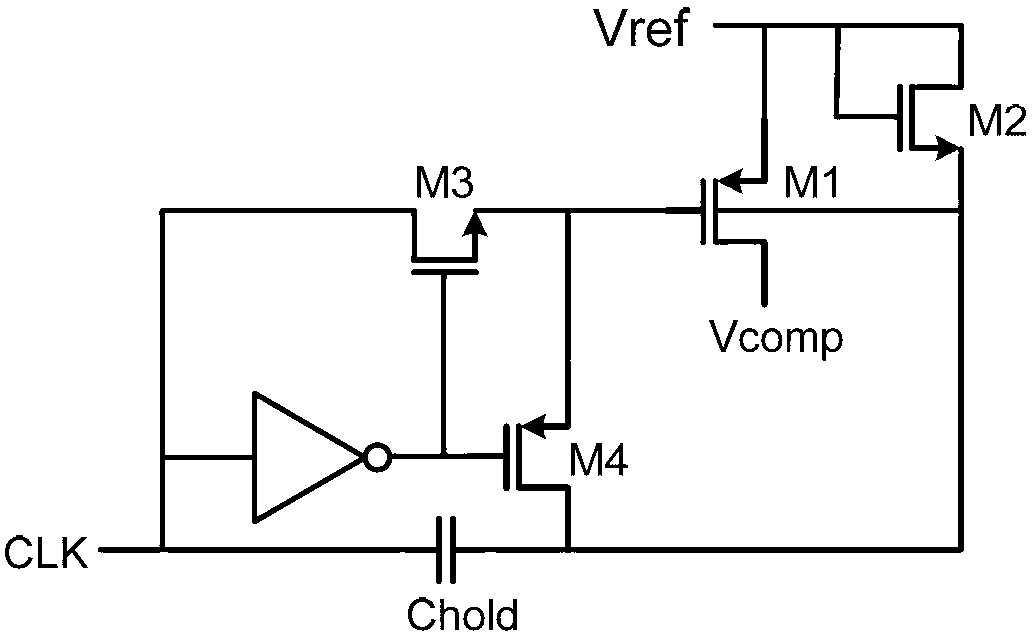
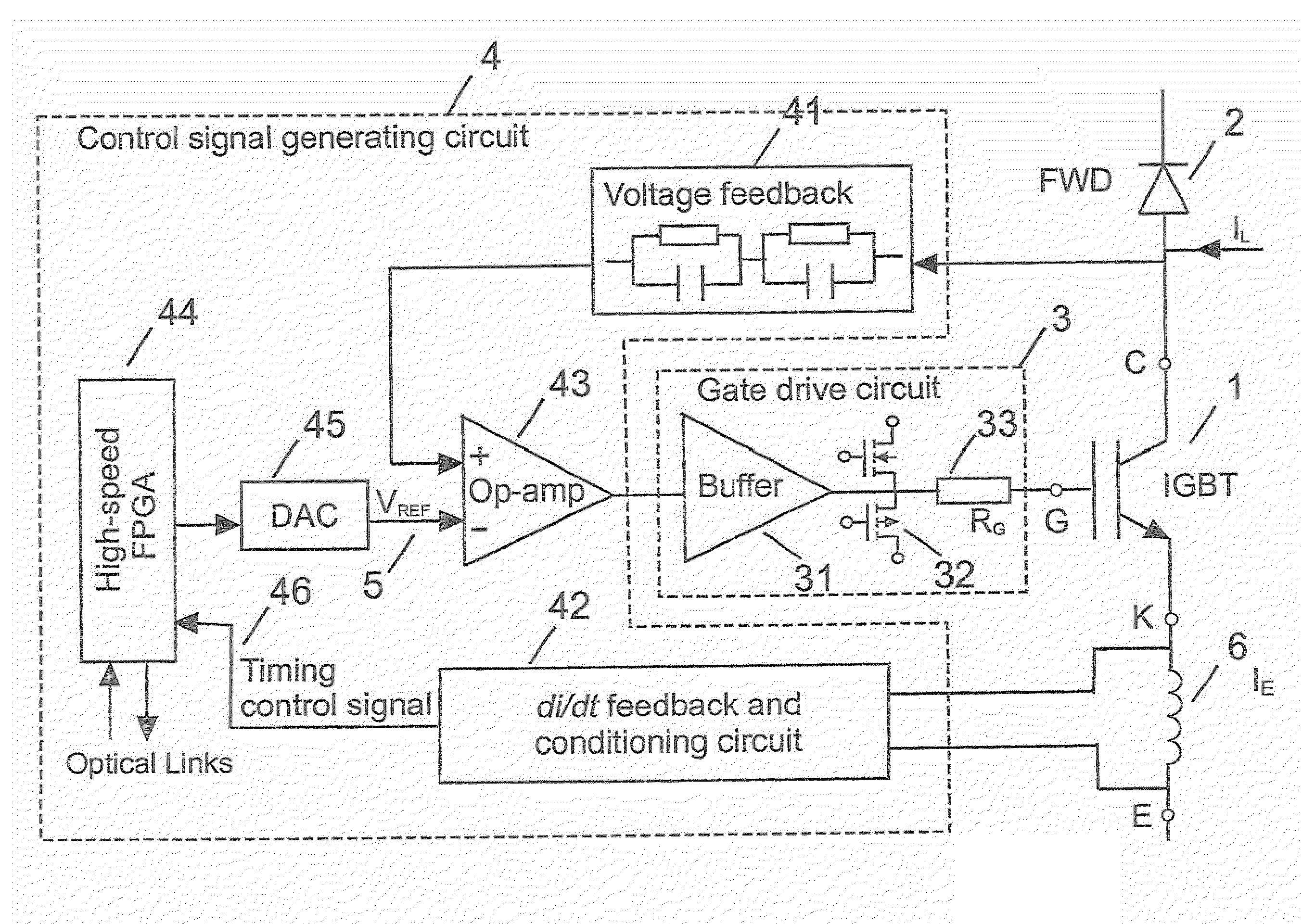
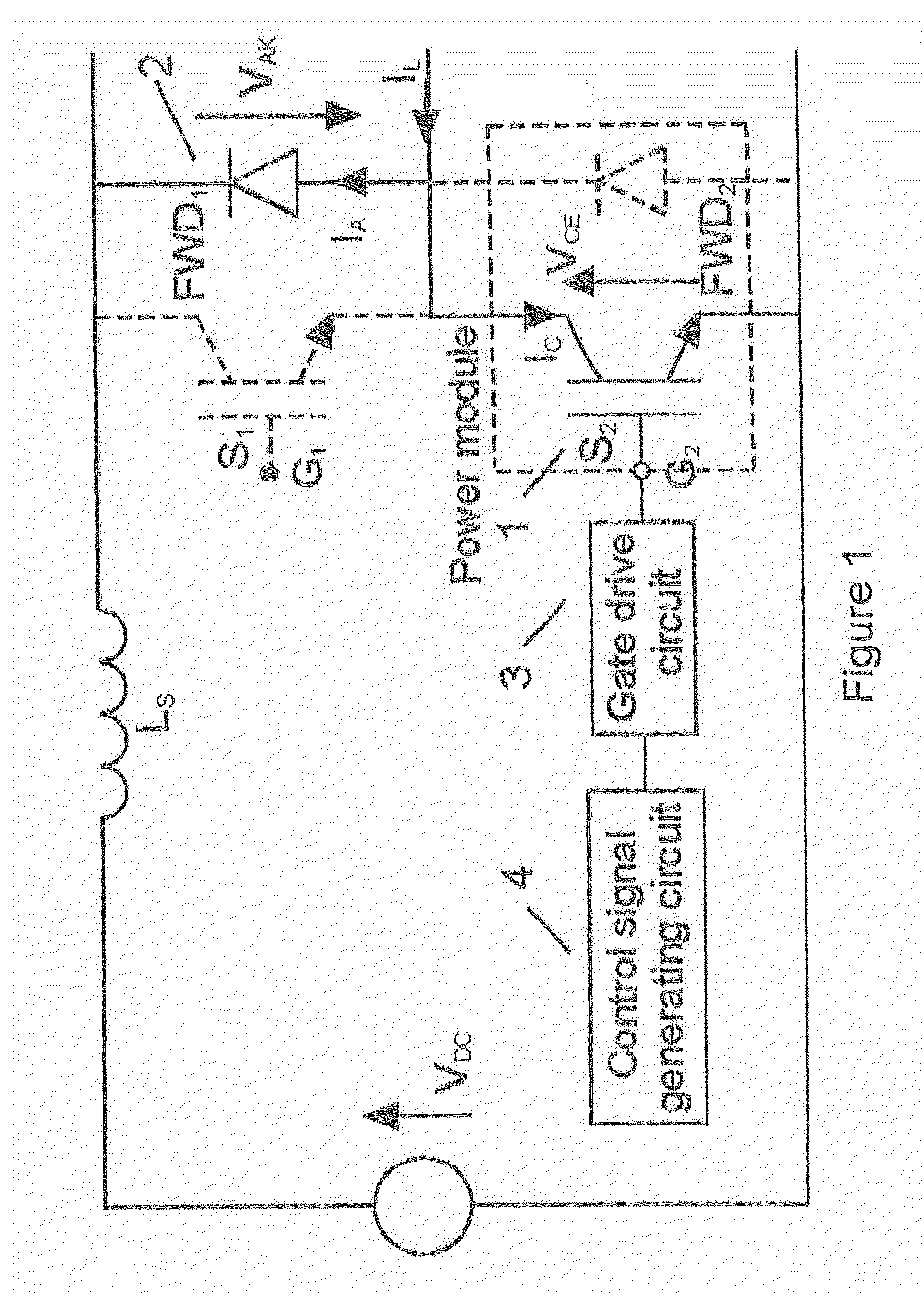
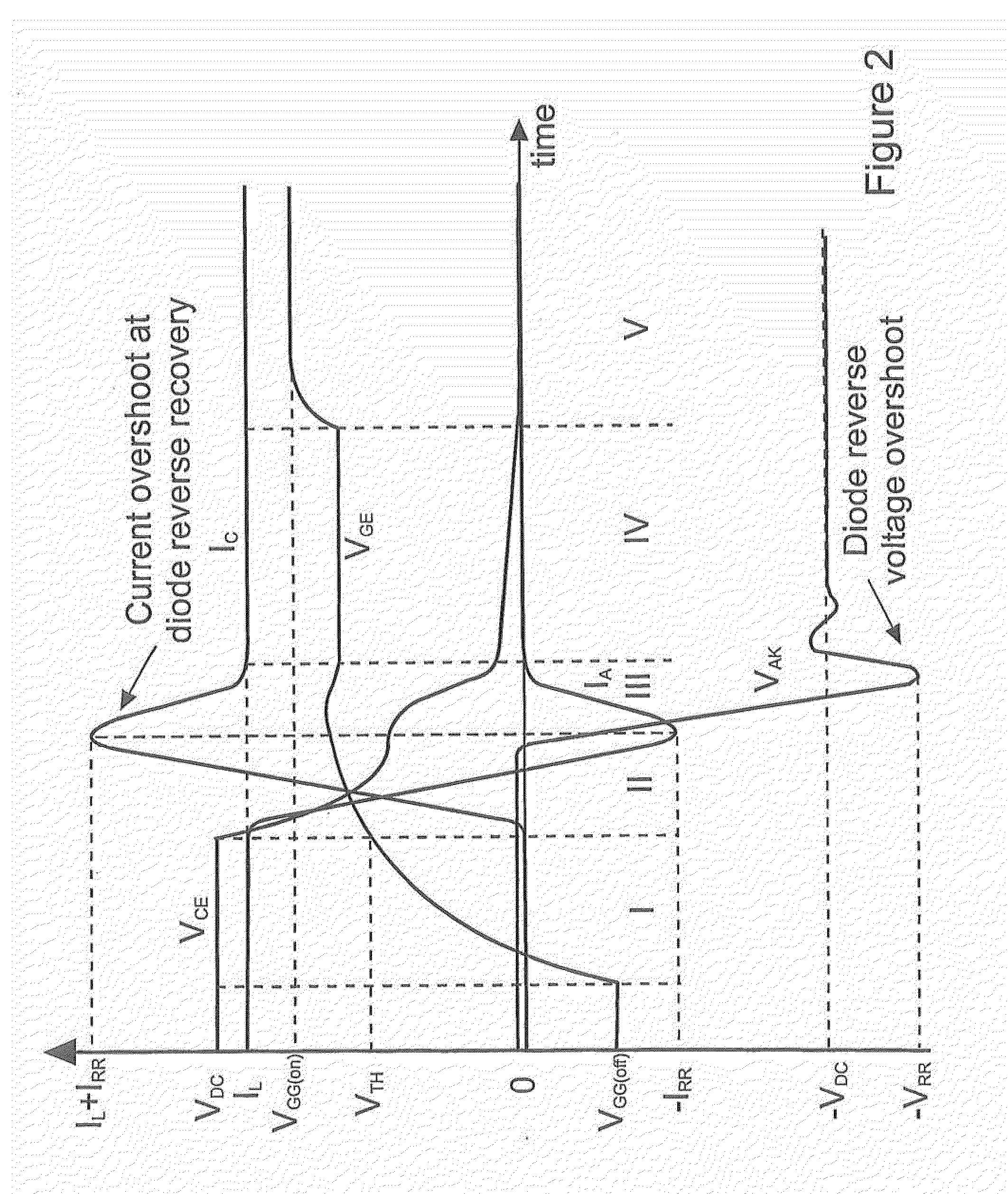
Patents
Literature
408 results about "Voltage overshoot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
As wire length or switching speed increases, the overshoot peak voltage also increases.The Variable Frequency Drive’s inverter circuit “switches” (transitions from the off state to the on state) rapidly, producing a carrier containing the fundamental voltage and frequency.
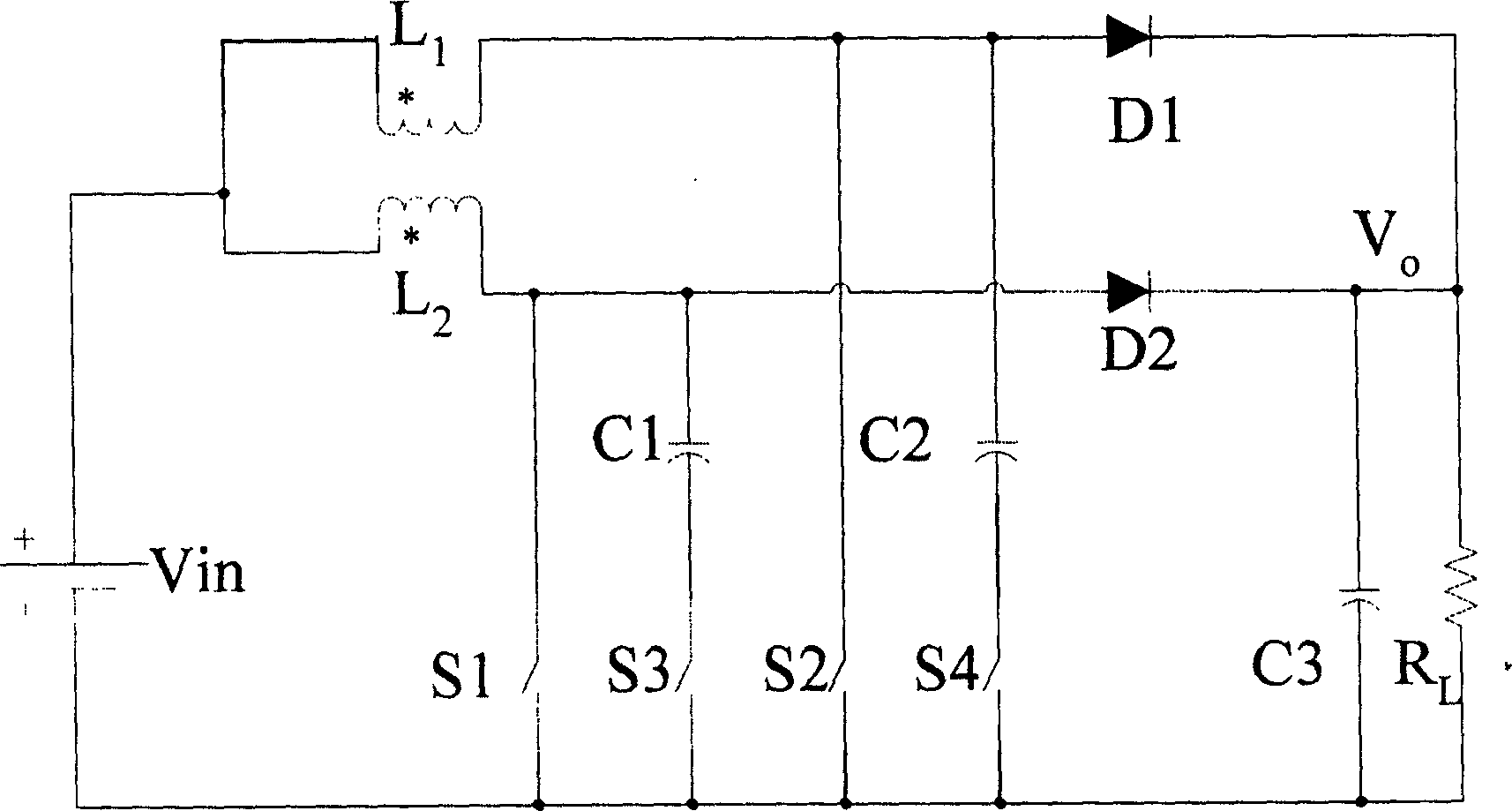
Boost type active interlaced parallel soft switch circuit
InactiveCN1588773AImprove efficiencySimple structureEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceVoltage overshoot
This invention relates to a voltage-boosting type active staggered parallel-connection soft switching circuit. It comprises: two phase coupled inductors, two follows current diodes, two power switching tubes. The drain electrode of the first power switching tube, the positive pole of the second diode and one end of the second inductor are connected. The drain electrode of the second power switching tube, the positive pole of the fist diode and one end of the first inductor are connected. The other end of the first inductor and second inductor are connected. The first power switching tube is paralllet connected with a series circuit composed of the first capacitor and the first auxiliary switching tube; while the second power switching tube is parallel connected with a series circuit composed of the second capacitor and the second auxiliary switching tube. Advantages are: less auxiliary devices, simple structure, no need of additional testing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
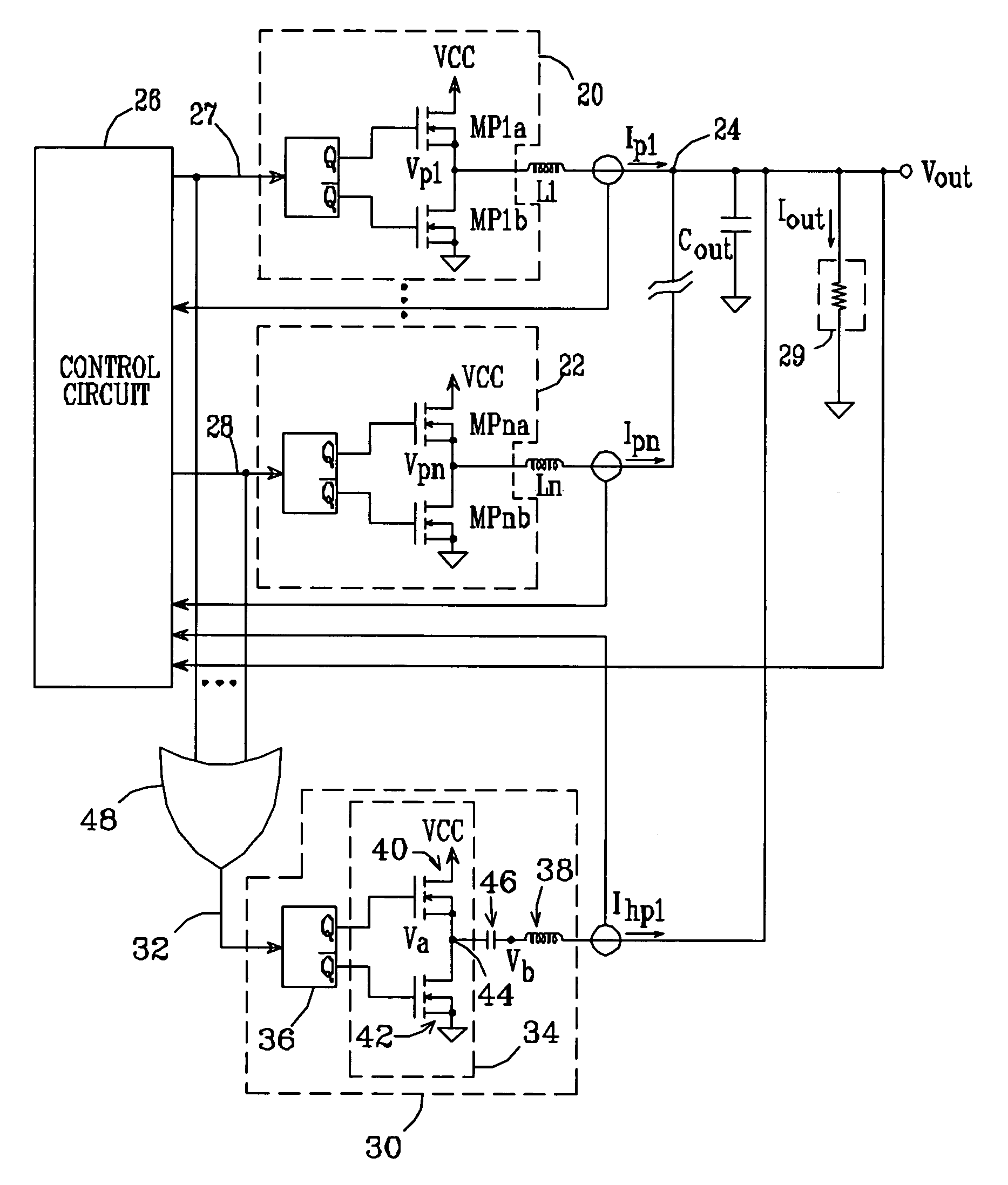
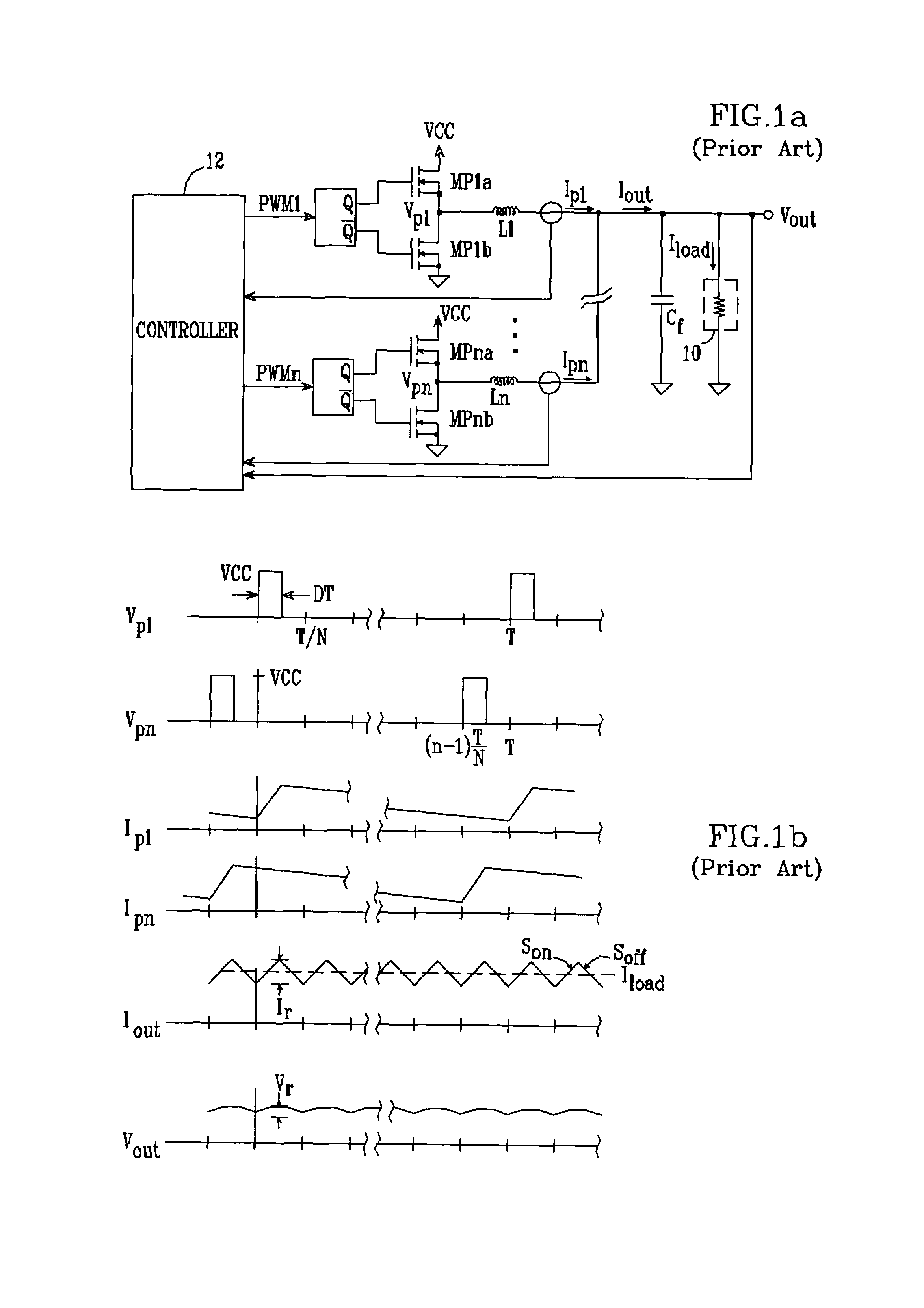
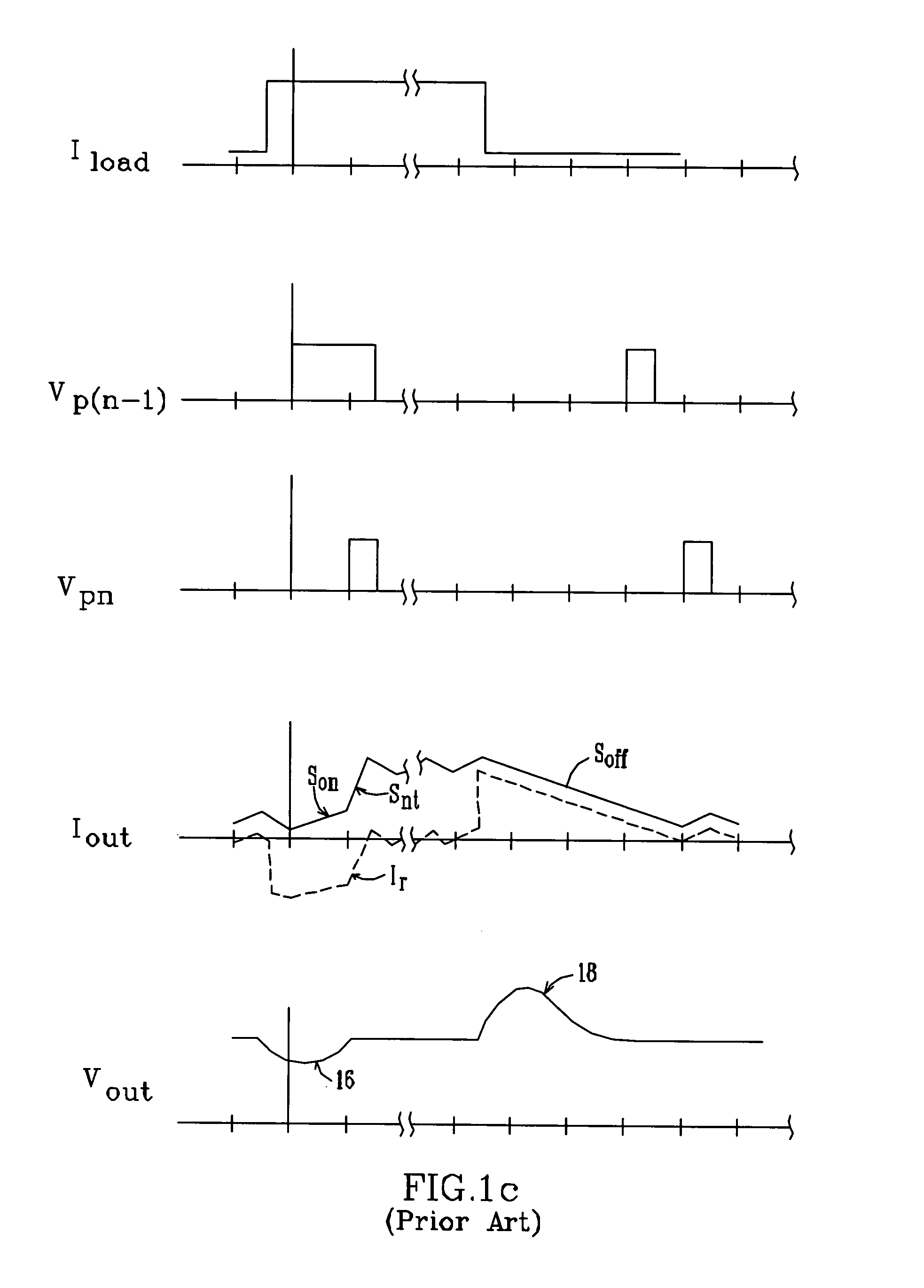
Multiple-phase DC-DC converter topology
ActiveUS6943535B1Improve responseIncrease speedDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentPhase currentsDc dc converter
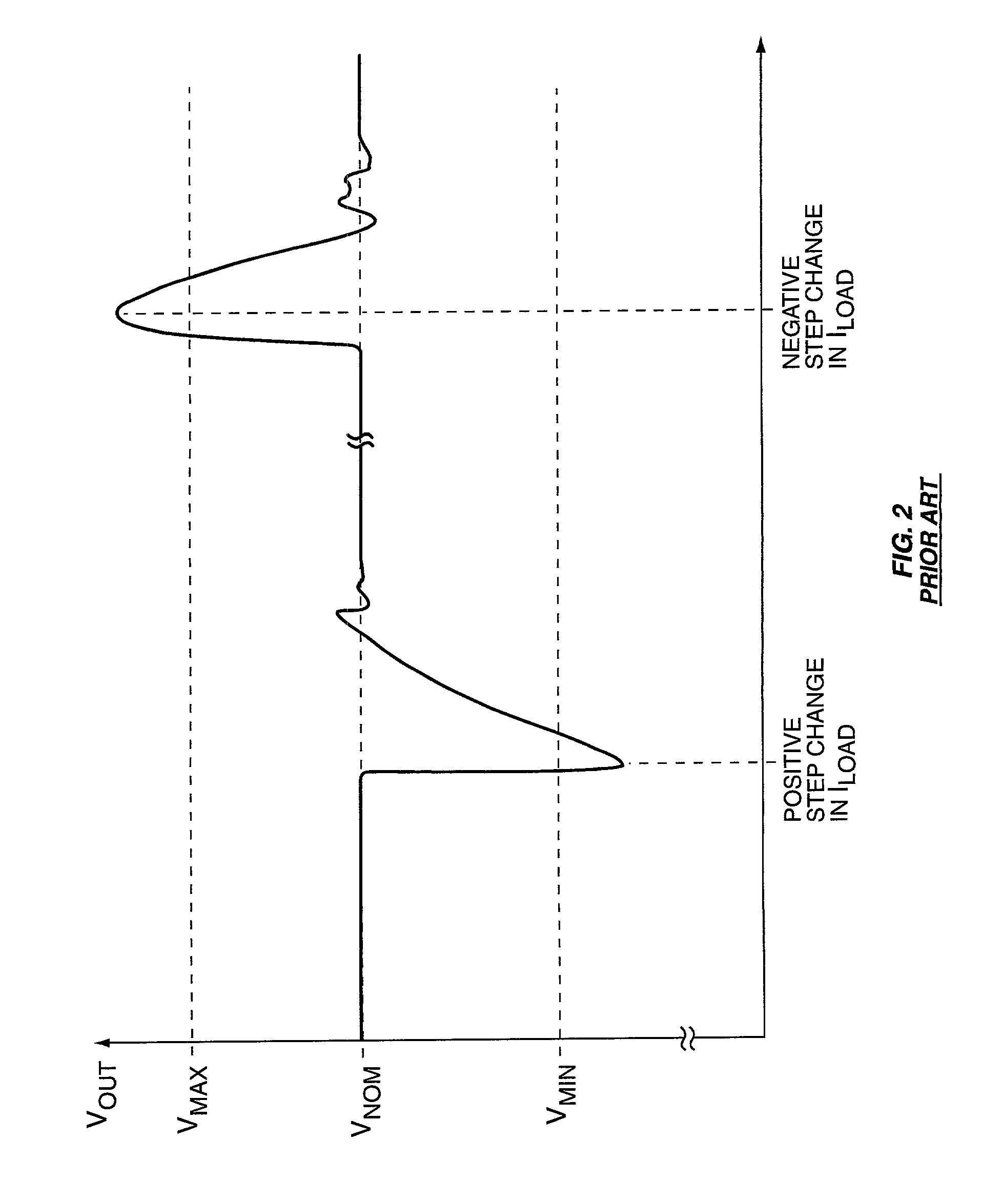
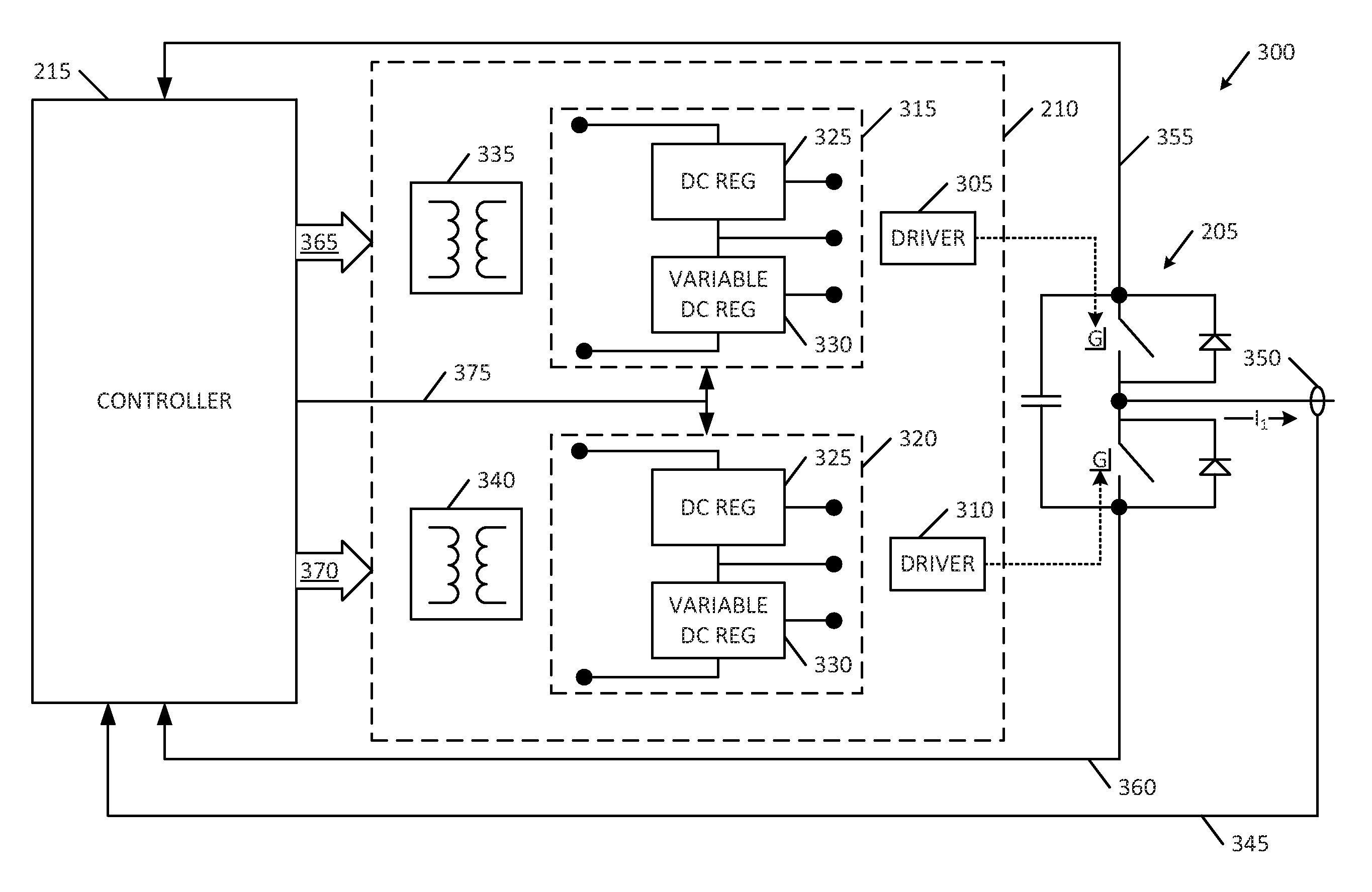
A multiple-phase DC—DC converter adds at least one additional phase to an N-phase DC—DC converter to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In one embodiment, an additional phase operates at a switching frequency greater than that of the N phases, to generate a current which is added to the N phase currents to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In another embodiment, an additional phase is configured to improve the converter's response to a load release. Here, the additional phase is kept off during load increase and steady-state conditions. However, when a load release occurs, the additional phase is turned on and acts to extract current from the converter's output terminal while the N phase currents slowly fall, to reduce the magnitude of output voltage overshoot that occurs on load release.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Low-cost 3D flip-chip packaging technology for integrated power electronics modules
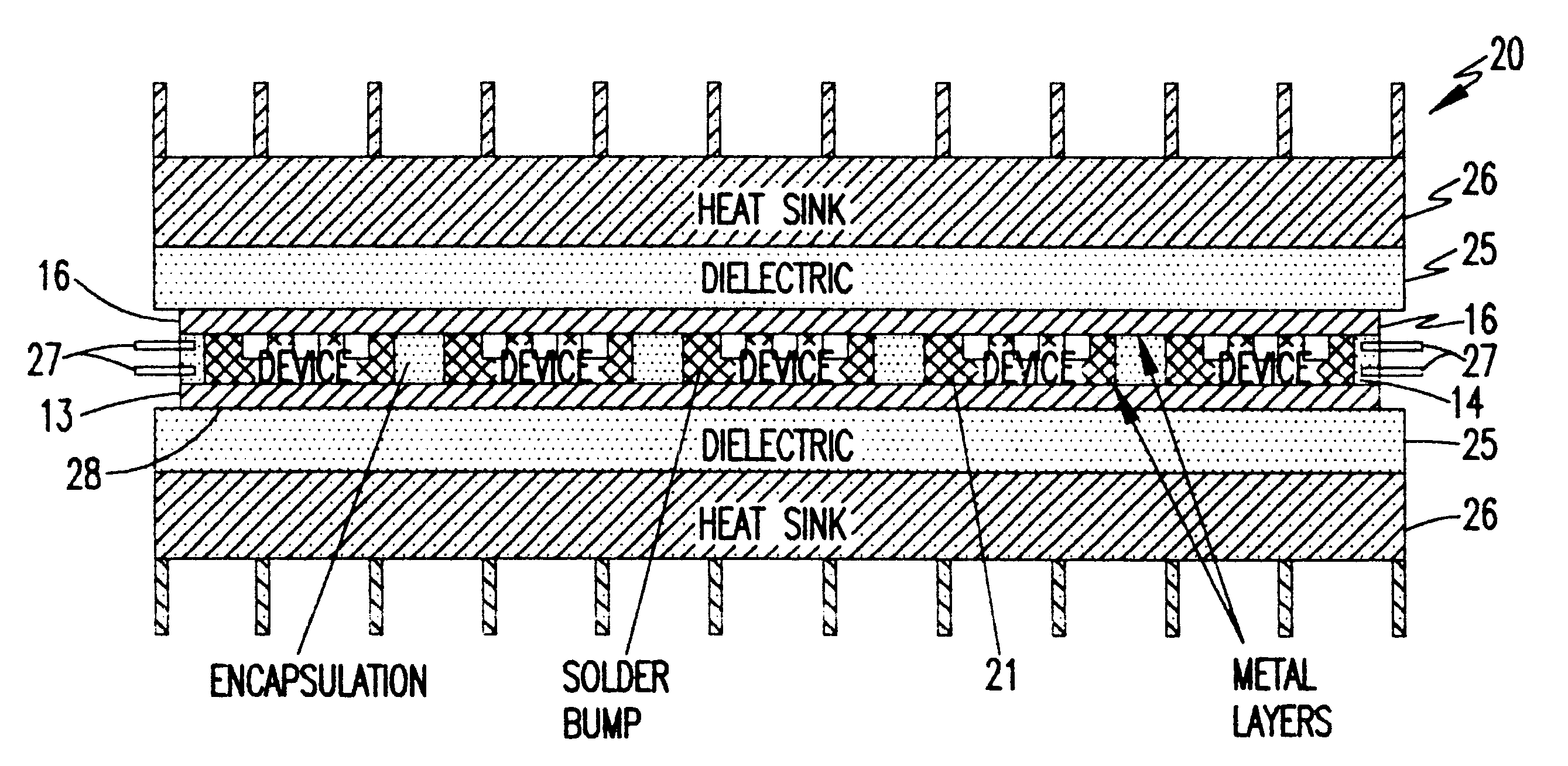
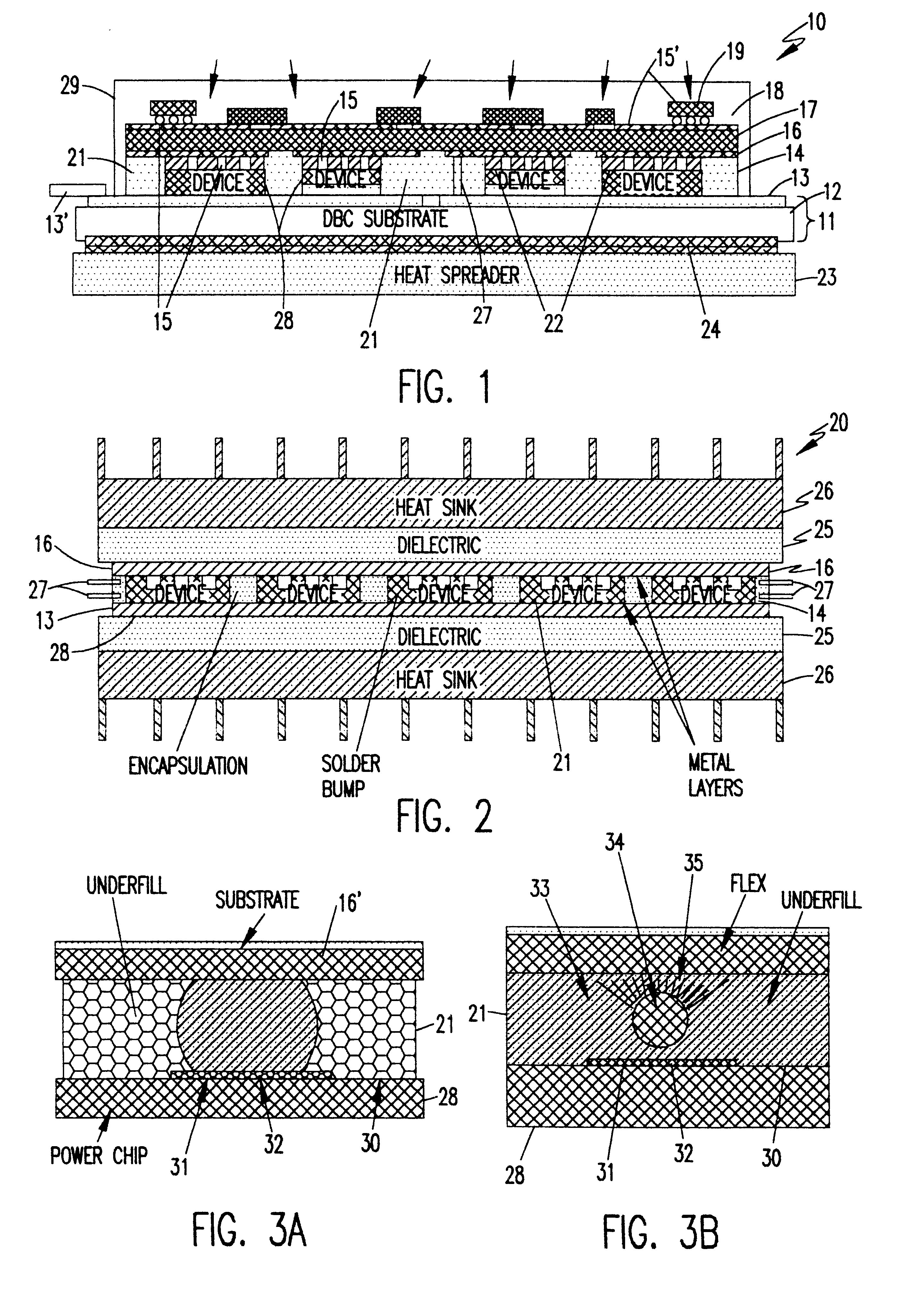
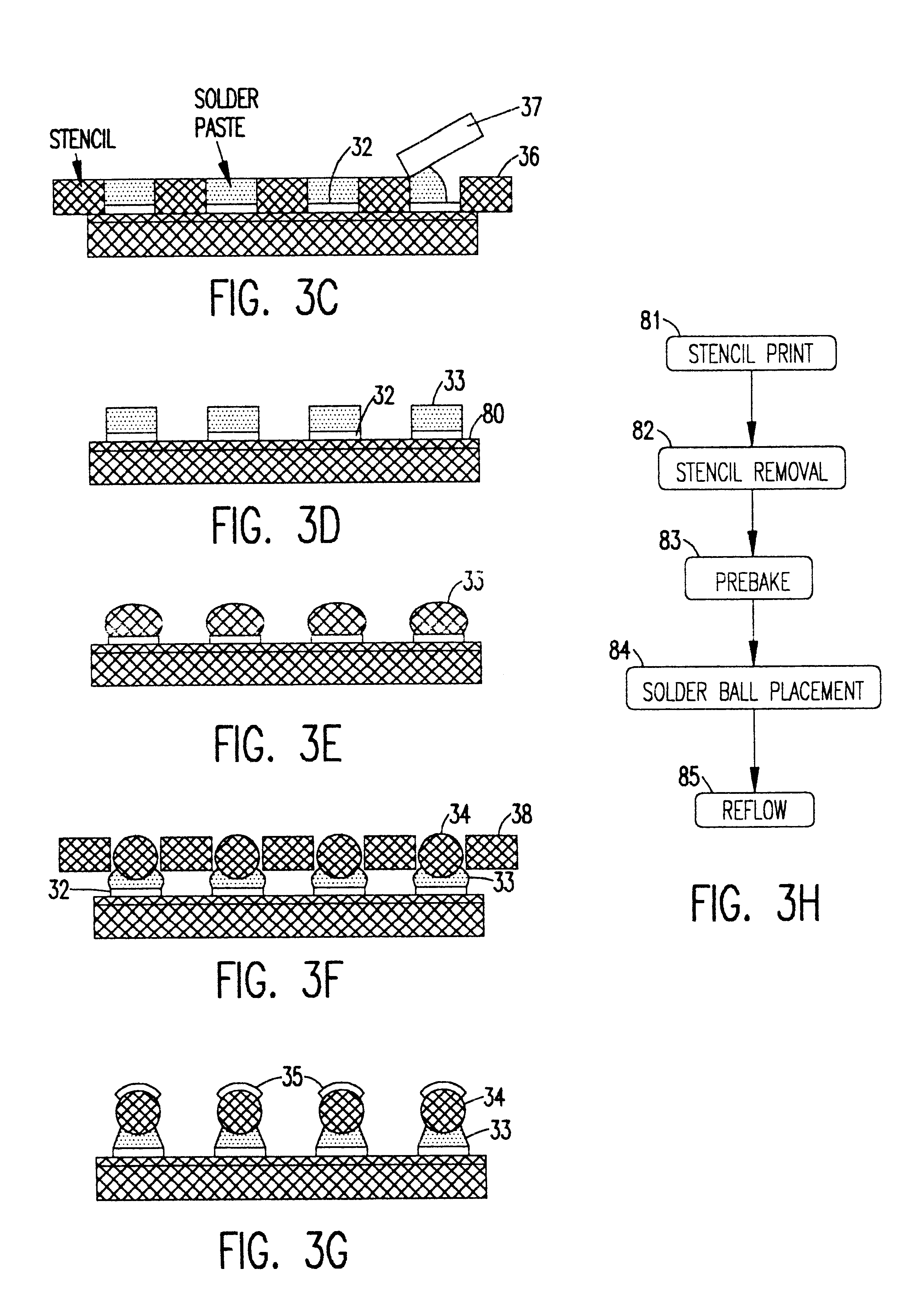
InactiveUS6442033B1Improve performanceLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVoltage overshootLead bonding
Resistance and parasitic inductance resulting from interconnection of semiconductor chips in power modules are reduced to negligible levels by a robust structure which completely avoids use of wire bonds through use of ball bonding and flip-chip manufacturing processes, possibly in combination with chip scale packaging and hourglass shaped stacked solder bumps of increased compliance and controlled height / shape. Turn-off voltage overshoot is reduced to about one-half or less than a comparable wire bond packaged power module. Hourglass shaped solder bumps provide increased compliance and reliability over much increased numbers of thermal cycles over wide temperature excursions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
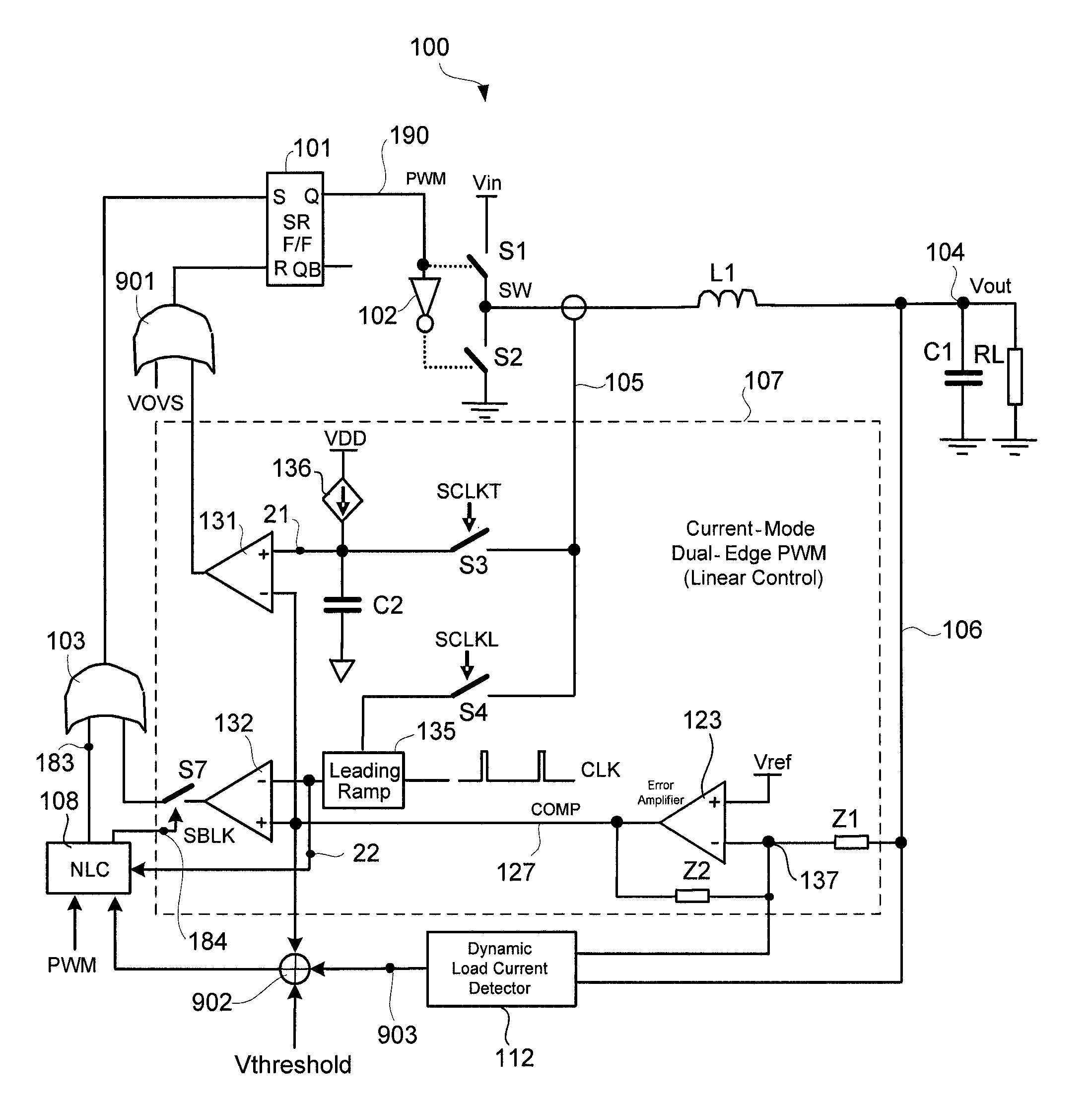
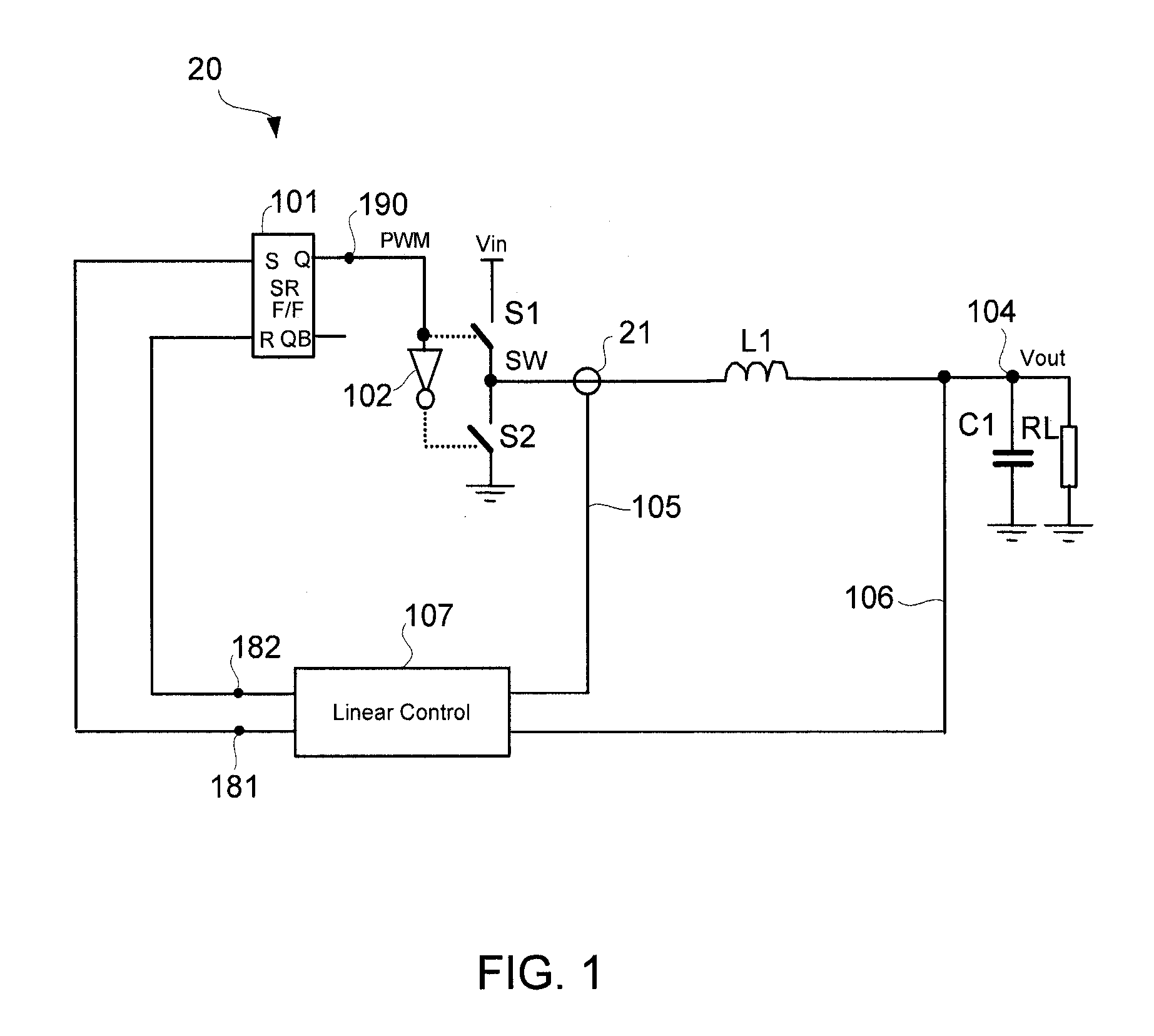
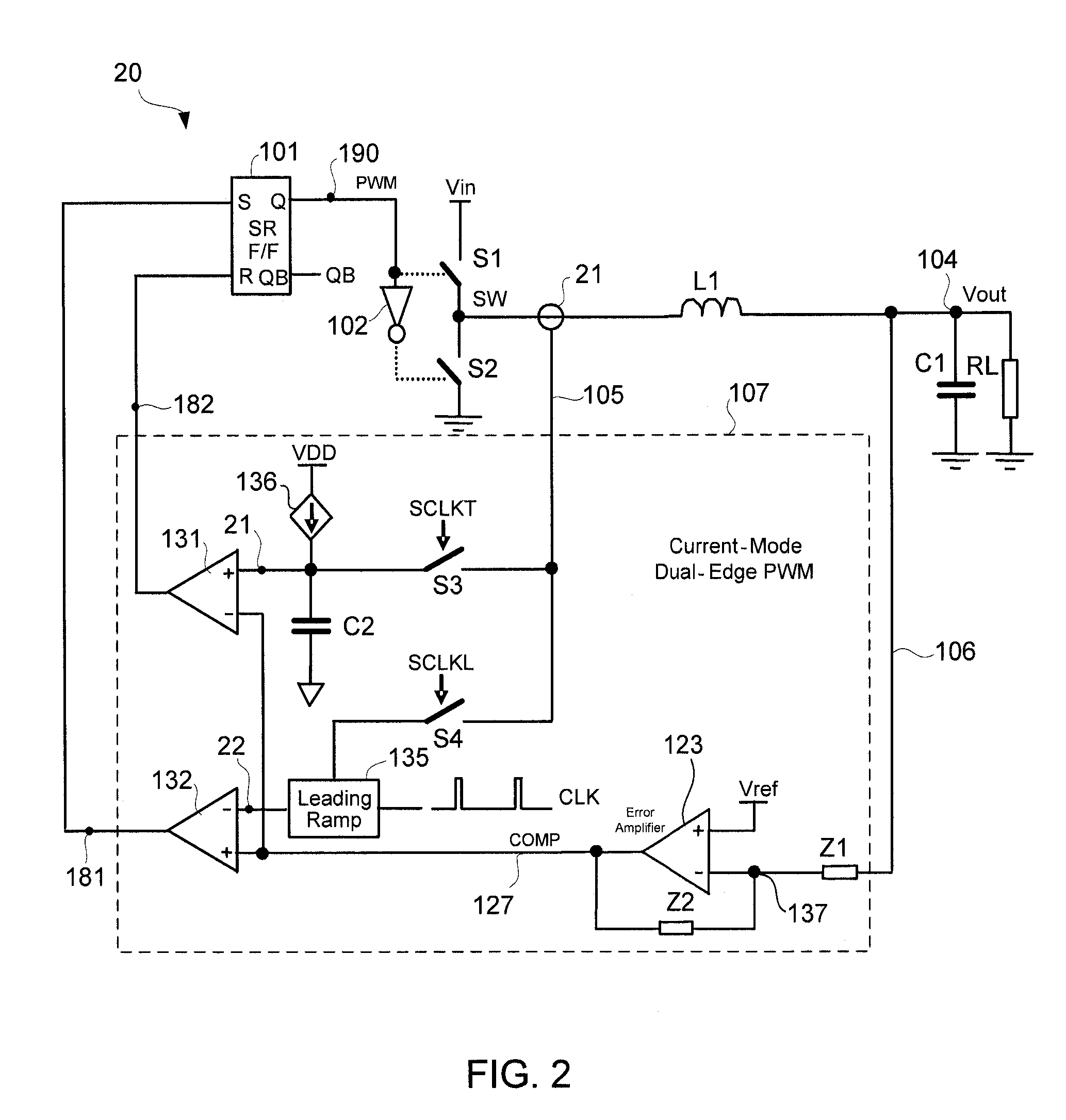
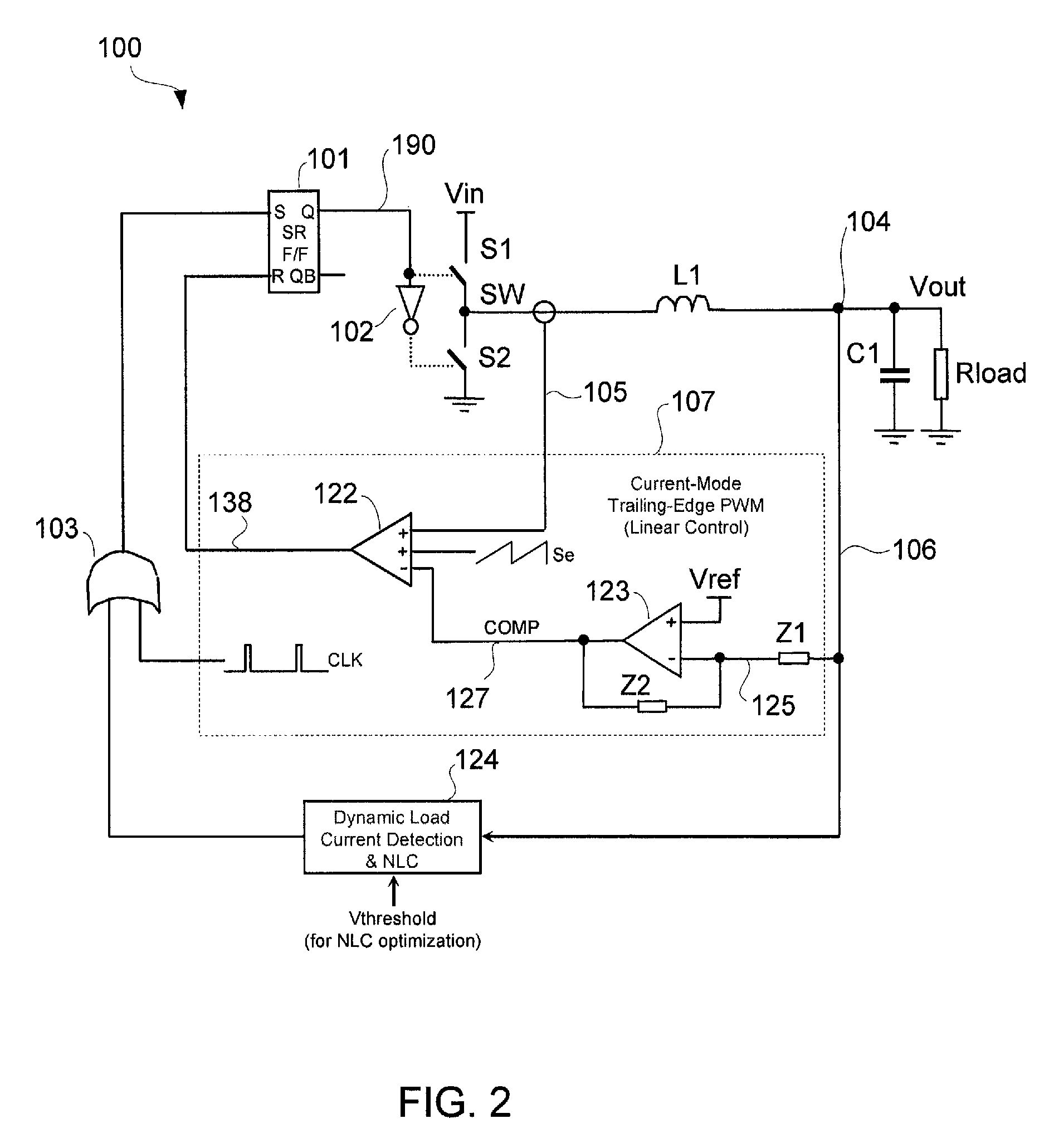
