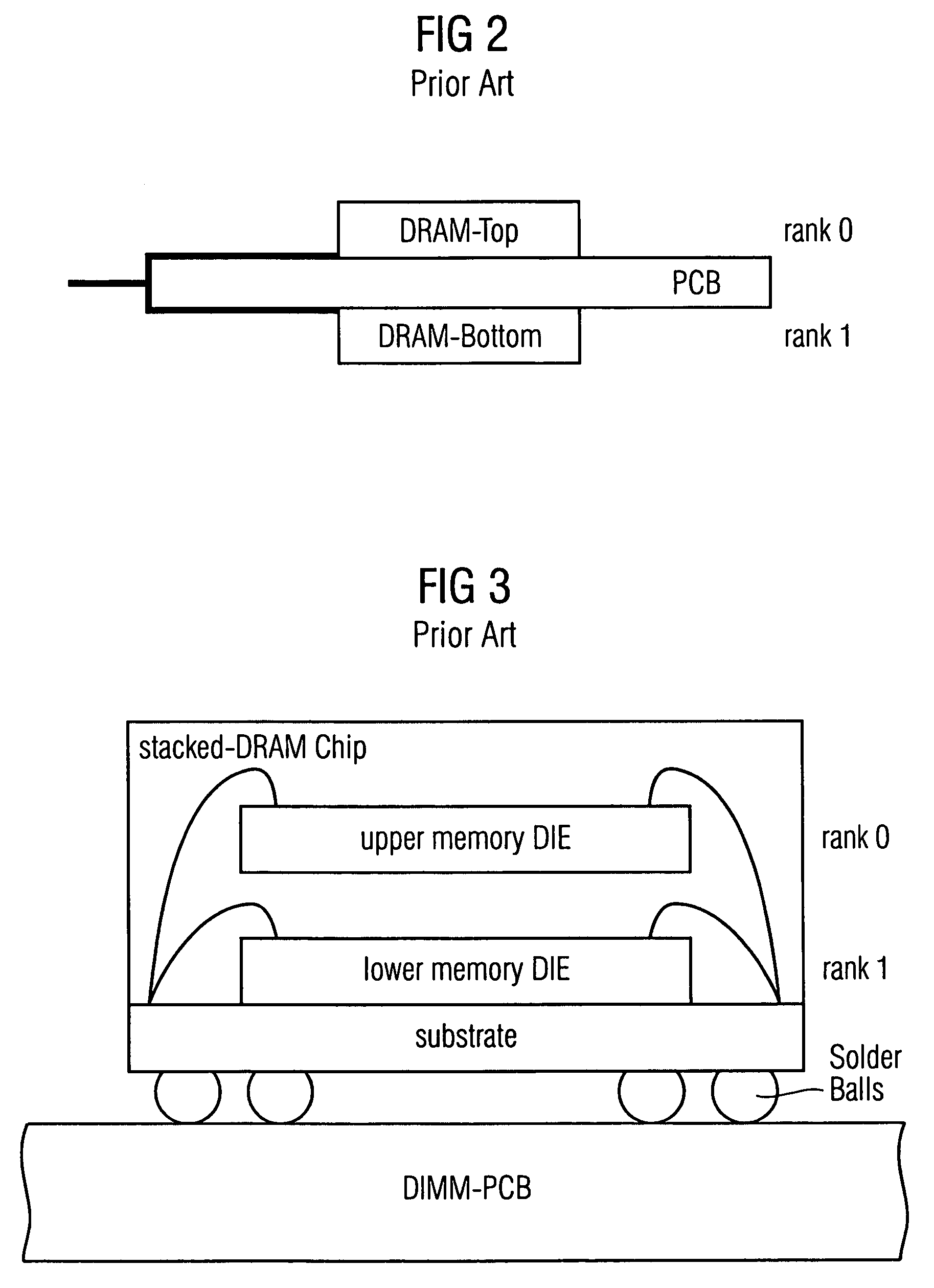
Stacked DRAM memory chip for a dual inline memory module (DIMM)
ActiveUS7200021B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsInternal memoryMemory chip
A stacked DRAM memory chip for a Dual In Line Memory Module (DIMM) is disclosed. According to one aspect, the DRAM memory chip comprises at least four stacked DRAM memory dies. Further, the memory dies are each selectable by a corresponding internal memory rank signal. Each memory die comprises an array of memory cells. A common internal address bus is provided for addressing the memory cells and is connected to all stacked DRAM memory dies. Internal data buses are provided for writing data into the memory cells and reading data out of the memory cells of the DRAM memory dies. An integrated redriving unit comprises buffers for all internal address lines provided for driving external address signals applied to address pads of the DRAM memory chip. A multiplexer / demultiplexer switches the internal data lines of the selected DRAM memory die. A memory rank decoder selects a corresponding memory die.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method of fabricating and architecture for vertical transistor cells and transistor-controlled memory cells
InactiveUS20050001257A1Increased area requirementLimited functionTransistorSolid-state devicesFloating body effectDram memory
In a substrate vertical transistor cells are formed and are arranged, in a transistor cell array, row by row in an x direction and column by column in a y direction. Lower source / drain regions of the transistor cells are connected to a common connection plate. Upper source / drain regions of the transistor cells impart a contact connection for instance to a storage capacitor of a DRAM memory cell. Active trenches running between the transistor cells with word lines are formed along the x direction. The word lines form gate electrodes in sections. A potential at the gate electrode controls a conductive channel in an active region arranged in each case between the upper and the lower source / drain connection region. According to the invention, the active regions of adjacent transistor cells are sections of a contiguous layer body and are connected to one another. An accumulation of charge carriers in the active region and floating body effects are avoided without increasing the area requirement of a transistor cell.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
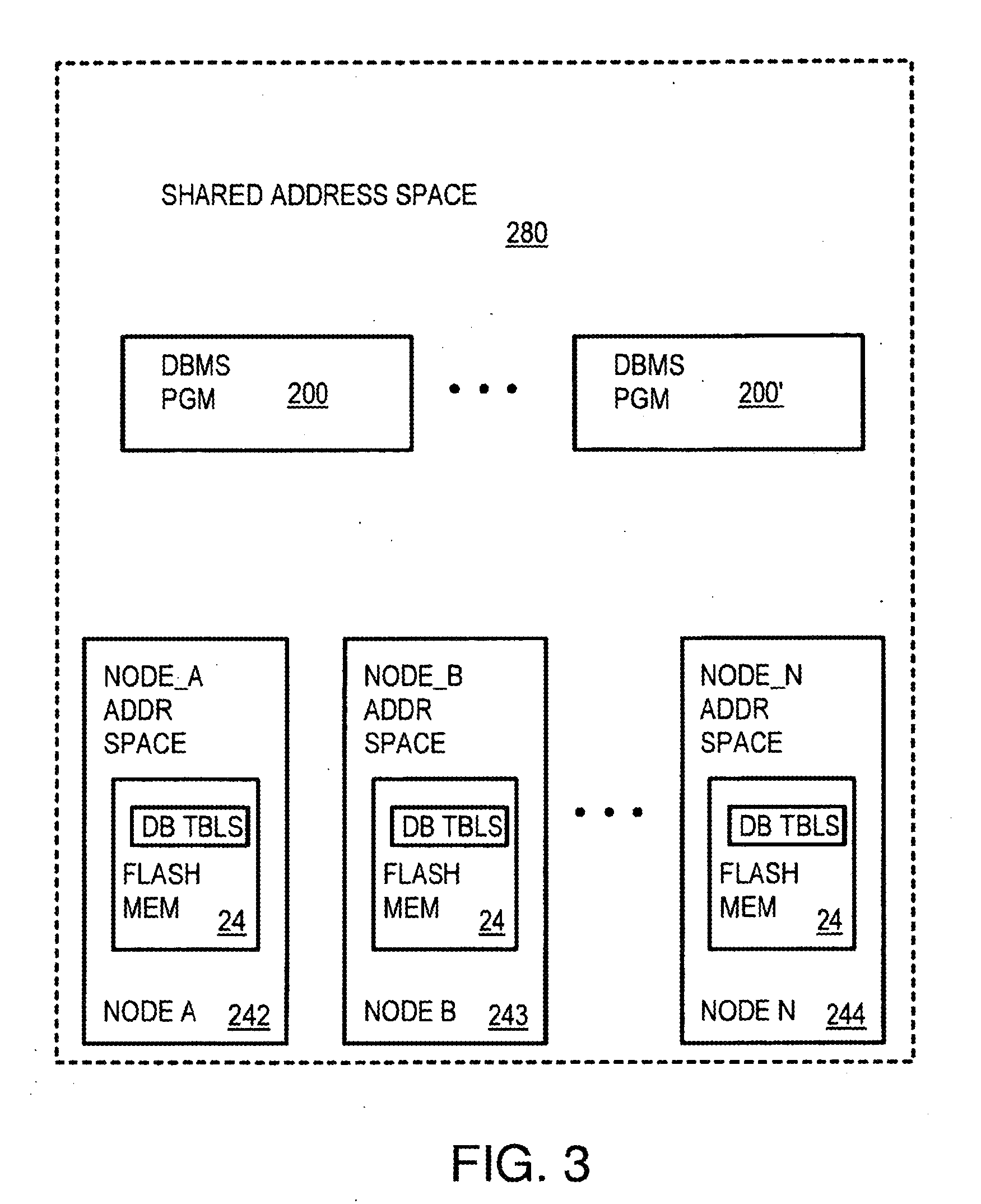
Cluster of processing nodes with distributed global flash memory using commodity server technology
InactiveUS20120017037A1Database management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsDram memoryMultiple applications
Approaches for a distributed storage system that comprises a plurality of nodes. Each node, of the plurality of nodes, executes one or more application processes which are capable of accessing persistent shared memory. The persistent shared memory is implemented by solid state devices physically maintained on each of the plurality of nodes. Each the one or more application processes, maintained on a particular node, of the plurality of nodes, communicates with a shared data fabric (SDF) to access the persistent shared memory. The persistent shared memory comprises a scoreboard implemented in shared DRAM memory that is mapped to a persistent storage. The scoreboard provides a crash tolerant mechanism for enabling application processes to communicate with the shared data fabric (SDF).
