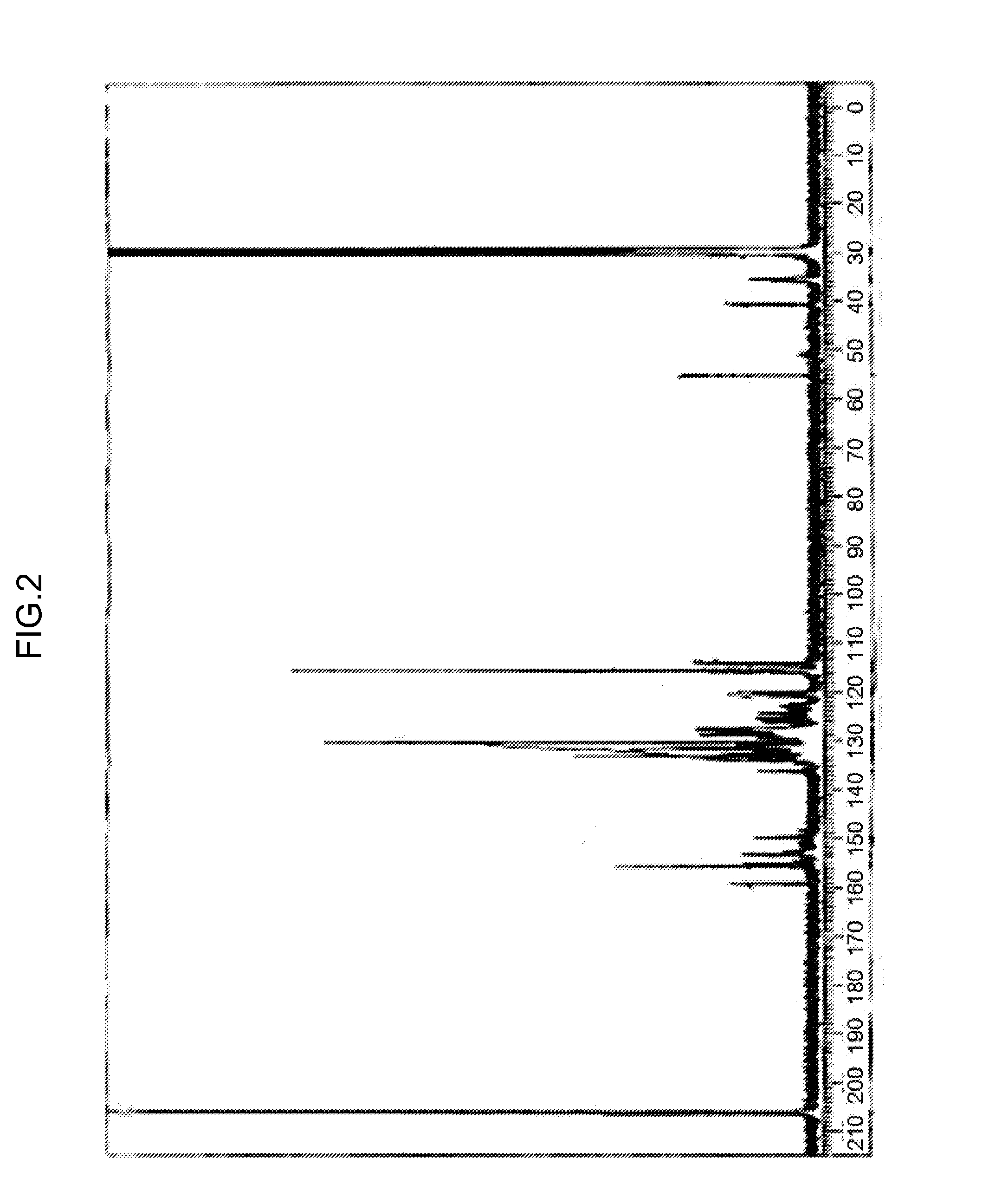
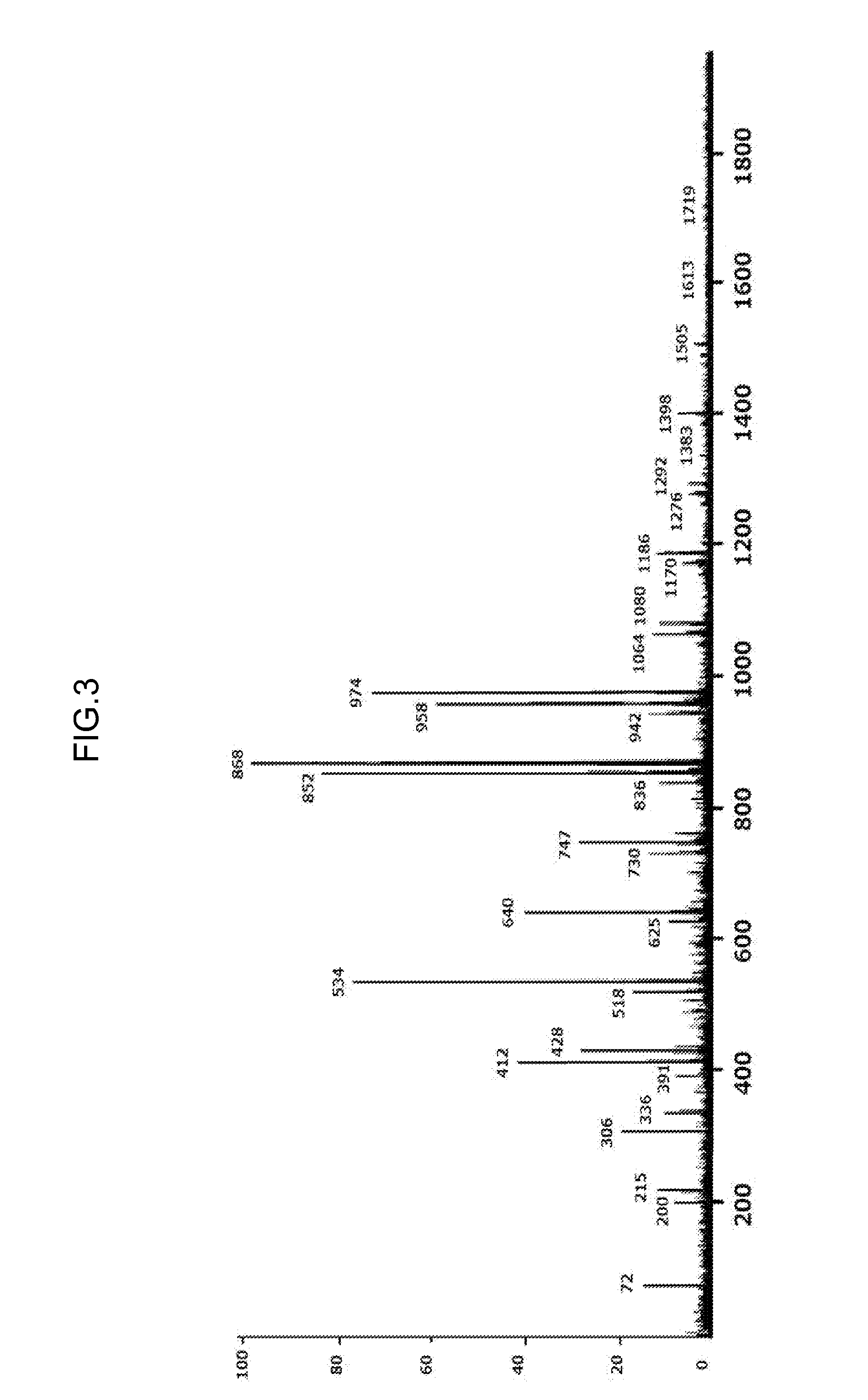
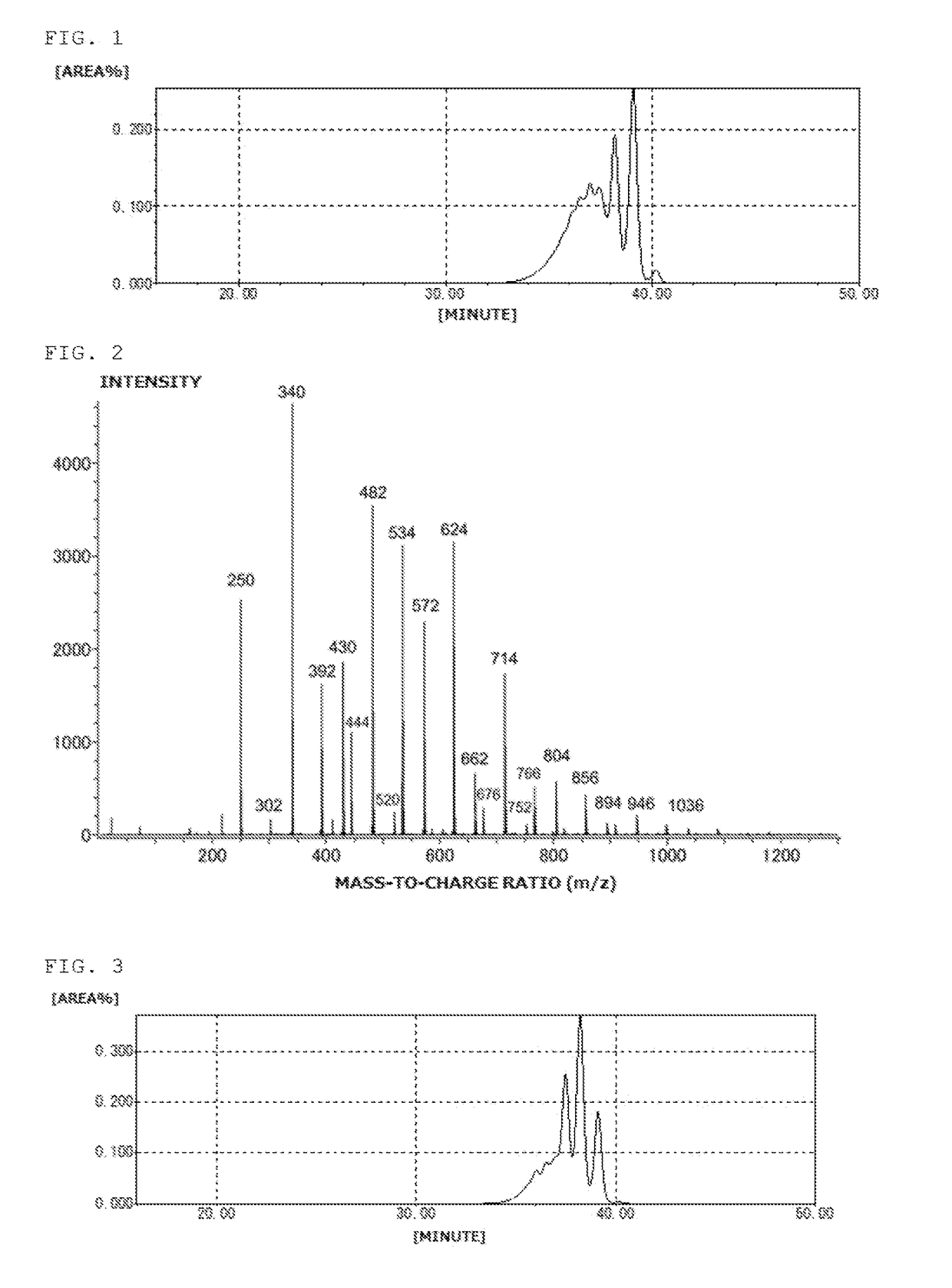
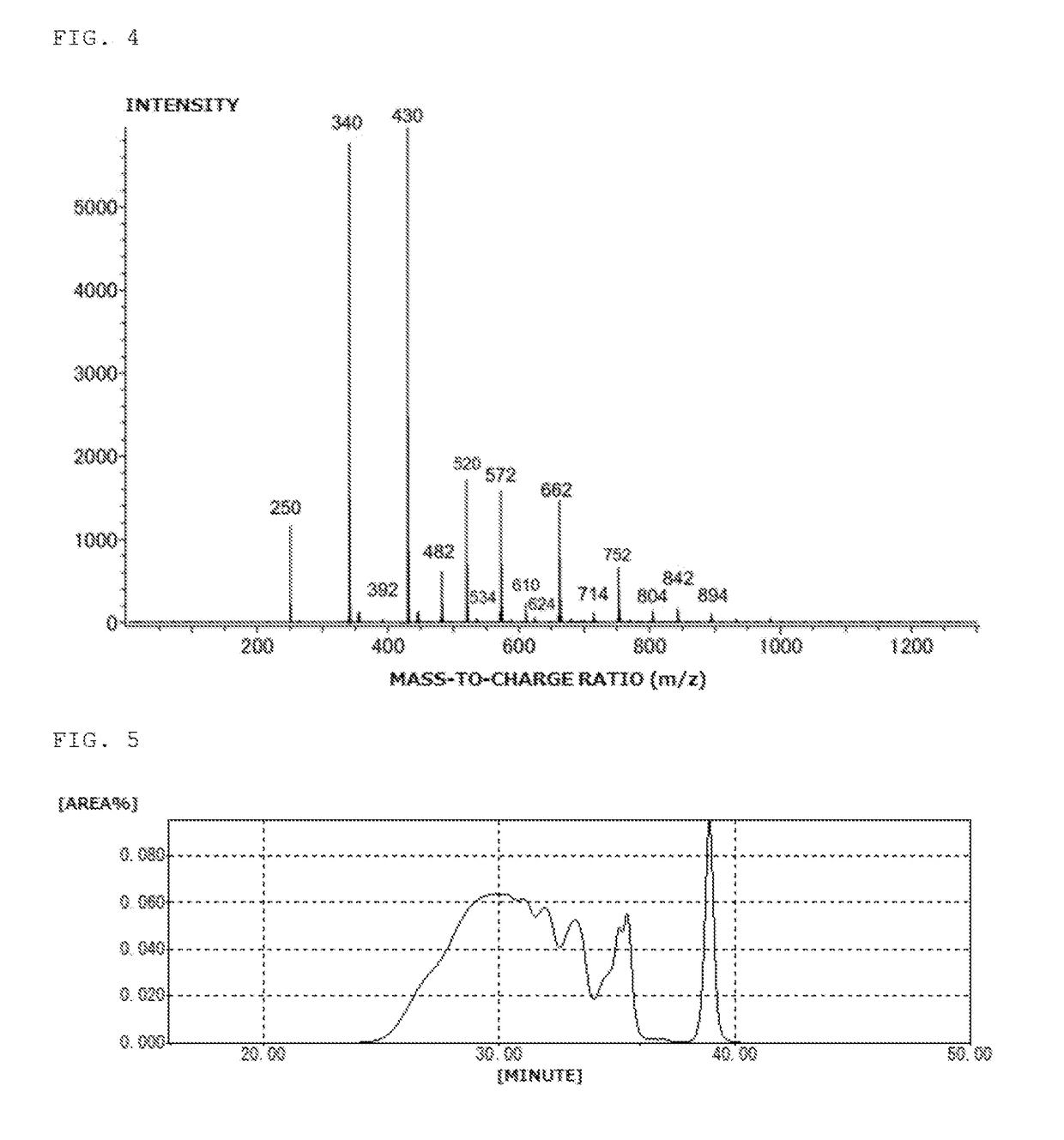
Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Low loss tangent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
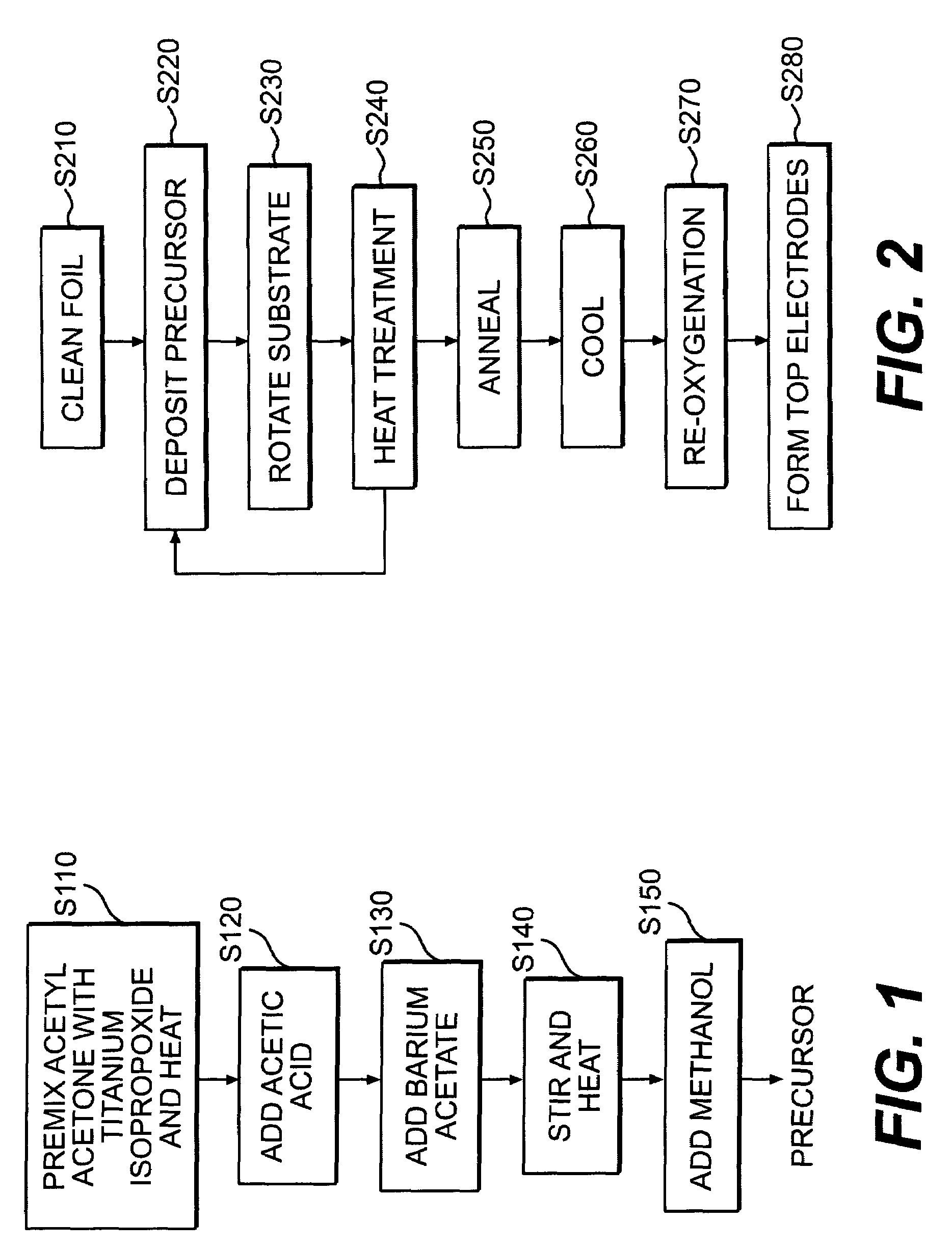
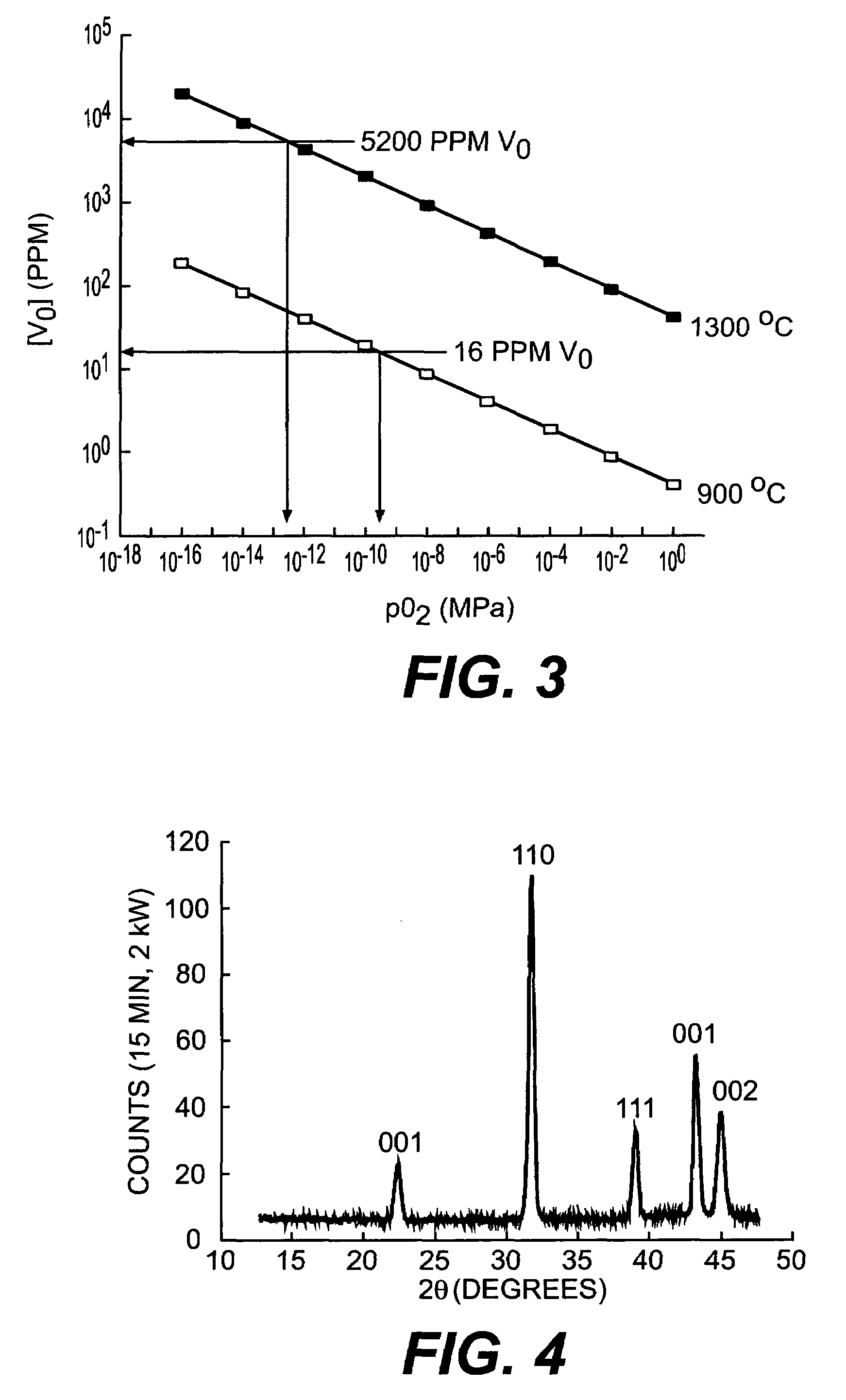
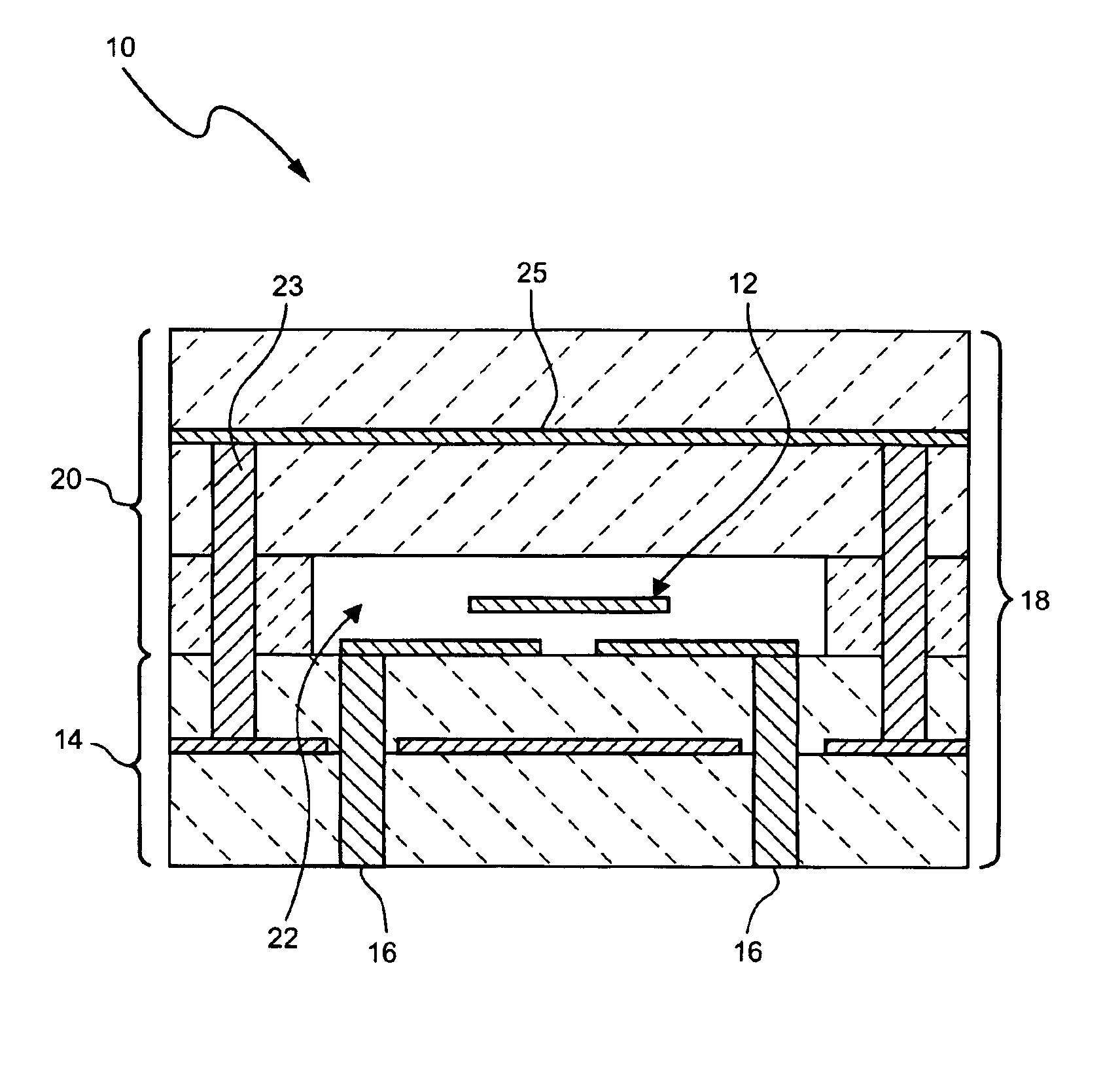
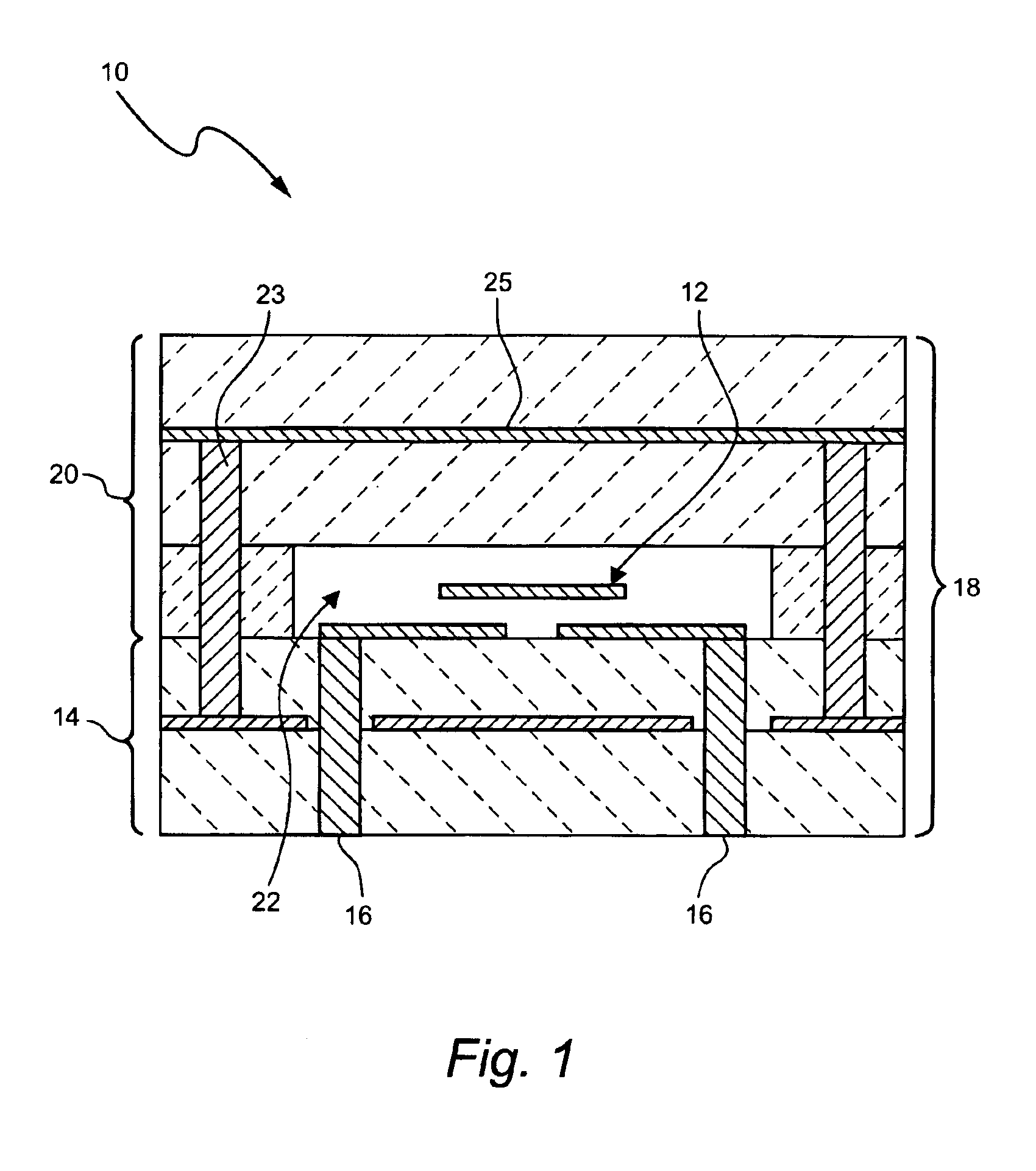
Thin film dielectrics for capacitors and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20050011857A1Increase capacitance densityLow loss tangentFixed capacitor dielectricPrinted circuit aspectsCopper foilHigh dielectric permittivity
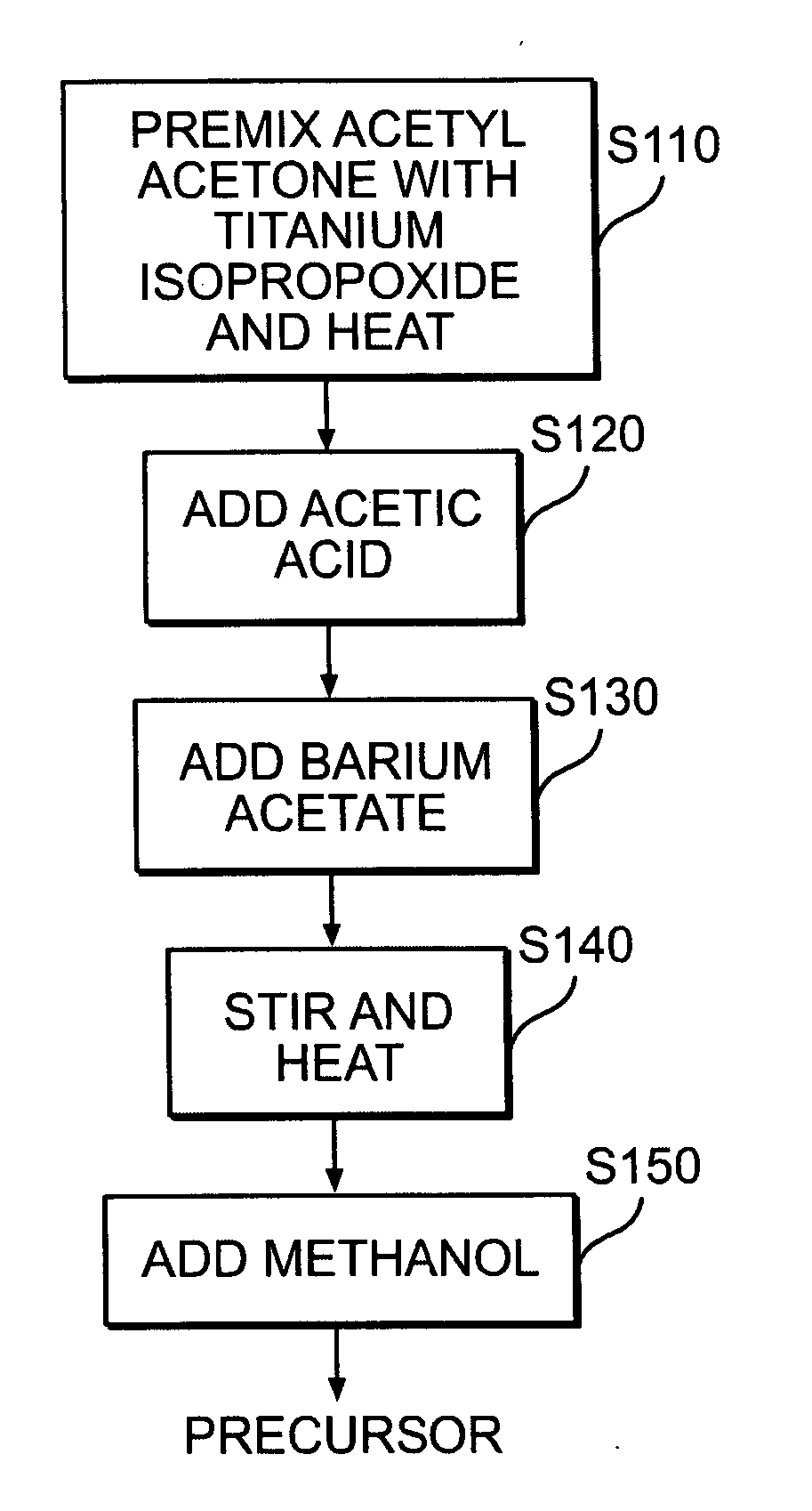
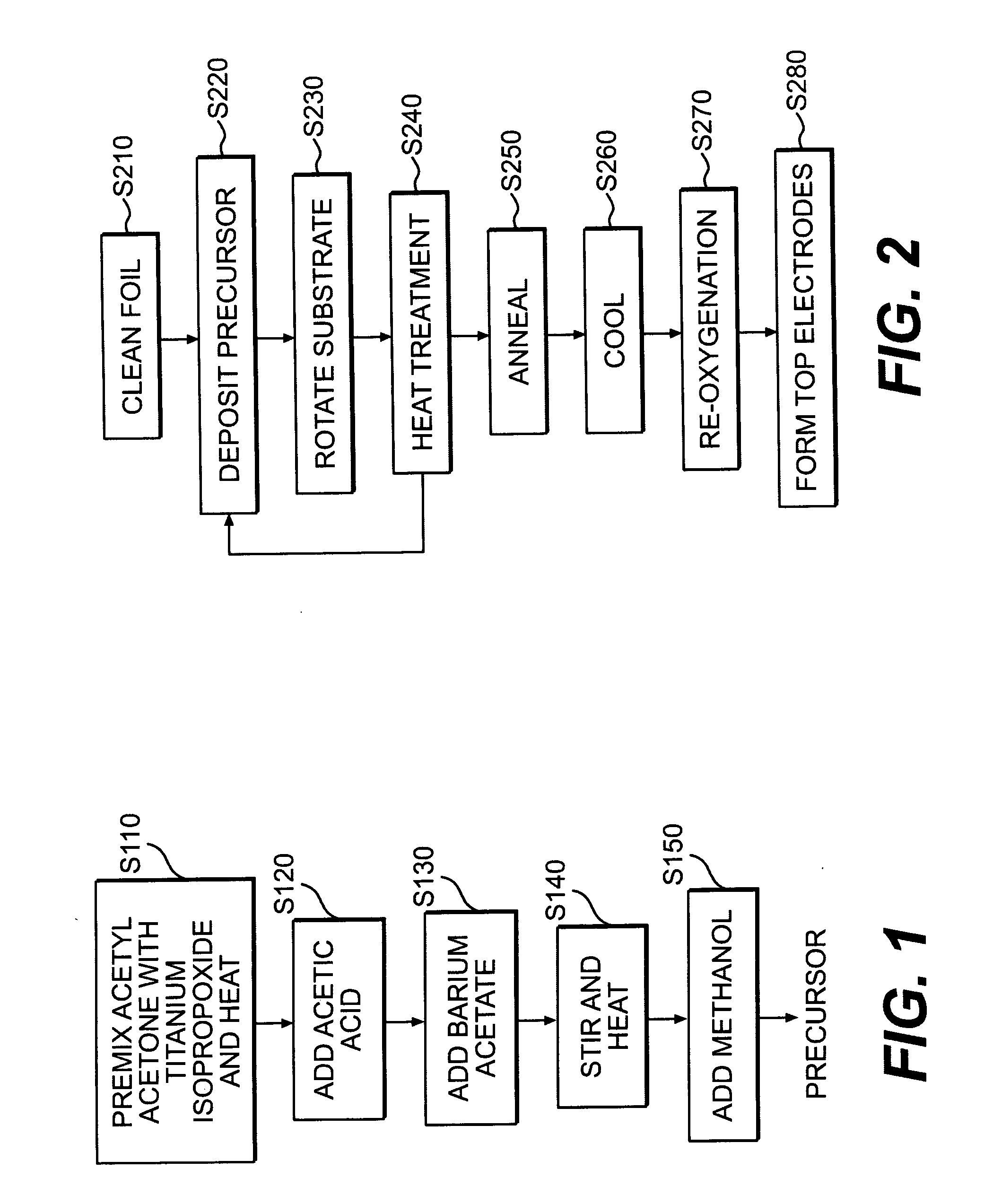
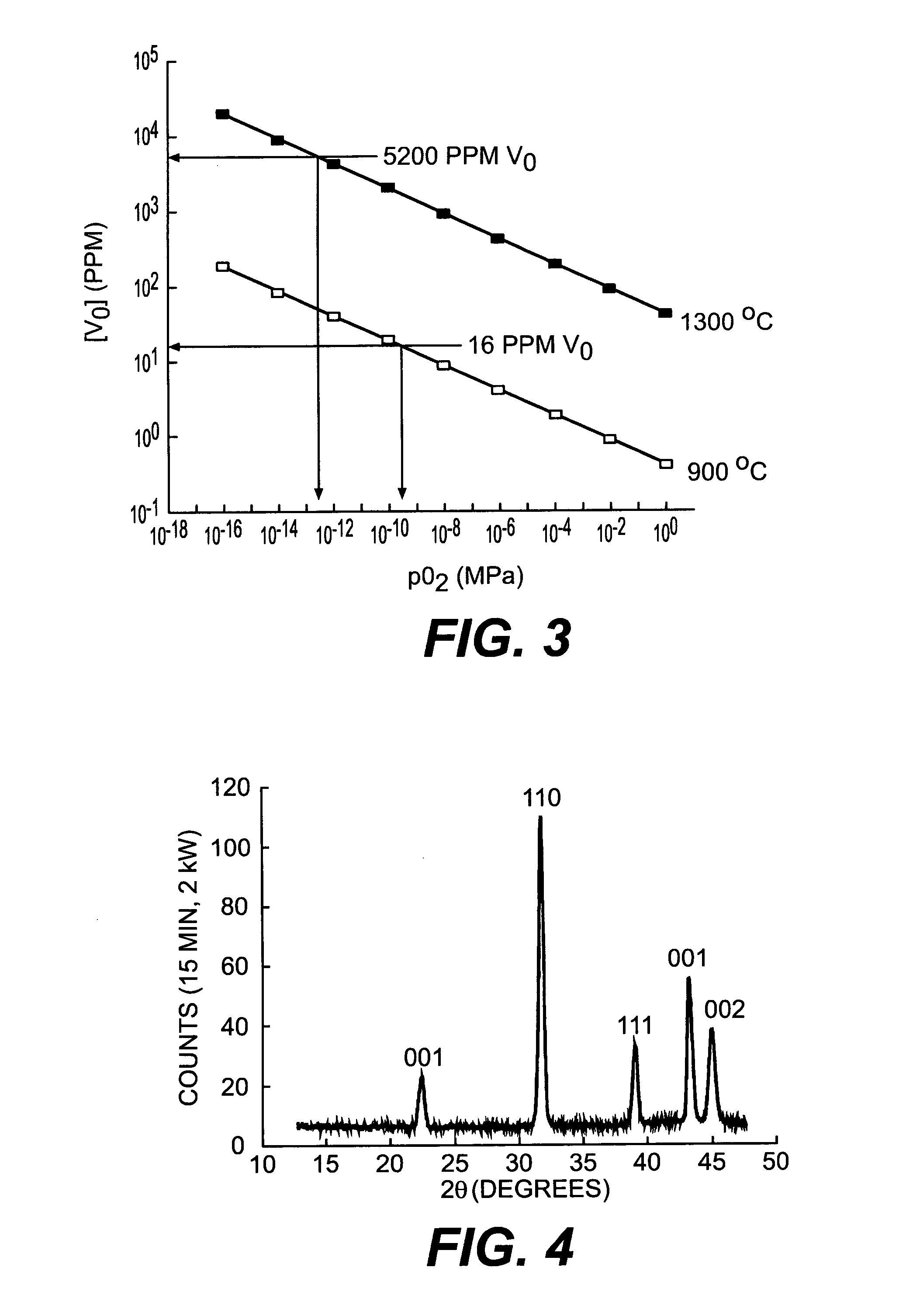
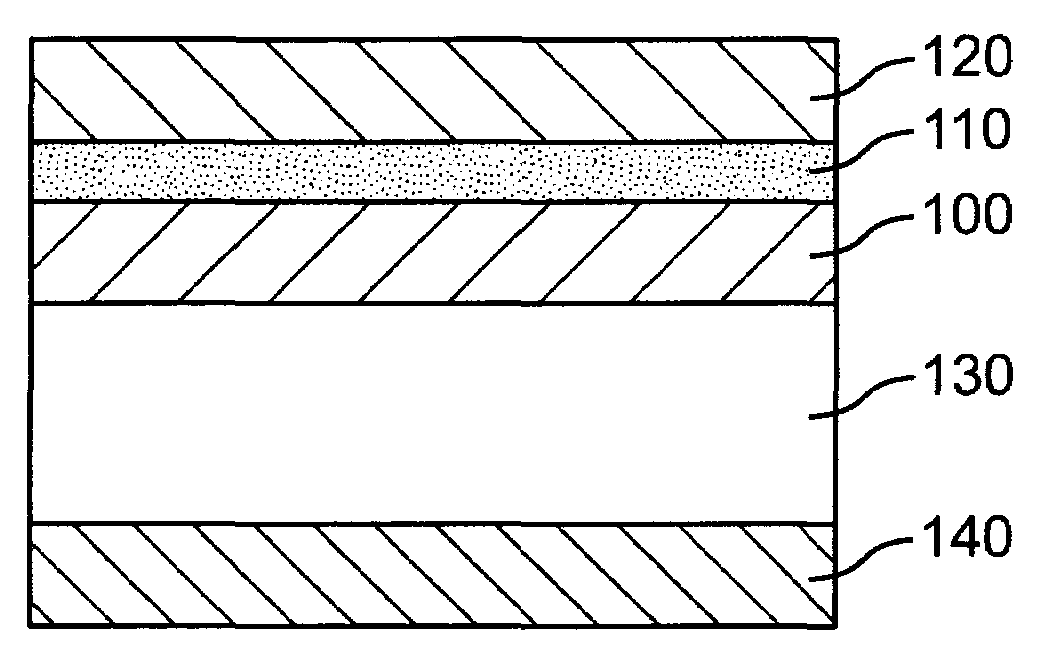
Dielectrics are formed having high dielectric constants, low loss tangents, and other desirable electrical and physical properties. The dielectrics are annealed at temperatures allowing the use of copper foil substrates, and at low oxygen partial pressures.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Thin film dielectrics for capacitors and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS7029971B2Increase capacitance densityLow loss tangentFixed capacitor dielectricPrinted circuit aspectsDielectricCopper foil
Dielectrics are formed having high dielectric constants, low loss tangents, and other desirable electrical and physical properties. The dielectrics are annealed at temperatures allowing the use of copper foil substrates, and at low oxygen partial pressures.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
MEMS-based variable capacitor
ActiveUS6909589B2Low loss tangentSimple processMechanically variable capacitor detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceClosed loop
A variable capacitor device using MEMS or micromachining techniques wherein thin-films of materials are deposited, patterned and etched to form movable micromechanical elements on the surface of a substrate composed of either semiconductor, glass, metal, or ceramic material. In one embodiment of the present invention to achieve higher frequency performance as well as other benefits, the substrate is comprised of Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramics (LTCC). The variable capacitor is an electrostatically actuated micromechanical device and if fabricated on a LTCC multi-layered substrate material has continuous electrical connections through the layers. The same LTCC substrate material can also be used to enclose the device by selectively removing a portion of the upper substrate so as to form a cavity. The two substrates are then bonded together to enclose and protect the variable capacitor. An integrated circuit can be incorporation onto the multi-level substrate structure to enable a electronic closed-loop controlled variable capacitor module. The integrated circuit is flip-chip bonded at the bottom of the substrate structure with appropriate electrical connections between the integrated circuit and the MEMS variable capacitor device. A variation of the present invention utilizes a zipper actuation method wherein the tuning ratio of the variable capacitor is increased to very high