Patents
Literature
378 results about "Hot electron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
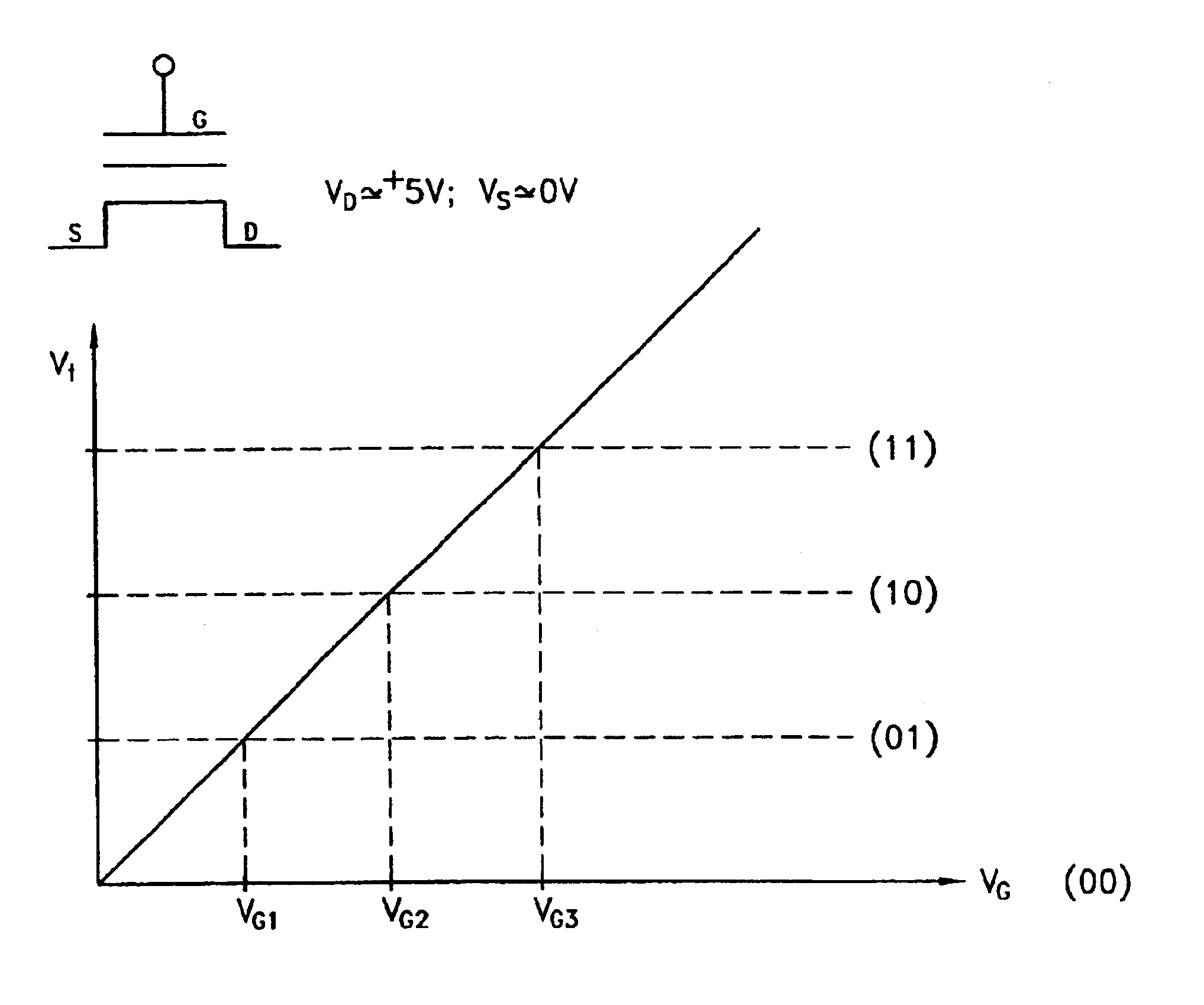
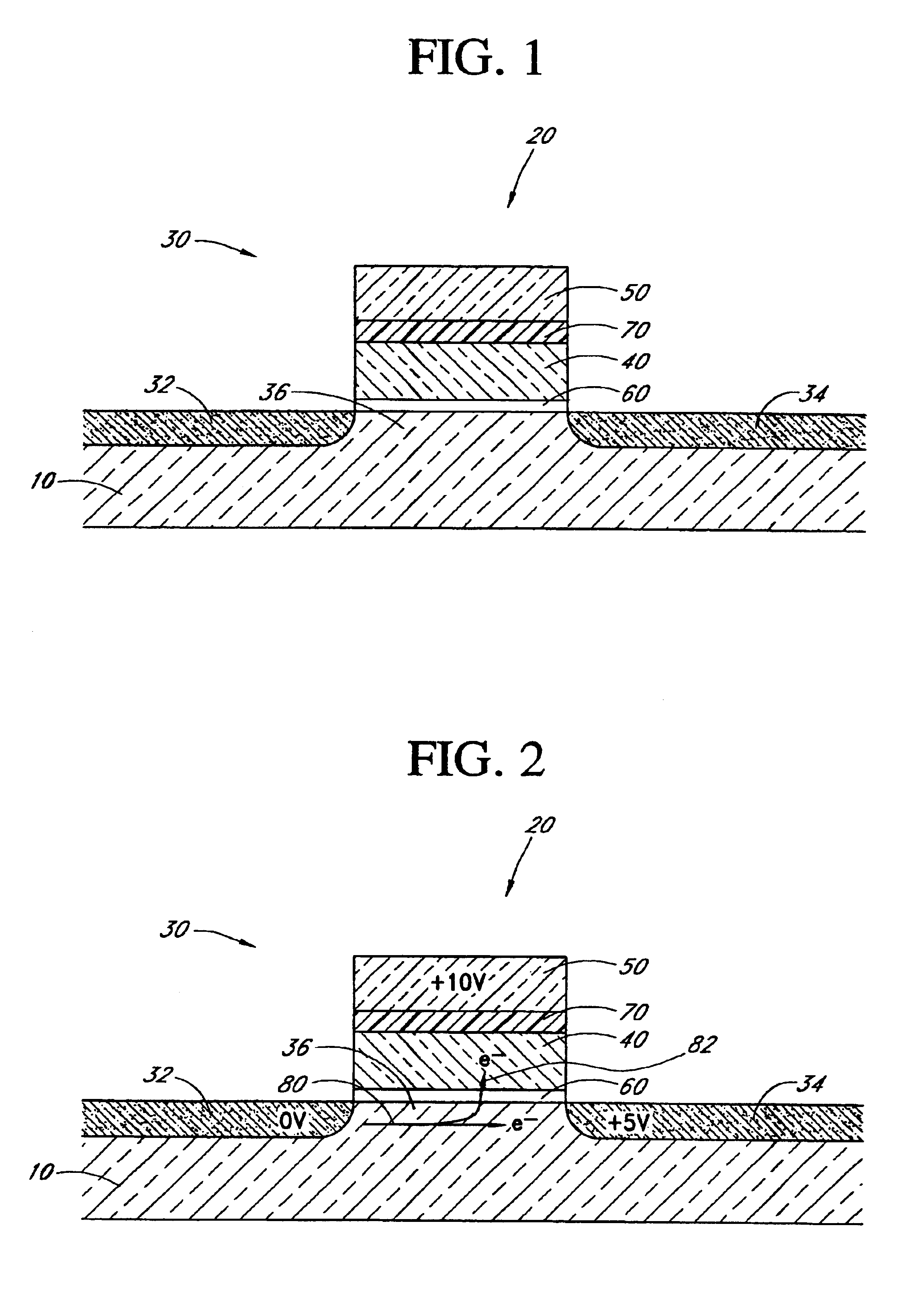
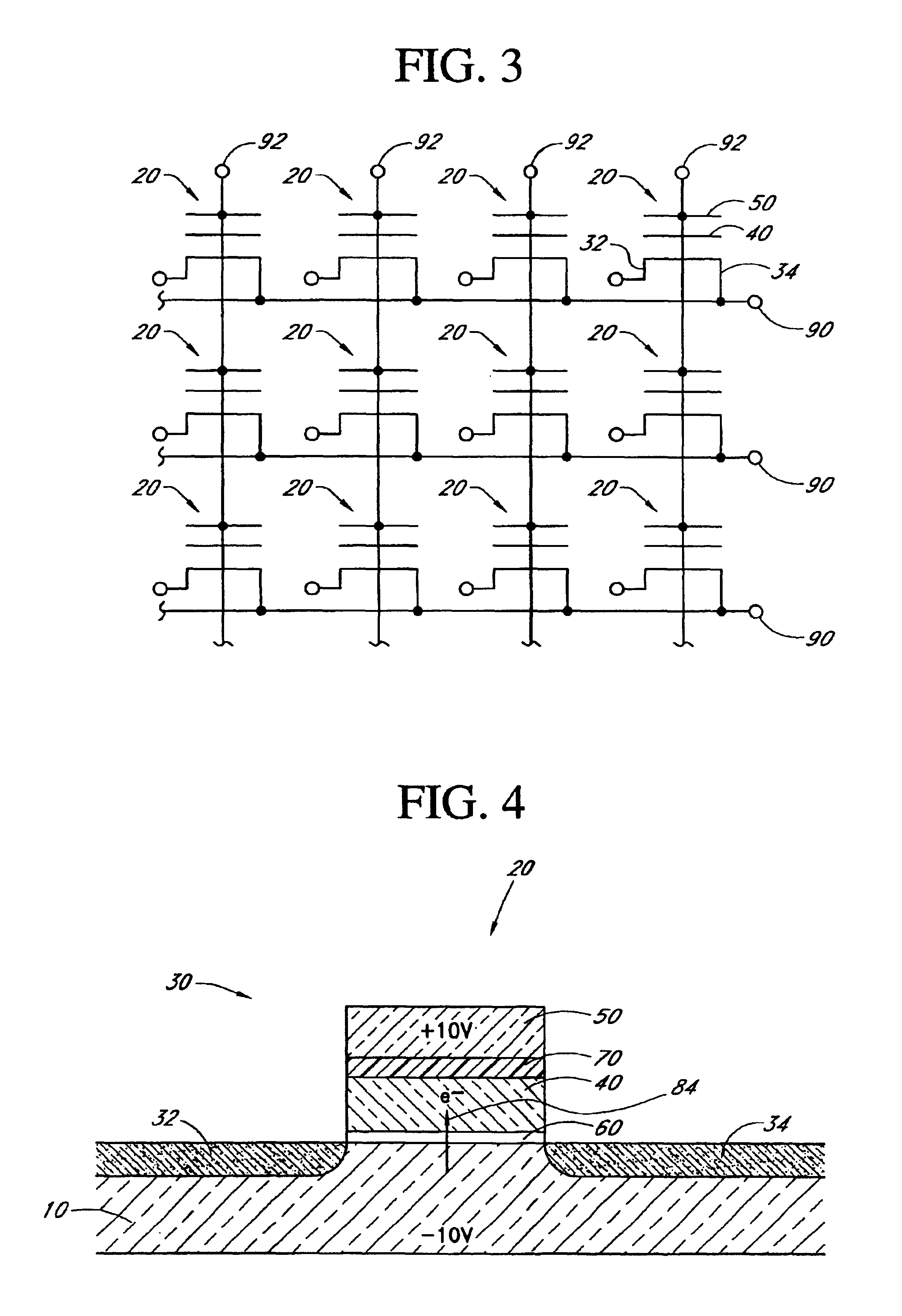
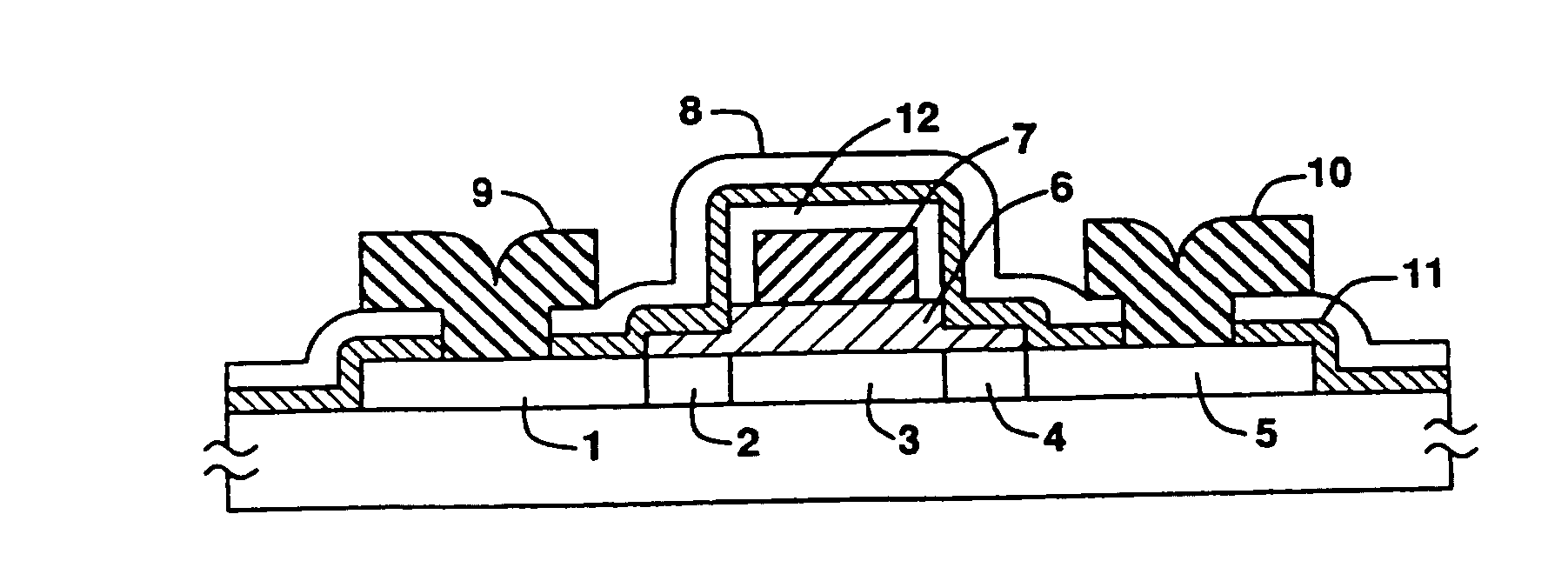
High Voltage Generation and Control in Source-Side Injection Programming of Non-Volatile Memory
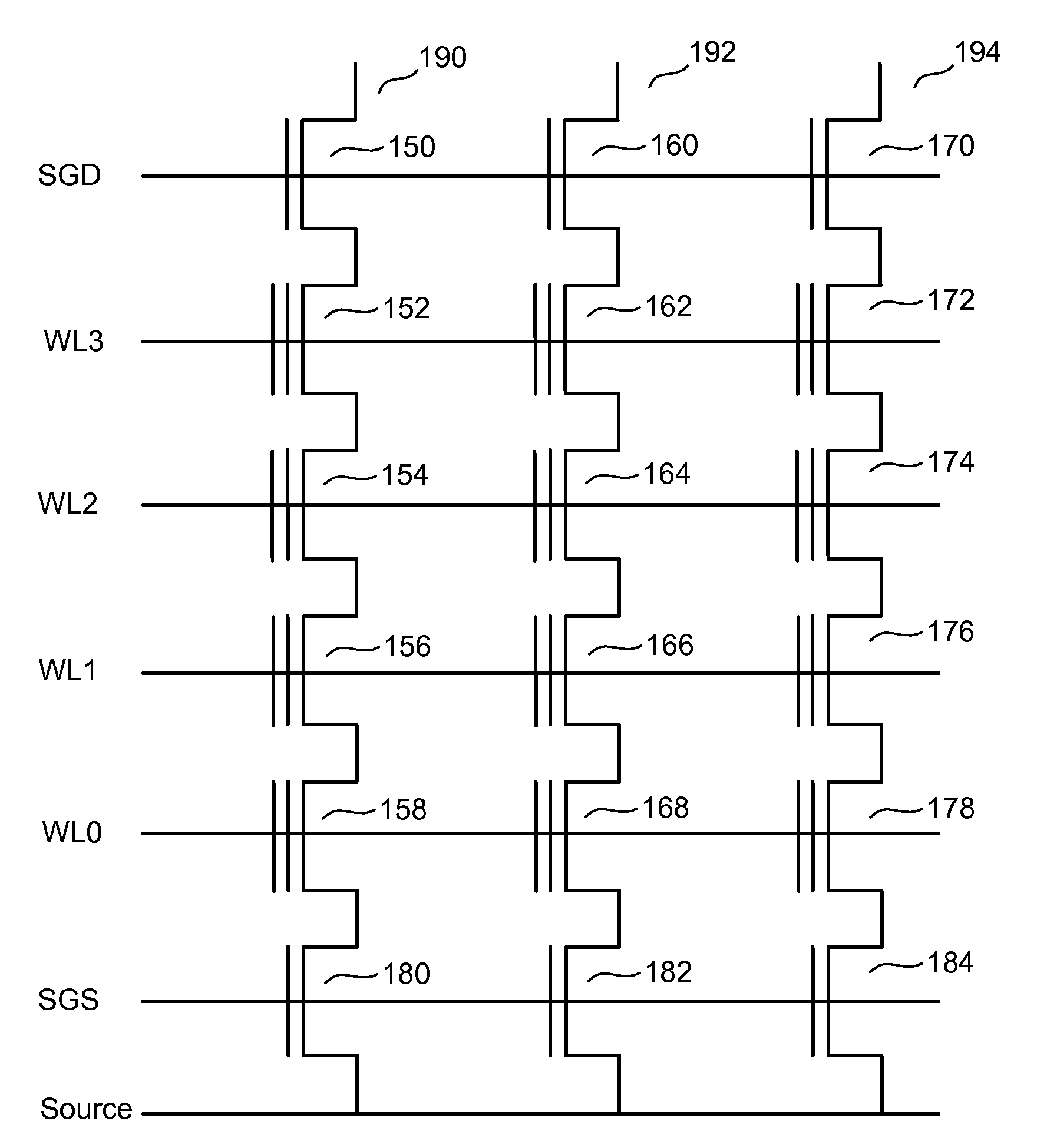
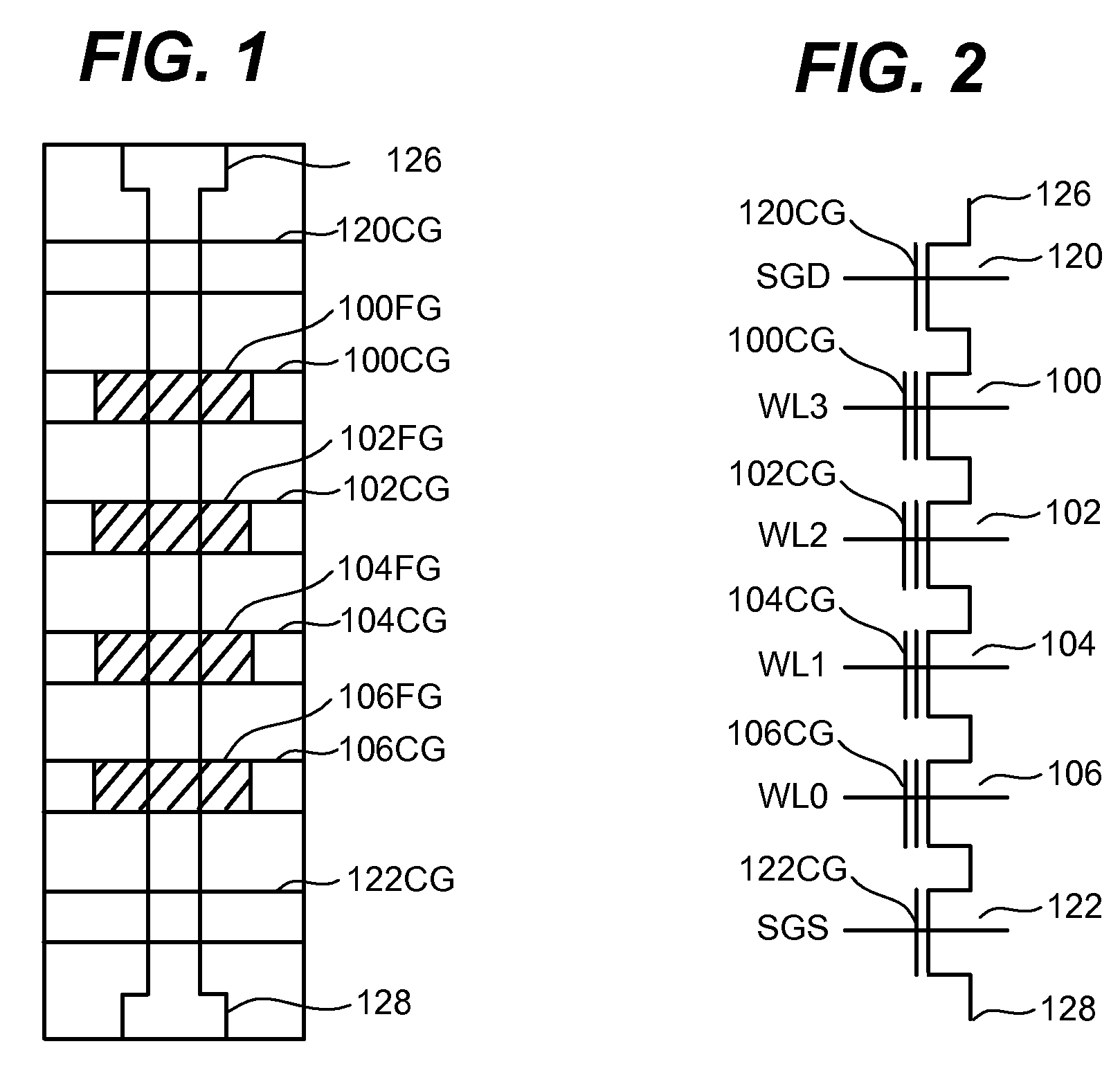
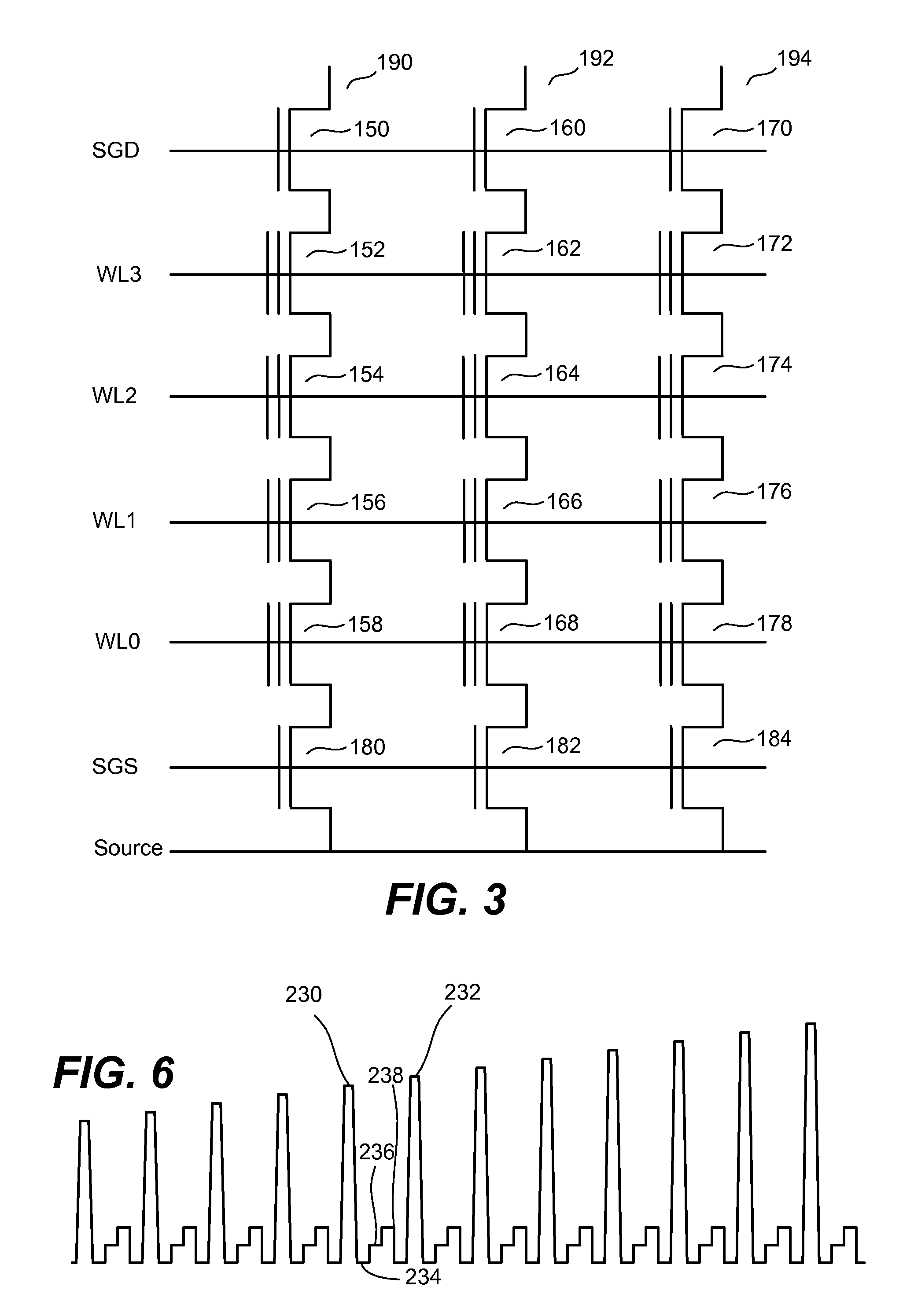
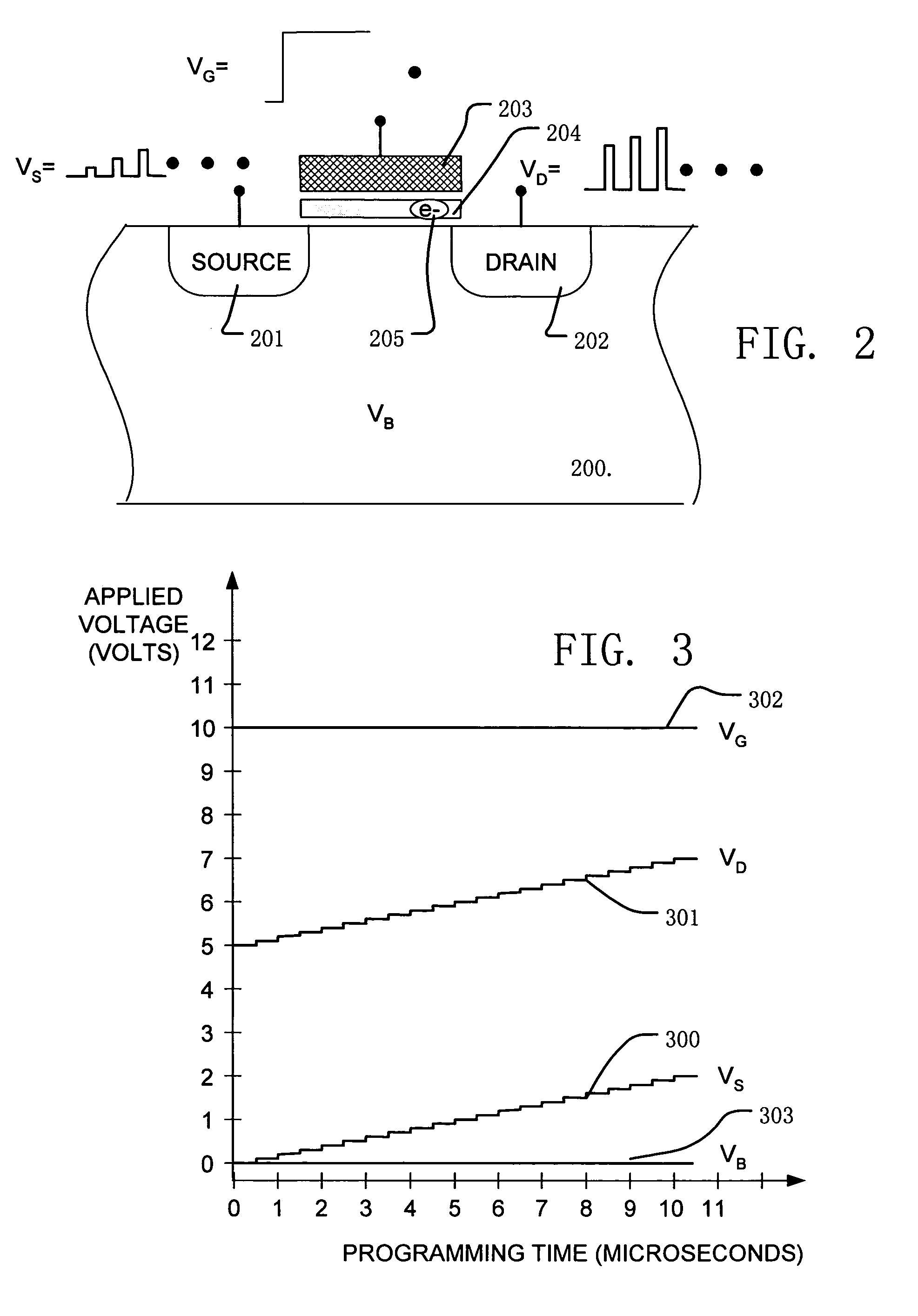
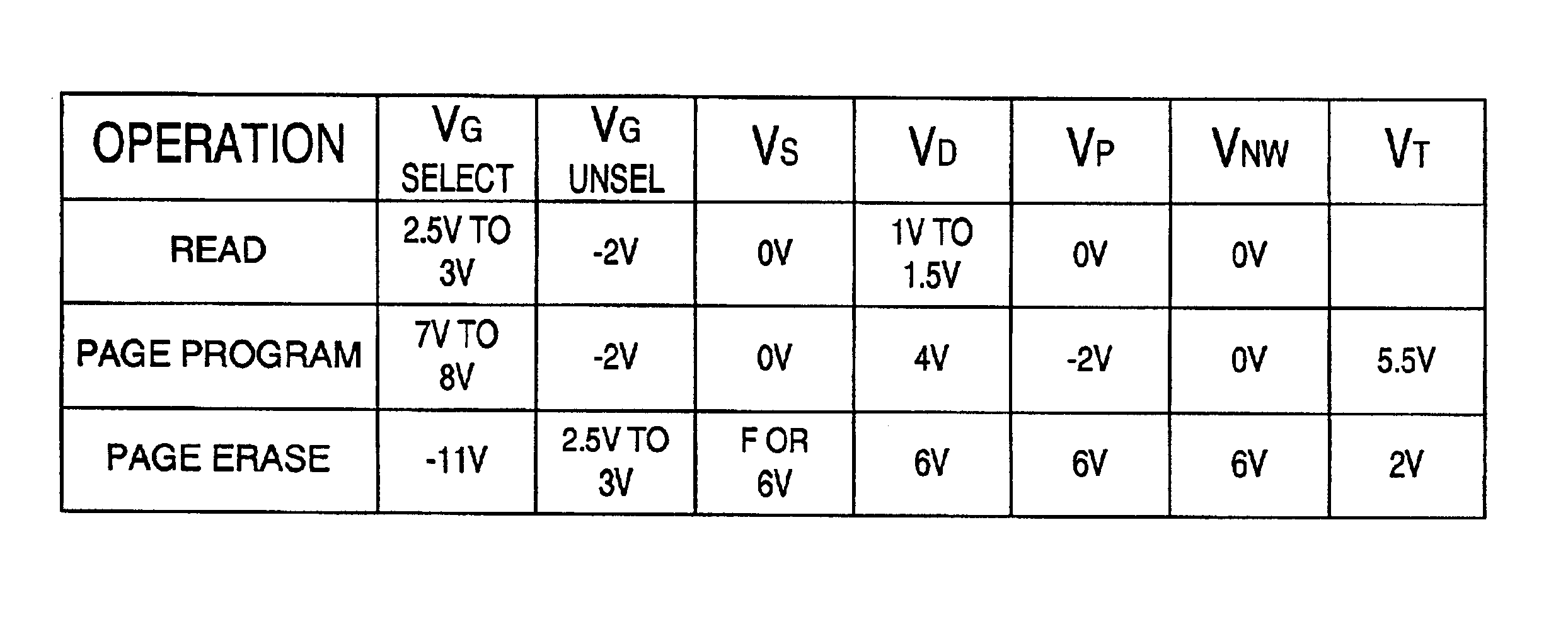
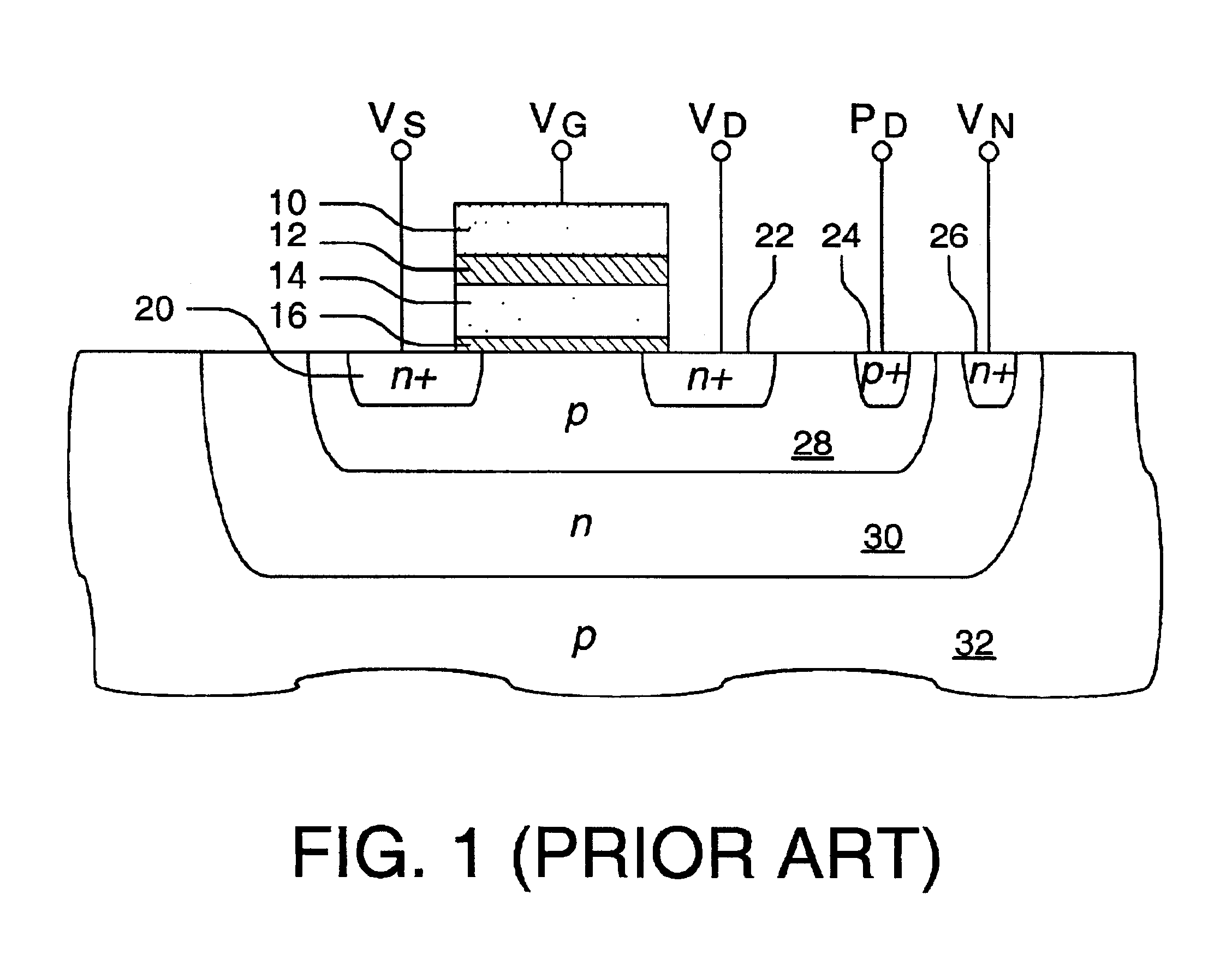
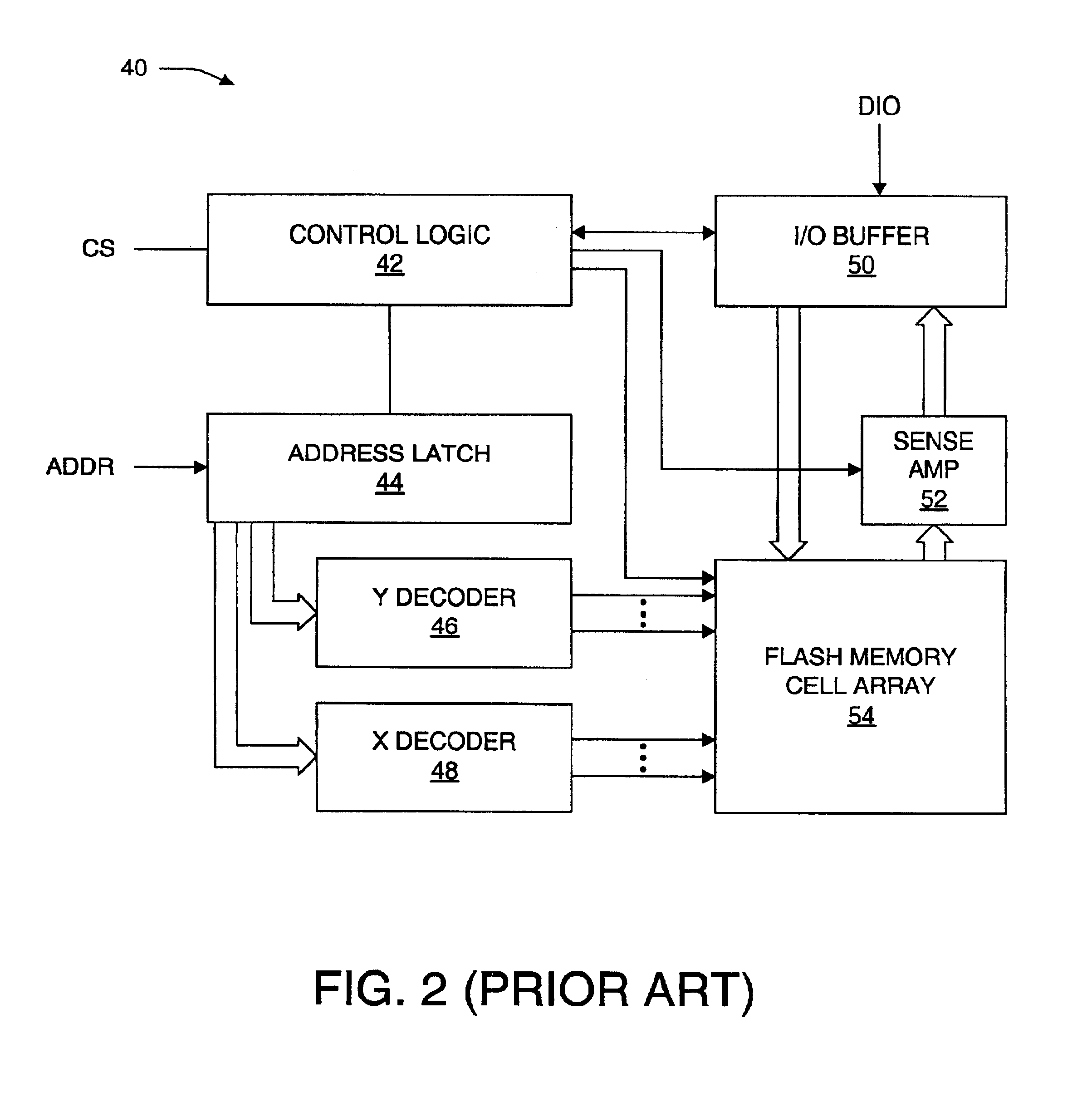
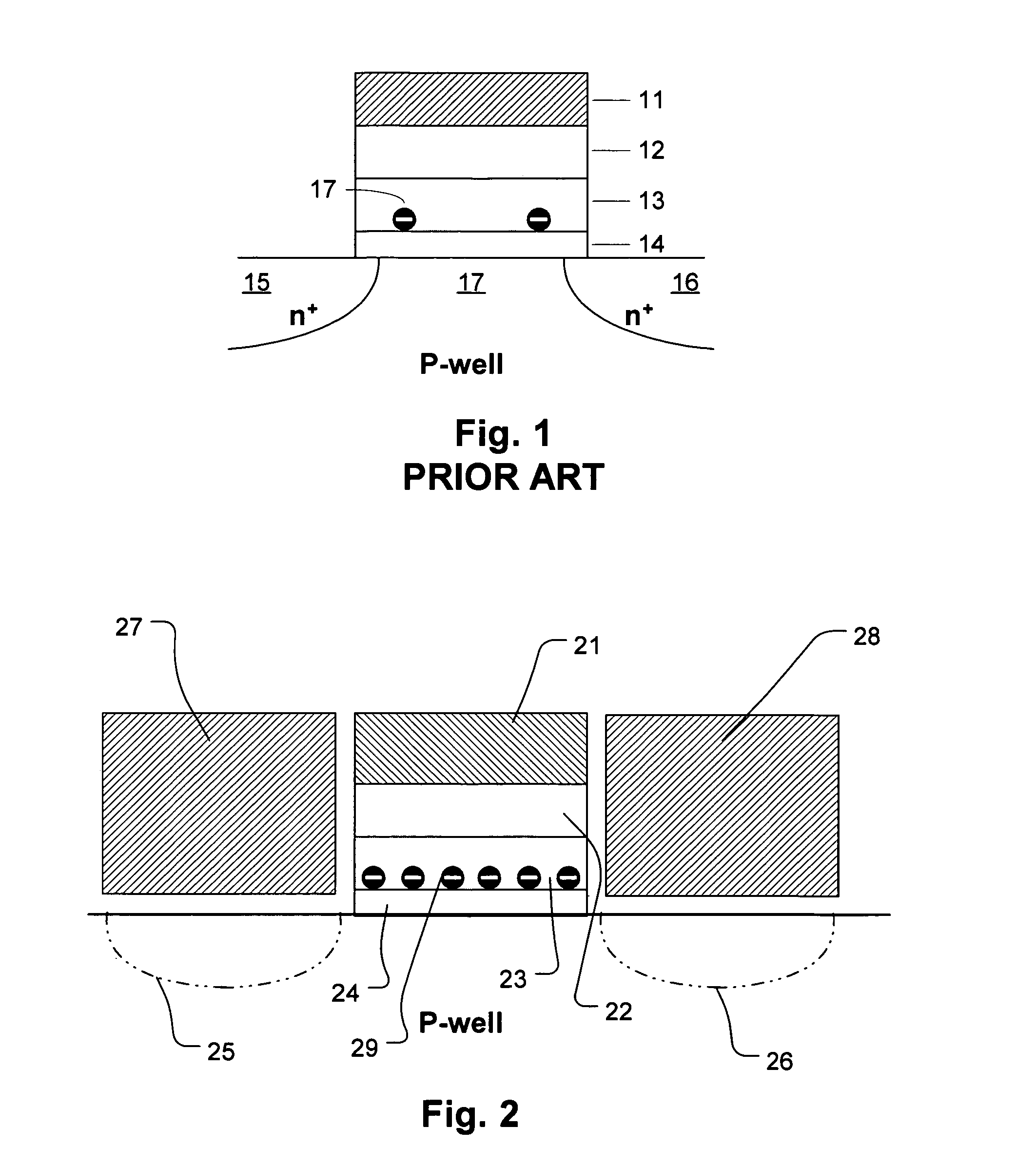
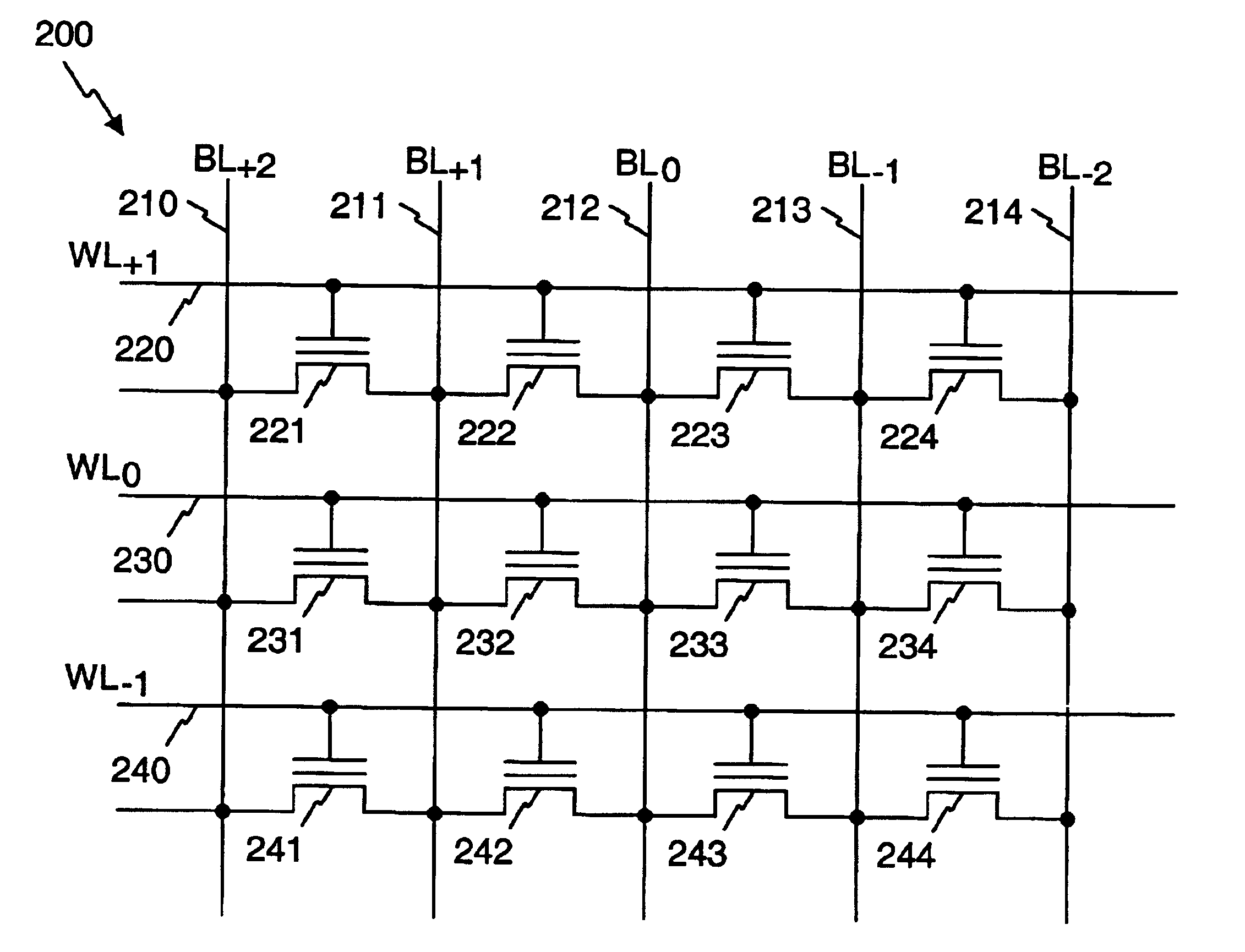
Non-volatile memory is programmed using source side hot electron injection. To generate a high voltage bit line for programming, the bit line corresponding to a selected memory cell is charged to a first level using a first low voltage. A second low voltage is applied to unselected bit lines adjacent to the selected bit line after charging. Because of capacitive coupling between the adjacent bit lines and the selected bit line, the selected bit line is boosted above the first voltage level by application of the second low voltage to the unselected bit lines. The column control circuitry for such a memory array does not directly apply the high voltage and thus, can be designed to withstand lower operating voltages, permitting low operating voltage circuitry to be used.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Molecular wire crossbar flash memory
InactiveUS6760245B2Process economyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsMolecular wire
A nano-scale flash memory comprises: (a) source and drain regions in a plurality of approximately parallel first wires, the first wires comprising a semiconductor material, the source and drain regions separated by a channel region; (b) gate electrodes in a plurality of approximately parallel second wires, the second wires comprising either a semiconductor material or a metal, the second wires crossing the first wires at a non-zero angle over the channel