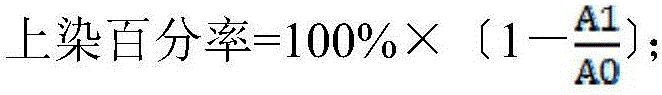Patents
Literature
1273 results about "Low vacuum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
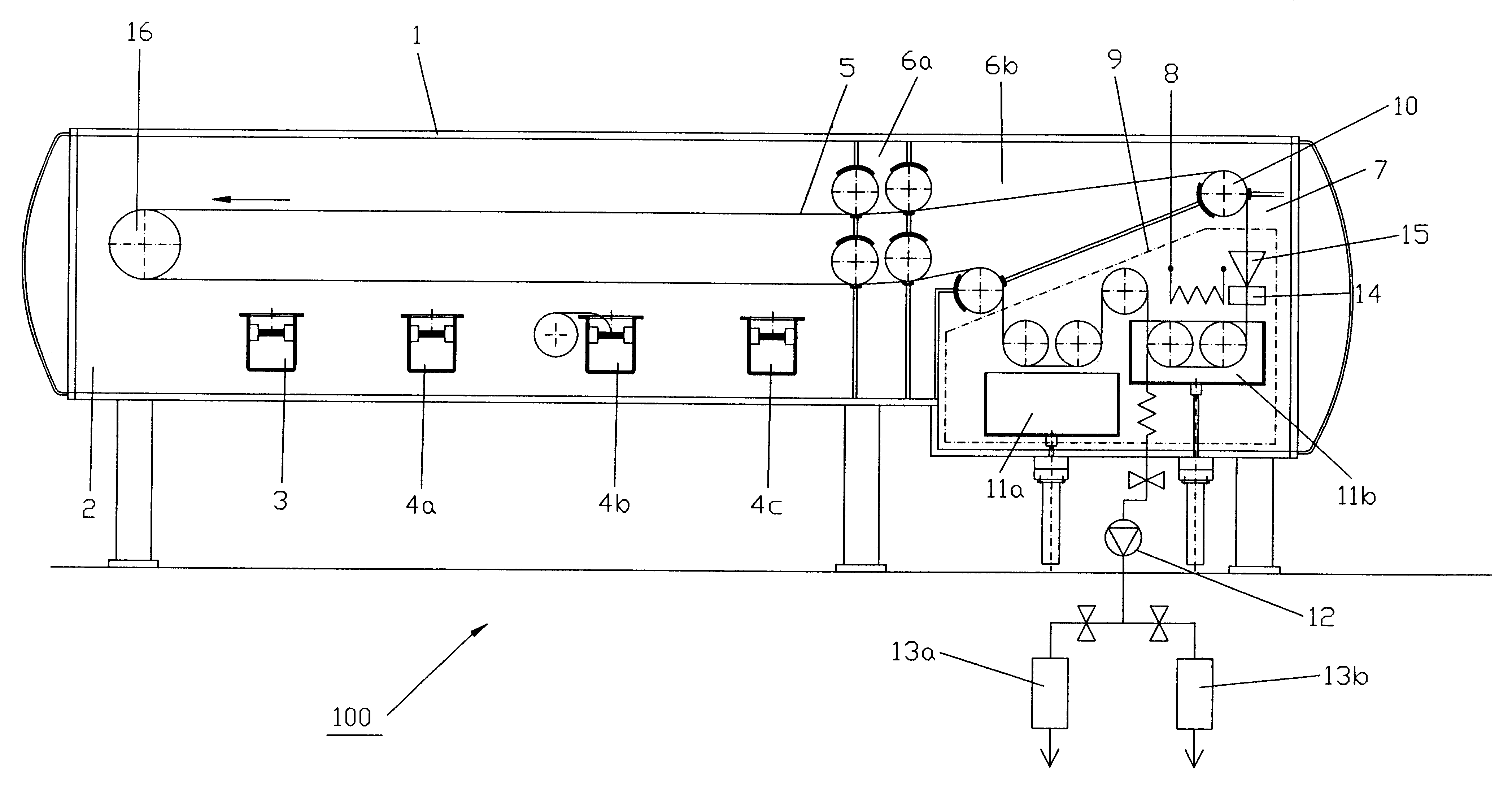
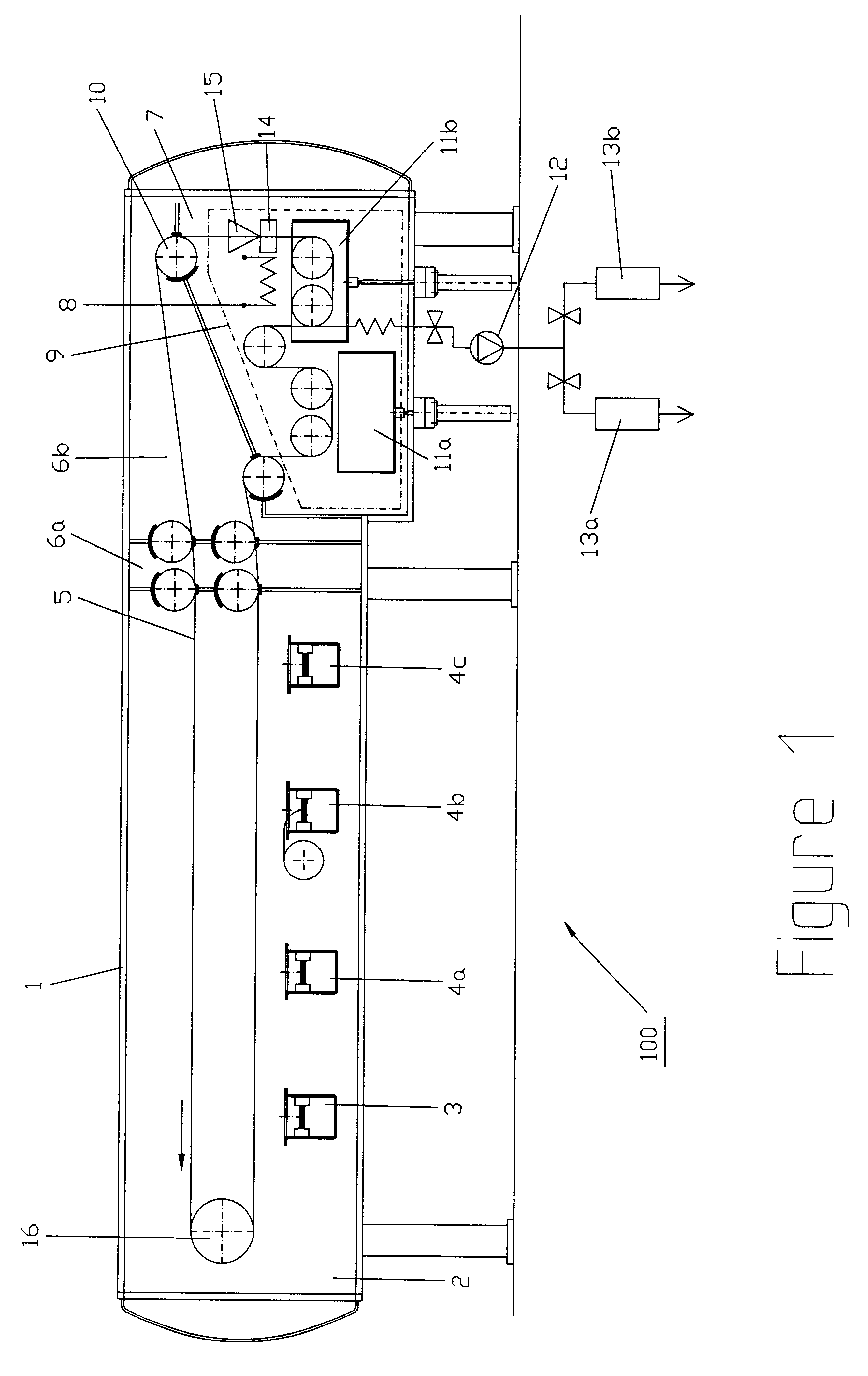
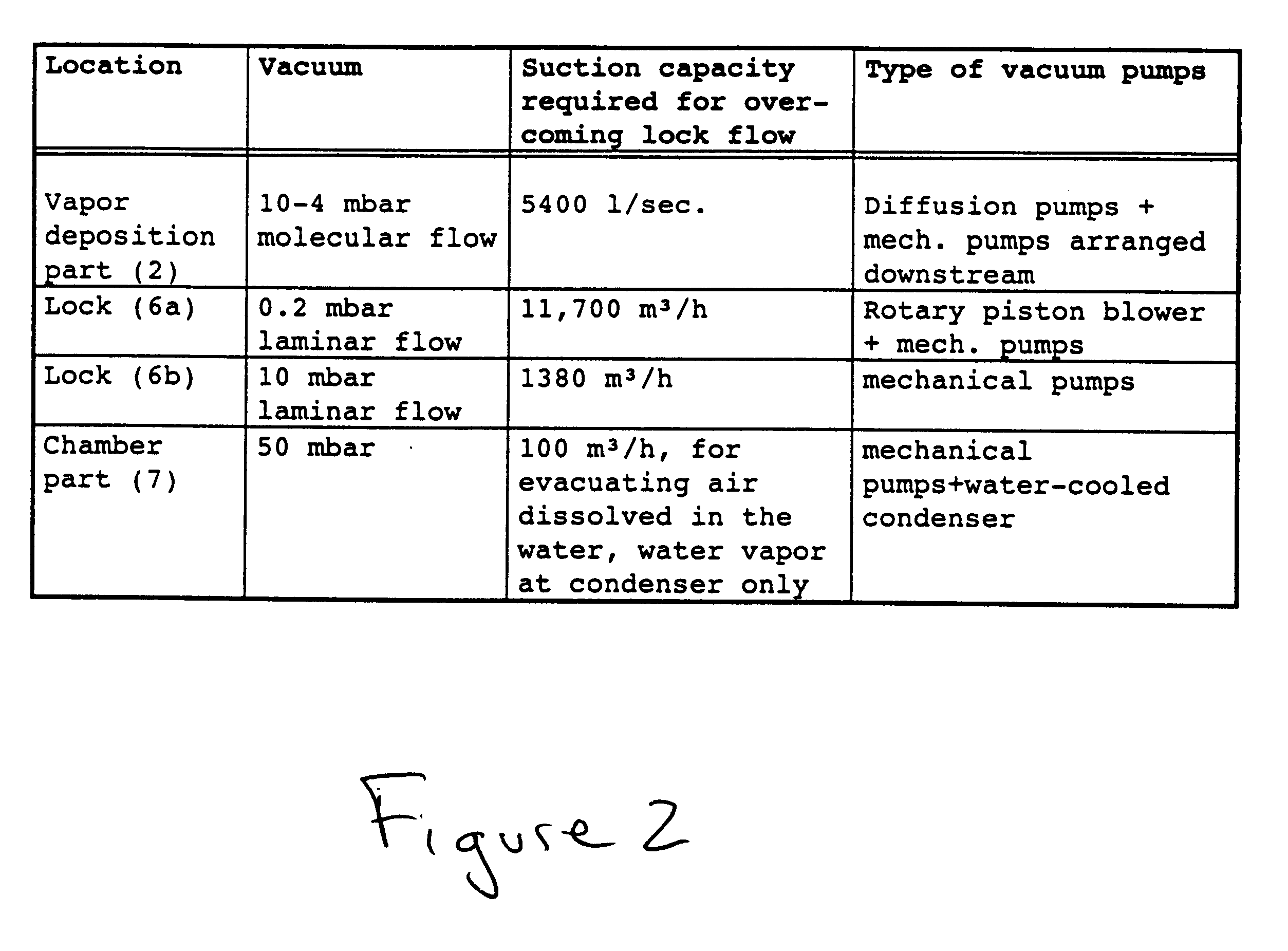
Low vacuum, also called rough vacuum or coarse vacuum, is vacuum that can be achieved or measured with rudimentary equipment such as a vacuum cleaner and a liquid column manometer. Medium vacuum is vacuum that can be achieved with a single pump, but the pressure is too low to measure with a liquid or mechanical manometer.
Refractory metal capped low resistivity metal conductor lines and vias formed using PVD and CVD
InactiveUS6323554B1High process yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricGas phase
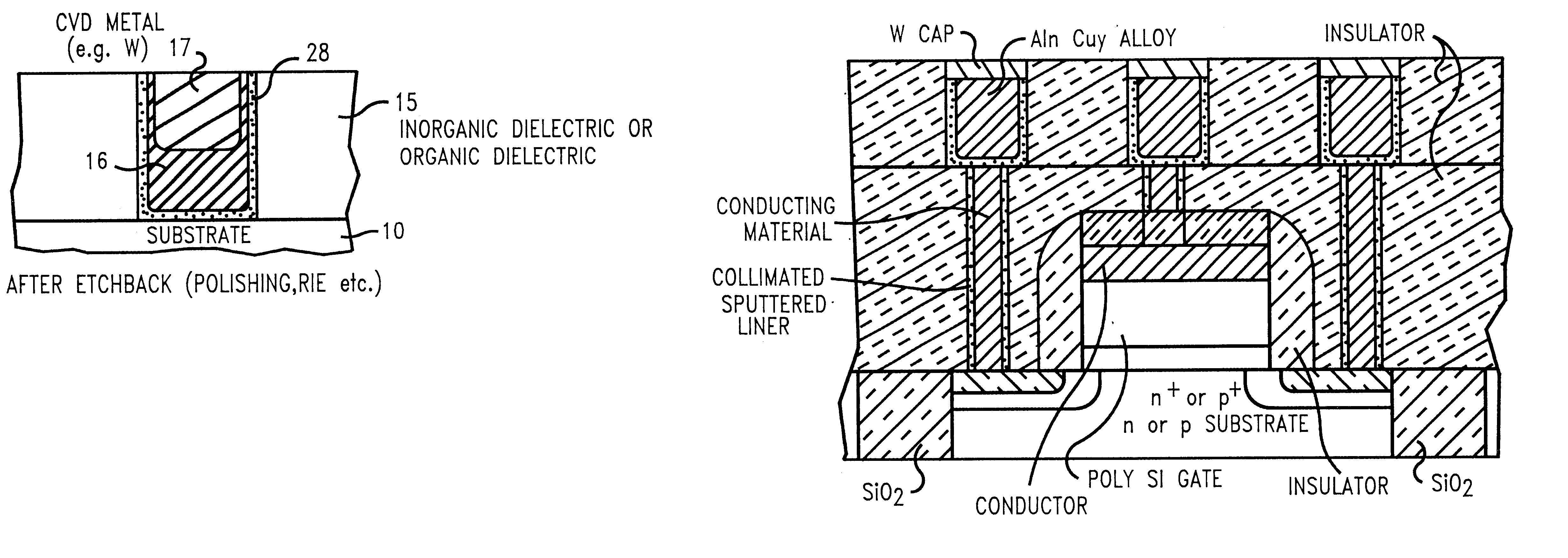
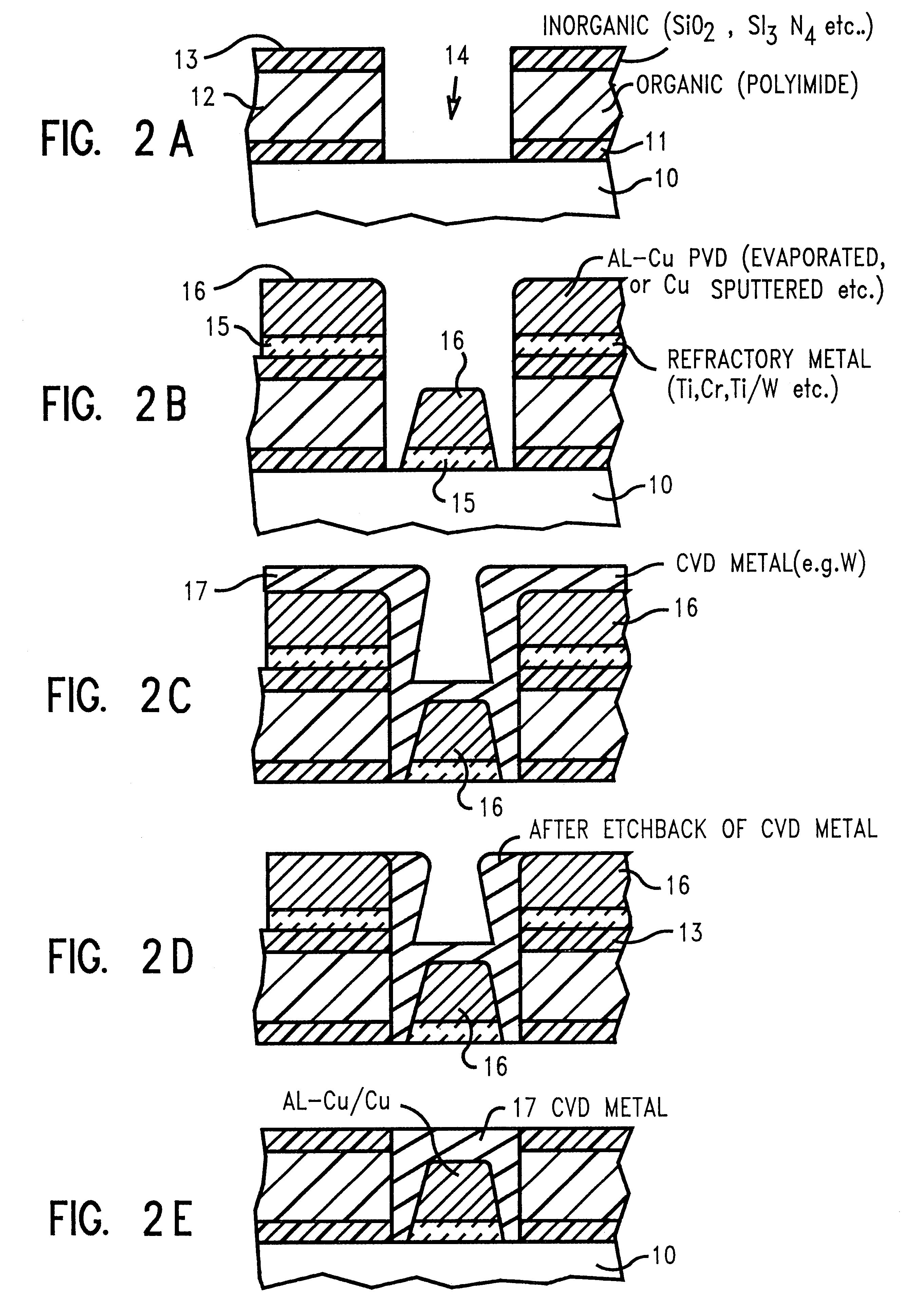
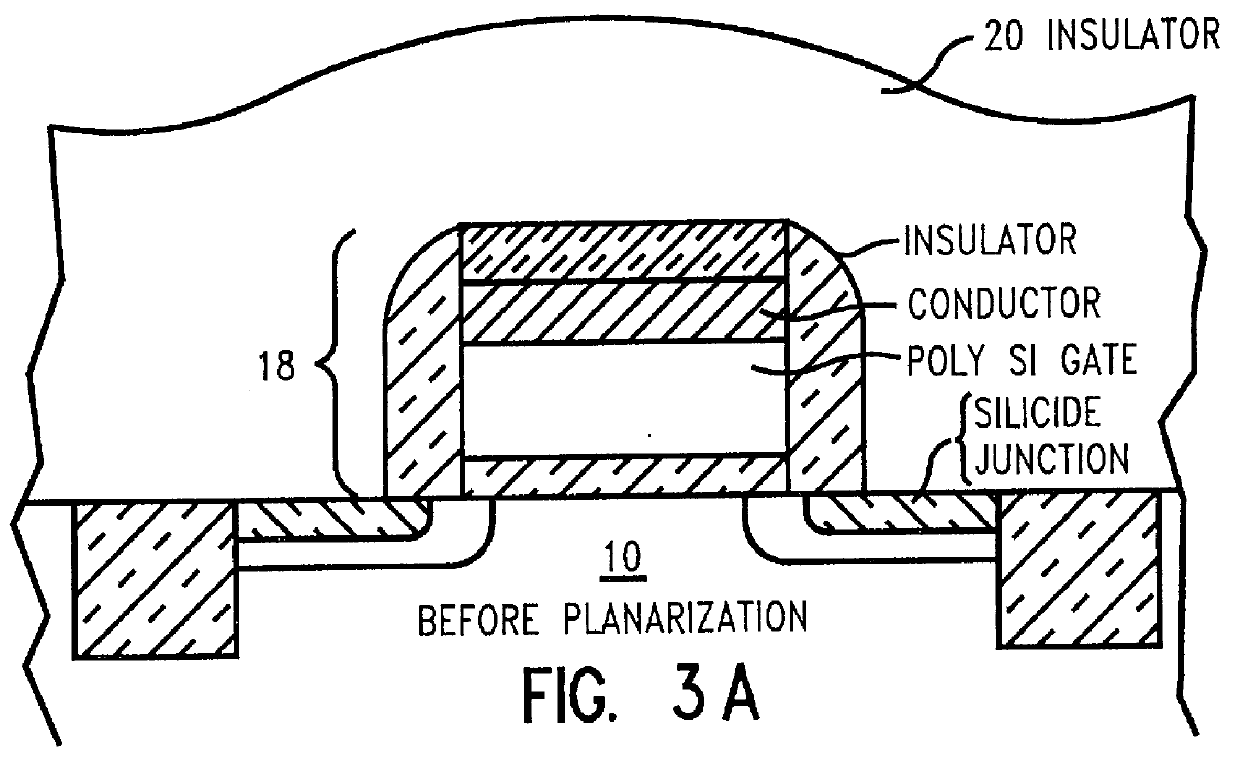
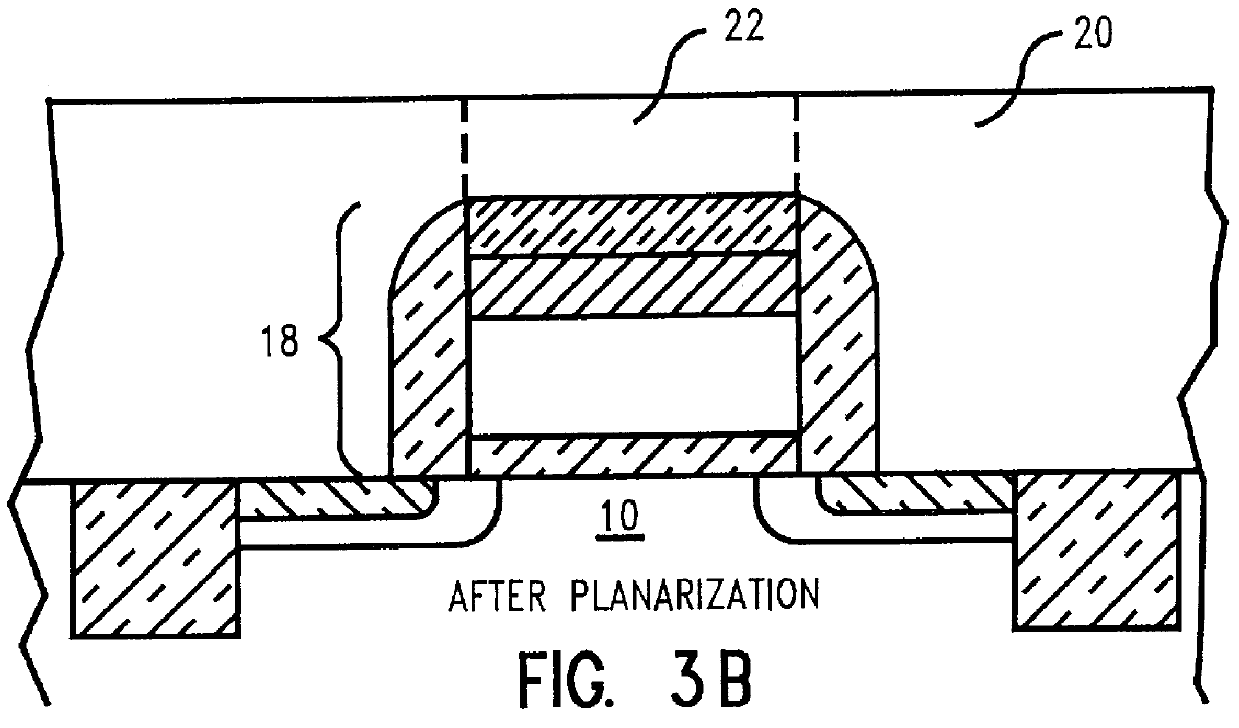
Capping a low resistivity metal conductor line or via with a refractory metal allows for effectively using chemical-mechanical polishing techniques because the hard, reduced wear, properties of the refractory metal do not scratch, corrode, or smear during chemical-mechanical polishing. Conductive lines and vias are created using a combination of both physical vapor deposition (e.g., evaporation or collimated sputtering) of a low resistivity metal or alloy followed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of a refractory metal and subsequent planarization. Altering a ratio of SiH4 to WF6 during application of the refractory metal cap by CVD allows for controlled incorporation of silicon into the tungsten capping layer. Collimated sputtering allows for creating a refractory metal liner in an opening in a dielectric which is suitable as a diffusion barrier to copper based metalizations as well as CVD tungsten. Ideally, for faster diffusing metals like copper, liners are created by a two step collimated sputtering process wherein a first layer is deposited under relatively low vacuum pressure where directional deposition dominates (e.g., below 1 mTorr) and a second layer is deposited under relatively high vacuum pressure where scattering deposition dominates (e.g., above 1 mTorr). For refractory metals like CVD tungsten, the liner can be created in one step using collimated sputtering at higher vacuum pressures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semi-rigid collapsible container
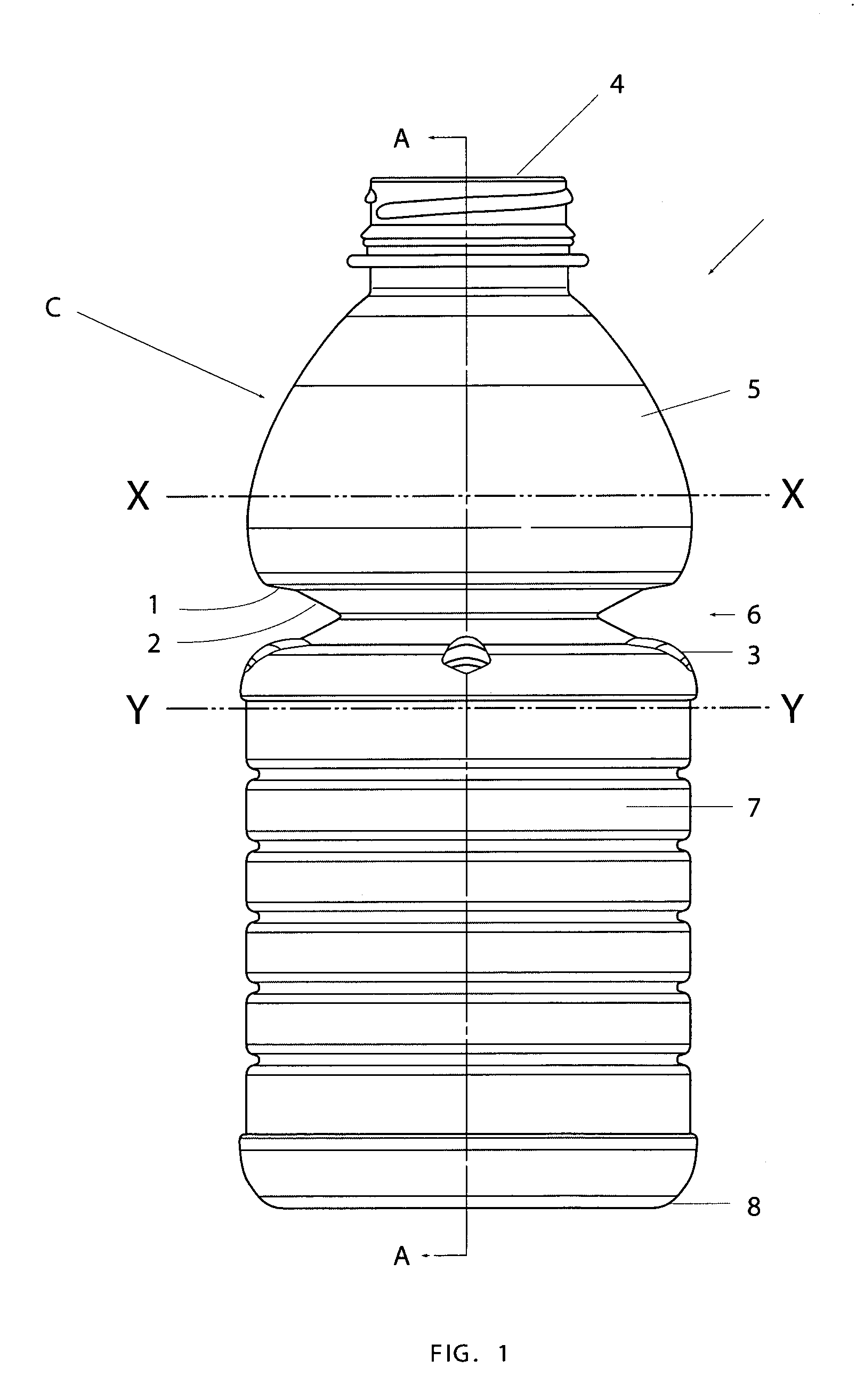
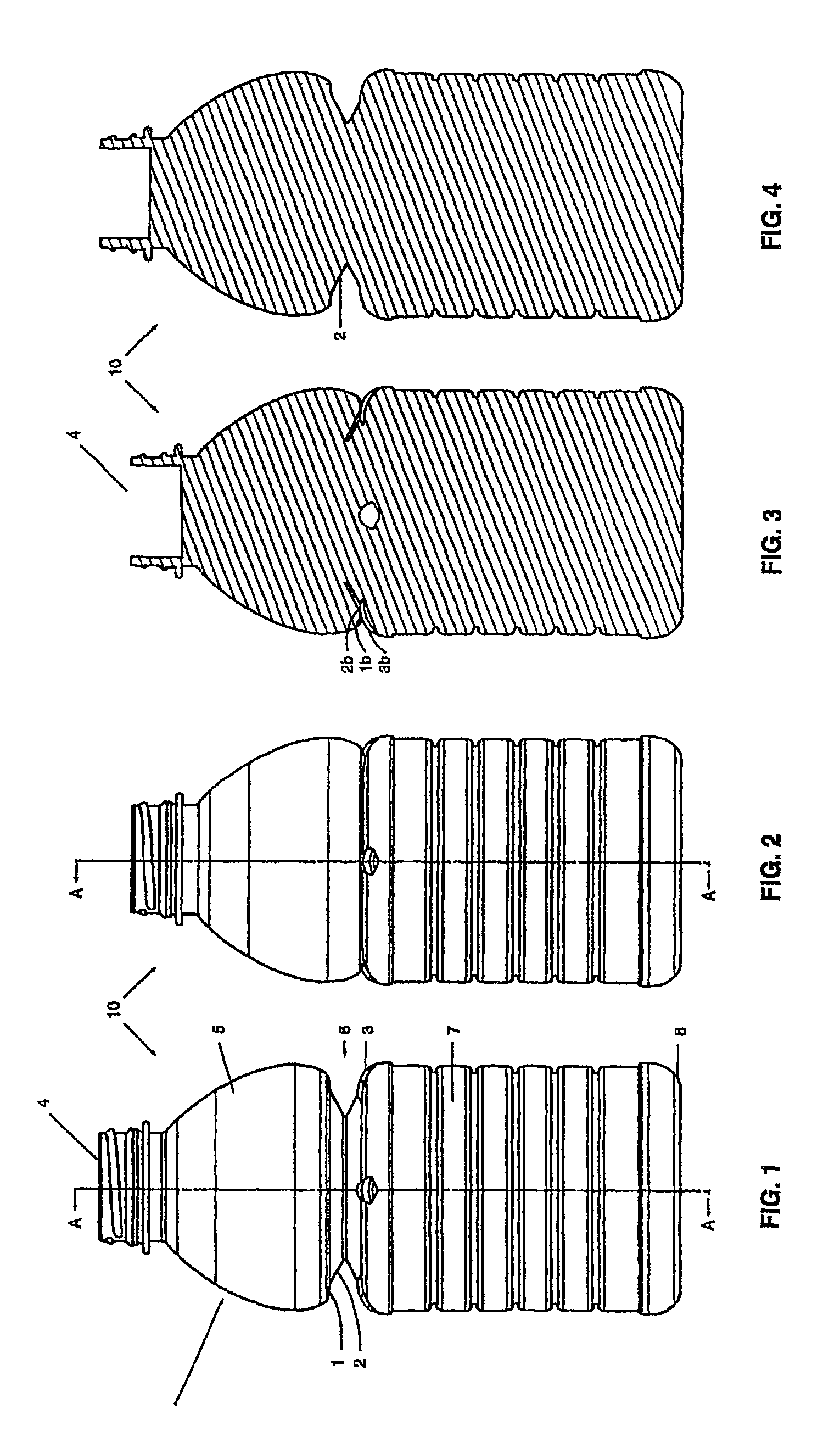
A semi-rigid collapsible container (10) has a side-wall with an upper portion (5), a central portion (6), a lower portion (7) and a base (8). The central protion (6) includes a vacuum panel portion having a control portion (2) and an initiator portion (1). The control portion (2) is inclined more steeply in a vertical direction, i.e. has a more acute angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the container (10), than the initiator portion (1). On low vacuum force being present within the container panel following the cooling of a hot liquid in the container (10), the initiator portion (1) will flex inwardly to cause the control protion (2) to invert and flex further inwardly into the container (10) and the central portion (6) to collapse. In the collapsed state upper and lower portions of the central portion (6) may be in substantial contact so as to contain the top-loading capacity of the container (10). Raised ribs (3) made an aditional support for the container in its collapsed state. In another embodiment the telescoping of the container back to its original position occurs when the vacuum force is released following removal of the container cap.
Owner:CO2 PAC
Precision Diagnostic Method For The Failure Protection And Predictive Maintenance Of A Vacuum Pump And A Precision Diagnostic System Therefor
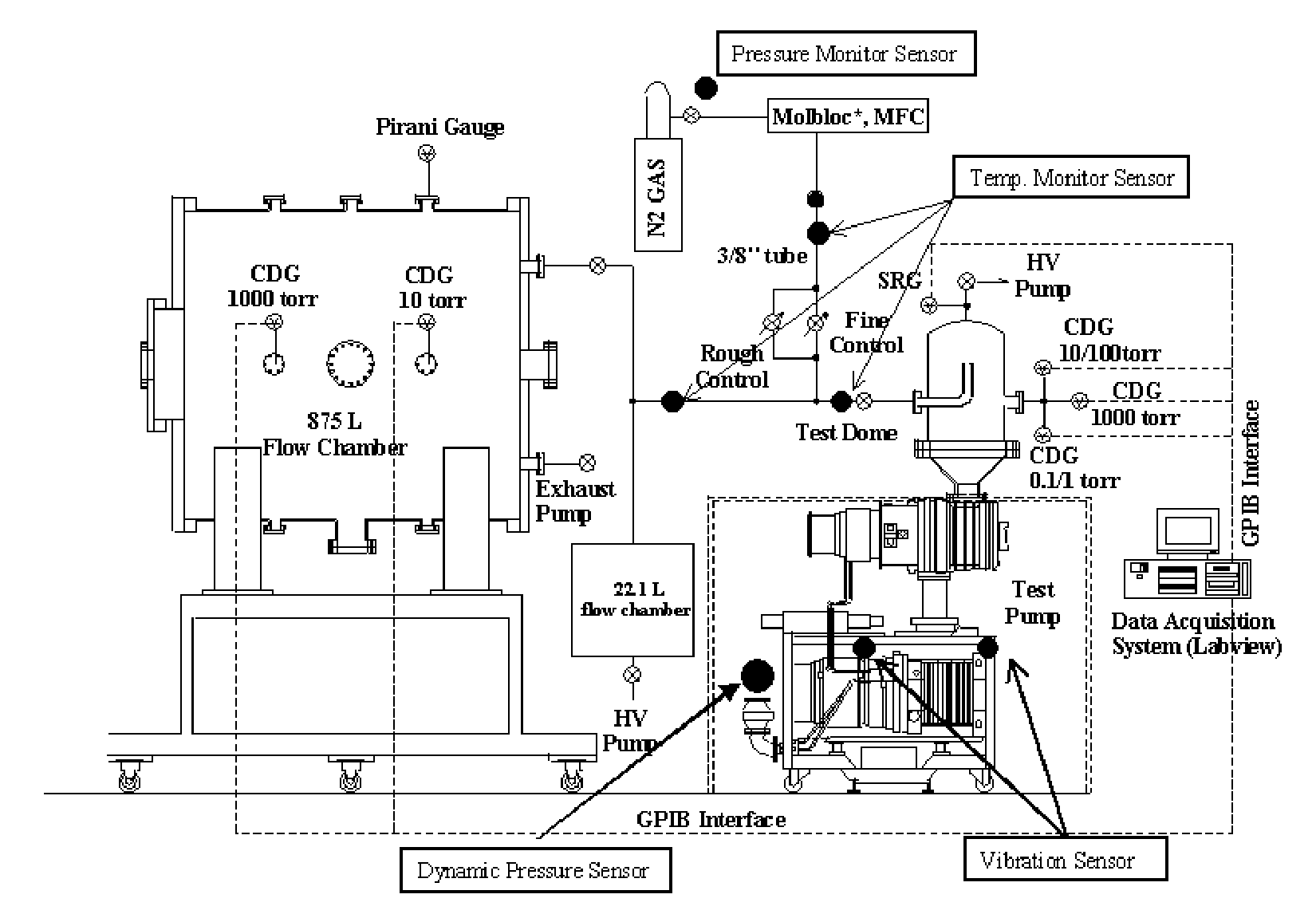
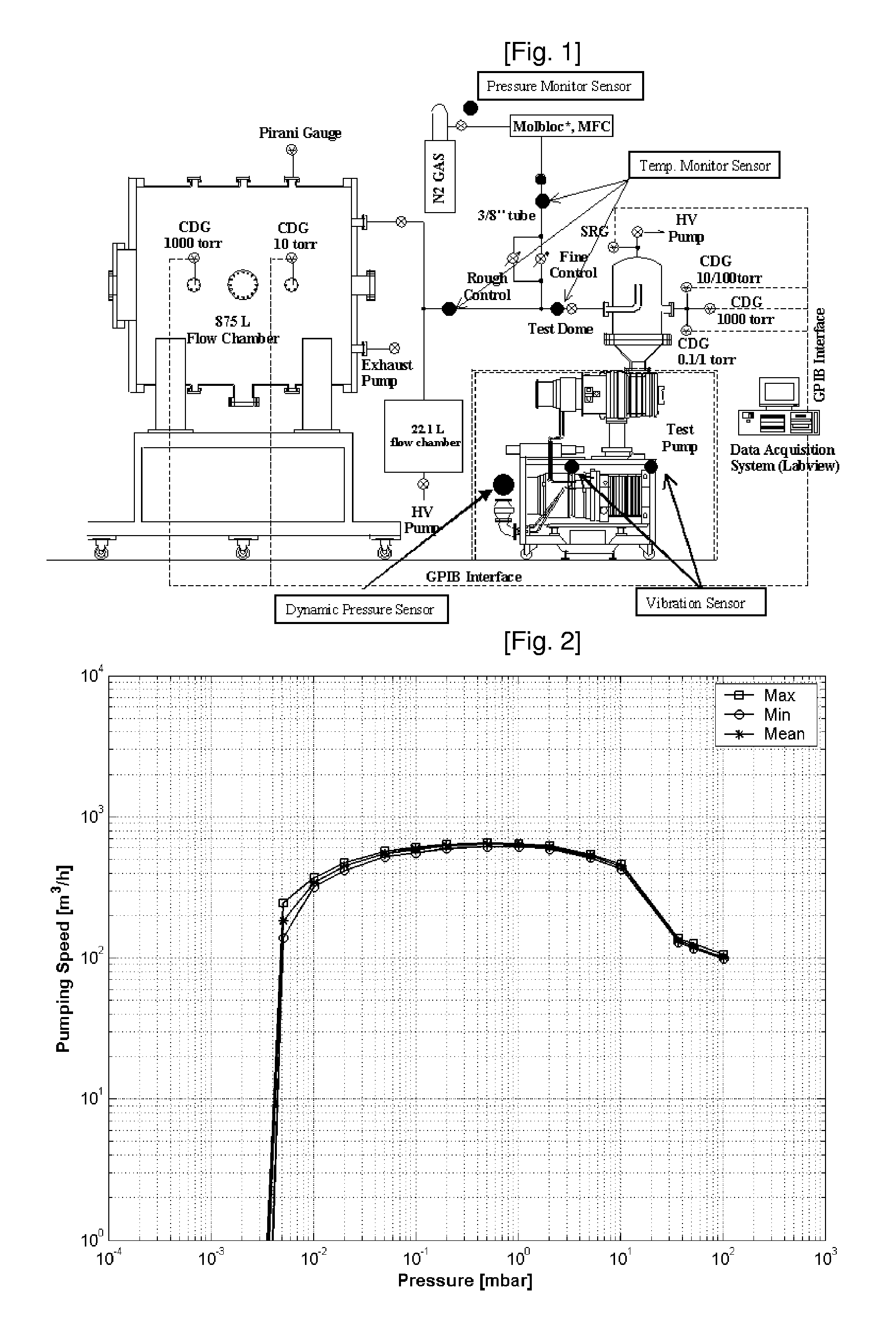
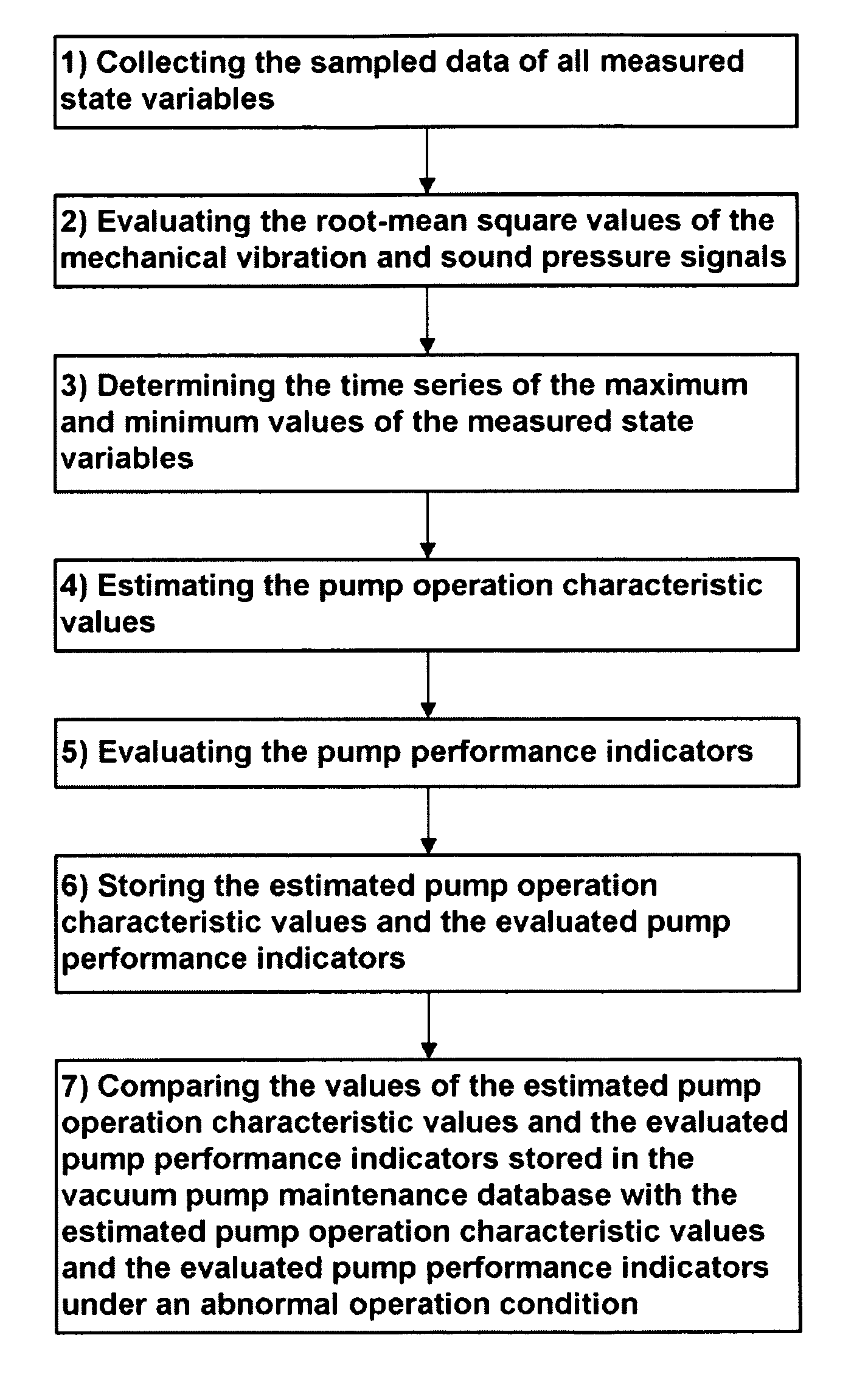
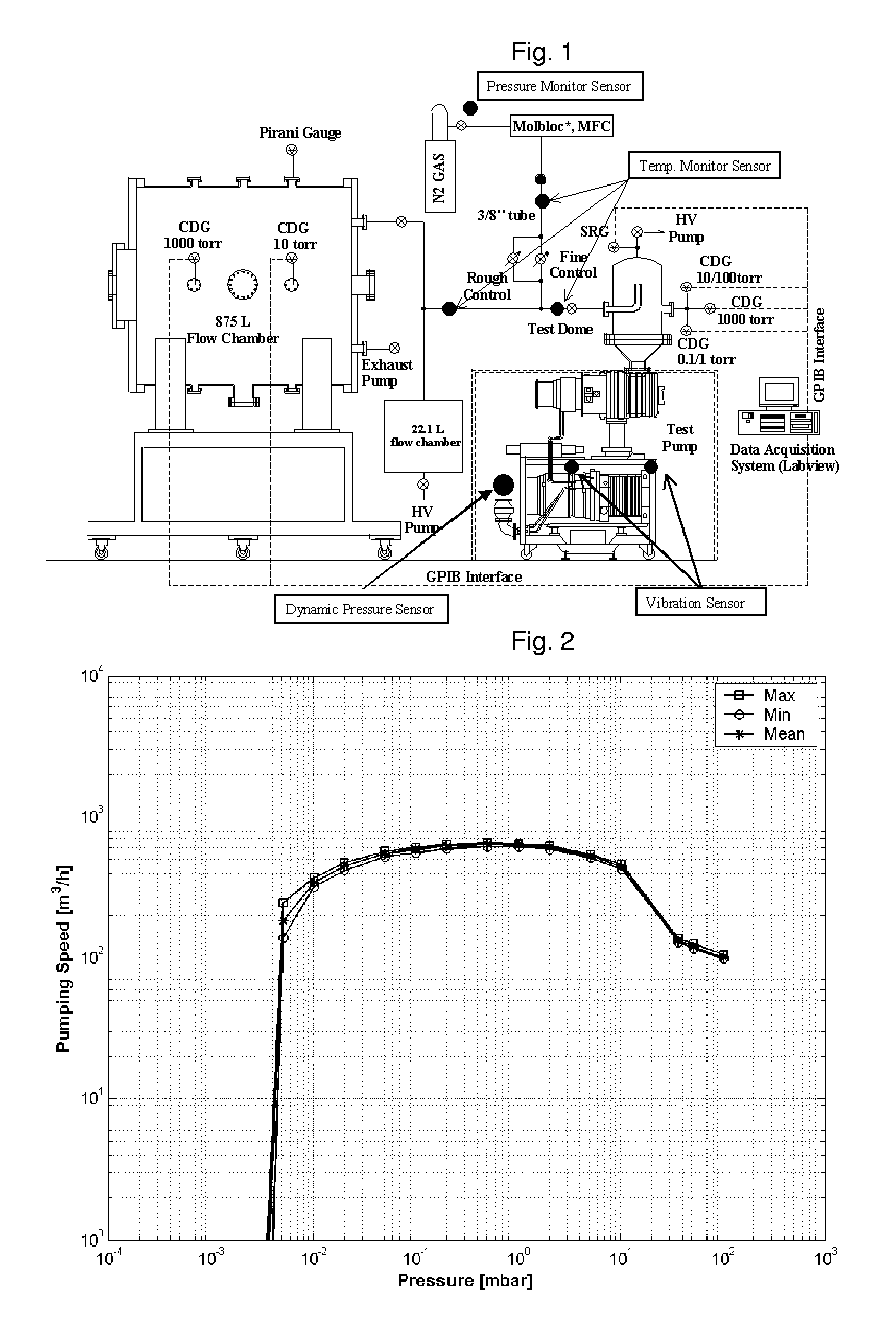
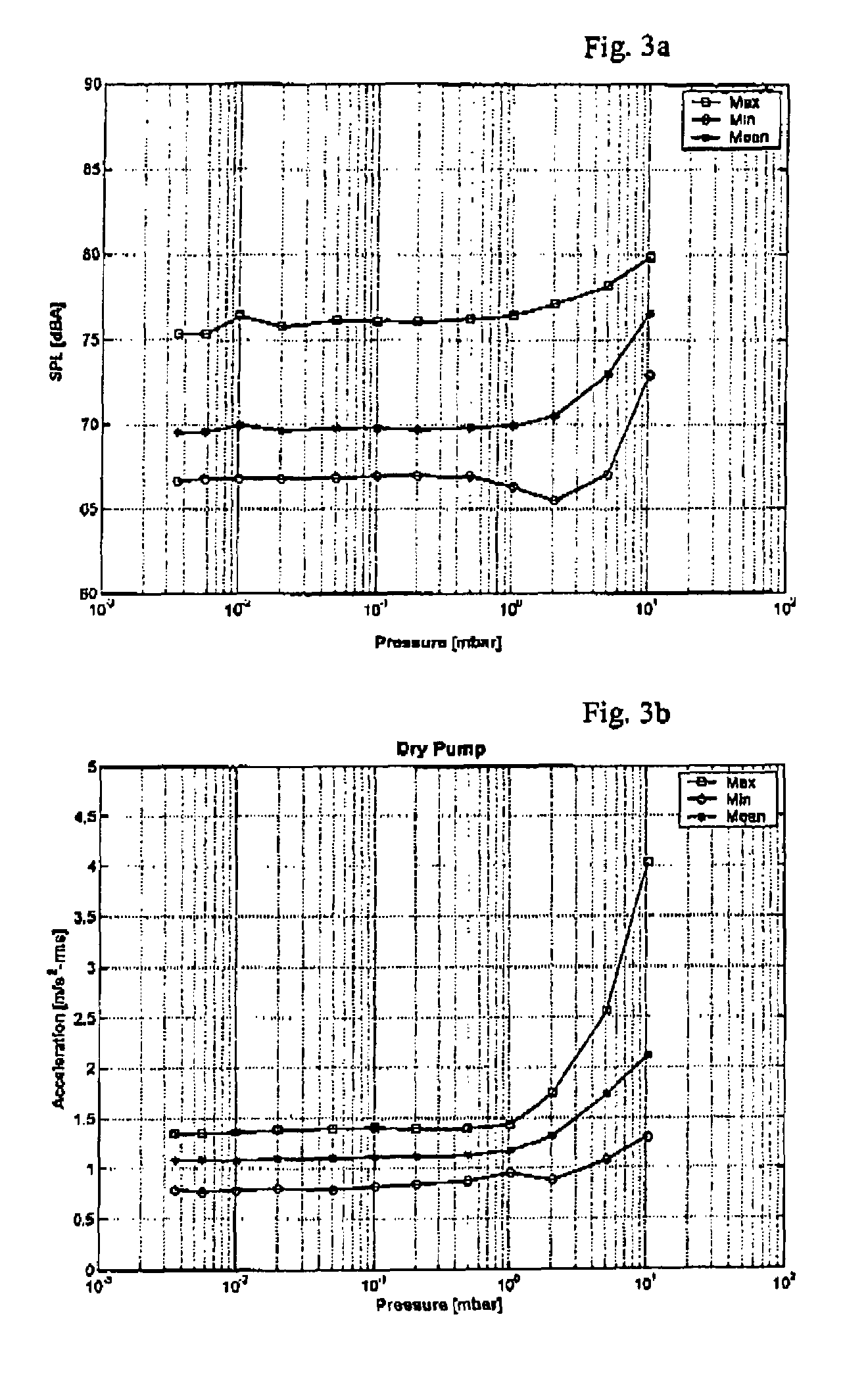
According to the present invention, the most challenging issues in this work have been to find systematic ways of enabling maintenance engineers to decide an adequate time for the replacement of vacuum pumps on the basis of their current performance assessment result. Further, the comparison of the currently evaluated diagnostics analysis results and the initial (or reference) data set is shown to enable maintenance engineers to decide the replacement of the considered vacuum pump according to the evaluated pump performance indicators. This quantitative diagnostic analysis result is expected not only to enable maintenance engineers to decide an adequate time for the replacement of vacuum pumps on the basis of their current performance assessment results but also to improve the reliability and confidence of the predictive maintenance of low vacuum pumps.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
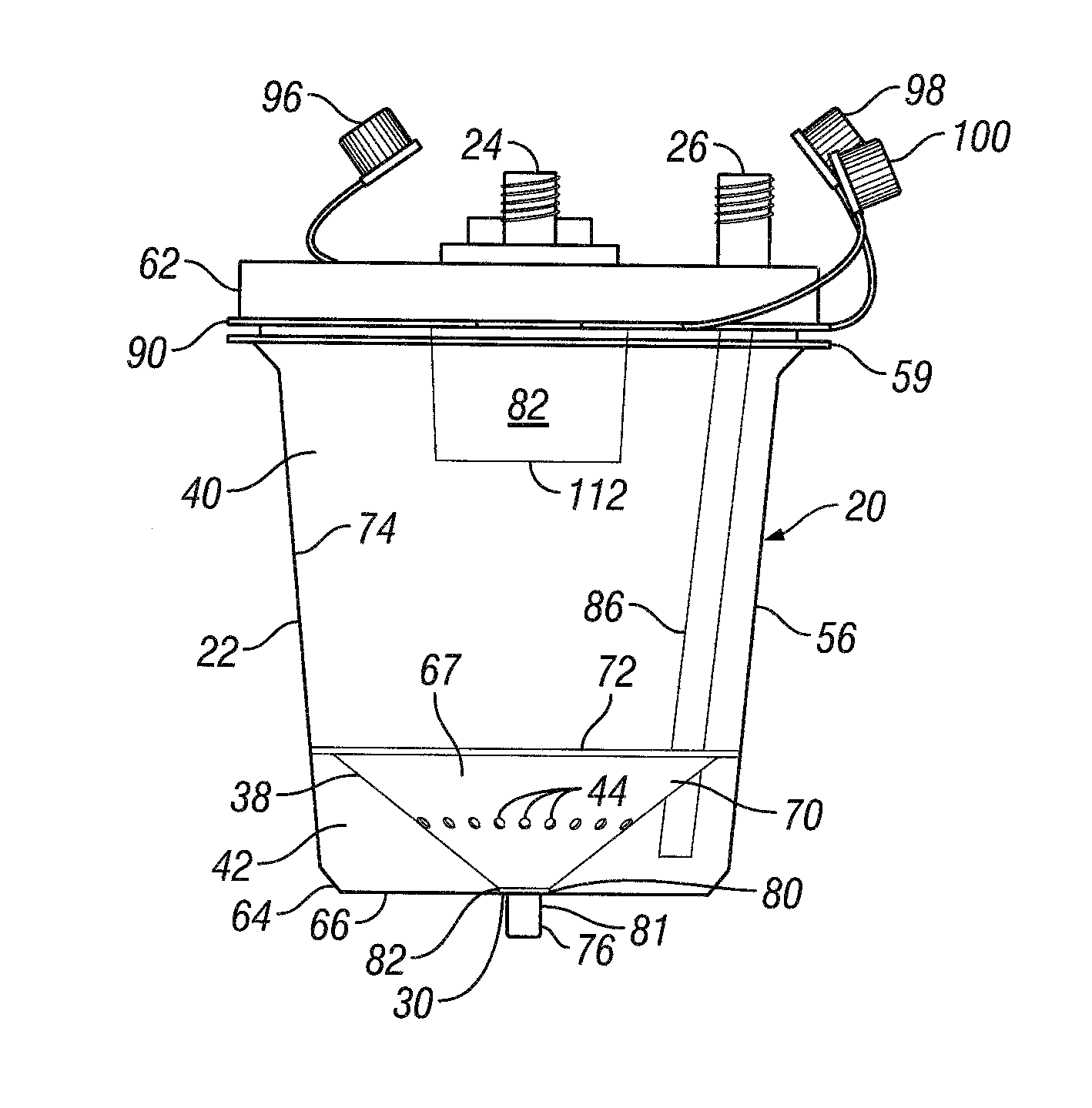
