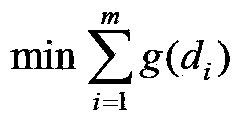Patents
Literature
71 results about "Normal rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The normal resting pulse range for adults is 60 to 100 beats per minute. Normal ranges vary by age, and women usually have slightly higher pulse rates compared to men.
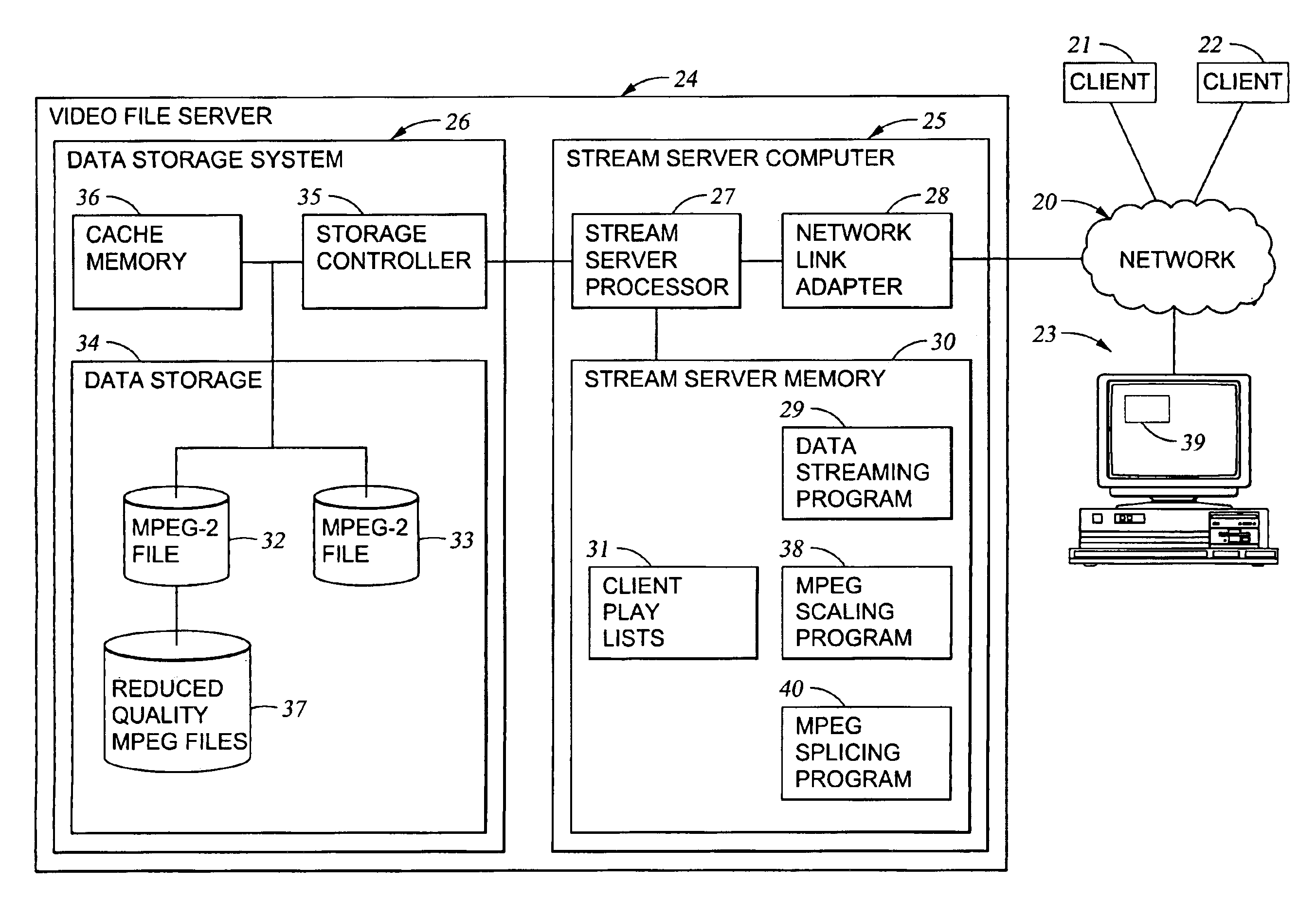
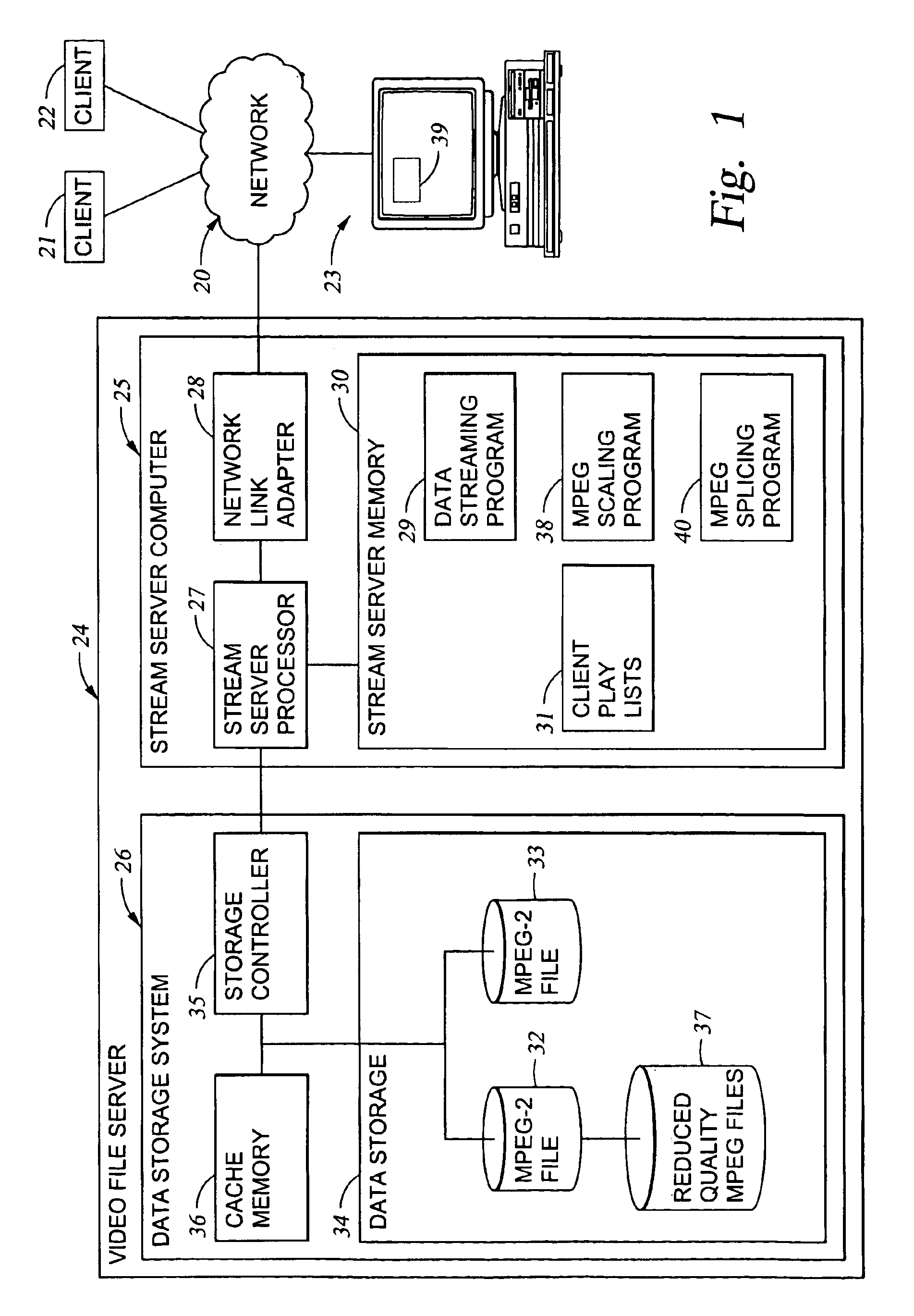
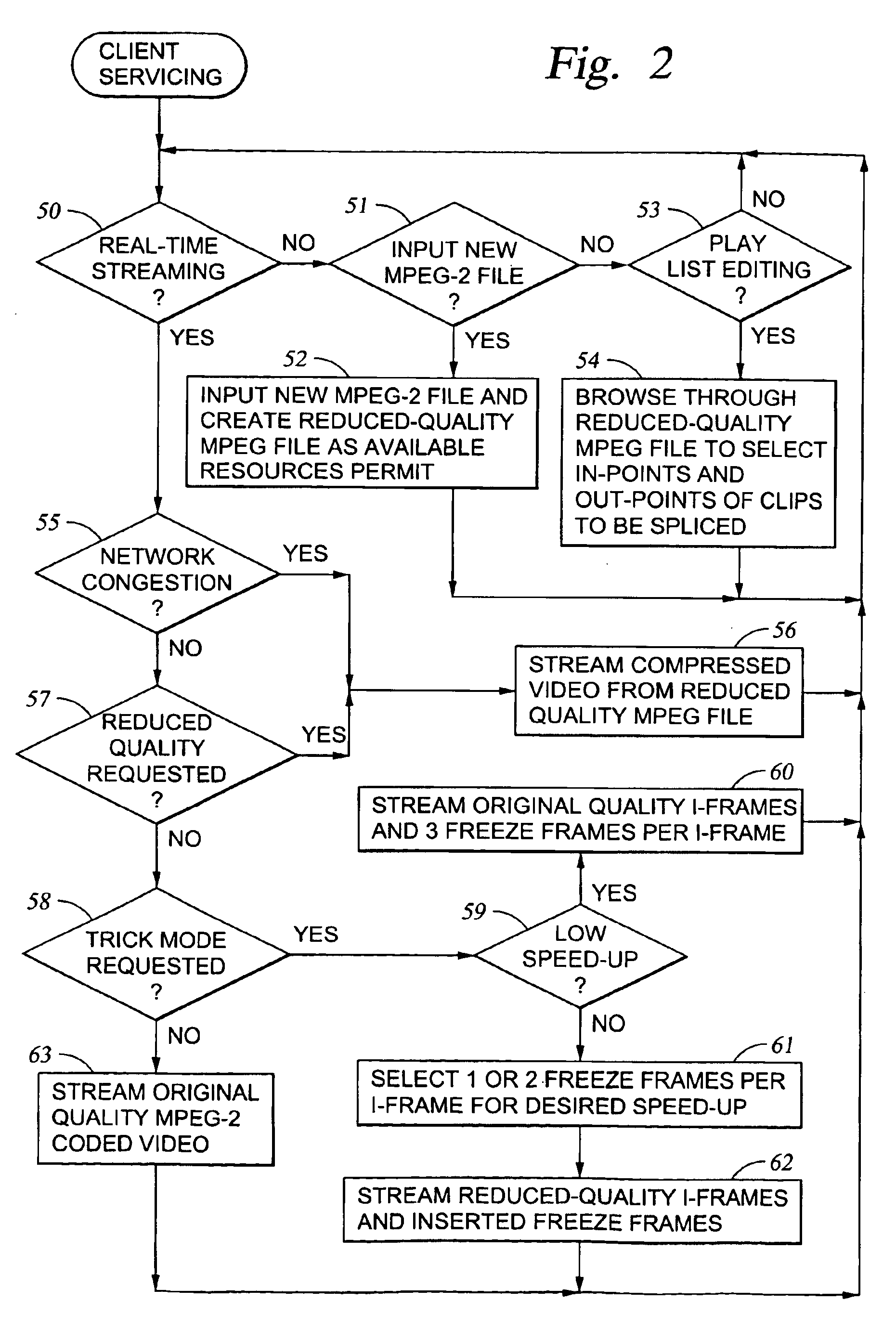
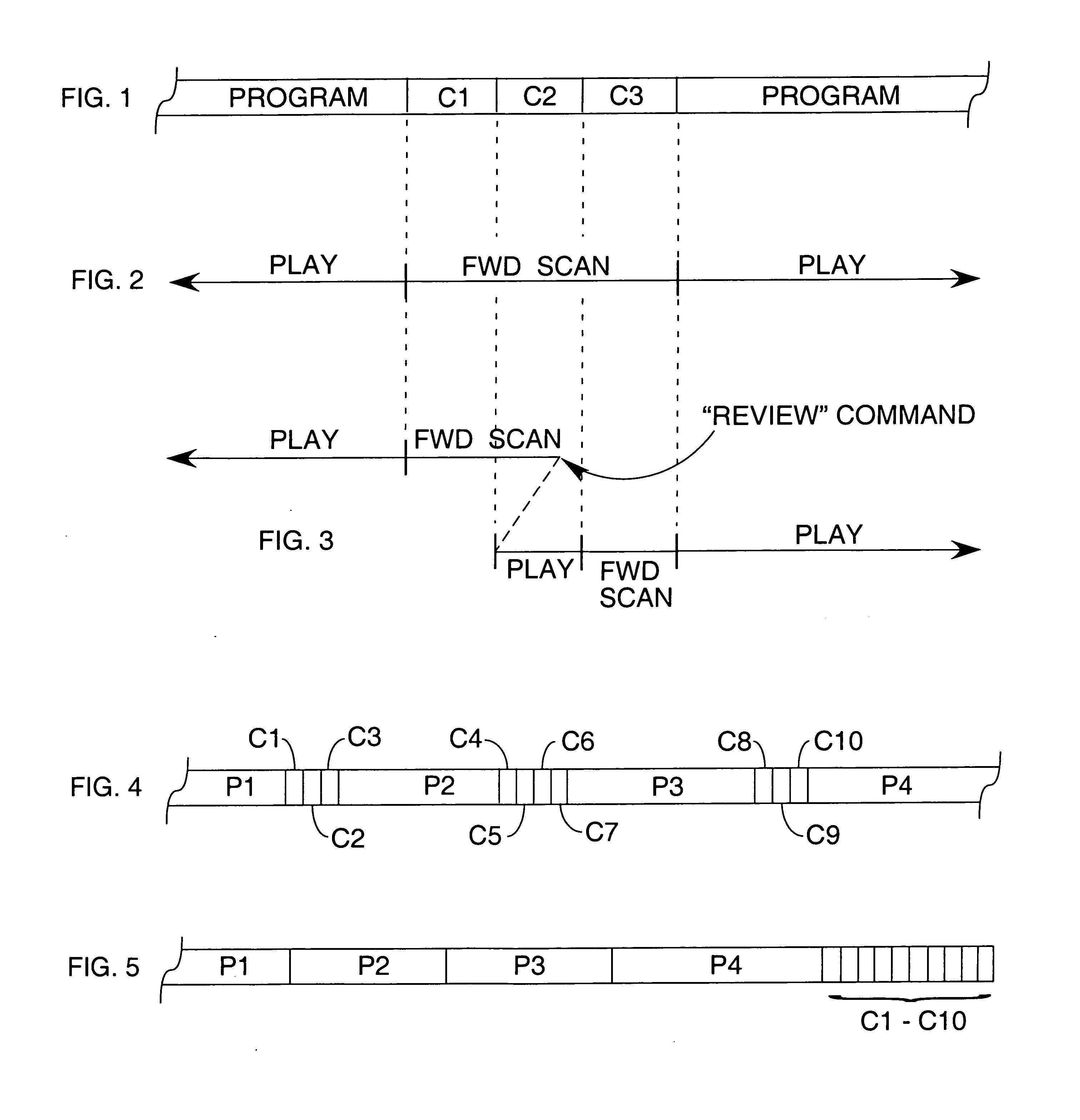
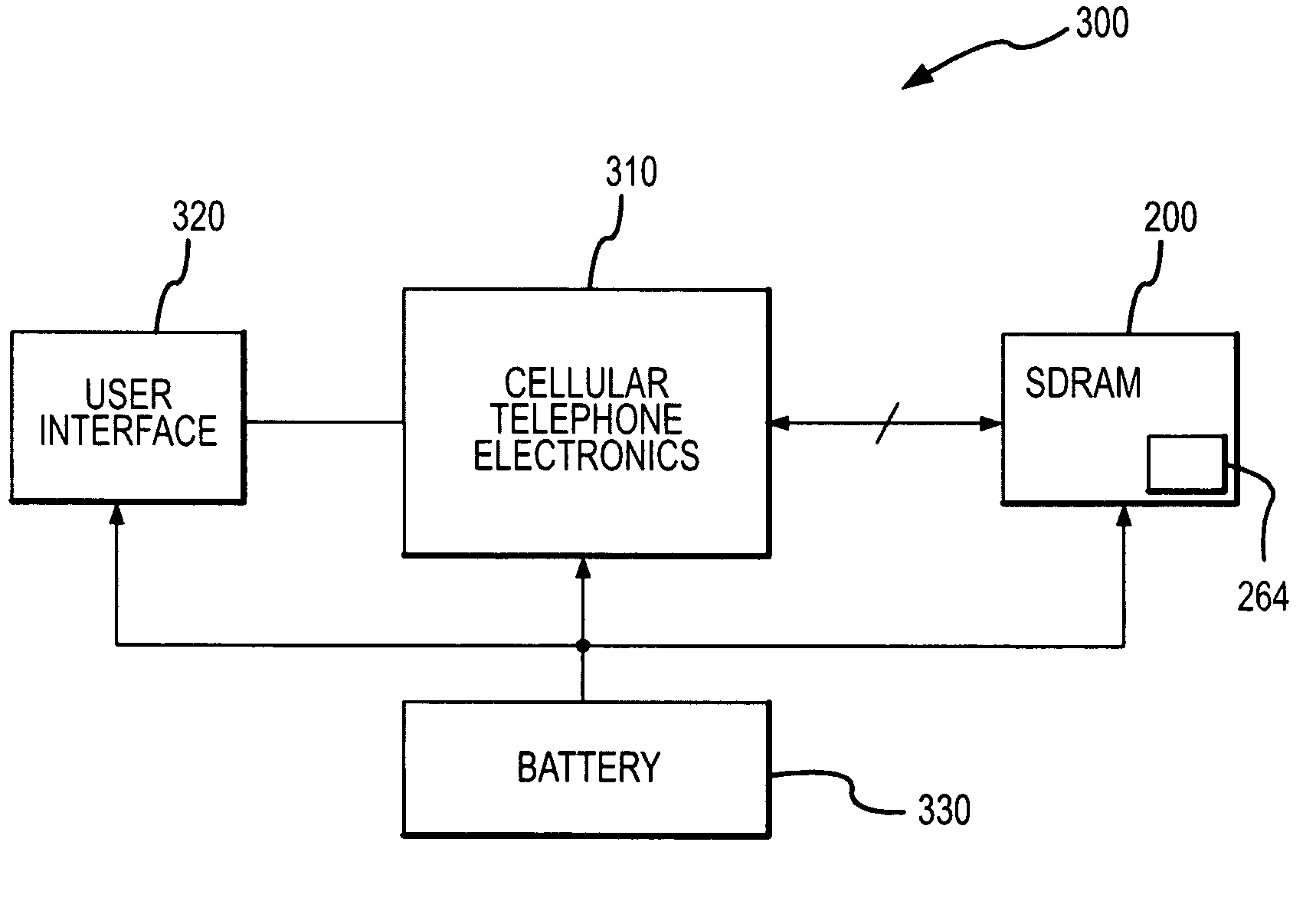
Processing of MPEG encoded video for trick mode operation
InactiveUS6871006B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVisual presentationMPEG transport stream
Original-quality MPEG coded video is processed to produce reduced-quality MPEG coded video for trick mode operation by removing non-zero AC DCT coefficients from the 8×8 blocks of I-frames of the MPEG coded video to produce I-frames of reduced-quality MPEG coded video, and inserting freeze frames in the reduced-quality MPEG coded video. Preferably, the coded video is stored in a main file, a fast-forward file and a fast-reverse file. The fast forward file and the fast reverse files contain reduced-quality I frames corresponding to original-quality I frames in the main file. A reading of the main file produces an MPEG transport stream for an audio-visual presentation at a normal rate, a reading of the fast-forward file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a forward direction at a fast rate, and a reading of the fast-reverse file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a reverse direction at a fast rate. Preferably, the files share a volume that includes at least one GOP index associating the corresponding I frames of the files.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
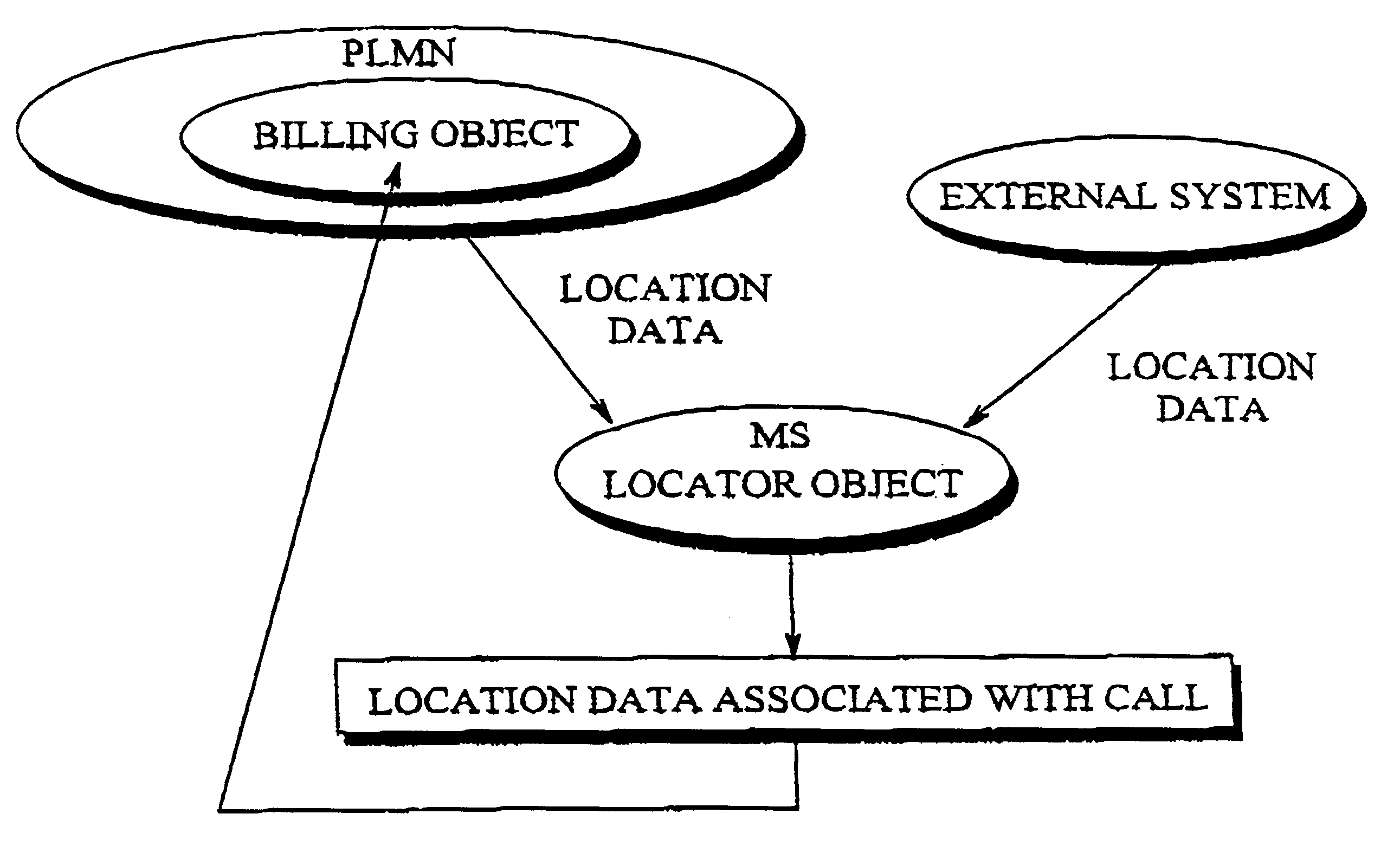
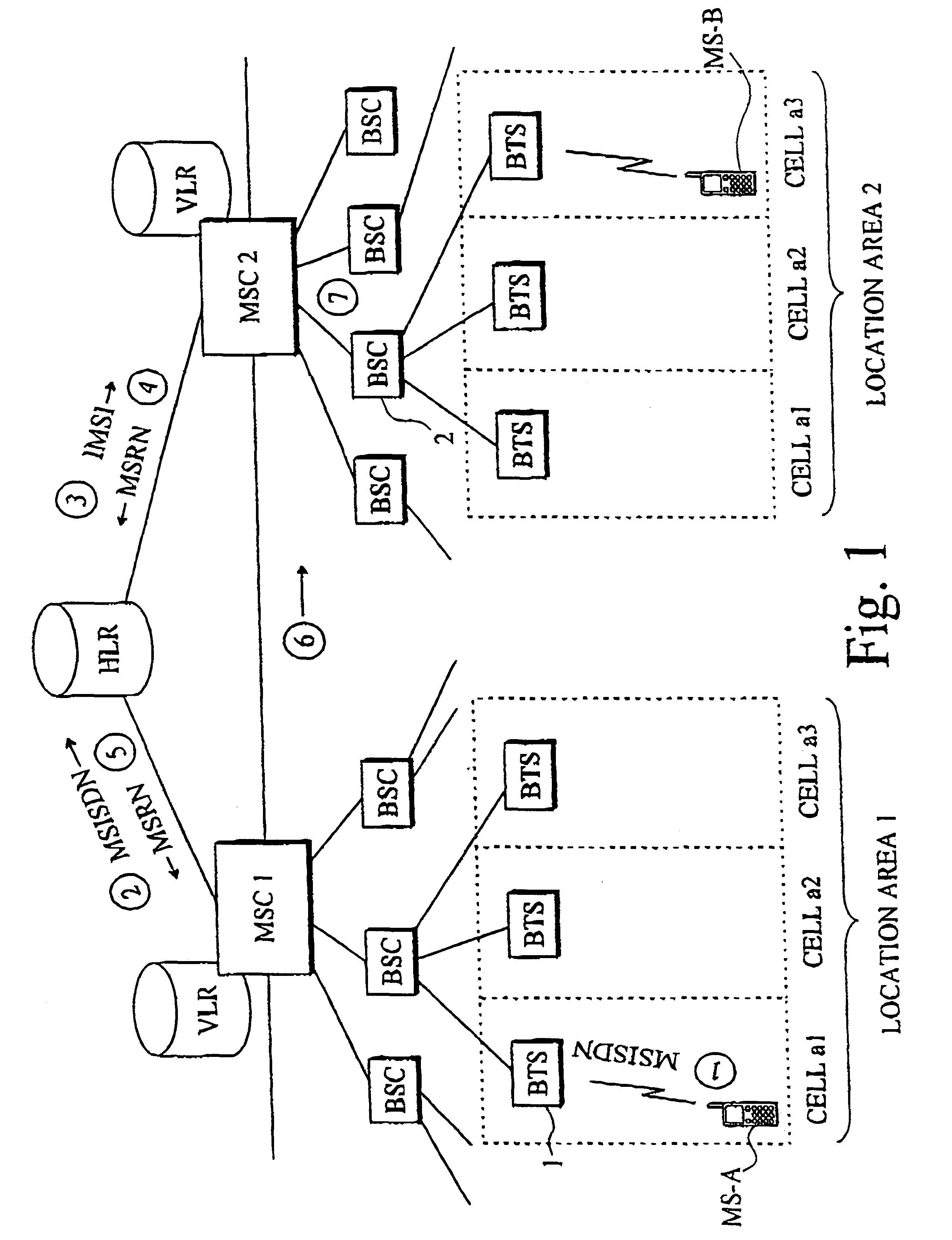
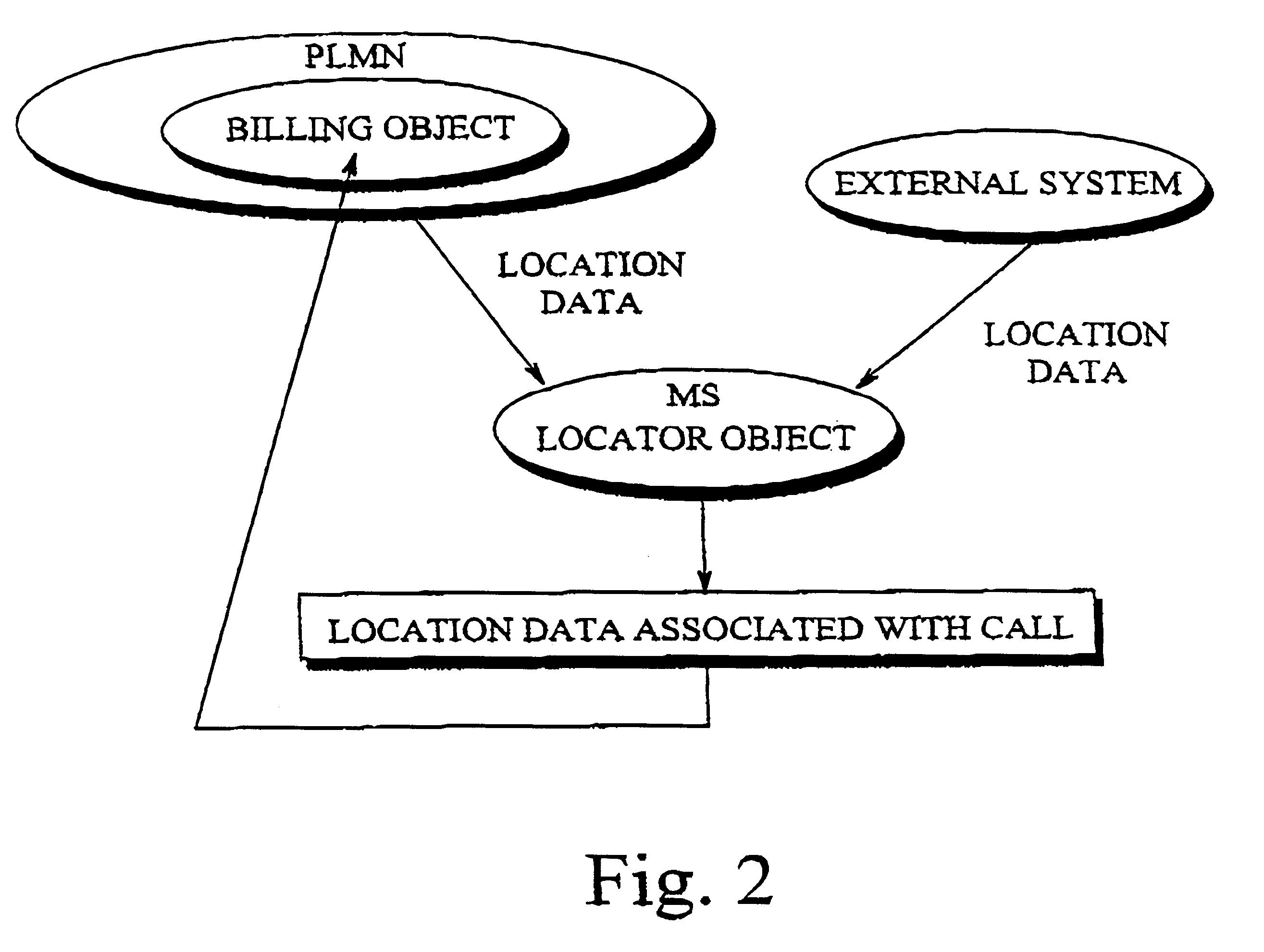
Method and apparatus for calculating call charge rates in a mobile telecommunication system
Rate charging rules and principles concerning mobile calls in a cellular communication system can be improved by providing the mobile station with a locator object which, at certain intervals, determines the cell in which the mobile station is currently located. Stored in the mobile station is a list of cells or areas in which a special rate is to be applied in charging for calls originating from the mobile station. The locator object monitors calls made from the mobile station and, when it detects that a call is being made, it determines whether the mobile station was in a denoted special rate area at the time that its location was most recently determined. If so, then the object informs the network that the call is entitled to the special rate. Since the last location function was executed just before call setup commenced, a special rate call is possible even if the mobile station