Patents
Literature
266 results about "Free carrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
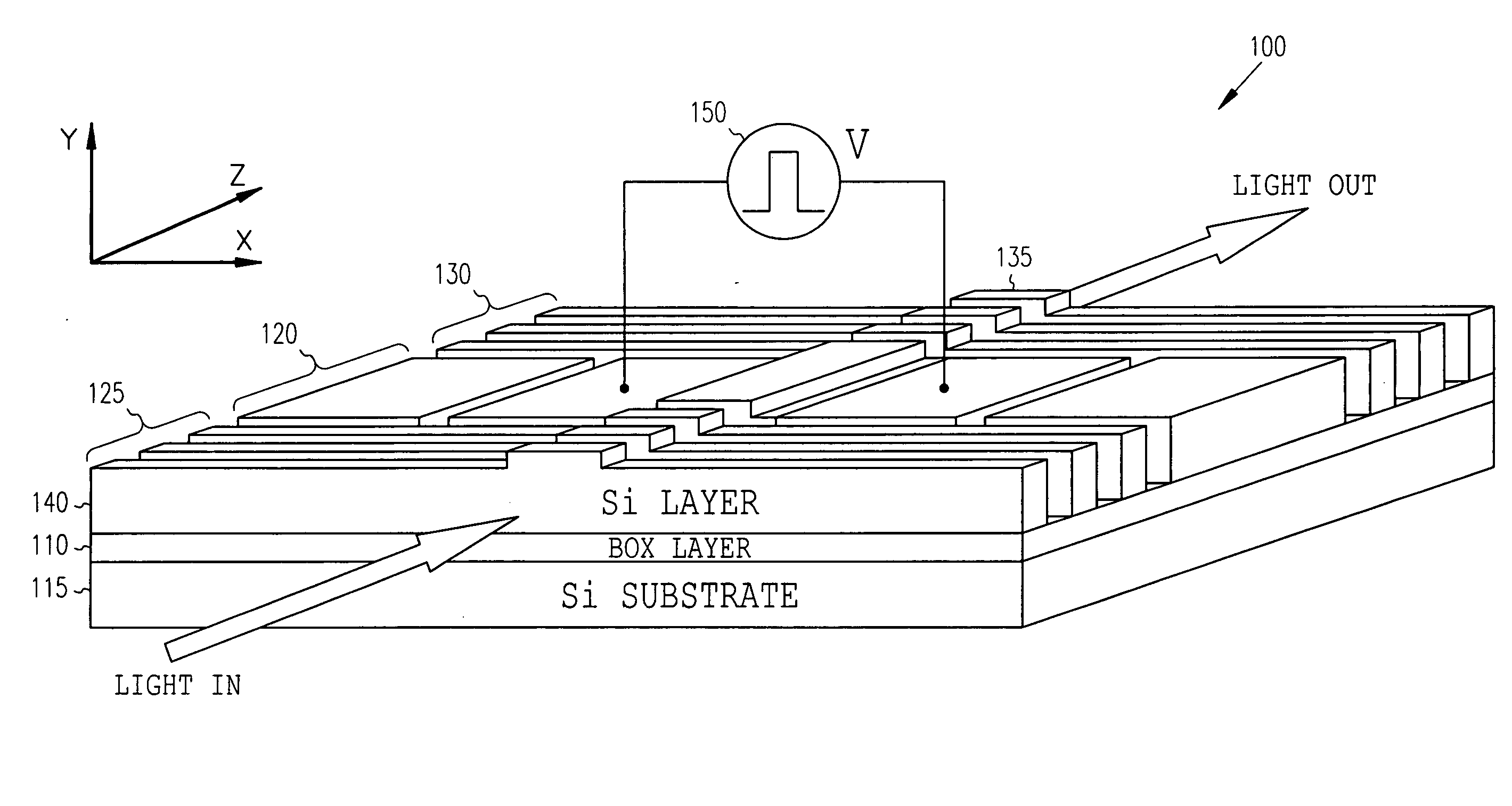
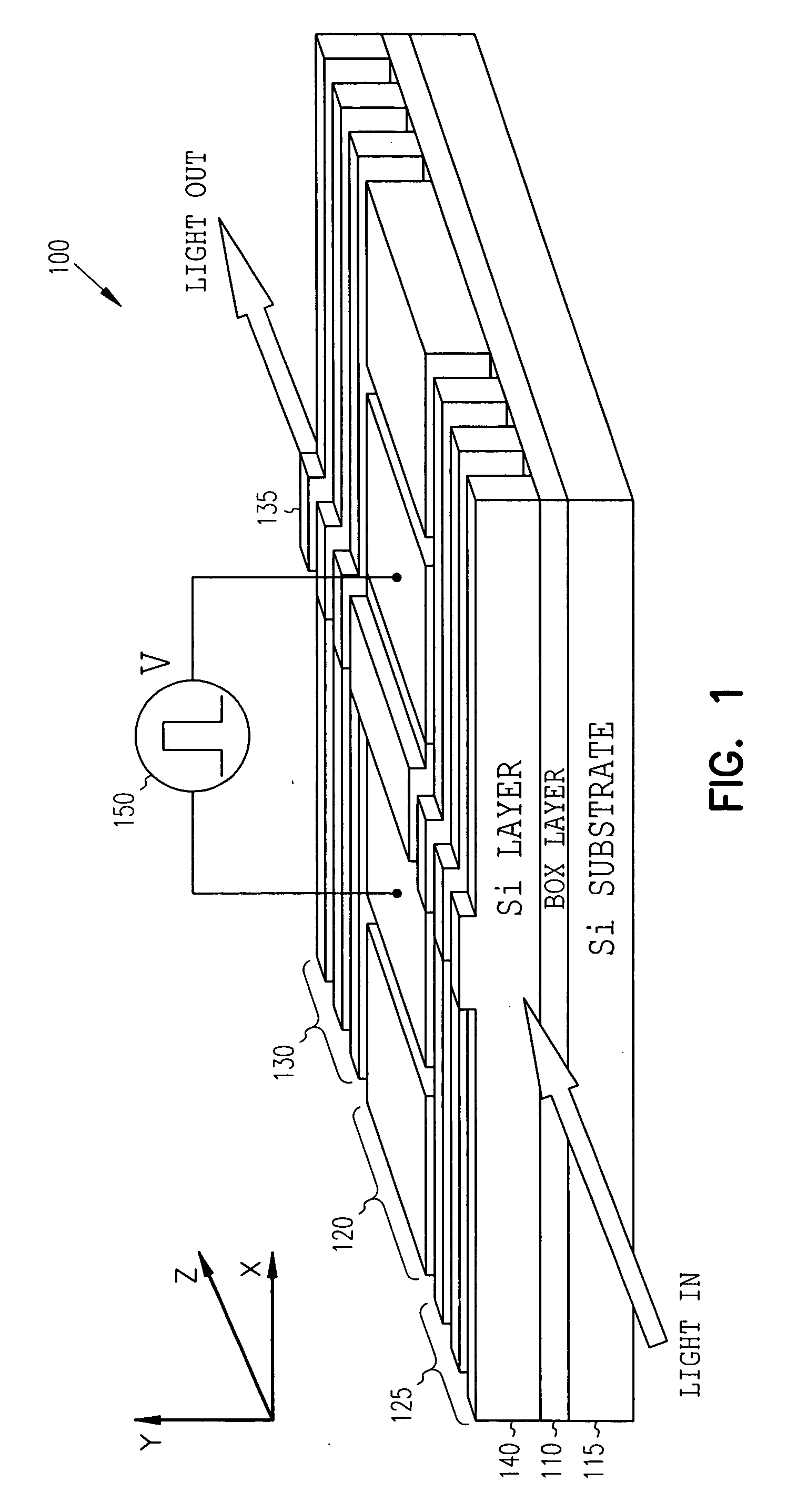
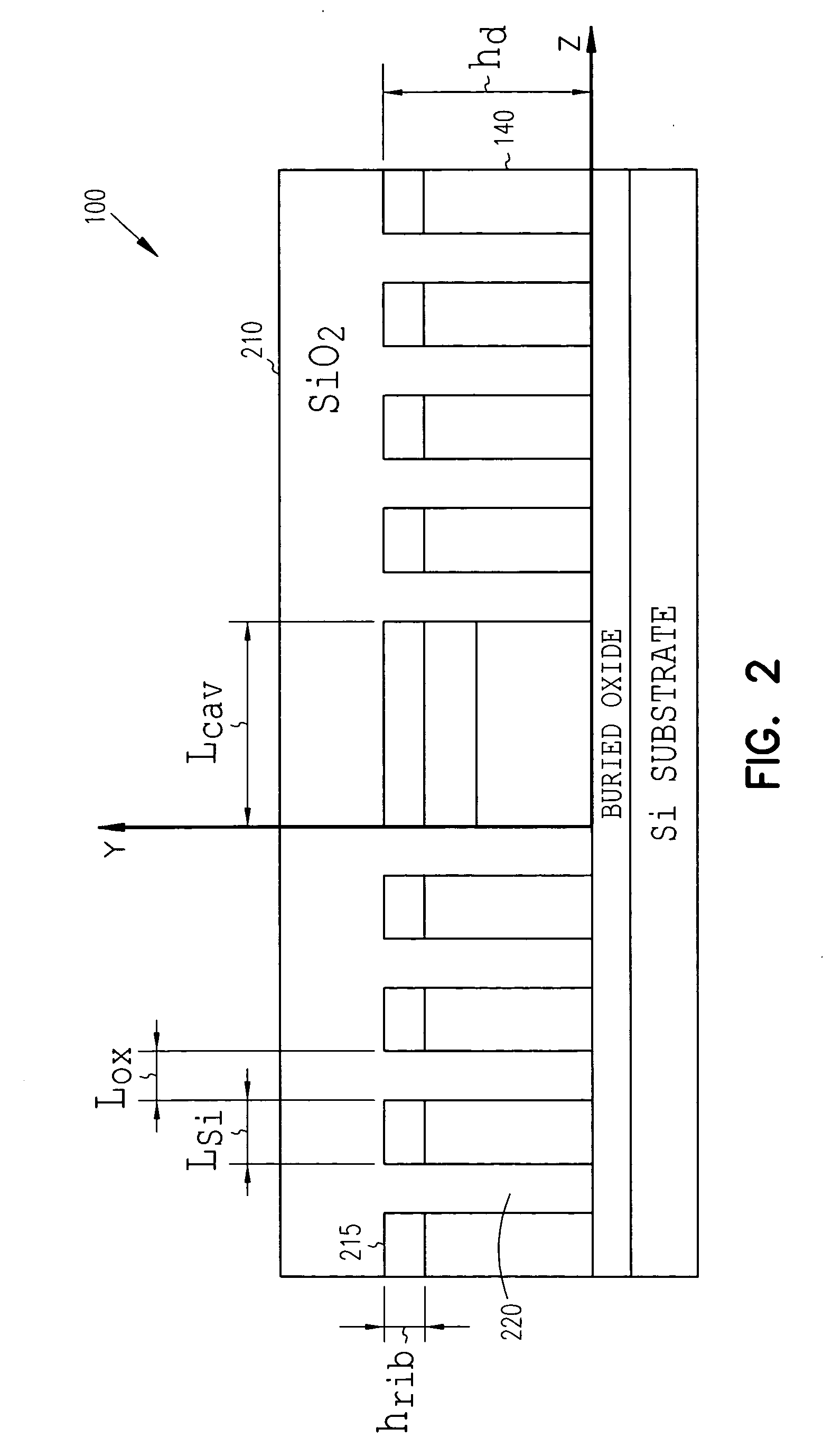
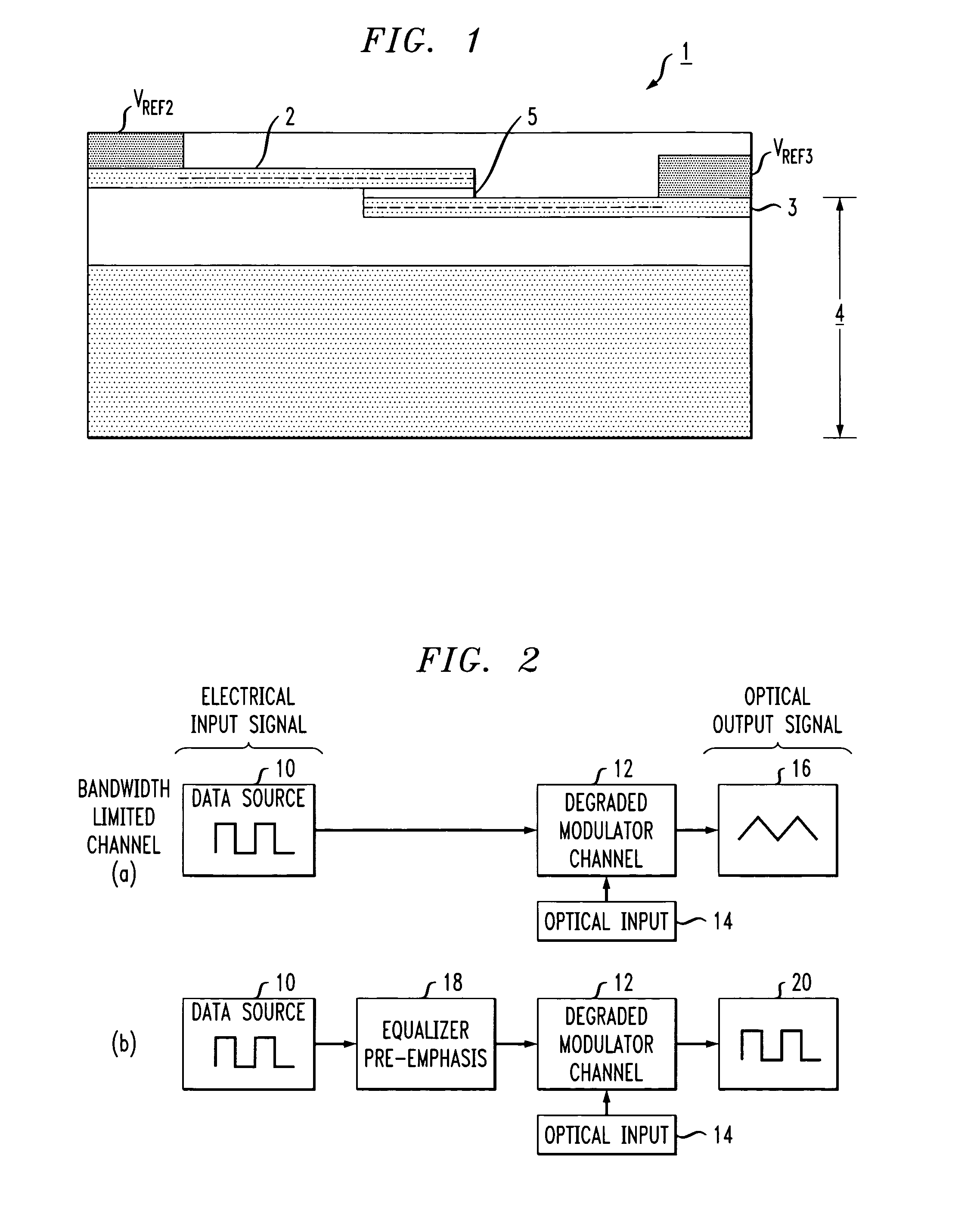
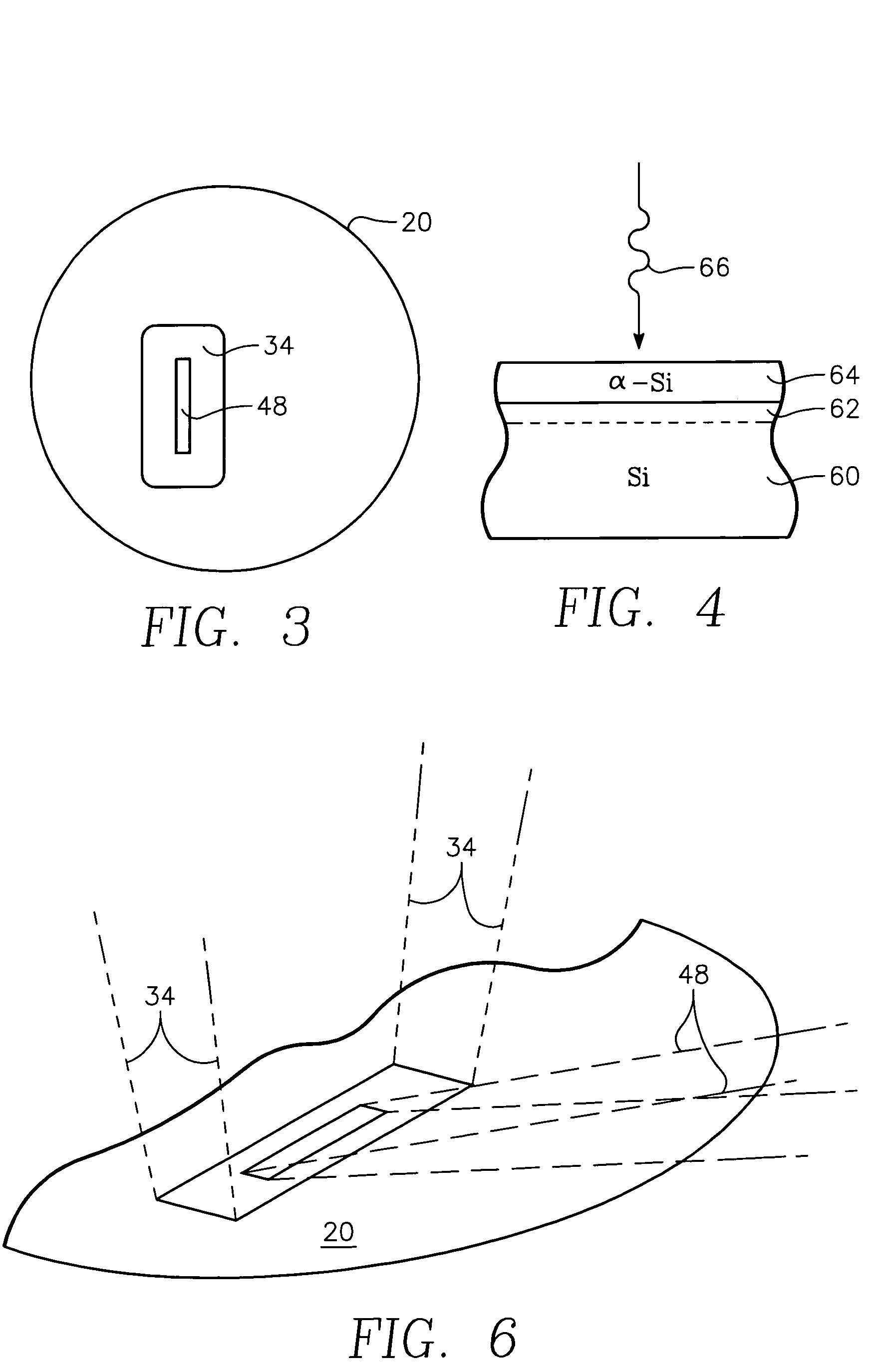
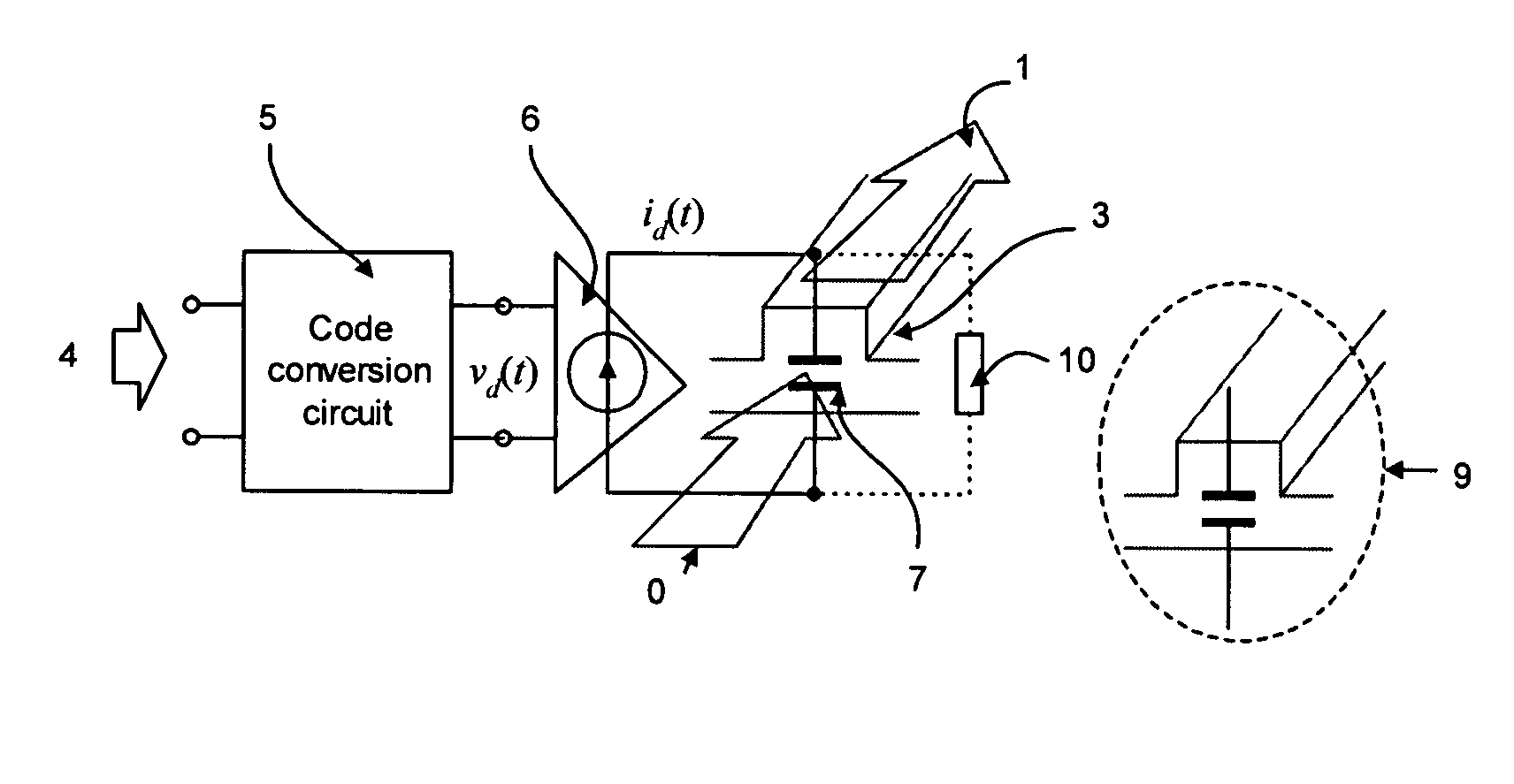
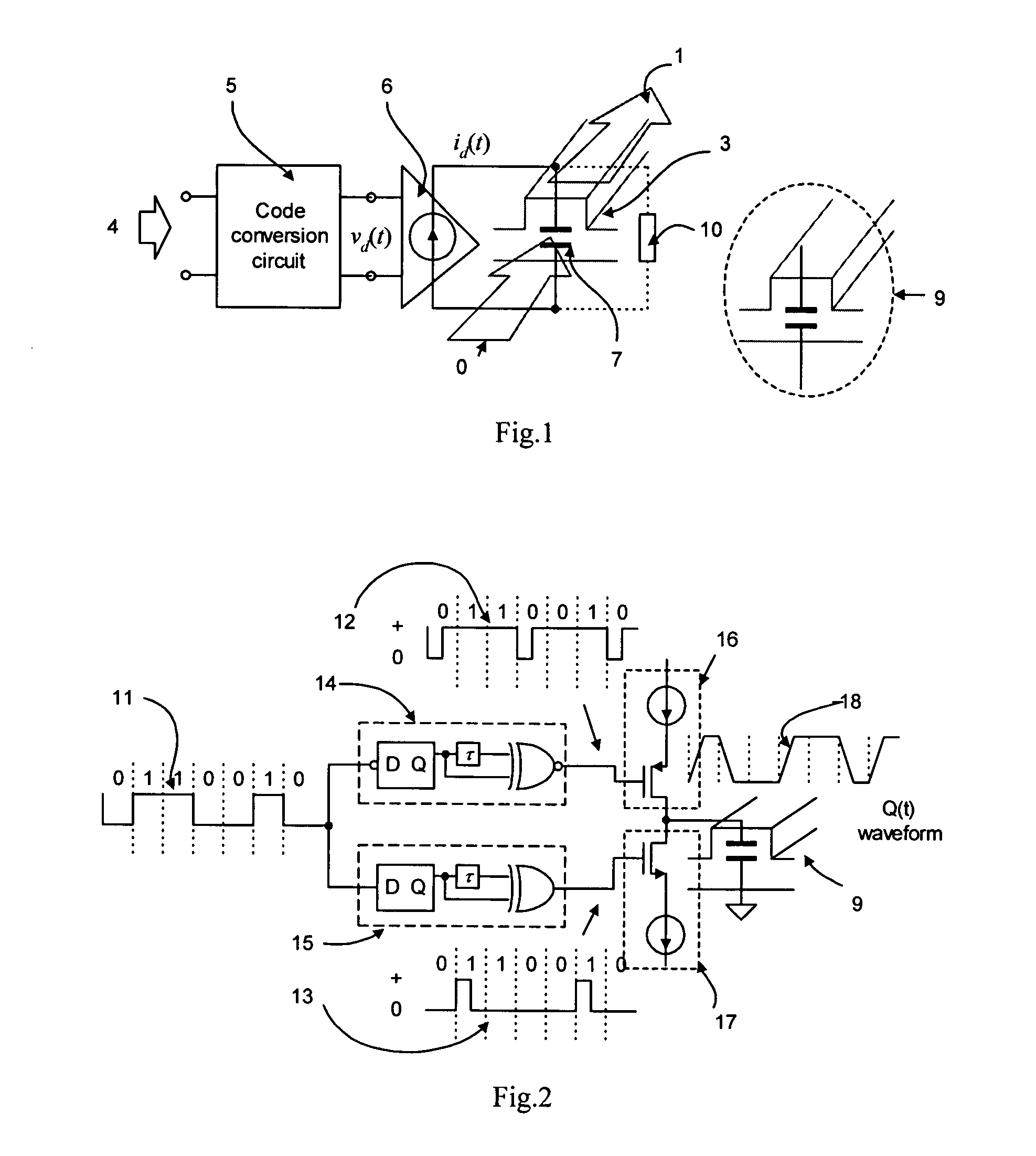
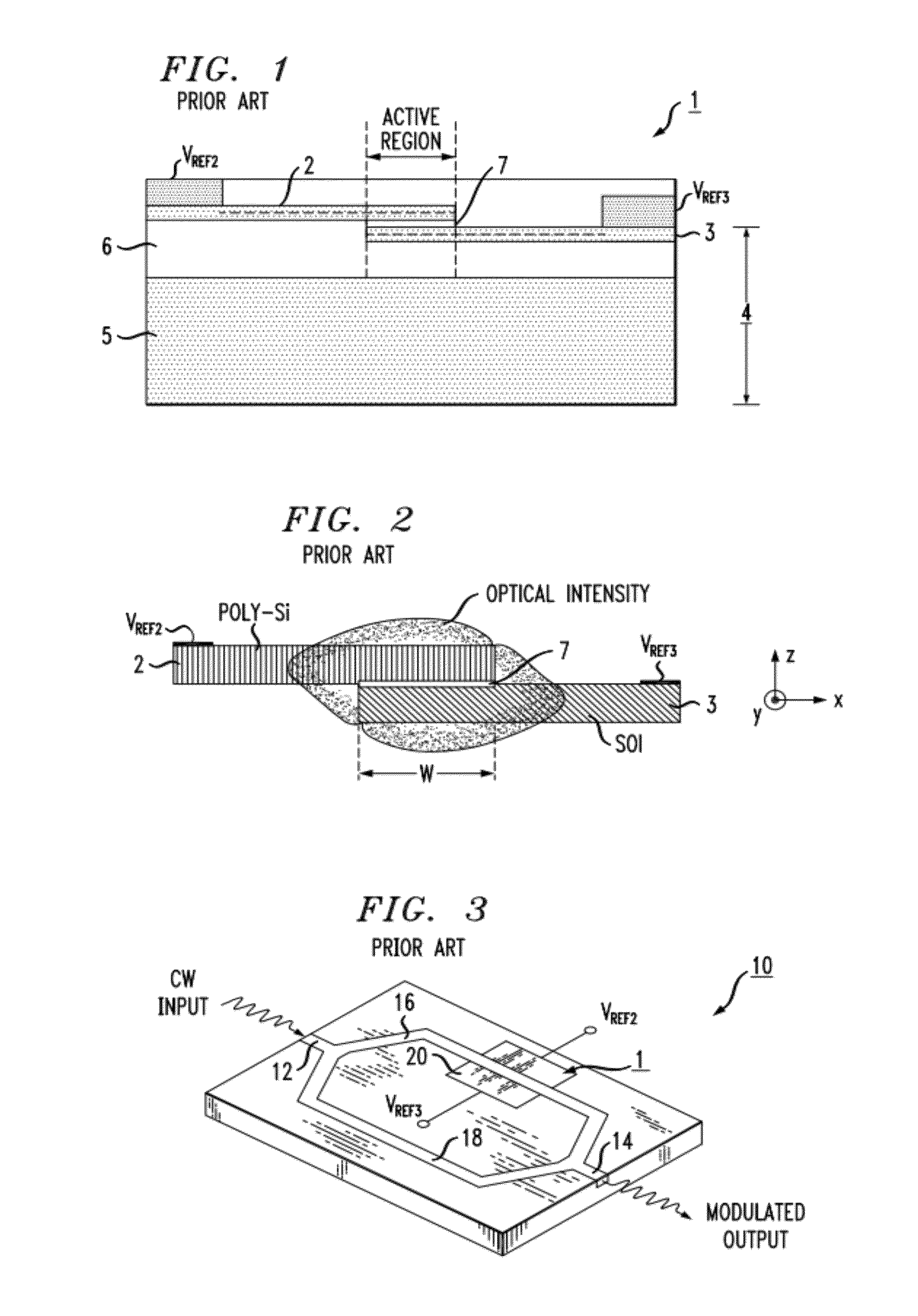
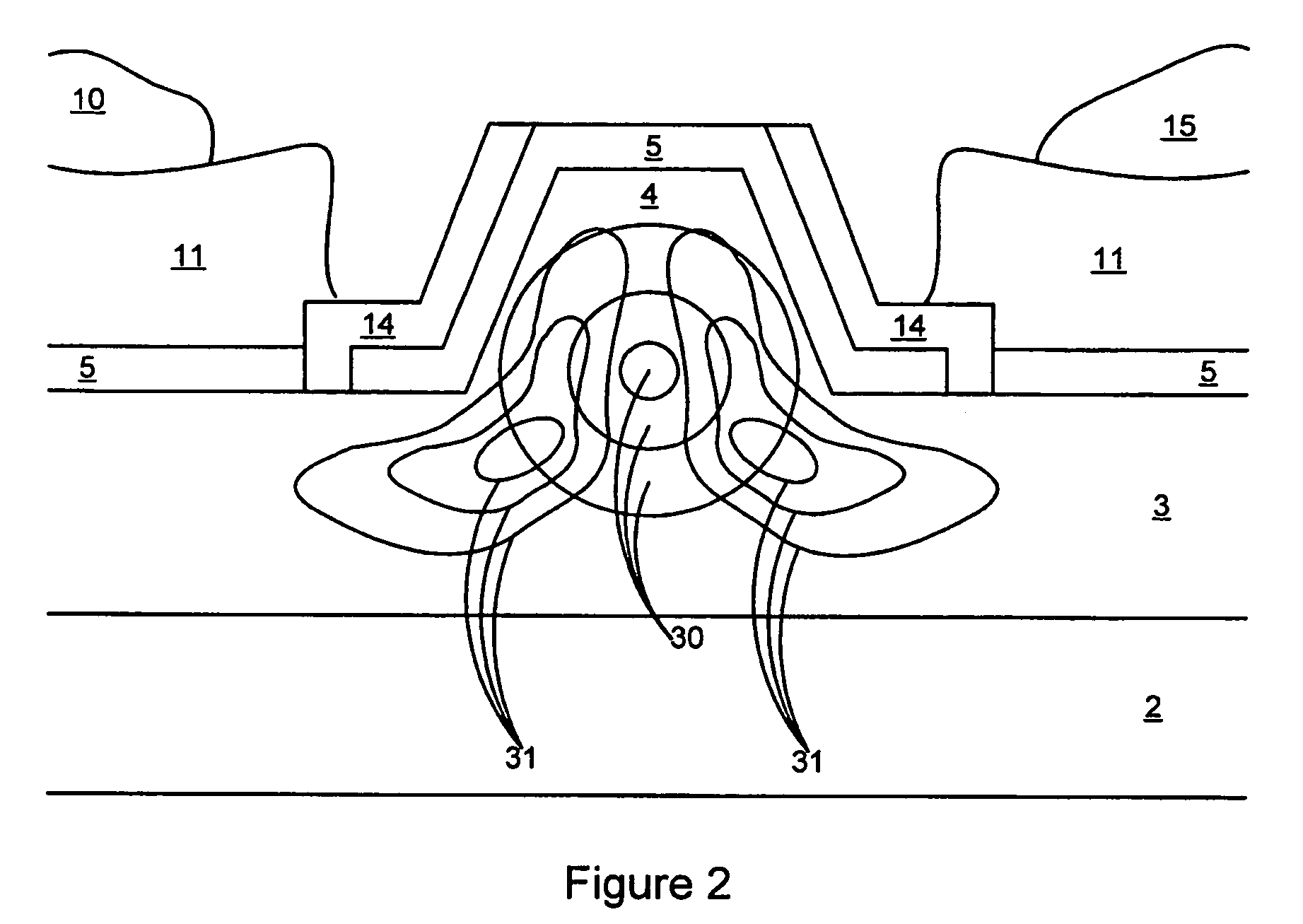
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
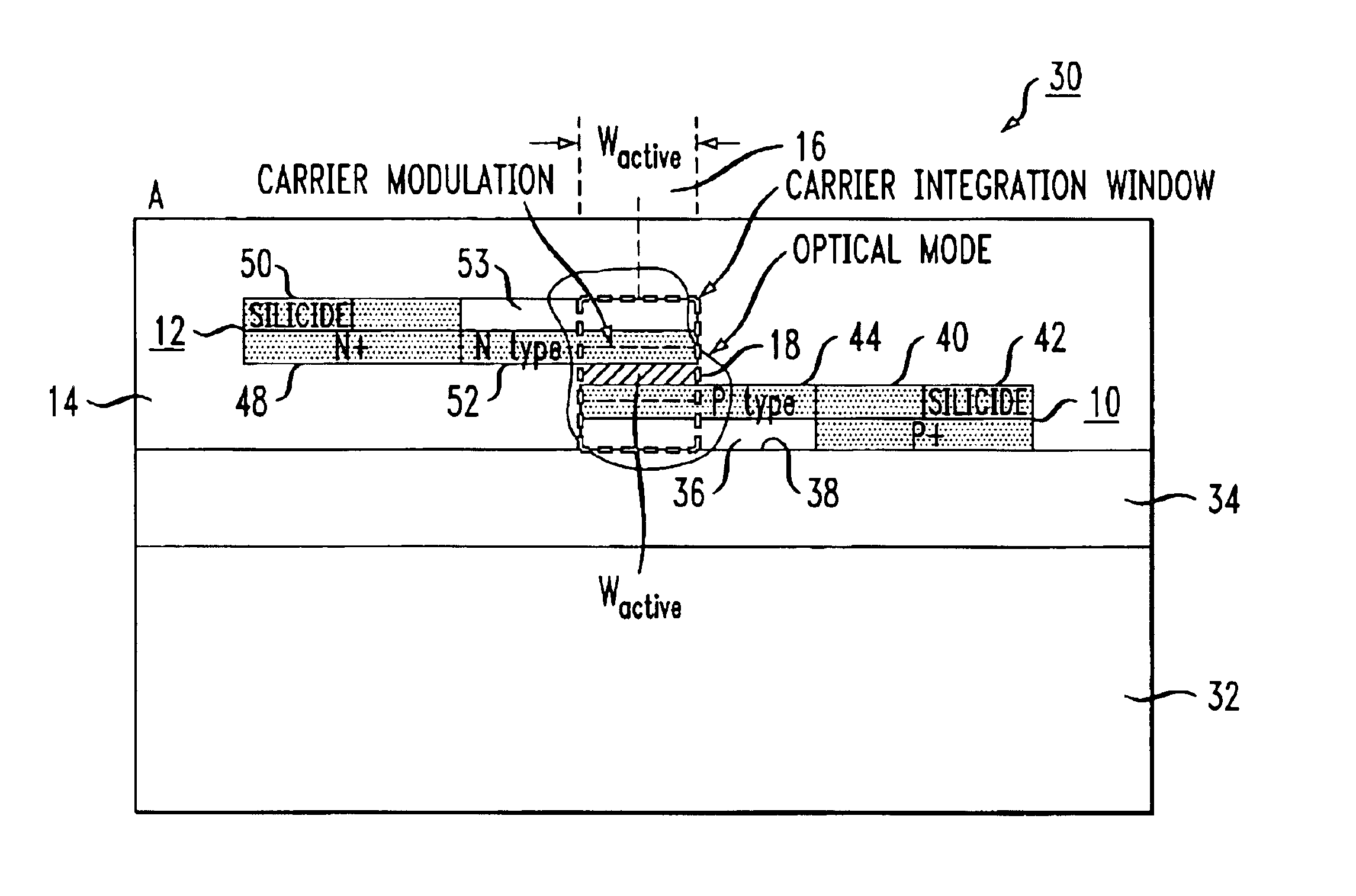
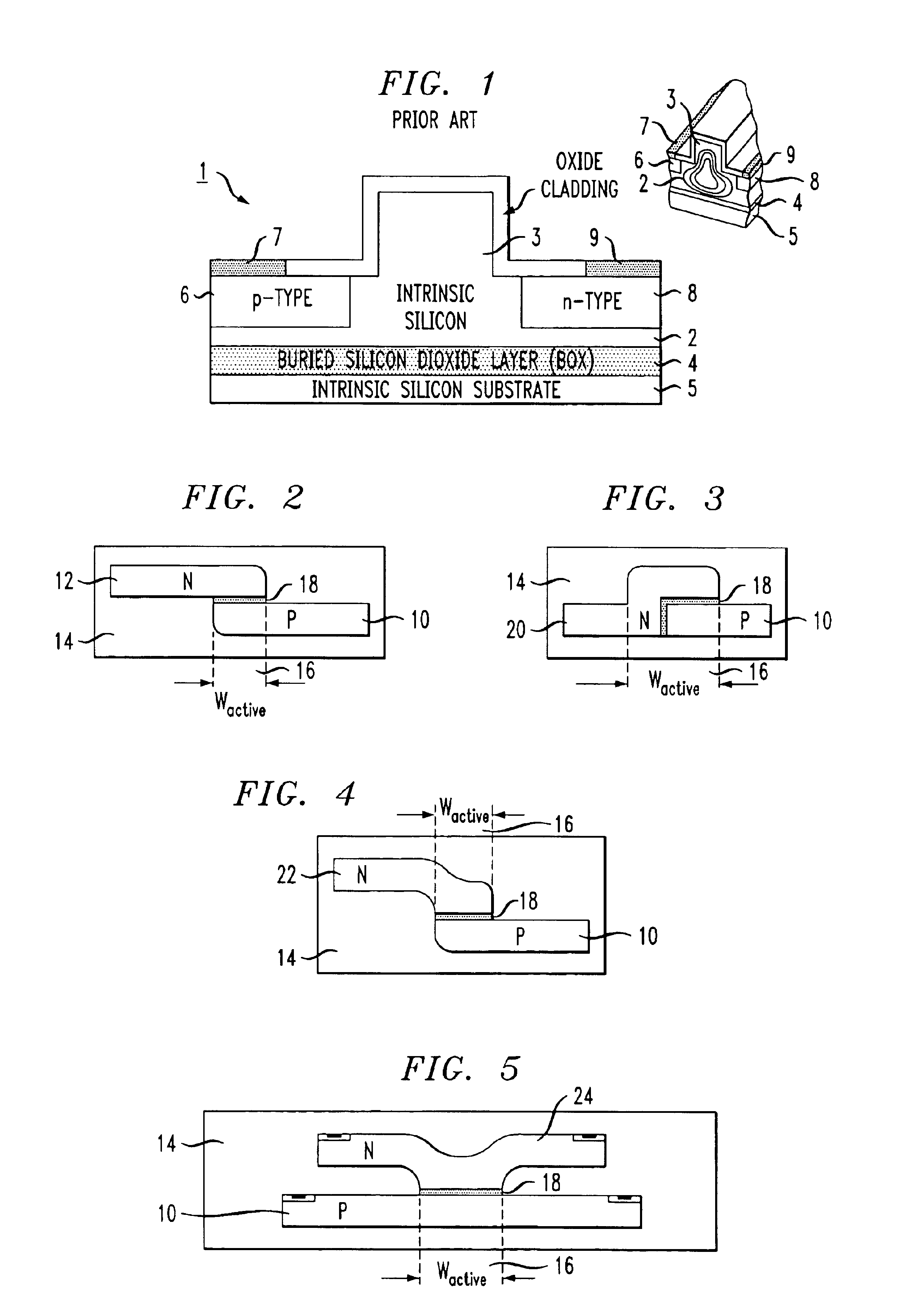
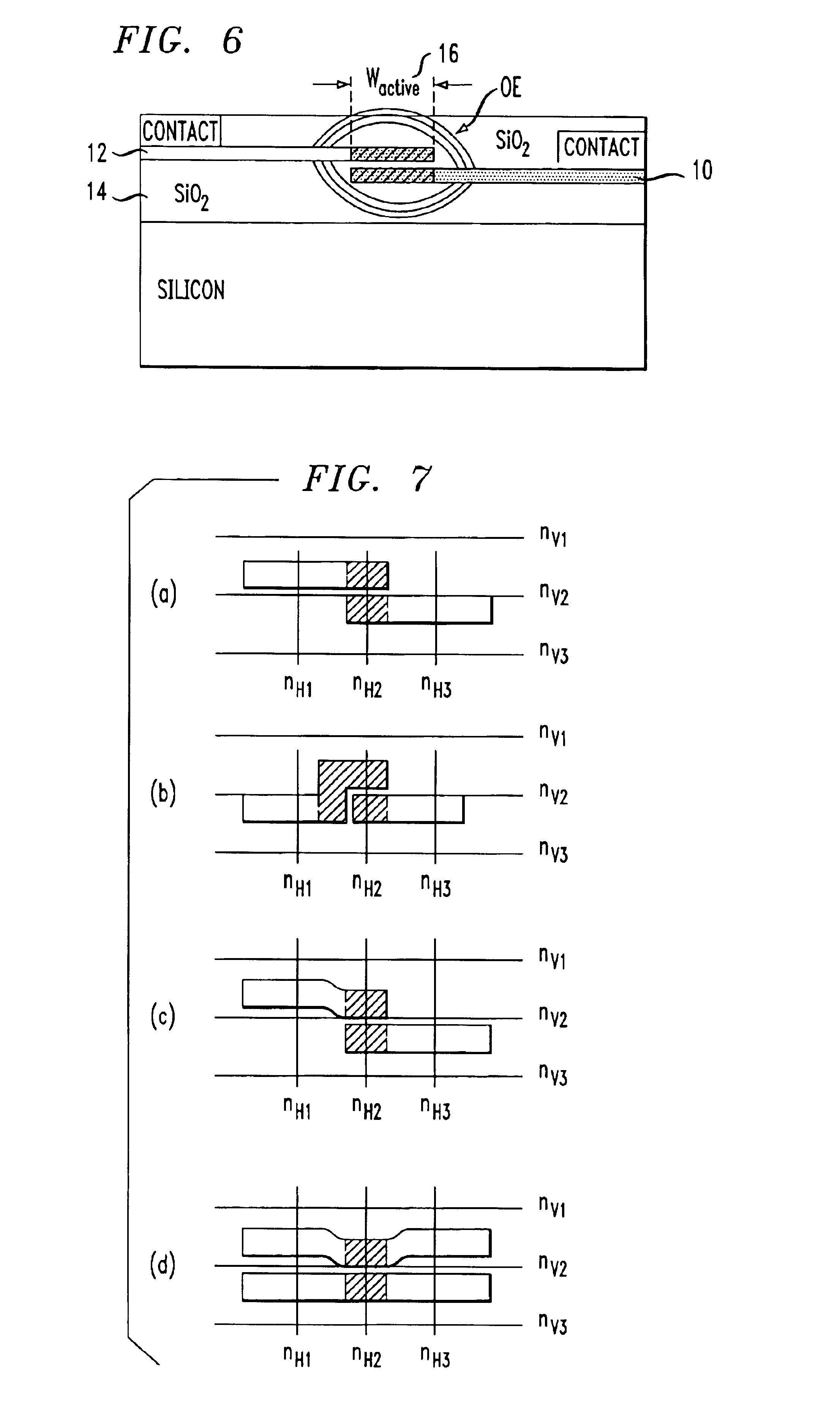
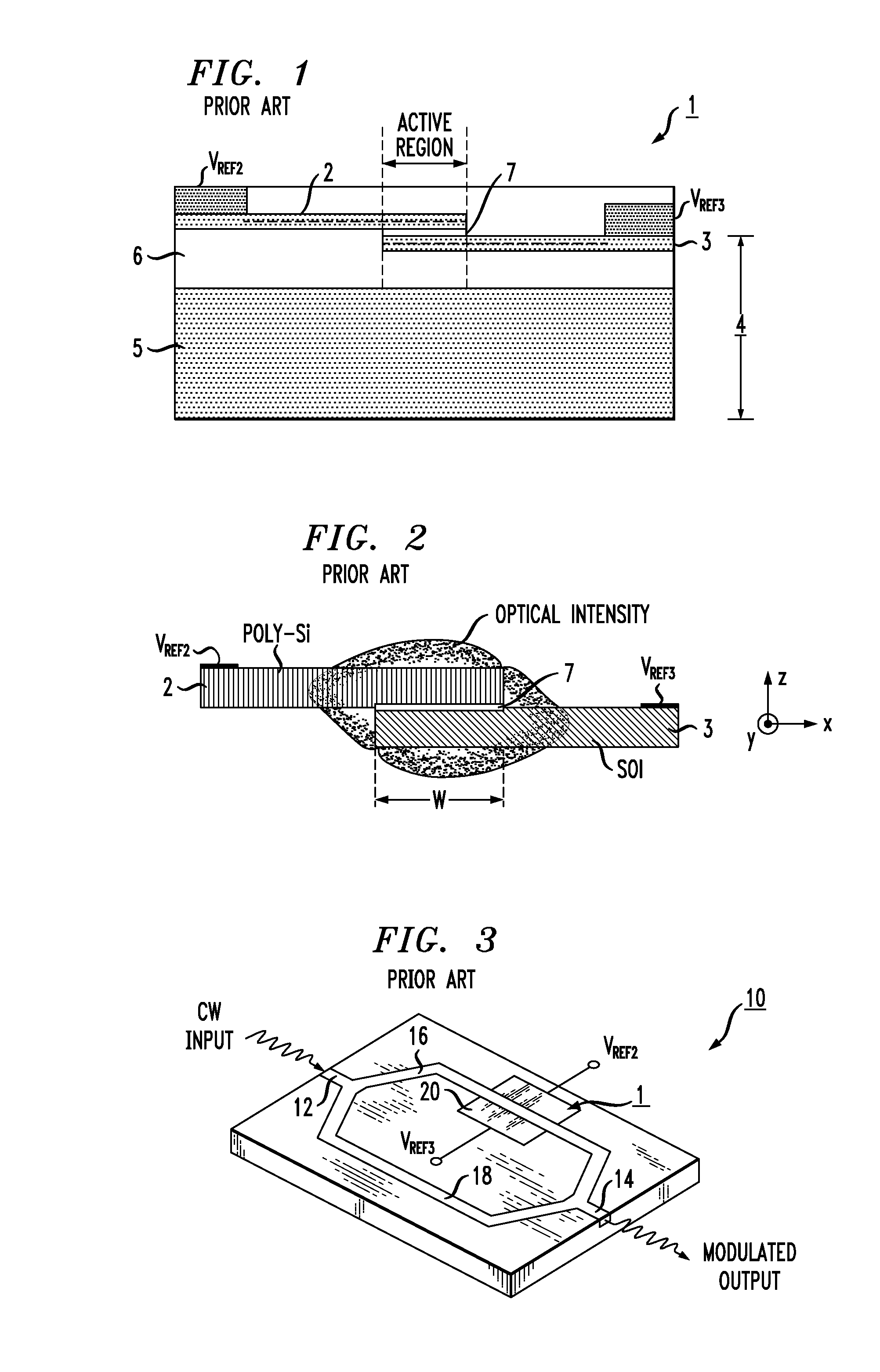
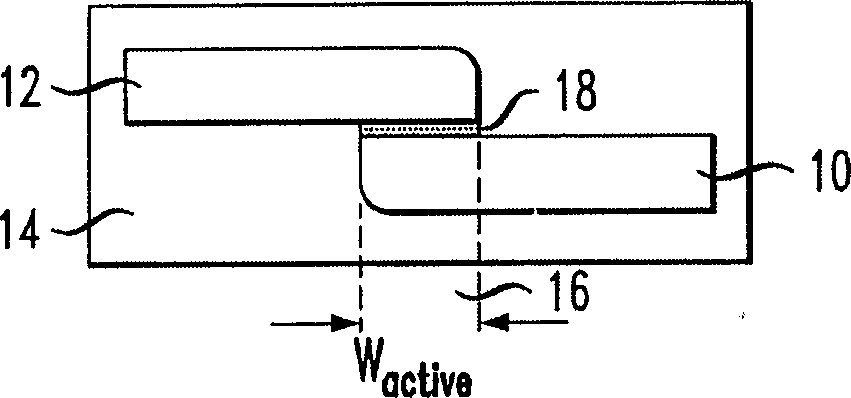
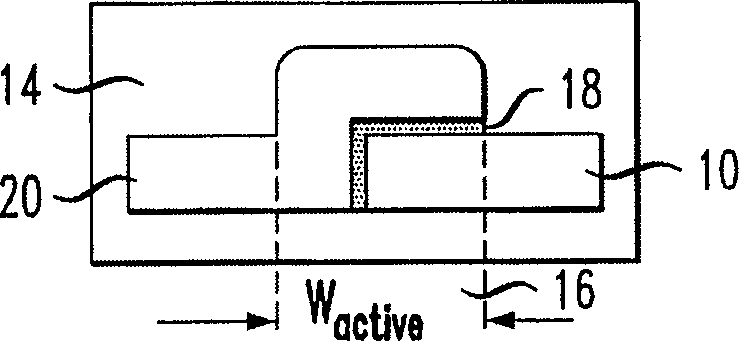
ActiveUS6845198B2Series resistance is minimizedLower optical lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
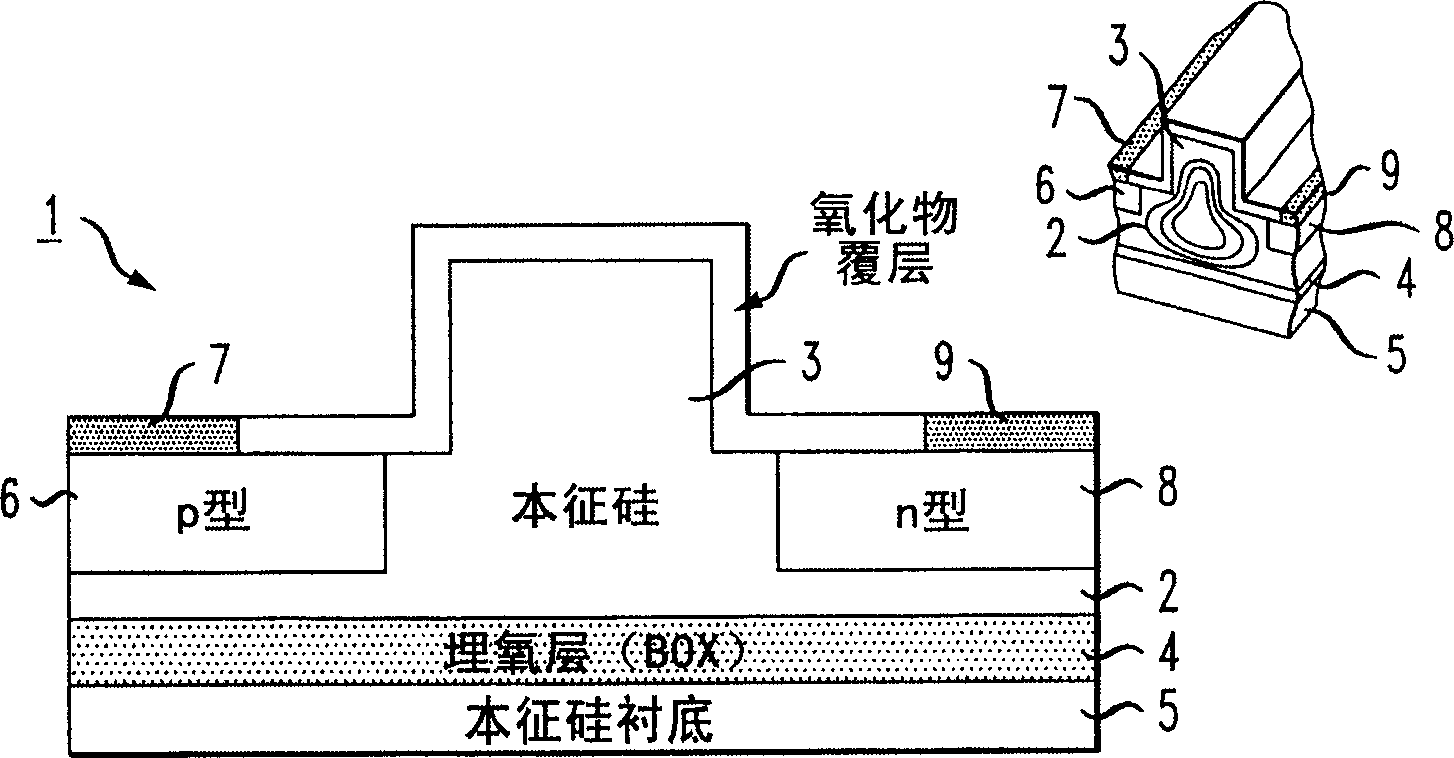
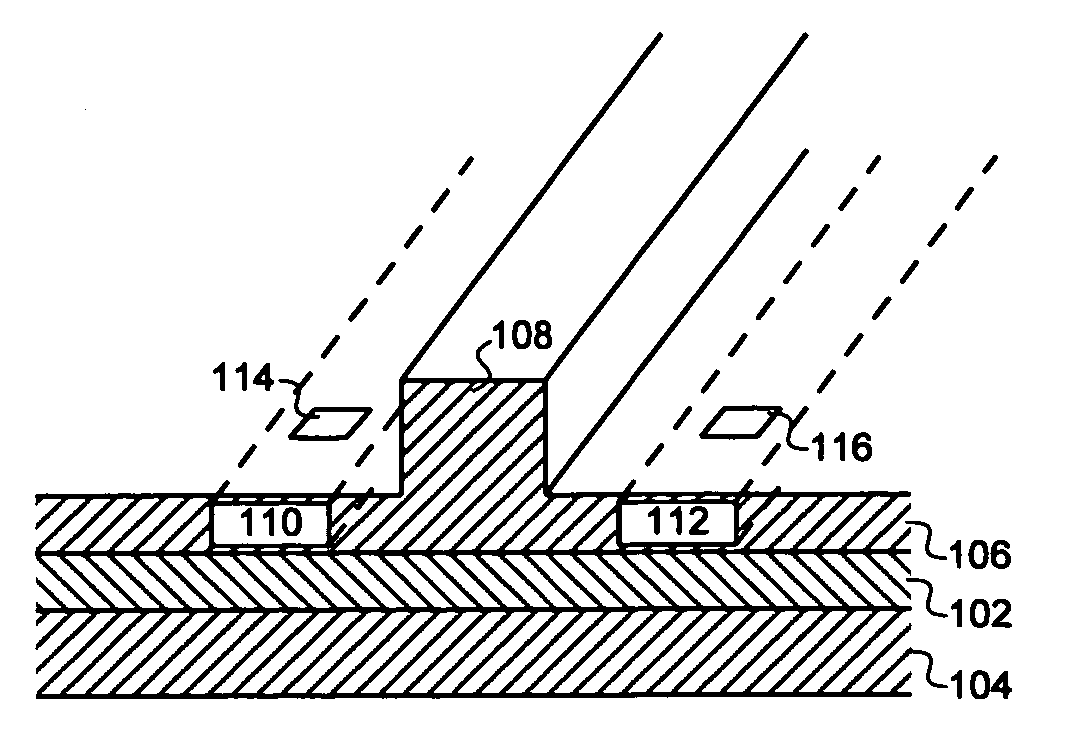
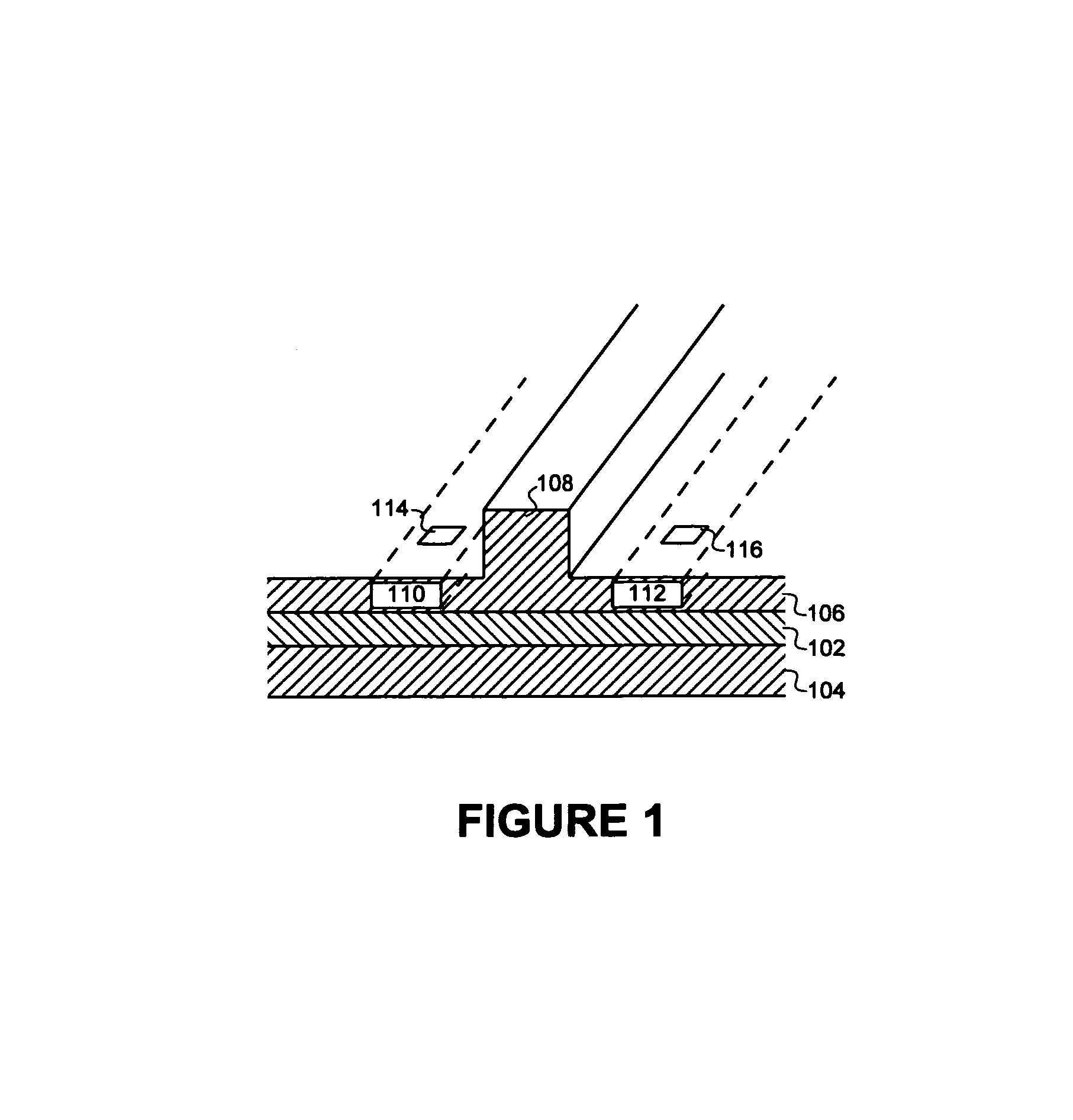
A silicon-based electro-optic modulator is based on forming a gate region of a first conductivity to partially overly a body region of a second conductivity type, with a relatively thin dielectric layer interposed between the contiguous portions of the gate and body regions. The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform, with the body region formed in the relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and the gate region formed of a relatively thin silicon layer overlying the SOI structure. The doping in the gate and body regions is controlled to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric, thus defining the active region of the device. Advantageously, the optical electric field essentially coincides with the free carrier concentration area in this active device region. The application of a modulation signal thus causes the simultaneous accumulation, depletion or inversion of free carriers on both sides of the dielectric at the same time, resulting in high speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
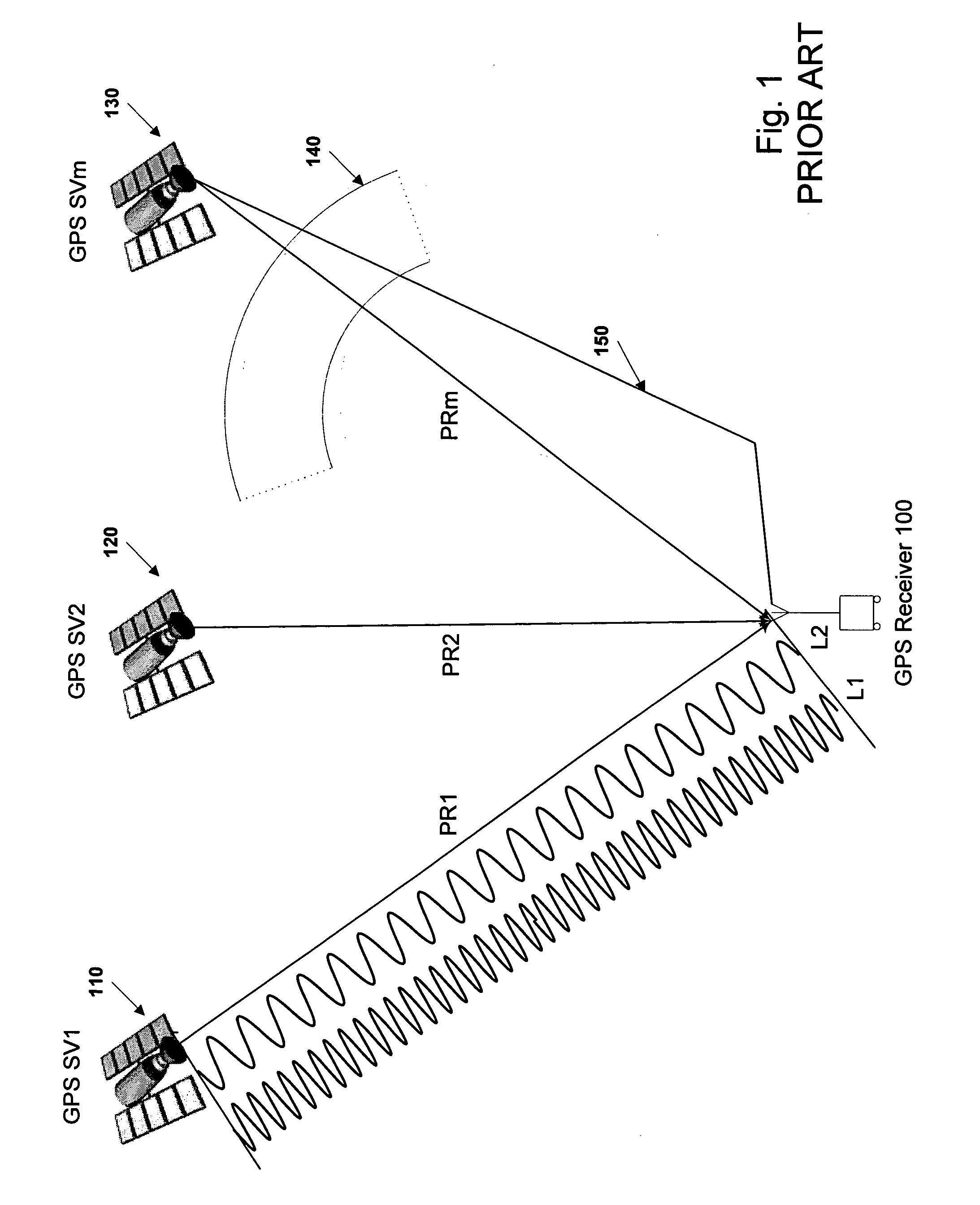
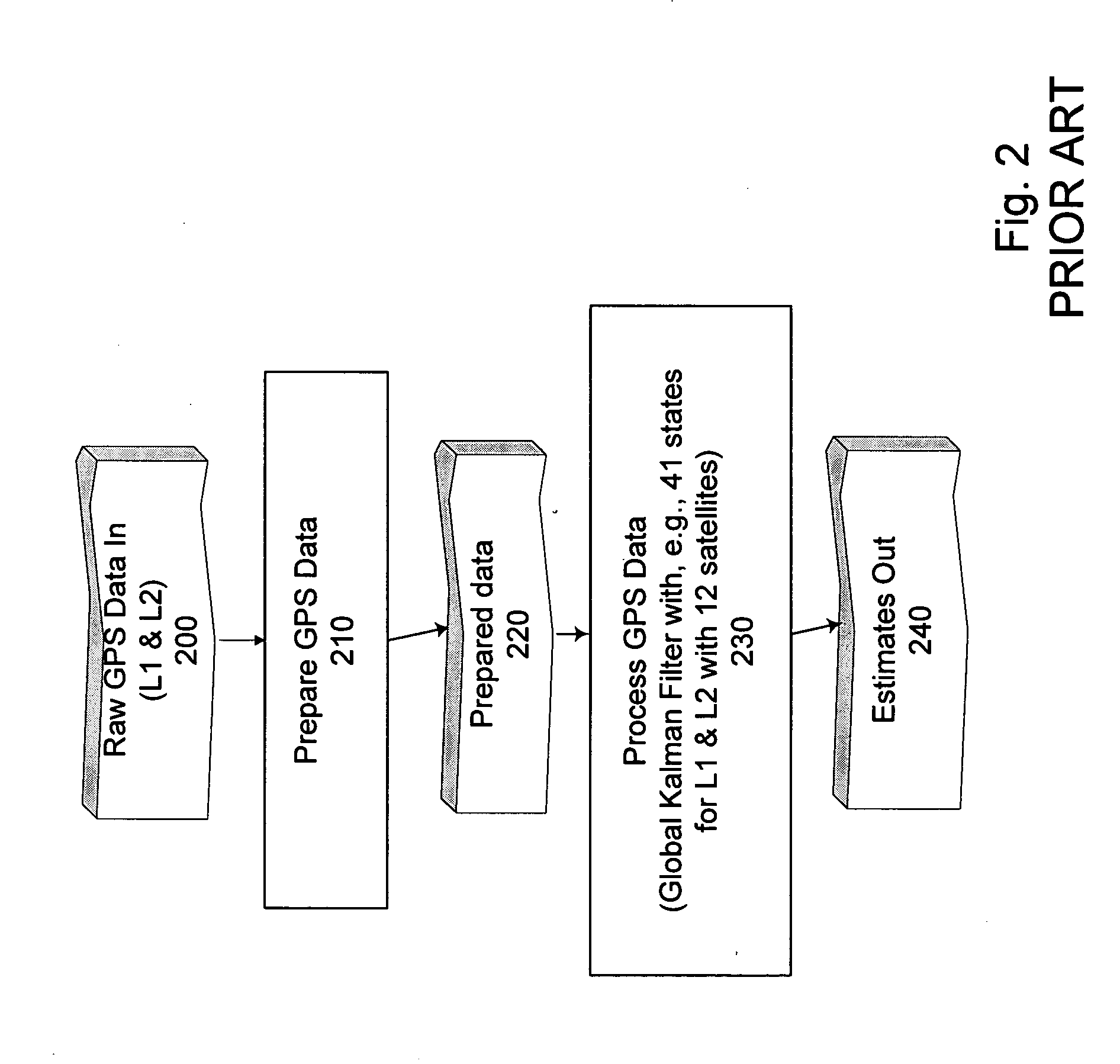
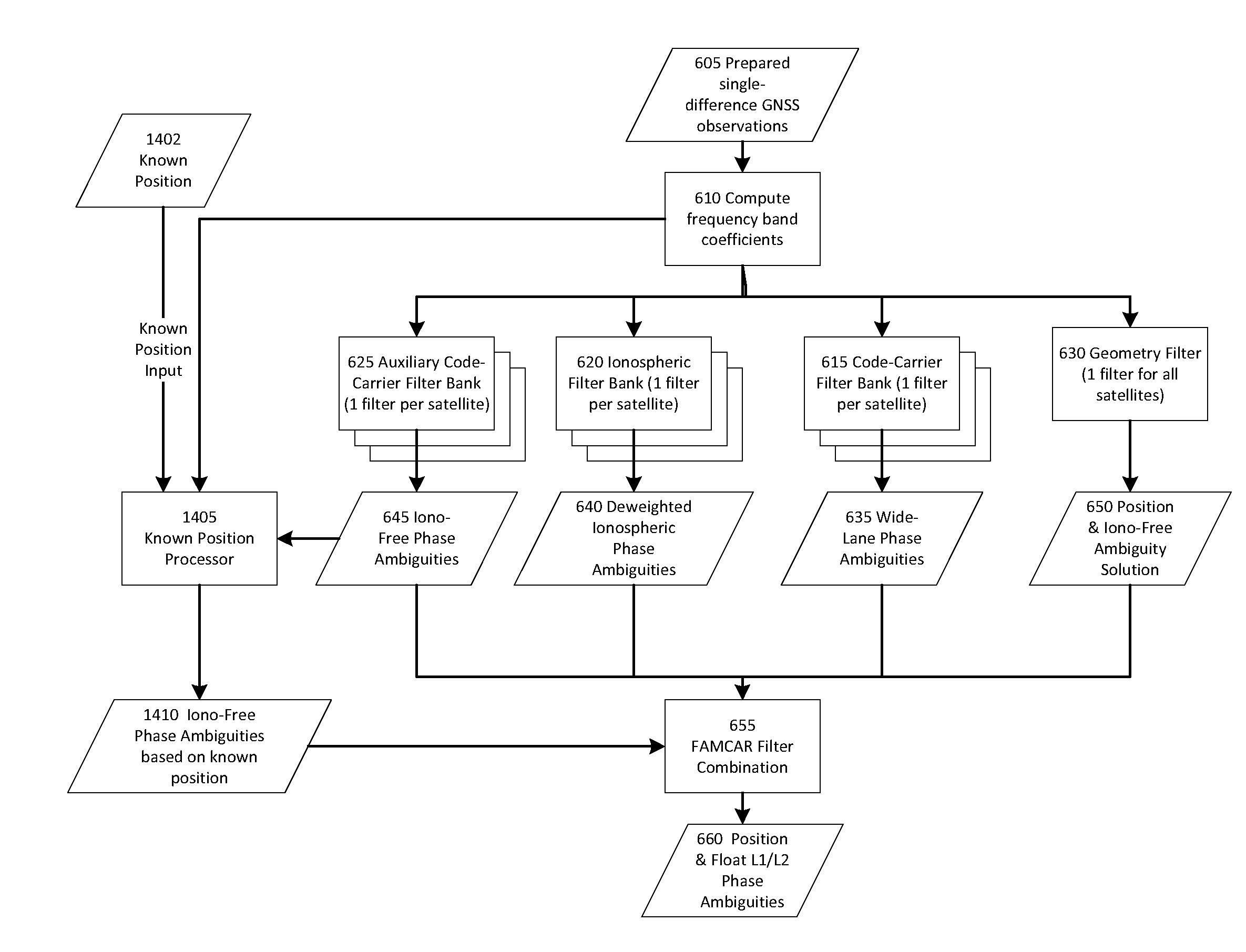
Ambiguity estimation of GNSS signals for three or more carriers
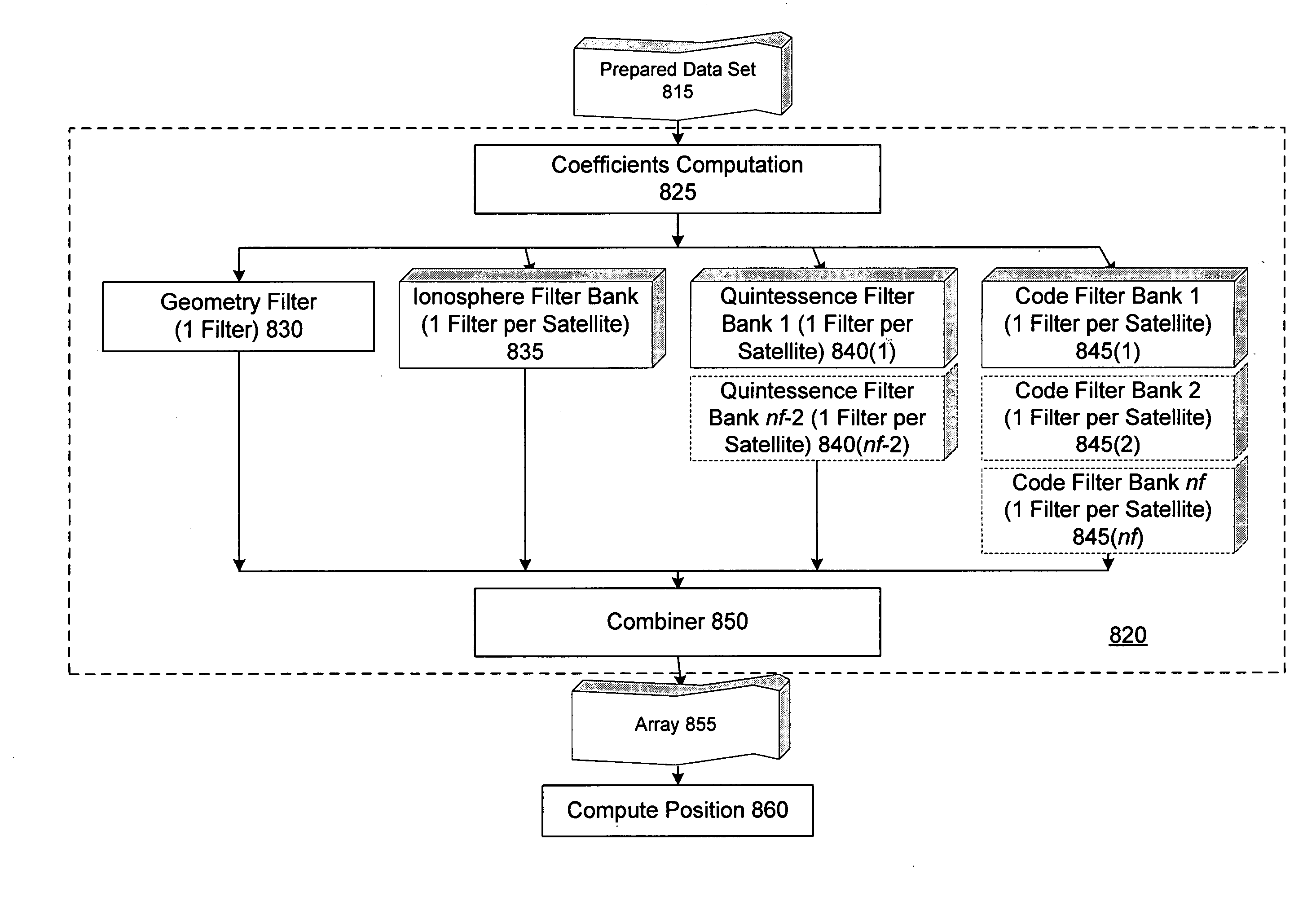
ActiveUS20050101248A1Reduce effortValidation is greatly reducedPosition fixationRadio transmissionCarrier signalComputer science
Methods and apparatus are provided for factorized processing of a set of GNSS signal data derived from signals having at least three carriers. A geometry filter is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the geometry carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. A bank of ionosphere filters is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry-free ionosphere carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the ionosphere carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. At least one bank of Quintessence filters is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry-free and ionosphere-free carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the geometry-free and ionosphere-free carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. At least one code filter is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a plurality of geometry-free and ionosphere-free code-carrier combinations to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the code-carrier combinations and associated statistical information. The resulting arrays are combined to obtain a combined array of ambiguity estimates for all carrier phase observations and associated statistical information.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Nanowhiskers with PN junctions, doped nanowhiskers, and methods for preparing them
InactiveUS20050006673A1Good electrical conductivityPermitted diffusionPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsHeterojunctionP–n junction