levels. Yet another variation of the present invention utilizes a differential gap between the top and bottom electrodes such that the actuation electrodes do not physically contact one another. Yet another implementation of the present invention uses an extra set of electrodes or mechanical mechanism so as to lock the value of the capacitor indefinitely. Yet another implementation uses shaped actuation electrodes so as to linearize the relationship between the applied actuation voltage and the resultant capacitance of the device.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Heavy duty tire
InactiveUS20070151649A1Reduce rolling resistanceDurability can be prevented being deterioratedSpecial tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsRolling resistanceEngineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Rubber Composition and Pneumatic Tire Using Same
ActiveUS20080289740A1High storage modulusHigh modulusSpecial tyresInflatable tyresConjugated dienePolystyrene
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Low loss glass-ceramic materials, method of making same and electronic packages including same
InactiveUS20050266252A1Low loss tangentHigh quality factorLayered product treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal expansionElectronic packaging
A glass-ceramic is provided having a thermal expansion coefficient in a range of 3-6 ppm / ° C., a dielectric constant that is less than 5 and a Quality factor Q of at least 400. The glass-ceramic consists essentially of SiO2 in a range of 45-58 wt %, Al2O3 in a range of 10-18 wt % and MgO in a range of 10-25 wt %. A method of making the glass-ceramic is also provided. Further, an electronic package is also provided, including a base member and a glass-ceramic substrate bonded to the base member.
Owner:KNOWLES CAZENOVIA
Ferroelectric nanocomposite based dielectric inks for reconfigurable RF and microwave applications
ActiveUS20170009090A1Low loss tangentAntenna arraysPrinted circuit detailsDielectricSemiconductor materials
A novel ferroelectric ink comprising multiphase Barium Strontium Titanate (BST) in a polymer composite is described. The ink can be employed using direct-ink writing techniques to print high dielectric constant, low loss, and electrostatically-tunable dielectrics on substrates. The substrates can be flexible such as plastics or rigid, such as substrates comprising semiconductor materials or ceramics and the like. The dielectric ink is made by suspending pre-sintered nano / submicron-sized particles of BST in a thermoplastic polymer with a solvent. After printing with the ink, a low temperature curing process is performed at temperatures below 200° C., a temperature too low to sinter BST. Fully printed devices, such as a varactor and a phase shifter using direct ink writing methodologies are described.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Glass-ceramic materials and electronic packages including same
InactiveUS20050266251A1Sufficient densificationLow melting pointSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionGlass-ceramic