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
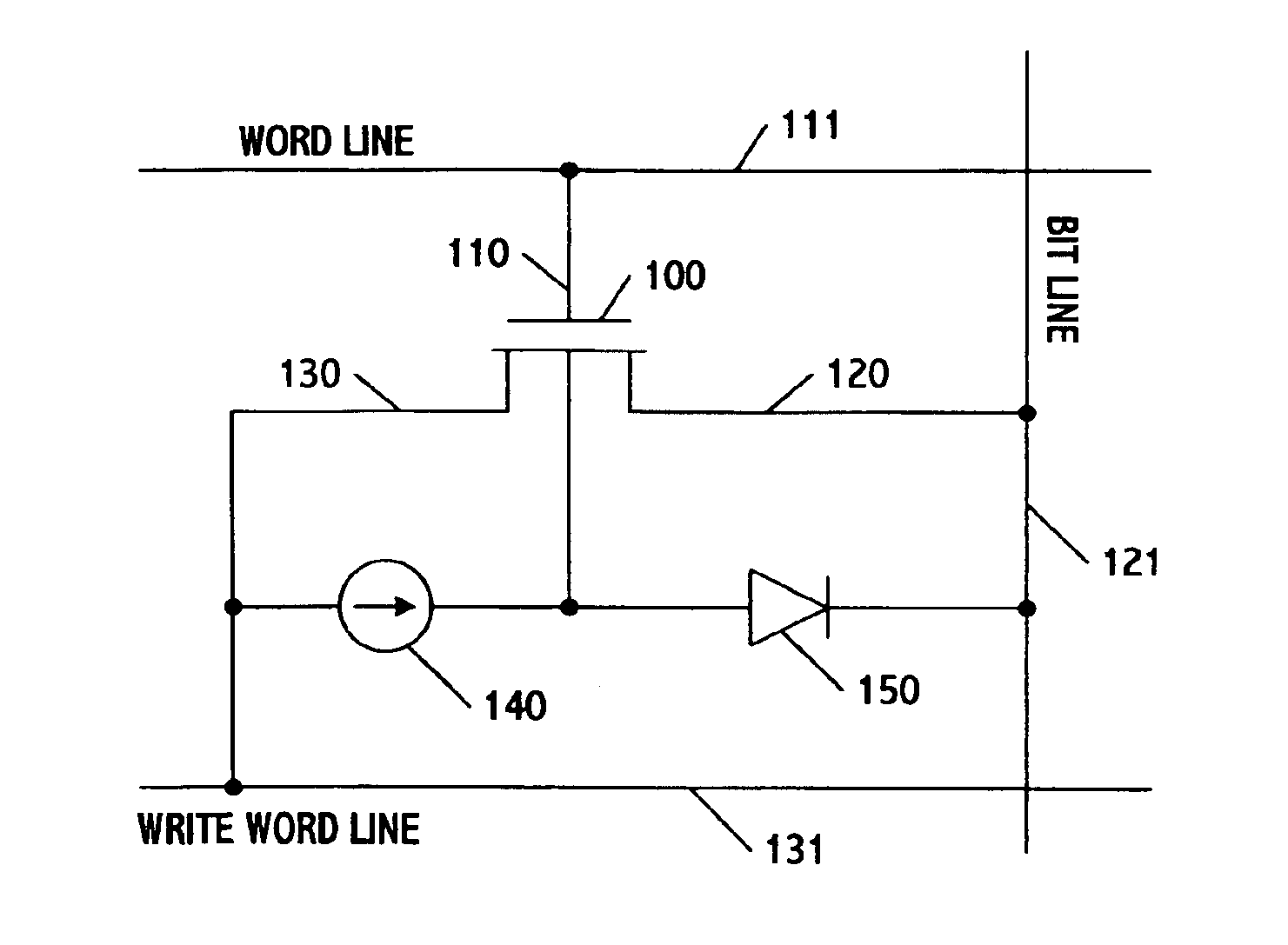
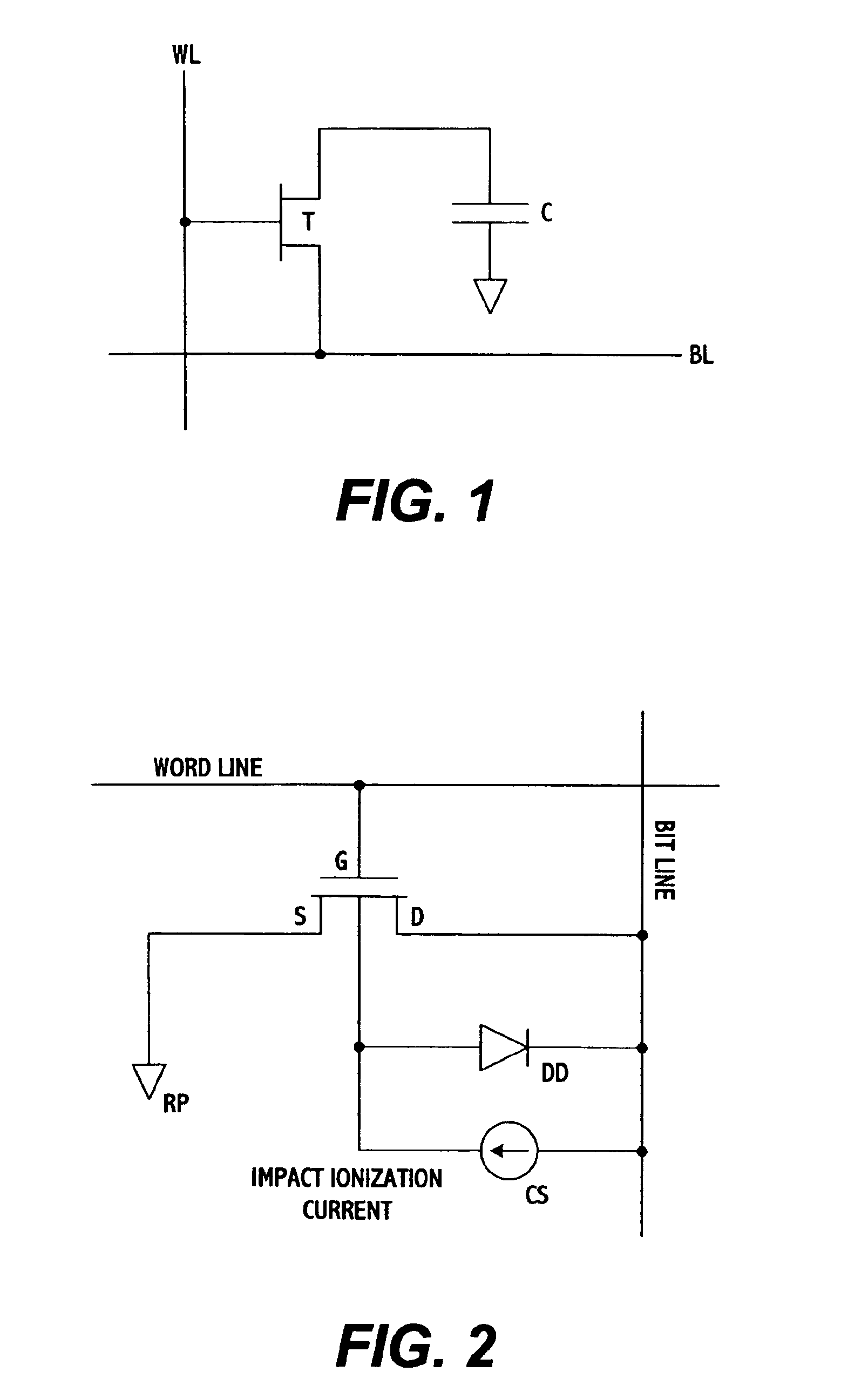
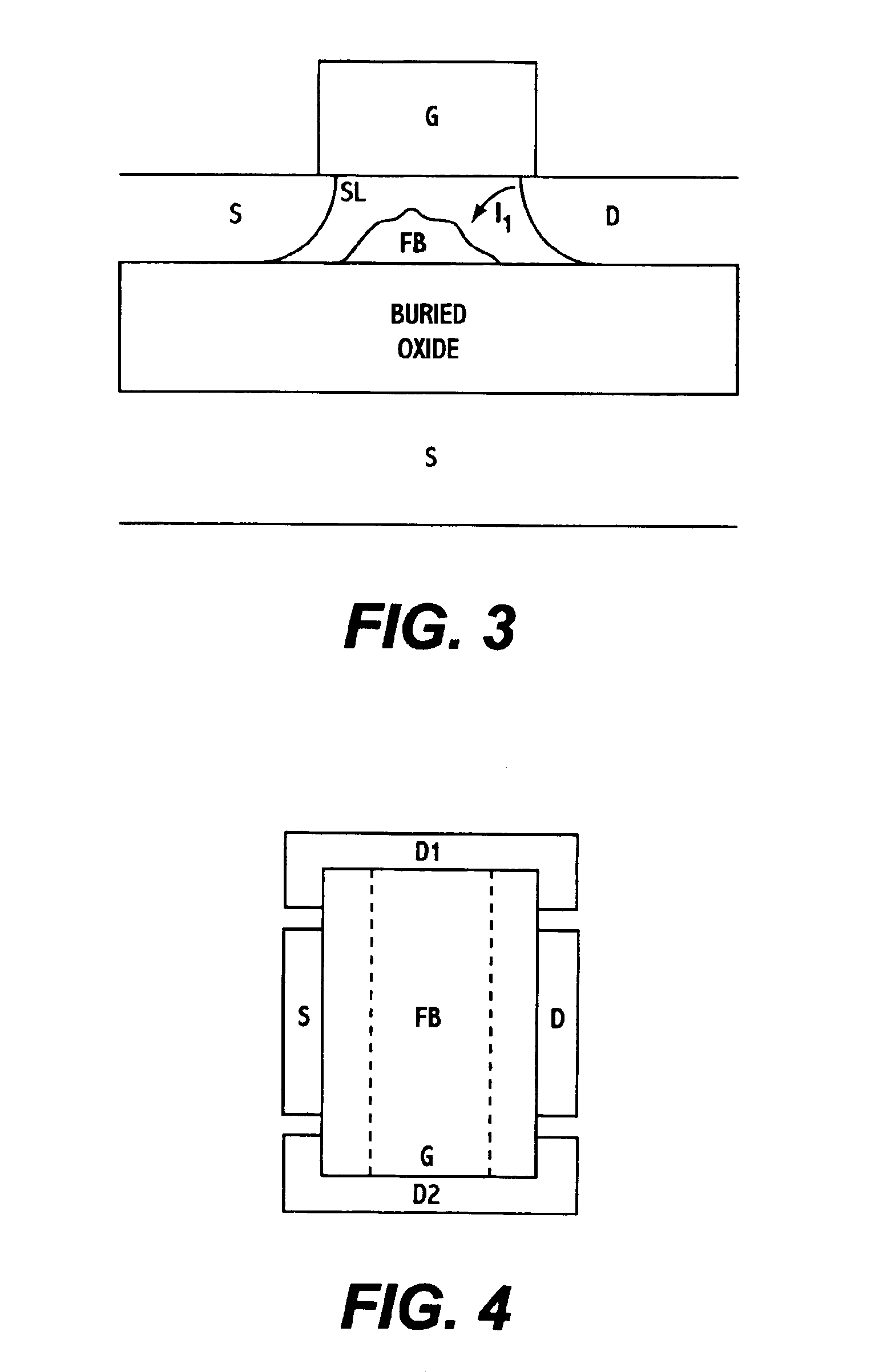
Floating-body DRAM using write word line for increased retention time
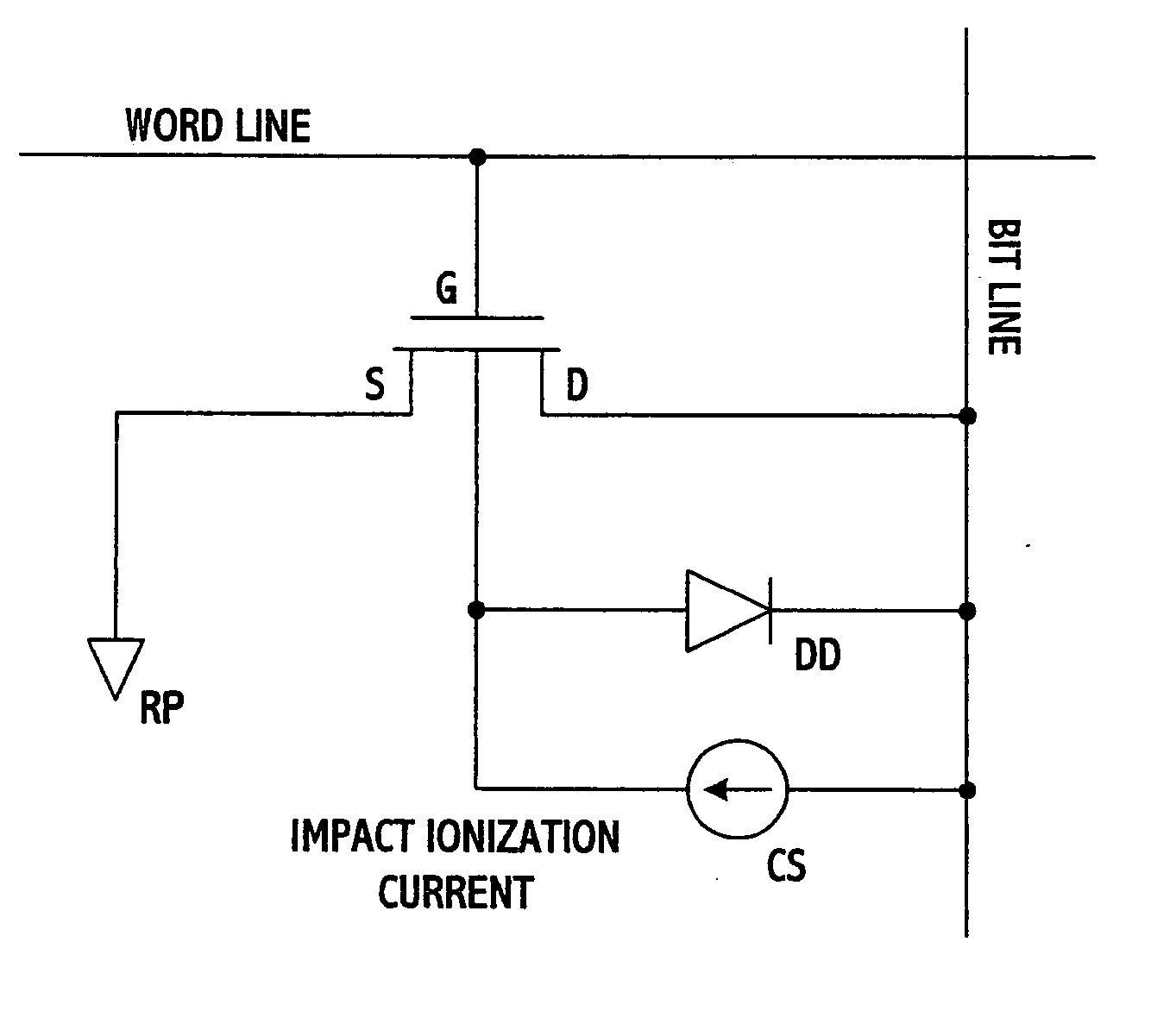
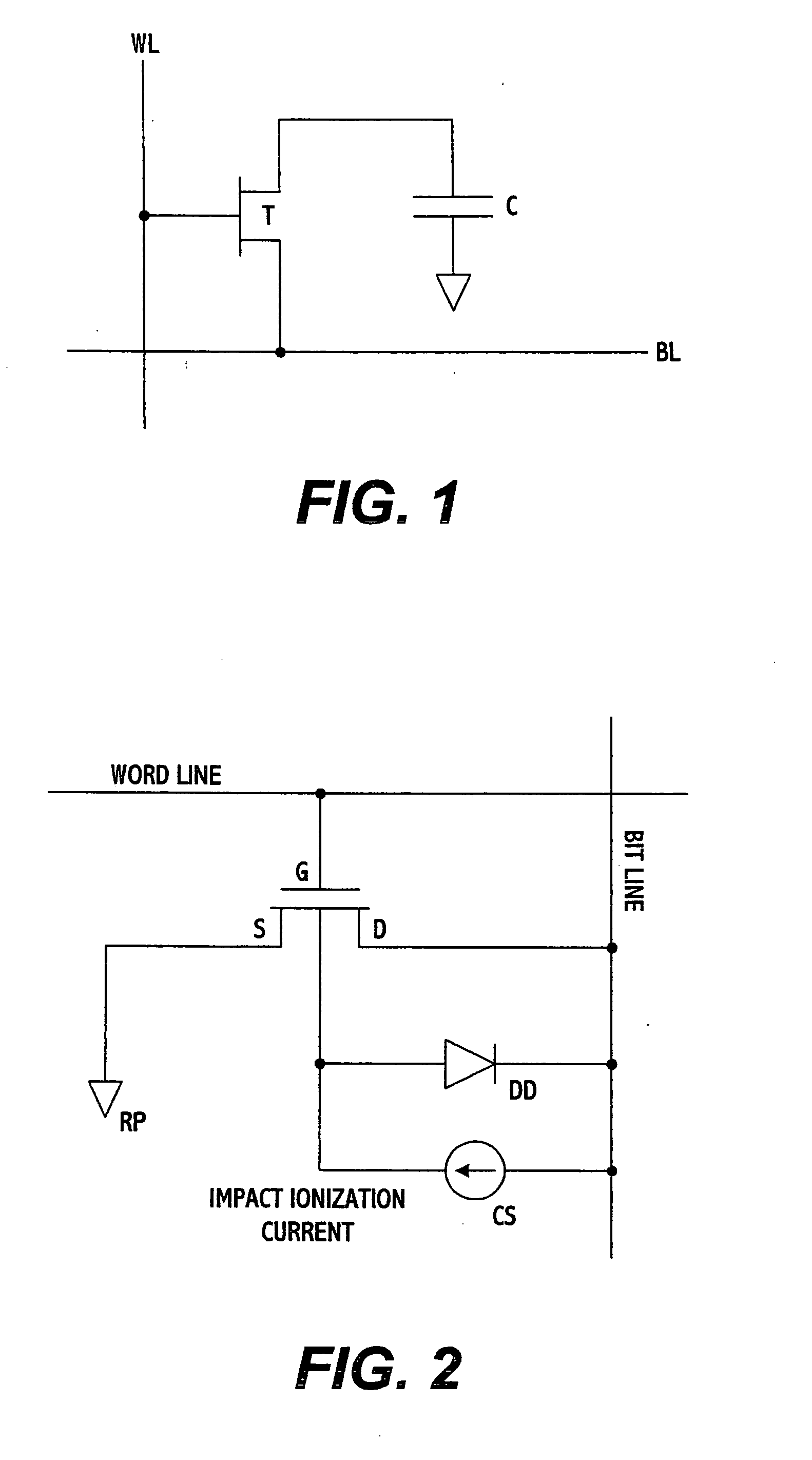
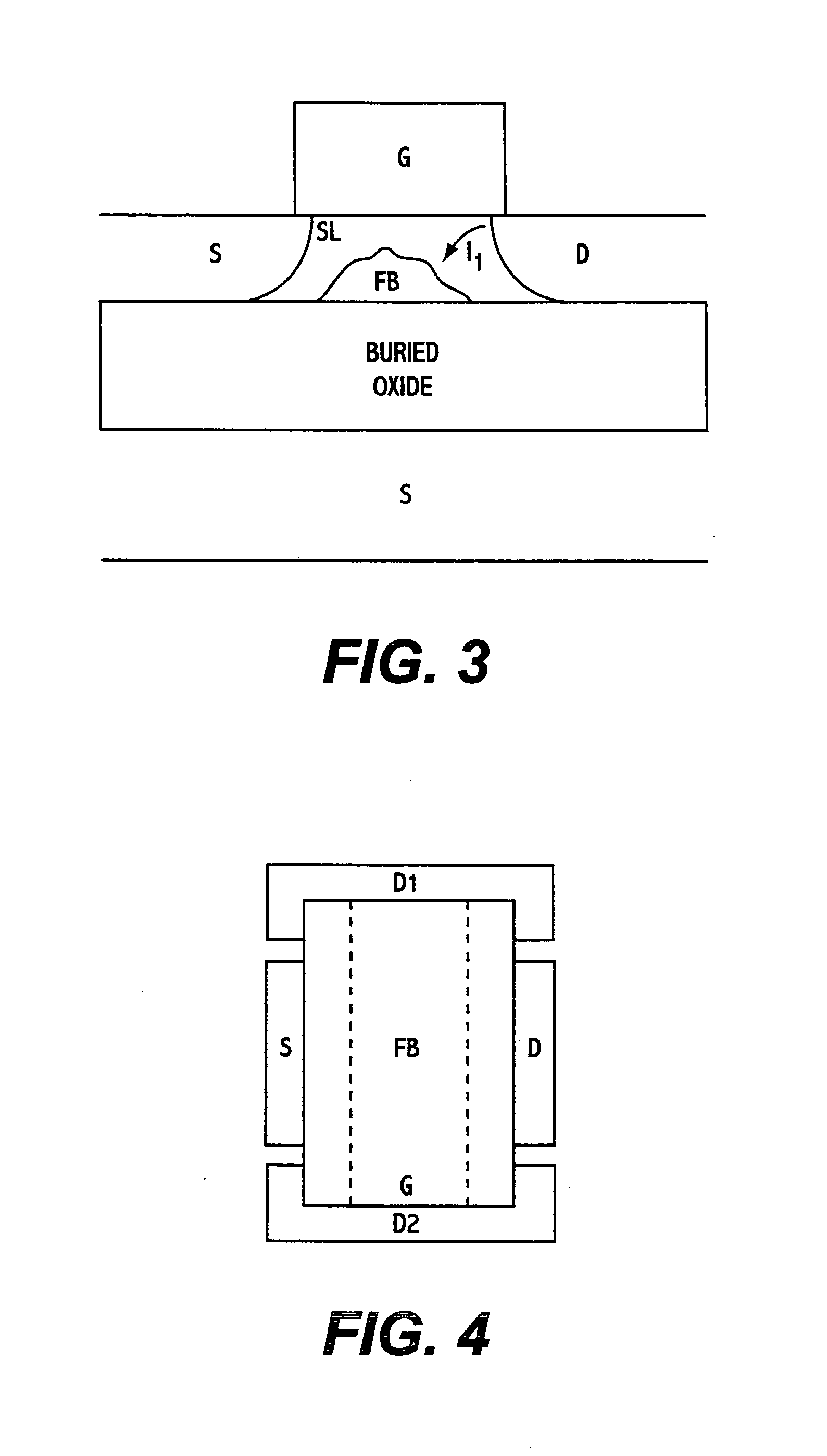
A DRAM memory cell uses a single transistor to perform the data storage and switching functions of a conventional cell. The transistor has a floating channel body which stores a potential that corresponds to one of two digital data values. The transistor further includes a gate connected to a first word line, a drain connected to a second word line, and a source connected to a bit line. By setting the word and bit lines to specific voltage states, the channel body stores a digital one potential as a result of impact ionization and a digital zero value as a result of forward bias of body-to-source junction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Architecture for vertical transistor cells and transistor-controlled memory cells
InactiveUS7109544B2Meet growth requirementsFunctional restriction of the transistor cells by a floating body effect is reducedTransistorSolid-state devicesTransistor arrayFloating body effect
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090003105A1Run at high speedSmall sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageAudio power amplifier
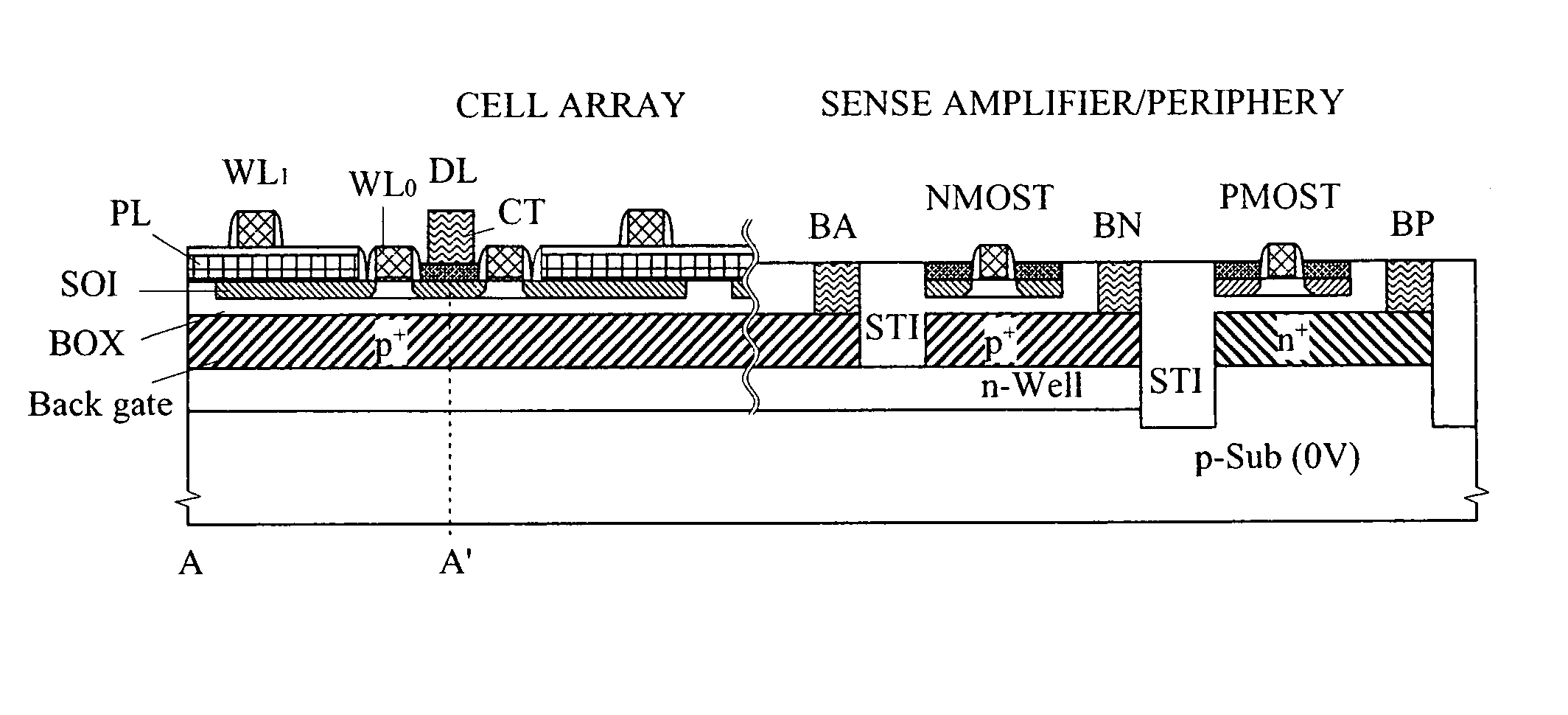
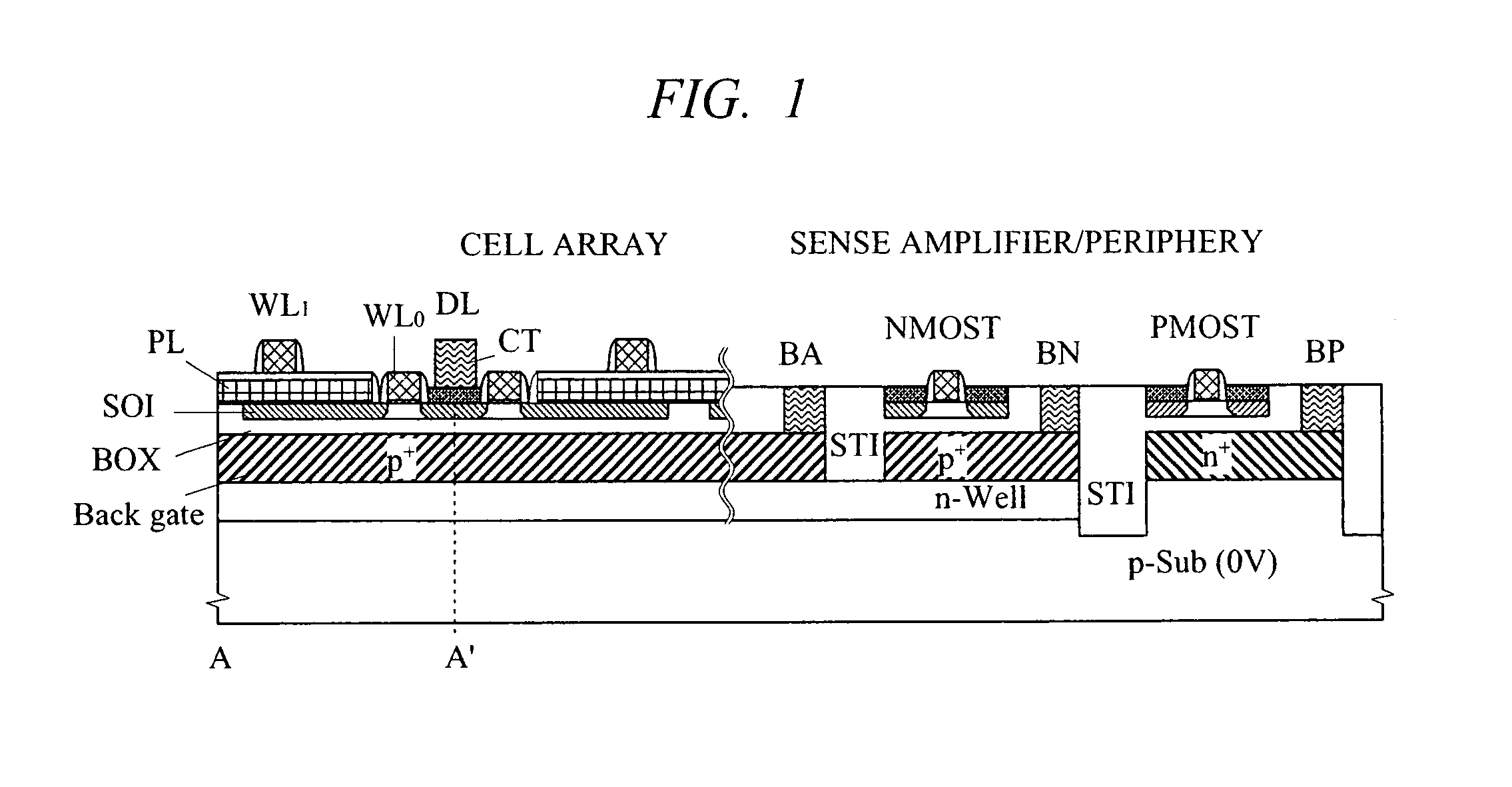
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
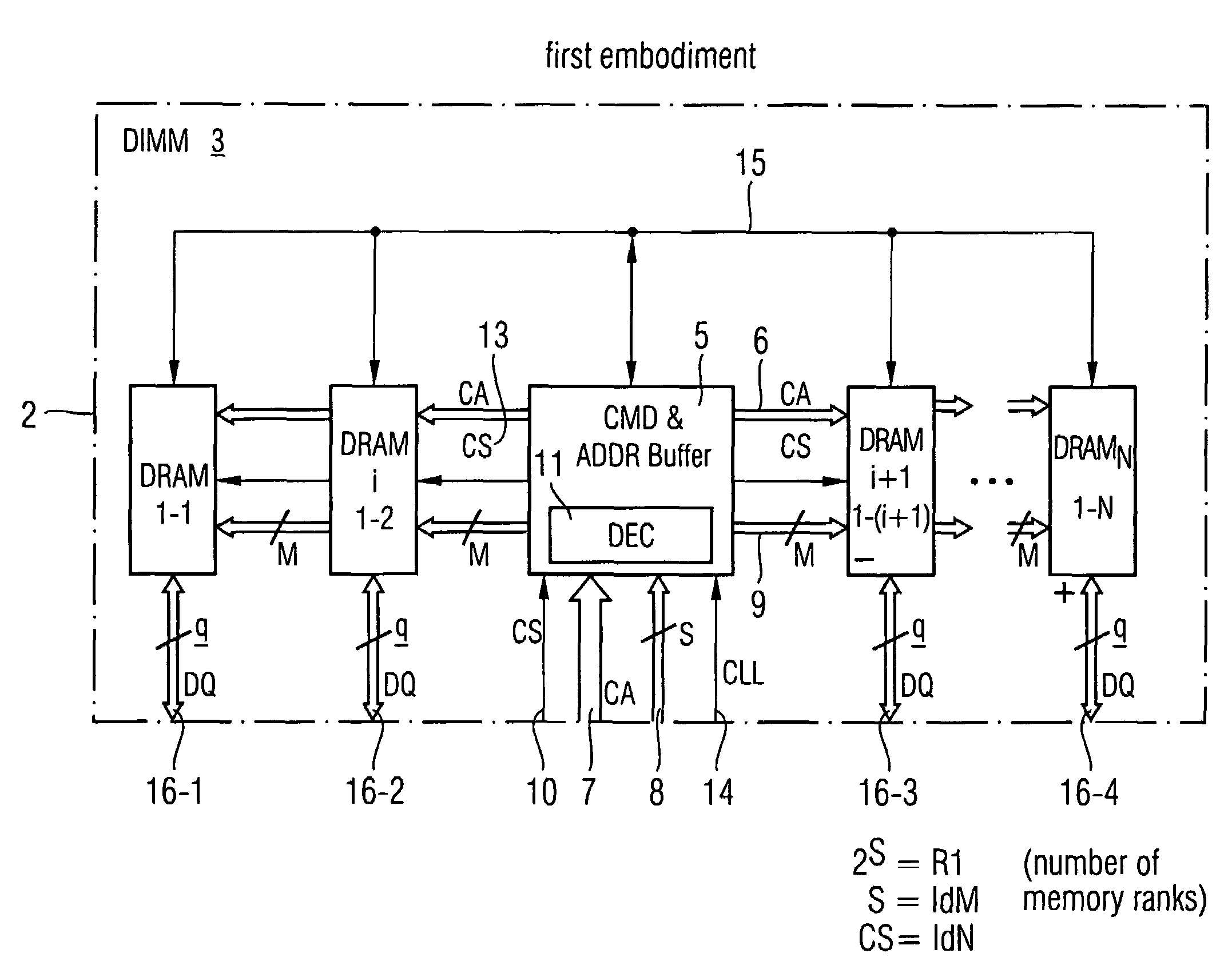
Memory rank decoder for a multi-rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM)
The invention refers to a Memory Rank Decoder for a Multi-Rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) having a predetermined number of DRAM memory chips mounted on a printer circuit board (PCB), wherein each DRAM memory chip comprises a predetermined number of stacked DRAM memory dies which are selectable by a memory rank selection signal (r), wherein the memory rank decoder generates the memory rank selection signal (r) in response to external selection signals applied to the dual inline module (DIMM).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Semiconductor device
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
High speed memory and input/output processor subsystem for efficiently allocating and using high-speed memory and slower-speed memory
ActiveUS7657706B2Easy to handleSimple taskMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh speed memoryMemory bank
