Patents
Literature
320 results about "Elementary stream" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
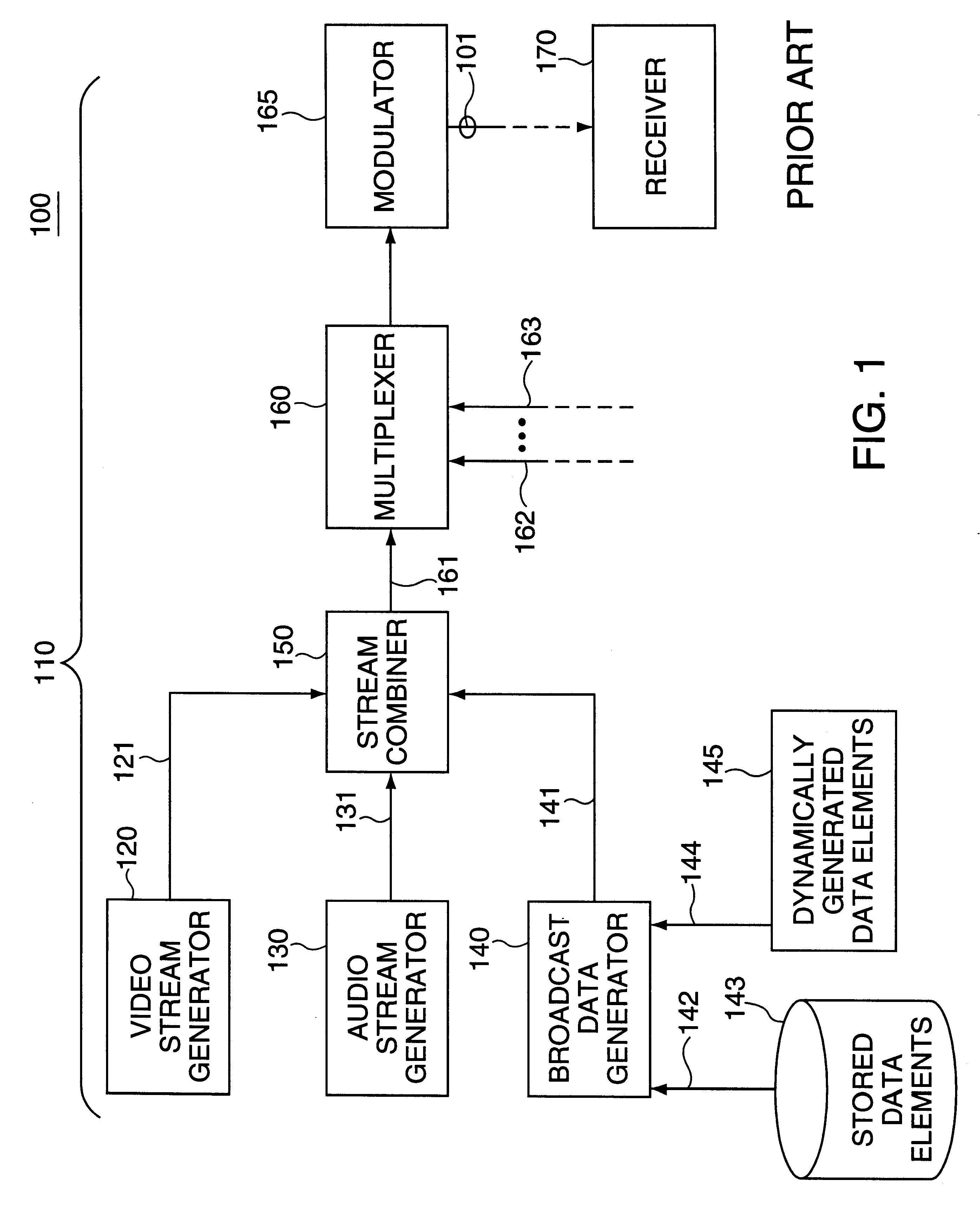
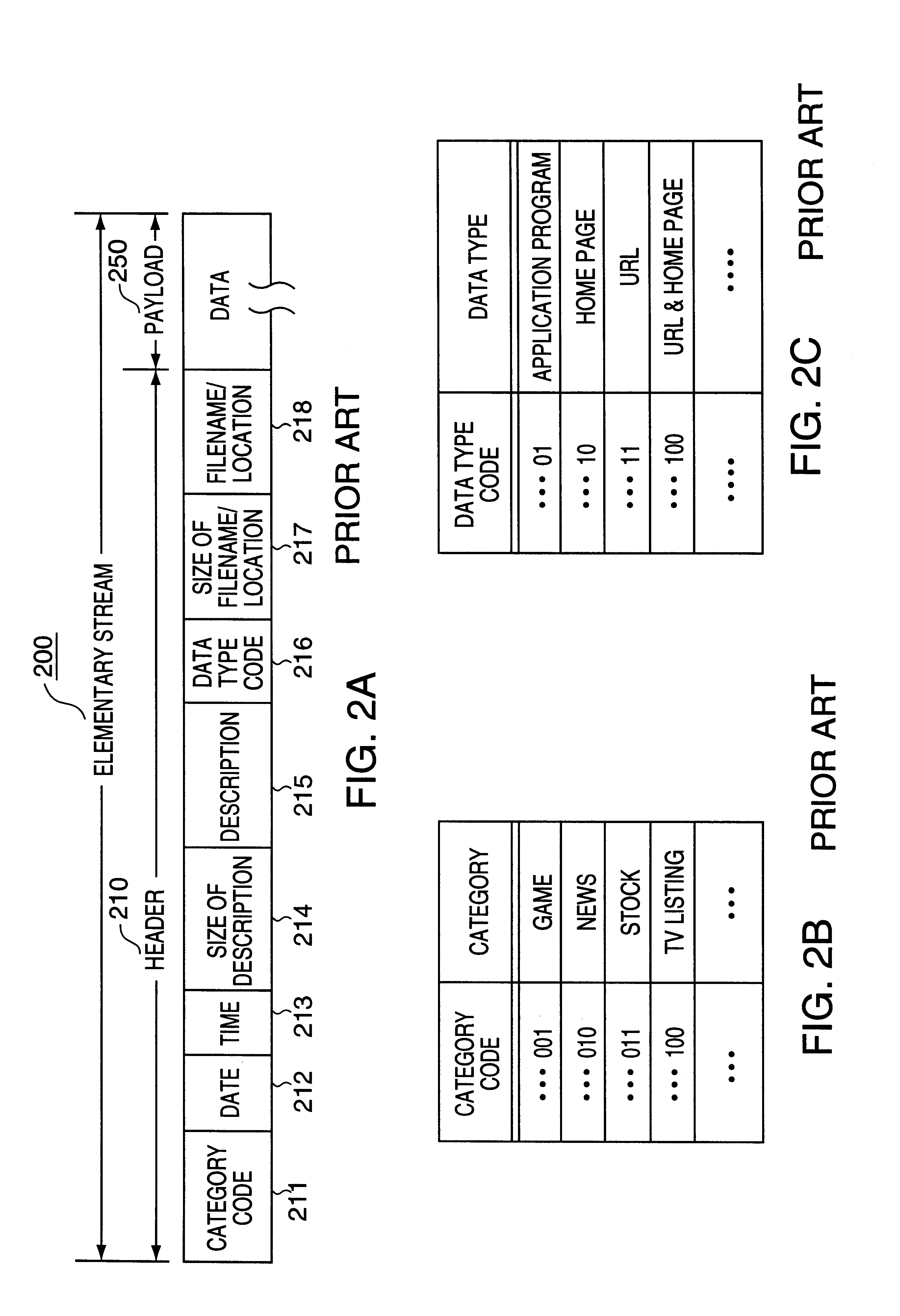
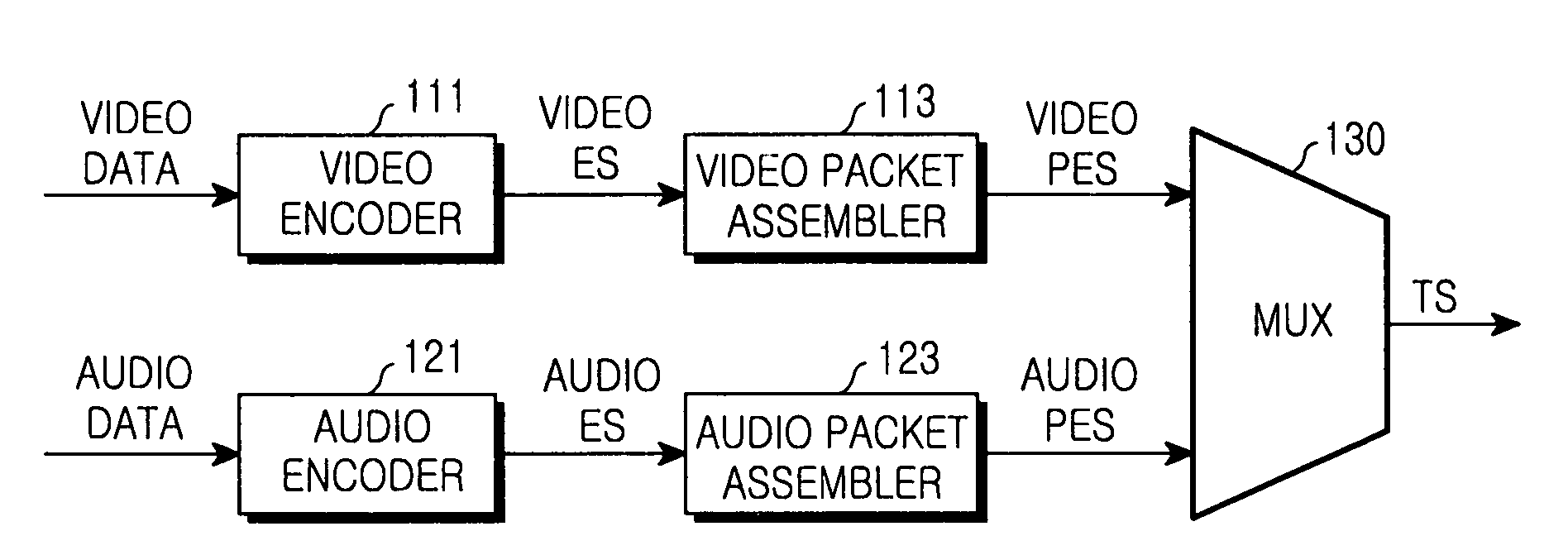
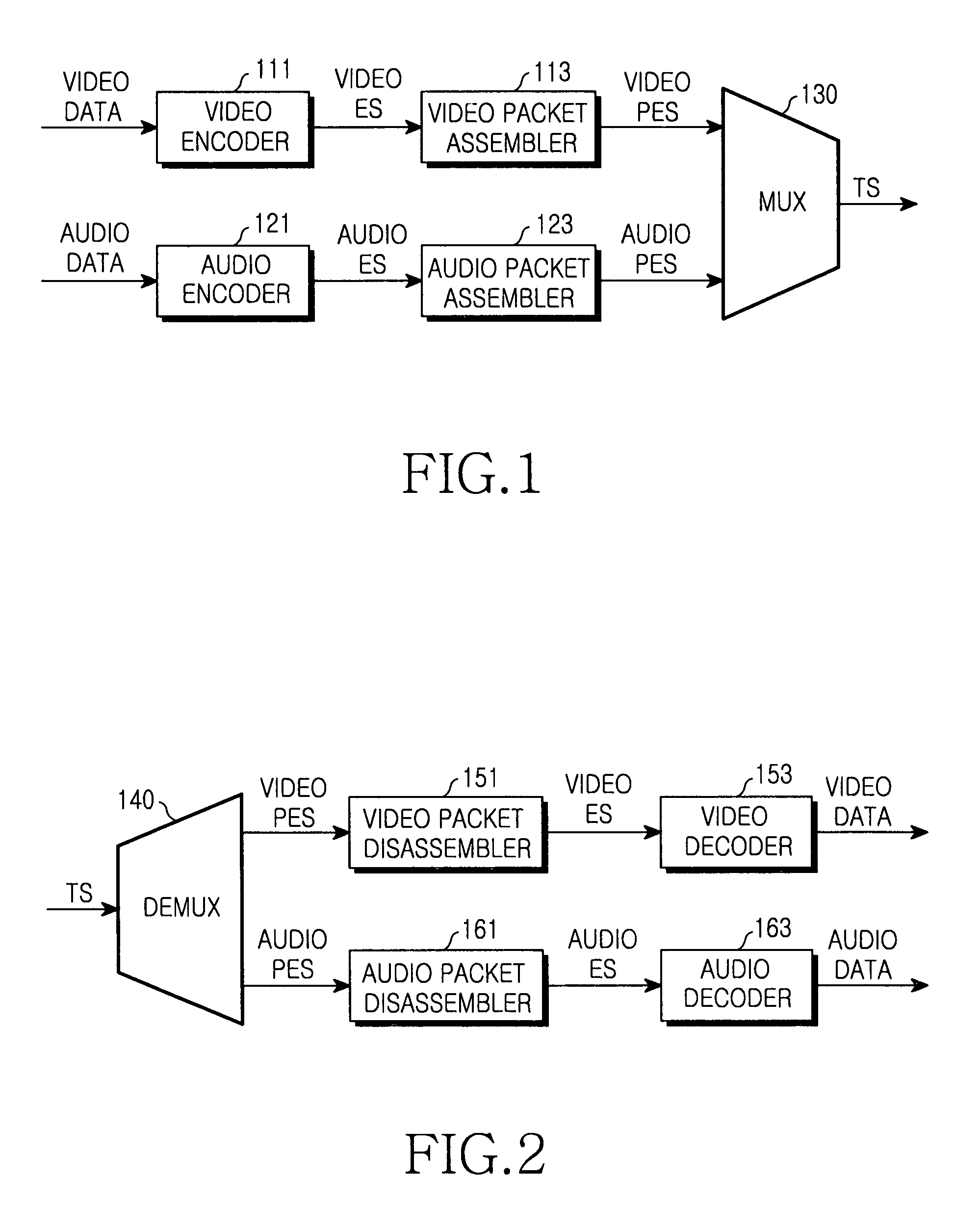
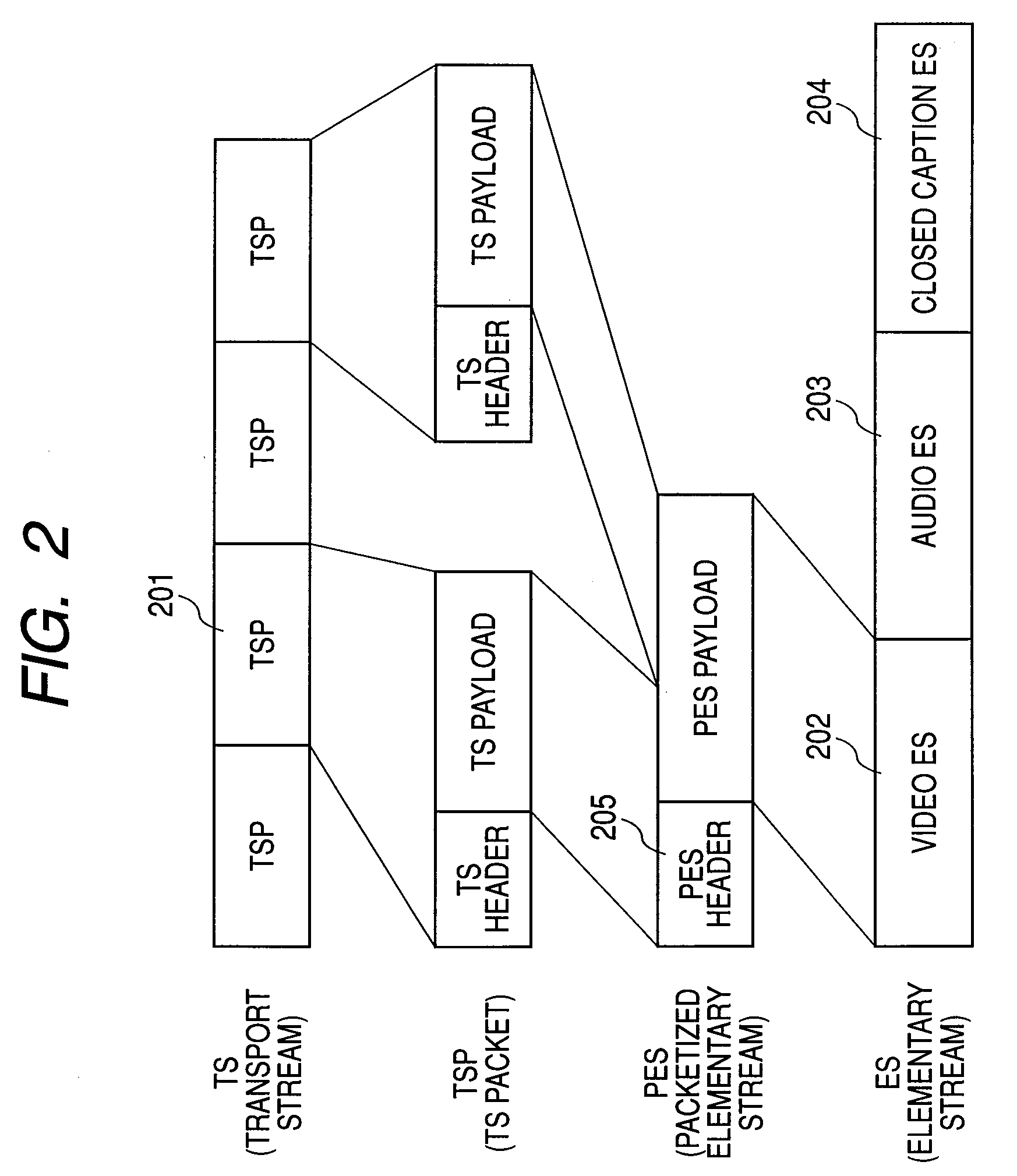
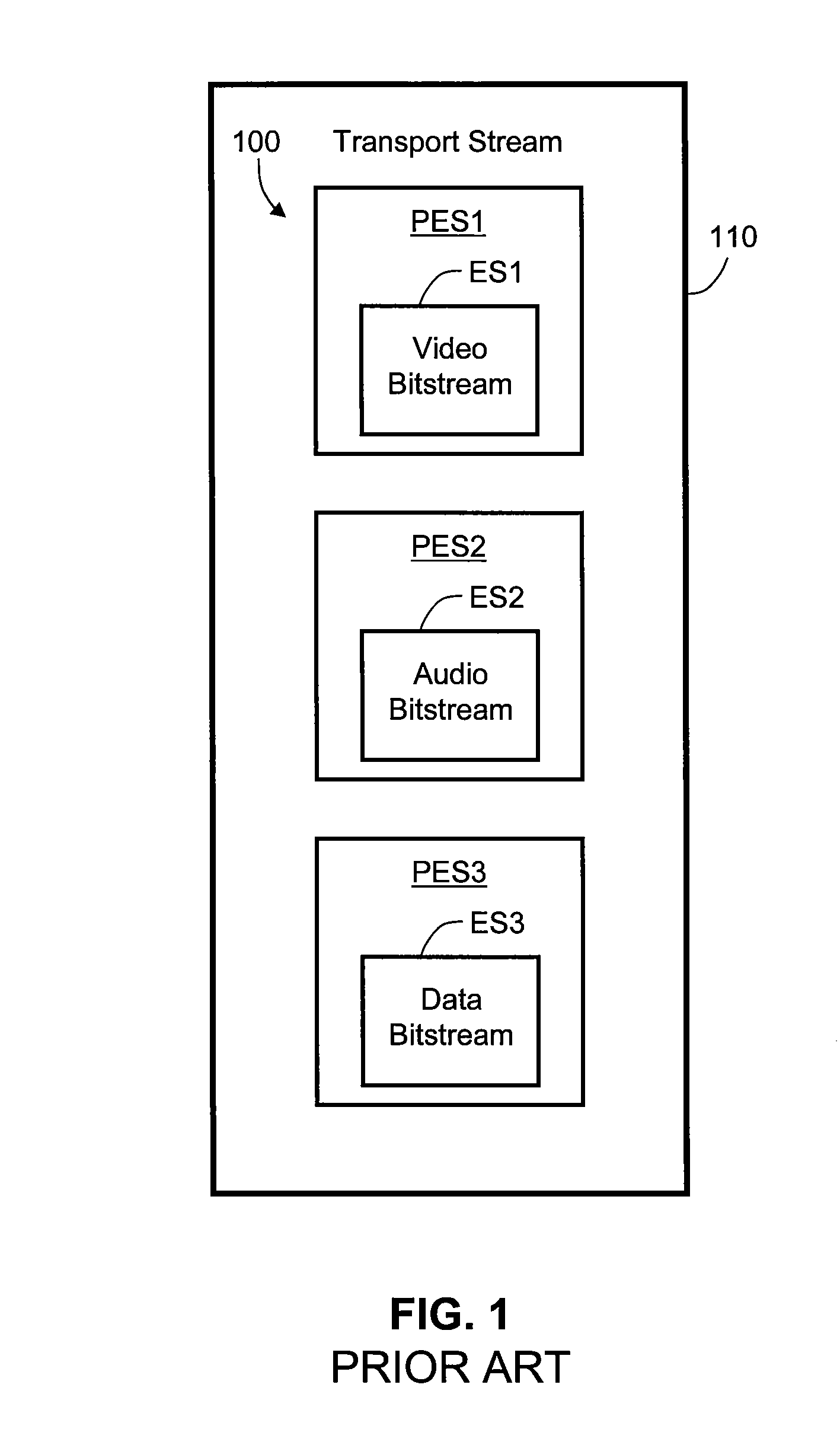
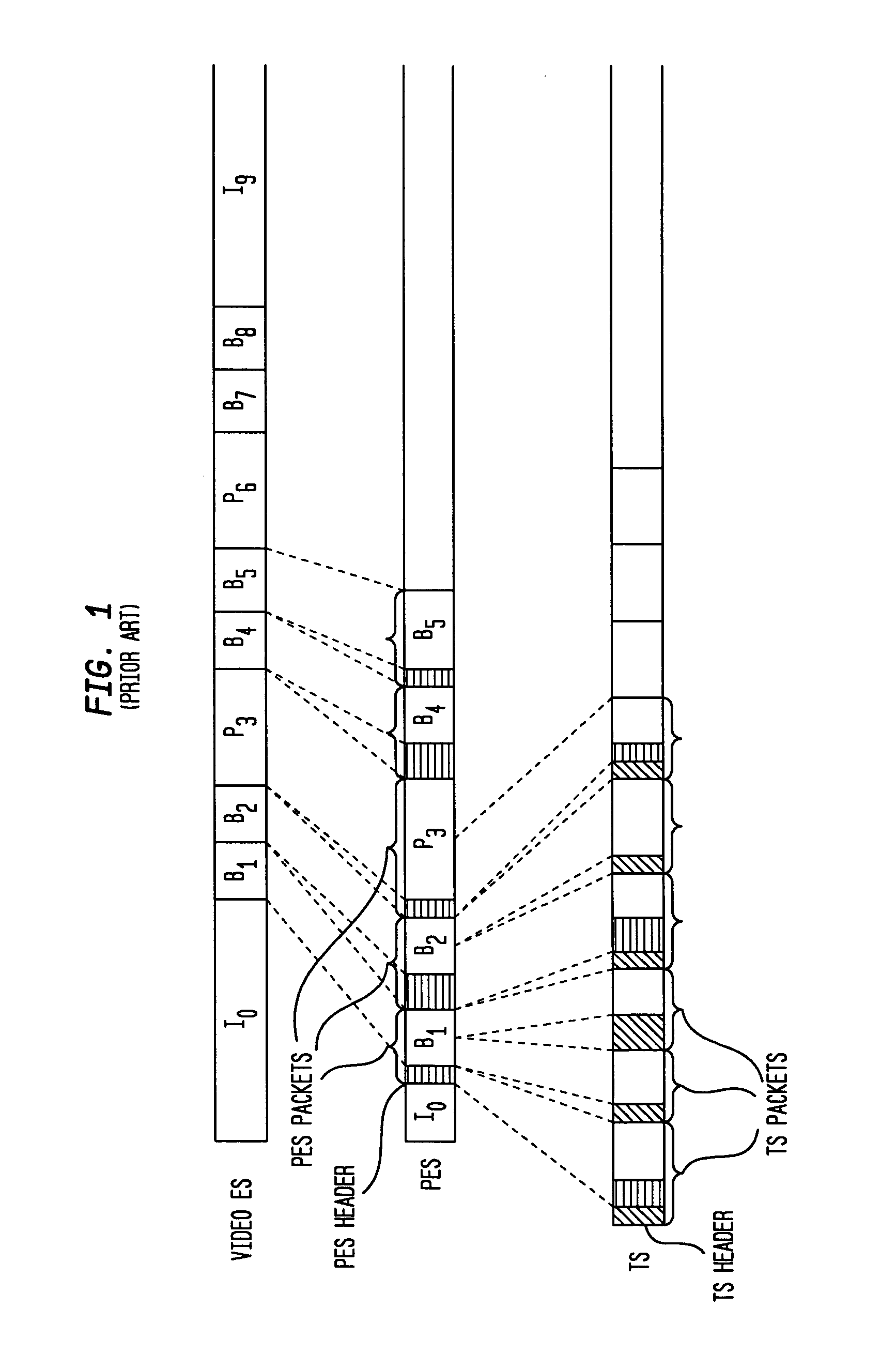
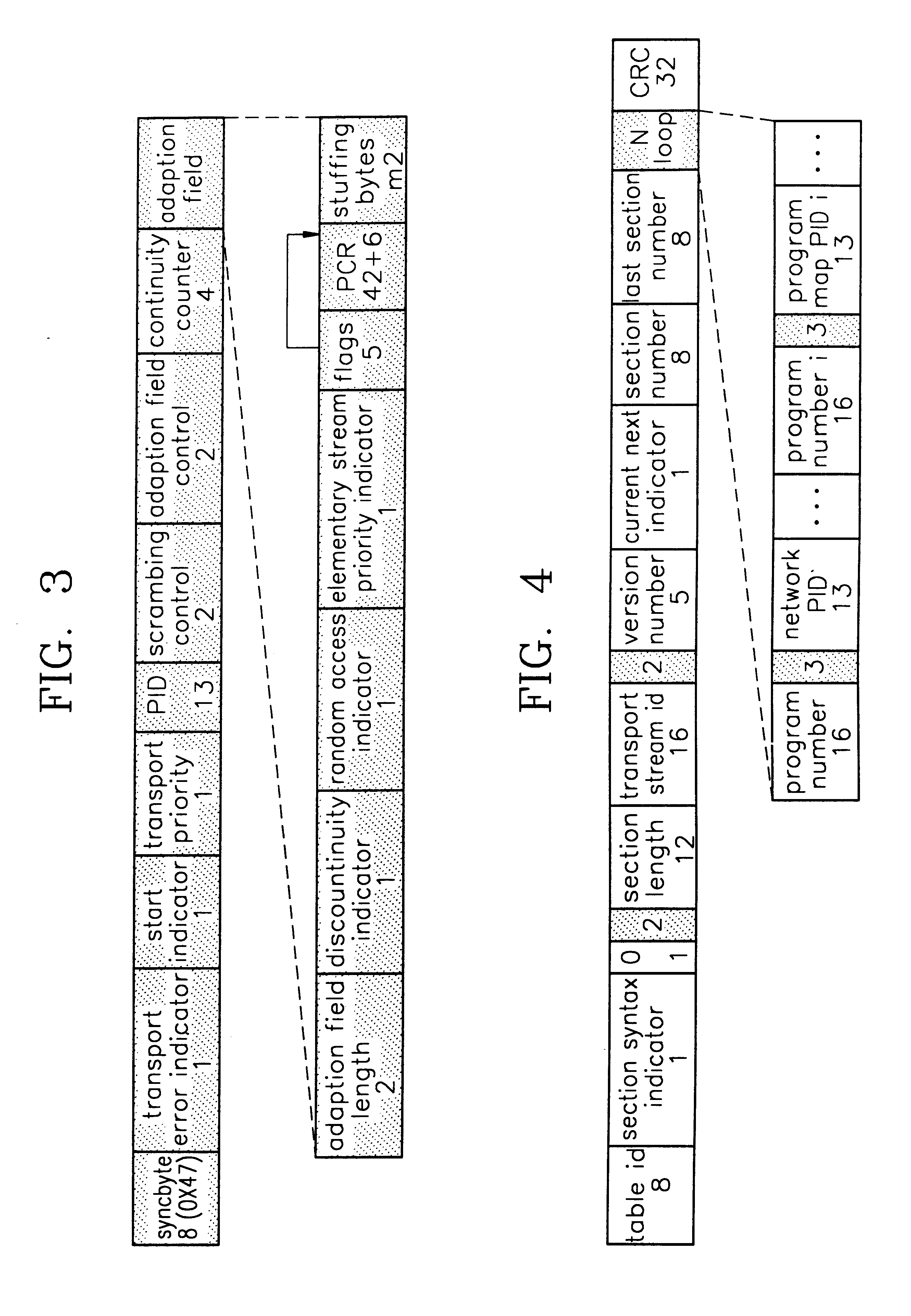
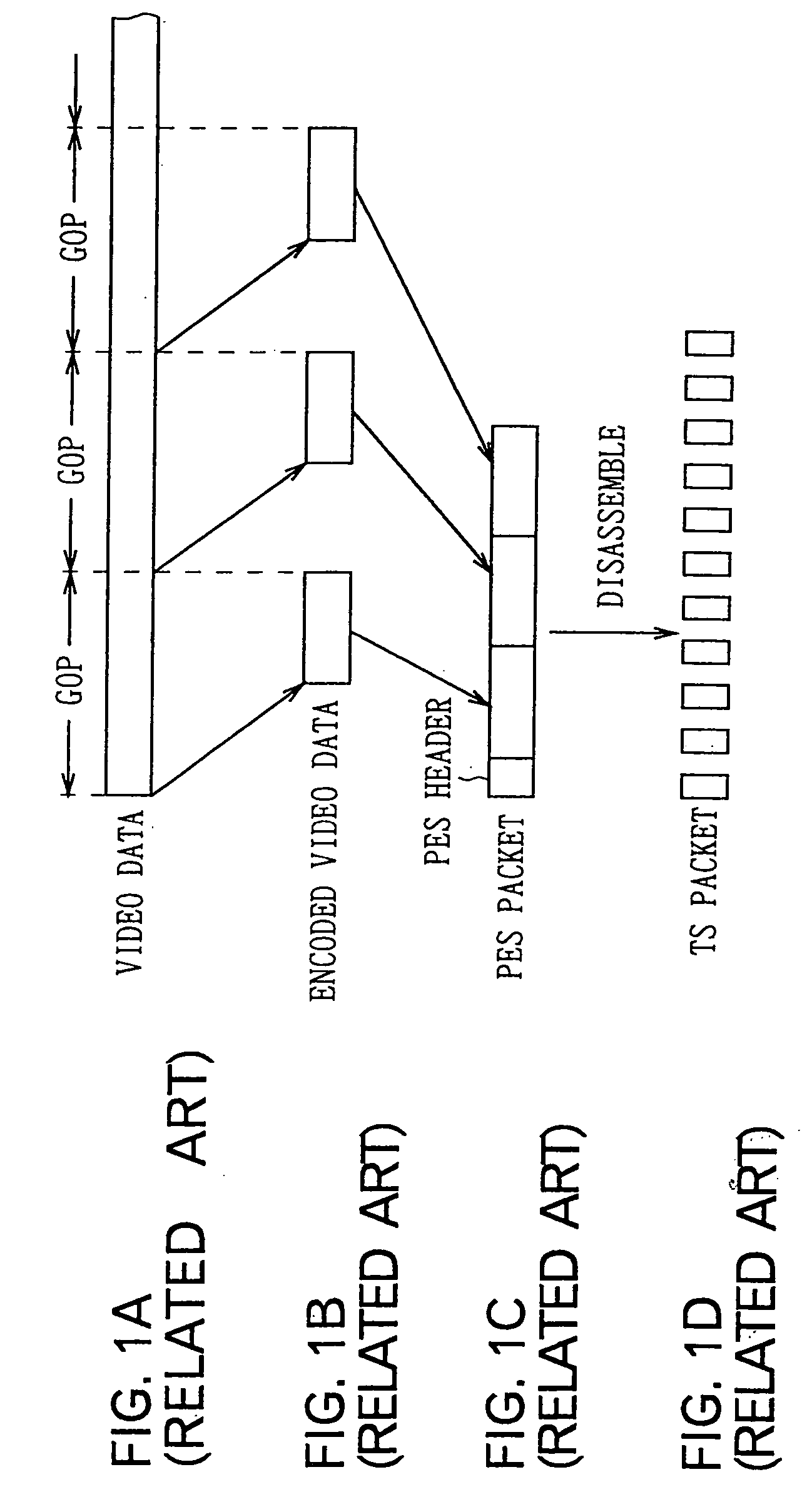
An elementary stream (ES) as defined by the MPEG communication protocol is usually the output of an audio or video encoder. ES contains only one kind of data (e.g. audio, video, or closed caption). An elementary stream is often referred to as "elementary", "data", "audio", or "video" bitstreams or streams. The format of the elementary stream depends upon the codec or data carried in the stream, but will often carry a common header when packetized into a packetized elementary stream.
