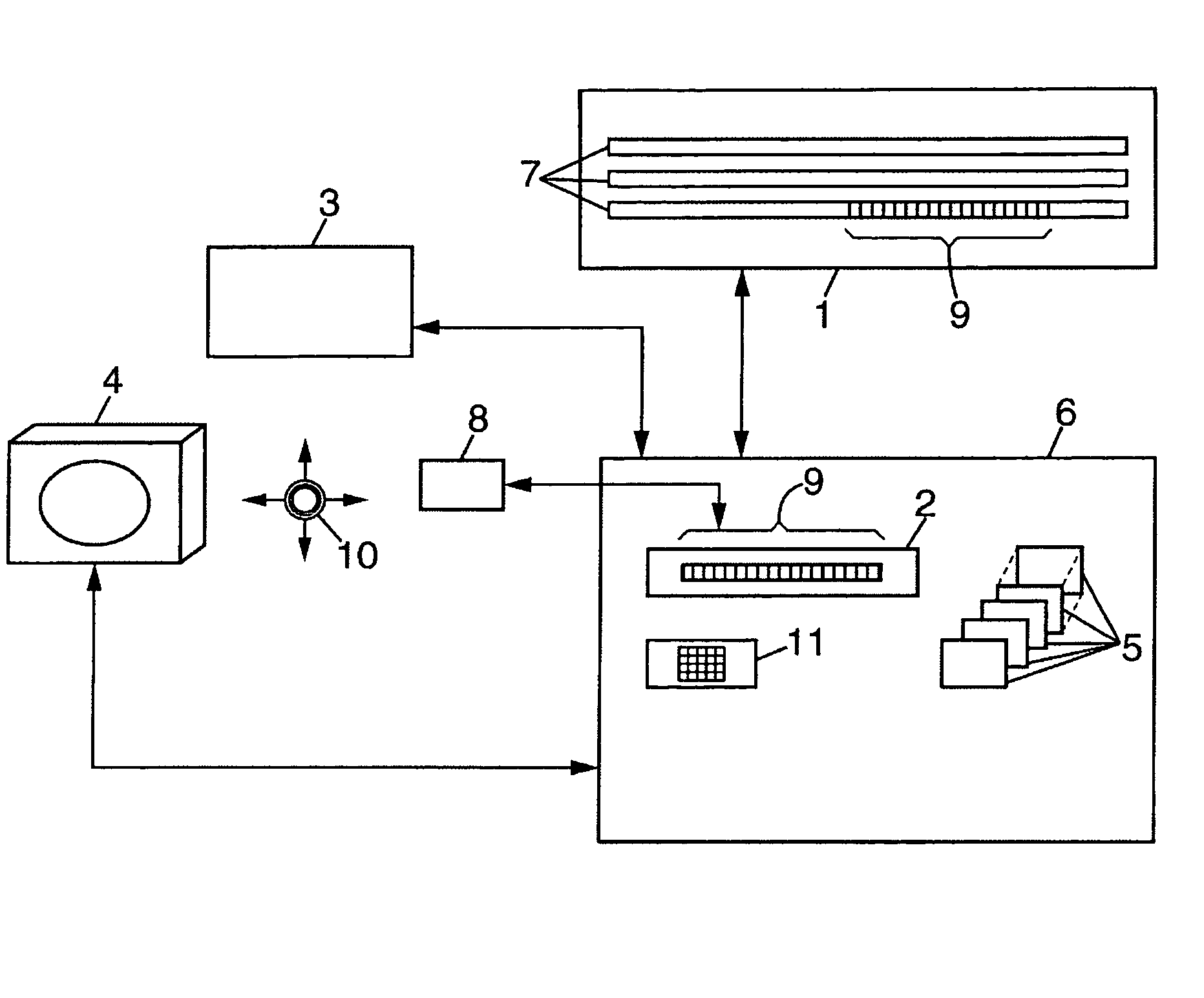
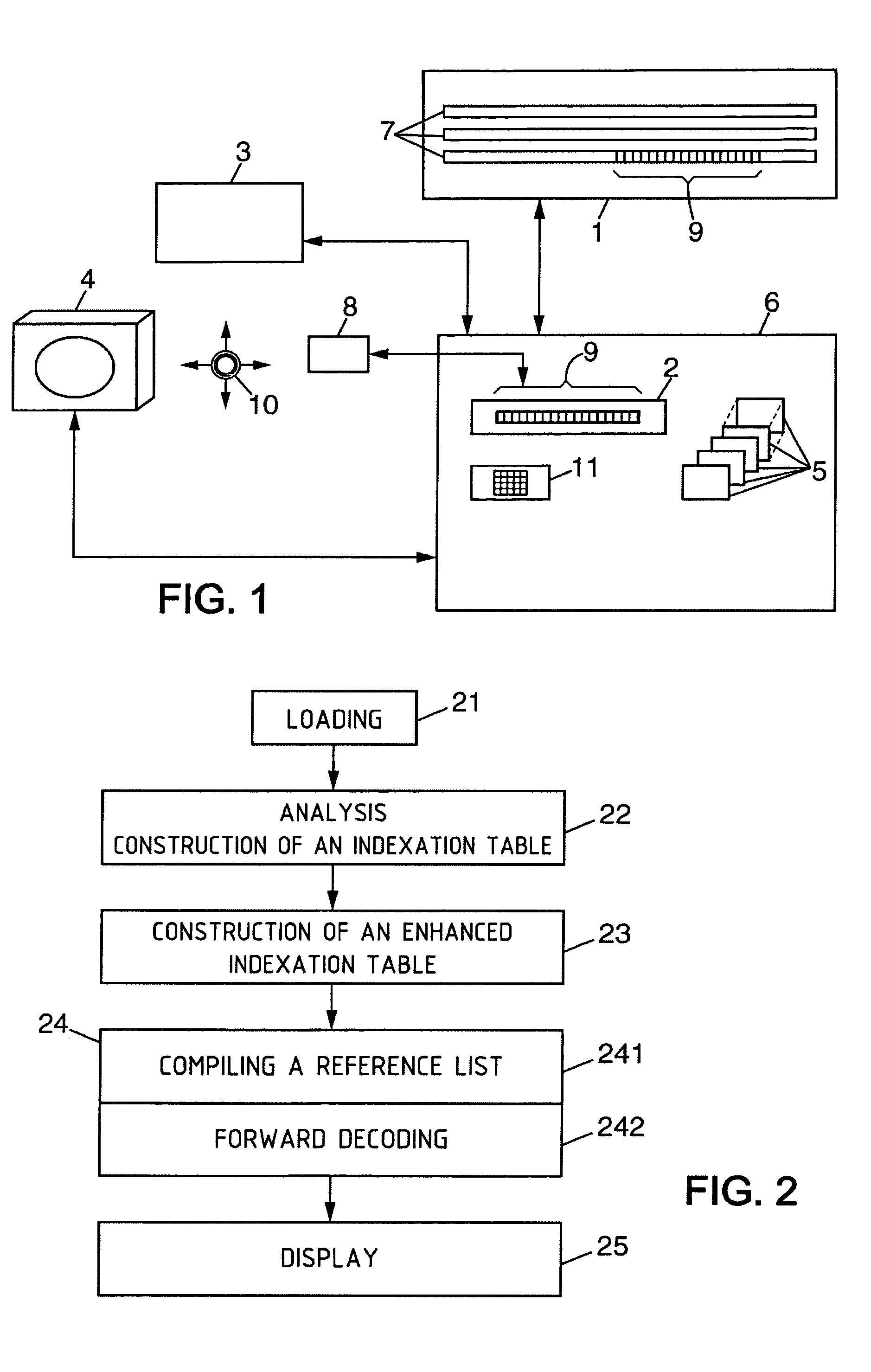
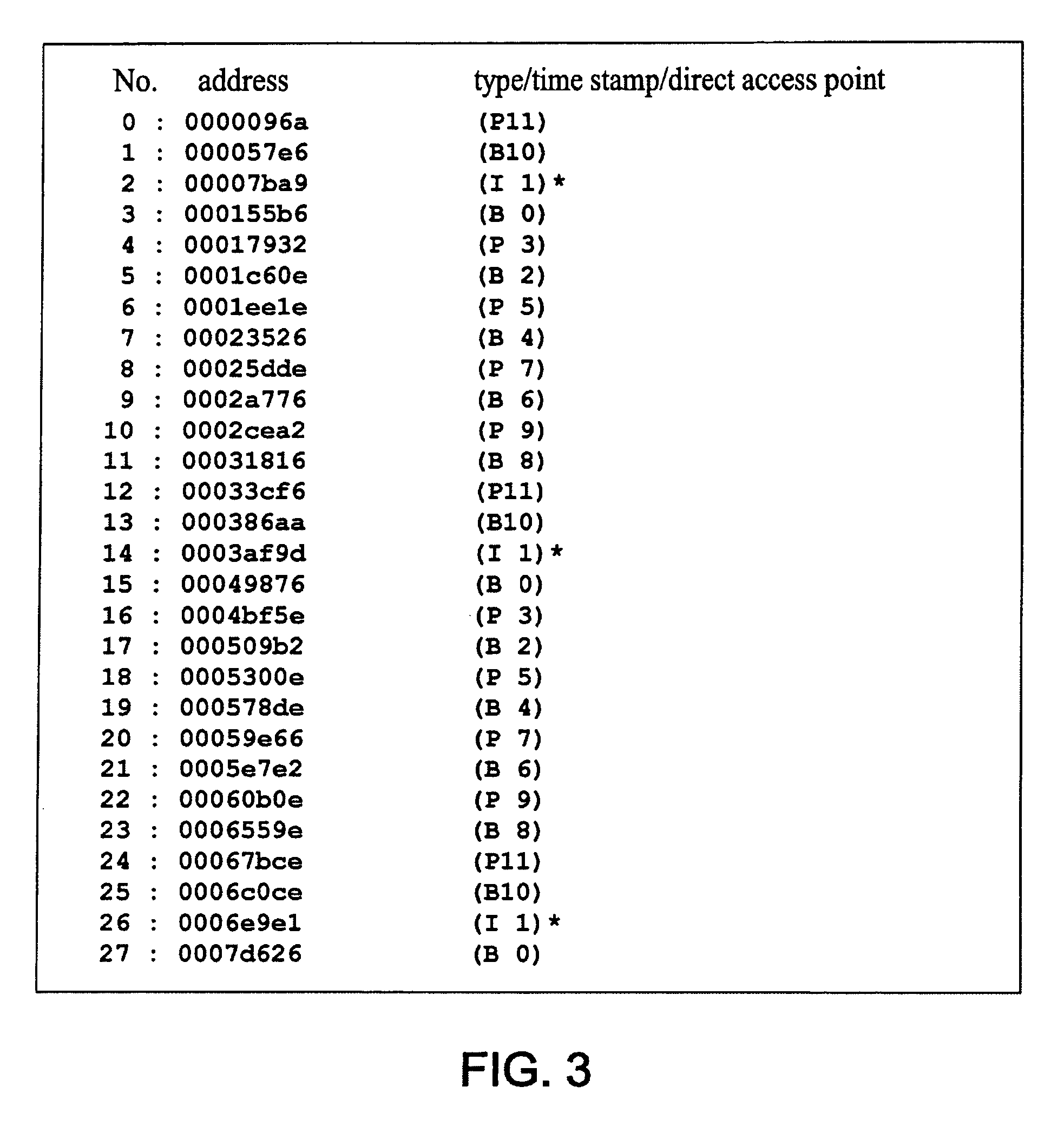
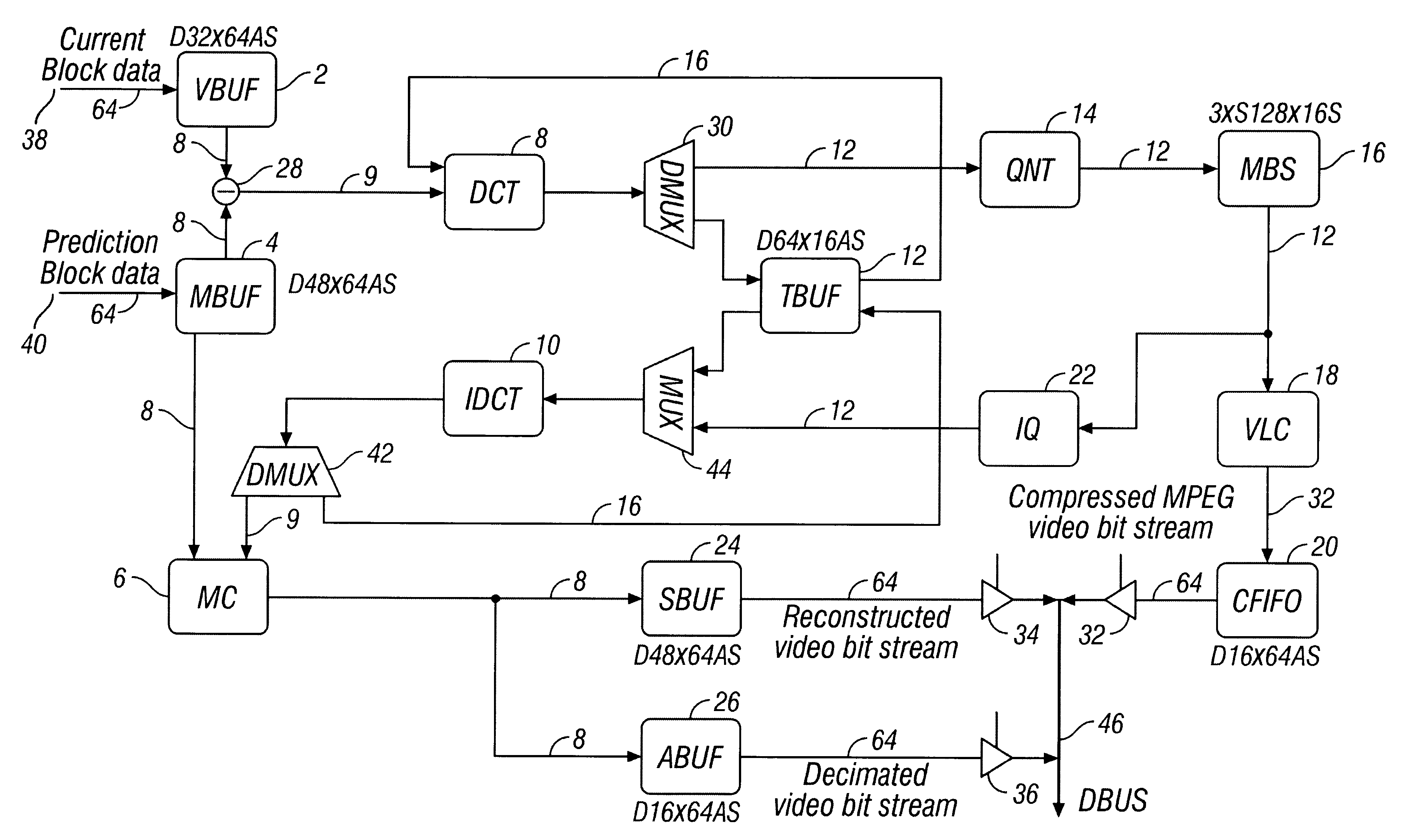
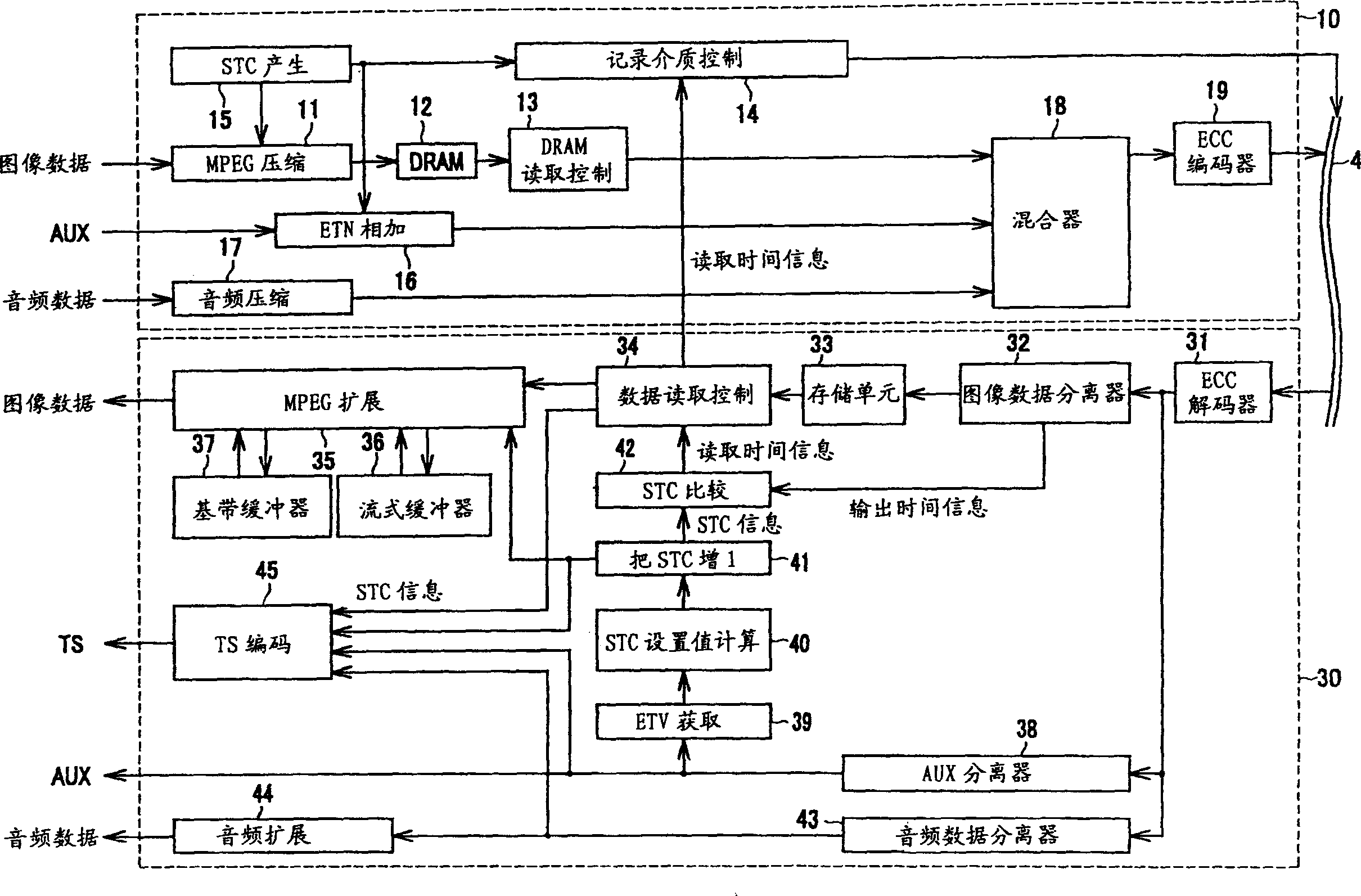
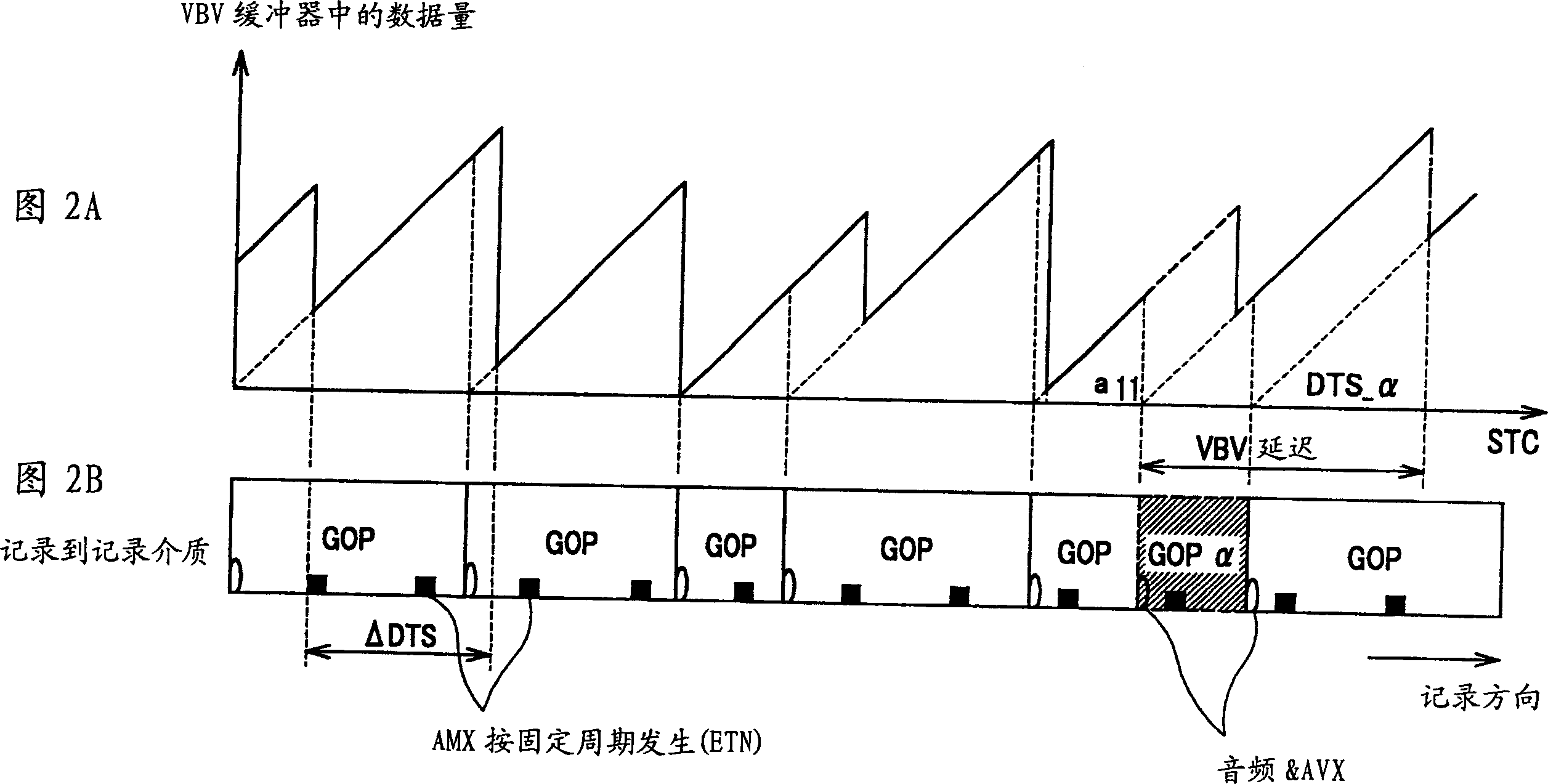
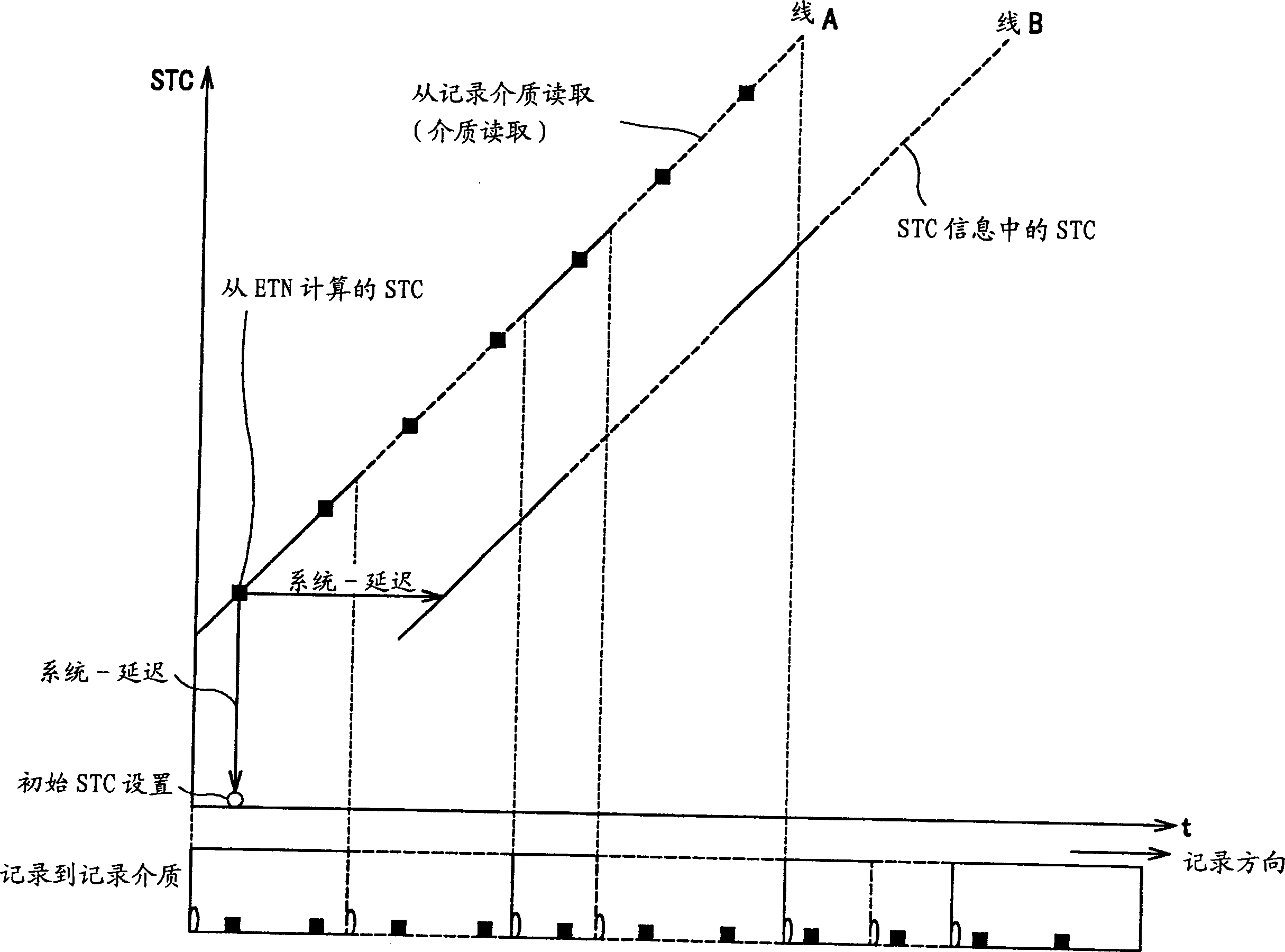
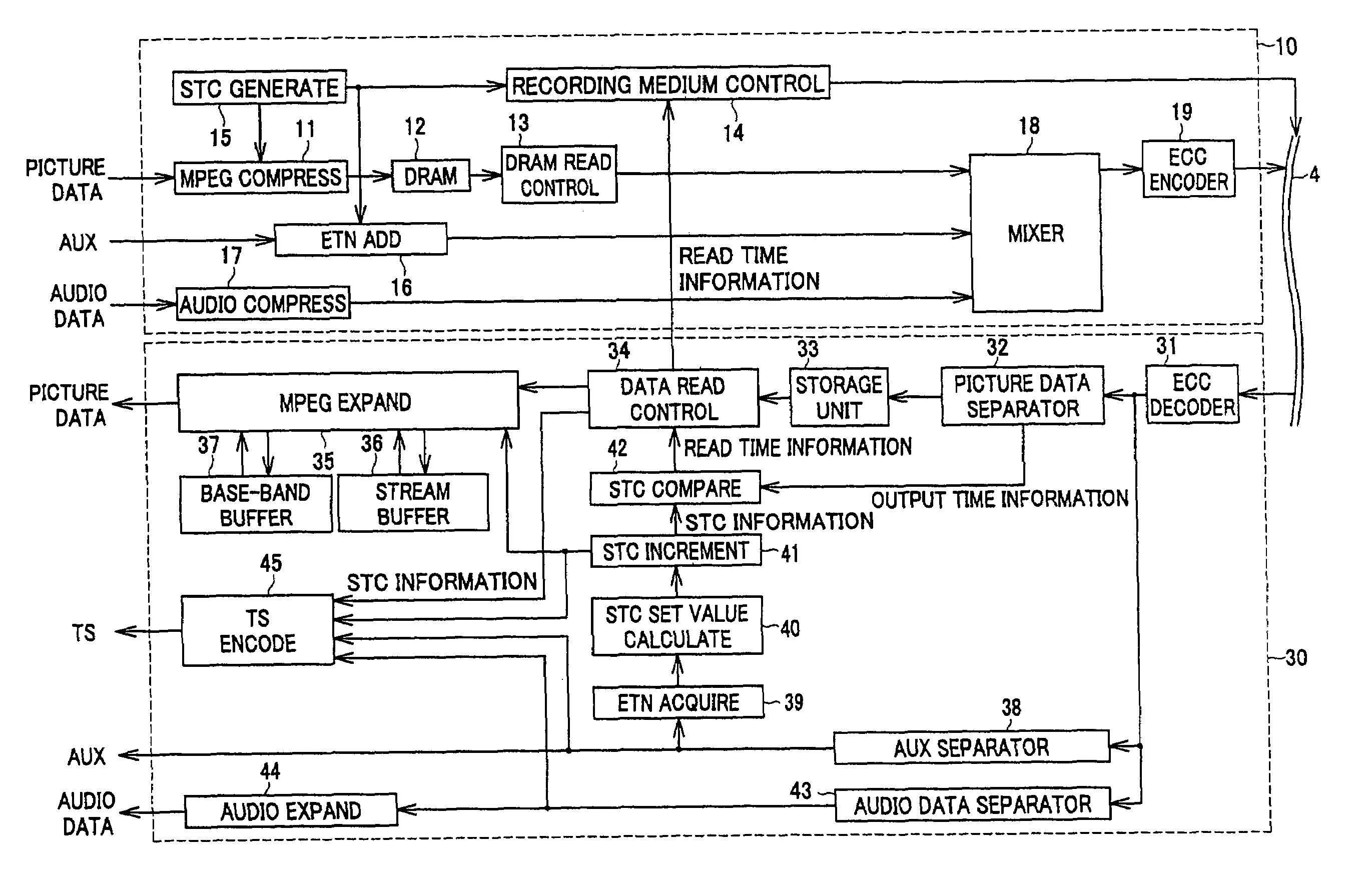
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Mpeg standards" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
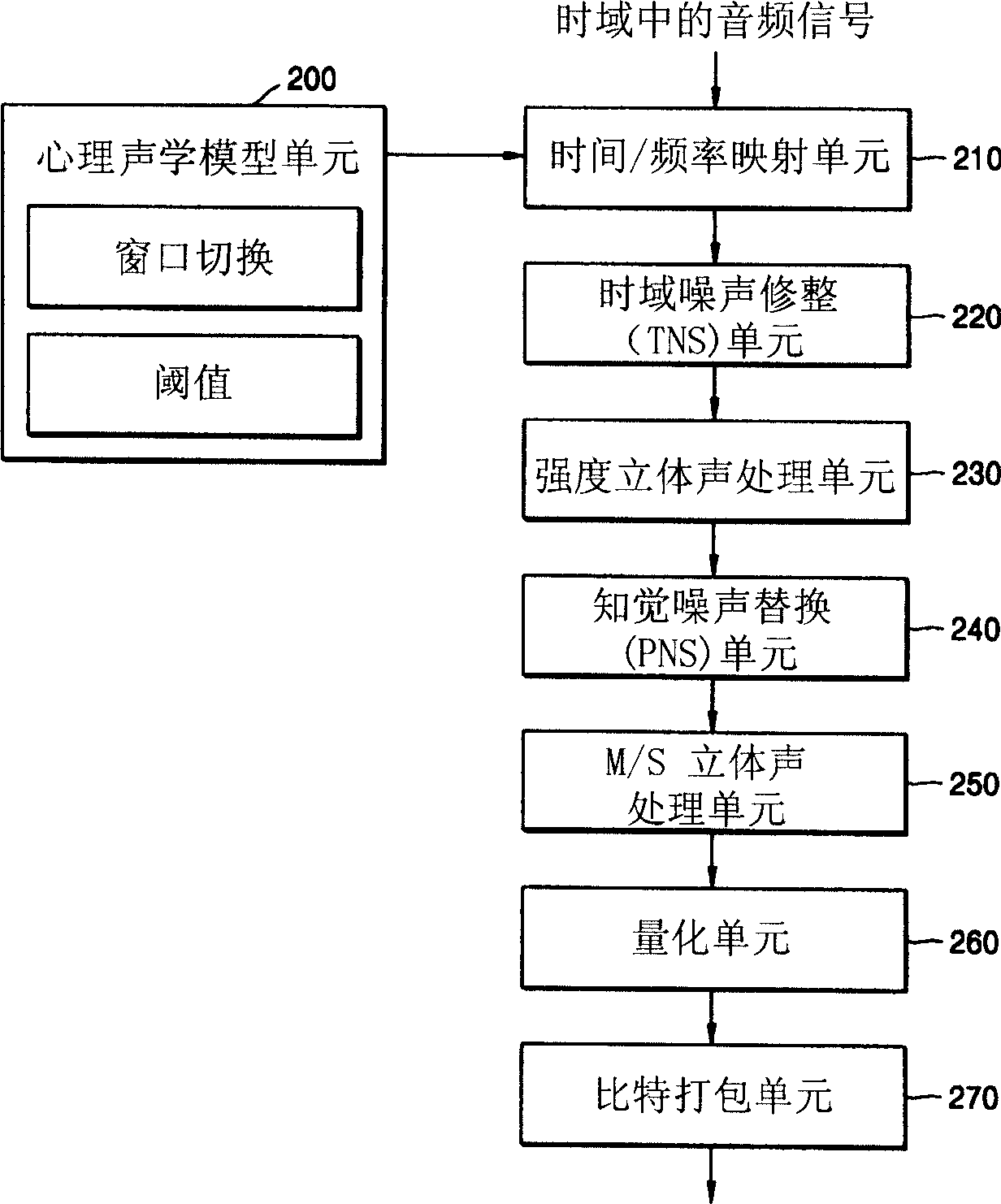
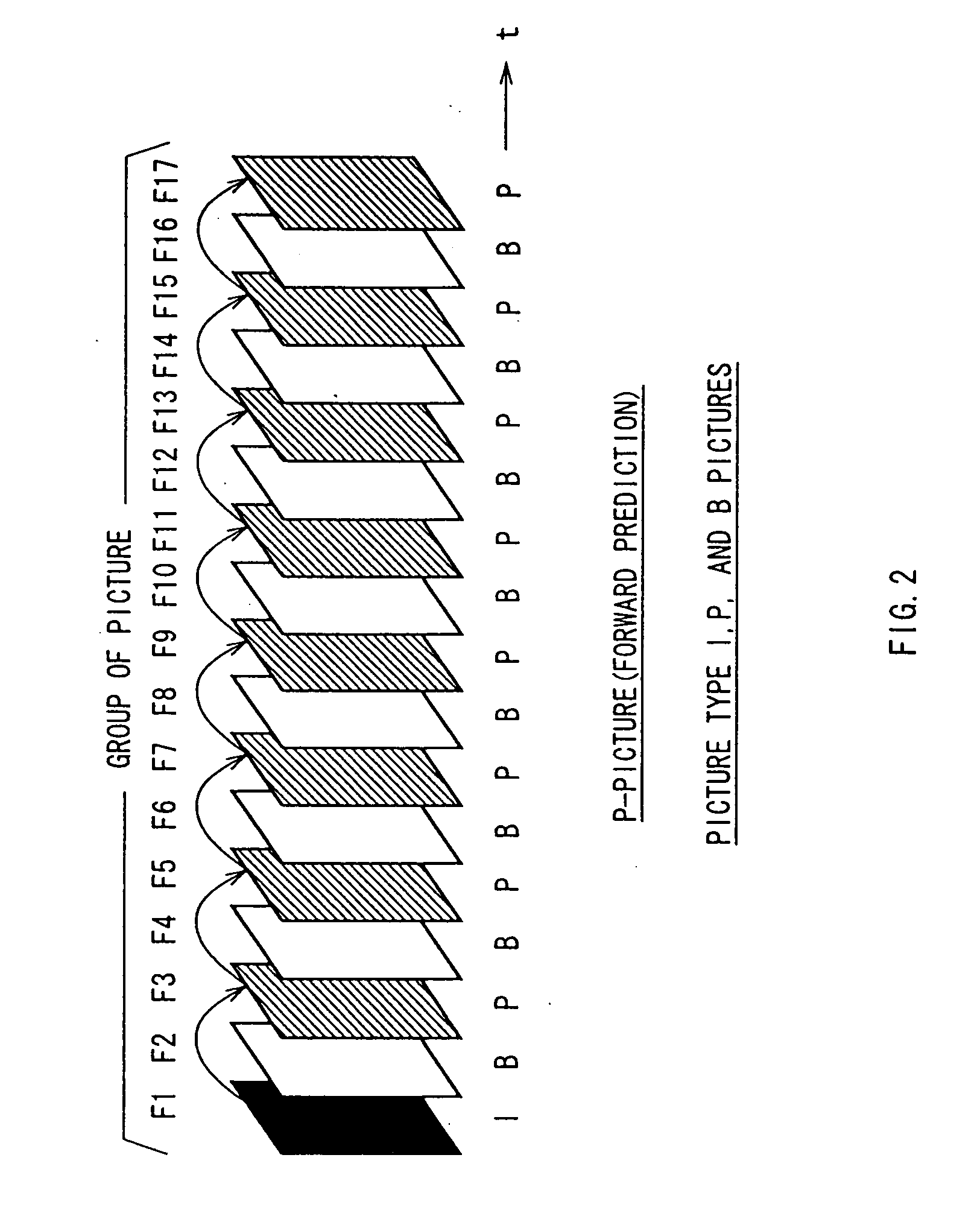
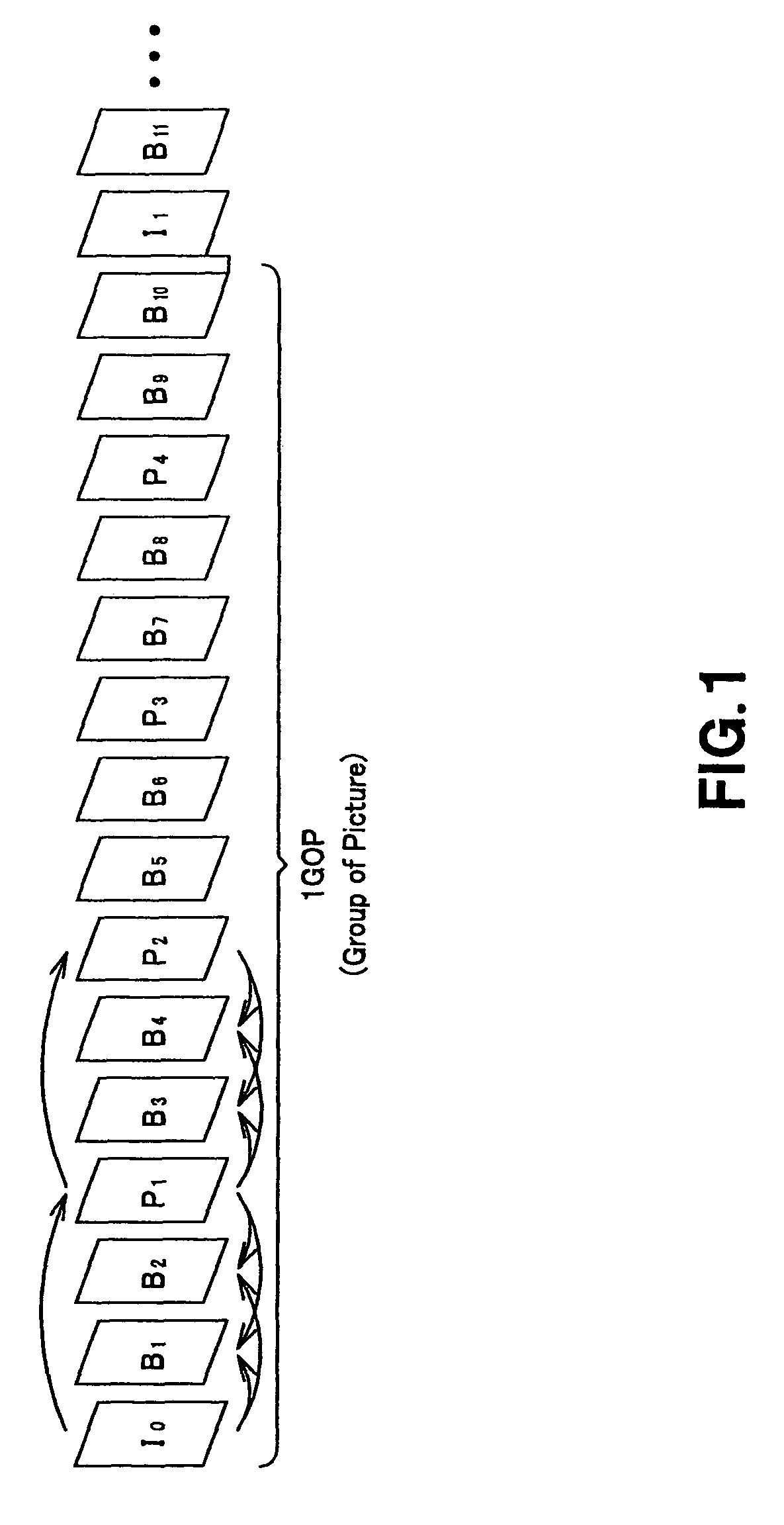
Some of the approved MPEG standards were revised by later amendments and/or new editions. MPEG has standardized the following compression formats and ancillary standards: MPEG-1 (1993): Coding of moving pictures and associated audio for digital storage media at up to about 1.5 Mbit/s (ISO/IEC 11172).
