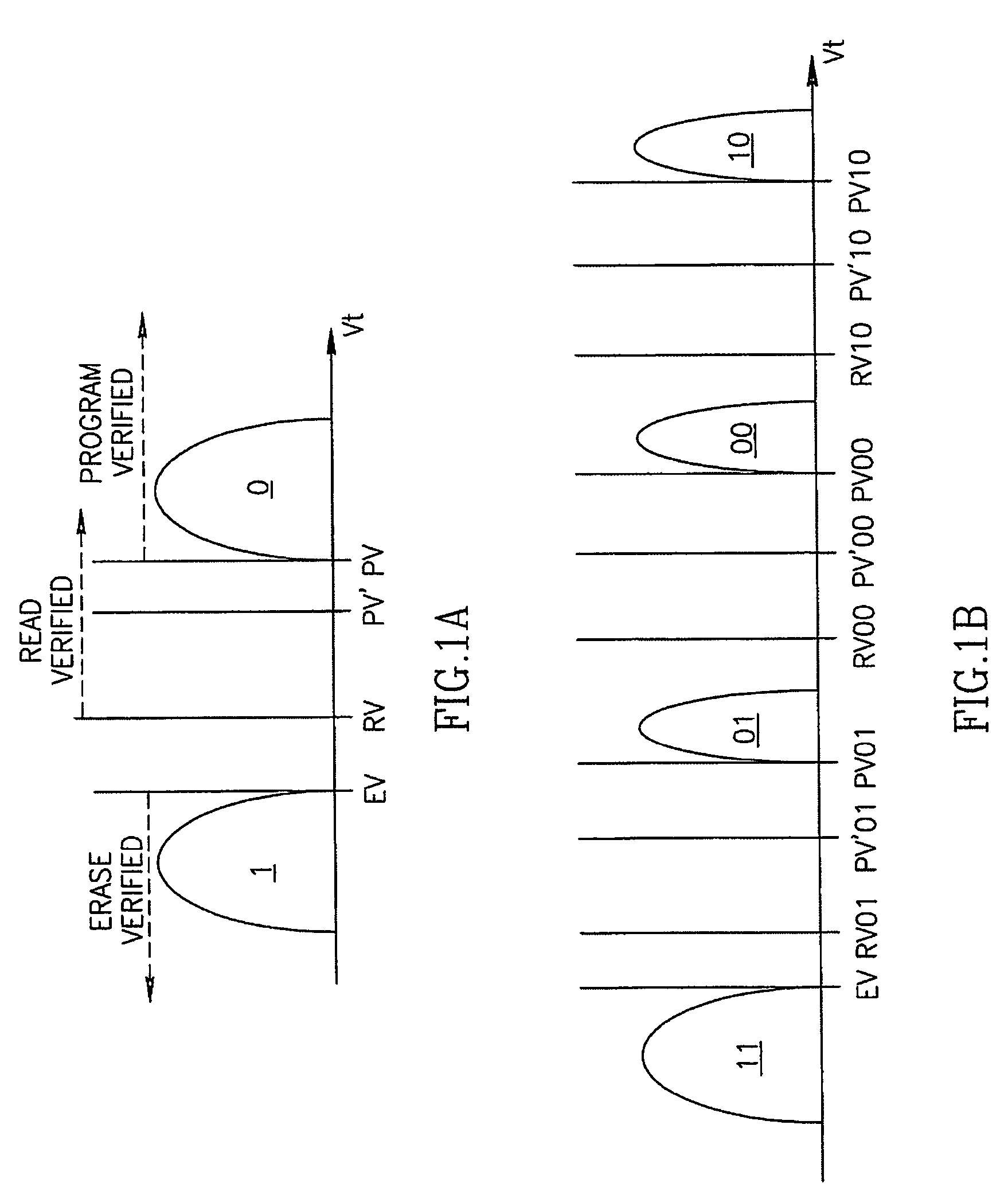
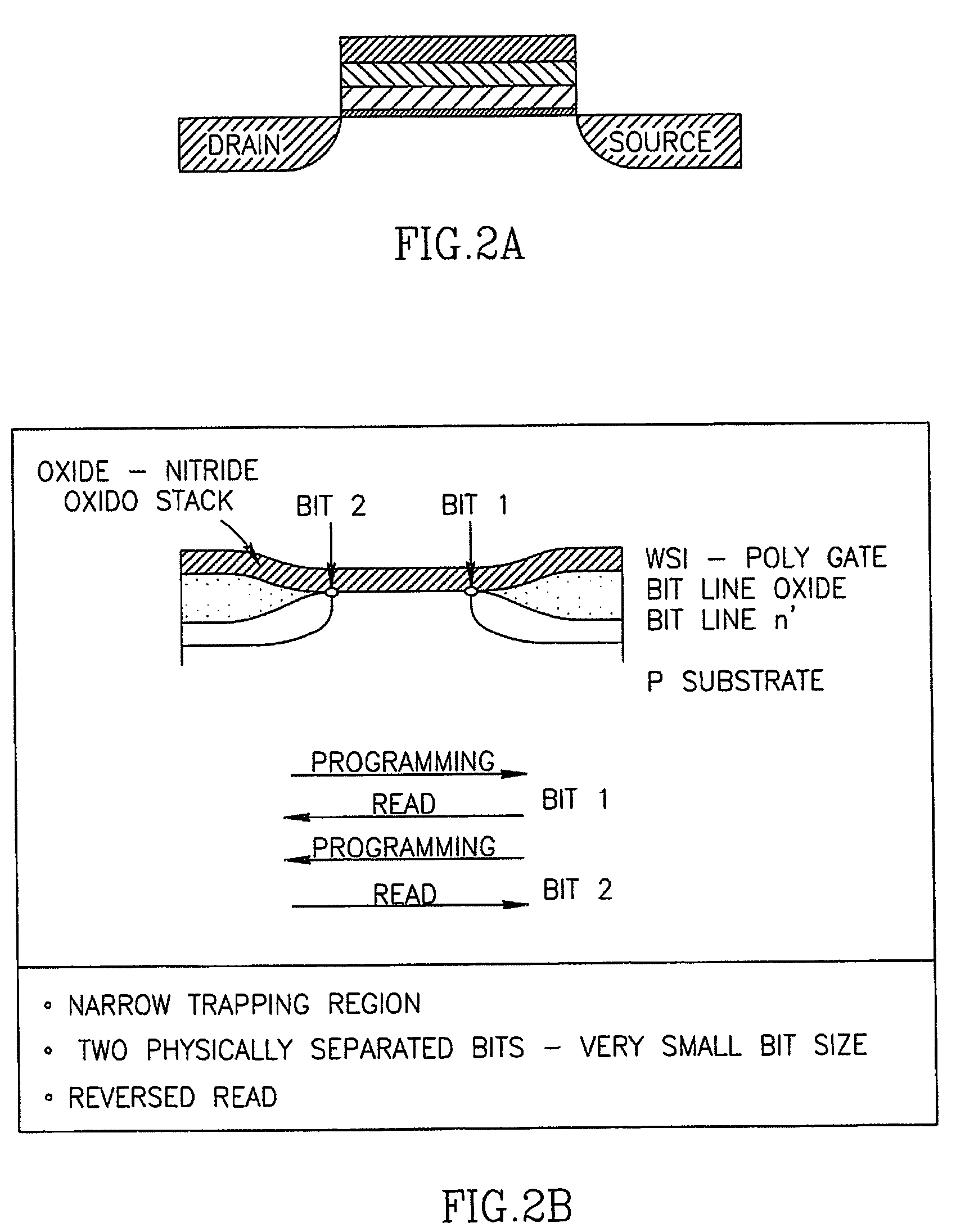
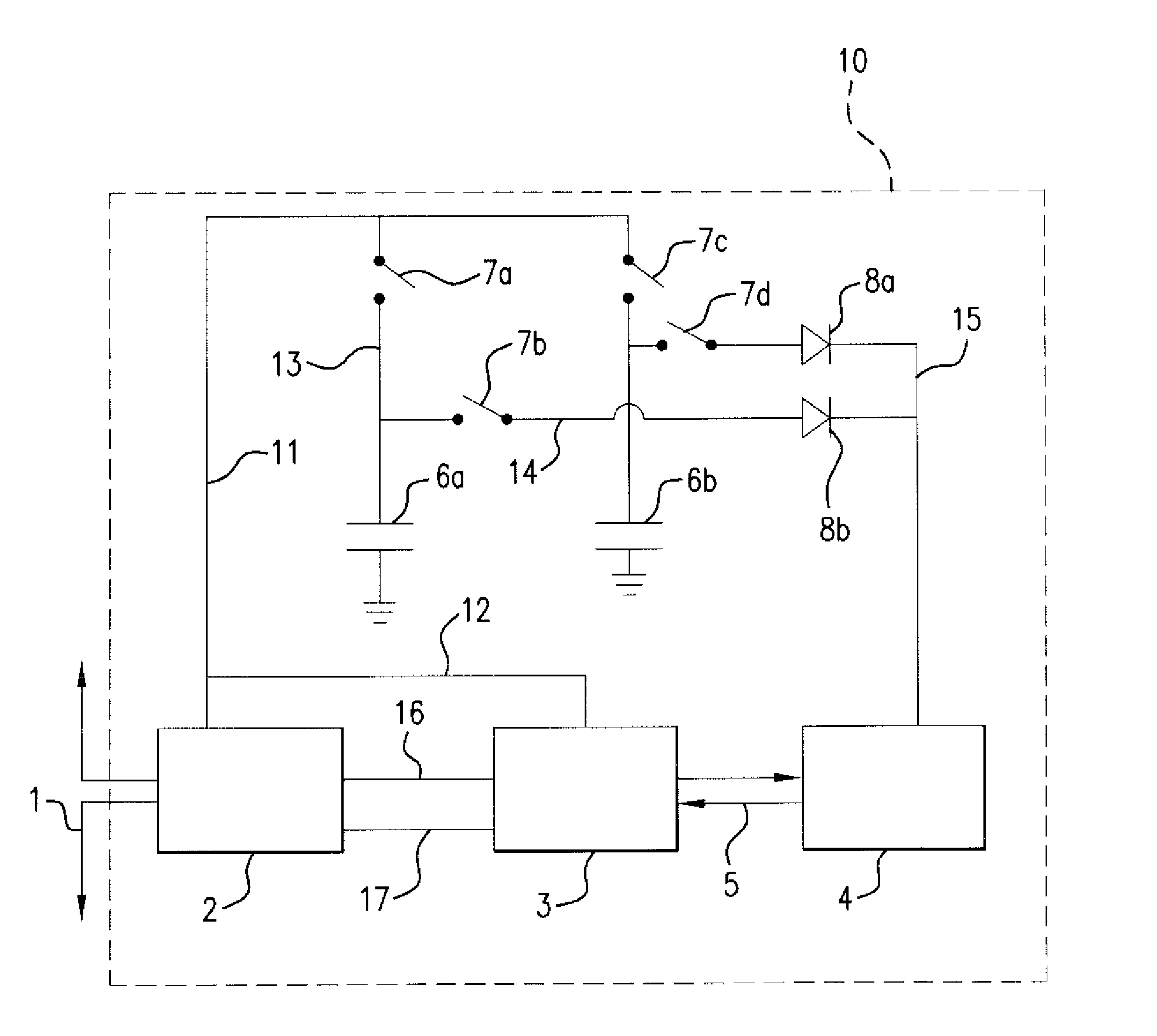
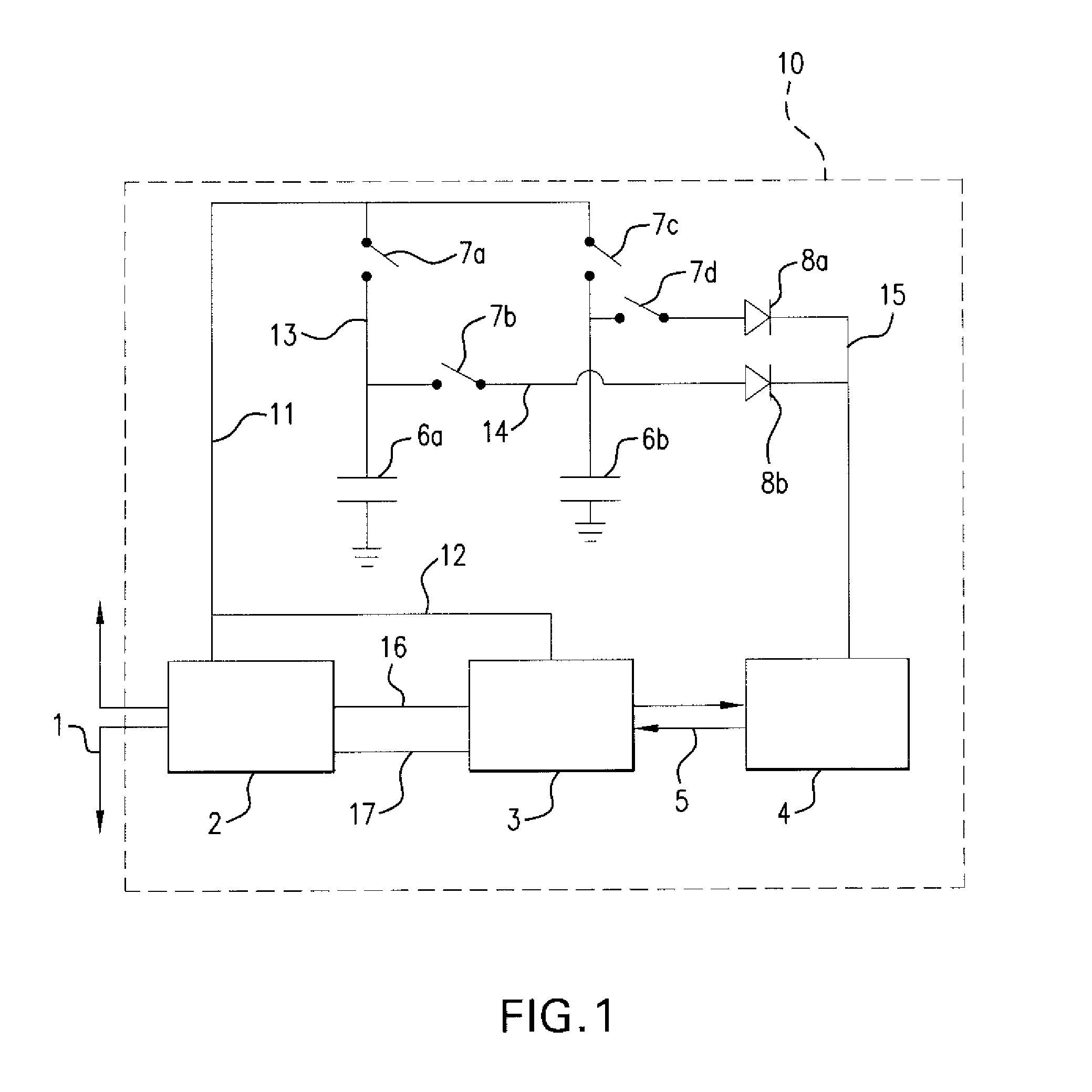
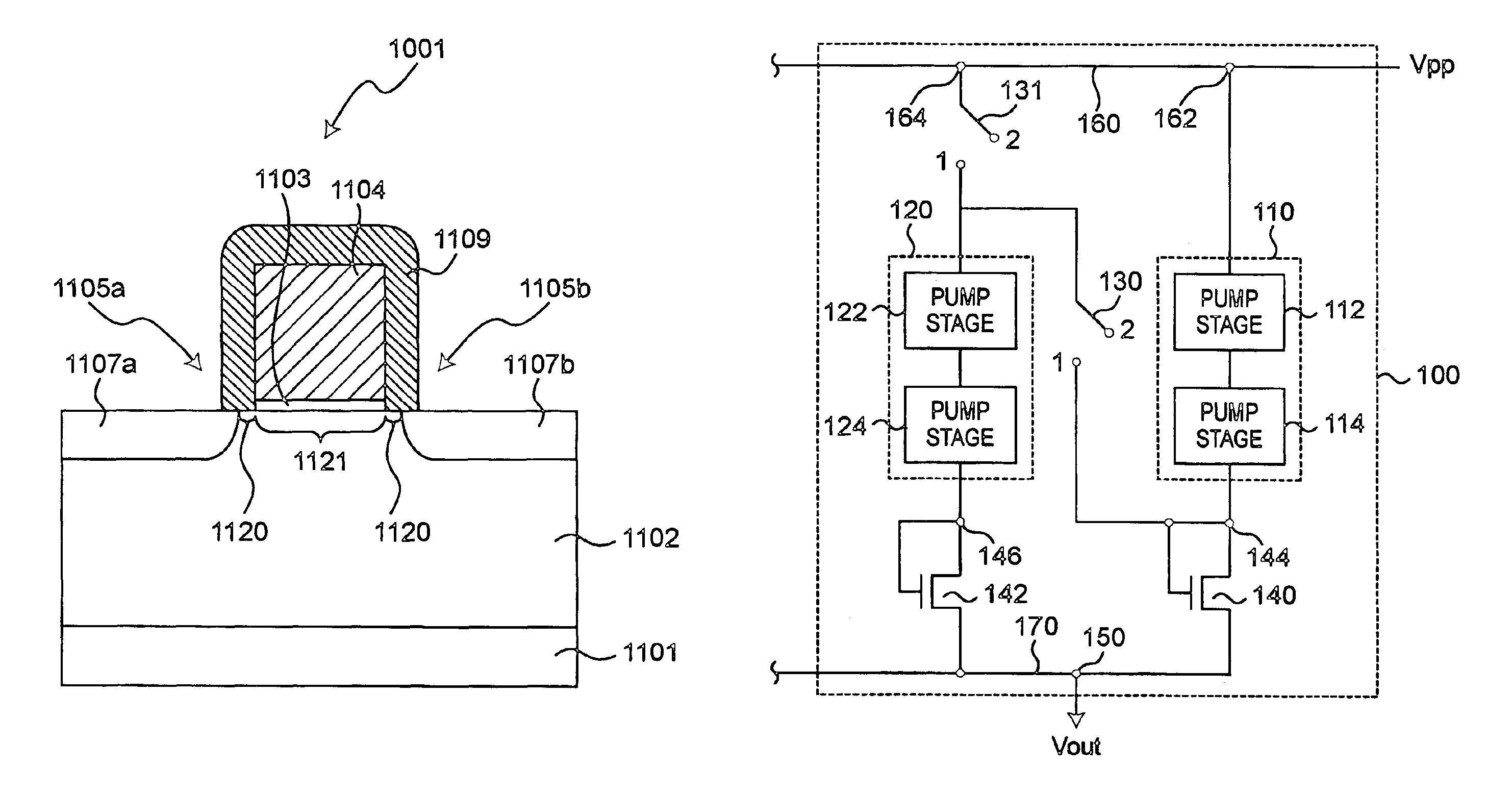
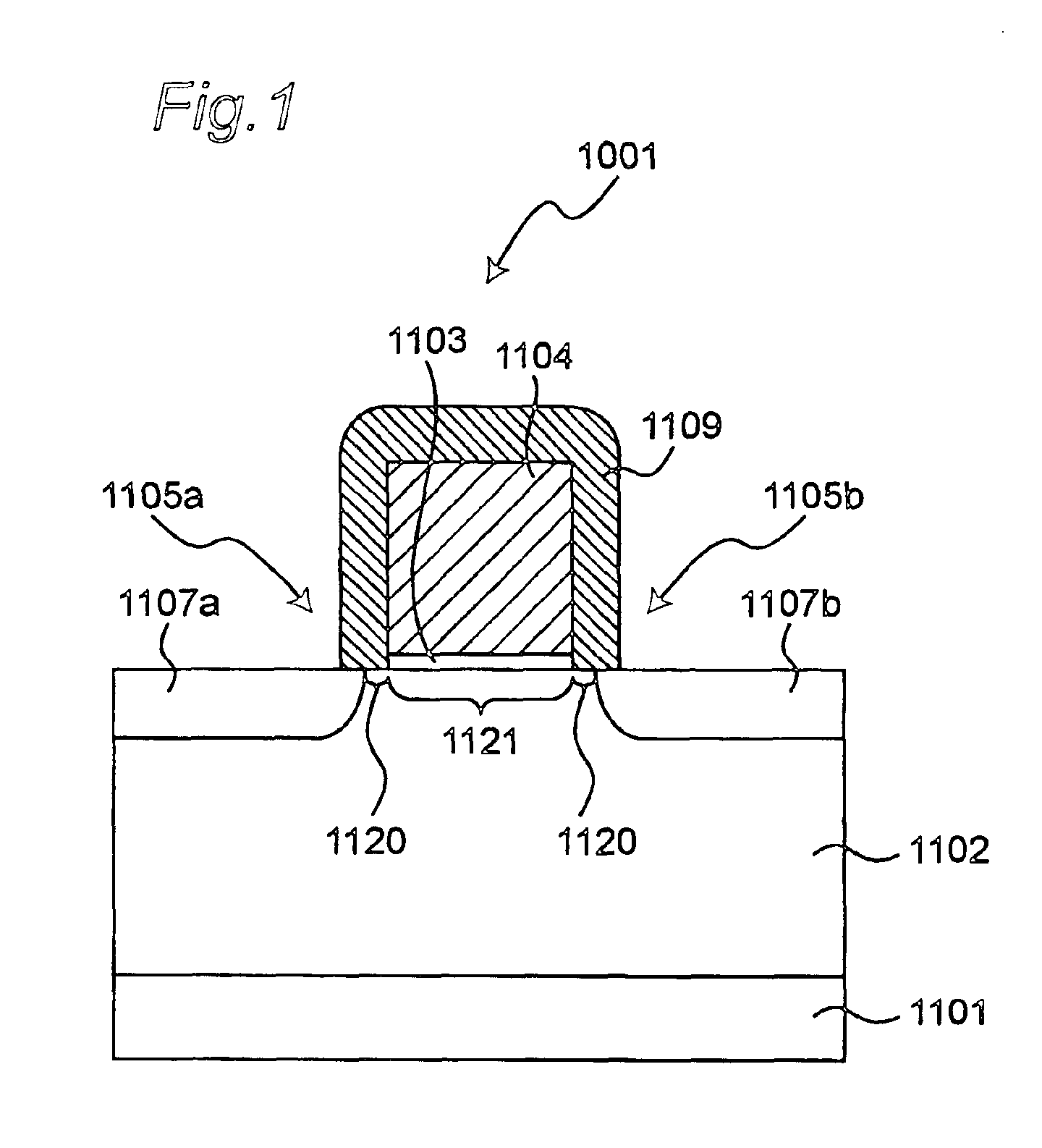
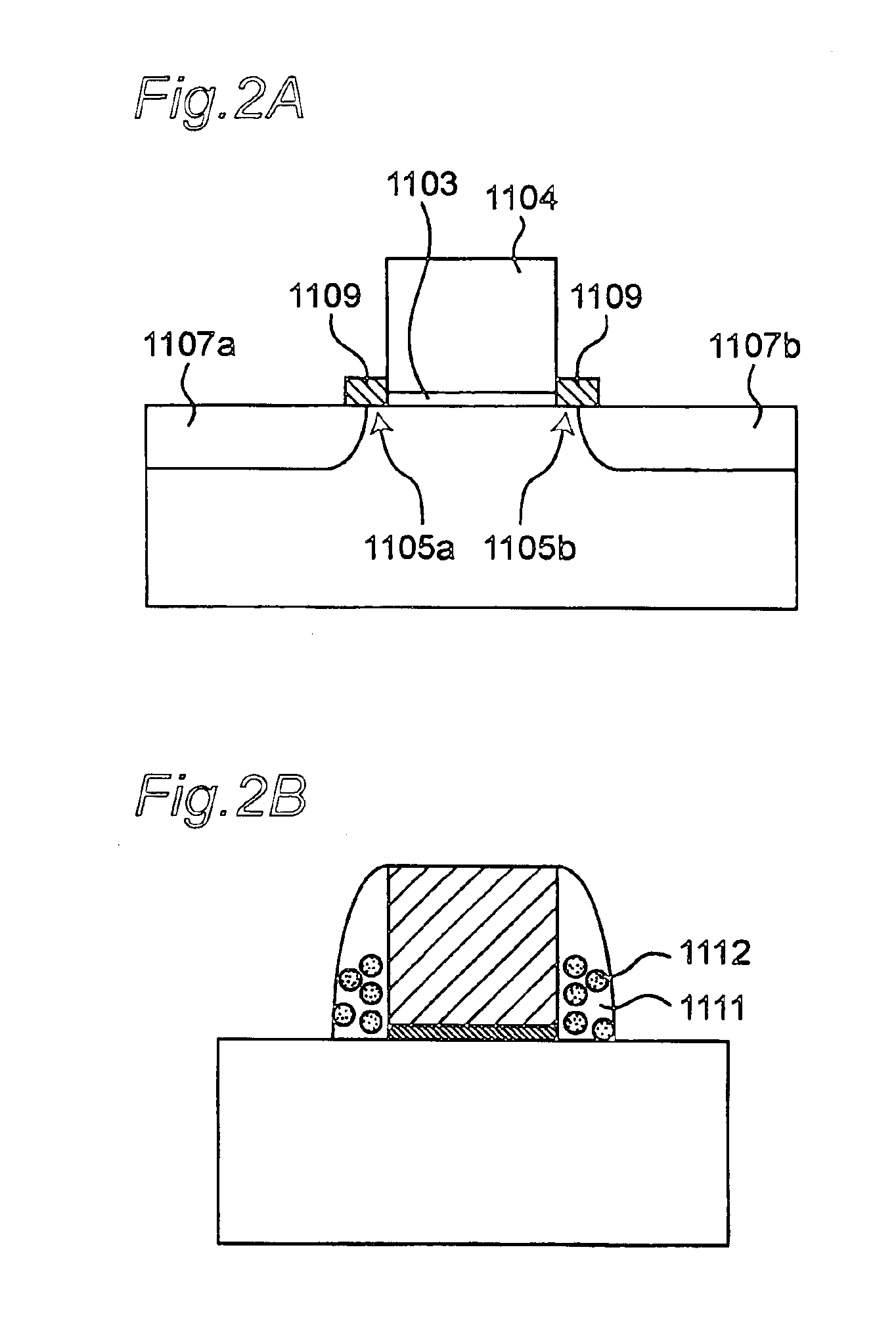
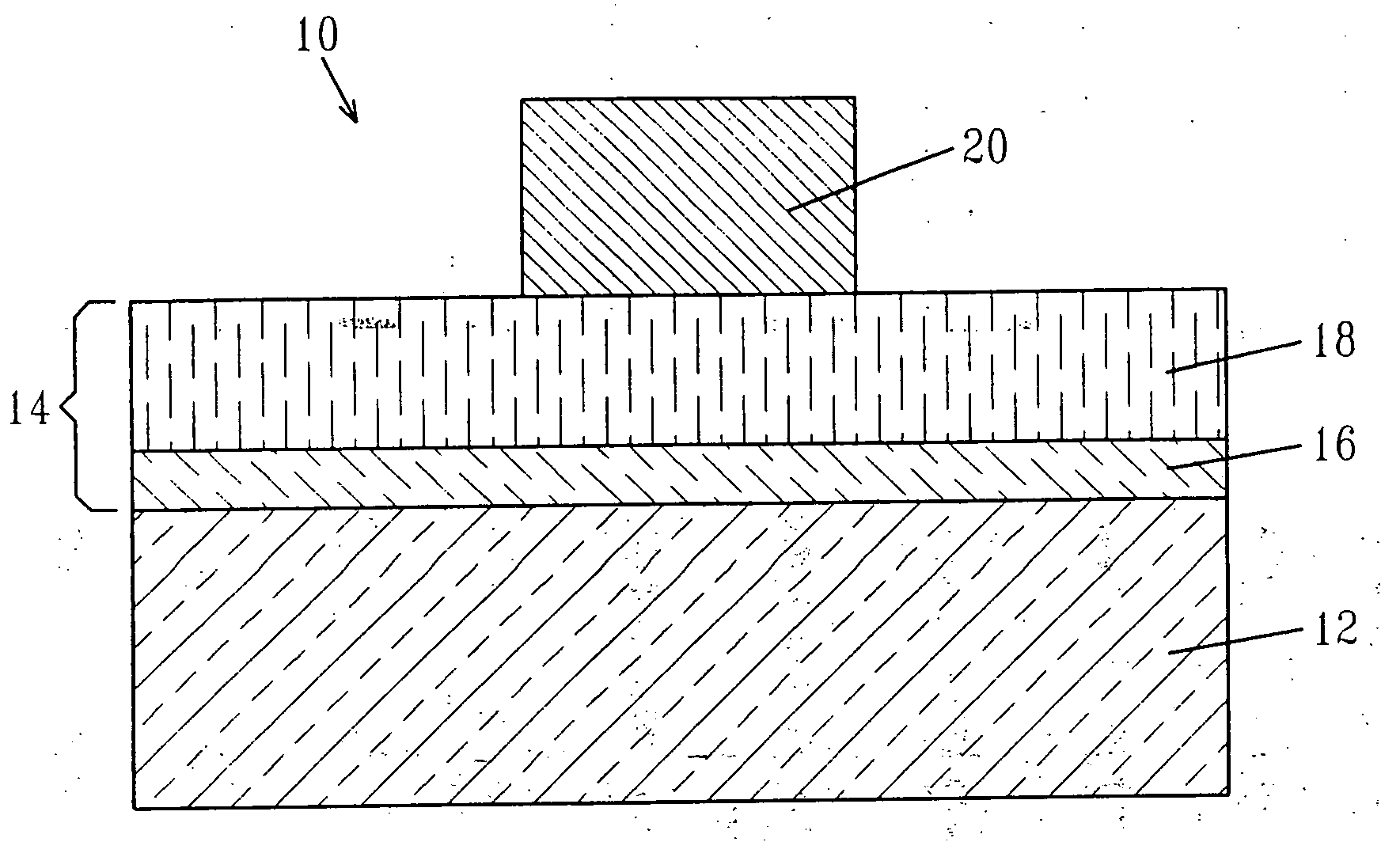
Patents
Literature
837 results about "Charge pumping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Charge Pump. A pump used to boost the pressure of a fluid before it enters the main pump(s) of a system. A charge pump is used to boost the pressure of a fluid before it enters the inlet of the main pump.