An input / output processor for speeding the input / output and memory access operations for a processor is presented. The key idea of an input / output processor is to functionally divide input / output and memory access operations tasks into a compute intensive part that is handled by the processor and an I / O or memory intensive part that is then handled by the input / output processor. An input / output processor is designed by analyzing common input / output and memory access patterns and implementing methods tailored to efficiently handle those commonly occurring patterns. One technique that an input / output processor may use is to divide memory tasks into high frequency or high-availability components and low frequency or low-availability components. After dividing a memory task in such a manner, the input / output processor then uses high-speed memory (such as SRAM) to store the high frequency and high-availability components and a slower-speed memory (such as commodity DRAM) to store the low frequency and low-availability components. Another technique used by the input / output processor is to allocate memory in such a manner that all memory bank conflicts are eliminated. By eliminating any possible memory bank conflicts, the maximum random access performance of DRAM memory technology can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
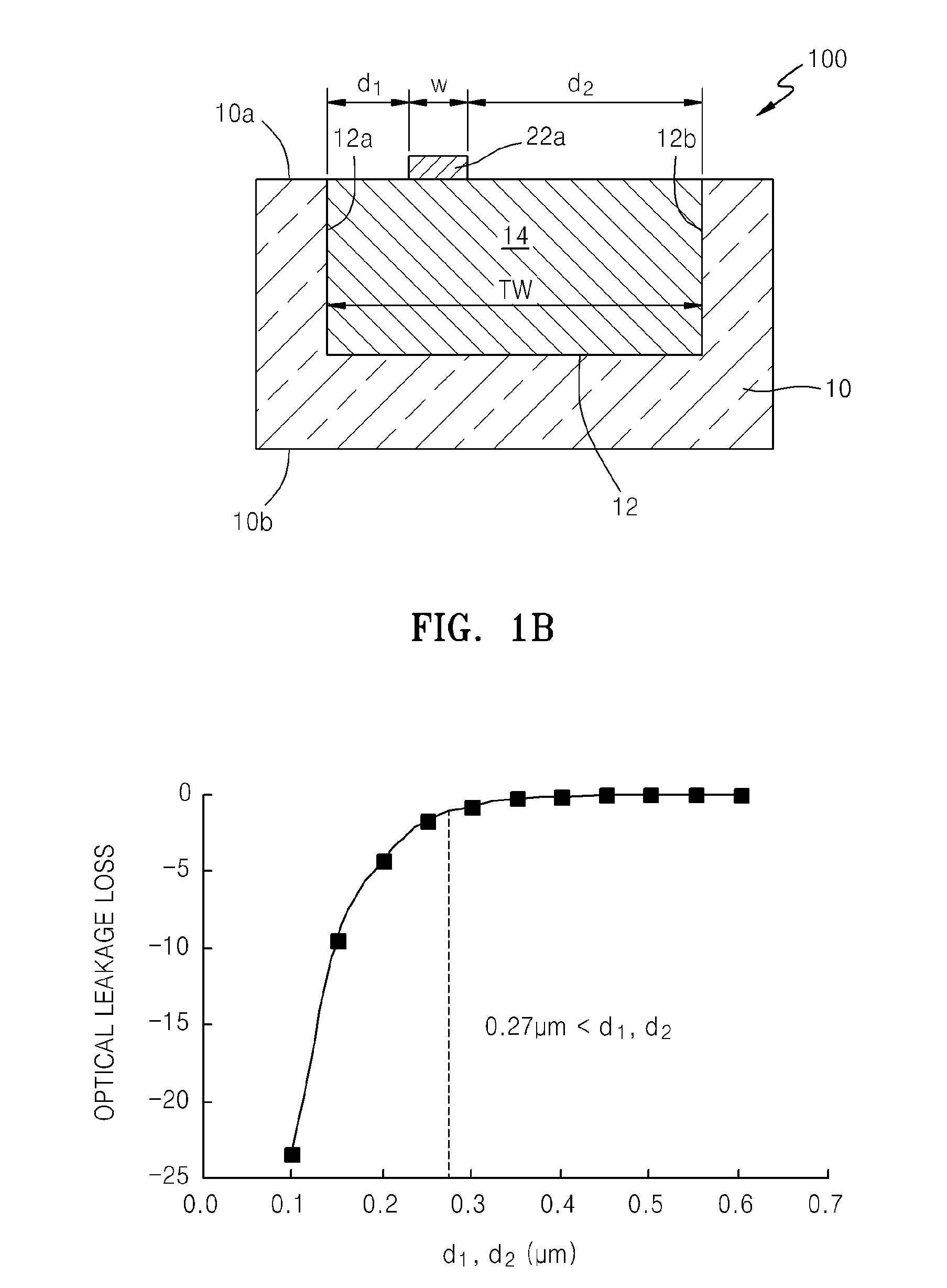
Optical waveguide and coupler apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110133063A1Cladded optical fibreSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon photonicsDram memory
Optical waveguide and coupler devices and methods include a trench formed in a bulk semiconductor substrate, for example, a bulk silicon substrate. A bottom cladding layer is formed in the trench, and a core region is formed on the bottom cladding layer. A reflective element, such as a distributed Bragg reflector can be formed under the coupler device and / or the waveguide device. Because the optical devices are integrated in a bulk substrate, they can be readily integrated with other devices on a chip or die in accordance with silicon photonics technology. Specifically, for example, the optical devices can be integrated in a DRAM memory circuit chip die.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
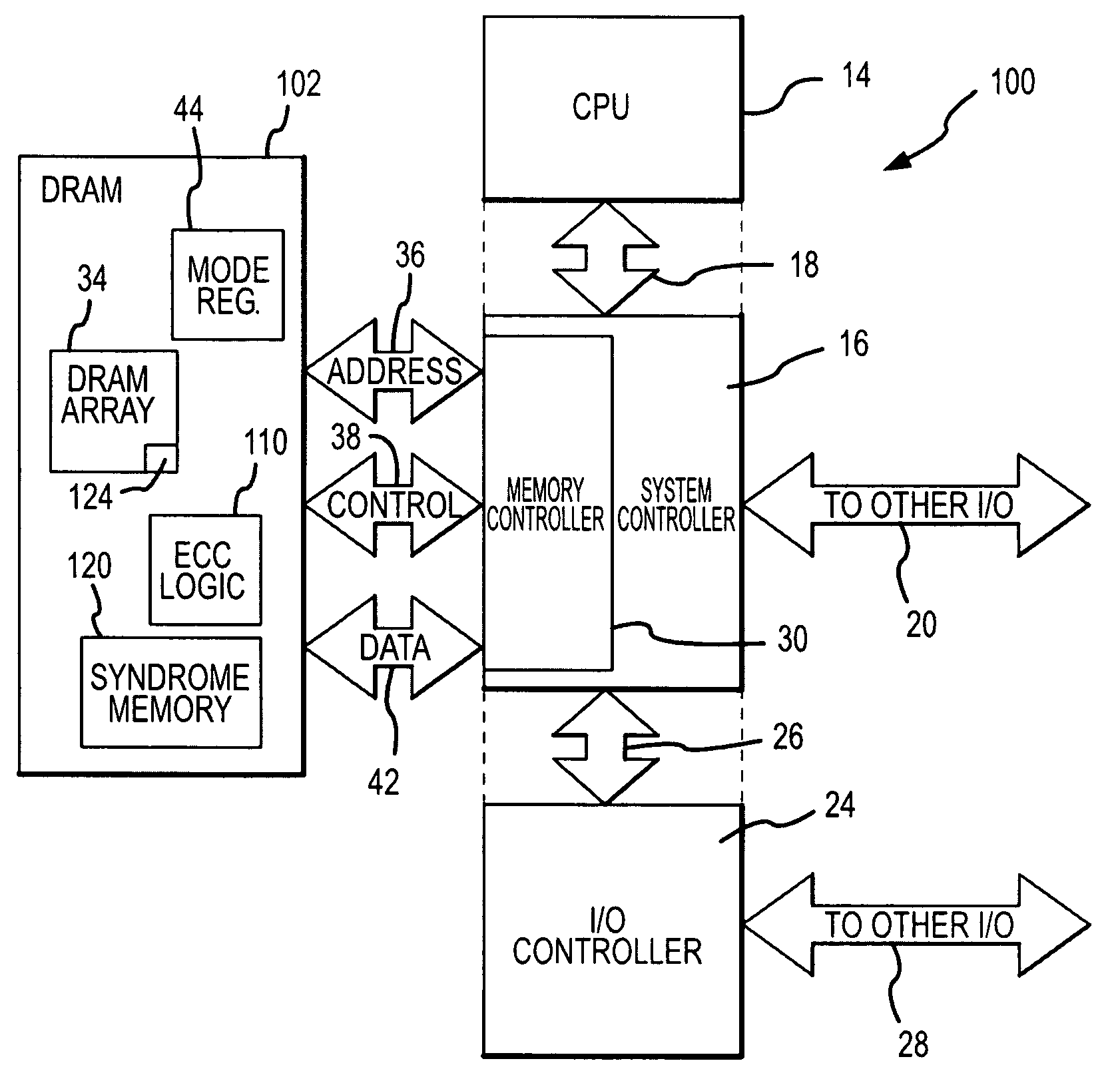
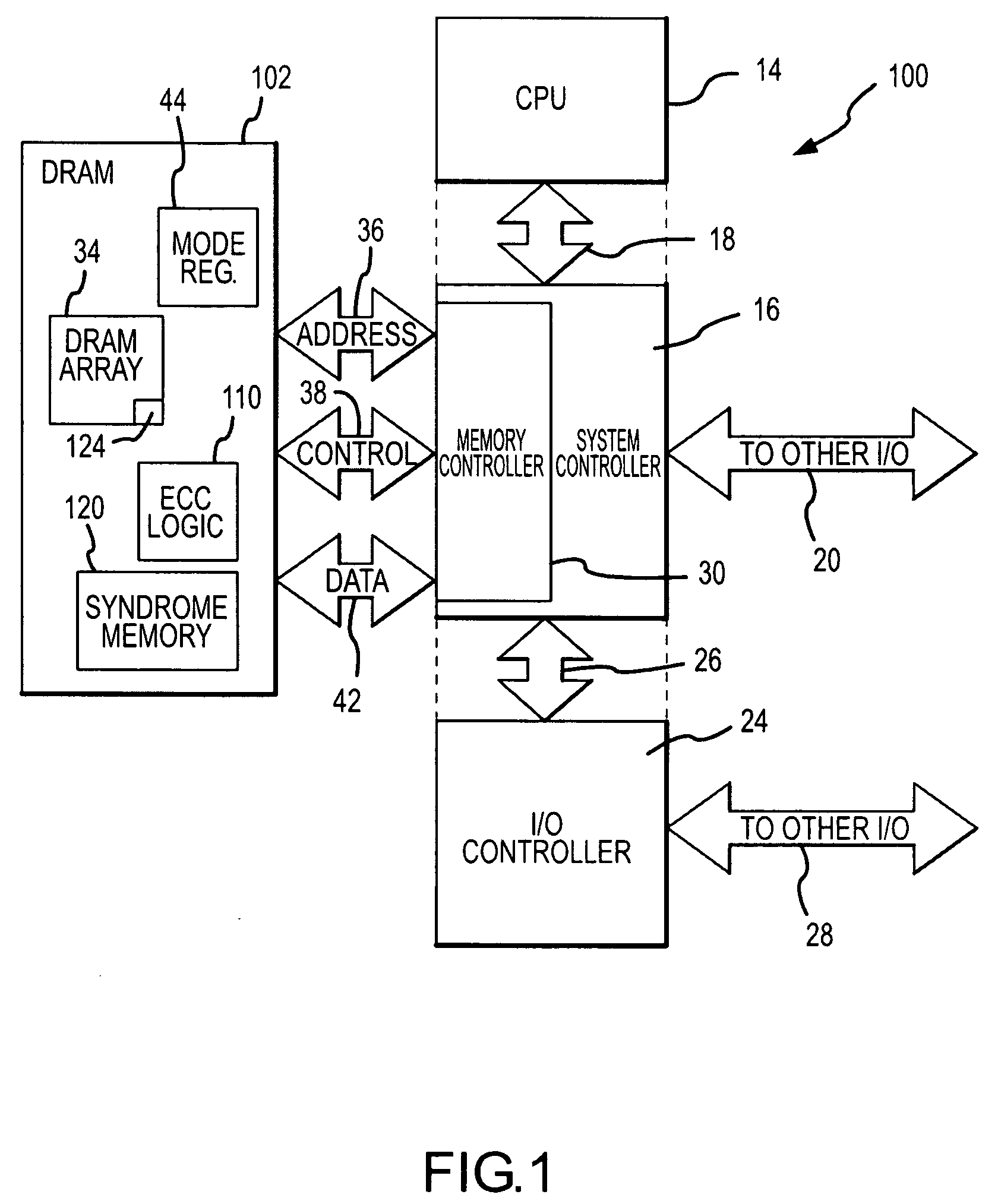
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and production method thereof
InactiveUS20050208716A1Improve refresh featureEasy to integrateTransistorSolid-state devicesDram memoryEngineering
A refresh characteristic of a DRAM memory cell is improved and the performance of a MISFET formed in the periphery thereof and constituting a logic circuit is improved. Each gate electrode in a memory cell area is formed of p type polycrystalline silicon, and a cap insulating film on each gate electrode and a sidewall film on the sidewall thereof are formed of a silicon oxide film. A polycrystalline silicon film formed on the gate electrodes and between the gate electrodes is polished by a CMP method, and thereby contact electrodes are formed. Also, sidewall films each composed of a laminated film of the silicon oxide film and the polycrystalline silicon film are formed on the sidewall of the gate electrodes in the logic circuit area, and these films are used as a mask to form semiconductor areas. As a result, it is possible to reduce the boron penetration and form contact electrodes in a self-alignment manner. In addition, the performance of the MISFET constituting the logic circuit can be improved.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Memory system and method using ECC to achieve low power refresh