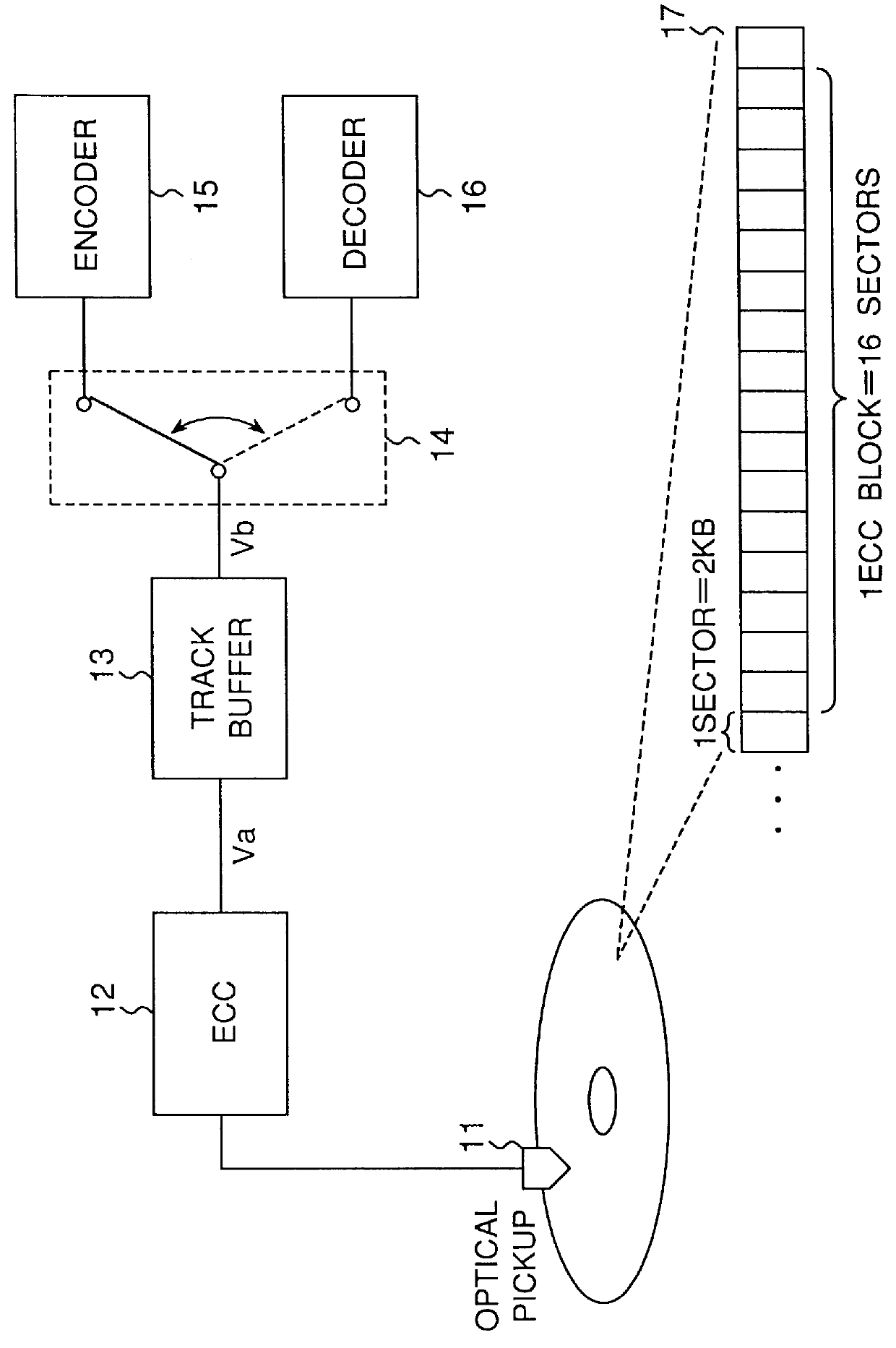
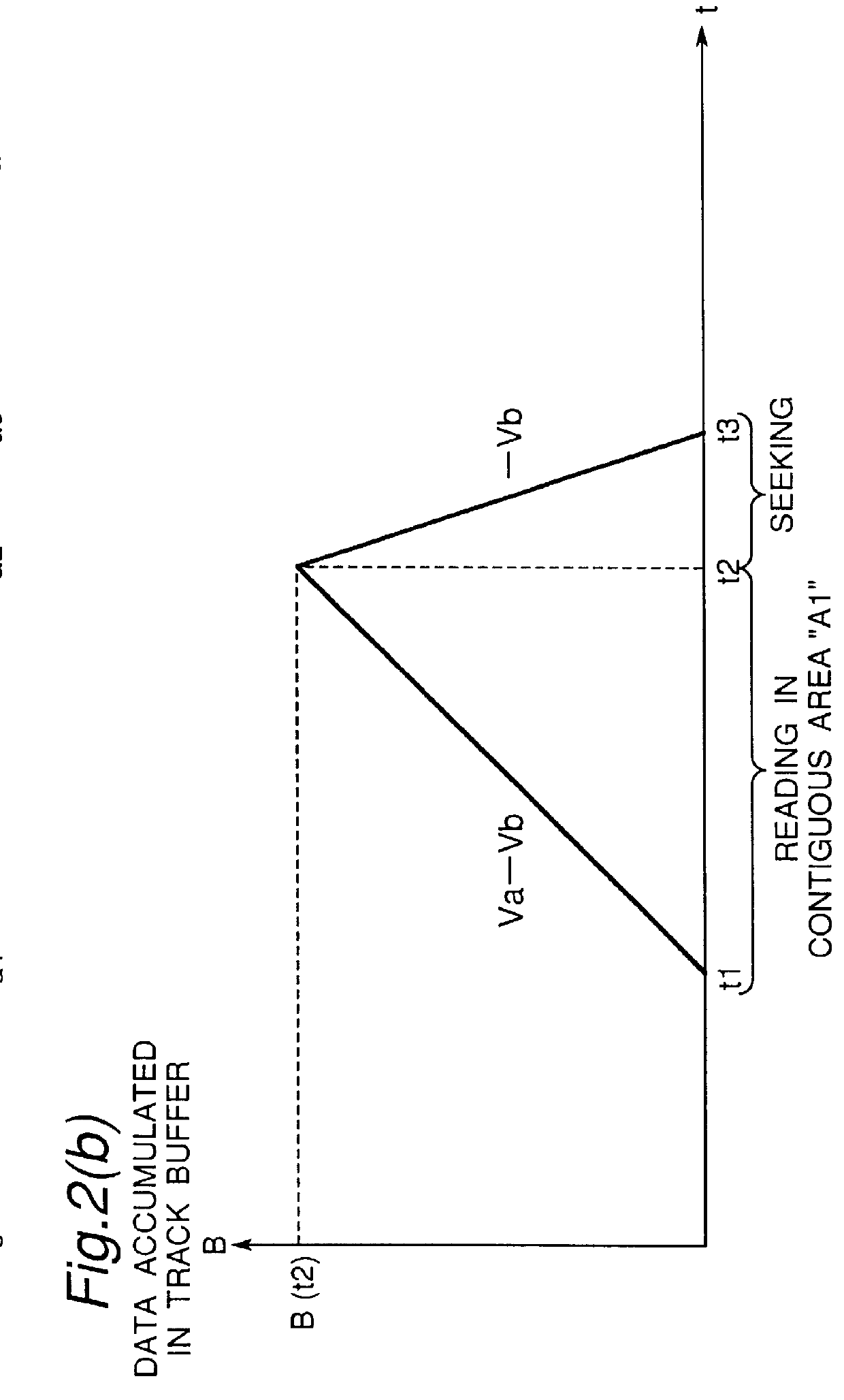
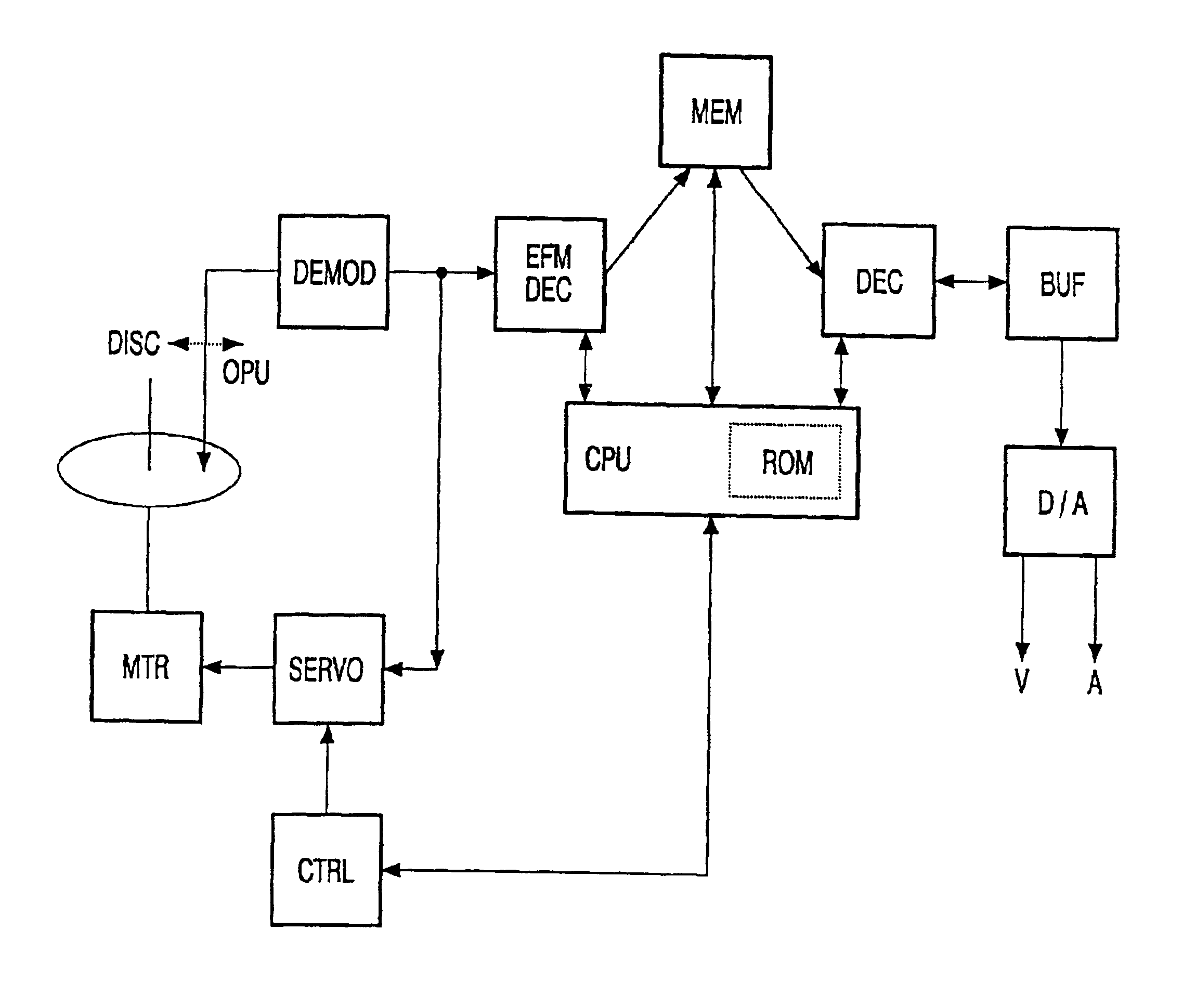
Optical disc, optical disc recording method and apparatus, and optical disc reproducing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6122436ATelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMpeg standardsAudio frequency
An optical disc that is reproducible by a reproducing apparatus has a still picture data and an audio data which are reproduced simultaneously. The still picture data is stored in a video part stream (ST1) comprising a plurality of units, and the audio data is stored in a second system stream (ST2) comprising one or a plurality of units. The units store time stamp information so that the second system stream (ST2) follows immediately after the video part stream (ST1). By changing the data in the second system stream (ST2), the audio data presented with a still picture can be freely and easily changed even after recording the still picture data using an MPEG standard format.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Coding system and its method, coding device and its method, decoding device and its method, recording device and its method, and reproducing device and its method
InactiveUS7236526B1Quality improvementMinimize degradation of image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging qualityGroup of pictures
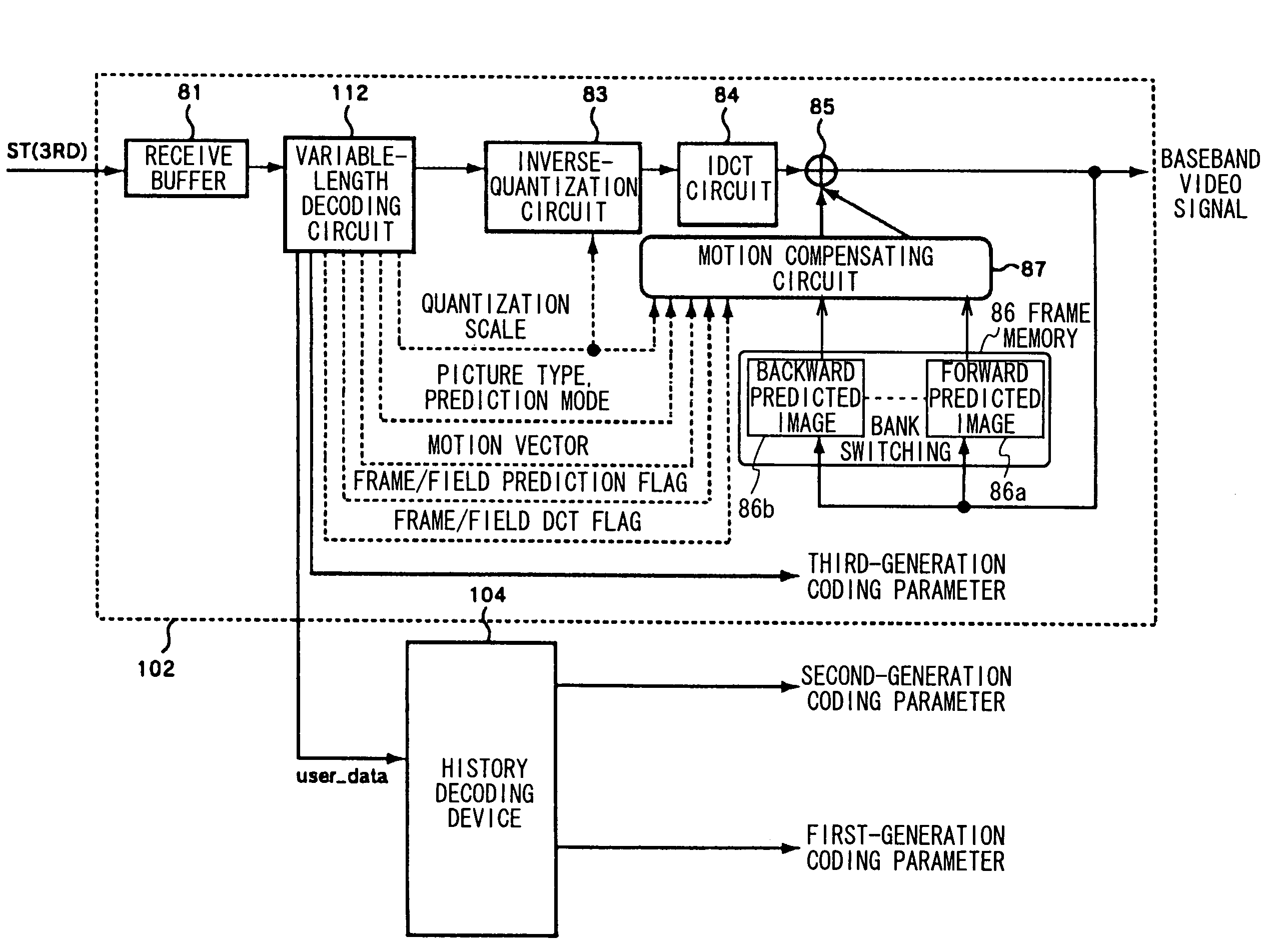
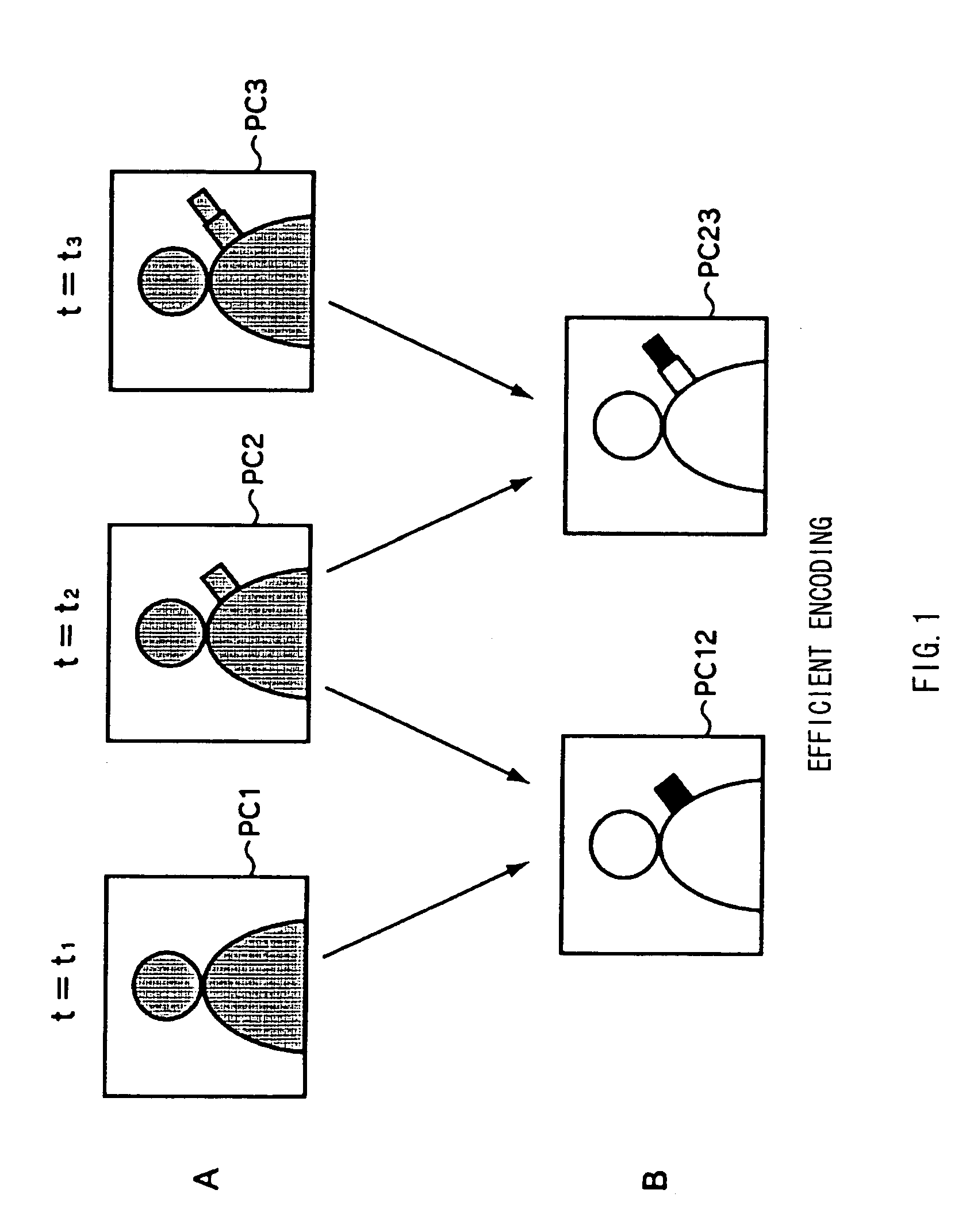
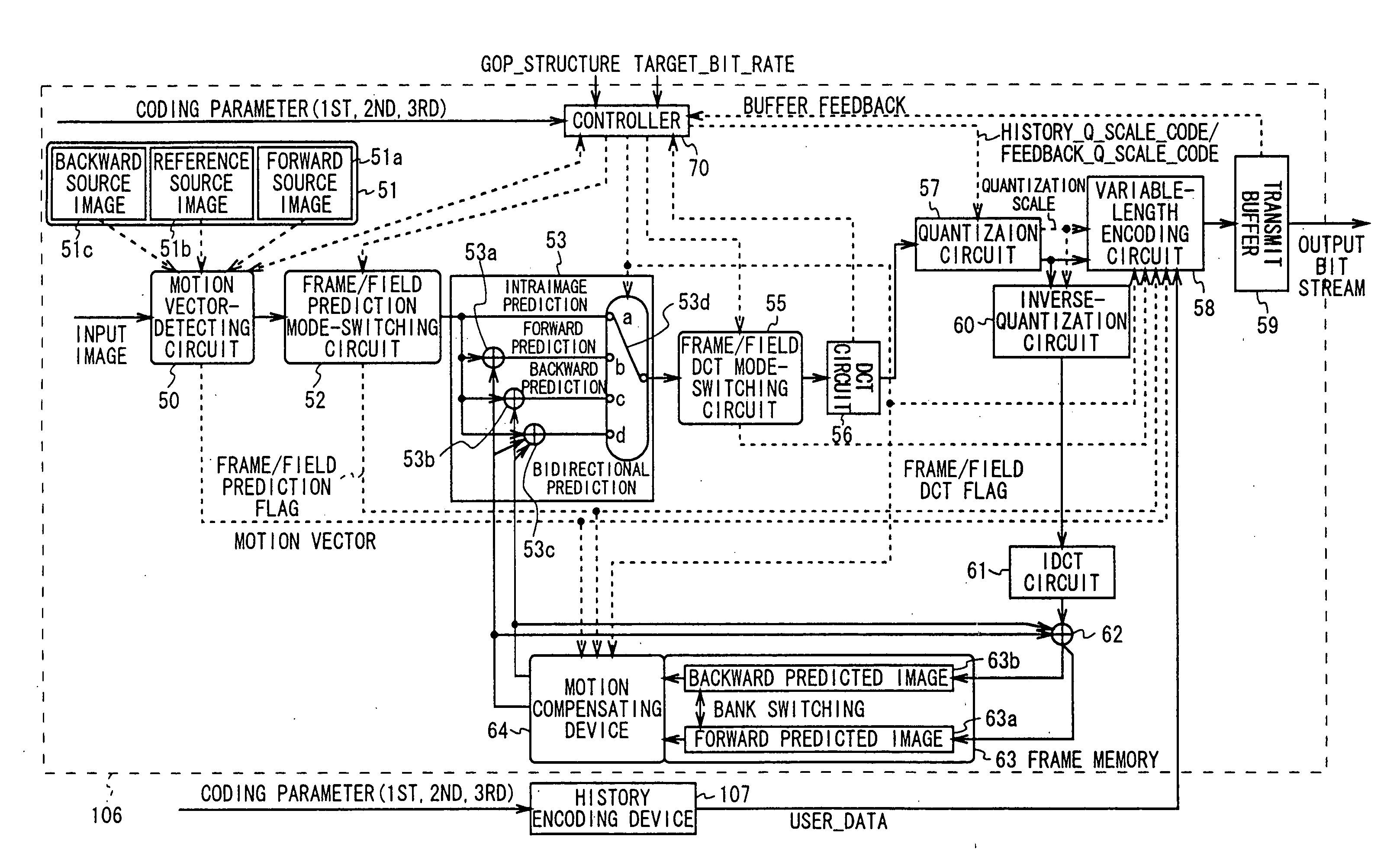
The present invention relates to a transcoder for executing a re-coding process on an encoded stream generated based on an MPEG standard in order to generate a re-coded stream having a different GOP (Group of Pictures) structure or bit rate.Specifically, a decoding device of a transcoder 106 decodes a source encoded stream to generate decoded video data and extracts past coding parameters superposed in the encoded stream as history_stream( ). In this case, the decoding device extracts the past coding parameters based on information superposed in the encoded stream as re_coding_stream_info( ).An encoding device receives the decoded video data and the past coding parameters and uses the past coding parameters to carry out an encoding process in a manner such that this process will not degrade image quality, thereby generating a re-coded stream. Further, the encoding device selects one of the past coding parameters which are optimal for an application connectively following the encoding device and describes only the selected past coding parameters in the encoded stream as history_stream( ). The encoding device superposes, as re_coding_stream_info( ), information indicating the selected past coding parameters so that the following application can properly extract the coding parameters for the history_stream( ) from the re-coded stream.