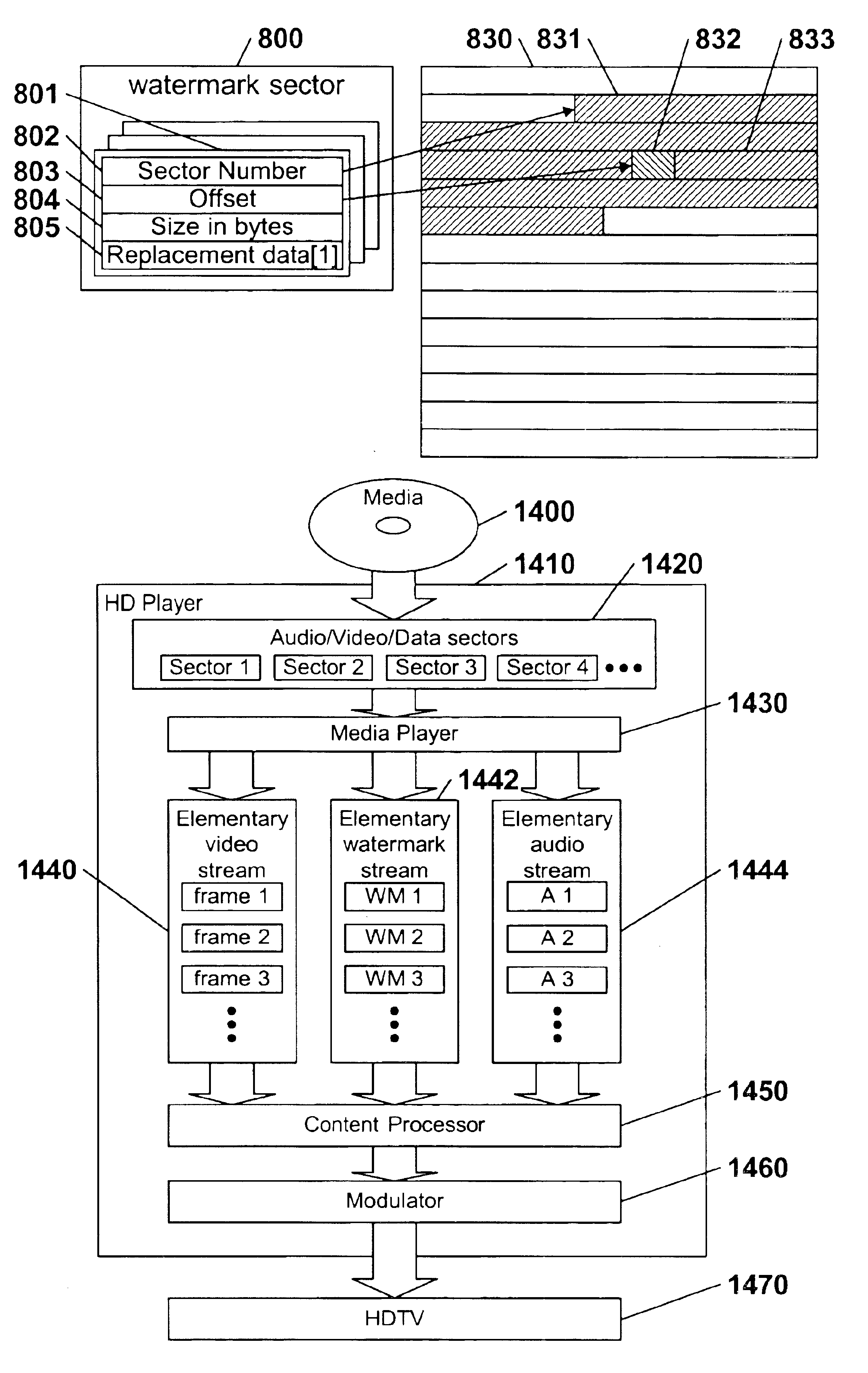
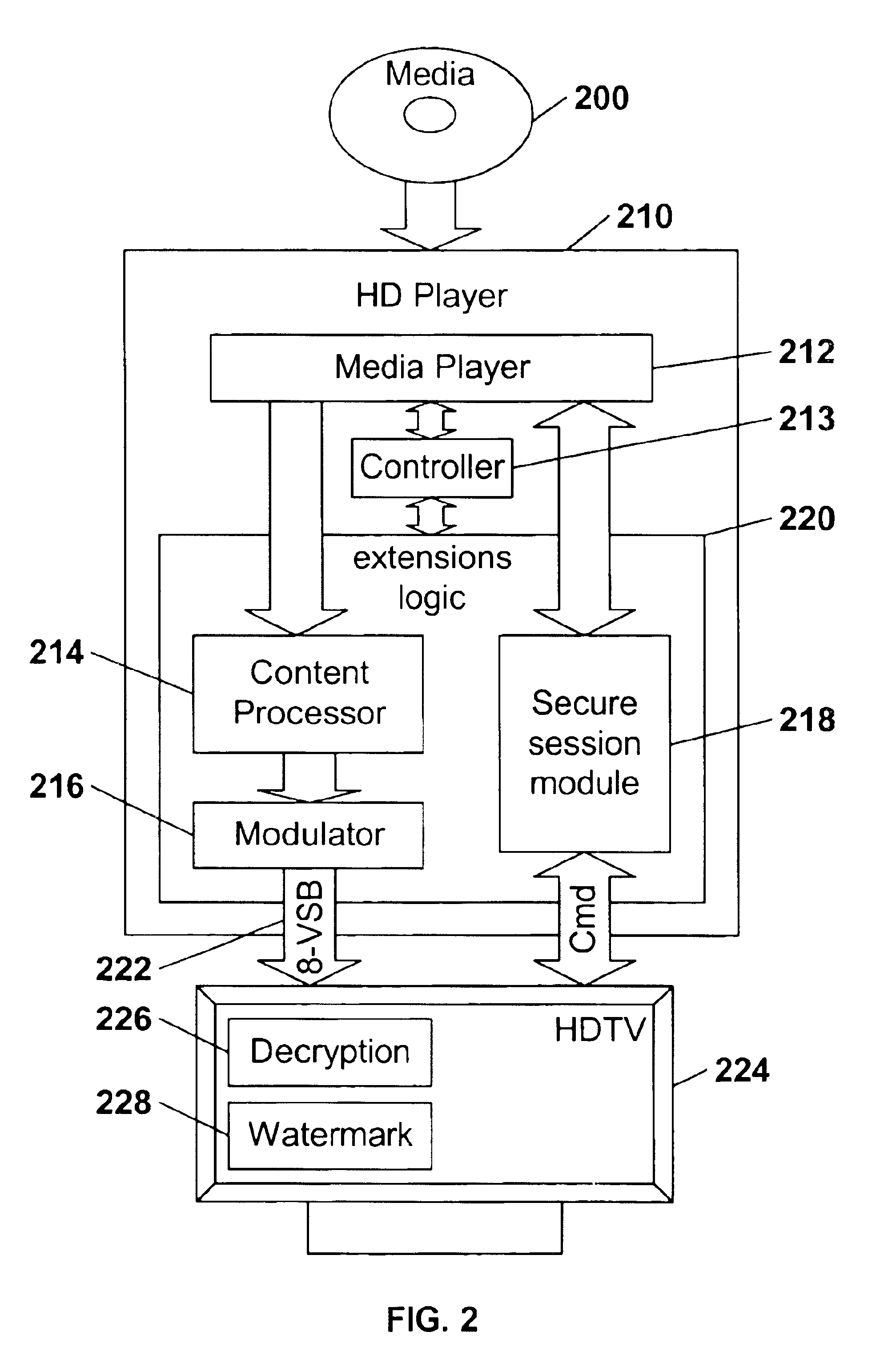
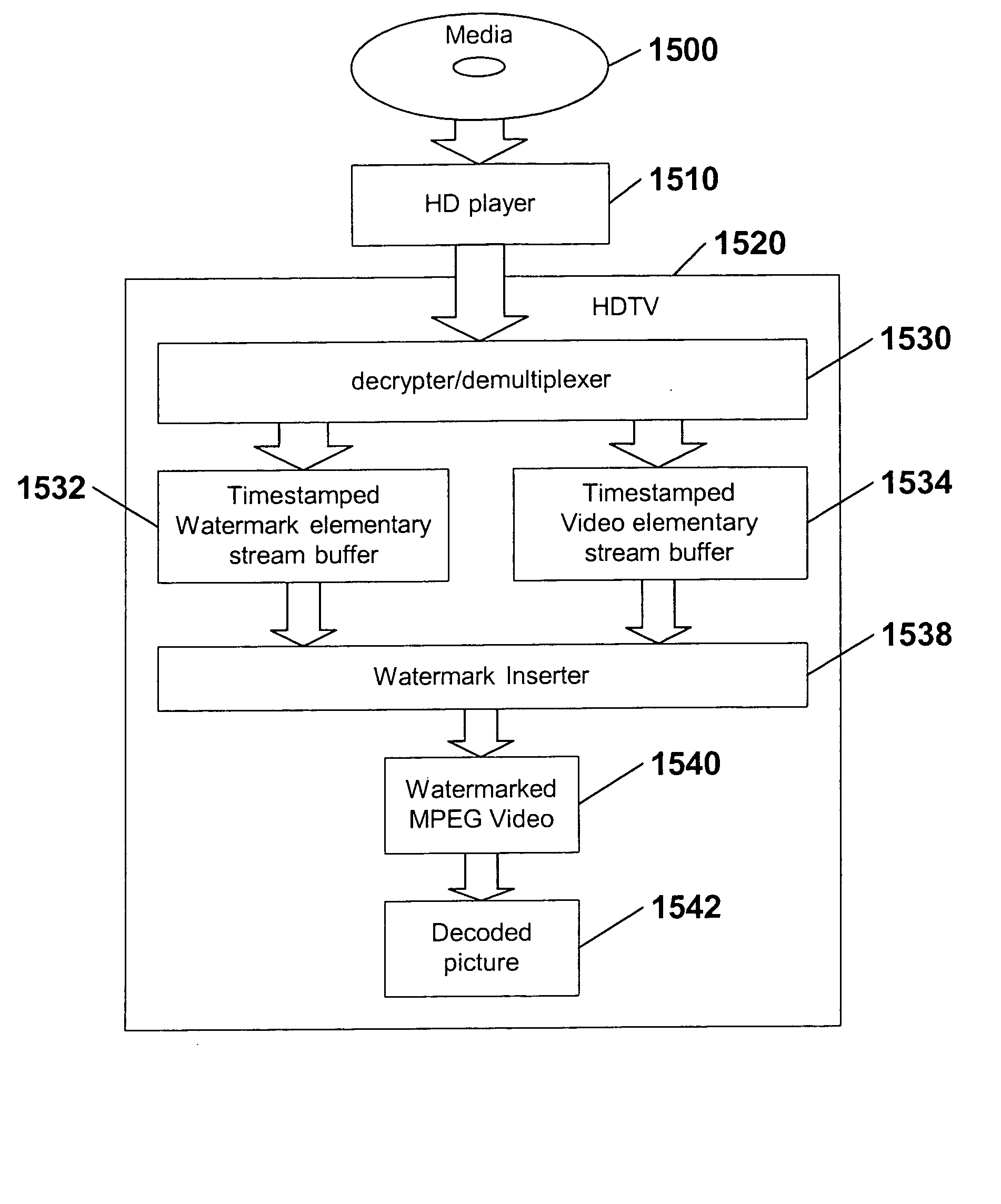
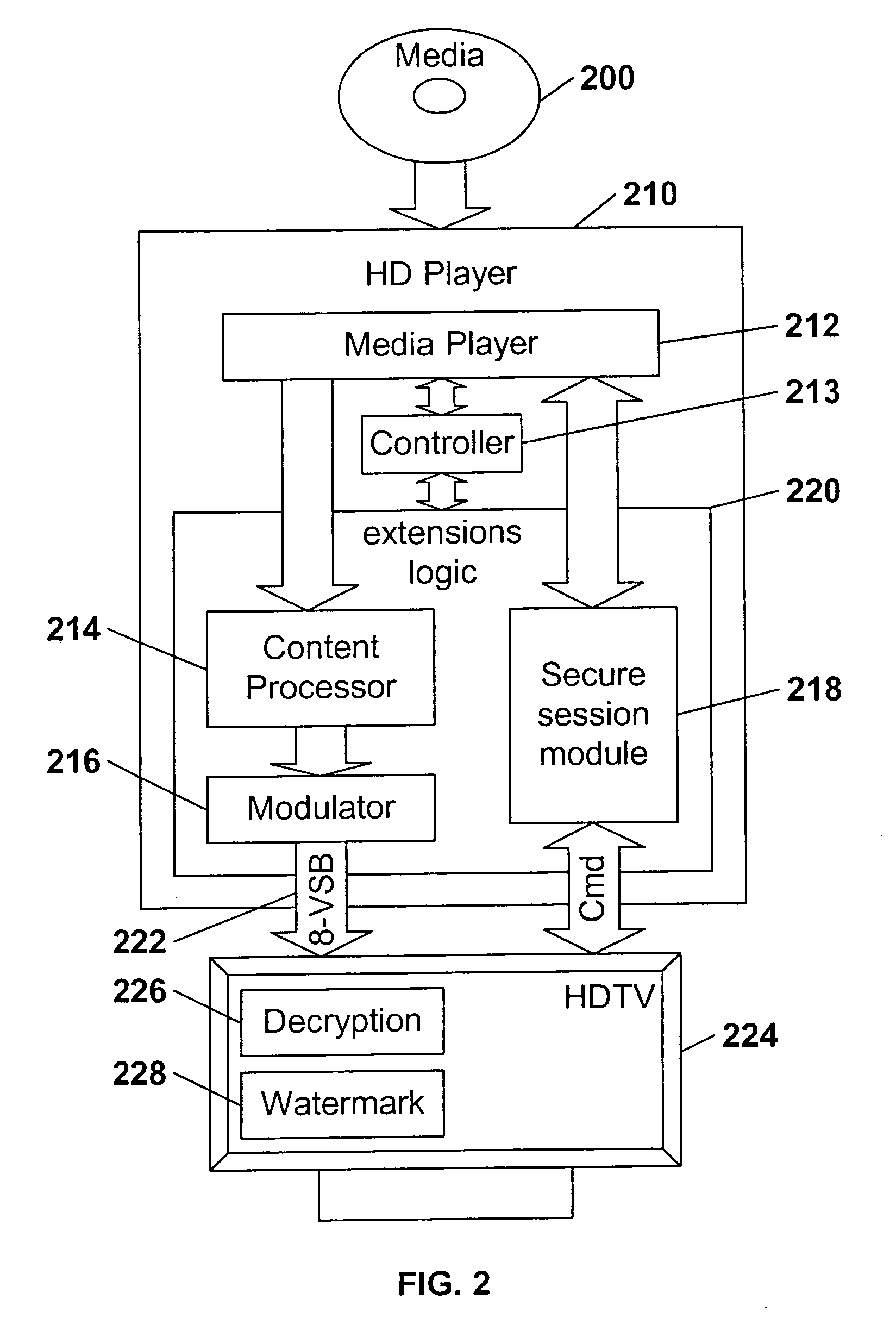
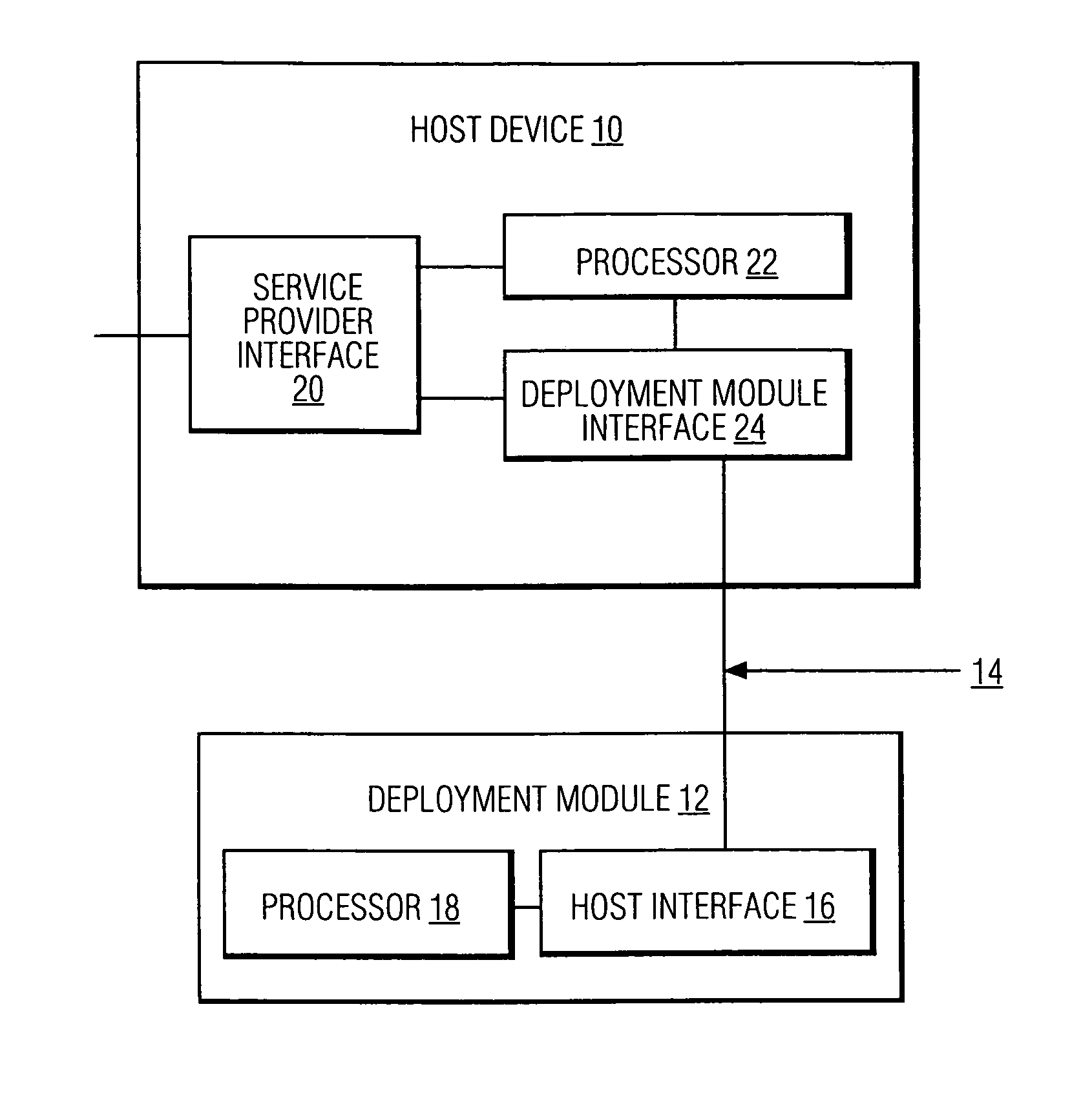
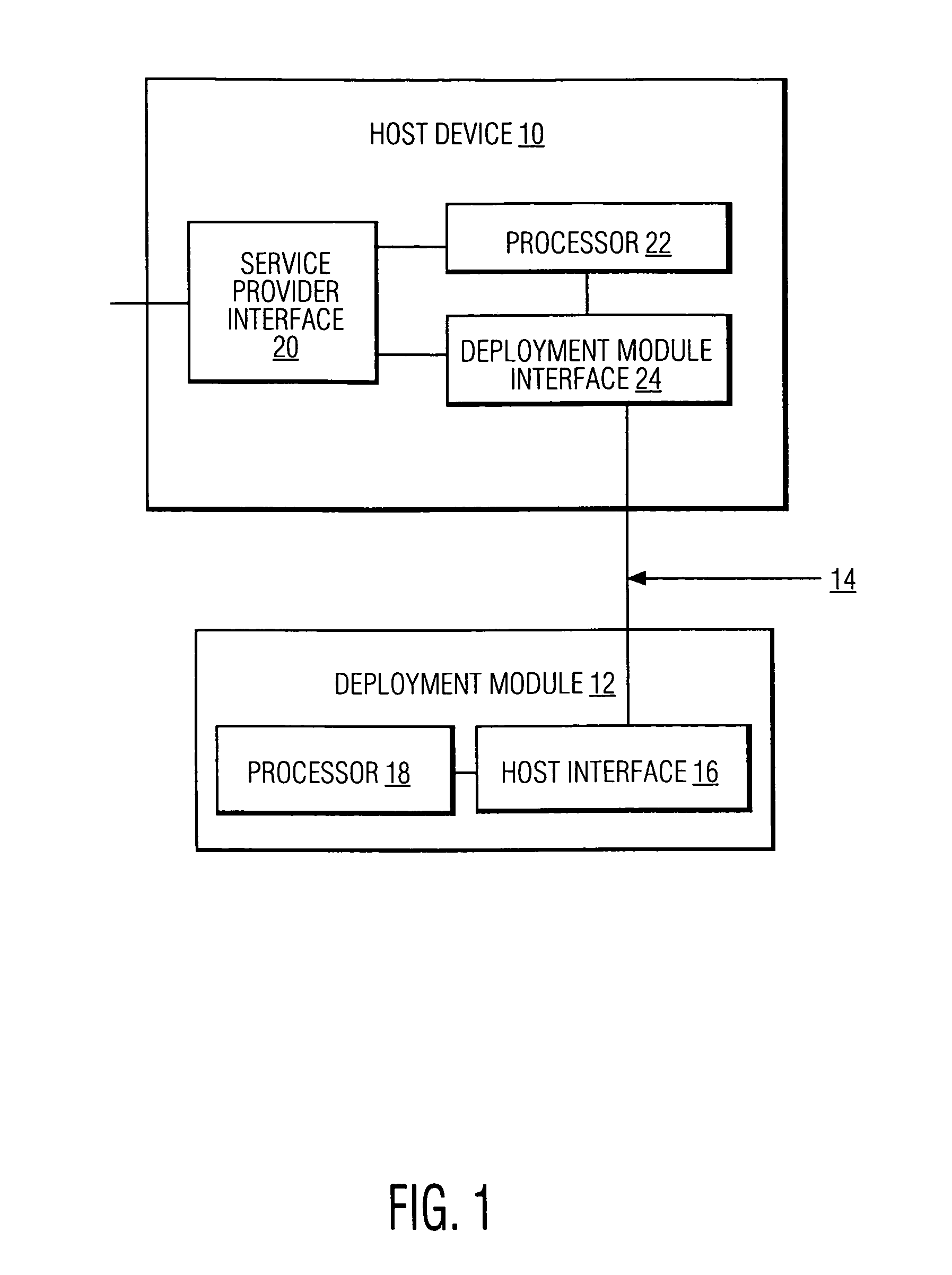
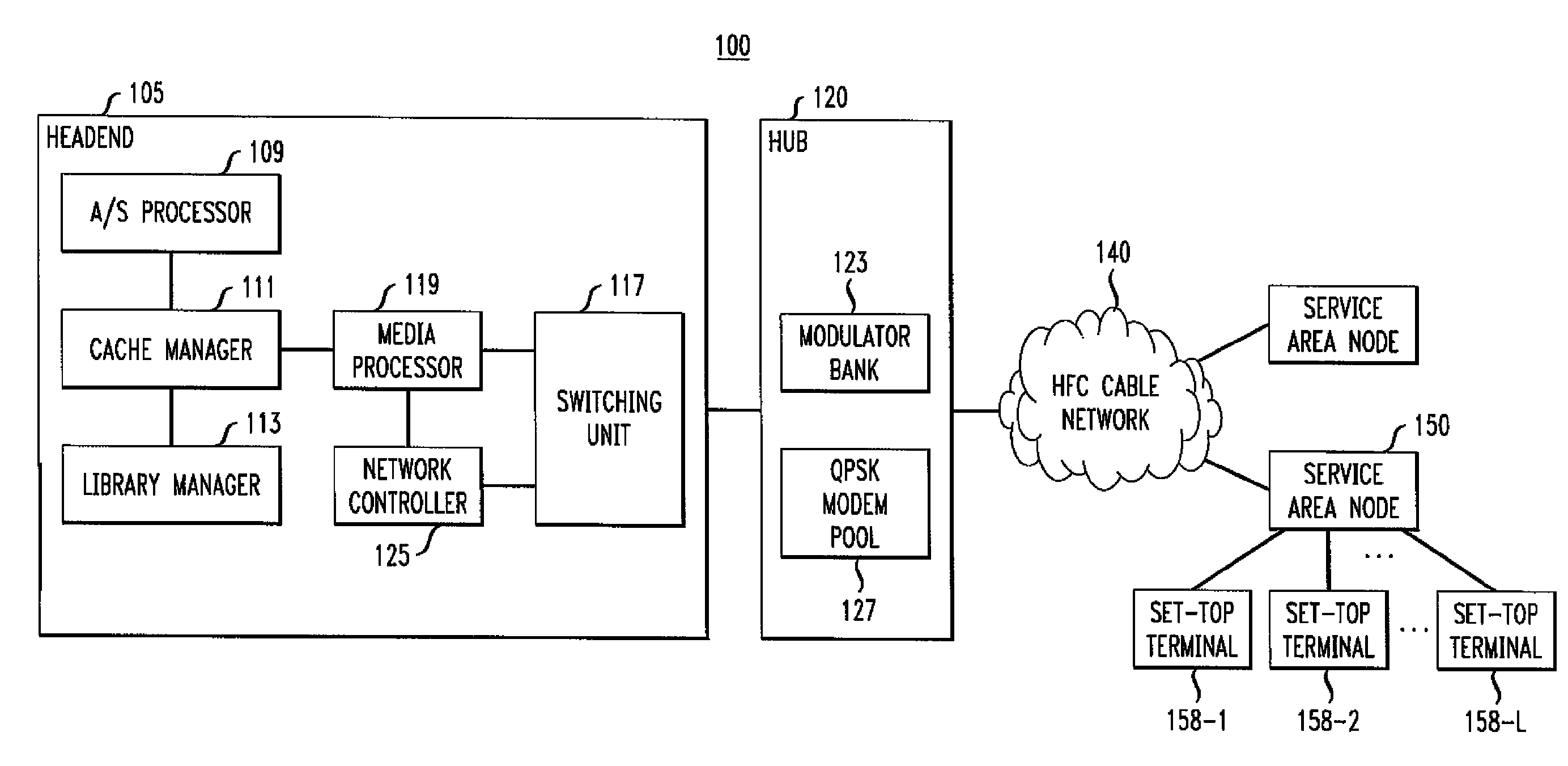
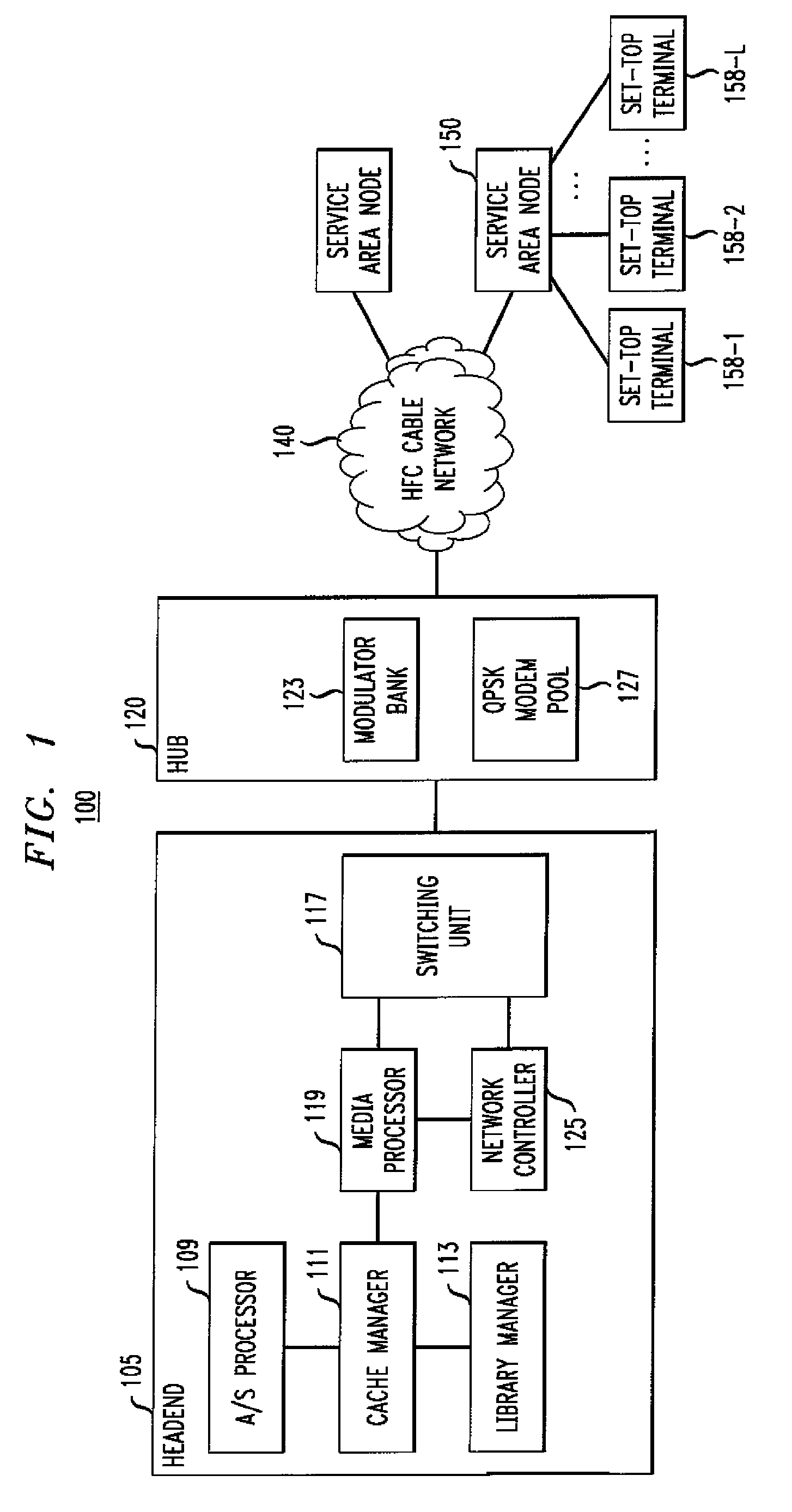
High definition media storage structure and playback mechanism
InactiveUS6865747B1Add featureTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer hardwareHigh definition
An apparatus and method for storing and playing high definition content is disclosed. This invention provides a mechanism for storing and playing back high definition content on a medium such as DVD optical disc. One aspect of the invention is that elementary streams may be multiplexed and processed in a high definition media player instead of at authoring time. Another aspect of the invention is that it provides for extended real-time features such as inserting watermarks into the content stream, decrypting selected sections of the content stream, and performing trick playback display modes.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
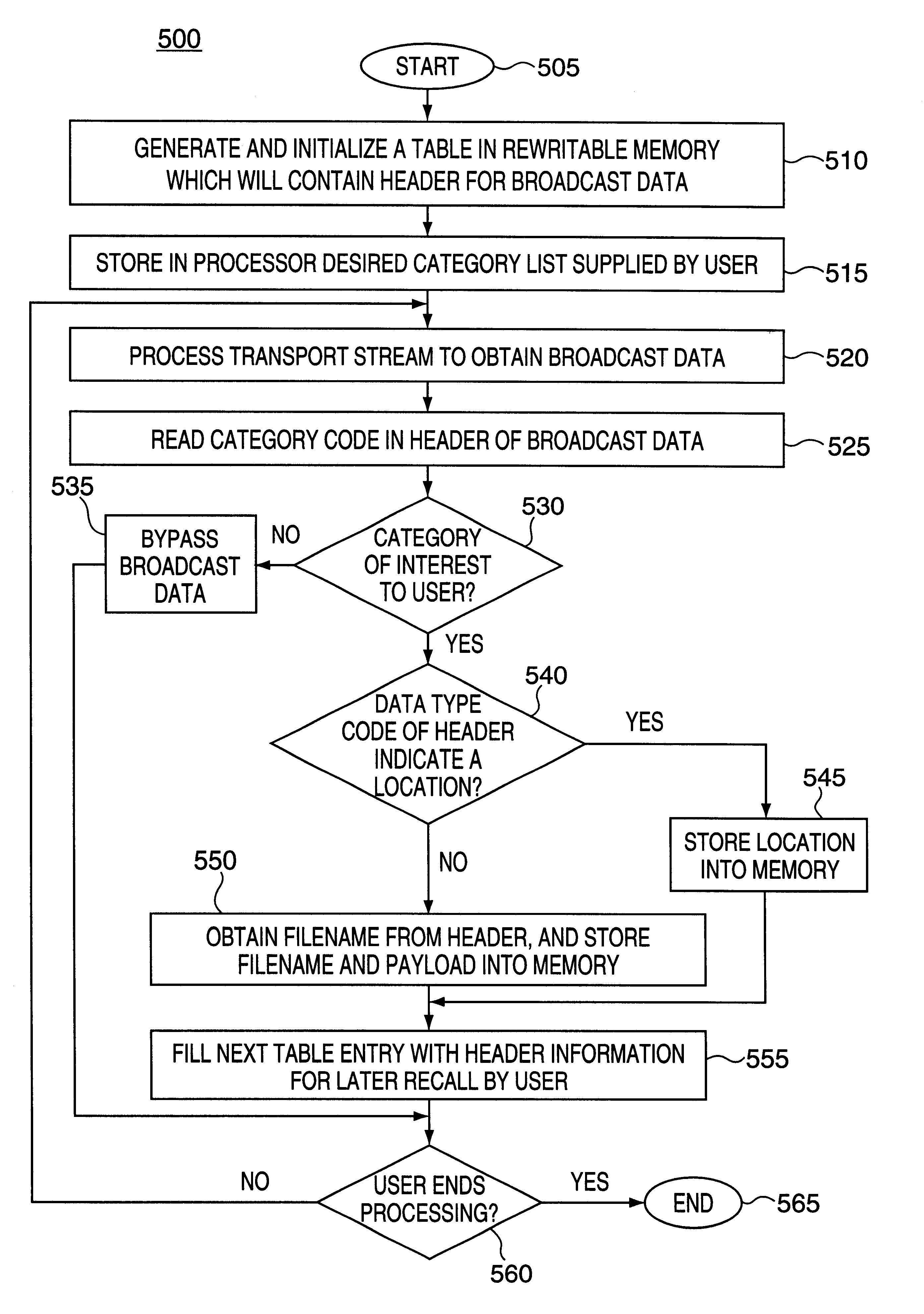
Methods and apparatus for recording video files and for generating a table listing the recorded files and links to additional information
InactiveUS6256071B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionElementary streamPower consumption
A receiver arranged to receive and store broadcast data transported by elementary stream of a multiplexed and modulated digital television signal in a rewritable memory during a low power consumption mode for later recall by a user of the receiver. For recall, the receiver is fully energized, and the receiver is further arranged to transfer the broadcast data stored in the rewritable memory to a receiver storage device for further processing of the data under control of the user.