has thereafter moved some distance into a cell applying a normal rate. Disposed in a billing center is a billing object, to which the locator object sends data indicating whether the call was initiated from a cell or area in which a special rate is applicable, as well as data identifying the particular call. The second object receives the billing records generated by the mobile switching center, which also contain call identifying data, and compares the call-specific data in those records with the data sent by the first object. In this way, the second object can identify from the billing records those calls that are entitled to a special rate, regardless of whether the mobile station has moved during call setup from the original cell into a cell where another rate, e.g. a higher rate, is applicable.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
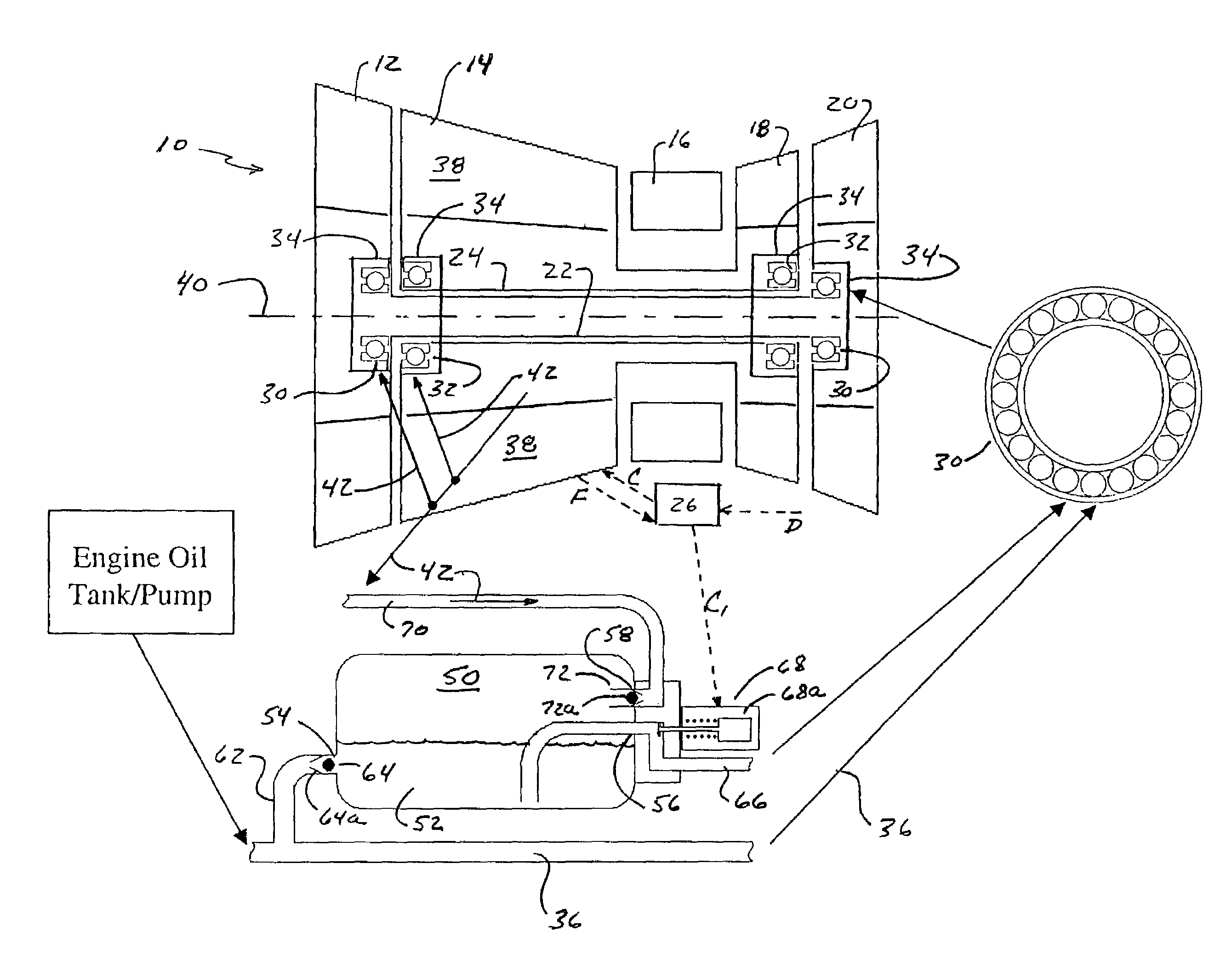
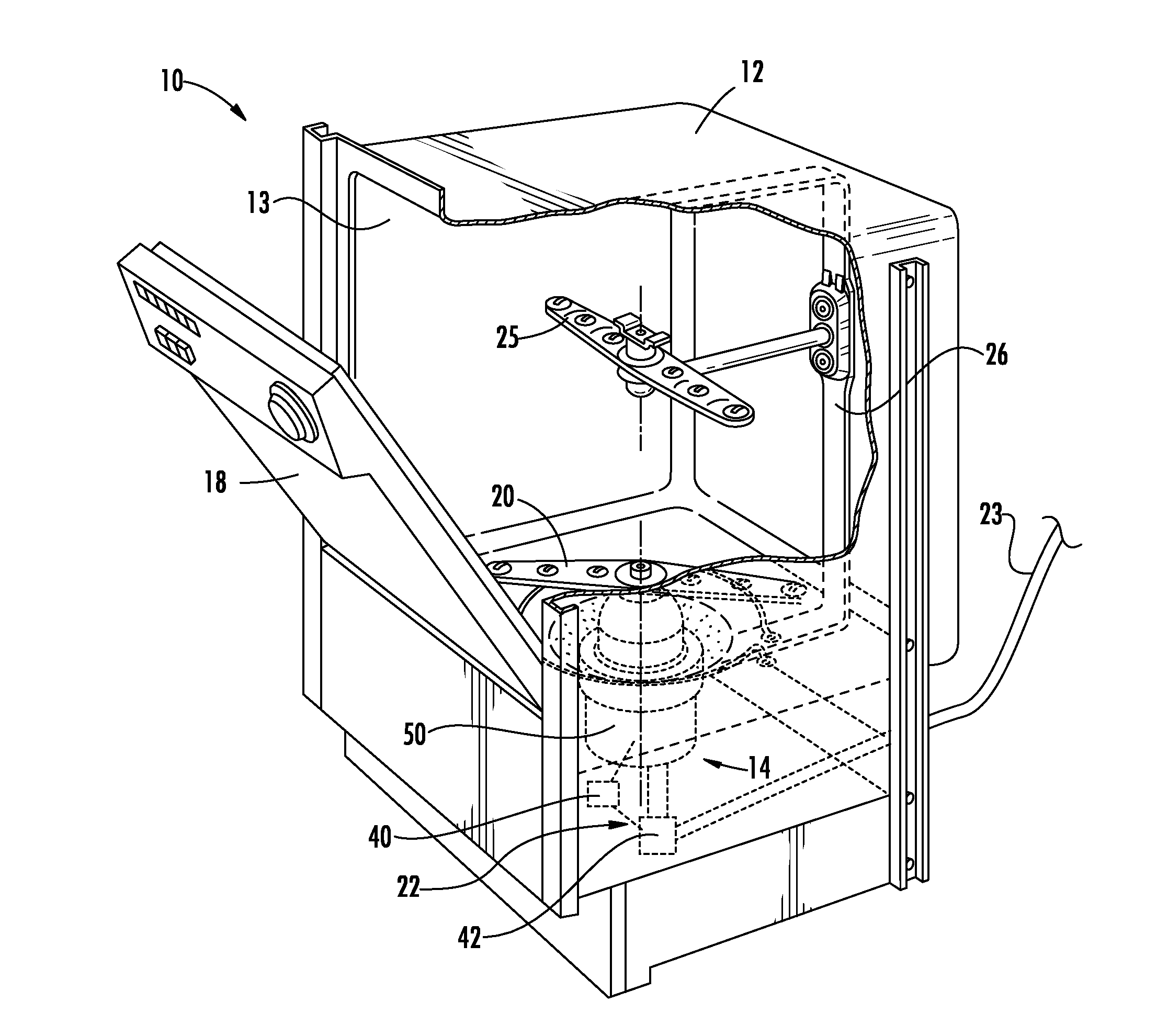
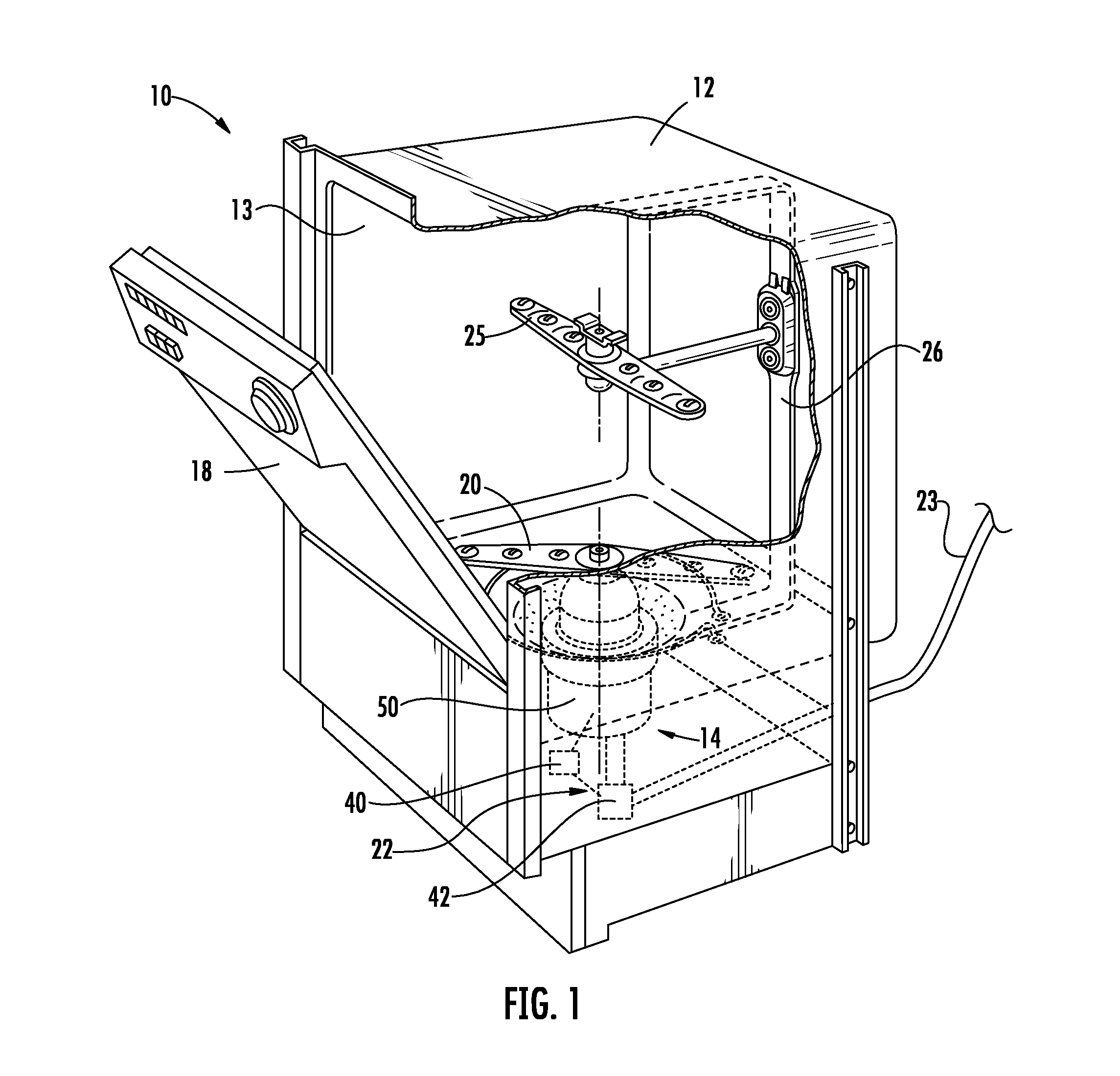
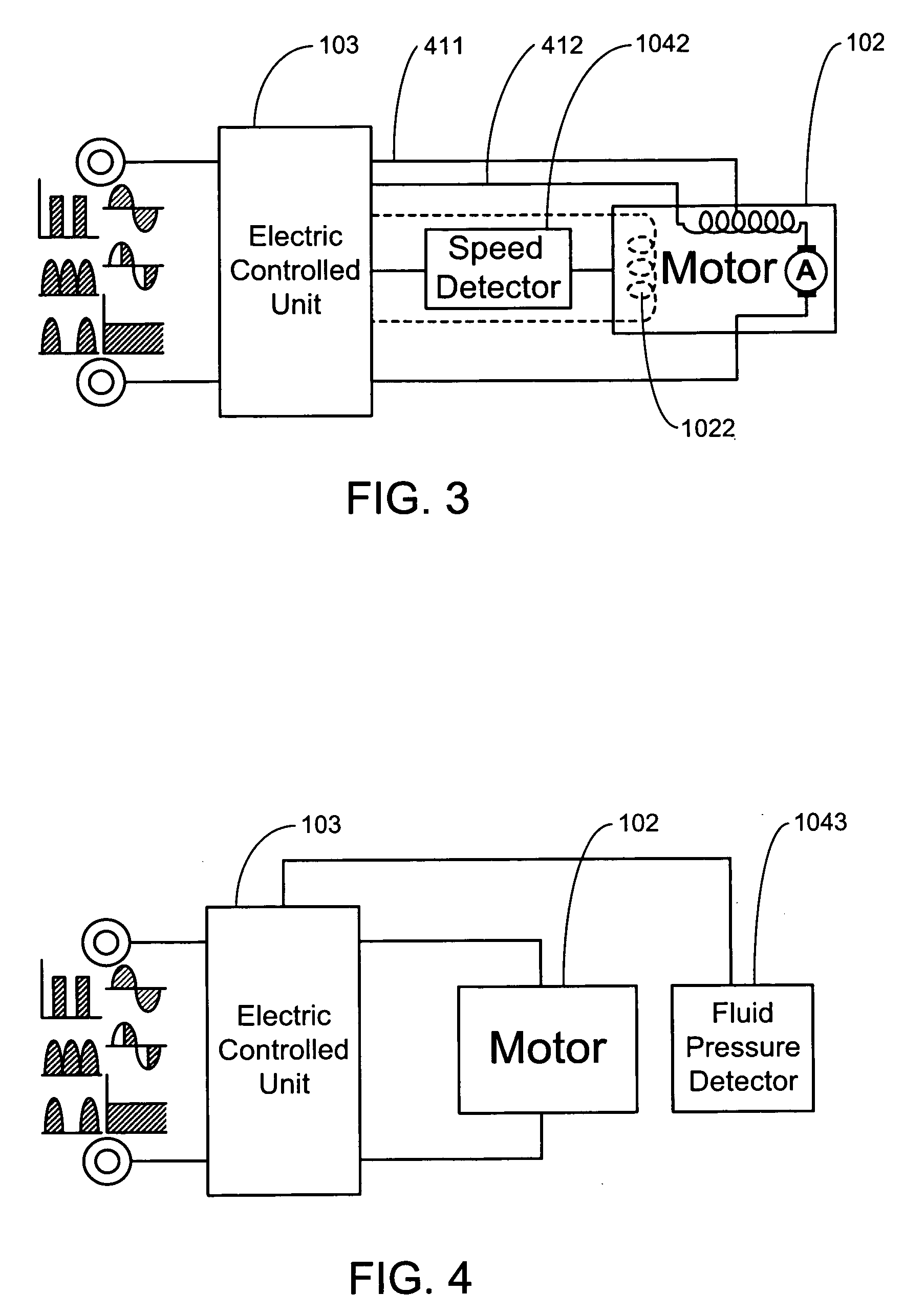
Emergency lubrication system
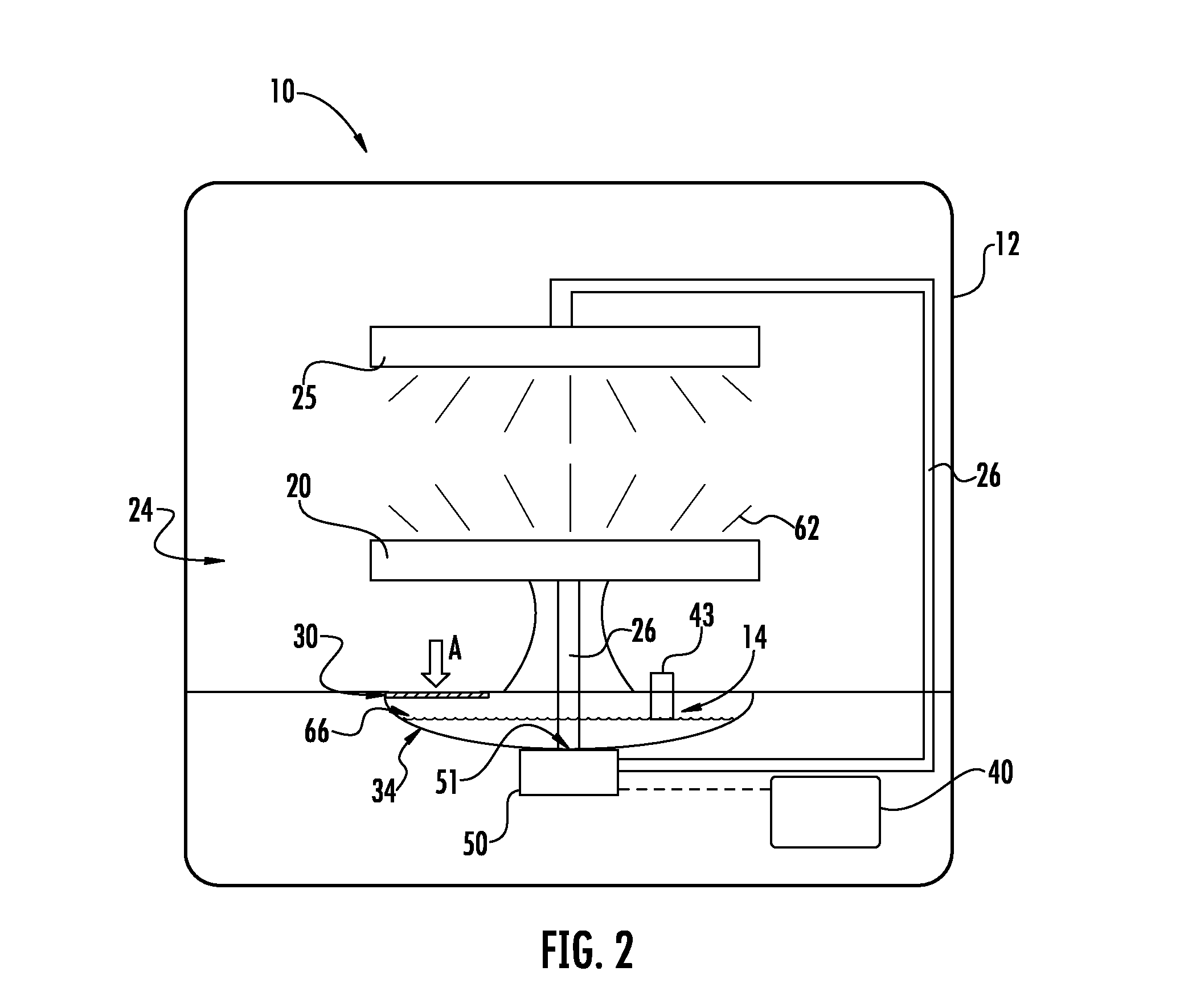
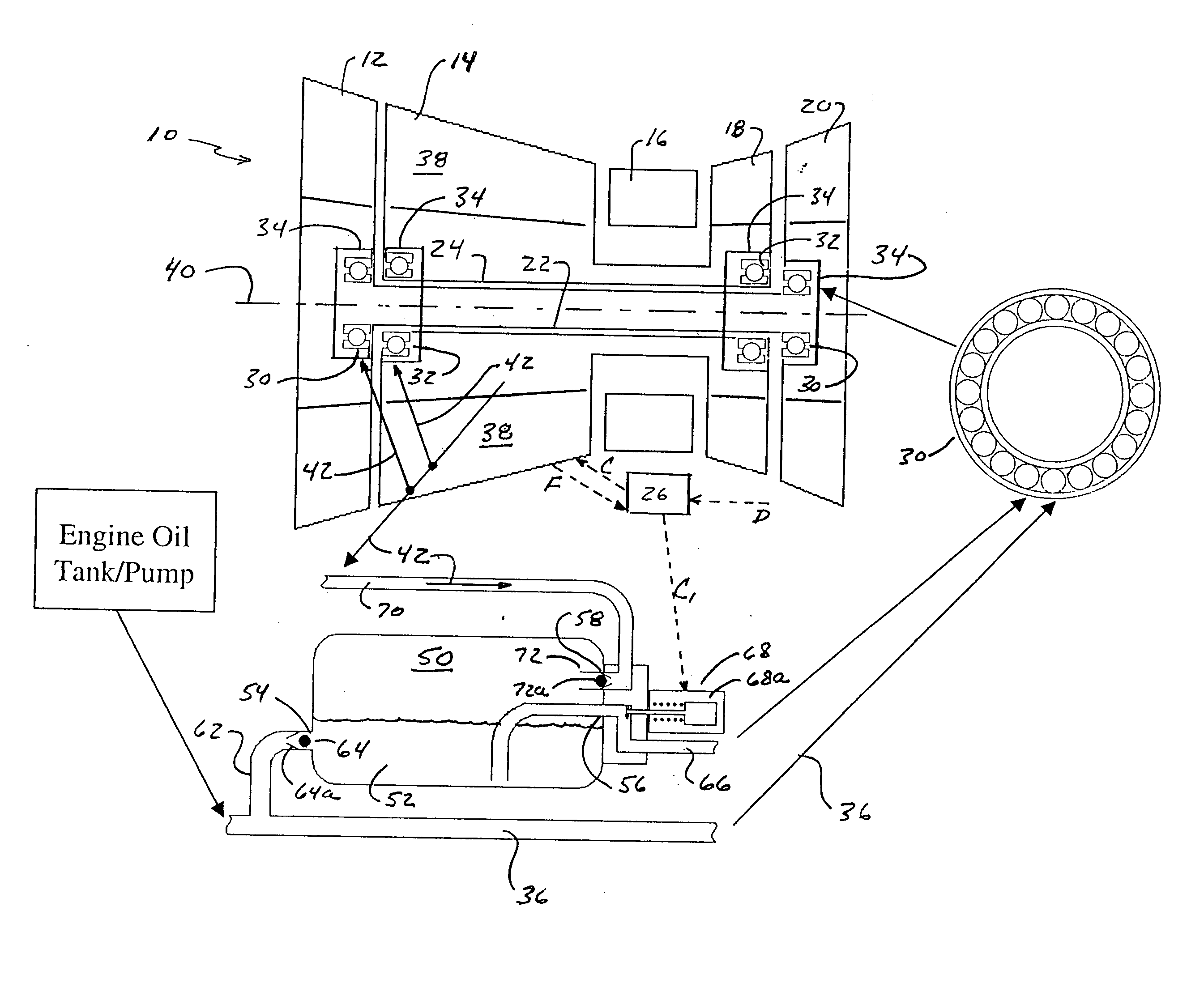
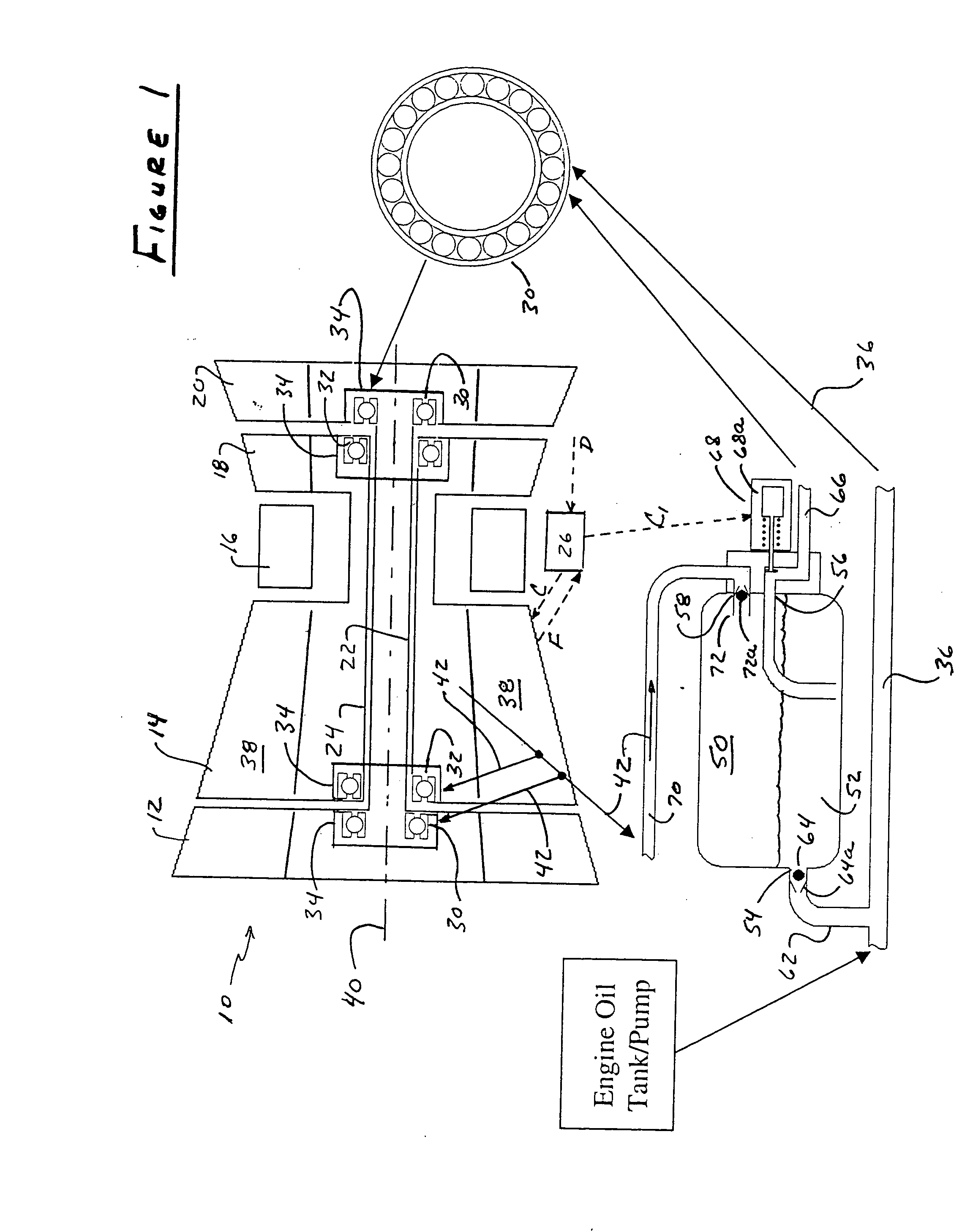
ActiveUS7387189B2Extended time intervalLight weightEfficient propulsion technologiesMachines/enginesNormal rateInlet valve
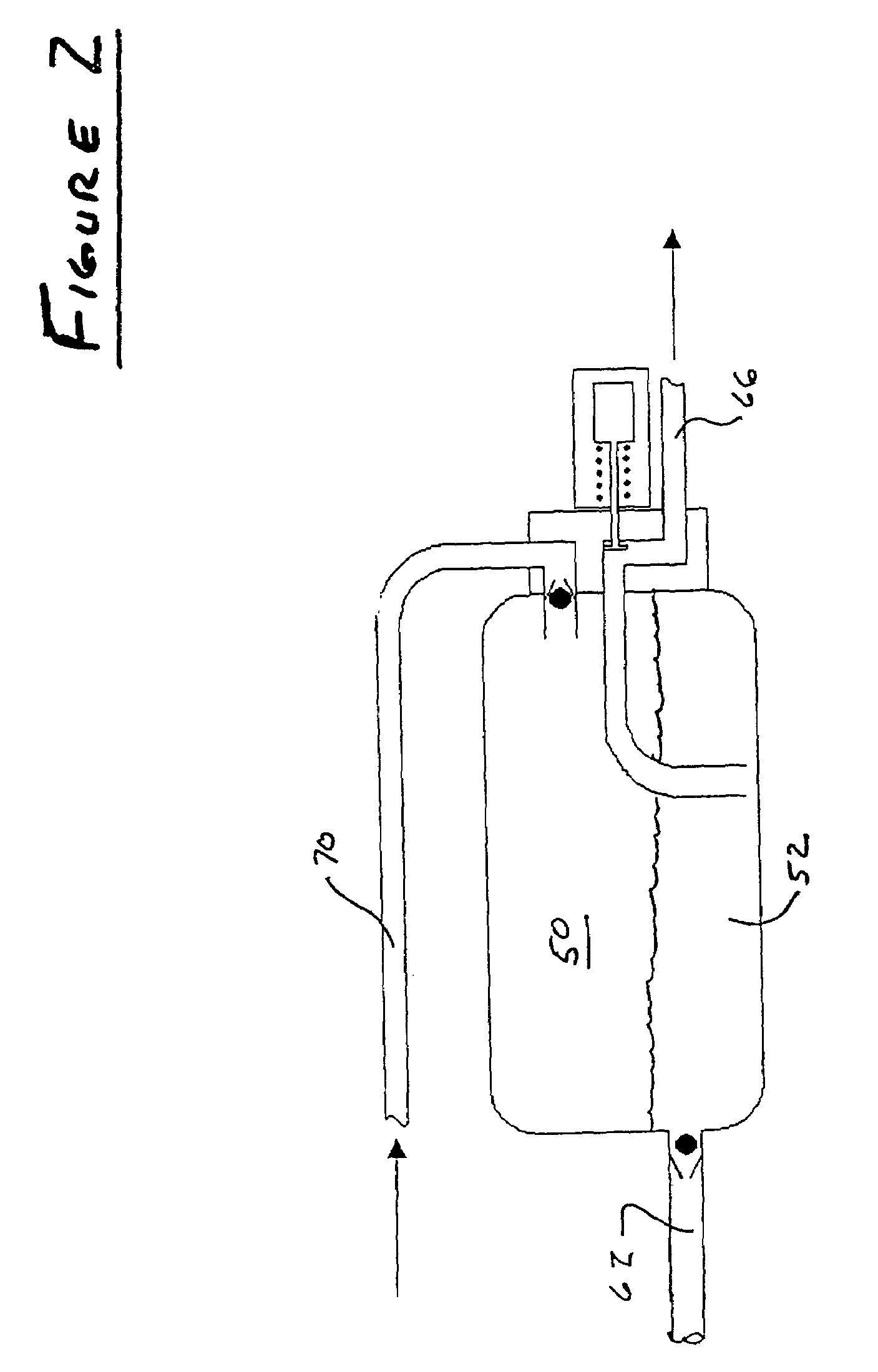
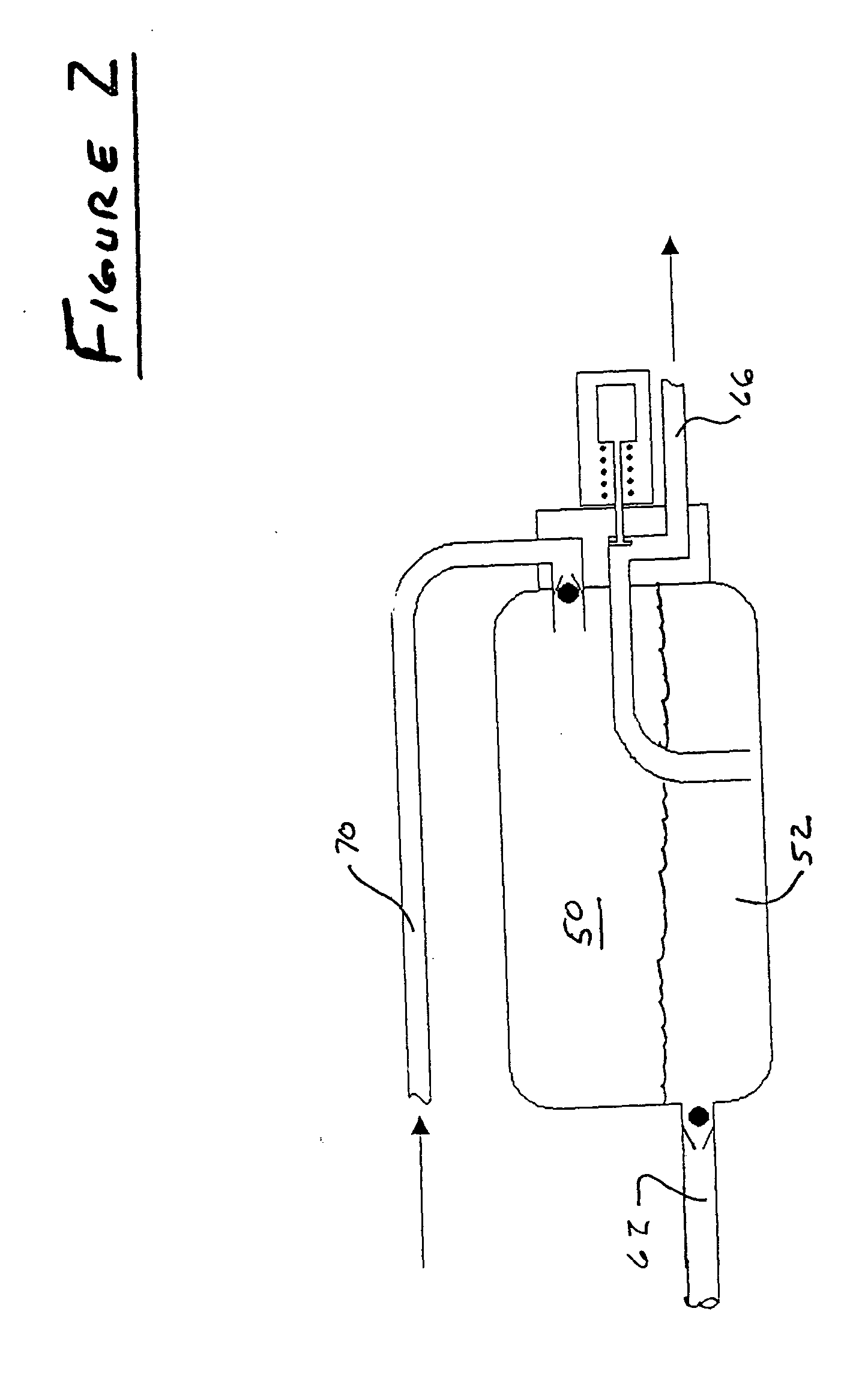
An emergency lubrication system for a turbine engine includes a reservoir 50 containing a reserve quantity of lubricant 52 and having a lubricant inlet 54 and a lubricant outlet 56. A lubricant supply line 62 and a lubricant outlet line 66 each have a respective valves 64, 68 for regulating lubricant flow into and out of the reservoir. A fluid supply line 70 includes a valve 72 for selectively establishing communication between the reserve quantity of lubricant and a source of pressurized fluid. During normal operation the lubricant outlet valve continuously releases lubricant at a normal rate to the component requiring lubrication while the lubricant inlet valve concurrently admits fresh lubricant into the reservoir. During abnormal operation, the lubricant inlet valve closes in response to abnormally low lubricant pressure outside the reservoir thereby preventing backflow of reserve lubricant out of the reservoir. The fluid inlet valve opens to admit pressurized fluid into the reservoir thus pressurizing the reserve lubricant. The lubricant outlet valve opens or cycles open and closed in response to a command from a controller 26 so that the pressurized fluid forces lubricant through the outlet 56 as a subnormal rate, which persists until the lubricant reserve is substantially depleted. The subnormal rate is ideally achieved by intermittently releasing lubricant from the reservoir, but may also be achieved by releasing a continuous stream of lubricant at a rate less than the normal rate of release.