Owner:SONY CORP
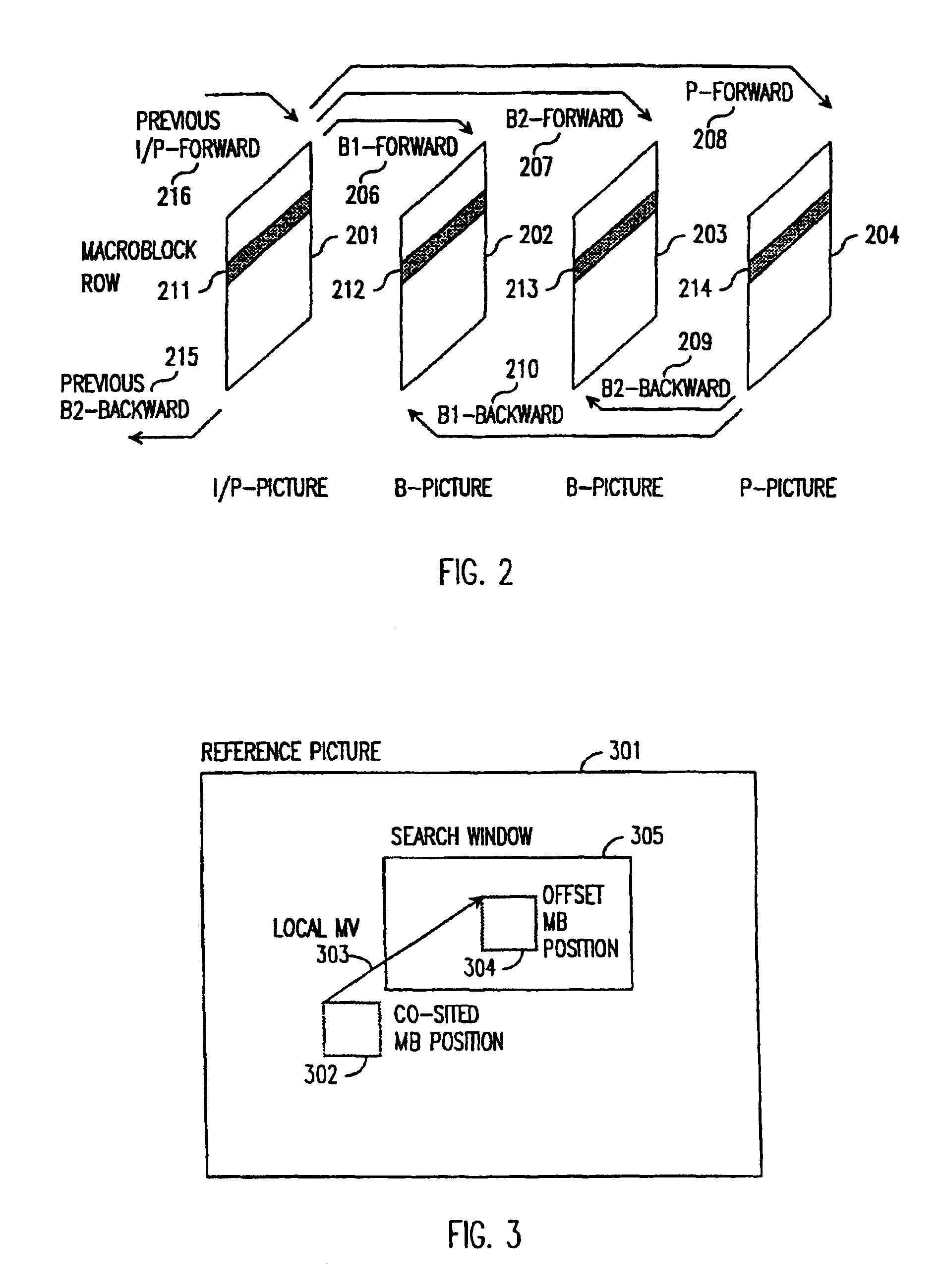
Motion vector detection with local motion estimator
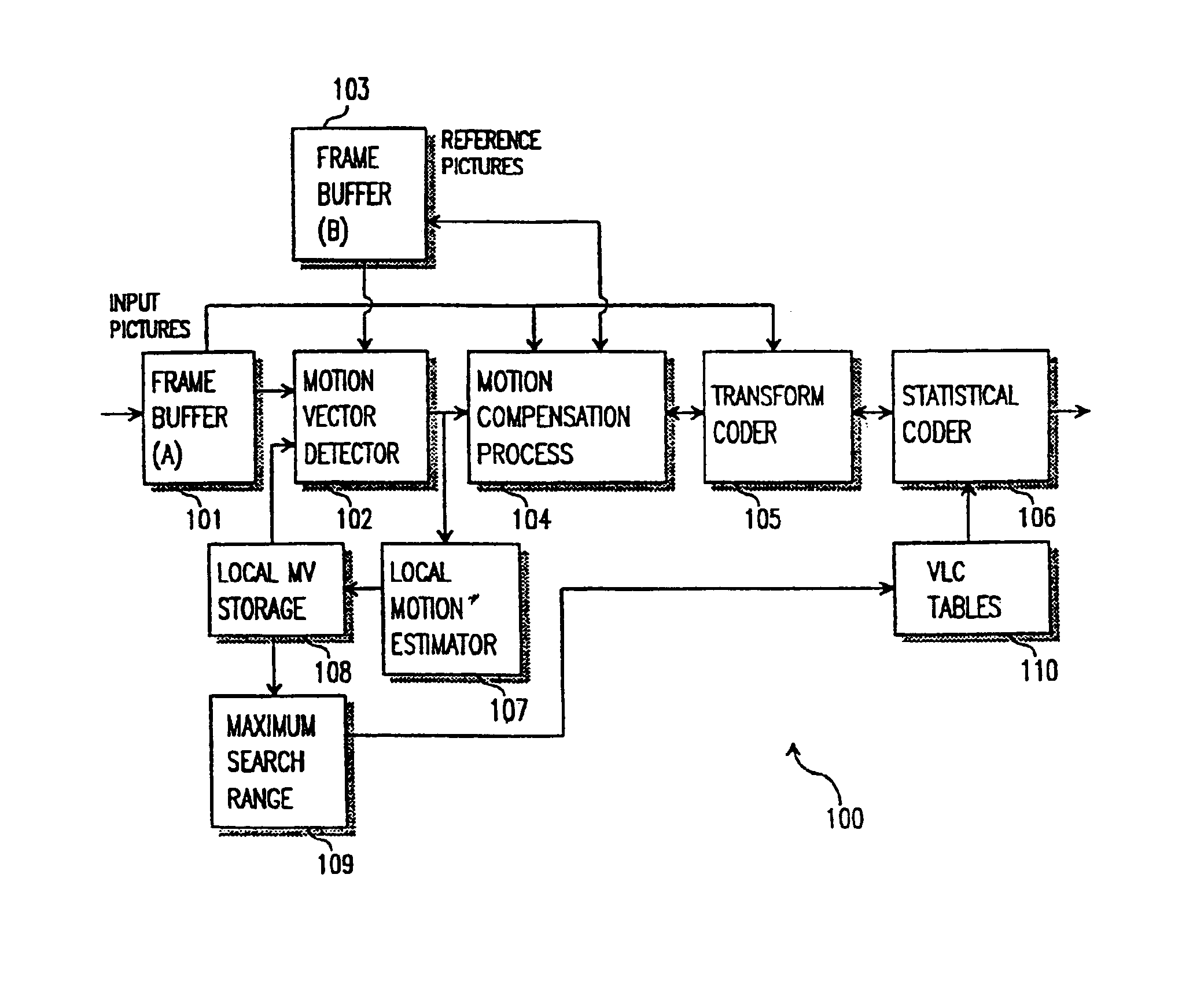
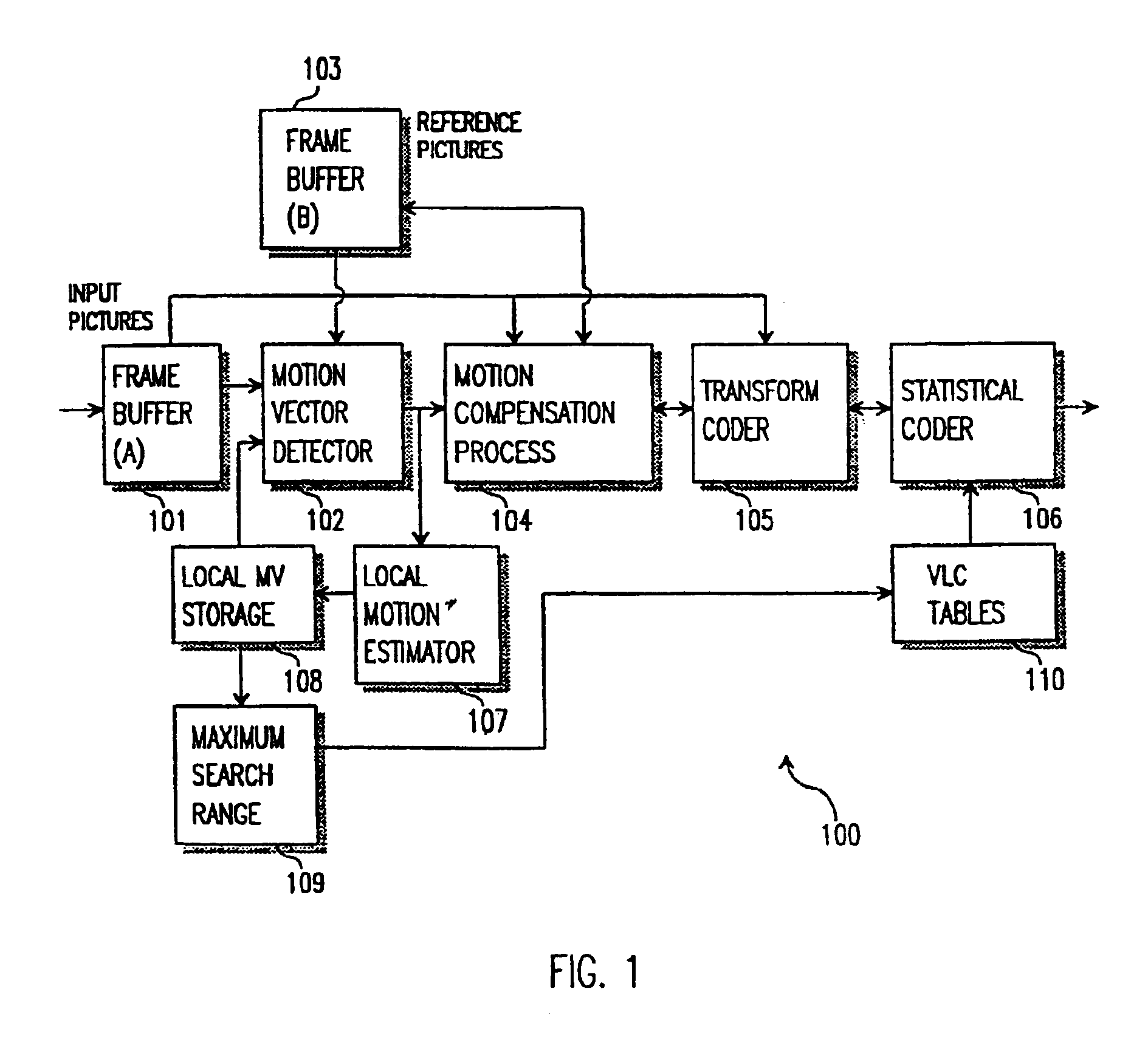
InactiveUS6876702B1Increase the search rangeMinimized search windowColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMPEG-1
A method and apparatus of encoding digital video, for example according to the ISO / IEC MPEG standards (ISO / IEC 11172-2 MPEG-1 and ISO / IEC 13818-2 MPEG-2), which employs a local motion estimator for determining respective local motion vectors for groups of adjacent macroblocks in a picture. A local motion vector is determined for each row of macroblocks in a picture from the motion vectors of the macroblocks in that row. Then, for macroblocks in the corresponding row of a subsequently coded picture, the local motion vector can be used to select the search window used for determining the motion vectors. The local motion estimator improves search range and accuracy of macroblock motion vector detection without increasing the search window accessing bandwidth and caching requirement, and computation lode of searching.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
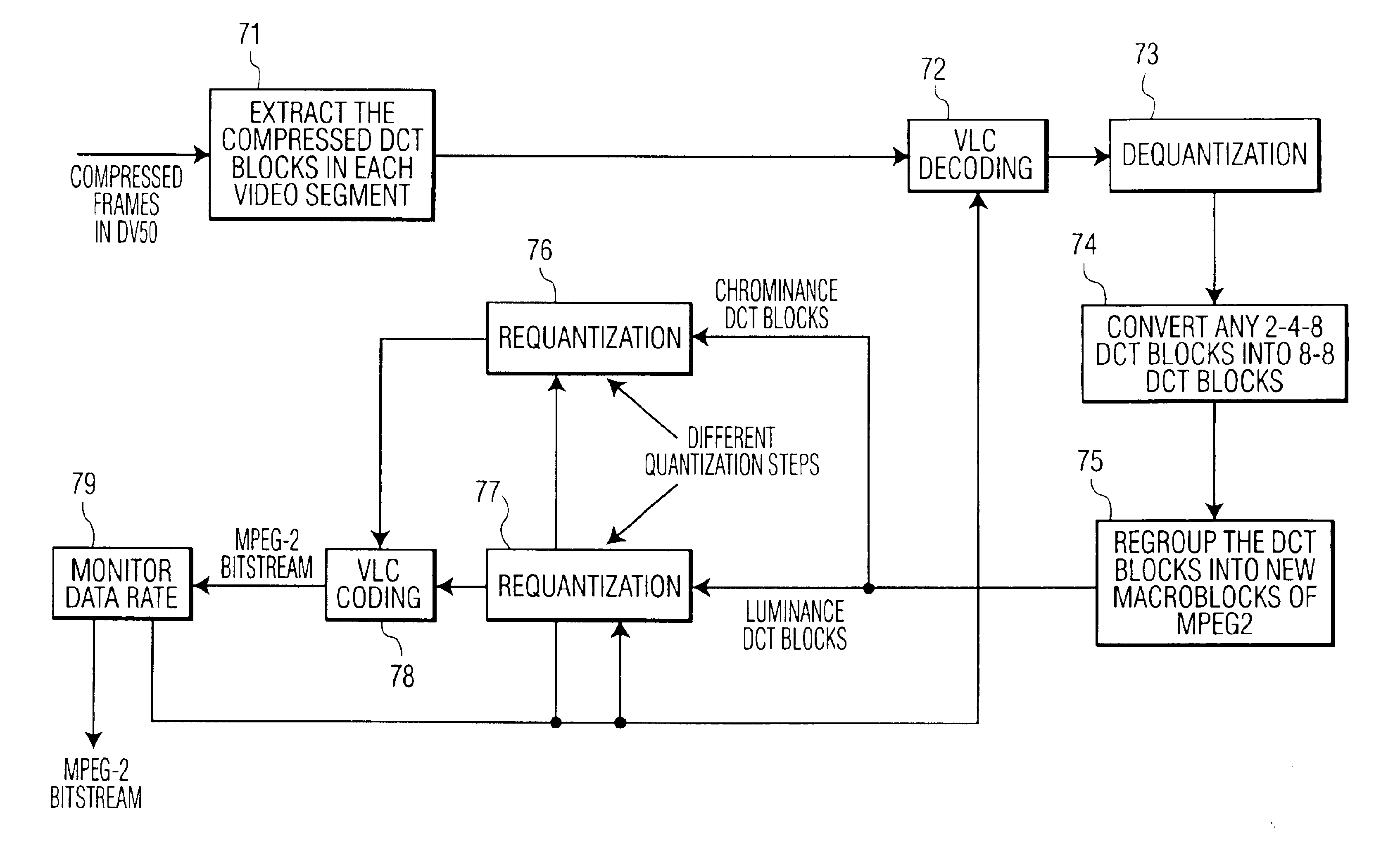
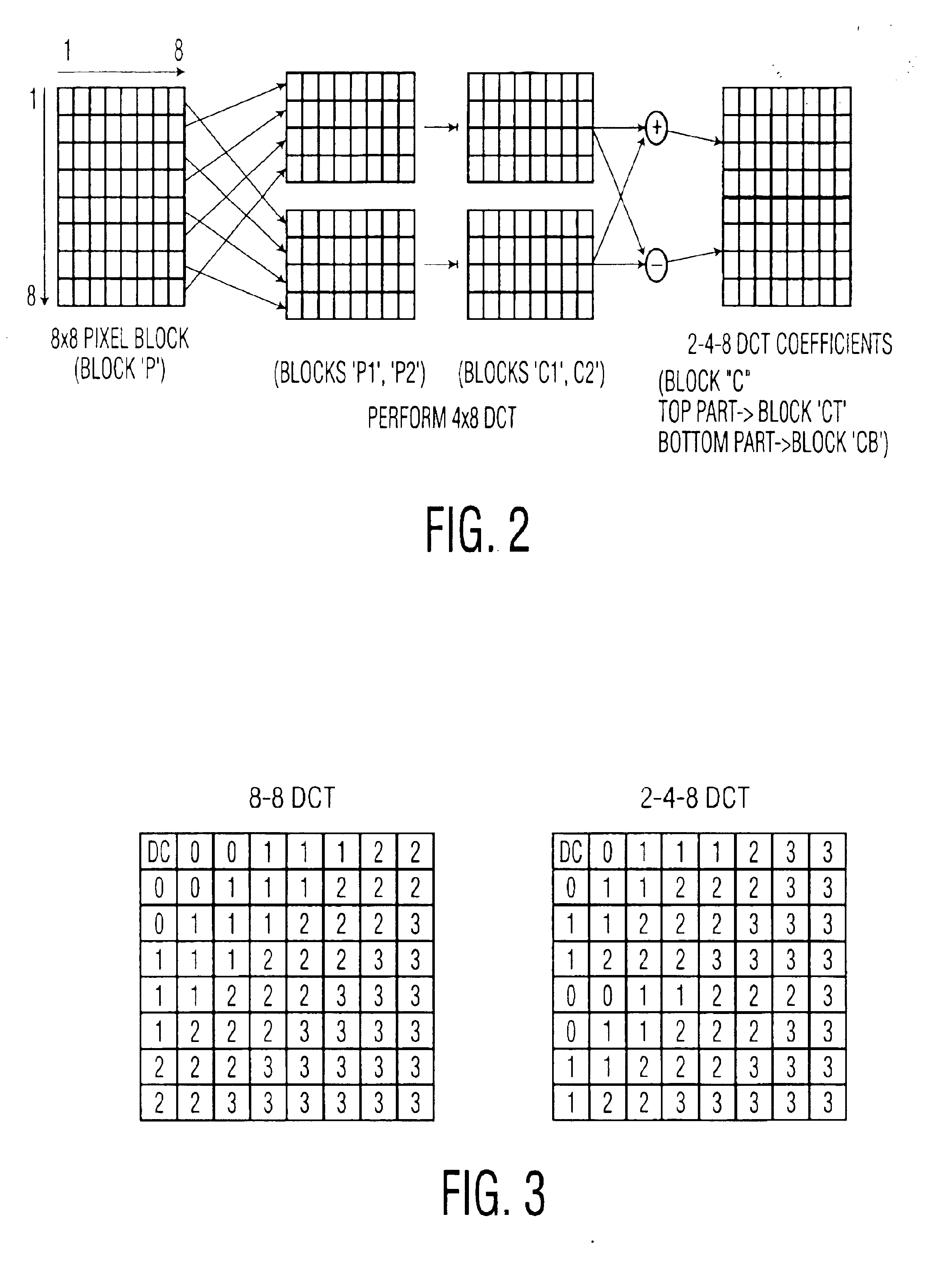
System and associated method for transcoding discrete cosine transform coded signals
InactiveUS6944226B1Low data rateTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMpeg standardsVariable length
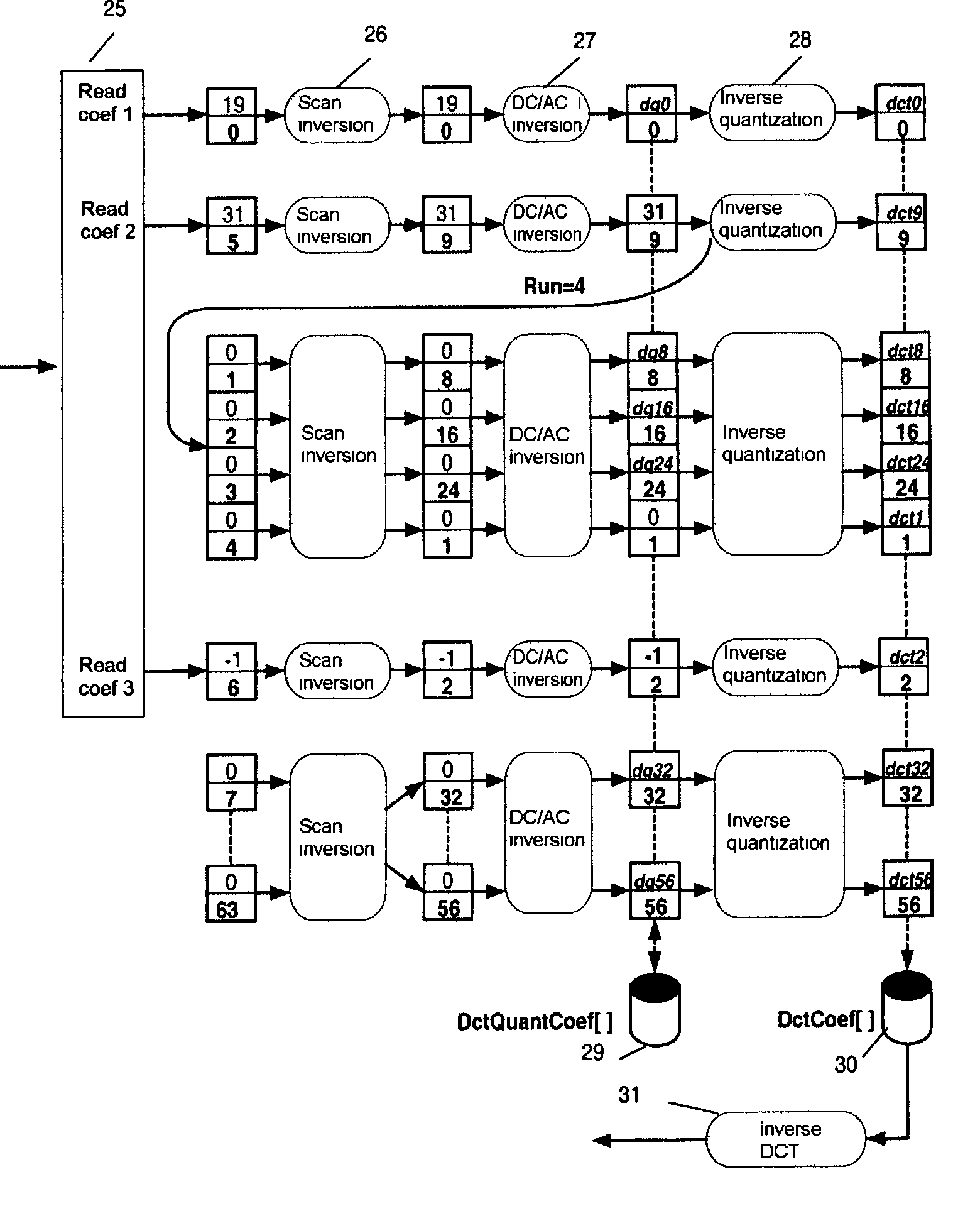
A method is provided for transcoding between video signals in two standards, DV and MPEG-2, each standard including discrete cosine transform (DCT) compressed signals. The each of the signals have macroblocks containing a plurality of DCT blocks. The DCT blocks are quantized according to respective quantization methods defined by the standards. The coefficients in each block are zigzag scanned, run-length coded and variable-length coded. The process variable-length decodes the coefficients and translates the quantized coefficients in the DV standard into quantized coefficients in the MPEG standard without fully dequantizing at least some of the DV coefficients and without performing an inverse DCT operation on any of the DCT coefficients. DV blocks that are encoded in a 248 format are translated into an 88 format before they are converted to MPEG-2 blocks. A method for transcoding from MPEG-2 to DV is also described. The MPEG-2 signals are intra-frame encoded, have a 4:2:2 chrominance format and an 88 frame-encoded block format. According to this method, converted 88 DV blocks that represent significant intra-field motion are converted from the 88 format to a 248 format. The method also controls which overflow coefficients in the DV signal are transcoded into corresponding coefficients in the MPEG-2 signal to control the data rate of the MPEG-2 signal.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
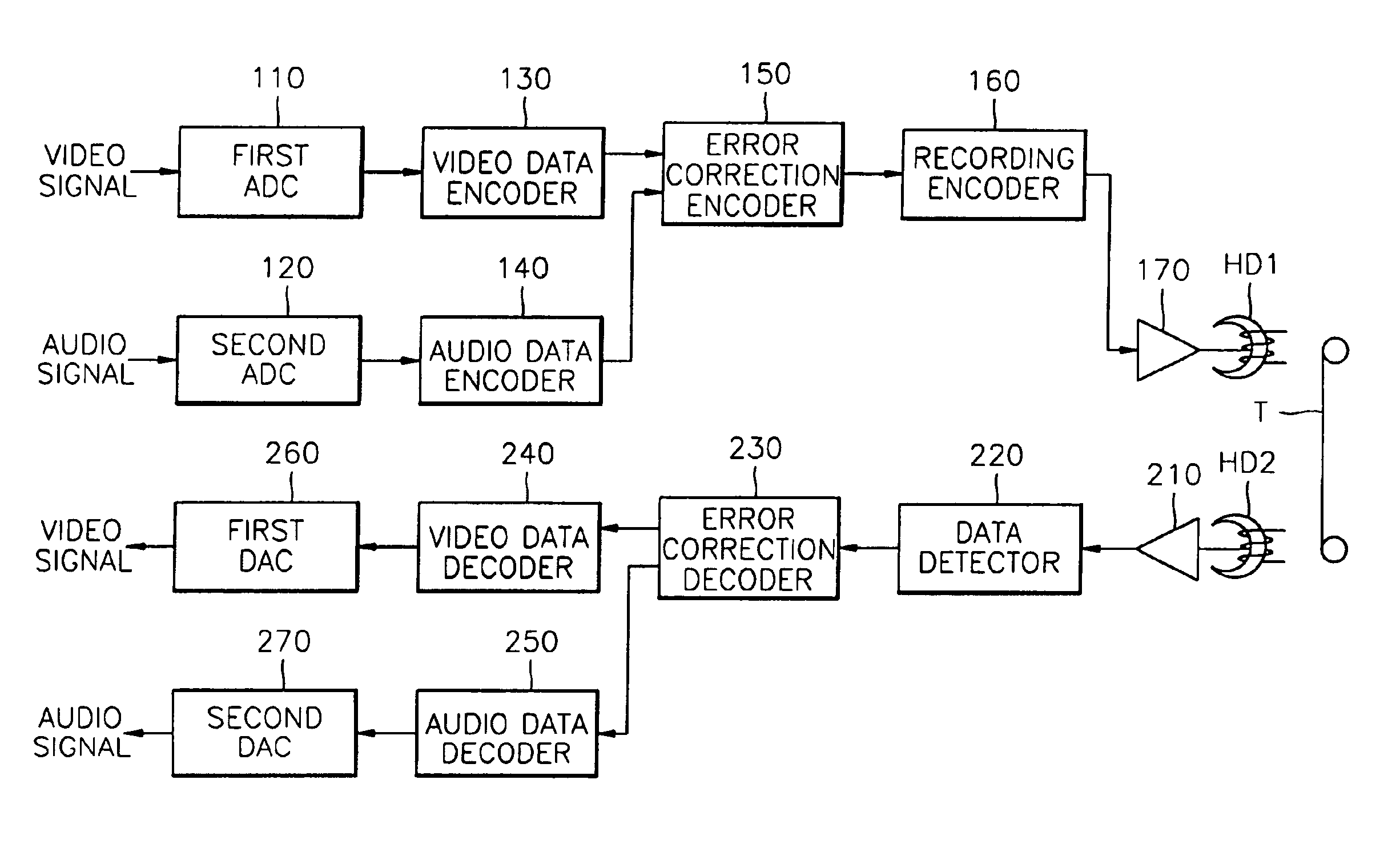
Digital recording and playback apparatus having MPEG CODEC and method therefor
InactiveUS6862402B2Increase speedTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMpeg standardsDigital recording
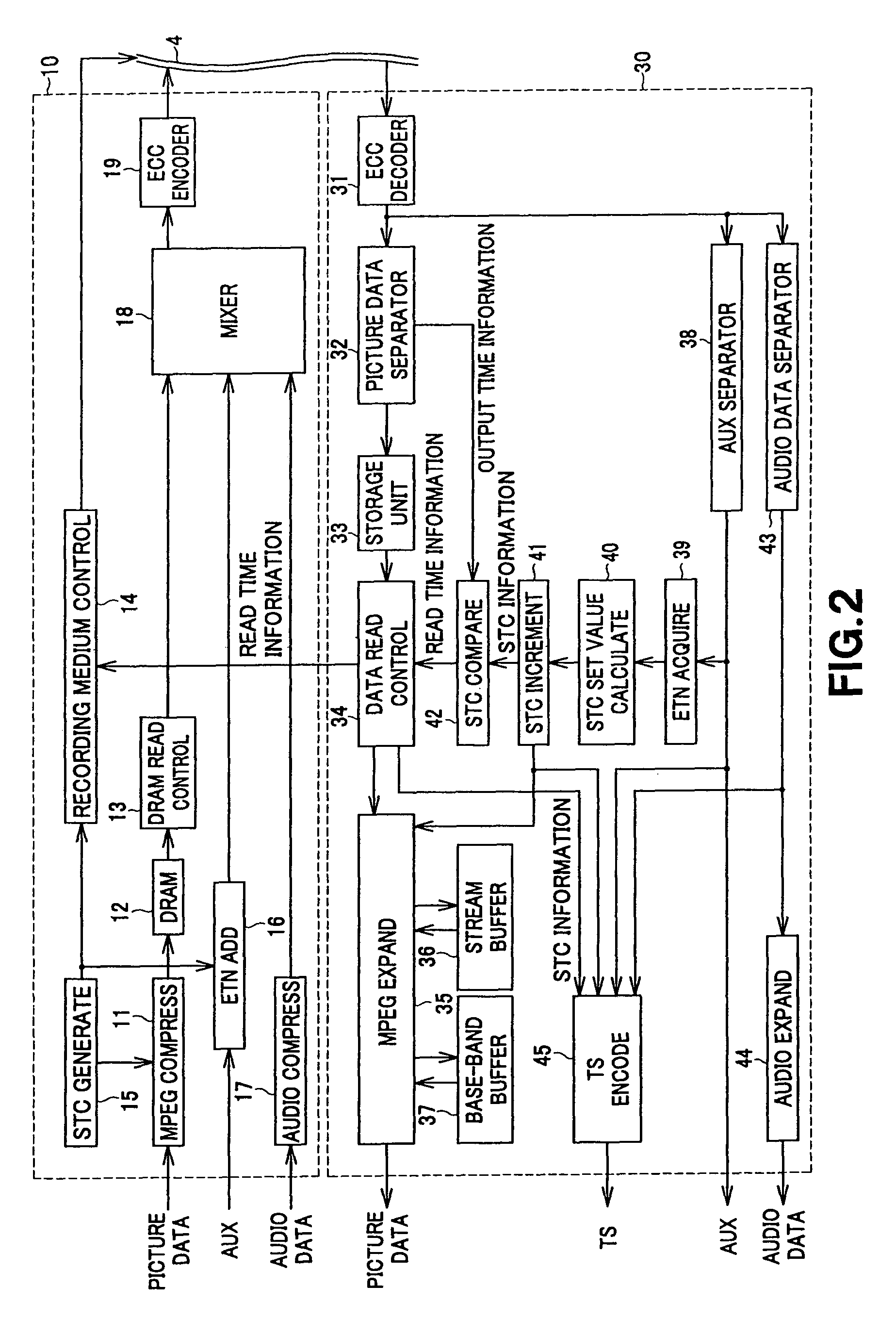
A digital recording and playback apparatus adopting an MPEG encoder and decoder, and a method thereof. The digital recording and playback apparatus includes: a first encoder for coding input video data in picture units, and outputting coded video data; a second encoder for coding input audio data and outputting coded audio data; a packetized elementary stream (PES) packetizer for packetizing the coded video data and audio data and user data into each PES, and outputting a video PES, audio PES and user PES; and a transport stream (TS) packetizer for multiplexing the video PES, audio PES and user PES into a TS. The digital recording and playback apparatus can be compatible with a digital television or multimedia applications adopting the MPEG standard, and can perform editing in picture units as well as high-speed search.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
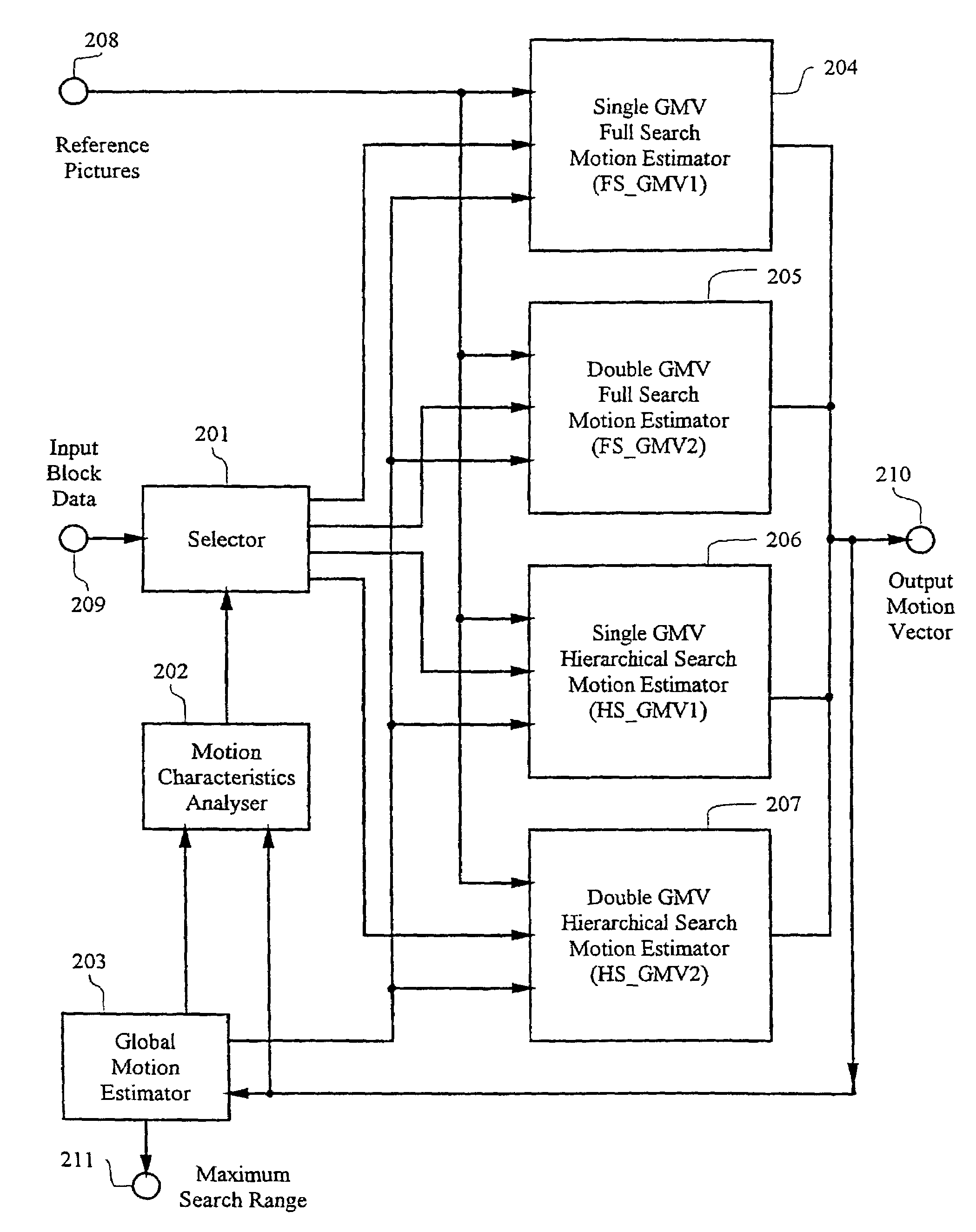