Owner:HITACHI AMERICA
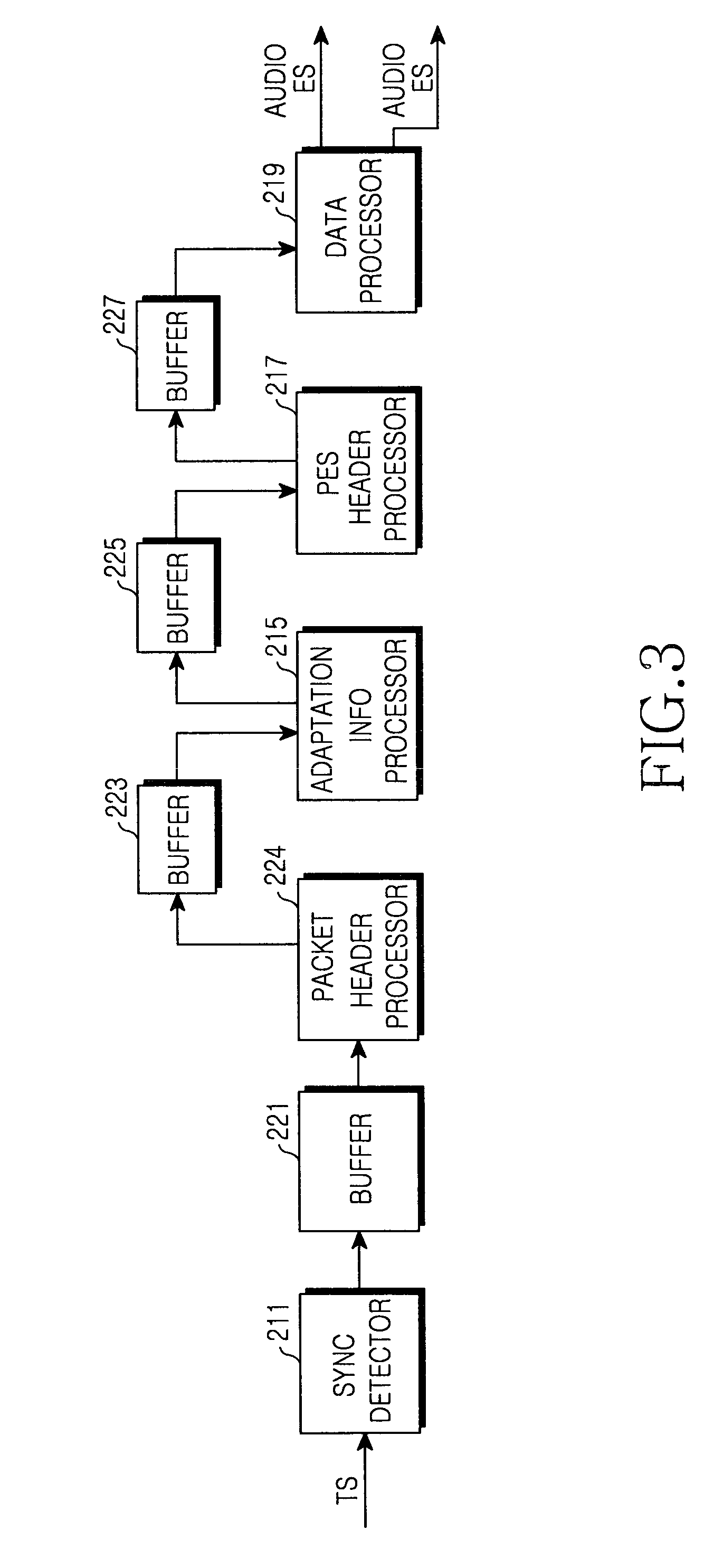
Device and method for demultiplexing received transport stream in digital broadcasting receiver
InactiveUS20060133429A1Television system detailsTime-division multiplexControl signalInformation processor
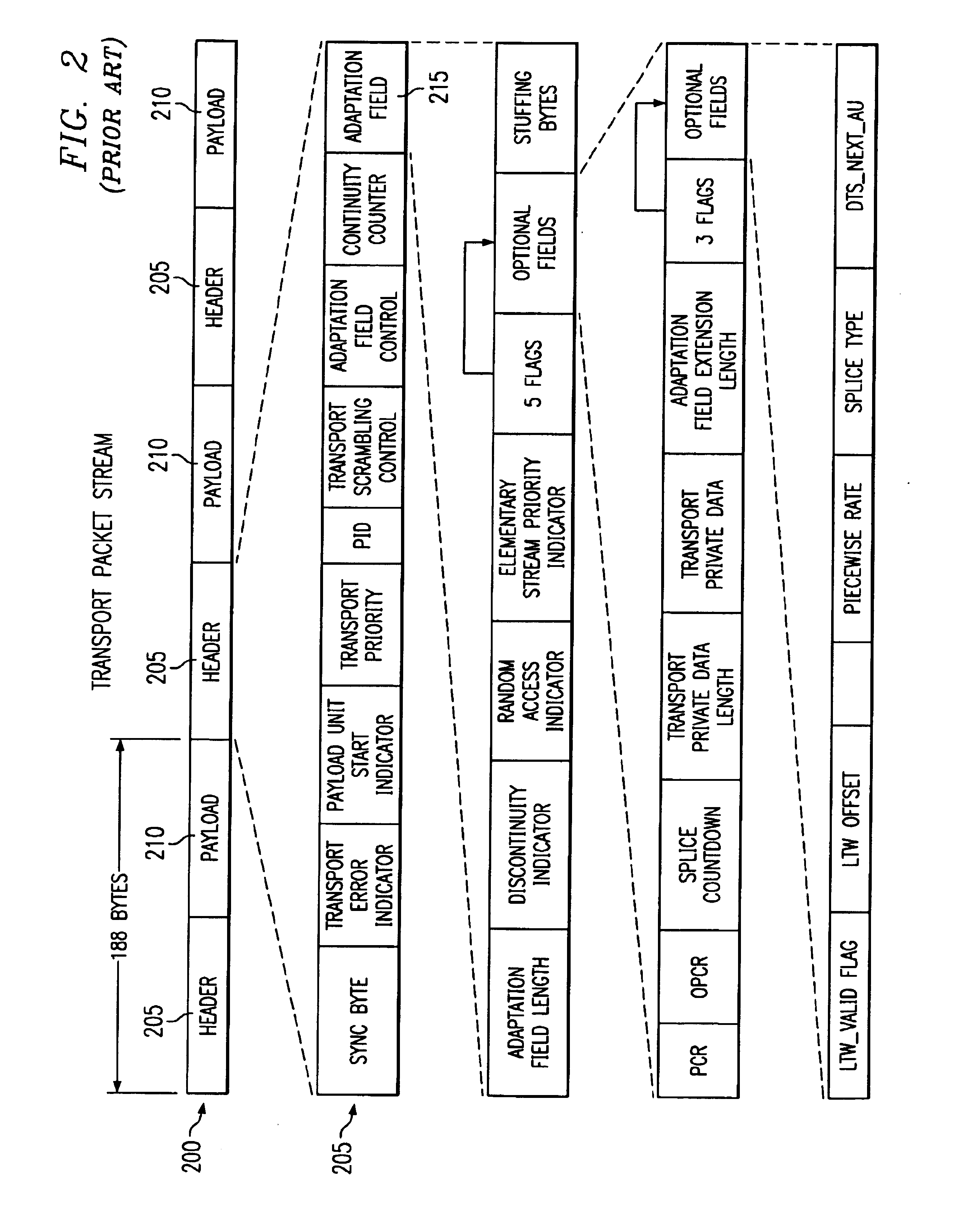
A device and method for demultiplexing in a digital broadcasting receiver for processing packet data configured by a packet header and a payload. A buffer buffers input packet data. Processors are parallel connected to the buffer. A packet header processor checks a packet header, identifies presence of adaptation information, and generates a control signal according to the presence of the adaptation information. An adaptation information processor processes the adaptation information of buffered payload data under control of the packet header processor. A packetized elementary stream (PES) header processor processes a PES header of the buffered payload data under the control of the packet header processor. A data processor generates an audio or video elementary stream (ES) from audio or video data of the buffered payload data under control of the PES header processor, and outputs the generated audio or video ES to an associated decoder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High definition media storage structure and playback mechanism
InactiveUS20050114909A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer hardwareHigh definition
An apparatus and method for storing and playing high definition content is disclosed. This invention provides a mechanism for storing and playing back high definition content on a medium such as DVD optical disc. One aspect of the invention is that elementary streams may be multiplexed and processed in a high definition media player instead of at authoring time. Another aspect of the invention is that it provides for extended real-time features such as inserting watermarks into the content stream, decrypting selected sections of the content stream, and performing trick playback display modes.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
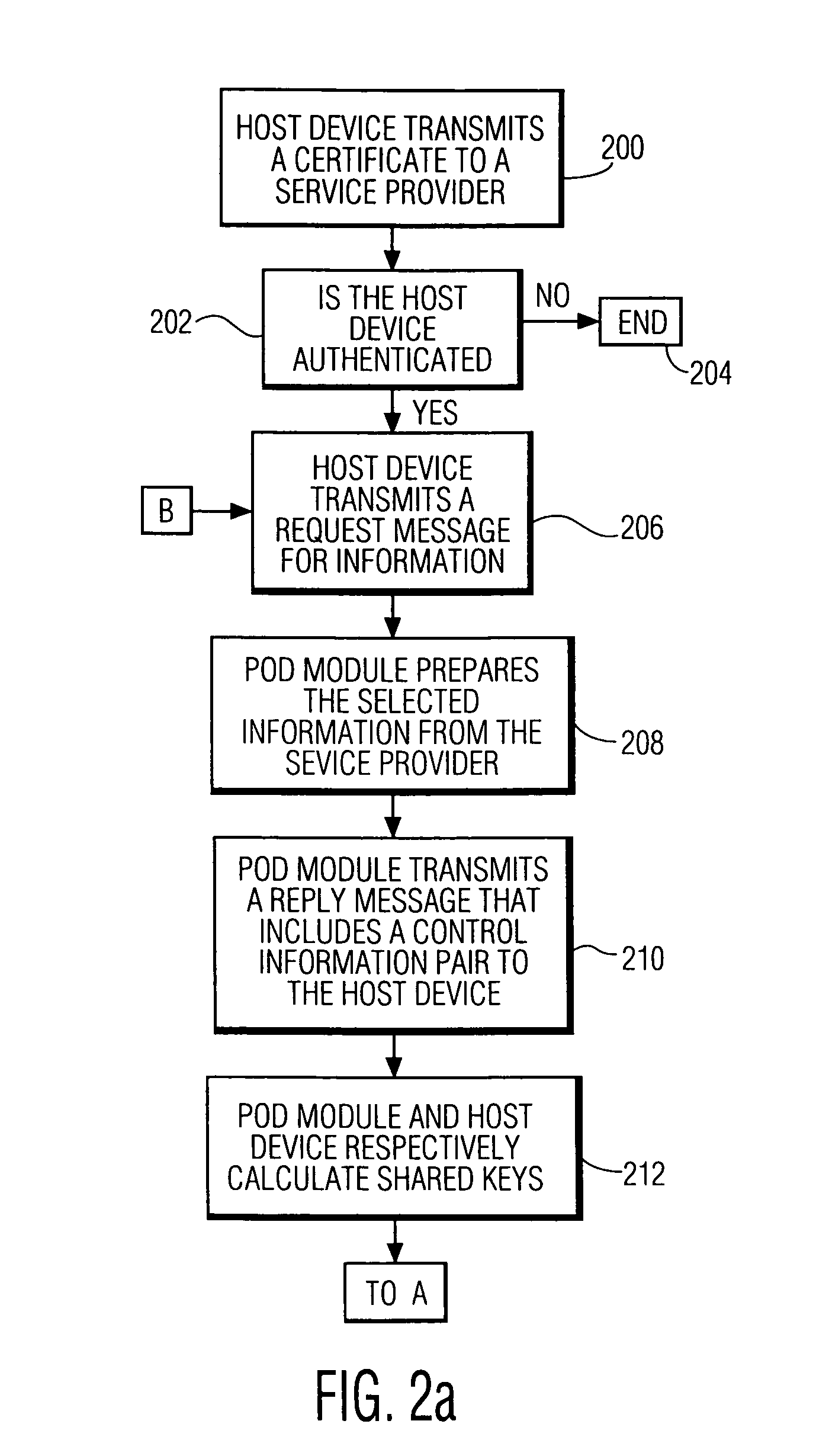
System and method for copy protecting transmitted information
InactiveUS7336785B1Protect informationEliminate useTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationTransfer procedureService provision
To afford copy protection for information, e.g. elementary streams, from a service provider while in transit between a point of deployment (POD) module and a set-top box, the information is accompanied by control information pairs. The pairs are respectively associated with the portions of the copy protected information and are incorporated into a shared key calculation in the POD module and set-top box. The shared keys are used by the POD module and set-top box to encrypt and decrypt the information. Tampering with a control information pair, as by an intruder or hacker, prevents keys shared by the set-top box and POD module from matching. A mismatch prevents the set-top box from correctly decrypting information received from the deployment module.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
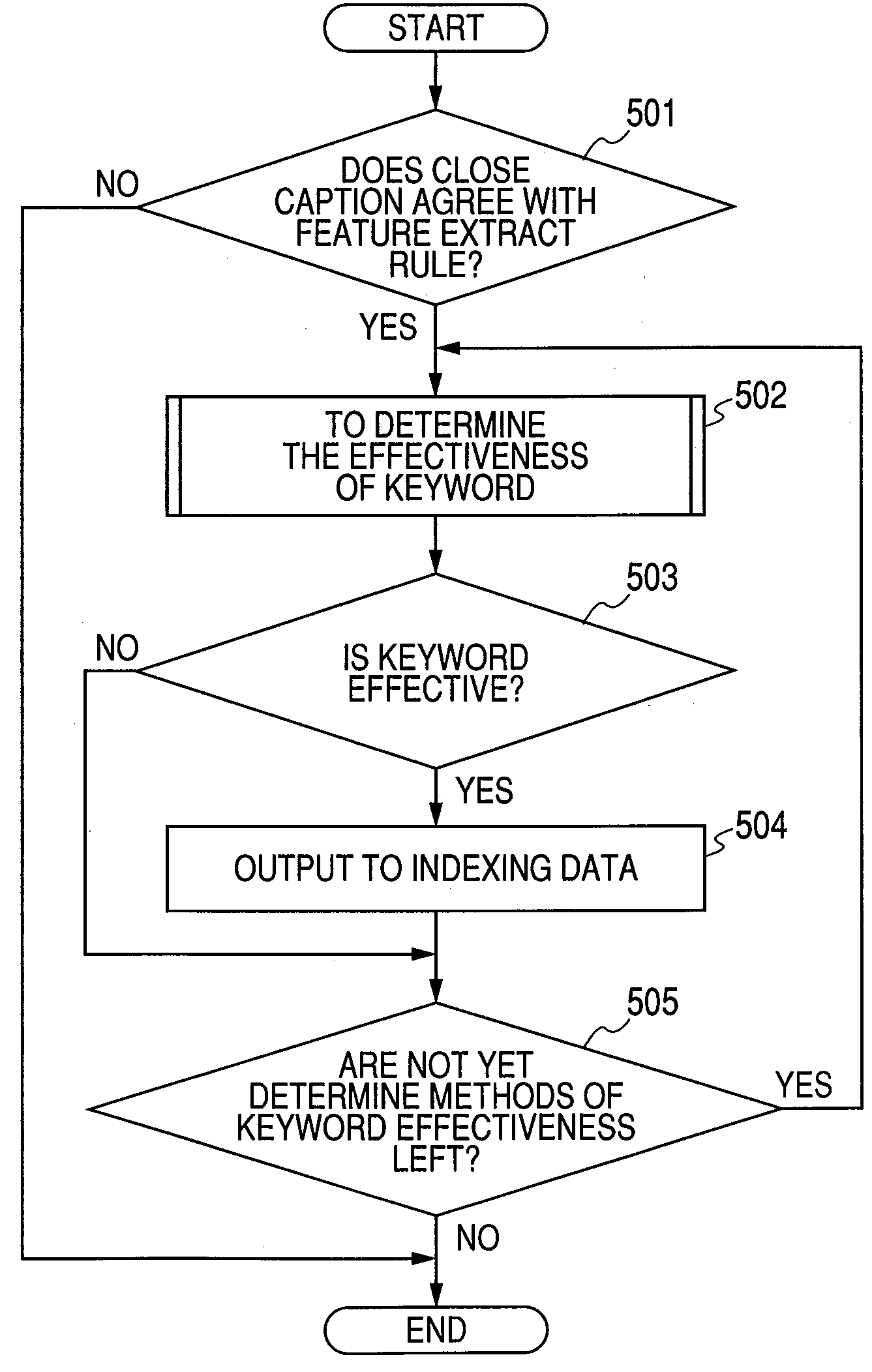
Video recorder and video reproduction method
InactiveUS20090129749A1Television system detailsDigital data information retrievalClosed captioningFeature extraction
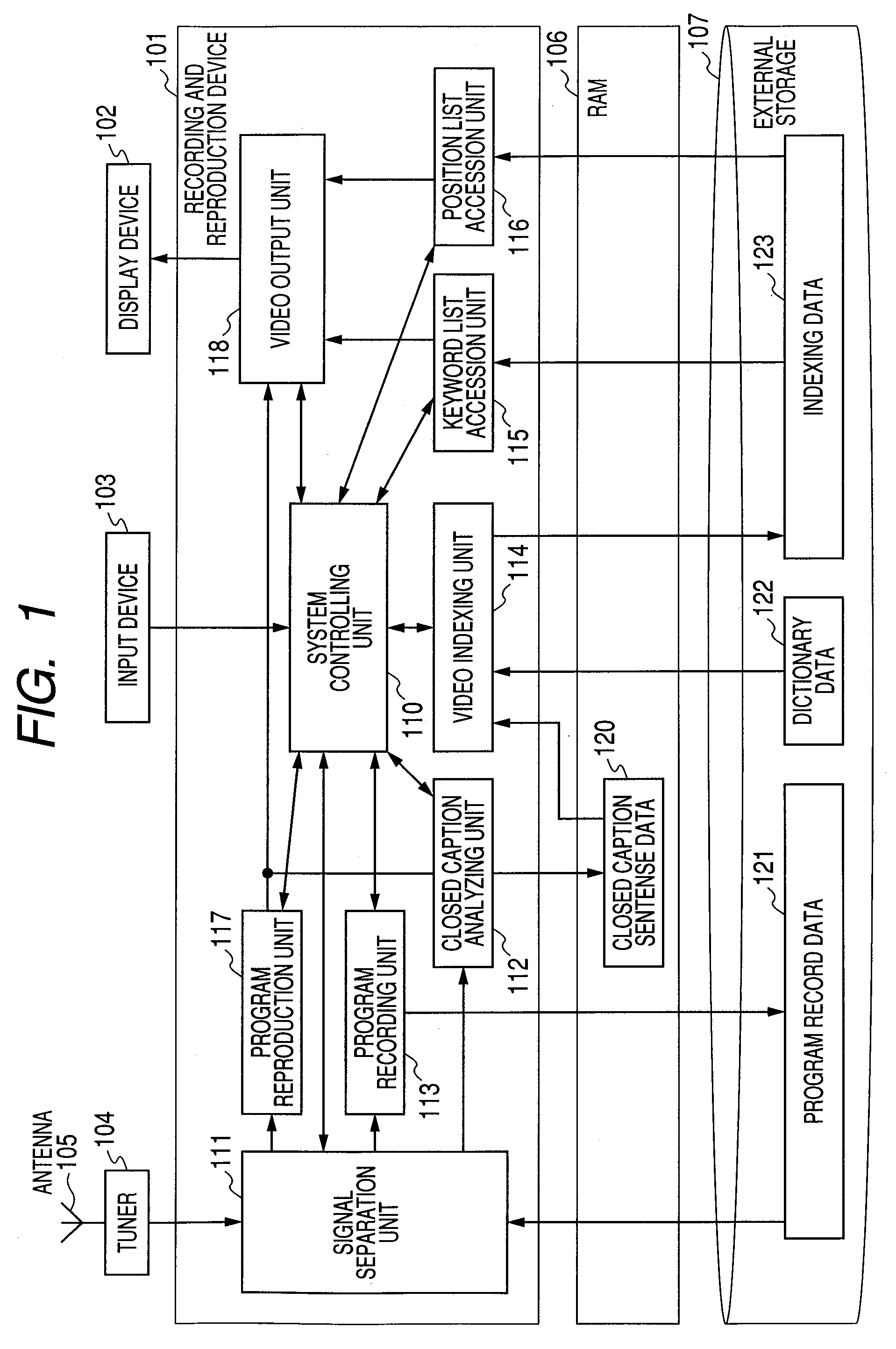
In a video recorder, closed caption sentence data is outputted by analyzing digital broadcasting data including closed caption information. Index data is generated on the basis of a feature extraction rule and the effectiveness of an appearing keyword by analyzing closed caption sentence data. Closed caption feature data including a type of a closed caption sentence and a display time is generated by analyzing a closed caption ES (Elementary Stream). The broadcasting data is stored as record data, the closed caption feature data is analyzed, chapter data for reproducing a program is generated by a chapter designated by the user, and the chapter data is outputted to a storage. In the case of recording and reproducing the digital broadcasting program, it is possible to perform both the reproduction by the optimal index using the closed caption and the reproduction by the keyword voluntarily inputted by the user.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
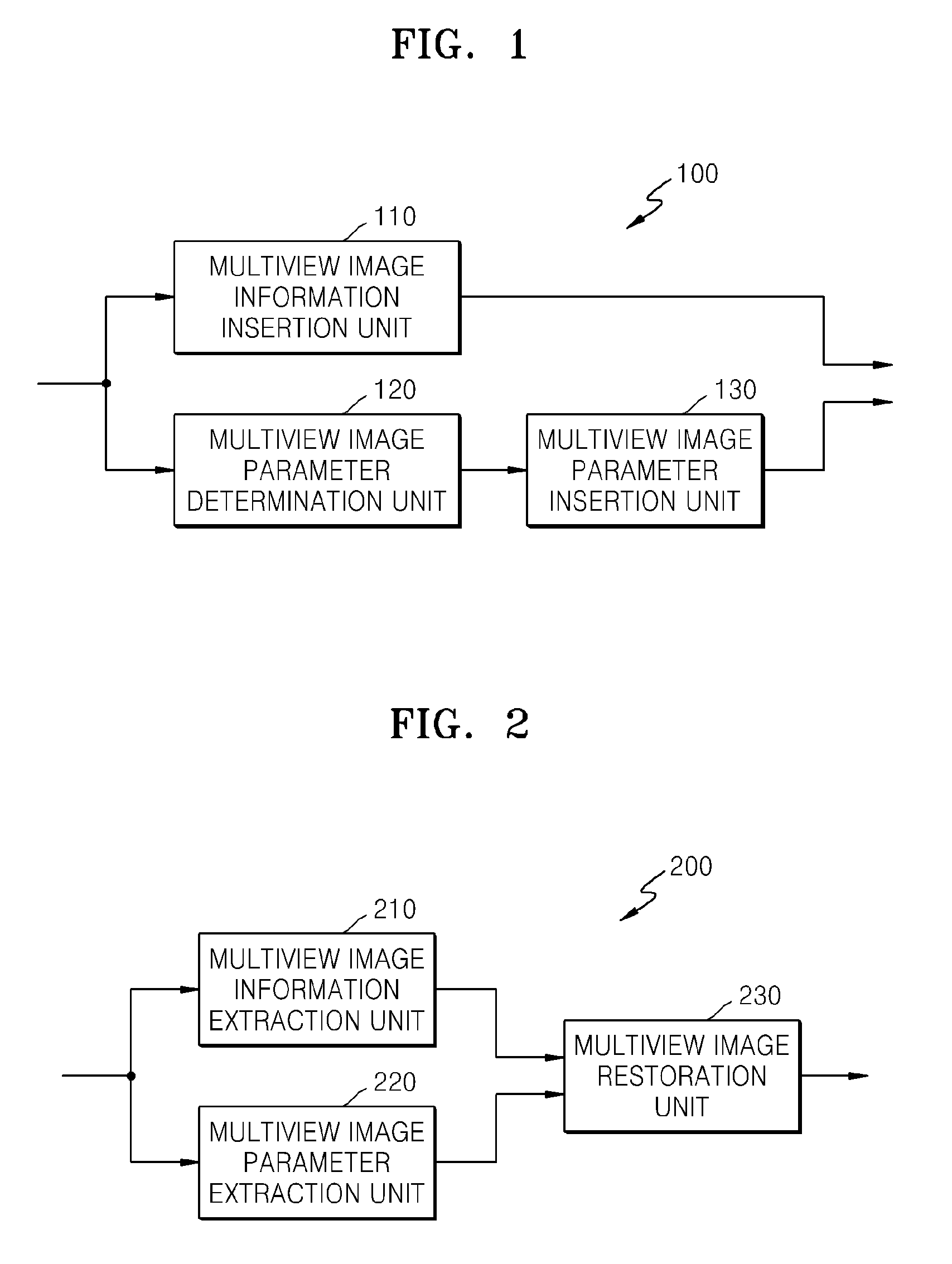
Method and apparatus for encoding datastream including additional information on multiview image and method and apparatus for decoding datastream by using the same
InactiveUS20090219282A1Efficient storageGuaranteed normal transmissionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamImage based
Provided are a method and apparatus for encoding and decoding a datastream into which multiview image information is inserted. The method of decoding a multiview image datastream includes extracting multiview image information including information on at least one view image of a multiview image, from at least one elementary stream of the multiview image datastream; extracting a multiview image parameter regarding the multiview image based on the number of elementary streams and a correlation between view images of the multiview image; and restoring the multiview image by using the extracted multiview image parameter and the extracted multiview image information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
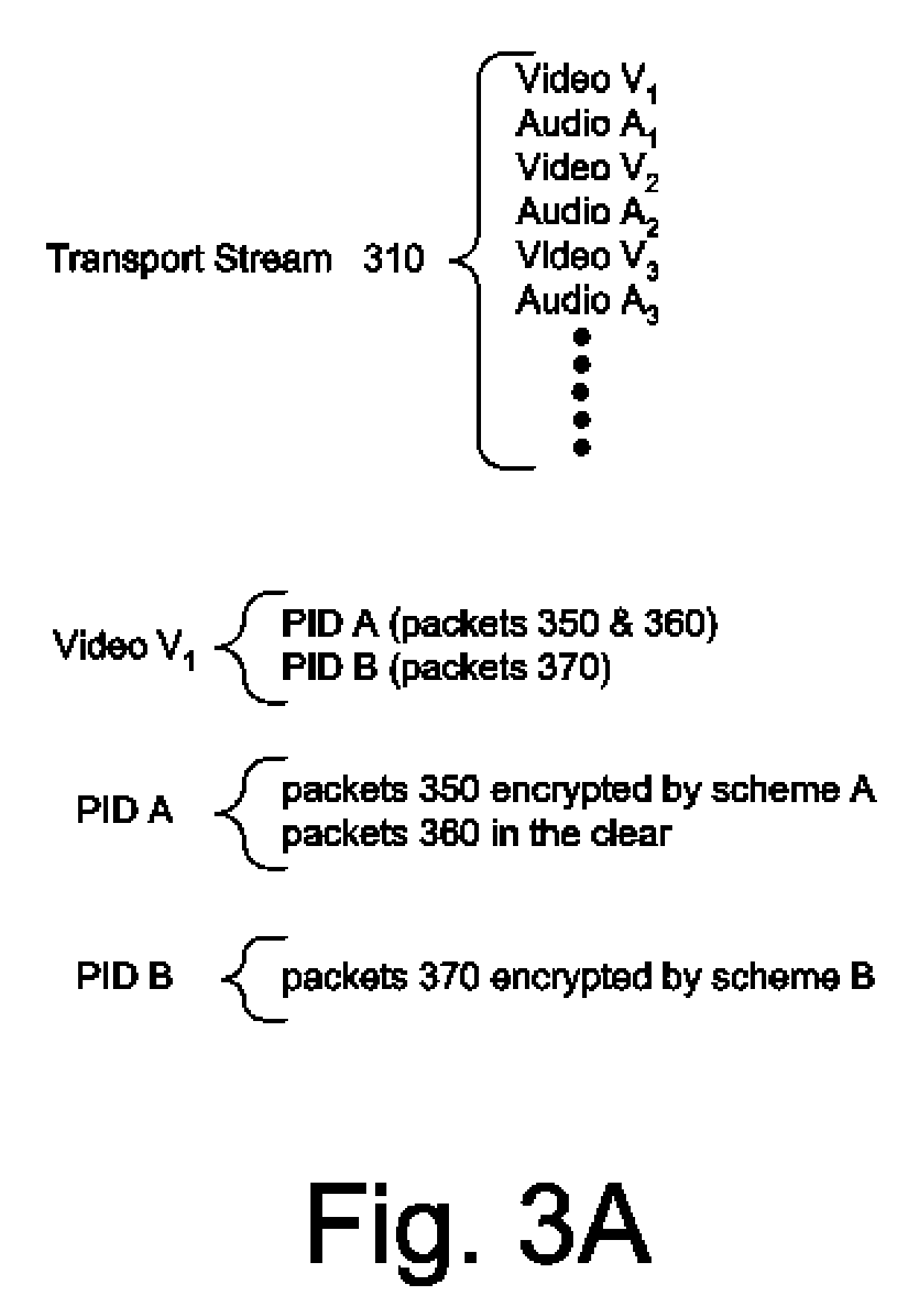
Partial dual encrypted stream utilizing program map tables
InactiveUS7496198B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareEncryption system
The present invention is suitable for use in a partial dual encrypted system. The present invention allows for two different decryption devices (e.g., an incumbent, or first, set-top and an overlay, or second, set-top) to be located in a single system having an incumbent encryption scheme and a second encryption scheme. Each set-top is designed to decrypt the first or second proprietary encryption schemes, respectively. In accordance with the present invention, the second set-top utilizes a novel program map table to ensure that the second set-top chooses correct elementary streams in the partial dual-encrypted stream (i.e., a combined stream including a first encrypted stream, a second encrypted stream, and a clear stream) for a desired program.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
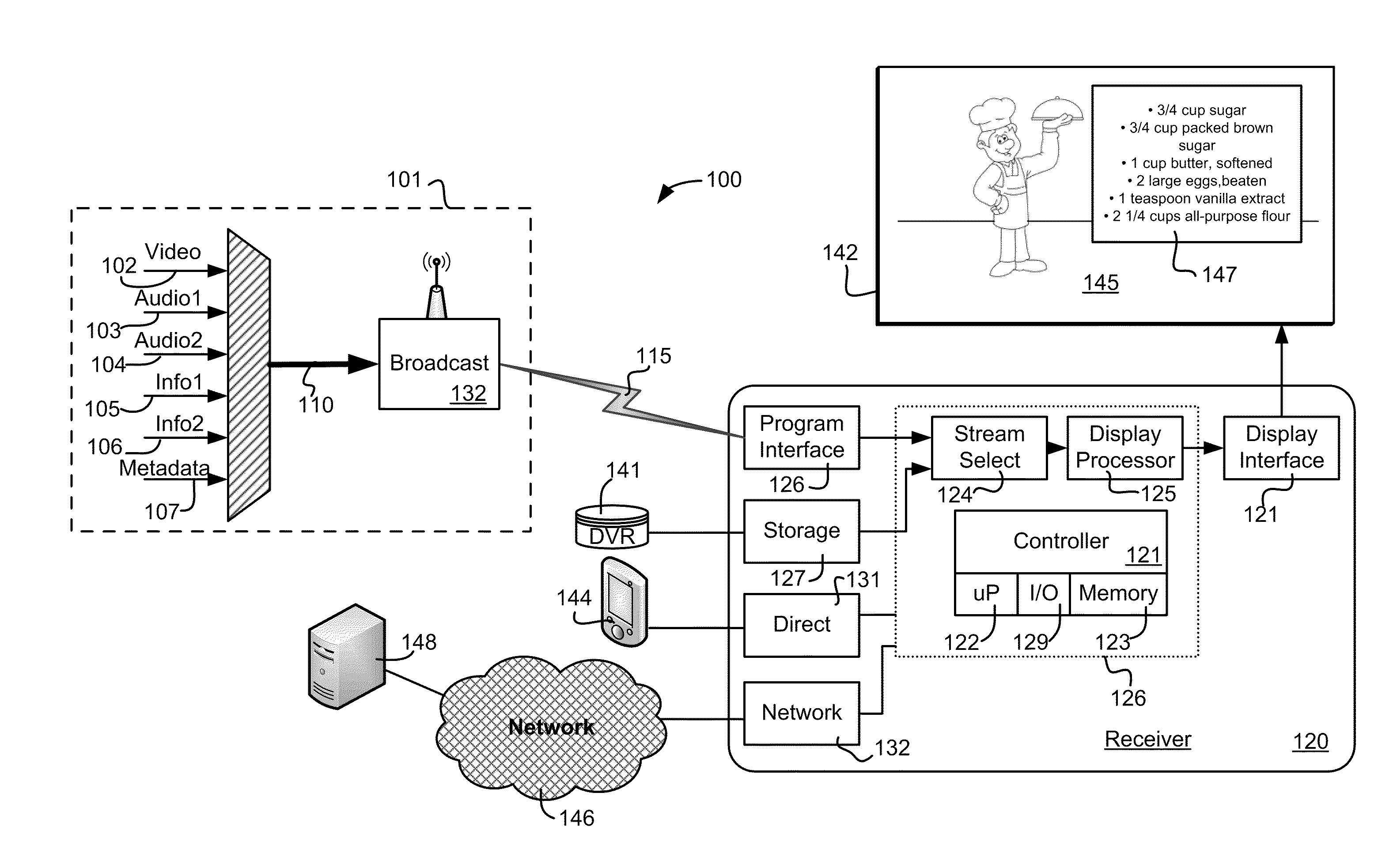
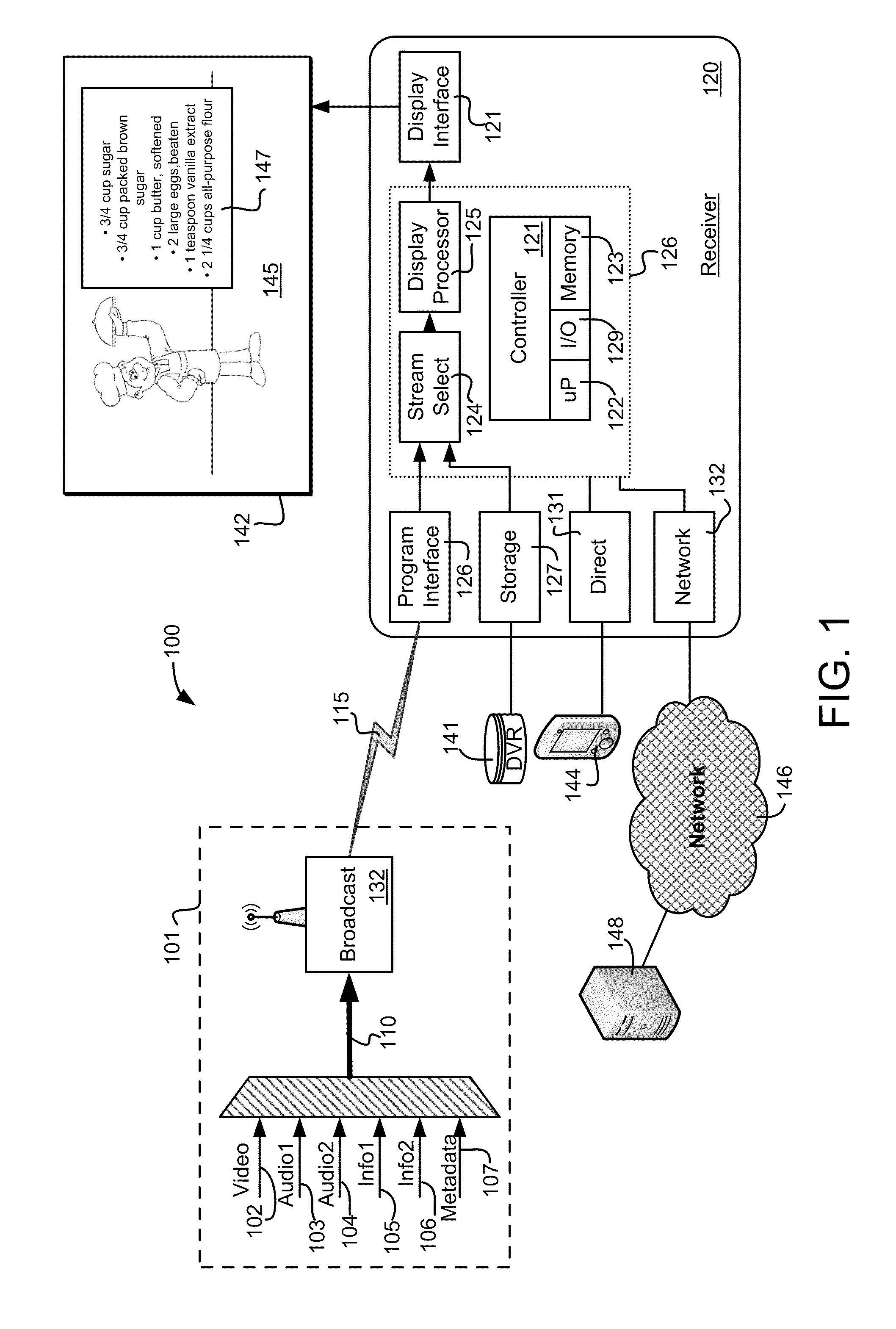
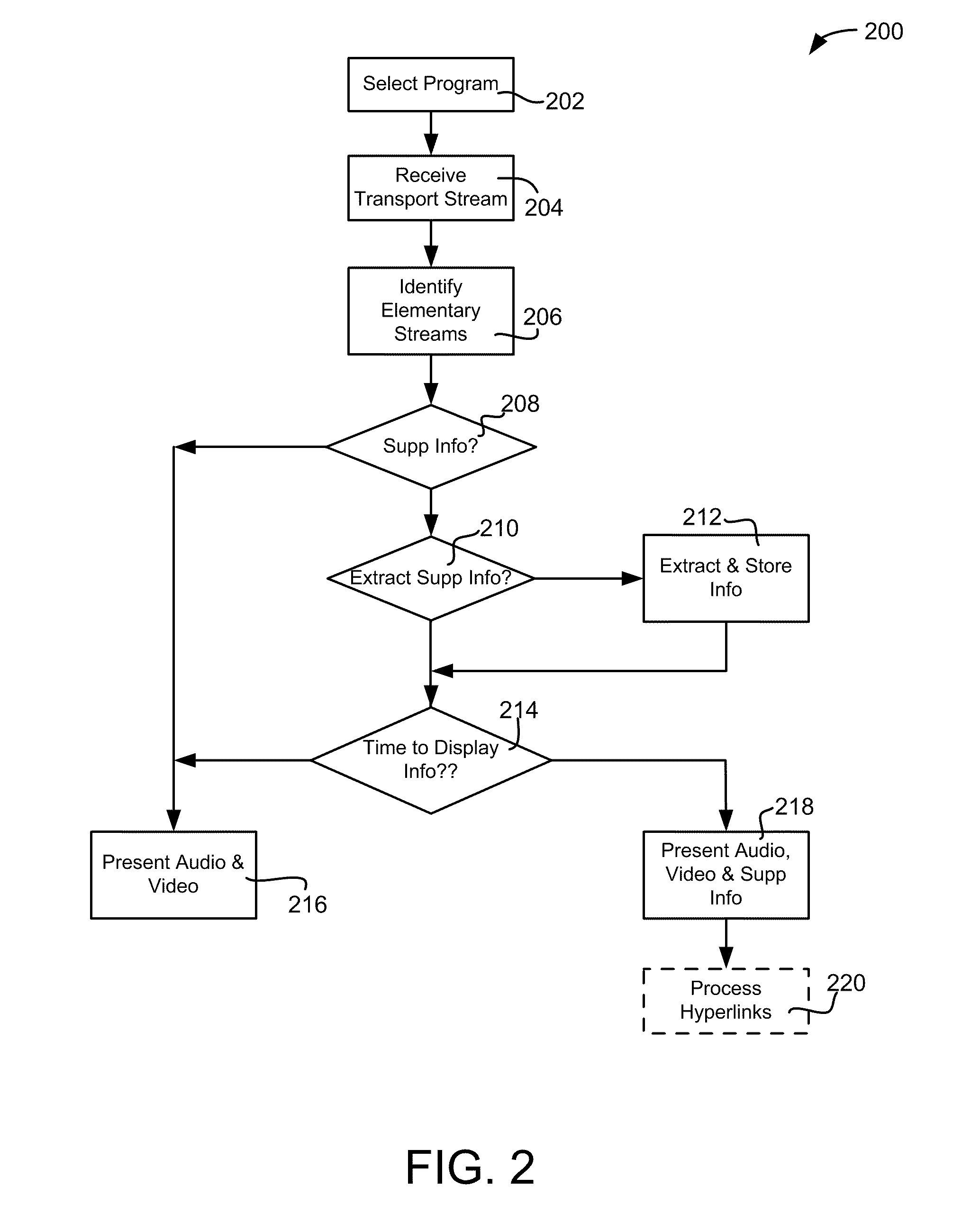
Systems and methods for processing supplemental information associated with media programming
ActiveUS20110321114A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsSelective content distributionElementary streamComputer network
Various systems and methods allow supplemental information such as recipes, parts lists, instructions, notes, outlines or other information associated with a television program to be delivered in the same transport stream that carries the television program to the viewer. The transport stream includes at least two elementary streams, wherein the first elementary stream conveys video content associated with the television program and the second elementary stream conveys supplemental information that summarizes at least a portion of the television program. The device receiving the digital transport stream identifies the first and second elementary streams in the digital transport stream, processes the first elementary stream to present the video content associated with the television program to the viewer, and makes the supplemental information in the second elementary stream available to the viewer.
