Patents
Literature
3510 results about "Voltage amplitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
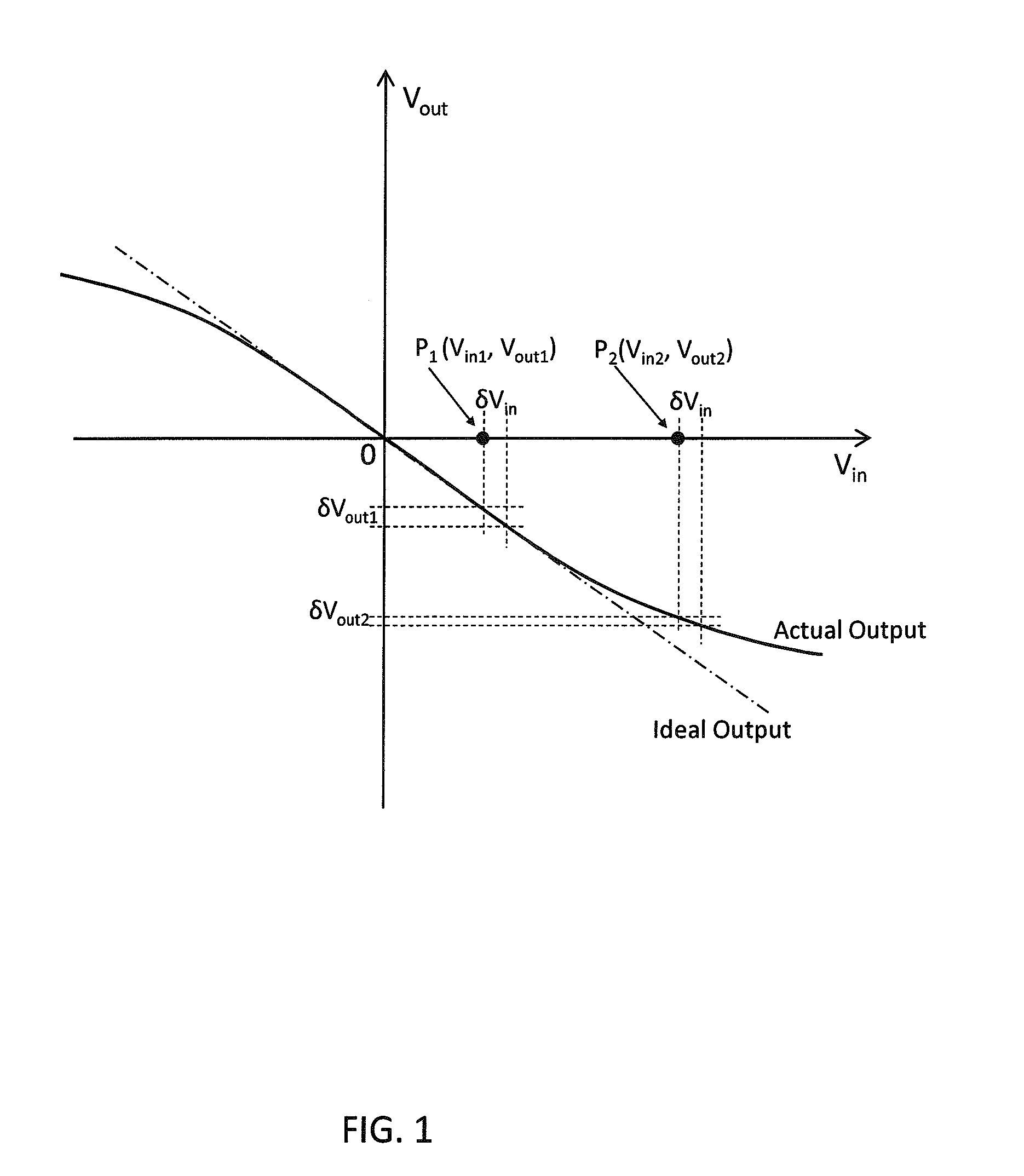
Amplitude is a measure of the intensity, loudness, power, strength, or volume level of a signal. In an electrical circuit operating on alternating current (ac), amplitude is measured as the Voltage (V) level and is expressed as +V and V, depending on the direction of the current.
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6975142B2Low costReduce manufacturing stepsTransistorSolid-state devicesVoltage amplitudeSemiconductor
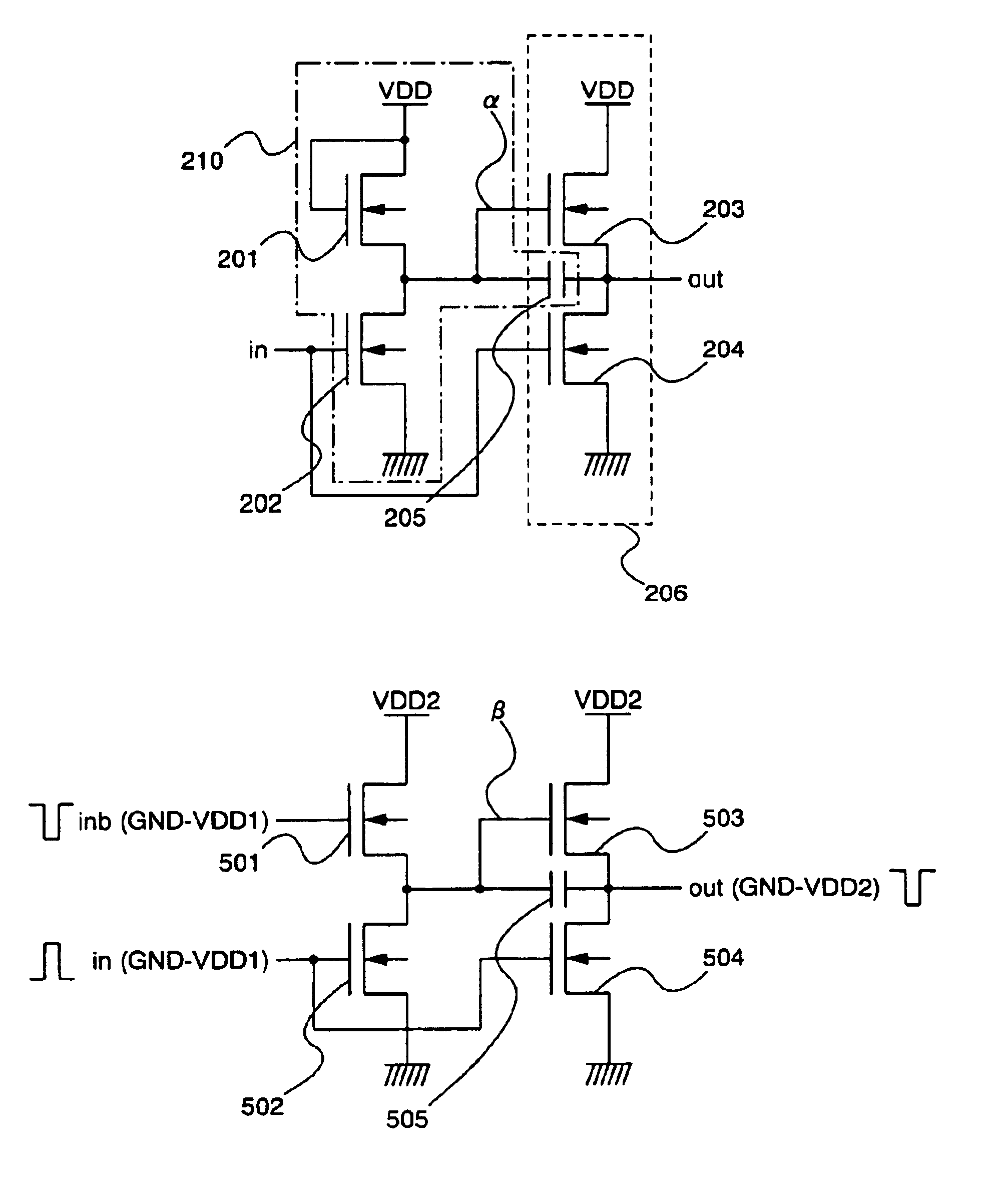
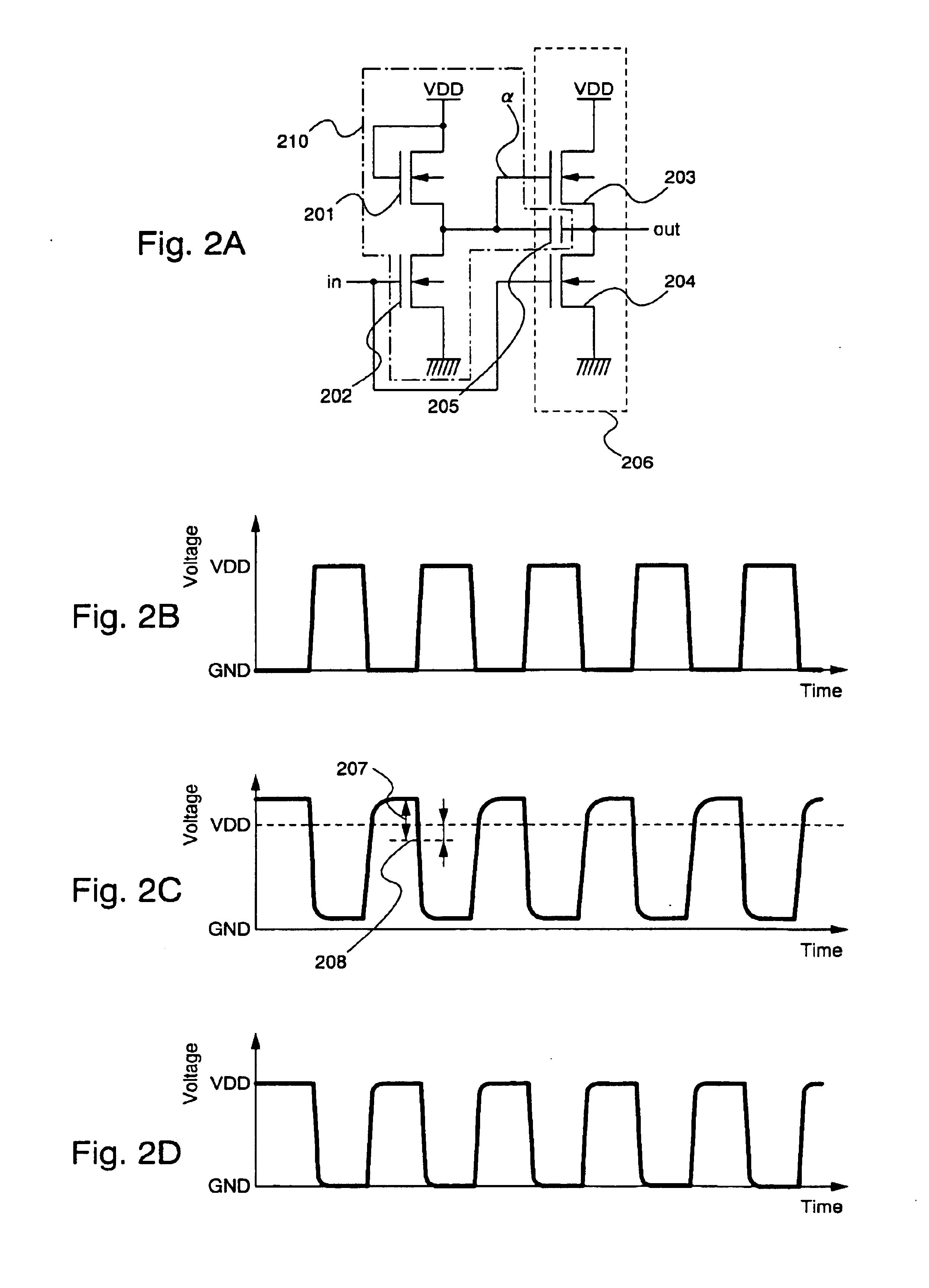
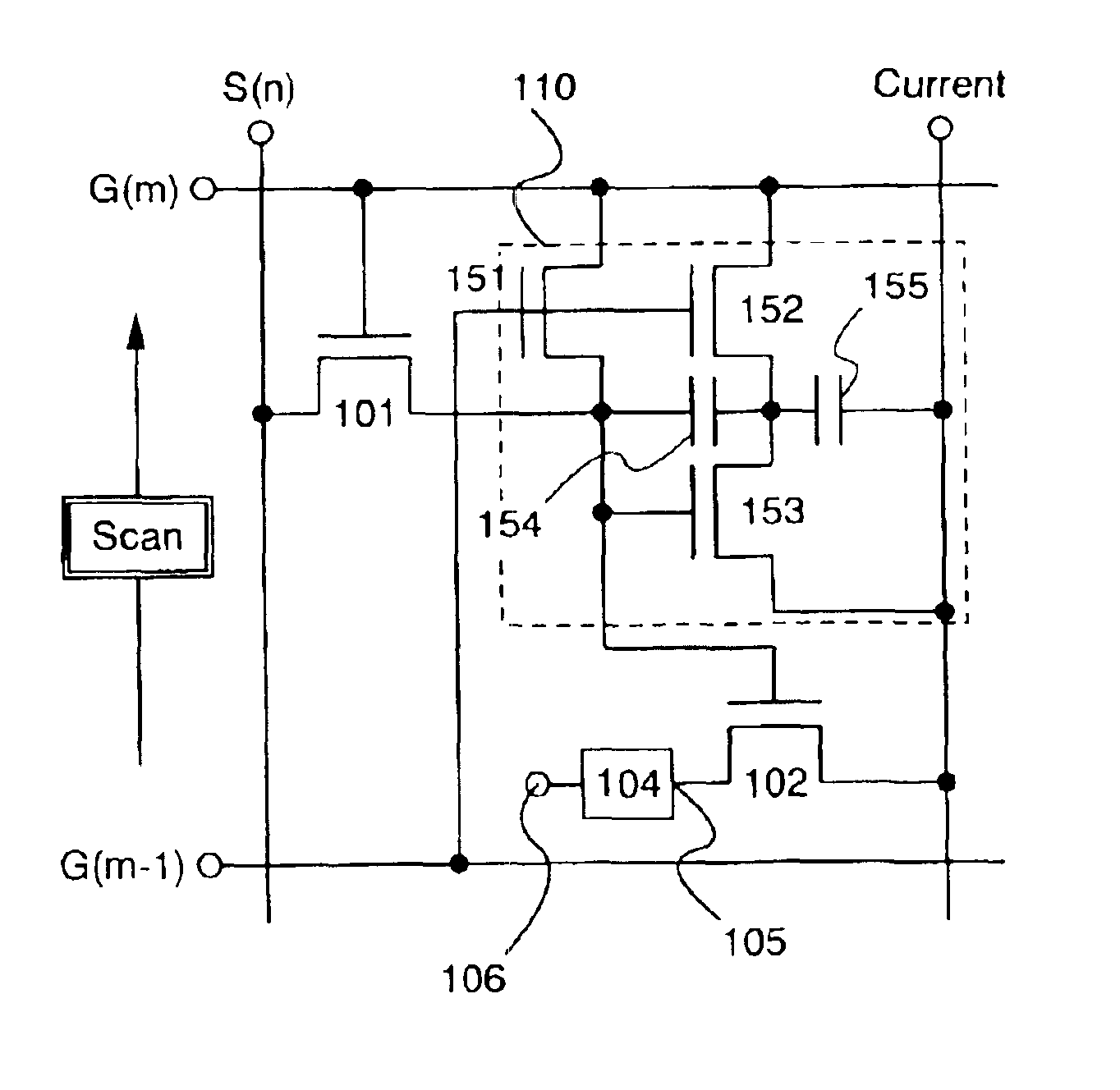
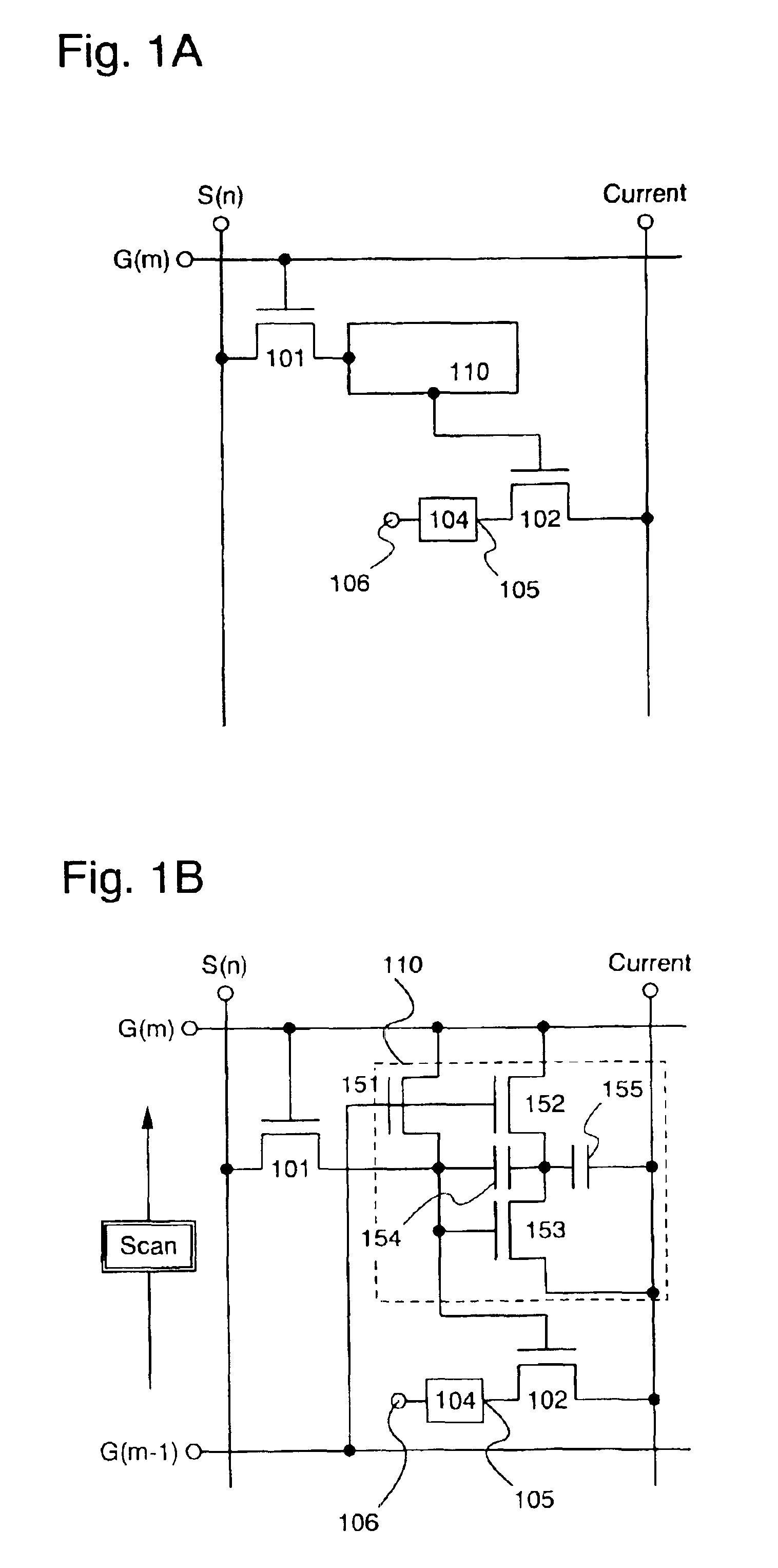
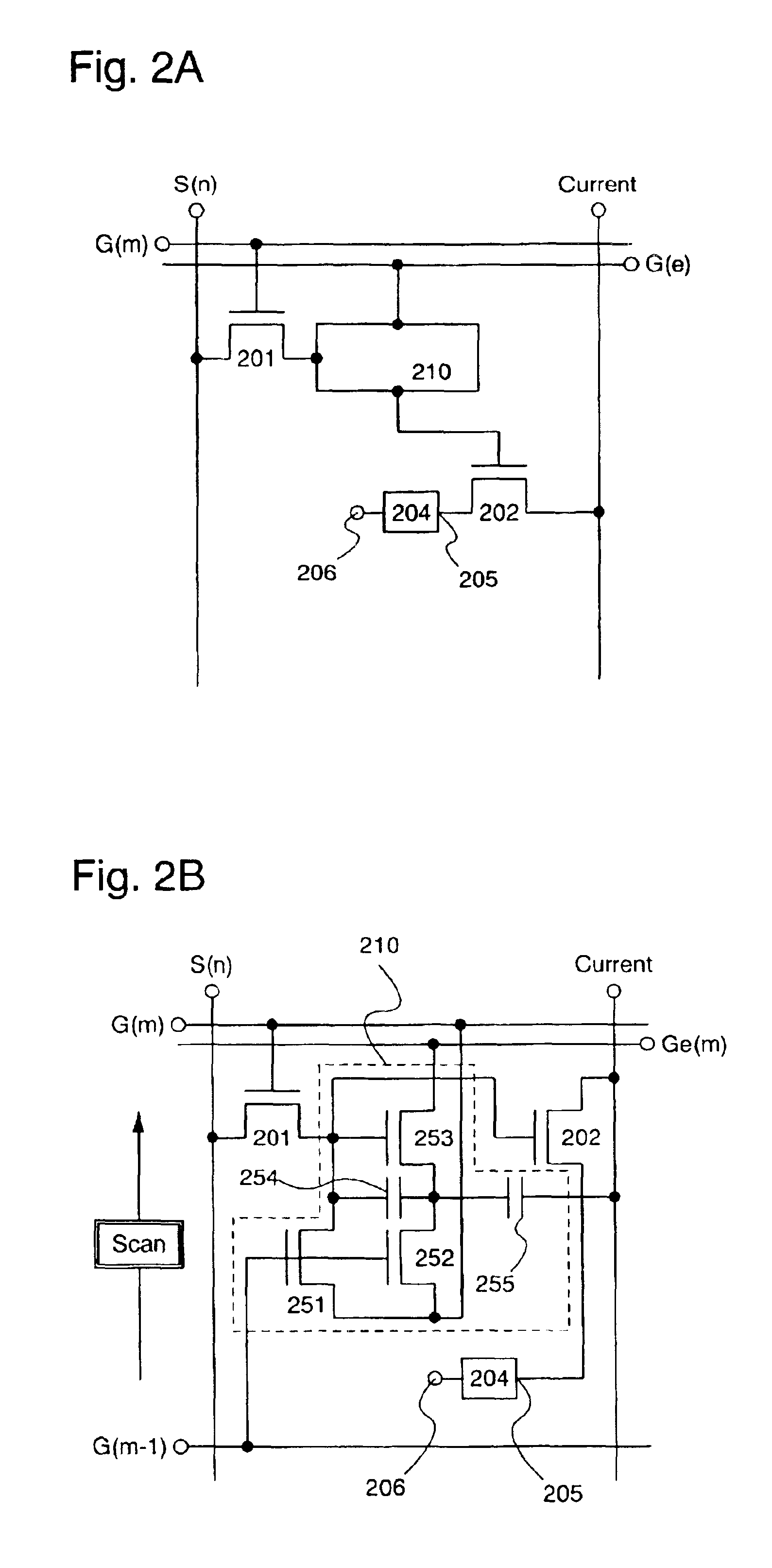
There is provided a semiconductor device in which fabrication steps can be reduced by constructing a circuit using only TFTs of one conductivity type and in which a voltage amplitude of an output signal can be normally obtained. A capacitance (205) is provided between a gate and a source of a TFT (203) connected to an output node, and a circuit formed of TFTs (201) and (202) has a function to bring a node a into a floating state. When the node α is in the floating state, a potential of the node a is caused higher than VDD by using gate-source capacitance coupling of the TFT (203) through the capacitance (205), thus an output signal having an amplitude of VDD-GND can be normally obtained without causing amplitude attenuation due to the threshold value of the TFT.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Amplifier with Variable Feedback Impedance
ActiveUS20150091650A1Reducing effect of variableMaintaining the characteristic output voltage range of the RF amplifierAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesRF amplifierVoltage amplitudeAudio power amplifier
A variable feedback impedance is presented capable of providing high linearity (e.g. as represented by 1P2 and 1P3) and high linear range (e.g. as represented by P1dB) when used in a feedback path of an RF amplifier in the presence of high voltage amplitudes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
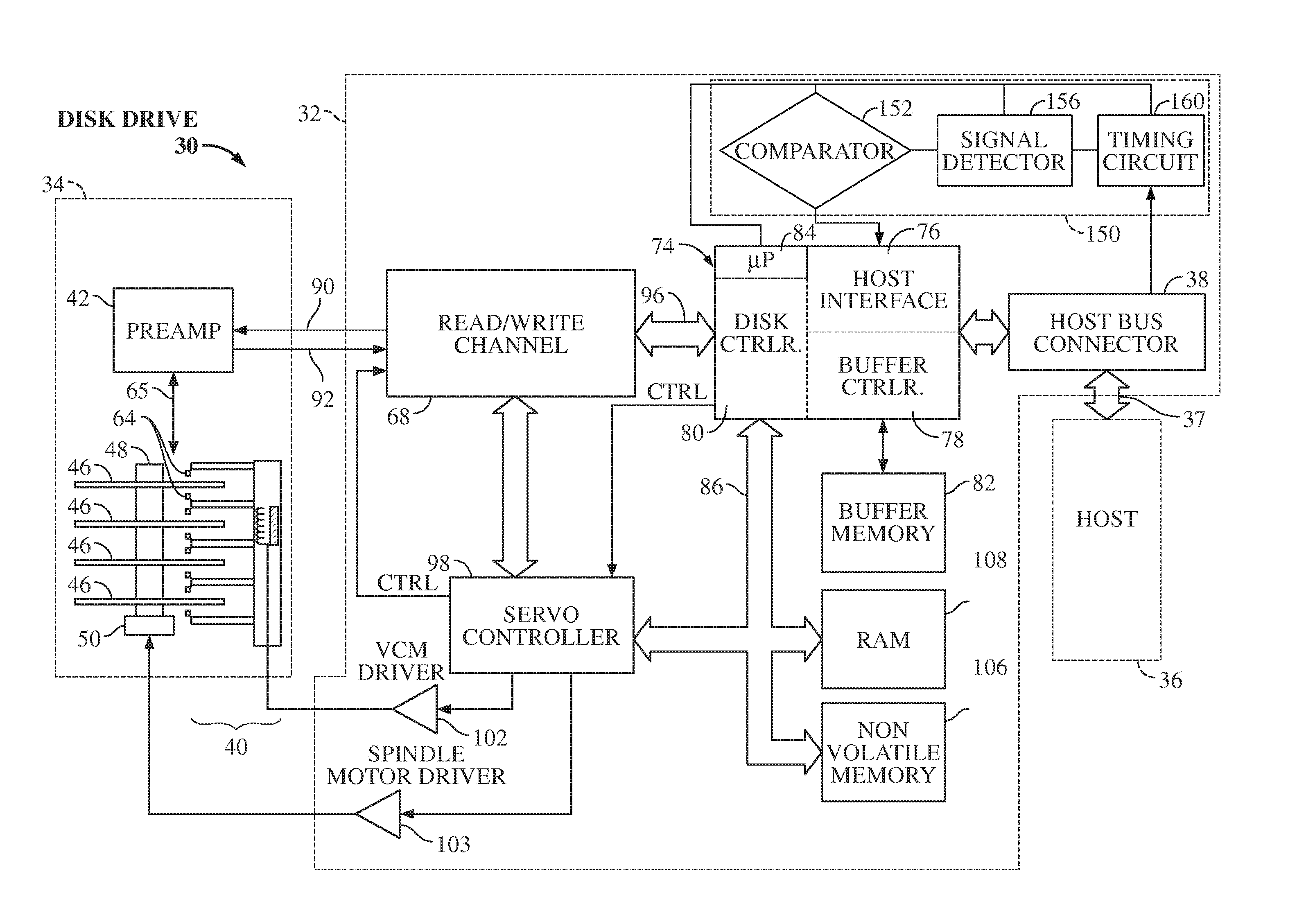
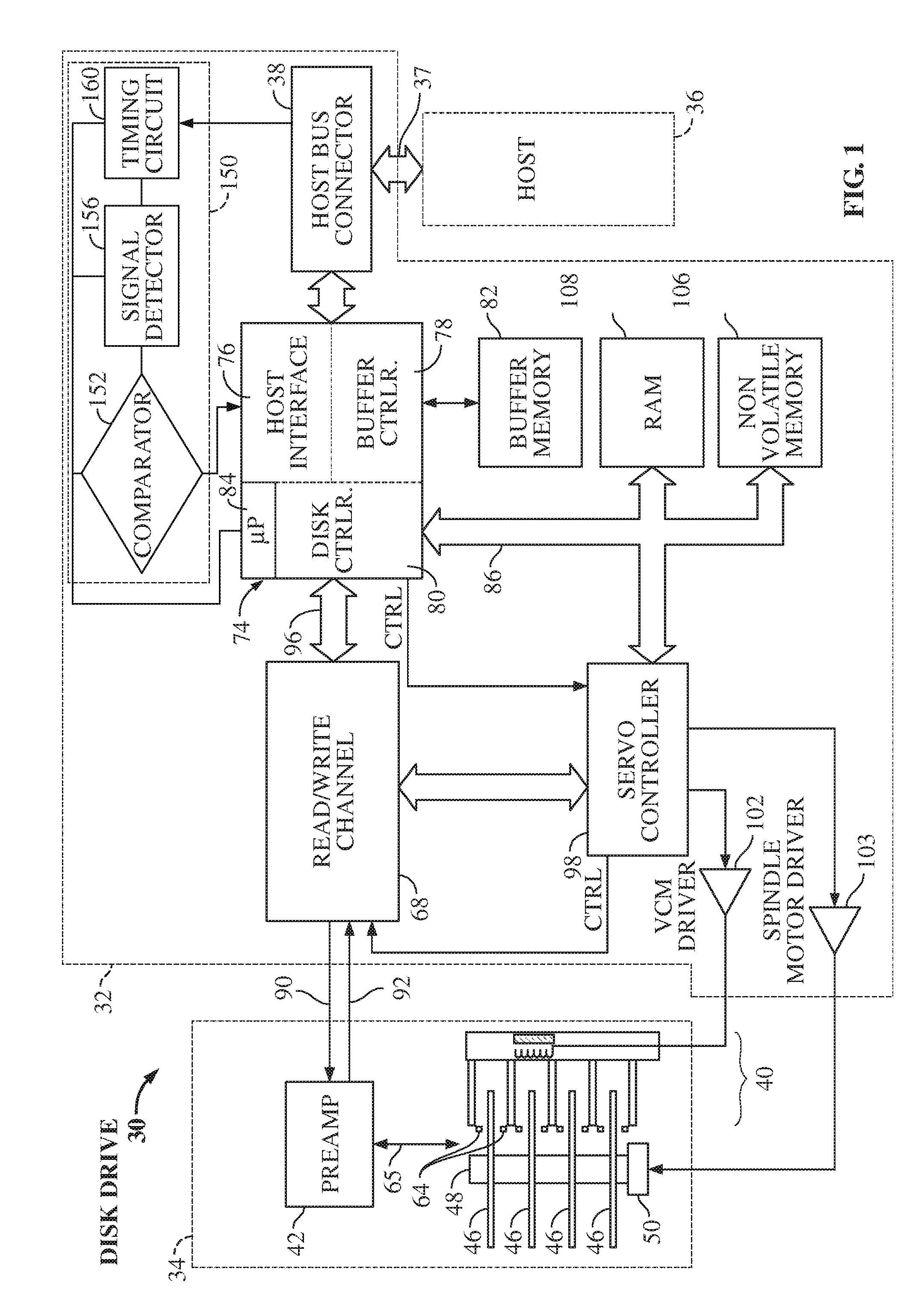
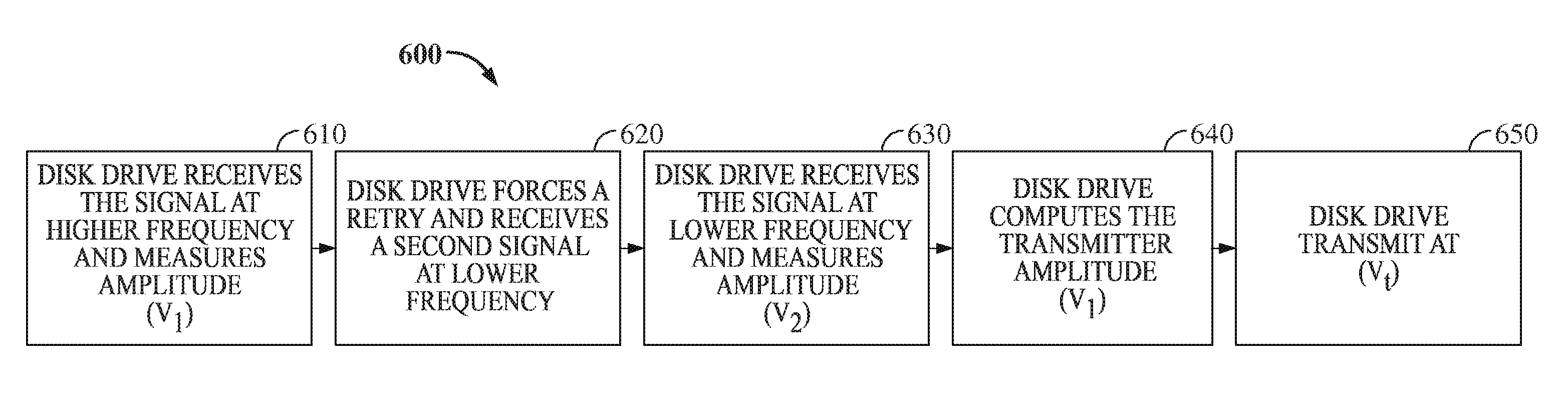
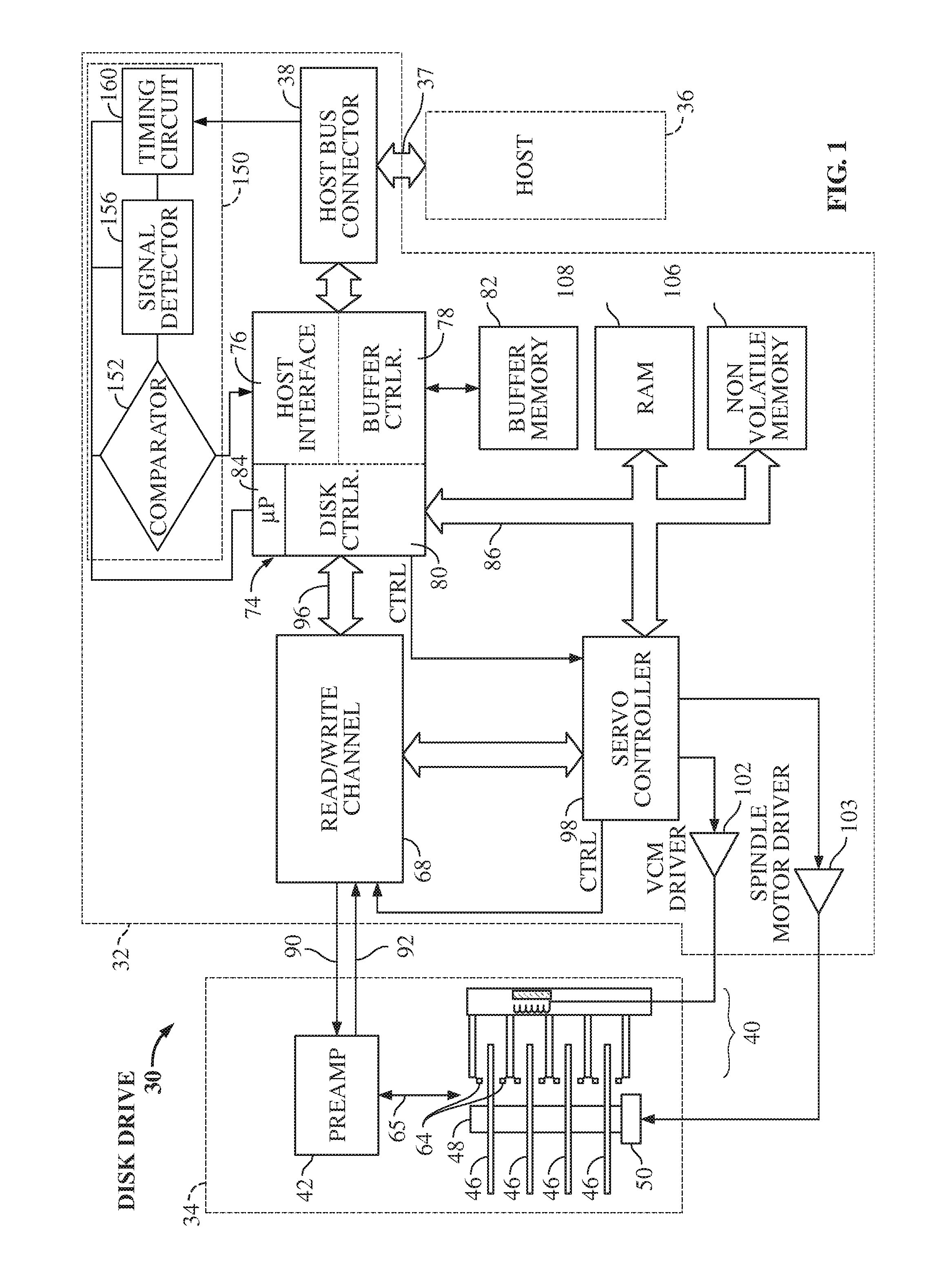
Serial interface amplitude selection for a disk drive in an unknown interconnect environment
InactiveUS8145452B1Energy efficient ICTCorrect operation testingVoltage amplitudeTransmission medium
A disk drive including a method for determining an amplitude for signal transmission over an interconnect is disclosed. The drive includes a processor that is coupled to a signal measurement circuit and is under the control of a program in conjunction with the signal measurement circuit to transmit a first signal to the host over a transmission medium at a first transmission frequency according to a first speed negotiation process, receive a second signal from the host at the first transmission frequency, determine a first voltage amplitude of the second signal, transmit a third signal to the host at a second transmission frequency according to a second speed negotiation process, receive a fourth signal from the host at the second transmission frequency, determine a second voltage amplitude of the fourth signal, and determine an approximate voltage loss in response to the first and second voltage amplitudes.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Light emitting device
InactiveUS6958750B2Reduce power consumptionReduce the number of processesCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsVoltage amplitudeLow voltage
A pixel having a structure in which low voltage drive is possible is provided by a simple process. A digital image signal input from a source signal line is input to the pixel through a switching TFT. At this point, a voltage compensation circuit amplifies the voltage amplitude of the digital image signal or transforms the amplitude, and applies the result to a gate electrode of a driver TFT. On-off control of TFTs within the pixel can thus be performed normally even if the voltage of a power source for driving gate signal lines becomes lower.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Serial interface amplitude selection for a disk drive in an unknown interconnect environment
A method for determining an amplitude for signal transmission over an interconnect is disclosed. The method includes transmitting a first signal to a host over a transmission medium at a first transmission frequency according to a first speed negotiation process and receiving a second signal from the host at the first transmission frequency. The method also includes measuring a first voltage amplitude of the second signal and transmitting a third signal to the host at a second transmission frequency according to a second speed negotiation process. The method further includes receiving a fourth signal from the host at the second transmission frequency, measuring a second voltage amplitude of the fourth signal, and determining an approximate voltage loss in response to the first and second voltage amplitudes.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus for varying the programming duration and/or voltage of an electrically floating body transistor, and memory cell array implementing same
There are many inventions described herein as well as many aspects and embodiments of those inventions, for example, circuitry and techniques for reading, writing and / or operating a semiconductor memory cells of a memory cell array, including electrically floating body transistors in which an electrical charge is stored in the body of the transistor. In one aspect, the present inventions are directed to one or more independently controllable parameters of a memory operation (for example, restore, write, refresh), to program or write a data state into a memory cell. In one embodiment, the parameter is the amount of time of programming or writing a predetermined data state into a memory cell. In another embodiment, the controllable parameter is the amplitude of the voltage of the control signals applied to the gate, drain region and / or source region during programming or writing a predetermined data state into a memory cell. Indeed, the controllable parameters may be both temporal and voltage amplitude. Notably, the memory cell array may comprise a portion of an integrated circuit device, for example, logic device (for example, a microprocessor) or a portion of a memory device (for example, a discrete memory).