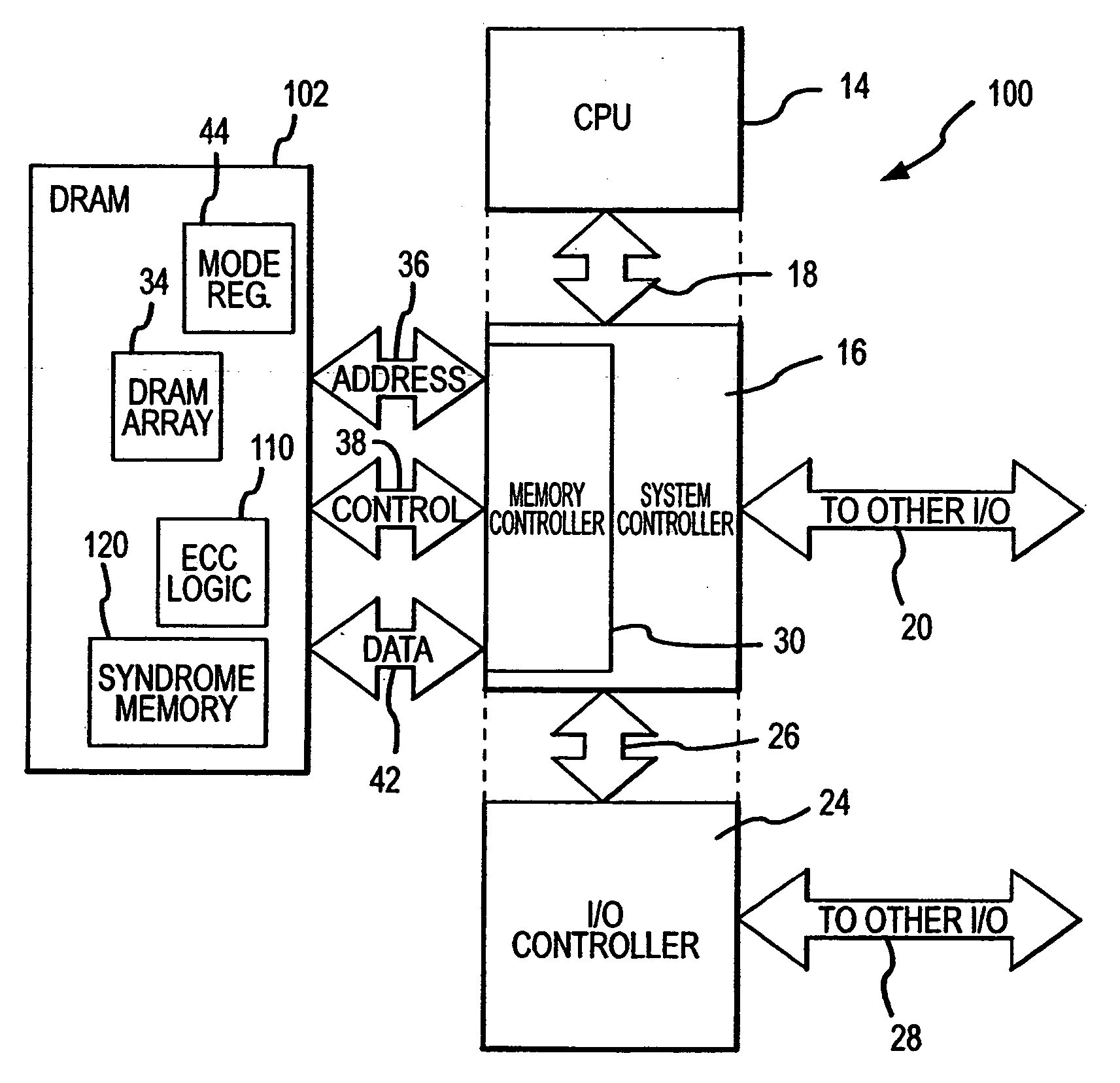
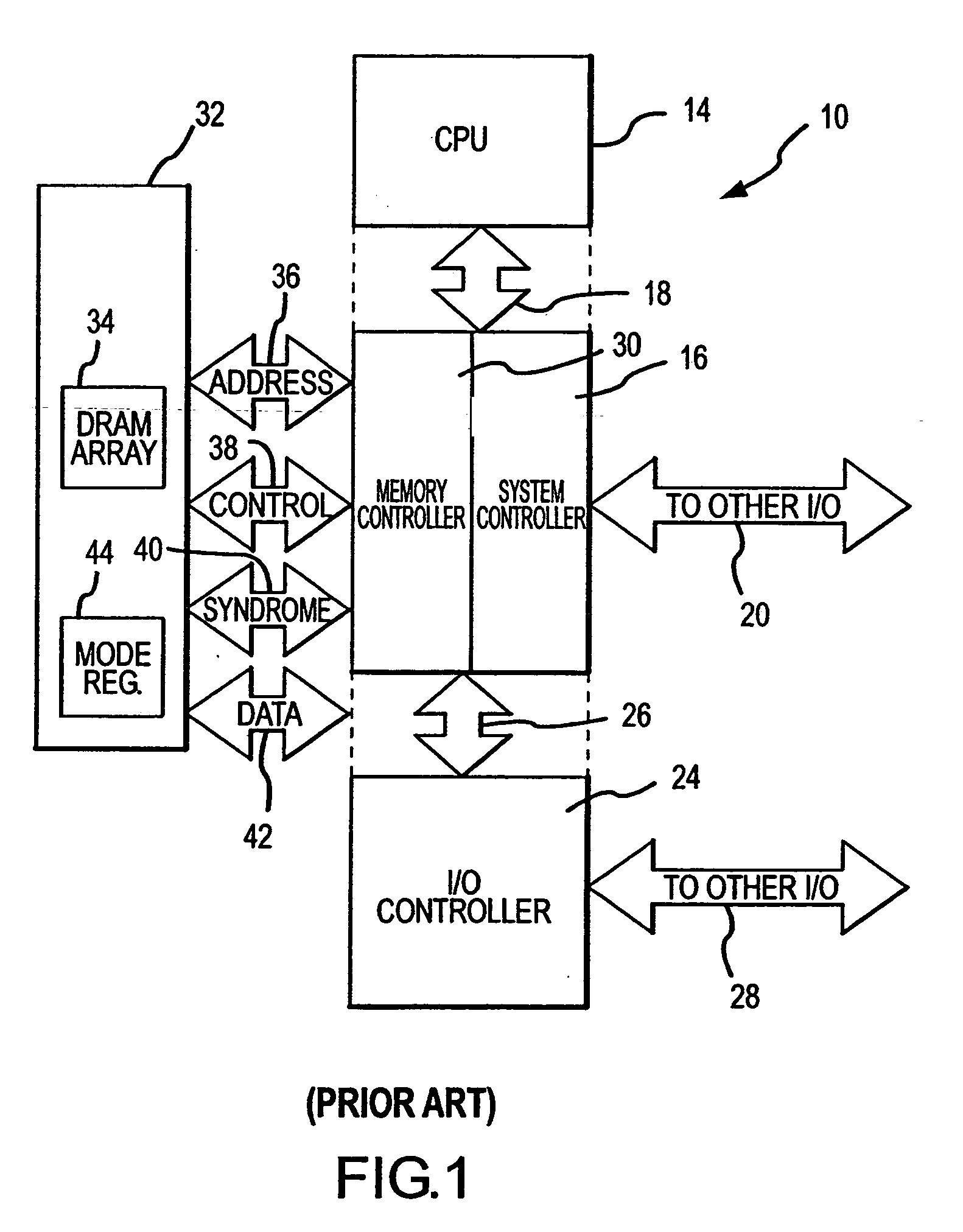
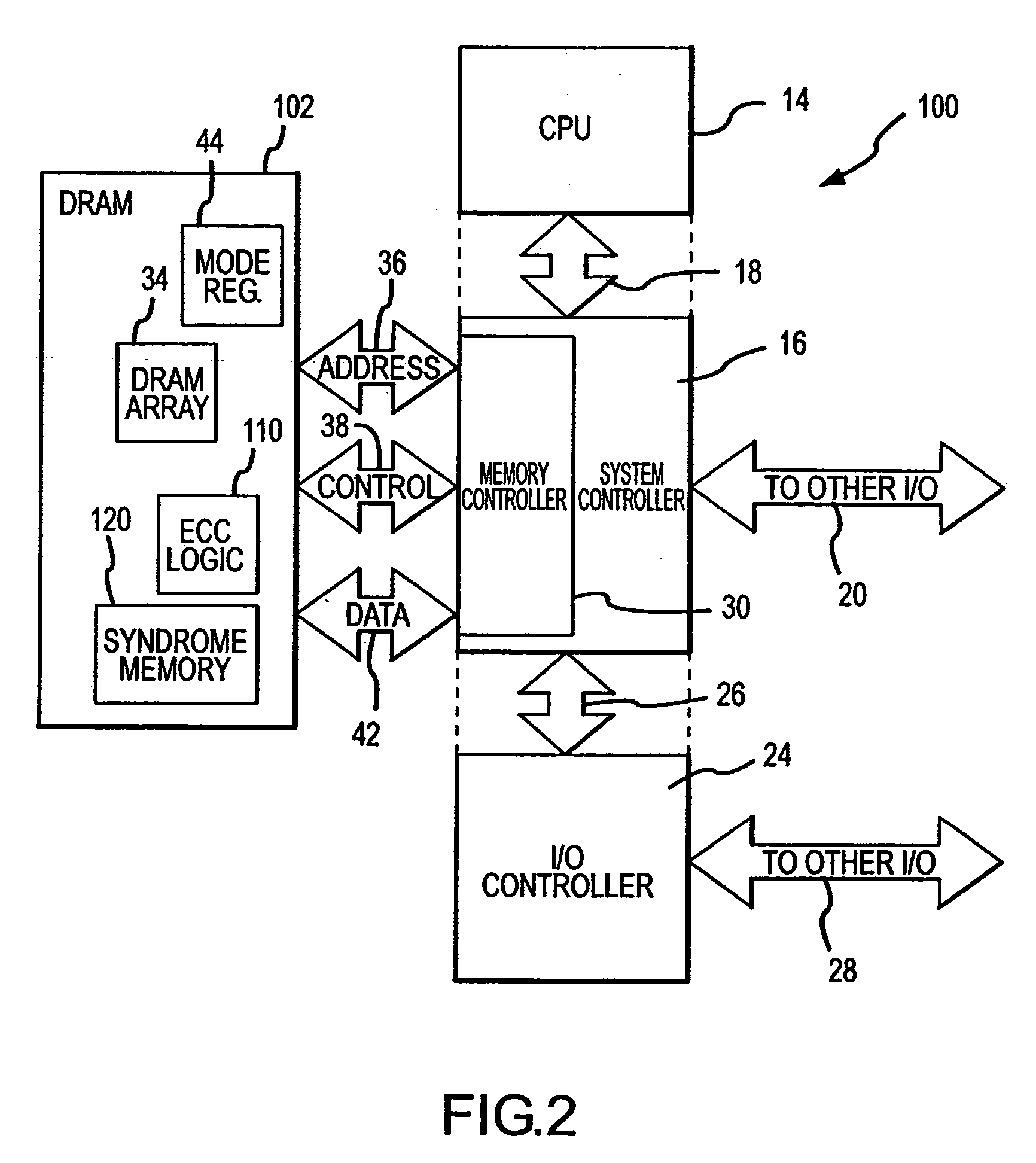
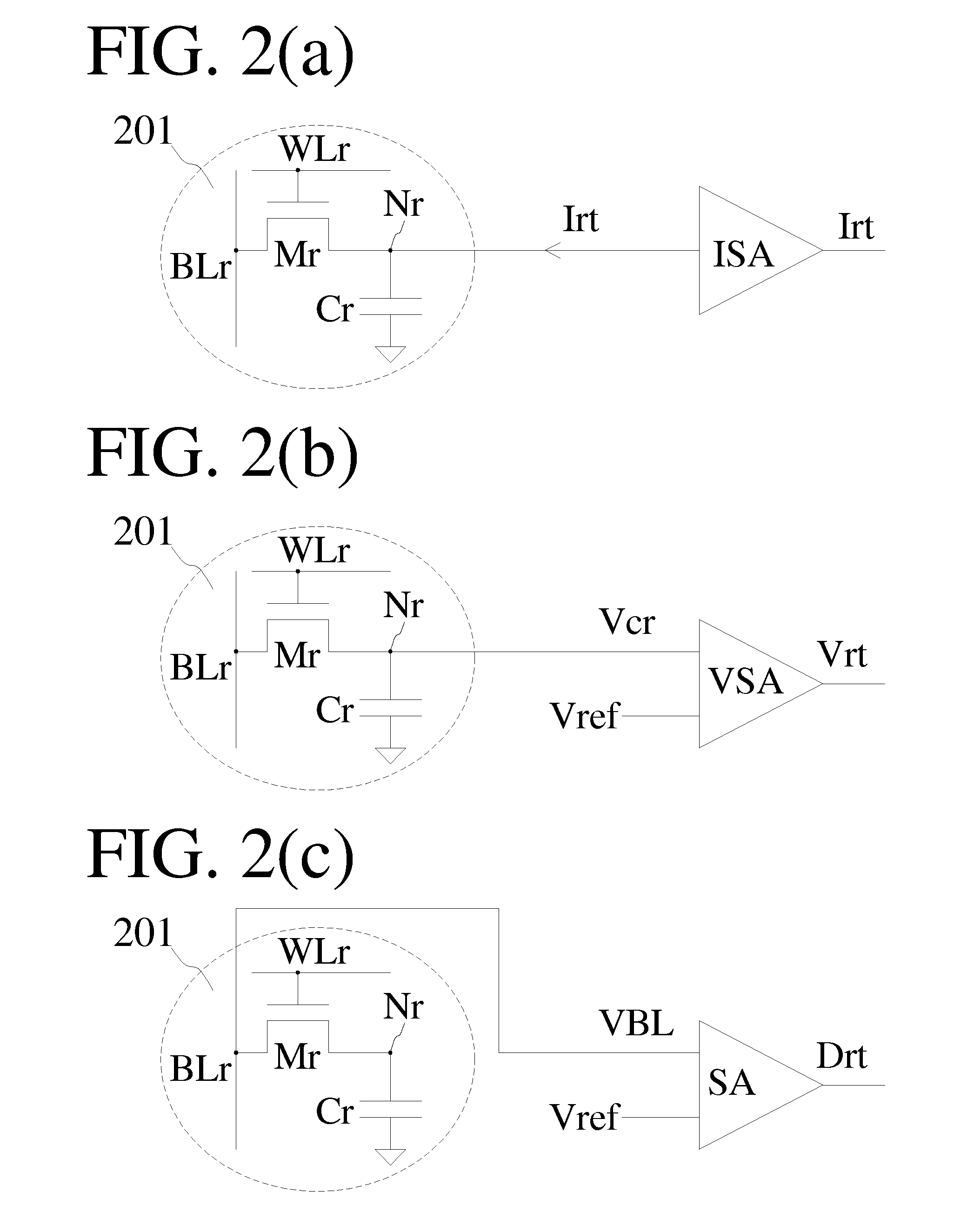
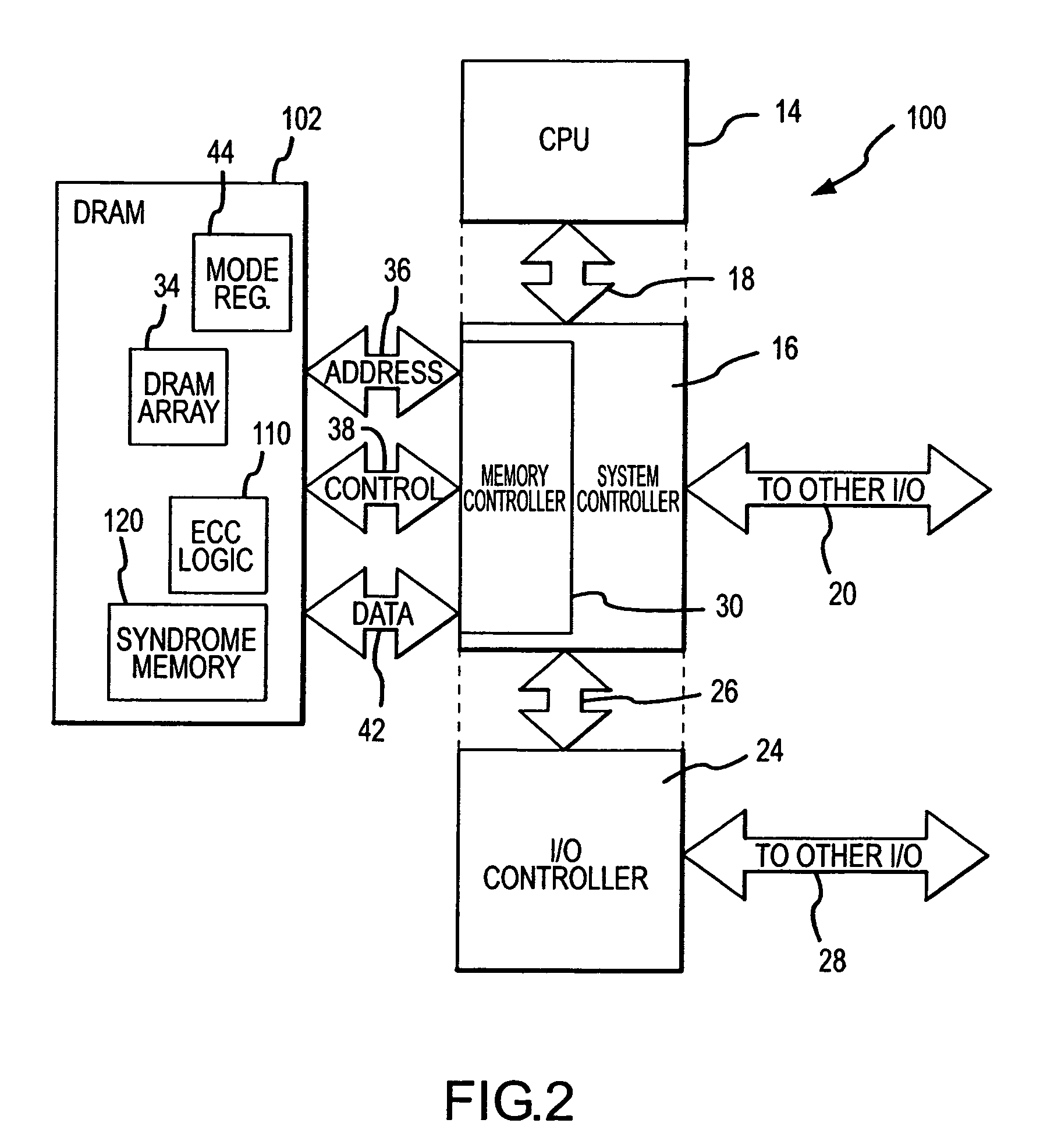
Rows of DRAM memory cells are refreshed at either a relatively high rate during normal operation or a relatively slow rate in a reduced power refresh mode. Prior to refreshing the rows of memory cells, the data are read from the memory cells, and corresponding syndromes are generated and stored. When transitioning from the reduced power refresh mode, data from the rows of memory cells are read, and the stored syndromes are used to determine if there are errors in the read data. The syndromes are also used to correct any errors that are found, and the corrected data are written to the rows of memory cells. By correcting any errors that exist when transitioning from the reduced power refresh mode, it is not necessary to use the syndromes to detect and correct errors while operating in the reduced power refresh mode.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
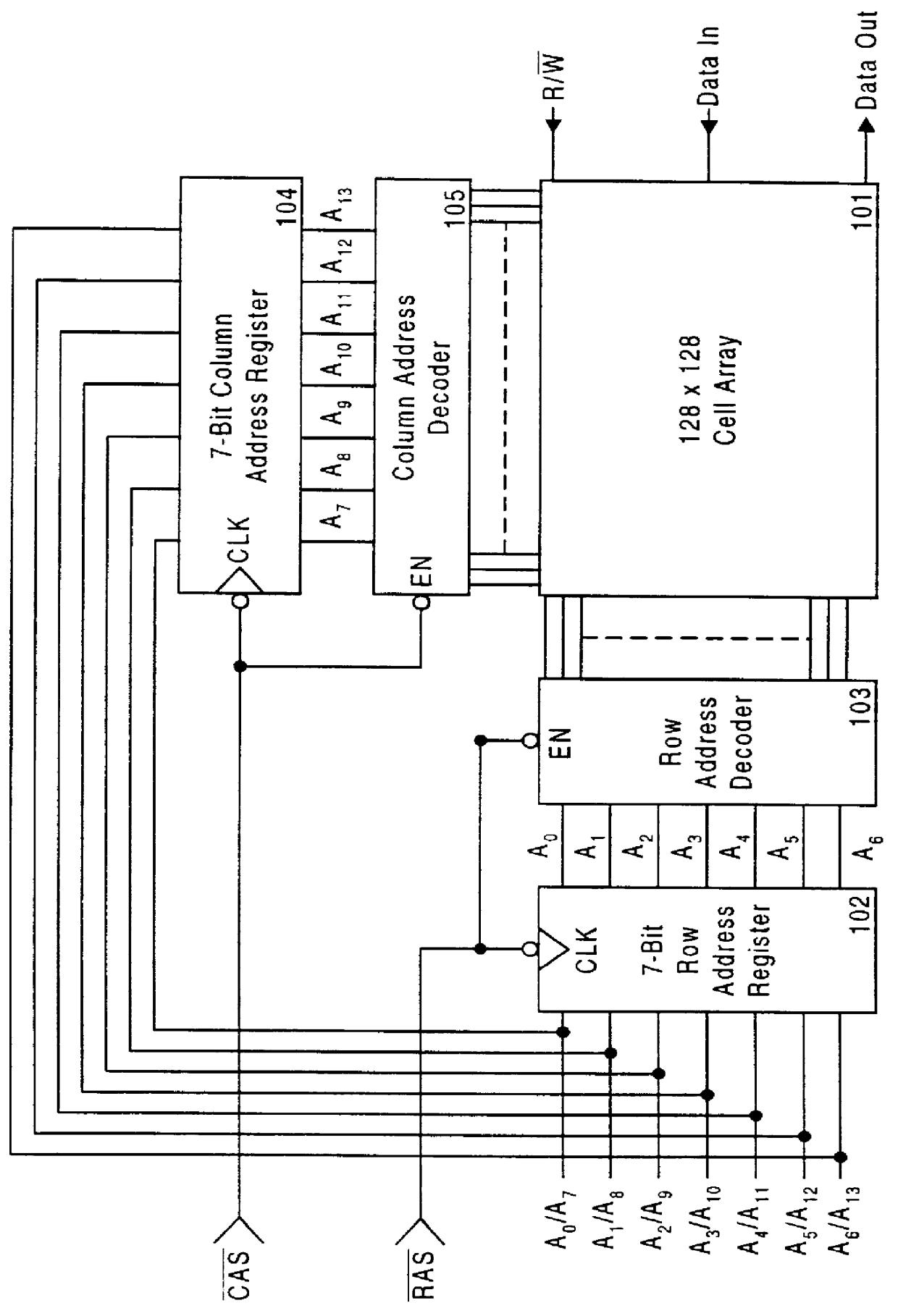
Scoreboarding for DRAM access within a multi-array DRAM device using simultaneous activate and read/write accesses
InactiveUS6023745AEfficient configurationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationArray data structureDram memory
A method and apparatus for performing memory array / row scoreboarding in a dynamic access memory (DRAM) having dual bank access. The DRAM of the present invention allows dual simultaneous memory accesses into a memory divided into a plurality of arrays (e.g., 48 arrays). Each array of the DRAM contains a plurality of rows (e.g., 256). Each row of the DRAM contains storage for a certain amount of data bits (e.g., 1024). The DRAM in one configuration contains 1.5 Megabytes of memory. During a dual bank DRAM access, the system allows a first access for pre-opening a row (e.g., a page) of DRAM memory within a first array while simultaneously allowing a second access for reading / writing data to an opened row of another array aside from the first array. The present invention scoreboarding system tracks the rows that are currently open so that immediate read / write accesses can take place. Upon presentation of a row and array, the scoreboard determines if the presented row is currently open, and if so, generates a hit signal that allows an immediate read / write access to the presented row. If the presented row is not open, the present invention generates a miss signal so that the row can be immediately opened before access is allowed. The scoreboard contains a memory unit containing row information for each array in the DRAM. The scoreboard, in addition to other novel features, allows an efficient DRAM configuration allowing dual memory accesses per cycle.