Owner:RTX CORP
Close-talk detector for personal listening device with adaptive active noise control
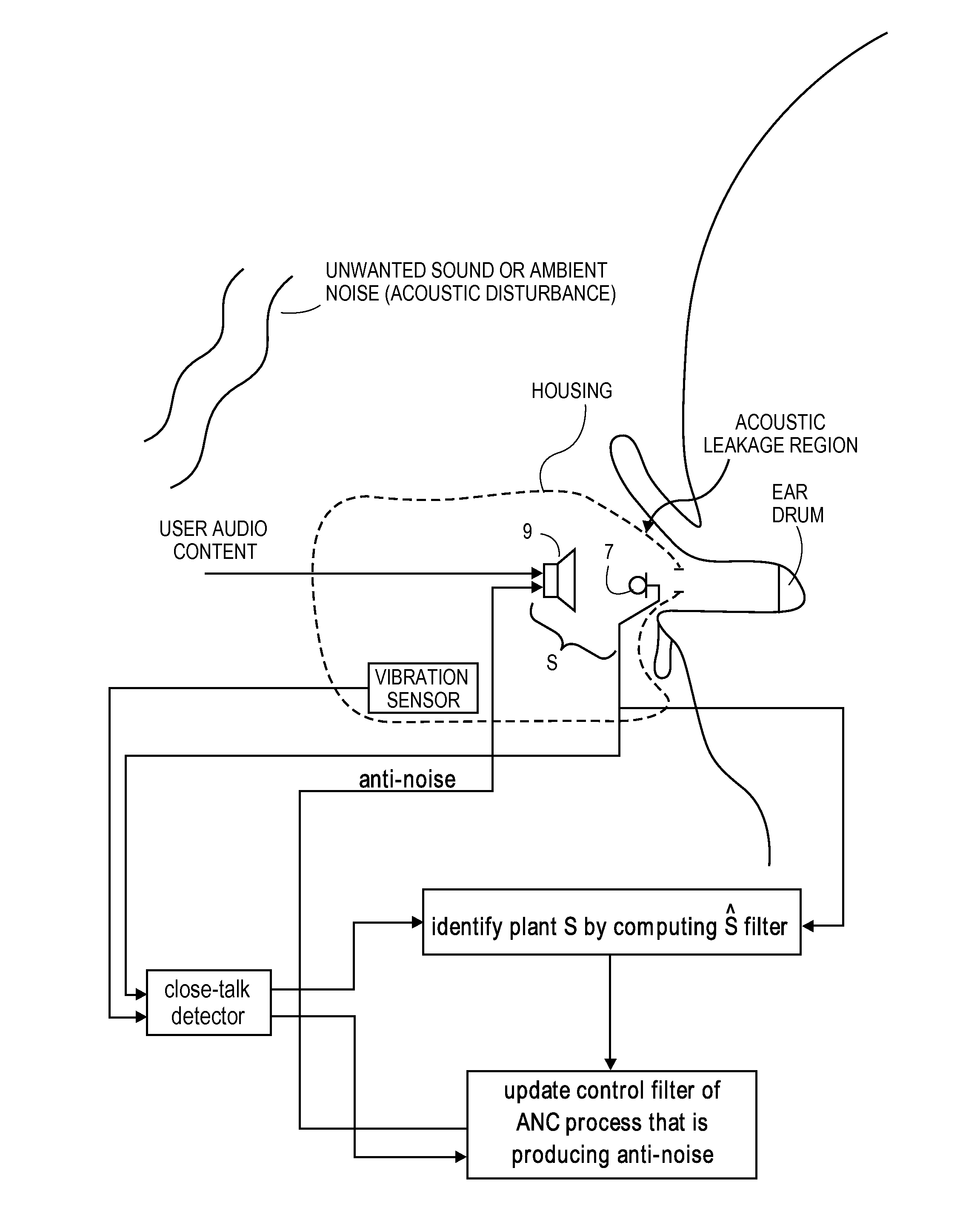
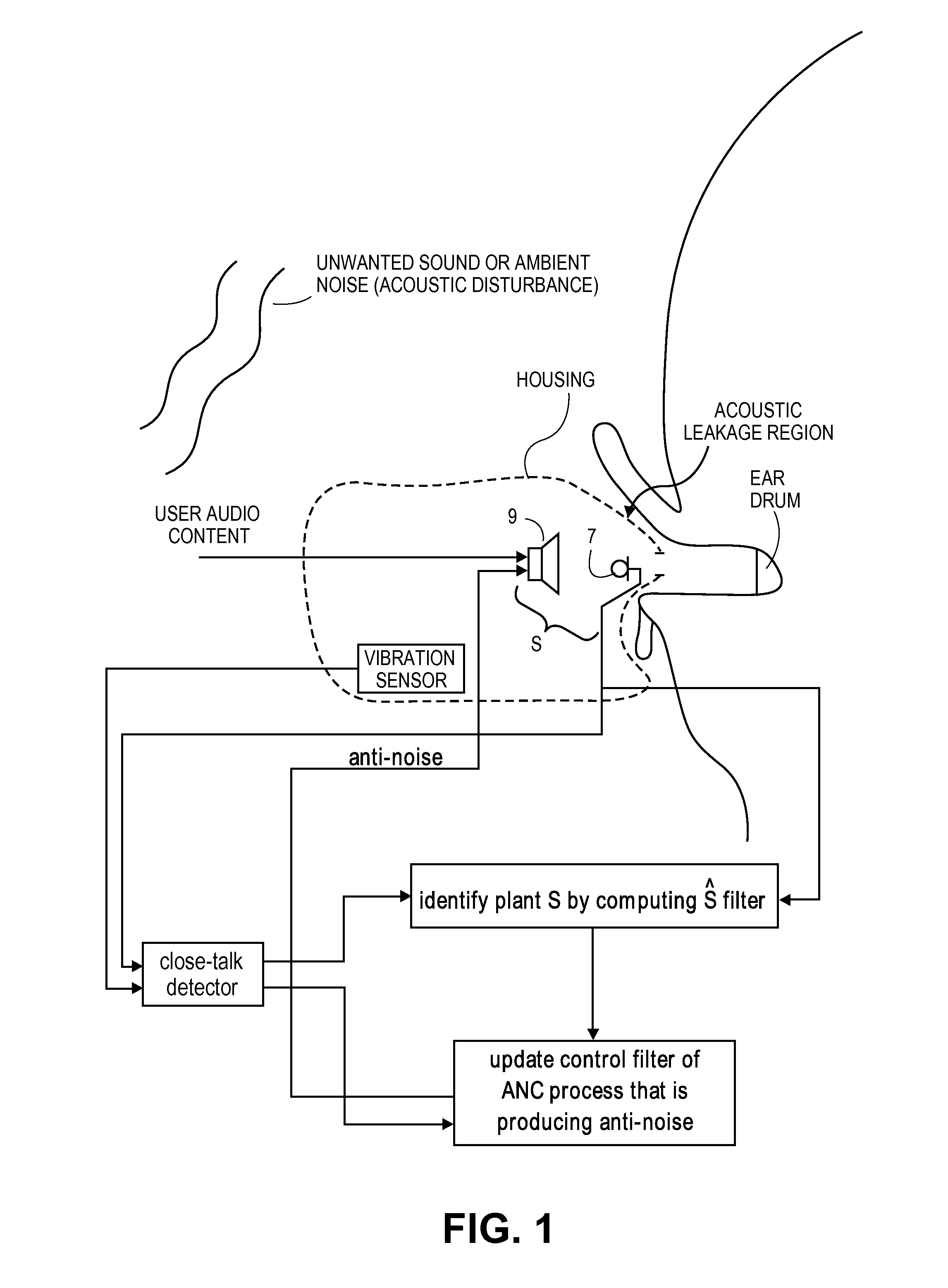
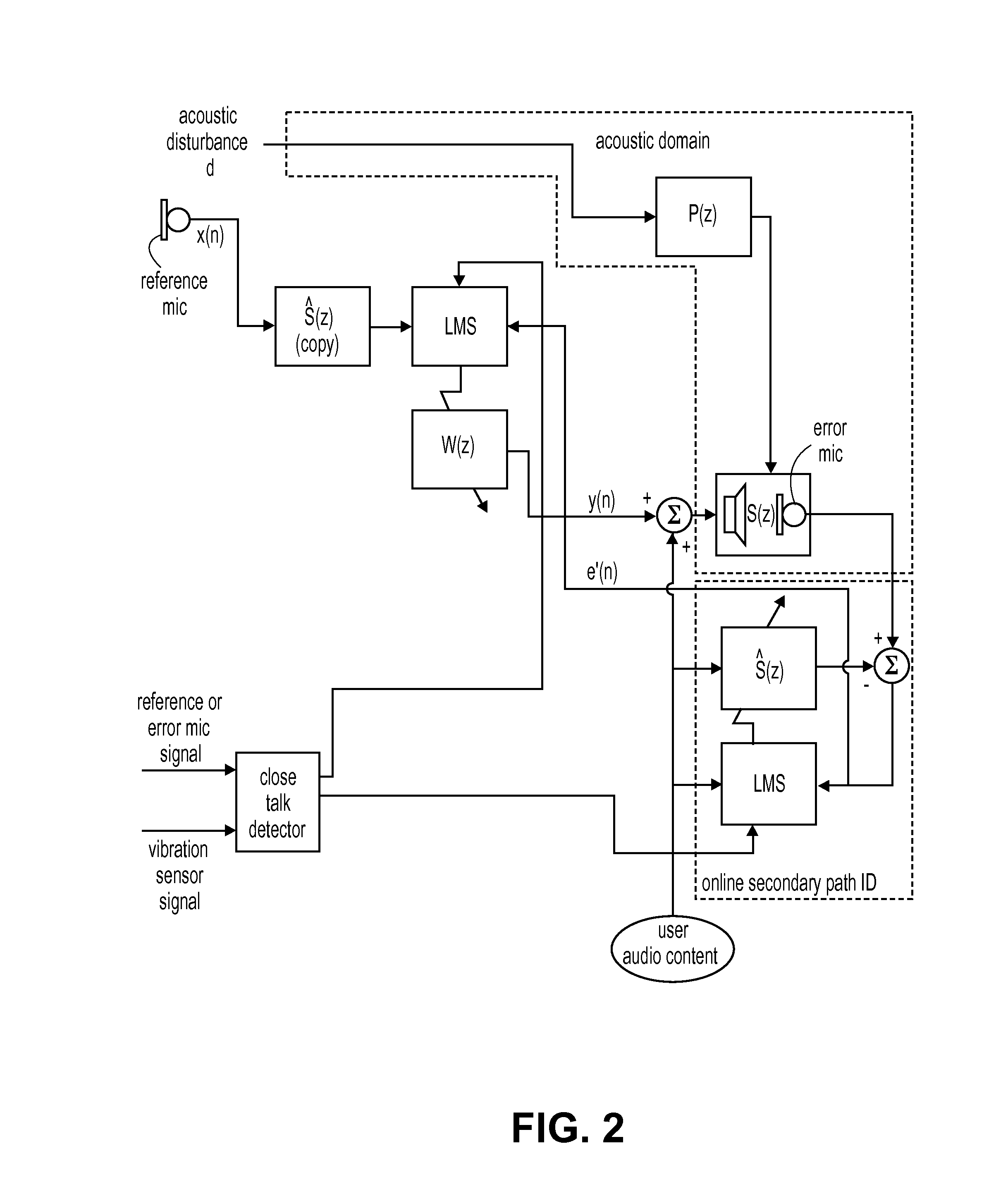
A close-talk detector detects a near-end user's speech signal, while an adaptive ANC process is running, and in response helps prevent the filter coefficients of an adaptive filter of the ANC process from being corrupted, thereby reducing the risk of the adaptive filters diverge. Upon detecting speech using a vibration sensor signal and one or more microphone signals, the detector asserts a signal that slows down, or even freezes or halts, the adaptation of the adaptive filter. The signal may be de-asserted when no more speech is being detected, thereby allowing the adaptive ANC process to resume its normal rate adaptation of the filter. The detector may continuously operate in this manner during the call, as the user talks and then pauses and then resumes talking. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:APPLE INC
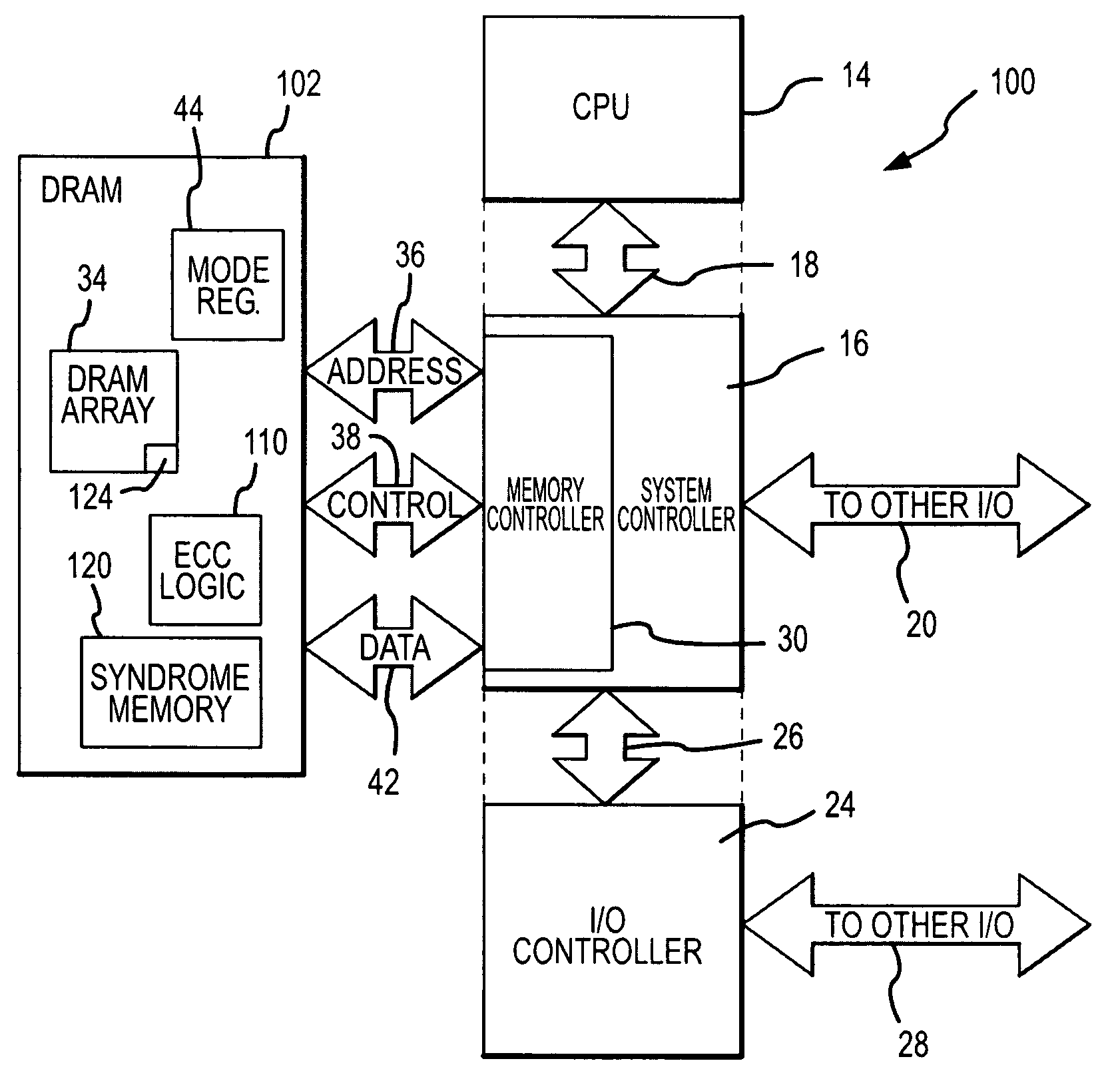
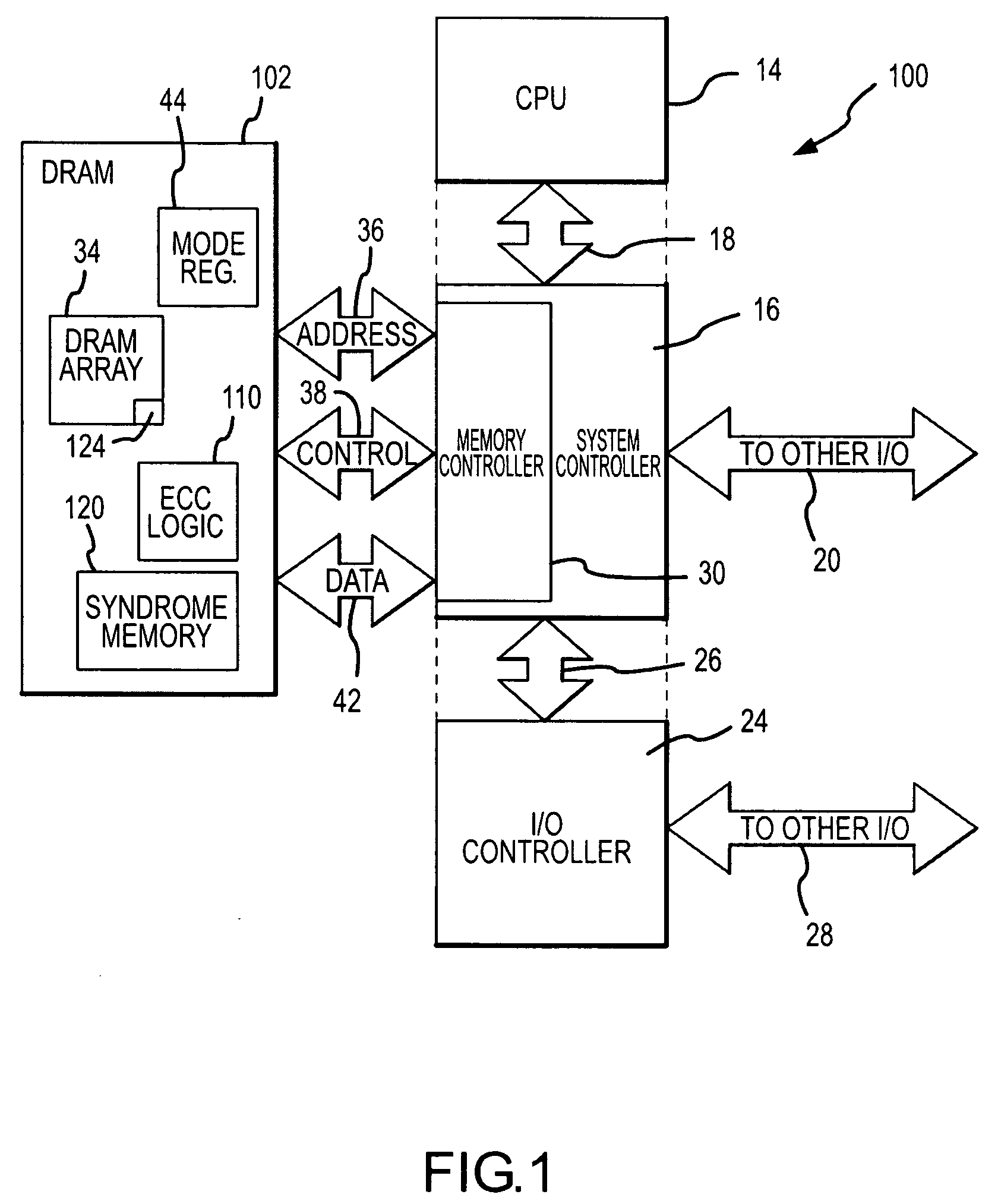
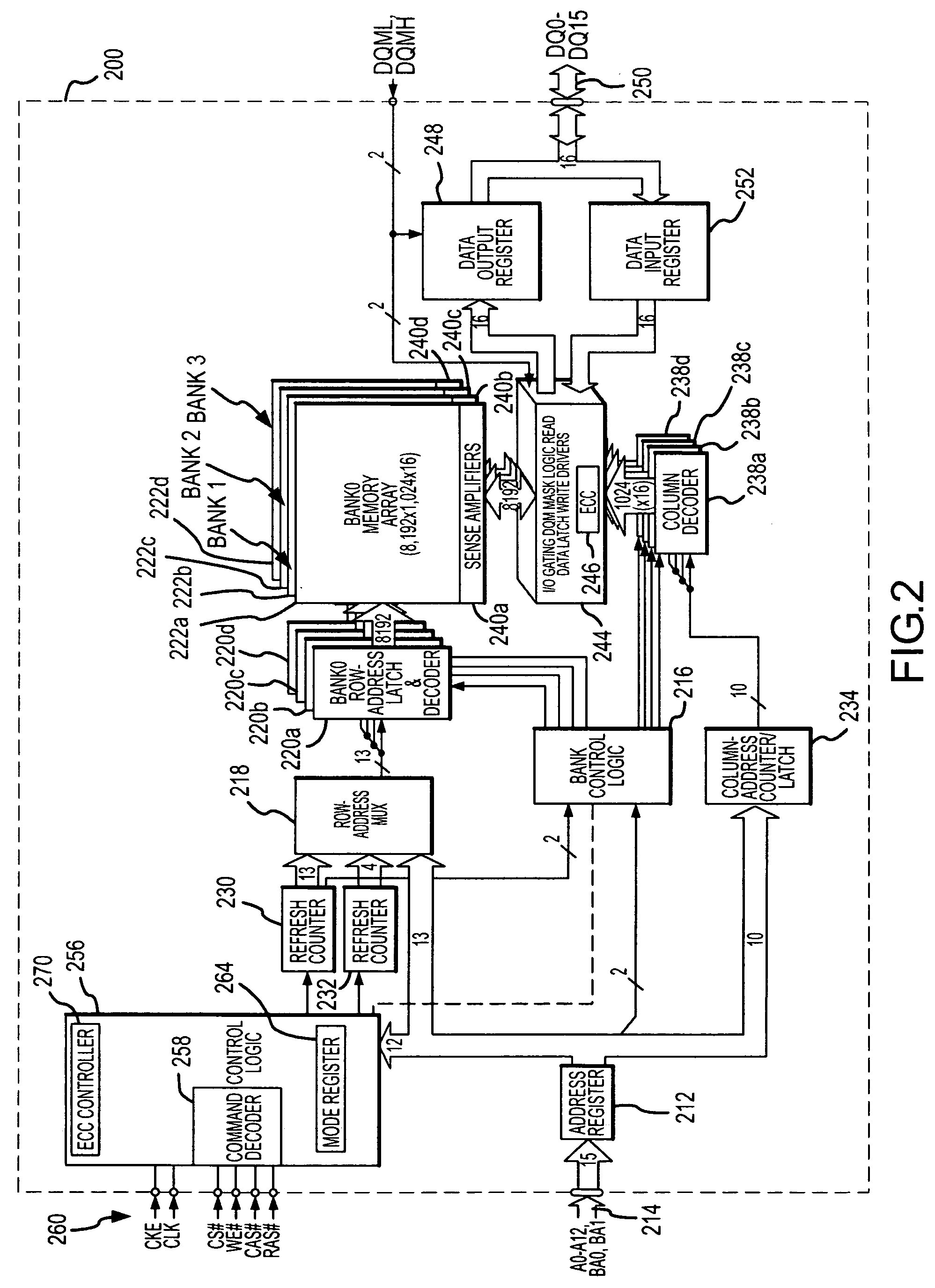
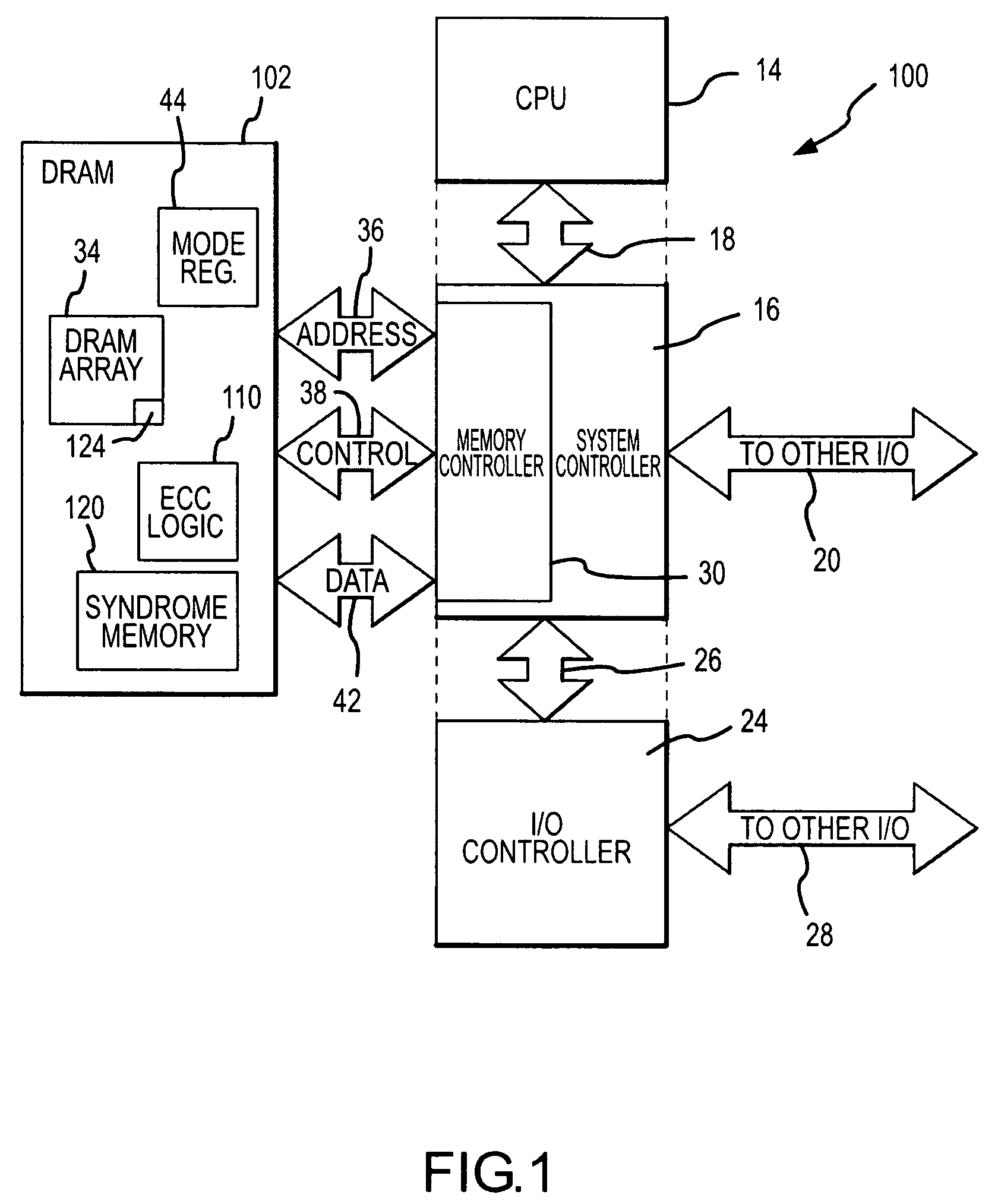
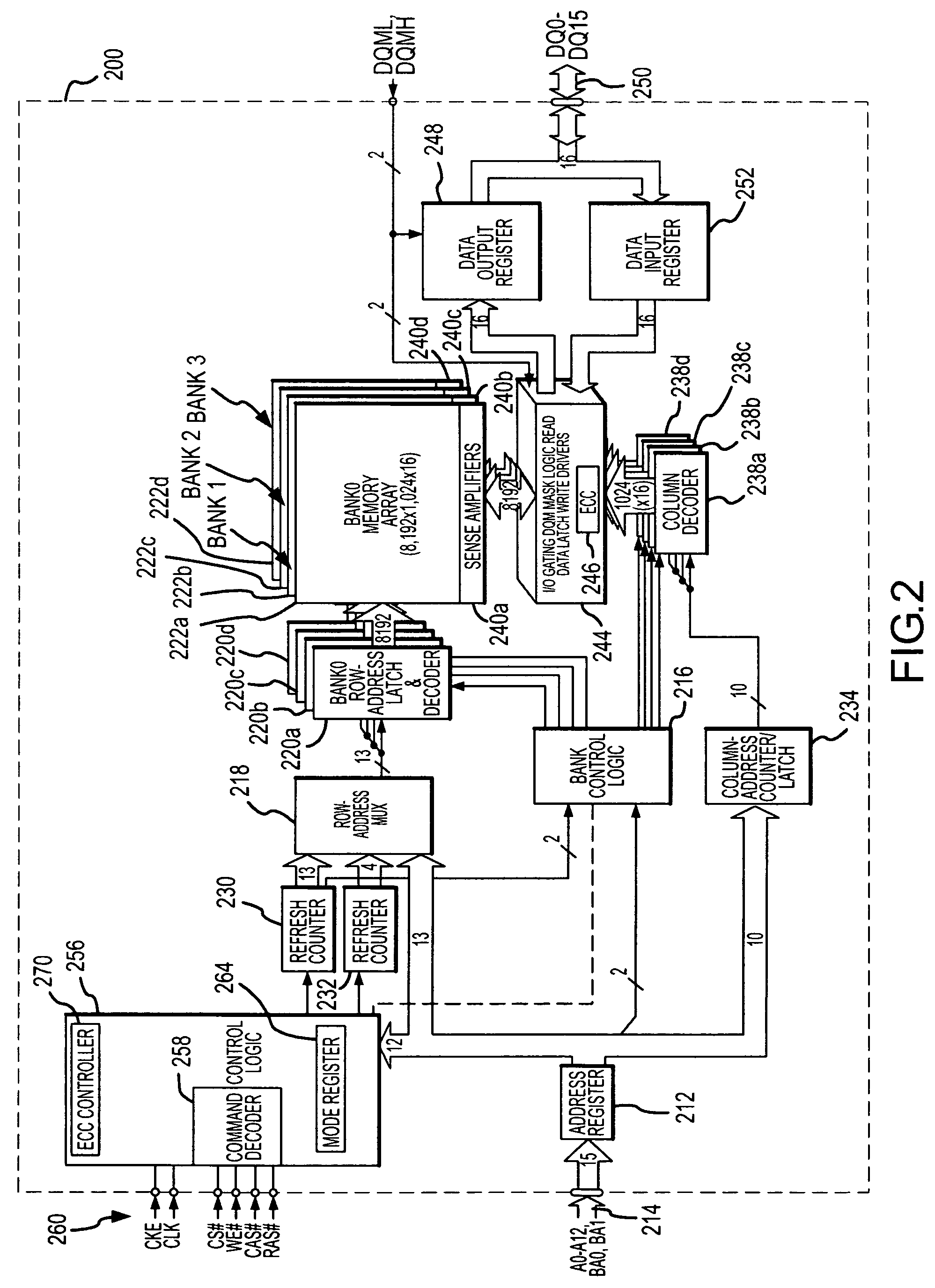
Memory system and method using partial ECC to achieve low power refresh and fast access to data
ActiveUS20080092016A1Reduced power refreshReduce power consumptionError detection/correctionCode conversionError checkingDram memory
A DRAM memory device includes several banks of memory cells each of which are divided into first and second sets of memory cells. The memory cells in the first set can be refreshed at a relatively slow rate to reduce the power consumed by the DRAM device. Error checking and correcting circuitry in the DRAM device corrects any data retention errors in the first set of memory cells caused by the relatively slow refresh rate. The memory cells in the second set are refreshed at a normal rate, which is fast enough that data retention errors do not occur. A mode register in the DRAM device may be programmed to select the size of the second set of memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
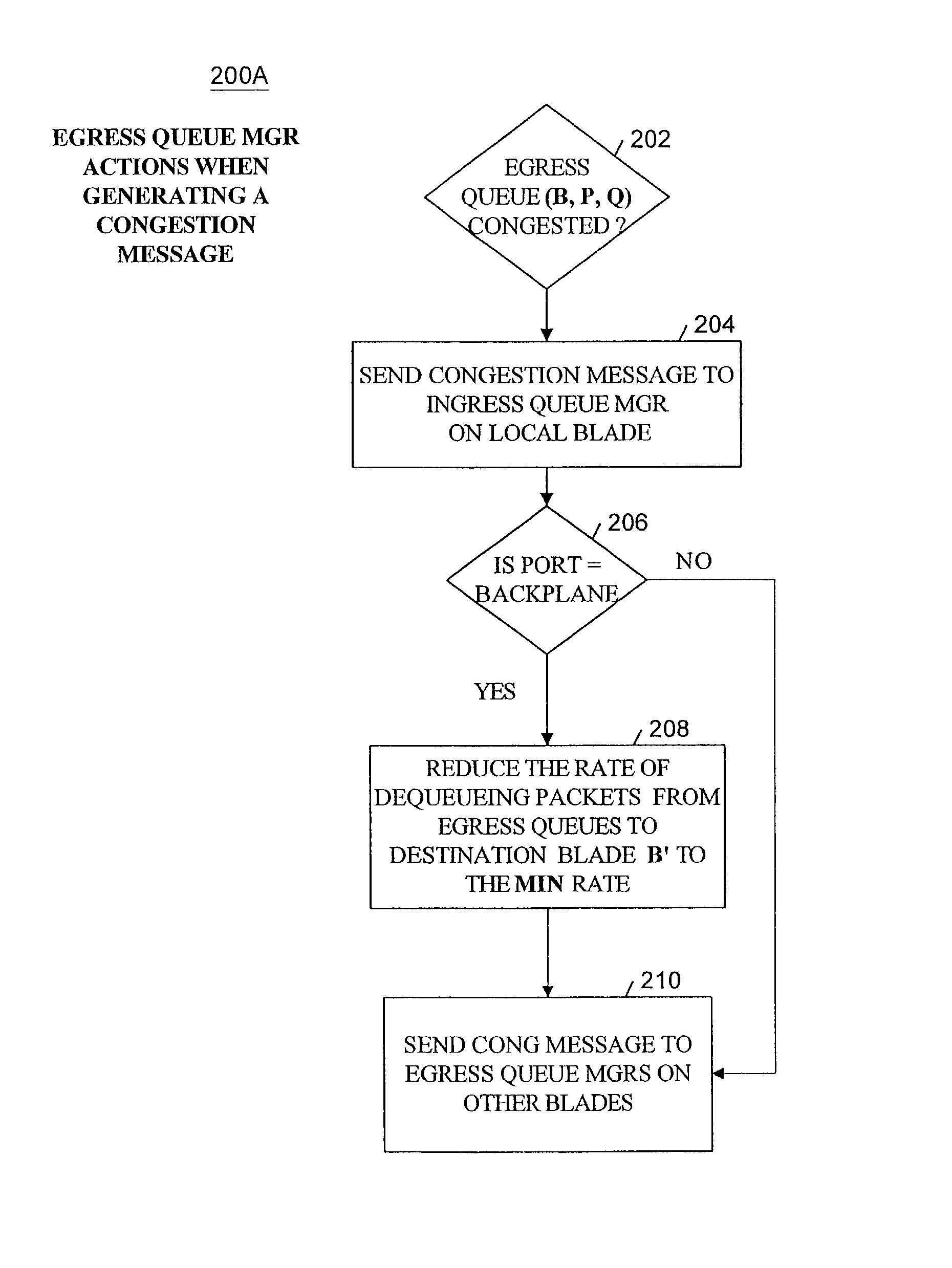
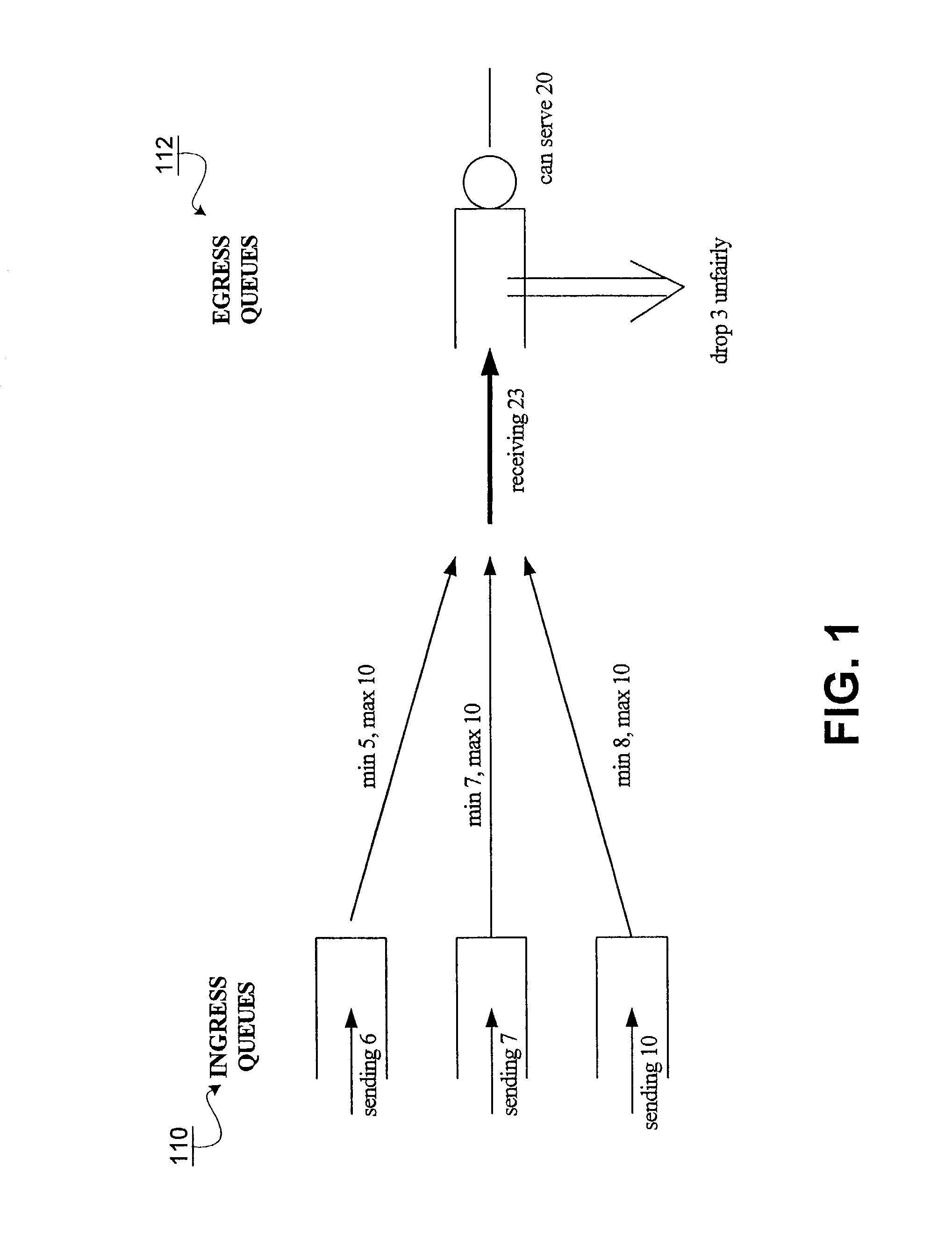
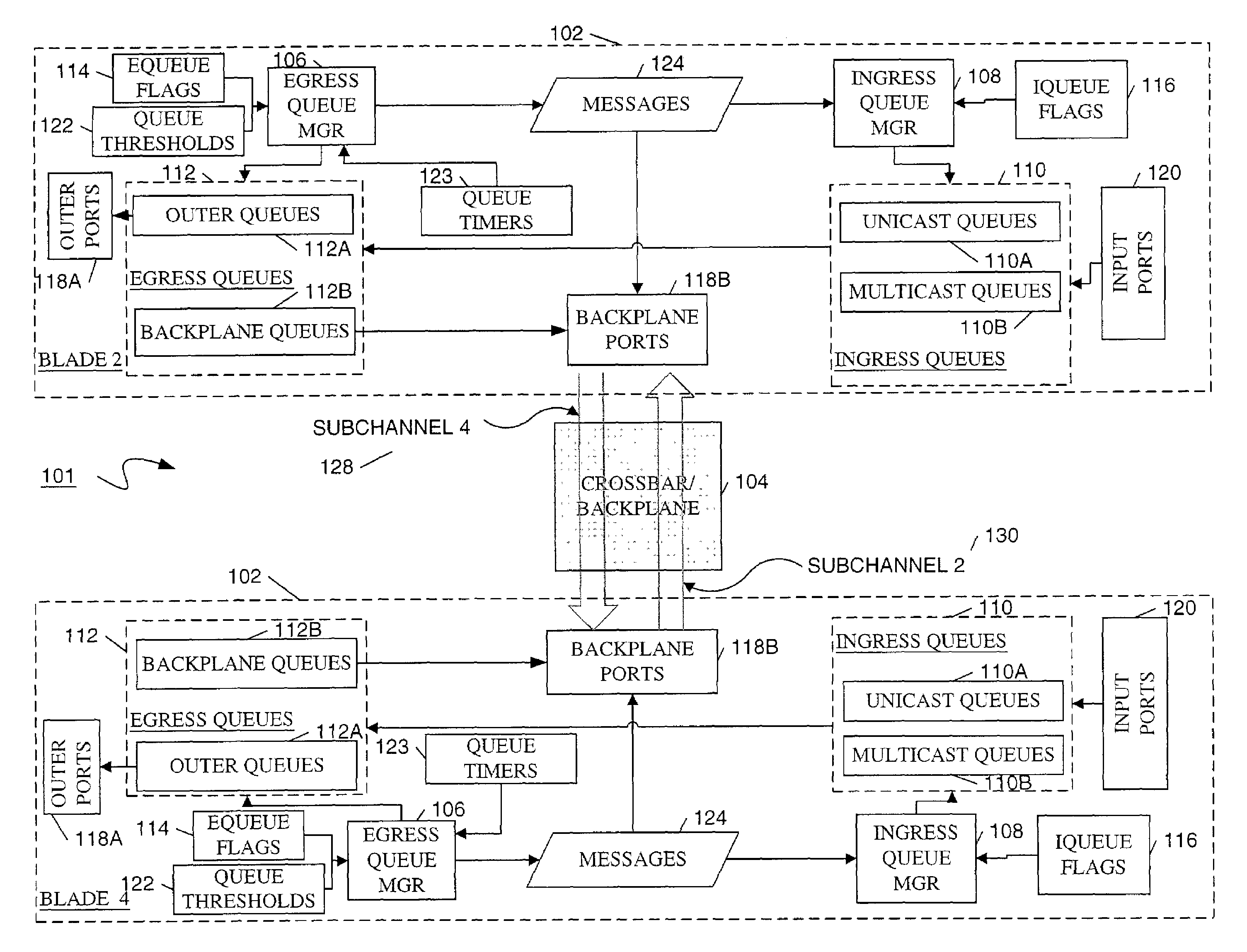
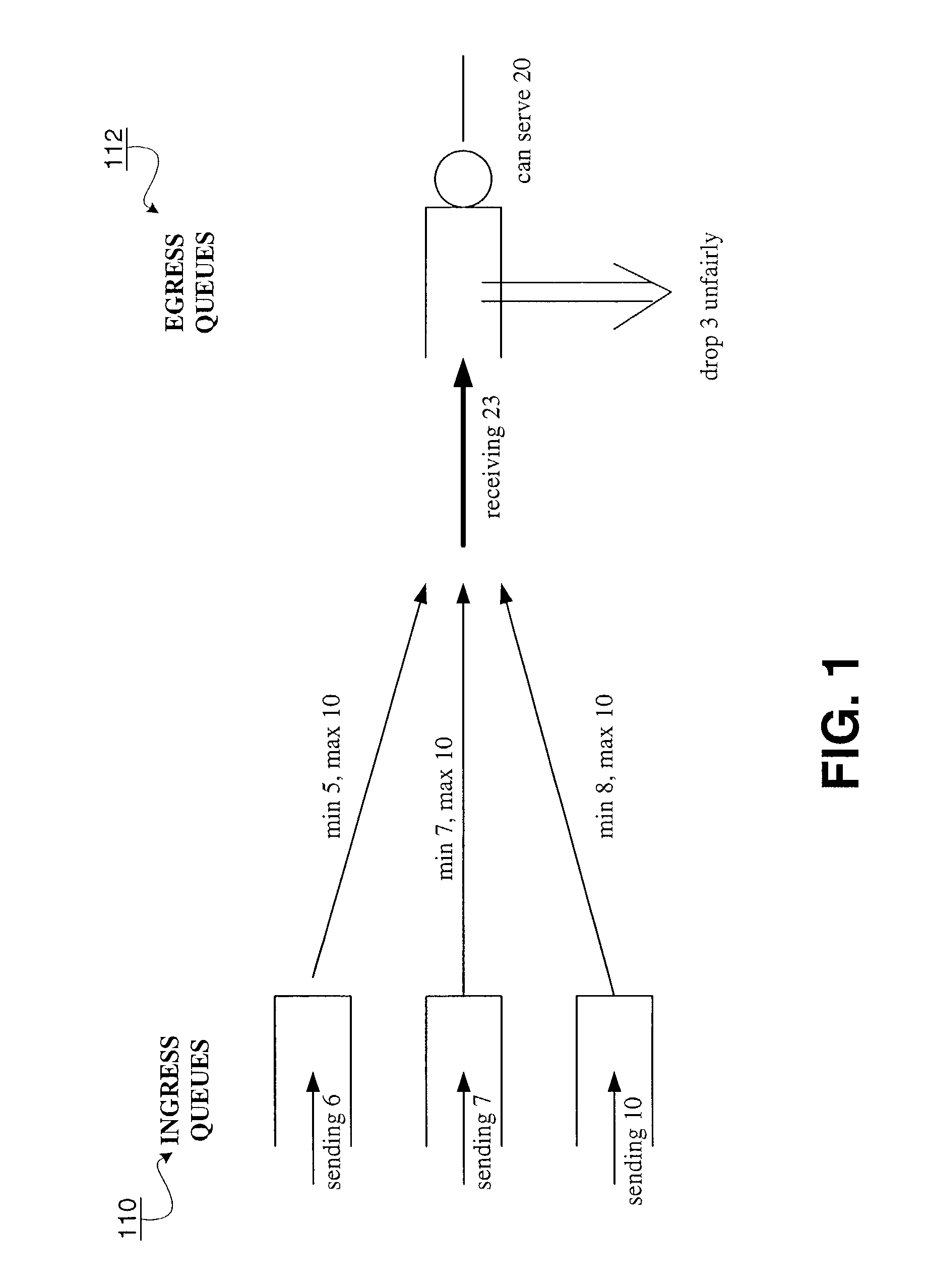
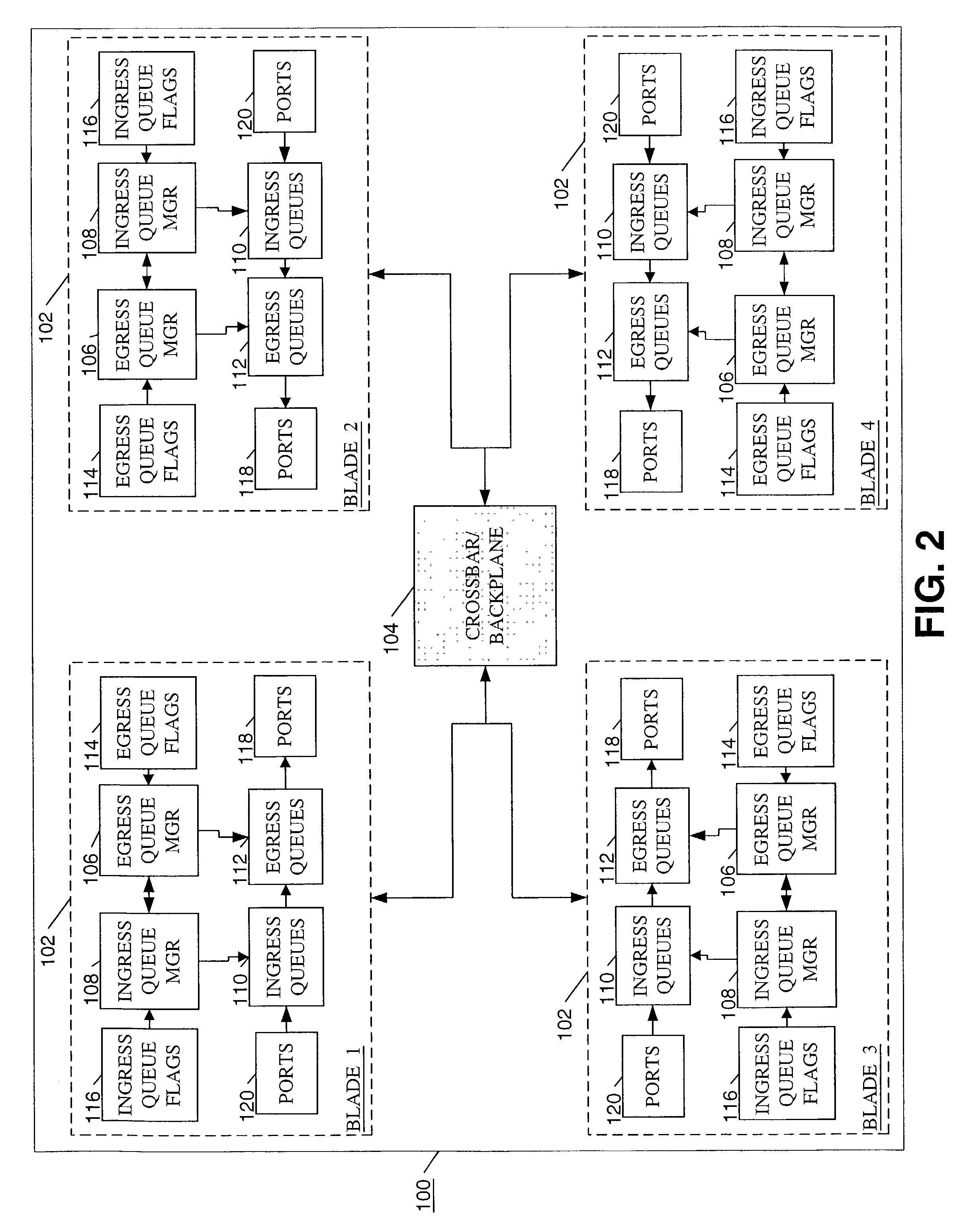
Method and apparatus for providing quality of service across a switched backplane between egress queue managers
ActiveUS7408876B1Improve robustnessReduce probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceNormal rate
A method and system is provided to enable quality of service across a backplane switch. An egress queue manager on one blade communicates with an egress queue manager on another blade where each blade is connected via a backplane switch. When a blade becomes congested, egress queues mapped to a destination on the congested blade also become congested. The egress queue managers determine when to reduce or resume the packet sending rates of egress queues mapped to destinations on congested blades using a messaging scheme. Each egress queue manager maintains notifications of the status of egress queue congestion on its own and other blades. Normal rates of dequeuing packets are resumed only when the related congestion on all of the blades has subsided.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Method and system for detecting and removing a clogging condition of a filter in a dishwasher
ActiveUS20140158163A1High degreeReduce the risk of failureWashing controlling processesWashing processesNormal rateWater level
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and systems for detecting and removing a clogging condition of a filter in a dishwasher. According to one embodiment, the method includes determining a normal water level or a normal rate of water level change for a wash cycle of the dishwasher and monitoring a water level or a rate of water level change during execution of the wash cycle. The method further includes detecting the clogging condition of the filter by detecting a deviation thereof. A current position of the wash cycle being executed may then be determined. The method further includes executing a remedial operation to facilitate removal of the clogging condition and determining if the clogging condition has been removed. Finally, the method includes resuming operation of the dishwasher at a wash cycle position based on the current position if the clogging condition has been removed.