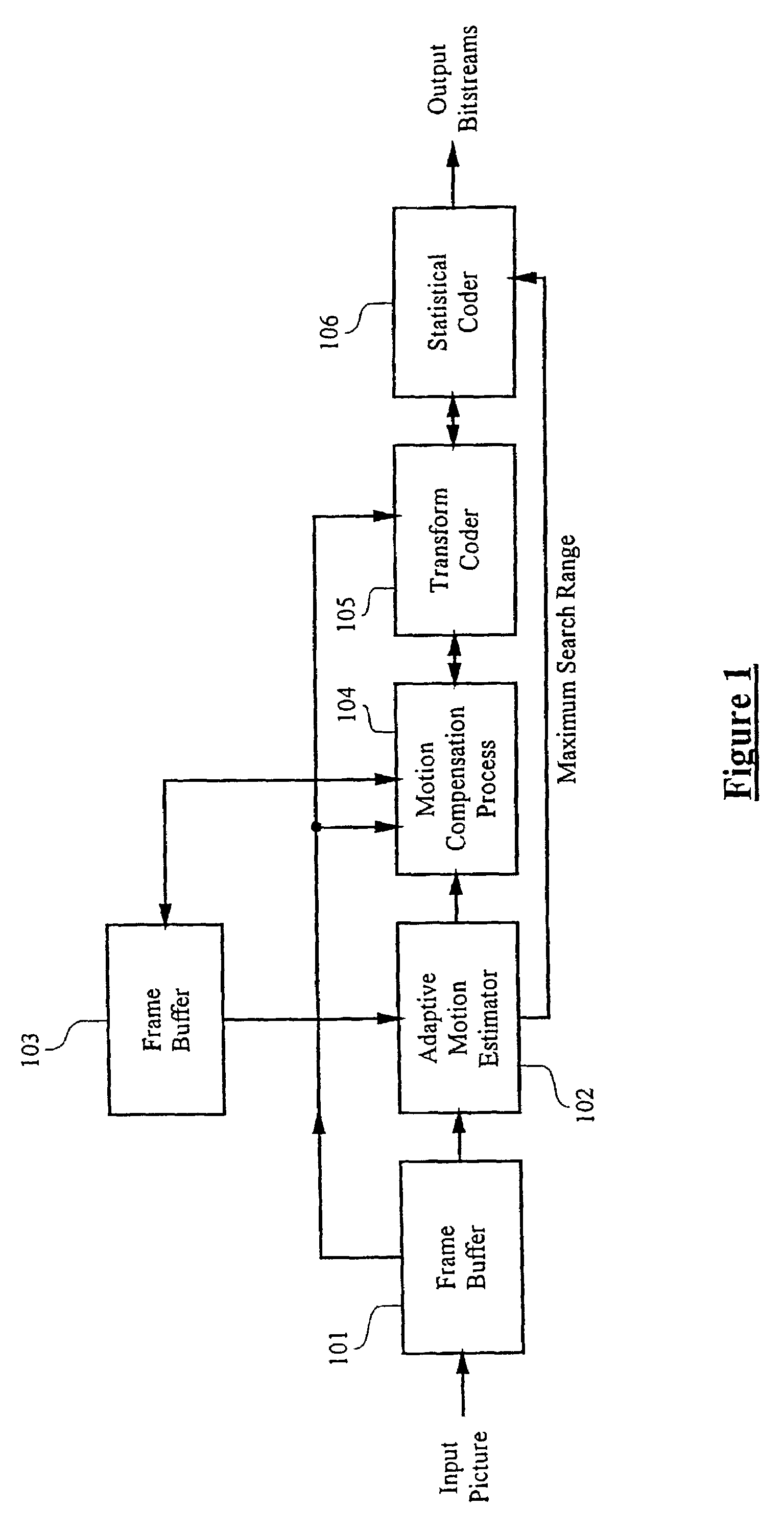
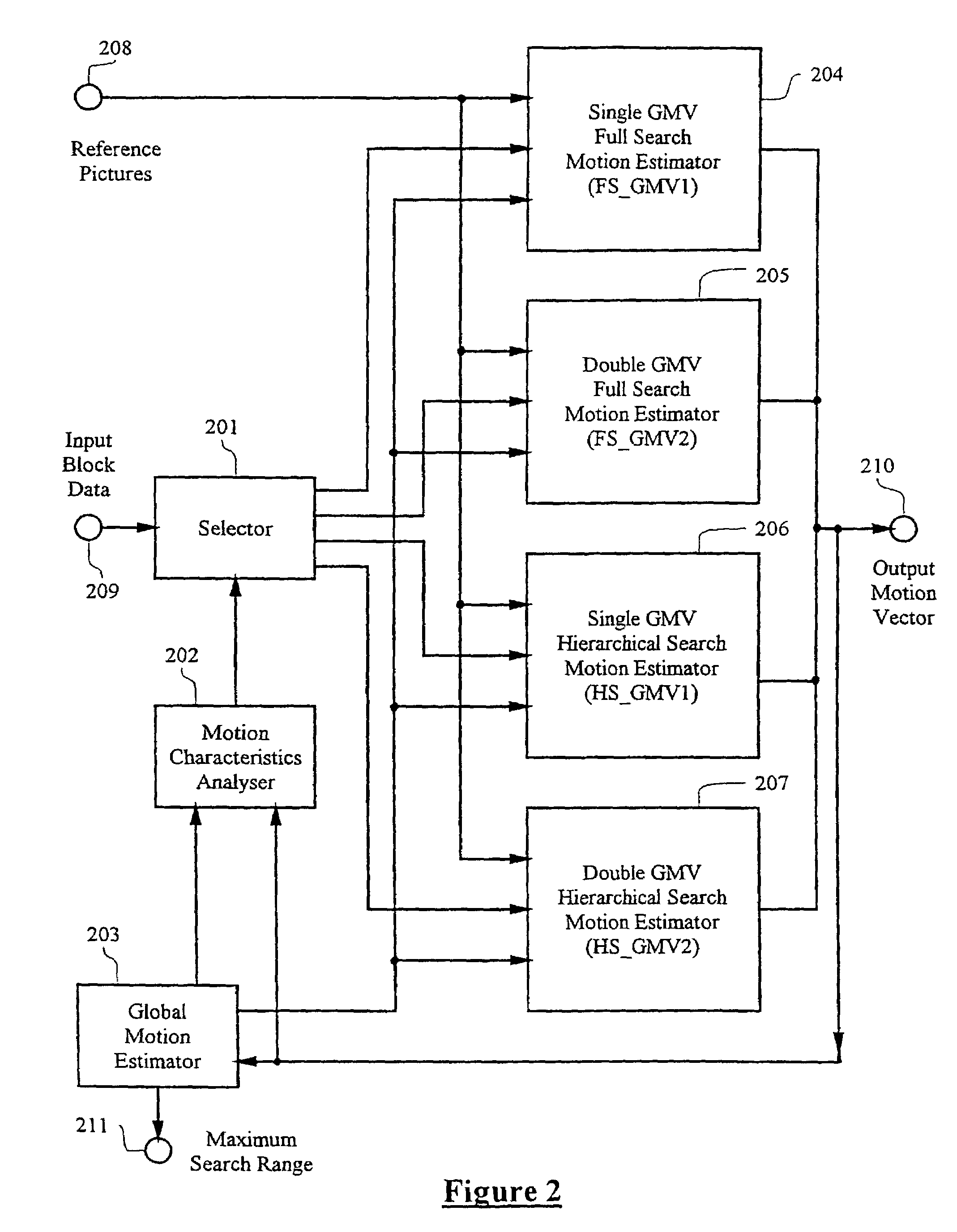
Adaptive motion estimator
InactiveUS7551673B1Expand effective search rangeMeet growth requirementsColor television with pulse code modulationImage analysisDigital videoMPEG-1
A method and apparatus of encoding digital video according to the ISO / IEC MPEG standards (ISO / IEC 11172-2 MPEG-1 and ISO / IEC 13818-2 MPEG-2) using an adaptive motion estimator. A plurality of global motion vectors are derived from the motion vectors of a previous picture in a sequence, and the global motion vectors are analyzed to determine motion characteristics. The video encoding is arranged to enable switching among different types of local motion estimators based on the motion characteristics of the moving pictures sequence. This gives rise to a motion estimation algorithm that can adaptively change its search range, search area and block matching scheme to suit different types of moving sequences.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
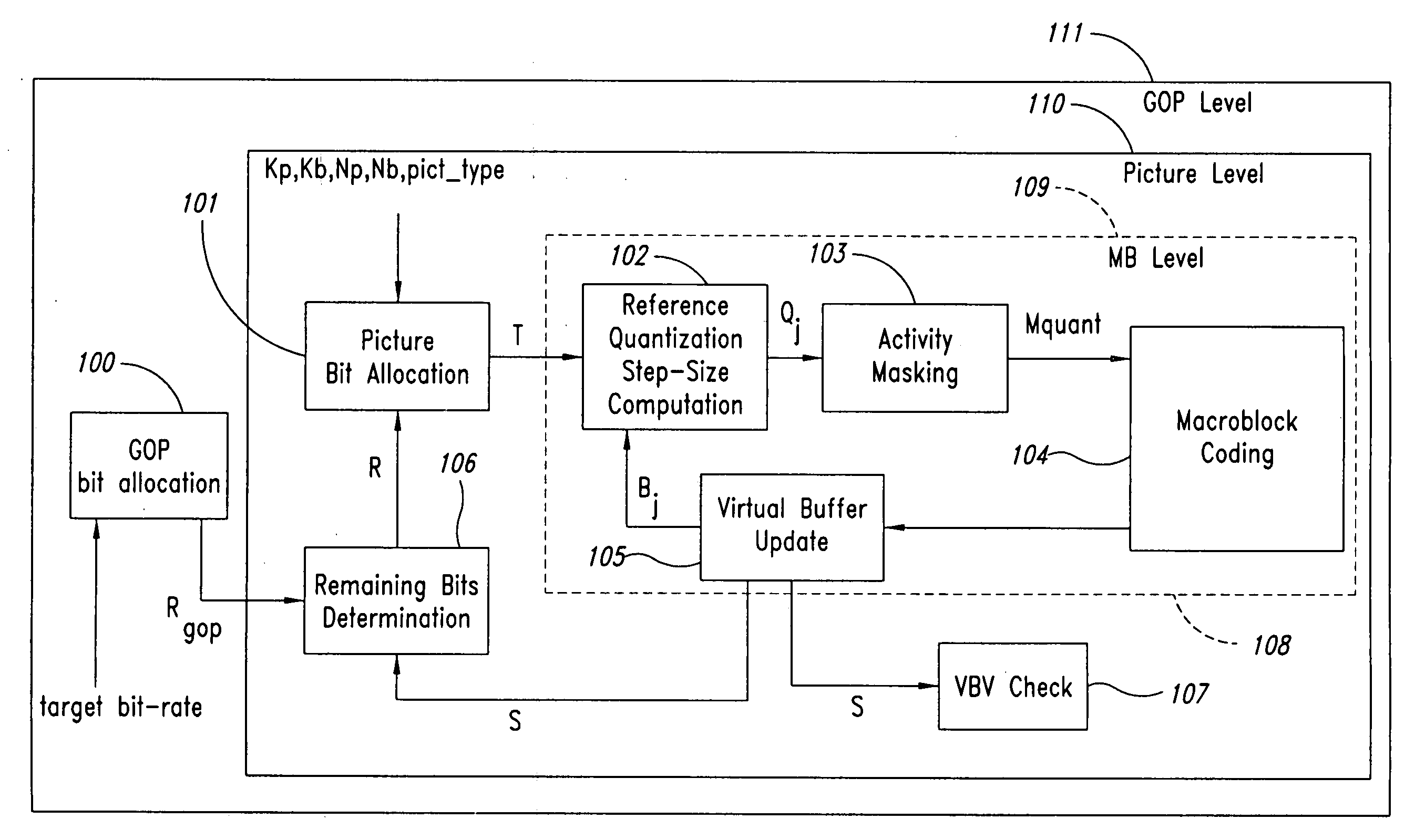
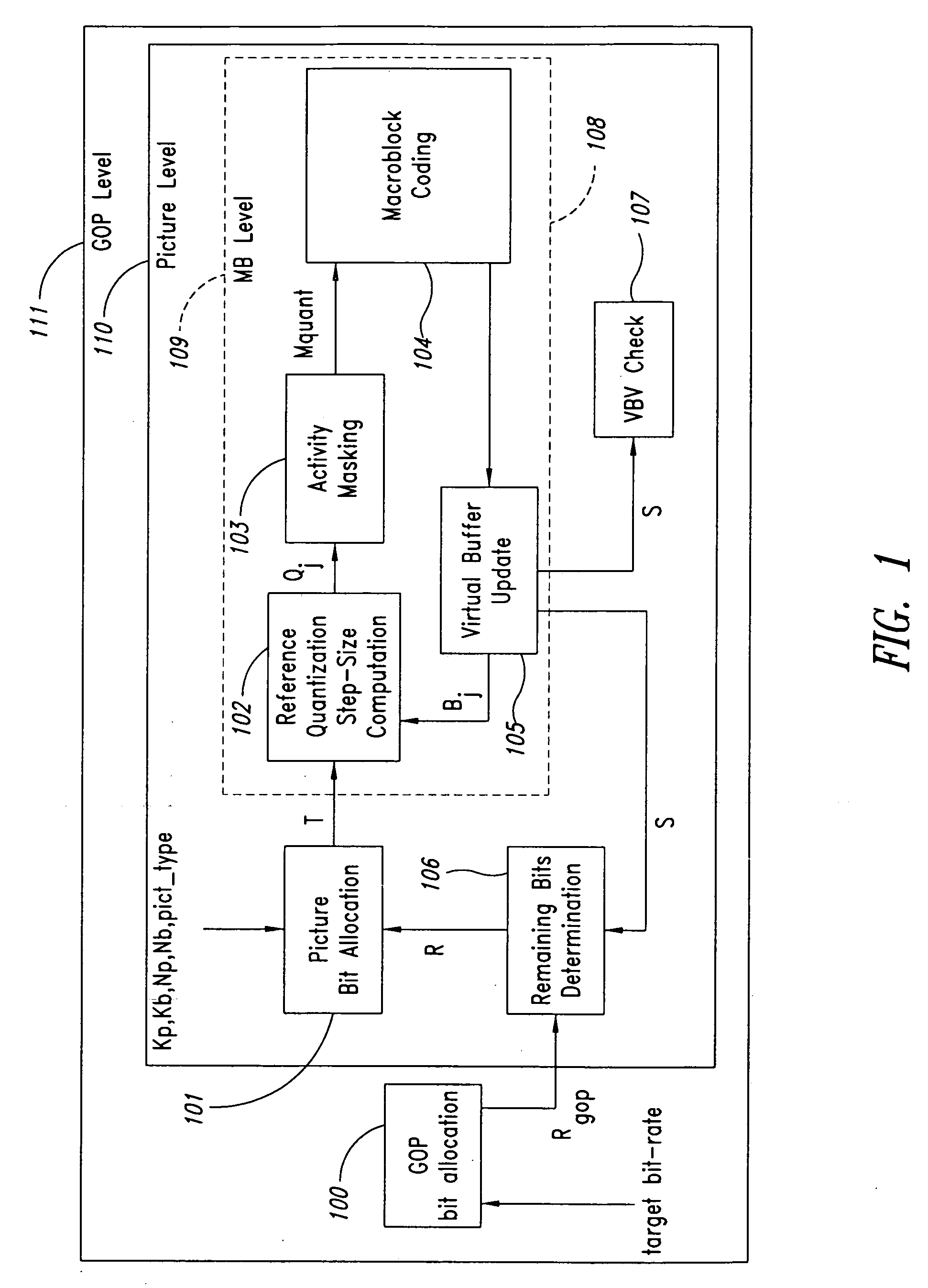
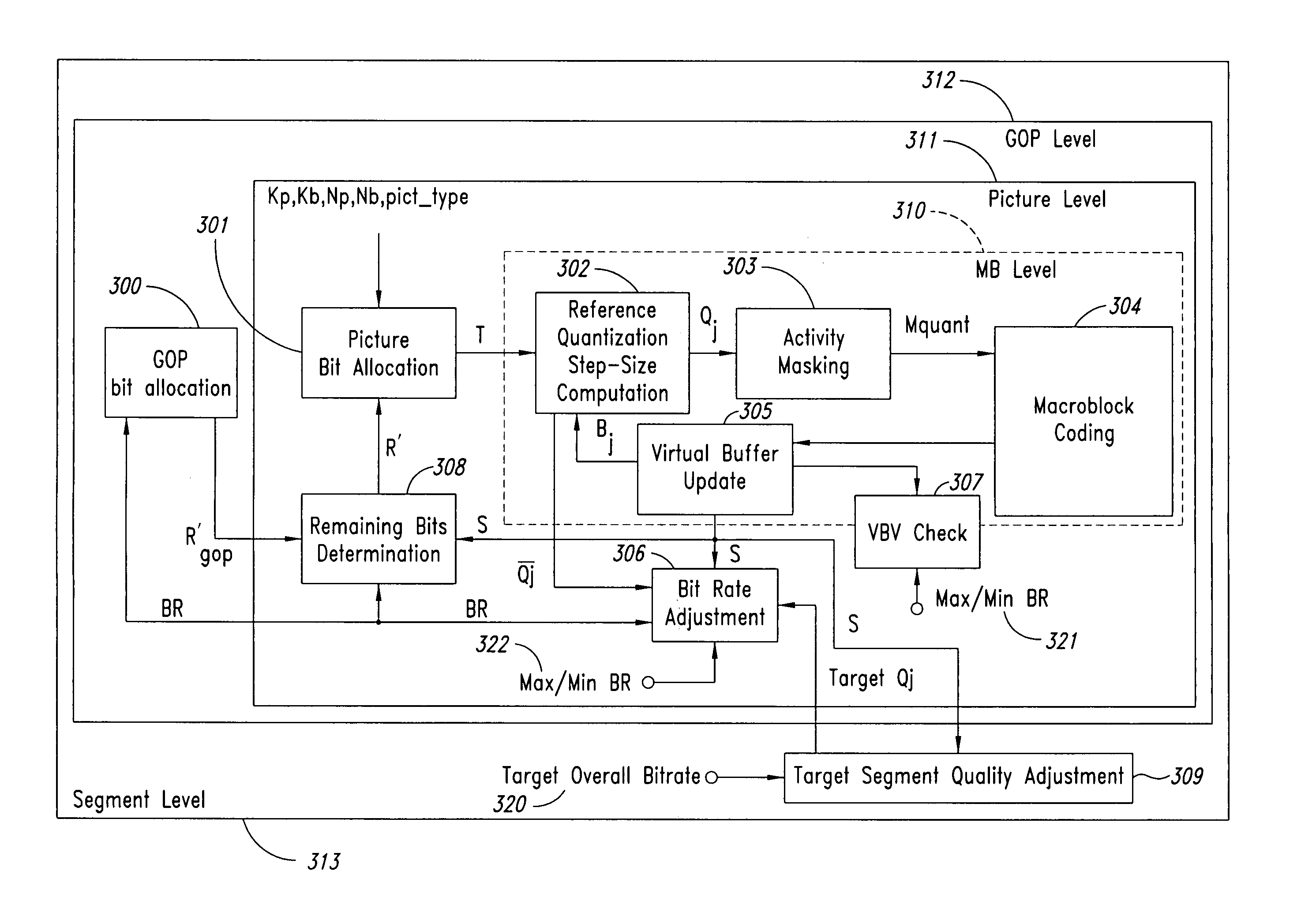
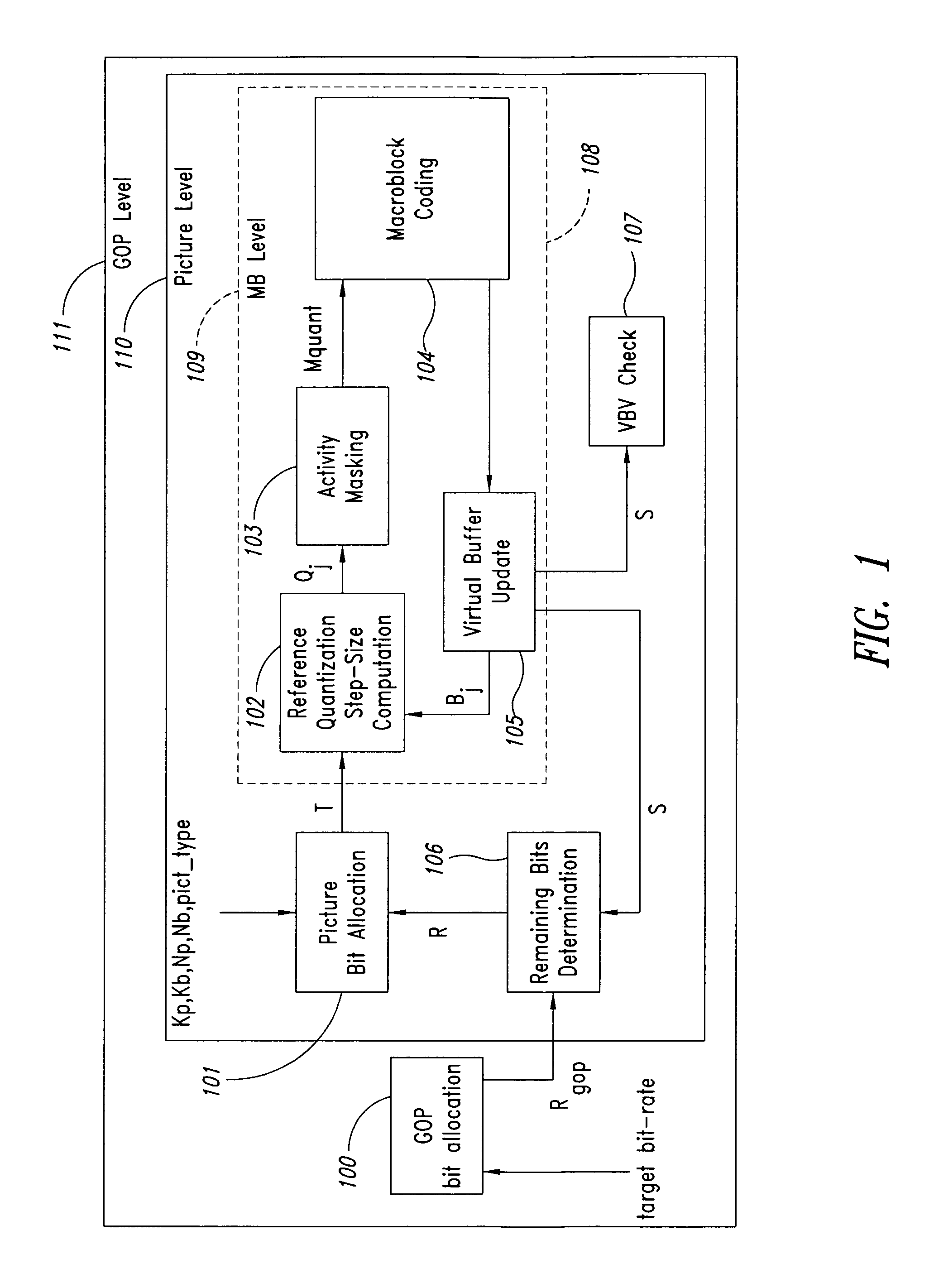
Moving pictures encoding with constant overall bit-rate
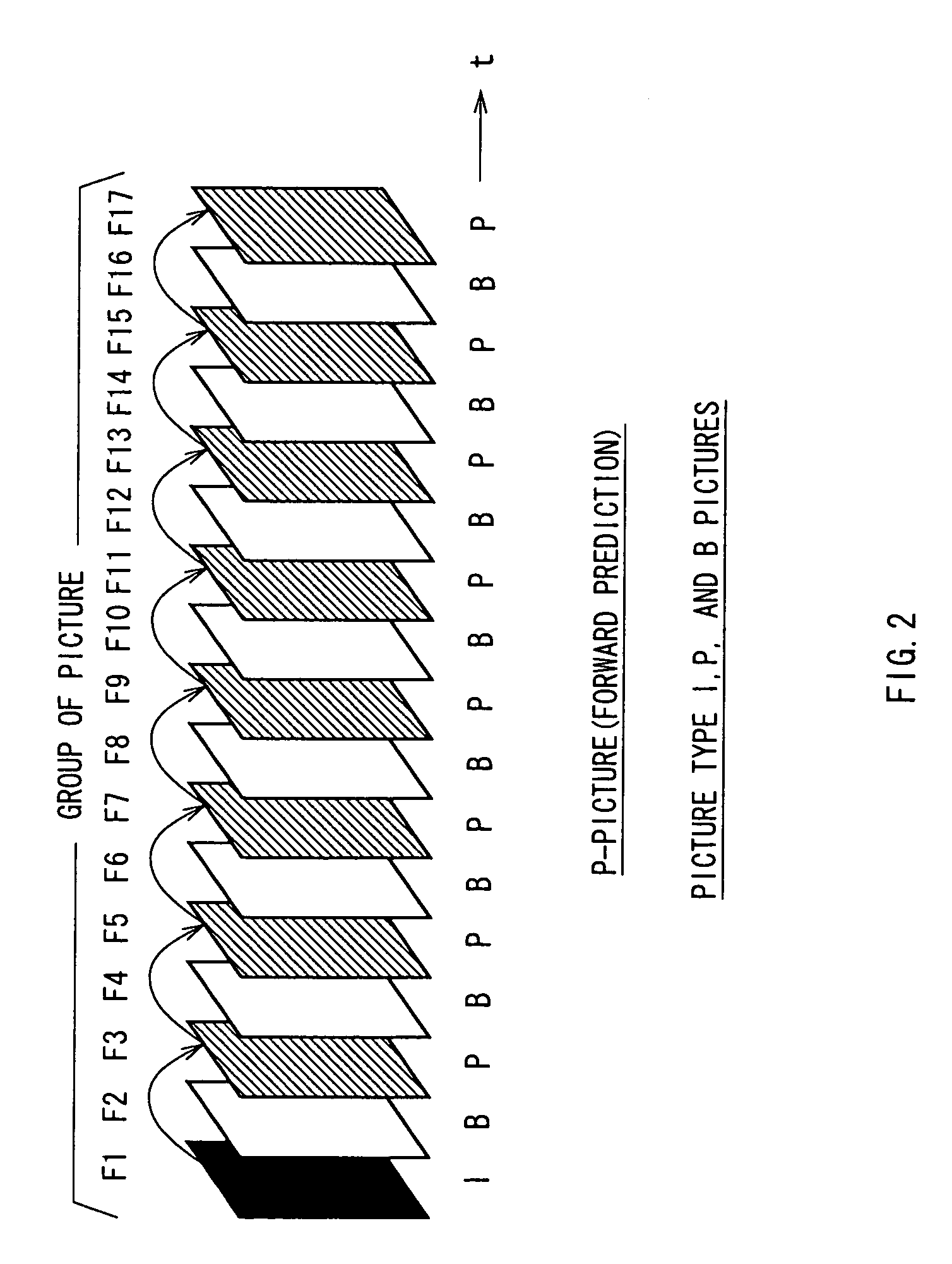
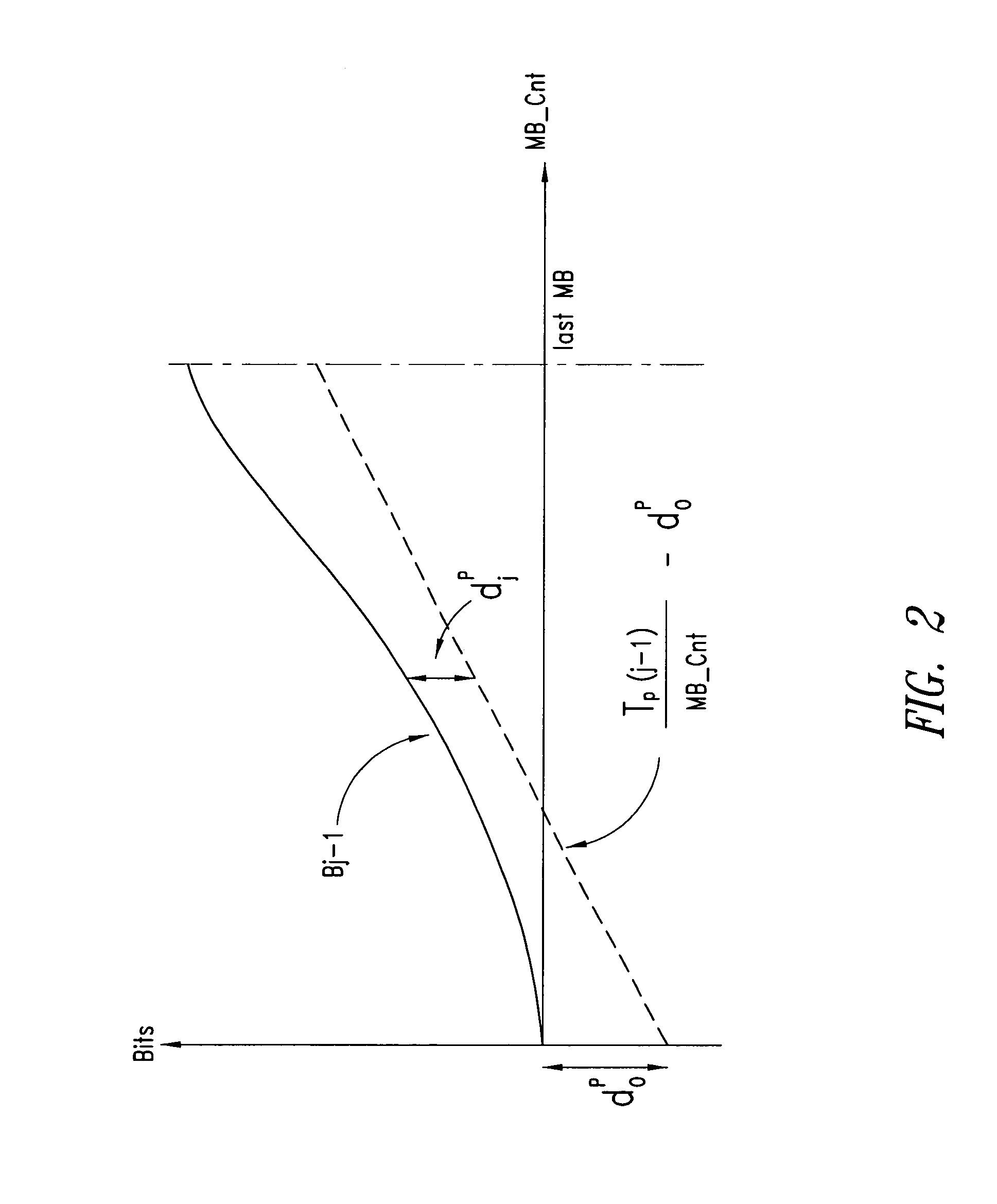
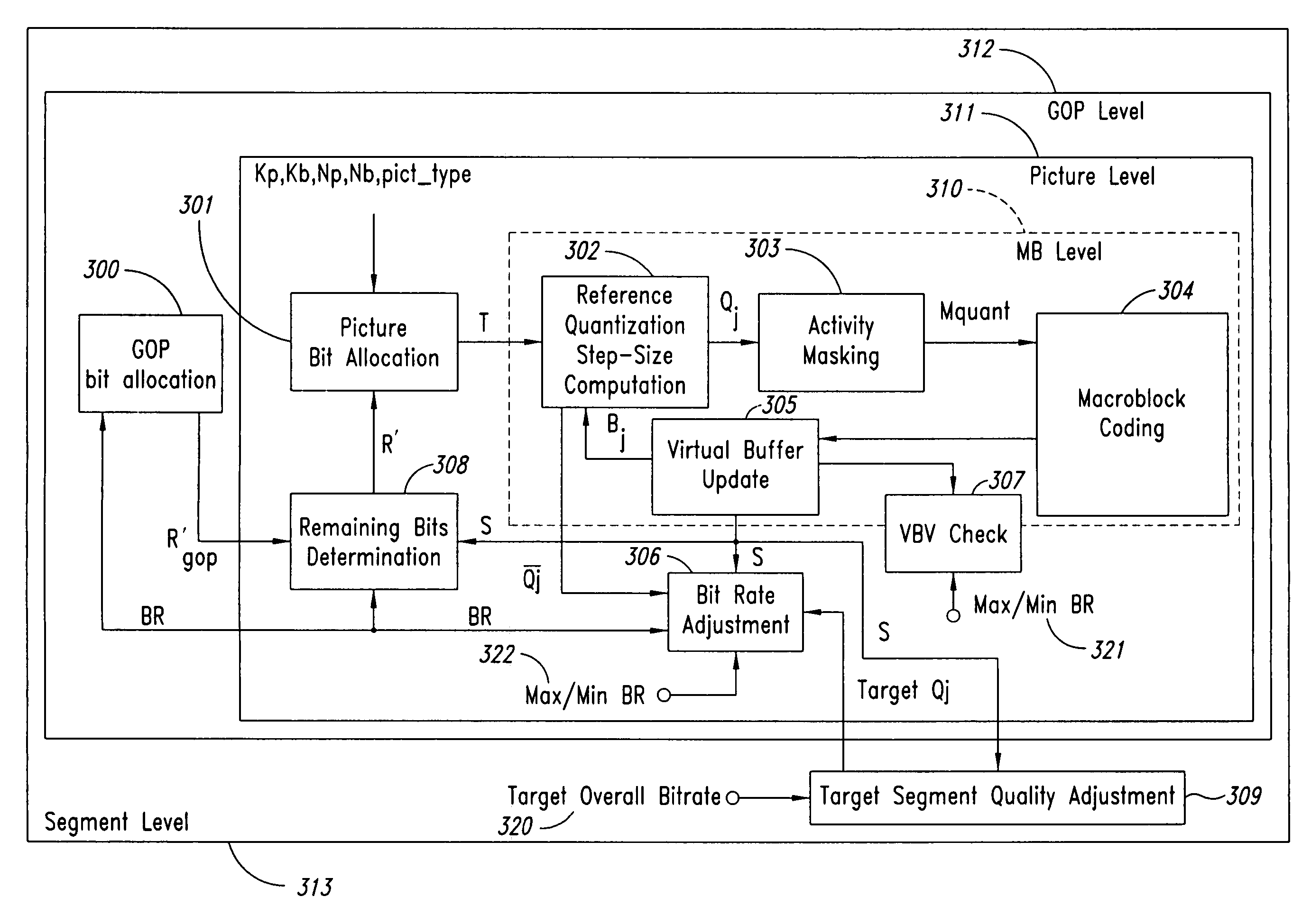
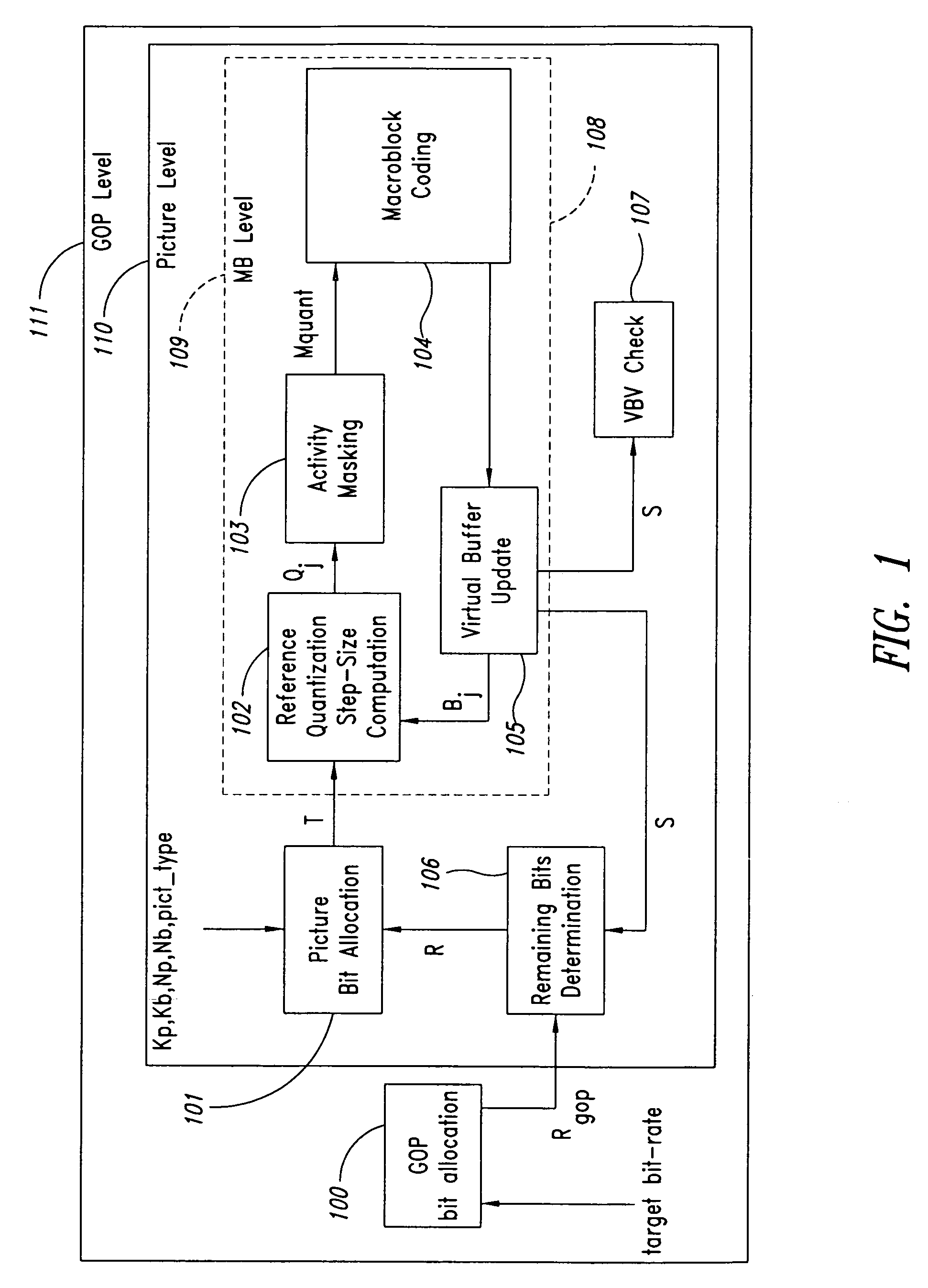
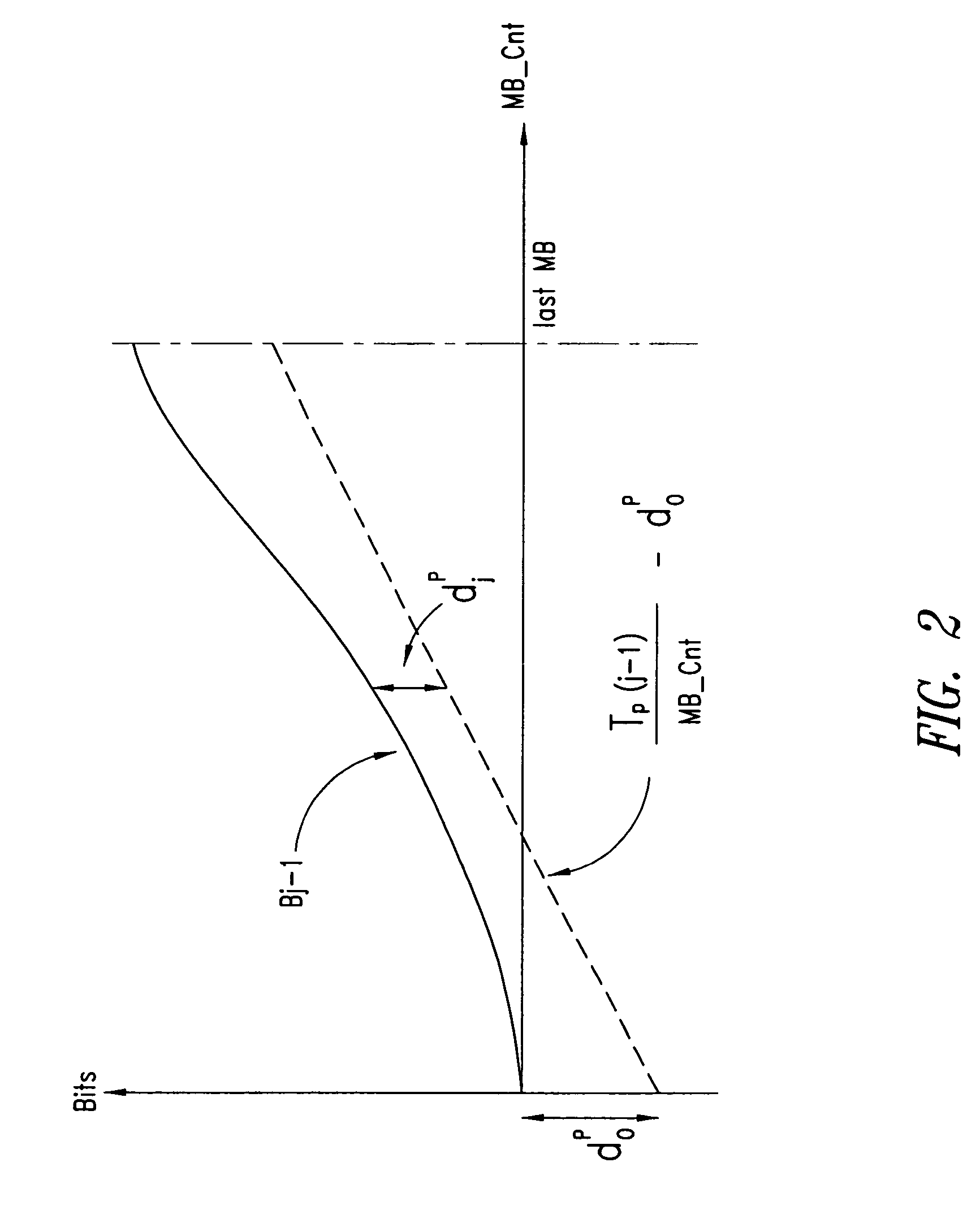
InactiveUS20060159169A1Minimize changesConstant rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGroup of picturesMpeg standards
A method and apparatus control bit rates used in a moving pictures encoder, such as an MPEG standard encoder. A sequence of moving pictures is divided into segments each of which comprises one or more groups of pictures. A constant overall bit rate is specified for the sequence of pictures, but variable bit rate encoding used within each segment. A difference between the number of bits allocated for encoding the segment and the actual bits used for encoding is determined, and the difference distributed over one or more subsequent segments.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
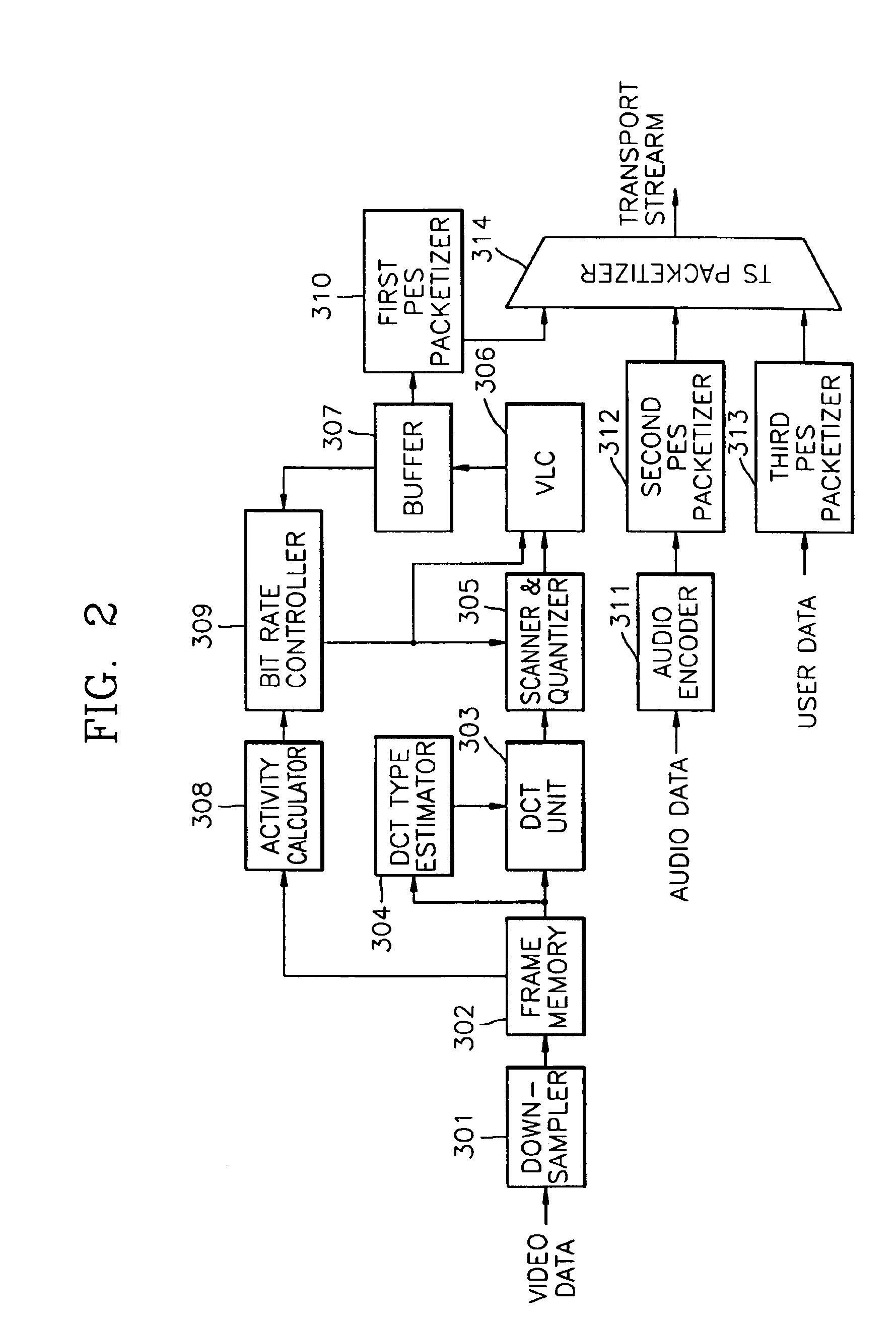
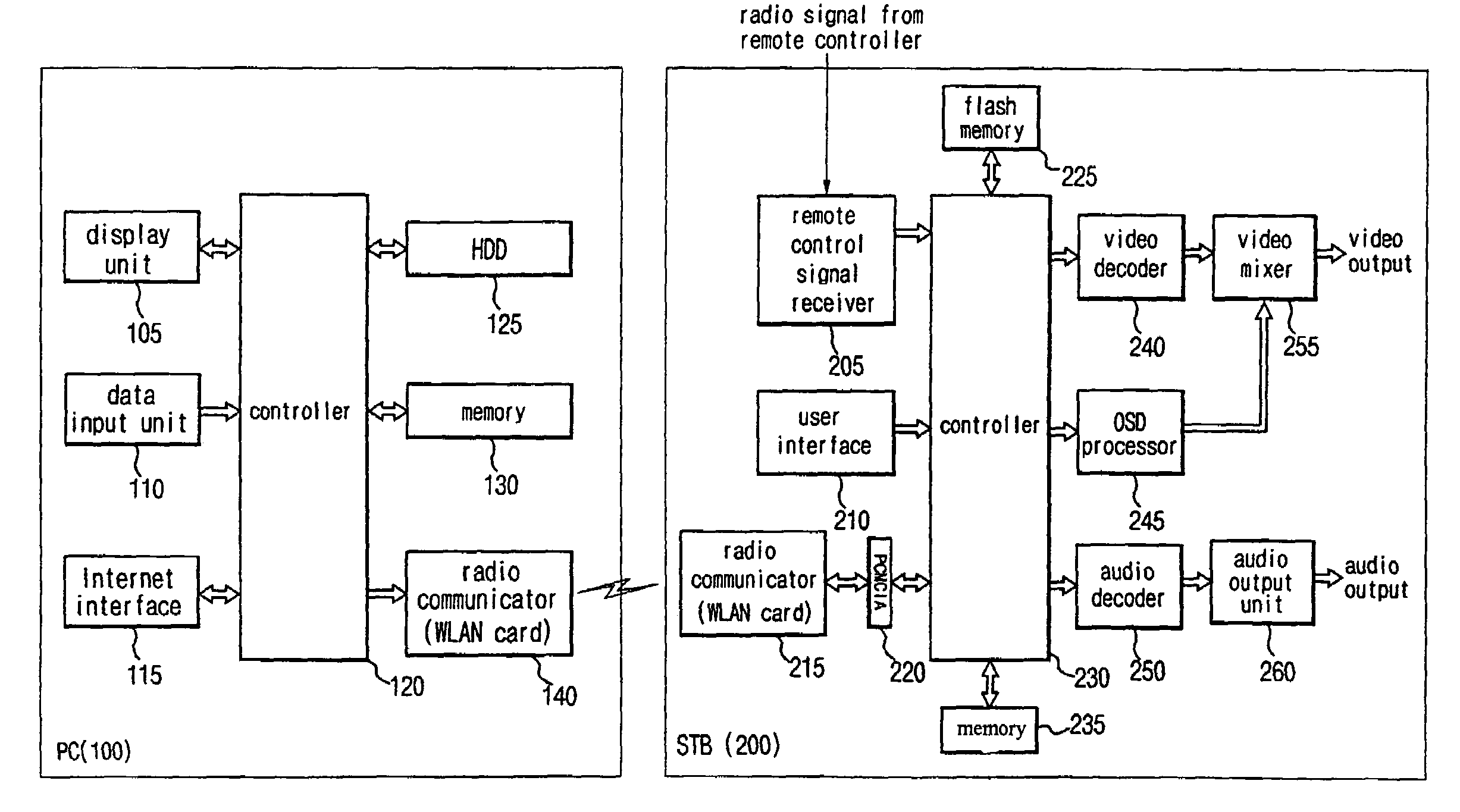
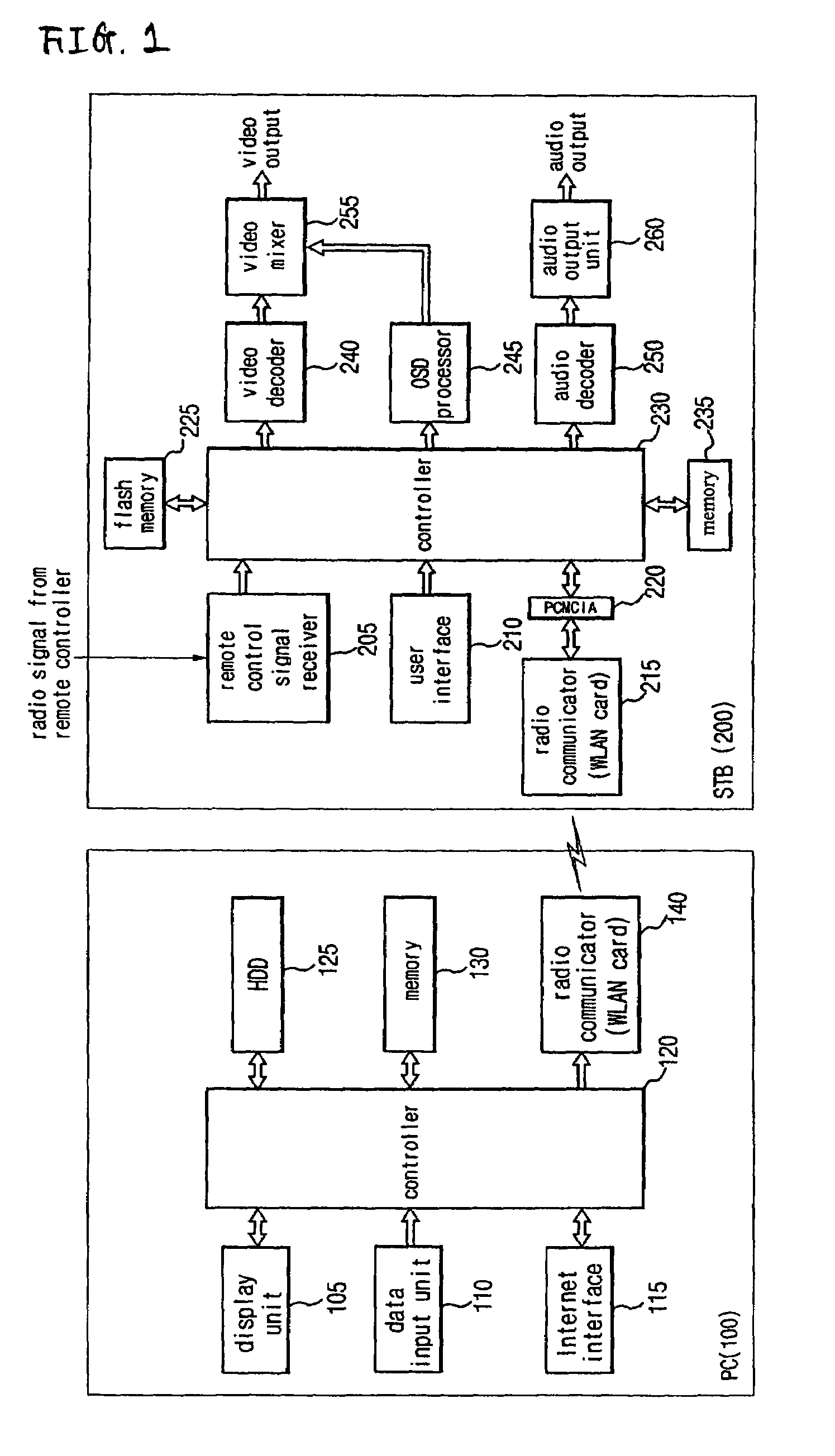
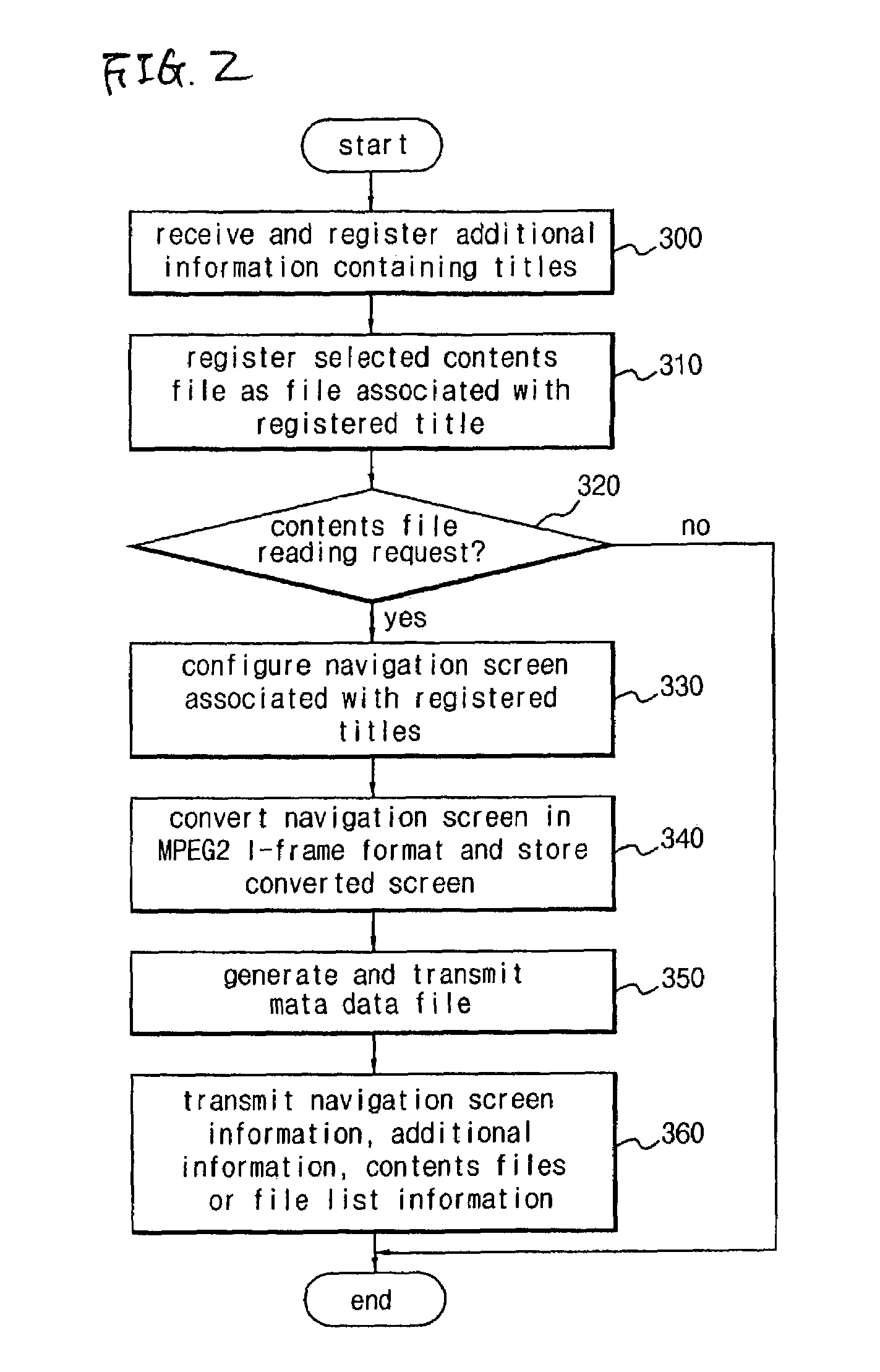
Wireless receiver for receiving multi-contents file and method for outputting data using the same
A wireless receiver for receiving a multi-contents file and a method for outputting data using the same, which can receive, navigation information for providing intuitively recognizable search interfaces to a user by radio in real time, receive various types of contents files by radio in real time, and output the received information and files through an AV device. A video decoder decodes a video stream on the basis of an MPEG standard. An audio decoder decodes an audio contents file. An OSD processor processes a text file and additional information. A video output unit selectively configures decoded video data and text data on one screen and performs encoding and outputting operations based on the format of a display unit. An audio output unit outputs decoded audio data. A user interface receives a user's command. A WLAN card communicates WLAN data with a computer system. A controller requests the computer system to transmit navigation screen information, at least one contents file or additional information of the contents file edited and processed by the computer system, analyzes a data stream received by radio from the computer system responsive to the request, and performs a control operation so that a result of the analysis is inputted into the decoder or OSD processor. A memory stores the stream and control program data.
Owner:EDITO CO LTD
Interface for compressed video data analysis
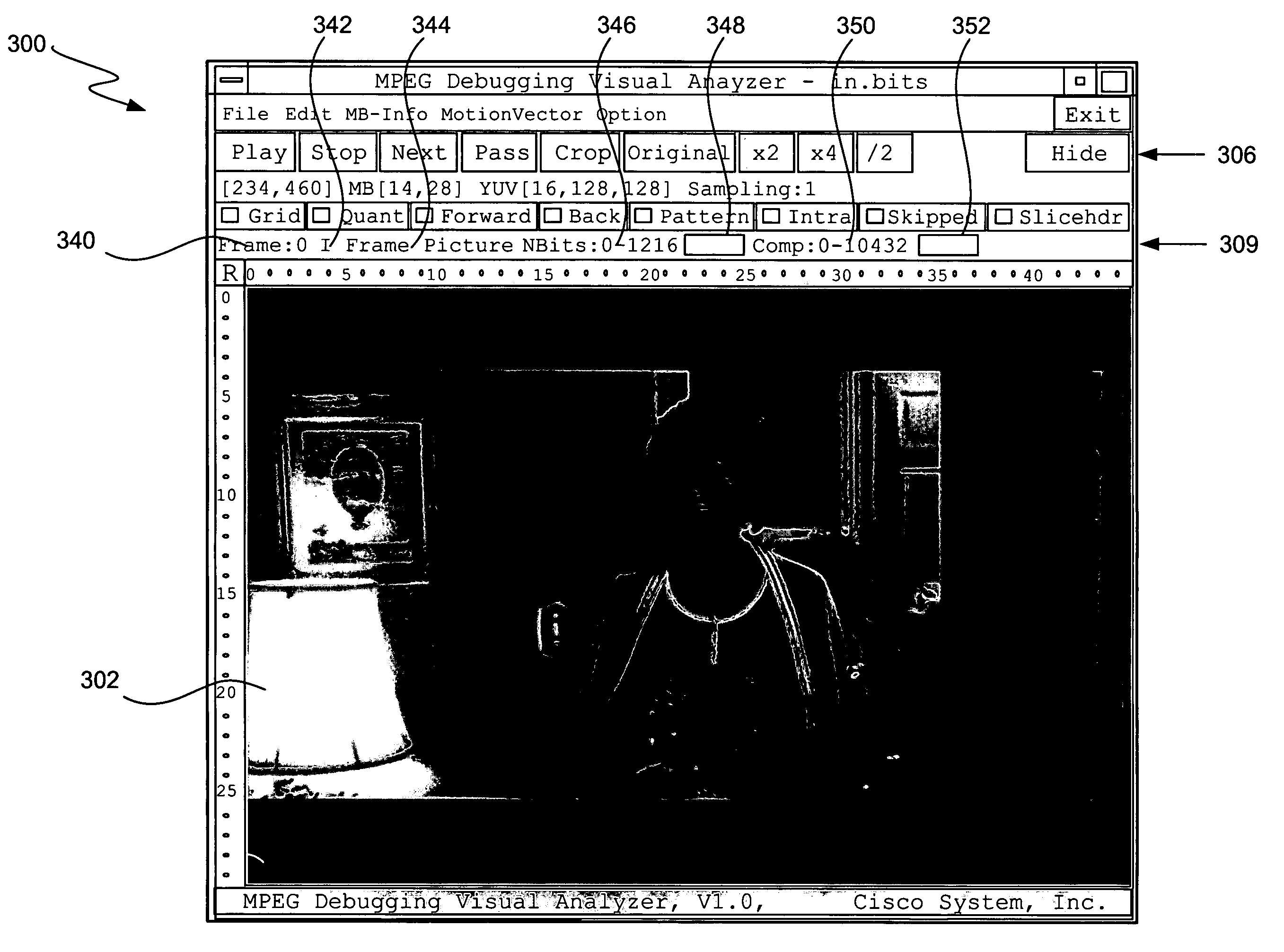
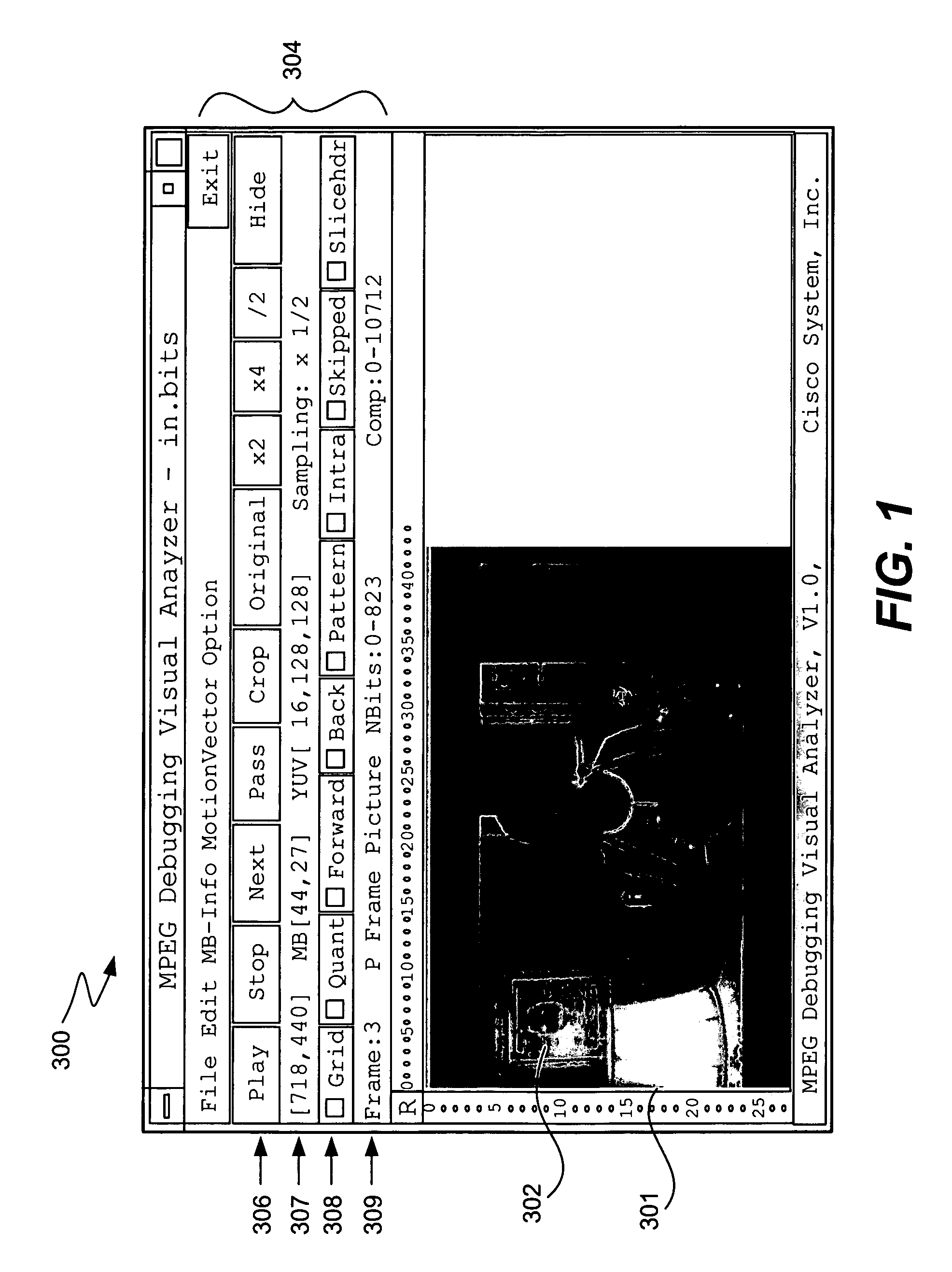
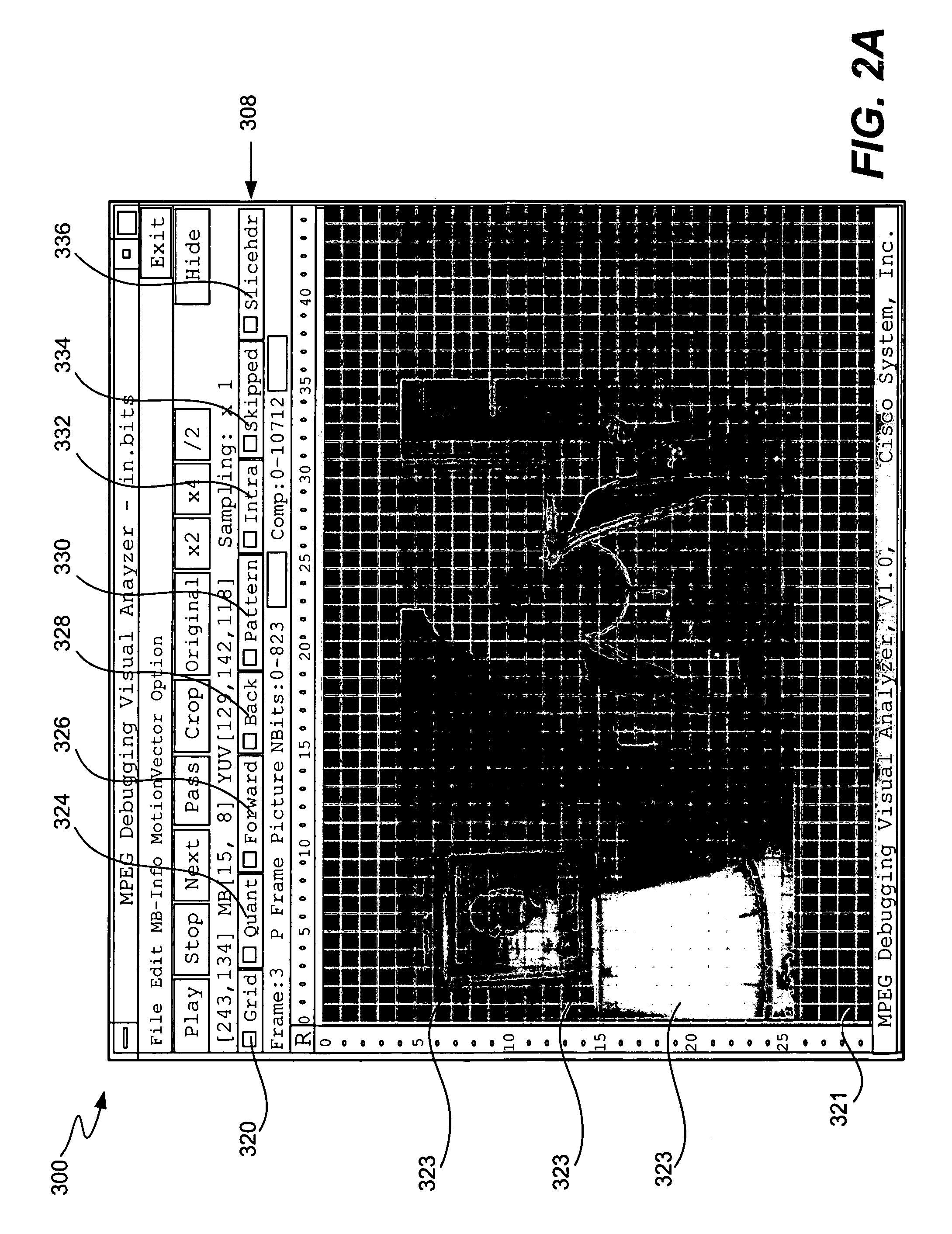
InactiveUS6948127B1Easy to interfaceEasy to useRecording carrier detailsError detection/correctionMpeg standardsComputer graphics (images)