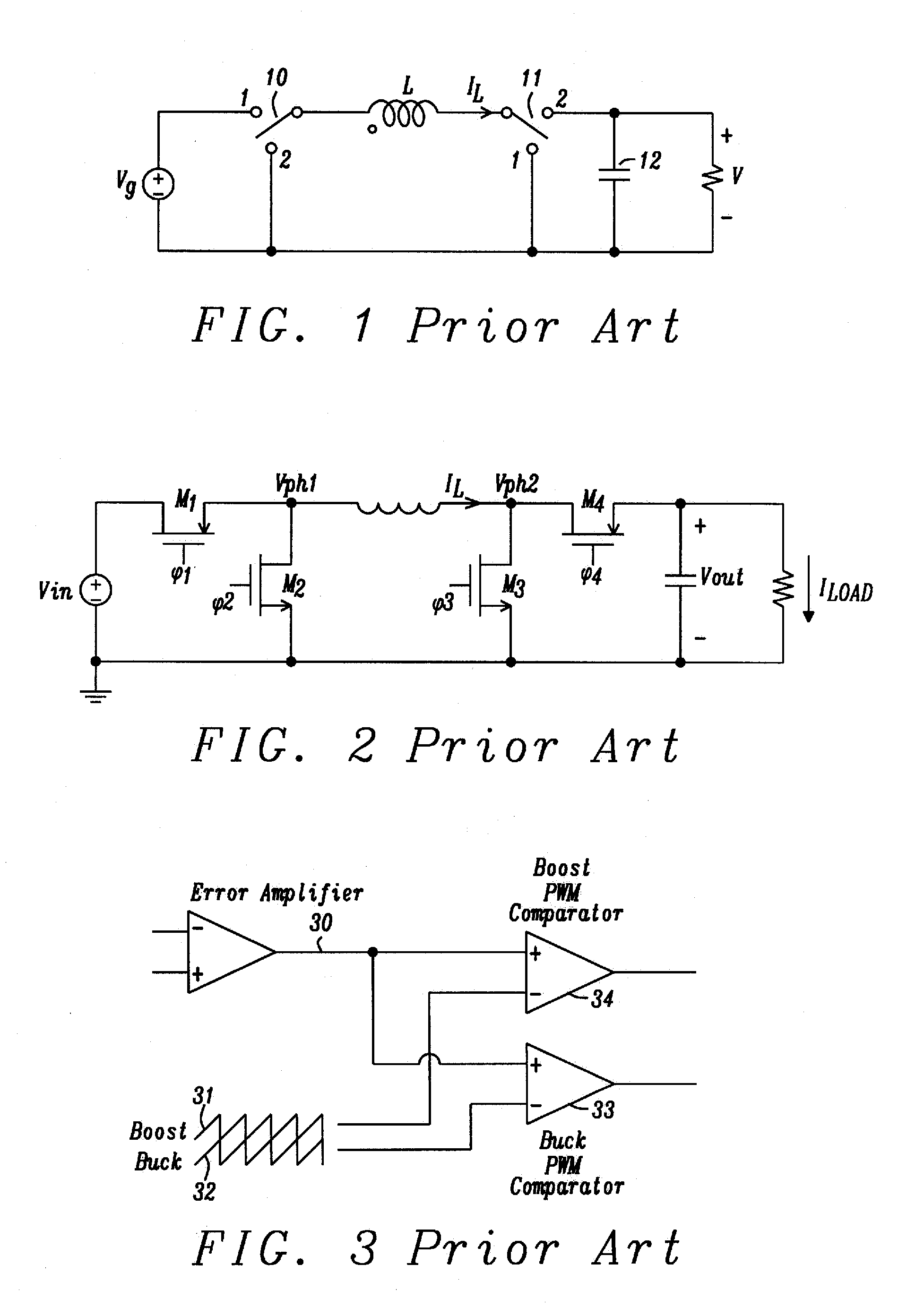
Voltage regulator with current-mode dual-edge pulse width modulation and non-linear control
ActiveUS7764054B1Prevent output voltage overshootMaintain output voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETVoltage overshoot
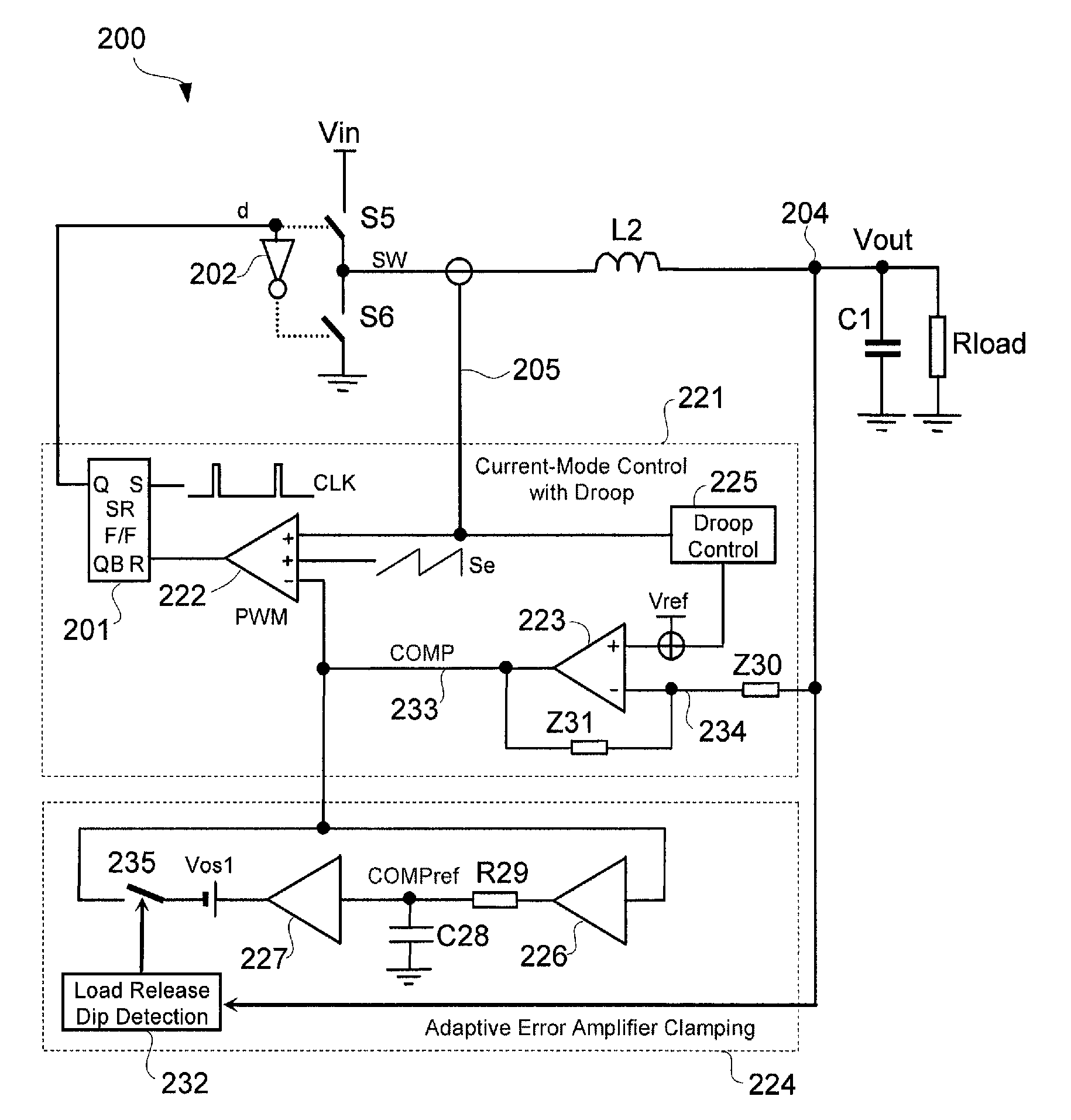
A voltage regulator with current-mode, dual-edge pulse width modulation (PWM) and non-linear control. The voltage regulator may include a top switch (e.g., MOSFET) configured to couple a power supply supplying an input voltage to a load. A linear control circuit of the regulator may use a first ramp signal to control turning ON of the top switch and a second ramp signal to control turning OFF of the top switch. A non-linear control circuit may turn ON the top switch upon detection of a load current step-up change to maintain an output voltage of the regulator within its regulation band. The non-linear control circuit may turn OFF the top switch upon a load current step-down change to prevent output voltage overshoot.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
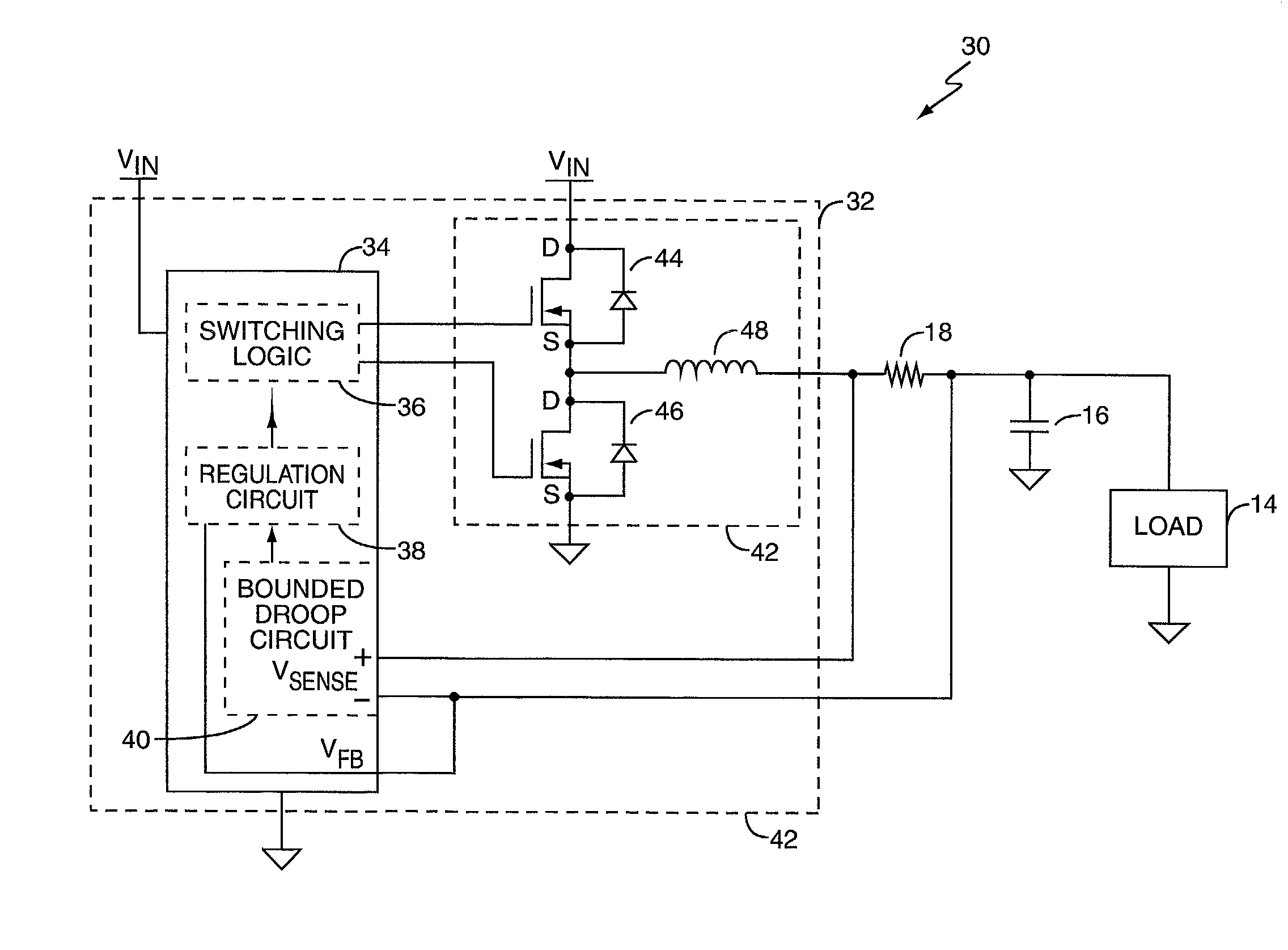
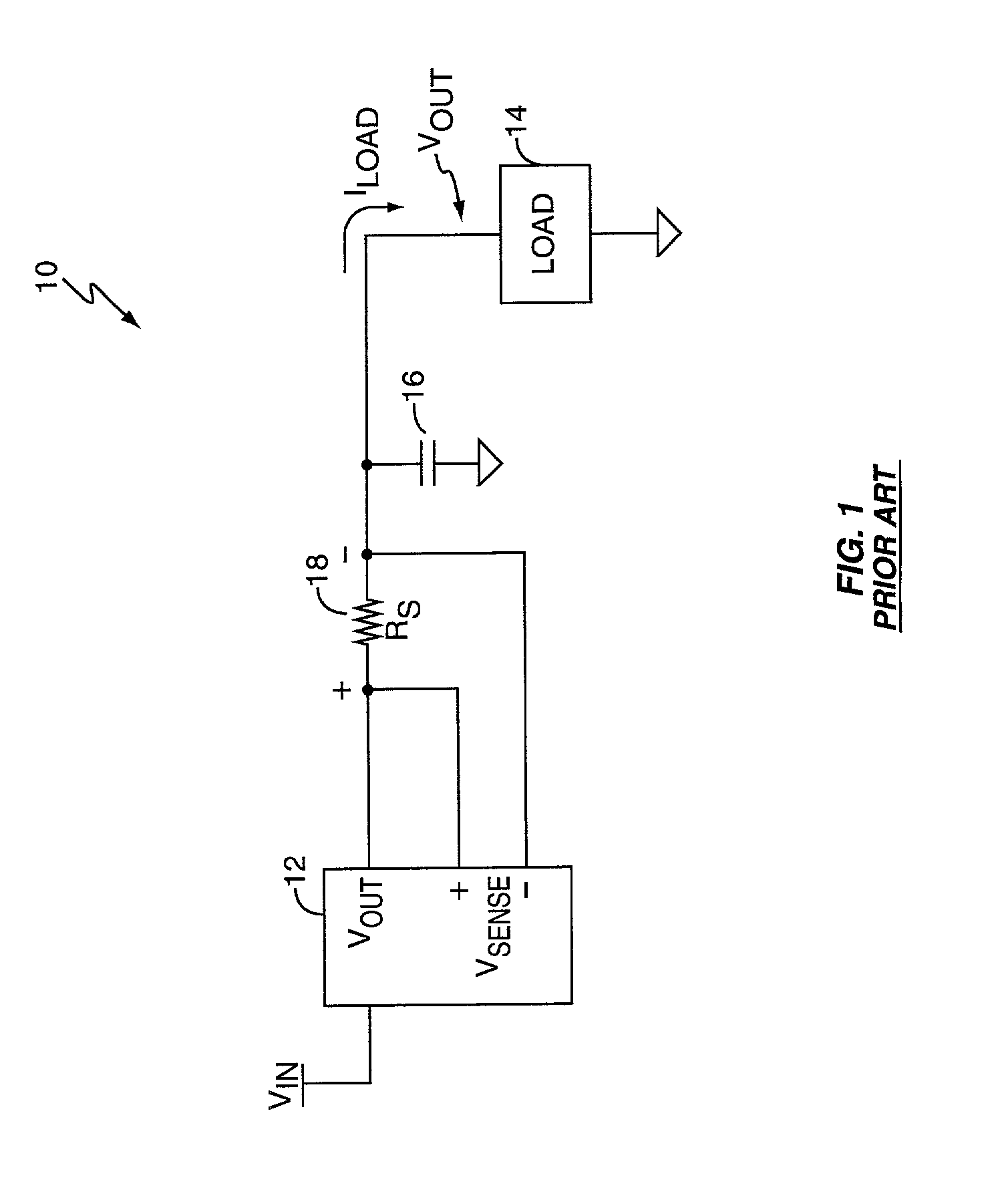
Bounded power supply voltage positioning
InactiveUS20020125871A1Facilitates active voltage positioningPrevent fallingDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage amplitudeLower limit
A voltage positioning technique allows a power supply controller to more fully exploit active voltage positioning as a way of maintaining supply voltage within the limits defined for an associated electrical load. The supply voltage is allowed to "droop" as a function of load current. Droop may be implemented in linear proportion to load current, or as a discrete droop function once load current exceeds a given threshold. In either case, the droop circuitry of the supply controller implements a bounding function that establishes an accurately known maximum droop voltage magnitude. This maximum droop voltage limit establishes a reliable lower limit for the supply voltage independent of increasing load current. This accurately set lower bound for the droop voltage enables the controller to more aggressively position the supply voltage at the lower voltage limit of the load, which minimizes voltage overshoot and load power consumption.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
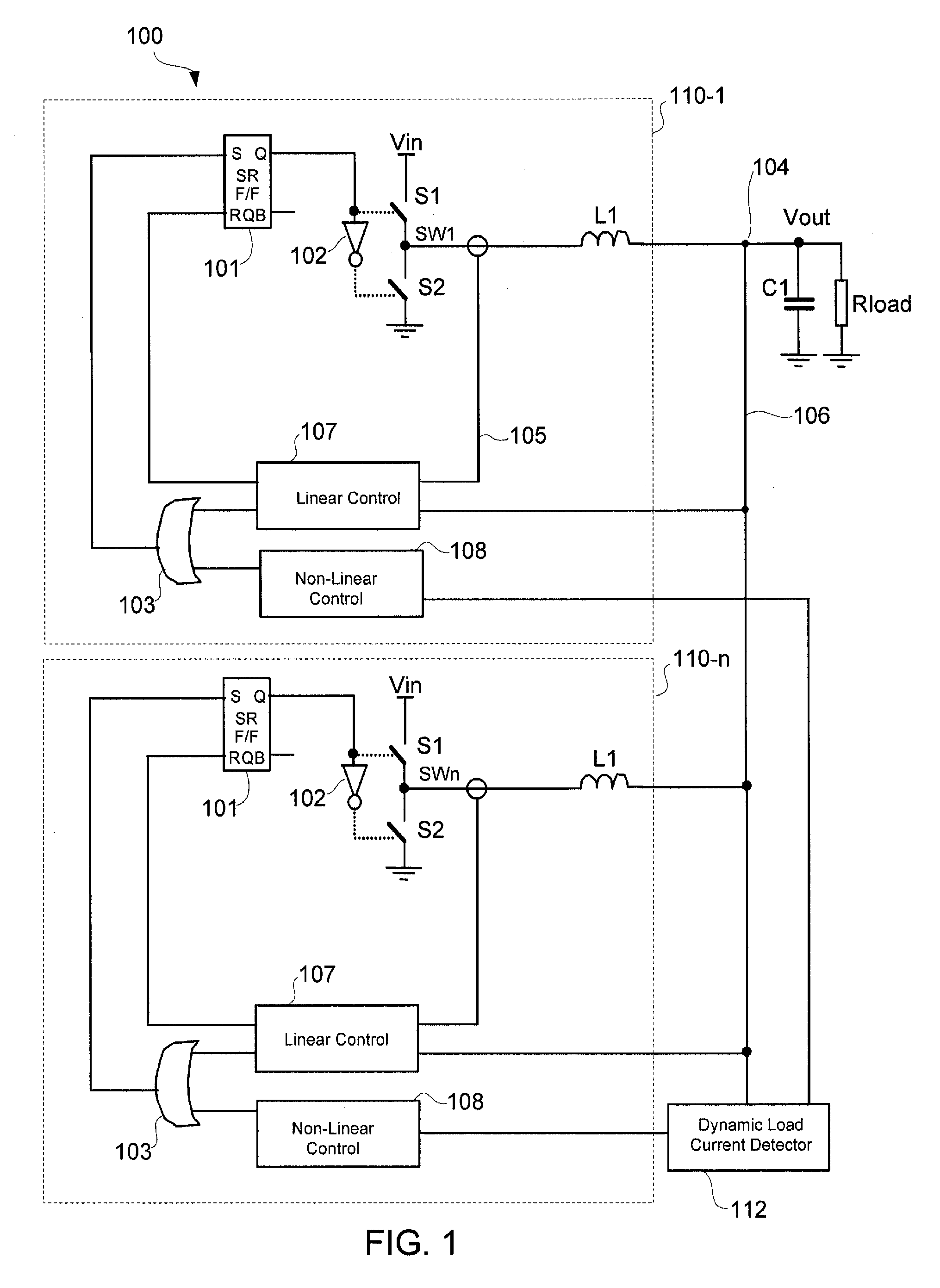
Non-linear control techniques for improving transient response to load current step change
ActiveUS7863875B1Limited to controlled bandwidthAvoid output voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage overshootLinear control
A voltage regulator may be configured to detect variation in load current and control transient response when the load current has a high slew rate or varies at high repetition rates. A linear control circuit may be employed to control charging of an output capacitor and a load of the regulator. Upon detection of high load current step-up change at high slew rates, a non-linear control circuit may be activated. The fast load current step change may be detected by comparing an output voltage of the regulator to a feedback input of an error amplifier of the linear control circuit. The output of the error amplifier may be clamped to prevent output voltage ring-back when using the non-linear control circuit or to control load release dip. Output voltage overshoot may be controlled by turning OFF a top switch that charges the output capacitor before the inductor current becomes zero.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Programmable voltage regulator with dynamic recovery circuits
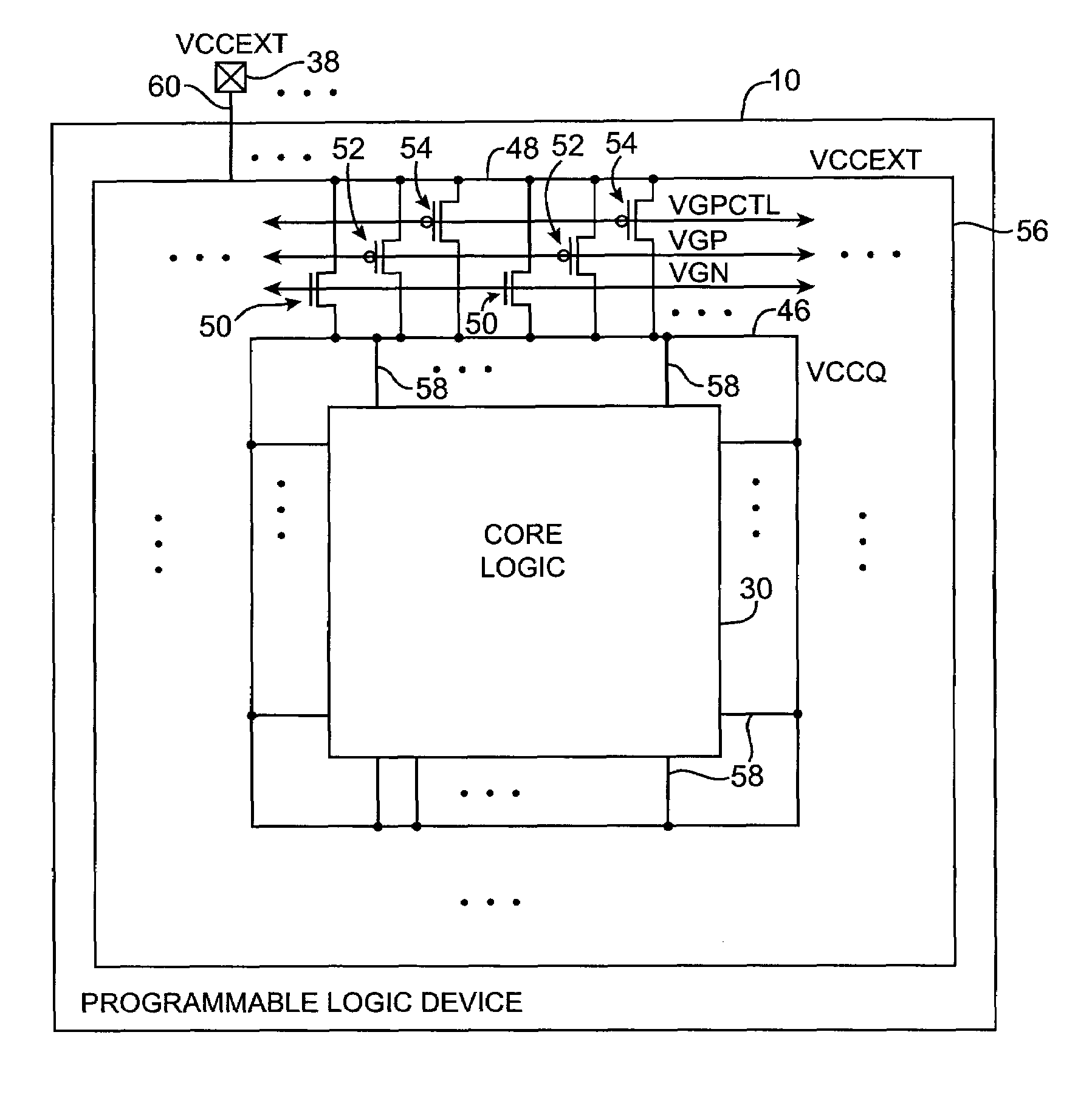
InactiveUS7589584B1Reduce potentially large external power supply voltage levelsReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingProgrammable logic deviceVoltage regulation