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
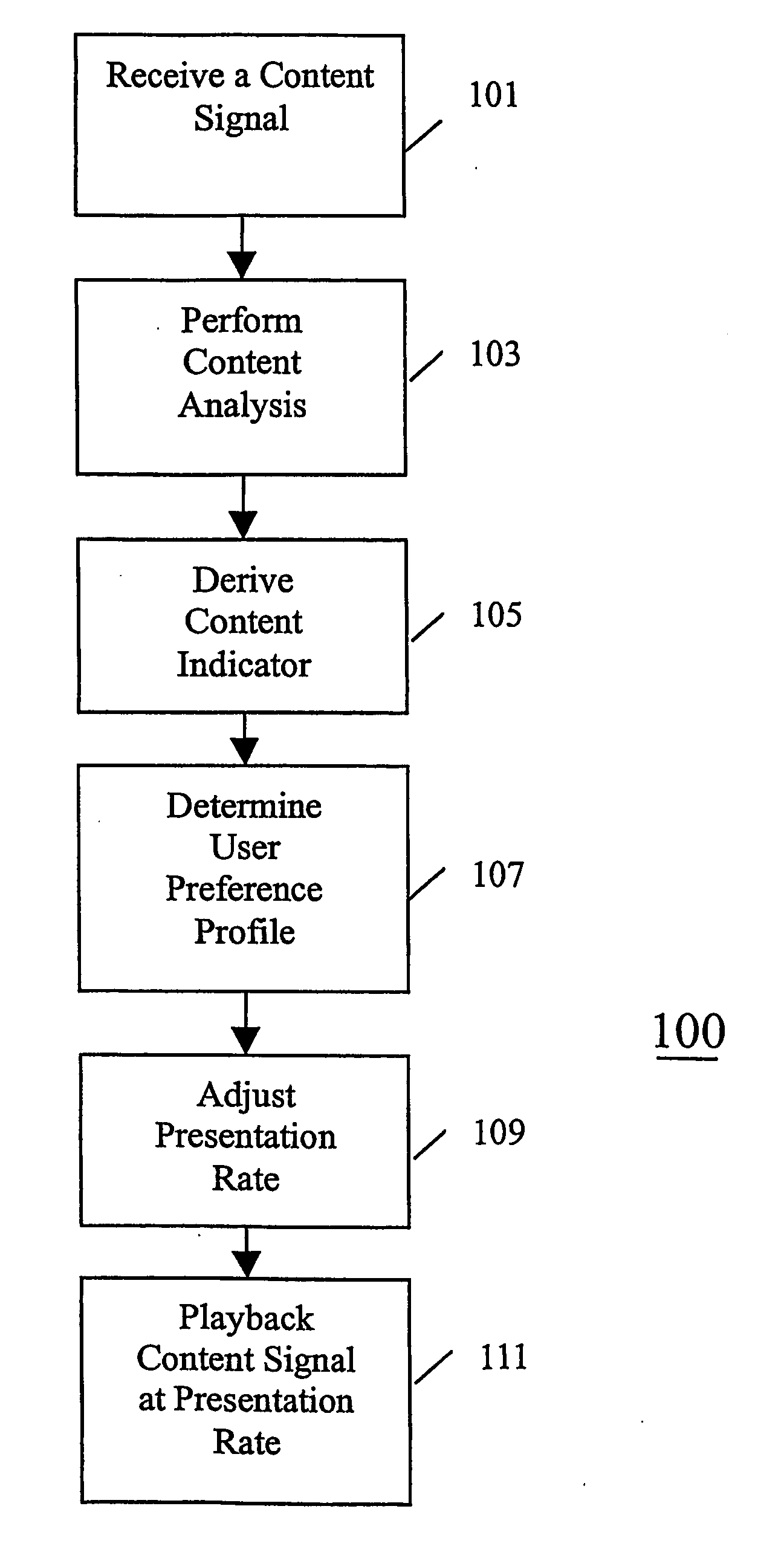
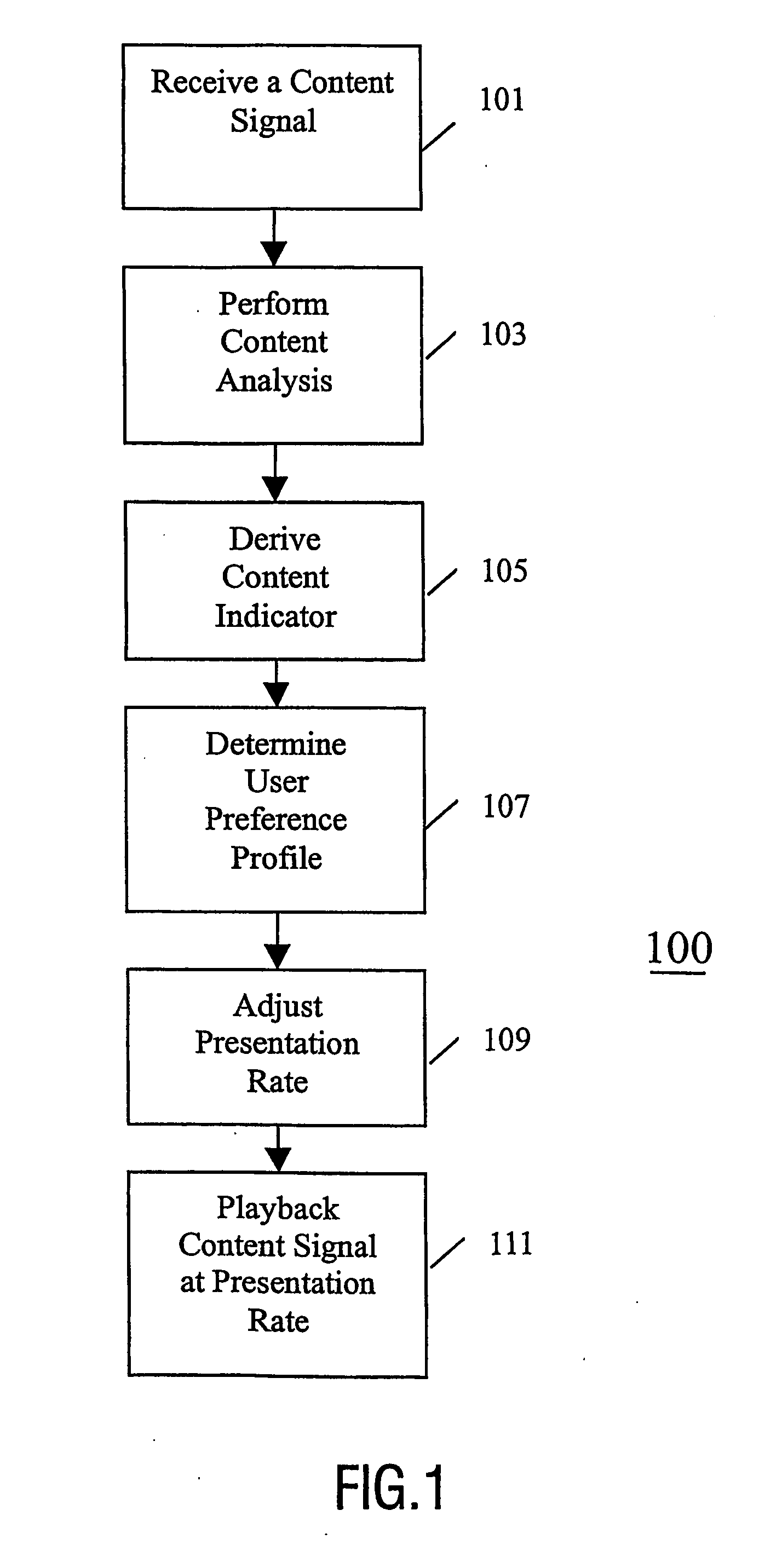
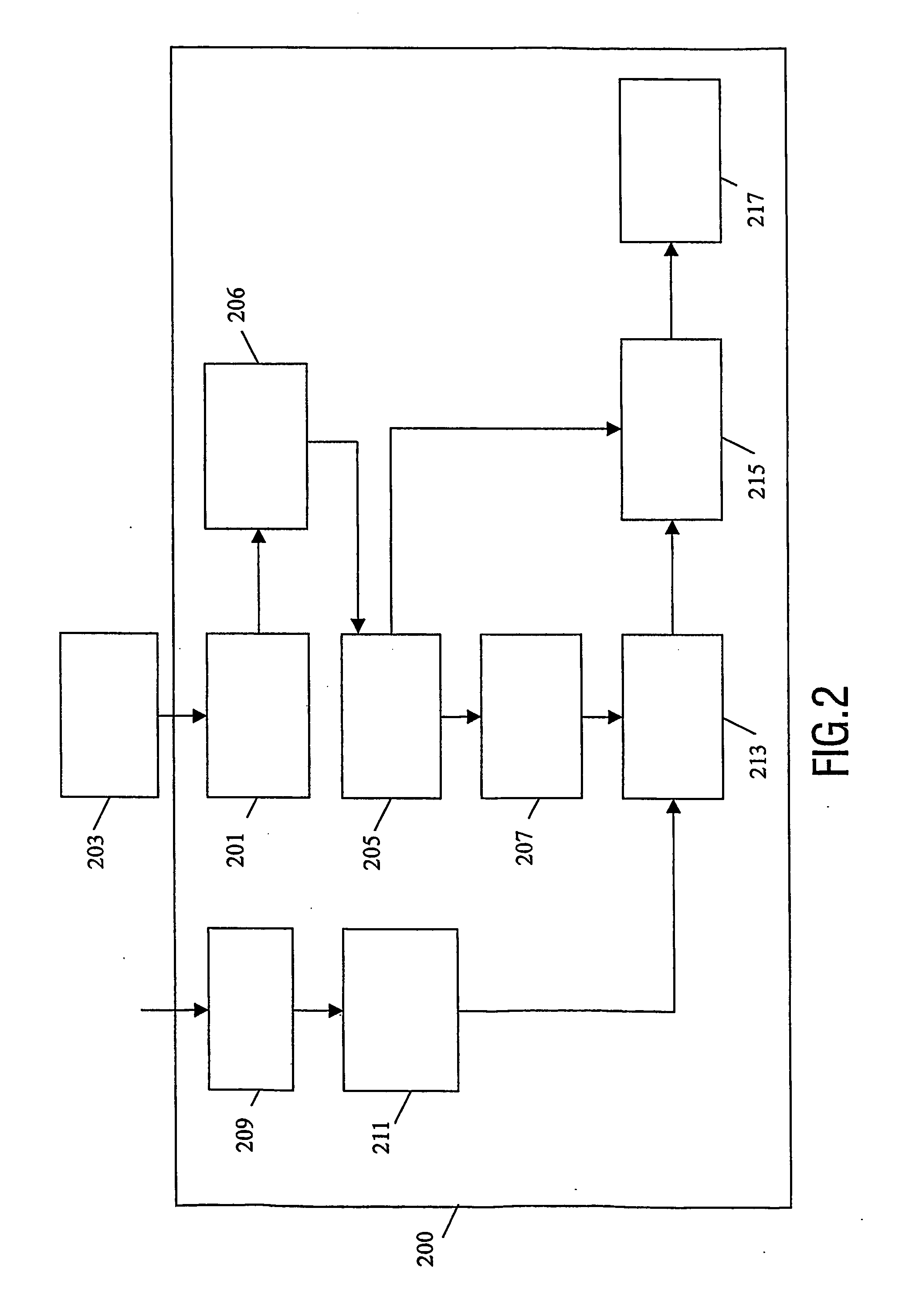
Method and apparatus for content presentation
InactiveUS20060036783A1Easy to controlIncreased flexibility and customisationTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNormal rateAnalyser
The invention relates to a system for content presentation of content signals such as video signals. A content presentation apparatus comprises a content signal receiver (201) receiving a content signal from a content source (203). The signal is stored in a memory (205). The memory is connected to a content analyser (207) which analyses the content and determines to which category of content this belongs. The apparatus further comprises a user preference profile processor (211) which determines a preferred presentation rate for different categories of content in response to a user input or a previous user behaviour. A playback controller (213) controls the playback of the content by setting the presentation rate to the preferred presentation rate of the user preference profile for the content category identified. Specifically, the invention provides for e.g. a fast forward button which fast forwards through unwanted content but plays at normal rate during user preferred content.
Owner:PACE MICRO TECH
Video buffer method for receiving end of network video service system
InactiveCN102665131AImprove coherenceImplement adaptive bandwidth playbackSelective content distributionNormal rateComputer science
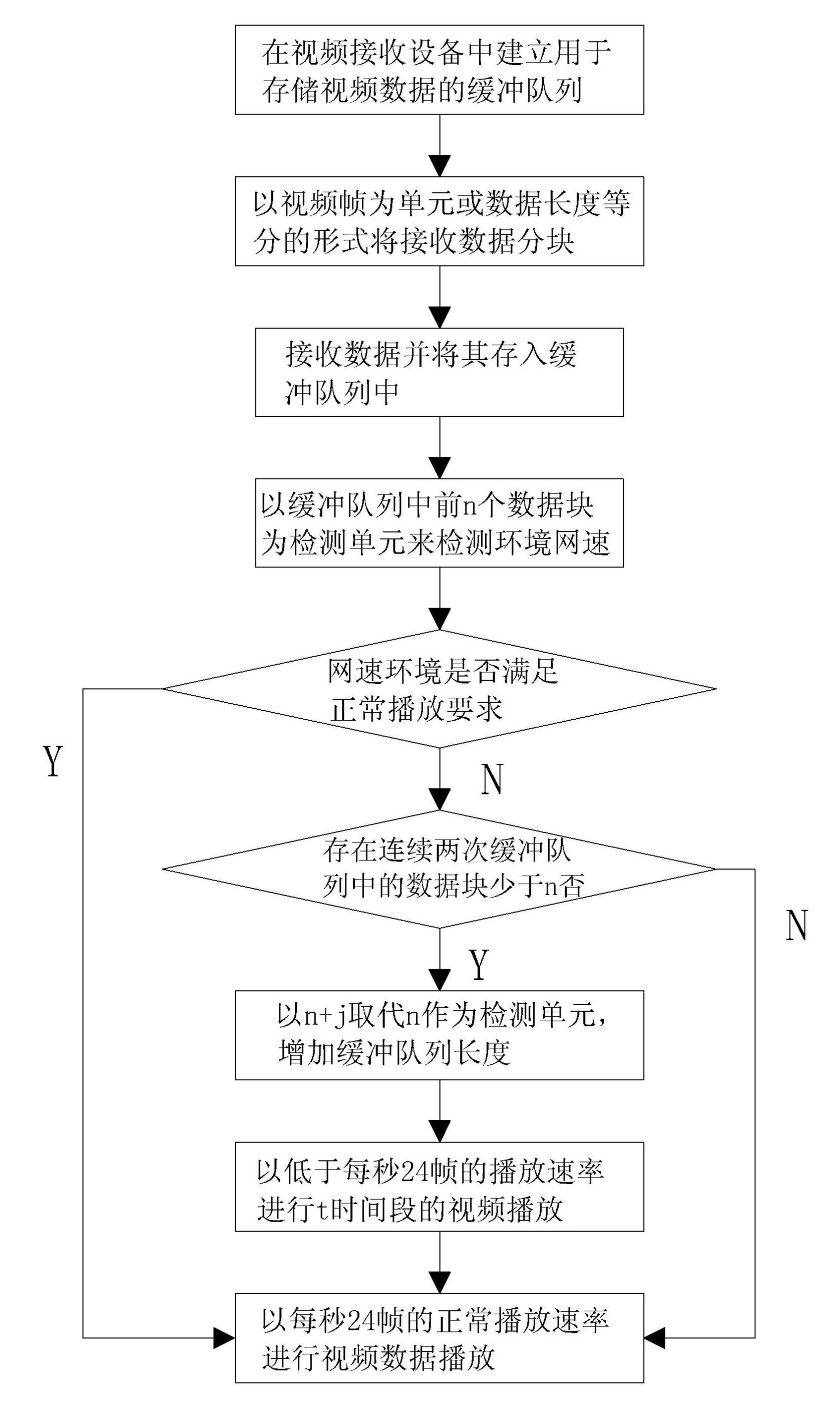
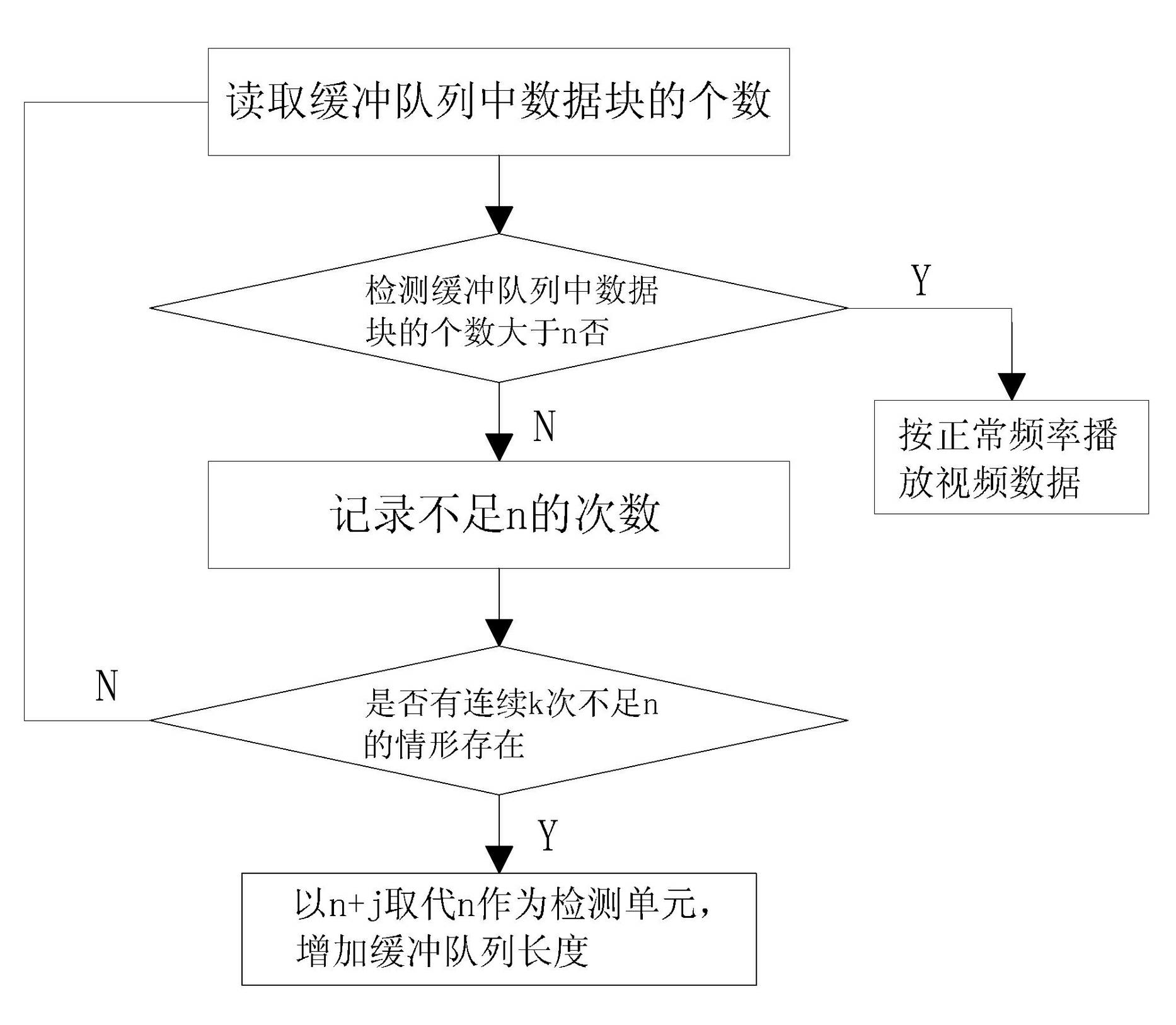
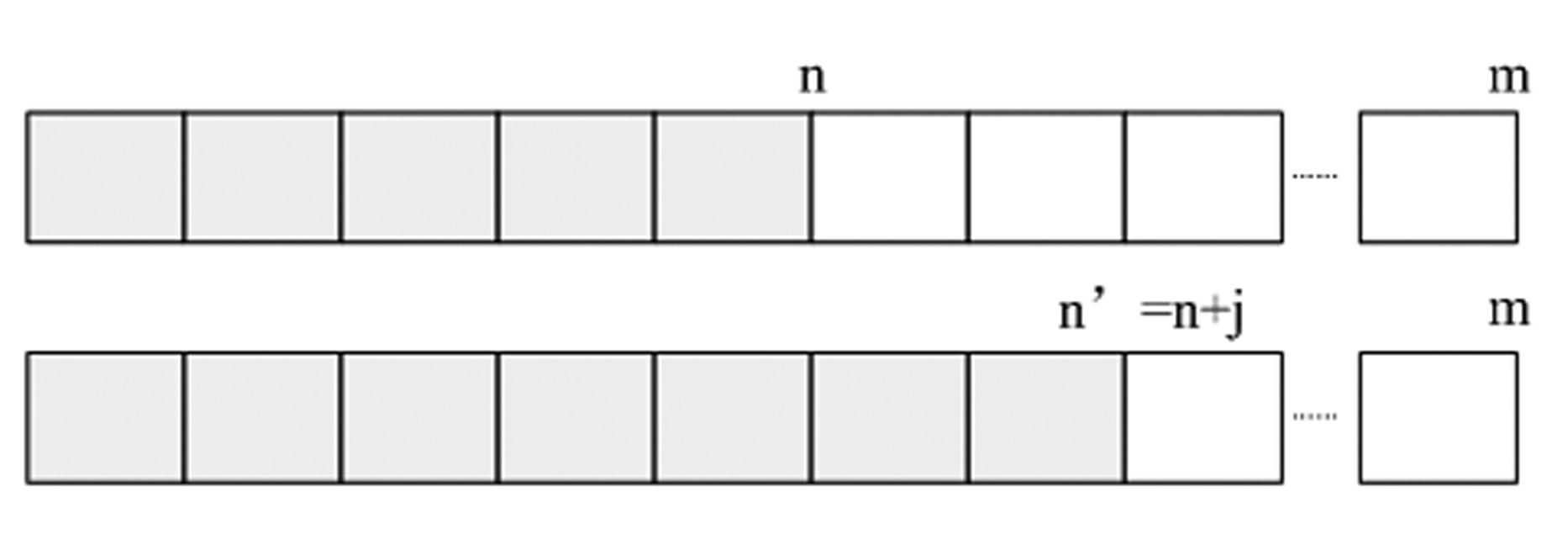
The invention discloses a video buffer method for the receiving end of a network video service system. The method comprises the following steps of: (a), establishing a buffer queue; (b), receiving and blocking data; (c), storing the data into the buffer queue; (d), comparing the receiving and play time of each of the first n data blocks to judge current network speed; (e), if the network speed is high enough, playing the data according to a normal rate; (f), if the network speed is not high enough, performing further judgment; and (g), lowering a play rate. The step (f) comprises the following steps of: (f-1), if the number of data blocks in the buffer queue is greater than n, normally playing the data; and (f-2) if the number of the data blocks is less than n continuously for k times, replacing n by utilizing n+j. According to the video buffer method, a network speed environment can be automatically sensed, and a buffer length and a play rate can be automatically regulated according to the network speed environment, so that the adaptive bandwidth play of a final user of the video service system in different network speed environments can be effectively realized; and in addition, high video play continuity is ensured, so that the service can obtain highly-satisfactory network streaming media service in different network environments.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
Method and apparatus for controlled viewing of recorded television programs
InactiveUS20070248314A1Simple methodTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsProgram segmentComputer graphics (images)
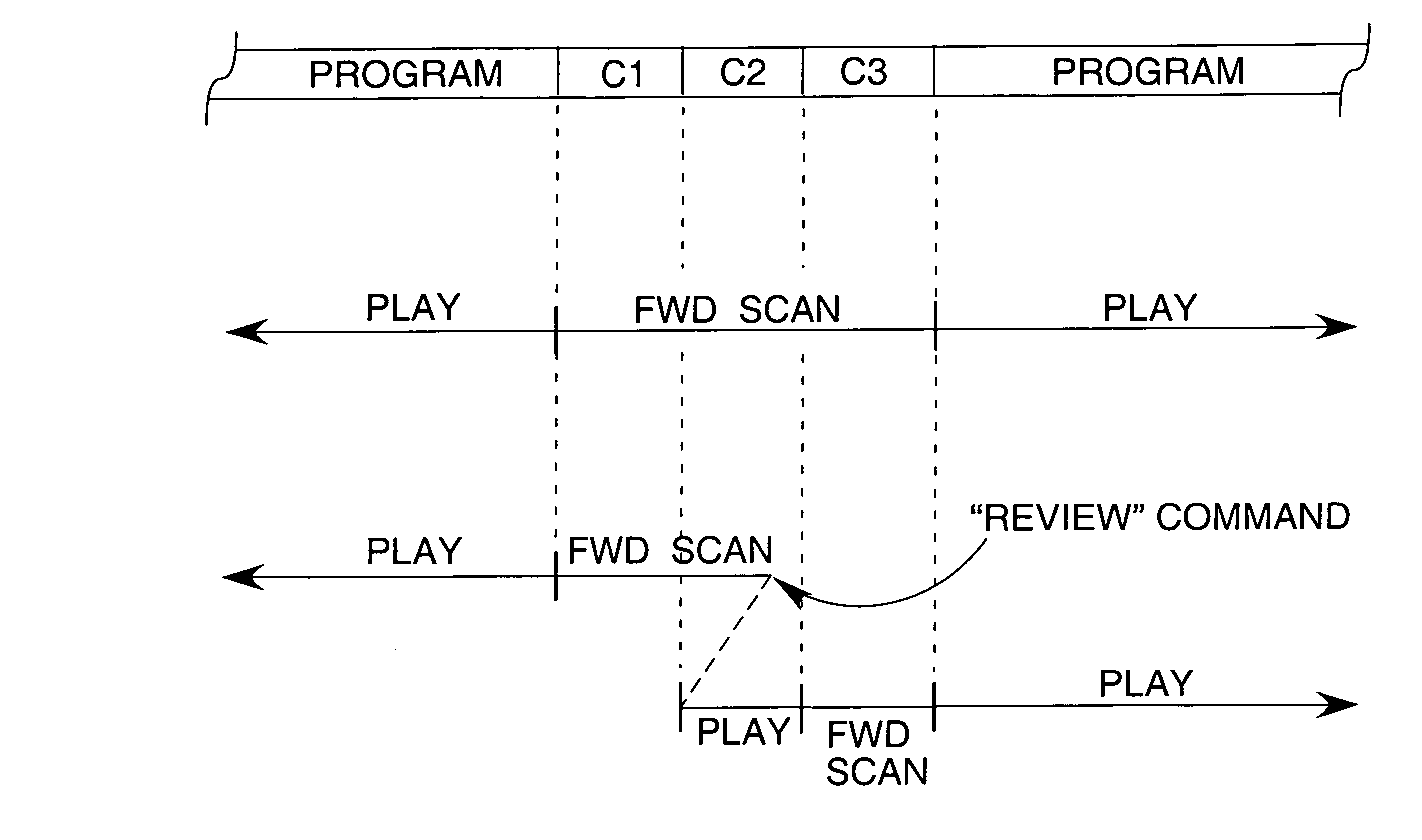
Segments of a recorded video program that are classified to be skipped during replay are scanned through at a predetermined rate, which is independent of viewer control. While faster than the normal play mode, the rate of forward scan is such that the content of the video segments being skipped can still be readily perceived. While in this controlled forward scan mode, viewer control of the scanning rate may be disabled. A viewer-controlled input may be provided so that a portion of a video segment being skipped can be viewed at a normal rate of play starting at the beginning of the portion that the viewer wishes to see. Once that portion of the video segment has been played at normal speed, the video playback device automatically switches to a predetermined mode of operation. Segments of a recorded video signal may be automatically rearranged for playback, allowing for all segments of one type to be played back contiguously, followed by playback of all segments of a second type.