Nano-engineered structures are disclosed, incorporating nanowhiskers of high mobility conductivity and incorporating pn junctions. In one embodiment, a nanowhisker of a first semiconducting material has a first band gap, and an enclosure comprising at least one second material with a second band gap encloses said nanoelement along at least part of its length, the second material being doped to provide opposite conductivity type charge carriers in respective first and second regions along the length of the of the nanowhisker, whereby to create in the nanowhisker by transfer of charge carriers into the nanowhisker, corresponding first and second regions of opposite conductivity type charge carriers with a region depleted of free carriers therebetween. The doping of the enclosure material may be degenerate so as to create within the nanowhisker adjacent segments having very heavy modulation doping of opposite conductivity type analogous to the heavily doped regions of an Esaki diode. In another embodiment, a nanowhisker is surrounded by polymer material containing dopant material. A step of rapid thermal annealing causes the dopant material to diffuse into the nanowhisker. In a further embodiment, a nanowhisker has a heterojunction between two different intrinsic materials, and Fermi level pinning creates a pn junction at the interface without doping.
Owner:QUNANO
Electro-optic modulator on rib waveguide
InactiveUS20050089257A1Refractive index variesOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsCharge carrierRefractive index
An electro-optic modulator is formed on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) rib waveguide. An optical field in the modulator is confined by using an electrically modulated microcavity. The microcavity has reflectors on each side. In one embodiment, a planar Fabry-Perot microcavity is used with deep Si / SiO2 Bragg reflectors. Carriers may be laterally confined in the microcavity region by employing deep etched lateral trenches. The refractive index of the microcavity is varied by using the free-carrier dispersion effect produced by a p-i-n diode formed about the microcavity. In one embodiment, the modulator confines both optical field and charge carriers in a micron-size region.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
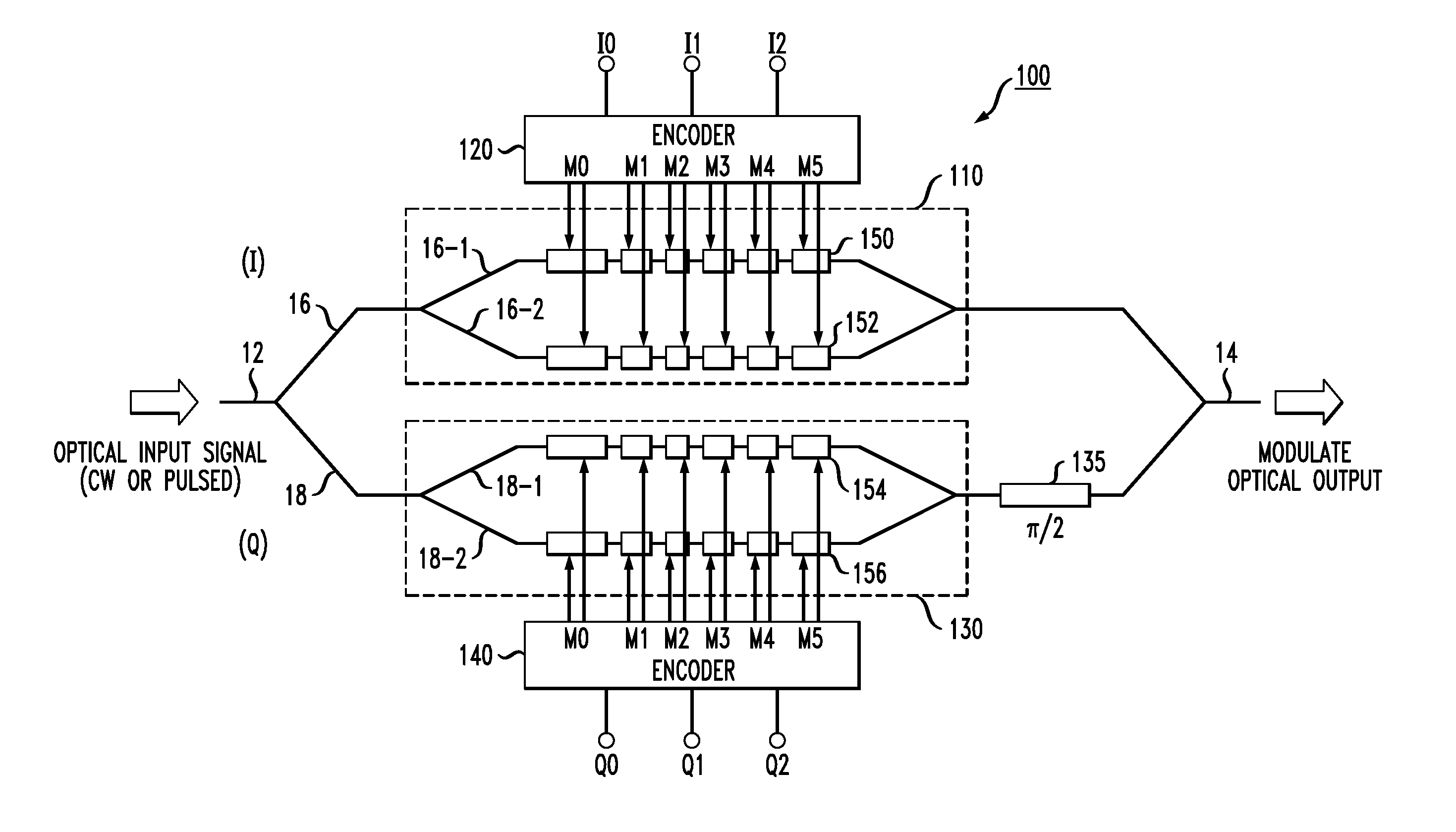
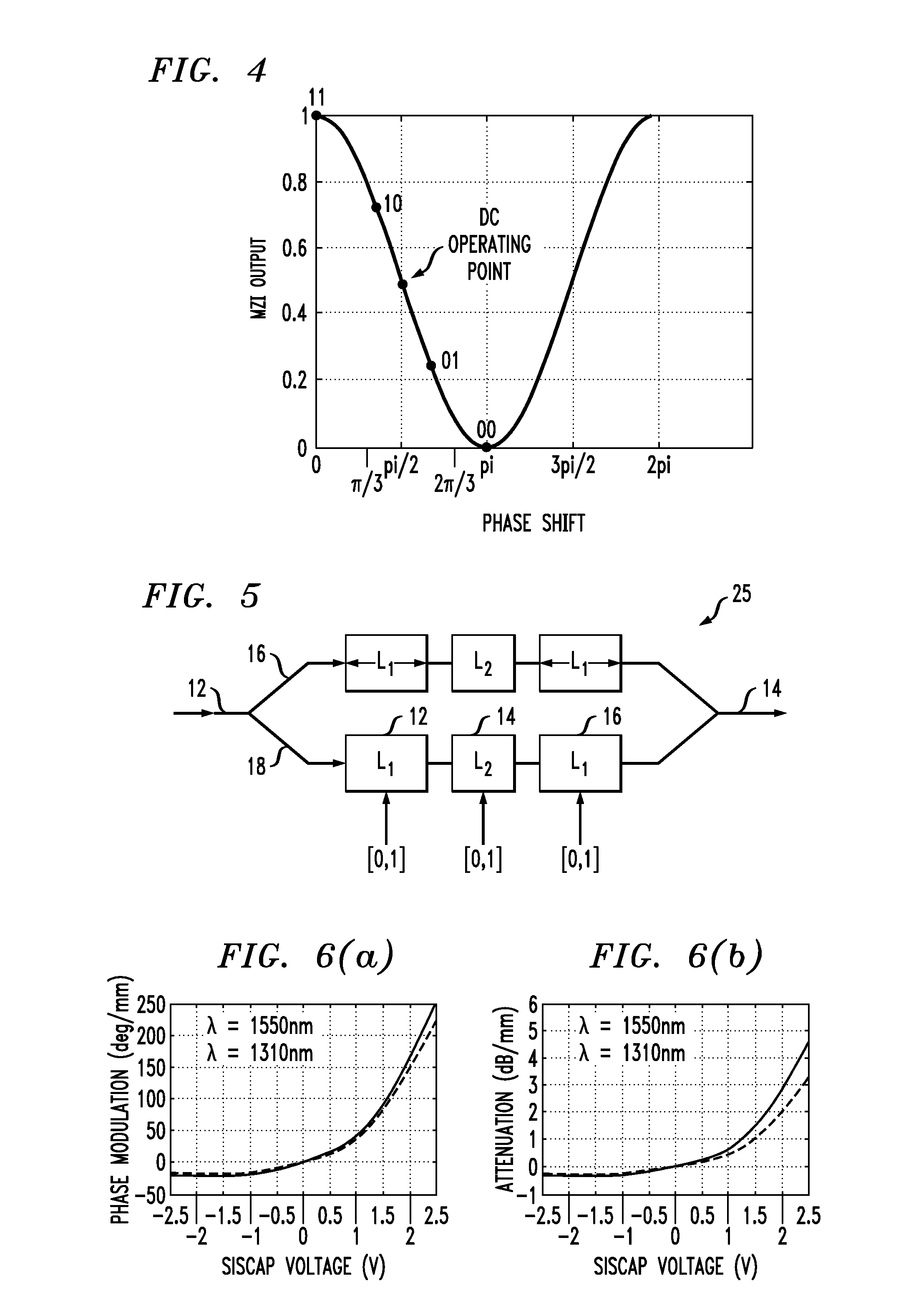
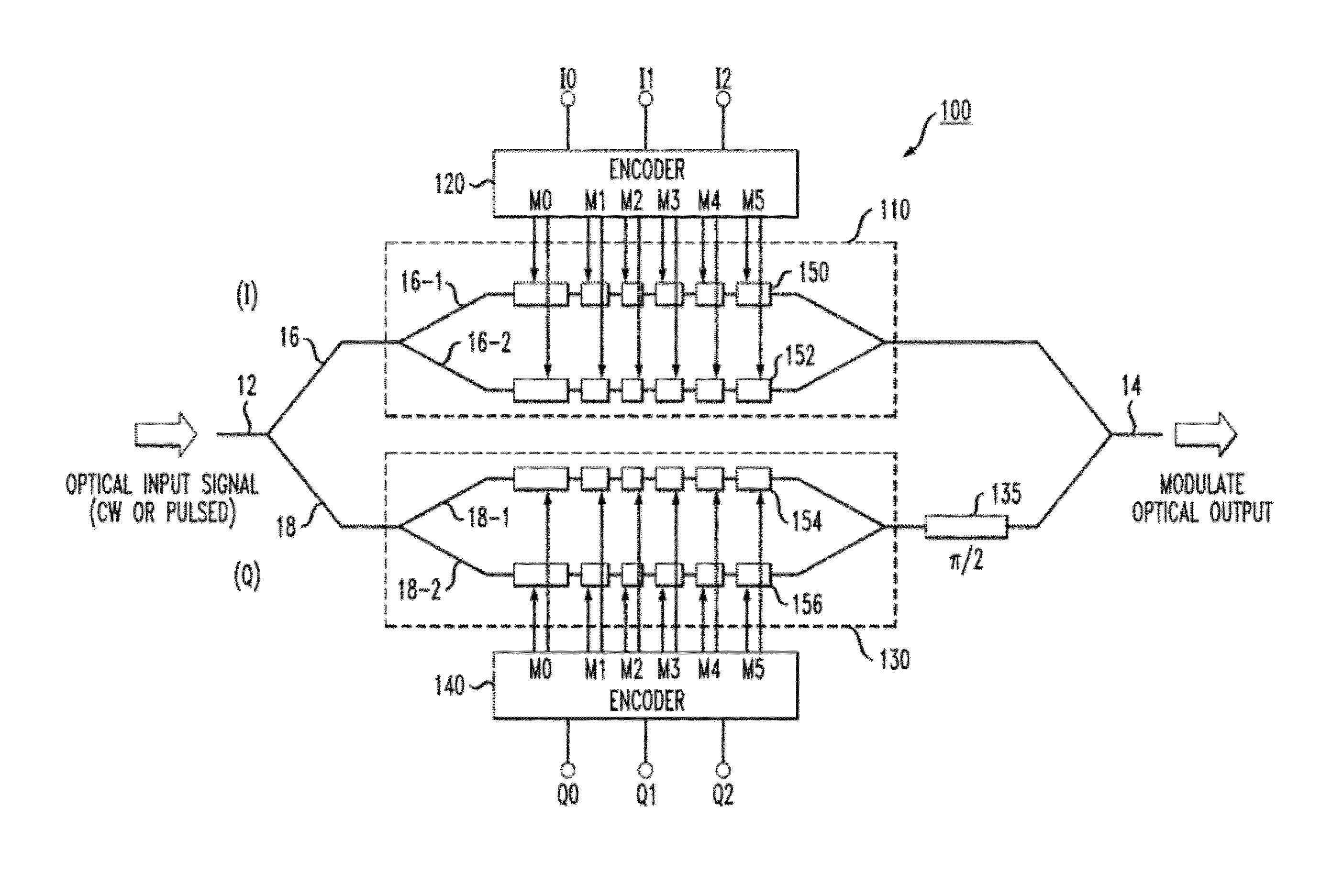
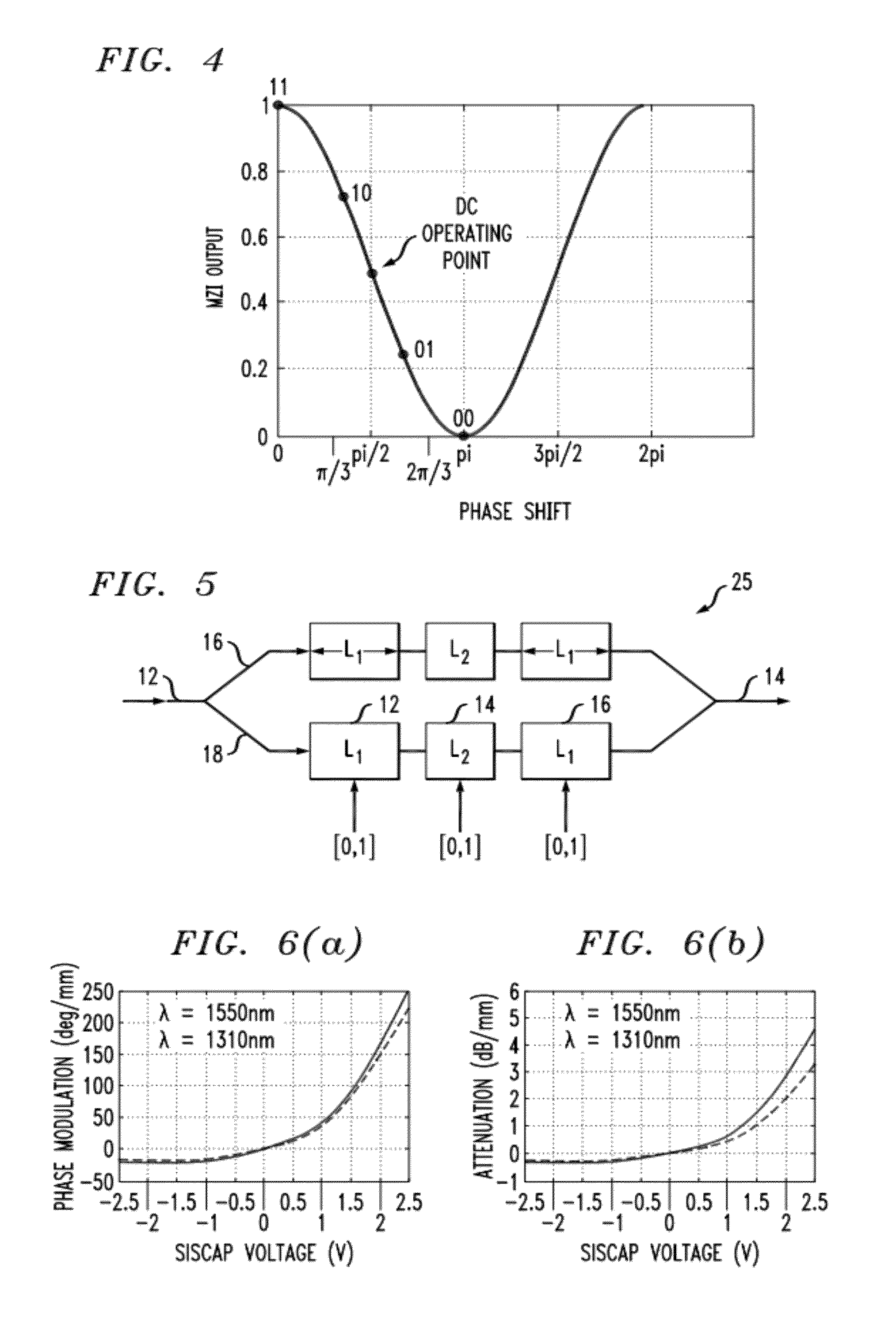
Advanced Modulation Formats for Silicon-Based Optical Modulators
ActiveUS20110044573A1Electromagnetic transmissionOptical waveguide light guideMulti segmentWaveguide
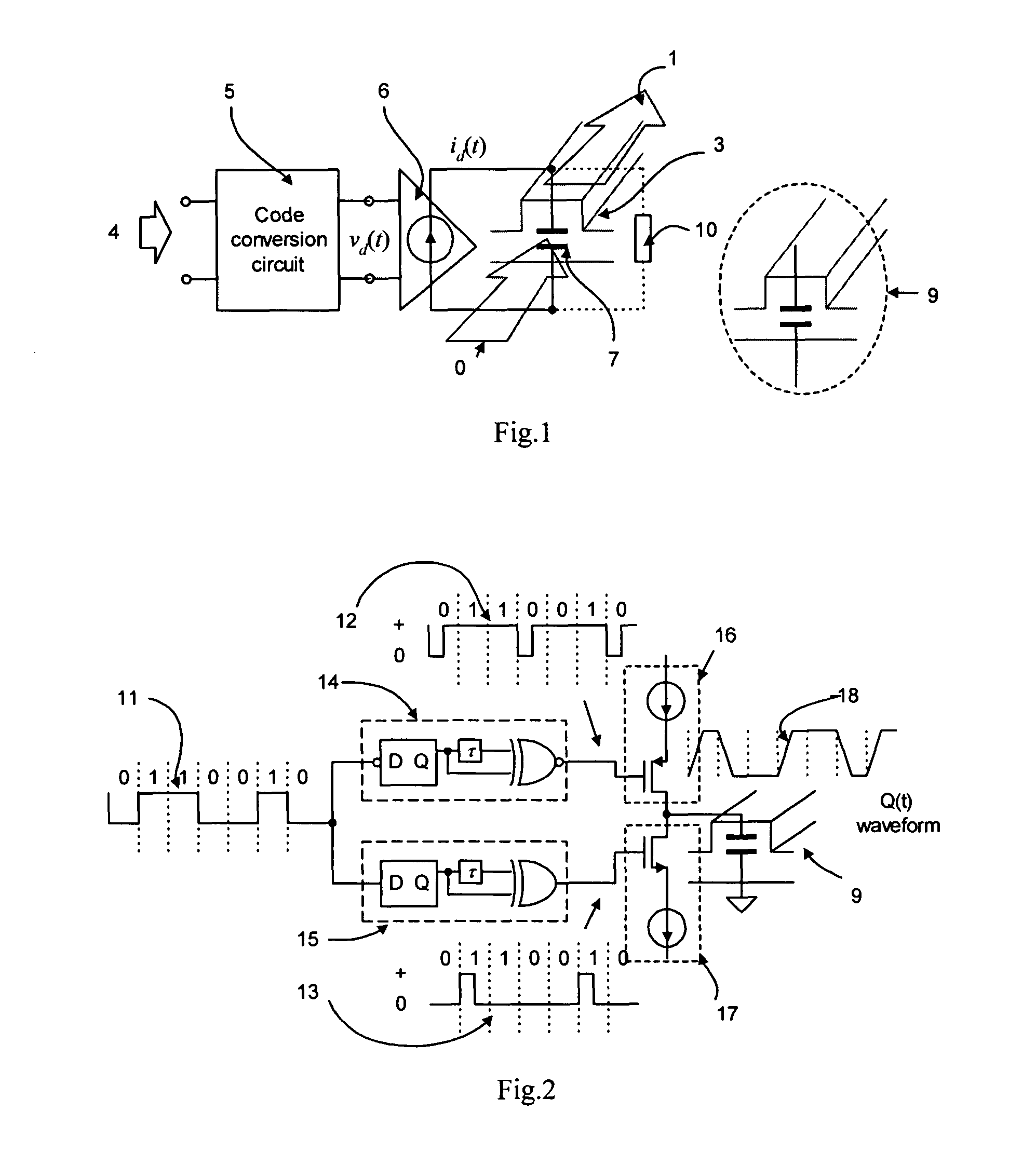
A silicon-based optical modulator is configured as a multi-segment device that utilizes a modified electrical data input signal format to address phase modulation nonlinearity and attenuation problems associated with free-carrier dispersion-based modulation. The modulator is formed to include M separate segments and a digital signal encoder is utilized to convert an N bit input data signal into a plurality of M drive signals for the M modulator segments, where M≧2N / 2. The lengths of the modulator segments may also be adjusted to address the nonlinearity and attenuation problems. Additional phase adjustments may be utilized at the output of the modulator (beyond the combining waveguide).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
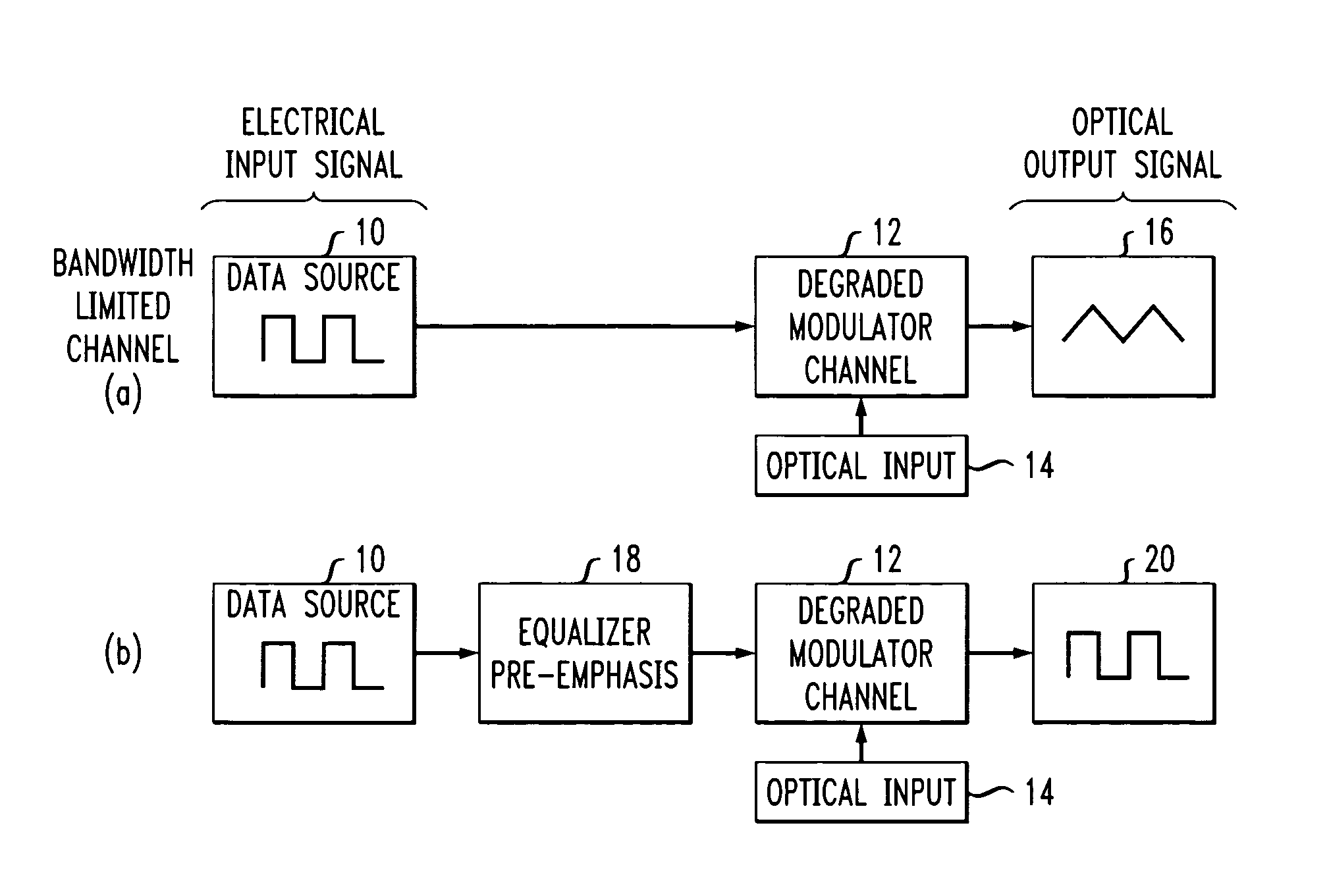
High speed, silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveUS7065301B2Fast switching speedReduce fallsElectromagnetic transmittersOptical light guidesCarrier signalRefractive index
An electro-optic modulator arrangement for achieving switching speeds greater than 1 Gb / s utilizes pre-emphasis pulses to accelerate the change in refractive index of the optical waveguide used to form the electro-optic modulator. In one embodiment, a feedback loop may be added to use a portion of the modulated optical output signal to adjust the magnitude and duration of the pre-emphasis pulses, as well as the various reference levels used for modulated. For free carrier-based electro-optic modulators, including silicon-based electro-optic modulators, the pre-emphasis pulses are used to accelerate the movement of free carriers at the transitions between input signal data values.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
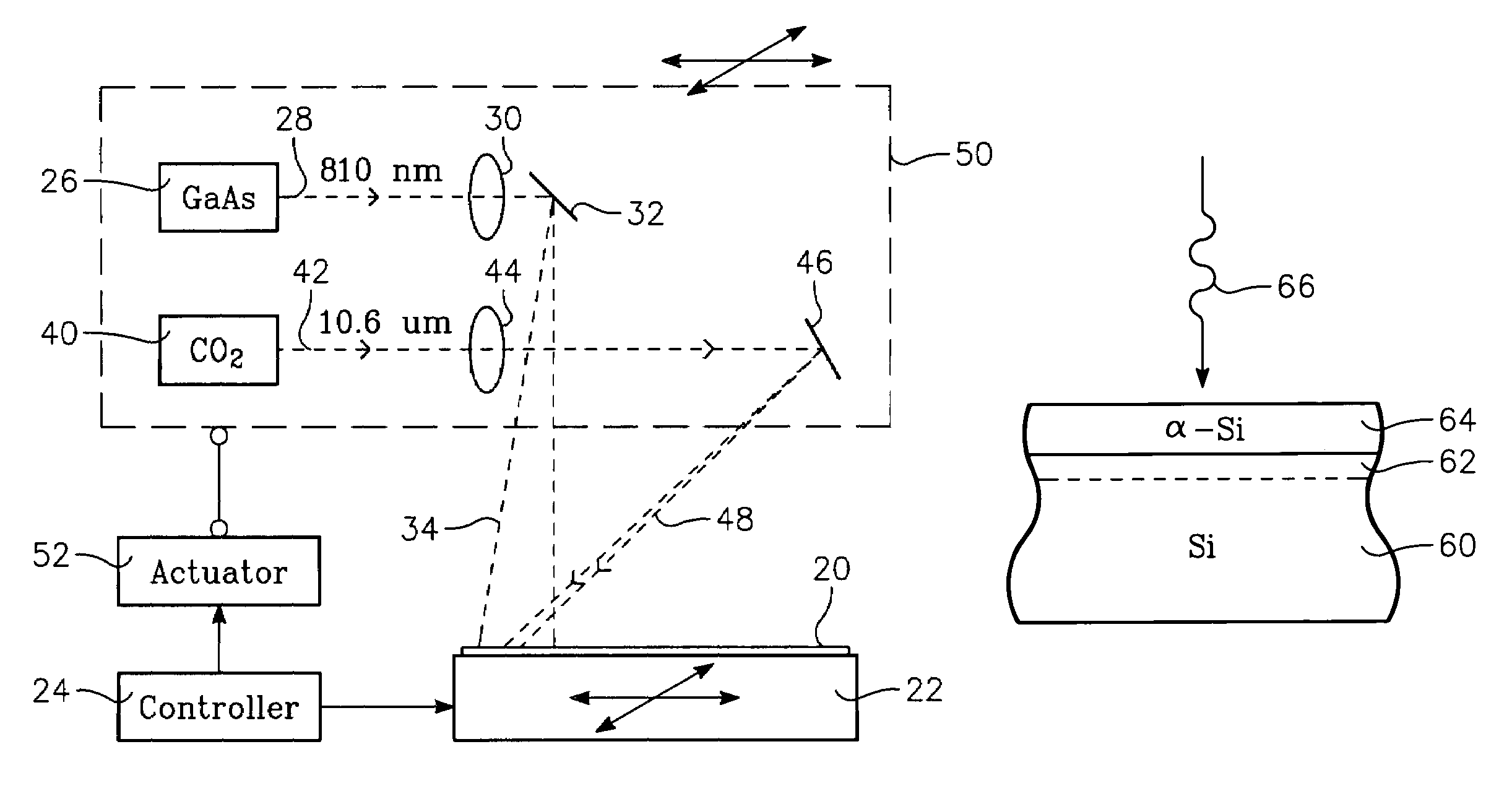
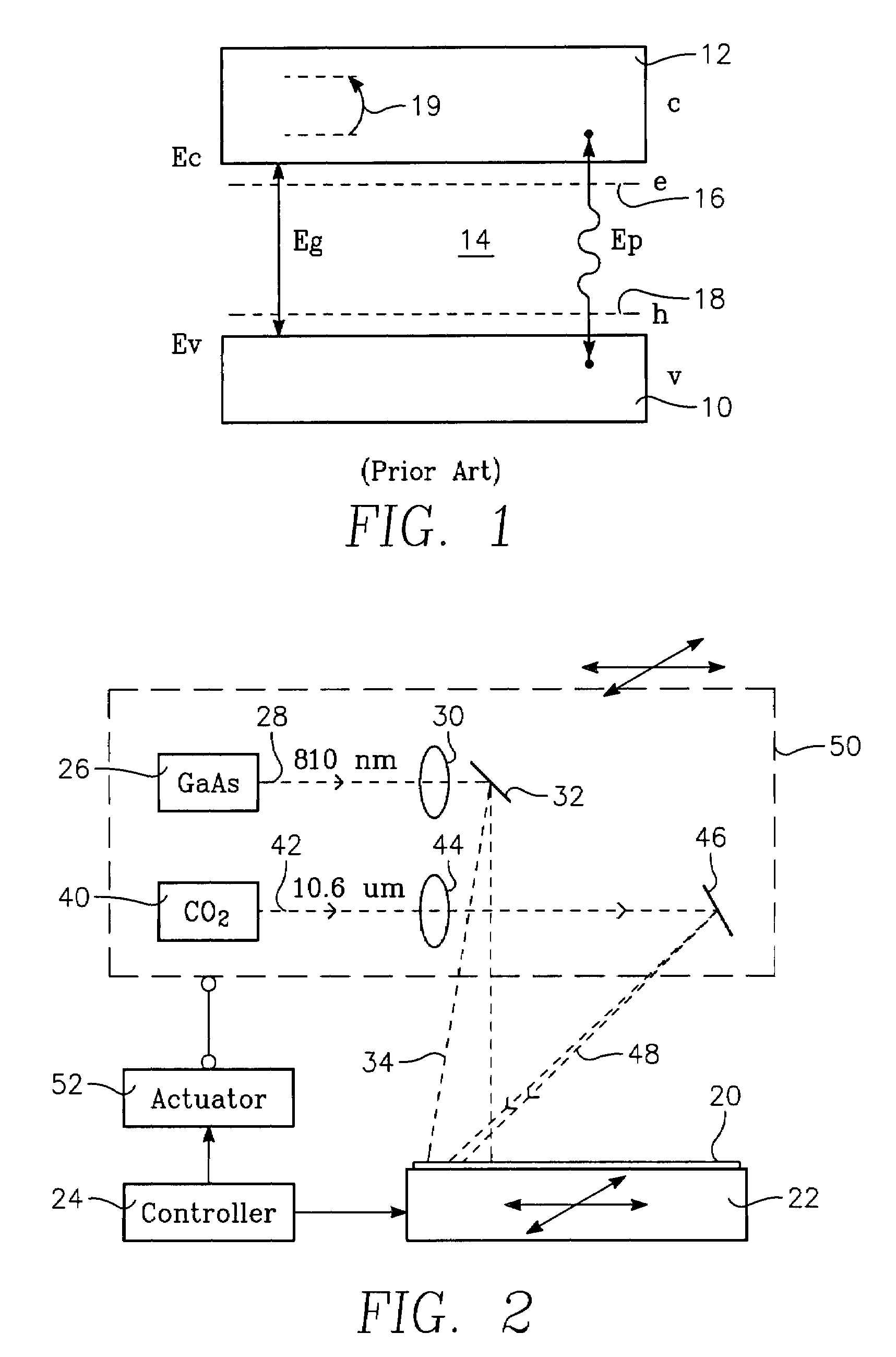
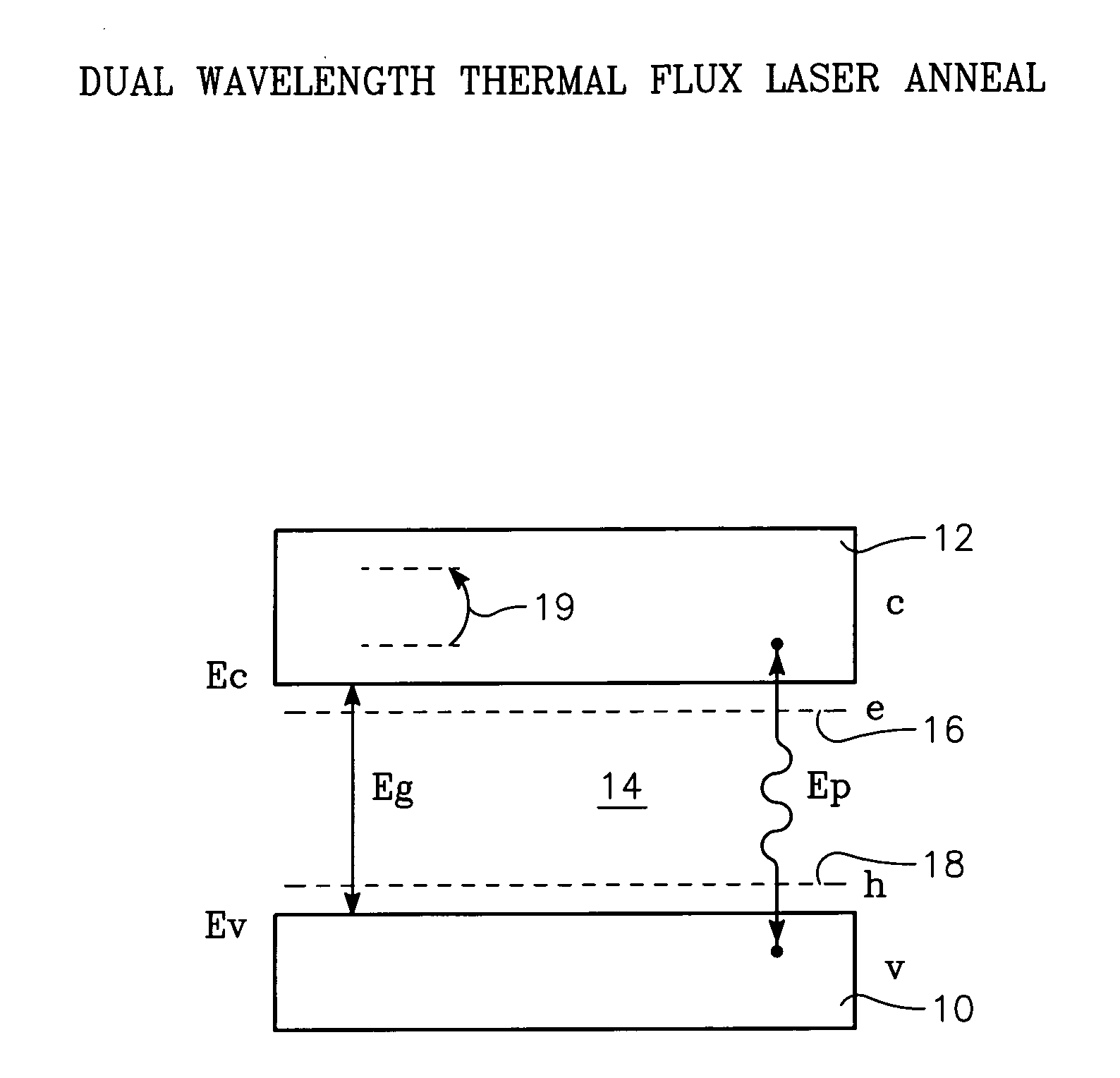
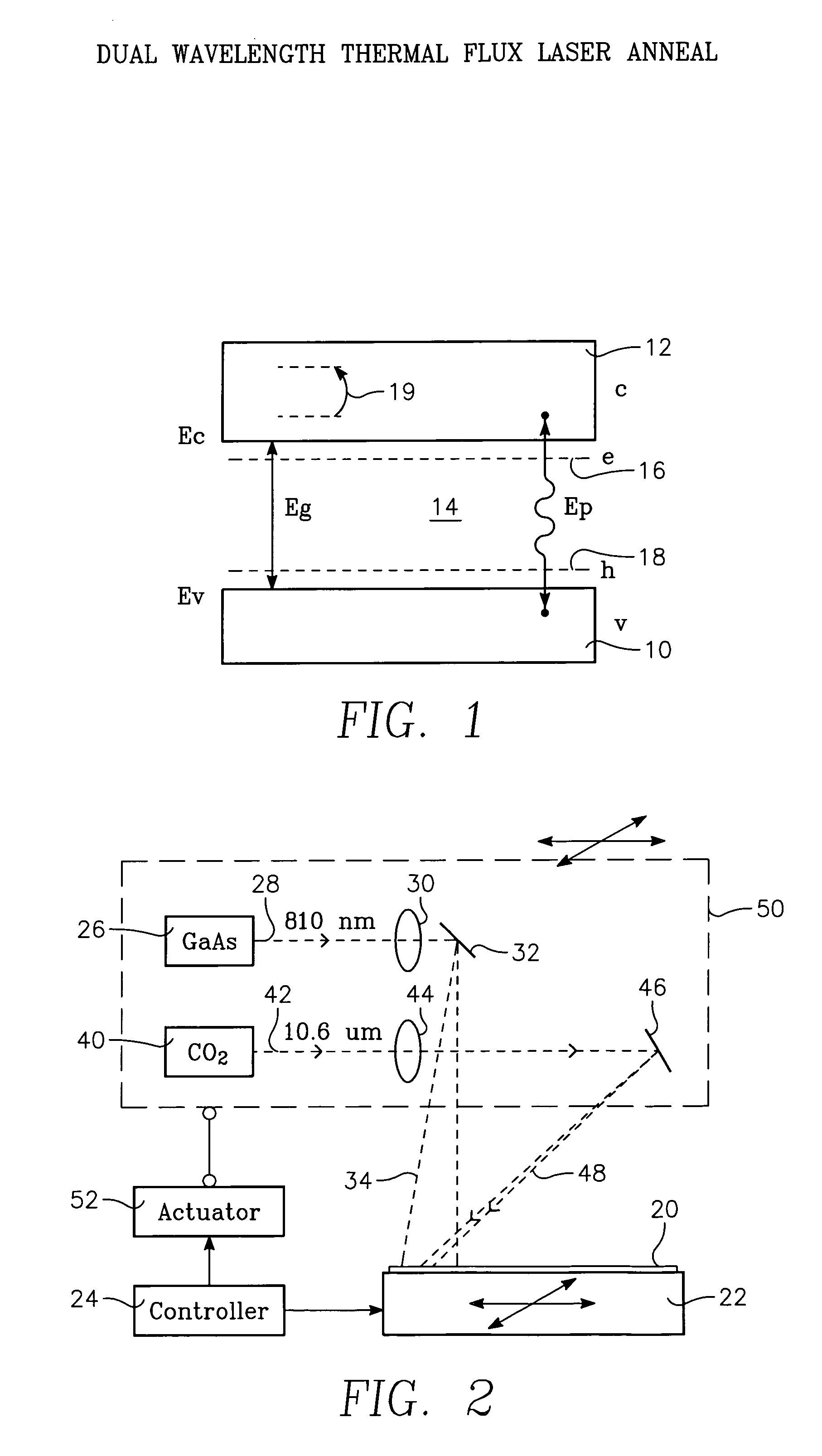
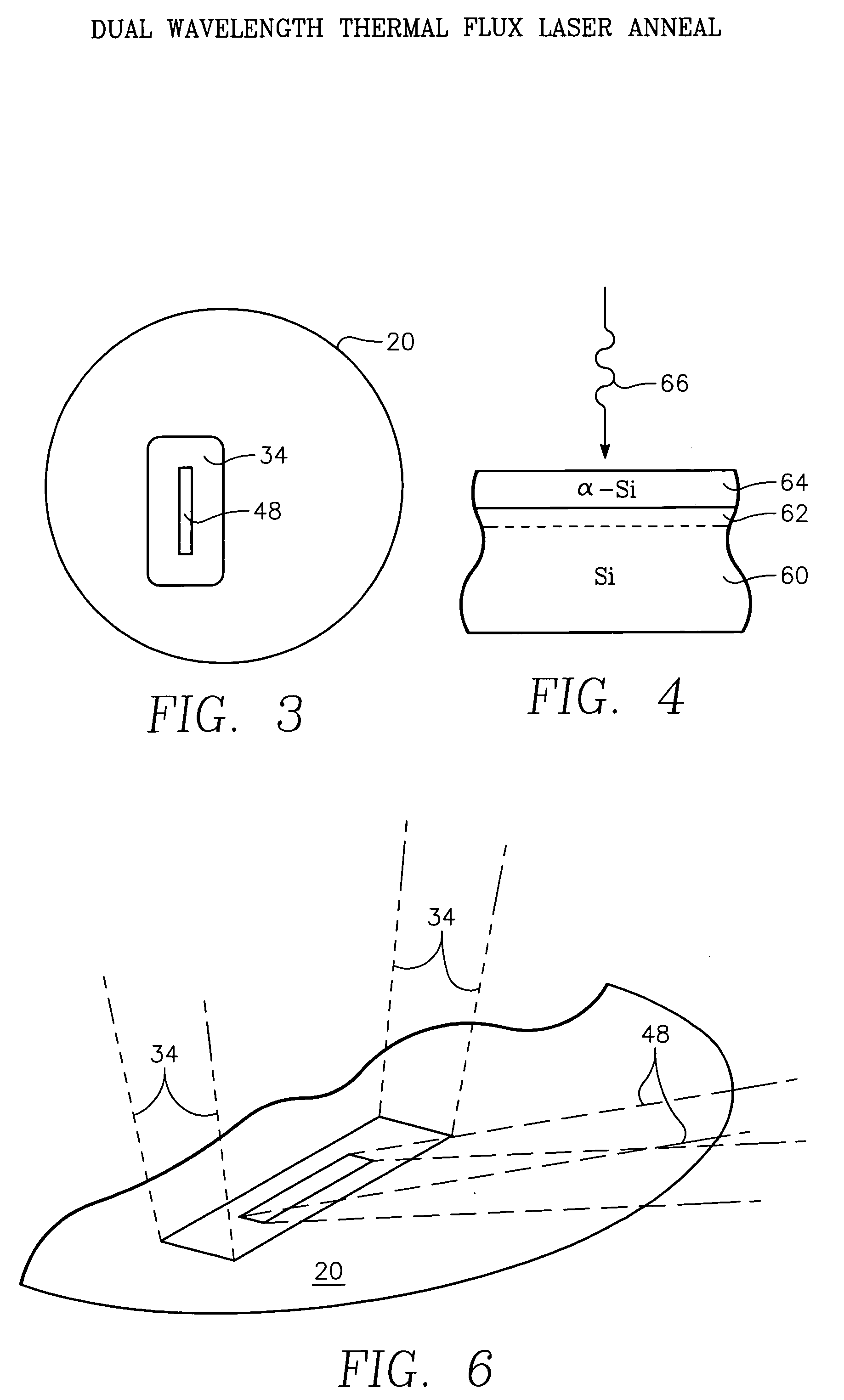
Dual wavelength thermal flux laser anneal
ActiveUS7279721B2Effective radiationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingLight beam