Voltage regulator circuitry is provided. The voltage regulator circuitry is suitable for powering core logic on a programmable logic device. The voltage regulator circuitry receives an external power supply voltage and reduces the external power supply voltage to a core power supply voltage if needed. If the external power supply voltage is at the same level needed to power the core logic, the voltage regulator circuitry passes the power supply voltage to the core logic. The voltage regulator circuitry monitors the core power supply voltage using a feedback path. Overshoot and undershoot fluctuations are minimized. The external power supply voltage may be supplied to a first bus. The core power supply voltage may be distributed on a second bus. A ring of transistors may be used to convey power from the first bus to the second bus. Control circuitry may control the ring of transistors based on programmable setpoint voltages.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
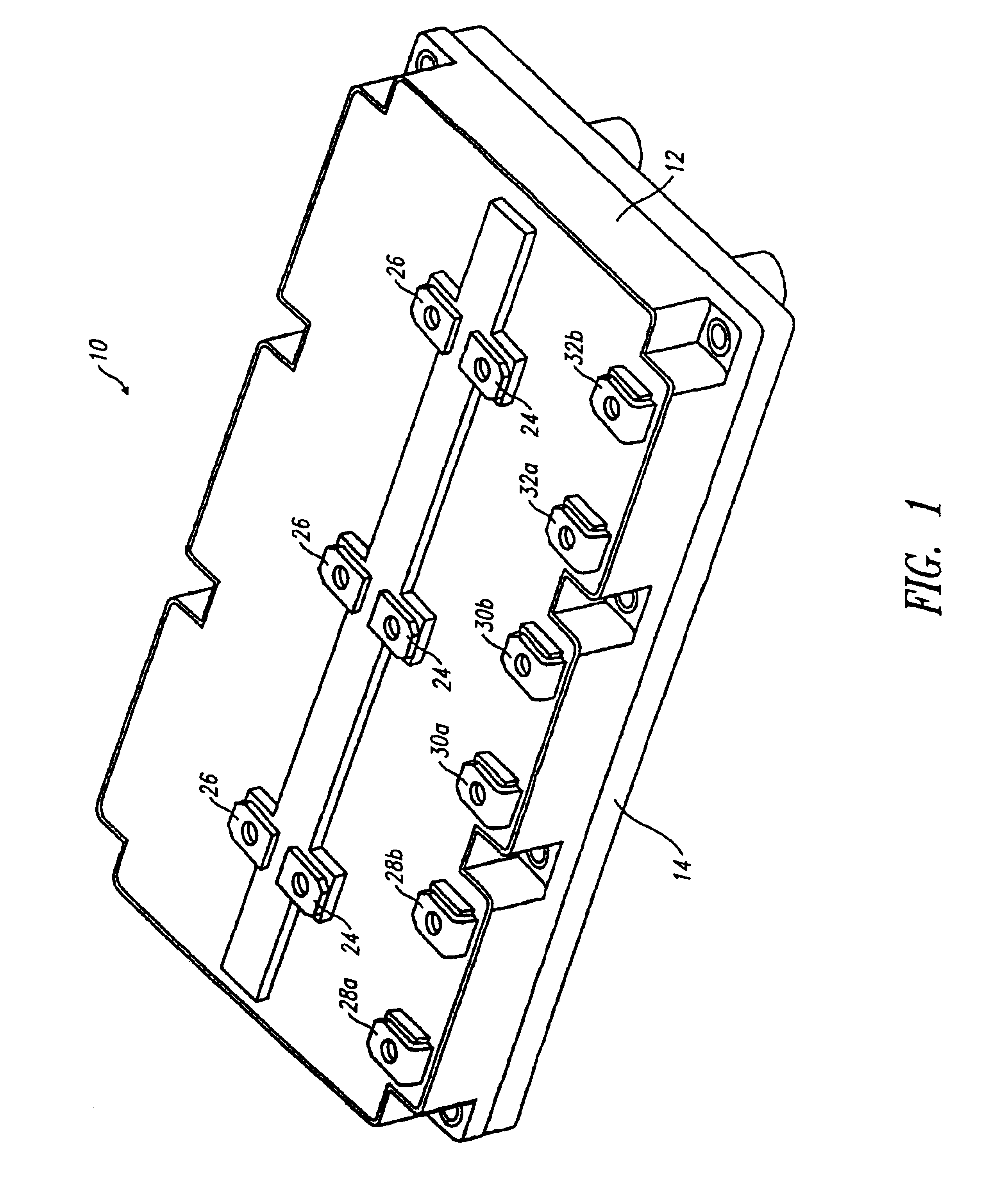
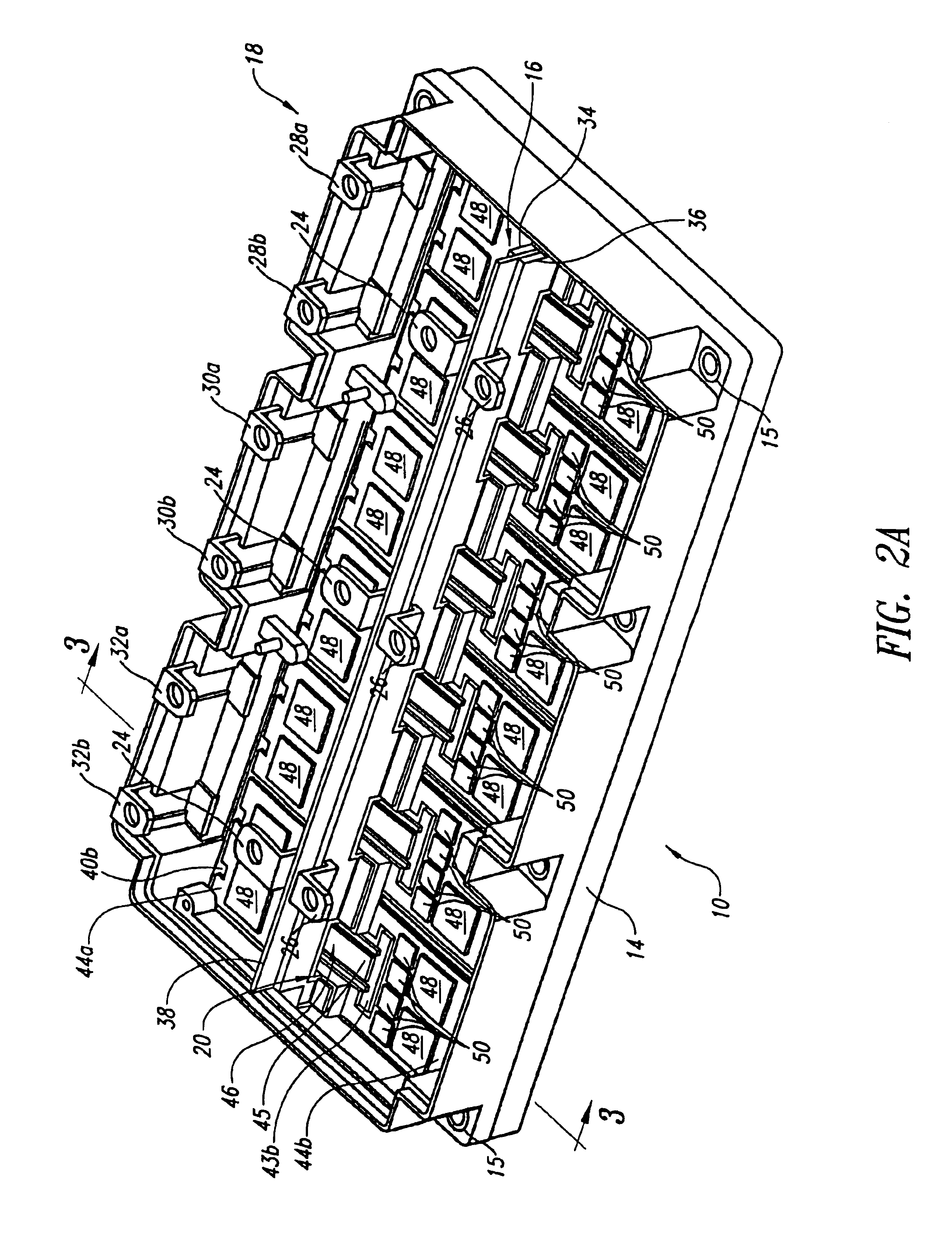
Power module with voltage overshoot limiting
InactiveUS6906404B2Handle large loadLow rateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementConversion constructional detailsElectricityVoltage overshoot
A power module employs at least one capacitor electrically coupled across the input terminals to reduce voltage overshoot. The capacitor may be surface mounted to a high side collector plating area and a low side emitter plating area. The power module may employ a lead frame and terminals accessible from an exterior of a module housing, for making electrical couplings to externally located power sources and / or loads.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
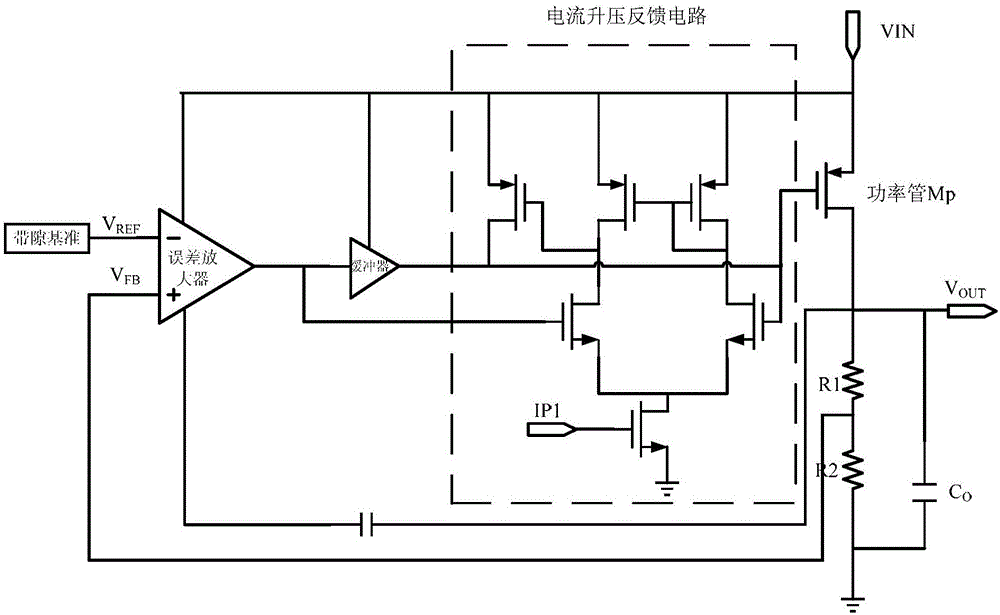
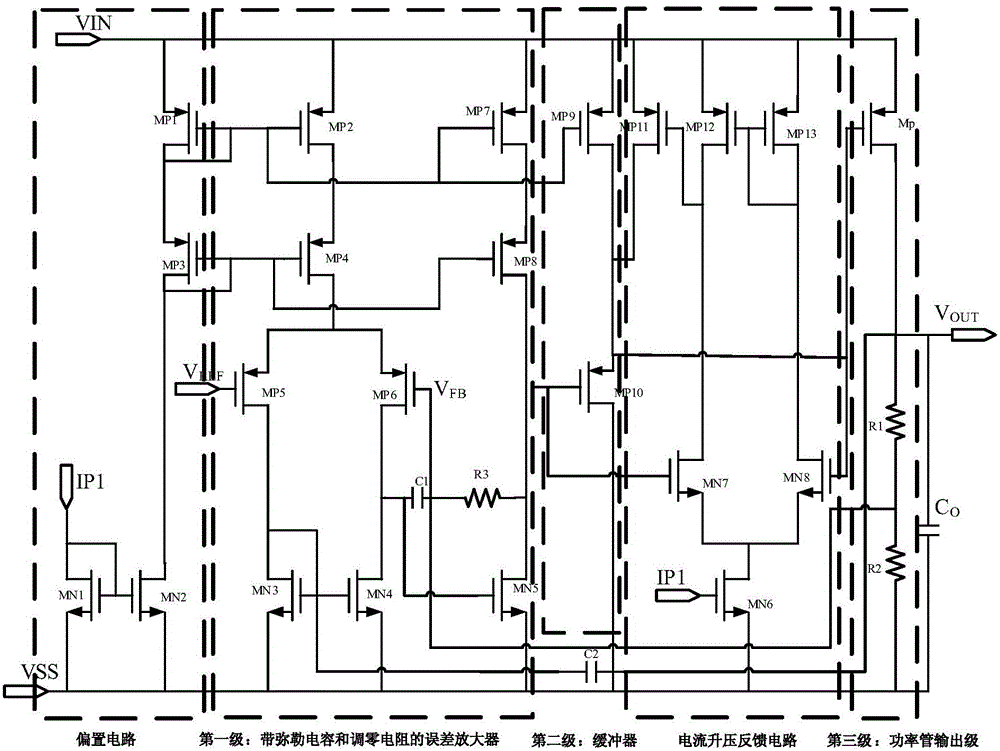
Transient enhancement circuit applied to full-integration LDO
InactiveCN105116955ASimple structureImprove transient response performanceElectric variable regulationVoltage overshootCharge current
The invention discloses a transient enhancement circuit applied to a full-integration LDO. The transient induction situation of the LDO is obtained by detecting the transient voltage of an LDO error amplifier output node. When load current changes suddenly from low current to high current or from high current to low current, output voltage is descended or ascended, at the moment, feedback voltage of a loop changes as well, and thus the output transient voltage of an error amplifier changes. When the output node voltage of the error amplifier is far lower than the grid voltage of an adjusting pipe, a buffer stage inserted between the error amplifier and a transistor provides large drop-down current for the grid of the adjusting pipe. When the output node voltage of the error amplifier is far higher than the grid voltage of the adjusting pipe, the current boosts, a feedback circuit is started, and sufficient charging current is provided for the grid of the adjusting pipe, so that the breakover current is controlled to meet the load requirement, and the effect of lowering the output voltage overshooting is achieved. The simulation result indicates that the transient enhancement circuit can remarkably improve the load transient response ability of the LDO.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
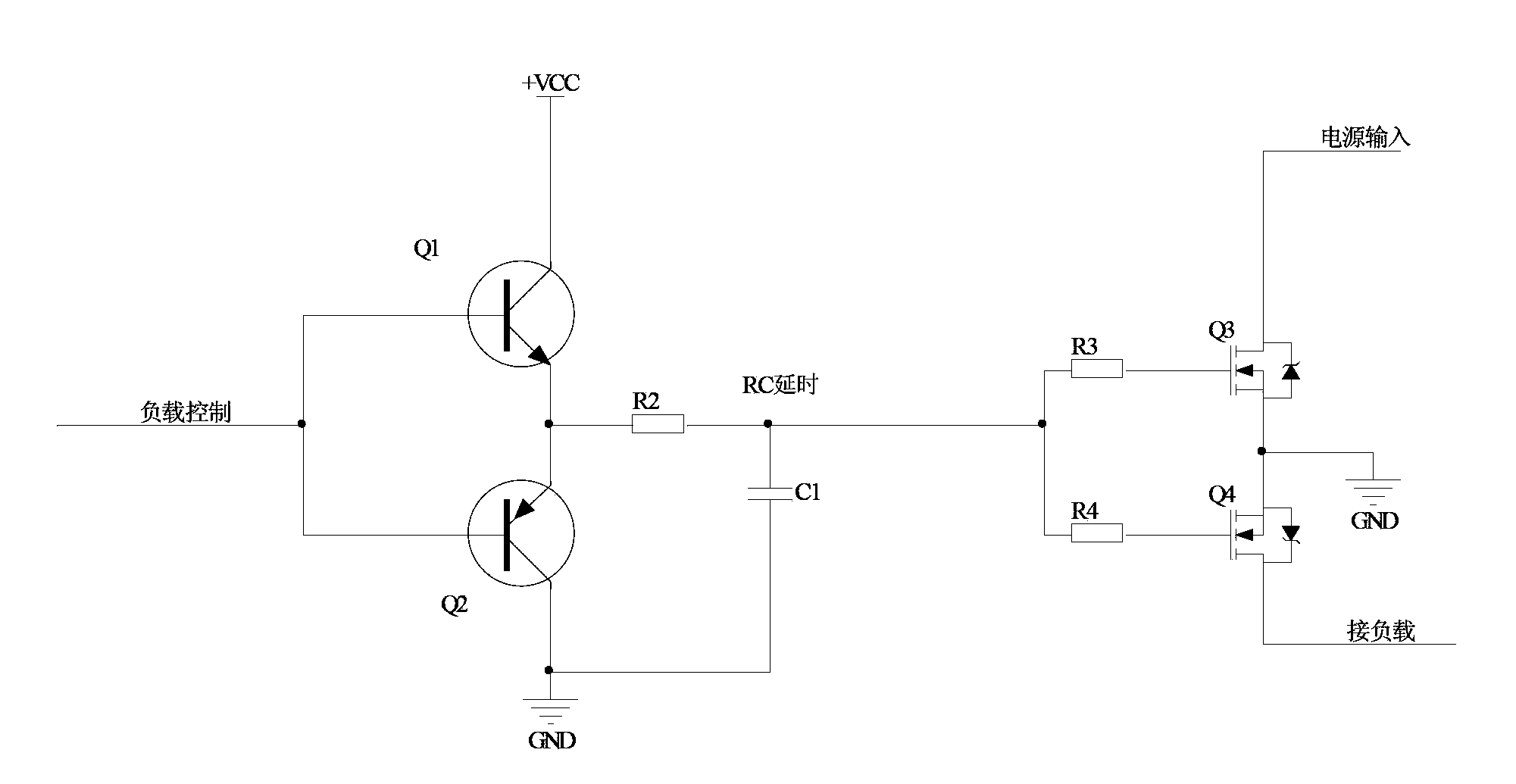
Synchronous rectification reverse-flow preventing circuit and method for parallel synchronous rectification converter
ActiveCN1571255AHigh parallel efficiencyLow costDc source parallel operationApparatus with intermediate ac conversionVoltage overshootTransfer switch
The invention discloses a synchronous rectification anti-backflow circuit and method of parallel synchronous rectifier converter, including auxiliary power supply, voltage detection and comparison circuit, PWM drive circuit and transfer switch, where the voltage output end of the auxiliary power supply is connected to the input end of the voltage detection and comparison circuit, the output end of the voltage detection and comparison circuit is connected to the control end of the transfer switch, PWM drive signal in the PWM drive circuit is coupled to the input end of the transfer switch, and the output end of the transfer switch is coupled to the control end of the synchronous rectifier tubes. It makes the synchronous rectifier converter have no problems of prestarting, output voltage overshoot and depression, etc., as parallel working and the parallel efficiency of the converter is high. The invention has simple and reliable circuit, low cost, and good effect after tested.