regions, to form an array of nanoscale transistors; and (c) a hot electron trap region at each intersection of the first wires with the second wires. Additionally, crossed-wire transistors are provided that can either form a configurable transistor or a switch memory bit that is capable of being set by application of a voltage. The crossed-wire transistors can be formed in a crossbar array.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Circuit and method for programming charge storage memory cells
ActiveUS6937511B2Increases the effective thresholdHot electron injection efficiencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringGate voltage
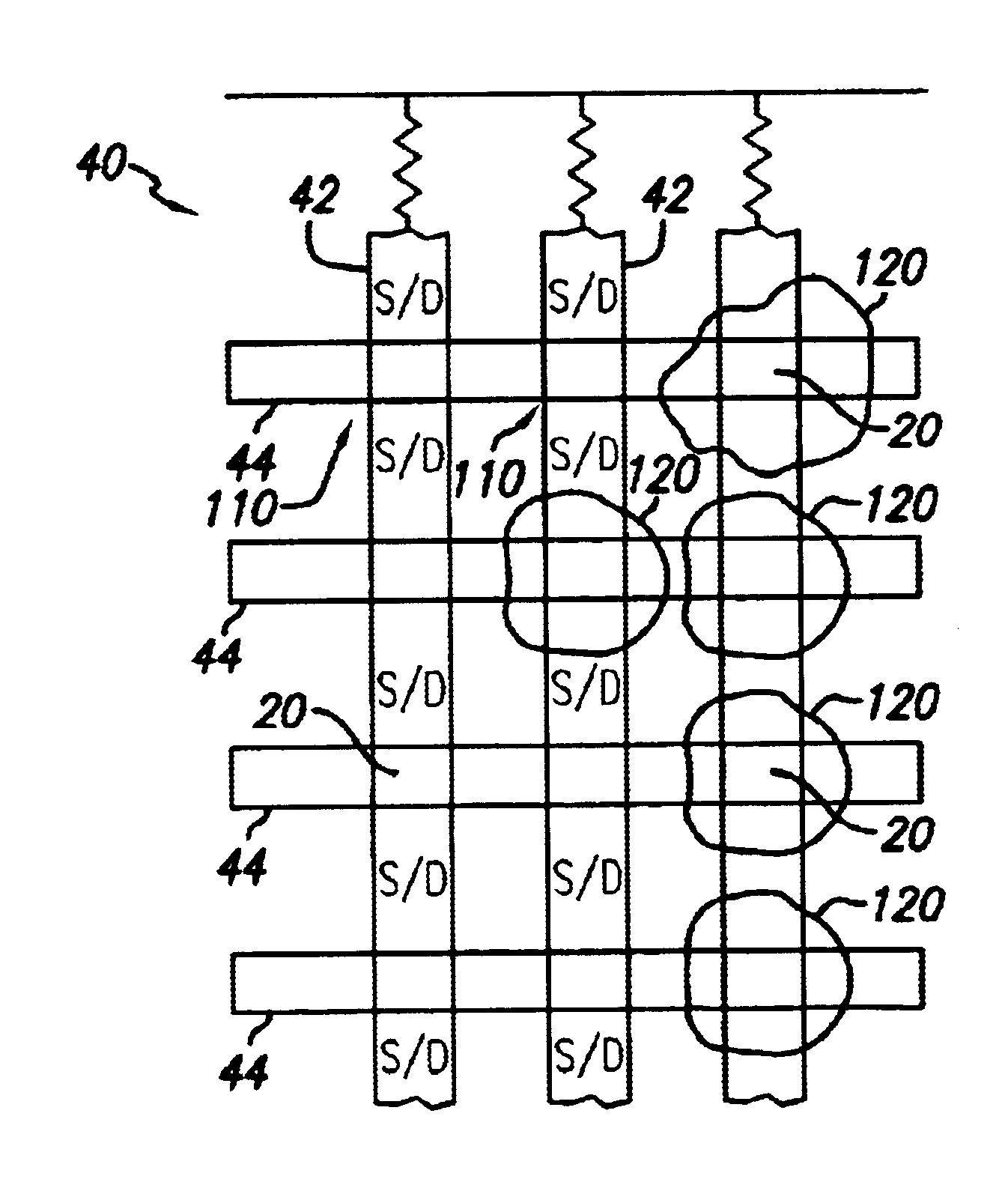
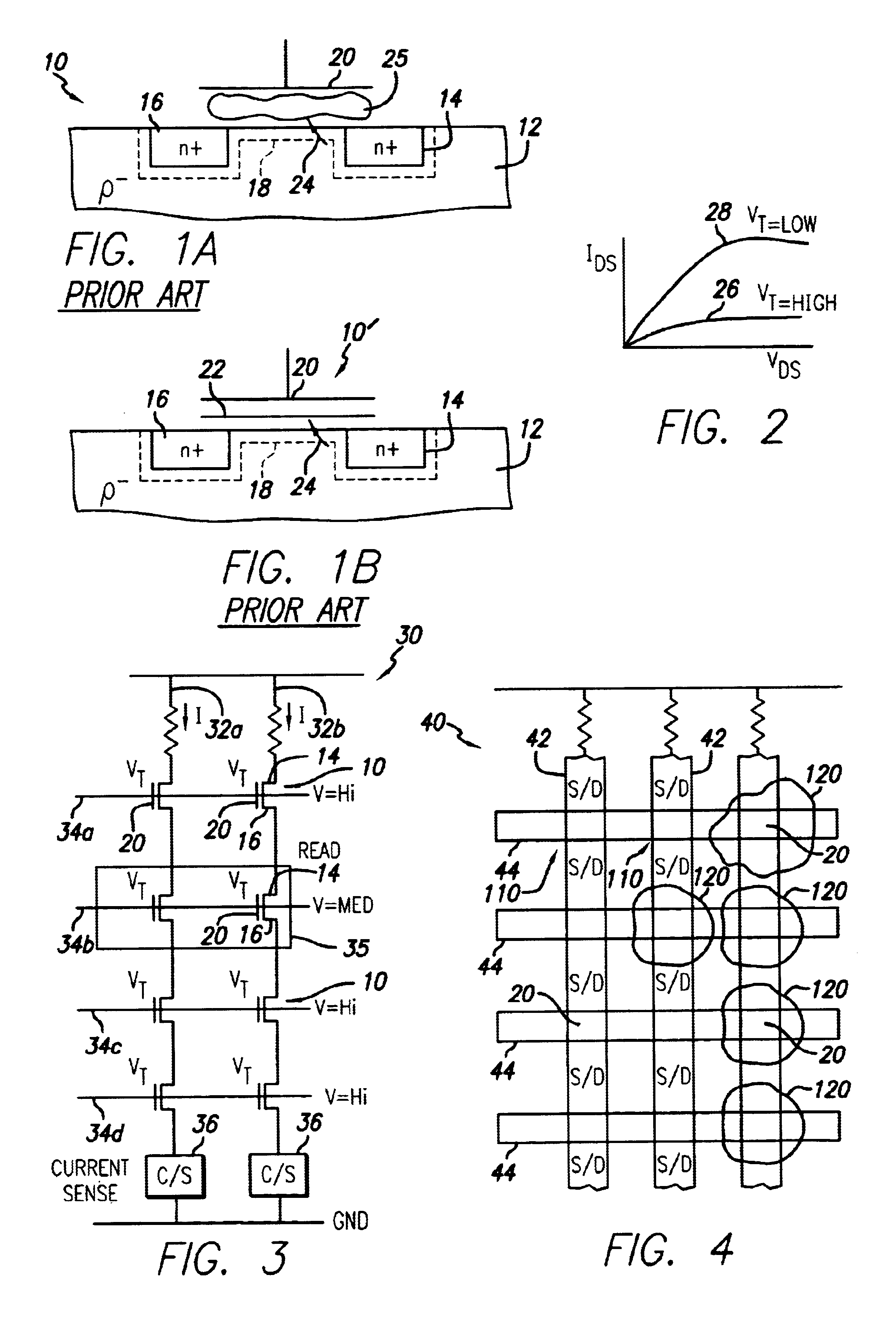
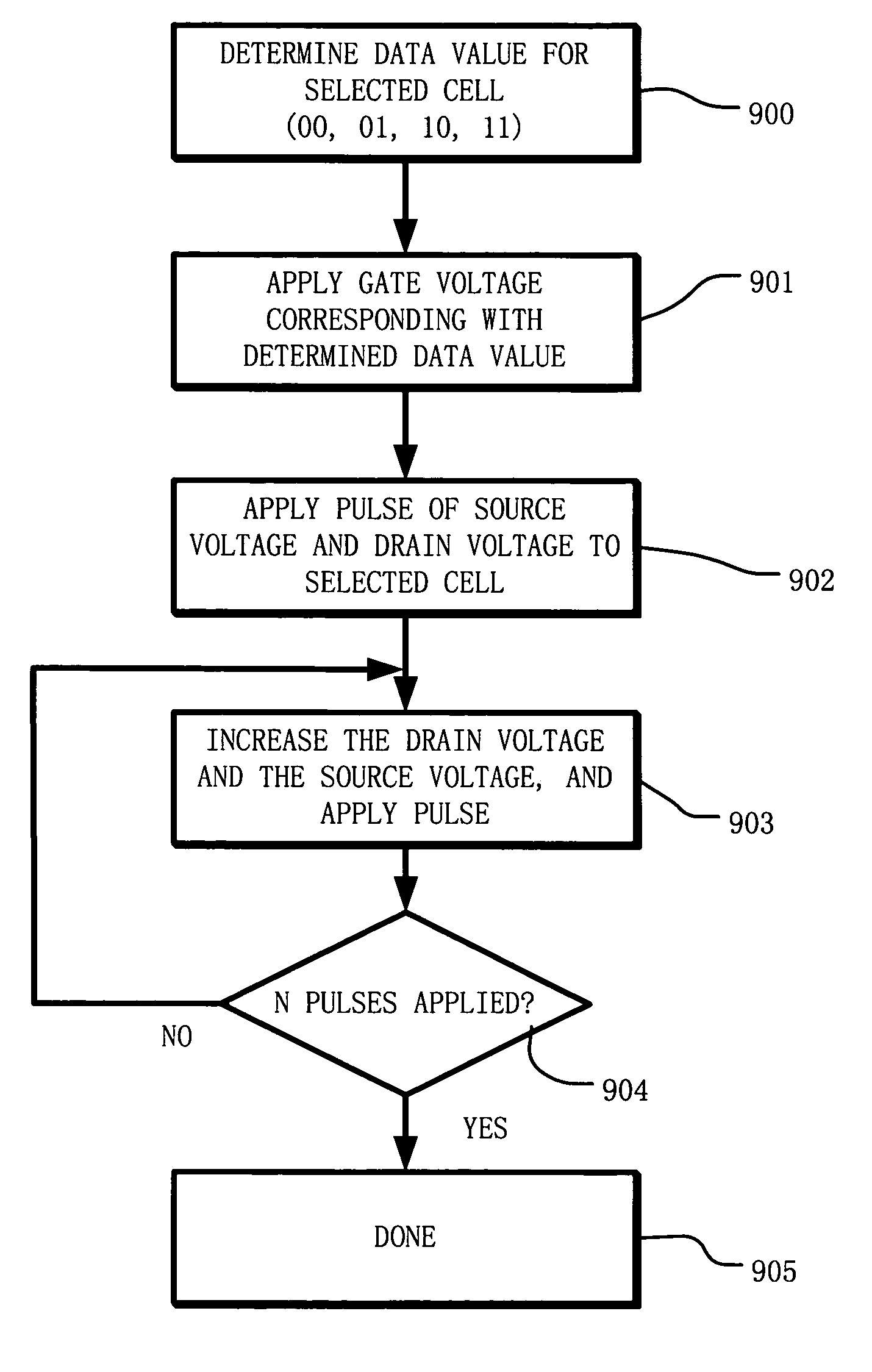
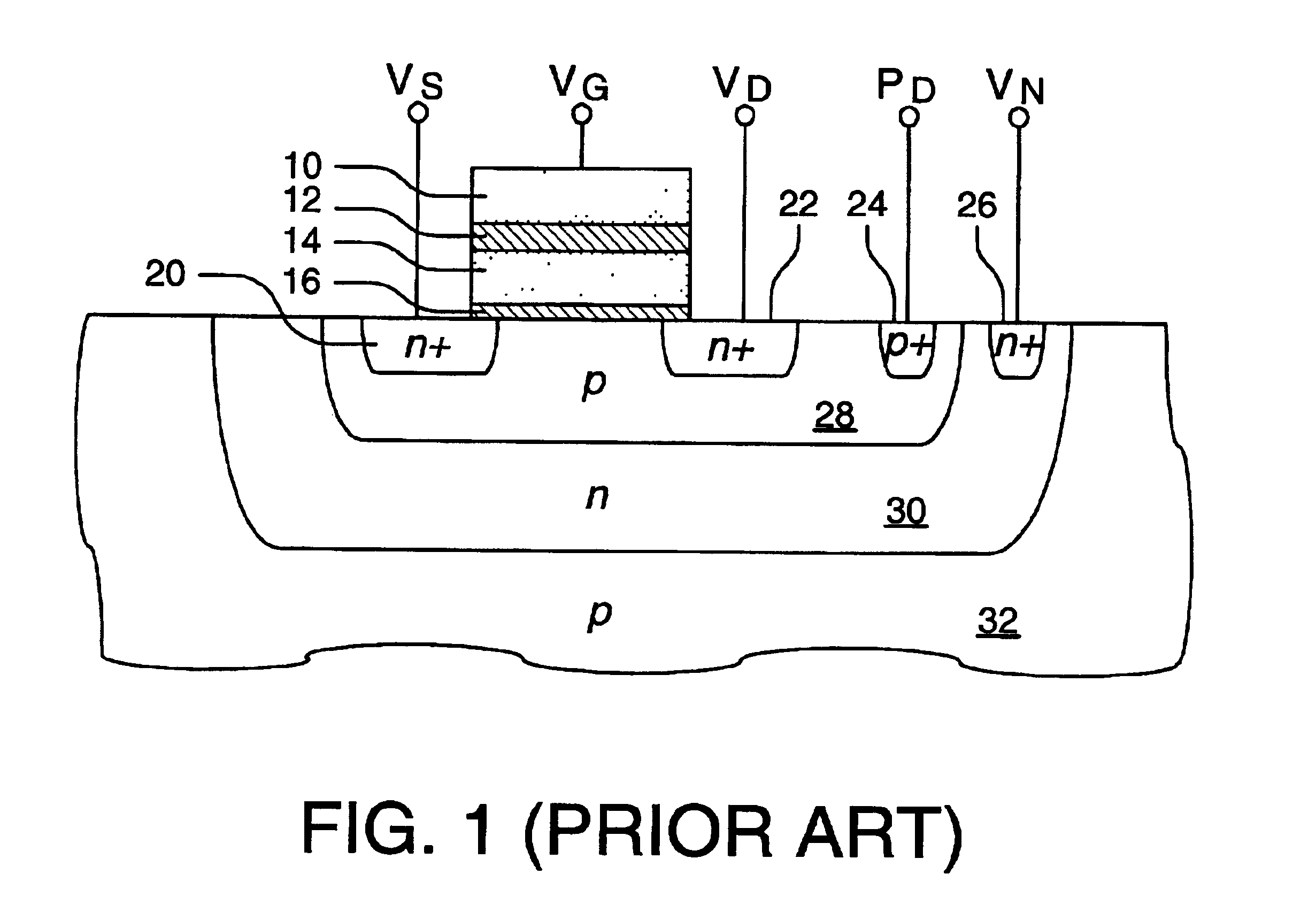
A circuit and method for self-converging programming of a charge storage memory cell, such as NROM or floating gate flash, having a source and a drain in a substrate, a charge storage element and a control gate. The method includes applying source voltage, inducing a body effect that increases the effective threshold, and increasing the source voltage along with the drain voltage to moderate hot electron injection efficiency during the program operation, at least during a portion of the program operation in which convergence on a target threshold occurs. A selected gate voltage is applied during the operation to establish the target threshold voltage. In multiple bit cells, the gate voltage is set according to the data values to be stored, enabling self-convergence at more than one target threshold.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
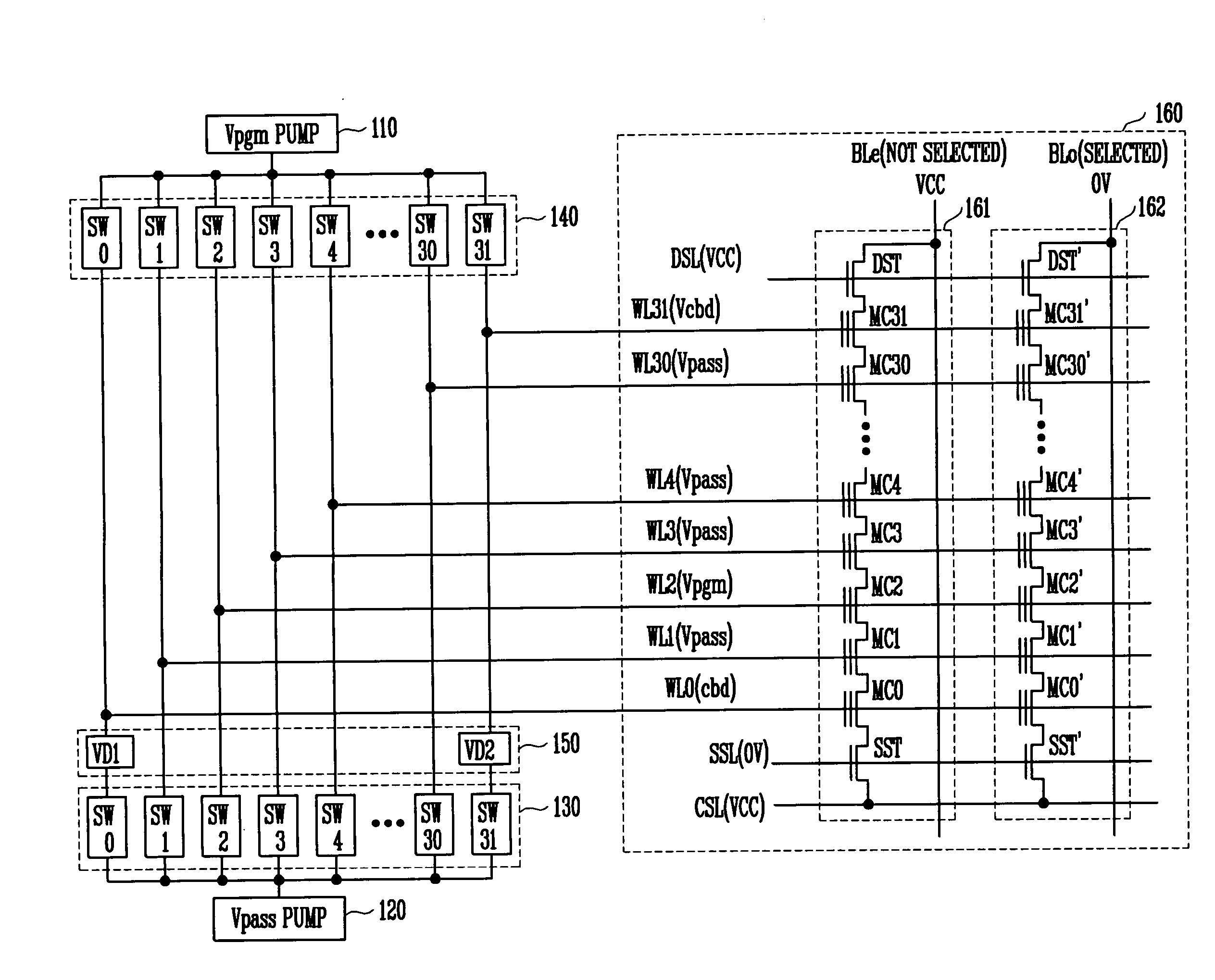
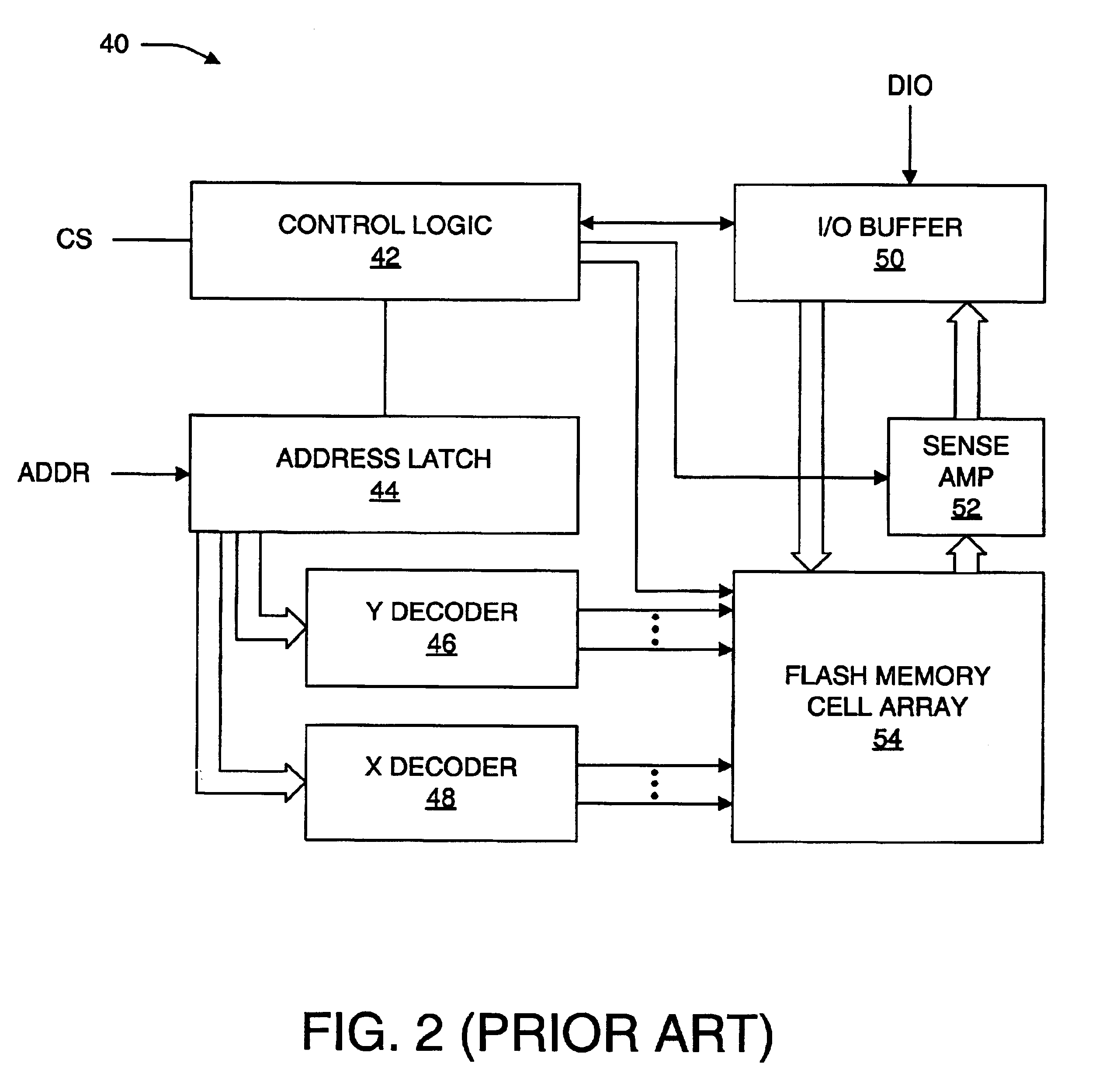
Method and apparatus for multiple byte or page mode programming and reading and for erasing of a flash memory array
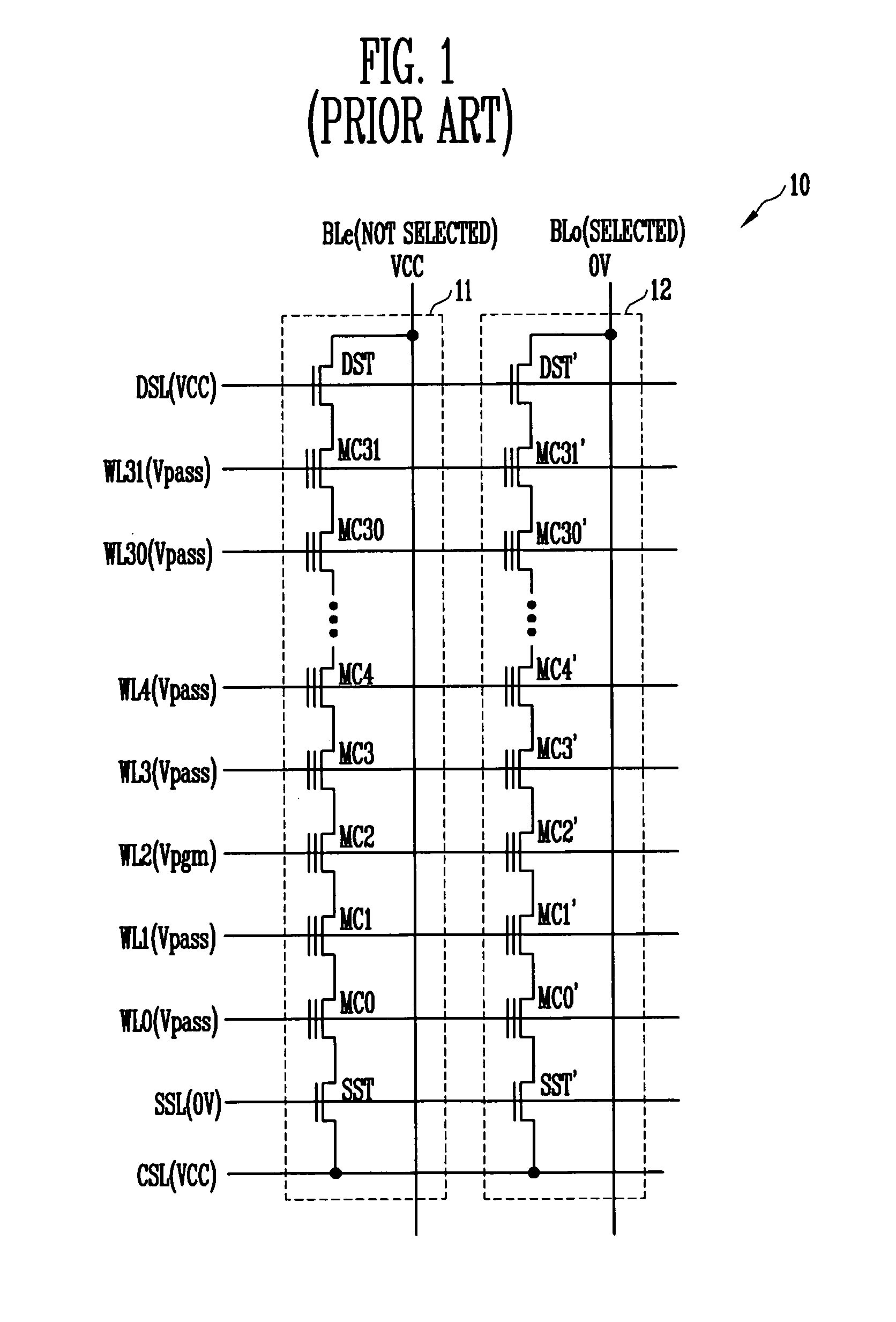
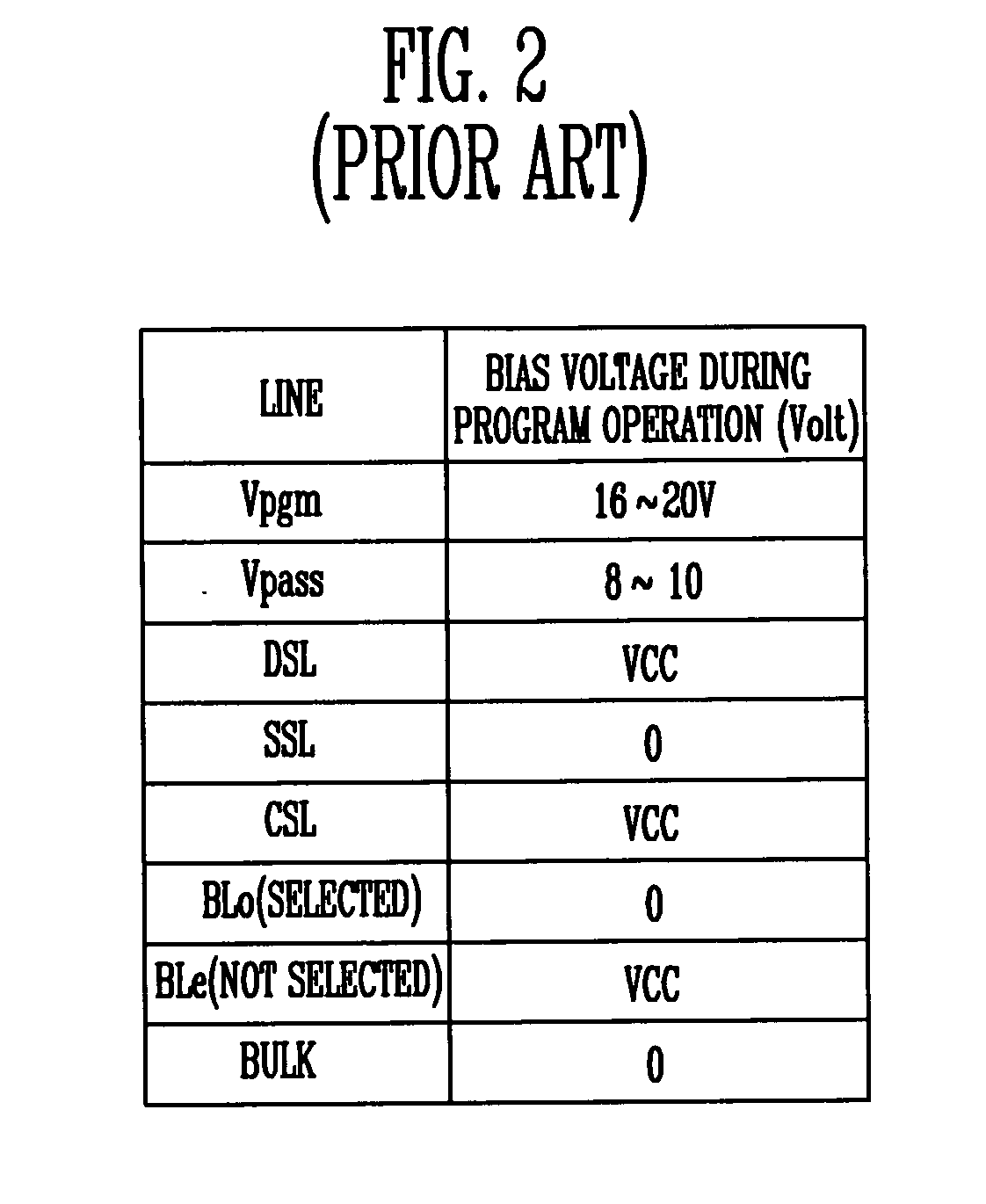
