Patents
Literature
598 results about "Potential well" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
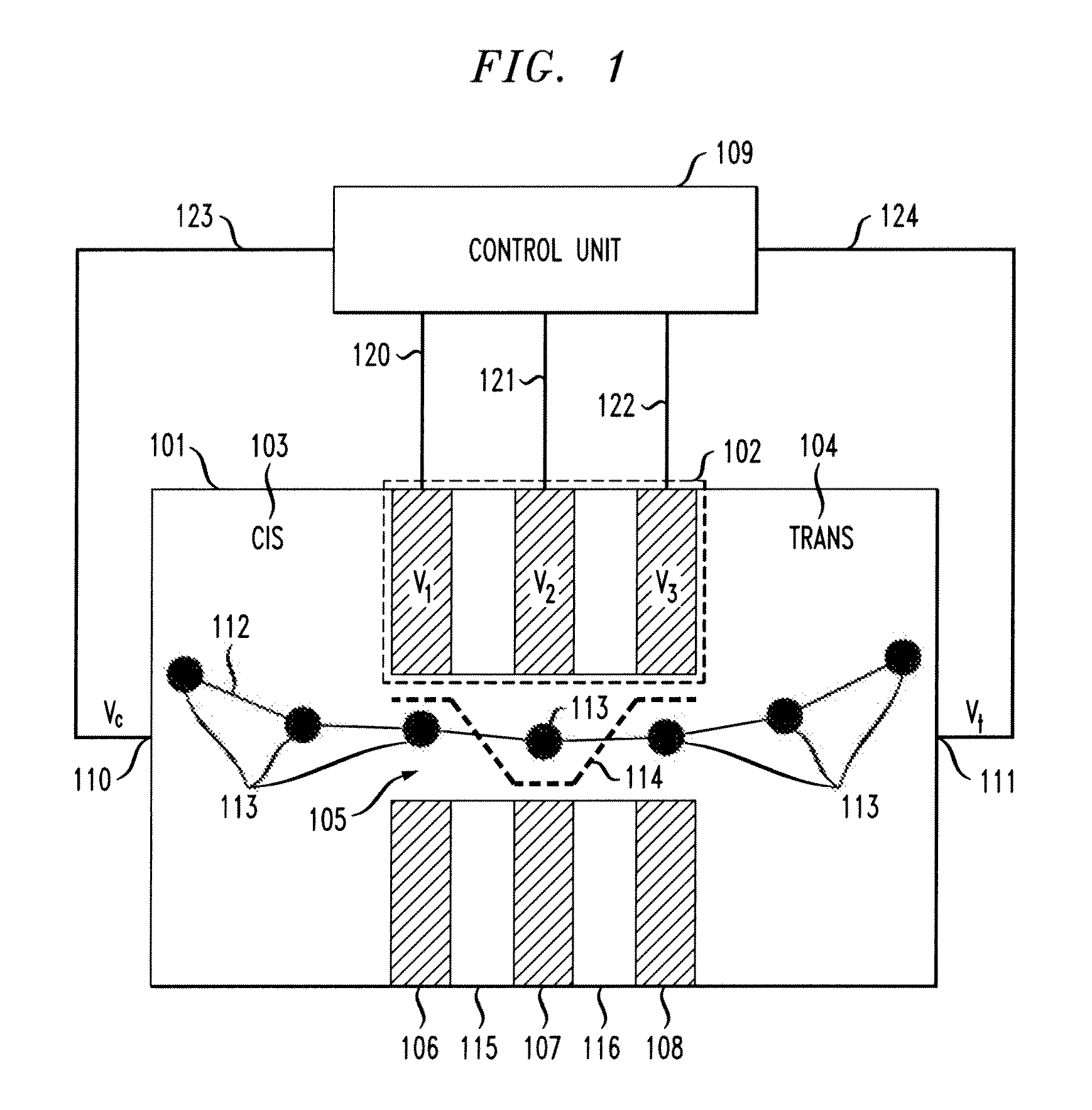
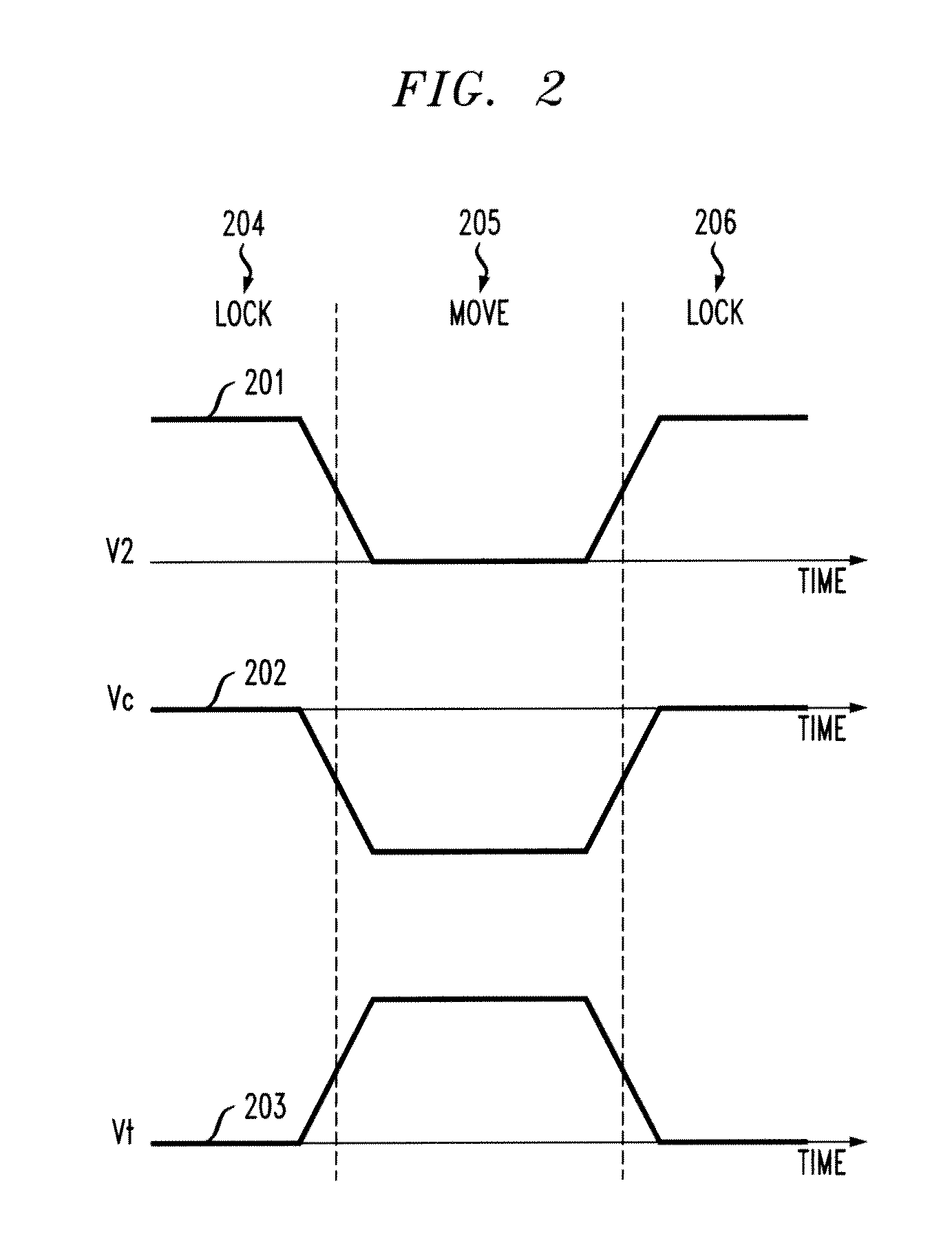