The invention described herein provides a video analysis tool to assist a computer programmer working on a program that effects video data. The tool may be integrated with program code. When enacted, the tool obtains statistical information related to the video data and information corresponding to functions of the code. The code may be responsible for encoding, transcoding, and / or decoding video data, for example. The tool is integrated with a video decoder to allow the information to be output with raw video data. The present invention is particularly useful for developing, debugging and analyzing programs responsible for encoding, transcoding, and / or decoding video data, such as video data compressed according to an MPEG standard.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multichannel audio data encoding/decoding method and apparatus
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Moving pictures encoding with constant overall bit rate
InactiveUS7092441B1Minimize changesConstant rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGroup of picturesMpeg standards
A method and apparatus control bit rates used in a moving pictures encoder, such as an MPEG standard encoder. A sequence of moving pictures is divided into segments each of which comprises one or more groups of pictures. A constant overall bit rate is specified for the sequence of pictures, but variable bit rate encoding is used within each segment. A difference between the number of bits allocated for encoding the segment and the actual bits used for encoding is determined, and the difference is distributed over one or more subsequent segments.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
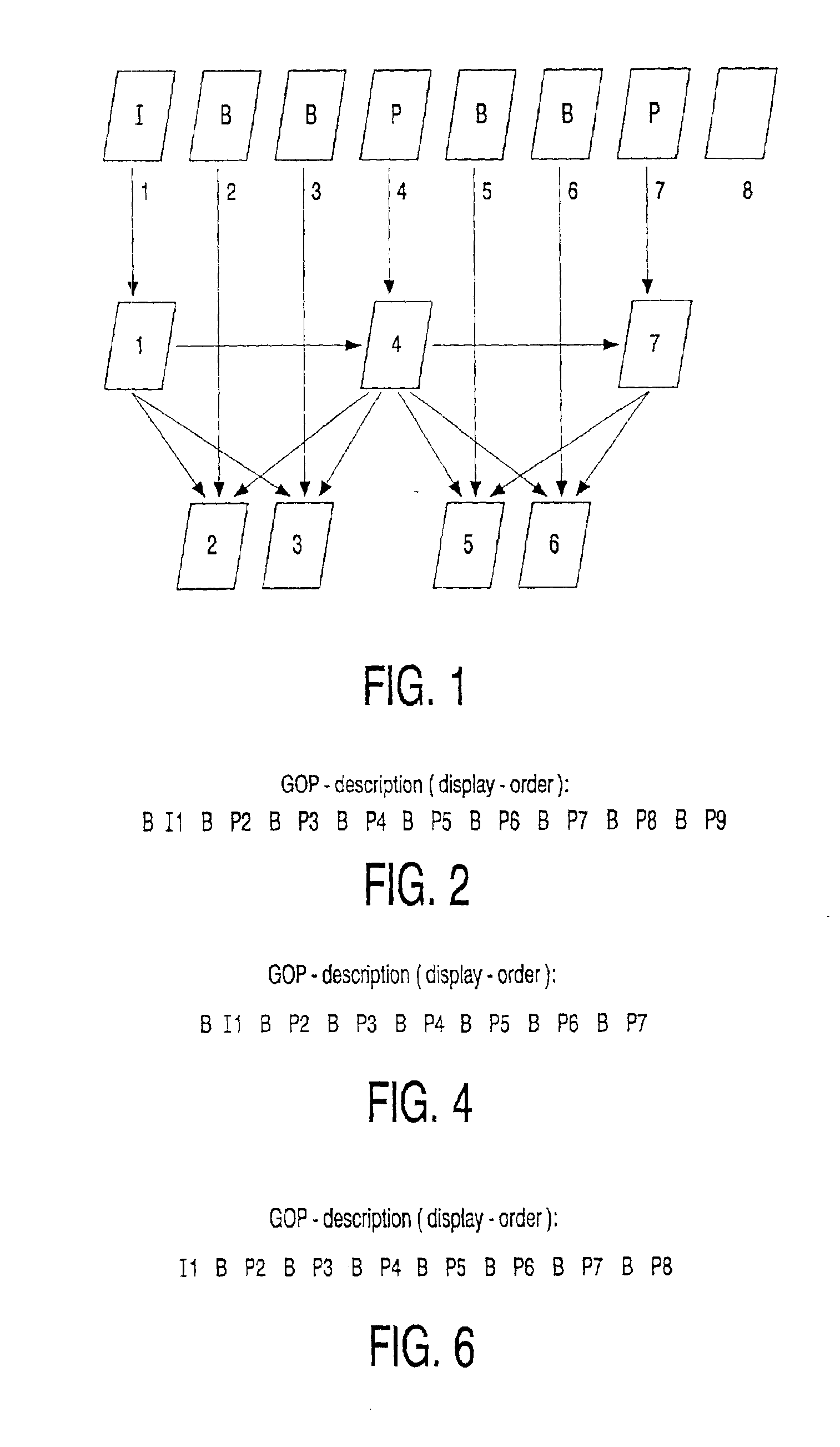
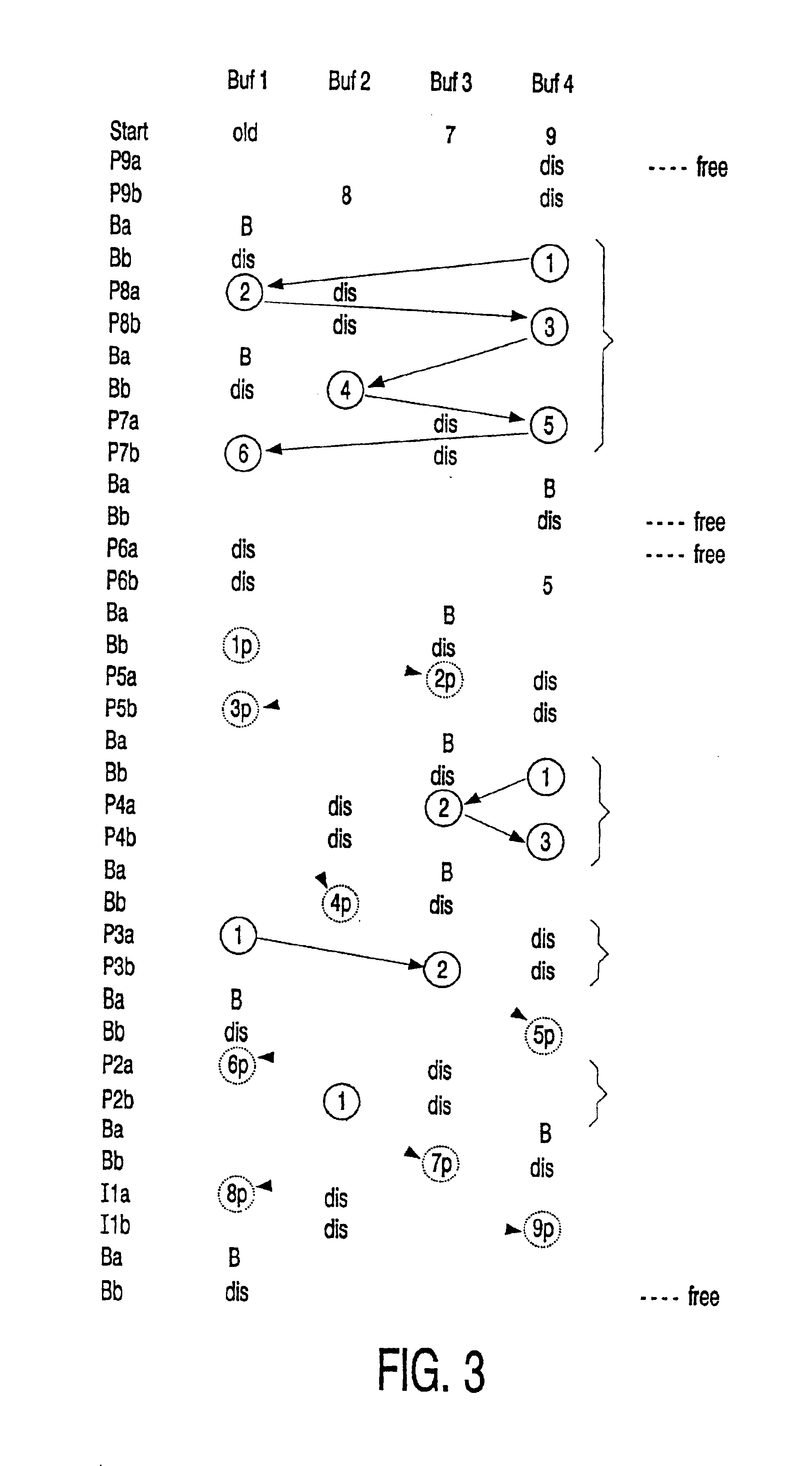
Method of reverse playback of a MPEG video stream
InactiveUS6879770B1Increase storage capacityDecoded is reducedTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital dataGroup of pictures
A method of decoding MPEG coded digital data, received in a forward reproduction order in least one Group Of Pictures (GOP) according to the MPEG standard, for producing decoded pictures for display in reverse playback order. Tho this purpose a limited number of decoded frames is temporarily stored while repeatedly same coded picture data is retrieved in a forward reproduction order to produce decoded picture data, employing the decoded temporarily stored picture data. This has as an advantage that the amount of temporarily storage capacity required, approximately equals the amount required for forward playback. In a specific embodiment, wherein the MPEG data cotains either NTSC GOPs or PAL GOPs, only temporarily storage capacity of four picture frames is required in case of reverse playback, compared with three in case of forward playback.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Process and device for decoding MPEG pictures and for displaying them in rewind mode, video driver circuit and decoder box incorporating such a device
ActiveUS7430361B2Compensation delayLow costTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingDriver circuitData stream
A process for decoding and for displaying in rewind mode pictures of a stream of picture data compressed according to the MPEG standard using a specified number N of frame memories each adapted for storing a decoded picture, where N is an integer greater than or equal to 4, applies rules for selecting a frame memory when a frame memory is to be overwritten so as to allow the storage of a new picture to be decoded.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
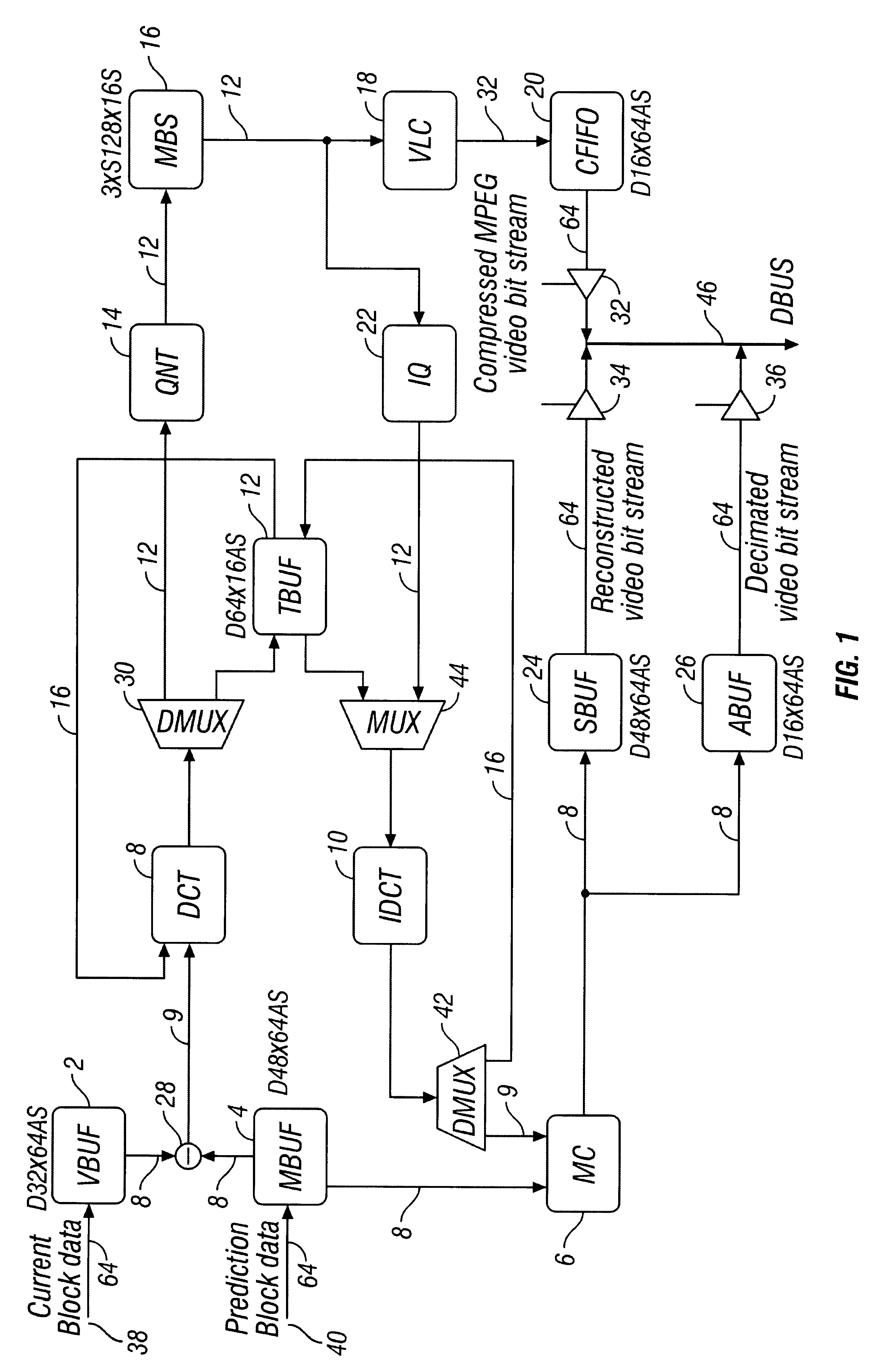
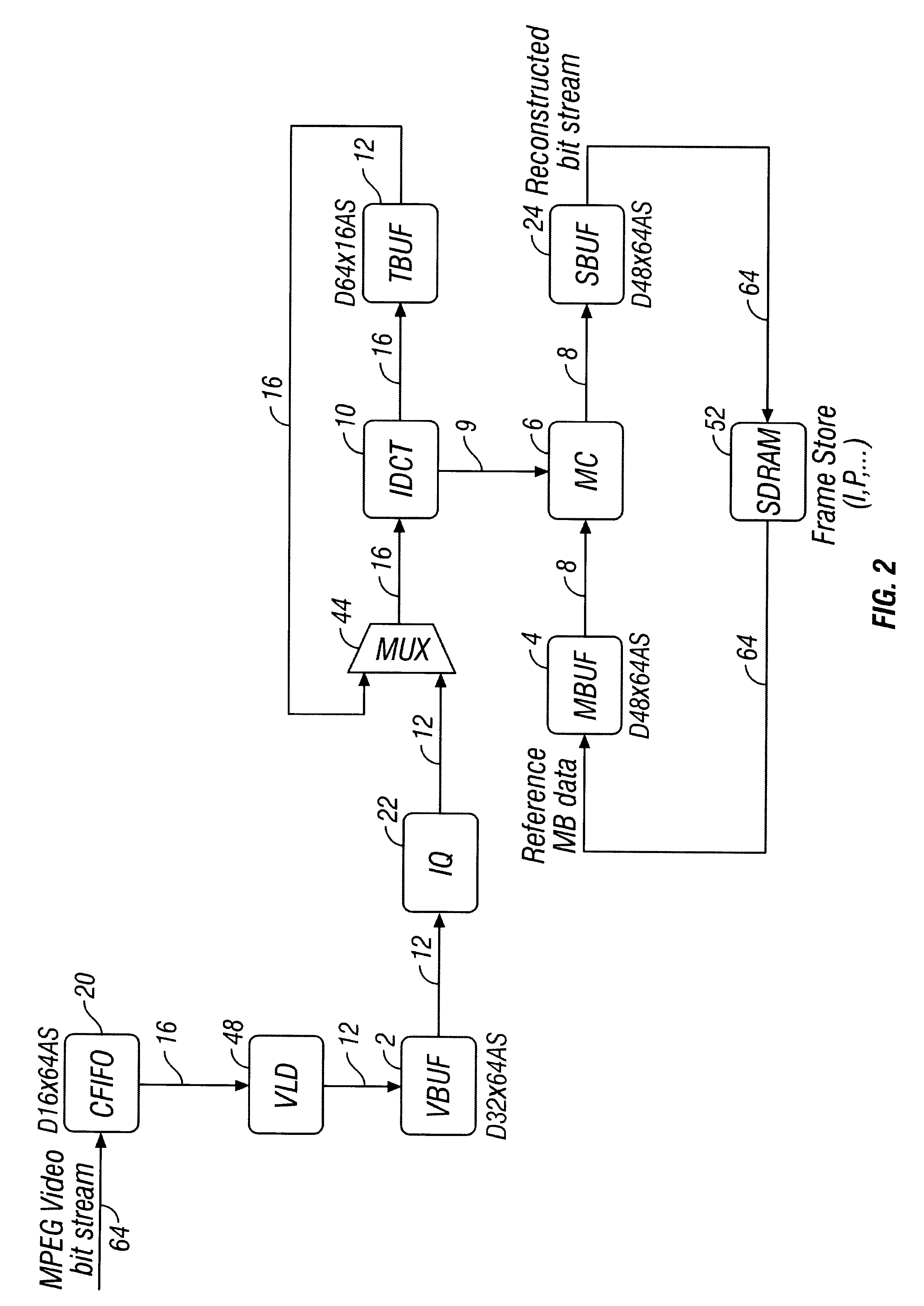
LSI Architecture and implementation of MPEG video codec
InactiveUS6584156B1Easy to processMinimizes total logicPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputation using non-contact making devicesVideo bitstreamComputer architecture