Owner:EMERSON NETWORK POWER CO LTD
Multi-phase switching regulator and driver circuit and control method thereof
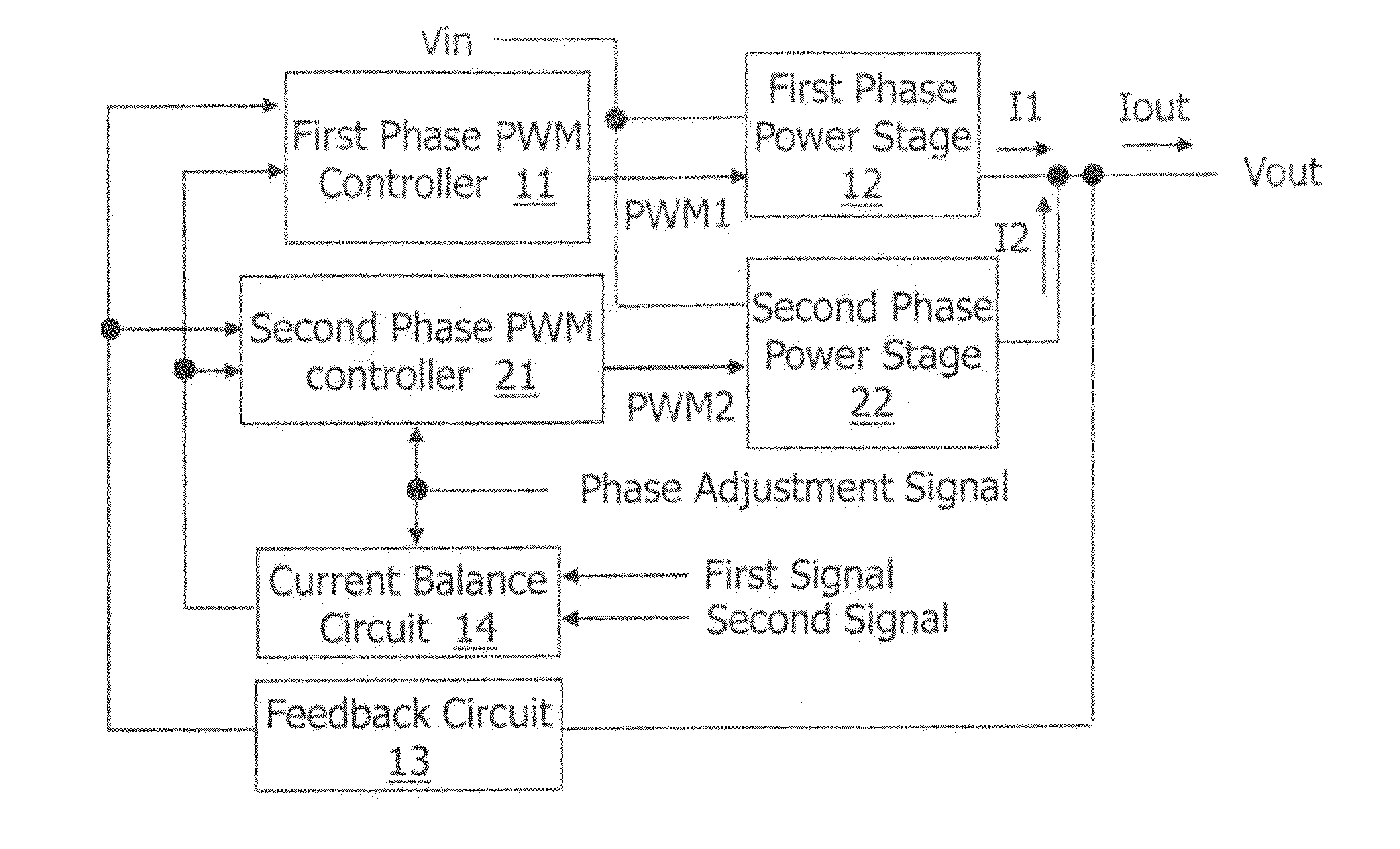
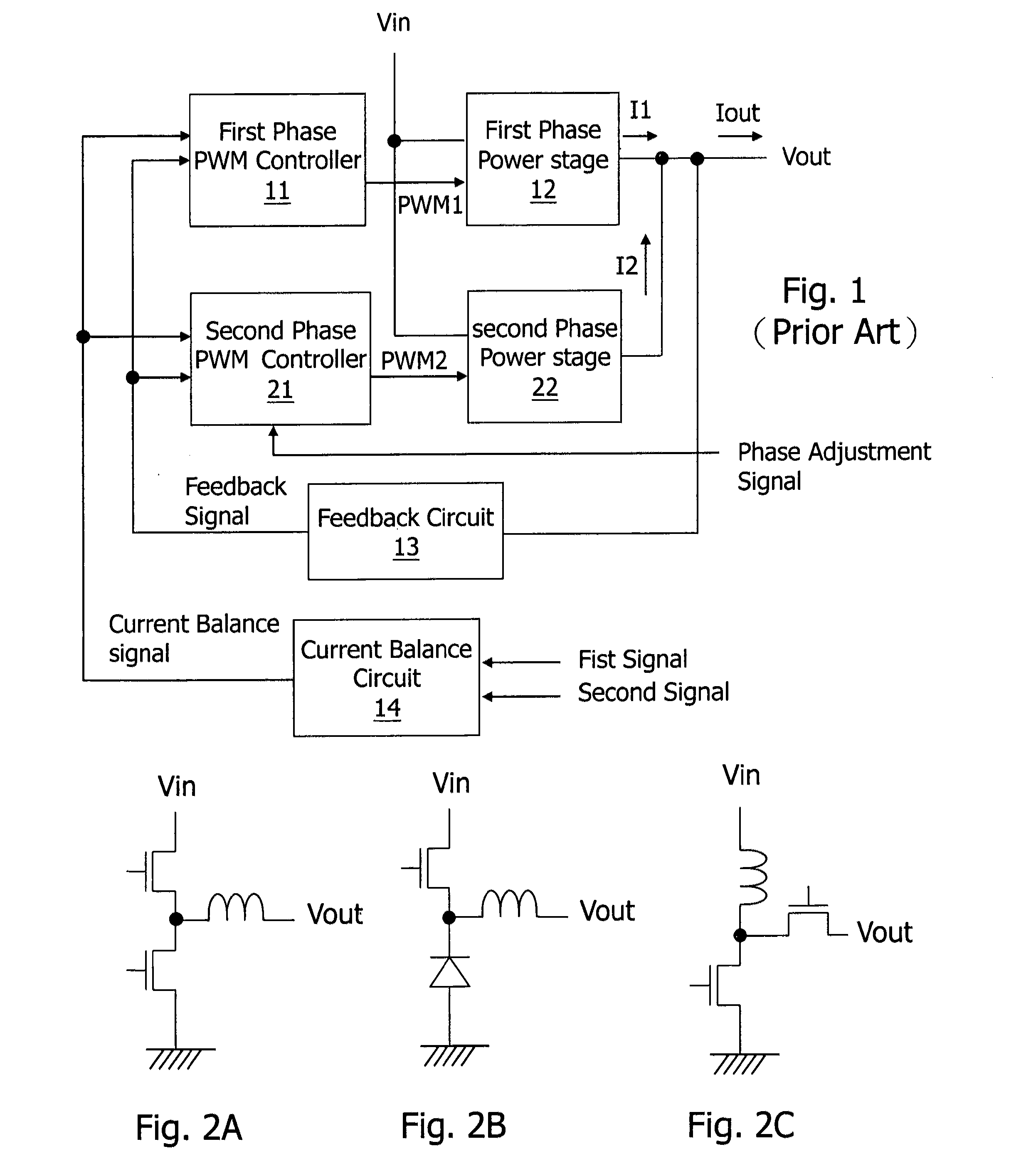
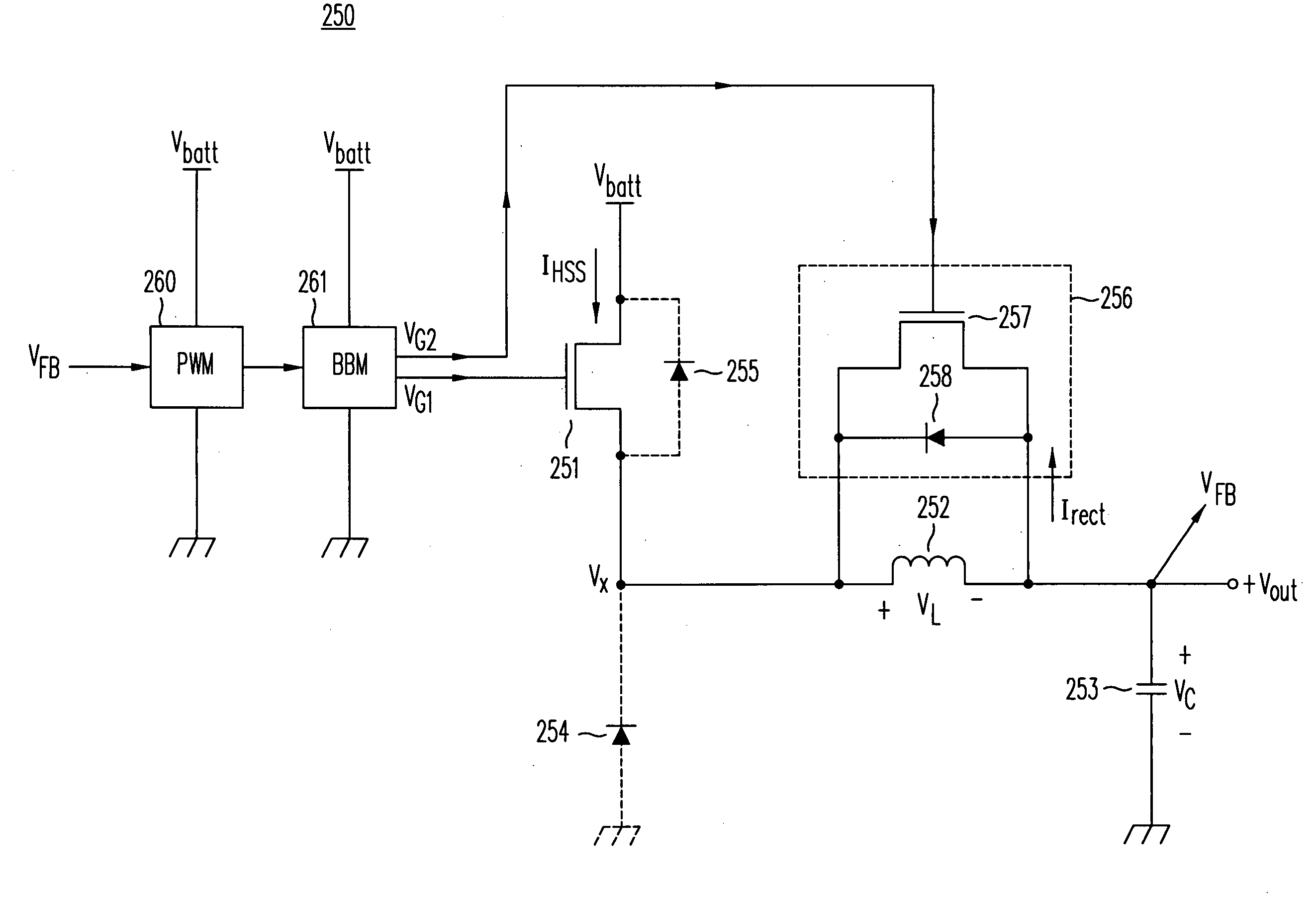
The present invention discloses a multi-phase switching regulator, a driver circuit of a multi-phase switching regulator, and a control method of a multi-phase switching regulator. The multi-phase switching regulator includes: at least two power stages, switching power transistors in the power stages to convert an input voltage to an output voltage according to pulse width modulation (PWM) signals generated by corresponding PWM controllers respectively; and a current balance circuit, generating a current balance signal according to the current of the corresponding power stage and a phase adjustment signal to averagely distribute current over the active power stages. In the present invention, the gain of the current balance circuit is adjustable, to avoid or reduce output voltage overshoot and undershoot when the phase number changes, while the current balance function is still achieved in normal operation.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Step-down switching regulator with freewheeling diode
ActiveUS20080291711A1High and voltage overshootEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMOSFETVoltage overshoot
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Successive approximation type analog/digital converter
ActiveCN102801422AReduce application complexitySolve the problem of voltage overshootAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceVoltage overshoot
The invention discloses a successive approximation type analog / digital converter, wherein a capacitor array digital / analog conversion circuit comprises a capacitor array, an auxiliary capacitor is connected between the capacitor array and the output end of a comparer, and the oscillation amplitude between the capacitor array and the output end of the comparer ranges from 0V to power voltage when the capacitance value of the auxiliary capacitor is selected in a range enabling the oscillation amplitude of the input voltage to be from 0V to the power voltage. A measure of carrying out limiting and compression on a quantification range or increasing complicated circuits, which is adopted for preventing voltage overshoot in the traditional scheme, is avoided. According to the circuit structure provided by the invention, the requirements on input offset of the comparer in the ADC (analog / digital converter) and performance of other internal circuits are reduced, so that higher resolution ratio can be achieved under the condition of not increasing power consumption of the ADC using the circuit structure.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD
Control of power semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20100060326A1Easy to controlBring this voltage down rapidlyElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorMOSFETPower semiconductor device
This invention relates to a control method and a circuit for MOS-gated power semiconductor switching devices such as IGBTs or MOSFETs, which allows control and optimisition of the current and voltage commutation of a power semiconductor switching device and freewheel diode pair in the basic half-bridge circuit found in a wide range of equipment. The method comprises the stages of: applying, upon receipt of a switch-on command signal, a voltage function to the control terminal or the gate of the power semiconductor switching device that allows a regulated current rise in the device whilst maintaining the voltage across the device falling at a predetermined rate; and at the instant when the voltage across the diode begins to change from the on-state towards the off-state level, applying a voltage function to the control terminal or the gate of the power semiconductor switching device to enable the voltage falling across the power semiconductor switching device to track the voltage falling across the diode in order to ensure a fast and controlled completion of the switching operation without diode reverse voltage overshoot. The gate drive automatically modifies the voltage function according to the working condition thereby accounting for the actual operating conditions.