A memory array contains memory cells designed to be erased using Fowler-Nordheim ("FN") tunneling through the channel area, and programmed using either channel hot electron injection ("CHE") or channel-initiated secondary electron injection ("CISEI"). To reduce disturbance of the floating gate potential of unselected memory cells during programming operations and read operations, the unselected word lines are brought to a negative potential rather than ground potential. To reduce disturbance of the floating gate potential of unselected memory cells during FN erase operations, the unselected word lines are brought to a positive potential rather than ground potential.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
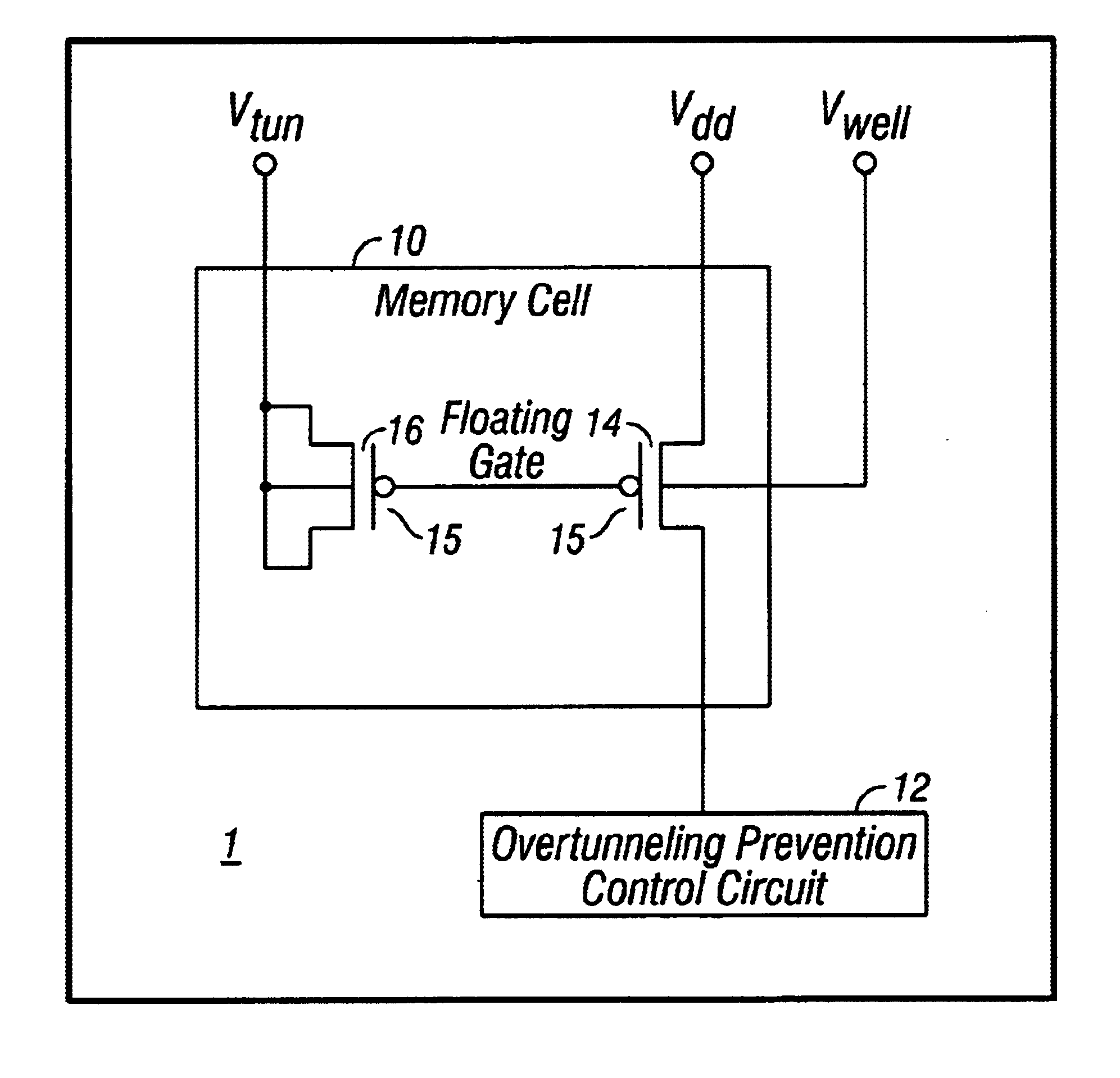
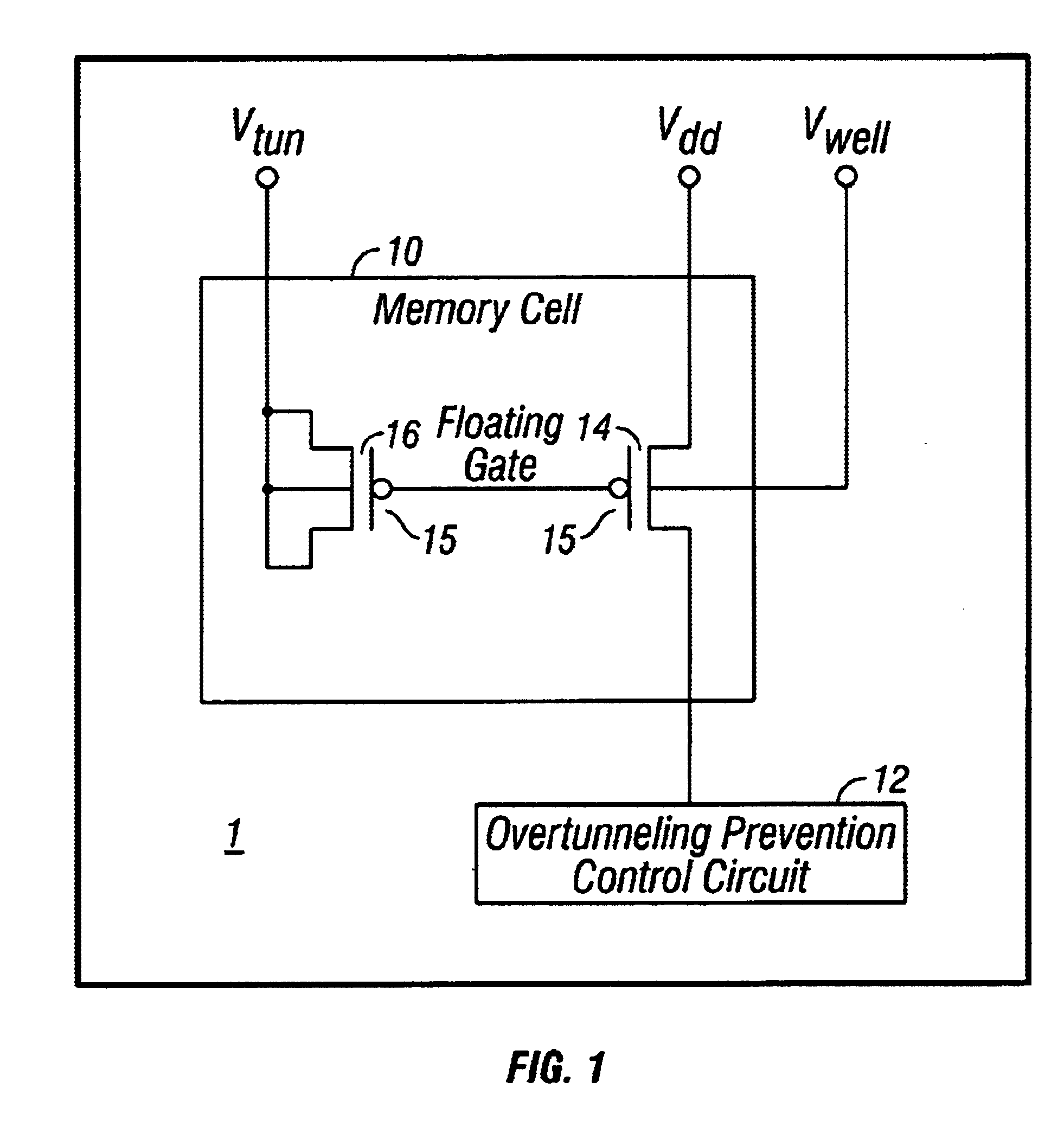
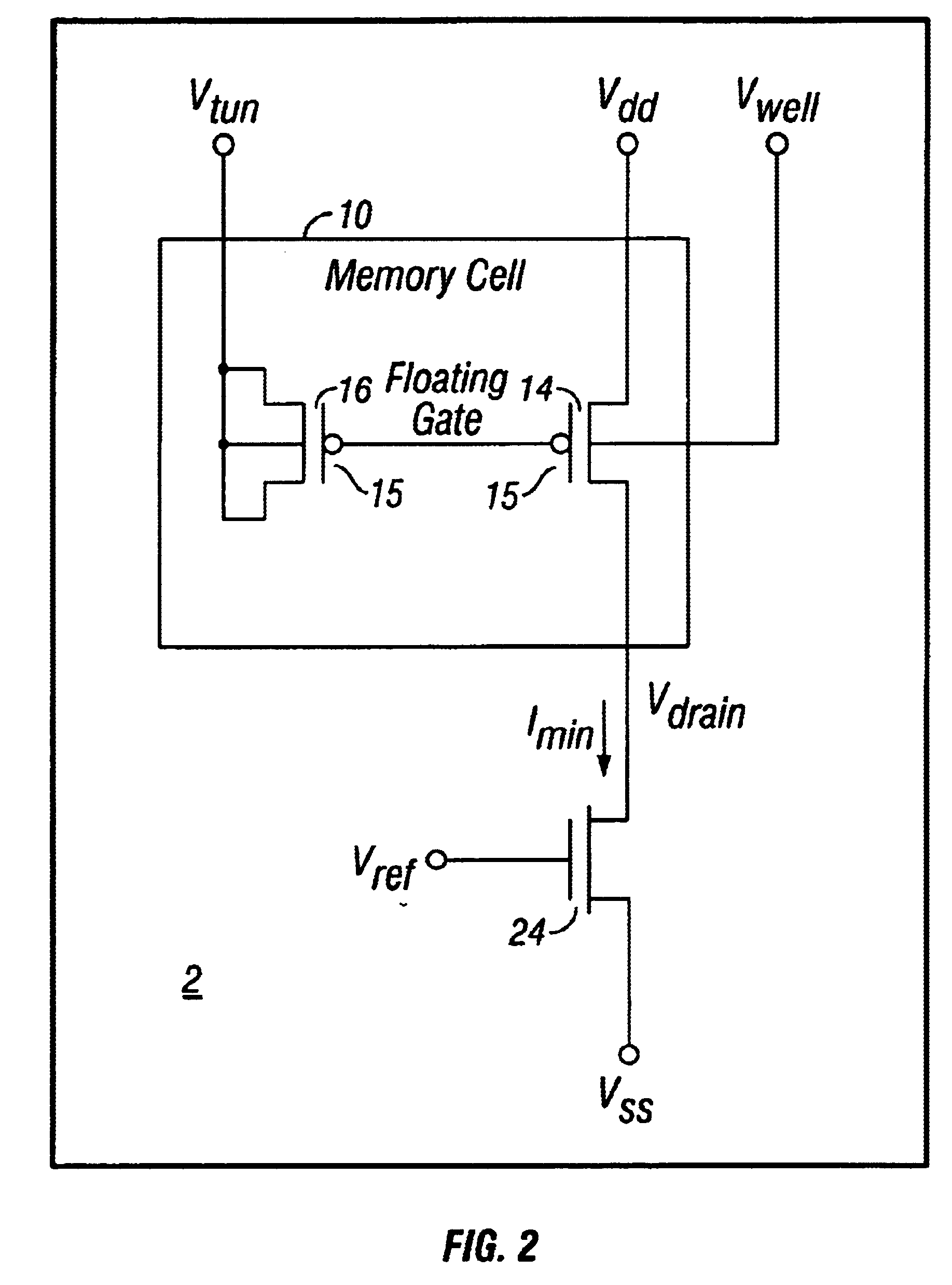
Method and apparatus for preventing overtunneling in pFET-based nonvolatile memory cells
Methods and apparatuses prevent overtunneling in pFET-based nonvolatile floating gate memory (NVM) cells. During a tunneling process, in which charge carriers are removed from a floating gate of a pFET-based NVM cell, a channel current of a memory cell transistor is monitored and compared to a predetermined minimum channel current required to maintain a conducting channel in an injection transistor of the memory cell. When the monitored channel current drops below the predetermined minimum channel current, charge carriers are injected onto the floating gate by impact-ionized hot-electron injection (IHEI) so that overtunneling is avoided.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Non-volatile memory device and method of preventing hot electron program disturb phenomenon
ActiveUS20060227613A1Weak electric fieldWeaker electric fieldRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceElectric field
A method for preventing generation of program disturbance incurred by hot electrons in a NAND flash memory device. A channel boosting disturb-prevention voltage lower than a program-prohibit voltage applied to other word lines is applied to edge word lines coupled to memory cells that are nearest to select transistors. As a result, an electric field between the memory cells coupled to the edge word lines and the select transistors is weakened, and the energy of the hot electrons is reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