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and apparatus for continuous electrode impedance monitoring
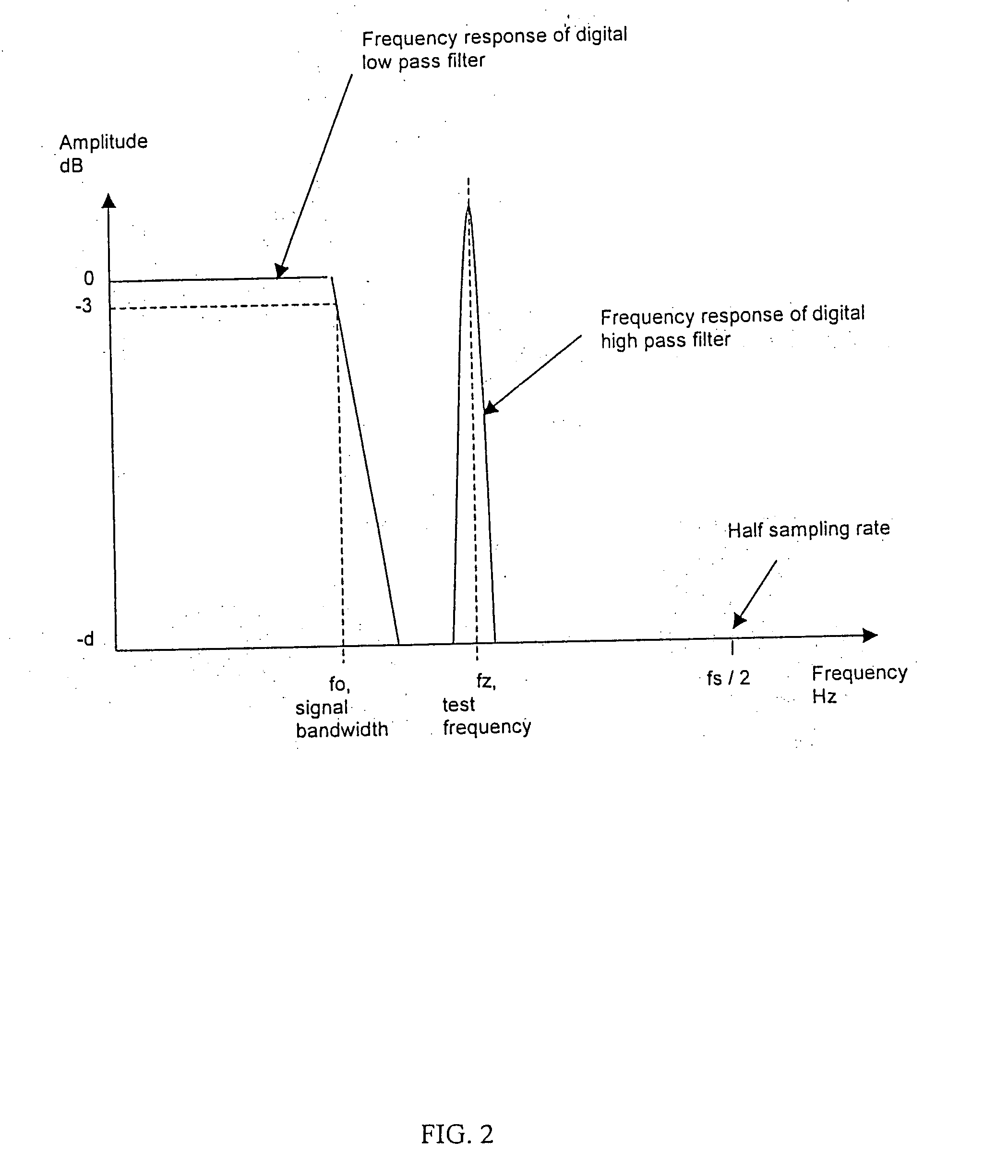
InactiveUS20060020218A1Continuous monitoringElectrocardiographyResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage amplitudeBandpass filtering
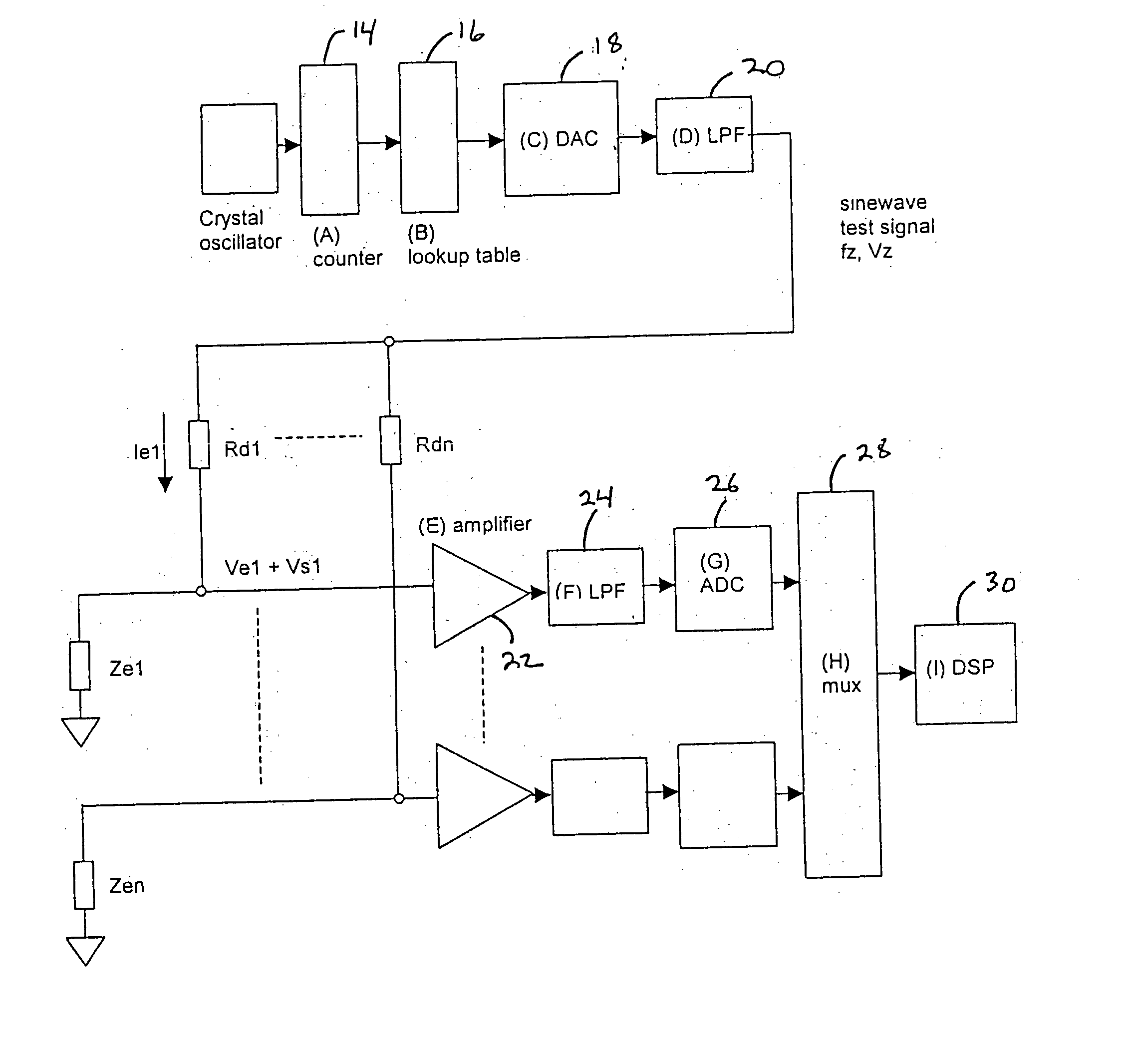
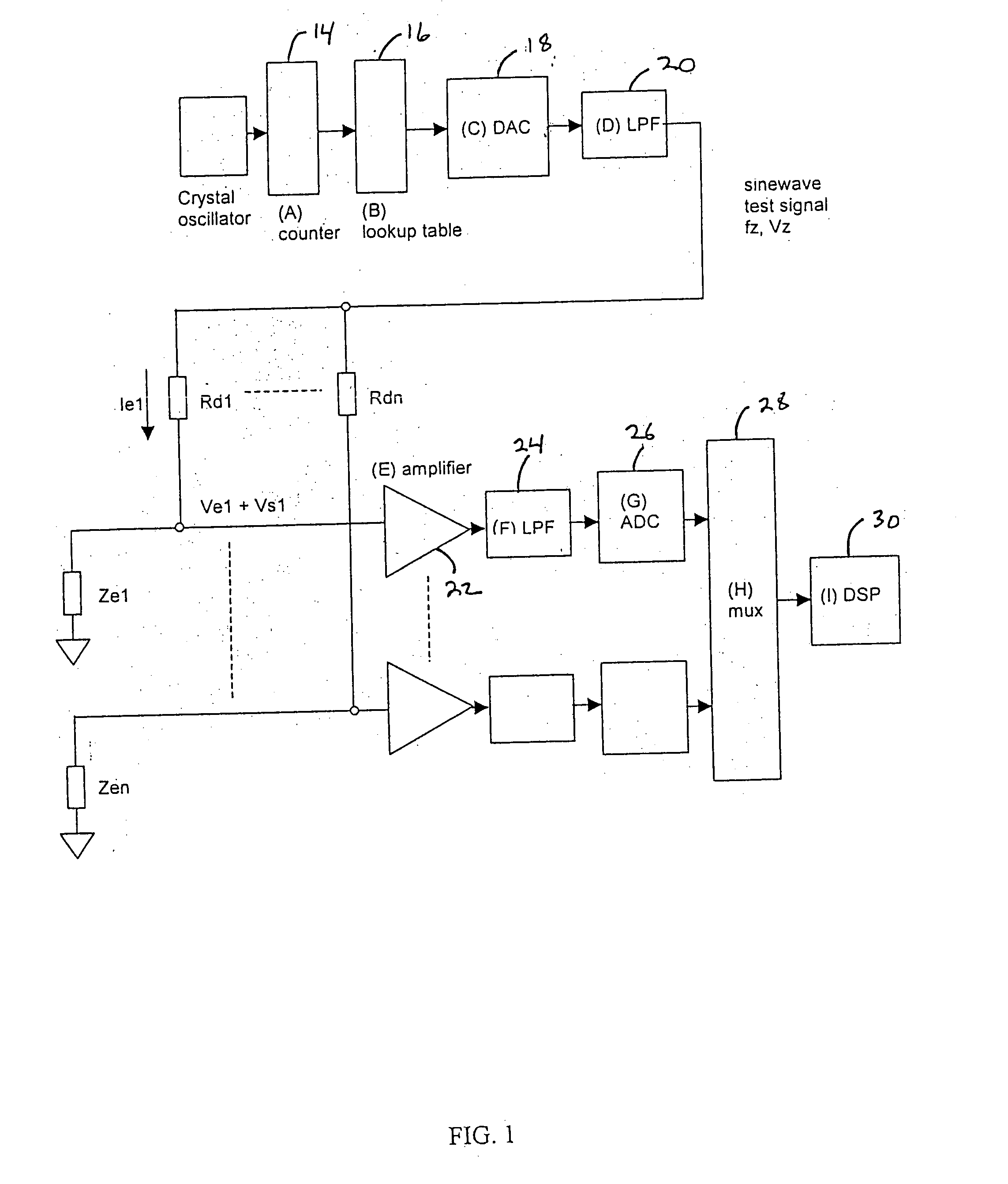
In one embodiment, the present invention includes a test signal generator capable of producing an impedance test signal comprising of a sine wave having a known frequency. The test signal generator may include a crystal oscillator, a counter, and a lookup table. The lookup table output is applied to a digital to analog converter and is then low pass filtered using a conventional analog filter to produce a sine wave of a known frequency and voltage amplitude. The test signal flows through the electrode and combines with an electrophysiological signal to form a combined signal. A signal processor is used to isolate the combined signal into the test signal component and the electrophysiological component. The signal processor digitally low pass filters the combined signal and the output of the low pass filter is the electrophysiological signal. The signal processor then digitally bandpass filters the combined signal using a filter with a center frequency which is the same as the test frequency. The output of this filter is then used to calculate the electrode impedance.
Owner:COMPUMEDICS
Non-contact current and voltage sensing clamp
InactiveUS20130076343A1Computing powerCurrent/voltage measurementBase element modificationsVoltage amplitudeElectrical conductor
A clamping current and voltage sensor provides an isolated and convenient technique for measuring current passing through a conductor such as an AC branch circuit wire, as well as providing an indication of an electrostatic potential on the wire, which can be used to indicate the phase of the voltage on the wire, and optionally a magnitude of the voltage. The device includes a body formed from two handle portions that contain the current and voltage sensors within an aperture at the distal end, which may be a ferrite cylinder with a hall effect sensor disposed in a gap along the circumference to measure current, or alternatively a winding provided through the cylinder along its axis and a capacitive plate or wire disposed adjacent to, or within, the ferrite cylinder to provide the indication of the voltage. When the handles are compressed the aperture is opened to permit insertion of a wire for measurement.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ground fault detector for vehicle
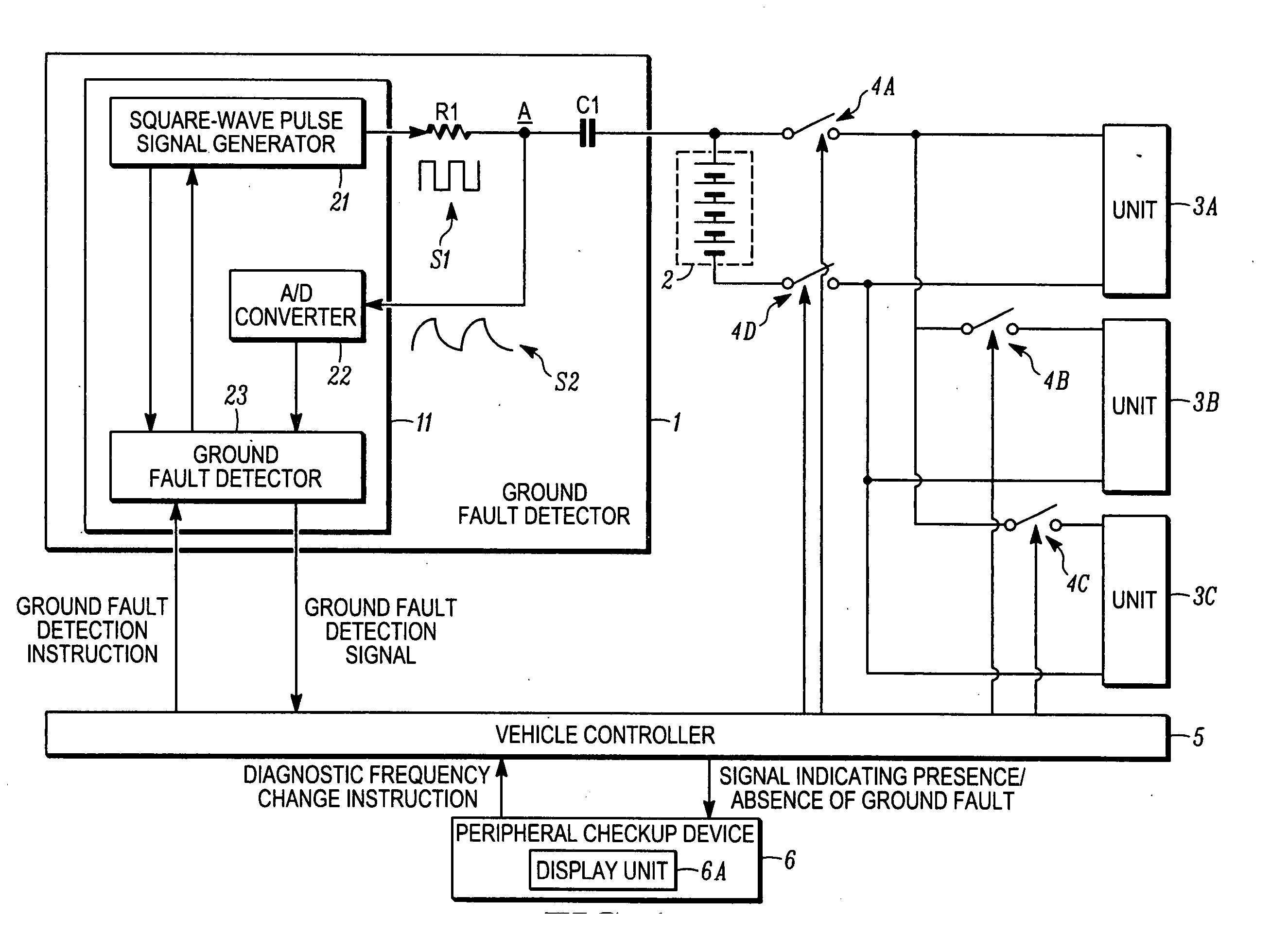
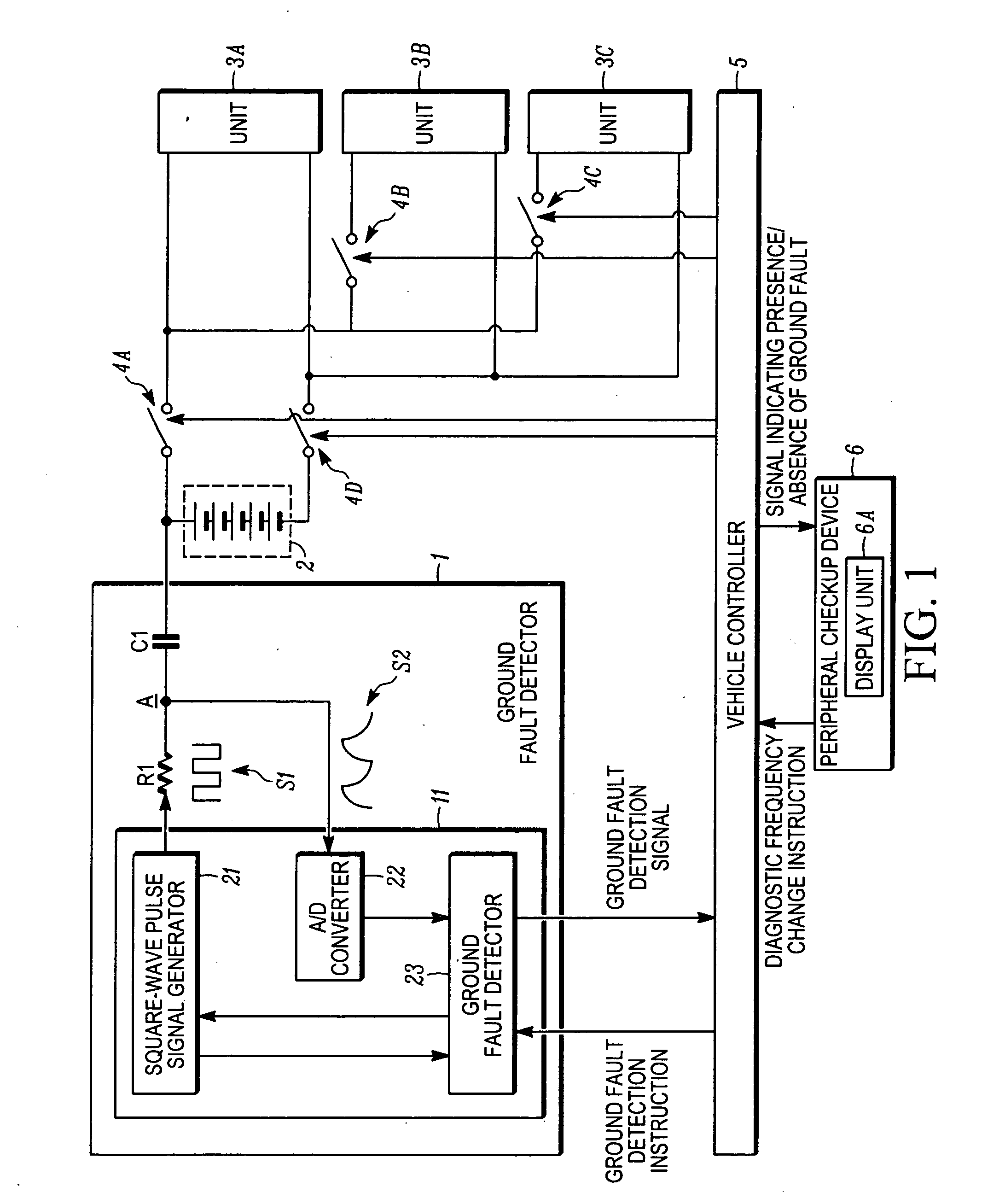
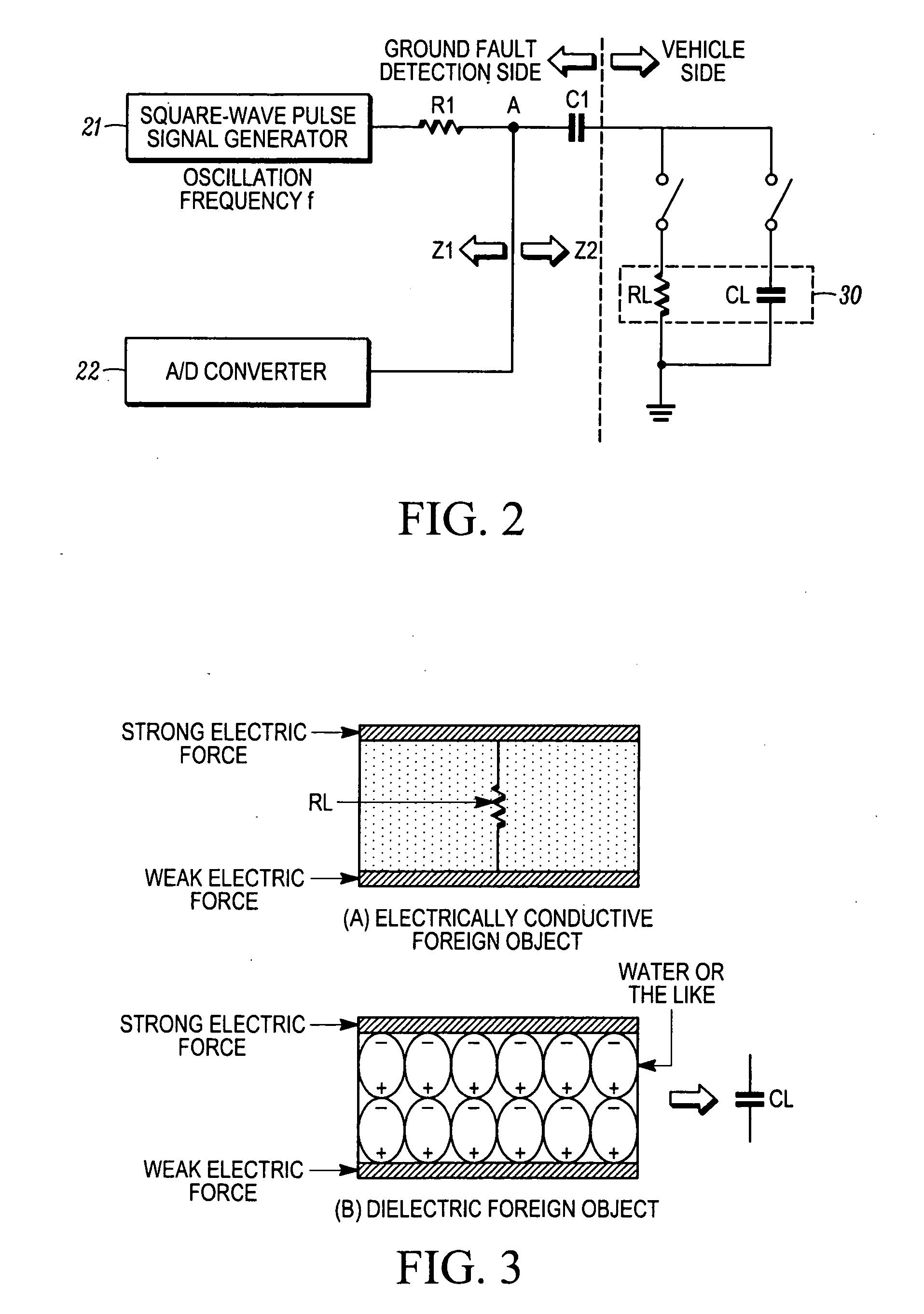
A ground fault detector and detection method for a vehicle that can determine the cause of the occurrence of a ground fault after detecting the presence of the ground fault. The output terminal of a high-voltage battery is connected to one side of a coupling capacitor. In operation, a pulse signal is applied to a measurement point on the other side of the coupling capacitor, and the voltage generated at that point is detected. Whether the high-voltage battery or the electrical equipment units are grounded is determined. To determine the cause of the ground fault, the oscillation frequency of the square-wave pulse signal is changed and applied to the measurement point. From the change in voltage amplitude detected, it is determined whether the cause of the ground fault is a resistive or a capacitive ground fault, according to the change in the impedance of the battery or the units.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Touch panel device
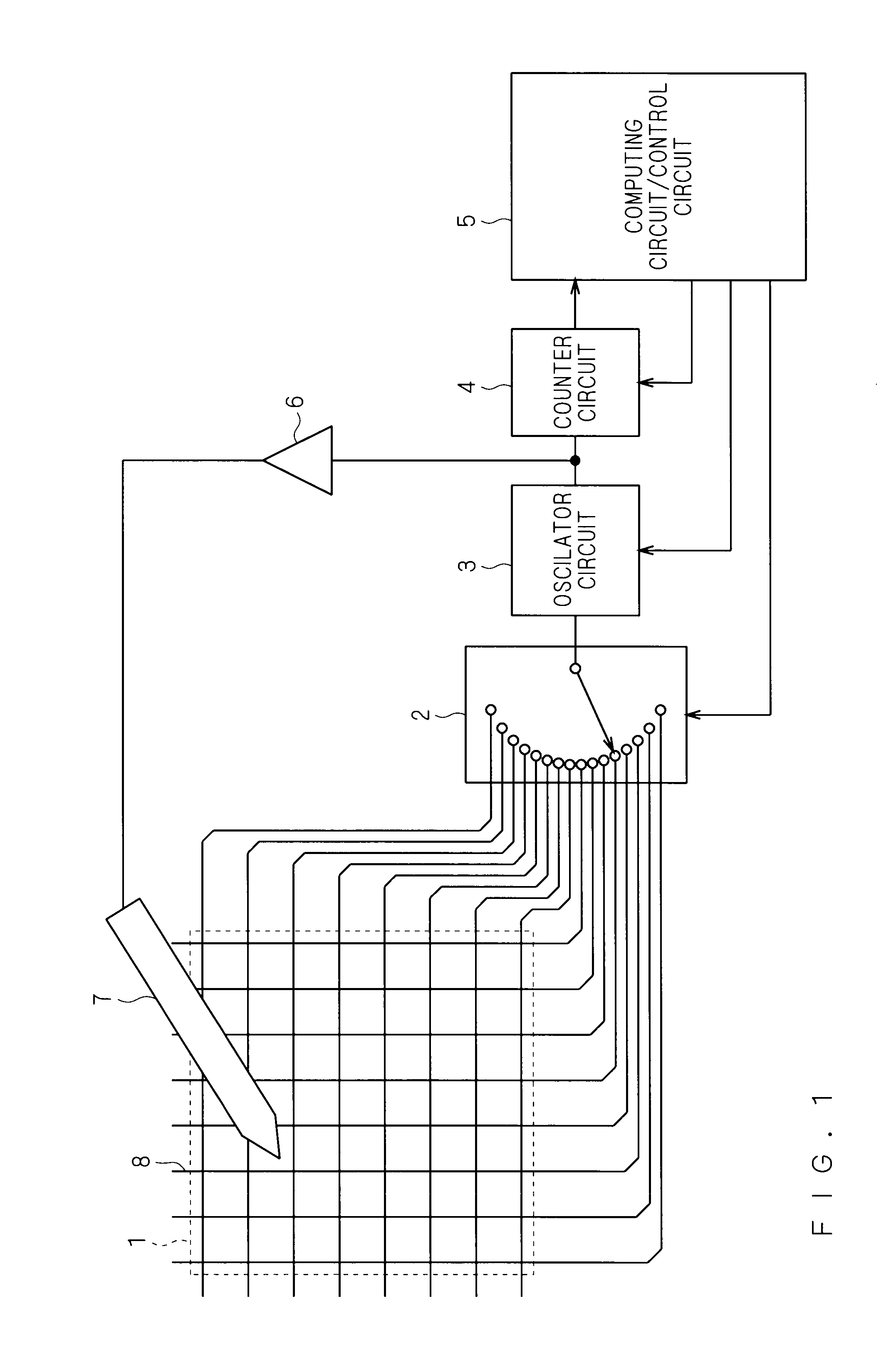
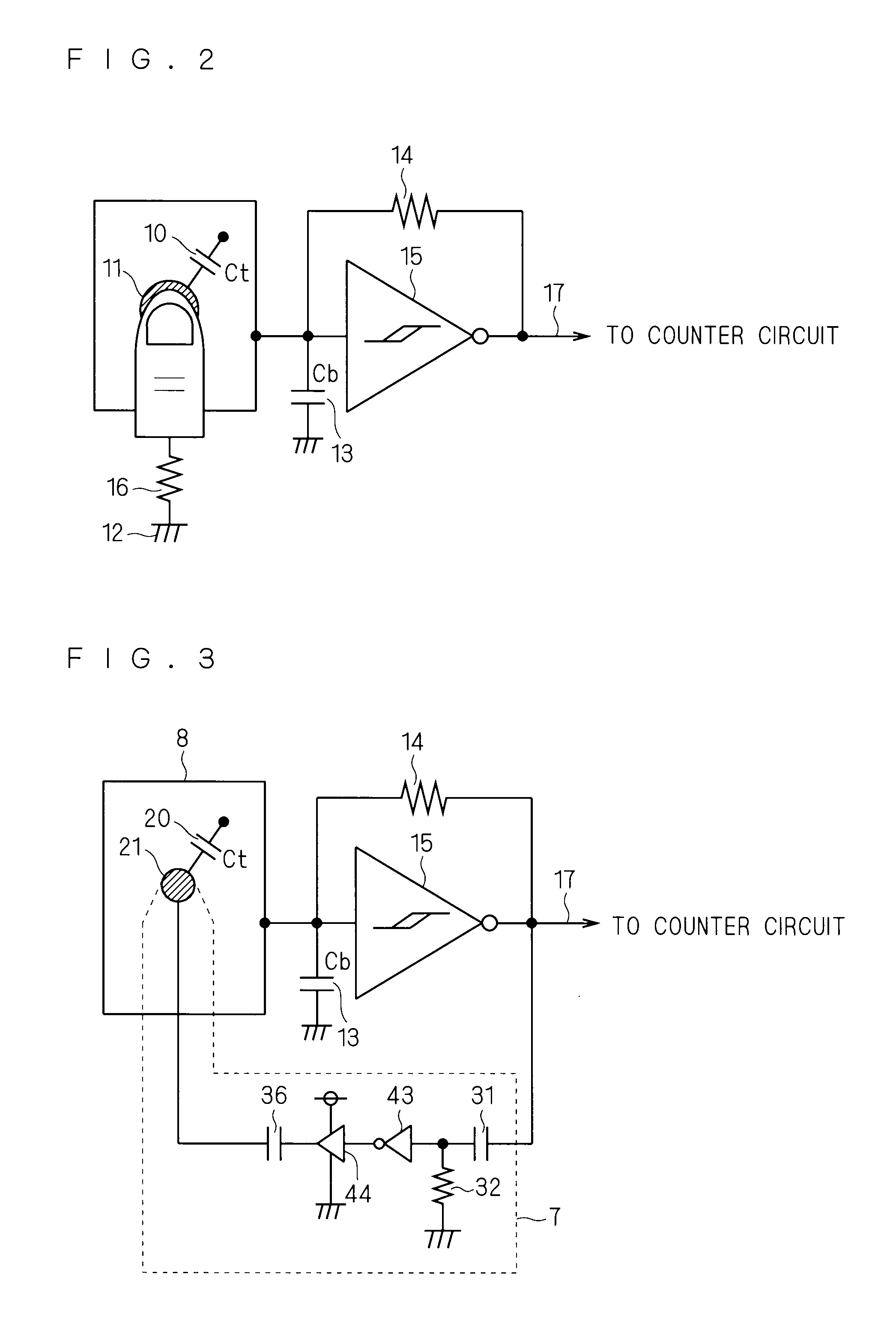
