Patents
Literature
679results about "Capacitor with electrode distance variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
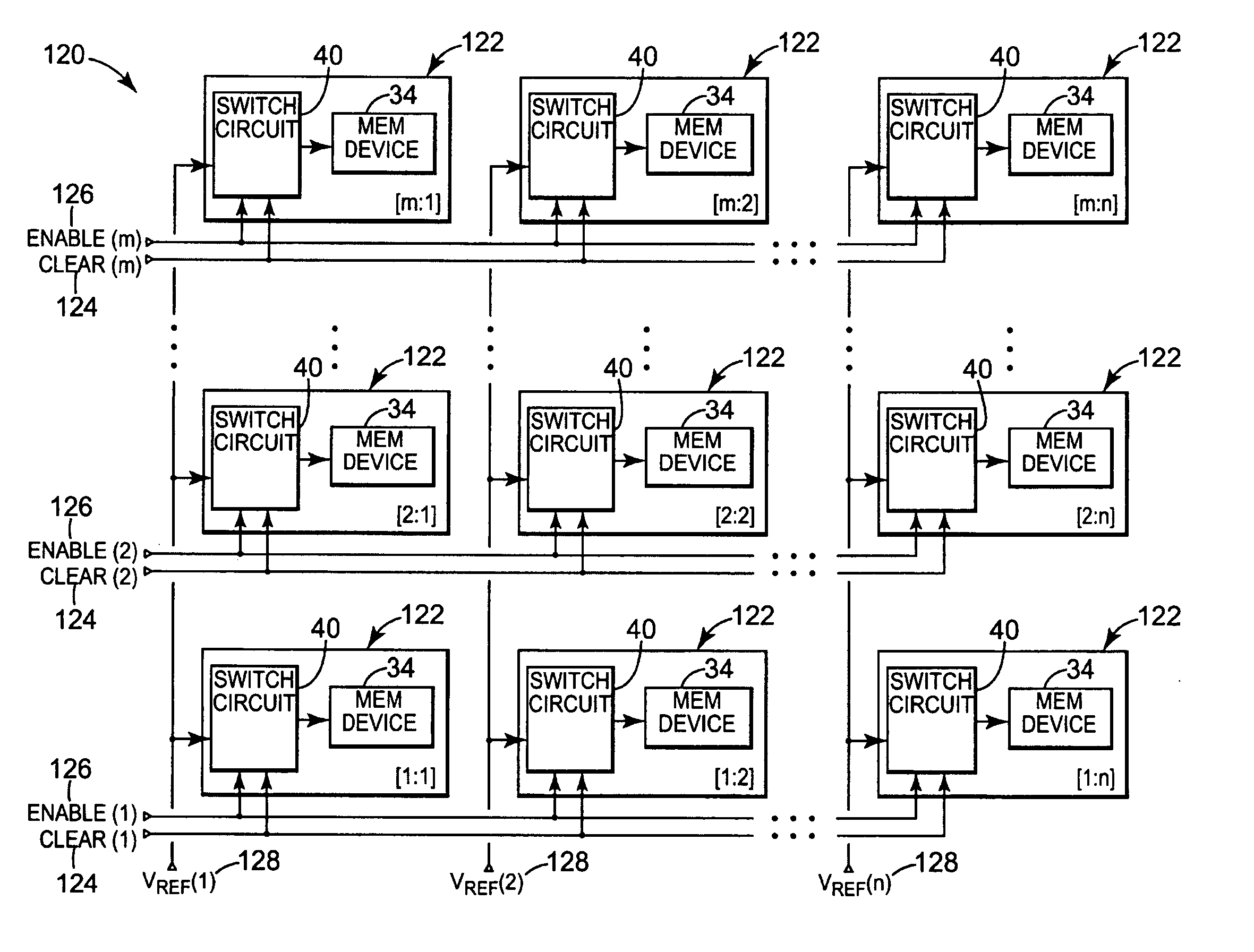
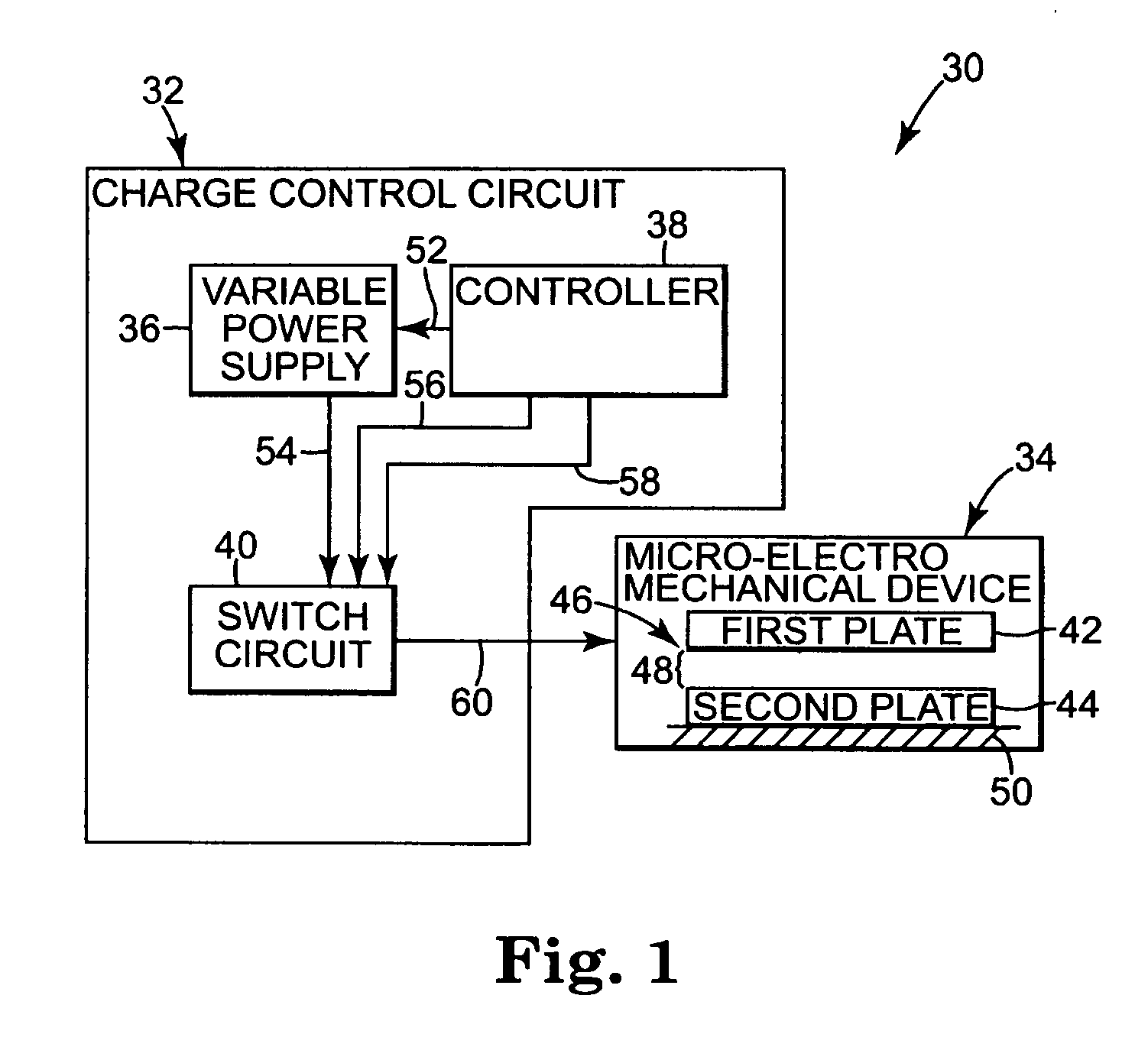
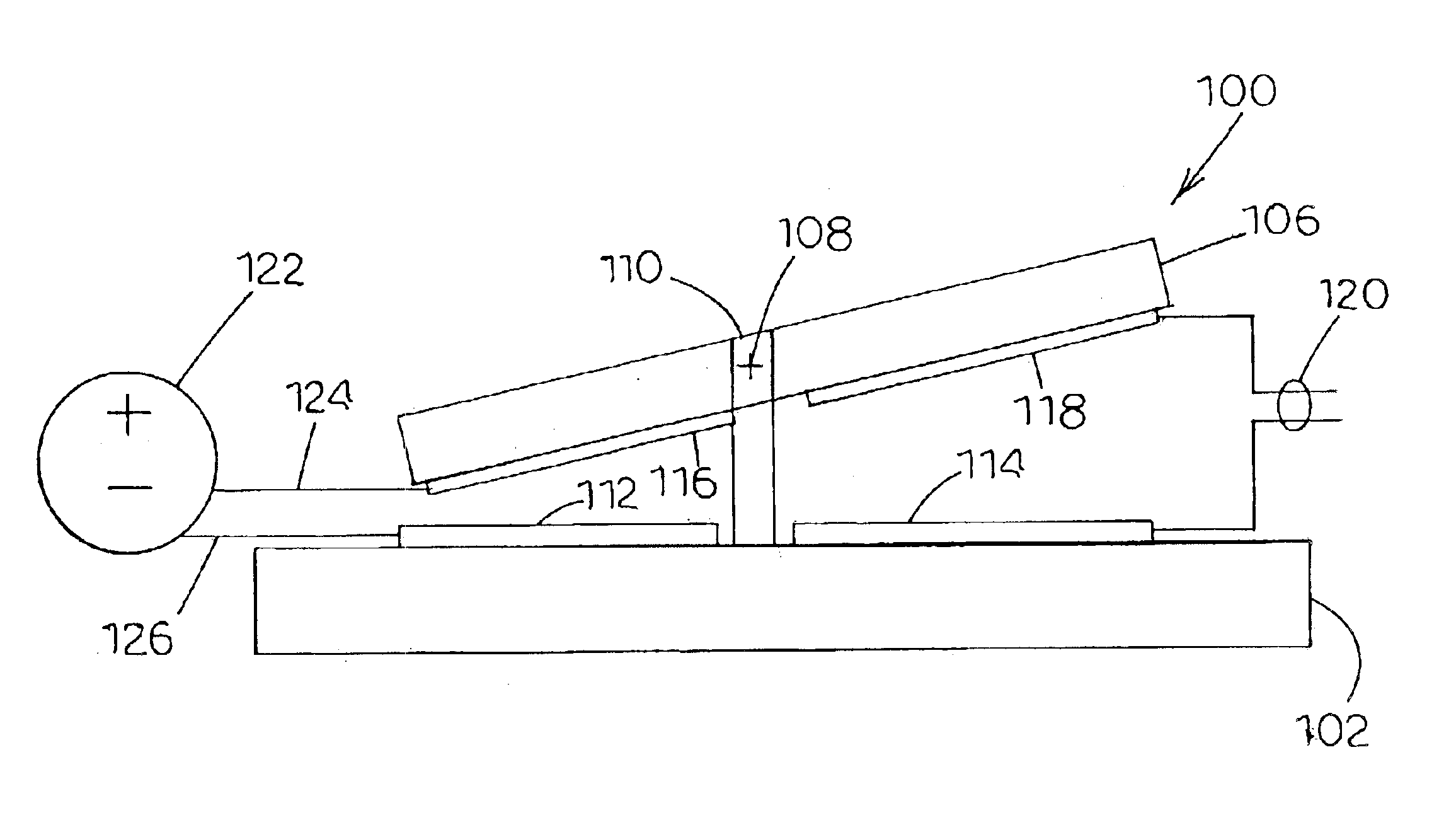
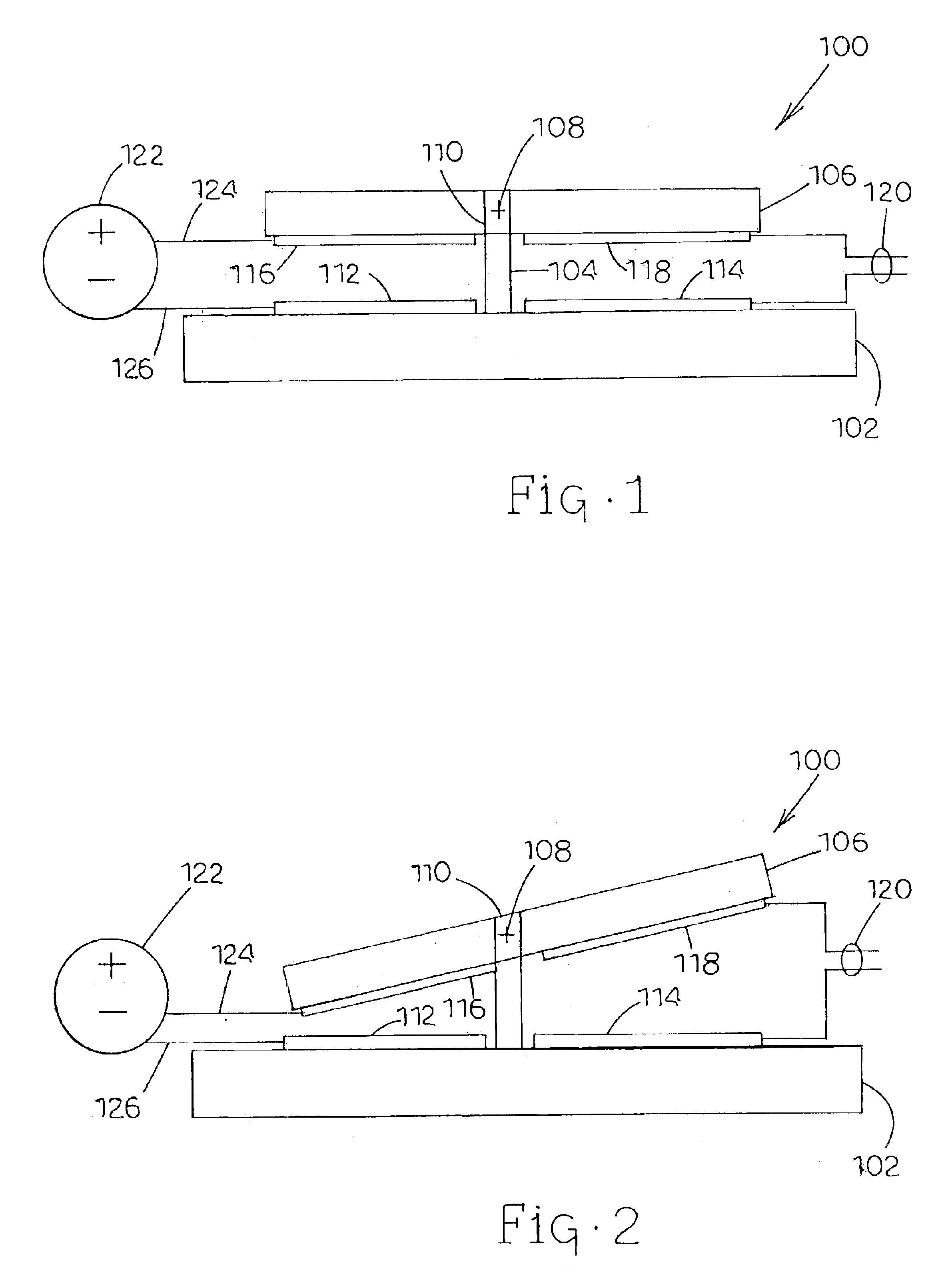
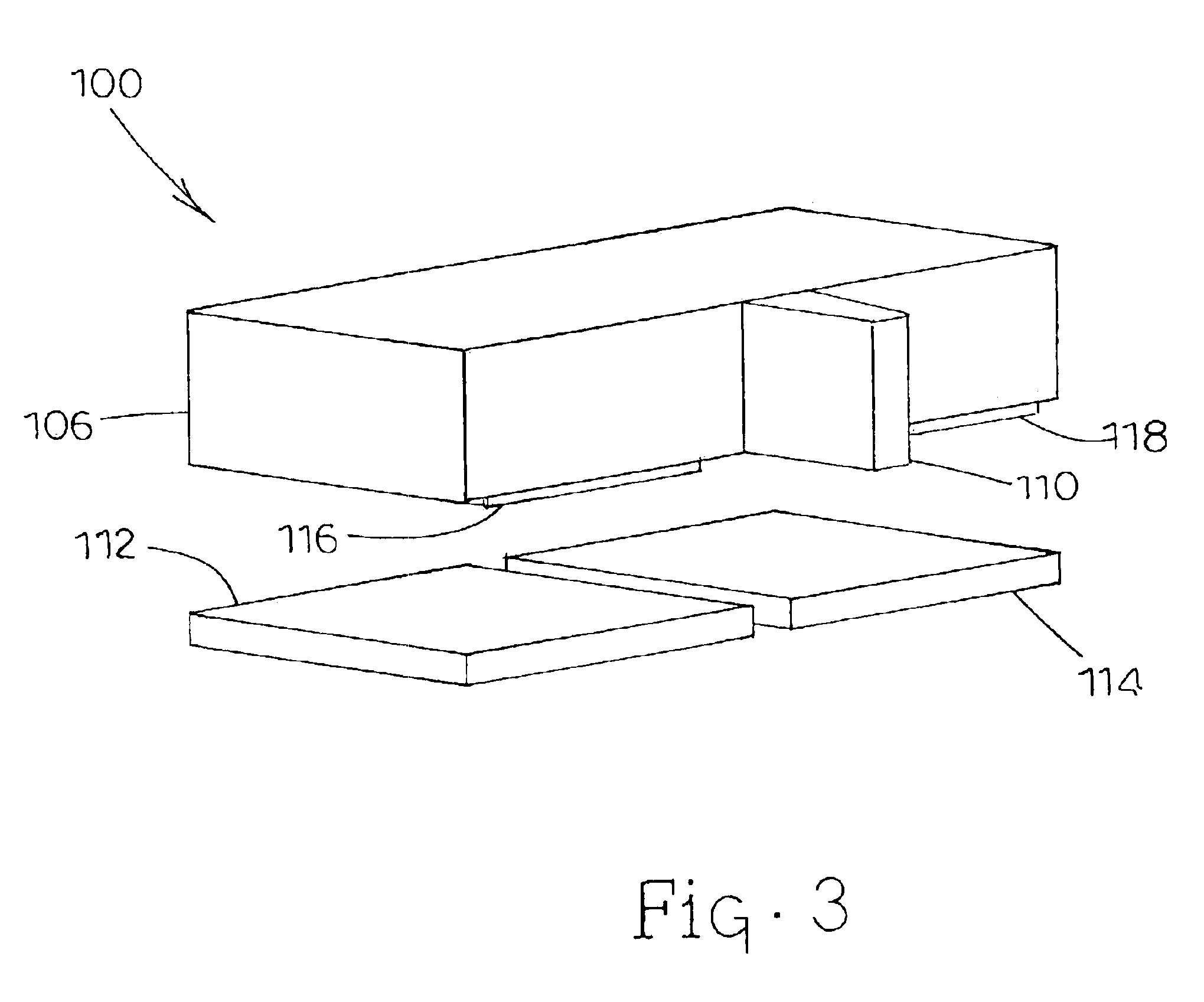
Charge control of micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS20050001828A1Capacitor with electrode distance variationPolarising elementsElectricityCharge control
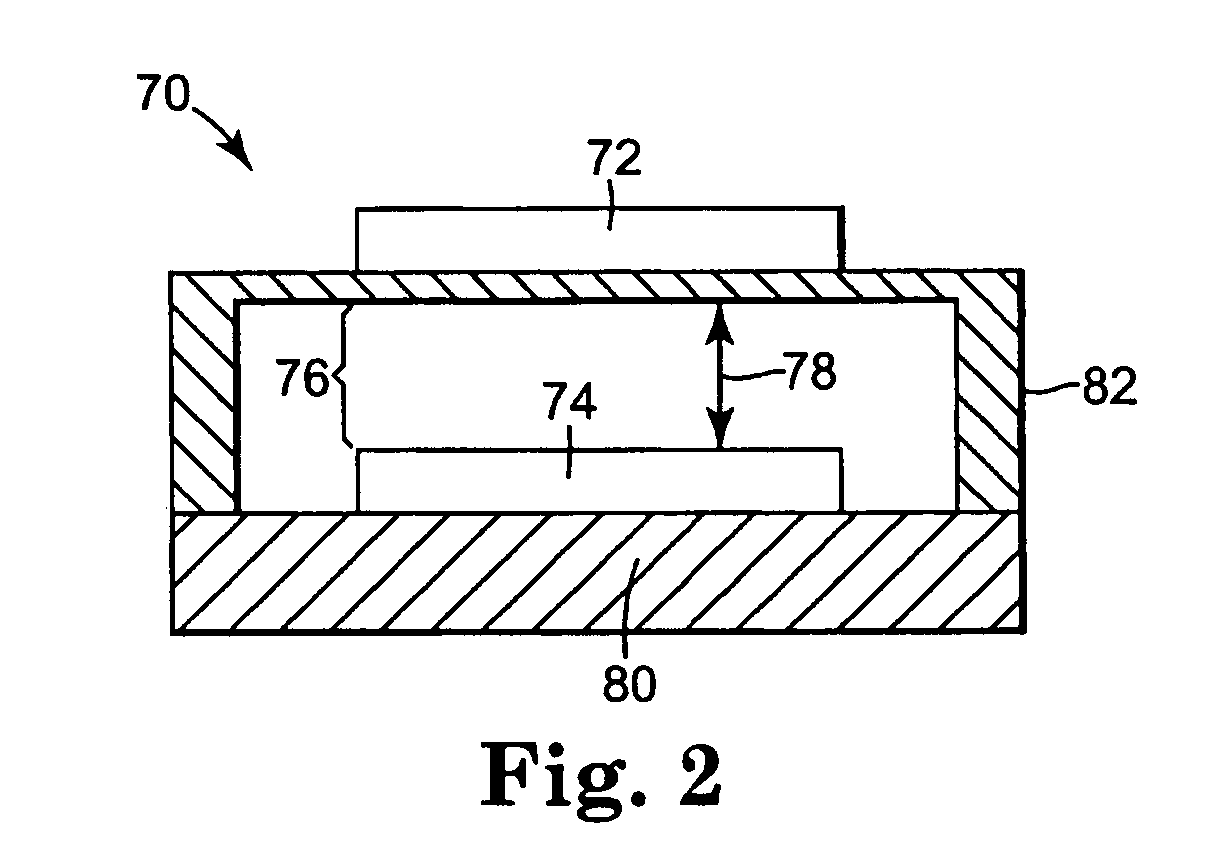
A charge control circuit for controlling a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) device having variable capacitor formed by first conductive plate and a second conductive plate separated by a variable gap distance. The charge control circuit comprises a switch circuit configured to receive a reference voltage having a selected voltage level and configured to respond to an enable signal having a duration at least as long as an electrical time constant constant of the MEMS device, but shorter than a mechanical time constant of the MEMS device, to apply the selected voltage level across the first and second plates for the duration to thereby cause a stored charge having a desired magnitude to accumulate on the variable capacitor, wherein the variable gap distance is a function of the magnitude of the stored charge.
Owner:MARTIN ERIC T +5
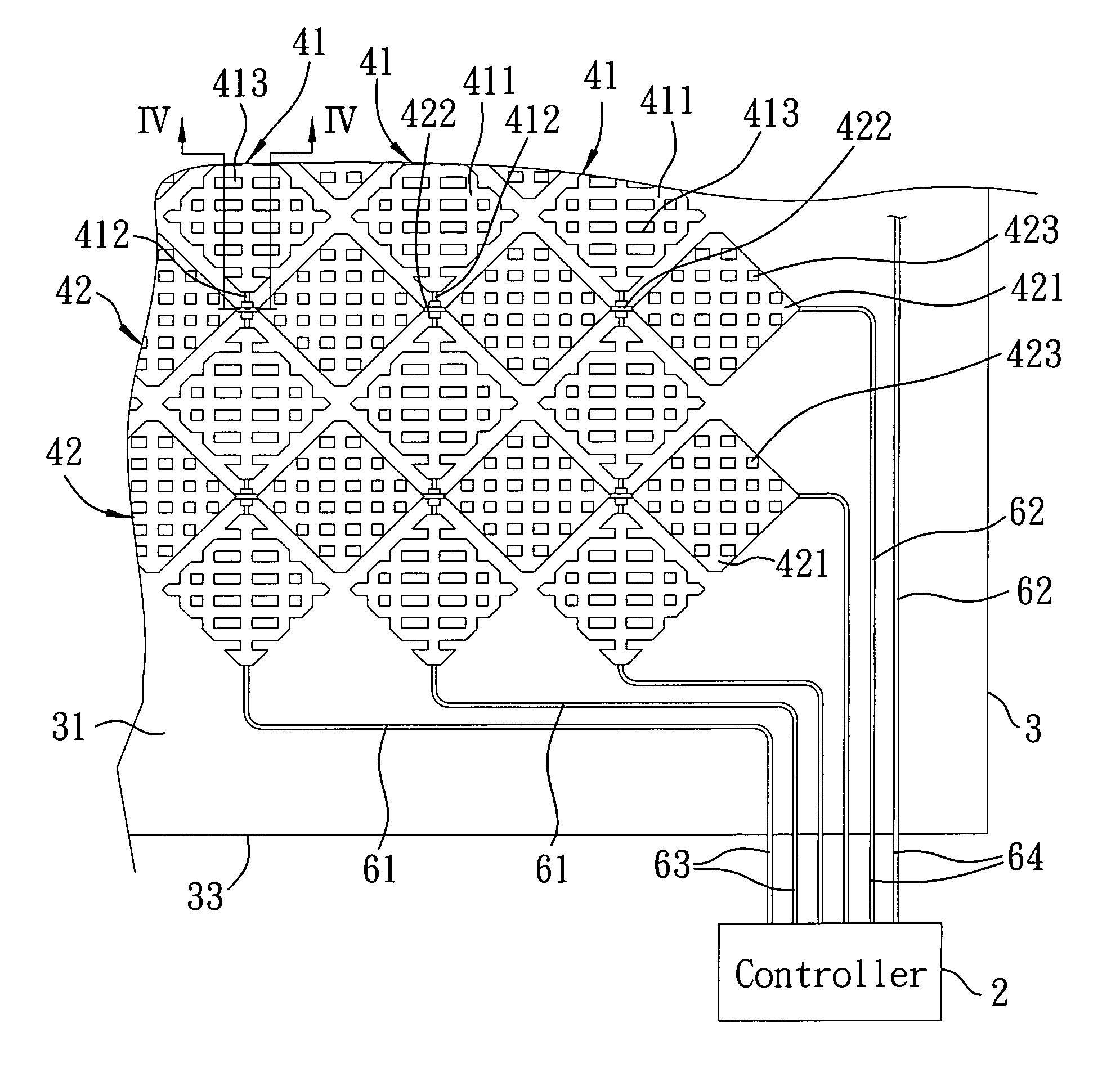
Capacitive type touch panel
ActiveUS7864503B2Overcomes drawbackContact materialsMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A capacitive type touch panel includes: a transparent substrate; an array of first conductors formed on a surface of the transparent substrate; an array of second conductors formed on the surface of the transparent substrate; a plurality of conductive first bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the first conductors; a plurality of conductive second bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the second conductors and each of which intersects insulatively a respective one of the first bridging lines; and a plurality of spaced apart insulators, each of which is disposed at an intersection of a respective one of the first bridging lines and a respective one of the second bridging lines to separate the respective first and second bridging lines.
Owner:TAZIK SOLUTIONS (SUZHOU) LTD
Capacitive type touch panel
ActiveUS20080277259A1Overcomes drawbackContact materialsMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrical conductorTouch panel
A capacitive type touch panel includes: a transparent substrate; an array of first conductors formed on a surface of the transparent substrate; an array of second conductors formed on the surface of the transparent substrate; a plurality of conductive first bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the first conductors; a plurality of conductive second bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the second conductors and each of which intersects insulatively a respective one of the first bridging lines; and a plurality of spaced apart insulators, each of which is disposed at an intersection of a respective one of the first bridging lines and a respective one of the second bridging lines to separate the respective first and second bridging lines.
Owner:TAZIK SOLUTIONS (SUZHOU) LTD
Method and apparatus for an improved single pole double throw micro-electrical mechanical switch