High data rate write process for non-volatile flash memories
InactiveUS6944058B2Reduce noiseIncrease data rateElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulationTotal current
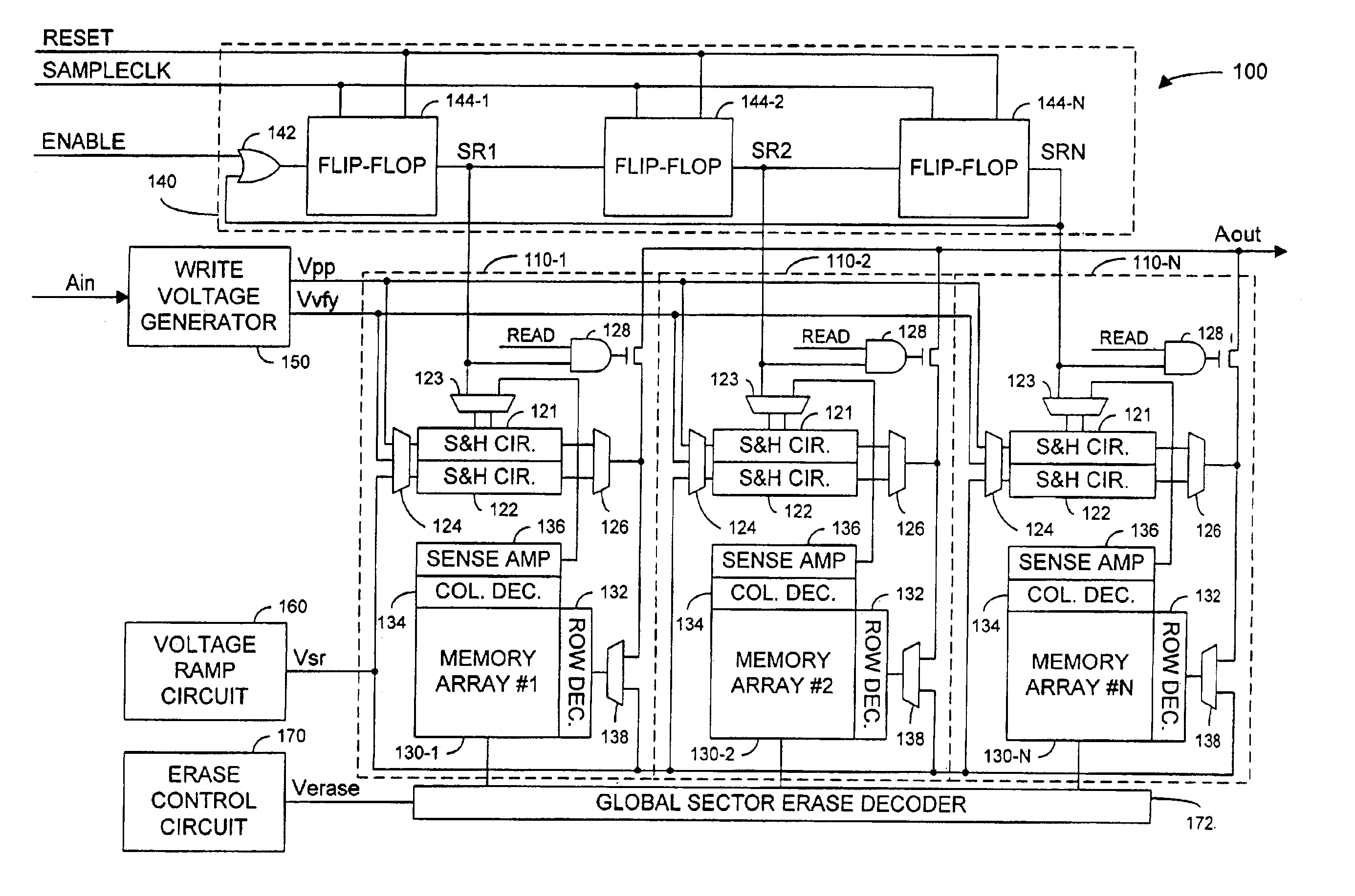
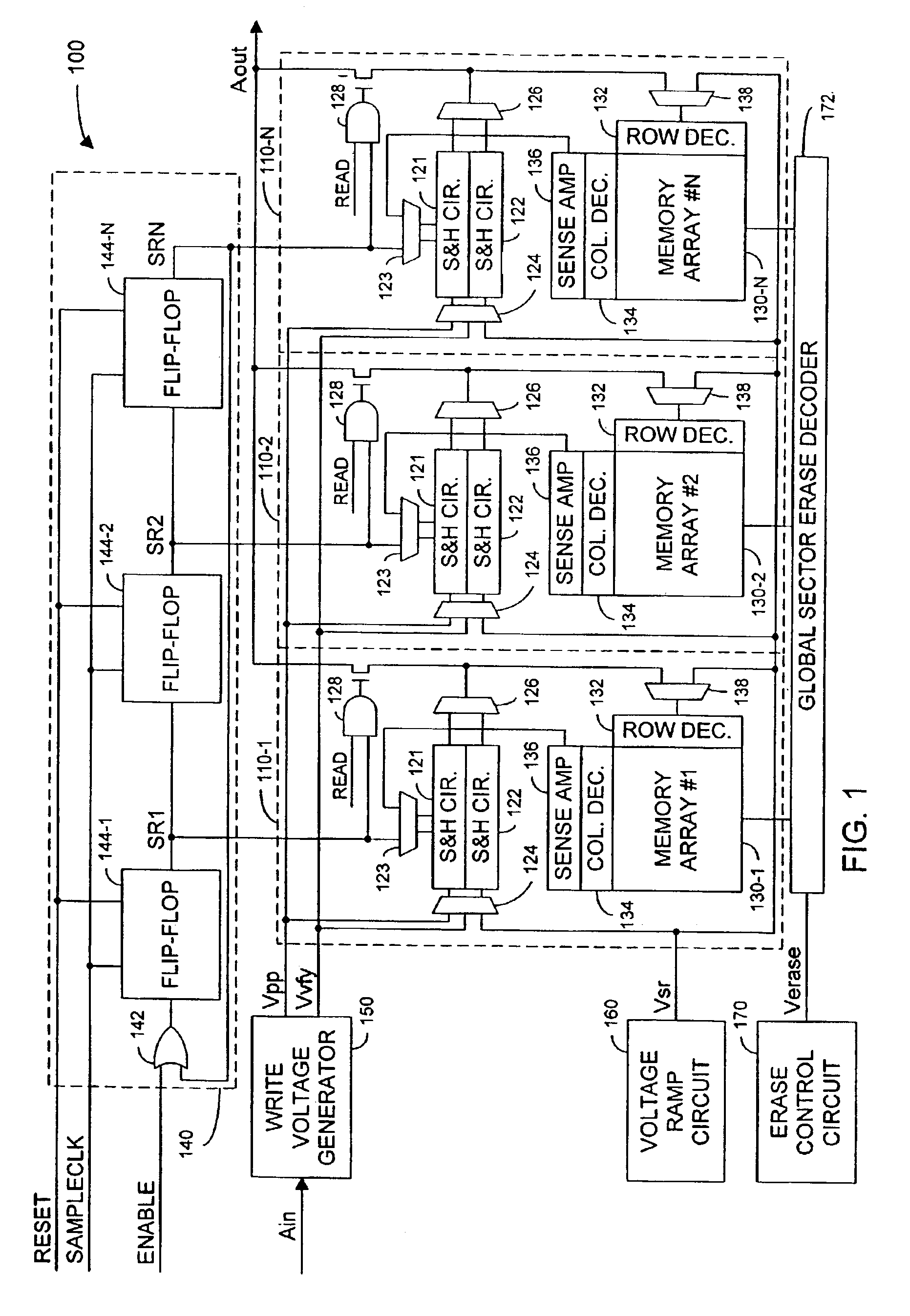
A non-volatile semiconductor memory includes: multiple write pipelines, each including a memory array; a timing circuit which sequentially starts programming operations in the pipelines; and a shared charge pump and voltage regulation circuit that drives a current through the memory cells being programmed. Staggering the starts of programming operations reduces the current demand on the charge pump because spikes that occur at the starts of programming operations, for example, when using channel hot electron injection, are distributed over time rather than occurring all at once. Noise, which can reduce the accuracy of write operations, is also reduced because the total current required from the charge pump is more nearly constant. As further aspect of the invention, each write pipeline can perform a write operation as alternating programming cycles and verify cycles. During a programming cycle, the shared charge pump drives a current through a selected memory cell to change the threshold voltage of the selected memory cell. During a verify cycle, the write circuit determines whether the selected memory cell has reached its target threshold voltage level. The write pipelines can be partitioned into two banks where pipelines in one bank perform programming cycles while pipelines in the other bank perform verify cycles. More generally the write pipelines are partitioned into multiple banks where each bank starts programming cycles at times that differ from the starts of programming cycles in the other banks.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
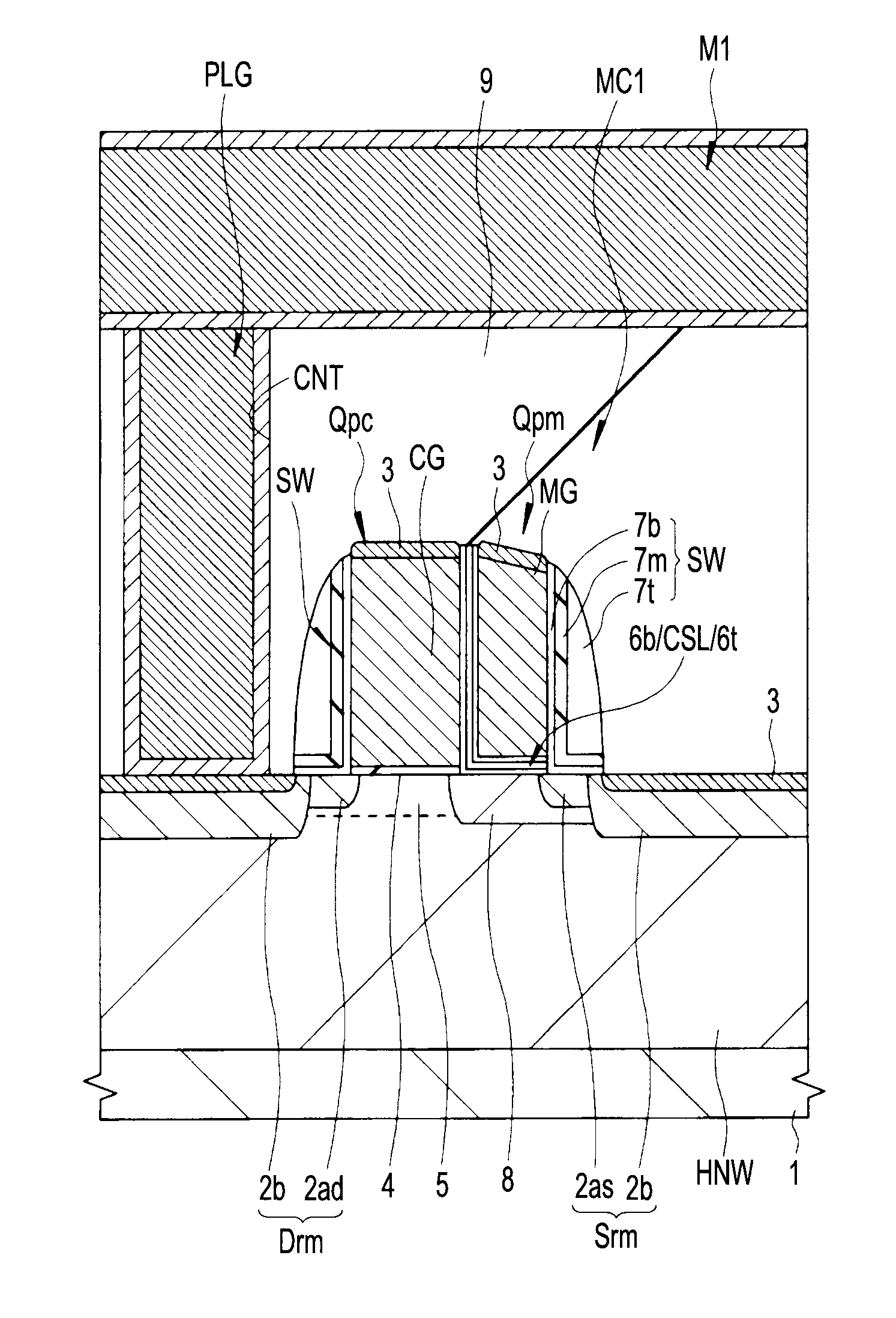
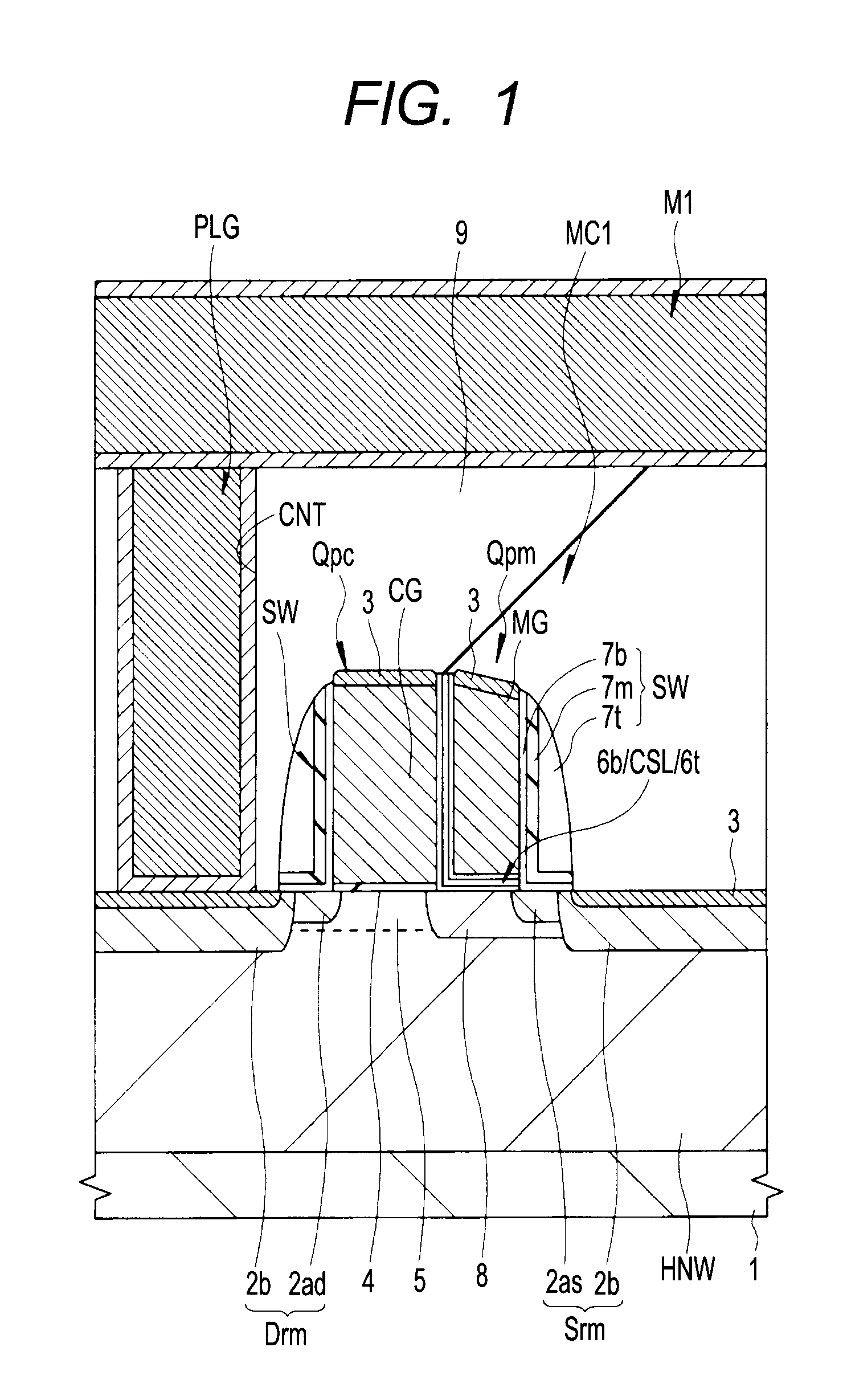
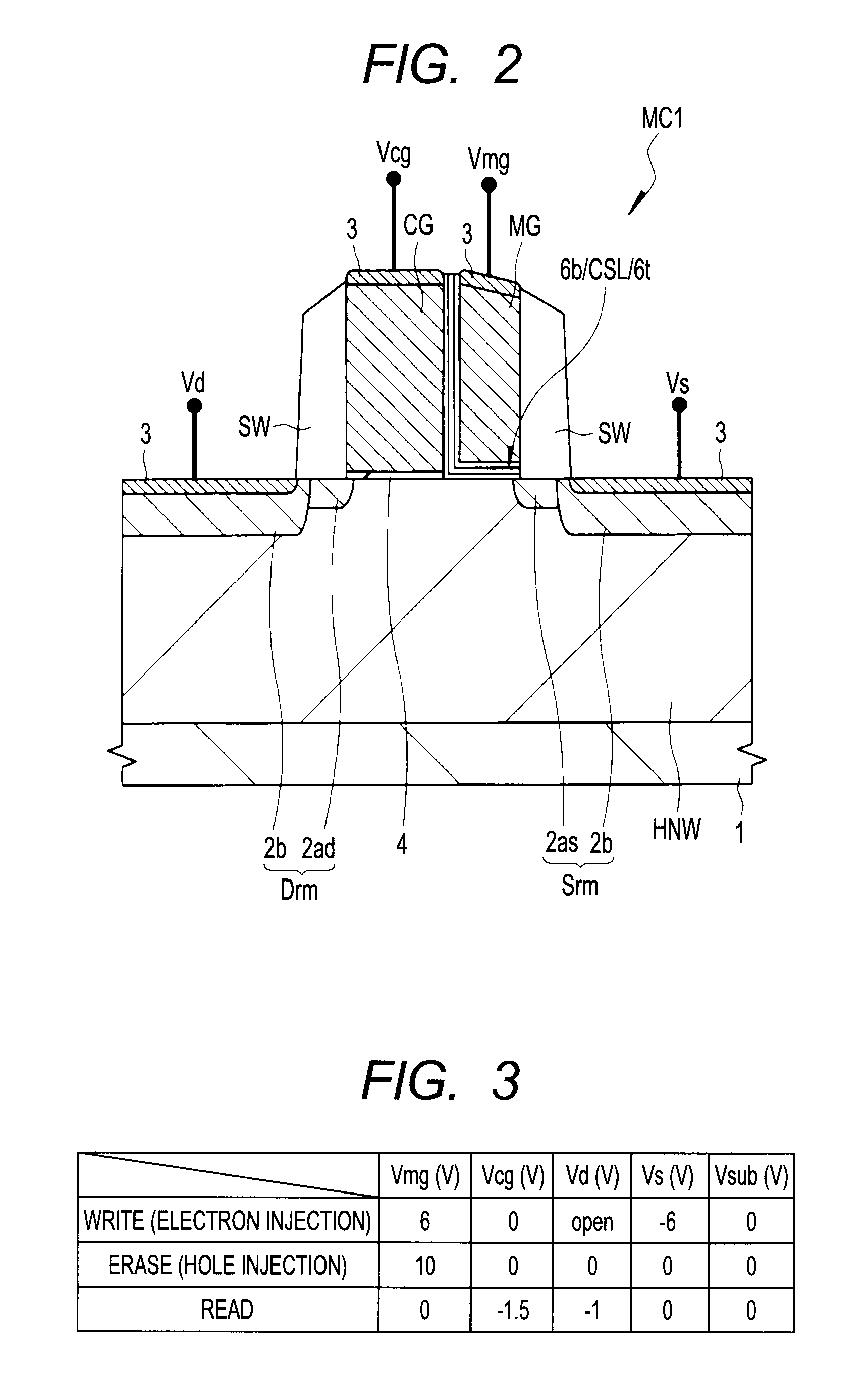
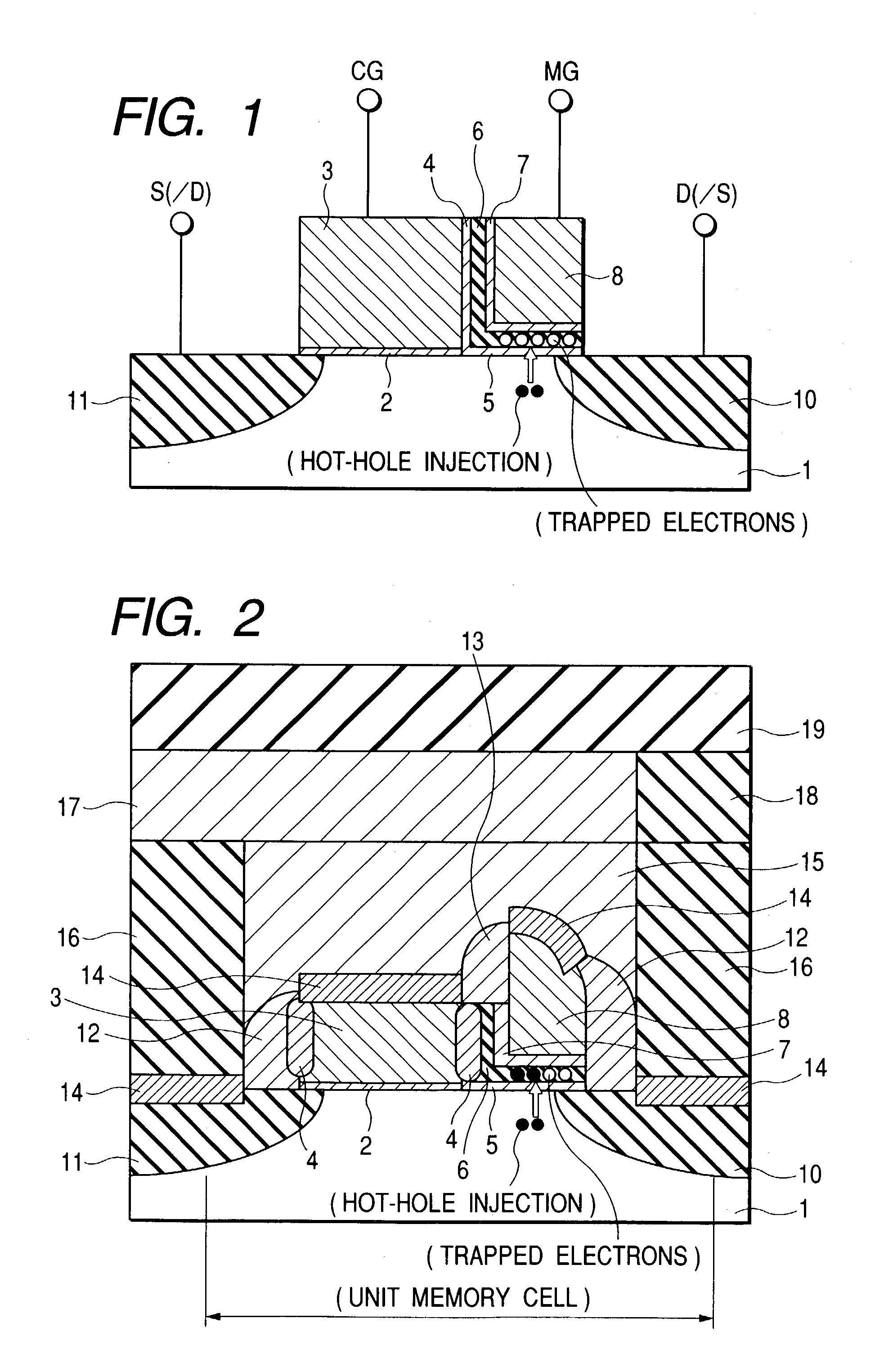
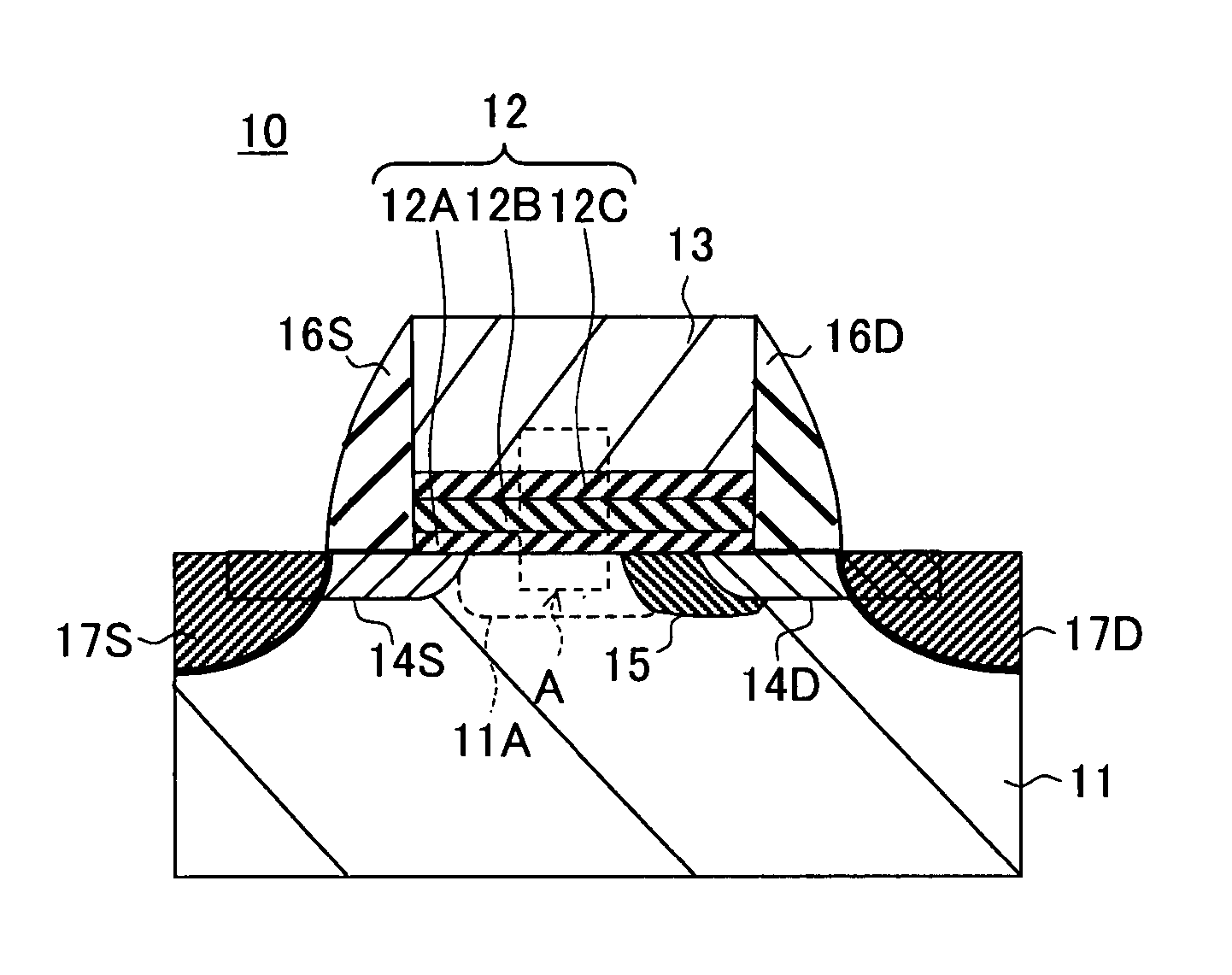
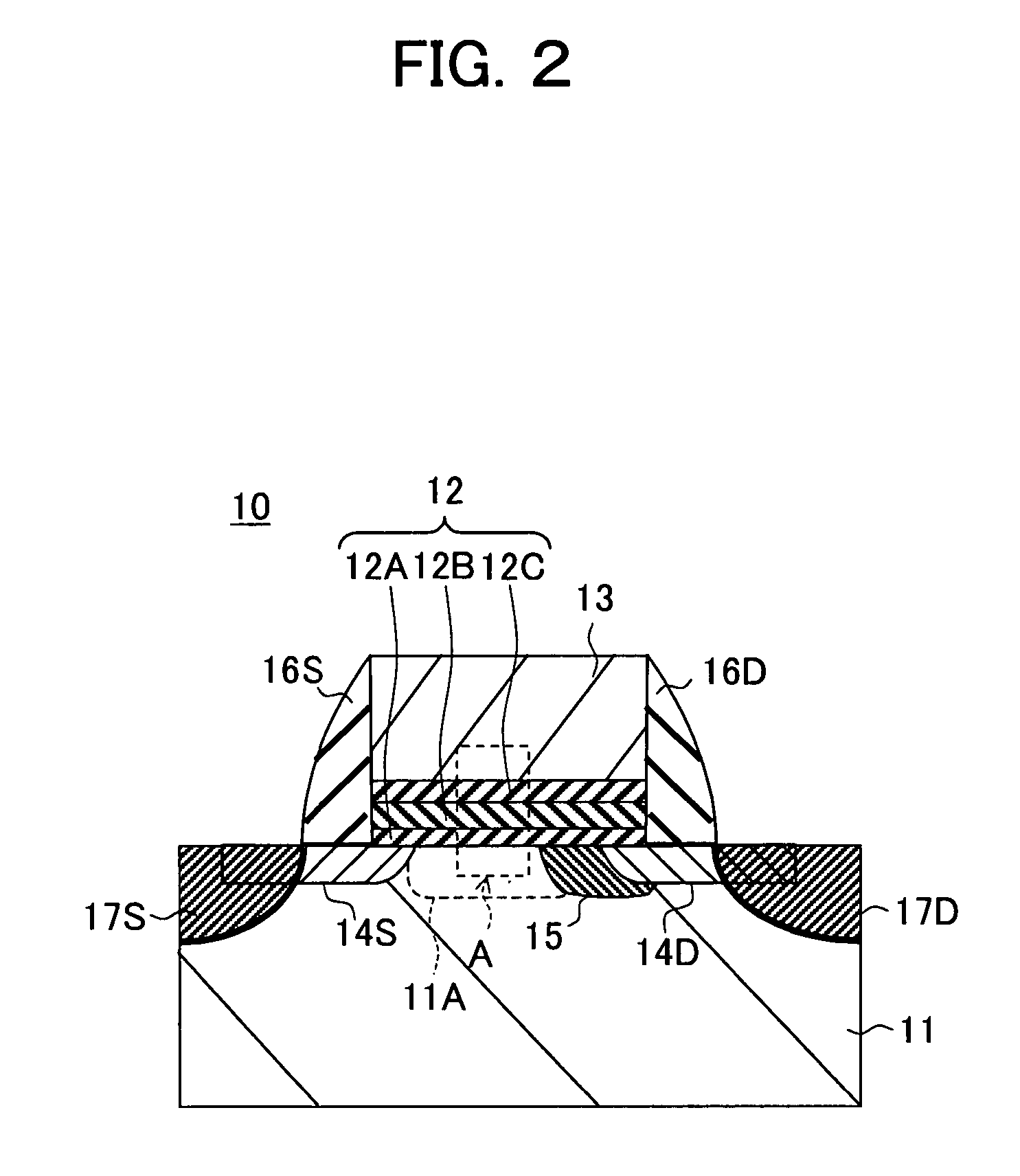
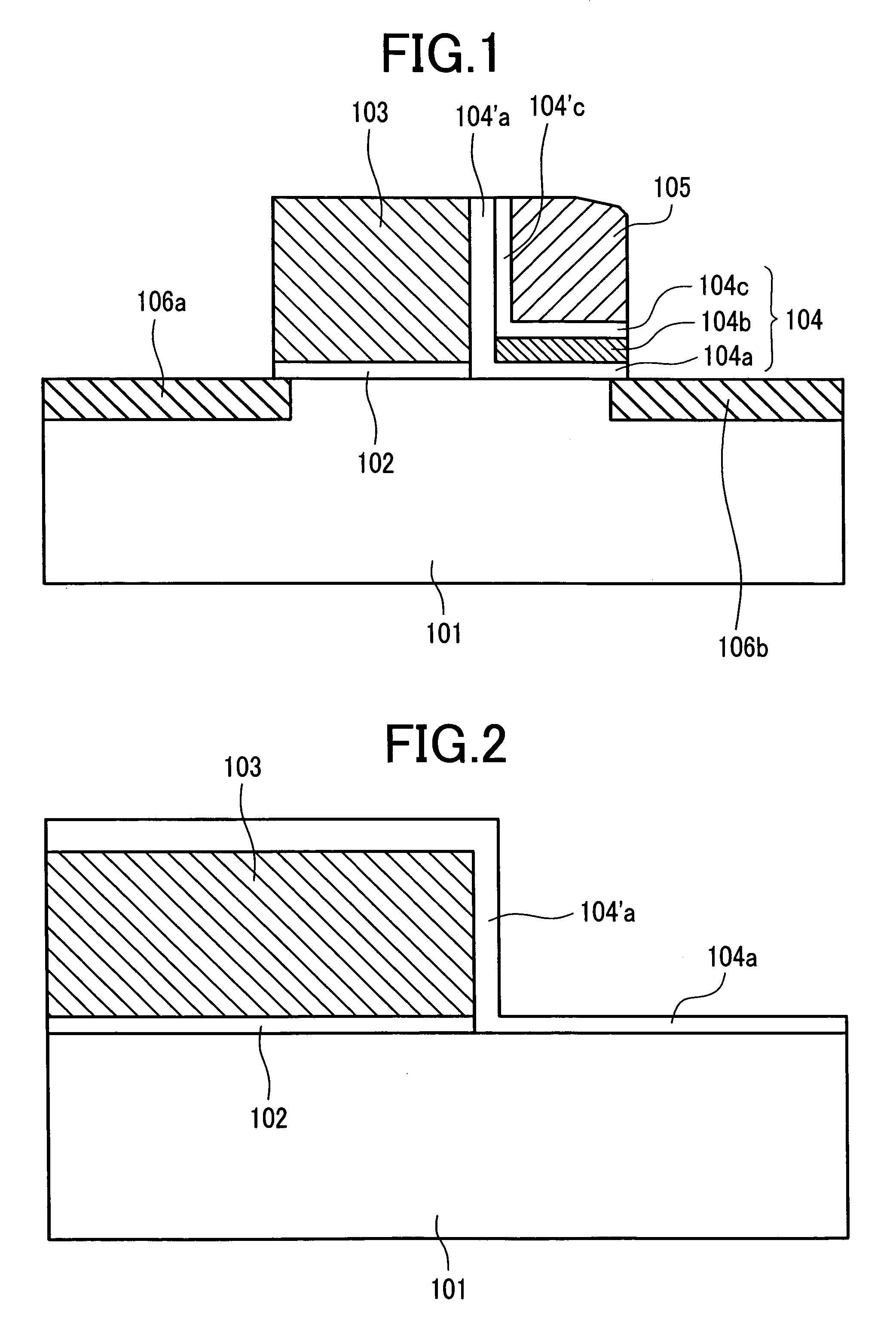