Owner:DISH TECH L L C
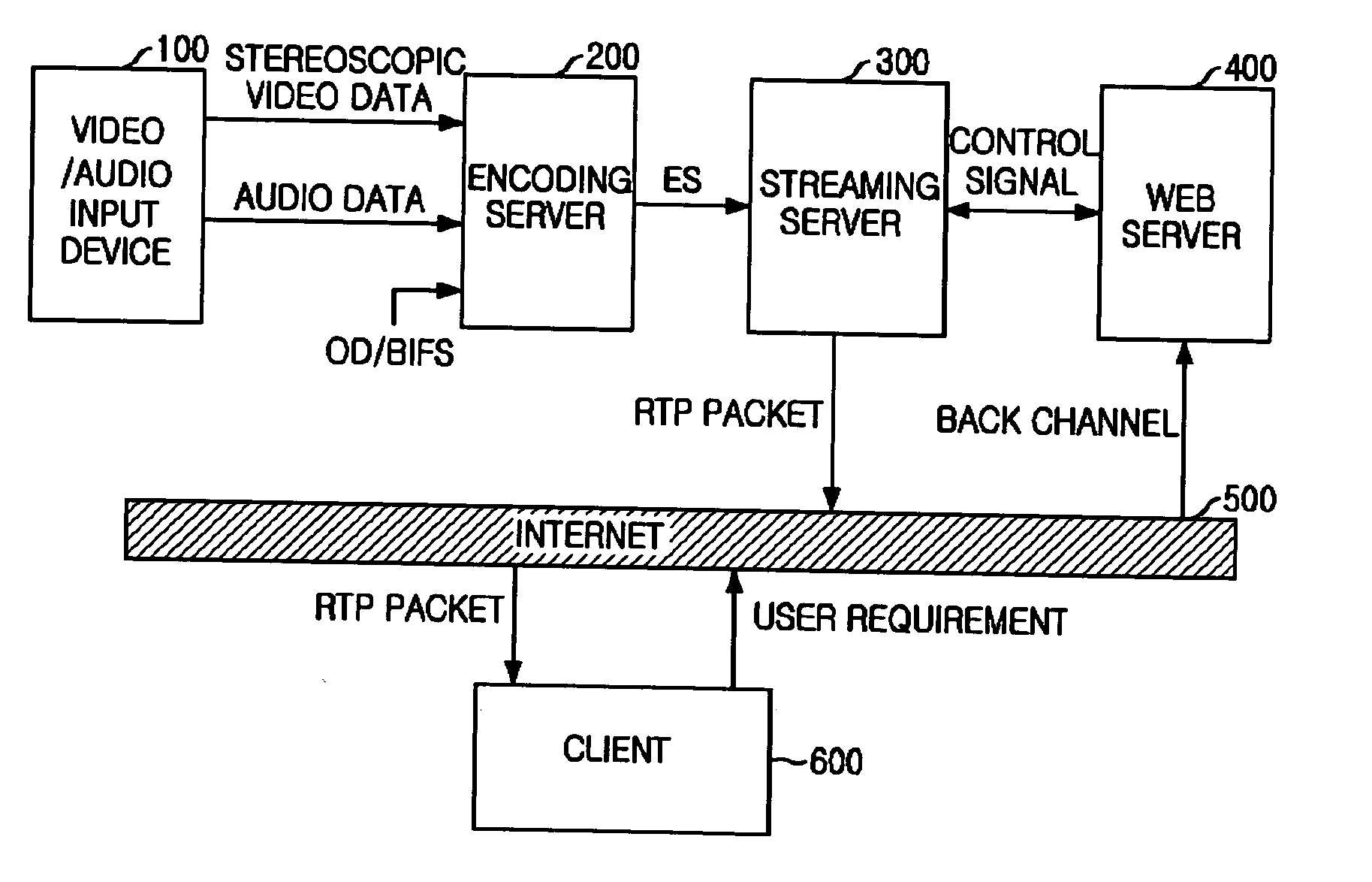
System and method for internet broadcasting of mpeg-4-based stereoscopic video
InactiveUS20060221178A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesStereoscopic videoMedia server
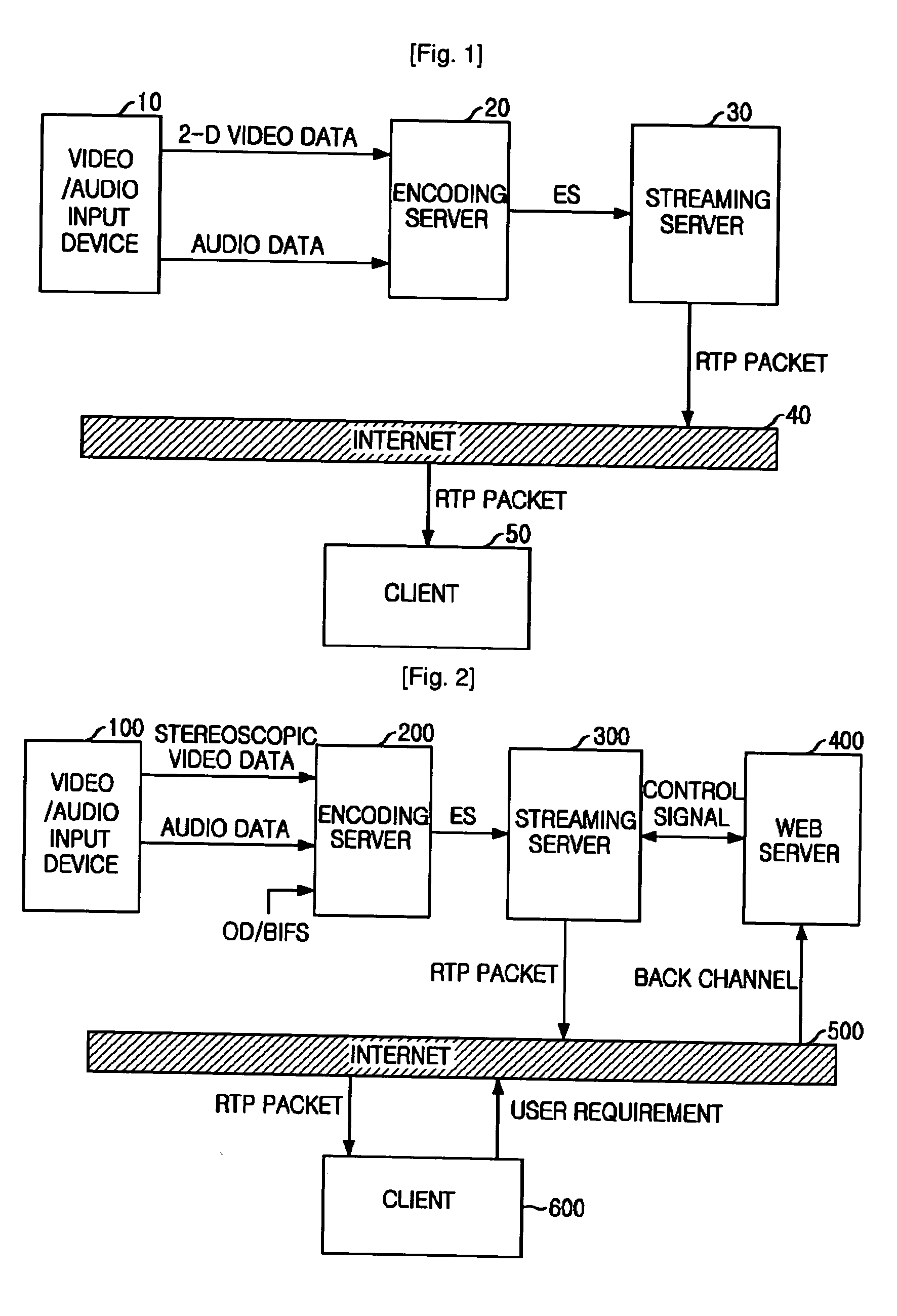
Provided is a system and method for broadcasting stereoscopic video data to users on the Internet based on Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG)-4. The system includes: an encoding server for receiving stereoscopic video data, audio data, and Object Descriptor / Binary Format for Scene (OD / BIFS), which is information for controlling a content, and encoding the data into elementary stream (ES) having an MPEG-4 structure; a web server for receiving from the client any one among two-dimensional video display mode, field-shuttering video display mode and frame-shuttering video display mode; and a streaming server for generating a RTP (RTP) packet for real-time data transmission on the Internet by multiplexing the ES based on the display mode inputted into the web server, and transmitting the RTP packet to the client.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Measuring Video Quality Using Partial Decoding
InactiveUS20100110199A1Measurement qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Video quality
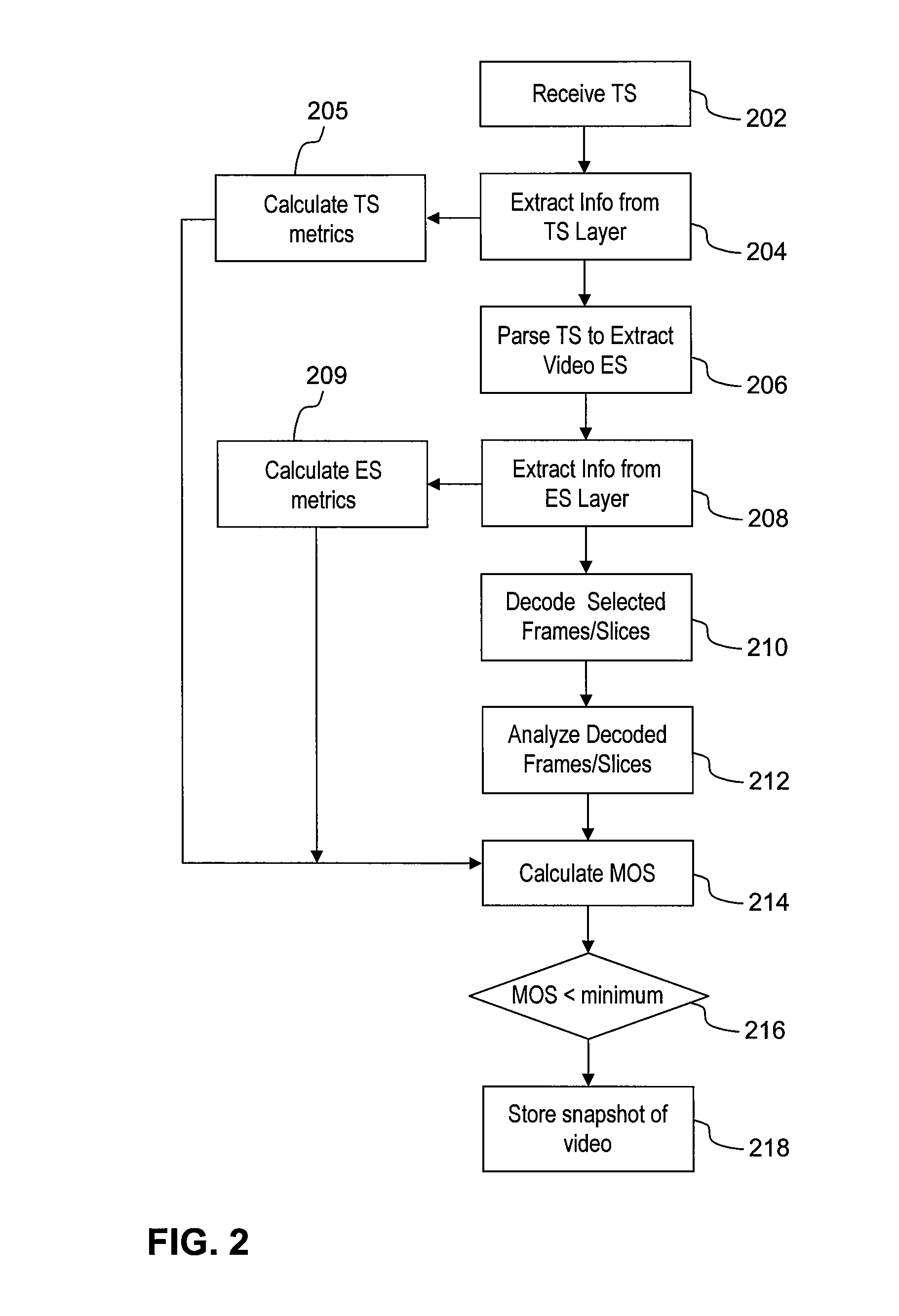
The quality of video that is broadcast as a packet-based video stream is measured using decoded pictures in combination with information extracted from the transport stream and elementary stream layers of the packet-based video stream. The decoded pictures include selected frames and / or slices decoded from the packet-based video stream and are used to generate video content metrics. A composite score for the video quality can be generated from the video content metrics in combination with quality metrics of the transport stream and / or the elementary stream. If the composite score falls below a minimum score, a snapshot of the video is captured for later analysis.
Owner:CHEETAH TECH
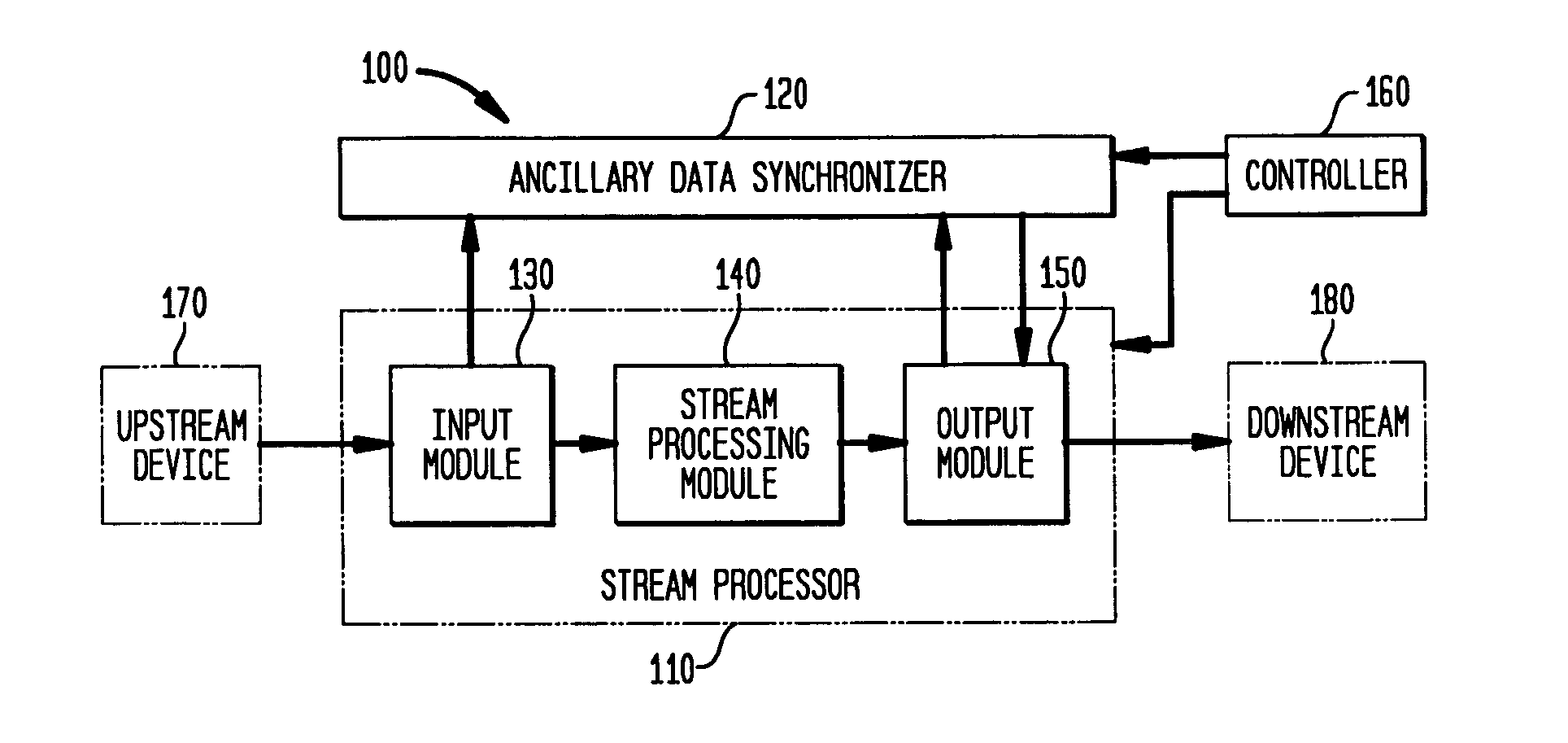
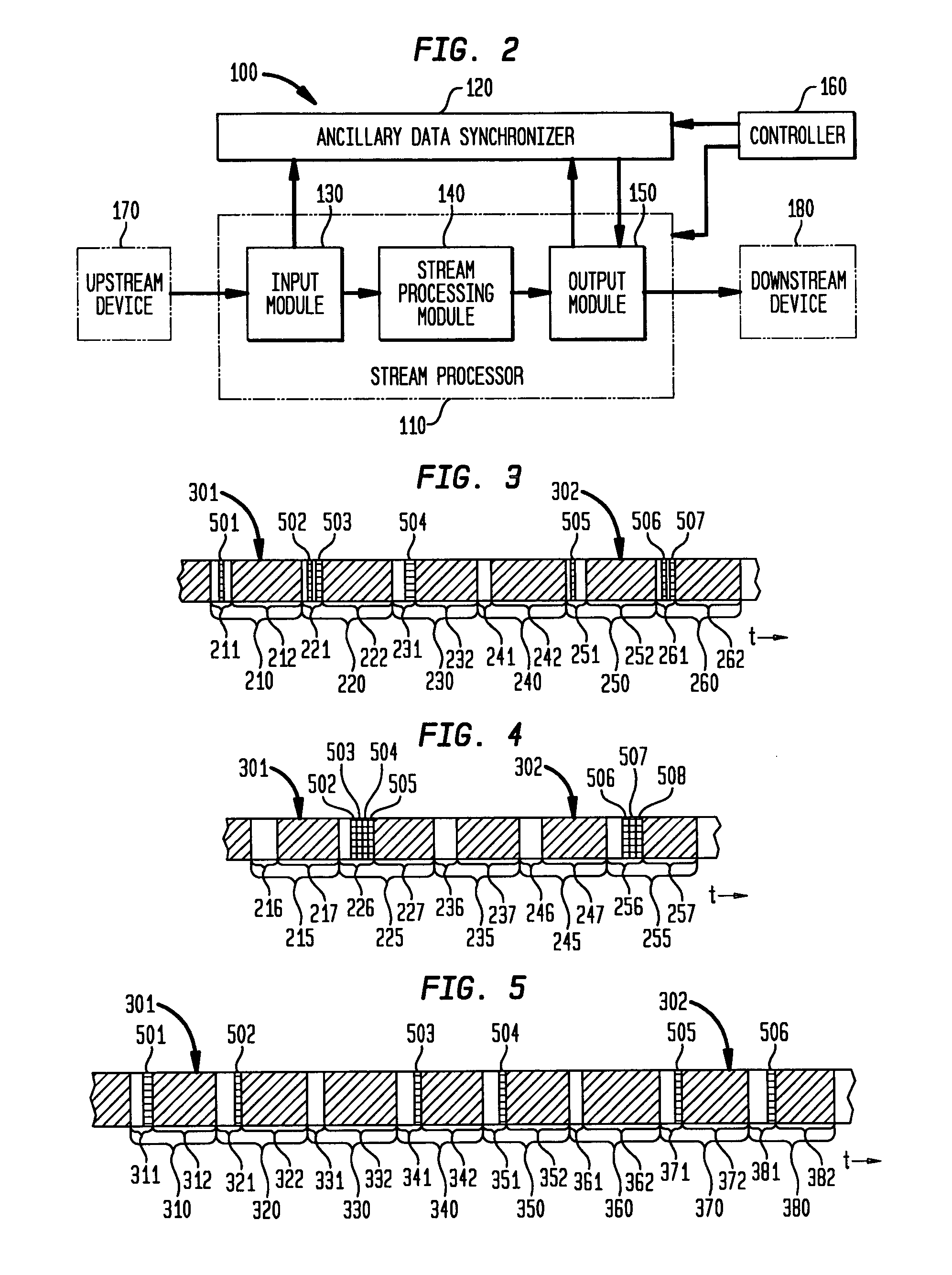
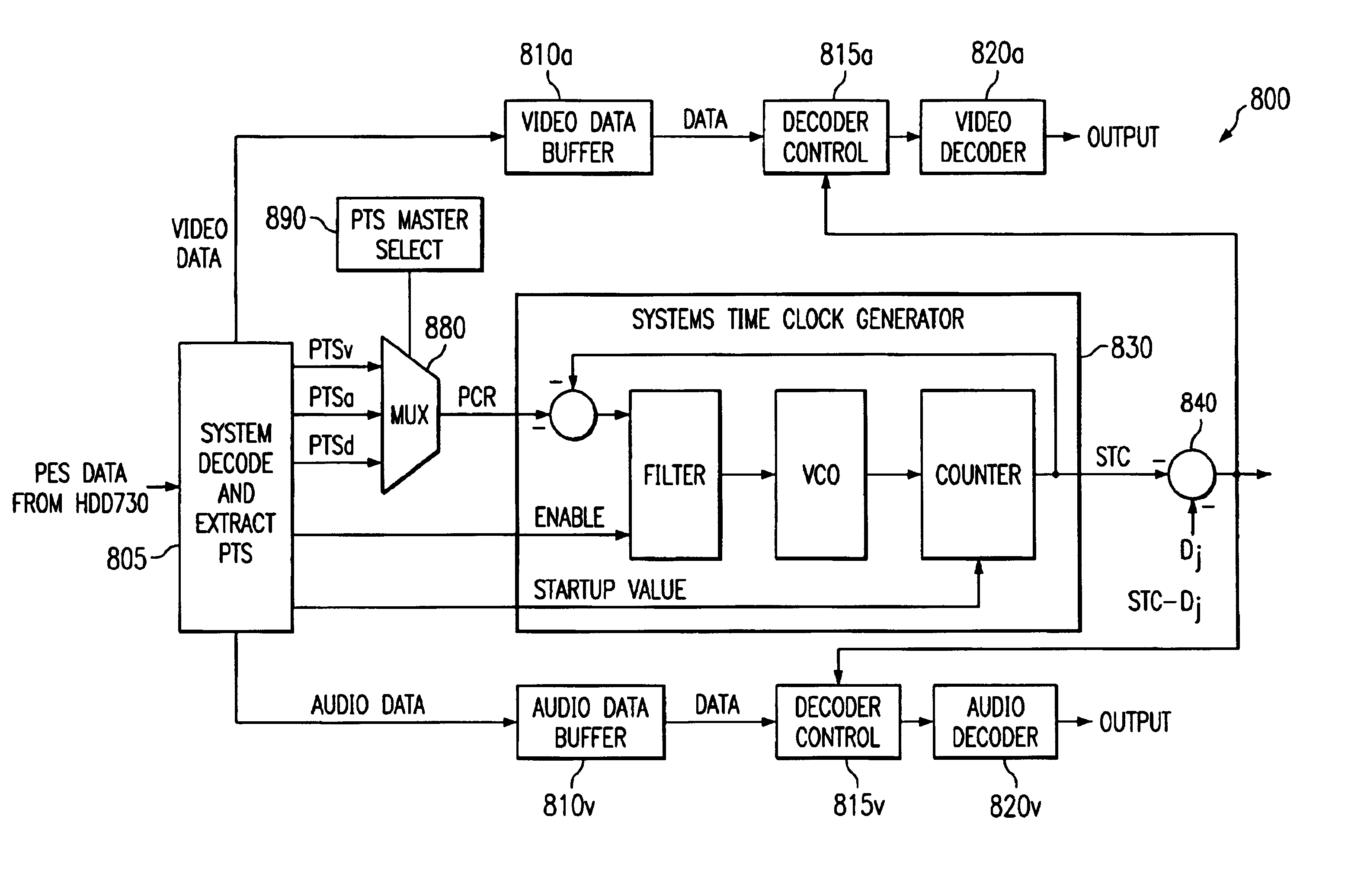
Method and system for time synchronized forwarding of ancillary information in stream processed MPEG-2 systems streams
InactiveUS20050036557A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionSystem timeHandling system
A method and system are provided for processing an elementary stream in a systems layer stream that is presumed to be ultimately consumed according a to predefined and deterministic schedule relative to a particular system time clock of a program that comprises the elementary stream. First and second synchronization points are identified in an elementary stream. The elementary stream is processed to produce a modified sequence of elementary stream information to be carried between the first and second synchronization points. The modified sequence has a different amount of information than the particular sequence of information. A series of one or more new systems layer stream segments carrying the first synchronization point, as well as the modified sequence of elementary stream information, are inserted into a new systems layer stream. At least one of the new systems layer stream segments comprises a systems layer information sub-segment containing the particular ancillary data. Each synchronization point is a type of sequential location of the elementary stream: (1) which recurs continually throughout the elementary stream; (2) is synchronized in time to the systems time clock of the program containing the elementary stream; and (3) is always present in an elementary stream both prior to, and after, the processing.
