Patents
Literature
361 results about "Mos capacitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
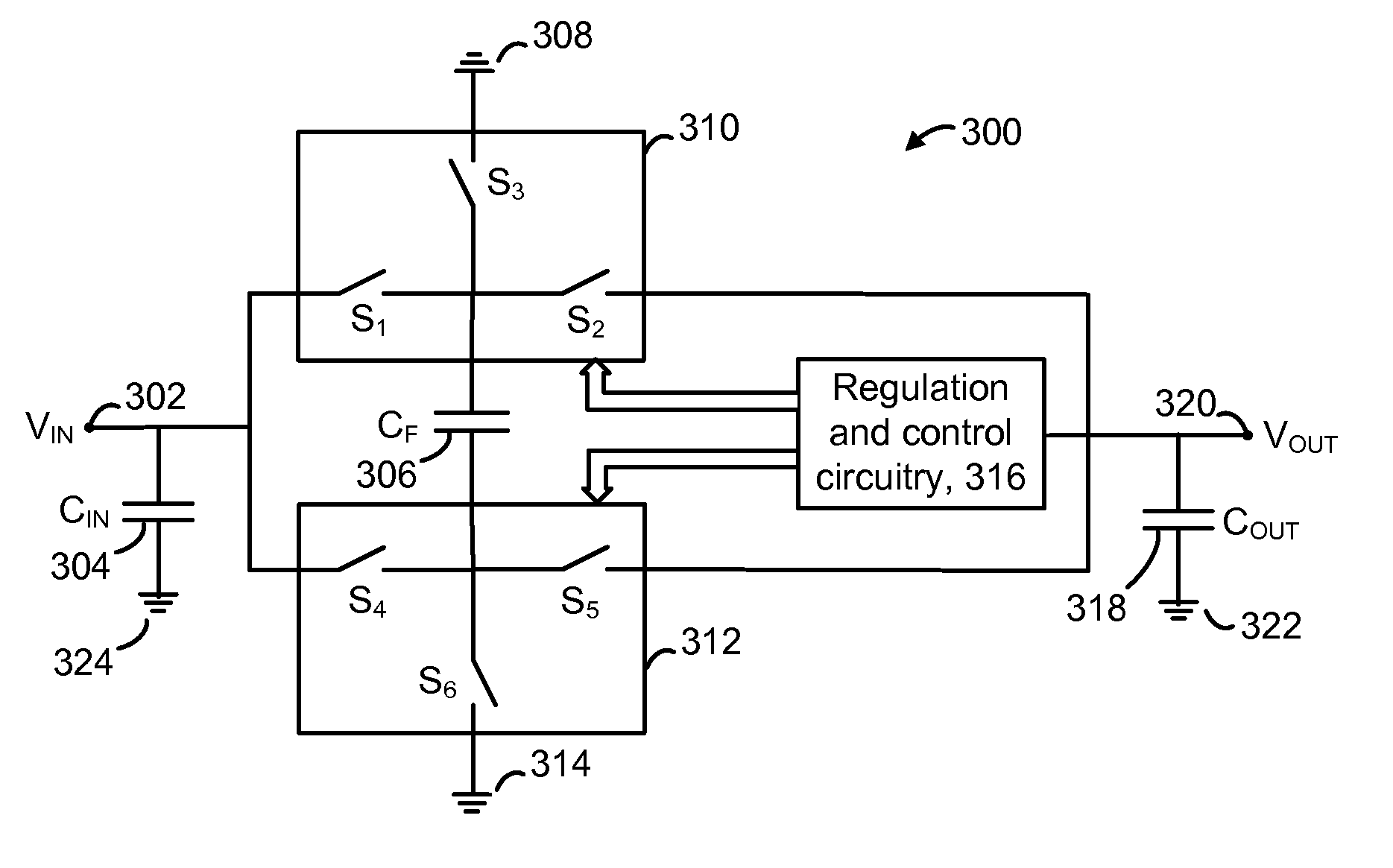
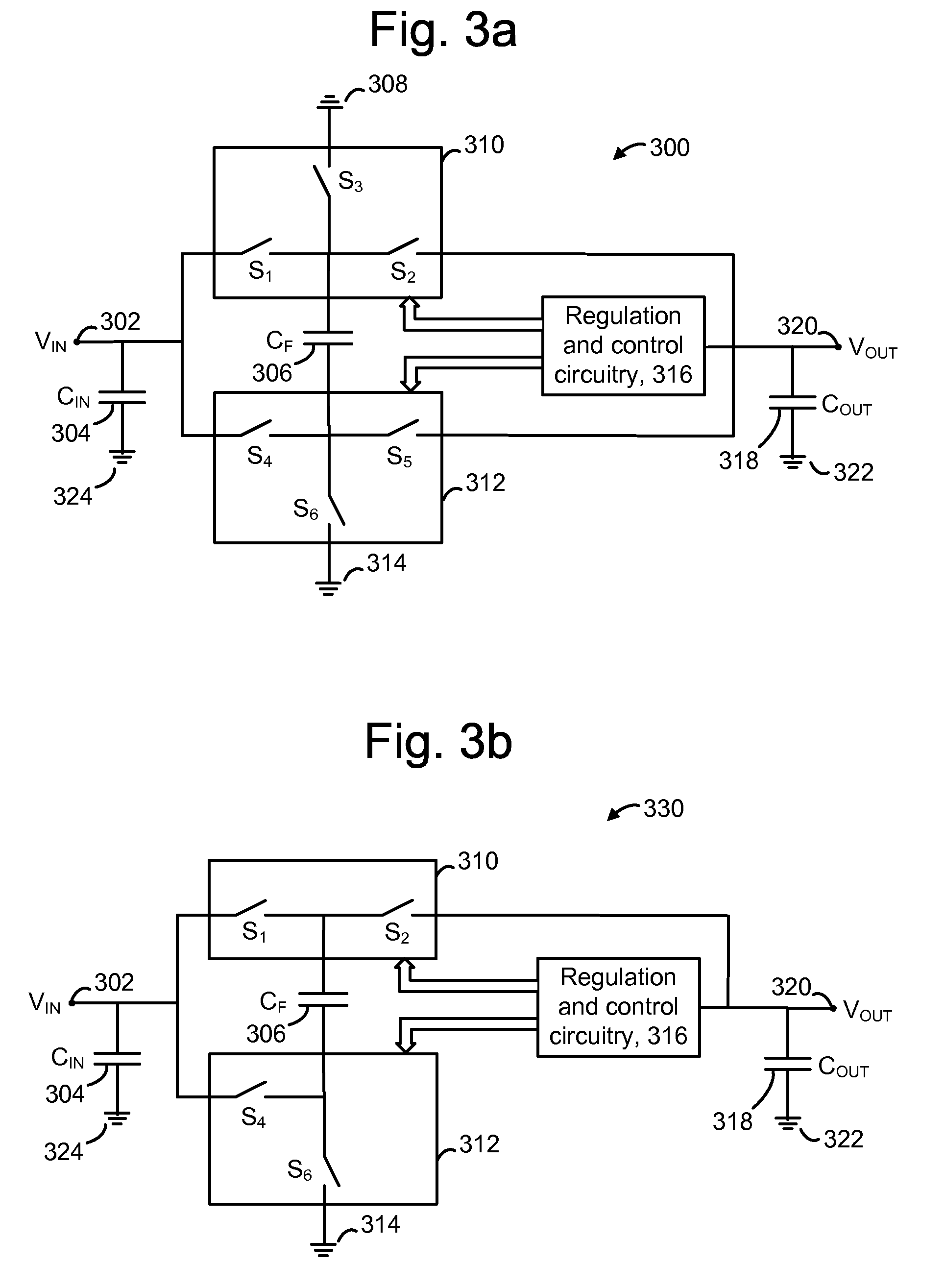
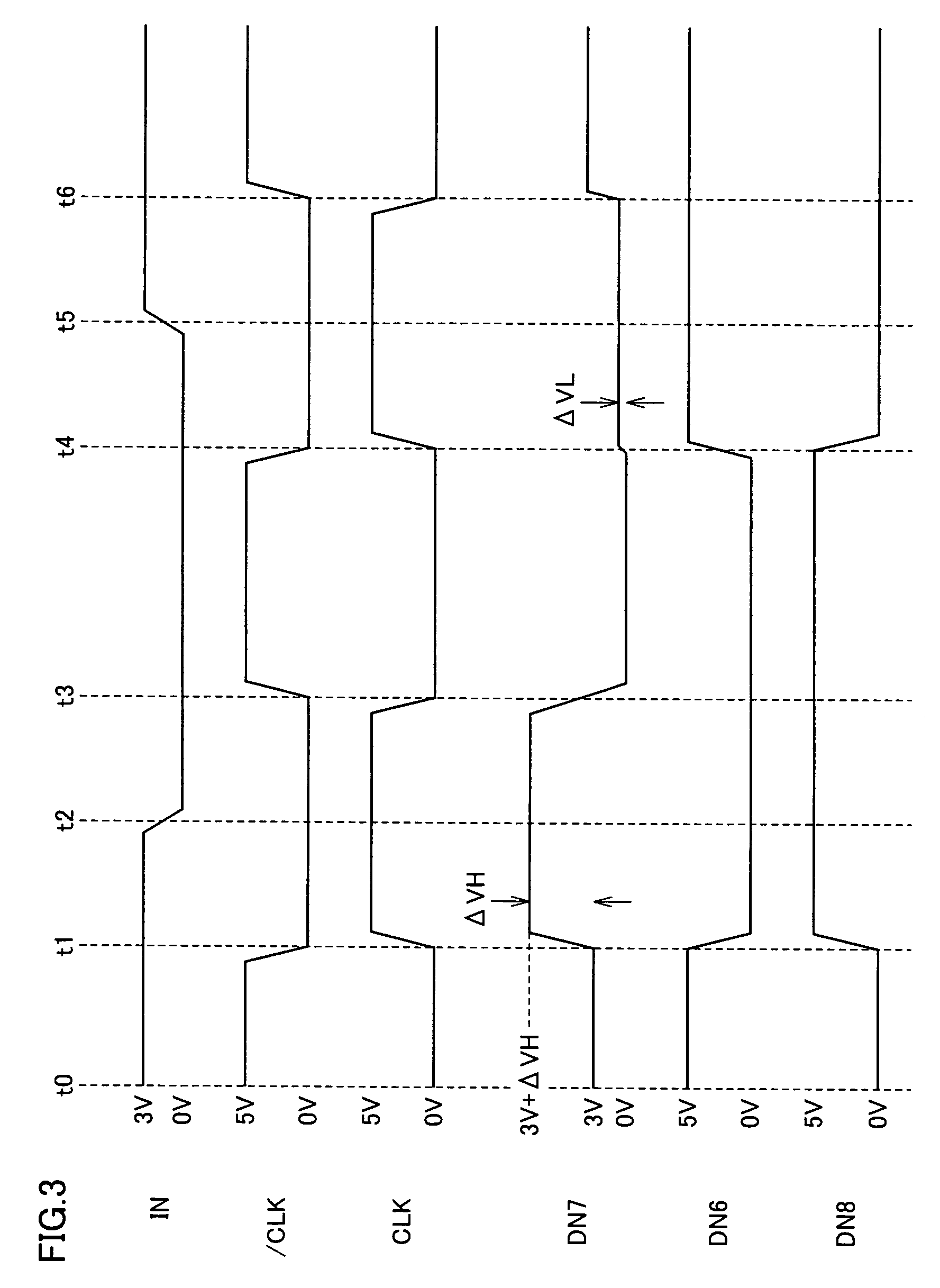
Charge coupled pump-efficient charge pump regulator with MOS capacitor
ActiveUS8040174B2Easy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCapacitanceVoltage multiplier
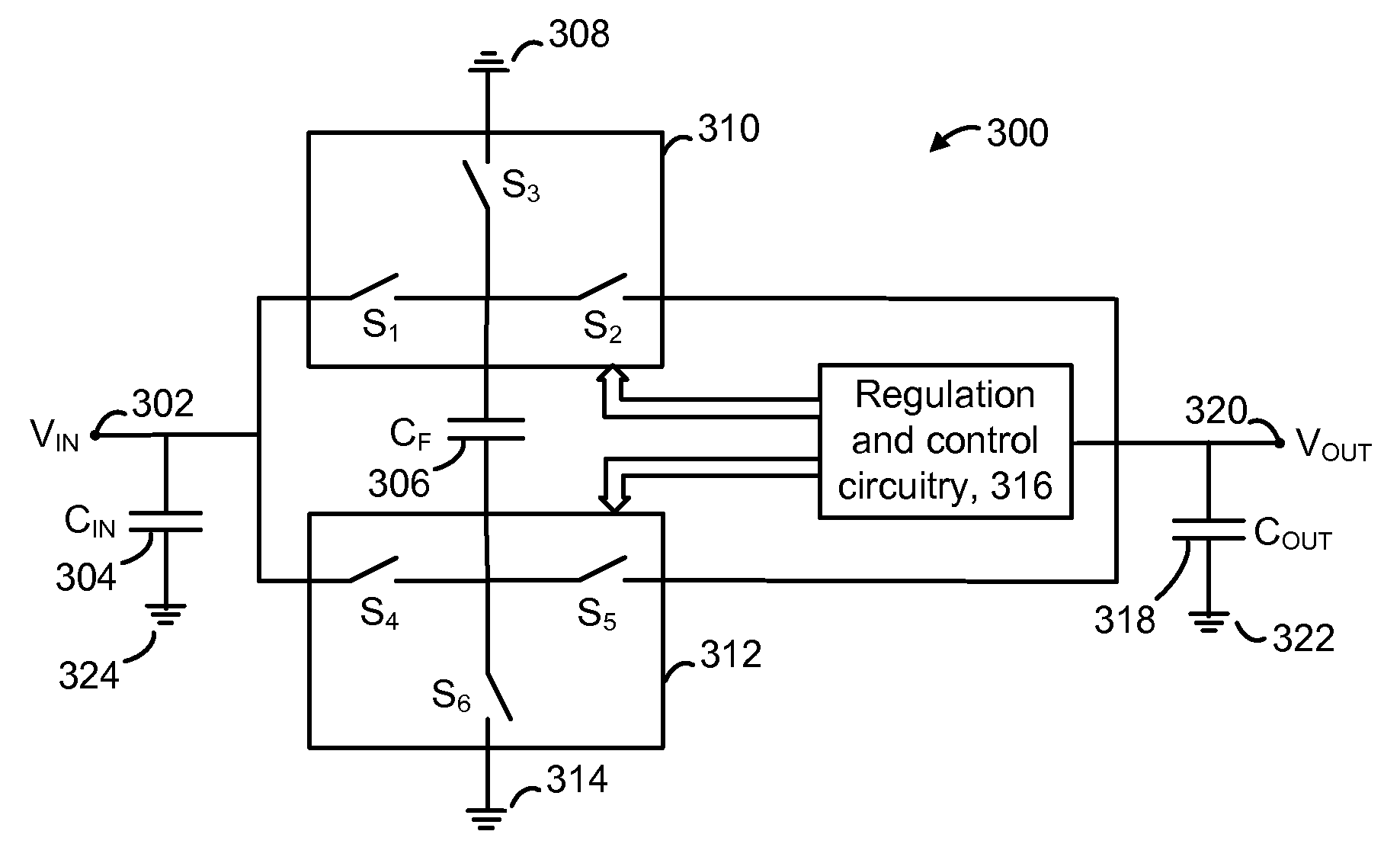
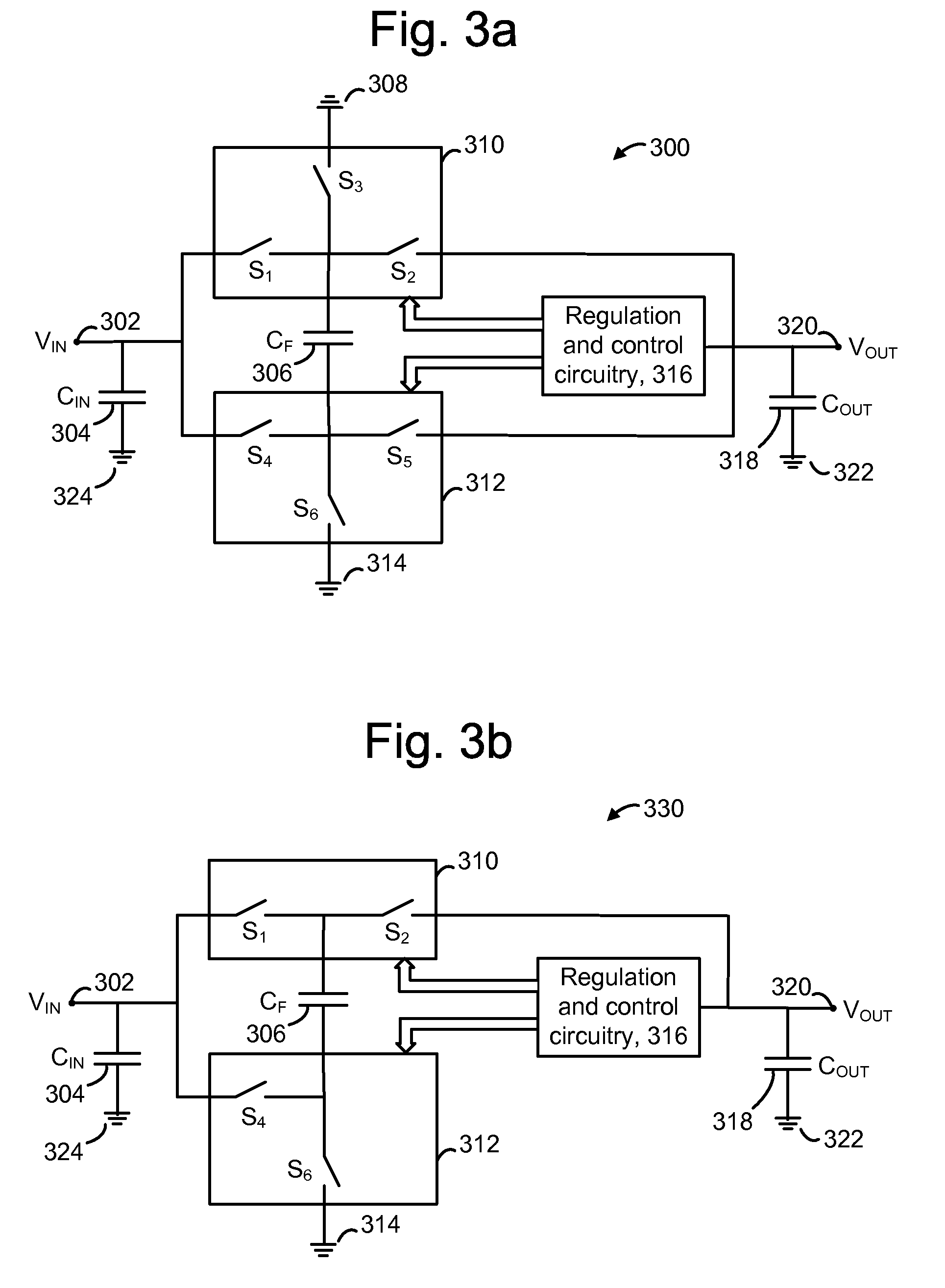
A charge pump with a MOS-type capacitor, where the MOS-type capacitor is operated in an inversion region in which capacitance varies as a function of the frequency of the applied signal. The charge pump is switched to transfer charge from an input node to the capacitor and from the capacitor to an output node. During a transition interval, a relatively high frequency switching signal is used to lower the capacitance and increase efficiency. During a settling interval, a relatively low frequency switching signal is used, in which case the capacitance is higher, but similar to a level which would be seen if the capacitor was operated in an accumulation region. MOS capacitor dimensions and switching intervals are mutually optimized to provide high efficiency and required throughput. The charge pump may be configured as a voltage multiplier, divider, inverter or follower, for instance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
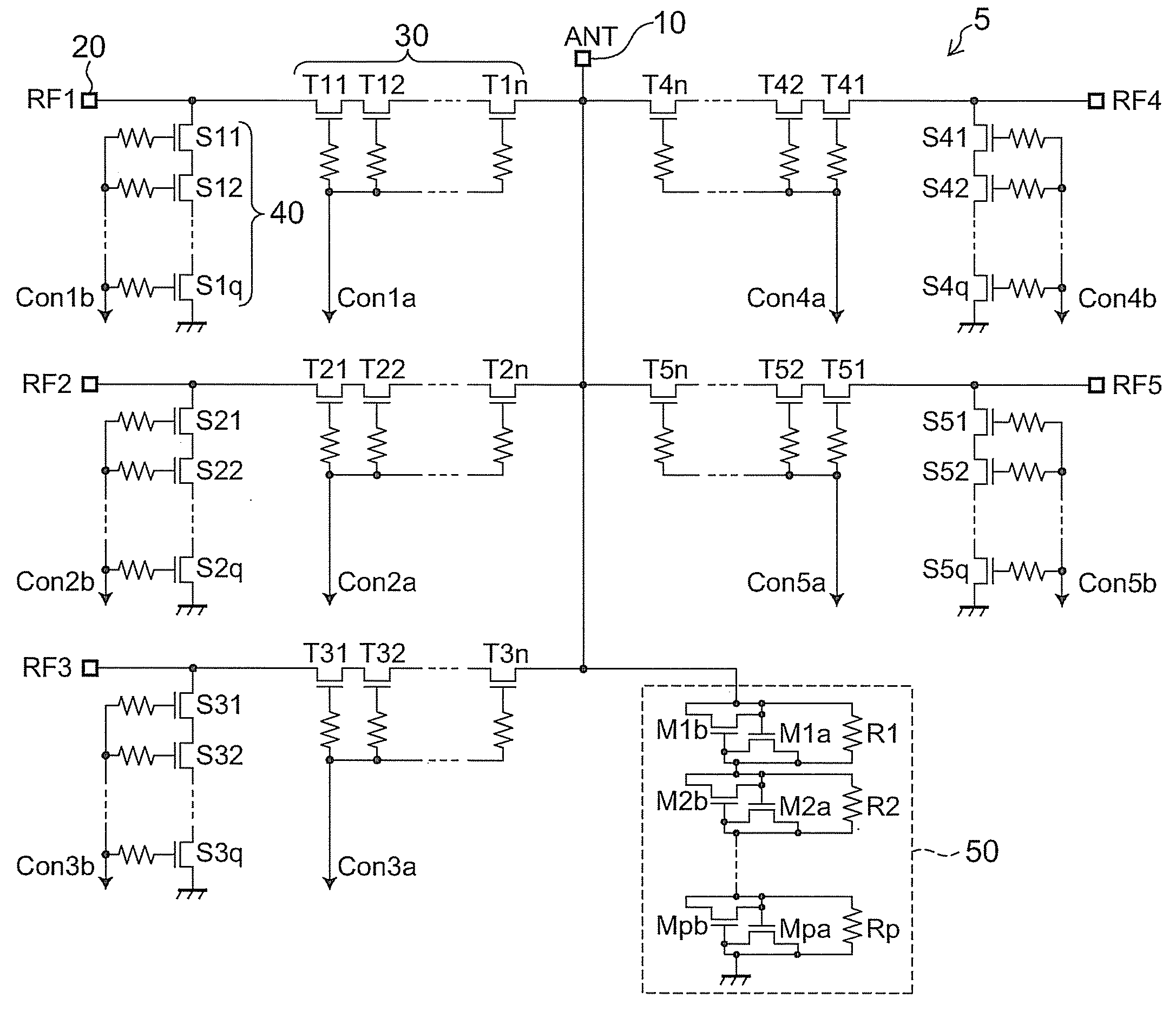
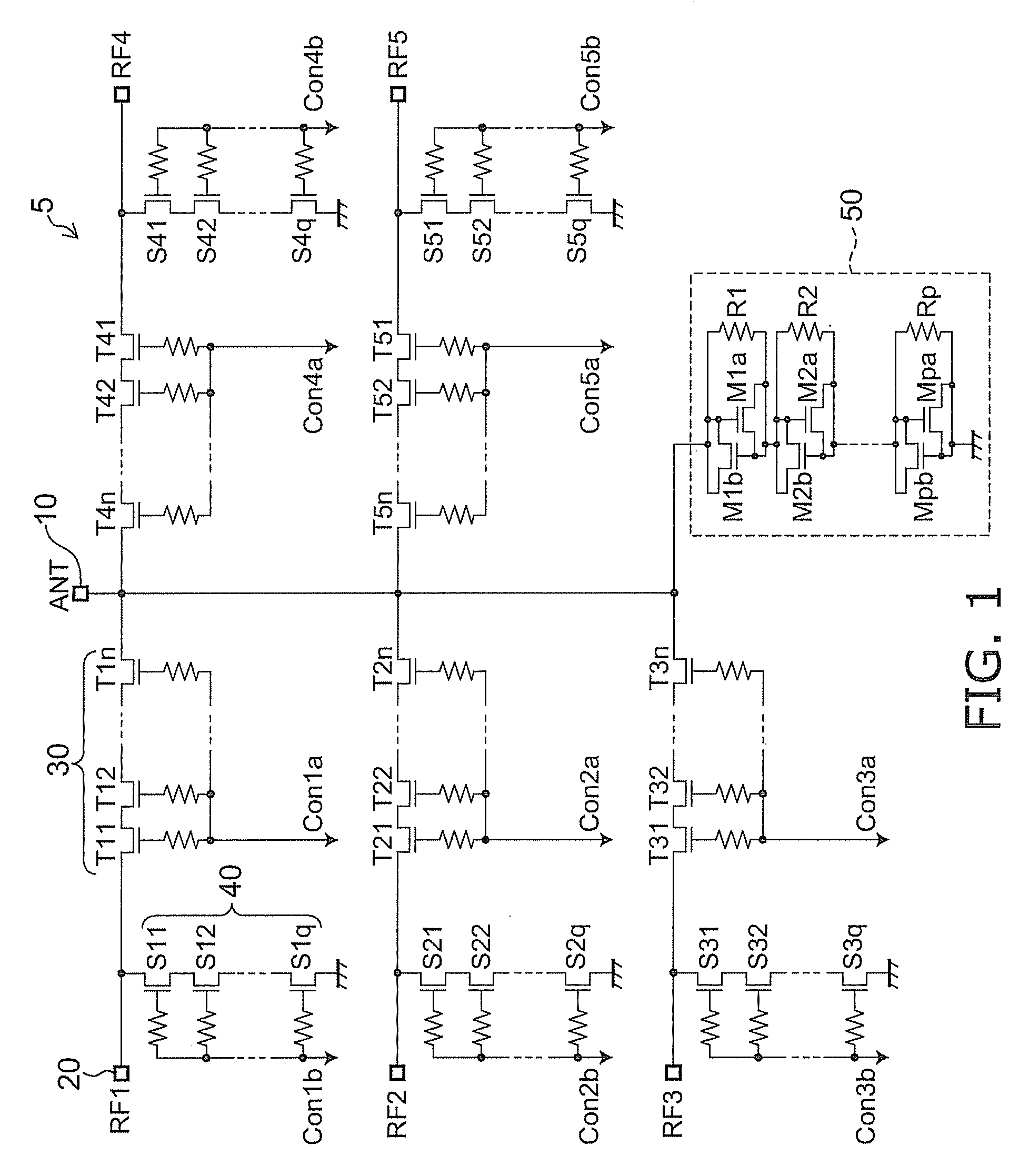
Radio frequency switch circuit
A radio frequency switch circuit includes: an antenna terminal; a first and second RF terminal; a first through transistor placed between the antenna terminal and the first RF terminal; a second through transistor placed between the antenna terminal and the second RF terminal; a first shunt transistor placed between ground and the first RF terminal; a second shunt transistor placed between the ground and the second RF terminal; and a distortion compensation circuit including a reverse parallel connected MOS capacitor whose capacitance around 0 volts has voltage dependence that is convex to the minus direction, the distortion compensation circuit being operable to compensate for voltage dependence of off-capacitance around 0 volts of the first and second through transistor and the first and second shunt transistor that is convex to the plus direction. Electrical connection between the antenna terminal and the first and second RF terminal is switchable.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
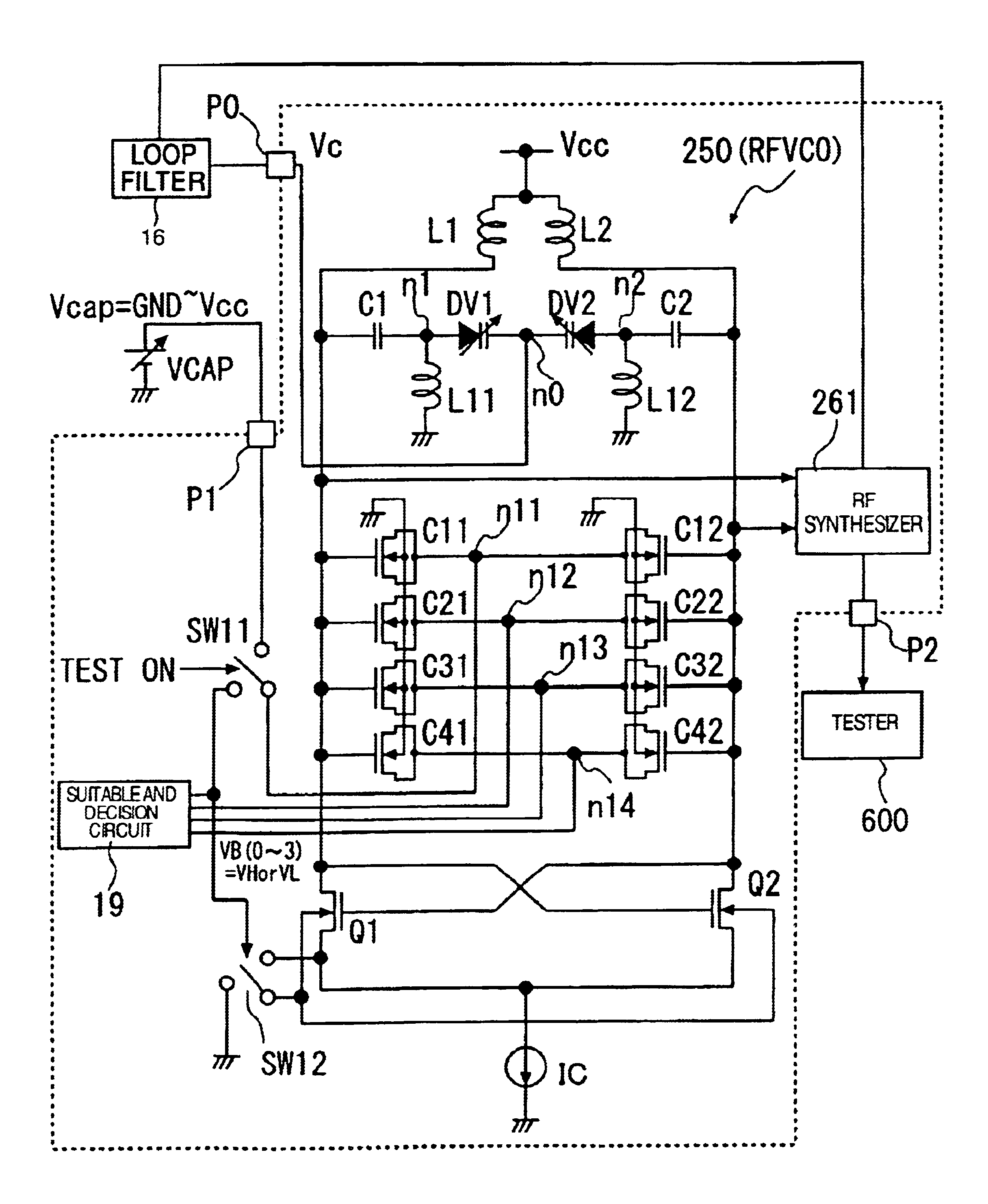
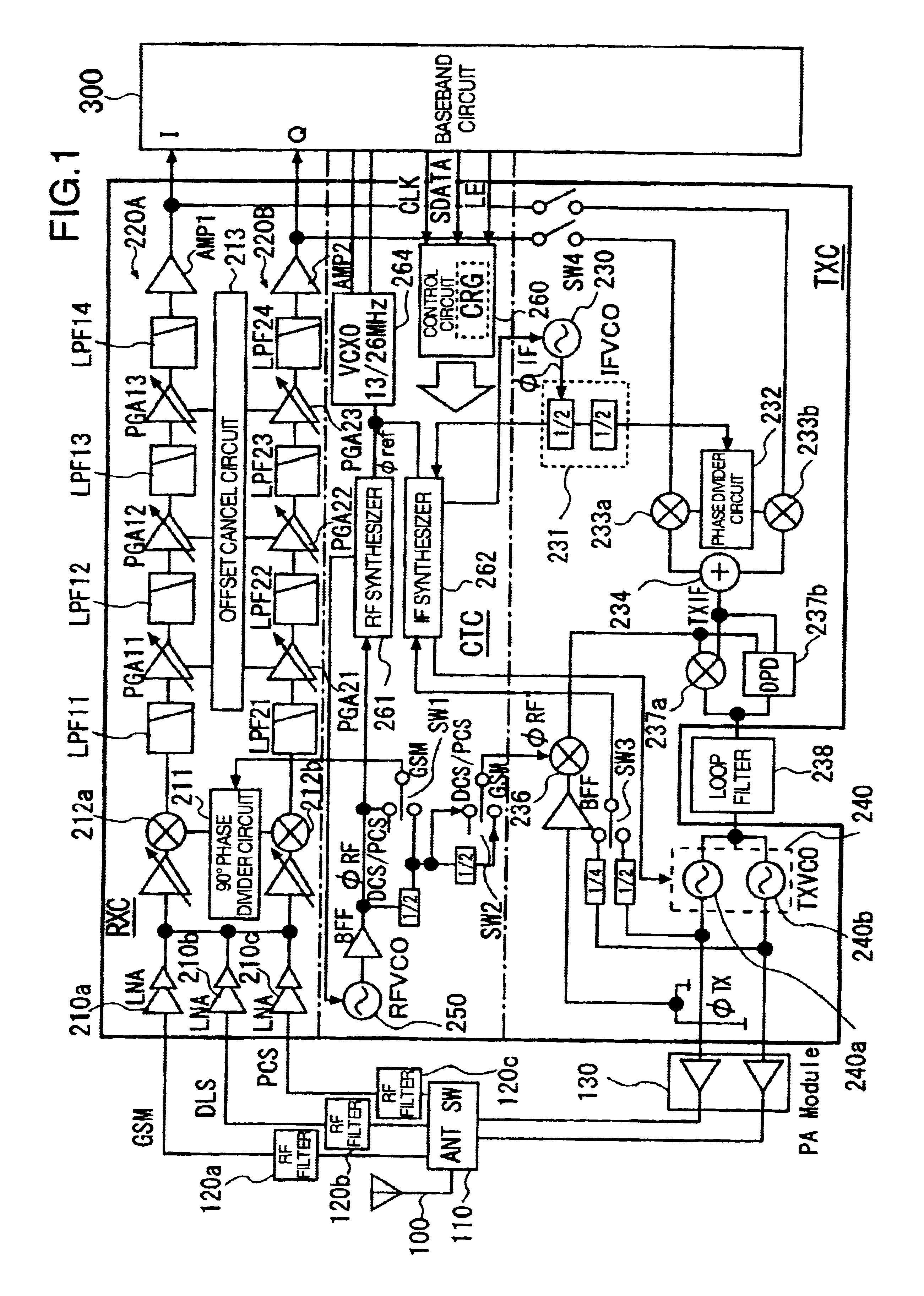
Oscillation circuit and a communication semiconductor integrated circuit
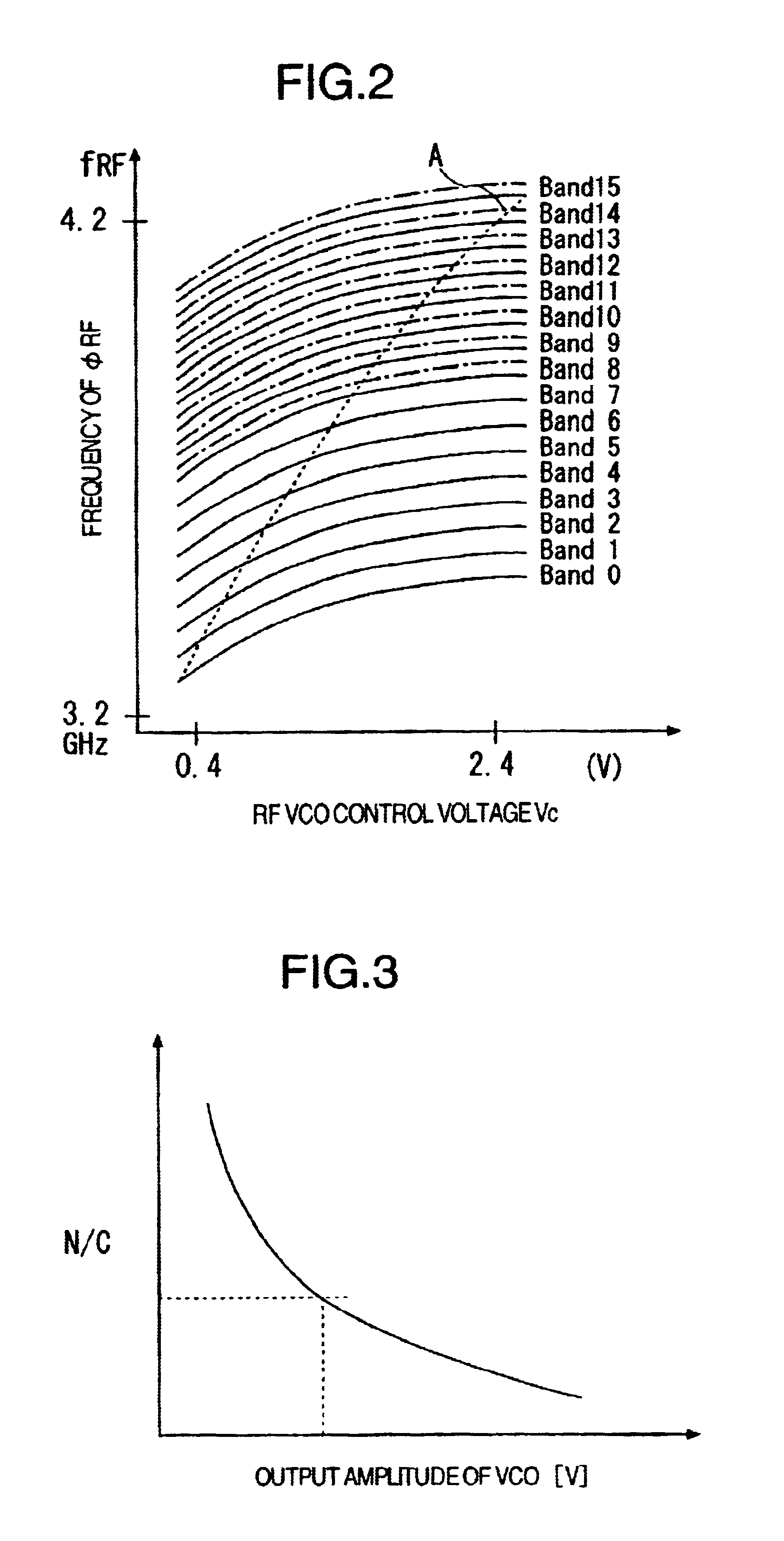
InactiveUS6906596B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceWide frequency conversion rangeAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlResonance oscillationLc resonant circuit
A voltage controlled LC resonance oscillation circuit has a plurality of capacitive elements connected to an output node. These capacitive elements are applied with voltages at opposing terminals for selecting an oscillating frequency band, so that the oscillating frequency band can be changed step by step in accordance with the selection voltage. The capacitive elements include at least one variable capacitive element such as a MOS capacitor, the capacitance of which is varied in accordance with a voltage applied thereto. The MOS capacitor is similar in structure to a MOS transistor. The variable capacitive element can be supplied at a terminal opposite to the output node with a voltage from a variable voltage source, for example, in place of the selection voltage. The voltage controlled LC resonance oscillation circuit can measure the output amplitude and oscillating frequency without affecting the characteristics thereof, and reduce the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:EPOCH MICROELECTRONICS +1
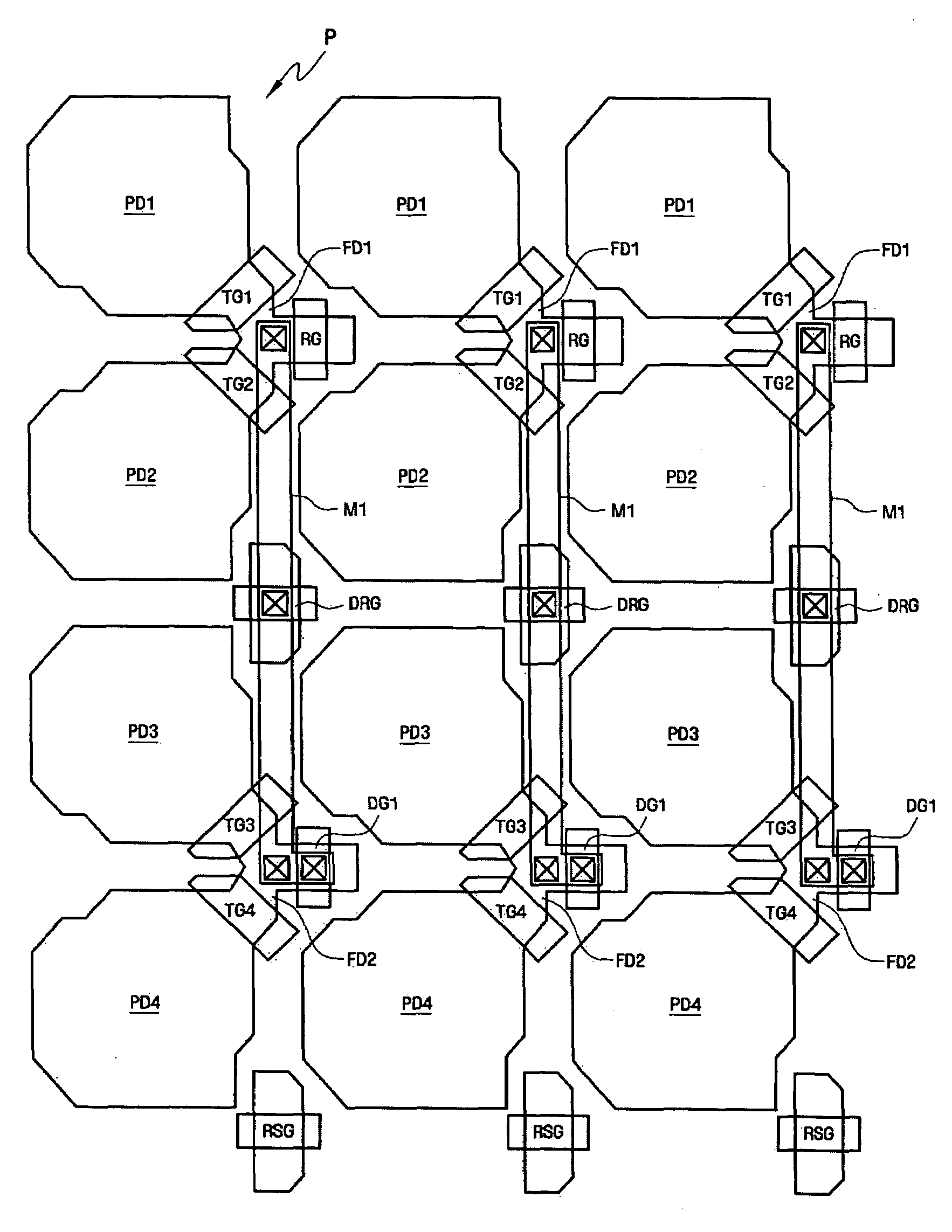
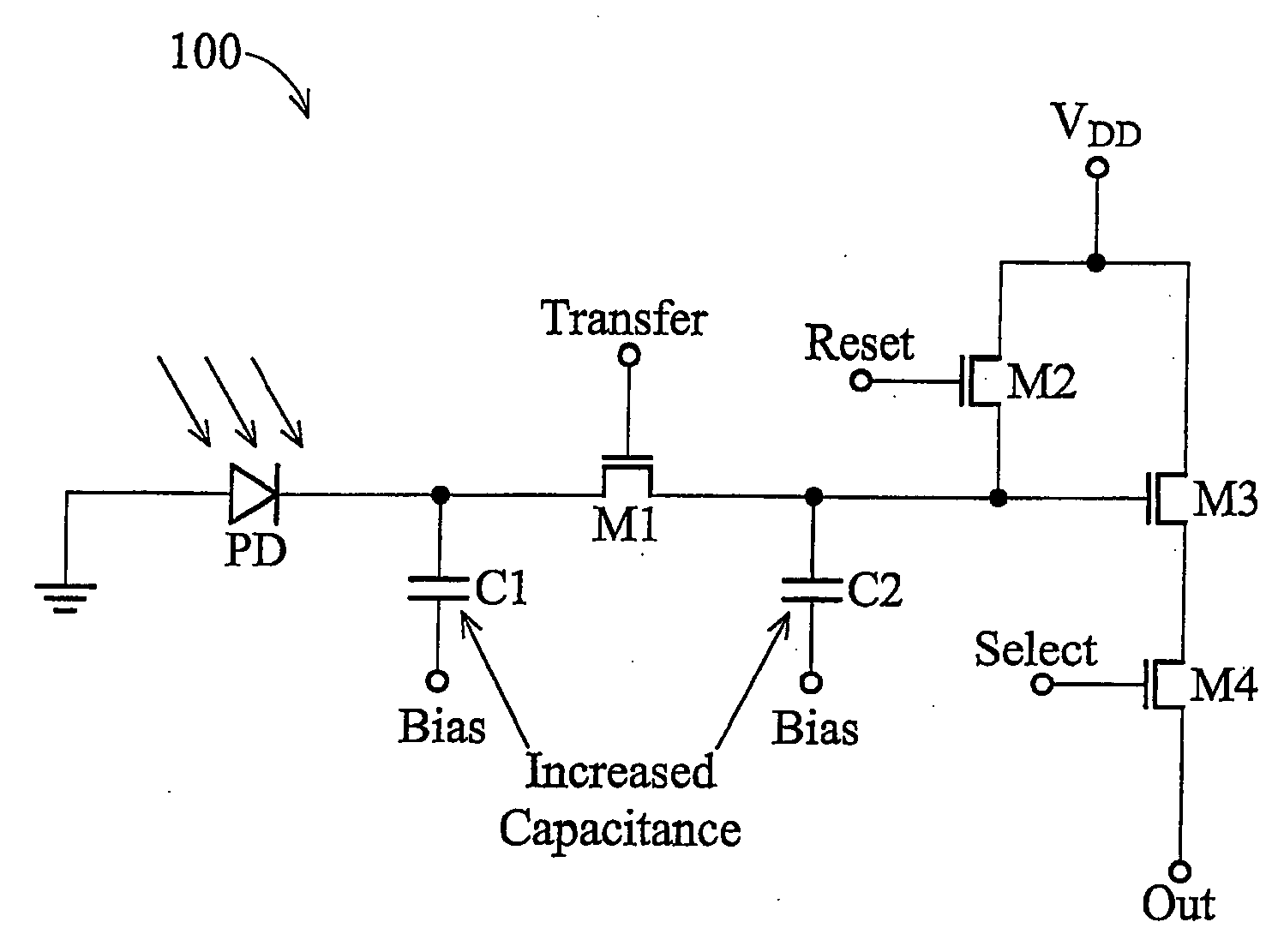
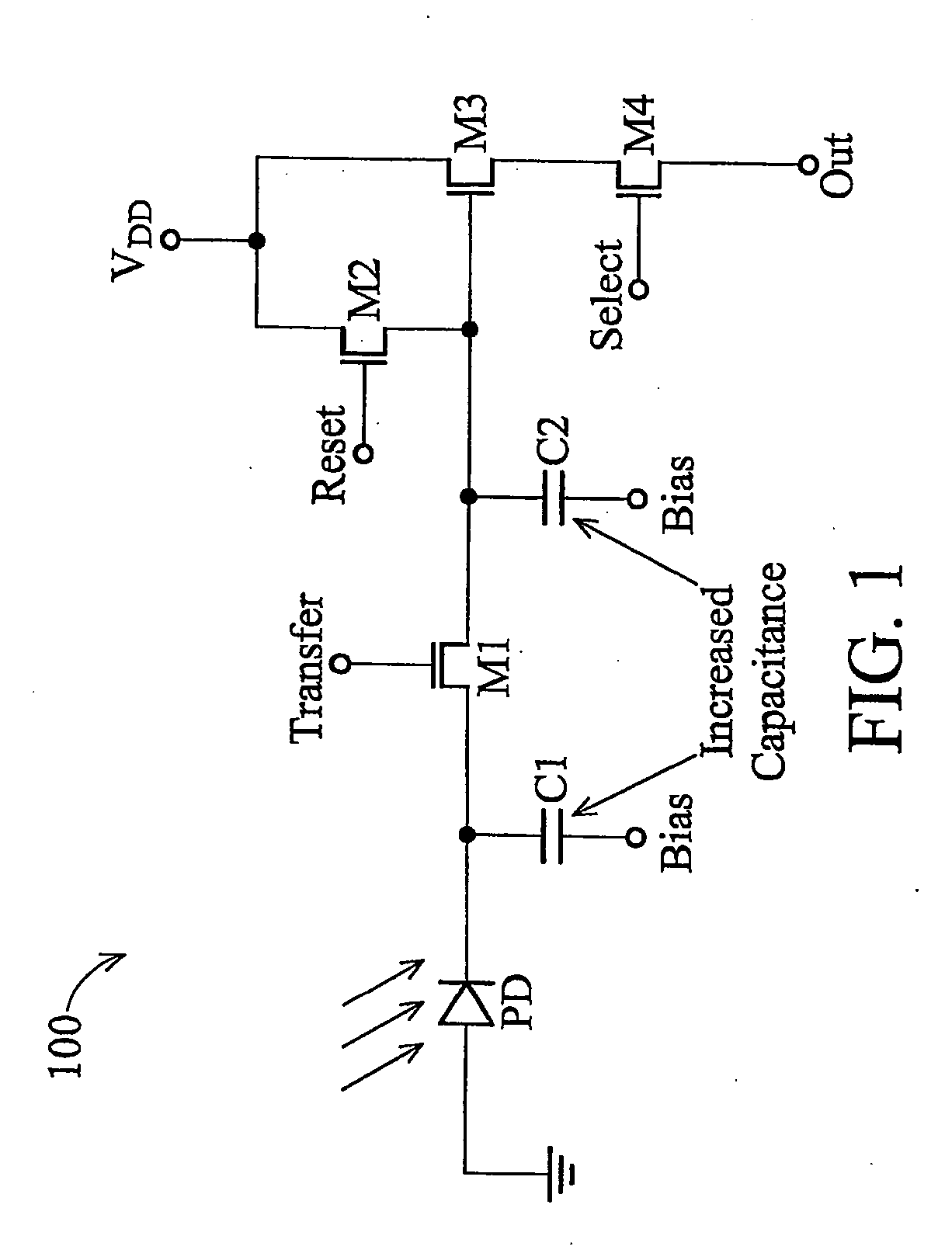
Shared-pixel-type image sensors for controlling capacitance of floating diffusion region
InactiveUS20070164332A1Improve fill factorIncrease the areaTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitancePhotoelectric conversion
