Patents
Literature
122results about How to "Limit voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
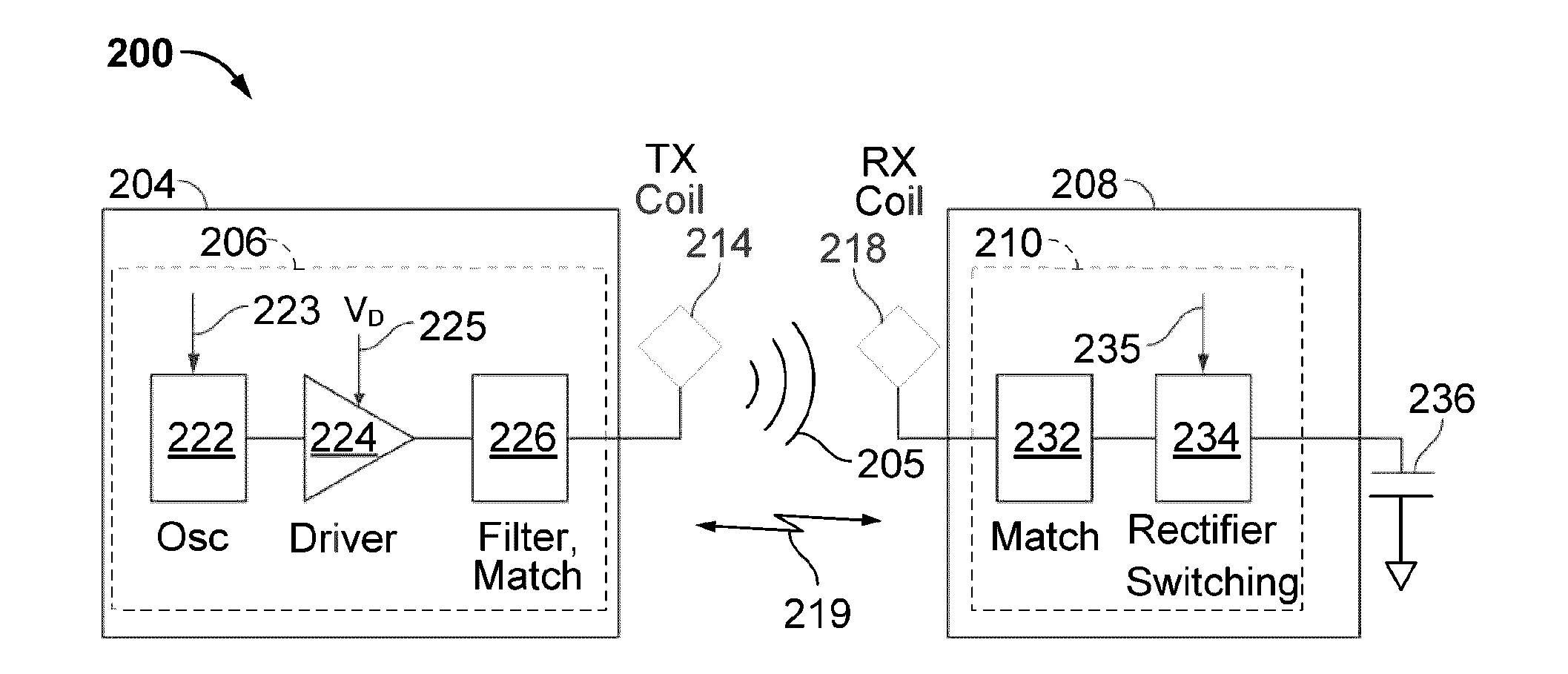
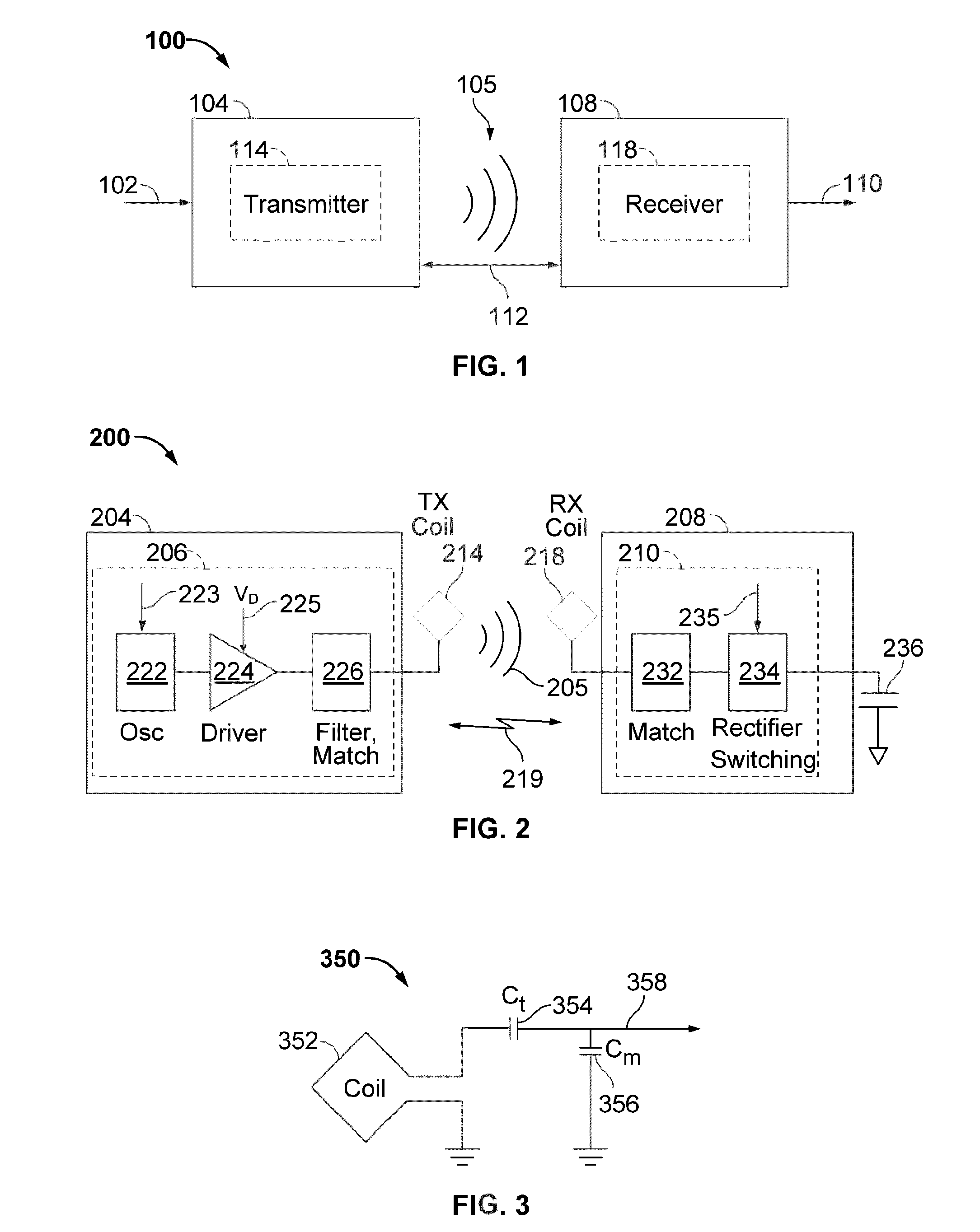
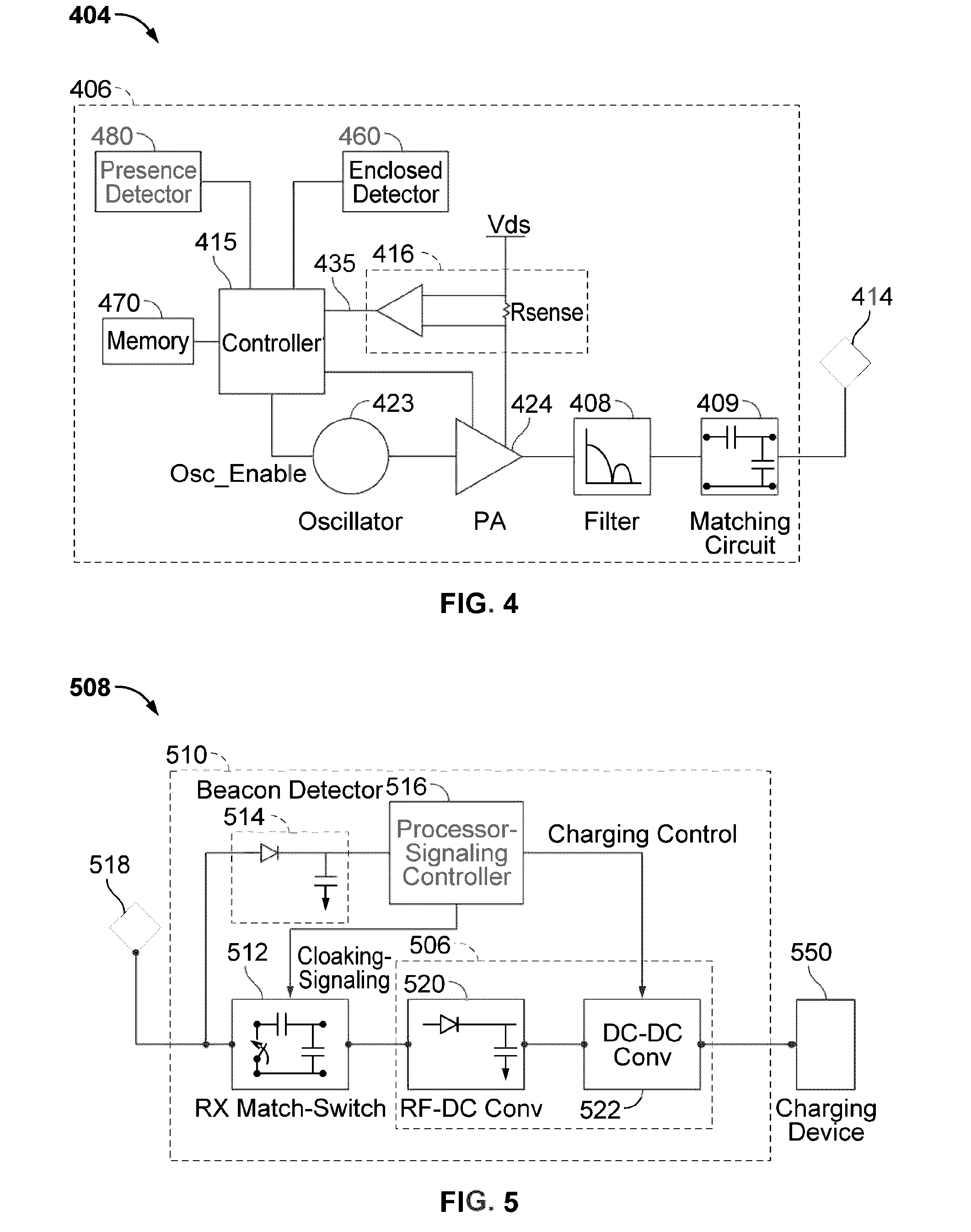
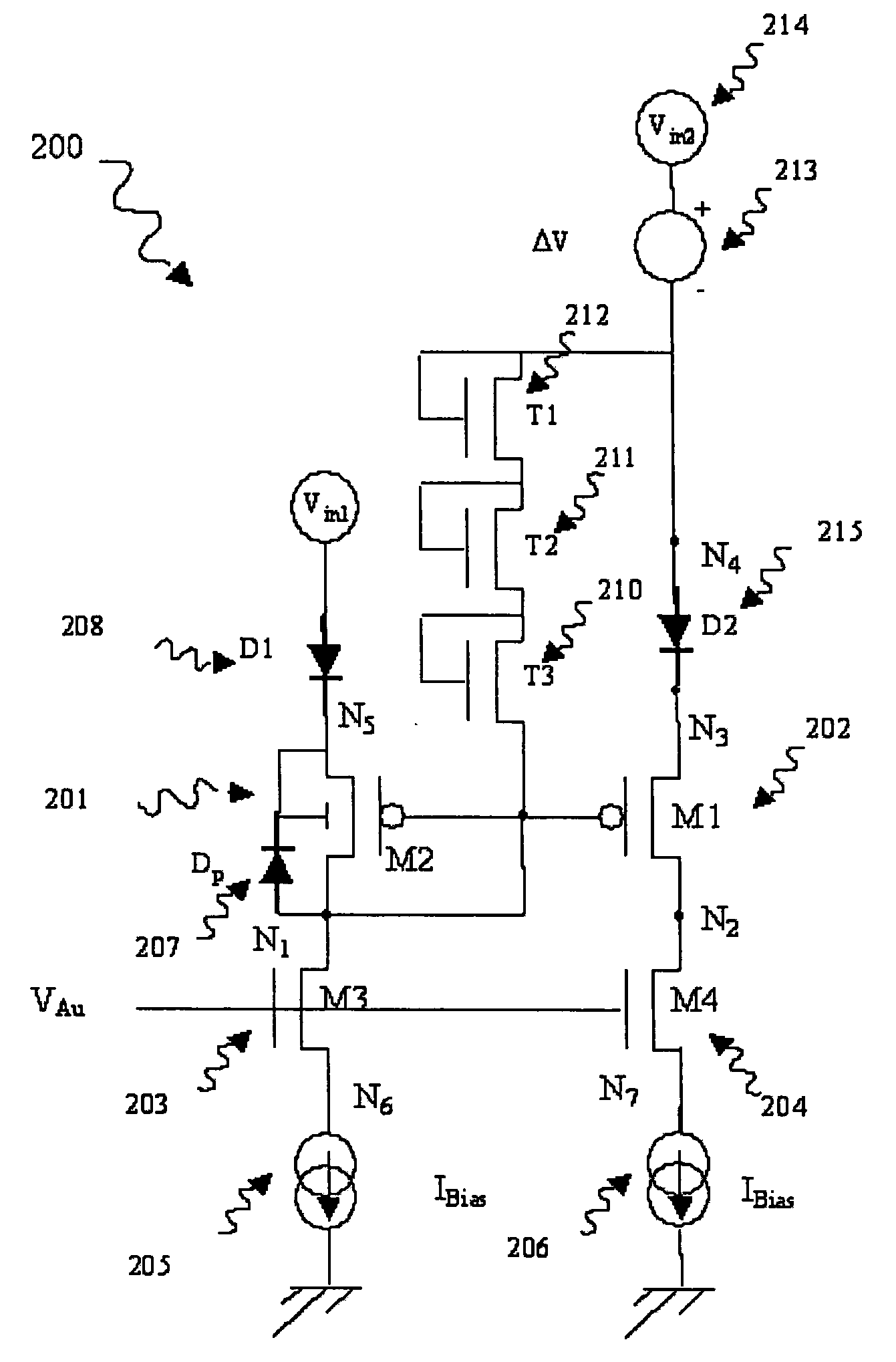
Systems and methods for limiting voltage in wireless power receivers
This disclosure provides systems, methods, and apparatus for the limiting of voltage in wireless power receivers. In one aspect, an apparatus includes a power transfer component configured to receive power wirelessly from a transmitter. The apparatus further includes a circuit coupled to the power transfer component and configured to reduce a received voltage when activated. The apparatus further includes a controller configured to activate the circuit when the received voltage reaches a first threshold value and configured to deactivate the circuit when the received voltage reaches a second threshold value. The apparatus further includes an antenna configured to generate a signal to the transmitter that signals to the transmitter that the received voltage reached the first threshold value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
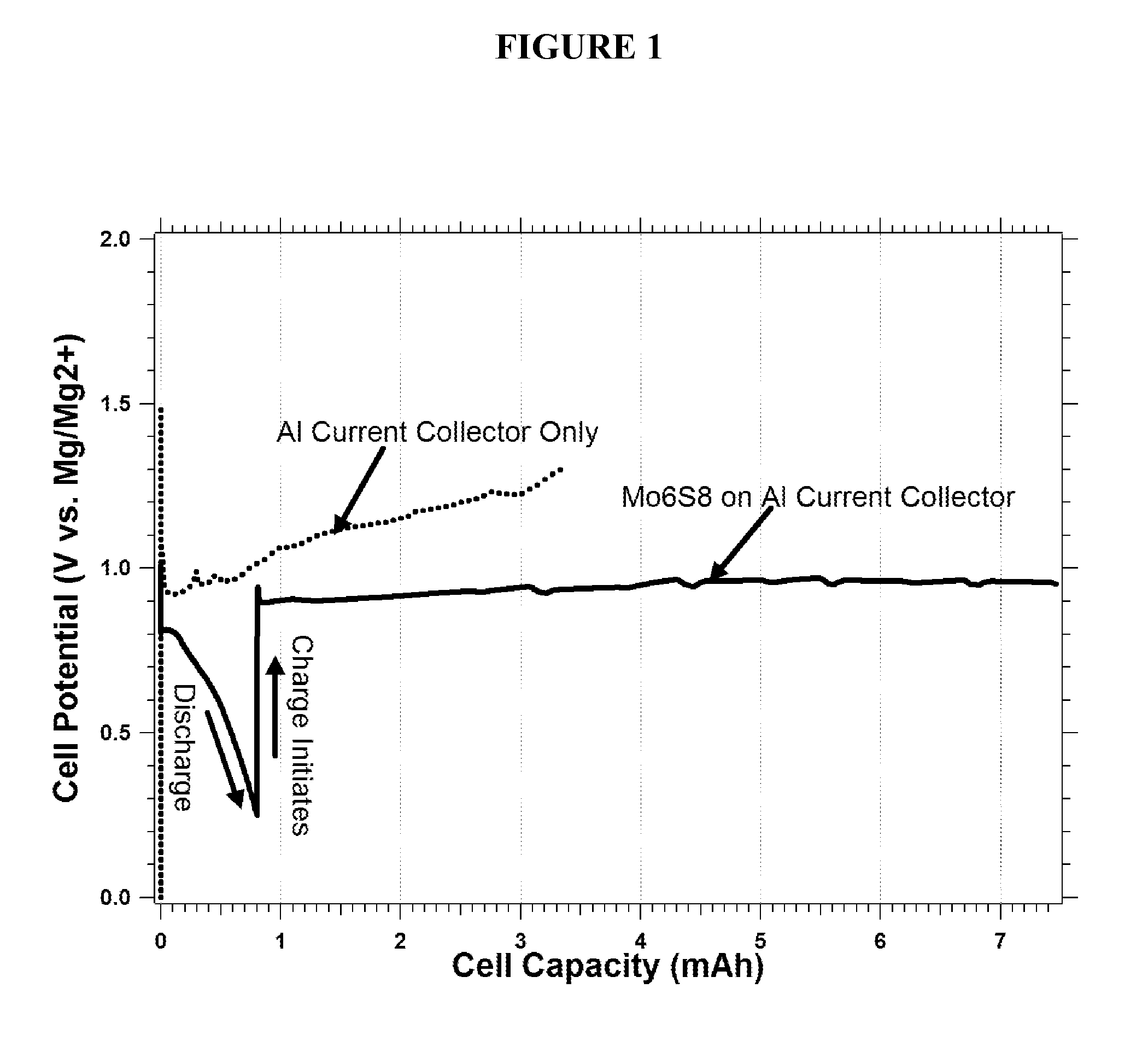
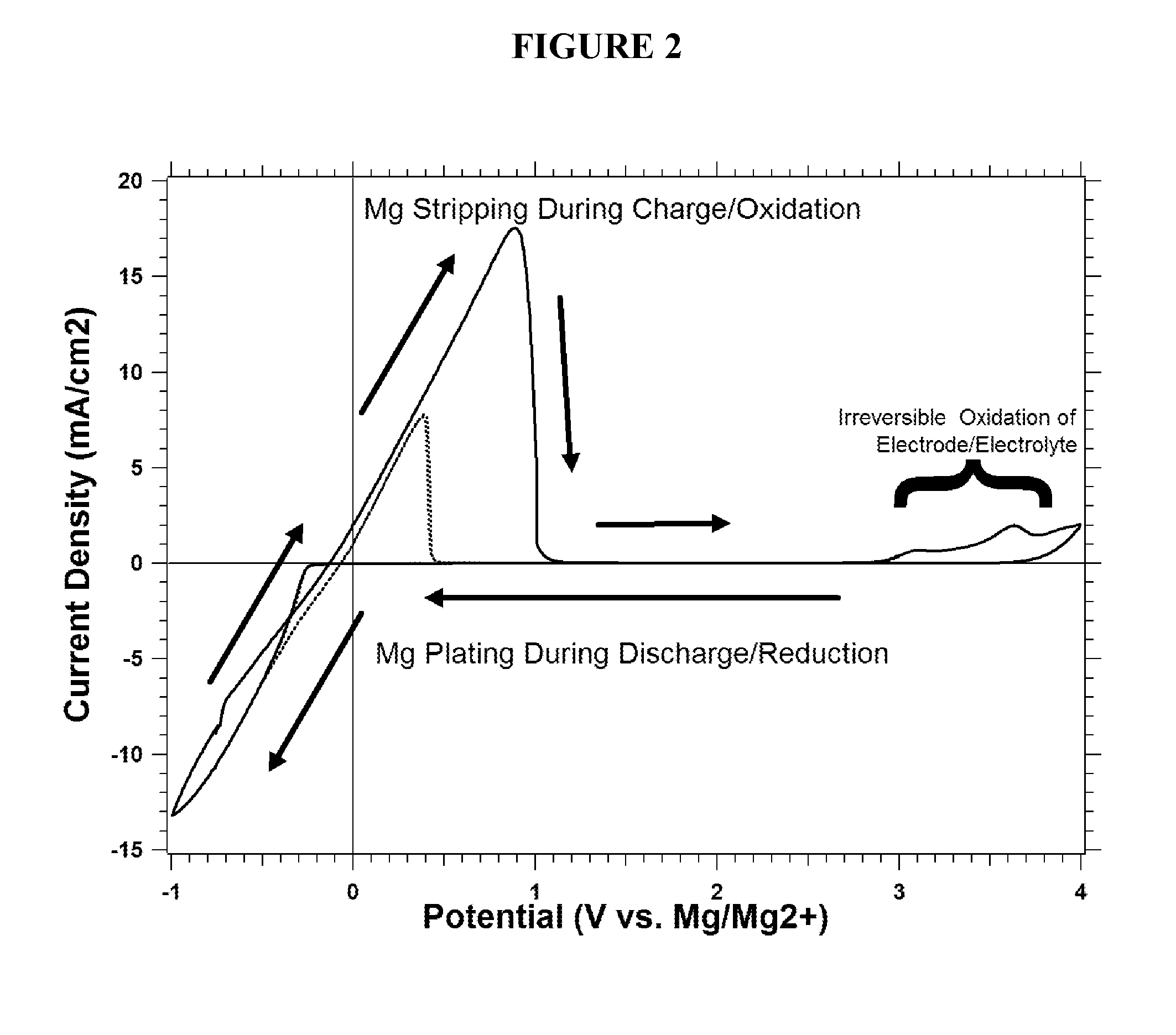
Rechargeable magnesium ion cell components and assembly
InactiveUS20110159381A1Cost-effective fabricationHigh voltageSilver accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsEngineeringMagnesium ion
A magnesium battery electrode assembly is described, including a current collector comprising a carbonaceous material and an electrode layer comprising an electrode active material disposed on the current collector.
