Patents
Literature
138 results about "MPEG encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
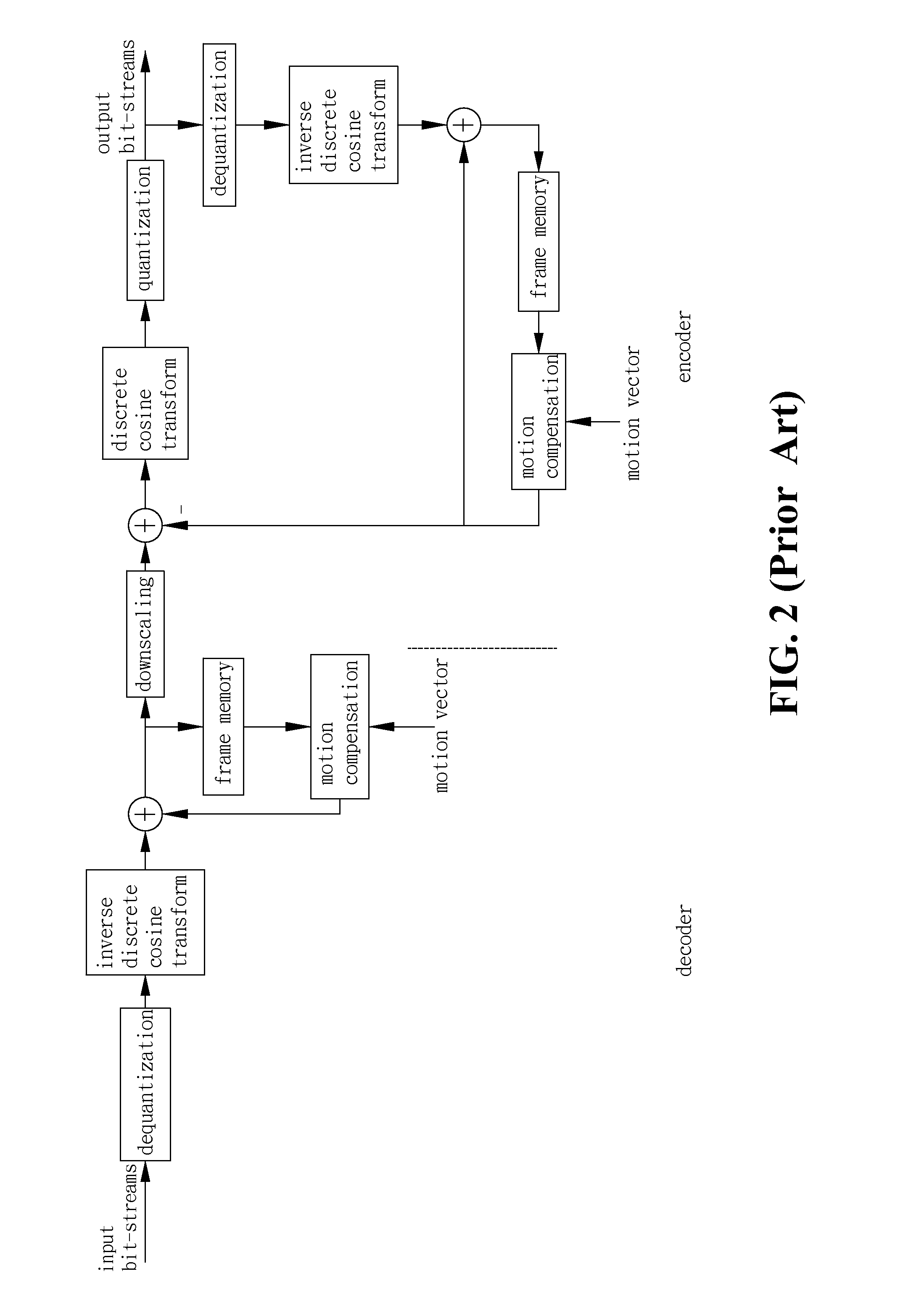
MPEG encoding is the process of capturing or converting video and/or audio to one of several MPEG video and/or audio standards for distribution or for archiving to optical disc. MPEG encoding can be done purely in software, or by using an MPEG capture card or a video editing card with in-built MPEG encoding capabilities, or via a dedicated hardware encoder like those built-into DVD-Video recorders.
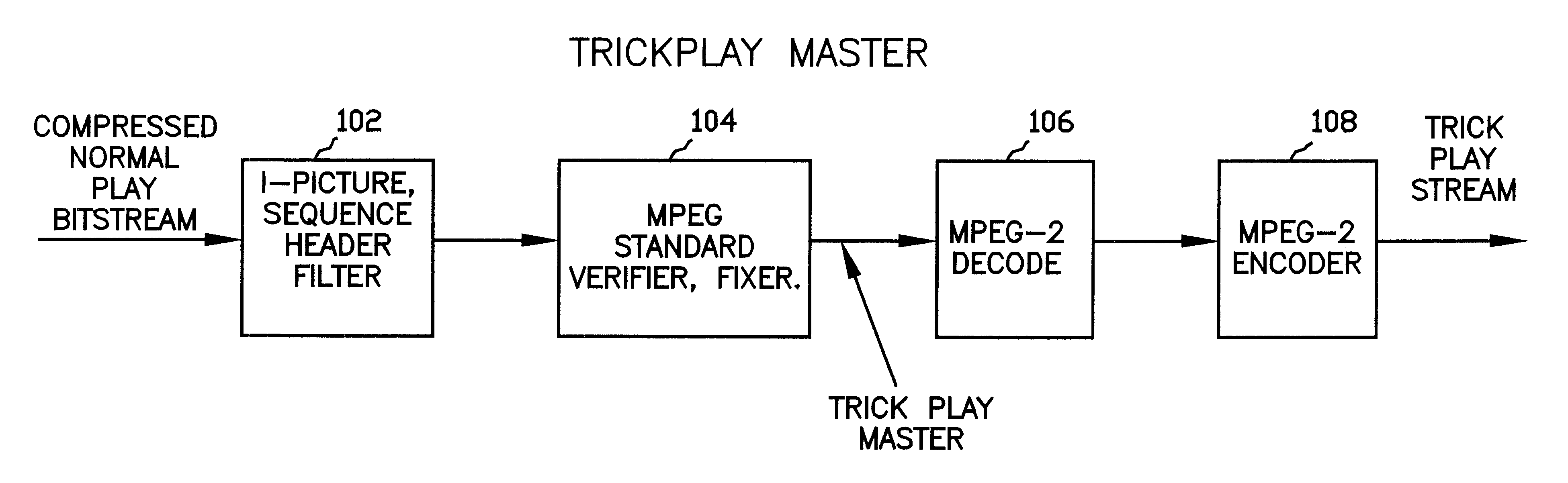
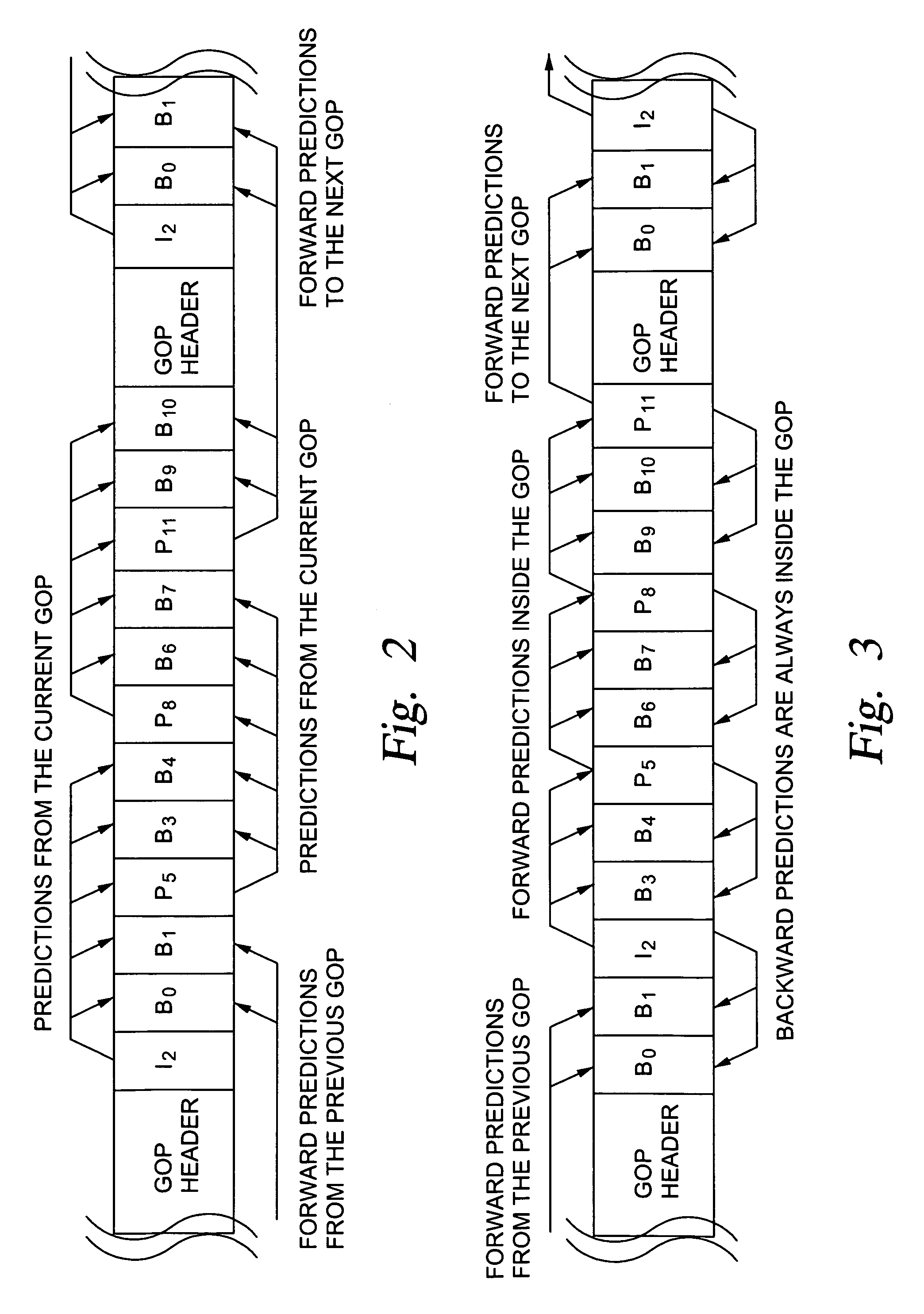
System and method for creating trick play video streams from a compressed normal play video bitstream
InactiveUS6445738B1Generate efficientlyReduced storage and data transfer data bandwidth requirementTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo bitstreamVideo sequence
A system and method for generating trick play video streams, such as fast forward and fast reverse video streams, from an MPEG compressed normal play bitstream. The system receives a compressed normal play bitstream and filters the bitstream by extracting and saving only portions of the bitstream. The system preferably extracts I-frames and sequence headers, including all weighting matrices, from the MPEG bitstream and stores this information in a new file. The system then assembles or collates the filtered data into the proper order to generate a single assembled bitstream. The system also ensures that the weighting matrixes properly correspond to the respective I-frames. This produces a bitstream comprised of a plurality of sequence headers and I-frames. This assembled bitstream is MPEG-2 decoded to produce a new video sequence which comprises only one out of every X pictures of the original, uncompressed normal play bitstream. This output picture stream is then re-encoded with respective MPEG parameters desired for the trickplay stream, thus producing a trickplay stream that is a valid MPEG encoded stream, but which includes only one of every X frames. The present invention thus generates compressed trick play video streams which require reduced storage and reduced data transfer bandwidth requirements.
Owner:OPEN TV INC +1
Processing of MPEG encoded video for trick mode operation
InactiveUS6871006B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVisual presentationMPEG transport stream
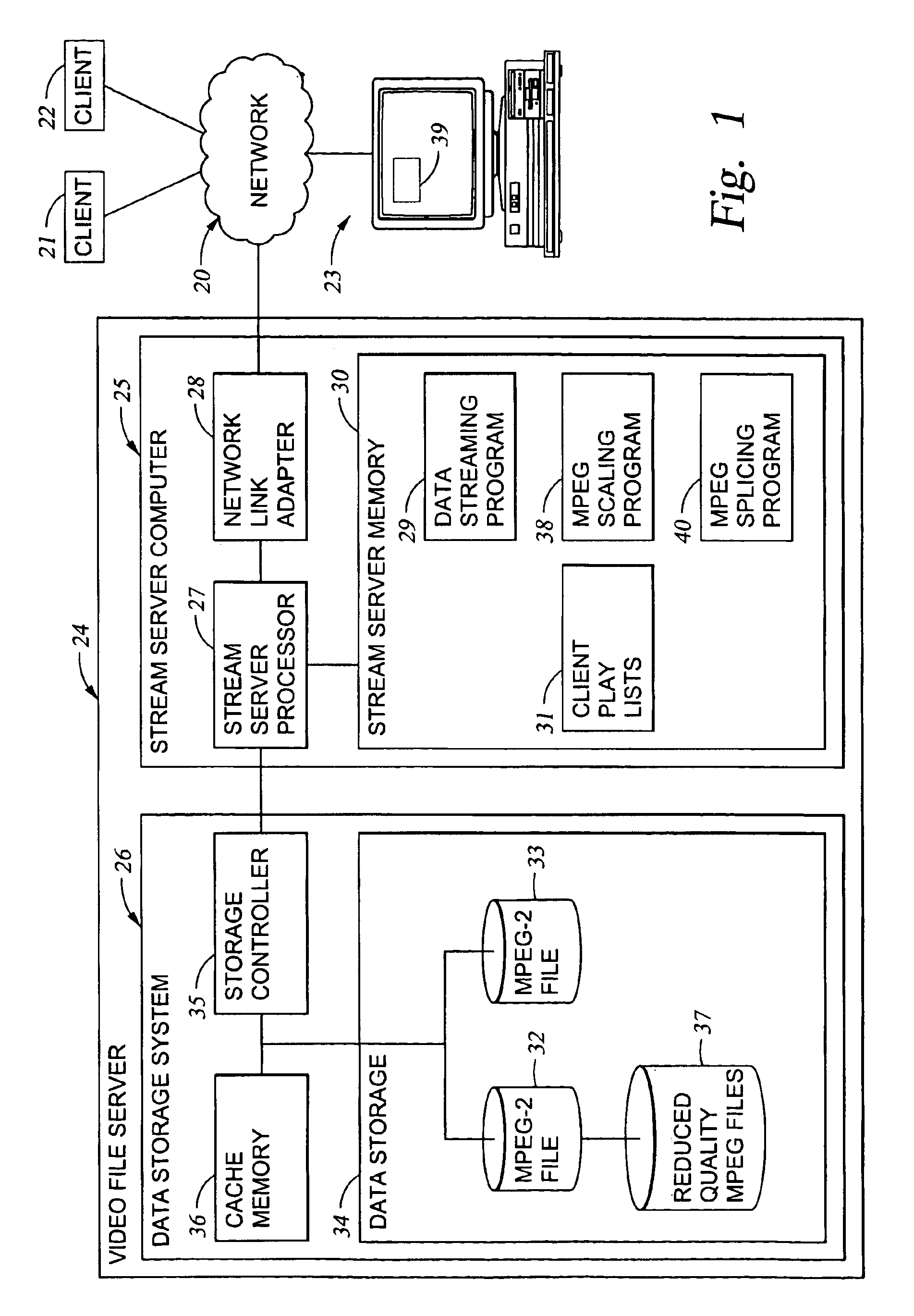
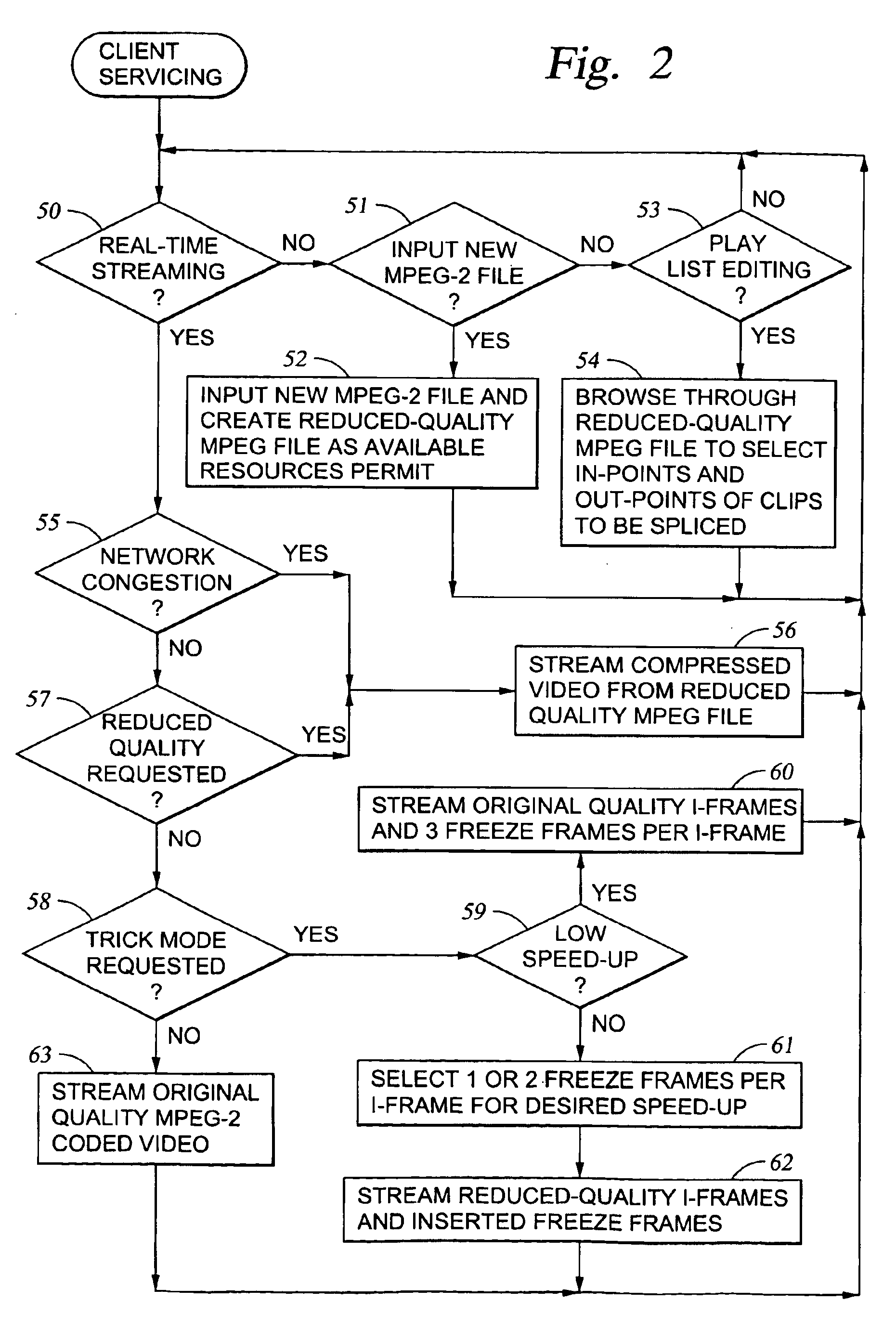
Original-quality MPEG coded video is processed to produce reduced-quality MPEG coded video for trick mode operation by removing non-zero AC DCT coefficients from the 8×8 blocks of I-frames of the MPEG coded video to produce I-frames of reduced-quality MPEG coded video, and inserting freeze frames in the reduced-quality MPEG coded video. Preferably, the coded video is stored in a main file, a fast-forward file and a fast-reverse file. The fast forward file and the fast reverse files contain reduced-quality I frames corresponding to original-quality I frames in the main file. A reading of the main file produces an MPEG transport stream for an audio-visual presentation at a normal rate, a reading of the fast-forward file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a forward direction at a fast rate, and a reading of the fast-reverse file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a reverse direction at a fast rate. Preferably, the files share a volume that includes at least one GOP index associating the corresponding I frames of the files.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
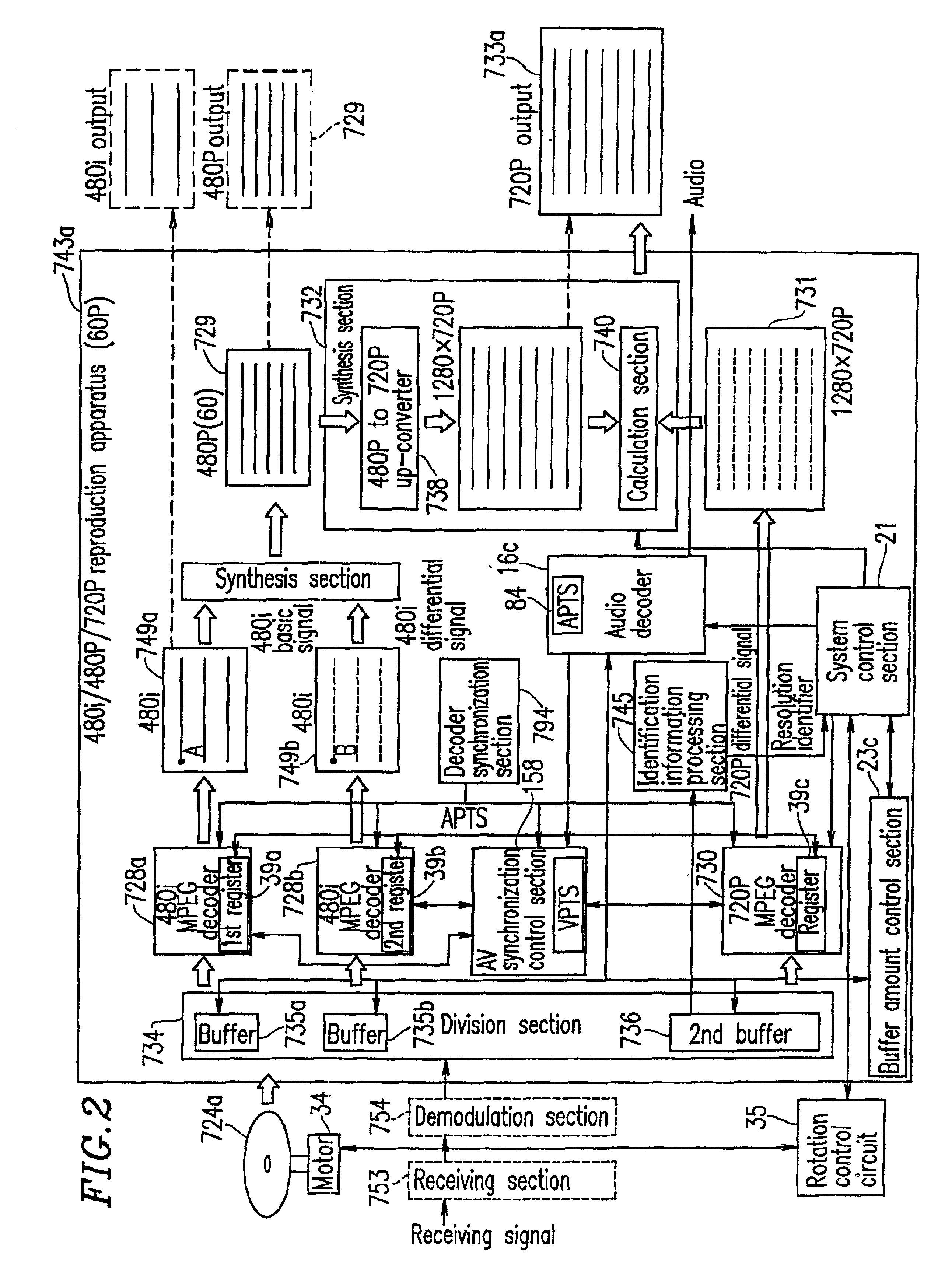
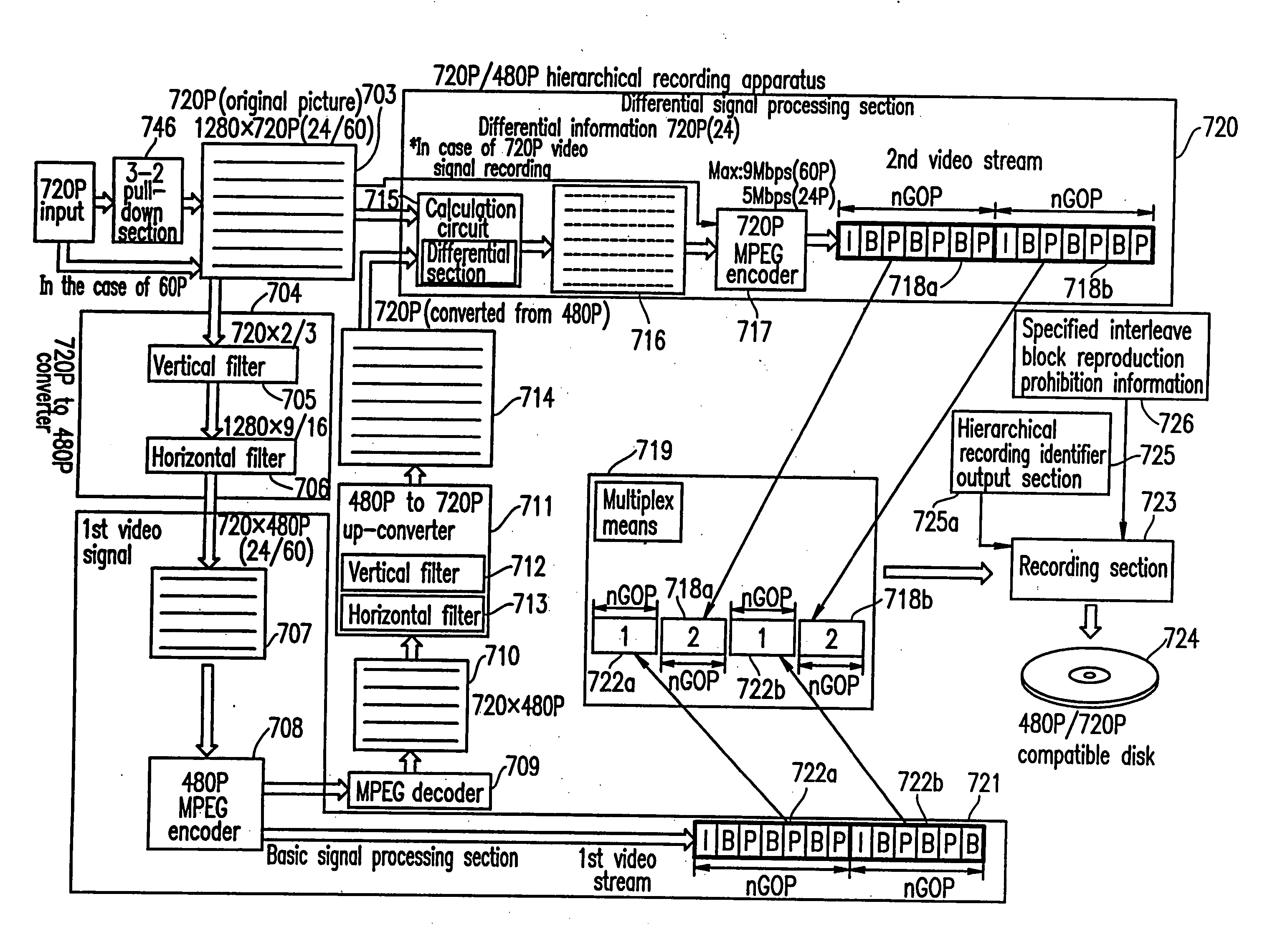
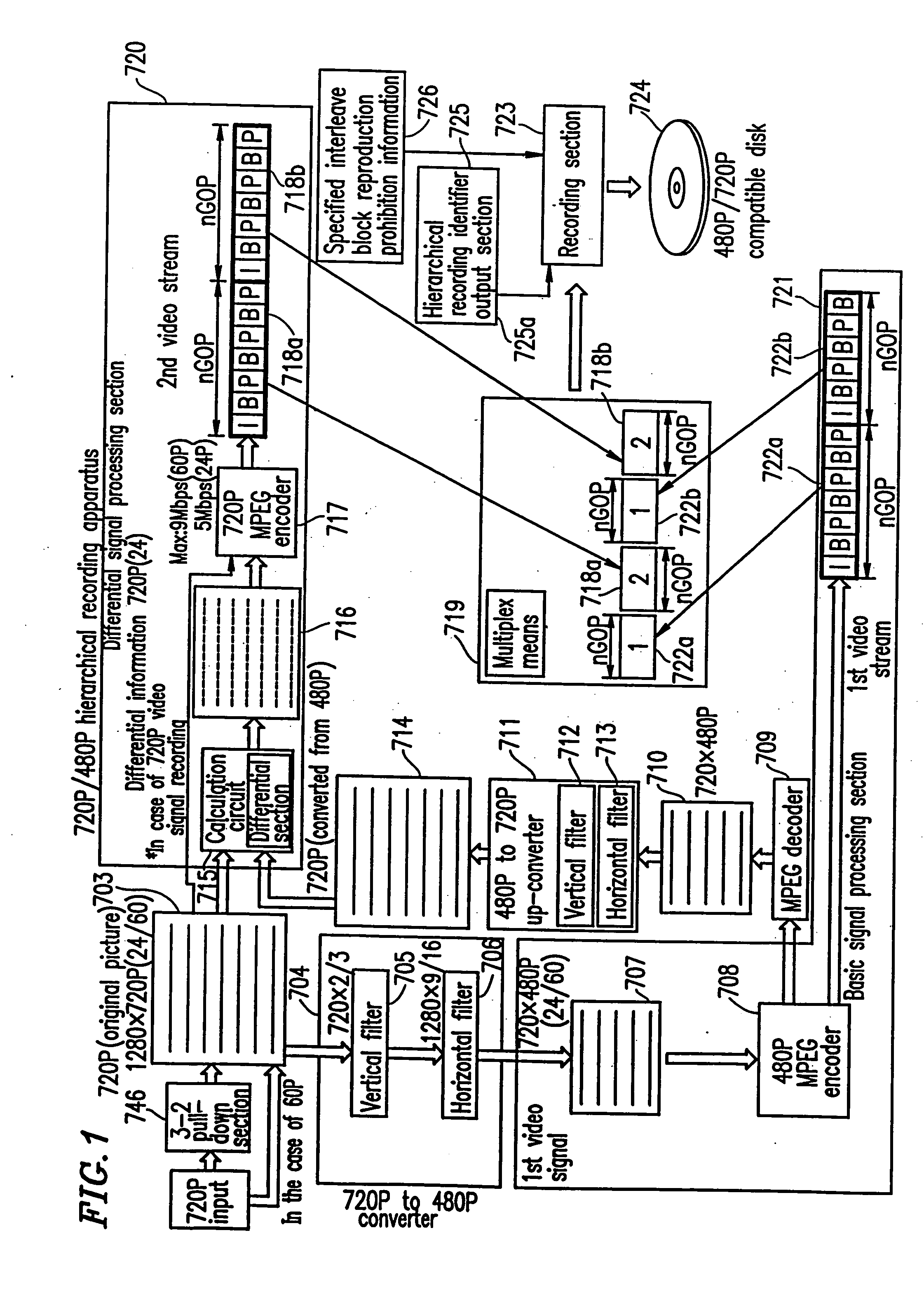
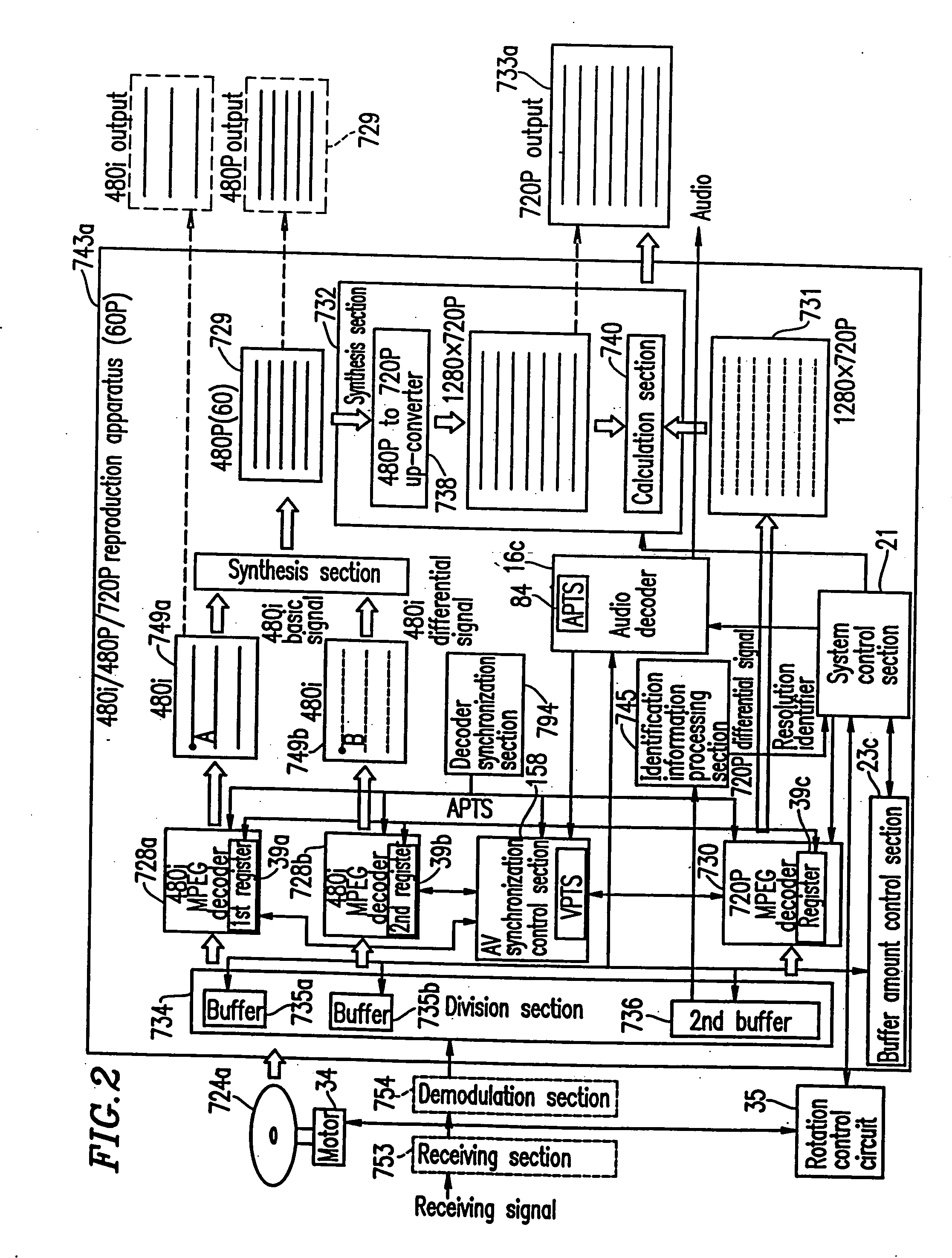
Optical disc for recording high resolution and normal image, optical disc player, optical disc recorder, and playback control information generator
InactiveUS6925250B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionMPEG encoding
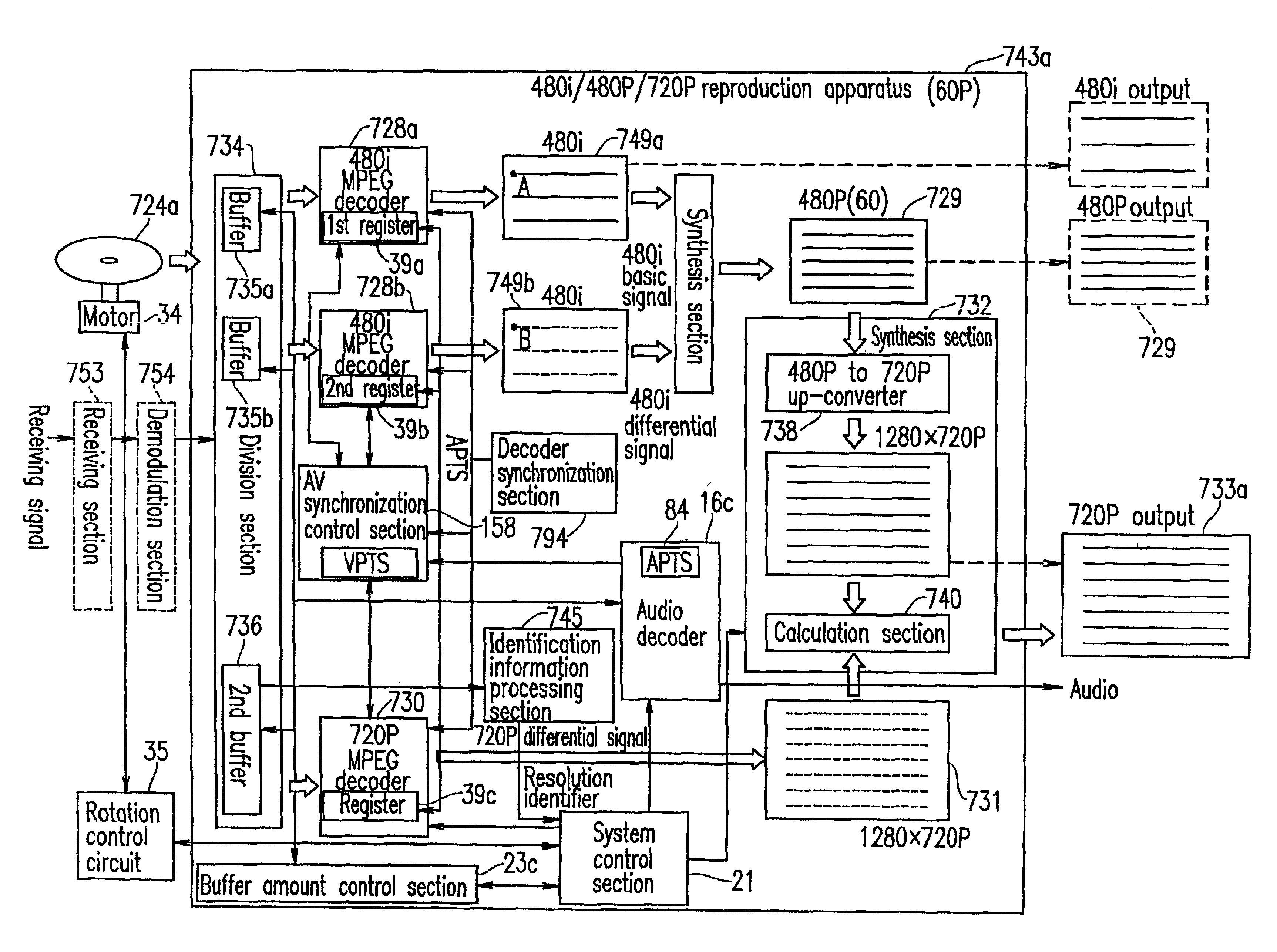
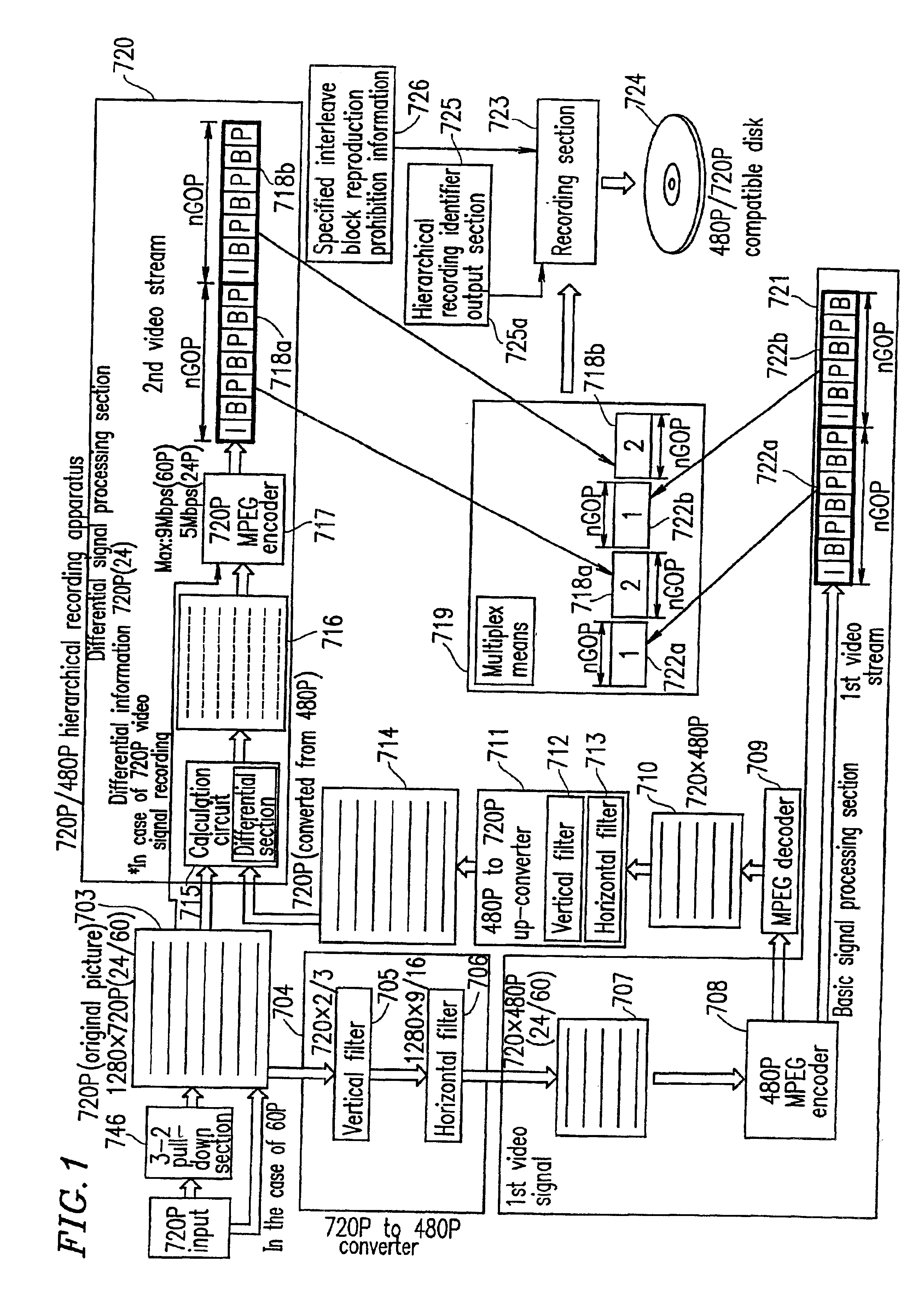
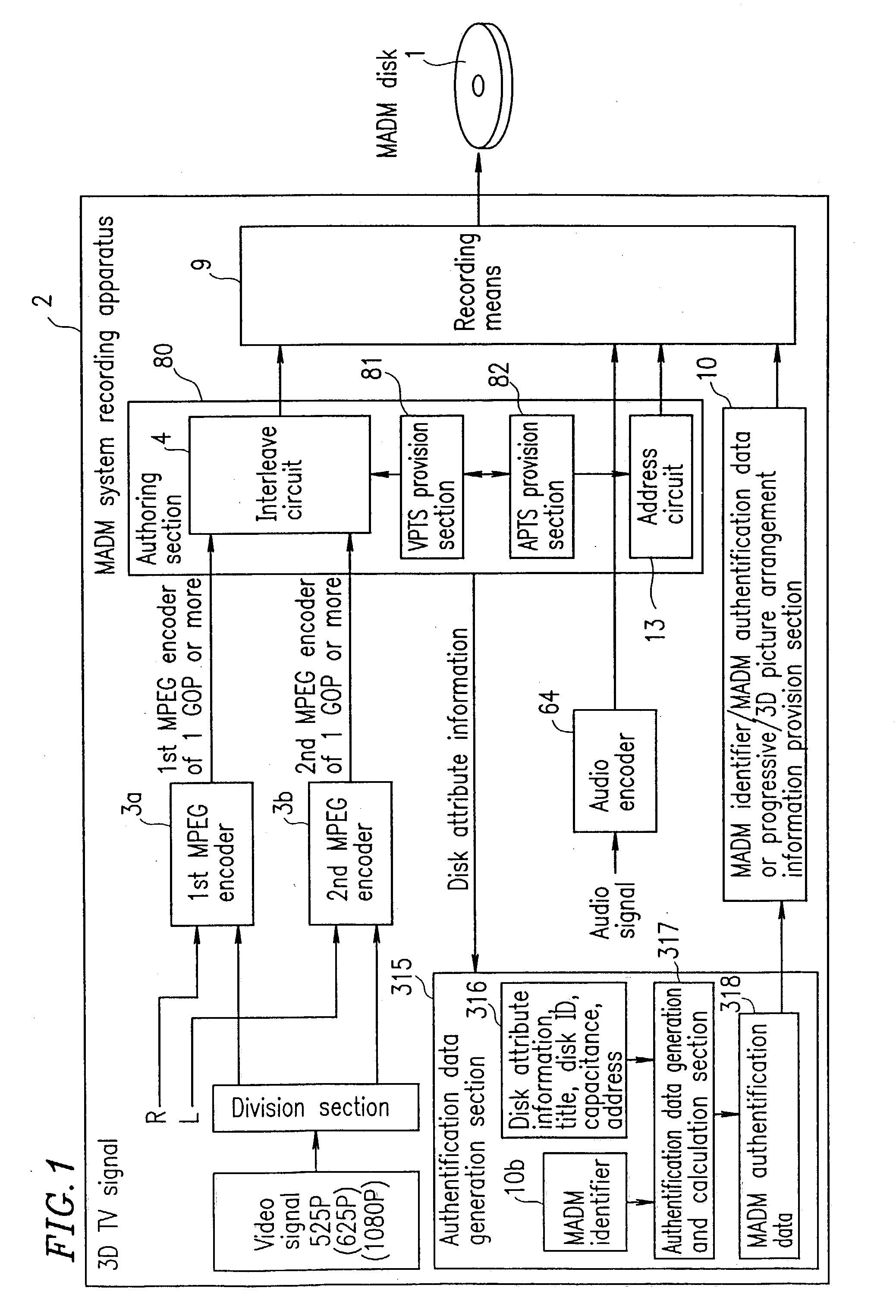
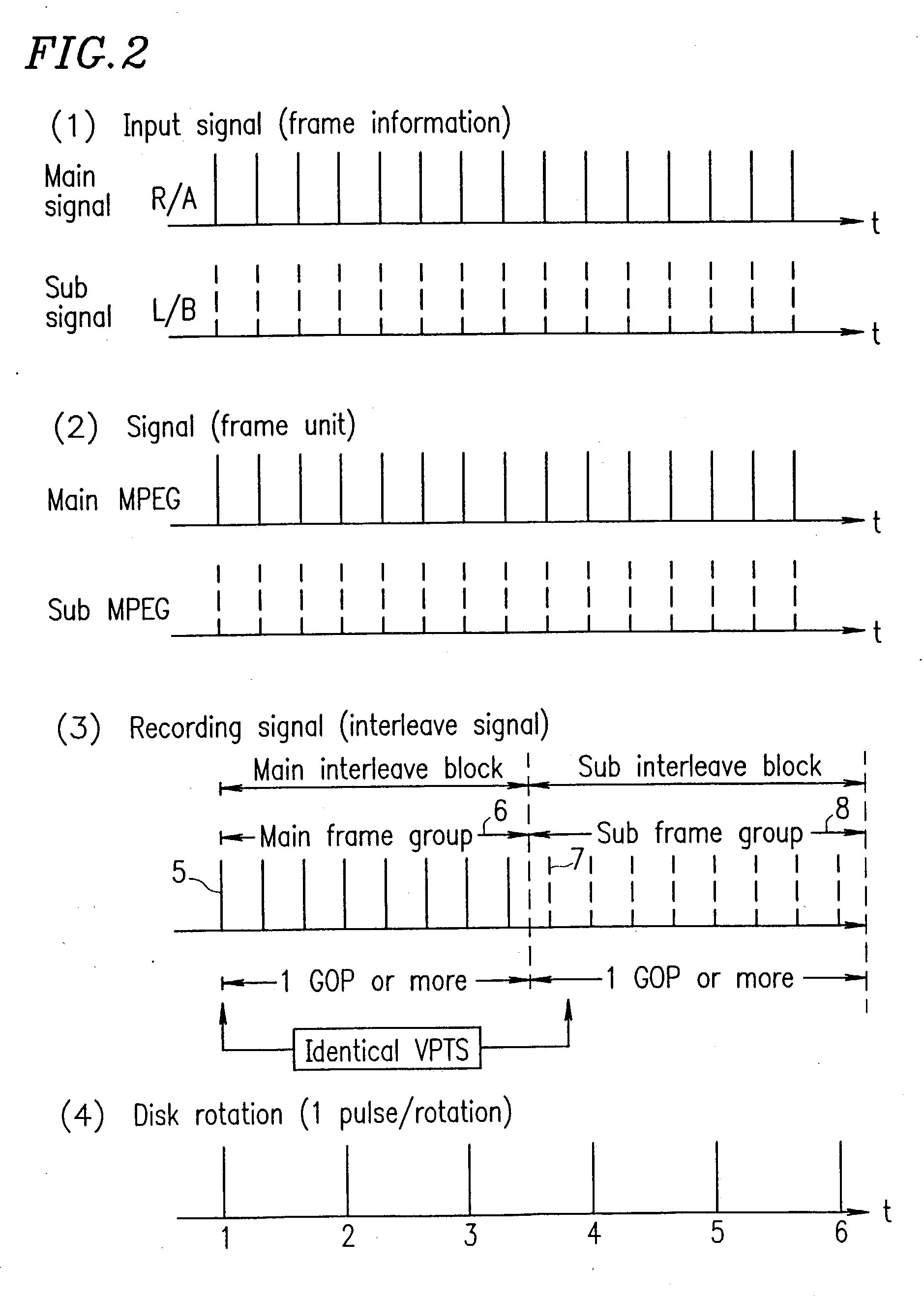