A shared-pixel-type image sensor includes a semiconductor substrate, four photoelectric conversion elements disposed adjacent to one another in one direction on the semiconductor substrate, two first transmission elements transmitting charges accumulated in two adjacent ones of the photoelectric conversion elements to a first floating diffusion region, respectively, two second transmission elements transmitting charges accumulated in the other two adjacent photoelectric conversion elements to a second floating diffusion region electrically coupled with the first floating diffusion region, respectively, MOS capacitors that are electrically coupled with the first or second floating diffusion region, a reset element resetting the charges of the first and second floating diffusion regions to a reference value, and a drive element and an select element outputting the charges of the first or second floating diffusion region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Metal capacitor stacked with a MOS capacitor to provide increased capacitance density
InactiveUS20060024905A1Increase capacitance densityIncrease processing costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceMetal interconnect
An on-chip capacitive device comprises a semiconductor substrate, a MOS capacitor formed on the semiconductor substrate, and a metal interconnect capacitor formed at least in part in a region above the MOS capacitor. The MOS capacitor and the metal interconnect capacitor are connected in parallel to form a single capacitive device. The capacitance densities of the MOS capacitor and the metal interconnect capacitor are, thereby, combined. Advantageously, significant capacitance density gains can be achieved without additional processing steps.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
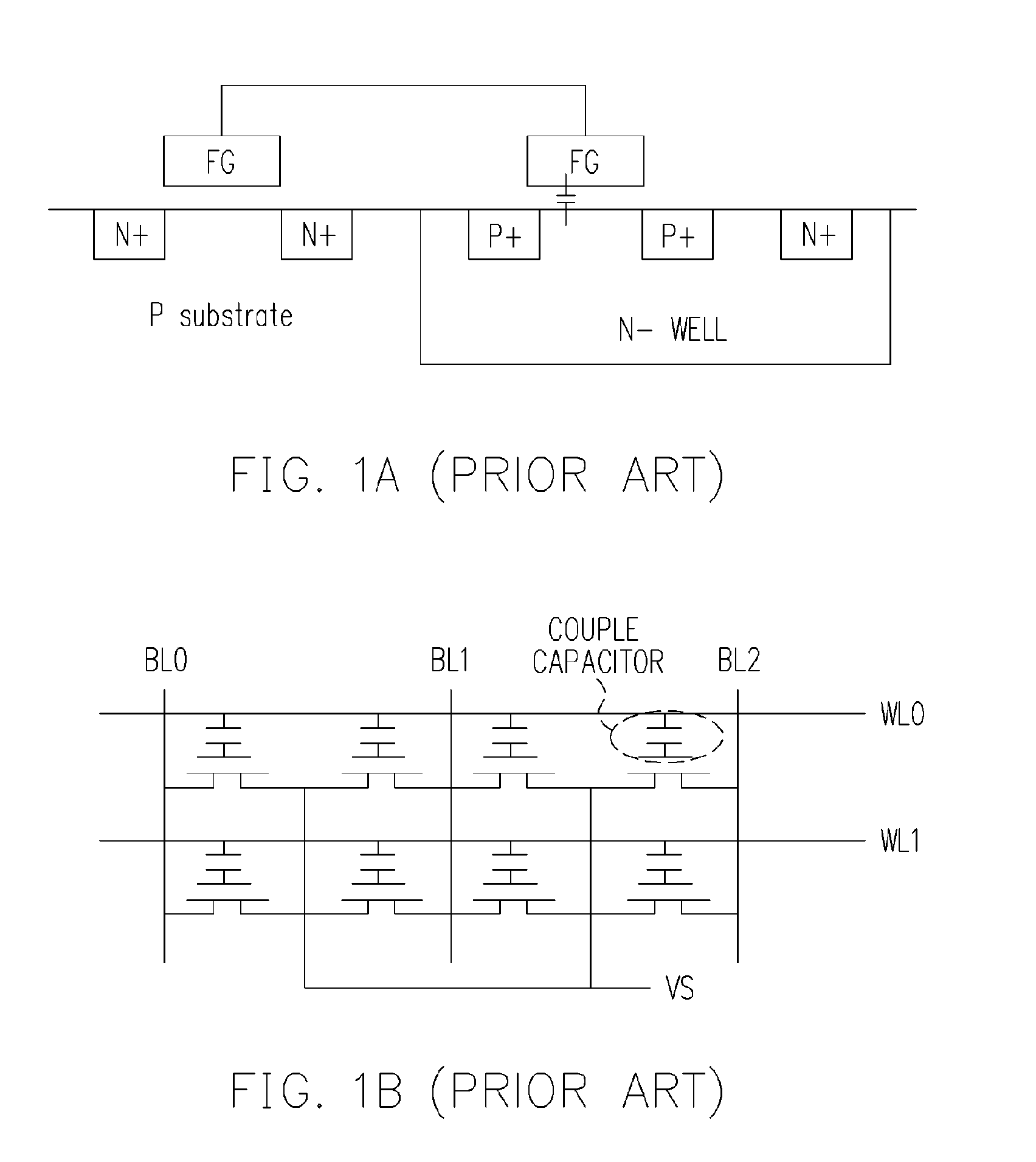
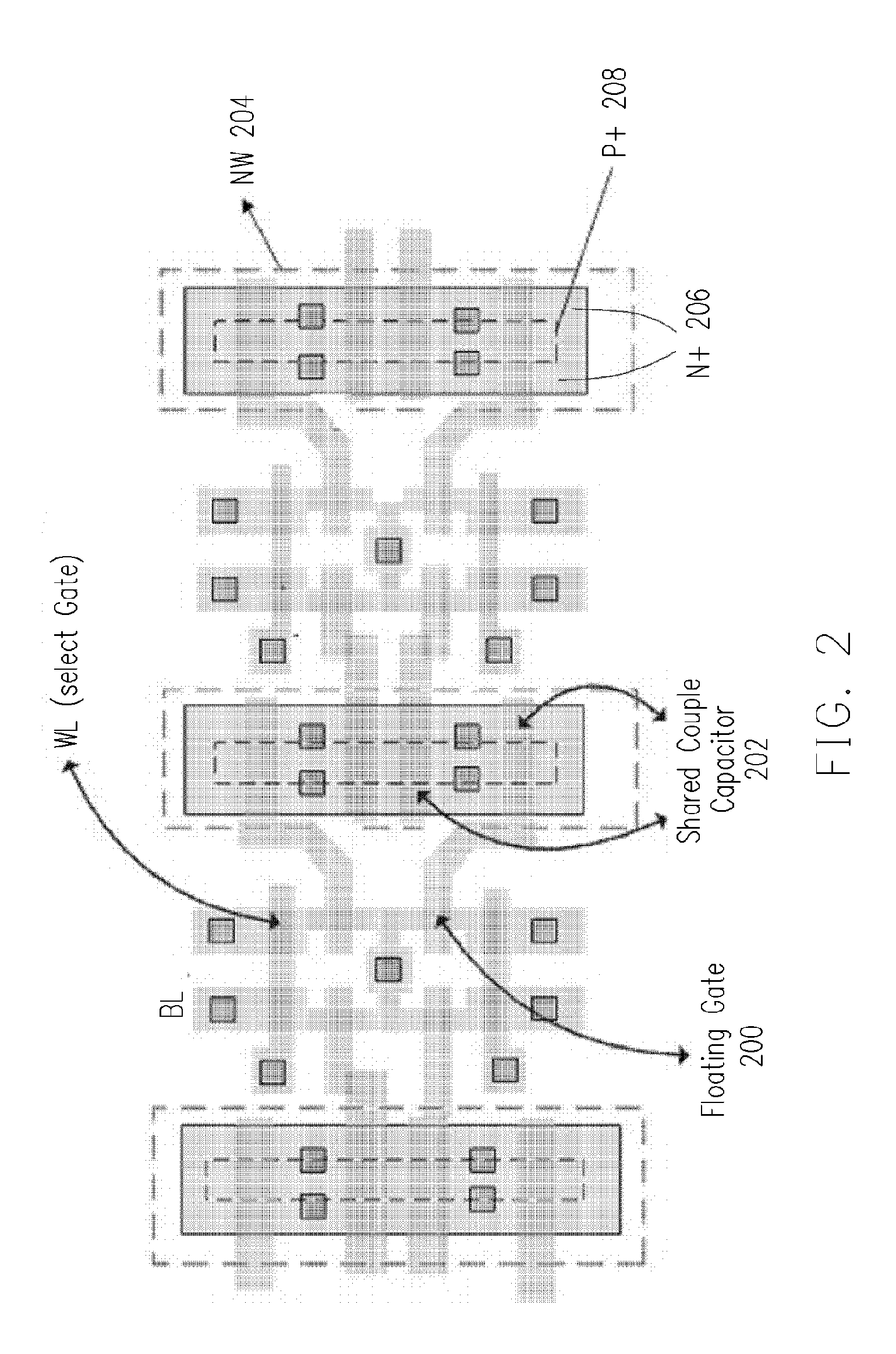
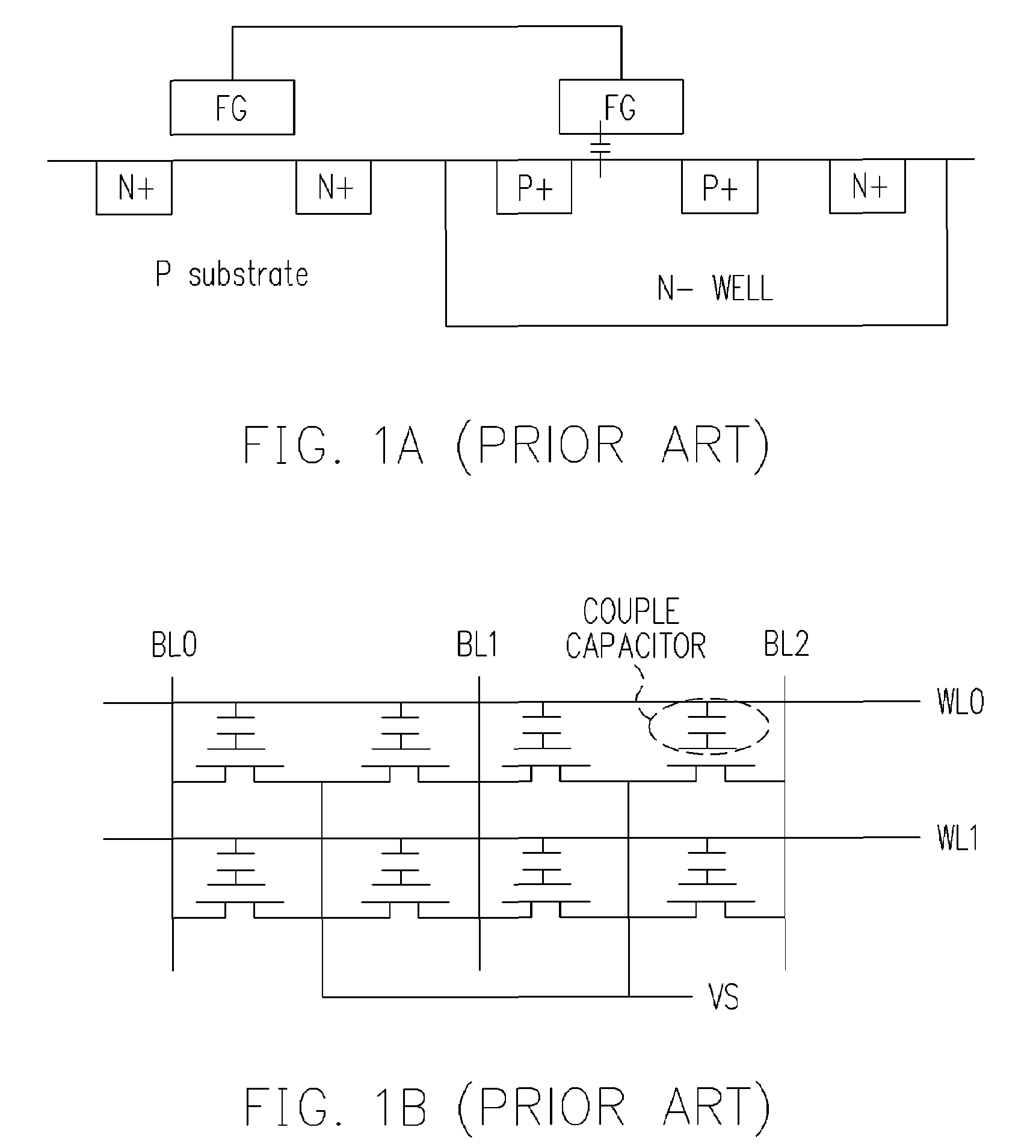
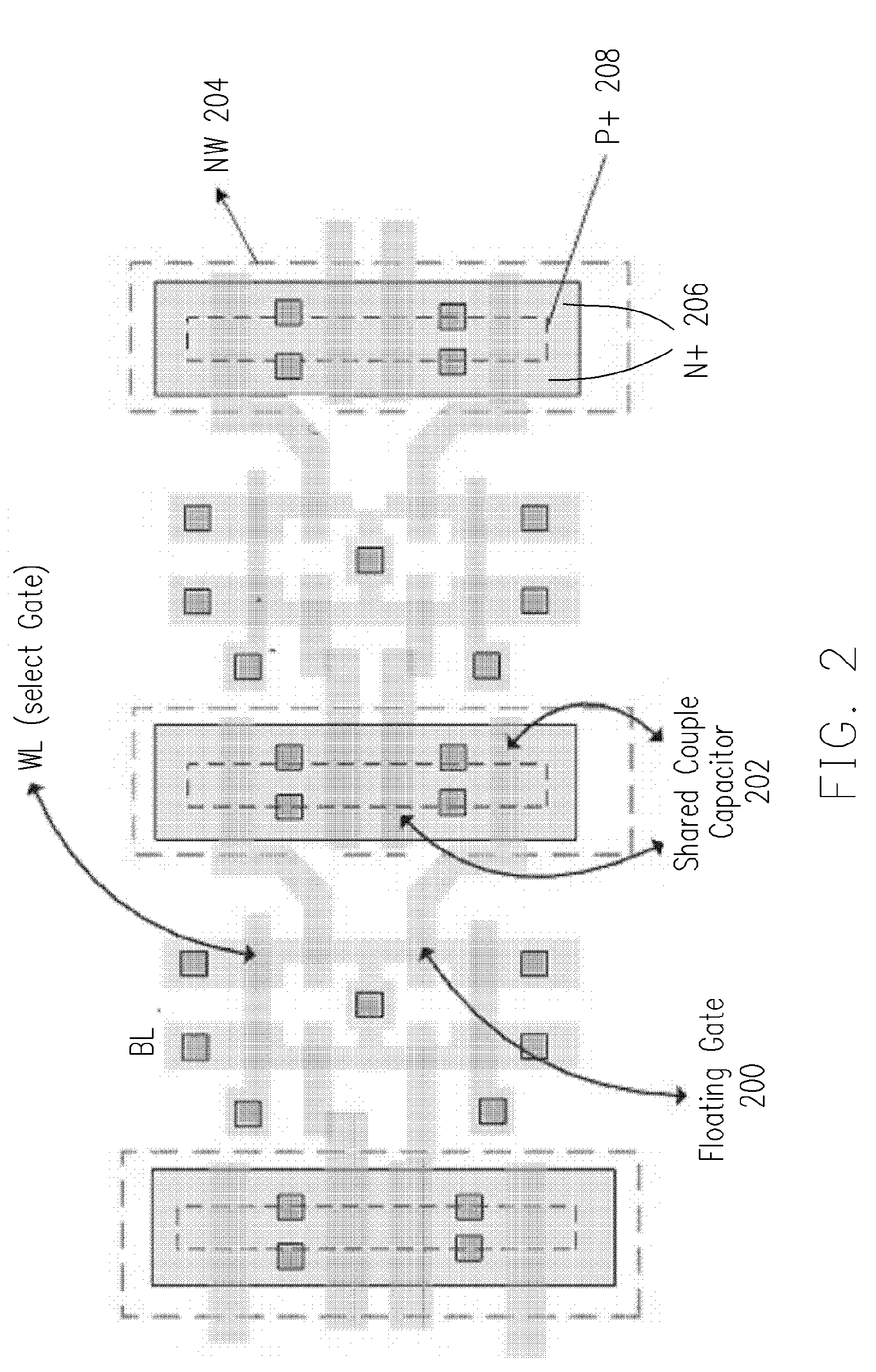
Nonvolatile memory structure
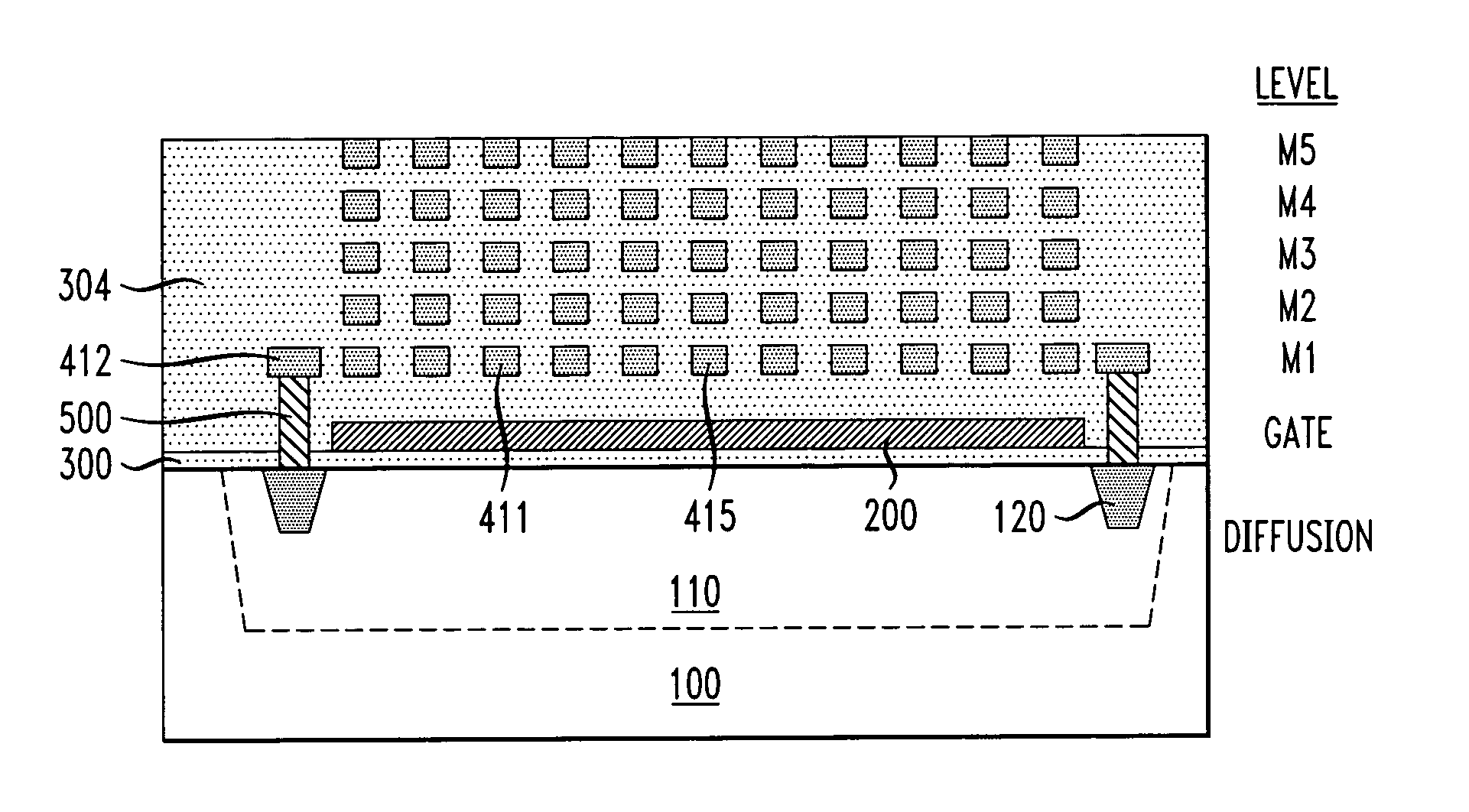
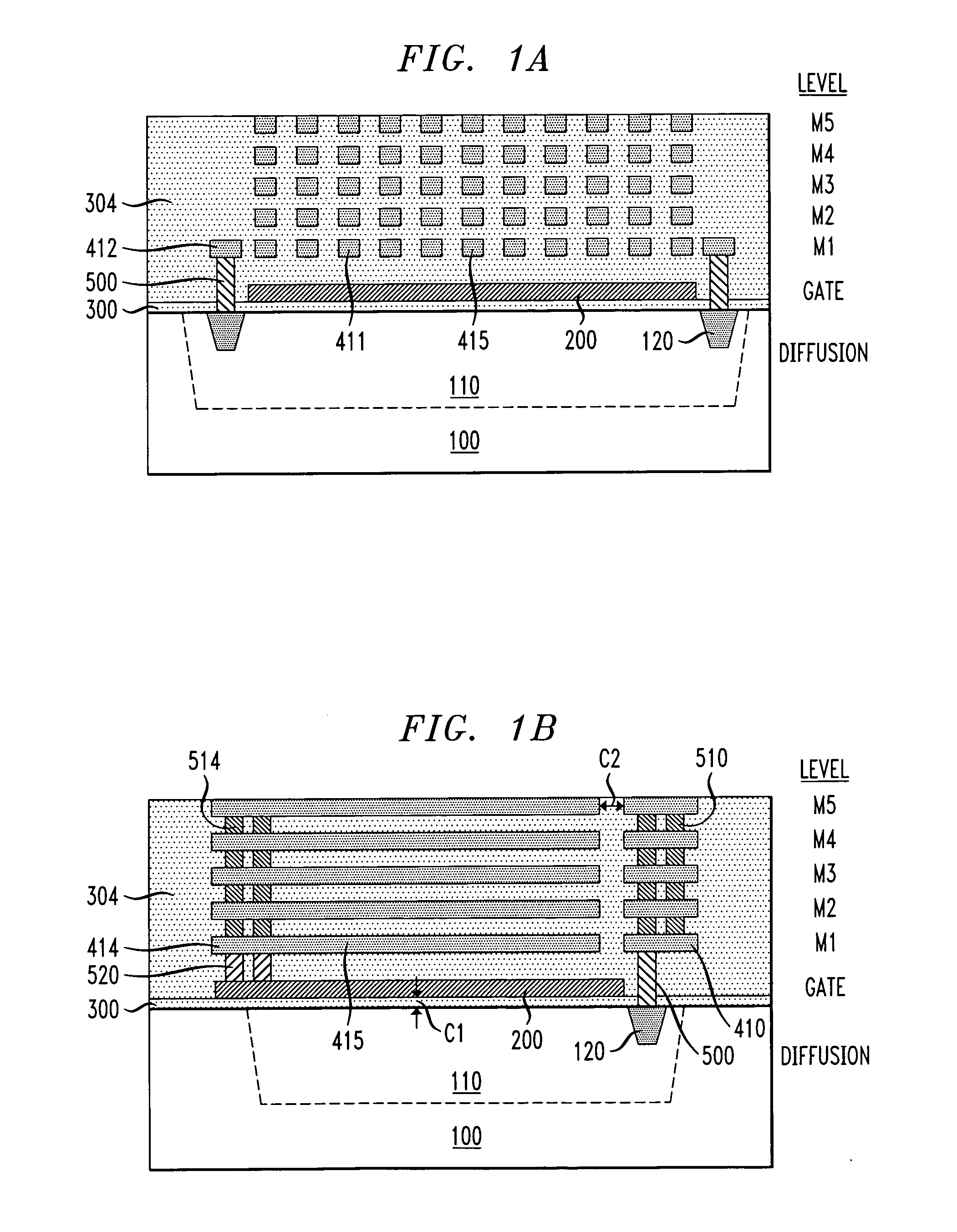
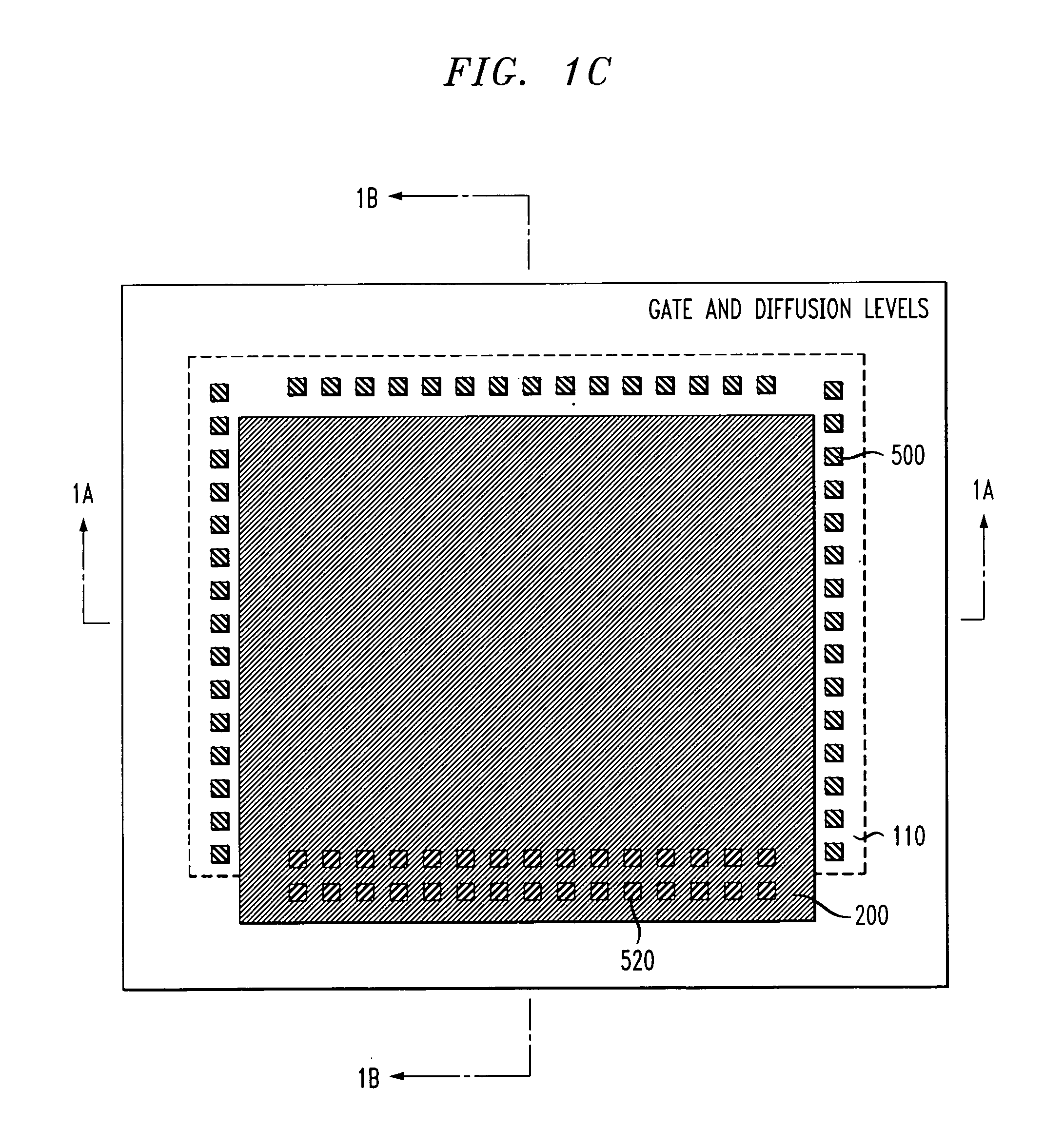
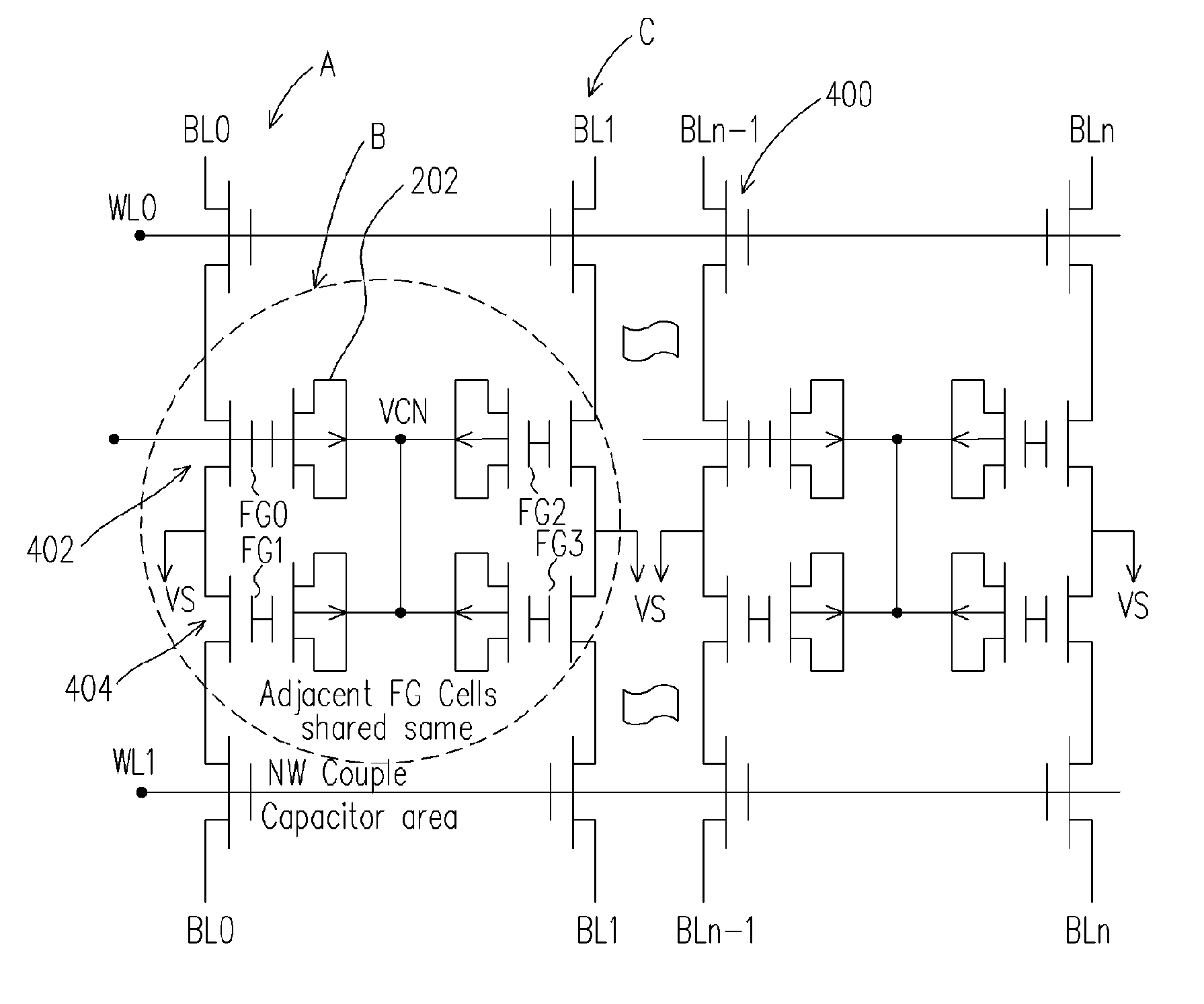
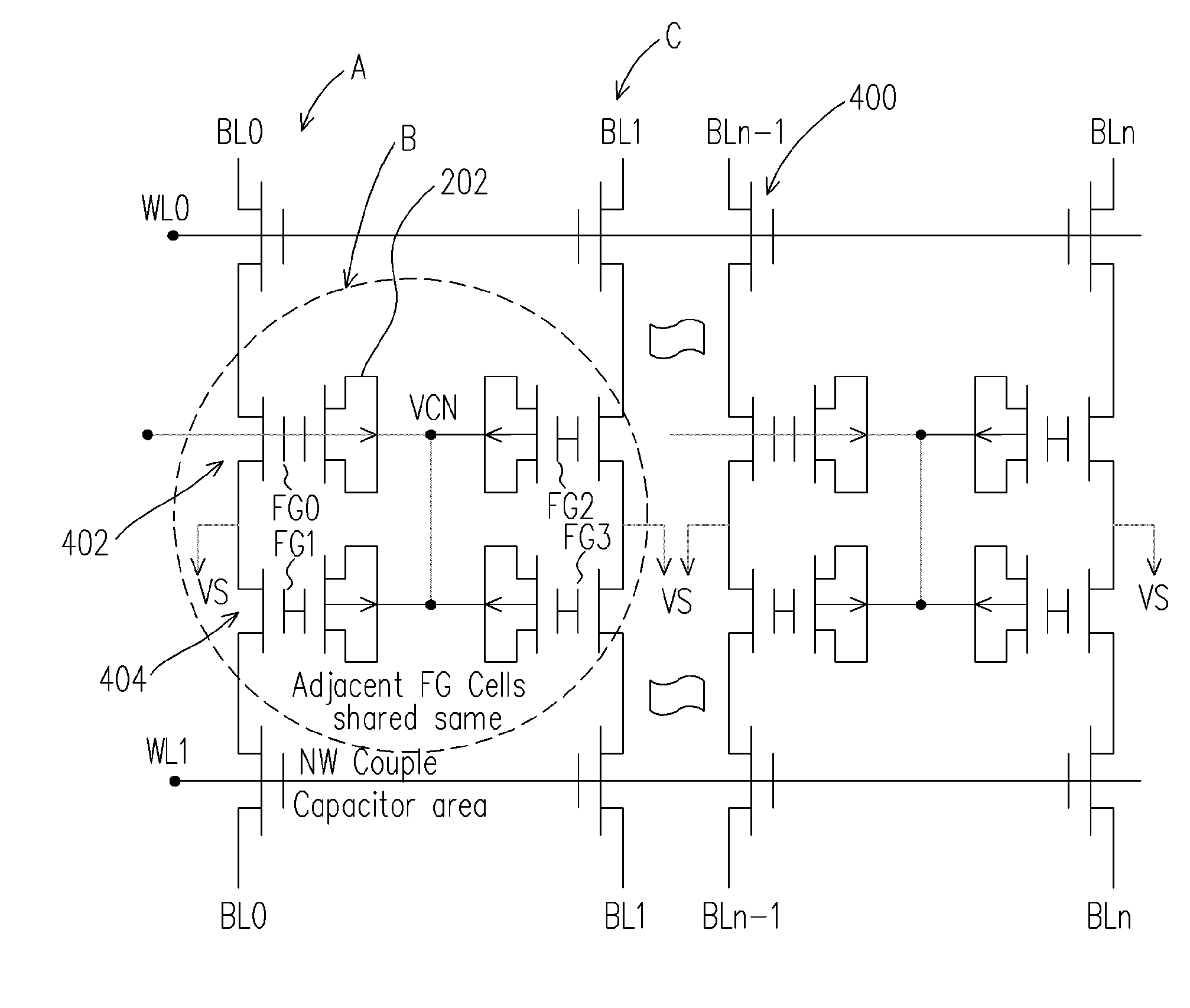
The invention is directed to a layout of nonvolatile memory device. The memory cell has a gate electrode, a first doped electrode, and a second doped electrode. The first doped electrode is coupled to the bit line. The gate electrode is coupled to one separated word line. A shared coupled capacitor structure is coupled between all of memory cells of the adjacent bit lines from the second doped electrode. The capacitor structure has at least two floating-gate MOS capacitors. Each floating-gate MOS capacitor has a floating-gate transistor having a floating gate, a first S / D region and a second S / D region; and a MOS capacitor coupled to the floating gate. The first S / D region is coupled to the second doped electrode of the corresponding one of the transistor memory cells, and the second S / D region is shared with an adjacent one of the floating-gate transistor.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
Single-polycrystalline silicon electrically erasable and programmable nonvolatile memory device
A single polycrystalline silicon floating gate nonvolatile memory cell has a MOS capacitor and a storage MOS transistor fabricated with dimensions that allow fabrication using current low voltage logic integrated circuit process. The MOS capacitor has a first plate connected to a gate of the storage MOS transistor to form a floating gate node. The physical size of the MOS capacitor is relatively large (approximately 10 time greater) when compared to a physical size of the storage MOS transistor to establish a large coupling ratio (approximately 90% between the second plate of the MOS capacitor and the floating gate node. When a voltage is applied to the second plate of the MOS capacitor and a voltage applied to the source region or drain region of the MOS transistor establishes a voltage field within the gate oxide of the MOS transistor such that Fowler-Nordheim edge tunnel is initiated.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Integrating the Formation of I/O and Core MOS Devices with MOS Capacitors and Resistors