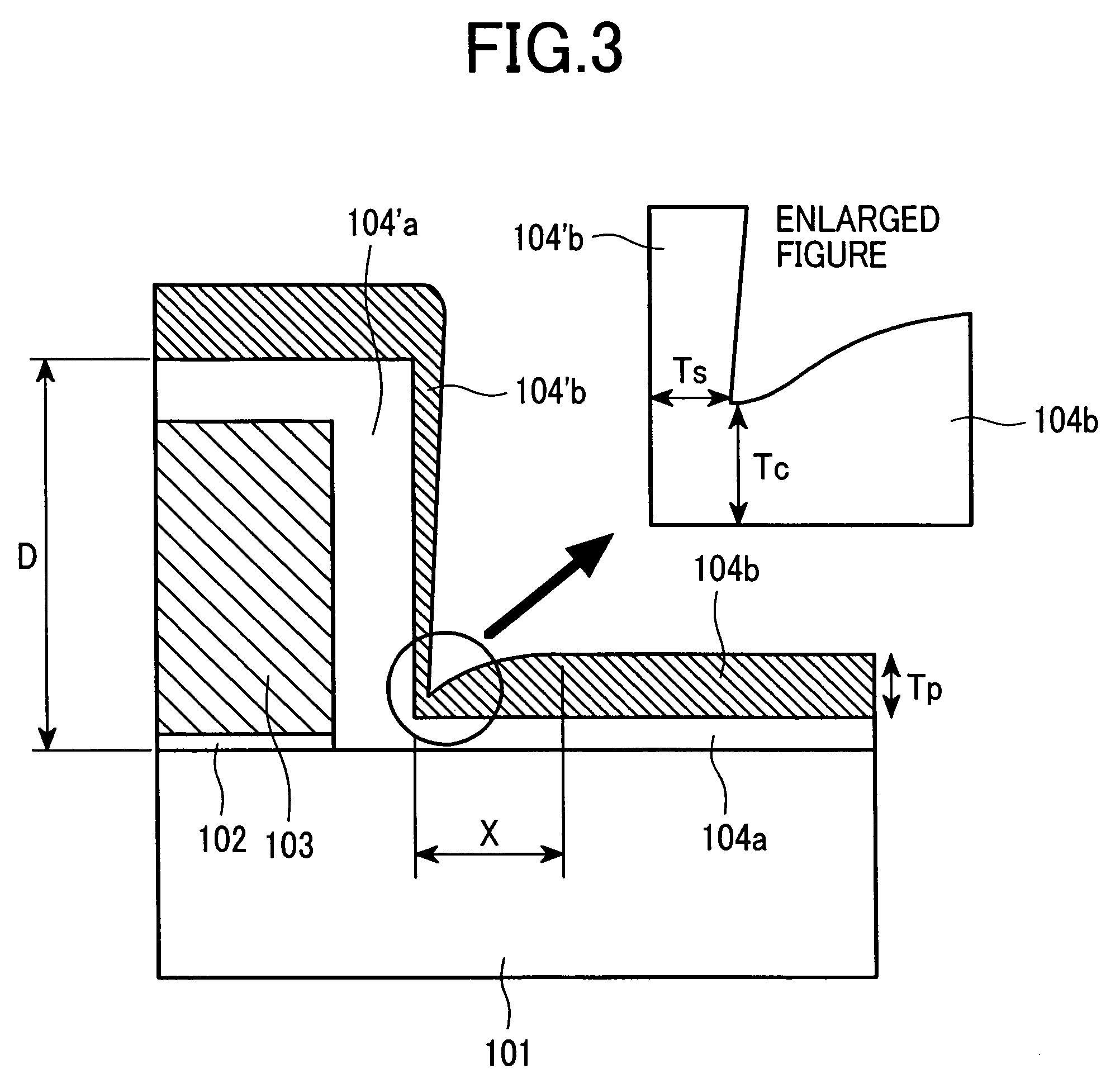
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20100200909A1Improve reliabilityReduce the driving forceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorStorage cell
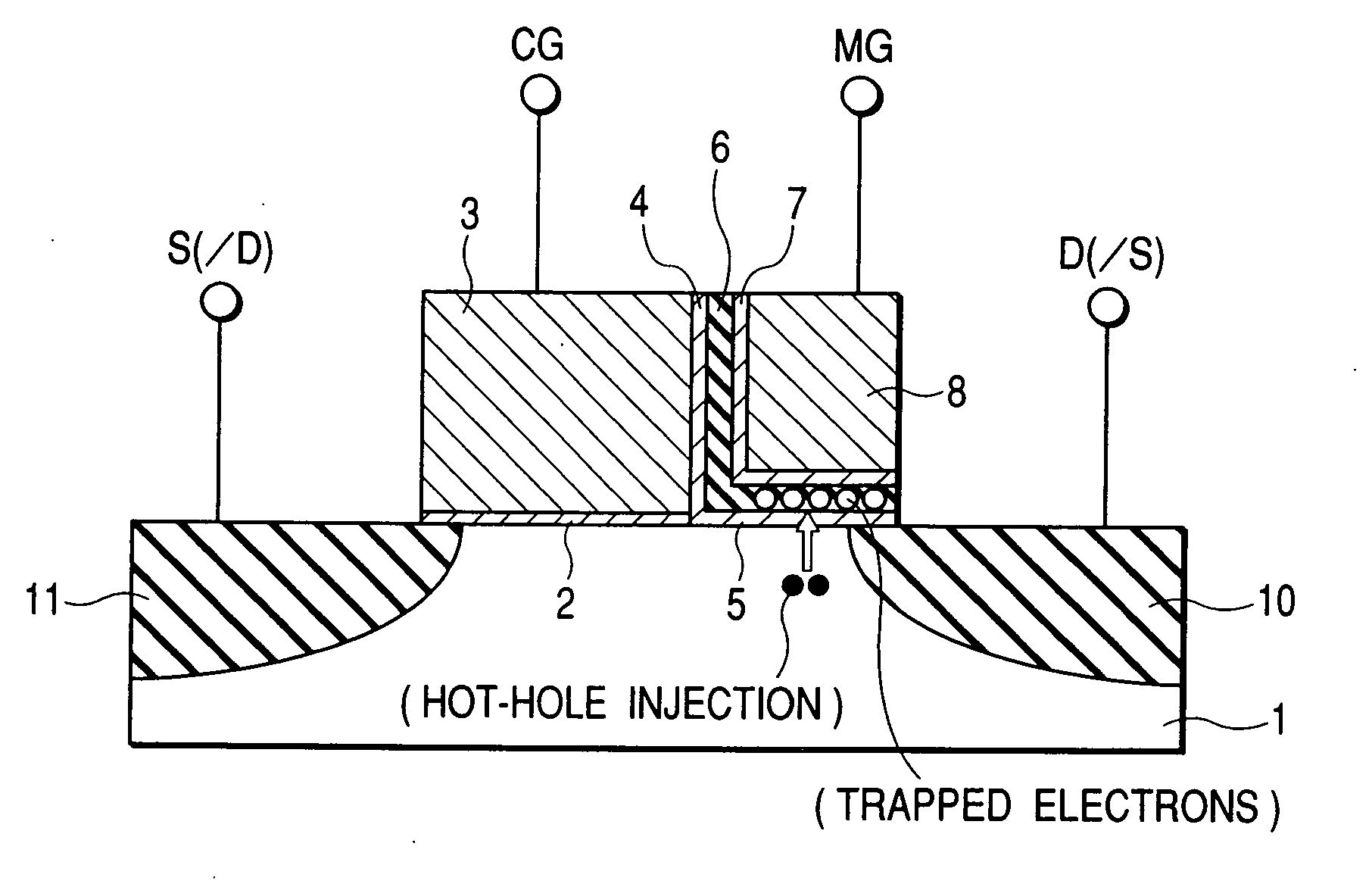
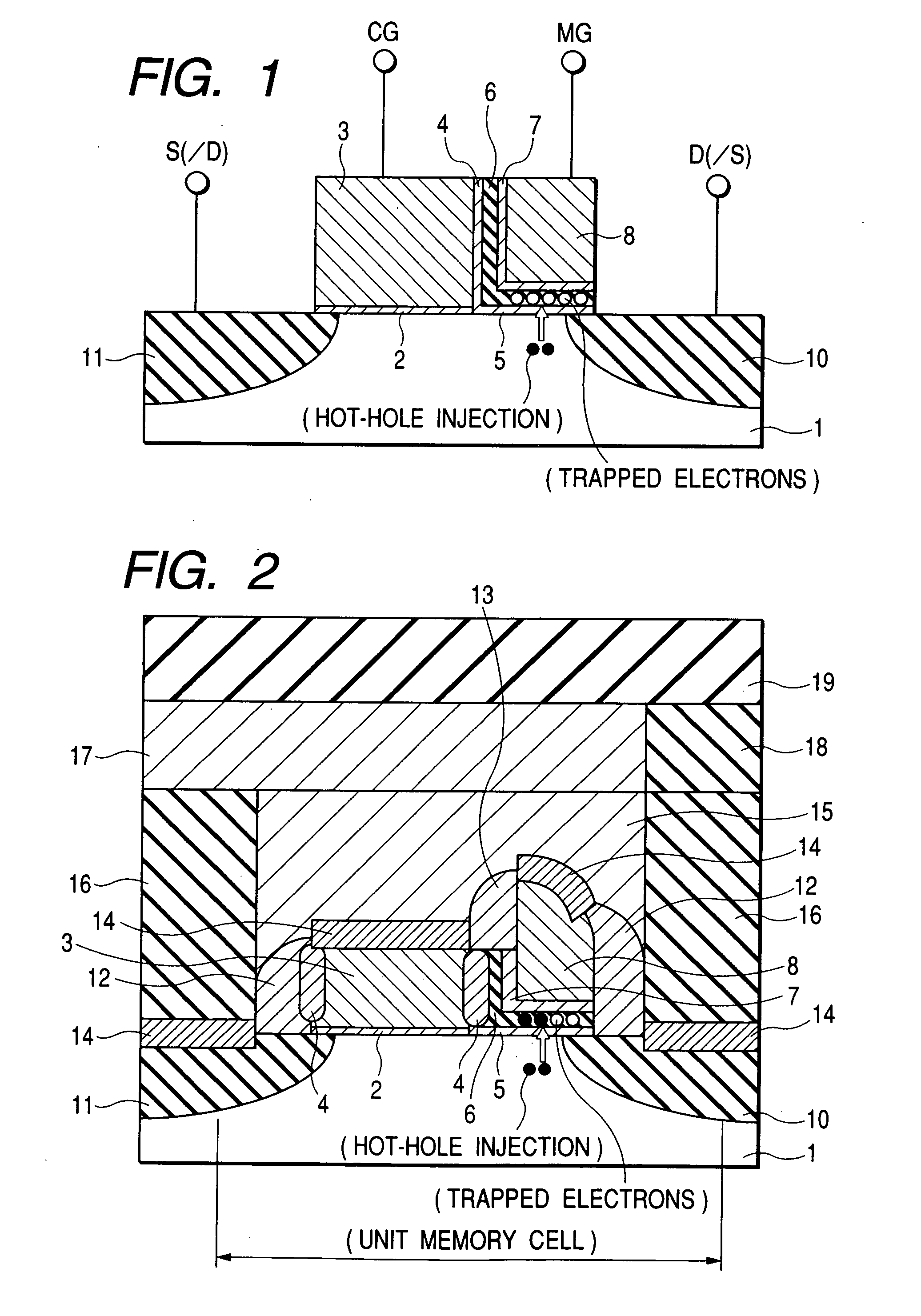
To provide a technique capable of improving reliability of a semiconductor device having a nonvolatile memory cell by suppressing the reduction of the drive force.A memory cell is configured by a selection pMIS having a selection gate electrode including a conductive film exhibiting a p-type conductivity and a memory pMIS having a memory gate electrode including a conductive film exhibiting a p-type conductivity, and at the time of write, hot electrons are injected into a charge storage layer from the side of a semiconductor substrate 1 and at the time of erase, hot holes are injected into the charge storage layer from the memory gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and method for operating the same
InactiveUS6949788B2Reduce the amount requiredLower energy barrierTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon dioxideImpurity
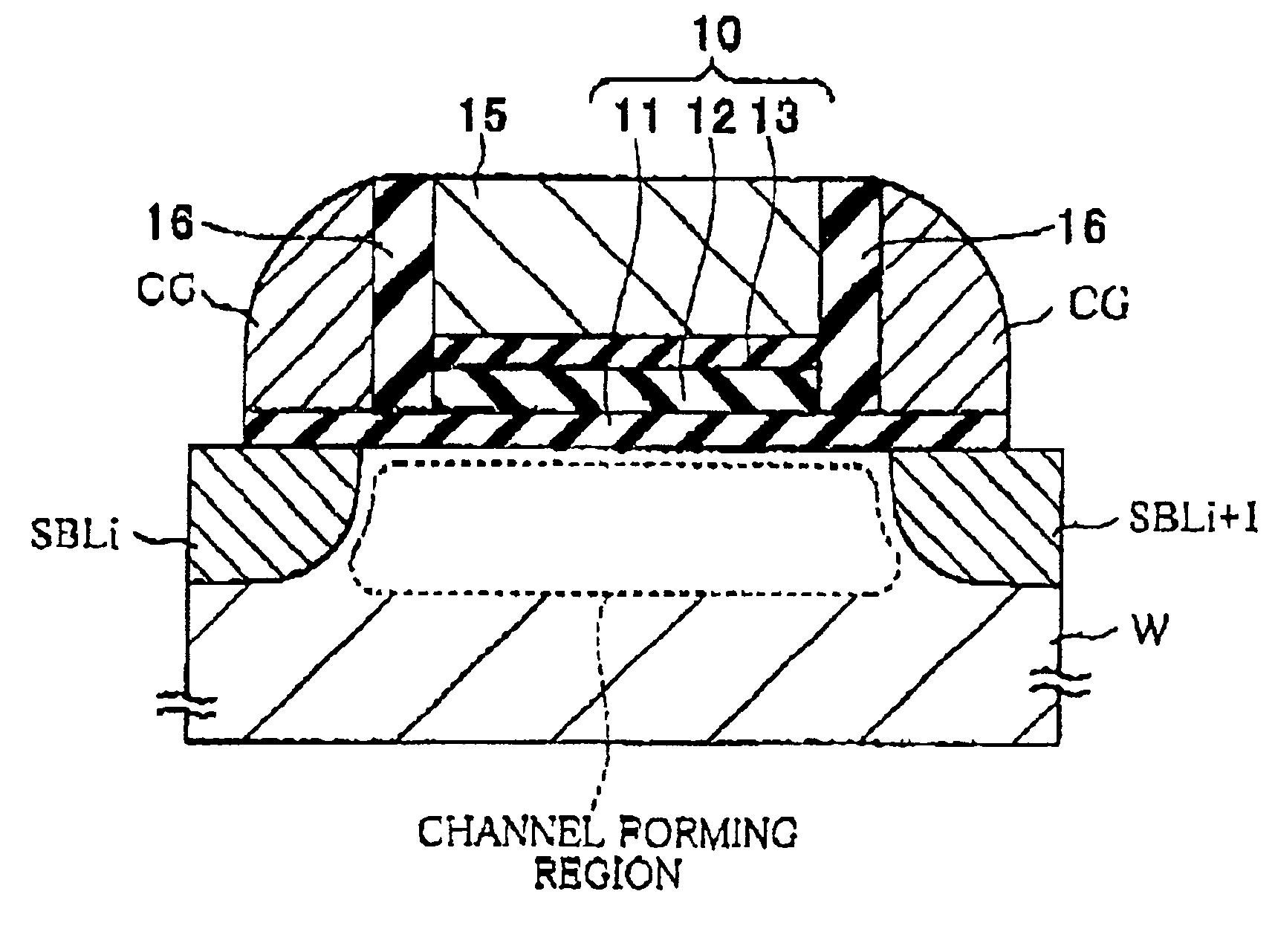
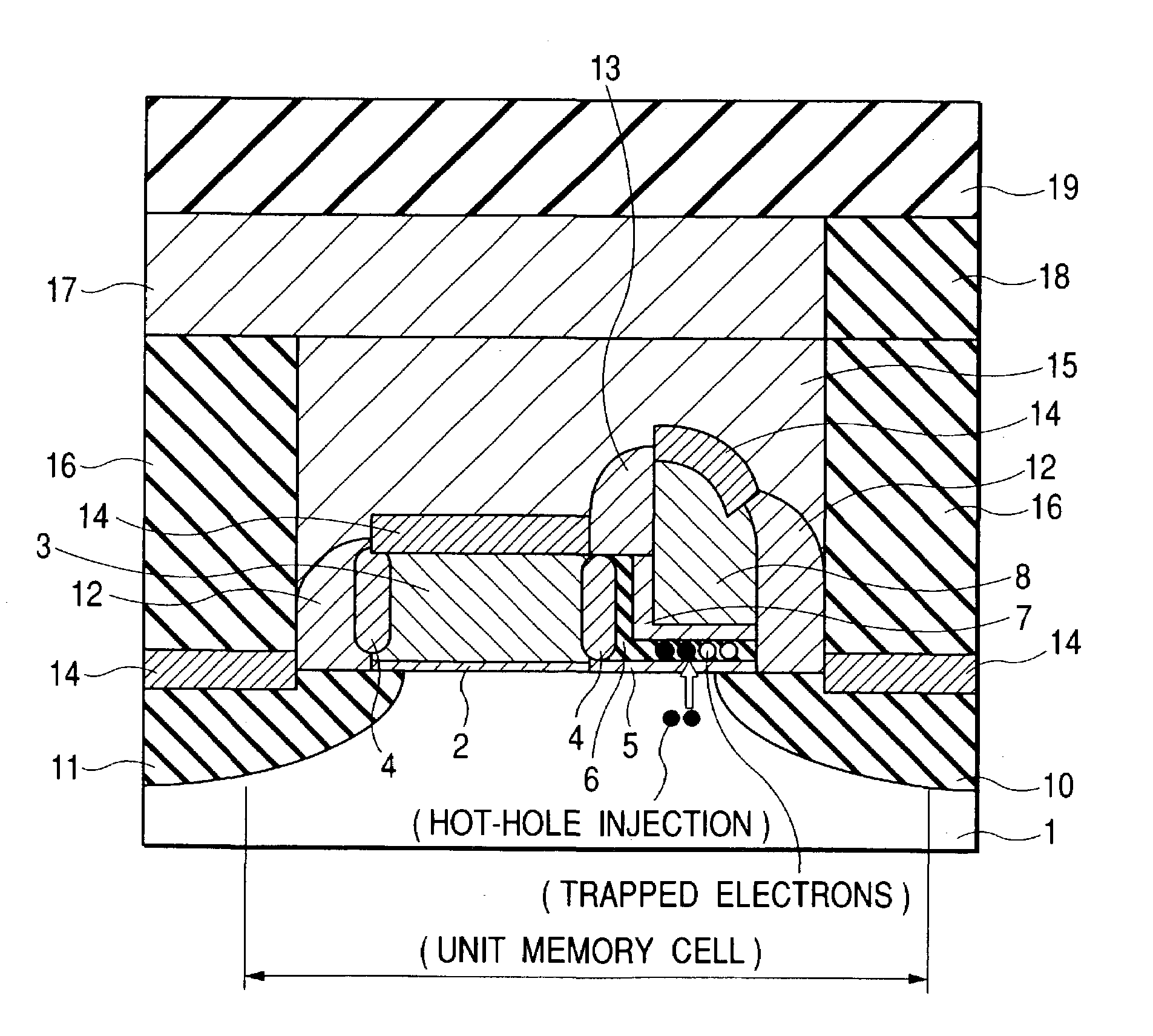
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device having MONOS type memory cells of increased efficiency by hot electron injection and improved scaling characteristics includes a channel forming region in the vicinity of a surface of a substrate, first and second impurity regions, acting as a source and a drain in operation, formed in the vicinity of the surface of the substrate sandwiching the channel forming region between them, a gate insulating film stacked on the channel forming region and having a plurality of films, and a charge storing means that is formed in the gate insulating film dispersed in the plane facing the channel forming region. A bottom insulating film includes a dielectric film that exhibits a FN type electroconductivity and makes the energy barrier between the bottom insulating film and the substrate lower than that between silicon dioxide and silicon.