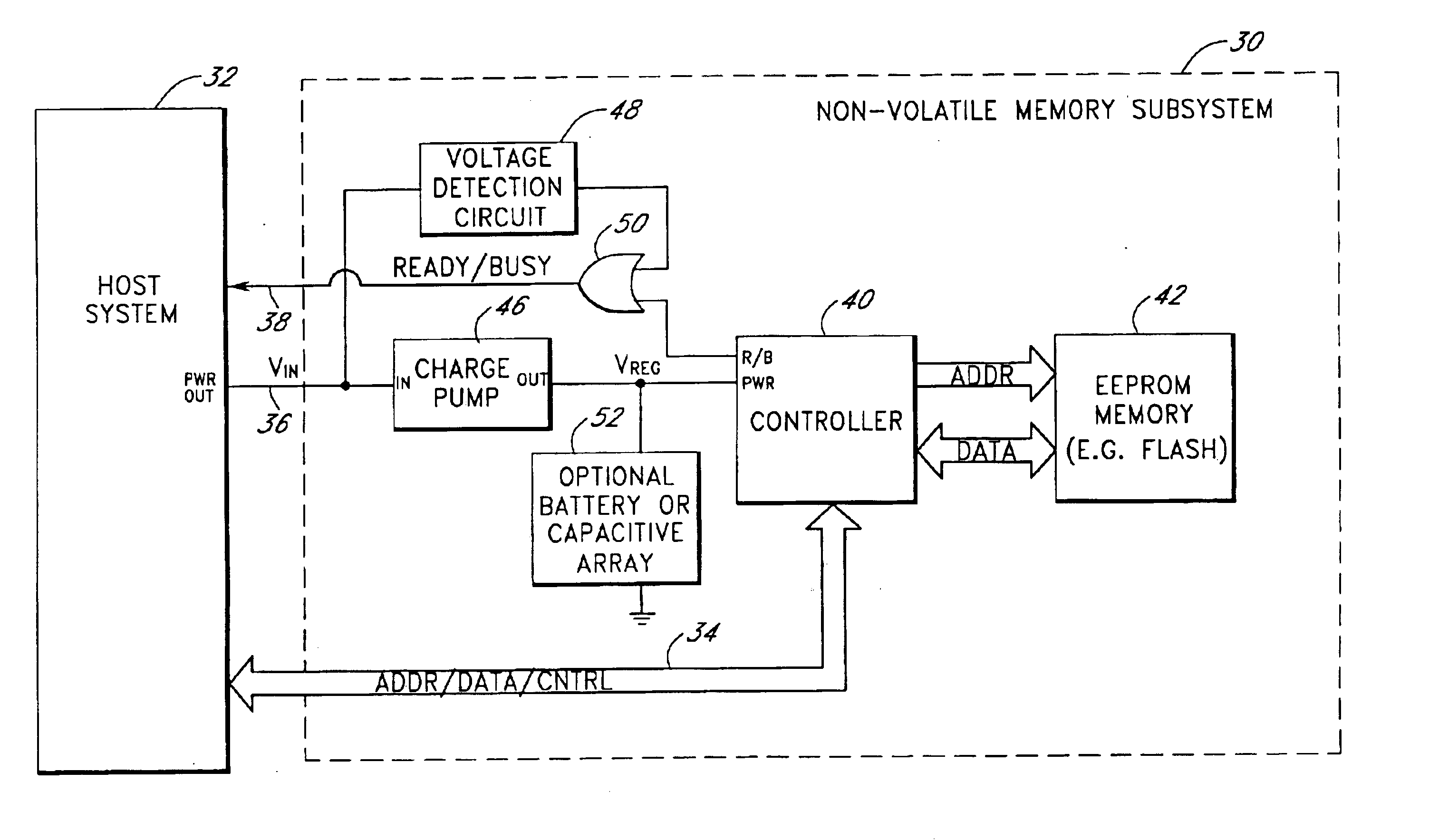
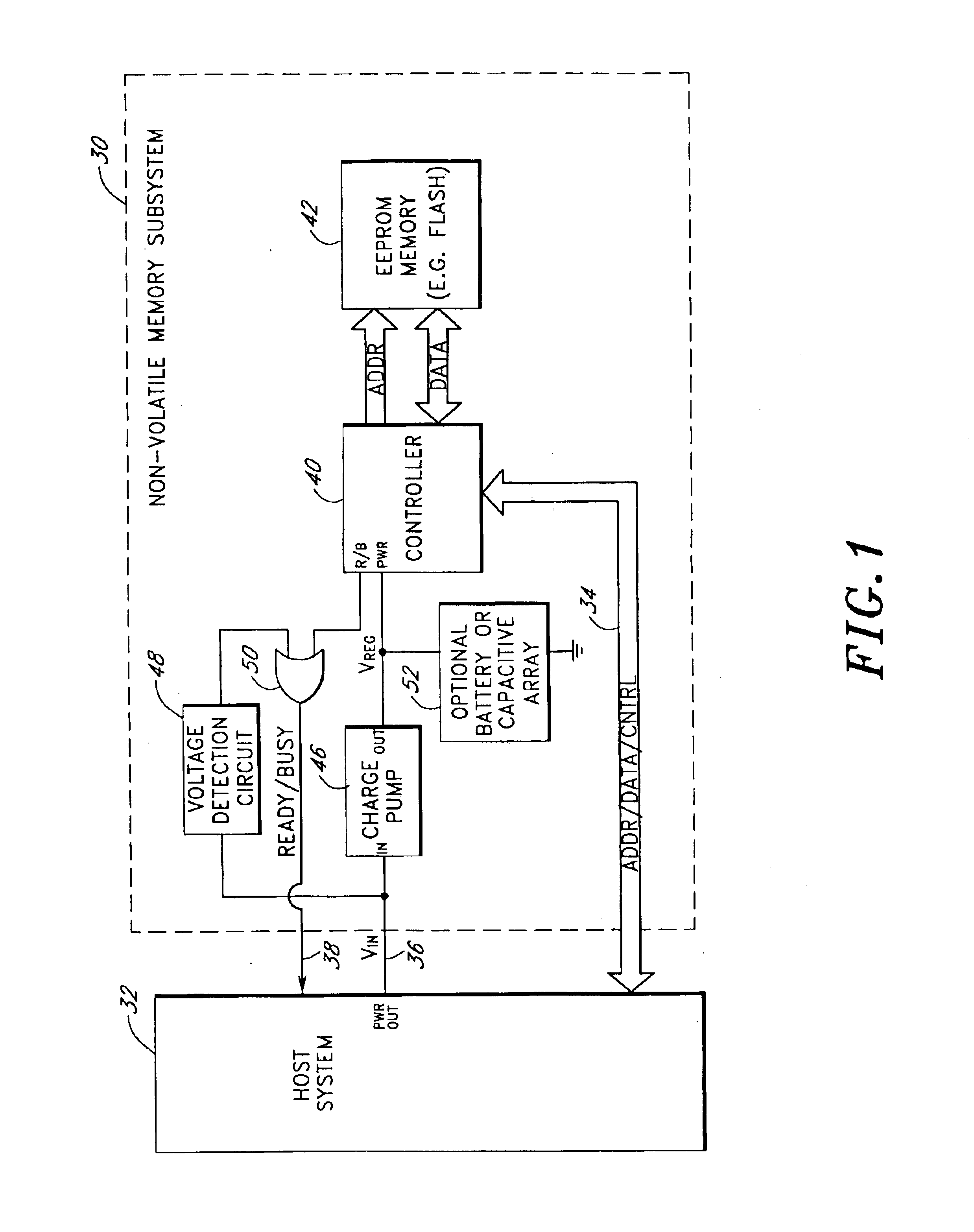
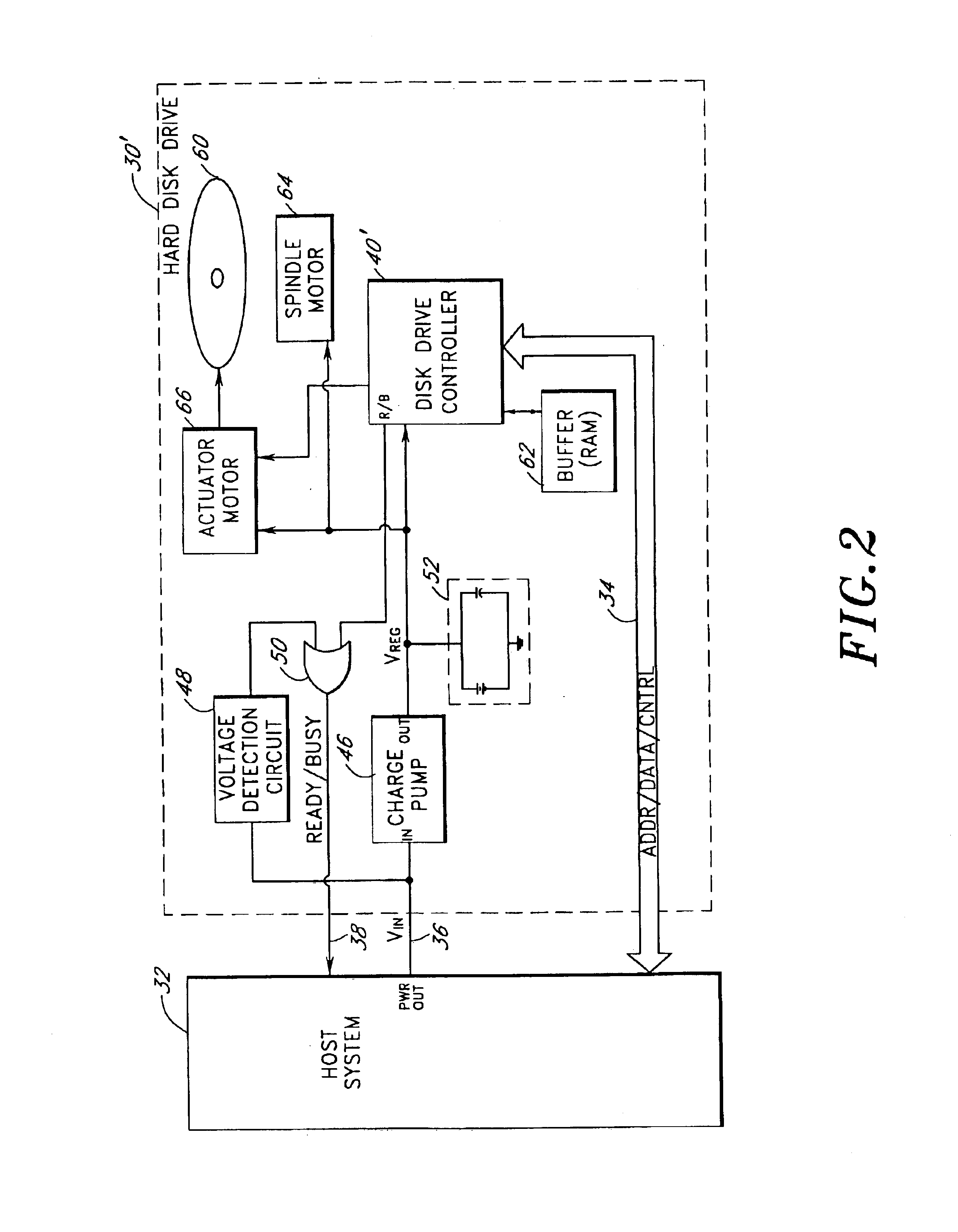
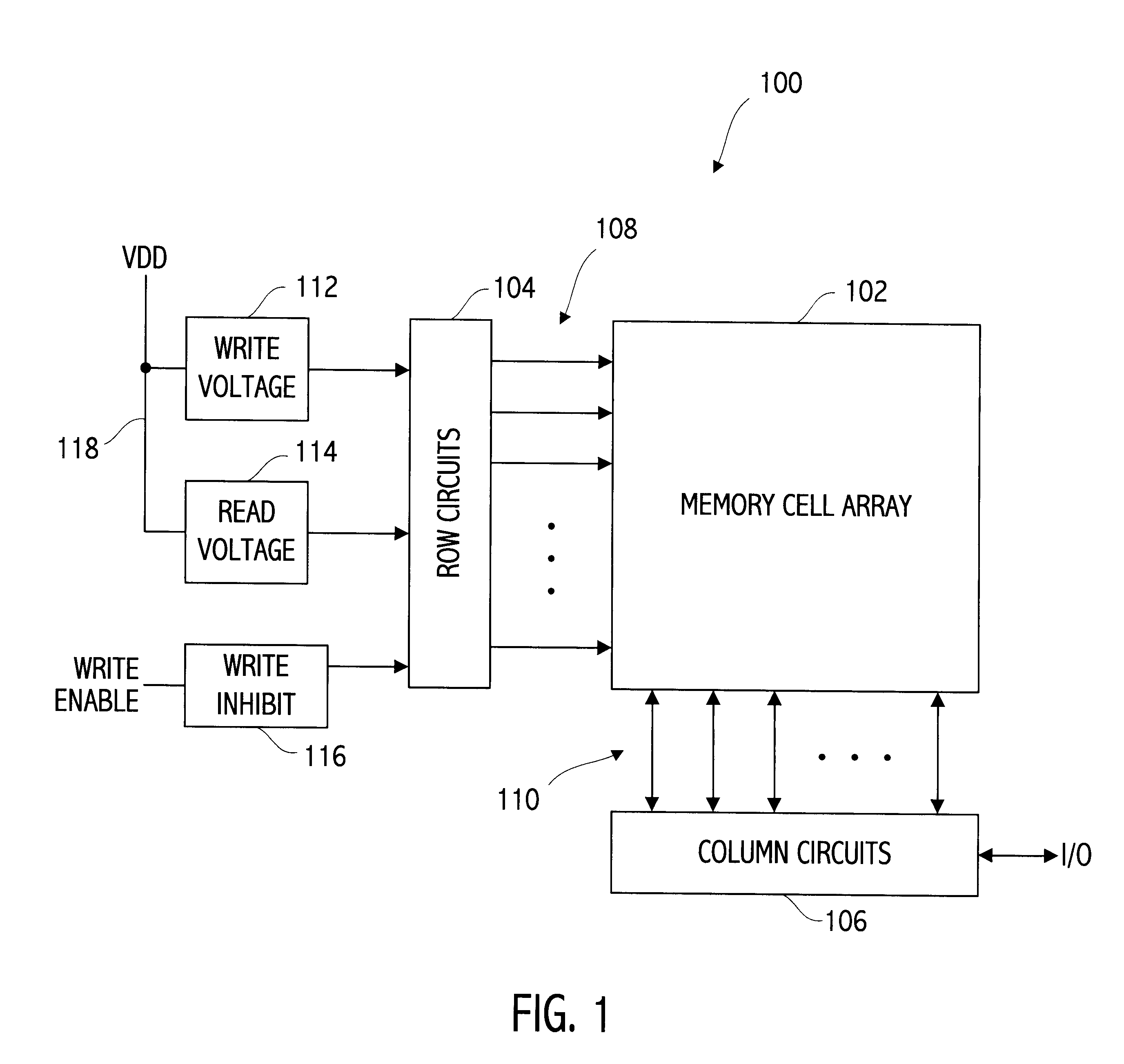
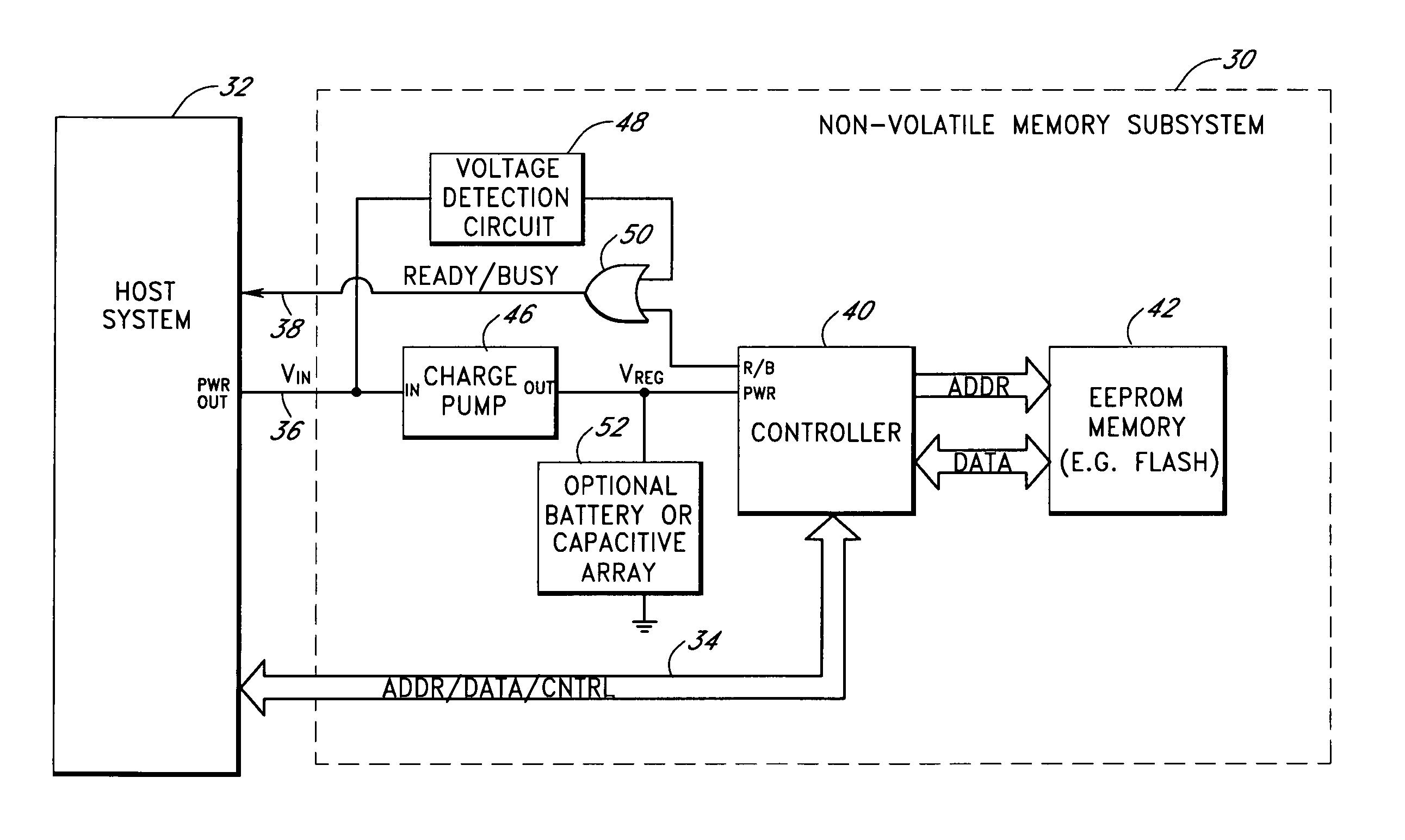
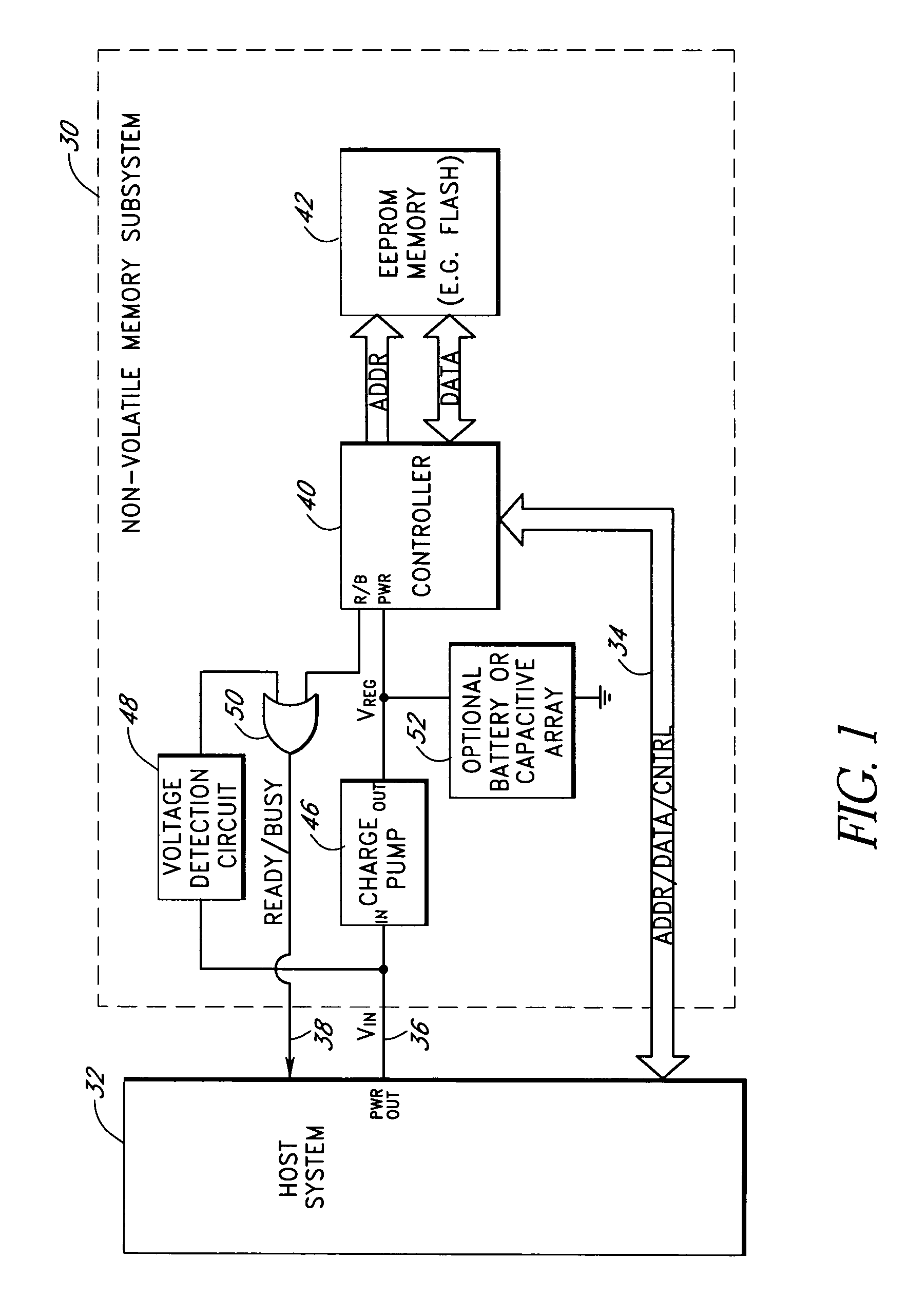
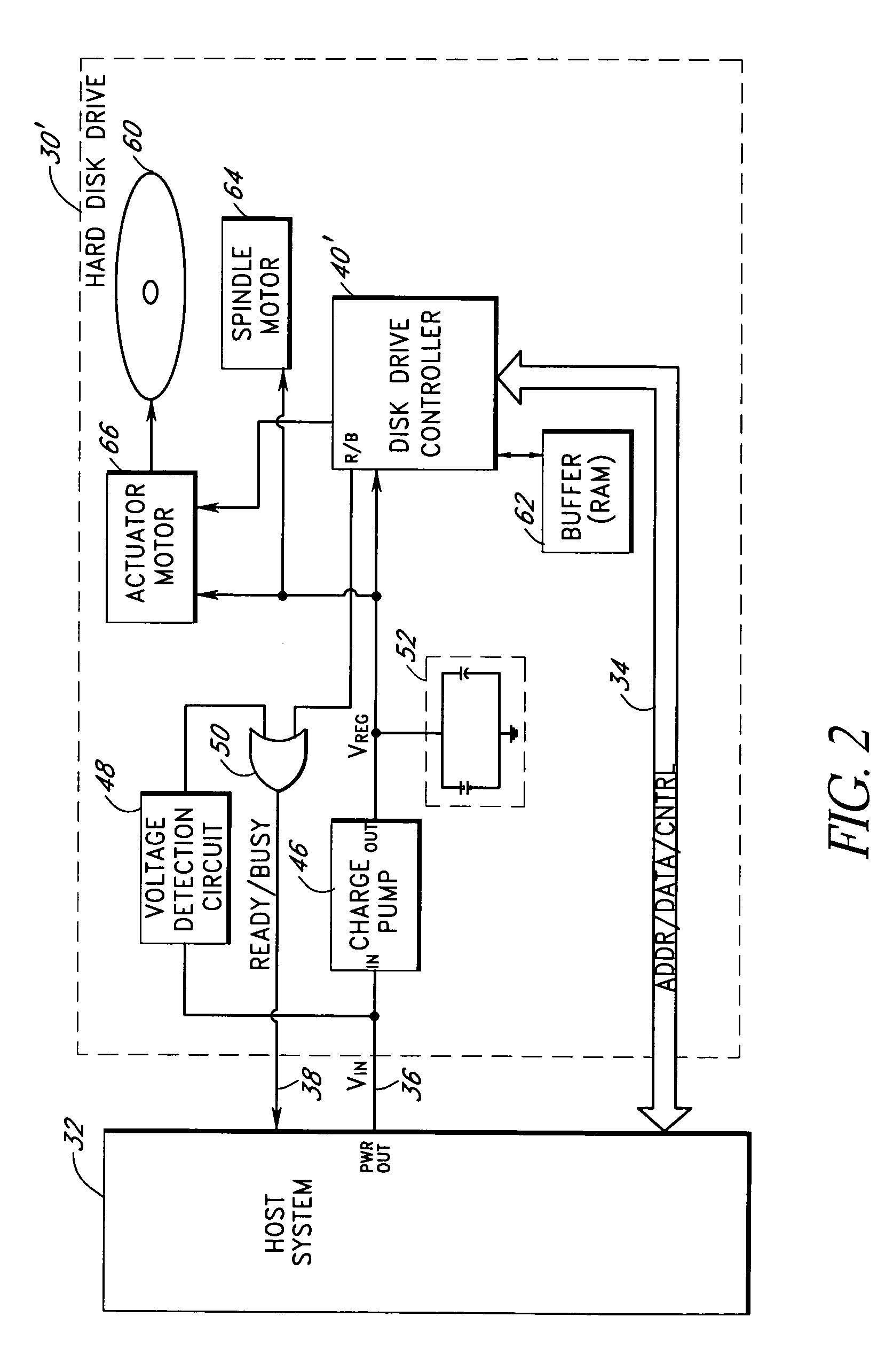
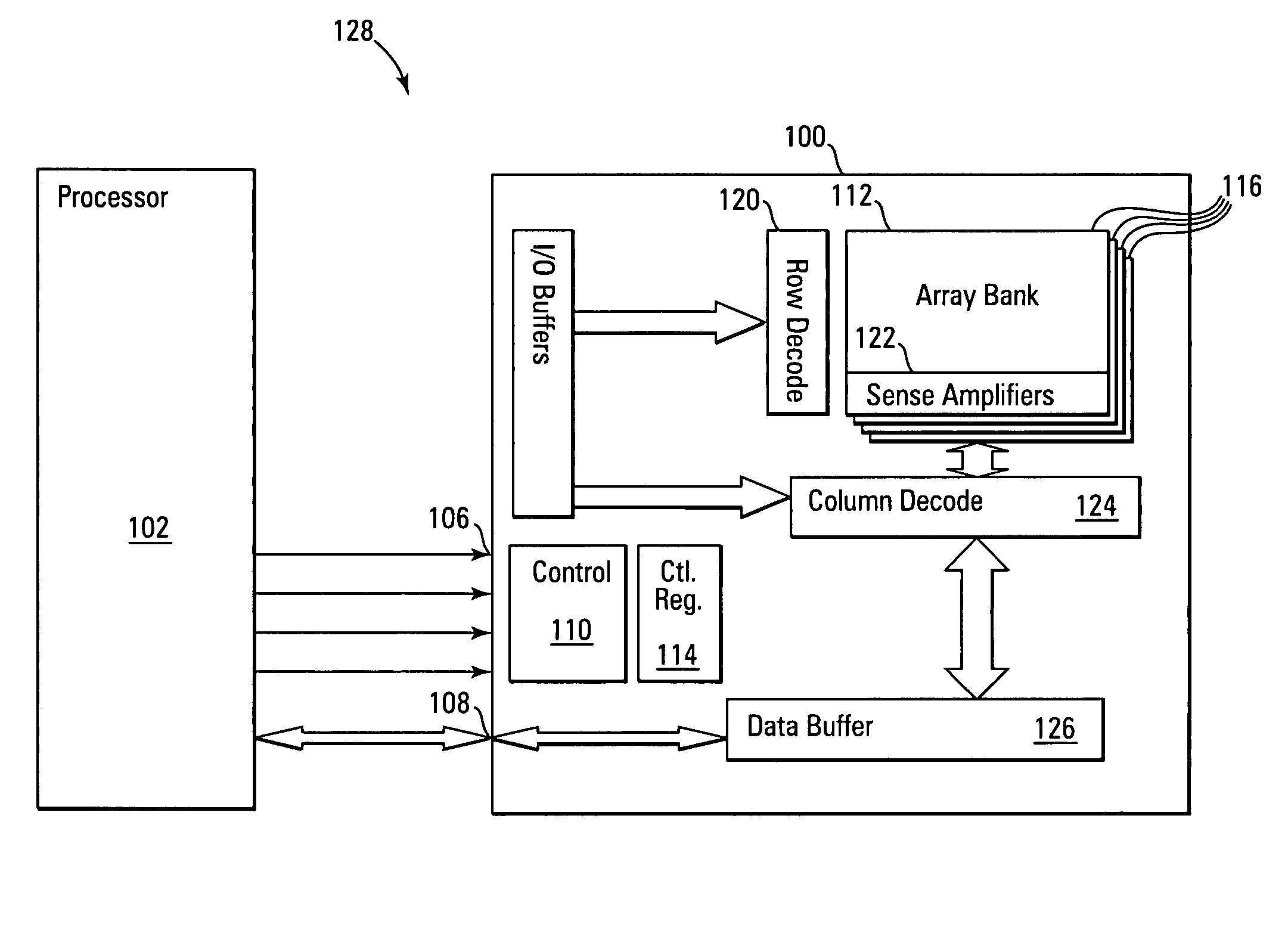
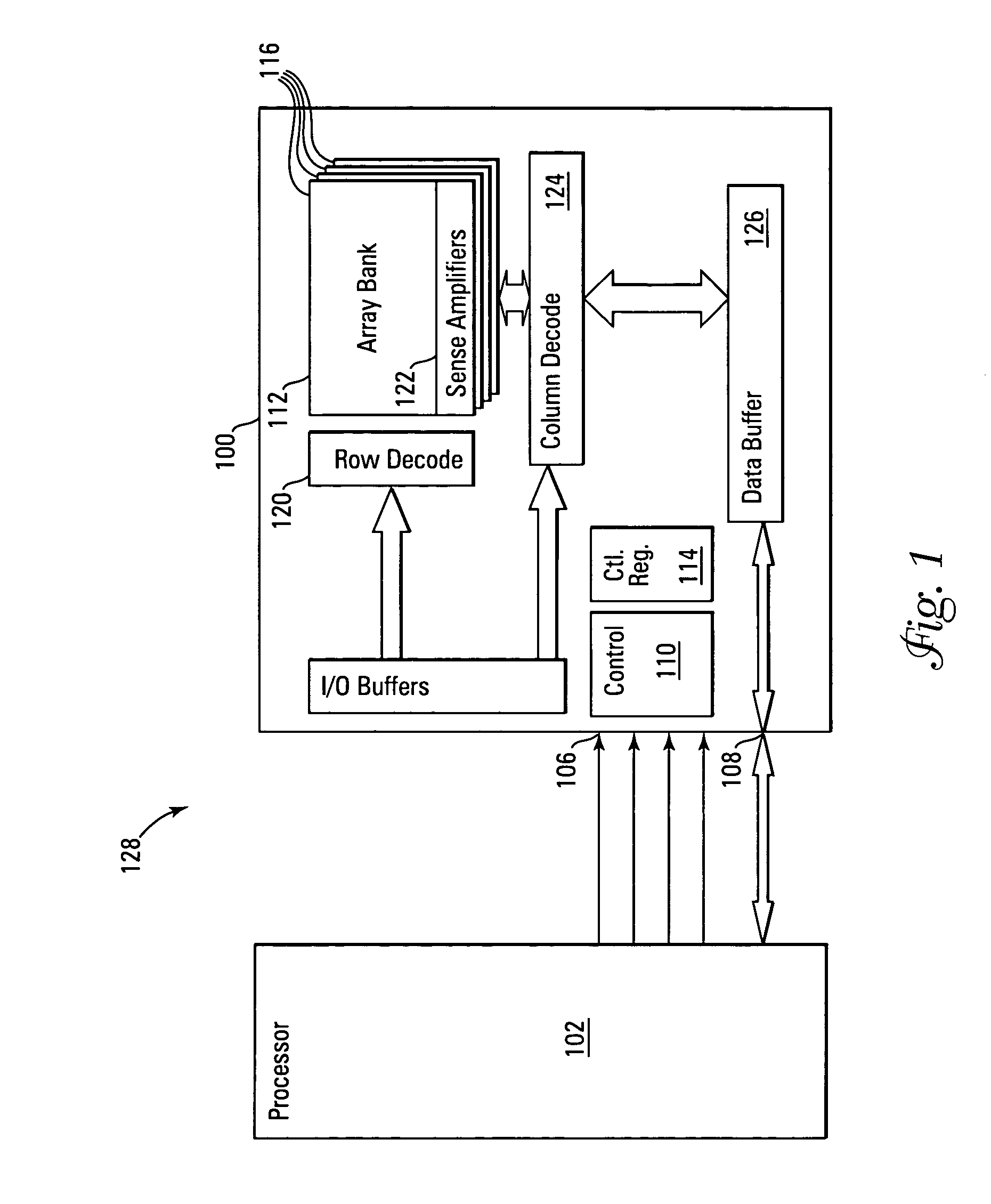
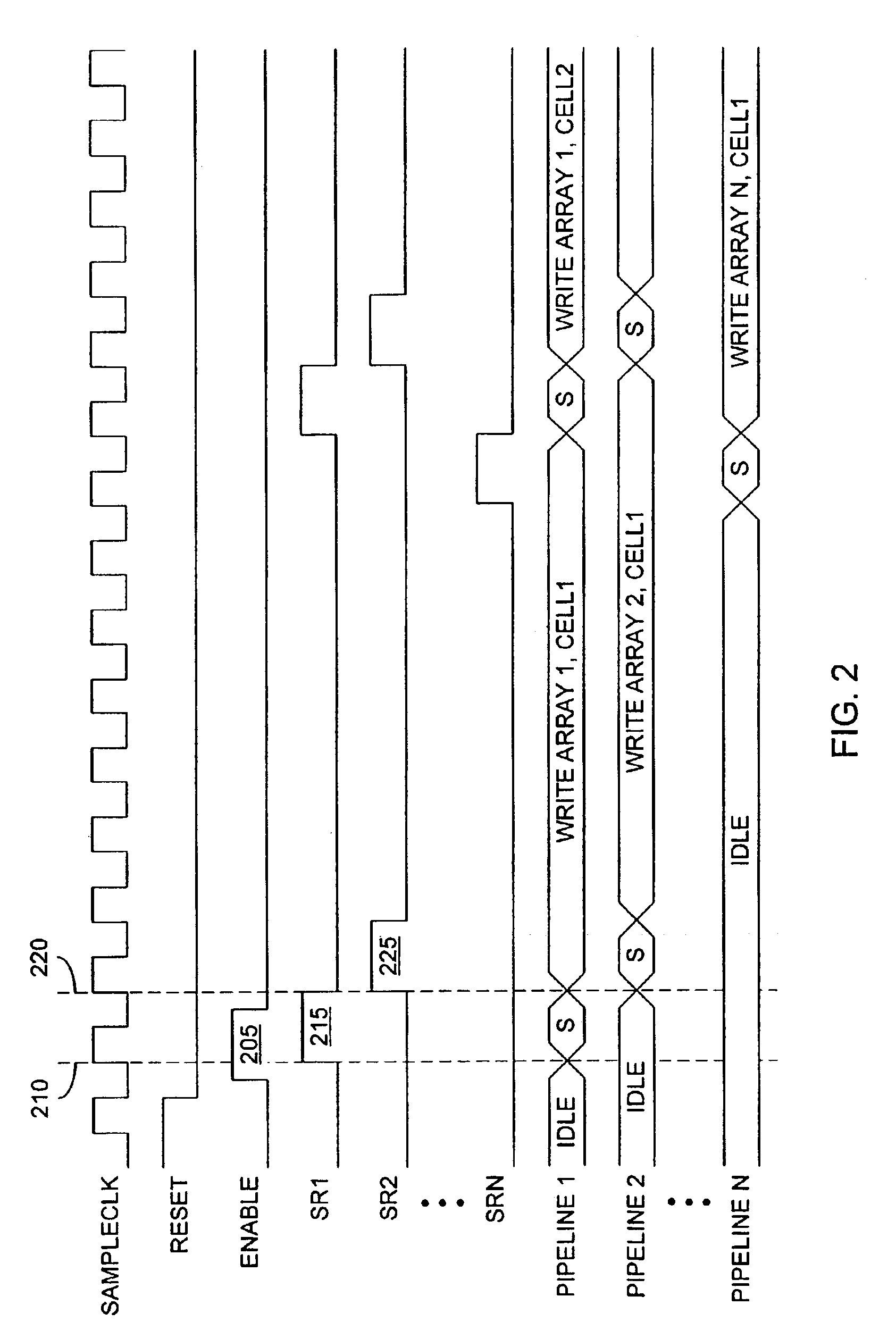
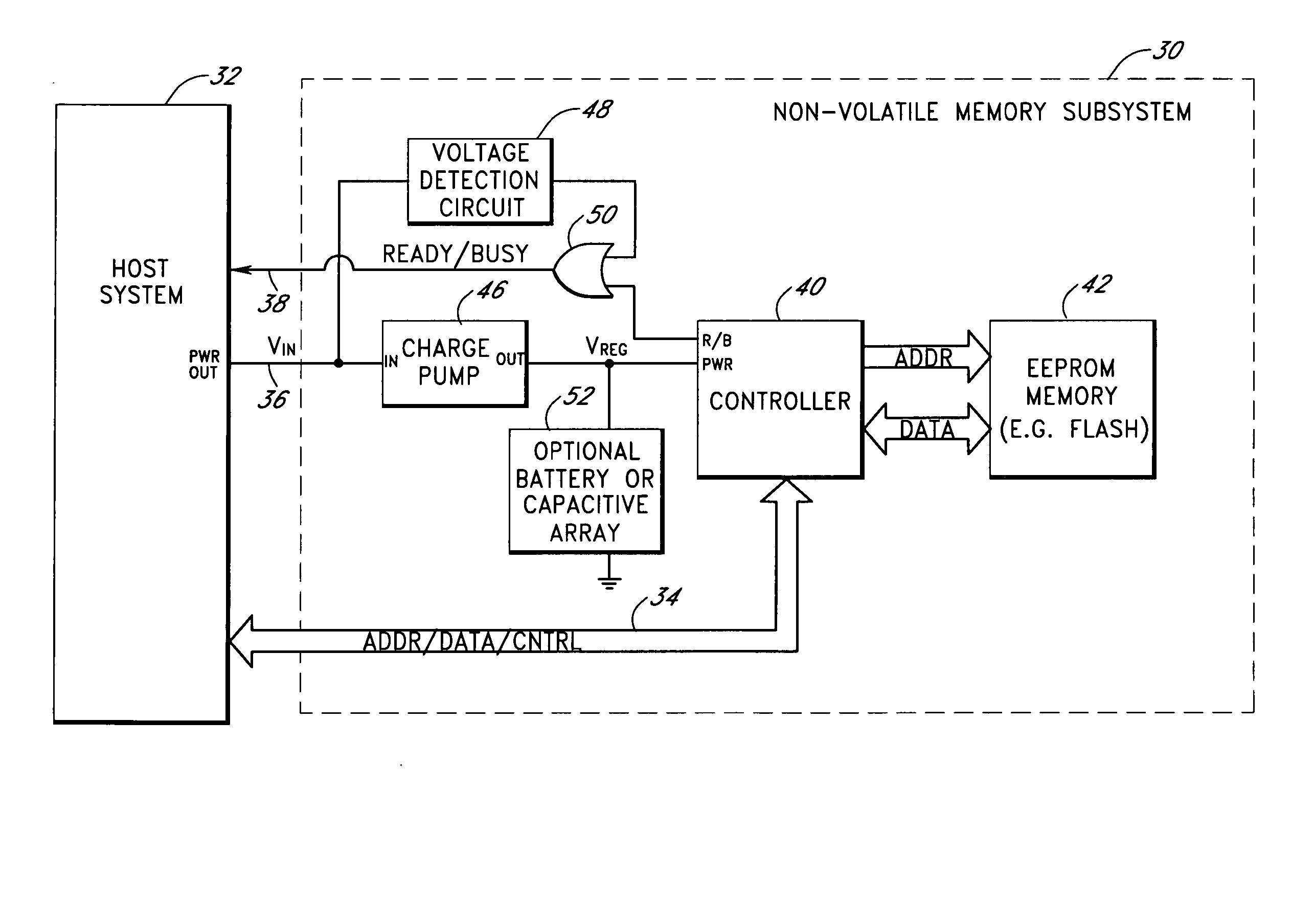
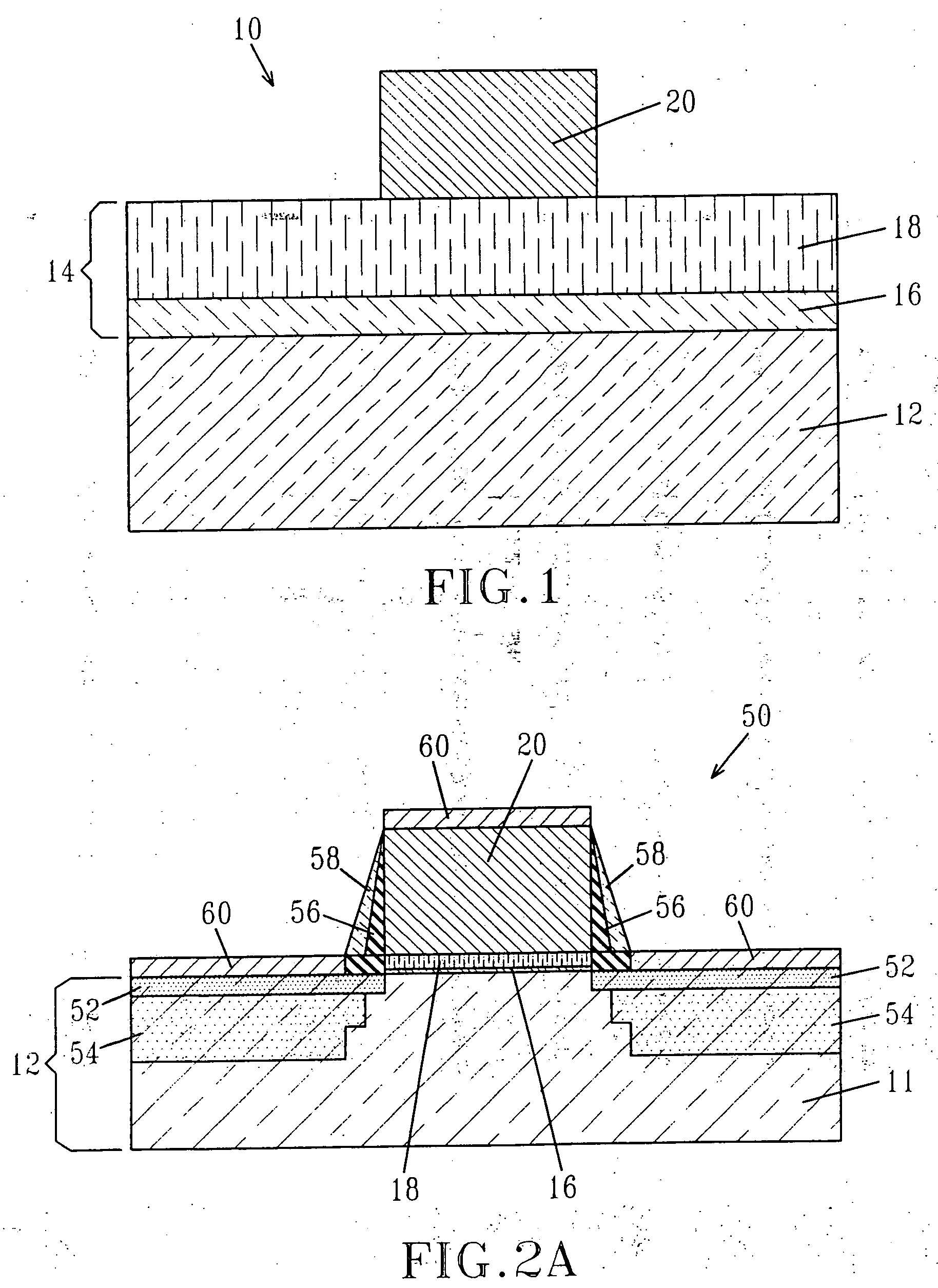
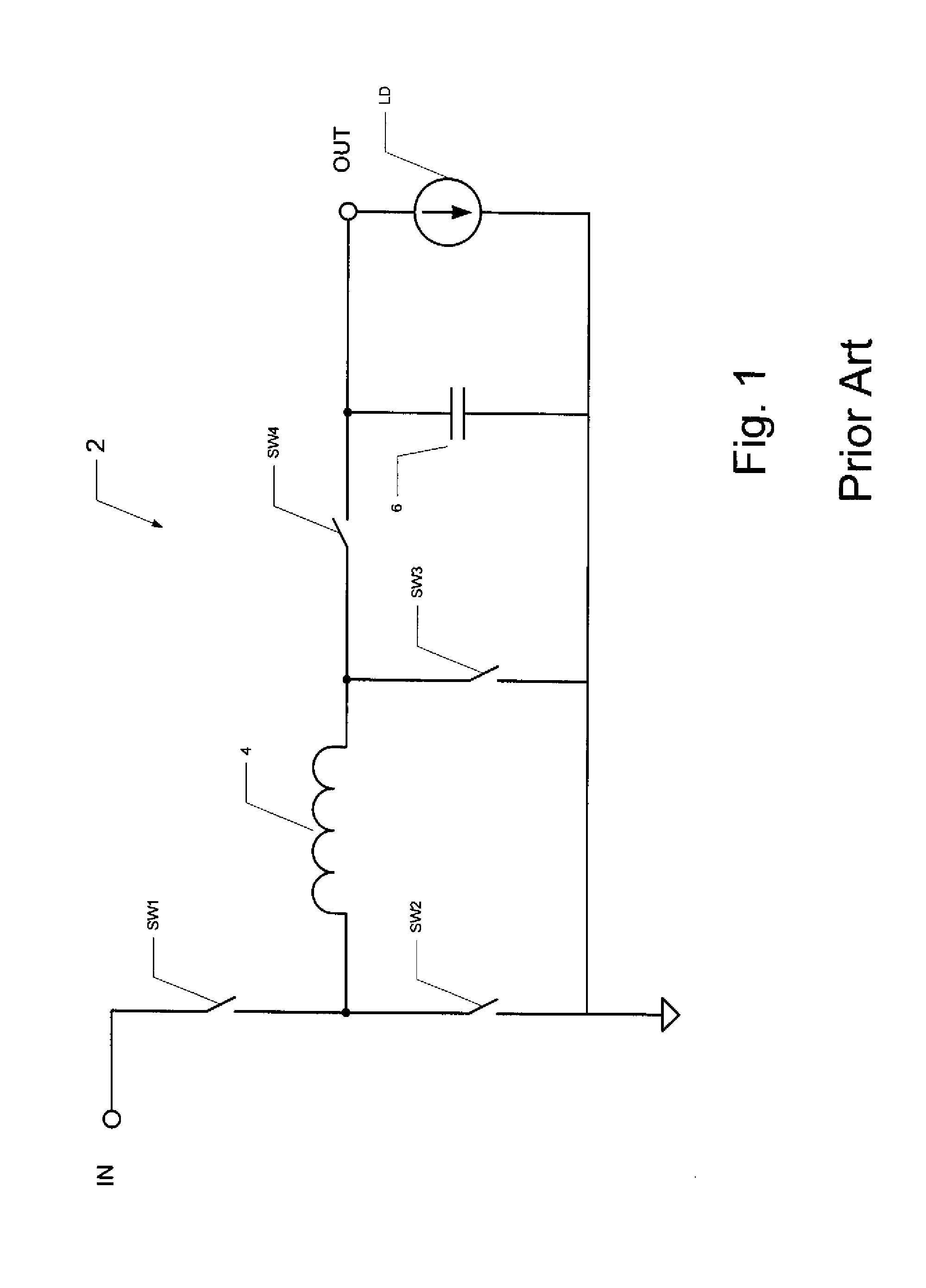
Storage subsystem with embedded circuit for protecting against anomalies in power signal from host
InactiveUS6856556B1Potential damageReduce the possibilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageStandby powerEngineering
A storage subsystem, such as a flash memory card, includes a charge pump that receives a power signal from a host system, and generates a regulated power signal that is provided to the storage subsystem's controller. When the power signal from the host is interrupted, the charge pump additionally acts as a backup power supply such that the storage subsystem can continue to operate temporarily. The storage subsystem also includes a voltage detection circuit that monitors the power signal from the host system to detect anomalies therein. The voltage detection circuit responds to detection of an anomaly by asserting a busy signal to block the host system from performing write operations to the storage subsystem. By asserting the busy signal, the voltage detection circuit substantially ensures that the backup, regulated power provided by the charge pump will be sufficient for the controller to complete all outstanding operations.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
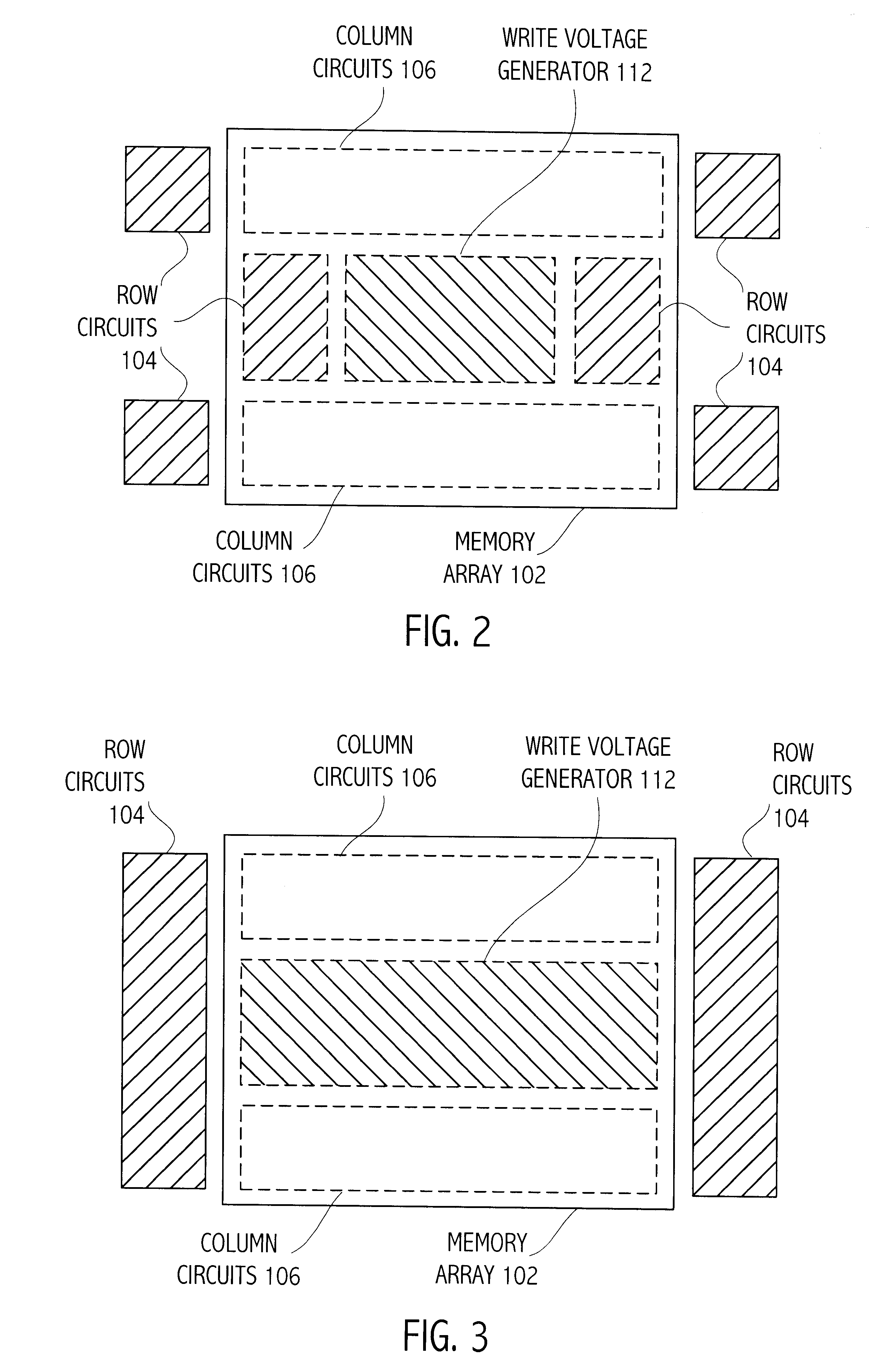
Integrated circuit structure including three-dimensional memory array
An integrated circuit device includes a three-dimensional memory array and array terminal circuitry for providing to selected memory cells of the array a write voltage different from a read voltage. Neither voltage is necessarily equal to a VDD power supply voltage supplied to the integrated circuit. The write voltage, particularly if greater than VDD, may be generated by an on-chip voltage generator, such as a charge pump, which may require an undesirably large amount of die area, particularly relative to a higher bit density three-dimensional memory array formed entirely in layers above a semiconductor substrate. In several preferred embodiments, the area directly beneath a memory array is advantageously utilized to layout at least some of the write voltage generator, thus locating the generator near the selected memory cells during a write operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
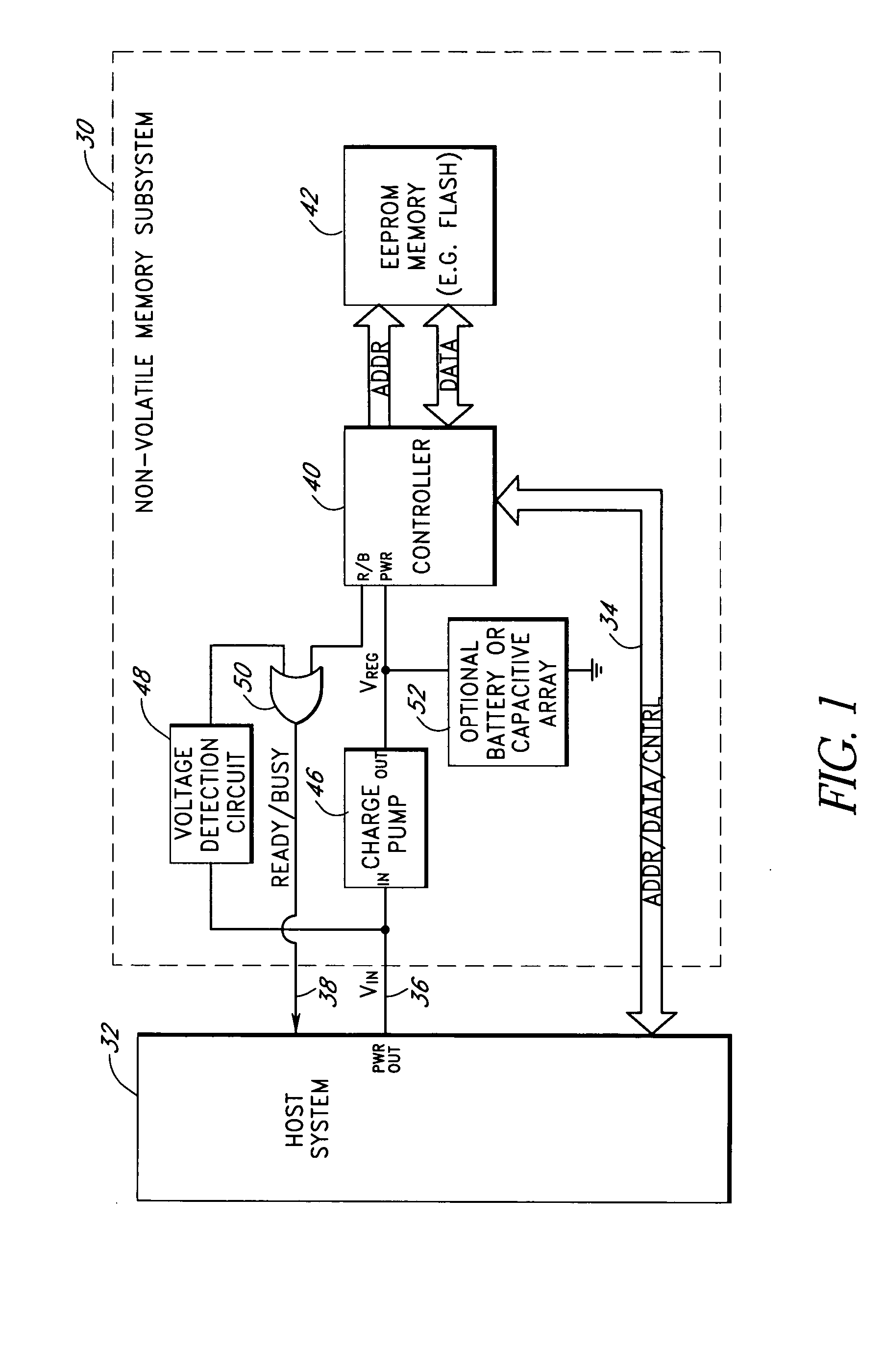
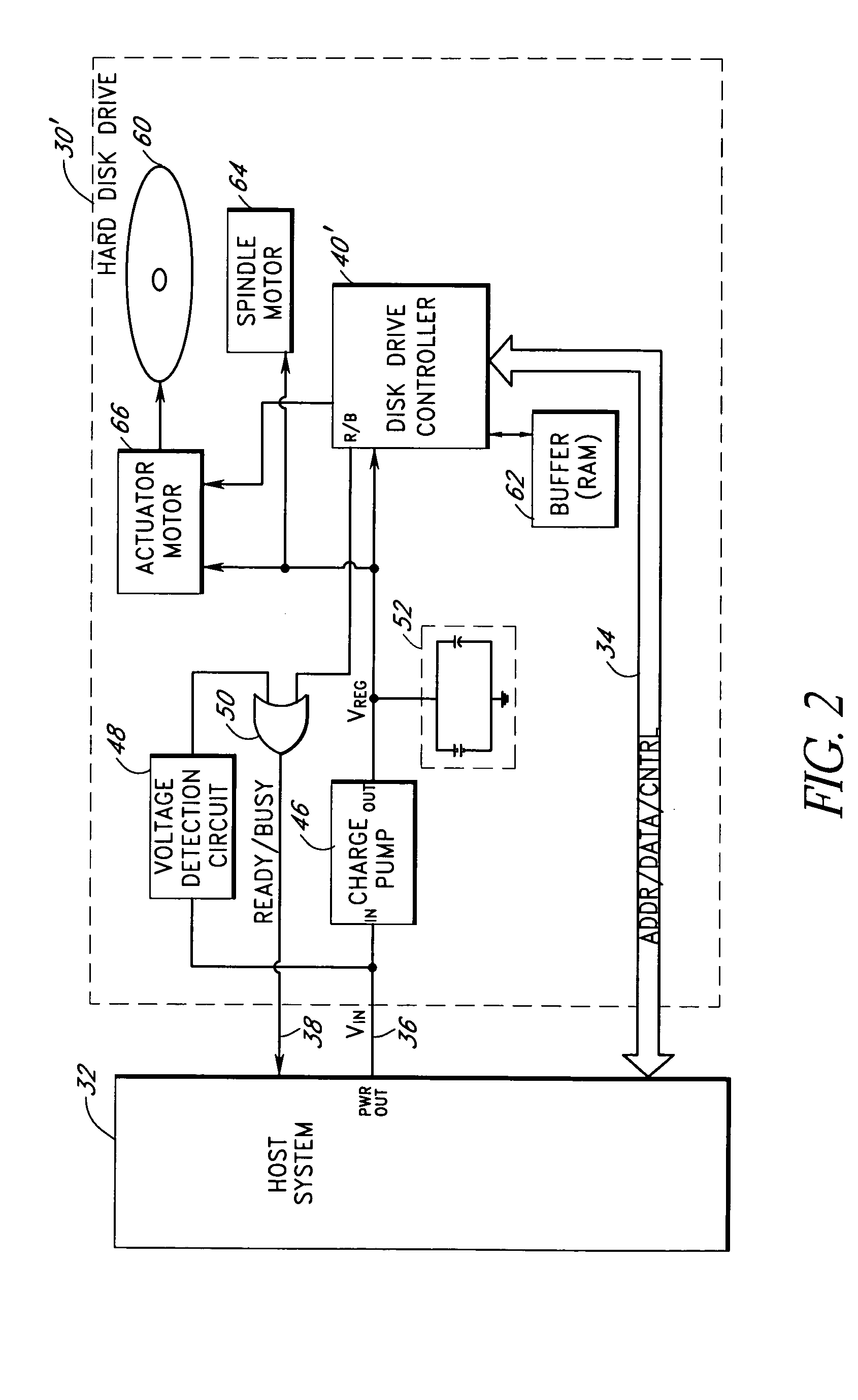
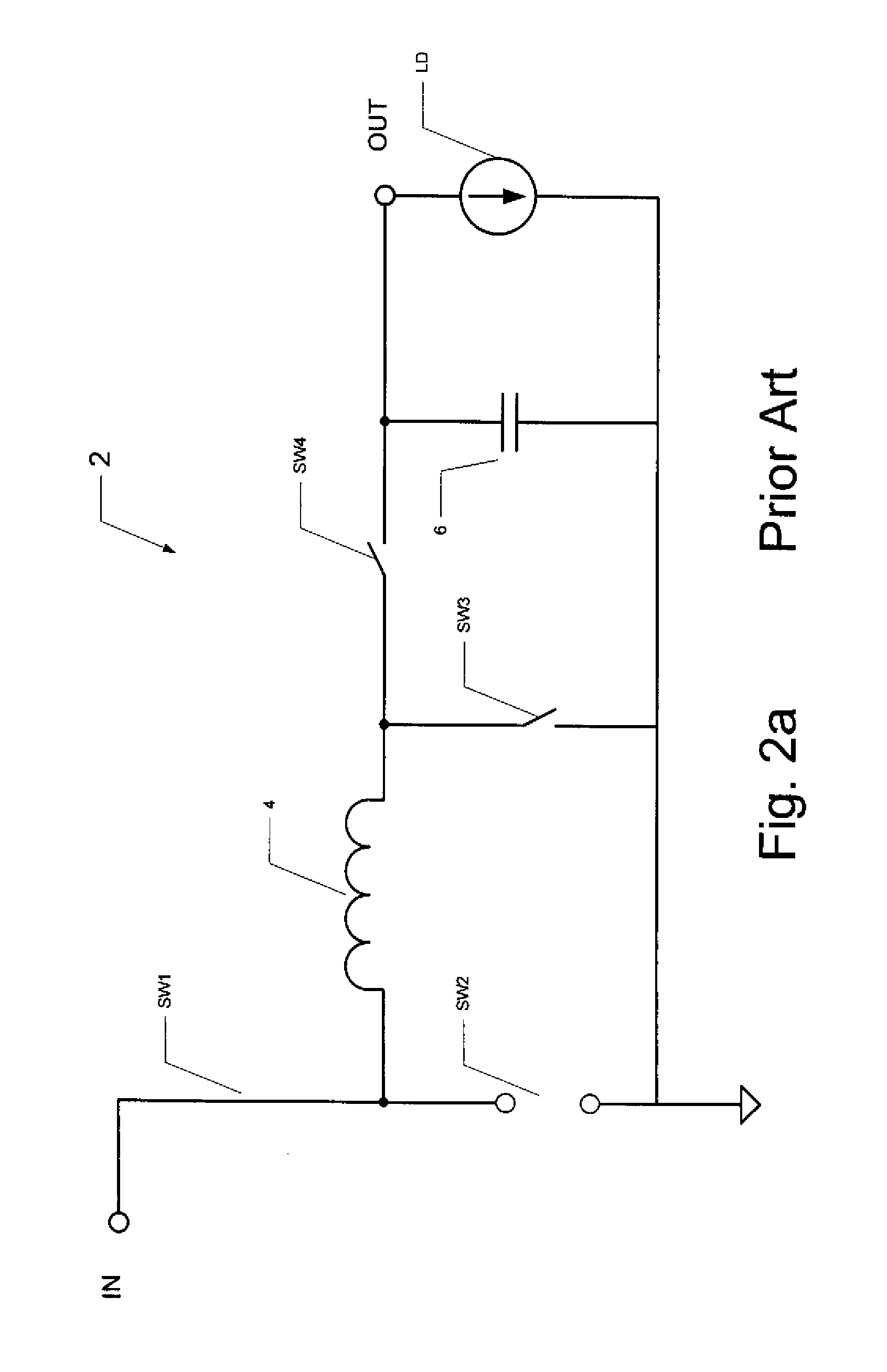
Storage subsystem with embedded circuit for protecting against anomalies in power signal from host