A thermal processing apparatus and method in which a first laser source, for example, a CO2 emitting at 10.6 μm is focused onto a silicon wafer as a line beam and a second laser source, for example, a GaAs laser bar emitting at 808 nm is focused onto the wafer as a larger beam surrounding the line beam. The two beams are scanned in synchronism in the direction of the narrow dimension of the line beam to create a narrow heating pulse from the line beam when activated by the larger beam. The energy of GaAs radiation is greater than the silicon bandgap energy and creates free carriers. The energy of the CO2 radiation is less than the silicon bandgap energy so silicon is otherwise transparent to it, but the long wavelength radiation is absorbed by the free carriers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fabrication of silicon nano wires and gate-all-around MOS devices
InactiveUS20070298551A1Quality improvementEnhance the quantum effectNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCapacitance
The invention relates to methods for manufacturing semiconductor devices. Processes are disclosed for implementing suspended single crystal silicon nano wires (NWs) using a combination of anisotropic and isotropic etches and spacer creation for sidewall protection. The core dimensions of the NWs are adjustable with the integration sequences: they can be triangular, rectangular, quasi-circular, or an alternative polygonal shape. Depending on the length of the NWs, going from the sub-micron to millimeter range, the NWs may utilize support from anchors to the side, during certain processing steps. By changing the lithographic dimensions of the anchors compared to the NWs, the anchors may be reduced or eliminated during processing. The method covers, among other things, the integration of Gate-All-Around NW (GAA-NW) MOSFETs on a bulk semiconductor. The GAA structure may consist of a silicon core fabricated as specified in the invention, surrounded by any usable gate dielectric, and finally by a gate material, such as polysilicon or metal. The source and drain of the GAA-NW may be connected to the bulk semiconductor to avoid self heating of the device over a wide range of operating conditions. The GAA-NW MOS capacitor can also be used for the integration of a Gate-All-Around optical phase modulator (GAA modulator). The working principle for the optical modulator is modulation of the refractive index by free carrier accumulation or inversion in a MOS capacitive structure, which changes the phase of the propagating light.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
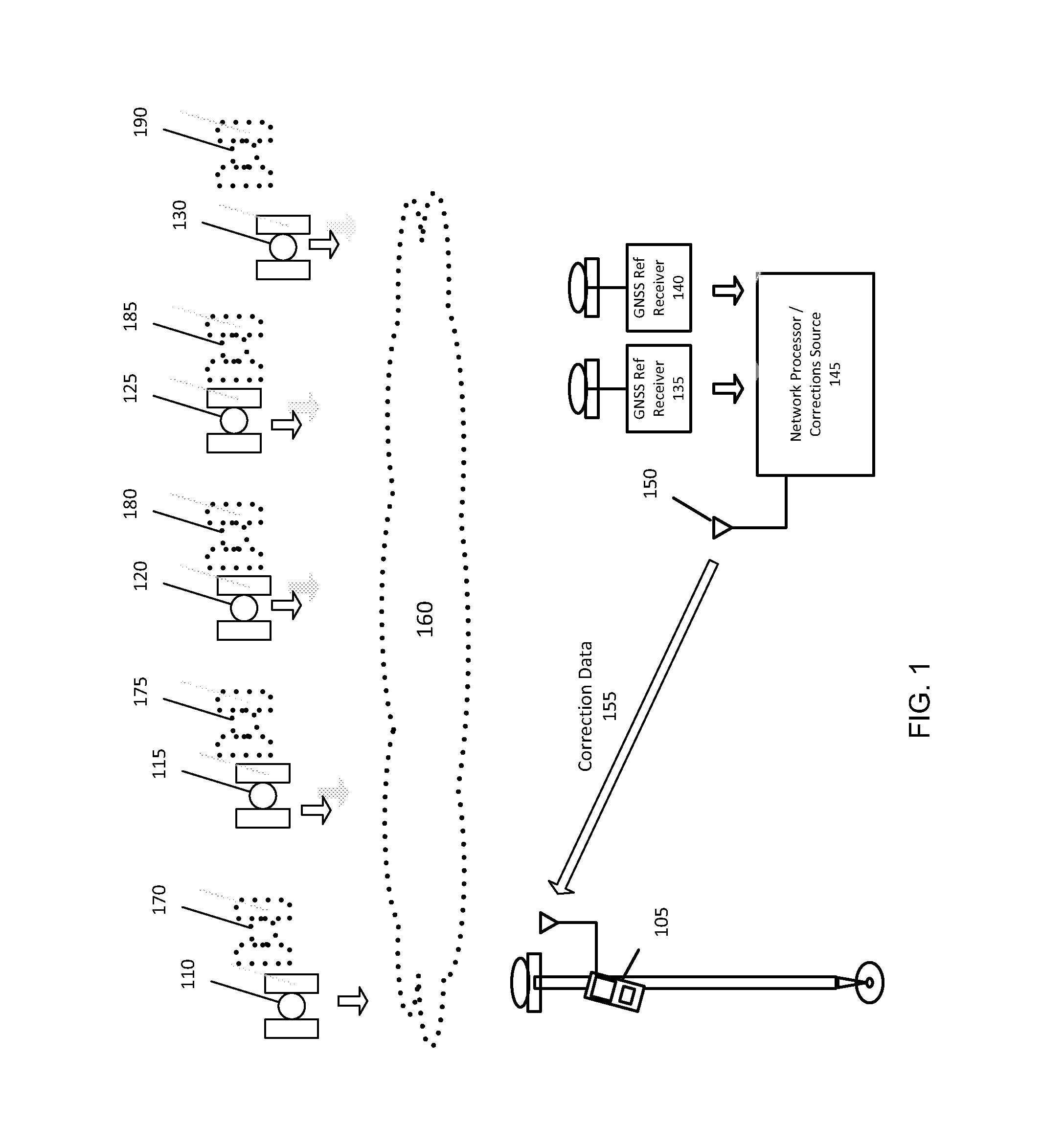
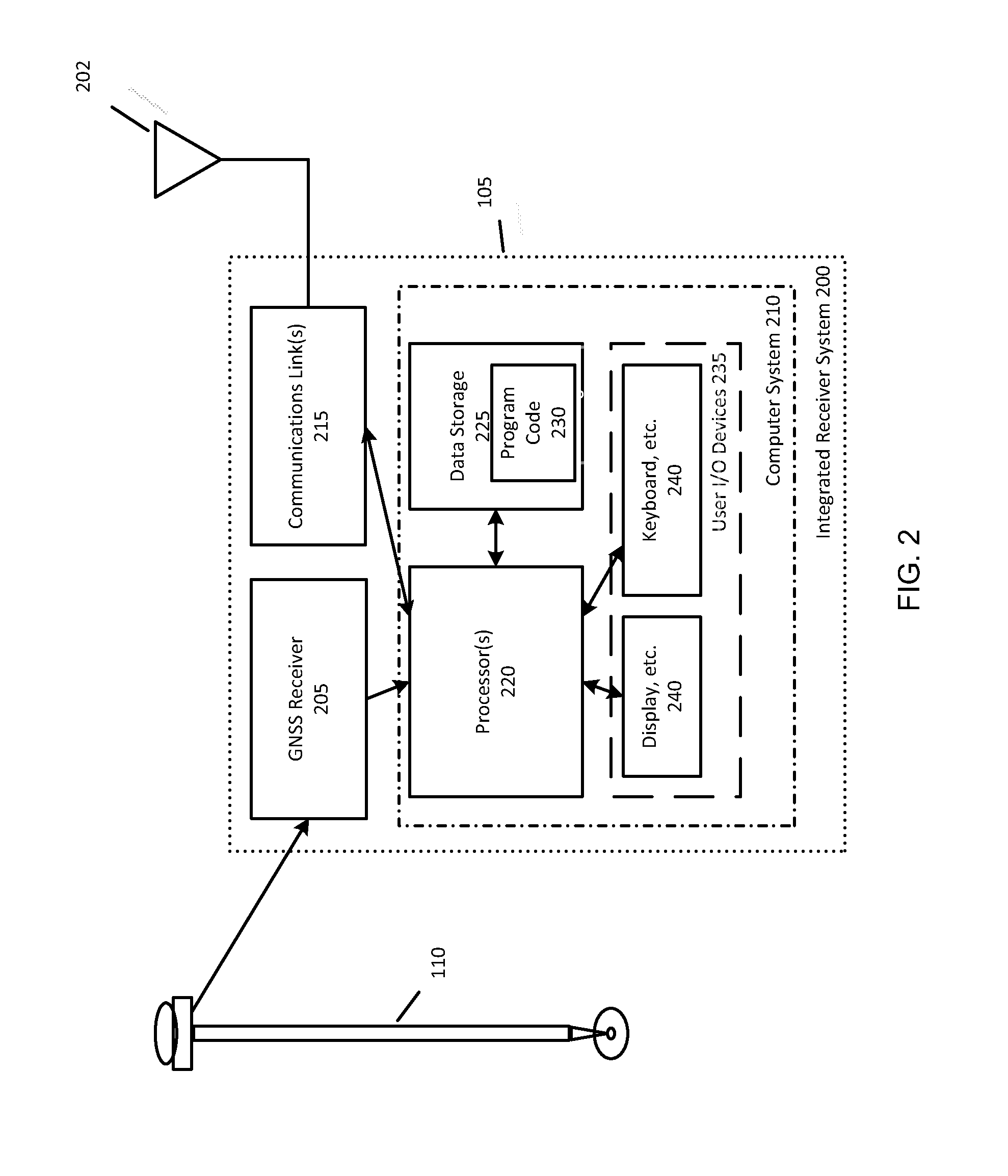
GNSS Signal Processing with Known Position for Reconvergence
ActiveUS20140002300A1Good precisionShorten the timeSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguitySignal processing
Methods and apparatus provide for positioning of a rover antenna from GNSS data derived from multi-frequency signals and correction data derived from a network of reference stations. At each of a plurality of epochs, the GNSS data and correction data are used to estimate values defining a rover antenna position and a set of multi-frequency ambiguities. An ionospheric-free carrier-phase ambiguity per satellite is estimated based on a known rover antenna position. The estimated ionospheric-free carrier-phase ambiguity is combined with an estimated widelane ambiguity and with an estimated ionospheric-free ambiguity and with values defining the known rover antenna position to obtain values defining an aided rover antenna position and aided multi-frequency ambiguities.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
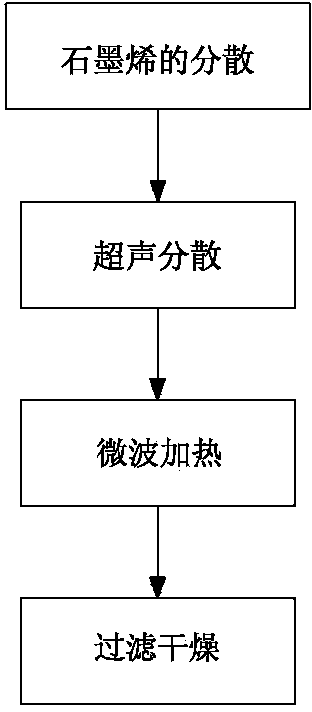
Method for preparing nitrogen-doped graphene with high nitrogen doping amount