InactiveUS20100066693A1Configuration economyMaintaining operability and simplicityInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceVoltage amplitude
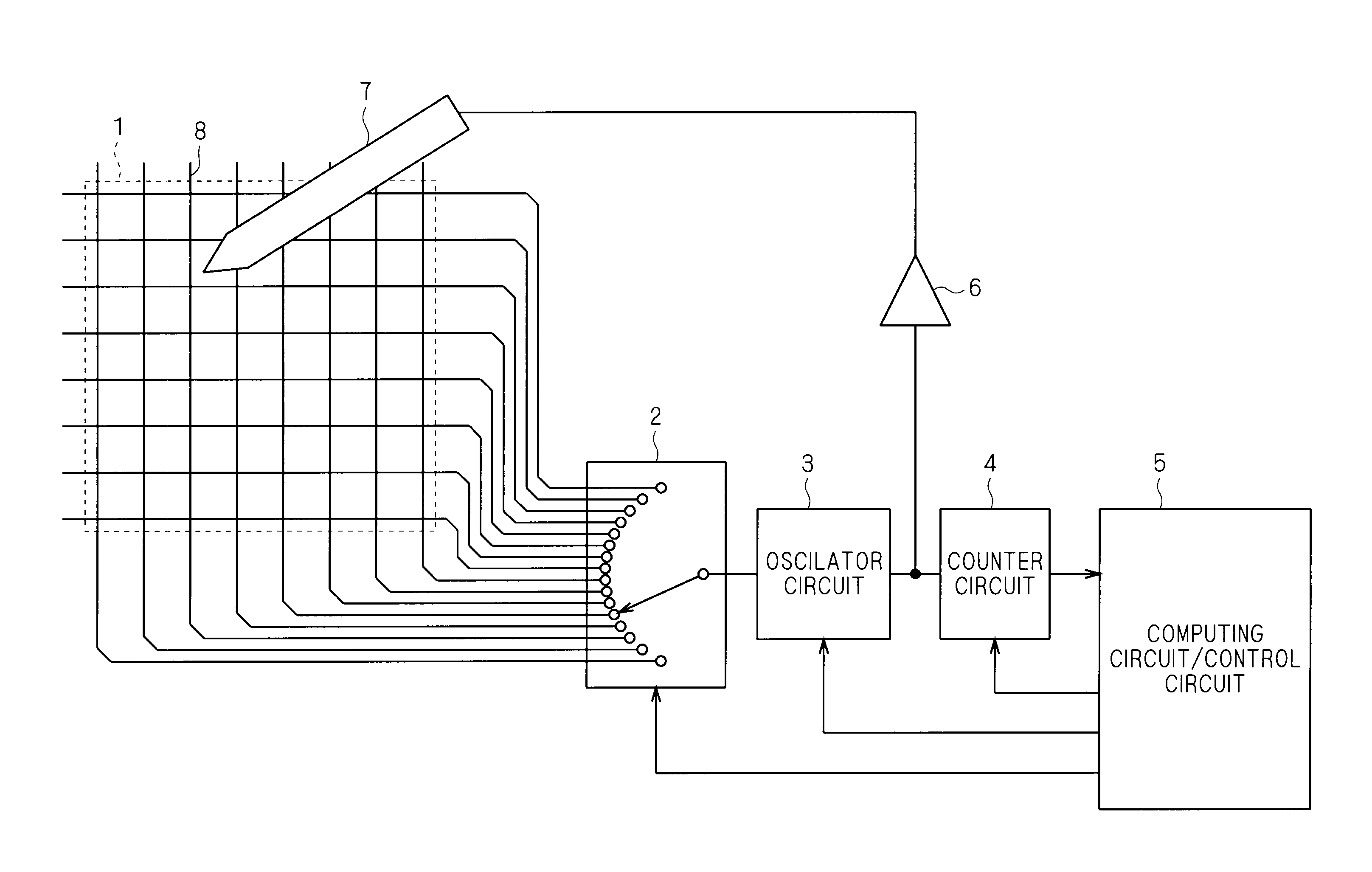
A touch panel device according to the present invention includes: a stylus pen including a conductive stylus pen electrode portion at a tip portion thereof; a plurality of capacitance detecting interconnections formed on a substrate in row and column directions; an oscillator circuit which outputs an oscillation signal for performing charging / discharging to each of the plurality of capacitance detecting interconnections, the oscillation signal having a cycle which changes in accordance with an amount of electric charges in the charging / discharging; and a counter circuit and a computing circuit / control circuit which compute, based on a change of the cycle being in accordance with a capacitance formed between the electrode portion of the stylus pen and the capacitance detecting interconnections, positional coordinates of the stylus pen brought in proximity to the capacitance detecting interconnections in a non-contact manner, wherein the stylus pen outputs to the electrode portion of the stylus pen an input pen signal which is in synchronization with the oscillation signal, has a phase different from a phase of the oscillation signal, and has a larger voltage amplitude compared with the oscillation signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
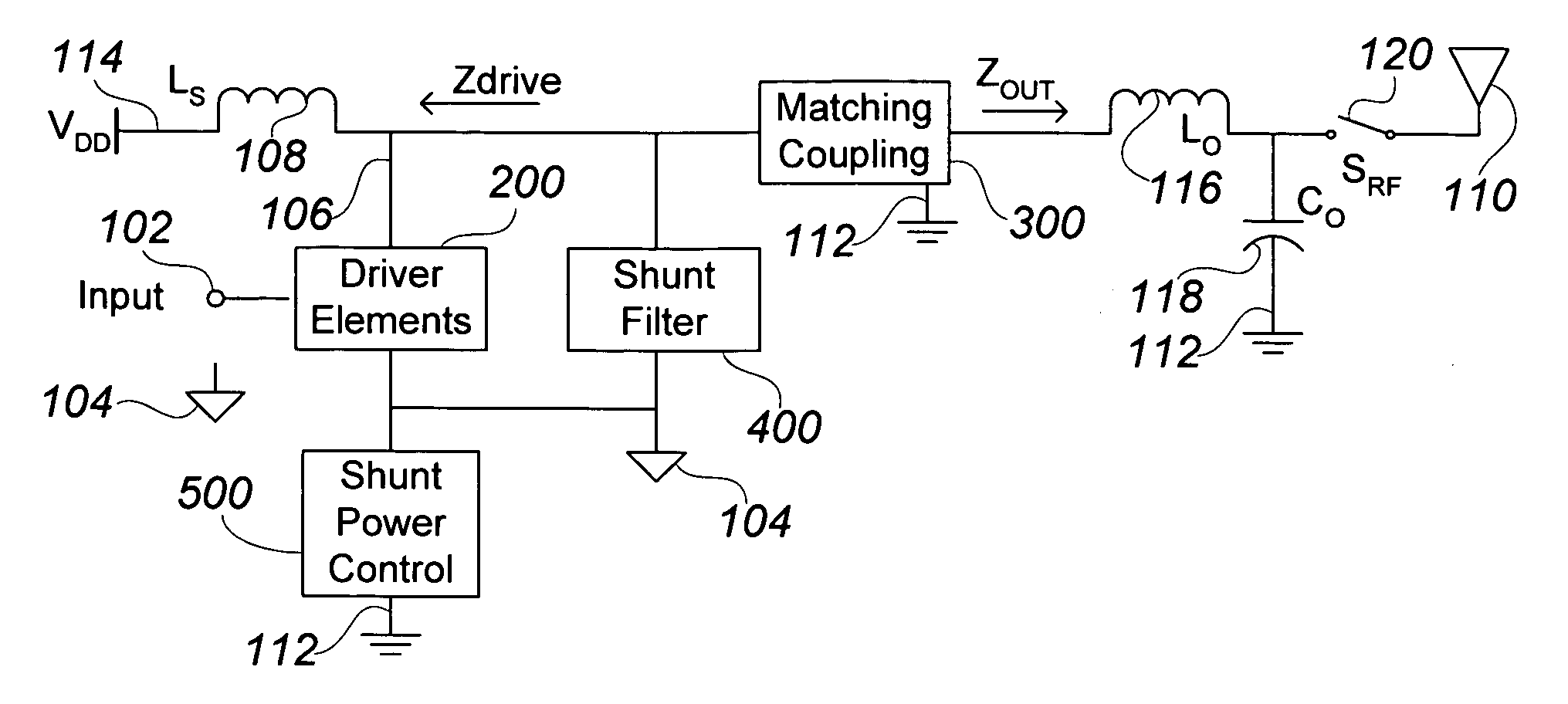
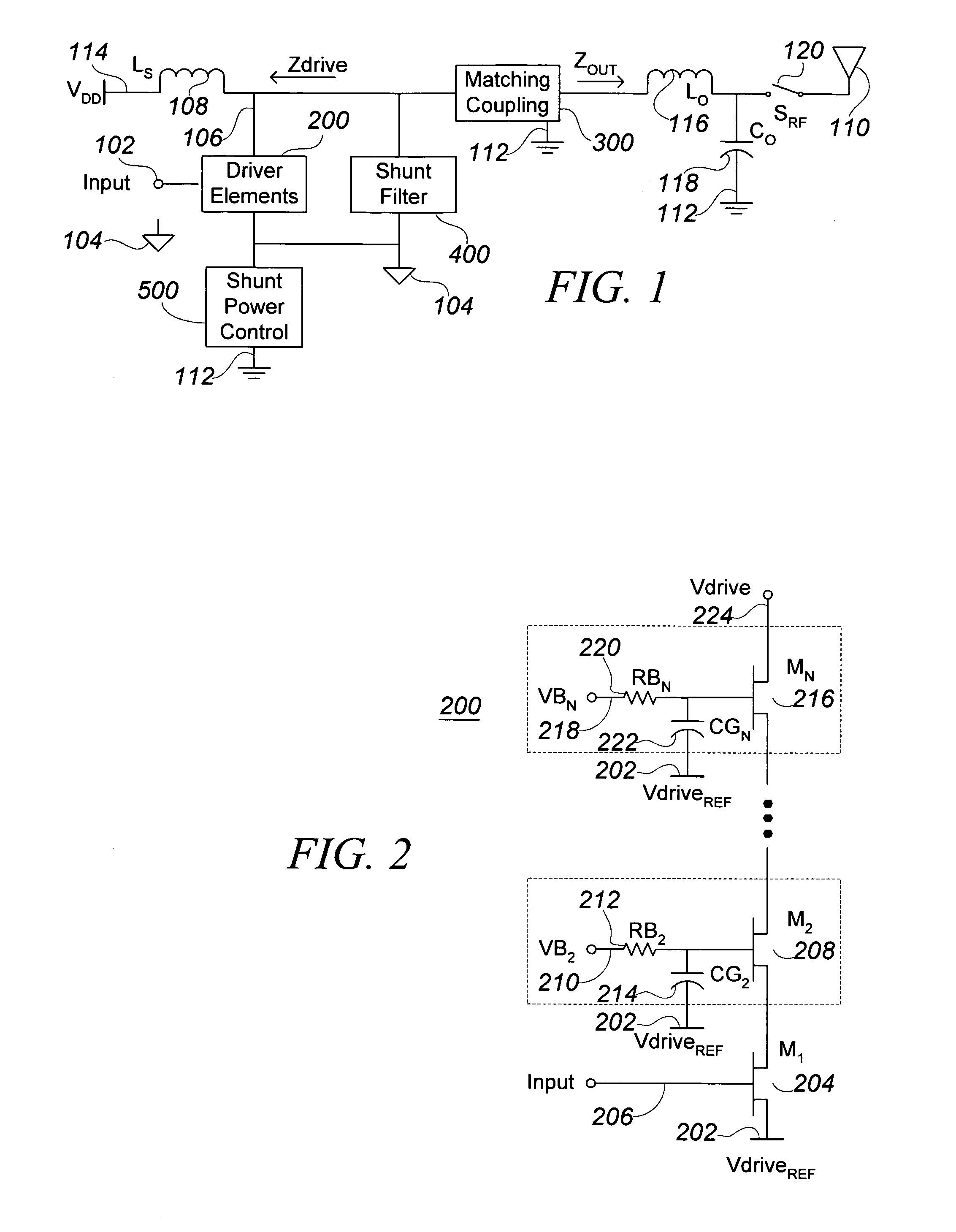
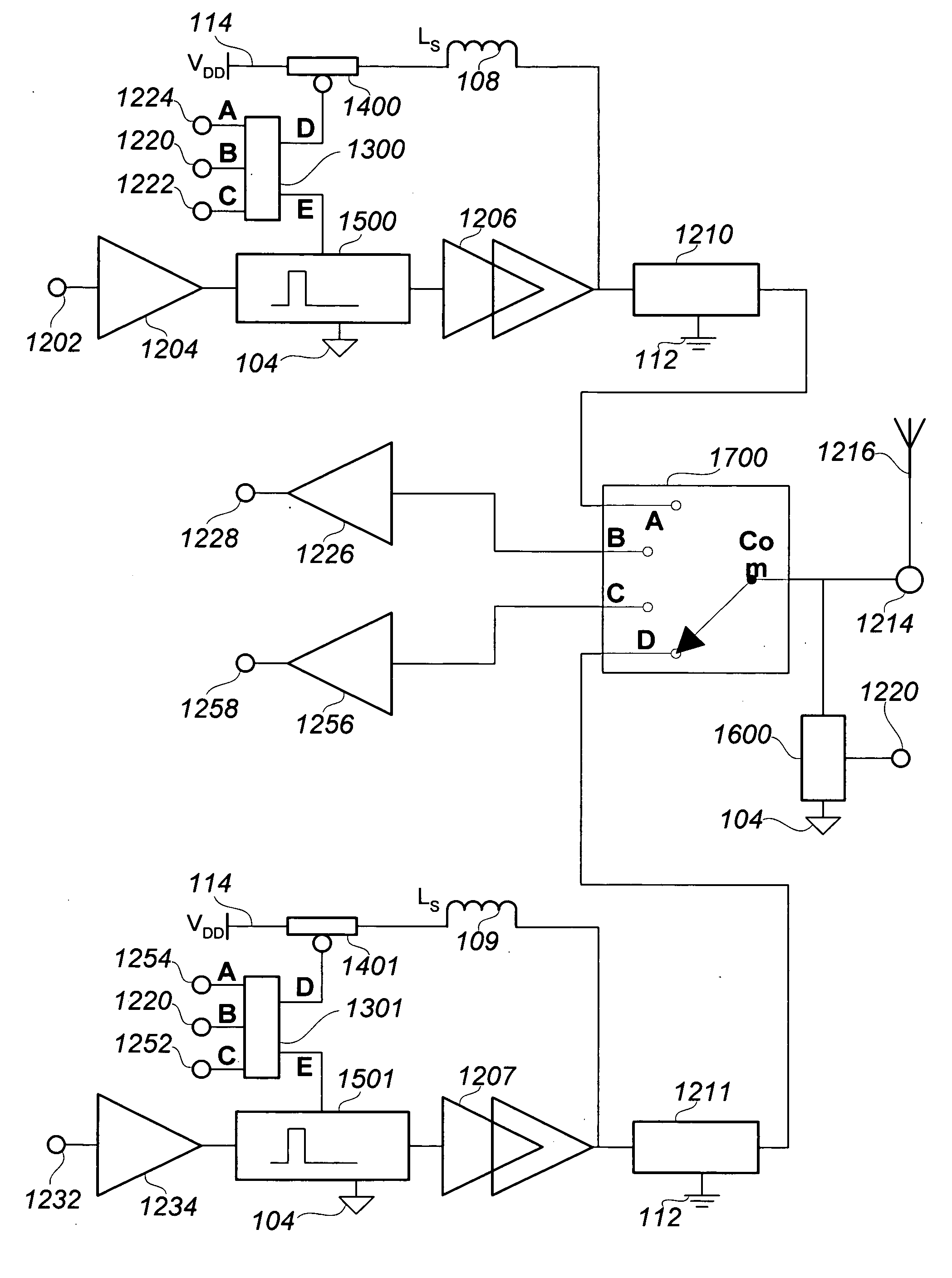
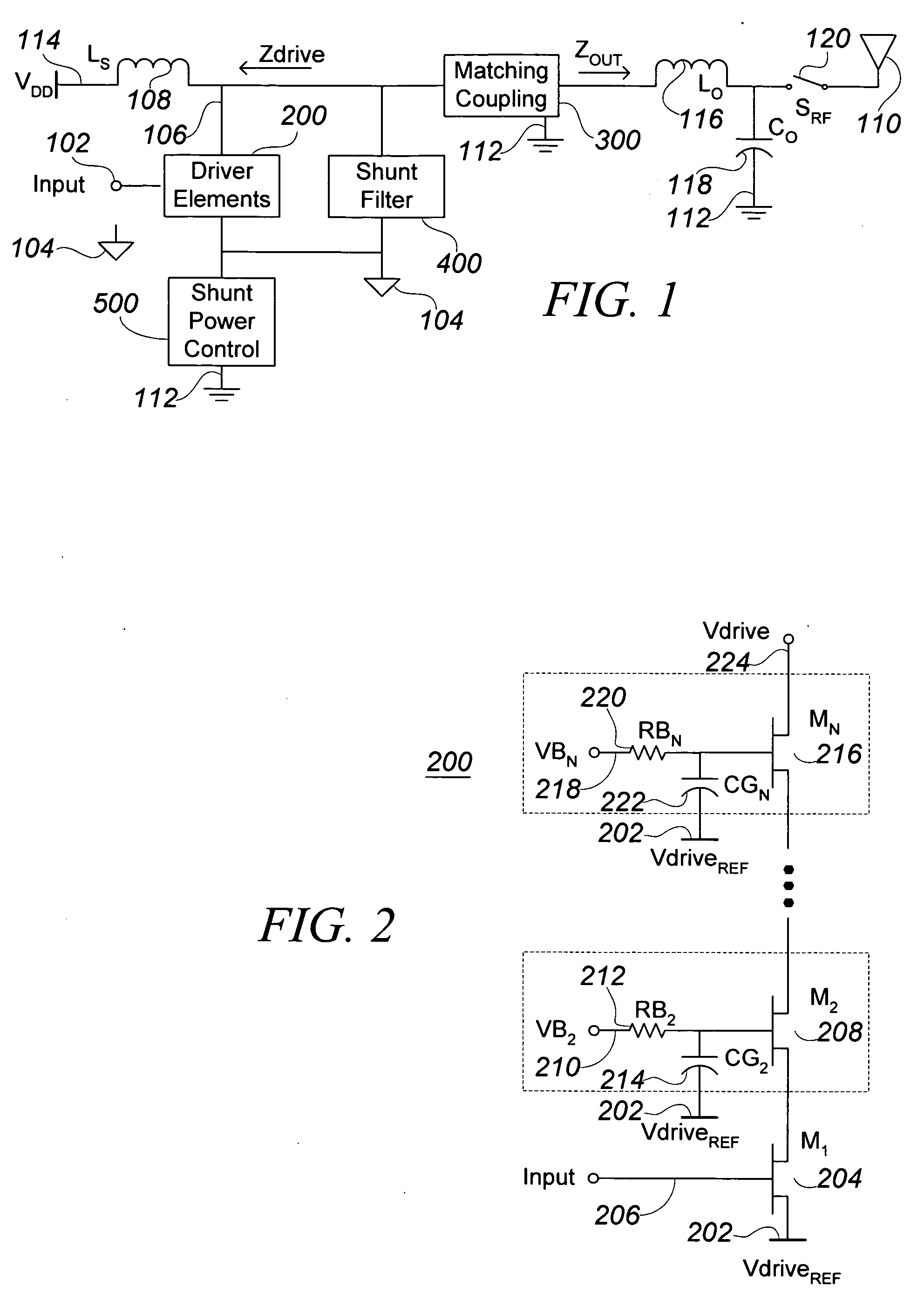
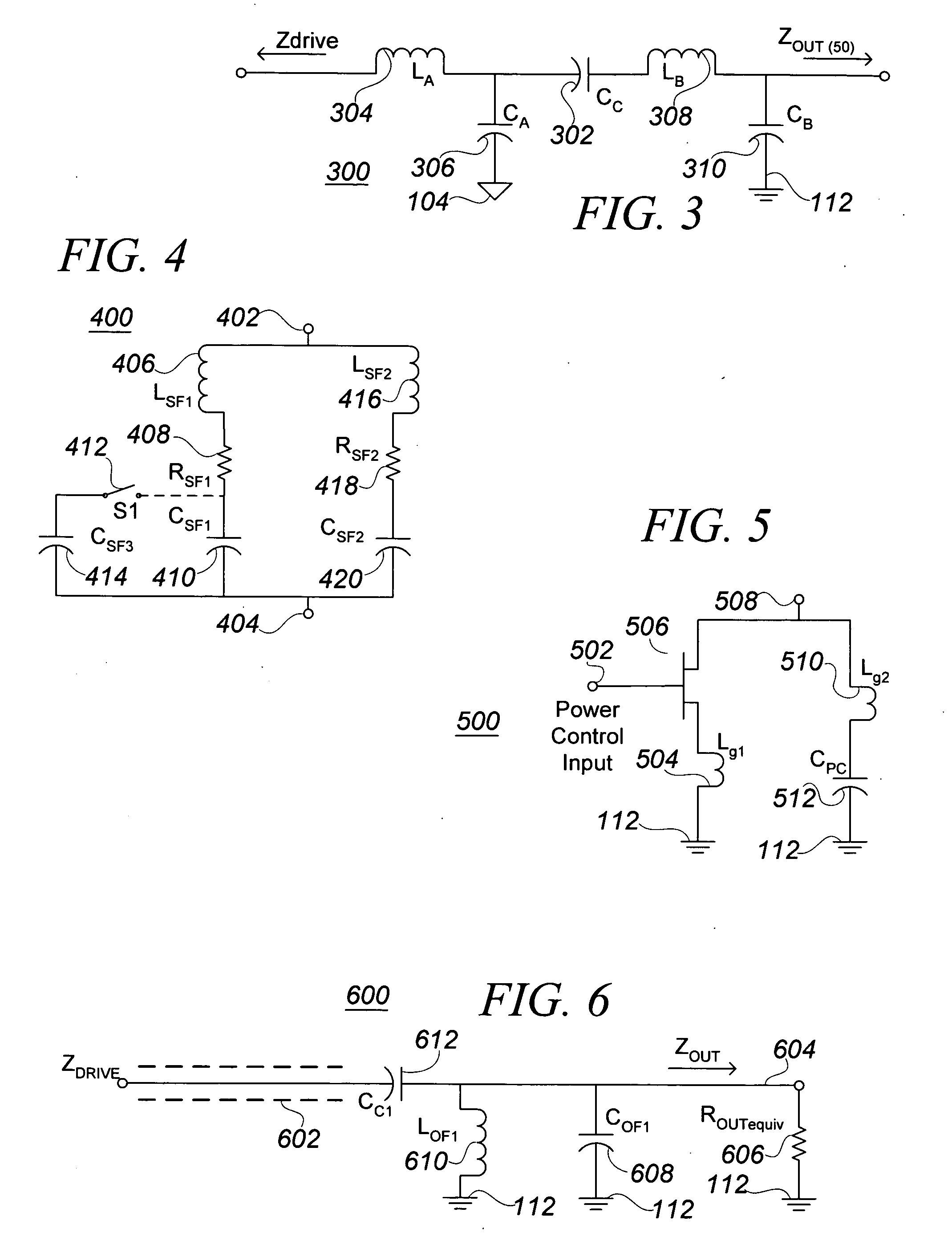
Integrated RF front end
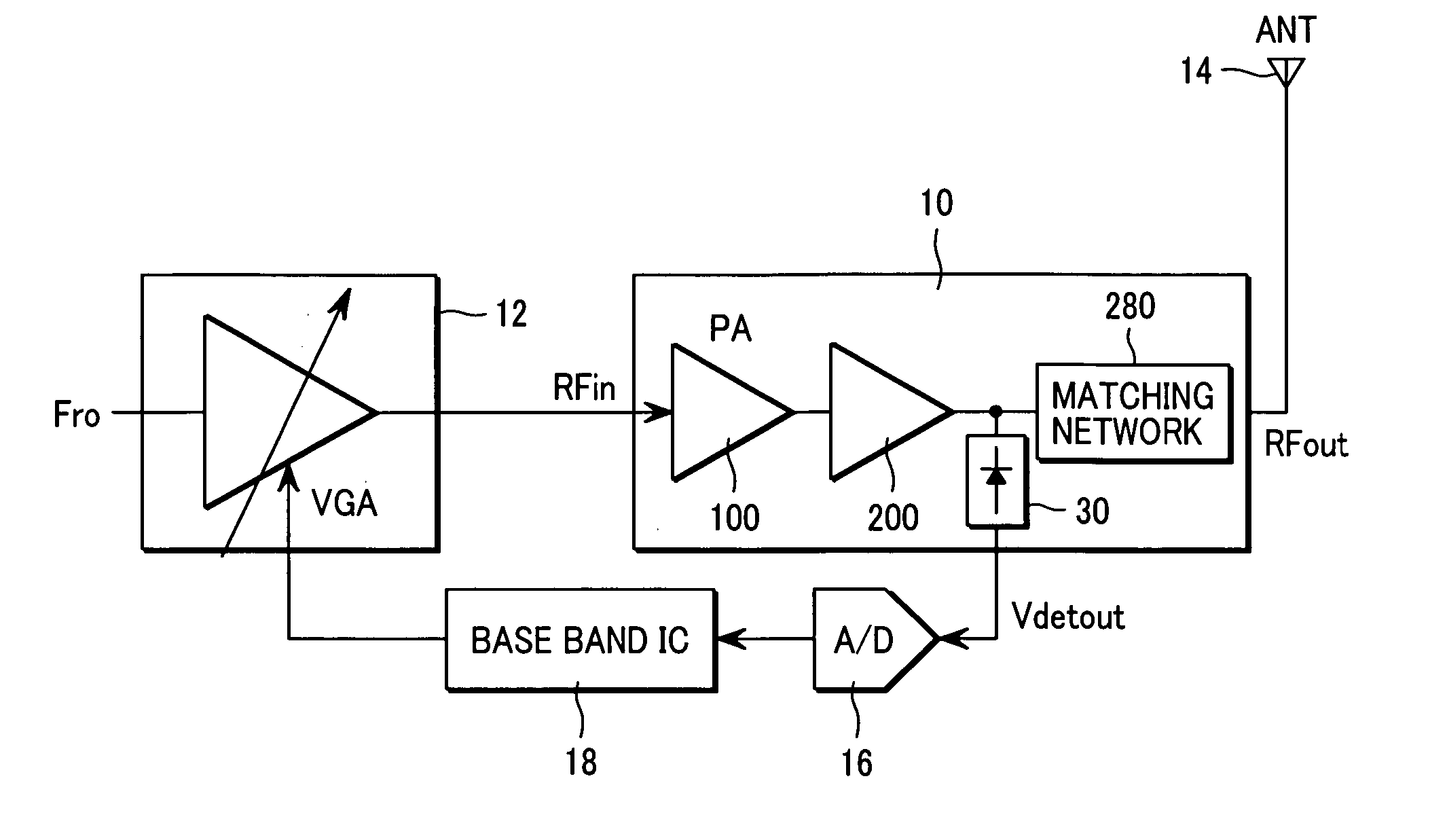
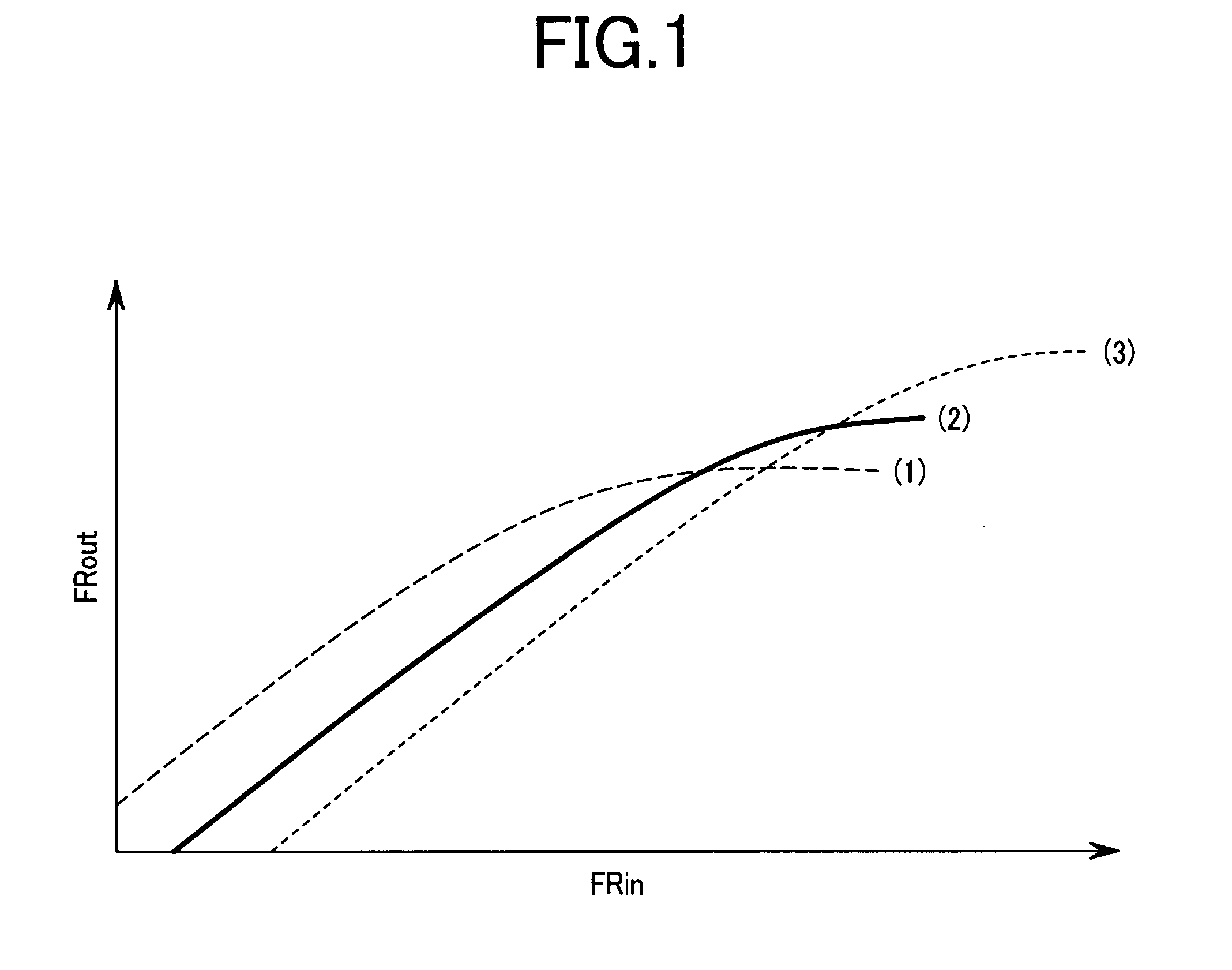
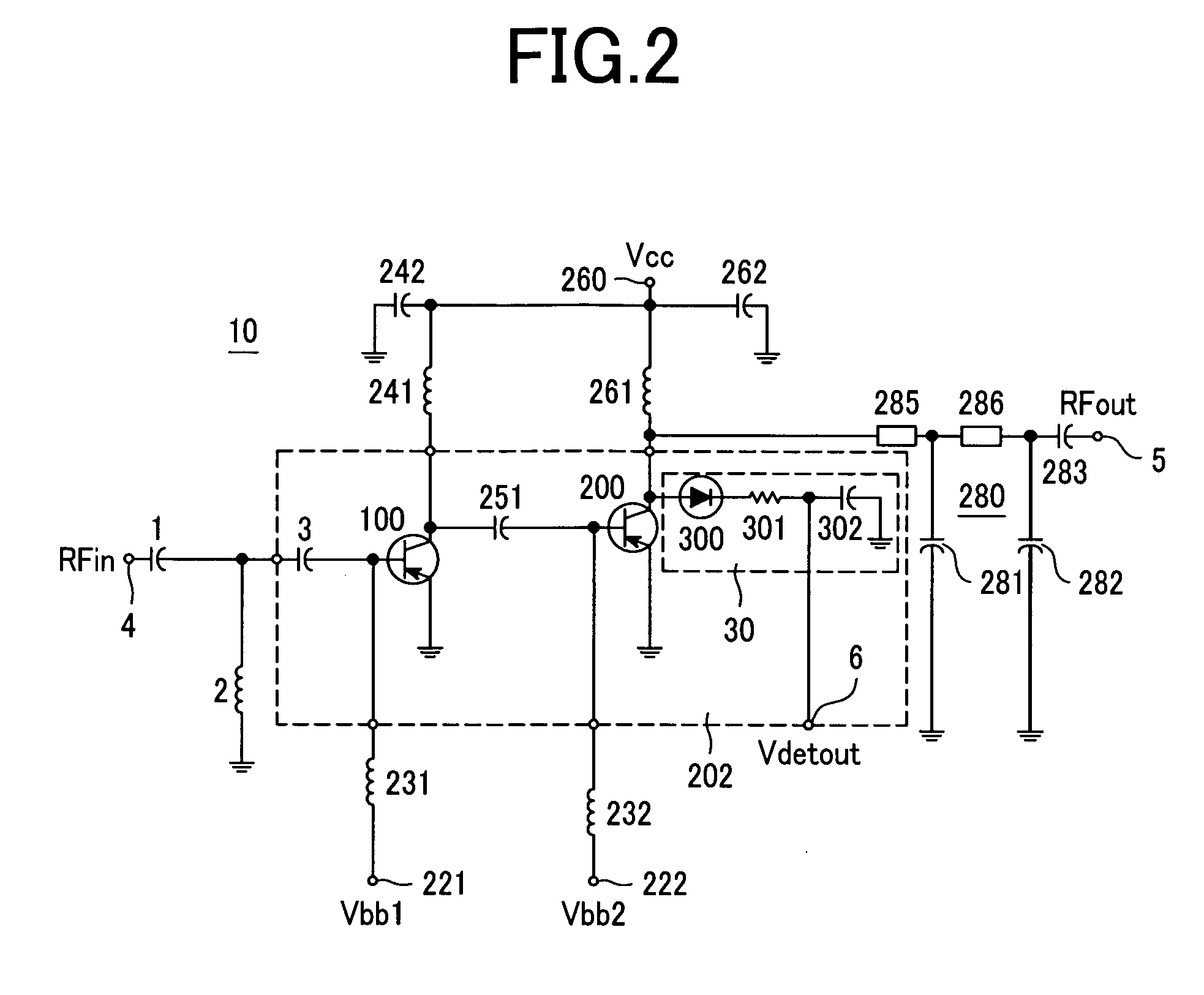
ActiveUS7088971B2Effective protectionResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersVoltage amplitudeTransceiver
A monolithic integrated circuit (IC), and method of manufacturing same, that includes all RF front end or transceiver elements for a portable communication device, including a power amplifier (PA), a matching, coupling and filtering network, and an antenna switch to couple the conditioned PA signal to an antenna. An output signal sensor senses at least a voltage amplitude of the signal switched by the antenna switch, and signals a PA control circuit to limit PA output power in response to excessive values of sensed output. Preferred fabrication techniques include stacking multiple FETs to form switching devices. An iClass PA architecture is described that dissipatively terminates unwanted harmonics of the PA output signal. A preferred embodiment of the RF transceiver IC includes two distinct PA circuits, two distinct receive signal amplifier circuits, and a four-way antenna switch to selectably couple a single antenna connection to any one of the four circuits.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
System for geophysical prospecting using induce electrokinetic effect
InactiveUS7042801B1Seismology for water-covered areasElectric/magnetic detectionVoltage amplitudeSeismic wave
Methods are disclosed employing seismic waves having infrasonic frequencies in the range of about 0.1–20 Hz for generating electromagnetic waves of similar infrasonic frequency in hydrocarbon bearing subterranean formations located at depths up to about 5000 meters, said electromagnetic waves having sufficient voltage amplitudes for detection at the earth's surface. Also disclosed are seismic sources capable of generating infrasonic seismic waves of sufficient amplitude for generating electromagnetic waves in hydrocarbon bearing formations at depths up to 5000 meters, said electromagnetic waves having voltage amplitudes sufficient for detection at the earth's surface.