Flexible VLSI architecture implements of MPEG video processing unit (VPU) for encoding and decoding. In encoding mode, VPU performs compression operations on digitized video input per MPEG standard; and in decoding mode, VPU performs decompression operations on video bitstream per MPEG standard. VPU modules include: Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT), Inverse Discrete Cosine Transformation (IDCT), Quantization (QNT), Inverse Quantization (IQ), Variable Length Encoding (VLC), Variable Length Decoding (VLD) and Motion Compensation (MC). VPU functions in half duplex, and hardware modules are shared between encode / decode modes. Architecture provides low-cost, flexible and efficient solution to implement real-time MPEG codec. Specific system configuration is not required, and general interface supports various operating conditions.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Coding system and method, encoding device and method, decoding device and method, recording device and method, and reproducing device and method
InactiveUS20070253488A1Quality improvementMinimize degradation of image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionSource encodingGroup of pictures
Owner:SONY CORP
Moving pictures encoding with constant overall bit-rate
InactiveUS7496142B2Minimize changesConstant rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGroup of picturesMpeg standards
A method and apparatus control bit rates used in a moving pictures encoder, such as an MPEG standard encoder. A sequence of moving pictures is divided into segments each of which comprises one or more groups of pictures. A constant overall bit rate is specified for the sequence of pictures, but variable bit rate encoding used within each segment. A difference between the number of bits allocated for encoding the segment and the actual bits used for encoding is determined, and the difference distributed over one or more subsequent segments.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
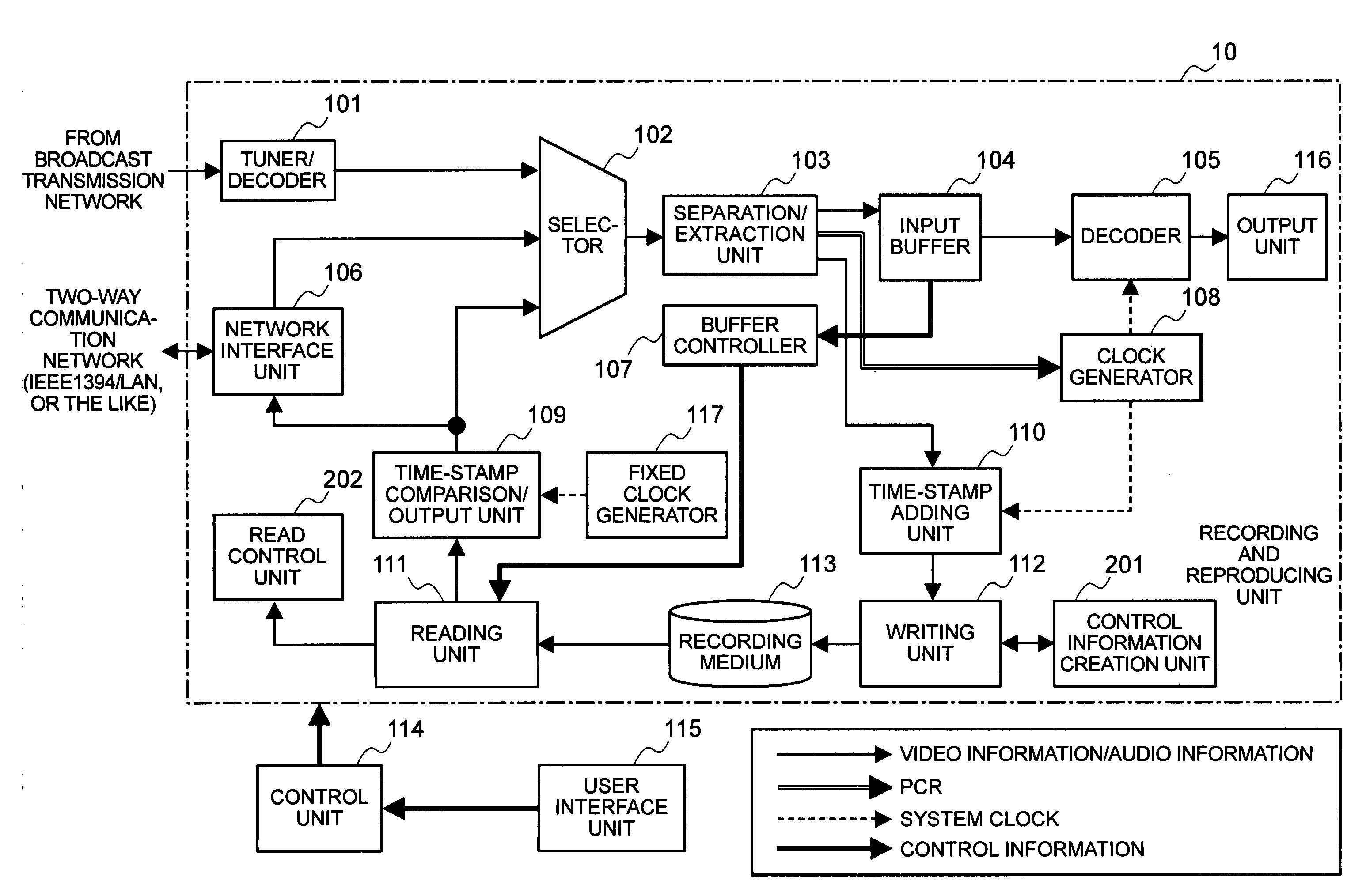
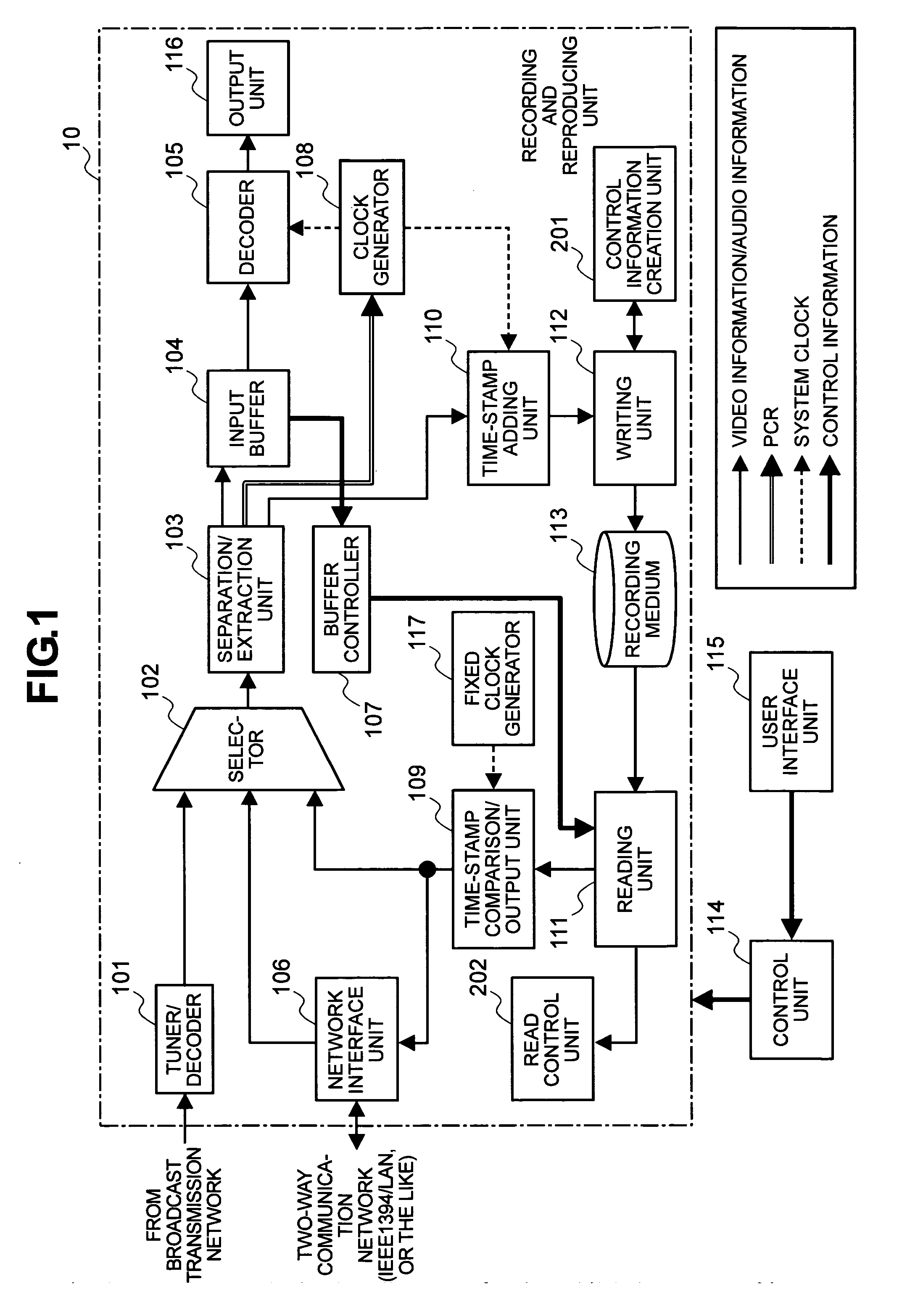
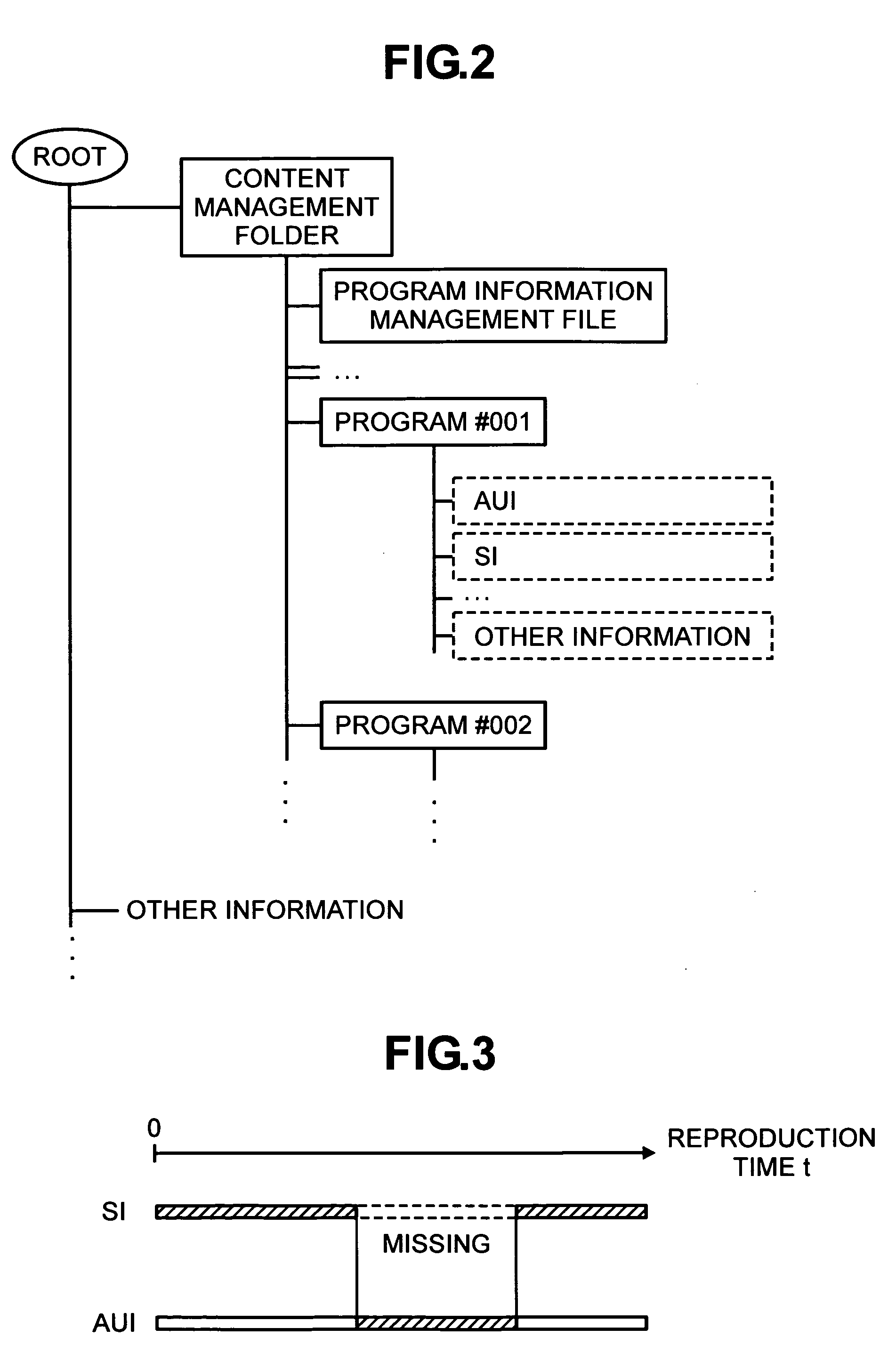
Recording apparatus, image reproducing apparatus, and special reproduction method therefor
ActiveUS20080232782A1Television system detailsRecording carrier detailsMpeg standardsDigital broadcasting
According to the present invention, there is provided an image reproducing apparatus for reproducing a digital broadcast based on the MPEG standard. When performing special reproduction by use of access-unit management information that is used to manage access units, the image reproducing apparatus reads ahead the access-unit management information and compares time stamps. As a result of the comparison, if it is judged that the absence of a piece of the access-unit management information exists, the special reproduction is then performed by use of simple information that is used to manage a stream.This makes it possible to continuously perform the special reproduction even if it becomes impossible to utilize the access-unit management information.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
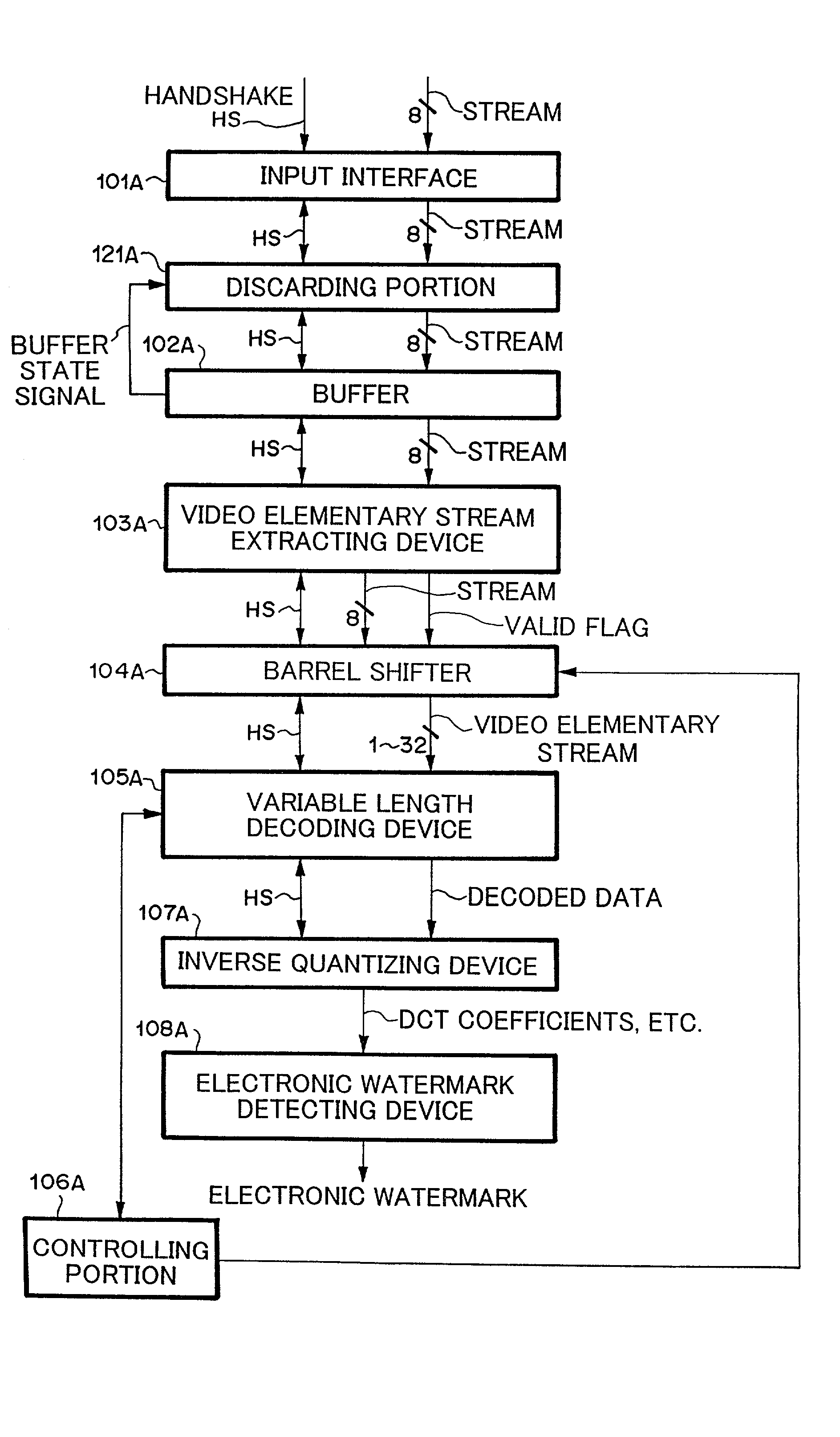
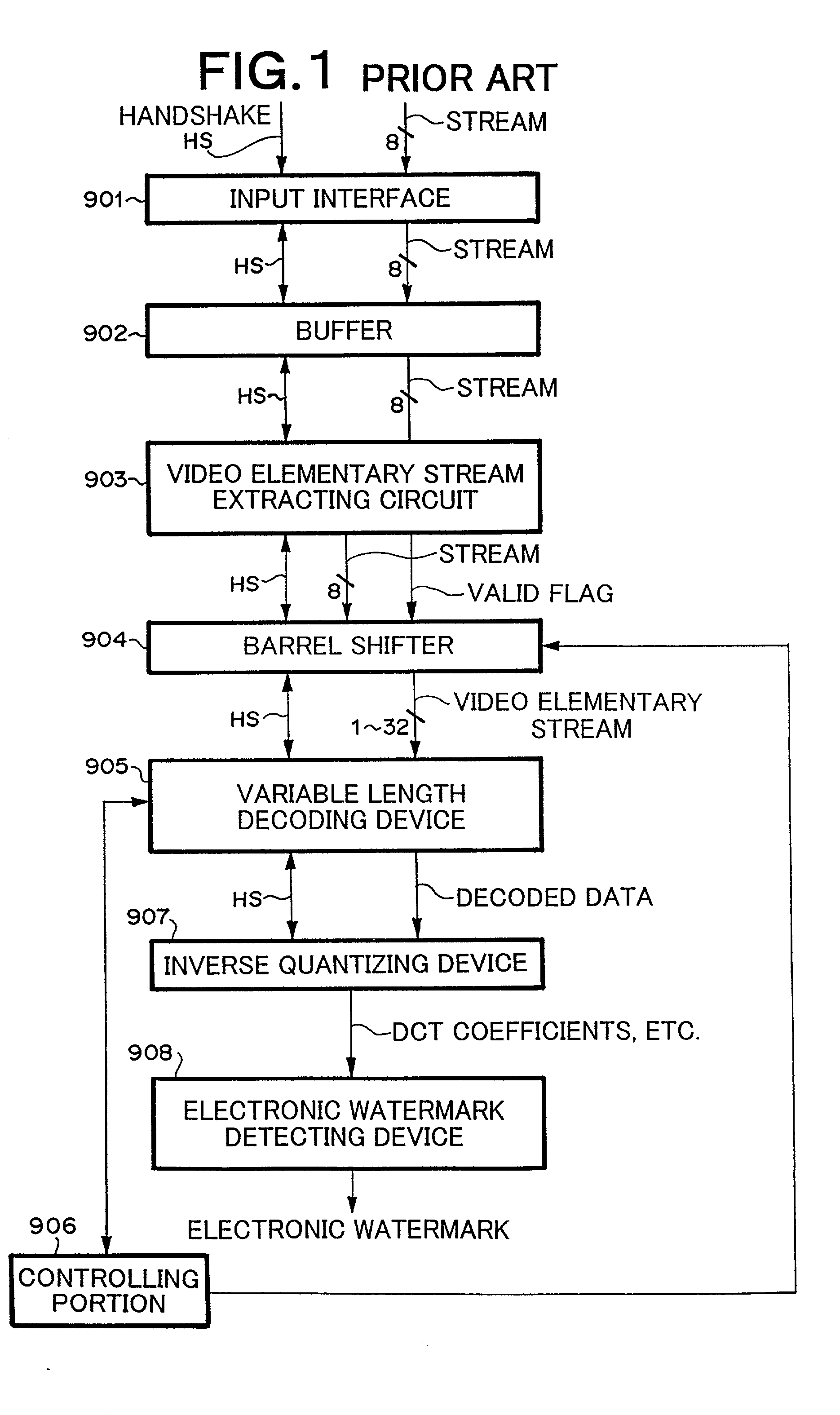
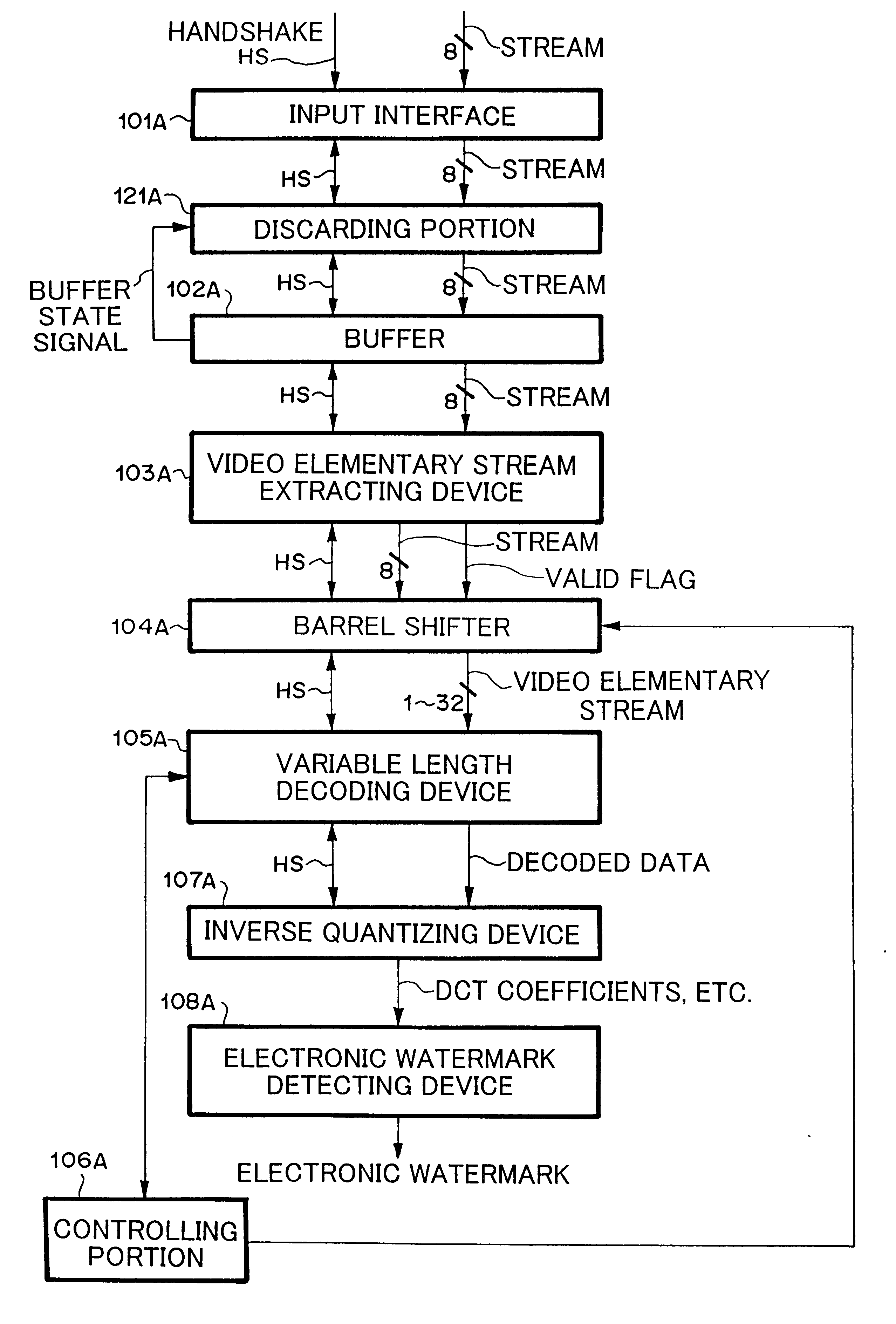
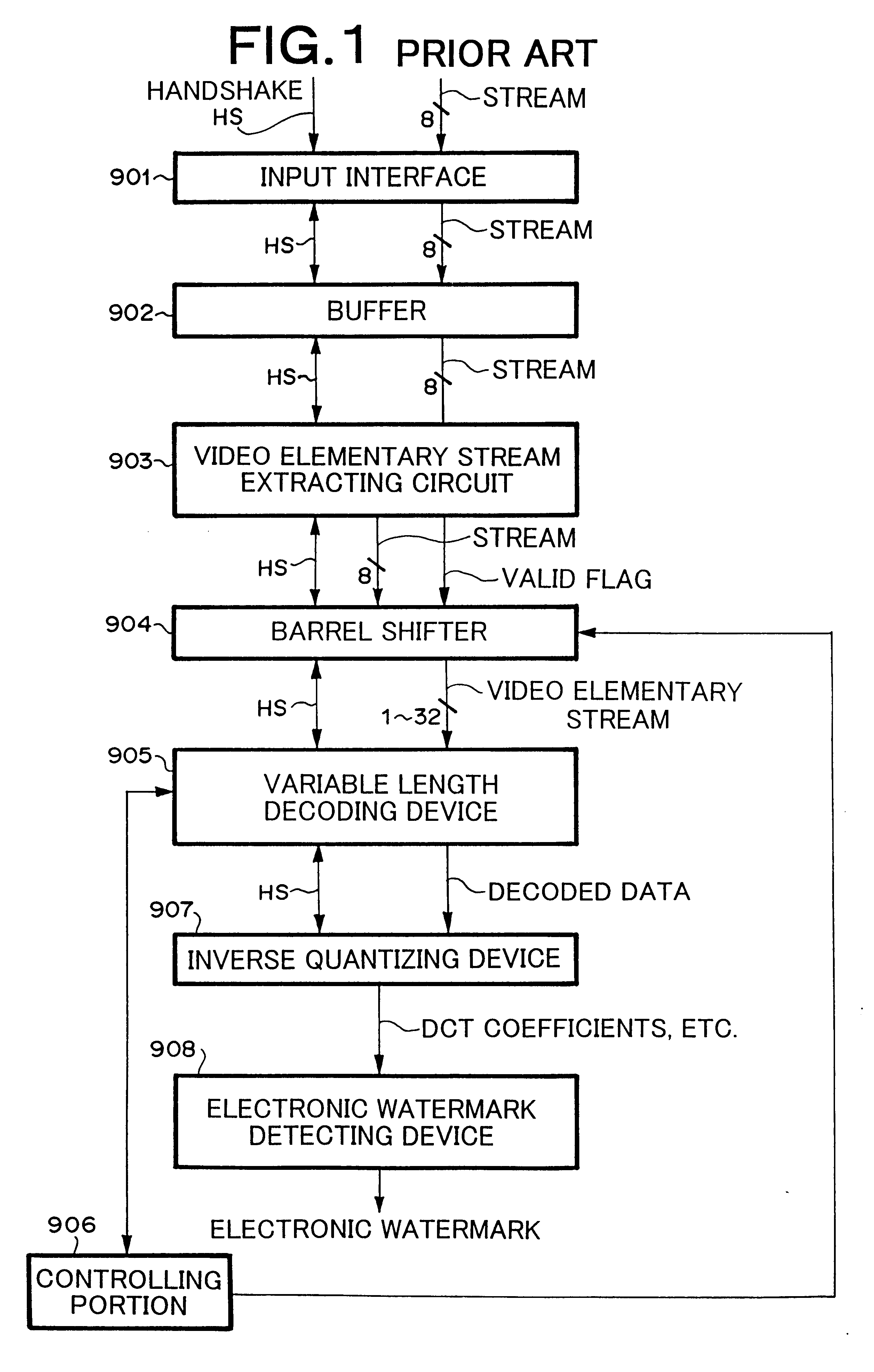
System and method for preventing input of variable length codes from being interrupted
InactiveUS20020167427A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeMpeg standards
A system and method that prevent an input of variable length codes in which short length codes continue from being interrupted without an increase of a circuit scale are provided. The system comprises a variable length decoding device for decoding variable length codes, a buffer for buffering the variable length codes to be supplied to the variable length decoding device, a detector for detecting whether or not a occupation rate of the variable length codes in the buffer has increased, and a discarder for discarding the variable length codes to be supplied to the buffer when the detected result by the detector represents that the occupation rate of the variable length codes in the buffer has increased. The system further comprises an elementary stream extractor, disposed between the discarding device and the buffer, for extracting an elementary stream defined in MPEG standard.