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen-doped graphene with high nitrogen doping amount. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dispersing of graphene; (2) ultrasonic dispersion; (3) microwave heating; and (4) filtering and drying. The nitrogen doping amount of the nitrogen-doped graphene prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is 10%-15.0%, the density of free carriers in graphene is greatly increased by the high nitrogen doping amount, the interaction of graphene and metal is enhanced, no oxidation pretreatment is carried out, no toxic solvent is used in the reaction process, reactants are simple in component, reaction conditions are mild, and the prepared nitrogen-doped graphene has excellent electrochemical property and can be used for preparation of new energy materials such as lithium ion battery, lithium-air battery, super capacitor electrode material and fuel cell oxygen reduction catalysts. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a high-pressure kettle is heated by using microwaves without high temperature; the method is low in energy consumption, is carried out in an airtight environment and therefore hardly causes environment pollution; in addition, the method is simple in process and convenient to operate and needs less production equipment, thus, the cost is further reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN XFH NEW ENERGY MATERIALS CO LTD
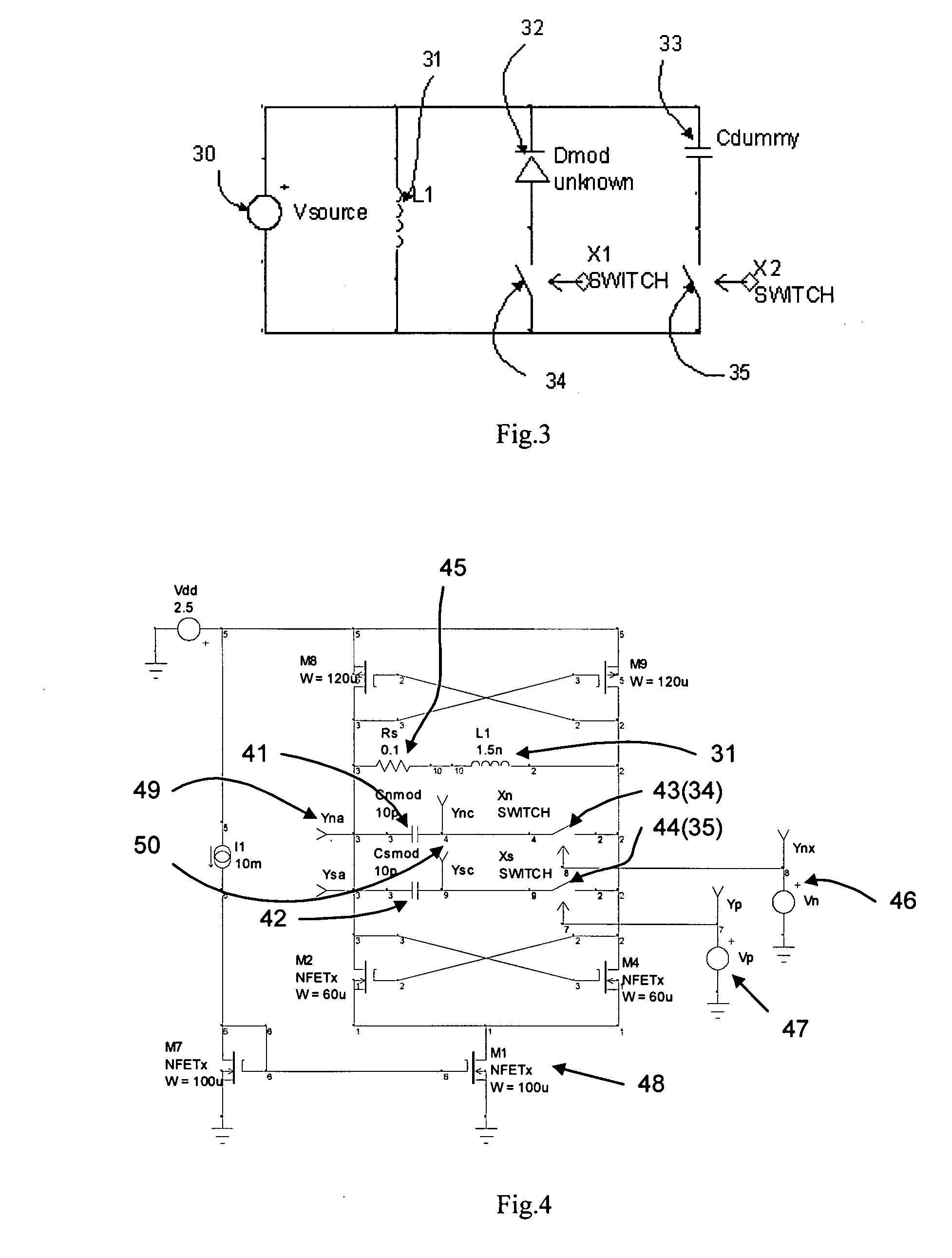
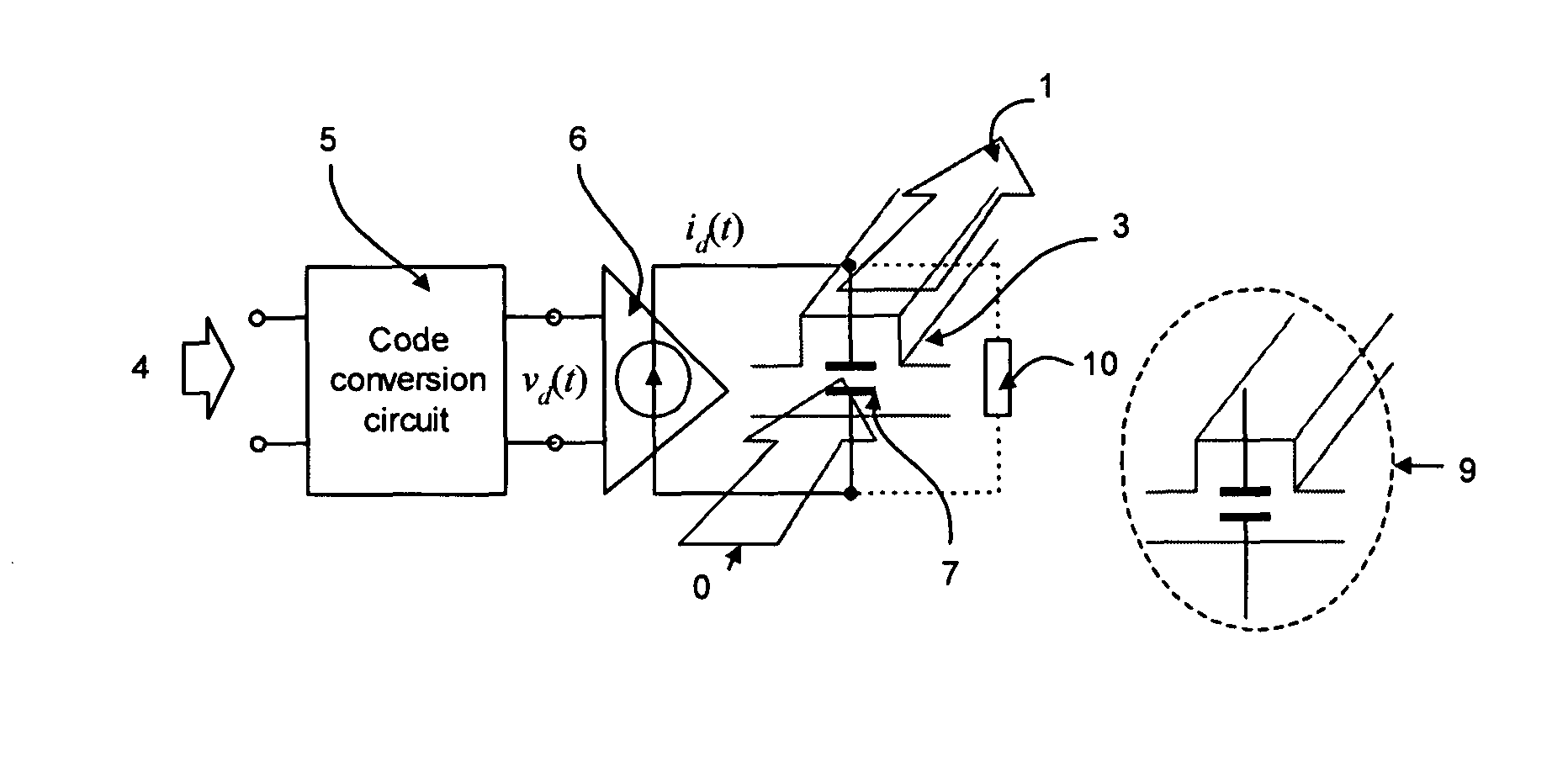
Circuit architecture for electro-optic modulation based on free carrier dispersion effect and the waveguide capacitor structures for such modulator circuitry using CMOS or Bi-CMOS process
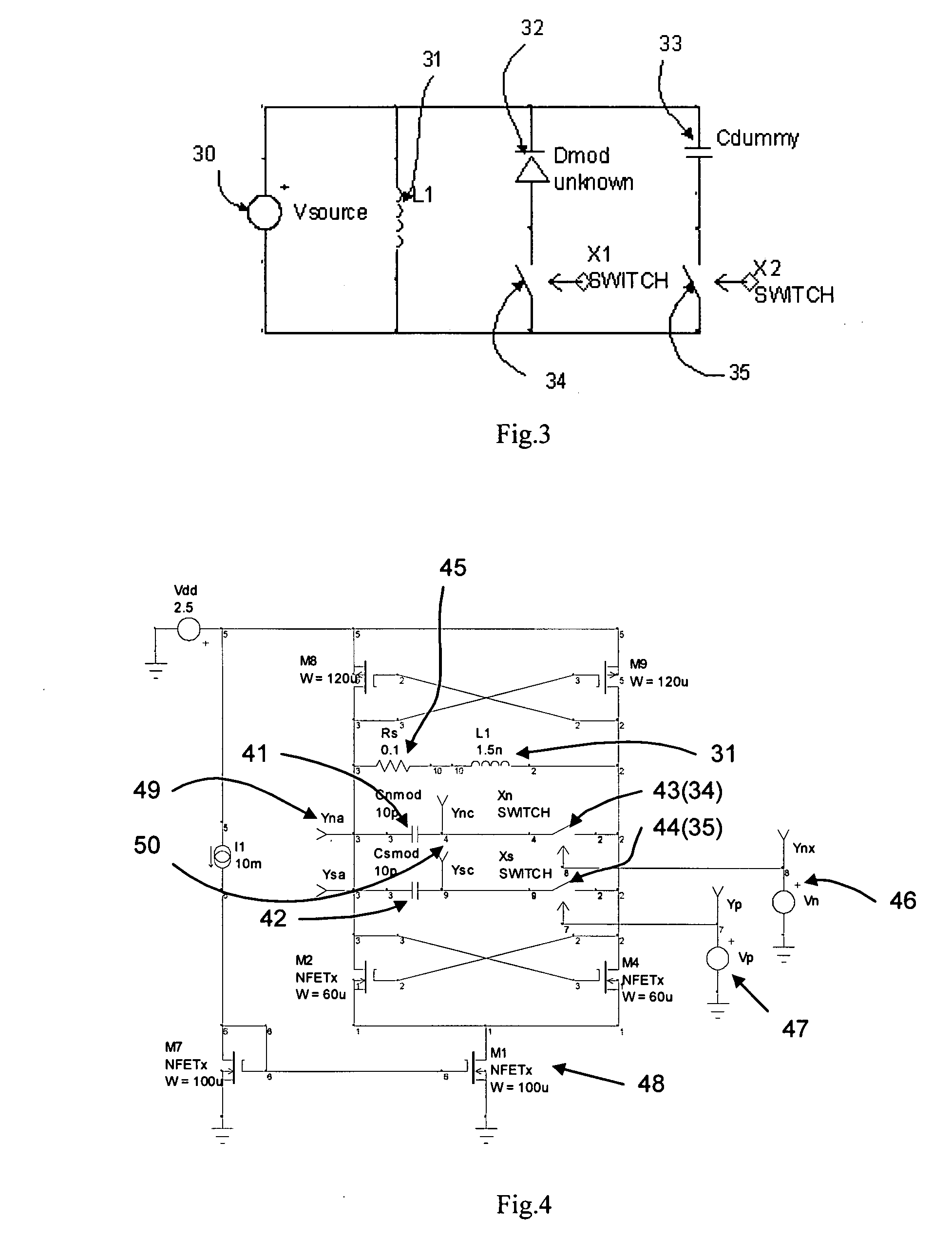
ActiveUS20070292073A1Improve performanceOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsHemt circuitsElectro-optic modulator
New circuit architecture for electro-optic modulator based on free-carrier dispersion effect is invented, in which the waveguide capacitor of the modulator is embed in the circuits and physically layout together with transistors, the switching of the modulator occurs in transistors, and as the result, the electro-optical modulation occurs in the waveguide capacitor. The invented modulator is not one physical device, it is actually a circuit. Several circuit design techniques are imported, leading to several new modulator circuits that have very high operation speed and very small power consumption. Several new waveguide capacitor structures are also invented that allow high efficient modulator circuits to be built.
Owner:LI BING
Dual wavelength thermal flux laser anneal
ActiveUS20060234458A1Effective radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusHeat fluxLaser source
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
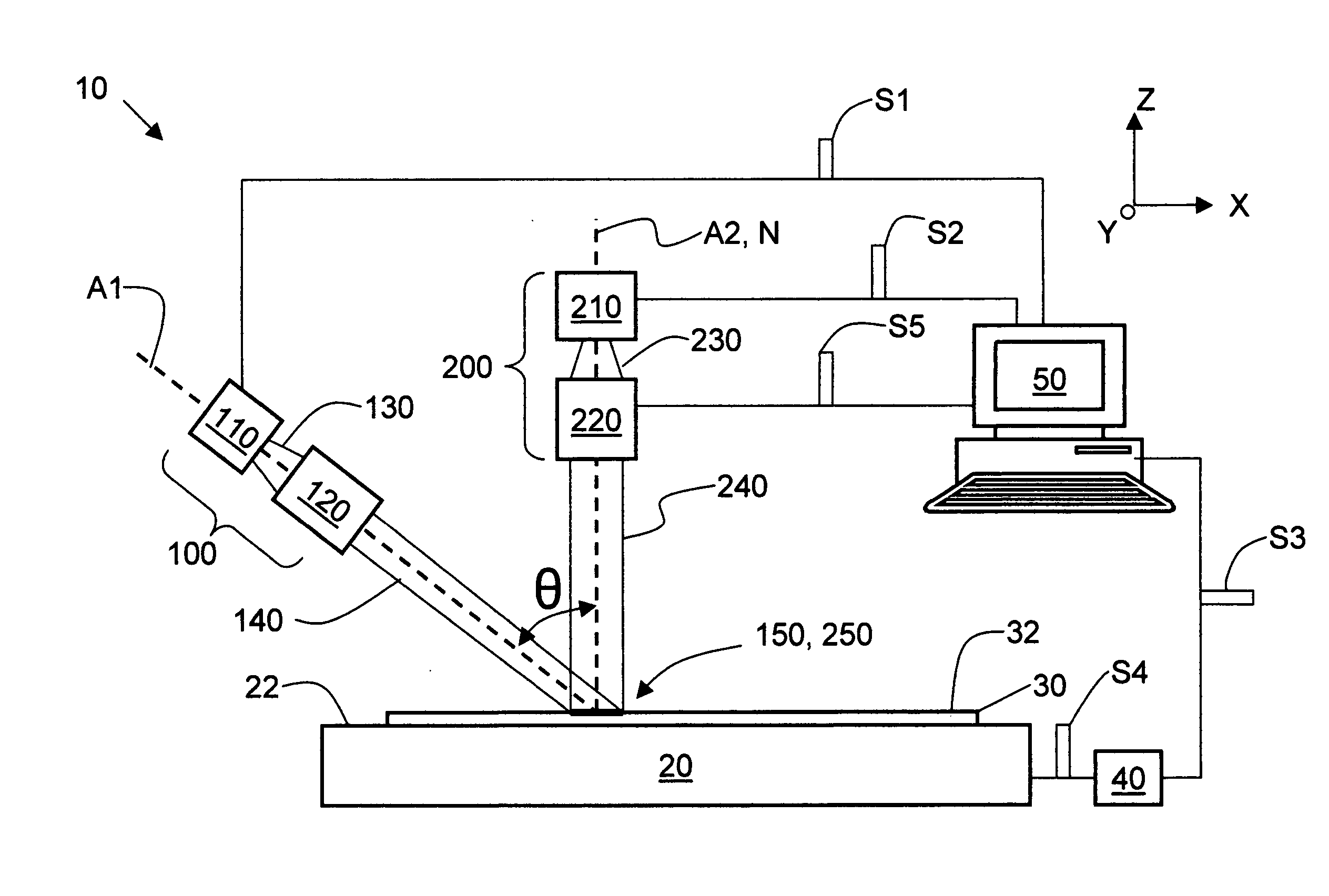
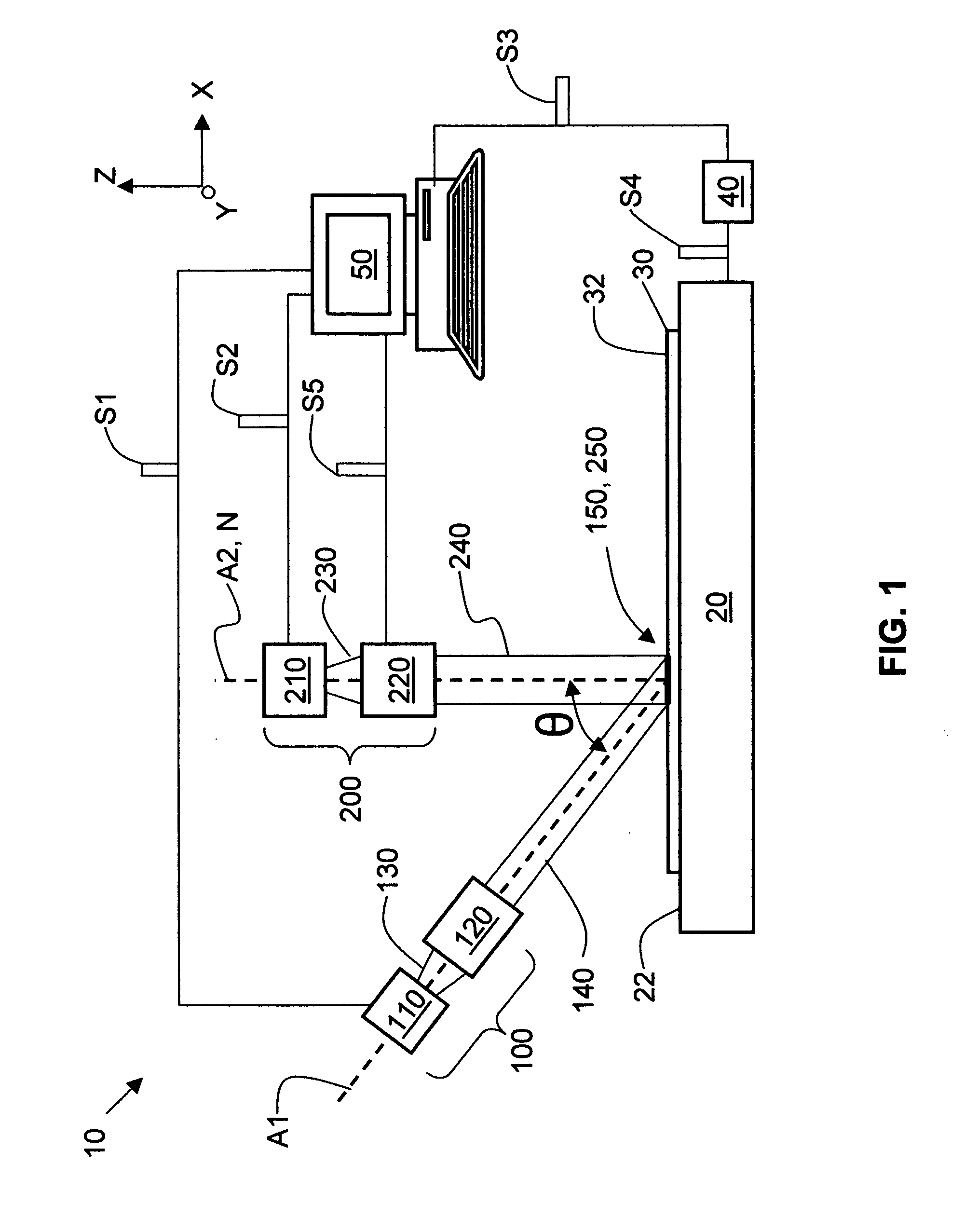
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing undoped and lightly doped substrates without pre-heating
InactiveUS20070072400A1Promote absorptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiological activationHeat treated
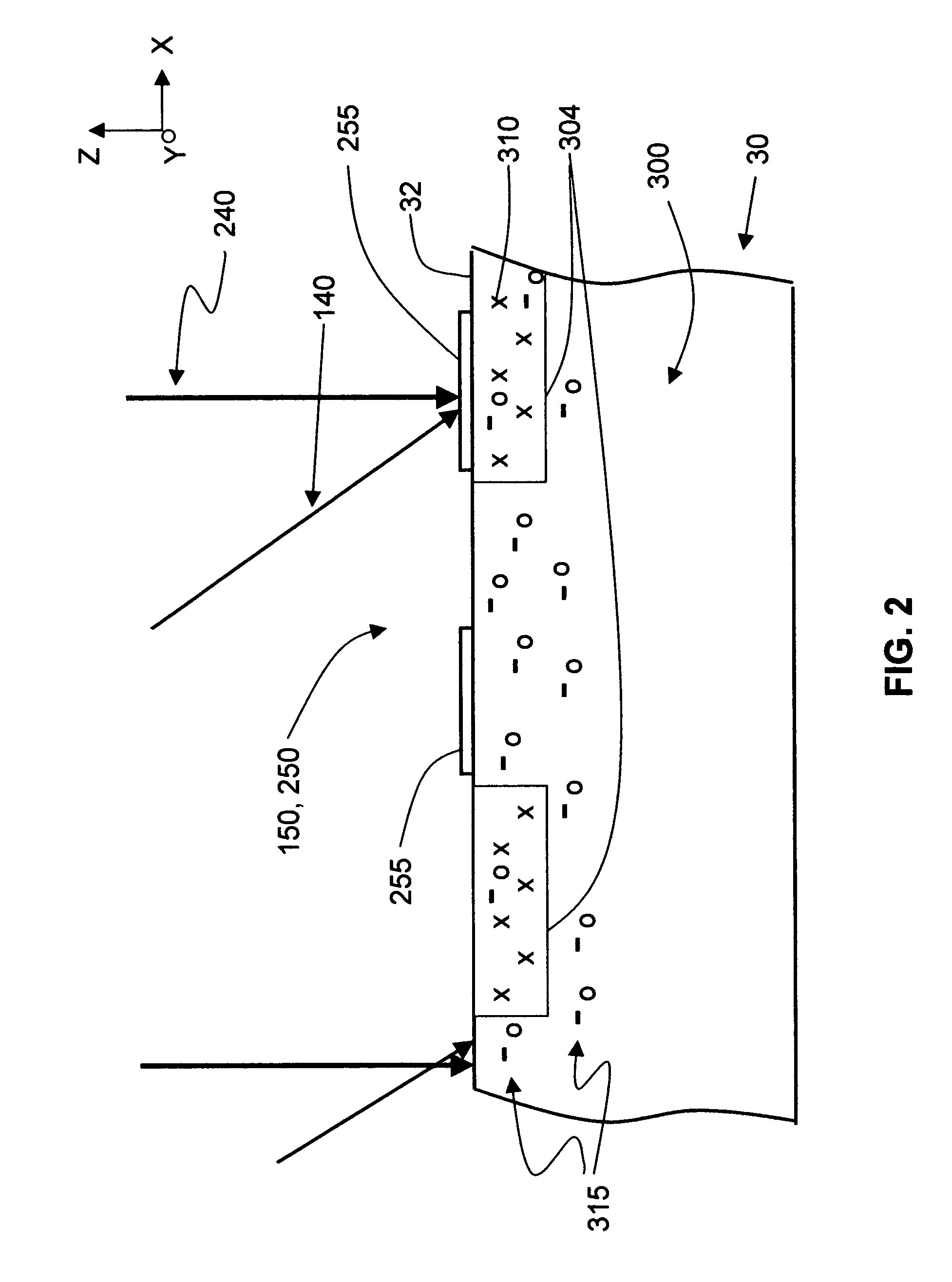
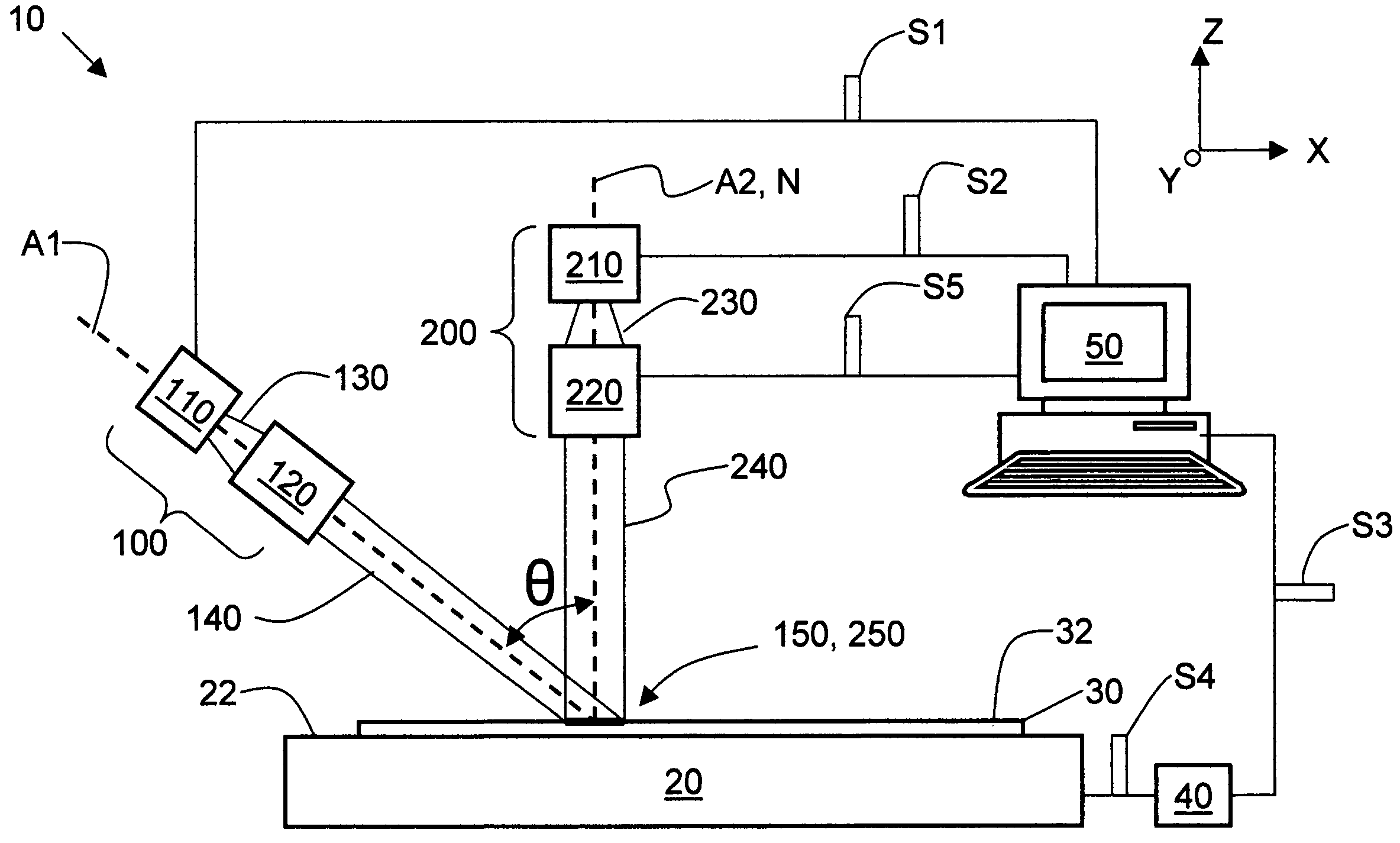
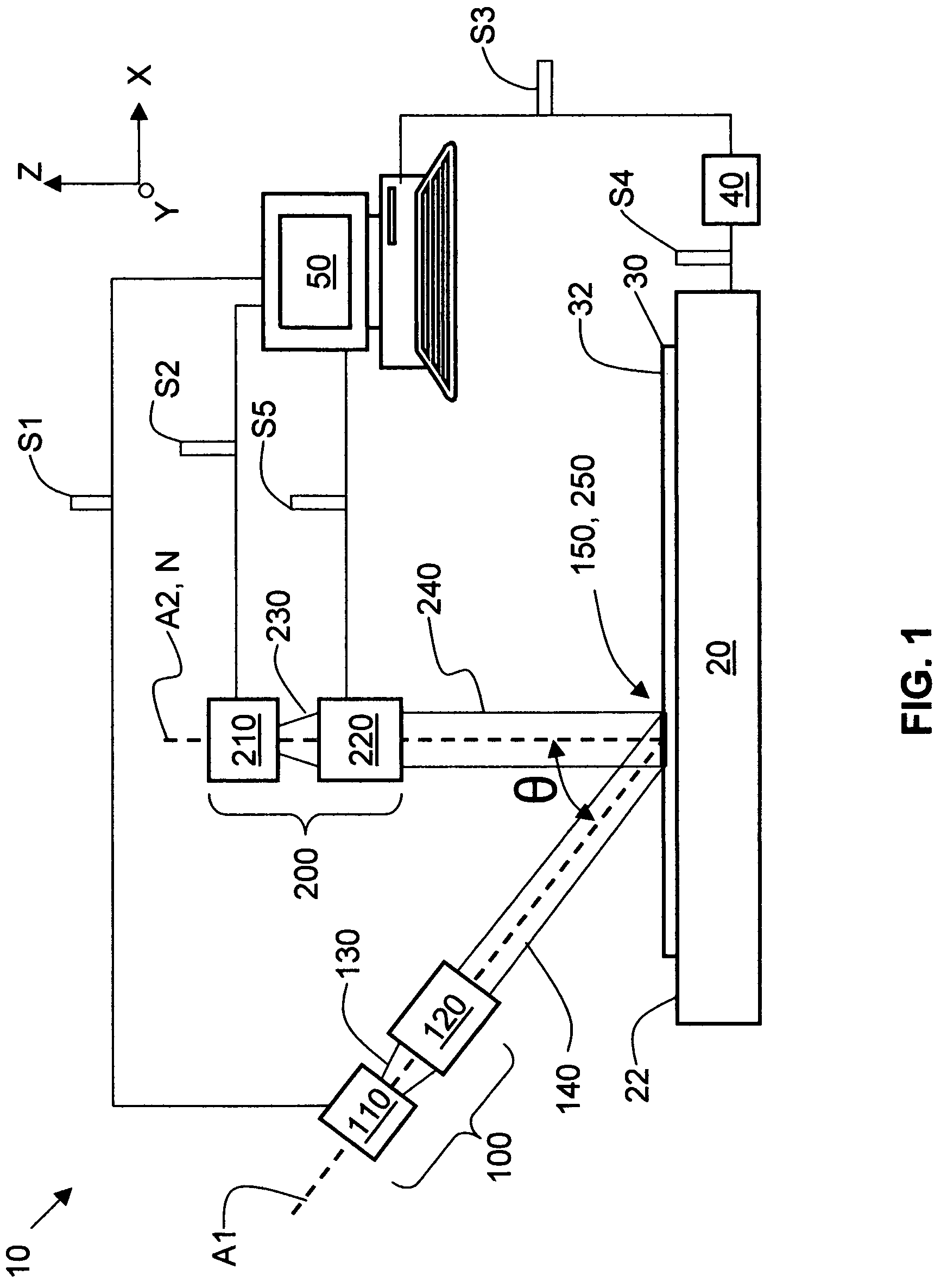
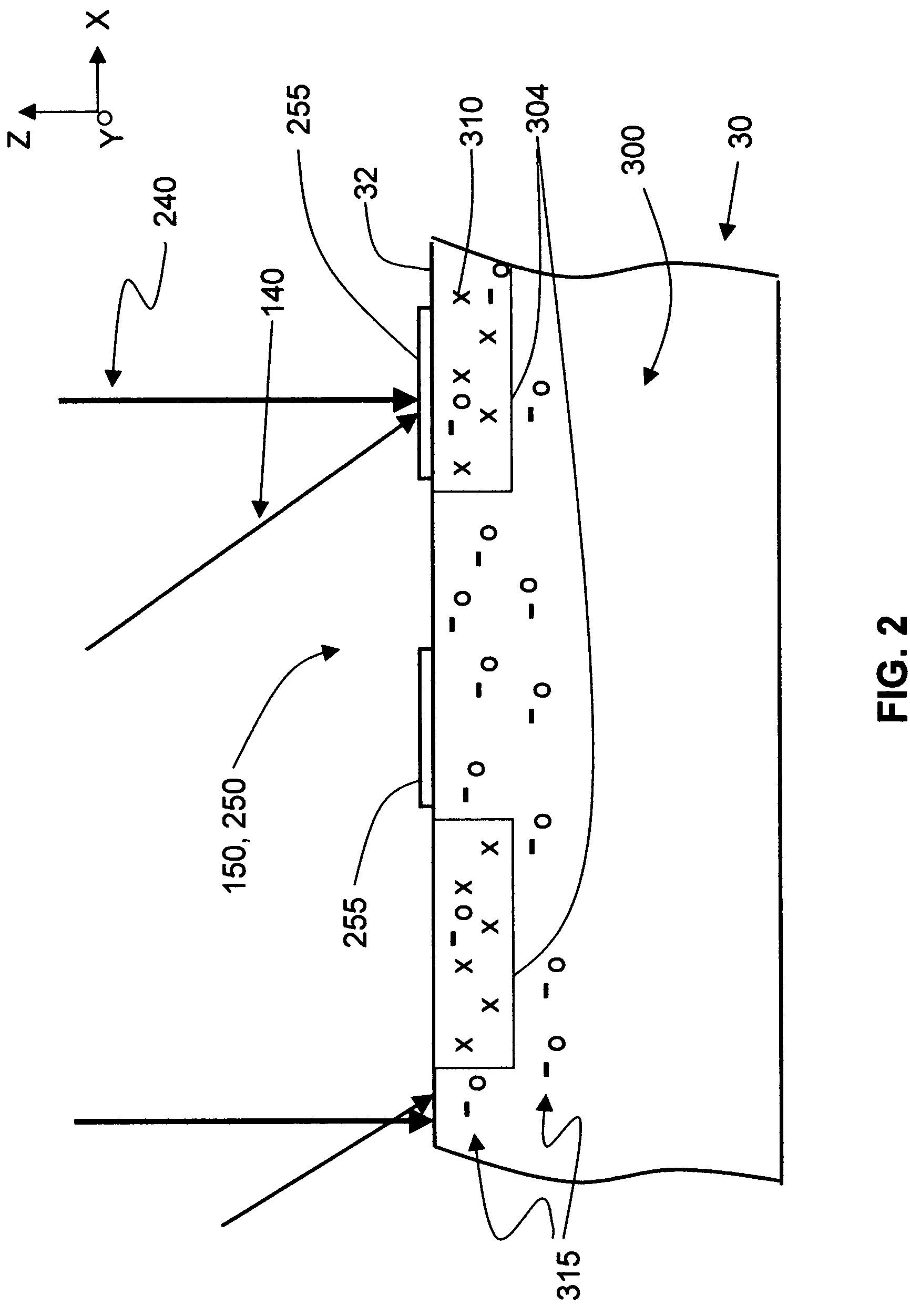
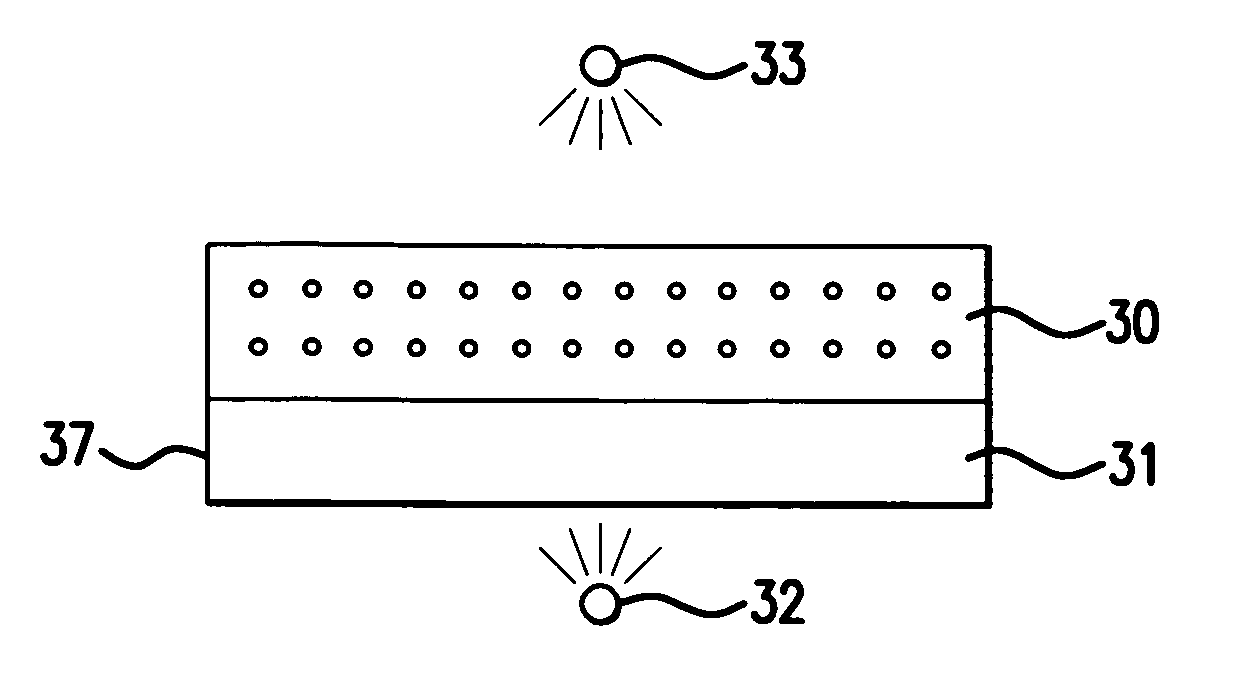
Apparatus for and methods of thermally processing undoped or lightly doped semiconductor wafers (30) that typically are not very absorptive of an annealing radiation beam (14) are disclosed. The apparatus (10) uses a relatively low power activating radiation beam (240) with a photon energy greater than the bandgap energy of the semiconductor substrate in order to generate free carriers (315) at and near the substrate surface (32). The free carriers so generated enhance the absorption by the substrate surface of the longer wavelength annealing radiation beam. The annealing radiation beam is thus able to rapidly heat the substrate surface and permit subsequent rapid cooling to obtain, for example, a high level of electrical activity (activation) of dopants (310) formed therein. The invention obviates the need to pre-heat the substrate in order to increase absorption of the annealing radiation beam when performing thermal processing.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Light-harvesting antennae for organic solar cells
InactiveUS20080087326A1Improve energy conversion efficiencyReduce photodegradationNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellUltraviolet
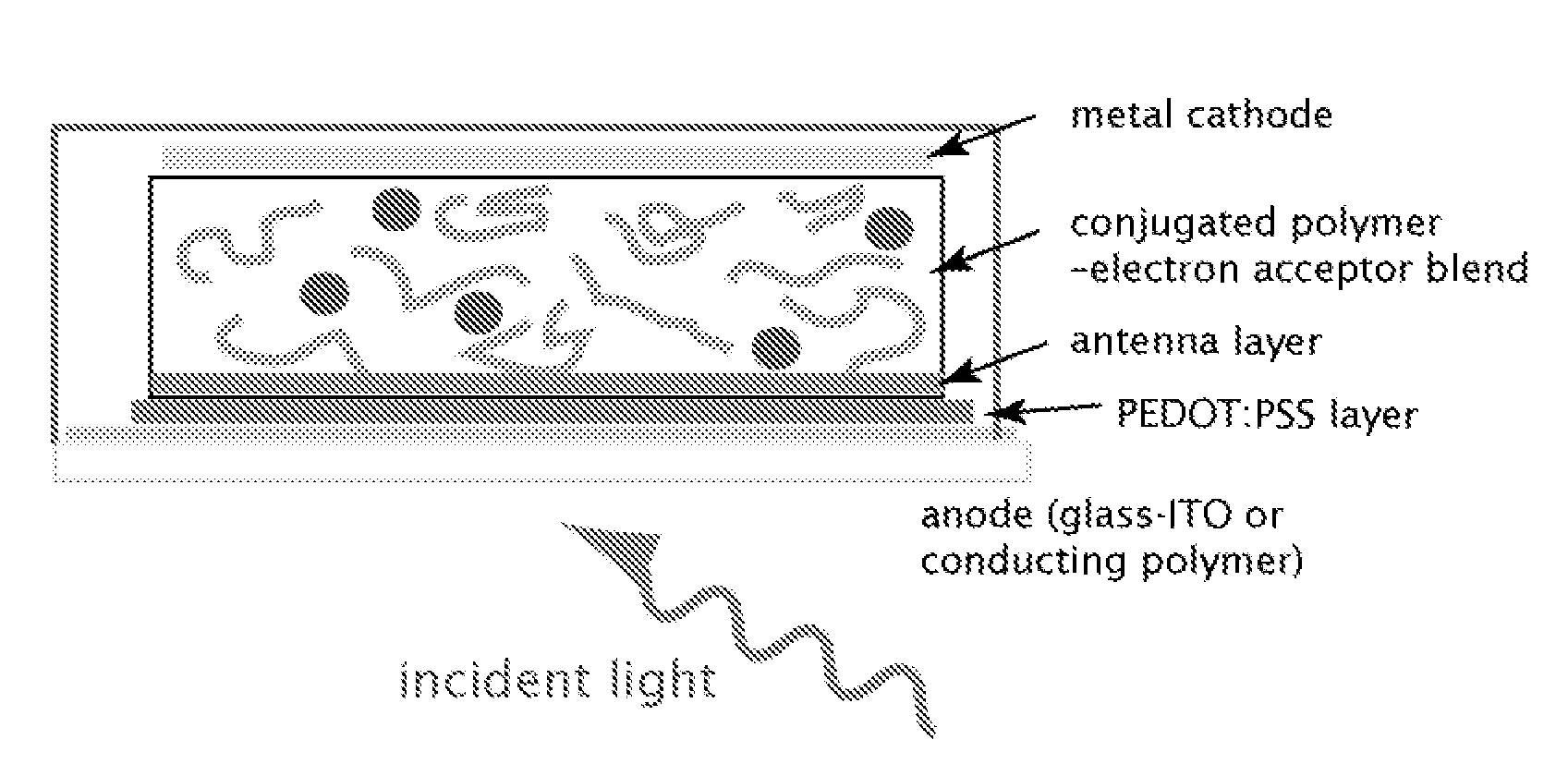
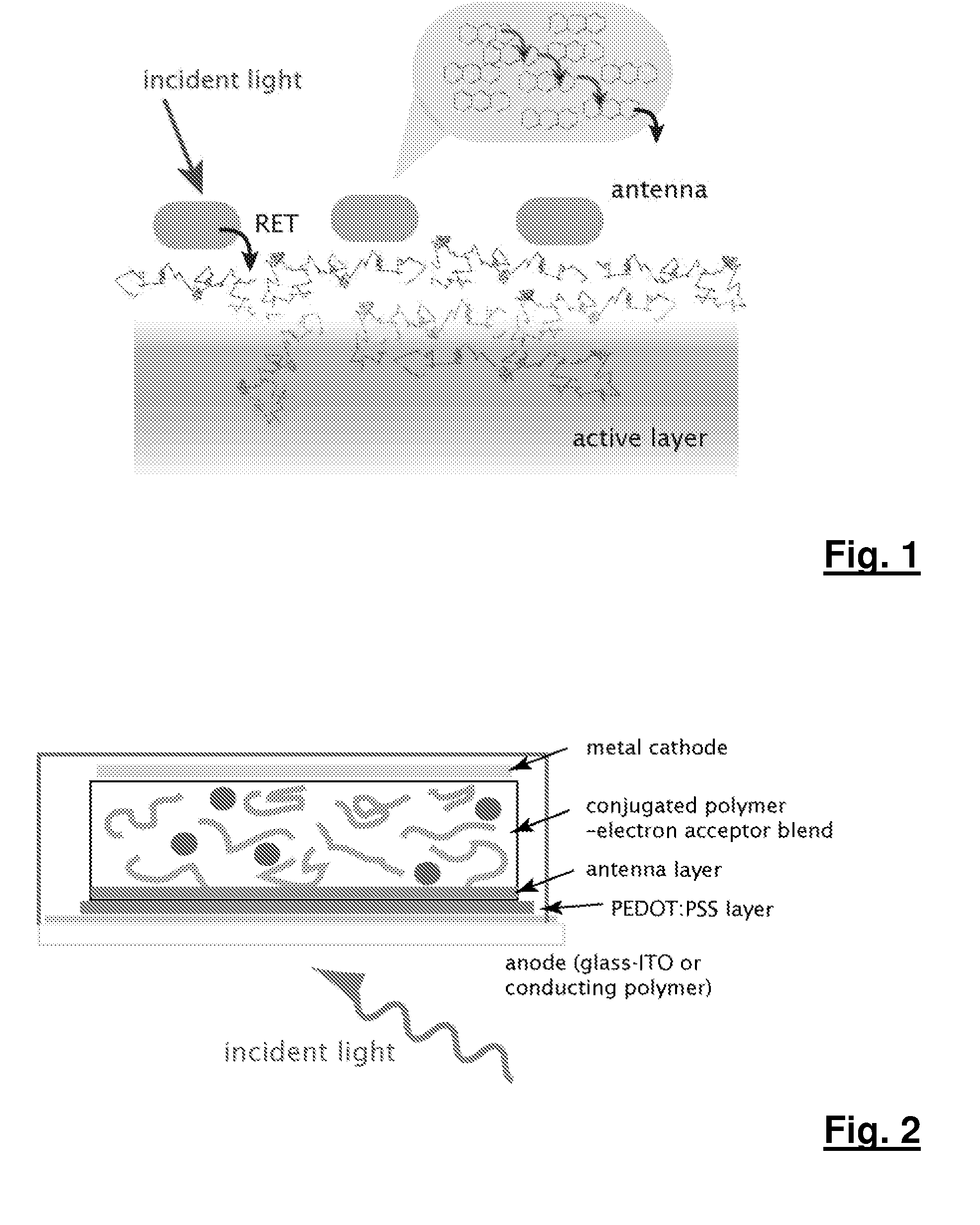