Owner:SEISMOELECTRIC SOUNDINGS
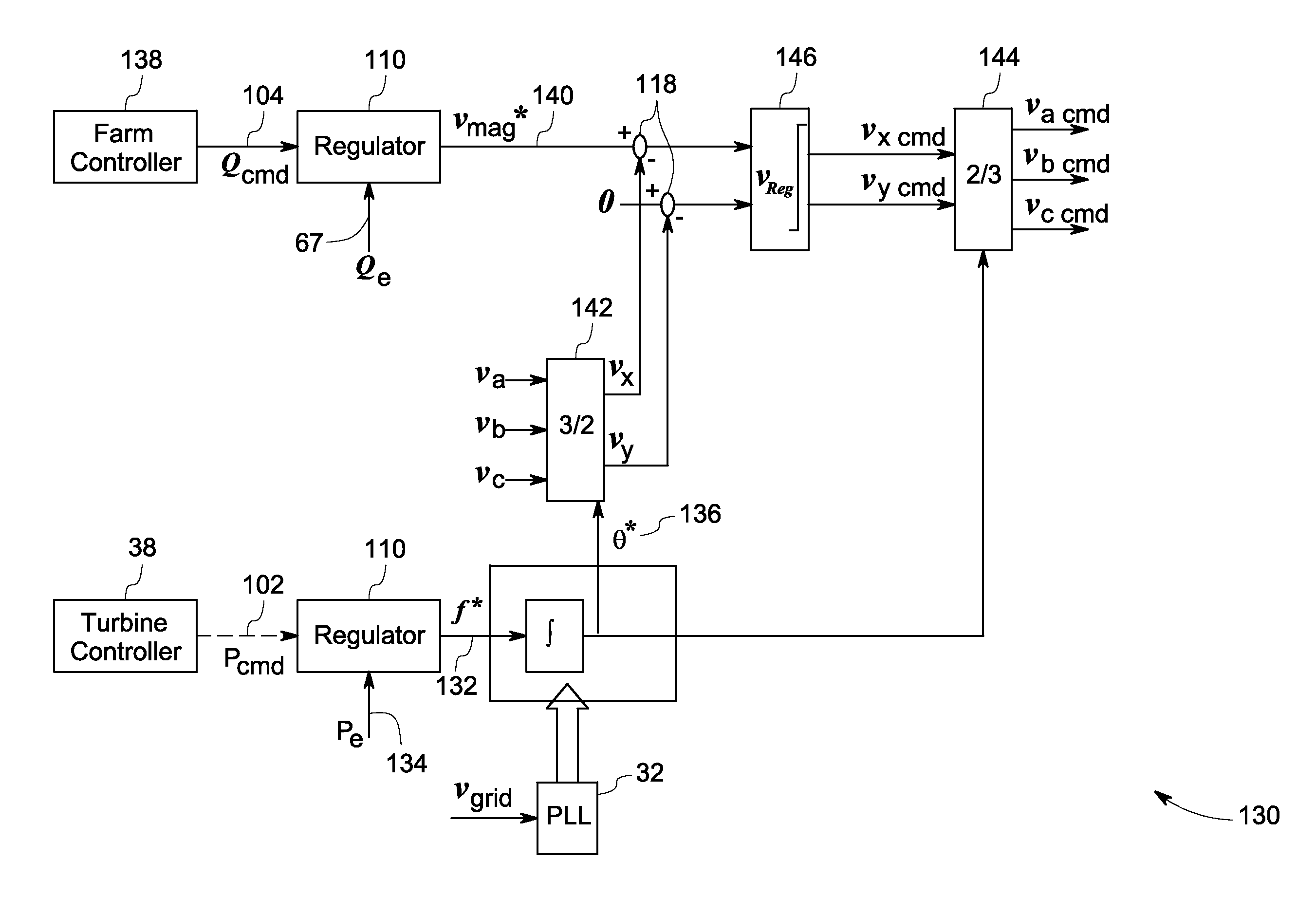
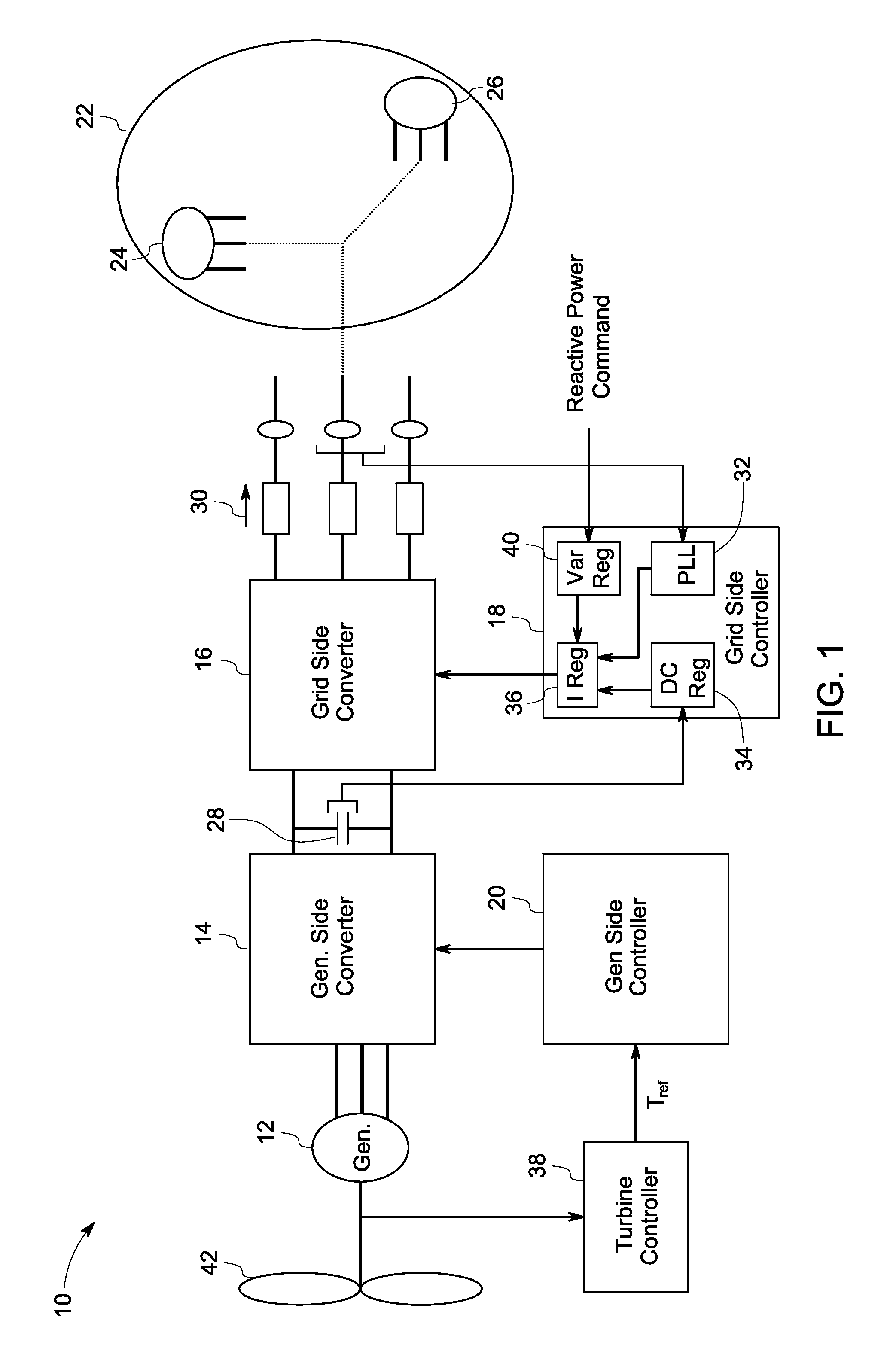
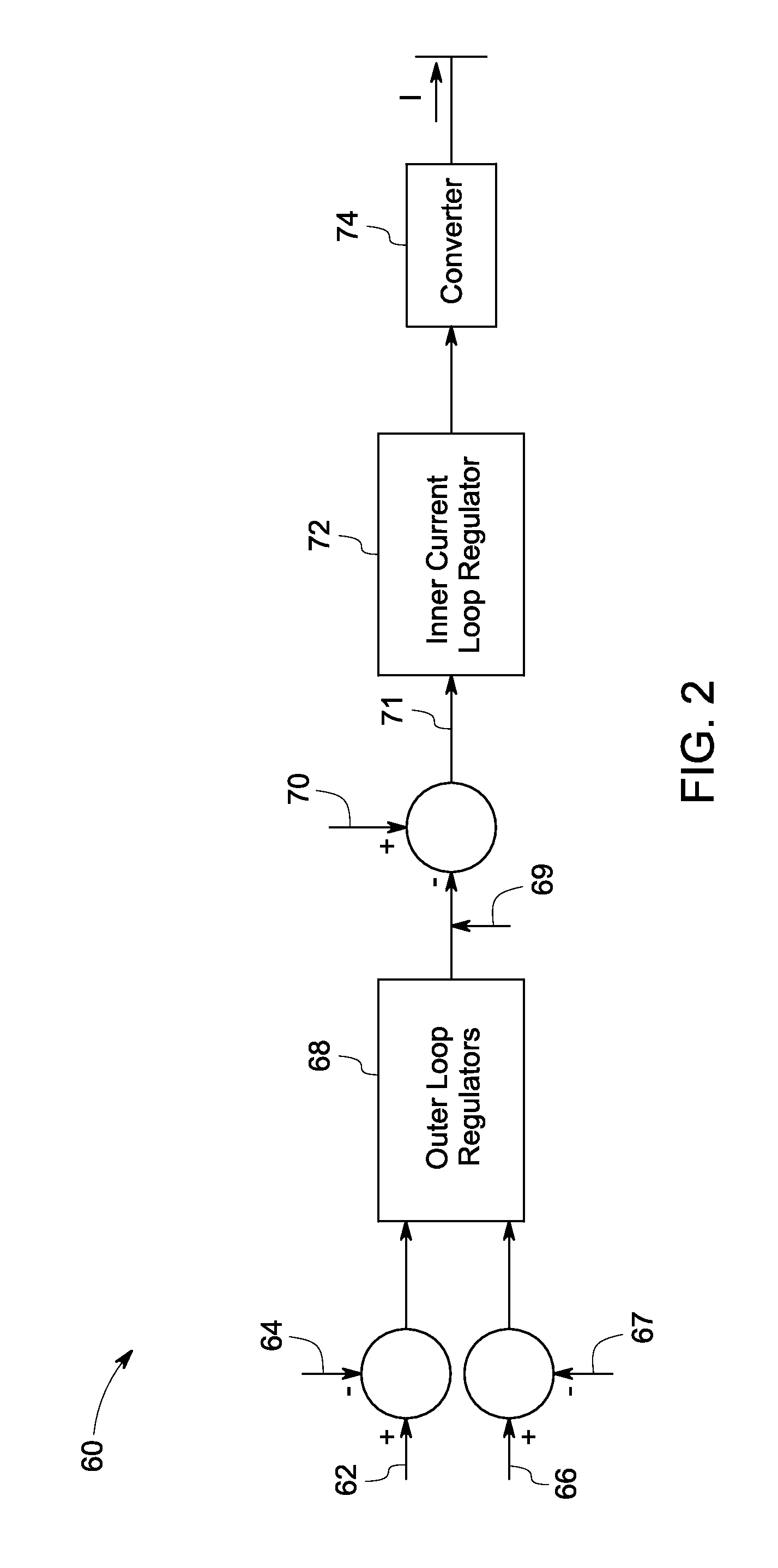
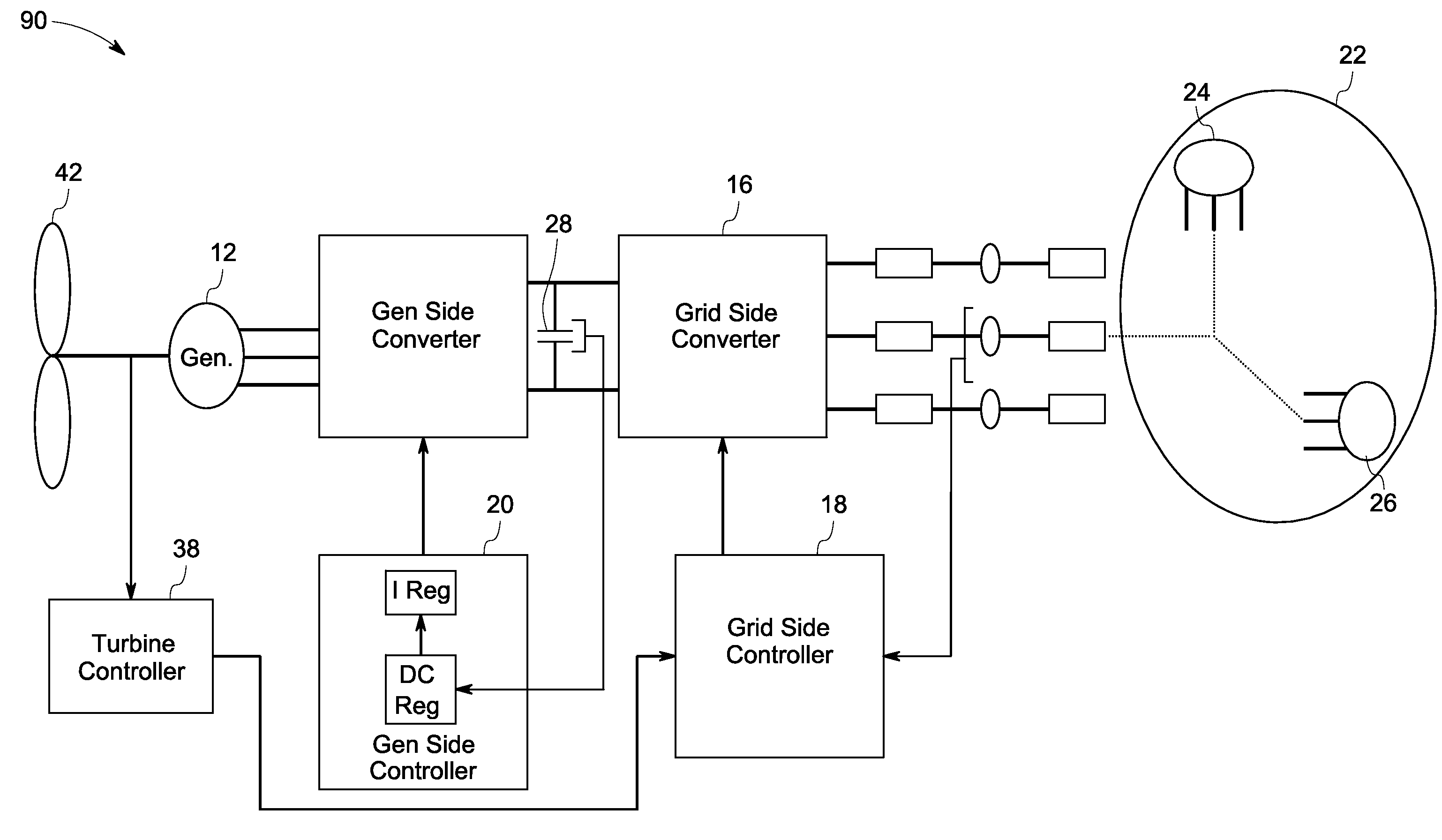
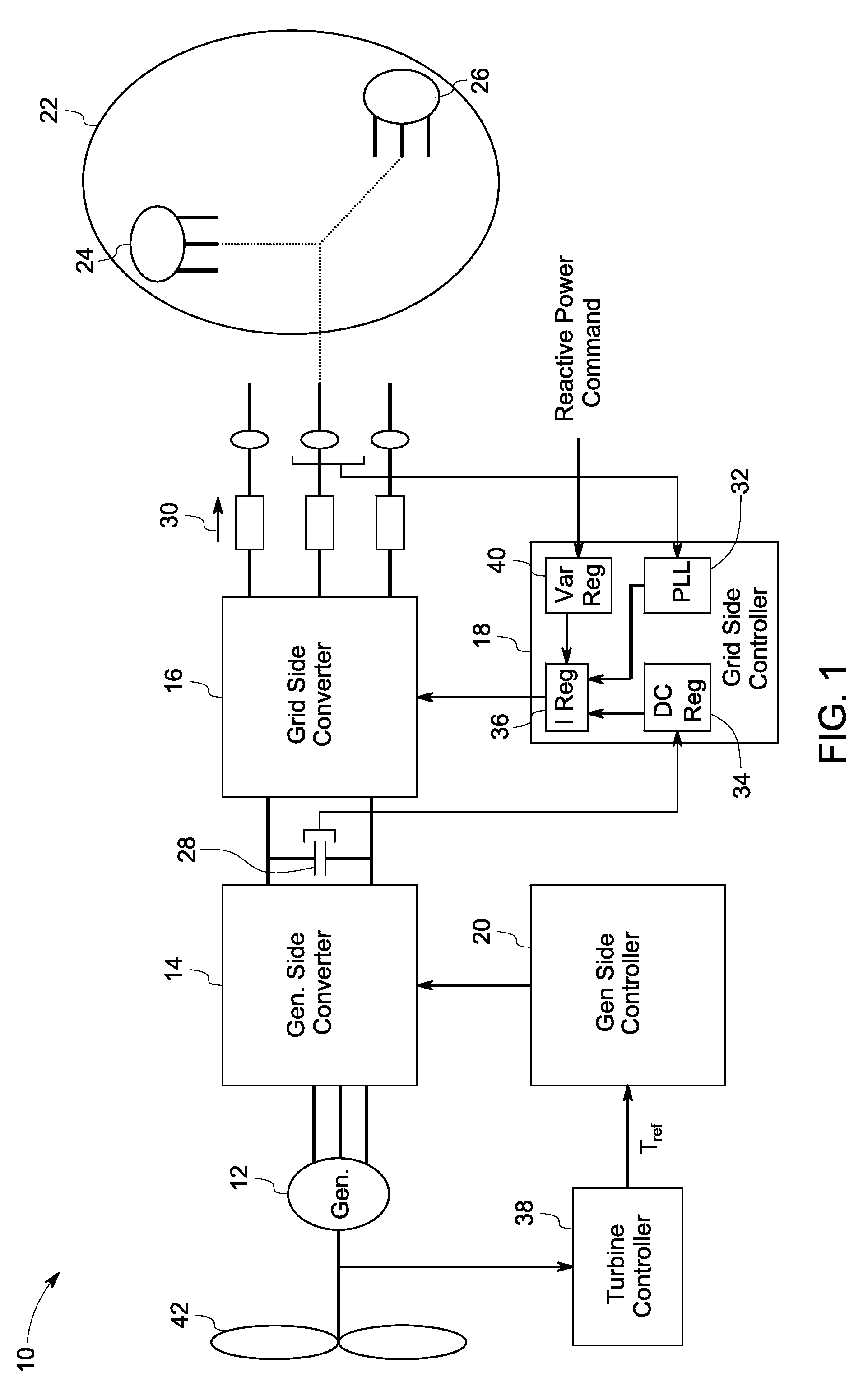
System and method for control of a grid connected power generating system
ActiveUS7804184B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage amplitudePower grid
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
System and method for control of a grid connected power generating system
ActiveUS20100142237A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage amplitudePower grid
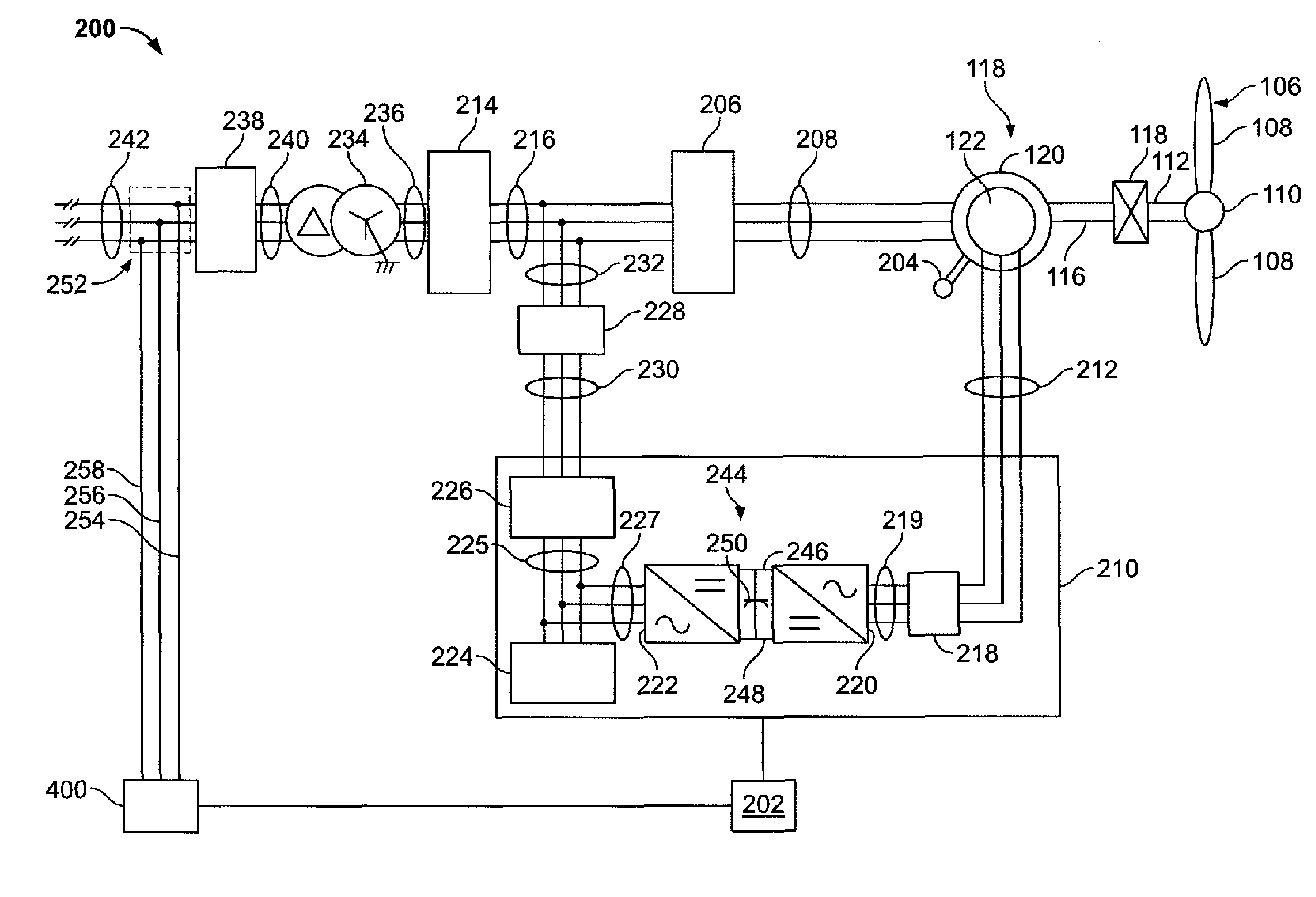
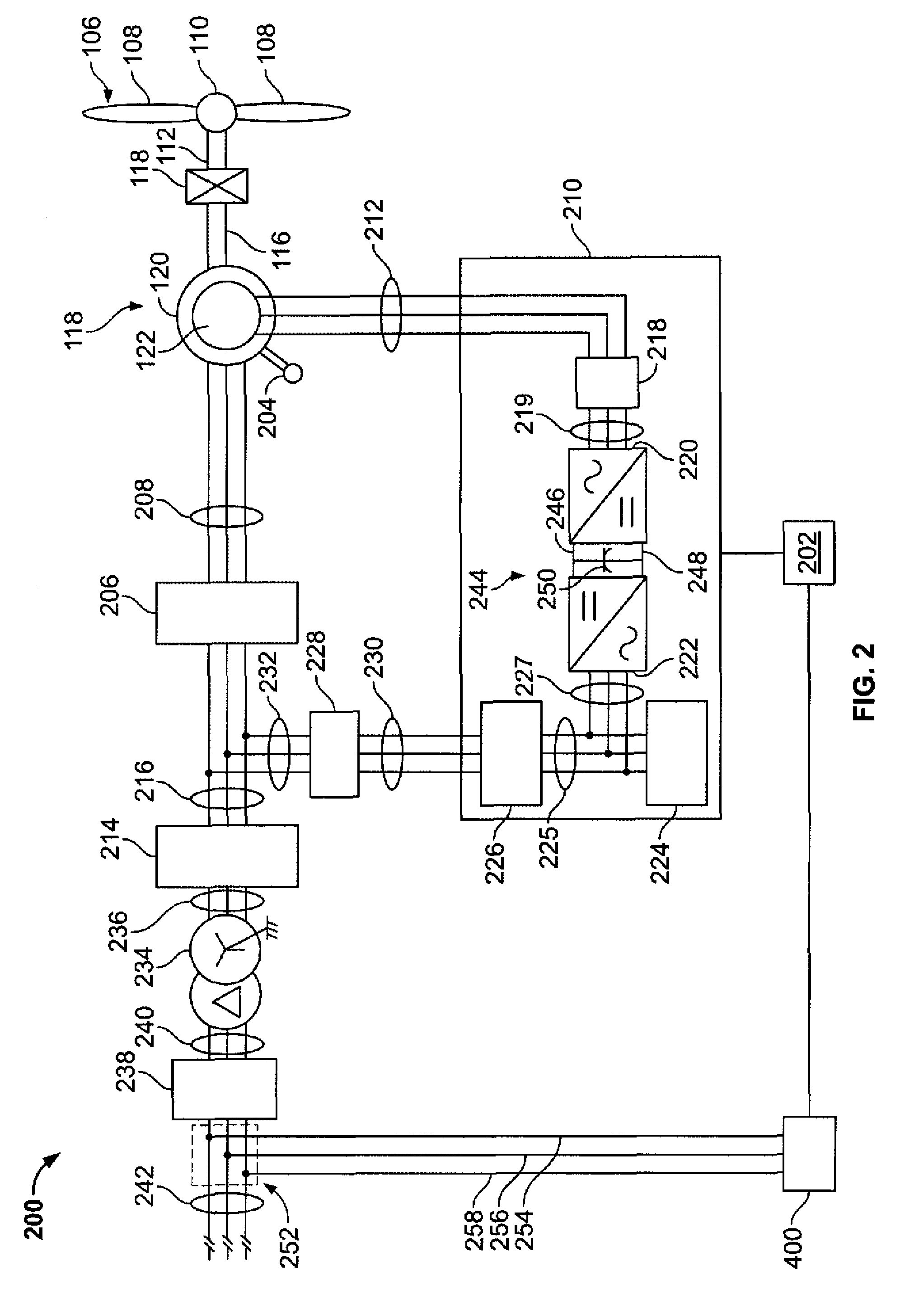
A system for controlling a grid connected power generating system is provided. The system includes a wind turbine, a converter, a first controller and a second controller. The wind turbine supplies electrical power to a power grid and the converter couples the wind turbine to the power grid. The first controller calculates voltage commands to emulate a phasor back electromotive force behind an inductance. The controller further generates converter switching commands from the voltage commands. The voltage commands include a voltage magnitude reference and an internal frequency reference calculated from a power imbalance between an active power reference and the electrical power. The second controller is used to limit a converter current.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
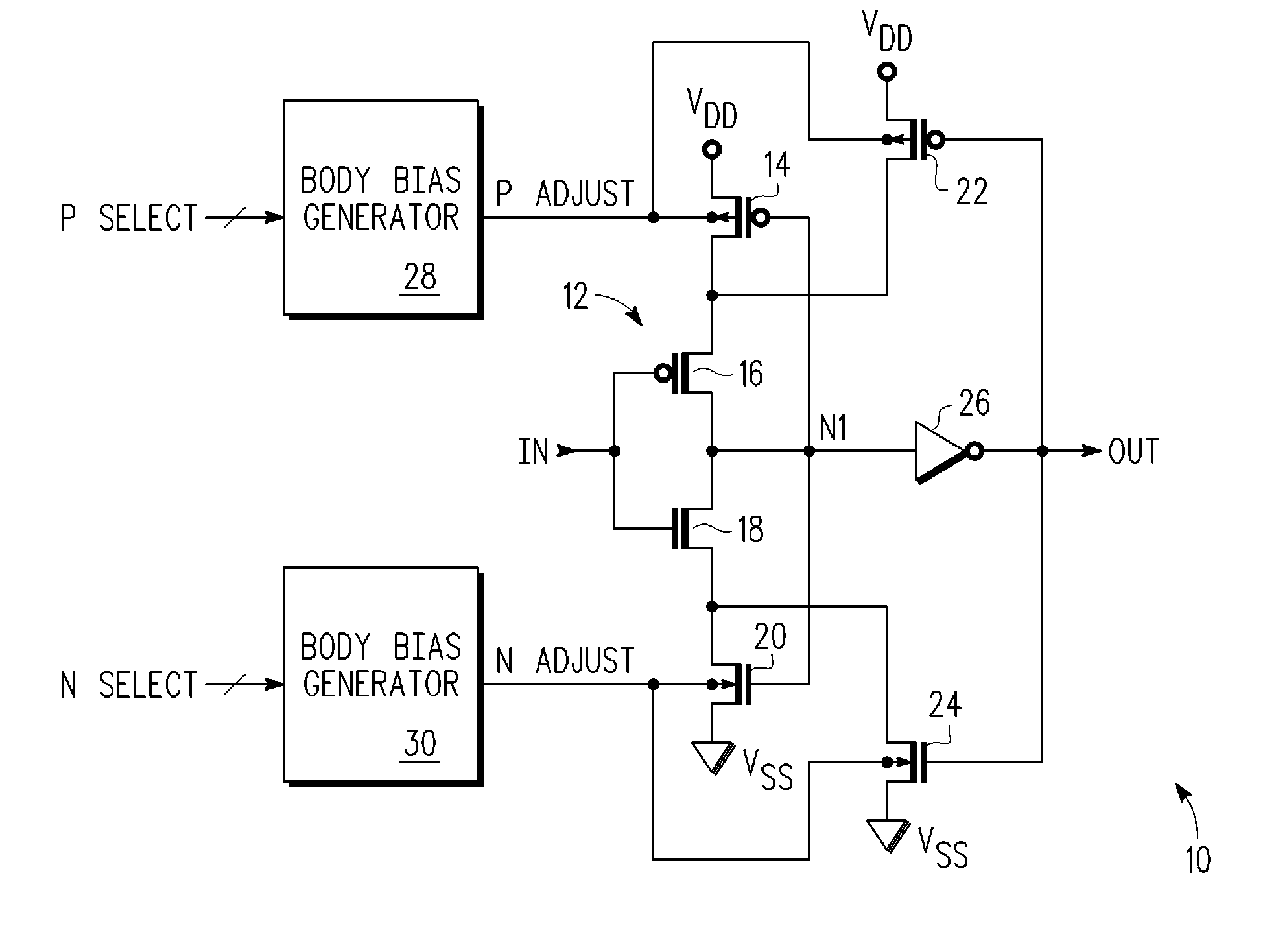
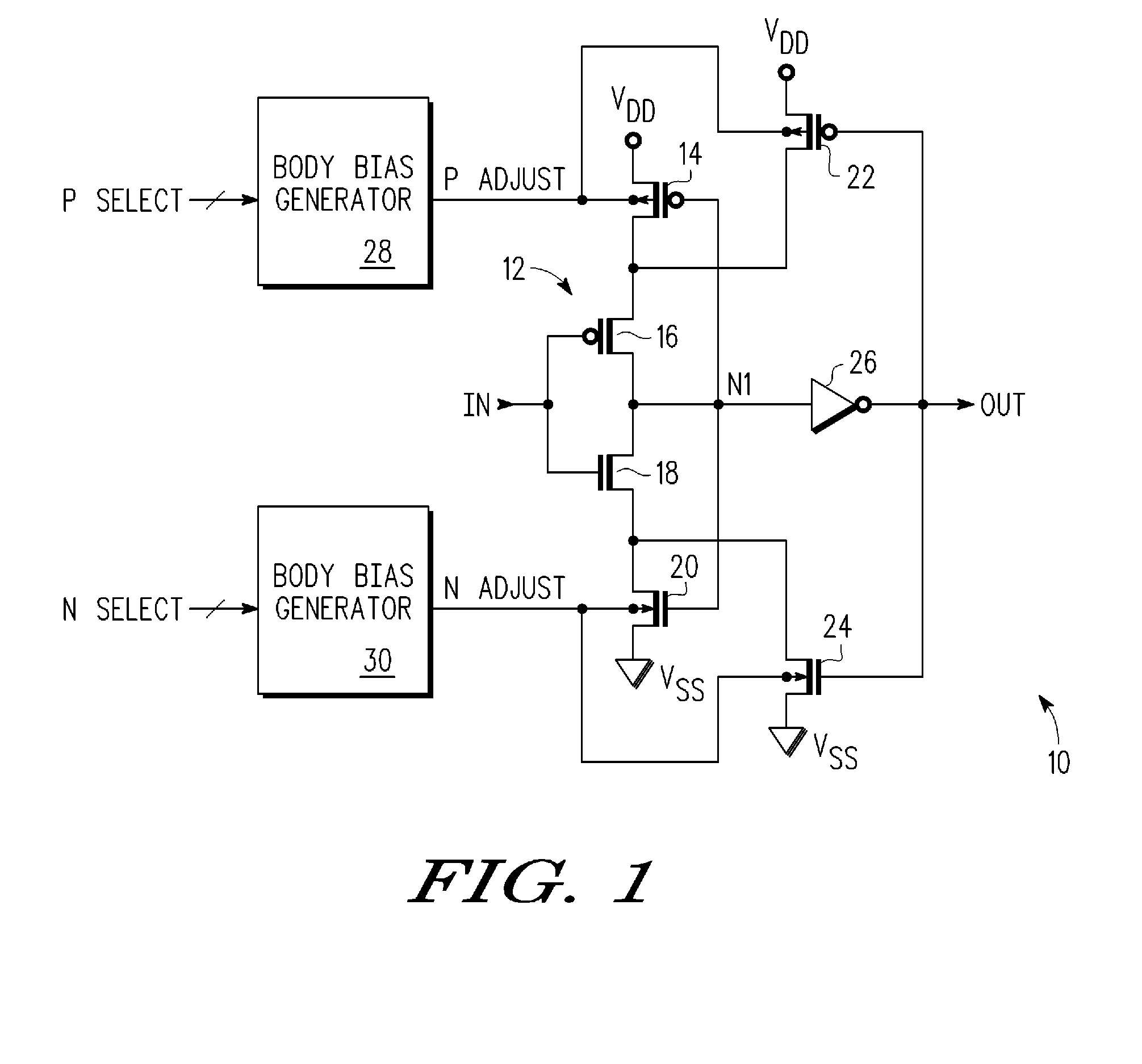
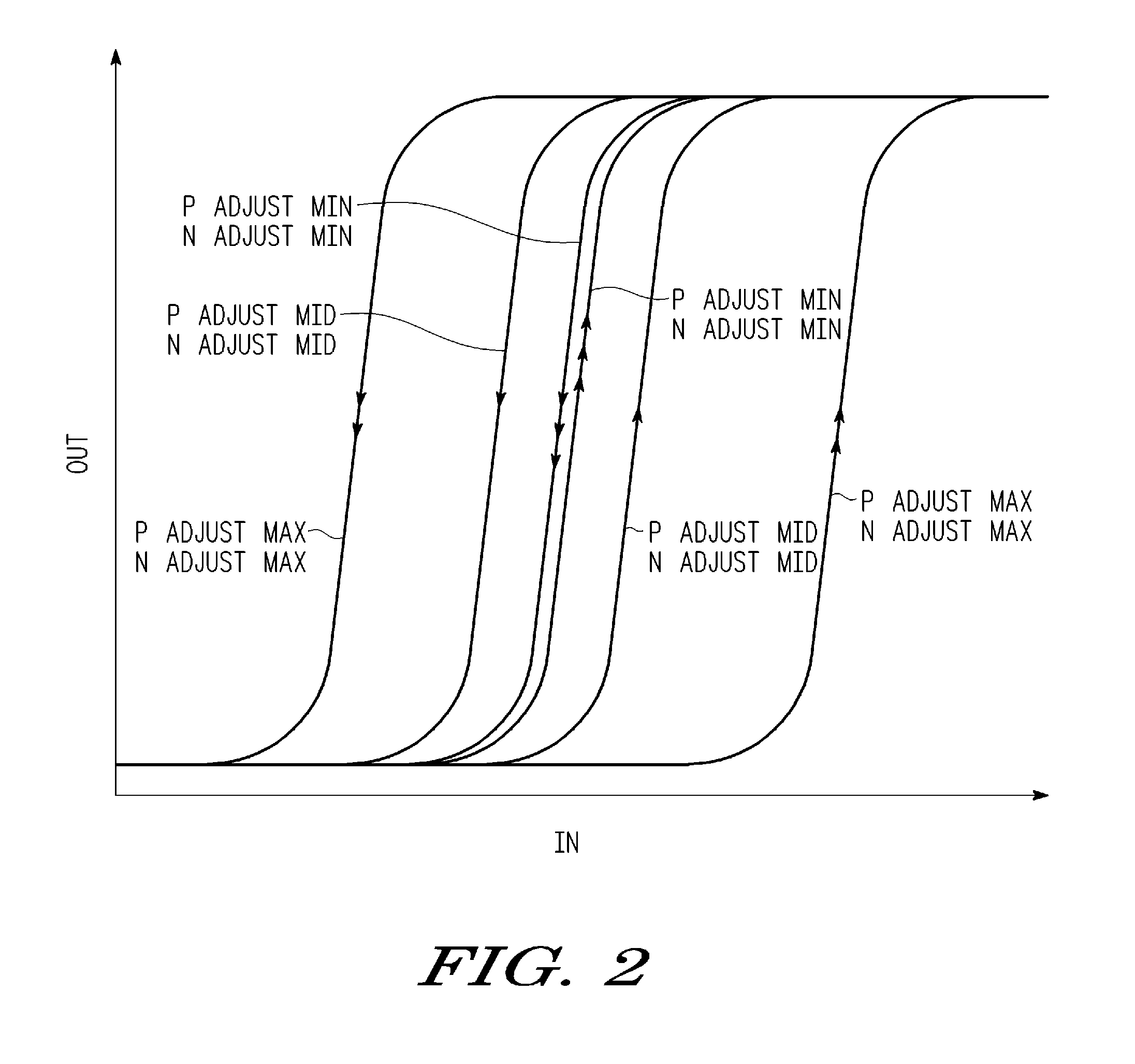
Schmitt trigger having variable hysteresis and method therefor
A Schmitt trigger has a first inverter, a second inverter, a bias means, and a transistor. The inverter has an input and an output. The second inverter has an input coupled to the output of the first inverter and has an output. The bias means provides a first bias voltage on a first output terminal. A magnitude of the bias voltage is selectable by a first input signal. The transistor has a first current electrode coupled to a first power supply terminal, a control electrode coupled to the output of the second inverter, a second current electrode coupled to the output of the first inverter, and a body coupled to the first output terminal. Selectability of the magnitude of the bias voltage provides selectability of the hysteresis of the Schmitt trigger.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
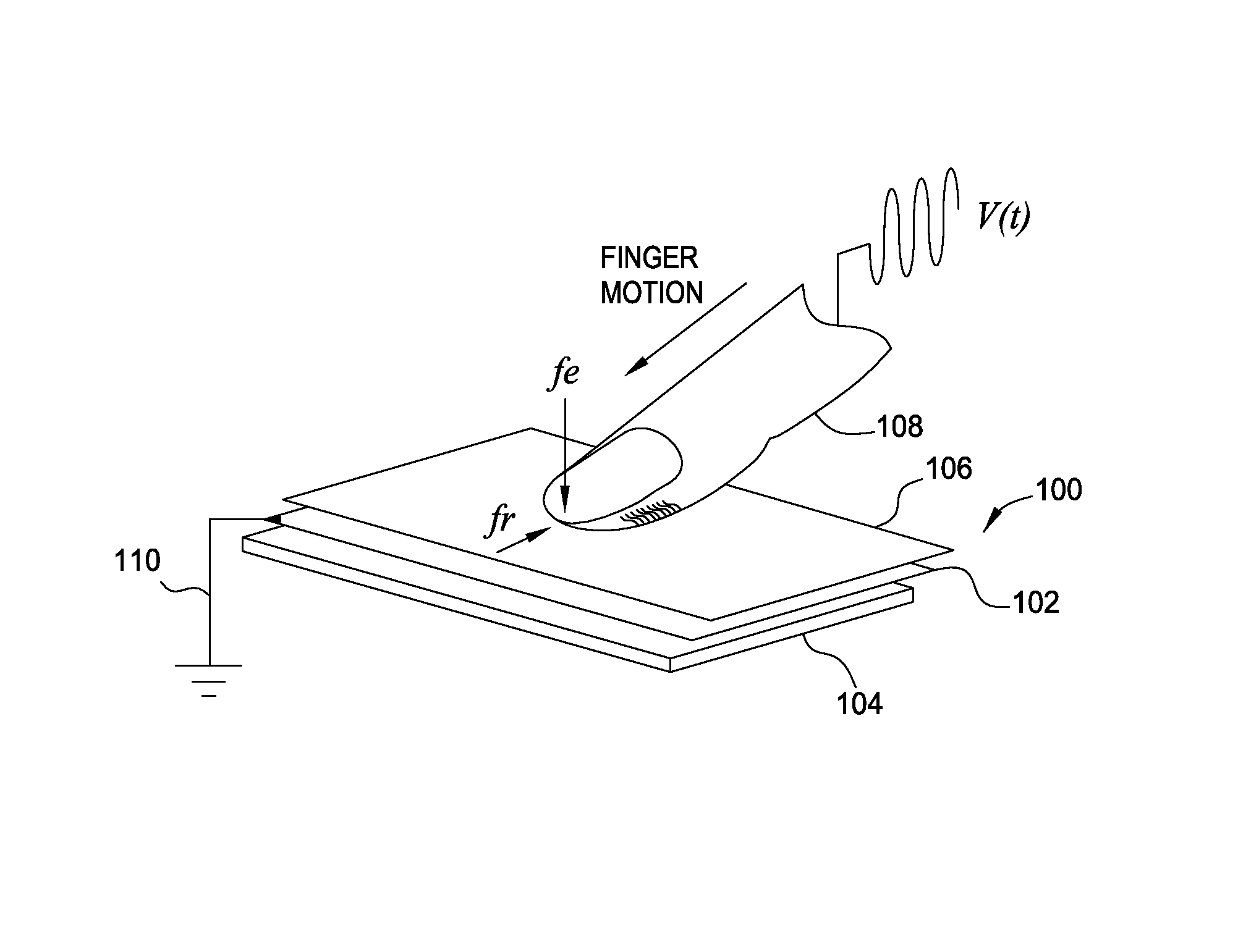
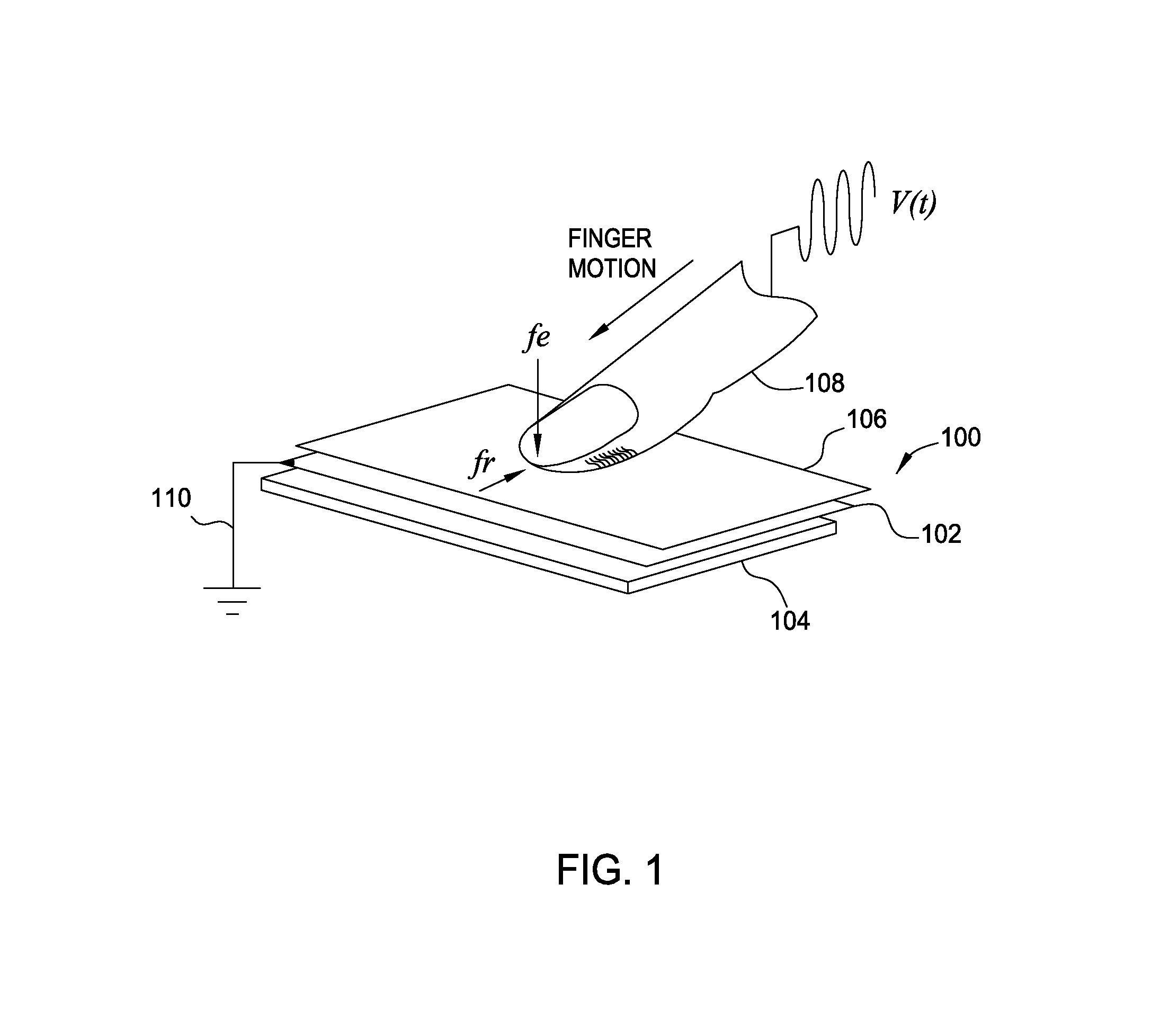
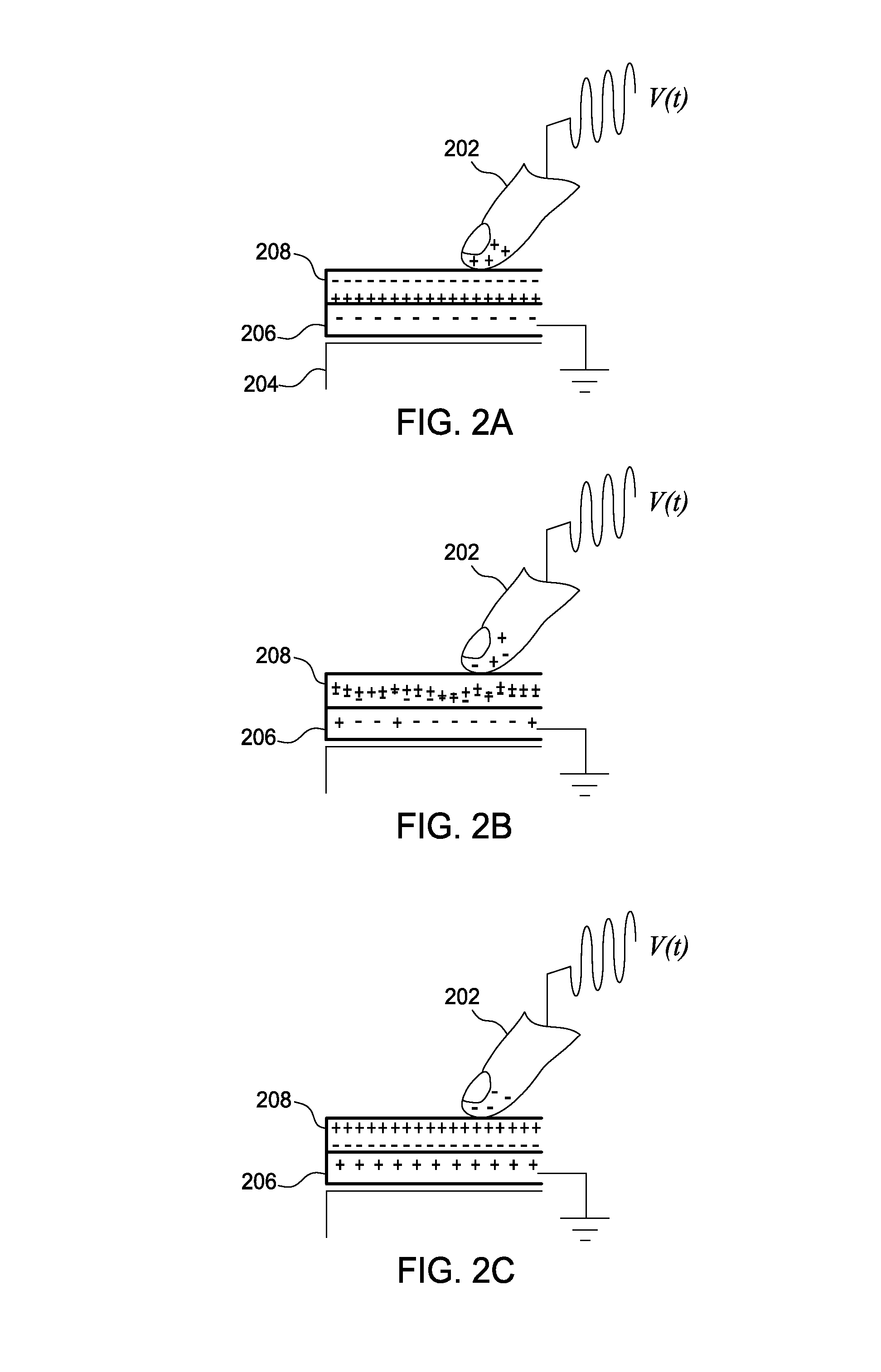
Controlling a user's tactile perception in a dynamic physical environment
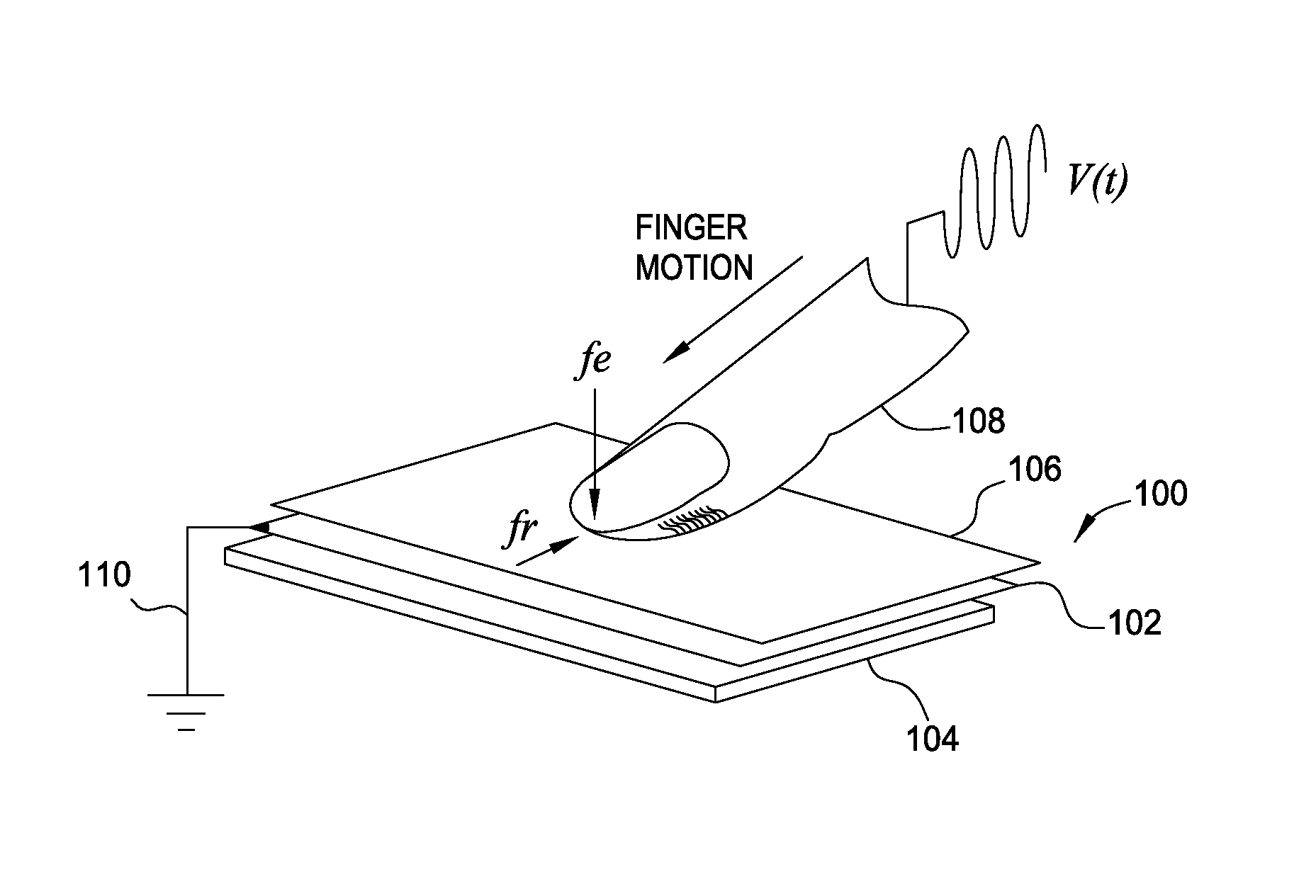
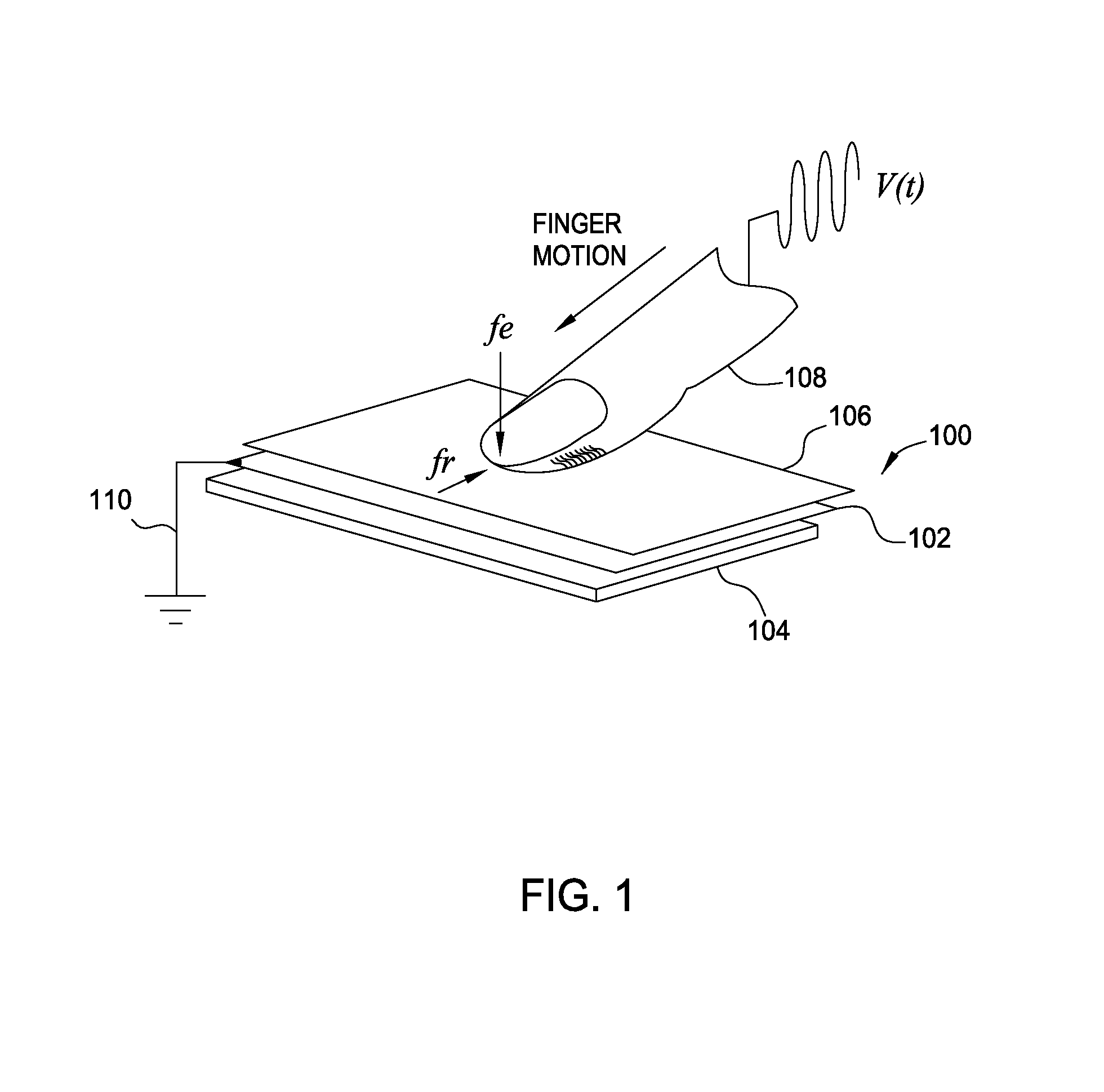
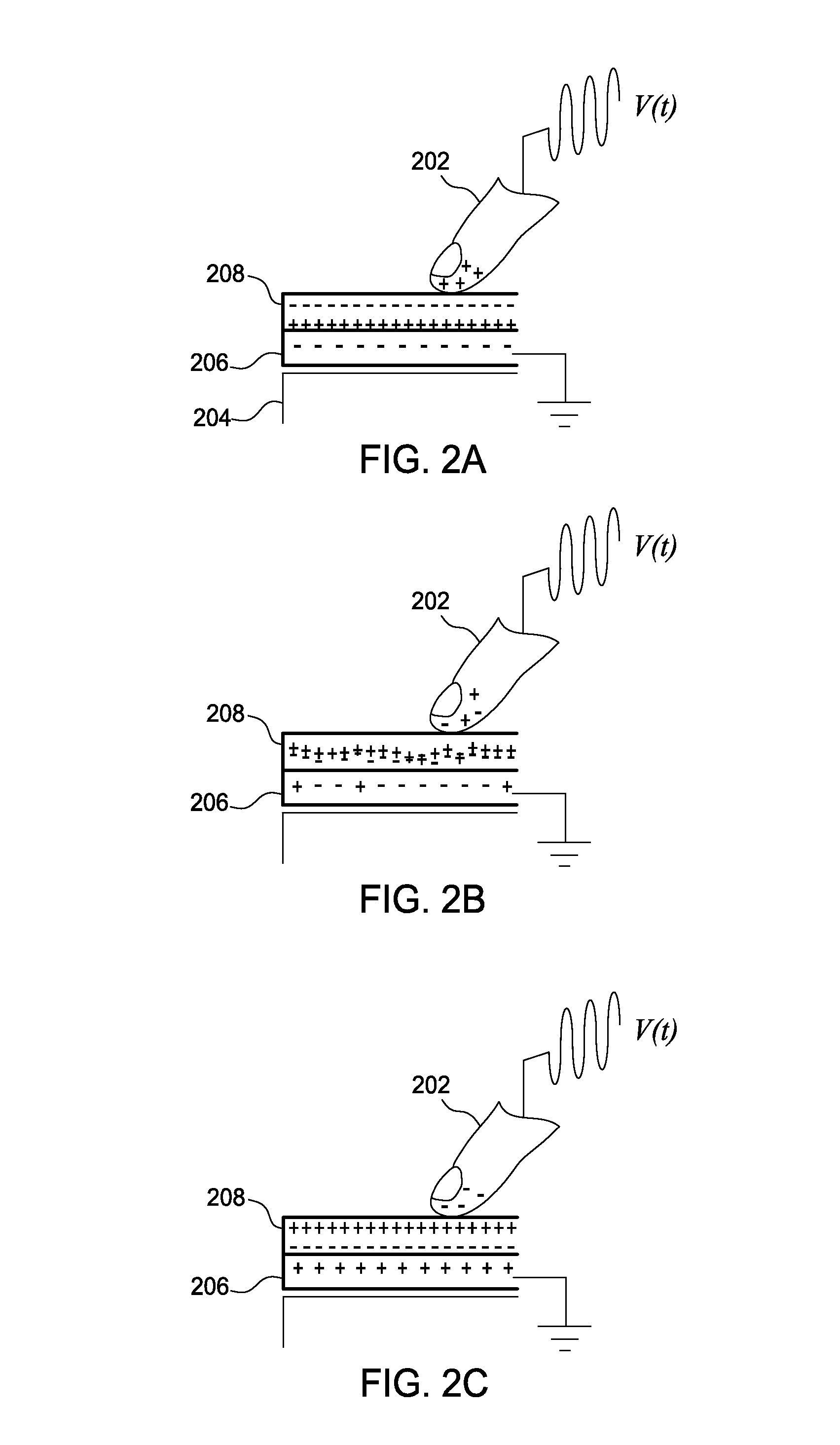
To maintain consistency in different environments with different impedances, a high voltage current driver may be used as a signal generator to output a tactile signal with a constant current. The constant current ensures that the voltage between the user's finger and the object's surface or electrode remains the same even if impedances in the electrical path change. Specifically, the current driver includes a current sensing circuit that determines the average current being generated. Using a feedback loop, the measured current is compared to a reference current to determine if the correct tactile sensation is perceived by the user. As the impedance changes, the current driver detects the resulting change in the signal's current and adjusts the voltage amplitude of the generated tactile signal in order to match the measured current to the reference current.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