Owner:PELLION TECH
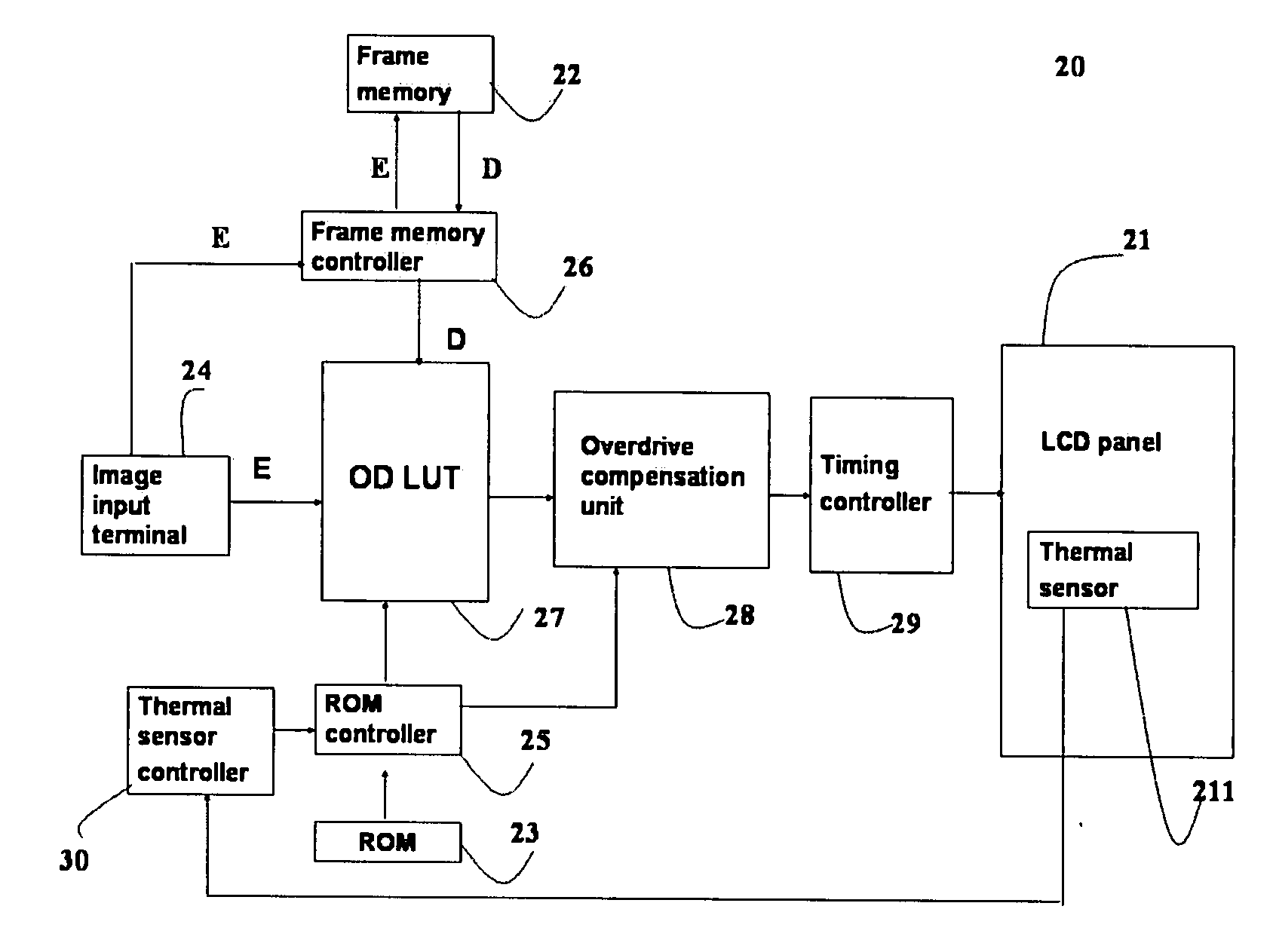
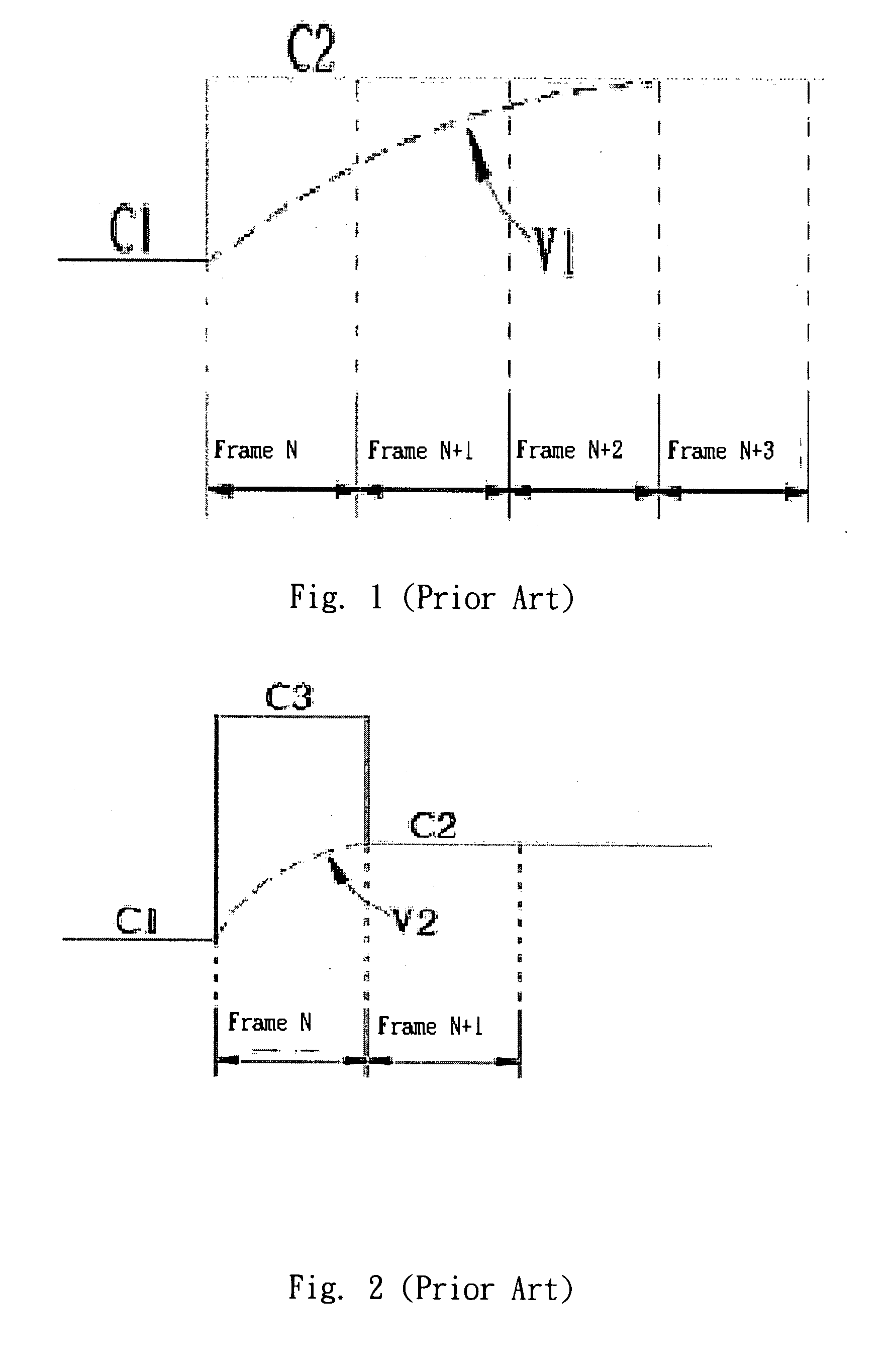
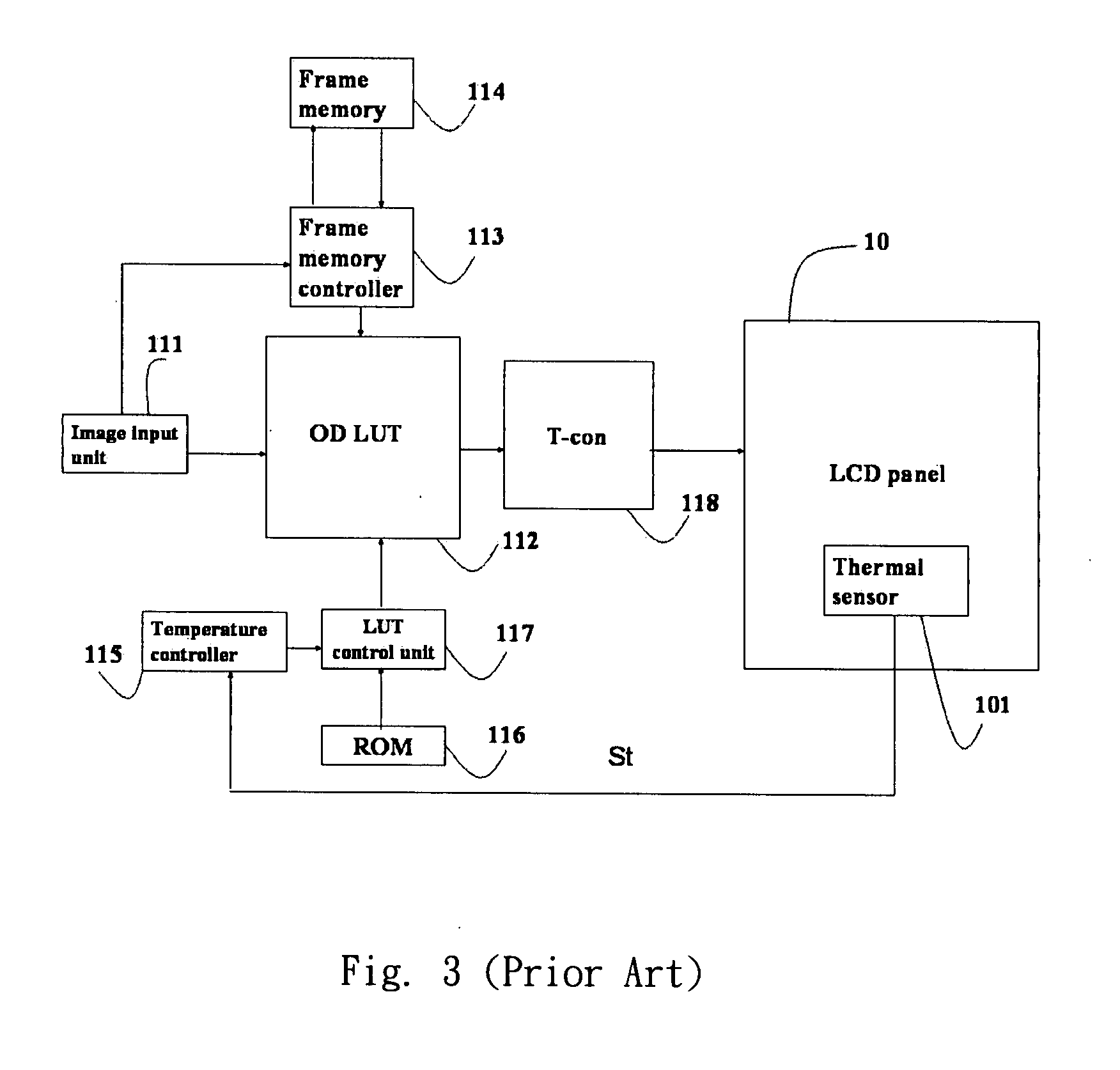
Liquid crystal display driving system and method for driving the same
InactiveUS20080284775A1Short response timeQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The present invention discloses a liquid crystal display driving system that uses at least one temperature sensor to detect a temperature of a LCD panel, and outputs a gamma compensation voltage value according to the detected temperature, and further uses an overdrive compensation unit to receive the gamma compensation voltage value, and obtains the overdrive compensation voltage value of two gamma overdrive compensation curves of a temperature gradient corresponding to a region of the LCD panel by a gamma mapping method, or uses an overdrive compensation unit to derive a corresponding partial compensation data table according to the temperature and the compensation data table, and at least one overdrive compensation table (OD compensation table) corresponding to the change of temperature gradient in a region of the LCD panel is derived, an outputted display image after being processed by an overdrive lookup table (OD LUT) is compensated, so as to adjust the overdrive voltage of the LCD panel and enhance the response time of the liquid crystal display.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
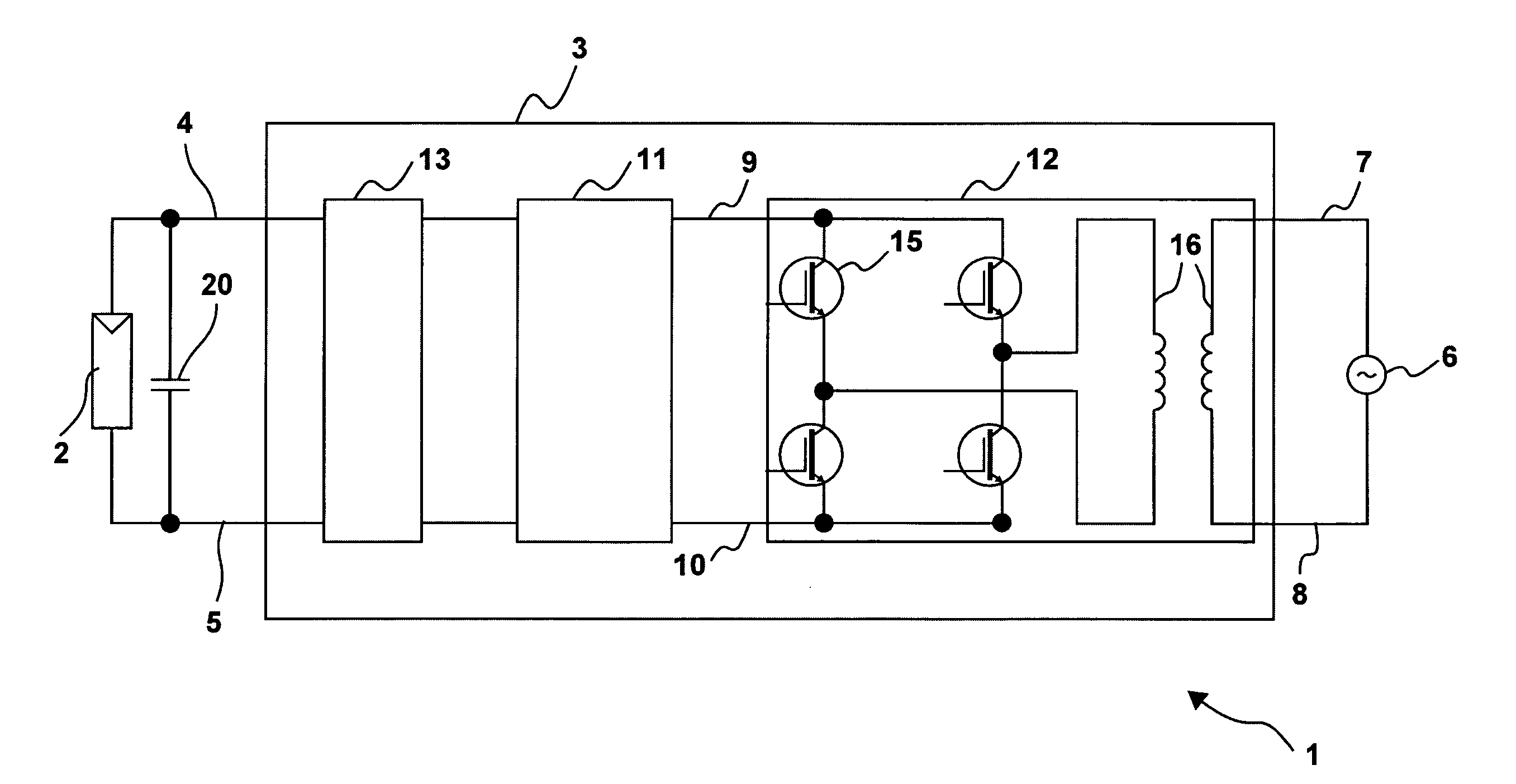
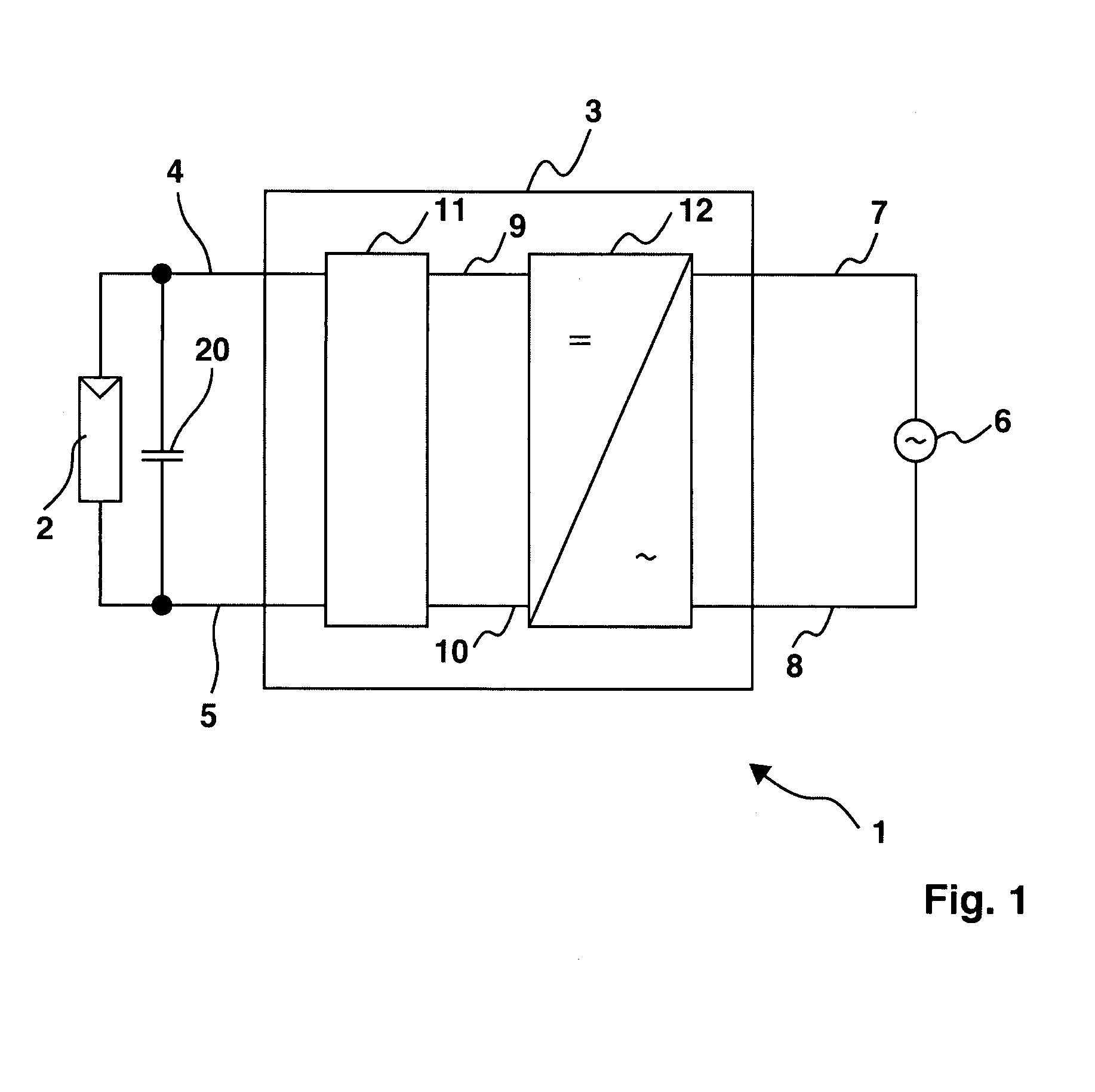
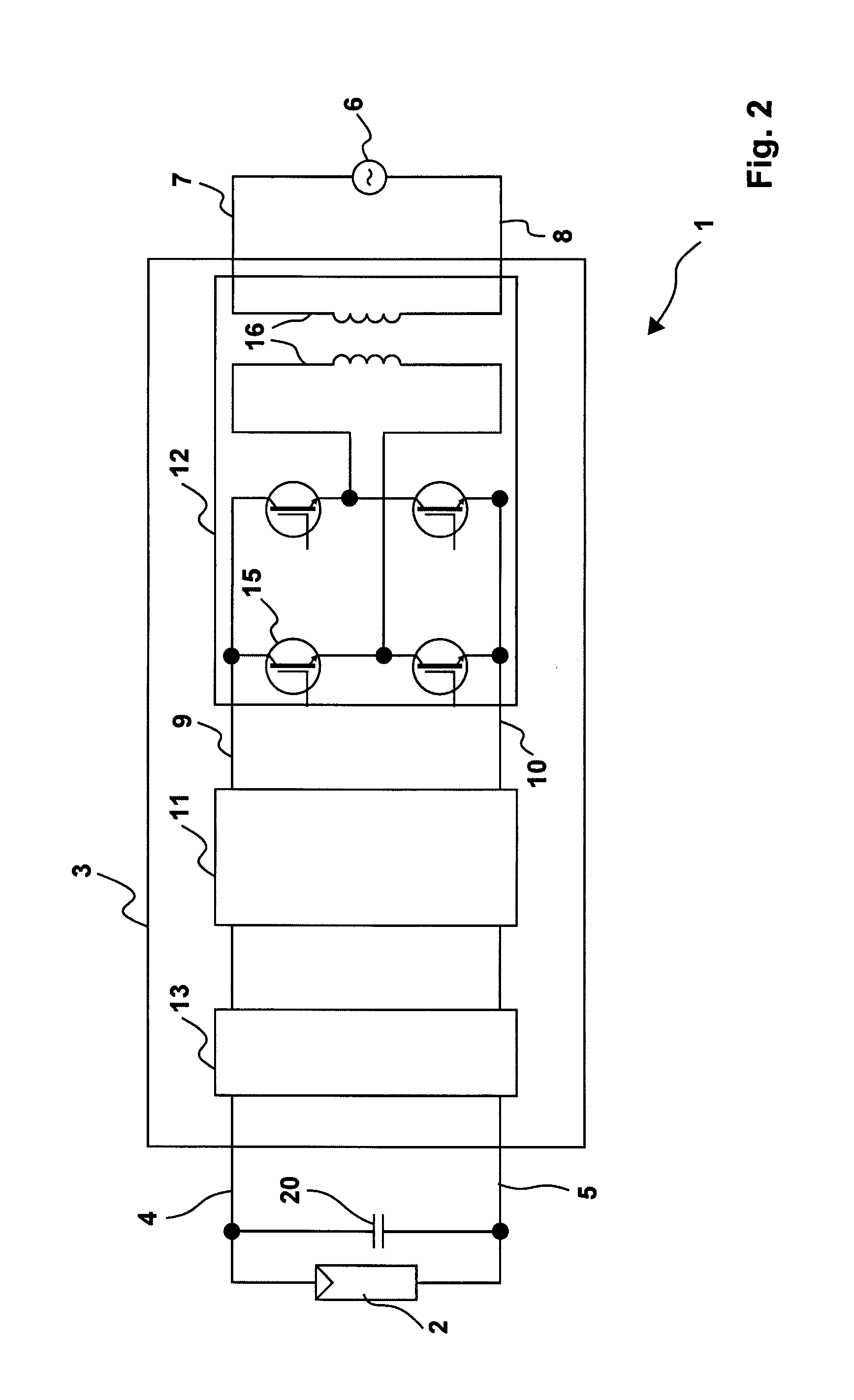
Switching device and method, in particular for photovoltaic generators
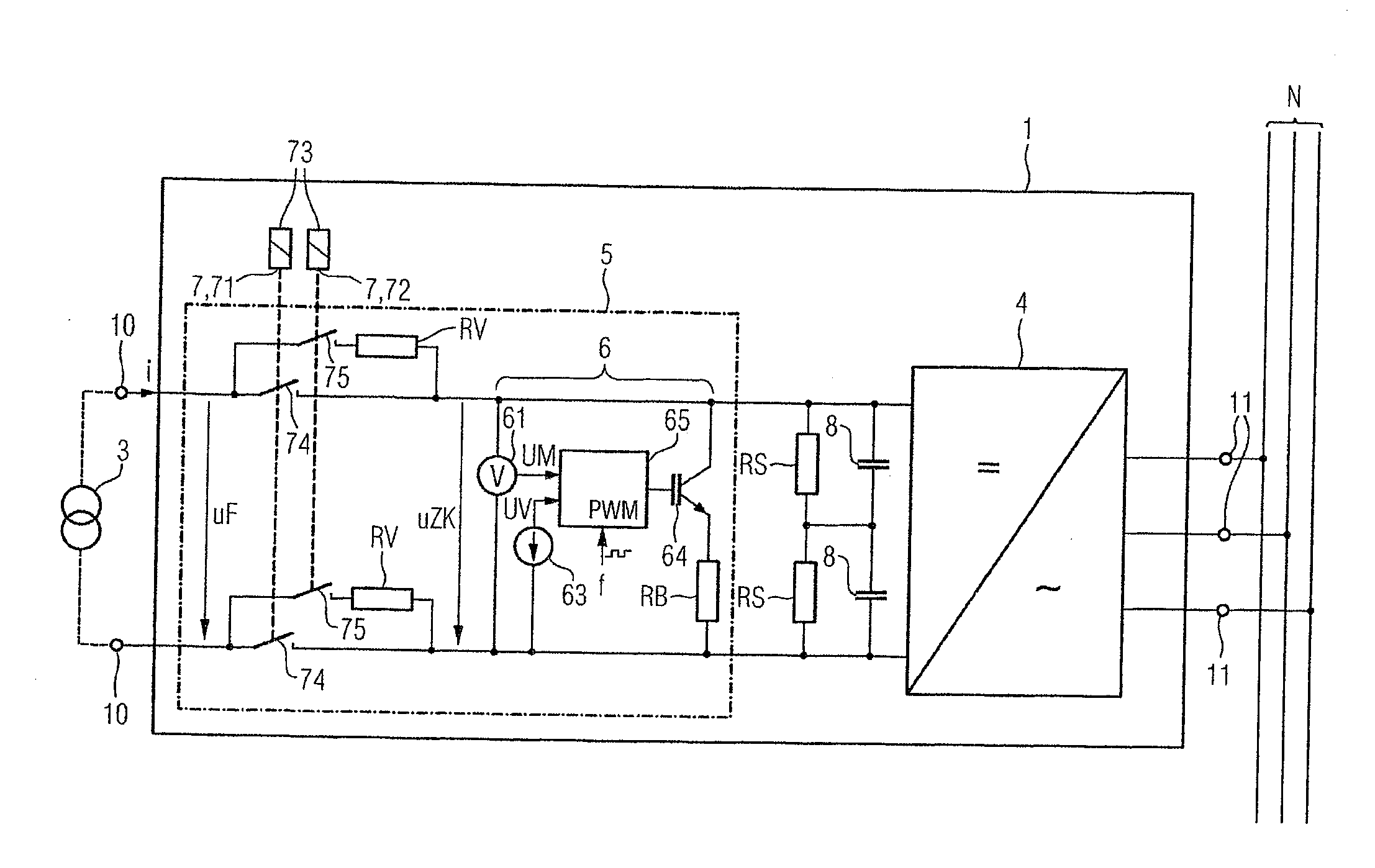
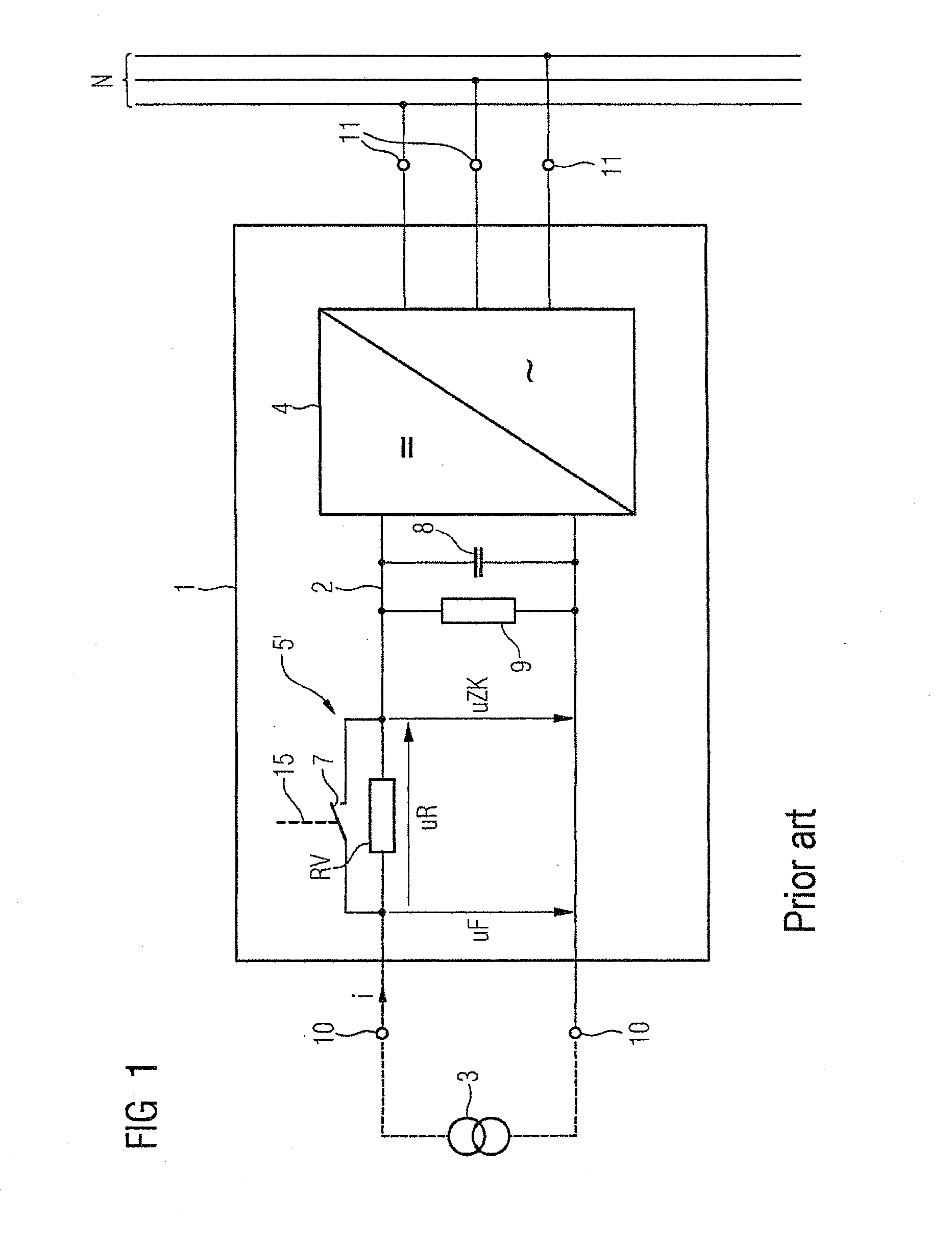
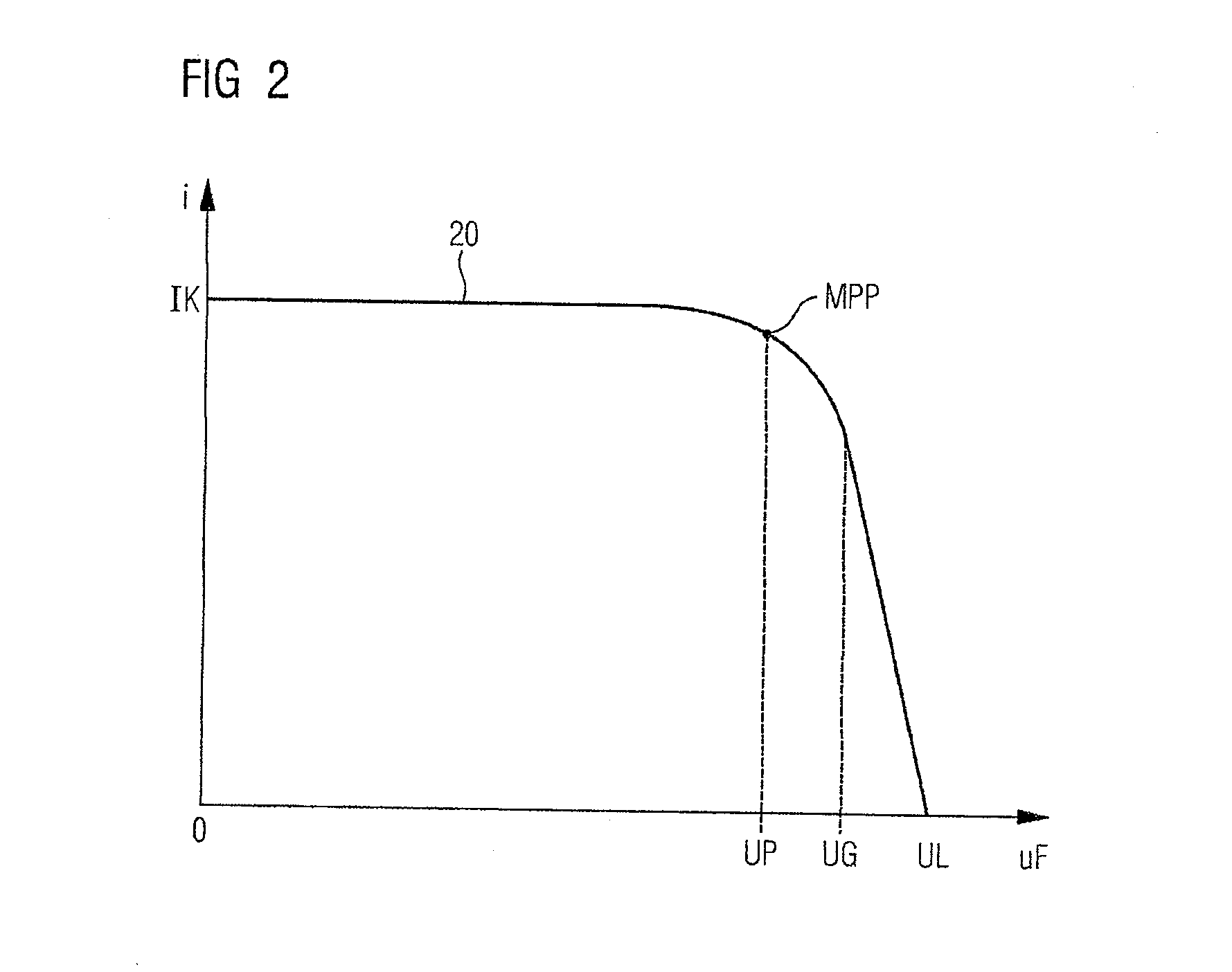
ActiveUS20080094867A1Quick correctionElegant simplificationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower supply linesDc ac converterEngineering
The subject matter of the invention is an inverter (3), more specifically for use in a photovoltaic plant (1) with a direct voltage input (connection terminals 4; 5) for connection to a generator (2) and an alternating voltage output (connection terminals 7; 8) for feeding into an energy supply network (6) as well as with a DC-AC converter (12) with semiconductor switch elements (15) and an intermediate circuit (11), at least one short-circuit switch element (18) being connected in parallel to the generator (2), so that the voltage will not exceed a maximum voltage value neither at the connection terminals (4; 5) of the generator (2) nor between the connection terminals (9; 10) of the inverter. This is achieved in that the inverter (3) comprises, in the intermediate circuit (12), a buffer capacitor (14) that is connected to the generator (2) through a protection diode (17) so that said buffer capacitor (14) will not be discharged upon actuation of the short-circuit switch element (18), the generator (2) working according to a clock rate in the short-circuit mode of operation.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
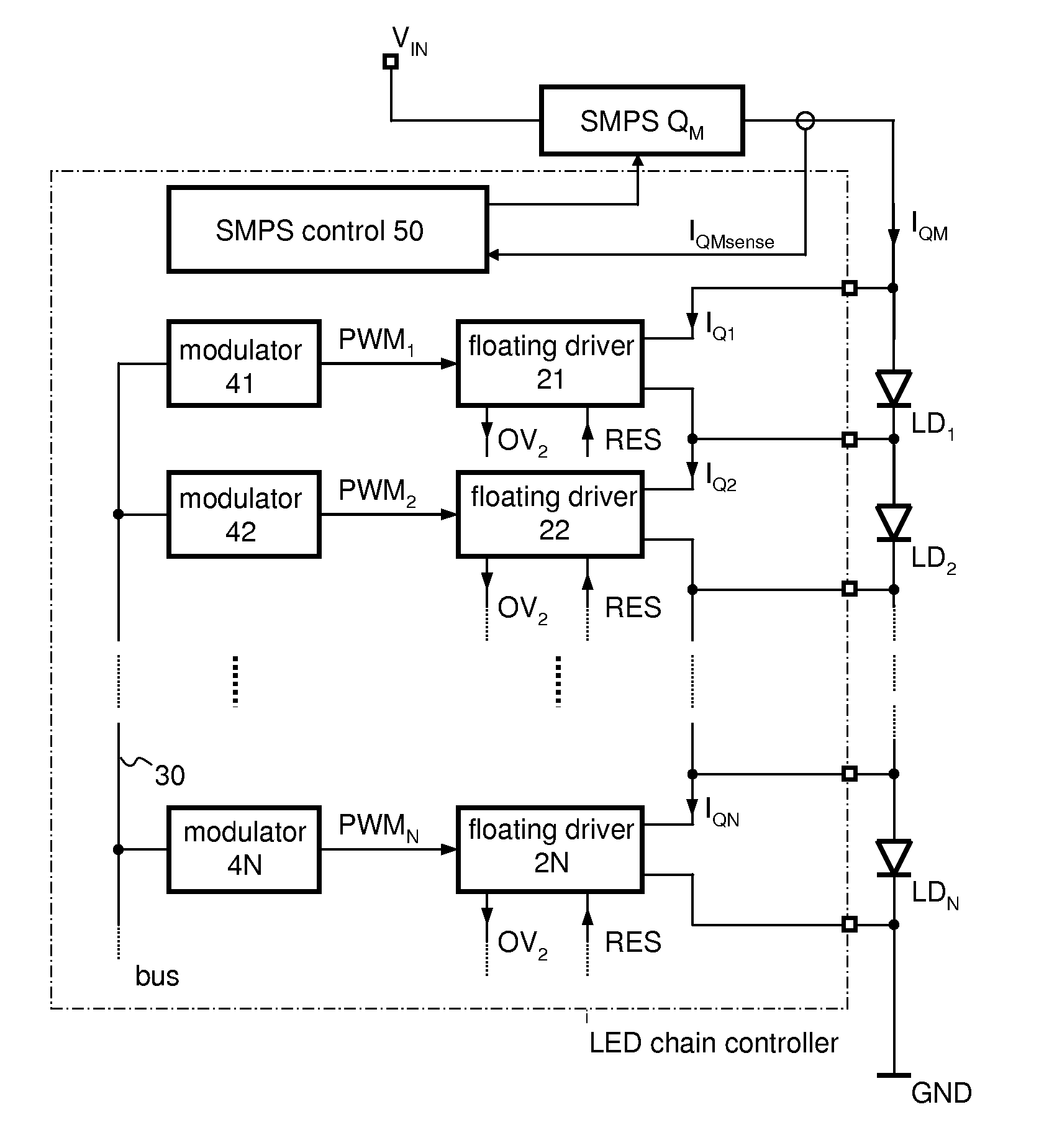
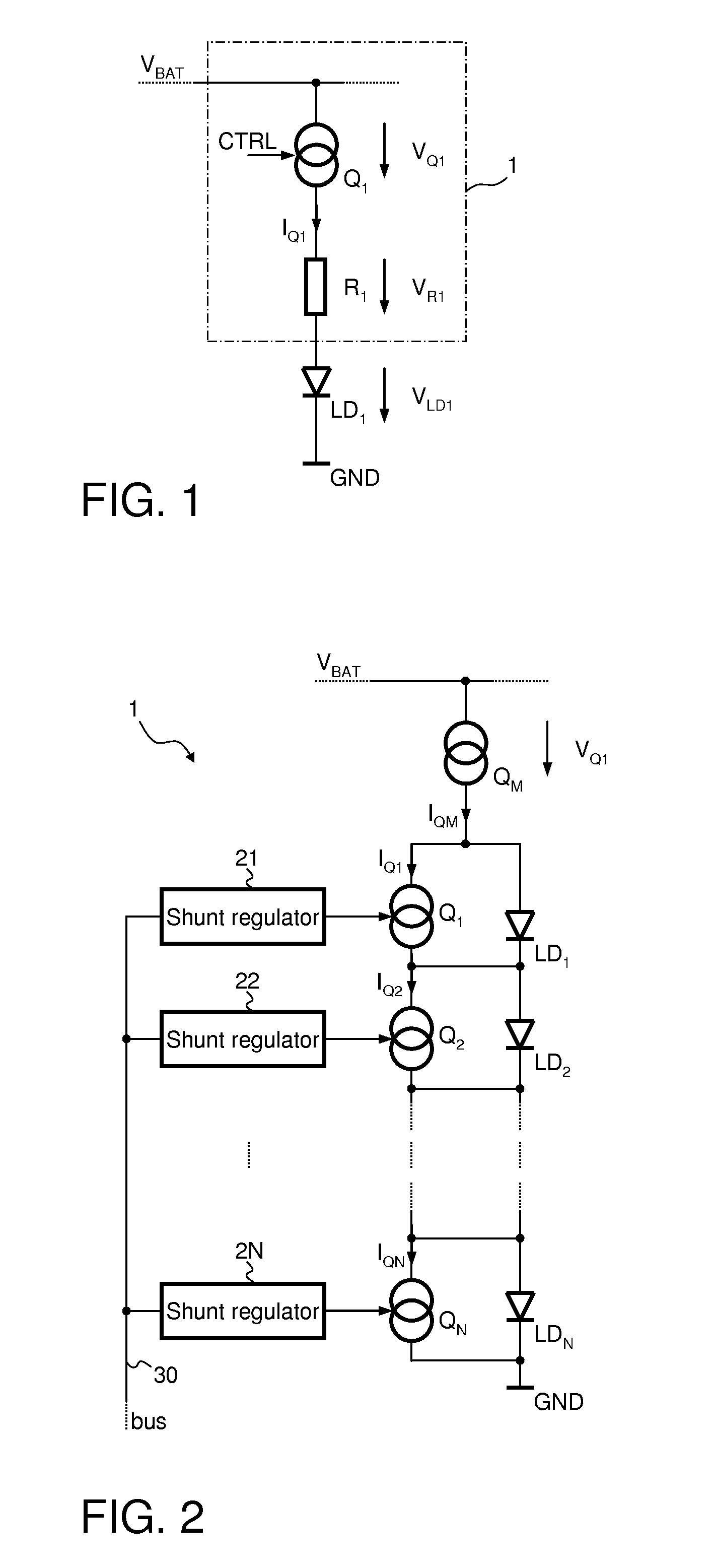
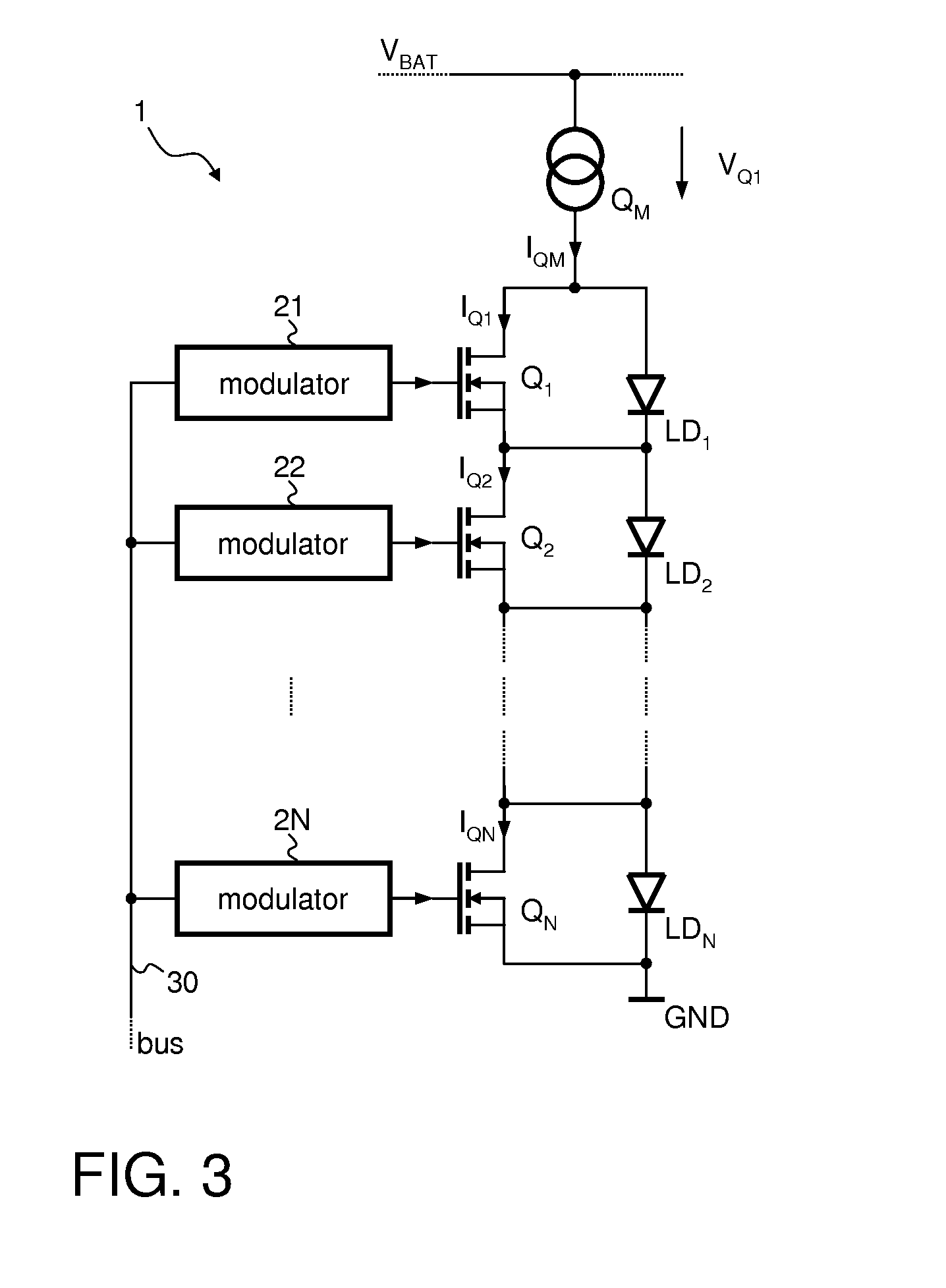
Driver Circuit for Efficiently Driving a Large Number of LEDs
ActiveUS20130049599A1Control intensityLimit voltageElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesInductorCapacitance
A circuit can be used for controlling a plurality of LEDs coupled in series. A switching converter operates as a current source coupled to the plurality of LEDs to provide a constant load current thereto. The switching converter includes an inductor coupled in series with the plurality of LEDs such that the same load current flows through the inductor and the plurality of LEDs. No substantial capacitance is coupled between the inductor and the plurality of LEDs. A floating driver circuit is coupled in parallel with each individual LED of the plurality of LEDs. The floating driver circuit is configured to fully or partially take over the load current thereby bypassing the respective LED in accordance with a respective modulated input signal to control the intensity of the light emitted by the LED.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
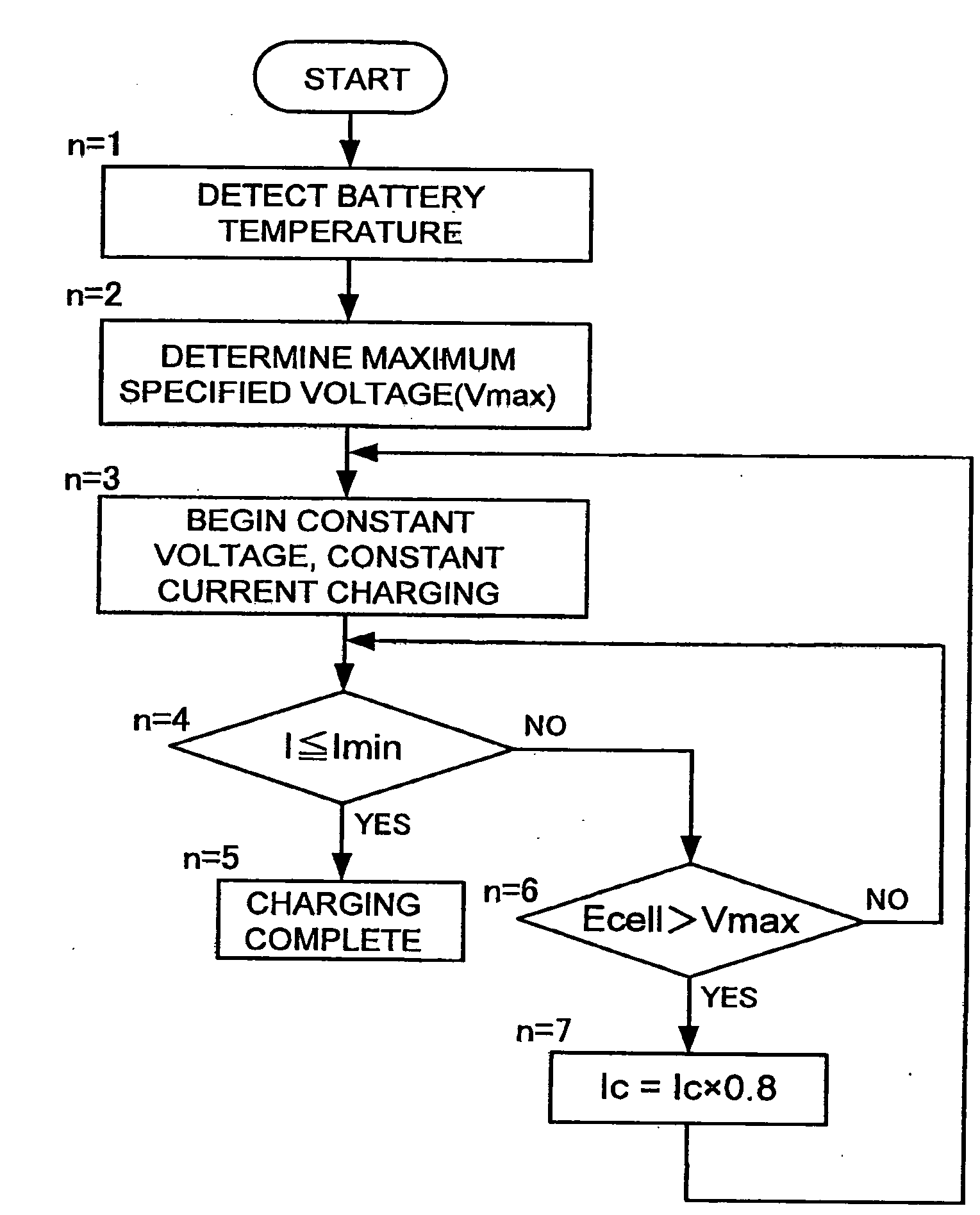
Method of charging a battery array
ActiveUS20090015209A1Simplifying charging voltage controlAvoid performanceElectric powerArrangements for several simultaneous batteriesBattery cellConstant current
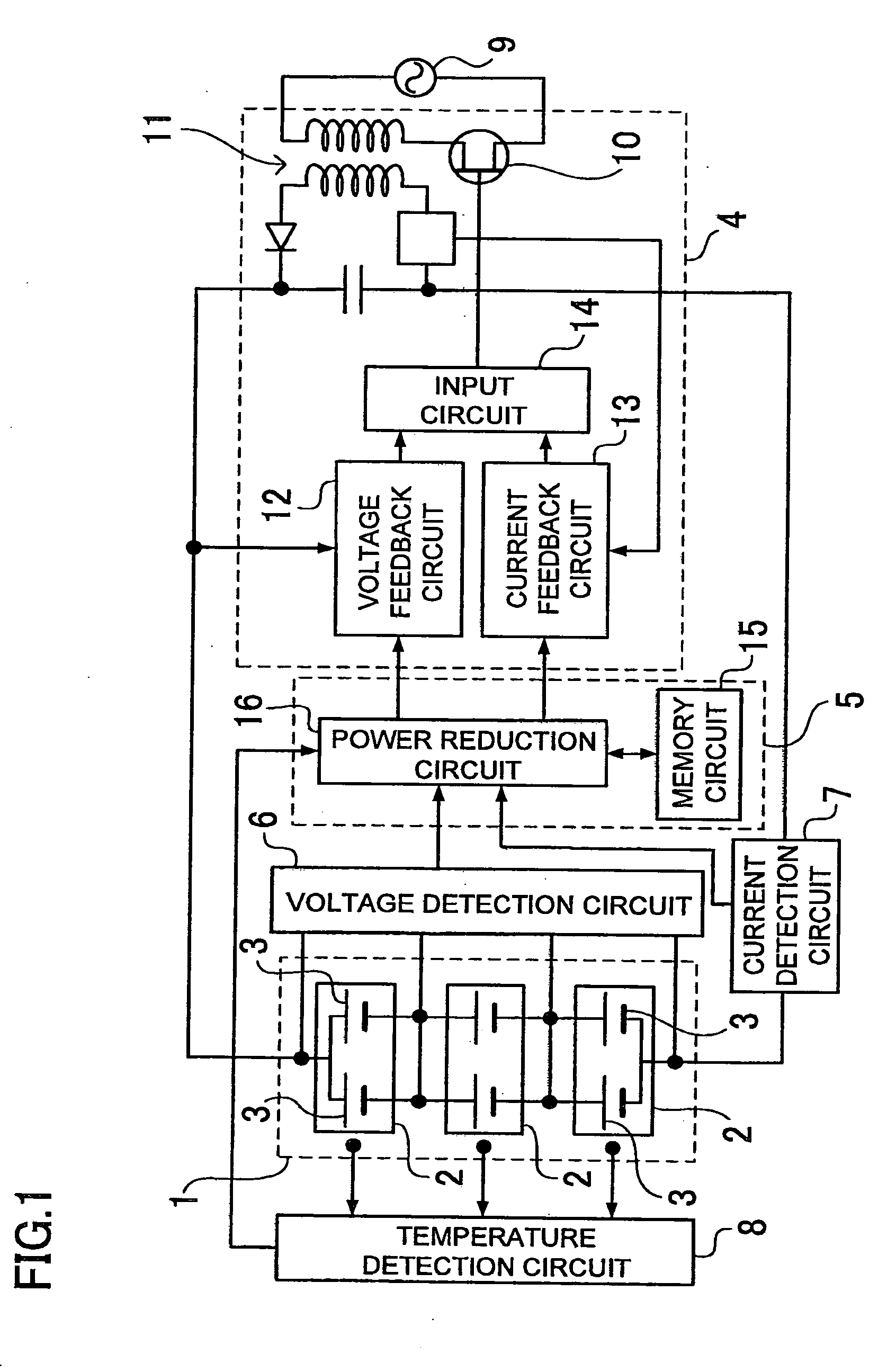
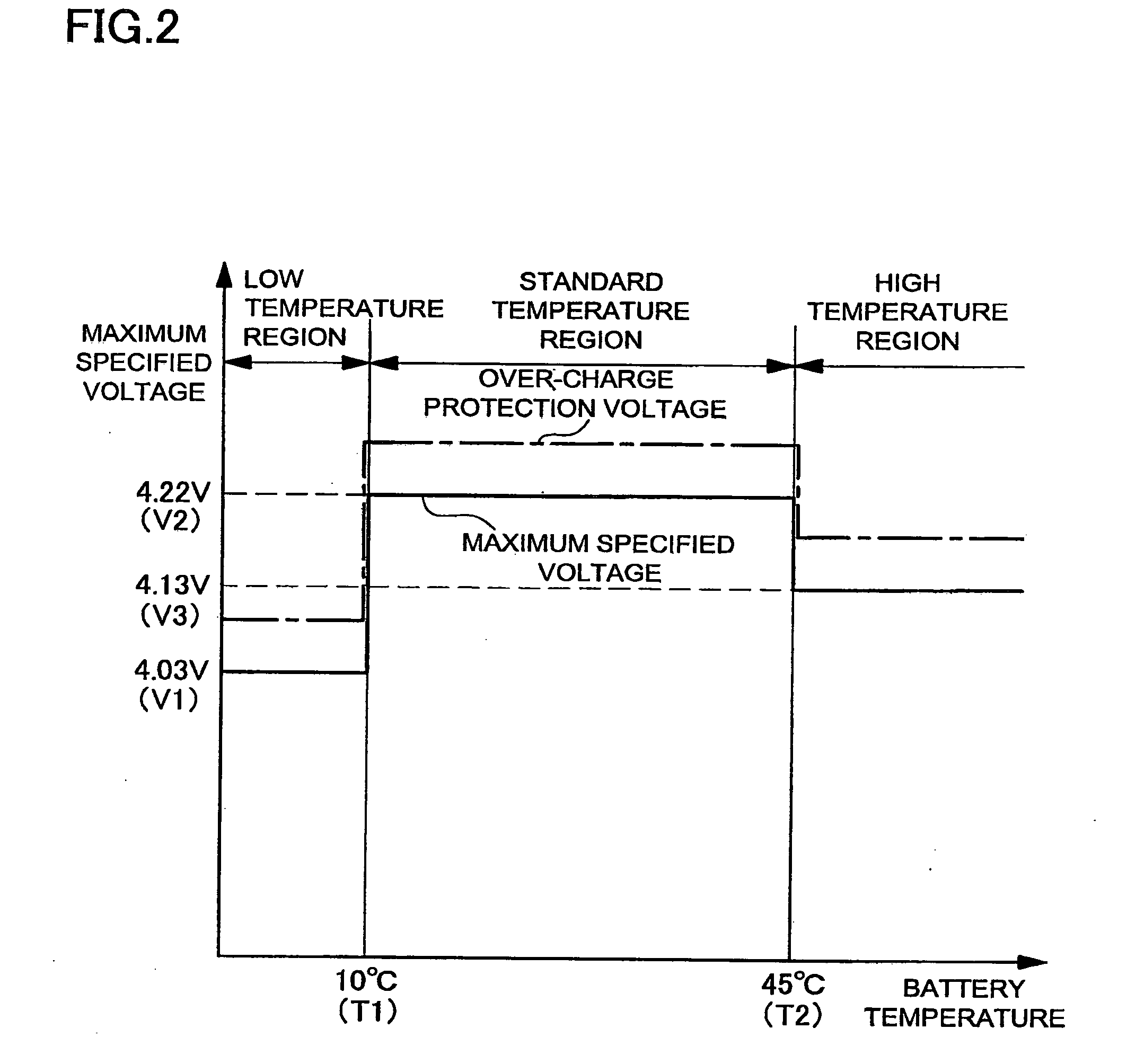
The method of charging a battery array performs constant current, constant voltage charging of a battery array while detecting the voltage of each battery. The battery array is a plurality of series connected batteries. The charging method detects the voltage of each battery cell at a prescribed sampling rate. When the voltage of any battery cell exceeds a preset maximum specified voltage, charging power is reduced for constant current, constant voltage charging of the battery array.
Owner:PANASONIC ENERGY CO LTD
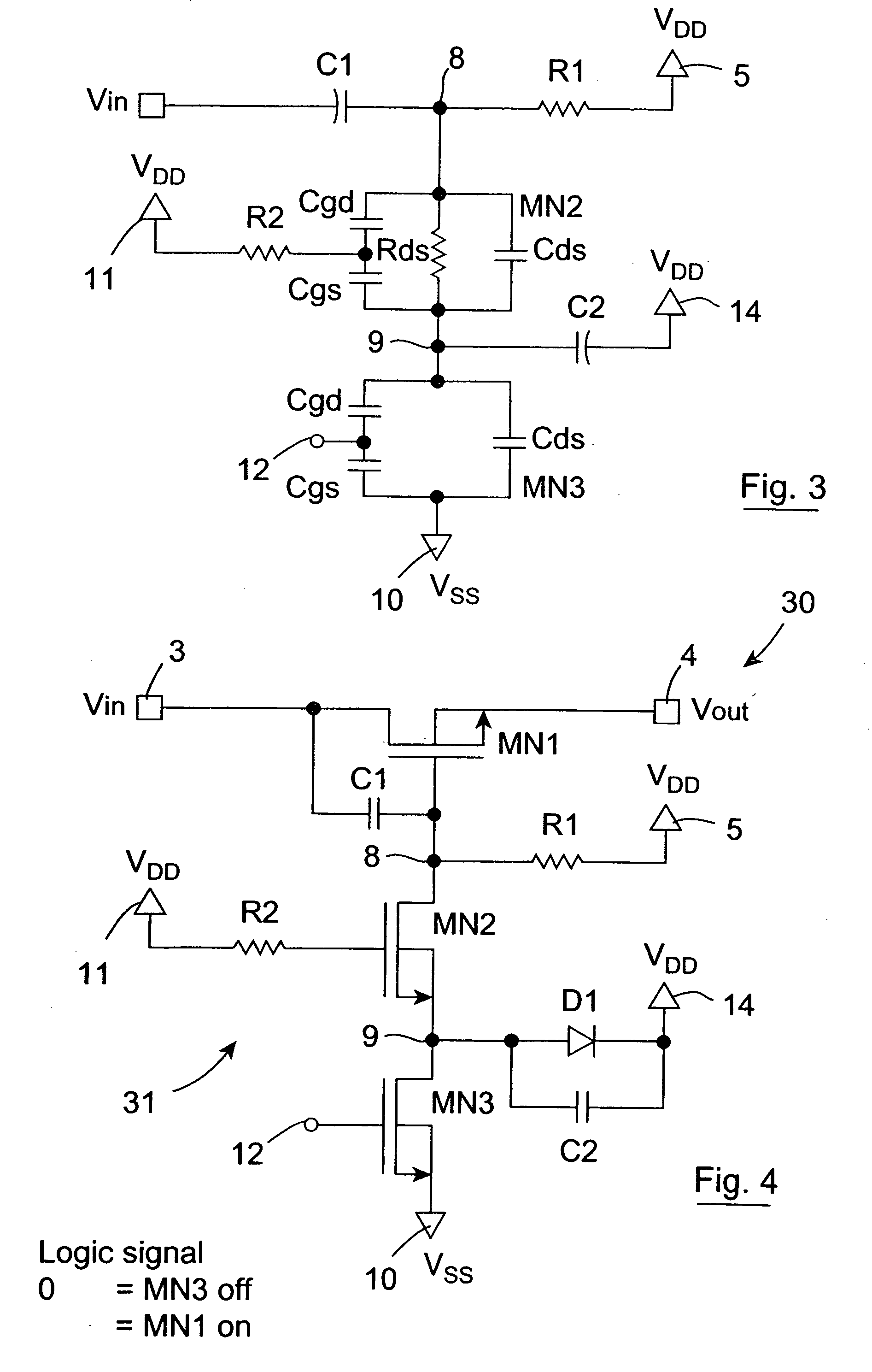
Open drain driver, and a switch comprising the open drain driver
ActiveUS20060255852A1Good overvoltage protectionSuitable for useTransistorElectrical testingMOSFETCapacitance
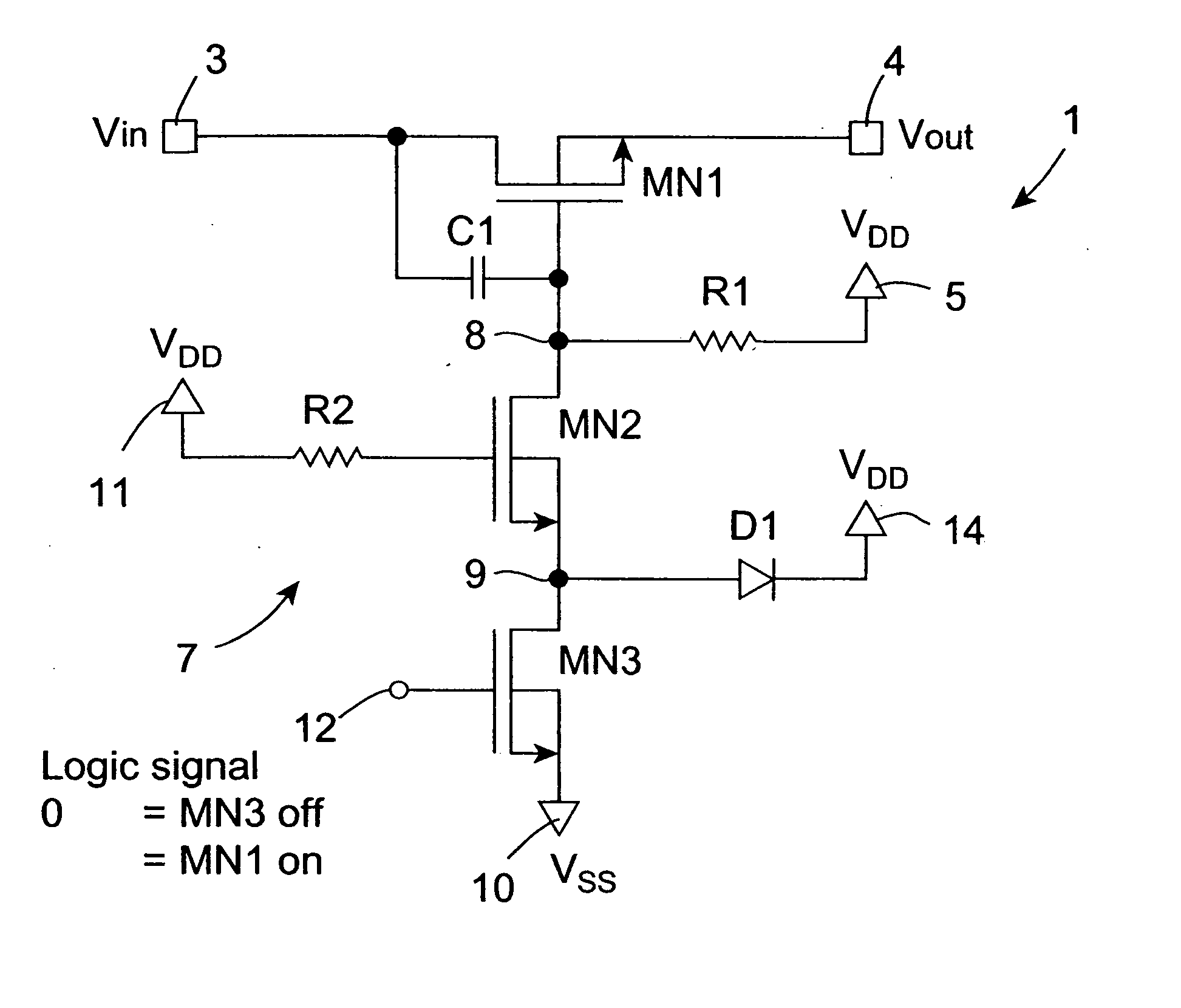
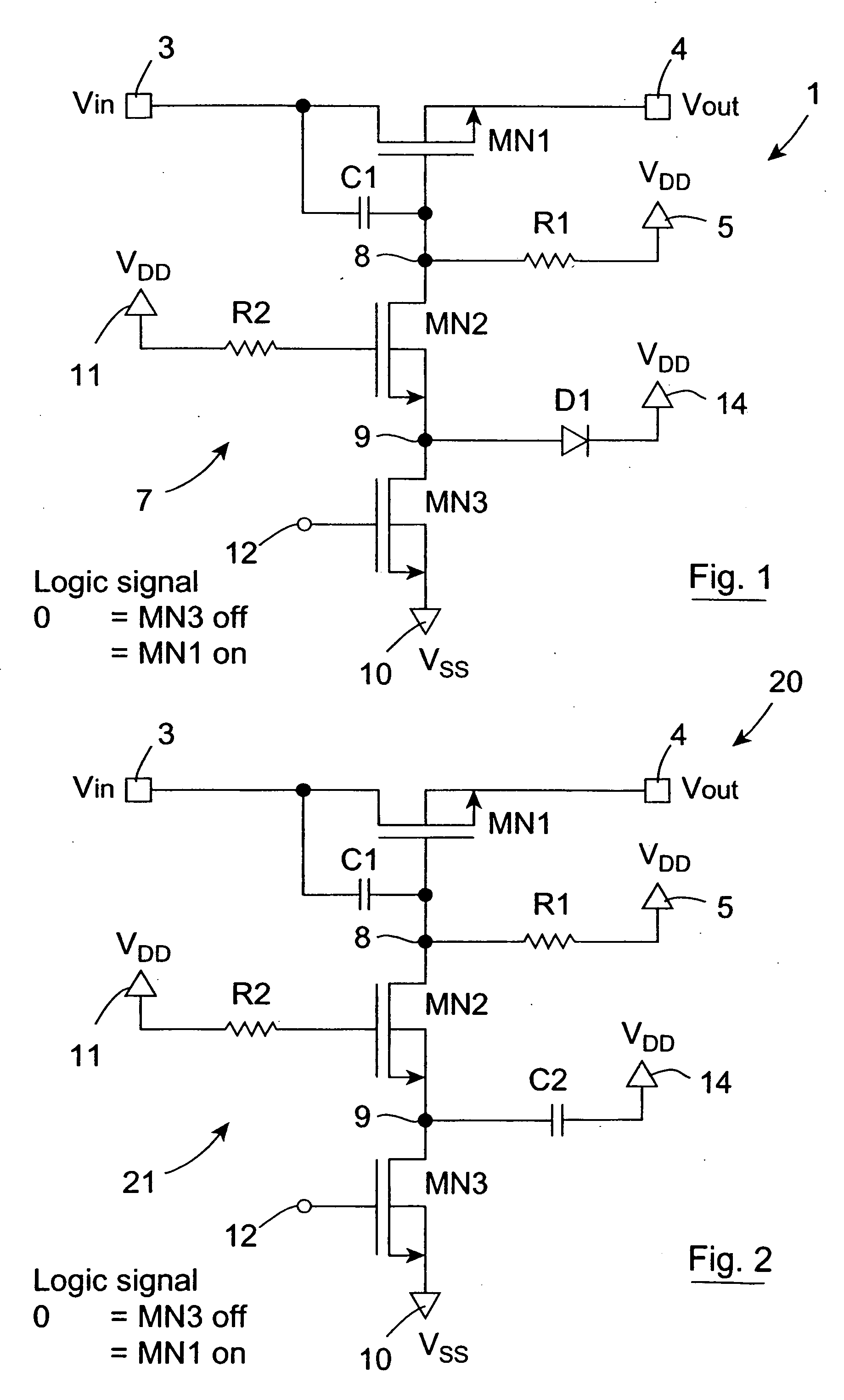
An open drain driver (7) selectively switches a MOSFET switch (MN1) which is passively held in the conducting state into the non-conducting state. The MOSFET switch (MN1) switches an AC analogue input signal on a main input terminal (3) to a main output terminal (4) and the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) is AC coupled by a capacitor (C1) to the drain thereof. The open drain driver (7) comprises a first MOSFET (MN2) and a second MOSFET (MN3) through which the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) is pulled to ground (Vss). The gate of the first MOSFET (MN2) is coupled to the supply voltage (VDD) for maintaining the first MOSFET (MN2) in the open state. A control signal is applied to the gate of the second MOSFET (MN3) for selectively operating the open drain driver (7) in the conducting state for operating the MOSFET switch (MN1) in the non-conducting state. When the second MOSFET (MN3) is in the non-conducting state, the first MOSFET (MN2) remains in the conducting state until the voltage on a coupling node (9) between the first and second MOSFETs (MN2,MN3) equals the difference between its gate voltage and its threshold voltage, at which stage, any over-voltages applied to the gate of the MOSFET switch (MN1) are divided between the first and second MOSFETs (MN2,MN3). A coupling diode (D1) coupling the coupling node (9) to the supply voltage (VDD) clamps the voltage on the coupling node (9) at the supply voltage (VDD) plus the conducting voltage of the diode (D1), in the event of the voltage on the coupling node (9) rising after the first MOSFET (MN2) has gone into the non-conducting state. The coupling node (9) may be capacitively coupled to the supply voltage (VDD) by a coupling capacitor instead of or as well as the diode (D1) for limiting the voltage on the coupling node (9).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