ActiveUS20100038692A1Reduce complexityLow costTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricEngineering
An integrated circuit structure includes a semiconductor substrate, and a first and a second MOS device. The first MOS device includes a first gate dielectric over the semiconductor substrate, wherein the first gate dielectric is planar; and a first gate electrode over the first gate dielectric. The second MOS device includes a second gate dielectric over the semiconductor substrate; and a second gate electrode over the second gate dielectric. The second gate electrode has a height greater than a height of the first gate electrode. The second gate dielectric includes a planar portion underlying the second gate electrode, and sidewall portions extending on sidewalls of the second gate electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fabrication of silicon nano wires and gate-all-around MOS devices
InactiveUS20070298551A1Quality improvementEnhance the quantum effectNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCapacitance
The invention relates to methods for manufacturing semiconductor devices. Processes are disclosed for implementing suspended single crystal silicon nano wires (NWs) using a combination of anisotropic and isotropic etches and spacer creation for sidewall protection. The core dimensions of the NWs are adjustable with the integration sequences: they can be triangular, rectangular, quasi-circular, or an alternative polygonal shape. Depending on the length of the NWs, going from the sub-micron to millimeter range, the NWs may utilize support from anchors to the side, during certain processing steps. By changing the lithographic dimensions of the anchors compared to the NWs, the anchors may be reduced or eliminated during processing. The method covers, among other things, the integration of Gate-All-Around NW (GAA-NW) MOSFETs on a bulk semiconductor. The GAA structure may consist of a silicon core fabricated as specified in the invention, surrounded by any usable gate dielectric, and finally by a gate material, such as polysilicon or metal. The source and drain of the GAA-NW may be connected to the bulk semiconductor to avoid self heating of the device over a wide range of operating conditions. The GAA-NW MOS capacitor can also be used for the integration of a Gate-All-Around optical phase modulator (GAA modulator). The working principle for the optical modulator is modulation of the refractive index by free carrier accumulation or inversion in a MOS capacitive structure, which changes the phase of the propagating light.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
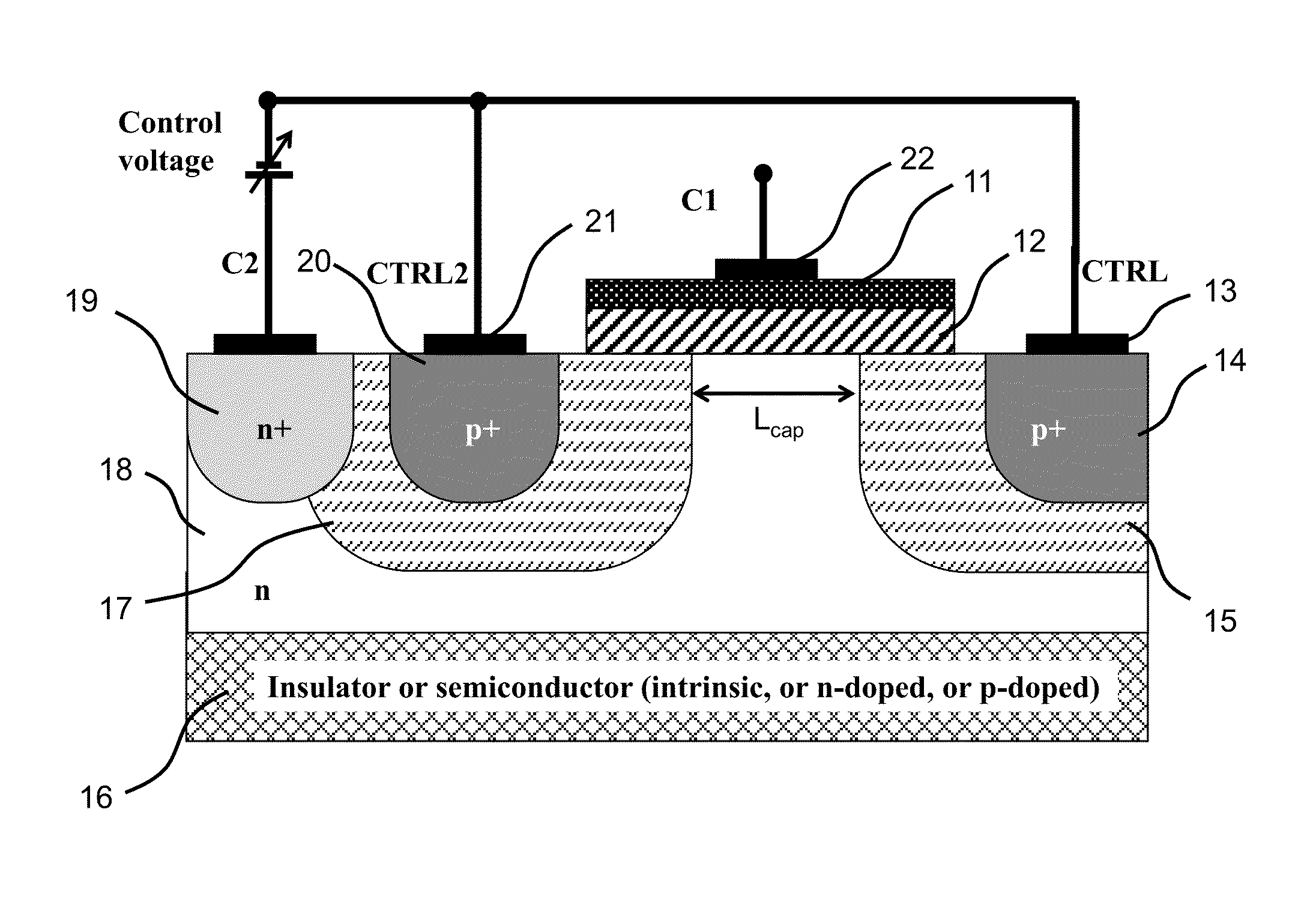
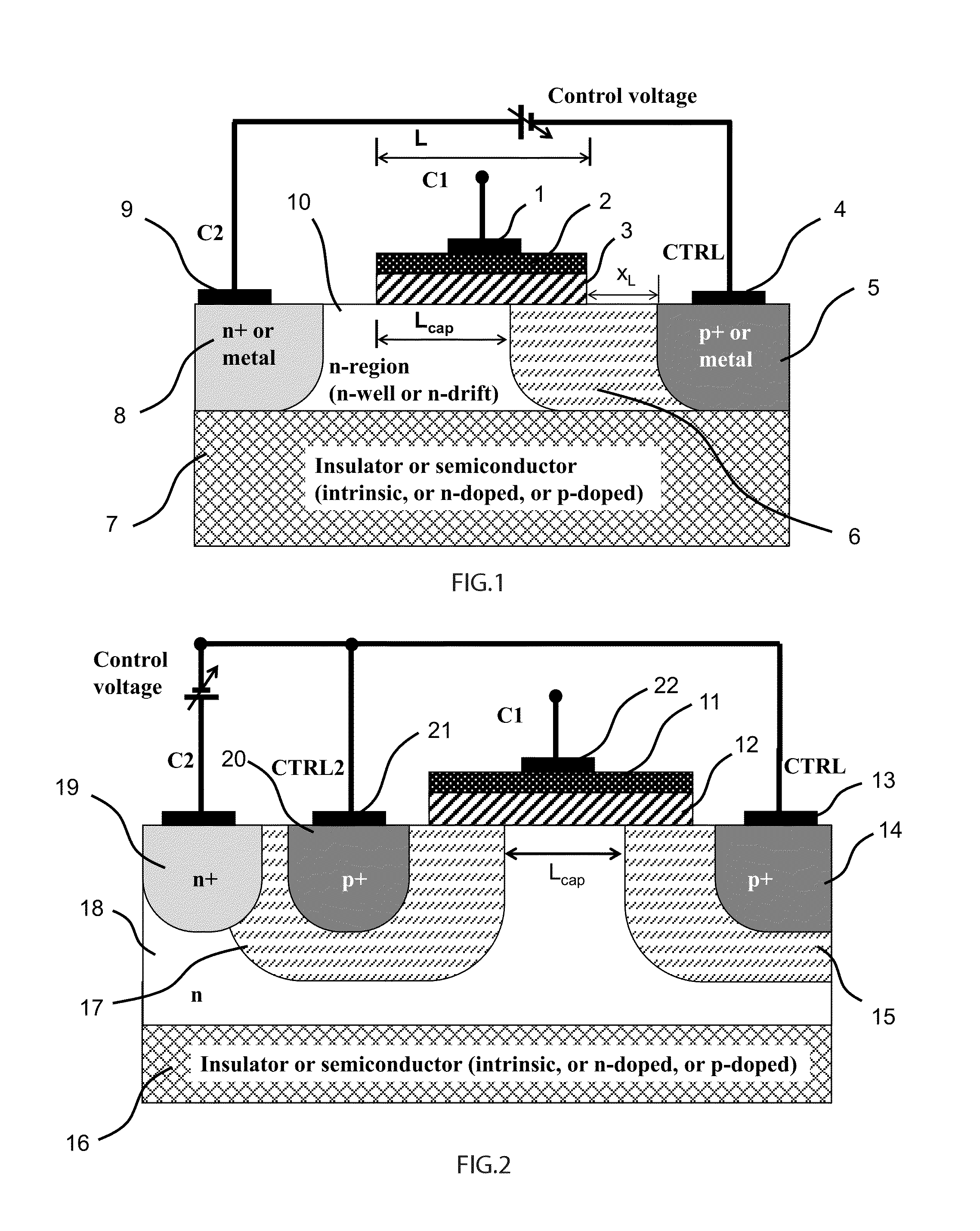
Multiple Control Transcap Variable Capacitor
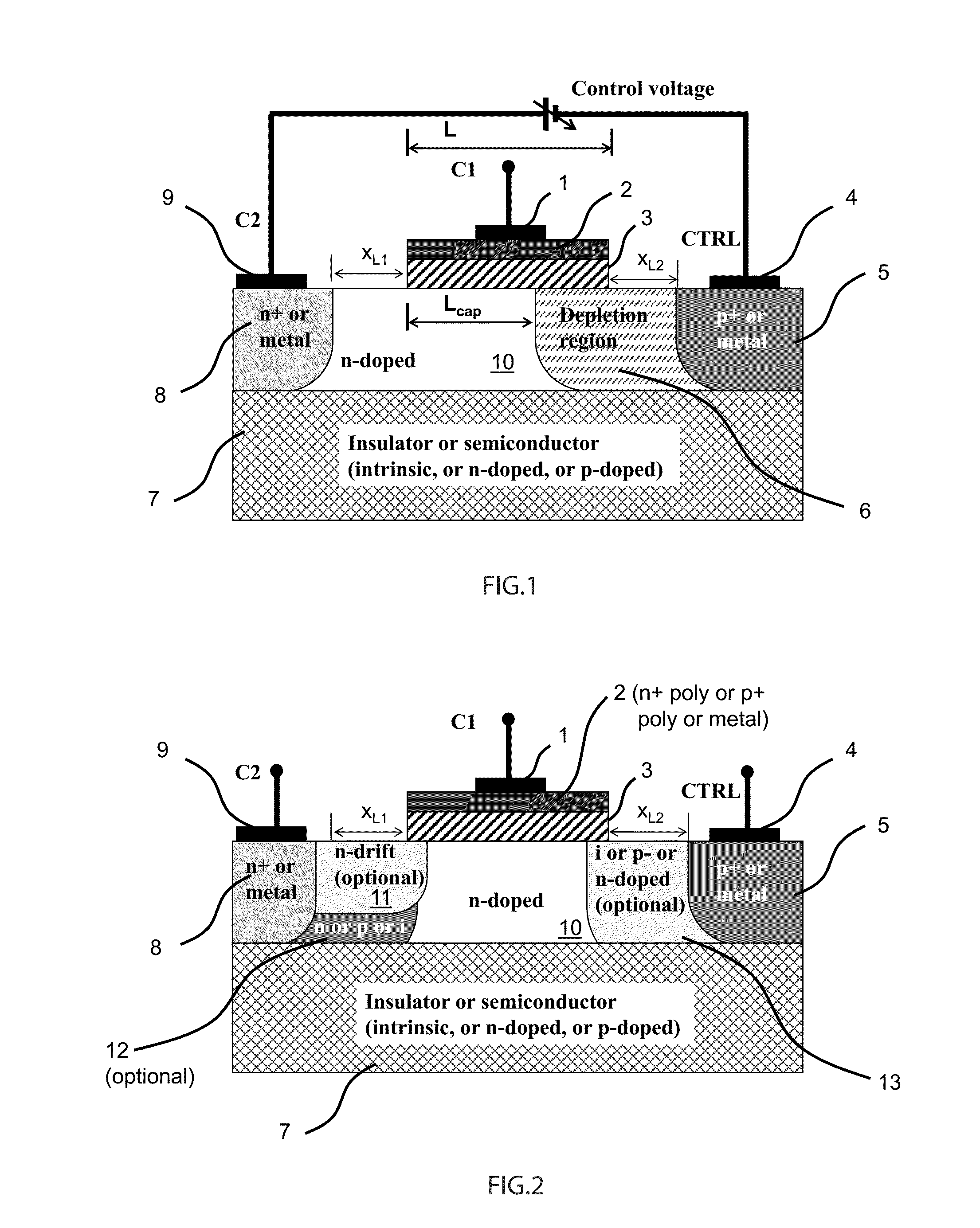
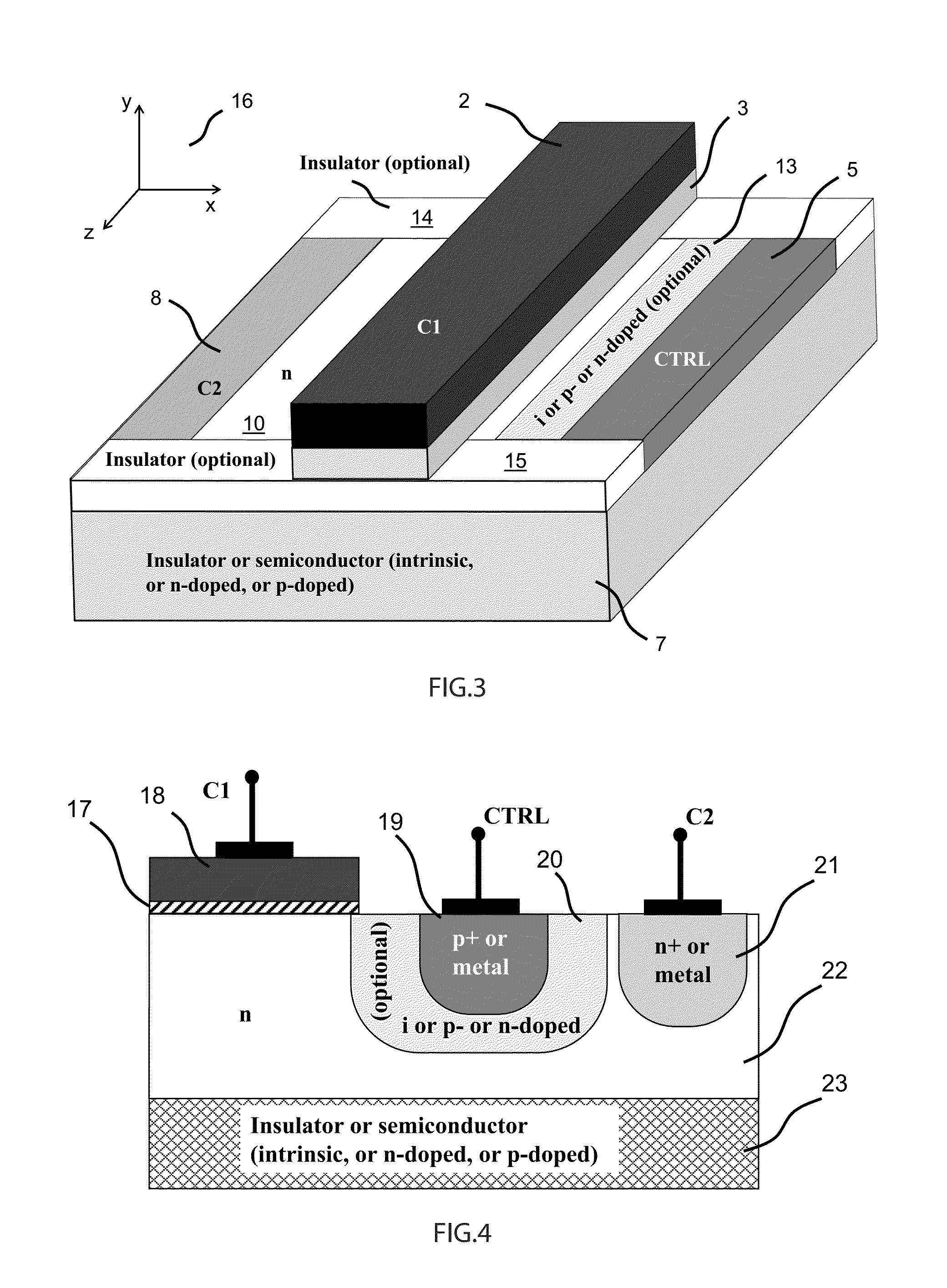
ActiveUS20150194538A1Improve device performanceAvoid distortionSolid-state devicesCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricCapacitanceManufacturing technology
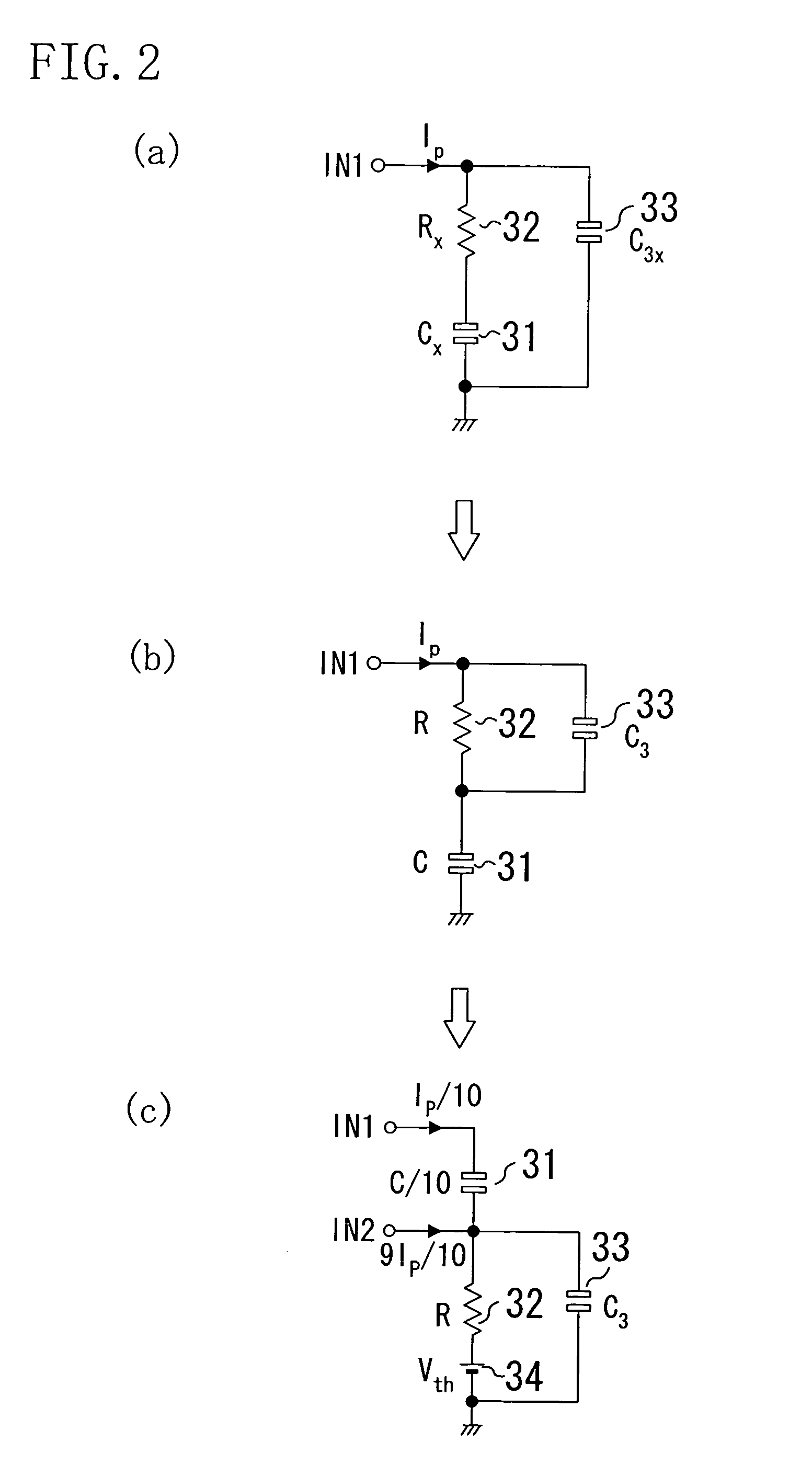
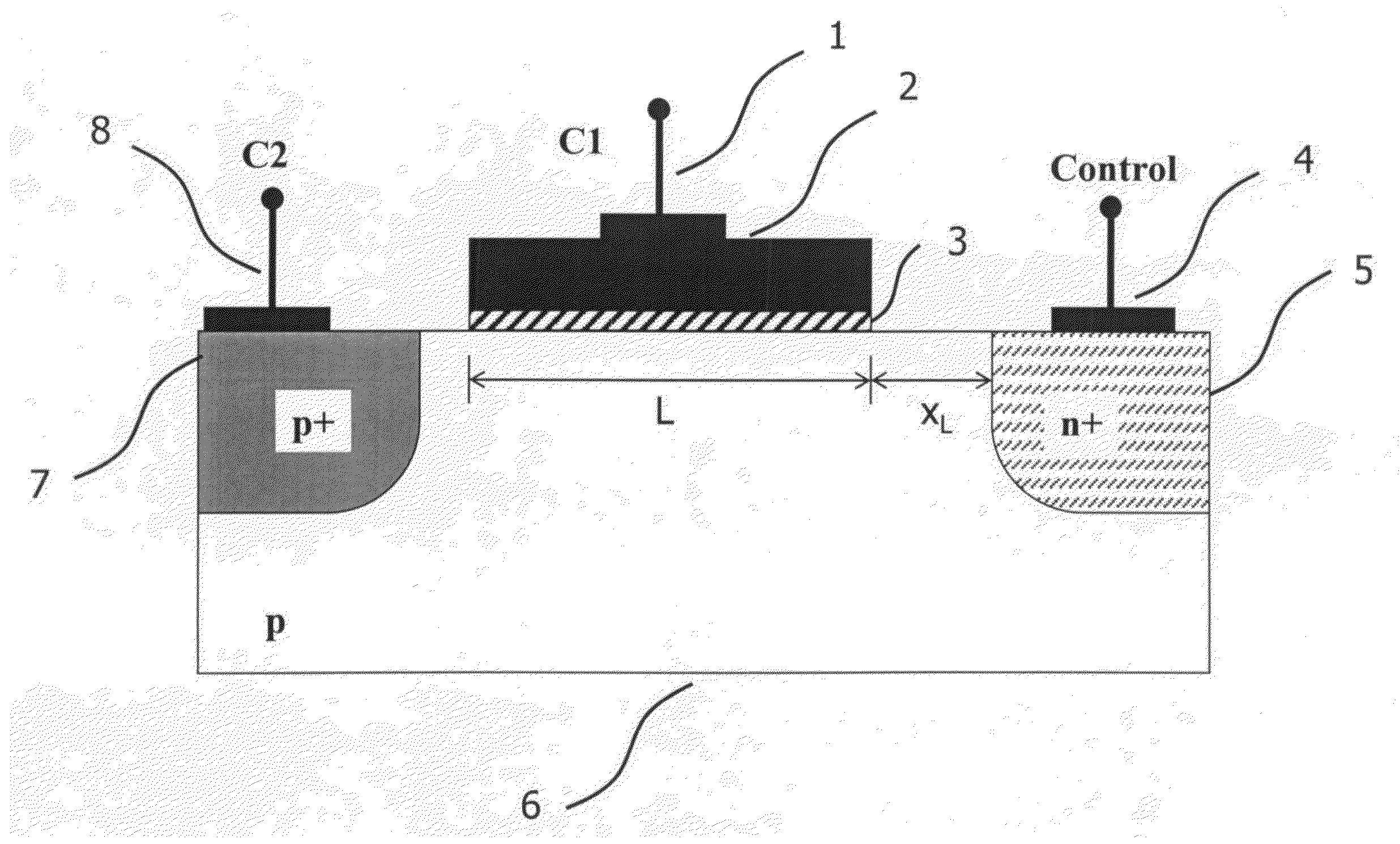
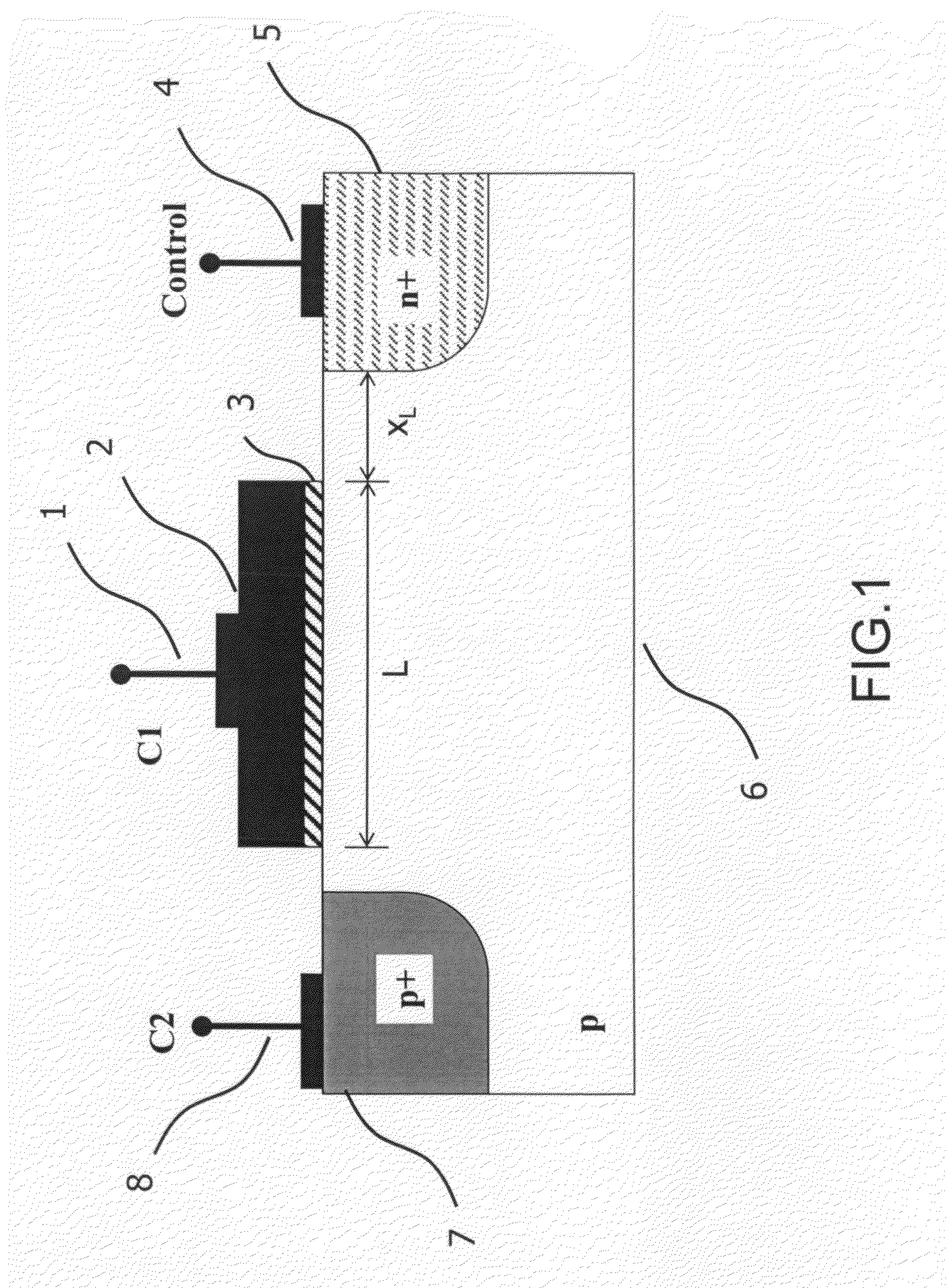
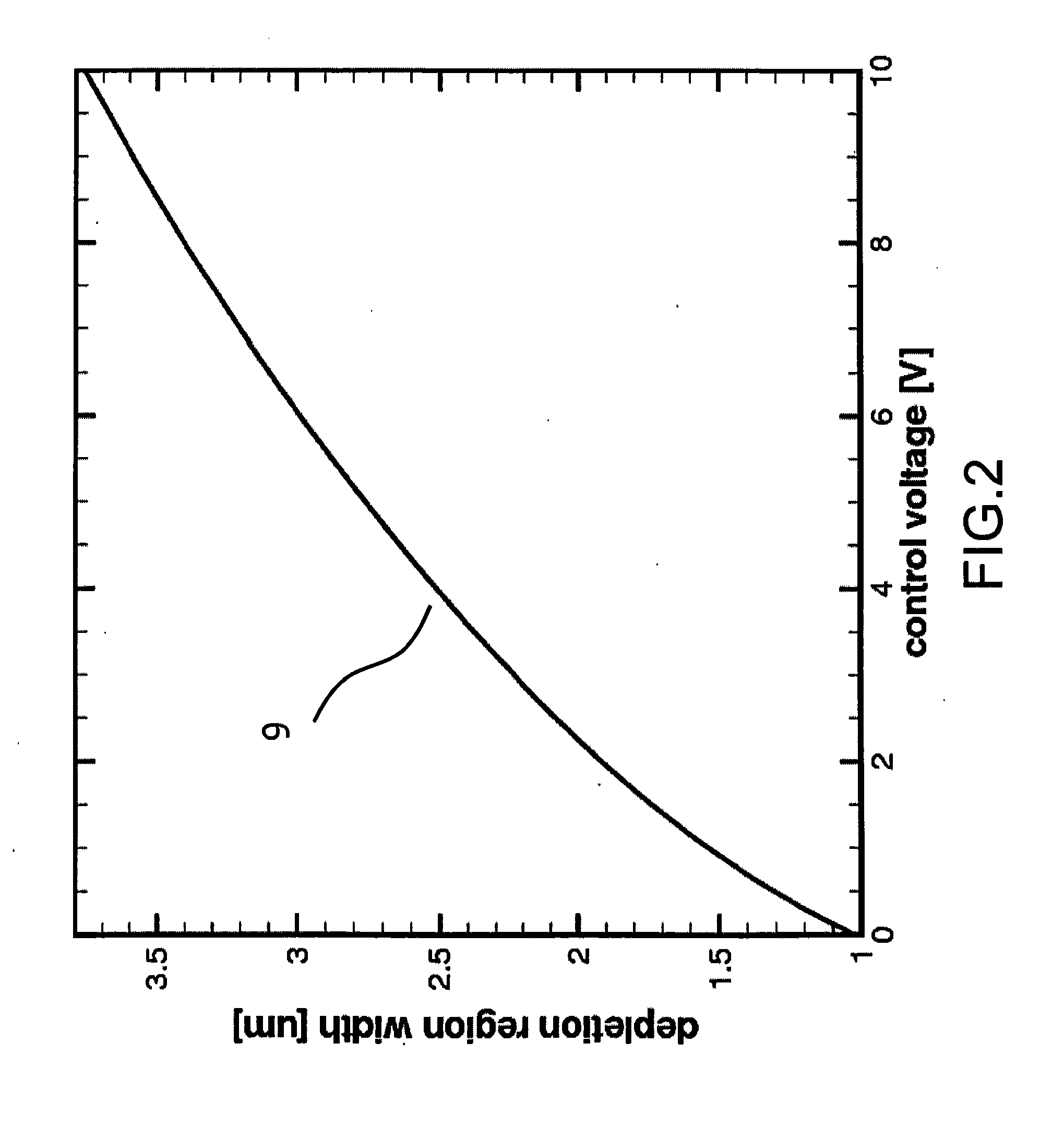
A novel semiconductor variable capacitor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a semiconductor variable MOS capacitor structure suitable for integrated circuits, which has at least three terminals, one of which is used to modulate the equivalent capacitor area of the MOS structure by increasing or decreasing its DC voltage with respect to another terminal of the device, in order to change the capacitance over a wide ranges of values. Furthermore, the present invention decouples the AC signal and the DC control voltage minimizing the distortion and increasing the performance of the device, such as its control characteristic. The present invention is simple and only slightly dependent on the variations due to the fabrication process. It exhibits a high value of capacitance density and, if opportunely implemented, shows a quasi linear dependence of the capacitance value with respect to the voltage of its control terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
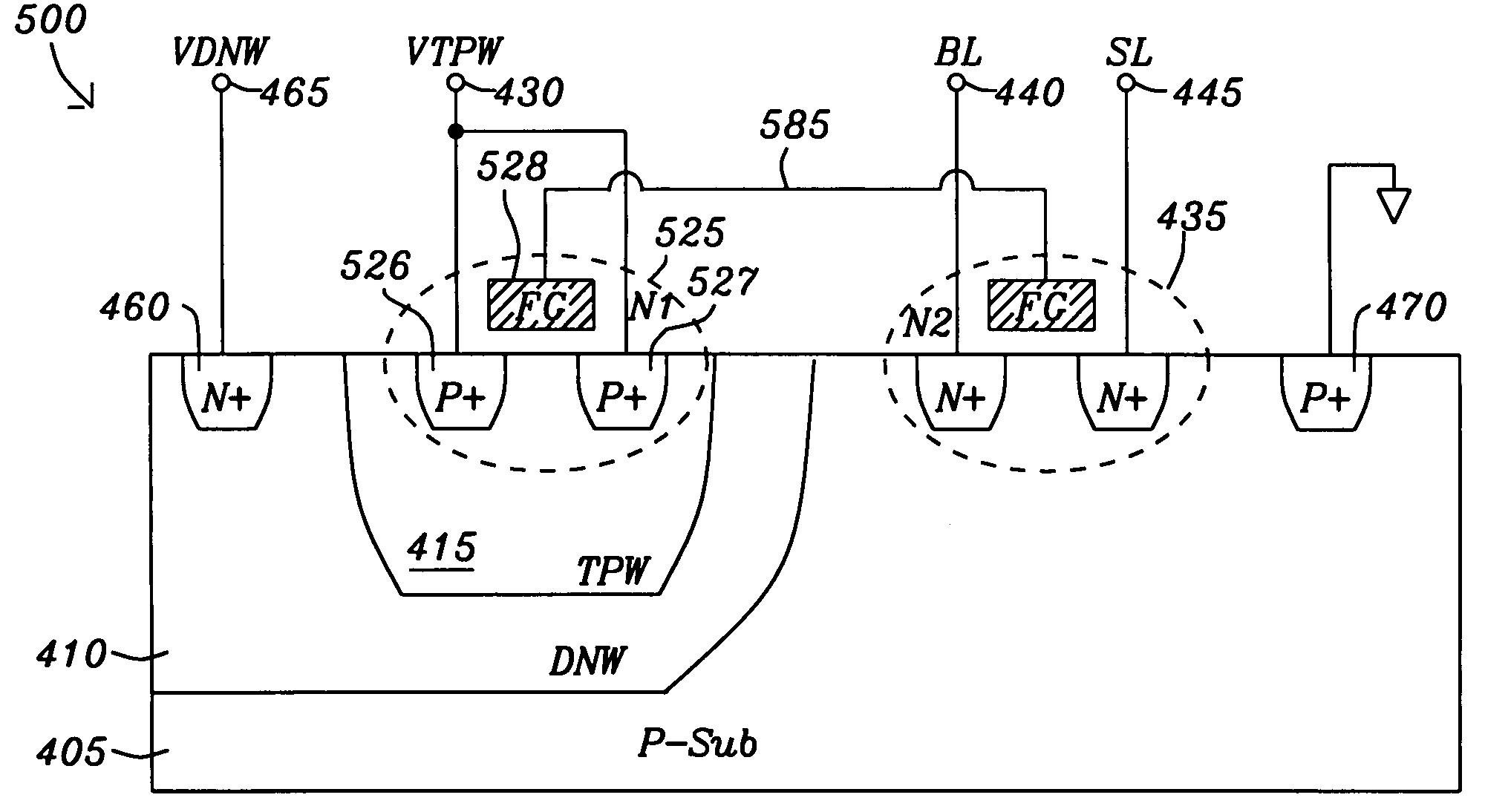
Soi device and method for its fabrication