The present invention has an objective of realizing compatibility of an optical disk having a high resolution video signal recorded thereon and a system for reproducing the optical disk, with a conventional system for producing a standard resolution video signal. A high resolution-video signal is divided by video division means into a main signal and a sub signal, and the main signal and the sub signal are MPEG-encoded. The stream of the main signal and the stream of the sub signal are divided into 1 GOP or more of frames. First interleave blocks 54 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the main signal and second interleave blocks 55 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the sub signal are recorded on an optical disk 1. A high resolution reproduction apparatus reproduces both the first and second interleave blocks to obtain a high resolution video output. A non-high quality picture reproduction apparatus reproduces only the first or second interleave blocks to obtain a standard resolution video output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Interactive encoded content system including object models for viewing on a remote device
InactiveUS20080170622A1Input/output for user-computer interactionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGraphicsUser input
A system for creating composite encoded video from two or more encoded video sources in the encoded domain. In response to user input, a markup language-based graphical layout is retrieved. The graphical layout includes frame locations within a composite frame for at least a first encoded source and a second encoded source. The system either retrieves or receives the first and second encoded sources. The sources include block-based transform encoded data. The system also includes a stitcher module for stitching together the first encoded source and the second encoded source according to the frame locations of the graphical layout to form an encoded frame. The system outputs an encoded video stream that is transmitted to a client device associated with the user. In response to further user input, the system updates the state of an object model and replaces all or a portion of one or more frames of the encoded video stream. The system may be used with MPEG encoded video.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
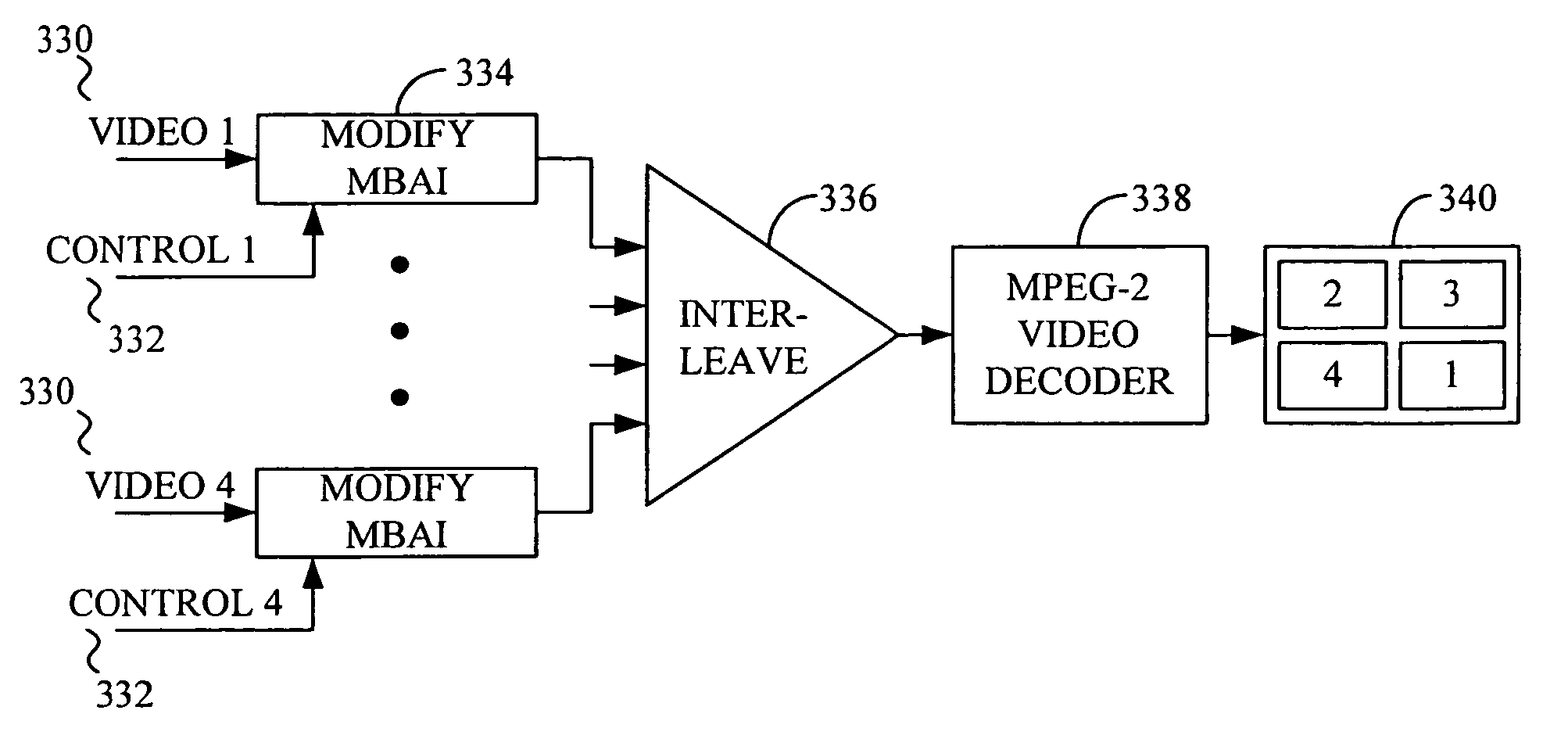
Interactive television system and method for simultaneous transmission and rendering of multiple MPEG-encoded video streams
InactiveUS6931660B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision systemDigital video
A system and method for the simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple MPEG-encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application are disclosed. Simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple MPEG-encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application generally comprises determining a value for a display position code corresponding to a display position of each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams, modifying the value of the display position code of each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams as necessary, and interleaving each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams as modified into a single composite video stream. The modifying preferably maintains bit-alignment of the display position code within a byte. The MPEG-encoded video streams are optionally MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 encoded video streams and the display position code is optionally a macroblock address increment variable length codeword and / or at least a byte of a slice startcode.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
Optical disk for high resolution and three-dimensional video recording, optical disk reproduction apparatus, and optical disk recording apparatus
InactiveUS20030108341A1Precise positioningWithout any changeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionImage segmentation