InactiveUS6160230AElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitor with electrode distance variationRepulsion forceCantilever
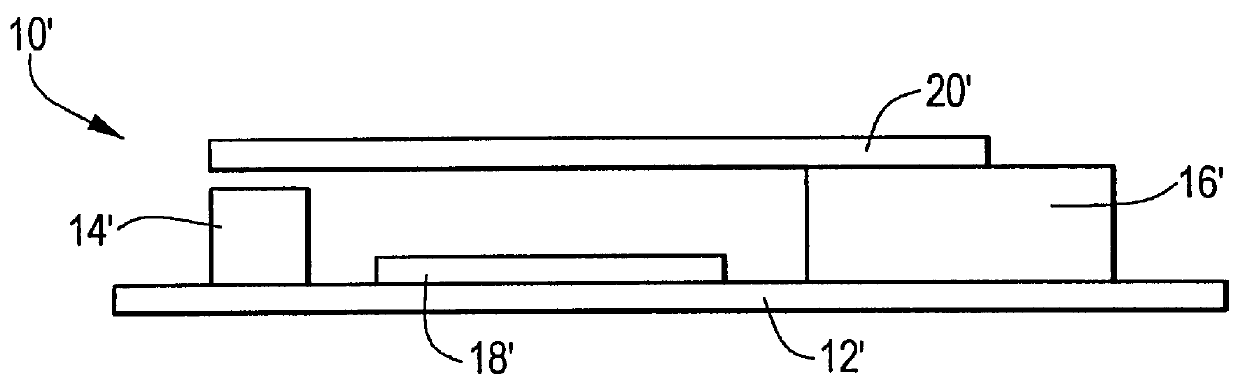
A single pole, double throw micro-electromechanical (MEM) switch. The inventive switch includes a first contact providing a first terminal of the switch. A second contact provides a second terminal of said switch. A cantilever beam provides a third terminal of the switch. The inventive switch includes a system for electrostatically pushing or pulling the beam to disengage the first contact and engage the second contact. In an illustrative implementation, the system for electrostatically operating the switch includes a first charge storage structure on the beam, a second charge storage structure on the switch, and an electrical supply for creating an electrical charge on the first and the second charge storage structures. The first and second charge storage structures are effective to create a force of repulsion therebetween on the application of an electrical charge thereto. The "pull" electrostatic force closes the MEM switch. The "push" force aids in opening the switch. The "push" capability is the result of the use of like (same polarity) electrostatic charges on the control surfaces. The like charges provide an electrostatic repulsion force during the switch opening process.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Capacitive Touch Panel with Low Impedance
ActiveUS20090085891A1Reduce resistanceSystem coupling capacitance and resistanceElectronic circuit testingStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceDielectric layer
A capacitive touch panel and a display device using the capacitive touch panel are provided. The capacitive touch panel includes a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, and a dielectric layer disposed between two layers. The first electrode layer has a plurality of first A electrode strings and first B electrode strings extended along a first direction. The first A electrode string and the first B electrode string respectively has a plurality of first direction electrodes. The second electrode layer has a plurality of second direction electrodes connected in series along a second direction. The first A and B electrode strings are disconnected in the first electrode layer while they are simultaneously detected for presence of signal variation.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Electroactive polymers
InactiveUS7049732B2Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to transducers, their use and fabrication. The transducers convert between mechanical and electrical energy. Some transducers of the present invention include a pre-strained polymer. The pre-strain improves the conversion between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention also relates to devices including an electroactive polymer to convert between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer included in a transducer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System and method of fabricating micro cavities
InactiveUS20080308920A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEpoxyMicroelectromechanical systems
A system and method for manufacturing micro cavity packaging enclosure at the wafer level using MEMS (MicroElectroMechanical Systems) process, wherein micro cavities are formed from epoxy-bonded single-crystalline silicon wafer as its cap, epoxy and deposited metal or insulator as at least part of its sidewall, on substrate wafers.