A silicon on insulator (SOI) device and methods for fabricating such a device are provided. The device includes an MOS capacitor coupled between voltage busses and formed in a monocrystalline semiconductor layer overlying an insulator layer and a semiconductor substrate. The device includes at least one electrical discharge path for discharging potentially harmful charge build up on the MOS capacitor. The MOS capacitor has a conductive electrode material forming a first plate of the MOS capacitor and an impurity doped region in the monocrystalline silicon layer beneath the conductive electrode material forming a second plate. A first voltage bus is coupled to the first plate of the capacitor and to an electrical discharge path through a diode formed in the semiconductor substrate and a second voltage bus is coupled to the second plate of the capacitor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Charge coupled pump-efficient charge pump regulator with mos capacitor
ActiveUS20090315615A1Easy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCapacitanceVoltage multiplier
A charge pump with a MOS-type capacitor, where the MOS-type capacitor is operated in an inversion region in which capacitance varies as a function of the frequency of the applied signal. The charge pump is switched to transfer charge from an input node to the capacitor and from the capacitor to an output node. During a transition interval, a relatively high frequency switching signal is used to lower the capacitance and increase efficiency. During a settling interval, a relatively low frequency switching signal is used, in which case the capacitance is higher, but similar to a level which would be seen if the capacitor was operated in an accumulation region. MOS capacitor dimensions and switching intervals are mutually optimized to provide high efficiency and required throughput. The charge pump may be configured as a voltage multiplier, divider, inverter or follower, for instance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
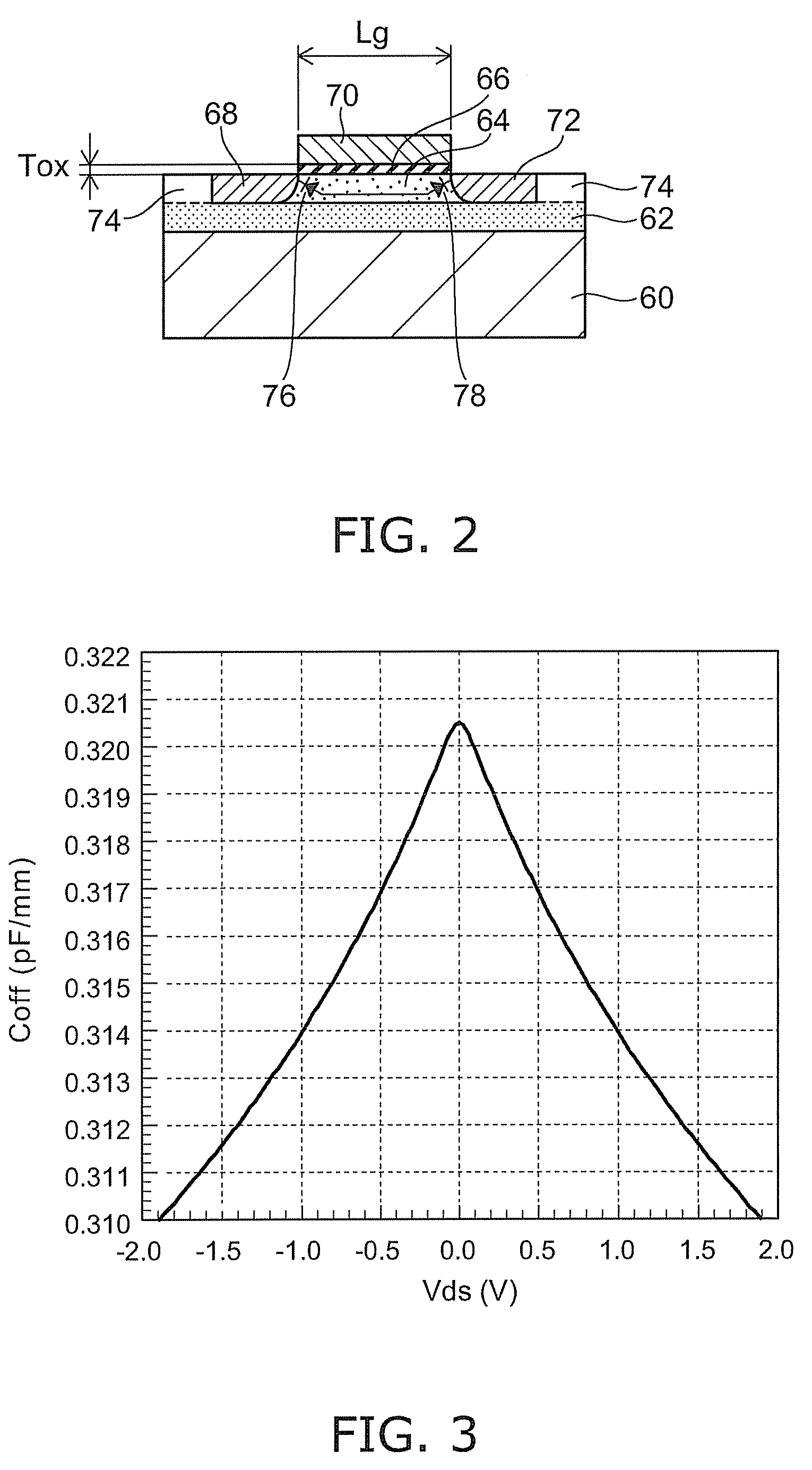
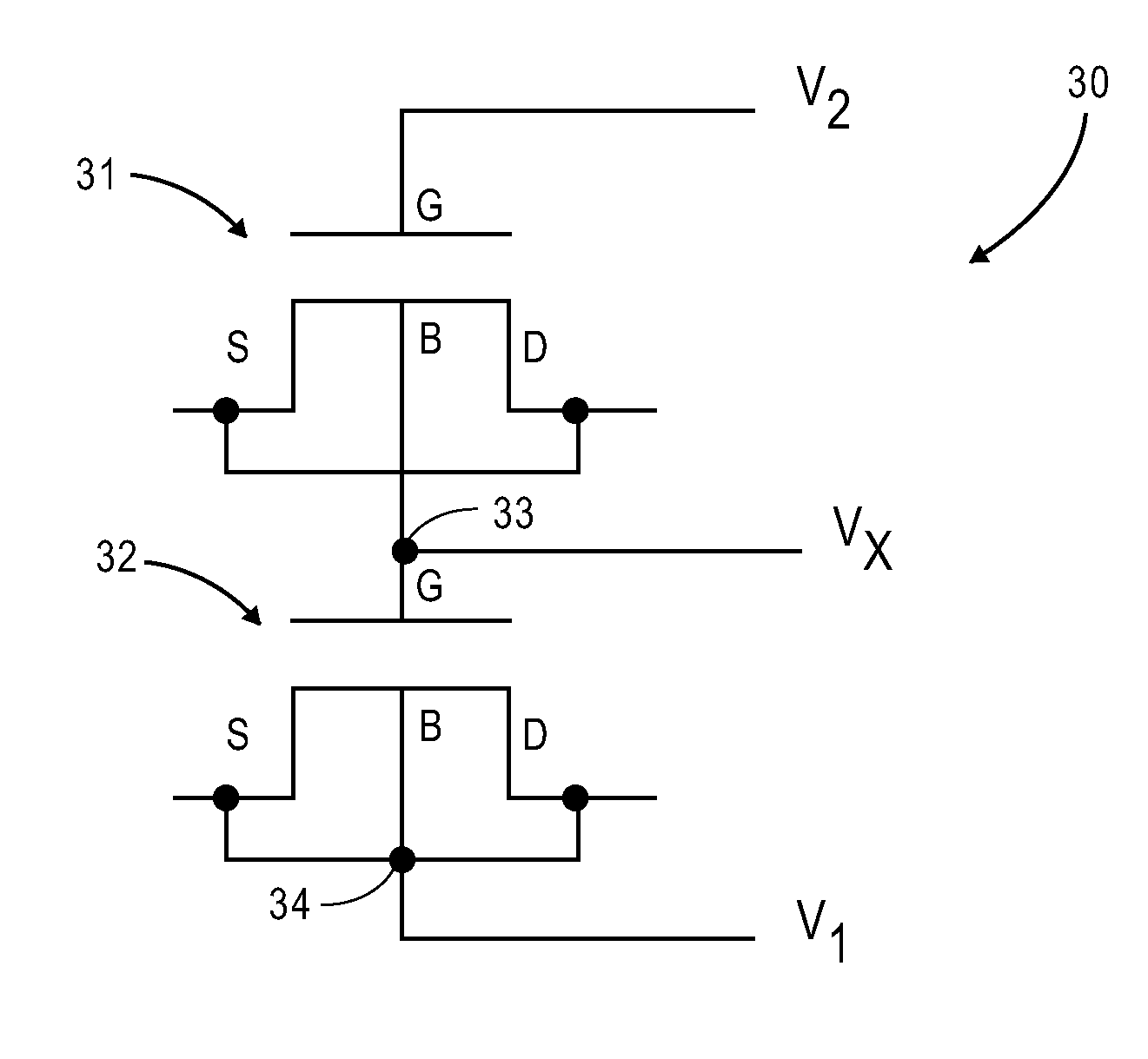
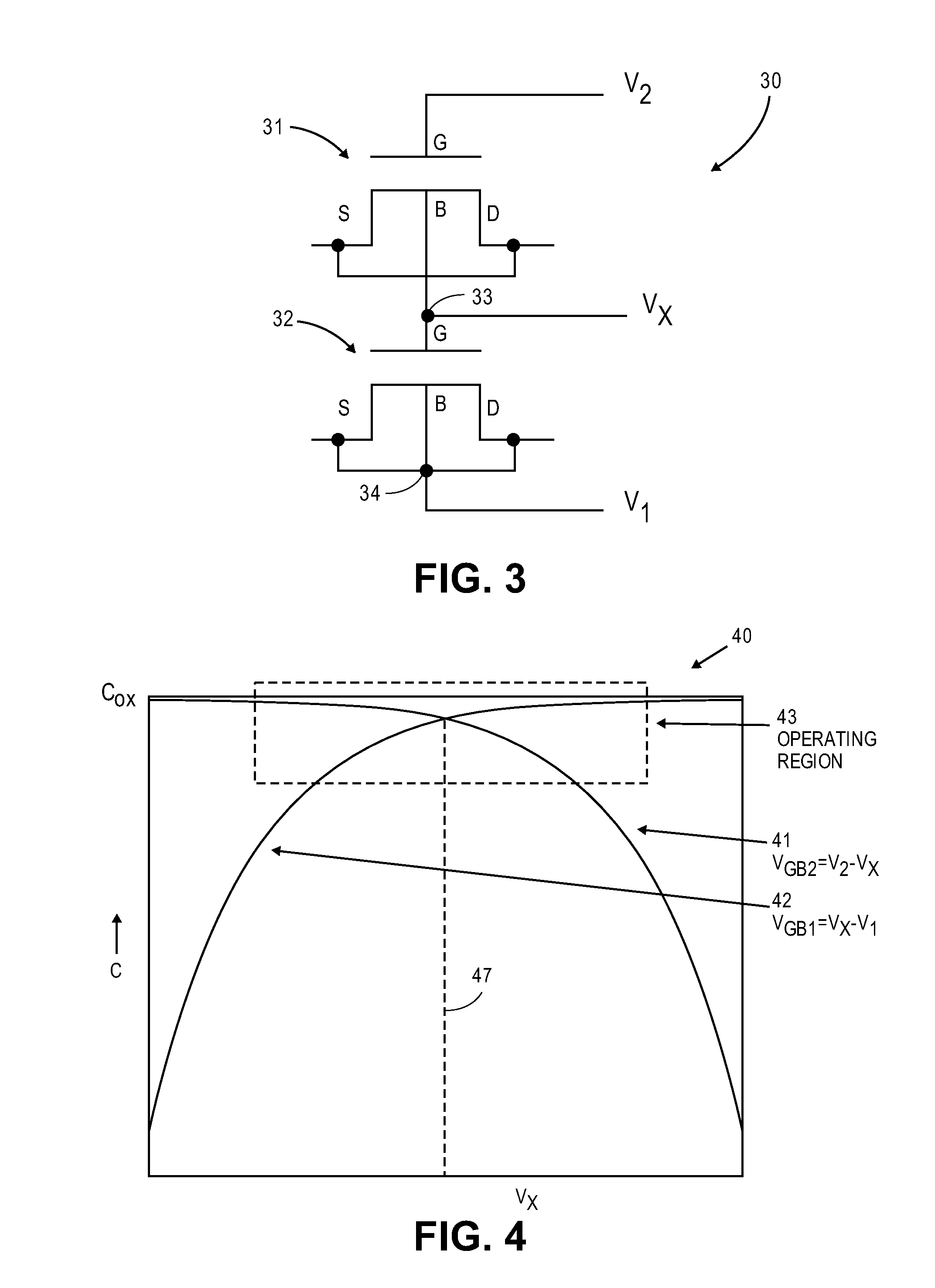
Mos capacitor structure and linearization method for reduced variation of the capacitance
A highly linearized capacitor structure is formed by a first capacitor, that is coupled between a first terminal and a common node, combine with a second capacitor, that is coupled between a second terminal and the common node. When a bias voltage is applied, the capacitance values of the first and second capacitors combine and a capacitance variation of the first capacitor is compensated by a capacitance variation of the second capacitor to reduce and linearize overall capacitance variation in the combined capacitor structure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Nonvolatile memory structure
The invention is directed to a layout of nonvolatile memory device. The memory cell has a gate electrode, a first doped electrode, and a second doped electrode. The first doped electrode is coupled to the bit line. The gate electrode is coupled to one separated word line. A shared coupled capacitor structure is coupled between all of memory cells of the adjacent bit lines from the second doped electrode. The capacitor structure has at least two floating-gate MOS capacitors. Each floating-gate MOS capacitor has a floating-gate transistor having a floating gate, a first S / D region and a second S / D region; and a MOS capacitor coupled to the floating gate. The first S / D region is coupled to the second doped electrode of the corresponding one of the transistor memory cells, and the second S / D region is shared with an adjacent one of the floating-gate transistor.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
Analog transcap device
ActiveUS8803288B1Improve device performanceAvoid distortionSolid-state devicesCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricCapacitanceSemiconductor structure
A novel semiconductor variable capacitor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a semiconductor variable MOS capacitor structure suitable for integrated circuits, which has at least three terminals, one of which is used to modulate the equivalent capacitor area of the MOS structure by increasing or decreasing its DC voltage with respect to another terminal of the device, in order to change the capacitance over a wide ranges of values. Furthermore, the present invention decouples the AC signal and the DC control voltage avoiding distortion and increasing the performance of the device, such as its control characteristic. The present invention is simple and only slightly dependent on the variations due to the fabrication process. It exhibits a high value of capacitance density and, if opportunely implemented, shows a quasi linear dependence of the capacitance value with respect to the voltage of its control terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
MOS capacitor and charge pump with MOS capacitor
InactiveUS20100226166A1Stable capacitanceImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
A MOS capacitor in a charge pump includes a MOS device with at least one body bias region and a device body of a same conductivity type for providing maximum capacitance over a wide voltage range. The MOS capacitor also includes a gate forming a first terminal of the MOS capacitor, and the at least one body bias region forms a second terminal of the MOS capacitor. The MOS capacitor further includes a multiple-well structure formed with the device body and a deep well in a substrate for enhanced noise immunity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mos Capacitor And Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20070210364A1Uniform thicknessIncrease capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialMos capacitor
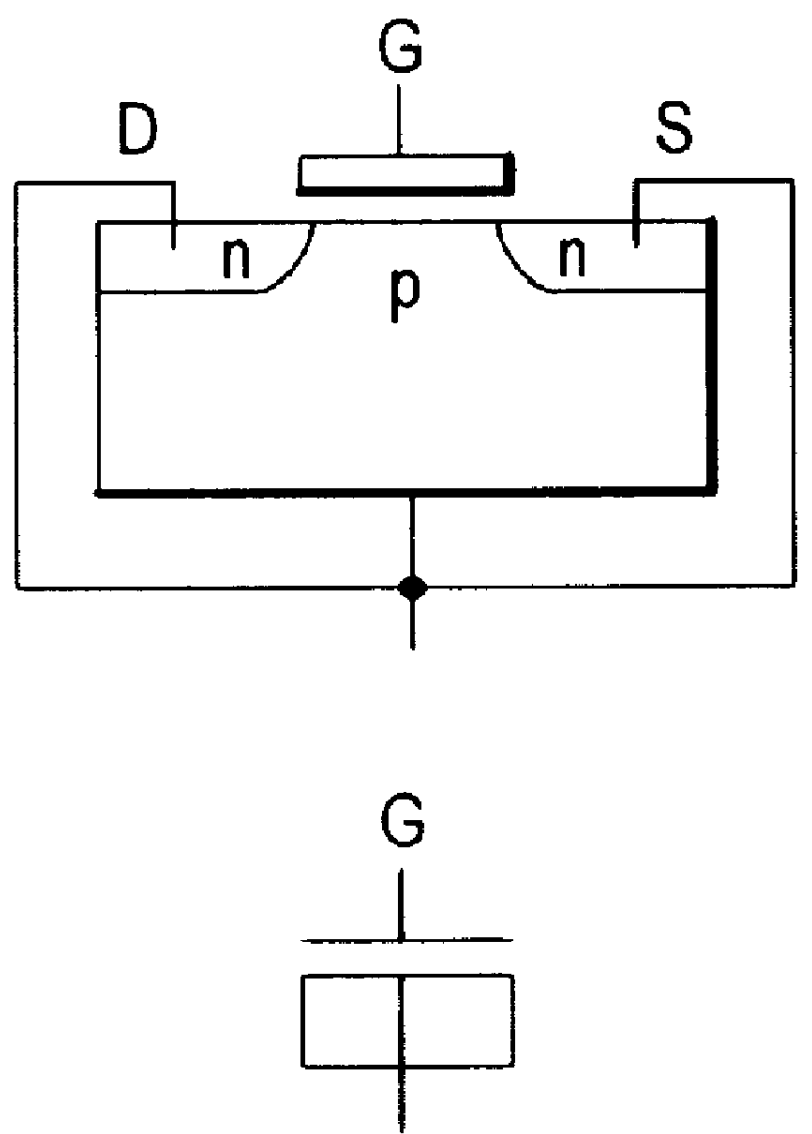
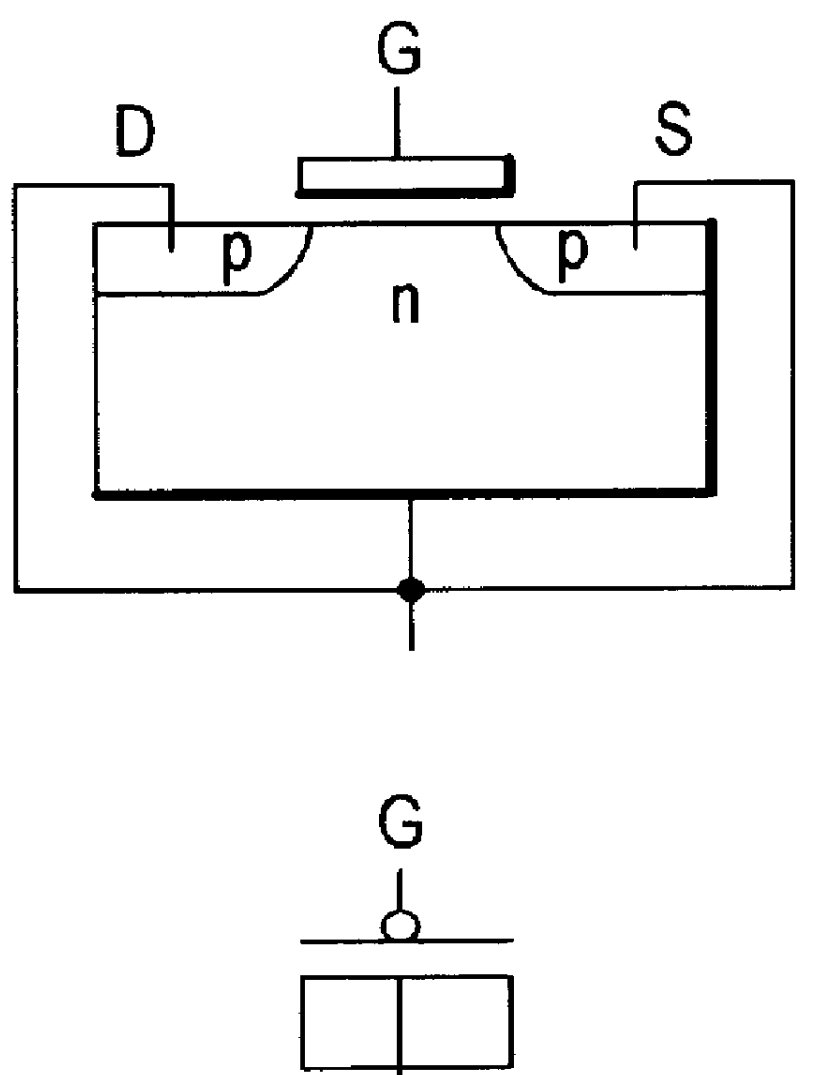
A capacitor capable of functioning as a capacitor even when an AC voltage is applied thereto is provided without increasing the manufacturing steps of a semiconductor device. A transistor is used as a MOS capacitor where a pair of impurity regions formed on opposite sides of a channel formation region are each doped with impurities of different conductivity so as to be used as a source region or a drain region. Specifically, assuming that an impurity region that is doped with N-type impurities is referred to as an N-type region while an impurity region that is doped with P-type impurities is referred to as a P-type region, a transistor is provided where a channel formation region is interposed between the N-type region and the P-type region, which is used as a MOS capacitor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
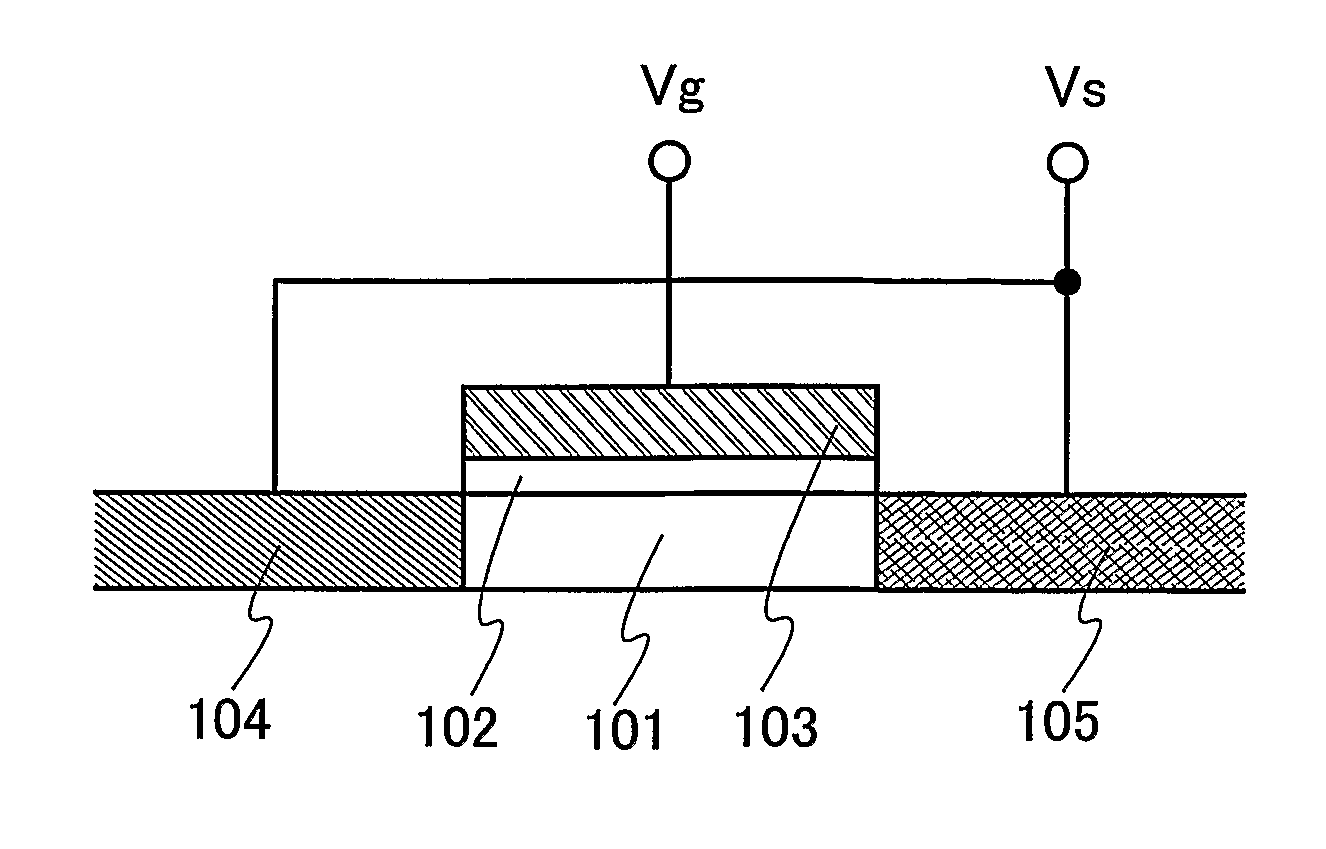
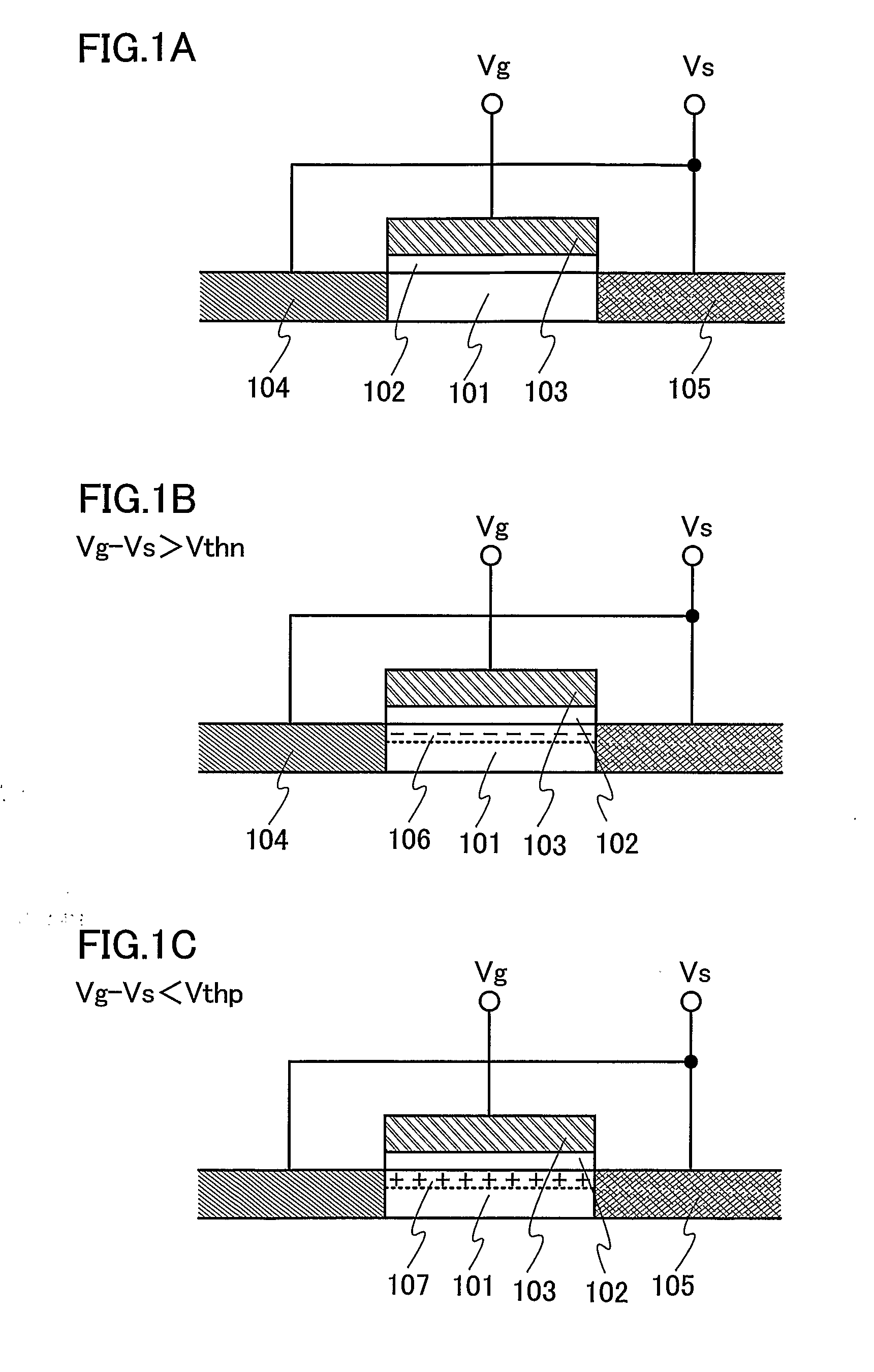
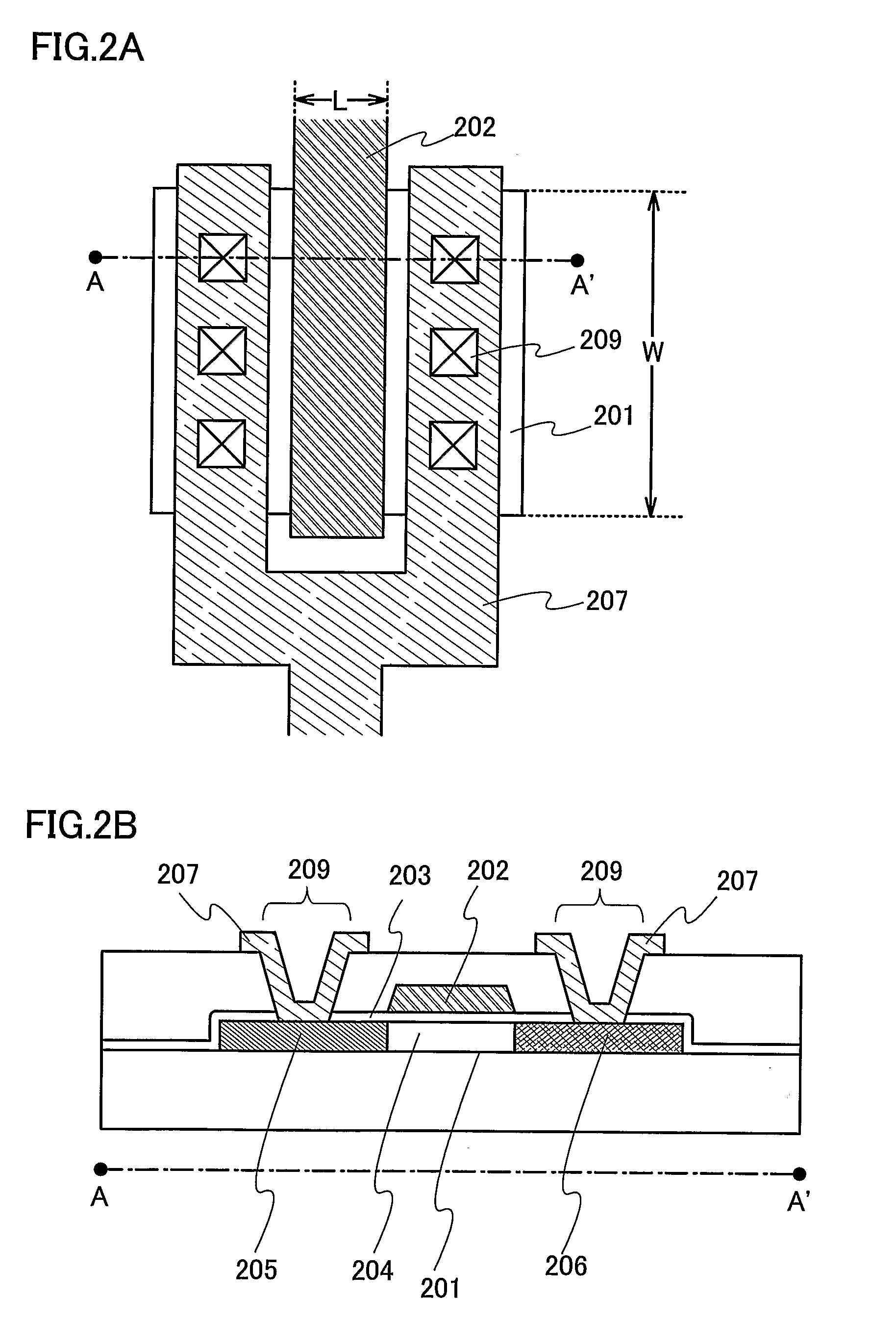
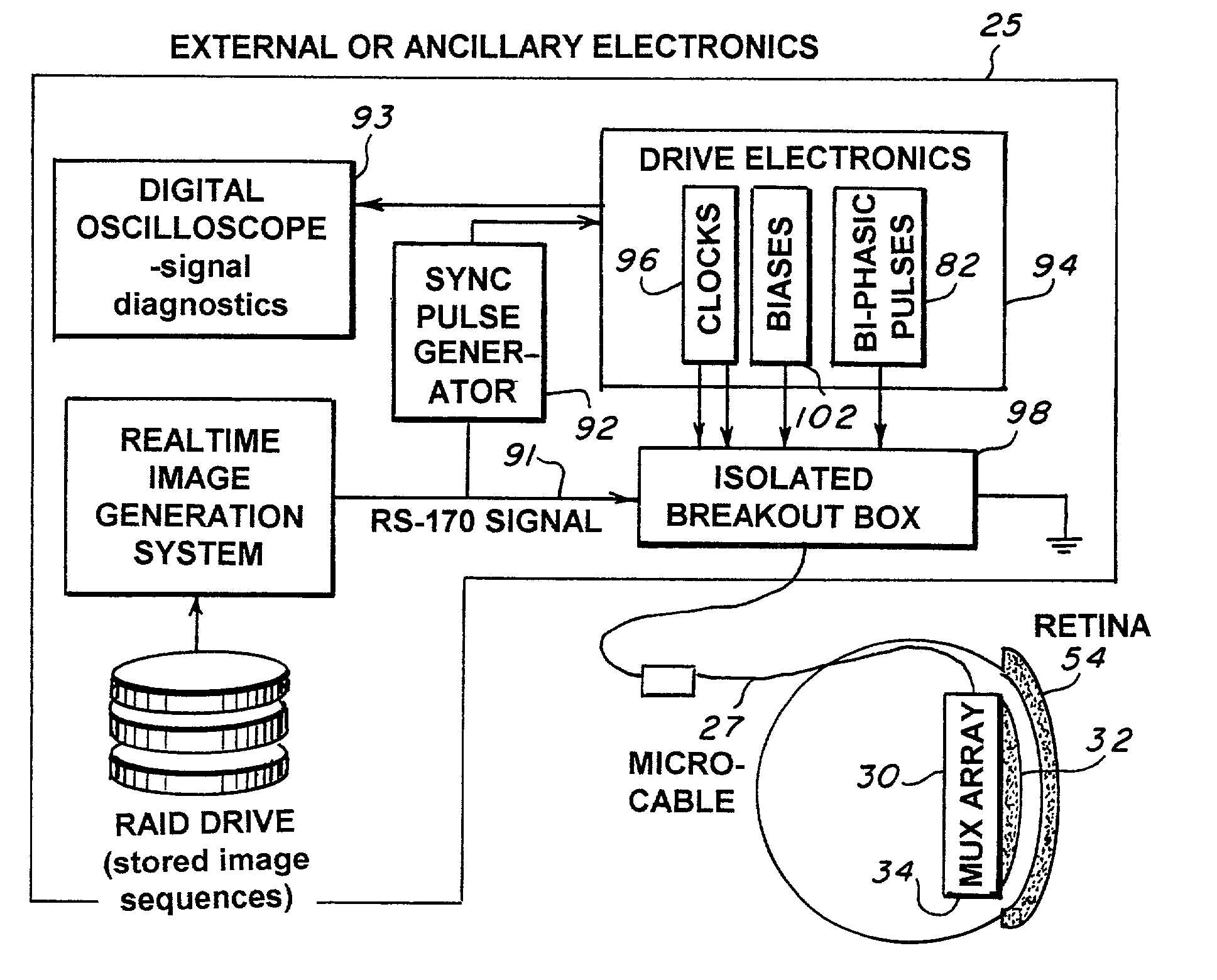
Microelectronic stimulator array for stimulating nerve tissue
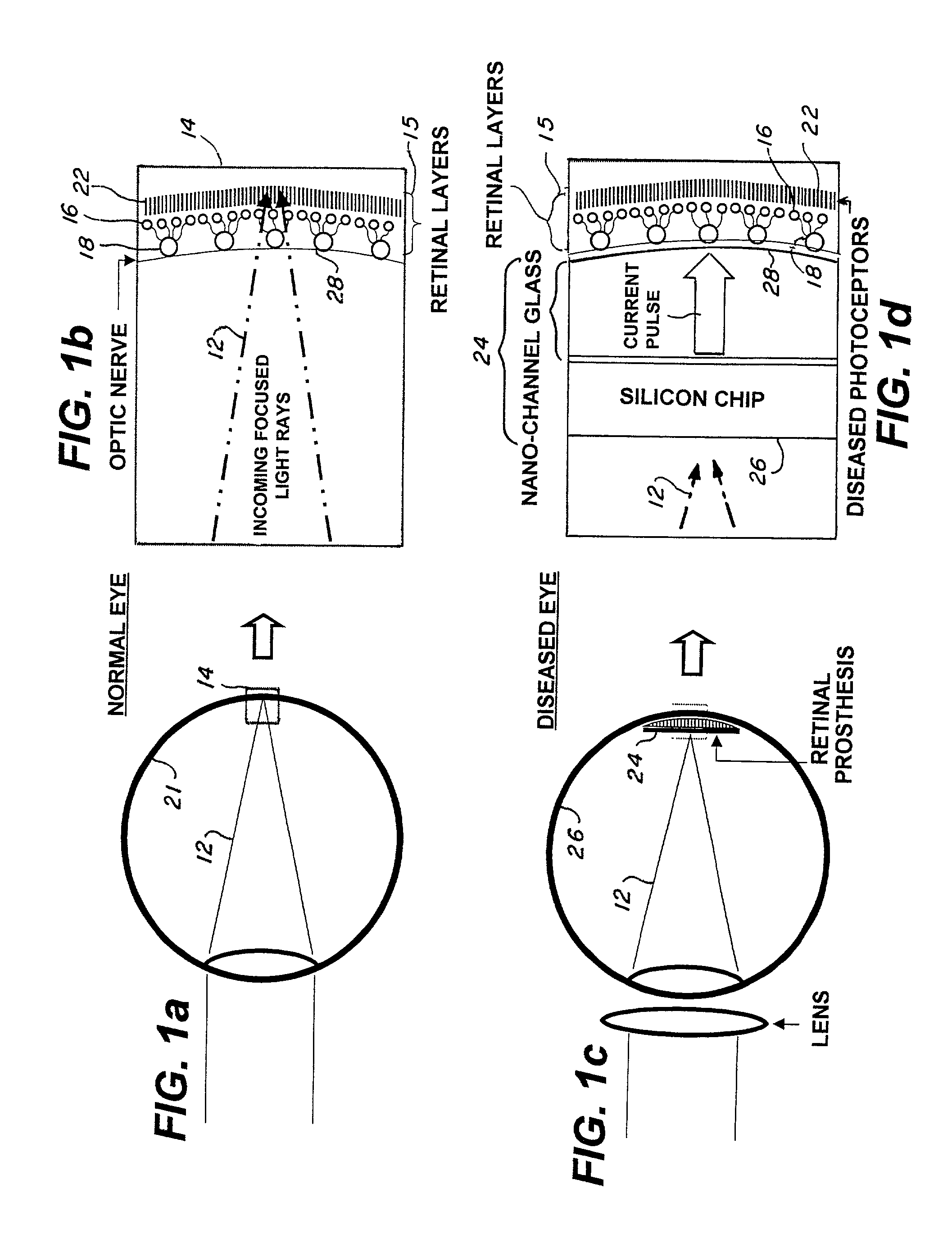
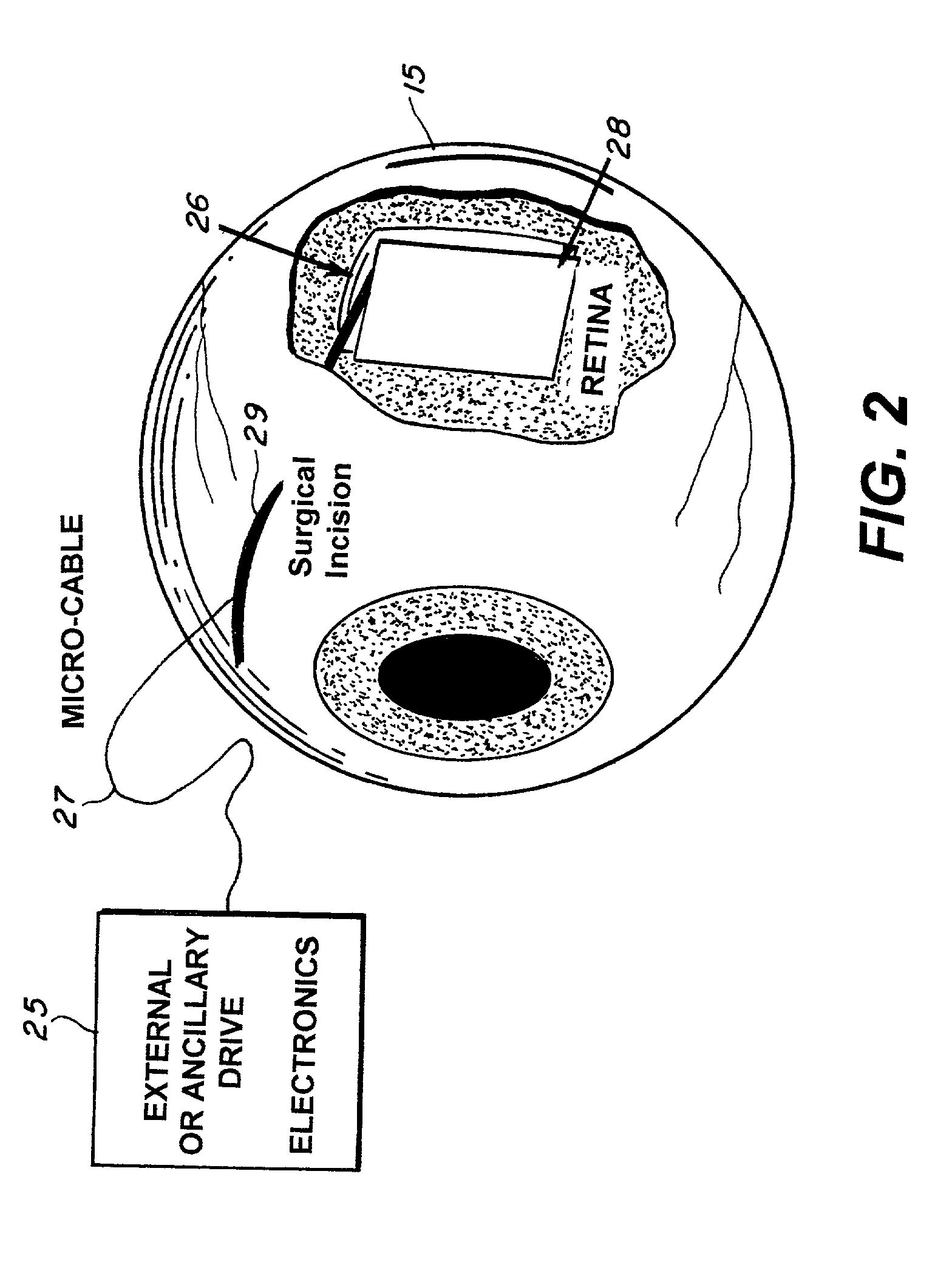
The retinal prosthesis test device is comprised of a thin wafer of glass made from nanochannel glass (NGC) with very small channels perpendicular to the plane of the wafer filled with an electrical conductor forming microwires. One surface of the glass is ground to a spherical shape consistent with the radius of curvature of the inside of the retina. The NGC is hybridized to a silicon de-multiplexer and a video image is serially input to a narrow, flexible micro-cable and read into a 2-D array of unit cells in a pixel-by-pixel manner which samples the analog video input and stores the value as a charge on a MOS capacitor. After all unit cells have been loaded with the pixel values for the current frame, a biphasic pulse is sent to each unit cell which modulates the pulse in proportion to the pixel value stored therein. Because the biphasic pulses flow in parallel to each unit cell from a global external connection, the adjacent retinal neurons are all stimulated simultaneously, analogous to image photons stimulating photoreceptors in a normal retina. A permanent retinal implant device uses a NGC array hybridized to a silicon chip, the image is simultaneously generated within each cell through a photon-to-electron conversion using a silicon photodiode. The photons propagate directly through into the backside of the device. Electrical power and any control signals are transmitted through an inductively driven coil or antenna on the chip. The device collects the charge in storage capacitors via the photon-to-electron conversion process, stimulates the neural tissue with biphasic pulses in proportion to the stored charges, and resets the storage capacitors to repeat the process.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