RFID tags with shielding structure for incorporation into microwavable food packaging
ActiveUS20180189623A1Limit voltageImprove the immunityContainer decorationsLevel indicationsDielectricElectricity
RFID tags are provided for incorporation into the packaging of a microwavable food item, with the RFID tag being configured to be safely microwaved. The RFID tag includes an antenna defining a gap and configured to operate at a first frequency. An RFID chip is electrically coupled to the antenna across the gap. A shielding structure is electrically coupled to the antenna across the gap and overlays the RFID chip. The shielding structure includes a shield conductor and a shield dielectric at least partially positioned between the shield conductor and the RFID chip. The shielding structure is configured to limit the voltage across the gap when the antenna is exposed to a second frequency that is greater than first frequency. In additional embodiments, RFID tags are provided for incorporation into the packaging of a microwavable food item, with the RFID tag being configured to be safely microwaved. The RFID tag includes an RFID chip and an antenna electrically coupled to the RFID chip. The antenna may have a sheet resistance in the range of approximately 100 ohms to approximately 230 ohms, optionally with an optical density in the range of approximately 0.18 to approximately 0.29. Alternatively, or additionally, the antenna may be configured to fracture into multiple pieces upon being subjected to heating in a microwave oven. Alternatively, or additionally, the RFID tag may be incorporated in an RFID label that is secured to the package by a joinder material with a greater resistance than that of the antenna, such as a sheet resistance in the range of approximately 100 ohms to approximately 230 ohms.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Arc welding method and arc welding apparatus
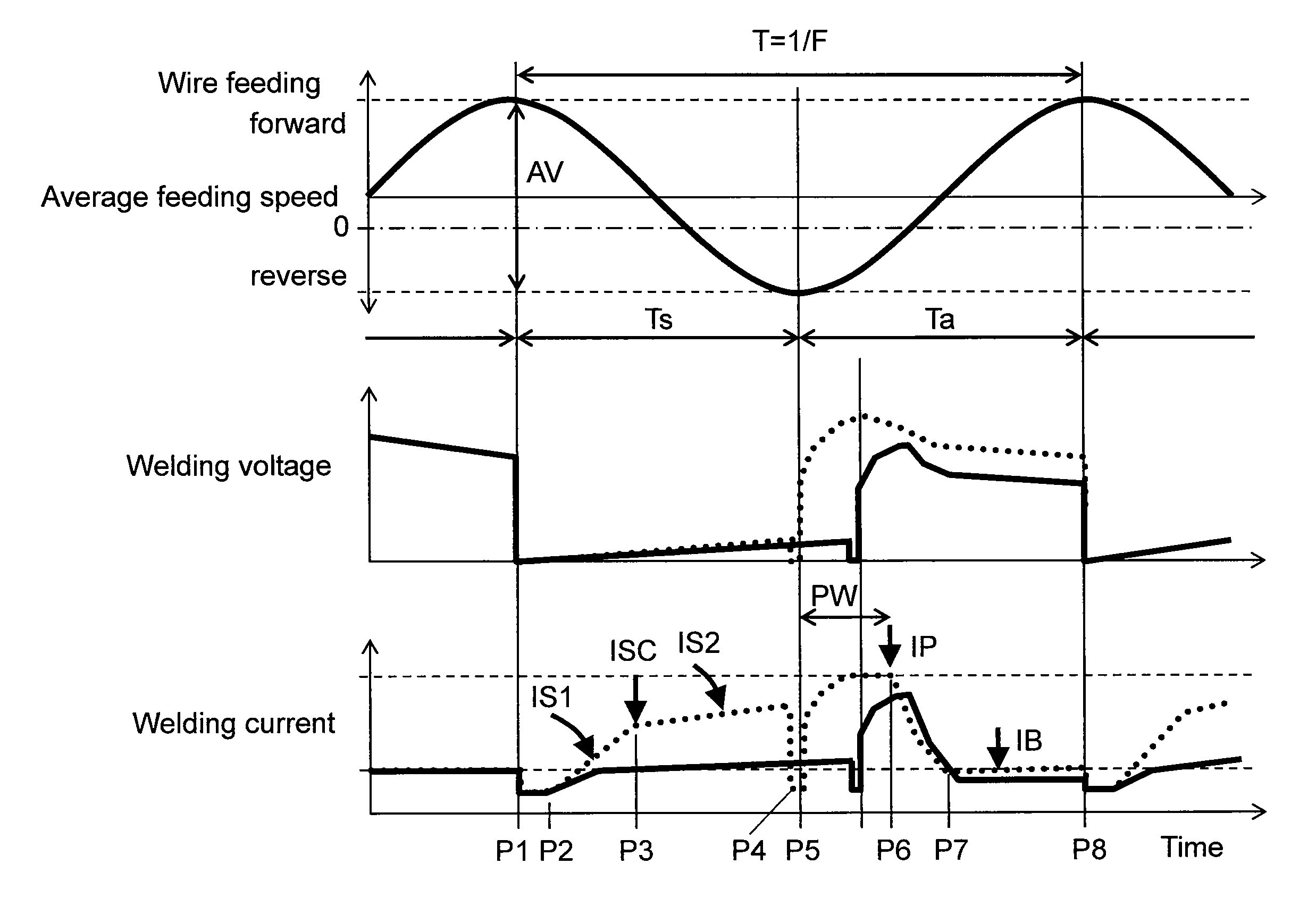
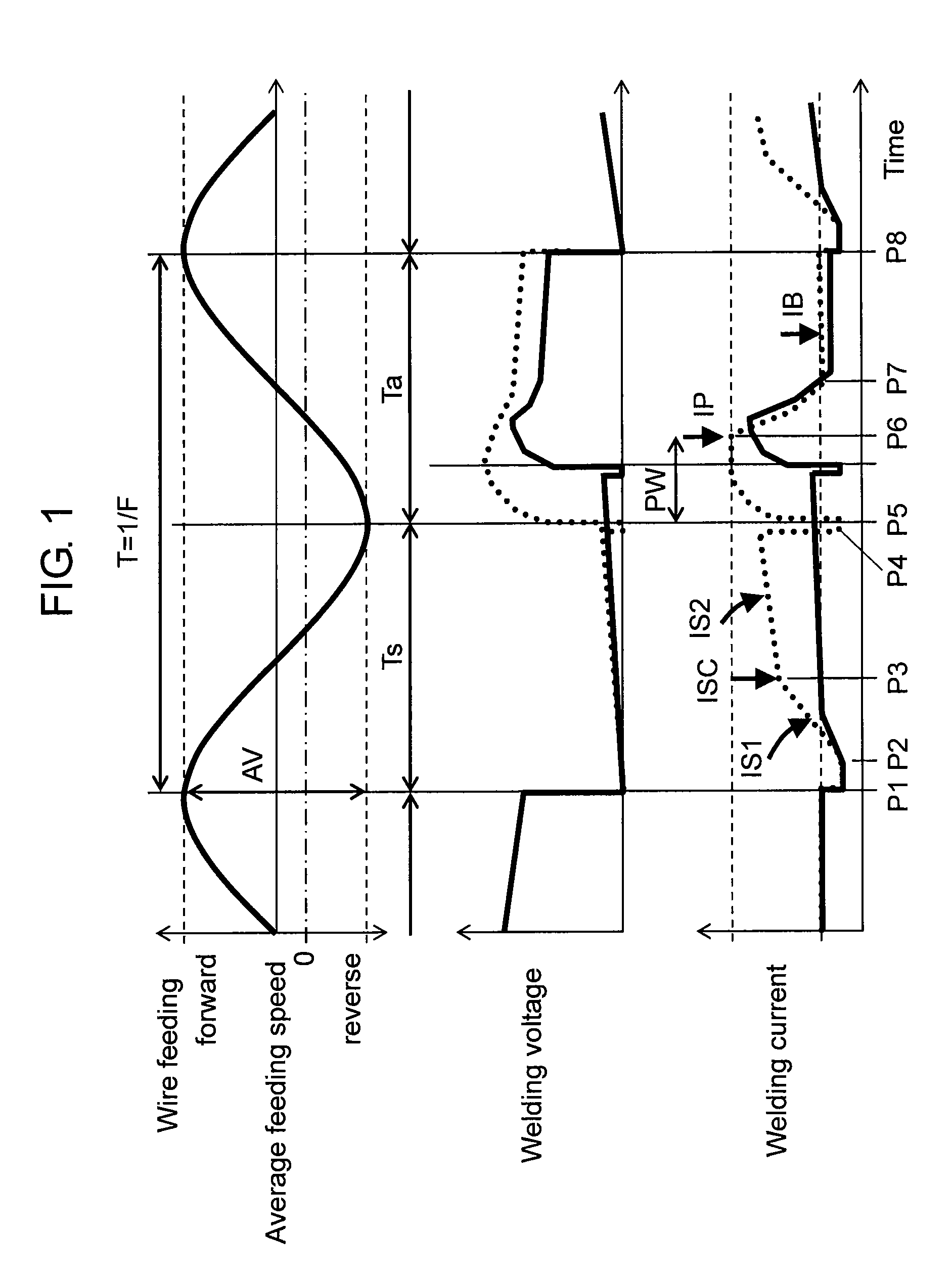
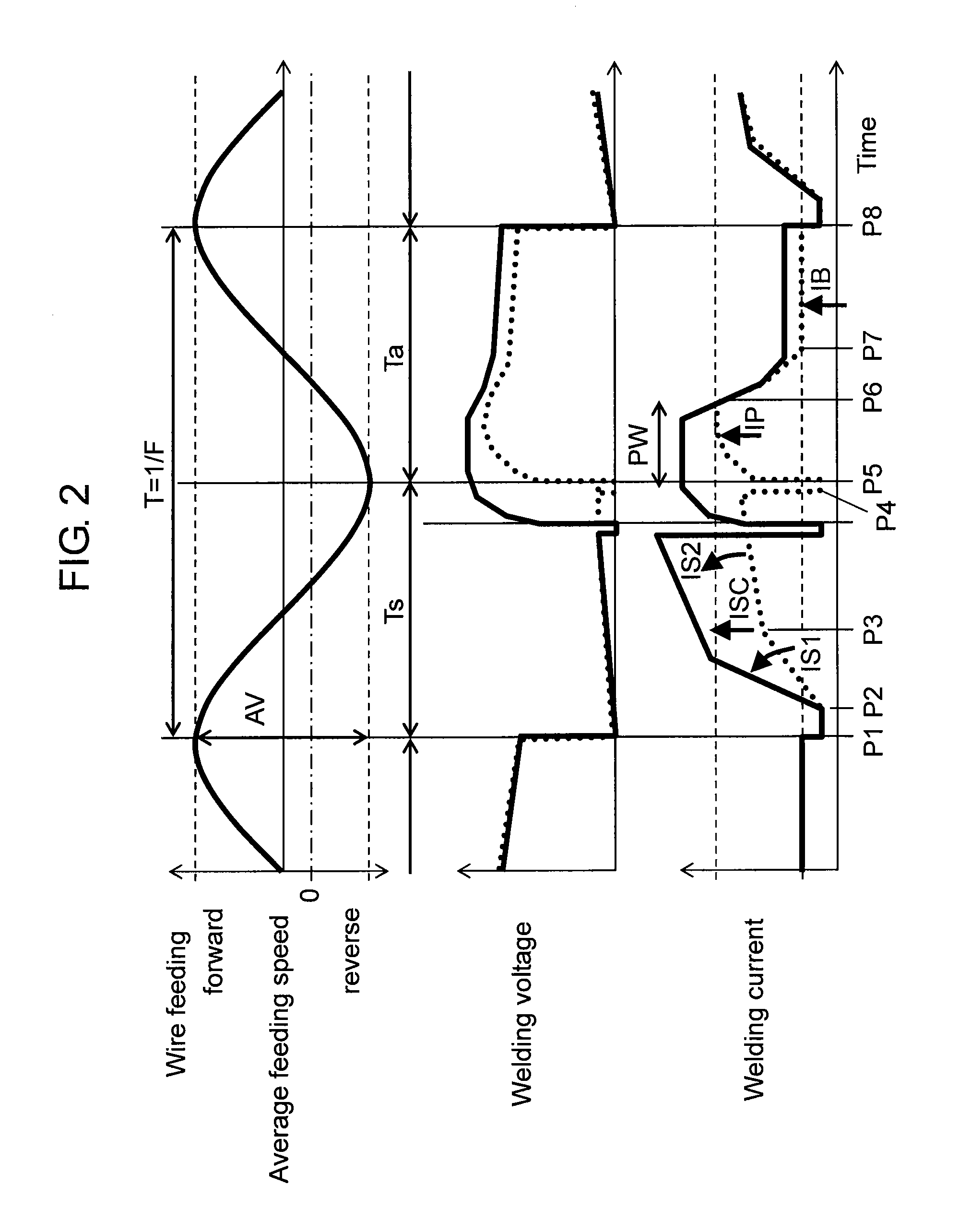
ActiveUS20120145691A1Stable controlReduce componentsArc welding apparatusEngineeringElectrical current
An arc welding method of the present invention controls a short-circuit current increasing gradient (di / dt), an inflection point at which the short-circuit current increasing gradient (di / dt) changes, the current in a peak period and in a base period, and the time of the peak period in accordance with a difference between a set voltage and an output voltage. This allows the output voltage to be matched with the set voltage, and stabilizes the arc. Thereby, a stable arc welding method can be implemented, even as a method for outputting a welding current based on a welding voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
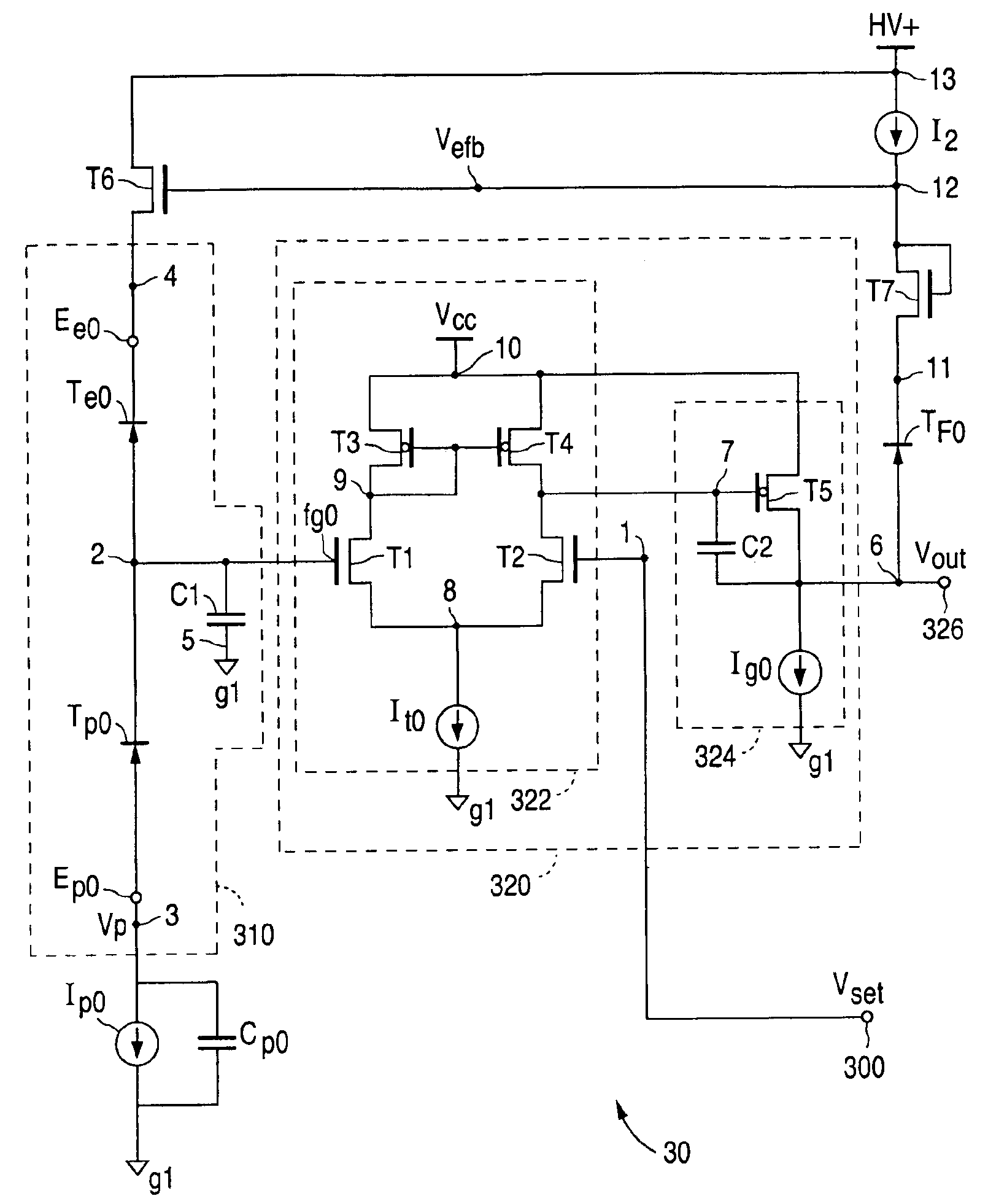
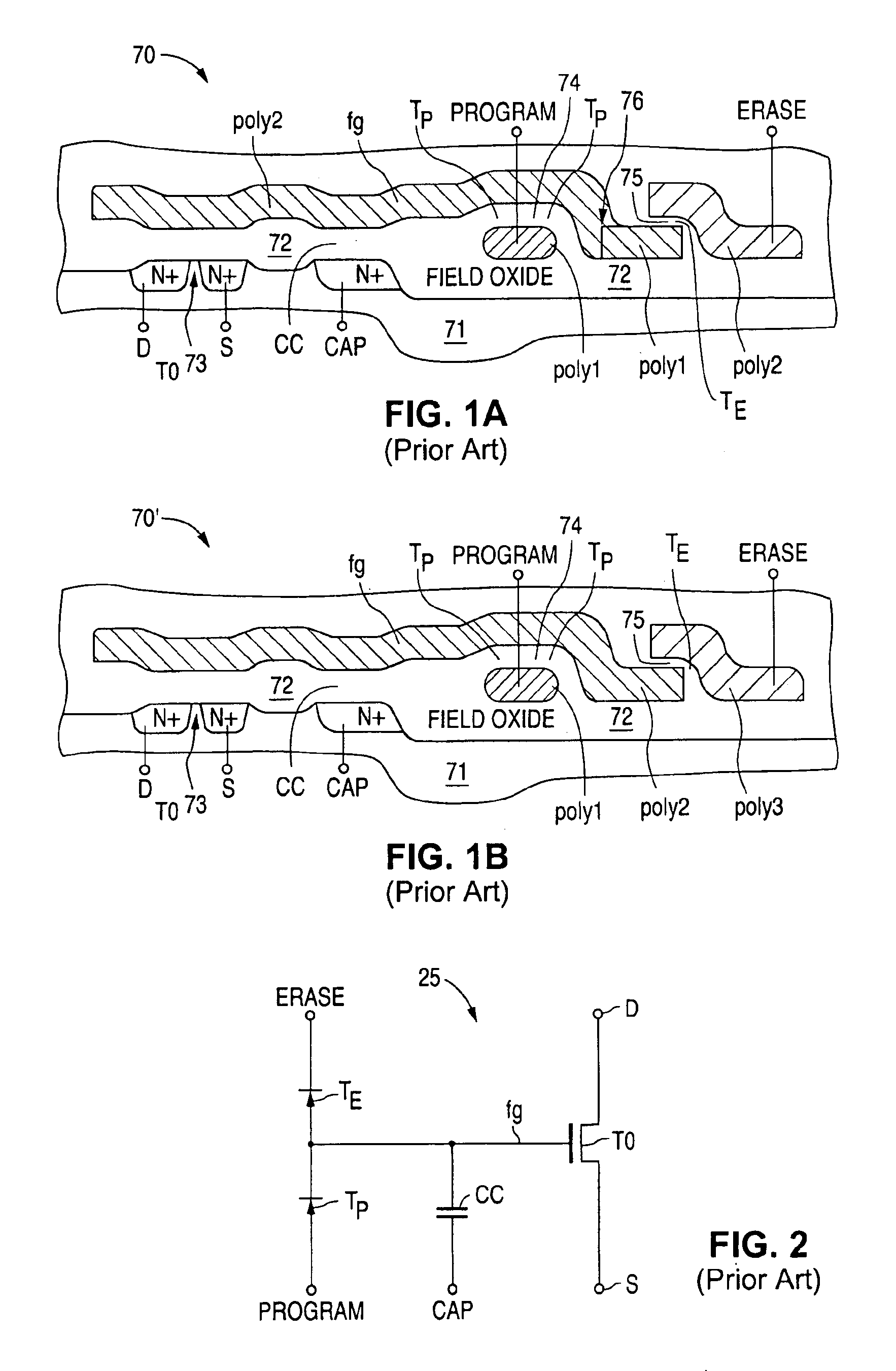
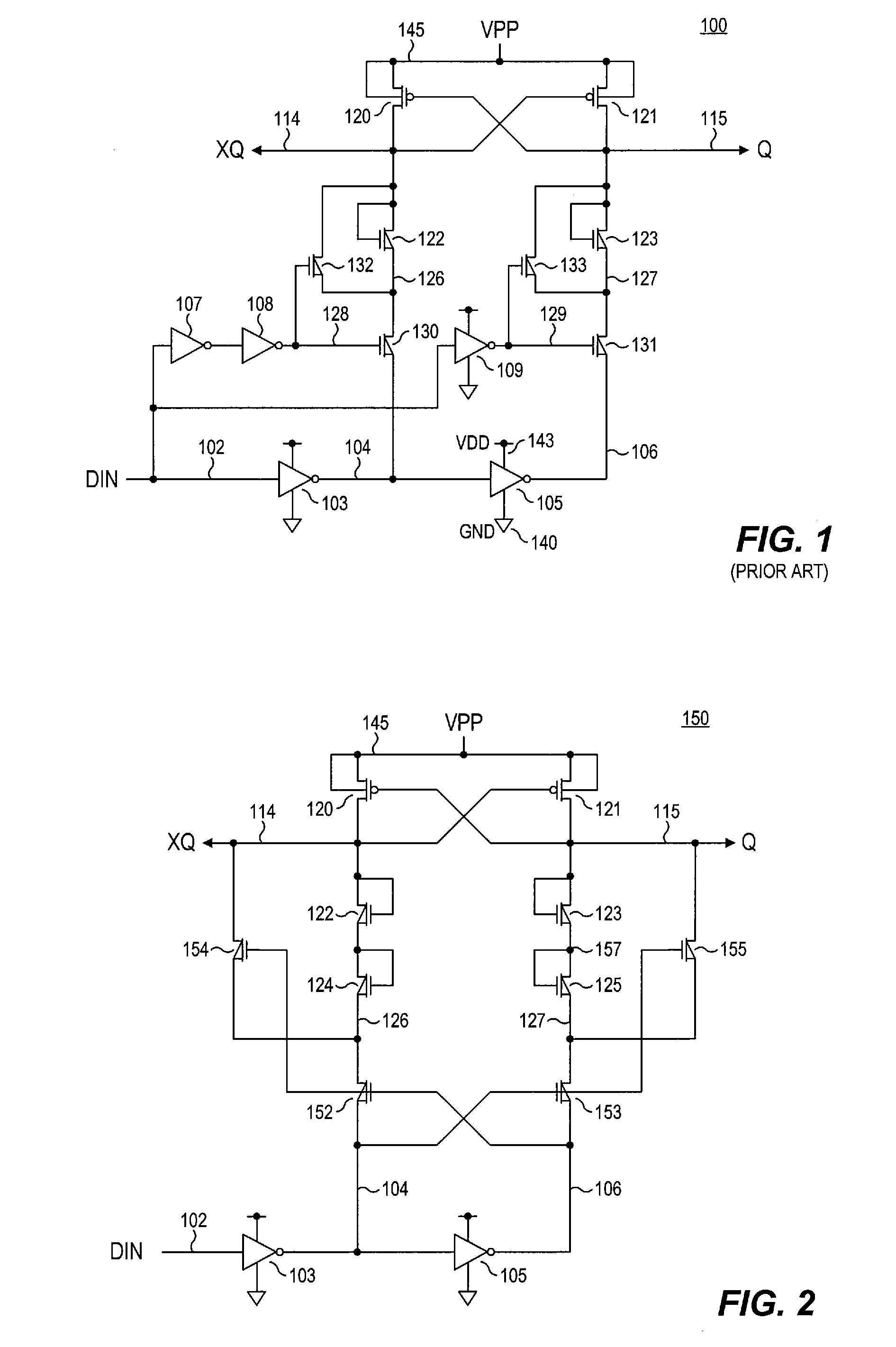
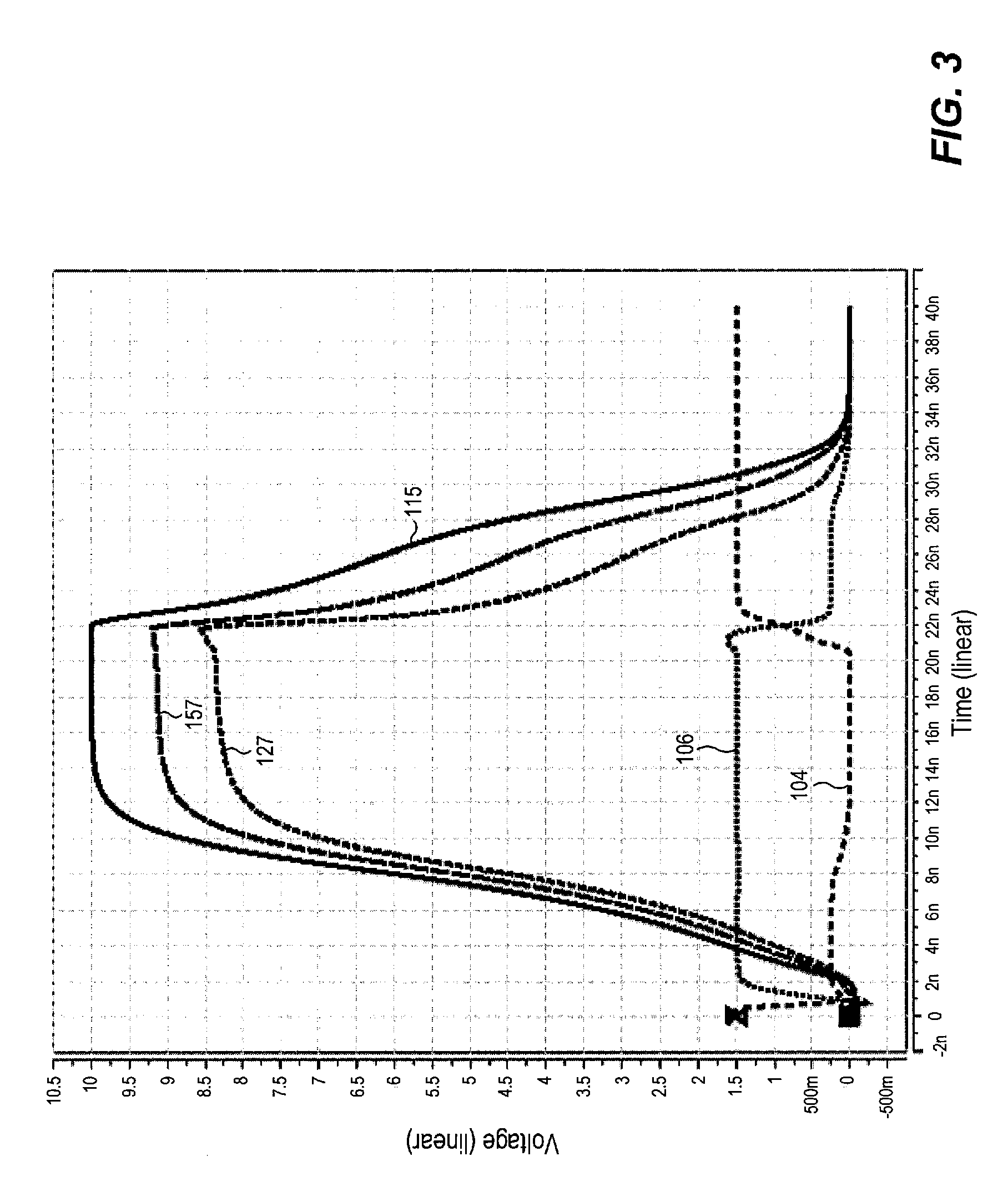
Differential dual floating gate circuit and method for programming
InactiveUS6898123B2Improved initial setting accuracyImprove accuracyElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A method and circuit for setting a reference voltage in a dual floating gate circuit is disclosed. During a set mode, a first and second floating gate are programmed to different charge levels that are a function of an input set voltage capacitively coupled to the first floating gate during the set mode. During a read mode, this difference in charge level is used by the dual floating gate circuit to generate a reference voltage that is a function of the input set voltage, and is preferably equal to the input set voltage.