Owner:SKYSTREAM NETWORKS
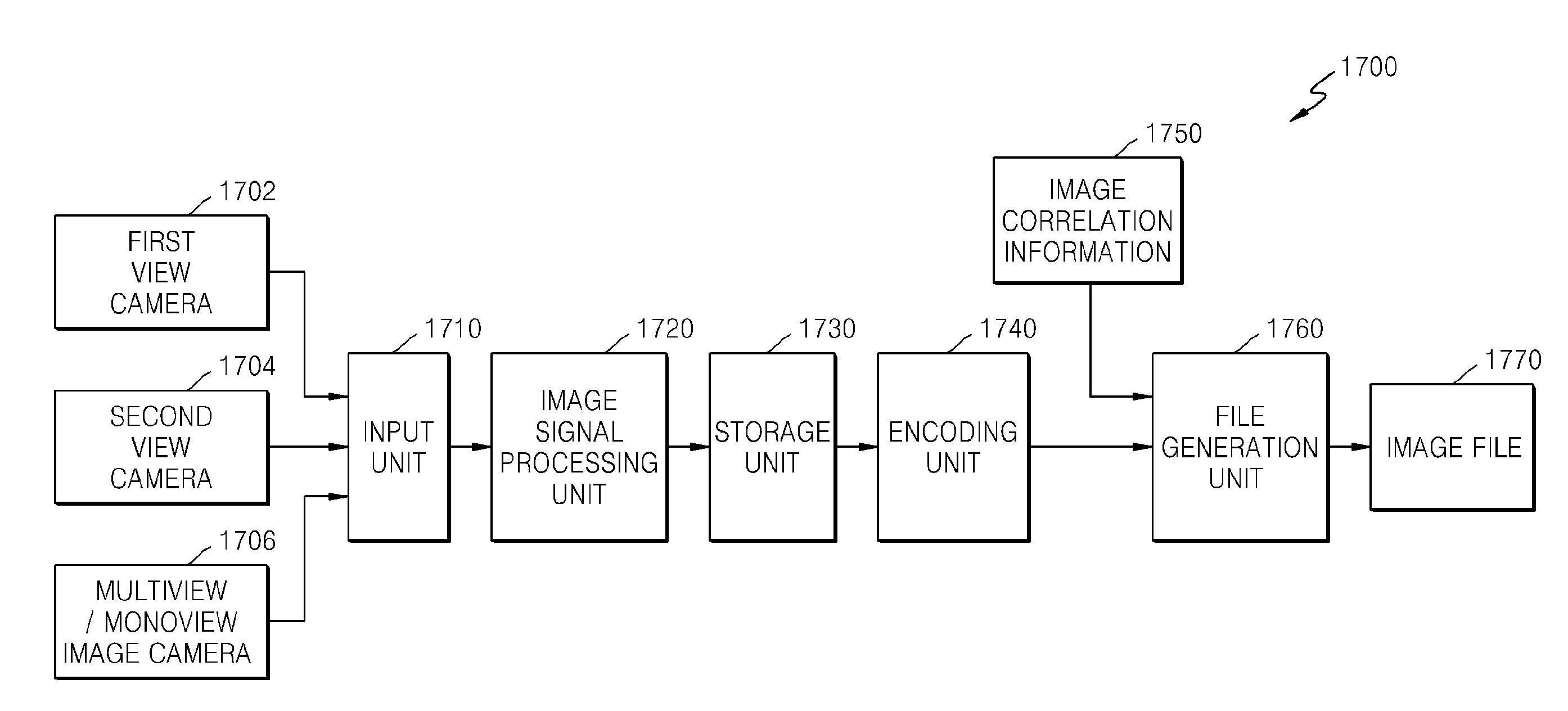
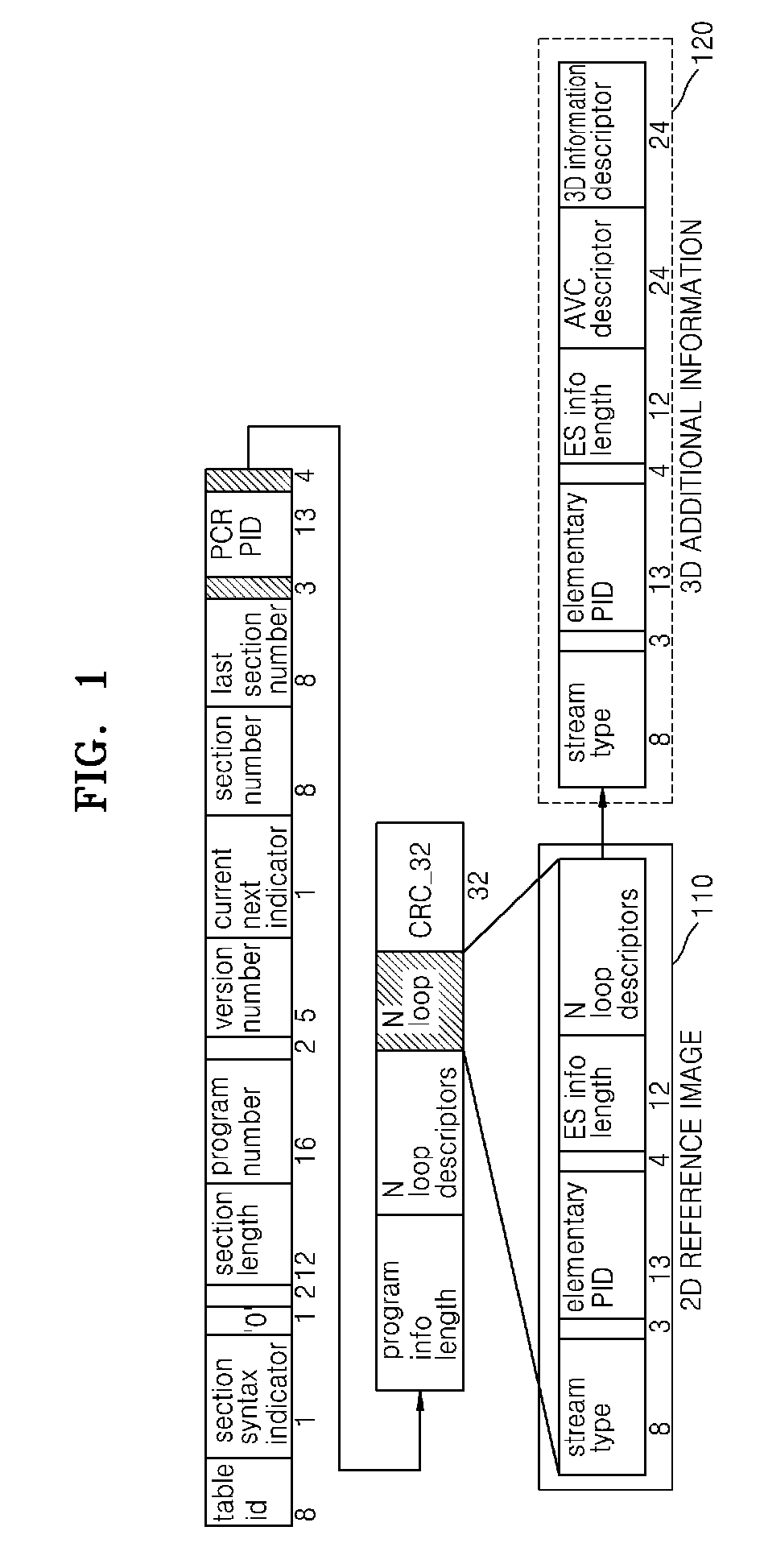
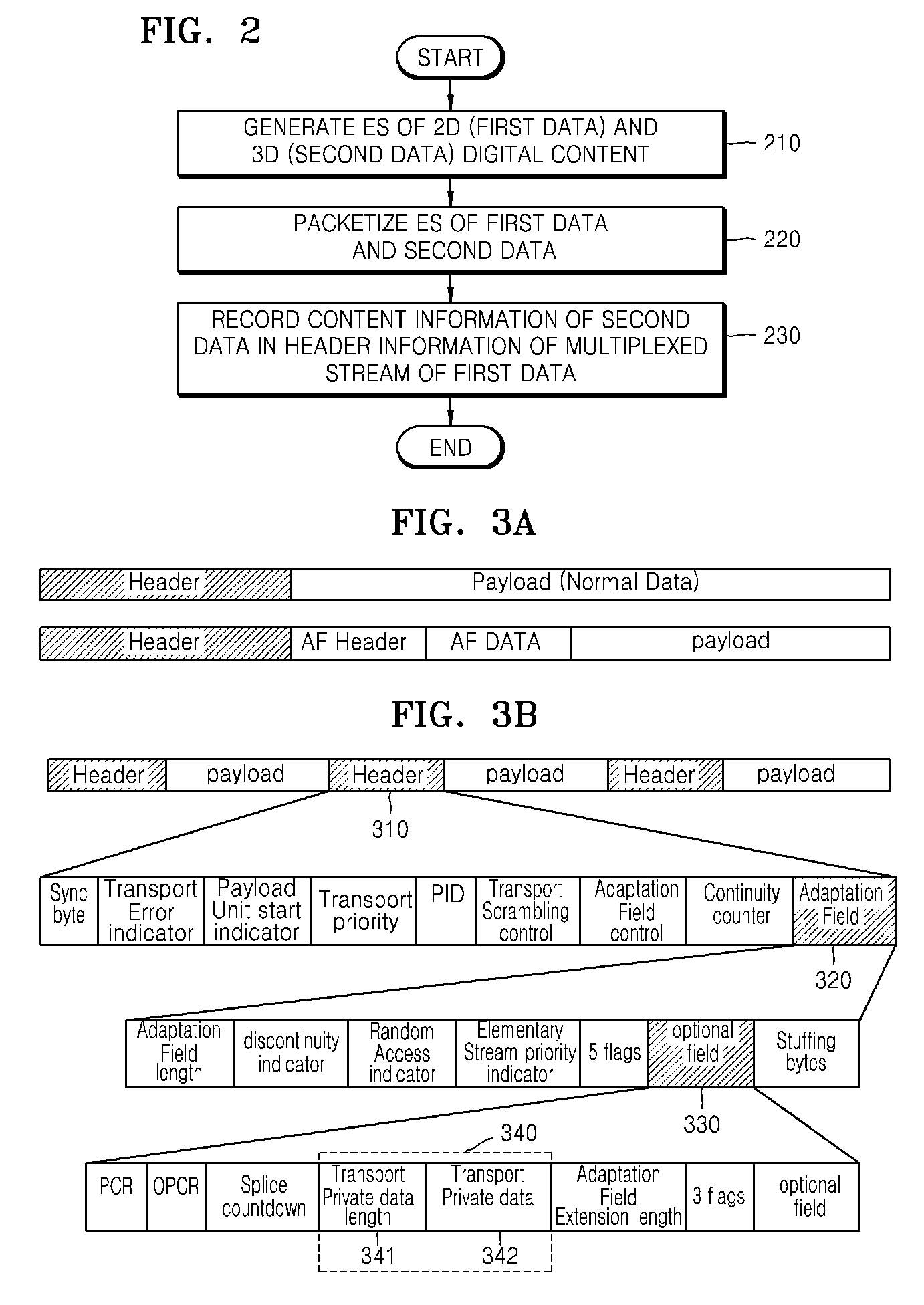
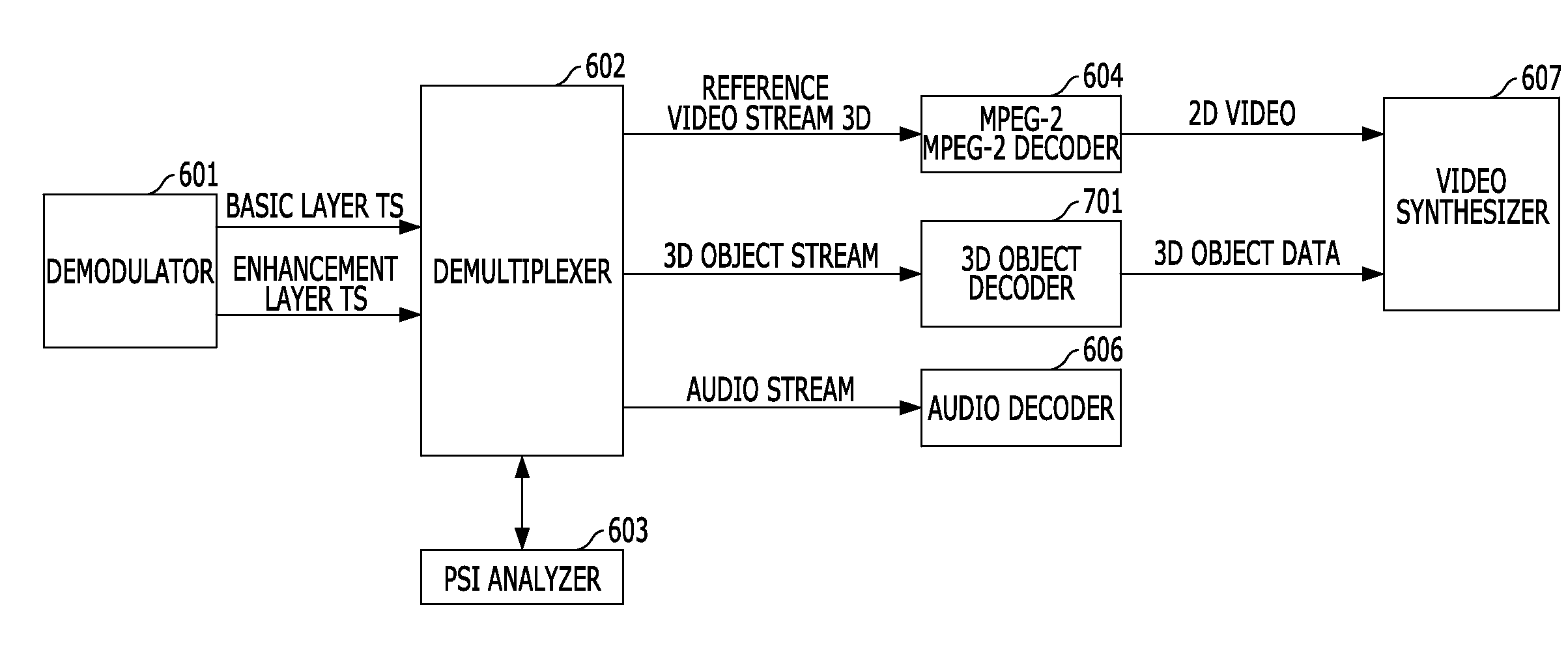
Method and apparatus for providing and receiving three-dimensional digital contents
InactiveUS20090257452A1Time-division multiplexData switching networksDigital contentElementary stream
Provided are a method and an apparatus for providing three-dimensional (3D) digital content by using a conventional system for providing two-dimensional (2D) digital content. The method includes generating an elementary stream (ES) regarding first data of 2D digital content, generating an ES regarding second data of 3D digital content, packetizing the ESs of the first data and the second data, and recording) the packetized second data and content information of the second data within header information of multiplexed stream of the packetized first data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
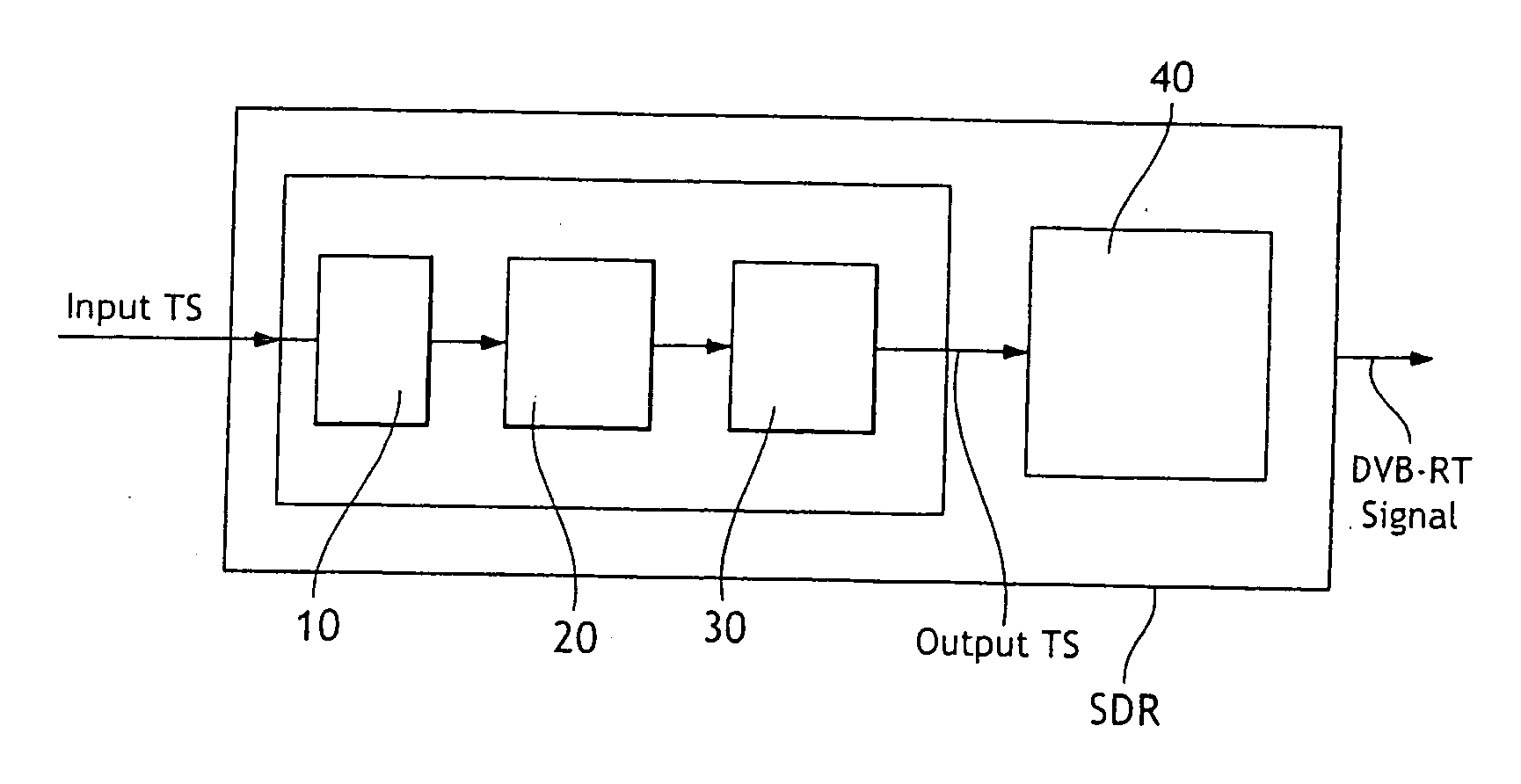
Method and device for processing a DVB-H compliant transport stream
InactiveUS20070074267A1Near-field transmissionResource management arrangementsTime informationComputer network
According to a first aspect, the invention proposes a method for processing a transport stream (TS) received as an input transport stream in a processing device (SDR), the transport stream comprising a plurality of elementary streams (ES), each elementary stream (ES) being a set of transport stream packets having the same Packet IDentifier (PID), at least one of these elementary streams being time-sliced so as to be sent in bursts, timing information indicating within a burst the time to the beginning of the next burst, characterized in that it comprises the steps of: applying a filtering operation to the input transport stream so as to filter out from the input transport stream part or all of one or more time-sliced elementary streams; modifying the bursts scheduling of the input transport stream so as to generate a DVB-H compliant output transport stream from the filtered input transport stream. The invention also relates to a device for processing a transport stream comprising a plurality of time-sliced elementary streams, said device means for performing the method according to the first aspect of the invention, and to a transport stream carrying in-band configuration messages intended to be interpreted by the device for determination of the filtering operation to be applied to the input transport stream.
Owner:UDCAST SA
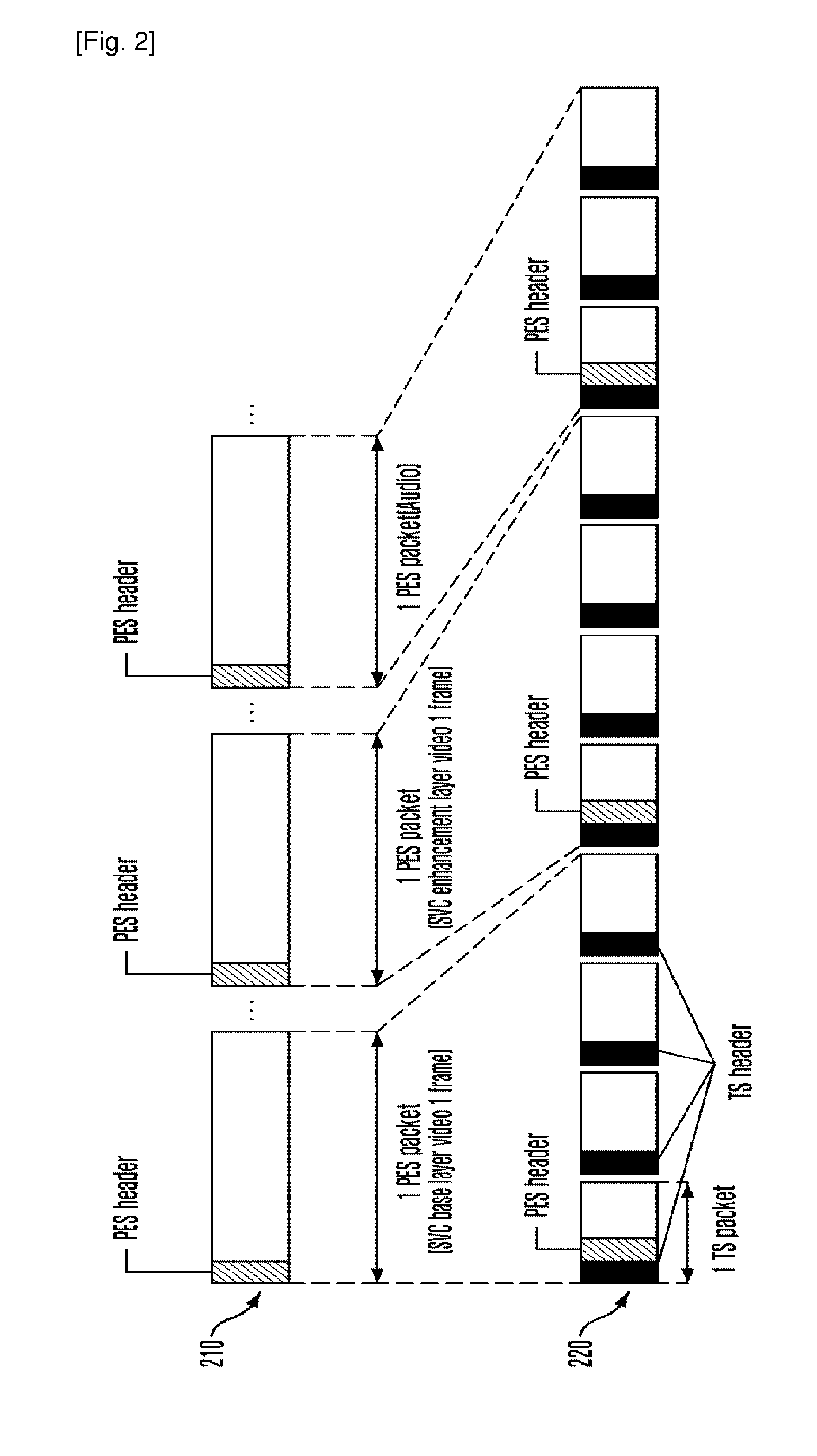
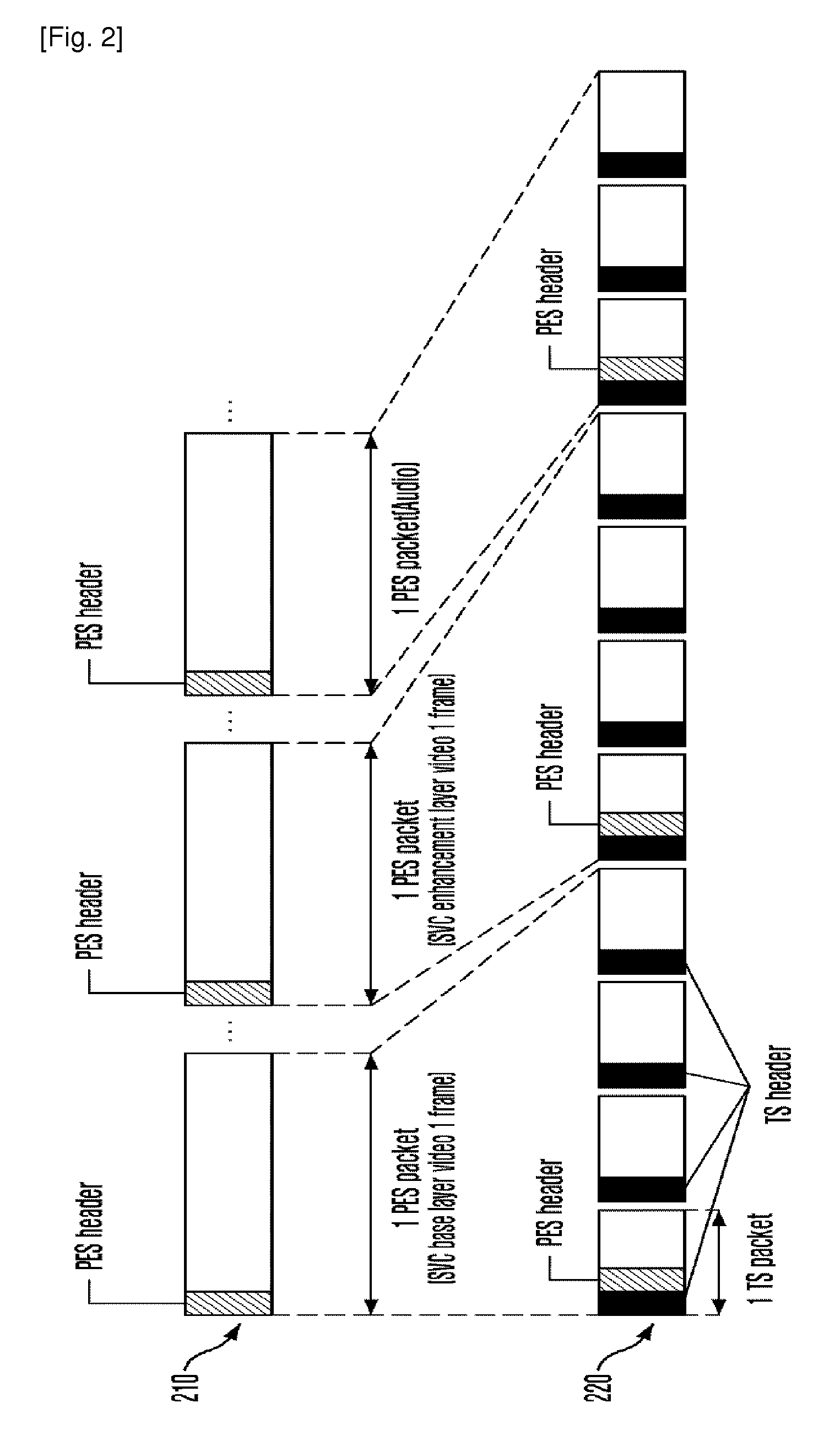
MPEG transport stream encoder and method for encoding MPEG transport stream
ActiveUS6912218B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareMPEG transport stream
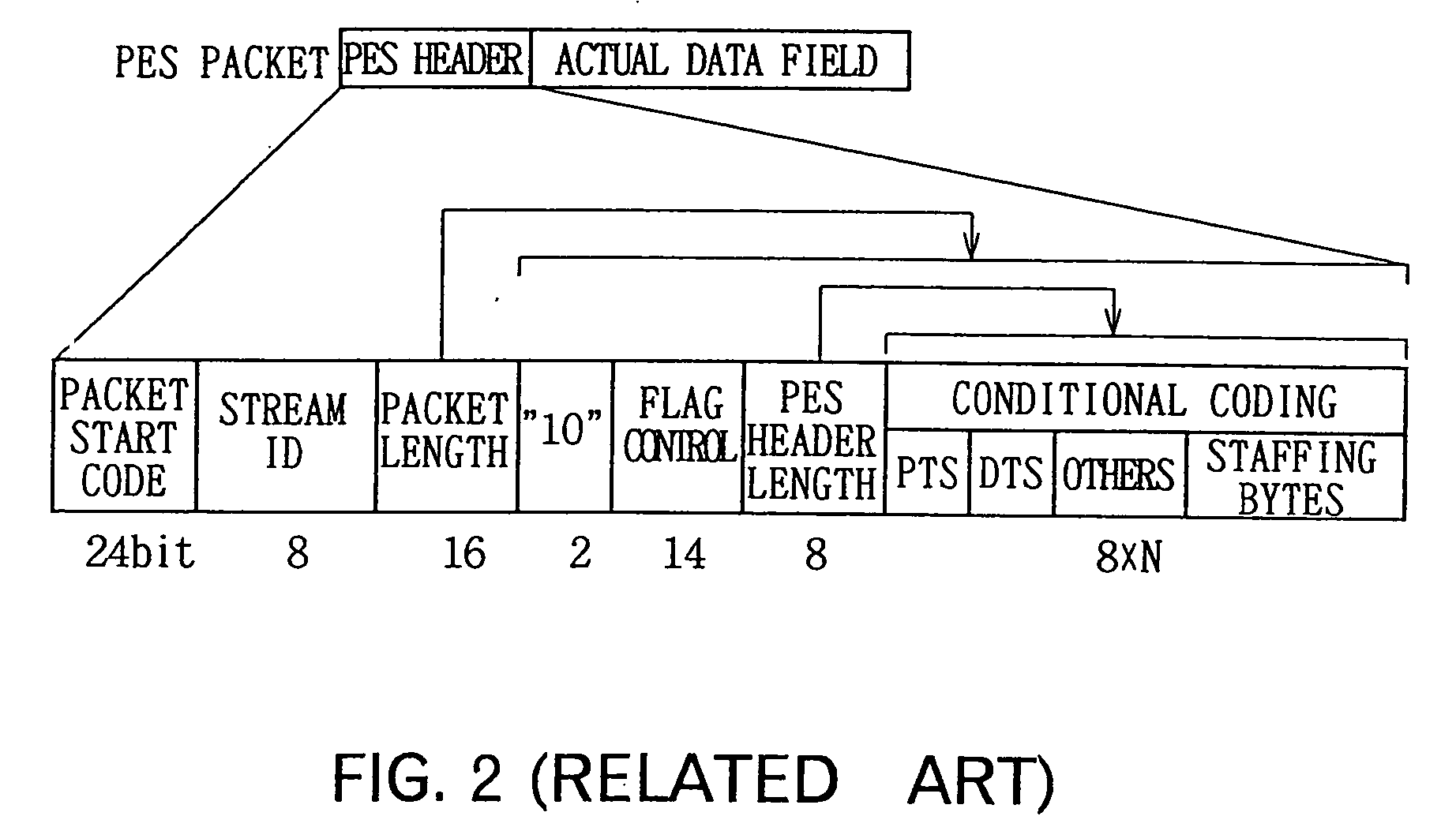
A TS encoder for encoding video and audio signals in units of fields is provided. A transport stream (TS) encoding method for receiving an MPEG elementary stream and generating a transport stream includes the steps of (a) generating a packetized elementary stream (PES) header in units of fields of the elementary stream, (b) generating a PES header valid period signal for denoting the valid period of the PES header generated in the step (a) in units of fields, (c) recording the PES header generated in the step (a) and the elementary stream in synchronization with the PES header valid period signal generated in the step (b), (d) generating a TS header period signal for denoting a period in which the TS header is to be recorded, (e) reading the PES header generated in the step (a) and the elementary stream in synchronization with the TS header period signal generated in the step (d), and (f) generating the TS packet by adding the TS header to the PES header read in the step (a) and to the elementary stream, according to the timing at which the TS header is to be recorded.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
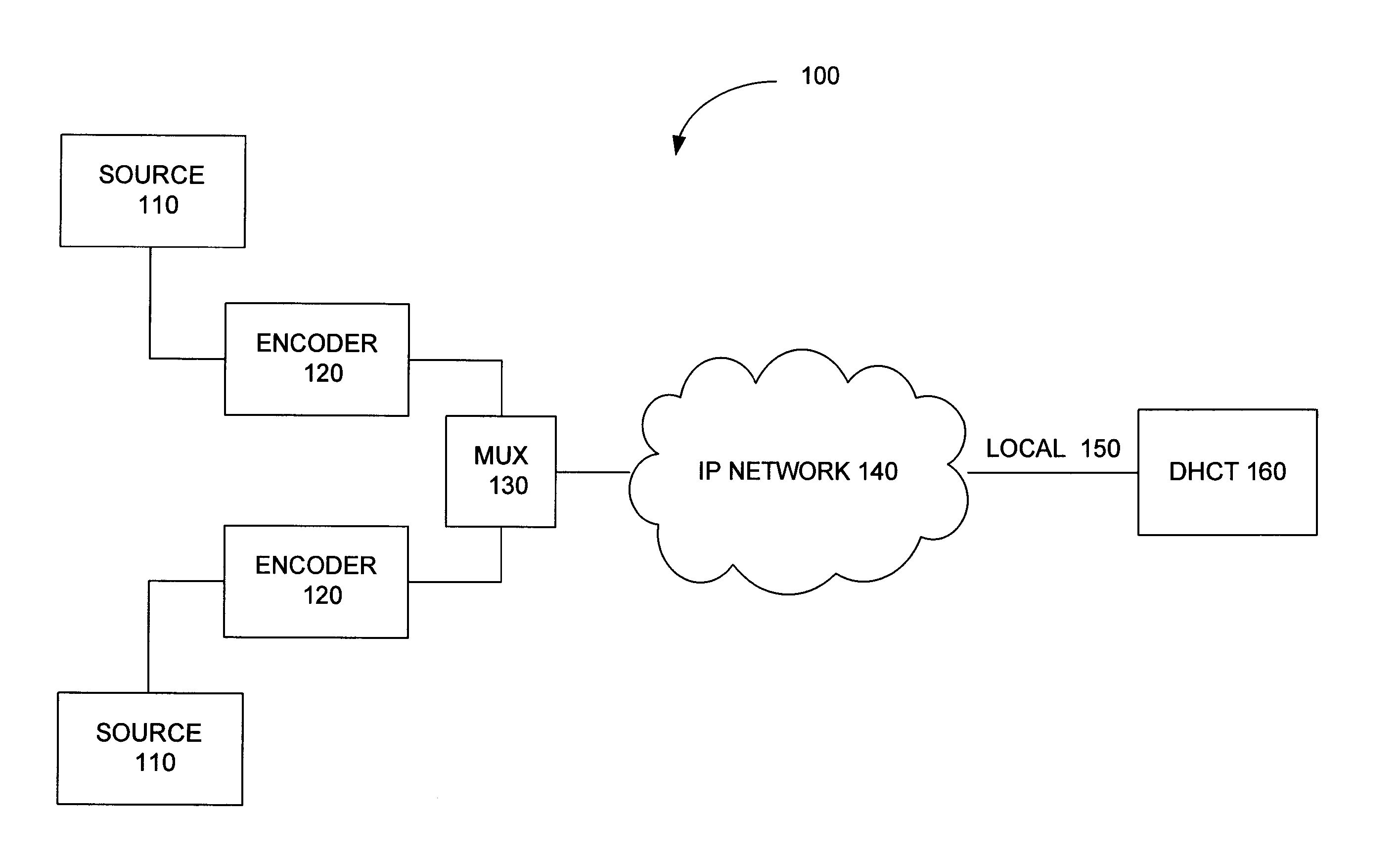
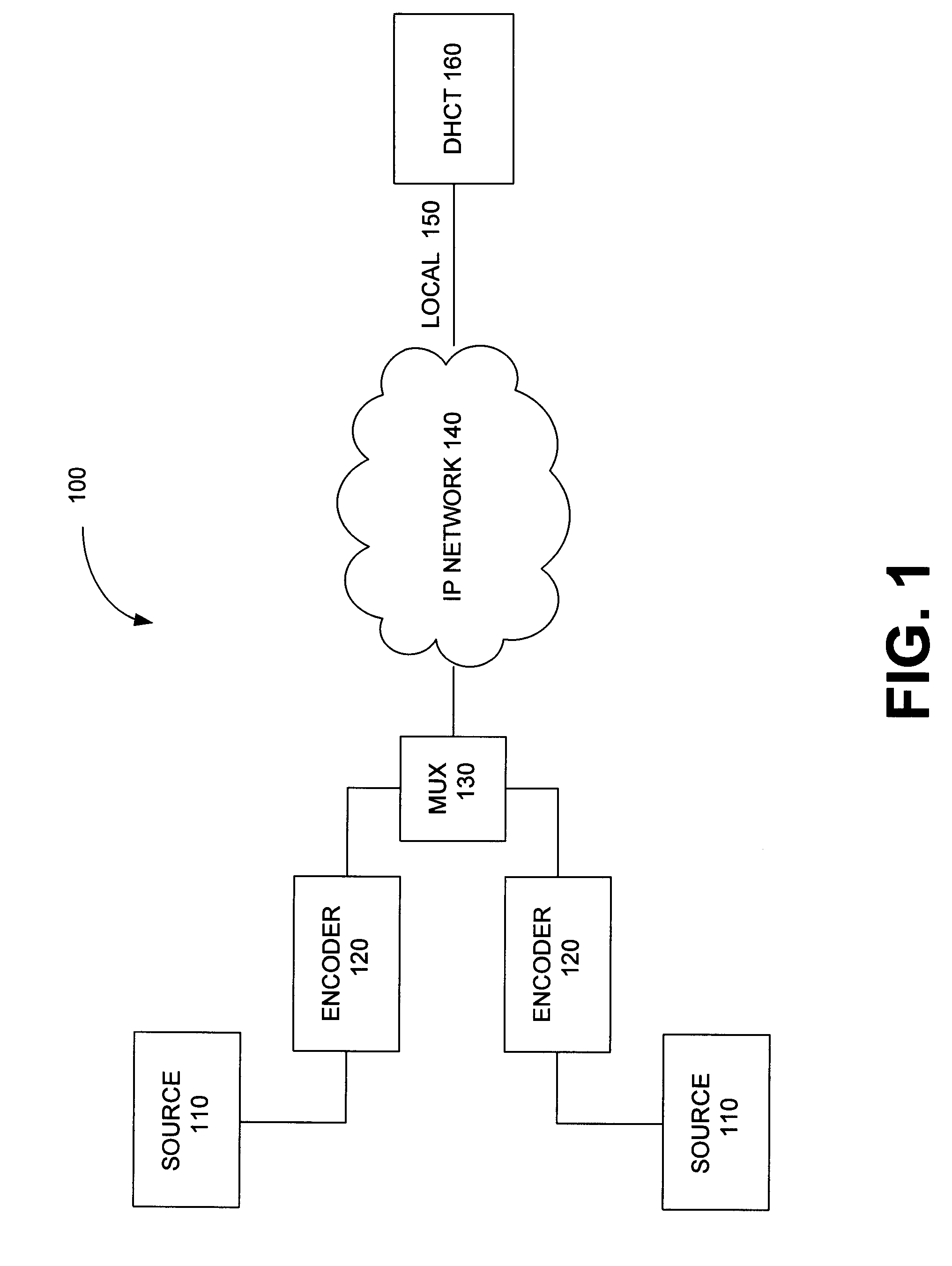
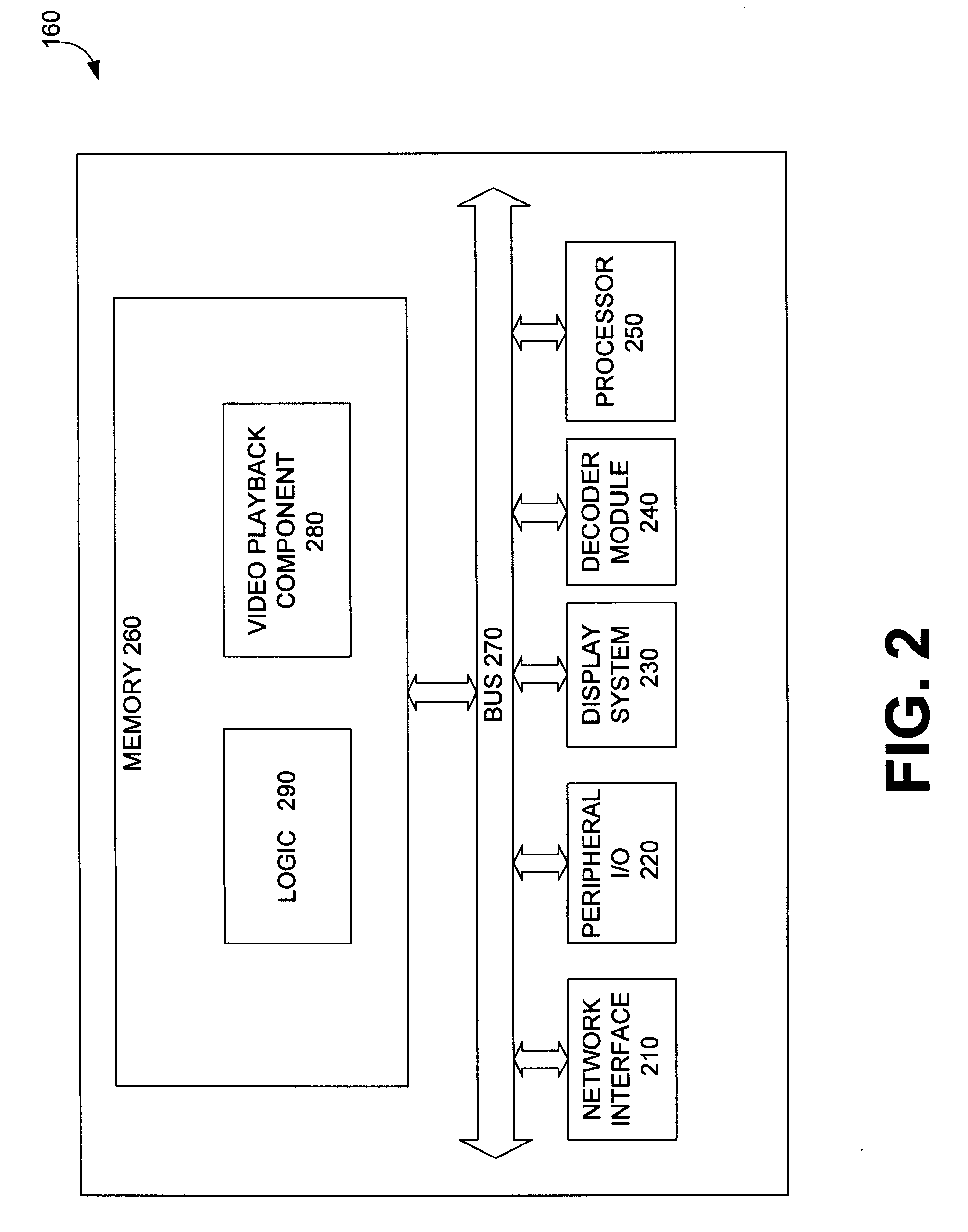
Systems and Methods of Assembling an Elementary Stream from an Encapsulated Multimedia Transport Stream
InactiveUS20080005776A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsElementary streamNetwork interface
Systems and methods of assembling an elementary stream from an encapsulated multimedia transport stream are disclosed. An exemplary method includes: receiving a command from a user mode video playback component; in response, processing layer-2 packets received through a network interface driver binding to assemble, into an MPEG elementary stream, multimedia transport packets encapsulated within; and supplying the stream to a decoder. The receiving and processing steps are performed in kernel mode. Also disclosed is an exemplary digital home communication terminal that includes a network interface, memory, and a processor. The processor executes code to: receive a command from a user mode video playback component; process layer-2 packets received through a network interface driver binding, in order to assemble into an MPEG elementary stream multimedia transport packets encapsulated within the received layer-2 packets; and supply the elementary stream to a decoder. The receive and process operations are performed in kernel mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Video editing apparatus and video editing method
InactiveUS20050259946A1Easy to implementAvoid discontinuitiesTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsComputer hardwareData stream
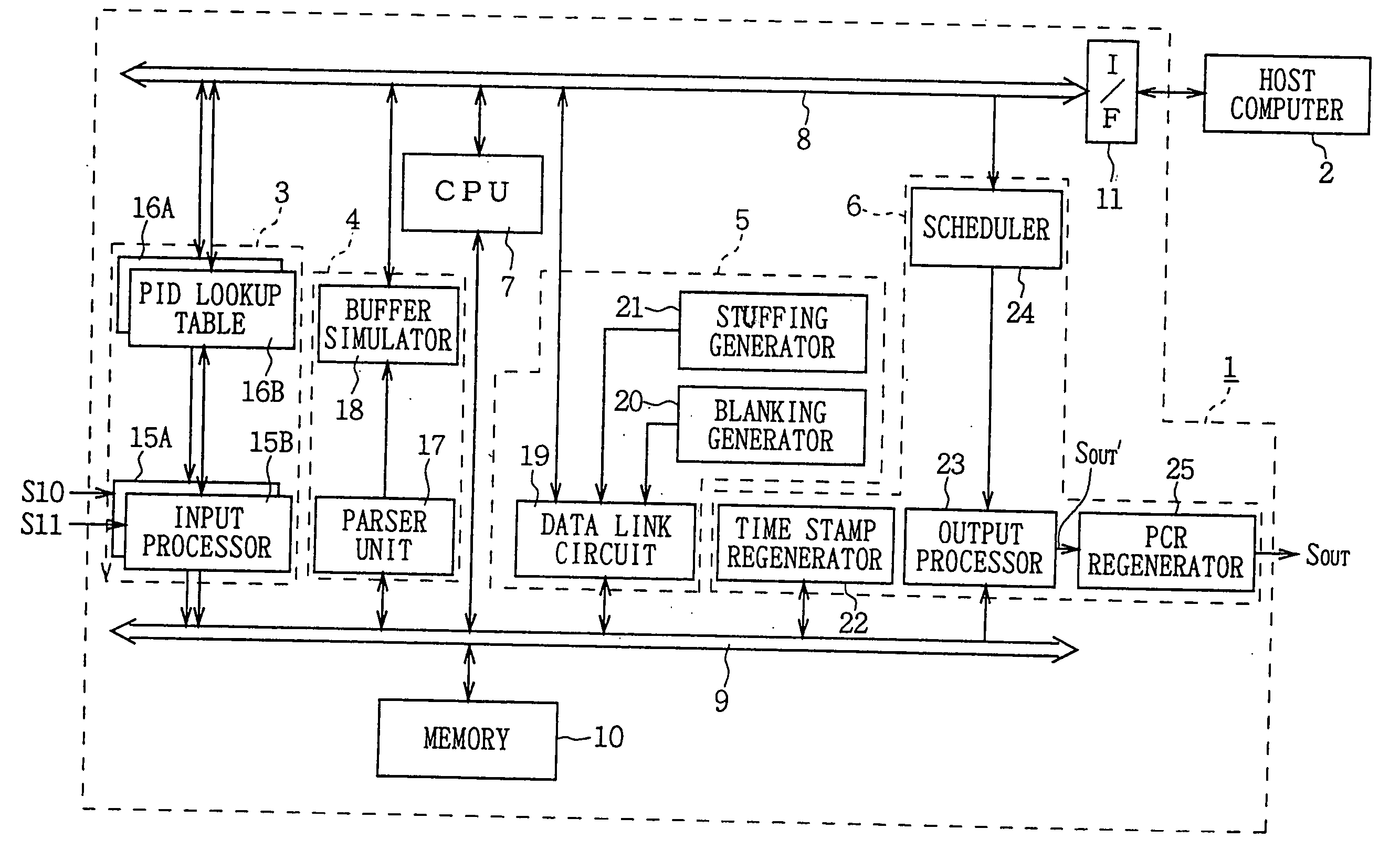
A video splicing apparatus for receiving a transport stream including a plurality of packetized encoded video data streams, and for splicing the encoded video data streams to generate a spliced video data stream. The video splicing apparatus includes an input processor for disassembling each of the plurality of packetized encoded video data streams in the transport stream into a pseudo-elementary stream before packetization, and for storing the disassembled pseudo-elementary streams in predetermined storage. An analyzer is also provided for analyzing the amount of coded bits of two data streams of the pseudo-elementary streams stored in the storage that will be generated upon decoding upon receipt of the two data streams to be subjected to a splicing operation. A data processor is provided for reading the data streams to be subjected to the splicing operation from the storage, splicing the streams, and inserting a desired amount of additional data at a splice point based on the result of the analysis by said analysis to produce a spliced video data stream and storing the spliced video data stream in the storage. An output processor is provided for determining output timing for the spliced video data stream based on the determined amount of coded bits, and outputting the spliced video data stream read from the storage based on the output timing.