Owner:WAN CHANG FENG
Stress bimorph MEMS switches and methods of making same
InactiveUS7053737B2Reduce capacitanceMinimize OFF-state capacitanceElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitor with electrode distance variationEngineeringCantilever
A micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) switch formed on a substrate, the switch comprising a transmission line formed on the substrate, a substrate electrostatic plate formed on the substrate, and an actuating portion. The actuating portion comprises a cantilever anchor formed on the substrate and a cantilevered actuator arm extending from the cantilever anchor. Attraction of the actuator arm toward the substrate brings an electrical contact into engagement with the portions of the transmission line separated by a gap, thus bridging the transmission line gap and closing the circuit. In order to maximize electrical isolation between the transmission line and the electrical contact in an OFF-state while maintaining a low actuation voltage, the actuator arm is bent such that the minimum separation distance between the transmission line and the electrical contact is equal to or greater than the maximum separation distance between the substrate electrostatic plate and arm electrostatic plate.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
Piezoelectric actuator and micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS20060055287A1Warpage suppressionImprove accuracyNanotechPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
A piezoelectric actuator includes a first beam including a first bottom electrode, a first piezoelectric film on the first bottom electrode, and a first top electrode on the first piezoelectric film, a fixed end assigned at an end of the first beam and fixed on a substrate, a connecting end assigned at another end of the first beam and suspended over a free space; and a second beam including a second piezoelectric film connected to the first piezoelectric film at the connecting end, a second bottom electrode under the second piezoelectric film, and a second top electrode on the second piezoelectric film, a working end assigned at an end of the second beam opposite to another end to which the connecting end is assigned and suspended over the free space; wherein a distance between centers of the fixed end and the working end is shorter than a distance from the working end to the connecting end.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of using a plurality of smaller MEMS devices to replace a larger MEMS device
ActiveUS20100116632A1Resolution in capacitanceDesired capacitancePrinted electric component incorporationCapacitor with electrode distance variationOxide semiconductorSignal averaging
Embodiments disclosed herein generally include using a large number of small MEMS devices to replace the function of an individual larger MEMS device or digital variable capacitor. The large number of smaller MEMS devices perform the same function as the larger device, but because of the smaller size, they can be encapsulated in a cavity using complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) compatible processes. Signal averaging over a large number of the smaller devices allows the accuracy of the array of smaller devices to be equivalent to the larger device. The process is exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based accelerometer switch array with an integrated analog to digital conversion of the inertial response. The process is also exemplified by considering the use of a MEMS based device structure where the MEMS devices operate in parallel as a digital variable capacitor.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Piezoelectric-driven MEMS device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050242687A1Fabricated reliably and consistentlyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin membraneEngineering