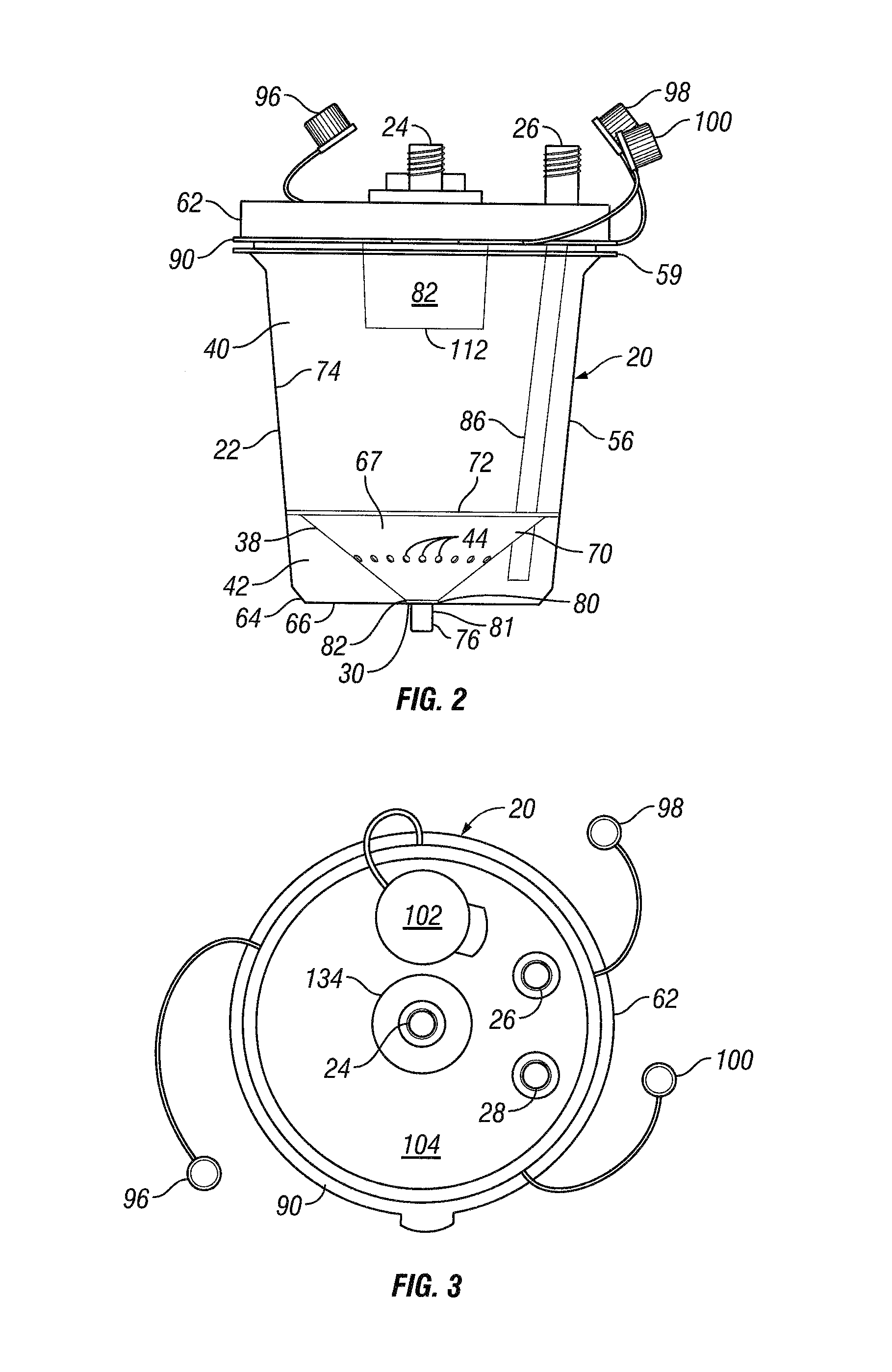
Tissue refining device
A device for use in a system or method of collecting and processing aspirated tissue received from a harvesting device is provided by a canister body having a vacuum port and an evacuation port operable to be placed in communication with a vacuum source, a tissue harvesting port for directing tissue into the canister body received from the harvesting device under suction, and a separator element dividing the canister body into an upper vacuum chamber in communication with the vacuum port and the tissue harvesting port and a lower vacuum chamber in communication with the evacuation port, the separator element including a plurality of apertures enabling fluid to pass between the chambers while restricting tissue from doing the same and a depression with a channel leading to a tissue retrieval port to facilitate processed tissue collection.
Owner:SUMMIT MEDICAL LLC
Low vacuum and vacuum release device for electric rice cooker
The present invention relates to a low vacuum and vacuum release device for an electric rice cooker, the device being capable of releasing a vacuum and maintaining a vacuum state by the rotation of an operation lever. The electric rice cooker has: the operation lever provided at the upper part of a lid; and the low vacuum and vacuum release device provided inside the lid, elastically connected to the operation lever such that when the operation lever is rotated, the device rises so as to open an air inlet, thereby releasing the vacuum while external air flows therein, and when the operation lever is released, the device lowers by the elastic force of a spring so as to maintain the vacuum state by blocking the air inlet, wherein the low vacuum and vacuum release device comprises: a housing provided in the inside of the lid; a first pressure opening / closing operation part provided inside the housing and rising or lowering according to the vapor pressure during cooking, thereby opening or closing the first vapor outlet of a first lower sealing member; a second vacuum release operation part provided inside the housing and rising or lowering according to the rotation of the operation lever, thereby opening or closing the air inlet of a second lower sealing member; and a raising / lowering operation connection part provided at the upper part of the housing and raising or lowering the second vacuum release operation part while being mounted with the operation lever.
Owner:SAMMY CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for producing plane-parallel flakes
InactiveUS6270840B1Increase productionLow production costTransportation and packagingPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsAlcoholFluoride
An apparatus and method technique for producing plane-parallel flakes is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention is realized through a multi-chamber apparatus for producing plane-parallel flakes from layers vapor deposited in vacuum on an endlessly circulating substrate. The present invention includes the sequential steps of: vapor deposition of a separating agent layer in high vacuum on the endlessly circulating substrate; vapor deposition of one or more layers of metal, oxides, fluorides, and nitrides in high vacuum on the separating agent layer; and stripping the vapor deposited layers from the endlessly circulating substrate under low vacuum. The vapor deposited layers are subsequently present in a separate vacuum stage separated from the vapor deposition chamber by dynamic locks as a suspension of fine flakes in a mixture of solvent. and separating agent. The suspension may continuously or intermittently be transferred out of the separate vacuum stage for further processing. The solvent may be water in a vacuum environment of more than 20 mbar or secondary or tertiary alcohols at more than 0.05 mbar.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM CORP +1
Dedicated Superconductor MRI Imaging System
ActiveUS20100066368A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceThermal isolationEngineering
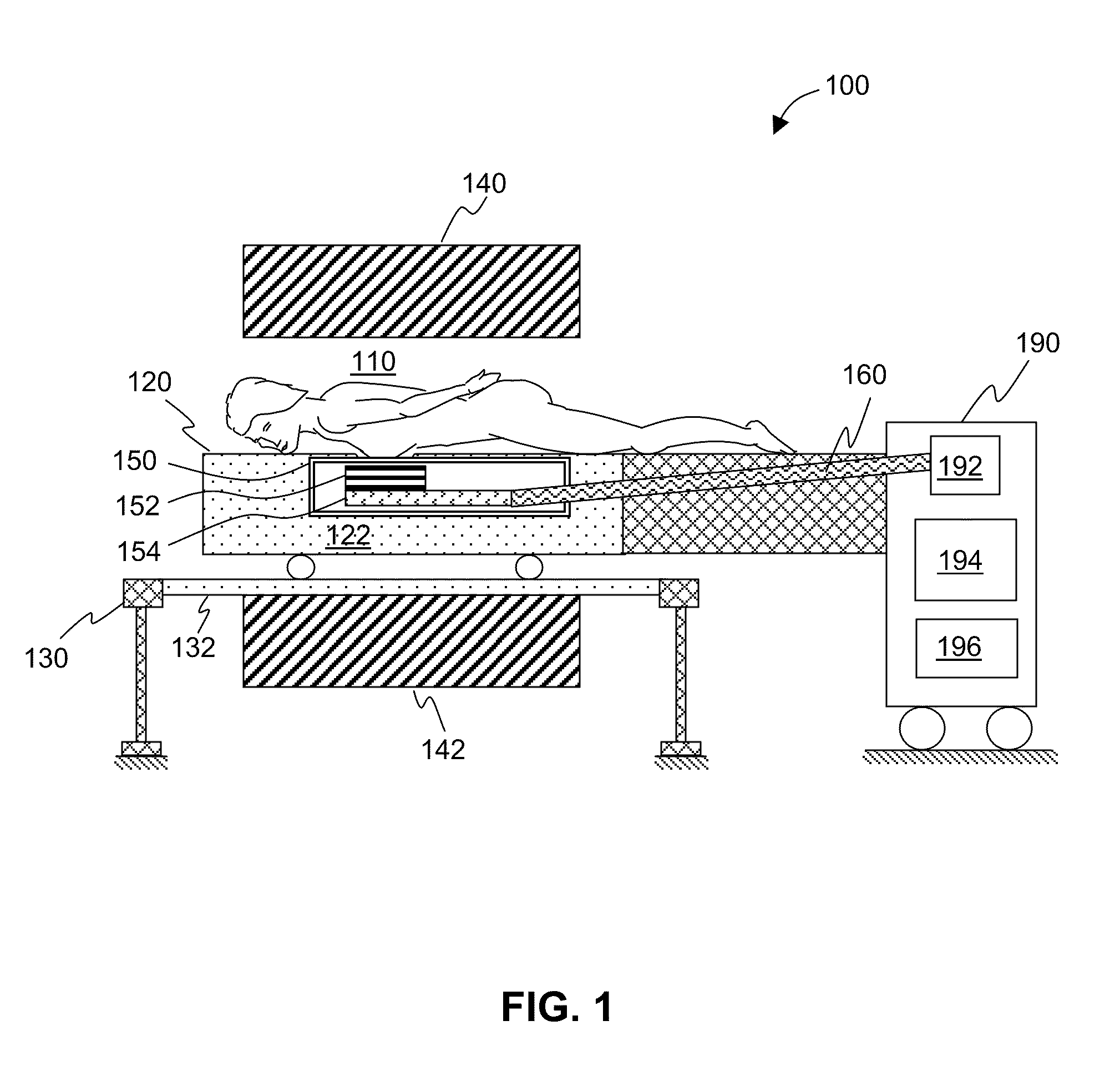
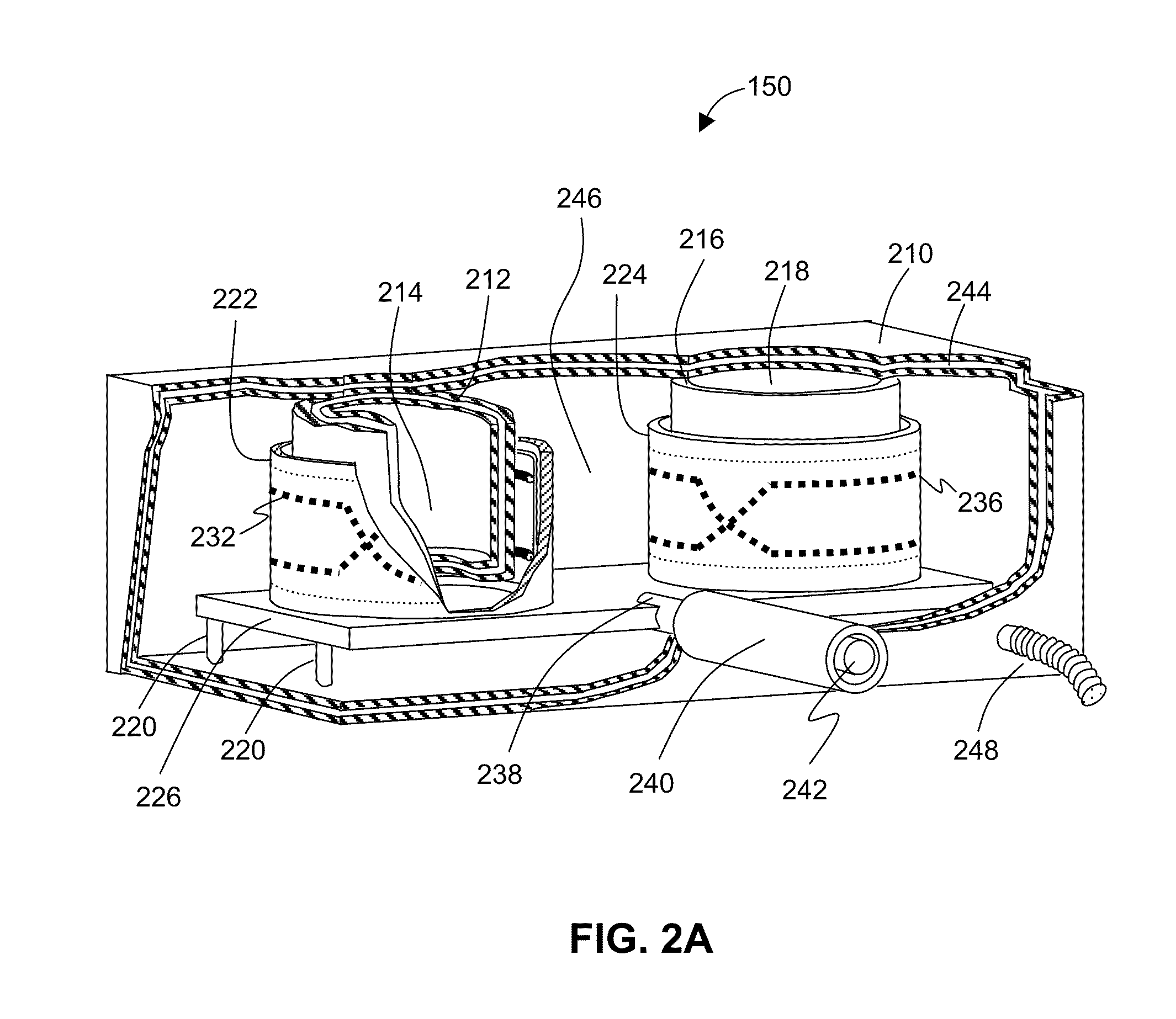
The present invention relates to dedicated superconductor magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF apparatus and method of constructing the same. One Embodiment of the present invention provides an MRI breast imaging apparatus comprising an examination region, a patient support, at least one vacuum thermal isolation housing, a main magnet system, and a cryogenic system. The vacuum thermal isolation housing comprises a low vacuum space between at least one inner and an outer high vacuum enclosure. The low vacuum space hosts at least one superconductor RF coil and a heat sink assembly therein. The RF coil is in thermal contact with the heat sink assembly that is coupled to the cryogenic system through a heat pipe to achieve and maintain a desired low temperature at the superconductor RF coil. The system provides a local examination region substantially surrounded by the superconductor RF coil.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Purification apparatus and method for solar energy level polysilicon