The present invention has an objective of providing an optical disk having a high resolution picture and a system for reproducing data on the optical disk, which are compatible with a conventional system for reproducing an ordinary resolution picture. A high resolution signal is divided into a main signal and a sub signal by picture division means and MPEG-encoded. The main signal and the sub signal are divided into frames each having 1 GOP or more. The resultant first interleave block 54 and second interleave block 55 are recorded alternately on an optical disk. A high resolution reproduction apparatus reproduced both the first and second interleave blocks, so that a high resolution picture is obtained. A non-high resolution reproduction apparatus reproduces only the first or second interleave block, so that an ordinary resolution picture.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Generation of MPEG slow motion playout
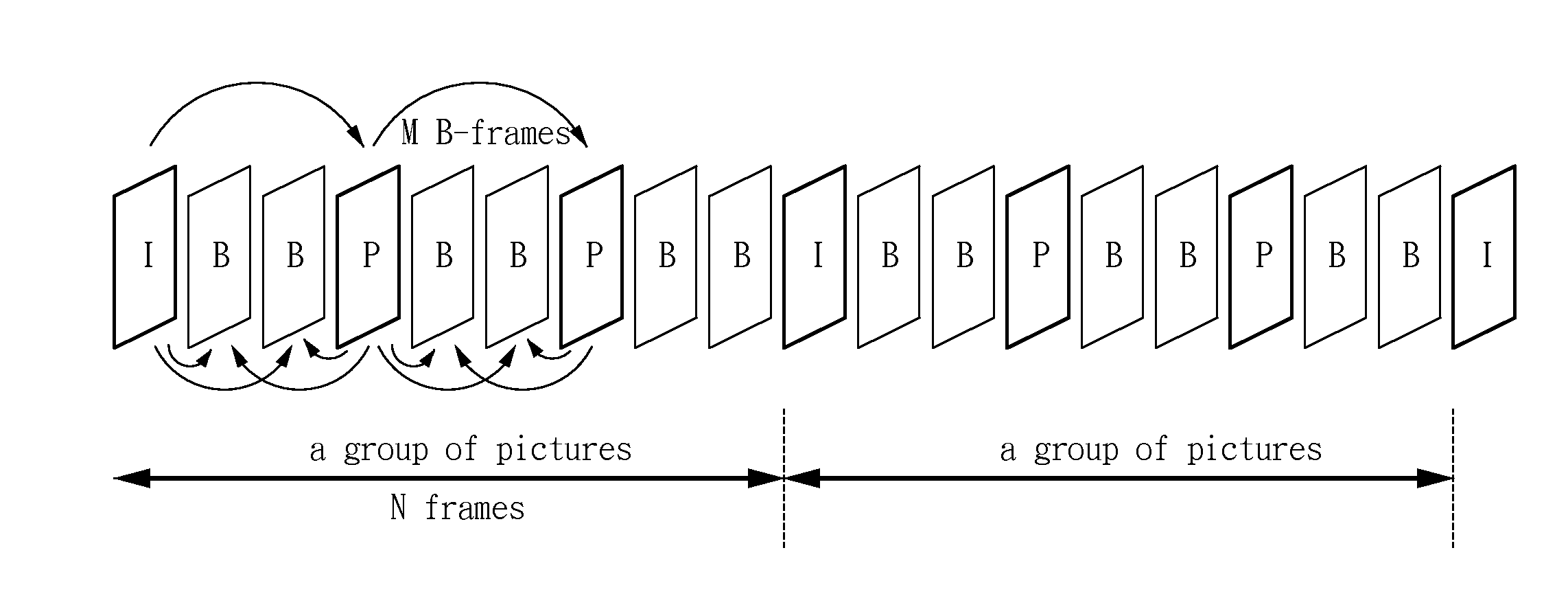
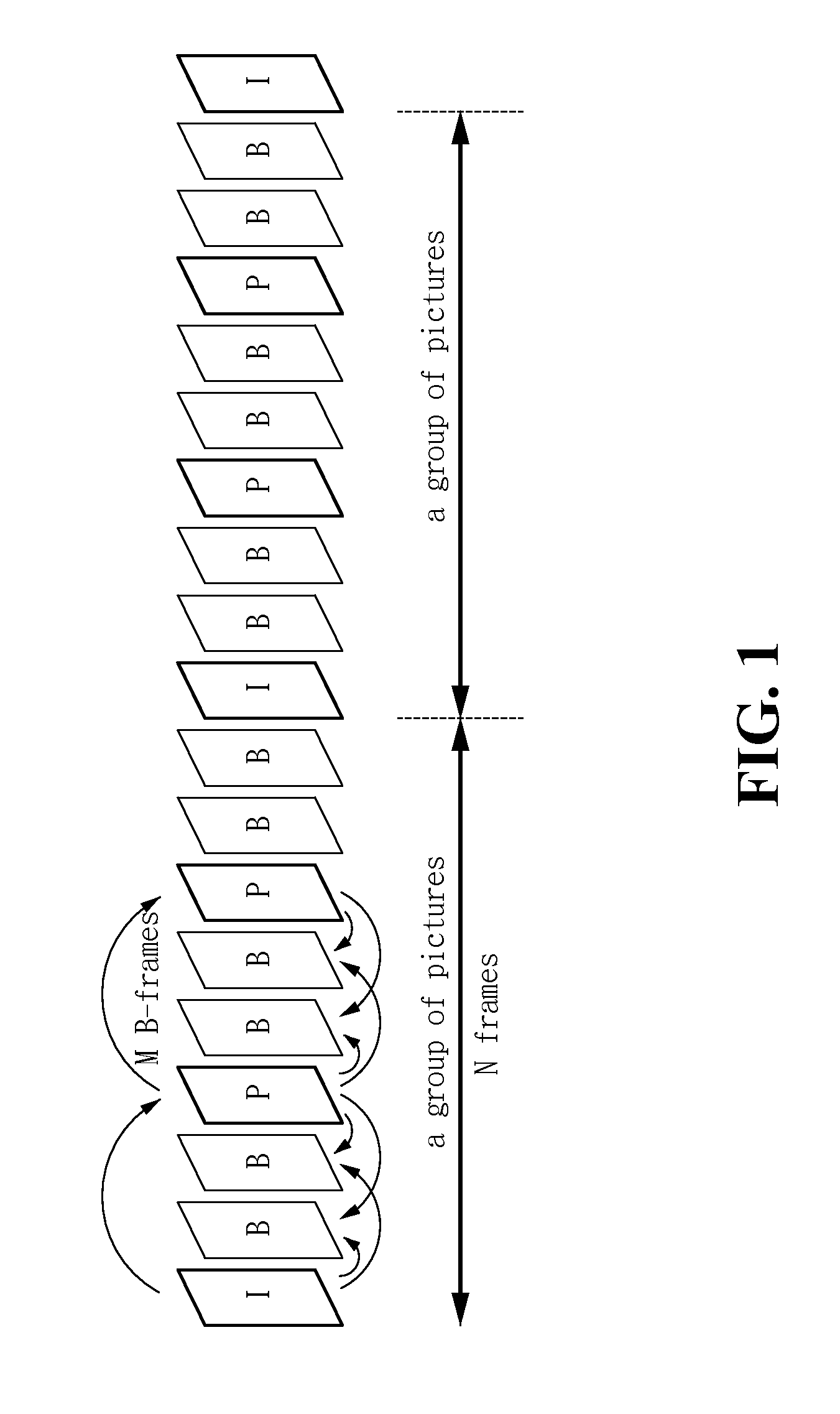
InactiveUS6980594B2Minimal costGuaranteed preservation qualityTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersGroup of picturesComputer graphics (images)
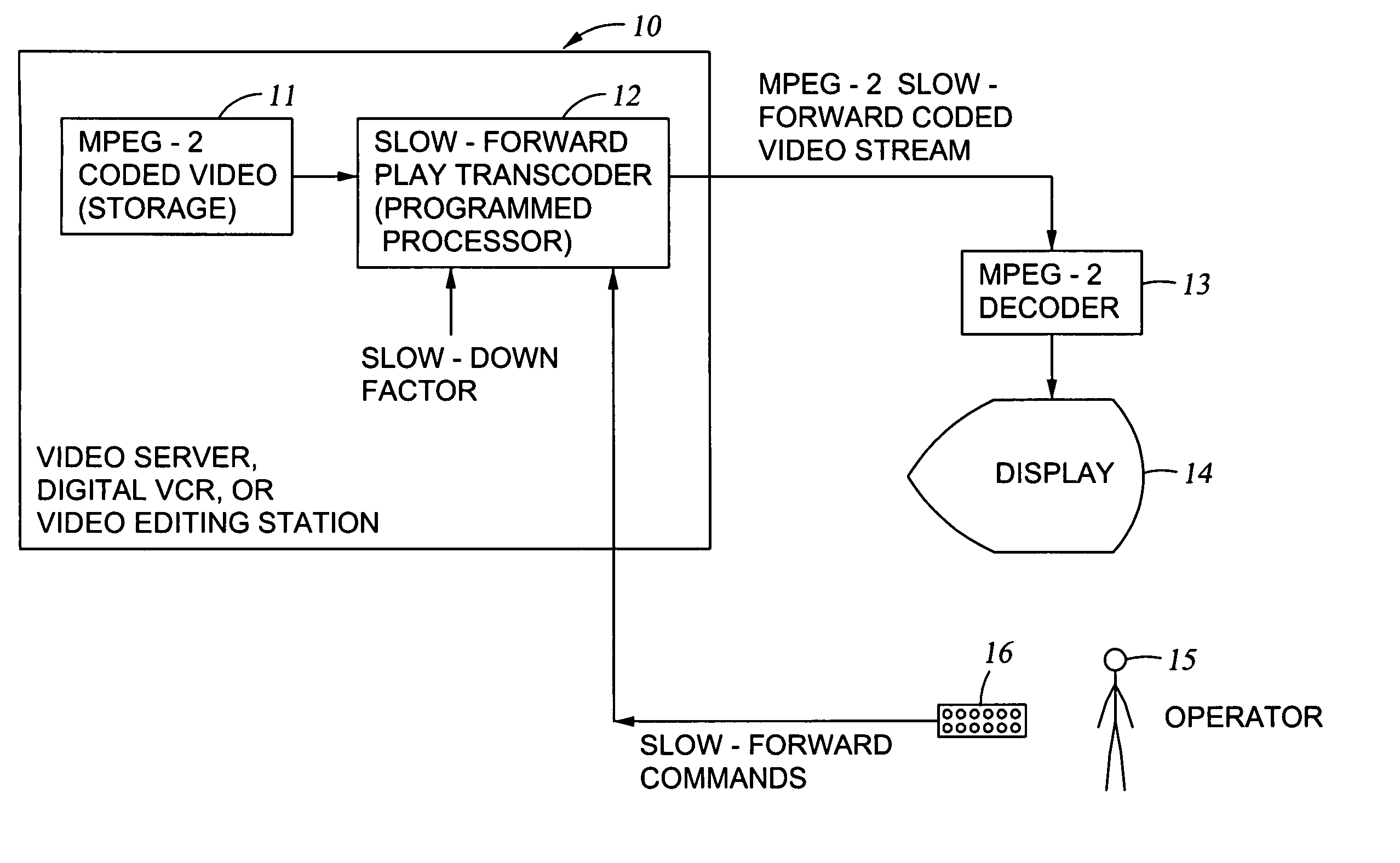
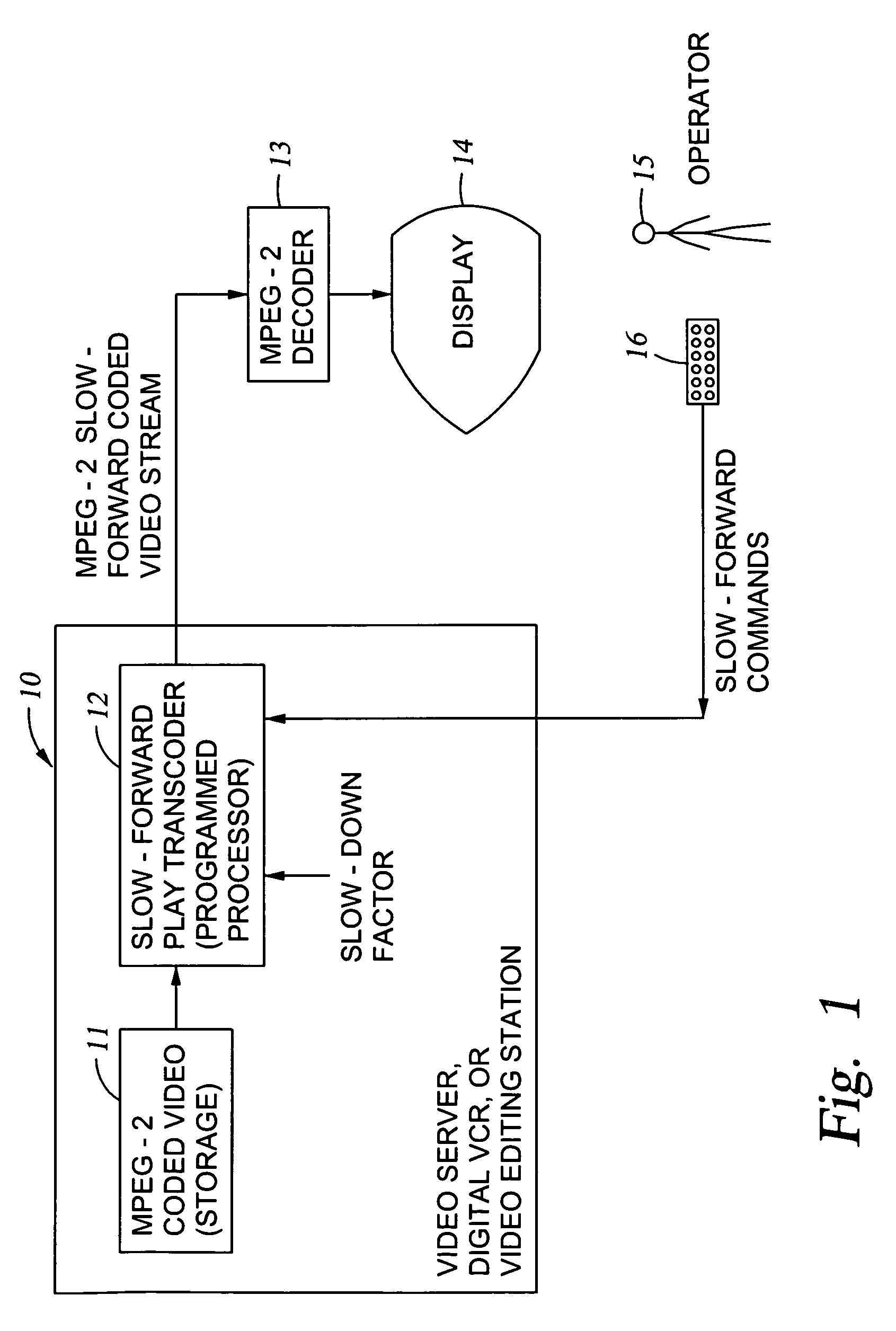
MPEG coded video data includes groups of pictures (GOPs). Each group of pictures includes one or more I-frames and a plurality of B- or P-frames. To produce an MPEG slow-forward coded video stream, the coding type of each frame in the MPEG coded video data is identified, and freeze frames are inserted as a predefined function of the identified coding type and as a predefined function of a desired slow down factor. In a preferred implementation, for a slow-down factor of n, for each original I- or P-frame, (n−1) backward-predicted freeze frames are inserted, and for each original B-frame, (n−1) copies of the original B-frames are added, and a selected amount of padding is added to each copy of each original B-frame in order to obtain a normal play bit rate and avoid video buffer overflow or underflow.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
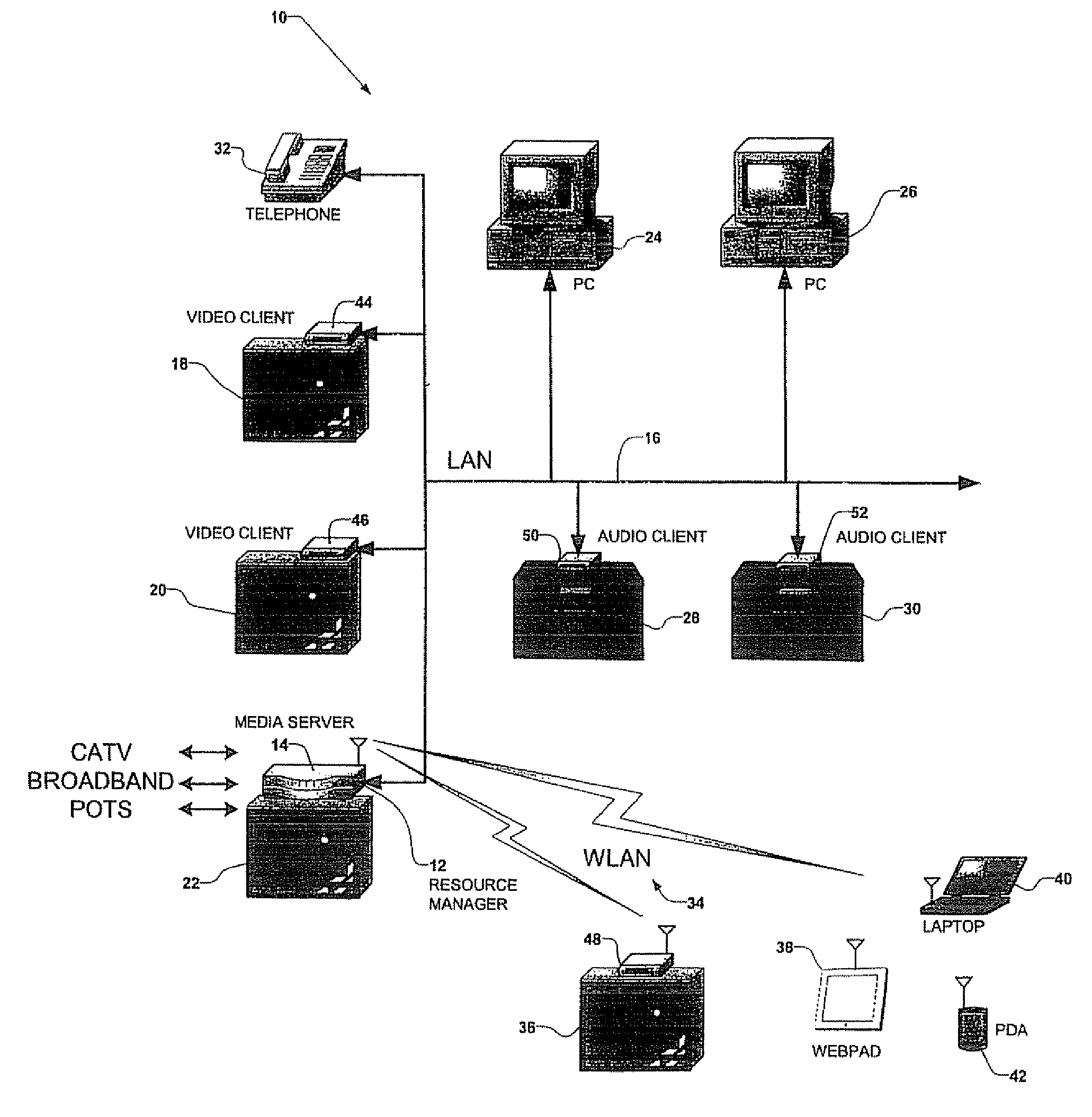
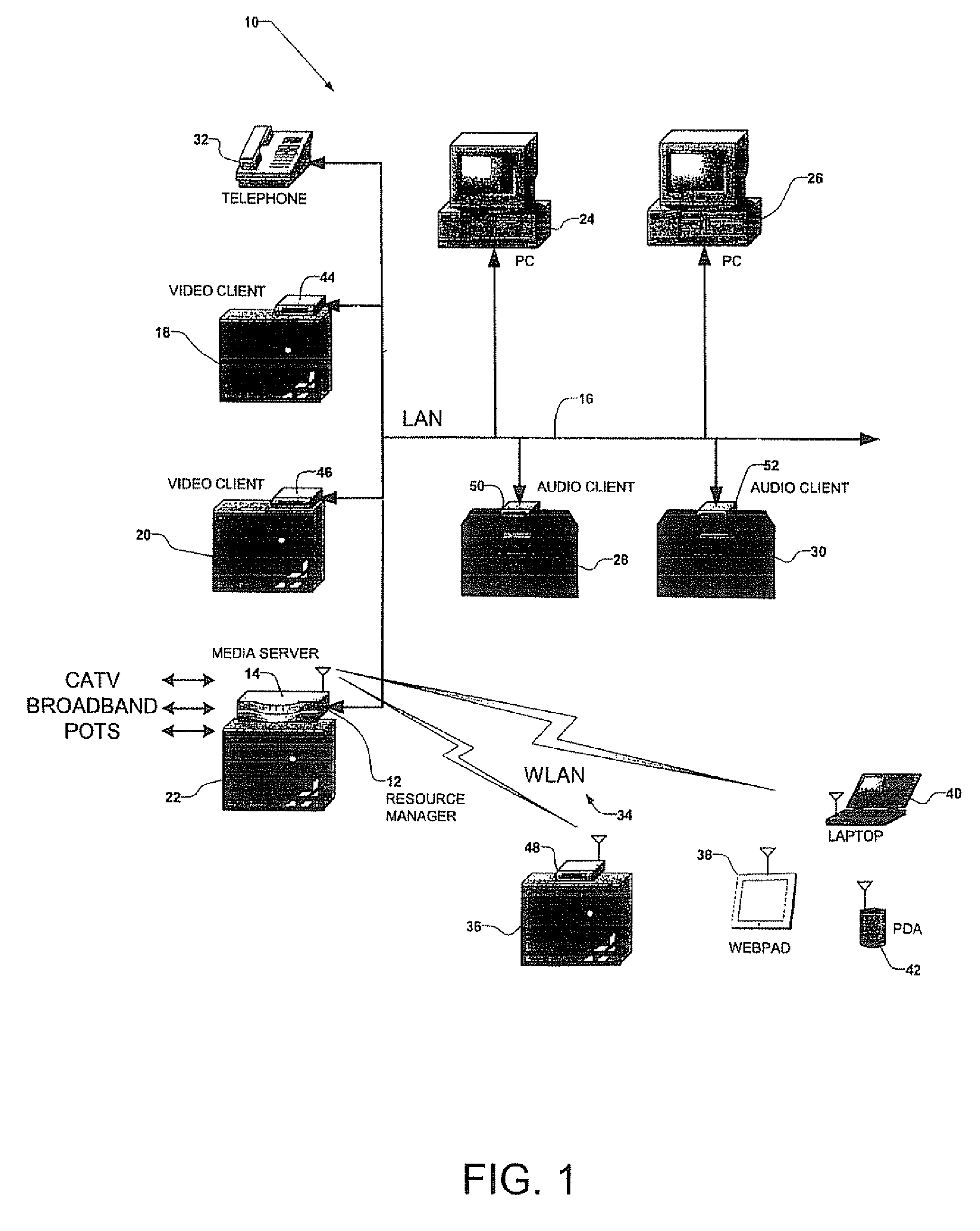
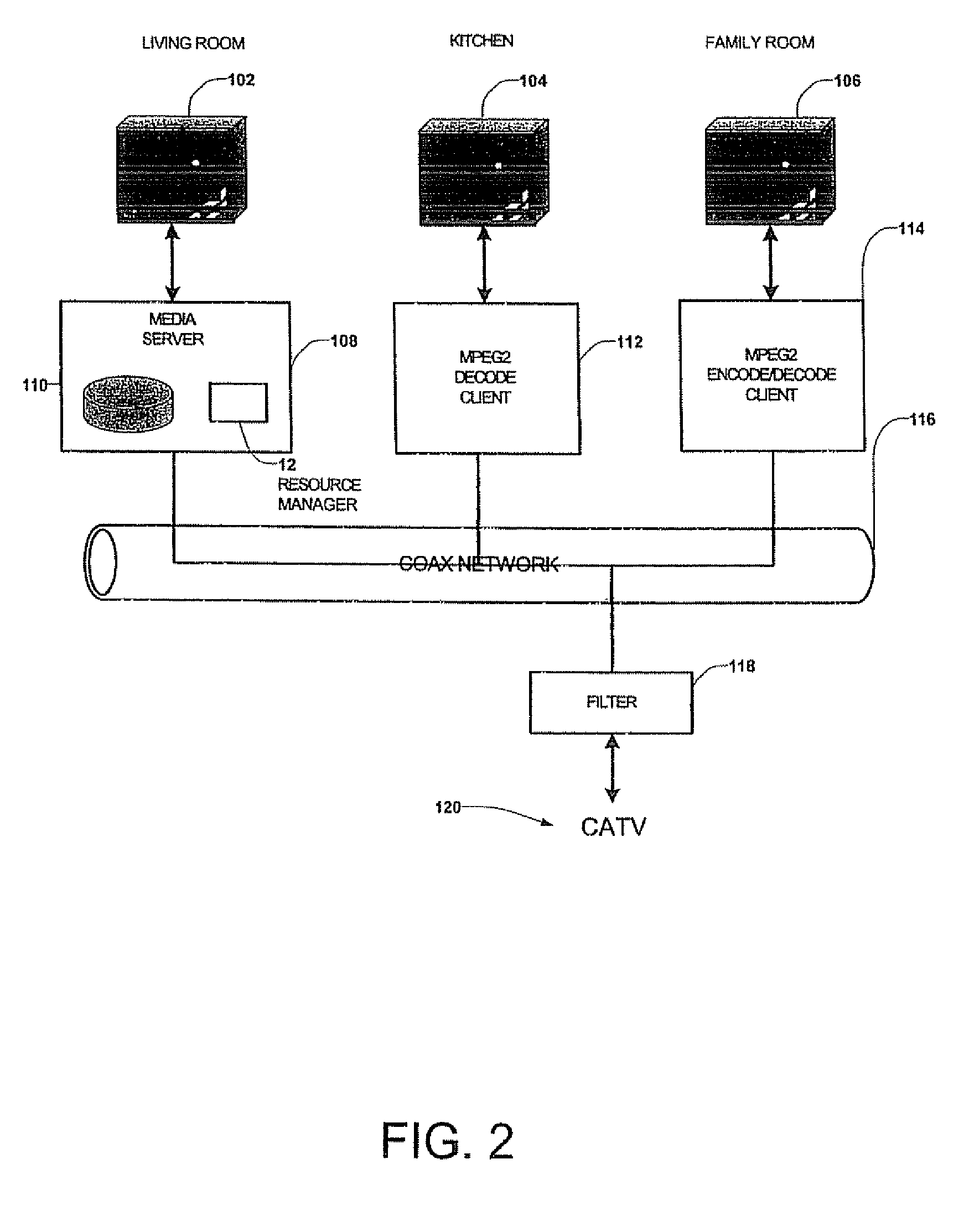
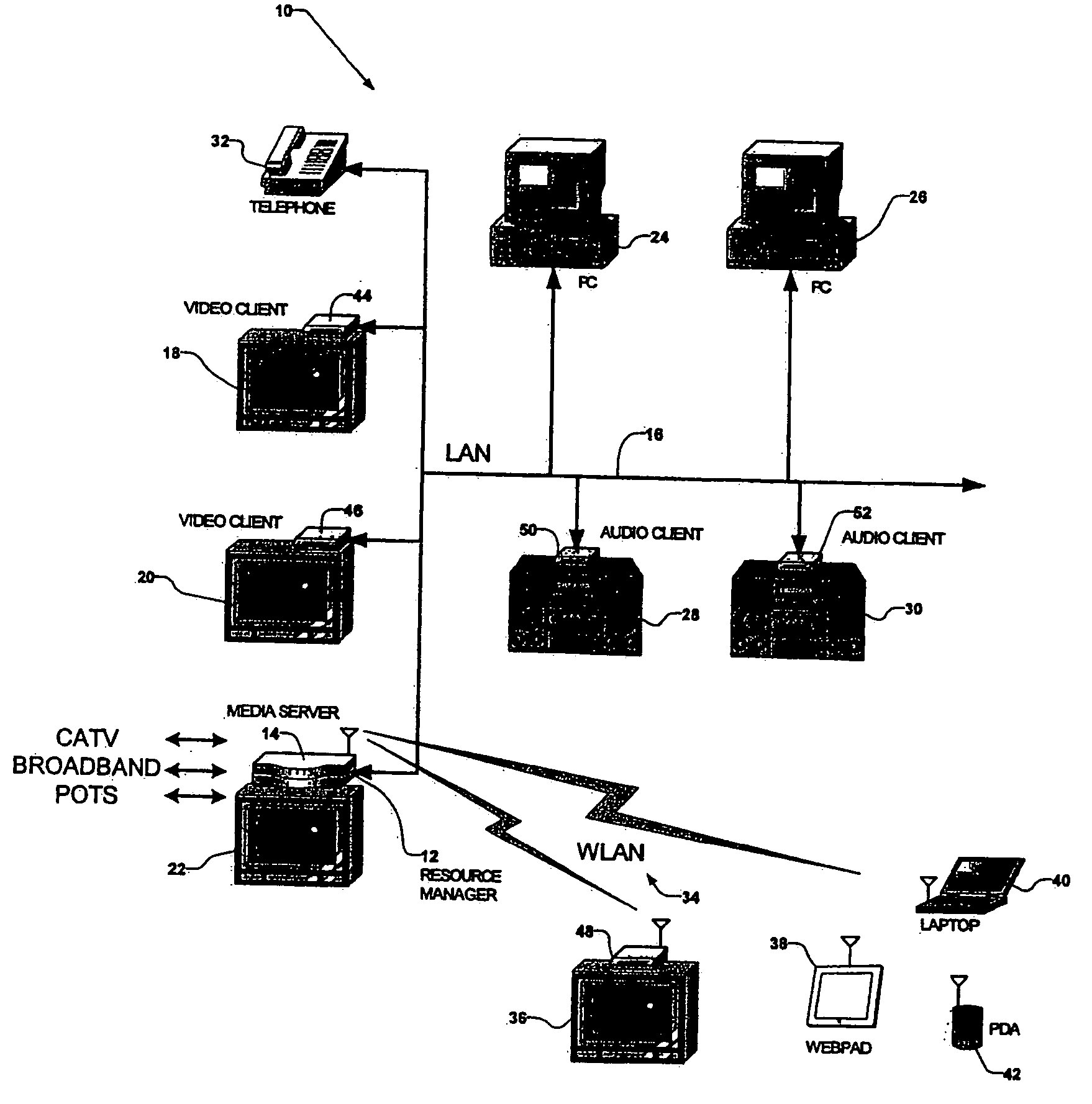
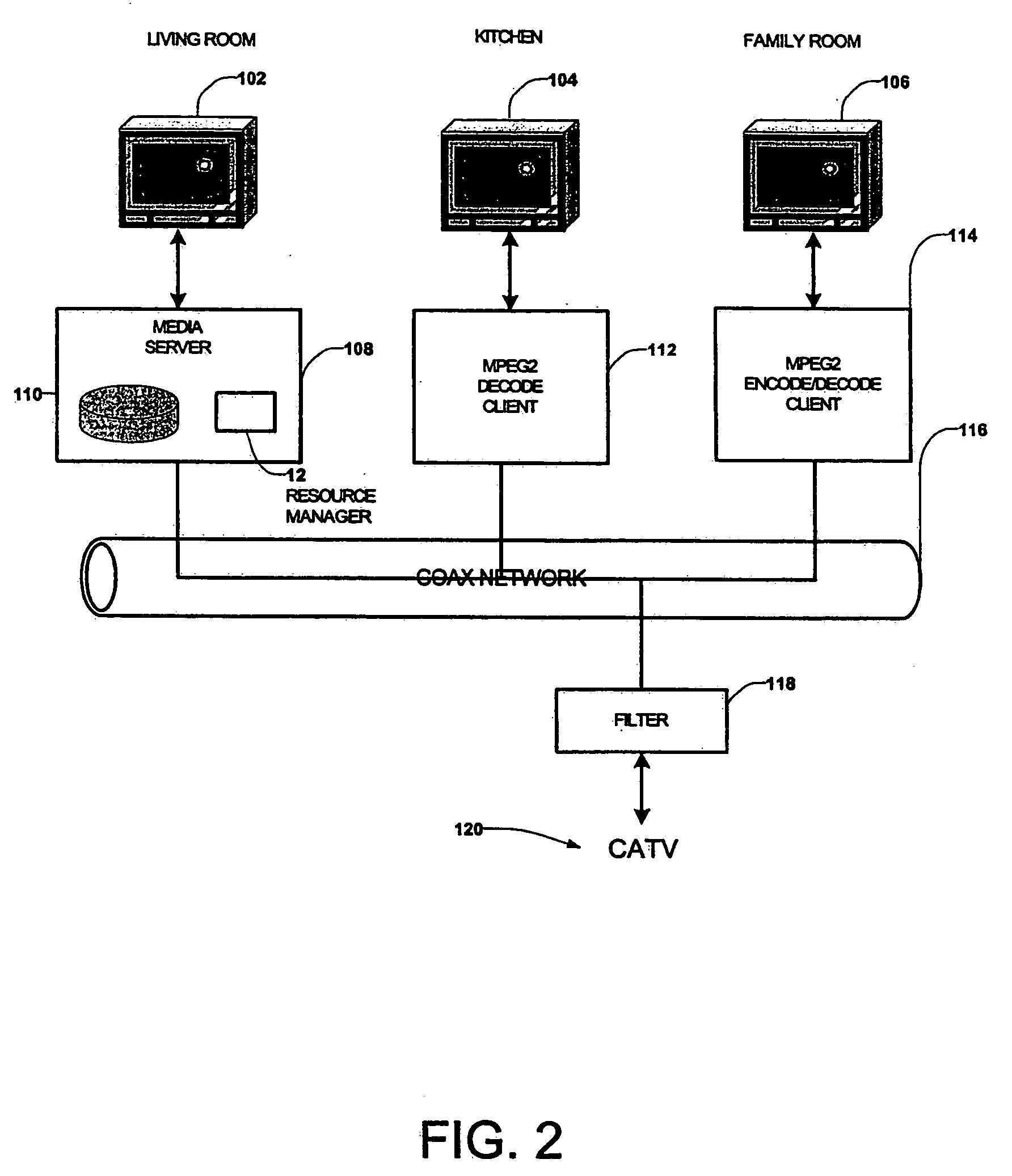
Centralized Resource Manager With Power Switching System
InactiveUS20070226344A1Overcome disadvantagesDigital computer detailsTransmissionPower switchingOutput device
A centralized resource manager for distributed networks manages resources available on the network, such as network bandwidth, CPU allocation, TV tuners, MPEG encoders and decoders, disk bandwidth, and input / output devices. The centralized resource manager also allocates the resources of network clients and a network-associated media server, in response to requests for media services via the distributed network. The centralized resource manager may include means for discovering when devices are added or removed from the network; a current, IR, or electromagnetic field sensing system for determining when video devices are turned off so that resources associated with any device not in use may be reallocated elsewhere; or a power switching system for controlling the ON or OFF state of such devices so that resources associated with any device in the OFF state may be reallocated elsewhere.
Owner:BUSINESS OBJECTS
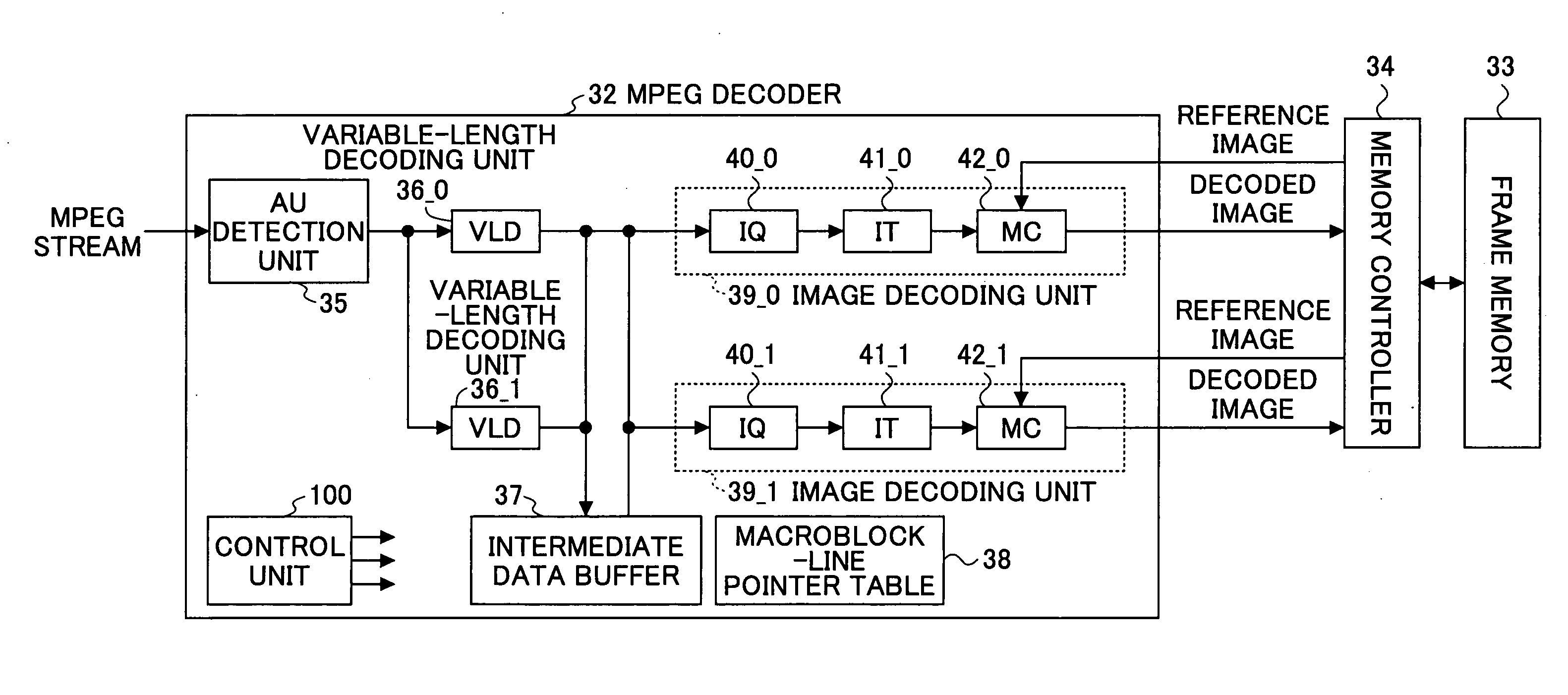
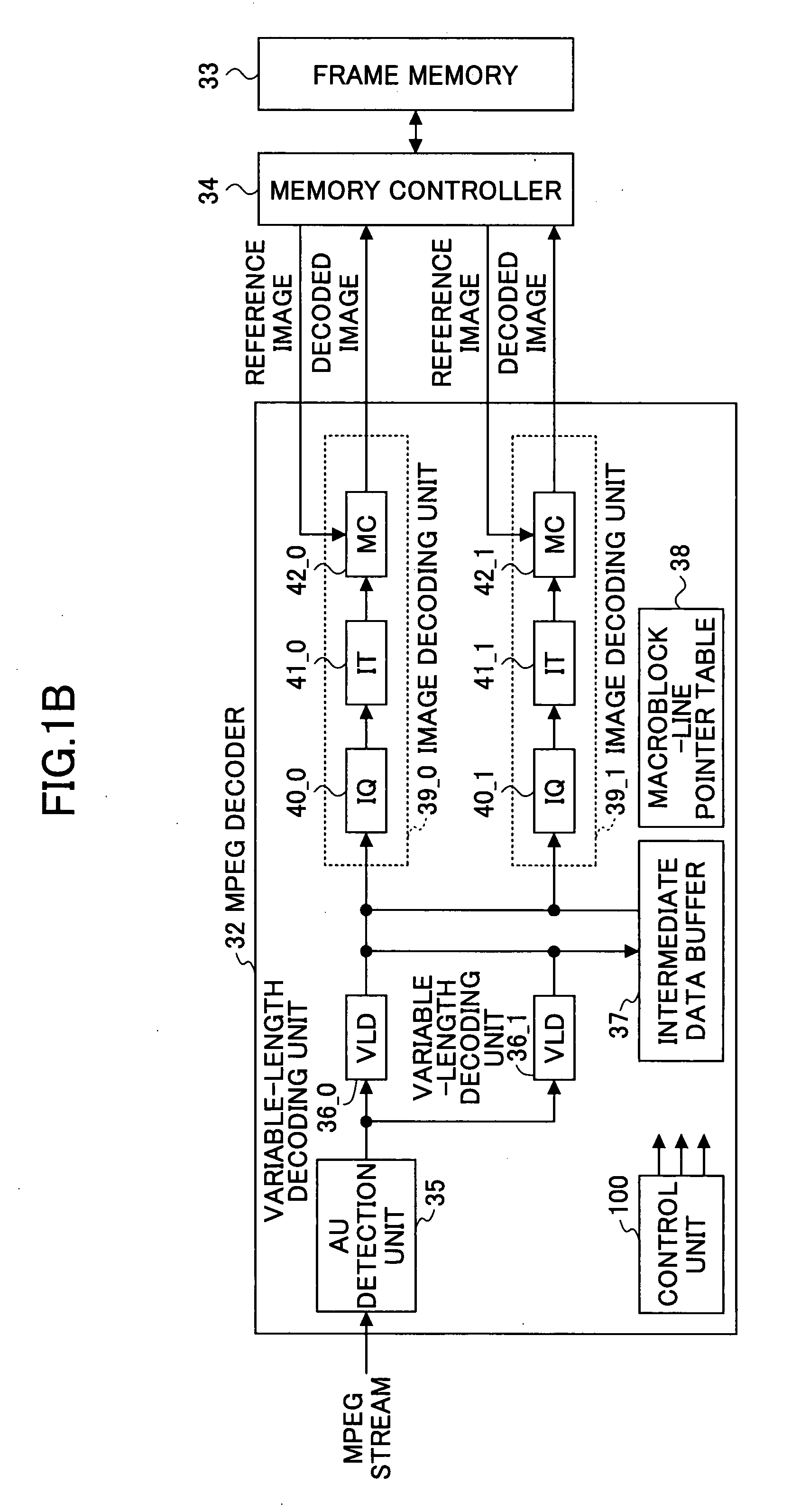
MPEG decoder and MPEG encoder
ActiveUS20080063082A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareVariable length
A moving picture decoding apparatus includes one or more variable-length decoding units, a data buffer configured to store data output from the one or more variable-length decoding units, and a plurality of image decoding units configured to read the data from the data buffer and to perform image decoding the data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Flexible use of MPEG encoded images
InactiveUS20060256865A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG encodingImage system
Systems and methods for encoding a sub-image, using conventional MPEG encoding technique, to generate a special image file that is smaller than the equivalent full-frame image file. This special image file can be used to regenerate any of a multiplicity of full-sized encoded image files, each of which results in the display of the sub-frame image at one of a multiplicity of positions within the full-sized image frame.