A piezoelectric-driven MEMS device can be fabricated reliably and consistently. The piezoelectric-driven MEMS device includes: a movable flat beam having a piezoelectric film disposed above a substrate with a recessed portion such that the piezoelectric film is bridged over the recessed portion, piezoelectric drive mechanisms disposed at both ends of the piezoelectric film and configured to drive the piezoelectric film, and a first electrode disposed at the center of the substrate-side of the piezoelectric film, and a second electrode disposed on a flat part of the recessed portion of the substrate and facing the first electrode of the movable flat beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Substantially rigid capacitive joystick designs
InactiveUS6888076B2Rigid designManual control with multiple controlled membersCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitanceJoystick
An economical, force-sensing “stiff” capacitive joystick includes a user-manipulable handle coupled to an electrically conductive drive plate, and an electrically conductive surface spaced apart from the drive plate. In the preferred embodiment, one or both of the drive plate and the conductive surface are segmented to produce multiple capacitive sensing elements, such that a force applied to the handle causes a slight deflection of the drive plate, enabling the force to be computed in at least two dimensions through changes detectable in the capacitive sensing elements. One or more electrical controls may be provided on the handle to accommodate different functions. For convenient construction, the electrically conductive drive plate is non-segmented, and the electrically conductive surface forms part of a printed-circuit board having a segmented pattern.
Owner:P I ENG
Method and apparatus for an improved micro-electrical mechanical switch
InactiveUS6127744ABatteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsElectricityFriction effect
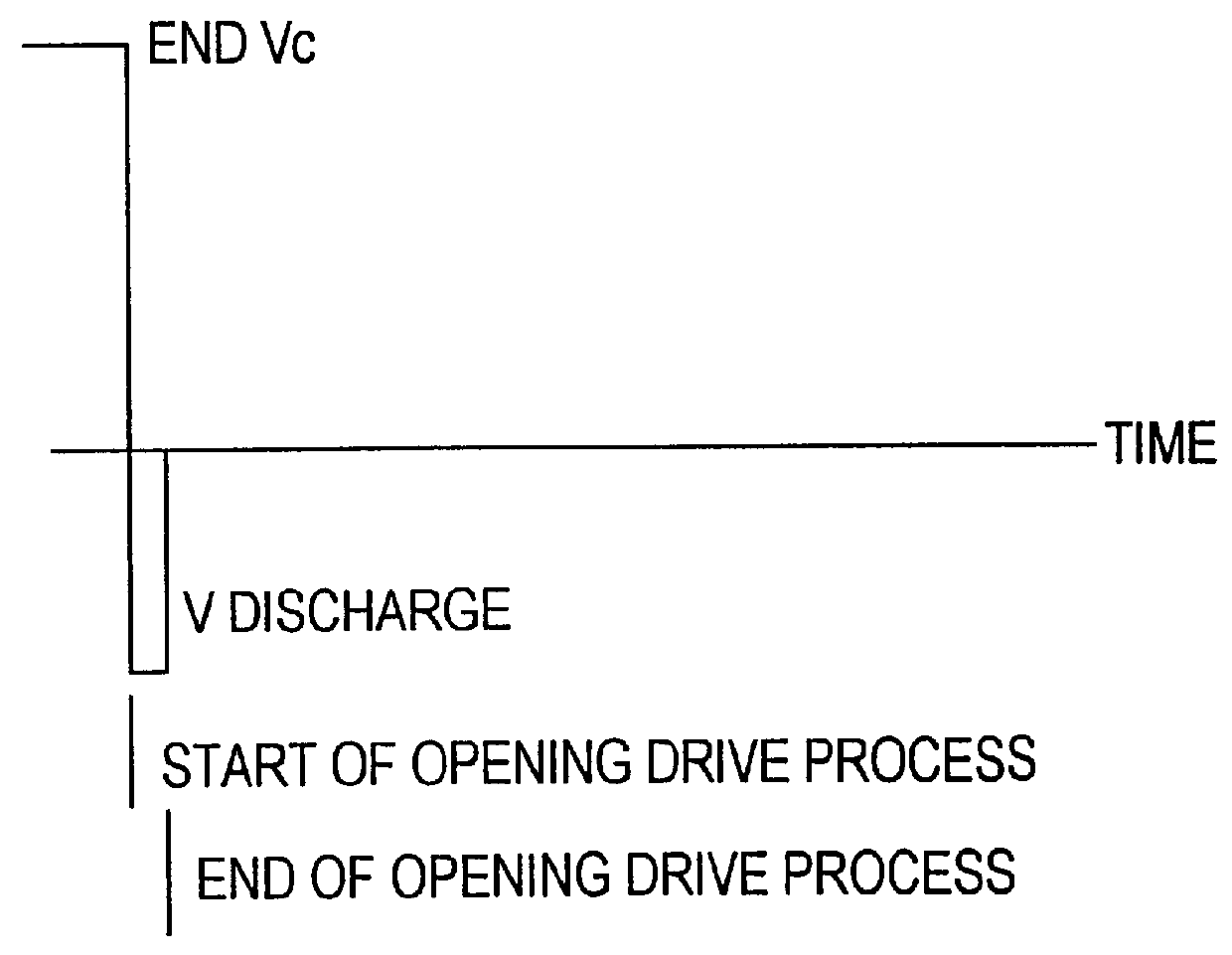
A method, device and circuit which applies an electrostatic repulsion pushing force to a MEM switch armature during an opening process. The repulsive force adds to the spring restoration force on the armature, increasing the opening speed of the switch and aids in overcoming stiction effects. The inventive switch includes a contact electrically connected to a first terminal of the switch. A throw is electrically connected to a second terminal of the switch. Finally, a mechanism is provided for opening the switch by electrostatically causing the throw to disengage the contact. In the illustrative implementation, the mechanism for opening the switch includes a first charge storage structure mounted on the throw and a second charge storage structure mounted in proximity to the first charge storage structure. When charges are applied between the first and the second charge storage structures, a force of repulsion is created or a force of attraction is created depending on the polarity of the potential.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20060113878A1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
MEMS tunable capacitor based on angular vertical comb drives
InactiveUS7085122B2Appreciates the drawbacks inherent in lateral drive MEMS capacitorsIncrease tuning rangeMultiple-port networksMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceComb finger
A MEMS tunable capacitor with angular vertical comb-drive (AVC) actuators is described where high capacitances and a wide continuous tuning range is achieved in a compact space. The comb fingers rotate through a small vertical angle which allows a wider tuning range than in conventional lateral comb drive devices. Fabrication of the device is straightforward, and involves a single deep reactive ion etching step followed by release and out-of-plane assembly of the angular combs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitor apparatuses and related methods