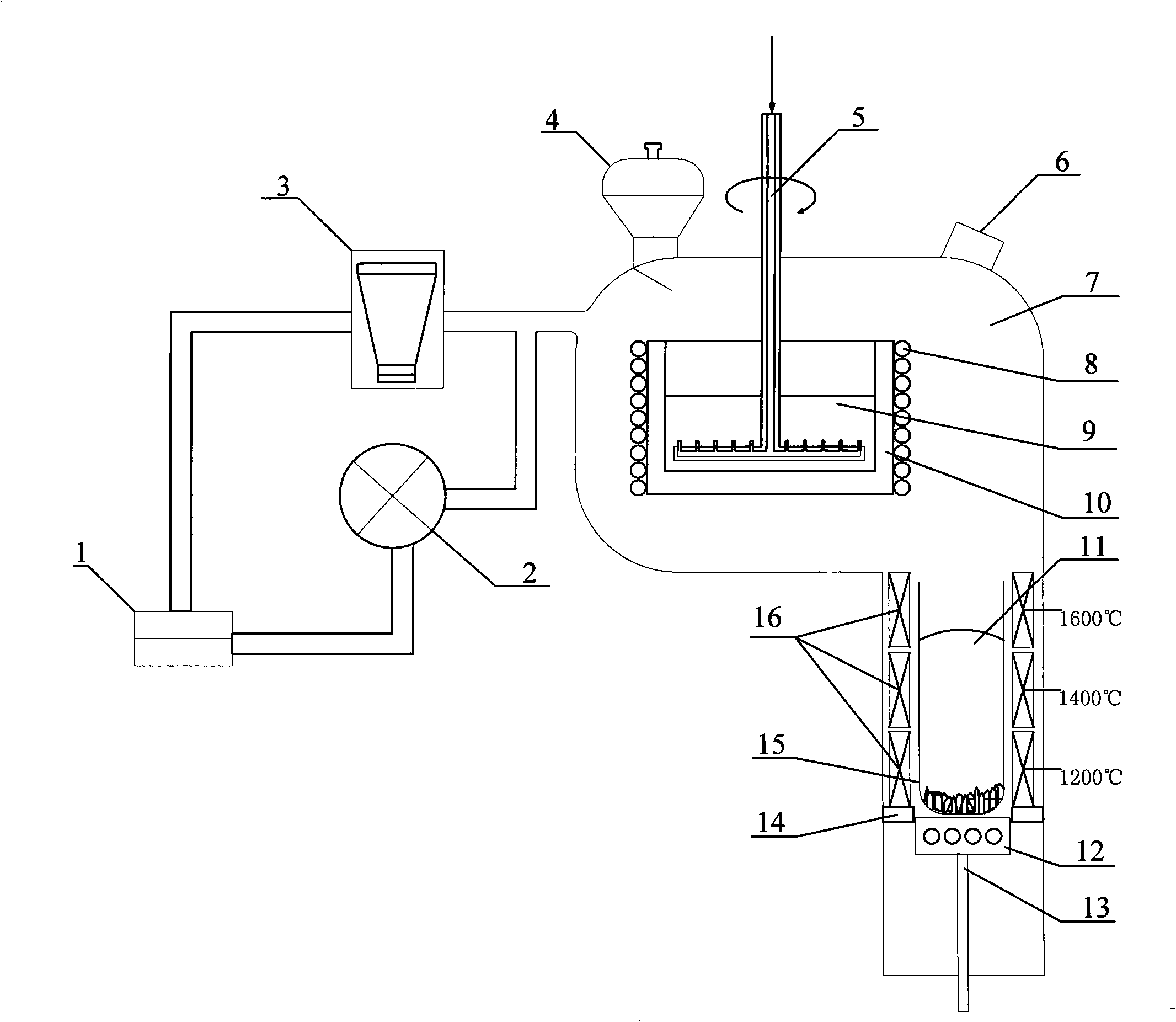
Disclosed are a purification device as well as a purification method of solar-grade polysilicon, relating to a polysilicon, which provides a purification device and a purification method of solar-grade polysilicon characterized by low cost, high purity, simple process, easy operation and suitability for large-scale production. The purification device is equipped with a vacuum system, a melting system and a directional solidification system; wherein the vacuum system is provided with a mechanical rotary vane pump, a lobed element pump and an oil diffusion pump, and the melting system is provided with a vacuum chamber, a secondary feeder, an observation window, a rotary ventilation device which can be raised and lowered, an induction coil and a graphite crucible; and the directional solidification system is disposed at the lower part of the vacuum chamber and is equipped with an electric resistance-wire heating and holding furnace, a graphite mold, a holding furnace frame, a water-cooled copper tray and an elevating lever which can control speed. The metal silicon is treated by induction heating to be molten, the oxidizing gas is fed under conditions of low vacuum and high temperature to remove boron, and then under conditions of high temperature and high vacuum to remove phosphorus, and finally the molten silicon solution is poured into a directional mold to strictly conduct directional solidification to remove metal impurities.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Precision diagnostic method for the failure protection and predictive maintenance of a vacuum pump and a precision diagnostic system therefor
InactiveUS7653512B2ConfidenceImprove reliabilityPlug gaugesMeasurement arrangements for variableData setLow vacuum
According to the present invention, the most challenging issues in this work have been to find systematic ways of enabling maintenance engineers to decide an adequate time for the replacement of vacuum pumps on the basis of their current performance assessment result. Further, the comparison of the currently evaluated diagnostics analysis results and the initial (or reference) data set is shown to enable maintenance engineers to decide the replacement of the considered vacuum pump according to the evaluated pump performance indicators. This quantitative diagnostic analysis result is expected not only to enable maintenance engineers to decide an adequate time for the replacement of vacuum pumps on the basis of their current performance assessment results but also to improve the reliability and confidence of the predictive maintenance of low vacuum pumps.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Miniature mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS20120138790A1Small sizeReduce weightMiniaturised spectrometersIsotope separationIon beamMass analyzer
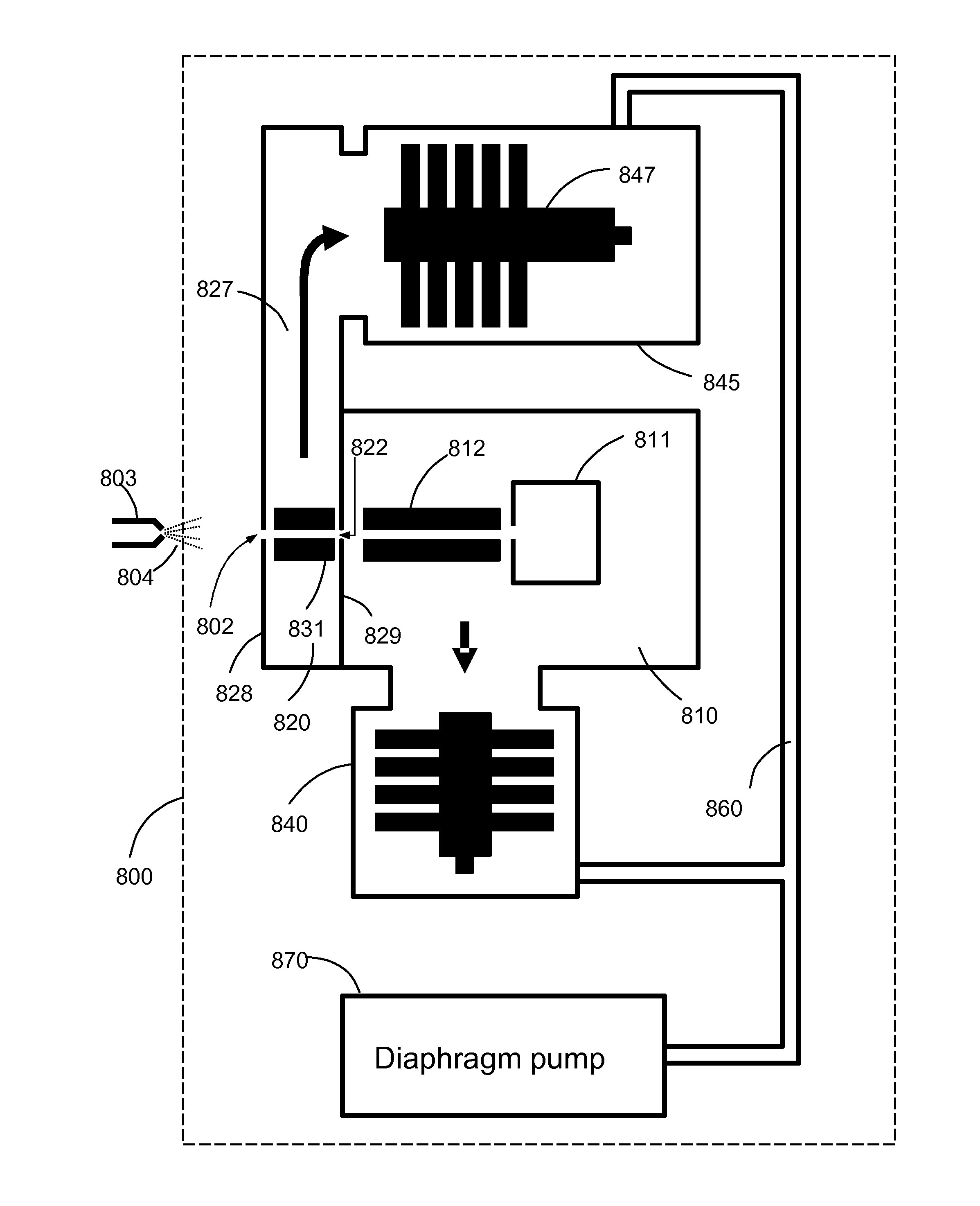
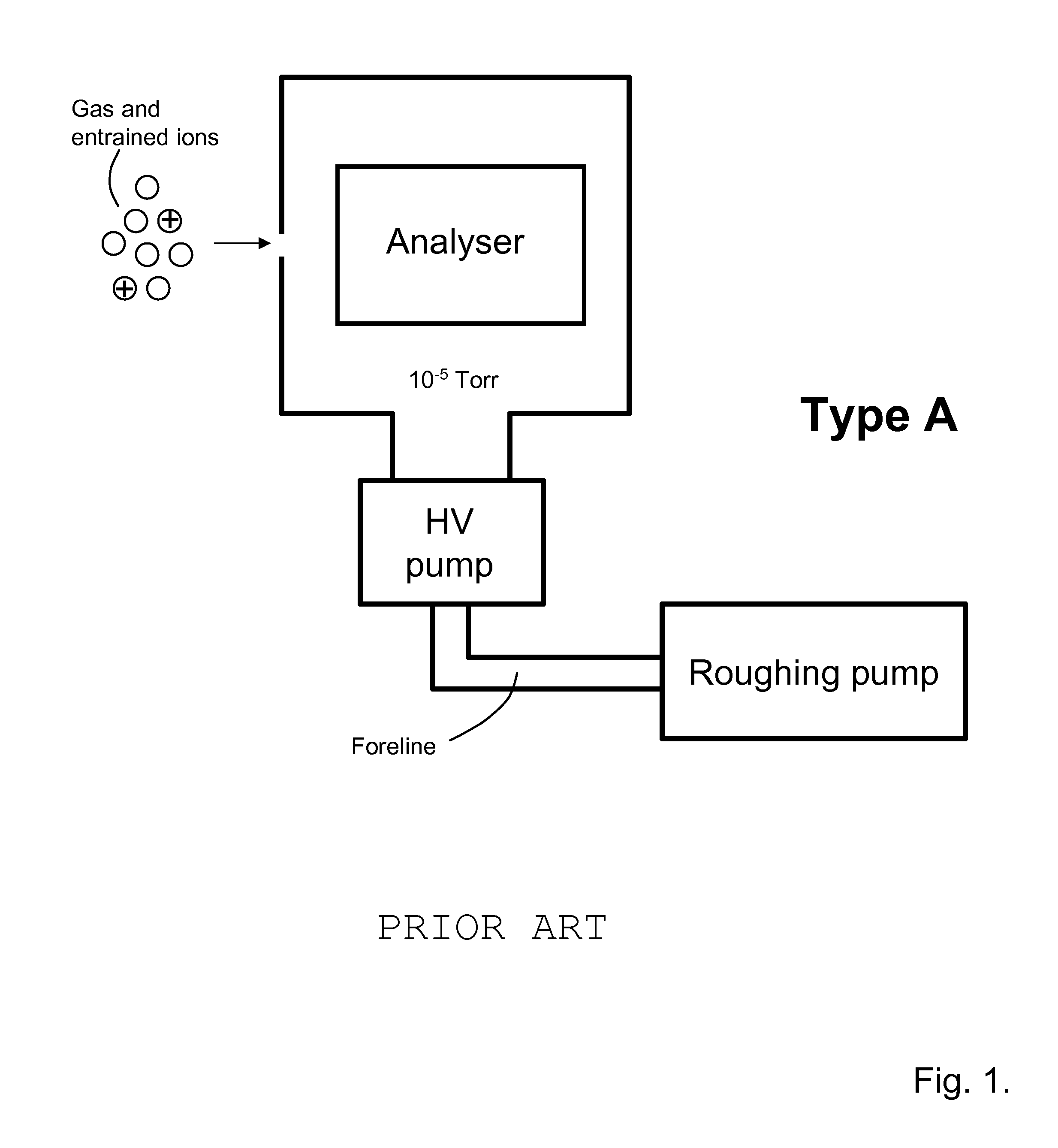
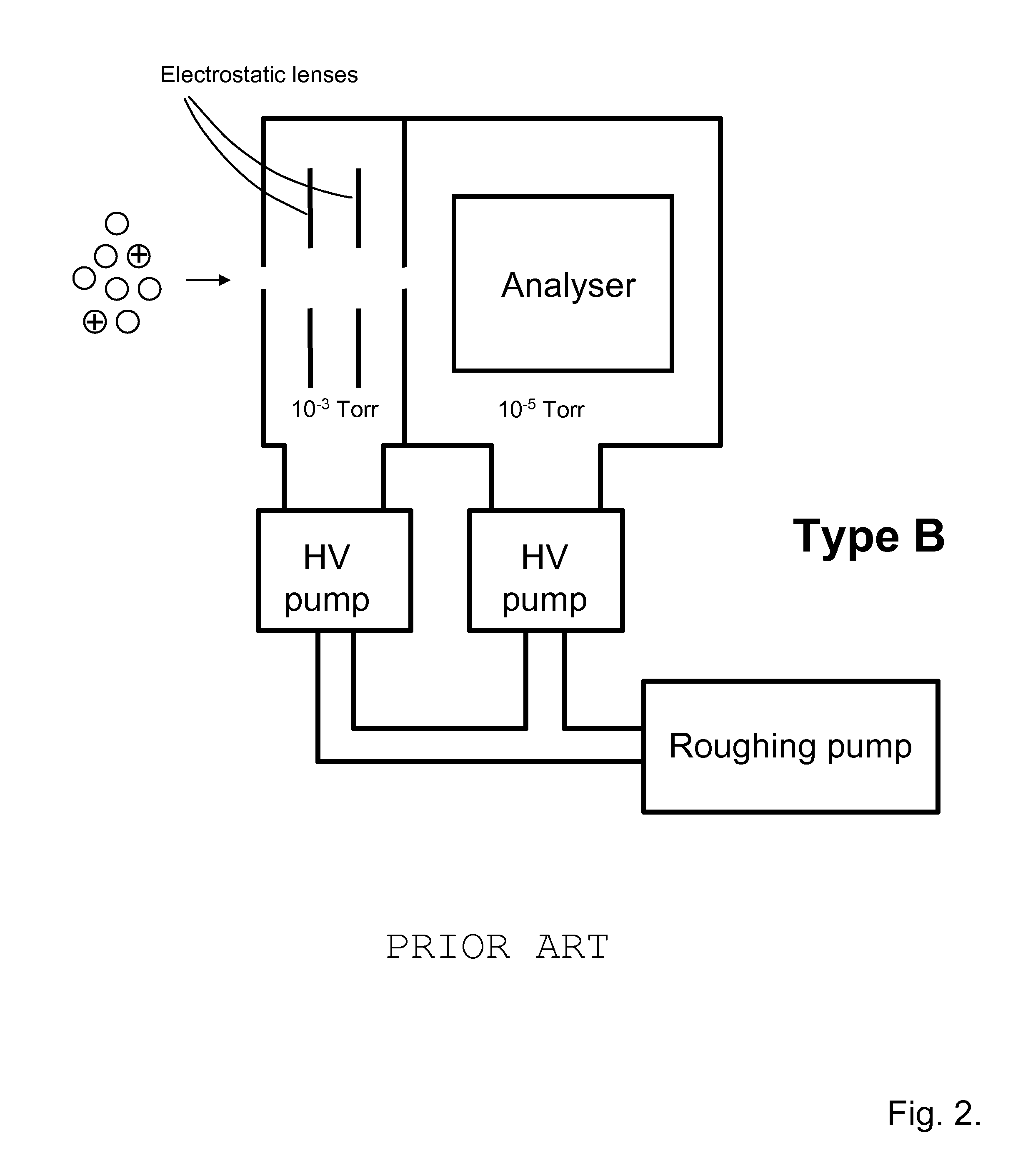
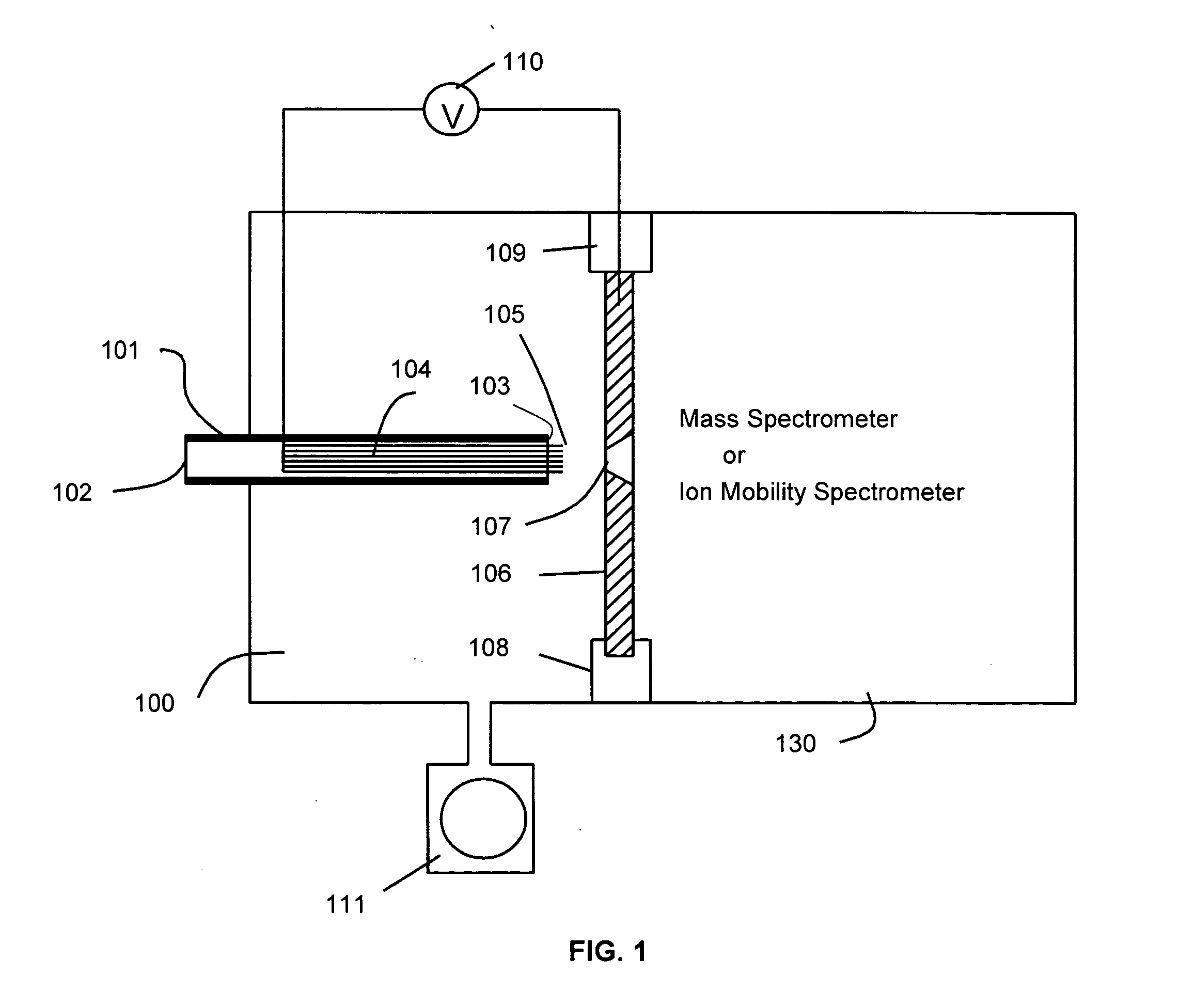
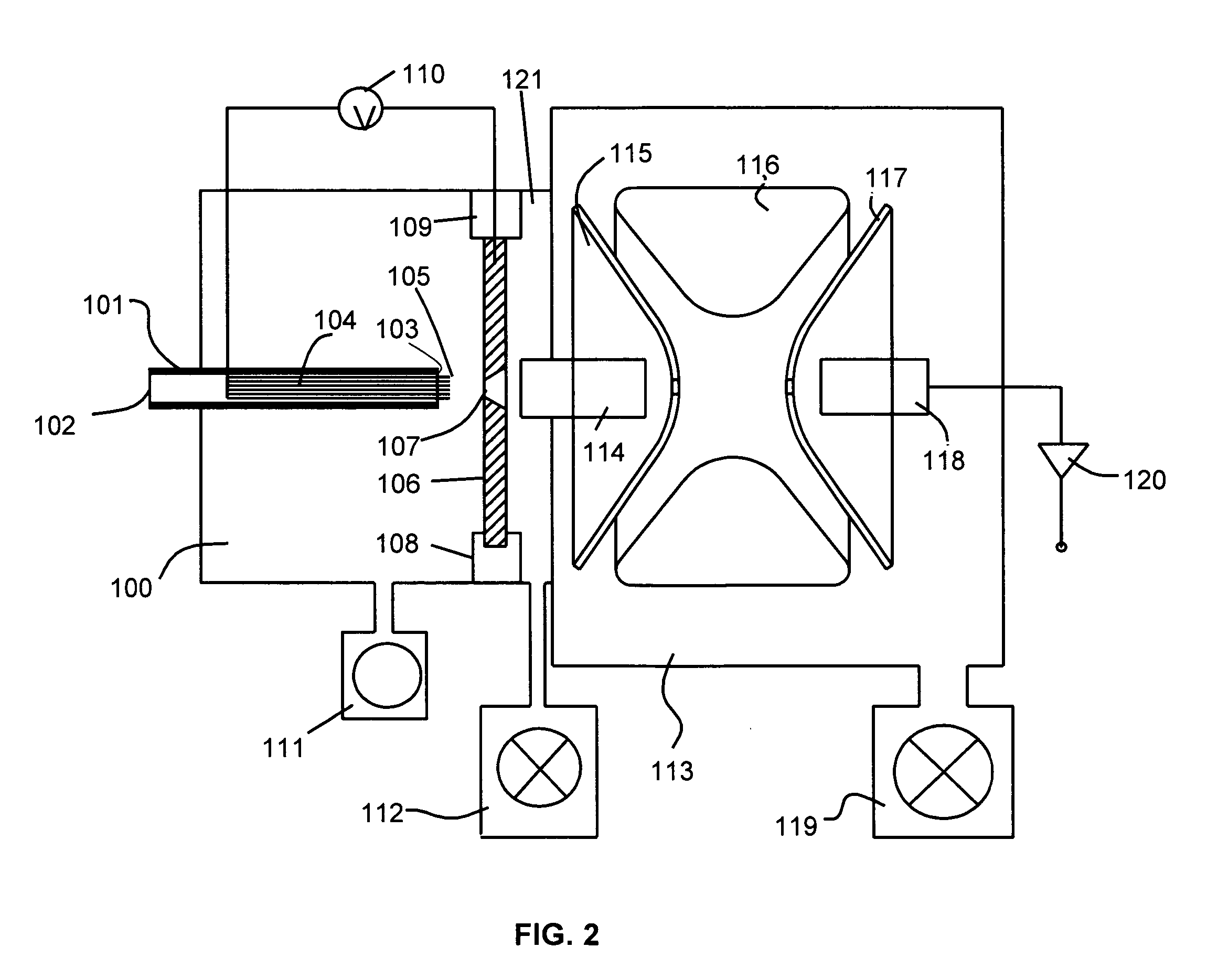
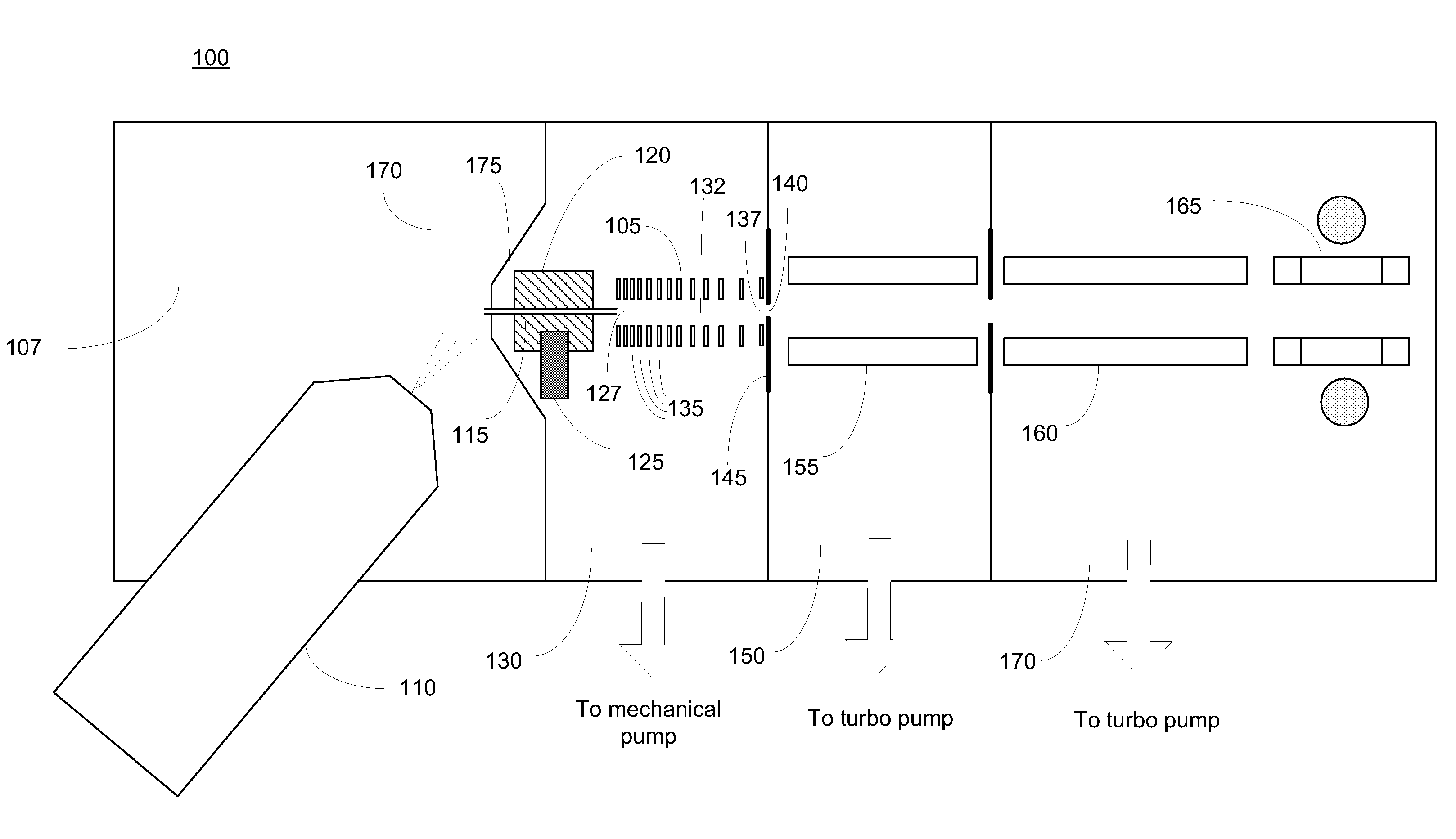
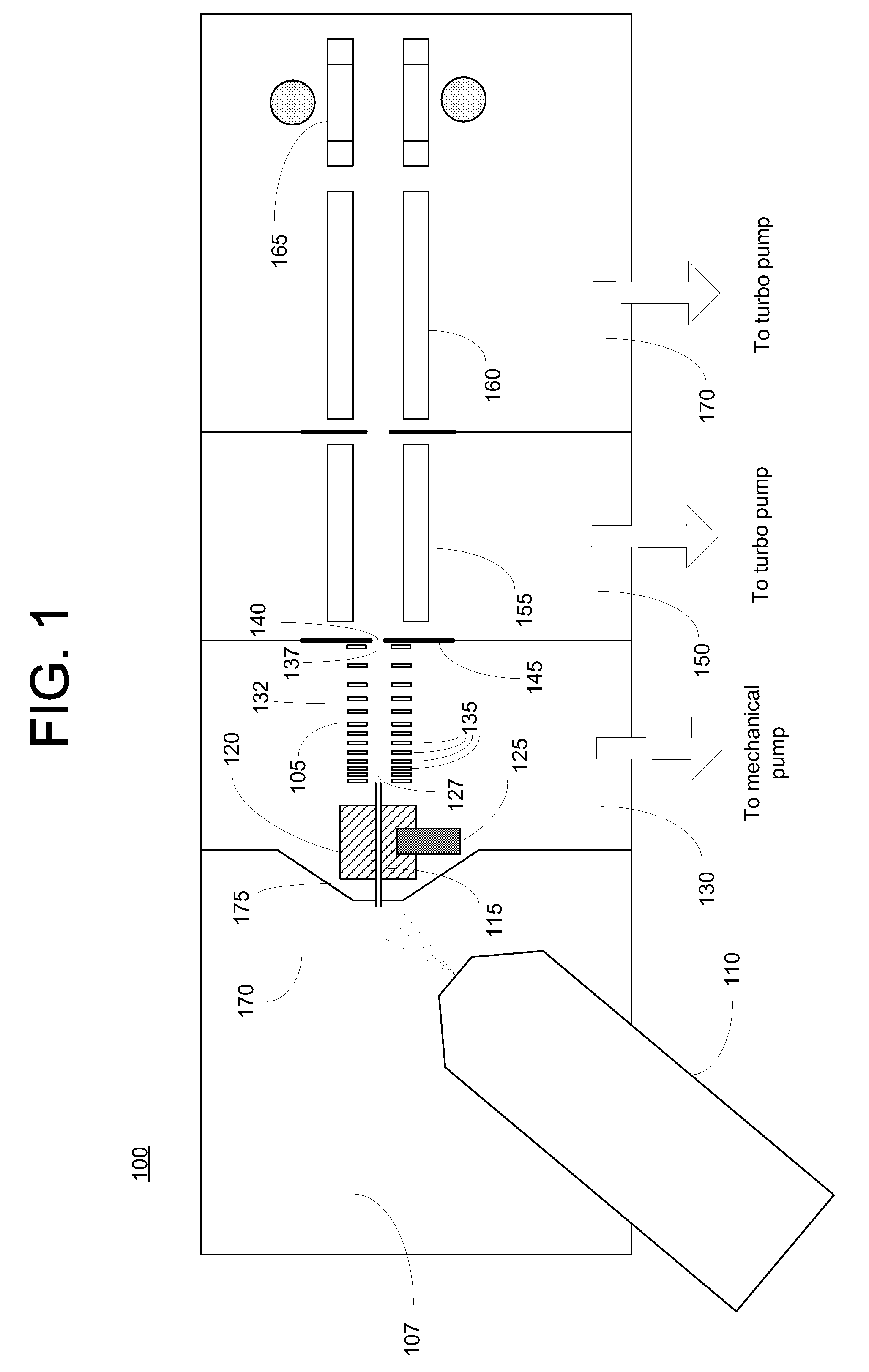
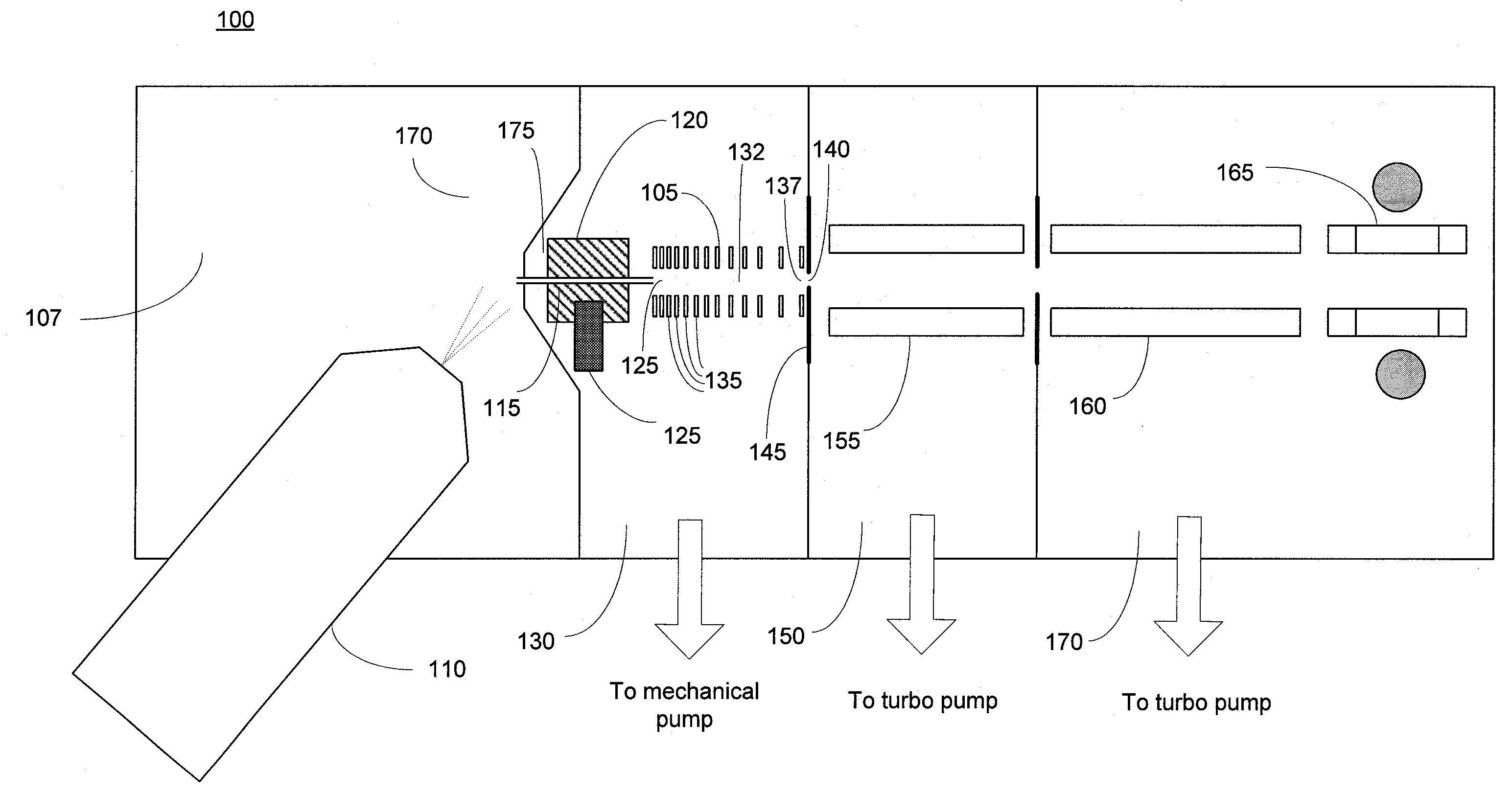
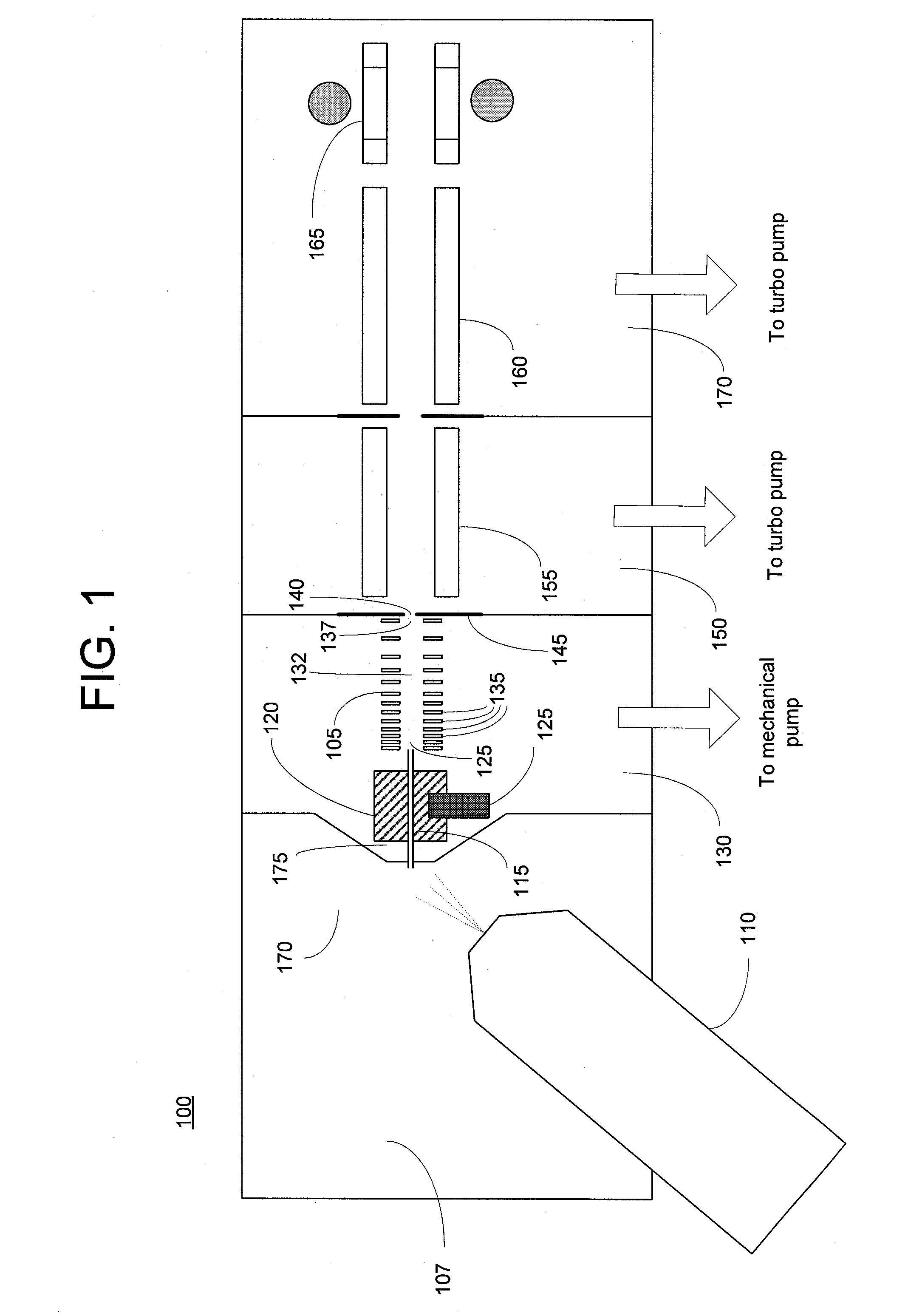
A miniature mass spectrometer that may be coupled to an atmospheric pressure ionisation source is described. Ions pass through a small orifice from a region at atmospheric pressure or low vacuum, and undergo efficient collisional cooling as they transit a very short, differentially pumped ion guide. A narrow beam of low energy ions is passed through a small aperture and into a separate chamber containing the mass analyser.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Corona discharge ionization sources for mass spectrometric and ion mobility spectrometric analysis of gas-phase chemical species
InactiveUS20070007448A1Improve ionization efficiencyImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsChemical speciesGas phase
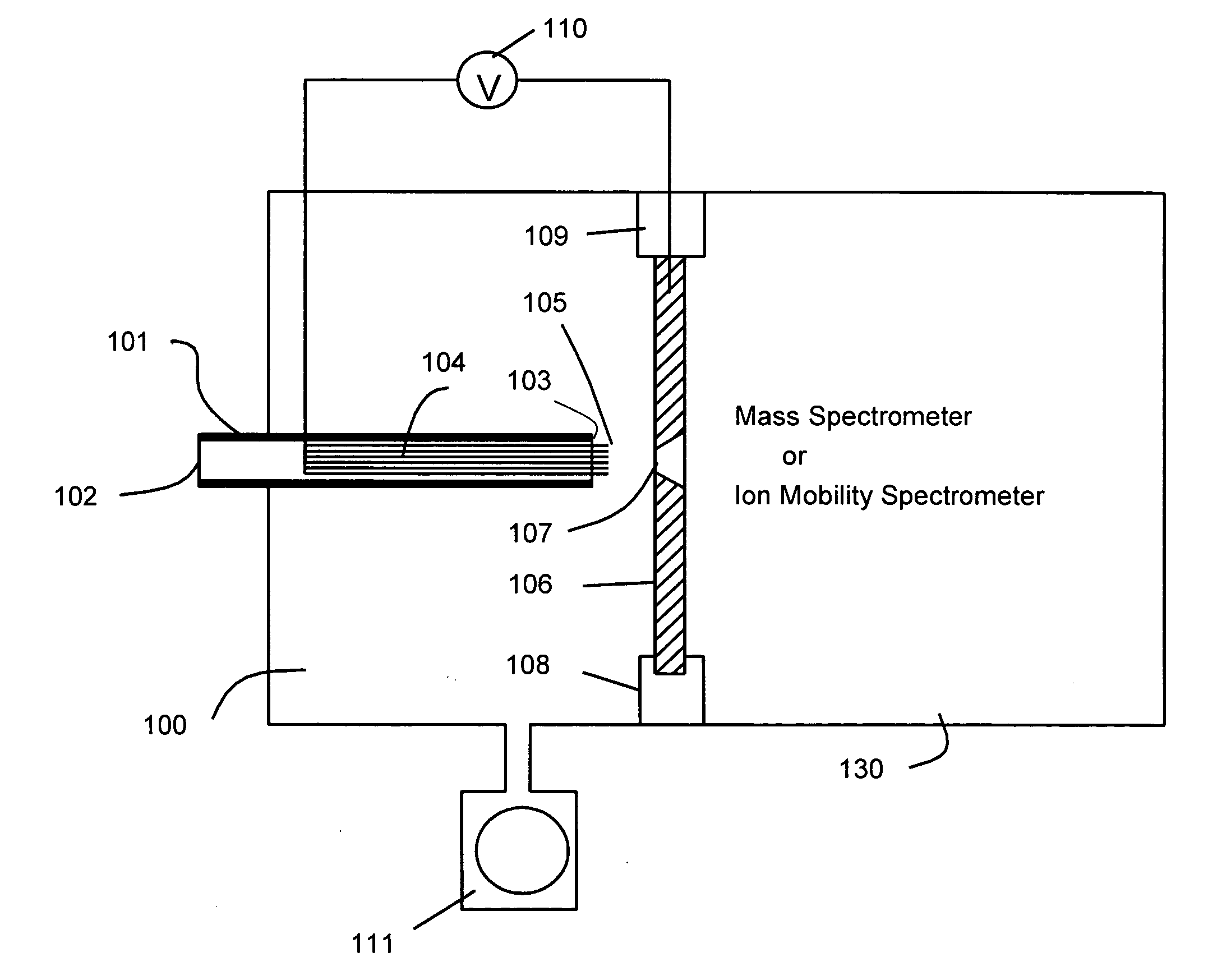
A corona discharge mass spectrometer or an ion mobility spectrometer is provided with a robust corona discharge ionization source. The corona discharge ionization source, which can be operated at atmospheric pressures or at low vacuum, includes a multi-thread electrode and plane electrode. The multiple thread electrode has multiple discharge tips which provide redundancy, and improve ionization stability and the reliability and efficiency of the ionization source.
Owner:WANG YANG
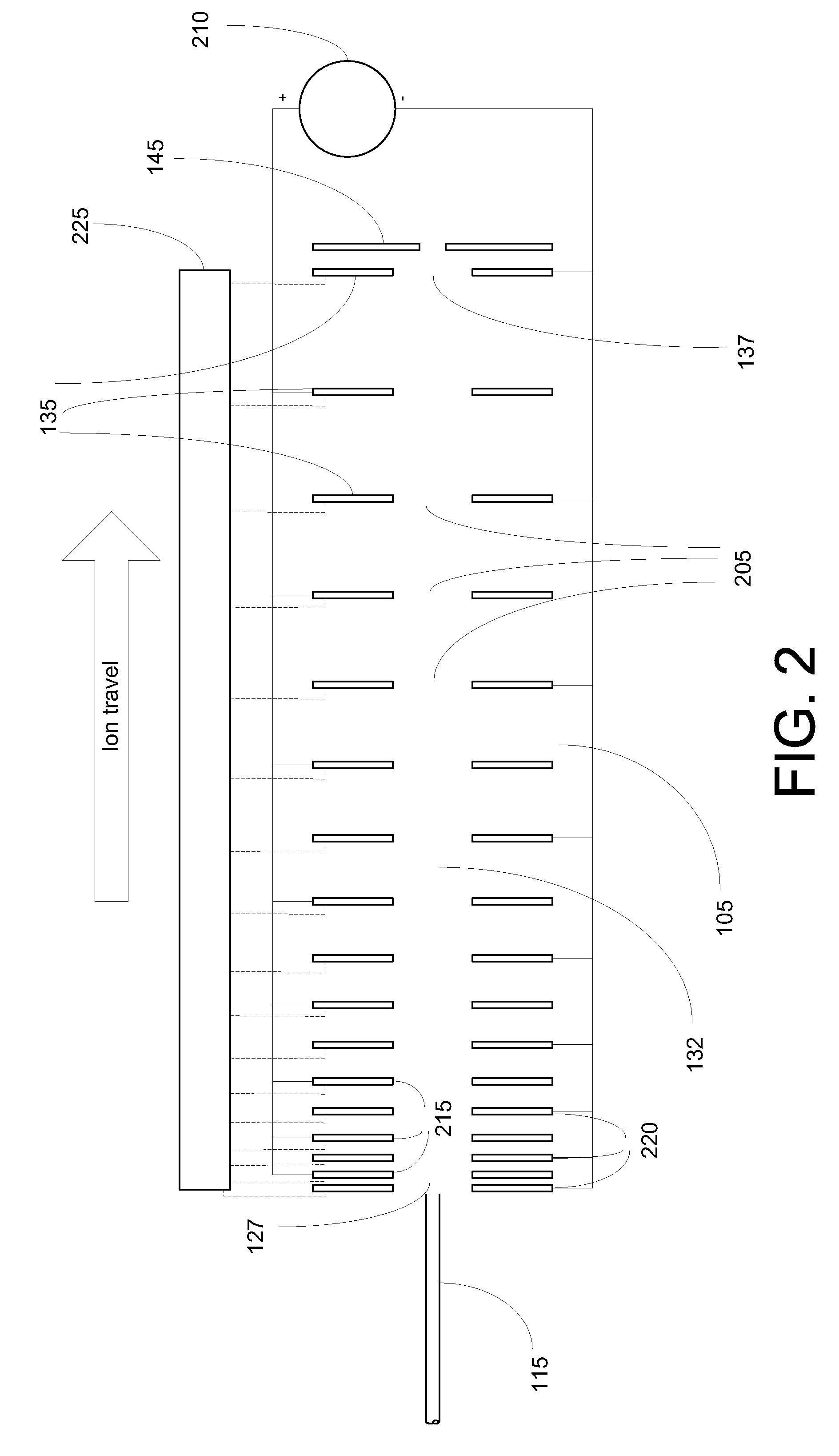
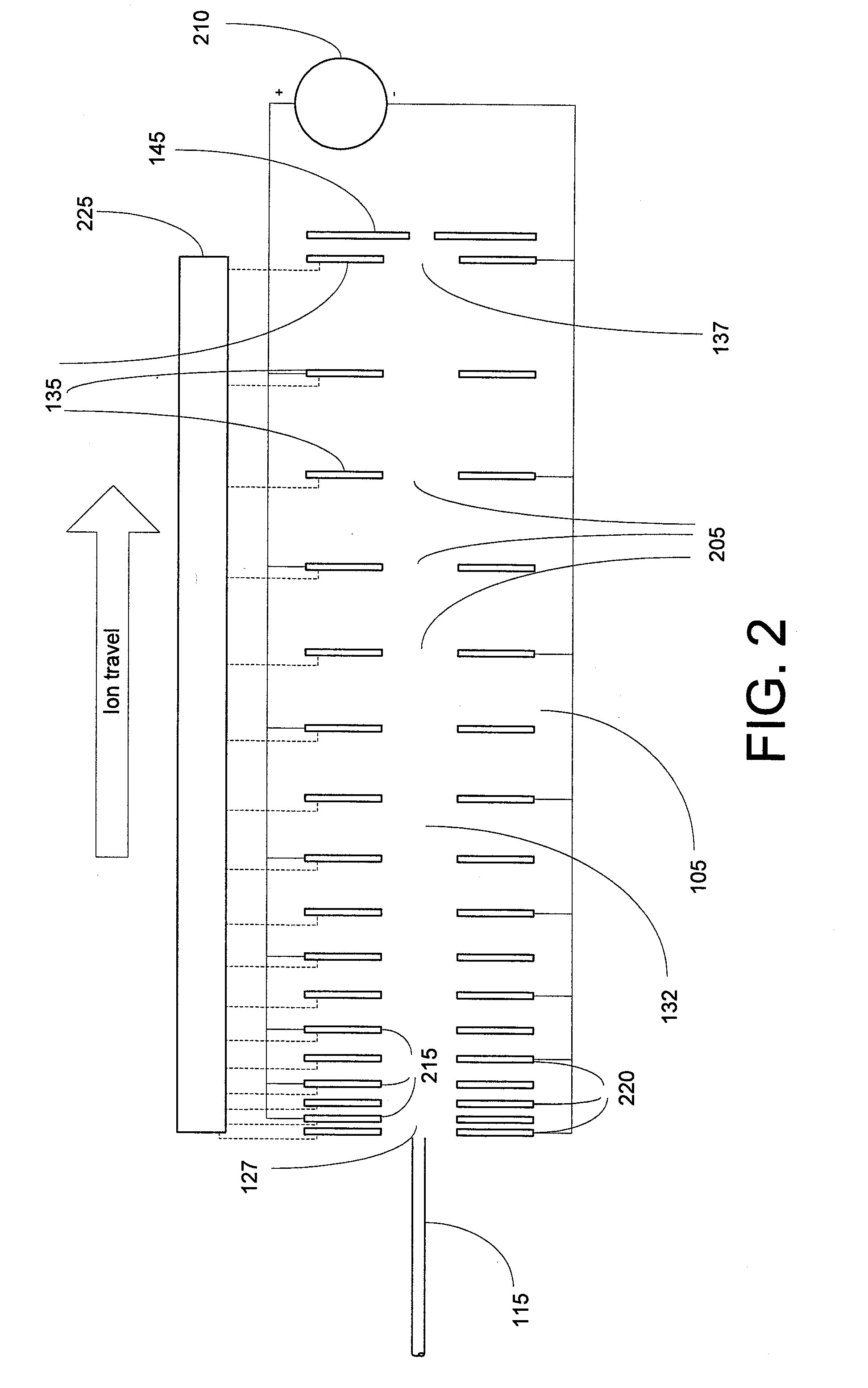
Ion transport device and modes of operation thereof
ActiveUS7781728B2Reduce streamingElectrostatic separatorsParticle separator tubesVoltage amplitudeLight beam