Owner:TELEVENTIONS
Off-load reduced input power energy saving low noise air vacuum cleaner
InactiveUS20080034532A1Reduce investmentReduce noiseVacuum cleaner apparatusElectric equipment installationLow noiseNoise level
An off-load reduced input power energy saving low noise air vacuum cleaner by detecting the operation status of the cleaner to control the size of the electricity inputted to an air pump drive motor, or exercise the control of power delivery or power cut off; normal rated voltage being inputted when the cleaner is in normal working status; or the power outputted to the air pump drive motor being reduced or cut off when the cleaning tool of the cleaner clears away from its working area to render the cleaner in full load operation status as were a blower to increase both noise level and power consumption for reduced noise level and energy saving.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
Memory system and method using partial ECC to achieve low power refresh and fast access to data
ActiveUS7894289B2Reduce power consumptionReduce the required powerError detection/correctionCode conversionError checkingDram memory
A DRAM memory device includes several banks of memory cells each of which are divided into first and second sets of memory cells. The memory cells in the first set can be refreshed at a relatively slow rate to reduce the power consumed by the DRAM device. Error checking and correcting circuitry in the DRAM device corrects any data retention errors in the first set of memory cells caused by the relatively slow refresh rate. The memory cells in the second set are refreshed at a normal rate, which is fast enough that data retention errors do not occur. A mode register in the DRAM device may be programmed to select the size of the second set of memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
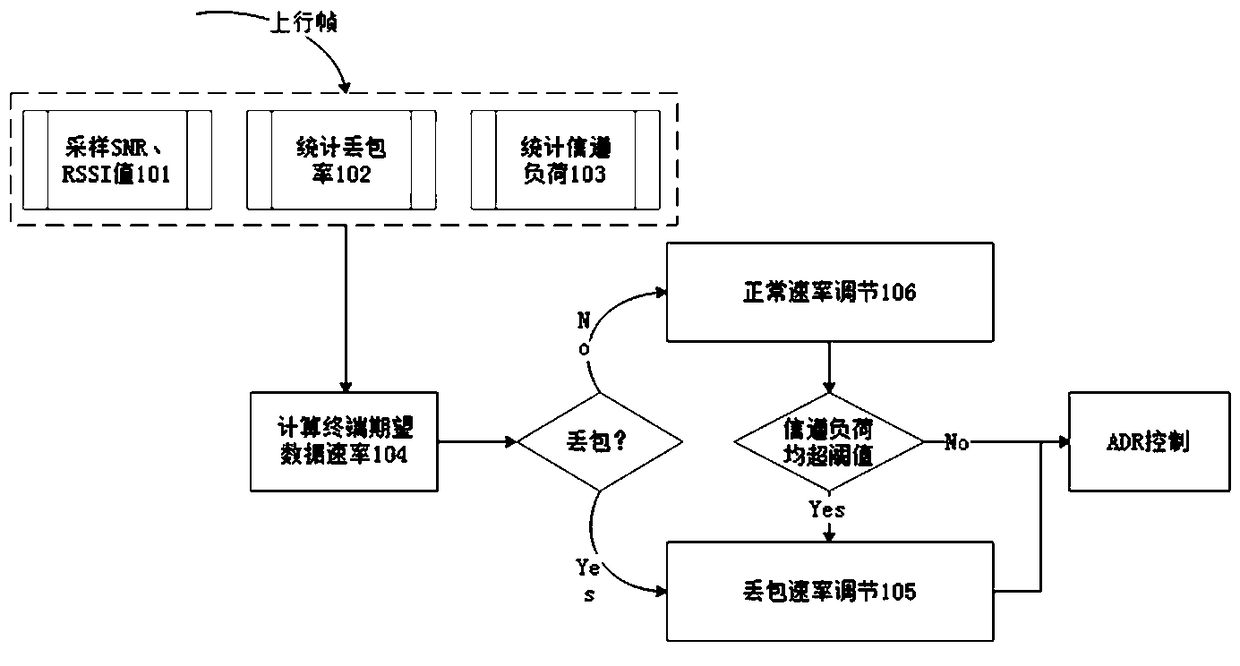
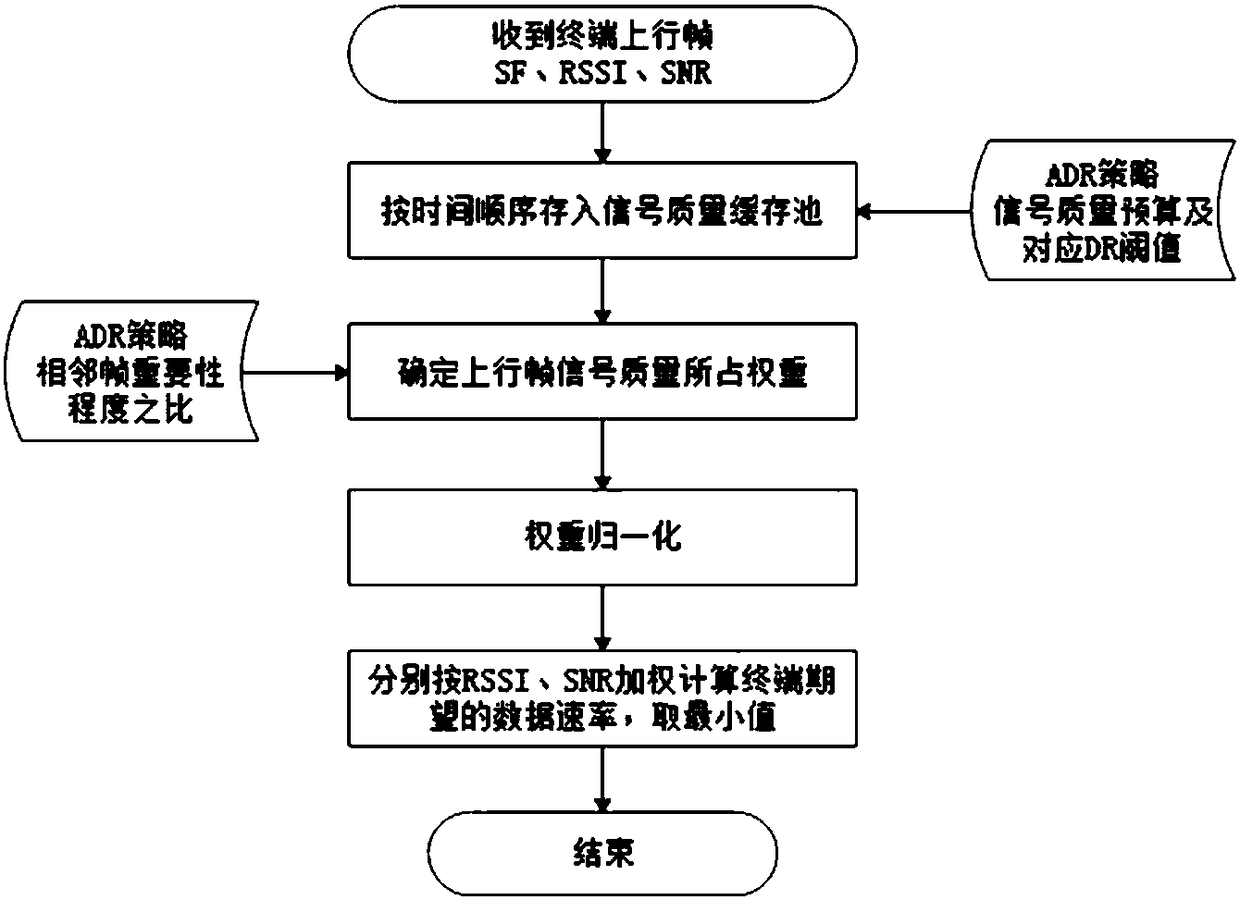
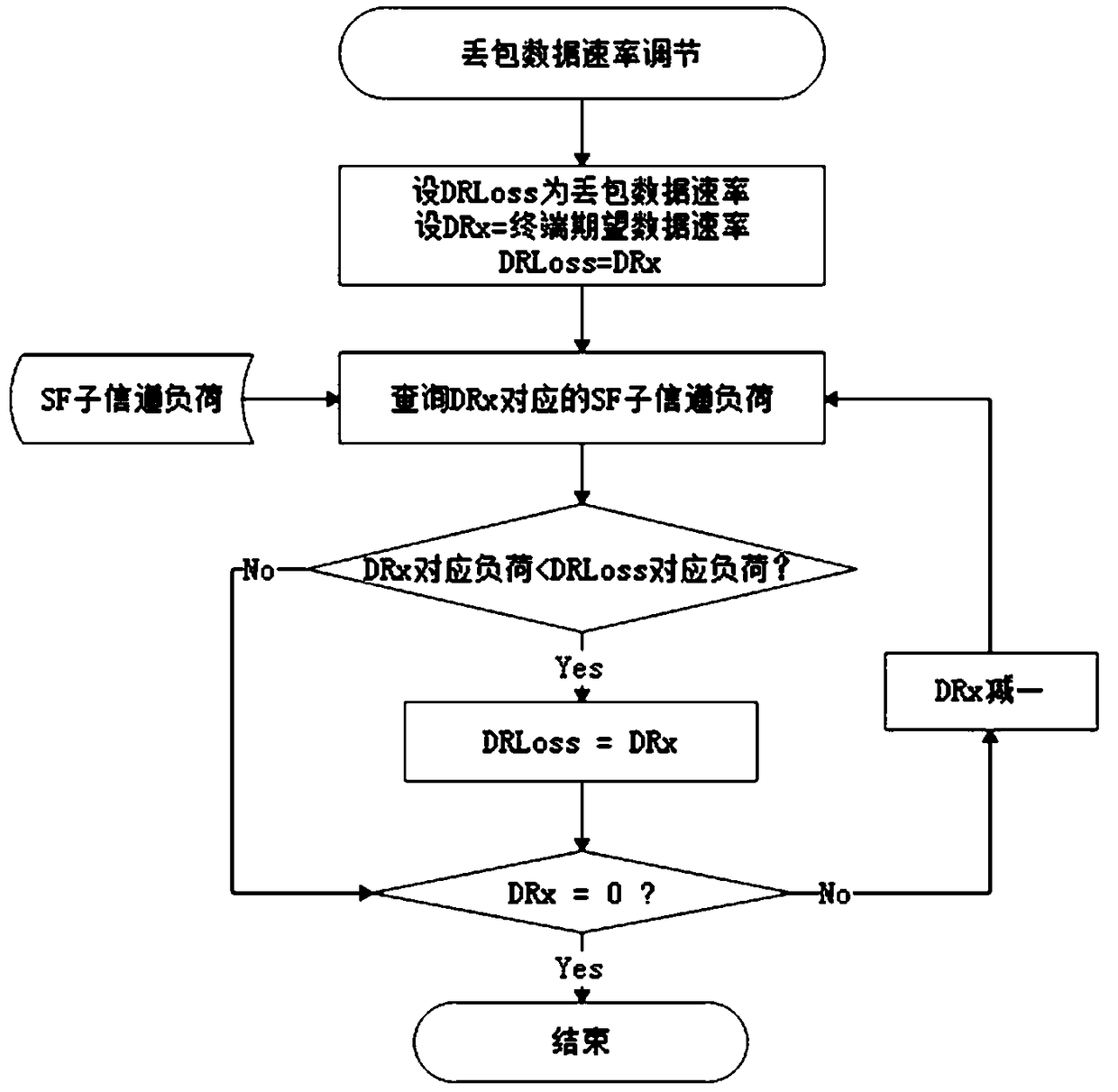
Adaptive rate adjustment method of LPWAN internet of things based on network condition
ActiveCN108093436AReduce power consumptionImprove network access capabilitiesNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh level techniquesNetwork conditionsSpreading factor
The invention is intended to provide an adaptive rate adjustment method of an LPWAN internet of things based on a network condition. The adaptive rate adjustment method comprises the steps of receiving uplink frames sent by a terminal; sampling SNR and RSSI values of latest N frames; making a statistics of a packet loss rate according to continuity of frame serial numbers; making a statistics of loads erl of SF (Spread Factor) sub-channels according to occupied channels and used SFs of the terminal; weighting to calculate an expected DR (Data Rate) <mote> of the terminal; when the packet lossrate of the terminal exceeds a packet loss threshold value in an ADR (Adaptive Data Rate) strategy, performing packet loss rate adjustment; when the packet loss rate of the terminal does not exceed the packet loss threshold value in the ADR strategy, performing normal rate adjustment; sending an ADR command to the terminal, and enabling the terminal to adjust a data transmission rate according toan own strategy after receiving the ADR command and make a response; and if a LoRaWAN server does not receive the response, considering that the sending is failed, and repeating to send till the response is received. The adaptive rate adjustment method has the following beneficial effects: the adaptive adjustment can be performed on the data rate of the terminal according to an own network condition including conditions such as a signal quality index, a channel load and the packet loss rate.
Owner:中兴克拉科技(苏州)有限公司
Low noise and energy saving air vacuum cleaner
InactiveUS20080180049A1Reduce noiseSave energyDC motor speed/torque controlAsynchronous induction motorsLow noiseNoise level
A low noise and energy saving air vacuum cleaner by detecting the operation status of the cleaner to control the size of the electricity inputted to an air pump drive motor, or exercise the control of power delivery or power cut off; normal rated voltage being inputted when the cleaner is in normal working status; or the power outputted to the air pump drive motor being reduced or cut off when the cleaning tool of the cleaner clears away from its work area to render the cleaner in full load operation status as were a blower to increase both noise level and power consumption, or when the cleaning tool is blocked due to excessive packing against the work area for reduced noise level and energy saving.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
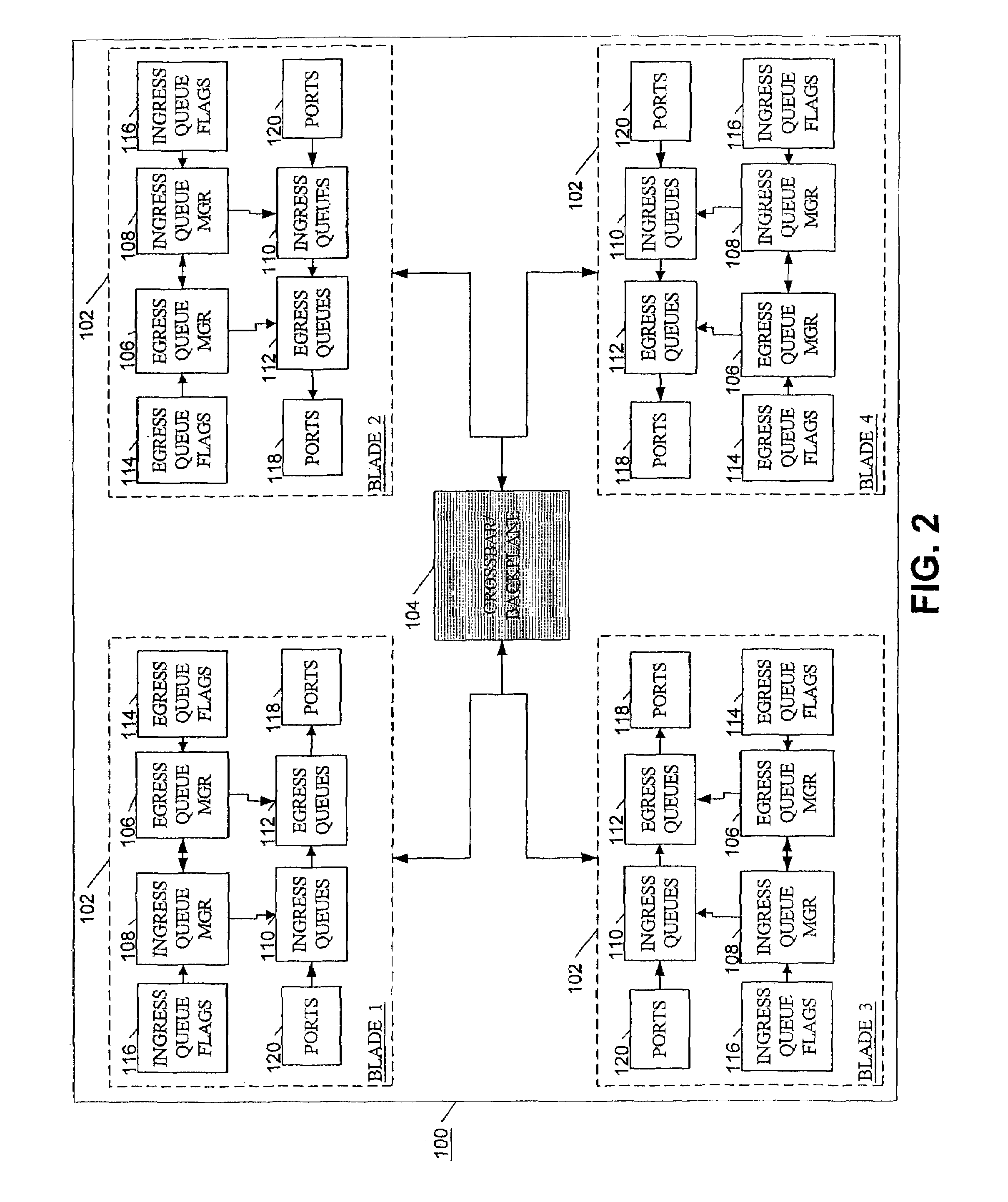
Method and apparatus for providing quality of service across a switched backplane between egress and ingress queue managers
ActiveUS7599292B1Improve robustnessReduce probabilitySpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTQuality of serviceNetwork packet
A method and system is provided to enable quality of service across a backplane switch. An egress queue manager on one blade communicates with an ingress queue manager on the same or on another blade where each blade is connected via a backplane switch. The egress queue managers communicate the congestion to ingress queue managers using a messaging scheme. The ingress queue managers determine when to reduce or resume the packet sending rates of ingress queues mapped to congested egress queues or to destinations on congested blades. Each ingress queue manager maintains information about the status of egress queue congestion on its own blades. Normal rates of dequeuing packets from ingress queues are resumed only when the related congestion on all of the egress queues or related destinations has subsided.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
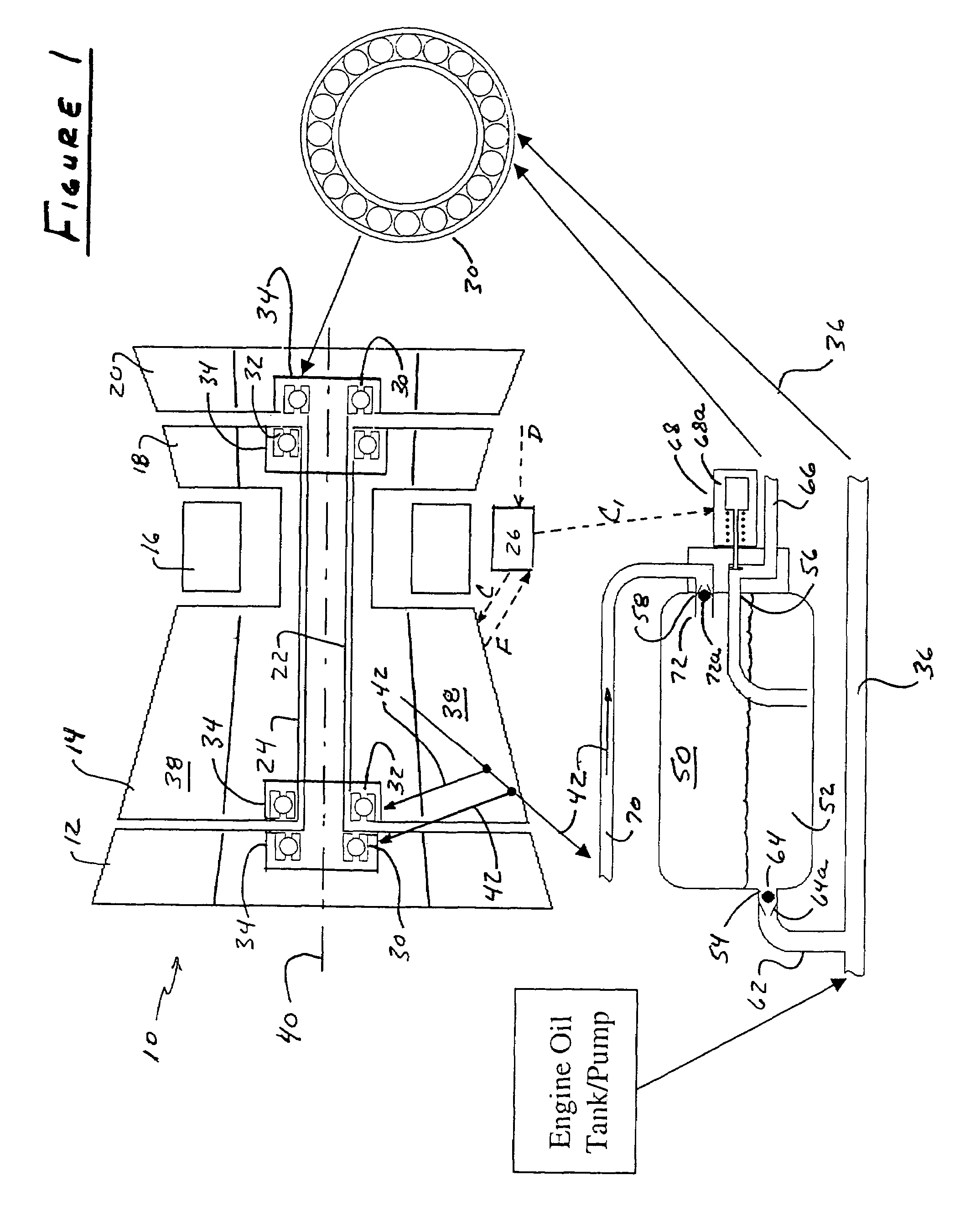
Emergency lubrication system
ActiveUS20050034924A1Extended time intervalLight weightEfficient propulsion technologiesMachines/enginesFuel tankNormal rate
An emergency lubrication system for a turbine engine includes a reservoir 50 containing a reserve quantity of lubricant 52 and having a lubricant inlet 54 and a lubricant outlet 56. A lubricant supply line 62 and a lubricant outlet line 66 each have a respective valves 64, 68 for regulating lubricant flow into and out of the reservoir. A fluid supply line 70 includes a valve 72 for selectively establishing communication between the reserve quantity of lubricant and a source of pressurized fluid. During normal operation the lubricant outlet valve continuously releases lubricant at a normal rate to the component requiring lubrication while the lubricant inlet valve concurrently admits fresh lubricant into the reservoir. During abnormal operation, the lubricant inlet valve closes in response to abnormally low lubricant pressure outside the reservoir thereby preventing backflow of reserve lubricant out of the reservoir. The fluid inlet valve opens to admit pressurized fluid into the reservoir thus pressurizing the reserve lubricant. The lubricant outlet valve opens or cycles open and closed in response to a command from a controller 26 so that the pressurized fluid forces lubricant through the outlet 56 as a subnormal rate, which persists until the lubricant reserve is substantially depleted. The subnormal rate is ideally achieved by intermittently releasing lubricant from the reservoir, but may also be achieved by releasing a continuous stream of lubricant at a rate less than the normal rate of release.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
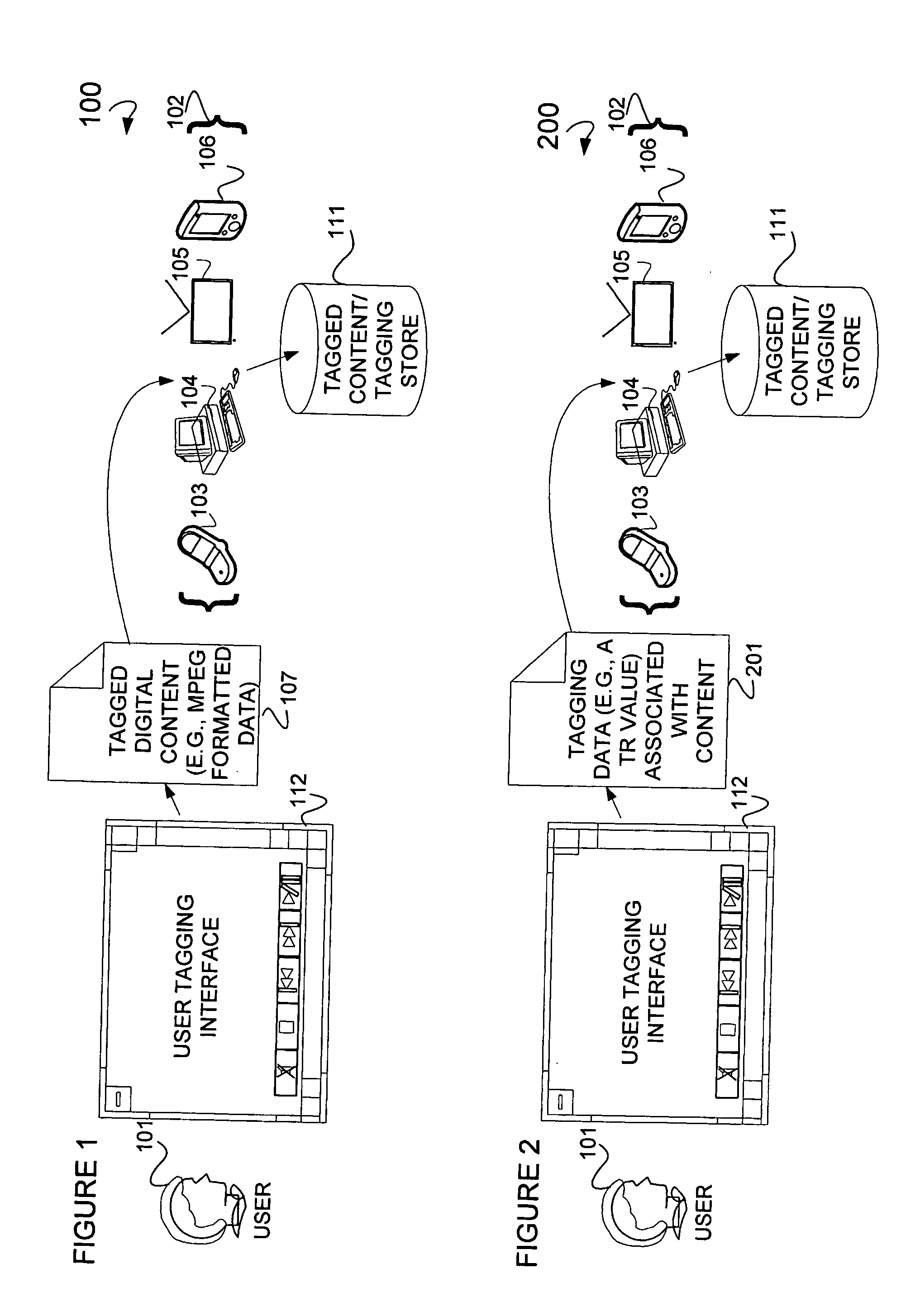
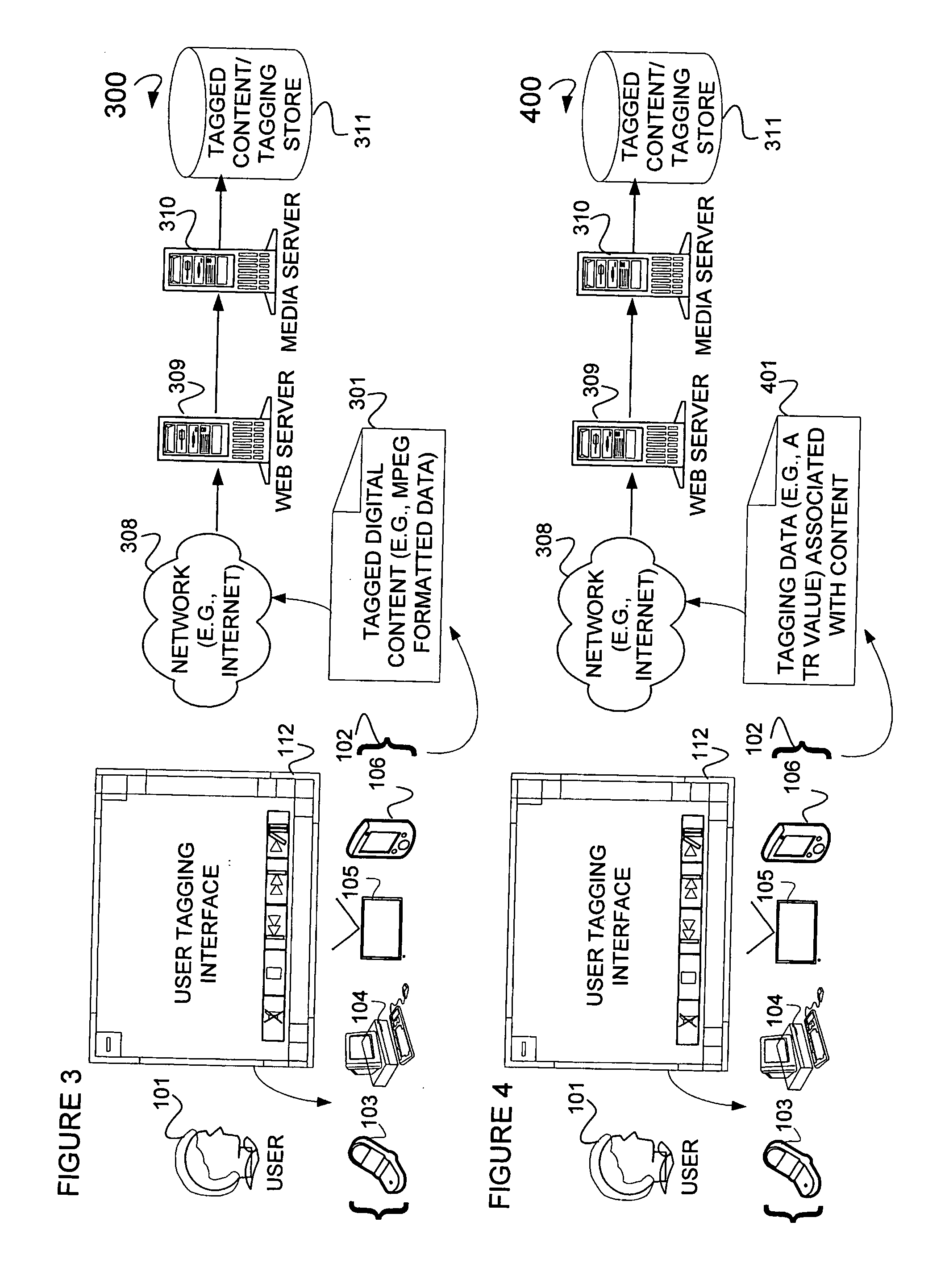
Audio/video content synchronization and display
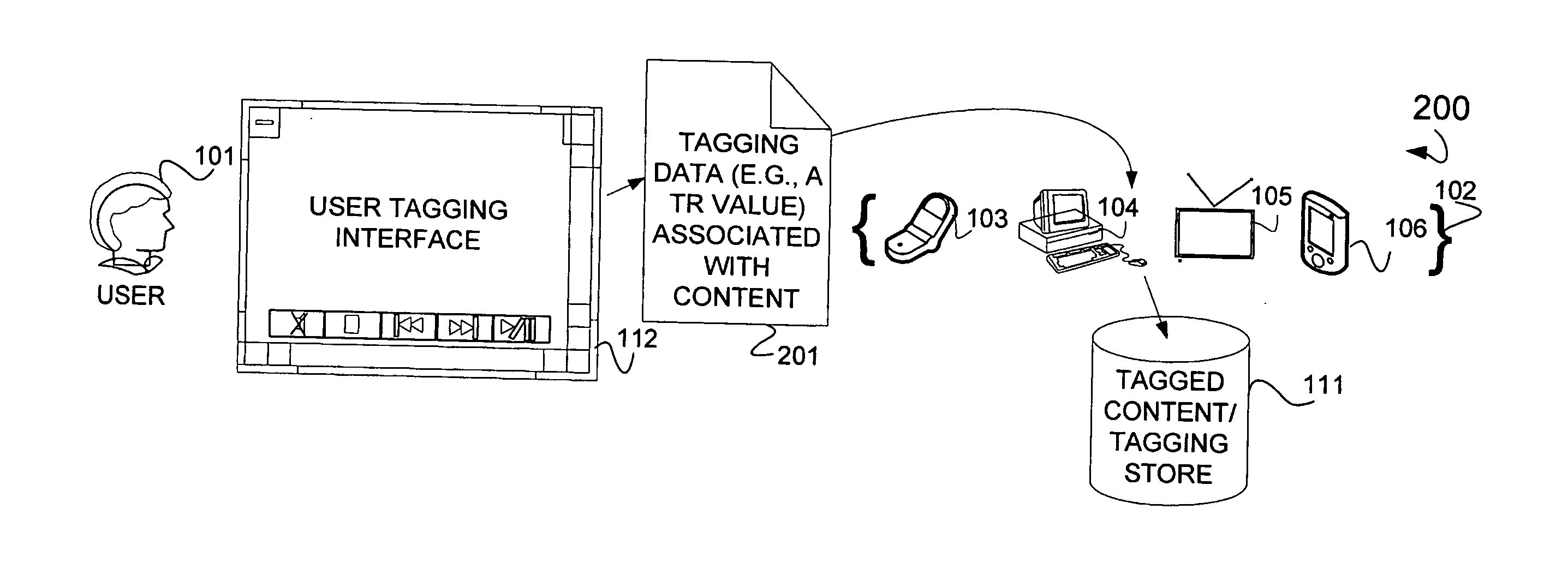
ActiveUS20140029916A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingDigital contentNormal rate
In one embodiment, a method is illustrated as including generating tagging data using a computer system to tag certain portions of digital content for playing at a normal rate and inserting the tagging data into a field of a data packet to create tagged digital content. In another embodiment, a further method is illustrated as including generating a metadata file using a computer system to denote certain portions of digital content for playing at a normal rate and inserting the metadata file into a media stream containing the certain portions of digital content. Additionally, in a further embodiment, a system is illustrated as including a generator residing on a device to generate tagging data to tag certain portions of digital content for playing at normal rate and an inserter residing on the device to insert the tagging data into a field of a data packet to create tagged digital content.