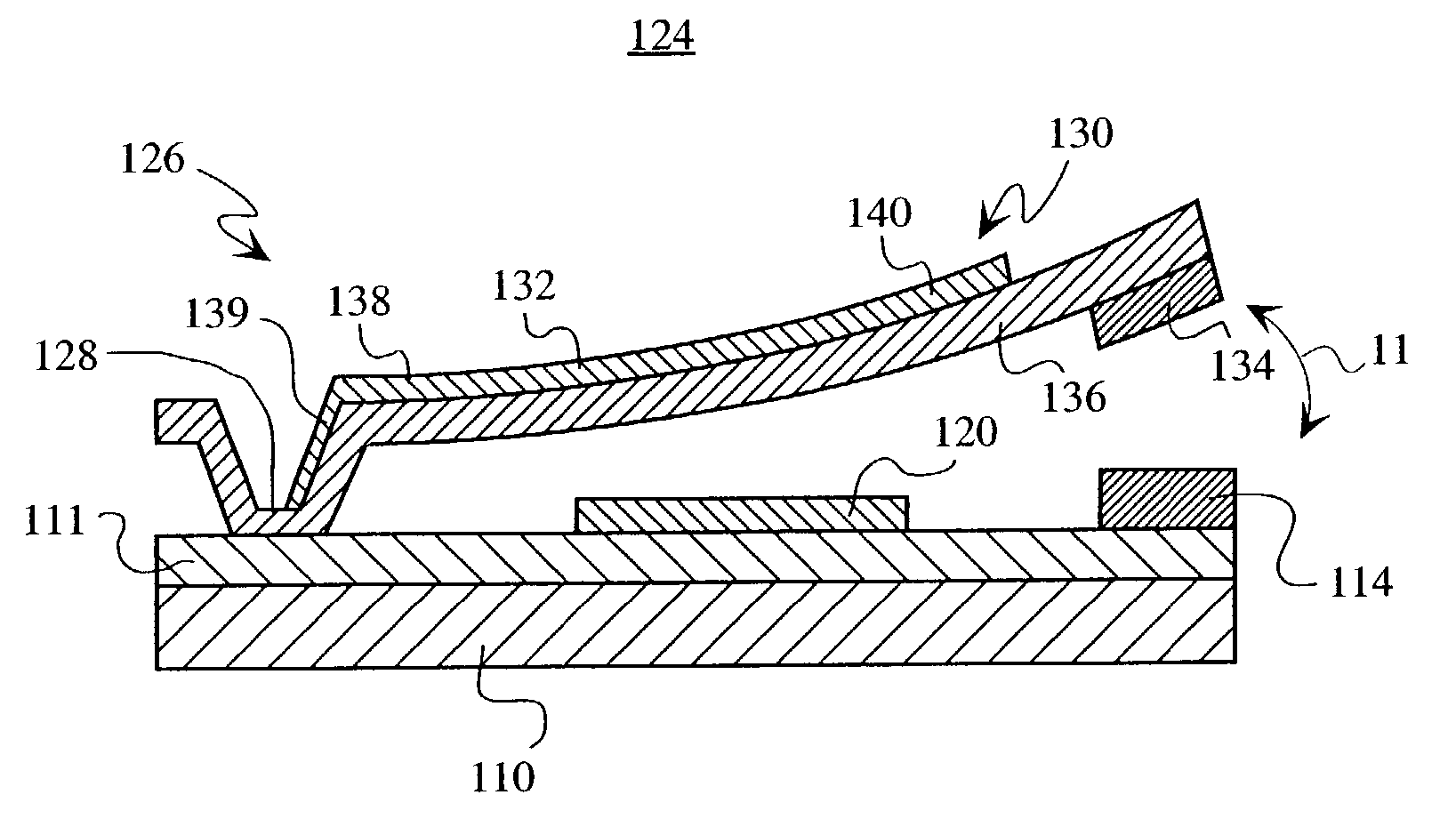
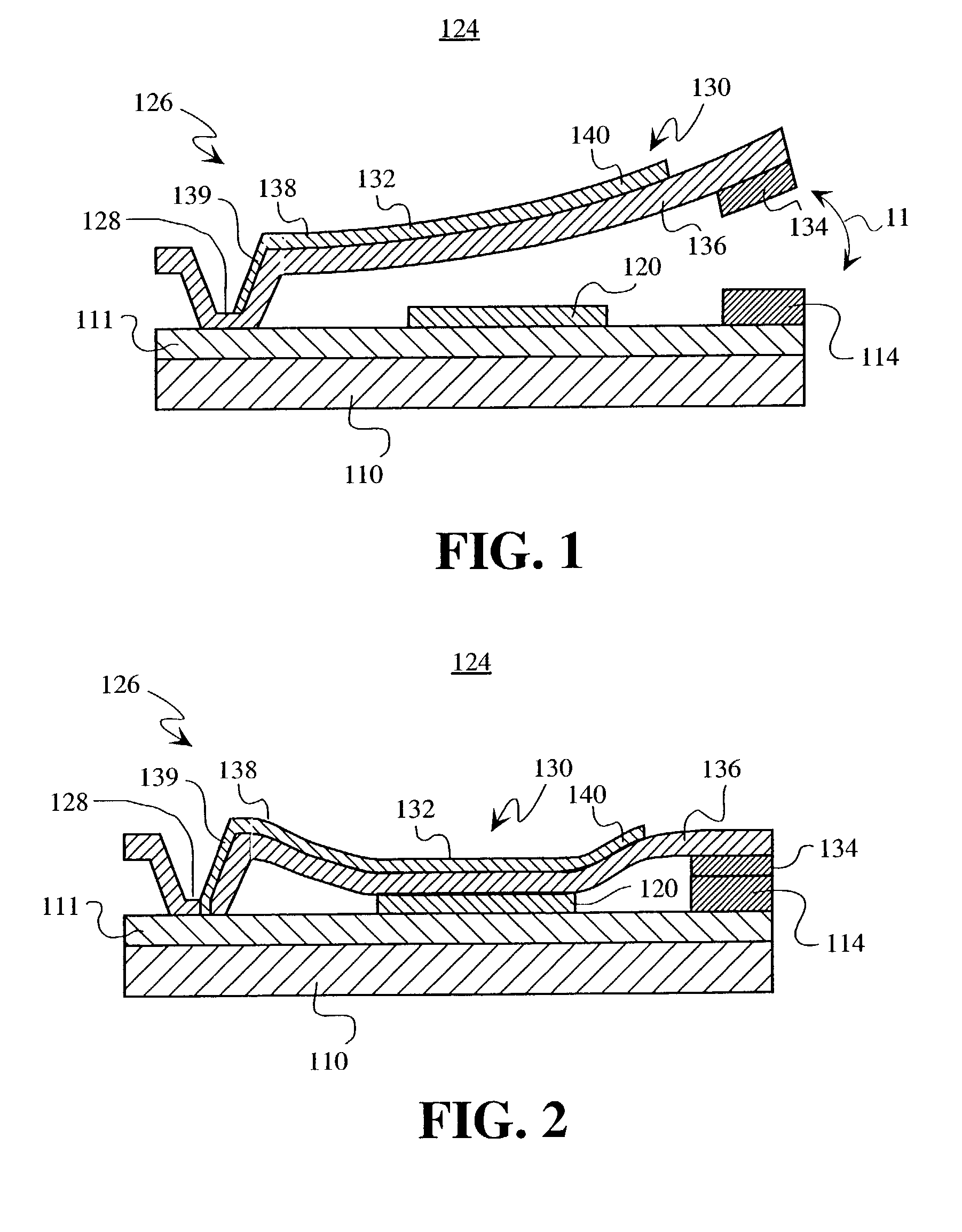
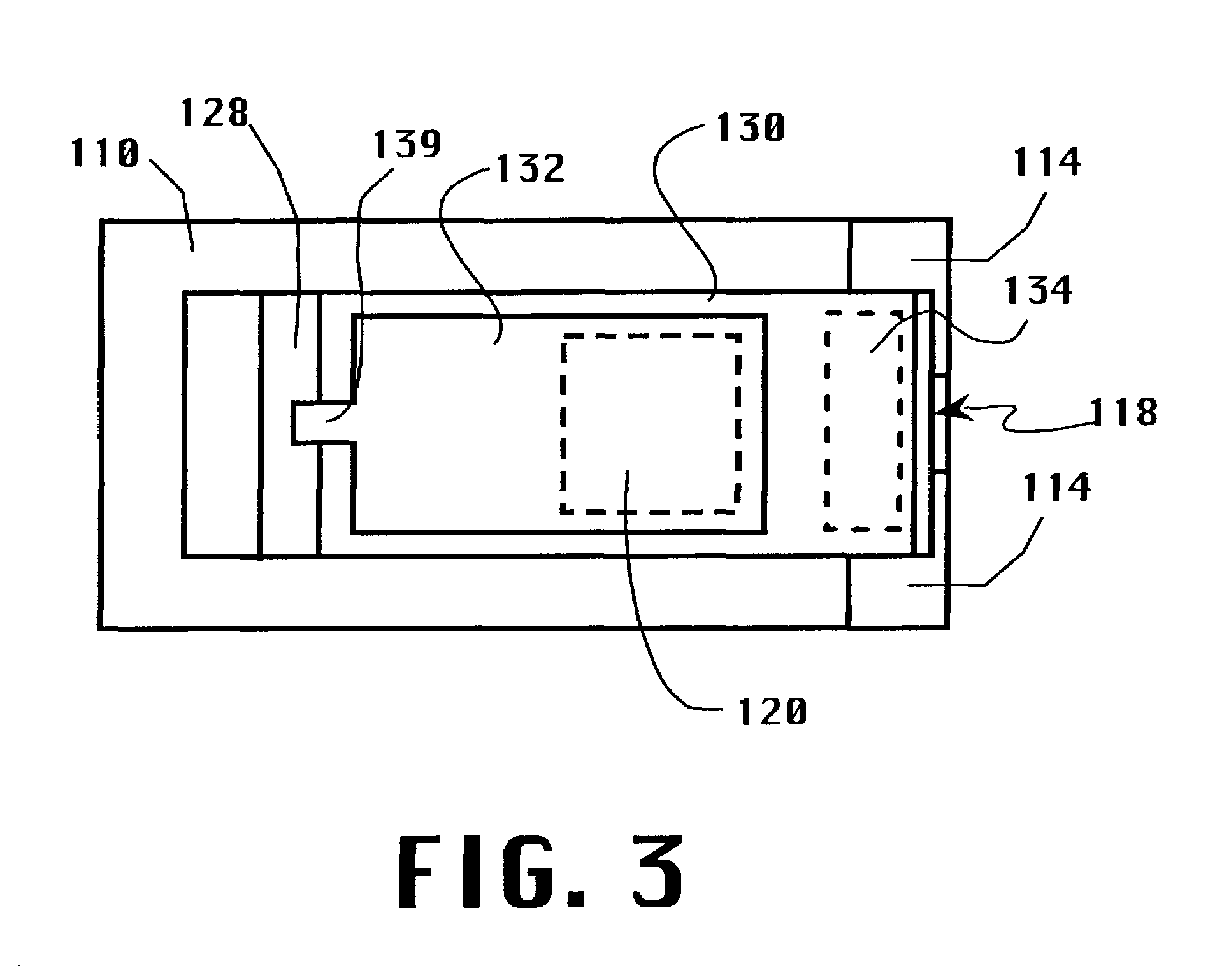
Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) Variable Capacitor Apparatus and Related Methods. According to one embodiment, a MEMS variable capacitor is provided. The variable capacitor can include first and second electrodes being spaced apart, and at least one of the electrodes being movable when a voltage is applied across the first and second electrodes. The variable capacitor can also include a first conductive plate attached to and electrically isolated from the first electrode. Furthermore, the variable capacitor can include a second conductive plate attached to the second electrode and spaced from the first conductive plate for movement of at least one of the plates with respect to the other plate upon application of voltage across the first and second electrodes to change the capacitance between the first and second plates.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
Stepping actuator and method of manufacture therefore
InactiveUS20050146241A1Reduce air gapReduce pull-in voltageCapacitor with electrode distance variationMultiple capacitorsParallel plateActuator
An embodiment of the present invention provides a stepping actuator, comprising a suspended membrane comprising a plurality of movable electrodes connected by plurality of spring hinges to a payload platform; and anchors connecting said membrane to a substrate, said substrate comprising a plurality of fixed electrodes; wherein said movable electrodes of said suspended membrane and said fixed electrodes from said substrate form parallel-plate electrostatic sub-actuators.
Owner:WAN CHANG FENG
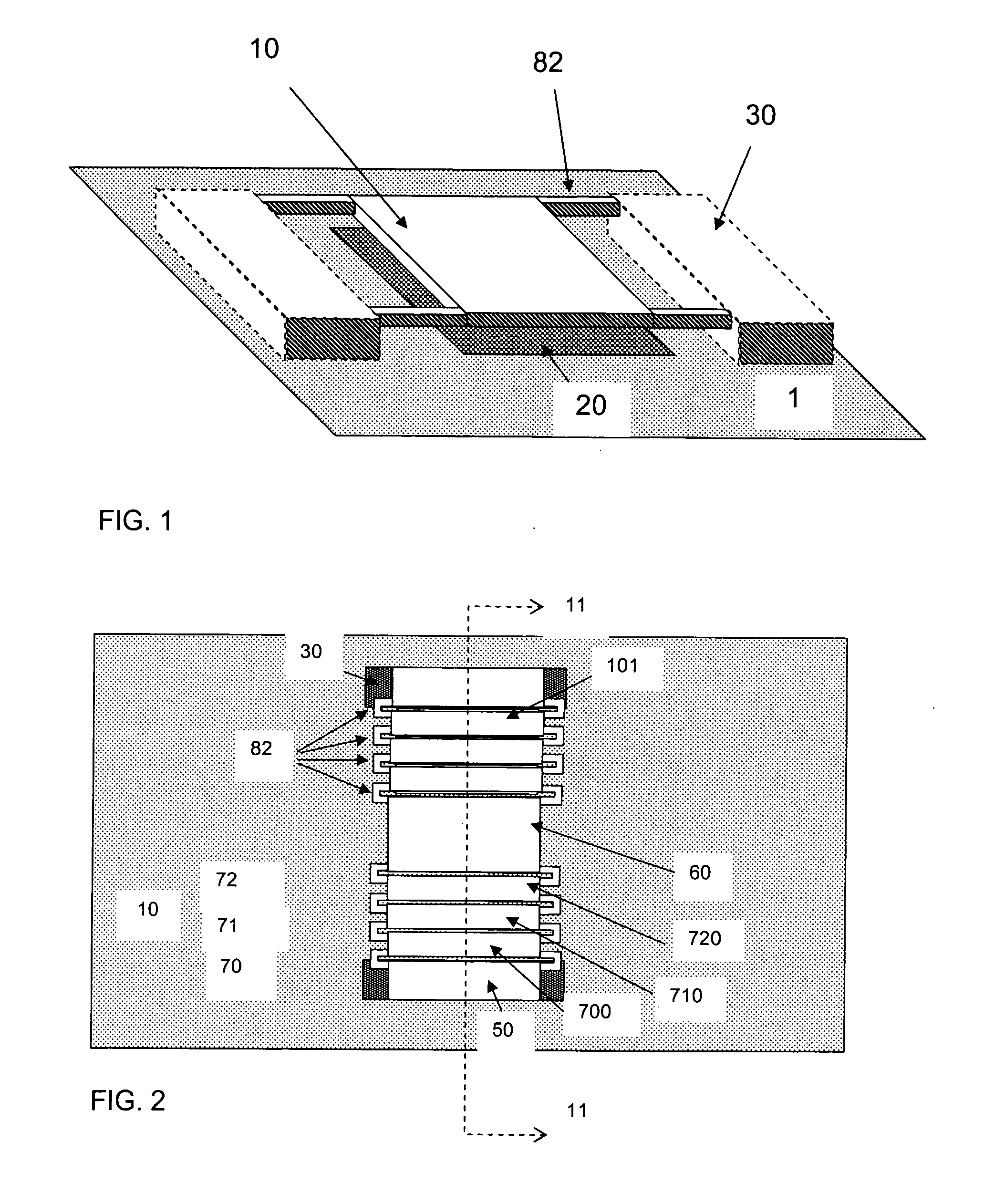
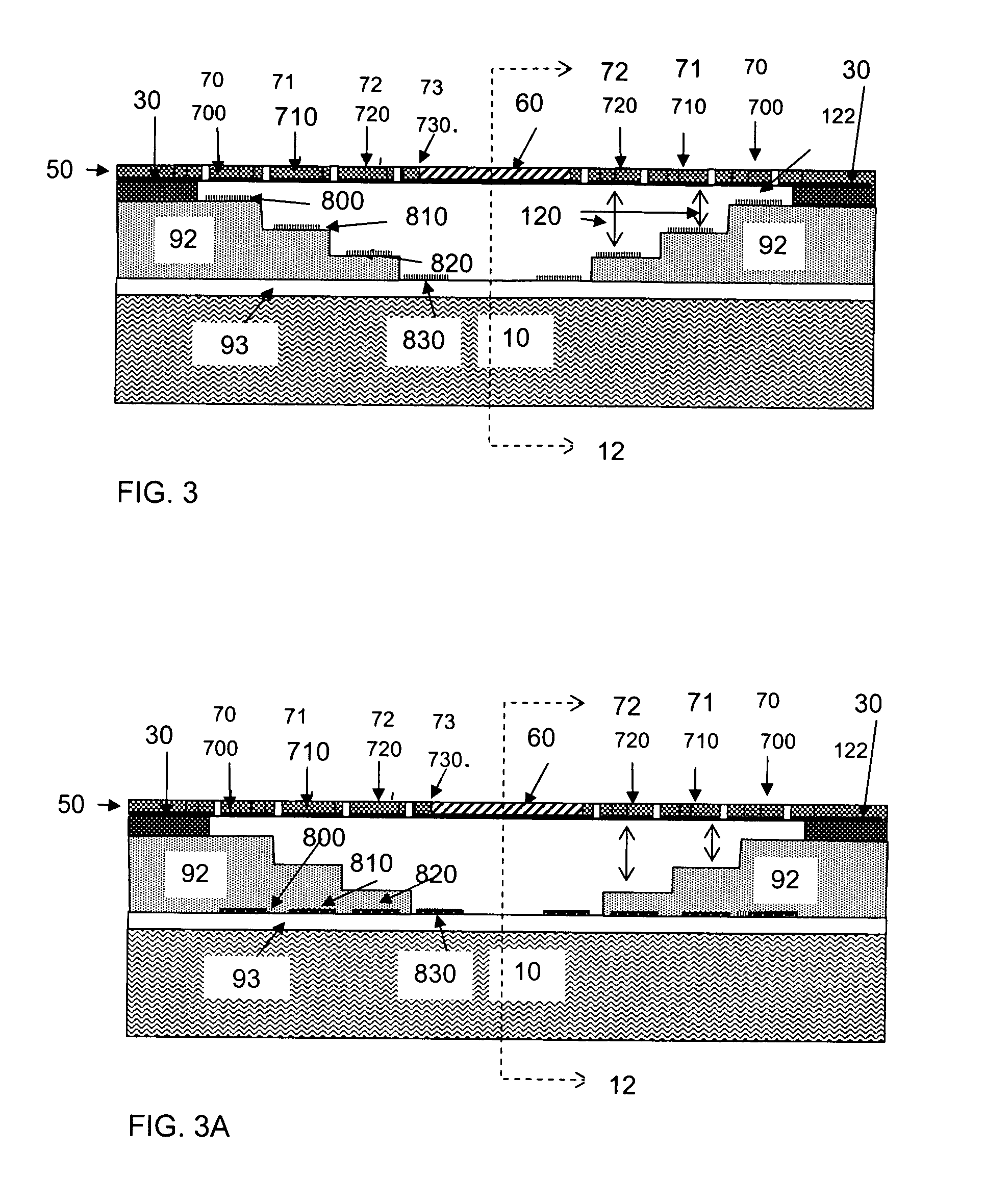
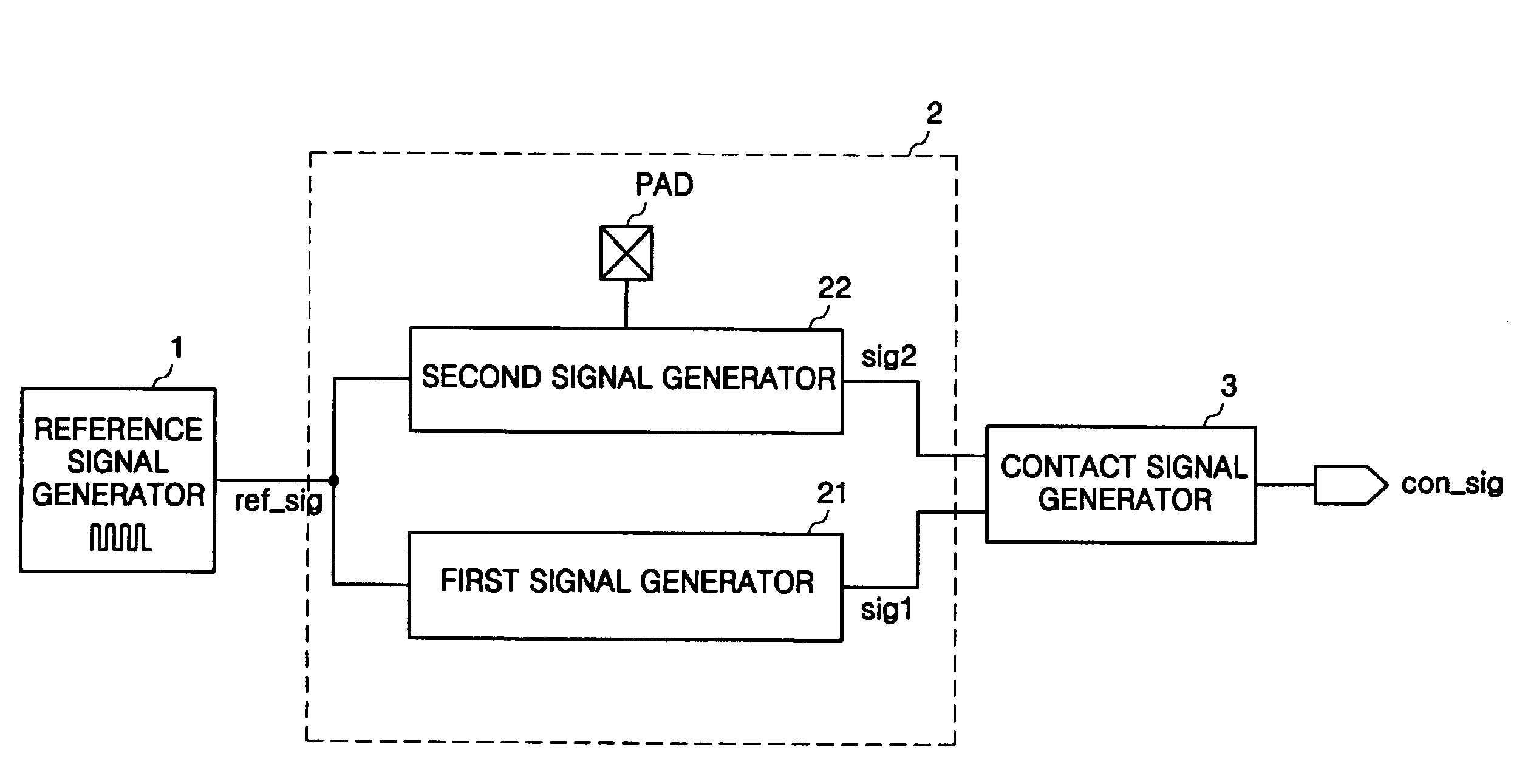
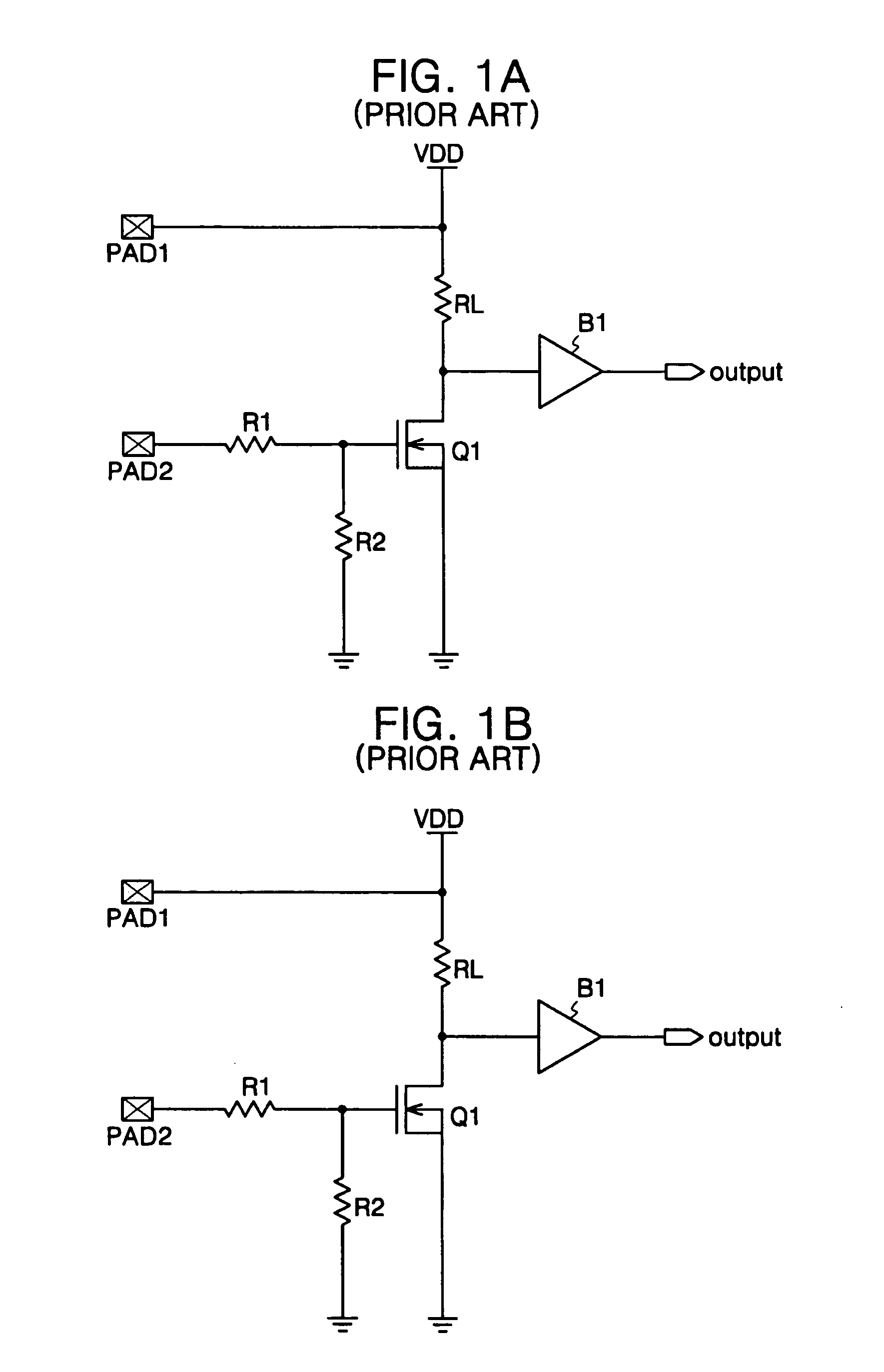
Electrical touch sensor and human interface device using the same
ActiveUS20060007181A1Accurate detectionMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitor with electrode distance variationTouchpadSignal generator
An electrical touch sensor is provided. The electrical touch sensor includes: a touch detection part having at least one touch pad and generating a first signal having a same delay time regardless of whether the object is in contact with the touch pad and a second signal having a varied delay time according to whether the object is in contact with the touch pad; and a contact signal generator generating a contact signal in response to the delay time-difference between the first and second signals. Therefore, it is possible to increase operation reliability by precisely determining whether the object is in contact with the pad, when the object has charge accumulation characteristics more than a certain level, although its conductive is insufficient. In addition, the electrical touch sensor can determine whether the object is in contact with the pad using only one pad to reduce a layout area of a product.
Owner:III HLDG 2
Oxide MEMS beam
InactiveUS20120133006A1Transducer detailsCapacitor with electrode distance variationSemiconductor structurePhysics
In one embodiment, a semiconductor structure includes a beam positioned within a sealed cavity, the beam including: an upper insulator layer including one or more layers; and a lower insulator layer including one or more layers, wherein a composite stress of the upper insulator layer is different than a composite stress of the lower insulator layer, such that the beam bends.
Owner:IBM CORP
Capacitance detection apparatus
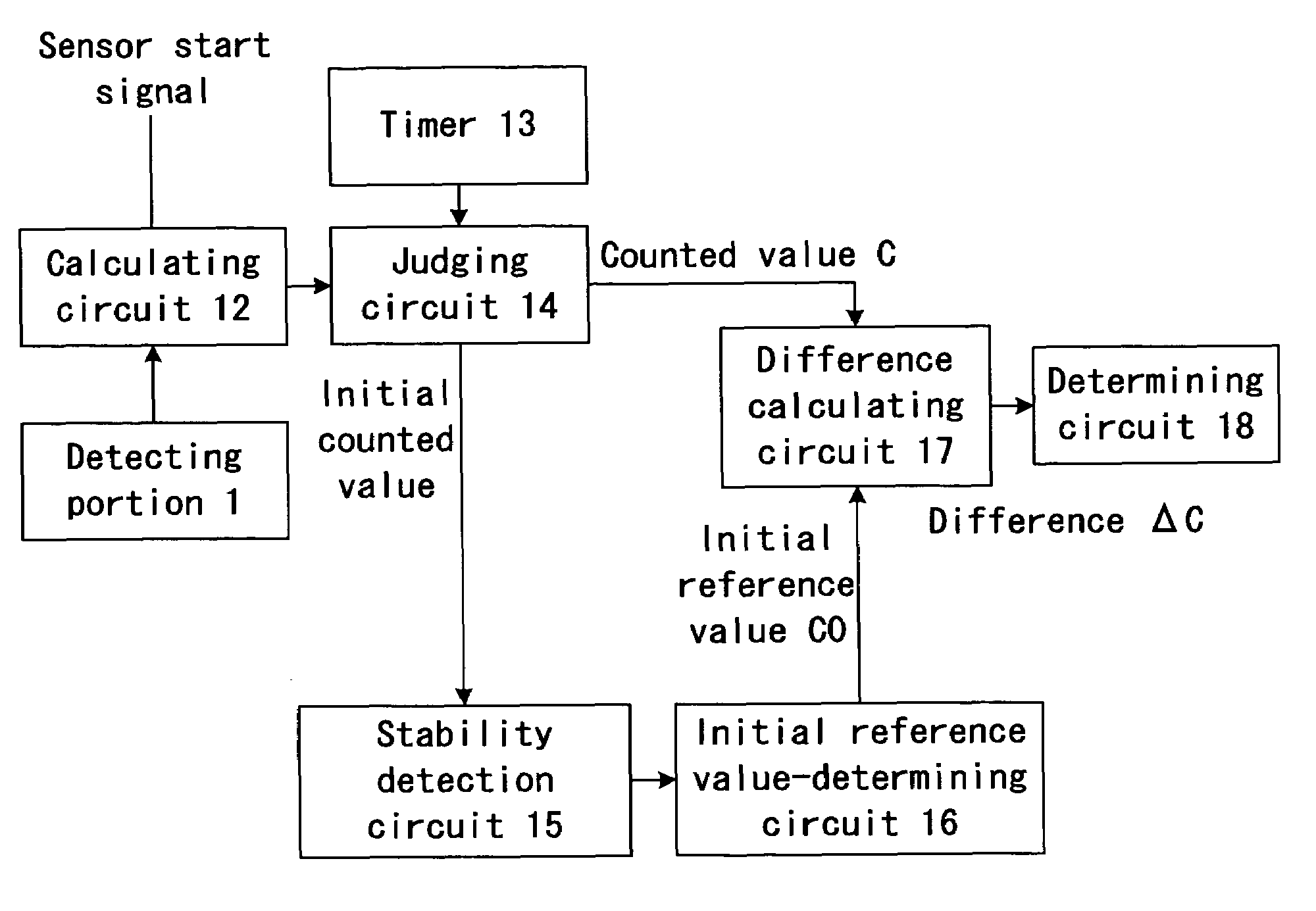
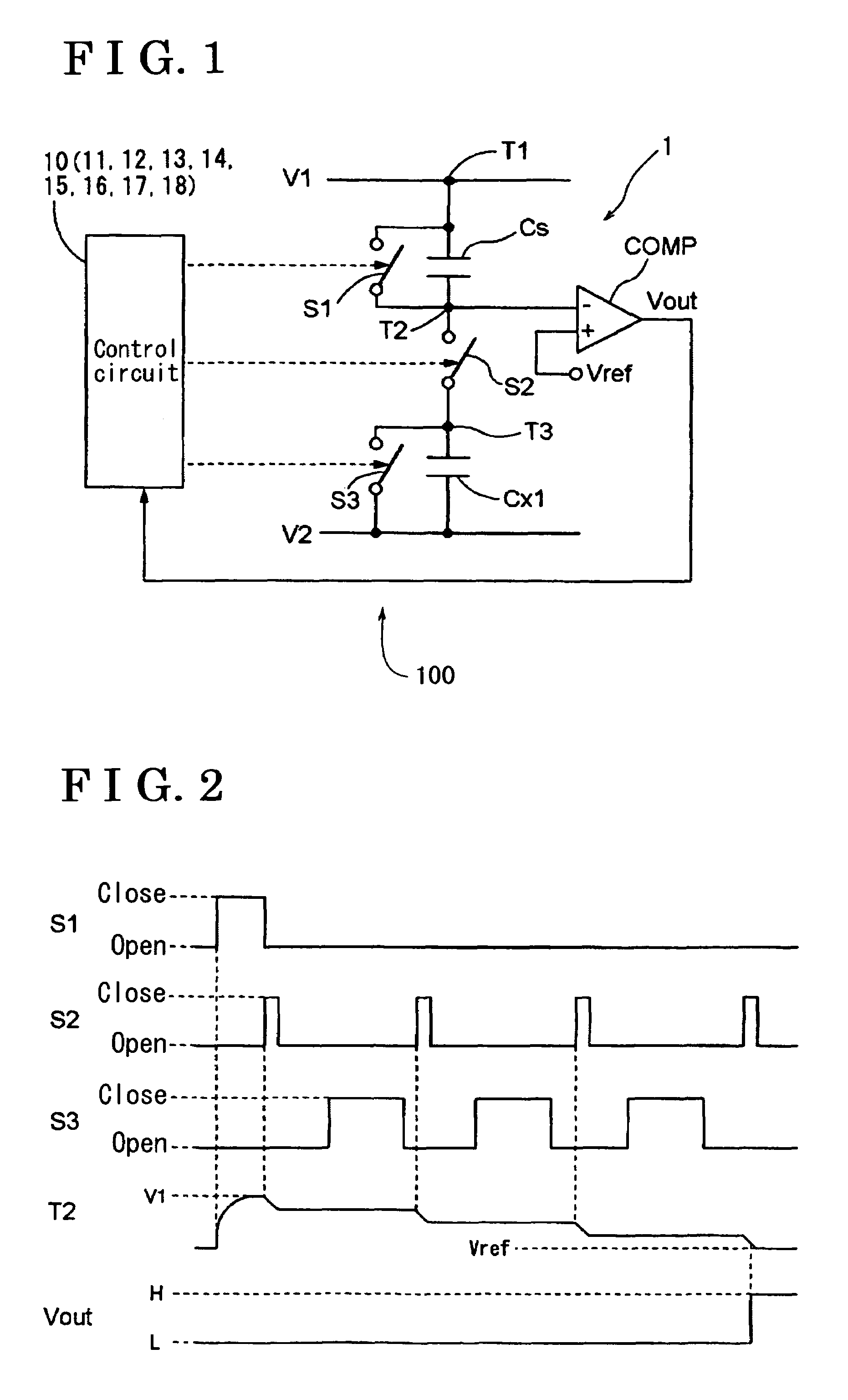
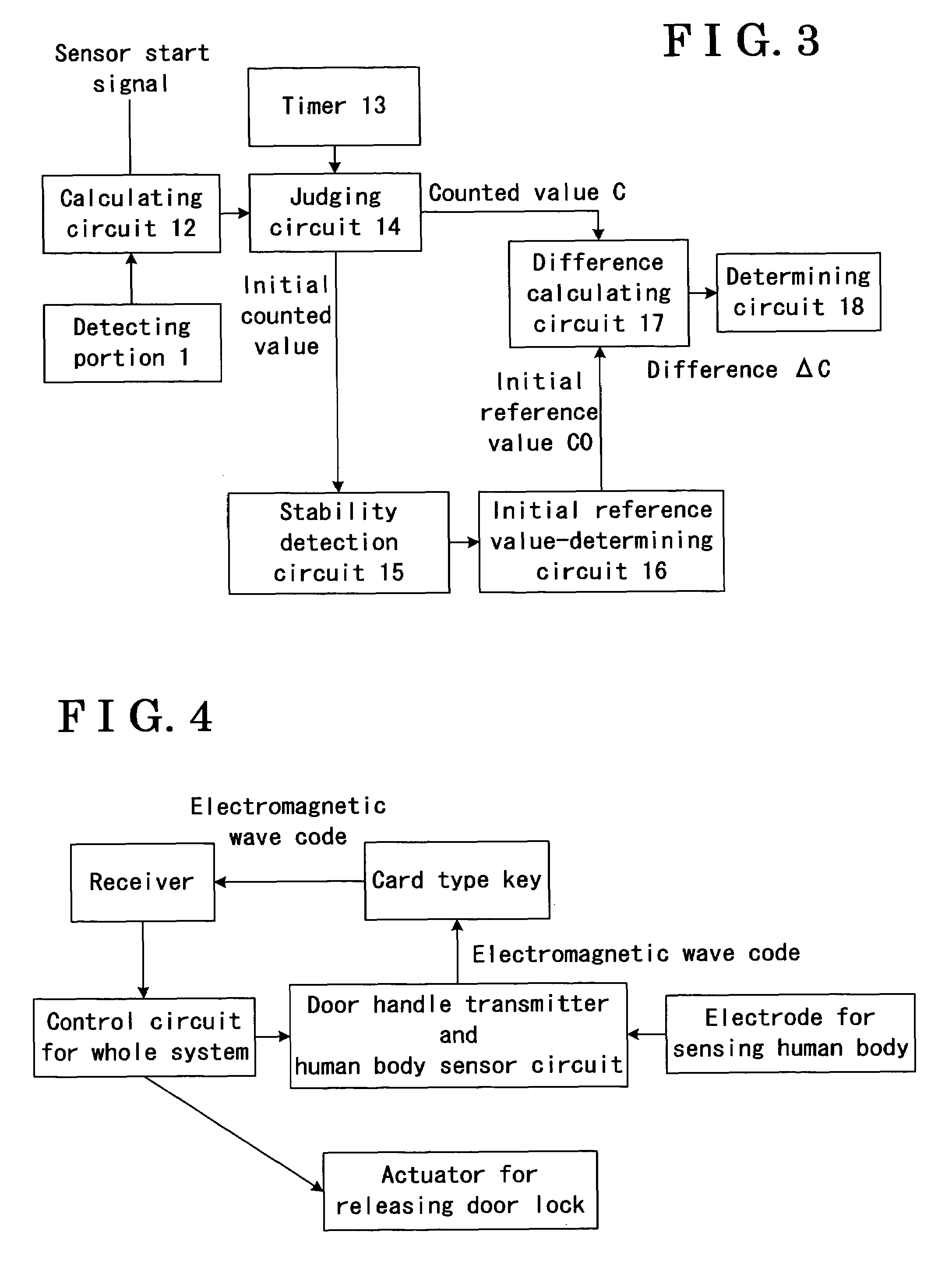
ActiveUS7245131B2Capacitance measurementsCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitanceStart time