Owner:MASCHFAB REINHAUSEN GEBR SCHEUBECK GMBH & CO KG
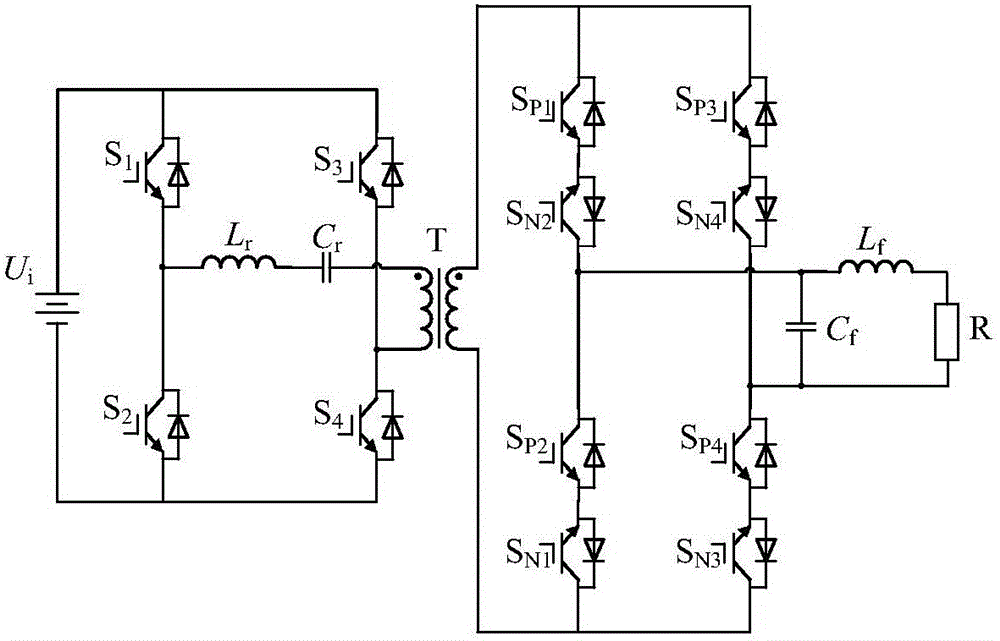
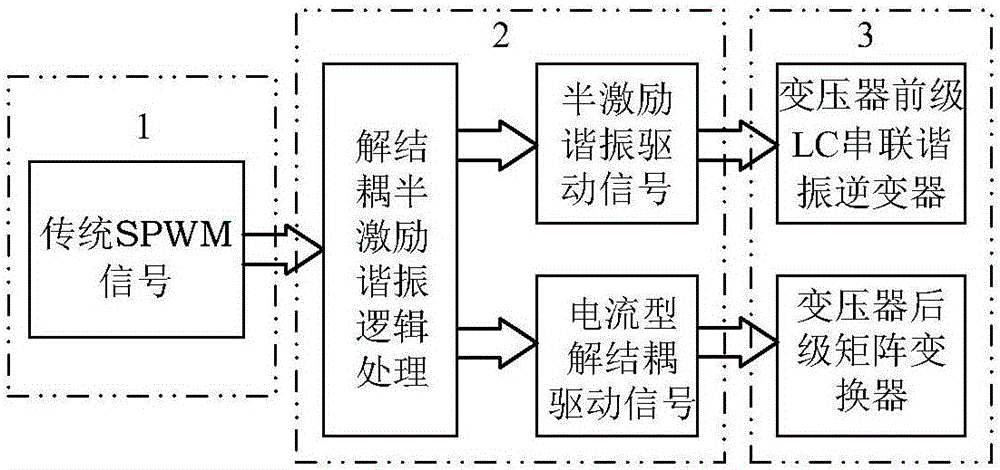
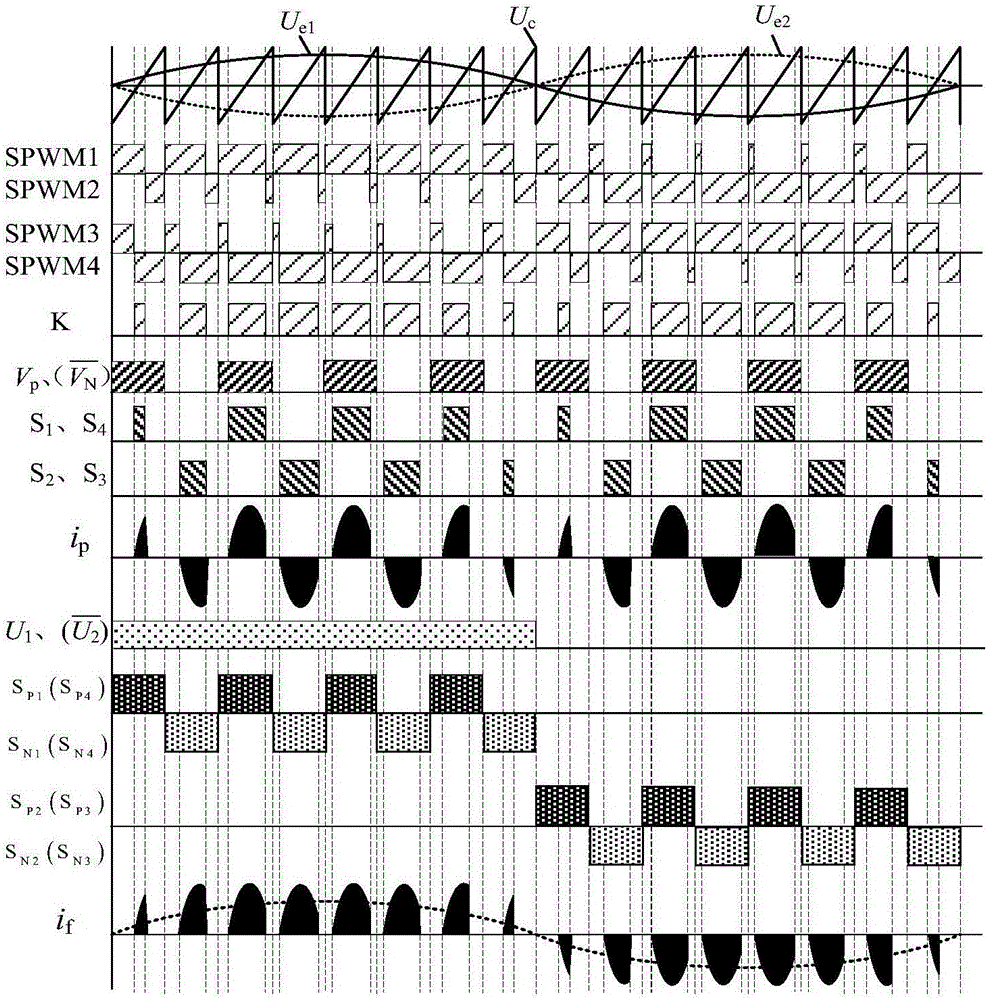
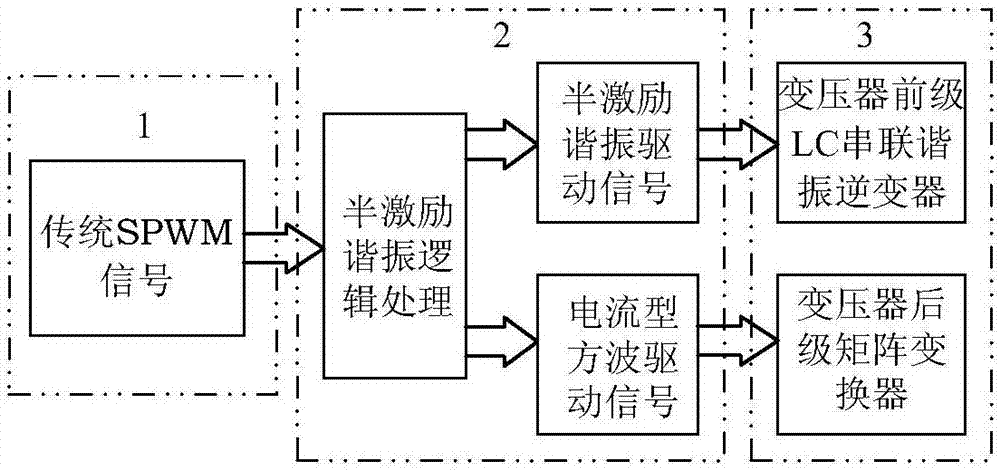
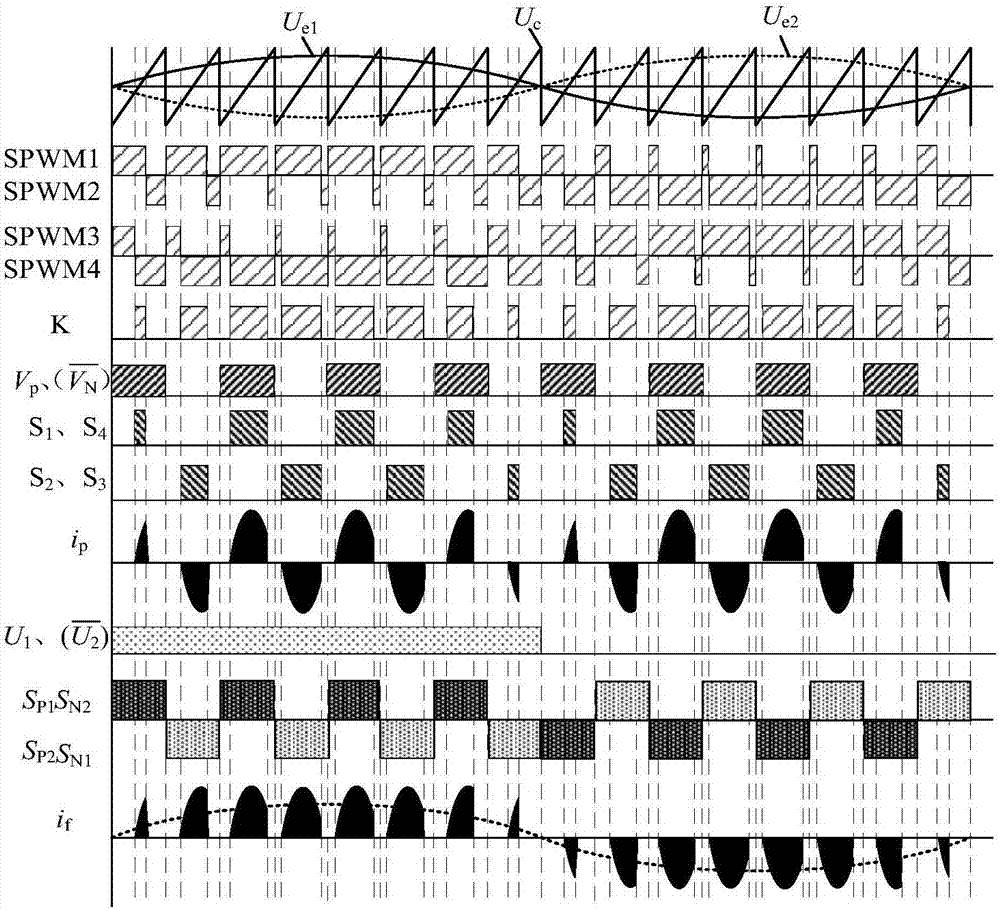
LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix-type inverter topology and resonance modulation method thereof
InactiveCN105915095AImprove reliabilityImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversionAc-ac conversionMatrix convertersVoltage overshoot
The present invention provides a LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix-type inverter topology and a resonance modulation method thereof. The topology comprises of a full bridge LC series resonance inverter, a high-frequency transformer T, a matrix converter and a CL-type filter which are connected in order. The modulation method is configured to process the SPWM wave through separation and link semi-excitation modulation logics to obtain driving signals of a transformer pre-stage LC series resonance inverter and a transformer post-stage matrix converter so as to allow the work duty ratio of the transformer pre-stage resonance circuit excitation resonance work state in the resonance half period to be controllable and realize the control of energy side transmission to the output load. The transformer post-stage matrix converter is modulated and decoupled to two common current-type inverters for controlling, a switch tube performs switching during the zero current outputting to realize zero current switching to avoid causing voltage overshoot problems and realize energy bidirectional flow and four-quadrant operation. The power transformation grades are few, the control method is simple, the circuit stability is high, and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
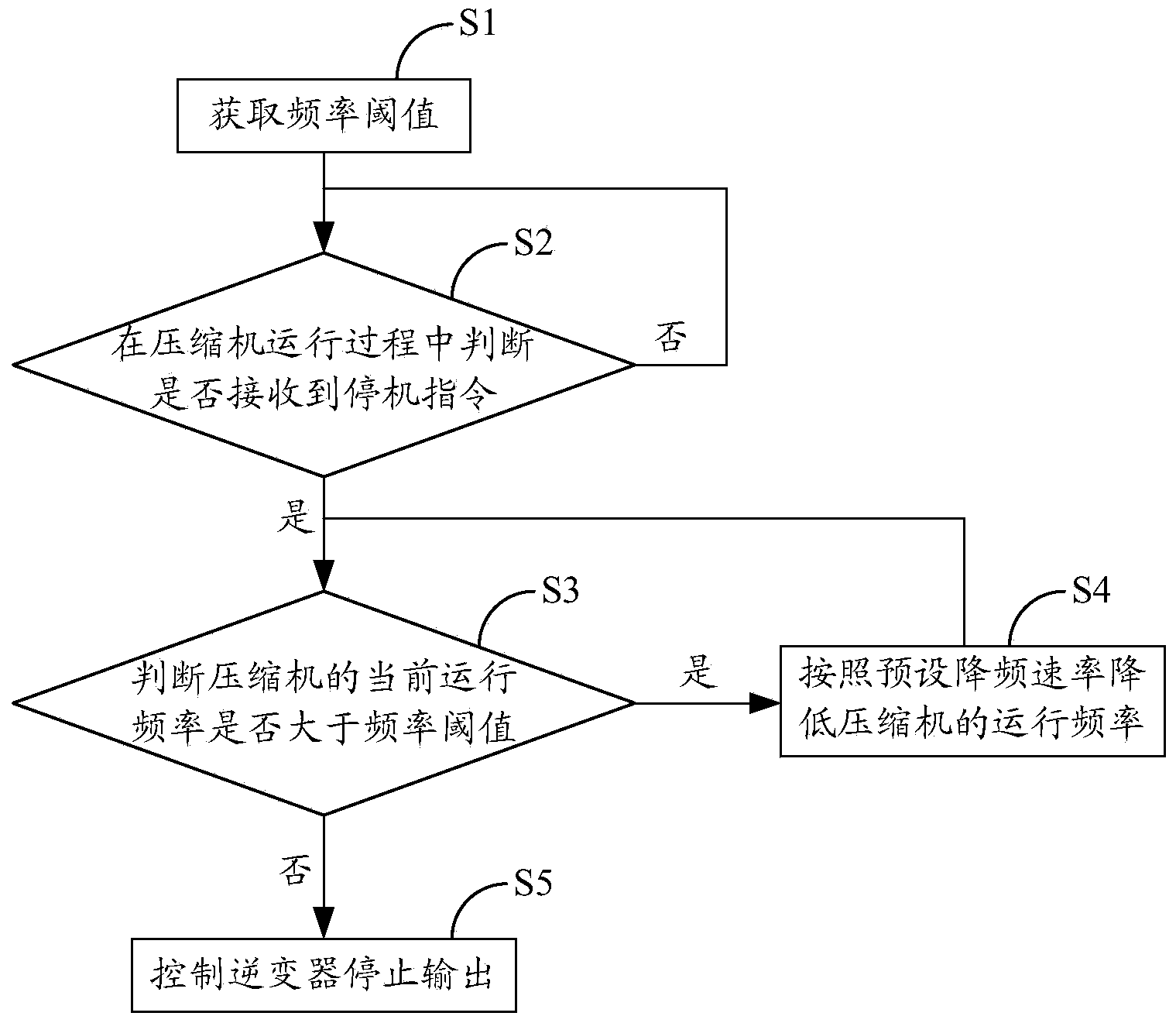
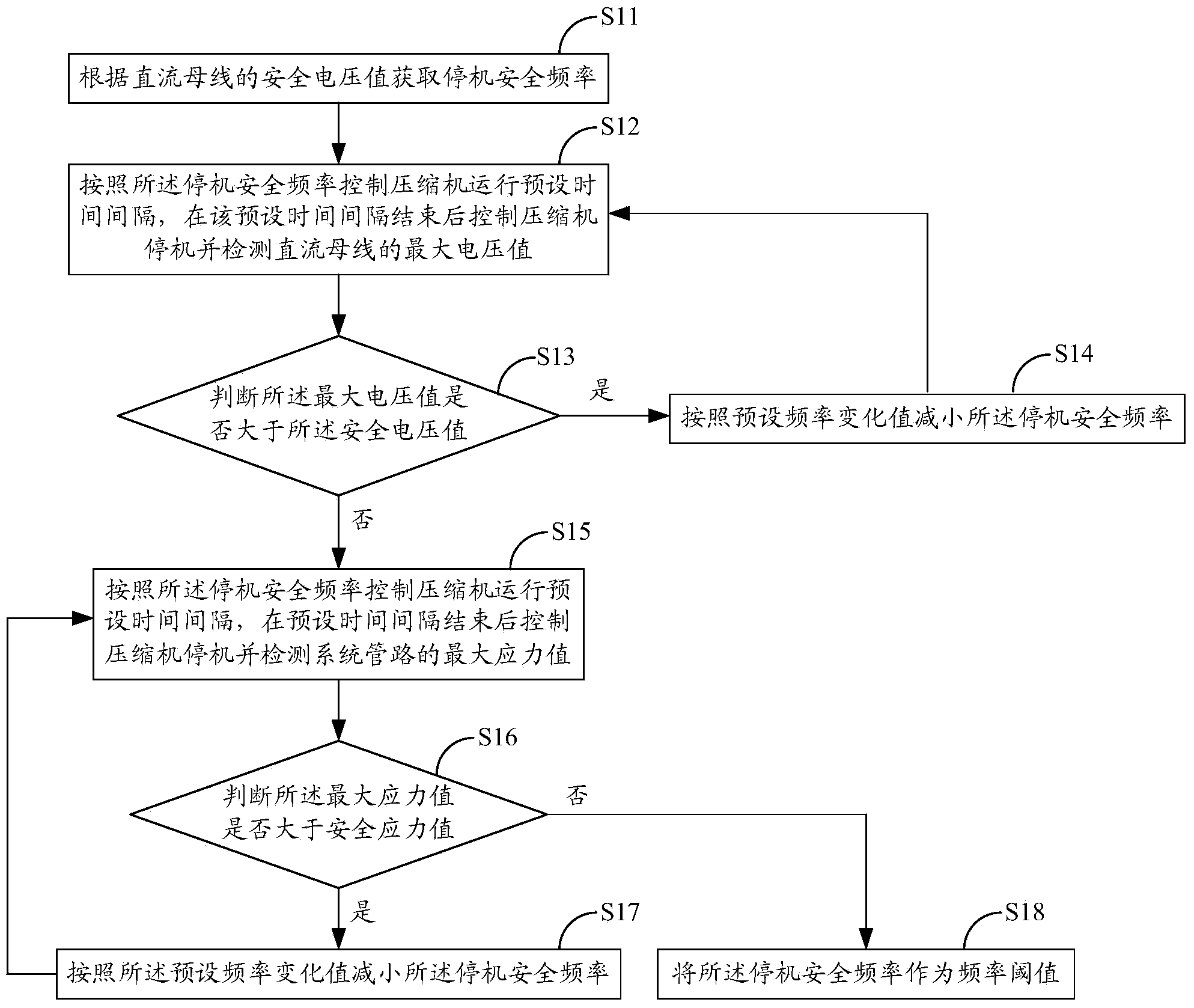
Frequency-conversion air conditioner operation control method and device
ActiveCN104110775AImprove reliabilityExtend your lifeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusVoltage overshootFrequency conversion
The invention belongs to the technical field of air conditioner controlling and provides a frequency-conversion air conditioner operation control method and device. The frequency-conversion air conditioner operation control method includes: acquiring a frequency threshold; judging whether a shutdown instruction is received or not during operation of a compressor, and judging whether current operation frequency of the compressor is larger than the frequency threshold or not when the shutdown instruction is received; if yes, reducing operation frequency of the compressor according to preset frequency reduction rate and continuously judging whether the current operation frequency of the compressor is larger than the frequency threshold or not, if not, controlling an inverter to stop outputting. Therefore, the operation frequency of the compressor can be sustained in the preset frequency threshold during shutdown, problems about voltage overshoot of a direct-current bus and overlarge stress impact upon a system pipeline when the compressor is shut down during high-frequency operation are solved, reliability of the high-frequency-conversion air conditioner can be beneficially improved, and service lives of internal electronic devices and cooling / heating system components of the frequency-conversion air conditioner can be favorably prolonged.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD
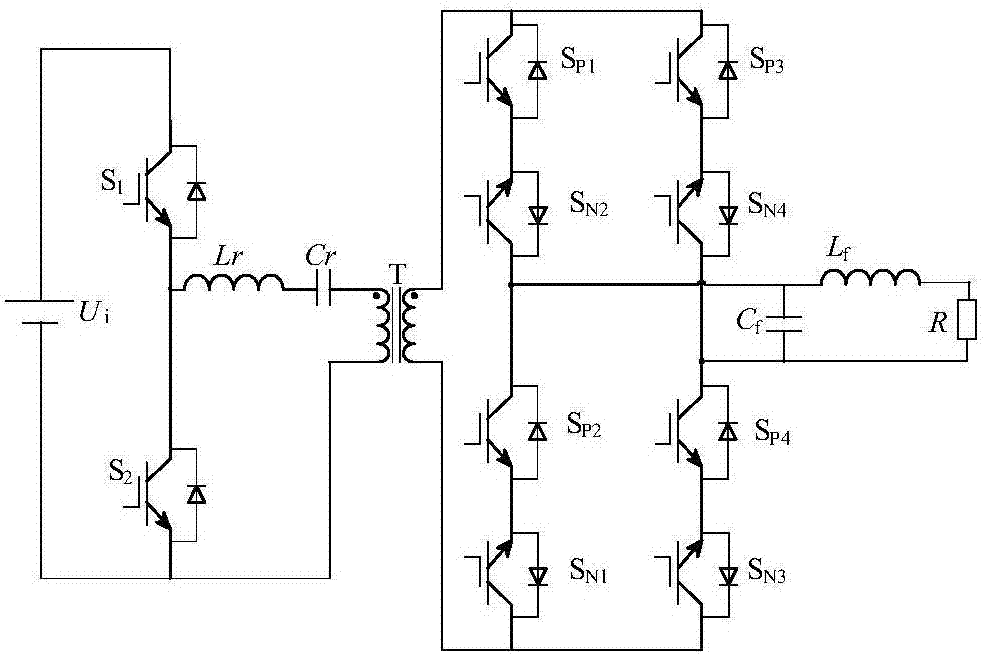
Method for controlling double-direction power flow high-frequency isolated active clamping rectifier
ActiveCN103595274ASolve Oscillation ProblemsRealize zero voltage breakingAc-dc conversionVoltage overshootClosed loop
The invention discloses a method for controlling a double-direction power flow high-frequency isolated active clamping rectifier. Through modulation conducted on a transformer primary side frequency converter and an active clamping circuit and modulation conducted on an auxiliary side H bridge circuit, the originally existing problem of voltage overshooting and oscillation of the rectifier of the type is solved, no-voltage switch-on and switch-off of all switches can be achieved, the operation efficiency is further improved, and electromagnetic interference is reduced. According to the method for controlling the double-direction power flow high-frequency isolated active clamping rectifier, closed-loop control is conducted on an output voltage, and a stable direct-current voltage is output by the rectifier on the resistor load condition or the rectifier load condition or the input alternating voltage fluctuation condition.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
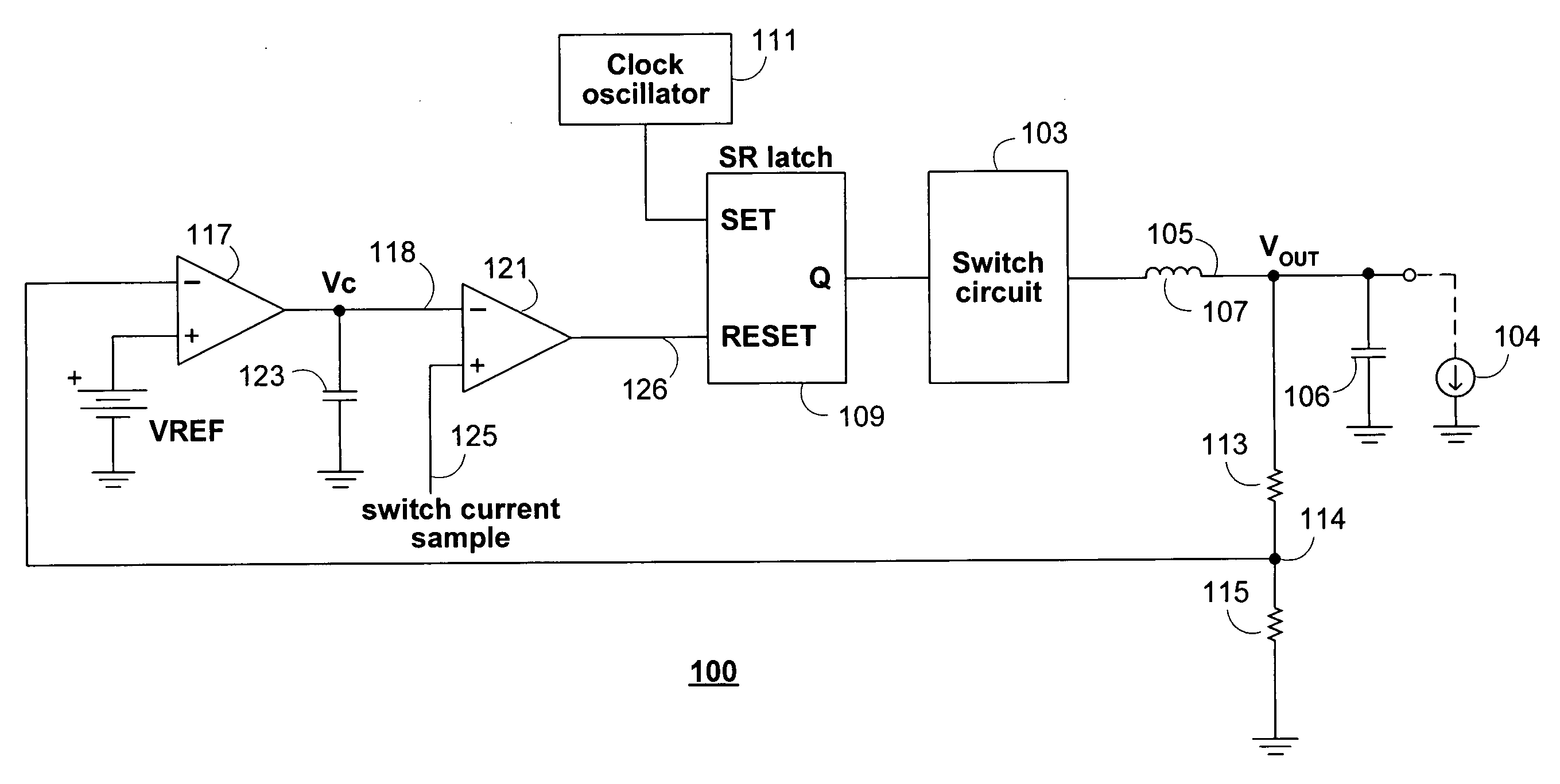
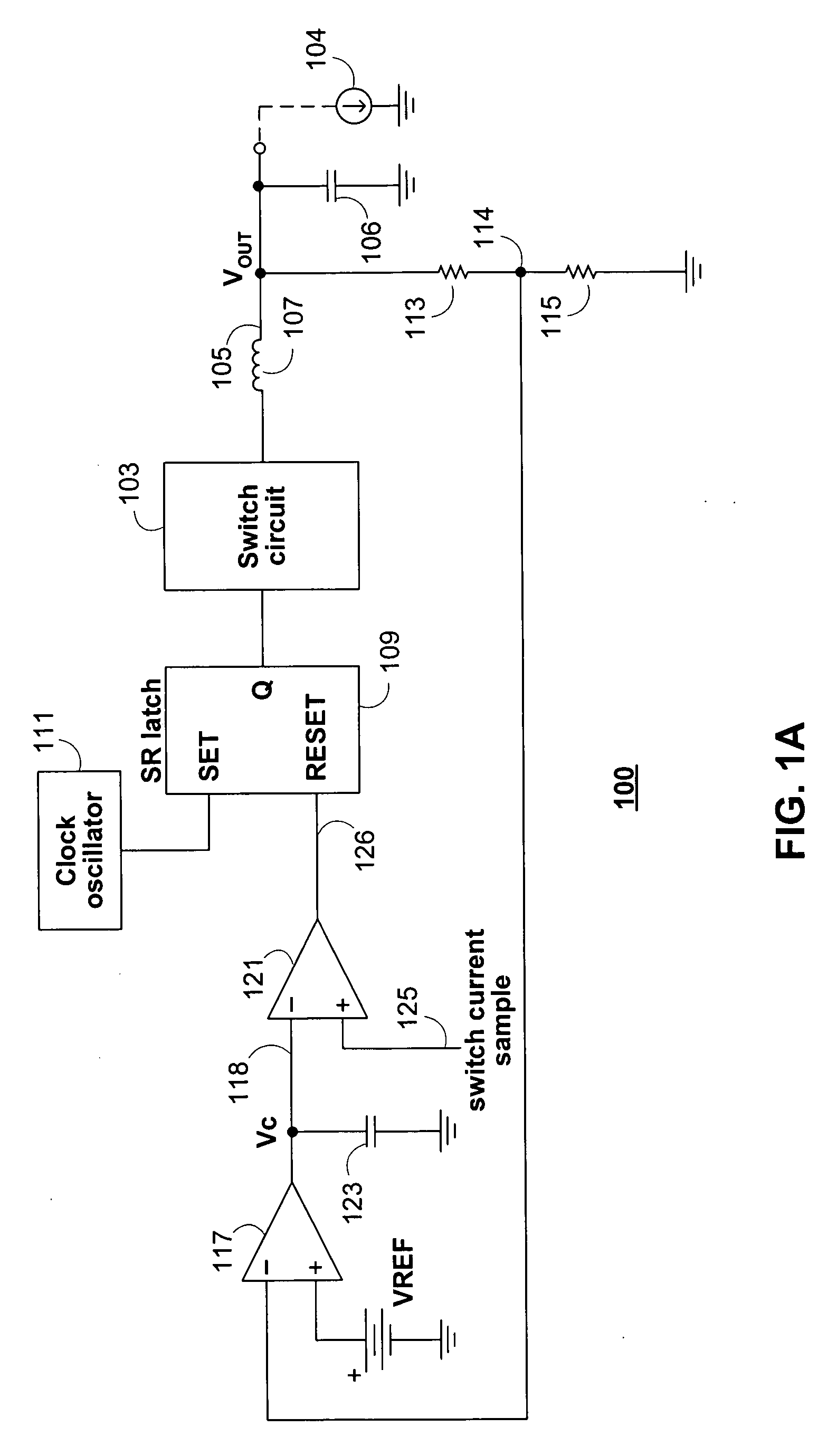
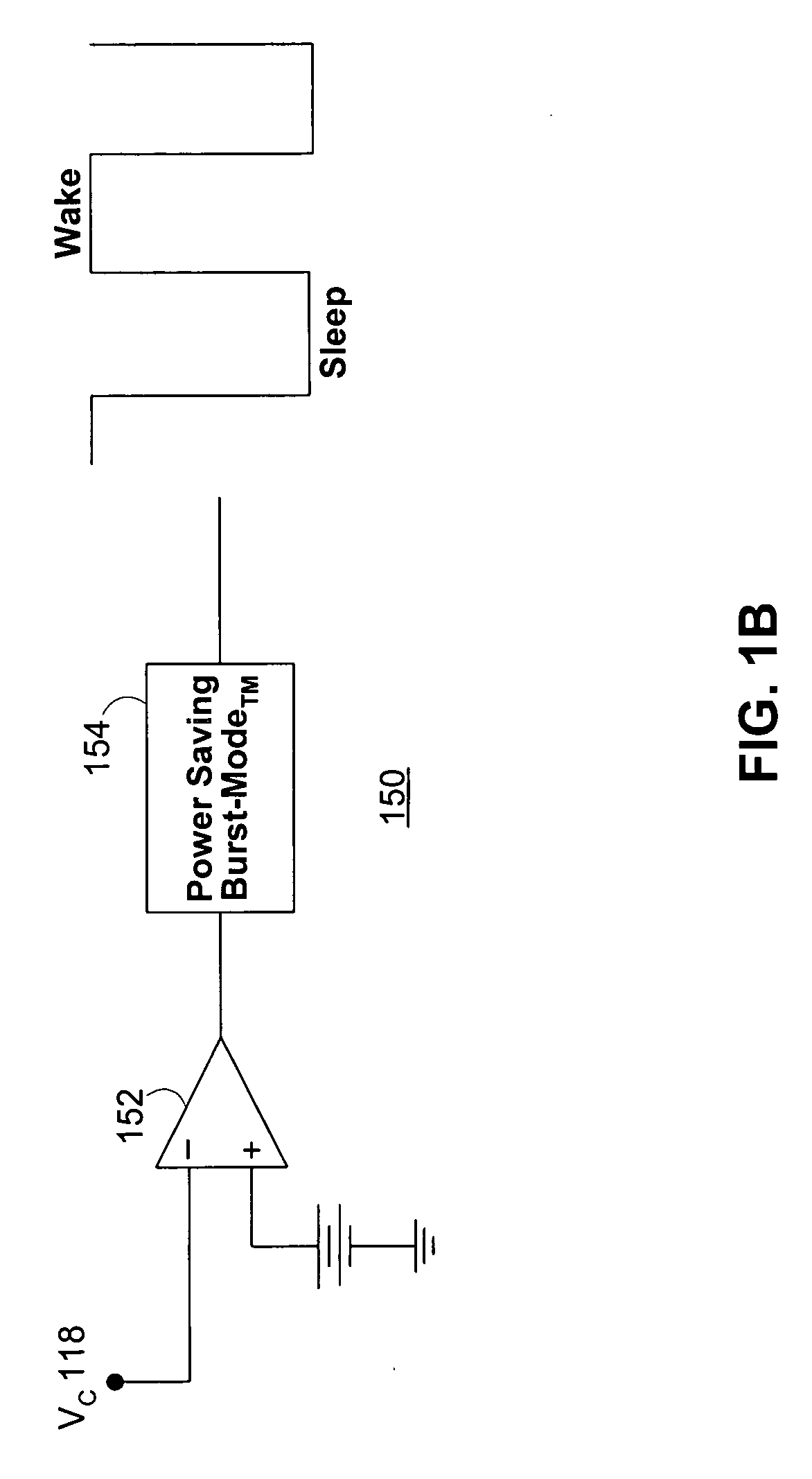
Methods and circuits for output over-voltage reduction in switching regulators
ActiveUS20070152647A1Reducing regulator output voltage overshootReduce voltageEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage overshootSleep state
Switching regulator Burst Mode control circuitry is provided for limiting voltage overshoot at the output of a switching regulator operating in power saving Burst Mode. The Burst Mode control circuitry may include regulator load current sensing circuitry which may be operative to put and maintain the regulator in the SLEEP state when the load current amplitude is below a threshold. The control circuitry may also include gated over-voltage comparator circuitry operative to reduce regulator output overshoot and to eliminate erroneous deactivation of the regulator switch circuitry when the regulator is not operating in Burst Mode. The gated over-voltage circuitry may include a one-shot timer circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
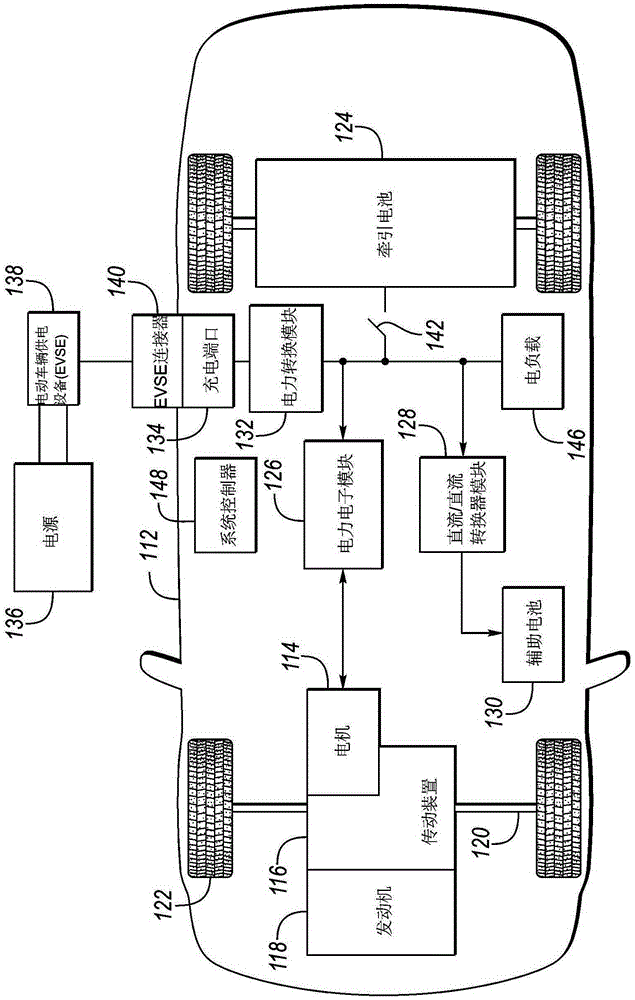
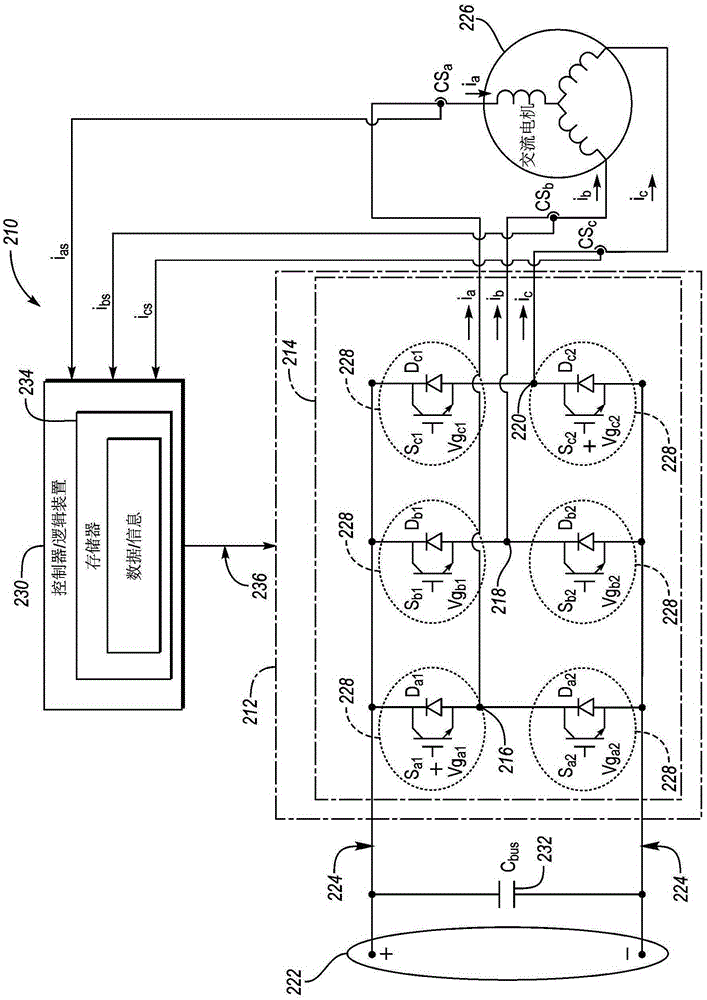
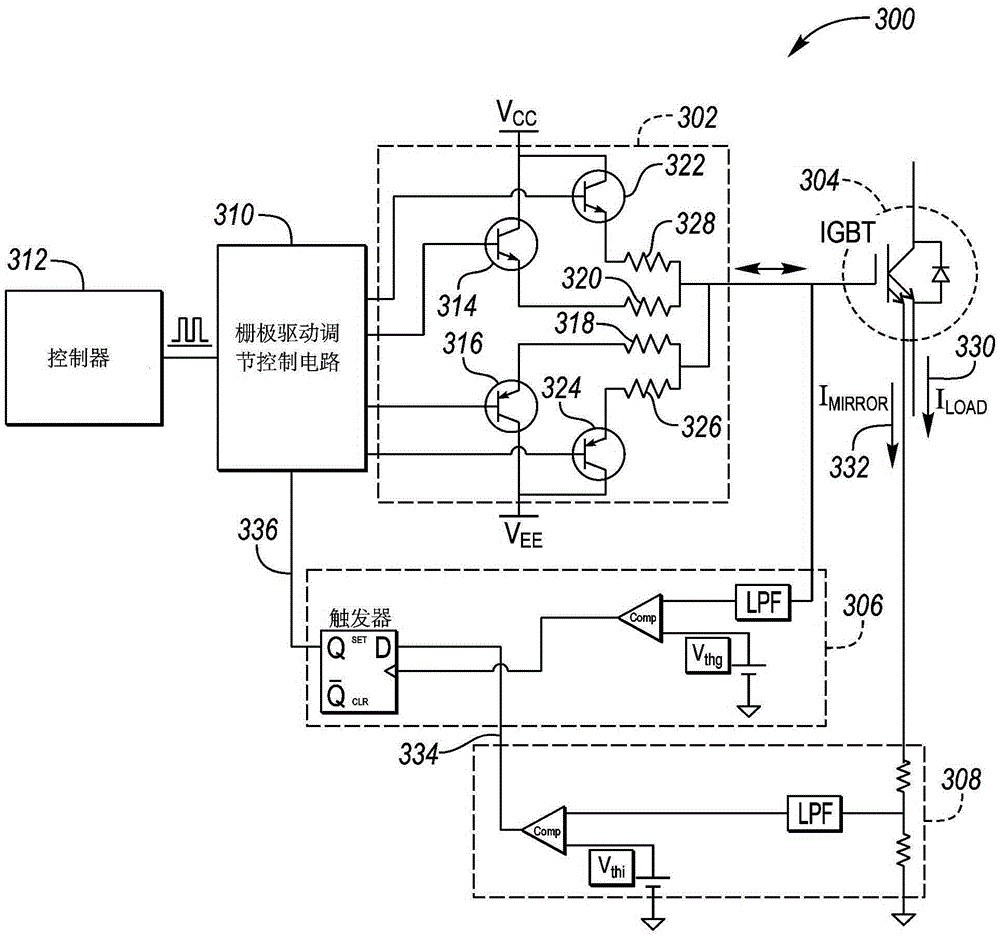
Dynamic igbt gate drive for vehicle traction inverters
A hybrid electric vehicle includes a traction battery, traction motor and power inverter therebetween. The power inverter converts the DC power of the traction battery to AC power to drive each phase of the traction motor. The power inverter includes Insulated Gate Bipolar junction Transistors (IGBTs) to modulate the power to the traction motor. The speed at which the IGBTs are modulated impacts the system performance including power loss, voltage overshoot and current overshoot. Using a dual emitter IGBT to provide a current mirror of the drive current, circuitry may be used with the gate drive circuitry such that the gate drive speed may be dynamically adjusted based on characteristics including temperature and traction motor rotational speed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
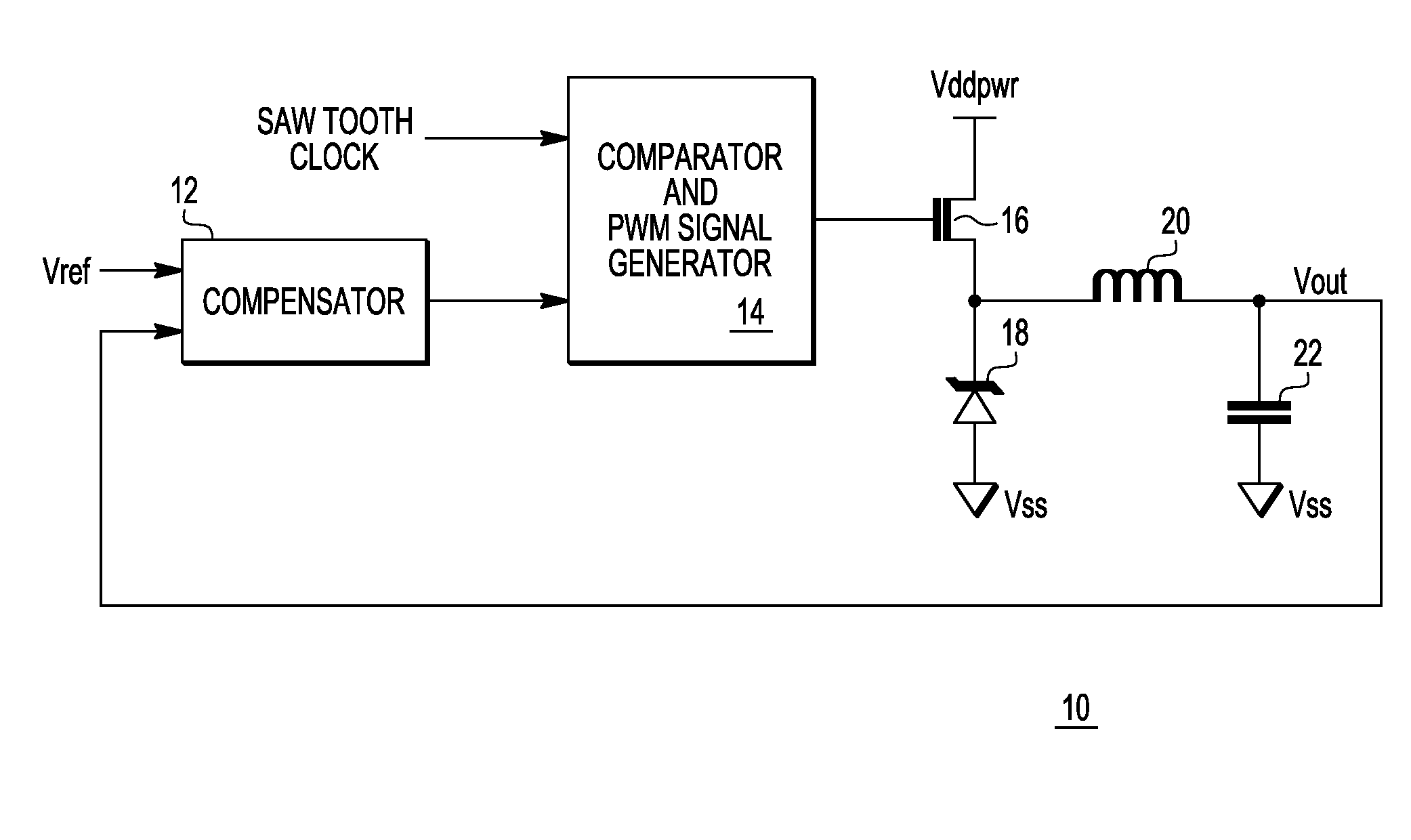
Switched mode voltage regulator and method of operation
ActiveUS20120086423A1Electric variable regulationPower conversion systemsRC time constantVoltage overshoot
A voltage regulator includes a transistor, a comparator, and a compensation circuit. The comparator has a first input terminal coupled to receive a clock signal, a second input terminal, and an output terminal coupled to a control electrode of the transistor. The compensation circuit has a first input terminal coupled to receive a reference voltage, a second input terminal coupled to the output terminal of the voltage regulator, and an output terminal coupled to the second input terminal of the comparator. The compensation circuit has a filter circuit. The filter circuit has a first RC time constant during startup of the voltage regulator, and the filter circuit has a second RC time constant during normal operation. Changing the RC time constant for startup prevents an overshoot of an output voltage of the voltage regulator.