A glass-ceramic is provided having a thermal expansion coefficient in a range of 4.0 to 8.5 ppm / ° C., a dielectric constant in a range of 5-7 and a Quality factor Q of at least 400. The glass-ceramic consists essentially of SiO2 in a range of 40-55 wt %, Al2O3 in a range of 7-22 wt %, MgO in a range of 6 to less than 26 wt %, and at least one of BaO in an amount up to 35 wt %, SrO in an amount up to 37 wt % and ZnO in an amount up to 17 wt %. An electronic package is also provided, including one of a metal and sintered ceramic base member and a glass-ceramic substrate bonded to the base member.
Owner:KNOWLES CAZENOVIA
Rubber composition and application thereof
ActiveCN105778179AGood physical and mechanical propertiesGood workmanshipBuilding insulationsPolymer scienceAdjuvant
The invention relates to a rubber composition. The rubber composition is prepared from the ingredients in parts by mass: 80-120 parts of crude rubber, 1-5 parts of peroxide initiator, 2-15 parts of bridging agent, 0.1-1 part of free-radical absorption and release regulator and reinforcing and anti-aging agents, wherein the crude rubber comprises any one to any three of polybutadiene rubber, natural rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber and accounts for 70 percent or more of mass of the crude rubber. According to the rubber composition and the application thereof, a formula of the rubber composition and adjuvants for product cross-linking and the like is provided, so that the requirements of a technical scheme for representatives, i.e., tires, shoe materials and wear resisting plates on good properties and good industrial adaptability effect can be met; cost and environmentally-friendliness can be taken into account simultaneously.
Owner:NANJING SIKAI RUBBER & PLASTIC PROD CO LTD
Methods and compositions for dielectric materials
ActiveUS20060281864A1Low dielectric constantGood dimensional stabilityDielectric materialsSynthetic resin layered productsComposite structureBelow sea level
The present invention comprises methods and compositions of dielectric materials. The dielectric materials of the present invention comprise materials having a dielectric constant of more than 1.0 and less than 1.9 and / or a dissipation factor of less than 0.0009. Other characteristics include the ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from both high temperatures of approximately +260° C. to low temperatures of approximately −200° C., operate in wide range of atmospheric conditions and pressures (e.g., a high atmosphere, low vacuum condition such as that found in the outer-space as well as conditions similar to those found at sea level or below sea level). The dielectric materials of the present invention may be used in the manufacture of composite structures that can be used alone or in combination with other materials, and can be used in electronic components or devices such as RF interconnects.
Owner:NELSON KEVIN G
High frequency film transmission line, antenna including the same and antenna-integrated image display device
ActiveUS20200076035A1Loss levelingSignal lossLiquid crystal compositionsPrinted circuit detailsCyclo olefin polymerDielectric layer
A film transmission line includes a dielectric layer including at least one of a liquid crystal polymer (LCP) structure or a cyclo olefin polymer (COP) structure, and an electrode line on the dielectric layer. A signal loss level (S21) defined of the film transmission line is −1.5 dB or more at a frequency in a range from 20 GHz to 30 GHz. The film transmission line may be applied to a high frequency thin film antenna and an image display device.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD
Methods and compositions for dielectric materials
InactiveUS20060210806A1Low dielectric constantLow loss tangentDielectric materialsSynthetic resin layered productsThermodynamicsElectronic component
The present invention comprises methods and compositions of dielectric materials. The dielectric materials of the present invention comprise materials having a dielectric constant of more than 1.0 and less than 1.9, or a dissipation factor of less than 0.0009, or a material having a dielectric constant of more than 1.0 and less than 1.9, and a dissipation factor of less than 0.0009. Other characteristics include the ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from both high temperatures of approximately +260° C. to low temperatures of approximately −200° C., operate in wide range of atmospheric conditions and pressures, such as a high atmosphere, low vacuum such as found in outer space as well as at sea level or below sea level, and is used in the manufacture of composite structures that can be used alone or in combination with other materials, and can be used in electronic components or devices.
Owner:NELSON KEVIN G
Glass-ceramic materials and electronic packages including same
InactiveUS7186461B2Easy to customizeLow loss tangentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionGlass-ceramic
Owner:KNOWLES CAZENOVIA
Dielectric waveguide line
ActiveUS20180040936A1High dielectric constantLoss tangentResistance/reactance/impedenceWaveguidesPermittivityMaterials science
The present invention provides a dielectric waveguide having excellent transmission efficiency. The dielectric waveguide includes a polytetrafluoroethylene molded article that has a permittivity of 2.05 or higher at 2.45 GHz or 12 GHz, a loss tangent of 1.20×10−4 or lower at 2.45 GHz or 12 GHz, and a hardness of 95 or higher.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20170217258A1Low loss tangentEasy maintenanceHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Methods and compositions for dielectric materials
ActiveUS7498392B2Low dielectric constantReduce absorptionDielectric materialsSynthetic resin layered productsElectricityElectronic component
The present invention comprises methods and compositions of dielectric materials. The dielectric materials of the present invention comprise materials having a dielectric constant of more than 1.0 and less than 1.9 and / or a dissipation factor of less than 0.0009. Other characteristics include the ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from both high temperatures of approximately +260° C. to low temperatures of approximately −200° C., operate in wide range of atmospheric conditions and pressures (e.g., a high atmosphere, low vacuum condition such as that found in the outer-space as well as conditions similar to those found at sea level or below sea level). The dielectric materials of the present invention may be used in the manufacture of composite structures that can be used alone or in combination with other materials, and can be used in electronic components or devices such as RF interconnects.