Owner:ENSEQUENCE
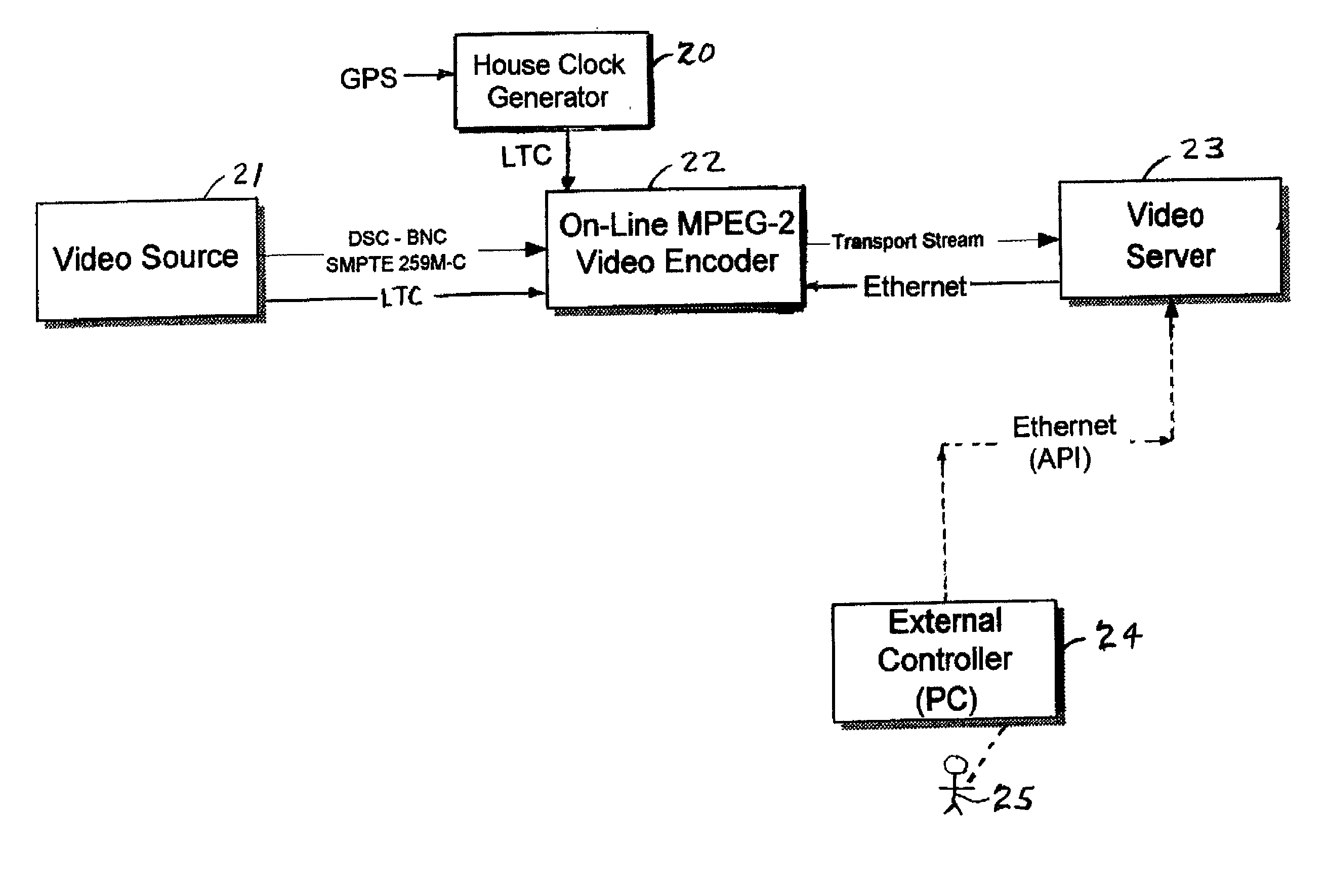
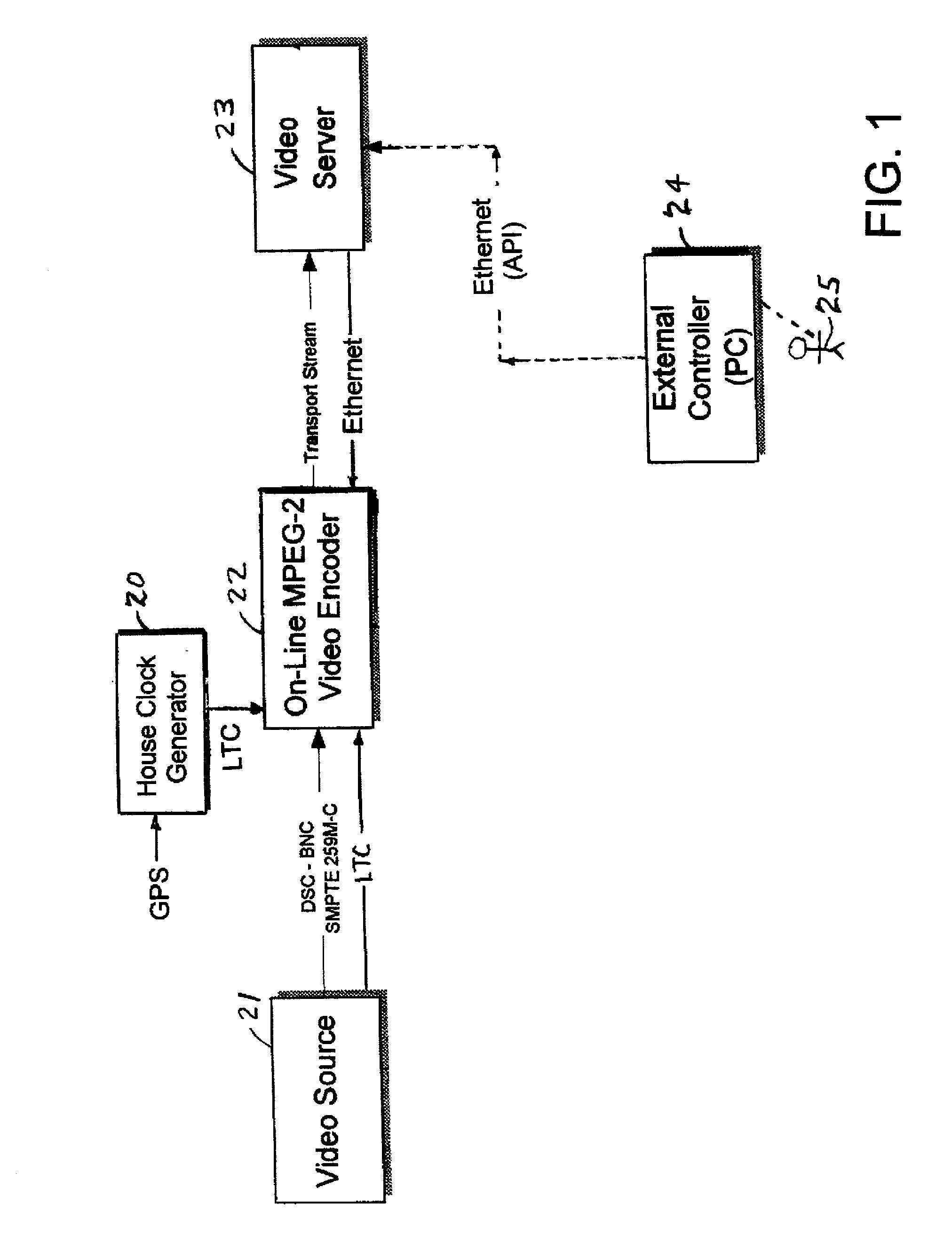
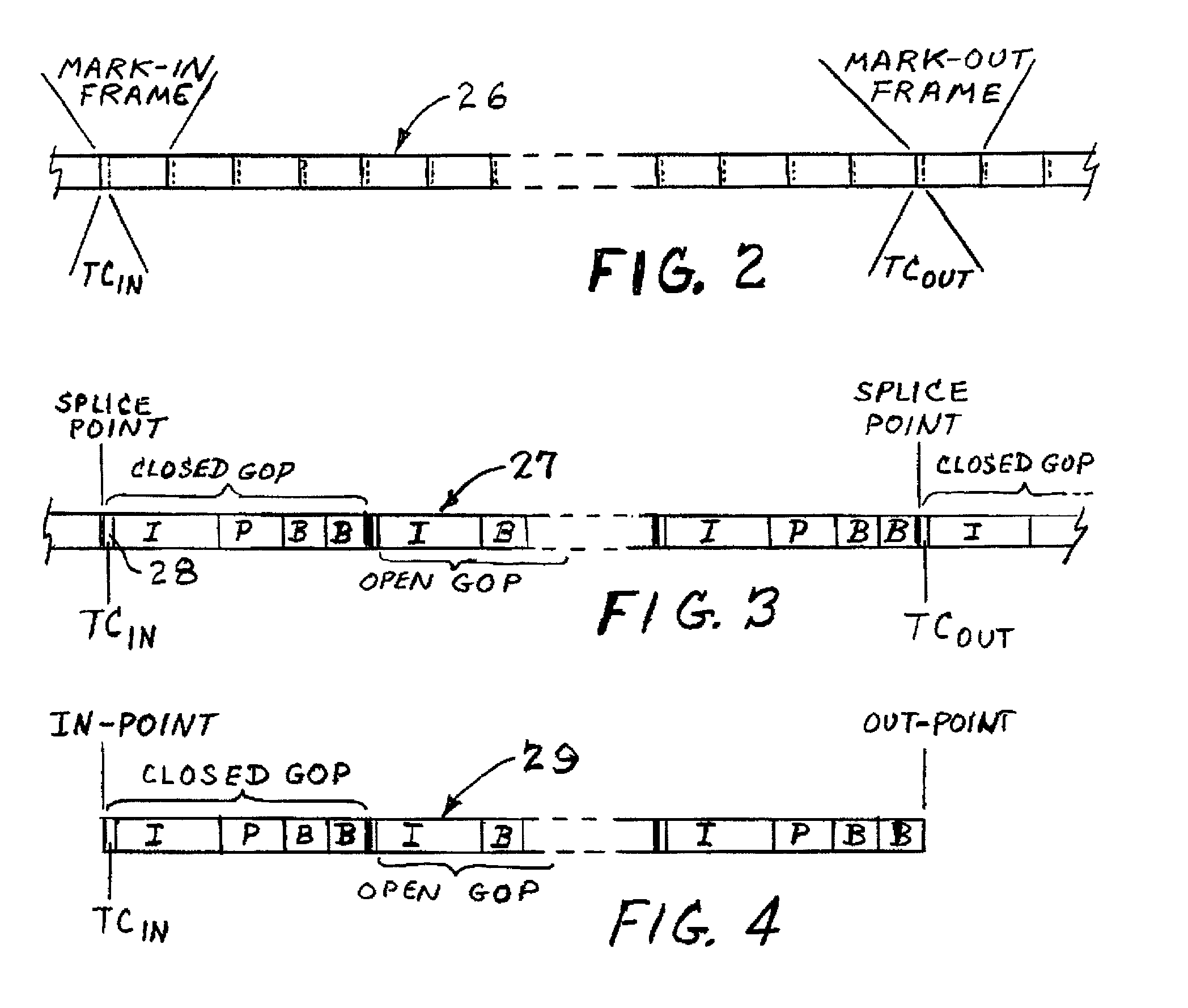
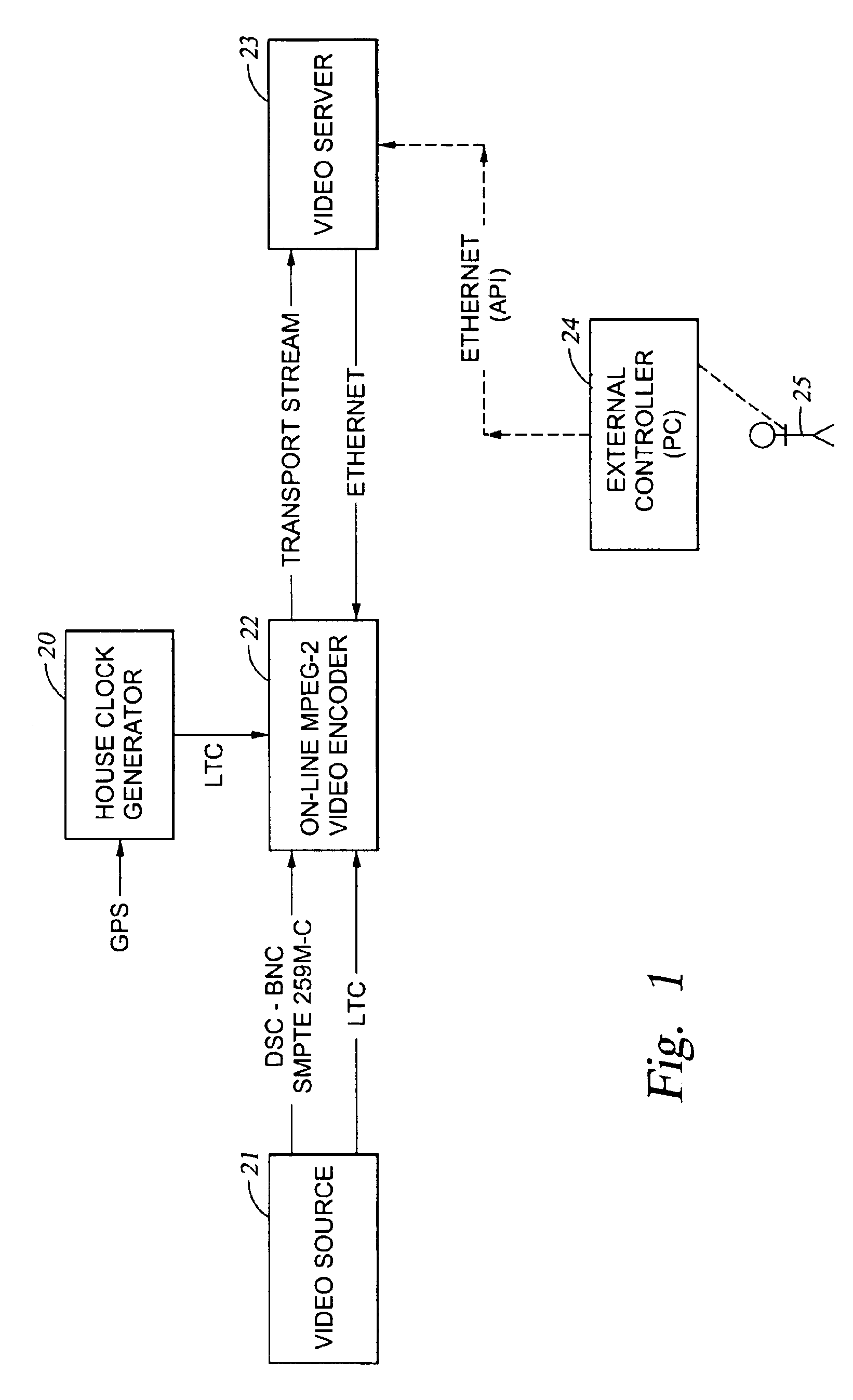
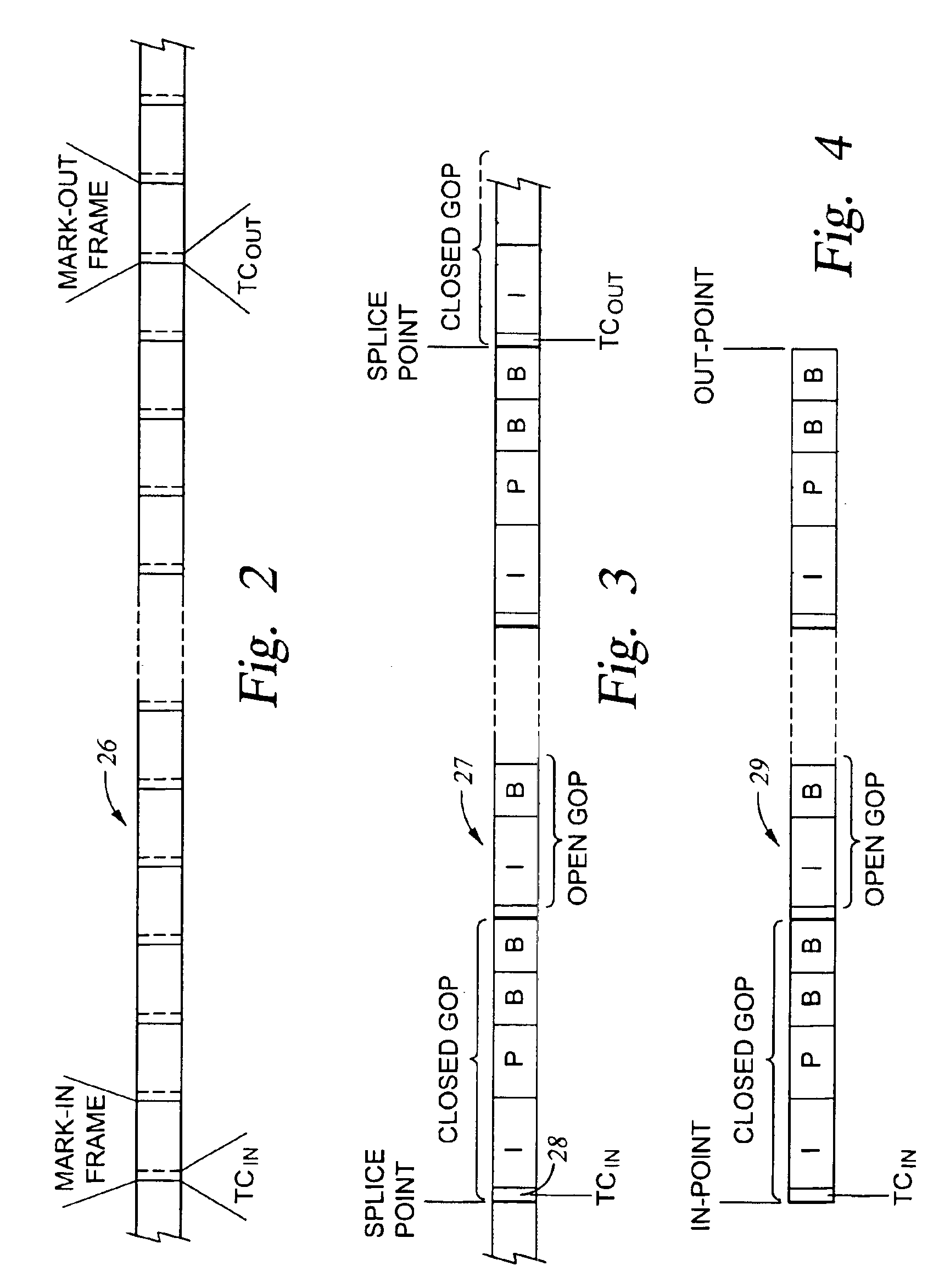
MPEG encoder control protocol for on-line encoding and MPEG data storage
ActiveUS20020172281A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Remote control
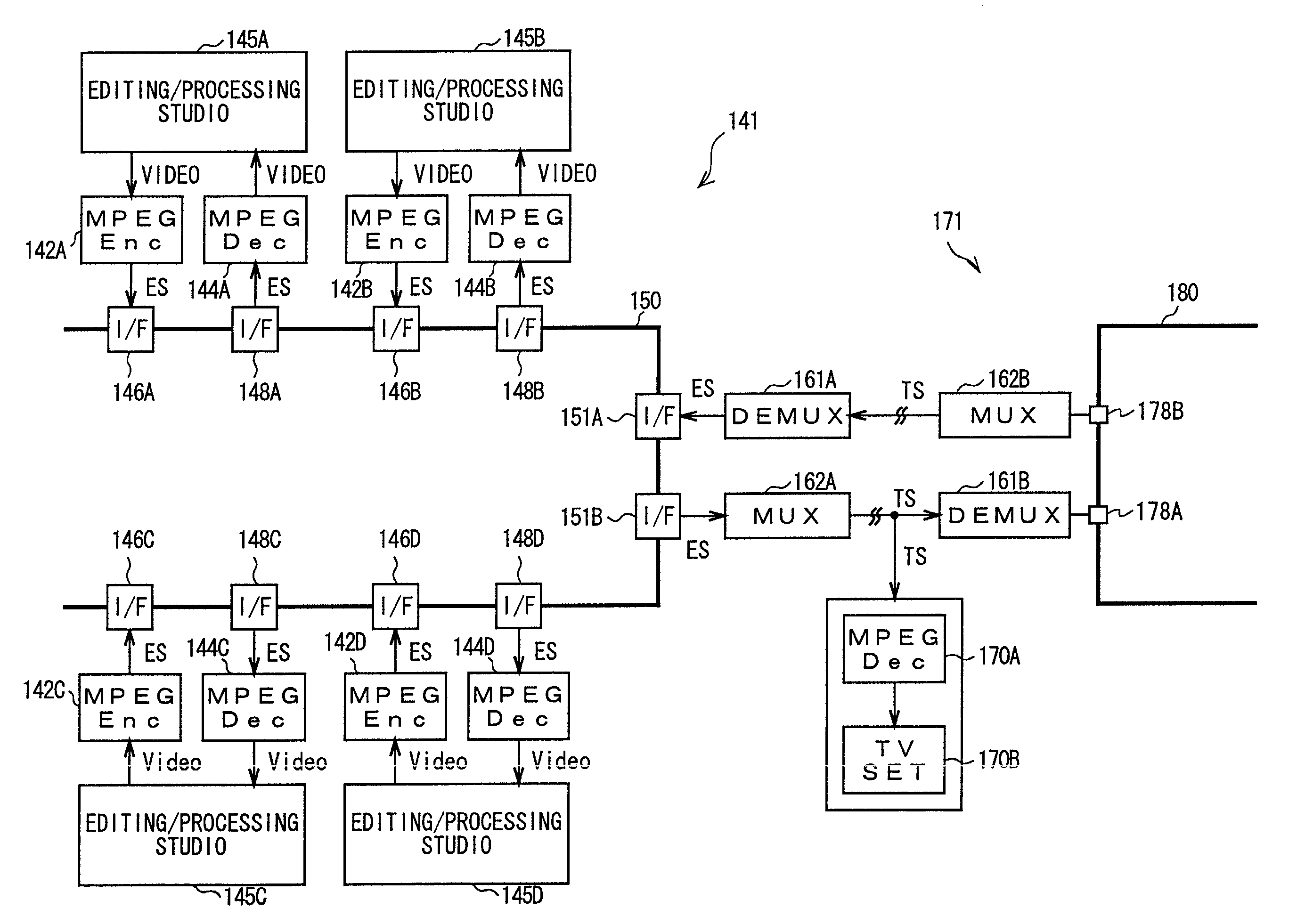
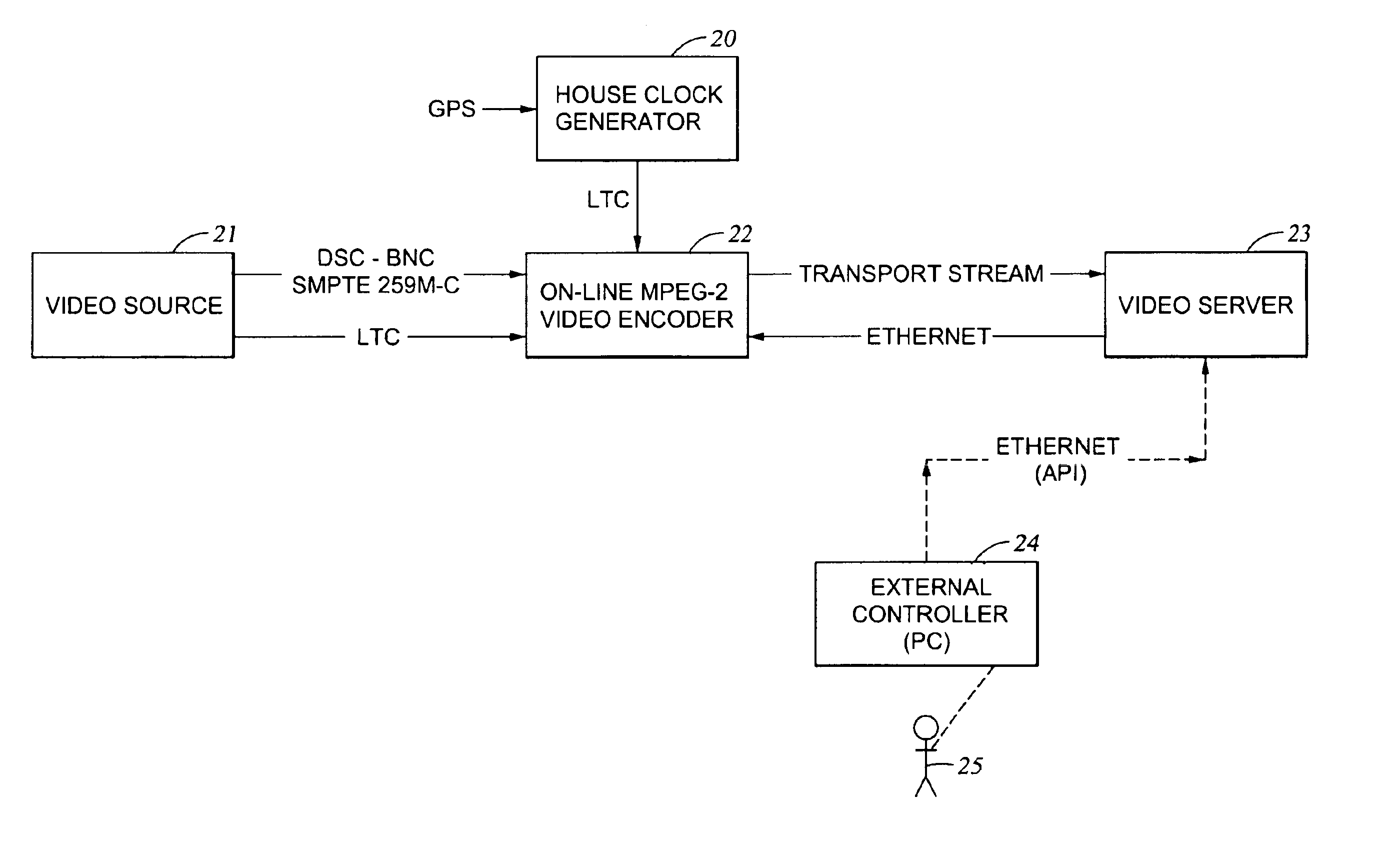
Coded video from an on-line MPEG video encoder is stored as a clip in a video server or is otherwise received in the video server and prepared or used for splicing. In order to reduce apparent frame inaccuracy that may result from the splicing process, the on-line MPEG video encoder and the server are coordinated so that the group-of-picture (GOP) structure in the encoder provides specified In-points and Out-points that are valid and desirable for splicing. An encoder control protocol is also provided for remote control of the on-line MPEG video encoder in order to coordinate the on-line MPEG video encoder with the video server.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Optical disk for high resolution and general video recording, optical disk reproduction apparatus, optical disk recording apparatus, and reproduction control information generation apparatus
InactiveUS20050180735A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionVideo recording
The present invention has an objective of realizing compatibility of an optical disk having a high resolution video signal recorded thereon and a system for reproducing the optical disk, with a conventional system for producing a standard resolution video signal. A high resolution video signal is divided by video division means into a main signal and a sub signal, and the main signal and the sub signal are MPEG-encoded. The stream of the main signal and the stream of the sub signal are divided into 1 GOP or more of frames. First interleave blocks 54 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the main signal and second interleave blocks 55 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the sub signal are recorded on an optical disk 1. A high resolution reproduction apparatus reproduces both the first and second interleave blocks to obtain a high resolution video output. A non-high quality picture reproduction apparatus reproduces only the first or second interleave blocks to obtain a standard resolution video output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
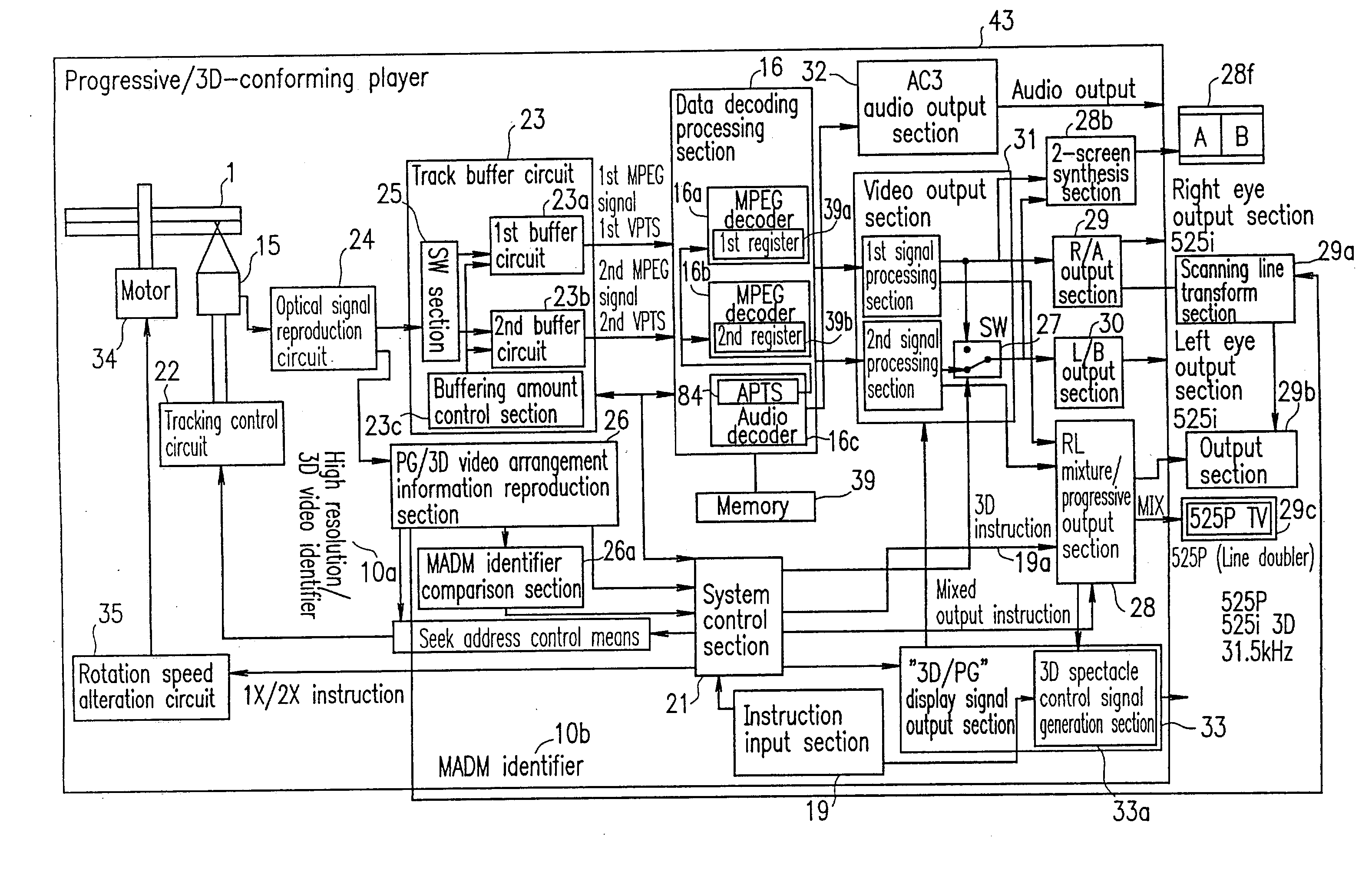
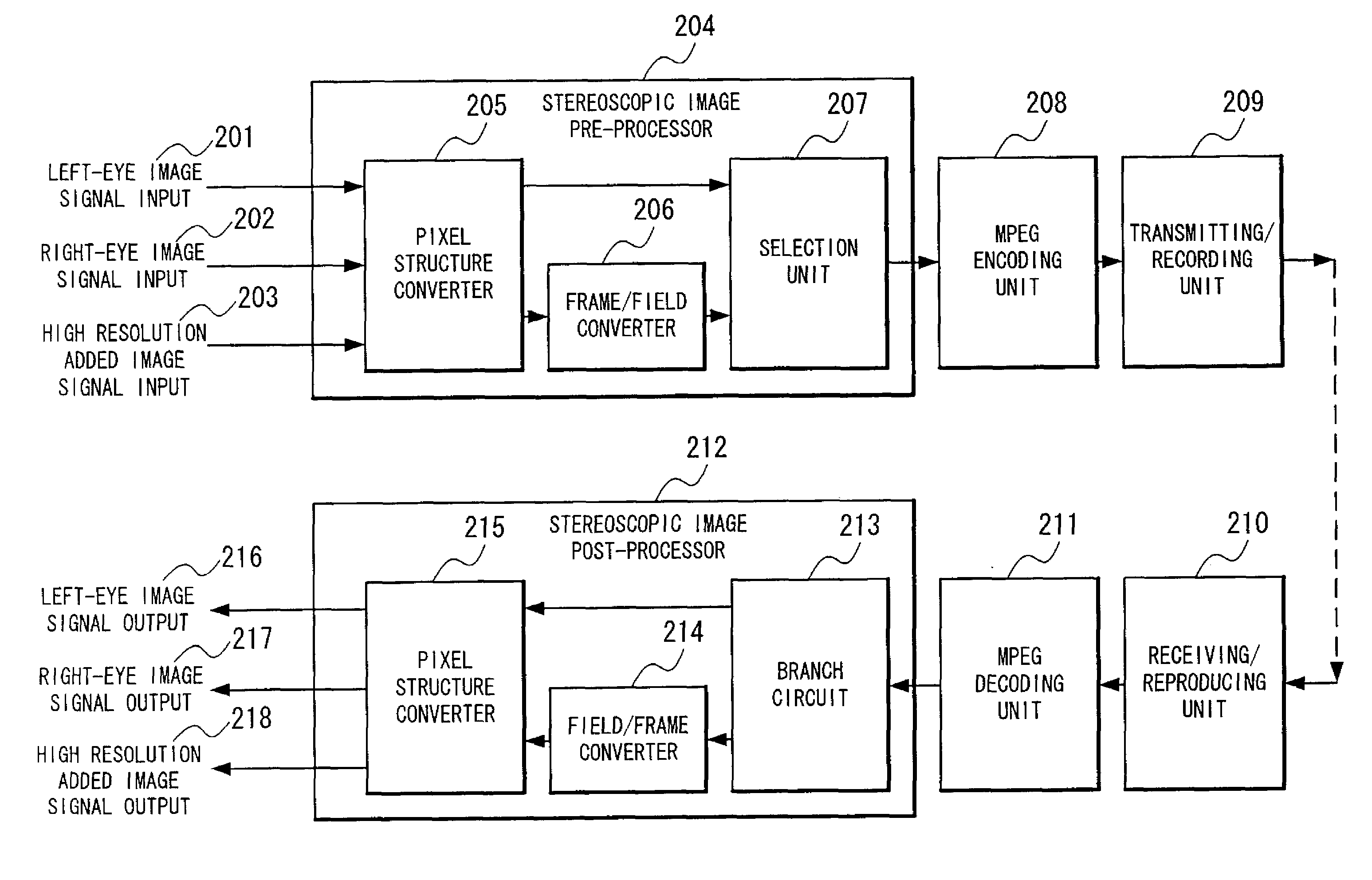
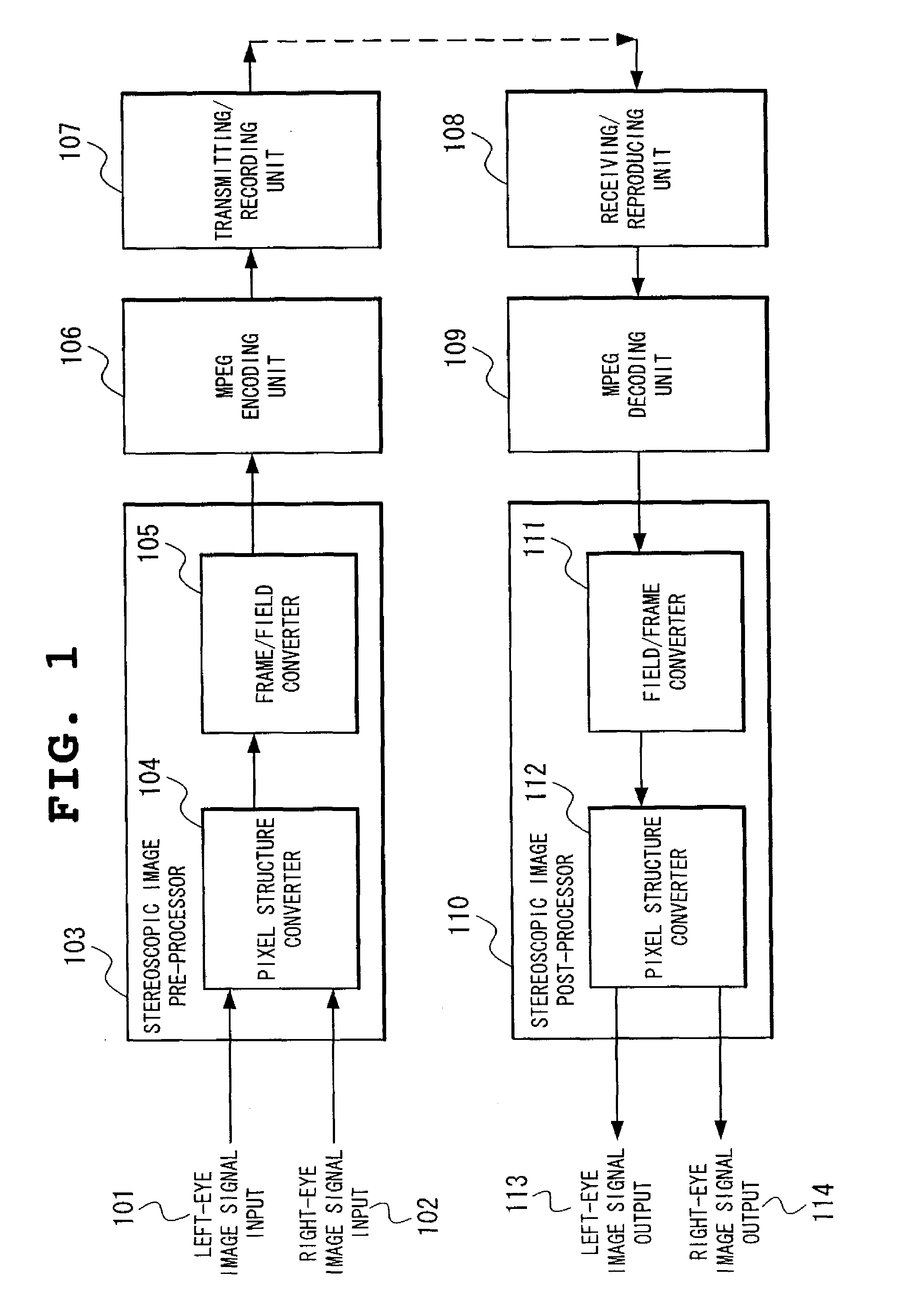
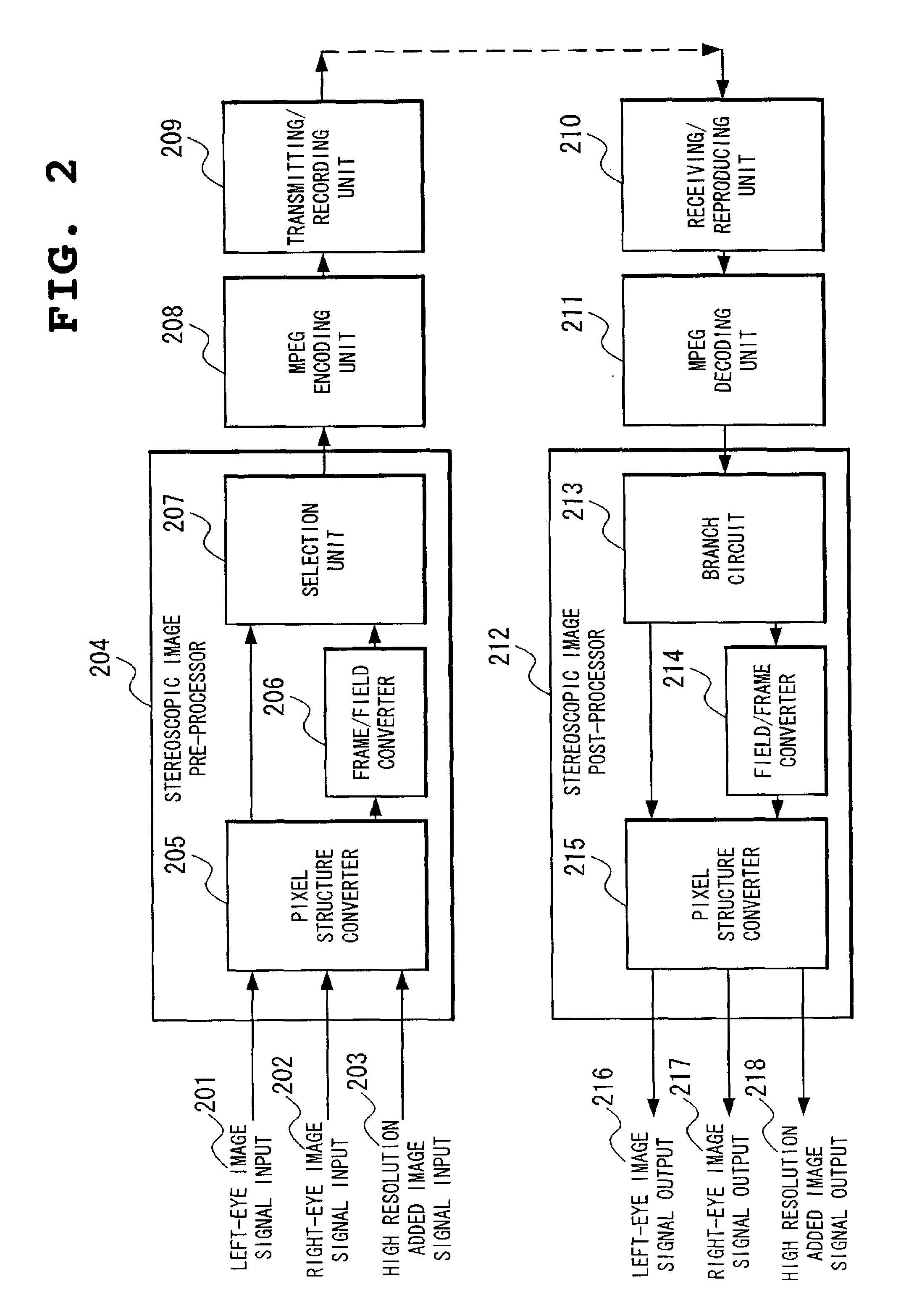
Stereoscopic image encoding and decoding device multiplexing high resolution added images
InactiveUS20080152241A1Efficiently encoding and transferring image dataEfficient codingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingMultiplexingComputer graphics (images)
A left-eye image signal and a right-eye image signal are supplied to a pixel structure converter of a stereoscopic image pre-processor, and multiplexed, so to form one image, an interlace image is formed by a frame / field converter, encoded in an MPEG format by an MPEG encoding unit, stored into a storage and transmitted outward by a transmitting / recording unit. The encoded stereoscopic image signal received from the outward and reproduced from the storage is decoded by am MPEG decoding unit after going through a receiving / reproducing unit, the interlace image is reproduced, returned to the frame image by a field / frame converter of a stereoscopic image post-processor, and reproduced as the left-eye image signal and the right-eye image signal and output by the pixel structure converter.