Owner:NXP USA INC
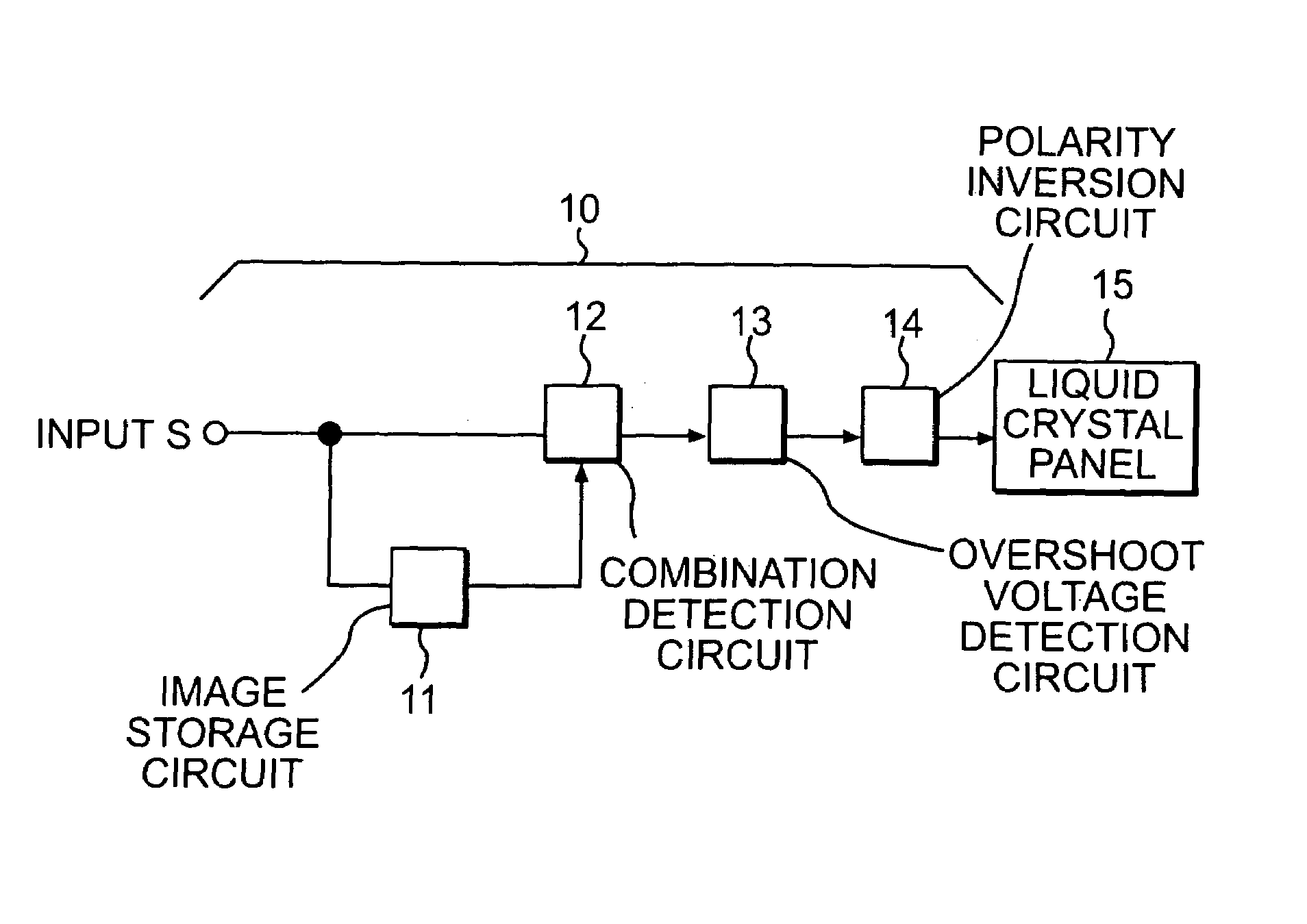
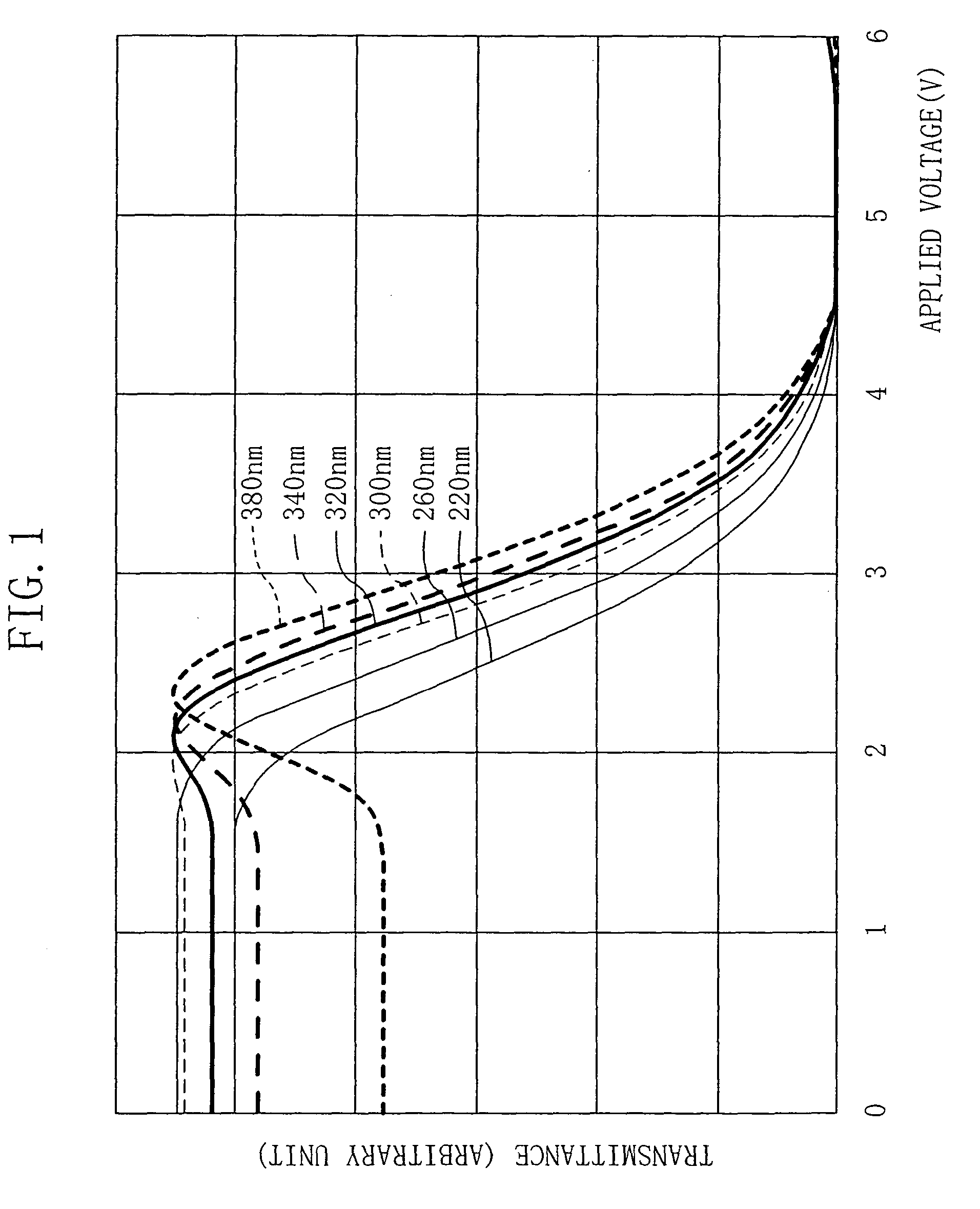
Liquid crystal display device
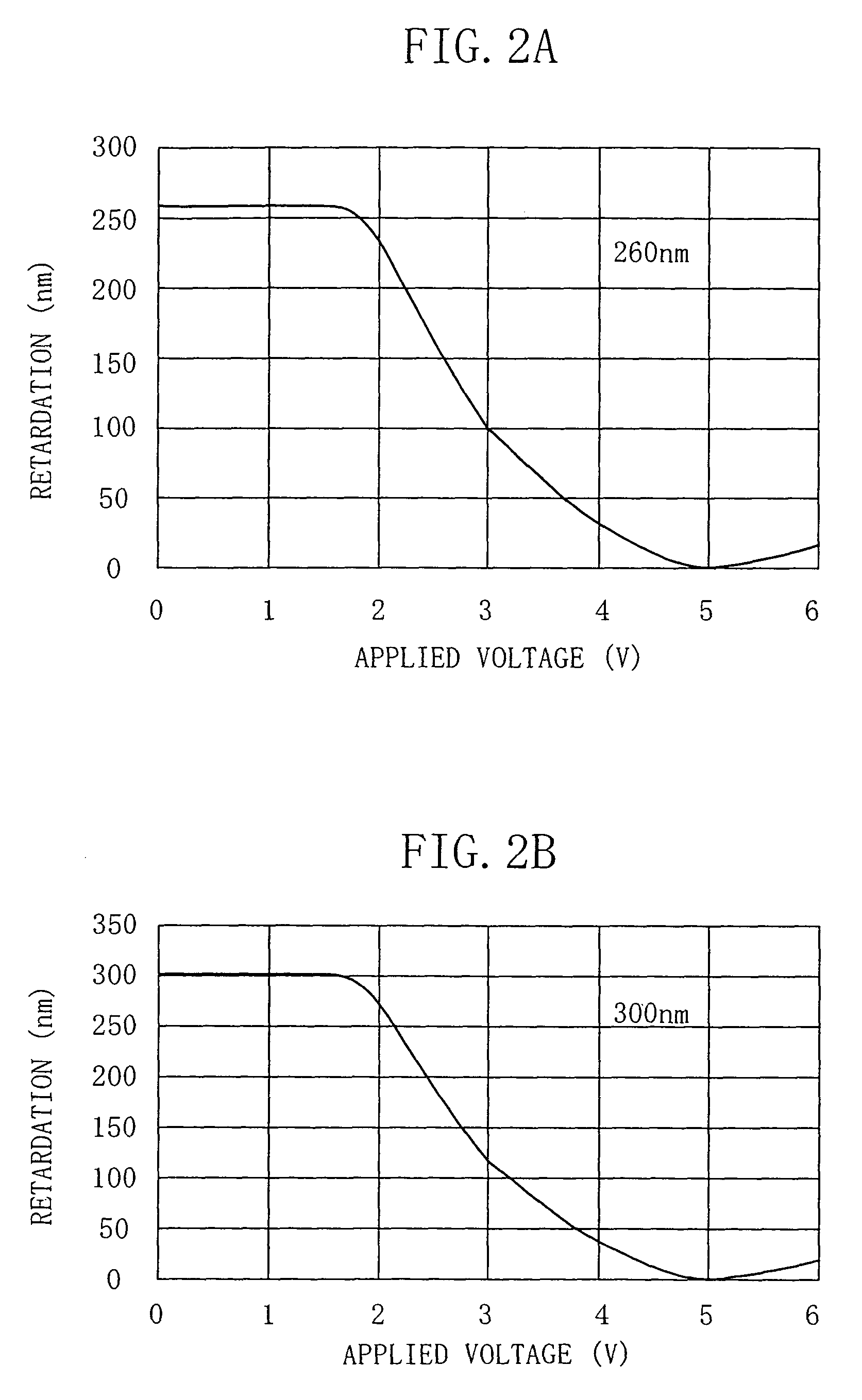
InactiveUS7084846B2Improved fall response characteristicImprove responsivenessCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsVoltage overshootLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal (LC) display device includes a LC panel and a driving circuit. The LC panel exhibits, in its voltage-transmittance characteristics, an extreme transmittance at a voltage equal to or lower than a lowest gray-level voltage. The driving circuit supplies to the LC panel a predetermined driving voltage overshooting a gray-level voltage corresponding to an input image signal of a current vertical period, according to a combination of an input image signal of an immediately preceding vertical period and the input image signal of the current vertical period.
Owner:SHARP KK
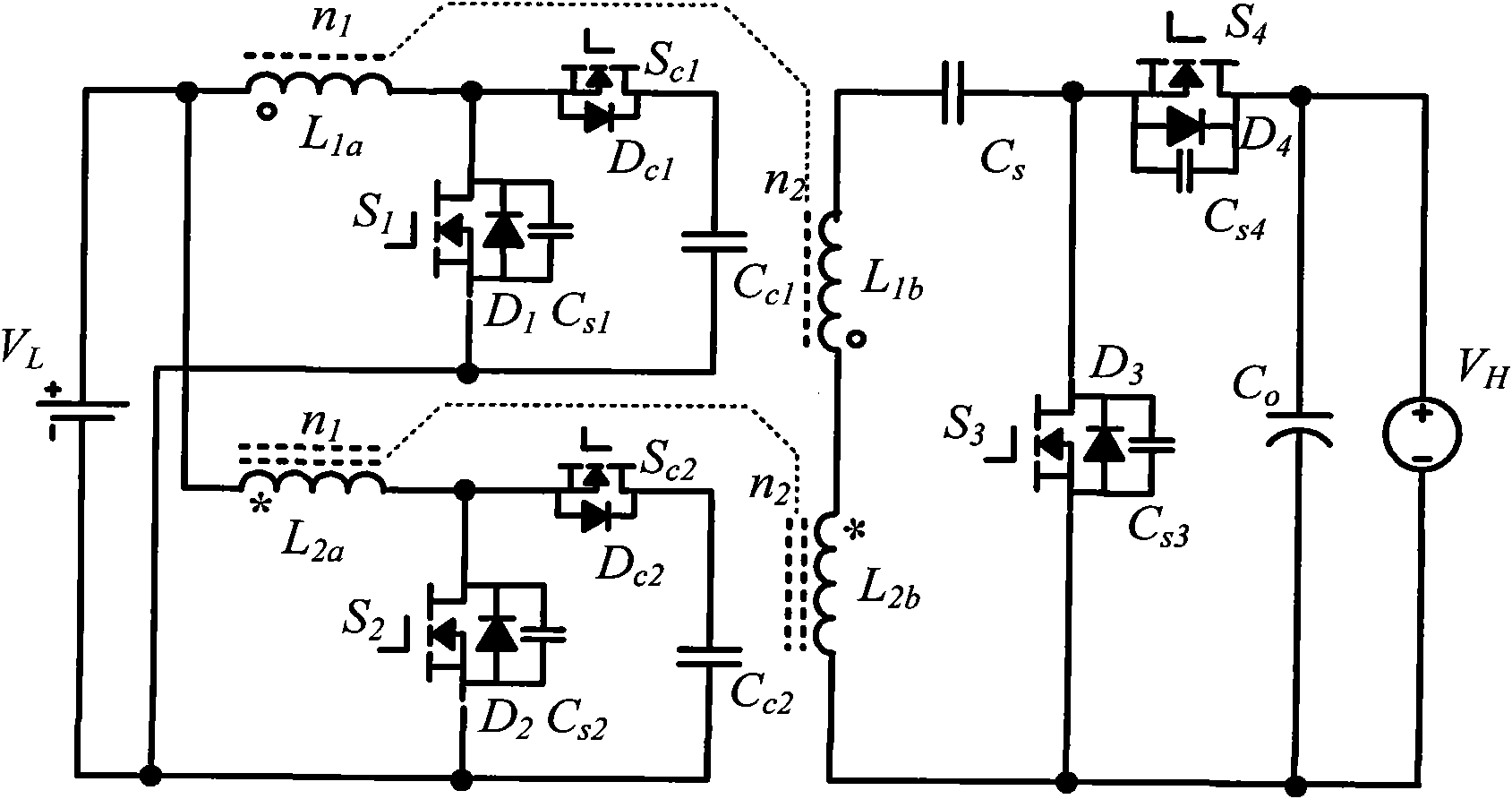
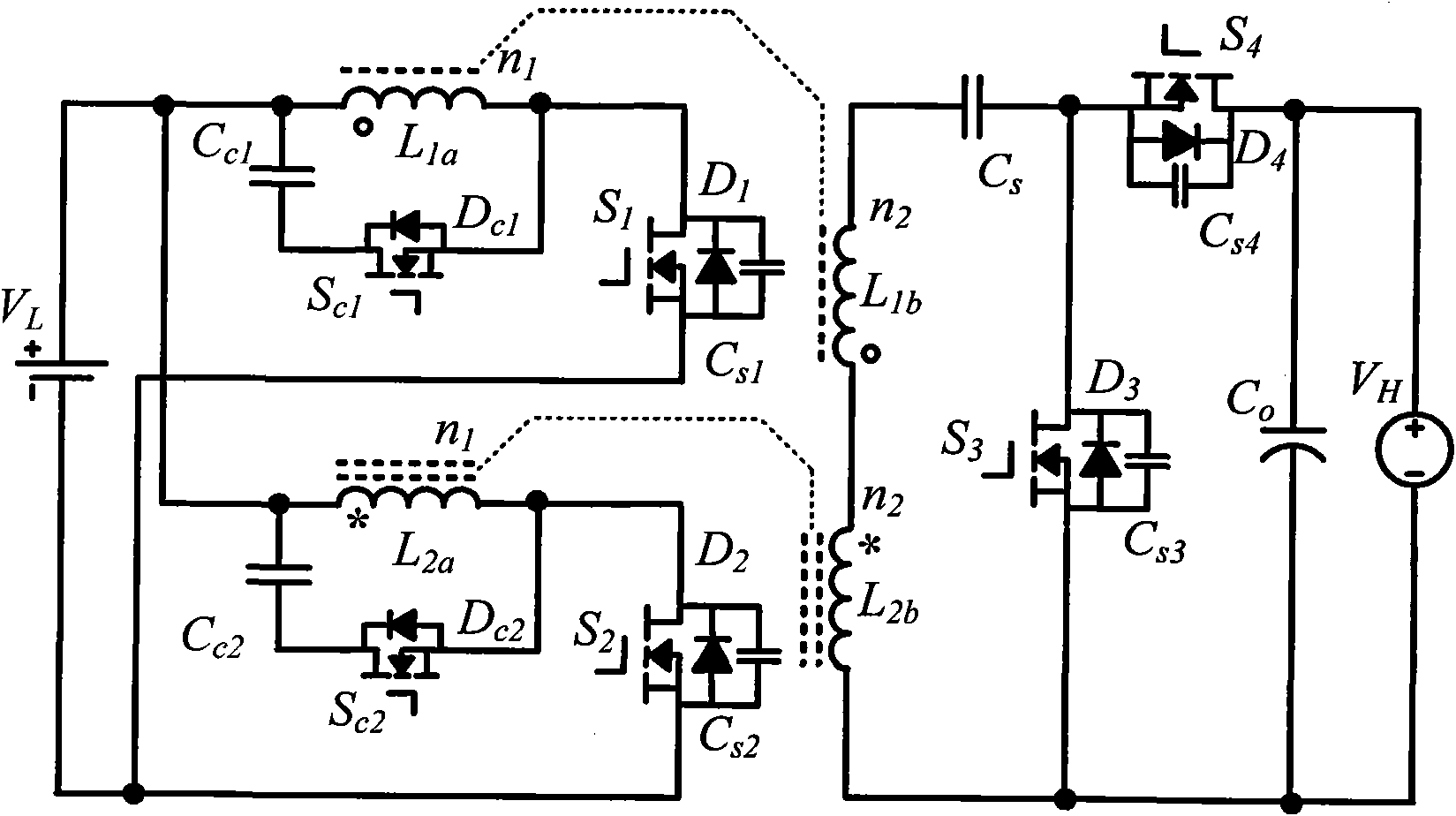
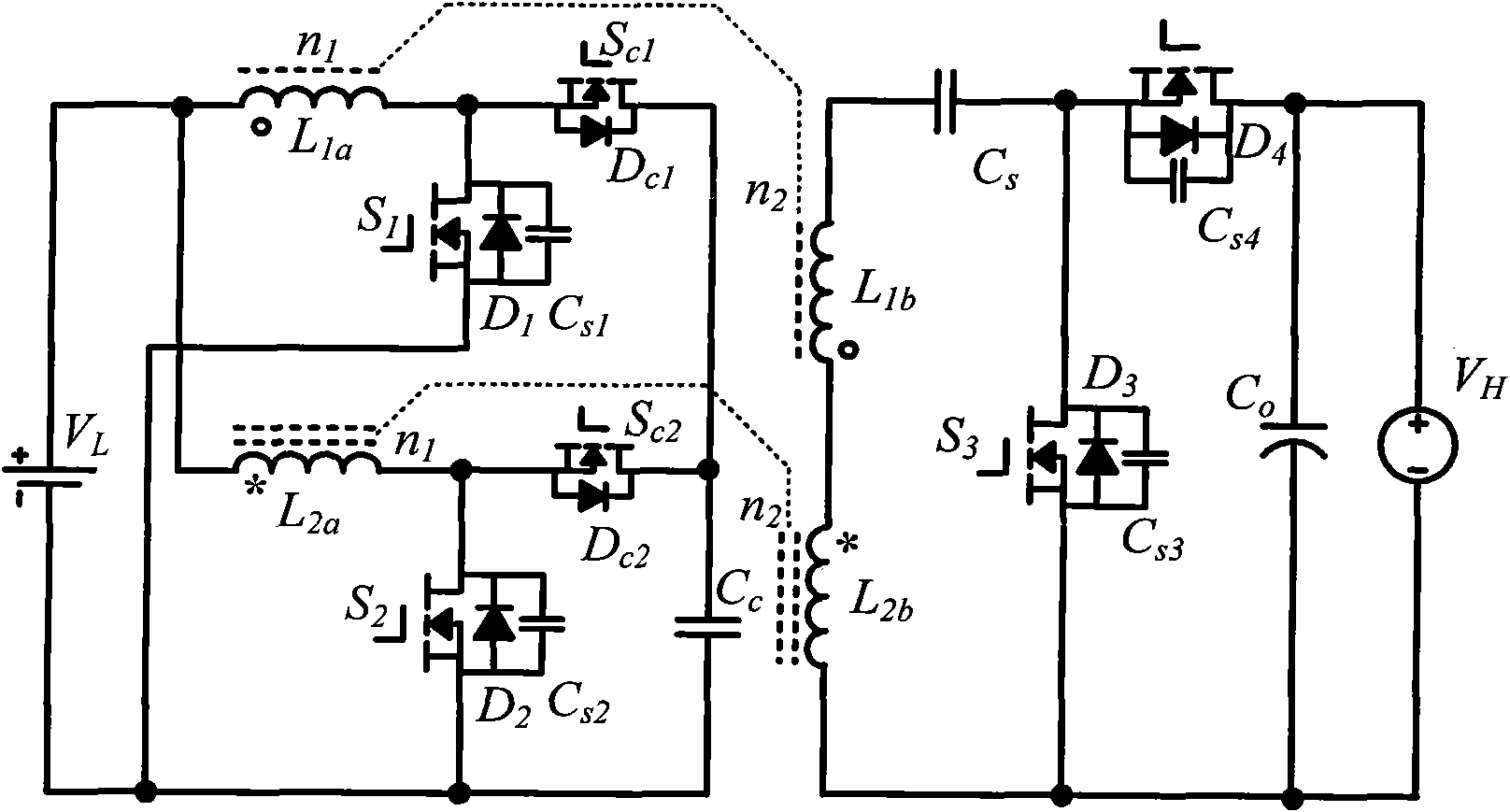
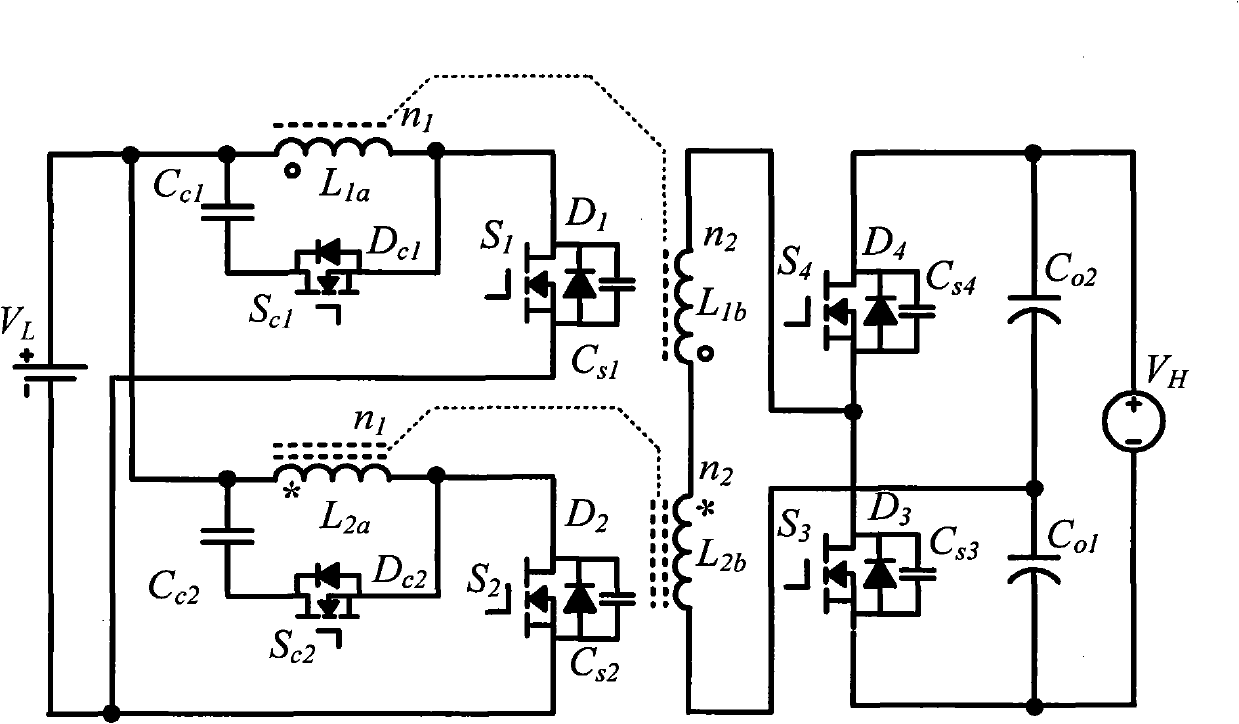
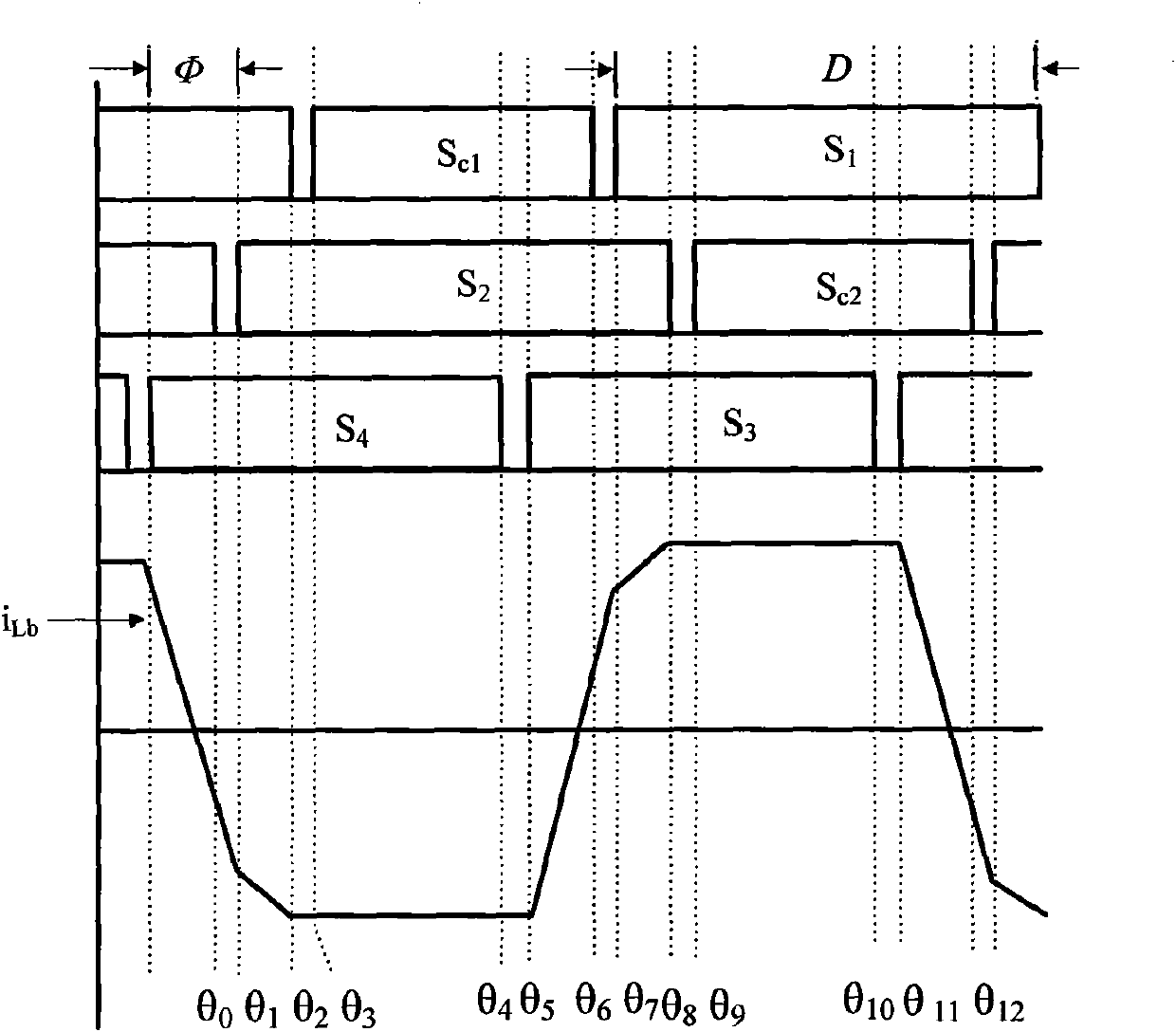
Isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter realized by coupling inductor
ActiveCN101976953AAchieve lossless transferSimple structureEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage overshootLow voltage
The invention discloses an isolated bidirectional DC-DC (direct current) converter realized by a coupling inductor, which comprises four power switch tubes with reverse parallel diodes and parallel capacitors, two auxiliary switch tubes with reverse parallel diodes, two clamping capacitors, a switch capacitor and two two-winding coupling inductors. The invention reduces the ripples of the low-voltage side current through the low-voltage side parallel structure, realizes the zero voltage shutoff of the power switch tubes through the parallel capacitors on the power switch tubes, realizes the zero voltage conduction of the power switch tubes through the leakage inductance of the coupling inductors, realizes lossless transfer of the leakage inductance energy through the auxiliary switch tubes and an active clamping circuit consisting of the reverse parallel diodes of the auxiliary switch tubes and the clamping capacitors, and increases / decreases the voltage of the converter through the serial structure of the high-voltage side windings of the two coupling inductors. The circuit has simple structure, all power switches work in a soft switch state, no energy consumption element is arranged in the circuit, and the converter efficiency is improved; and moreover, during the current conversion, the switch device does not experience voltage overshoot.