A device for transporting and focusing ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart electrodes to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. In order to create a tapered field that focuses ions to a narrow beam near the device exit, the inter-electrode spacing or the oscillatory voltage amplitude is increased in the direction of ion travel.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Polyester fibres and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106367835AImprove dyeing effectEasy to processSpinnerette packsMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentSlurryLow vacuum
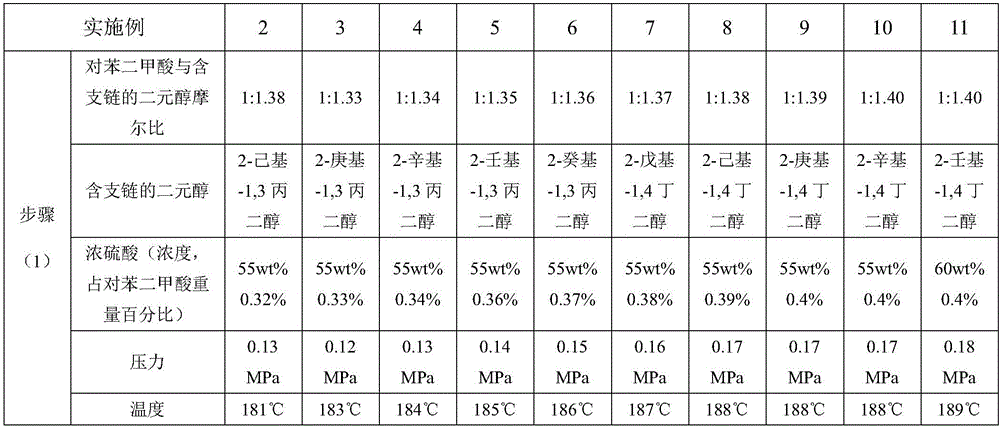
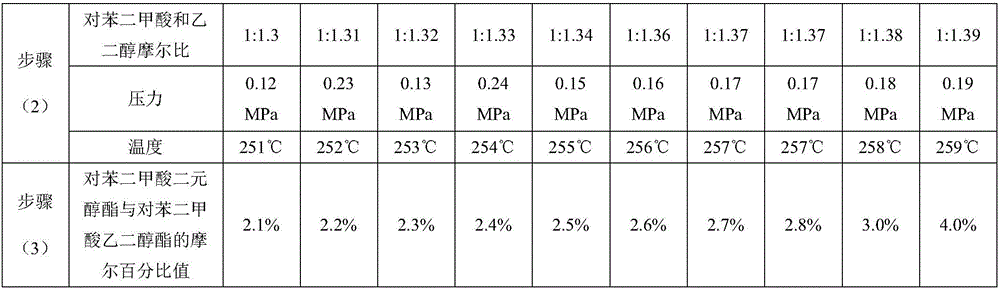
The invention relates to polyester fibres and a preparation method thereof. The raw material of the polyester fibres is modified polyester which consists of a terephthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment and a branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol chain segment. The preparation method of the polyester fibres comprises the following steps: performing esterification reaction on terephthalic acid and branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol under the catalysis of concentrated sulphuric acid to obtain terephthalic acid dihydric alcohol ester; then, preparing the terephthalic acid and the ethylene glycol into slurry, and performing the esterification reaction on the slurry to obtain the terephthalic acid ethylene glycol ester; finally, stirring and mixing the terephthalic acid dihydric alcohol ester and the terephthalic acid ethylene glycol ester, and performing condensation polymerization in a low vacuum stage and a high vacuum stage under the action of a catalyst and a stabilizing agent to obtain modified polyester; metering, extruding, cooling, oiling, stretching, heat-setting and winding the polyester to prepare the polyester fibres. The increasing amplitude of the spatial gaps of the polyester fibres is much higher than that of branched chain-free polyester fibres at the same temperature, which is beneficial to the degree of micro particles, such as a dye, that enter the polyester; the dyeing rate is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS20090230304A1Low costSave spaceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning tunneling microscopeScanning electron microscope
In a VP-SEM that uses gas multiplication induced within a low-vacuum sample chamber and uses a method of detecting a positive displacement current, a secondary electron detector for the VP-SEM that responds at high speed, which can acquire a TV-Scan rate image at a low cost while saving a space is provided. A secondary electron detector is formed by forming the electron supplying electrode and the detection electrode on the flexible thin film type substrate such as a polyimide film, etc., by an etching method. Thereby, the space can be saved while realizing low cost due to mass production. Further, the ion horizontally moving with respect to the surface of the secondary electron detector is detected and the ion moving in a vertical direction returned to the sample holder is not detected, making it possible to realize a high-speed response.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
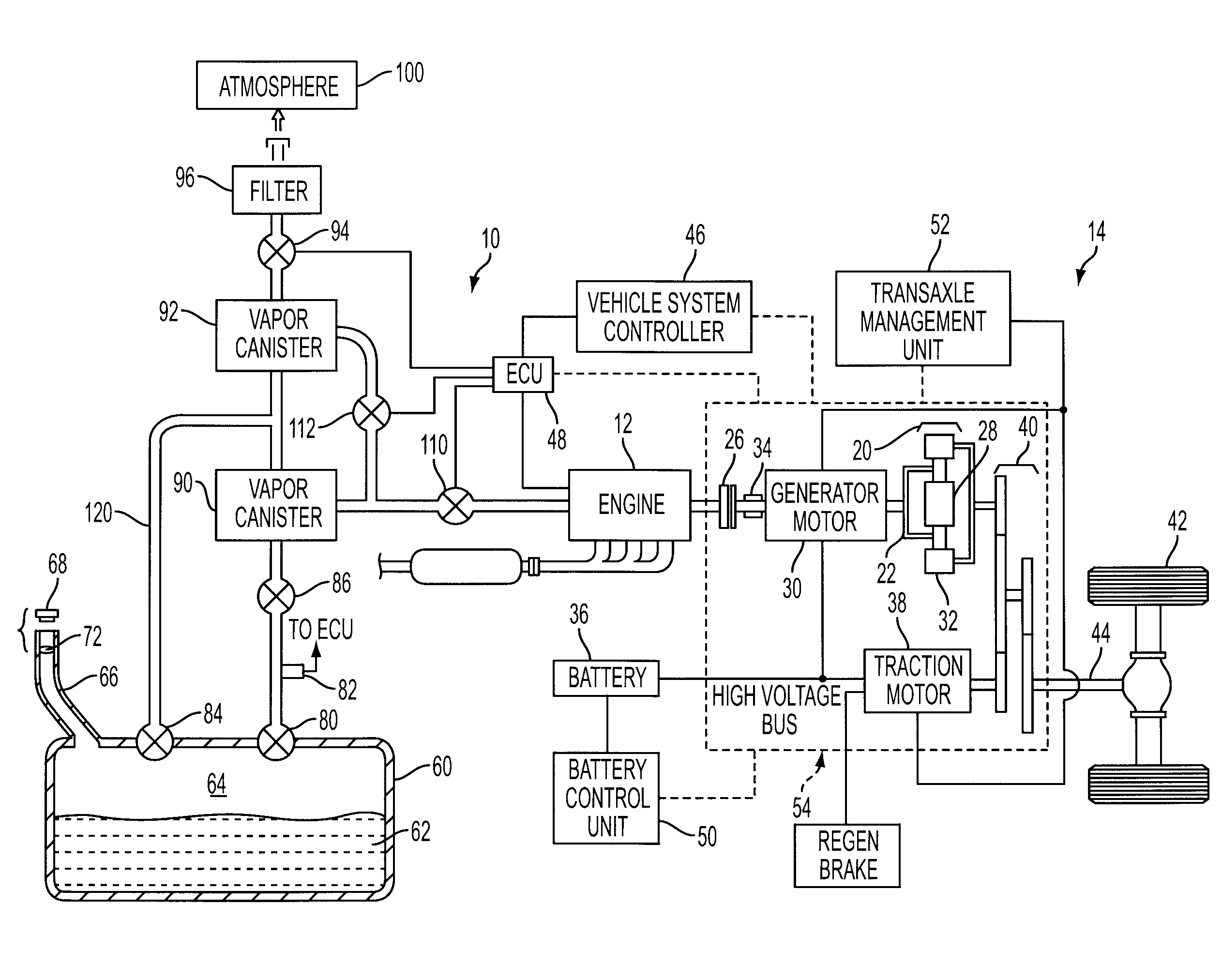
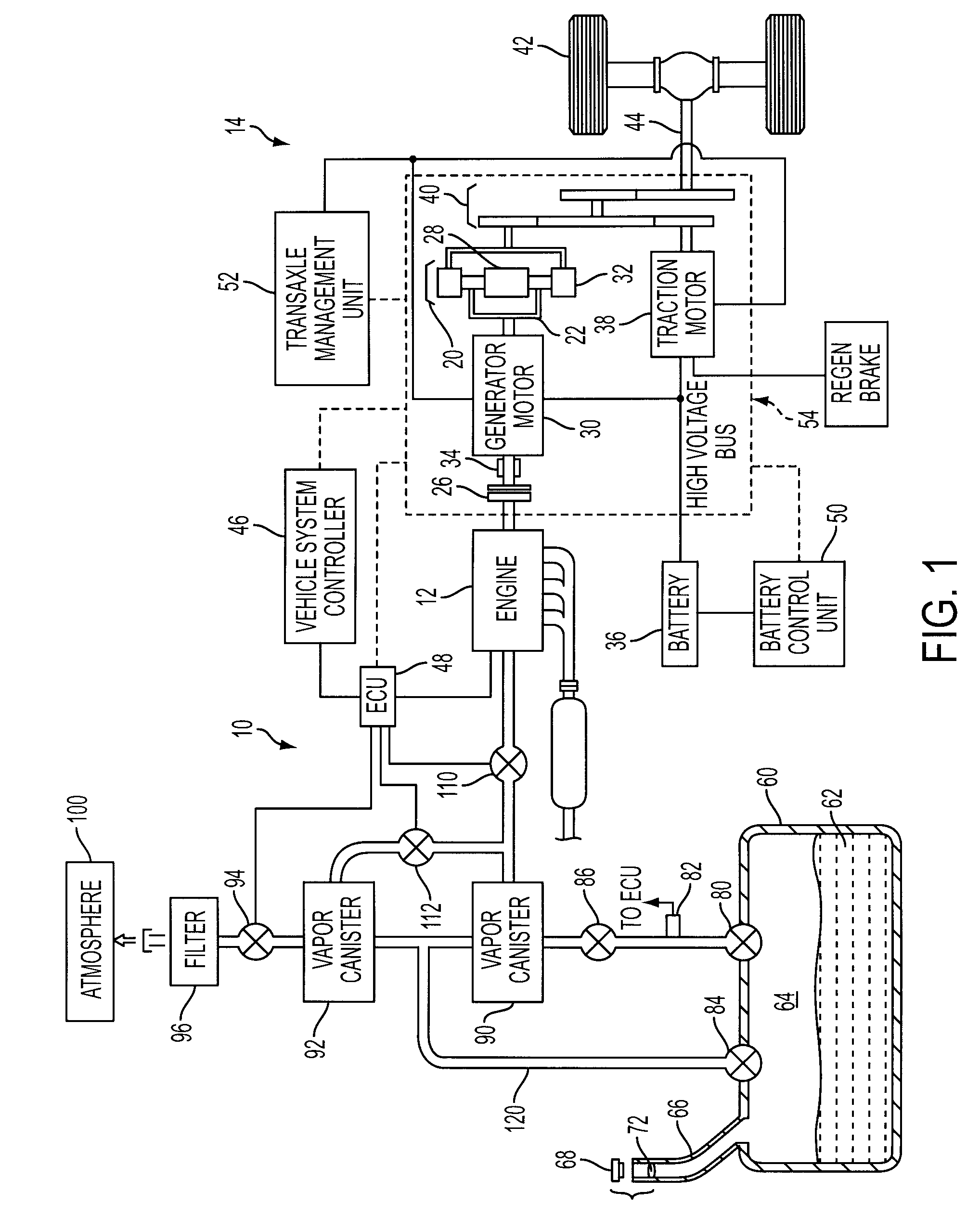
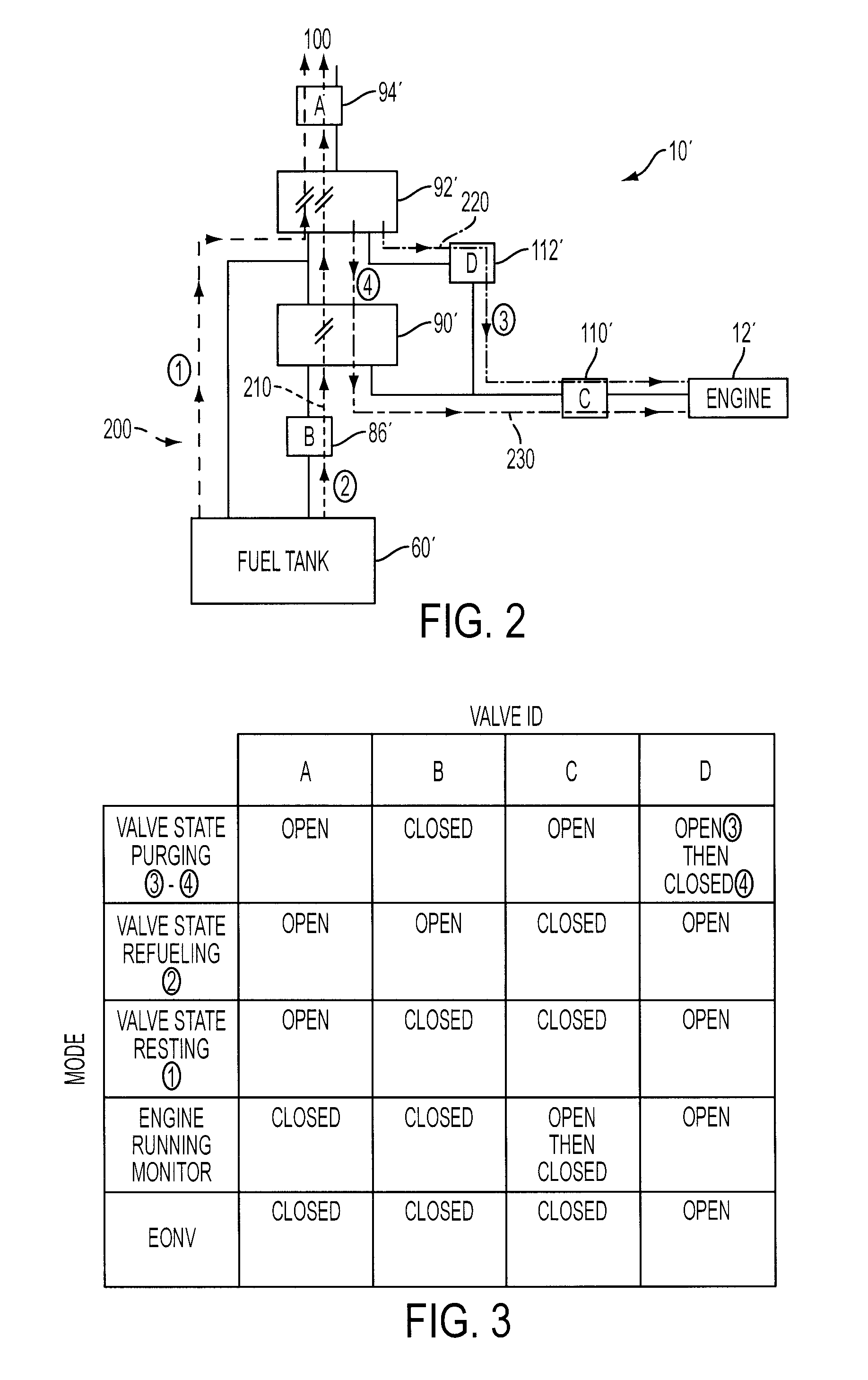
Evaporative Emission Management For Vehicles
ActiveUS20090288645A1Additional vapor storage capacitySmall sizeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesAtmospheric airEngineering
Evaporative emissions management for a vehicle having a fuel tank and a low-vacuum internal combustion engine, including hybrid electric vehicles, include first and second canisters with the second canister disposed between the first canister and atmosphere. A refueling valve routes fuel vapors from the fuel storage tank through the first canister, and to the second canister when the first canister becomes saturated, during refueling. Other than during refueling, the refueling valve is closed to route fuel vapors around the first canister and directly into the second canister. First and second purge valves are controlled during canister regeneration or purging so air from atmosphere is routed primarily through the second canister to the engine to purge the second canister before the purge valves are operated to route air from atmosphere through both the second and first canisters to purge the first canister.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Bag sealing system and method
InactiveUS6862867B2Rapid and frequent temperature fluctuationAvoid problemsPackaging by pressurising/gasifyingPackaging under vacuum/special atmosphereThermoplasticHermetic seal