Owner:XYLON LLC
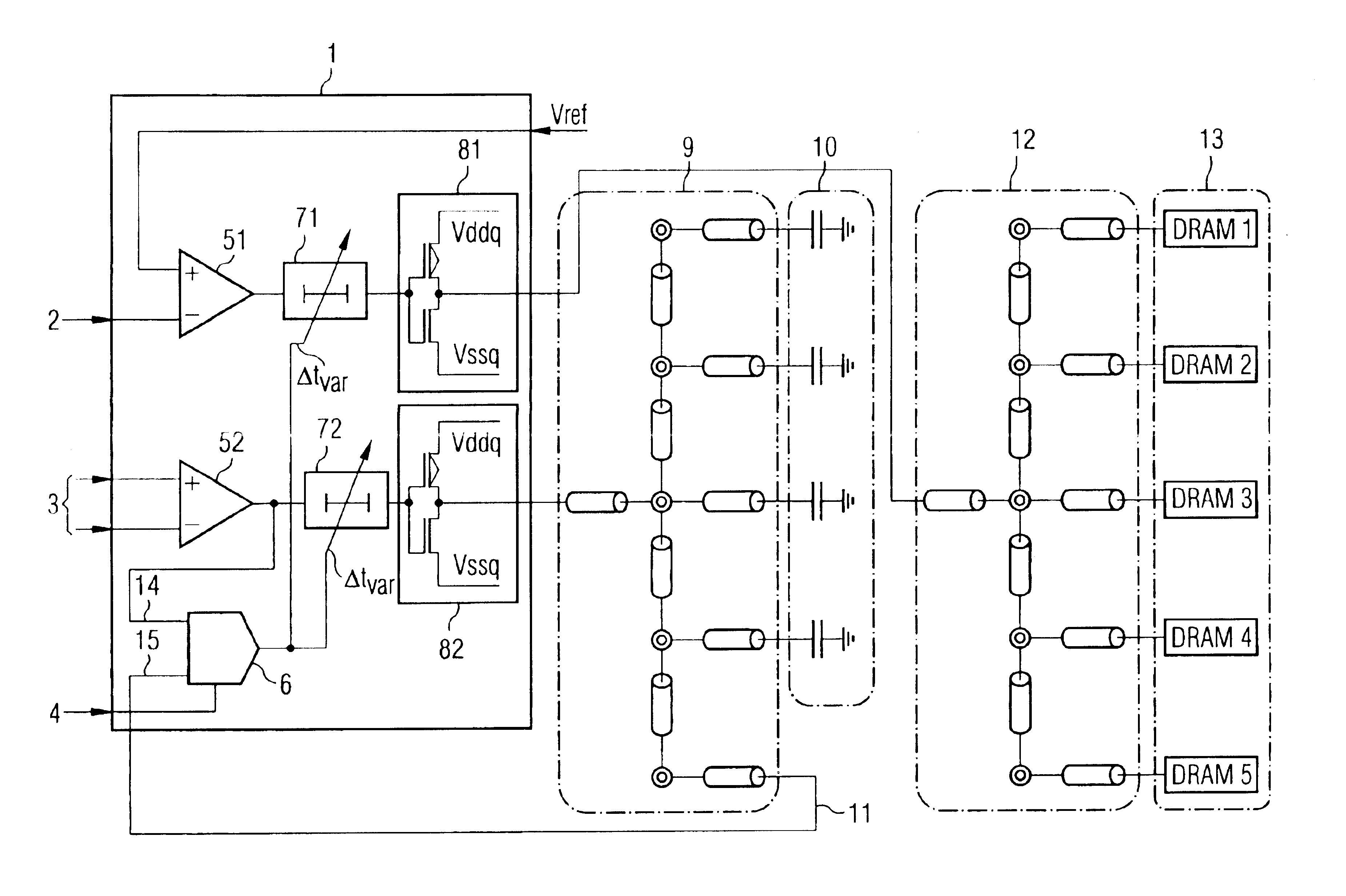
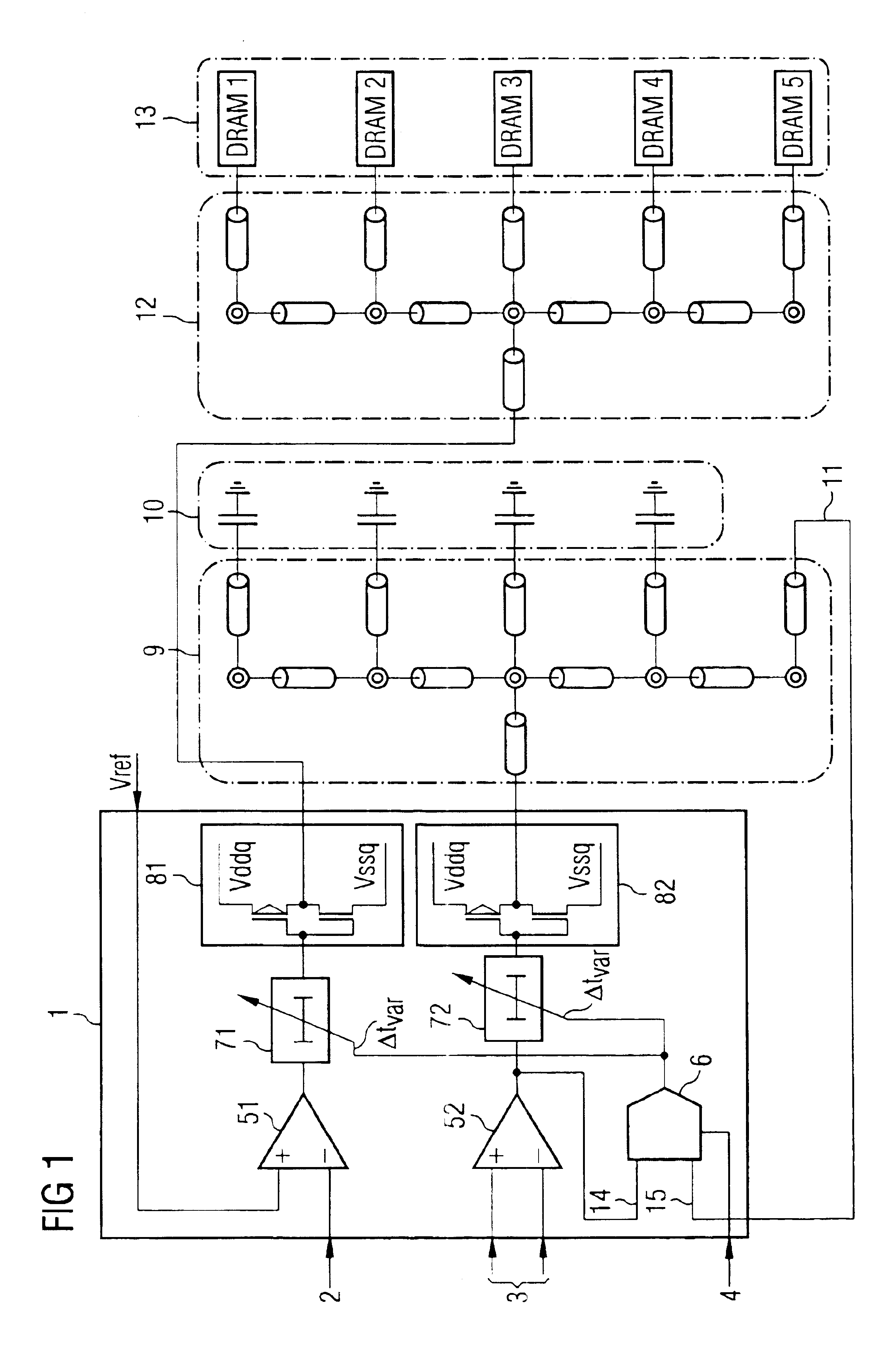
Buffer amplifier architecture for semiconductor memory circuits
A buffer amplifier architecture for buffering signals which are supplied in parallel to identical chips, particularly DRAM chips, on a semiconductor memory module, is disclosed. The architecture has adjustable delay circuits in each signal line and a delay detector circuit which receives a clock signal from the buffer amplifier architecture at the input and at the output of the buffer amplifier architecture, and takes the phase difference between the two signals to produce a control signal for setting the variable delay time of the delay circuits. To ensure that the delay time set by the delay detector circuit is independent of variations in parameters of the DRAM memory chips, the feedback path routed to the input of the delay detector circuit has a reference line network of the same structure and having the same electrical properties as capacitance elements which terminate the line network routed to the DRAM memory chips and the reference line network, and which have the same capacitances as the signal inputs on the DRAM memory chips.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
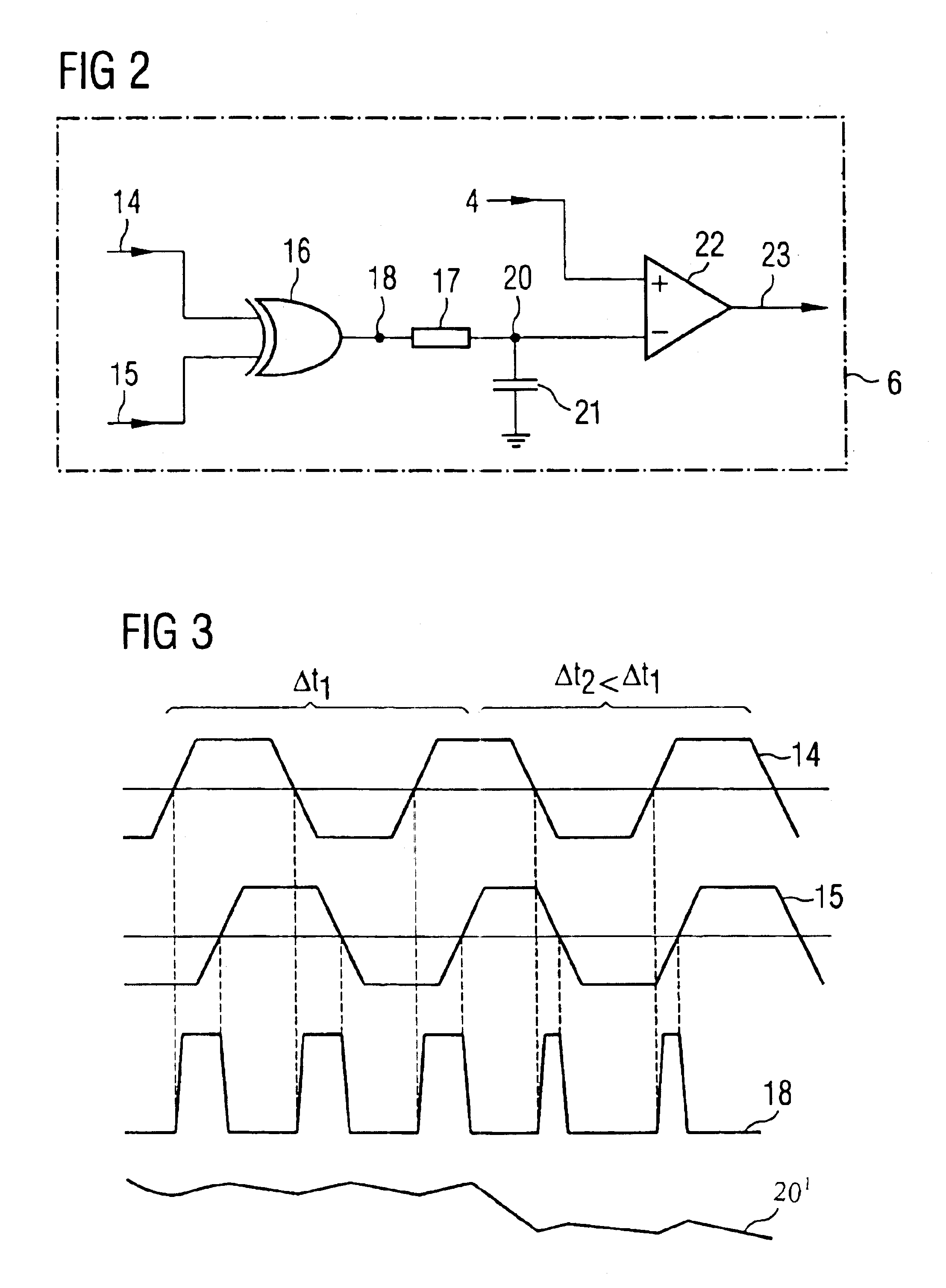
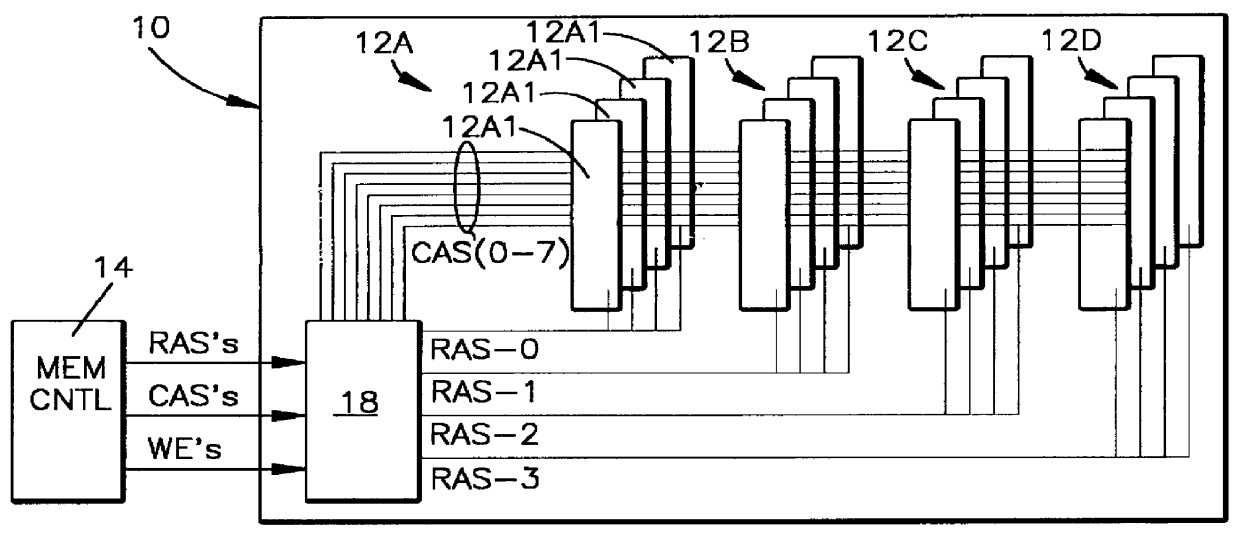
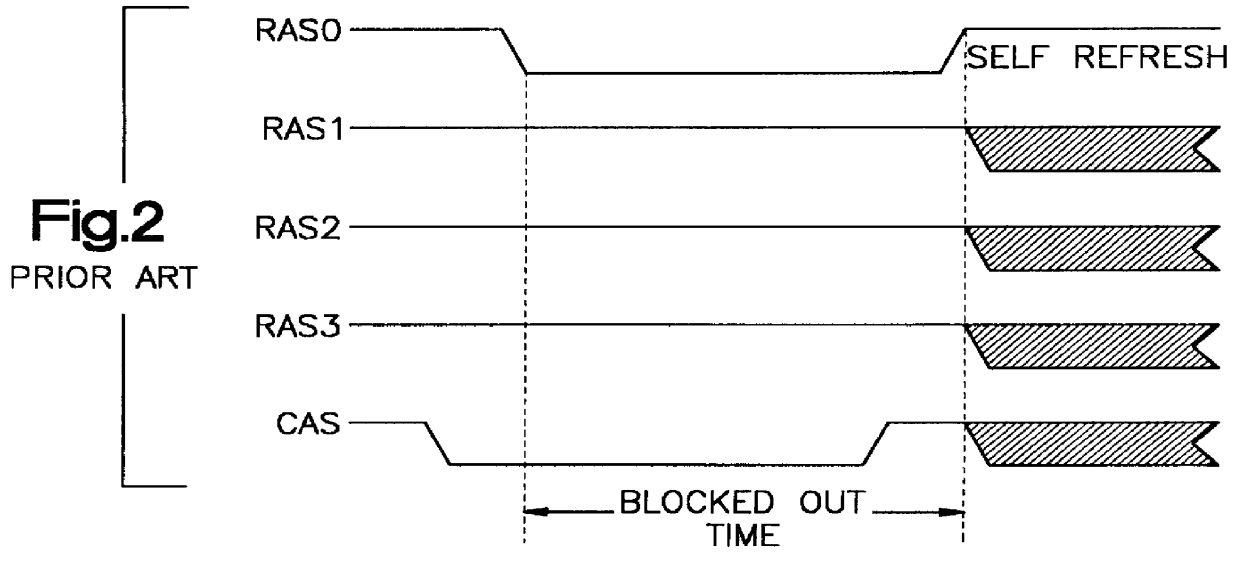
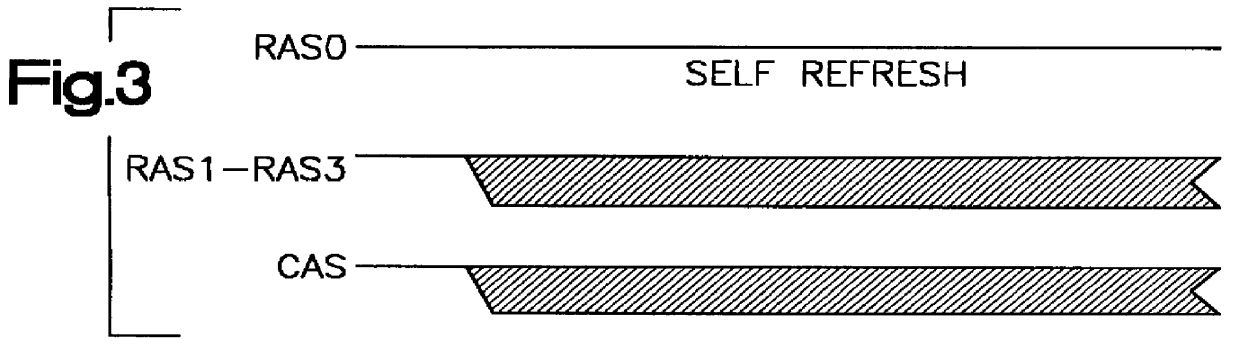
Self-initiated self-refresh mode for memory modules
A method and apparatus for selectively causing each bank of a number of banks of DRAMs of a DRAM memory card to enter into the self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. In the computer system incorporating the SIMM or DIMM type DRAM cards, each bank of memory on each card has a RAS signal specific to that specific bank. One or more CAS signals are supplied across all of the memory banks, on all cards. Thus, each memory bank is accessed separately for a read / write operation by the RAS becoming active before the CAS becomes active; and refresh takes place by the CAS signal becoming active before the RAS signal becomes active. The number of clock cycles or refresh cycles between active RAS signals to each memory bank are counted. If RAS does not become active for N clock or refresh cycles, a signal is provided within each respective memory bank and that memory bank will immediately, or preferably after M additional clock or refresh cycles enter self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. At the same time, the memory controller counts cycles of RAS inactivity for each DRAM bank it controls. A signal is also provided to a register to require a double read / write on the next active read / write cycle to that bank, for reactivating that bank from the self-refresh mode when RAS signal specific to that bank becomes active while CAS is inactive.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Semiconductor memory
InactiveUS20060076549A1Short switching timeLow programming voltageDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesSilicon matrixRetention time
The object of providing a non-volatile semiconductor memory that stands out by good scalability and a high retention time as well as ensures low switching voltages at low switching times and achieves a great number of switching cycles at good temperature stability is solved by the present invention with a semiconductor memory whose memory cells comprise at least one silicon matrix material layer with open or disturbed nanocrystalline or amorphous network structures and structural voids which has a resistively switching property between two stable states, utilizing the ion drift in the silicon matrix material layer. The memory concept suggested in the present invention thus offers an alternative to the flash and DRAM memory concepts since it is not based on the storing of charges, but on the difference of the electric resistance between two stable states that are caused by the mobility of ions in the amorphous silicon matrix material with an externally applied electric field.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Power efficient dynamic random access memory devices
InactiveUS20120243299A1Improve DRAM power efficiencyReduce DRAM refresh powerDigital storagePower efficientCharge retention
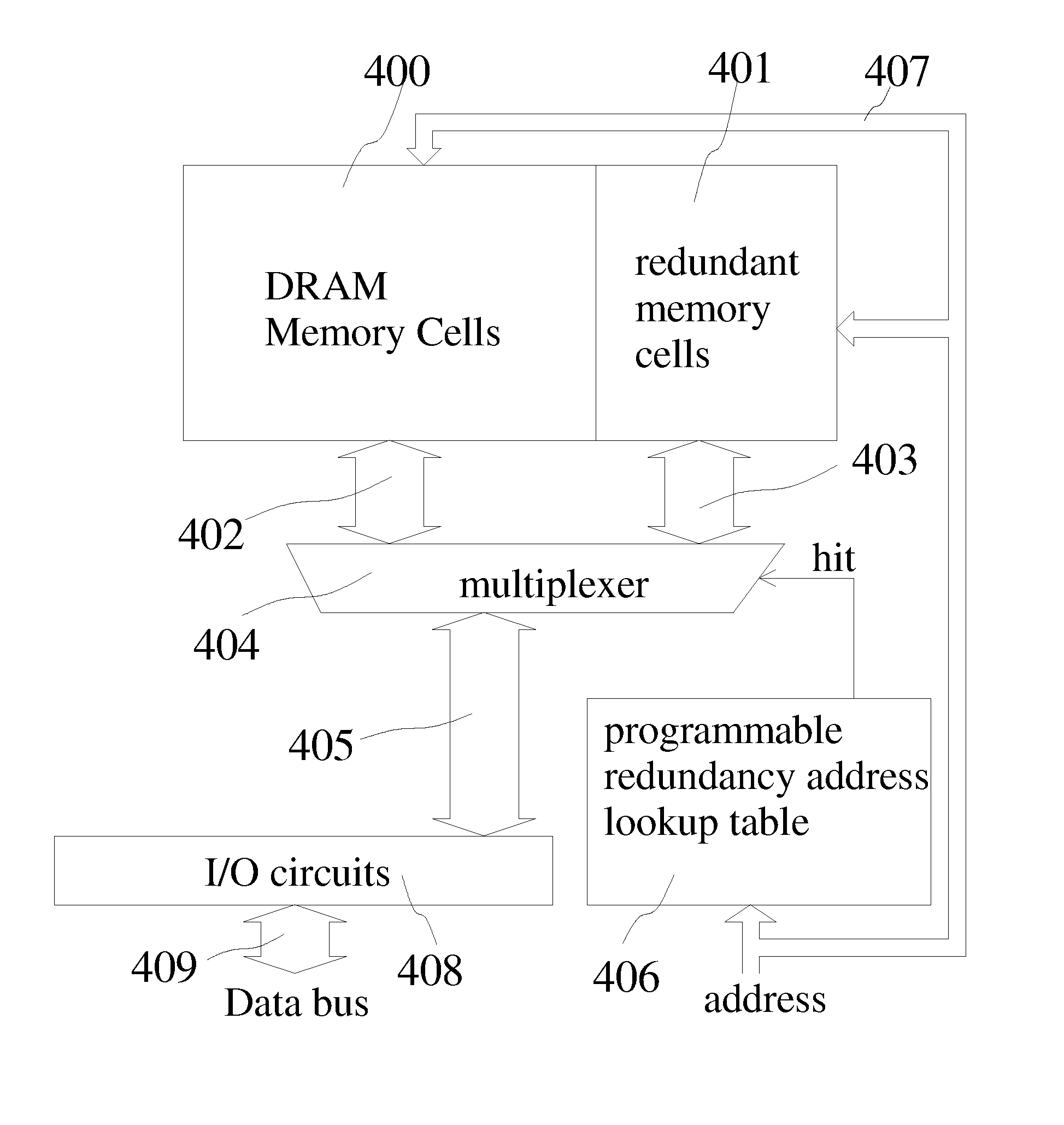
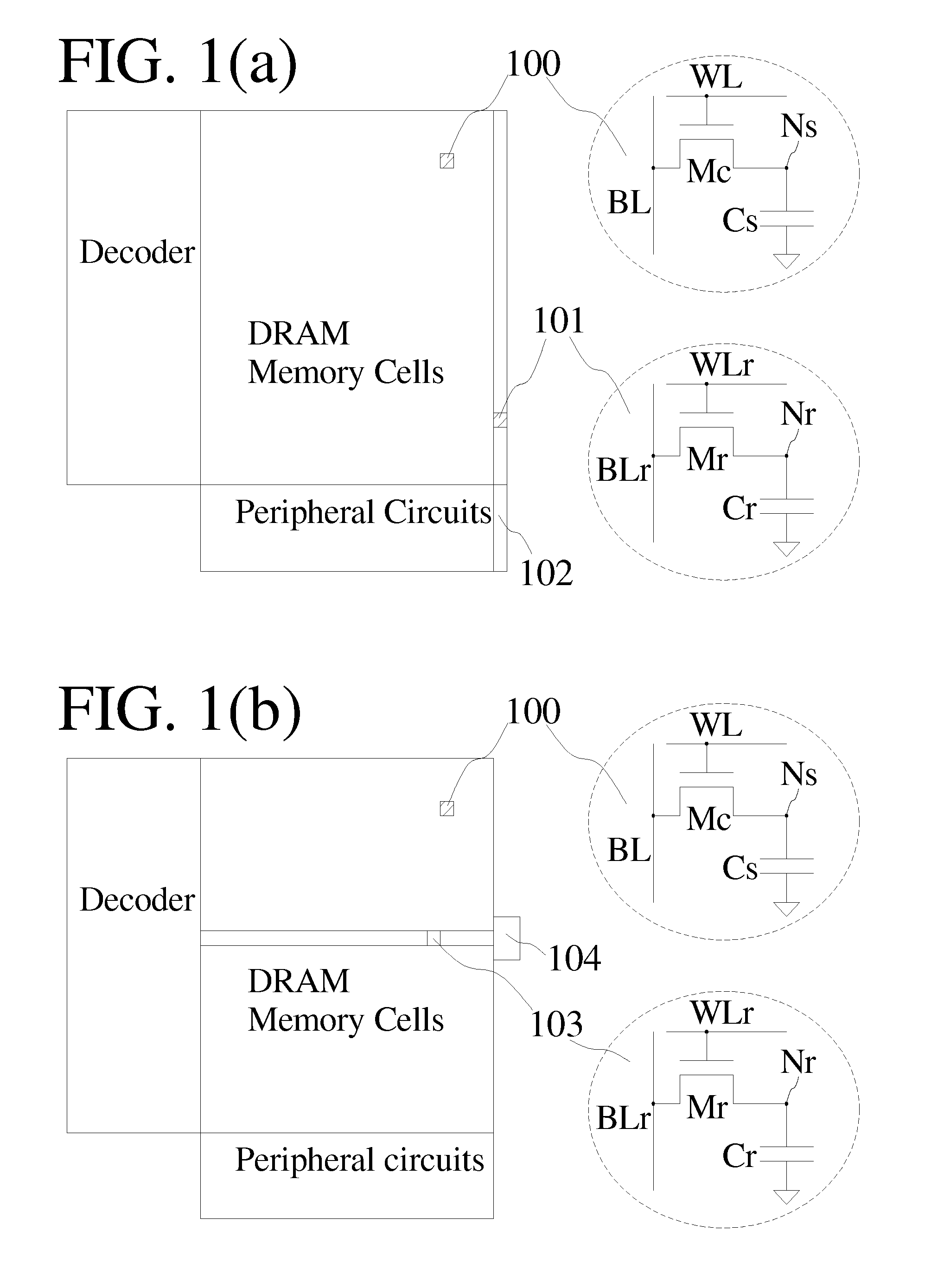
The present invention provides methods and structures for improving refresh power efficiency of dynamic random access memory devices. By measuring charge retention properties of reference cells that have substantially the same structures as normal DRAM memory cells, the refresh rate of DRAM devices can be adjusted with better reliability. The reliability is further improved by using ECC circuits and / or field programmable redundancy circuits.