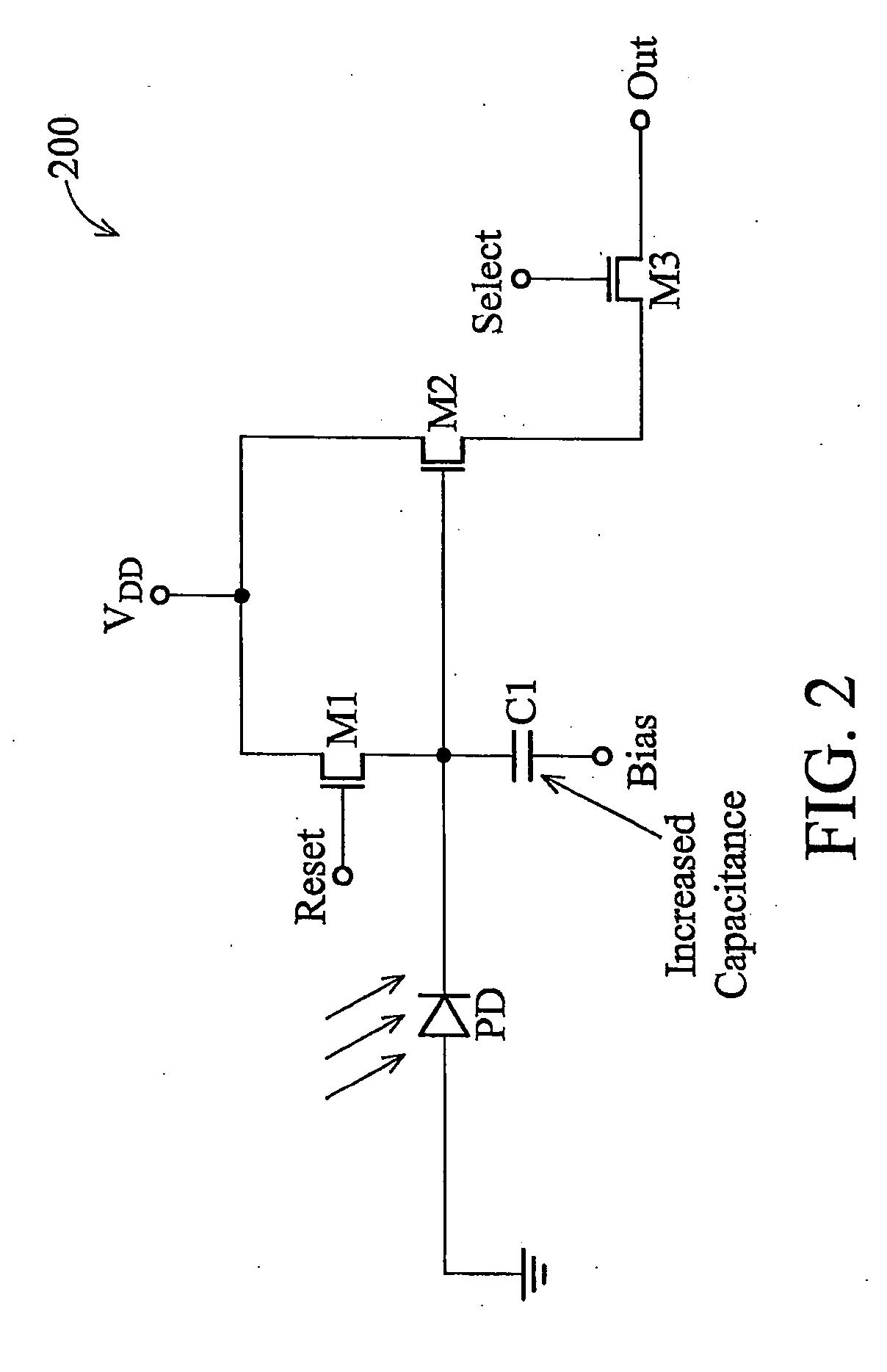
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100032741A1Reduce defective rateReduce initial failure rateTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationCapacitance
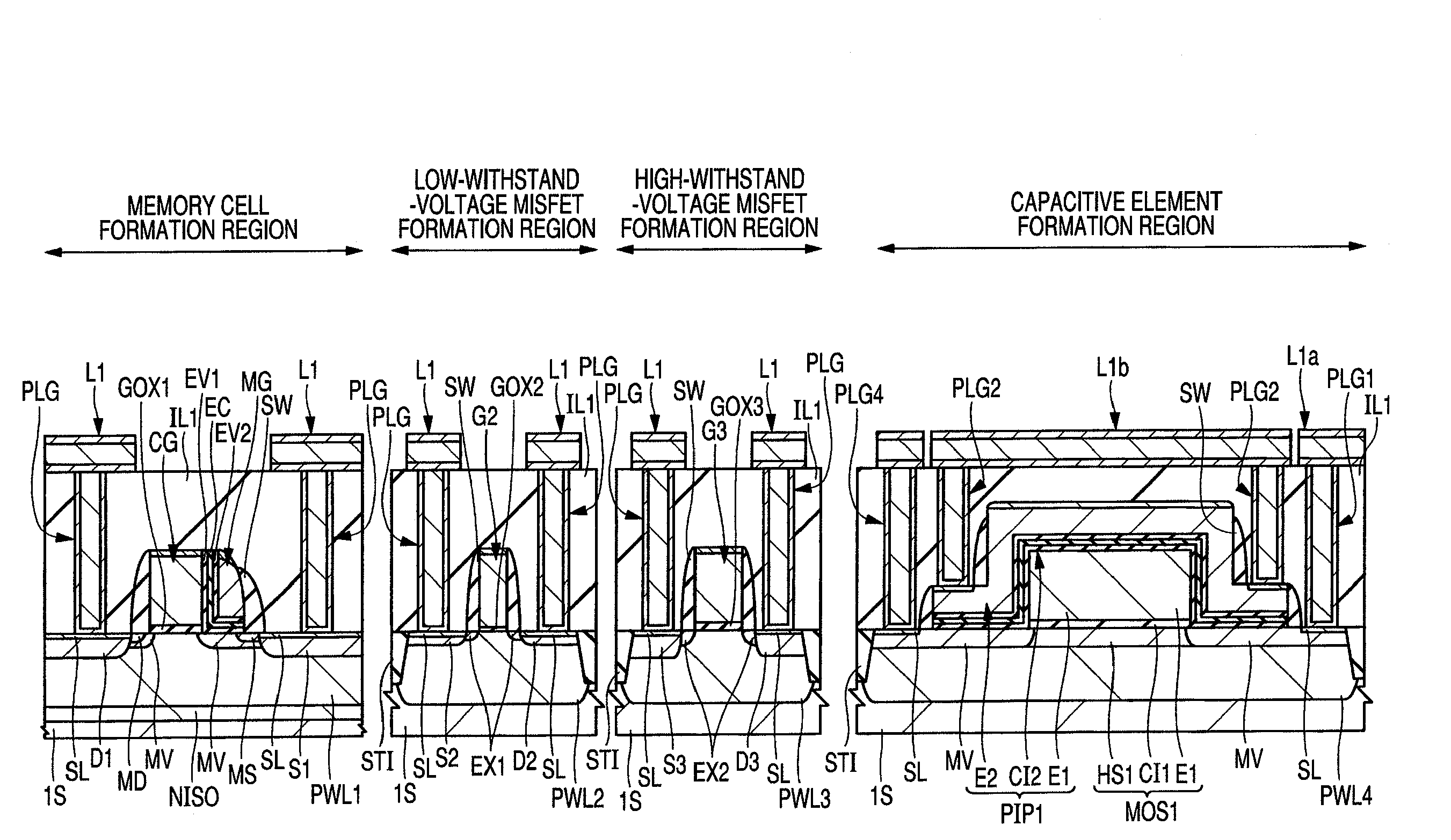
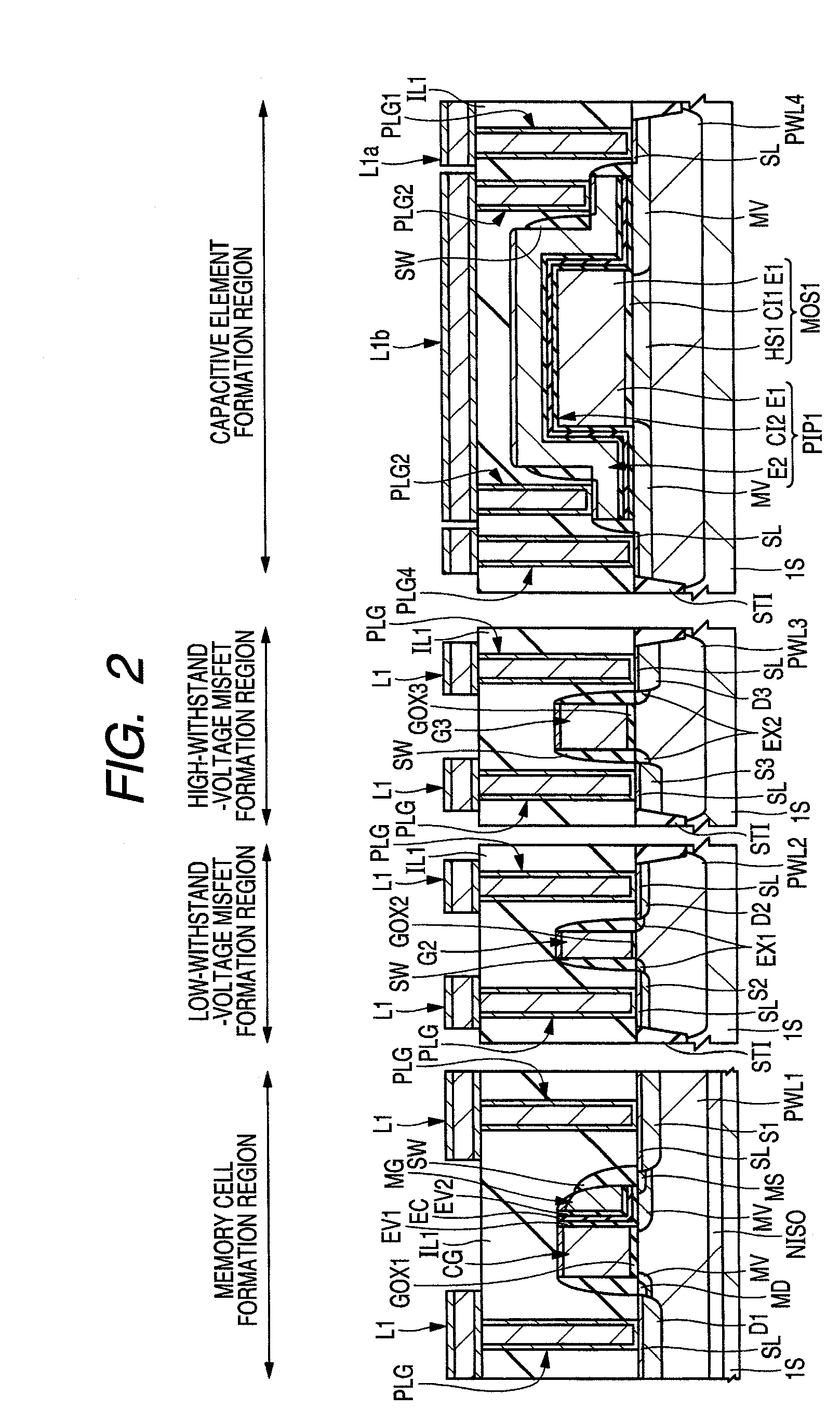
A technology capable of reducing the fraction defective of a MOS capacitor without the need to perform a screening is provided.A MOS capacitor MOS1 and a MOS capacitor MOS2 are coupled in series between a high potential and a low potential to form a series capacitive element. Then, a polysilicon capacitor PIP1 and a polysilicon capacitor PIP2 are coupled in parallel with the series capacitive element. Specifically, a high-concentration semiconductor region HS1 constituting a lower electrode of the MOS capacitor MOS1 and a high-concentration semiconductor region HS2 constituting a lower electrode of the MOS capacitor MOS2 are coupled. Further, an electrode E1 constituting an upper electrode of the MOS capacitor MOS1 is coupled to the low potential (for example, GND) and an electrode E3 constituting an upper electrode of the MOS capacitor MOS2 is coupled to the high potential (for example, power source potential).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
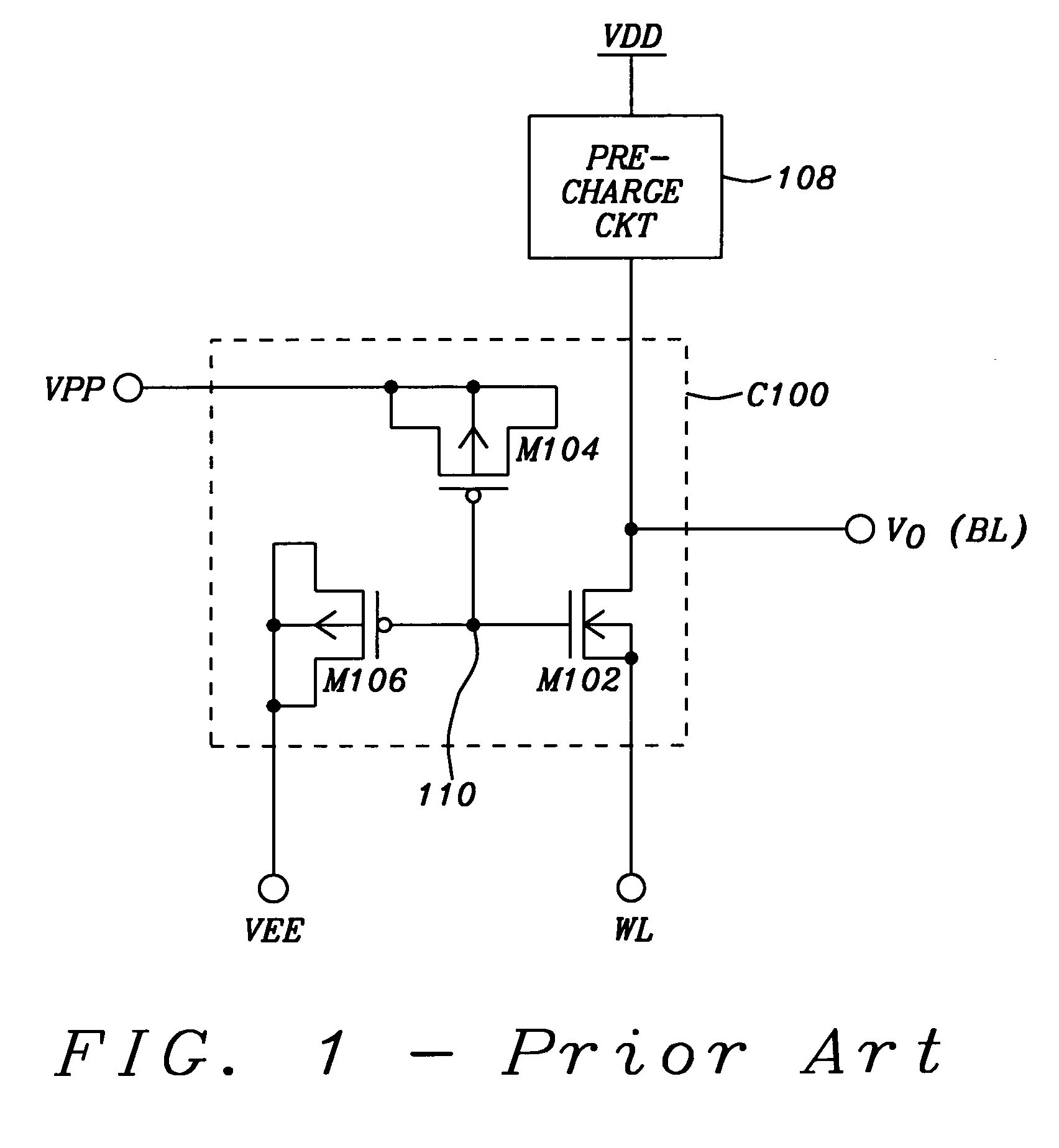
Methods and apparatus for a high efficiency charge pump that includes a MOSFET capacitor operating in an accumulation region
InactiveUS6166585AApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceMOSFET
A charge pump circuit includes MOS capacitors configured to operate in the accumulation region, resulting in a substantially constant capacitance over the operational range. In a particularly preferred embodiment, a char ge pump uses multiple stages of p-channel MOS capacitors. In accordance with a further aspect of the present invention, oxide thicknesses of the p-channel MOS capacitors are optimized in accordance with the requirements of each stage.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Structure for CMOS image sensor
ActiveUS20060164531A1Susceptibility to noiseReduce output signalTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCMOS
A CMOS image sensor having increased capacitance that allows a photo-diode to generate a larger current is provided. The increased capacitance reduces noise and the dark signal. The image sensor utilizes a transistor having nitride spacers formed on a buffer oxide layer. Additional capacitance may be provided by various capacitor structures, such as a stacked capacitor, a planar capacitor, a trench capacitor, a MOS capacitor, a MIM / PIP capacitor, or the like. Embodiments of the present invention may be utilized in a 4-transistor pixel or a 3-transistor pixel configuration.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
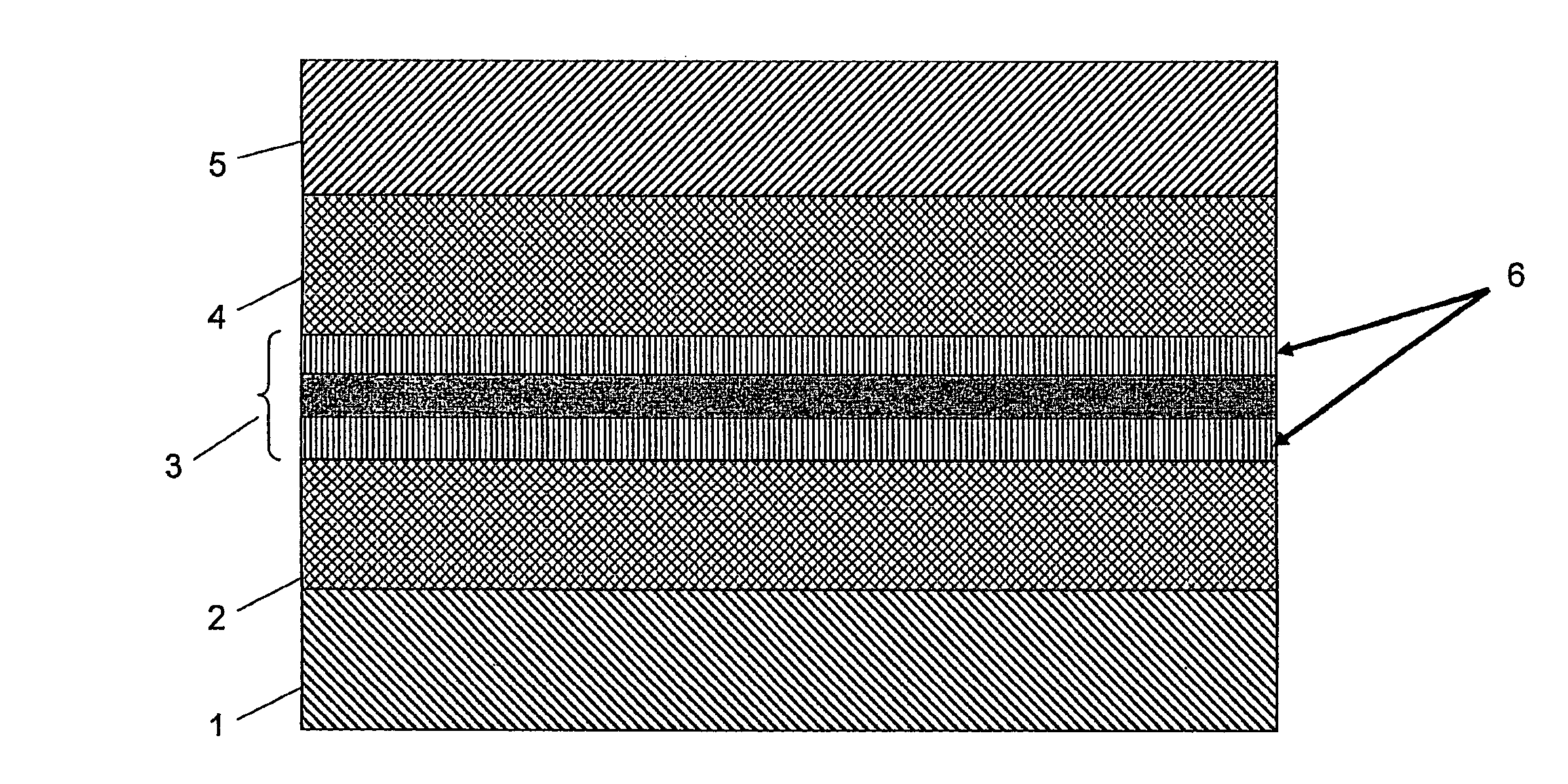
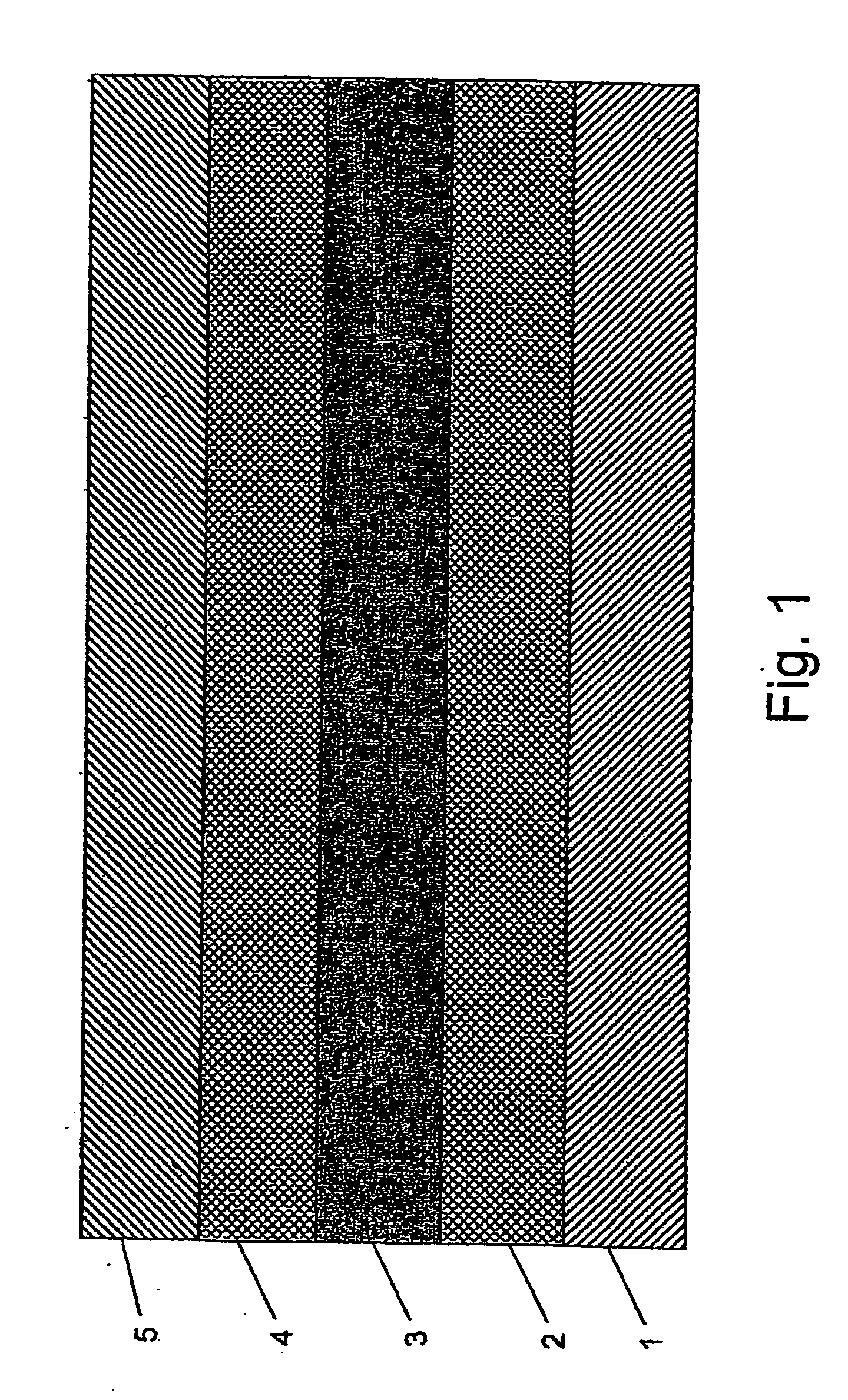
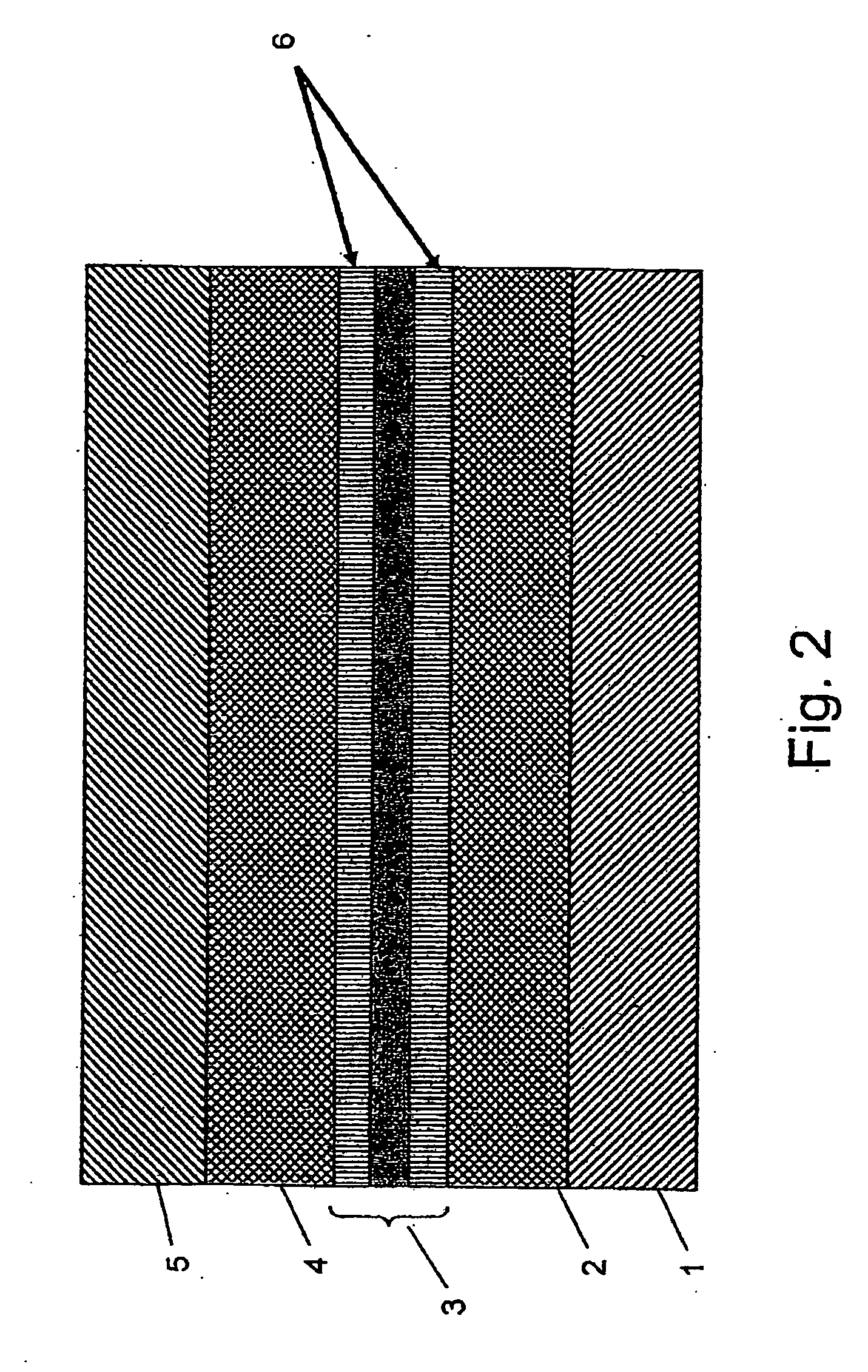
Silicon light waveguide with MOS capacitors positioned on the waveguide
The present invention provides a silicon wave-guide (3), with a silicon oxide cladding (2, 4) on a silicon substrate (1). At predetermined positions along the length of the wave-guide, are created metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structures. A poly-silicon, or any other conductive layer (5), is deposited and patterned above the upper cladding (4) and electrical contacts are made to the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5). Upon the application of a potential difference between at least two of the layers from the group comprising the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5), the free carrier concentration at the top and / or bottom layer of the silicon wave-guide (3) is changed by the electric field. The change in the electric field results in a change in the index of refraction, and the change in the index of refraction causes a change in the optical mode propagating in the waveguide (3). The propagation is controlled by controlling the changes in the electric field, which can be enhanced by localized changes in the optical properties of the wave-guide (3) induced by ion implantation (6) or trapping of photo-carriers.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