Owner:XICOR
Method of automatically adjusting voltage level and voltage level adjusting device thereof
ActiveCN103425169AAvoid burnsLimit voltageEfficient power electronics conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage referenceEngineering
A method of automatically adjusting a voltage level used in an induction type power supply system includes detecting an output voltage of a signal analysis circuit; adding a first threshold value to the output voltage to generate a first determination voltage and subtracting a second threshold value from the output voltage to generate a second determination voltage; outputting the first determination voltage as a reference voltage; and comparing a trigger signal of the signal analysis circuit and the reference voltage, in order to generate a first data code; wherein when the step of comparing the trigger signal of the signal analysis circuit and the reference voltage in order to generate the first data code fails, the method further includes outputting the second determination voltage as the reference voltage and comparing the trigger signal of the signal analysis circuit and the reference voltage, in order to generate a second data code.
Owner:FU TONG TECH
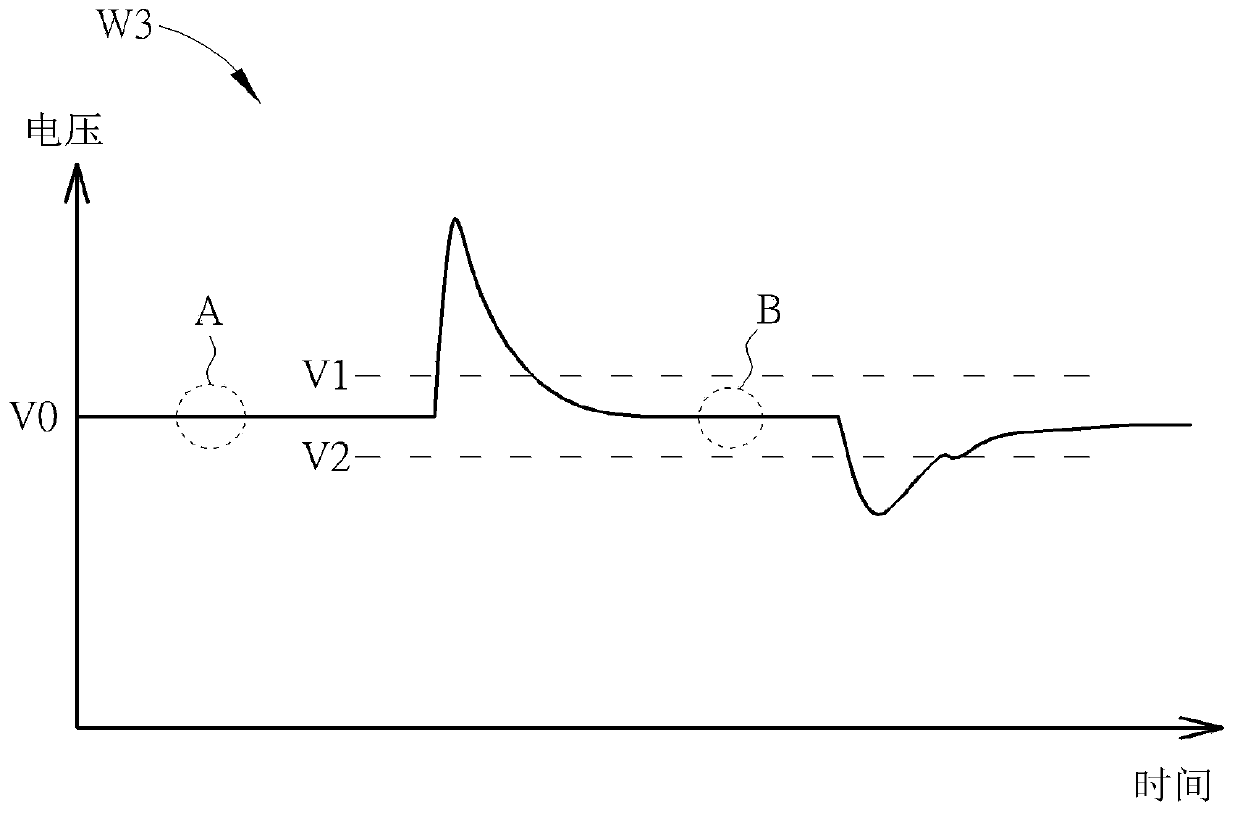
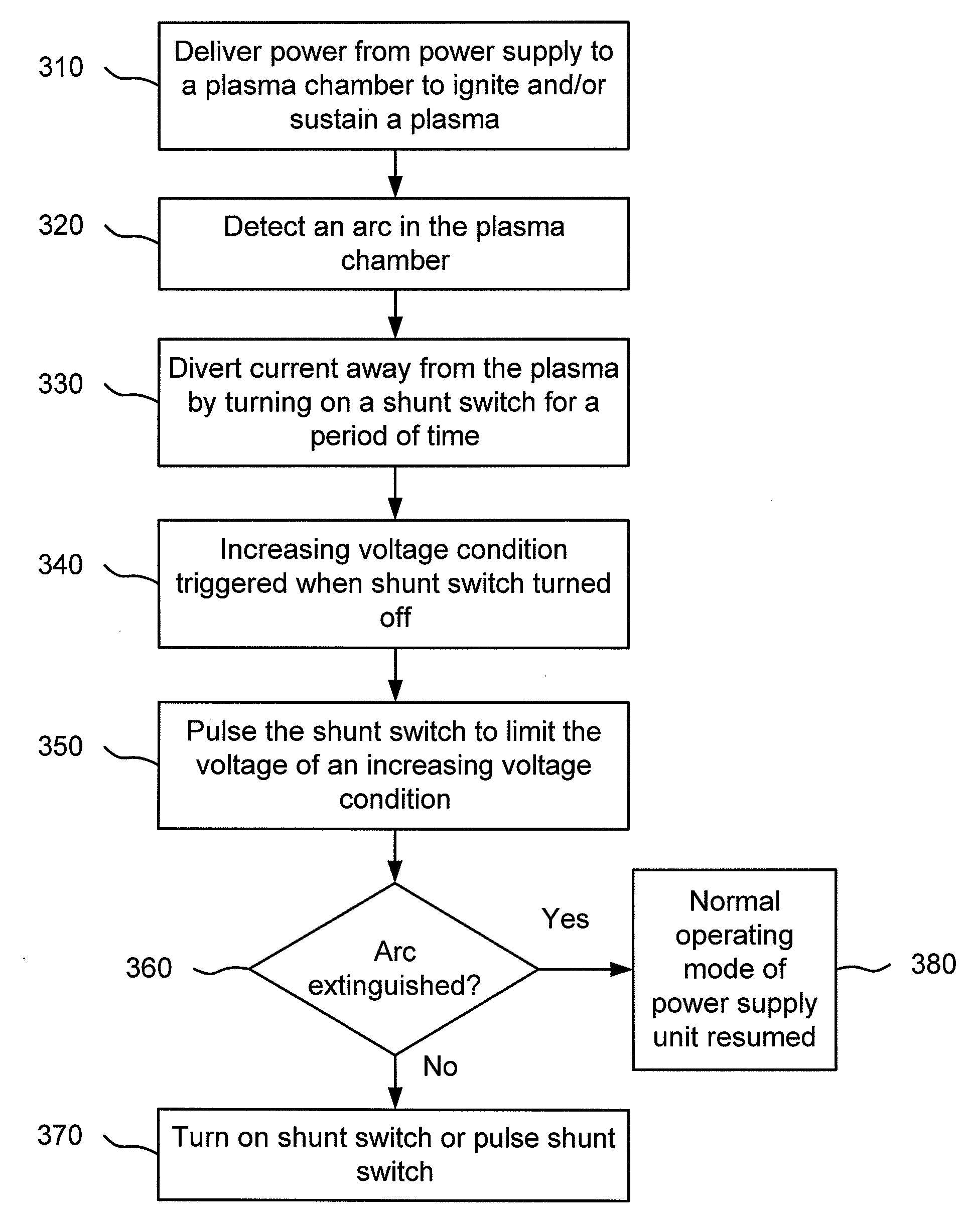
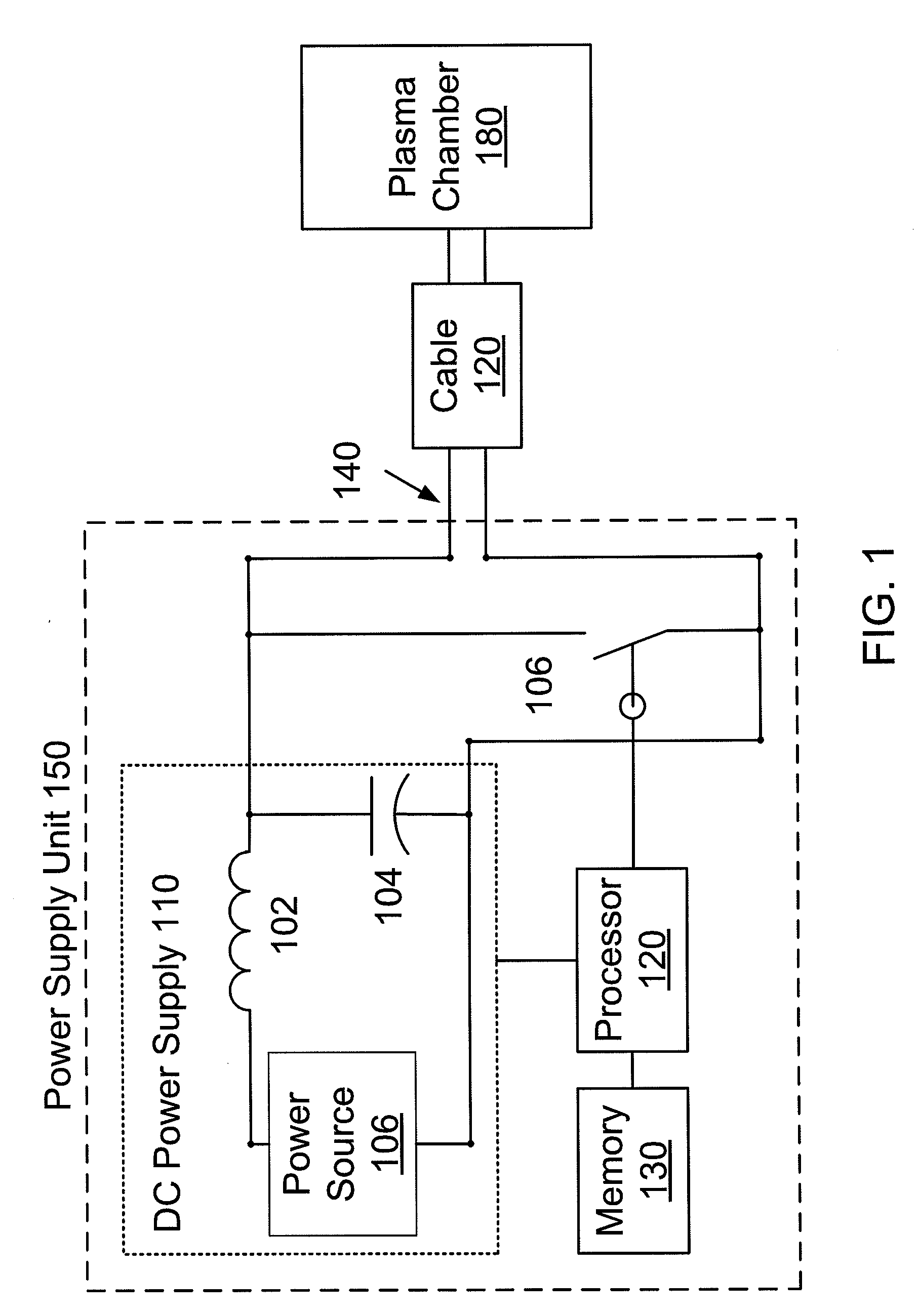
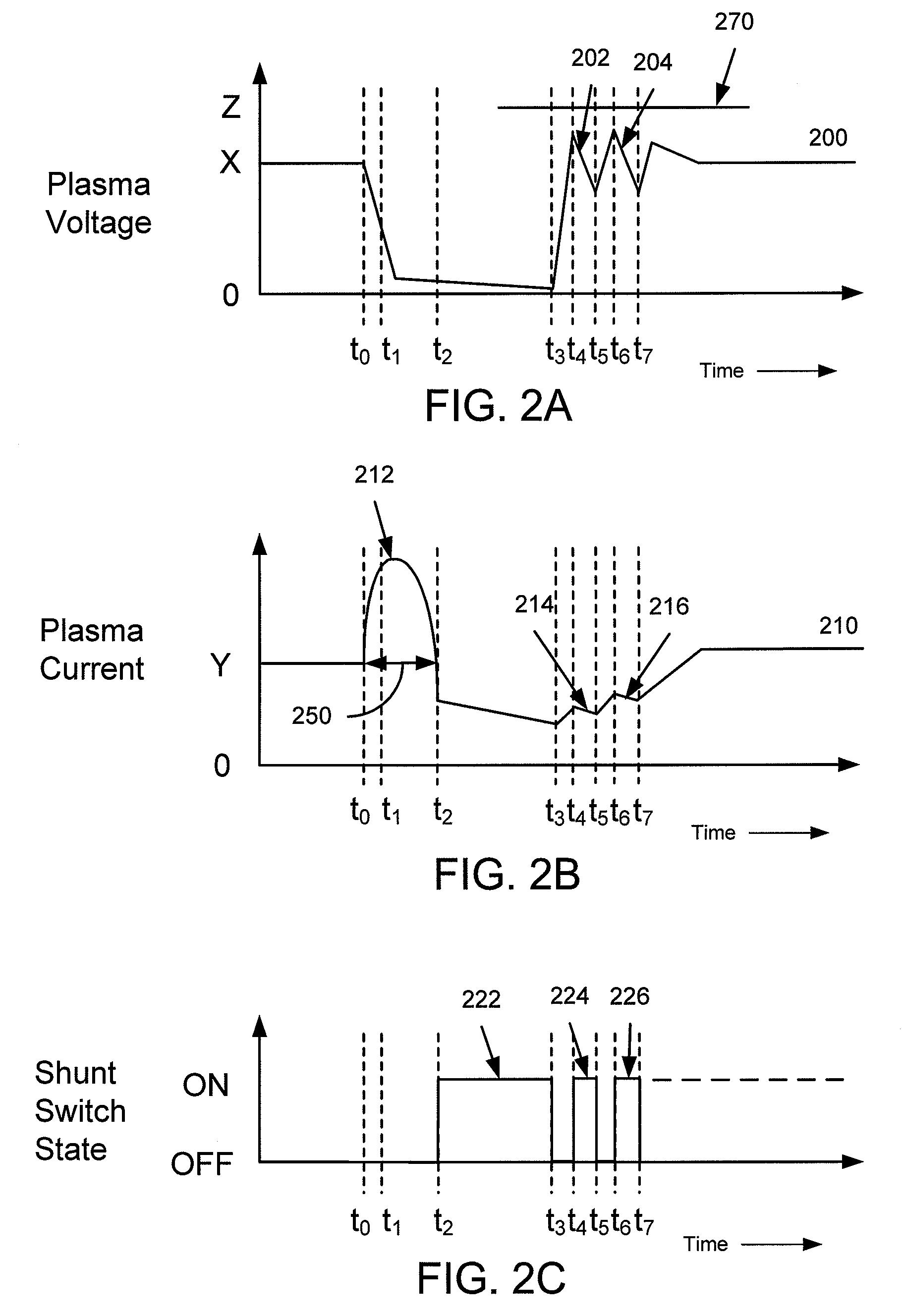
Arc recovery without over-voltage for plasma chamber power supplies using a shunt switch
A system and method for over-voltage protection is described. In one embodiment of the invention, an apparatus includes an output port configured to deliver power to a plasma chamber to ignite a plasma. The apparatus also includes a shunt switch in parallel with the output port and a processor configured to receive an indicator of an arc in the plasma. The processor is configured to close the shunt switch for a period of time to divert current away from the arc. The processor is also configured to trigger a pulse of the shunt switch to limit a voltage of an increasing voltage condition associated with the arc.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
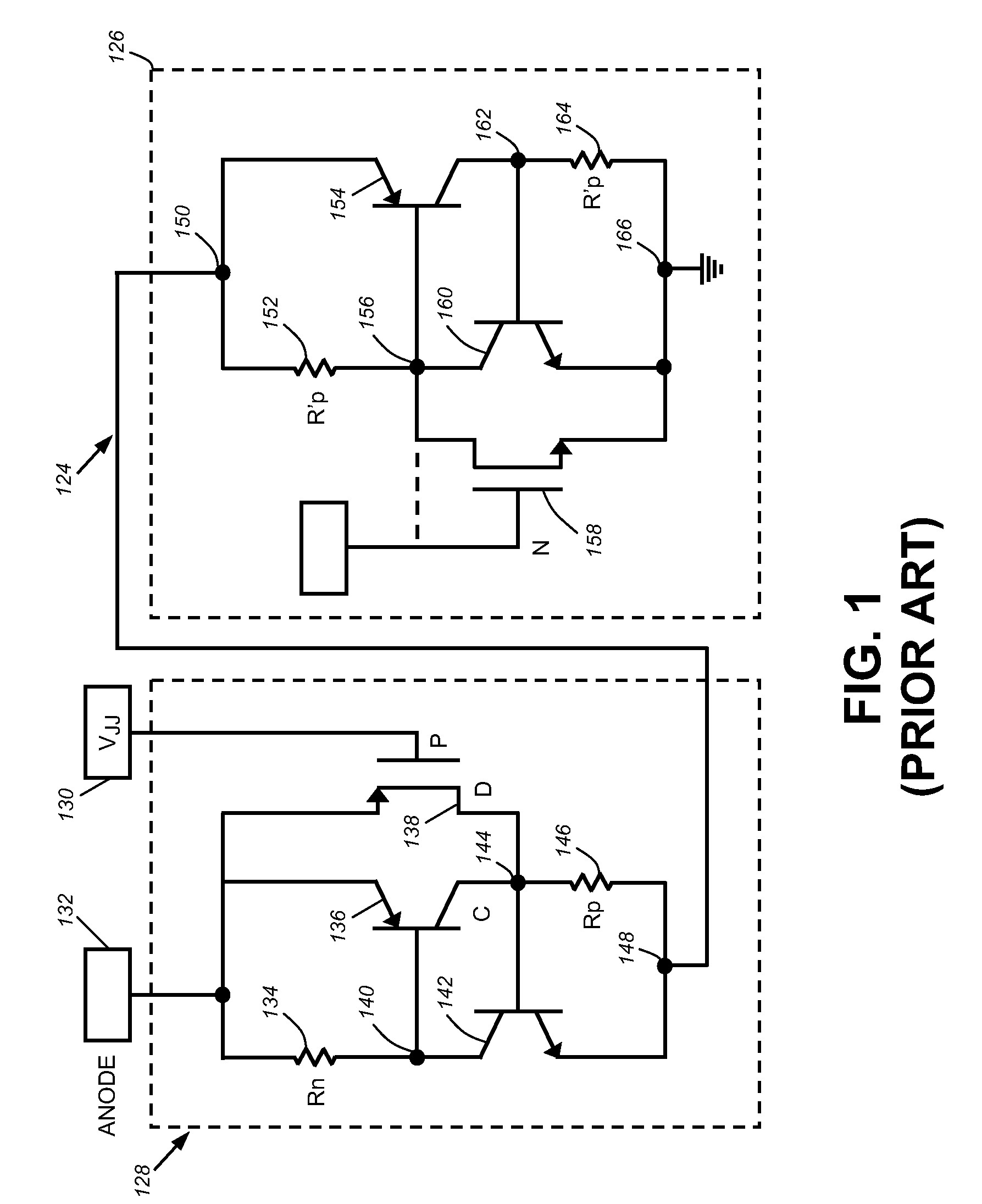
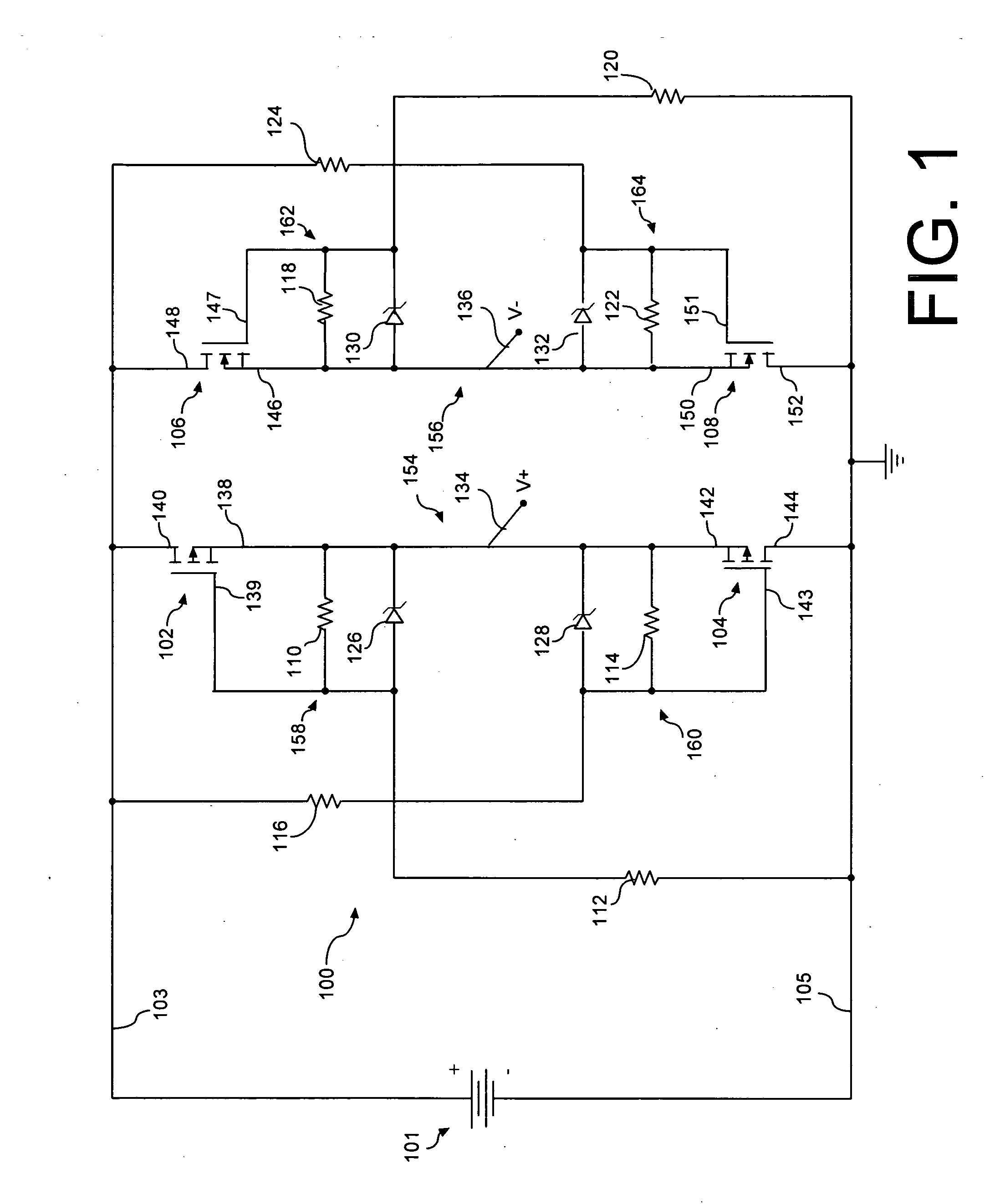
Biased-MOSFET active bridge
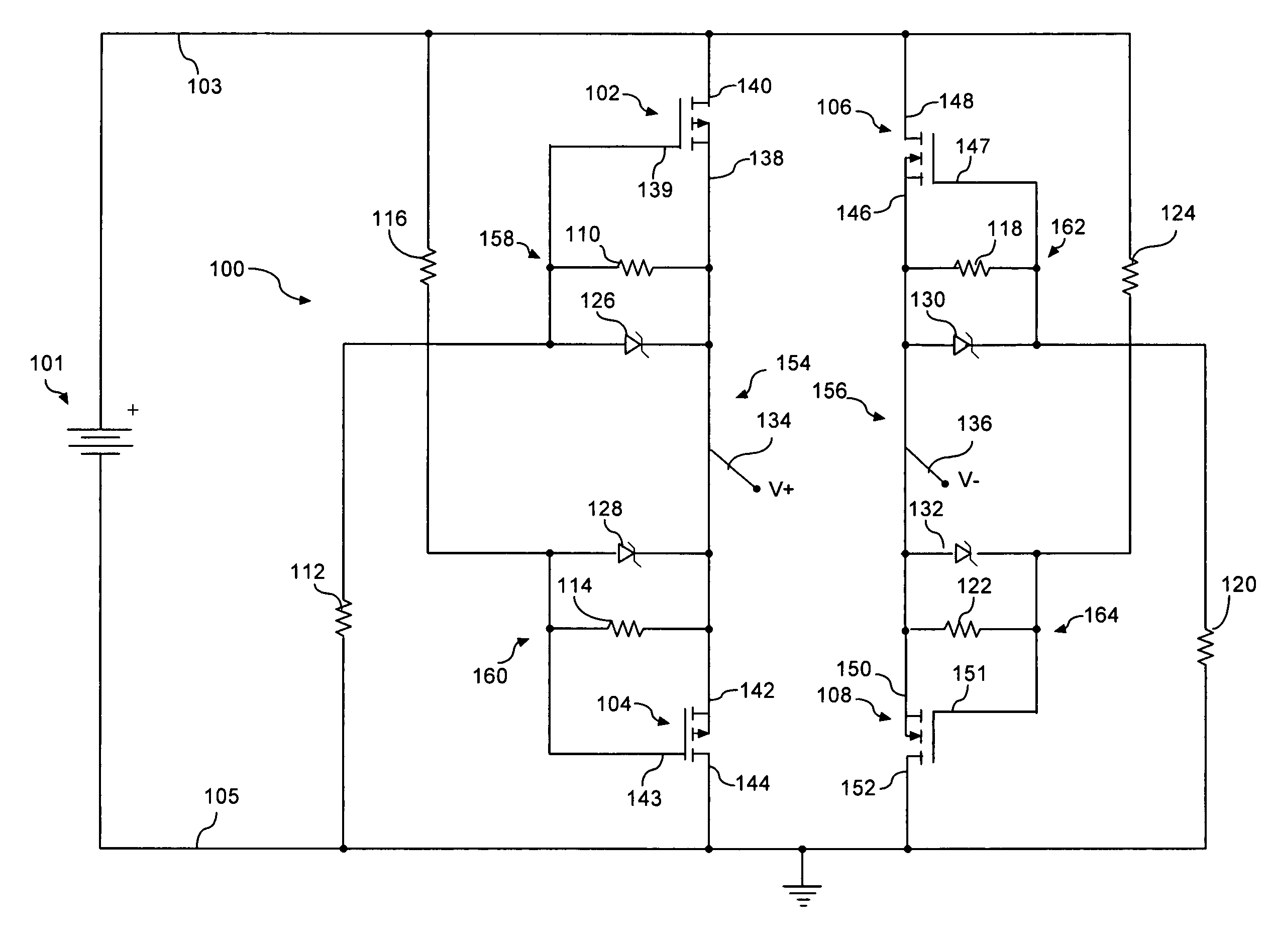
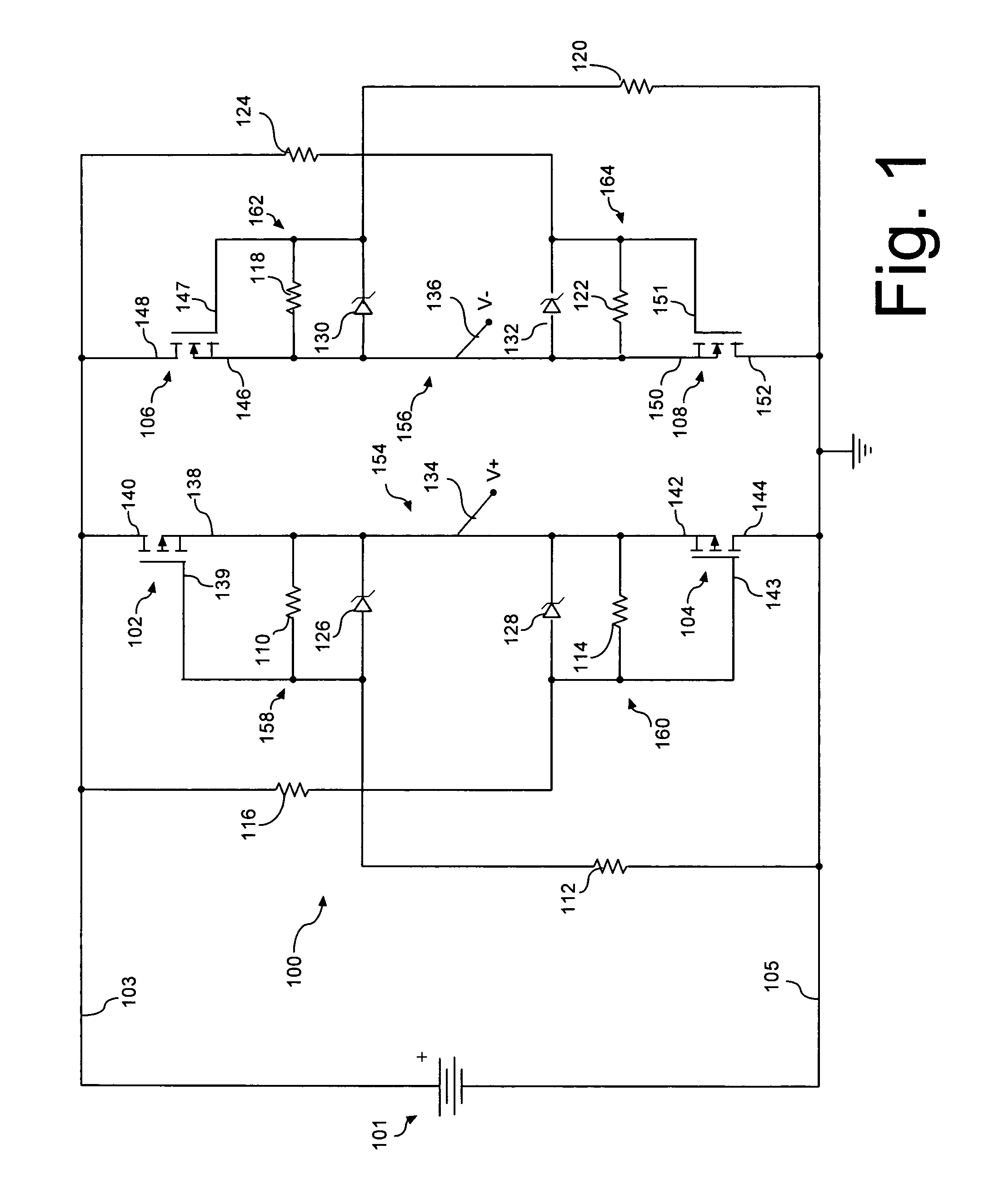
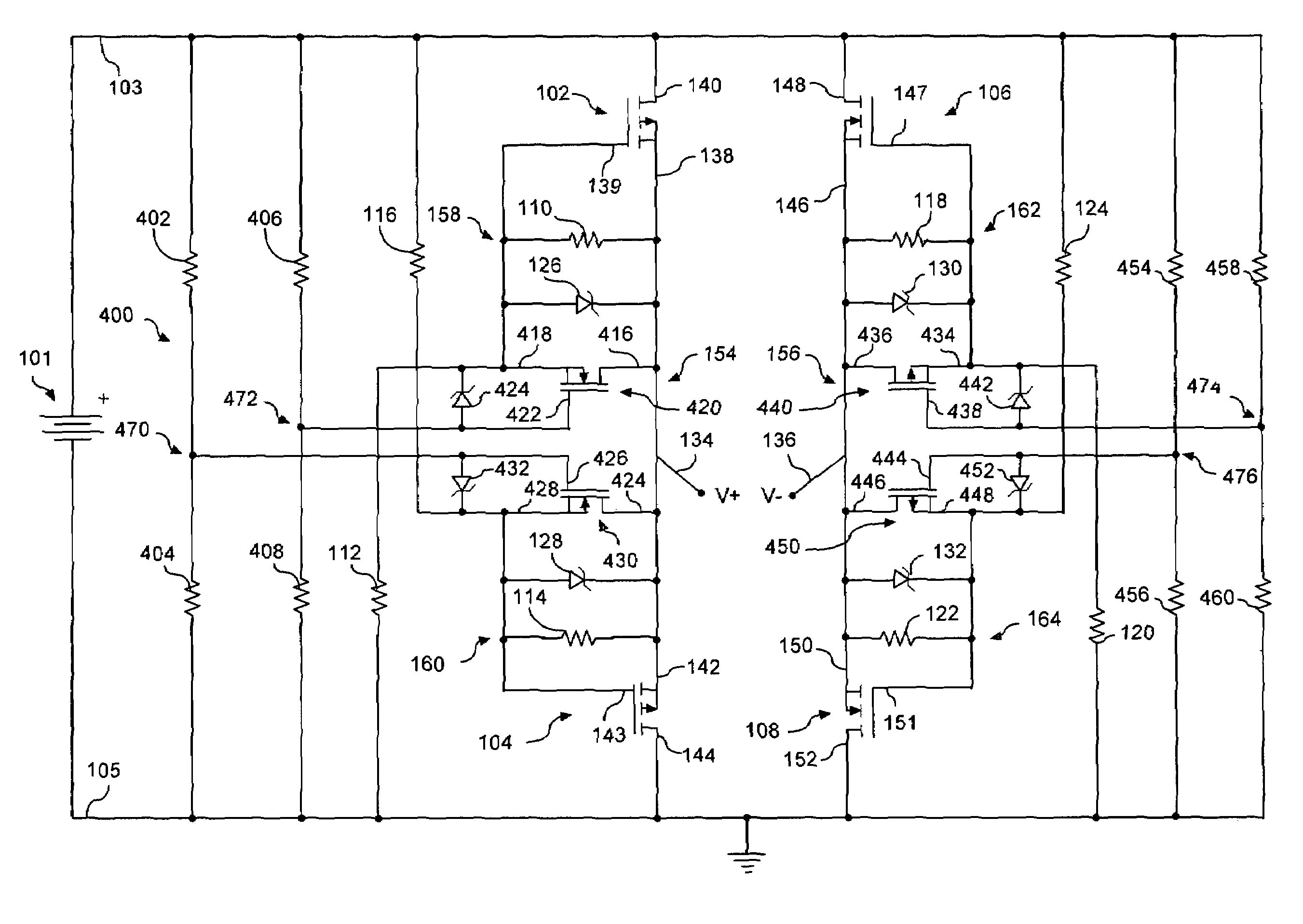
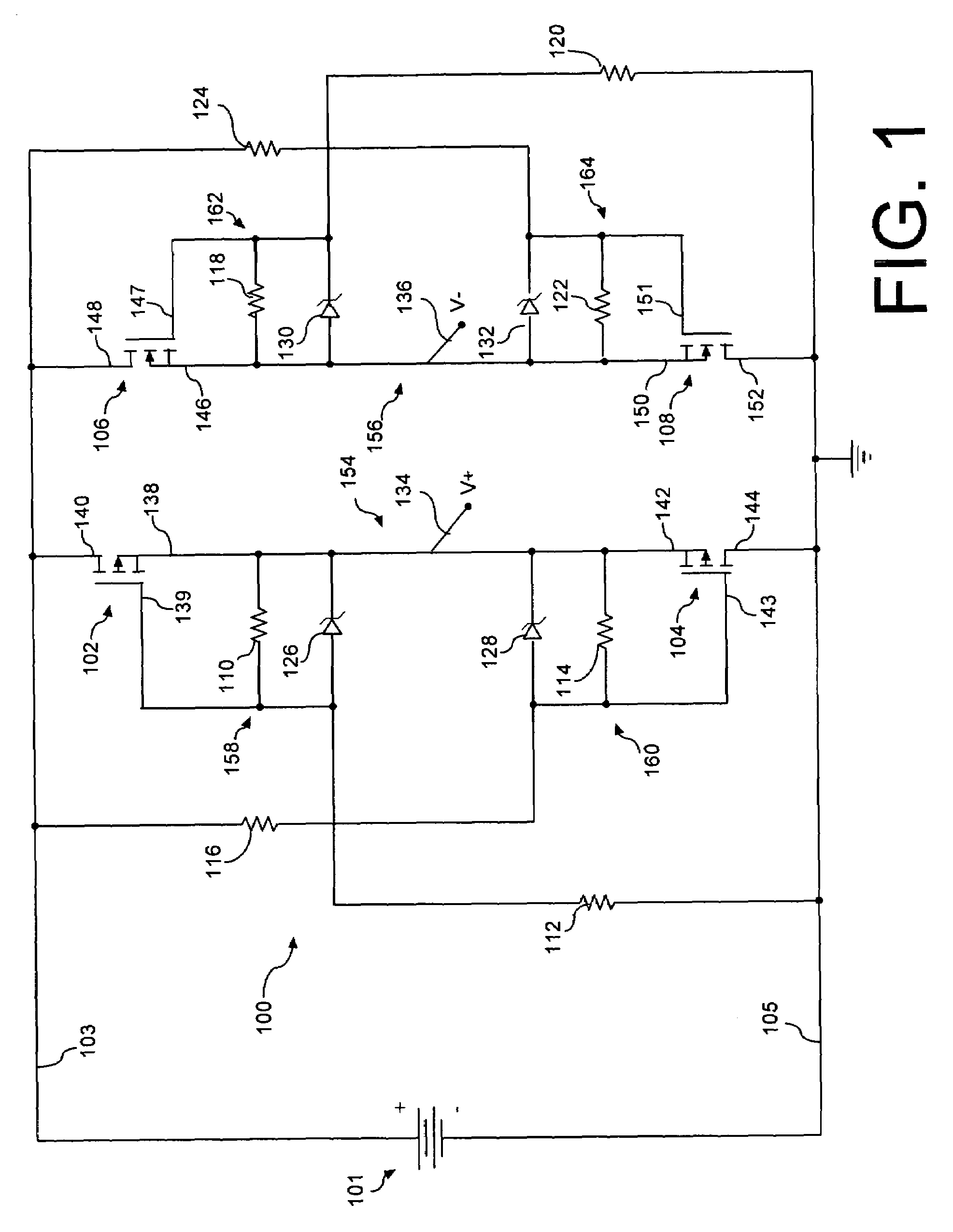
InactiveUS7561404B2Reduce voltageLimit voltageEmergency protective circuit arrangementsReverse polarity correctionMOSFETElectrical polarity
A transistor active bridge circuit (100) provides operation and protection for devices from the effects of battery polarity reversal. The circuit includes first and second field-effect transistors (102, 104) of a first channel type, and third and fourth field-effect transistors (106, 108) of a second channel type that is different from the first channel type. A set of voltage dividers (110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124) and voltage clamping devices (126, 128, 130, 132) permit the circuit (100) to efficiently operate over a wider range of input voltages, without potential damage to the field-effect transistors.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Downhole measurement tool circuit and method to balance fault current in a protective inductor
ActiveUS8149552B1Limit voltageFluid removalEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionInductorEngineering
A downhole measurement tool circuit and method to balance fault current in a protective inductor, which keeps an alternating current balanced in a protective choke during a phase-to-ground fault condition in a power cable or a downhole motor of an electrical submersible pump. The downhole measurement tool circuit and method cause a conducting of current during the negative polarity voltage portions of a phase-to-ground fault condition, but do not cause a conduction of negative polarity voltage during use of a negative polarity megger.
Owner:ACE DOWNHOLE LLC
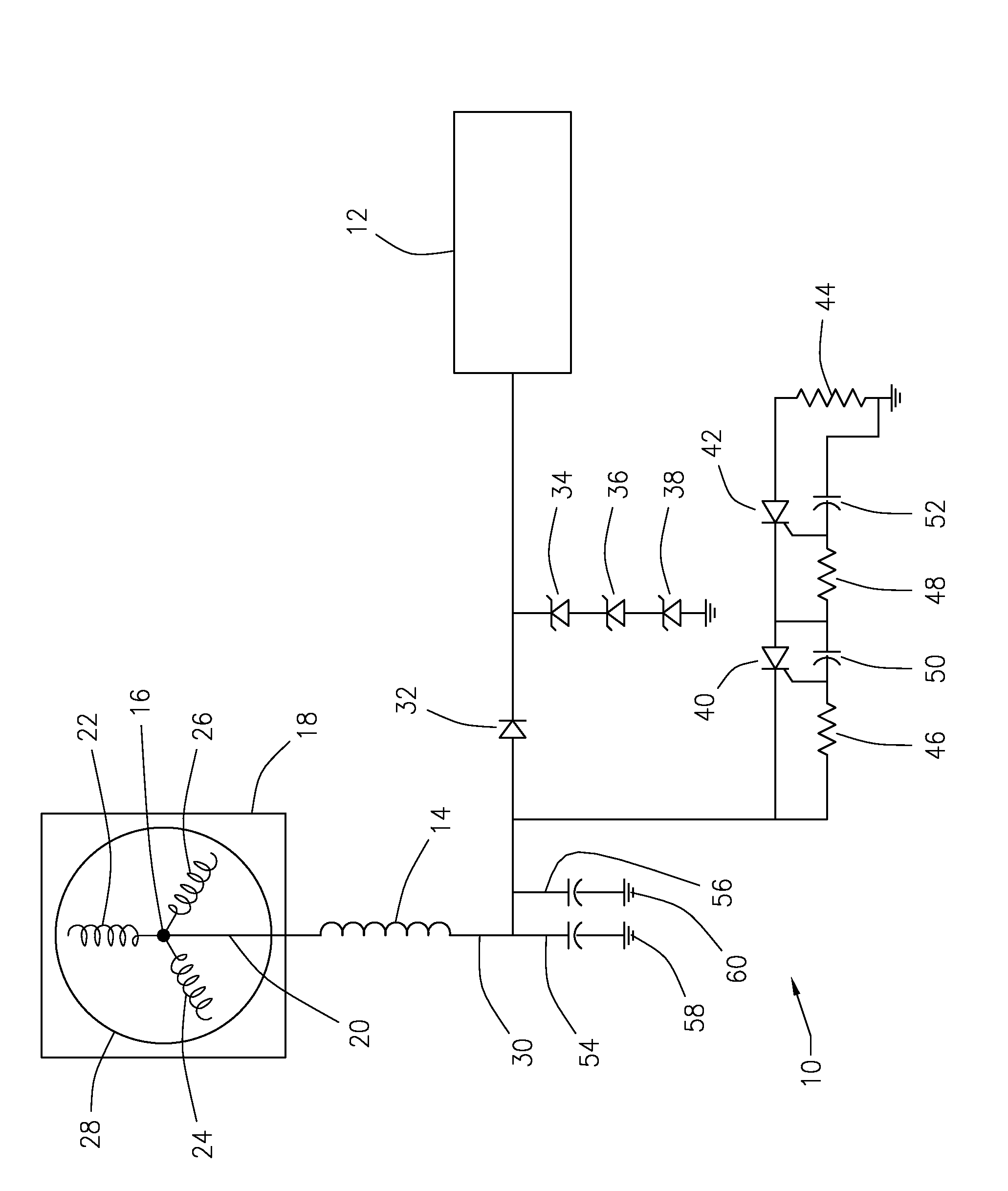
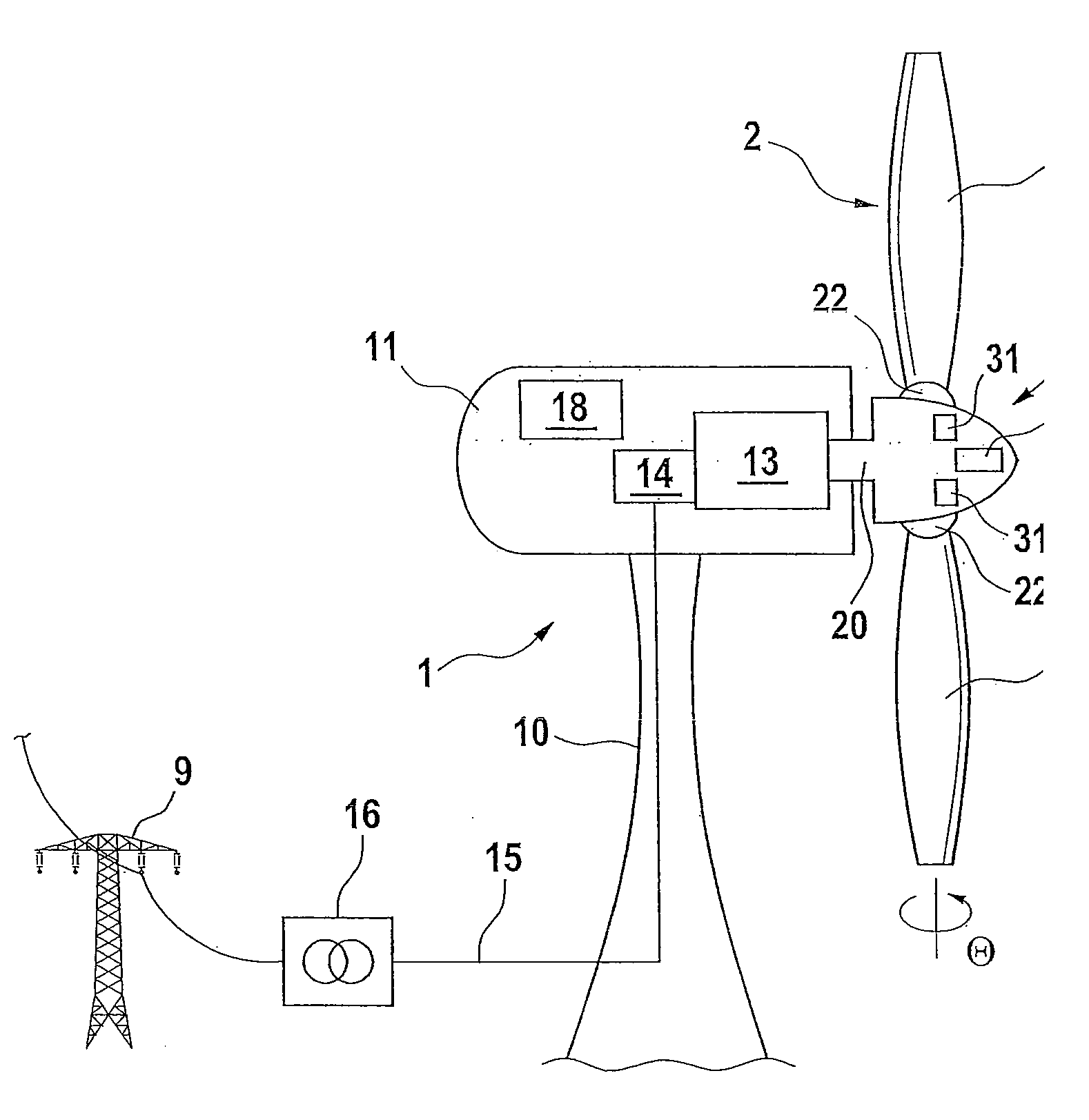
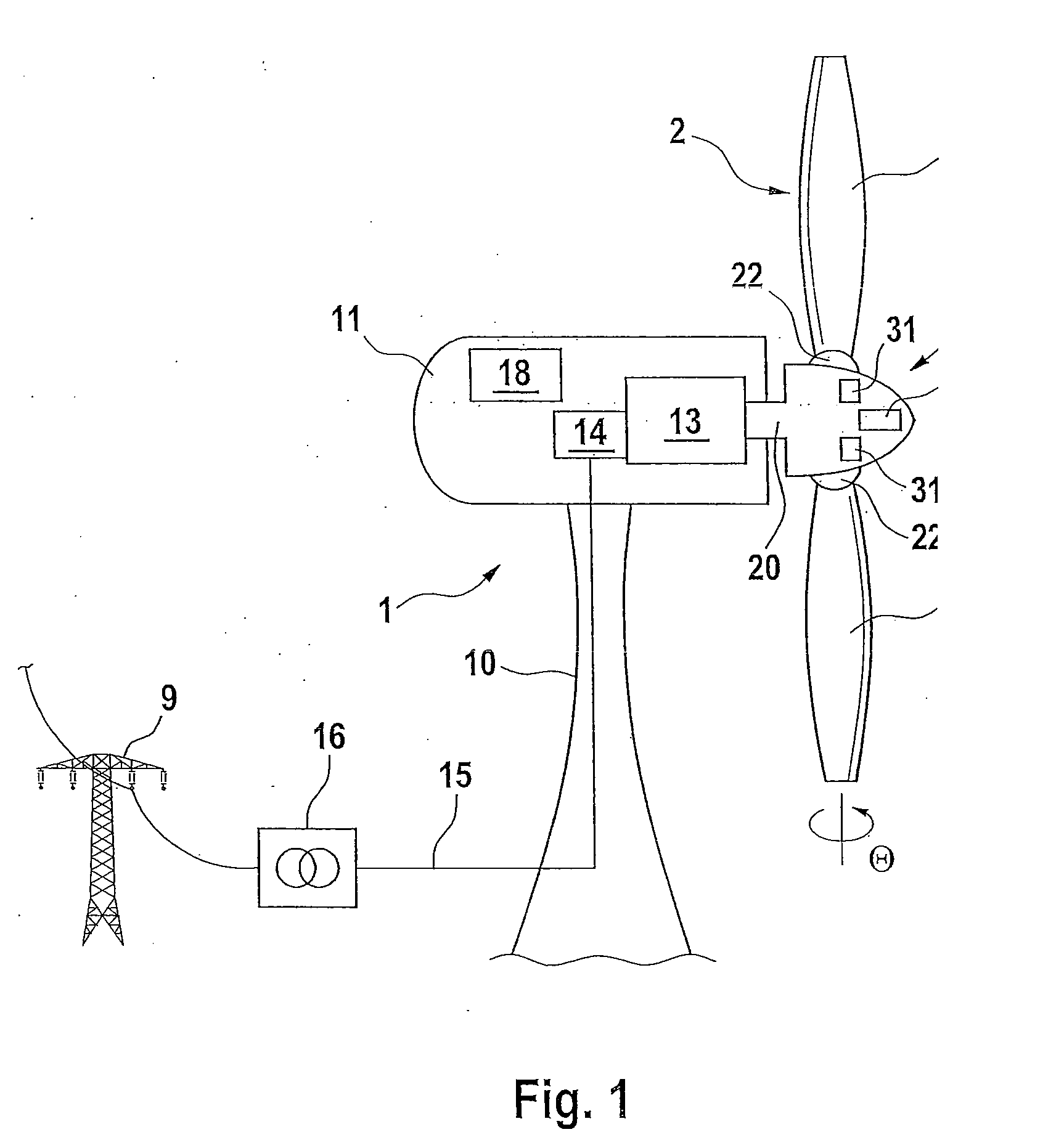
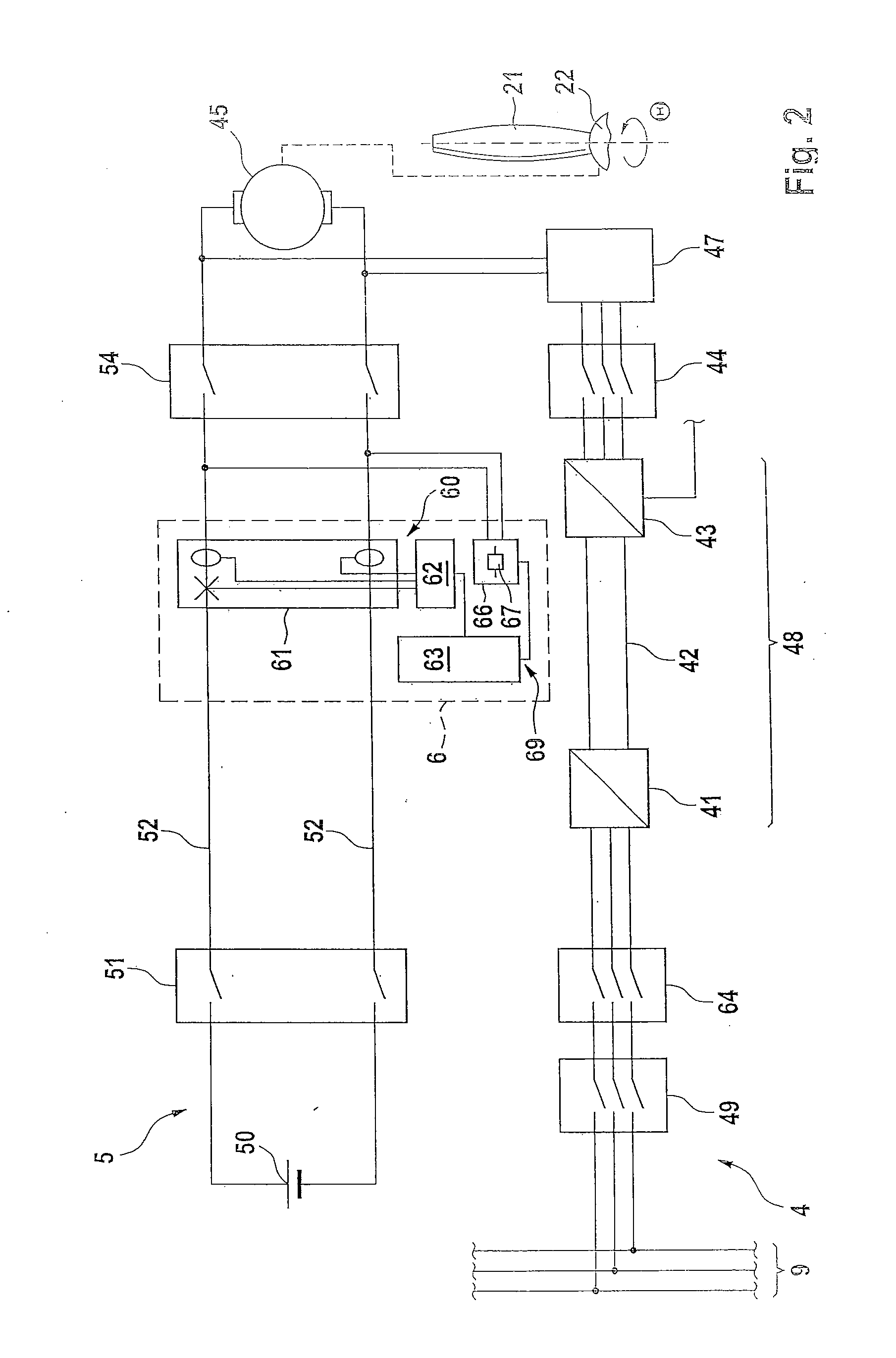