Owner:SONY CORP
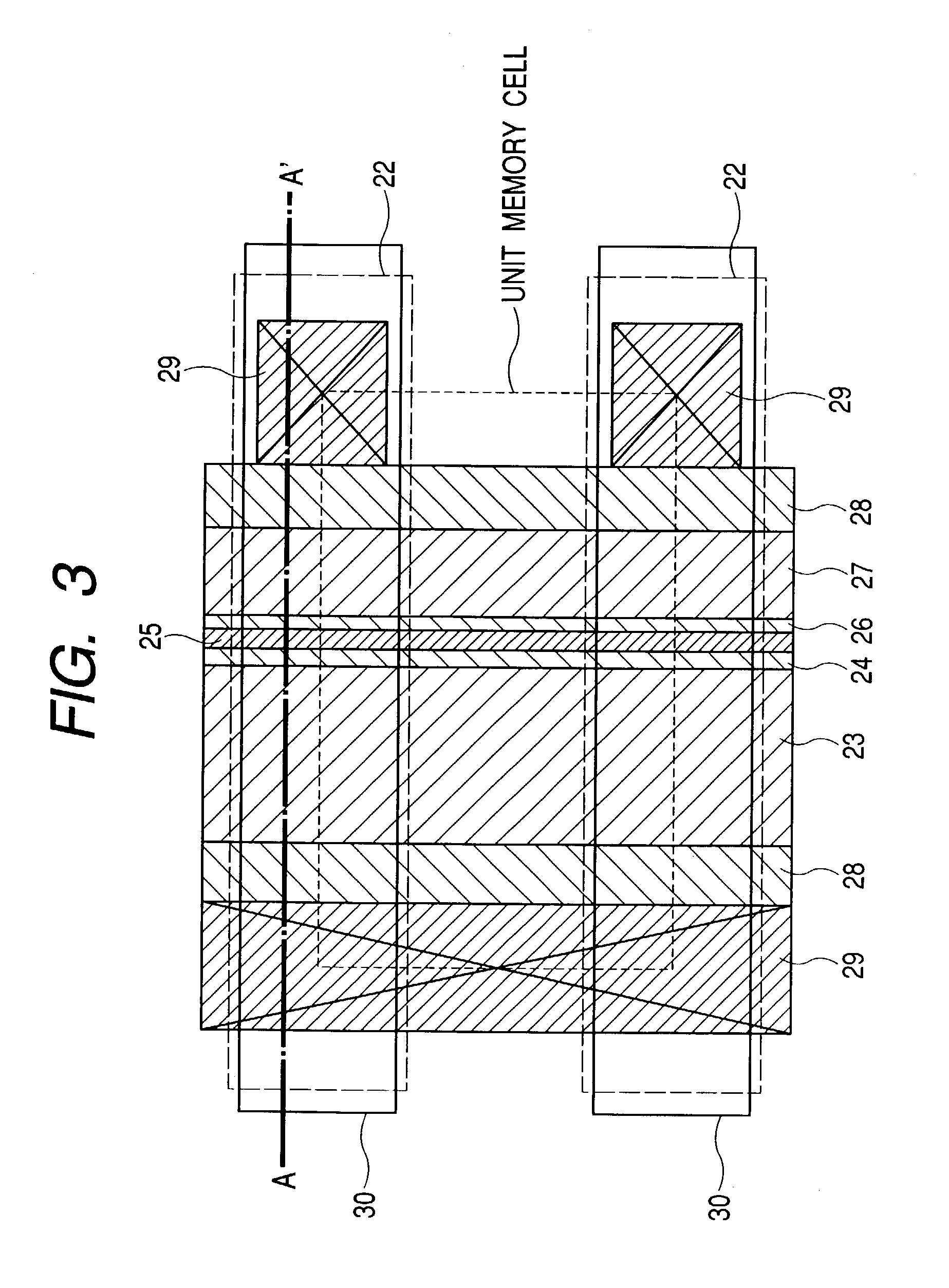
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7045848B2Increase speedHigh speed readTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsReverse biasSemiconductor
The memory cell transistor includes, in a first well region, a pair of memory electrodes, one of which serves as source electrode and the other serves as a drain electrode and a channel region interposed between the pair of memory electrodes. There is, on a channel region, a first gate electrode disposed near its corresponding memory electrode with an insulating film interposed therebetween, and a second gate electrode disposed through insulating films and a charge storage region and electrically isolated from the first gate electrode. A first negative voltage is applied to the first well region to form a state of a reverse bias greater than or equal to a junction withstand voltage between the second gate electrode and the memory electrode near the second gate electrode, thereby enabling injection of hot electrons into the charge storage region and injection of electrons from the well region to the charge storage region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
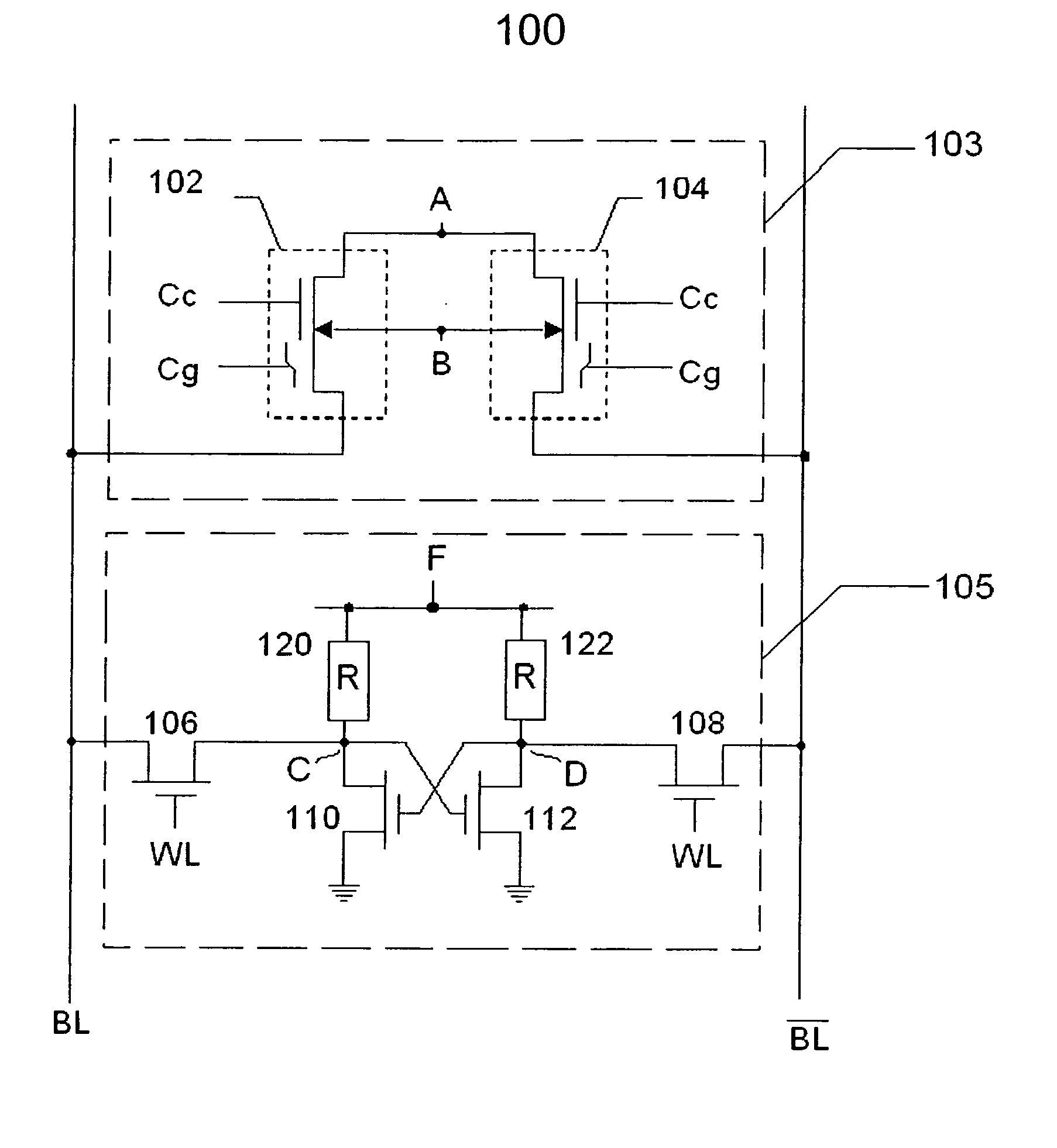
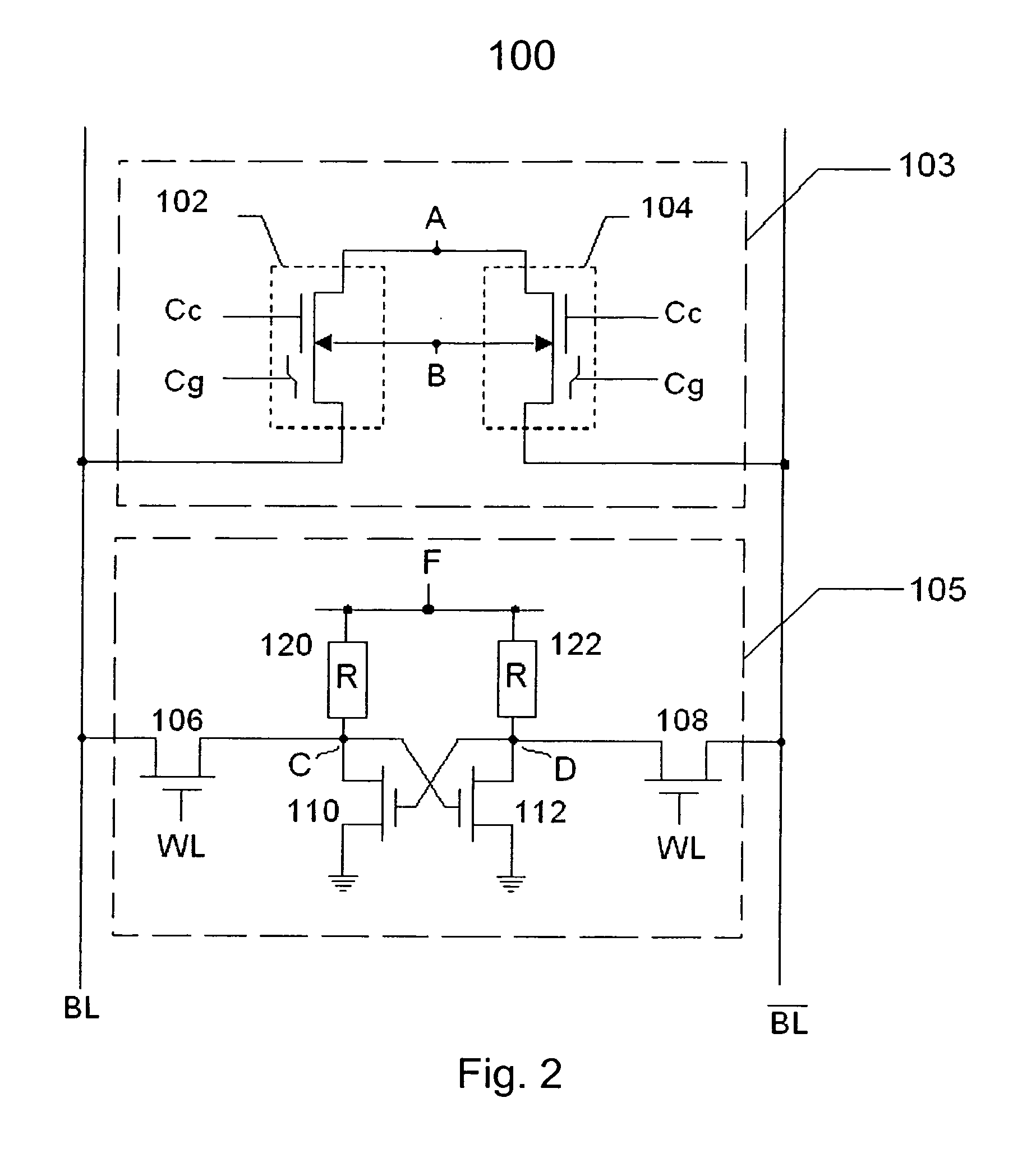
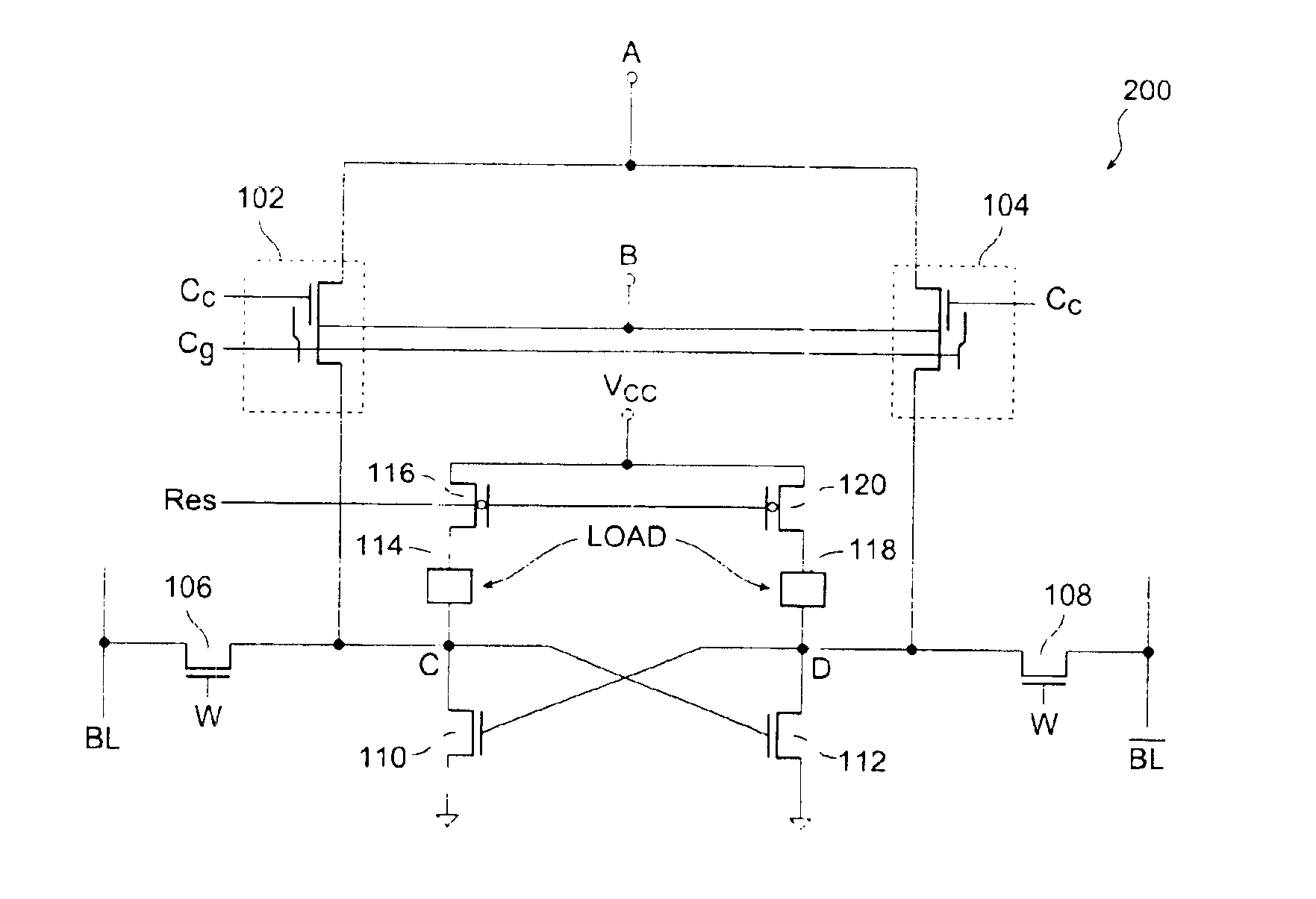
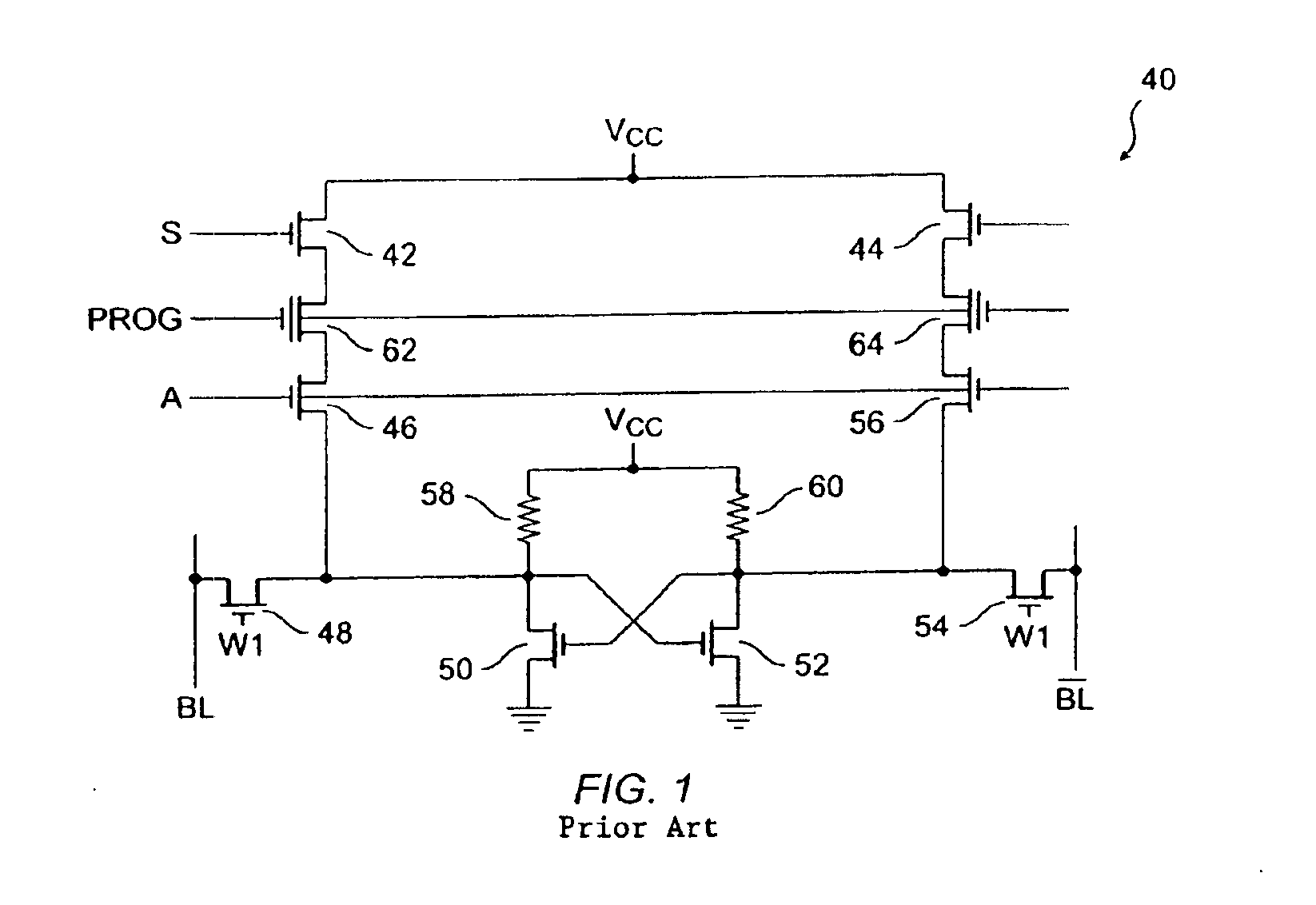
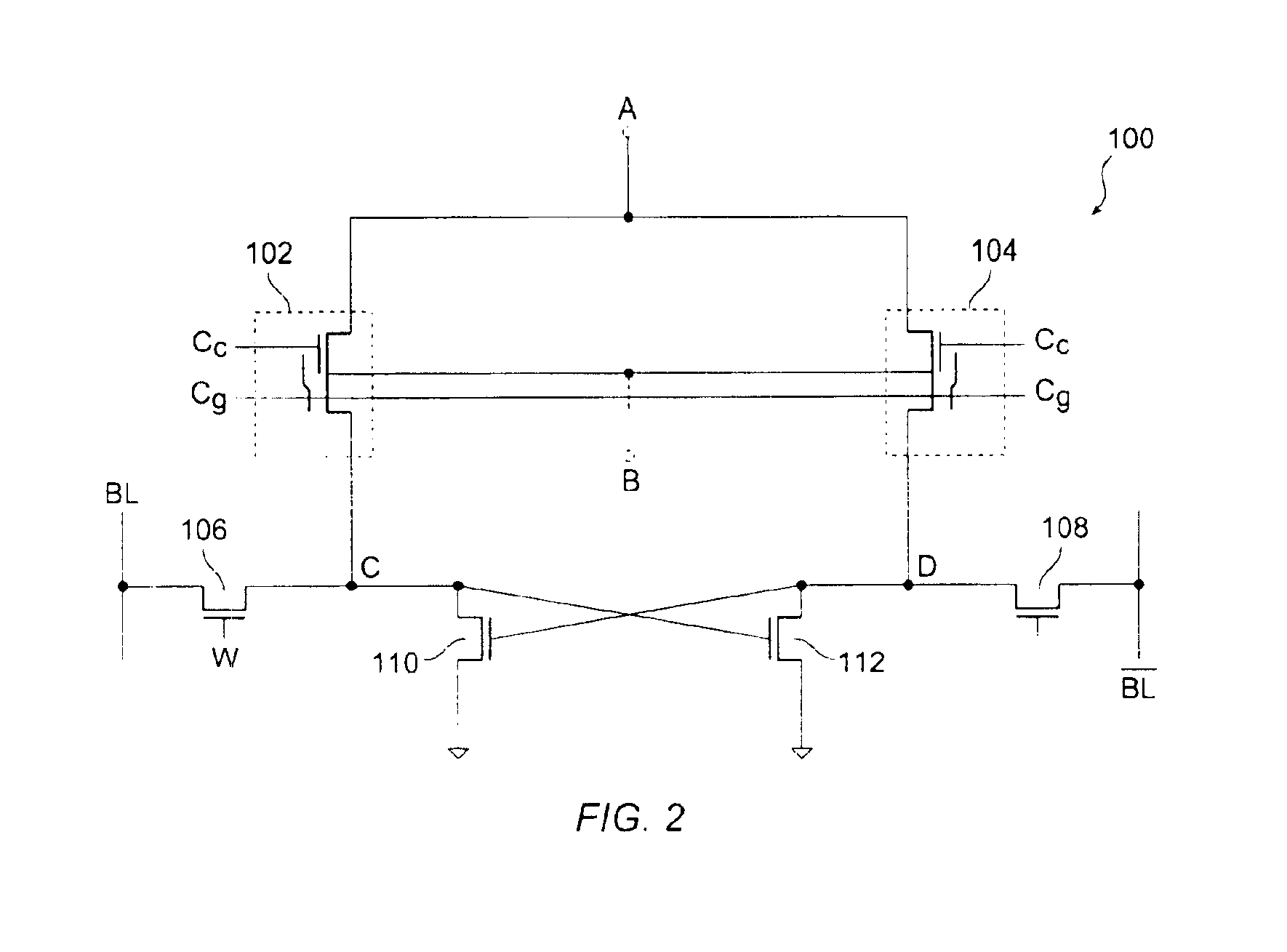
Non-volatile and static random access memory cells sharing the same bitlines
A memory cell structure includes non-volatile as well as SRAM memory cells that share the same bitline and operate differentially. The SRAM cell includes first and second MOS transistors that are coupled to the same true and complementary bit lines that the non-volatile memory cells are coupled to. The non-volatile memory cells are erased prior to being programmed. Programming of the non-volatile memory cells may be carried out via hot-electron injection or Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. Data stored in the non-volatile memory cells may be transferred to the SRAM cell. The differential reading and writing of data reduces over-erase of the non-volatile devices.
Owner:O2IC
Ballistic injection nrom flash memory
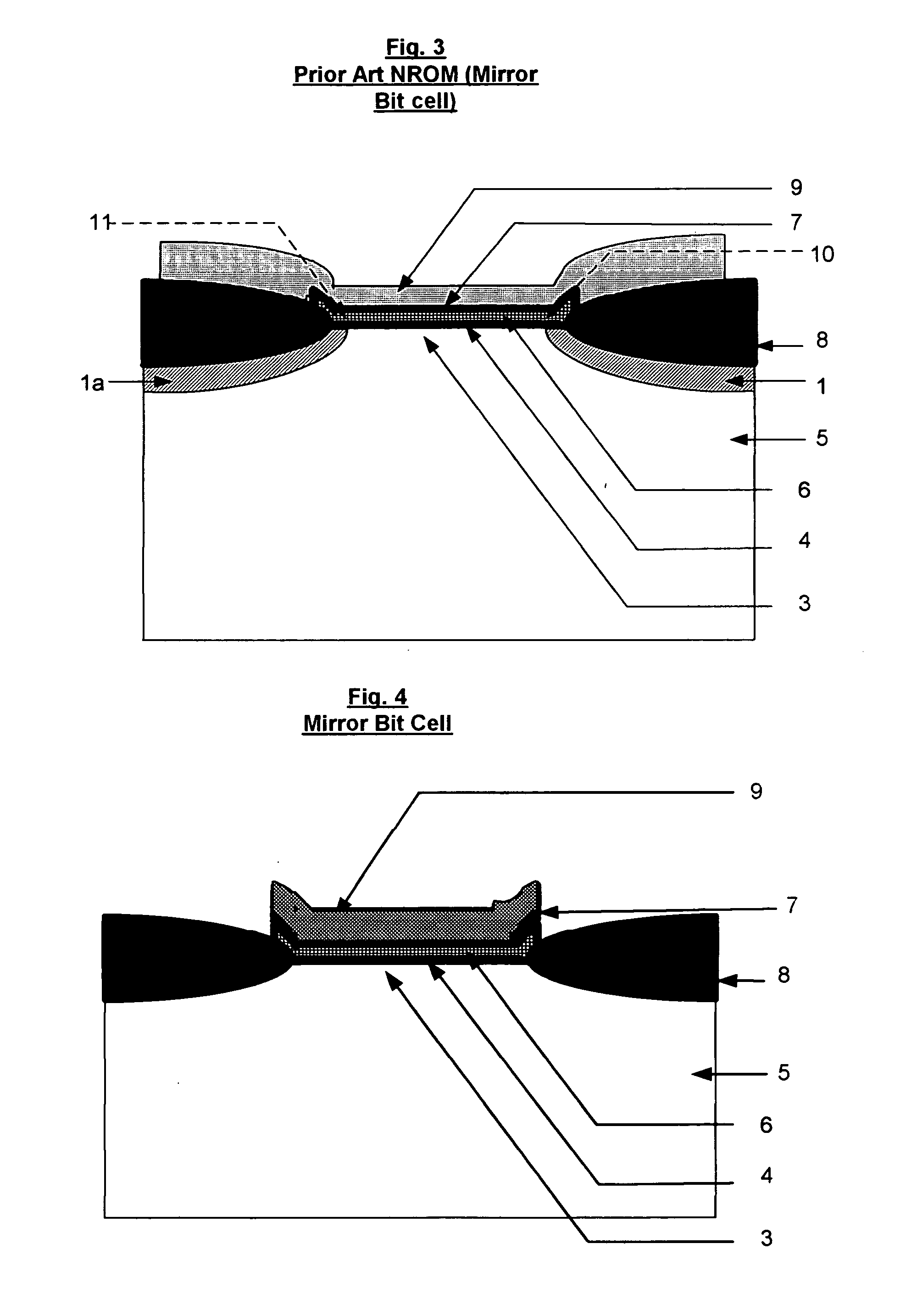
ActiveUS20050259475A1Read-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrideHot electron
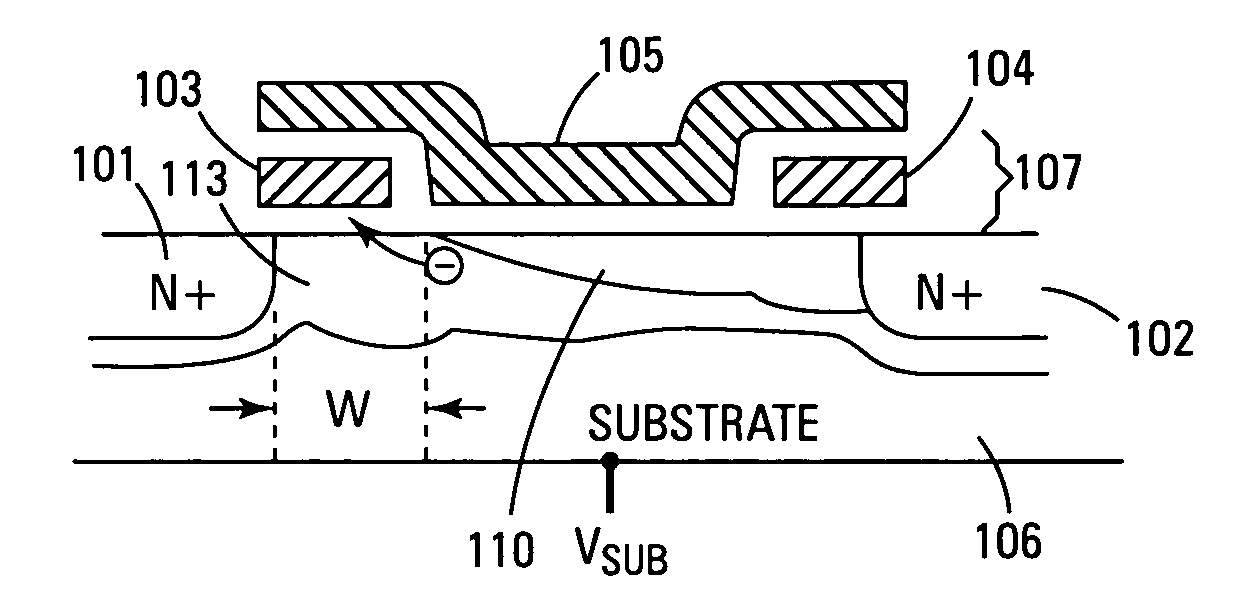
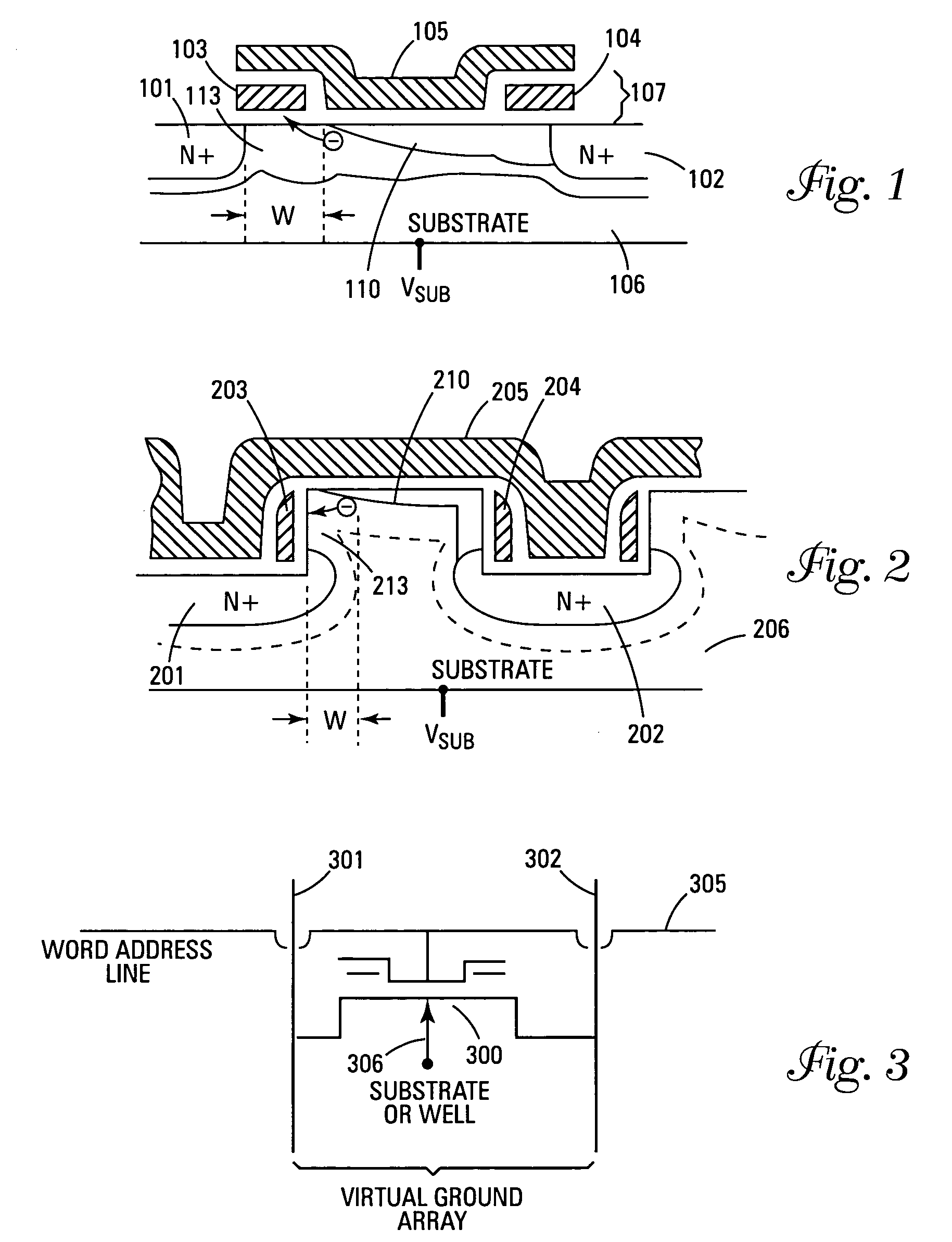
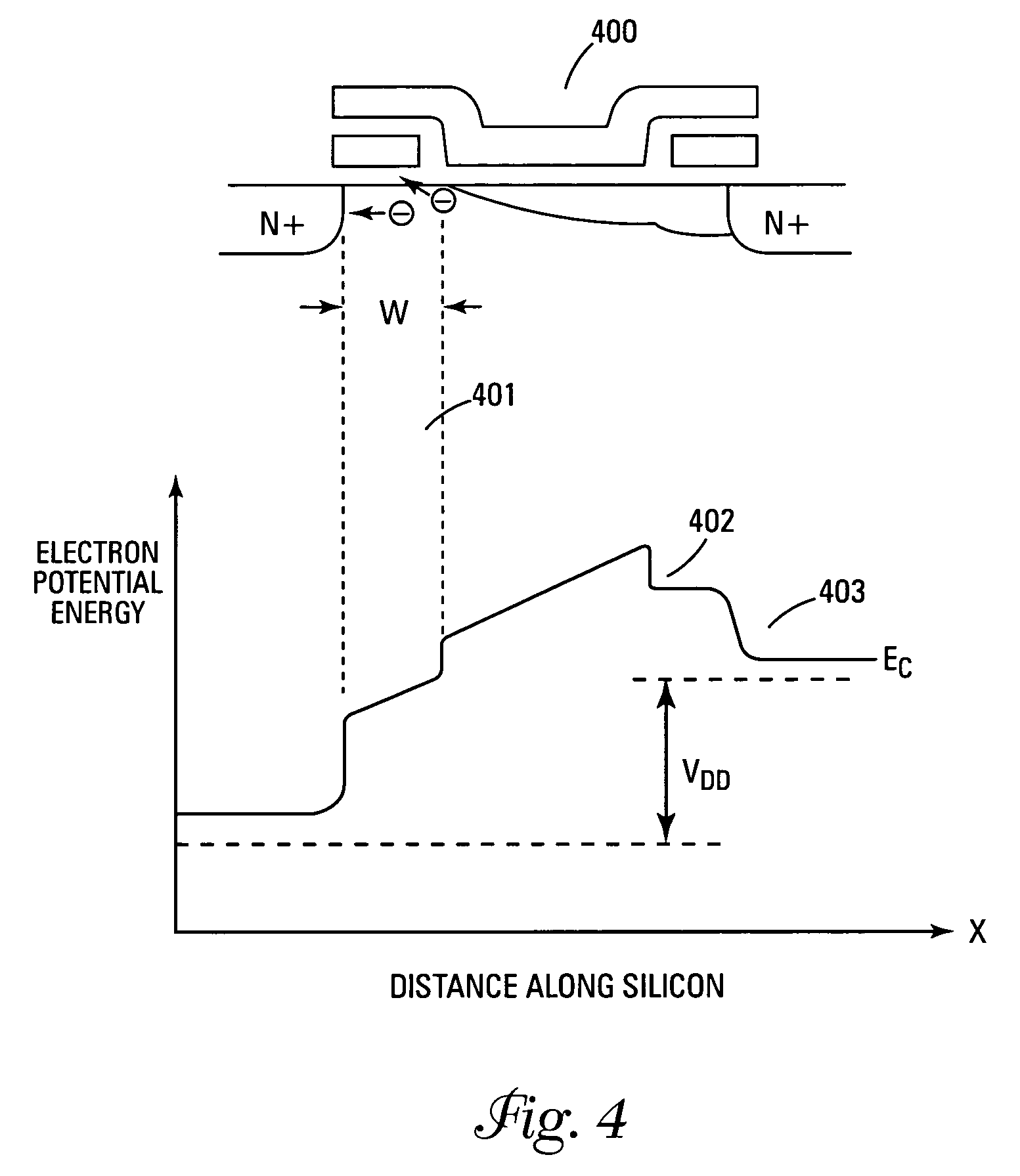
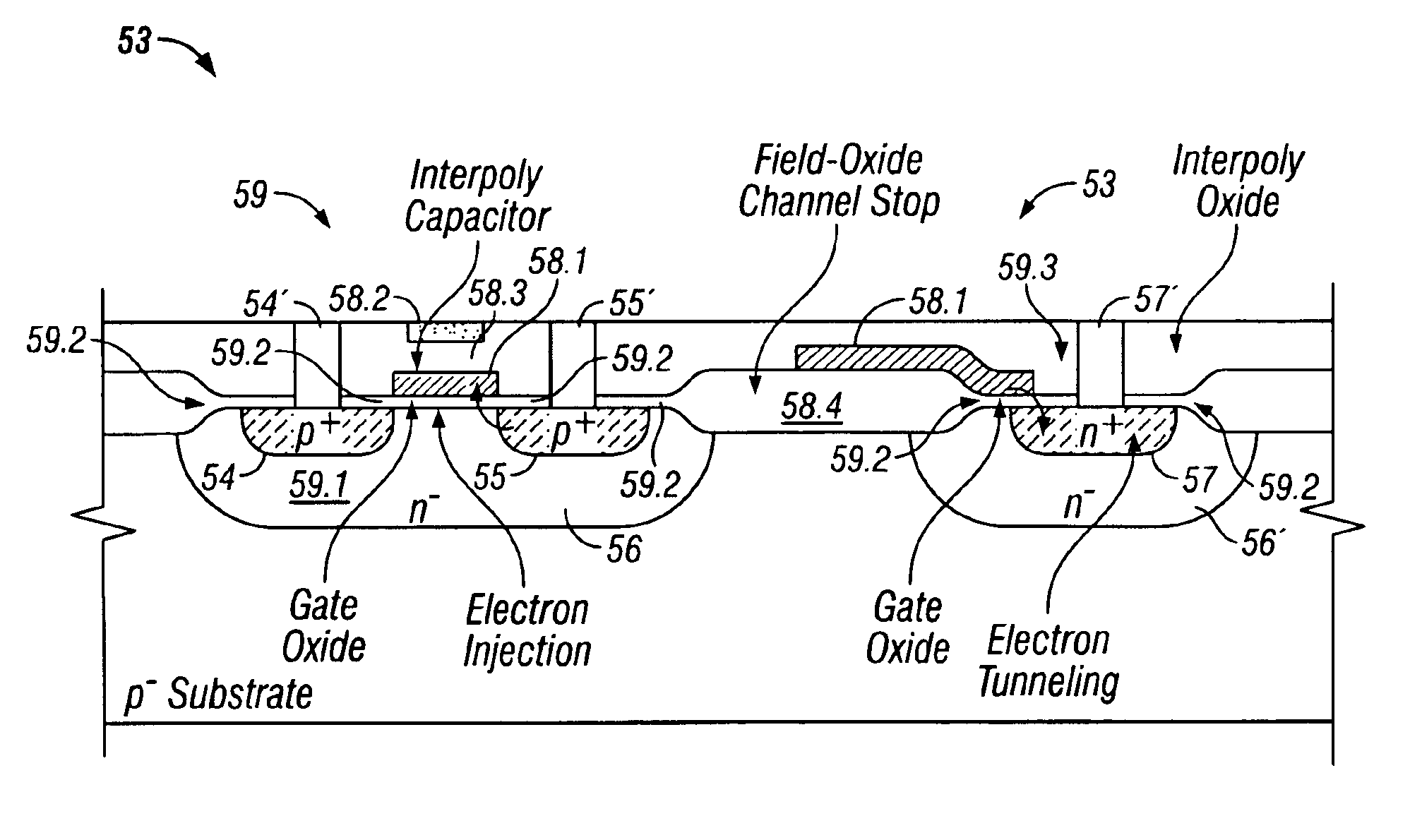
A split NROM flash memory cell is comprised of source / drain regions in a substrate. The split nitride charge storage regions are insulated from the substrate by a first layer of oxide material and from a control gate by a second layer of oxide material. The nitride storage regions are isolated from each other by a depression in the control gate. In a vertical embodiment, the split nitride storage regions are separated by an oxide pillar. The cell is programmed by creating a positive charge on the nitride storage regions and biasing the drain region while grounding the source region. This creates a virtual source / drain region near the drain region such that the hot electrons are accelerated in the narrow pinched off region. The electrons become ballistic and are directly injected onto the nitride storage region that is adjacent to the pinched off channel region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and apparatus for multiple byte or page mode programming of a flash memory array
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Inversion bit line, charge trapping non-volatile memory and method of operating same
ActiveUS7158420B2Easy to scaleLower average currentRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineFowler nordheim
A charge trapping memory device in which a field induced inversion layer is used to replace the source and drain implants. The memory cell are adapted to store two bits, one on the left side and one on the right side of the charge trapping structure. A positive threshold voltage erase state is induced using negative gate voltage Fowler Nordheim FN tunneling which establishes a charge balance condition at a positive voltage. A low current, source side, hot electron injection programming method is used.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
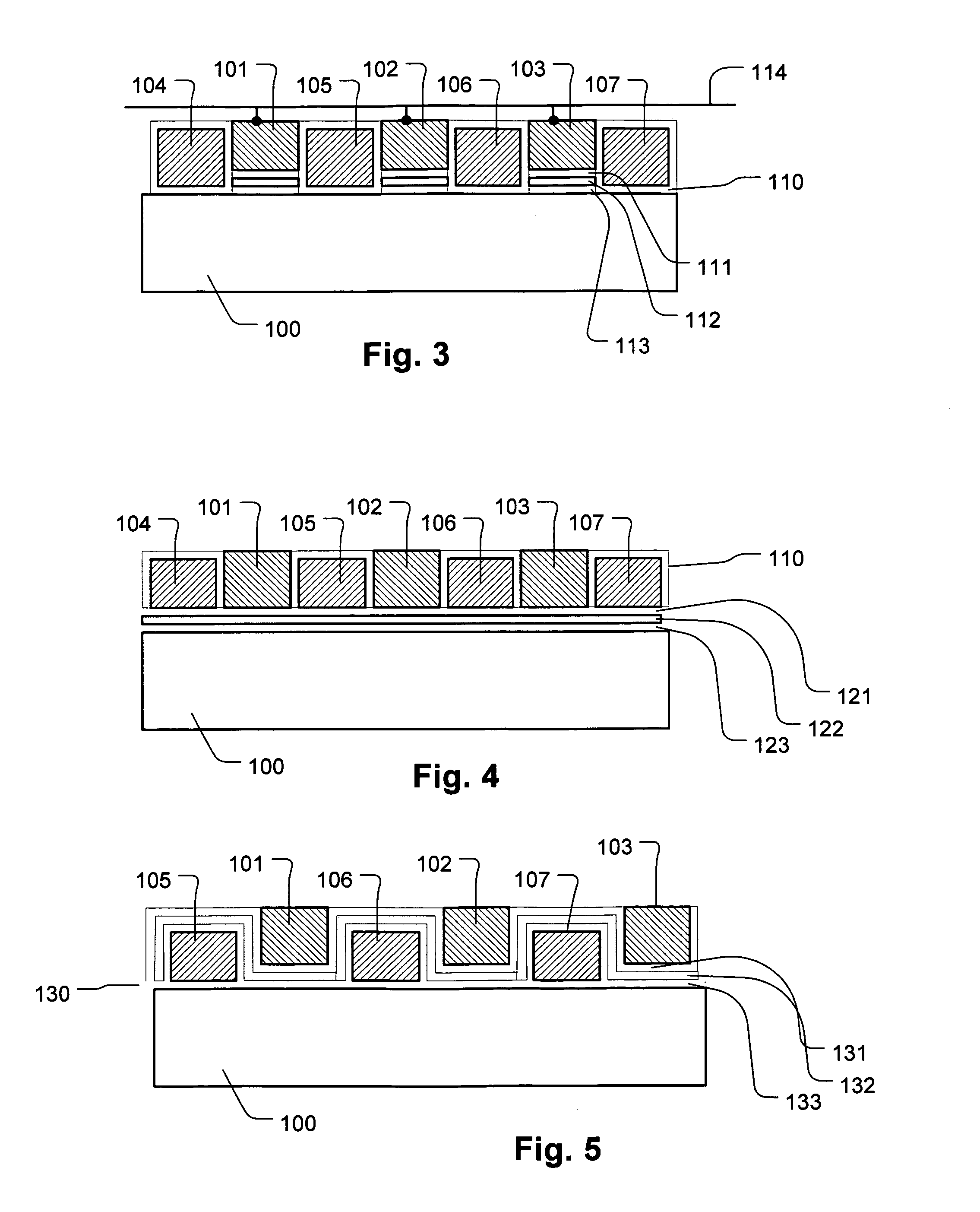
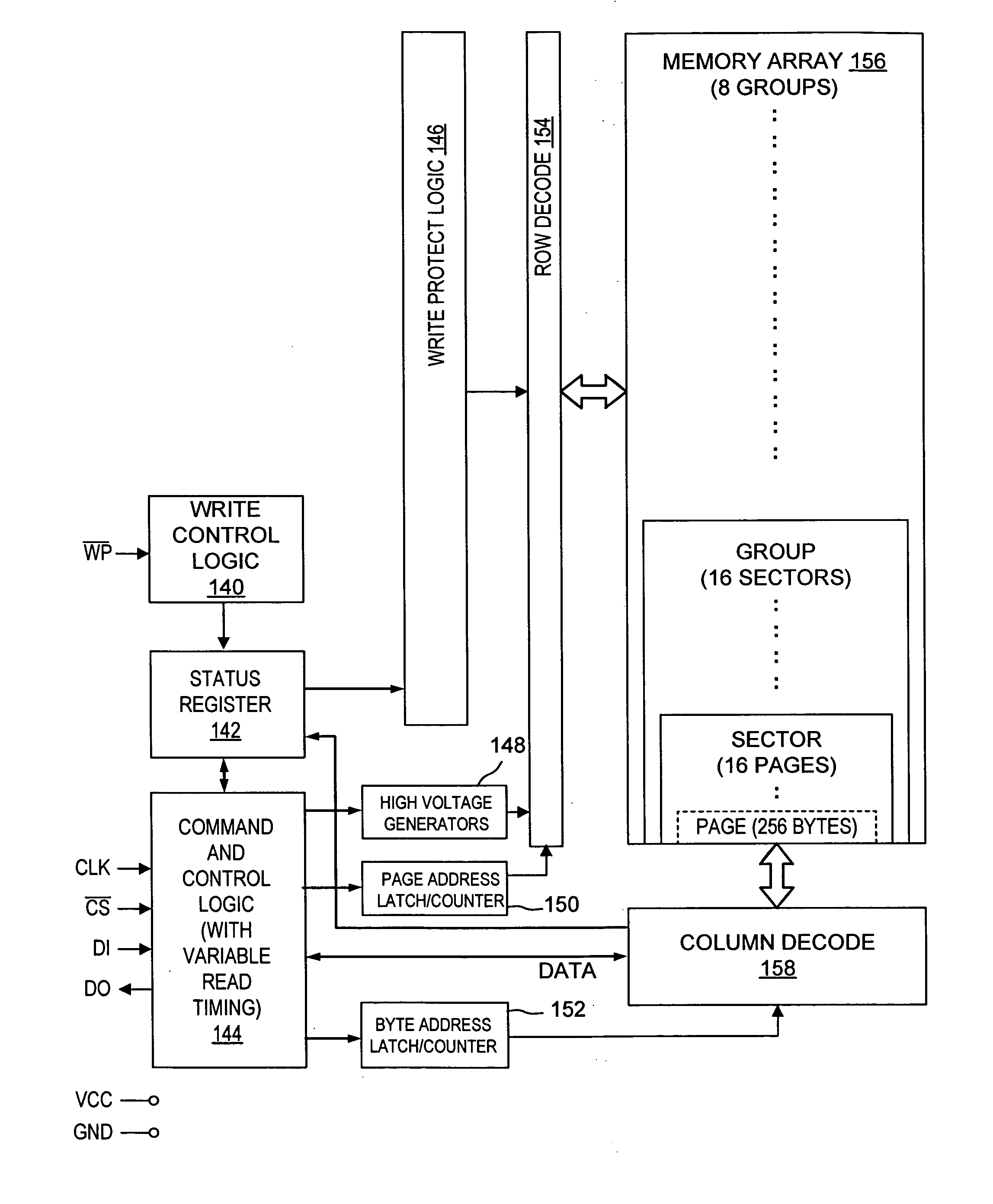
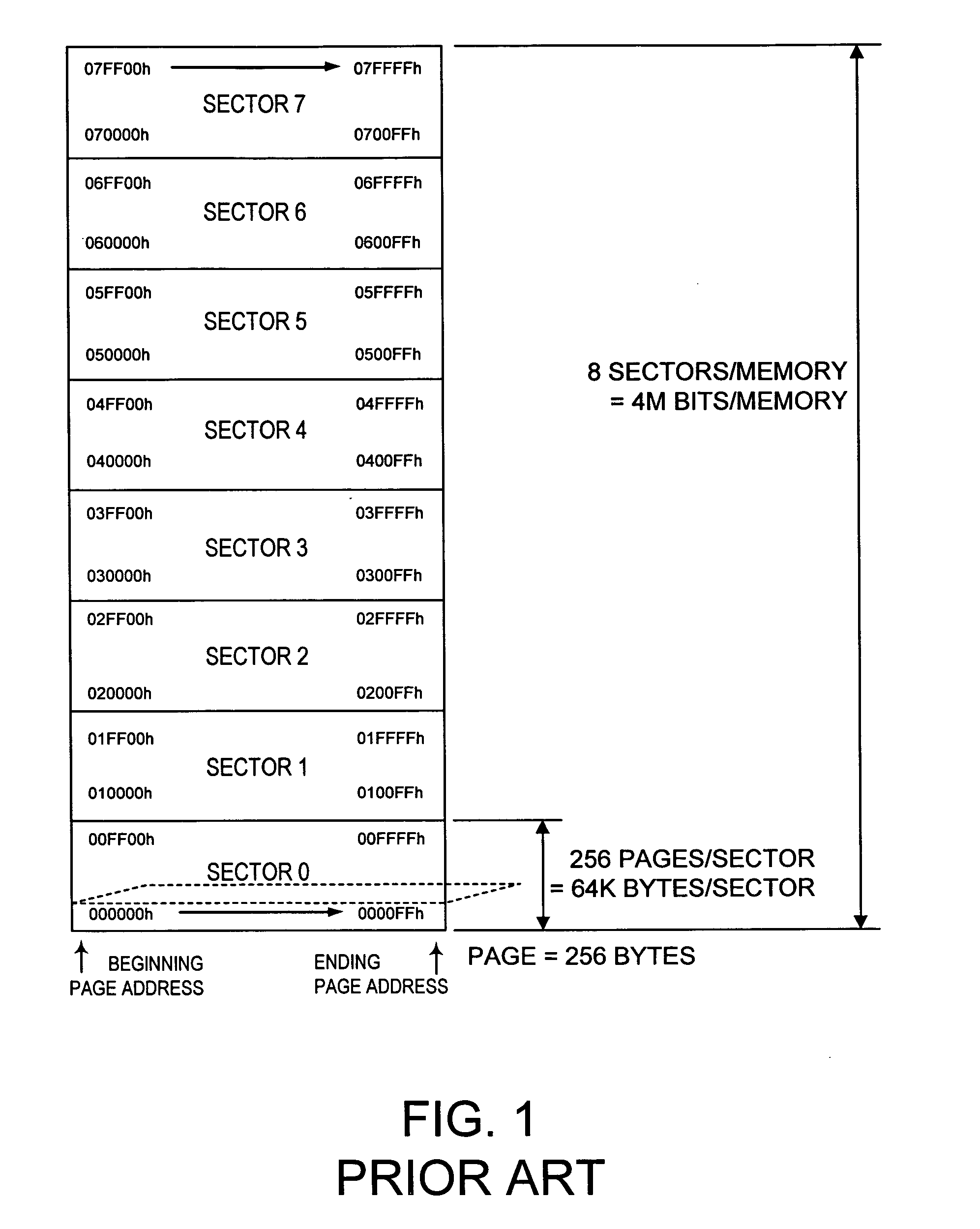
Small sector floating gate flash memory
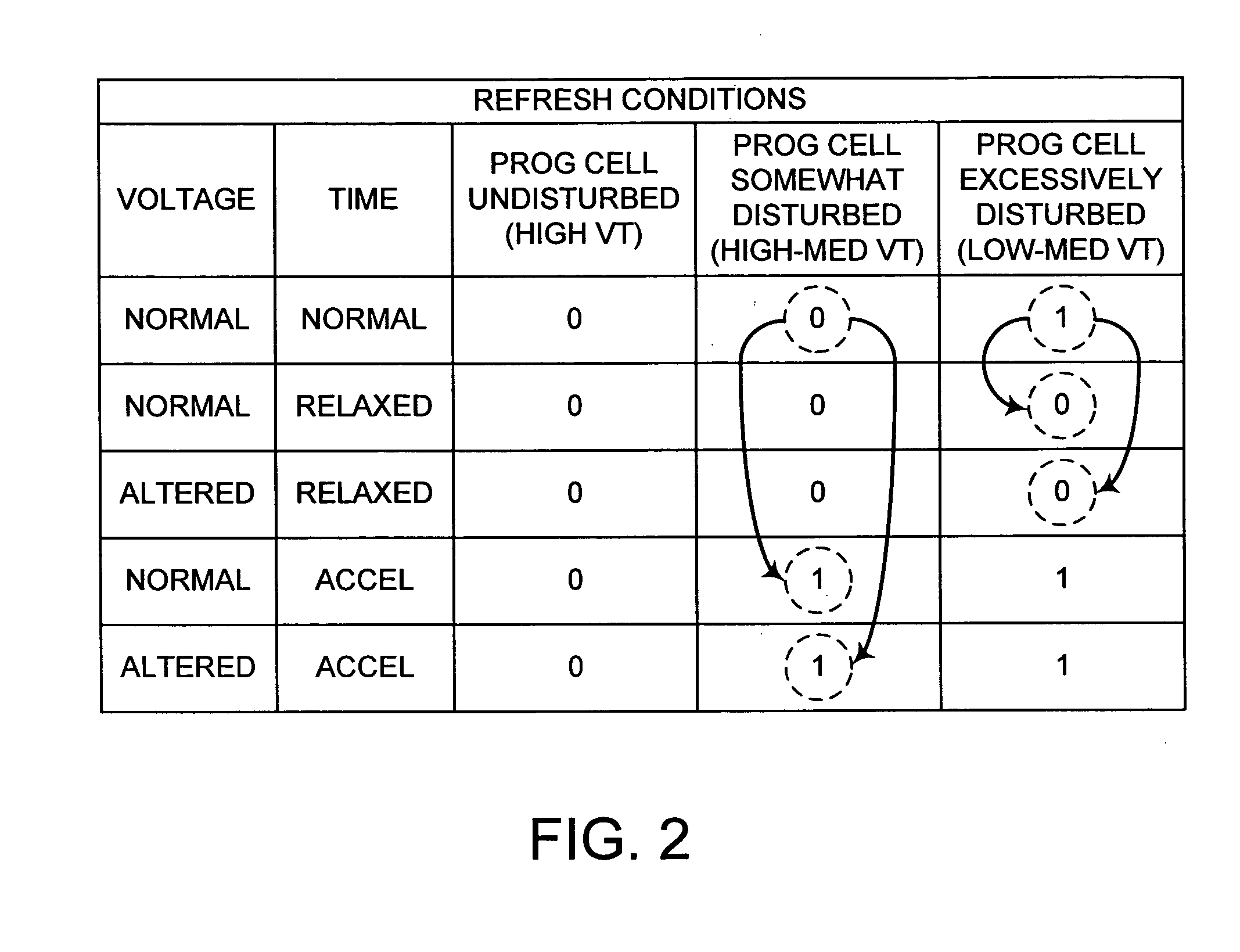
ActiveUS20060256606A1Small sector sizeSacrificing original benefitRead-only memoriesDigital storageFowler nordheimMemory array
To control the problem of program and erase disturb in flash memory arrays having multiple sectors of cells grouped in each isolation wells of the flash memory array, a refresh procedure is used that involves two readings of each of the cells in a “refresh area” of a group under different read timing conditions, with other read conditions being constant or varied as desired. Cells that yield the same result in both reads are not excessively disturbed and need not be reprogrammed. However, cells that read differently may be excessively disturbed and should be reprogrammed. The refresh procedure is particularly suitable for memory arrays with small sector size and many sectors per group. The memory arrays preferably incorporate memory cells that use hot electron programming and Fowler-Nordheim erase.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Floating-gate semiconductor structures
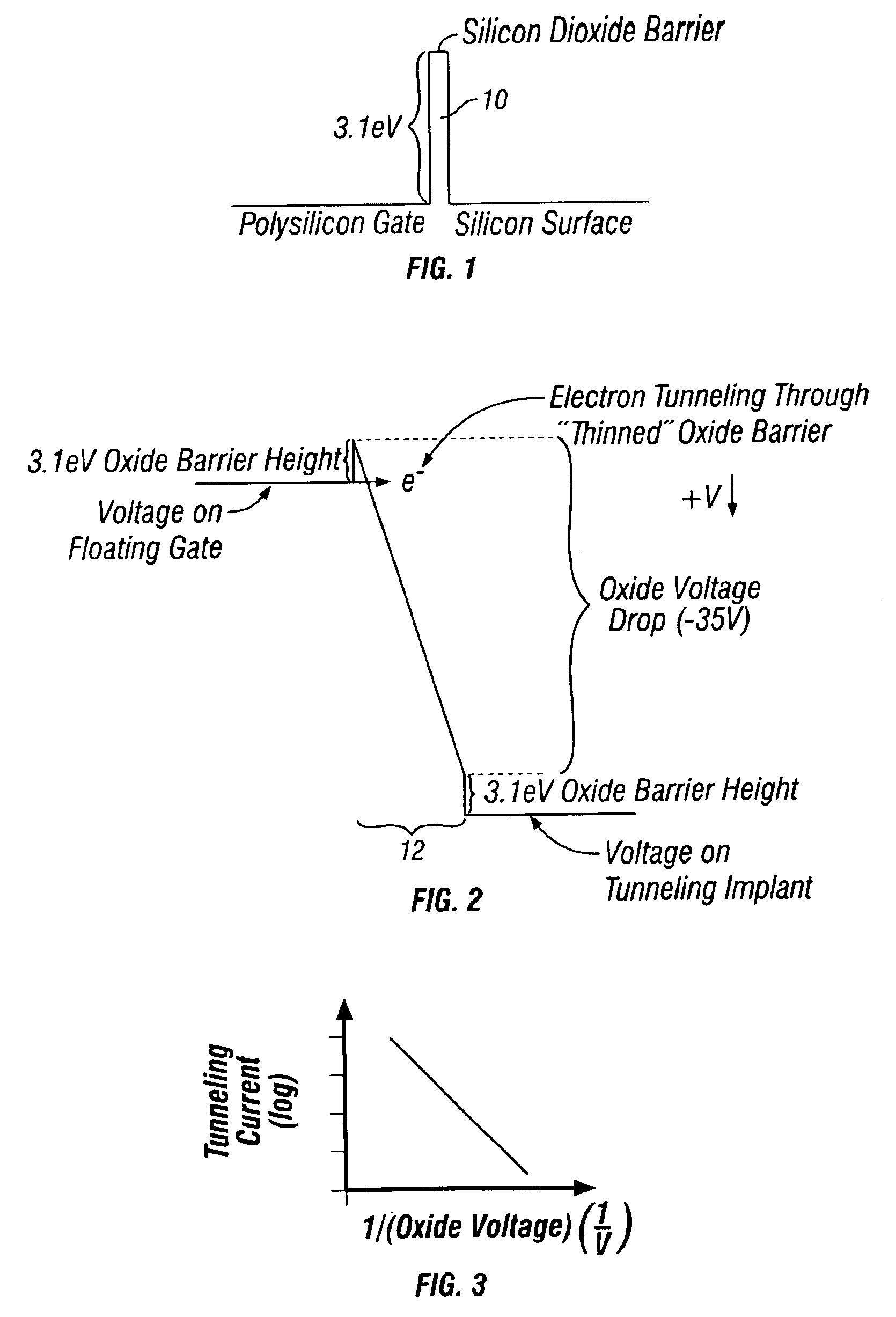