Owner:NELSON KEVIN G
Rubber composition and pneumatic tire using the same
InactiveUS8030406B2High modulusReduce heat buildupSpecial tyresInflatable tyresPolymer sciencePolystyrene
This invention relates to a rubber composition having a high storage modulus (G′) and a low loss tangent (tan δ), and more particularly to a rubber composition comprising 2 to 60 parts by mass of a low-molecular weight aromatic vinyl compound-conjugated diene compound copolymer (B) having an aromatic vinyl compound content of 5 to 80% by mass, a vinyl bond content in a conjugated diene compound portion of 5 to 80% by mass, a weight average molecular weight as measured through a gel permeation chromatography and converted to polystyrene of 5,000 to 500,000 and at least one functional group based on 100 parts by mass of a rubber component (A) composed of at least one of natural rubber and synthetic diene-based rubbers.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Porous glass ceramic material, preparation method and prepared metamaterial substrate
ActiveCN102603192AThe preparation method is scientific and reasonableLow dielectric constantAntennasLow-k dielectricPorous glass
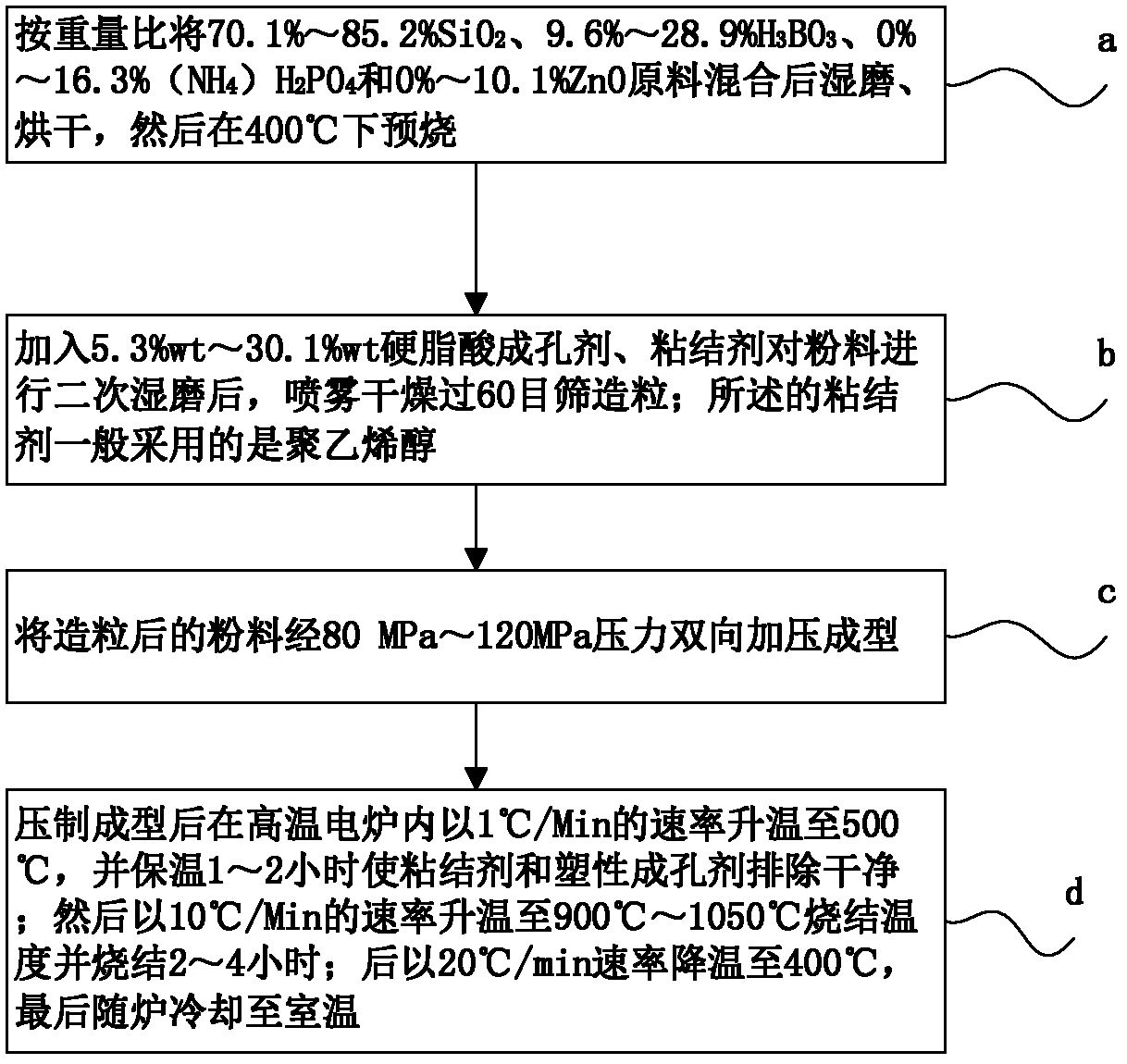
The invention provides a porous glass ceramic material, a preparation method and a prepared metamaterial substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting ZnO-B2O3-P2O5-SiO2 system glass ceramic, adopting and adding a plastic pore-forming agent and sintering to prepare the porous glass ceramic material; the dielectric constant of the prepared porous glass ceramic material can be reduced to 2-3, and the loss tangent angle can also be reduced to about 0.0001; furthermore, the preparation method has the advantages of science, reasonableness and simplicity and easiness in operation; and the substrate with low dielectric constant and low loss, which is prepared by the porous glass ceramic material, can meet the requirements of the metamaterial substrate on the dielectric constant and the loss and be widely applied in the field of metamaterials.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Active ester resin, thermosetting resin composition, cured product of same, semiconductor encapsulation material, prepreg, circuit board, and build-up film
ActiveUS20150118499A1Increase resistanceLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsCarboxylic acidAldehyde formation
A cured product exhibits good heat resistance and flame retardancy as well as low dielectric constant and low loss tangent. A phosphorus-containing compound (i) obtained by a reaction between an aromatic aldehyde (a1) having an alkoxy group as a substituent on a nucleus and an organic phosphorus compound (a2) having a P—H group or a P—OH group in a molecular structure is reacted with a phenolic substance (a3) to obtain a phosphorus-containing phenolic substance (A1). Then the phosphorus-containing phenolic substance (A1) is reacted with an aromatic dicarboxylic acid or an anhydride or dihalide of an aromatic dicarboxylic acid or a C2-6 saturated dicarboxylic acid or an anhydride or dihalide of a C2-6 saturated dicarboxylic acid (A2) so that all or some of hydroxyl groups of the phenolic substance (A1) form ester bonds.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Thermosetting resin composition, cured product obtained therefrom, and active ester resin for use therein