Owner:HOYMILES POWER ELECTRONICS INC
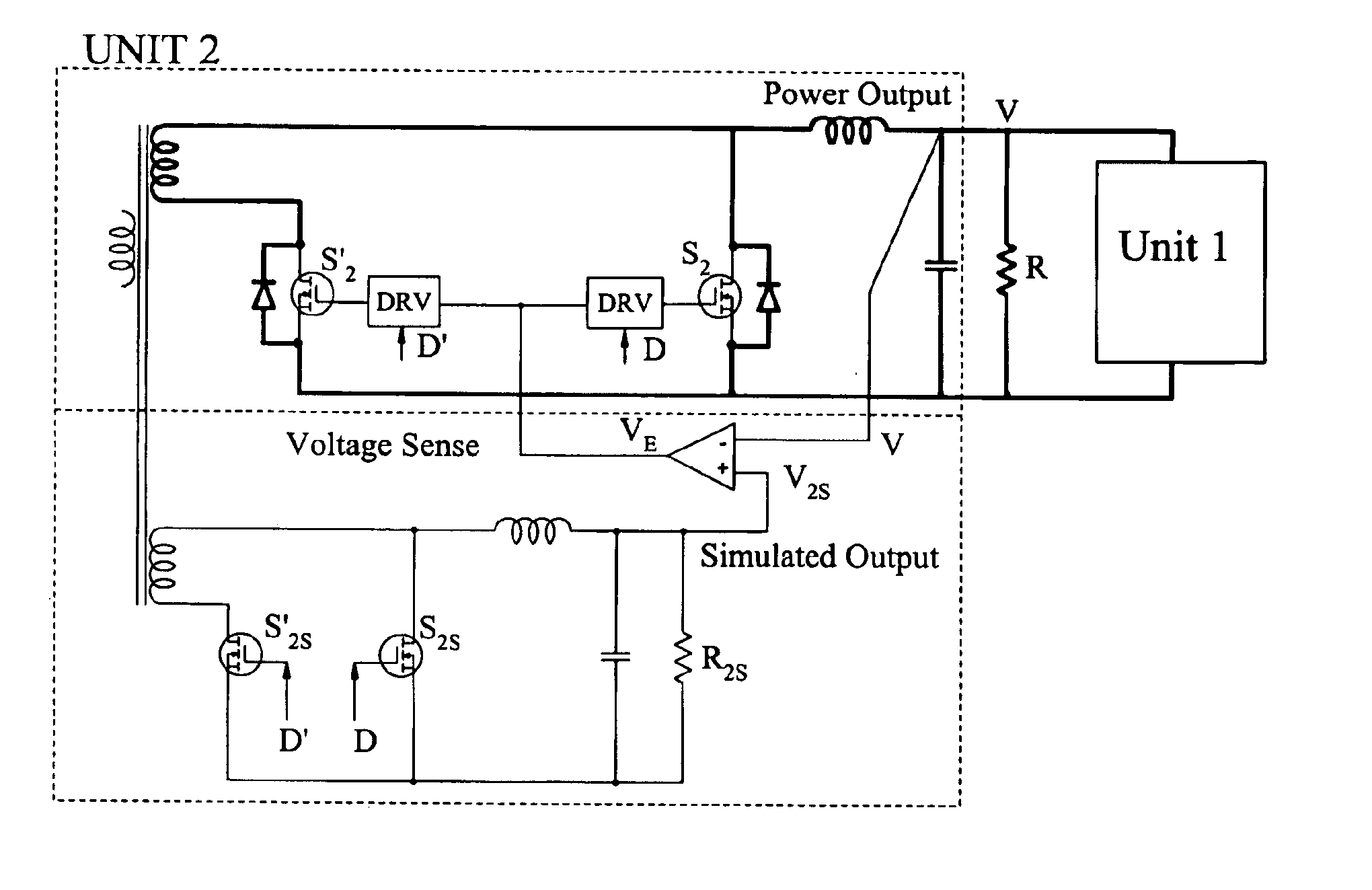
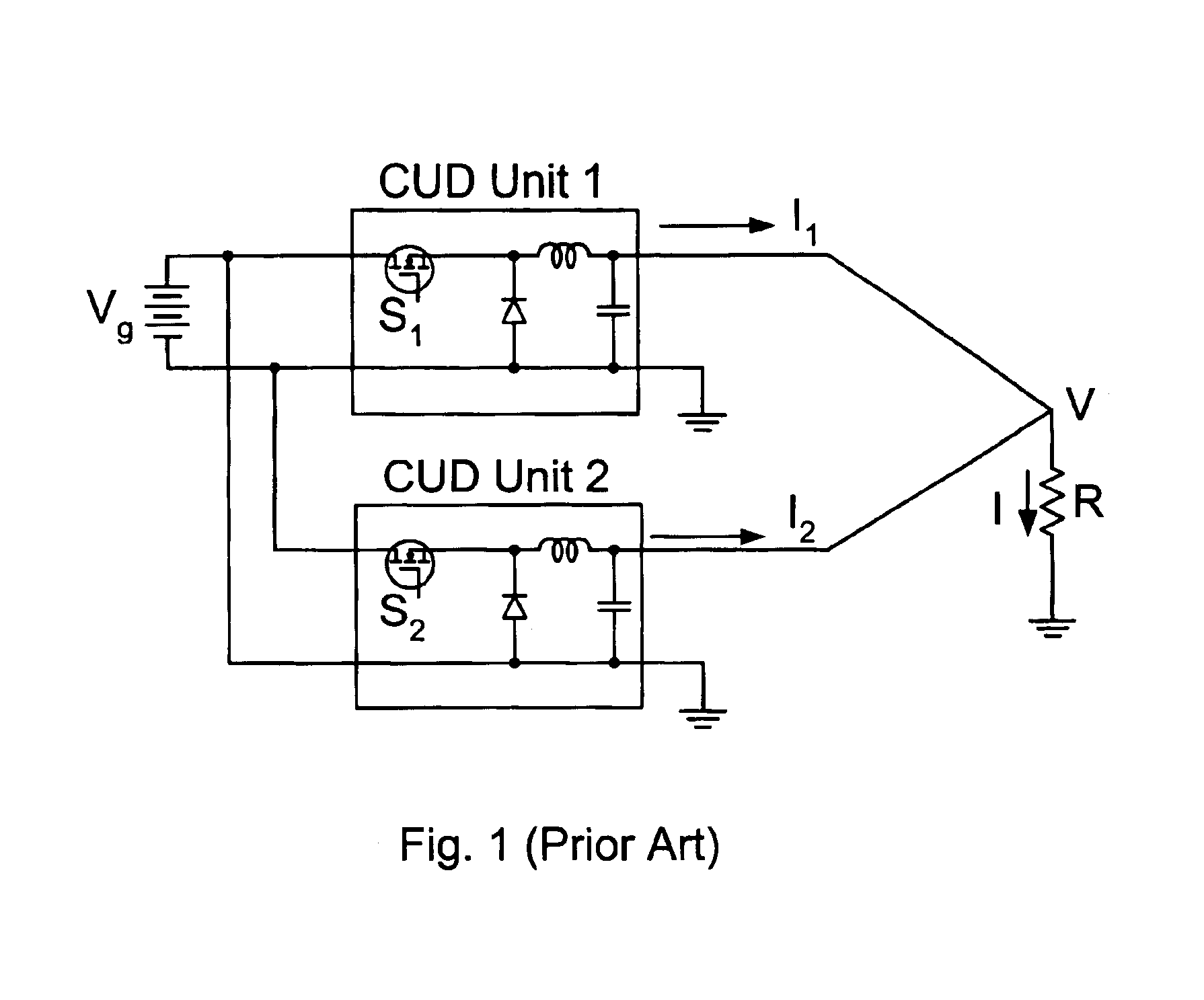
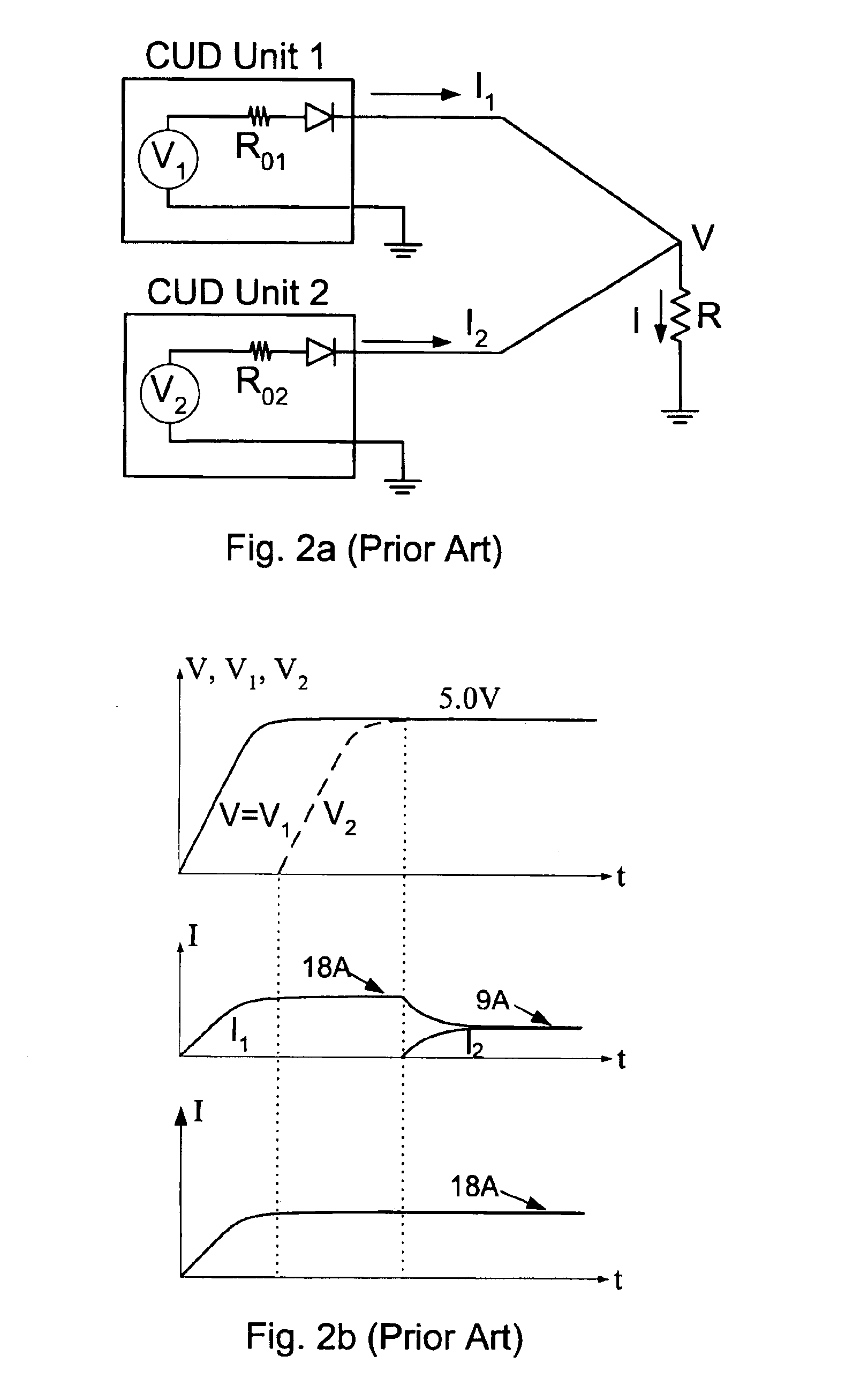
Voltage sense method and circuit which alleviate reverse current flow of current bi-directional converters
InactiveUS6853562B2Eliminate stressHigh pressureEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage overshootReverse current
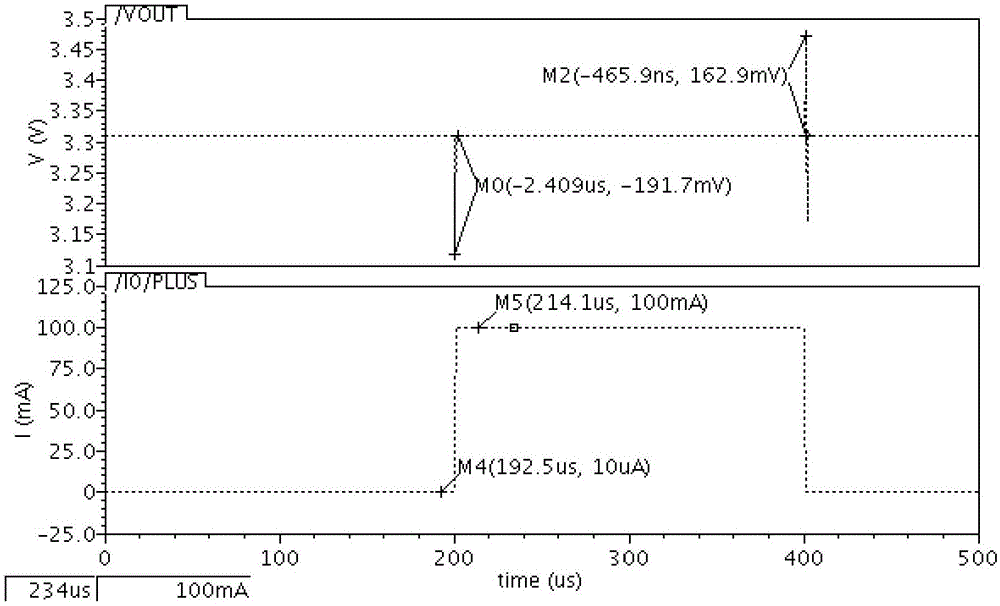
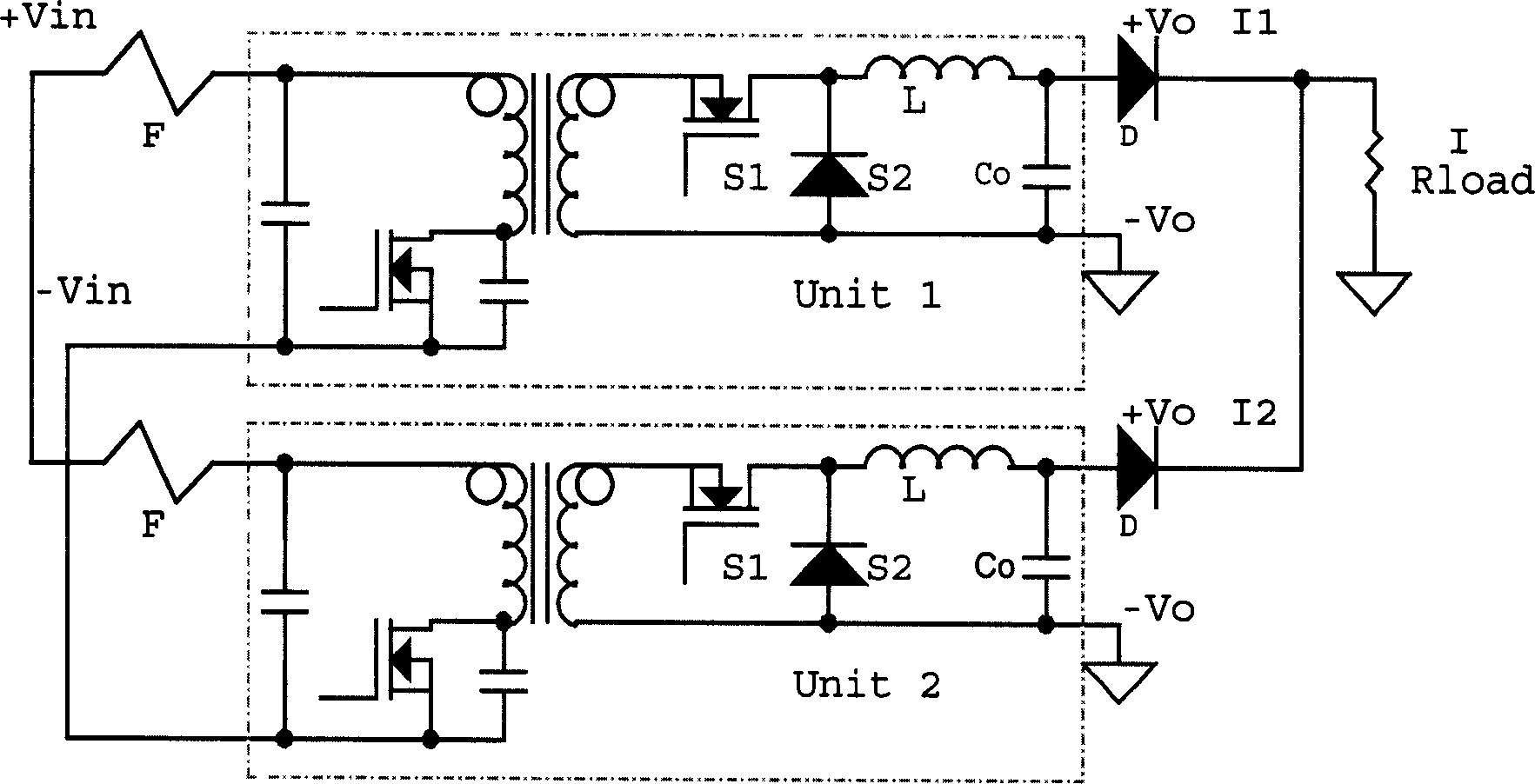
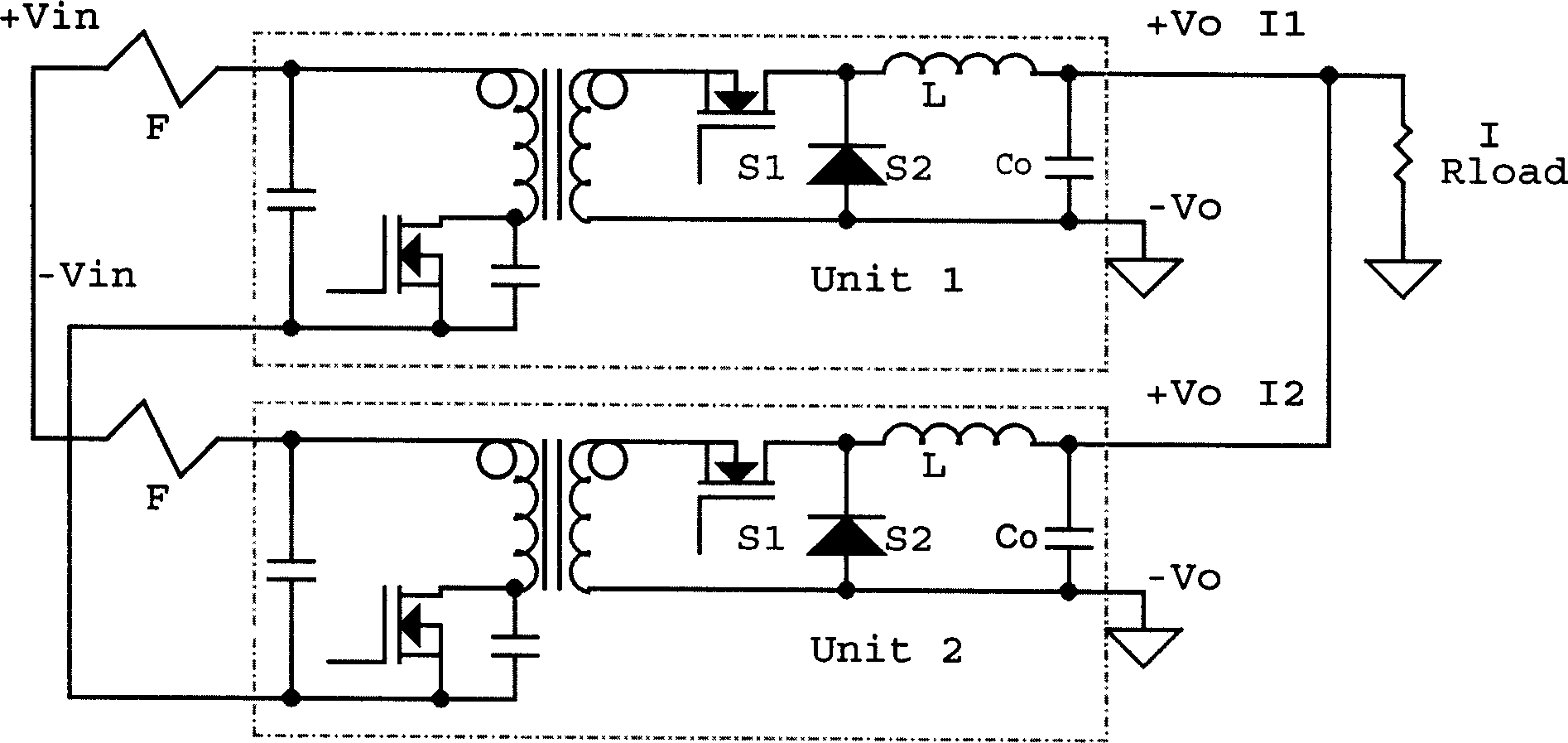
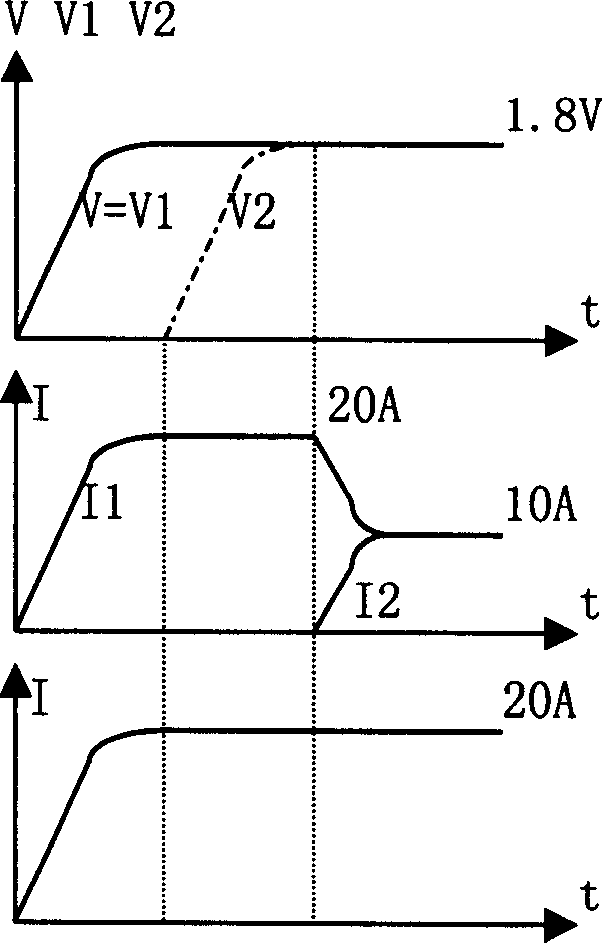
The Voltage Sense Method is introduced and a number of its implementations using Voltage Sense Circuit are demonstrated to solve problems associated with the start-up of parallel switching converters, each converter having output synchronous rectifiers or more general Current Bi-directional Switches: prevention of the excessive reverse current, elimination of the excess voltage stress of the input switches and elimination of the voltage overshoot in the common output voltage. The Voltage Sense circuit added to each converter generates a Simulated Output Voltage, which predicts how would the output voltage of each particular unit rise during the start-up with enabled synchronous rectifiers if that particular unit were to operate alone. When the simulated output voltage of one converter reaches the actual common output voltage, synchronous rectifiers / CBS switches of that particular converter are all enabled so that their body-diodes, used up until that time to prevent reverse current flow, are by-passed eliminating all start-up problems. The introduced Voltage Sense Method and a number of its Voltage Sense Circuitries are also applicable to solve problems associated with the start-up of the current bi-directional converters with a battery load.
Owner:TESLACO
LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix type half-bridge inverter topology and modulation method
InactiveCN107070281AImprove reliabilityImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMatrix convertersVoltage overshoot
The invention relates to an LC series resonance high frequency chain matrix type half-bridge inverter topology and a modulation method. The topology comprises a half-bridge LC series resonance inverter, a high-frequency transformer T, a matrix converter and a CL type filter. The modulation method comprises steps that SPWM waves generated in a SPWM signal generation link are processed through series resonance modulation logics to acquire driving signals of a transformer front-level LC series resonance inverter and a transformer back-level matrix converter, a work duty ratio of an excitation resonance work state of a transformer front-level resonance circuit is made to be controllable within a half period, and output load side energy transmission control is realized; the transformer back-level matrix converter is taken as a common current type inverter to control, switching of a switch tube during a transformer zero current output period is carried out to realize a zero current switch, a voltage overshoot problem caused by break of a transformer secondary side leakage current flow path can be avoided, and bidirectional energy flow is realized. The method has advantages of small-quantity power conversion grades, small-quantity switch tubes, simple control and high circuit stability.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
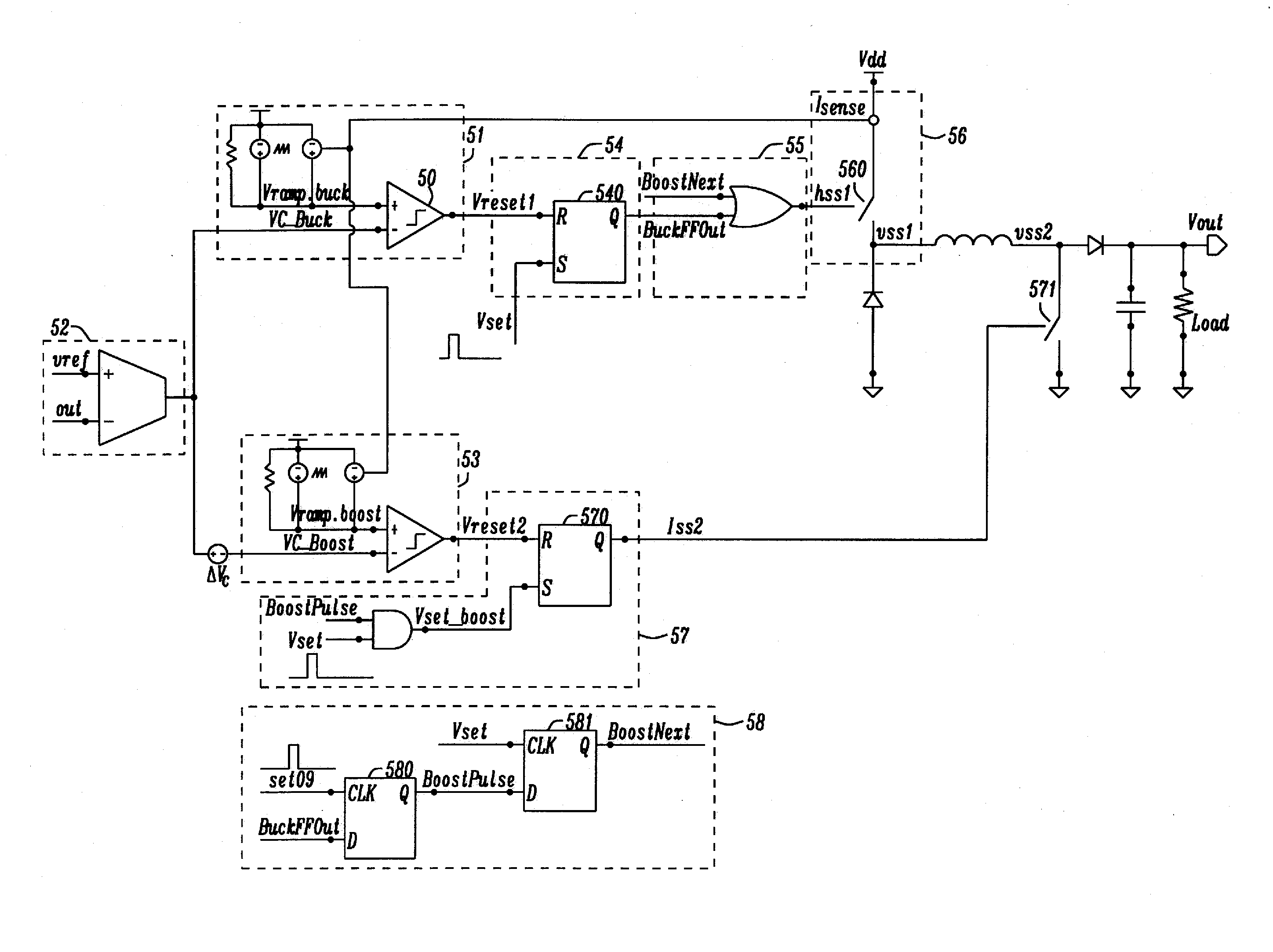
Method for a Current Mode Buck-Boost Converter
ActiveUS20150357914A1Reduce switching lossesReduce resistance lossApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlVoltage overshoot
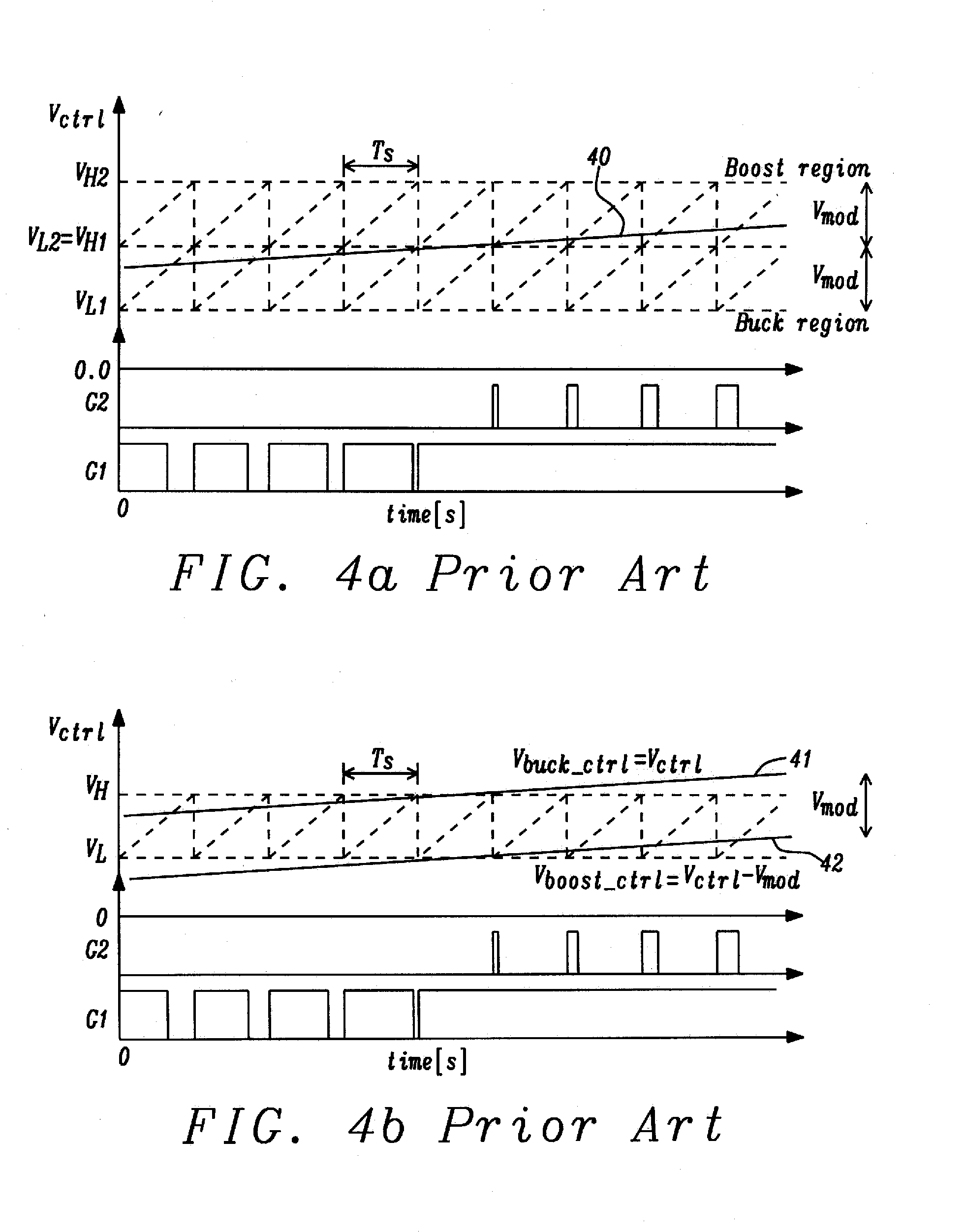
A current mode control buck-boost converter with improved performance utilizes separate buck and boost pulses. The buck-boost converter utilizes a buck / boost decision method with continuous control voltage for buck and boost mode, therefore eliminating transients in the control loop between operation modes and preventing voltage overshoots. If switching in Boost mode and the buck duty cycle is smaller than a set duty cycle, then in the next cycle Buck mode switching will occur. It is possible to track a Buck comparator output and the related duty cycle during Boost mode operation. Thus a mode change decision will only be dependent on a single input. A control loop will incorporate a single loop filter and error amplifier, wherein control voltages for Buck comparator and Boost comparator will be related.