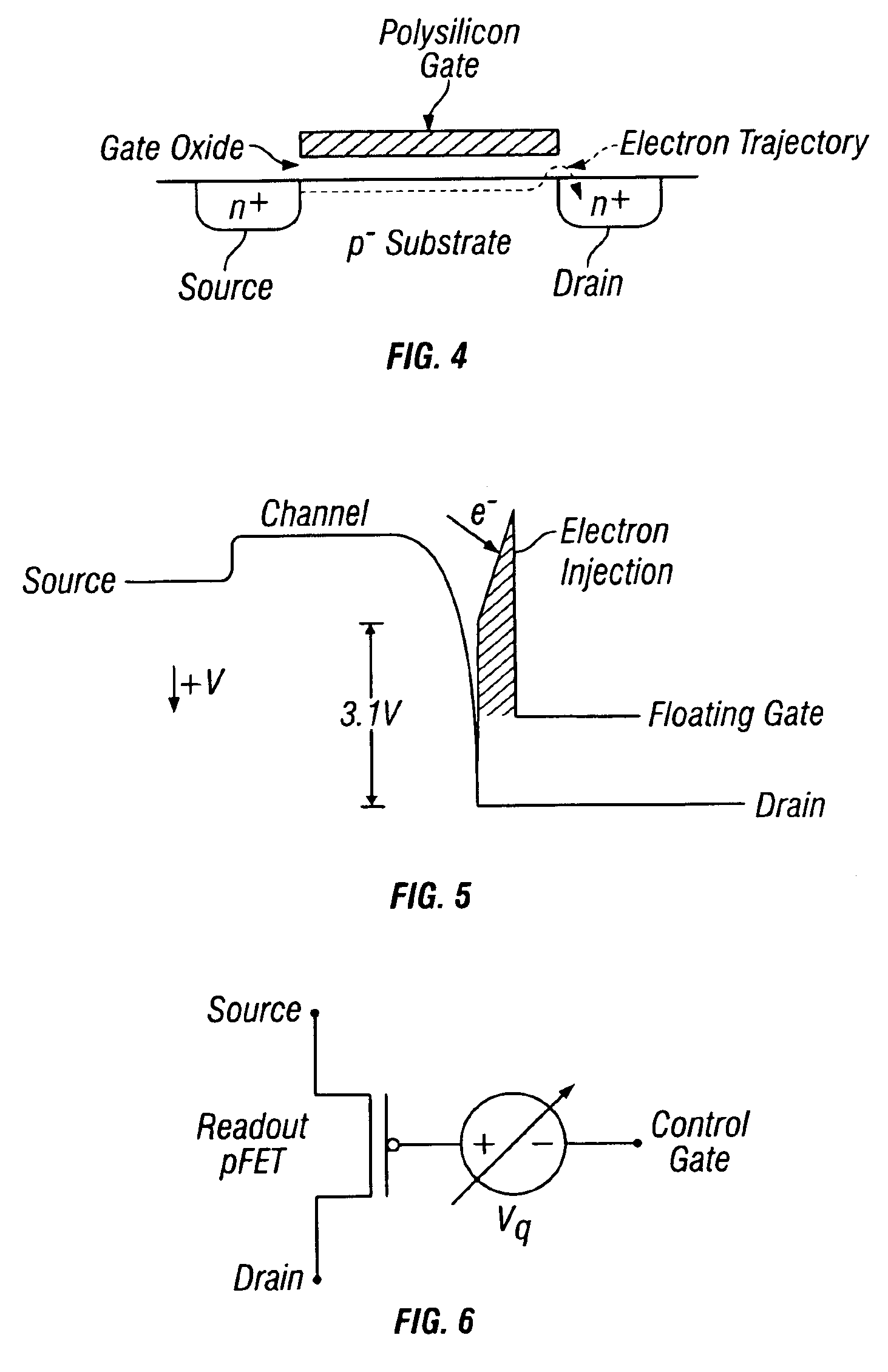
Hot-electron injection driven by hole impact ionization in the channel-to-drain junction of a p-channel MOSFET provides a new mechanism for writing a floating-gate memory. Various pFET floating-gate structures use a combination of this mechanism and electron tunneling to implement nonvolatile analog memory, nonvolatile digital memory, or on-line learning in silicon. The memory is nonvolatile because the devices use electrically isolated floating gates to store electronic charge. The devices enable on-line learning because the electron injection and tunneling mechanisms that write the memory can occur during normal device operation. The memory updates and learning are bidirectional because the injection and tunneling mechanisms add and remove electrons from the floating gate, respectively. Because the memory updates depend on both the stored memory and the pFETs terminal voltages, and because they are bidirectional, the devices can implement on-line learning functions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC +1
Method and apparatus for multiple byte or page mode programming of a flash memory array
A memory array contains memory cells designed to be erased using Fowler-Nordheim ("FN") tunneling through the channel area, and programmed using either channel hot electron injection ("CHE") or channel-initiated secondary electron injection ("CISEI"). To reduce disturbance of the floating gate potential of unselected memory cells during programming operations and read operations, the unselected word lines are brought to a negative potential rather than ground potential. To reduce disturbance of the floating gate potential of unselected memory cells during FN erase operations, the unselected word lines are brought to a positive potential rather than ground potential.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for operating NOR type flash memory device including SONOS cells
InactiveUS6847556B2Easy to integrateSimple processTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineFowler nordheim
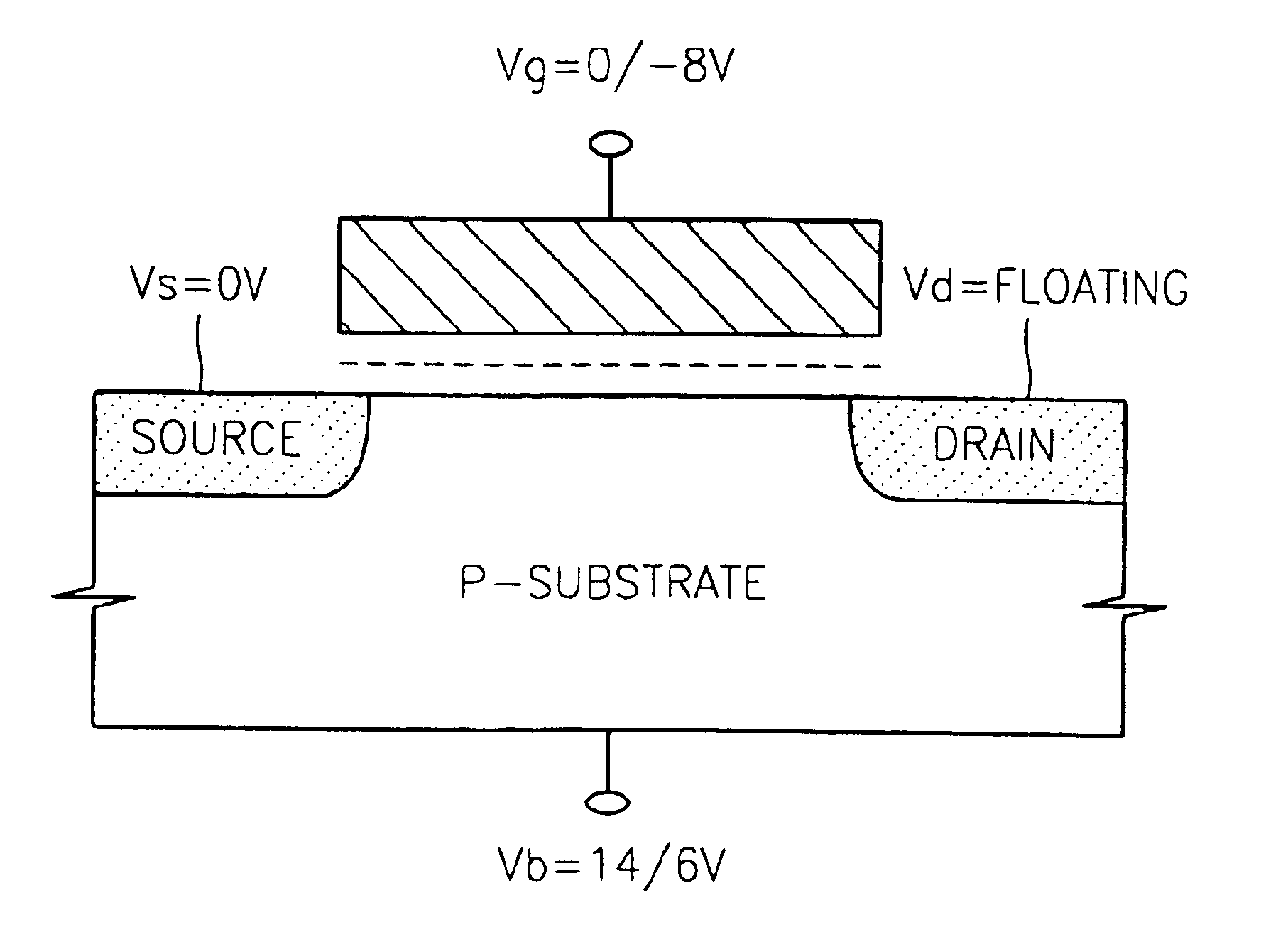
Provided is a method for operating a NOR-type flash memory device using SONOS cells. The SONOS cells are selectively programmed using channel hot electron injection and erased using Fowler-Nordheim tunneling and hot hole injection. When the SONOS cells are programmed, a voltage within a range of 8V-12V is applied to a selected word line and a voltage within a range of 3V-6V is applied to a selected bit line. When the SONOS cells are erased, the selected word line is ground and a voltage within a range of 13V-18V is applied to a substrate. Alternatively, a voltage of about −8V is applied to the selected word line, a voltage of about 6V is applied to the substrate, and a bit line and a source line float.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050199940A1Reduce the impactReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
A MONOS nonvolatile memory of a split gate structure, wherein writing and erasing are performed by hot electrons and hot holes respectively, is prone to cause electrons not to be erased and to remain in an Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall and that results in the deterioration of rewriting durability. When long time erasing is applied as a measure to solve the problem, drawbacks appear, such as the increase of a circuit area caused by the increase of the erasing current and the deterioration of retention characteristics. In the present invention, an Si nitride film is formed by the reactive plasma sputter deposition method that enables oriented deposition and the Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall is removed at the time when a top Si oxide film is formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-volatile memory cell having a silicon-oxide nitride-oxide-silicon gate structure
A non-volatile memory cell able to be written in a first direction and read in a second direction is described. The memory cell includes one or two charge trapping regions located near either the source or the drain, or both the source and the drain. During a programming operation, electrons can be injected into the charge trapping region by hot electron injection. During an erasing operation, holes can be injected into the charge trapping region. Embodiments of the invention include a charge trapping region that is overlapped by the control gate only to an extent where the electrons that were injected during a programming operation can be erased later by injecting holes in the charge trapping region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060065919A1Reduce voltageImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesExtinctionPeak value
To provide a nonvolatile memory device suppressing a reduction of a data retention characteristic even if charges injected and stored into a local area of a nitride film is redistributed to achieve a reduction of voltage, the nonvolatile memory device in which hot electrons are injected into the local area of the nitride film at one or both of source•drain regions side to store data in a memory transistor is satisfied with a standard for evaluating a film quality of the nitride film, the standard being defined by one of the followings: a density of the bond group of silicon and hydrogen being under 1×1021 cm−3; an extinction coefficient in an ultraviolet region at a wavelength of 240 nm being under 0.10 or the extinction coefficient in 230 nm being under 0.14; an optical energy, a peak wavelength of an luminance spectrum, or a peak energy thereof.