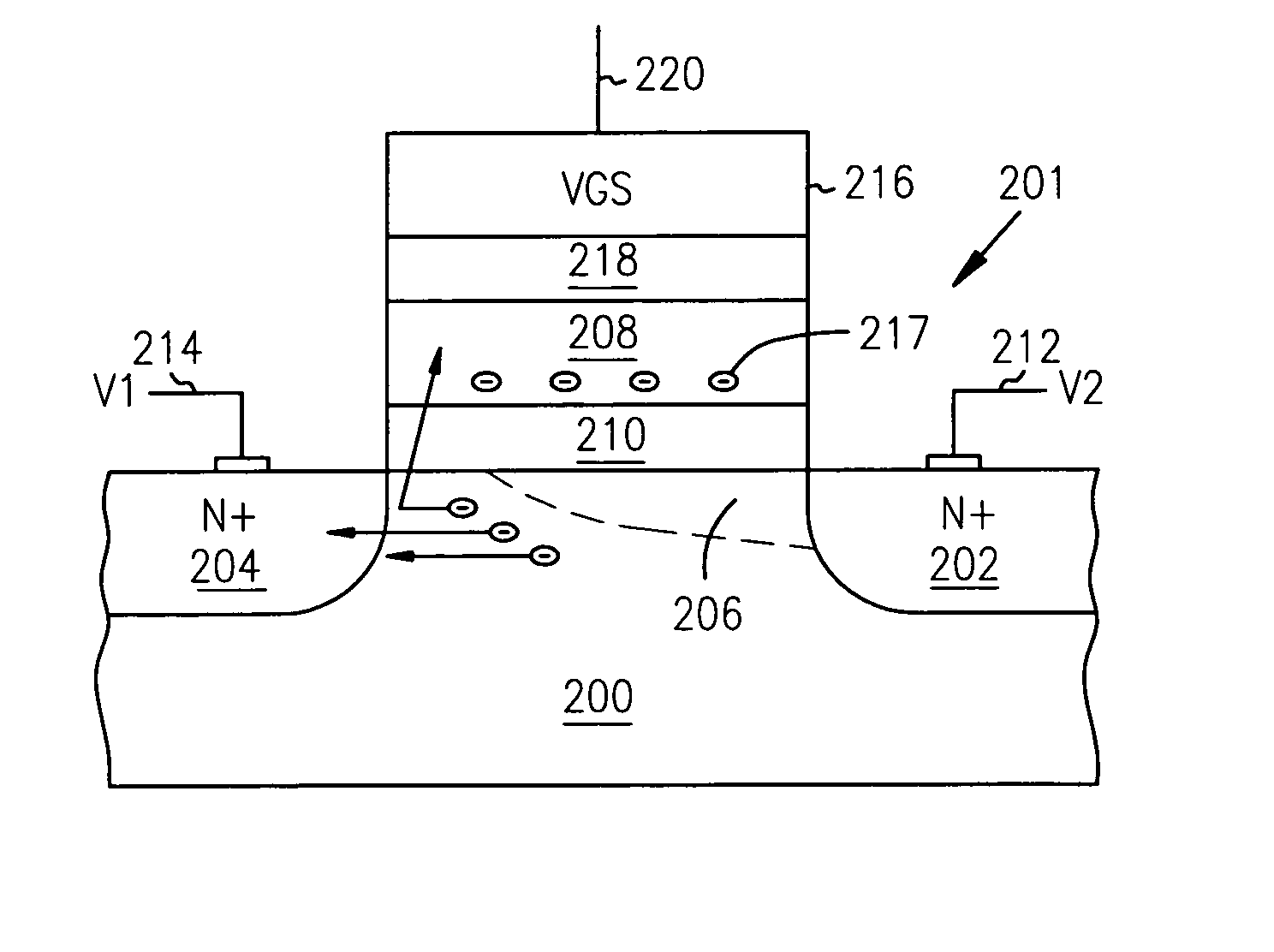