A storage subsystem, such as a flash memory card, includes a voltage detection circuit that monitors the power signal from a host system to detect anomalies. The voltage detection circuit responds to a power signal anomaly by asserting a signal, such as a busy signal on a standard ready / busy signal line, to block the host system from performing write operations to the storage subsystem during presence of the anomaly. The storage system may also include a backup power source, such as a charge pump circuit, a capacitive array, and / or a rechargeable battery, that provides power to a controller of the storage subsystem during the presence of the anomaly, such that the storage system can complete outstanding operations.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
Charge pump circuit adjustable in response to an external voltage source
InactiveUS6370075B1Prolong lifeImprove reliabilityElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesEngineeringVoltage source
An integrated circuit detects the voltage level of the supply voltage to the integrated circuit. Circuity on the integrated circuit including the charge pump circuity adjusts to operate more effectively or efficiently at the voltage level of the supply voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
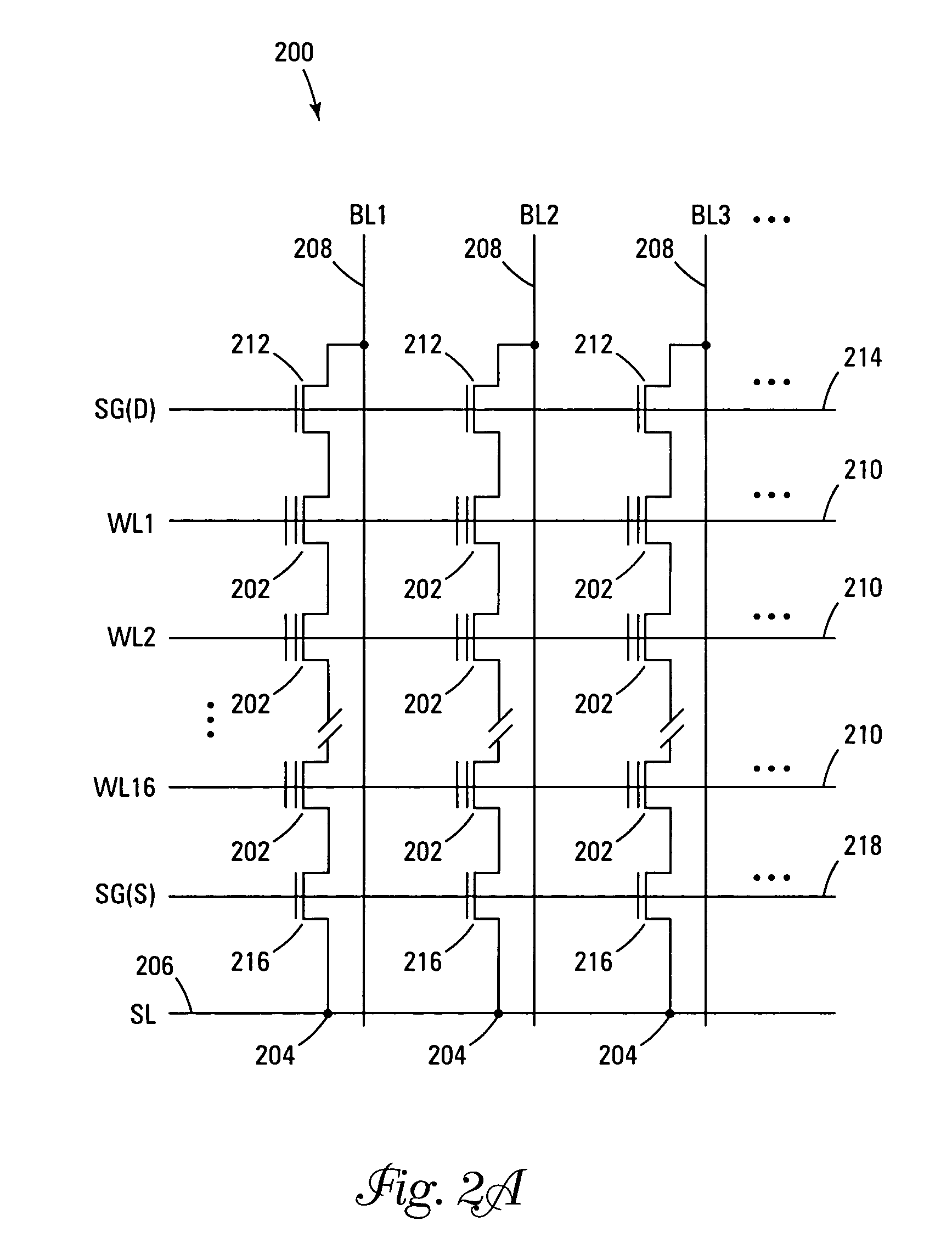
NAND flash depletion cell structure
InactiveUS20060044872A1Scale upIncrease supplyRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceRC time constant
NAND architecture Flash memory strings, memory arrays, and memory devices are described that utilize depletion mode floating gate memory cells. Depletion mode floating gate memory cells allow for increased cell current through lower channel rdS resistance and decreased “narrow width” effect, allowing for increased scaling of NAND memory cell strings. In addition, the required voltages for reading and programming operations are reduced, allowing the use of more efficient, lower voltage charge pumps and a reduction circuit element feature sizes and layouts. Cell inhibit of unselected cells is also increased, reducing the likelihood of cell disturb in the memory array. Operation speed is improved by increasing read current of the selected NAND string and by increasing the ability to overcome the RC time constants of circuit lines and capacitances through lowered voltage swings and increased current supplies.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High data rate write process for non-volatile flash memories
InactiveUS6944058B2Reduce noiseIncrease data rateElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulationTotal current