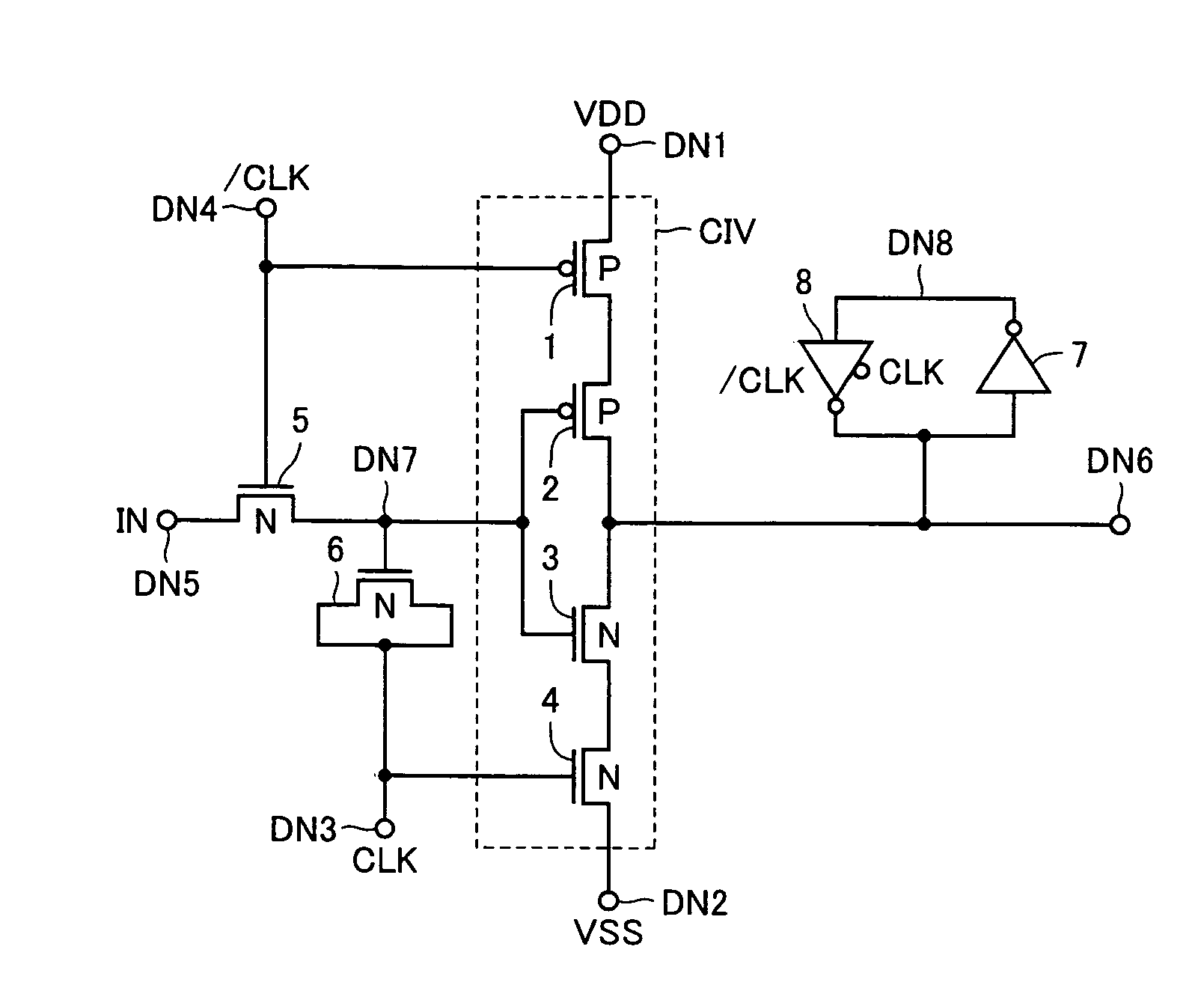
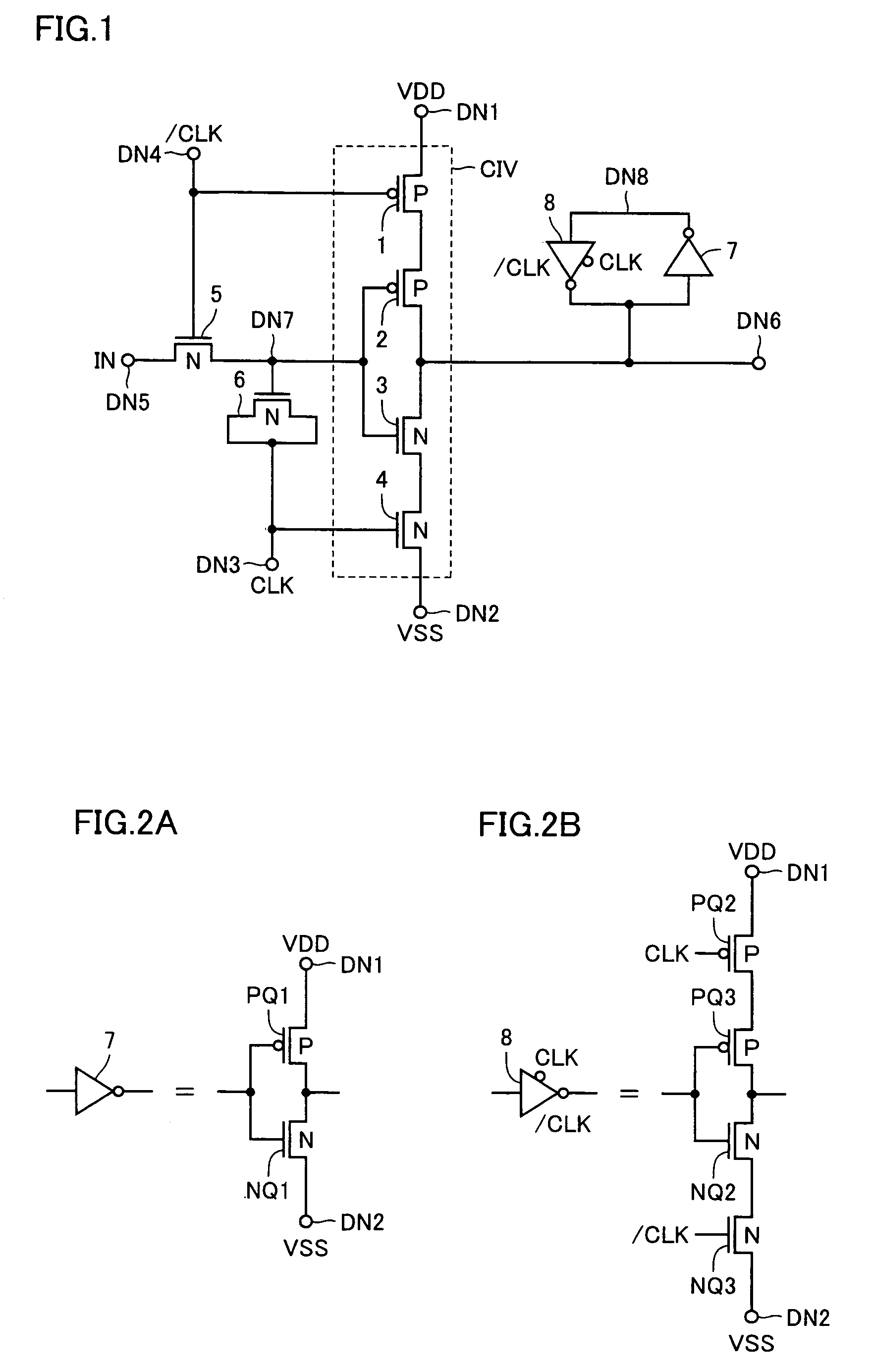
Level conversion circuit and serial/parallel conversion circuit with level conversion function
InactiveUS7138831B2Increase speedReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionPulse automatic controlVoltage amplitudeBiological activation
A MOS capacitor receiving a clock signal complementary to a sampling clock signal is provided at an input of a clocked inverter that is activated after sampling an input signal to perform level conversion. A charge pump operation of the MOS capacitor is performed in parallel with the activation of the clocked inverter. The power consumption of and the area occupied by a level conversion circuit converting a voltage amplitude of the input signal are reduced without deteriorating a high-speed operating characteristics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
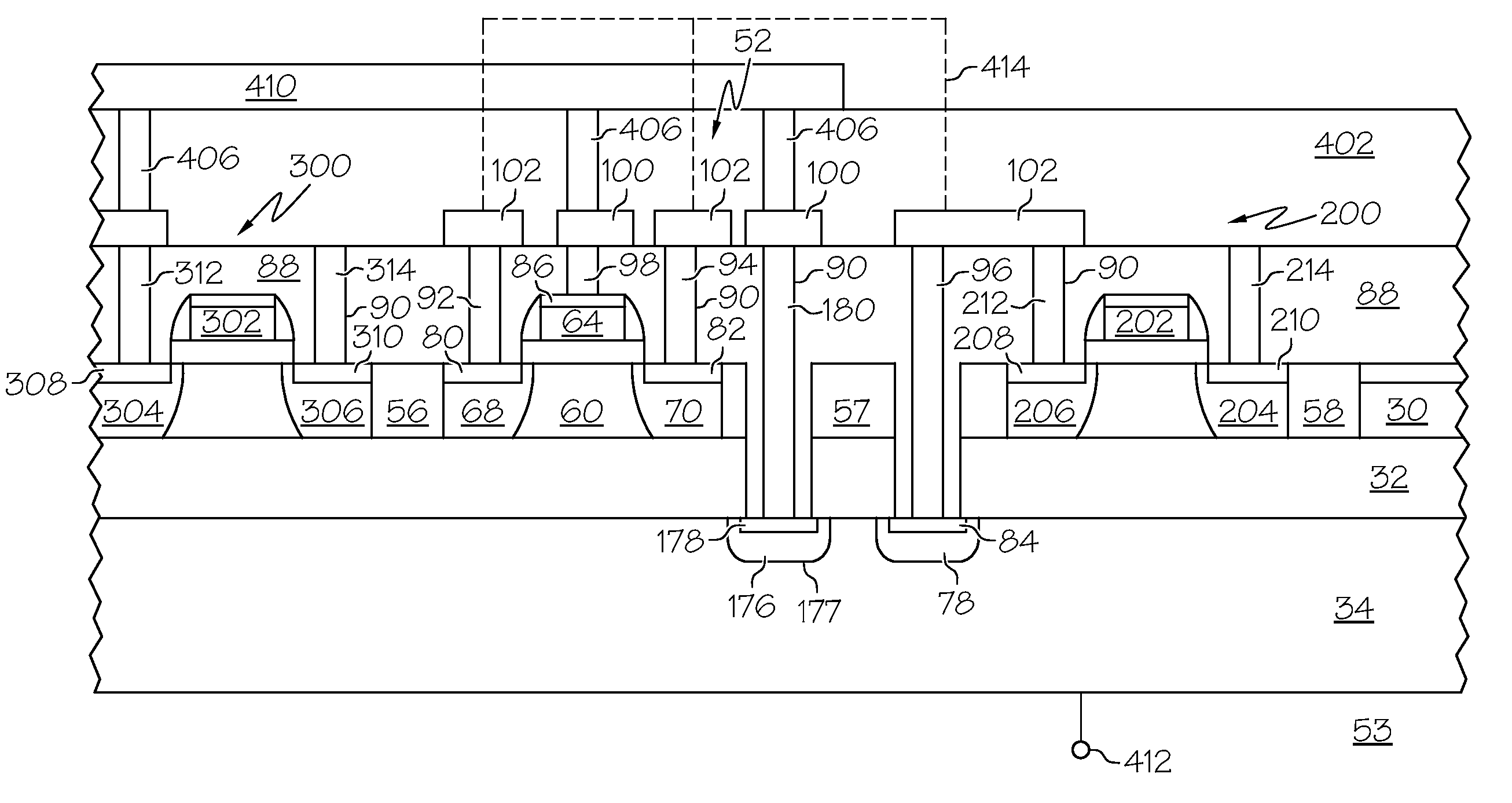
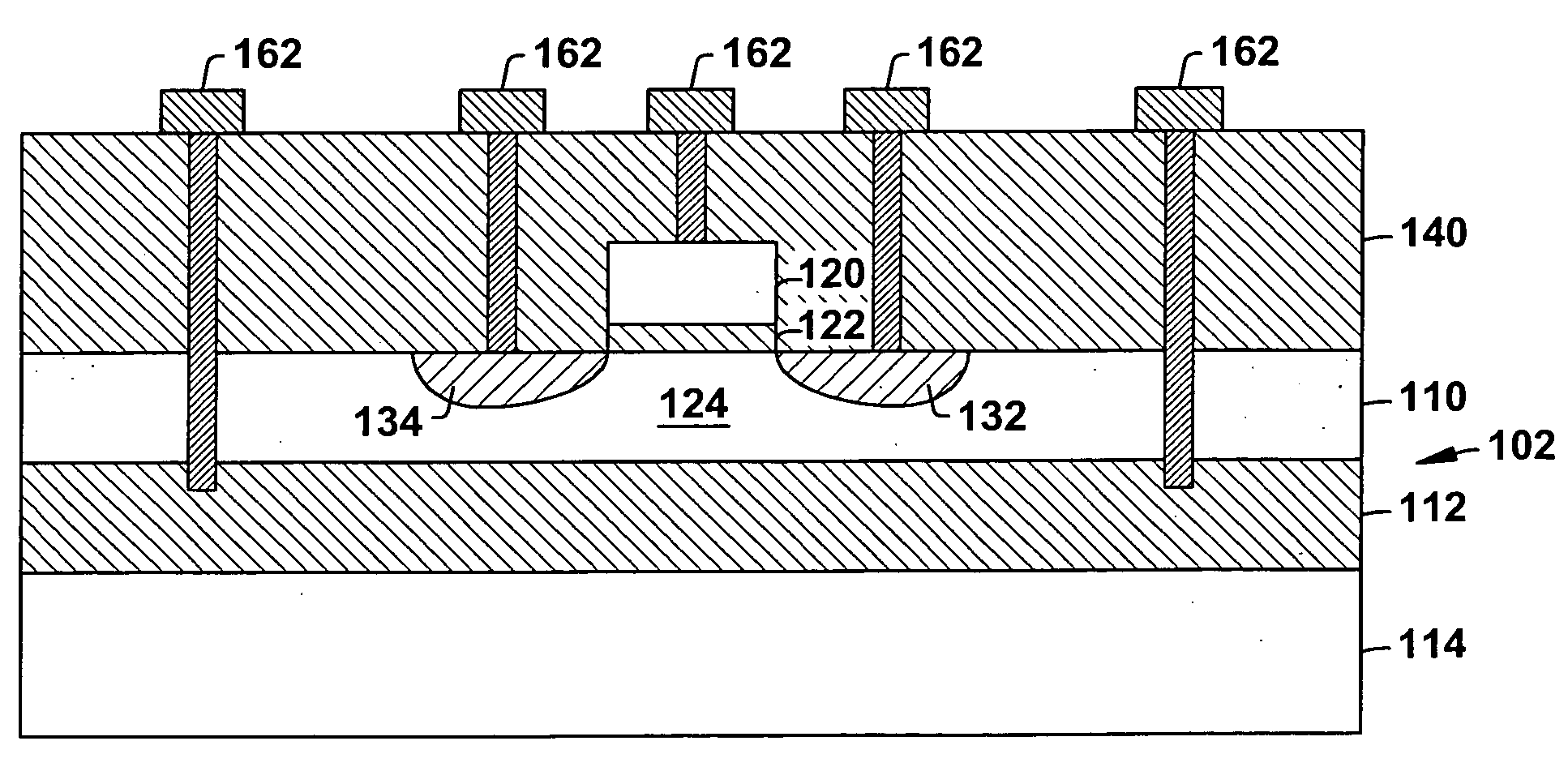
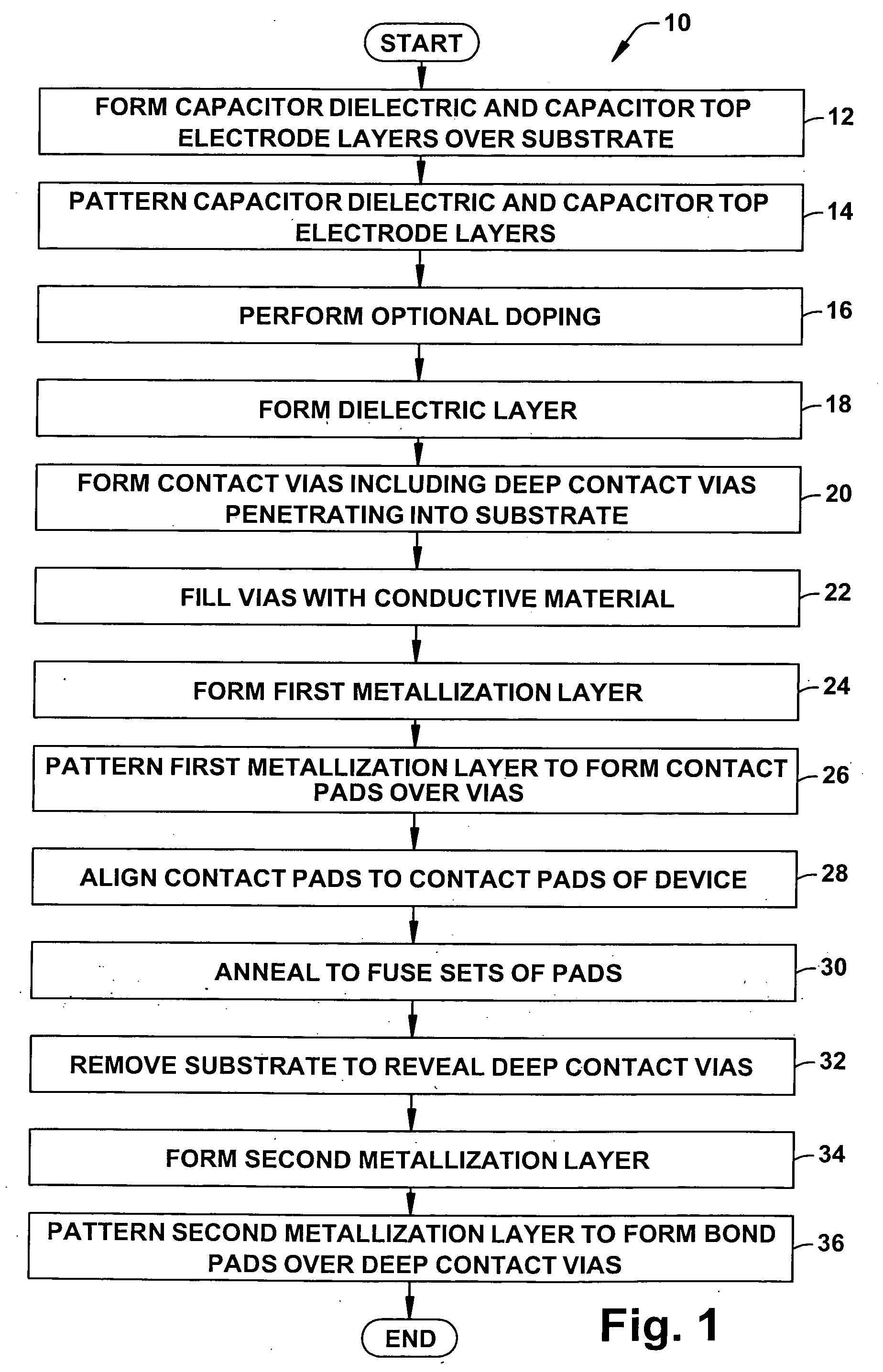
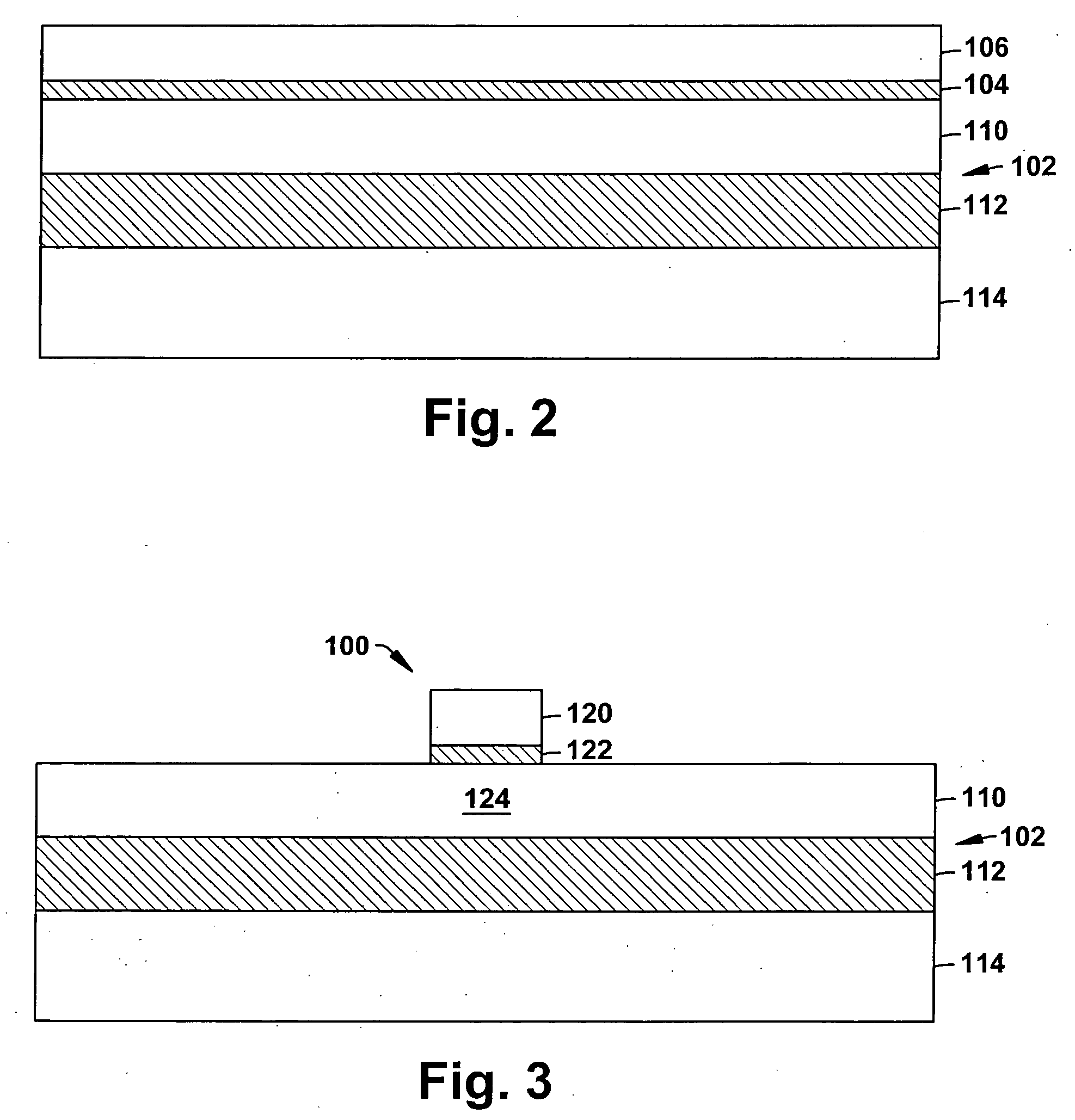
Wafer bonded MOS decoupling capacitor
ActiveUS20060128092A1Well formedCost-effectively formedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceManufacturing technology
A technique for forming a MOS capacitor (100) that can be utilized as a decoupling capacitor is disclosed. The MOS capacitor (100) is formed separately from the particular circuit device (170) that it is to service. As such, the capacitor (100) and its fabrication process can be optimized in terms of efficiency, etc. The capacitor (100) is fabricated with conductive contacts (162) that allow it to be fused to the device (170) via conductive pads (172) of the device (170). As such, the capacitor (100) and device (170) can be packaged together and valuable semiconductor real estate can be conserved as the capacitor (100) is not formed out of the same substrate as the device (170). The capacitor (100) further includes deep contacts (150, 152) whereon bond pads (180, 182) can be formed that allow electrical connection of the capacitor (100) and device (170) to the outside world.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Implementation of MOS capacitor in CT scanner data acquisition system
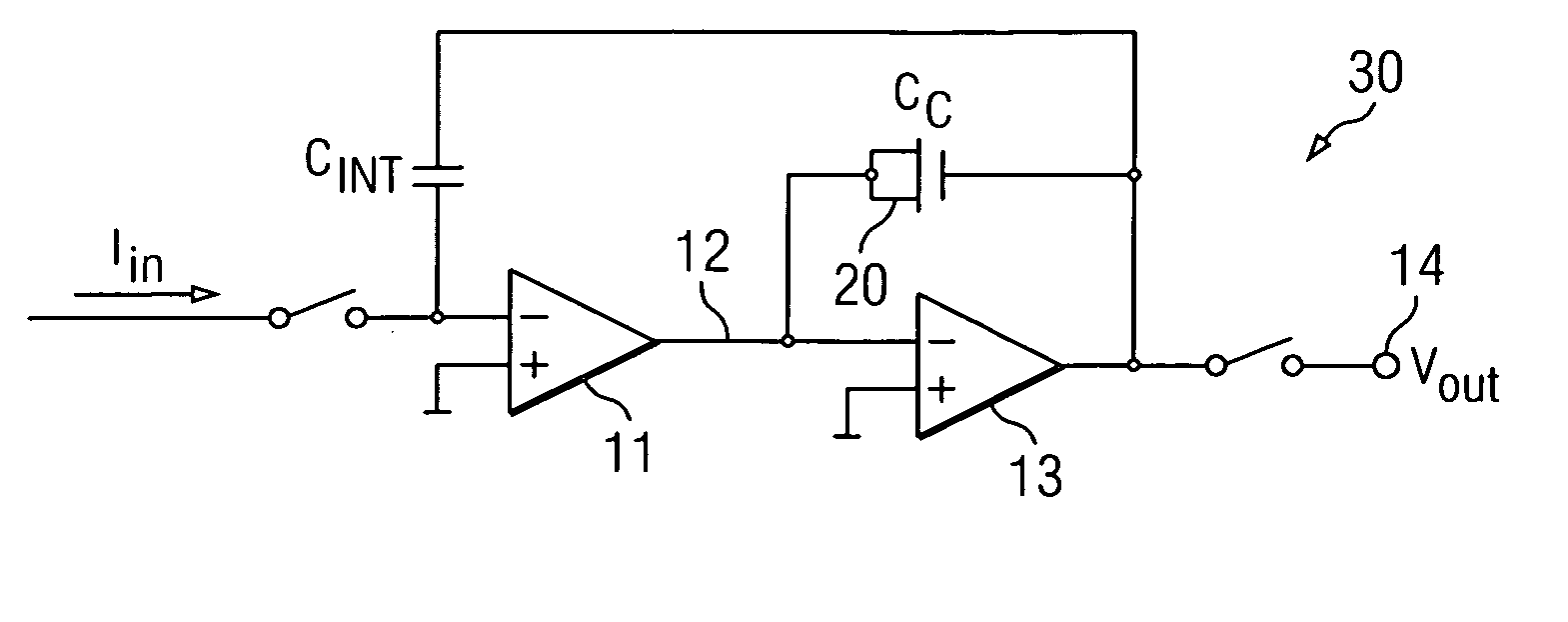
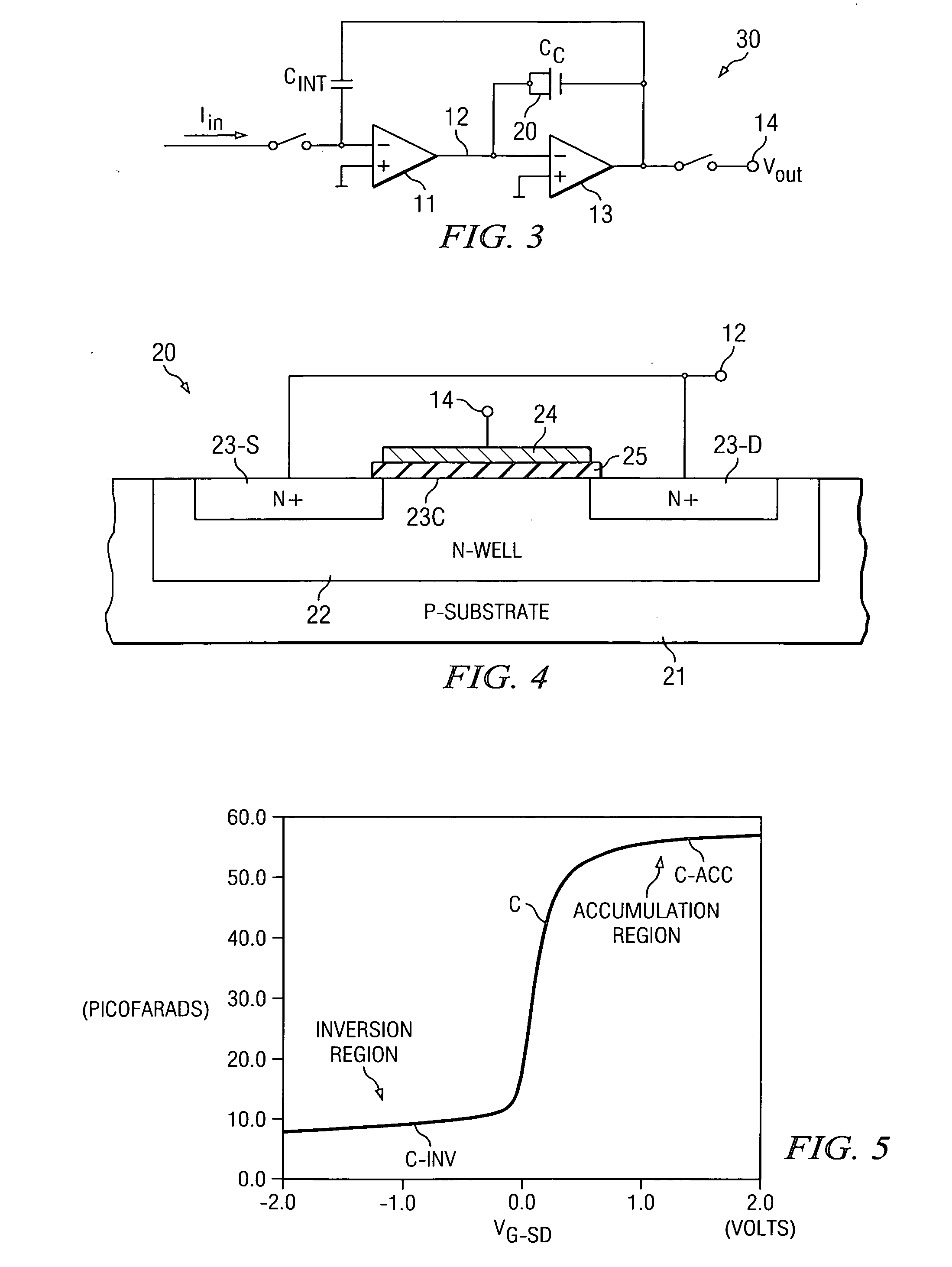
InactiveUS20050179468A1Reduce in quantityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical conductorIntegrator
An integrator circuit includes an input conductor for conducting an input current, a first amplifier stage having a first input coupled to the input conductor and a second input coupled to receive a reference voltage and a second amplifier stage having a output and an input coupled to an output of the first amplifier stage. An integrating capacitor is coupled between the first input of the first amplifier stage and the output of the second amplifier stage, and a compensation capacitor comprised of an MOS capacitor is coupled between the input and the output of the second amplifier stage. The integrator circuit is especially adapted for use in a CT scanner data acquisition system.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
MOS capacitors with a finfet process
Capacitors include a first electrical terminal that has fins formed from doped semiconductor on a top layer of doped semiconductor on a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate; a second electrical terminal that has an undoped material having bottom surface shape that is complementary to the first electrical terminal, such that an interface area between the first electrical terminal and the second electrical terminal is larger than a capacitor footprint; and a dielectric layer separating the first and second electrical terminals.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Low-pass filter and feedback system
InactiveUS6995607B2Easy to useSmall sizeMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlCapacitanceBand-pass filter