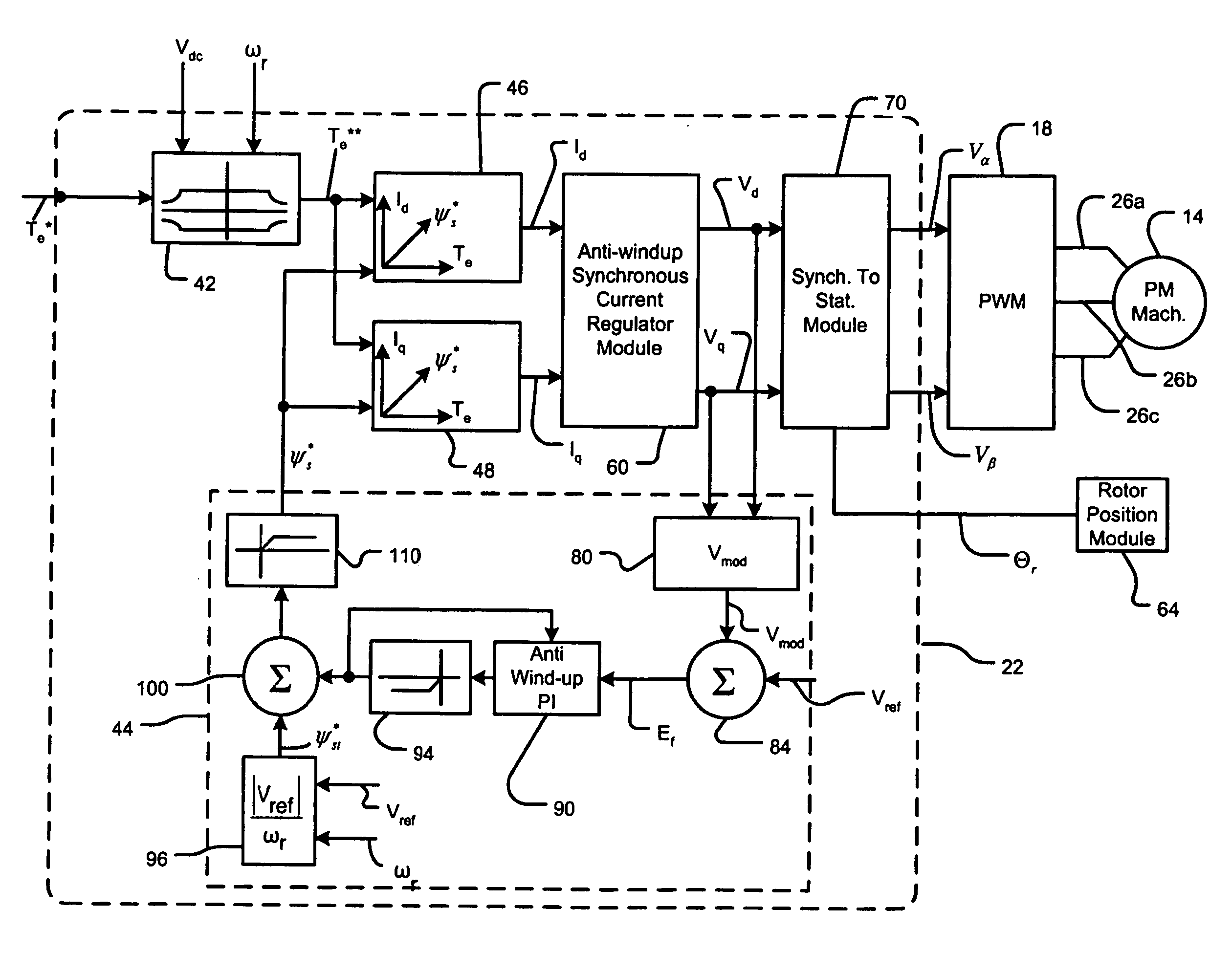
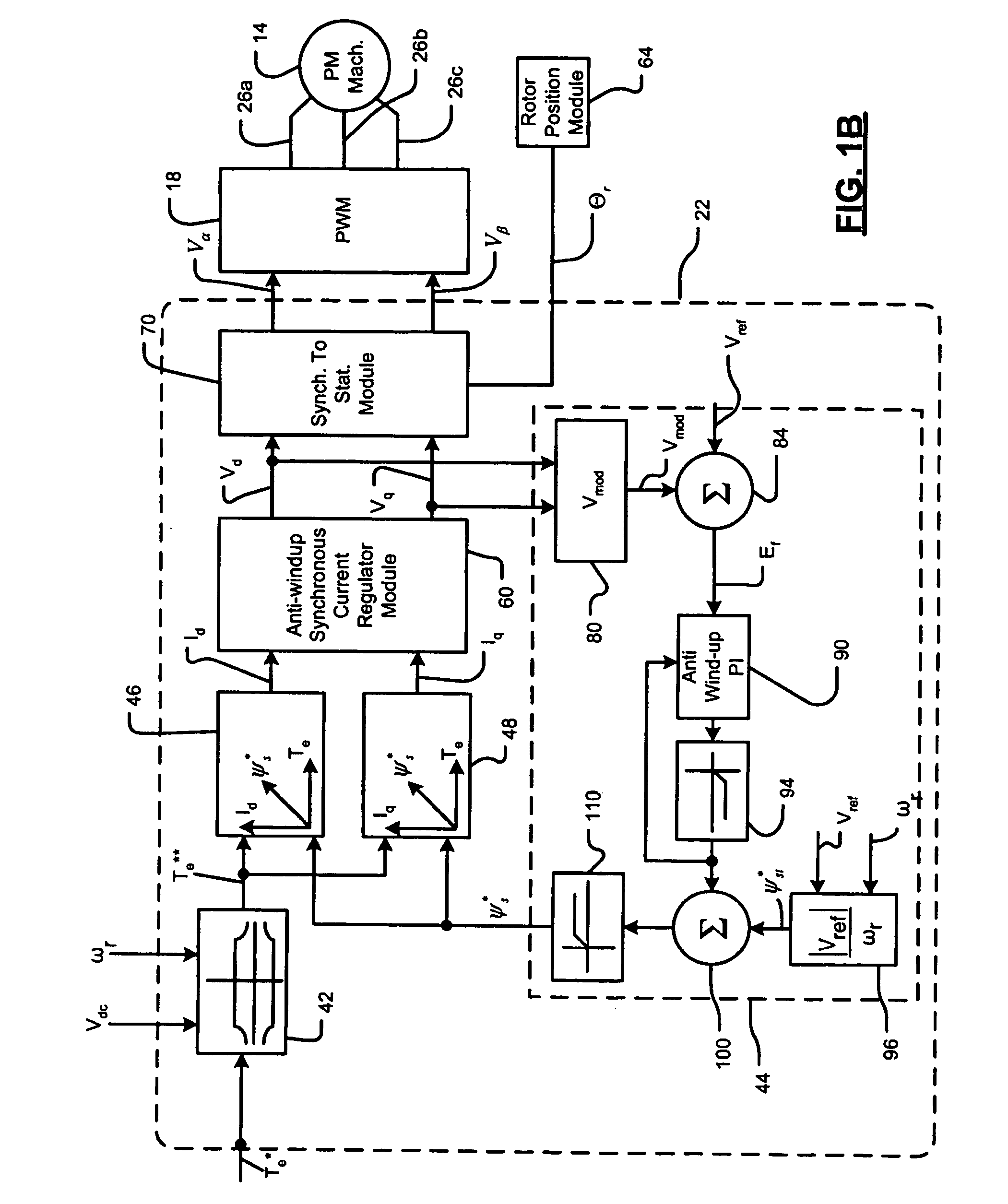
Field weakening motor control system and method
InactiveUS20060055363A1Improve stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersVoltage amplitudeFlux correction
A control system for an electric machine includes a flux weakening module, which includes a voltage magnitude calculator that receives d-axis and q-axis command voltages and that generates a voltage magnitude. An error circuit compares the voltage magnitude to a reference voltage and generates an error signal. A controller receives the error signal and generates a feedback flux correction signal. A limiter limits the feedback flux correction signal to a predetermined flux value and generates a limited feedback flux correction signal. A feedforward stator flux generating circuit generates a feedforward stator flux signal. A summing circuit sums the feedforward stator flux signal and the limited feedback flux correction signal to generate a final stator flux command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
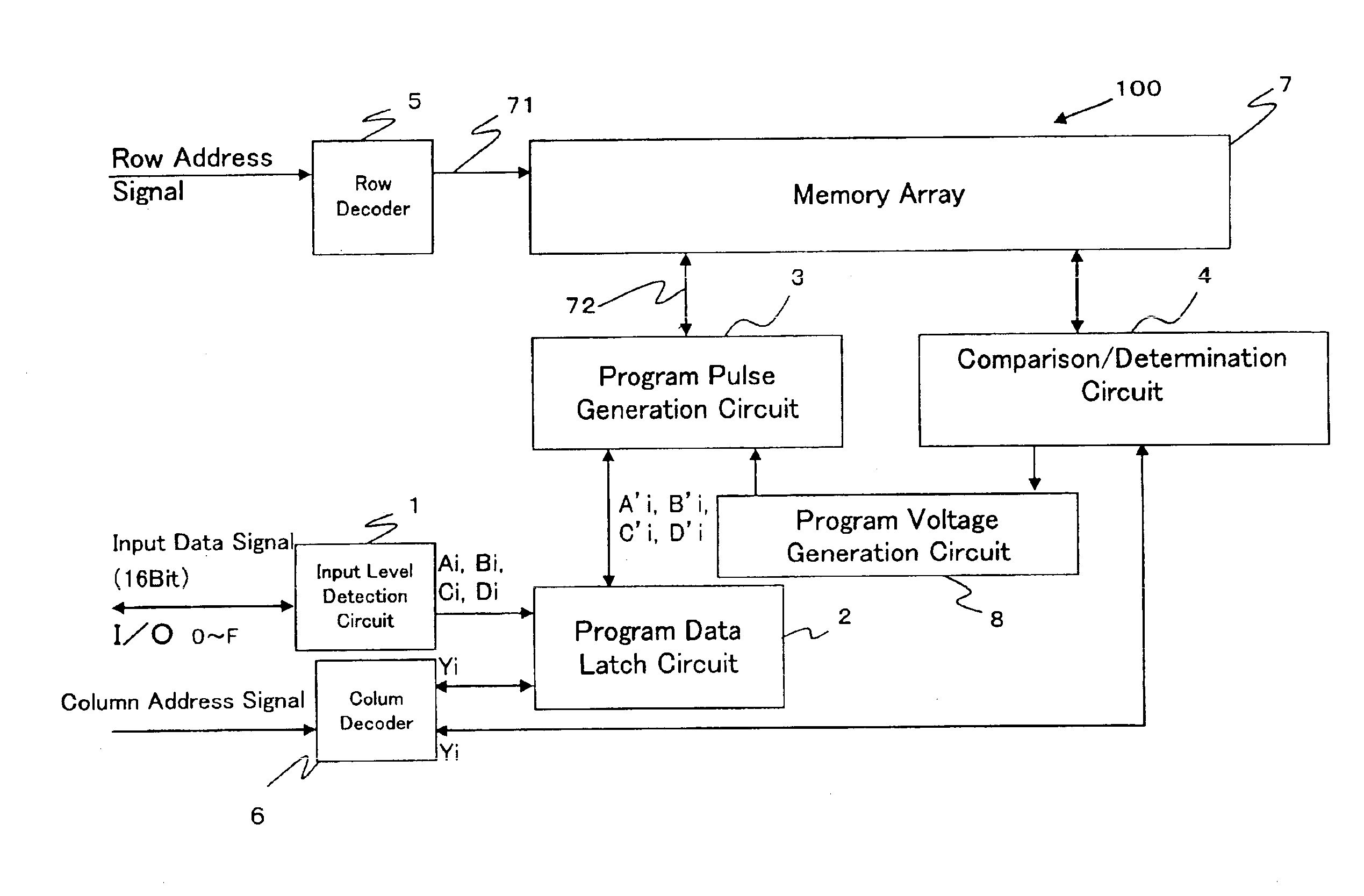
Nonvolatile memory device
ActiveUS6888745B2Increase speedSteady read operationSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage amplitudeMass storage
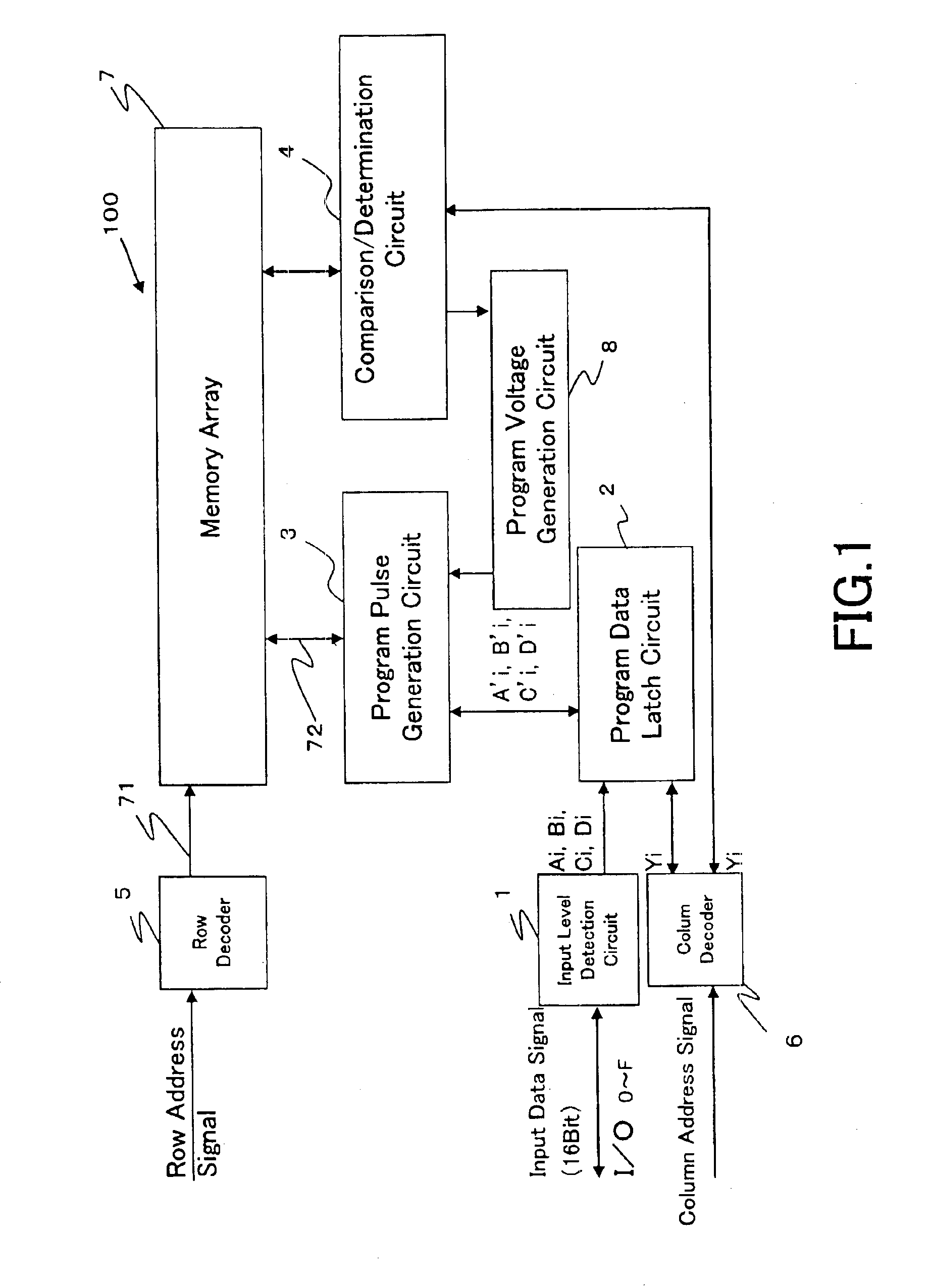
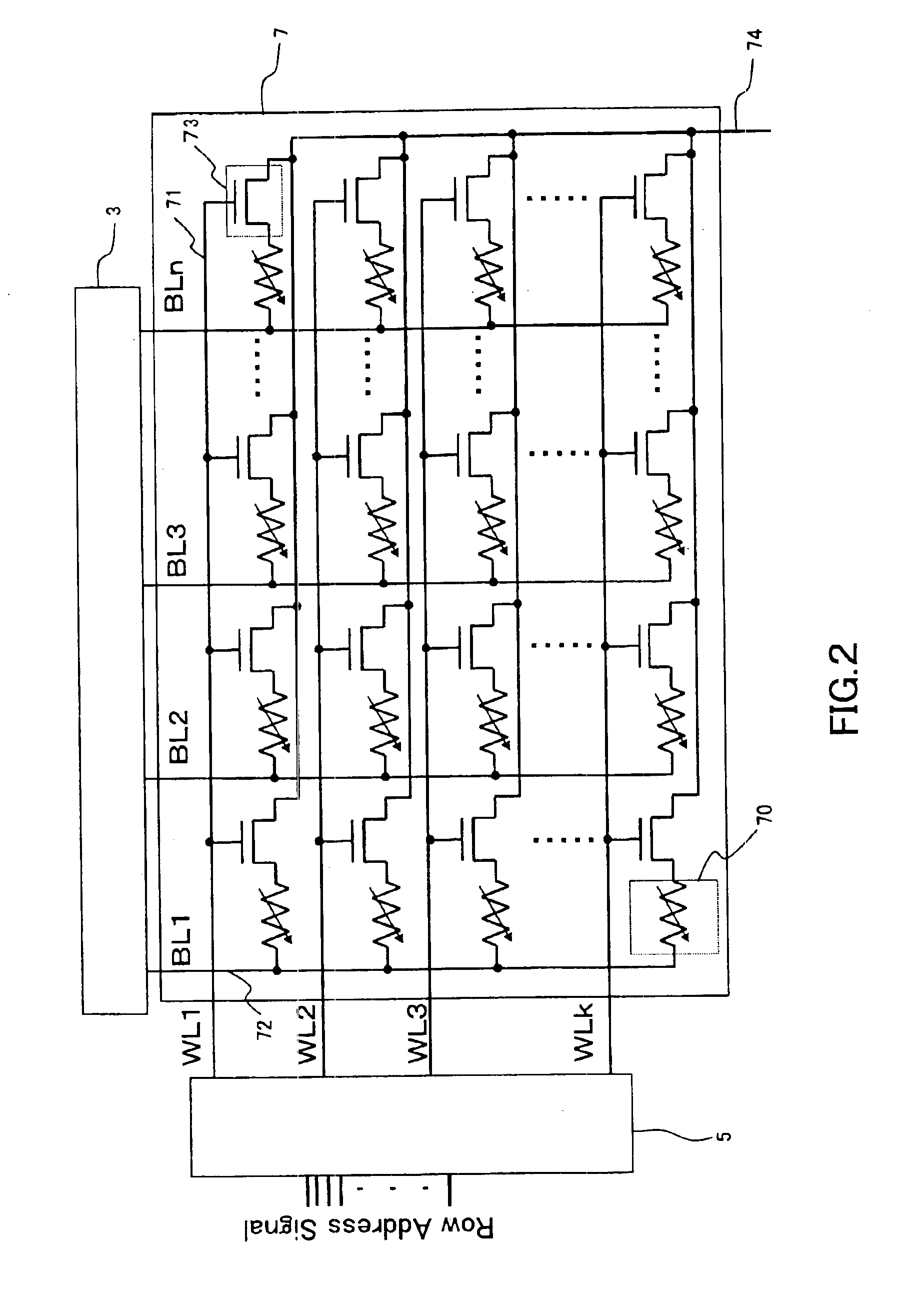
An object of the present invention is to provide a mass-storage nonvolatile memory device capable of performing high speed operation. The nonvolatile memory device comprises a memory array comprising a plurality of memory cells arranged in a matrix, each of the memory cells comprising a variable resistor element formed of a manganese-containing oxide having a perovskite structure in which an electric resistance is varied by application of a voltage pulse and a variation amount of the electric resistance is variable depending on the magnitude of the voltage amplitude; and a program pulse generation circuit that, in order to program 3-level or larger multi-level data corresponding to one erase state and two or more program states into the variable resistor element, is capable of performing generation of program pulses having two or more different voltage amplitudes corresponding to the program states, the generation being separately performed corresponding to program data.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
High Voltage Word Line Driver
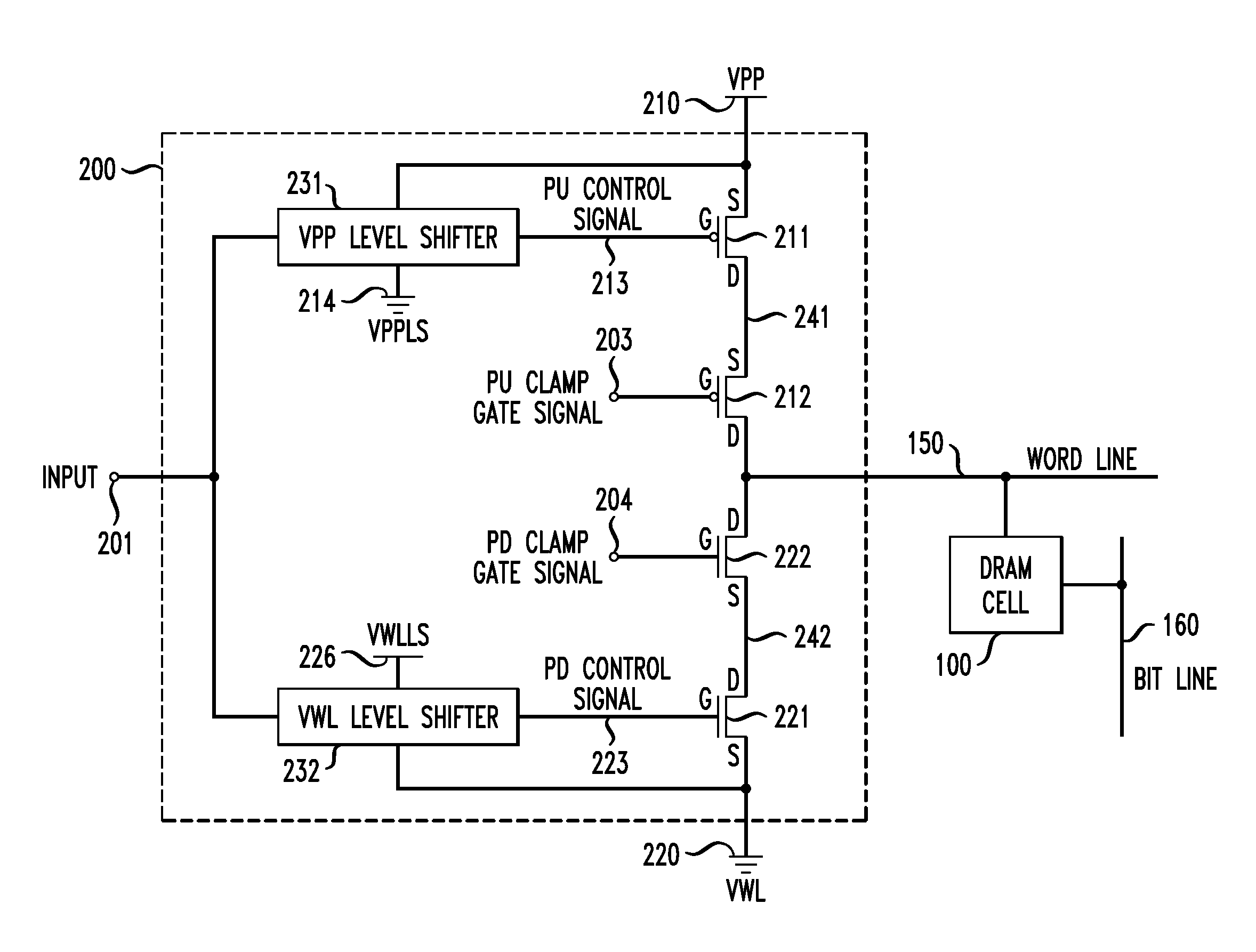
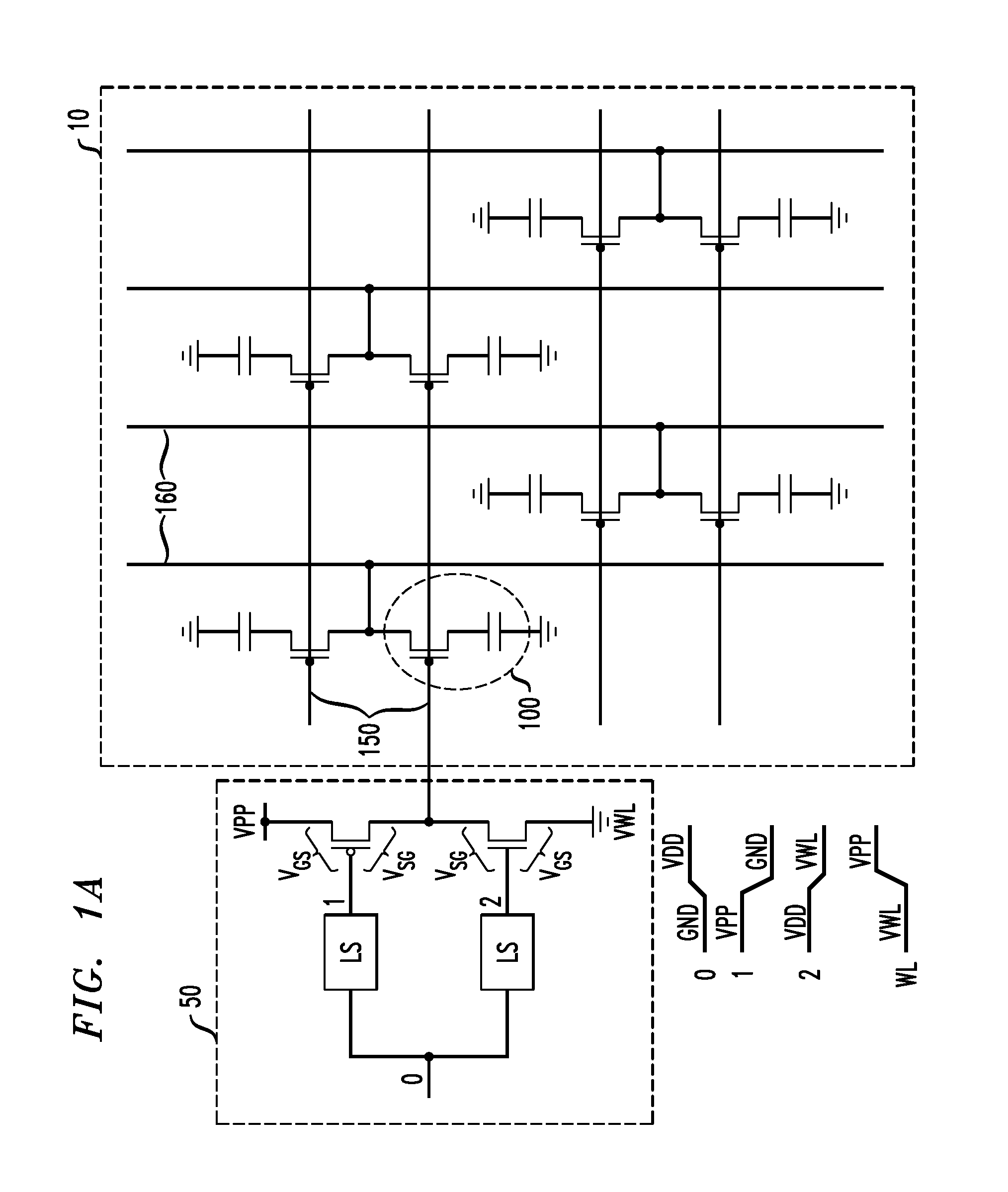
InactiveUS20110199837A1Excellent driving voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageHigh pressureMemory circuits
A word line driver circuit coupled to a memory circuit word line includes pull-up, pull-up clamp, pull-down and pull-down clamp transistors, each having a source, a drain and a gate. For the pull-up transistor, the source is coupled to a first power supply, and the gate to a pull-up control signal. For the pull-up clamp transistor, the source is coupled to the drain of the pull-up transistor, the drain to the word line, and the gate to a pull-up clamp gate signal. For the pull-down transistor, the source is coupled to a second power supply, and the gate to a pull-down control signal. For the pull-down clamp transistor, the source is coupled to the drain of the pull-down transistor, the drain to the word line, and the gate to a pull-down clamp gate signal. The word line is coupled to one or more DRAM cells. Source to drain voltage magnitudes of the pull-up and pull-down transistors are less than a voltage between the first and second power supplies.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for operating electrical machines