A system for sealing thermoplastic film includes one or more bag sealing units, each comprising a lower vacuum platen and a vacuum chamber cover adapted for sealing engagement on the platen to form a vacuum chamber. A sealing bar assembly includes a sealing bar designed for constant heated operation and a pair of cooling plates which function as heat sinks. The sealing bar assembly is pneumatically reciprocated between a raised, disengaged position and a lowered position with the sealing bar engaging the neck of a bag for hermetically sealing same. The cooling plates clamp the bag neck against a sealing support assembly. A method of sealing a thermoplastic film bag includes the steps of placing a packaging object in a thermoplastic bag and placing the bag on a cradle with the bag neck extending over a bag support assembly. A vacuum chamber cover is placed on the platen and evacuated to form a vacuum chamber. A sealing bar assembly melds the thermoplastic to form a sealed area across the bag neck. A cutoff knife blade severs the end of the bag beyond a sealed area, which extends across its neck.
Owner:PACKTECH
Tissue refining device
A device for use in a system or method of collecting and processing aspirated tissue received from a harvesting device is provided by a canister body having a vacuum port and an evacuation port operable to be placed in communication with a vacuum source, a tissue harvesting port for directing tissue into the canister body received from the harvesting device under suction, a pressure equalization passage, and a separator element dividing the canister body into an upper vacuum chamber in communication with the vacuum port and the tissue harvesting port and a lower vacuum chamber in communication with the evacuation port, the separator element including a plurality of apertures enabling fluid to pass between the chambers while restricting tissue from doing the same and a depression with a channel leading to a tissue retrieval port to facilitate processed tissue collection.
Owner:MIAMI FAT SUPPLY
Integrated Superconductor MRI Imaging System
ActiveUS20100066367A1Quality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsWave amplification devicesThermal isolationEngineering
The present invention relates to an integrated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF apparatus and method of constructing the same. One Embodiment of the present invention provides an MRI apparatus comprising an examination region, a patient support, at least one vacuum thermal isolation housing, a main magnet system for generating a main magnetic field in the examination region, and a cryogenic system. The vacuum thermal isolation housing comprises a hermetically sealed high vacuum jacket that encloses a low vacuum space hosting at least one superconductor RF coil and a heat sink assembly therein. The RF coil is in thermal contact with the heat sink assembly that is coupled to the cryogenic system through a heat pipe to achieve and maintain a desired low temperature at the superconductor RF coil.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
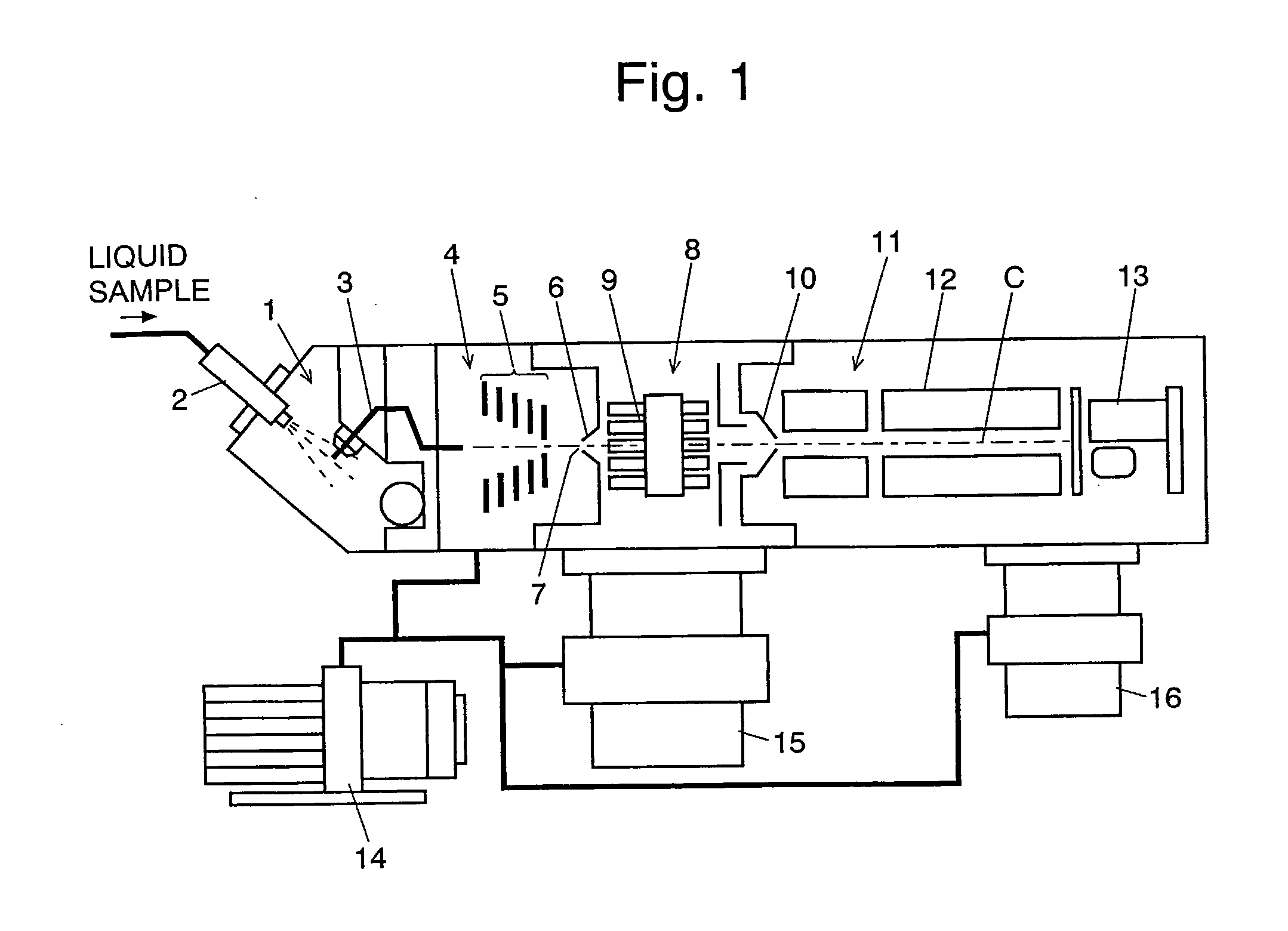
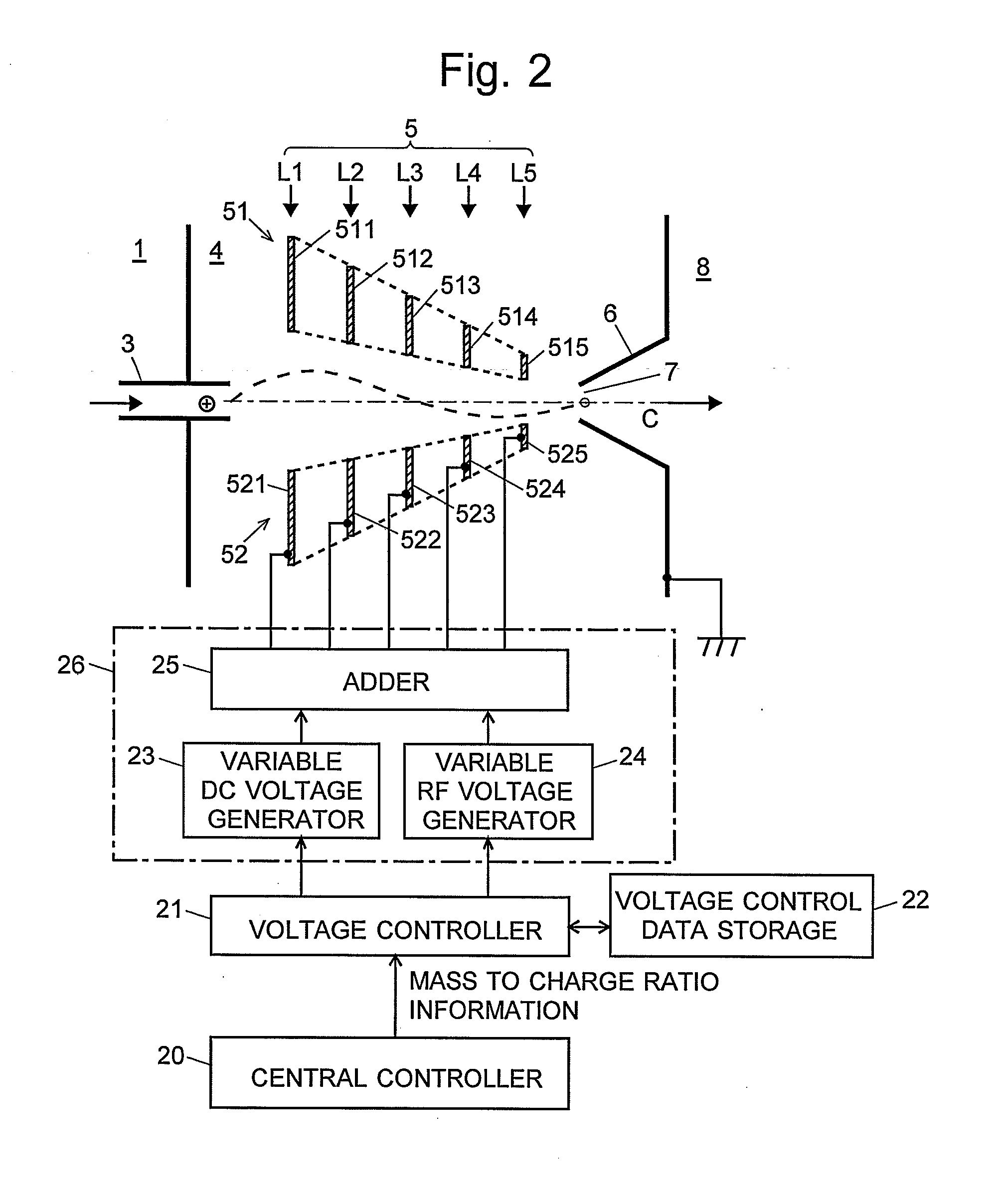
Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20080283742A1Improve efficiencyEfficient transportIsotope separationMass spectrometersElectric dischargeMass analyzer
The present invention provides a mass spectrometer having an ion lens capable of transporting an ion having a large mass to charge ratio with a high level of ion-passing efficiency even under a low-vacuum atmosphere. In conventional atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometers or similar mass spectrometers, applying an excessively high voltage to the ion lens undesirably causes an electric discharge. Therefore, the passing efficiency for an ion having a large mass to charge ratio cannot be adequately improved, which leads to a poor detection sensitivity. To solve this problem, the mass spectrometer according to the present invention includes a voltage controller 21 that controls a variable radiofrequency (RF) voltage generator 24 so that both the amplitude and the frequency of the RF voltage applied to the lens electrodes of an ion lens 5 are changed according to the mass to charge ratio of an ion to be analyzed. This control enables the ion lens 5 to focus an ion and transport it to the subsequent stage with a high level of passing efficiency even in the case of analyzing an ion having a large mass to charge ratio. Thus, the detection sensitivity is improved. The aforementioned control is conducted on the basis of the control data stored in a voltage control data storage 22. These data are obtained in advance by a measurement of a sample containing a substance having a known mass to charge ratio, in which the intensity of the signal of an ion detector is maintained while the analysis conditions are changed.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Papermaking machine for forming tissue employing an air press
InactiveUS20050150626A1Shorten the lengthIncrease speedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperLow vacuumPaper machine