Owner:NEC CORP
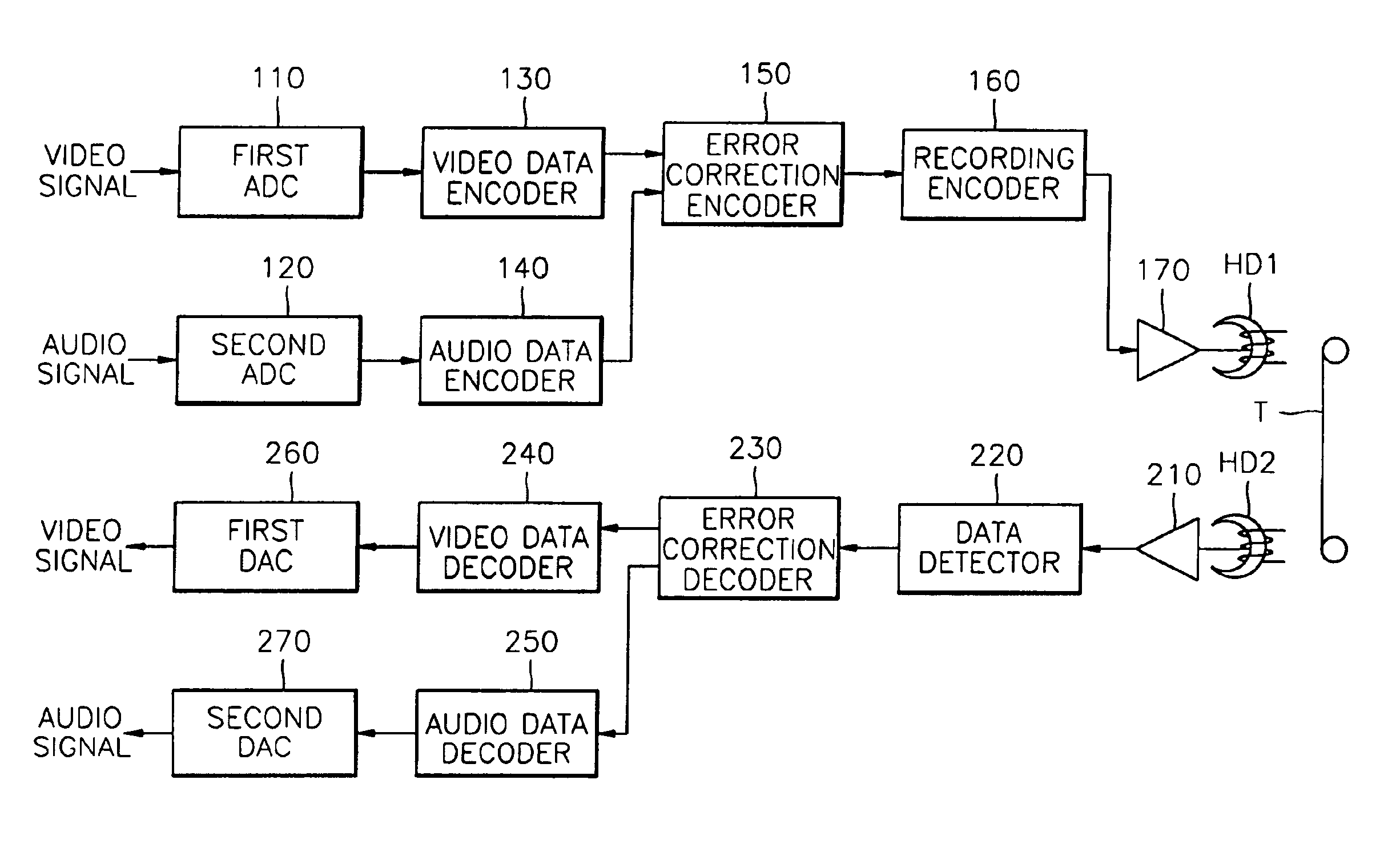
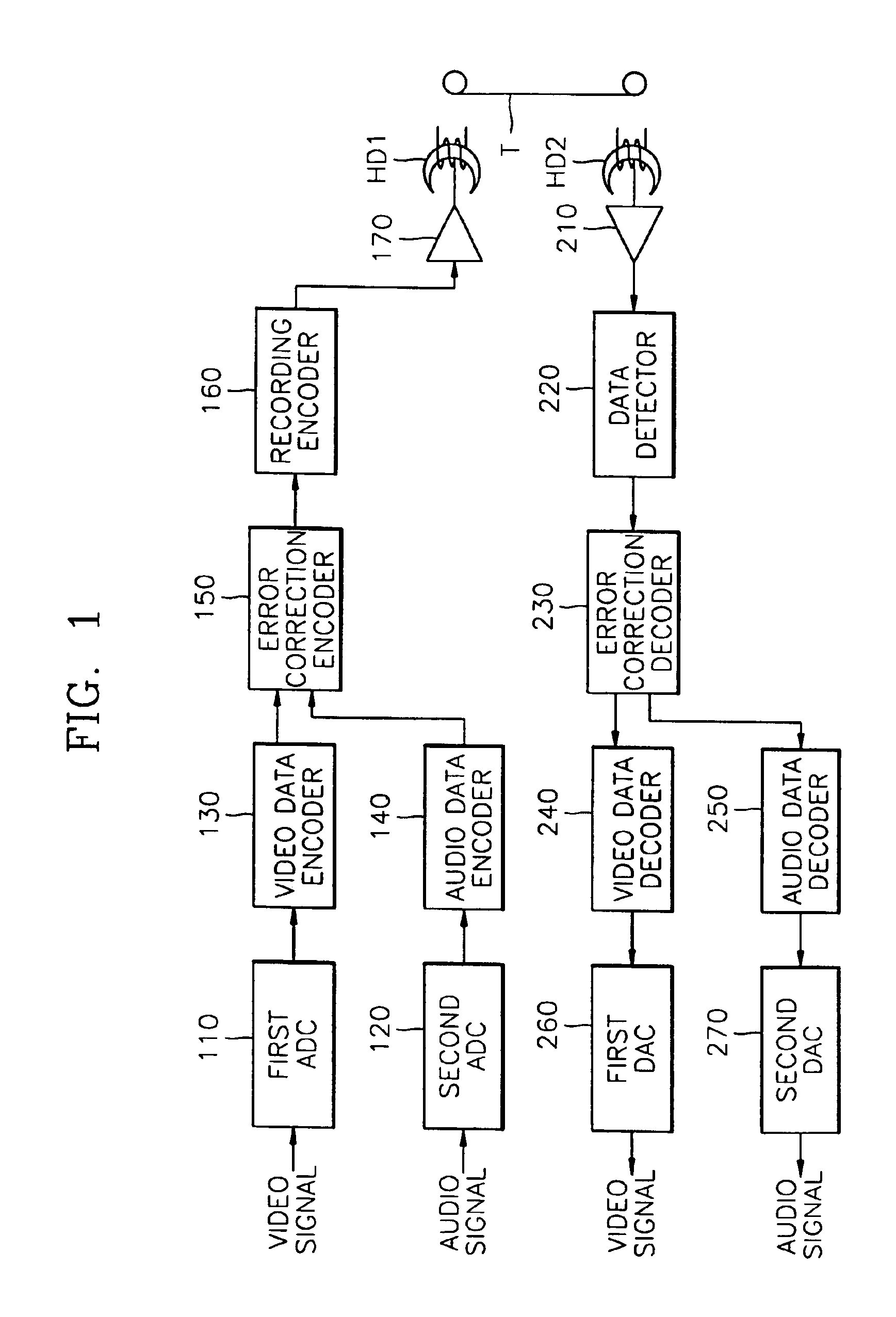
Digital recording and playback apparatus having MPEG CODEC and method therefor
InactiveUS6862402B2Increase speedTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMpeg standardsDigital recording
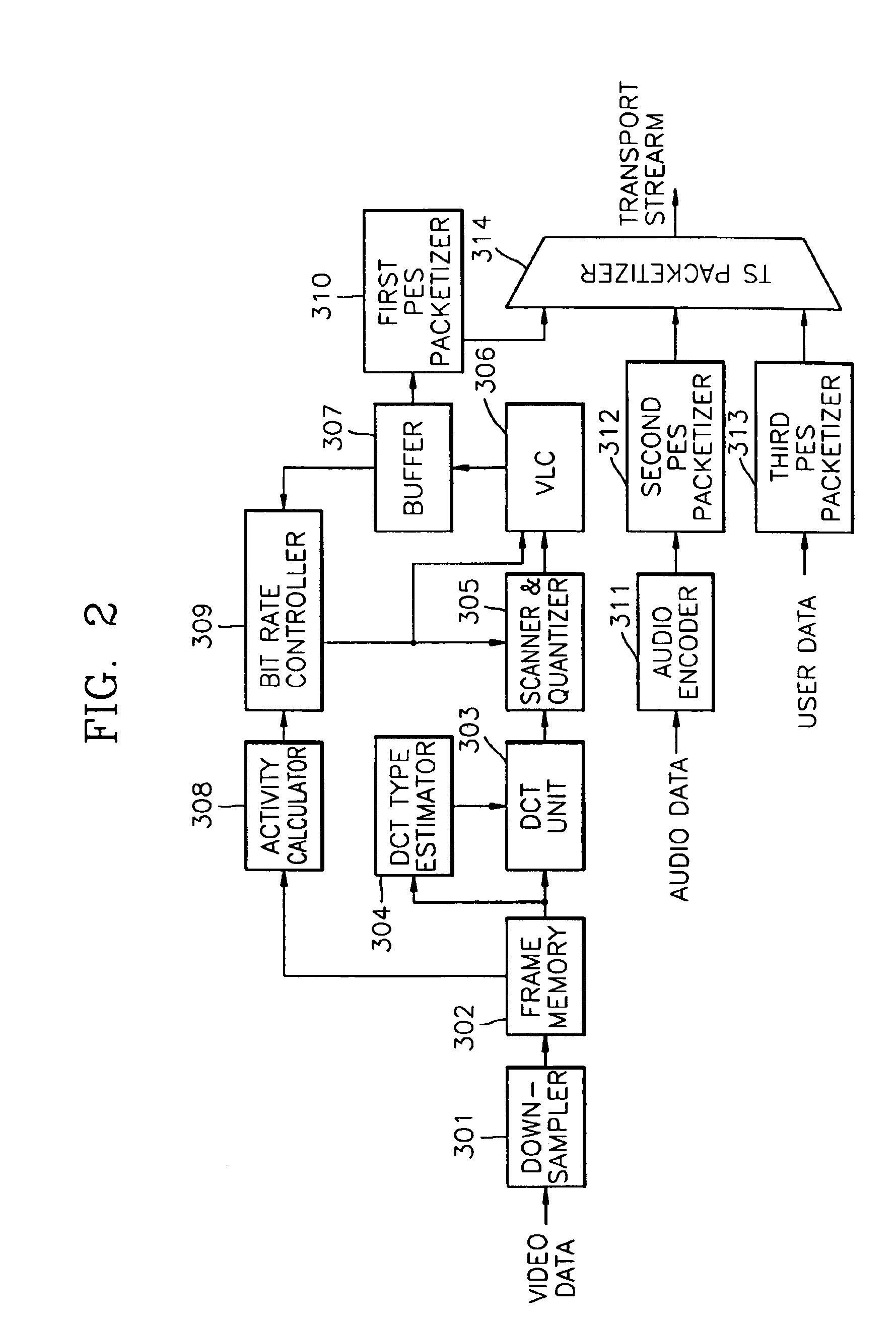
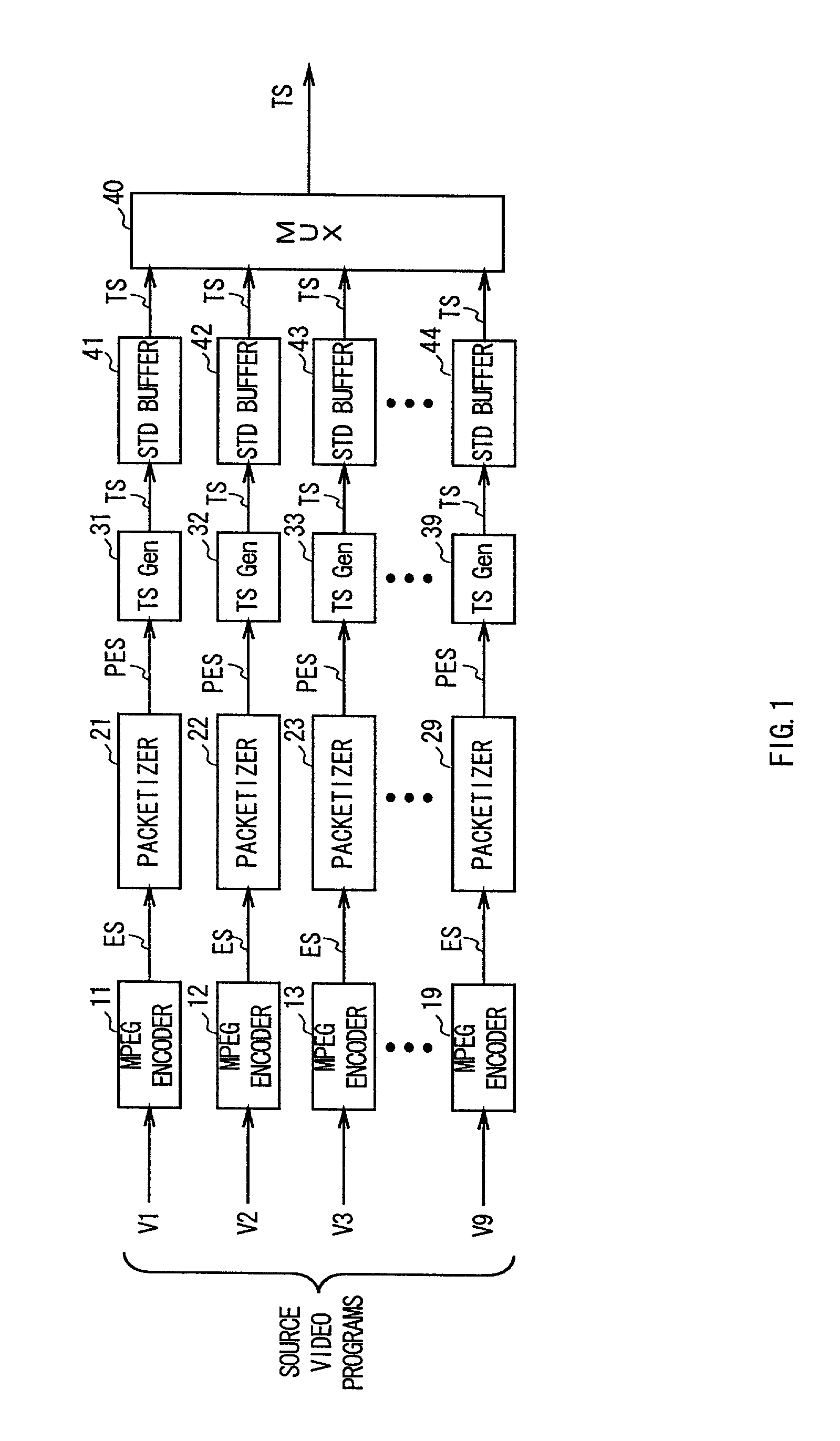
A digital recording and playback apparatus adopting an MPEG encoder and decoder, and a method thereof. The digital recording and playback apparatus includes: a first encoder for coding input video data in picture units, and outputting coded video data; a second encoder for coding input audio data and outputting coded audio data; a packetized elementary stream (PES) packetizer for packetizing the coded video data and audio data and user data into each PES, and outputting a video PES, audio PES and user PES; and a transport stream (TS) packetizer for multiplexing the video PES, audio PES and user PES into a TS. The digital recording and playback apparatus can be compatible with a digital television or multimedia applications adopting the MPEG standard, and can perform editing in picture units as well as high-speed search.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
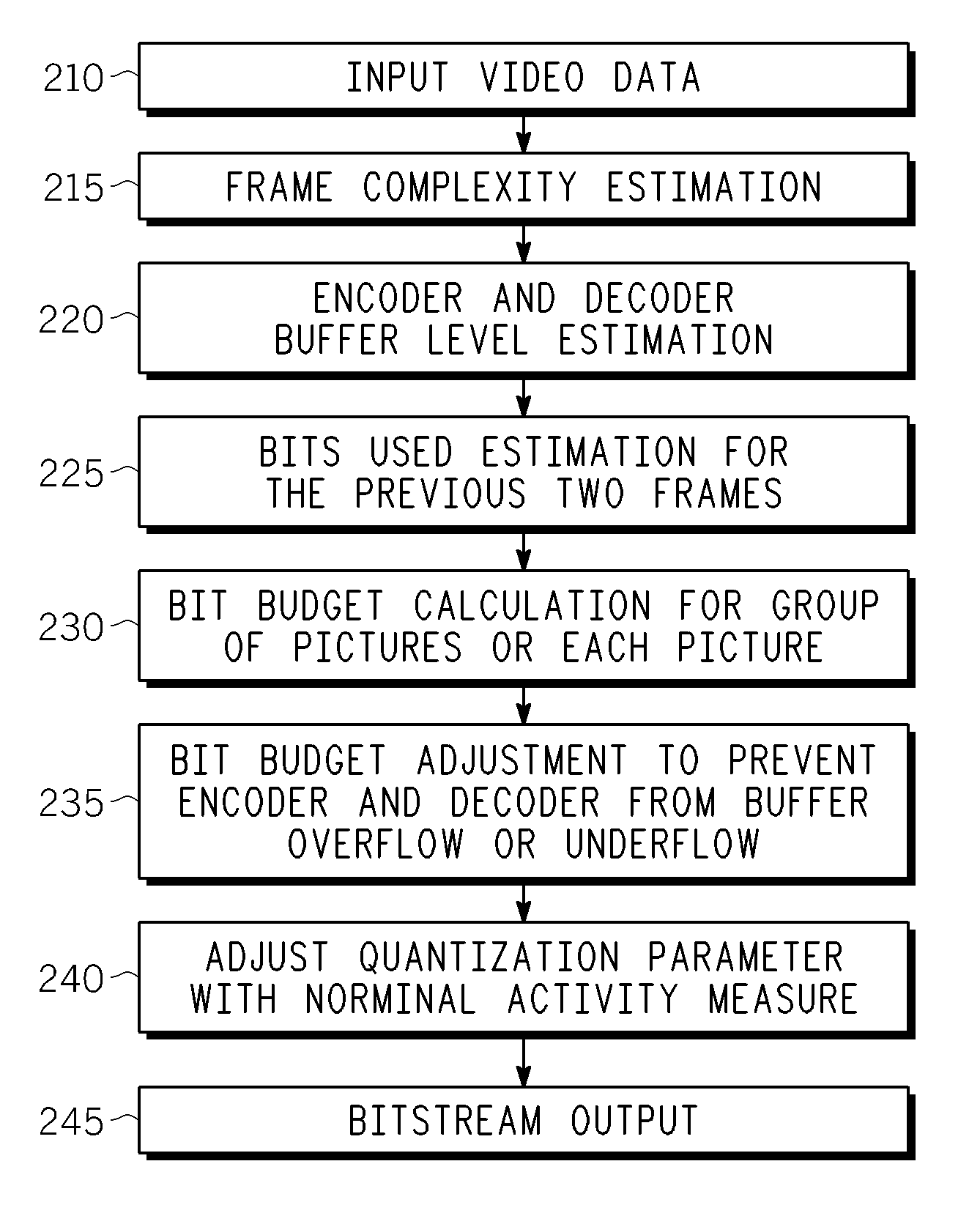
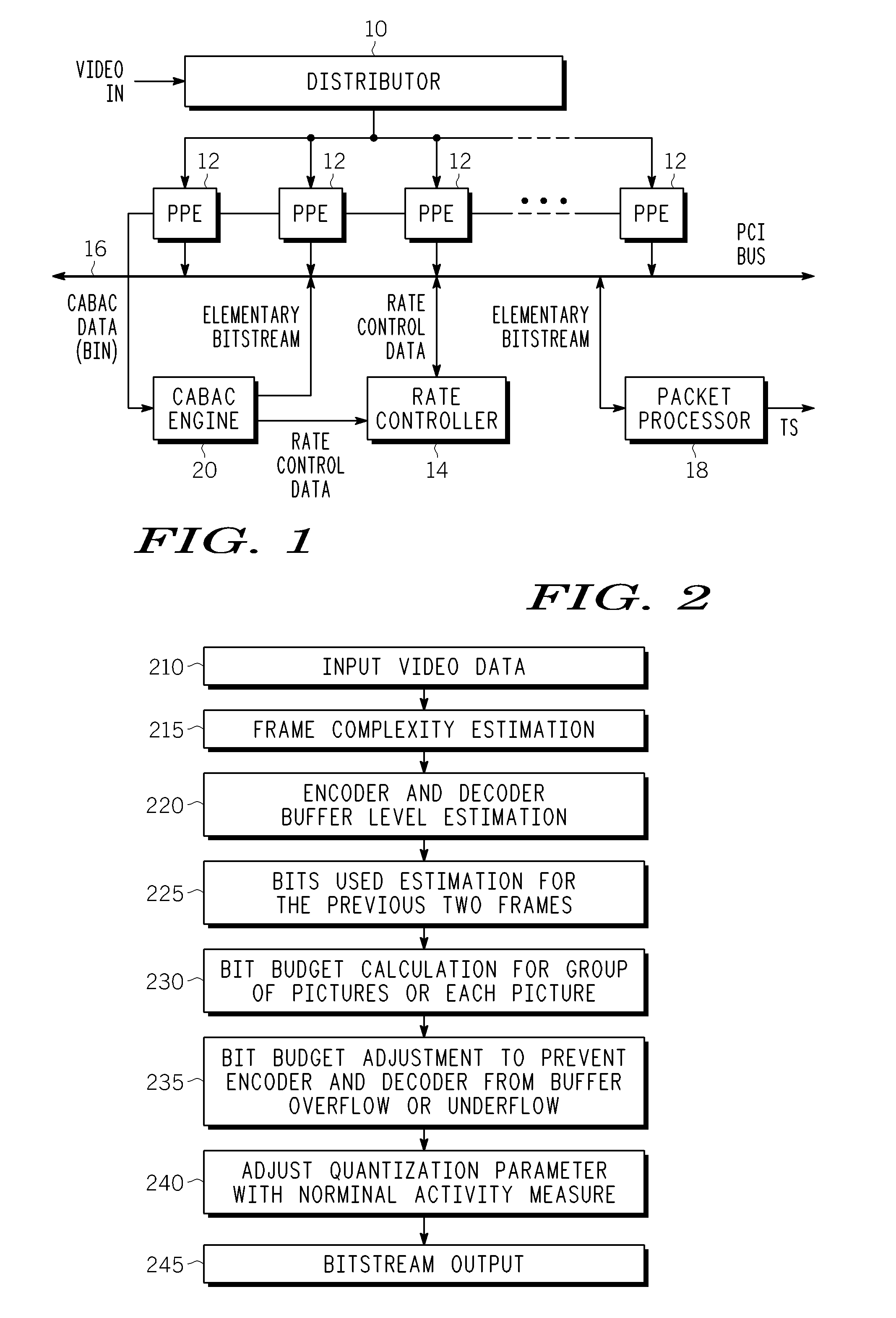
Method and Apparatus for Providing Rate Control for Panel-Based Real Time Video Encoder
InactiveUS20080151998A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSimulationMPEG encoding
A method and apparatus is provided for panel-based rate control in an MPEG encoder. In one embodiment, the method begins by estimating a complexity measure of pictures in a GOP and calculating a GOP bit budget for the GOP. Portions of the GOP bit budget are assigned to the pictures in the GOP based at least in part on the estimated complexity measure. A quantization parameter is adjusted for the picture to achieve the assigned portion of bit budget for each picture in the GOP.
Owner:GENERAL INSTR CORP
Macroblock level no-reference objective quality estimation of video
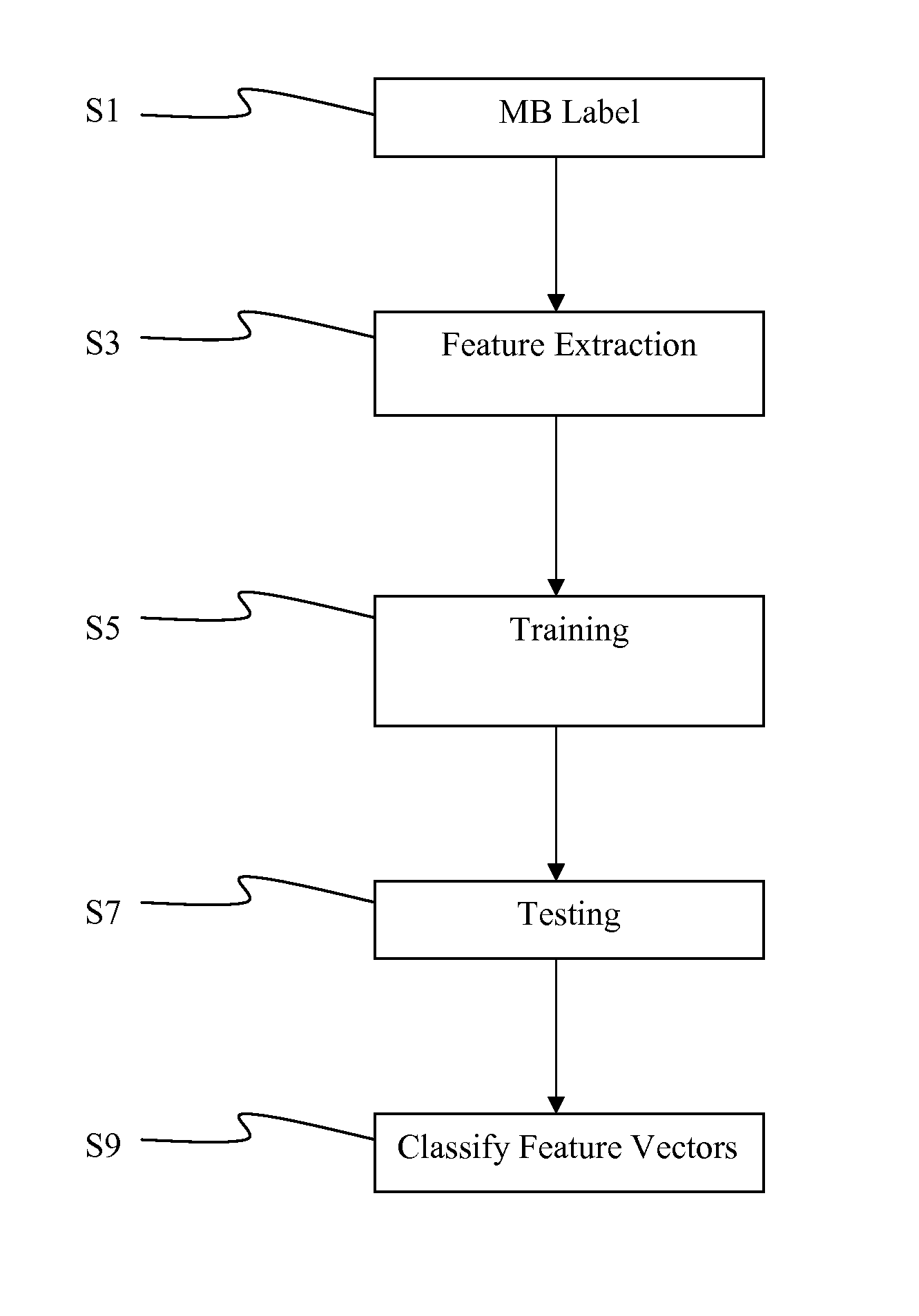
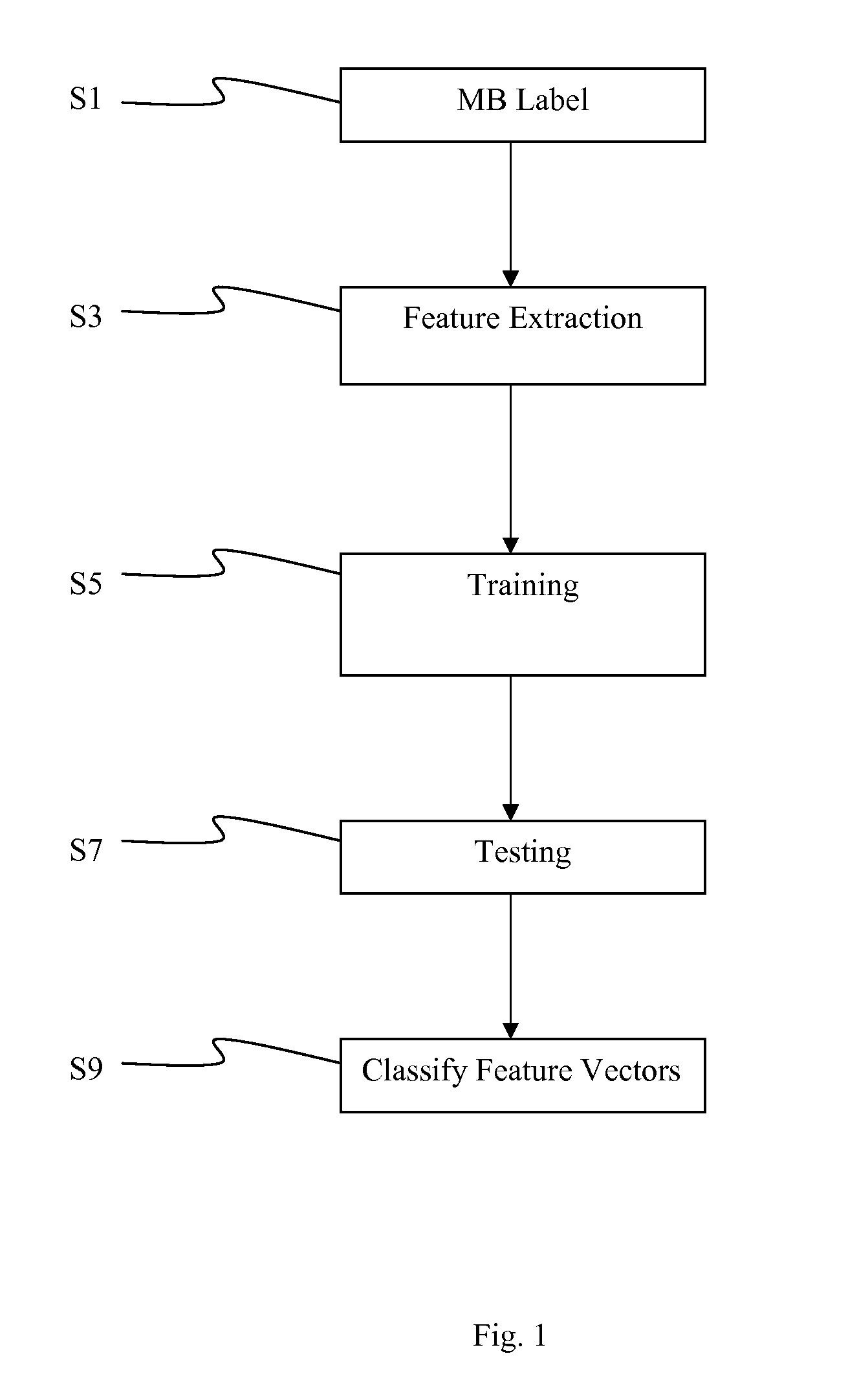
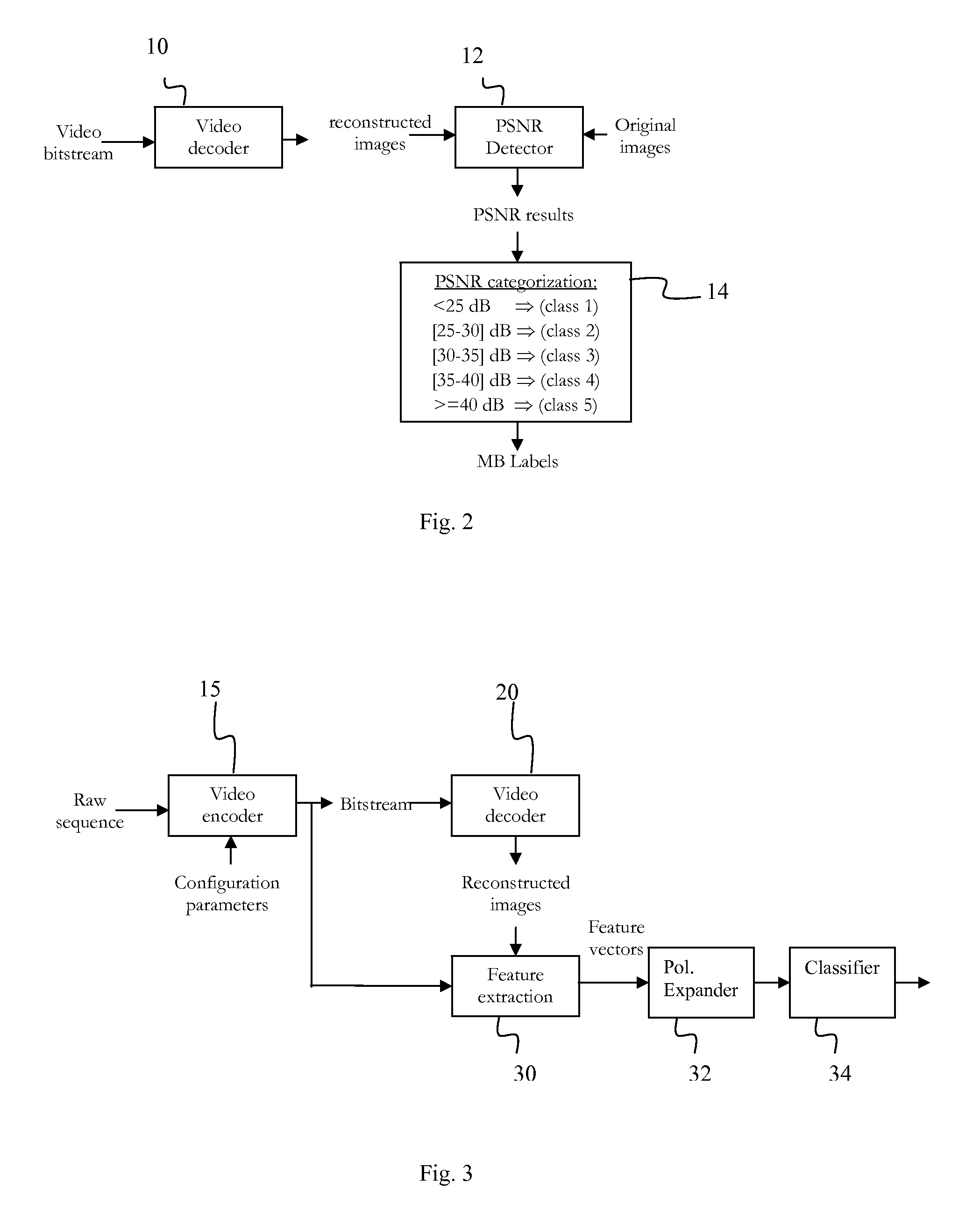
InactiveUS20100316131A1Image enhancementPulse modulation television signal transmissionReduced modelFeature vector
A no-reference estimation of video quality in streaming video is provided on a macroblock basis. Compressed video is being deployed in video in streaming and transmission applications. MB-level no-reference objective quality estimation is provided based on machine learning techniques. First the feature vectors are extracted from both the MPEG coded bitstream and the reconstructed video. Various feature extraction scenarios are proposed based on bitstream information, MB prediction error, prediction source and reconstruction intensity. The features are then modeled using both a reduced model polynomial network and a Bayes classifier. The classified features may be used as feature vector used by a client device assess the quality of received video without use of the original video as a reference.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Parallel encoding and decoding processor system and method
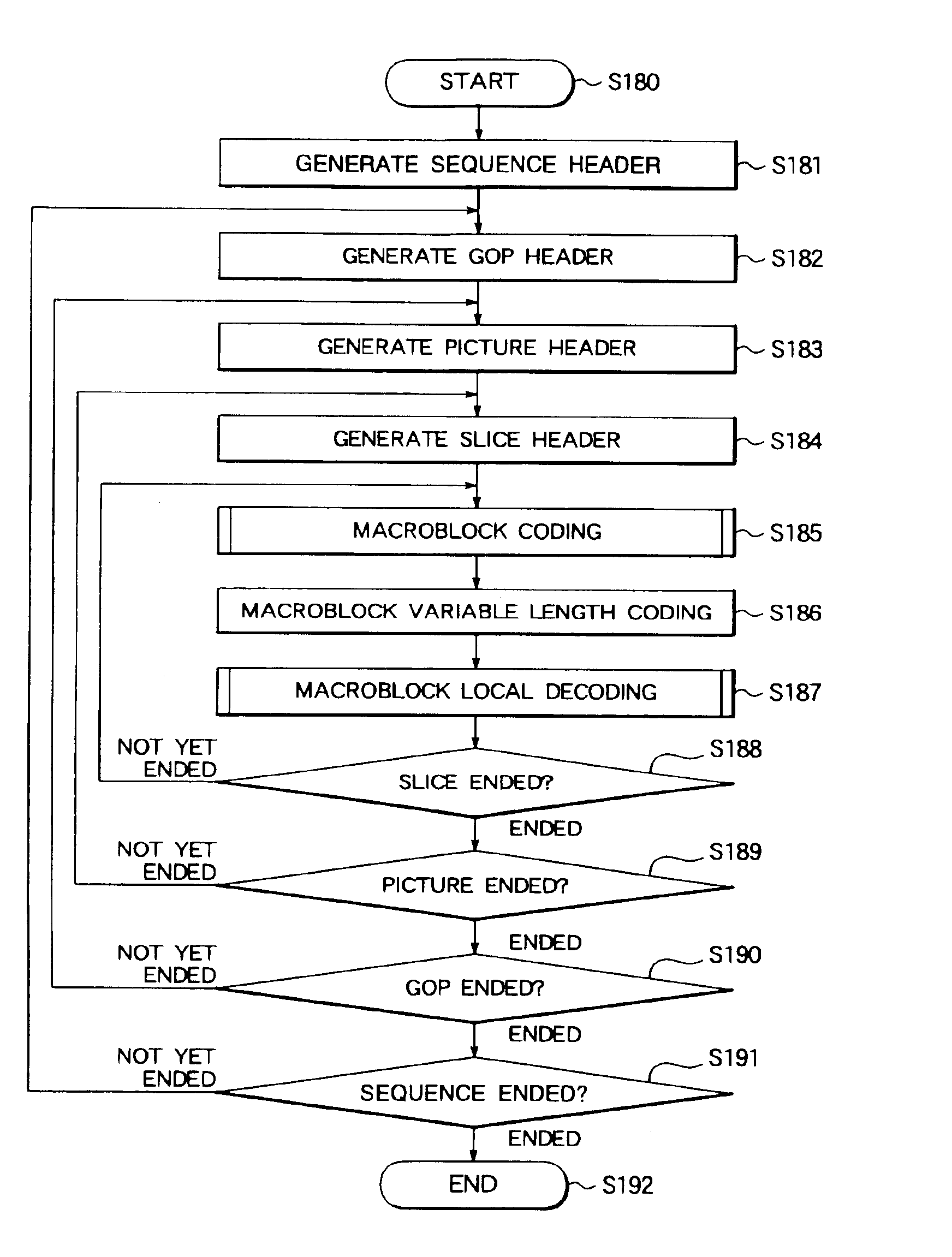
InactiveUS6870883B2Simple configurationIncrease speedResource allocationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeParallel encoding
Encoding and decoding systems for MPEG encoding and decoding at a high speed using a parallel processing system, wherein macroblocks to be processed are designated for first to third processors which are made to carry out all processings of encoding, variable length coding, and local decoding of those macroblocks; the variable length coding is carried out after confirming that the variable length coding with respect to the previous macroblock is ended; the variable length coding which was normally sequentially carried out at a specific processor is carried out at all of the processors; and the encoding and local decoding are carried out at all of the processors; whereby the loads are dispersed, the efficiency is improved as a whole, and the processing speed becomes fast.