A non-volatile semiconductor memory includes: multiple write pipelines, each including a memory array; a timing circuit which sequentially starts programming operations in the pipelines; and a shared charge pump and voltage regulation circuit that drives a current through the memory cells being programmed. Staggering the starts of programming operations reduces the current demand on the charge pump because spikes that occur at the starts of programming operations, for example, when using channel hot electron injection, are distributed over time rather than occurring all at once. Noise, which can reduce the accuracy of write operations, is also reduced because the total current required from the charge pump is more nearly constant. As further aspect of the invention, each write pipeline can perform a write operation as alternating programming cycles and verify cycles. During a programming cycle, the shared charge pump drives a current through a selected memory cell to change the threshold voltage of the selected memory cell. During a verify cycle, the write circuit determines whether the selected memory cell has reached its target threshold voltage level. The write pipelines can be partitioned into two banks where pipelines in one bank perform programming cycles while pipelines in the other bank perform verify cycles. More generally the write pipelines are partitioned into multiple banks where each bank starts programming cycles at times that differ from the starts of programming cycles in the other banks.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
Storage subsystem with embedded circuit for protecting against anomalies in power signal from host
A storage subsystem, such as a flash memory card, includes a voltage detection circuit that monitors the power signal from a host system to detect anomalies. The voltage detection circuit responds to a power signal anomaly by asserting a signal, such as a busy signal on a standard ready / busy signal line, to block the host system from performing write operations to the storage subsystem during presence of the anomaly. The storage system may also include a backup power source, such as a charge pump circuit, a capacitive array, and / or a rechargeable battery, that provides power to a controller of the storage subsystem during the presence of the anomaly, such that the storage system can complete outstanding operations.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
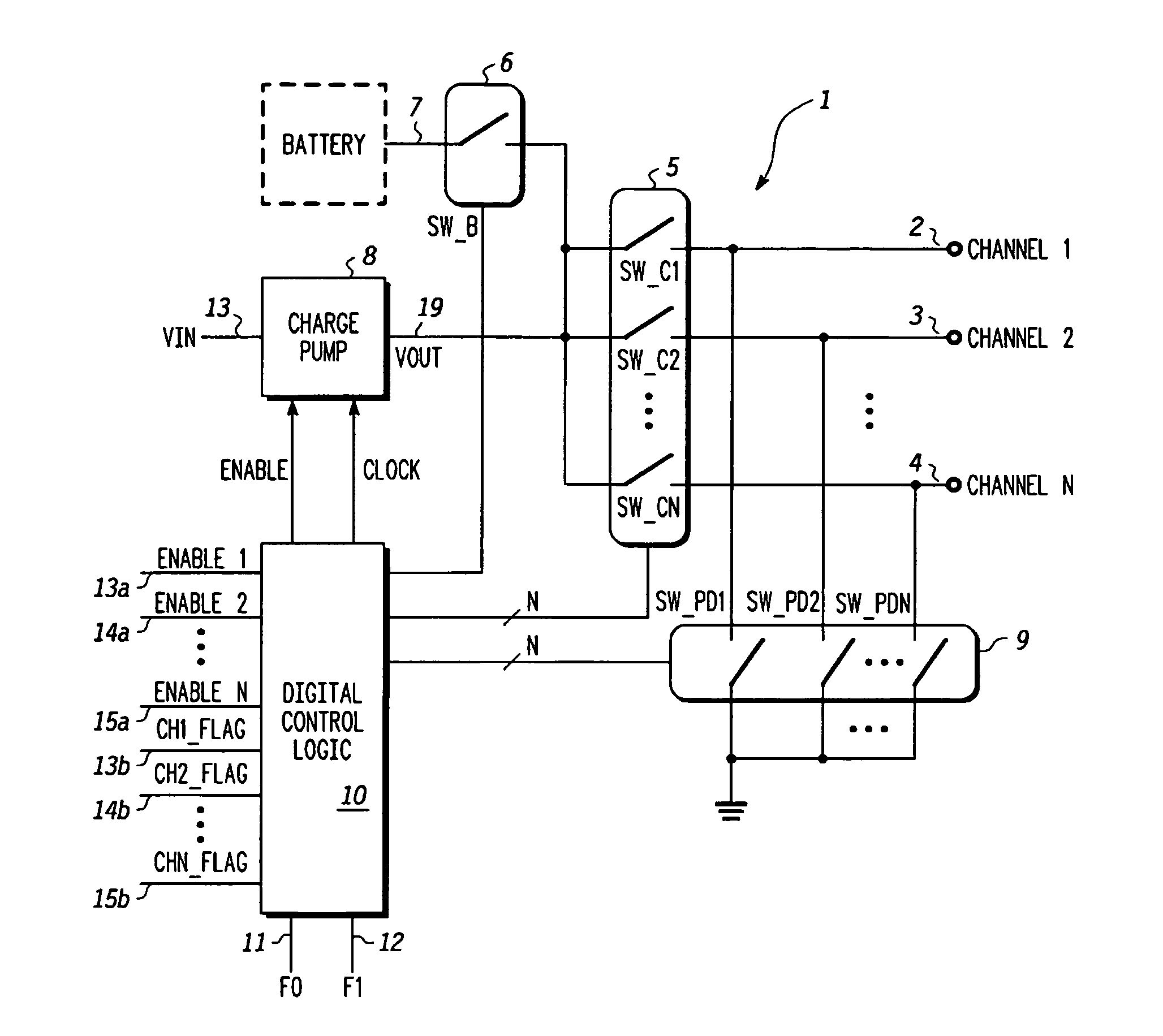
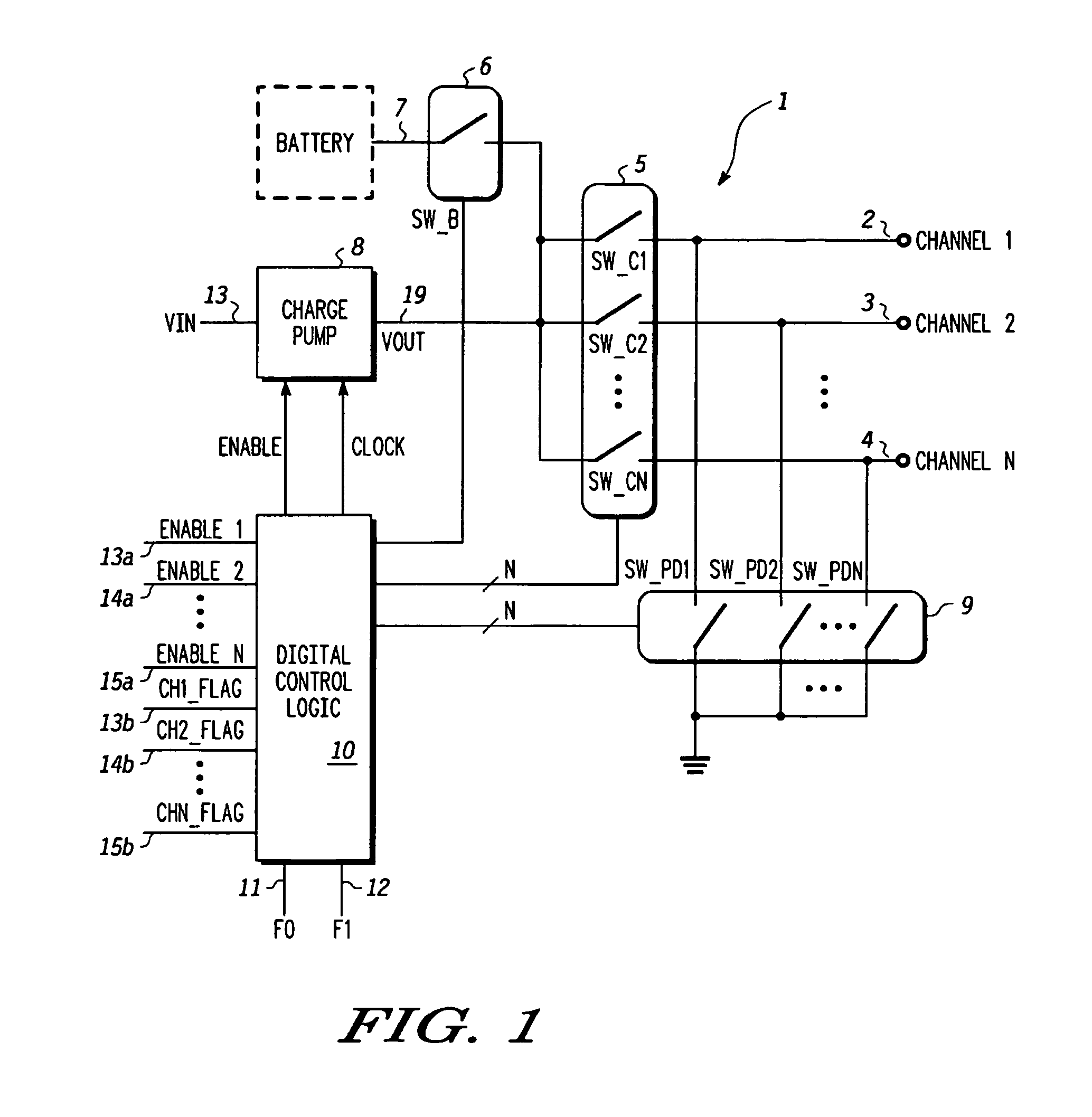
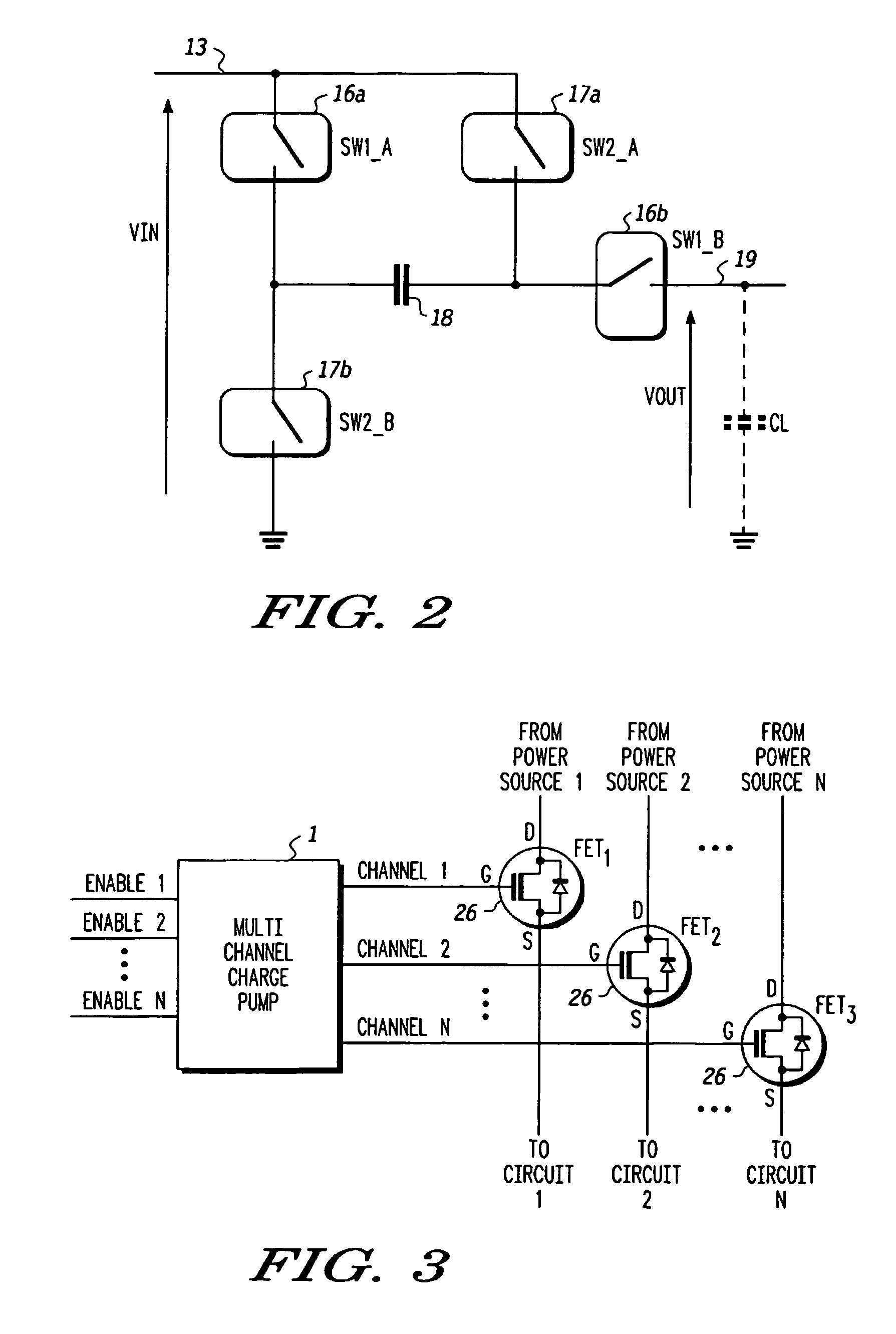
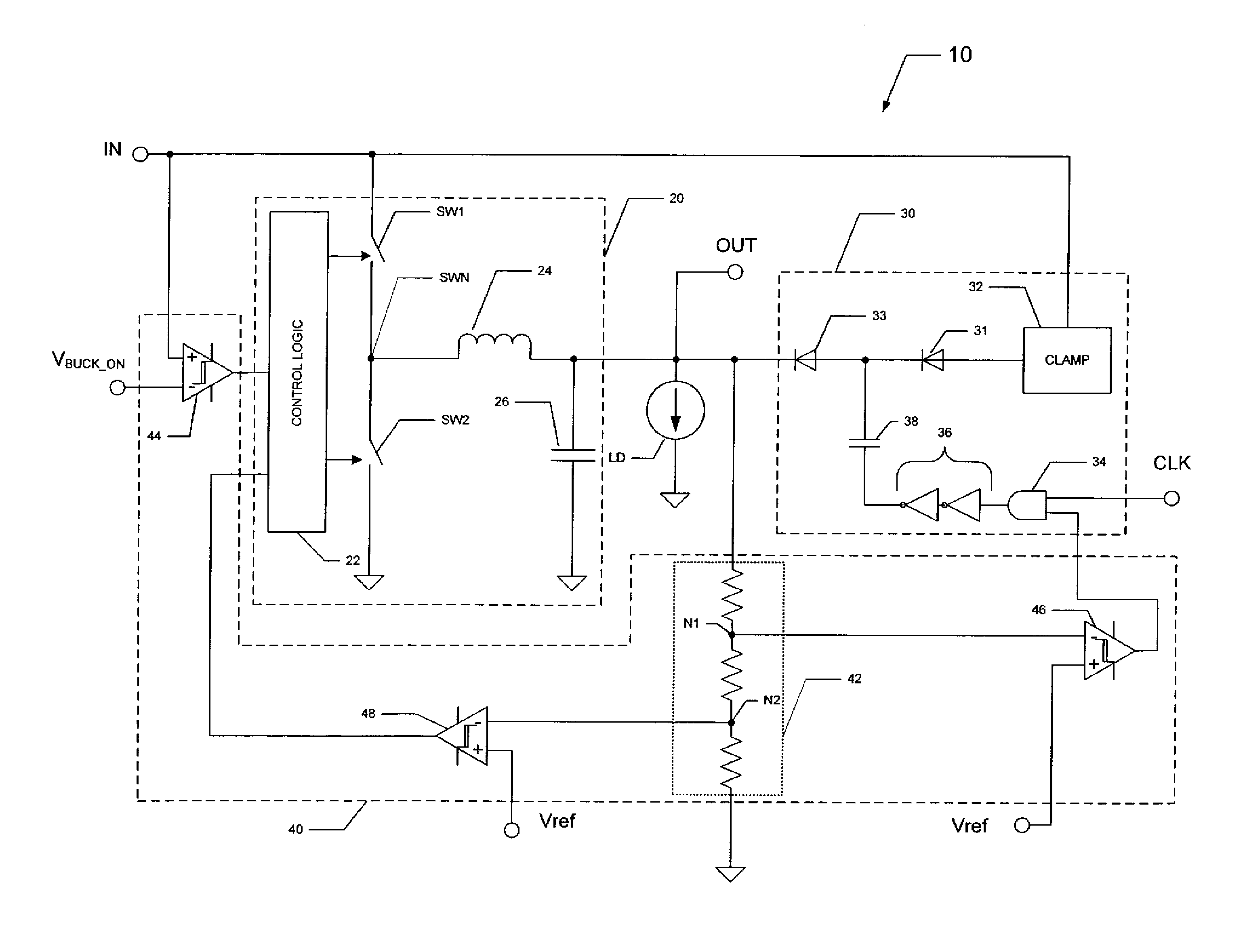
Charge pump and control scheme
A switch controller has a charge pump, a selector switch connected to the charge pump, and a pre-charge power supply input connectable to the input of the selector switch. For each of the output channels being controlled, a power control switch is connected to an output of the selector switch. In response to commands, output channels are enabled and disabled, causing corresponding actions in the power control switches. When an output channel is to be activated, the output channel is selected by the selector switch and the pre-charge power supply connected to the input of the selector switch. The charging is completed by the charge pump and the enabled status of the power control switch is maintained by the charge pump.