Energy Supply for a Blade Adjustment Device Pertaining to a Wind Energy Installation
A wind energy installation includes a tower provided with rotor blades that are adjusted using a servomotor connected to a pitch circuit and an emergency circuit. During normal operation the rotor blades are actuated by the pitch circuit and during emergency operation are actuated by the emergency circuit. The emergency circuit has an electric energy store, a switching device, connection lines to the servomotor and a protection device which includes comprises a power flow detector module (60) designed for determining whether electric power flows into or from the servomotor and a discharge module designed to limit the voltage and / or current in the emergency circuit in the case of a power flow from the servomotor.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Protection Circuit for Protecting an Intermediate Circuit of a Solar Inverter Against Overvoltages
InactiveUS20110194216A1Little power lossSimple circuit designEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower conversion systemsPower inverterOvervoltage
An input-side protective circuit for protecting an intermediate circuit of an inverter against overvoltages, wherein the input-side protective circuit includes an upstream element for limiting the voltage of the intermediate circuit connected upstream of the intermediate circuit and which is bridgeable by a mechanical switching device that is controllable such that it opens in a feed-in operation of the inverter when an intermediate circuit voltage is greater than a specified voltage limit. The protective circuit also includes an electronic voltage limiter connected downstream of the upstream element and connected in parallel to the intermediate circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
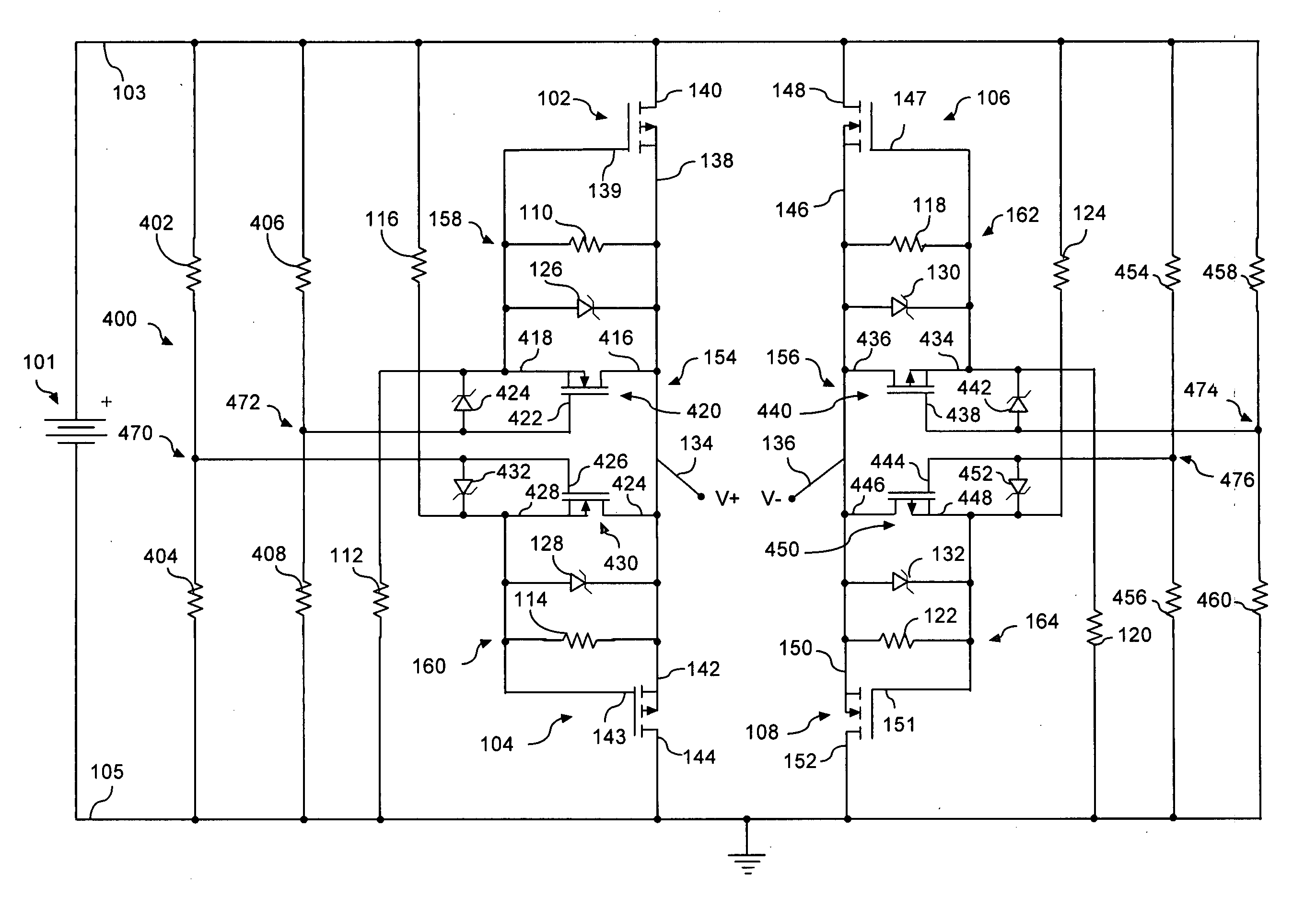
Low-loss rectifier with shoot-through current protection
InactiveUS7411768B2Reduce power consumptionReduce voltageBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringField-effect transistor
A transistor active bridge circuit (400) rectifies domestic AC mains (for example, 120V, 60 Hz) and / or foreign AC mains (for example, 230V, 50 Hz) with low power loss. The circuit includes first and second field effect transistors (102, 104) of a first channel type, and third and fourth field effect transistors (106, 108) of a second channel type that is different from the first channel type. A set of voltage dividers (110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124) and voltage clamping devices (126, 128, 130, 132) permit the circuit (400) to efficiently operate over a wider range of input voltages, without potential damage to the field effect transistors. Shoot-through protection devices (420, 430) provide a means for preventing the first and second field effect transistors (102, 104) from conducting simultaneously. Shoot-through protection devices (440, 450) provide a means for preventing the third and fourth field effect transistors (106, 108) from conducting simultaneously.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Hot-pluggable voltage regulator module
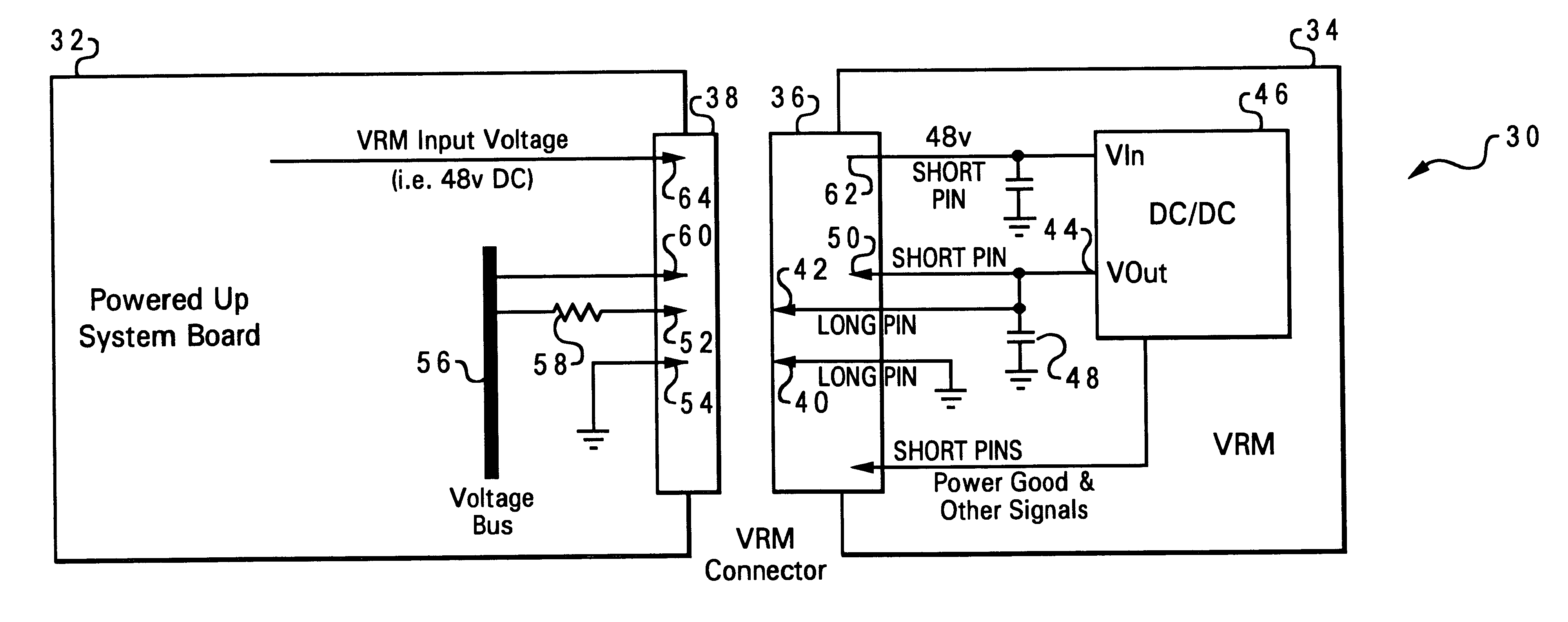
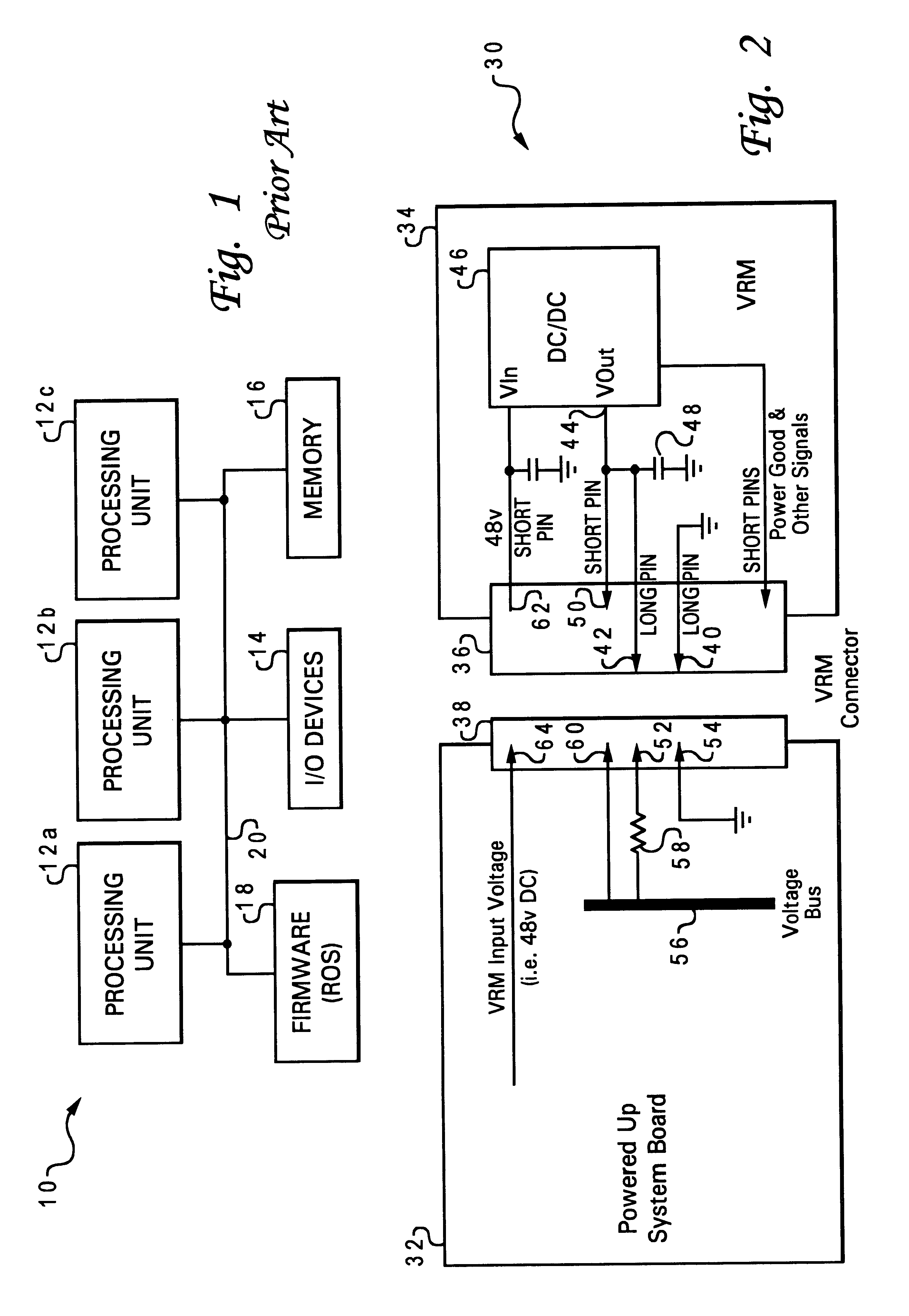
InactiveUS6449676B1Easy maintenanceLimit voltageVolume/mass flow measurementDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator moduleEngineering
A power subsystem for a computer system allows a voltage regulator module (VRM) to be removably connected to a system board, while limiting disturbances on the voltage rails of the system board. The electrical disturbances are prevented by charging voltage outputs of the DC / DC circuit of the VRM prior to directly connecting the voltage outputs to the voltage rails. To ensure that the voltage outputs are properly charged, a VRM connector may be used in which the voltage output pins are shorter than charge pins which are coupled to respective capacitors and to the voltage outputs of the DC / DC circuit. In this manner, as the connector is mated with a corresponding connector on the system board, the capacitors are first charged via resistive paths connected to the voltage rails, prior to directly connecting the voltage outputs to the voltage rails. The VRMs are thus "hot-pluggable," enabling a user to upgrade or service the system with no interruption.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