Owner:SONY CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7115943B2Improve performanceReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
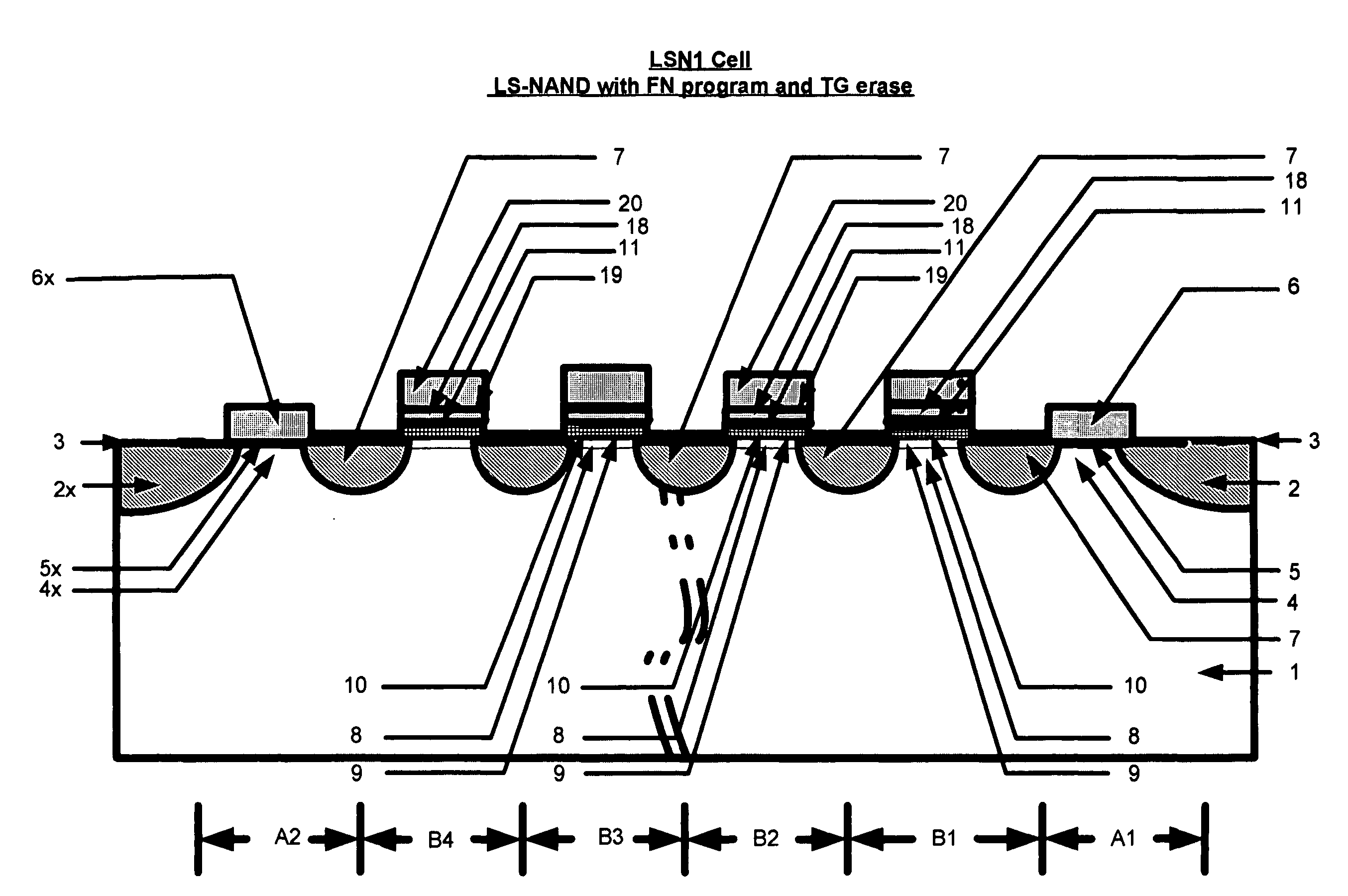
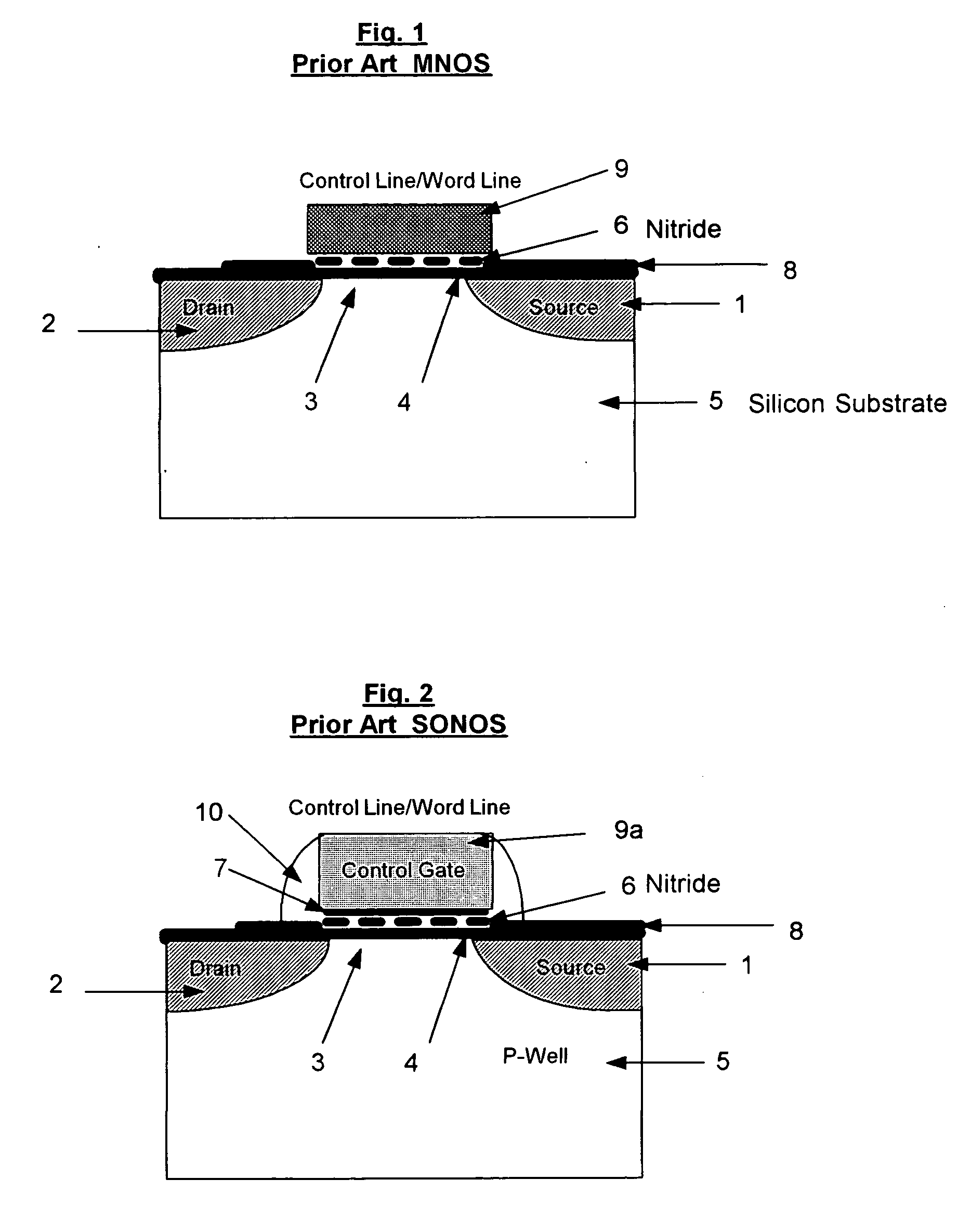
Location-specific NAND (ls NAND) memory technology and cells
The use of a Nitride layer or a silicon-nodule layer capable of location-specific (LS) charge storage, allow easy vertical scaling and implementation of NOR and NAND NVM array and technology. If the charge is stored in the traps in the Nitride storage layer, a Oxide Nitride Oxide is used as the storage element and if charge is stored in potential wells of discrete silicon-nodules, or Carbon Bucky-ball layers, an Oxide silicon-nodule Oxide storage element, or an Oxide Bucky-ball Oxide layer is used as the storage element. The problem of location-specific NAND memory is the inability to erase the cells with repeatable results. A novel erase method, Tunnel Gun (TG) method, that generate holes for consistent erase of LS storage elements and typical NAND Cells that erase by the disclosed method and programmed by either by Fouler-Nordheim (FN) tunneling or Low Current Hot Electron (LCHE) method are disclosed.
Owner:THOMAS MAMMEN
Solid state surface catalysis reactor
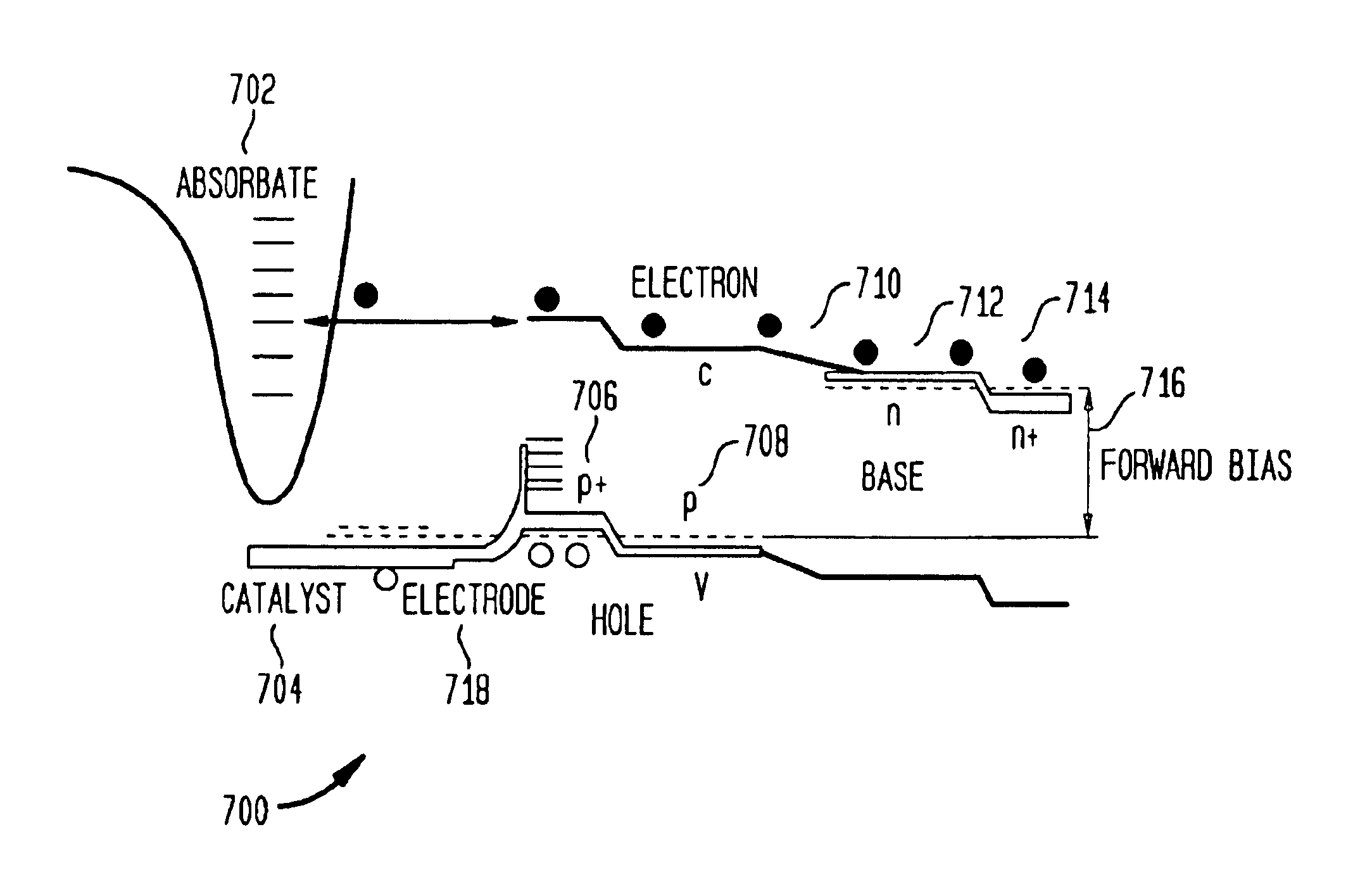
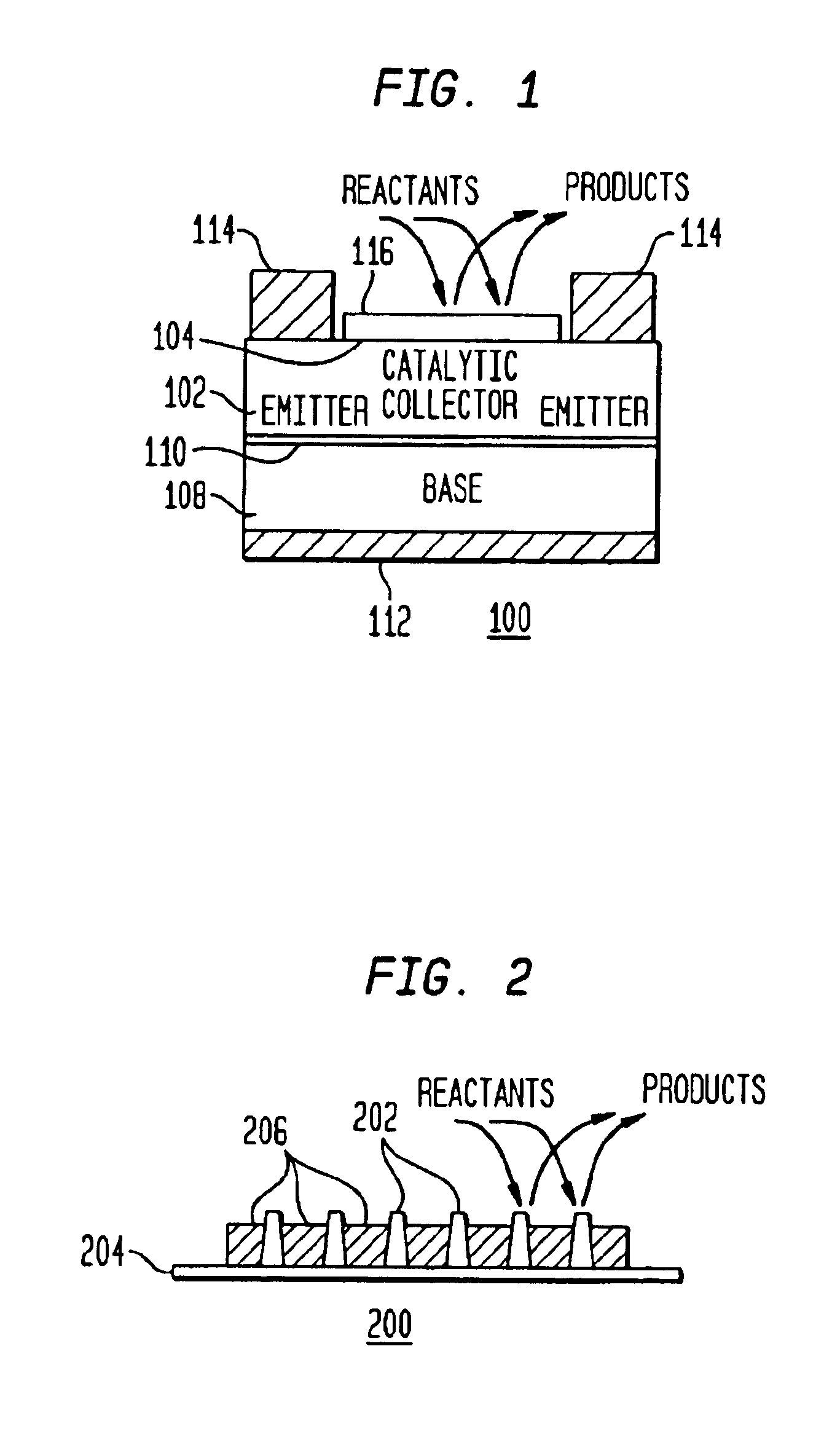
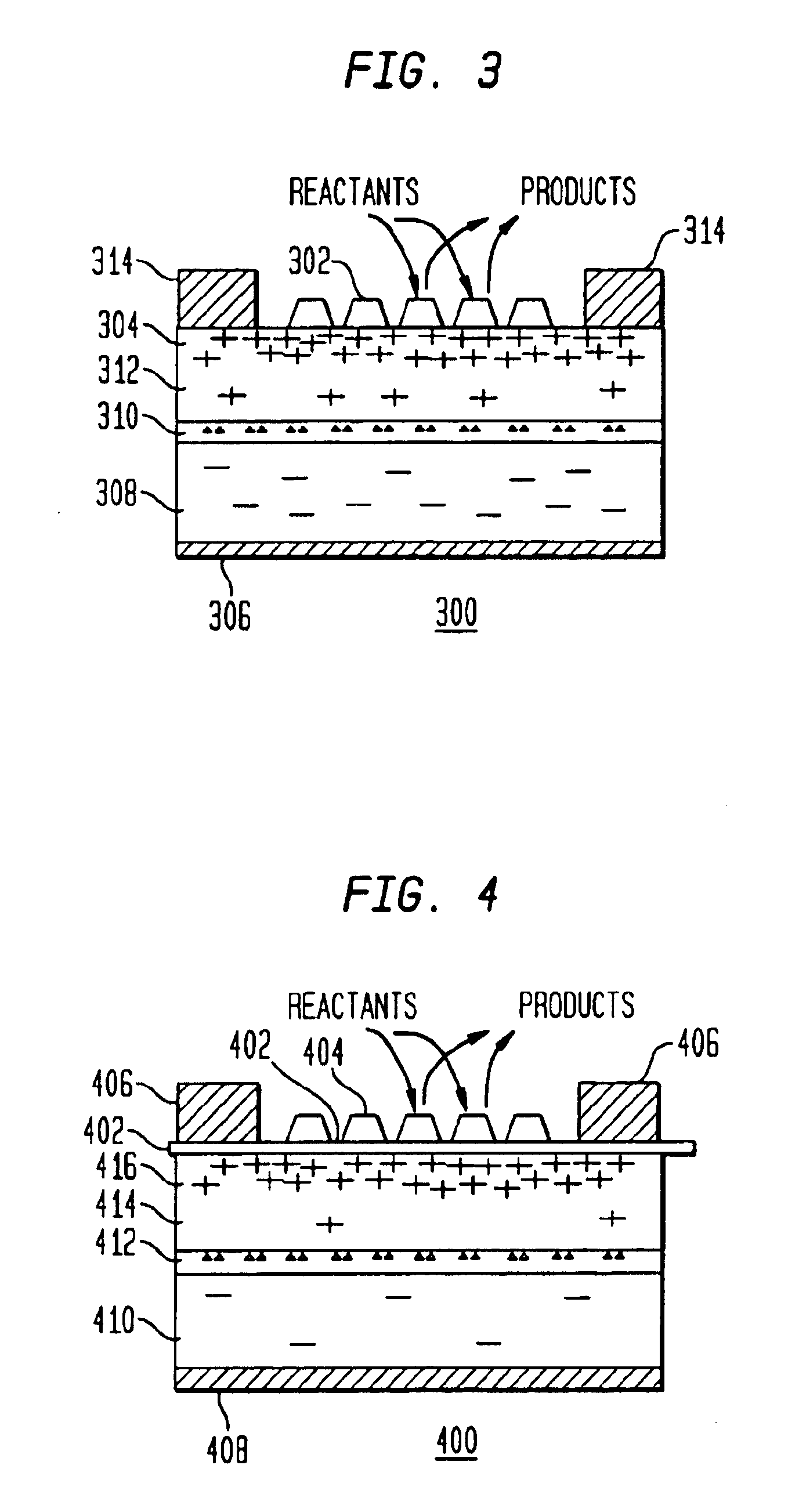
InactiveUS6916451B1Physical/chemical process catalystsPhotovoltaicsChemical reactionElectric generator
A method and apparatus to stimulate chemical reactions on a catalyst surface using electricity, and the reverse process to convert energy released from chemical reactions into electricity. A reversible emitter generates electrons which are injected into reactants on the catalyst surface, exciting chemically reactive vibrational resonances. Hot electrons created in the emitter region of a semiconductor junction diffuse to the co-located collector region and catalyst surface. Catalyst clusters or films bonded on the collector surface transfer the hot electrons to or from the catalyst surface having adsorbed reactants. The dimension of the catalyst-collector is less than the energy mean free path of hot electrons. The hot electrons excite reactant vibrations before thermalizing with the substrate lattice thereby accelerating reactions. The hot electrons are also generated by the same reactions on a catalyst surface. The method and apparatus is reversible and may be operated as an electric generator using chemical reactions.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
Programming methods for multi-level flash EEPROMS
InactiveUS6845039B2Faster multi-level programmingRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgrammable read-only memoryDrain current
A method is provided for programming a memory cell of an electrically erasable programmable read only memory. The memory cell is fabricated on a substrate and comprises a source region, a drain region, a floating gate, and a control gate. The memory cell has a threshold voltage selectively configurable into one of at least three programming states. The method includes generating a drain current between the drain region and the source region by applying a drain-to-source bias voltage between the drain region and the source region. The method further includes injecting hot electrons from the drain current to the floating gate by applying a gate voltage to the control gate. A selected threshold voltage for the memory cell corresponding to a selected one of the programming states is generated by applying a selected constant drain-to-source bias voltage and a selected gate voltage.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
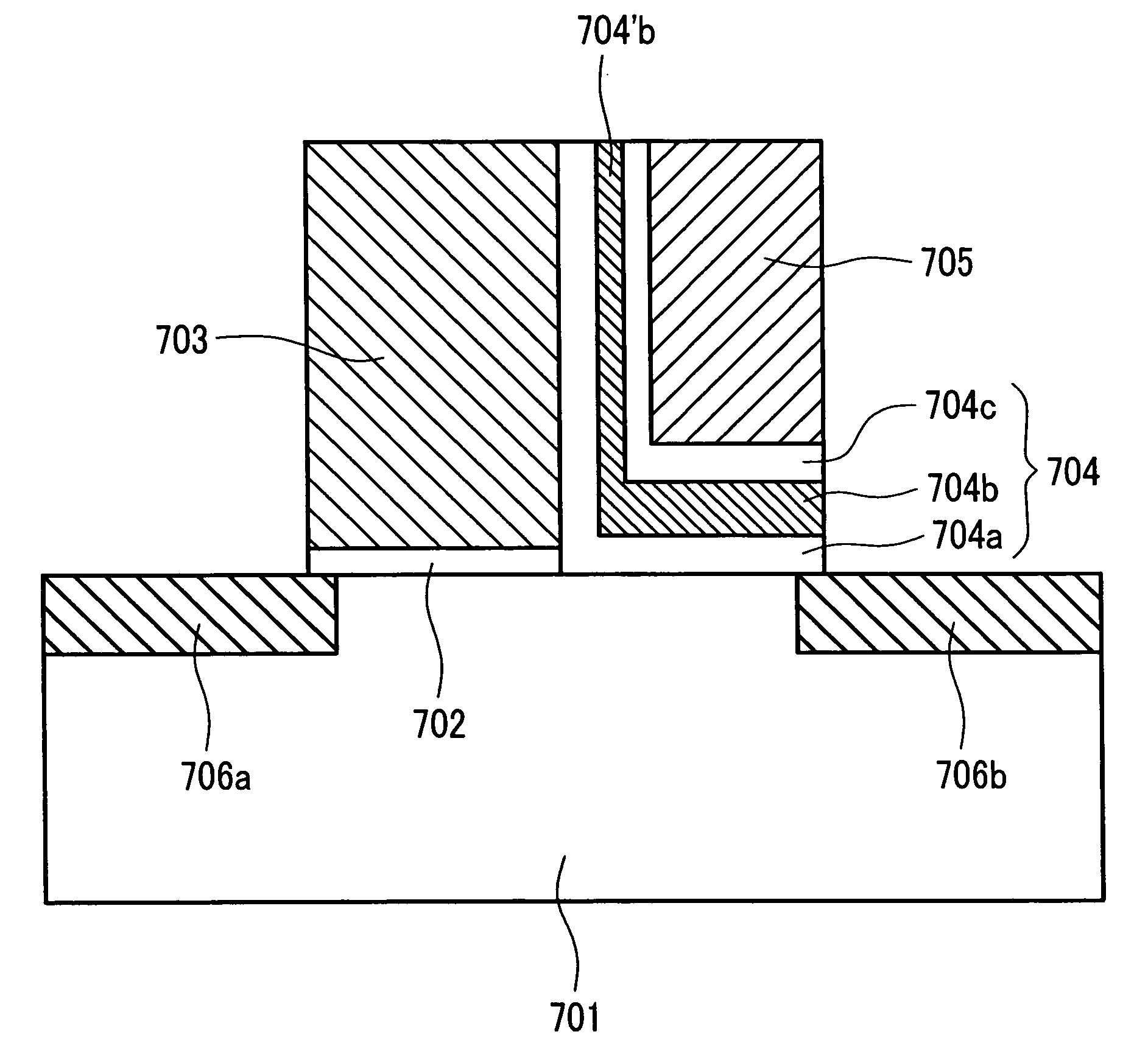
Semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070096224A1Quality improvementHigh yieldTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDevice material
A thin film transistor of the present invention has an active layer including at least source, drain and channel regions formed on an insulating surface. A high resistivity region is formed between the channel region and each of the source and drain regions. A film capable of trapping positive charges therein is provided on at least the high resistivity region so that N-type conductivity is induced in the high resistivity region. Accordingly, the reliability of N-channel type TFT against hot electrons can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Monolithic, combo nonvolatile memory allowing byte, page and block write with no disturb and divided-well in the cell array using a unified cell structure and technology with a new scheme of decoder and layout
InactiveUS7064978B2Large positive voltageSmaller memory cell.Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerFowler nordheim
A nonvolatile memory array has a single transistor flash memory cell and a two transistor EEPROM memory cell which maybe integrated on the same substrate. The nonvolatile memory cell has a floating gate with a low coupling coefficient to permit a smaller memory cell. The floating gate placed over a tunneling insulation layer, the floating gate is aligned with edges of the source region and the drain region and having a width defined by a width of the edges of the source the drain. The floating gate and control gate have a relatively small coupling ratio of less than 50% to allow scaling of the nonvolatile memory cells. The nonvolatile memory cells are programmed with channel hot electron programming and erased with Fowler Nordheim tunneling at relatively high voltages.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Transistor with nanocrystalline silicon gate structure
A memory is described which has memory cells that store data using hot electron injection. The data is erased through electron tunneling. The memory cells are described as floating gate transistors wherein the floating gate is fabricated using a conductive layer of nanocrystalline silicon particles. Each nanocrystalline silicon particle has a diameter of about 10 Å to 100 Å. The nanocrystalline silicon particles are in contact such that a charge stored on the floating gate is shared between the particles. The floating gate has a reduced electron affinity to allow for data erase operations using lower voltages.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Non-volatile static random access memory
InactiveUS6965524B2Easy to optimizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryFowler nordheim
In accordance with the present invention, a memory cell includes a non-volatile device and a SRAM cell. The SRAM cell includes first and second MOS transistors. The non-volatile device is a load to the SRAM cell. The memory cell may be adapted to operate differentially if a second SRAM cell and a second non-volatile device is disposed therein. If so adapted, the SRAM cells and / or the non-volatile devices when programmed store and supply complementary data. The non-volatile devices are erased prior to being programmed. Programming of the non-volatile devices may be done via hot-electron injection or Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. When a power failure occurs, the data stored in the SRAM are loaded in the non-volatile devices. After the power is restored, the data stored in the non-volatile devices are restored in the SRAM cells. The differential reading and wring of data reduces over-erase of the non-volatile devices.
Owner:O2IC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and a method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060008992A1Shorten the timeTime to erase be shortenedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringReverse bias
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com