Owner:ADOBE INC
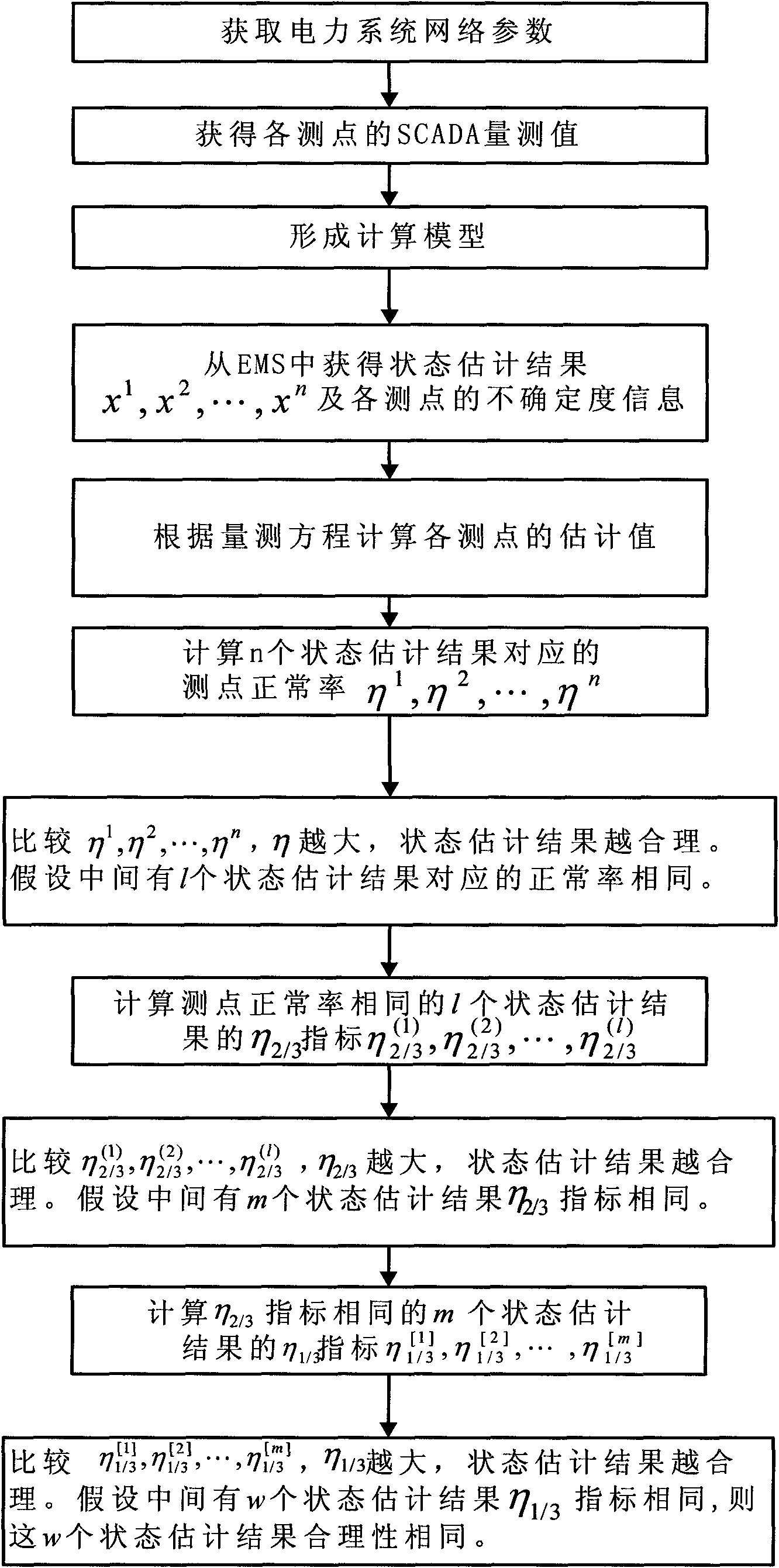
Evaluation method of power system state estimated result based on expanded uncertainty
InactiveCN101615213ASimple calculationPracticalSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemElectric power systemNormal rate
The invention relates to an evaluation method of a power system state estimated result based on expanded uncertainty, which belongs to the field of the analysis and computation of power system state. The method is characterized in that the expanded uncertainty of each measuring point is defined according to the international evaluation and expression of uncertainty of measurement; measuring point normal rate eta index, eta 2 / 3 index and eta 1 / 3 index are constructed based on the expanded uncertainty; then all the results obtained by performing state evaluation and computation to measured values are evaluated by adopting the indexes; the state estimated result of larger index is selected to be output. The method has rationality, practicability and popularization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
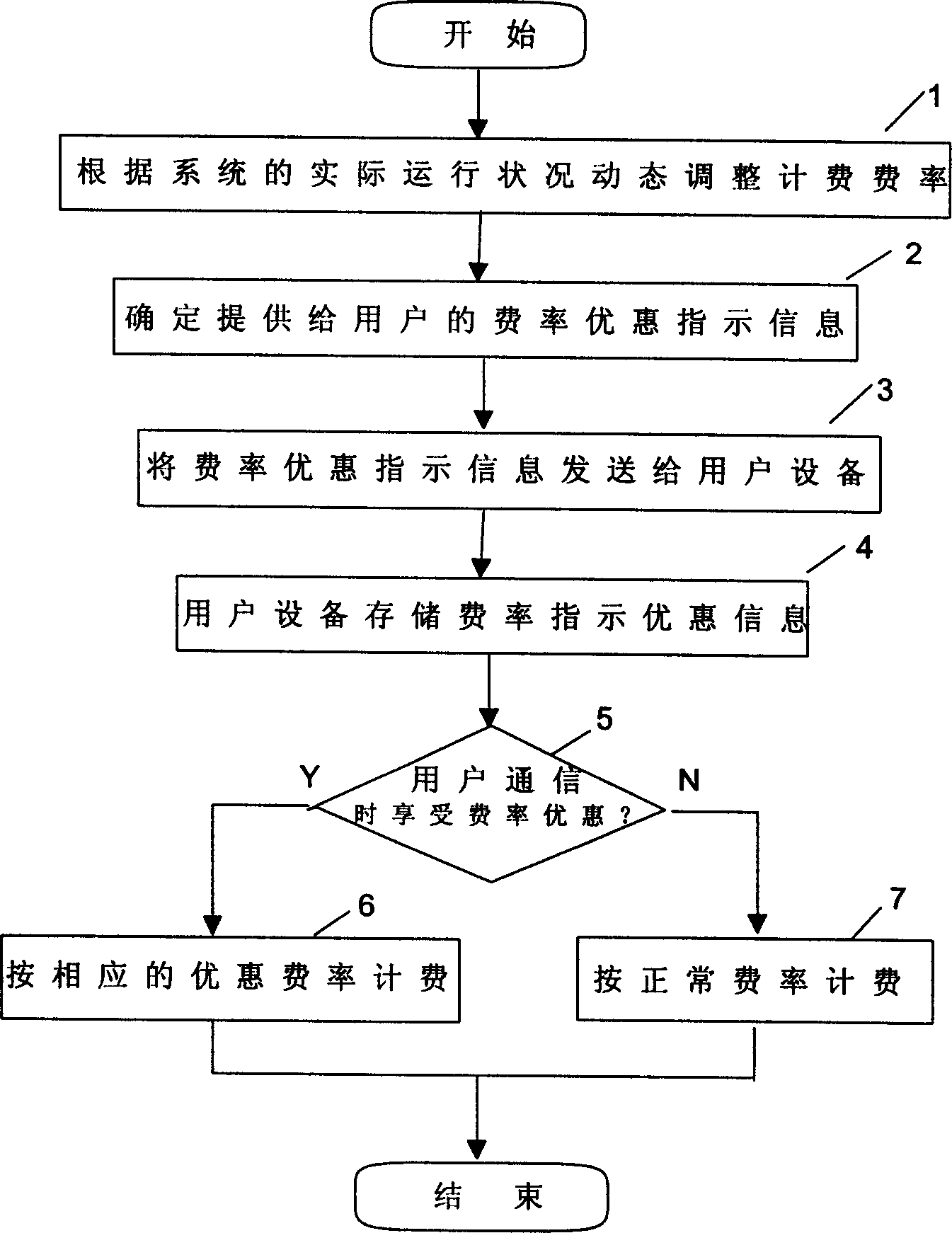
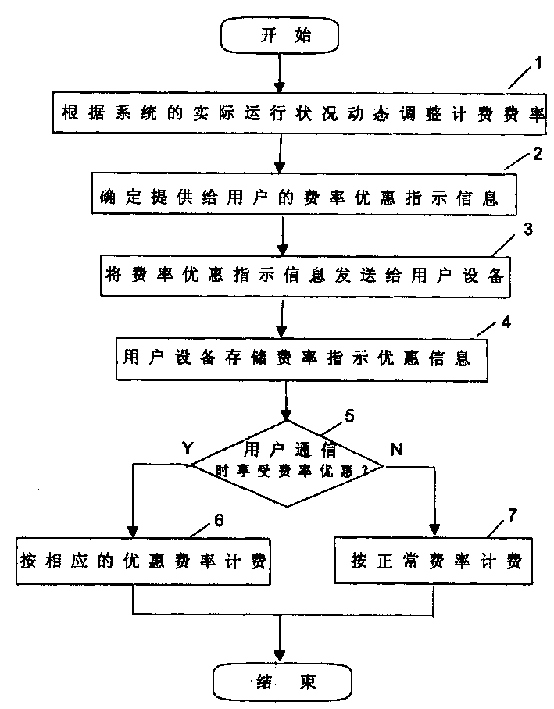
Charging method of mobile communication system
InactiveCN1464757AReduce communication costsExtended use timeMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesNormal rateMobile communication systems
The invention discloses a charging method in mobile communication system characterized by that, the rate for user charging can be adjusted dynamically according to the real operation status reflected by the system operation parameters e.g., service period, service user category and application type, operation stage and operation location. Then determine the rate concession indicating information for the user, and send it to the user's equipment (UE) by the system. When the user proceeds communication, determine whether the user enjoys the rate concession, if so, proceed charging according to the corresponding rate, otherwise charge with the normal rate.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
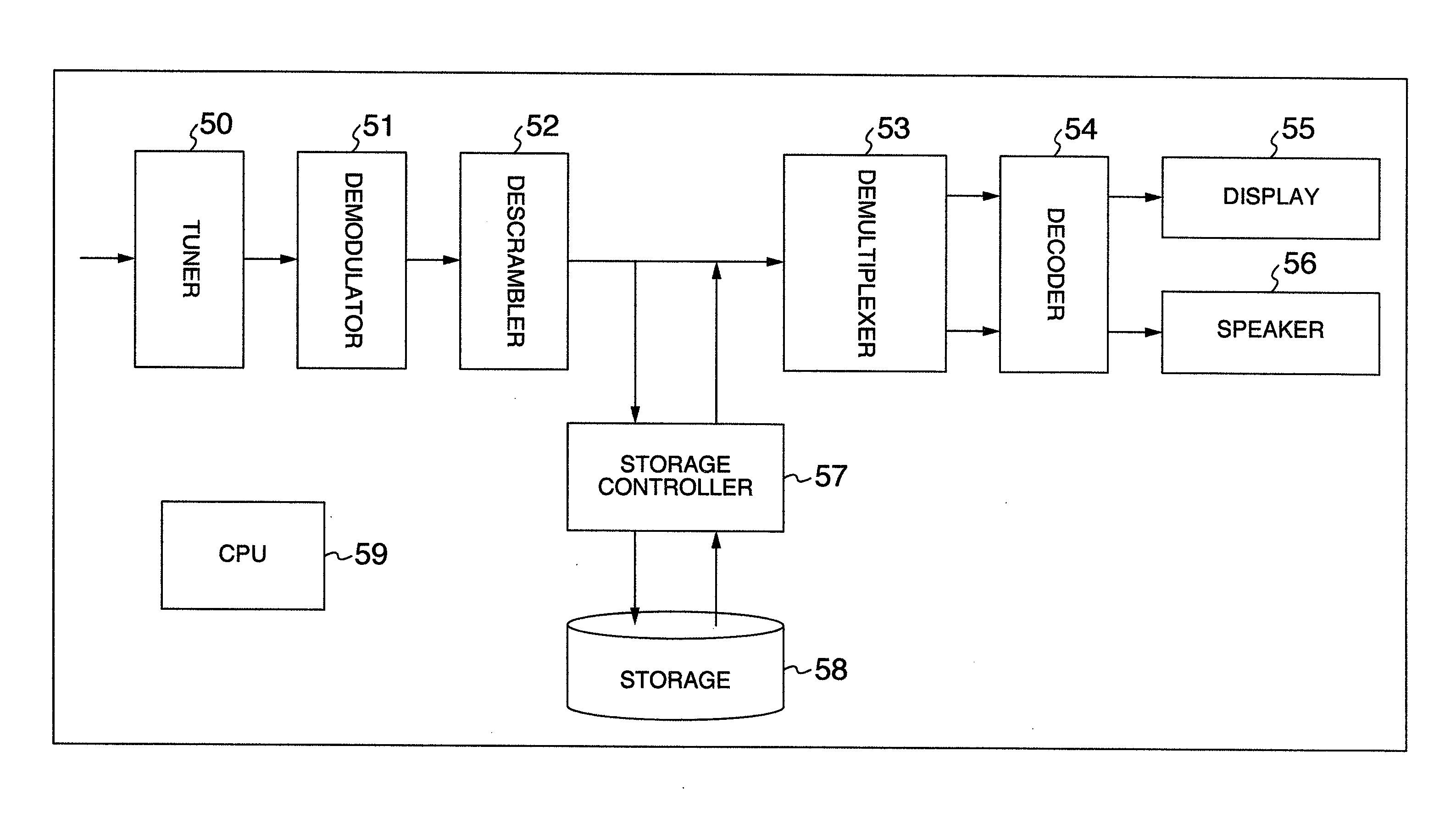
Receiver and information processing method
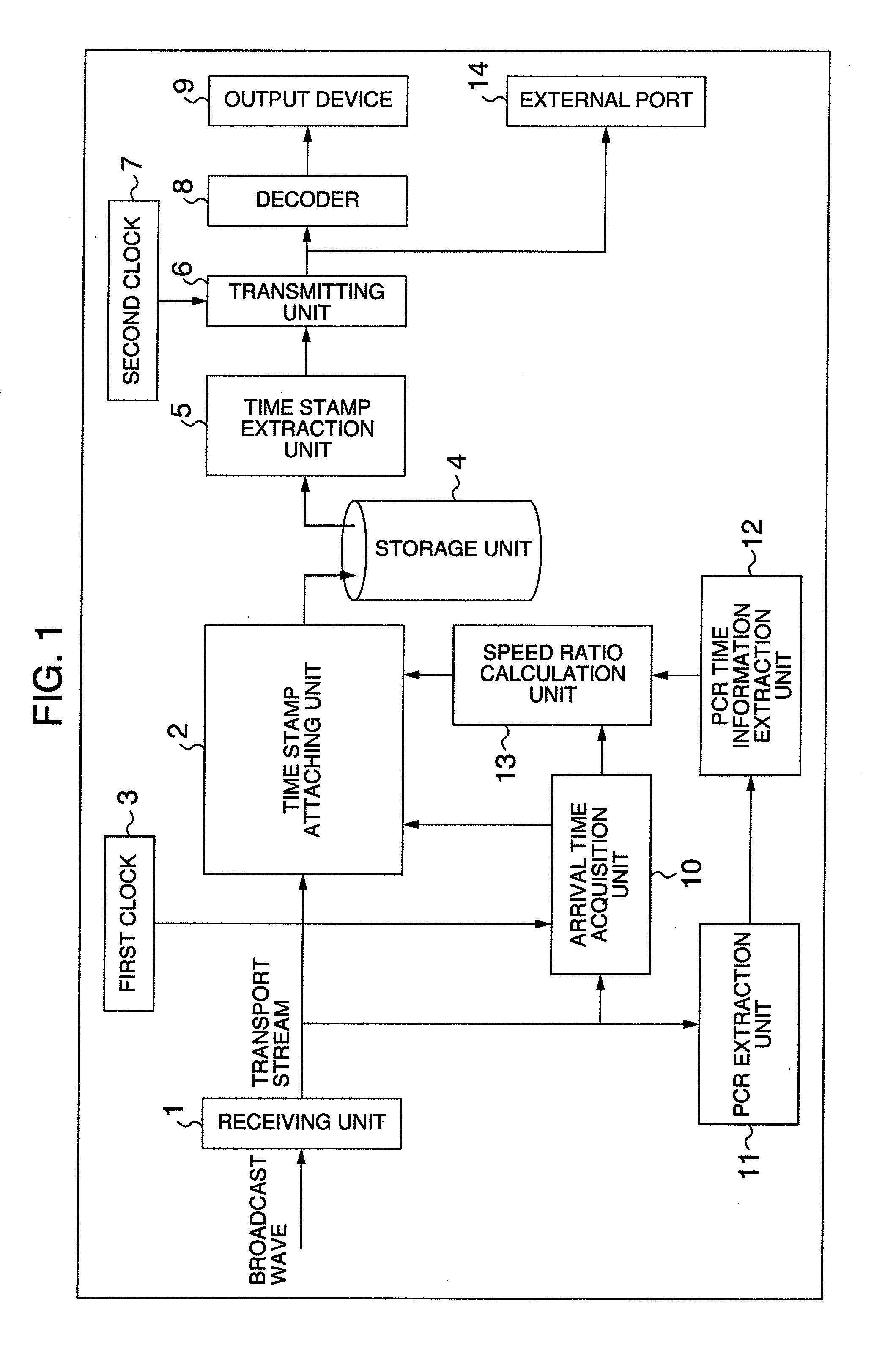
InactiveUS20080056666A1Improve playbackTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsInformation processingNormal rate
An object of this invention is to provide a receiver that downloads a transport stream at a bit rate different from the normal playback rate, attaches to the transport stream timestamps representing a playback timing for playback at the normal rate and then stores the time-stamped stream. When the receiver receives the transport stream at a transmission rate different from the normal playback rate and stores the stream, the receiver calculates timestamps representing a playback timing for playback at the normal rate according to the speed ratio of the received transport stream and attaches the timestamps to the transport stream before storing it as a time-stamped transport stream.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
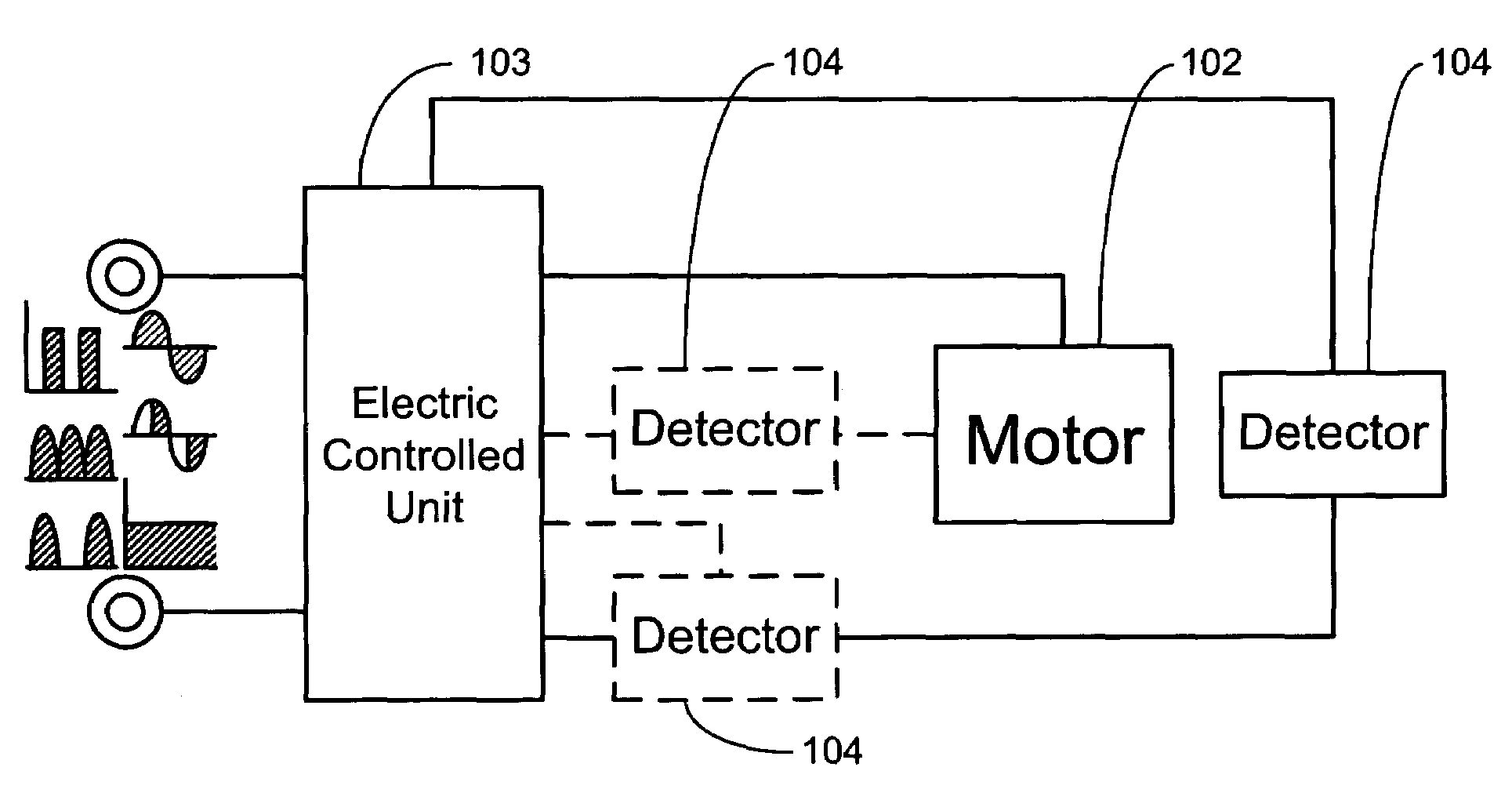
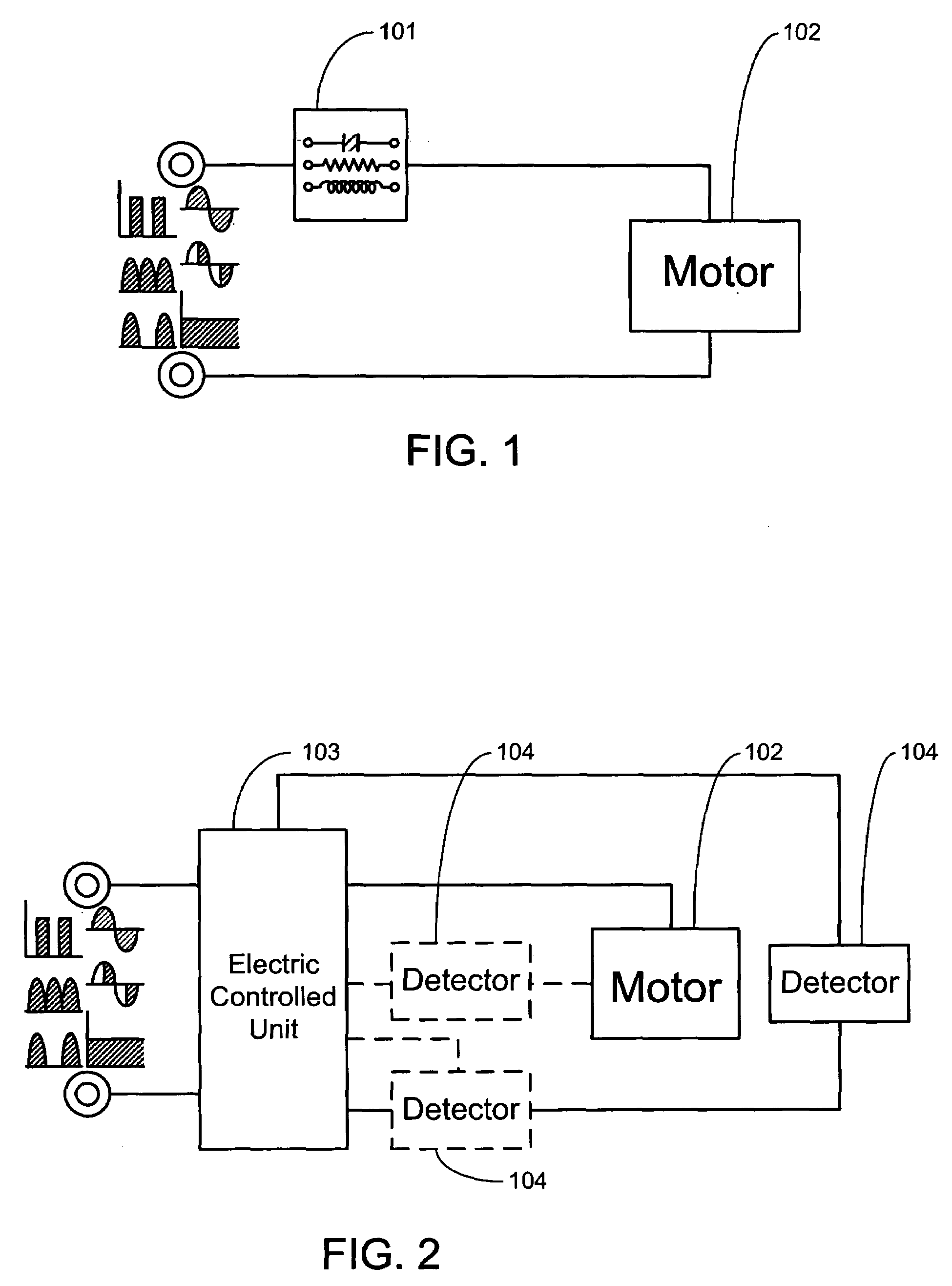
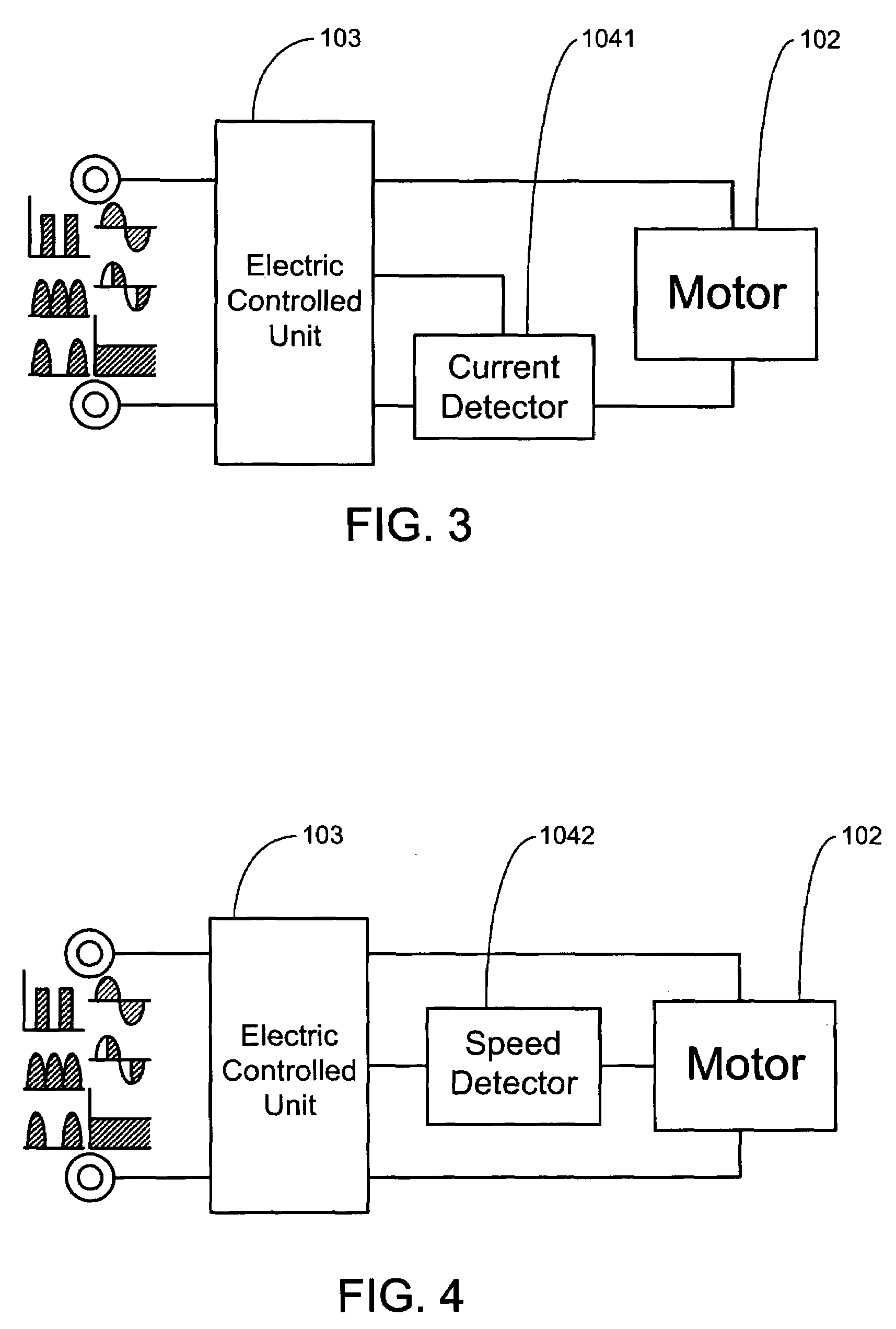
Illumination device and control method thereof
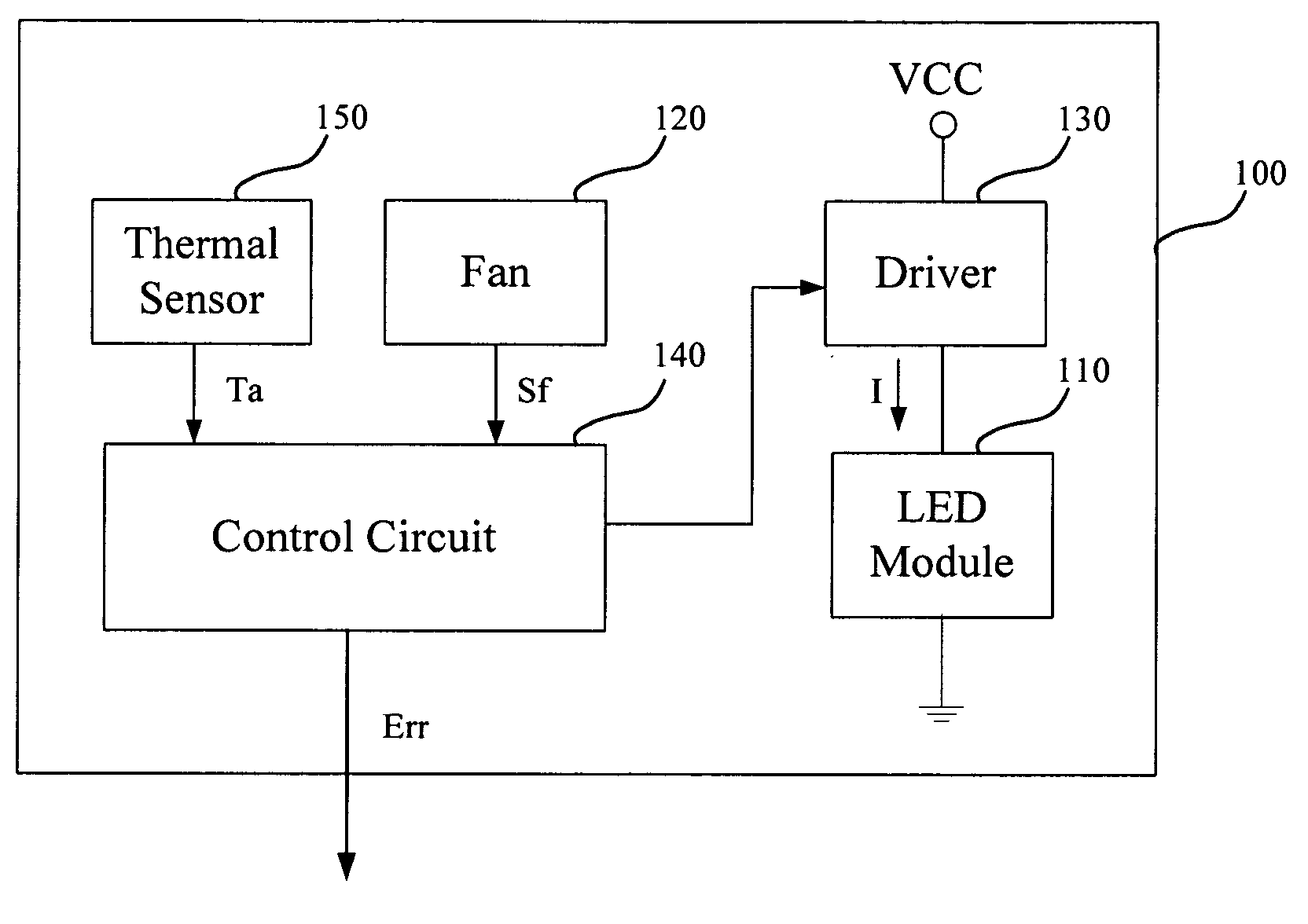
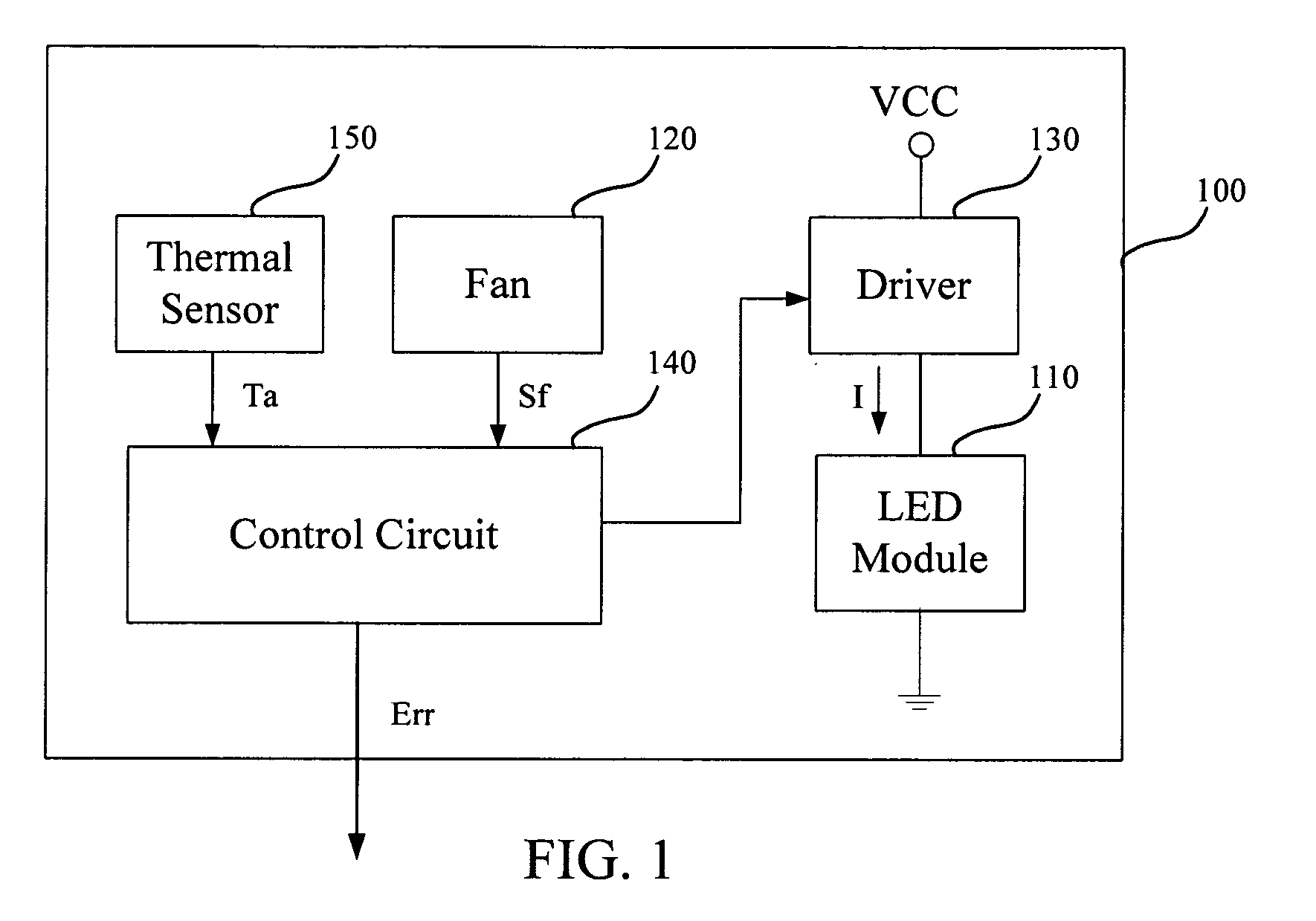
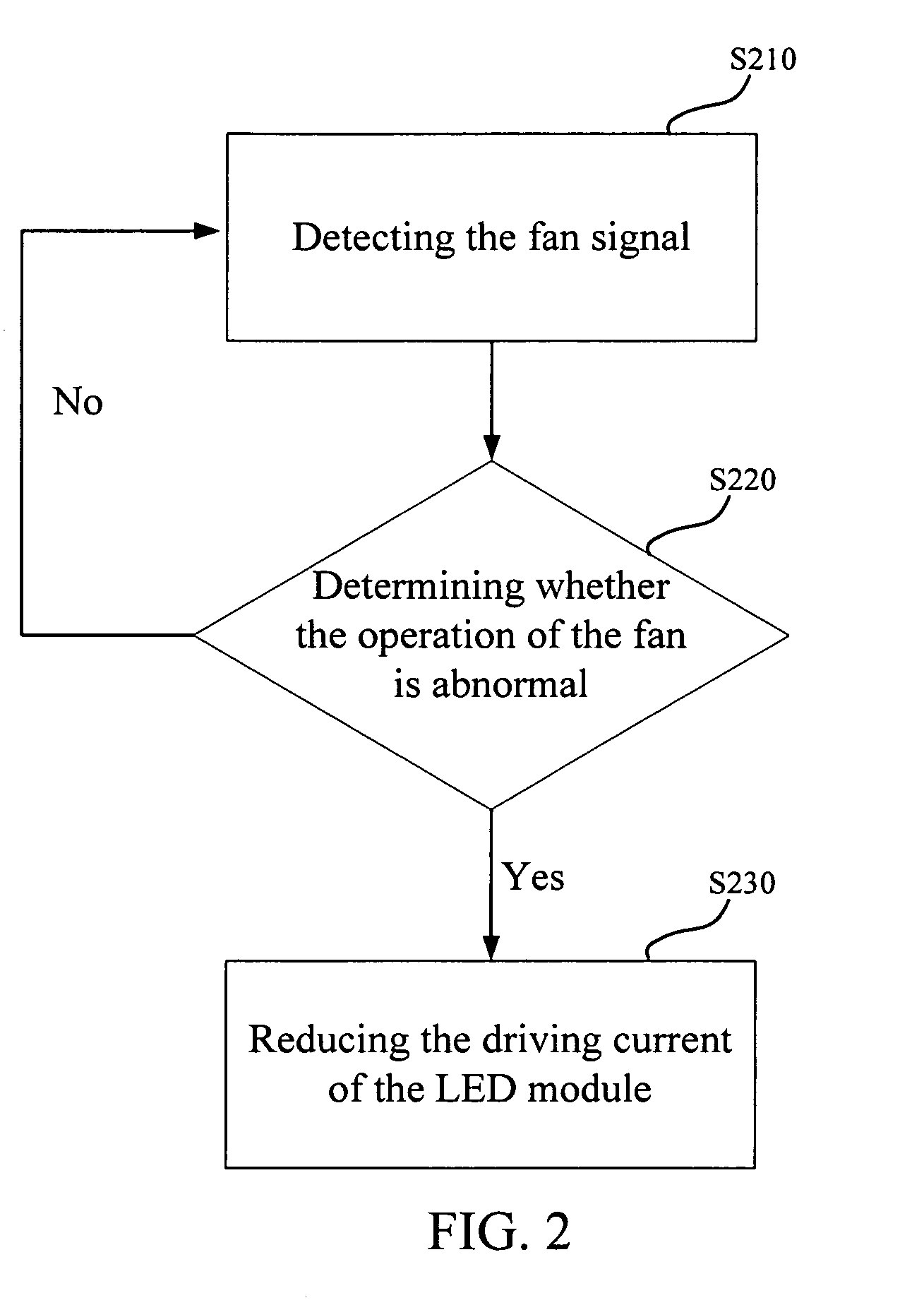
InactiveUS20100289410A1Heat dissipationElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid cathode detailsDriving currentLight beam
An illumination device and a control method thereof are provided. The illumination device includes a fan and a light emitting diode module capable of emitting a light beam. The control method includes: detecting a fan signal of the fan; determining whether an operation of the fan is abnormal according to the fan signal, wherein a driving current of the LED module is reduced when the operation of the fan is determined to be abnormal; and a driving current of the LED module is reduced to a predetermined rang of the normal rated driving current when the fan is determined to be stop according to the fan signal.