A capacitance detection apparatus includes a detection electrode for detecting approach of an object on the basis of a change of capacitance, a calculating circuit for calculating a value associated with the capacitance change, a judging circuit for judging whether the calculated value is a normal or initial value calculated after or before a predetermined period of time lapse from a start time of the capacitance detection apparatus, an initial reference value-determining circuit for determining an initial reference value, a difference calculating circuit for calculating a difference between the normal value and a value calculated earlier than a time when the normal value is calculated by the predetermined period of time or longer or between the initial value and the initial reference value, and a determining circuit for determining whether the object is approaching by comparing the difference with a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20060113880A1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
The present invention relates to transducers, their use and fabrication. The transducers convert between mechanical and electrical energy. Some transducers of the present invention include a pre-strained polymer. The pre-strain improves the conversion between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention also relates to devices including an electroactive polymer to convert between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer included in a transducer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Elastomeric CMOS based micro electromechanical varactor
InactiveUS20060003482A1Increase capacitance densityIncreased side wall areaCapacitor with electrode distance variationMultiple capacitorsElastomerElectrical polarity
A micro electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitor is described, wherein movable comb electrodes of opposing polarity are fabricated simultaneously on the same substrate and are independently actuated. The electrodes are formed in an interdigitated fashion to maximize capacitance. The MEMS variable capacitor includes CMOS manufacturing steps in combination with elastomeric material selectively used in areas under greatest stress to ensure that the varactor will not fail as a result of stresses that may result in the separation of dielectric material from the conductive elements. The combination of a CMOS process with the conducting elastomeric material between vias increases the overall sidewall area, which provides increased capacitance density.
Owner:IBM CORP
MEMS-based variable capacitor
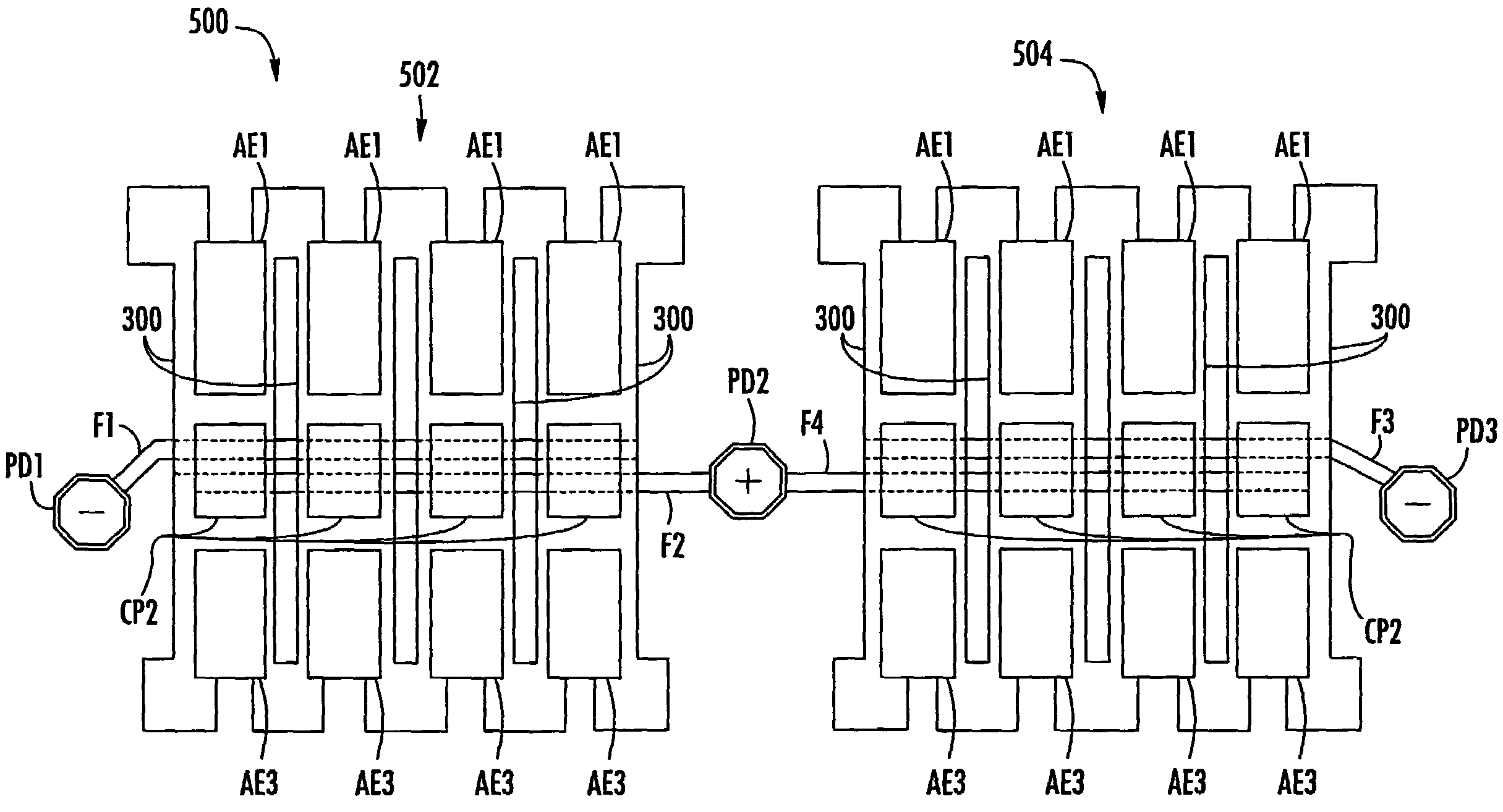
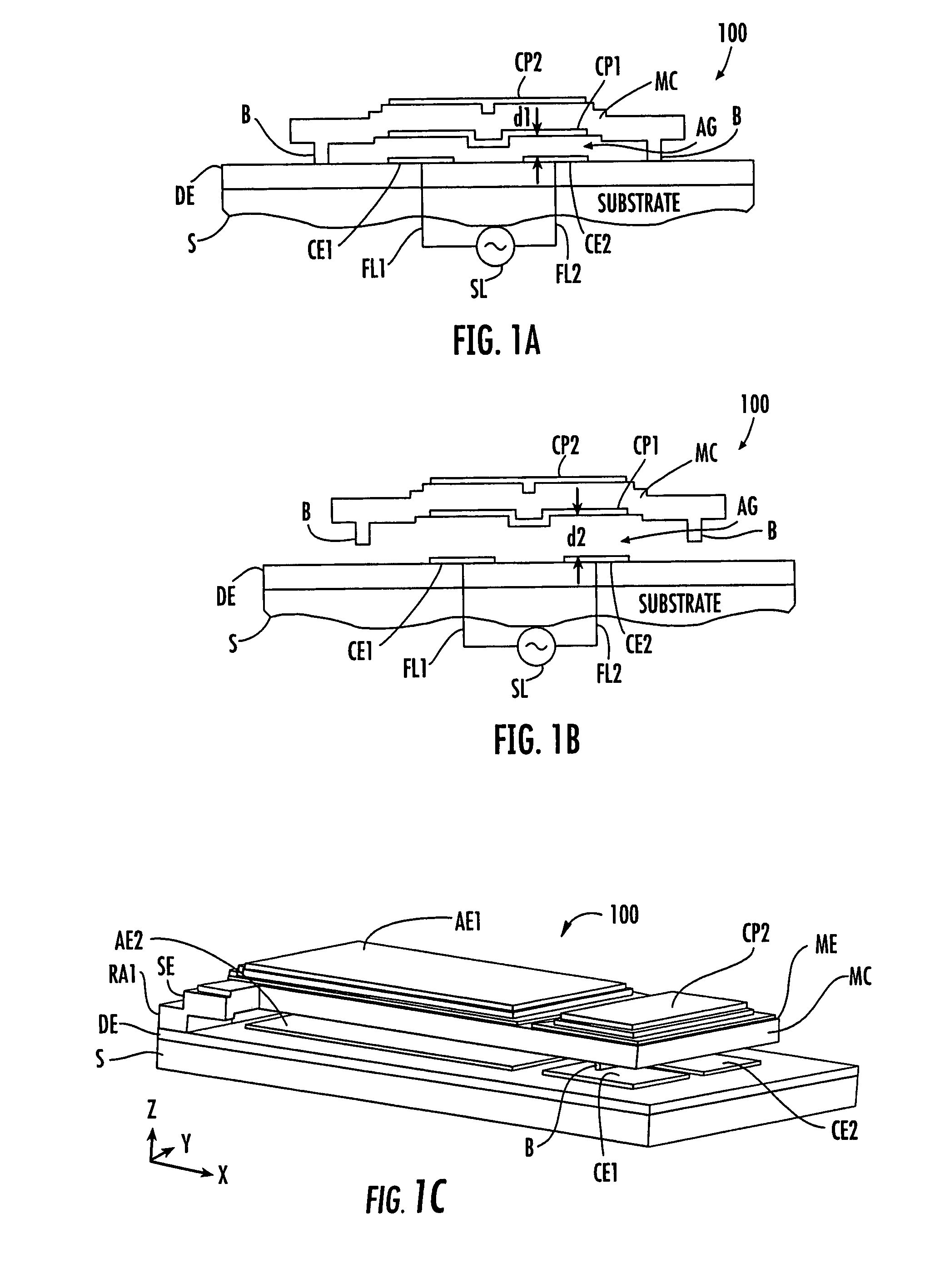
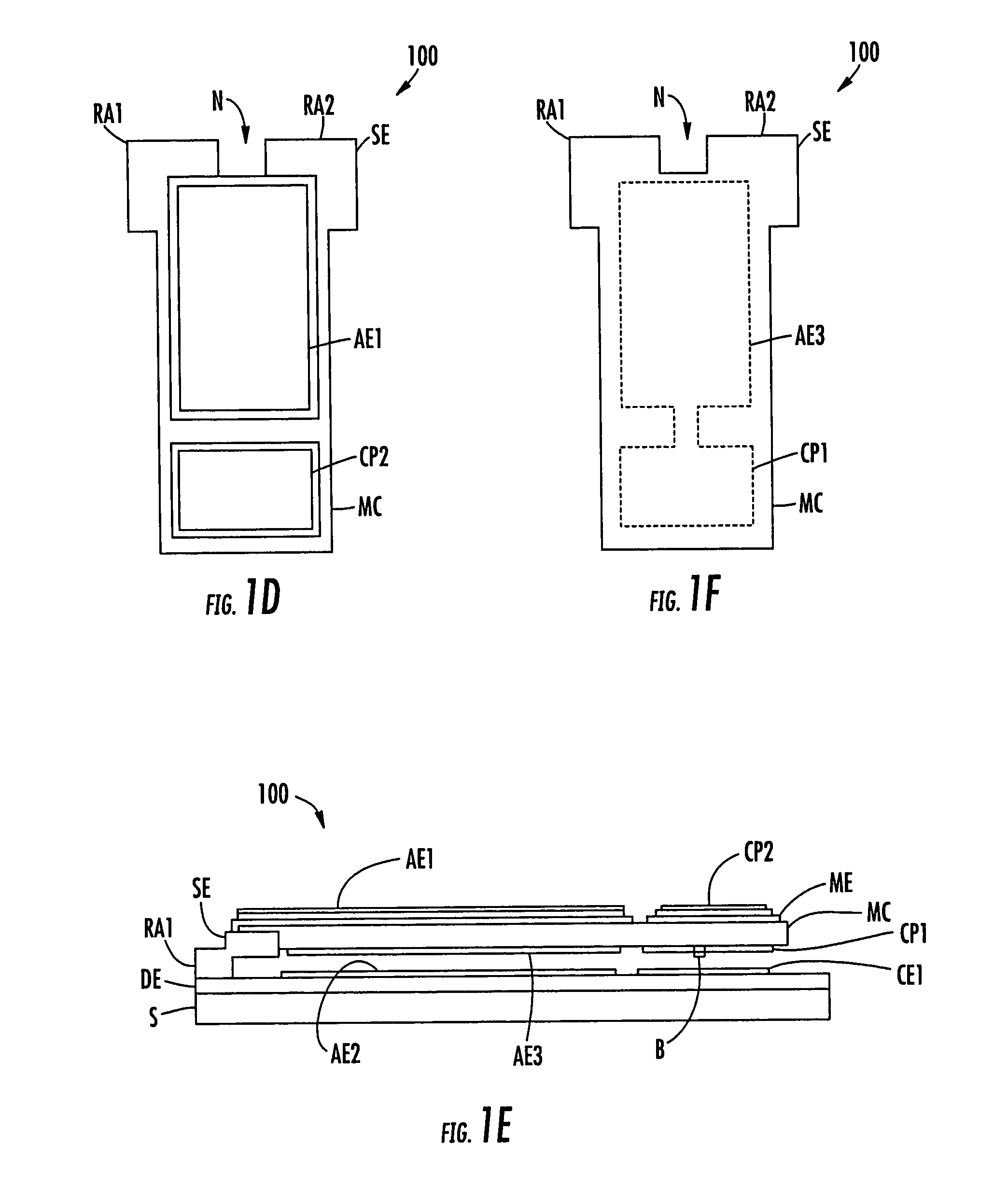
ActiveUS6909589B2Low loss tangentSimple processMechanically variable capacitor detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceClosed loop
A variable capacitor device using MEMS or micromachining techniques wherein thin-films of materials are deposited, patterned and etched to form movable micromechanical elements on the surface of a substrate composed of either semiconductor, glass, metal, or ceramic material. In one embodiment of the present invention to achieve higher frequency performance as well as other benefits, the substrate is comprised of Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramics (LTCC). The variable capacitor is an electrostatically actuated micromechanical device and if fabricated on a LTCC multi-layered substrate material has continuous electrical connections through the layers. The same LTCC substrate material can also be used to enclose the device by selectively removing a portion of the upper substrate so as to form a cavity. The two substrates are then bonded together to enclose and protect the variable capacitor. An integrated circuit can be incorporation onto the