Owner:NXP USA INC
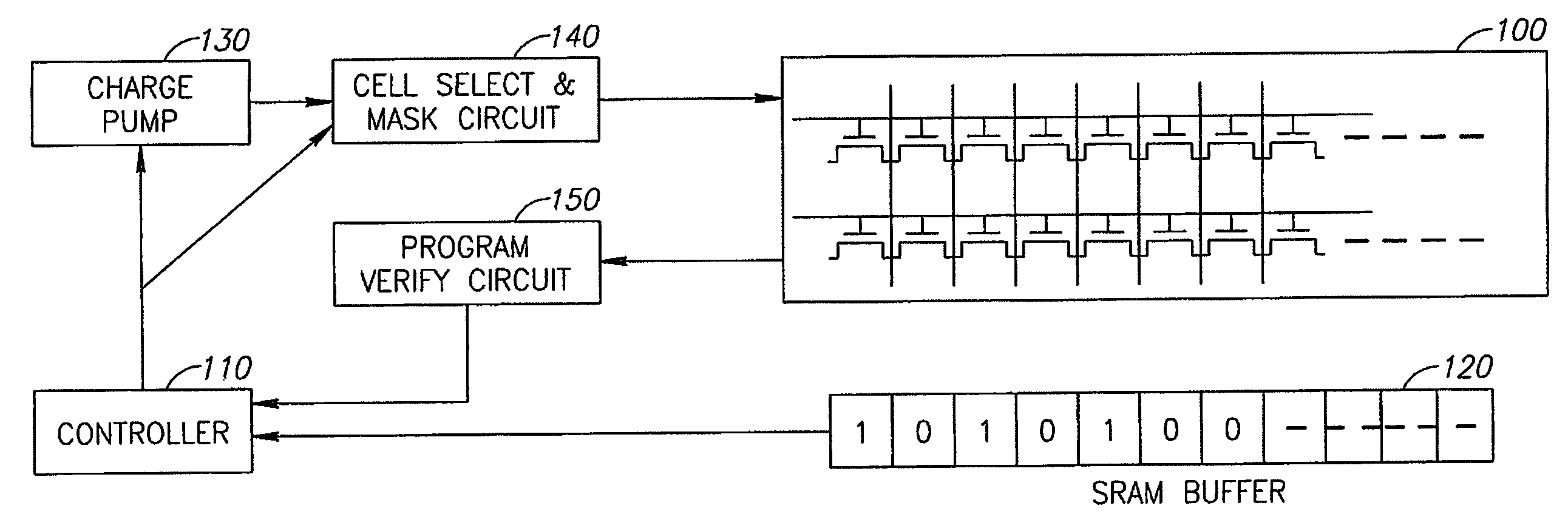
Method, system and circuit for programming a non-volatile memory array
InactiveUS7136304B2Low programming rateSlow changeRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer terminalMulti phase
Owner:SAIFUN SEMICONUCTIORS
Method and apparatus for protecting RFID tags from power analysis
InactiveUS20100005533A1Cheap and effective solutionEliminate power consumption informationError detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementElectromagnetic fieldPower attack
RFID tags were believed to be immune to power analysis since they have no direct connection to an external power supply. However, recent research has shown that they s are vulnerable to such attacks, since it is possible to measure their power consumption remotely via a completely passive attack. The method and apparatus of the invention protects RFID tags against simple and differential power attacks. The invention is particularly useful regarding inventory control systems or secure documents such as epassports. The basic technique is to use two capacitors embedded in the RFID tag in lo such a way that at any given time one of them is storing energy that is being generated by the charge pump of the tag that sucks energy from the electromagnetic or magnetic field of a tag reader, and the other one is discharging and powering the computational element of the tag chip.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Non volatile memory
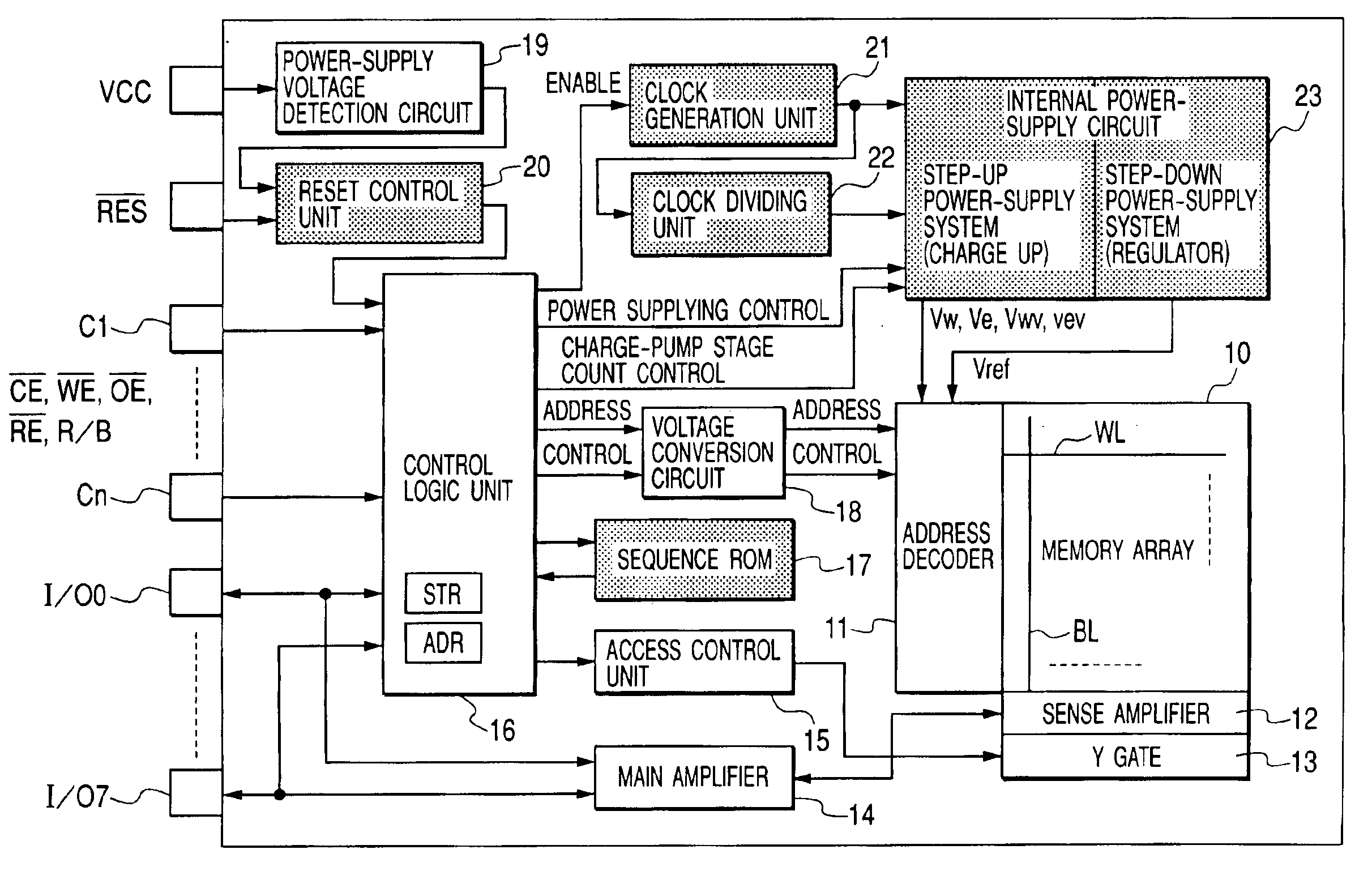
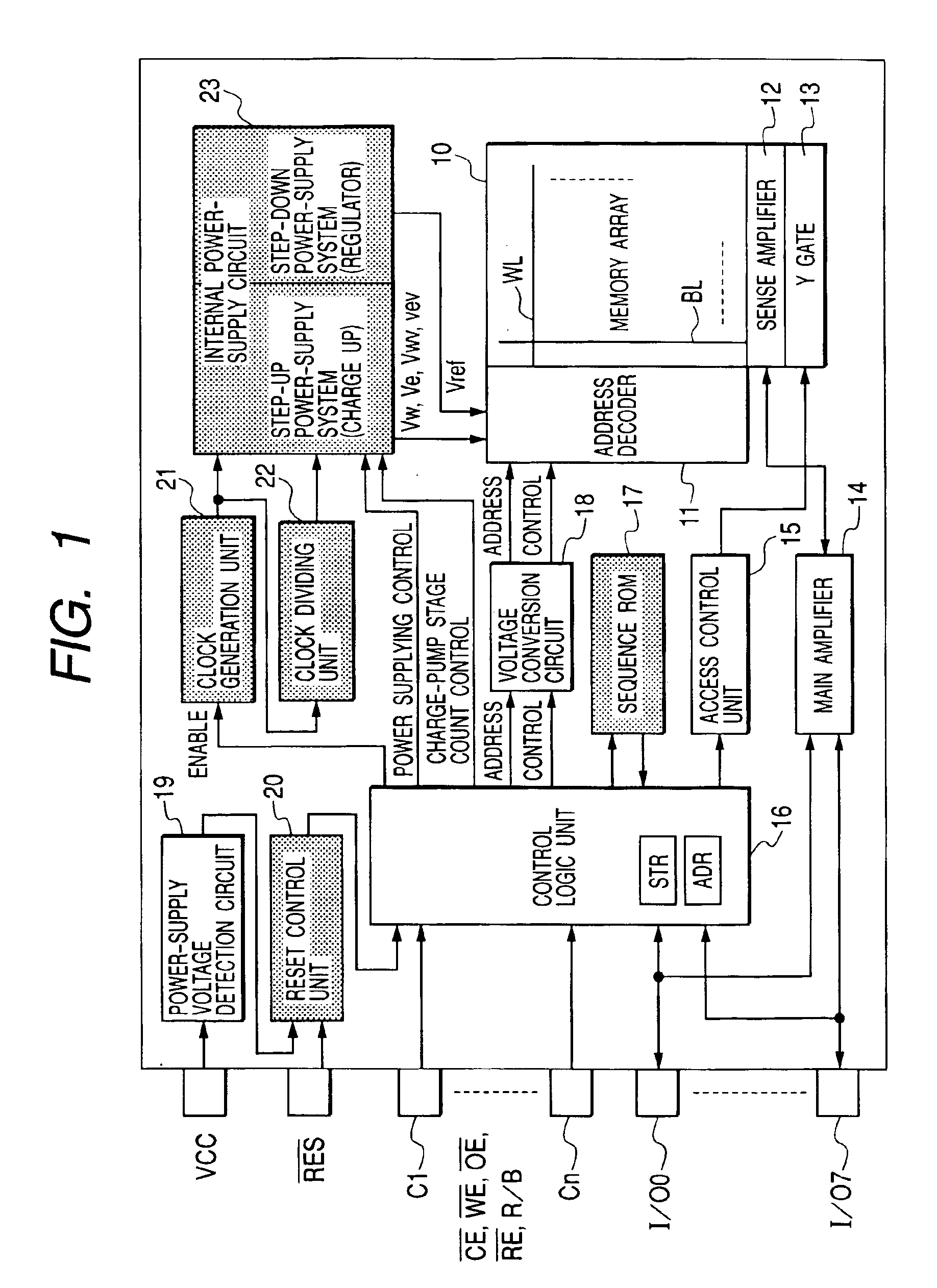
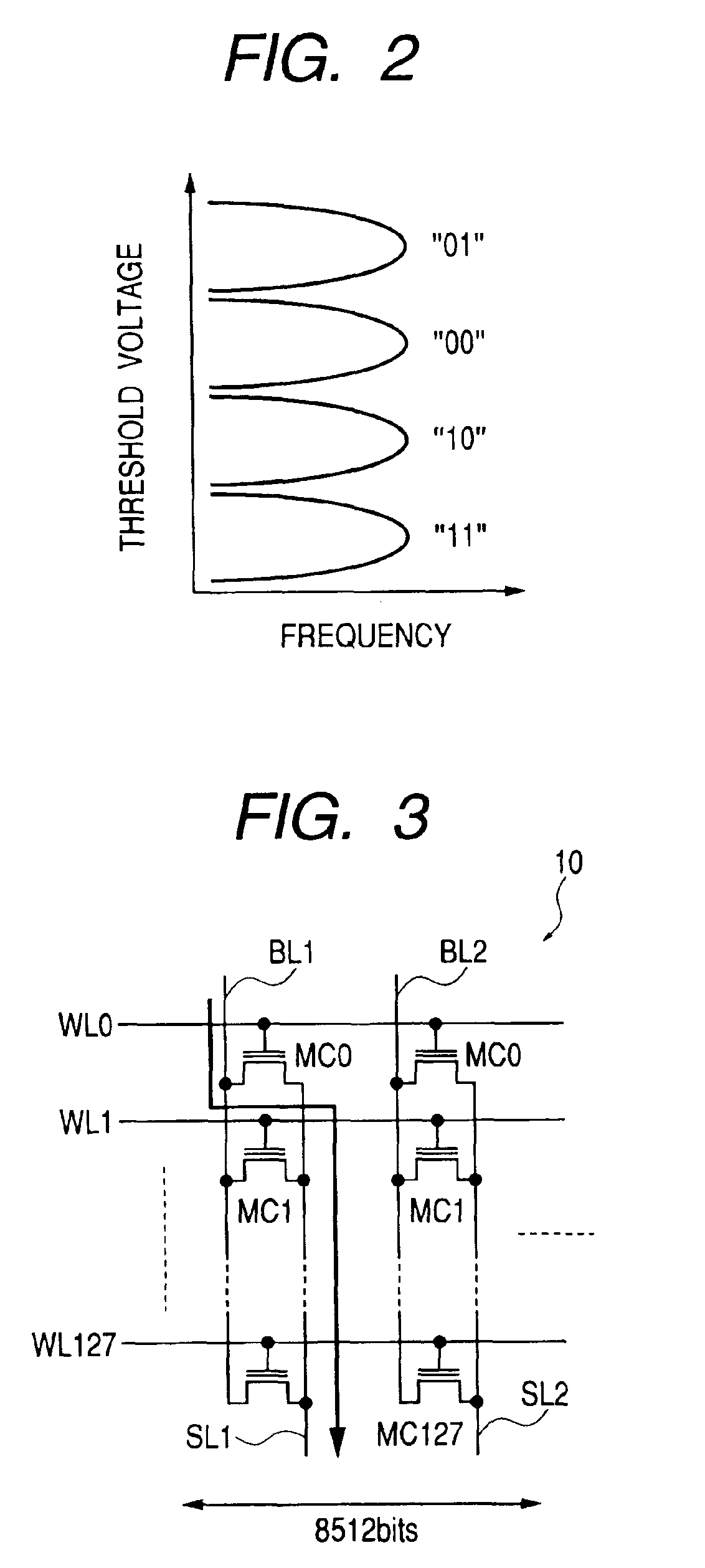
An electrically programmable and erasable nonvolatile semiconductor memory such as a flash memory is designed into a configuration in which, when a cutoff of the power supply occurs in the course of a write or erase operation carried out on a memory cell employed in the non-volatile semiconductor memory, the operation currently being executed is discontinued and a write-back operation is carried out to change a threshold voltage of the memory cell in the reversed direction. In addition, the configuration also allows the number of charge-pump stages in an internal power-supply configuration to be changed in accordance with the level of a power-supply voltage so as to make the write-back operation correctly executable. As a result, no memory cells are put in deplete state even in the event of a power-supply cutoff in the course of a write or erase operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
3D semiconductor device and structure
ActiveUS20170213821A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor device3d integrated circuit
A 3D integrated circuit device, including: a first layer including first transistors, overlaid by a second layer including second transistors, overlaid by a third layer including third transistors, where the first layer, the second layer and the third layer are each thinner than 2 microns, where the first layer includes first circuits including at least one of the first transistors, where the second layer includes second circuits including at least one of the second transistors, and where the third layer includes a charge pump circuit and control circuits to control the first circuits and the second circuits
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
Method for operating nonvolatile memory cells
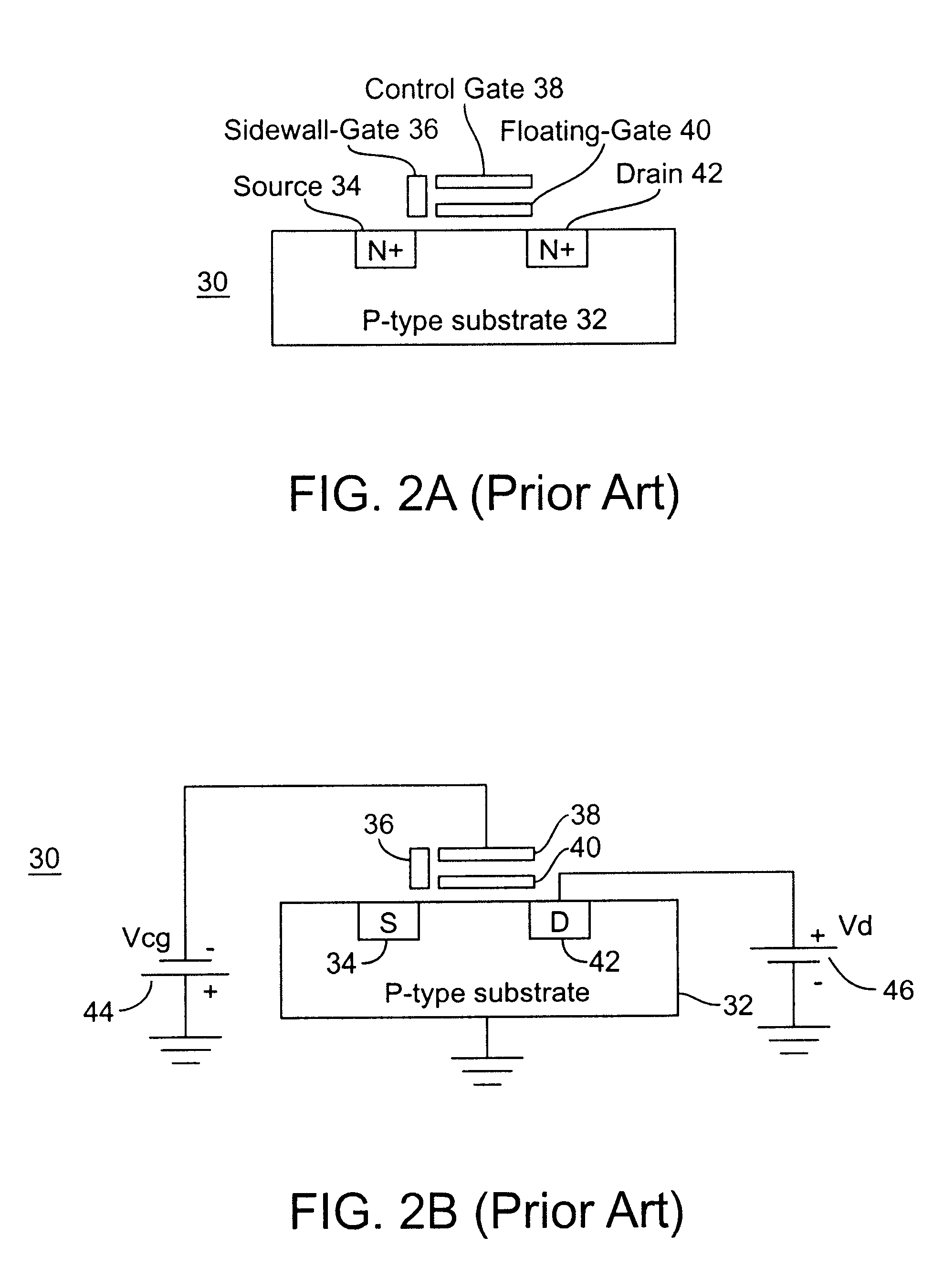
The present invention is directed at a new nonvolatile memory cell structure, and a new erase method and apparatus for operating this and other nonvolatile memory cells, with special emphasis on source-side injection flash EEPROM cells, which enhances the erase efficiency of the cell. By activating the select-gate terminal of the cell using a negative voltage, it has been found for the first time that the erase performance can be improved. In one preferred embodiment, the present invention provides for three overlapping voltage signals applied to the cell terminals, of which two are negative and one positive. In another preferred embodiment, the memory cell is built on an "internal P-well" within an isolating N-well on the P-type substrate. In this case, by shifting the memory cell's body potential, the erase-mode uses four overlapping erase signals, two of which are negative, and two positive. With experimental data, it is demonstrated that better "magnitude balance" has been achieved for the highest erase voltages of opposite polarities. Since only moderate voltages are needed for the erase operation while maintaining the erase speed, the otherwise stringent requirement on transistor breakdown voltages for on-chip charge pumps and driver circuitry can be relaxed.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
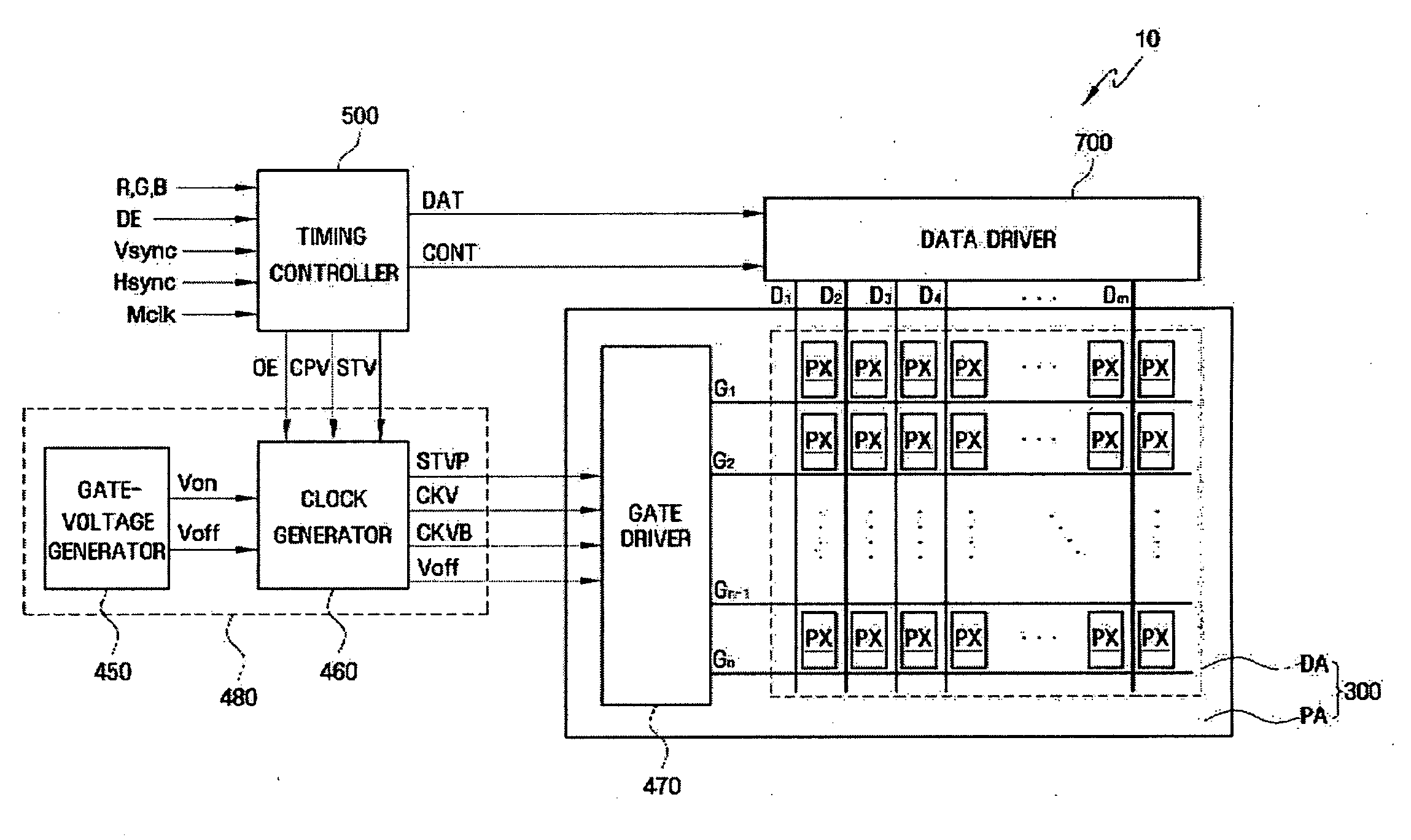
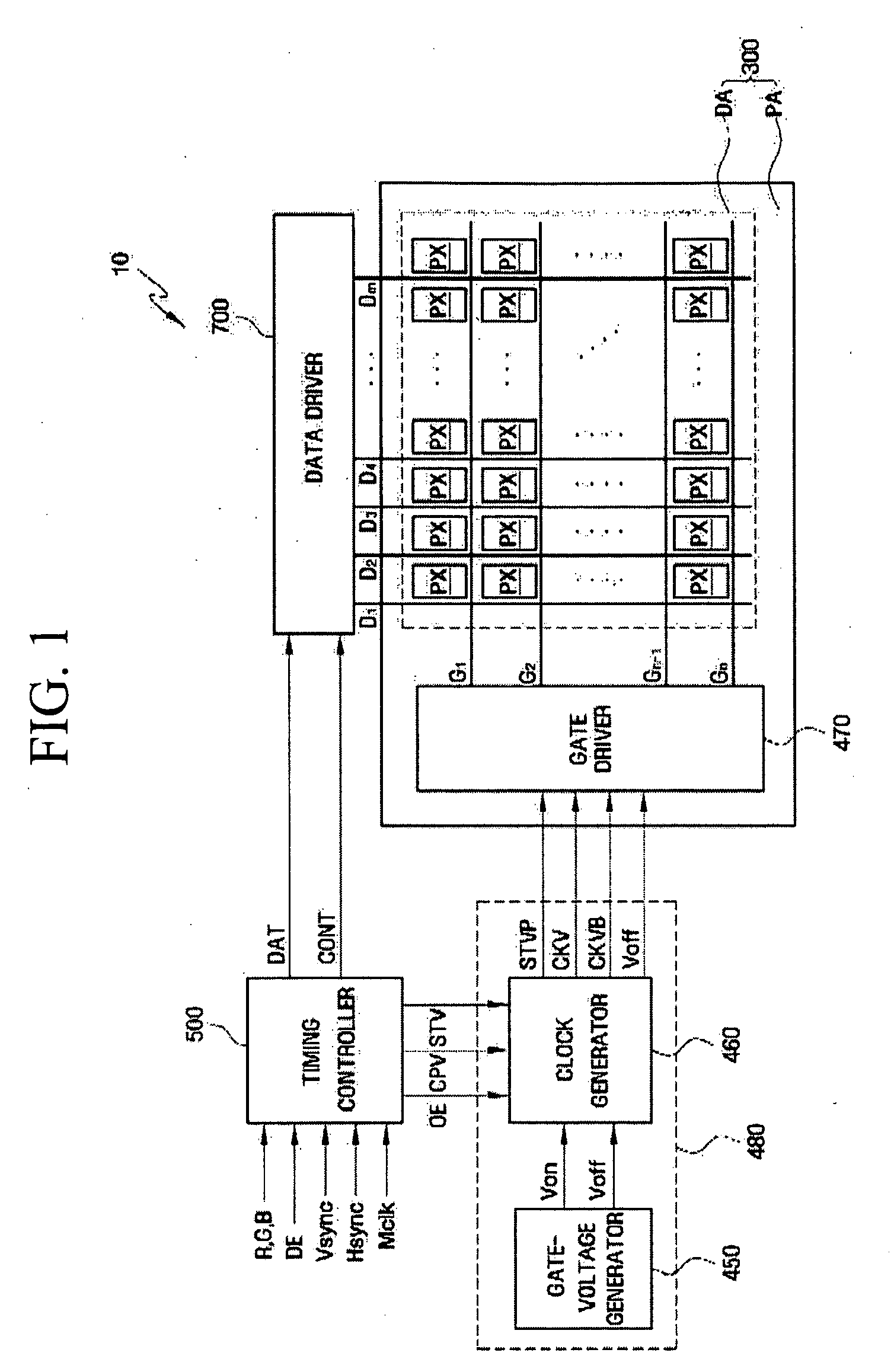
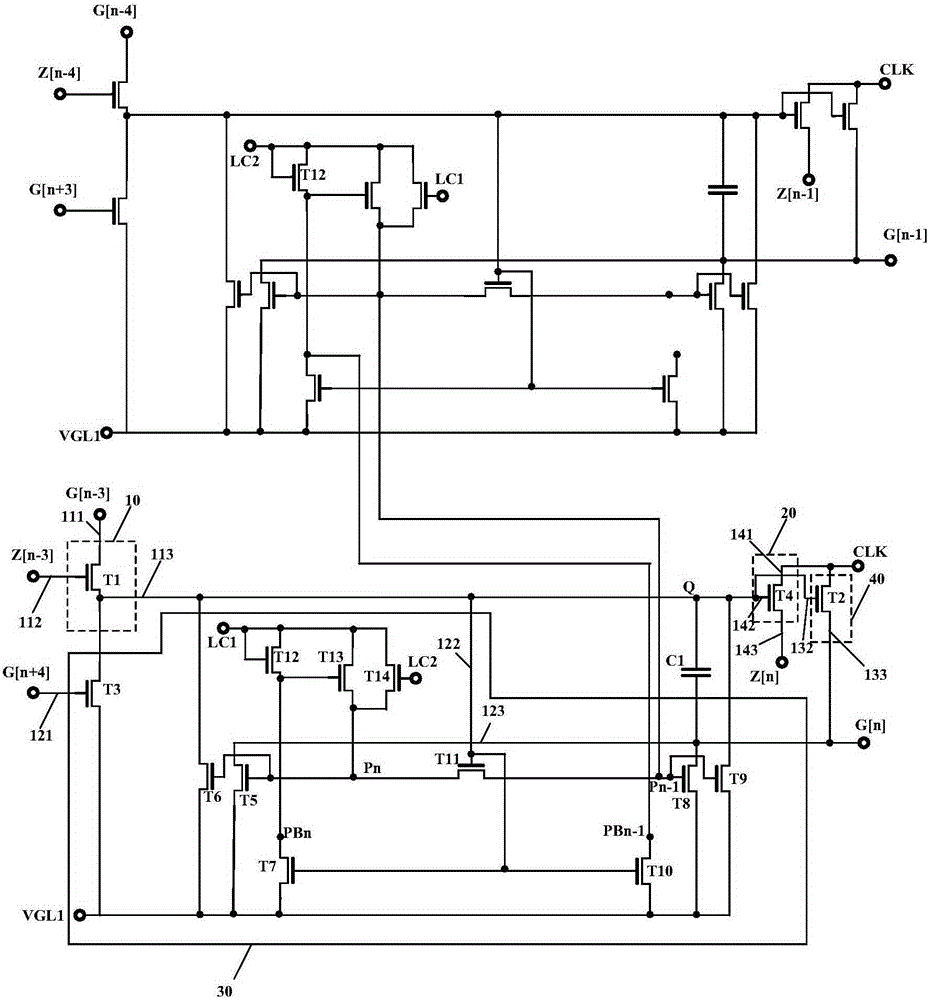
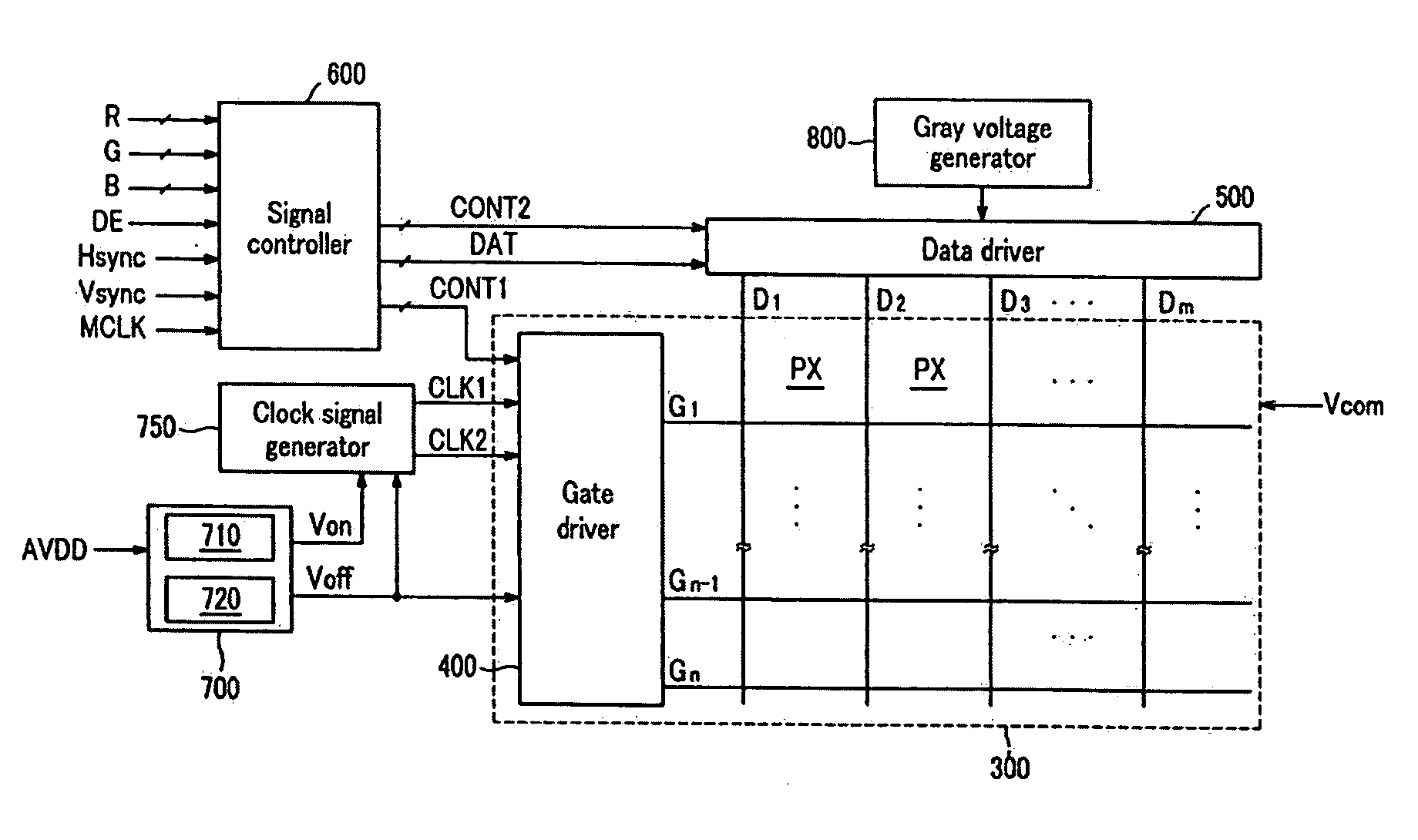
Gate-off volatage generating circuit, driving device and liquid crystal dispaly including the same
InactiveUS20090102779A1Improve display qualityThermometer detailsElectronic switchingVoltage generatorLiquid-crystal display
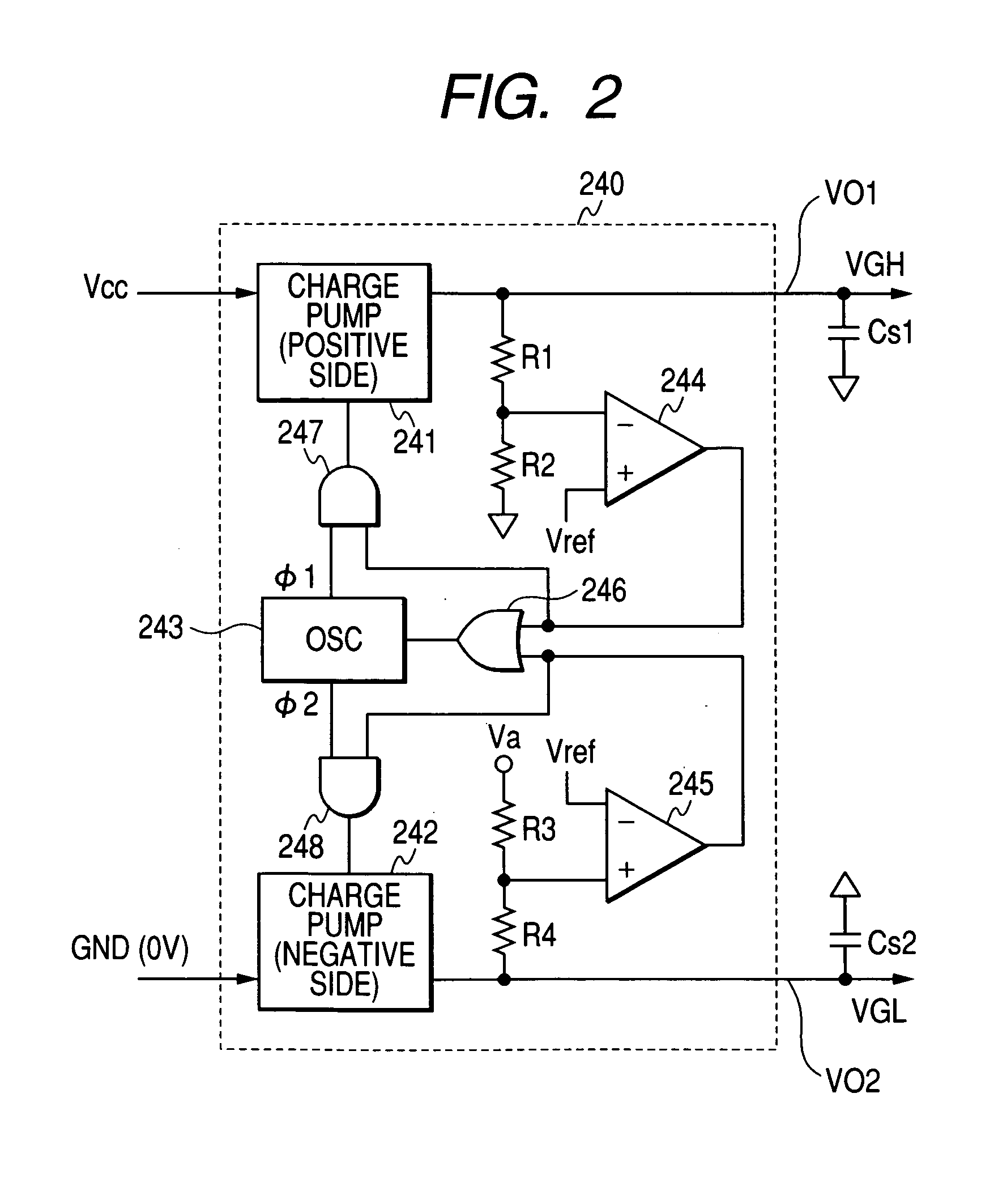