An antenna layer is provided separate from an active layer in a solar cell device based on organic materials, enabling improved energy conversion in the solar cell devices by increasing the efficiency and spectral cross-section for the capture of incident light. The antenna layer may be anthracene or an anthracene derivative, for example. The antenna layer is operable to harvest light and transfer captured excitation energy to the active layer of the solar cell device using an energy transfer mechanism, wherein the charge separation and / or the formation of free carriers takes place. The antenna layer also limits the ultraviolet exposure of the active layer thus extending the operating life of the solar cell. The active layer and the antenna layer of a solar cell device may be independently optimized such that there is an increased spectral range and / or cross-section of light absorption and thus a higher photovoltaic efficiency.
Owner:SCHOLES GREGORY DENTON +2
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing undoped and lightly doped substrates without pre-heating
Apparatus for and methods of thermally processing undoped or lightly doped semiconductor wafers (30) that typically are not very absorptive of an annealing radiation beam (14) are disclosed. The apparatus (10) uses a relatively low power activating radiation beam (240) with a photon energy greater than the bandgap energy of the semiconductor substrate in order to generate free carriers (315) at and near the substrate surface (32). The free carriers so generated enhance the absorption by the substrate surface of the longer wavelength annealing radiation beam. The annealing radiation beam is thus able to rapidly heat the substrate surface and permit subsequent rapid cooling to obtain, for example, a high level of electrical activity (activation) of dopants (310) formed therein. The invention obviates the need to pre-heat the substrate in order to increase absorption of the annealing radiation beam when performing thermal processing.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
High-speed silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveCN1764863AReduce light lossReduce power consumptionCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideElectricitySurface layer
A silicon-based electro-optical modulator (30) based on a gate region of the first conductivity formed to partially cover the body region of the second conductivity type, having interposed between the contact portions of the gate region and the body region (12, 10) A relatively thin dielectric layer (10). The modulator may be formed on an SOI platform with a body region formed in a relatively thin silicon surface layer of the SOI structure and a gate region formed with a relatively thin silicon layer (10) overlying the SOI structure. The doping of the control gate and body regions is used to form lightly doped regions above and below the dielectric layer, thereby defining the active region of the device (16). Advantageously, the photoelectric field in the active device region is substantially identical to the free carrier concentration region. Therefore, the application of the modulation signal causes the free carriers on both sides of the dielectric layer to accumulate, deplete or invert simultaneously, resulting in high-speed operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
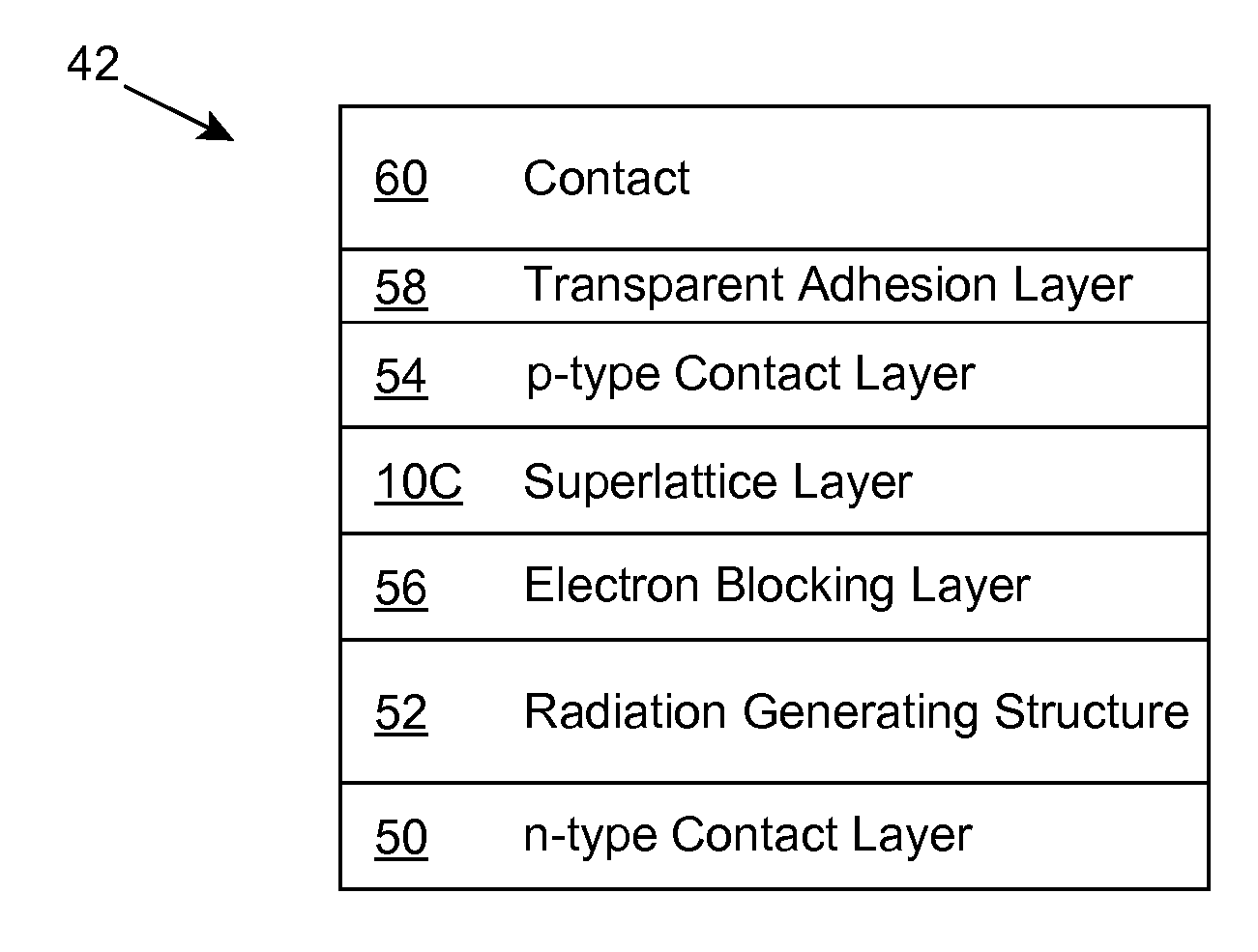
Steady-state non-equilibrium distribution of free carriers and photon energy up-conversion using same
InactiveUS6995371B2Easy to detectImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconSilicon dioxide
Methods and specialized media adapted to the formation of a steady-state, non-equilibrium distribution of free carriers using mesoscopic classical confinement. Specialized media is silicon-based (e.g., crystalline silicon, amorphous silicon, silicon dioxide) and formed from mesoscopic sized particles embedded with a matrix of wide-bandgap material, such as silicon dioxide. An IR to visible light imaging system is implemented around the foregoing.
Owner:SIRICA CORP
Silicon light waveguide with MOS capacitors positioned on the waveguide