InactiveUS20180327541A1Low dielectric constantImprove flame retardant performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEpoxyHeat resistance
Provided are a thermosetting resin composition whose cured product exhibits a low dielectric constant and a low loss tangent as well as excellent flame retardancy, heat resistance, and thermal decomposition resistance, a cured product obtained from the thermosetting resin composition, and an active ester resin for use in the thermosetting resin composition. Specifically, the thermosetting resin composition contains, as essential components, an epoxy resin and an active ester resin having a resin structure that has a structural segment represented by formula (I) below and monovalent aryloxy groups at both terminals:
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Method for machining signal transmission device, signal transmission device, and mobile terminal
InactiveCN109379834ALow dielectric constantLow loss tangentHigh frequency circuit adaptationsCircuit susbtrate materialsFiberComputer terminal
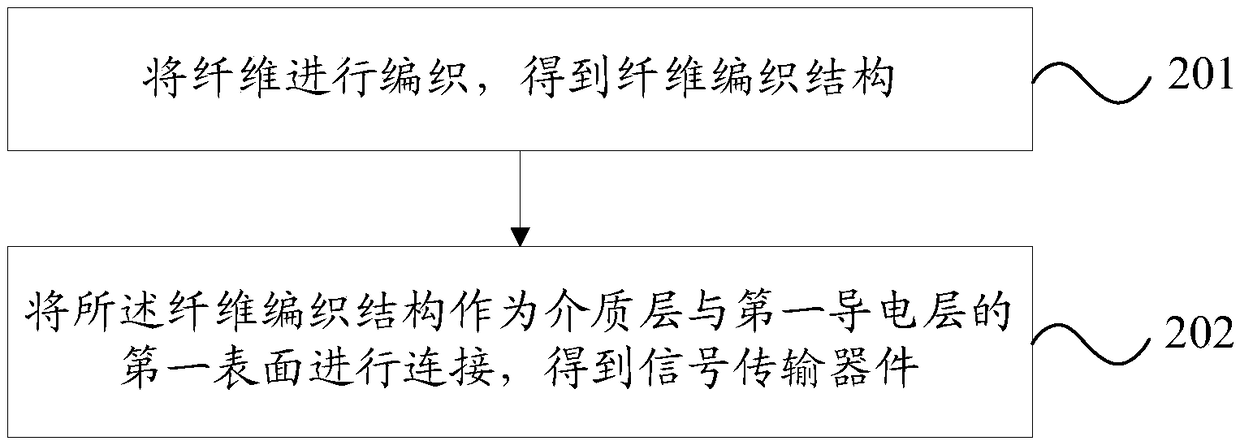
The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for machining a signal transmission device, a signal transmission device, and a mobile terminal. The signal transmission device specifically includes a first conductive layer and a dielectric layer, wherein a first surface of the first conductive layer is connected to the dielectric layer; and the dielectric layer is a fiber woven structure. In the embodiment of the present invention, when configured to transmit a high-frequency signal, the signal transmission device can reduce the transmission loss of the high-frequency signal, and improve the integrity of the high-frequency signal. Moreover, the dielectric layer can achieve reliably support the first conductive layer, and improves the overall strength of the signal transmission device.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Low loss glass-ceramic materials, method of making same and electronic packages including same
InactiveUS7387838B2Low loss tangentHigh quality factorLayered product treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal expansionGlass-ceramic
A glass-ceramic is provided having a thermal expansion coefficient in a range of 3-6 ppm / ° C., a dielectric constant that is less than 5 and a Quality factor Q of at least 400. The glass-ceramic consists essentially of SiO2 in a range of 45-58 wt %, Al2O3 in a range of 10-18 wt % and MgO in a range of 10-25 wt %. A method of making the glass-ceramic is also provided. Further, an electronic package is also provided, including a base member and a glass-ceramic substrate bonded to the base member.
Owner:KNOWLES CAZENOVIA
Active ester resin, thermosetting resin composition, cured product of same, semiconductor encapsulation material, prepreg, circuit board, and build-up film