multi-level substrate structure to enable a electronic closed-loop controlled variable capacitor module. The integrated circuit is flip-chip bonded at the bottom of the substrate structure with appropriate electrical connections between the integrated circuit and the MEMS variable capacitor device. A variation of the present invention utilizes a zipper actuation method wherein the tuning ratio of the variable capacitor is increased to very high levels. Yet another variation of the present invention utilizes a differential gap between the top and bottom electrodes such that the actuation electrodes do not physically contact one another. Yet another implementation of the present invention uses an extra set of electrodes or mechanical mechanism so as to lock the value of the capacitor indefinitely. Yet another implementation uses shaped actuation electrodes so as to linearize the relationship between the applied actuation voltage and the resultant capacitance of the device.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitors and actuation components and related methods
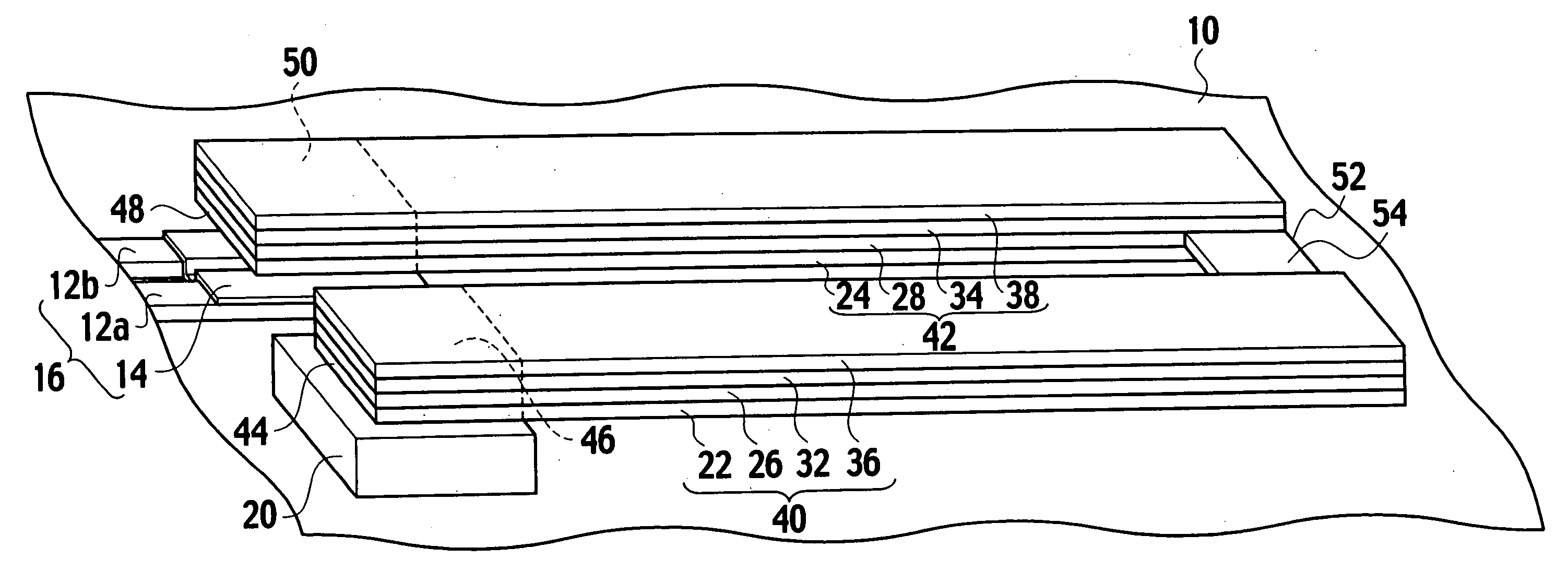
Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitors and actuation components and related methods are provided. A MEMS variable capacitor can include first and second feed lines extending substantially parallel to one another. Further, MEMS variable capacitors can include first and second capacitive plates being spaced apart from the first and second feed lines. The first and second capacitive plates can be separately movable with respect to at least one of the first and second feed lines for varying the capacitance between the first and second feed lines over a predetermined capacitance range.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
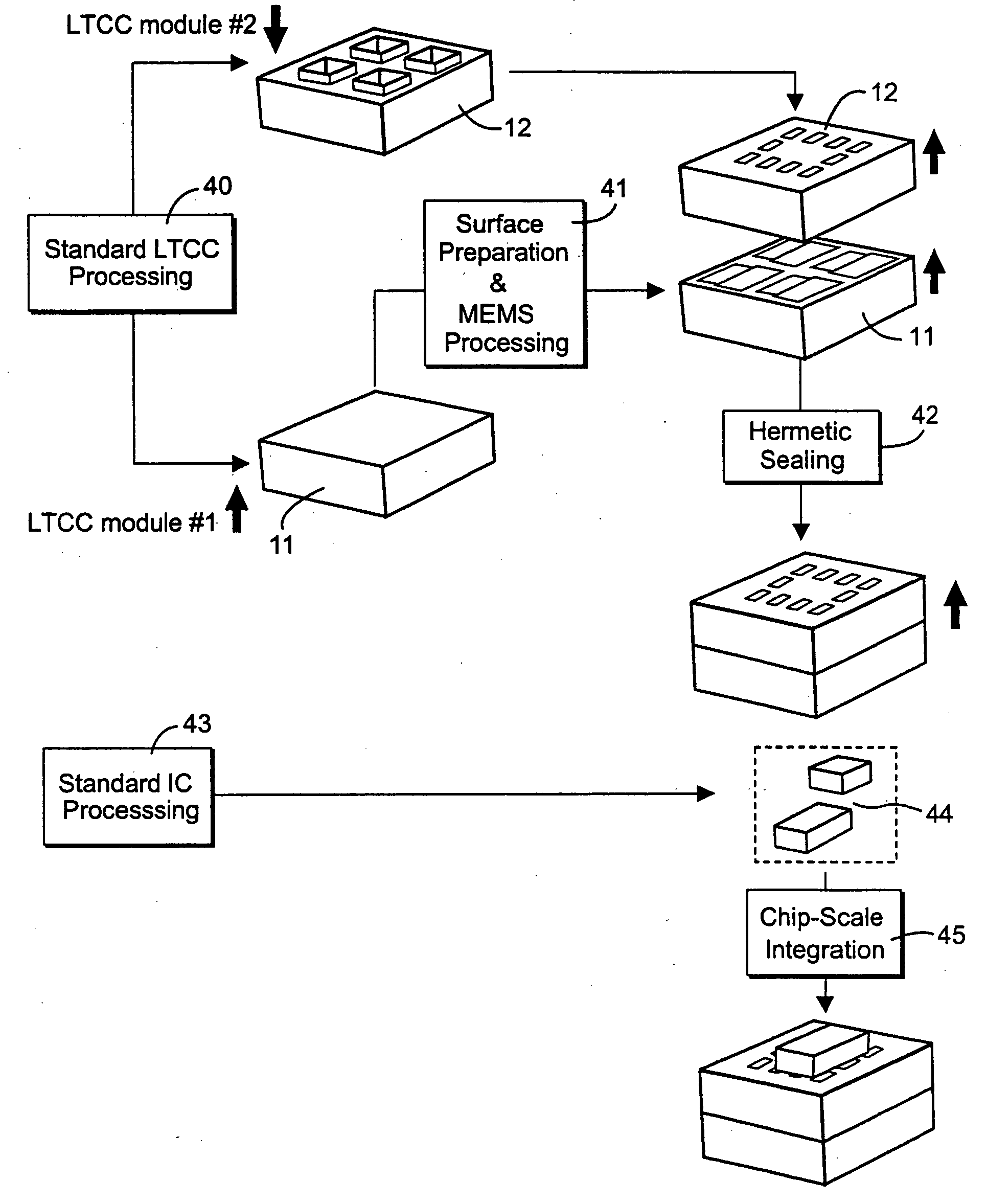
Method of fabricating radio frequency microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrates
InactiveUS20050161753A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricRadio frequency microelectromechanical system
A phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices and systems using microelectromechanical switches (“MEMS”) and low-temperature co-fired ceramic (“LTCC”) technology and a method of fabricating such phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices are disclosed. Each antenna or other type of device includes at least two multilayer ceramic modules and a MEMS device fabricated on one of the modules. Once fabrication of the MEMS device is completed, the two ceramic modules are bonded together, hermetically sealing the MEMS device, as well as allowing electrical connections between all device layers. The bottom ceramic module has also cavities at the backside for mounting integrated circuits. The internal layers are formed using conducting, resistive and high-k dielectric pastes available in standard LTCC fabrication and low-loss dielectric LTCC tape materials.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Capacitive micro-electro-mechanical sensors with single crystal silicon electrodes
ActiveUS7539003B2Mechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitor with electrode area variationIn planeAccelerometer
The devices presented herein are capacitive sensors with single crystal silicon on all key stress points. Isolating trenches are formed by trench and refill forming dielectrically isolated conductive silicon electrodes for drive, sense and guards. For pressure sensing devices according to the invention, the pressure port is opposed to the electrical wire bond pads for ease of packaging. Dual-axis accelerometers measuring in plane acceleration and out of plane acceleration are also described. A third axis in plane is easy to achieve by duplicating and rotating the accelerometer 90 degrees about its out of plane axis Creating resonant structures, angular rate sensors, bolometers, and many other structures are possible with this process technology. Key advantages are hermeticity, vertical vias, vertical and horizontal gap capability, single crystal materials, wafer level packaging, small size, high performance and low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