A gate-off-voltage-generating circuit that can enhance display quality at low temperatures, a driving device, and a liquid crystal display having the same are provided. The driving device includes a boost converter to receive and boost a first input voltage, and output a driving voltage and a pulse signal; a gate-on voltage generator to receive the driving voltage and output a gate-on voltage; and a gate-off voltage generator including a first temperature-compensation unit to receive the driving voltage and output a first temperature-dependent variable voltage, the level of which varies according to the ambient temperature, a first voltage follower to receive and transfer the first temperature-dependent variable voltage, and a first charge-pumping unit to shift the first temperature-dependent variable voltage by the amplitude of the pulse signal and output a gate-off voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit for liquid crystal display driver
InactiveUS20060132417A1Reduce chip costReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
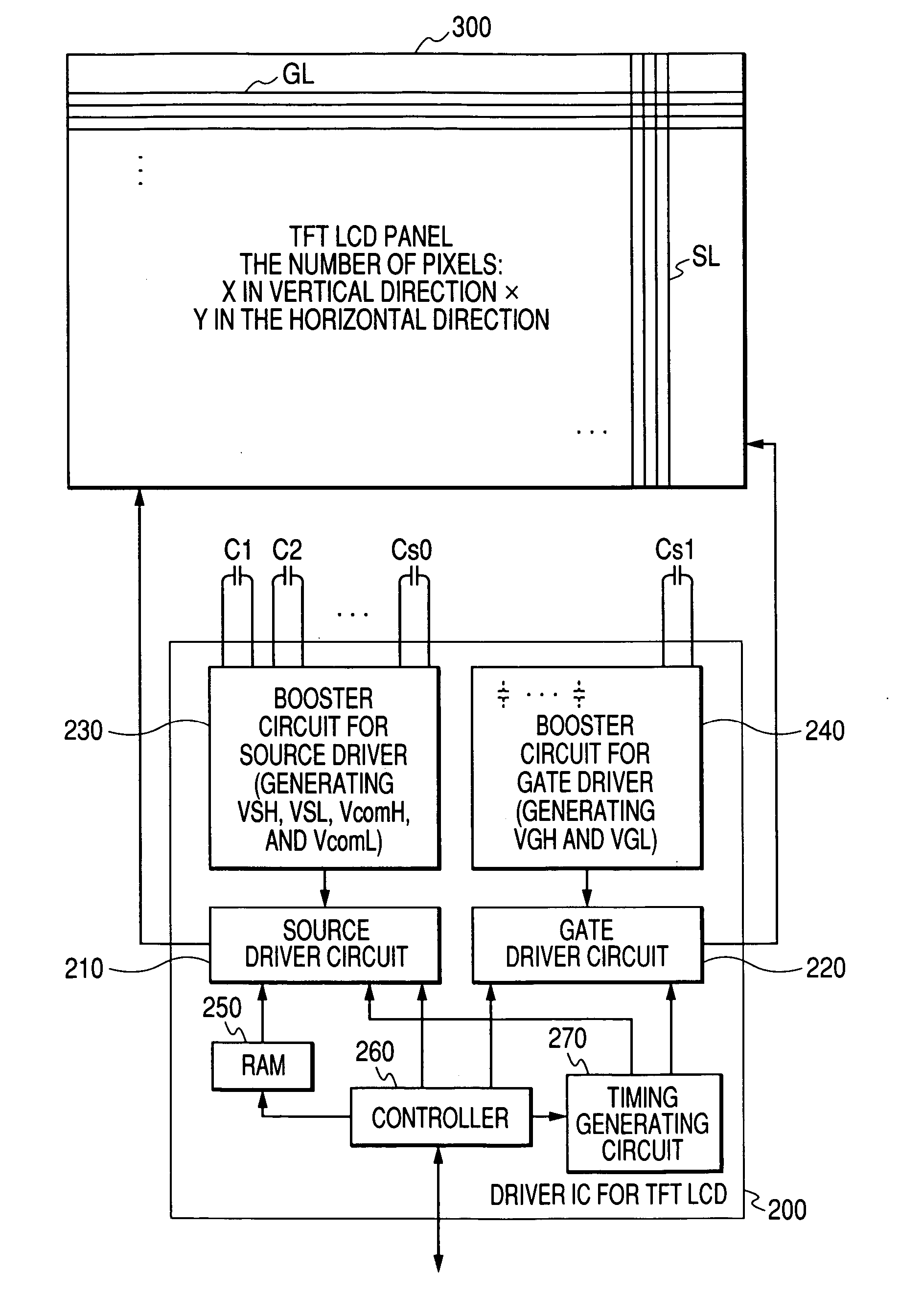
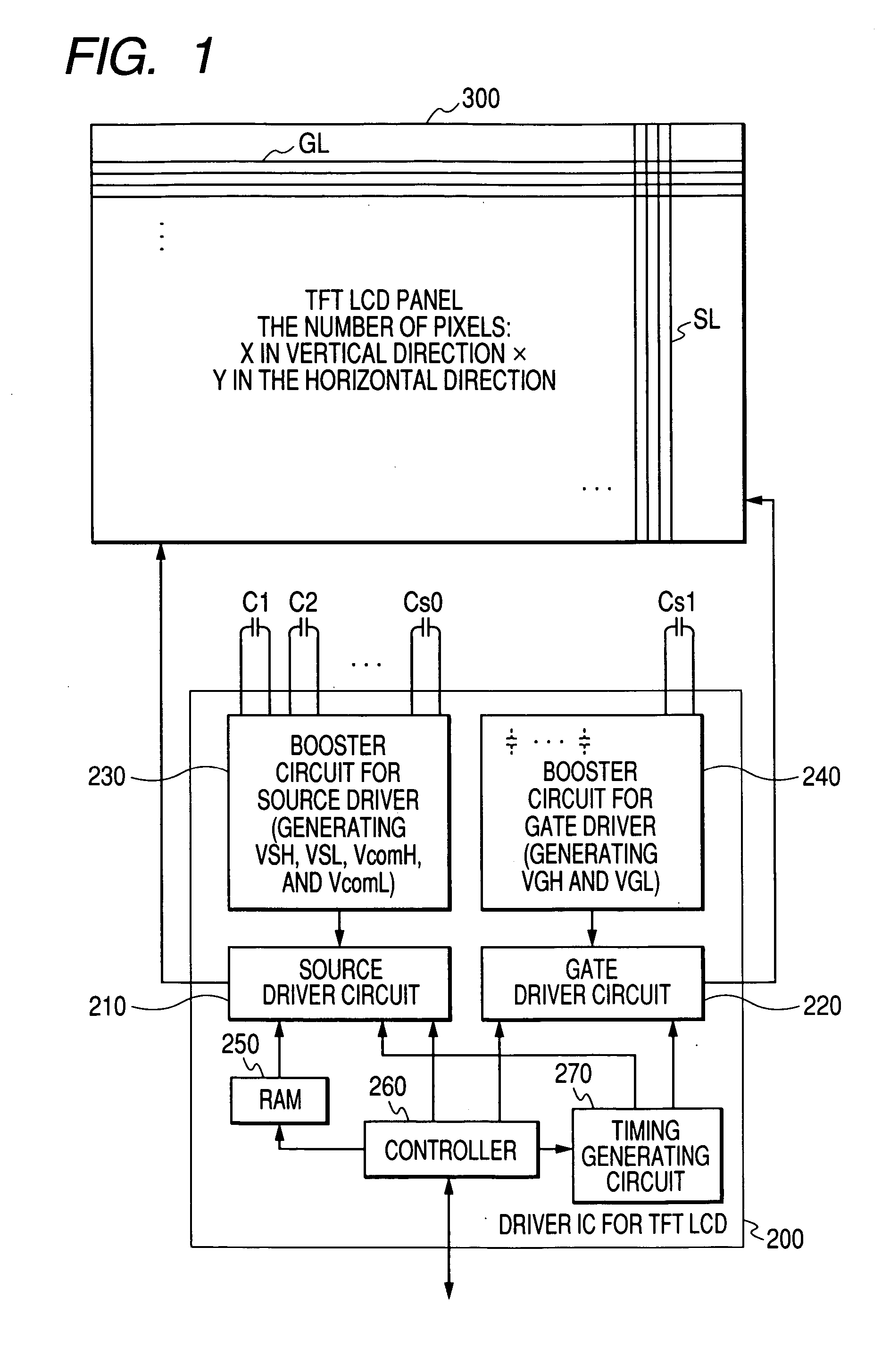
In a liquid crystal drive controller formed as a semiconductor integrated circuit having therein a power source circuit including a boosting circuit and driving a source line and a gate line of a TFT liquid crystal panel, the number of external capacitive elements and the number of external terminals for connecting the external capacitive elements are reduced, thereby reducing the size and cost of the chip and an electronic device on which the chip is mounted. As a boosting circuit for generating a voltage for driving a source line of the TFT liquid crystal panel in the liquid crystal controller having therein the power source including the boosting circuit, a boosting circuit having an external capacitive element is used. On the other hand, as a boosting circuit for generating a voltage for driving a gate line, a charge pump having a built-in (on-chip) capacitive element is used.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Technology device and method for preparing propylene by dehydrogenating propane or propane-enriched low carbon hydrocarbon
ActiveCN102040445AReduce energy consumptionLow unit priceHydrogen separationDistillation purification/separationGas phaseAlkali metal oxide
The invention provides a technology device and method for preparing propylene by dehydrogenating propane or propane-enriching low carbon hydrocarbon. The device comprises a reacting / regenerating part and a product fractionating part. A reacting / regenerating system is divided into a parallel type arrangement scheme and a coaxial type arrangement scheme by a fluidized bed reacting / regenerating technology, wherein a raising pipe of the parallel type reacting / regenerating system is an internal or external raising pipe, and a raising pipe of the coaxial type reacting / regenerating system is an external raising pipe. The method comprises the steps: leading raw materials and reaction products to enter into a raising pipe reactor after heat exchange; performing a dehydrogenating conversion reaction under the conditions that the reaction temperature is 500-700 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-0.4MPa, and the ratio of a microspherical catalyst to oil is 5-60, wherein the microspherical catalyst consists of chromium, rare earth oxides, alkali metal oxides and a gamma-Al2O3 carrier, preferably, the temperature is 550-670 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-0.15MPa, and the ratio of the microspherical catalyst to oil is 6-14; leading the reaction products and the raw materials to enter into a gas-oil separator to separate a gas phase, a liquid phase from a water phase after heat exchange and cooling; leading the separated gas to enter into a gas compressor to be compressed and be transported to an absorbing / stabilizing part; pumping the liquid to an absorbing tower; transporting the liquefied gas from a return tank at the top of a stabilizing tower to a propylene / propane separating tower by a charging pump of a propylene tower; discharging the fine propylene separated from the top of the tower out of the device as a product; discharging the separated byproduct hydrogen out of the device; and returning products at bottom of the tower to the reacting / regenerating part to be recycled.
Owner:卓润生 +1
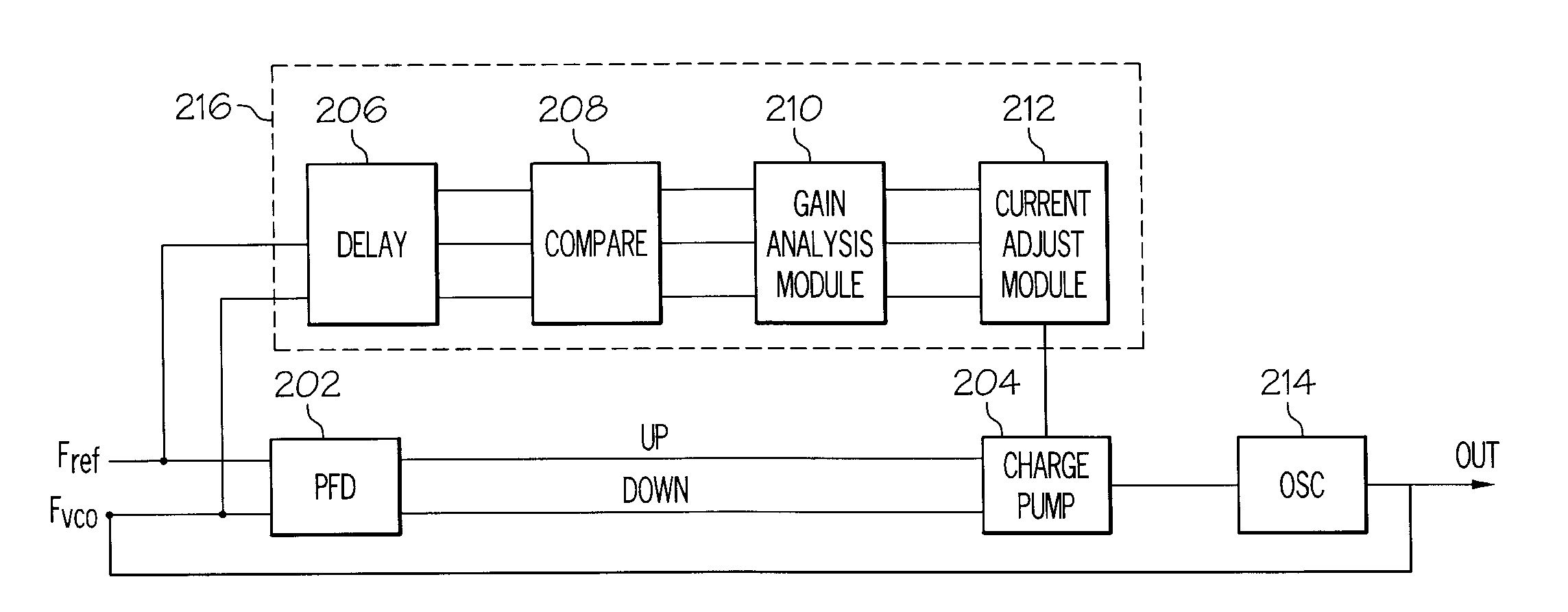
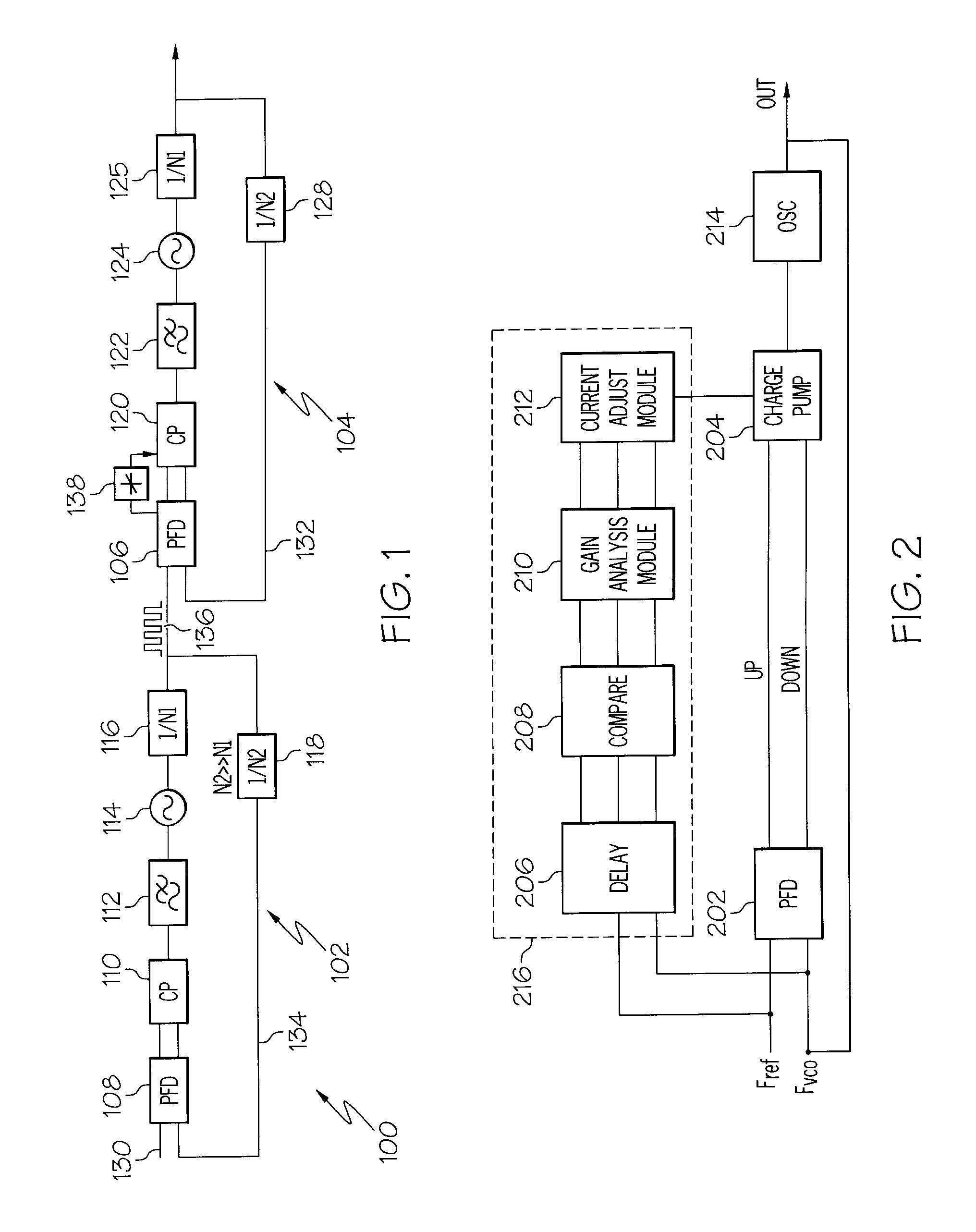
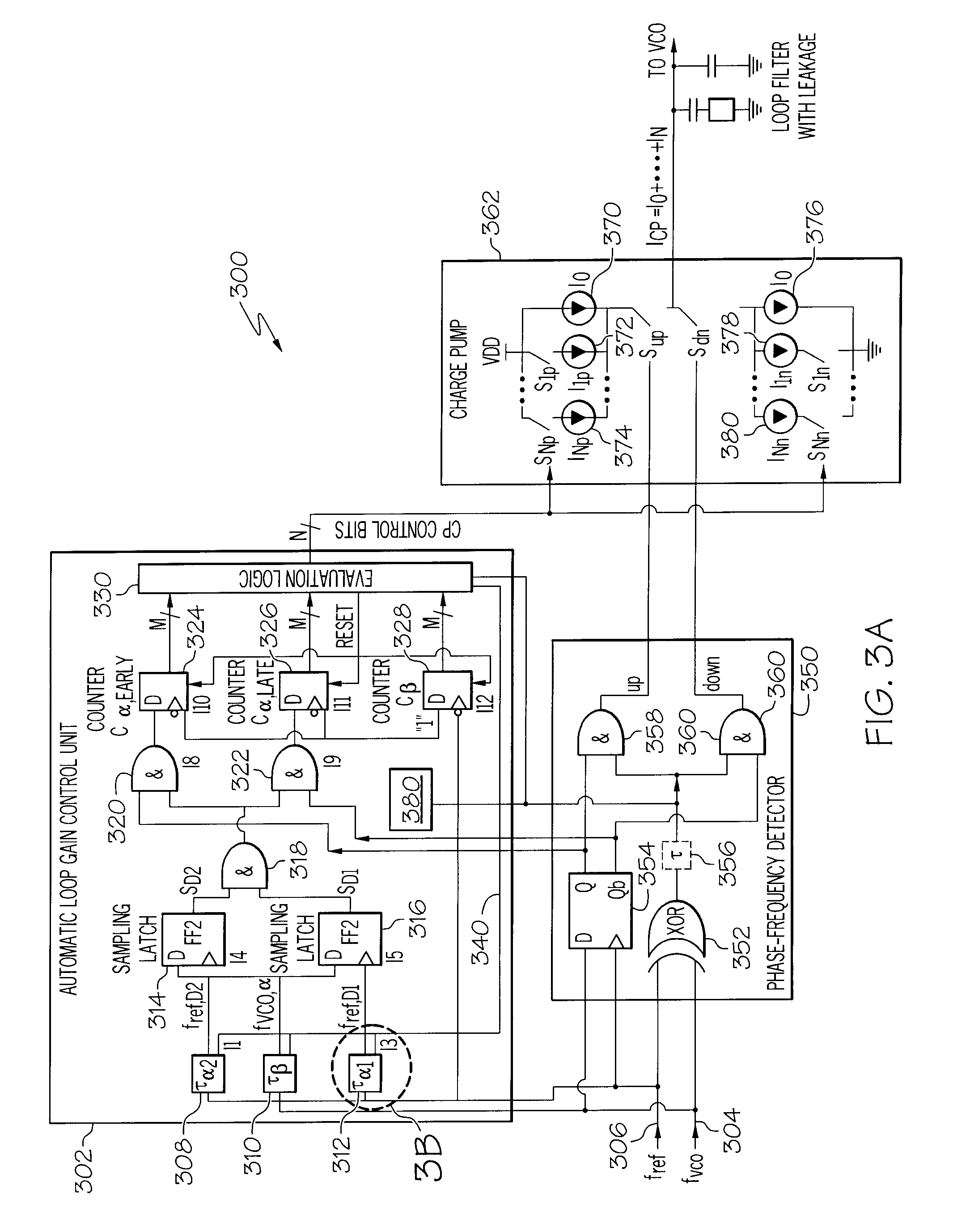
Systems and Arrangements for Controlling Phase Locked Loop
A multi-Gigahertz, low jitter phase locked loop (PLL) with adjustable gain is disclosed. In one embodiment, properties of a fVCO signal of a PLL can be acquired. Properties can include the occurrences of different types of jitter on the fVCO signal and the lock status of the PLL. A gain control module can control at least a portion of the PLL based on an analysis of the acquired properties. For example, when the loop is locked or when there is loop filter leakage, the gain of a charge pump in the PLL can be reduced. When a charge pump mismatch is detected based on the acquired properties, additional control signals can be provided to the charge pump to correct the mismatch.
Owner:IBM CORP
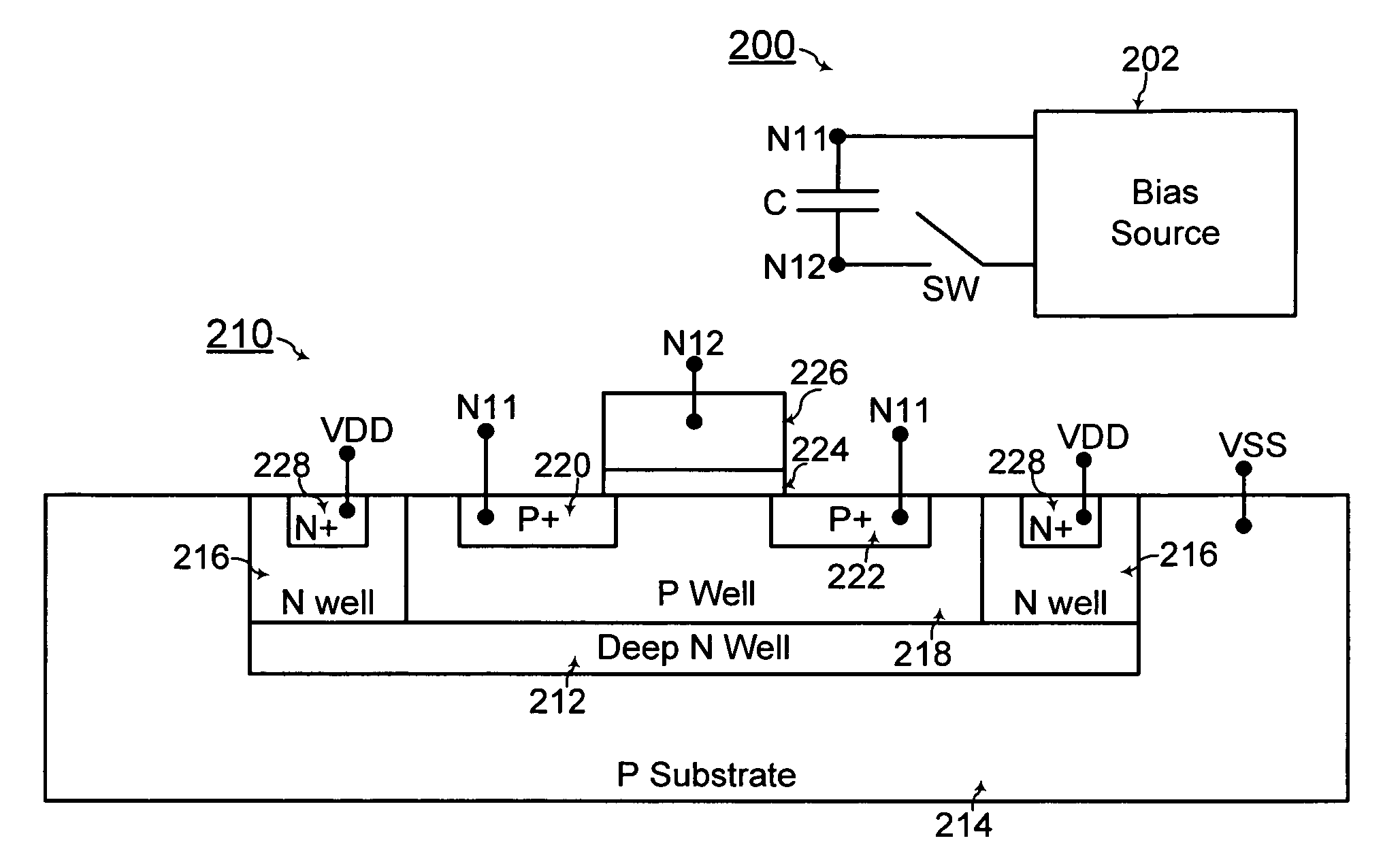
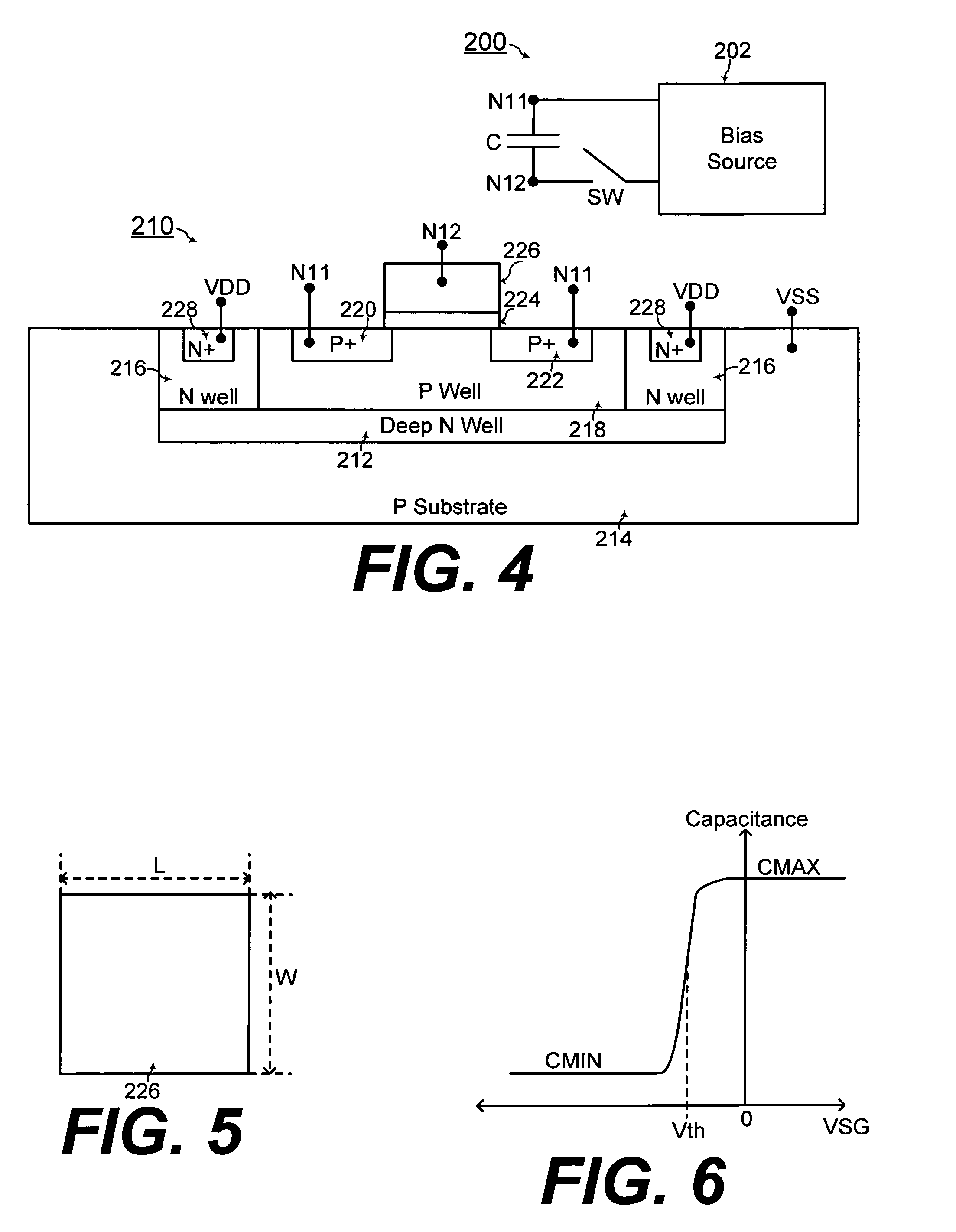
MOS capacitor and charge pump with MOS capacitor