ActiveUS9217053B2Increase resistanceLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsCarboxylic acidChemistry
A cured product exhibits good heat resistance and flame retardancy as well as low dielectric constant and low loss tangent. A phosphorus-containing compound (i) obtained by a reaction between an aromatic aldehyde (a1) having an alkoxy group as a substituent on a nucleus and an organic phosphorus compound (a2) having a P—H group or a P—OH group in a molecular structure is reacted with a phenolic substance (a3) to obtain a phosphorus-containing phenolic substance (A1). Then the phosphorus-containing phenolic substance (A1) is reacted with an aromatic dicarboxylic acid or an anhydride or dihalide of an aromatic dicarboxylic acid or a C2-6 saturated dicarboxylic acid or an anhydride or dihalide of a C2-6 saturated dicarboxylic acid (A2) so that all or some of hydroxyl groups of the phenolic substance (A1) form ester bonds.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20170217257A1Low loss tangentEasy maintenanceHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleEngineeringBase line
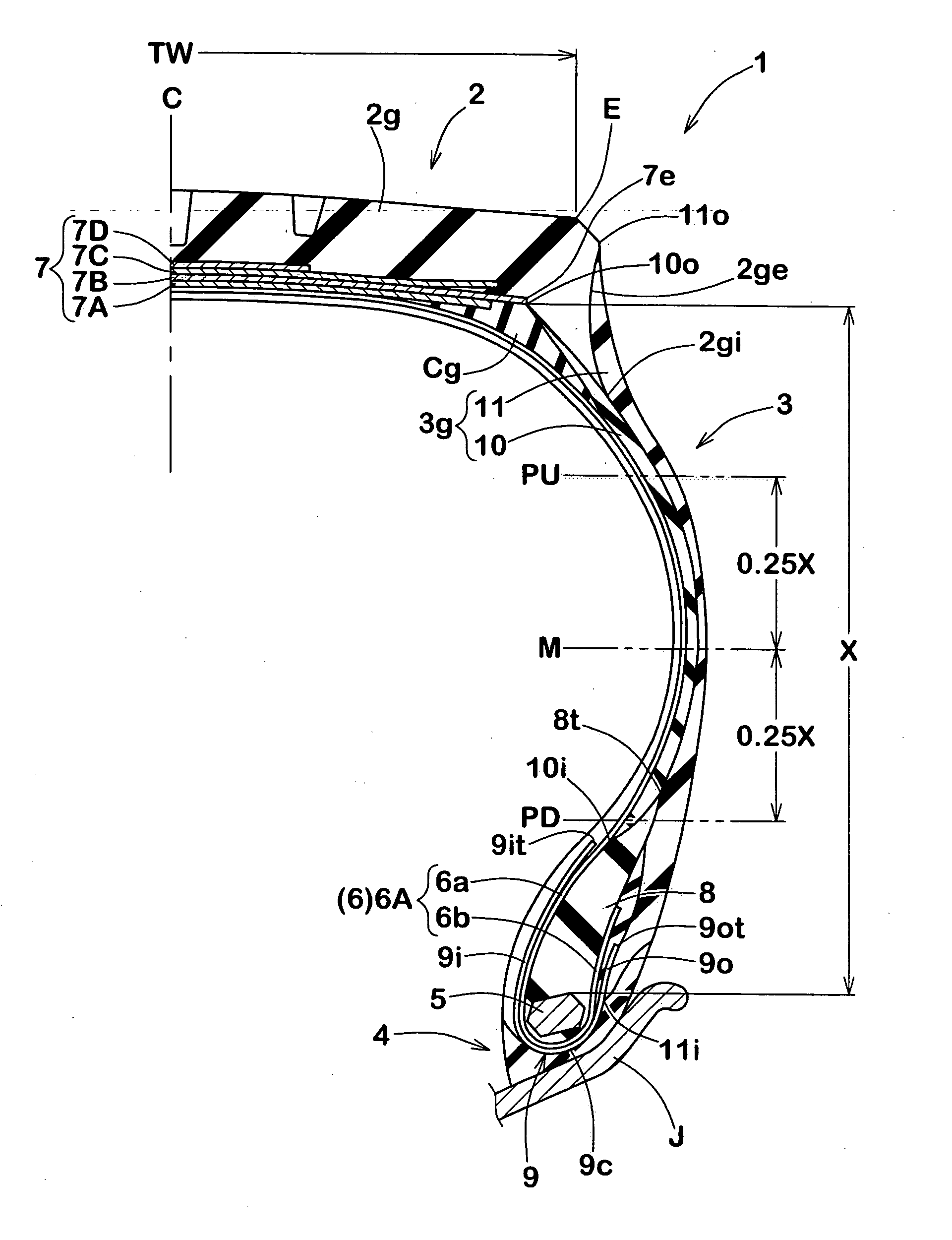
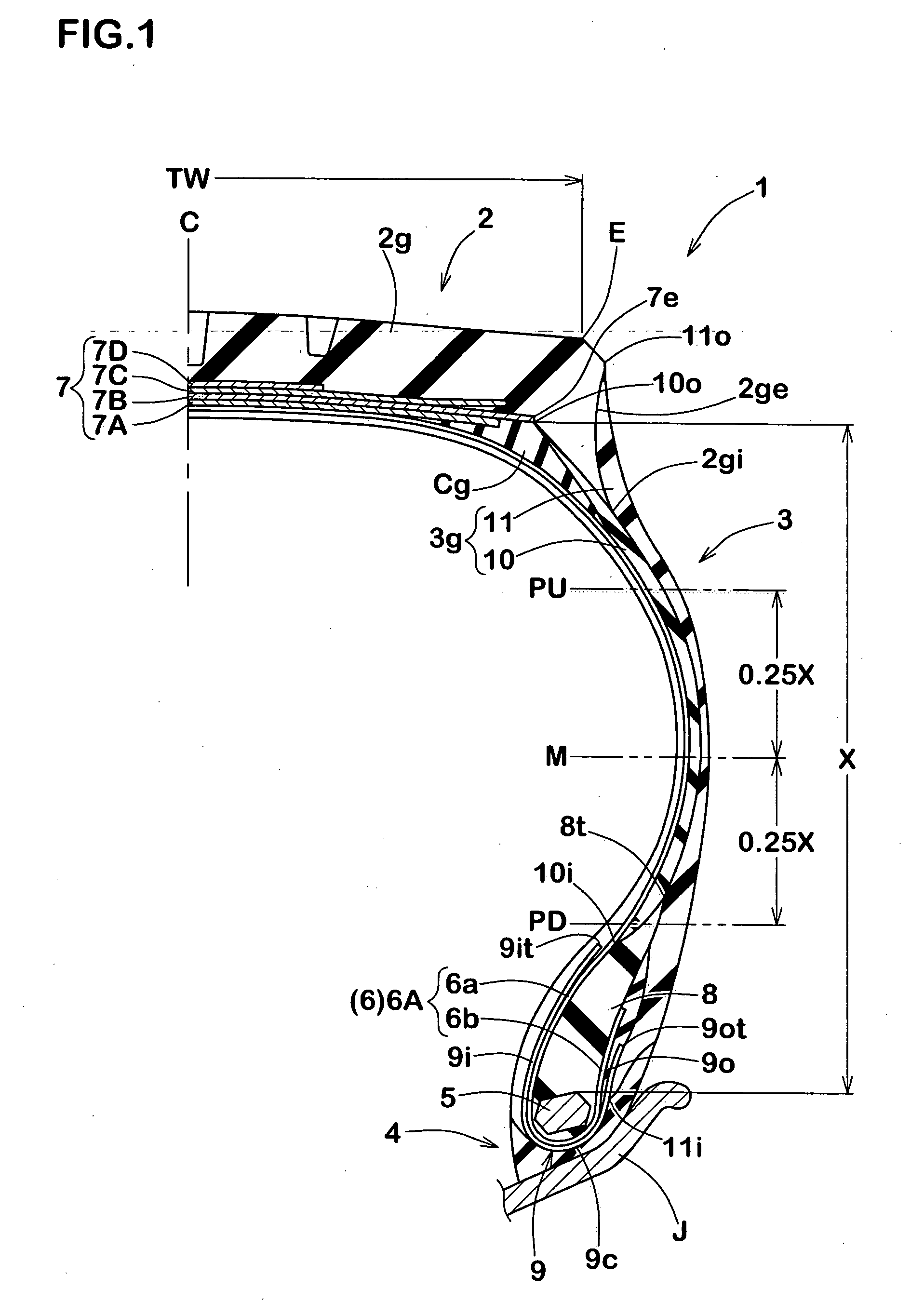
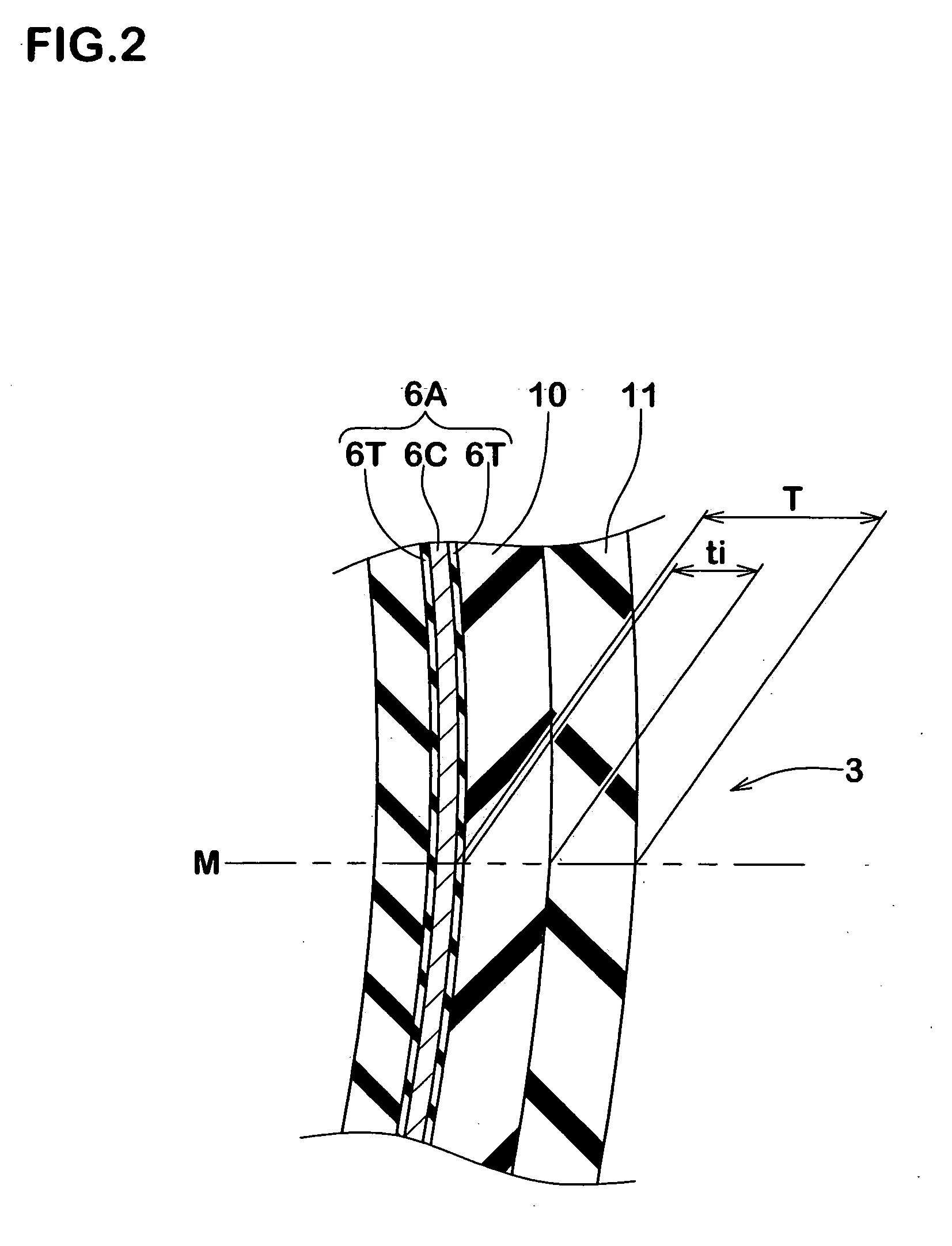
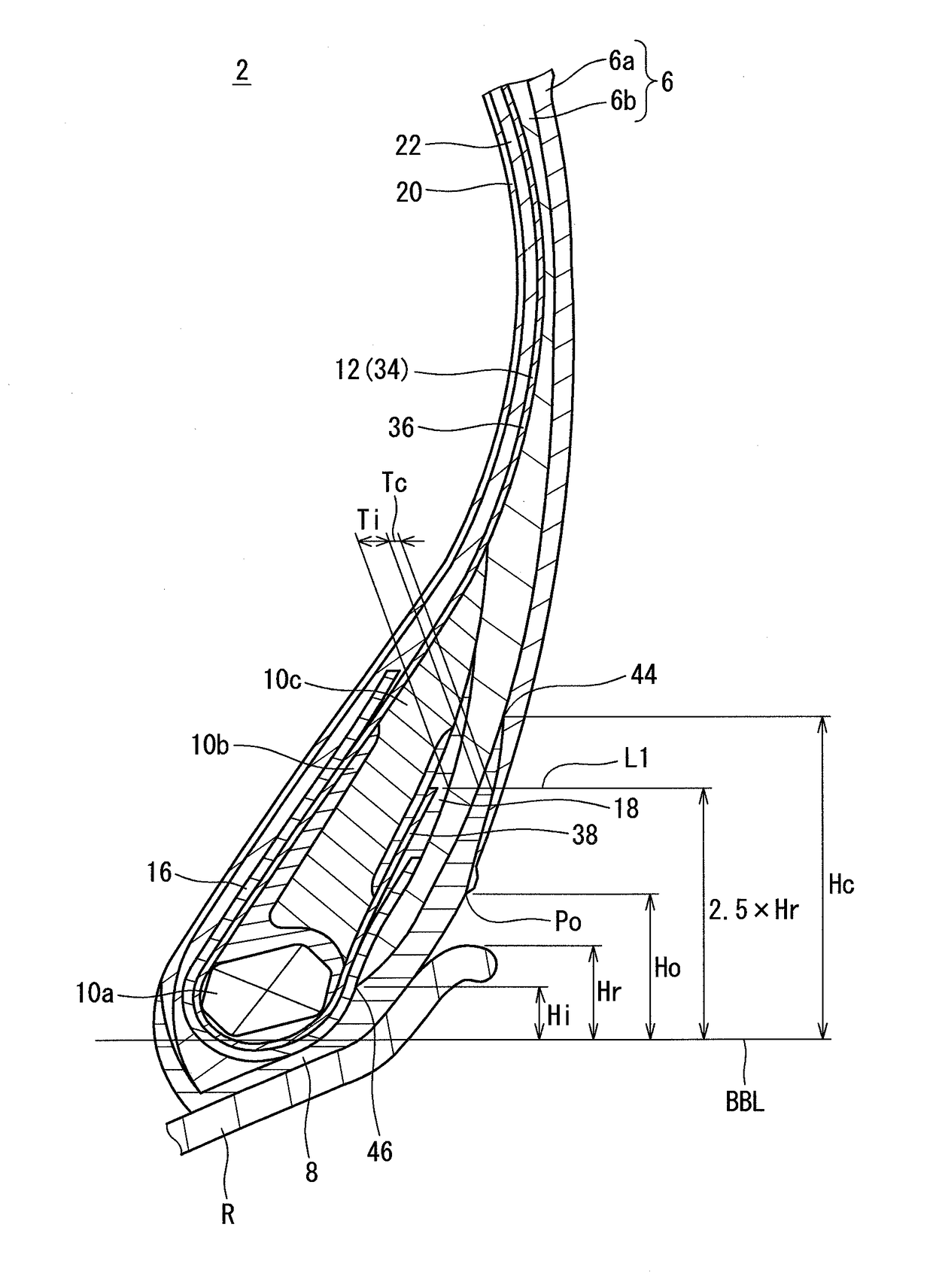
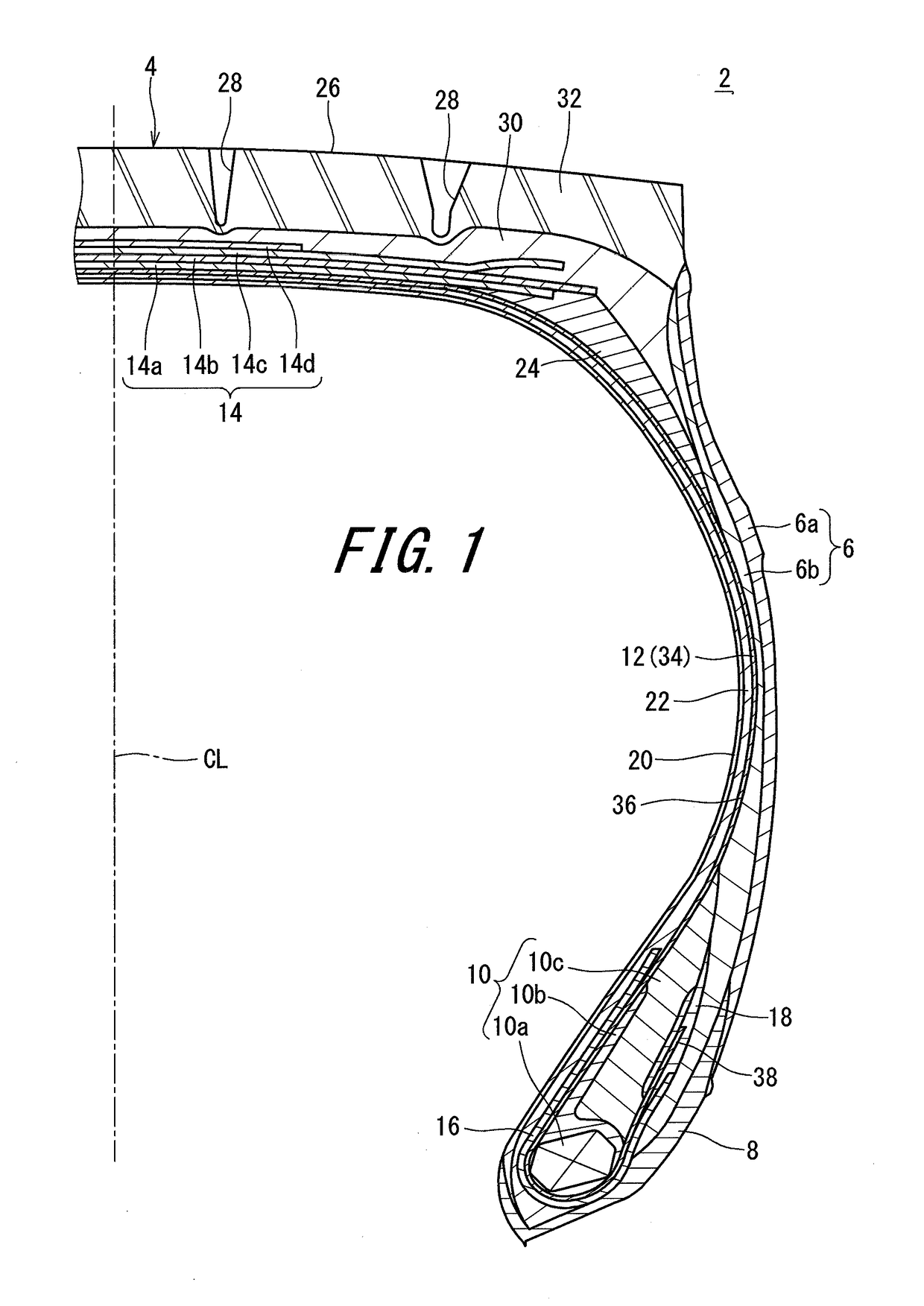
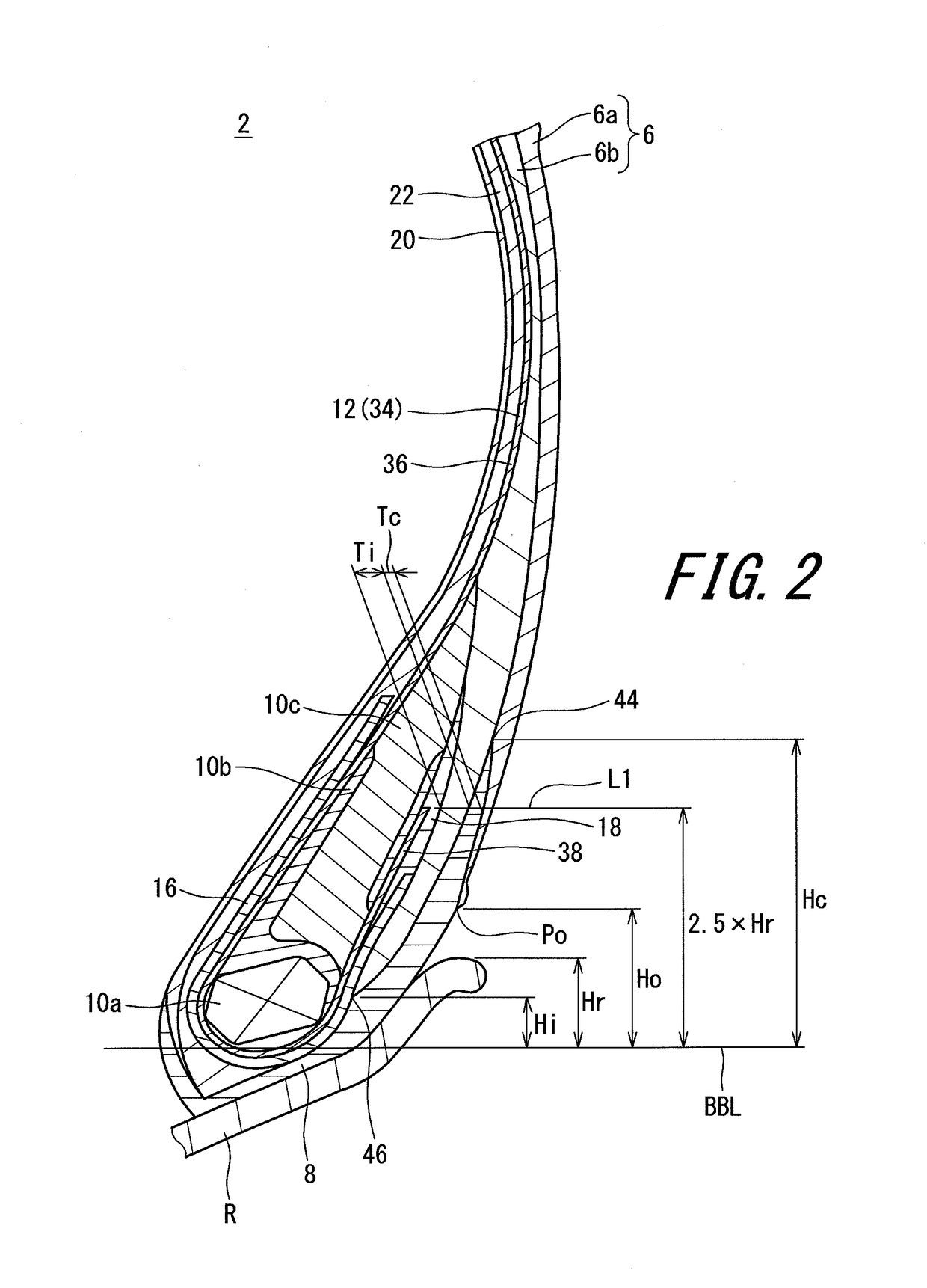
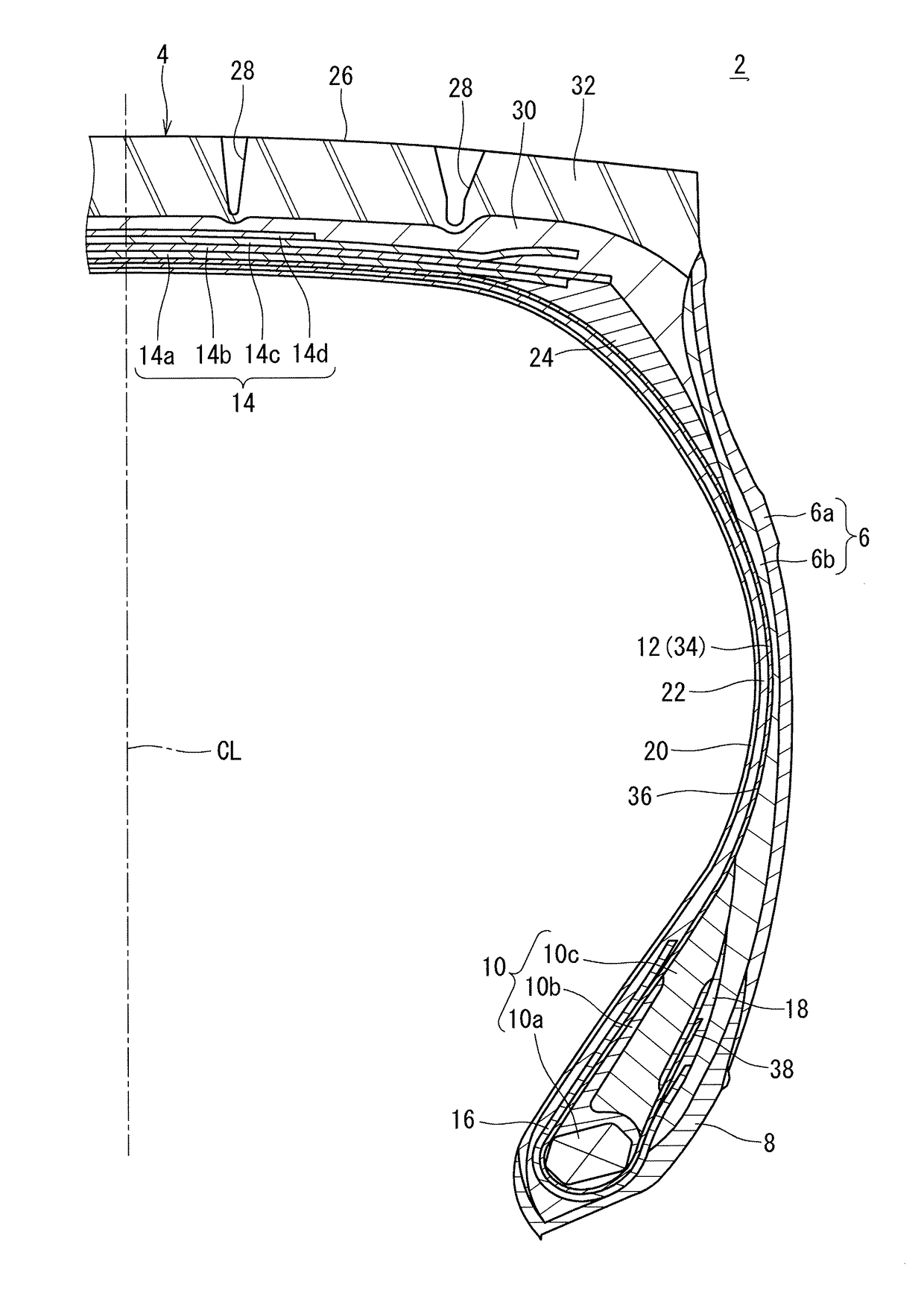
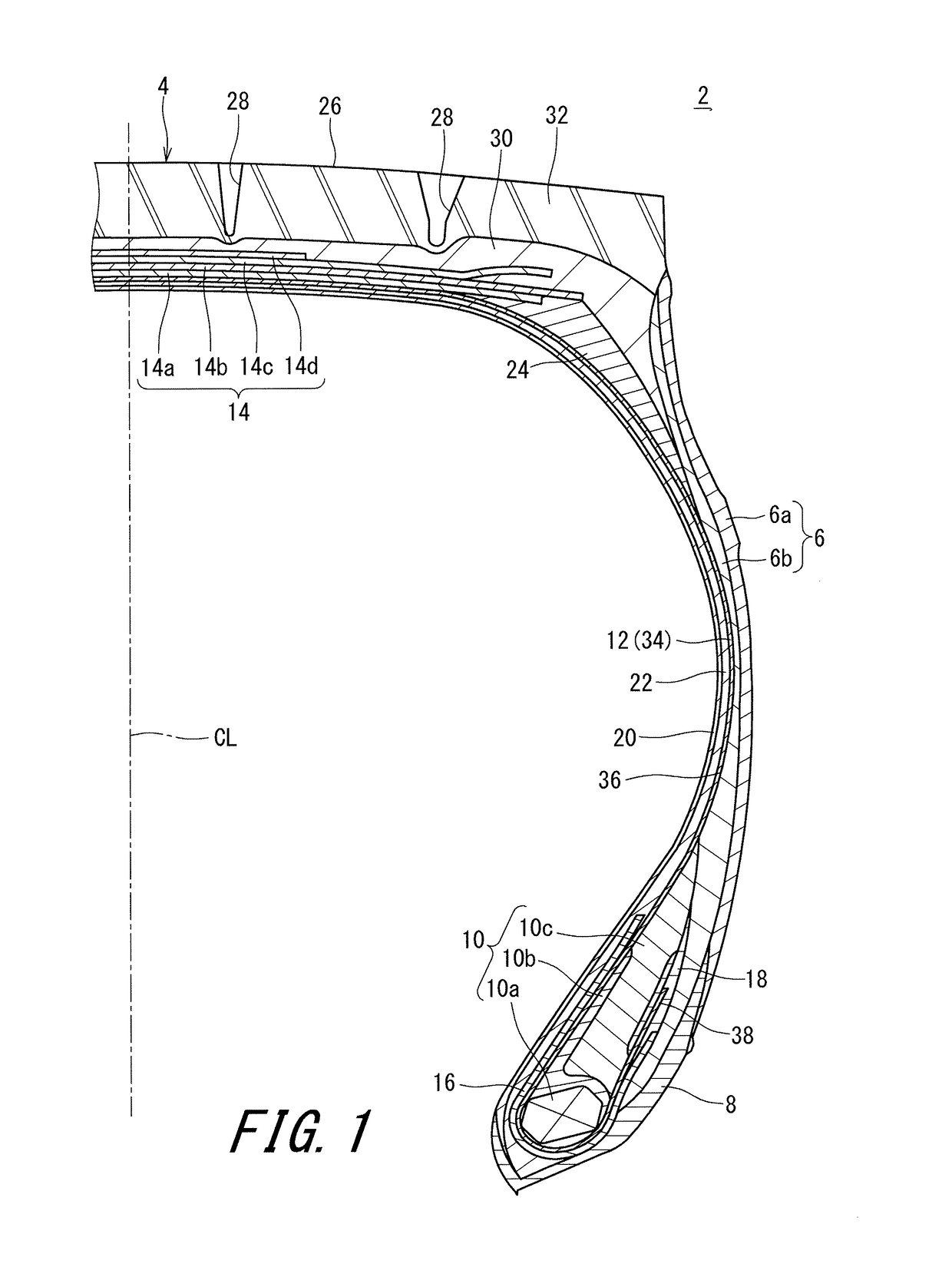
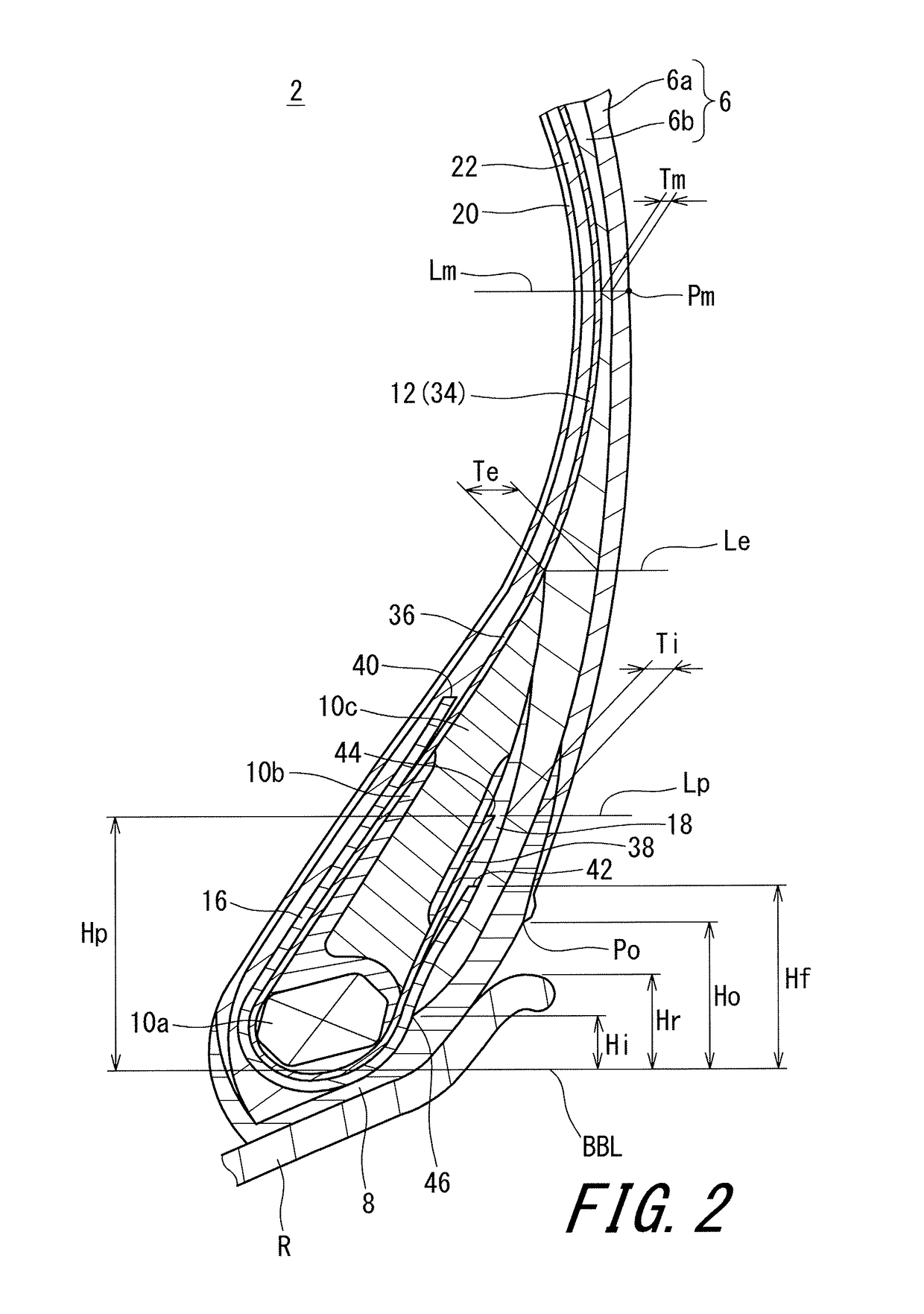
In a tire 2 of the present invention, sidewalls 6 each include an outer layer 6a, and an inner layer 6b disposed inward of the outer layer 6a in the axial direction. A loss tangent of the inner layer 6b is less than a loss tangent of the outer layer 6a. When Hr represents a height, in the radial direction, from a bead base line BBL to an outer side end of a rim R, and Hi represents a height, in the radial direction, from the bead base line BBL to an inner side end 46 of the inner layer 6b, a ratio (Hi / Hr) of the height Hi to the height Hr is greater than or equal to 0.0 and not greater than 3.0.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Insulating film, adhesive film and flat cable
PendingCN113272921AGood chemical resistanceExcellent heat and humidity resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsFlat/ribbon cablesElastomerPolymer science
Provided are an adhesive film, a flat cable, and an insulating film excelling in toughness and adhesive strength, and capable of achieving a lower dielectric constant and a lower dielectric loss tangent. More specifically, an insulating film 4 is used in a flat cable 1. The insulating film 4 is formed from a resin composition containing: a polyarylene sulfide-based resin (A); a polyphenylene ether-based resin (B); and a modified elastomer (C) having a reactive group capable of reacting with the polyarylene sulfide-based resin (A) and / or the polyphenylene ether-based resin (B). In the resin composition, the content of the polyarylene sulfide-based resin (A) is 50-93 mass%, and the content of the polyphenylene ether-based resin (B) is 3-40 mass%.