Owner:SHAU JENG JYE
Memory system and method using ECC to achieve low power refresh
Rows of DRAM memory cells are refreshed at either a relatively high rate during normal operation or a relatively slow rate in a reduced power refresh mode. Prior to refreshing the rows of memory cells, the data are read from the memory cells, and corresponding syndromes are generated and stored. When transitioning from the reduced power refresh mode, data from the rows of memory cells are read, and the stored syndromes are used to determine if there are errors in the read data. The syndromes are also used to correct any errors that are found, and the corrected data are written to the rows of memory cells. By correcting any errors that exist when transitioning from the reduced power refresh mode, it is not necessary to use the syndromes to detect and correct errors while operating in the reduced power refresh mode.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Captured synchronous DRAM fails in a working environment
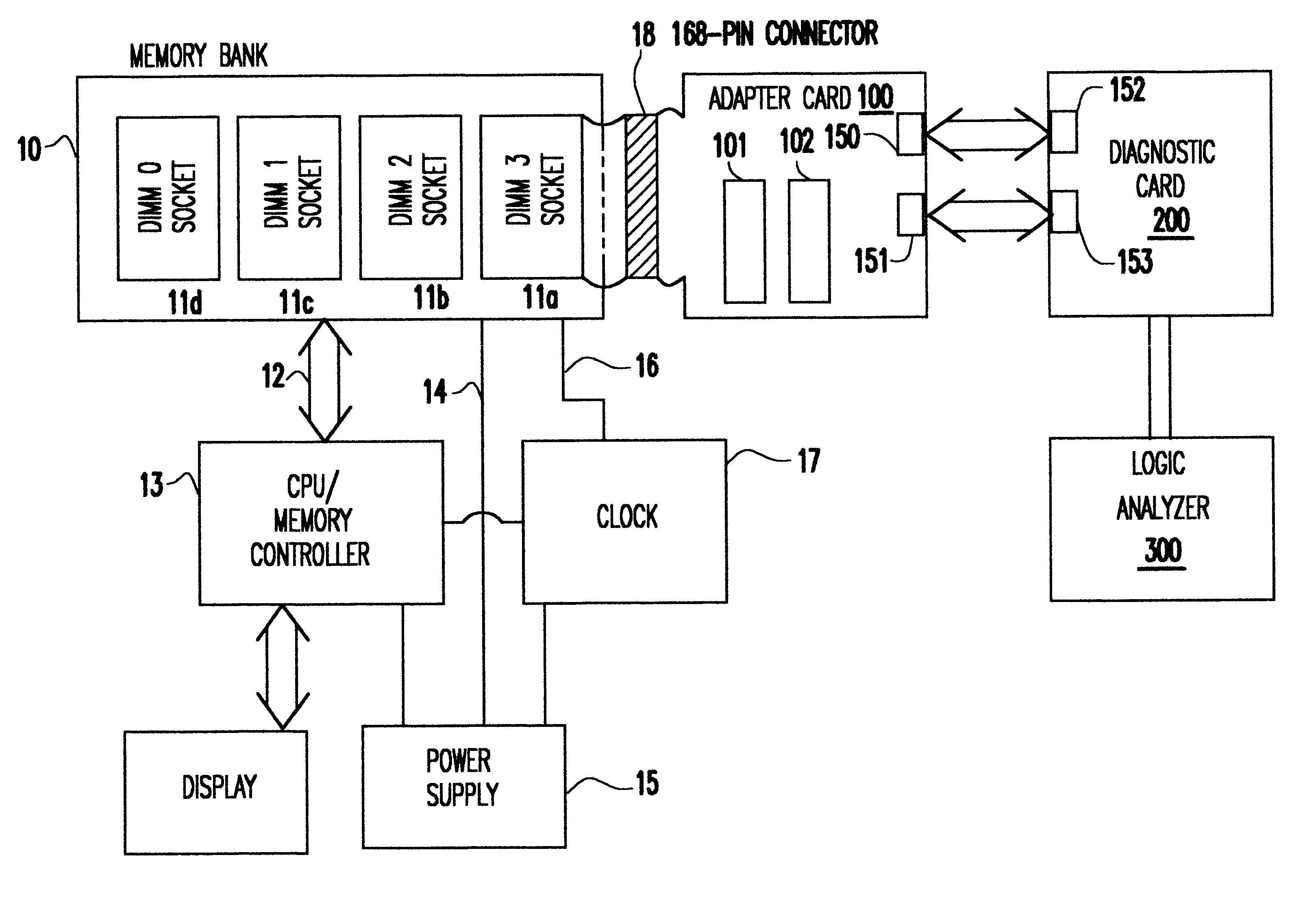
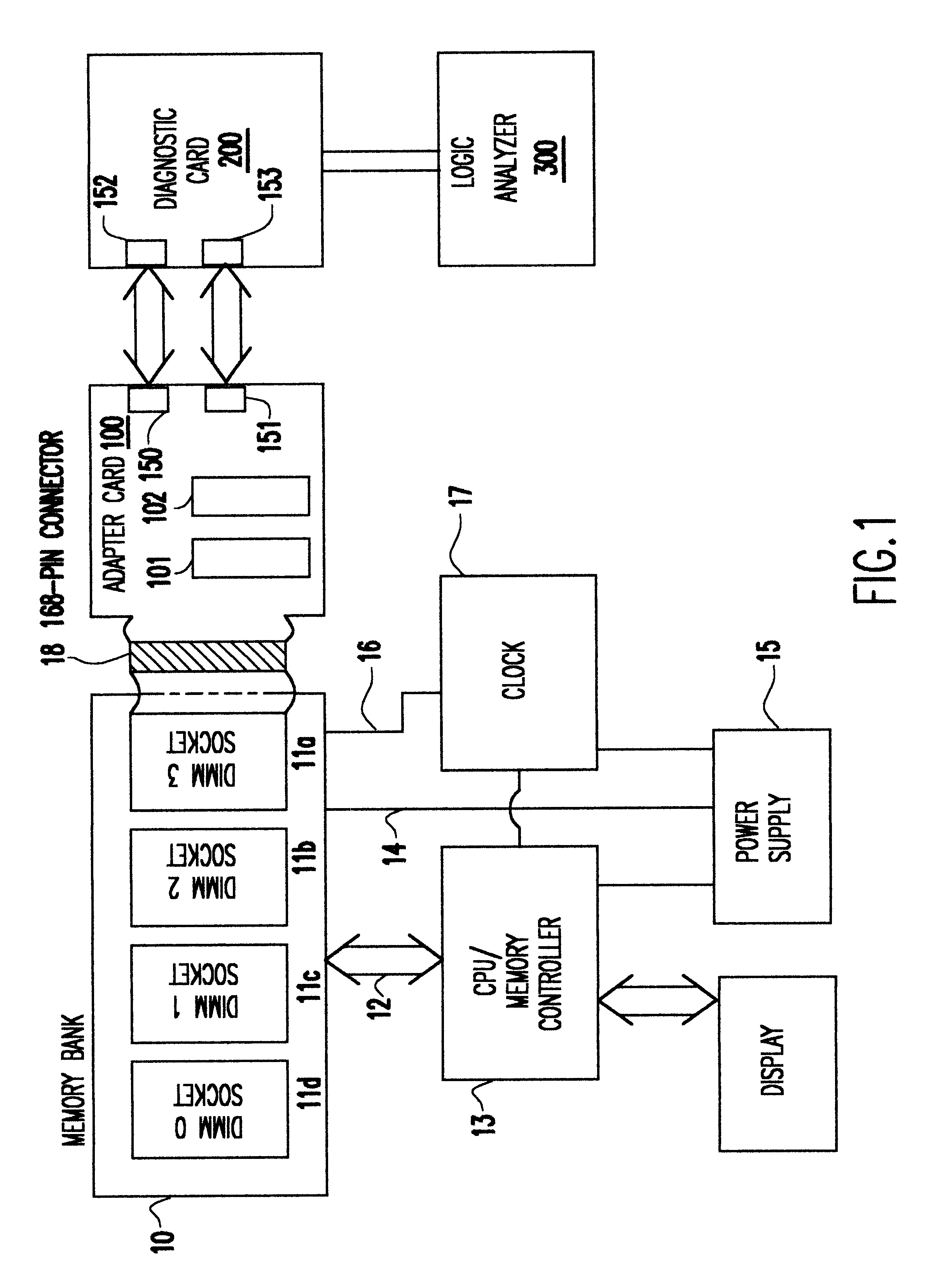
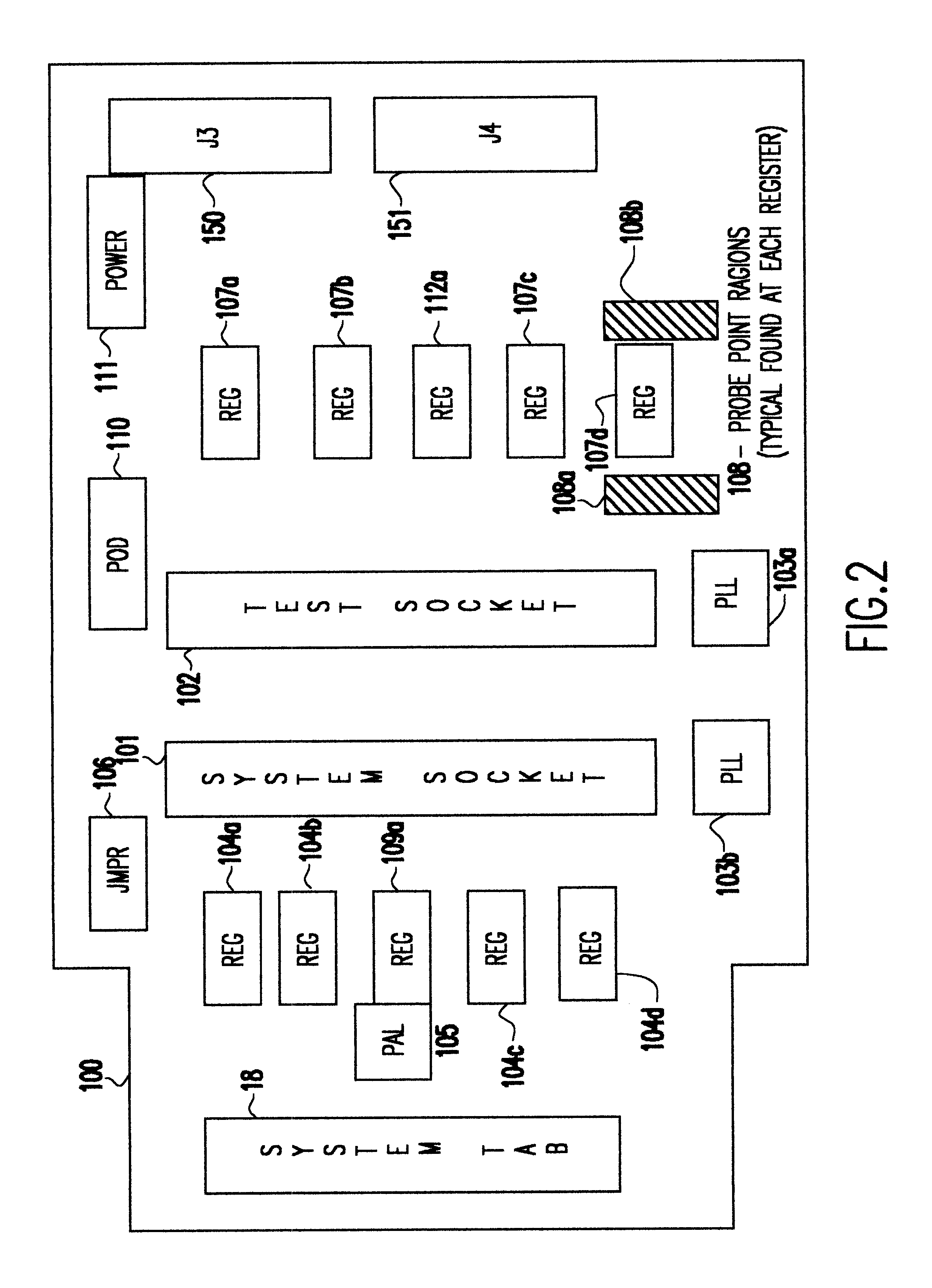
InactiveUS6467053B1Minimize degradationError detection/correctionComponent plug-in assemblagesLength variationDram memory
A Synchronous DRAM memory test assembly that converts a normal PC or Workstation with a synchronous bus into a memory tester. The test assembly may be split into two segments: a diagnostic card and an adapter card to limit mechanical load on the system socket as well as permit varying form factors. This test assembly architecture supports memory bus speeds of 66 MHz and above, and provides easy access for a logic analyzer. The test assembly supports Registered and Unbuffered Synchronous DRAM products. The test assembly permits good and questionable synchronous modules to be compared using an external logic analyzer. It permits resolution of in-system fails that occur uniquely in system environments and may be otherwise difficult or impossible to replicate. The test assembly re-drives the system clocks with a phase lock loop (PLL) buffer to a memory module socket on the test assembly to permit timing adjustments to minimize the degradation to the system's memory bus timings due to the additional wire length and loading. The test assembly is programmable to adjust to varying bus timings such as: CAS (column address strobe) Latencies and Burst Length variations. It is designed with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) to allow for changes internally without modifying the test assembly.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
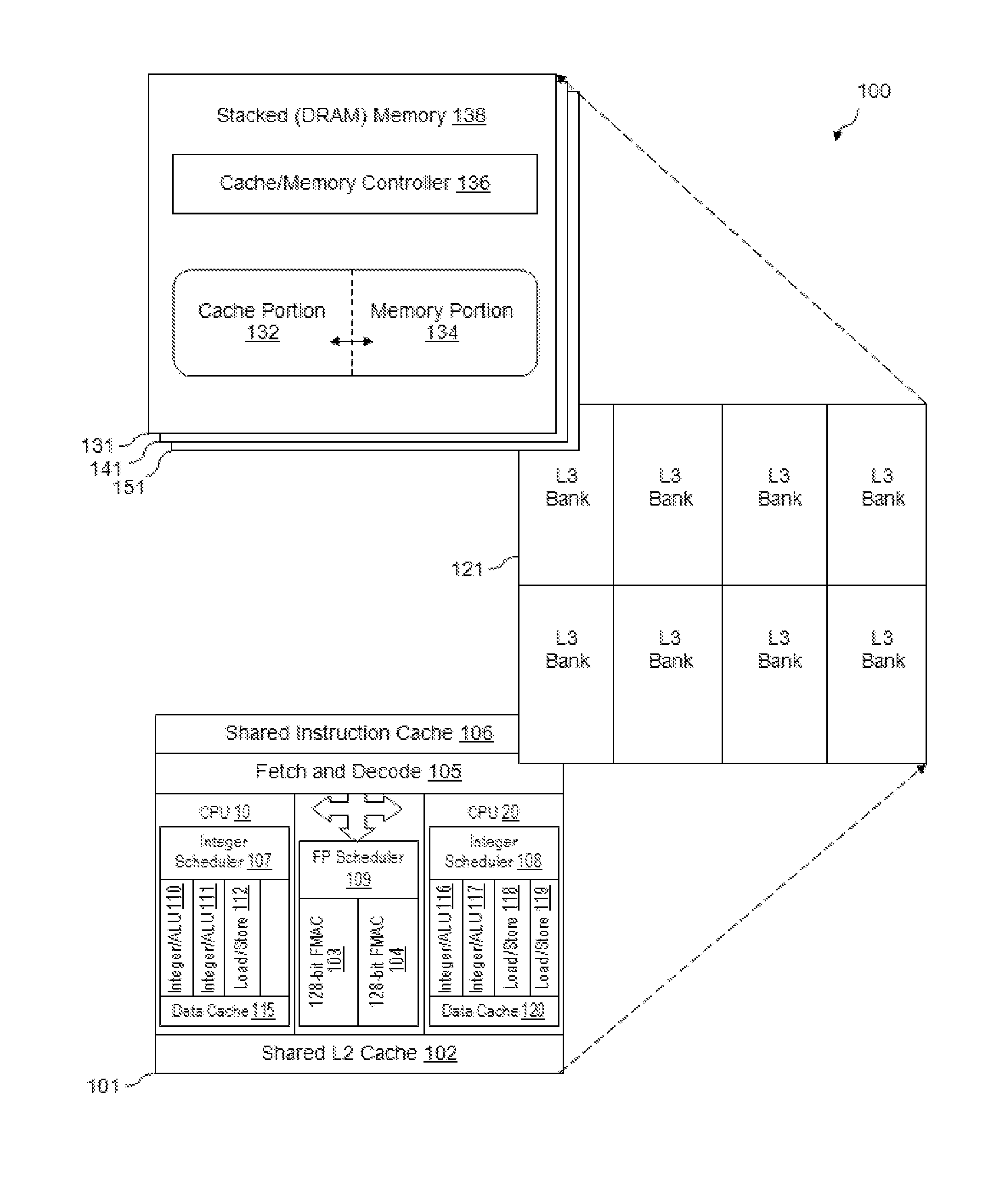
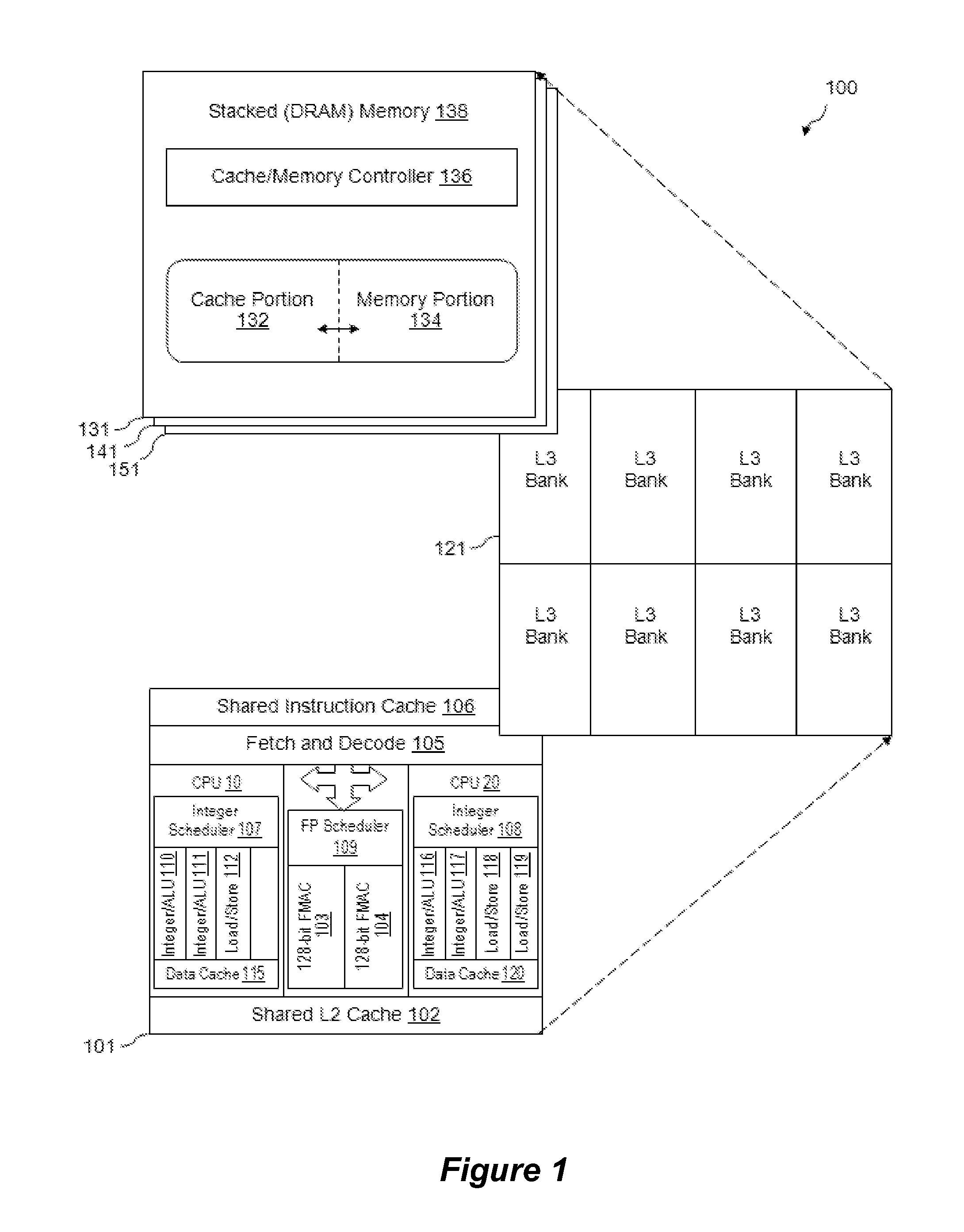
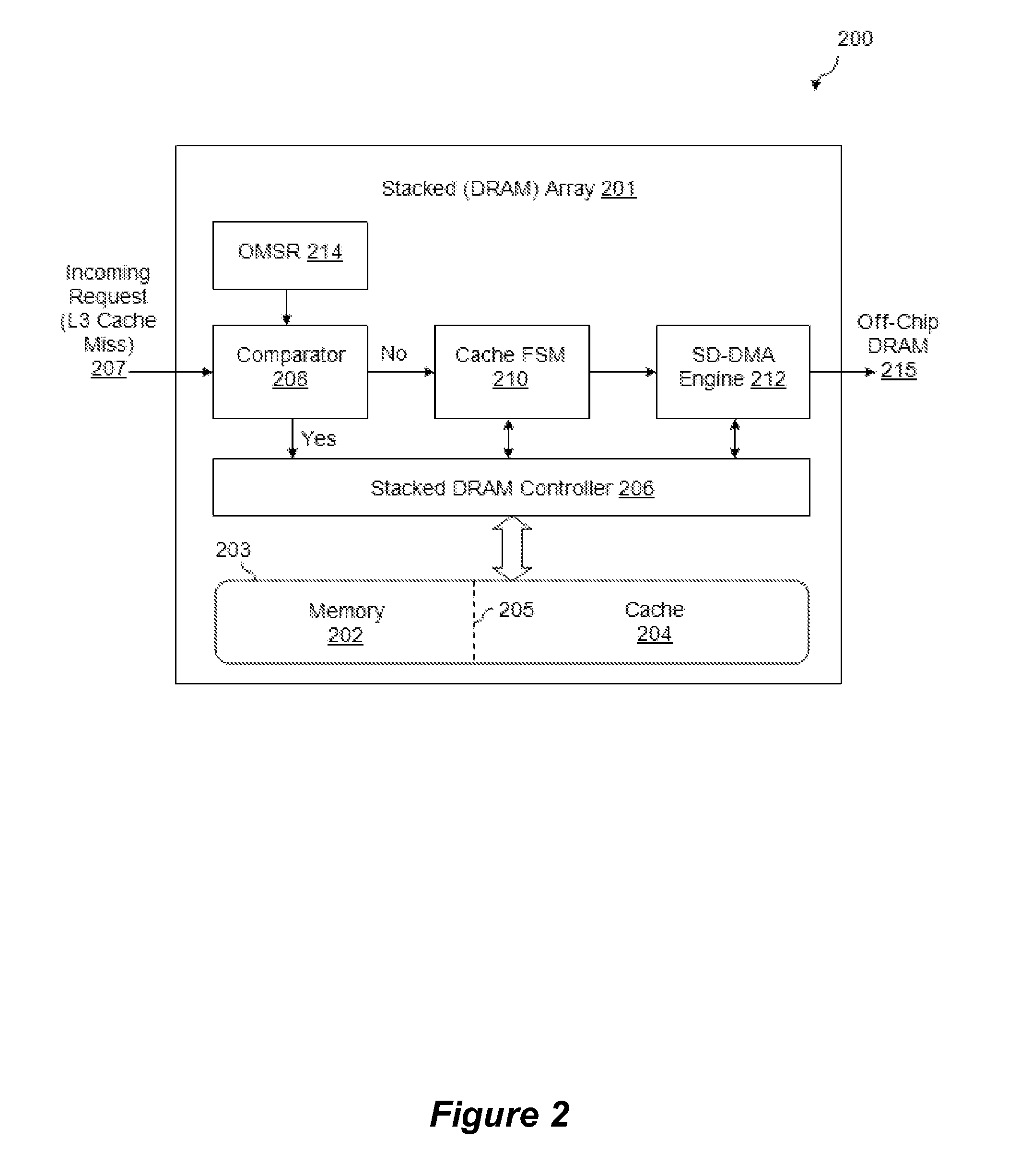
Polymorphic Stacked DRAM Memory Architecture
InactiveUS20120221785A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDram memoryParallel computing