The present invention provides a silicon wave-guide (3), with a silicon oxide cladding (2, 4) on a silicon substrate (1). At predetermined positions along the length of the wave-guide, are created metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structures. A poly-silicon, or any other conductive layer (5), is deposited and patterned above the upper cladding (4) and electrical contacts are made to the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5). Upon the application of a potential difference between at least two of the layers from the group comprising the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5), the free carrier concentration at the top and / or bottom layer of the silicon wave-guide (3) is changed by the electric field. The change in the electric field results in a change in the index of refraction, and the change in the index of refraction causes a change in the optical mode propagating in the waveguide (3). The propagation is controlled by controlling the changes in the electric field, which can be enhanced by localized changes in the optical properties of the wave-guide (3) induced by ion implantation (6) or trapping of photo-carriers.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Advanced modulation formats for silicon-based optical modulators
A silicon-based optical modulator is configured as a multi-segment device that utilizes a modified electrical data input signal format to address phase modulation nonlinearity and attenuation problems associated with free-carrier dispersion-based modulation. The modulator is formed to include M separate segments and a digital signal encoder is utilized to convert an N bit input data signal into a plurality of M drive signals for the M modulator segments, where M≧2N / 2. The lengths of the modulator segments may also be adjusted to address the nonlinearity and attenuation problems. Additional phase adjustments may be utilized at the output of the modulator (beyond the combining waveguide).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Semiconductor material doping based on target valence band discontinuity
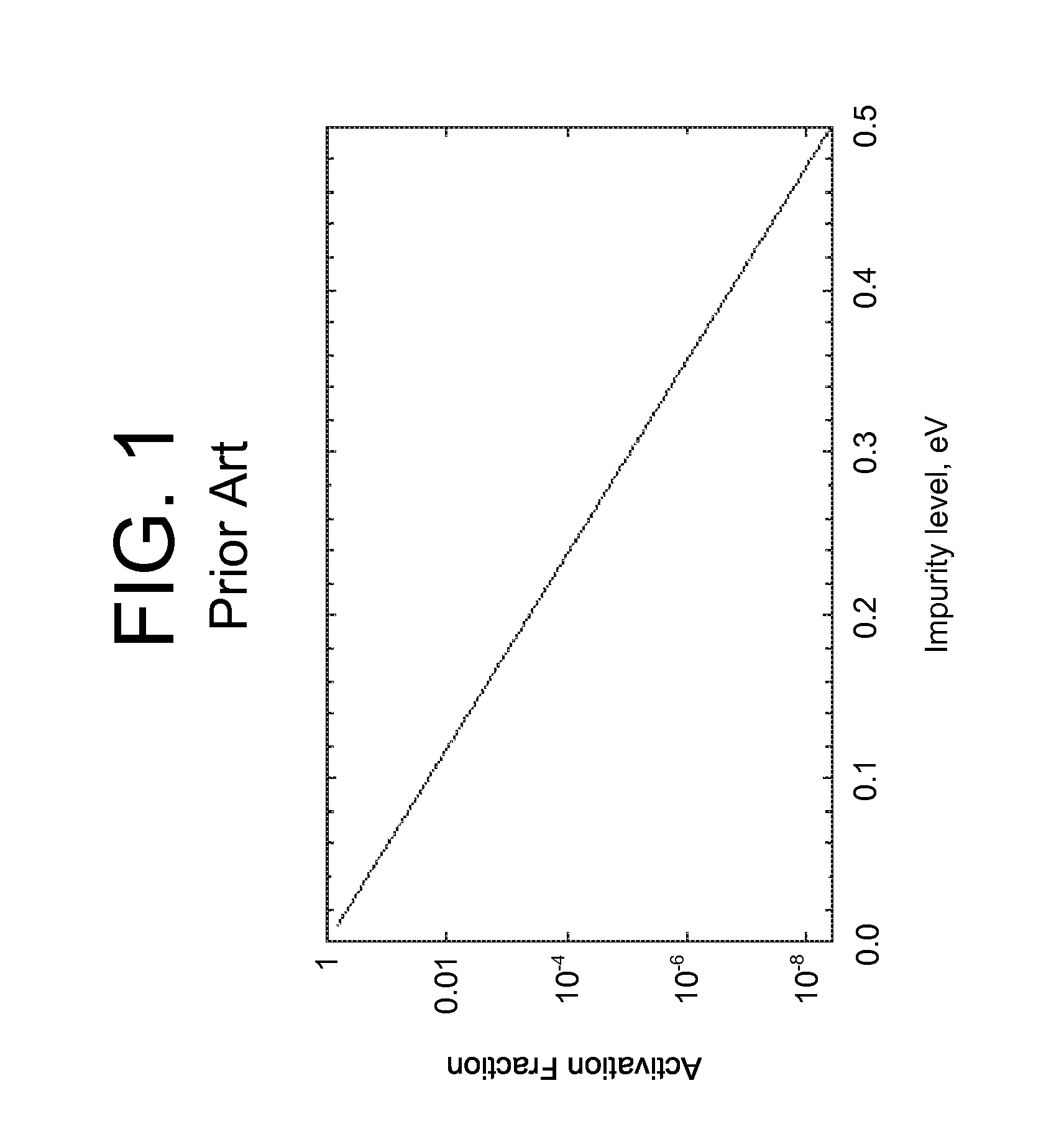
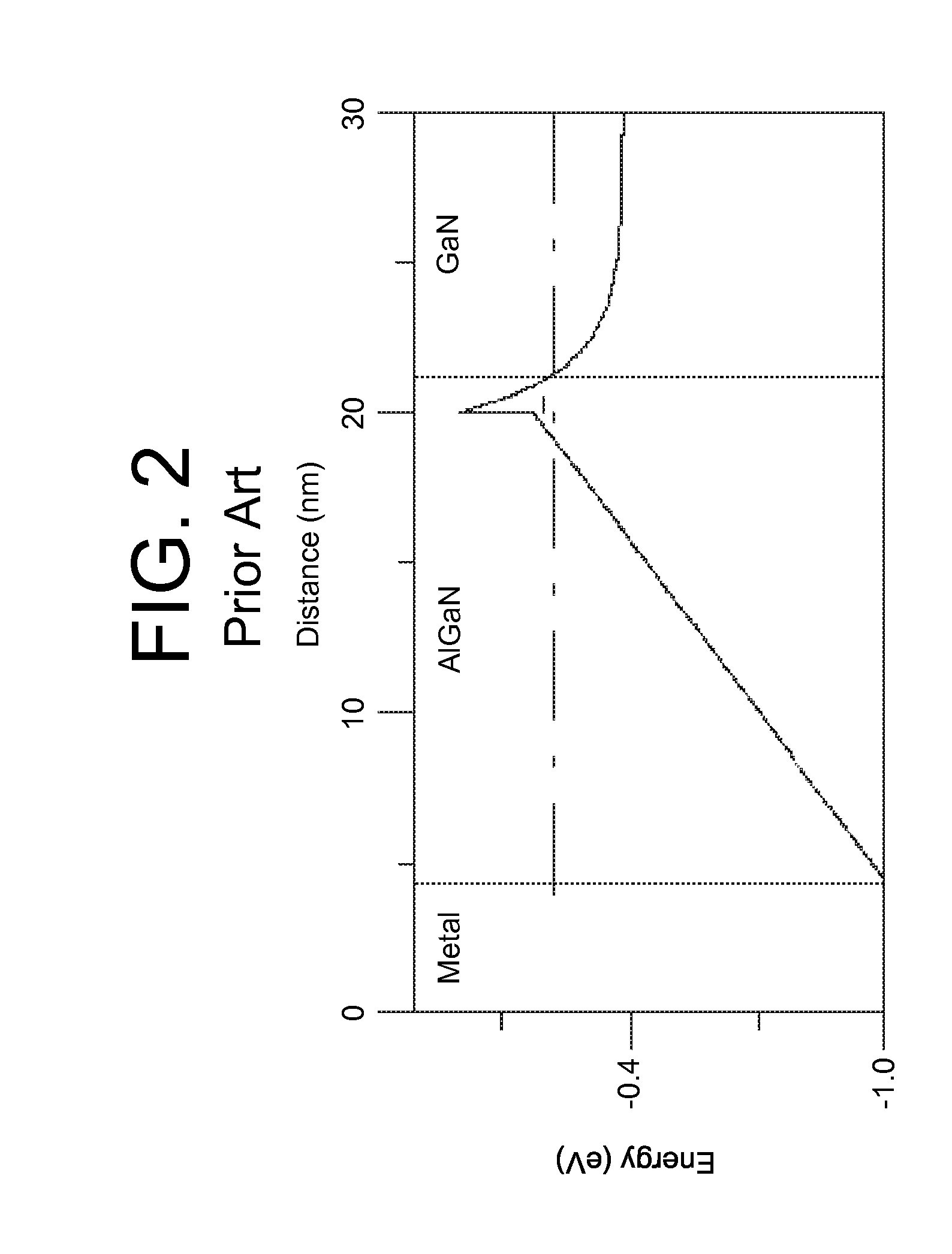
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Enhanced performance mode converter
ActiveUS7242821B2Reduce accumulationPropagation delayCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor materialsSchottky barrier
An optical mode converter comprising a slow wave electrode structure and including Schottky barriers for preventing an accumulation of free carriers in the optical waveguide region of the converter. The Schottky barriers are also used for suppressing higher order modes in the waveguide. Low refractive index insulators are used to allow efficient driving of the device without hindering the impedance or the microwave index of the optical mode converter. Two-photon absorption processes are eliminated through the use of a waveguide semiconductor material having a bandgap of at least twice the photon energy of the light beam propagating through the optical mode converter.
Owner:OPTELIAN ACCESS NETWORKS
Nanowhiskers with pn junctions, doped nanowhiskers, and methods for preparing them
InactiveUS7432522B2Permitted diffusionReduce the amount requiredPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsHeterojunctionNon doped
Nano-engineered structures are disclosed, incorporating nanowhiskers of high mobility conductivity and incorporating pn junctions. In one embodiment, a nanowhisker of a first semiconducting material has a first band gap, and an enclosure comprising at least one second material with a second band gap encloses said nanoelement along at least part of its length, the second material being doped to provide opposite conductivity type charge carriers in respective first and second regions along the length of the of the nanowhisker, whereby to create in the nanowhisker by transfer of charge carriers into the nanowhisker, corresponding first and second regions of opposite conductivity type charge carriers with a region depleted of free carriers therebetween. The doping of the enclosure material may be degenerate so as to create within the nanowhisker adjacent segments having very heavy modulation doping of opposite conductivity type analogous to the heavily doped regions of an Esaki diode. In another embodiment, a nanowhisker is surrounded by polymer material containing dopant material. A step of rapid thermal annealing causes the dopant material to diffuse into the nanowhisker. In a further embodiment, a nanowhisker has a heterojunction between two different intrinsic materials, and Fermi level pinning creates a pn junction at the interface without doping.