Owner:DIC CORP
A kind of rubber composition and application
A rubber composition, comprising: 80-120 parts by weight of a raw rubber; 1-5 parts by weight of a peroxide initiator; 2-15 parts by weight of a crossbridging agent; 0.1-1 parts by weight of a free radical-absorbing and releasing modulator; and a strengthening and anti-aging agent. At least 70% by weight of the raw rubber comprises any one or any combination of a polybutadiene rubber, natural rubber, and styrene-butadiene rubber. The invention provides a formulation of a crossbridging and auxiliary agent for an unfinished good of the rubber composition, and offers a technical solution with excellent performance and industrial applicability in representative industries including tires, footwear materials, and wear plates. The invention is also cost effective and friendly to the environment.
Owner:NANJING SIKAI RUBBER & PLASTIC PROD CO LTD
High-capacitance density thin film dielectrics having columnar grains formed on base-metal foils
ActiveUS7981741B2Increase capacitance densityImprove breakdown voltageTransistorThin/thick film capacitorCapacitanceDielectric
Deposited thin-film dielectrics having columnar grains and high dielectric constants are formed on heat treated and polished metal foil. The sputtered dielectrics are annealed at low oxygen partial pressures.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
High frequency film transmission line, antenna including the same and antenna-integrated image display device
ActiveUS11316238B2Improved signaling efficiency and reliabilityLoss levelingLiquid crystal compositionsPrinted circuit detailsEngineeringCyclo olefin polymer
A film transmission line includes a dielectric layer including at least one of a liquid crystal polymer (LCP) structure or a cyclo olefin polymer (COP) structure, and an electrode line on the dielectric layer. A signal loss level (S21) defined of the film transmission line is −1.5 dB or more at a frequency in a range from 20 GHz to 30 GHz. The film transmission line may be applied to a high frequency thin film antenna and an image display device.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD
Porous glass ceramic material, preparation method and prepared metamaterial substrate
The invention provides a porous glass ceramic material, a preparation method and a prepared metamaterial substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting ZnO-B2O3-P2O5-SiO2 system glass ceramic, adopting and adding a plastic pore-forming agent and sintering to prepare the porous glass ceramic material; the dielectric constant of the prepared porous glass ceramic material can be reduced to 2-3, and the loss tangent angle can also be reduced to about 0.0001; furthermore, the preparation method has the advantages of science, reasonableness and simplicity and easiness in operation; and the substrate with low dielectric constant and low loss, which is prepared by the porous glass ceramic material, can meet the requirements of the metamaterial substrate on the dielectric constant and the loss and be widely applied in the field of metamaterials.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Broadband light splitting and frequency splitting element and preparation method thereof
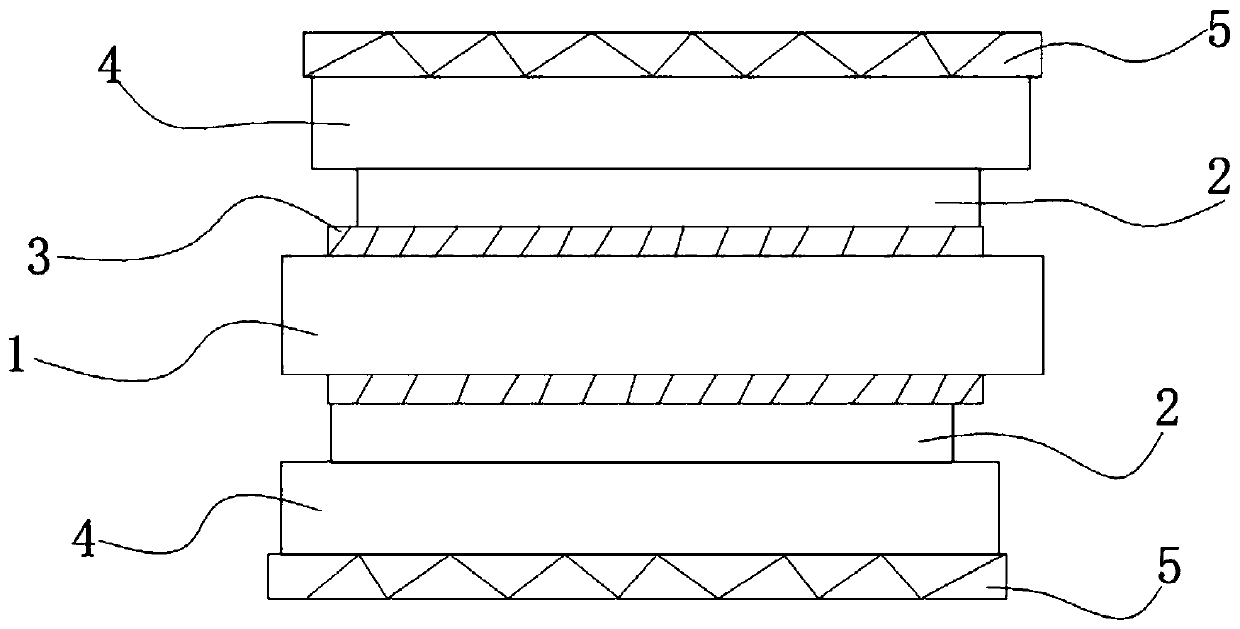
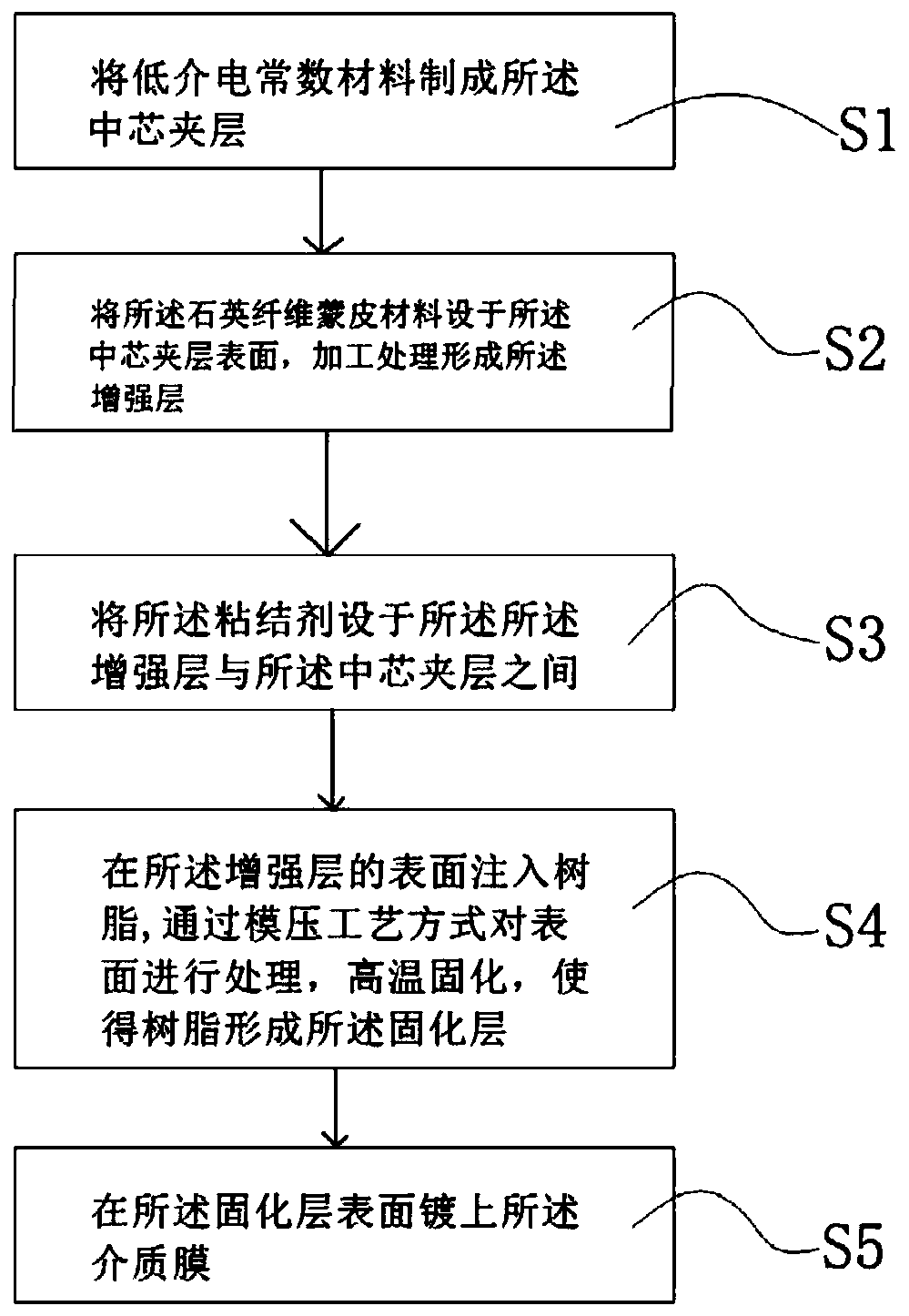
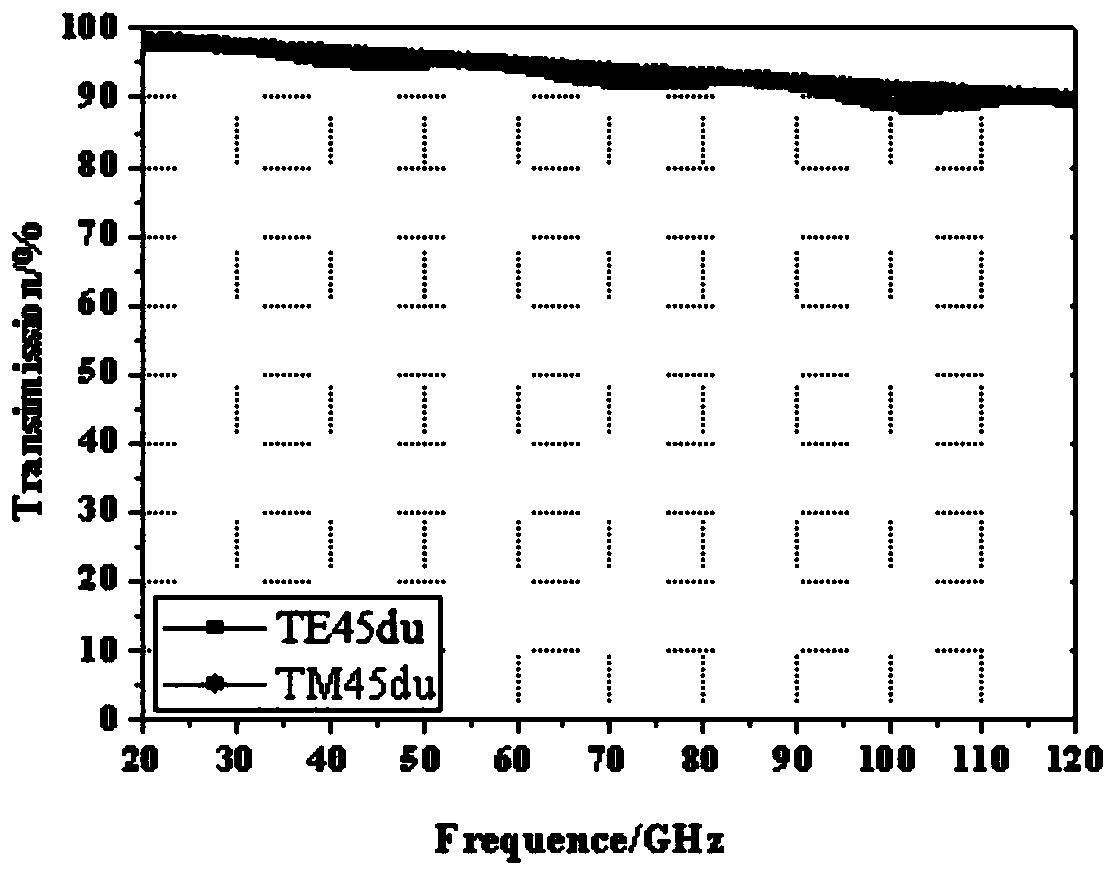
The invention relates to the fields of optical technology and high-frequency radio receiving technology, and specifically discloses a broadband light-splitting and frequency-dividing element and a preparation method thereof. The traditional sandwich structure of the present invention is used to produce a broadband light splitter and frequency division element with transparent wave characteristics, and ensure that the surface of a single quartz fiber skin material has a level of mechanical parallelism, and then add cured resin on the surface of the quartz fiber skin material , the requirements for optical surface precision are achieved by the cured resin. For the analysis and design of millimeter wave transmission characteristics, the reinforcement layer formed by the solidified layer, the quartz fiber skin material, and the core interlayer are comprehensively analyzed and designed, and the thickness of the core interlayer is adjusted to make the reinforcement The reflections of the layers cancel each other out, so that the characteristics of high-frequency broadband wave transmission can be obtained in a wide bandwidth. For optical signal reflection properties, adding the dielectric film on the surface of the high-temperature-resistant resin can ensure high reflectivity of optical signals.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com