A web of tissue is formed in a twin wire former, followed by an air press for water removal in the pressing section, passing onto a Yankee dryer. A headbox injects stock between upper and lower dryer fabrics brought together on a breast roll. The fabrics moves over vacuum boxes, and the web is heated with steam and passed between an upper pressure box and a lower vacuum box forming an air press which dewaters the web. A sheet transfer pickup vacuum box holds the sheet to the upper fabric as the lower fabric diverges from the upper fabric. A pressure roller transfers the web onto a Yankee dryer. The fabrics are cleaned on vertical runs before returning to the breast roll. A final forming fabric is arranged to operated at a lower speed than the penultimate forming fabric so that a rush transfer and creping like action takes place.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
Refractory metal capped low resistivity metal conductor lines and vias
InactiveUS6147402AHigh process yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricElectrical conductor
Capping a low resistivity metal conductor line or via with a refractory metal allows for effectively using chemical-mechanical polishing techniques because the hard, reduced wear, properties of the refractory metal do not scratch, corrode, or smear during chemical-mechanical polishing. Superior conductive lines and vias are created using a combination of both physical vapor deposition (e.g., evaporation or collimated sputtering) of a low resistivity metal or alloy followed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of a refractory metal and subsequent planarization. Altering a ratio of SiH4 to WF6 during application of the refractory metal cap by CVD allows for controlled incorporation of silicon into the tungsten capping layer. Collimated sputtering allows for creating a refractory metal liner in an opening in a dielectric which is suitable as a diffusion barrier to copper based metalizations as well as CVD tungsten. Ideally, for faster diffusing metals like copper, liners are created by a two step collimated sputtering process wherein a first layer is deposited under relatively low vacuum pressure where directional deposition dominates (e.g., below 1 mTorr) and a second layer is deposited under relatively high vacuum pressure where scattering deposition dominates (e.g., above 1 mTorr). For refractory metals like CVD tungsten, the liner can be created in one step using collimated sputtering at higher vacuum pressures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Process and device for removing phosphorus and metal impurities in polycrystalline silicon
InactiveCN101289188AHigh purityImprove efficiencyChemical industrySilicon compoundsMetal impuritiesLow vacuum
The invention relates to a method and a device for removing impurity phosphorus and metal impurities in polycrystalline silicon, which pertains to the technical field of purifying the polycrystalline silicon by a physical metallurgy technology, particularly relates to the method for removing the impurity phosphorus and the metal impurities in the polycrystalline silicon by an electron-beam fusion technology. Cooperative ways of electron-beam fusion and induction heating are used for completing the fusion and solidification process of the polycrystalline silicon. Silicon powder with high purity is used for spreading in a hollow-out space at a water cooled copper base which is filled with quartz crucibles; polycrystalline silicon material is put into the quartz crucibles and the cover of a vacuum device is closed; in the process of vacuumization, a mechanical pump and a lodz pump are firstly used for vacuumizing a vacuum room to low vacuum and then a diffusion pump is used for vacuumizing to high vacuum; the device used is provided with a vacuum device cover and a vacuum drum which are formed into the outer shell of the device; the inner cavity of the vacuum drum is the vacuum room, in which a fusion system is arranged. The method and the device of the invention effectively improve the purity of the polycrystalline silicon, which have the advantages of high efficiency, simple device and saving energy.
Owner:QINGDAO NEW ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Electron emitting element and image forming apparatus employing it
ActiveUS20060186786A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsSimple Organic CompoundsLow vacuum
An electron emitting element is of a structure in which a semiconductor layer is formed between an upper electrode and a lower electrode, wherein an organic compound adsorption layer is formed on a semiconductor surface of the semiconductor layer by causing the organic compound to be adsorbed on the semiconductor surface. Herein, the semiconductor layer can be made of silicon or polysilicon and partly or as a whole porous. The absorbed organic compound can be a non-cyclic hydrocarbon, a compound obtained by coupling at least an aldehyde group to a non-cyclic hydrocarbon, or a non-cyclic hydrocarbon having an unsaturated bond. As a result, there can be provided an electron emitting element capable of stably operating in the atmosphere or in a low vacuum even when being operated in the atmosphere or in the low vacuum and an imaging device using the electron emitting element.