Owner:QUNANO
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
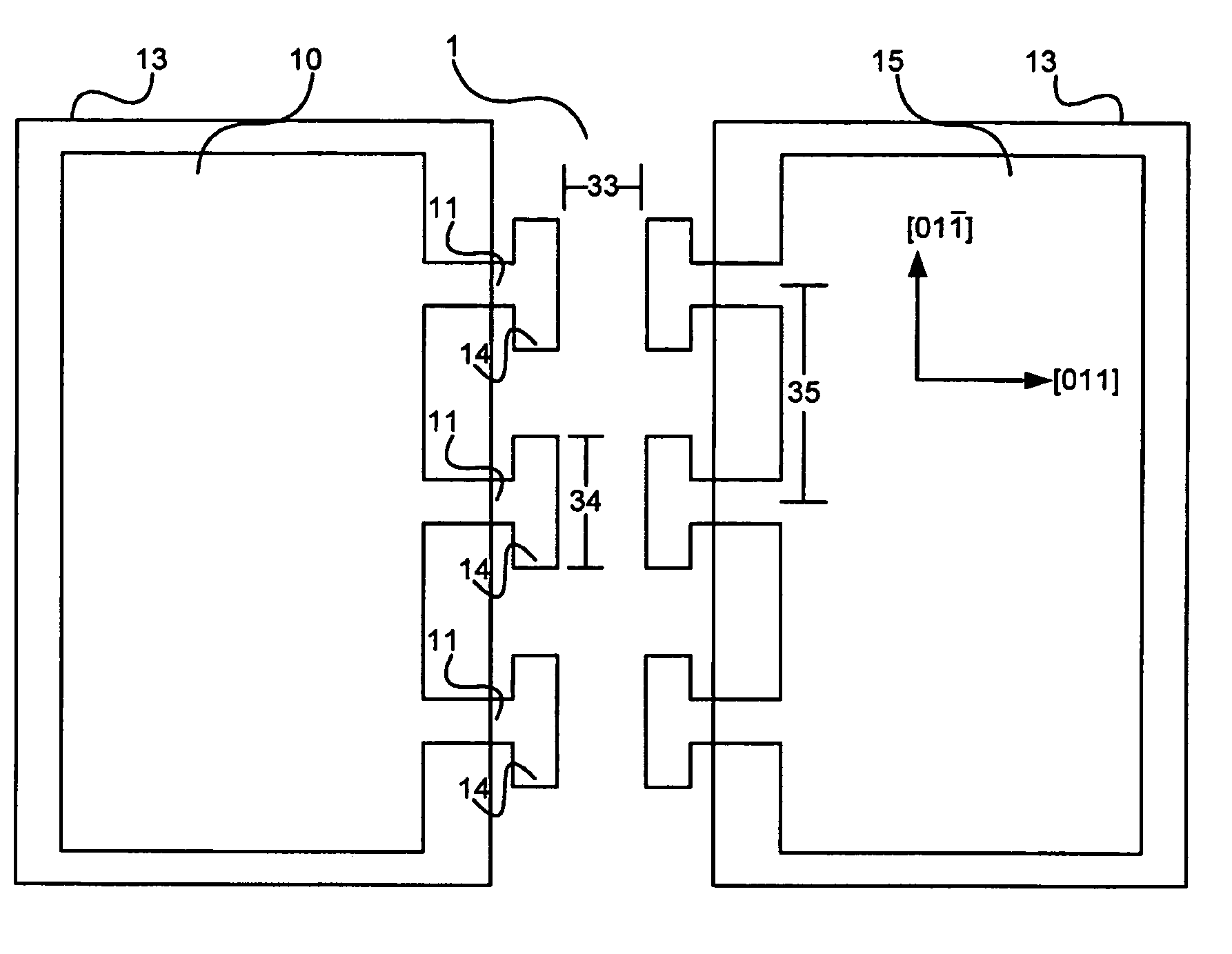
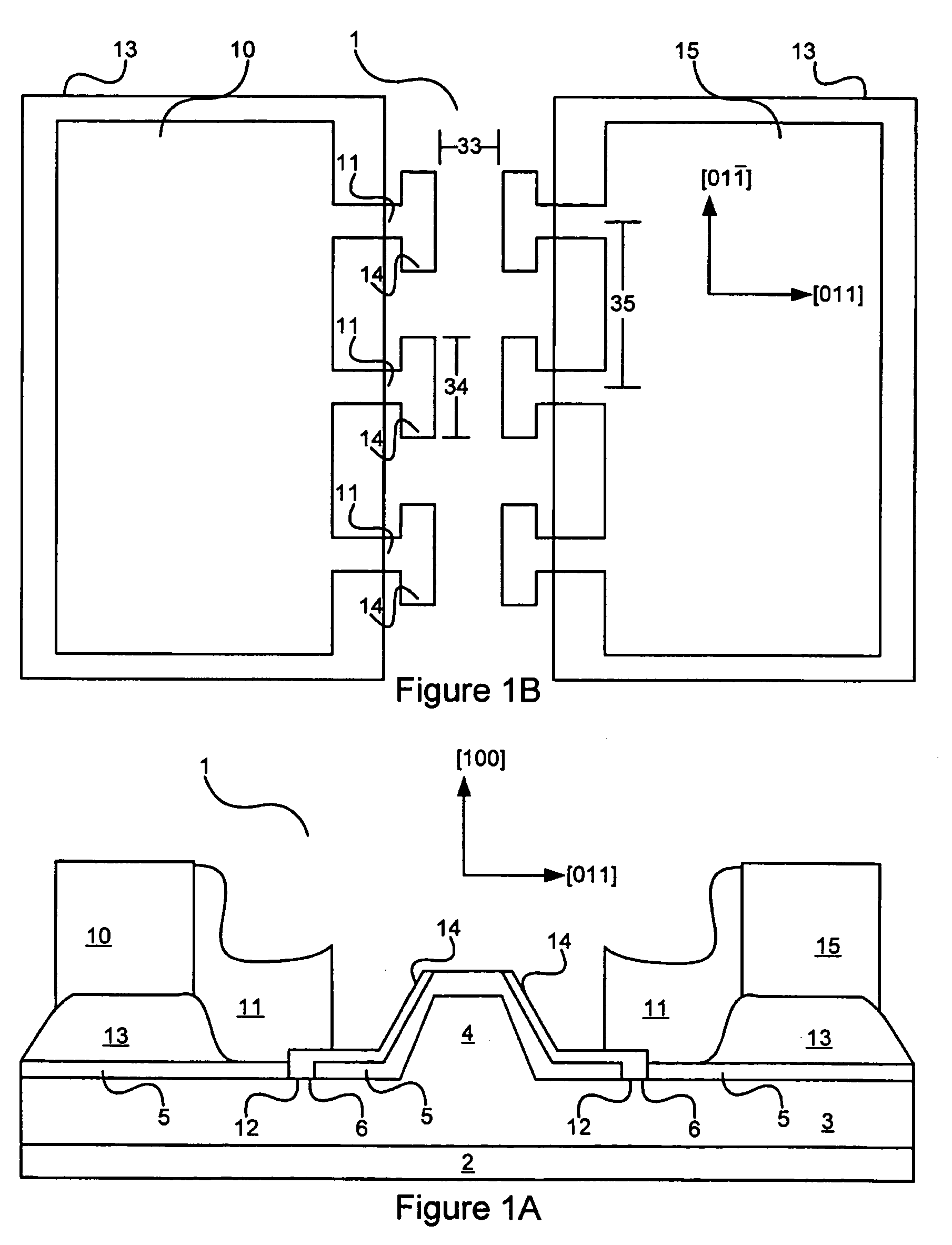
Semiconductor Material Doping
ActiveUS20110253975A1Facilitate real space transferEasy transferNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeDopant
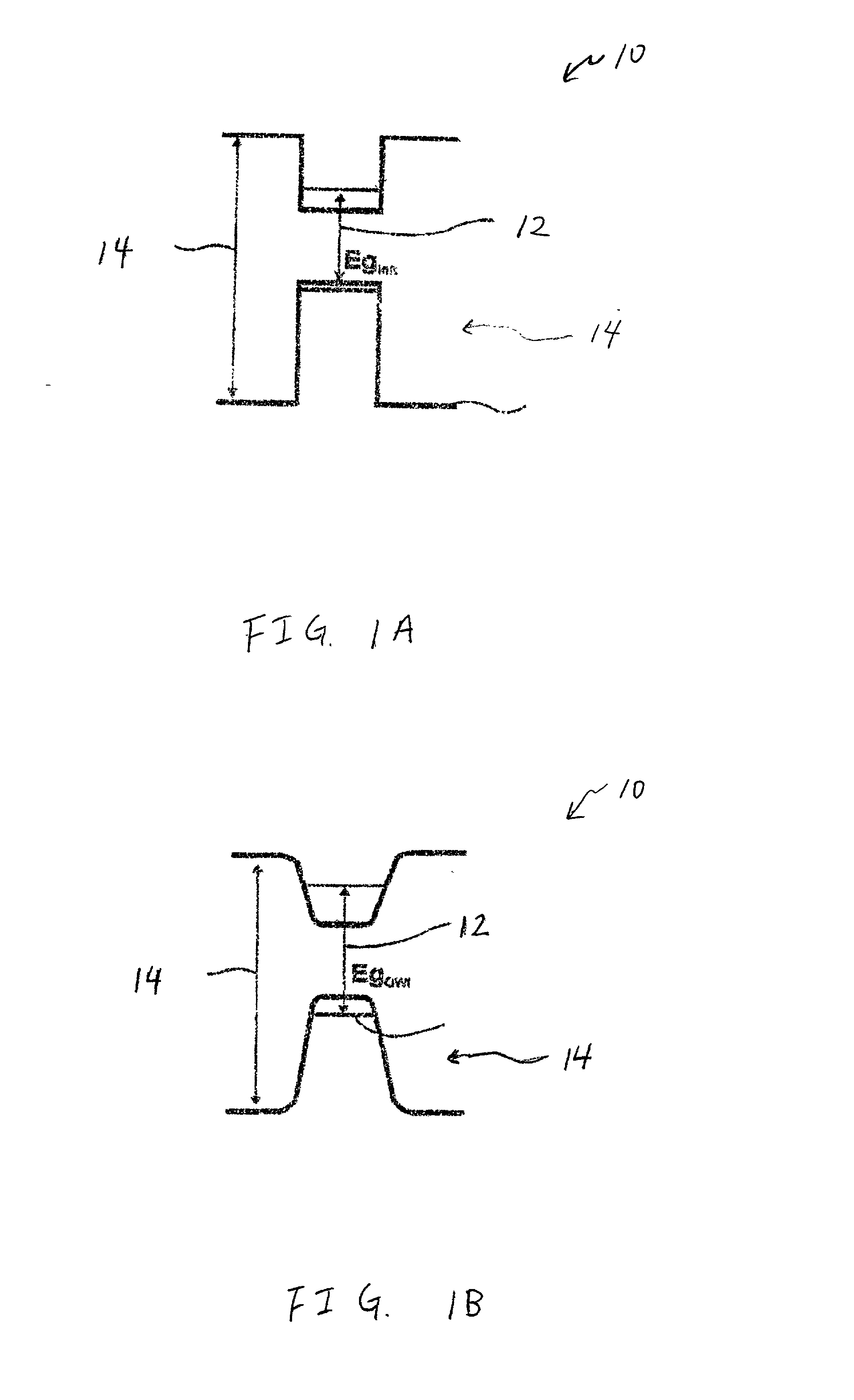
A solution for designing and / or fabricating a structure including a quantum well and an adjacent barrier is provided. A target band discontinuity between the quantum well and the adjacent barrier is selected to coincide with an activation energy of a dopant for the quantum well and / or barrier. For example, a target valence band discontinuity can be selected such that a dopant energy level of a dopant in the adjacent barrier coincides with a valence energy band edge for the quantum well and / or a ground state energy for free carriers in a valence energy band for the quantum well. Additionally, a target doping level for the quantum well and / or adjacent barrier can be selected to facilitate a real space transfer of holes across the barrier. The quantum well and the adjacent barrier can be formed such that the actual band discontinuity and / or actual doping level(s) correspond to the relevant target(s).
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
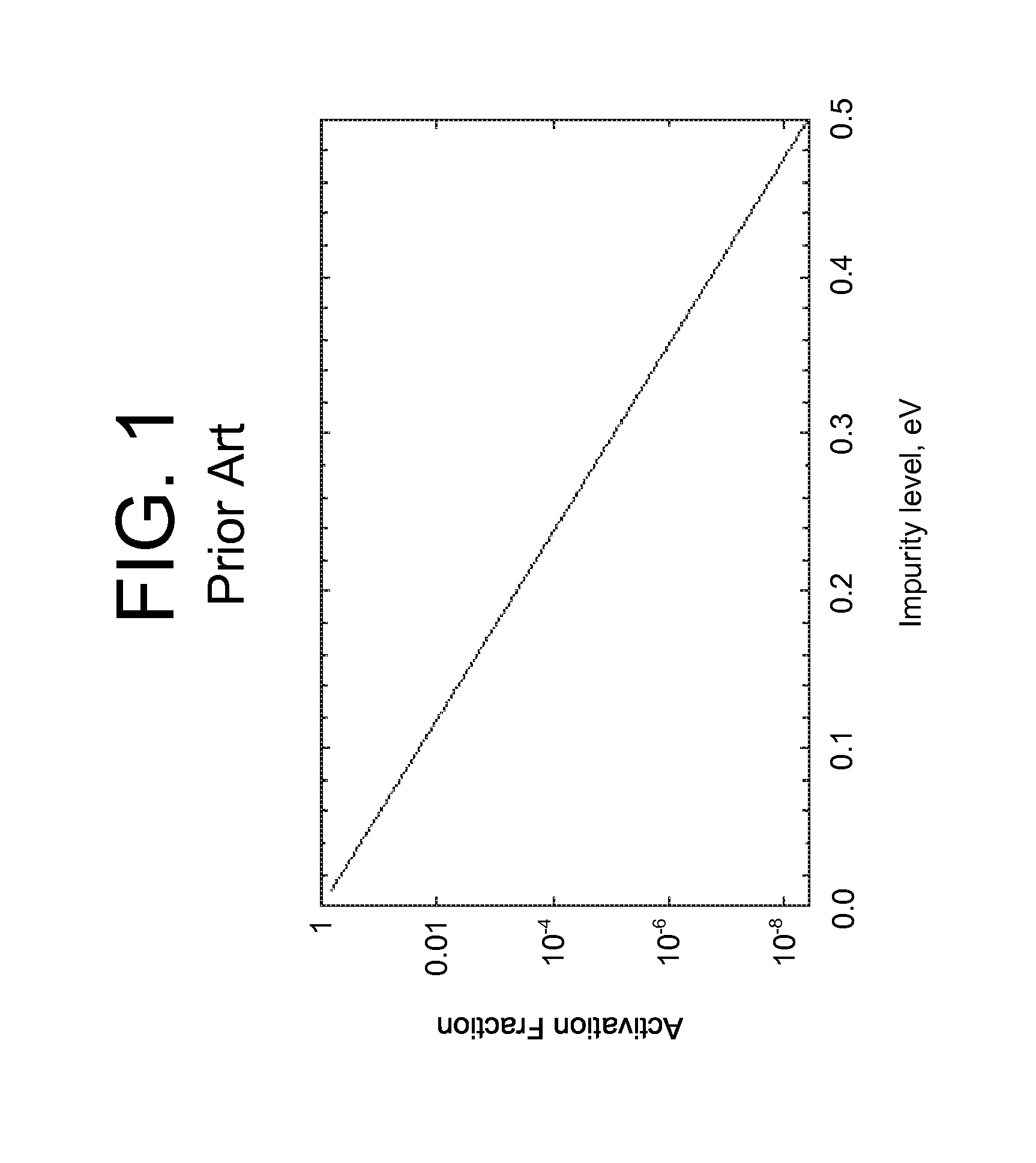
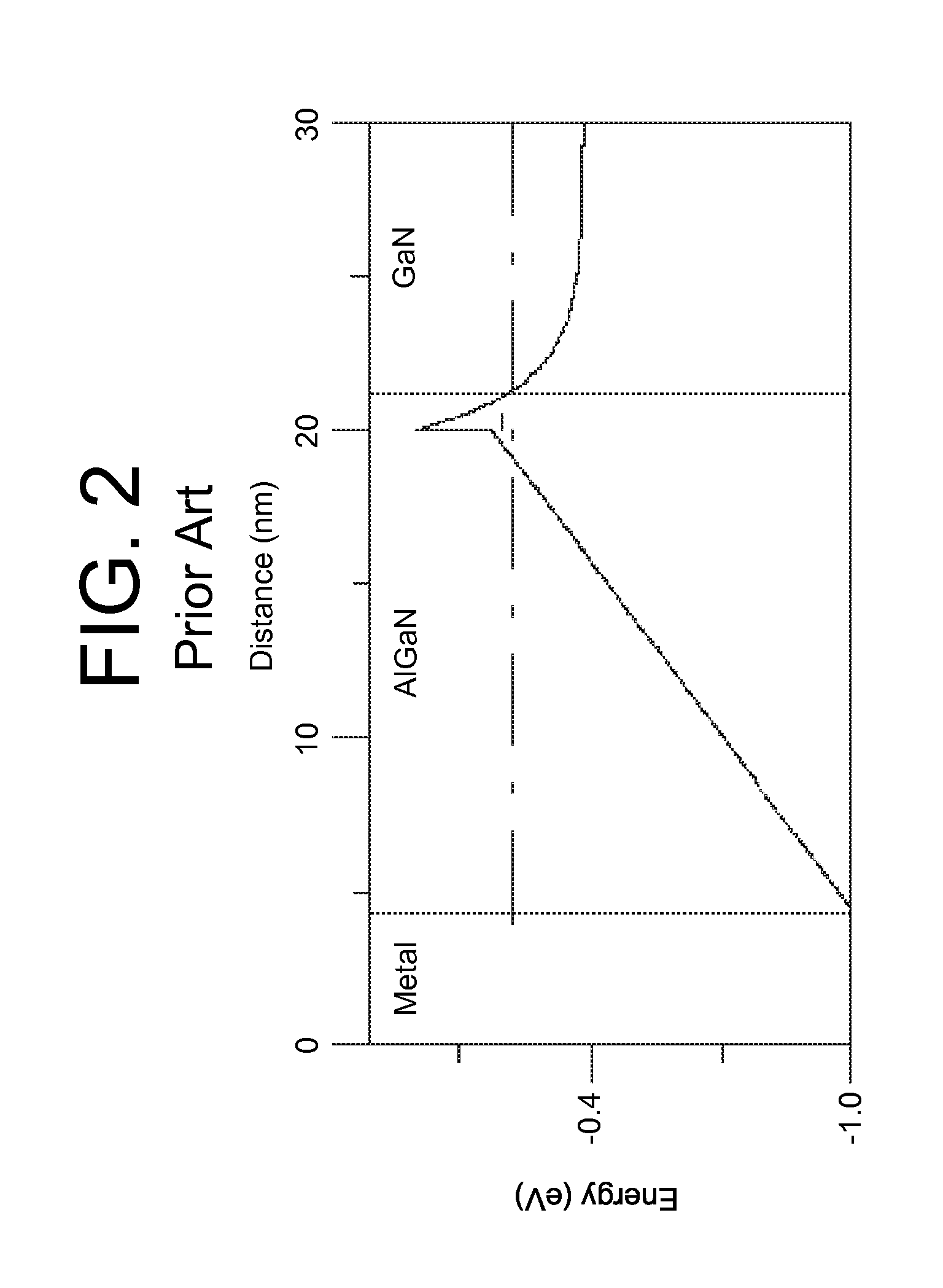
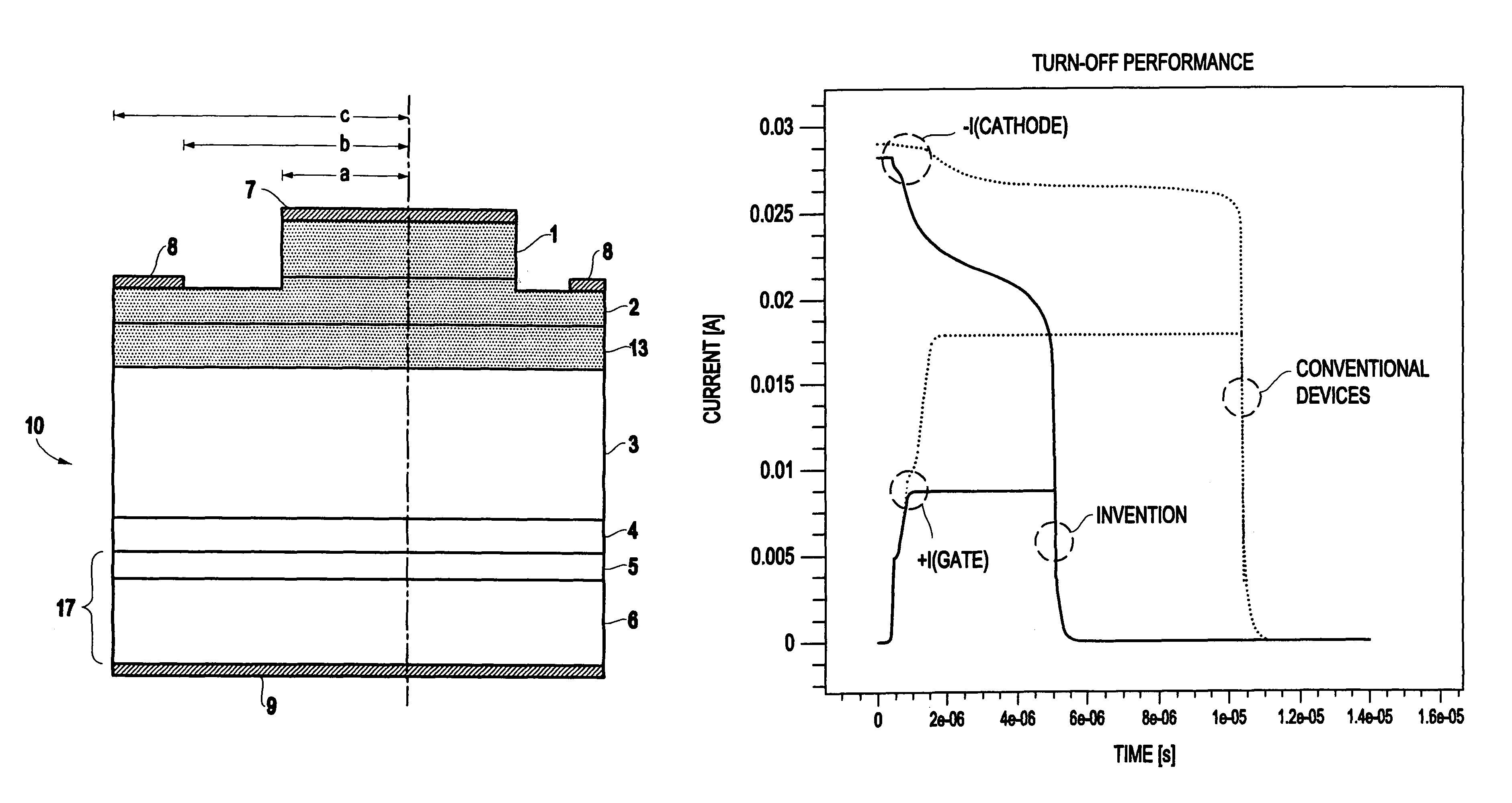
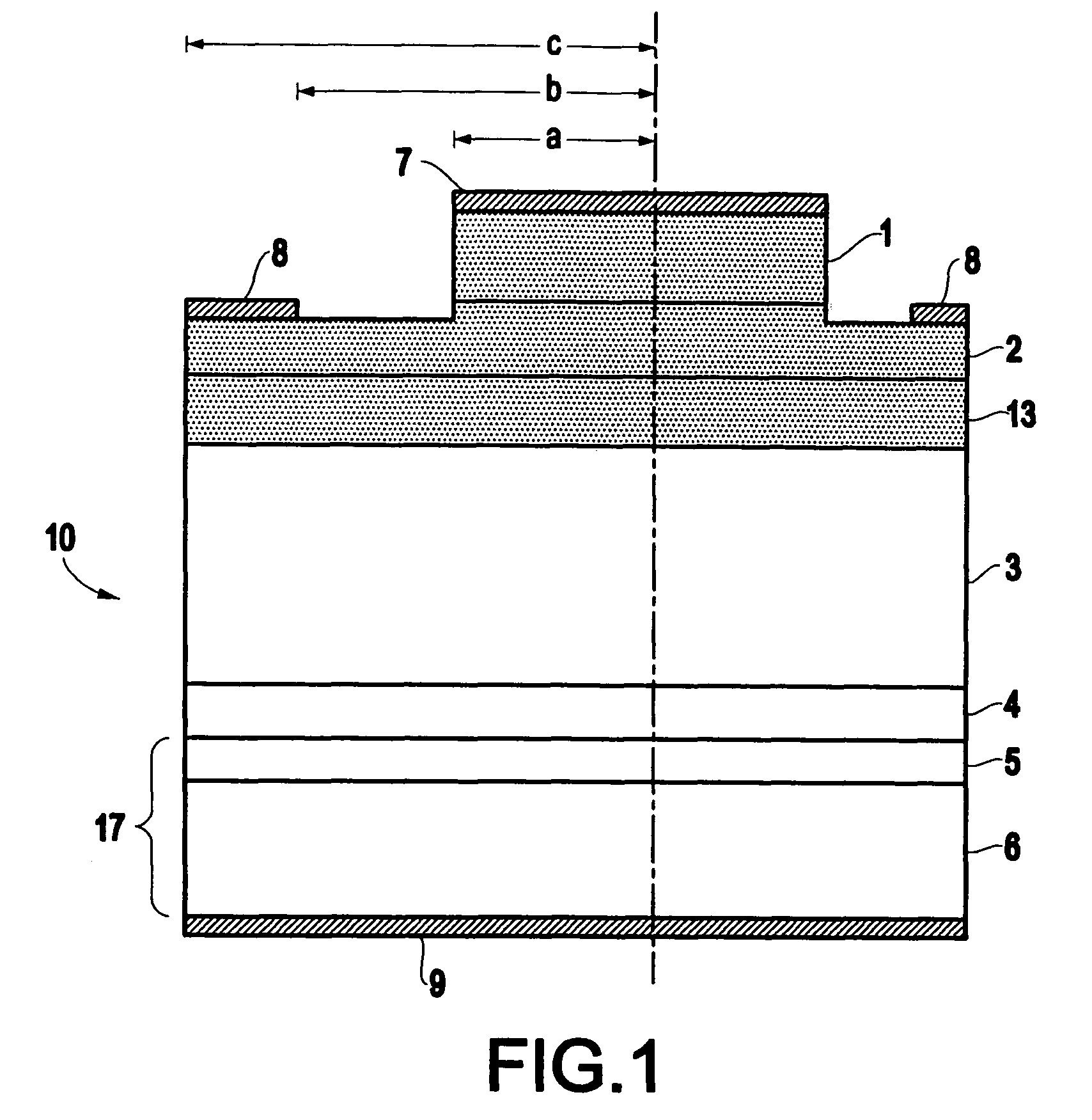
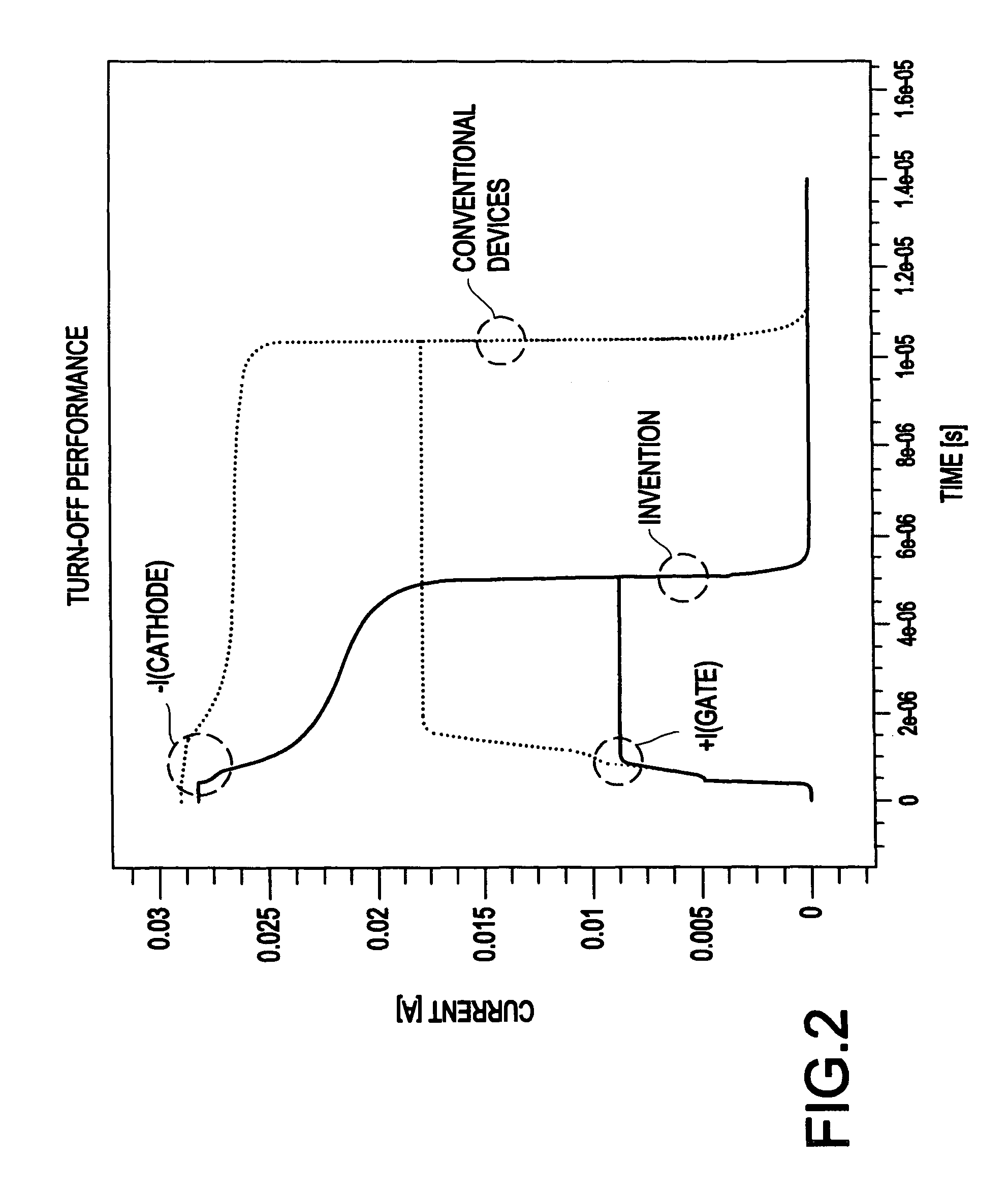
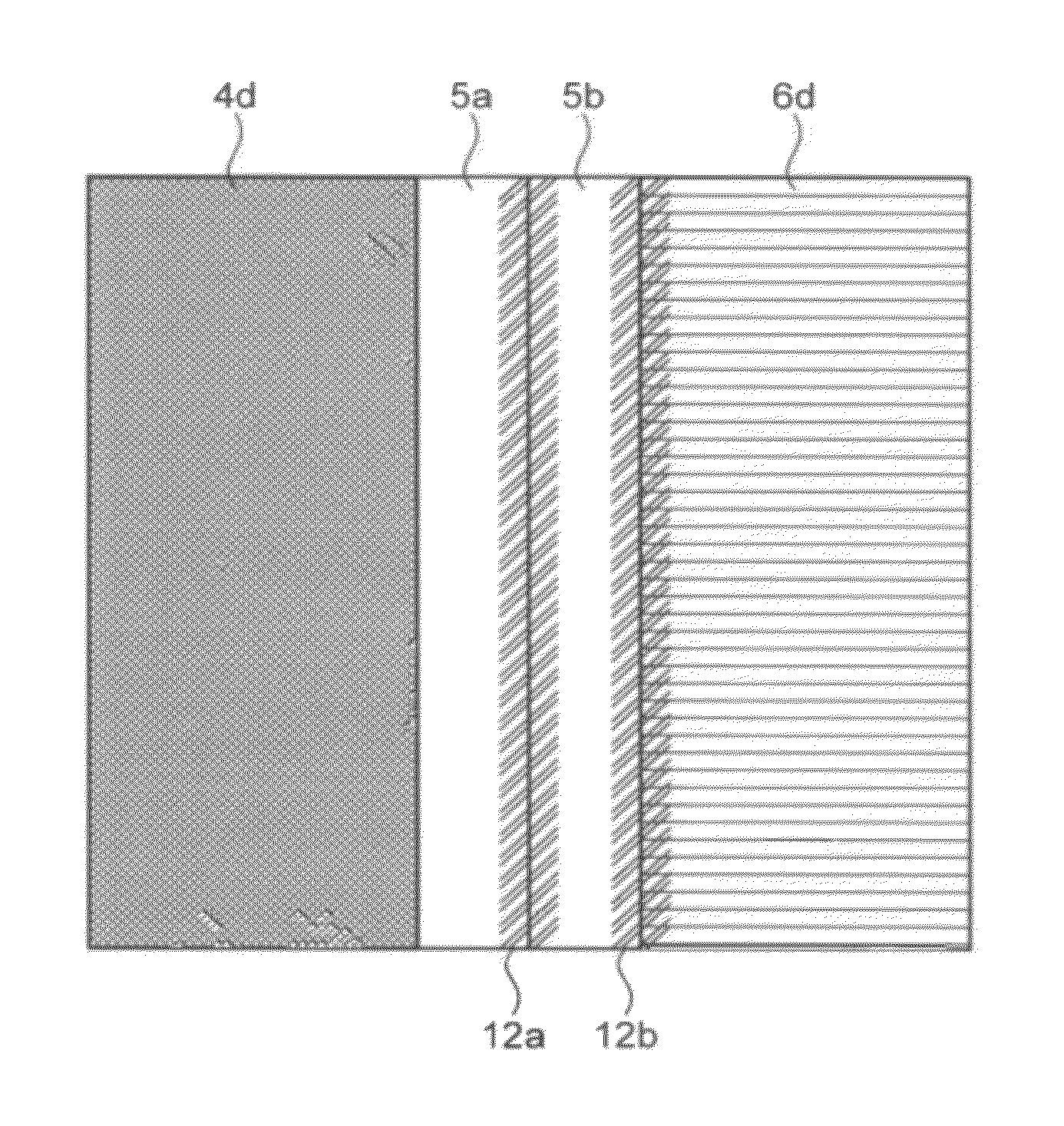
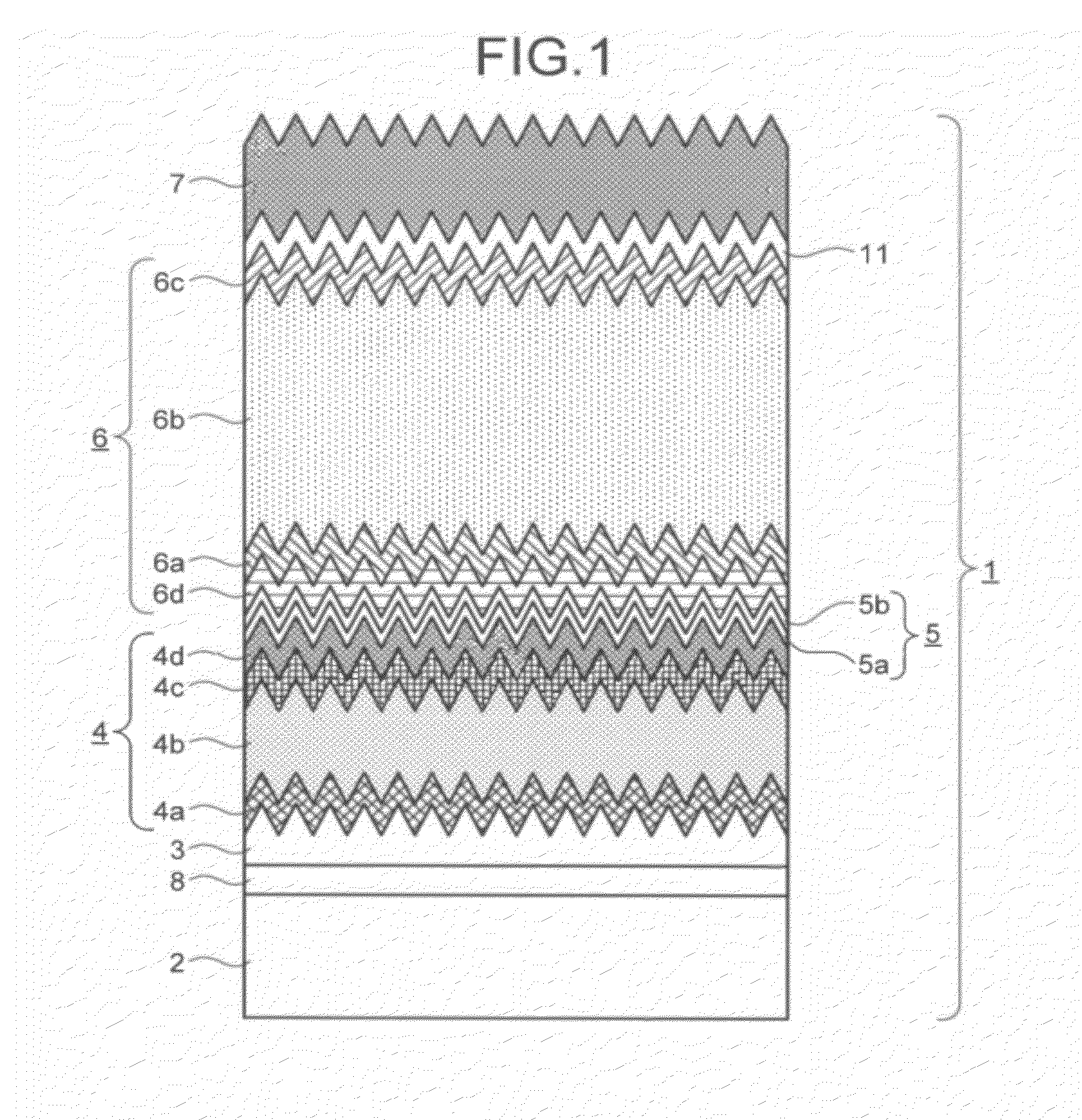
Processing technique to improve the turn-off gain of a silicon carbide gate turn-off thyristor
ActiveUS7851274B1Increased turnLow mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate turn-off thyristorNanosecond
A structure and method for a silicon carbide (SiC) gate turn-off (GTO) thyristor device operable to provide an increased turn-off gain comprises a cathode region, a drift region having an upper portion and a lower portion, wherein the drift region overlies the cathode region, a gate region overlying the drift region, an anode region overlying the gate, and at least one ohmic contact positioned on each of the gate region, anode region, and cathode region, wherein the upper portion of the drift region, the gate region, and the anode region have a free carrier lifetime and mobility lower than a comparable SiC GTO thyristor for providing the device with an increased turn-off gain, wherein the free carrier lifetime is approximately 10 nanoseconds. The reduced free carrier lifetime and mobility are affected by altering the growth conditions, such as temperature under which epitaxy occurs.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Photoelectric converter and manufacturing method thereof, and photoelectric conversion module
InactiveUS20120160298A1Solve problemsPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric converter in which an intermediate layer is provided between a first photoelectric-conversion-layer including a first p-type-semiconductor-layer and a first n-type-semiconductor-layer and a second photoelectric-conversion-layer including a second p-type-semiconductor-layer and a second n-type-semiconductor-layer. The intermediate layer includes an n-type-transparent conductive-oxide-film in contact with the first n-type-semiconductor-layer and a p-type-transparent-conductive oxide-film in contact with the second p-type-semiconductor-layer respectively having a bandgap equal to or higher than 1.5 electron volts. A width of a low carrier concentration region in a film thickness direction, in which a concentration of a free carrier formed near at least one of an interface on which the p-type-transparent-conductive-oxide-film comes into contact with the n-type-transparent-conductive-oxide-film and an interface on which the p-type-transparent-conductive-oxide-film comes into contact with the second p-type-semiconductor-layer is equal to or lower than 1×1018 cm−3, is equal to or less than 5 nanometers.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Circuit architecture for electro-optic modulation based on free carrier dispersion effect and the waveguide capacitor structures for such modulator circuitry using CMOS or Bi-CMOS process
ActiveUS7817881B2Improve performanceOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsHemt circuitsElectro-optic modulator
New circuit architecture for electro-optic modulator based on free-carrier dispersion effect is invented, in which the waveguide capacitor of the modulator is embed in the circuits and physically layout together with transistors, the switching of the modulator occurs in transistors, and as the result, the electro-optical modulation occurs in the waveguide capacitor. The invented modulator is not one physical device, it is actually a circuit. Several circuit design techniques are imported, leading to several new modulator circuits that have very high operation speed and very small power consumption. Several new waveguide capacitor structures are also invented that allow high efficient modulator circuits to be built.