Owner:YOUNG GREEN ENERGY
Data processing device, encoding device, encoding method, decoding device decoding method, and program
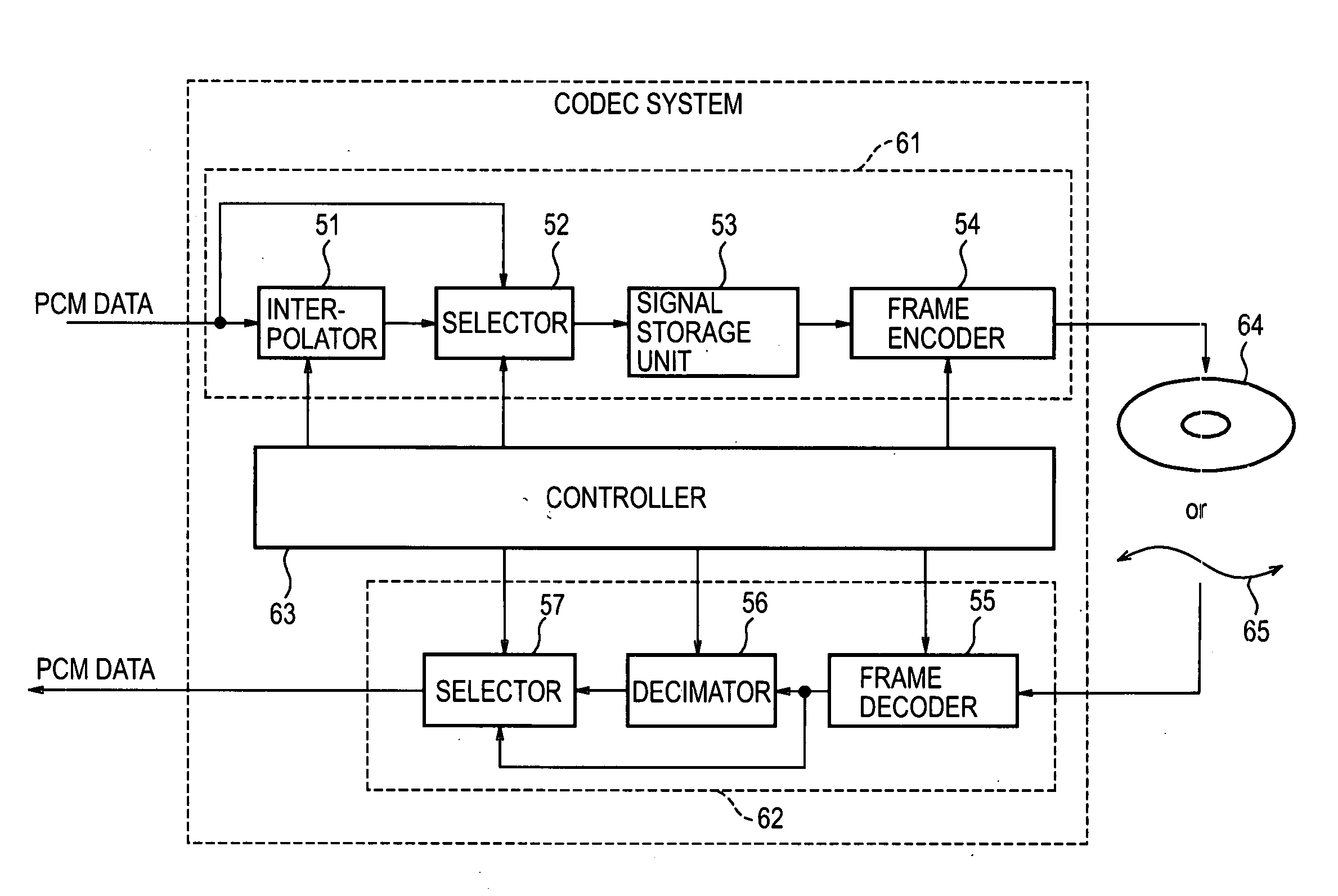
InactiveUS20070025446A1Reducing algorithm delayReduce delaysInterconnection arrangementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer hardwareOriginal data
The present invention relates to a data processing apparatus, a method and apparatus for encoding, a method and apparatus for decoding, and a program, that allow a reduction in an algorithm delay. An interpolator 51 produces interpolated PCM data by performing R-times oversampling on original PCM data. A frame encoder 54 fetches a predetermined number of samples of the oversampled data as one frame, encodes the oversampled data on a frame-by-frame basis, and outputs resultant encoded data. A frame decoder 55 decodes the encoded data on a frame-by-frame basis at a rate R times higher than a predetermined normal rate. A decimator 56 decimates data obtained as a result of the decoding such that the number of samples is reduced to 1 / R of the number of sampled included in the original data. The present invention is applicable, for example, to an IP telephone system.
Owner:SONY CORP
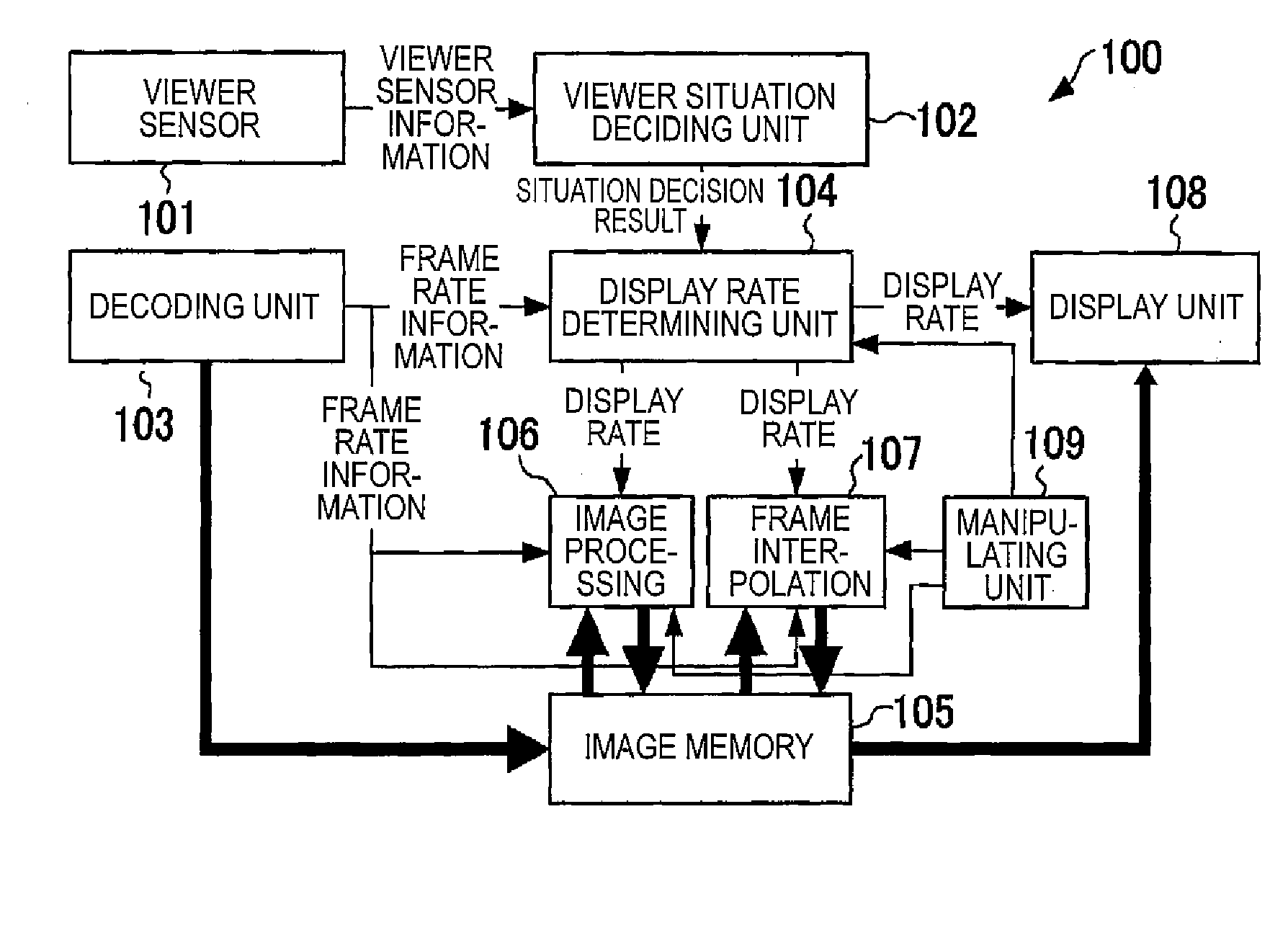
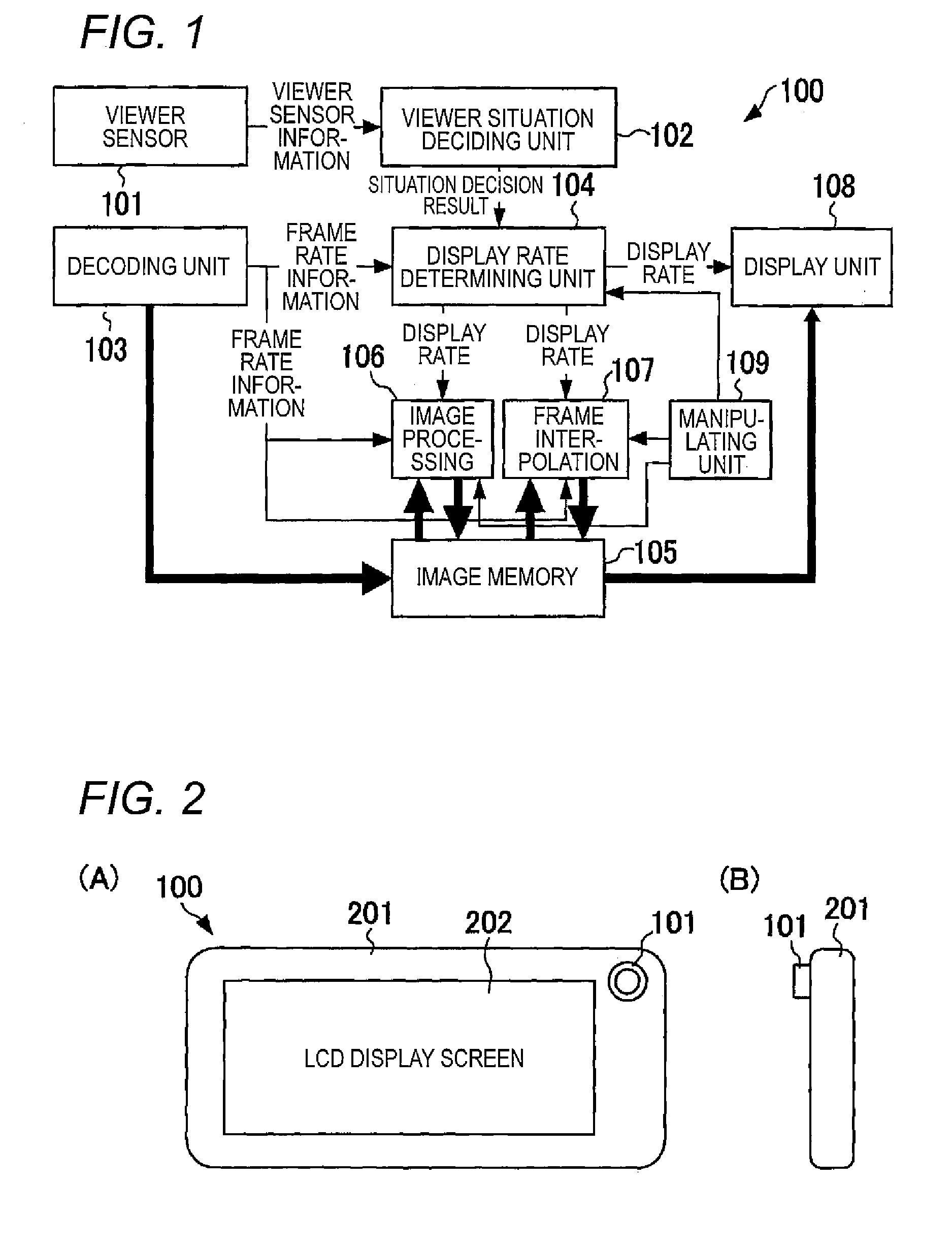
Display device, display control method, cellular phone, and semiconductor device
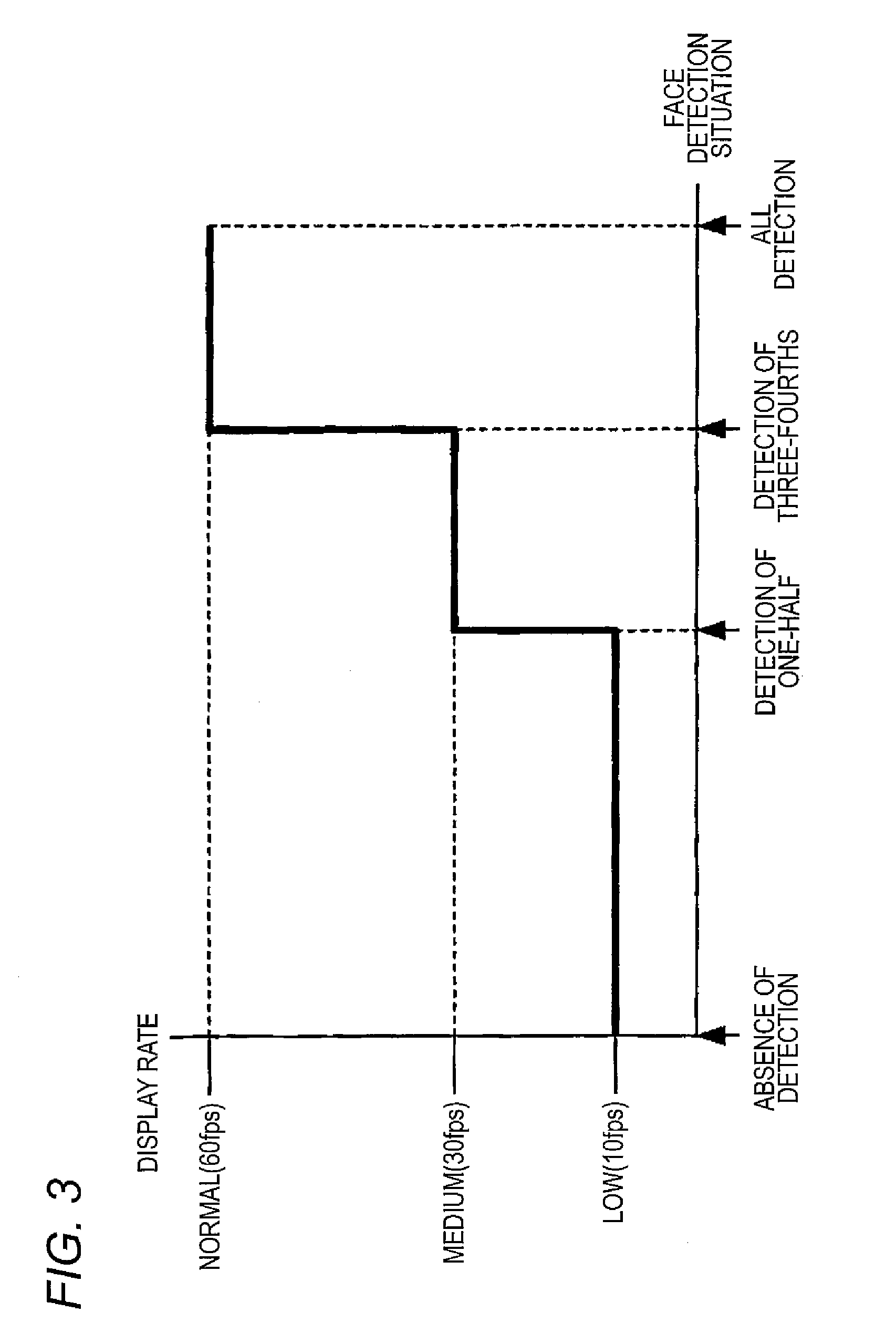
InactiveUS20130242187A1Save electricityDecrease in display rateTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesFace detectionNormal rate
A display device decides a face detection situation. When the face detection situation is in the range from the absence of face detection, in which a face facing an LCD display screen is not detected, to detection of one-half of the face, a display rate is set at a low rate by a display rate determining unit. When the face detection situation is in the range from detection of one-half of the face to detection of three-fourths of the face, the display rate is set at a medium rate by the display rate determining unit. When the face detection situation is in the range from detection of three-fourths of the face to detection of all of the face, the display rate is set at a normal rate by the display rate determining unit.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Method of playing streaming media video file with variable rate
ActiveCN106331824ARealize fast forward and slow playbackReserve the right to chooseSelective content distributionValue setComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a method of playing a streaming media video file with a variable rate, which comprises two parts of video information editing and video playing. In a manual editing method, a speed multiplication label of the video is generated in advance and the speed multiplication label is provided in a certain format; and according to the speed multiplication label information, video data in a label description range are played according to a speed multiplication value set by the label, needed fast and slow video file playing is realized, and the user still can watch the video with a normal rate. Thus, according to the method of the invention, while variable-speed playing of the video is realized, the right of selection of audience is still kept.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARCVIDEO TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
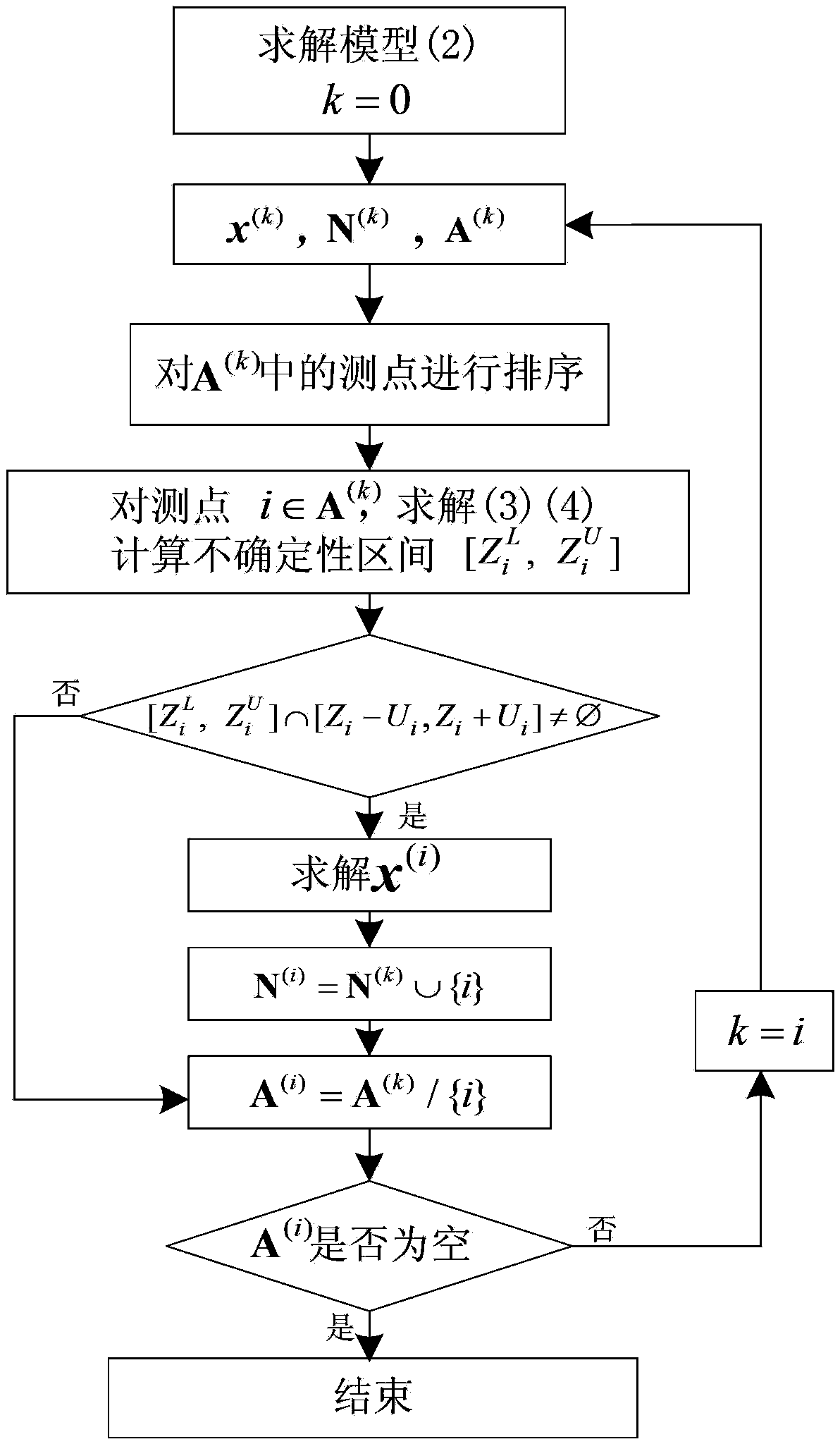
Method for solving state estimation problem taking maximum normal rate of measurement point as target
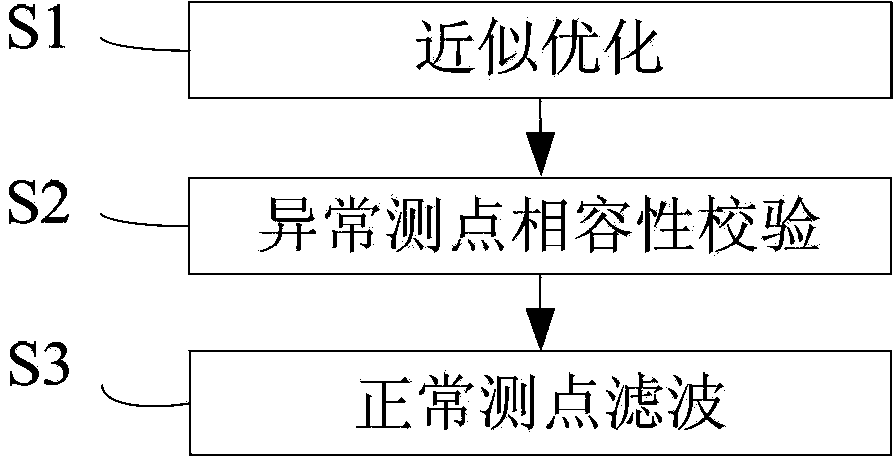
InactiveCN103400201AImprove the normal rate of measuring pointsHeavy calculationForecastingMeasurement pointAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for solving a state estimation problem taking a maximum normal rate of a measurement point as a target. The method comprises the following steps of performing approximate optimization, namely serializing an evaluation function of the normal rate of the measurement point to build a non-linear continuous variable optimization model of the problem and perform solving, thus obtaining an approximately optimal estimation state of the measurement point normal rate; checking the compatibility of an abnormal measurement point, namely analyzing an uncertainty region of the current abnormal measurement point according to a system state corresponding to the approximately optimal result, judging whether a state that enables the abnormal measurement point to be compatible with the current normal measurement point exists, if the state exists, determining that the measurement point is a normal measurement point in the state and the normal rate of the measurement point corresponding to the state is higher, repeating the execution to obtain a system state with higher normal rate of the measurement point; and performing filtration on the normal measurement point, namely performing least square estimation on the system state under the condition that an existing normal measurement point set is not changed. The method has the advantages of high tolerance resistance performance, high precision and small calculation gain.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
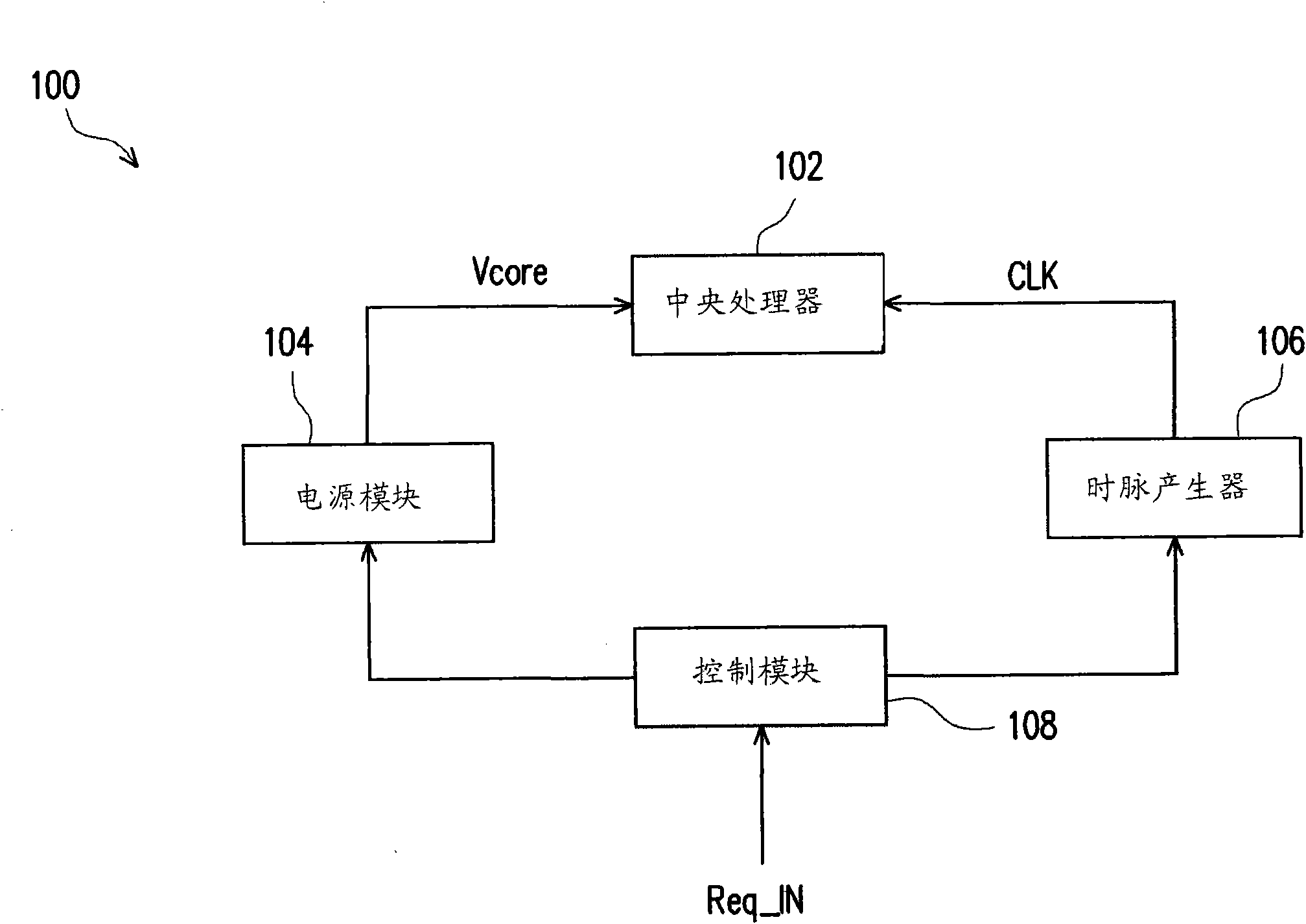
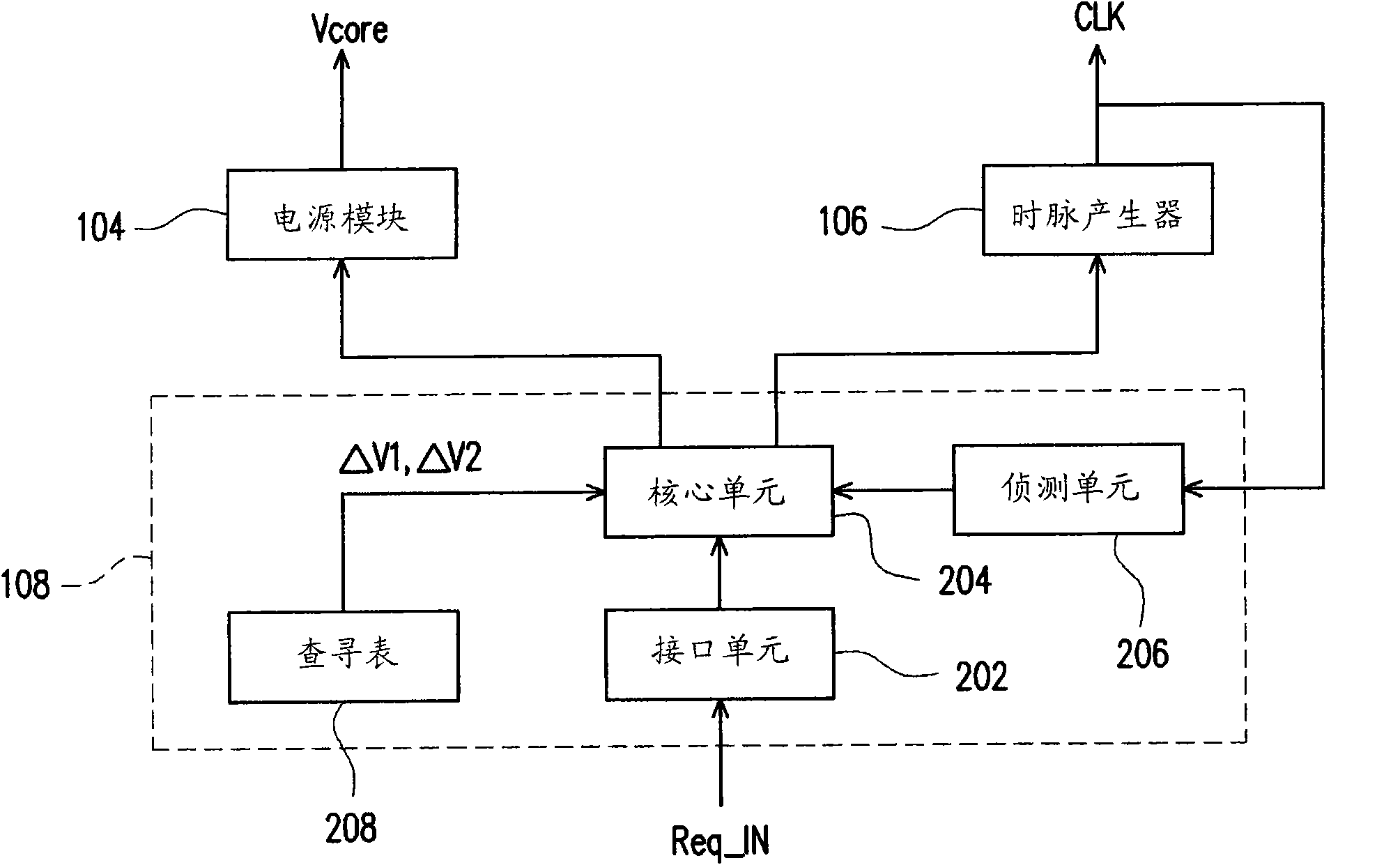
Overclocking control method and overclocking control program of central processing unit
ActiveCN101876845AEasy to operateVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingStable stateNormal rate
The invention relates to an overclocking control method and an overclocking control program of a central processing unit (CPU). The method comprises the following steps of: when the CPU needs to perform overclocking, supplying an overclocking working voltage to the CPU; regulating an internal work clock pulse according to the overclocking working voltage by using the CPU; and adding an extra voltage into the overclocking working voltage according to a normal rated working voltage of the CPU, so the CPU enters an overclocking mode (namely the frequency of the work clock pulse is higher than a frequency value of a standard work clock pulse); and when the frequency value of the work clock pulse of the CPU under the overclocking mode enters a stable state, lowering the working voltage under the overclocking mode, which is supplied to the CPU and keeping the CUP continuously working under the overclocking mode.