ActiveUS7629705B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlElectric power transmissionVoltage amplitude
A method for operating an electrical machine includes coupling the electrical machine to an electric power system such that the electric power system is configured to transmit at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine. The method also includes configuring the electrical machine such that the electrical machine remains electrically connected to the electric power system during and subsequent to a voltage amplitude of the electric power system operating outside of a predetermined range for an undetermined period of time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
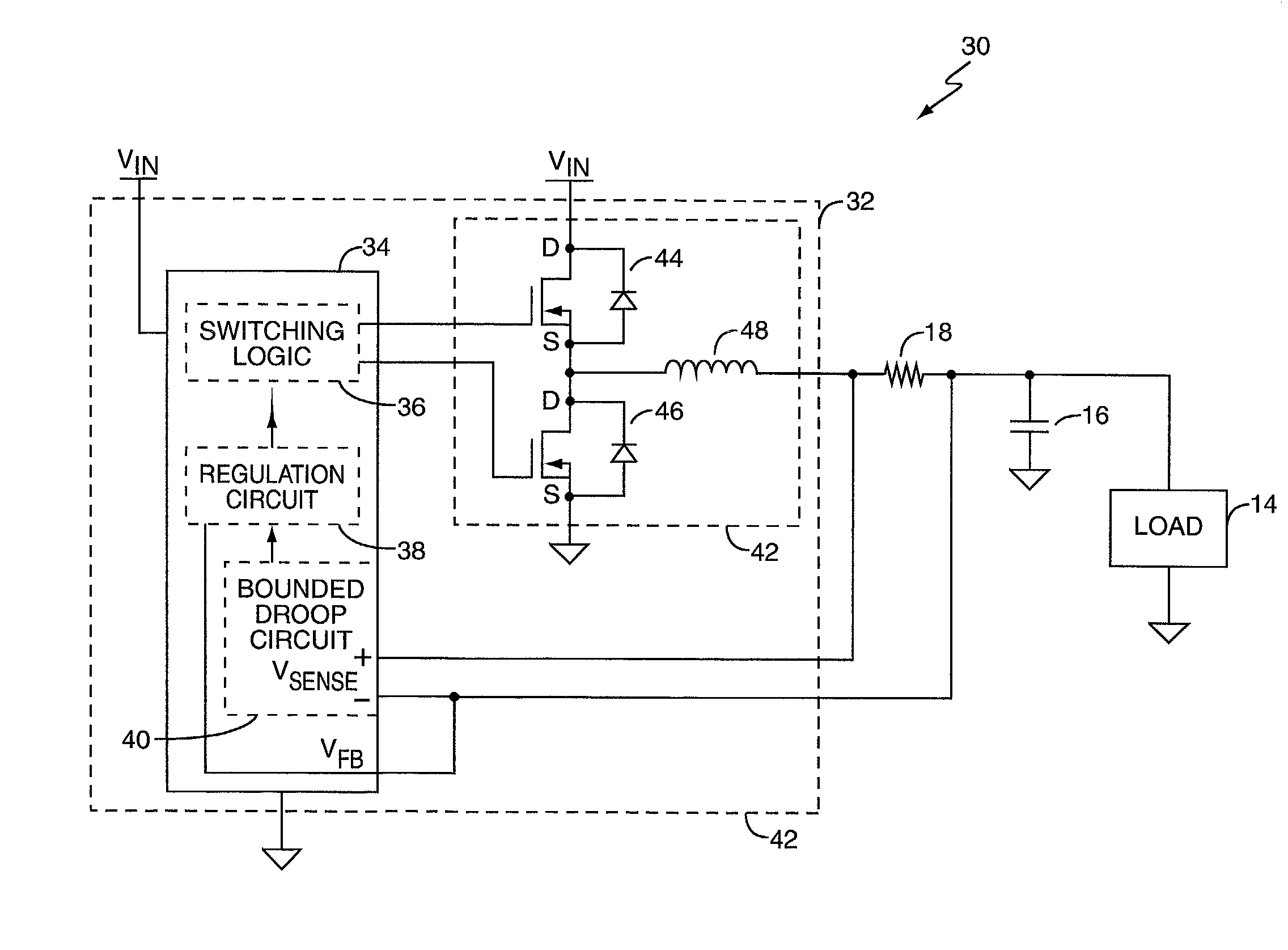
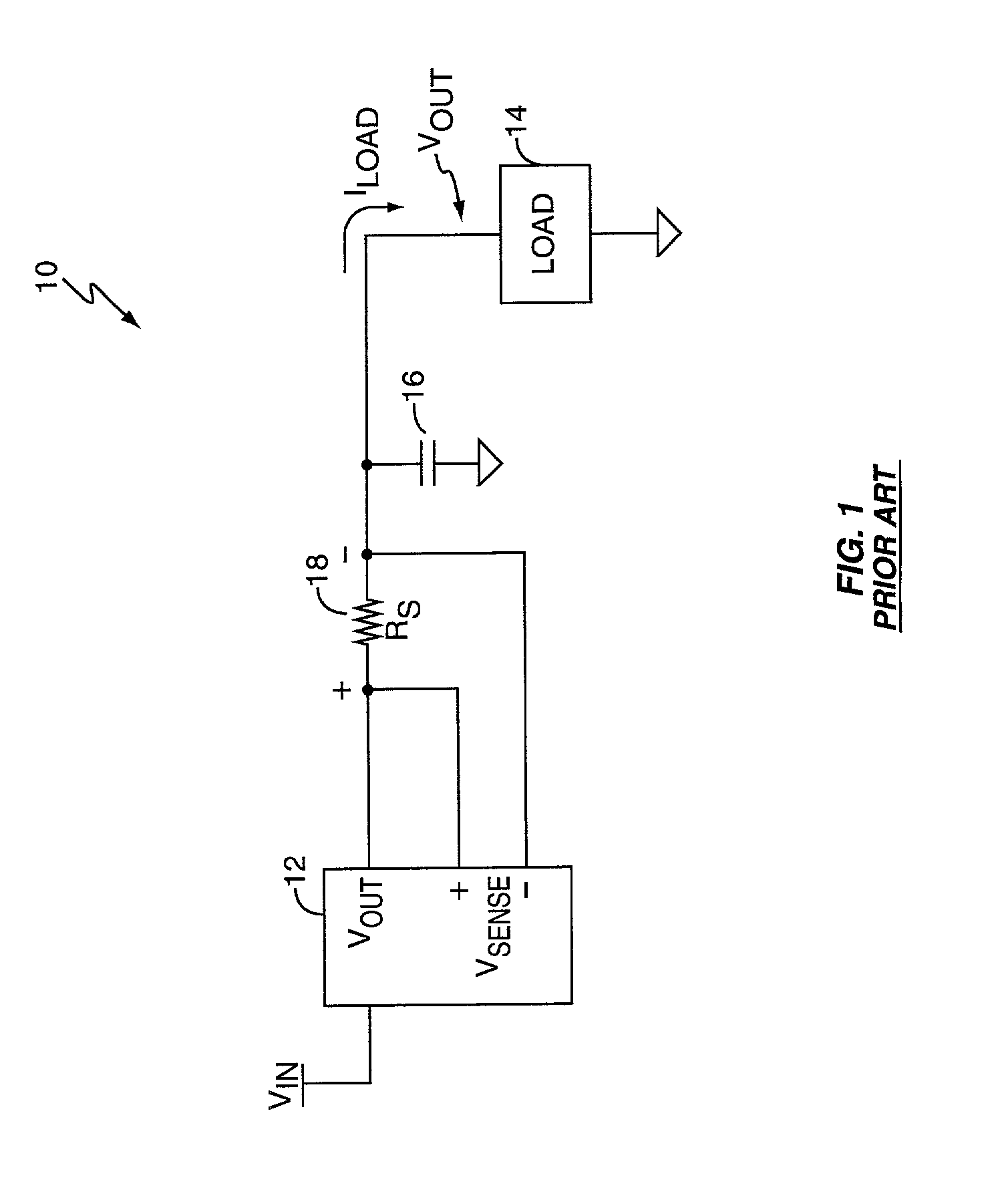
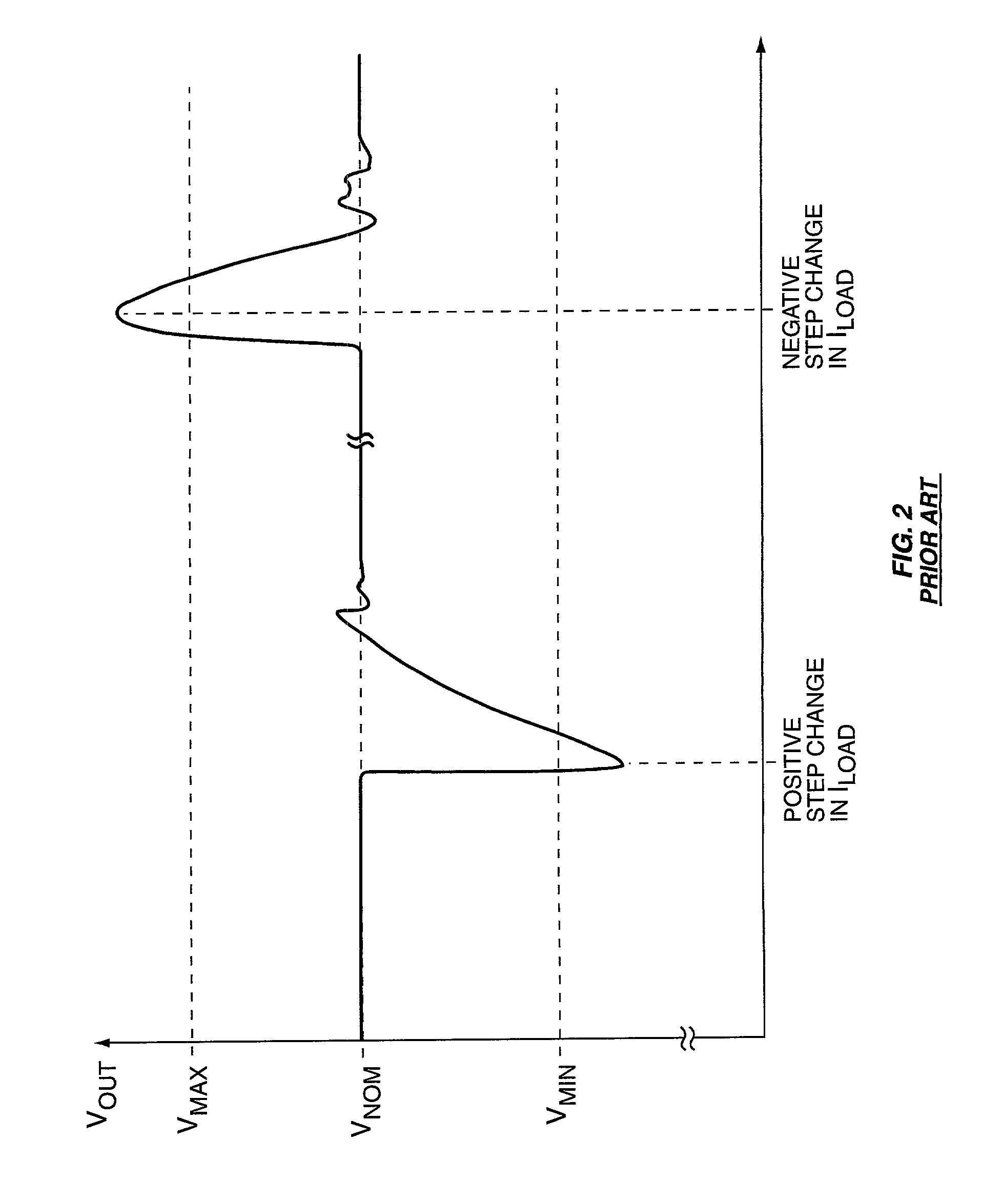
Bounded power supply voltage positioning
InactiveUS20020125871A1Facilitates active voltage positioningPrevent fallingDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage amplitudeLower limit
A voltage positioning technique allows a power supply controller to more fully exploit active voltage positioning as a way of maintaining supply voltage within the limits defined for an associated electrical load. The supply voltage is allowed to "droop" as a function of load current. Droop may be implemented in linear proportion to load current, or as a discrete droop function once load current exceeds a given threshold. In either case, the droop circuitry of the supply controller implements a bounding function that establishes an accurately known maximum droop voltage magnitude. This maximum droop voltage limit establishes a reliable lower limit for the supply voltage independent of increasing load current. This accurately set lower bound for the droop voltage enables the controller to more aggressively position the supply voltage at the lower voltage limit of the load, which minimizes voltage overshoot and load power consumption.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
Controlling a user's tactile perception in a dynamic physical environment
ActiveUS9122330B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTactile signalling systemsVoltage amplitudeReference current
To maintain consistency in different environments with different impedances, a high voltage current driver may be used as a signal generator to output a tactile signal with a constant current. The constant current ensures that the voltage between the user's finger and the object's surface or electrode remains the same even if impedances in the electrical path change. Specifically, the current driver includes a current sensing circuit that determines the average current being generated. Using a feedback loop, the measured current is compared to a reference current to determine if the correct tactile sensation is perceived by the user. As the impedance changes, the current driver detects the resulting change in the signal's current and adjusts the voltage amplitude of the generated tactile signal in order to match the measured current to the reference current.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
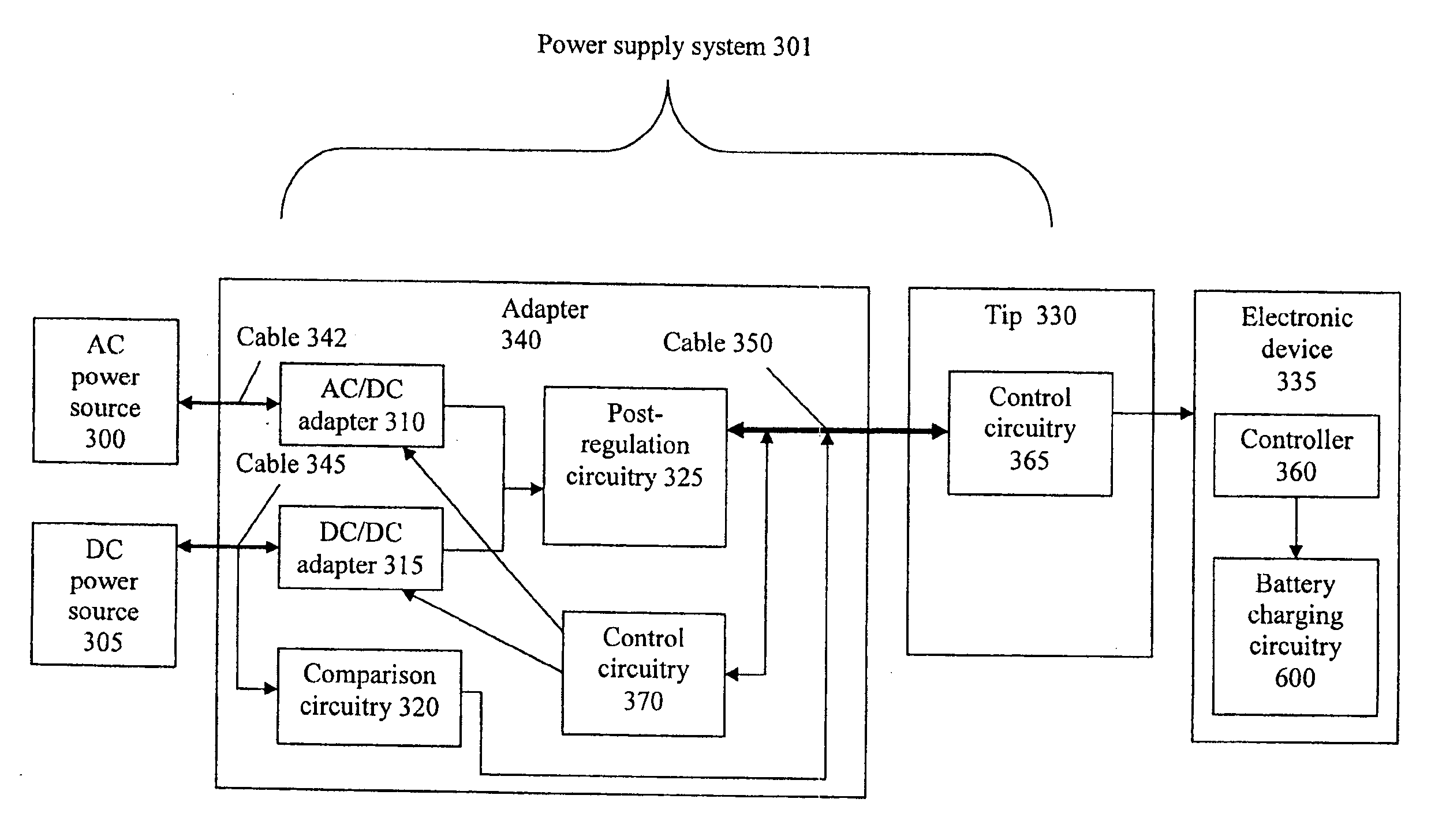
DC power source determination circuitry for use with an adapter
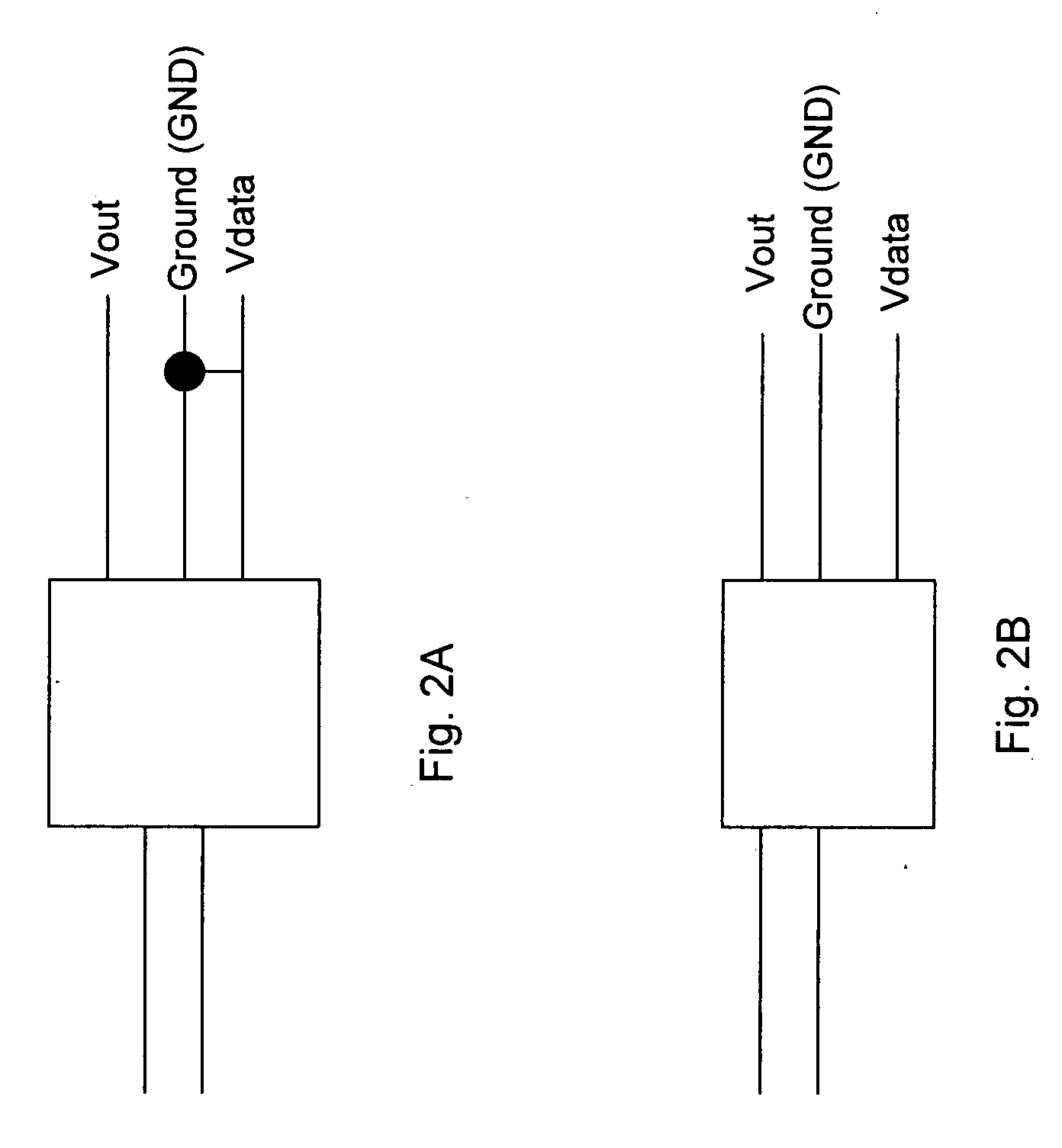
InactiveUS20050162020A1Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsElectric switchesVoltage amplitudeVoltage reference