Owner:LI BING
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20050077571A1Avoid flowAvoid failureTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectromotive force
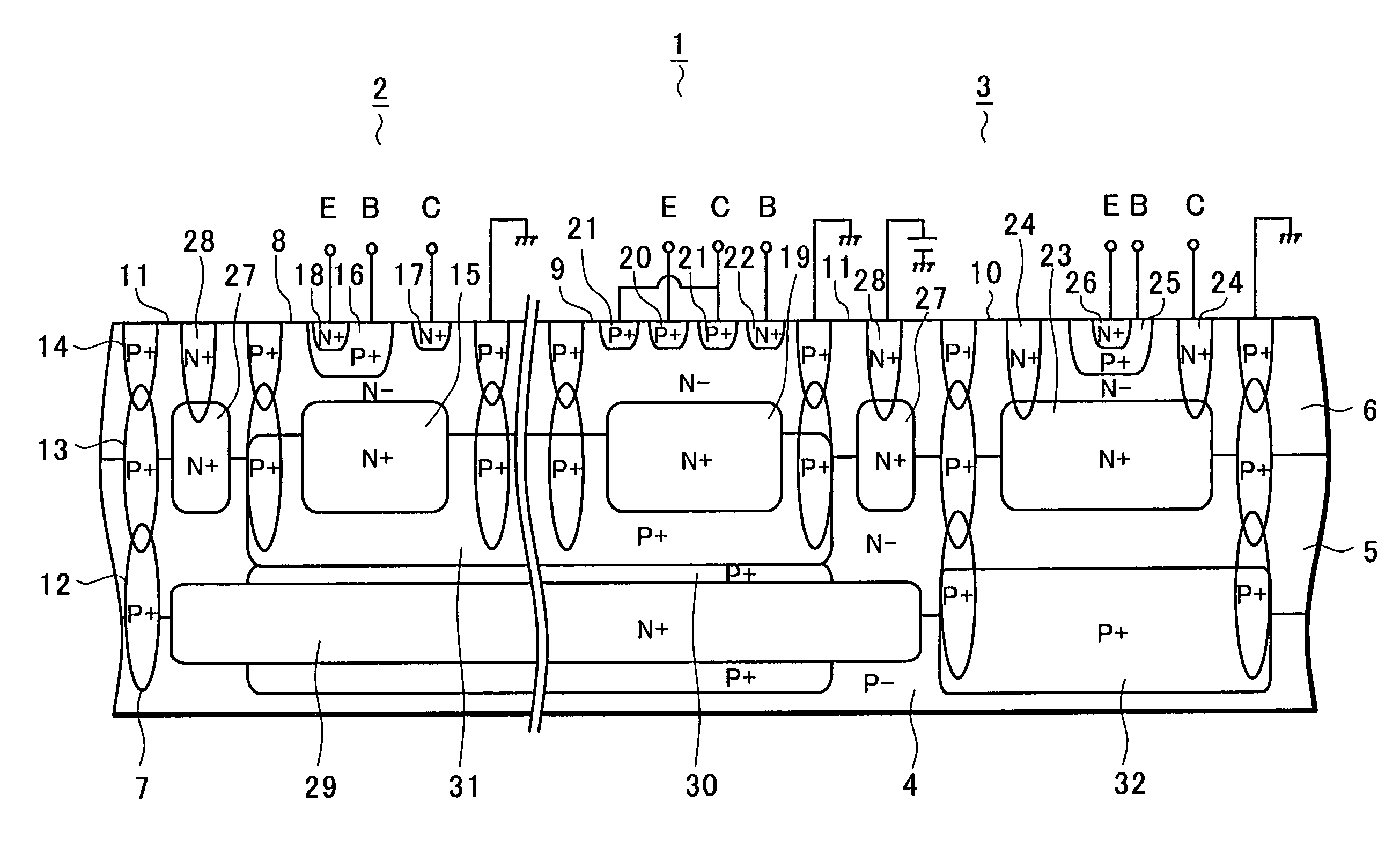
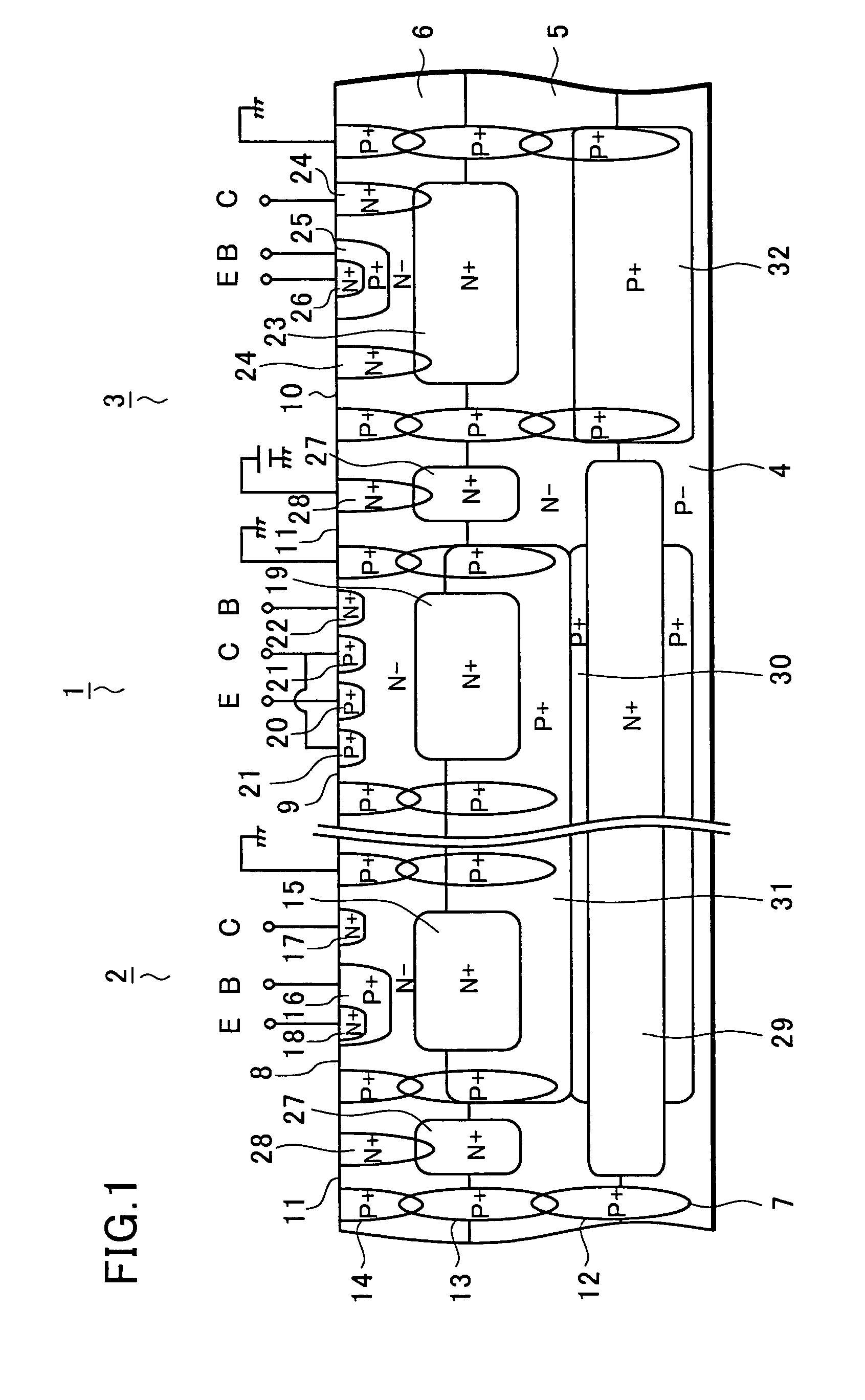
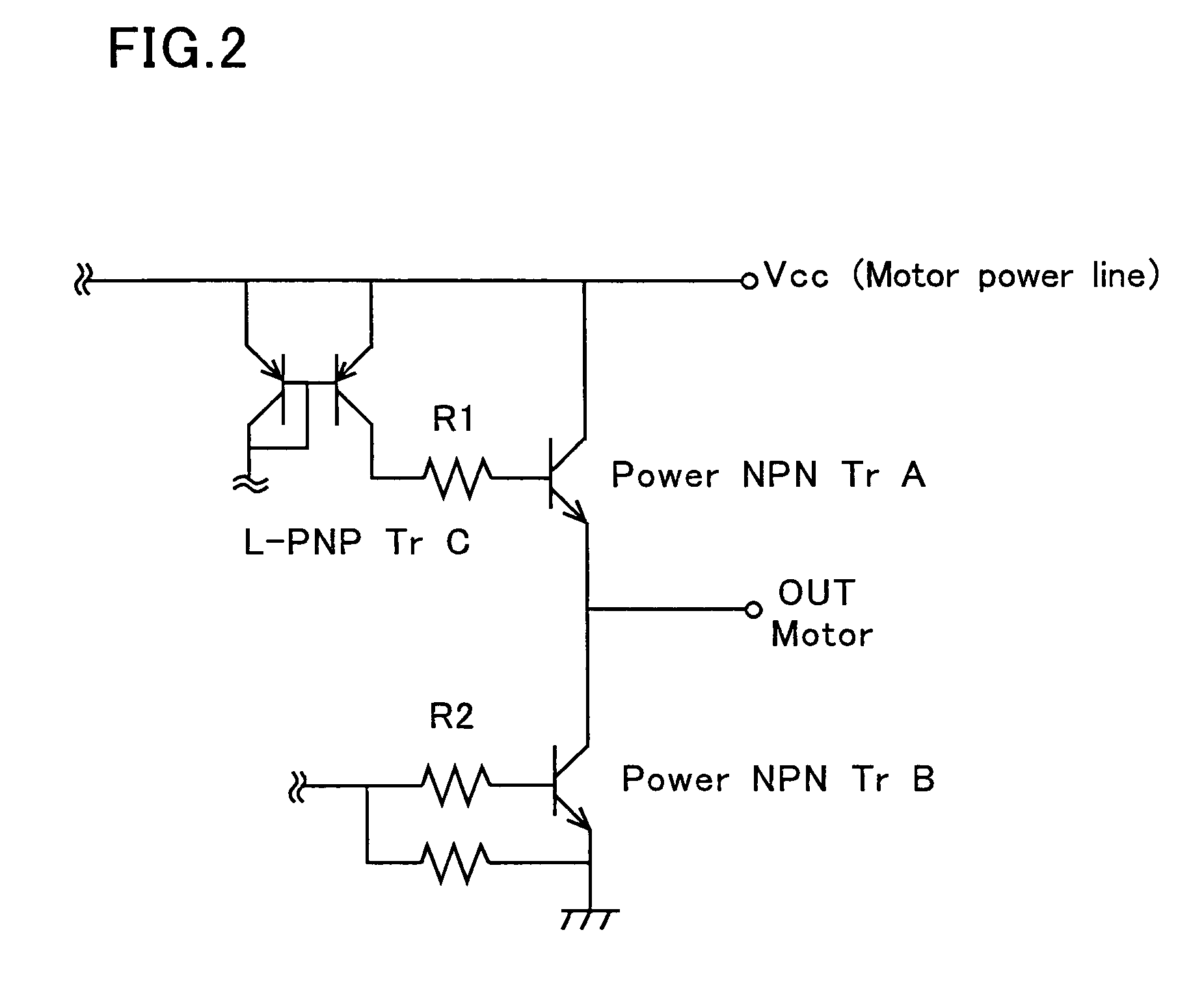
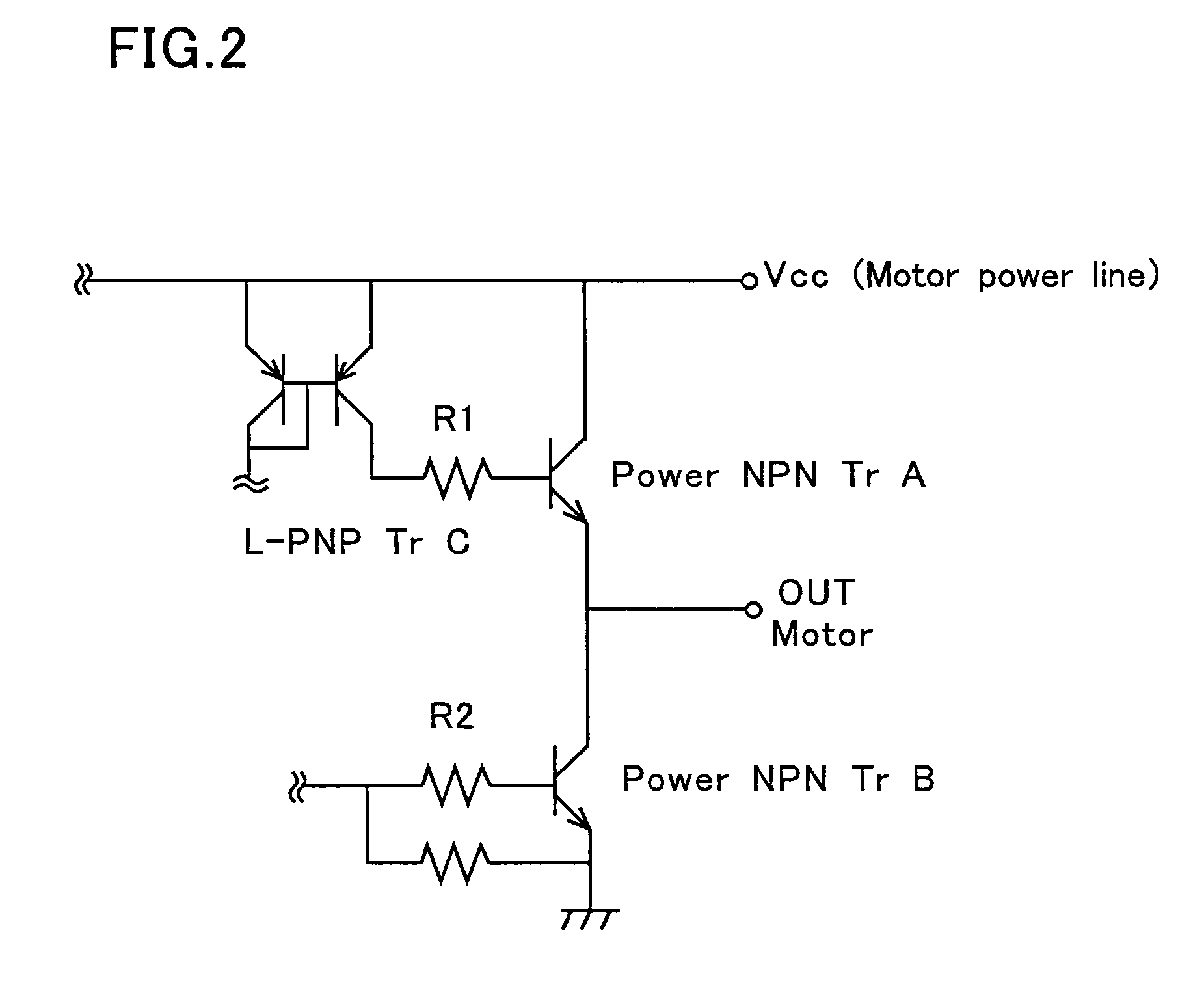
A semiconductor integrated circuit device according to the invention includes an N-type embedded diffusion region between a substrate and a first epitaxial layer in island regions serving as small signal section. The substrate and the first epitaxial layer are thus partitioned by the N-type embedded diffusion region having supply potential in the island regions serving as small signal section. This structure prevents the inflow of free carriers (electrons) generated from a power NPN transistor due to the back electromotive force of the motor into the small signal section, thus preventing the malfunction of the small signal section.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method for shifting the bandgap energy of a quantum well layer
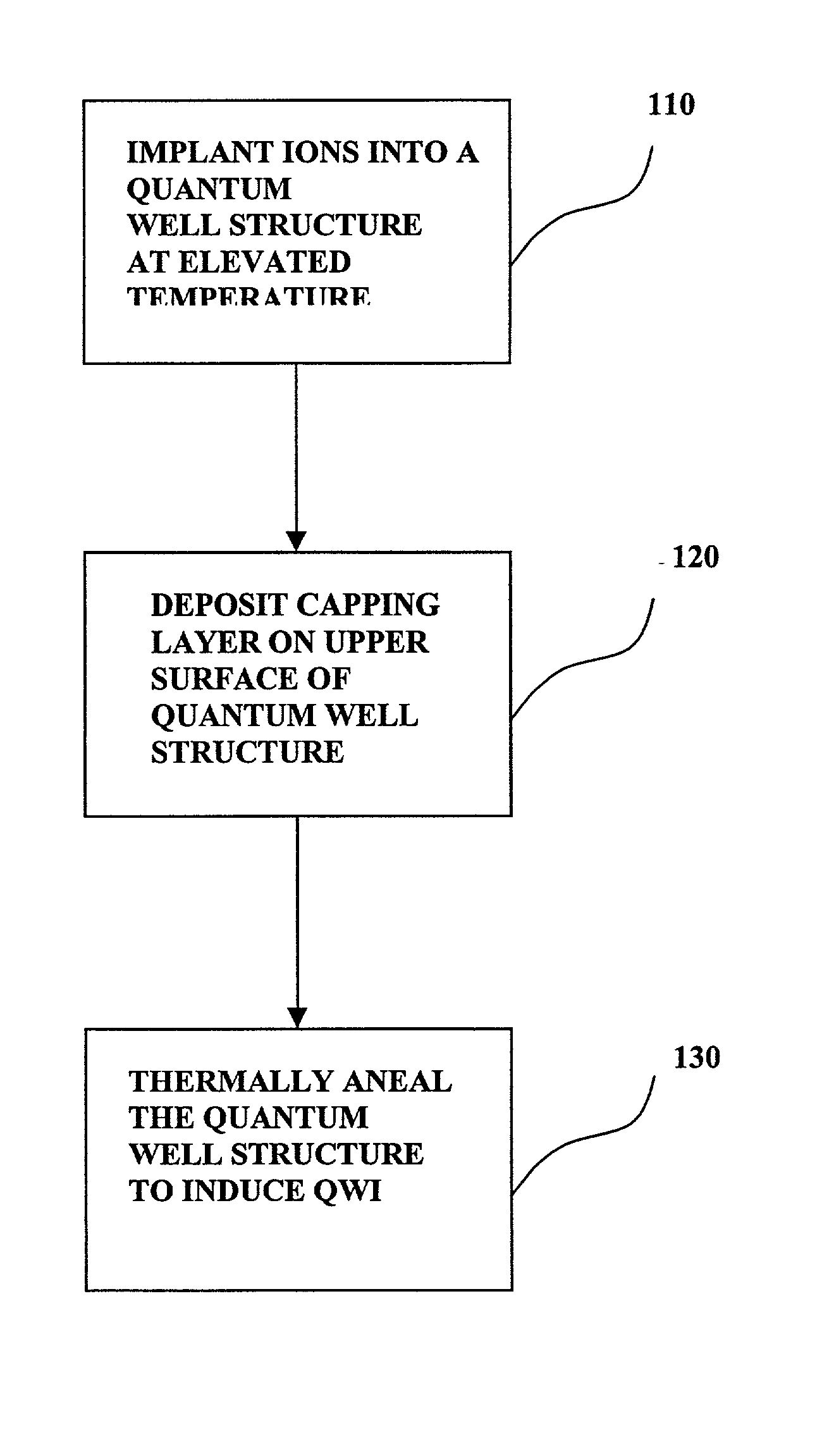
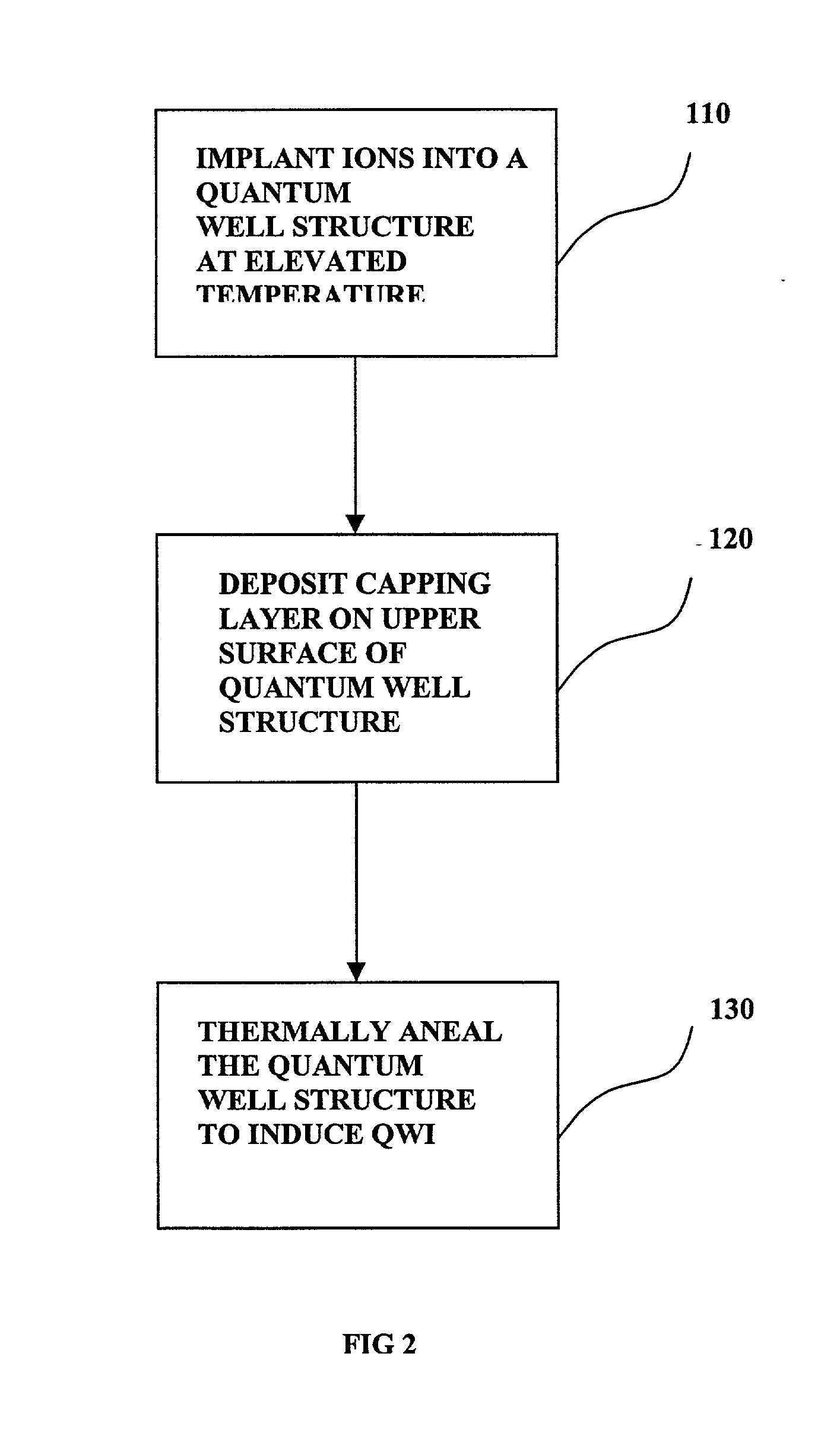
A process for shifting the bandgap energy of a quantum well layer (e.g., a III-V semiconductor quantum well layer) without inducing complex crystal defects or generating significant free carriers. The process includes introducing ions (e.g., deep-level ion species) into a quantum well structure at an elevated temperature, for example, in the range of from about 200 ° C. to about 700 ° C. The quantum well structure that has had ions introduced therein includes an upper barrier layer, a lower barrier layer and a quantum well layer. The quantum well layer is disposed between the upper barrier layer and the lower barrier layer. The quantum well structure is then thermally annealed, thereby inducing quantum well intermixing (QWI) in the quantum well structure and shifting the bandgap energy of the quantum well layer. Also, a photonic device assembly that includes a plurality of operably coupled photonic devices monolithically integrated on a single substrate using the process described above.
Owner:HO SENG TIONG
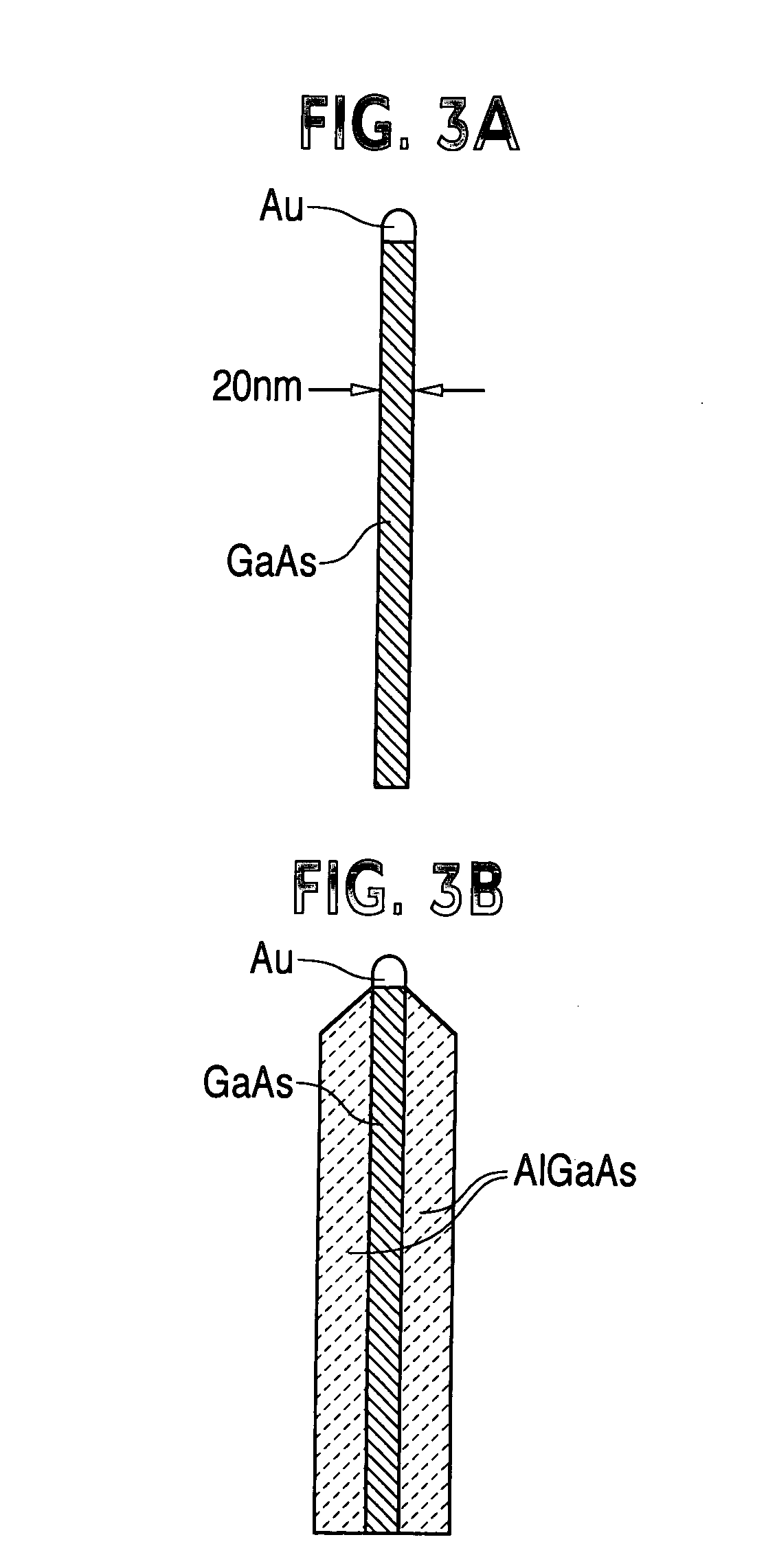
Method to realize fast silicon-on-insulator (SOI) optical device
A fast silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguide-based optical device enhanced with minority charge carrier lifetime modifiers enables faster modulation speeds in optical attenuators, optical intensity / phase-modulators, and optical switches whose operation principles are based on free-carrier injection into a waveguide. The waveguide is doped with gold (Au) or platinum (Pt) such that when a drive voltage (applied to the device) is turned off, the minority charge carriers rapidly annihilate because gold doping reduces the minority carrier lifetime, which improves transient characteristics of the optical device. Integration of the fast active device with passive devices such as WDM demultiplexers / multiplexers on the SOI optical waveguide platform enables realization of monolithic integrated optical components for advanced functionality such as dynamic spectral equalization.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com