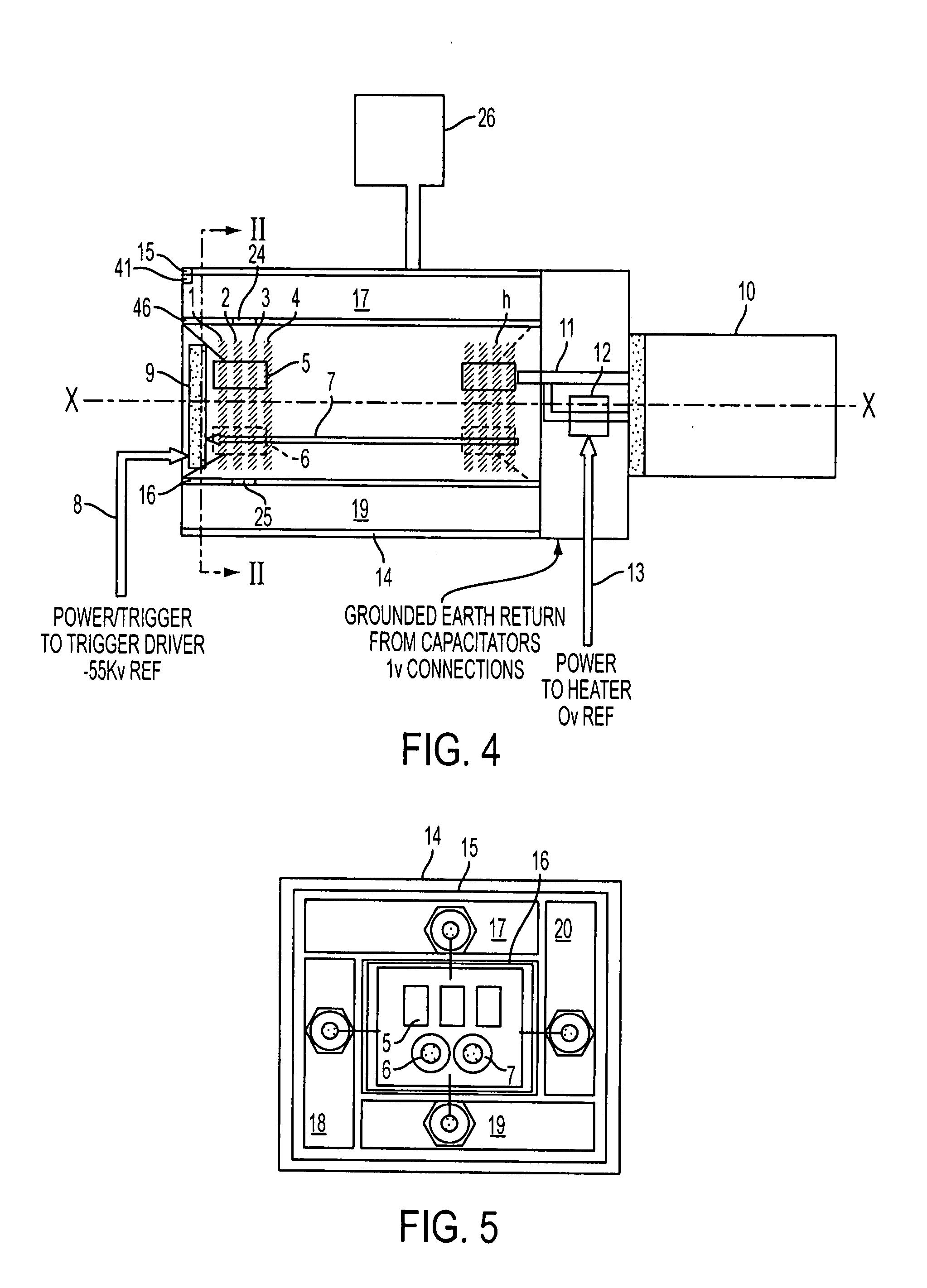
High-voltage protection circuitry in a data access arrangement
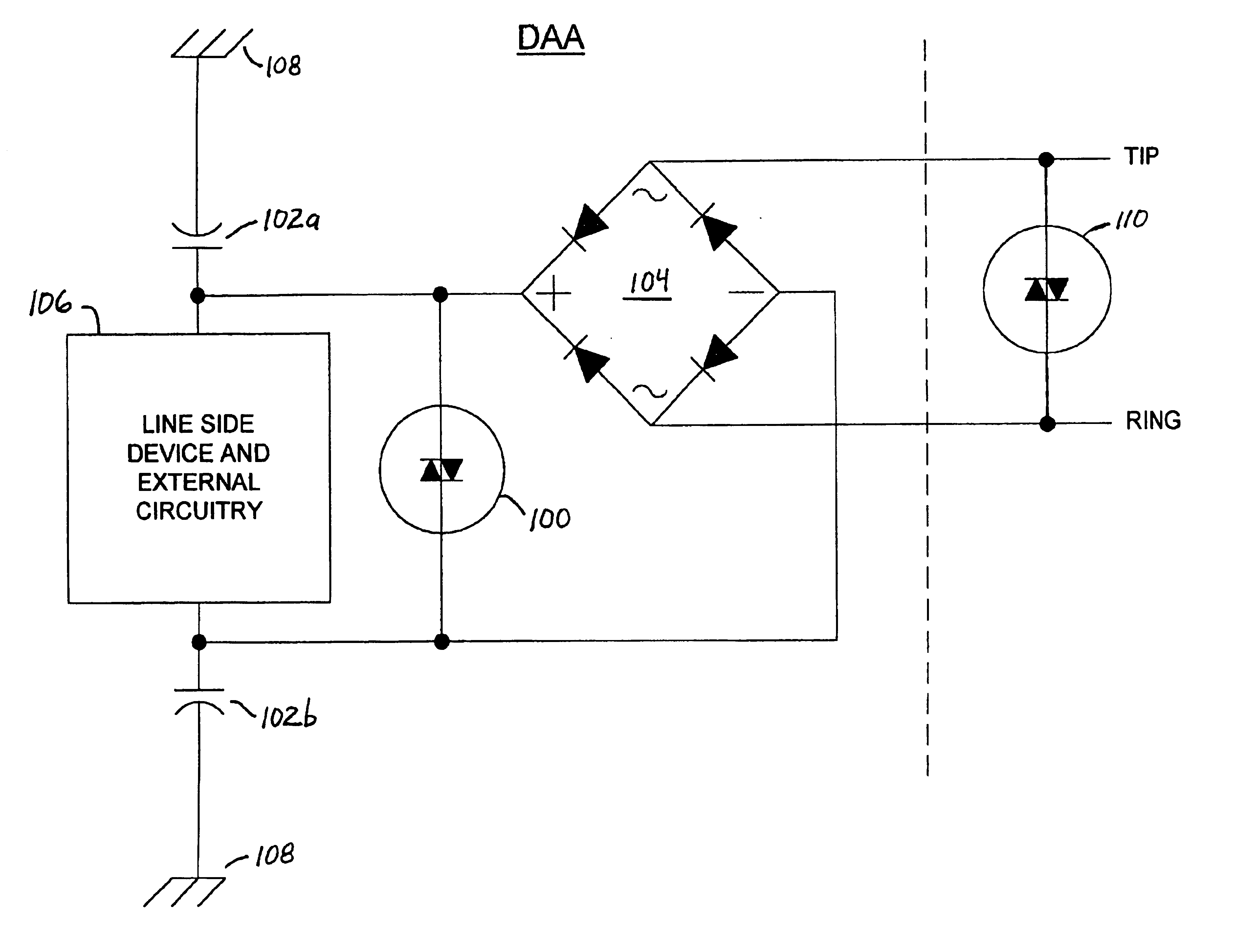
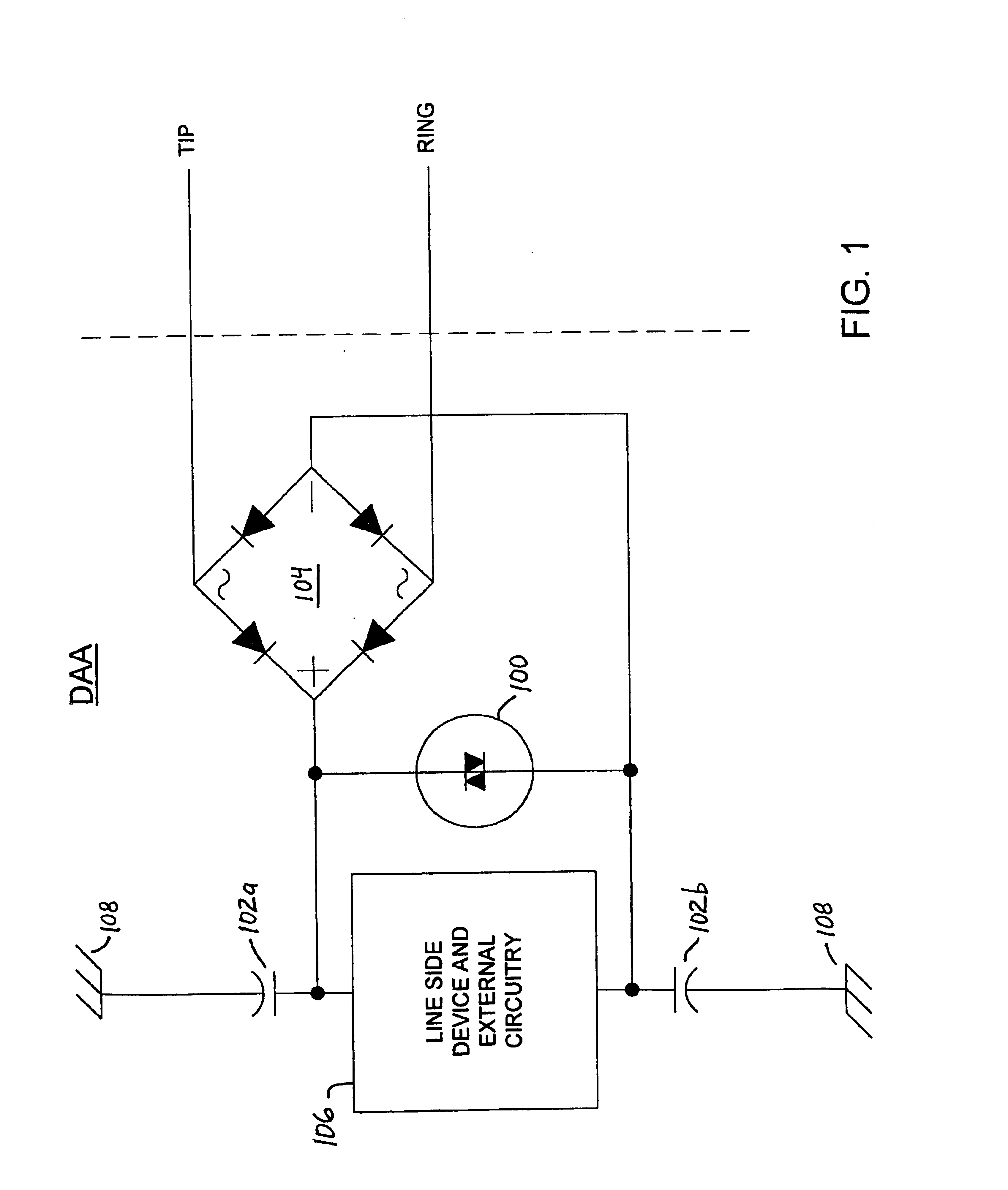
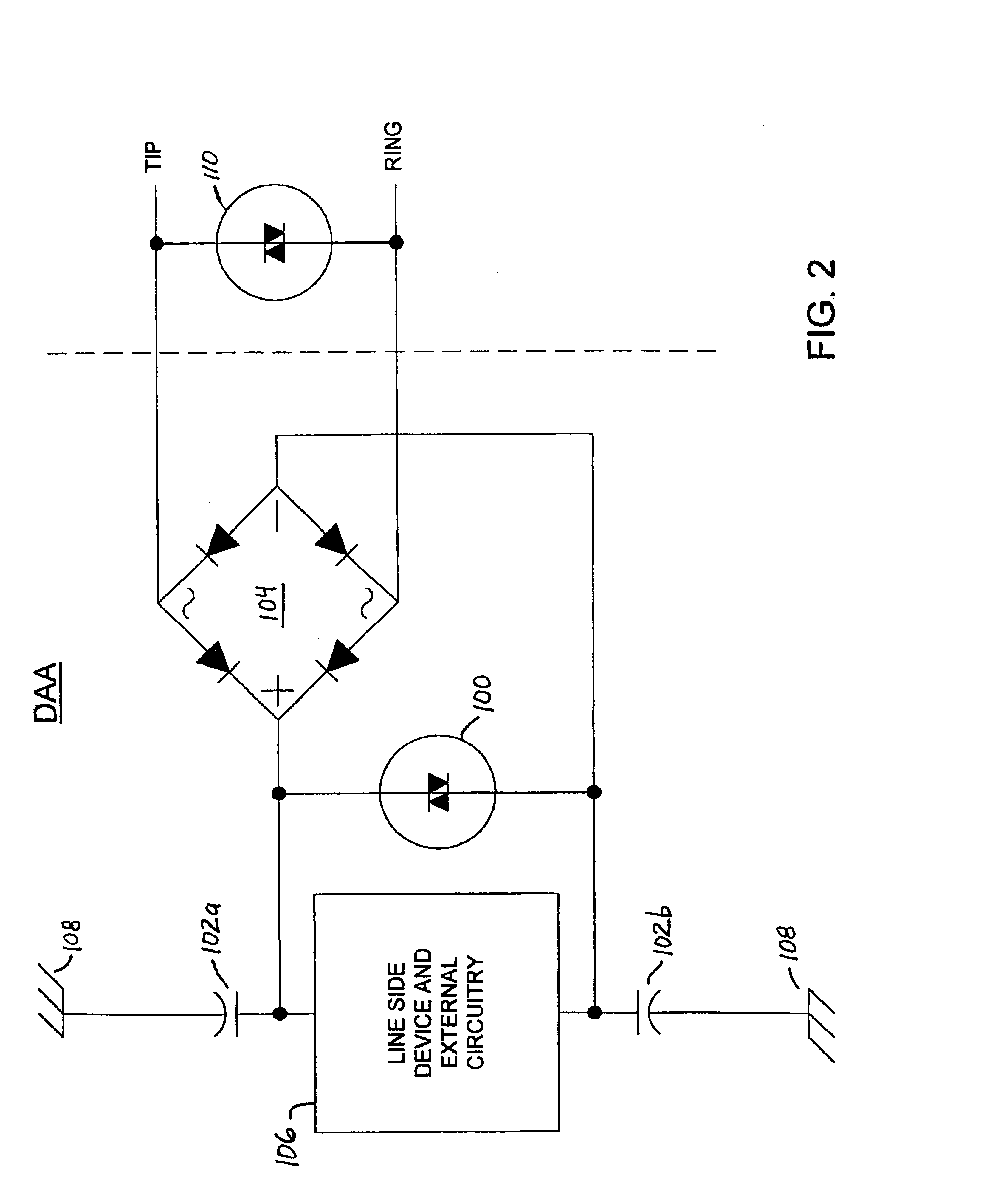
InactiveUS6876742B1Negative efficiencySuccessfully and economically withstand surge voltageTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsData accessPeak value
A data access arrangement (DAA) having improved surge protection. The DAA incorporates a high voltage clamping device functioning to protect line side circuitry from signal paths created by EMI capacitors. In one embodiment of the invention, EMI capacitors are added between the “plus” and “minus” terminals of the diode bridge of the DAA to balance and reduce noise injection onto the TIP and RING lines. These EMI capacitors also reduce EMI interference. However, by adding EMI capacitors on this side (the “rectified side” or “line side”) of the diode bridge, a high voltage signal path to earth ground is created that may have deleterious effects on the line side circuitry. To effectively negate undesirable signal paths through the EMI capacitors, the DAA includes a high voltage clamping device (e.g., a MOV, SIDACTor™, gas discharge tube or similar device) disposed between the plus and minus terminals of the diode bridge for suppressing high voltage spikes. The high voltage clamping device limits the voltage seen by the line side circuitry as a result of high voltage longitudinal surges by providing a current path from the plus terminal to the minus terminal of the diode bridge, thereby effectively bypassing the line side circuitry. The present invention recognizes and takes advantage of the fact that the diodes of a typical diode bridge are capable of withstanding the peak currents associated with most voltage surges.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
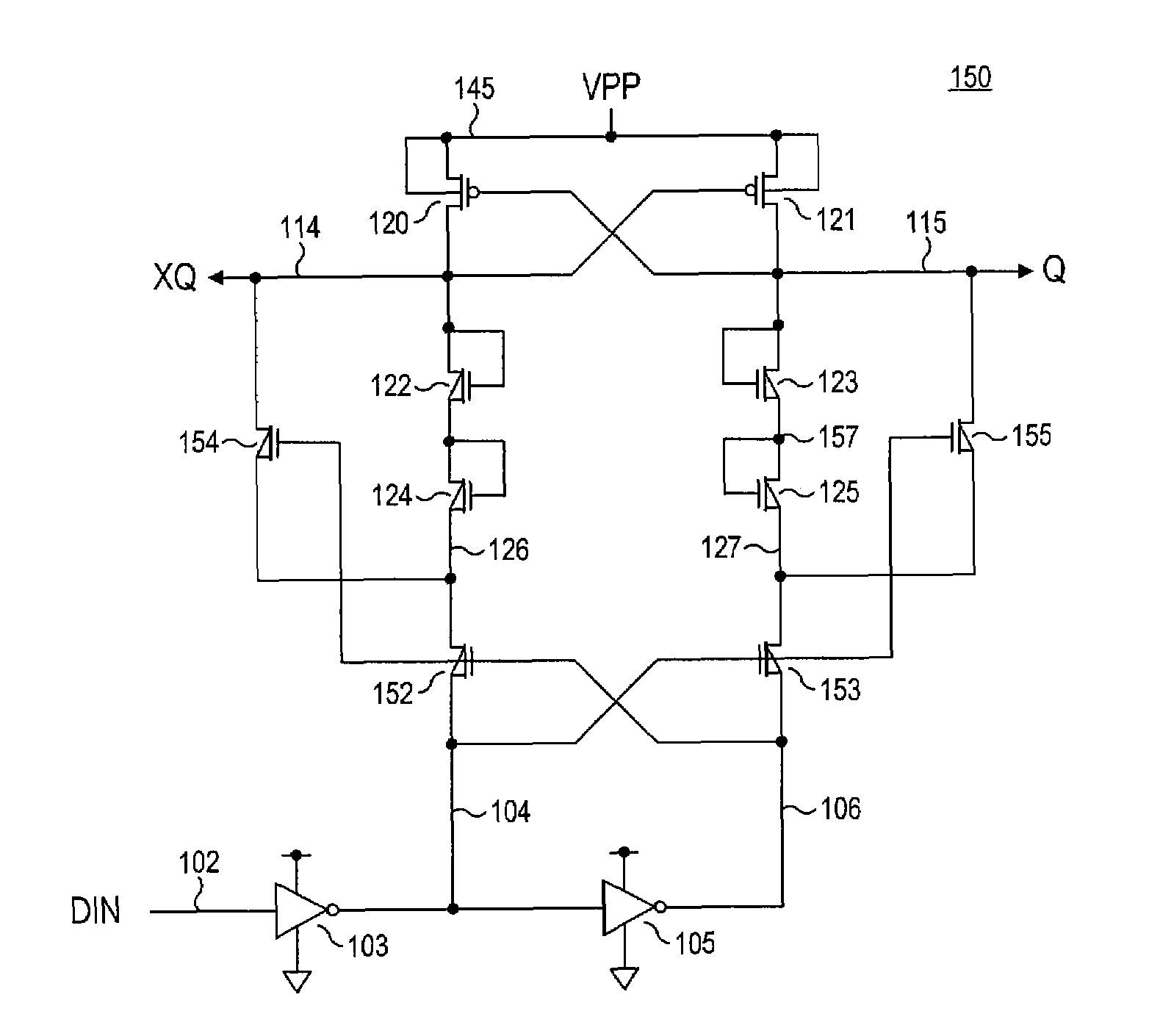
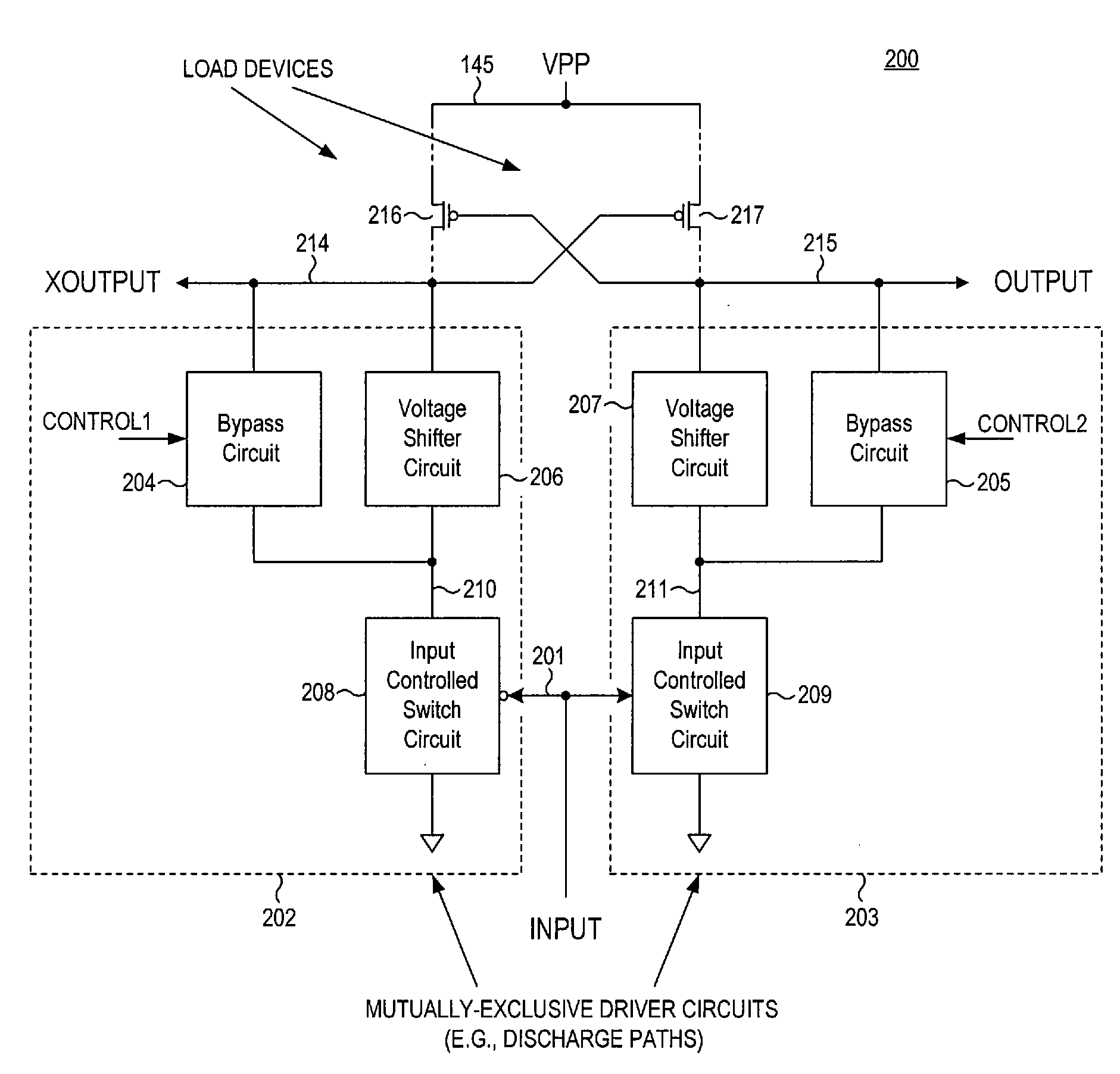
Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
ActiveUS7696805B2Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Superconducting FCL using a combined inducted magnetic field trigger and shunt coil
InactiveUS7283339B2Increase speedReduce creationMagnetsMagnetic materialsShunt impedanceHigh temperature superconducting
A single trigger / shunt coil is utilized for combined induced magnetic field triggering and shunt impedance. The single coil connected in parallel with the high temperature superconducting element, is designed to generate a circulating current in the parallel circuit during normal operation to aid triggering the high temperature superconducting element to quench in the event of a fault. The circulating current is generated by an induced voltage in the coil, when the system current flows through the high temperature superconducting element.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
ActiveUS20080238523A1Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Comparator for input voltages higher than supply voltage
ActiveUS20060125529A1Improve the immunityHigh voltageMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsVoltage dropEngineering
A comparator has first and second current paths, each passing from an input through a transistor, through a current source to ground, the second current path also having a reference voltage drop element coupled in series with the second input. The gates of the transistors are coupled to form a current mirror. The reference voltage drop element enables higher voltages to be input and compared to higher thresholds above an internal supply voltage level without the need for dividing resistors to reduce the input voltage. Avoiding such resistors means the power dissipation and the silicon area used can be kept lower. ESD vulnerability is reduced since the inputs are not coupled to gates of MOS transistors. Overvoltage protection across the source and gate of the second transistor can be added.