Owner:SONY CORP
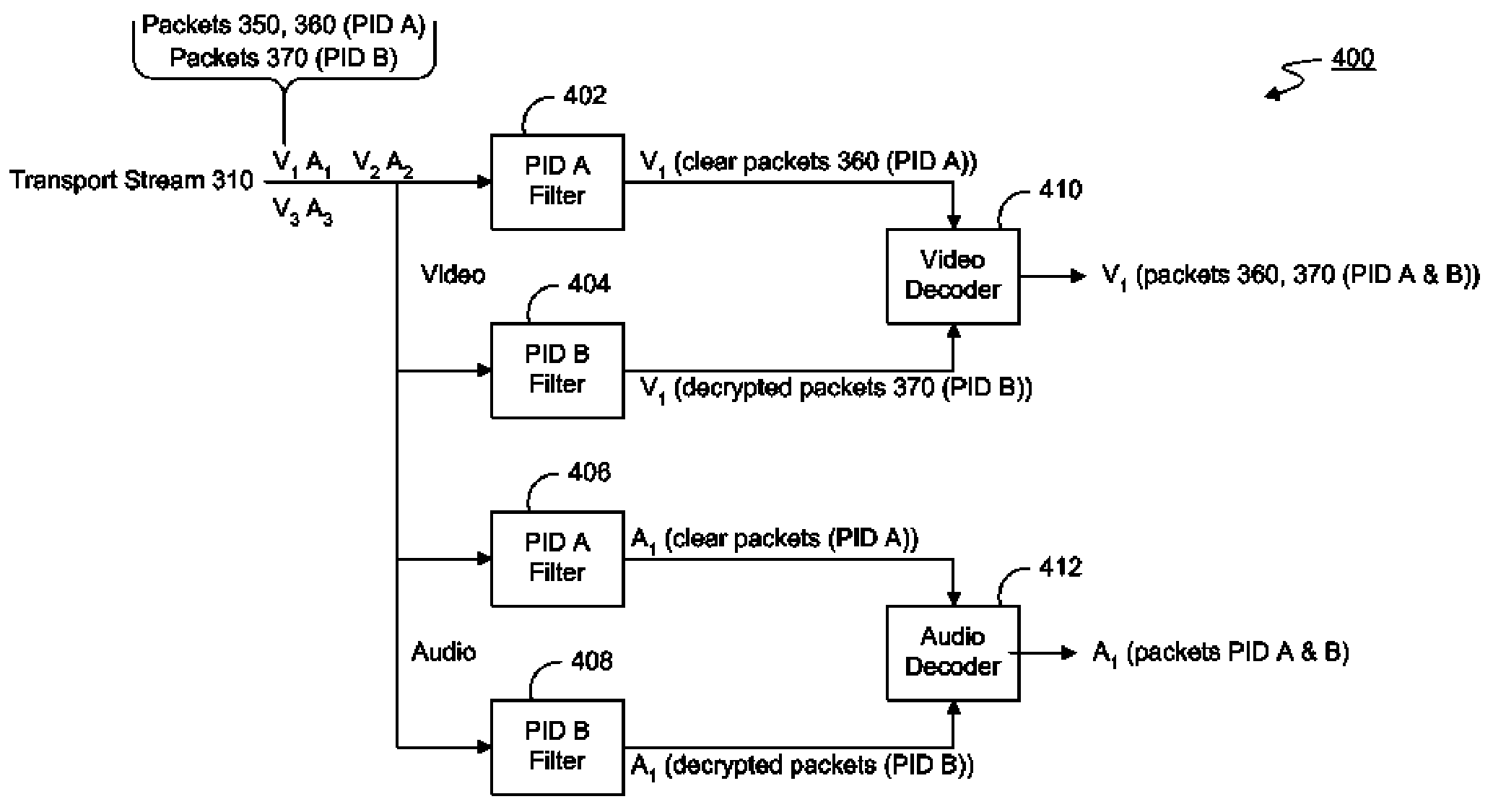
Processing an MPEG elementary stream in a conditional access overlay environment
InactiveUS7555123B2Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsConditional accessFilter system
Processing an MPEG elementary stream contained in multiple PID streams in a conditional access overlay environment. A multi-program transport stream contains numerous video and audio elementary streams. Critical packets in the elementary streams are encrypted with two different encryption schemes creating a stream having multiple PID values. The streams are then sent from the headend to individual set-top boxes. One encryption scheme can be decoded by the incumbent set-top box and the second encryption scheme can be decoded by the overlay set-top box. The overlay set-top box uses a dual filter system to filter and decode the PIDs for each video and audio stream of the desired program.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
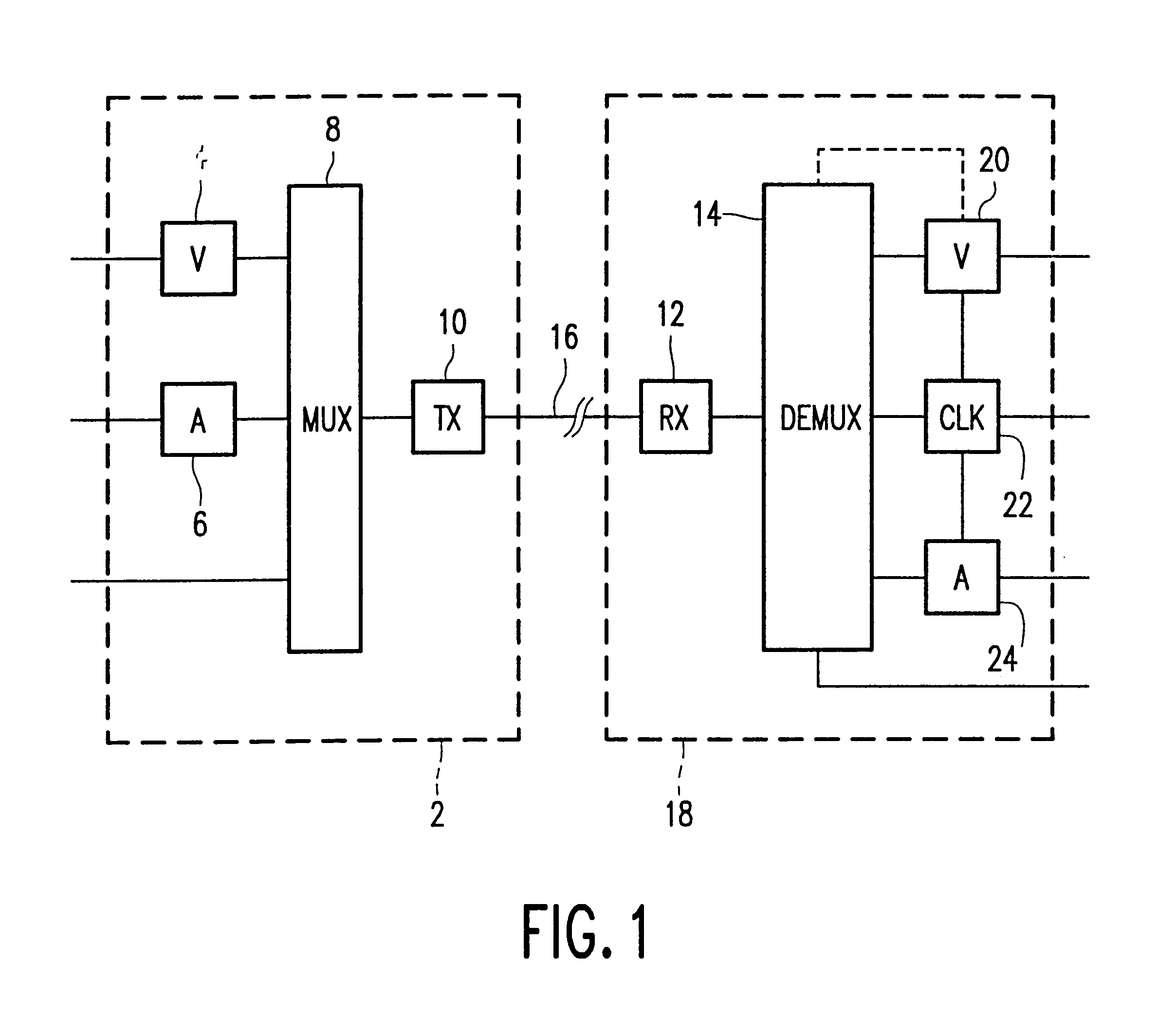
Transmission system for transmitting a flexible multiplex signal
InactiveUS6175577B1Reduce effortPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexerComputer science
In an MPEG-2 transmission system a plurality of programs each consisting of a plurality of elementary streams are multiplexed on a transport stream by a multiplexer (8). The transport stream is transmitted by the transmitting means (10) via a transmission medium (16) to a receiver (18). In the receiver (10) the signal is demodulated by the receiving means (12) and demultiplexed by the demultiplexer (14).In order to be able to find the different elementary streams which form a program several tables are used. Said tables which can change over time, are updated by information present in the transport stream. The tables are identified by a version number in order to be able to distinguish different versions of them. The version numbers are not necessarily subsequent numbers. In a prior art transmission system filtering has to be performed on all possible version numbers to find updates of a table.In the transmission system according to the present invention, filtering is performed by only selecting sections having a version number which is different from the previous version numbers.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
3d stereoscopic/multiview video processing system and its method
InactiveCN1613263ACode conversionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Video processing
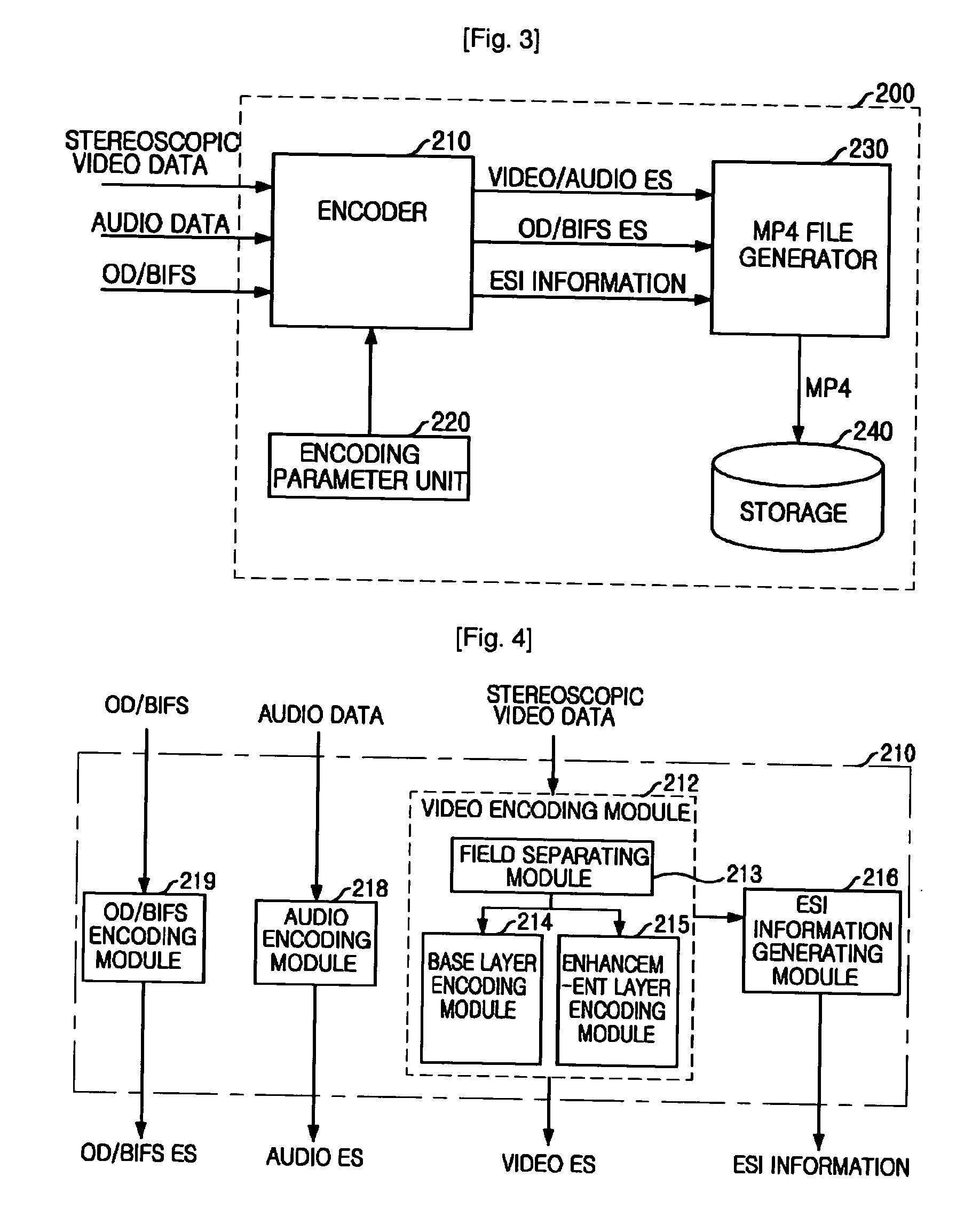
Disclosed is a stereoscopic / multiview three-dimensional video processing system and its method. In the present invention, stereoscopic / multiview three-dimensional video data having a plurality of images at the same time are coded into a plurality of elementary streams. The plural elementary streams output at the same time are multiplexed according to the user's selected display mode to generate a single elementary stream. After packetization of the single elementary stream continuously generated, information about the stereoscopic / multiview three-dimensional video multiplexing method and the selected display mode information are added to the packet header of the stream. Then the packetized elementary stream is sent to the image reproducer or stored in storage media. The present invention multiplexes the multi-channel elementary streams having the same temporal and spatial information, thereby minimizing the overlapping header information, and performs streaming of data suitable for the user's demand and the user system environments.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Transport stream encapsulated trick modes
ActiveUS7941823B2Reduce processing overheadEasier propagationTime-division multiplexTwo-way working systemsMPEG transport streamComputer network
A representation of an audiovisual asset is obtained and is processed to obtain at least one normal playback video elementary stream, (optionally, at least one audio elementary stream), and at least one trick mode video elementary stream. A transport stream is formed from the at least one normal playback video elementary stream, the at least one audio elementary stream (where present), and the at least one trick mode video elementary stream, with the at least one trick mode video elementary stream encapsulated in the transport stream. Streaming of the transport stream within a network is facilitated, for example, to a VOD server (for de-encapsulation), and in some approaches, to a set-top box.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
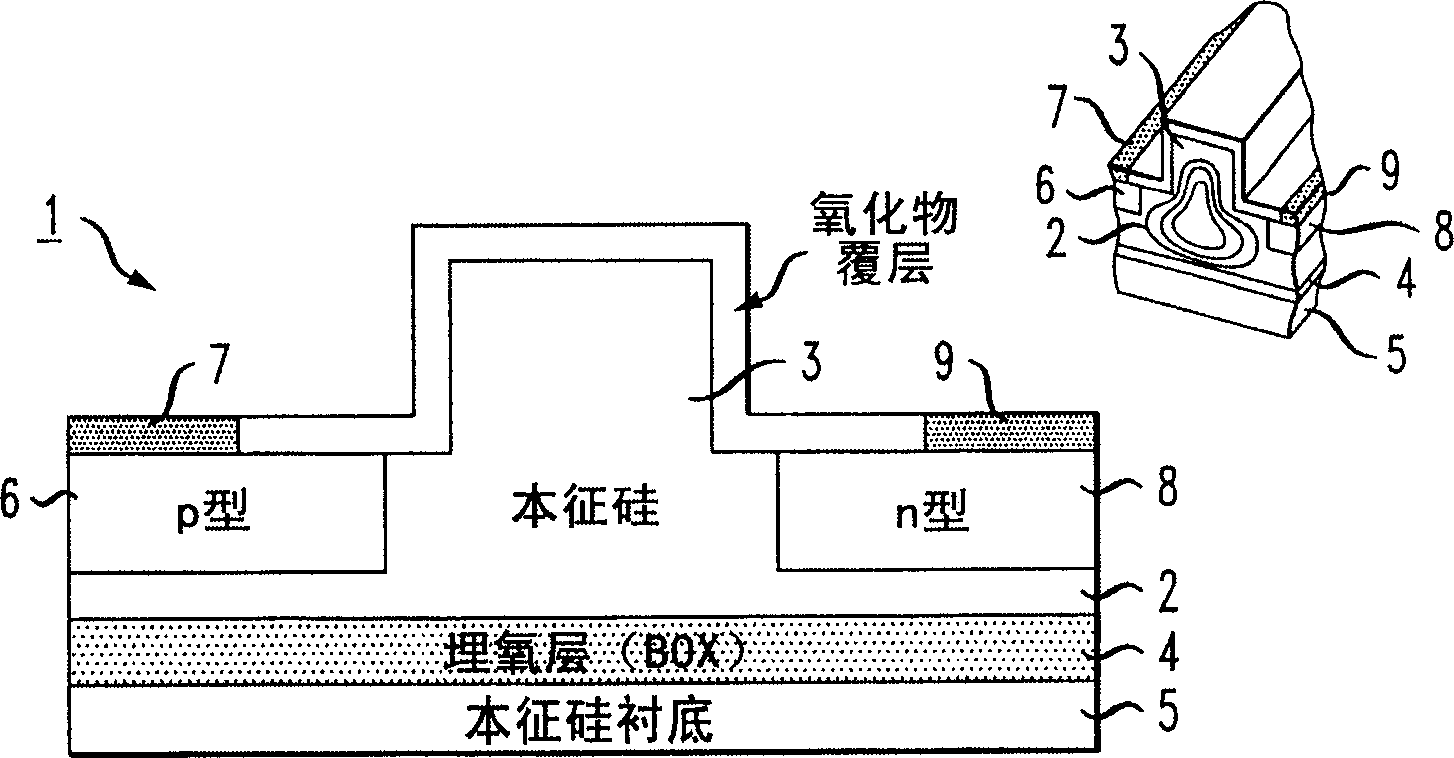
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveCN1764863AReduce light lossReduce power consumptionCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