InactiveUS20100226166A1Stable capacitanceImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
A MOS capacitor in a charge pump includes a MOS device with at least one body bias region and a device body of a same conductivity type for providing maximum capacitance over a wide voltage range. The MOS capacitor also includes a gate forming a first terminal of the MOS capacitor, and the at least one body bias region forms a second terminal of the MOS capacitor. The MOS capacitor further includes a multiple-well structure formed with the device body and a deep well in a substrate for enhanced noise immunity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor storage device and portable electronic equipment having the same
InactiveUS6985397B2MiniaturizationFunctionalTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor storage devicesSemiconductor
A semiconductor storage device has a variable-stage charge pump, and a memory cell array to which an output from an output line of the variable-stage charge pump is fed. In the variable-stage charge pump, first and second charge pumps are connected in parallel between a common input bus and a common output bus. A first n-channel MOSFET is provided on a line connecting an output terminal of the first charge pump and the common output bus, and another n-channel MOSFET is provided on a line connecting the second charge pump and the common output bus. First switches are provided between the output terminal of the first charge pump and the first n-channel MOSFET, and between the input terminal of the second charge pump and the second switch. A second switch is provided on a line connecting an input terminal of the second charge pump and the common input bus.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method of forming metal/high-k gate stacks with high mobility
ActiveUS20050280105A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorDevice material
The present invention provides a gate stack structure that has high mobilites and low interfacial charges as well as semiconductor devices, i.e., metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) that include the same. In the semiconductor devices, the gate stack structure of the present invention is located between the substrate and an overlaying gate conductor. The present invention also provides a method of fabricating the inventive gate stack structure in which a high temperature annealing process (on the order of about 800° C.) is employed. The high temperature anneal used in the present invention provides a gate stack structure that has an interface state density, as measured by charge pumping, of about 8×1010 charges / cm2 or less, a peak mobility of about 250 cm2 / V-s or greater and substantially no mobility degradation at about 6.0×1012 inversion charges / cm2 or greater.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
GIA circuit and display device
ActiveCN105185292AGuaranteed Fall TimeReduce occupancyStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitElectricity
Owner:KUSN INFOVISION OPTOELECTRONICS
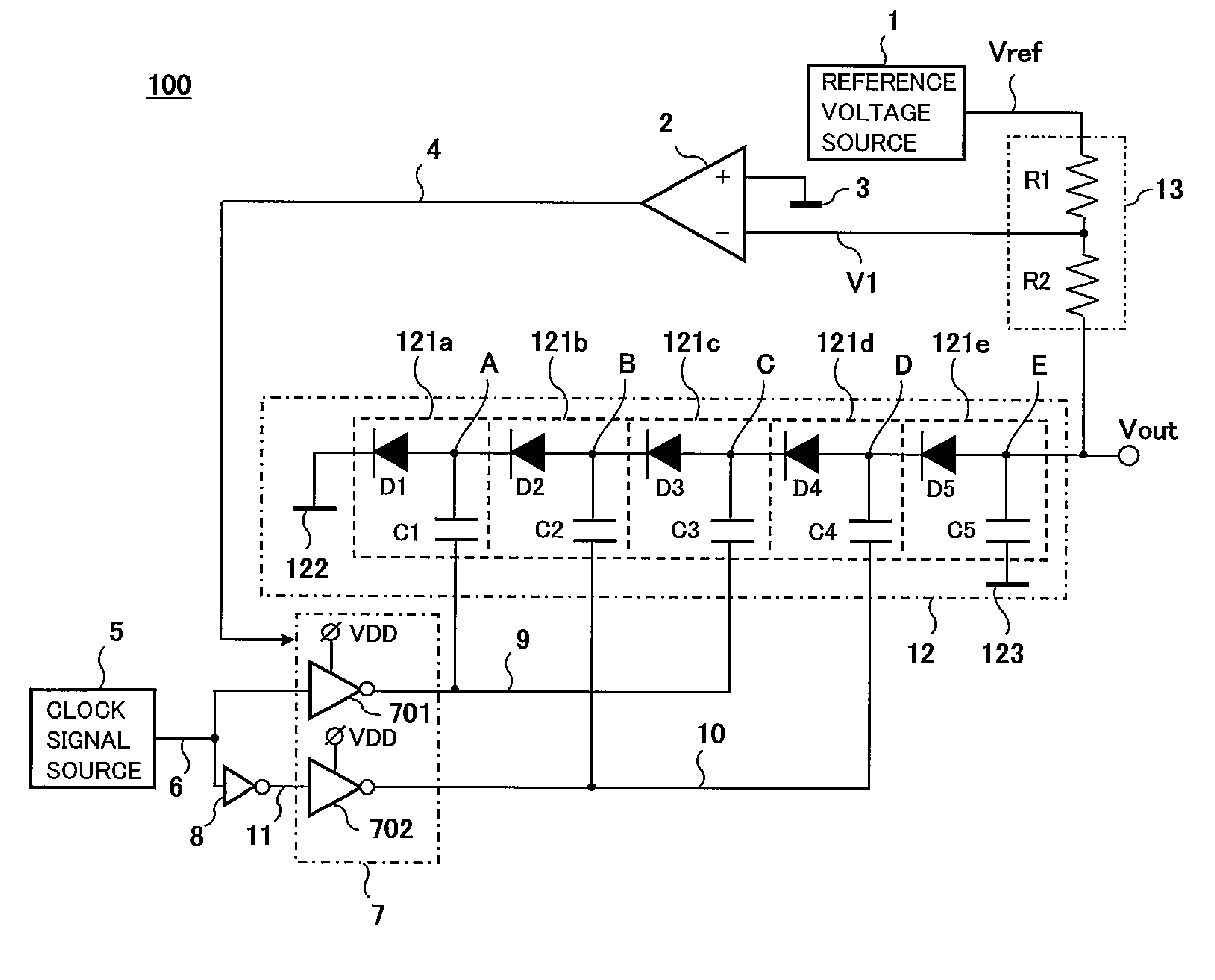
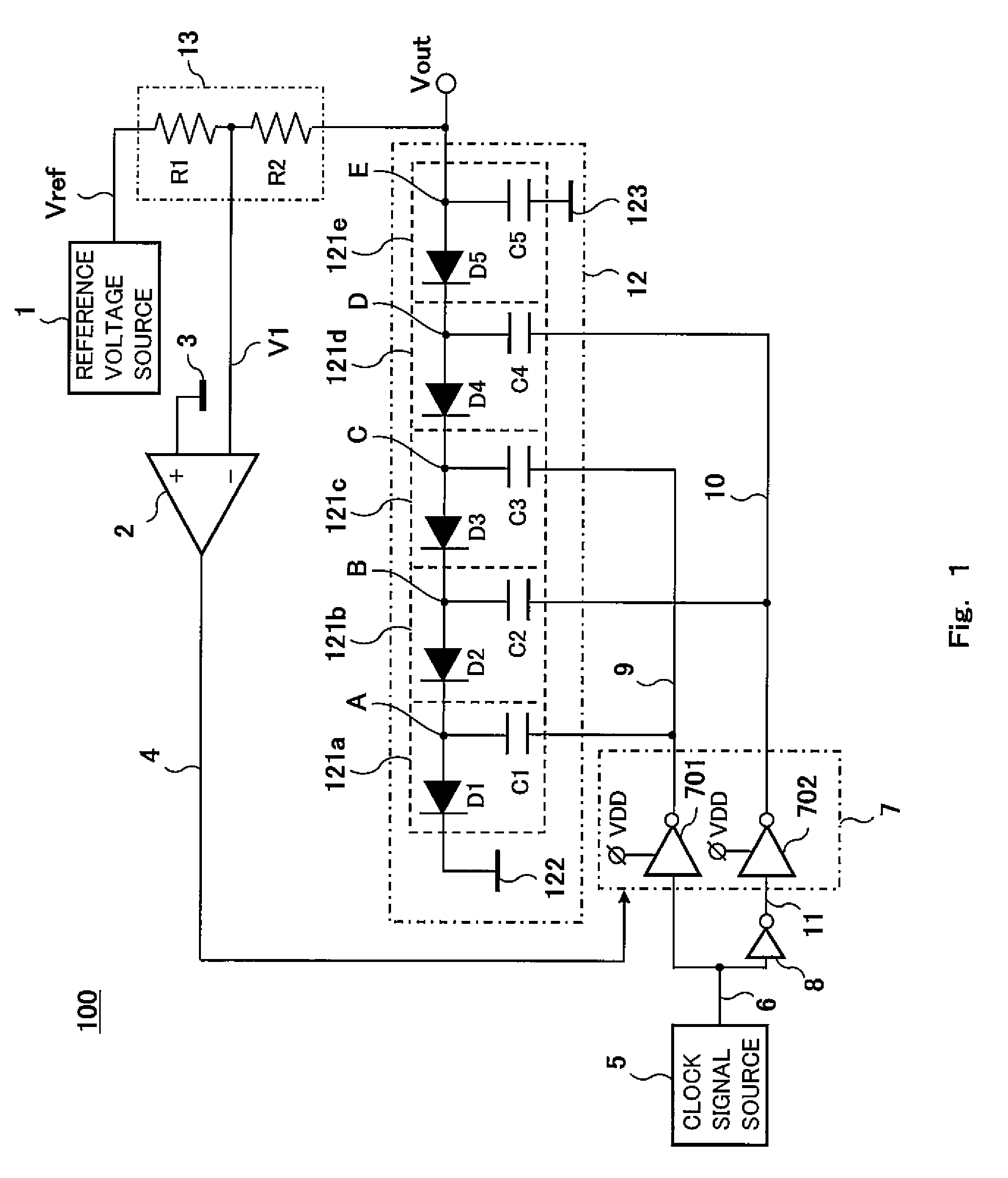
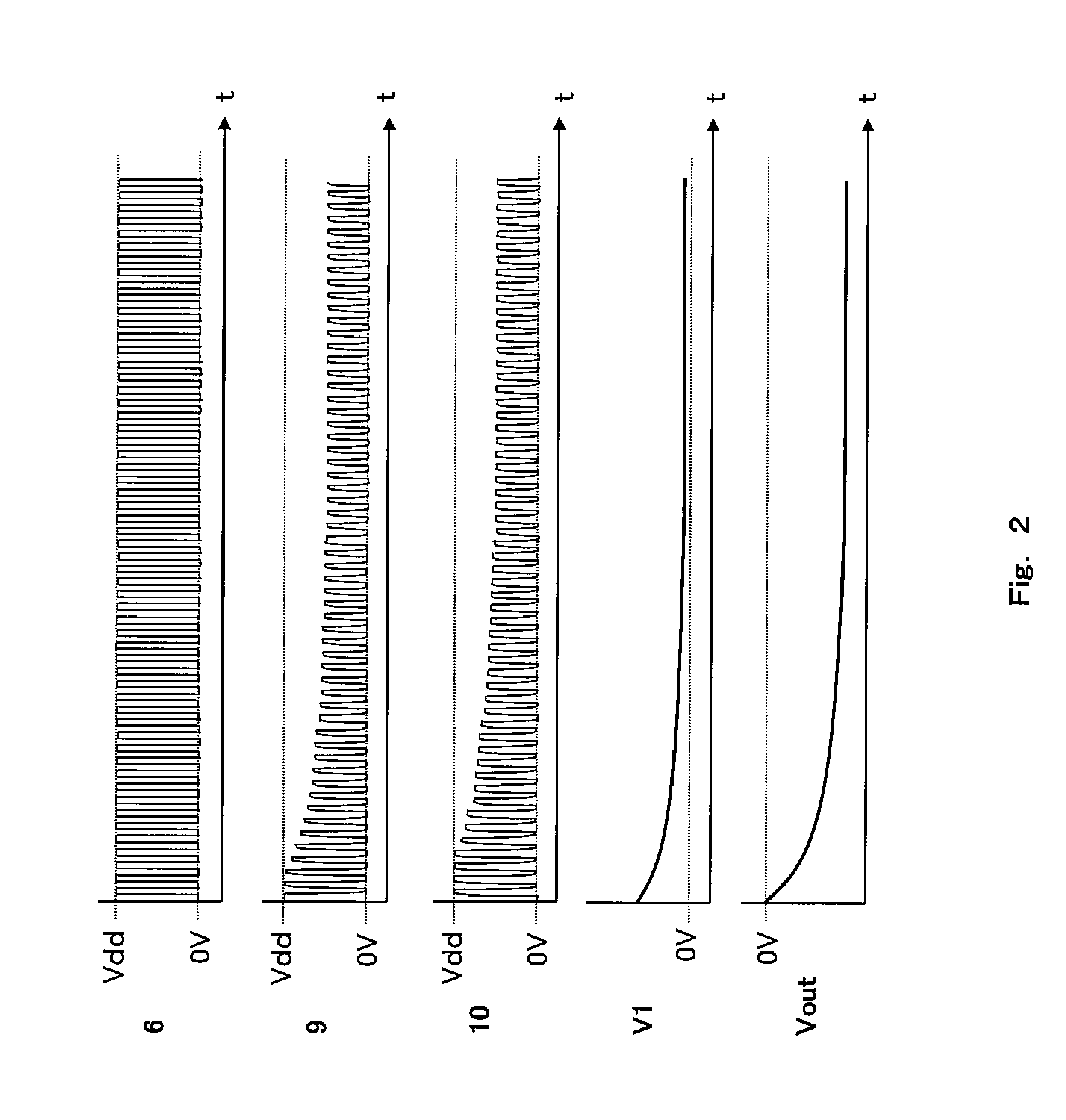
Charge pump circuit, and method of controlling charge pump circuit
InactiveUS20110080198A1Suppresses noise generationStable output voltagePulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionPotential differenceVoltage regulation
A charge pump circuit of the present invention comprises a resistance voltage divider provided between a reference voltage source and an output terminal, a differential amplifier which has an inverting input terminal applied with a divided voltage portion from the resistance voltage divider and a non-inverting input terminal applied with a comparison voltage and is configured to output an output signal obtained by amplifying a potential difference between the divided voltage portion and the comparison voltage through an output terminal, a clock feeder configured to output first and second clock signals according to an original clock signal, and a pump circuit section which is applied with the first and second clock signals alternately and control an output voltage at an output terminal, and the clock feeder is configured to regulate amplitude levels of the first and second clock signals according to the voltage of the output signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Driving apparatus for a liquid crystal display and liquid crystal display including the same
InactiveUS20080309597A1Code of PracticeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageVoltage generatorElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention is related to a driving apparatus for a liquid crystal display, and a liquid crystal display including the same. A gate-on voltage generator includes first and second resistors connected between a predetermined reference voltage and a ground voltage, a voltage follower connected to a contact between the first resistor and the second resistor, a charge pump circuit connected to an output terminal of the voltage follower, and a gate-on voltage output terminal connected to the charge pump circuit. The voltage follower is disposed in front of the charge pump circuit such that an influence due to load changes is blocked to thereby prevent an excessive increase of the gate-on voltage during a blank time. Furthermore, two resistors having the same resistance are used to divide the reference voltage such that stress on the resistors may be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