An adapter device includes a DC / DC adapter to receive DC power from a DC power source, and output a regulated DC voltage (Vout). A source determination circuitry receives the DC power from the DC power source and compares a magnitude of a voltage of the DC power with a reference magnitude of a reference voltage (Vref). When the magnitude of the voltage of the DC power is greater than the reference magnitude, a data signal (Vdata) having a first value is output. When the magnitude of the voltage of the DC power is less than the reference magnitude, the Vdata signal having a second value is output. The Vdata signal is received by control circuitry of an electronic device. When the Vdata signal has the first value, the electronic device operates in a first mode where battery charging circuitry is disabled. When the Vdata signal has the second value, the battery charging circuitry is enabled.
Owner:COMARCO WIRELESS SYST LLC
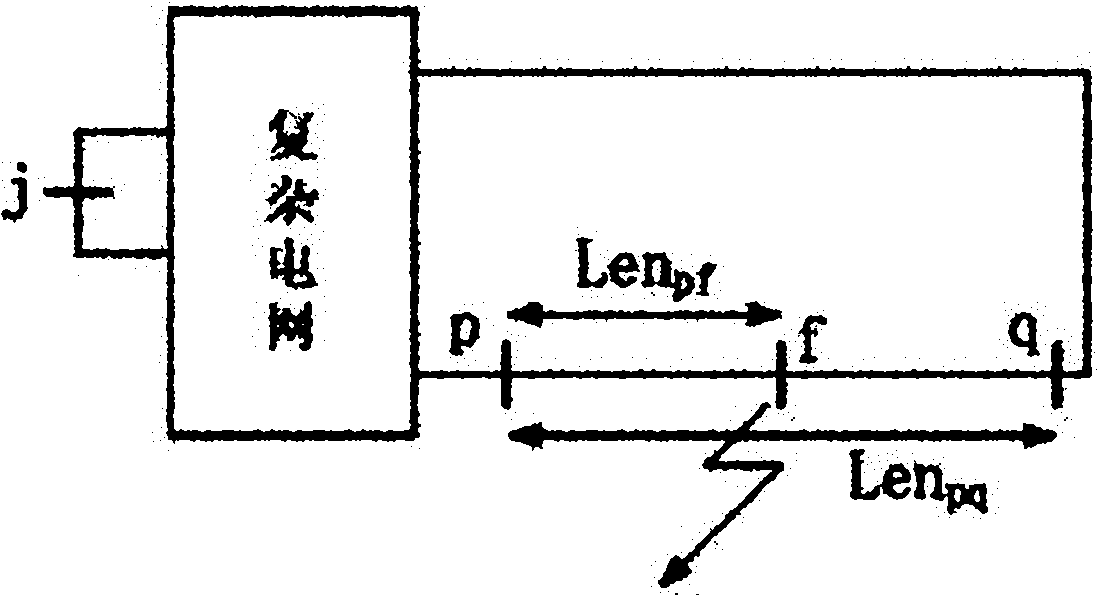
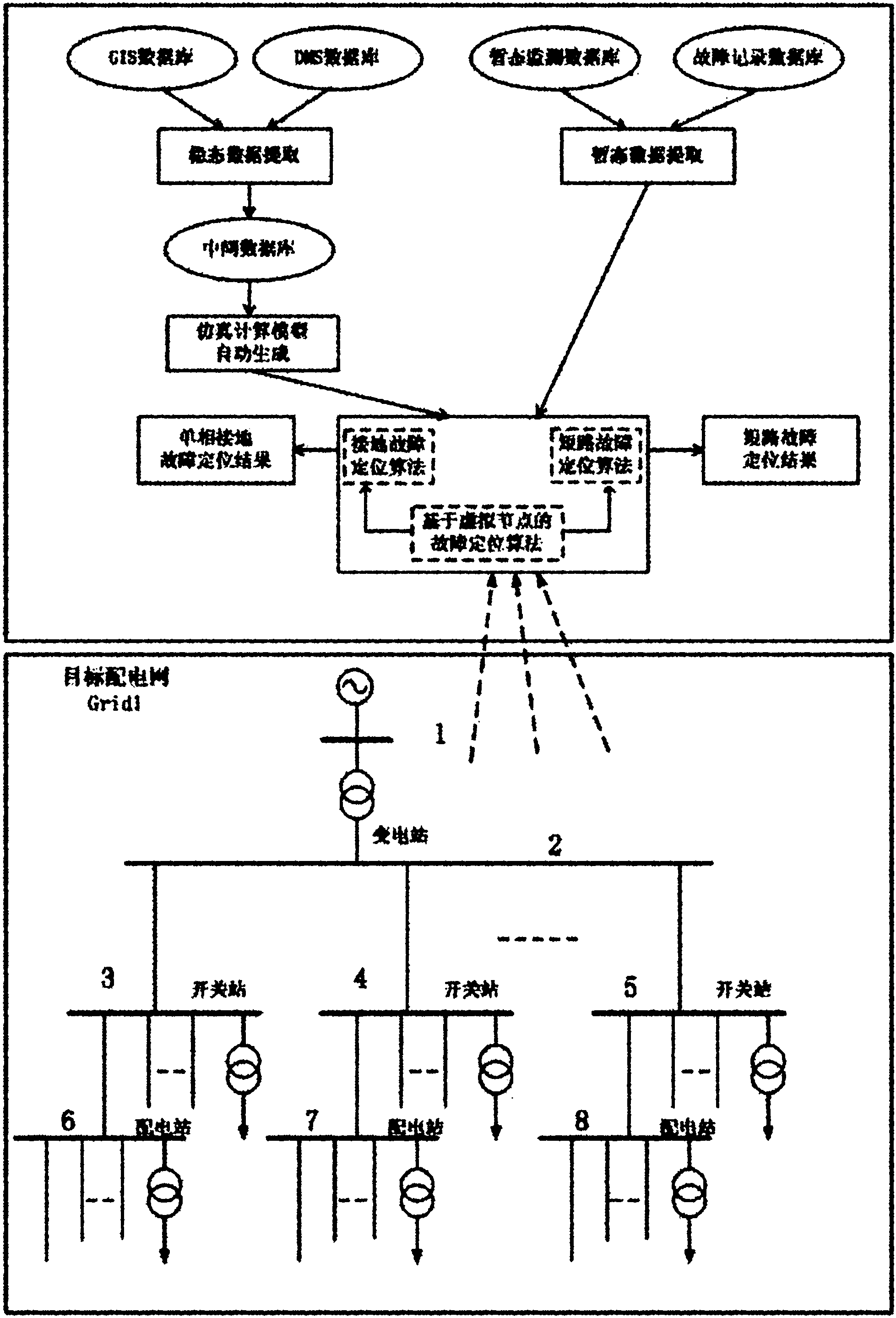
Fault positioning method for power distribution network by combining simulation calculation and real-time monitoring
ActiveCN101968525AAccurate and effective reflectionHigh precisionFault locationSpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudeFunctional relation
The invention discloses a fault positioning method for a power distribution network by combining simulation calculation and real-time monitoring, and belongs to the technical field of fault detection of the power distribution network. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting information of a target power distribution network from the conventional power distribution network geographic information system and a power distribution network energy management system through an organizational data analysis interface to automatically generate a real-time simulation calculation model of the target network; putting forward a virtual node-based fault positioning algorithm according to the simulation calculation model so as to solve functional relation between voltage amplitude of any node and a fault position parameter when a symmetric and asymmetric fault occurs at any point in the target network; and finally calculating an accurate position of the actual fault of the power distribution network by using a small amount of real-time data of voltage drop amplitude in a fault process. By using the fault positioning method for the power distribution network by combining the simulation calculation and the real-time monitoring, the state and the parameter of the network are accurately and effectively reflected when the fault occurs, the accuracy of the fault positioning is improved, and the method is suitable for various network structures and fault types.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
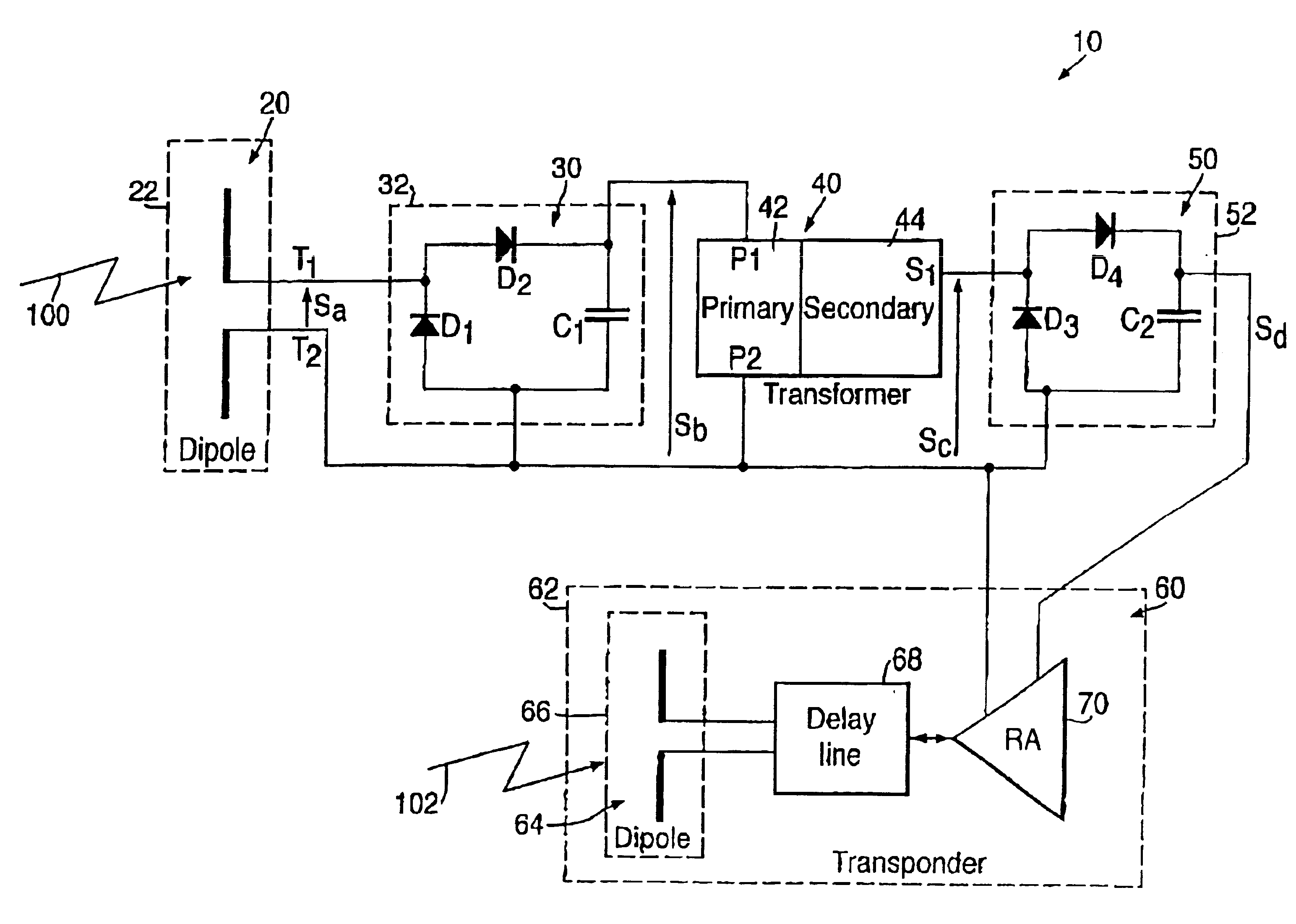
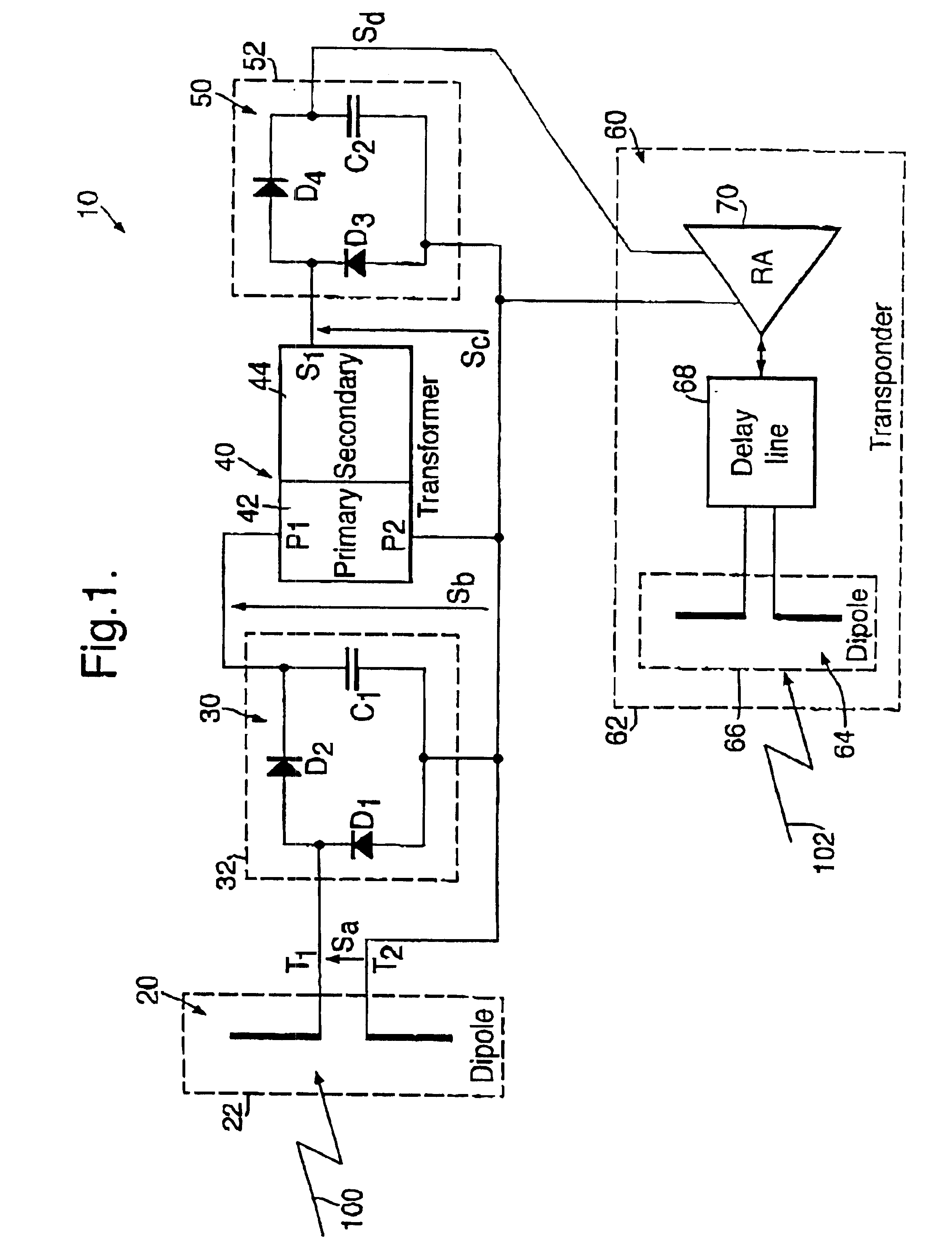
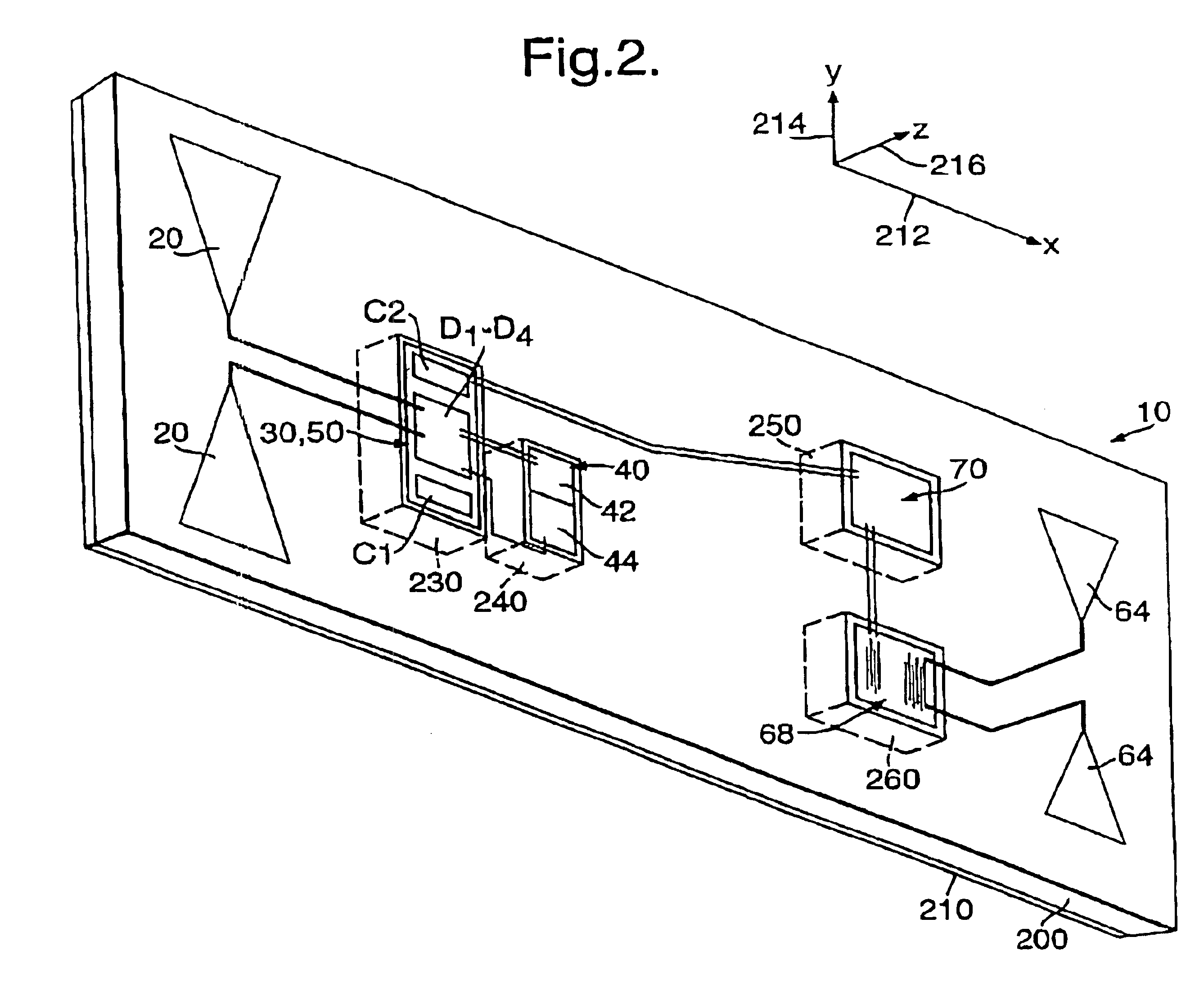
Piezo-electric tag
A piezo-electric tag in the form of a card has a first dipole antenna, a first rectification circuit, a piezo-electric transformer, a second rectification circuit, and a transponder circuit. In operation, the antenna receives incoming radiation and generates a corresponding signal which propagates to the first circuit which demodulates and filters it to generate a signal which is applied to the transformer to excite it. The transformer increases the voltage amplitude of the signal by generating a relatively higher voltage amplitude signal which is used in the tag to generate a signal for supplying power to the transponder. The transformer provides voltage magnitude enhancement to generate potentials suitable for operating active electronic circuits incorporated into the tag. The tag can be personnel wearable and even adapted for permanent inclusion into biological systems.