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
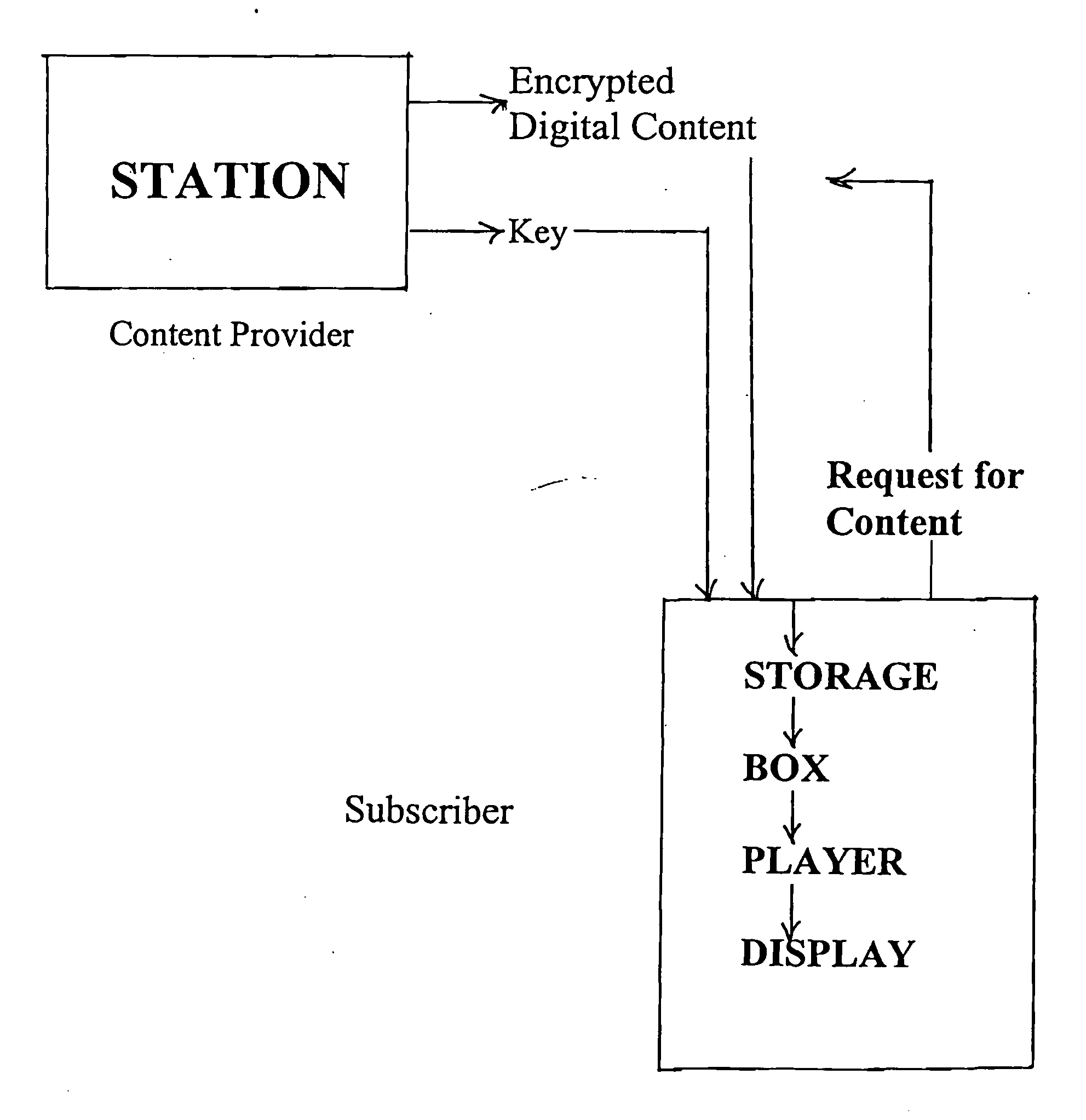
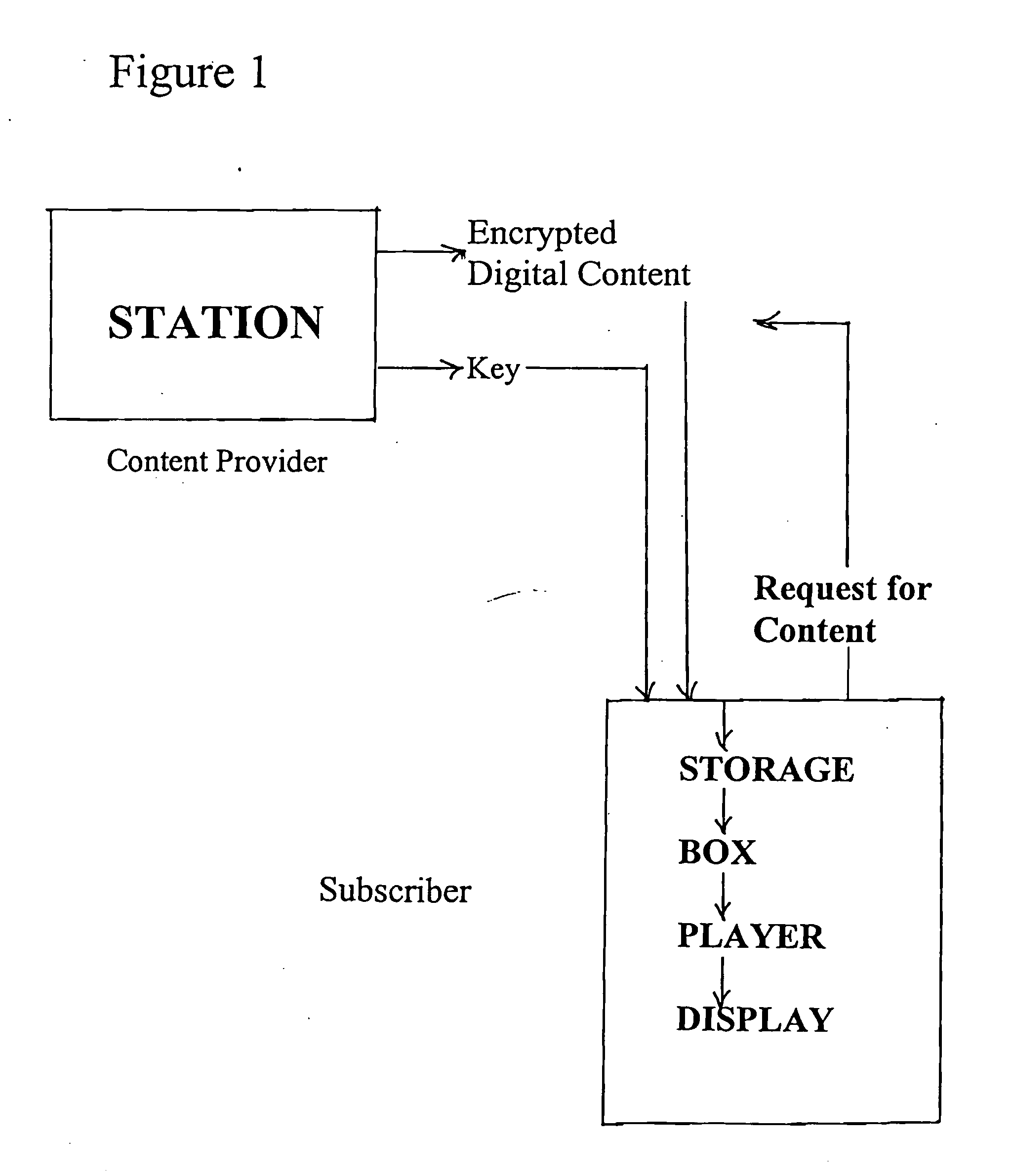
Method for secure delivery of digital content
InactiveUS20110066857A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsTamper resistanceHash function
Methods and apparatus for the secure and copy-proof distribution of digital content are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention cryptographic primitives (encryption algorithms, message-authentication codes, hash functions, random-number generators, etc.) are used in a novel security protocol. The invention may be utilized to protect a first-run movie that has been digitized in accordance with one of the current or forthcoming MPEG standards (e.g., MPEG-7). Content receivers or users first register their boxes. This registration information is stored in a secure database. When a subscriber registers, he then receives a box (interface to his player) that has been initialized to contain a number of tamper-proof secrets that are shared between the station and that particular box. The station stores an encrypted version of the digital content. This encrypted version ultimately arrives at some unprotected storage medium local to the player. Upon demand, the station delivers to the box the use-once computational ability to decrypt the content and display it on the player or terminal.
Owner:PASCALS POCKET
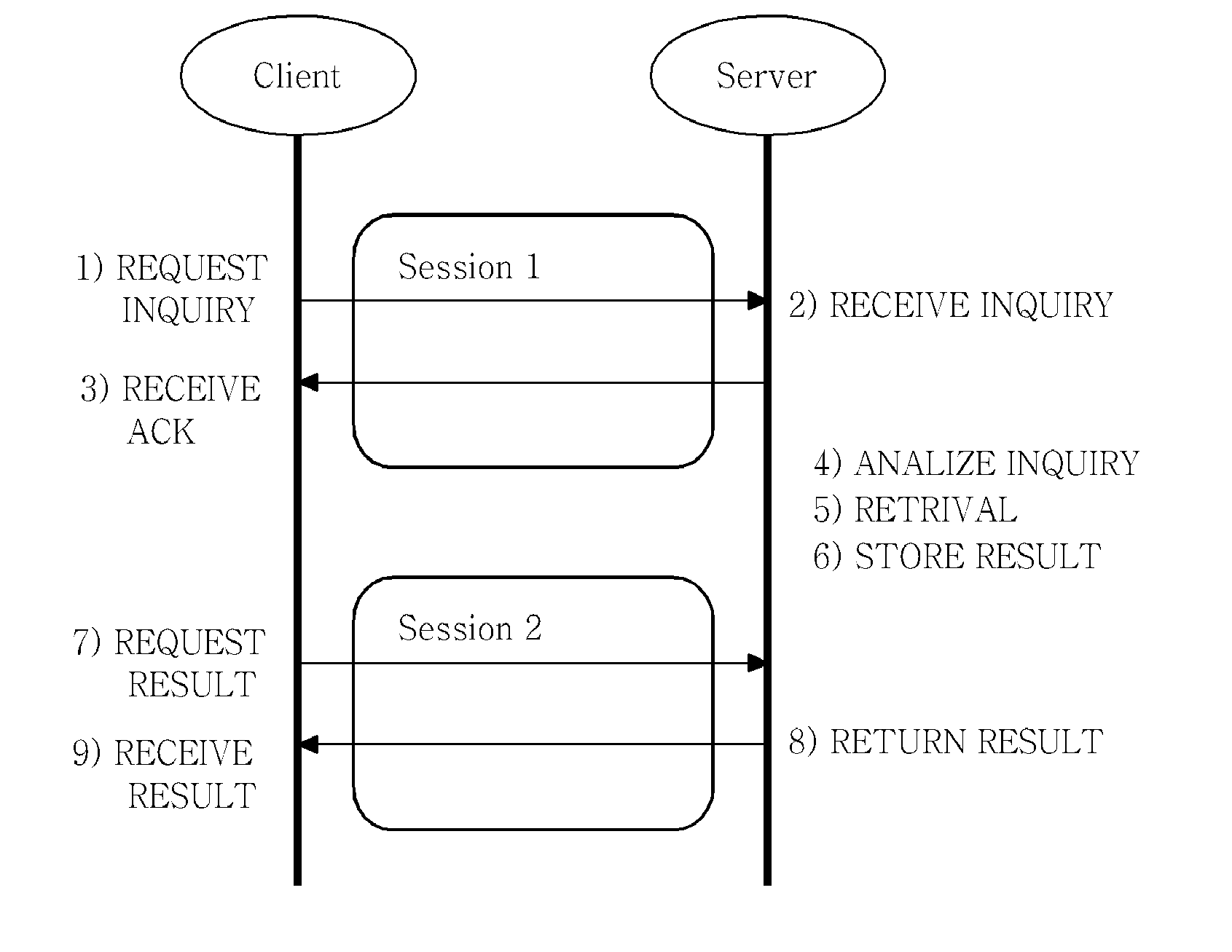
Method for asynchronous multimedia retrieval
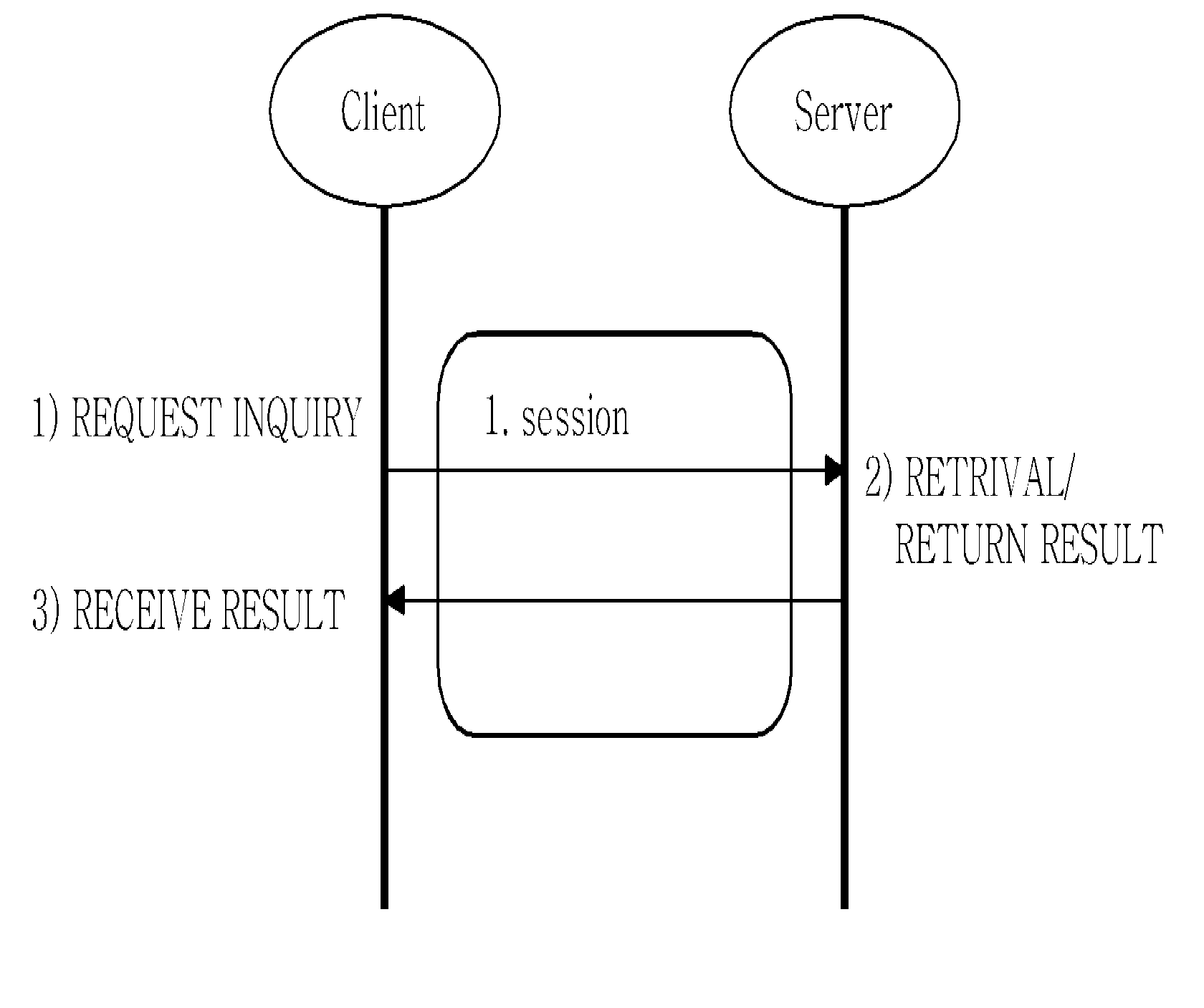
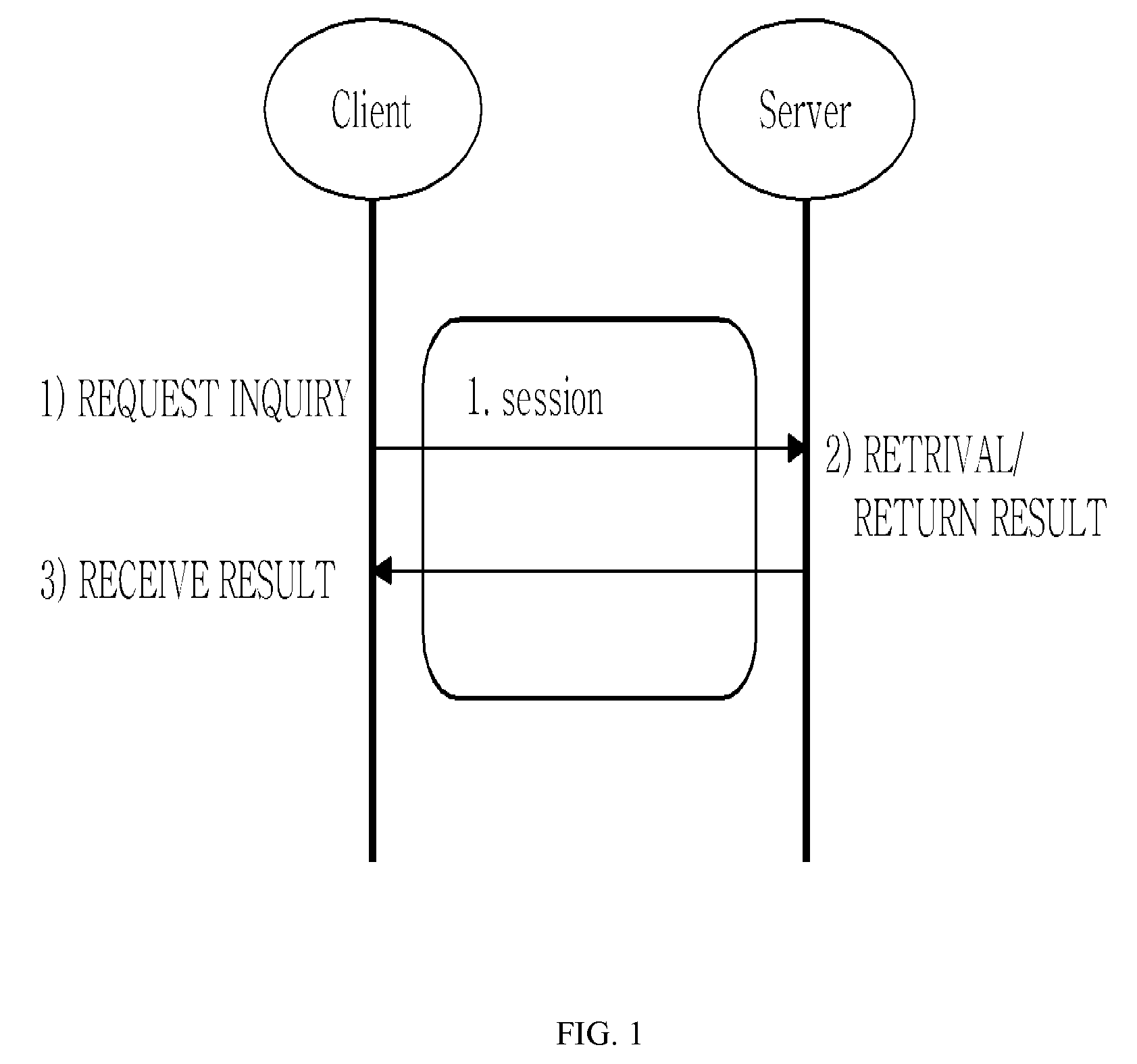
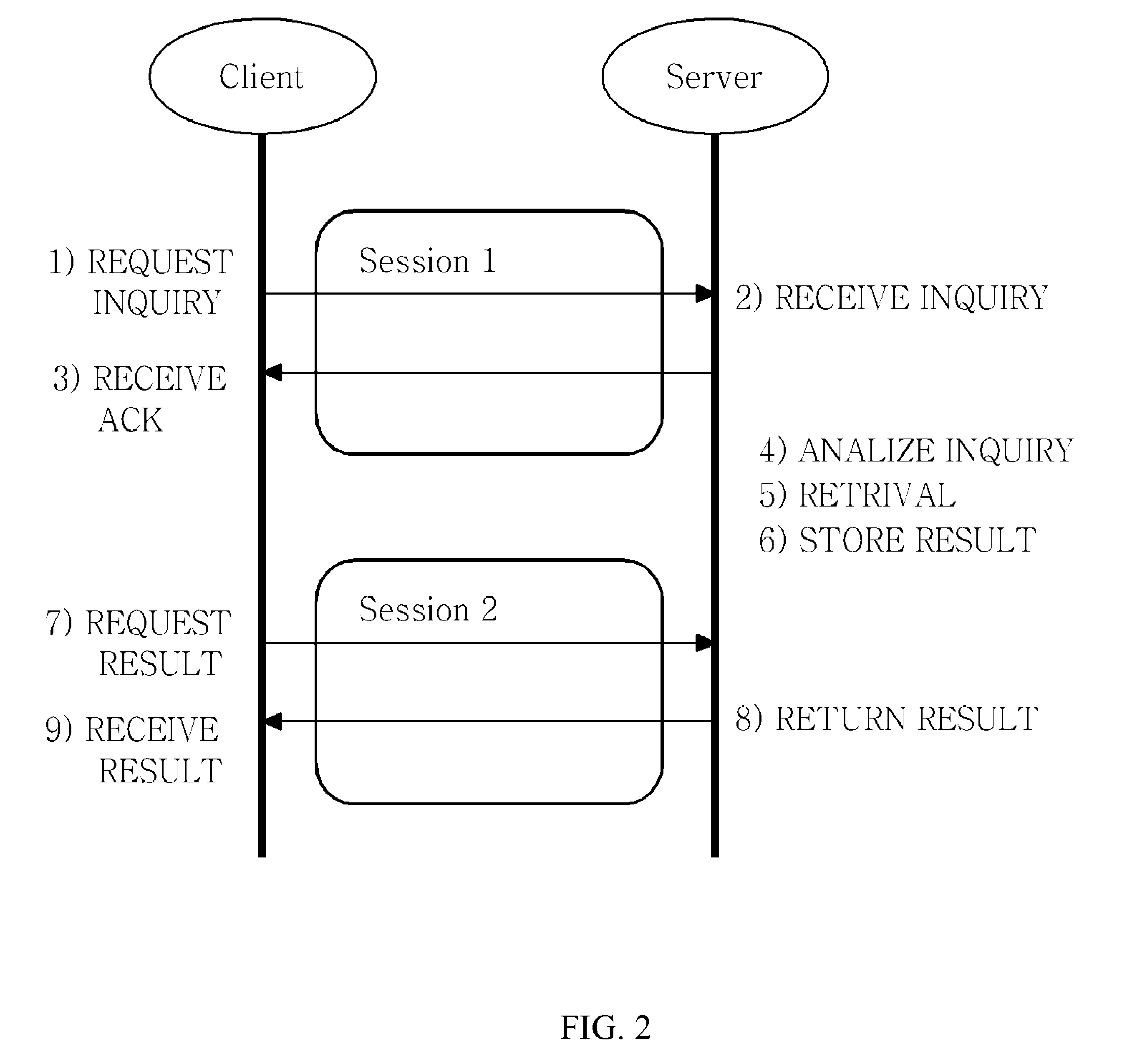
ActiveUS8239545B2Effective controlAppropriate load balanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsTV-AnytimeComputer network
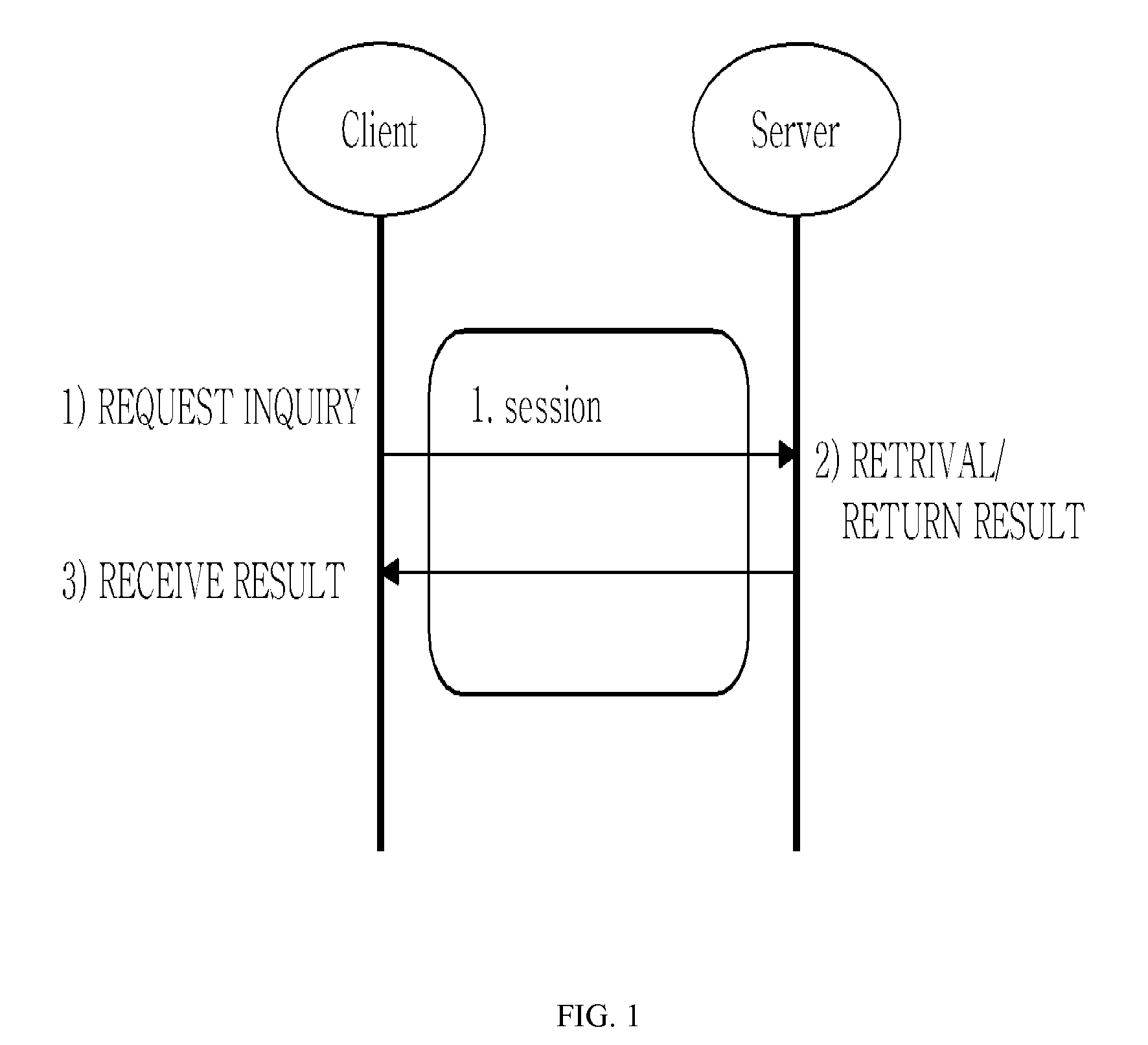
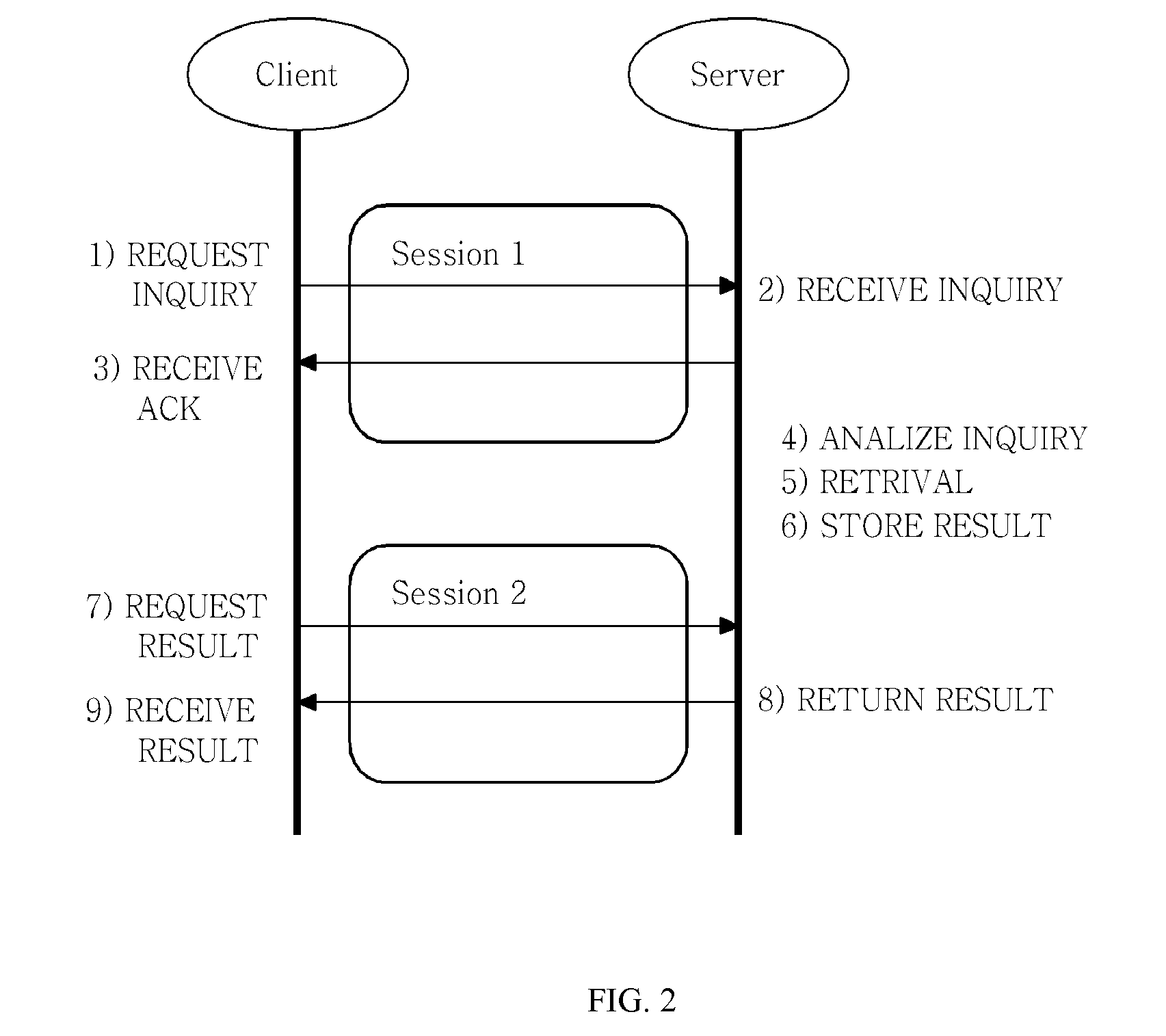
The present invention relates to a method for asynchronous multimedia content retrieval, which can be applied to TV-Anytime standard or MPEG standard. In summary, an asynchronous multimedia retrieval method is provided as including: a client establishing the first session as requesting to the server; transmitting to the server the retrieval inquiry message for contents that the server needs; terminating the first session after the retrieval inquiry; establishing the second session and requesting to the server the result for the retrieval inquiry at a certain point in time that the previously set time has passed; and receiving the retrieval result from the server and terminating the second session.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
System and method for preventing input of variable length codes from being interrupted
InactiveUS6717535B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeMpeg standards
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
Method For Asynchronous Multimedia Retrieval
ActiveUS20110055401A1Efficient load controlAppropriate load balanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsTV-AnytimeMpeg standards
The present invention relates to a method for asynchronous multimedia content retrieval, which can be applied to TV-Anytime standard or MPEG standard. In summary, an asynchronous multimedia retrieval method is provided as including: a client establishing the first session as requesting to the server; transmitting to the server the retrieval inquiry message for contents that the server needs; terminating the first session after the retrieval inquiry; establishing the second session and requesting to the server the result for the retrieval inquiry at a certain point in time that the previously set time has passed; and receiving the retrieval result from the server and terminating the second session.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
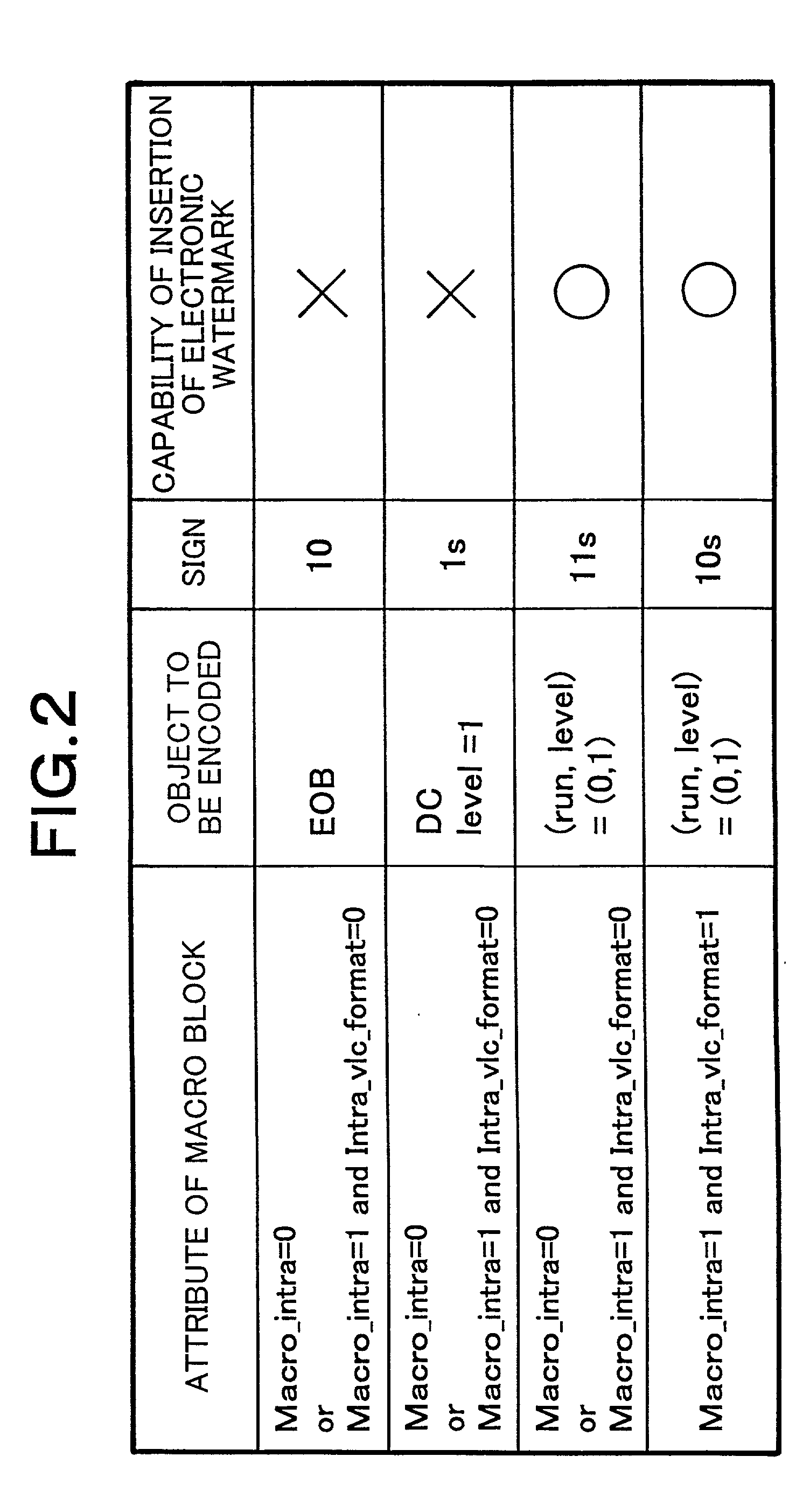
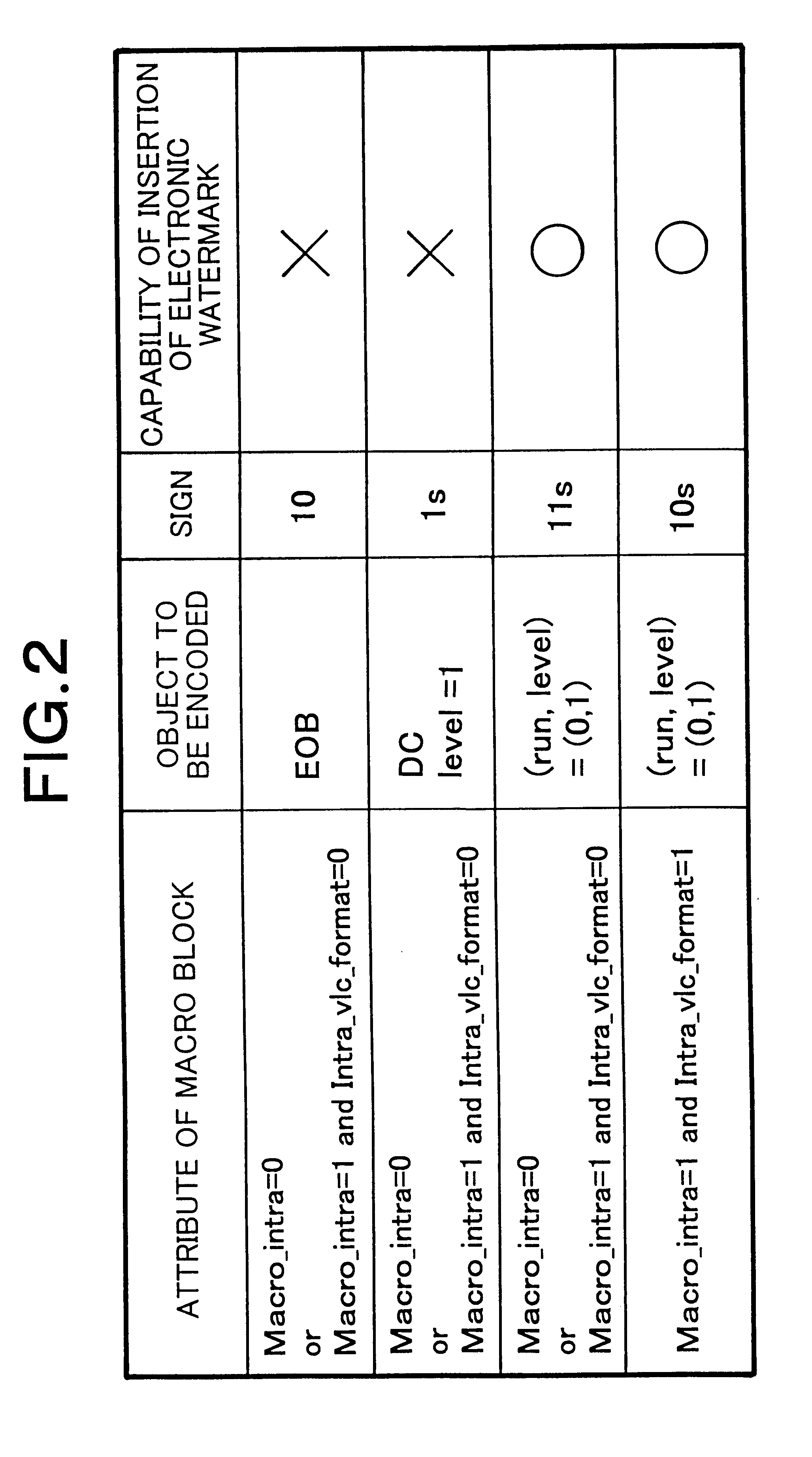
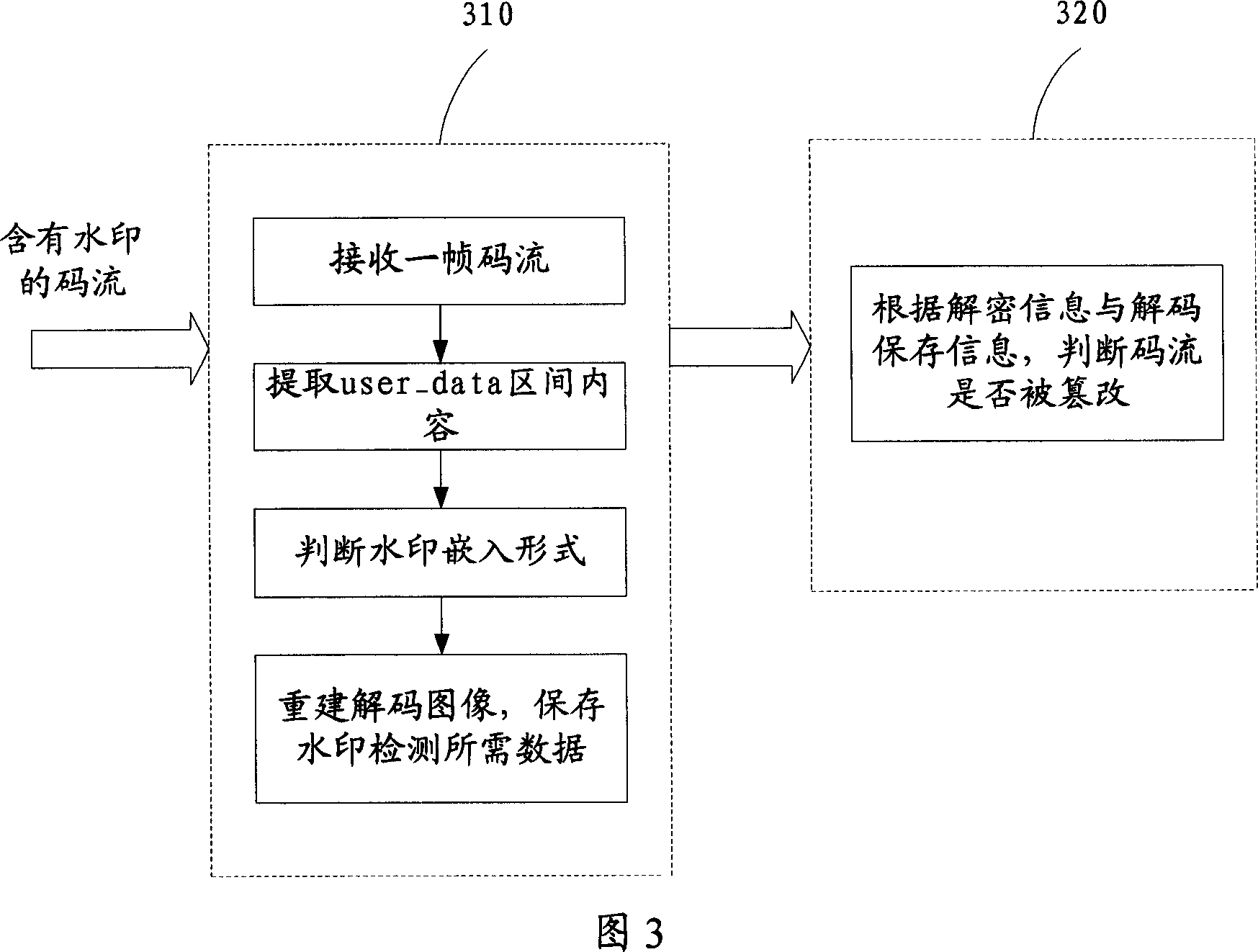
Coding and decoding equipment with watermark encrypting
InactiveCN1976437AEasy to implementVarious formsTelevision systemsImage data processing detailsMpeg standardsComputer science
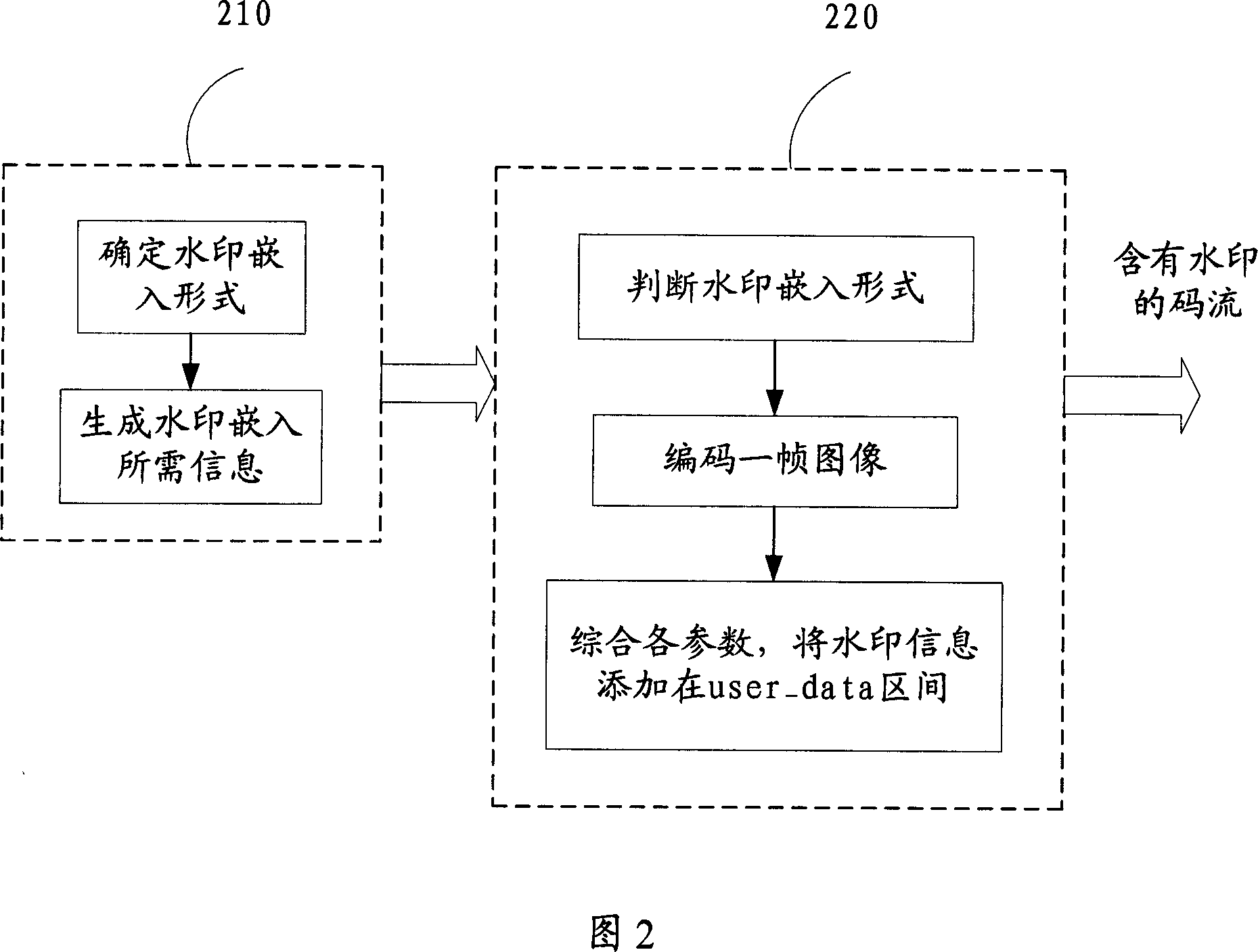
A coding / decoding device with watermark encipherment is prepared as forming coding device by watermark generator for generating watermark information and coder for carrying out coding according to MPEG standard and for embedding said watermark on, forming decoding device by decoder for analyzing MPEG code stream to pick watermark up and for restructuring decoded image and watermark detector used for judging whether code stream is distorted or not.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Picture data reproducing apparatus and method