Owner:KOSHIDA NOBUYOSHI +1
Papermaking machine for forming tissue employing an air press
InactiveUS6863777B2Increases web bulk and absorbencyShorten the lengthNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperLow vacuumAirflow
A web of tissue is formed in a twin wire former, followed by an air press for water removal in the pressing section, passing onto a Yankee dryer. A headbox injects stock between upper and lower dryer fabrics brought together on a breast roll. The fabrics move over vacuum boxes, and the web is heated with steam and passed between an upper pressure box and a lower vacuum box forming an air press which dewaters the web. A sheet transfer pickup vacuum box holds the sheet to the upper fabric as the lower fabric diverges from the upper fabric. A pressure roller transfers the web onto a Yankee dryer. The fabrics are cleaned on vertical runs before returning to the breast roll.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
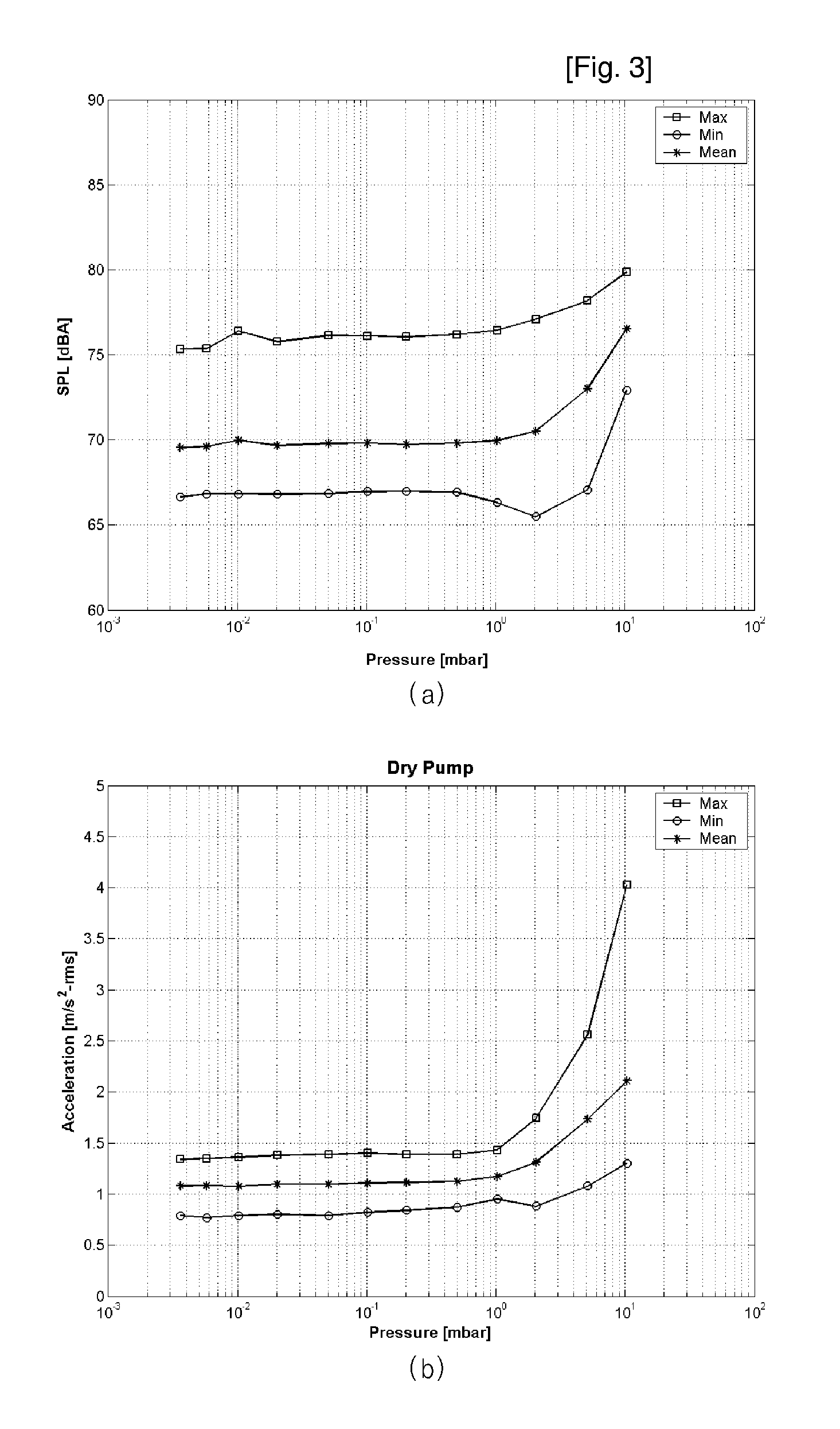
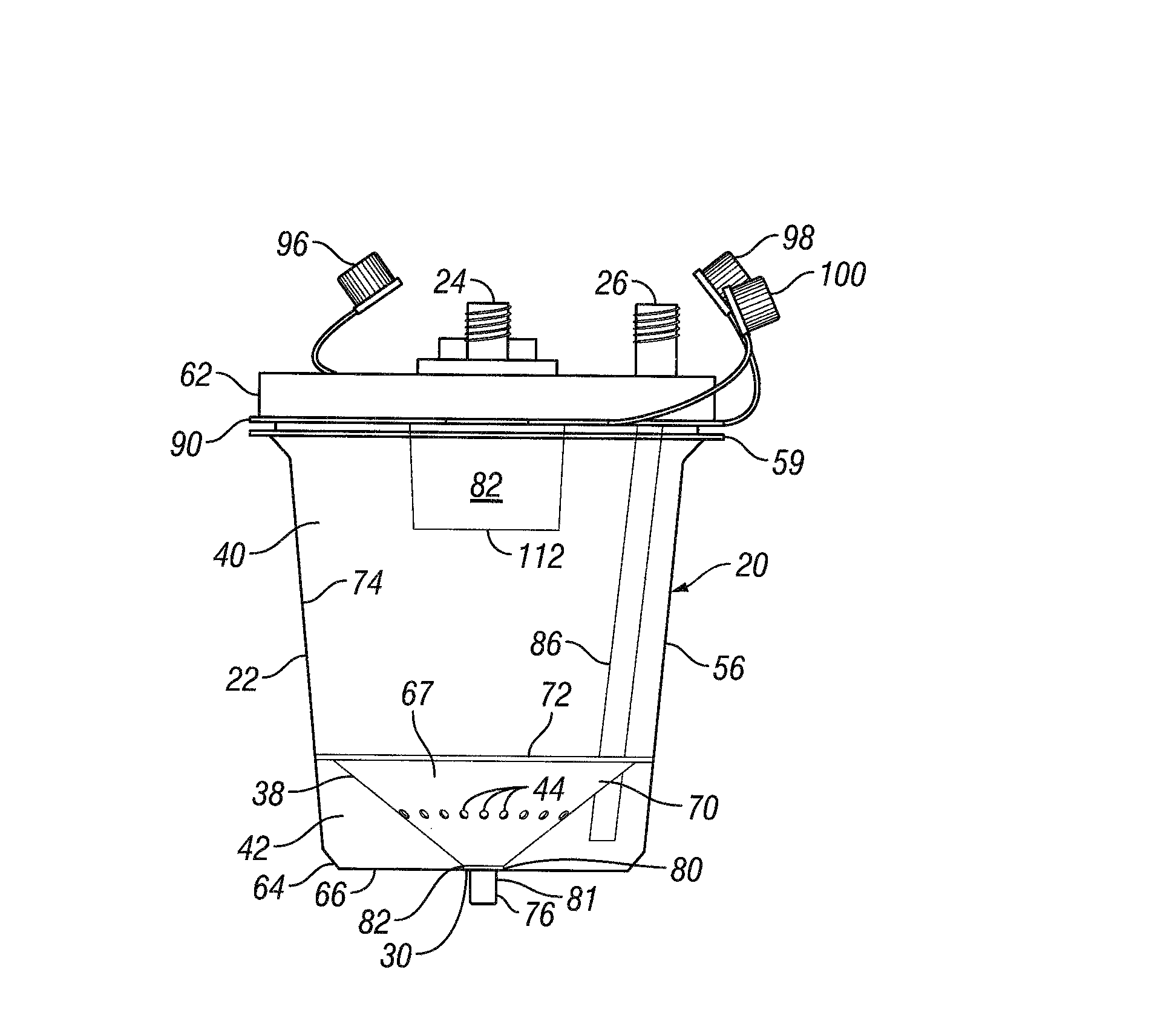
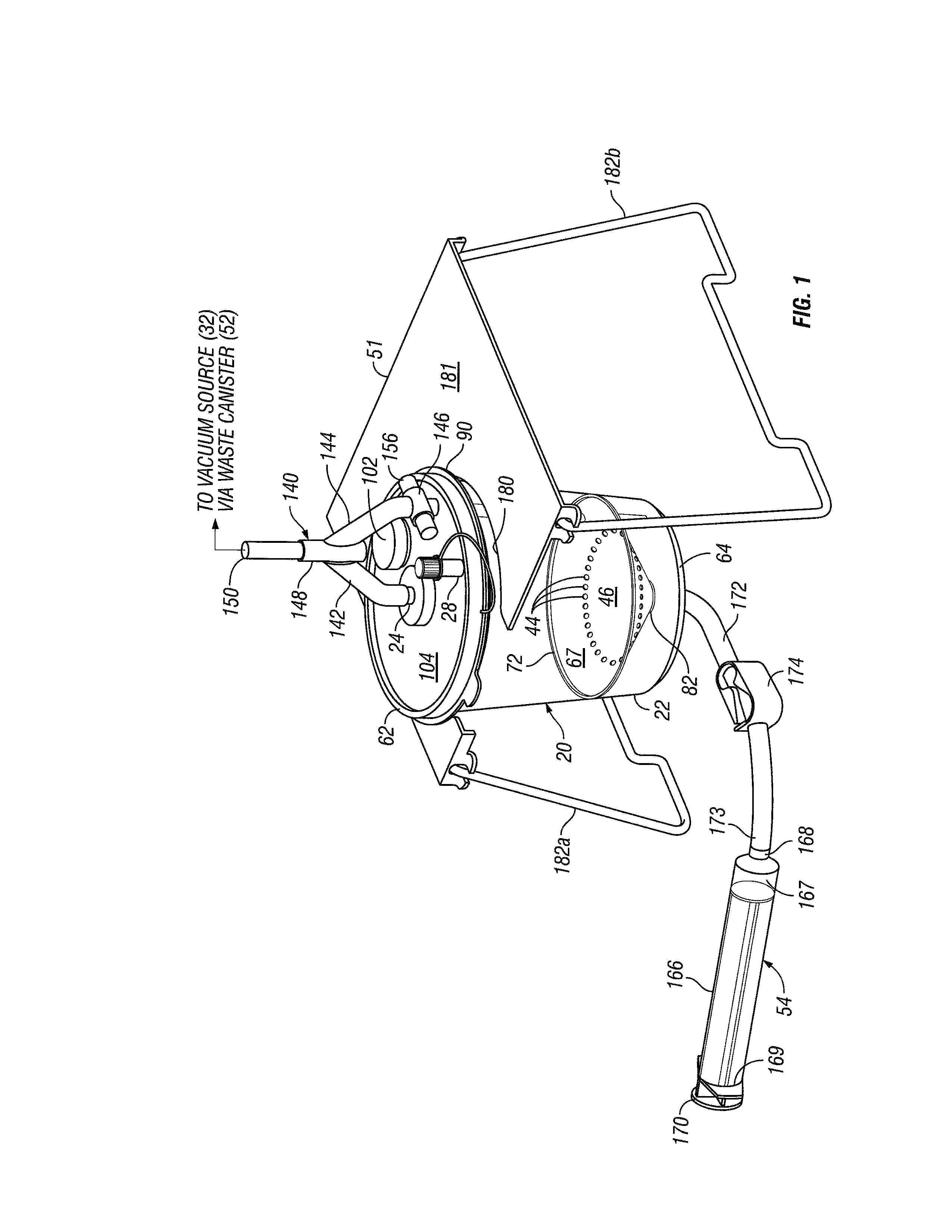
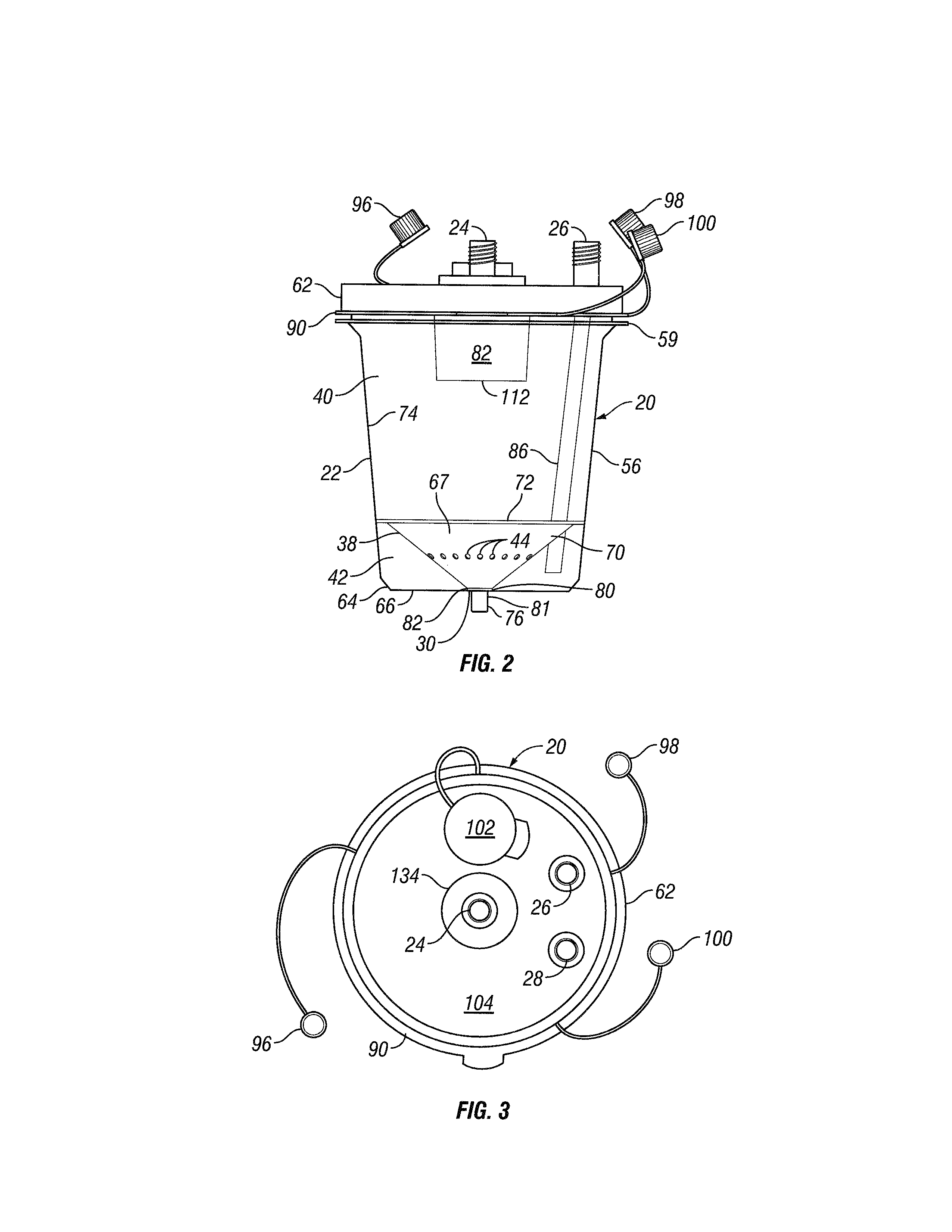
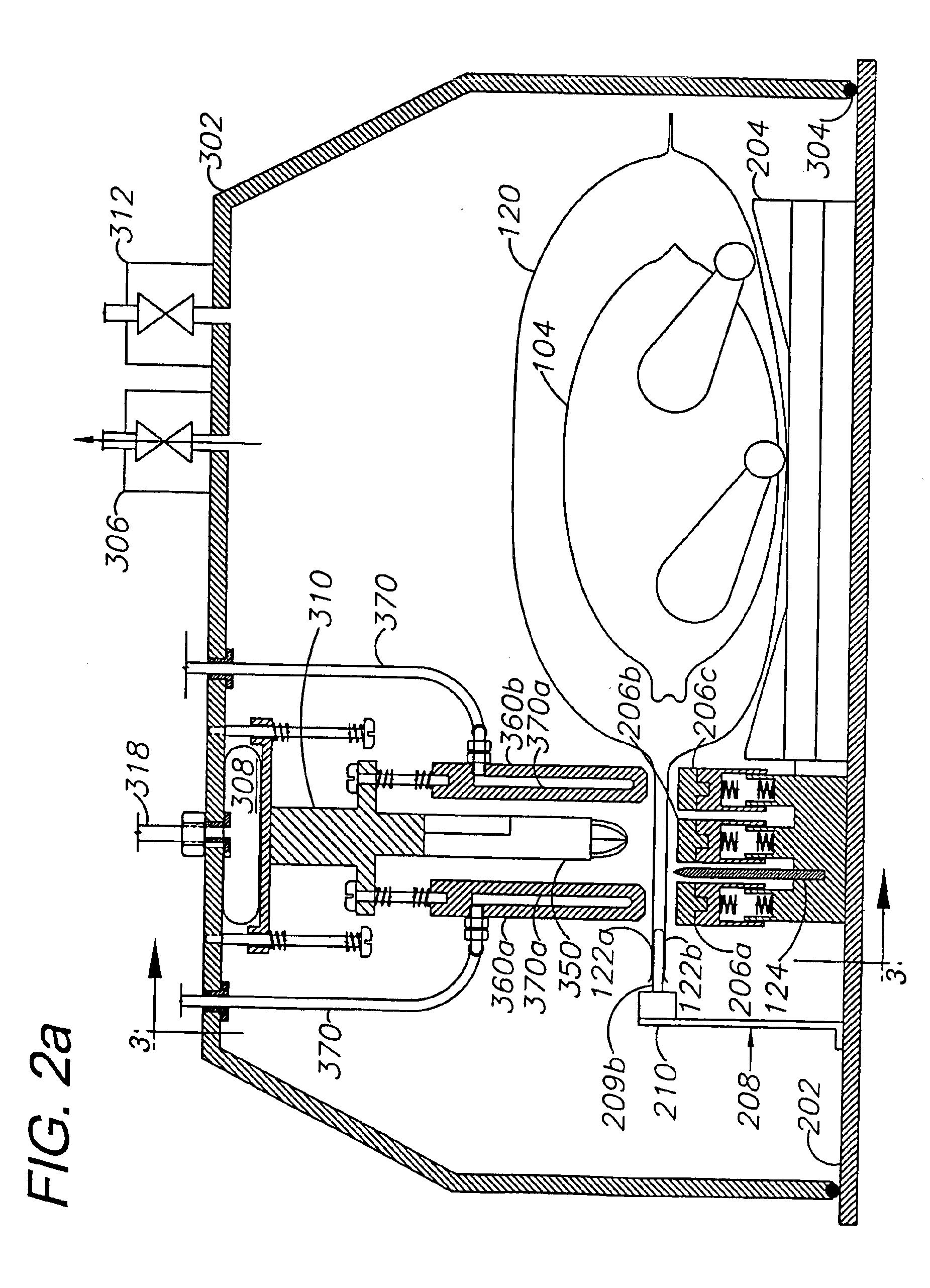
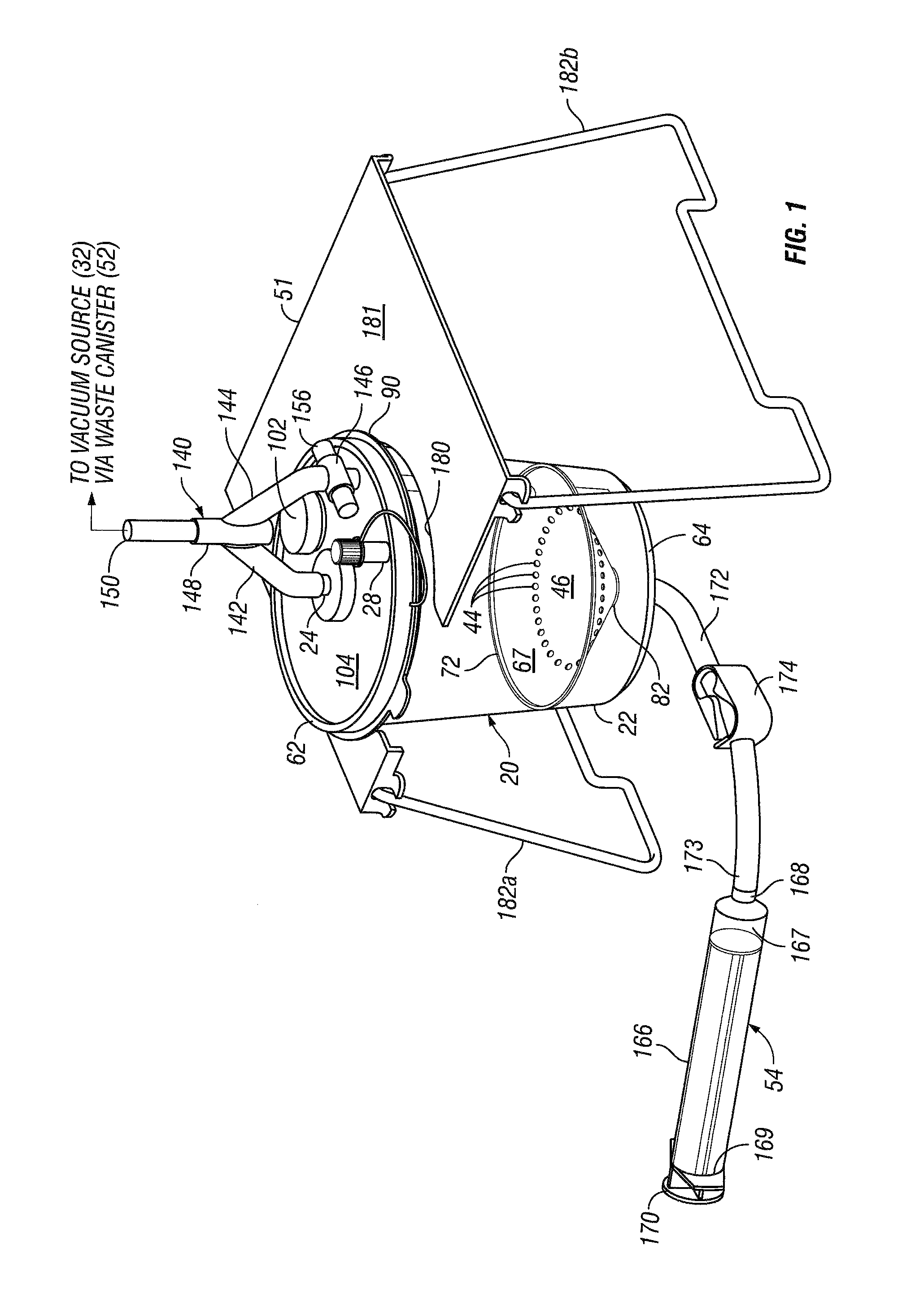
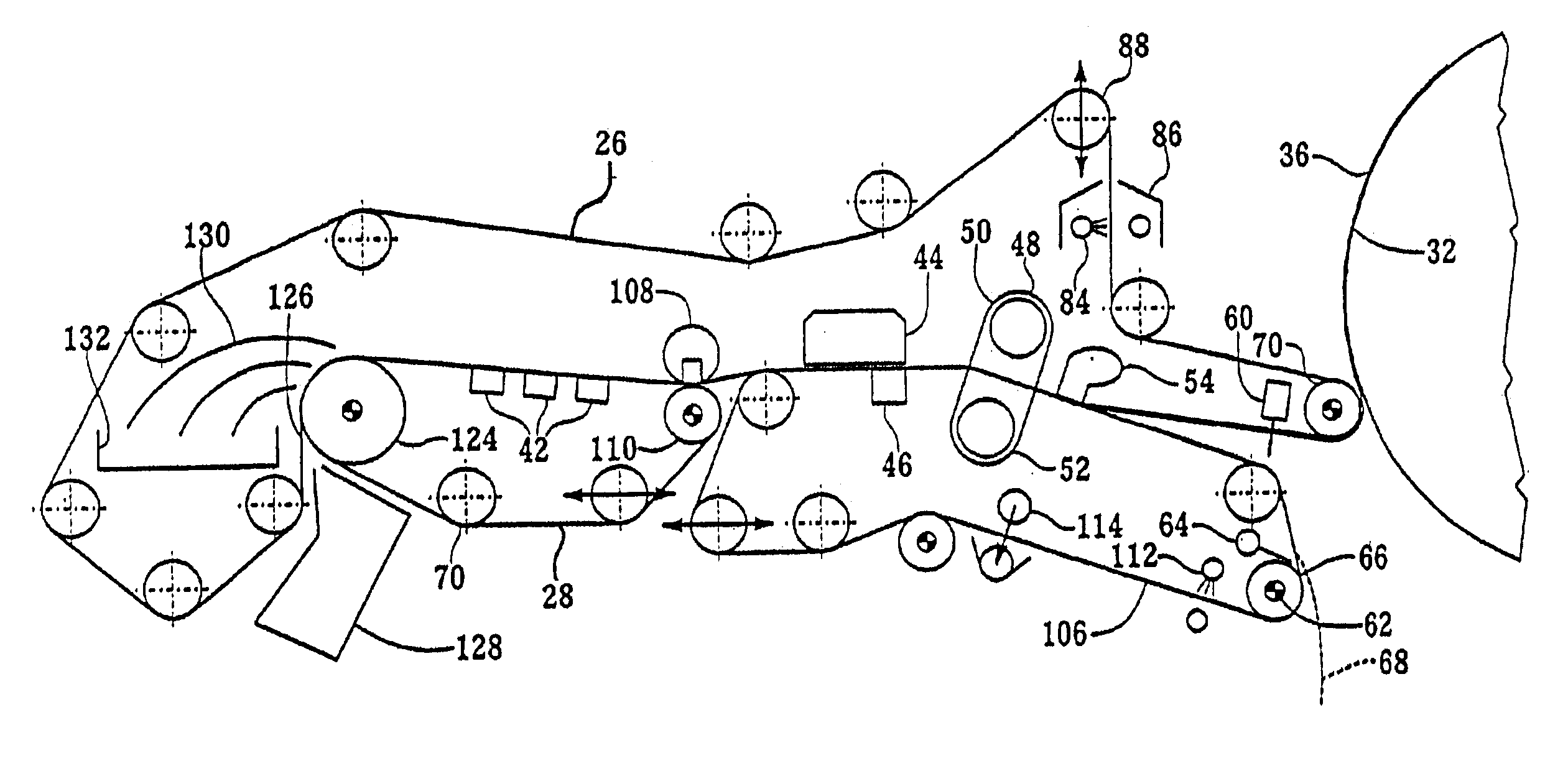
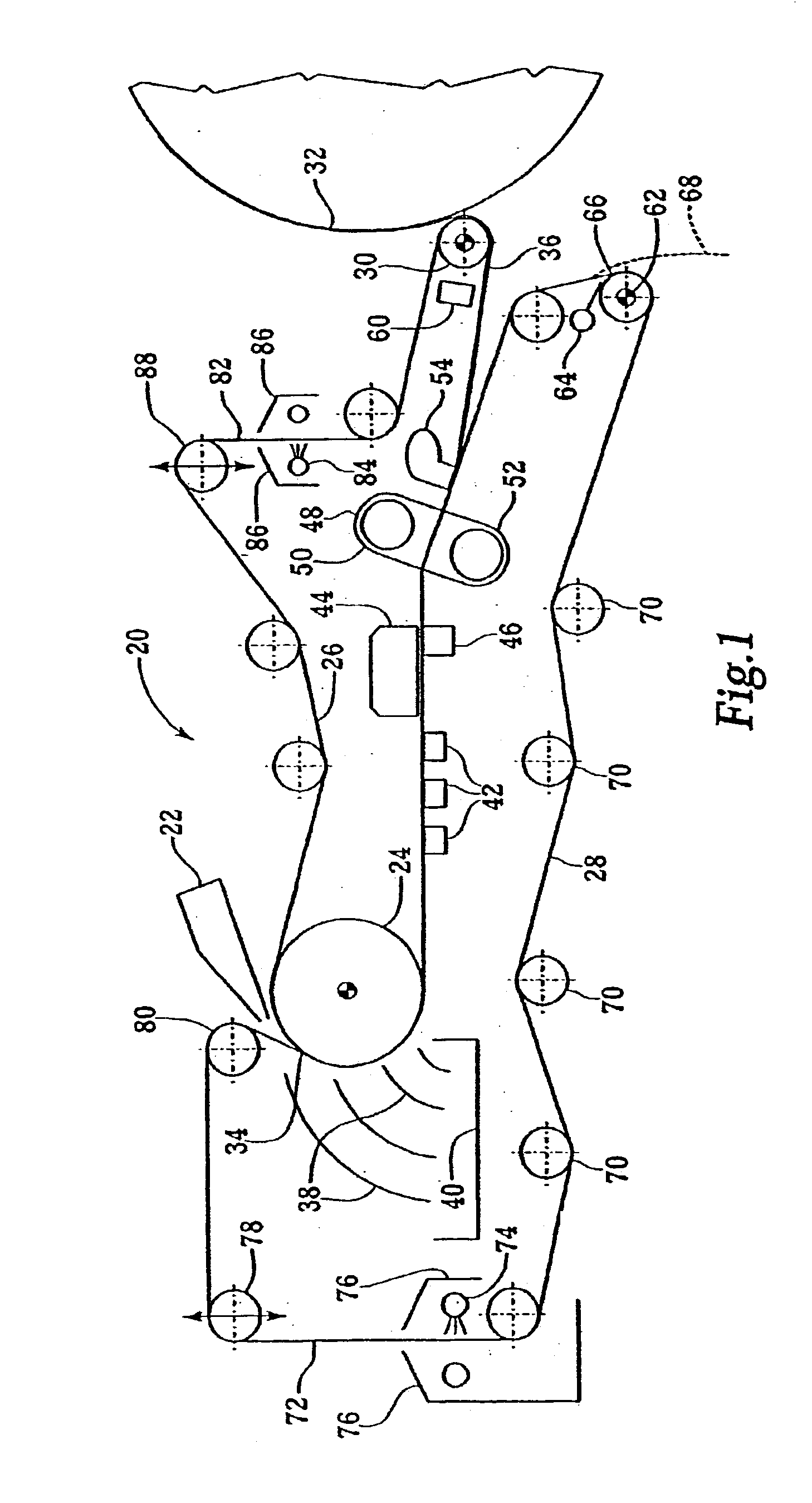
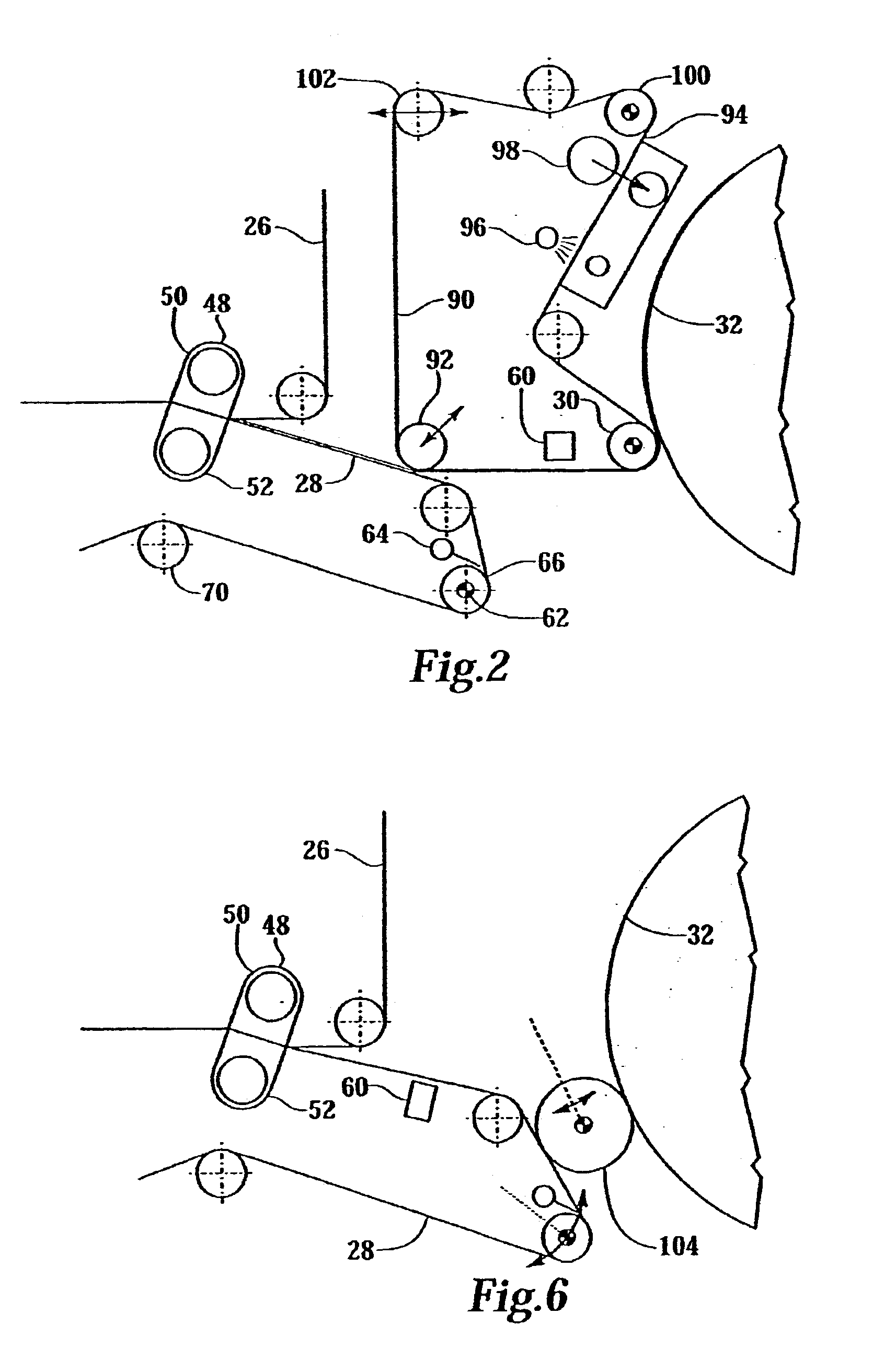
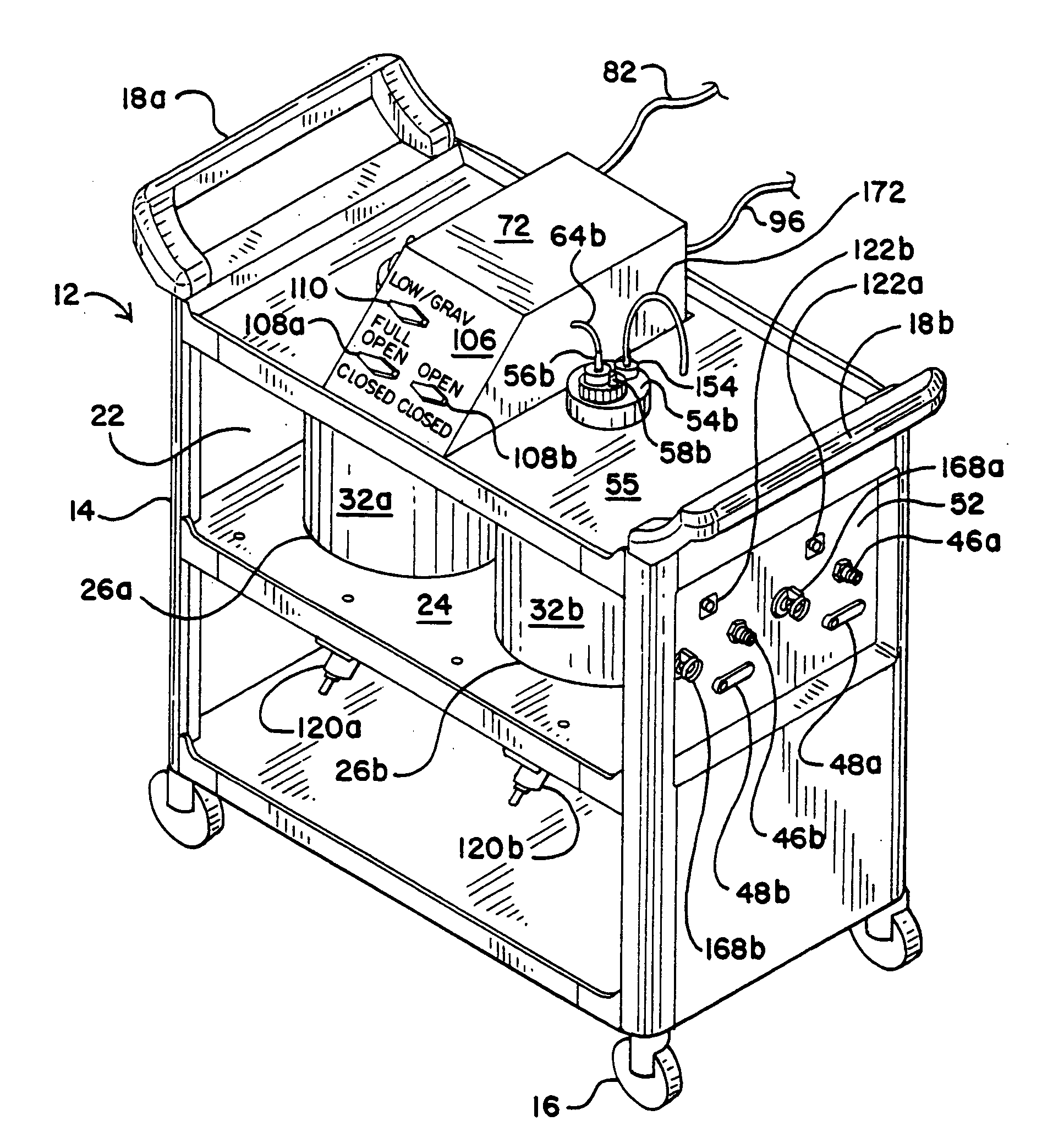
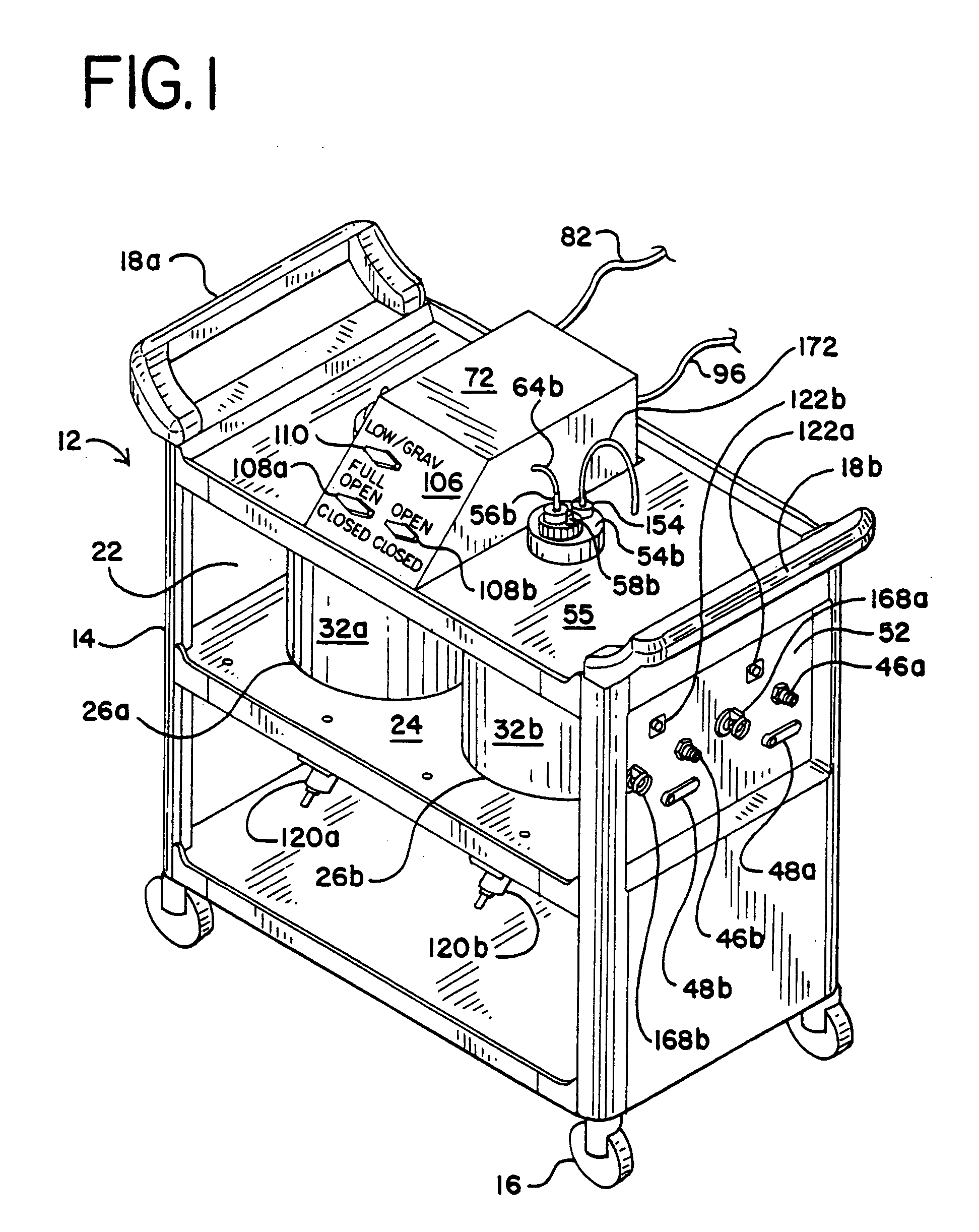
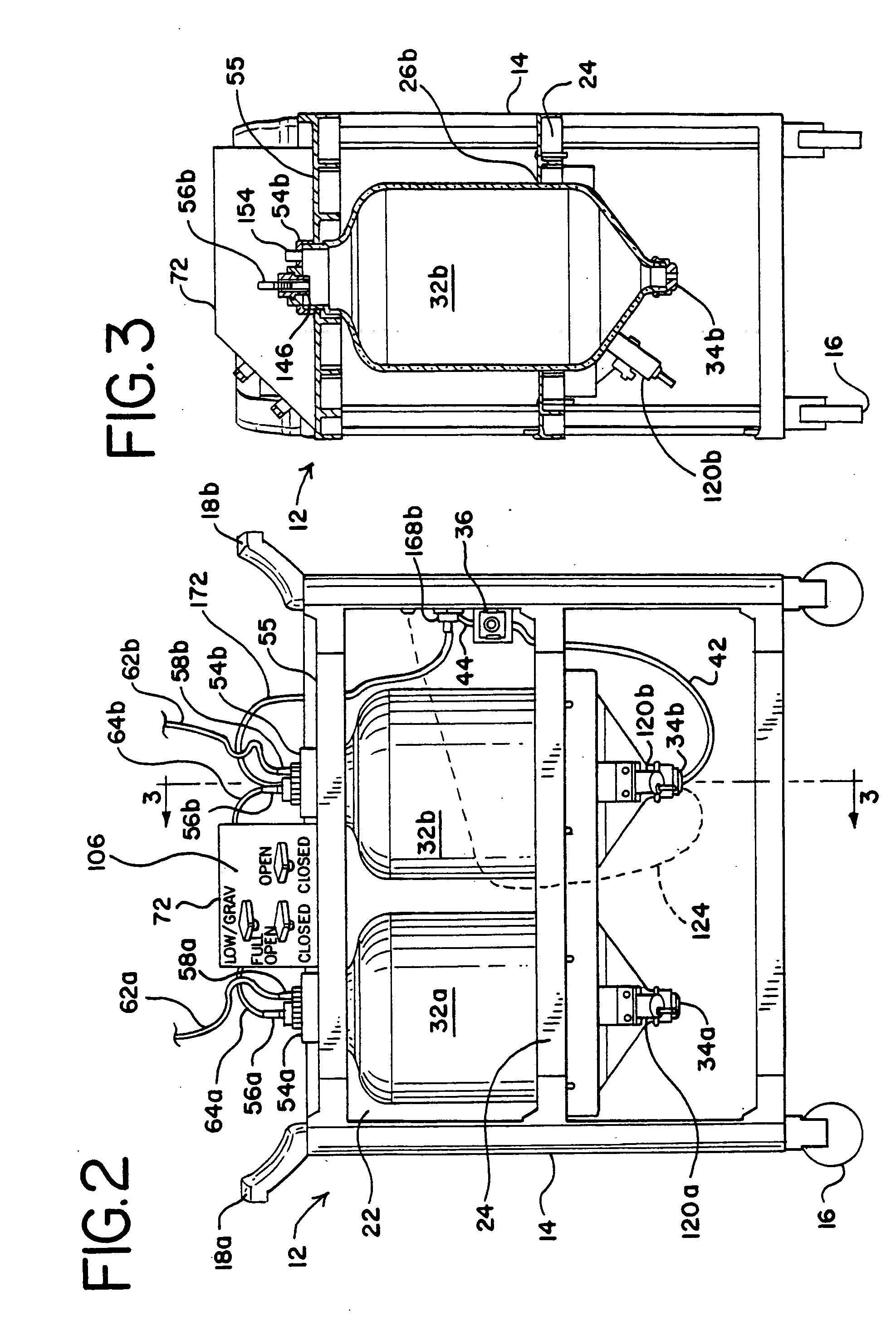
High volume liquid waste collection and disposal system
A system for collecting and disposing of liquid medical waste includes a fluid collection cart and a draining and cleaning station. The fluid collection cart includes a pair of containers, each of which includes a draining port and a cap. Each cap includes an outer portion having a flushing port and a bore formed therein and an inner portion having vacuum and patient ports formed therein. The inner cap portion is disposable and removably positioned within the bore of the outer cap portion. Liquid level detectors also communicate with each container. The cart also includes a regulator so a low vacuum level may be pulled on one of the containers while a full vacuum level is pulled on the other container. Fluids are collected in the containers via suction tubes connected to the patient ports. The flushing and drain ports of the containers are connected to corresponding flushing and drain connectors on the station when the containers are full so that they may be drained and flushed. The cart liquid level detectors communicate with the station microprocessor so that the draining and flushing cycles may be properly sequenced. The station may also clean suction canisters.
Owner:DORNOCH MEDICAL SYST
High-uniformity polyester industrial yarn used for safety belt and production method thereof
ActiveCN106381557AIncreased free volumeReduce melt viscositySpinnerette packsHollow filament manufactureYarnLow vacuum
The invention relates to a high-uniformity polyester industrial yarn used for a safety belt and a production method thereof. The raw material of the high-uniformity polyester industrial yarn is modified polyester composed of a terephthalic acid chain segment, a glycol chain segment and a branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol chain segment. The production method is characterized in that terephthalic acid and branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol are subjected to an esterification reaction under catalysis of concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain dihydricalcohol terephthalate; then terephthalic acid and glycol are prepared for the esterification reaction to obtain ethylene terephthalate; finally ethylene terephthalate and dihydricalcohol terephthalate are stirred and mixed, under a catalyst and a stabilizing agent, the condensation polymerization reactions under a low vacuum phase and a high vacuum phase are carried out to prepare the modified polyester, and the modified polyester is subjected to metering, extrusion by a porous spinneret, cooling, oiling, stretching, thermoforming and reeling to prepare the high-uniformity polyester industrial yarn.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Ion transport device