Owner:SONY CORP
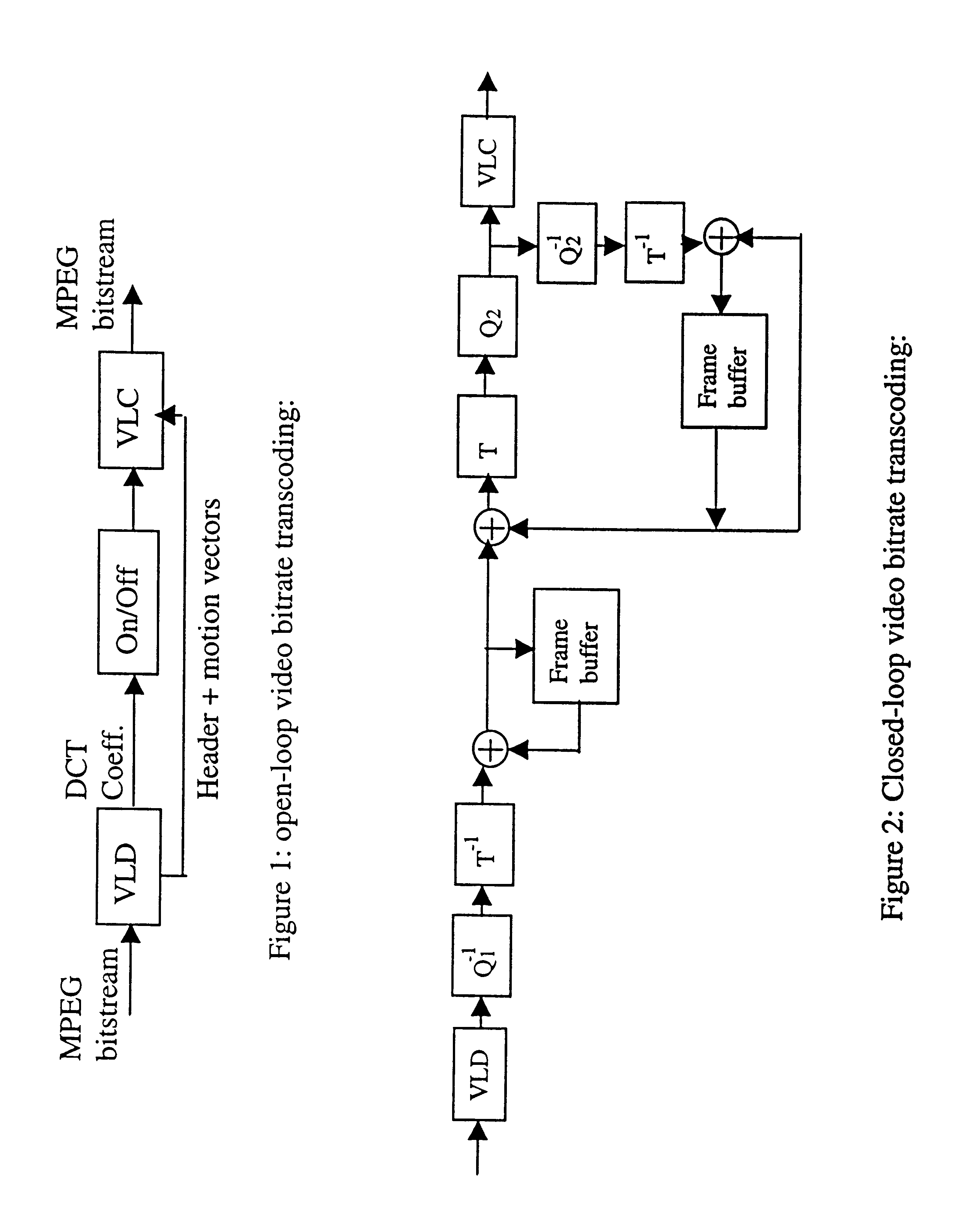
Stream based bitrate transcoder for MPEG coded video
InactiveUS6700935B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorMPEG encoding
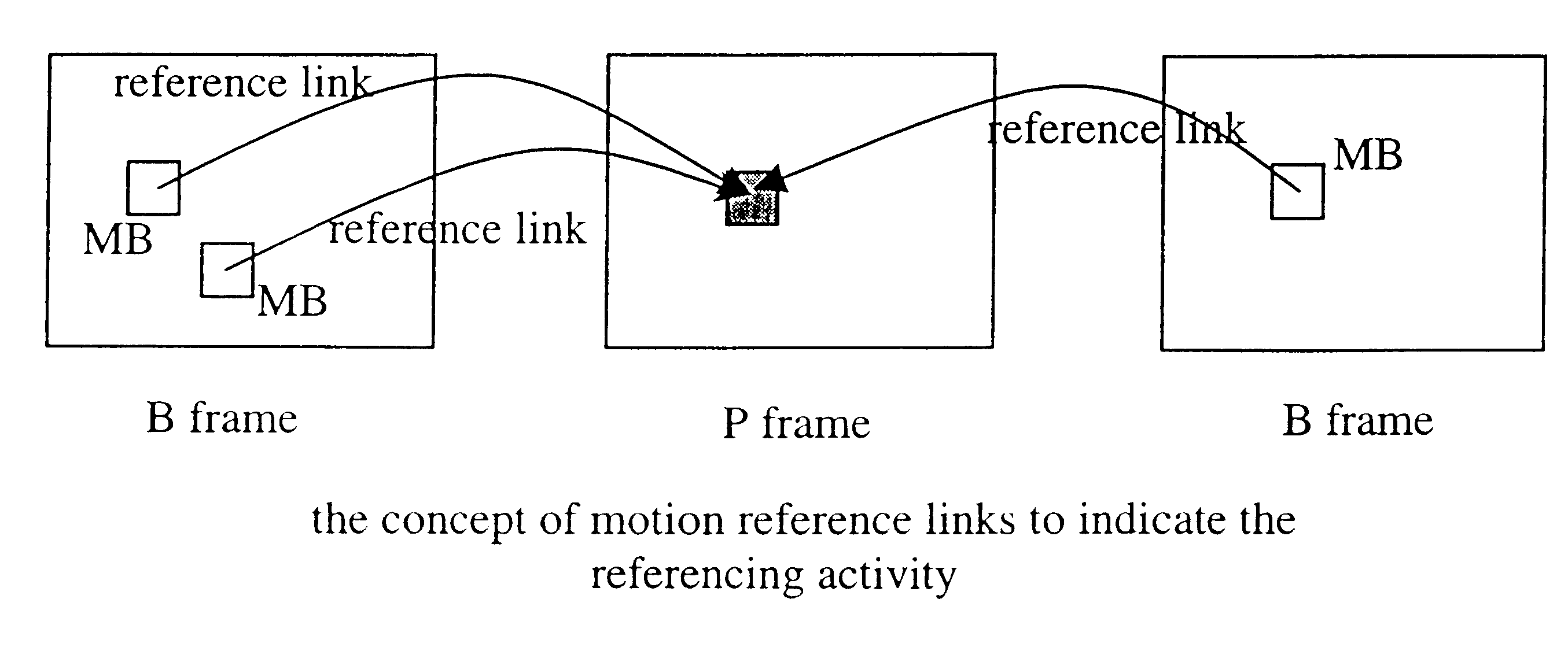
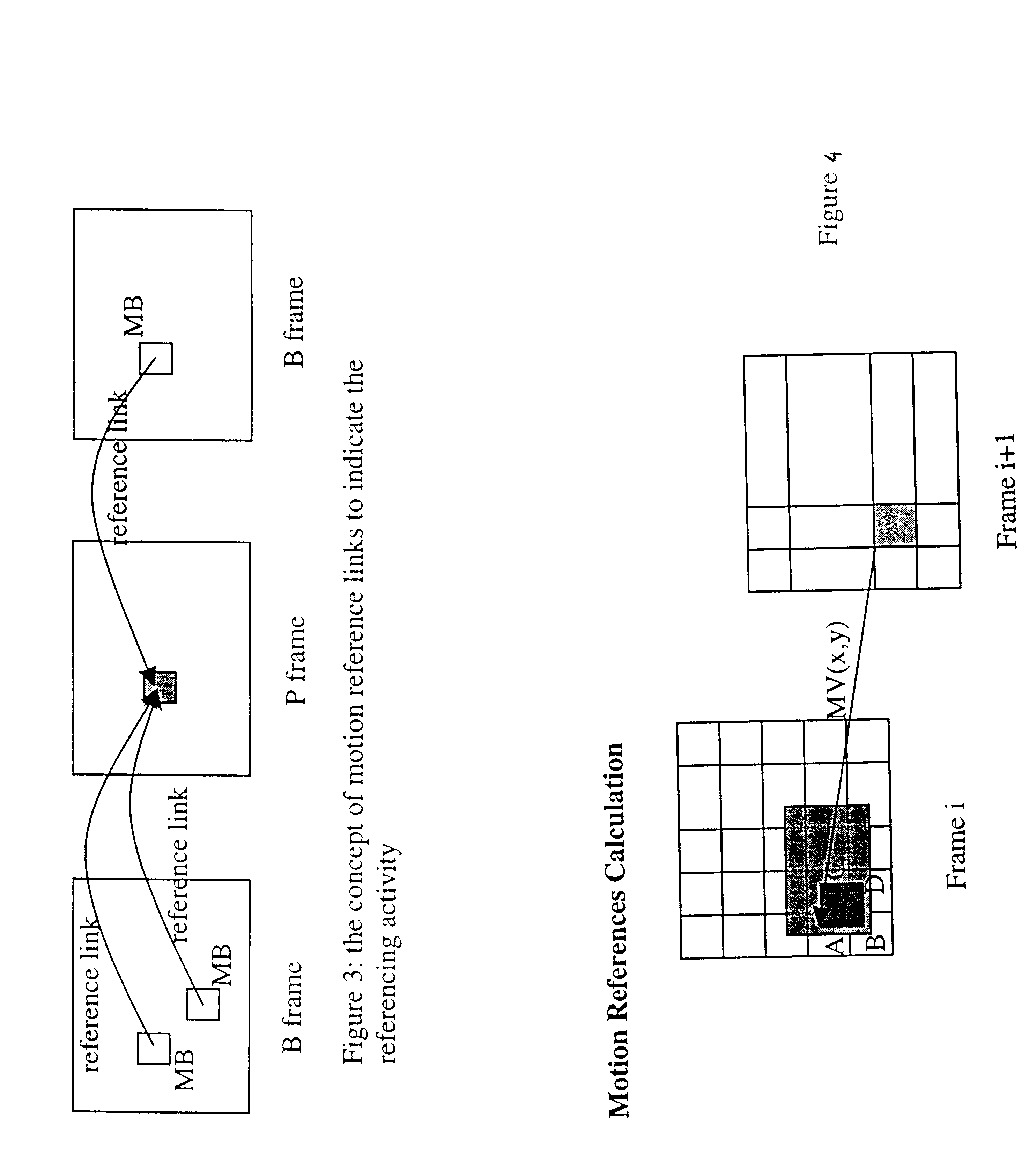
A stream based bitrate transcoder for MPEG bitstreams that utilizes information extracted from MPEG bitstreams, such as picture-type, coding complexity, motion vector and MB-mode. Using this information, a stream-based bitrate conversion of rhythm is realized. DCT coefficients are dropped with regard to two components, specifically, picture / MB-level classification and motion reference calculation.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
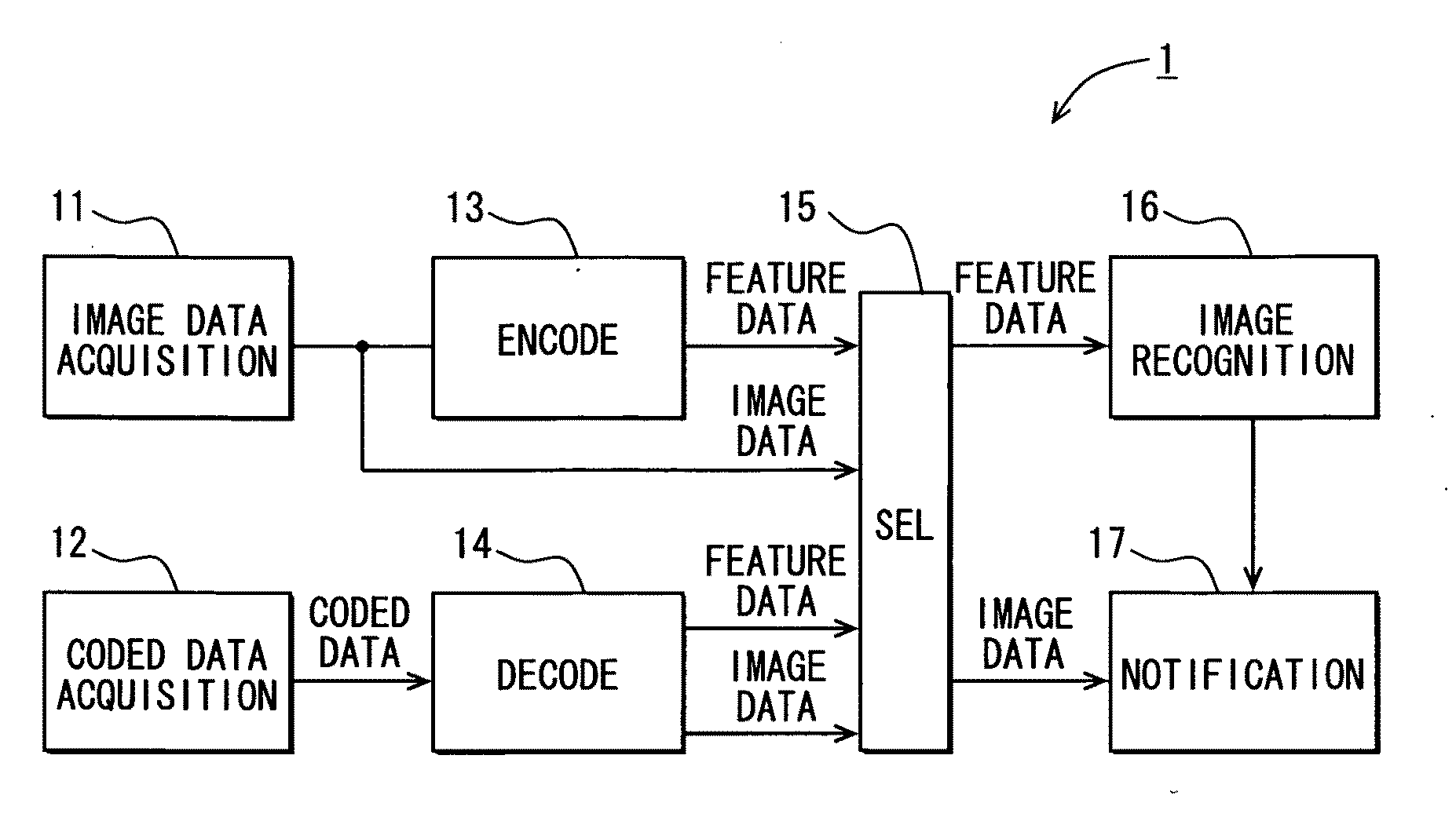
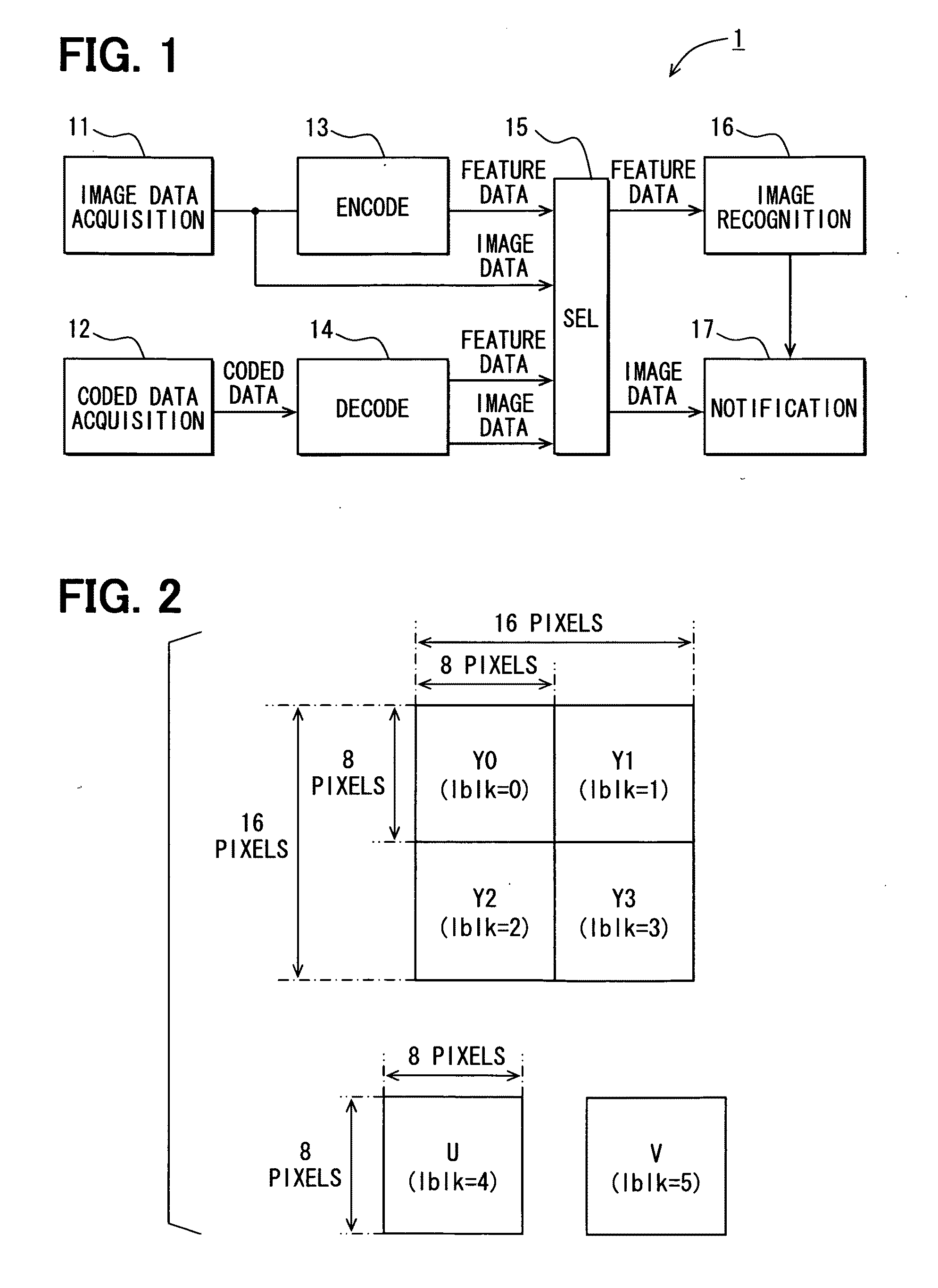
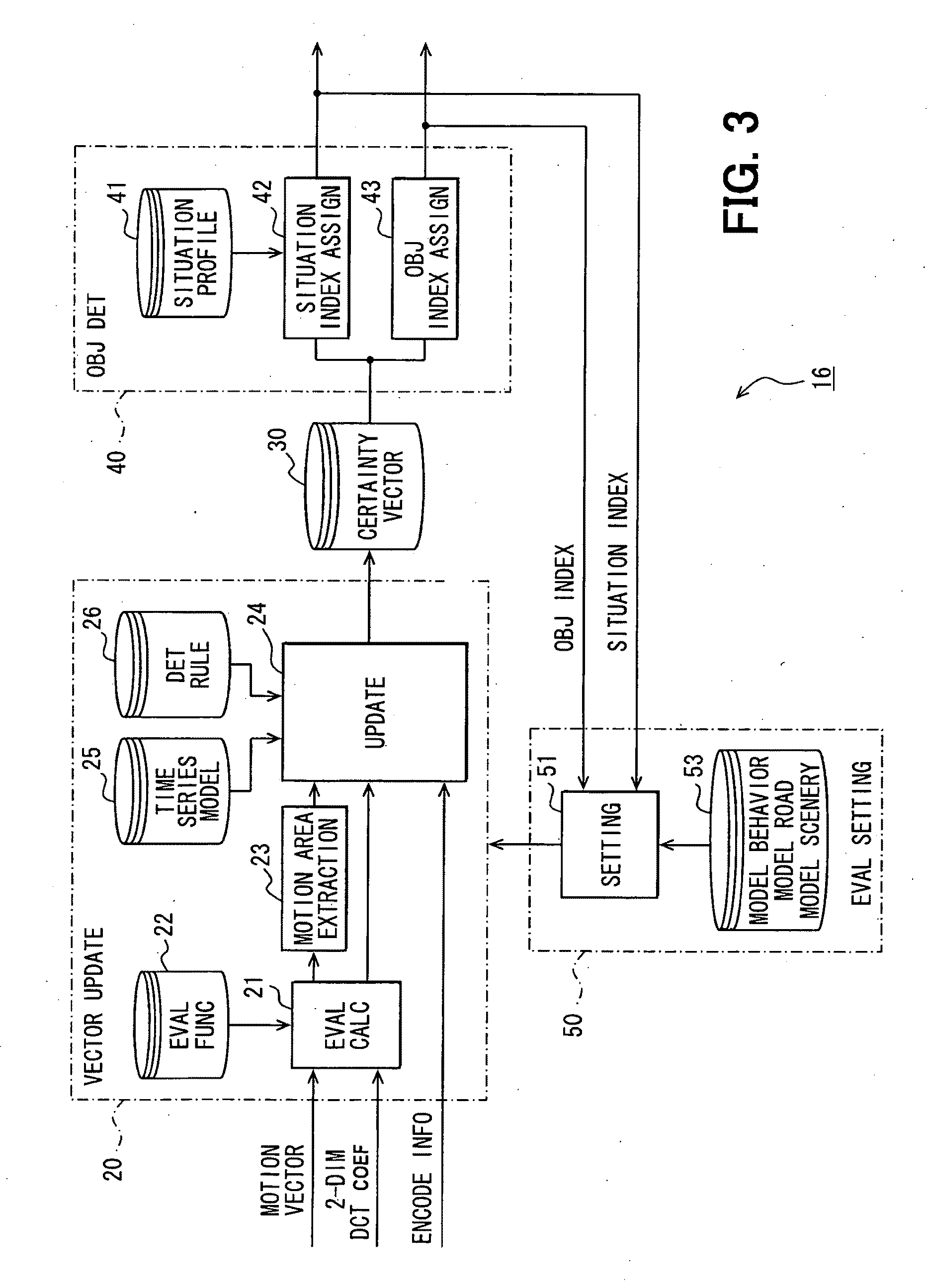
Apparatus for image recognition
InactiveUS20090279738A1Highly-accurate mannerHighly accurate object recognition of objectImage analysisAnti-collision systemsPattern recognitionObject based
An image recognition apparatus includes an image recognition unit, an evaluation value calculation unit, and a motion extraction unit. The image recognition unit uses motion vectors that are generated in the course of coding image data into MPEG format data or in the course of decoding the MPEG coded data by the evaluation value calculation unit and the motion extraction unit as well as two dimensional DCT coefficients and encode information such as picture types and block types for generating the evaluation values that represent feature of the image. The apparatus further includes an update unit for recognizing the object in the image based on the determination rules for a unit of macro block. The apparatus can thus accurately detect the motion of the object based on the evaluation values derived from DCT coefficients even when generation of the motion vectors is difficult.
Owner:DENSO CORP
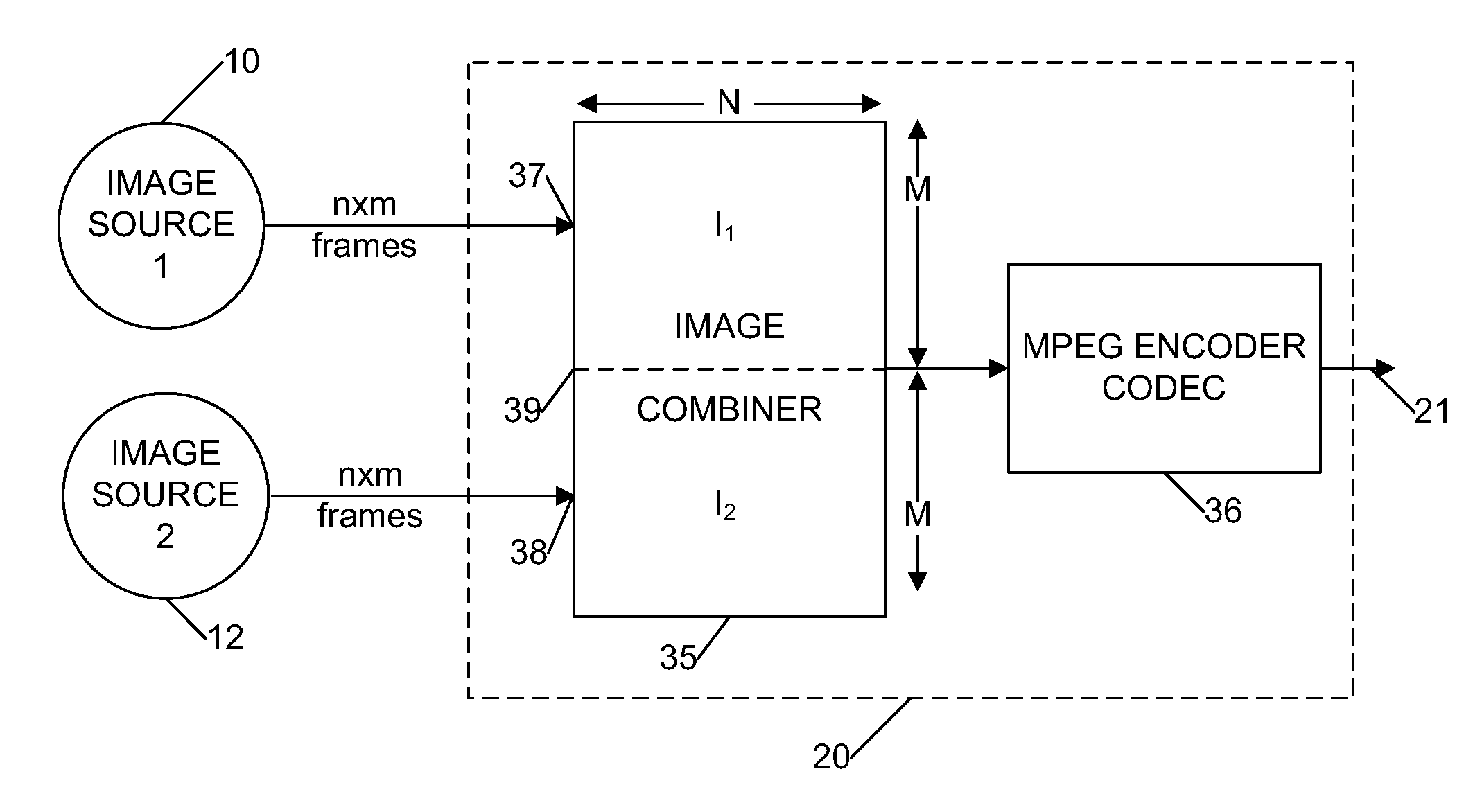
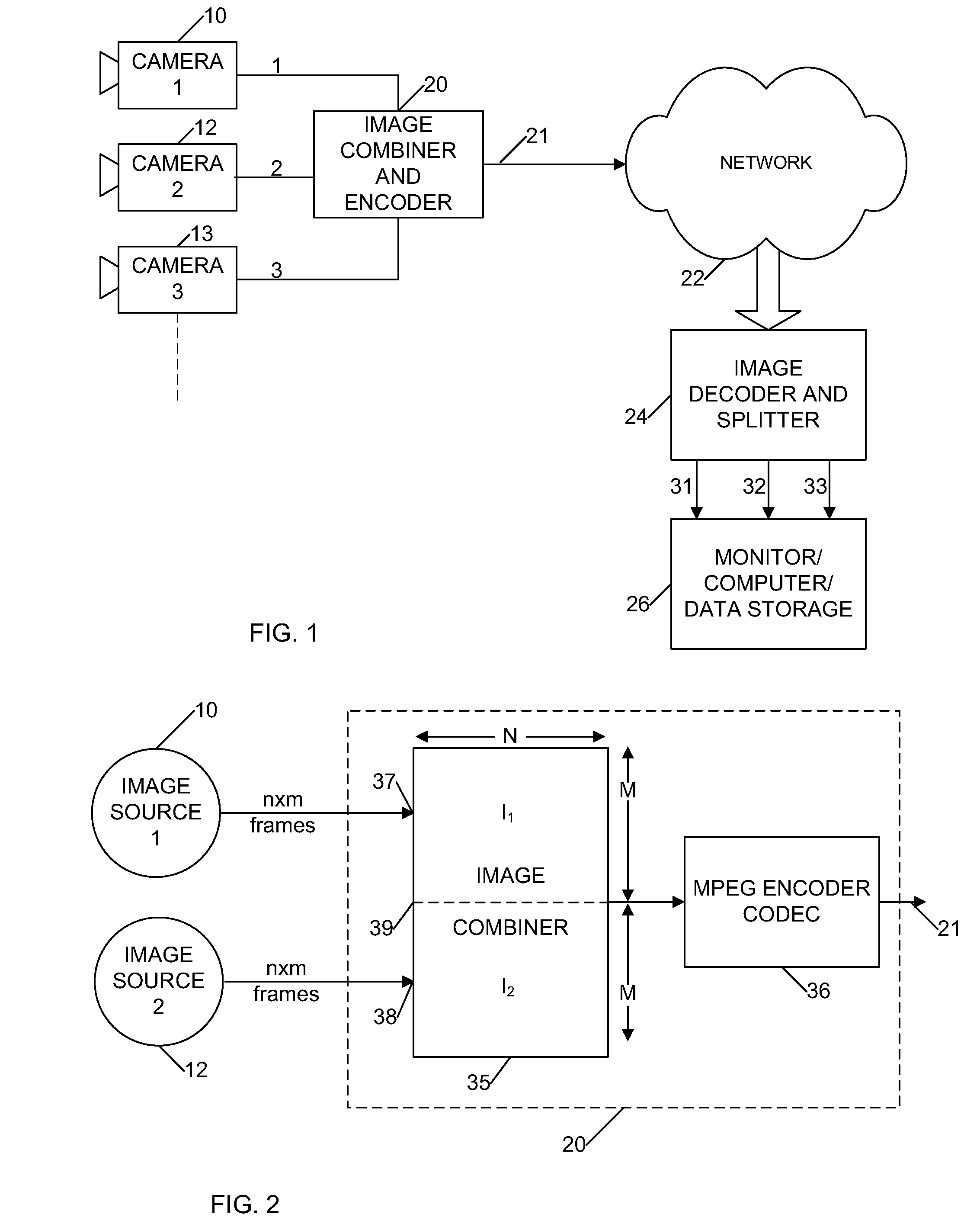
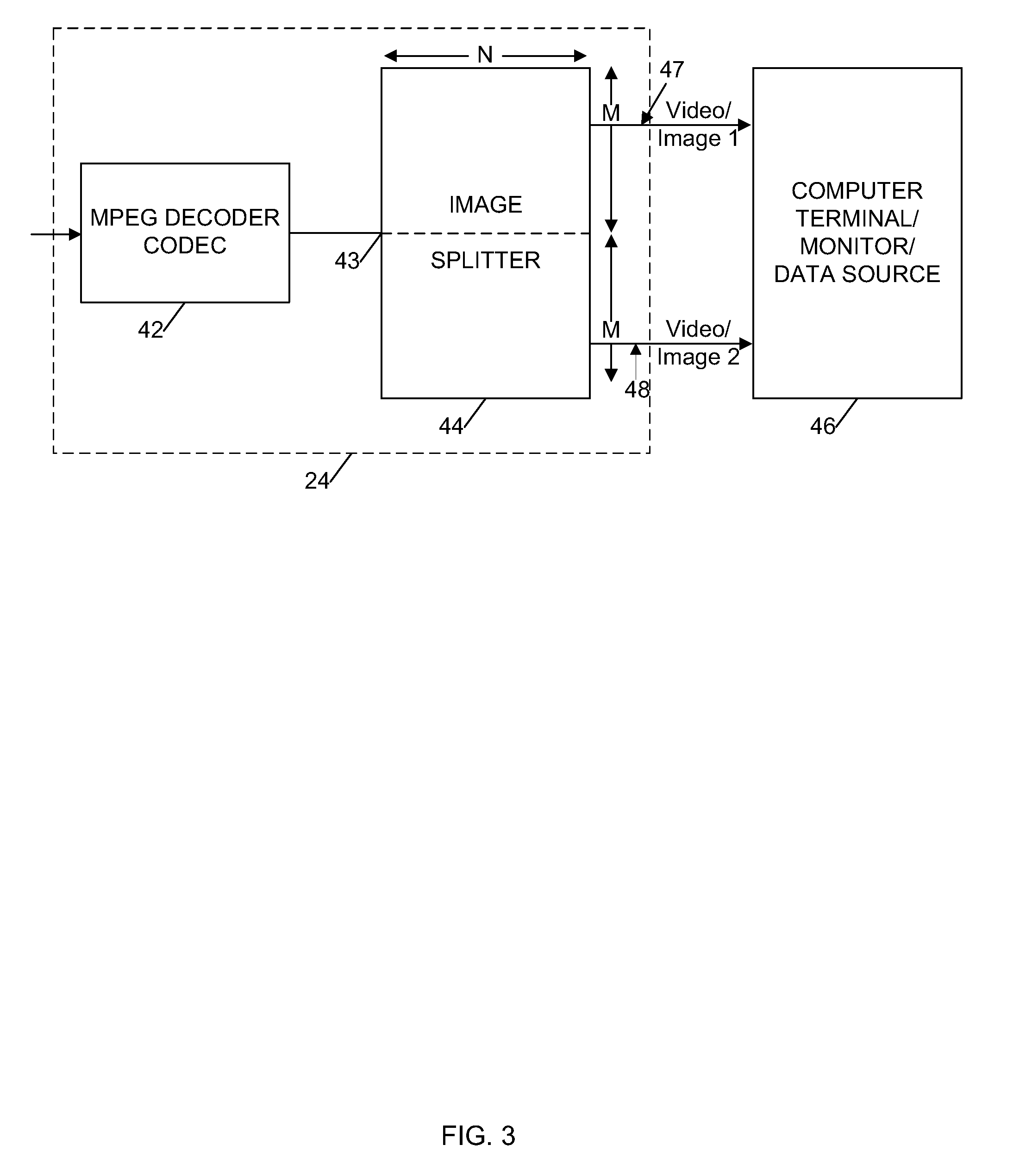
Multiple Image Source Processing Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20080049830A1Readily apparentColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG encodingMultiple image
Separate first and second input streams of image frames are received by a frame combiner module, which combines an image frame from the first stream with an image frame from the second stream to produce a single output stream of combined frames. The single output stream is encoded by an encoder module such as an MPEG encoder to produce an encoded output signal, which may be stored or transmitted over a network.