Owner:AMI SEMICON BELGIUM
Method for incorporating transistor snap-back protection in a level shifter circuit
ActiveUS20080238522A1Limit voltagePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLevel shifting
Level shift circuits are disclosed for level shifting an input signal corresponding to a first voltage domain, to generate a pair of complementary output signals corresponding to a second, higher-voltage domain. Snap-back sensitive devices in a discharge circuit for a high voltage output node are protected, irrespective of the loading on the output node, and without requiring precise transistor sizing as a function of the output loading. The snap-back sensitive devices are protected by a voltage shifter circuit in series with the sensitive devices, to limit the voltage across the sensitive devices, even for a high capacitance output node at its highest output voltage. The voltage shifter circuit is then bypassed to provide for an output low level that fully reaches the lower power supply rail.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
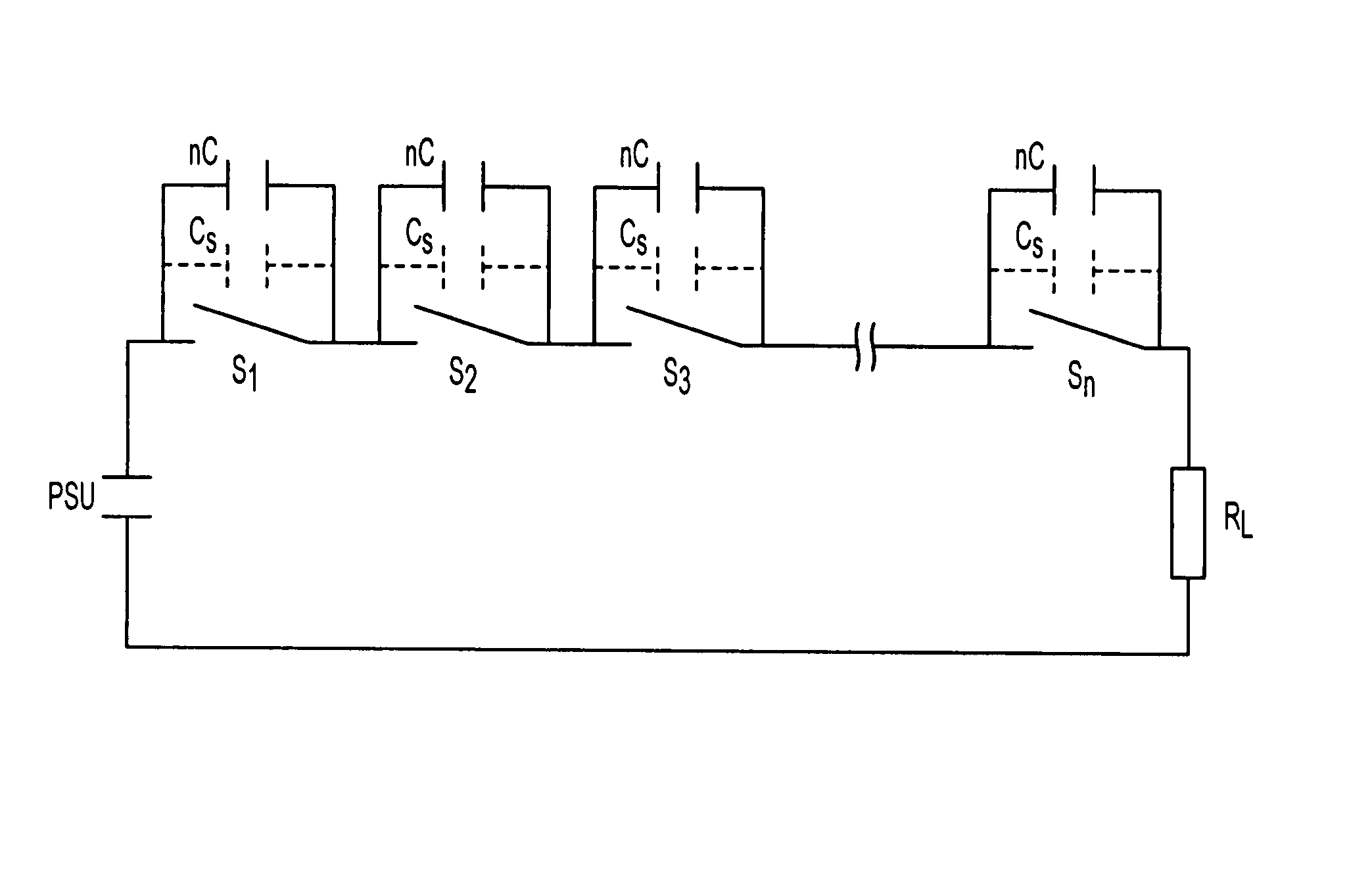
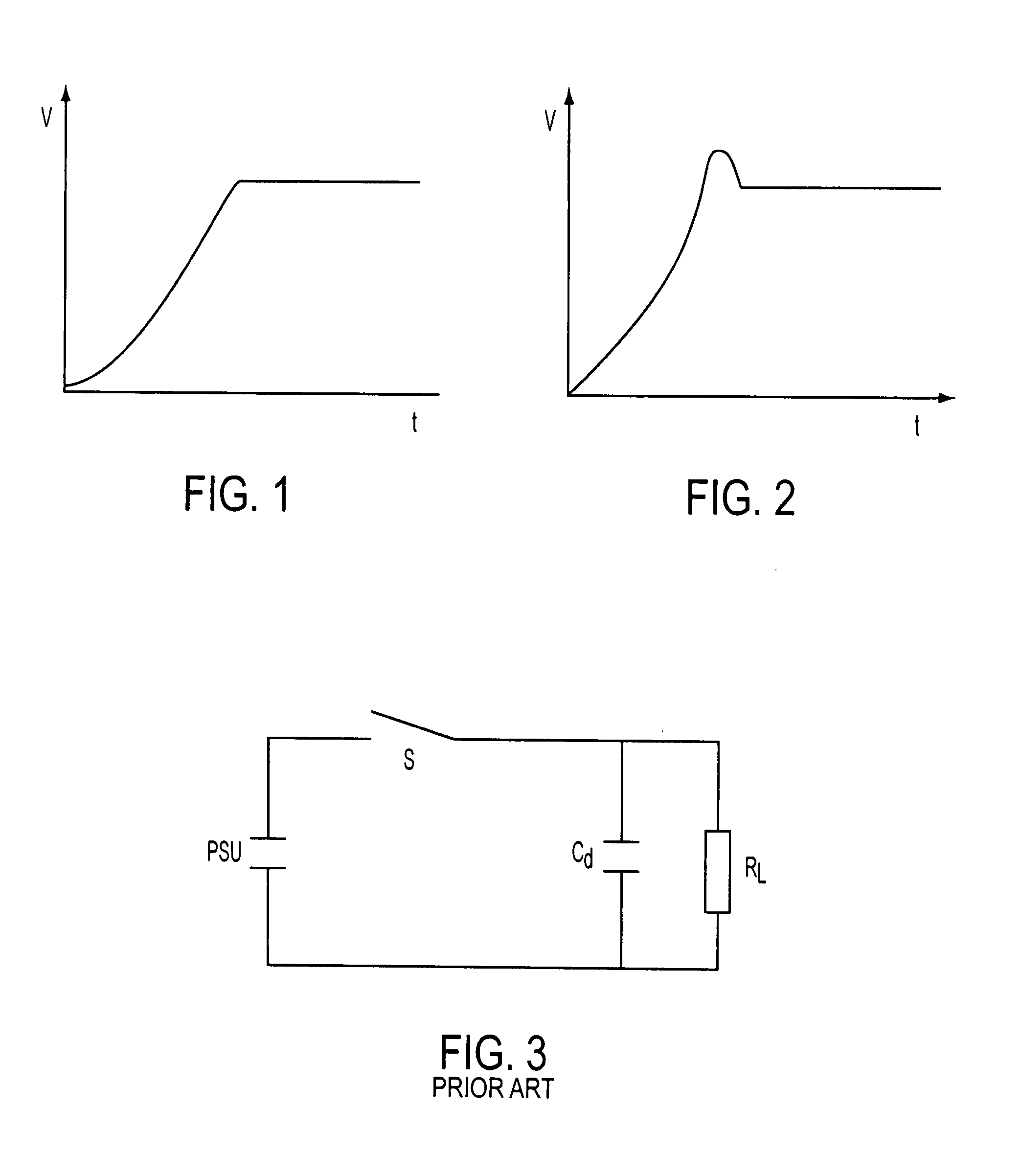
High voltage switching apparatus
InactiveUS7256637B2Limit voltageInhibitionAc-dc conversionTransit-time tubesCapacitanceVoltage overshoot
A switching arrangement for a high voltage load provides high voltage pulses to the load. The switching arrangement includes switching modules, where n is typically (75). A load capacitance is Cd is required to avoid voltage overshoot at the load and is provided by a capacitance of nCd arranged in parallel with each switch.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
Surge clamp protection circuit
InactiveUS7266195B1Limit voltageAvoid accumulationInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentEngineeringCharge pump
A surge clamp circuit that may be implemented with DAA circuitry to limit the total voltage developed across one or more line side capacitors due to charge pumping phenomenon during a multi-transient events such as lightning strikes. The surge clamp circuit is capable of electronically sensing a transient event (e.g., lightning strike) and of momentarily turning on one or more components of a DAA hookswitch circuit during on hook mode to discharge the voltage developed across one or more line side capacitors before it reaches critical breakdown levels. The surge clamp circuit may be configured with a clamping sensitivity selected so that the DAA hookswitch circuitry is only activated or turned on upon occurrence of relatively large and potentially damaging transient events, and not upon occurrence of non-damaging transient events, such as operational signals.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
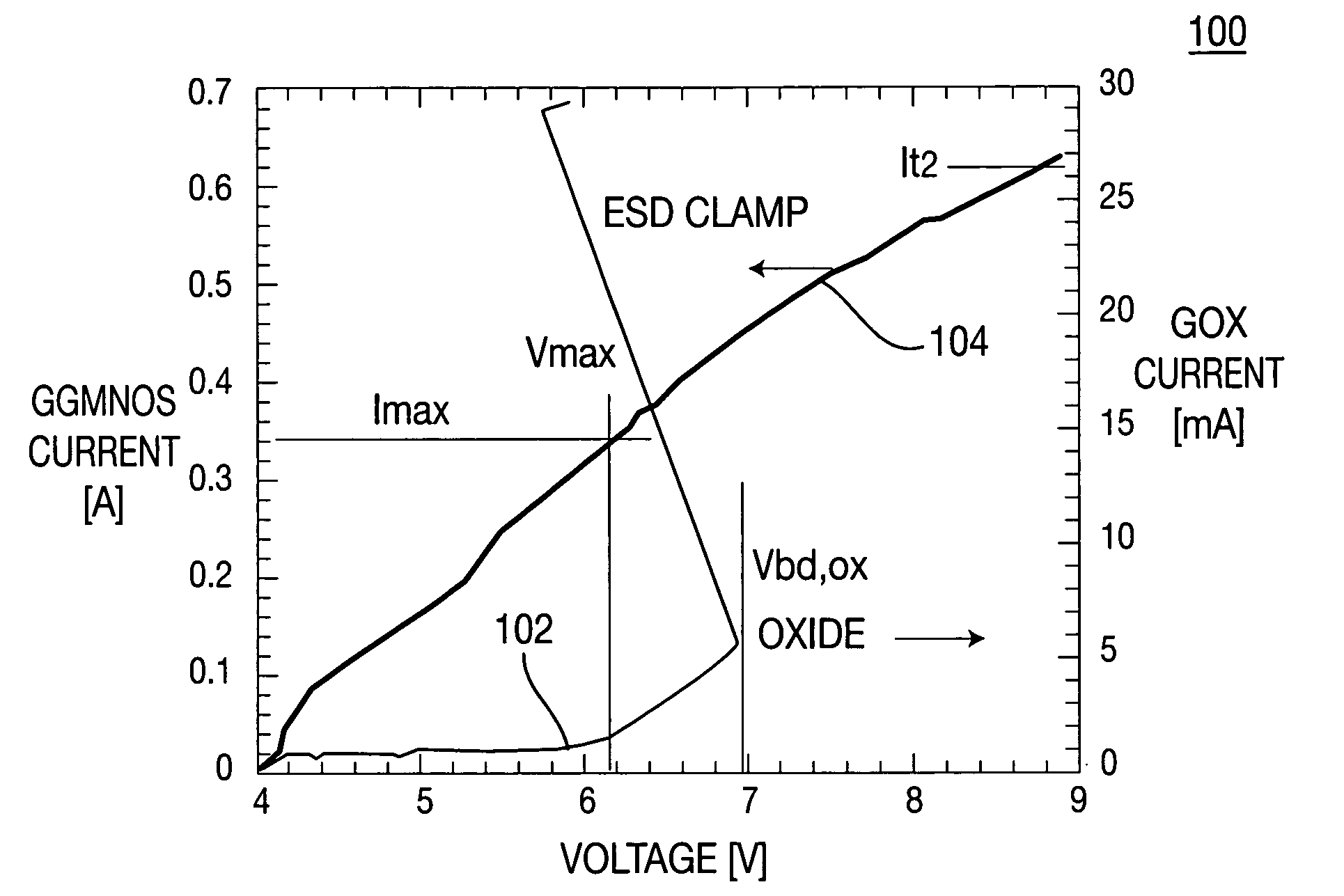
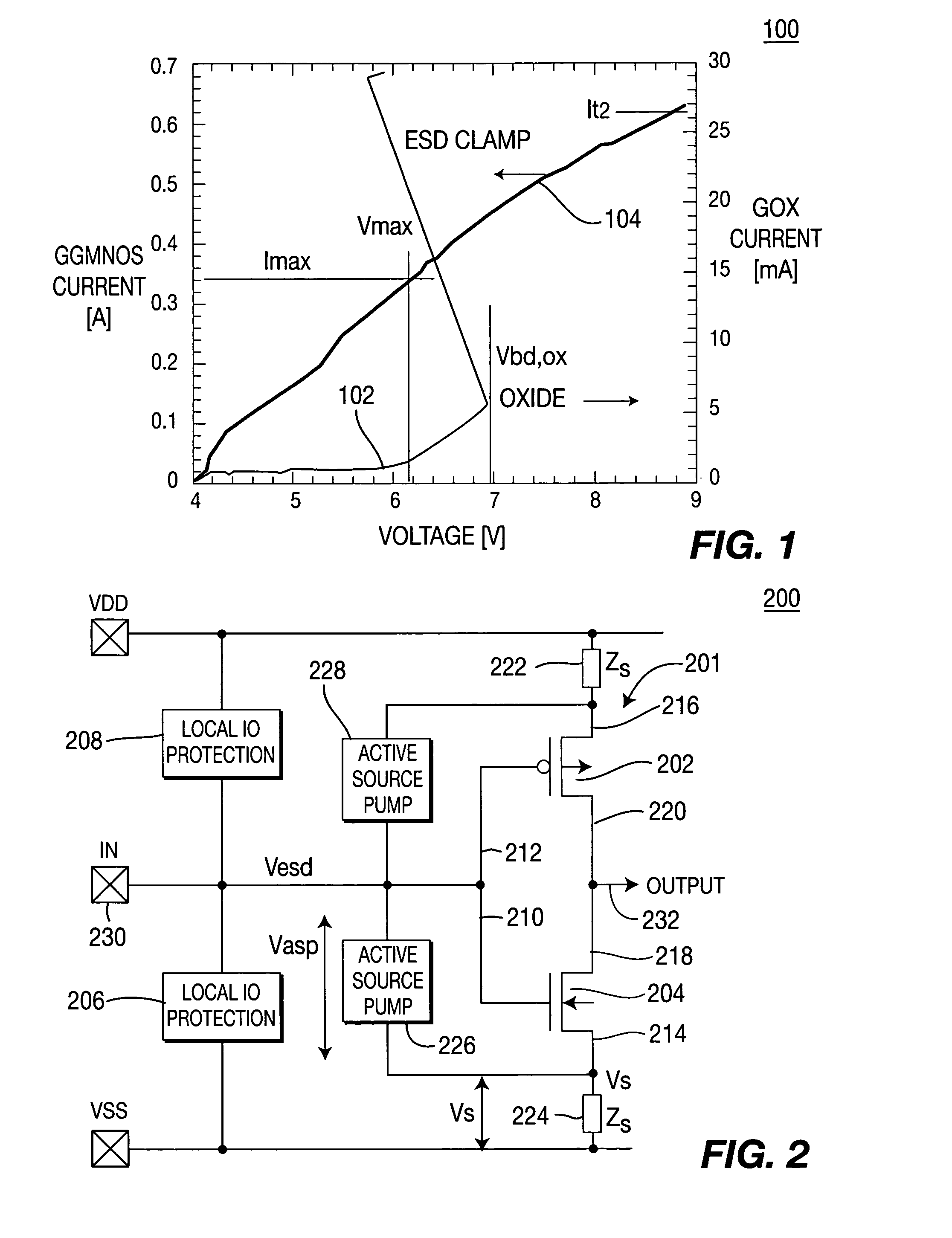
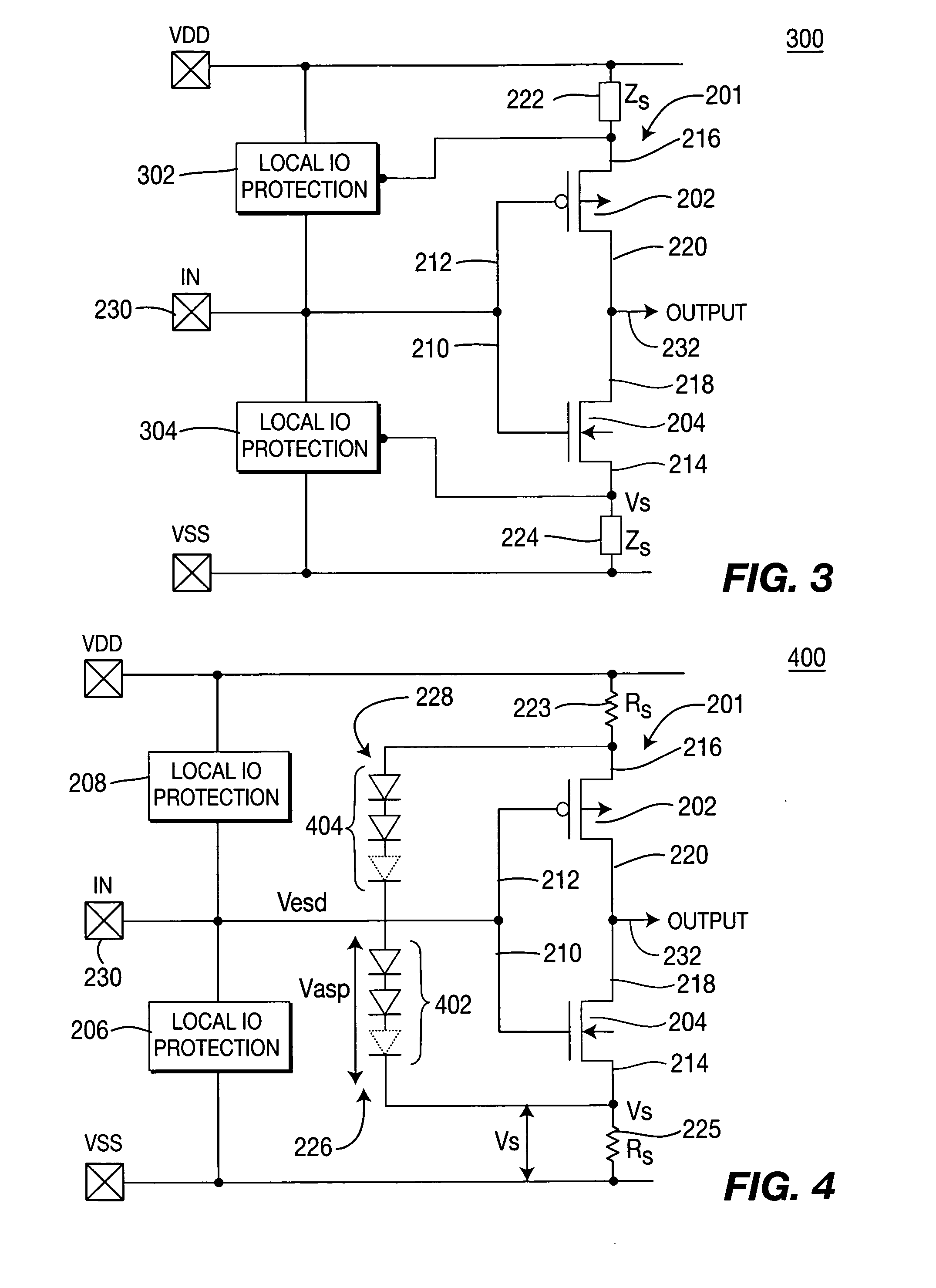
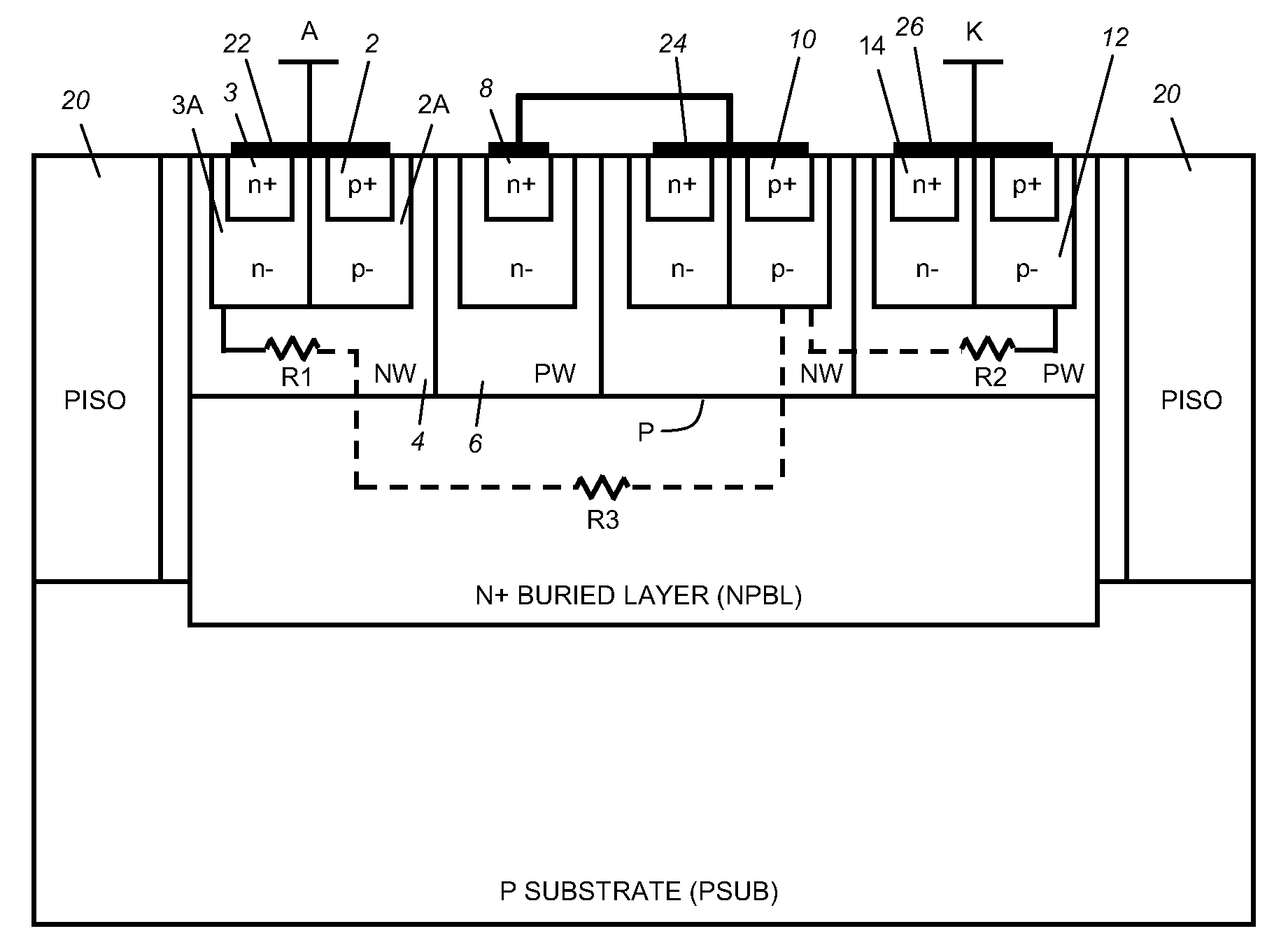
Method and apparatus for protecting a gate oxide using source/bulk pumping
A method and apparatus for providing ESD event protection for a circuit using a source or bulk pump to increase the bulk and / or source potential level during an ESD event. The apparatus comprises a protection circuit that, in response to an ESD event, limits the voltage formed between two terminals of a transistor by adjusting a potential level on the second terminal.
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Stacked scr with high holding voltage
ActiveUS20090237847A1Reduce voltageLimit voltageTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentAnode voltageEngineering
Stacked SCR's are disclosed with a resistor connecting an internal portion of the upper SCR to an internal portion of the lower SCR. The anode of the protective circuit is connected to a contact on a target circuit to be protected and the cathode of the protective circuit is connected to ground or a reference voltage on the target circuit. The anode voltage is directed to the lower SCR via the resistor such that when the voltage on the anode reaches the triggering voltage of the lower SCR, that SCR triggers and that triggering triggers the upper SCR, such that the stacked SCR's both trigger and thereby limit the voltage between the anode and the cathode and thereby protecting the target circuit.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Low-loss rectifier with shoot-through current protection
InactiveUS20070279821A1Reduce power consumptionReduce voltageBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringField-effect transistor
A transistor active bridge circuit (400) rectifies domestic AC mains (for example, 120V, 60 Hz) and / or foreign AC mains (for example, 230V, 50 Hz) with low power loss. The circuit includes first and second field effect transistors (102, 104) of a first channel type, and third and fourth field effect transistors (106, 108) of a second channel type that is different from the first channel type. A set of voltage dividers (110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124) and voltage clamping devices (126, 128, 130, 132) permit the circuit (400) to efficiently operate over a wider range of input voltages, without potential damage to the field effect transistors. Shoot-through protection devices (420, 430) provide a means for preventing the first and second field effect transistors (102, 104) from conducting simultaneously. Shoot-through protection devices (440, 450) provide a means for preventing the third and fourth field effect transistors (106, 108) from conducting simultaneously.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Transponder with an improved voltage limiter circuit
ActiveUS7786870B2Efficiently and flexibly adjust voltage limitImprove performanceCo-operative working arrangementsTransmissionHemt circuitsEngineering
A transponder with an antenna and an antenna voltage limiting unit for limiting an antenna voltage to a first voltage limit when the transponder is receiving data and to a second voltage limit when the transponder is sending data. Dynamic voltage limitation may be implemented by using a computer program or implemented in hardware. Additionally, it is possible to introduce a third voltage limit when the transponder is in a third mode of operation such as standby or sleeping mode.
Owner:NXP BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com