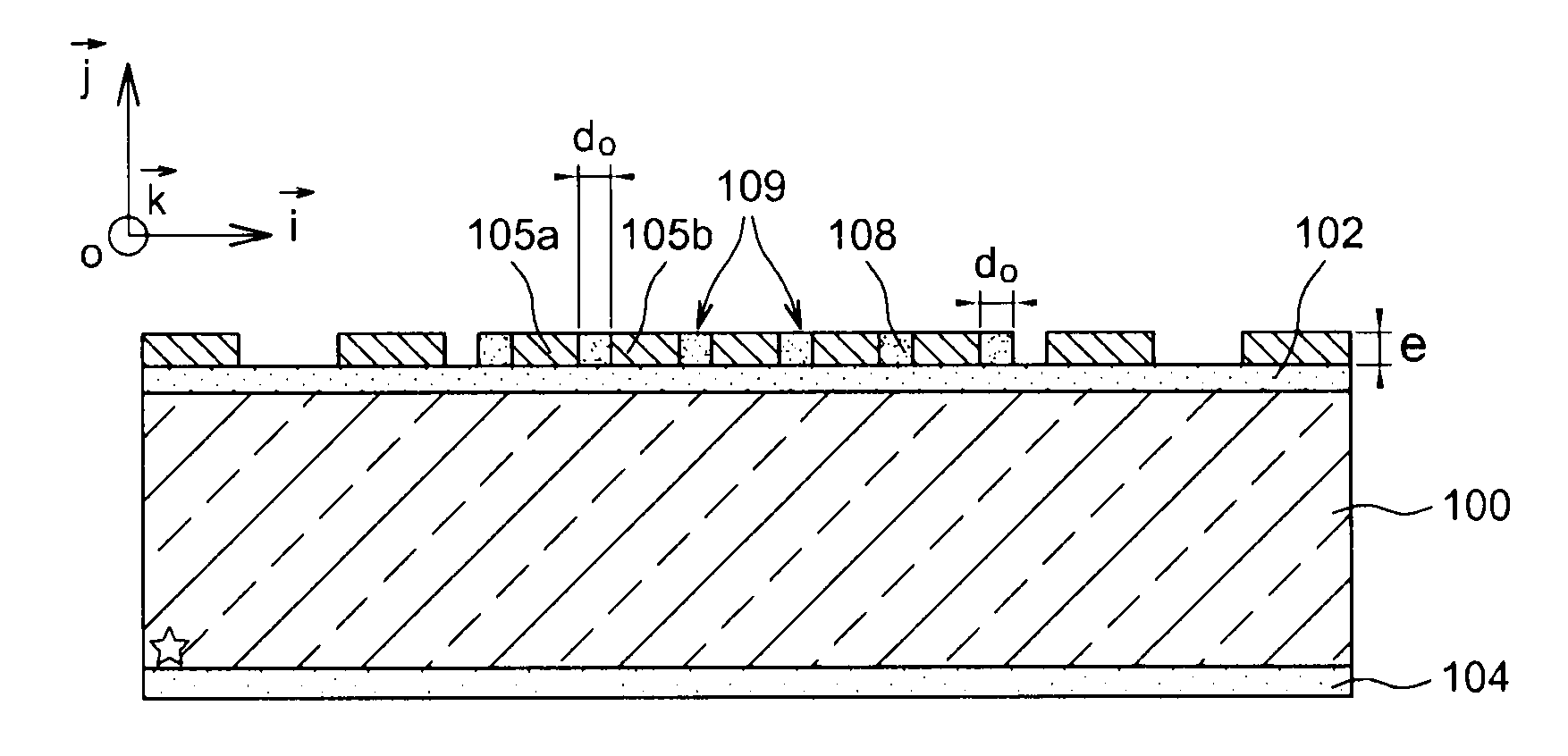
Micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20130056841A1Increase capacitanceReduce thicknessSemiconductor electrostatic transducersCapacitor with electrode distance variationMicro electrical mechanical systemsEngineering
A MEMS device includes a substrate. The substrate has a plurality of through holes in the substrate within a diaphragm region and optionally an indent space from the second surface at the diaphragm region. A first dielectric structural layer is then disposed over the substrate from the first surface, wherein the first dielectric structural layer has a plurality of openings corresponding to the through holes, wherein each of the through holes remains exposed by the first dielectric structural layer. A second dielectric structural layer with a chamber is disposed over the first dielectric structural layer, wherein the chamber exposes the openings of the first dielectric structural layer and the through holes of the substrate to connect to the indent space. A MEMS diaphragm is embedded in the second dielectric structural layer above the chamber, wherein an air gap is formed between the substrate and the MEMS diaphragm.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
Device with beam structure, and semiconductor device
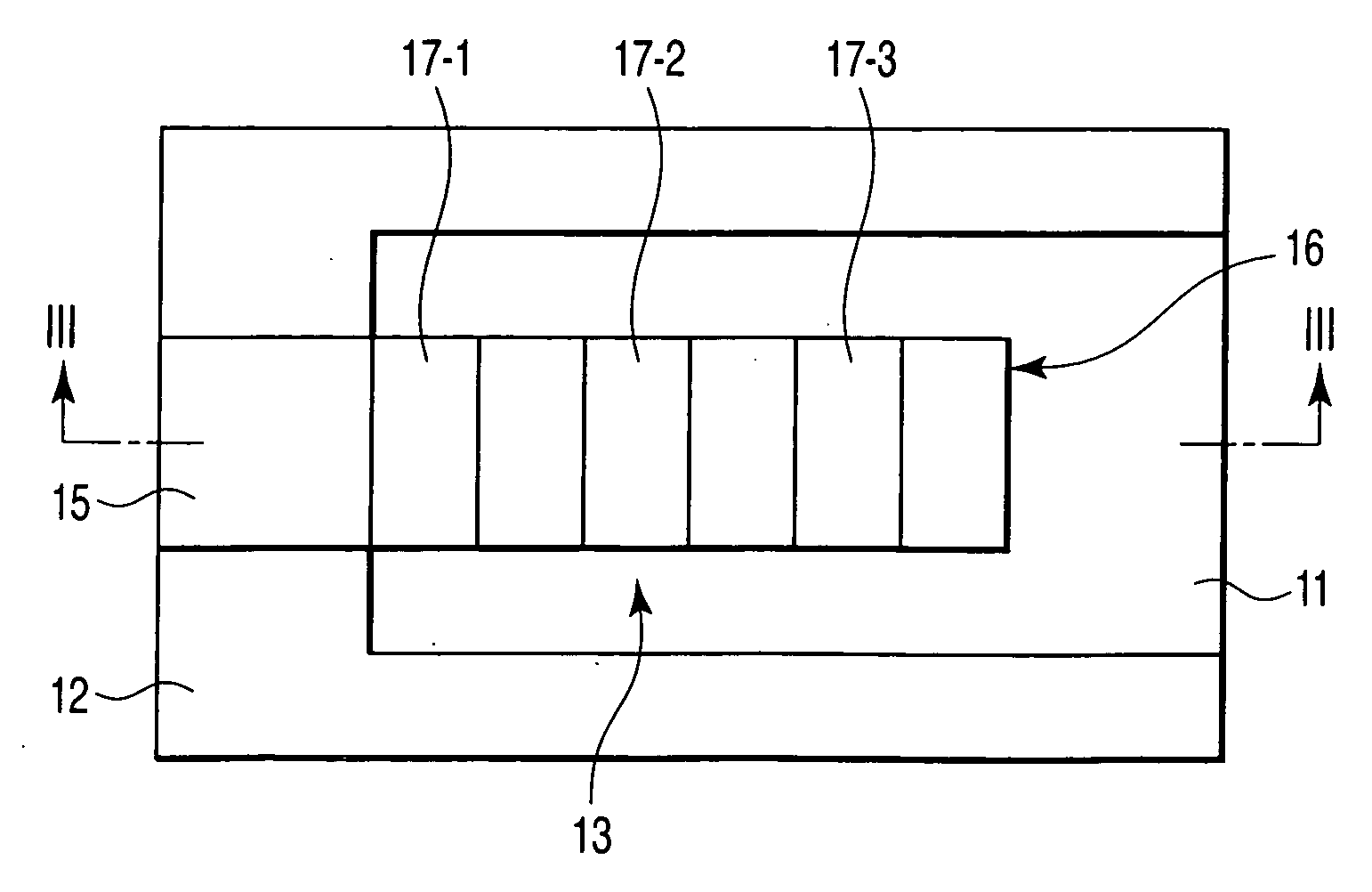
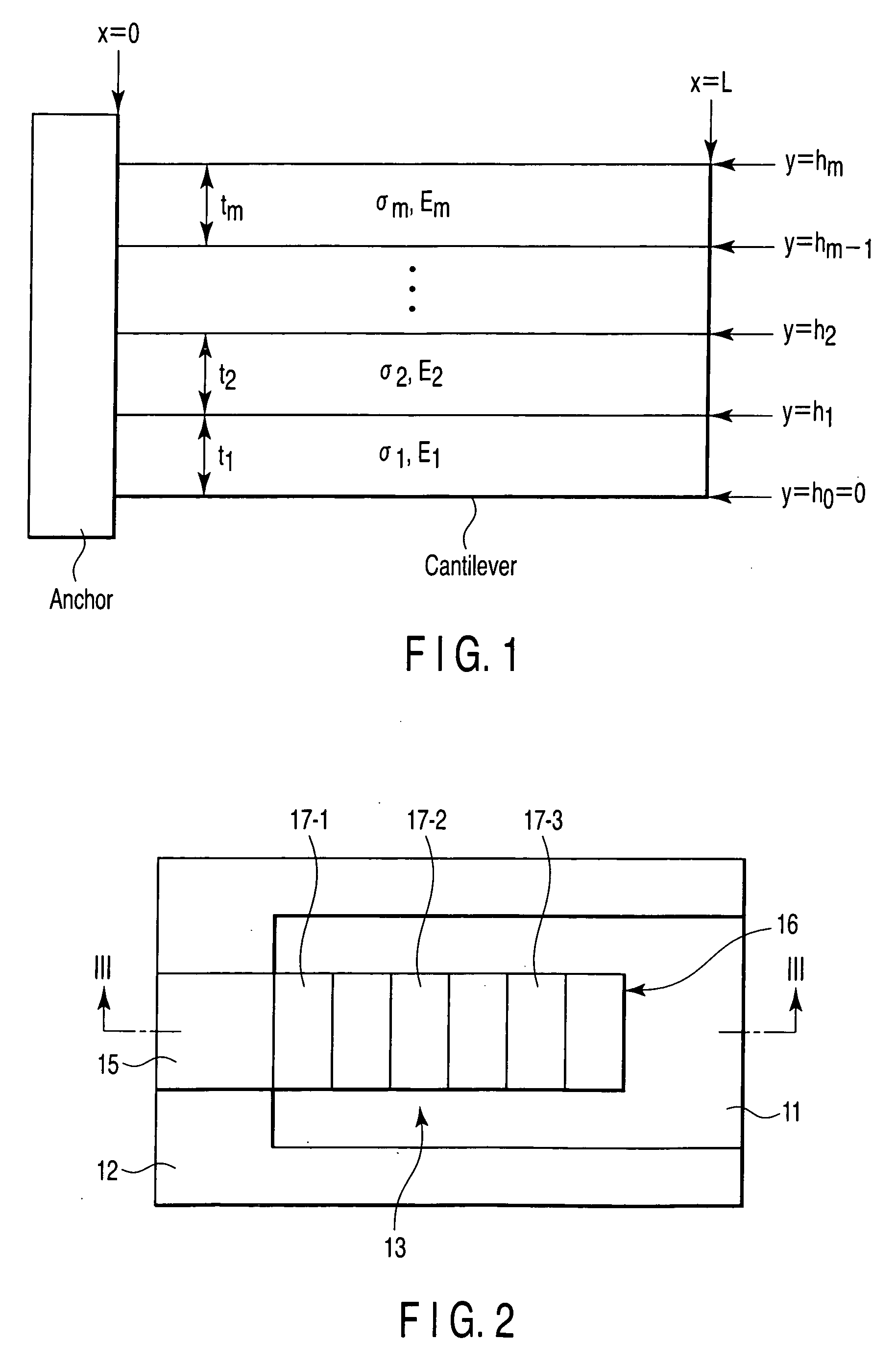
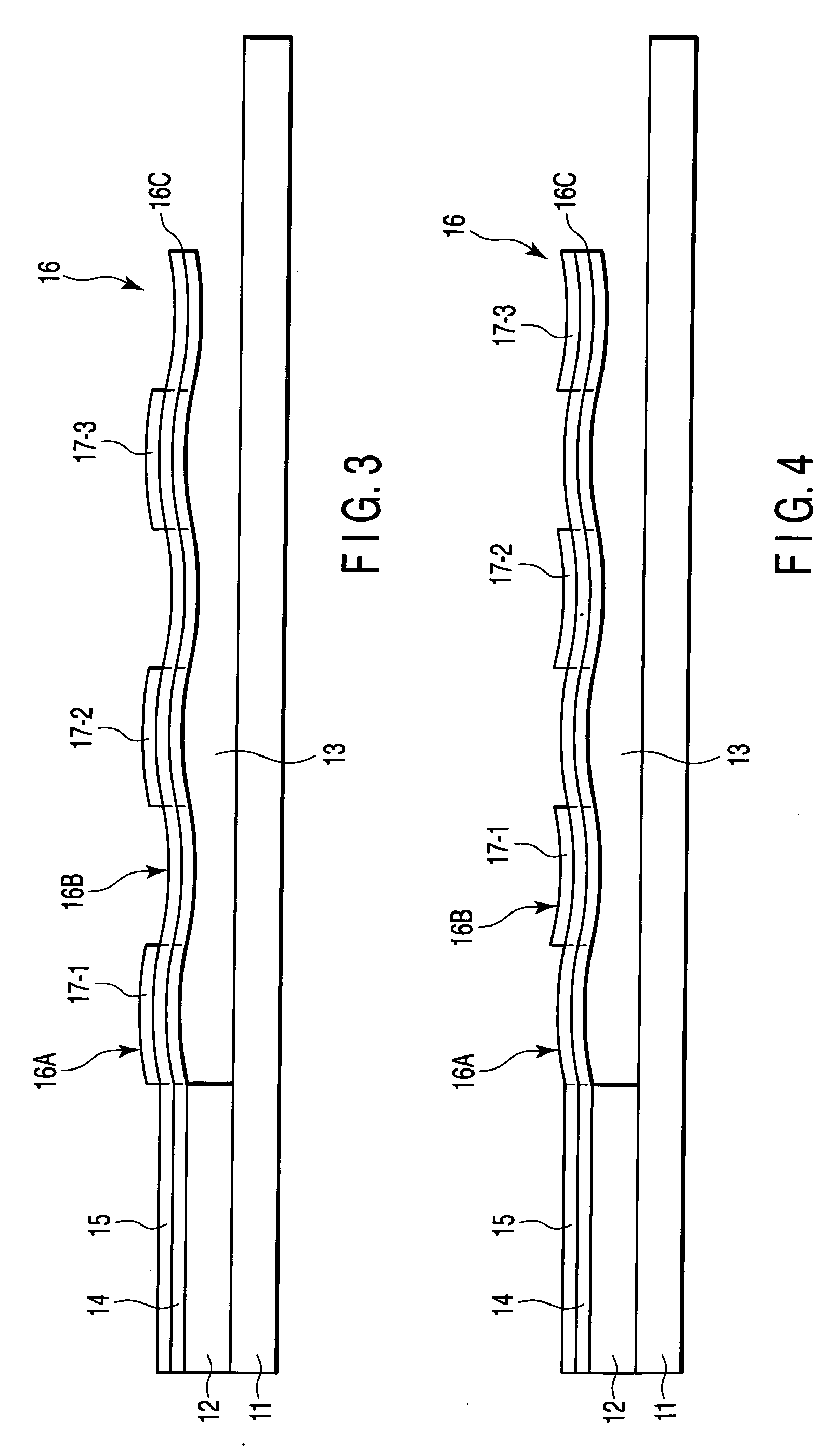
InactiveUS20070138608A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitor with electrode distance variationDevice materialEngineering
A device with a beam structure includes a substrate, an anchor and a cavity which are provided on and over the substrate, respectively, and a beam structure which is provided on the anchor and over the cavity, extends in a first direction and includes a plurality of convex portions and a plurality of concave portions, each of the convex portions having such a stress gradient as to provide a convex warp, and each of the concave portions having such a stress gradient as to provide a concave warp. The convex portions and the concave portions are alternately repeatedly arranged.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Capacitive humidity detector with nanoporous hydrophilic dielectric
InactiveUS20110179861A1High sensitivityImprove hydrophilicityCapacitor with electrode distance variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricAcoustics
A humidity sensor of capacitive type, a device for detecting or measuring humidity including the sensor, and a method to fabricate the sensor. The humidity sensor includes at least one nanoporous dielectric material positioned between at least one first electrode of a capacitor and at least one second electrode of the capacitor.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Stepping actuator and method of manufacture therefore
InactiveUS7265477B2Reduce air gapReduce pull-in voltageElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitor with electrode distance variationParallel plateActuator
An embodiment of the present invention provides a stepping actuator, comprising a suspended membrane comprising a plurality of movable electrodes connected by plurality of spring hinges to a payload platform; and anchors connecting said membrane to a substrate, said substrate comprising a plurality of fixed electrodes; wherein said movable electrodes of said suspended membrane and said fixed electrodes from said substrate form parallel-plate electrostatic sub-actuators.
Owner:WAN CHANG FENG
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com