Owner:APPLE INC
Fast switching for power inverter
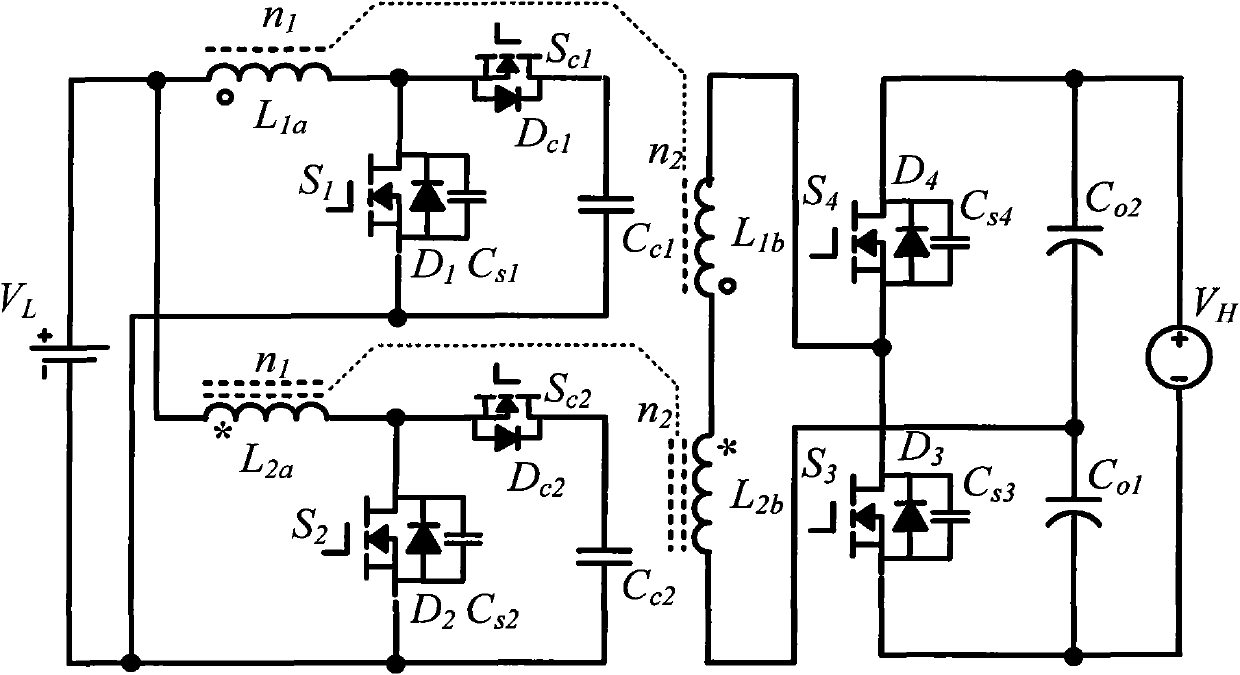
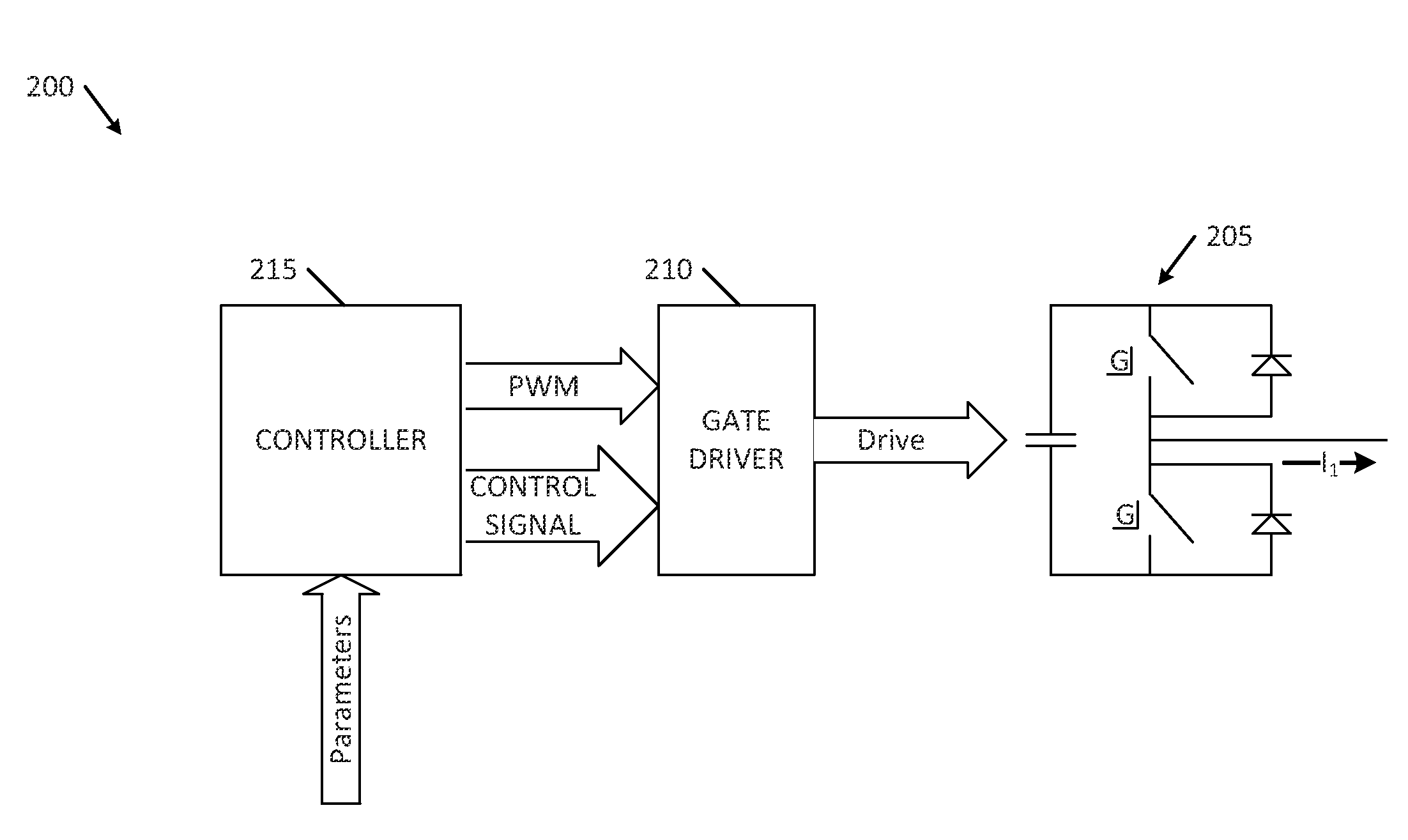
ActiveUS20120195079A1Efficiently and economically reduce excessive voltage overshootReduce riskAc-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower inverterDriving current
An apparatus includes an inverter including a high-side switch coupled to a low-side switch, the inverter generating a time-varying drive current from a plurality of drive control signals, a positive rail voltage, and a negative rail voltage wherein controlling the switches to generate the time-varying drive current produces a potential transitory overshoot condition for one of the switches of the inverter; a drive control, coupled to the inverter, to generate the drive control signals and to set a level of each of the rail voltages responsive to a plurality of controller signals; and a controller monitoring one or more parameters indicative of the potential transitory voltage overshoot condition, the controller dynamically adjusting, responsive to the monitored parameters, the controller signals to reduce a risk of occurrence of the potential transitory voltage overshoot condition.
Owner:TESLA INC
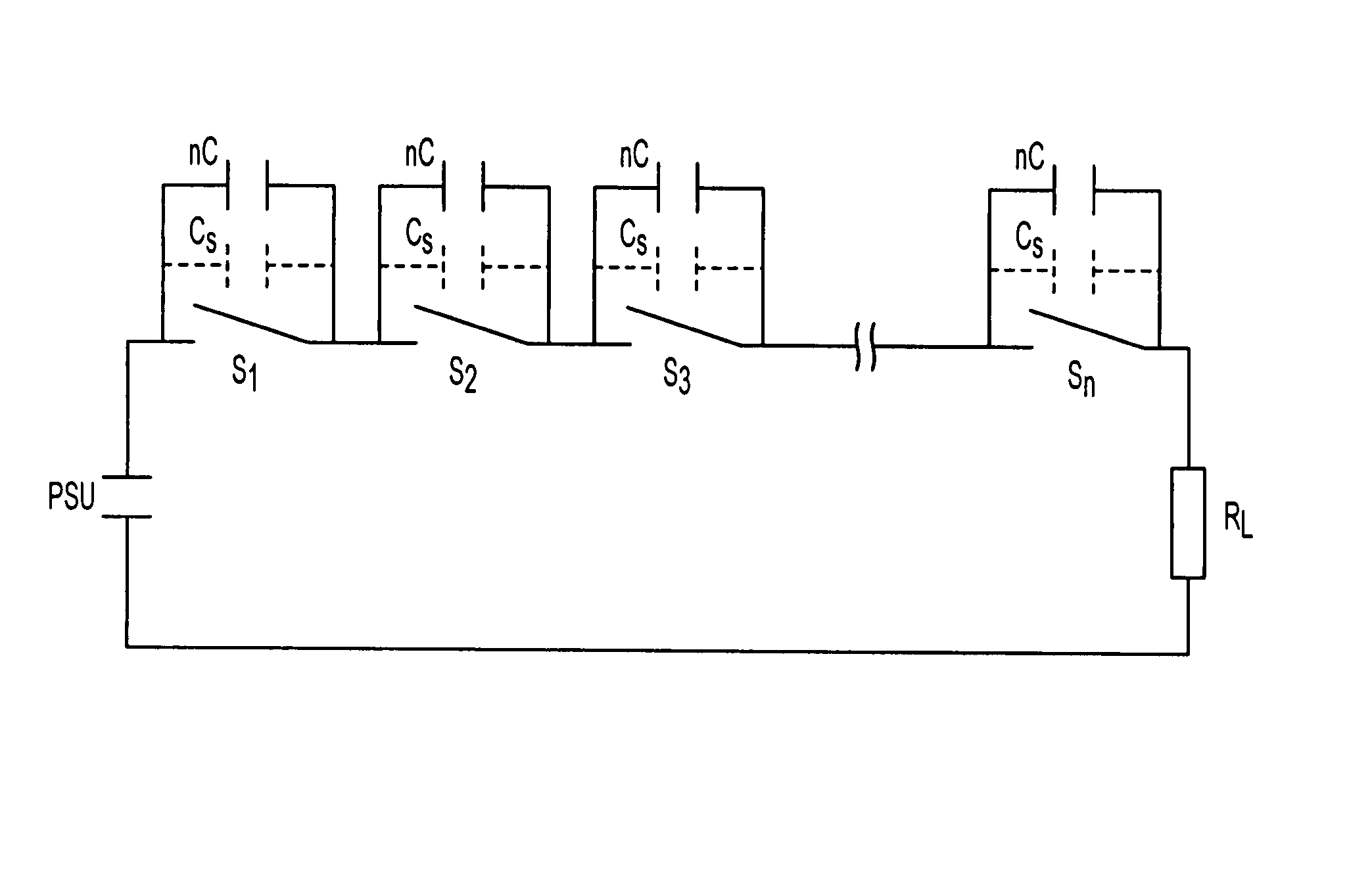
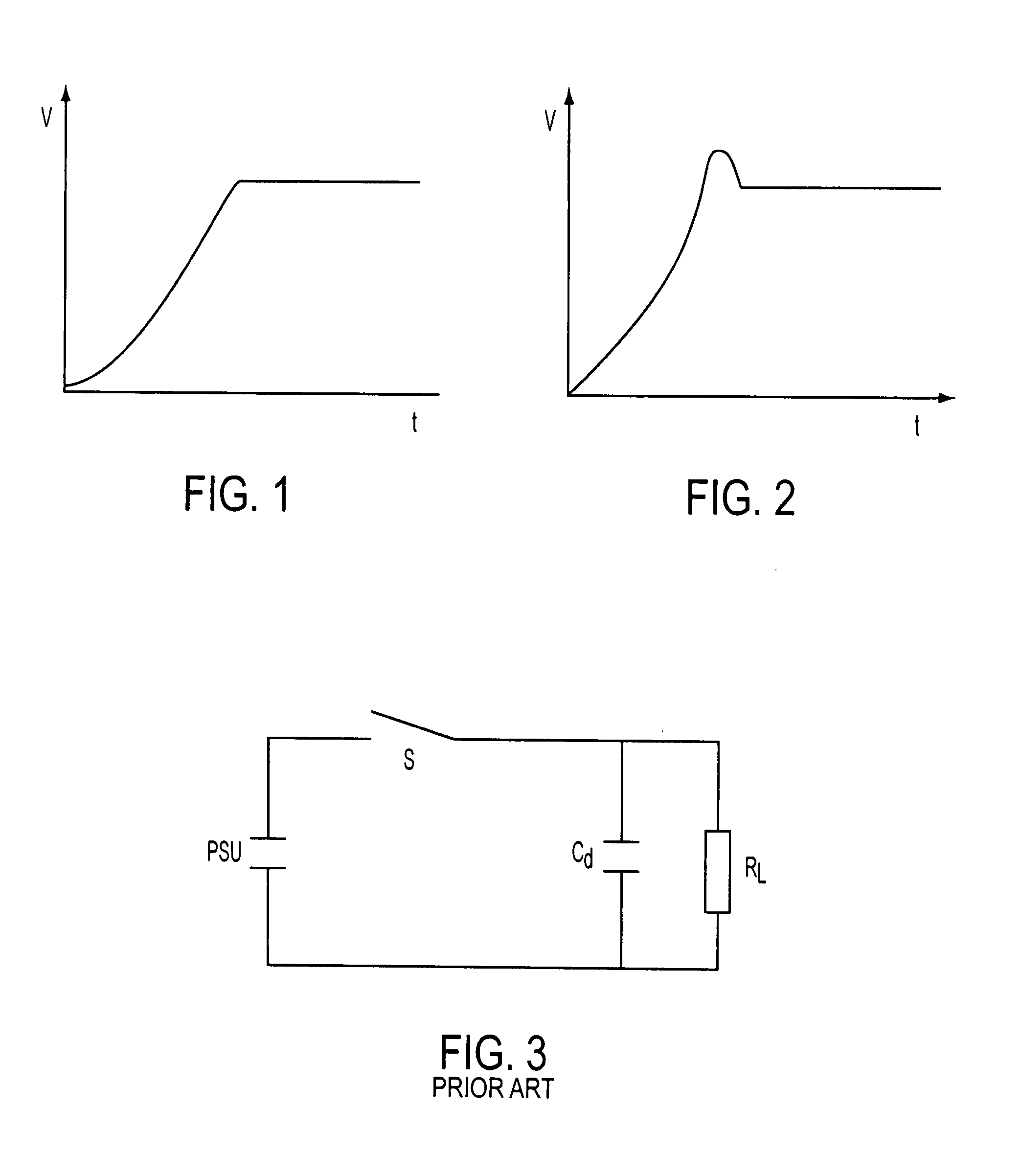
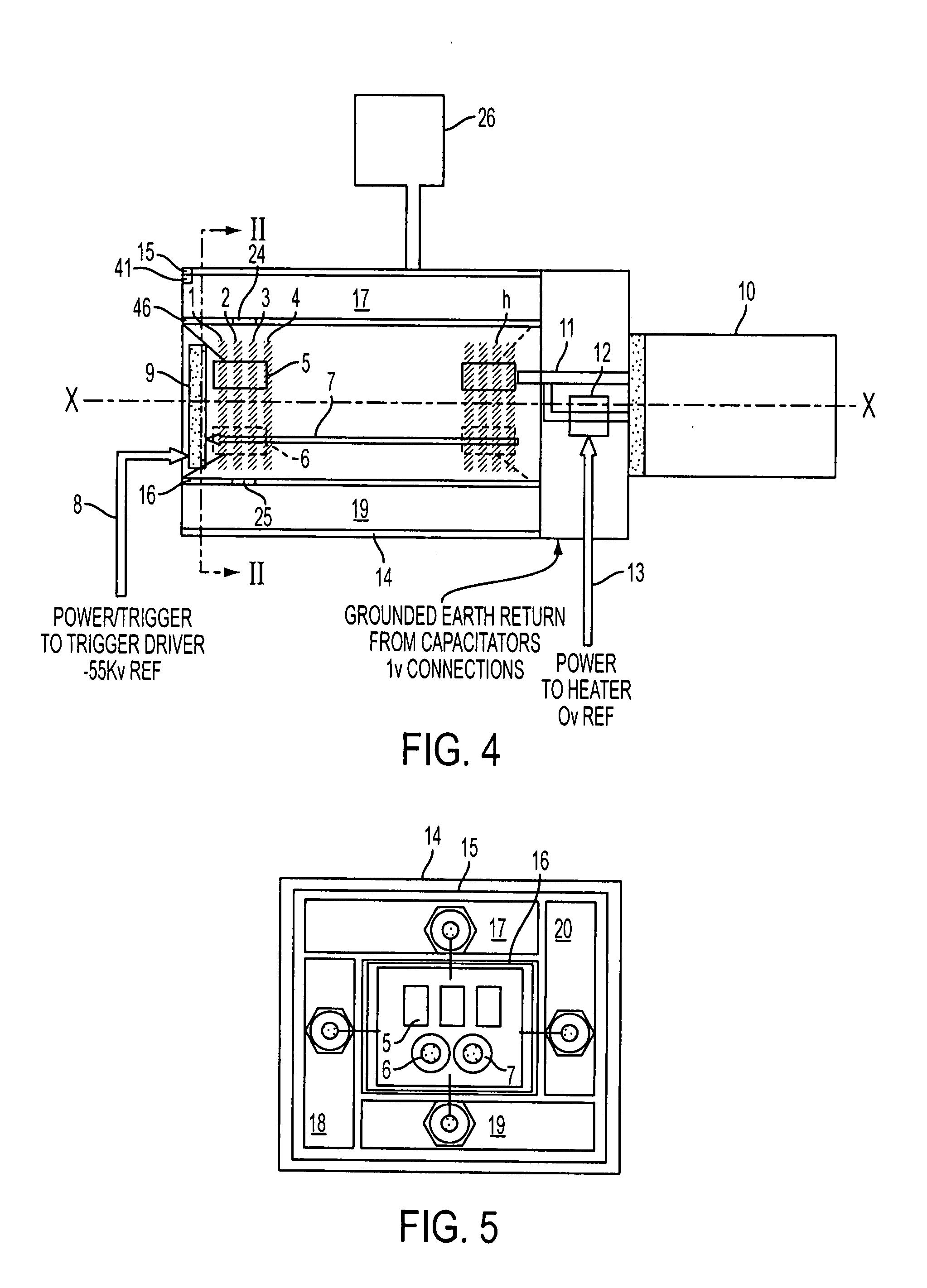
High voltage switching apparatus
InactiveUS7256637B2Limit voltageInhibitionAc-dc conversionTransit-time tubesCapacitanceVoltage overshoot
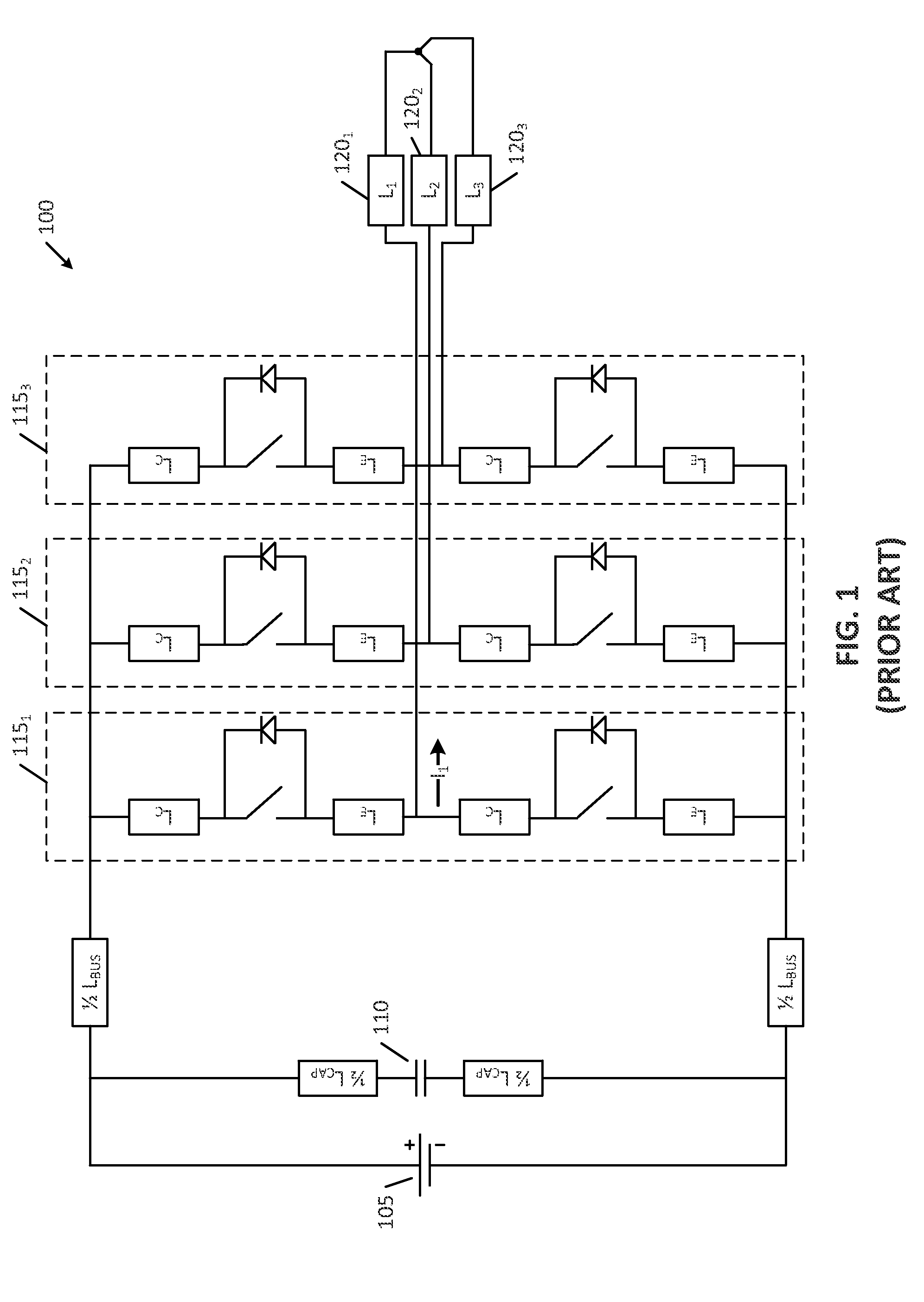
A switching arrangement for a high voltage load provides high voltage pulses to the load. The switching arrangement includes switching modules, where n is typically (75). A load capacitance is Cd is required to avoid voltage overshoot at the load and is provided by a capacitance of nCd arranged in parallel with each switch.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
Wireless power transmission system adaptive to multi-load dynamic switching
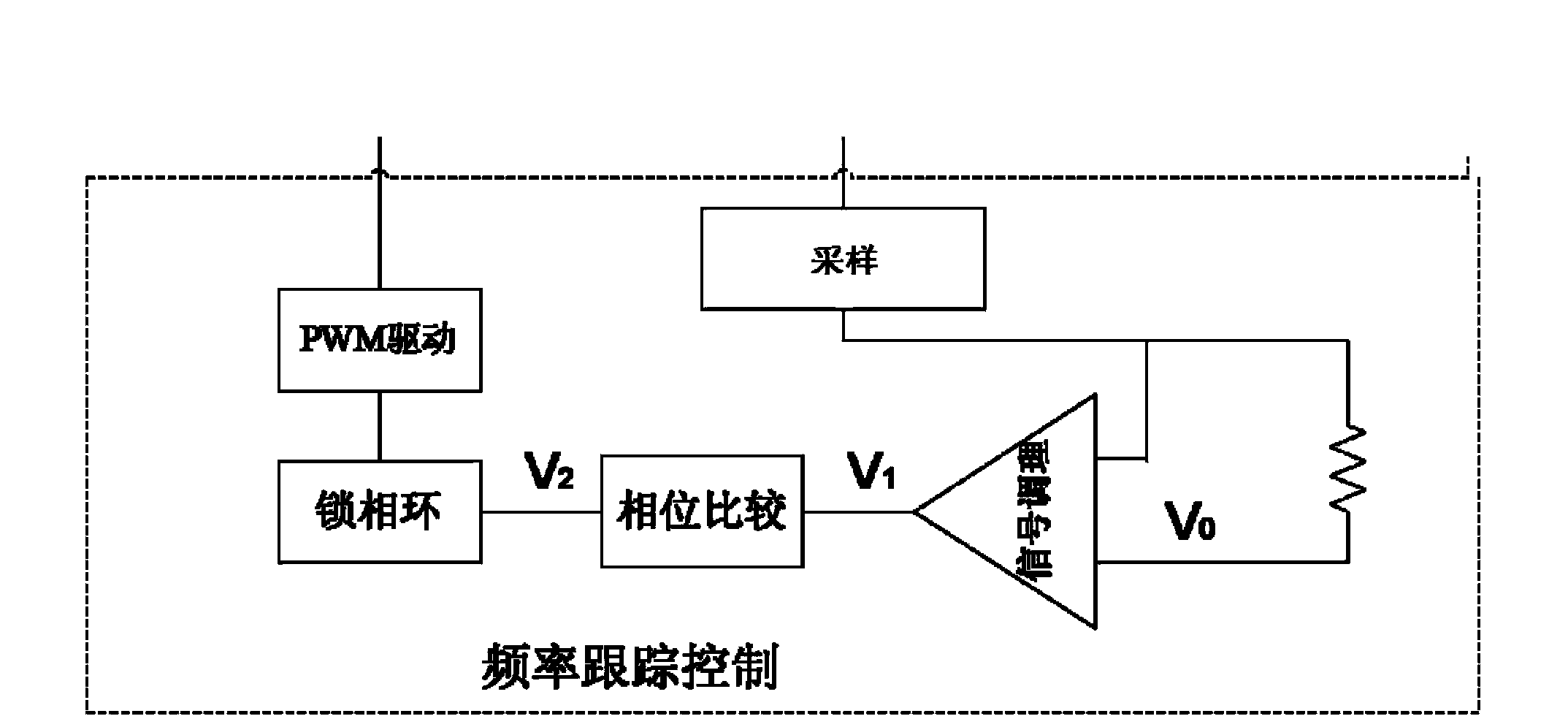
ActiveCN104052161AGuaranteed stabilityAvoid mutationElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectromagnetic coupling
A wireless power transmission system adapted for multiload dynamic switching comprises a primary module for transmitting electric energy and a second module for picking up electric energy. The primary module transmits electric energy to the secondary module by using electromagnetic coupling resonance, and when the secondary module switches different power loads, the secondary module gradually changes, by using soft switching, a secondary reflected impedance by using a mode of gradually increasing voltages on two sides of a load, so that changes of a resonance frequency and a phase of the primary module are kept in a self-adaptive range of frequency tracking and control. The primary module can make stable adjustment according a dynamic change of the load, making the primary module stably work; in addition, for an output voltage of a system, because soft switching is used to change the load in load switching, the impact of a load change on the system resonance is reduced, and the stability of a secondary output voltage is ensured.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Isolation type active clamping interleaving paralleled bidirectional DC-DC converter
ActiveCN101951154AImprove efficiencySmall rippleApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationSoft switchingVoltage overshoot
The invention discloses an isolation type active clamping interleaving paralleled bidirectional DC-DC converter which comprises four power switch tubes with anti-parallel diodes and parallel capacitors, two auxiliary switch tubes with anti-parallel diodes, two clamping capacitors, two high voltage side capacitors and two winding coupled inductors. The invention utilizes a low voltage side parallel structure to reduce ripples of a low voltage side current, utilizes the parallel capacitors of the power switch tubes to realize zero voltage turn-off of the power switch tubes, utilizes the leakage inductance of the coupled inductors to realize zero voltage switching of the power switch tubes, utilizes the auxiliary switch tubes and an active clamping circuit consisting of the anti-parallel diodes and the clamping capacitors of the auxiliary switch tubes to realize lossless transfer of the leakage inductance energy and utilizes serial structures of high voltage side windings of the two coupled inductors to realize high voltage rising / reduction of the converter. In the invention, a circuit structure is simple, all power switches work in a soft switching state, and an energy loss element does not exist in the circuit, therefore the converter efficiency is enhanced, and voltage overshoot does not occur on a switch device in a current commutating process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fast switching for power inverter
ActiveUS20120194119A1Efficiently and economically reduce excessive voltage overshootReduce riskAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersPower inverterDriving current
An apparatus includes an inverter including a high-side switch coupled to a low-side switch, the inverter generating a time-varying drive current from a plurality of drive control signals, a positive rail voltage, and a negative rail voltage wherein controlling the switches to generate the time-varying drive current produces a potential transitory overshoot condition for one of the switches of the inverter; a drive control, coupled to the inverter, to generate the drive control signals and to set a level of each of the rail voltages responsive to a plurality of controller signals; and a controller monitoring one or more parameters indicative of the potential transitory voltage overshoot condition, the controller dynamically adjusting, responsive to the monitored parameters, the controller signals to reduce a risk of occurrence of the potential transitory voltage overshoot condition.
Owner:TESLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com