A silicon-based electro-optical modulator (30) based on a gate region of the first conductivity formed to partially cover the body region of the second conductivity type, having interposed between the contact portions of the gate region and the body region (12, 10) A relatively thin dielectric layer (10). The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform with a body region formed in a relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and a gate region formed with a relatively thin silicon layer (10) overlying the SOI structure. The doping of the control gate and body regions is used to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric layer, thereby defining the active region of the device (16). Advantageously, the photoelectric field in the active device region is substantially identical to the free carrier concentration region. Therefore, the application of the modulation signal causes the free carriers on both sides of the dielectric layer to accumulate, deplete or invert simultaneously, resulting in high-speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
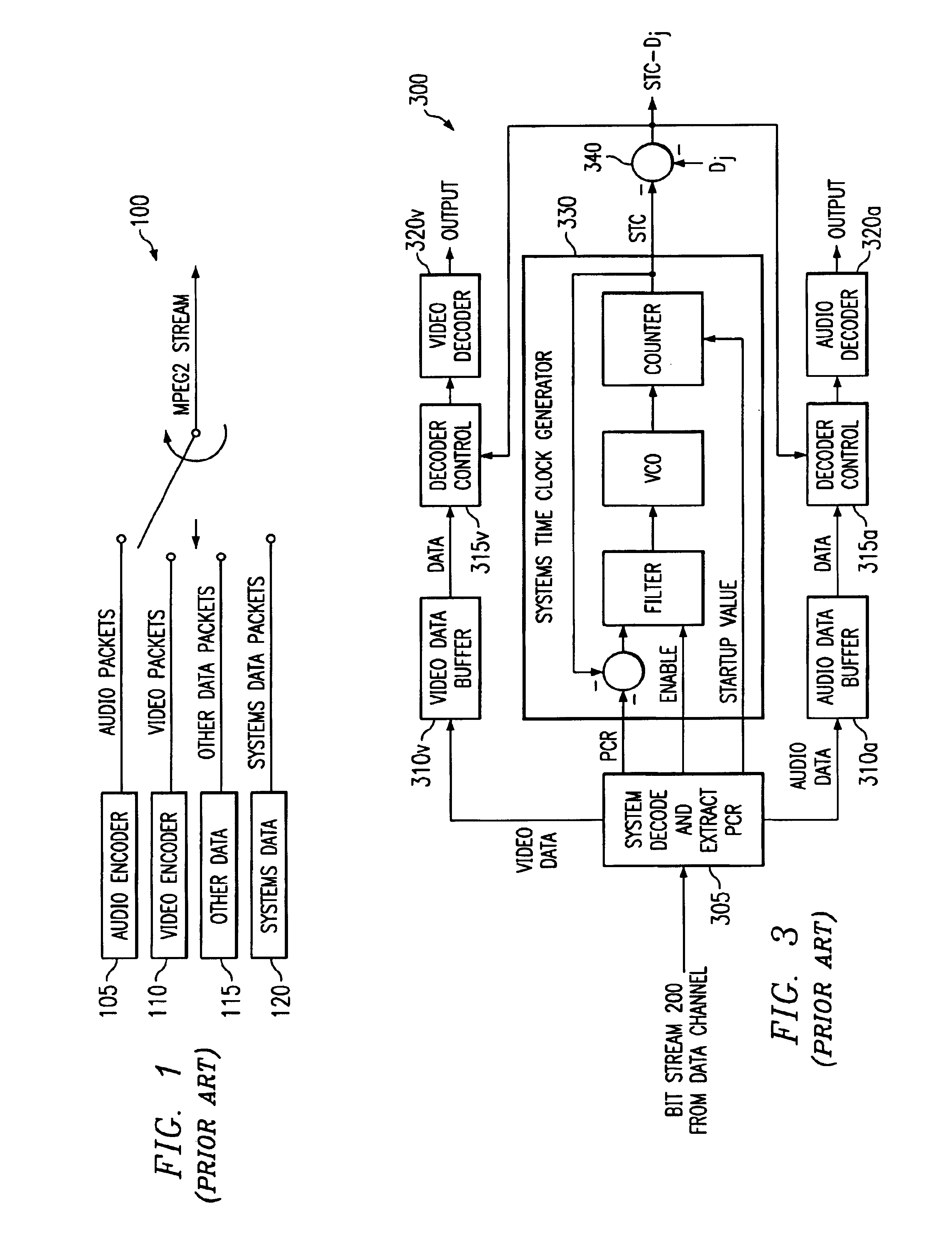
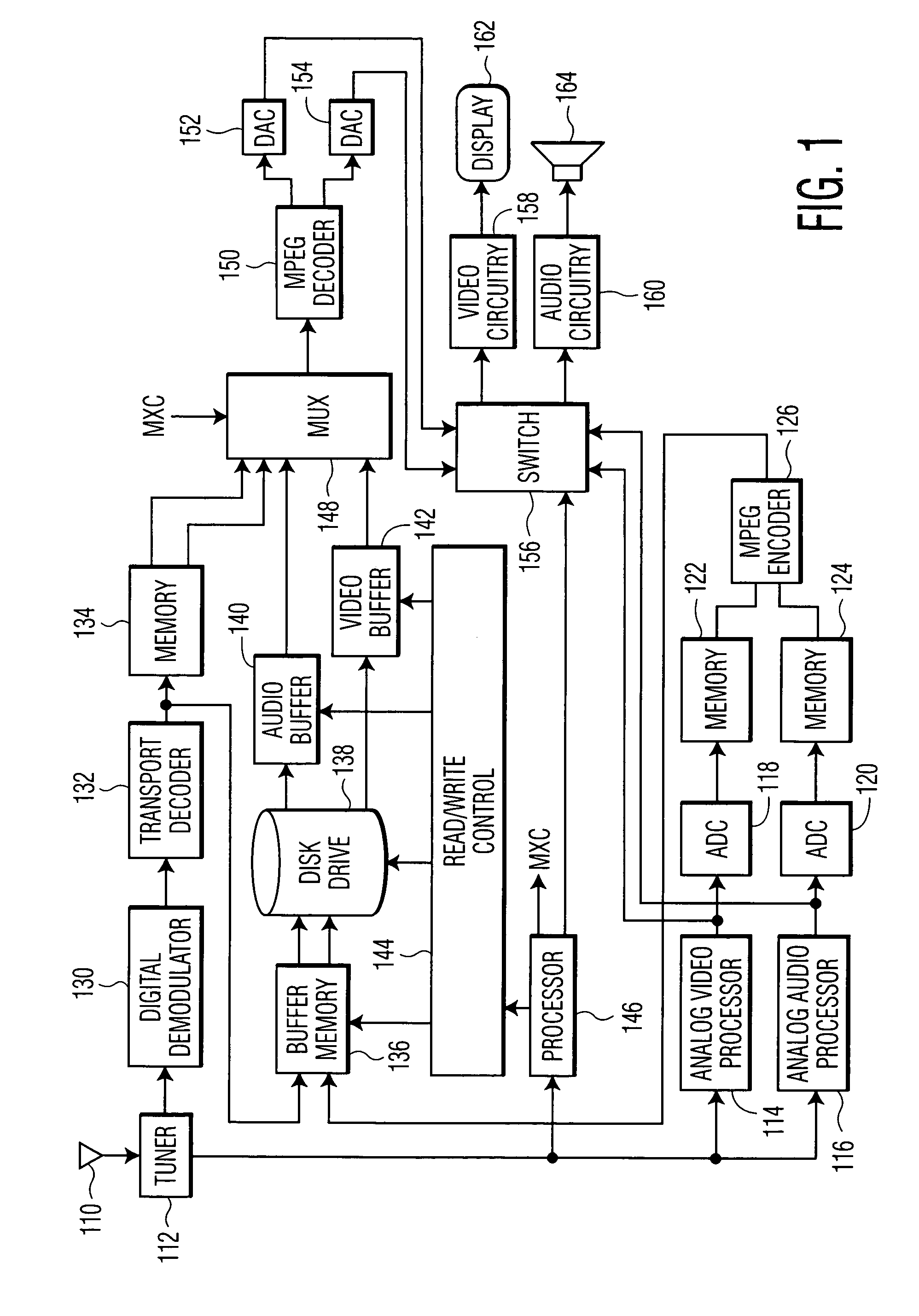
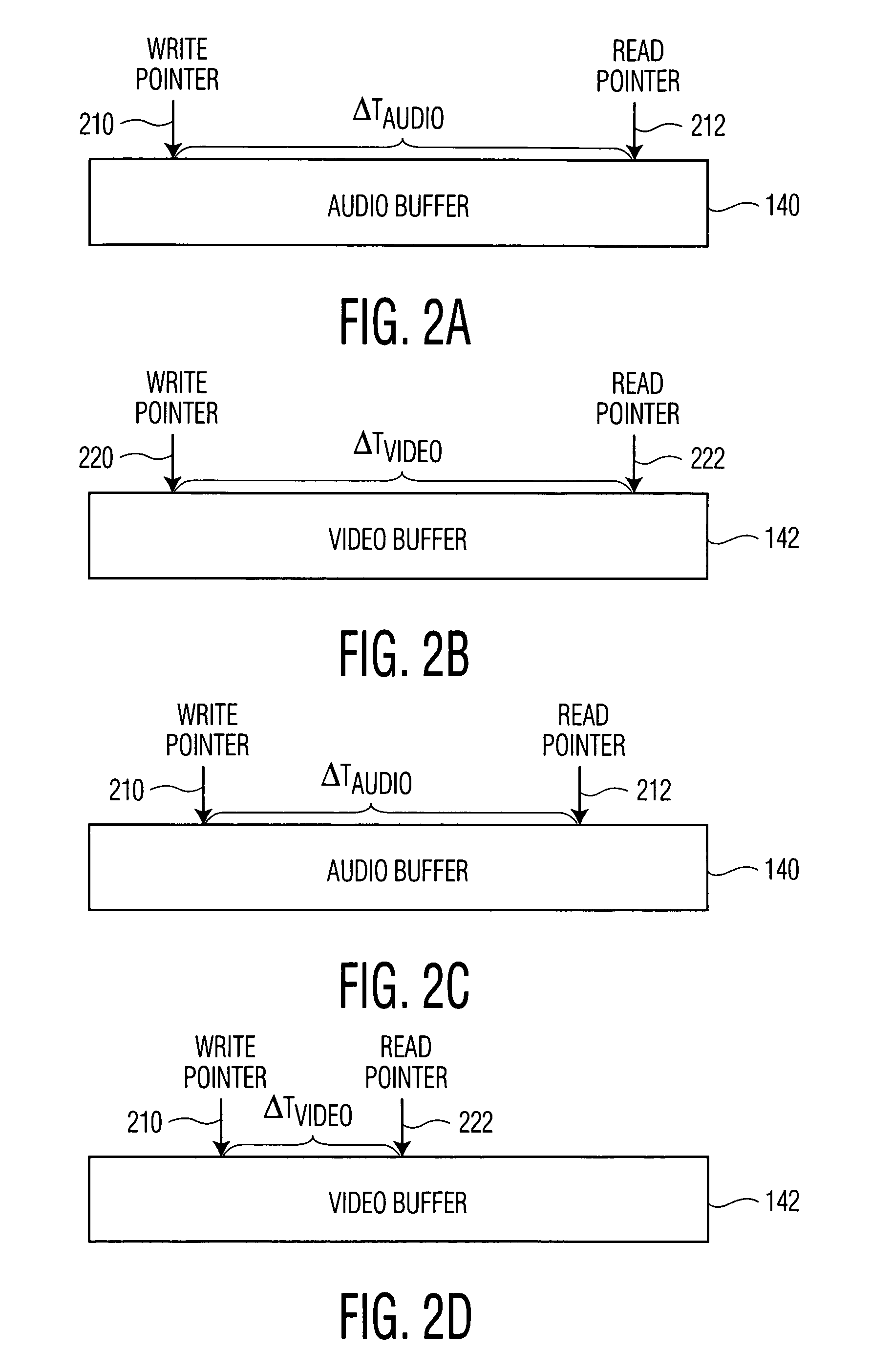
Apparatus and method for synchronizing video and audio MPEG streams in a video playback device
InactiveUS6931071B2Robust solutionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPacketized elementary streamElementary stream
There is disclosed an MPEG decoder comprising: 1) a packetized elementary stream (PES) interface for receiving a plurality of packetized elementary streams associated with a single video program; 2) a presentation time stamp (PTS) detection circuit for detecting presentation time stamps in the packetized elementary streams and extracting the presentation time stamps therefrom; and 3) a selection circuit for selecting presentation time stamps associated with a first one of the plurality of packetized elementary streams and transmitting the selected presentation time stamps to a clock generation circuit, wherein the clock generation circuit generates a first reference clock signal used by a first decoder to decode the first packetized elementary stream. The clock generation circuit further generates a second reference clock signal synchronized to the first reference clock signal, wherein the second reference clock signal is used by a second decoder to decode a second packetized elementary stream in synchronization with the first packetized elementary stream.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
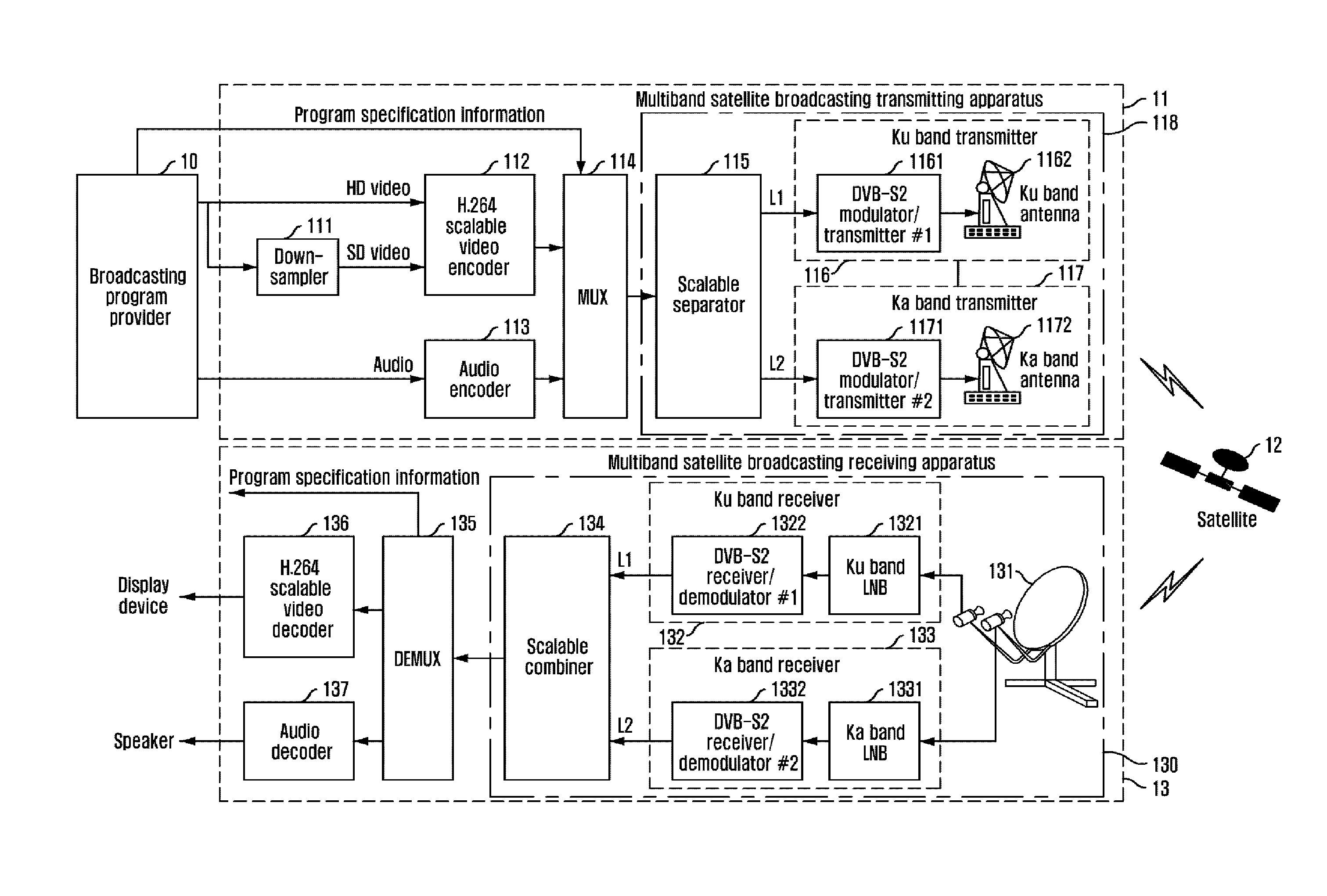
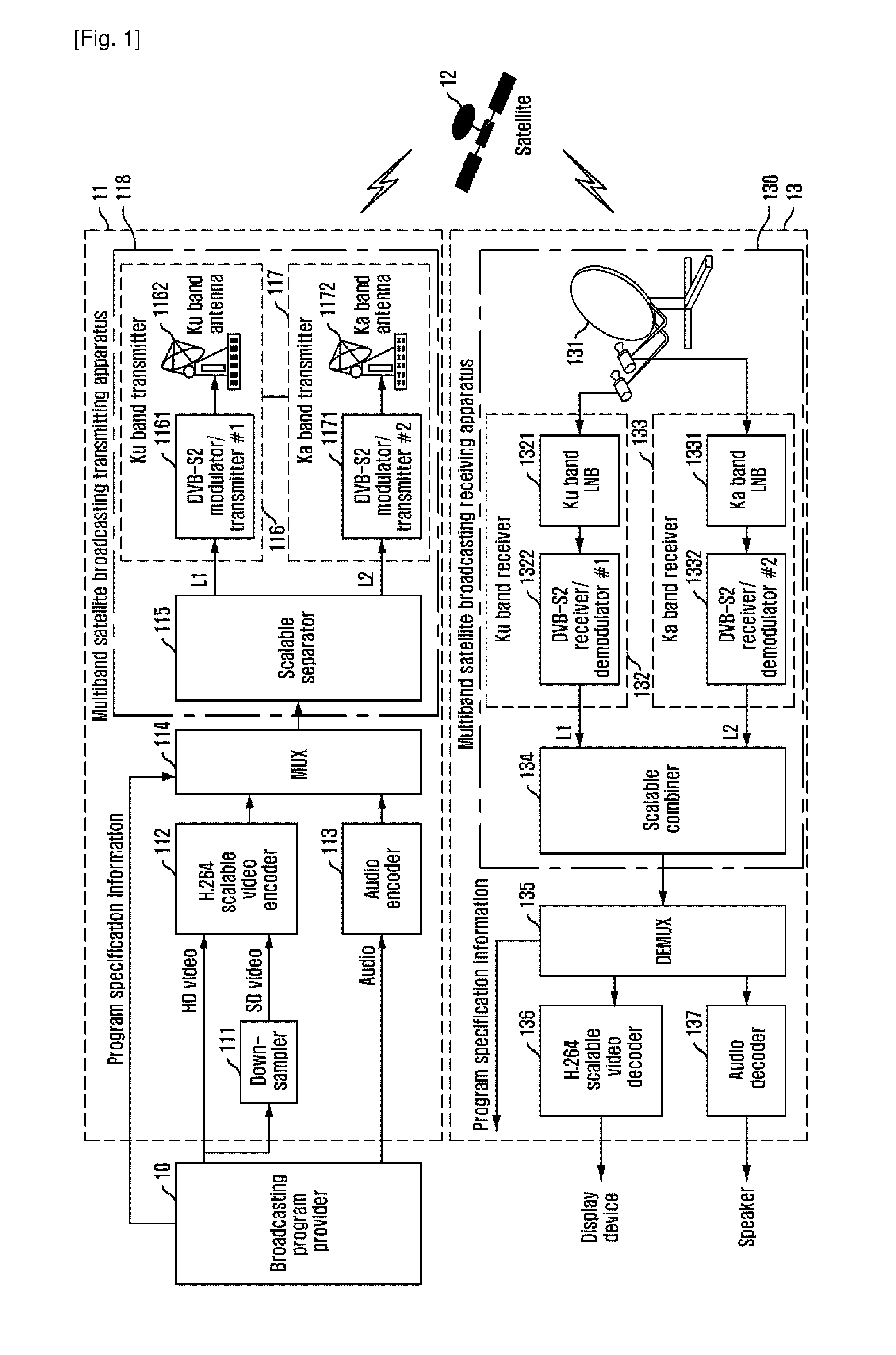
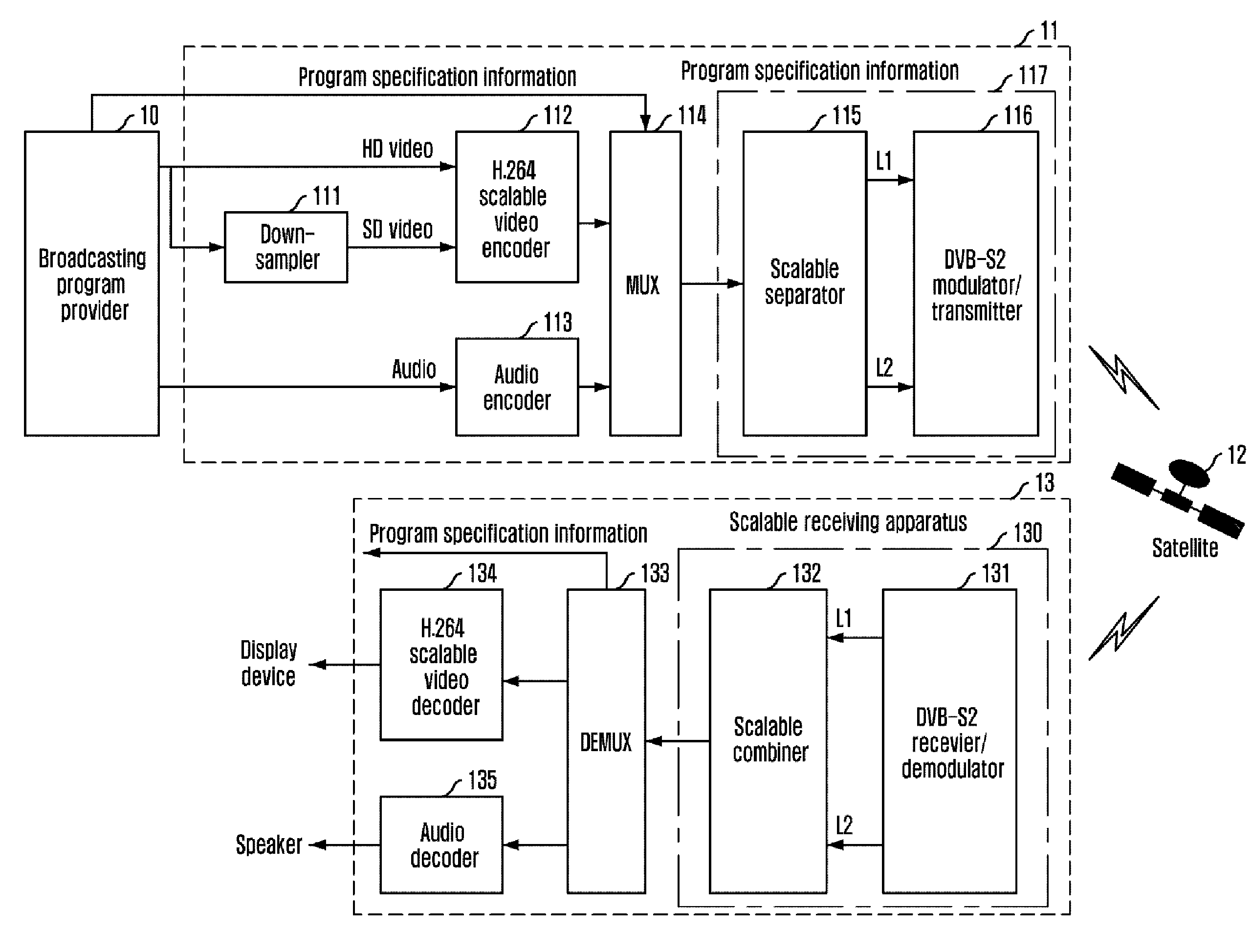
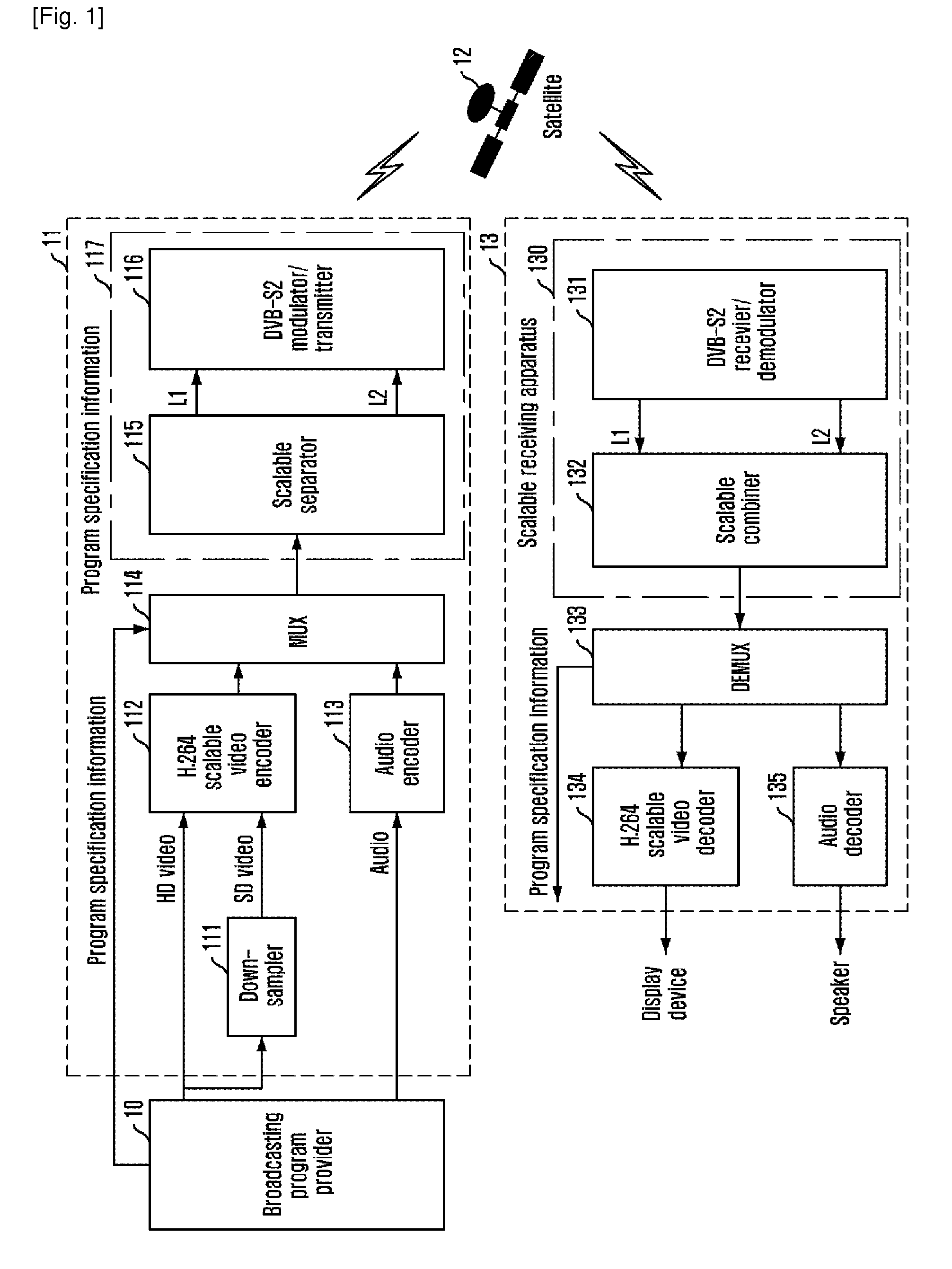
Scalable video broadcasting apparatus and method over multiband satellite channel
InactiveUS20110235701A1Low use efficiencySolve problemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGHz frequency transmissionSatellite broadcastingBroadcasting
Provided is an apparatus and method for transmitting / receiving multiband broadcasting using scalable video coding, which can solve a limitation of a transmission band in a multichannel satellite broadcasting service and increase availability of a satellite broadcasting service by scalably encoding video data and transmitting the data using a different transmission band for each layer. The apparatus for transmitting multiband broadcasting using scalable video coding includes: a scalable video encoder for scalably encoding video data to generate a scalable video stream having multiple layers; a multiplexer for multiplexing the scalable video elementary stream having multiple layers, a compressed audio elementary stream, and program specification information to generate a transport stream (TS); and a multiband transmitter for separating packets of the TS into multiple TSs according to pre-given priority information and transmitting the packet streams using a different transmission band.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Scalable transmitting/receiving apparatus and method for improving availability of broadcasting service
InactiveUS20100272190A1Increase frame rateImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexerVideo encoding
Provided is a scalable transmitting / receiving apparatus and method for improving availability of a broadcasting service, which can allow a reception party to select an optimum video according to an attenuation degree of a broadcasting signal by scalably encoding video data and transmitting it by a different transmission scheme for each layer. The scalable transmitting apparatus for improving availability of a broadcasting service includes: a scalable video encoder for scalably encoding video data to generate scalable video elementary streams having logical layers; a multiplexer for multiplexing the multiple scalable video elementary stream, a compressed audio elementary stream, and program specification information to generate a transport stream; and a scalable transmitter for separating the transport stream into multiple TS packet streams according to pre-given priority information, and transmitting the packet streams by a different transmission scheme for each layer. down-sampler
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
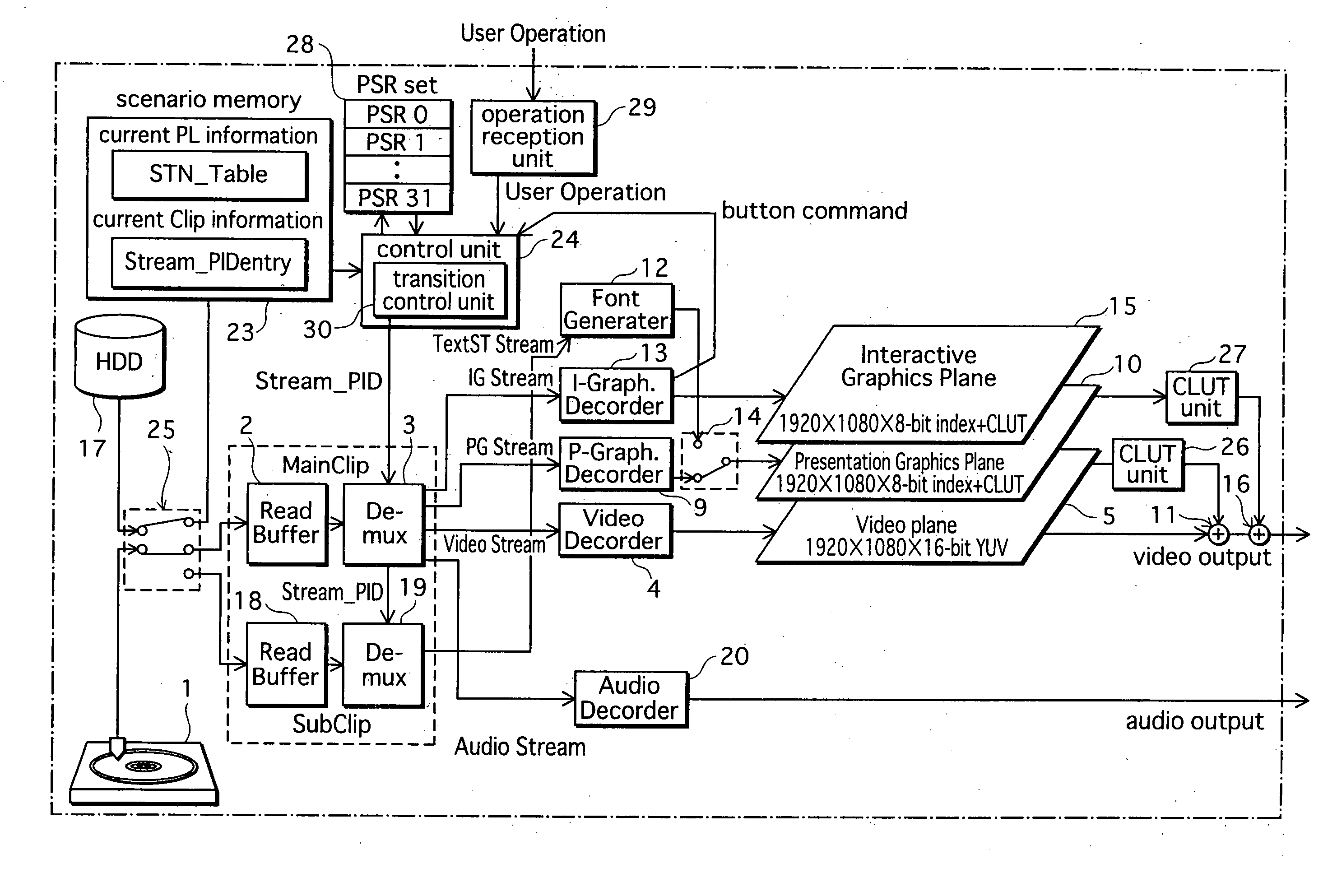
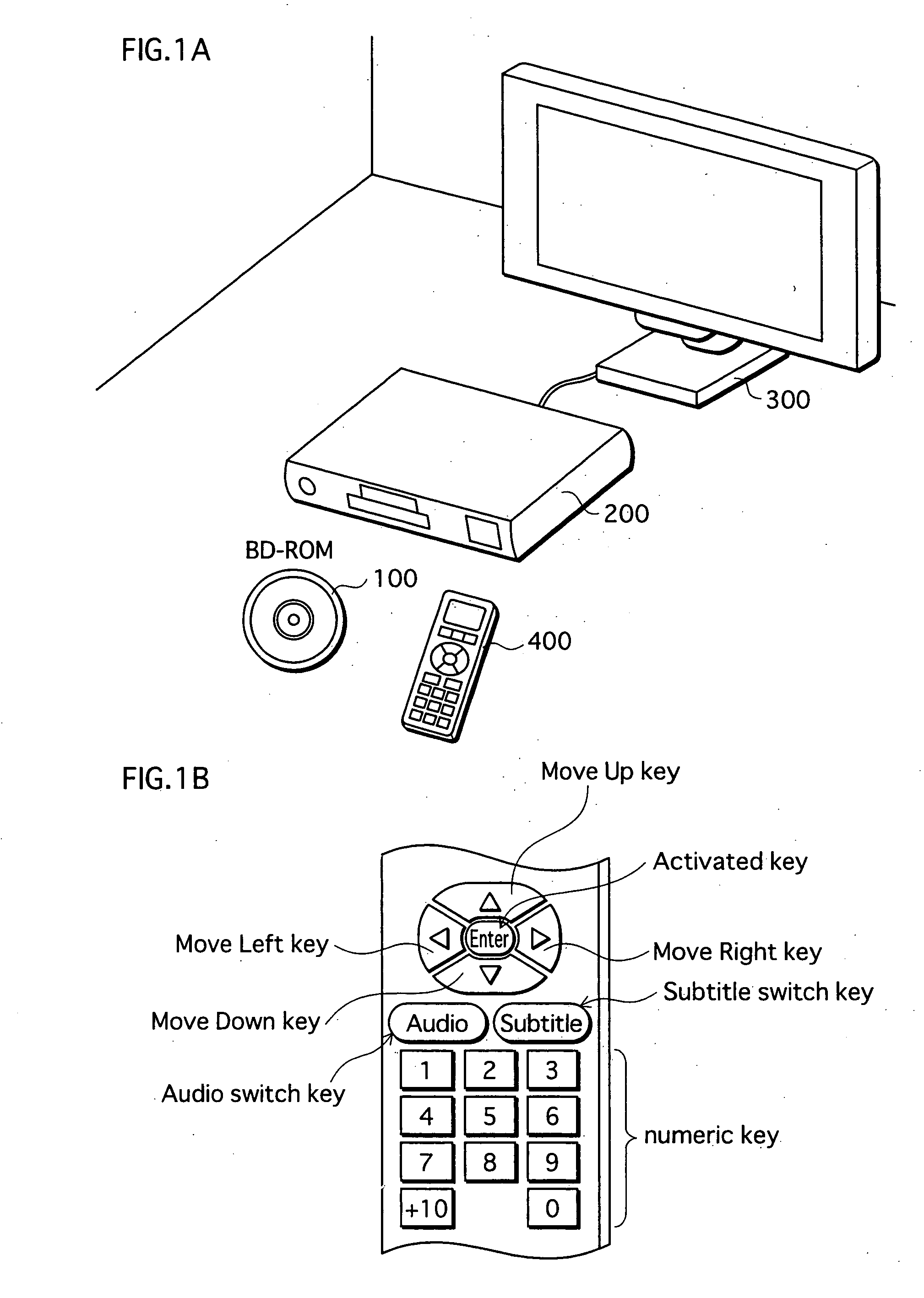
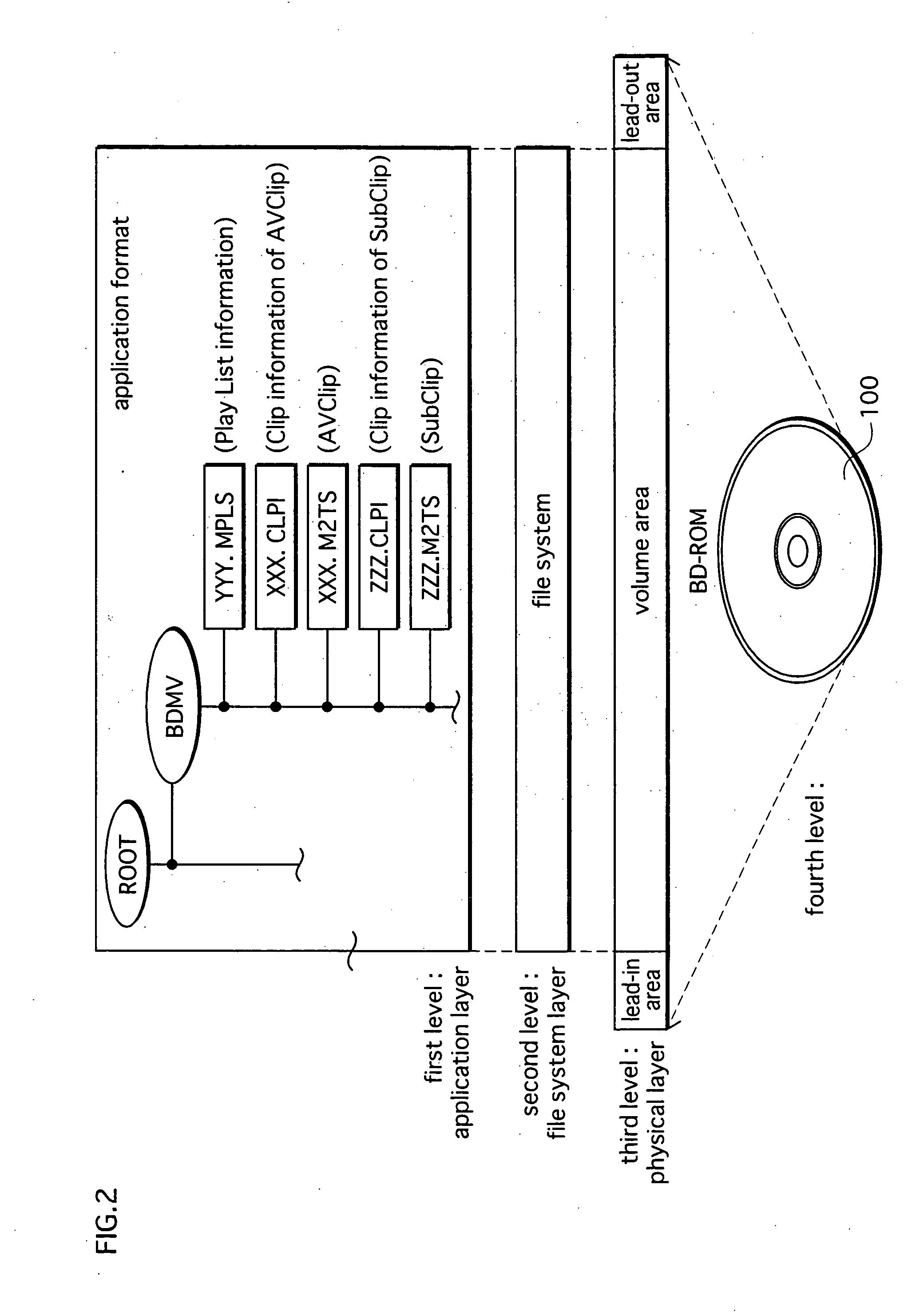
Playback apparatus, program and playback method
ActiveUS20070160350A1Television system detailsRecord information storageComputer scienceHuman language