Owner:LIBERTY PATENTS LLC +1
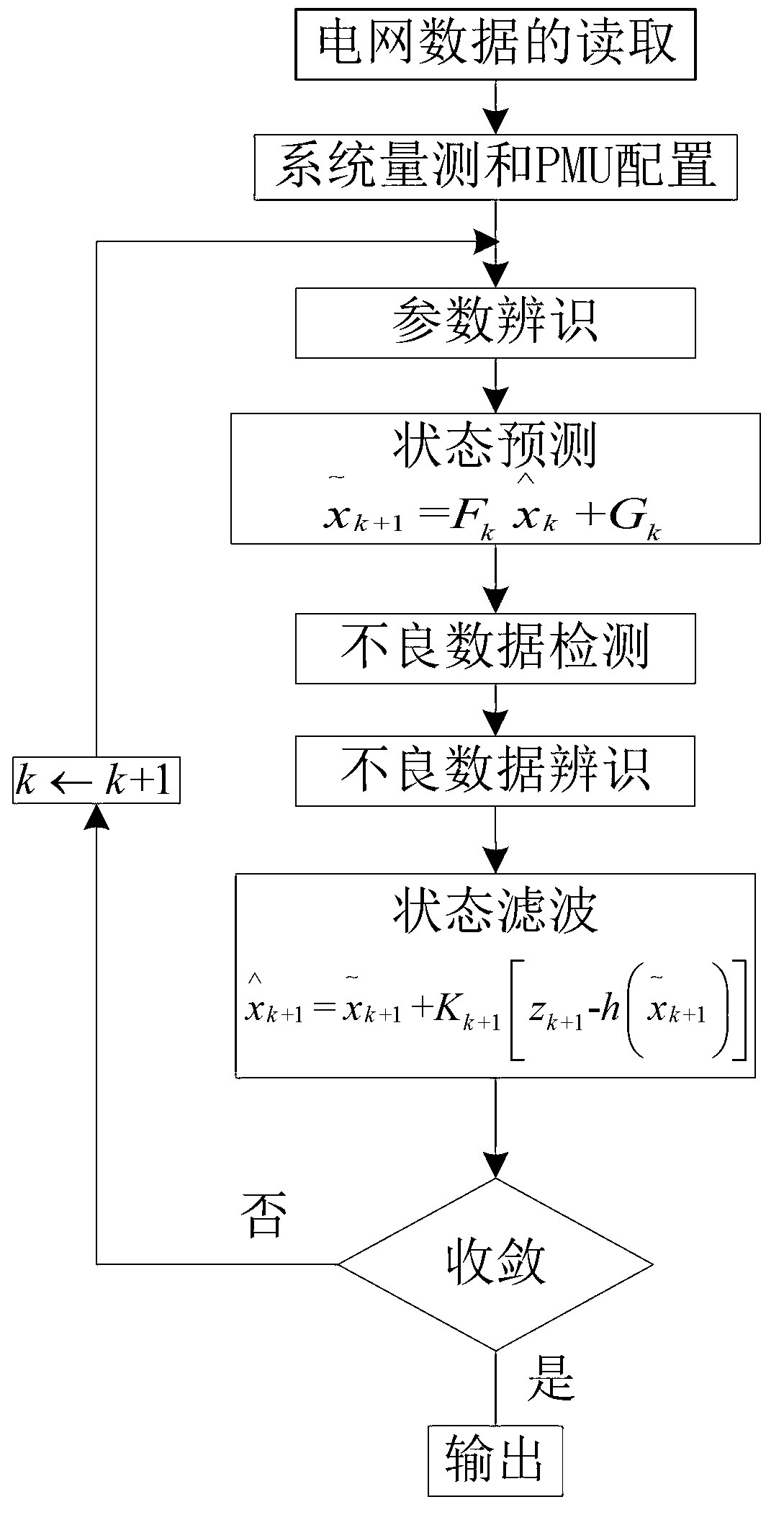
Method for detecting and identifying dynamic bad data of electric power system
InactiveCN103324847AMeet development requirementsEfficient Economic DispatchSpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudeElectric power system
The invention relates to the technical field of operation and control of an electric power system and discloses a method for detecting and identifying dynamic bad data of the electric power system. The method comprises the steps of A, reading a current network parameter and a network topology of the electric power system and forming a node admittance matrix and a branch circuit-node incidence matrix; B, establishing an equivalent circuit according to the network topology of the electric power system and configuring measurement functions and a power management unit (PMU) of the electric power system, wherein system measurement includes node voltage amplitude measurement, node current amplitude measurement, node power injection measurement and node trend measurement; C, detecting and identifying the dynamic bad data of the electric power system; D, judging the convergence condition. By means of the method, accidentally arisen bad data from a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system and in the PMU measurement can be found and eliminated, and accordingly an accurate operation state, voltage amplitude and phase angles of nodes of a power grid are obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
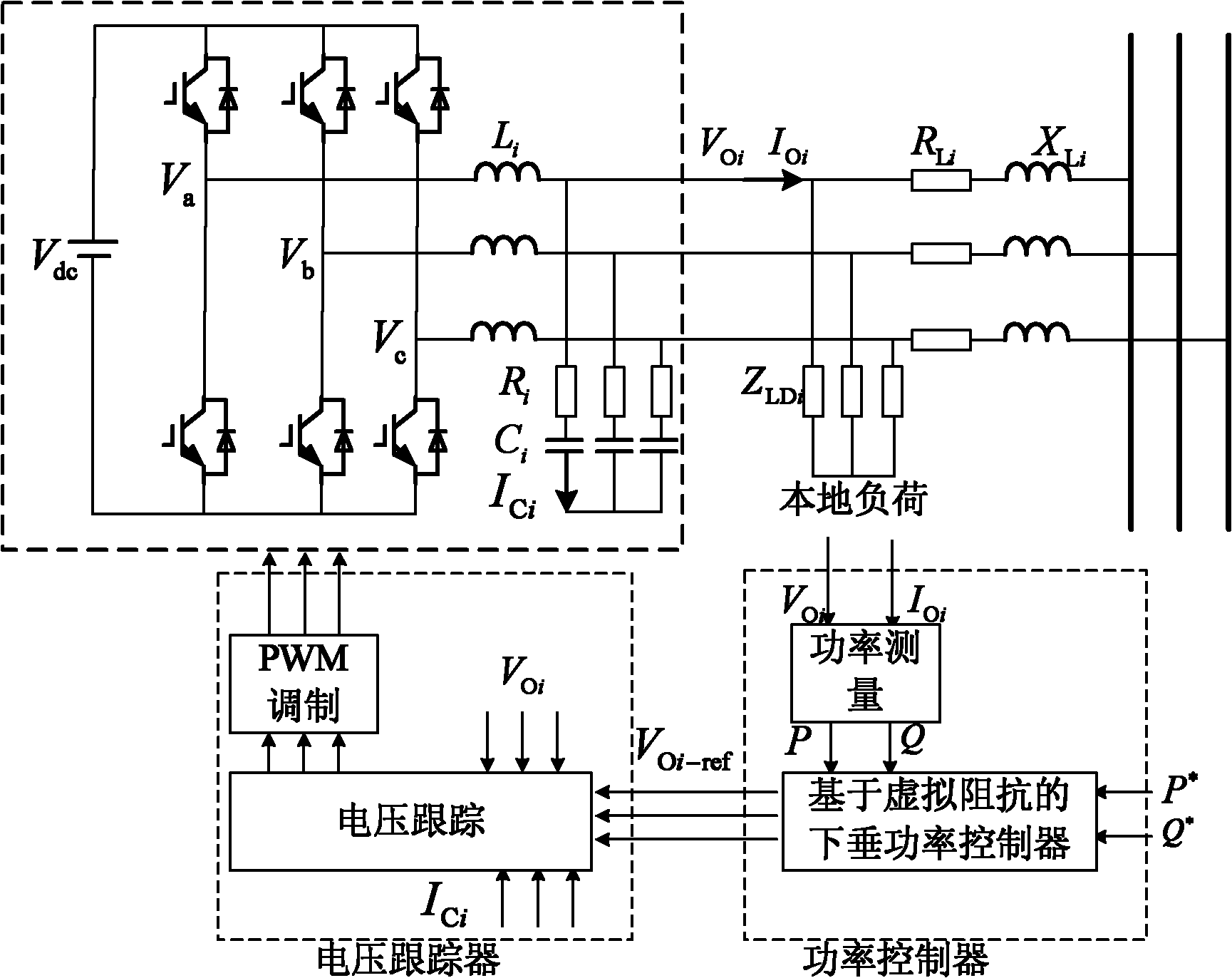
Virtual-impedance-based inverter parallel running method
ActiveCN102157956AIncrease investmentEasy to useFlexible AC transmissionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower inverterVoltage amplitude
The invention provides a virtual-impedance-based inverter parallel running method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: for each inverter, introducing a virtual generator which is connected to a point with the inverter by virtual impedance; performing droop control on the virtual generators, regulating the frequency and voltage amplitude of each virtual generator by utilizing the active power and reactive power of the corresponding inverters respectively, and further calculating voltage directive values of the virtual generators; and based on the voltage directive values, further calculating output voltage directive values of the inverters, and controlling the inverters to output voltages to track the directive values, thereby realizing control over the voltages of the virtual generators and finally realizing the decoupling regulation of the active power and the reactive power. In the method, a control policy for the wireless parallel running of the inverters is realized by utilizing the virtual impedance; and compared with the conventional control methods, the invention is not required to remarkably increase hardware investment, and betters the using effects of droop characteristics to make applicable the droop characteristics to resistive environments.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Integrated RF front end
ActiveUS20050287976A1Reduce the required powerEffective protectionResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersVoltage amplitudeManufacturing technology
A monolithic integrated circuit (IC), and method of manufacturing same, that includes all RF front end or transceiver elements for a portable communication device, including a power amplifier (PA), a matching, coupling and filtering network, and an antenna switch to couple the conditioned PA signal to an antenna. An output signal sensor senses at least a voltage amplitude of the signal switched by the antenna switch, and signals a PA control circuit to limit PA output power in response to excessive values of sensed output. Preferred fabrication techniques include stacking multiple FETs to form switching devices. An iClass PA architecture is described that dissipatively terminates unwanted harmonics of the PA output signal. A preferred embodiment of the RF transceiver IC includes two distinct PA circuits, two distinct receive signal amplifier circuits, and a four-way antenna switch to selectably couple a single antenna connection to any one of the four circuits.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
High frequency power amplifier, transmitter and mobile communication terminal using the power amplifier
ActiveUS20060267688A1Improve linearityEasily downsizedResonant long antennasGain controlVoltage amplitudeAudio power amplifier
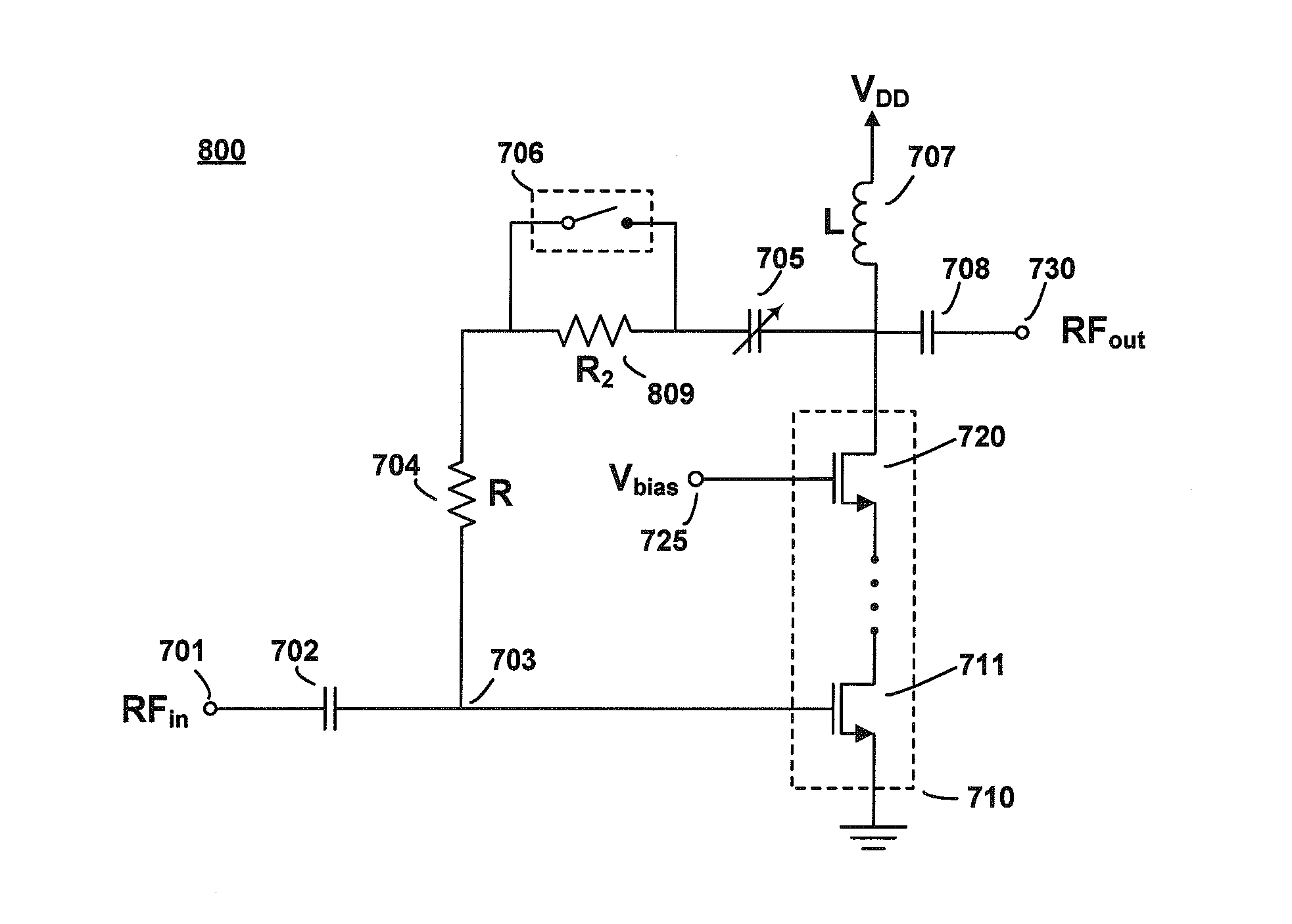
A high frequency power amplifier maintains an excellent linearity regardless of a fluctuation of a load impedance and is downsized. The high frequency power amplifier detects an AC voltage amplitude at an output terminal of a final amplification stage transistor, and suppresses an input signal amplitude of a power amplifier when the voltage amplitude exceeds a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Field weakening control method for built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor
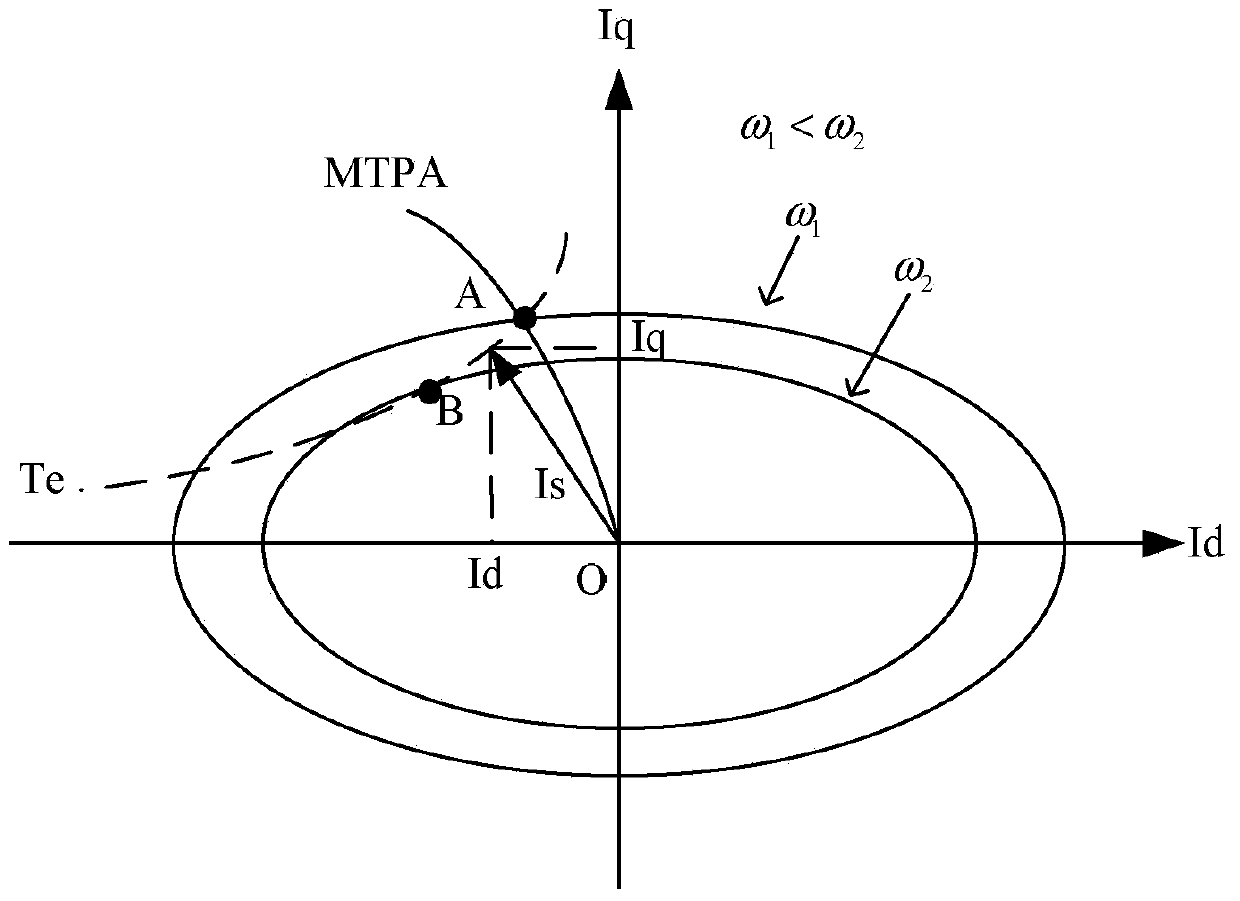
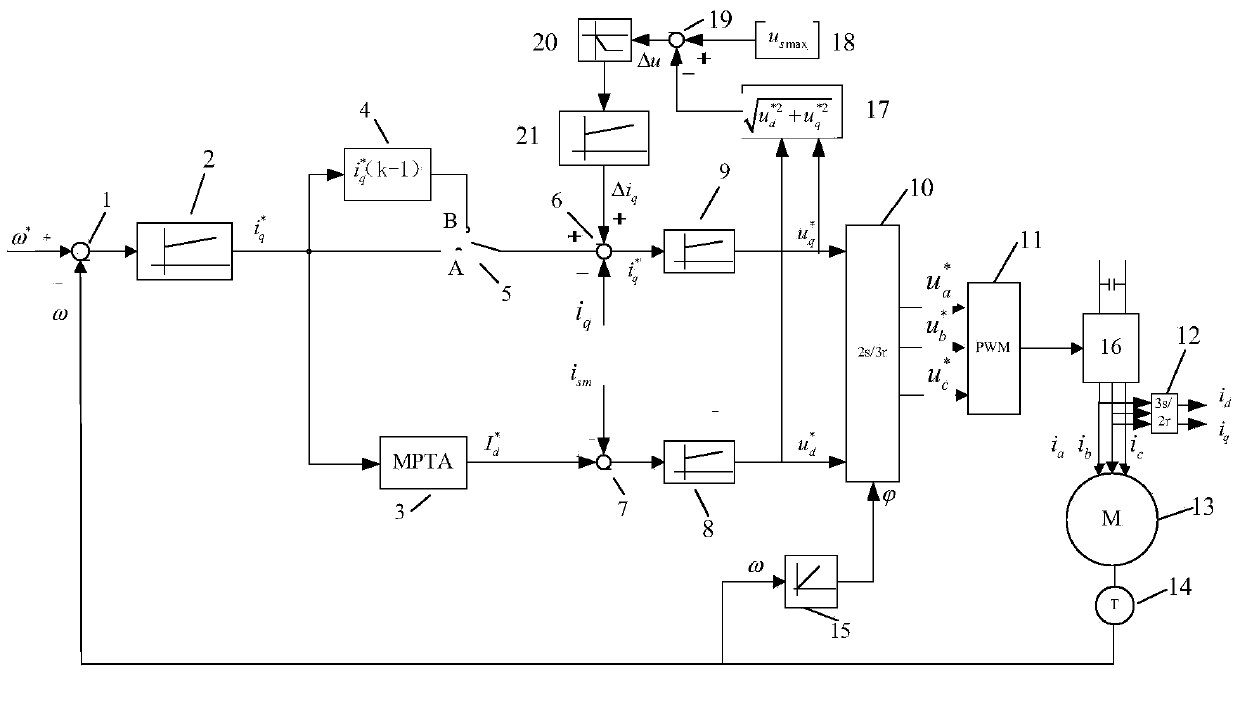
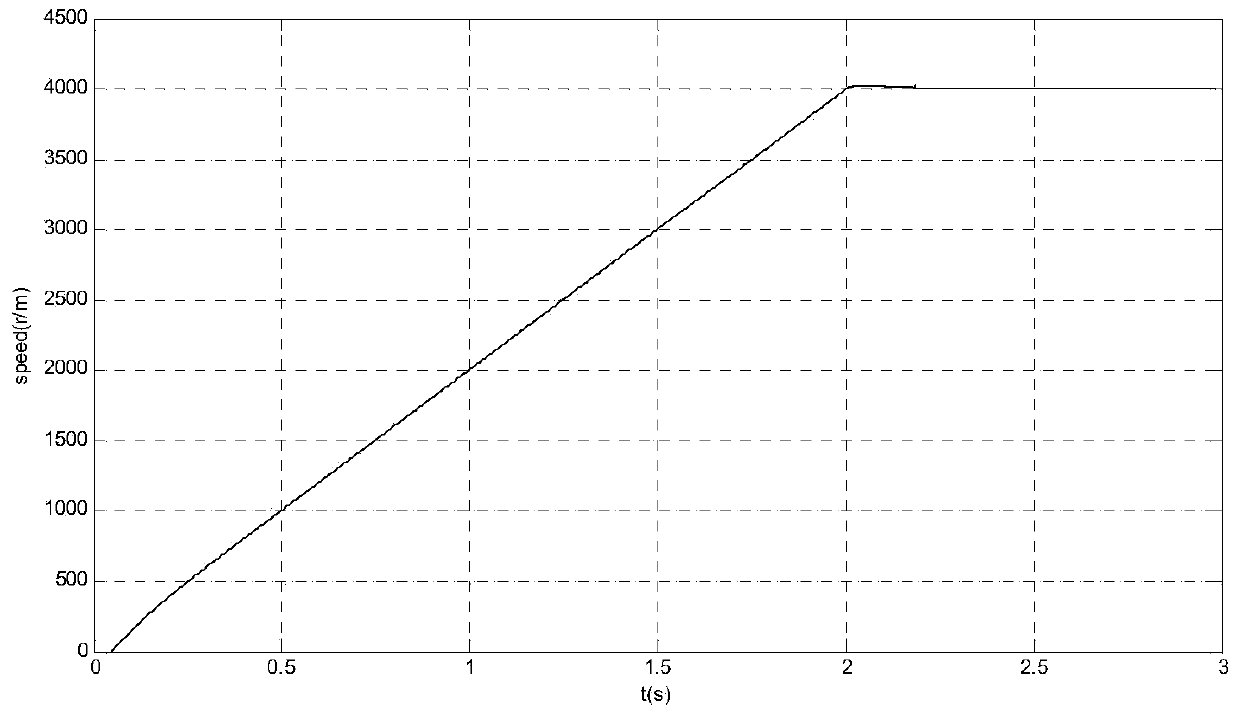
ActiveCN103701384ASimple designImprove stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedVoltage amplitude
The invention provides a field weakening control method for a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: motor speed closed-loop control in a field non-weakening region: the output of a speed loop is the current directive value i<*>q of an axis q, the current directive value i<*>d of an axis d is calculated from i<*>q according to an MTPA relation, and i<*>d, i<*>q and the actual feedback values id and iq thereof are subjected to closed-loop control to output the voltage directive values of the axis d and the axis q; difference value amplitude-limiting processing: whether to enter a field weakening region is judged, if yes, an output voltage amplitude value controls a PI (Proportional-Integral) controller to work and controls a PI adjustor to perform difference value amplitude-limiting processing and output Deltaiq, otherwise, the output voltage amplitude value controls the PI controller not to work, and the output is 0; in case of entering the field weakening region, the output i<*>q of the speed loop is only used as the current directive value of the axis d after MTPA calculation, and the sum of the output of the front beat of the speed loop before entering the field weakening region and Deltaiq serves as the current directive value of the axis q in the field weakening region.
Owner:WISDRI WUHAN AUTOMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com