ActiveUS20080308721A1Reduce transmissionStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersVoltage amplitudeLight beam
A device for transporting and focusing ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart electrodes to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. In order to create a tapered field that focuses ions to a narrow beam near the device exit, the inter-electrode spacing or the oscillatory voltage amplitude is increased in the direction of ion travel.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
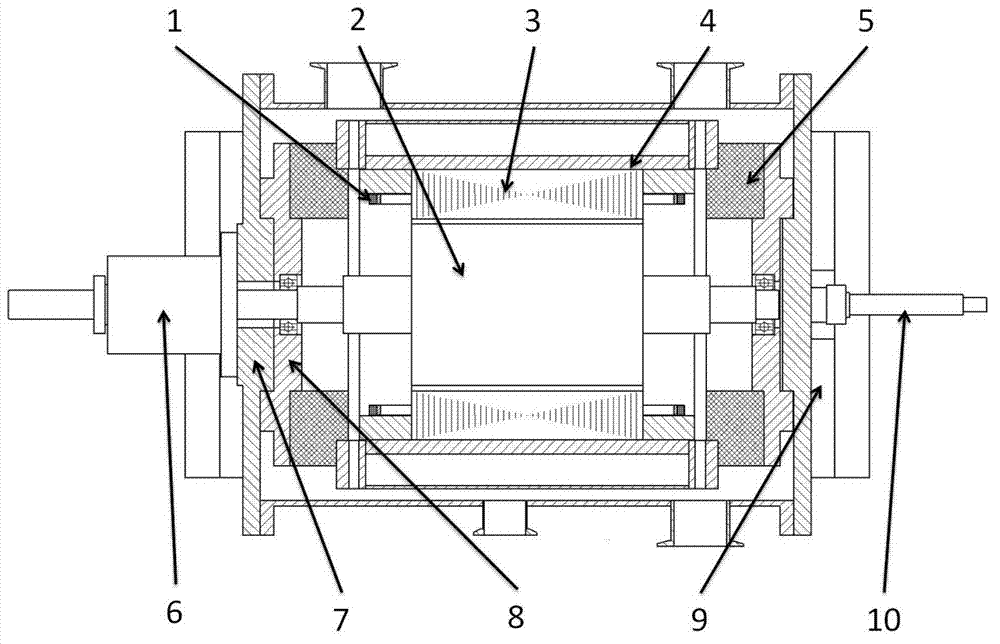
High-temperature superconducting motor
ActiveCN102969873AEfficient power outputNo mutual interferenceDynamo-electric machinesMarine propulsionSuperconducting electric machine
The invention relates to the field of superconducting technologies and the field of motor technologies, and particularly relates to a high-temperature superconducting motor. The motor comprises an electromotor and a generator, an armature winding is manufactured by winding a high-temperature superconducting wire, and a current passing through the armature winding has an alternating component. A refrigerating Dewar vessel of the motor is placed on the outside of a stator core, and cools a high-temperature superconducting coil in a contact conduction refrigerating mode. No heat insulating layer is arranged between a stator and a rotor of the motor, and an inner cavity of the motor is pumped as a low-vacuum cavity, so that no heat convection and no heat conduction are formed between the stator and the rotor. The torque transmission between the inside and outside of the vacuum cavity is realized through a magnetofluid sealing part. Stator windings are distributed in a centralized winding form. The coil adopts a runway coil or a rounded square coil, and no space mutual-interference situation occurs at the end part of the coil; a low-frequency alternating current is used, so that the loss is reduced; and due to the low-frequency characteristic, the motor is especially applicable to the fields such as wind power generation, marine propulsion power, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Ion transport device
ActiveUS7514673B2Reduce transmissionStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersVoltage amplitudeLight beam
A device for transporting and focusing ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart electrodes to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. In order to create a tapered field that focuses ions to a narrow beam near the device exit, the inter-electrode spacing or the oscillatory voltage amplitude is increased in the direction of ion travel.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Wide-range combination vacuum gauge
InactiveUS7207224B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDifferential pressureUltra-high vacuum
A combination vacuum gauge provides simultaneous absolute and differential pressure measurements over a wide range of pressures ranging from atmospheric pressures to ultrahigh vacuum by processing the readings from an absolute high vacuum gauge (e.g., an ionization gauge and / or a heat-loss sensor), a differential low vacuum gauge providing a differential relative to ambient pressure (e.g., a diaphragm sensor), and a barometric absolute pressure sensor exposed to the ambient atmosphere outside the measurement region. The barometric absolute pressure sensor reading is used to convert the differential vacuum gauge reading from uncalibrated differential pressure to calibrated absolute pressure.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com