InactiveCN1476243AReproduce smooth shiftingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMpeg standardsRecording media
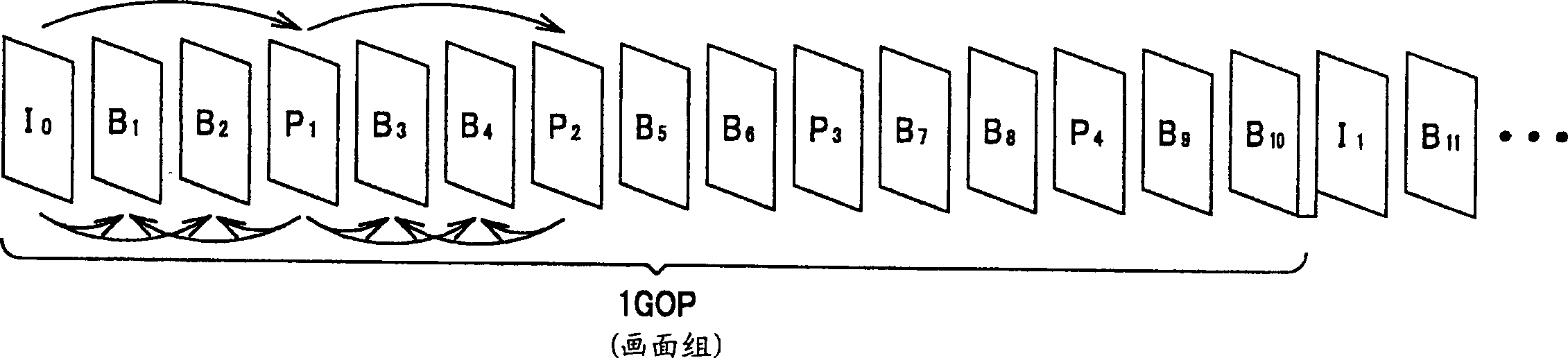
In a picture data reproducing method of reproducing picture data recorded to a recording medium according the MPEG standard, there is provisionally stored, into a stream buffer, picture data grouped as a GOP which begins with an I picture, the picture data provisionally stored in the stream buffer is read sequentially starting with a previous picture and the read picture data is decoded in the course of a FORWARD reproduction being done, and picture data acquired from the recording medium is additionally supplied to the stream buffer. When the picture data provisionally stored in the stream buffer have been read in the decoding step to before last N frames, a predetermined amount of picture data is additionally supplied, in the data adding step, beginning at the head of a GOP including picture data in the remaining N-th frame in the stream buffer. Thus, a smooth variable-speed reproduction can be done according to the MPEG Standard.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image data reproducing device and method
Owner:SONY CORP
Picture data reproducing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7321715B2Smoothly reproducedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMpeg standardsRecording media
In a picture data reproducing method of reproducing picture data recorded to a recording medium according the MPEG standard, there is provisionally stored, into a stream buffer, picture data grouped as a GOP which begins with an I picture, the picture data provisionally stored in the stream buffer is read sequentially starting with a previous picture and the read picture data is decoded in the course of a FORWARD reproduction being done, and picture data acquired from the recording medium is additionally supplied to the stream buffer. When the picture data provisionally stored in the stream buffer have been read in the decoding step to before last N frames, a predetermined amount of picture data is additionally supplied, in the data adding step, beginning at the head of a GOP including picture data in the remaining N-th frame in the stream buffer. Thus, a smooth variable-speed reproduction can be done according to the MPEG Standard.
Owner:SONY CORP
Digital video image frame reducing storage method
InactiveCN1694519AReduce processing speed requirementsEasy to implementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
This invention discloses a digital video image frame-reduction storage method including the following steps: On the basis of compatible known MPEG standard, MPEG standard is applied to encode digital video images to form a basic MPEG video flow, then to reduce frames to every GDP set of said flow and store the frame-reduced MPEG digital video image in a video flow-like document. Advantage: when storing MPEG video images, it can store and display high quality of MPEG images in the limited space of hard disks and at low process speed of microprocessors by reducing or eliminating P, B or partial B frames of each GOP set.
Owner:CHENGDU NAWEITE SCI & TECH DEV
Method, system and device for displaying image
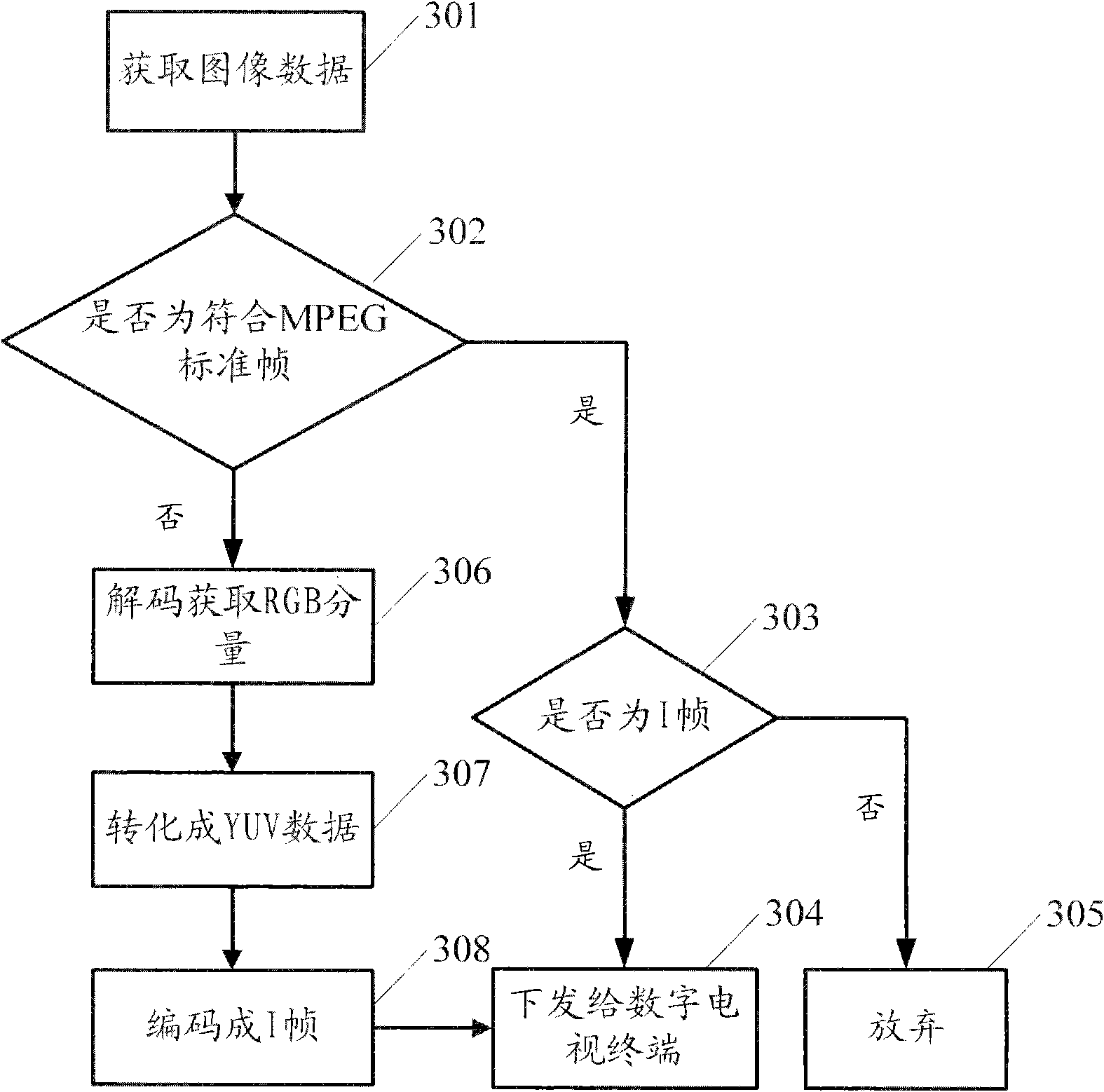
ActiveCN101783950ASave resourcesImprove decoding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Mpeg standards
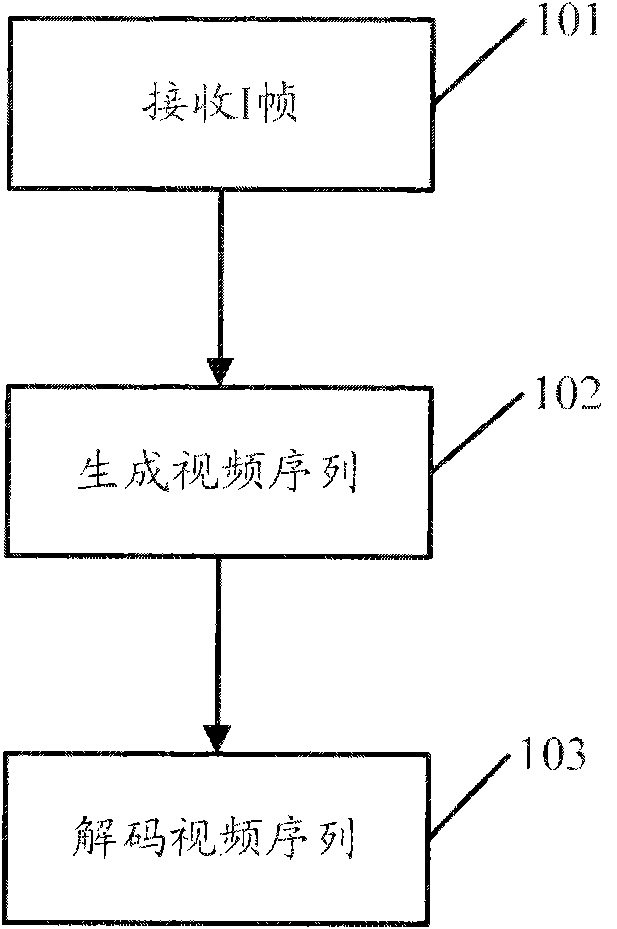
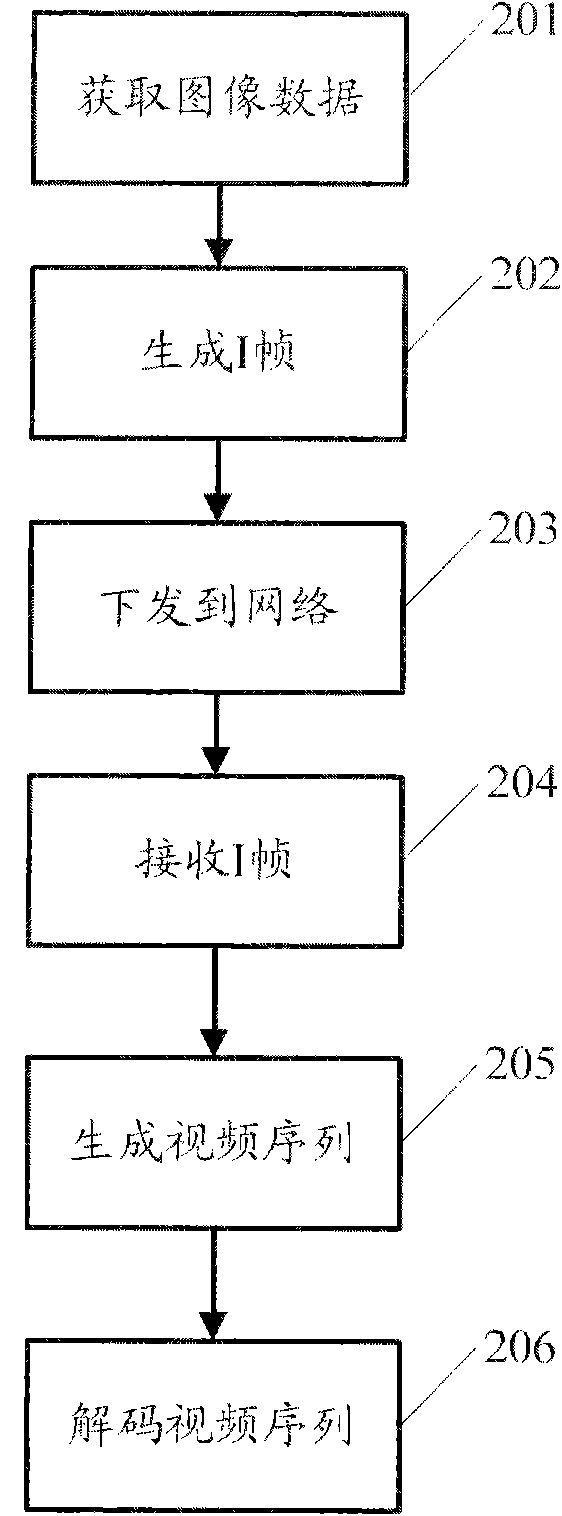
The invention discloses a method, a system and a device for displaying a static image in a digital TV. The method comprises the steps of: receiving an I frame, and generating a video sequence which is in accordance with a moving picture experts group (MPEG) standard by referring to the I frame; and then, transmitting the generated video sequence to an MPEG hardware decoder for decoding. In the embodiment of the invention, a P frame and a B frame are generated by referring to the I frame, so that the video sequence which is in accordance with the MPEG standard can be generated and then transmitted to the MPEG hardware decoder for decoding, and decoded image is not processed by a CPU; an therefore, the invention saves resource of the CPU, and improves the decoding efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN IPANEL TECH LTD
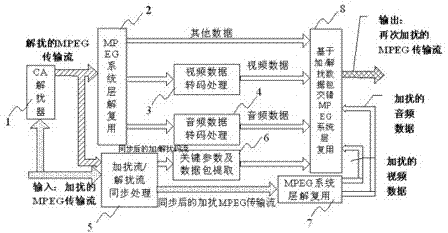
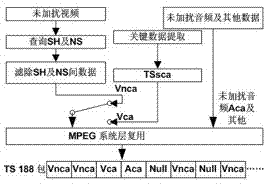
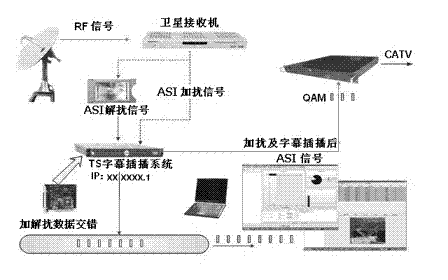
Scrambled/descrambled-data-scattering-based video scrambling system
InactiveCN102238418ASolve a practical problemLow costSelective content distributionMultiplexingConditional access systems
Owner:昆明亿尚科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com