When playing an AV Clip recorded on a BD-ROM, a judgment is made, for each elementary stream, which of a plurality of predetermined conditions the elementary stream satisfies. The plurality of predetermined conditions include (a) a condition that a playback apparatus has a capability of playing the elementary stream, (b) a language attribute of the elementary stream matches a language setting of the playback apparatus, and (c) a channel attribute of the elementary stream is surround sound and the playback apparatus has a surround output capability. The playback apparatus assigns a priority to each elementary stream based on which conditions the elementary stream satisfies, selects an elementary stream having a highest priority, and plays the selected elementary stream.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
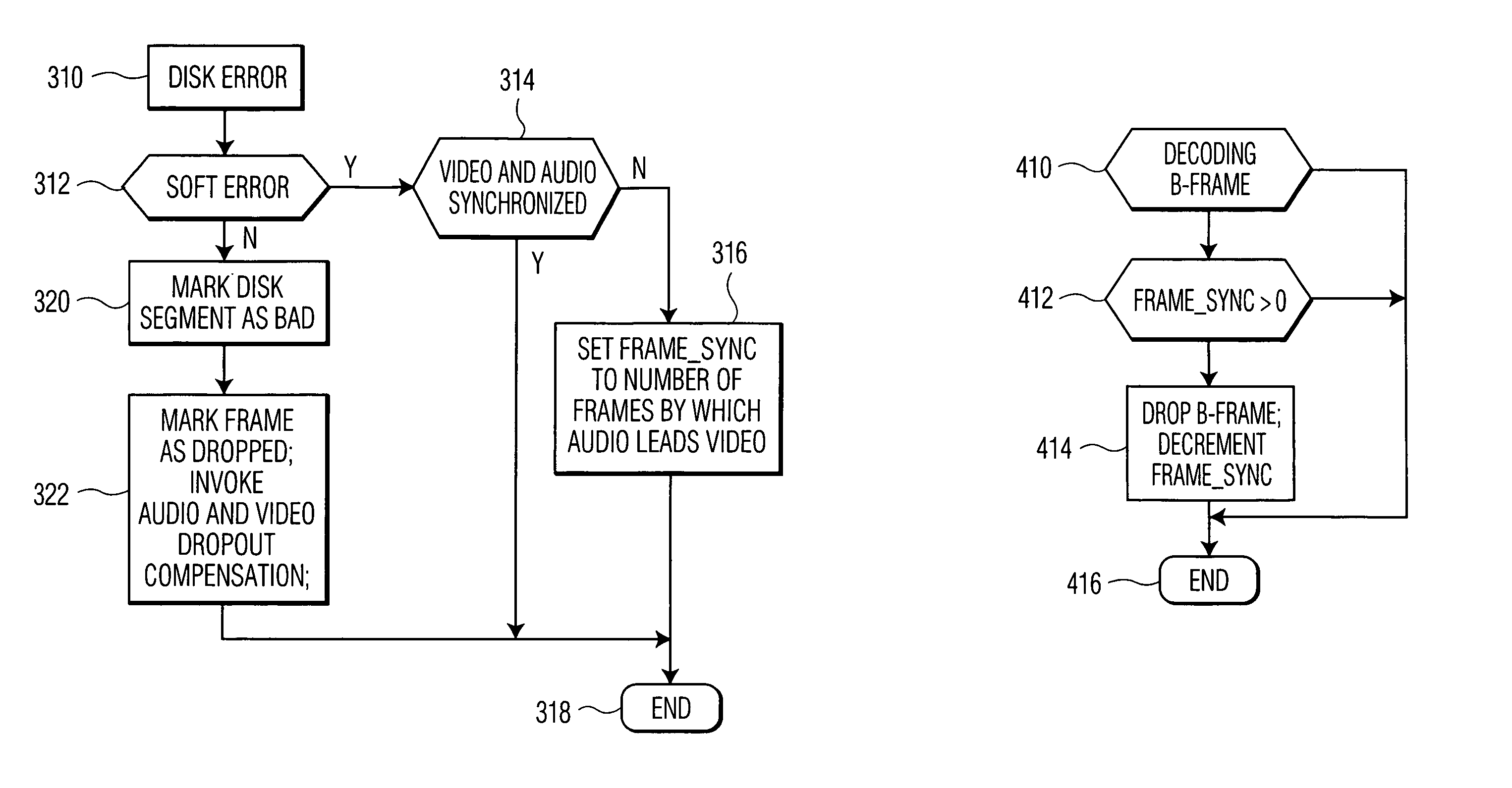
Method and apparatus for concealing disk soft errors in recorded digital television signals
InactiveUS6993251B1Minimize disruptionTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingHard disc driveData stream
A video data storage system holds MPEG compressed video data on a hard disk drive. A transport decoder receives a bit-stream including the compressed audio and video data formatted as transport packets and that reformats the compressed audio and video data into respective program elementary stream (PES) packets. The system stores the audio and video PES packets onto a disk. The system also includes separate audio and video buffer memories that hold the audio and video PES packets when they are read from the disk drive. An MPEG decoder separately accesses the audio and video data from the respective audio and video buffer memories. The audio buffer memory has an amount of memory sufficient to provide the MPEG decoder with audio data representing ten seconds of decoded audio signal. In one embodiment, when a soft error occurs, the MPEG decoder continues to read and decode data from the audio buffer, but stops reading and decoding data from the video buffer. During this time, the MPEG decoder continually displays a current image. After the disk has recovered from the soft error, the MPEG decoder continues to retrieve and decode video data from the video buffer memory and drops P or B frames to resynchronize the video data stream to the audio data stream.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
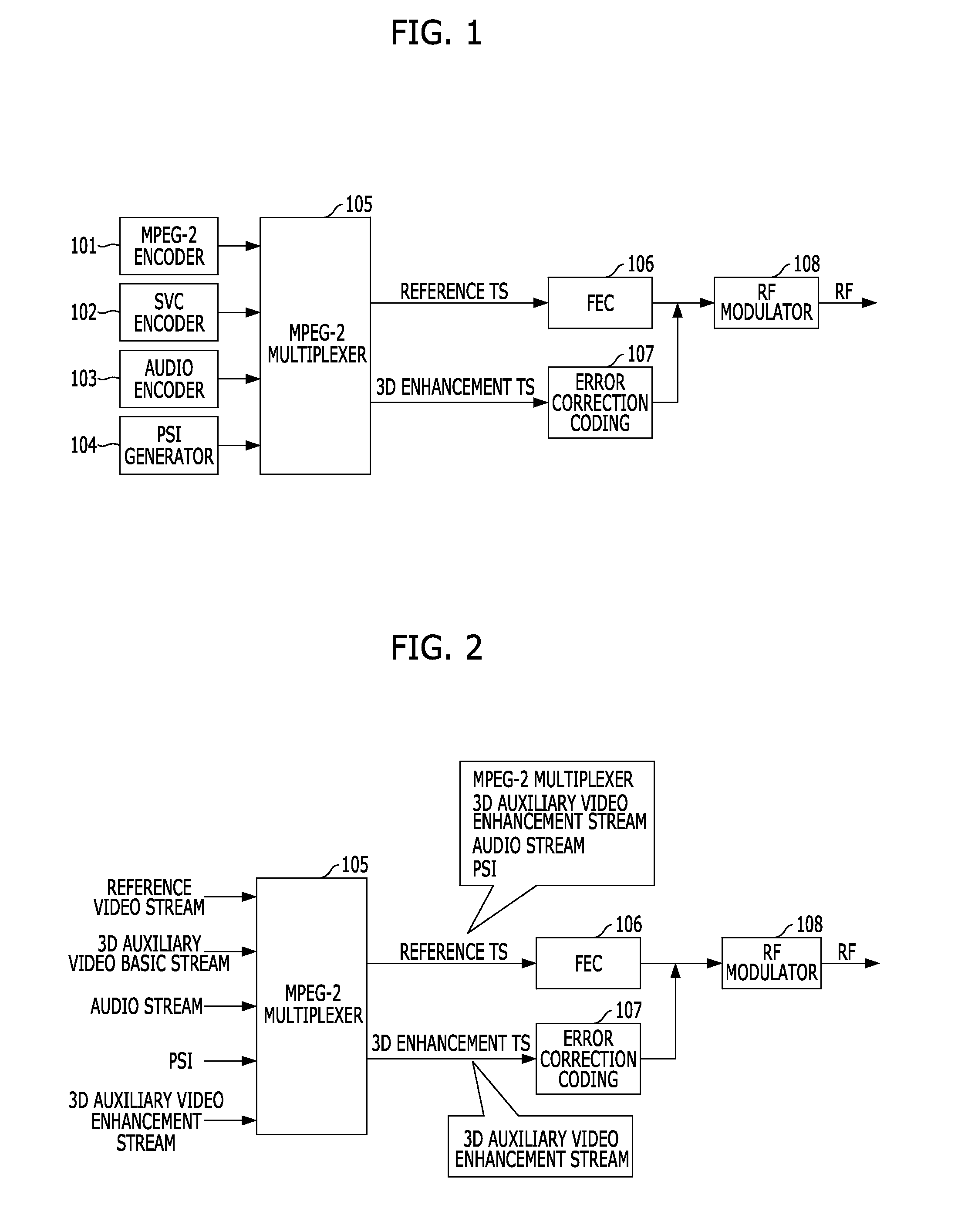
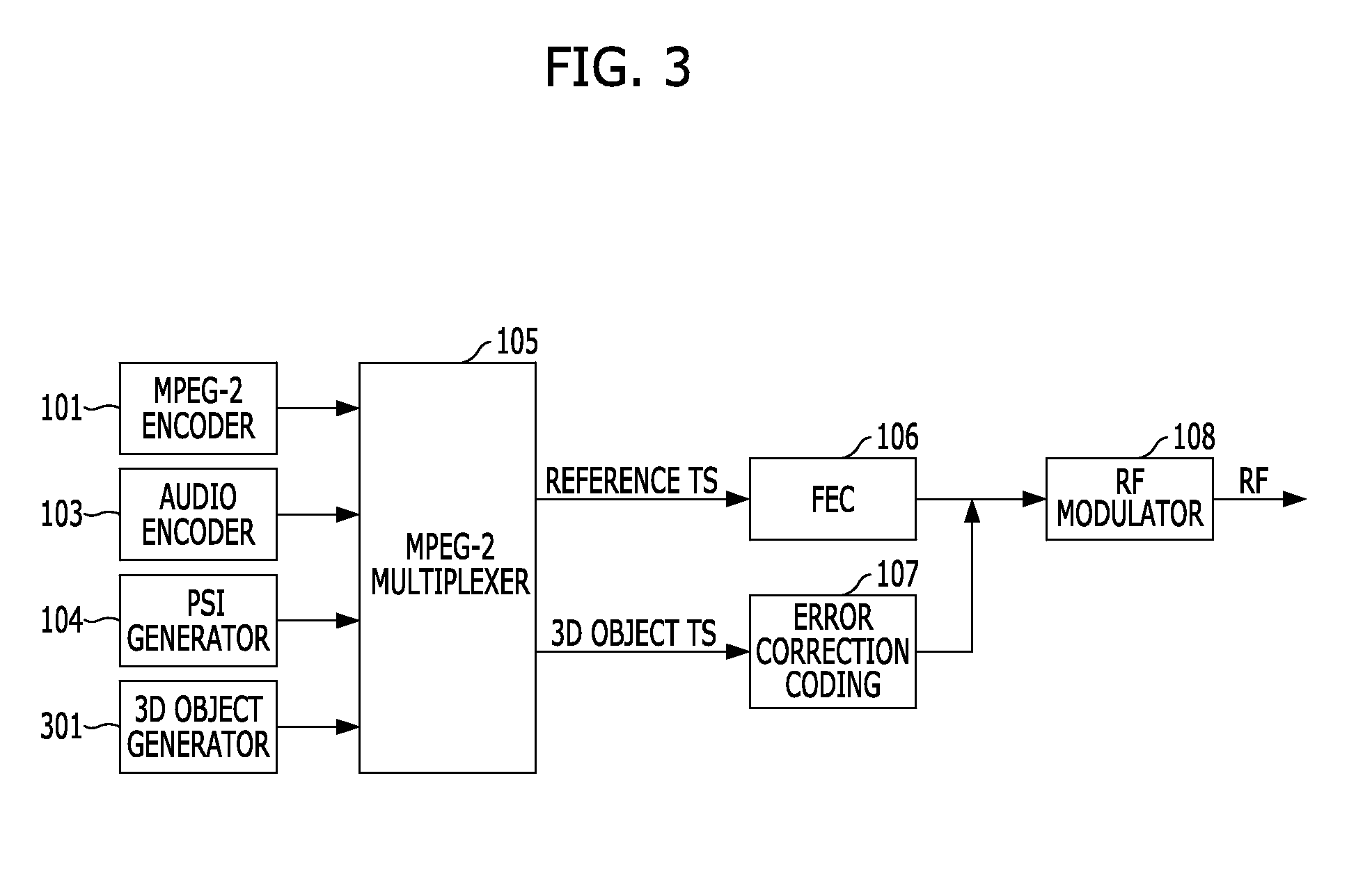
Method and apparatus for transmission and reception in the provision of a plurality of transport interactive 3dtv broadcasting services
InactiveUS20120320168A1Quality improvementMaintain compatibilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionSimultaneous/sequential multiple television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Service configuration
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for providing a plurality of transport interactive 3DTV broadcasting services in the provision of higher definition 3D video service and 3D data service, while maintaining the compatibility with the existing digital TV broadcasts or 3DTV services. To this end, an input 3D video is encoded to generate a 3D additional video base stream and a 3D additional video enhanced stream. Engineer information for defining engineers, which includes 3D broadcasting service configuration information, is generated, and then an encoded 2D base video stream, an encoded audio stream, the encoded 3D additional video base stream and the engineer information are multiplexed and transmitted via a base layer. The 3D additional video enhanced stream is multiplexed and transmitted via an enhanced layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Reproduction device and reproduction method
InactiveUS20060080094A1Program control using stored programsSpeech analysisComputer hardwareSyncword
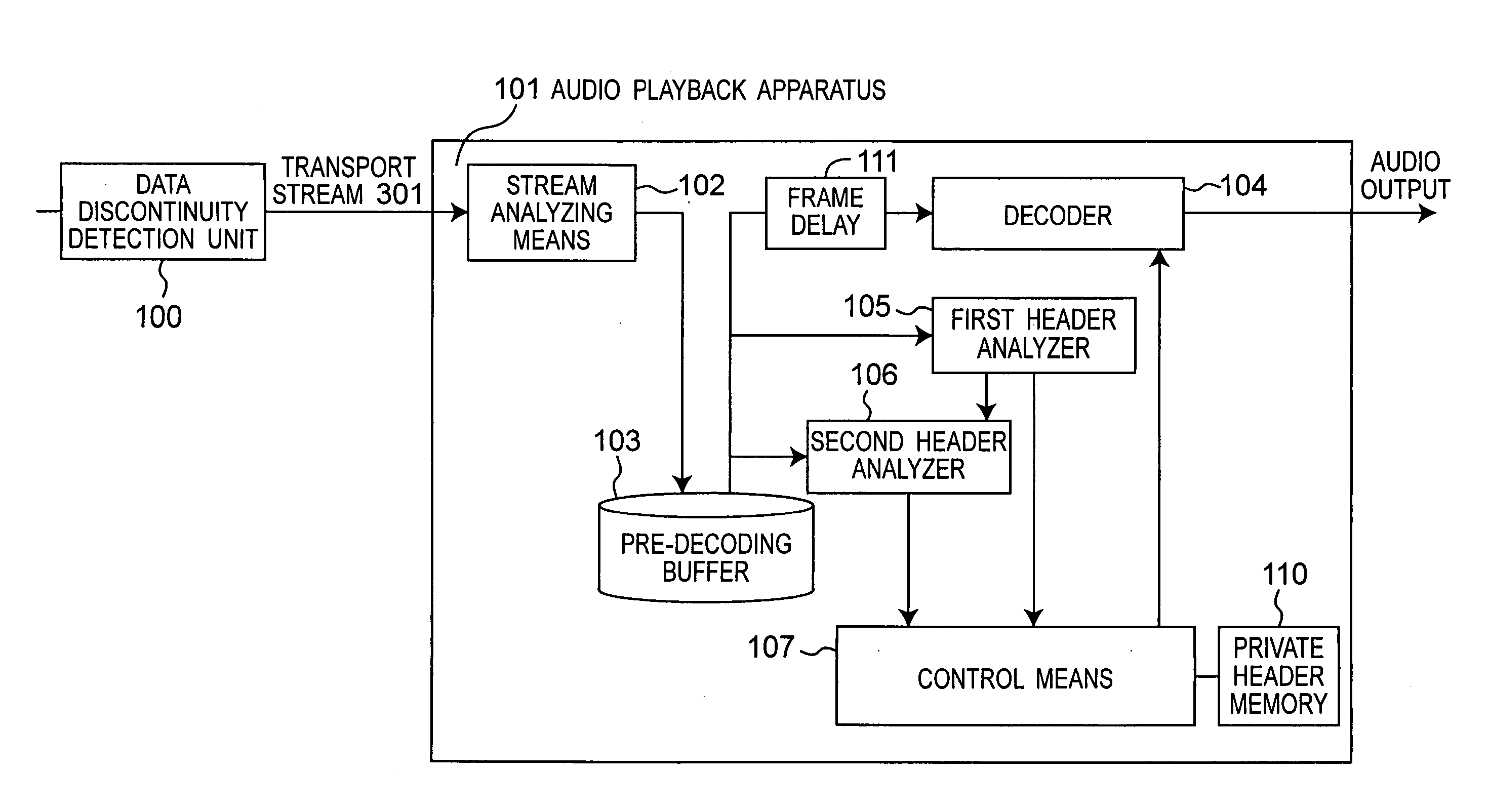
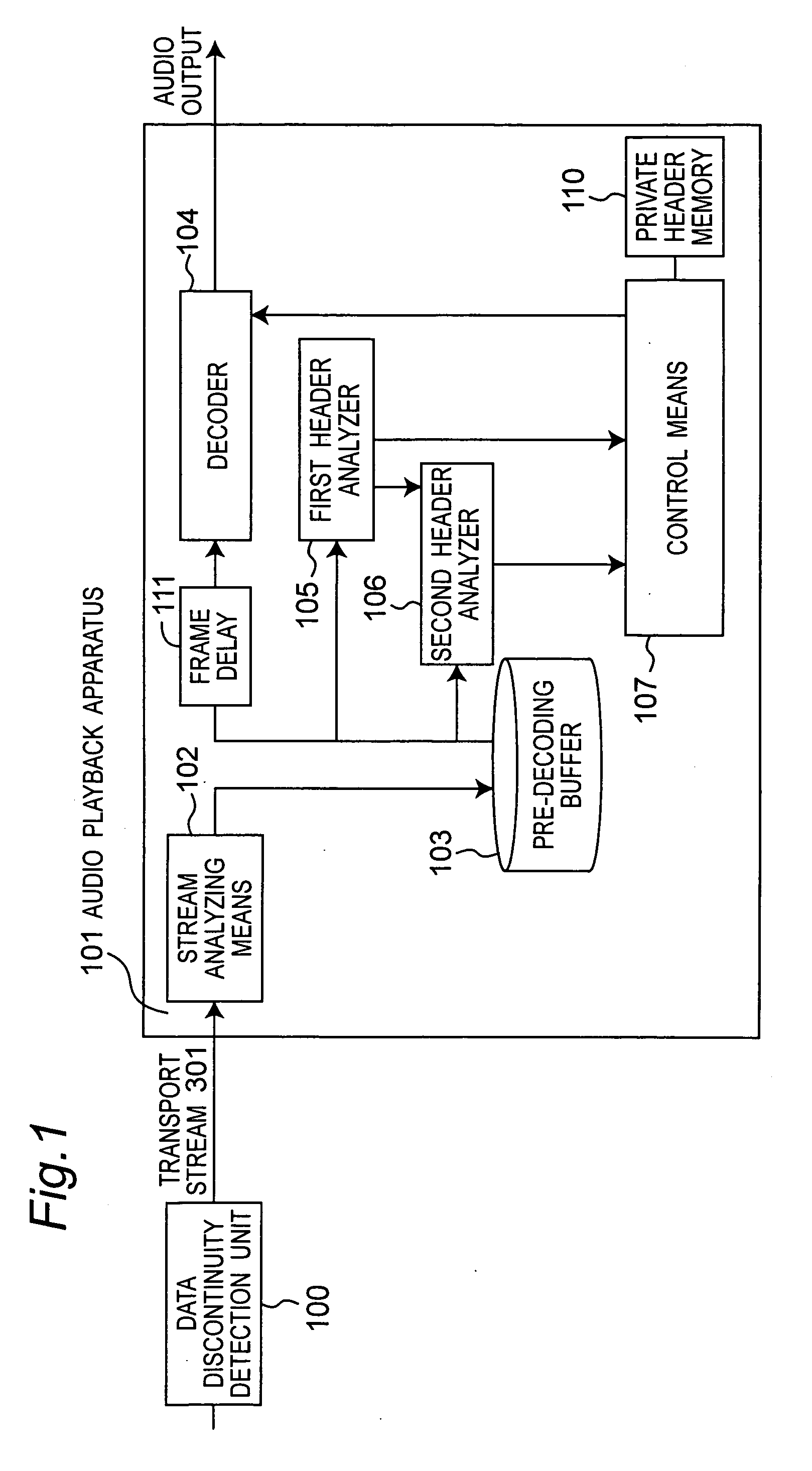
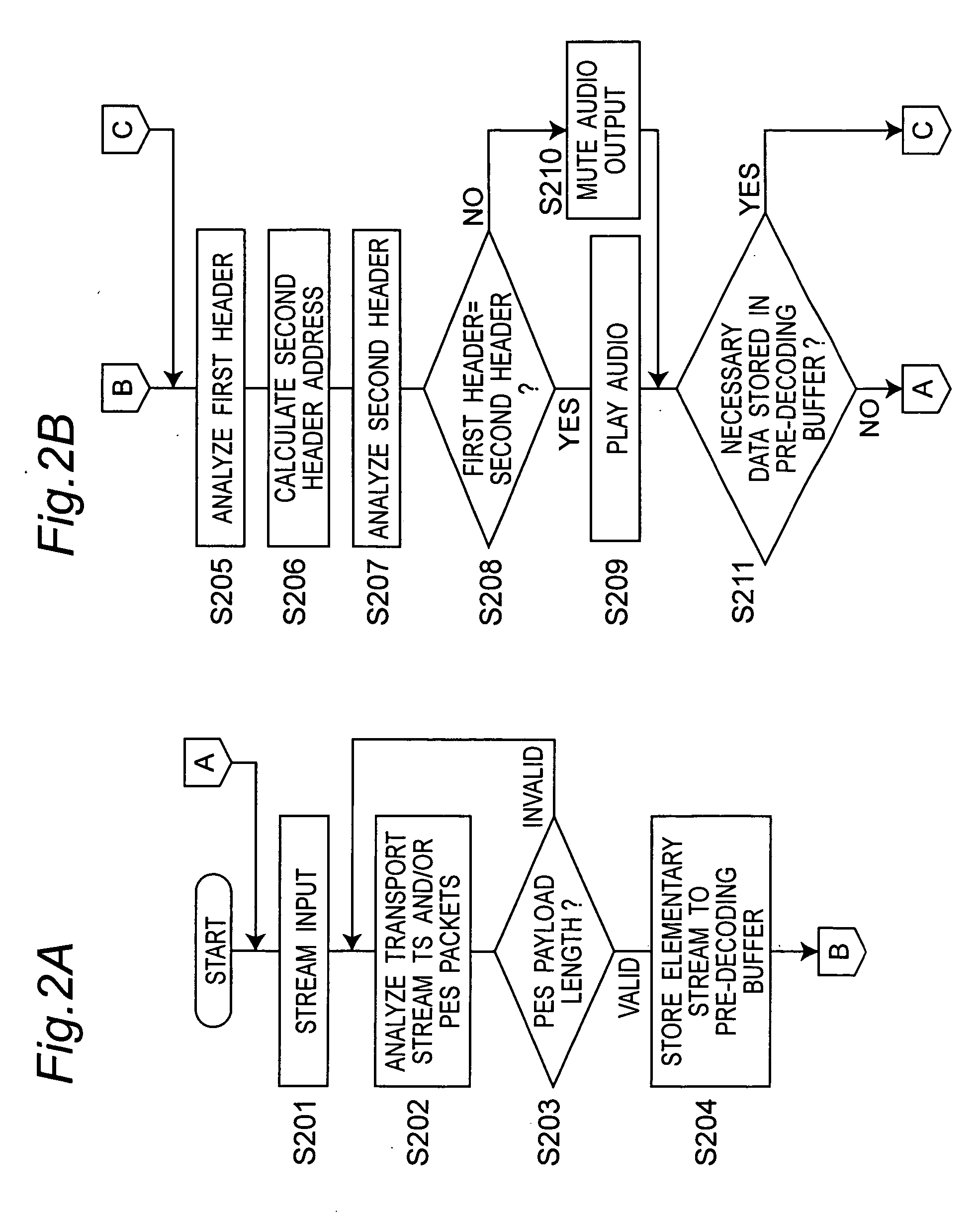
Noise is prevented when decoding an audio stream not containing syncwords or CRC bits in the elementary stream. When decoding a current frame, the private header of the next frame is analyzed and the current frame is muted if the private header of the next frame is not valid. When there is a data discontinuity caused by editing, decoding resumes from the start address of the next frame determined by the stream analyzing means.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
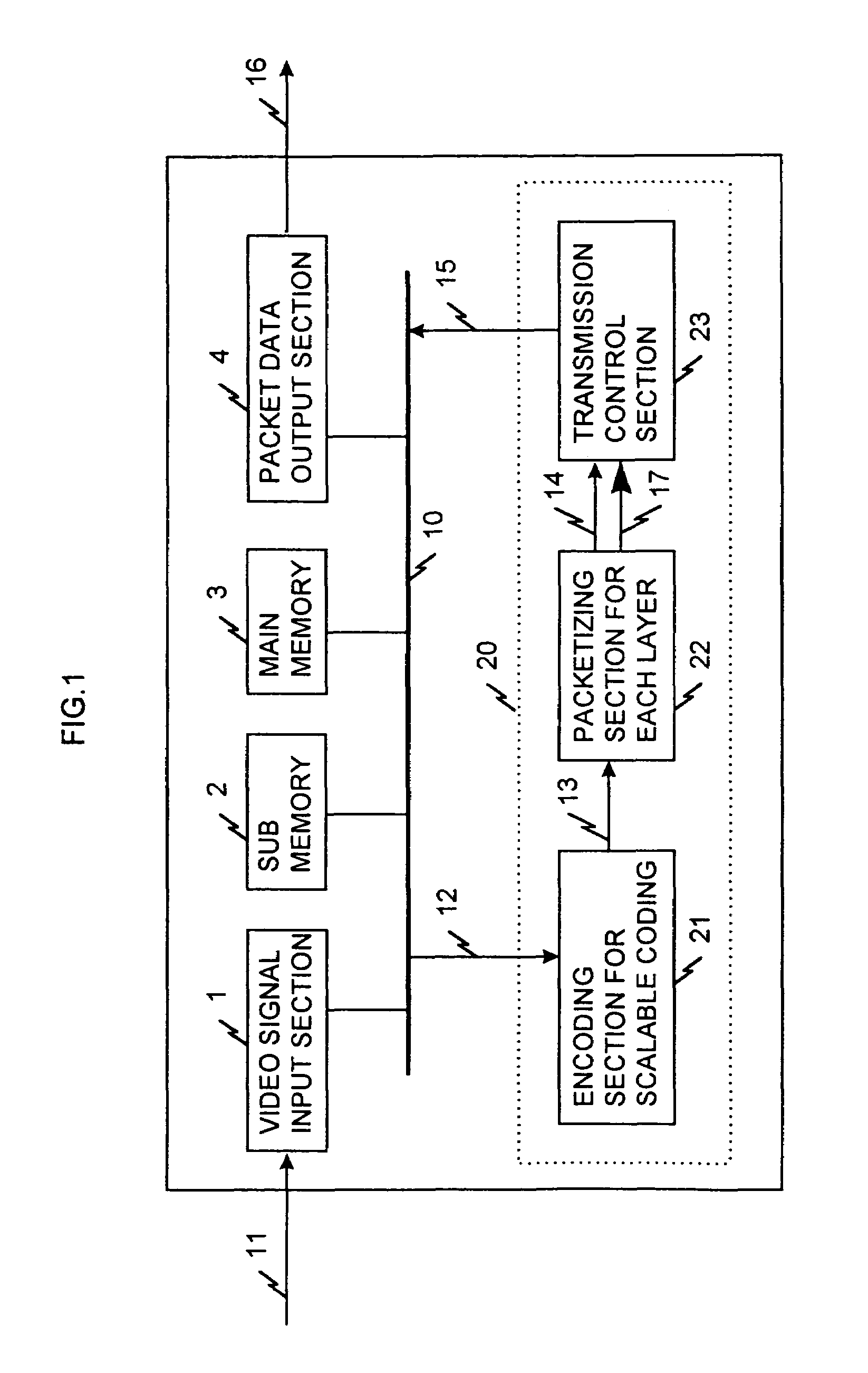
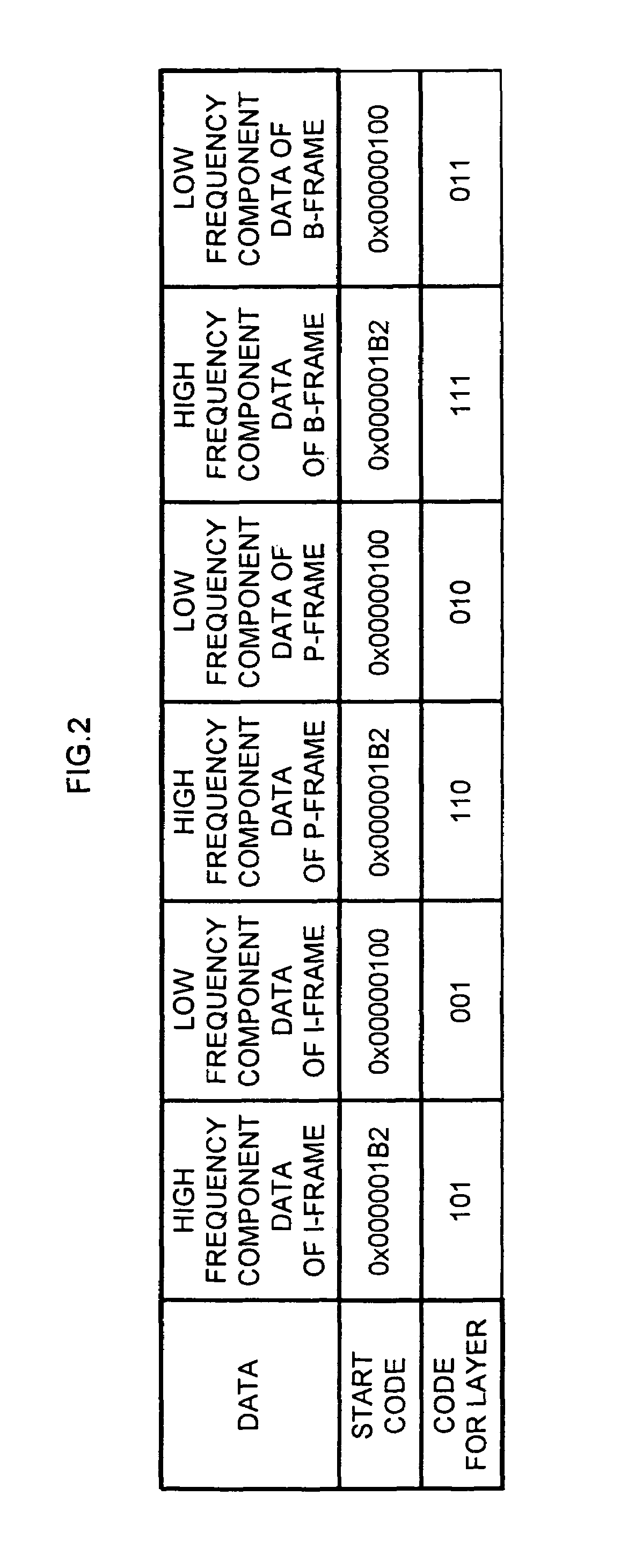
Layer-coded data transmitting apparatus
InactiveUS6975645B1Time-division multiplexTwo-way working systemsTime ProtocolUser Datagram Protocol
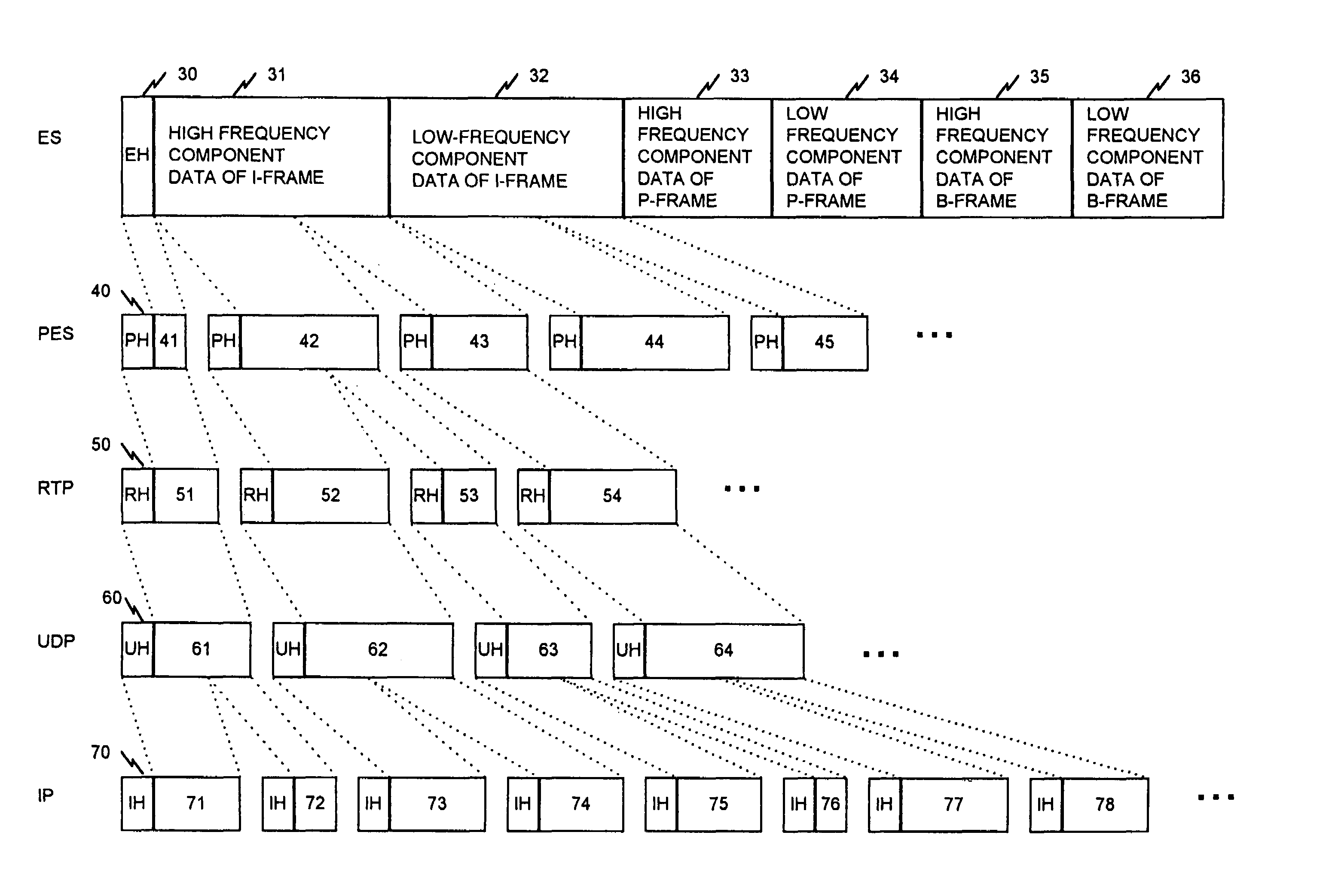
When one-video program data (layer-coded data) of a plurality of layers is transmitted in a single channel, a video signal is layer-coded in an MPEG system, the layer-coded ES (Elementary Stream) data is converted to a PES (Packetized Elementary Stream) for each layer, and the PES is then converted to a RTP (Real-Time Protocol) packet, which is then converted to a UDP (User Datagram Protocol). An identifier is then annexed to a UDP packet data for each layer to form an IP (Internet Protocol) packet.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com