In a low-pass filter, the filter characteristics equivalent to those of a conventional low-pass filter are maintained, the size of a capacitive element is decreased, and the low-pass filter operates stably. Further, a MOS capacitor is used as a capacitive element. For such purposes, in a low-pass filter including a first capacitive element, and a resistive element and a second capacitive element which are connected in series to the first capacitive element, a first electric current is supplied to the first input terminal connected to one end of the first capacitive element, and a second electric current is supplied to the second input terminal connected to the other end of the first capacitive element. Herein, the capacitance value of the first capacitive element is set according to the magnitude of the first electric current. Further, the resistive element is provided with a power supply that is connected in series to the resistive element, and a voltage equal to or higher than the threshold voltage of a MOS transistor is always applied between the second input terminal and the ground.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor variable capacitor
ActiveUS20120281336A1Avoid distortionIncrease valueMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitanceSemiconductor structure
A novel semiconductor variable capacitor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a semiconductor variable MOS capacitor structure suitable for integrated circuits, which has at least three terminals, one of which is used to modulate the equivalent capacitor area of the MOS structure by increasing or decreasing its DC voltage with respect to another terminal of the device, in order to change the capacitance over a wide ranges of values. Furthermore, the present invention decouples the AC signal and the DC control voltage avoiding distortion and increasing the performance of the device, such as its control characteristic. The present invention is simple and only slightly dependent on the variations due to the fabrication process. It exhibits a high value of capacitance density and, if opportunely implemented, shows a linear dependence of the capacitance value with respect to the voltage of its control terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Ge-based semiconductor structure fabricated using a non-oxygen chalcogen passivation step
InactiveUS20070093074A1Reducing unwanted diffusionReduce reduction reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceSemiconductor structure
A method and structure in which Ge-based semiconductor devices such as FETs and MOS capacitors can be obtained are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of forming a semiconductor device including a stack including a dielectric layer and a conductive material located on and / or within a Ge-containing material (layer or wafer) in which the surface thereof is non-oxygen chalcogen rich. By providing a non-oxygen chalcogen rich interface, the formation of undesirable interfacial compounds during and after dielectric growth is suppressed and interfacial traps are reduced in density.
Owner:IBM CORP
Silicon light waveguide with mos capacitors positioned on the waveguide
InactiveUS20050220405A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor structureRefractive index
The present invention provides a silicon wave-guide (3), with a silicon oxide cladding (2, 4) on a silicon substrate (1). At predetermined positions along the length of the wave-guide, are created metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structures. A poly-silicon, or any other conductive layer (5), is deposited and patterned above the upper cladding (4) and electrical contacts are made to the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5). Upon the application of a potential difference between at least two of the layers from the group comprising the substrate (1), the silicon wave-guide (3), and the poly-silicon layer (5), the free carrier concentration at the top and / or bottom layer of the silicon wave-guide (3) is changed by the electric field. The change in the electric field results in a change in the index of refraction, and the change in the index of refraction causes a change in the optical mode propagating in the wave-guide (3). The propagation is controlled by controlling the changes in the electric field, which can be enhanced by localized changes in the optical properties of the wave-guide (3) induced by ion implantation (6) or trapping of photo-carriers.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com