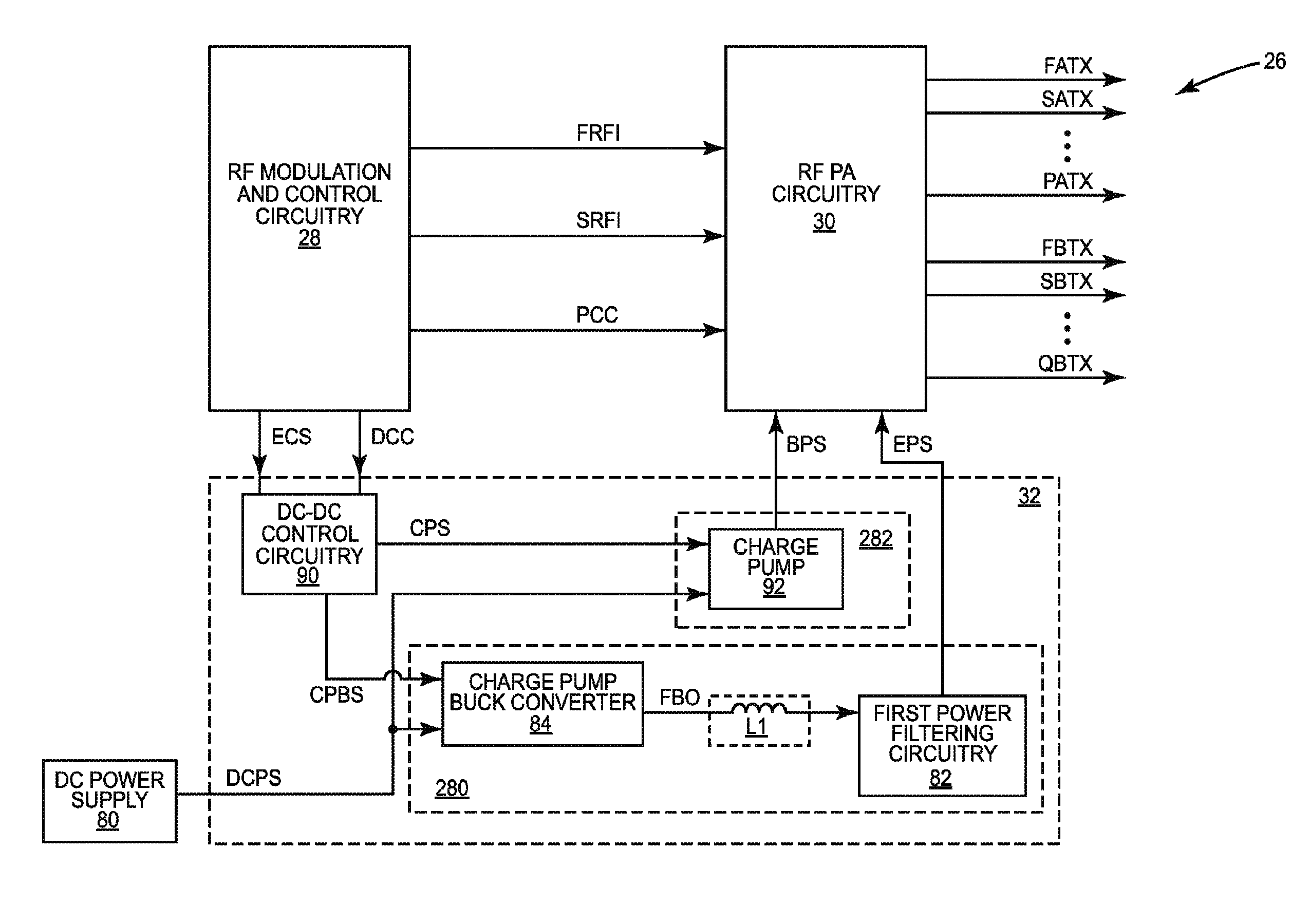
Low-loss step-up and step-down voltage converter
ActiveUS20150145497A1Reduce resistance lossSmooth transitEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage converterPower flow
A switch-mode DC-DC voltage converter including a boost stage in the form of a charge pump and a buck stage. Control circuitry is provided that enables the operation of the buck stage while the charge pump stage is also enabled, followed by disabling of the charge pump stage as the input voltage and output voltage increase. The buck converter stage is constructed so that it regulates the output voltage at a voltage above that which disables the charge pump stage. Conduction losses in the main current path, due to the necessity of a power FET or other switching device, are avoided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
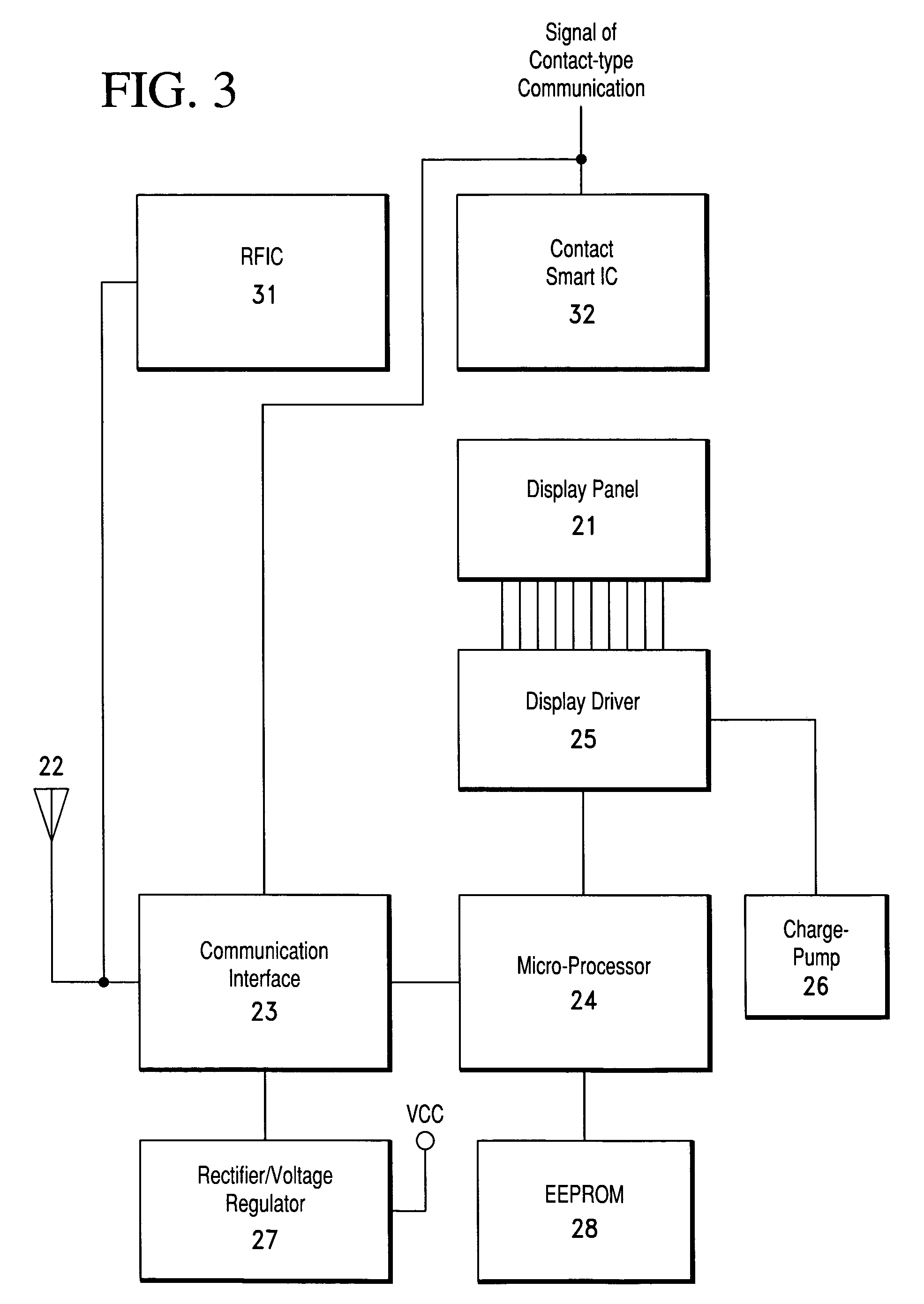
IC card with display panel but without batteries
InactiveUS7156313B2Improve disadvantagesRecord carriers used with machinesCommunication interfaceElectrical battery
Owner:SMARTDISPLAYER TECH CO LTD
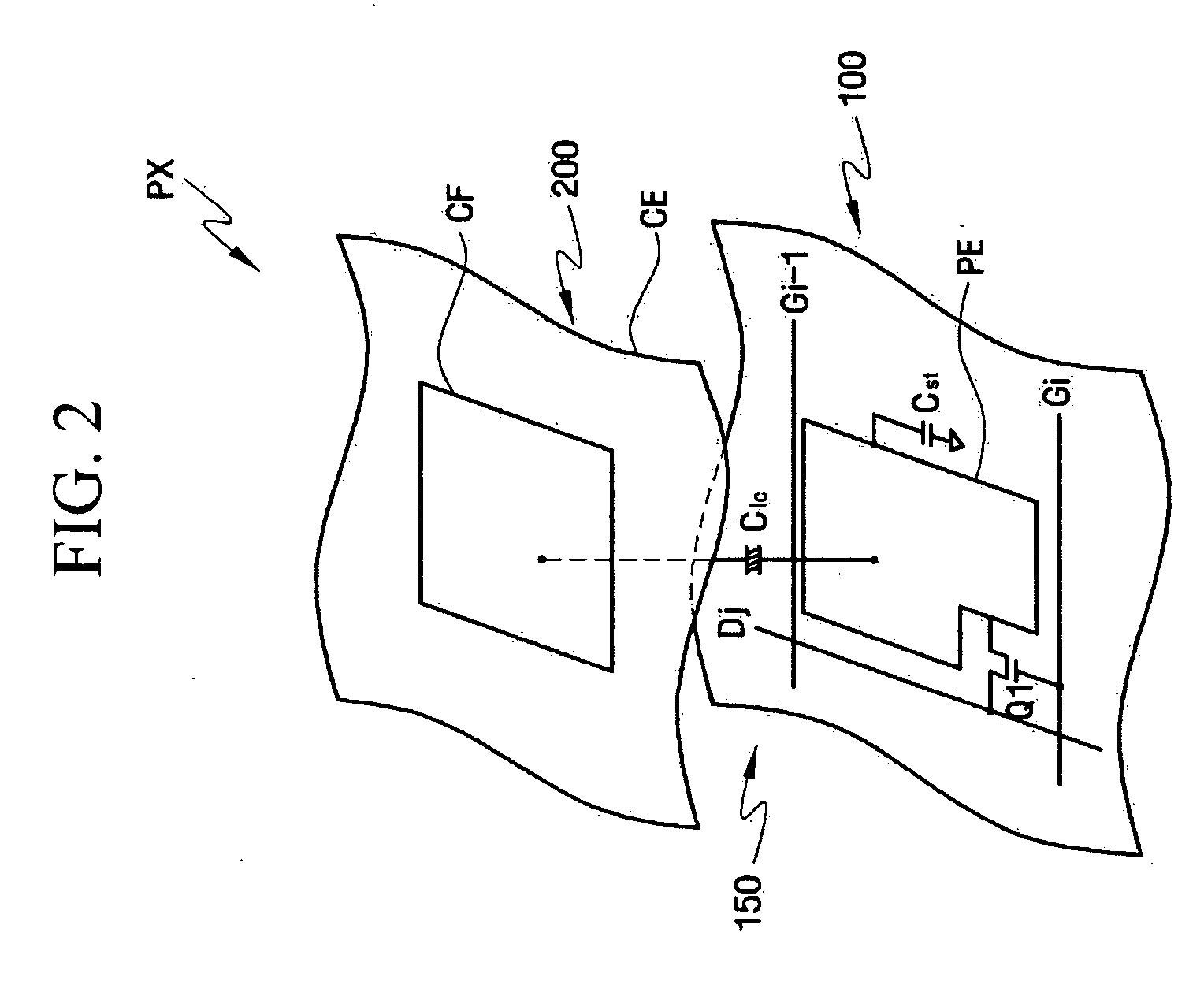
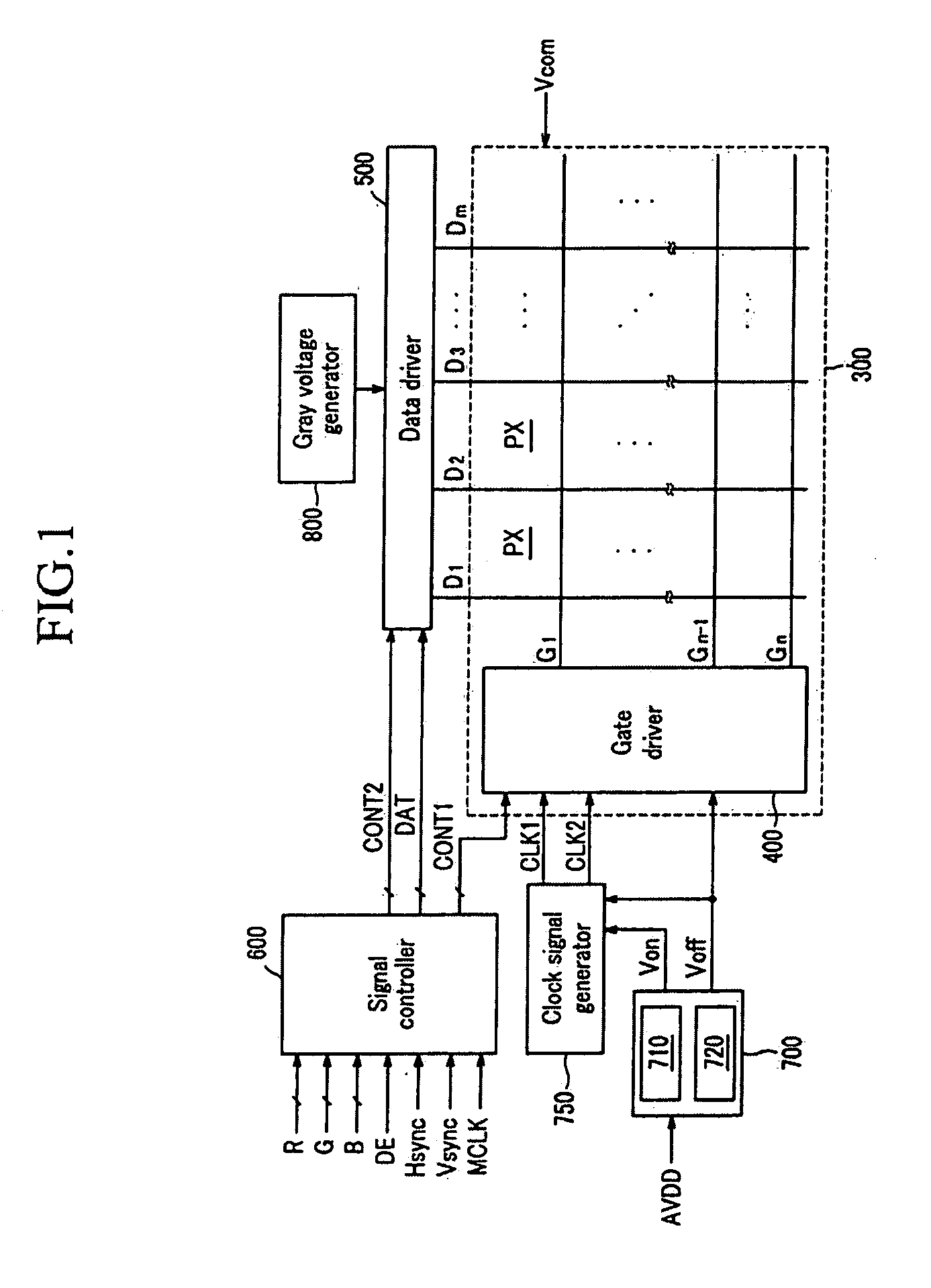
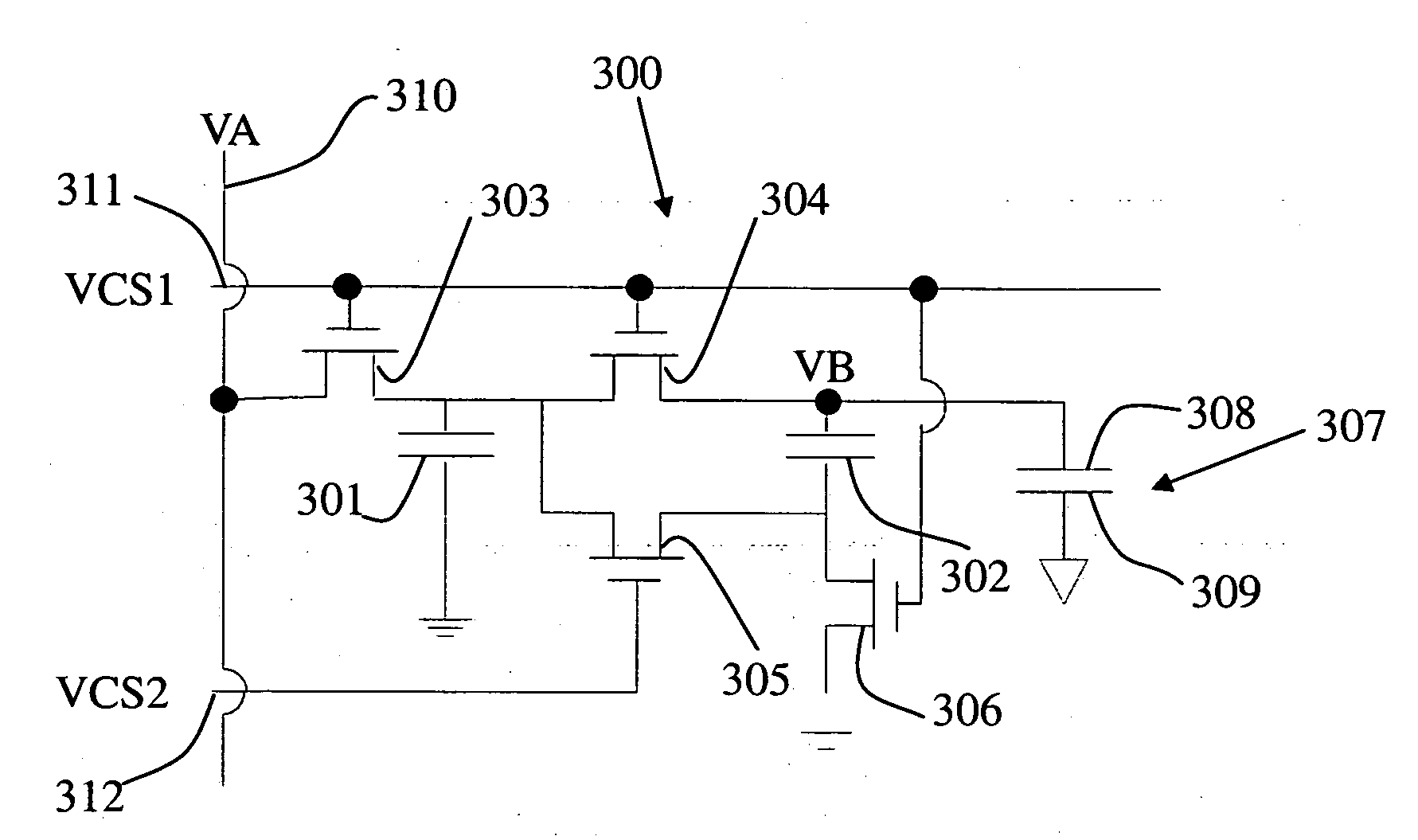
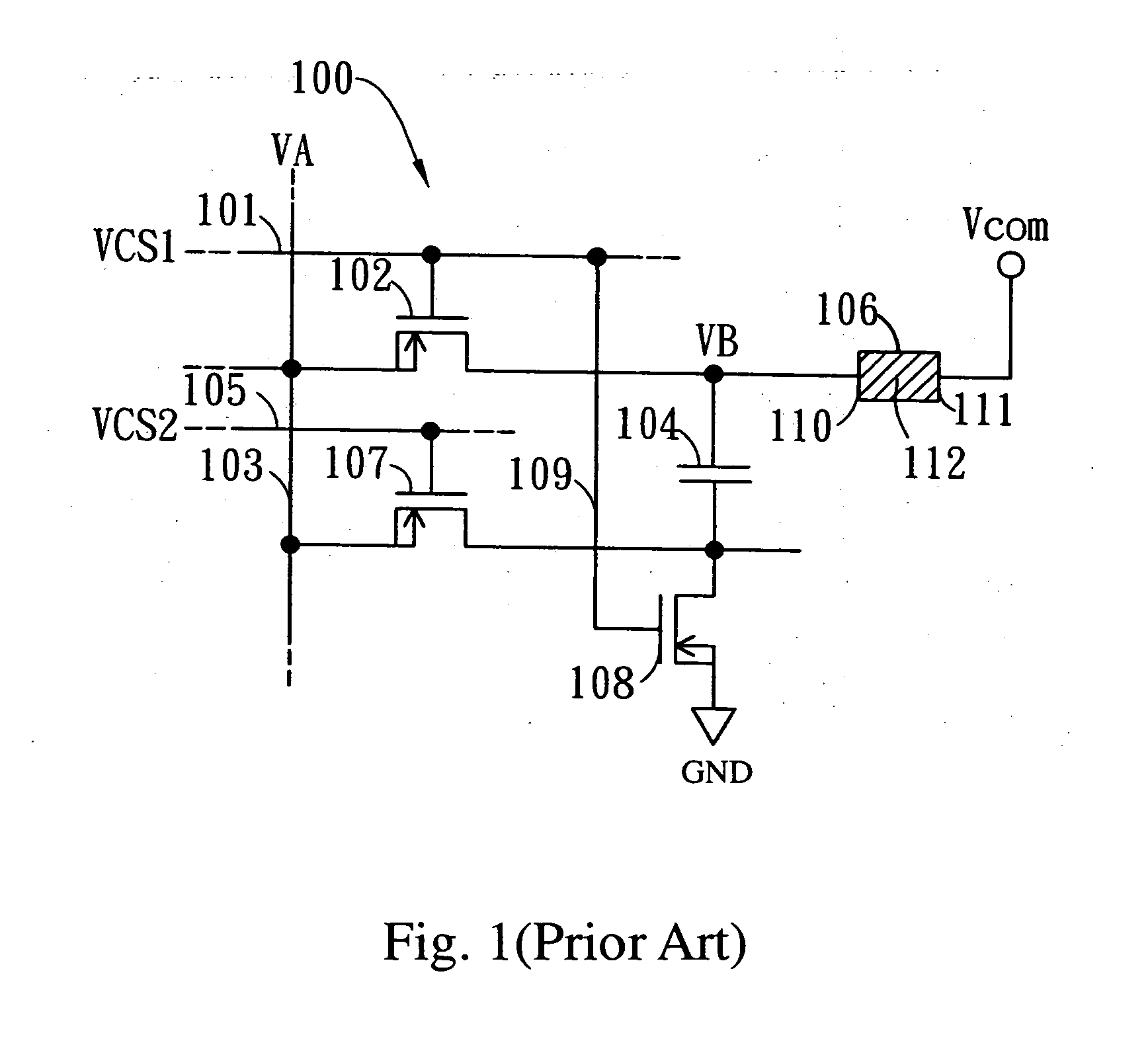
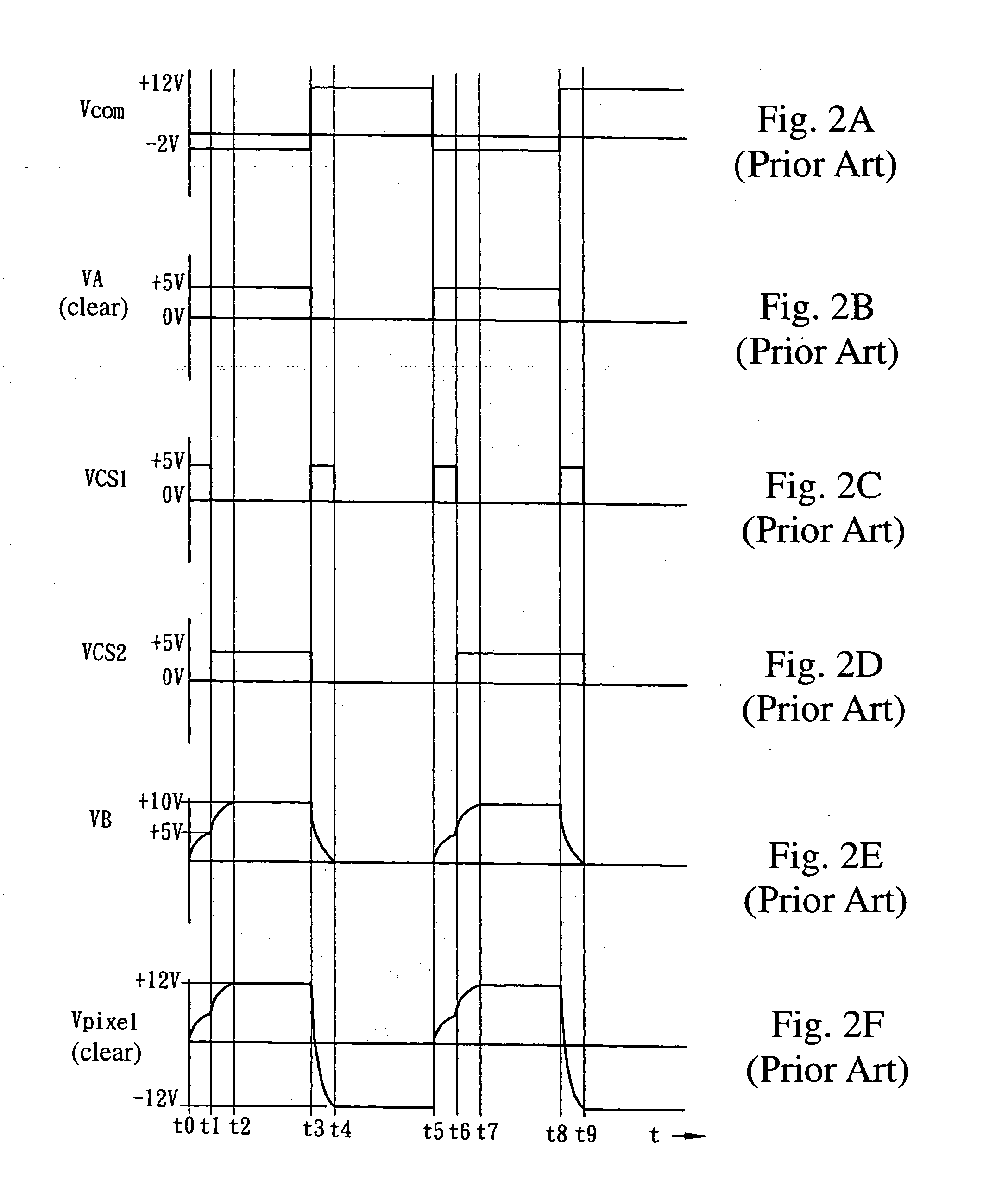
Charge pump pixel driving circuit
InactiveUS20080055222A1Keep the colorSimple designStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceControl signal
The present invention provides a charge pump pixel driving circuit, which includes a first storage capacitor, a second storage capacitor and switch means. The first end of the second storage capacitor is coupled to a pixel electrode. The switch means responsive to a control signal to couple a signal voltage to the first ends of the first storage capacitor and second capacitor until the first ends of the first storage capacitor and second capacitor are charged to a voltage equal to the signal voltage. Then, the signal voltage is decoupled from the first storage capacitor and second storage capacitor, and the first end of the first storage capacitor is coupled to the second end of the second storage capacitor so that the first end of the second storage capacitor provides a voltage twice the signal voltage to the pixel electrode.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
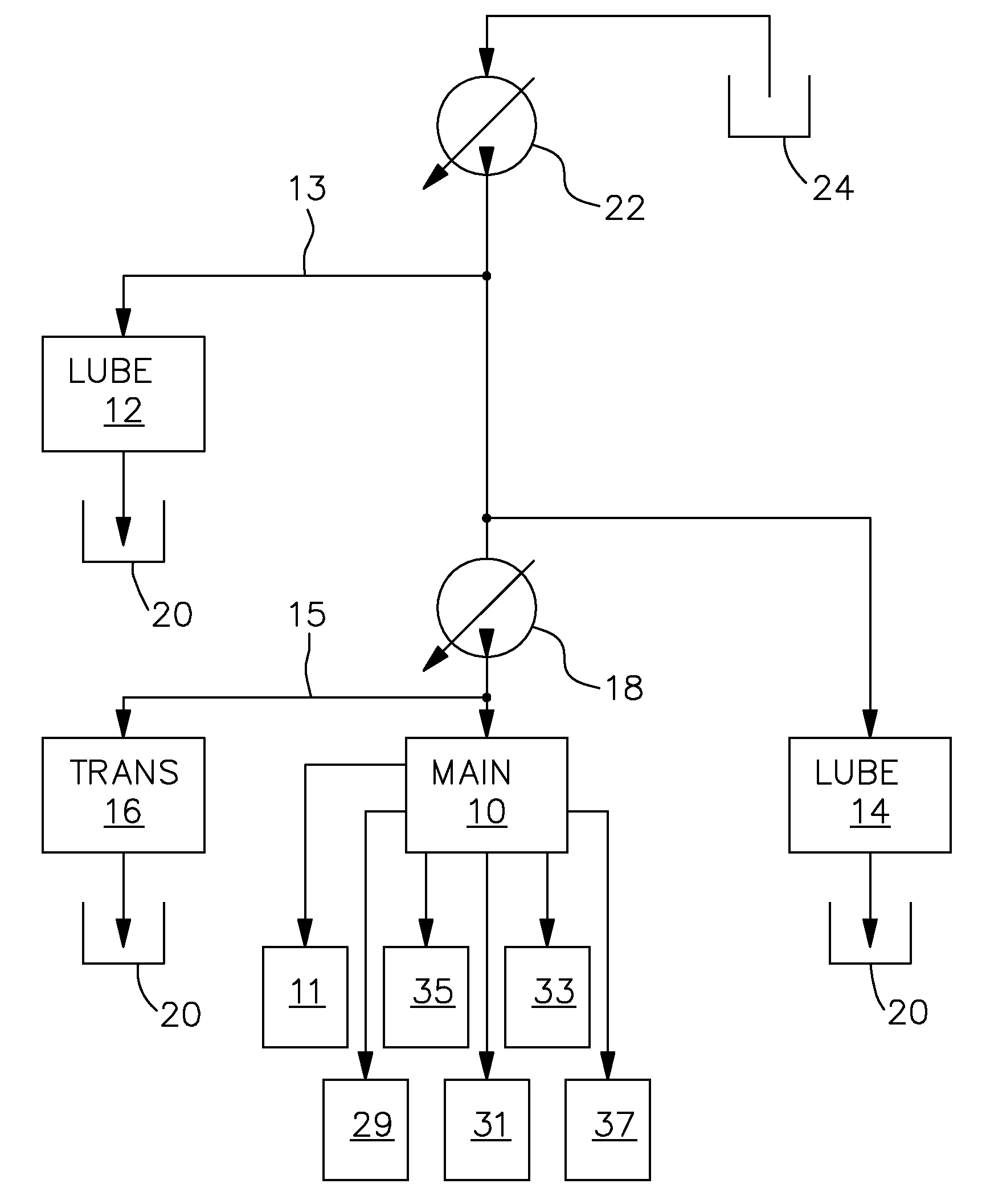
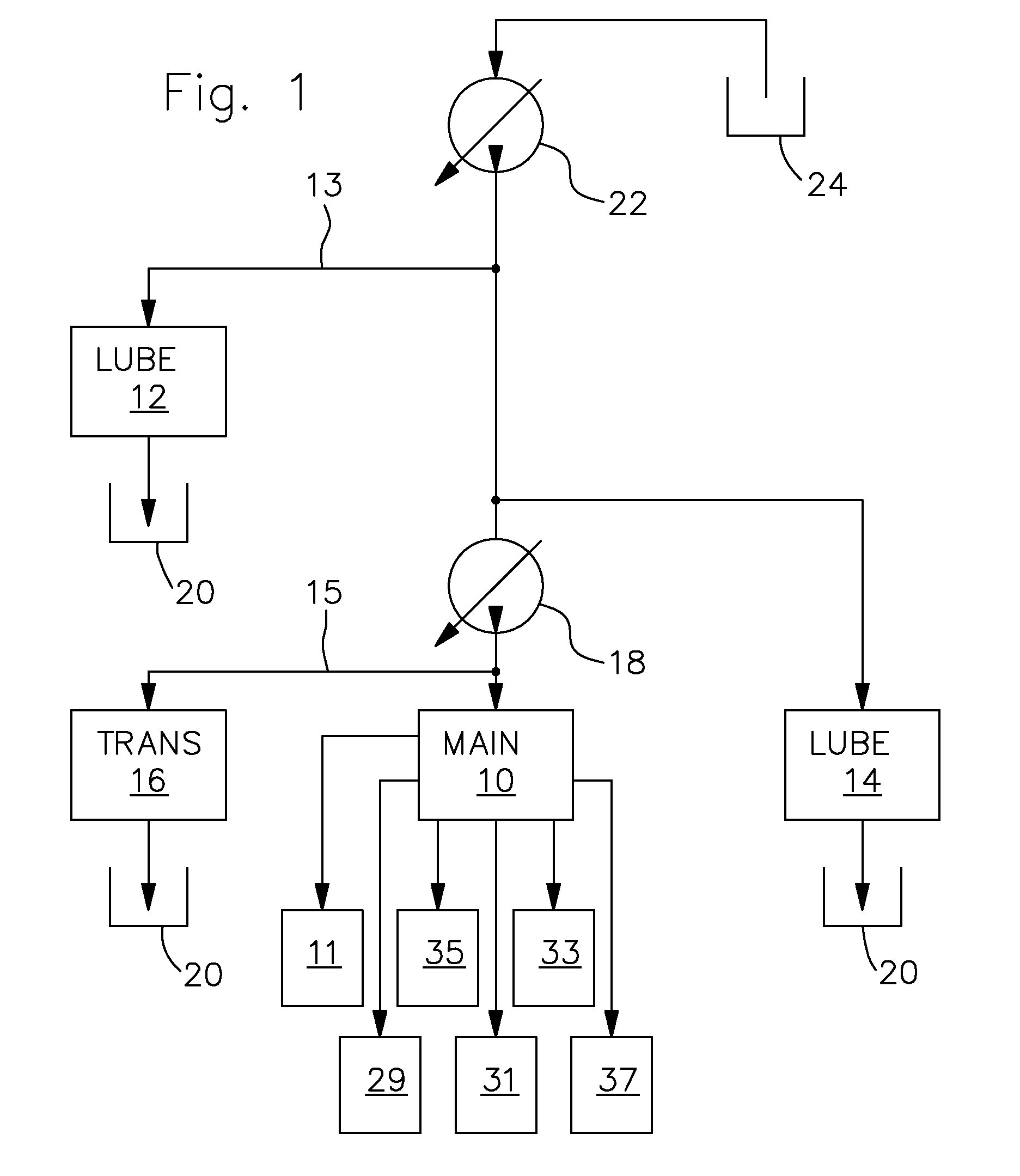
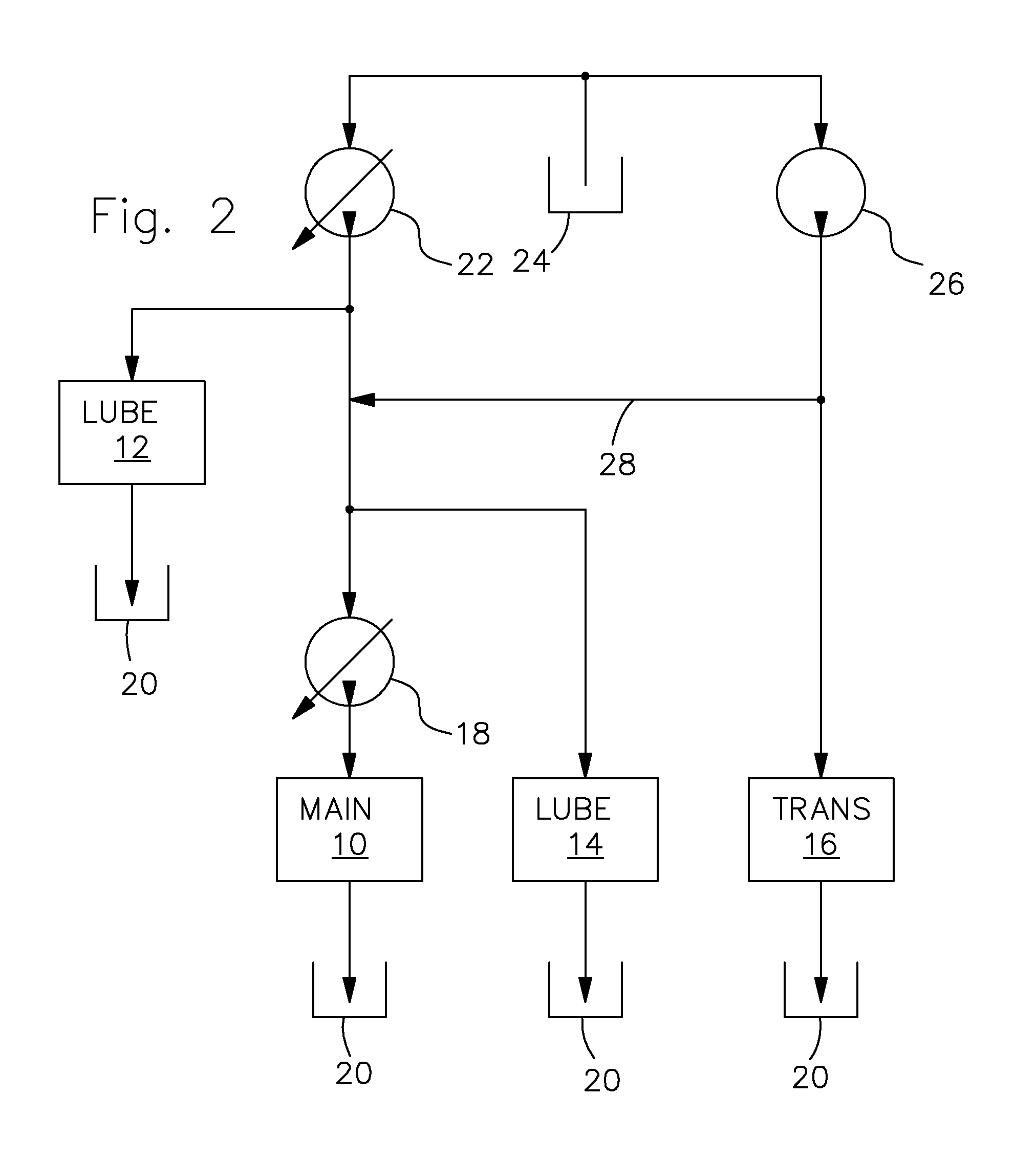
Hydraulic system
ActiveUS20090158727A1Advantage in of complexityDevelopment complexityFluid couplingsGearing controlHydraulic circuitHydraulic pump
A hydraulic system for an agricultural vehicle is proposed. The hydraulic system comprises a main hydraulic circuit, which is fed with hydraulic fluid by a main hydraulic pump, a variable displacement charge pump which supplies charge pressure to the main hydraulic pump, and a lubricating hydraulic circuits. In order to keep efficiency losses on the vehicle to a minimum, particularly at high engine speeds, part of the hydraulic fluid delivered by the charge pump can be diverted to the lubricating hydraulic circuit.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Control circuit of gate driving circuit, working method and display device
InactiveCN104036740AReduce power consumptionExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesElectric pulse generatorDisplay deviceDigital control
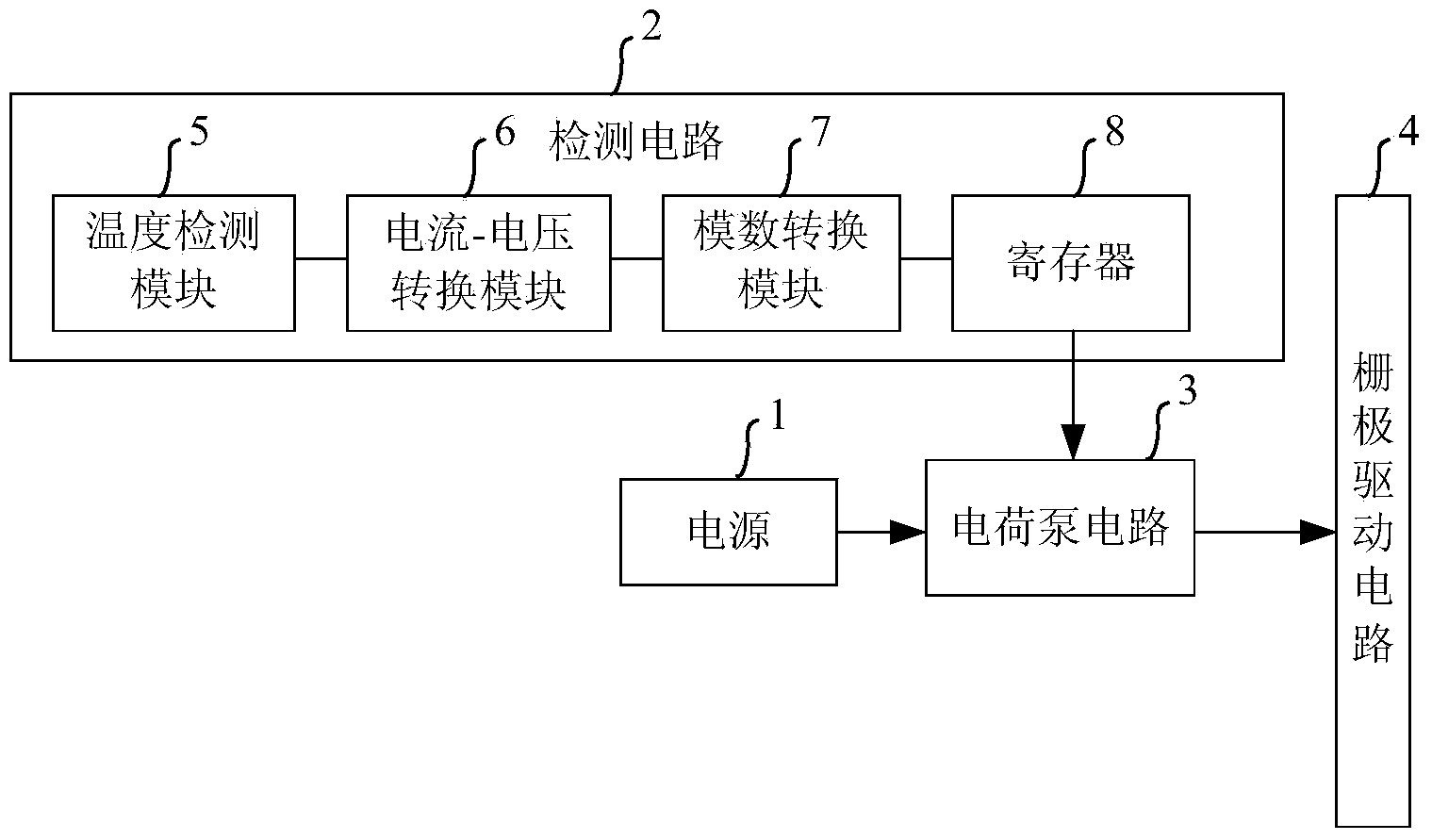
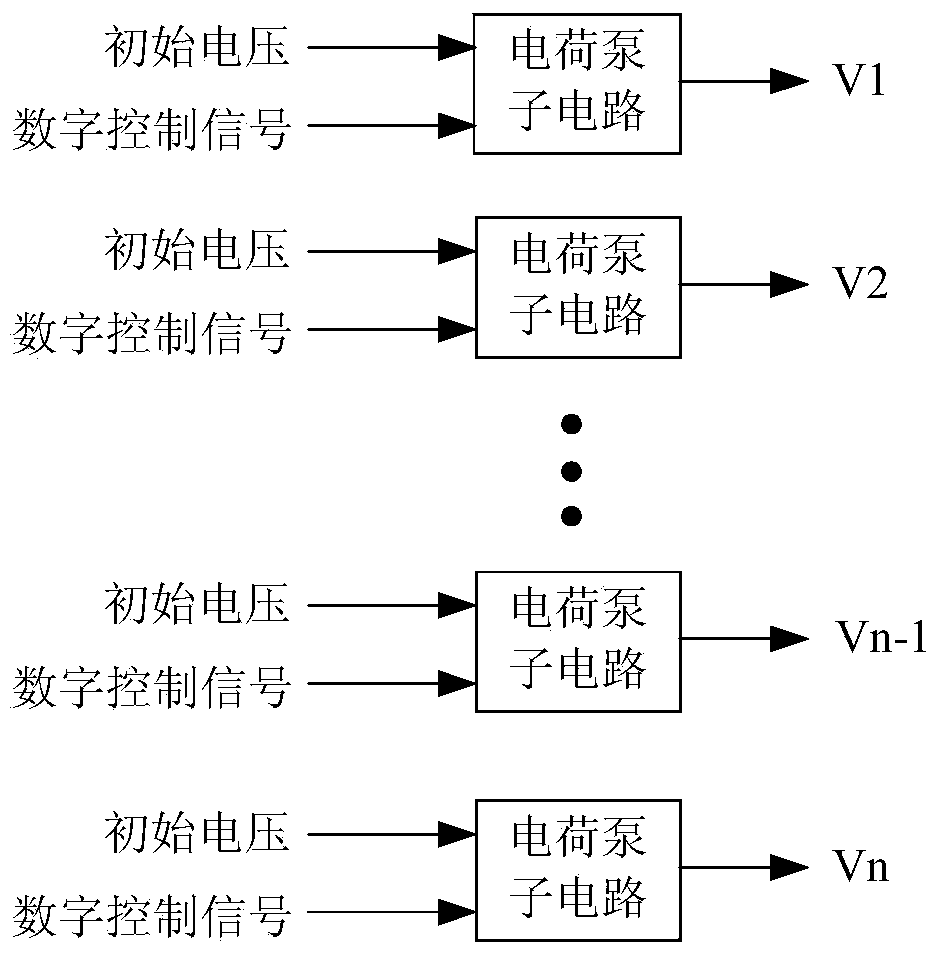
The invention discloses a control circuit of a gate driving circuit, a working method and a display device. The control circuit comprises a detection circuit, a power source and a charge pump circuit, wherein the detection circuit is used for generating digital control signals corresponding to environment temperature according to the environment temperature of the gate driving circuit, the power source is used for providing initial voltage for the charge pump circuit, and the charge pump circuit is used for adjusting the initial voltage according to the digital control signals so as to generate driving voltage, and outputting the driving voltage to the gate driving circuit. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the driving voltage is dynamic and adjustable, and therefore, the power consumption of the gate driving circuit can be reduced, and the service life of a thin film transistor of the gate driving circuit can be prolonged.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Booster circuit and semiconductor device having same
InactiveUS7274248B2Guaranteed current efficiencyCurrent consumptionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
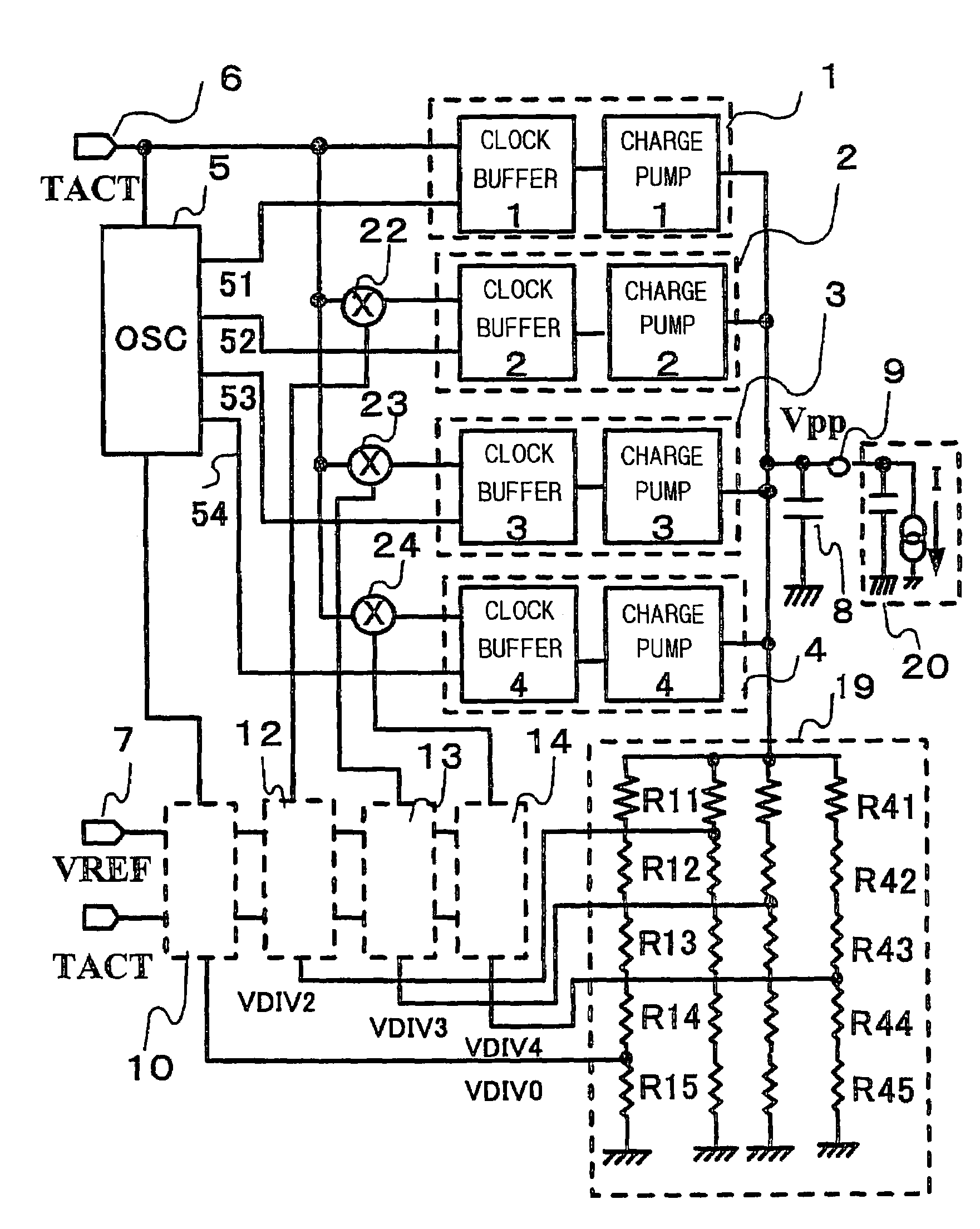
A booster circuit for boosting an externally supplied voltage includes a plurality of parallel-connected charge pump units. The charge pump units are activated successively in accordance with a boosted voltage to suppress peak current at start-up of the booster circuit and reduce fluctuation of power supply voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com