Owner:DRIVECAM
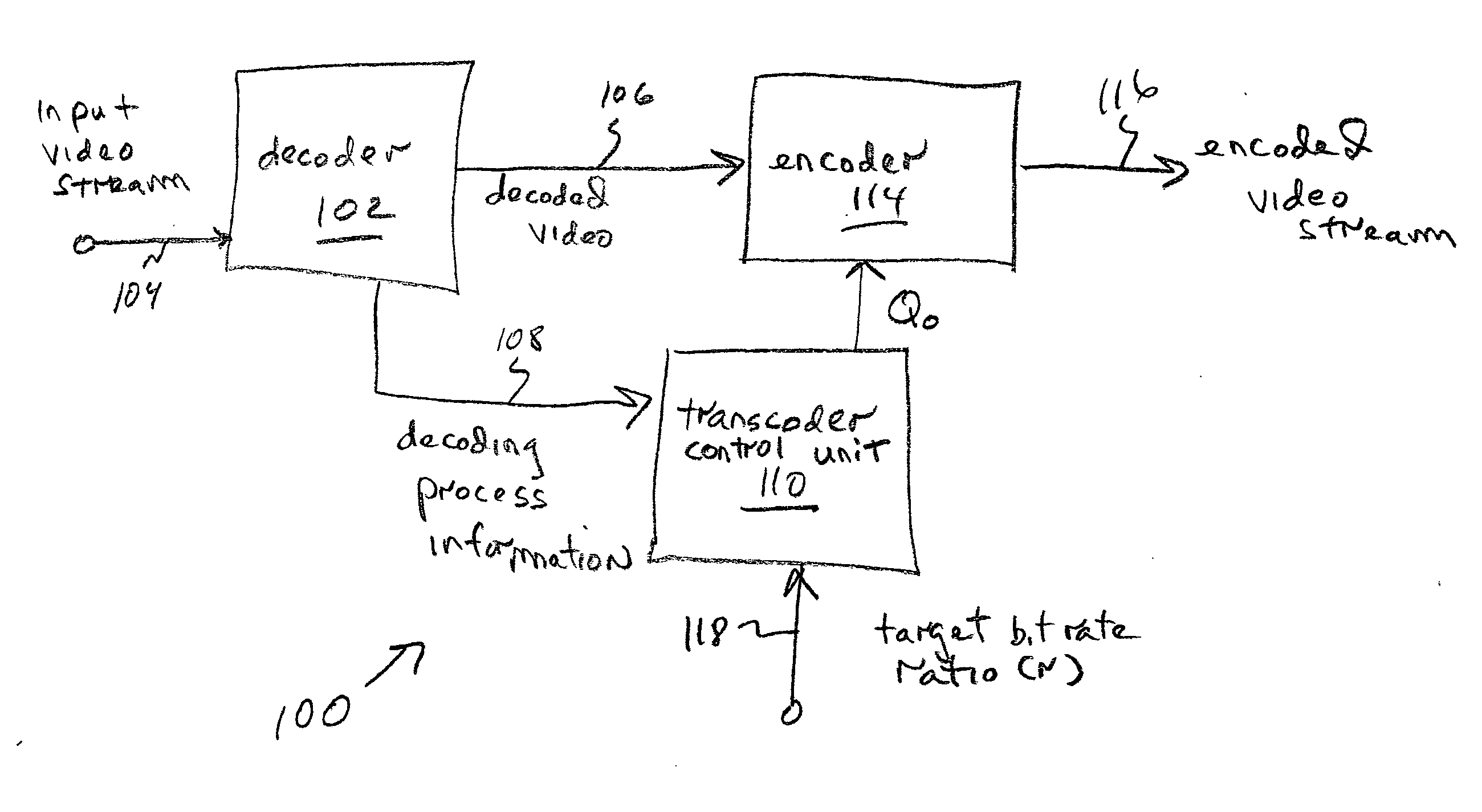
System and method for transcoding with adaptive bit rate control
InactiveUS20050058198A1Improve visual qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Transcoding
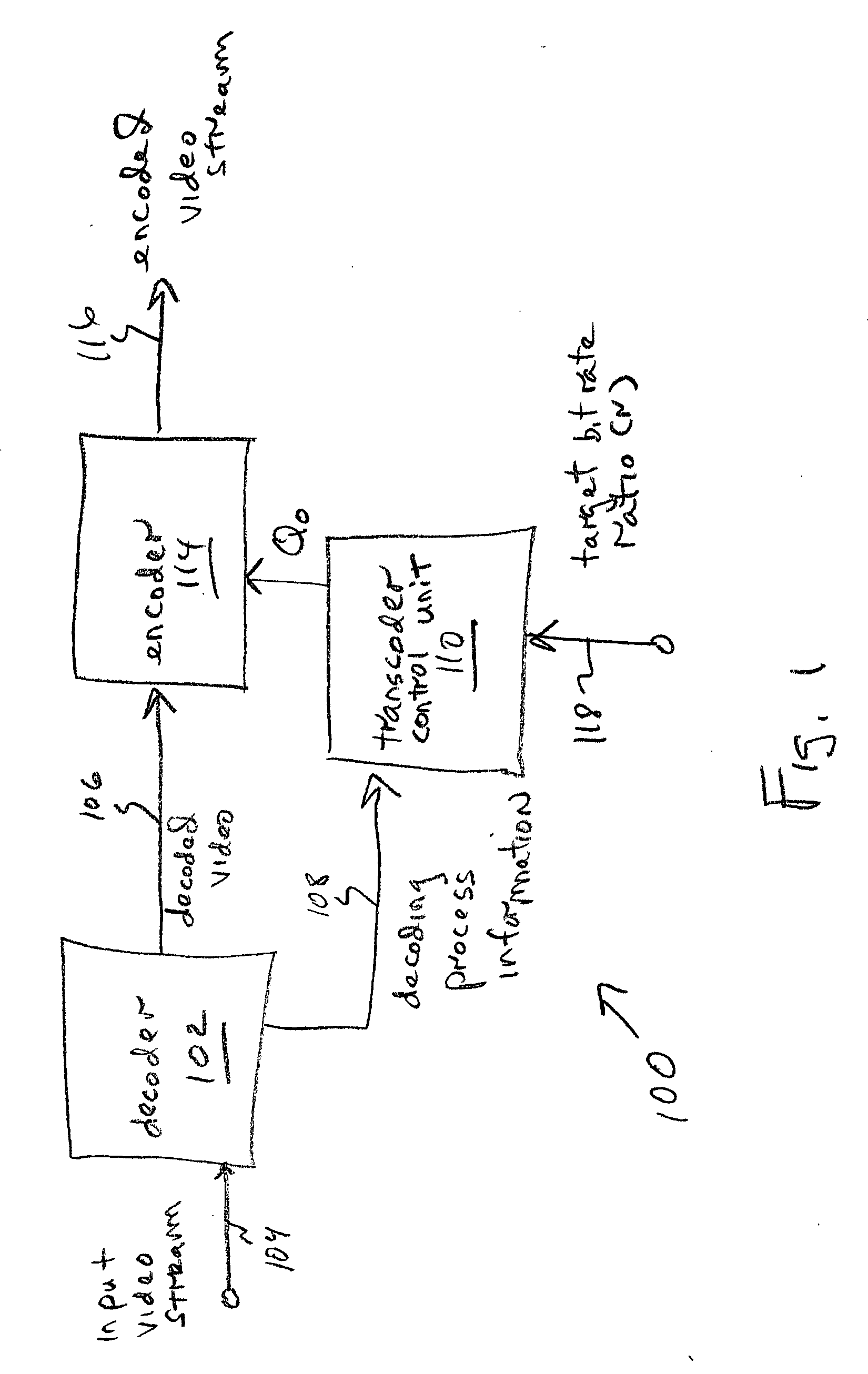
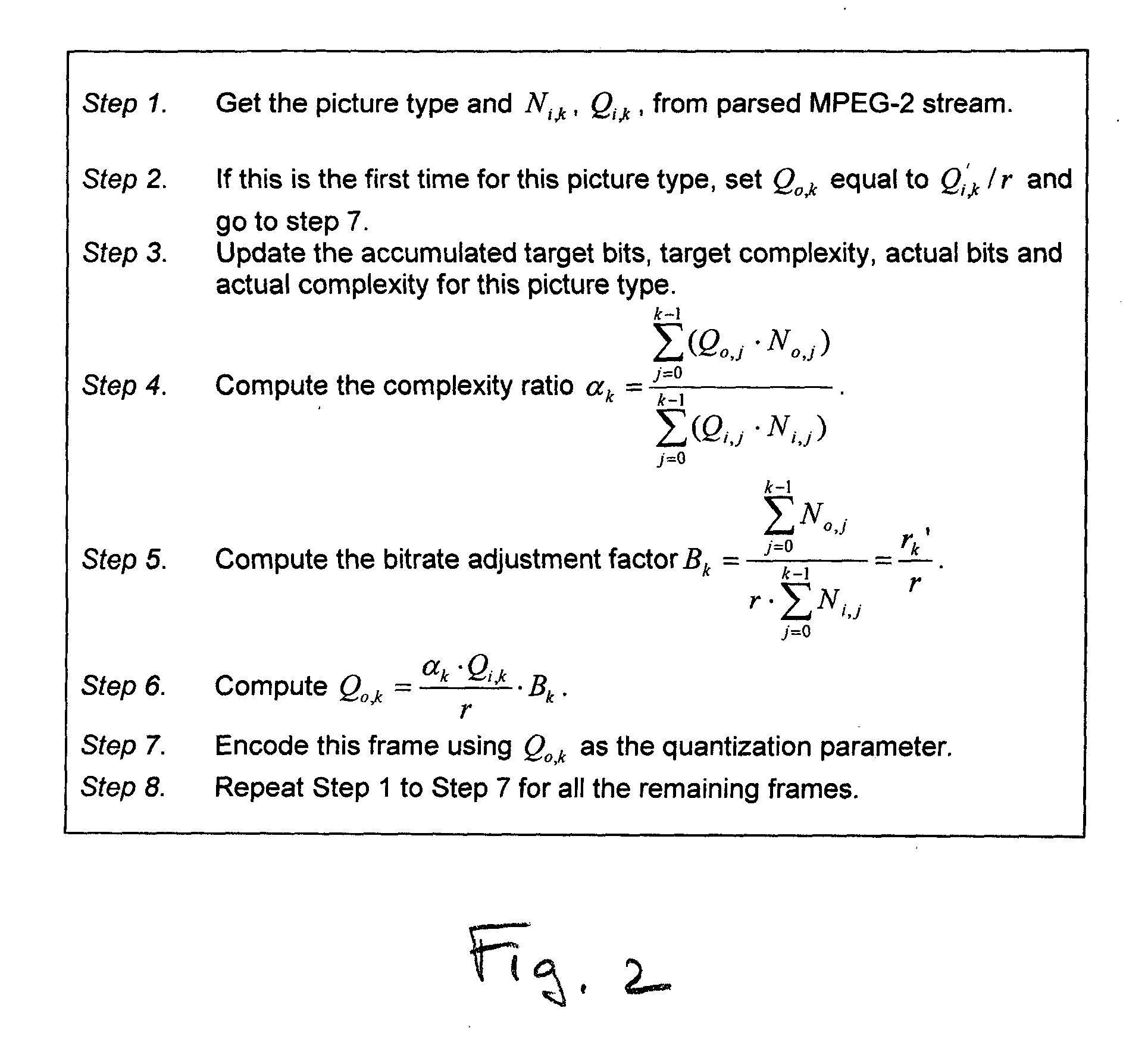
A system and method are provided for adaptive rate control in the transcoding of video streams. The method comprises: accepting frames of an input MPEG encoded video stream; decoding the video stream; determining video stream complexity; for each frame, calculating an output video stream quantization parameter (Qo) responsive to determined video stream complexity; and, encoding the output video stream into a protocol using Qo. Some aspects further comprise accepting a target bit rate ratio (r) for transcoding that is equal to the ratio of the target output video stream number of bits per frame (No), to the input video stream number of bits per frame (Ni). Then, Qo is also calculated in response to the value of r. More explicitly, Qo is calculated in response to a complexity ratio of: an accumulated complexity in the output video stream, to an accumulated complexity in the input video stream.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method of transmitting and receiving compressed television signals
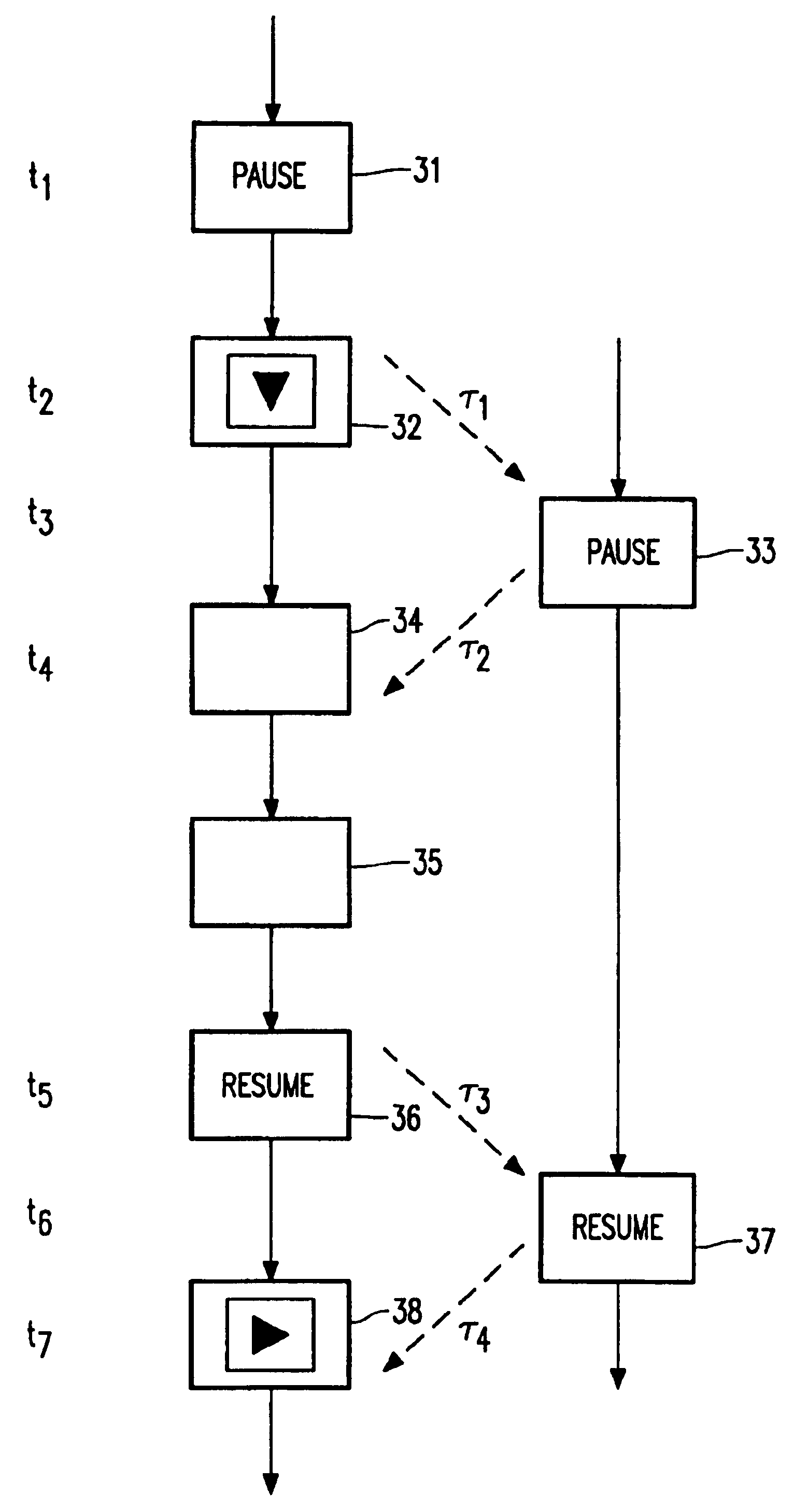
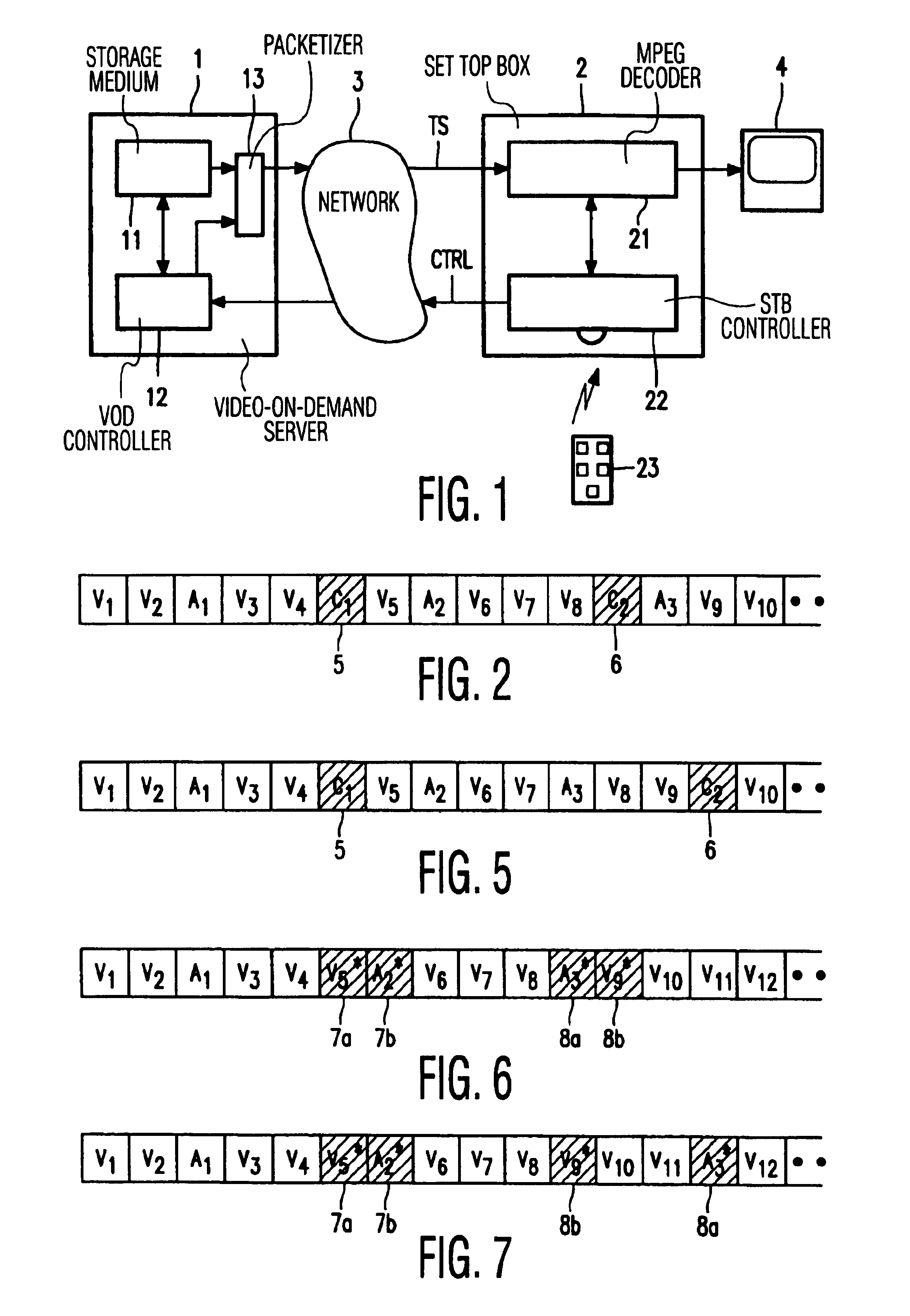
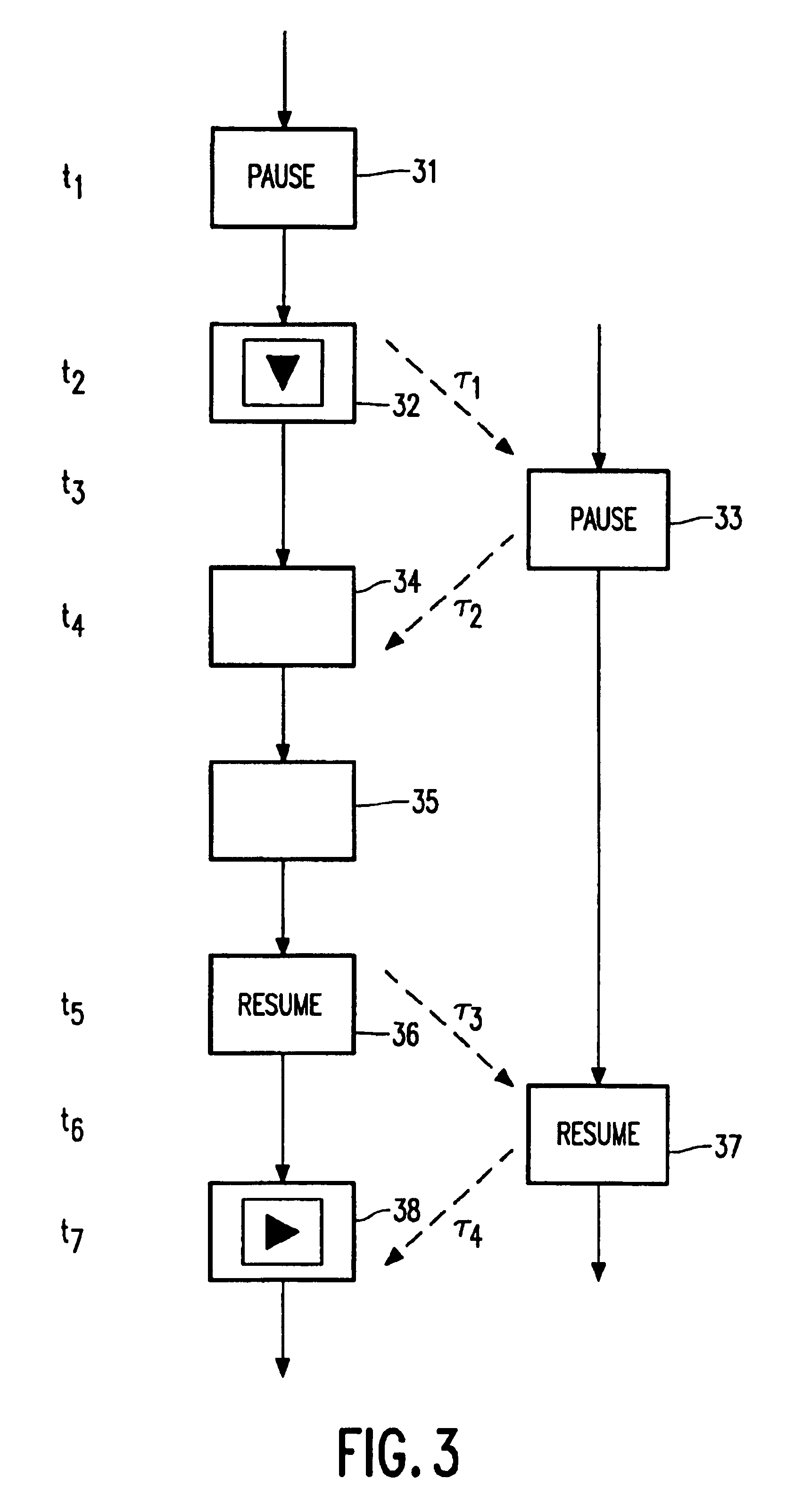
The invention relates to the transmission of MPEG encoded television signals from a Video-On-Demand server (1) to a receiver (2) via a network (3). Non-linear playback functions such as 'pause' and 'resume' require a very accurate control of the bit stream, taking account of typical network aspects such as network latency and remultiplexing. In order to allow the receiver to flawlessly resume signal reproduction after a pause, position labels (p; 5,6; 7a,7b,8a,8b) are inserted into the bit stream at positions where the server can resume transmission of the signal after an interruption. Upon a pause request, the decoder initially continues the reproduction until such a position label is detected. The subsequent bits delivered by the network are ignored, i.e. they are thrown away. Upon a request to resume reproduction, the receiver requests the server to retransmit the signal starting at the detected position.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
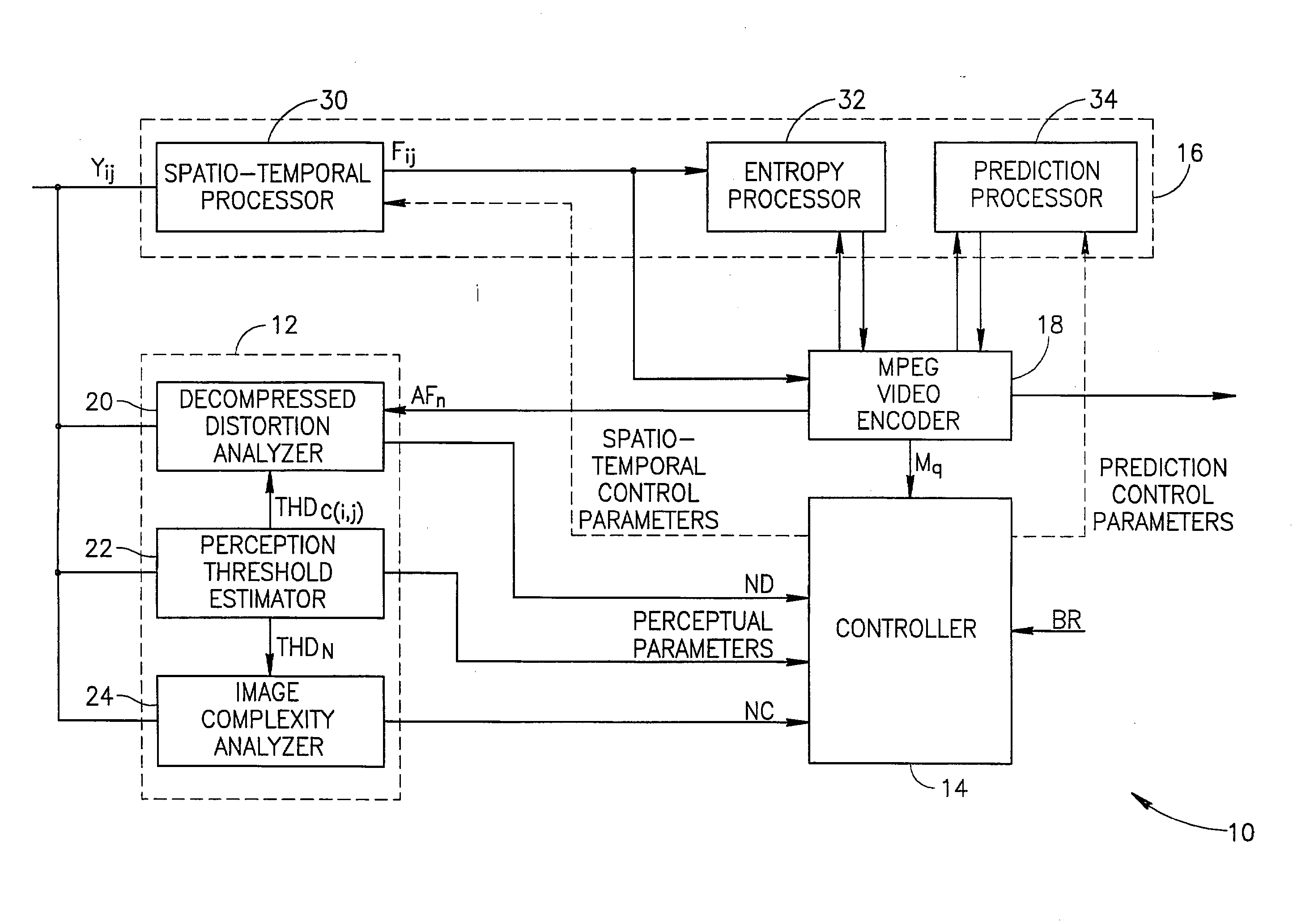
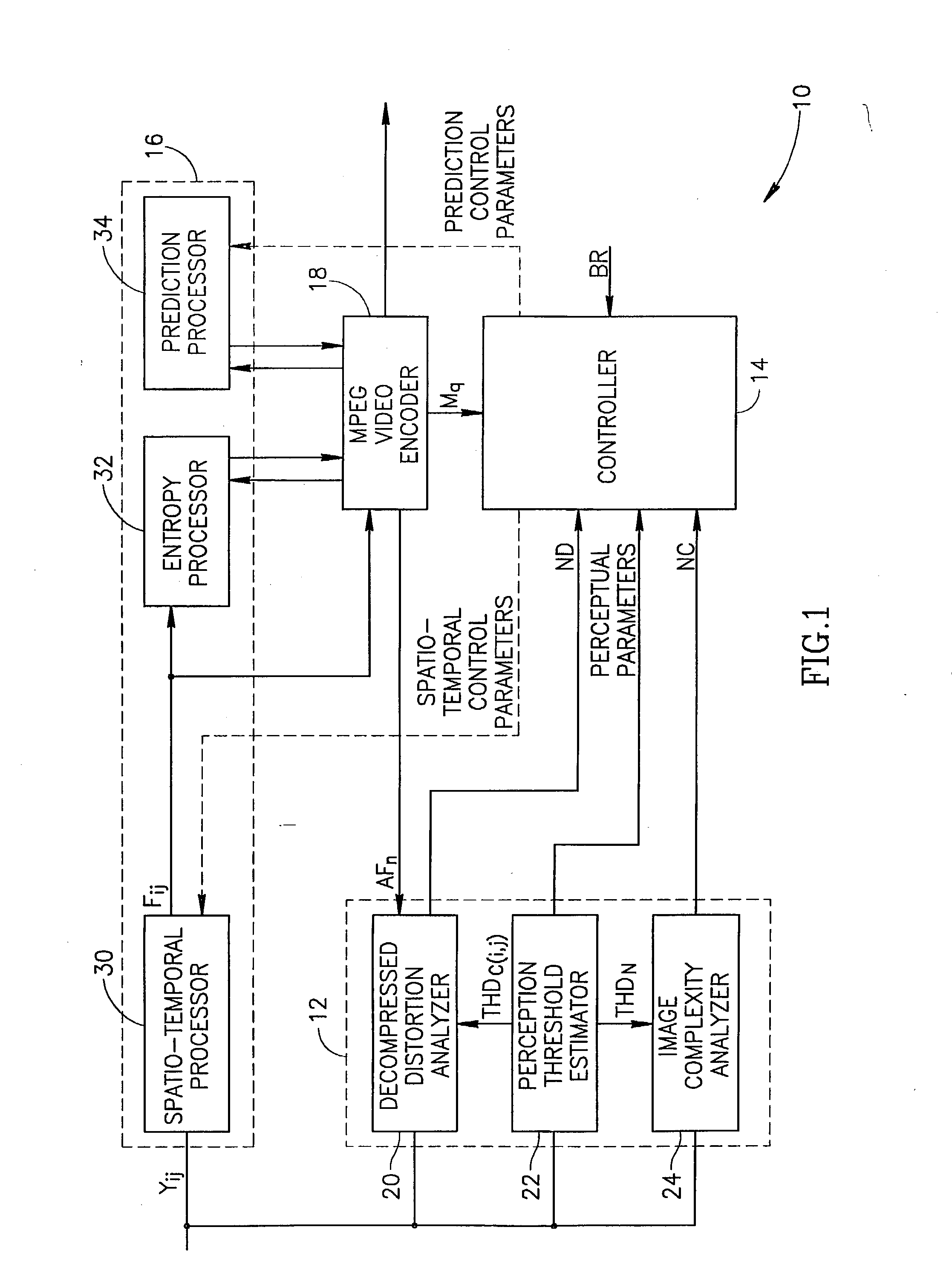
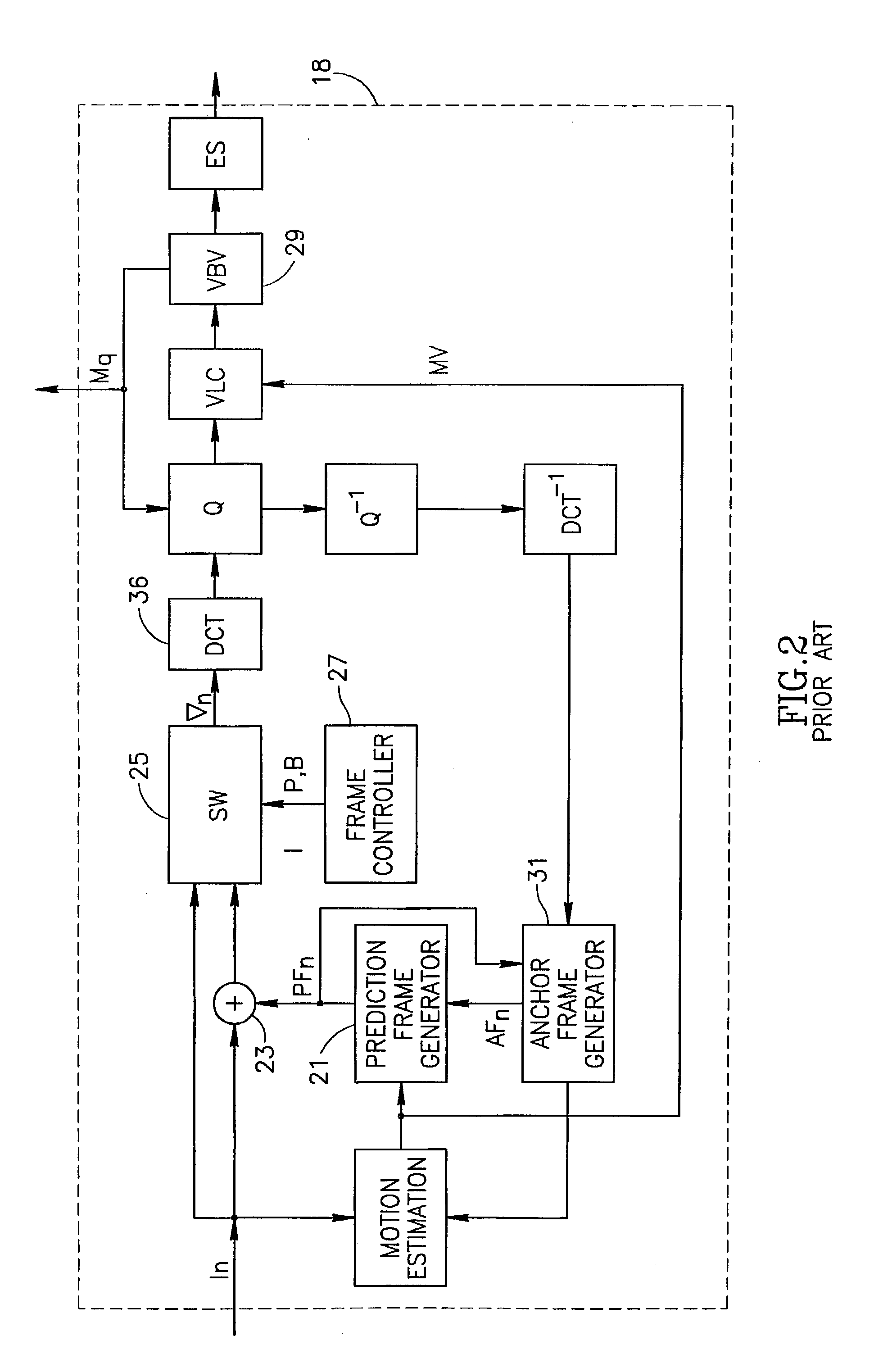
Apparatus and methods for adaptive digital video quantization
InactiveUS6782135B1Character and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
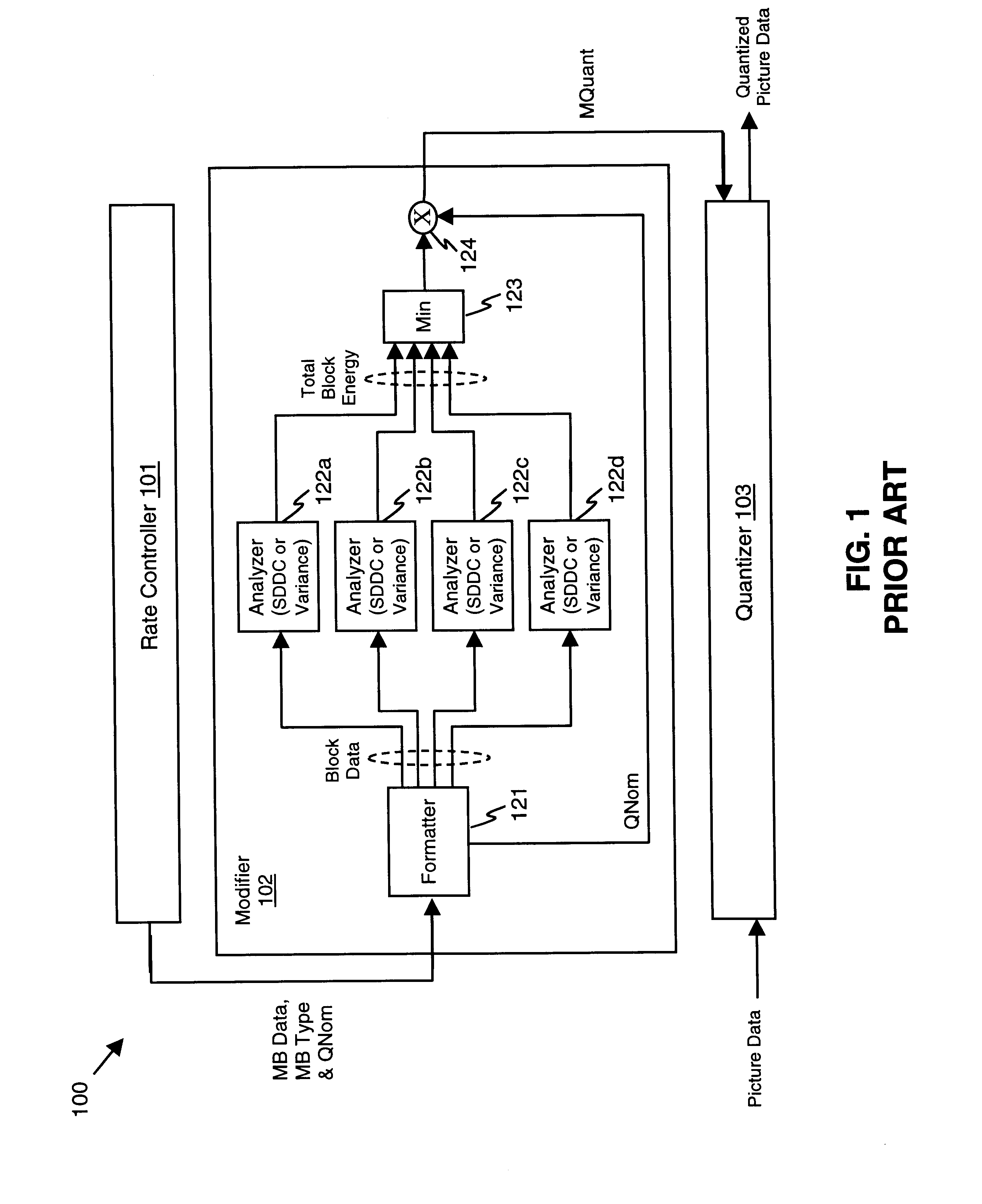
A video quantizer provides for performing quantization adaptively in accordance with perceptual masking characteristics of the human visual system. In a preferred MPEG encoder-IC, a block-based activity quantization modification or "activity-modification" is formed from the combined correlation of block-energy and edge analyses. A luminance-sensitivity modification is then formed and correlated with the activity modification to form an intermediate modification. A nominal-quantization modification is further formed and correlated with the intermediate modification, which is then limited and correlated with a nominal quantization value to form a base modification. Next, a positional-sensitivity modification is formed as a perimeter offset, which offset is correlated with the base modification to form a modified quantization value, and which modified quantization value is then rounded and returned to a rate controller.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof
ActiveUS7180944B2Reduce calculationExtensive computationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionMotion vector
A low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof are disclosed. The transcoder comprises a decoder having a reduced DCT-MC unit, a DCT-domain downscaling unit, and an encoder. The decoder performs the DCT-MC operation at a reduced-resolution for P- / B-frames in an MPEG coded bit-stream. The DCT-domain downscaling unit is used for spatial downscaling in the DCT-domain. After the downscaling and the motion vectors re-sampling, the encoder determines the encoding modes and outputs the encoded bit-stream. Compared with the original CDDT, this invention can achieve significant computation reduction and speeds up the transcoder without any quality degradation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for performing digital-to-digital video insertion
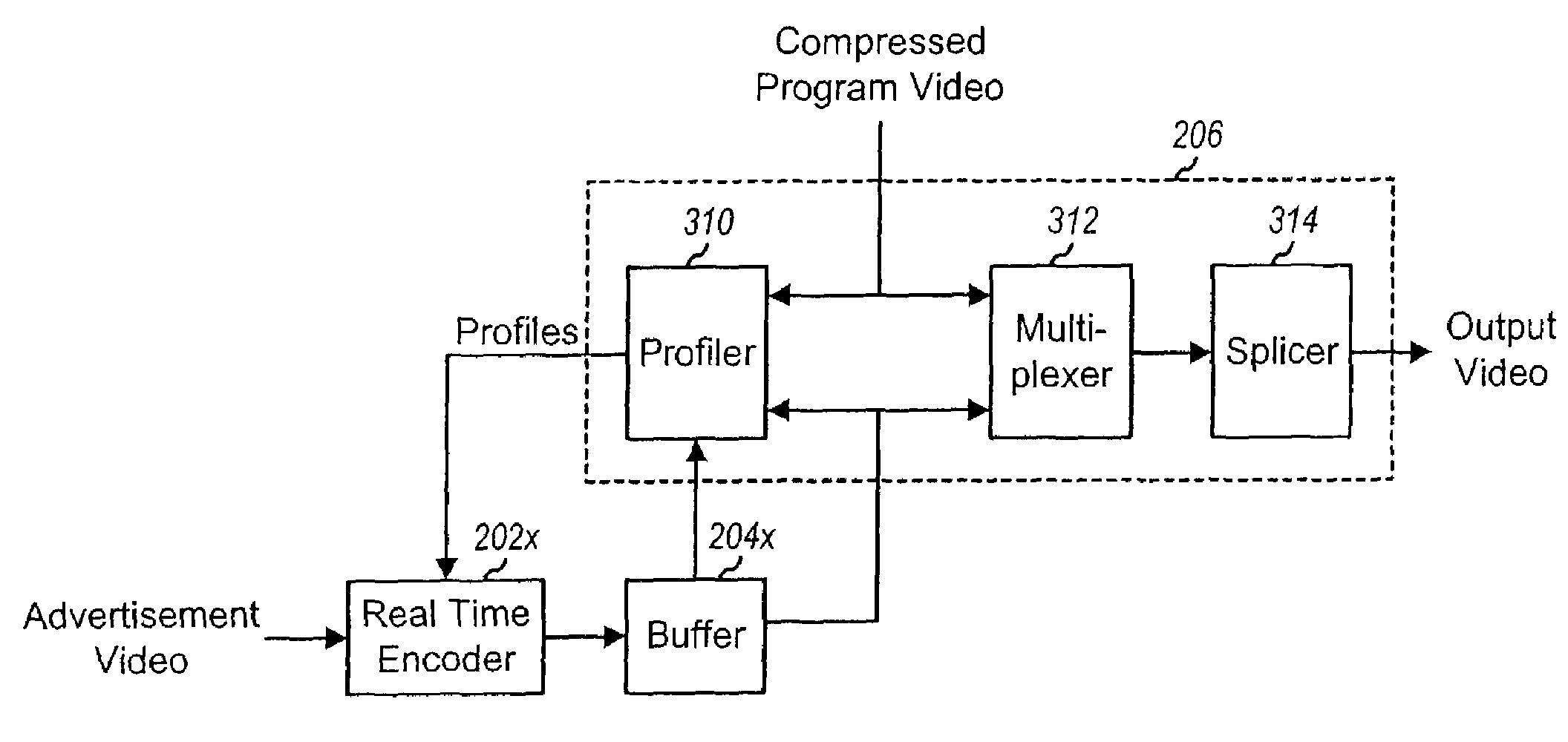
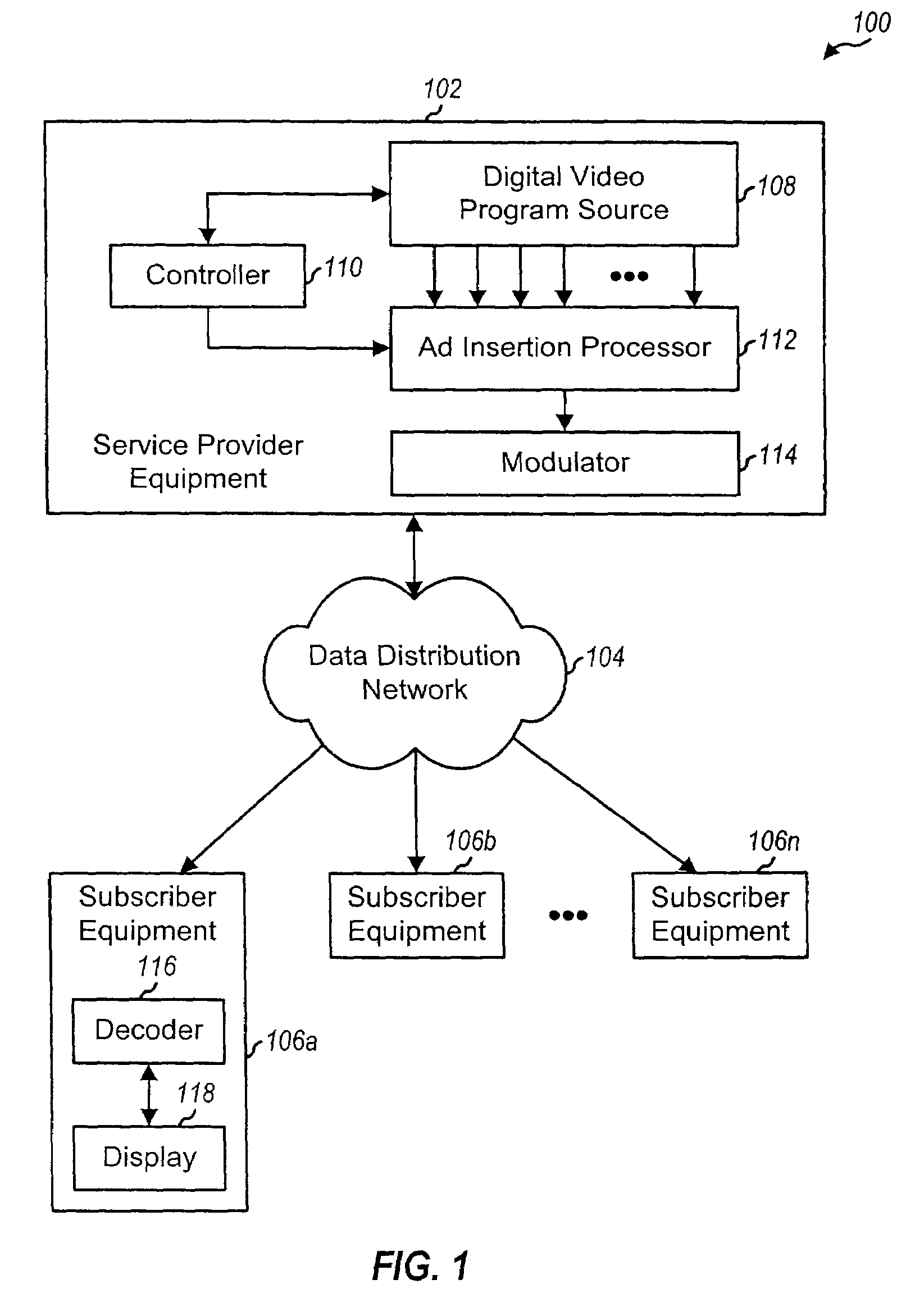
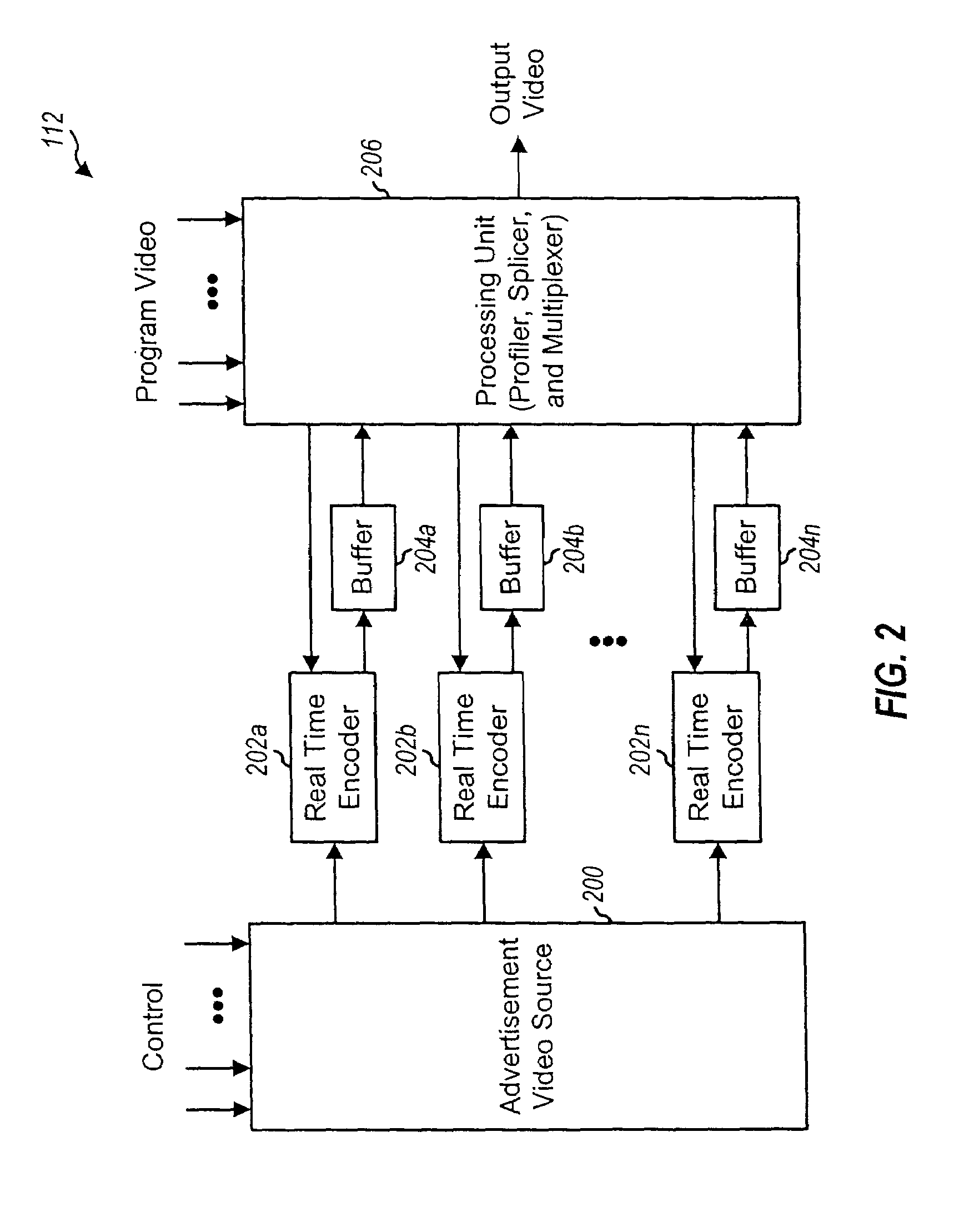
InactiveUS7394850B1Overcome disadvantagesFacilitating splicingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMultiplexer
Techniques for seamlessly inserting a second compressed video stream (e.g., for an advertisement) into a first compressed video stream (e.g., for a program video), which can be implemented in an ad insertion processor that typically includes a real time encoder (e.g., an MPEG encoder), a buffer, a profiler, a multiplexer, and a splicer. The profiler receives the first compressed video stream and provides a “profile” for the stream, which may include bit rate and other information about the stream. The real time encoder receives and encodes a second video in accordance with a particular encoding scheme to generate the second compressed video stream. The real time encoder further controls the encoding of the second video based at least in part on the profile of the first compressed video stream such that the profiles for the two streams are approximately similar at the point in time the second stream is inserted into the first stream. The buffer stores the first compressed video stream from the real time encoder until it is needed. The multiplexer inserts the second compressed video stream into the first compressed video stream, and the splicer splices the two streams together to form the output video stream.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Centralized resource manager
InactiveUS20060031887A1Overcome disadvantagesClosed circuit television systemsSelective content distributionPower switchingResource management
A centralized resource manager for distributed networks manages resources available on the network, such as network bandwidth, CPU allocation, TV tuners, MPEG encoders and decoders, disk bandwidth, and input / output devices. The centralized resource manager also allocates the resources of network clients and a network-associated media server, in response to requests for media services via the distributed network. The centralized resource manager may include means for discovering when devices are added or removed from the network; a current, IR, or electromagnetic field sensing system for determining when video devices are turned off so that resources associated with any device not in use may be reallocated elsewhere; or a power switching system for controlling the ON or OFF state of such devices so that resources associated with any device in the OFF state may be reallocated elsewhere.
Owner:UCENTRIC SYST
Method and apparatus for improving MPEG picture compression
InactiveUS20040131117A1Reduce componentsSharpens high contrast componentTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A processor changes frames of a videostream according to how an MPEG (Motion Picture Expert Group) encoder will encode them so that the output of the MPEG encoder has a minimal number of bits but a human eye generally does not detect distortion of the image in the frame.
Owner:SOMLE DEV
Encoding system and method, decoding system and method, multiplexing apparatus and method, and display system and method
InactiveUS7551672B1Avoid delayPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMPEG encodingPacketized elementary stream
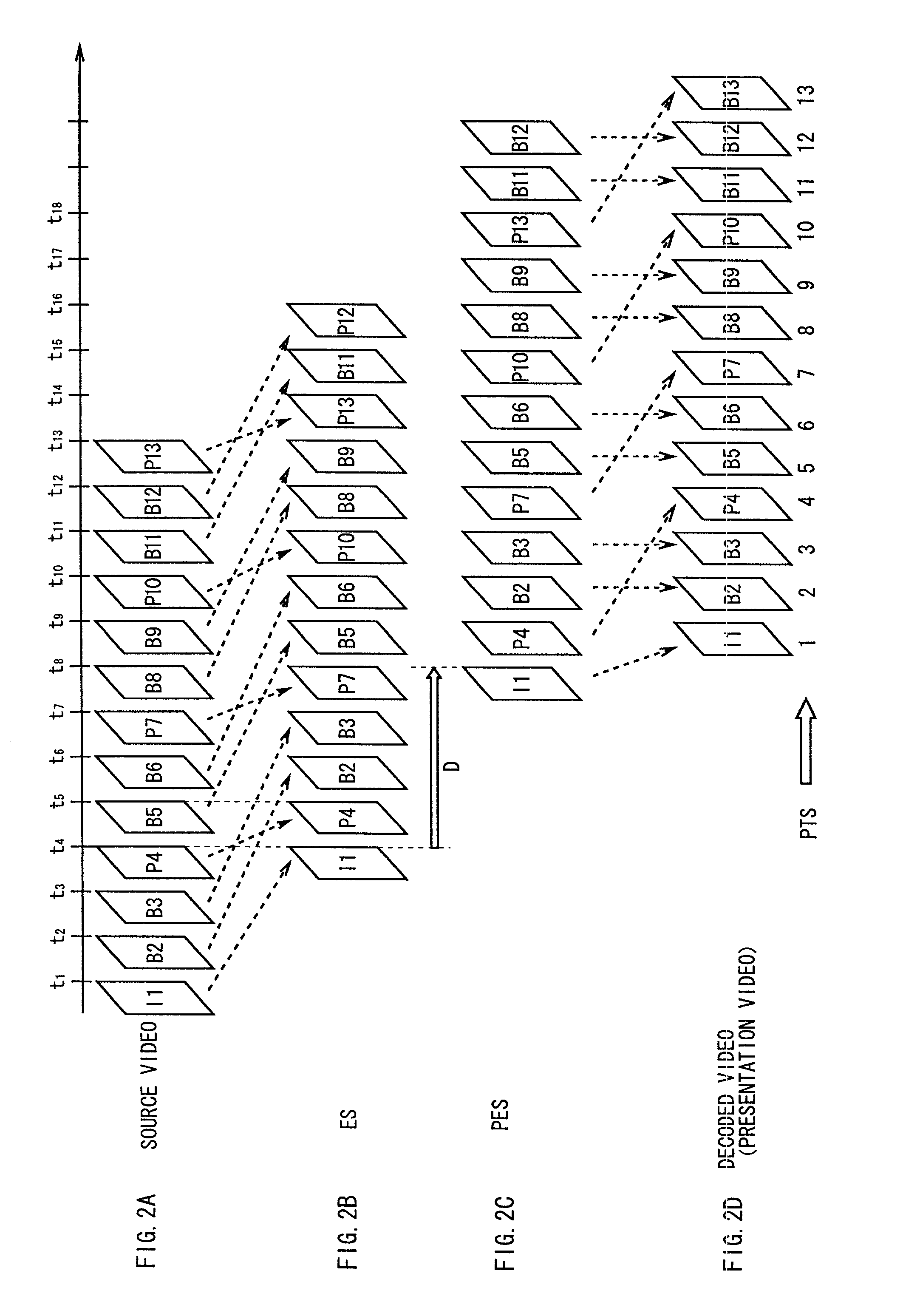
The present invention relates to an encoding system for encoding input video data and a multiplexing system for multiplexing a plurality of encoded streams. More particularly, it proposes a system and method that involve describing, in encoded streams, information on the picture order of input video data, and using the picture order information when generating packetized elementary stream (PES) packets, to prevent delays associated with the PES packet generation.MPEG encoders generate PTS_count and DTS_count based on the information obtained from the number of fields in the input video data and describe the PTS_count and DTS_count data as picture order information in encoded streams. The packetizers for generating packetized elementary stream take out PTS_count and DTS_count described in the encoded streams, generate presentation time stamps and decoding time stamps based on PTS_count and DTS_count, and add these time stamps as PES header data.
Owner:SONY CORP
MPEG encoder control protocol for on-line encoding and MPEG data storage
InactiveUS6907081B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionRemote controlGroup of pictures
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
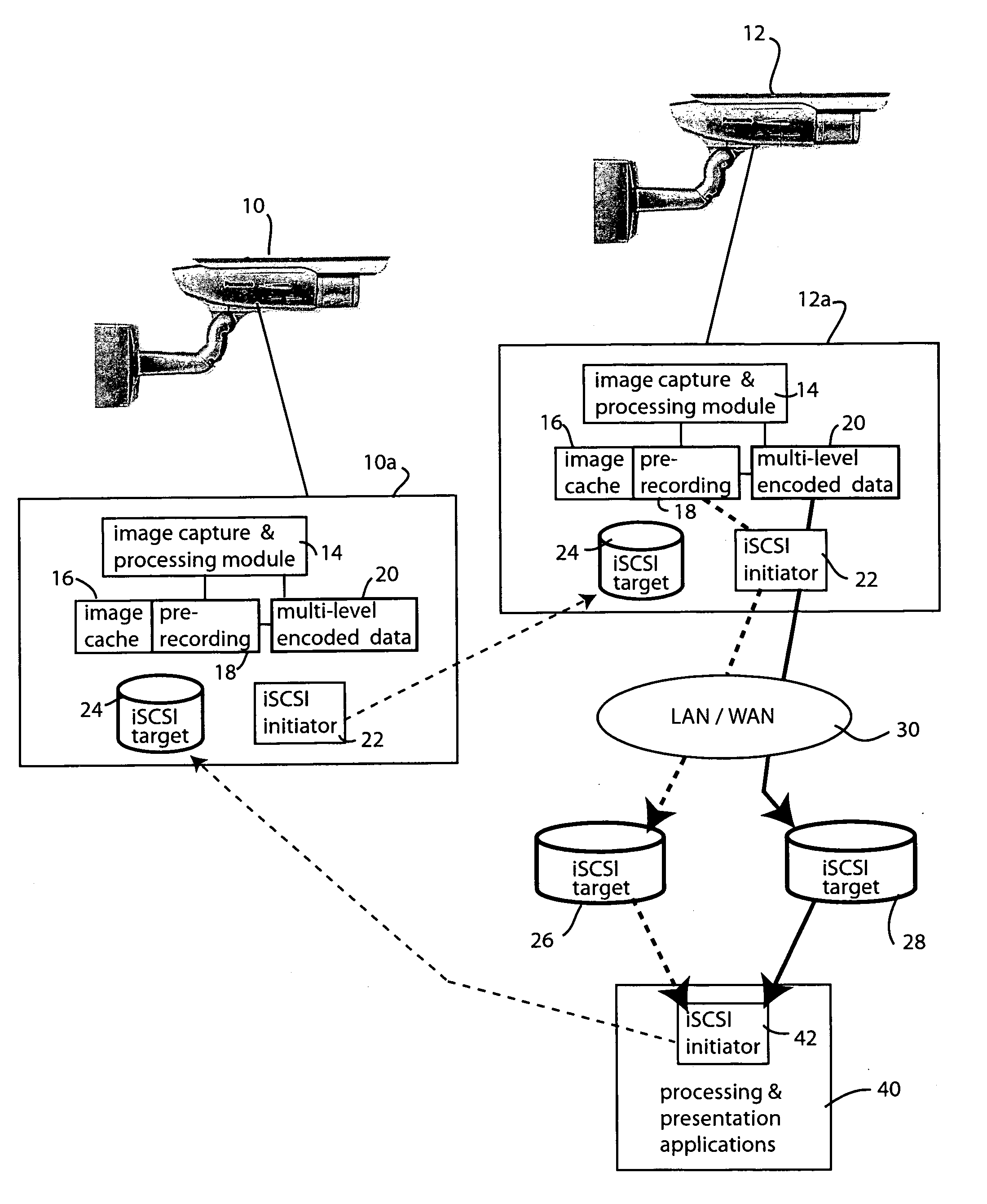
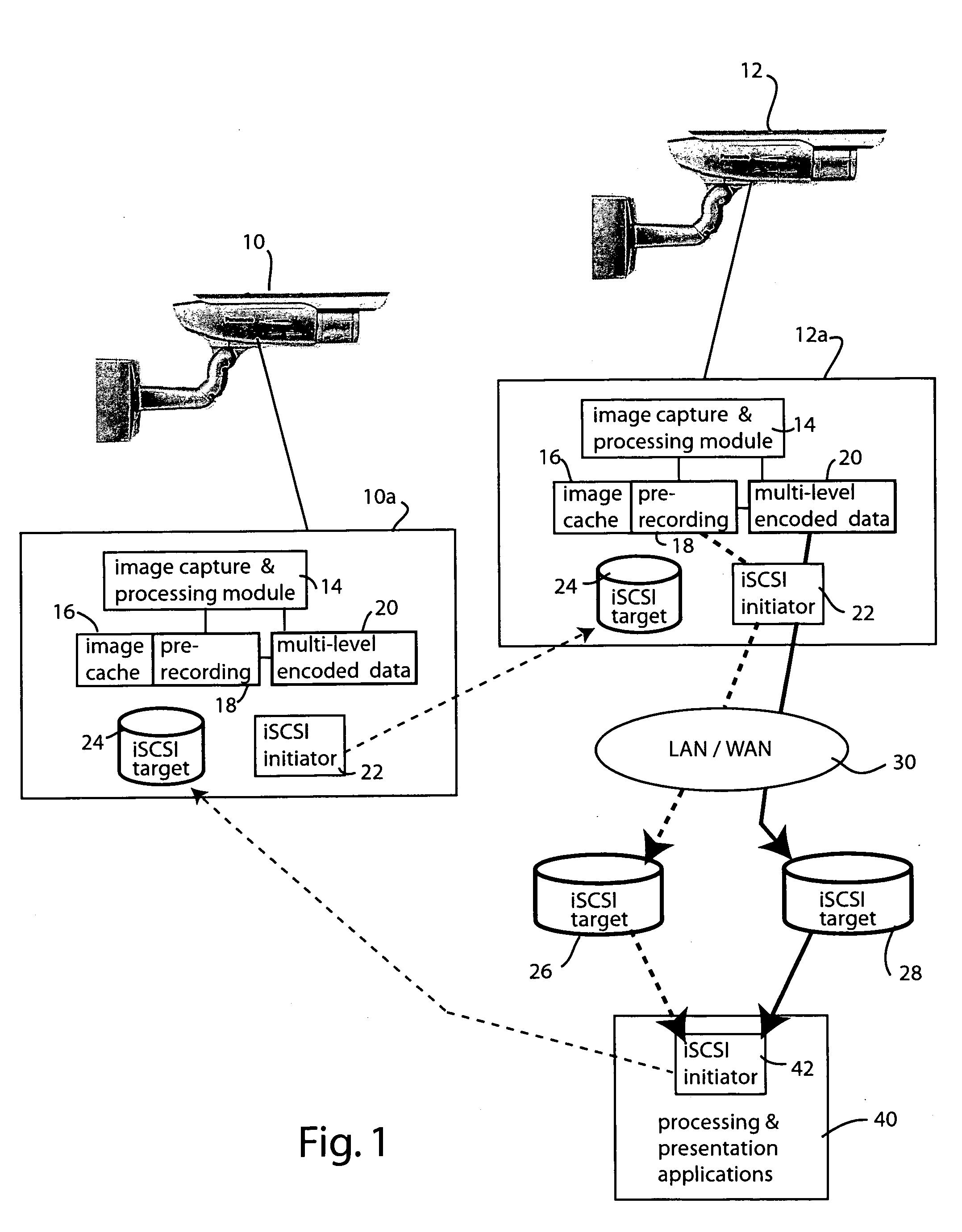
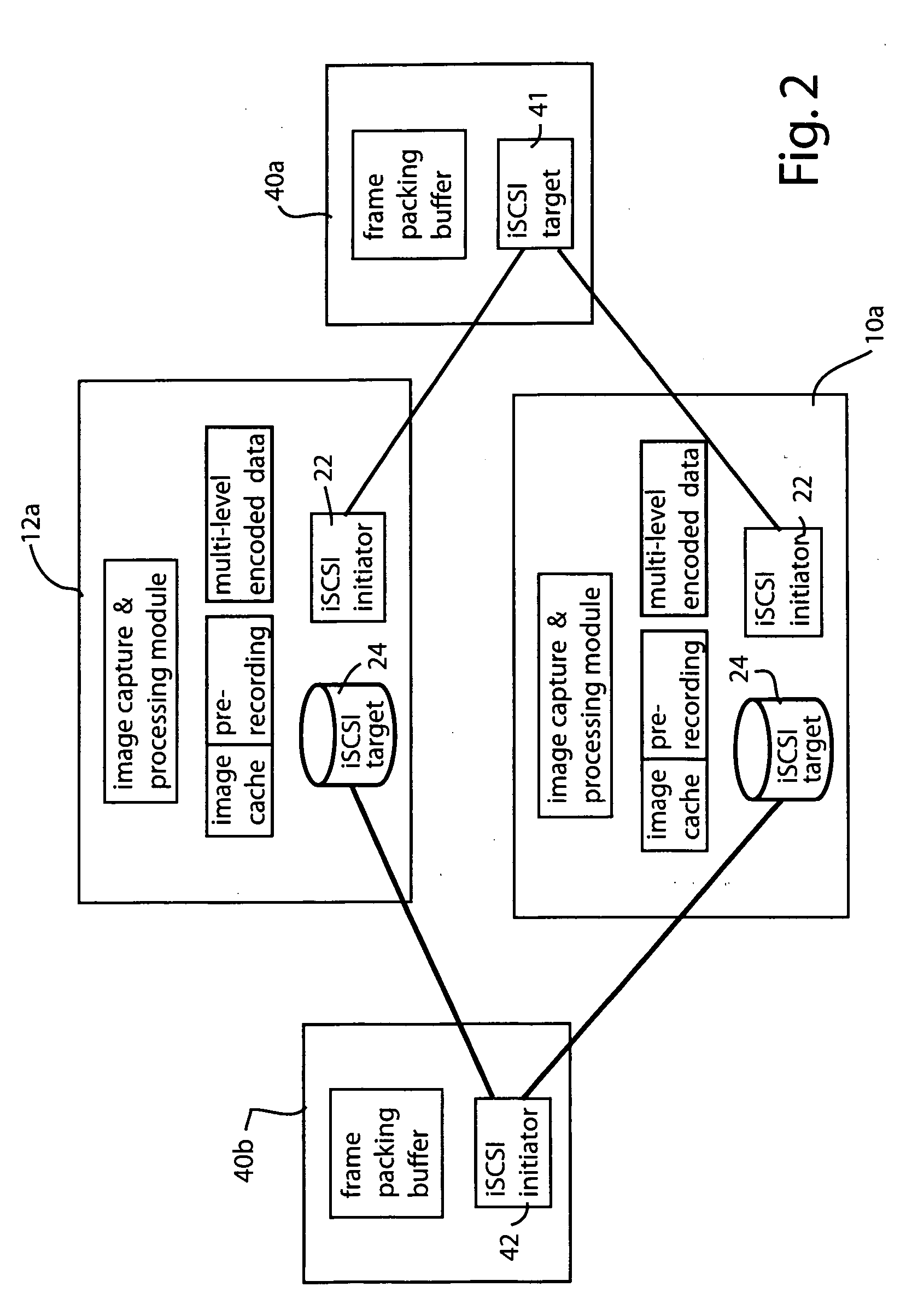
Secure and private iSCSI camera network
InactiveUS20060181612A1Efficient processingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer hardwareThe Internet
A peer-to-peer camera sensor network is defined using intelligent cameras that employ iSCSI initiators and iSCSI targets to read and write data and to send control commands directly across the network as iSCSI blocks. Because data transfer rides on top of the internet protocol, cameras can be directly attached to the internet without requiring attachment to a host computer. Image data represented as video frames are mapped onto iSCSI data blocks and are shared among the cameras directly to form an efficient virtual block level video image frame storage that can be directly manipulated by multiple cameras without data replications. Transport of multiple streams, associated with scalable or multilevel MPEG encoding scheme for instance, are automatically sequenced and realigned as the iSCSI data blocks are time-aligned.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com