A 3D stacked processor device is described which includes a processor chip and a stacked polymorphic DRAM memory chip connected to the processor chip through a plurality of through-silicon-via structures, where the stacked DRAM memory chip includes a memory with an adjustable memory portion and an adjustable cache portion such that memory can operate simultaneously in both memory and cache modes.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Memory system and method using partial ECC to achieve low power refresh and fast access to data
ActiveUS20080092016A1Reduced power refreshReduce power consumptionError detection/correctionCode conversionError checkingDram memory
A DRAM memory device includes several banks of memory cells each of which are divided into first and second sets of memory cells. The memory cells in the first set can be refreshed at a relatively slow rate to reduce the power consumed by the DRAM device. Error checking and correcting circuitry in the DRAM device corrects any data retention errors in the first set of memory cells caused by the relatively slow refresh rate. The memory cells in the second set are refreshed at a normal rate, which is fast enough that data retention errors do not occur. A mode register in the DRAM device may be programmed to select the size of the second set of memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
6F2 access transistor arrangement and semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20060281250A1Improve insulation performanceImprove isolationTransistorSolid-state devicesDopantBit line
An access transistor arrangement is provided for a 6F2 stacked capacitor DRAM memory cell layout with shared bit line contacts. The access transistors are arranged in pairs along semiconductor lines. The two transistors of each pair of transistors are arranged laterally reversed opposing the respective common bit line section. Each pair of access transistors is separated from the adjacent pair of access transistors by an isolation transistor which is permanently turned off. The access transistors and the isolation transistors are formed as identical recessed channel transistors with elongated channel and enhanced isolation properties. The same dopant concentration may be provided for both junctions of the access transistors. As identical devices are provided both as access transistor and as isolation transistors, the complexity of lithographic patterning processes is reduced.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
DRAM memory cell and array having pass transistors with surrounding gate
InactiveUS6207985B1Easy to controlAdvantageous charge storage capabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDram memorySilicon
A dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell and associated array are disclosed. In a first embodiment, the DRAM (300) includes a storage capacitor (308) and a pass transistor (306). The pass transistor (306) is formed within a silicon mesa (314), and includes a source region (320), a drain region (322), and a channel region (324) that extends in a length direction between the source region (320) and drain region (322). When viewed with respect to a width direction, the channel region (324) has a narrower width than that of the source region (320) and drain region (322). Further, the channel region (324) has a top surface and opposing side surfaces. A surrounding gate (318) is disposed around the channel region (324), adjacent to the top and side surfaces, and separated therefrom by a gate insulating layer (316). Due to the reduced channel region width and surrounding gate (318), greater control of the operation of the pass transistor (302) is provided, including an off state with reduced source-to-drain leakage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
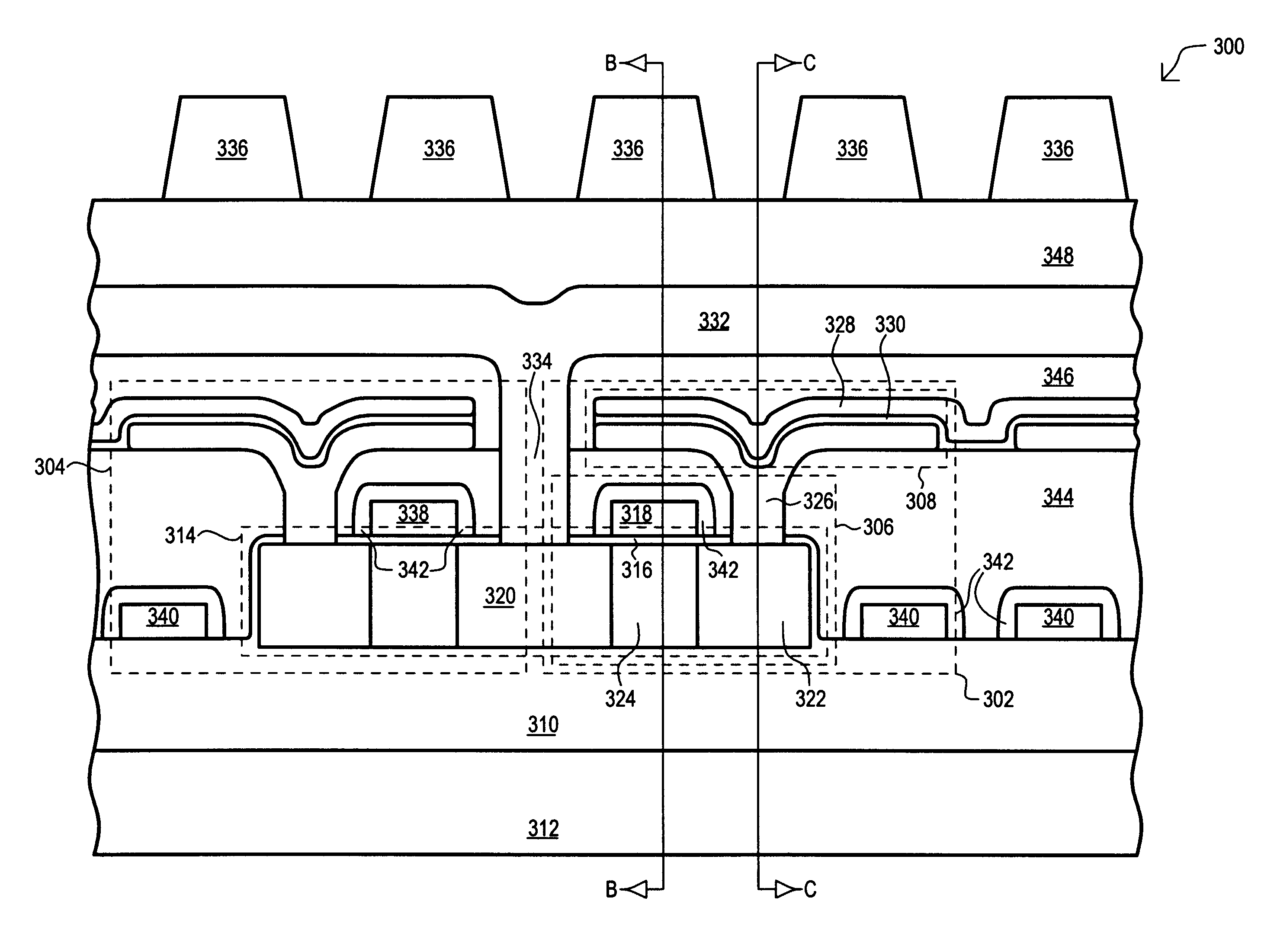
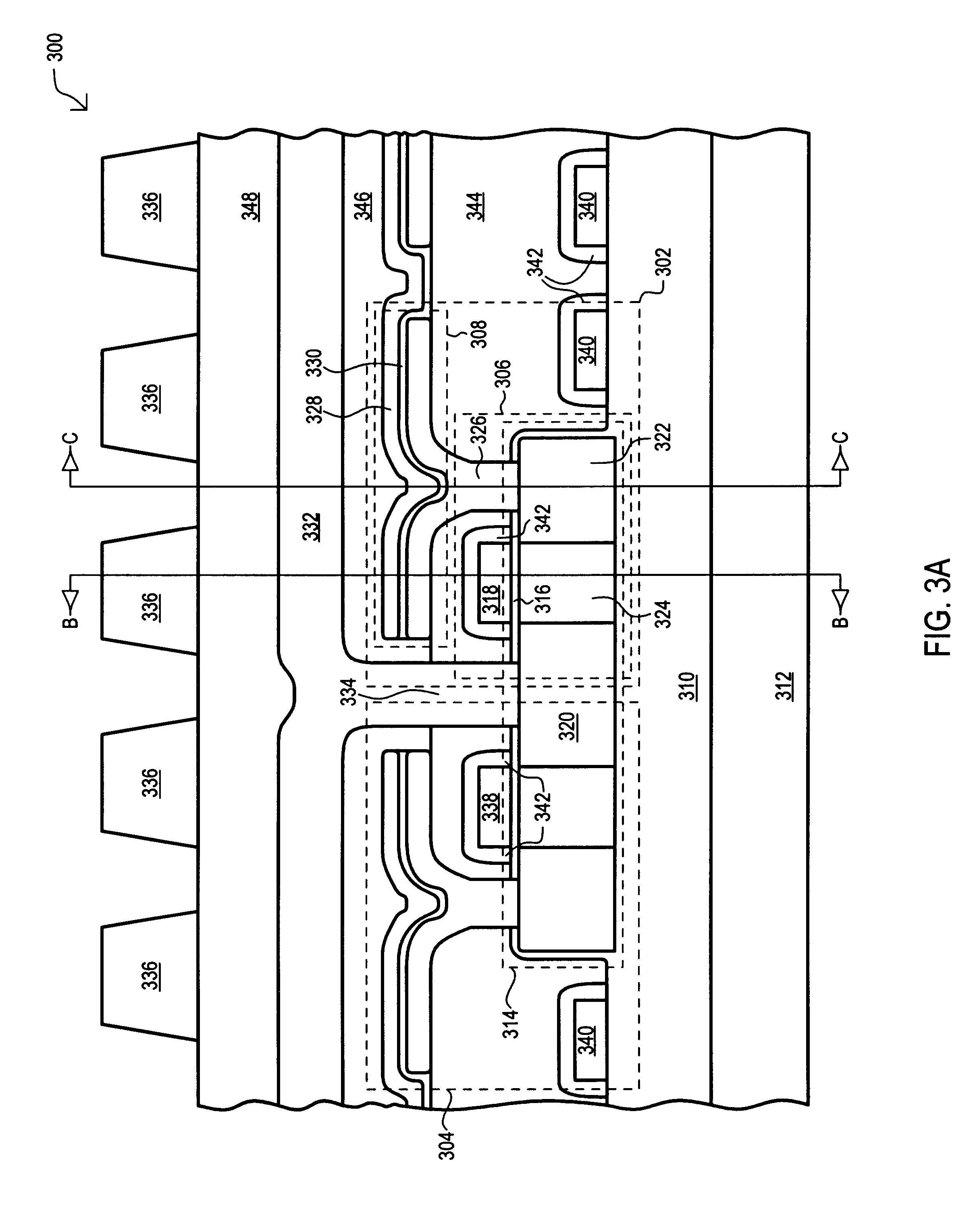
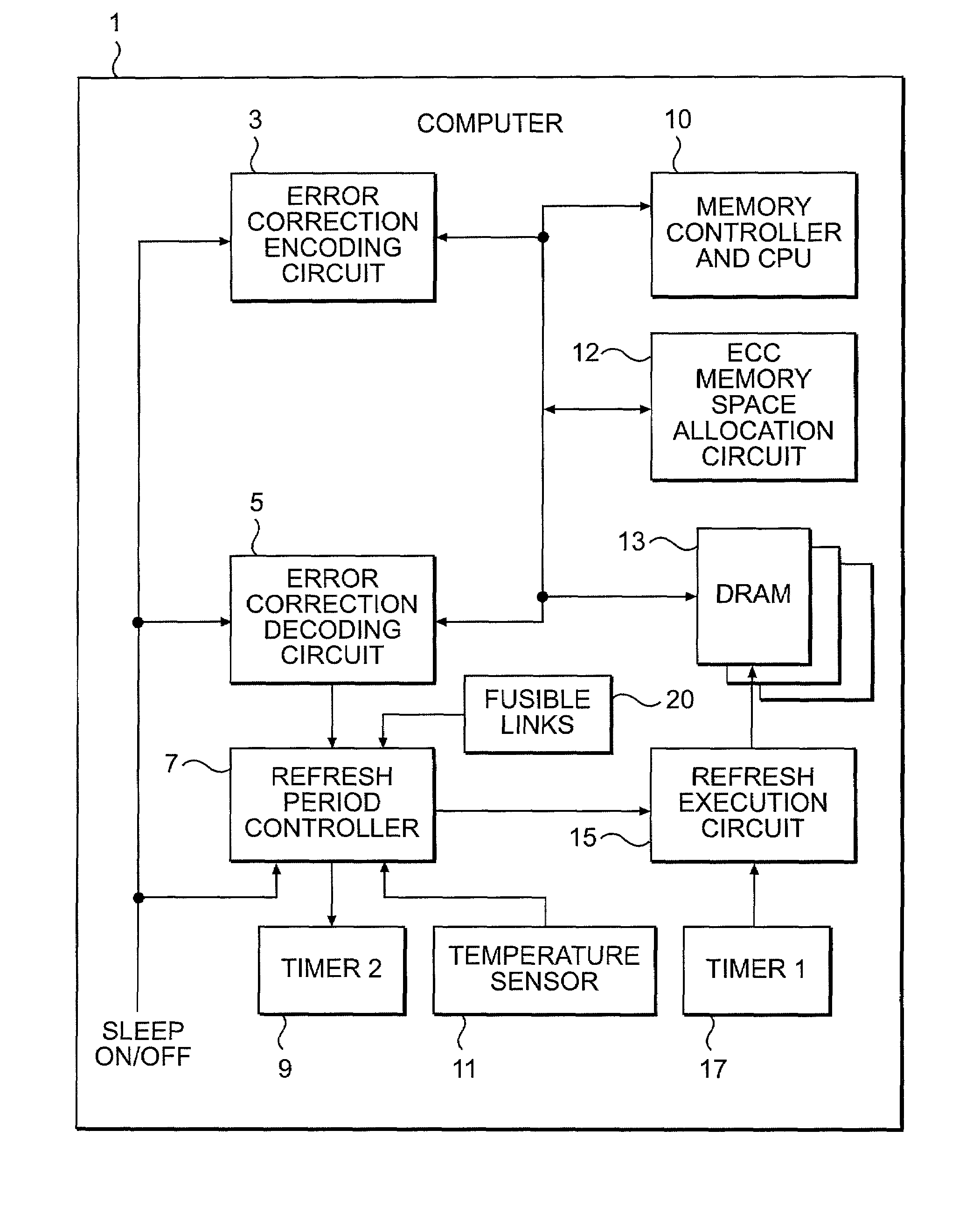
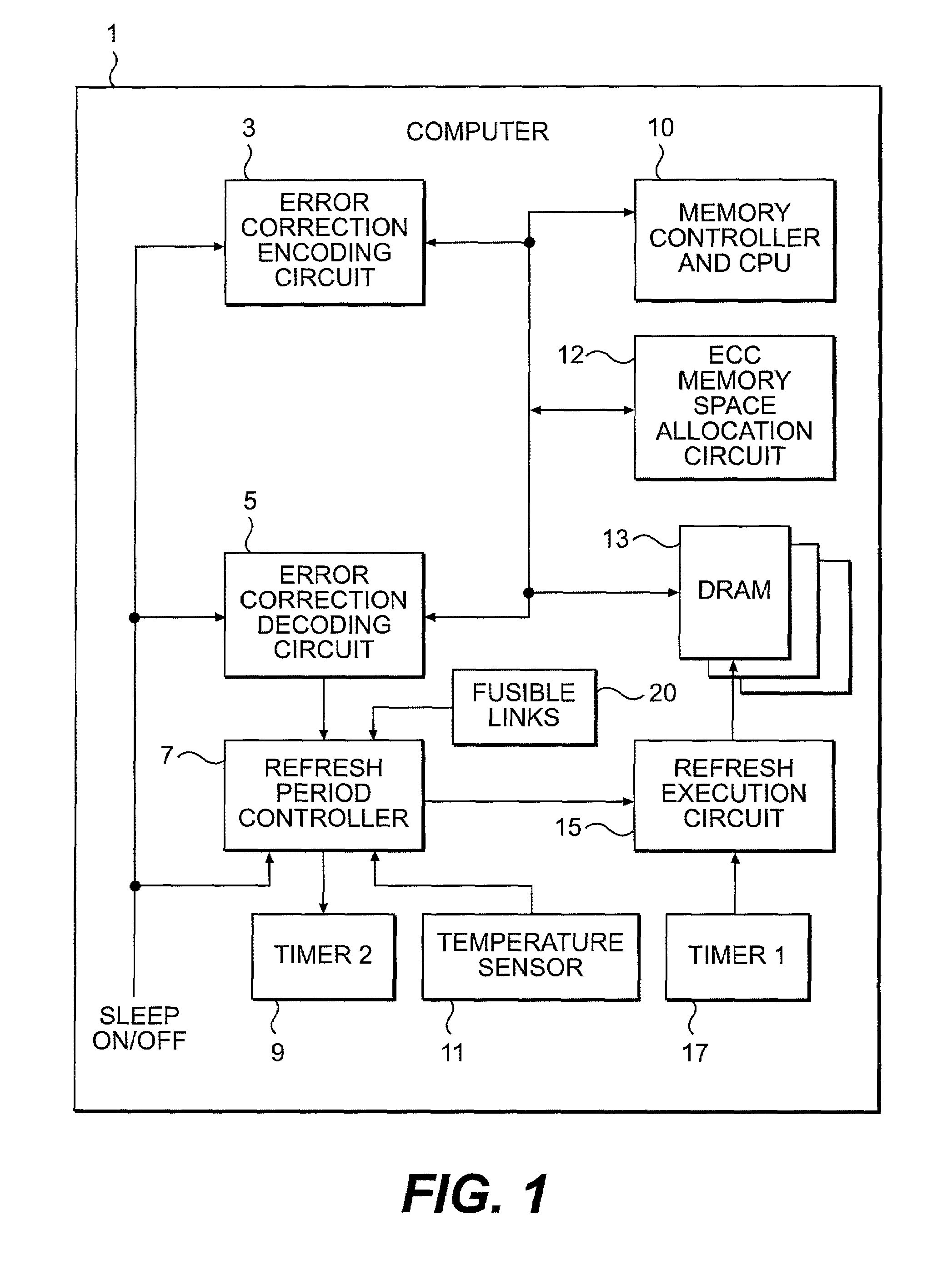
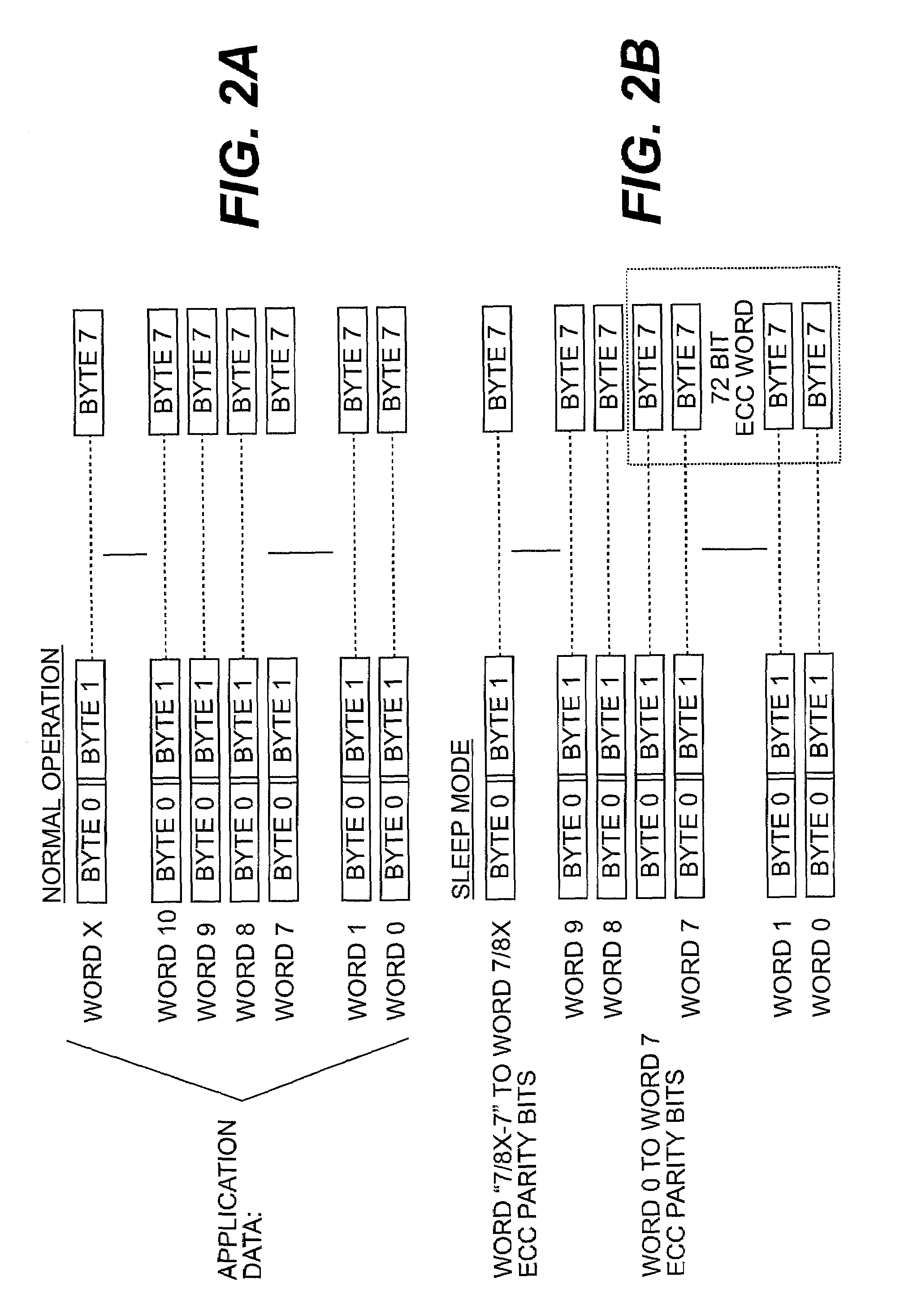
Check bit free error correction for sleep mode data retention
A DRAM memory has a reduced refresh rate in a sleep mode to conserve power. Error Correction Codes (ECC) are used to correct errors that may arise due to the reduced refresh rate. ECC encoding occurs at the time of entering the sleep mode and ECC decoding for error detection and correction need only take place upon wake up when resuming active mode. In addition, the memory system reassigns a portion of the memory for storing the additional parity bits required for the error correcting code (ECC).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
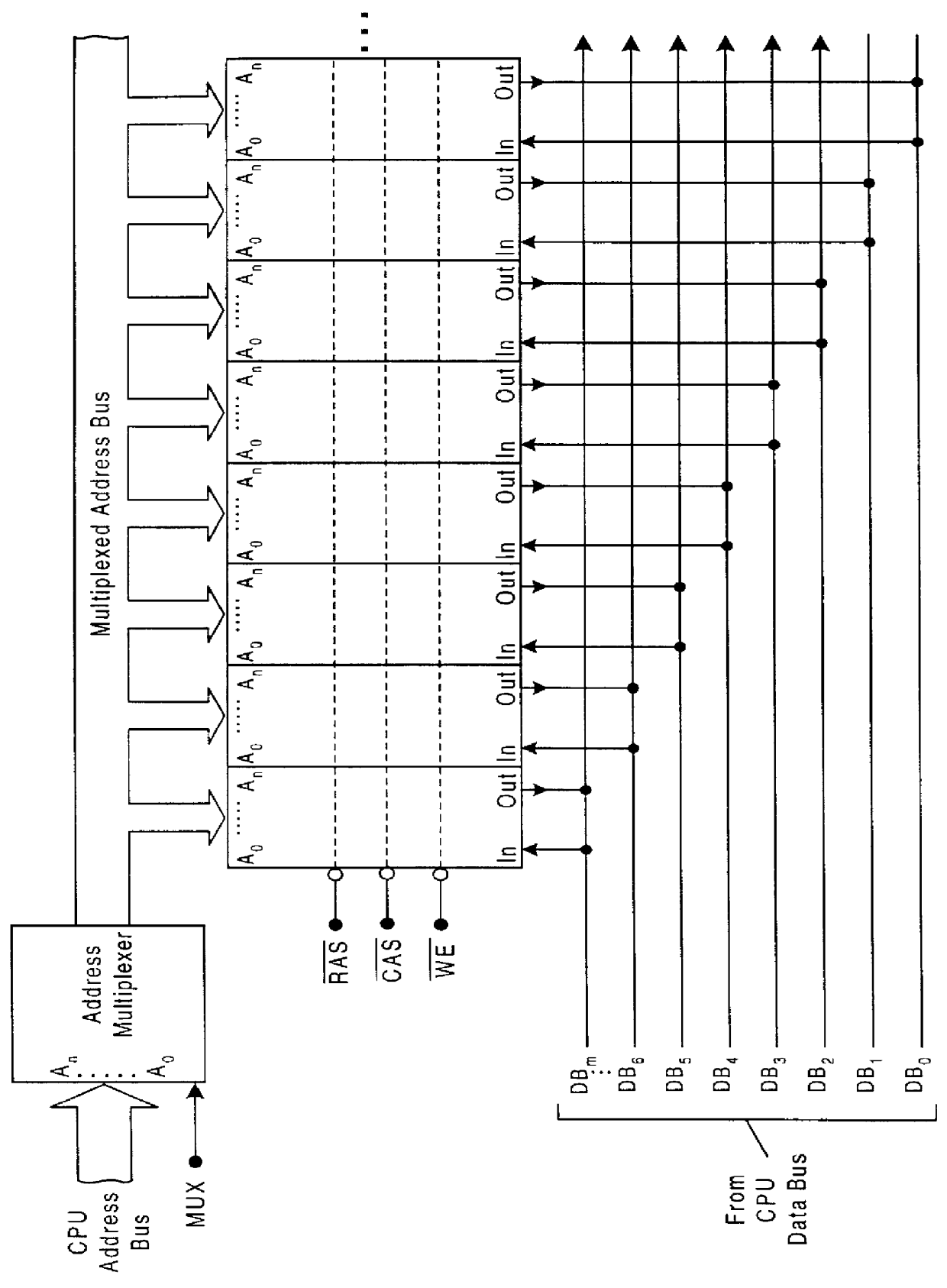
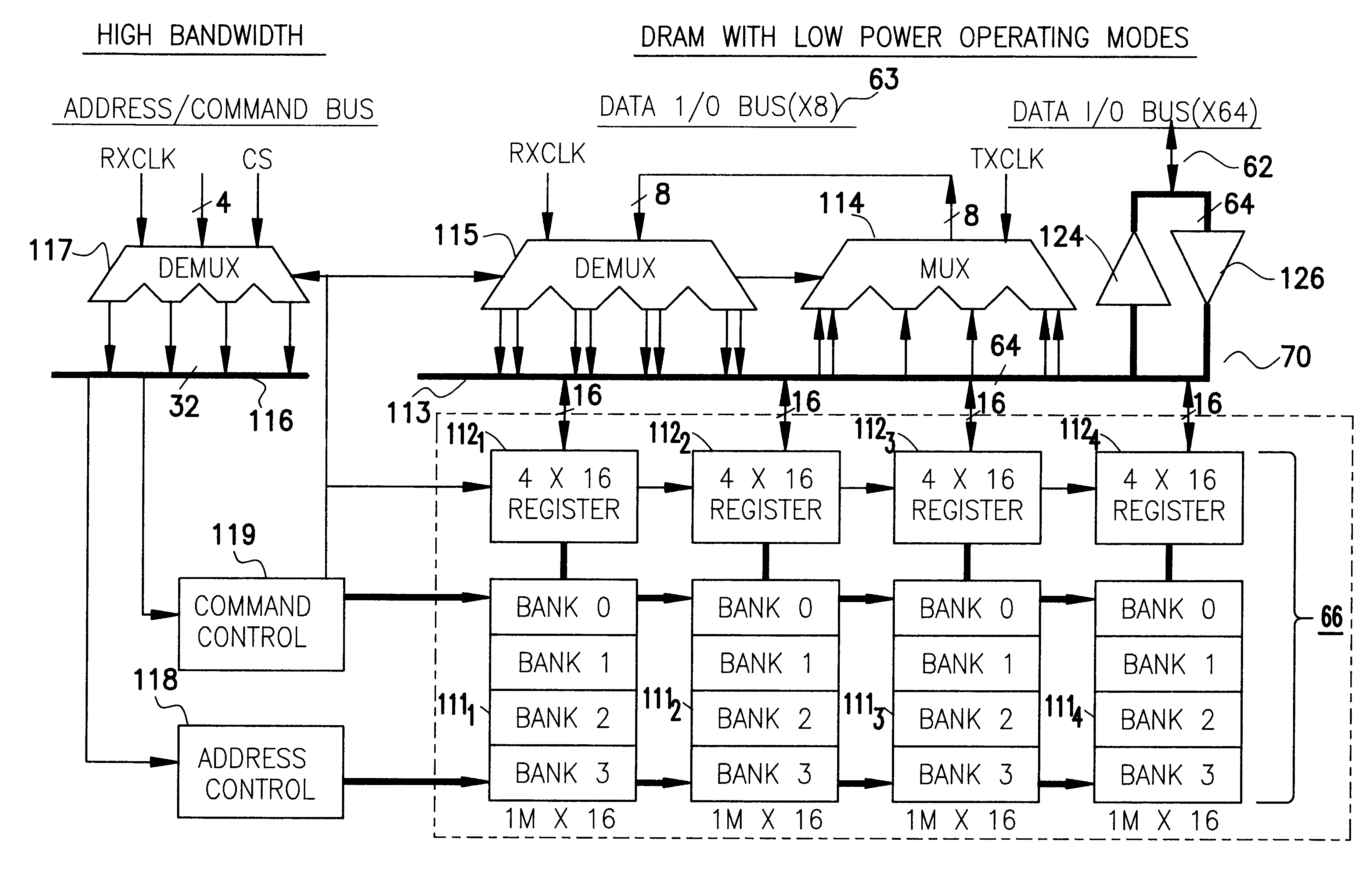
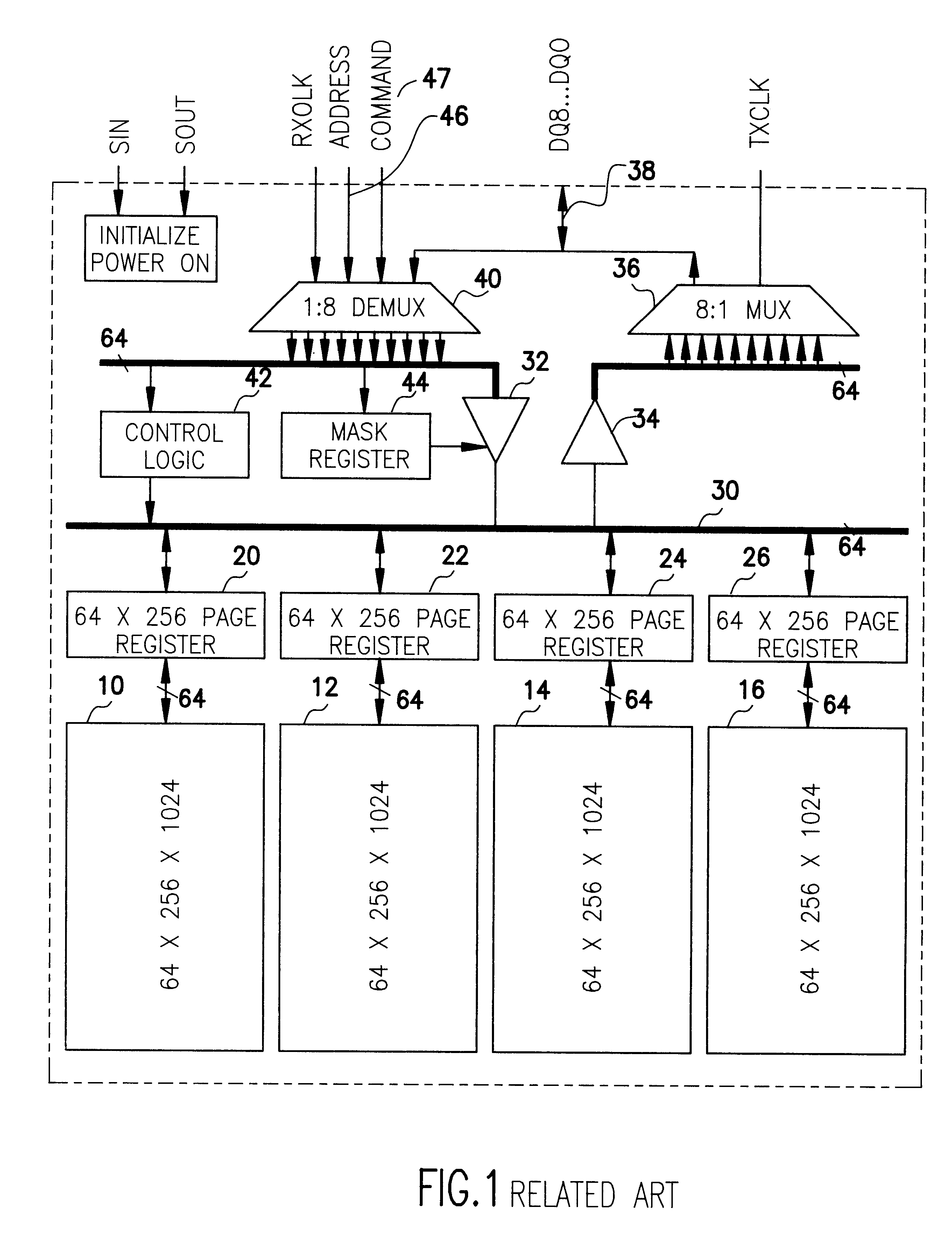
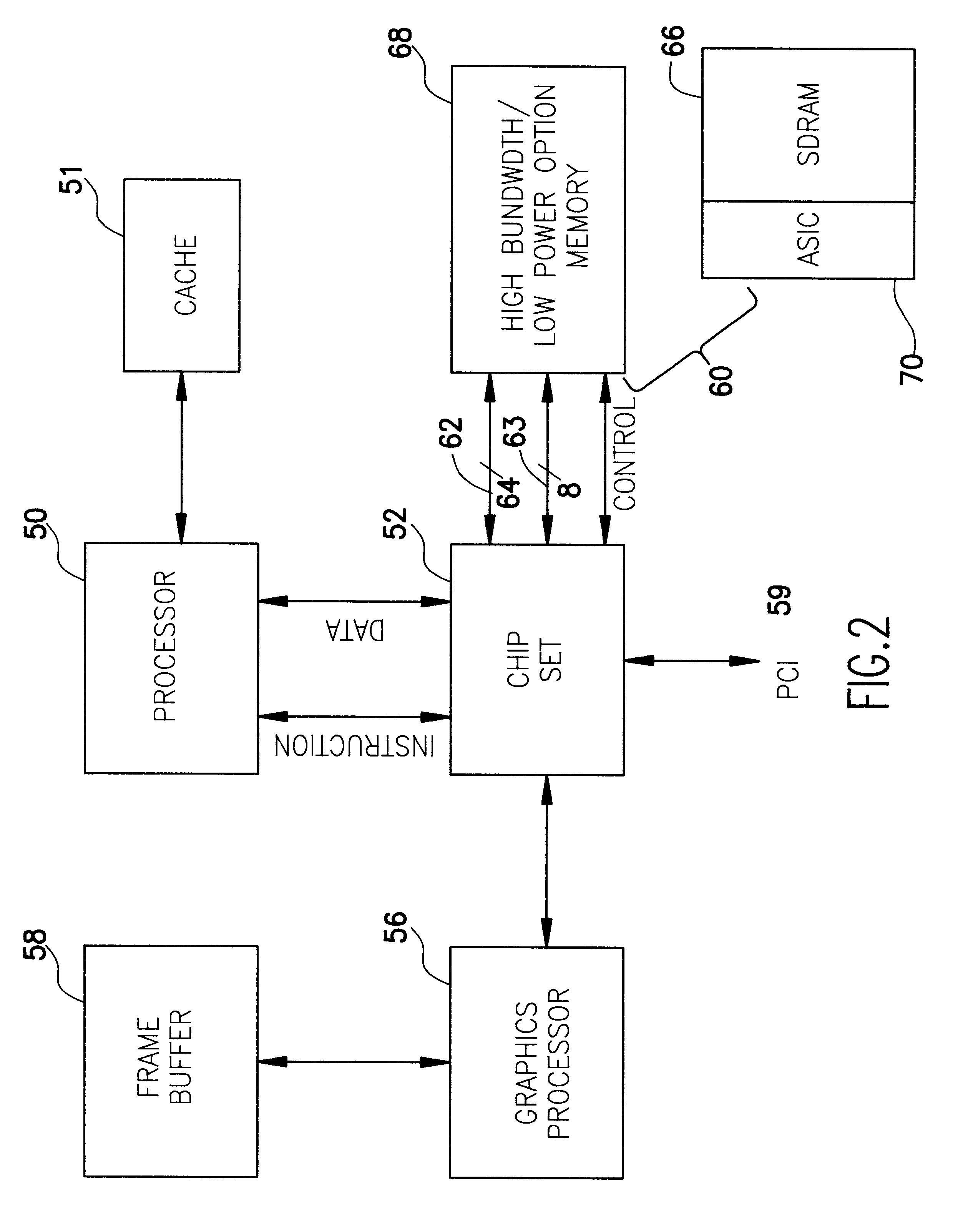
High bandwidth DRAM with low operating power modes
InactiveUS6178517B1Adjustable speedEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsPower modeGraphics
A high bandwidth DRAM is provided with two separate bus networks connecting the DRAM to a processor. One bus network is a high speed (e.g., 500 MHZ) 8:1 or 16:1 multiplexed I / O bus and the second is a slower (e.g., 64-bit) bus. The high-speed bus is used for example for graphic intensive applications which require fast access to large numbers of bits in the DRAM memory array. This of course results in higher power requirements. Since, not all applications require such large amounts of data to be transferred between the DRAM and the processor, the slower bus is provided for these less demanding applications such as word processors, spreadsheets, and the like. The slower bus requires less power to operate and therefore results in a power saving mode which, among other things, facilitates longer battery life.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com