Owner:ASUSTEK COMPUTER INC
Method for the diagnosis, prognosis and monitoring of muscular degeneration
InactiveUS20130316933A1Reduce delaysSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesTypes diseasesAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The invention relates to methods based on the quantification of a set of biomarkers, preferably in biological samples isolated from skeletal muscle, for performing the diagnosis, prognosis and / or monitoring of muscular degeneration, preferably muscular degeneration caused by motor neuron diseases, more preferably amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); and to a kit for the diagnosis, prognosis and monitoring of said type of diseases. The method in the invention for the prognosis and / or monitoring of muscular degeneration makes it possible to determine the rate of progression of said degeneration (fast or slow rate of progression in relation to the normal rate of progression).
Owner:UNIV DE ZARAGOZA +2
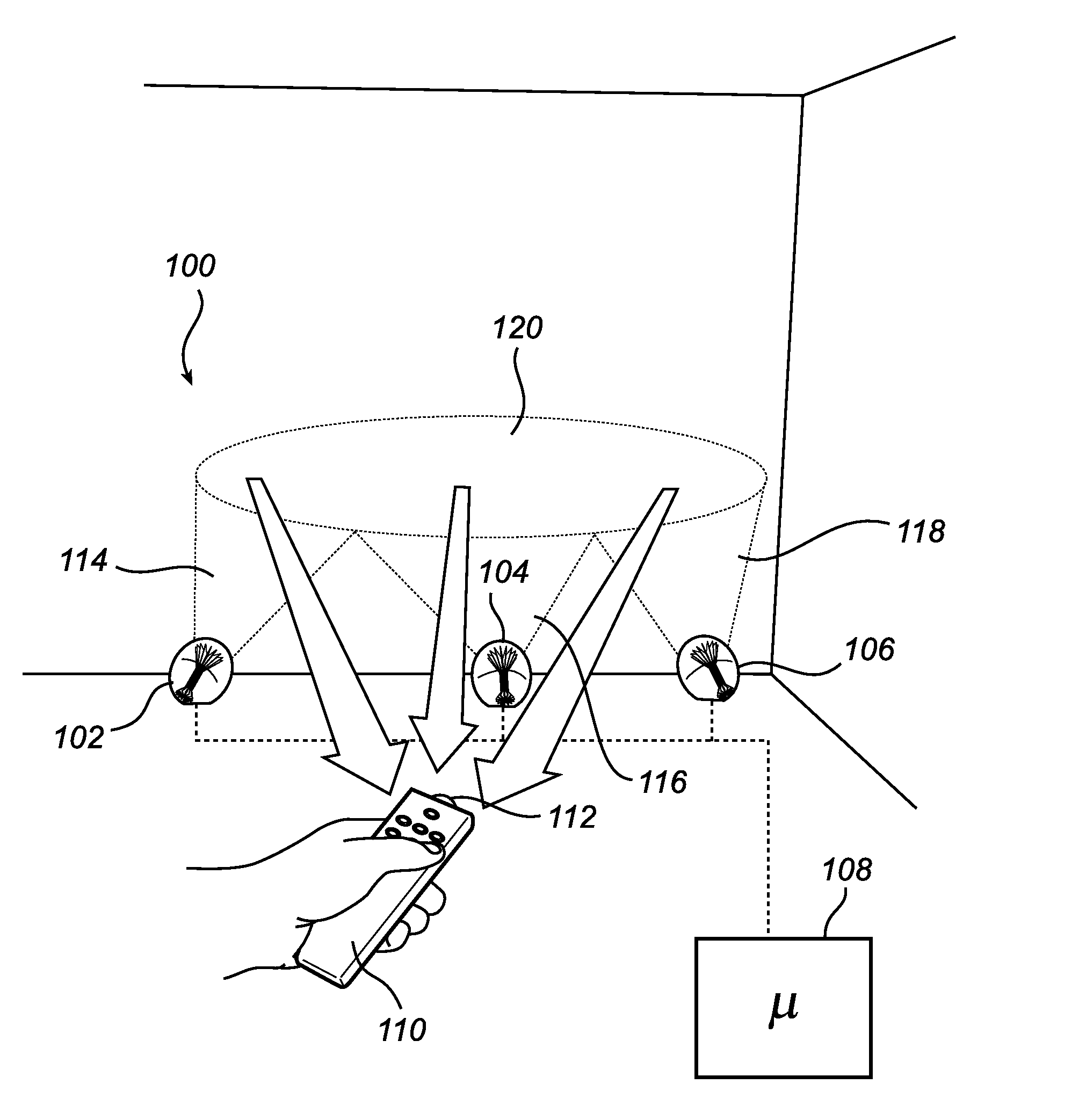
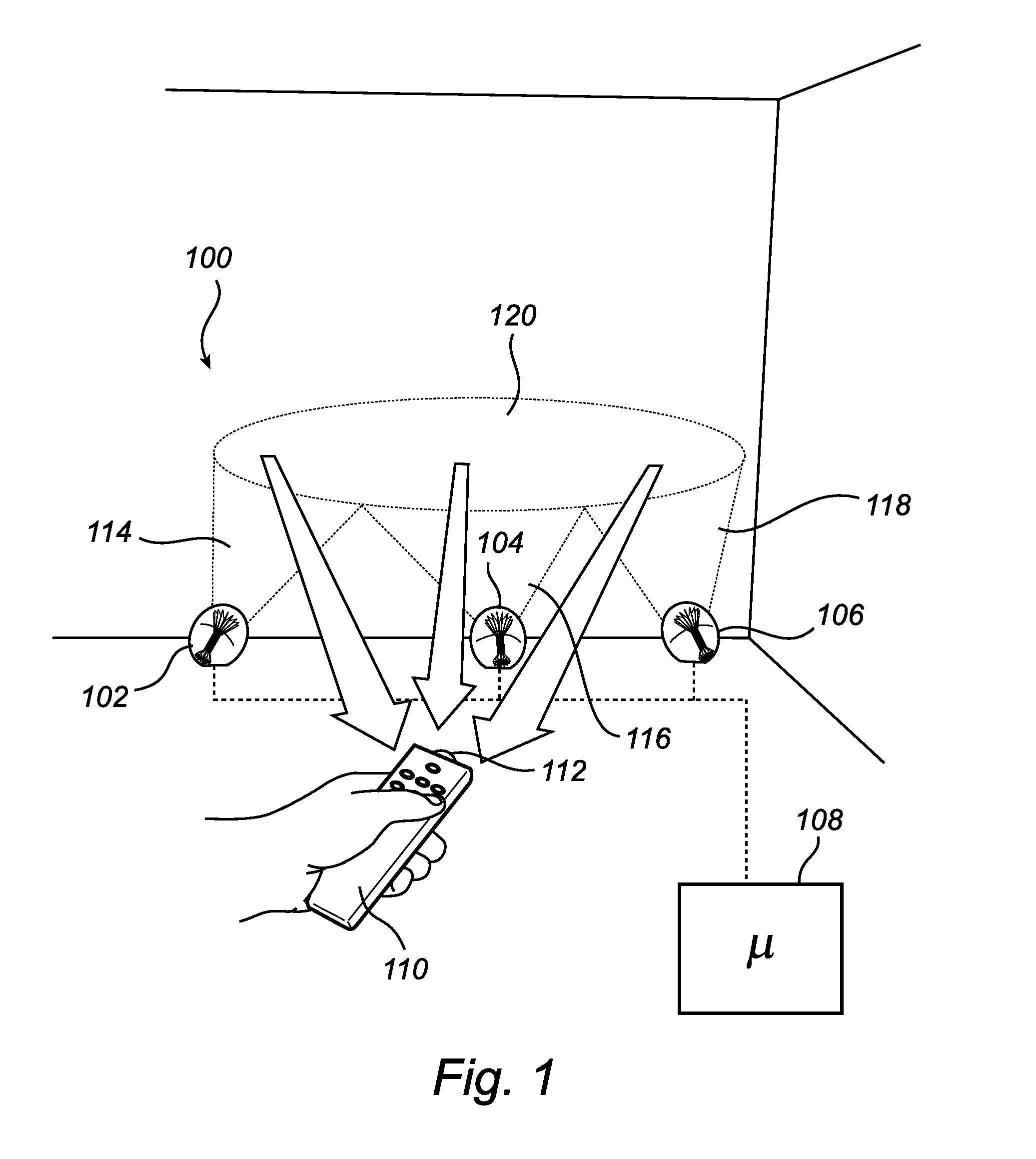
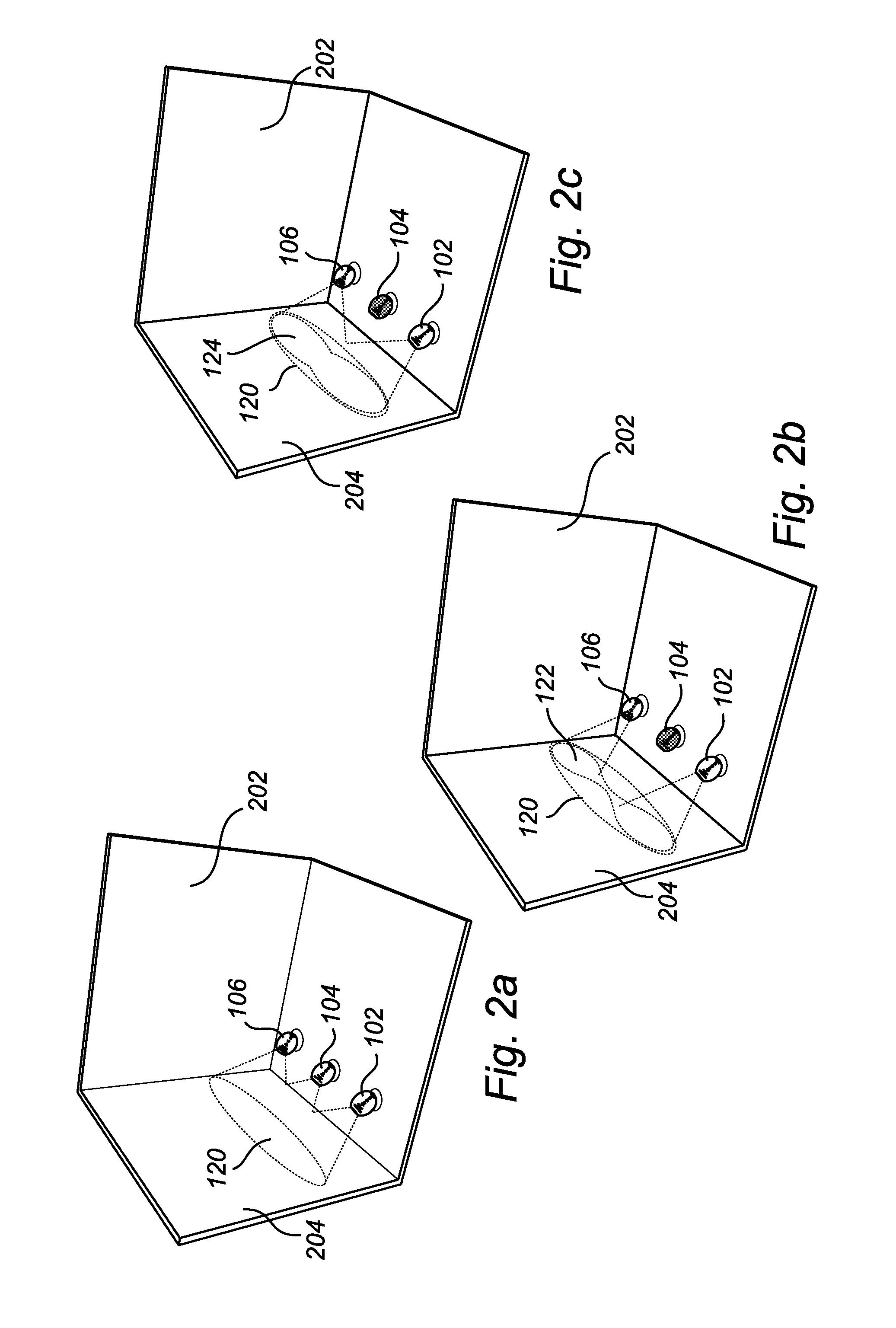
Adaptable lighting system
ActiveUS20120299510A1Self healing featureExtended service lifeElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementNormal rateEngineering
The present invention relates to a control unit (108) for a lighting system (100) comprising at least two individually controllable light sources (102, 104), wherein the control unit (108) is connectable to the at least two individually controllable light sources (102, 104) and configured to control the at least two individually controllable light sources (102, 104), wherein the control unit (108) is further configured to control a first lighting system configuration comprising the at least two individually controllable light sources (102, 104) so as to cause it to emit a first illumination pattern (120) provided jointly by the at least two light sources (102, 104) of the first lighting system configuration, detect and store an initial set of illumination parameters being indicative of the first illumination pattern (120), determine a subsequent set of illumination parameters being indicative of a second illumination pattern (122) provided by a second lighting system configuration comprising individually controllable light sources (102, 106), the second lighting system configuration being different from the first lighting system configuration, and control, in dependence on the initial set and the subsequent set of illumination parameters, the second lighting system configuration so as to cause it to emit a third illumination pattern (124), the third illumination pattern (124) being an approximation of the first illumination pattern (120). The present invention provides advantages in respect of e.g. automatic “healing” of the lighting system (100), for example in the case where a light source (102, 104) of the lighting system (100) fails or is only capable of providing less than the normal rated light output.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system of analyzing dredging operation of cutter-suction dredger
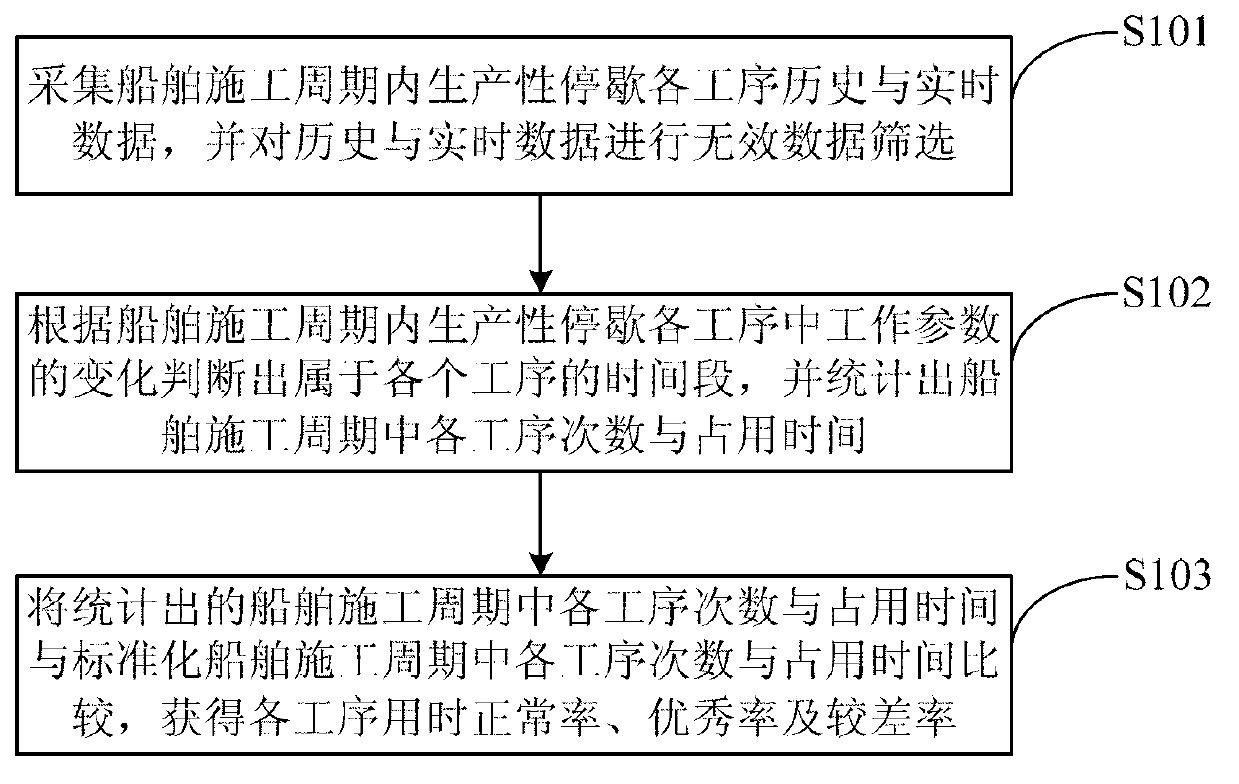
InactiveCN103136704AIncrease profitImprove productivityData processing applicationsProduction rateReal-time data
The invention discloses a method and a system of analyzing dredging operation of a cutter-suction dredger. The method comprises the following steps: collecting historic and real-time data of each production break working procedure during construction period of the cutter-suction dredger, and carrying out invalid data screening on the collected historic and real-time data; judging time quantum of each working procedure according to operating parameter variation in each production break working procedure in the ship construction period, and counting each frequency and occupied time in the ship construction period; at last, comparing the time consumption of each working procedure and the occupied time in the ship construction period with the time consumption of each working procedure and occupied time in a standardized ship construction period to obtain normal rates, excellent rates and bad rates of the time consumption of each working procedure. By the adoption of the method, the frequency and occupied time of each production break working procedure can be analyzed, various accurate and important parameter data under the condition that output is kept highly stable are provided, an accurate and timely ship construction procedure operation is achieved according to a degree of parametric variation, and an utilization rate and a production rate of ship time are improved.
Owner:CCCC TDC BINHAI ENVIRONMENTAL CHANNEL DREDGING
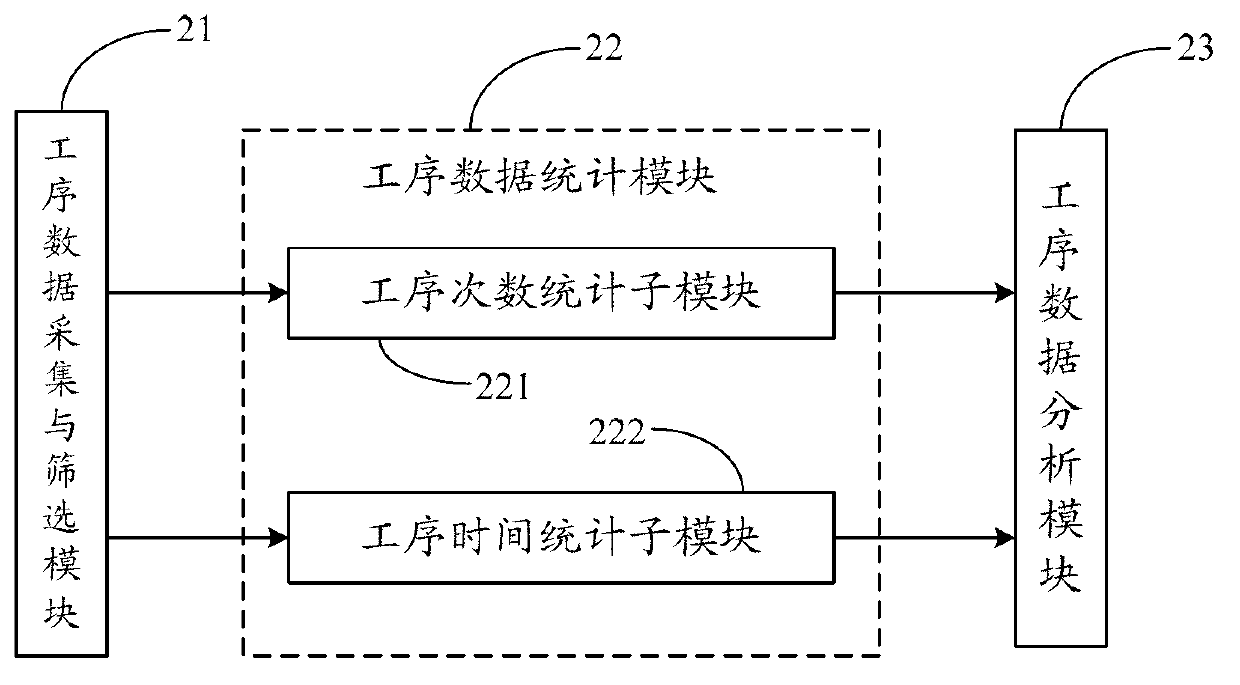
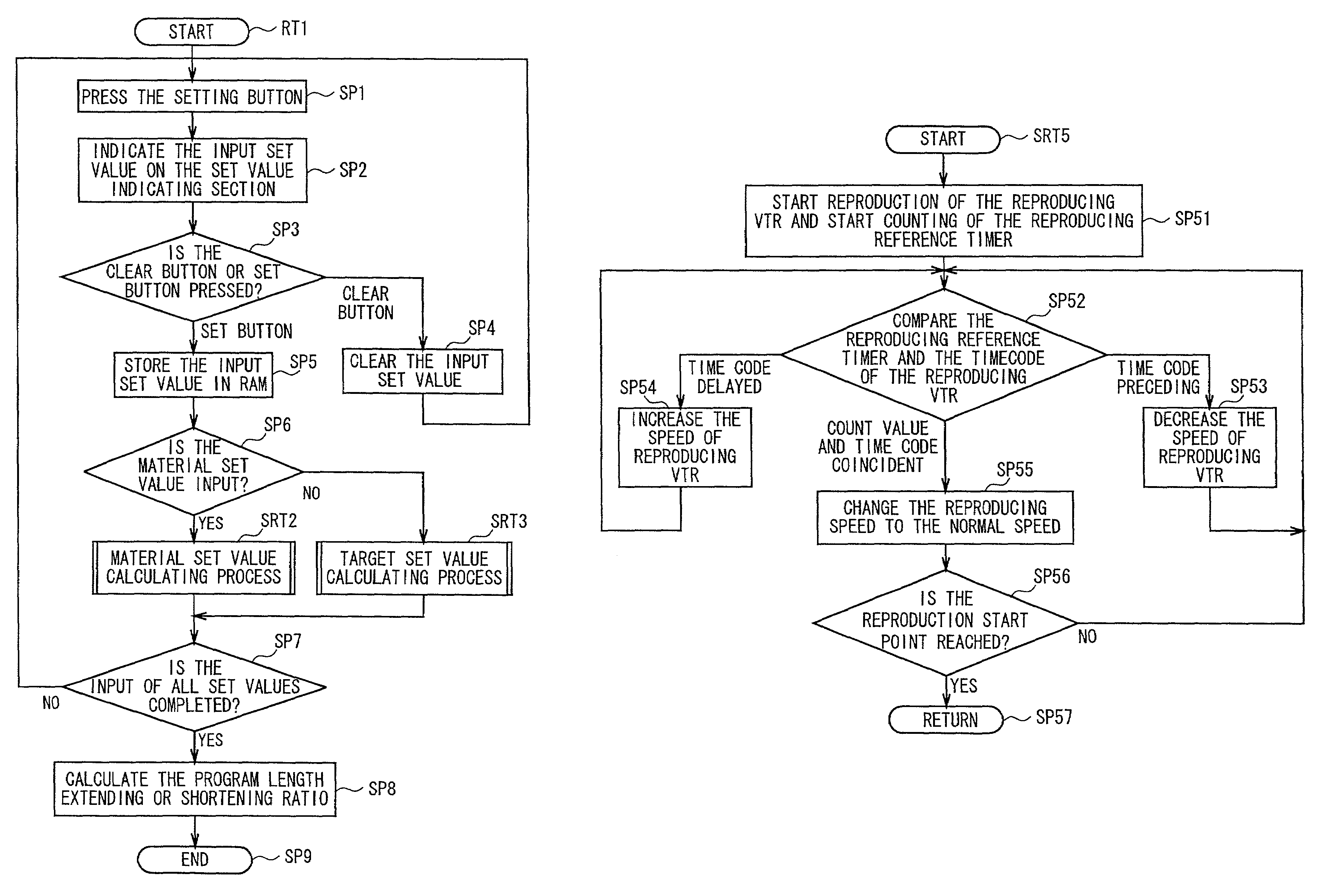
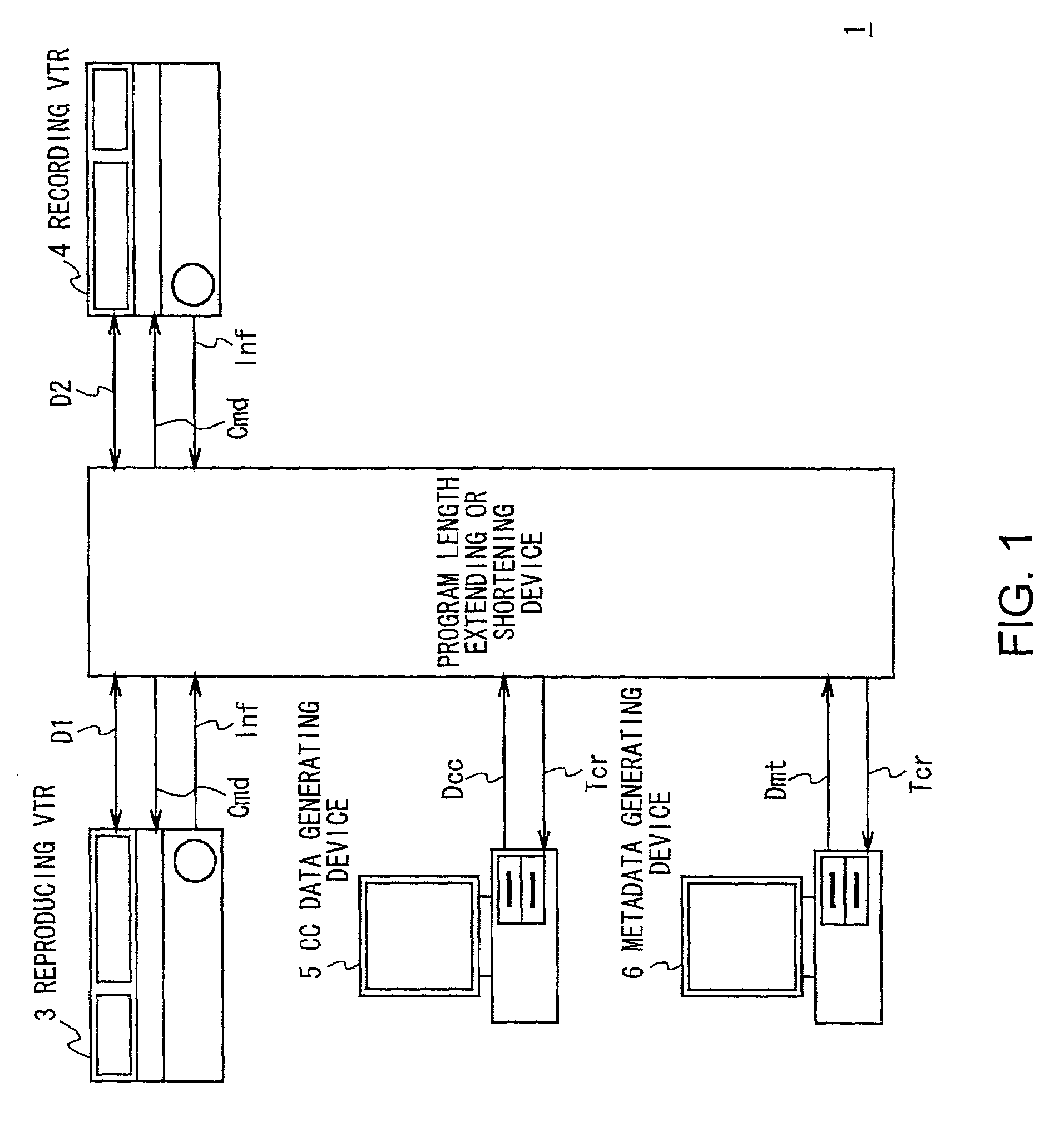
Program length extending or shortening device and method, and program length adjusting system
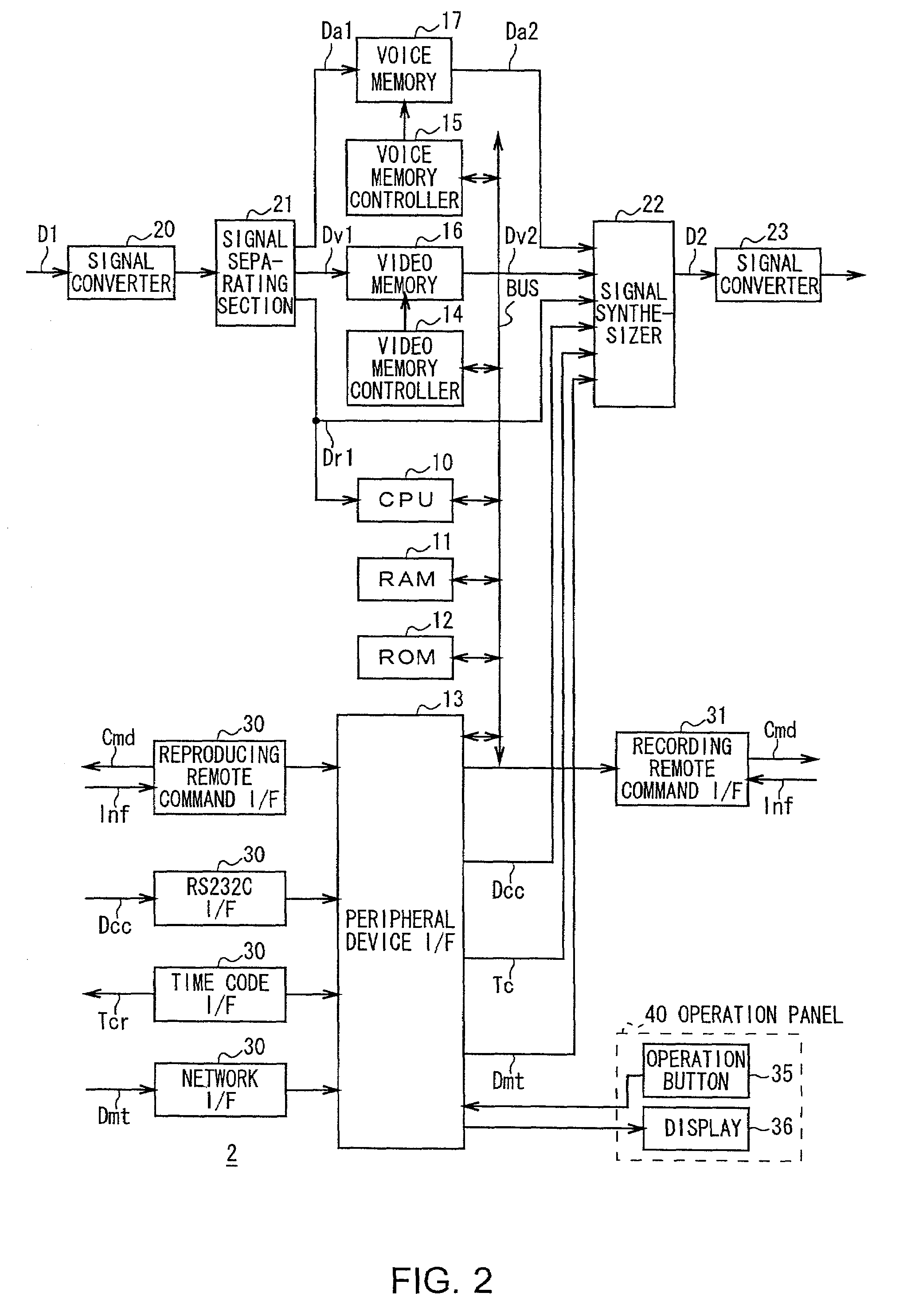
InactiveUS7043136B2Securely extended and shortenedTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital videoMagnetic tape
A program length extending or shortening device for extending or shortening the program length in a digital video tape recorder of the image information compression recording method. The device comprises storage means for storing an image of a material video program reproduced and supplied from a predetermined recording medium by a reproducing device, and extending or shortening control means for extending or shortening the program length of the material video program to produce a target video program by skipping or reading duplicately the image of the material video program from the storage means in accordance with a program length extending or shortening ratio N based on the program lengths of the material video program and the target video program. According to the present invention, the program length can be freely extended or shortened using storage means of a small capacity while the recording device is being operated at a normal rate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com