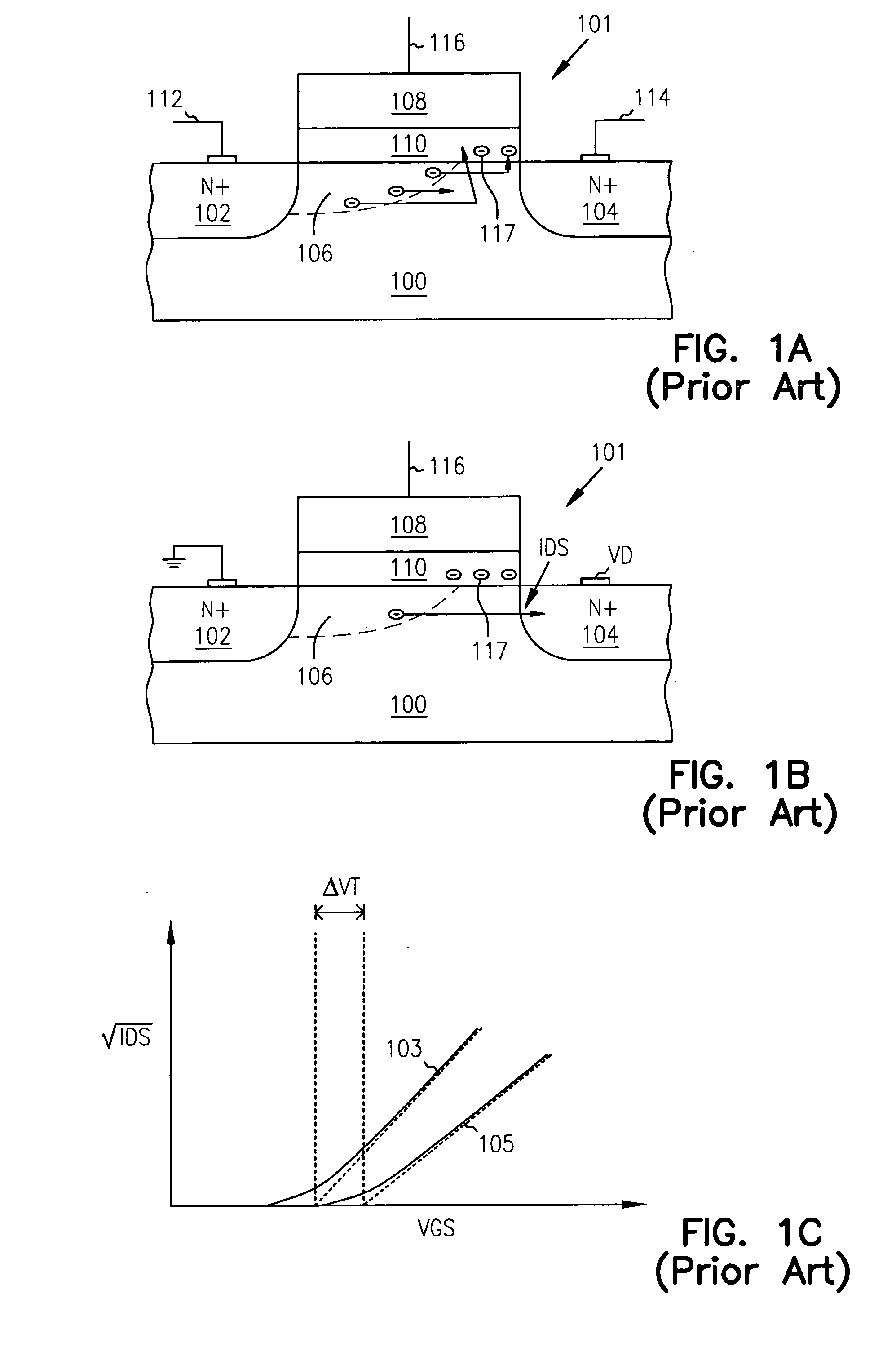
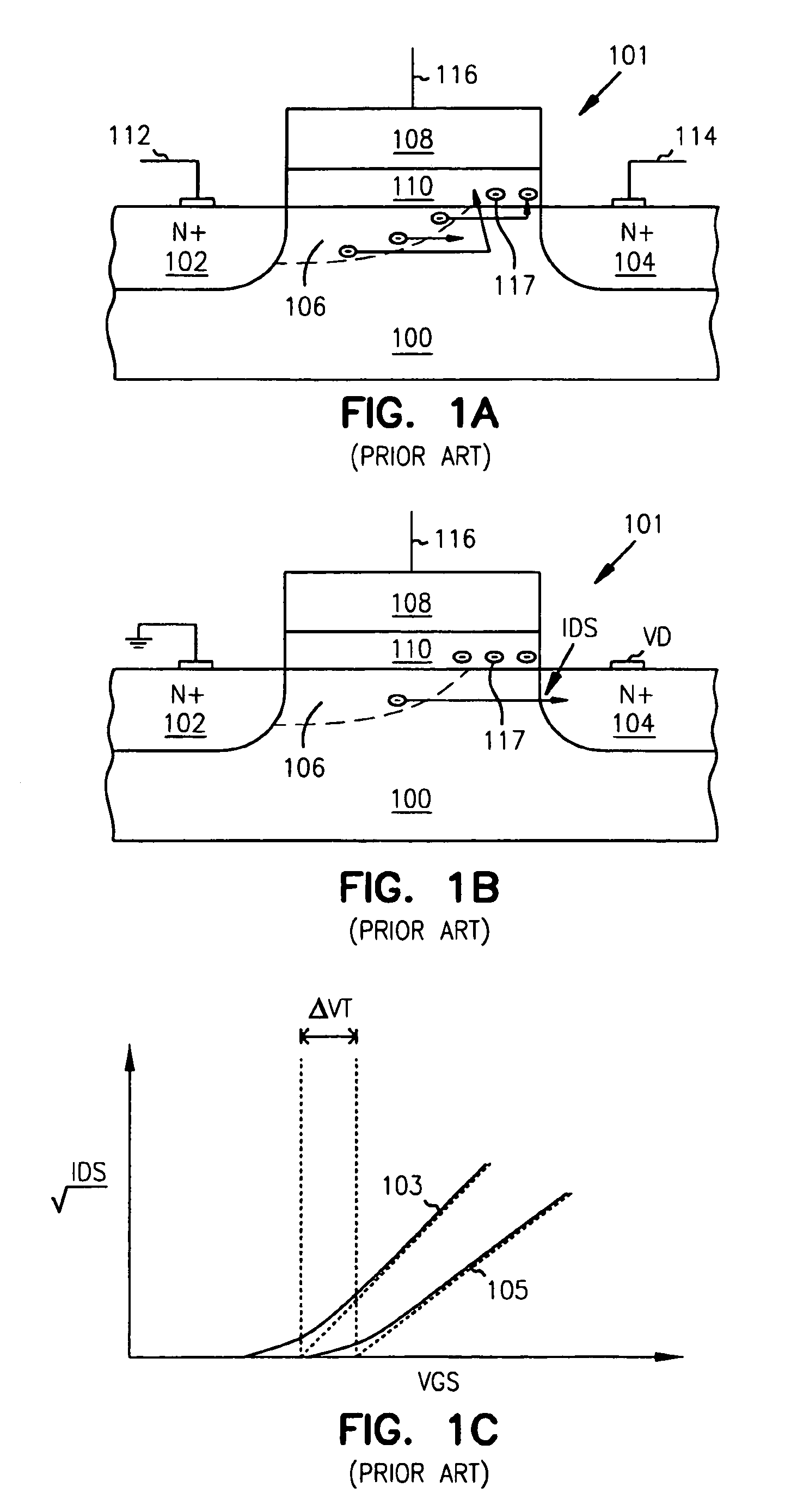
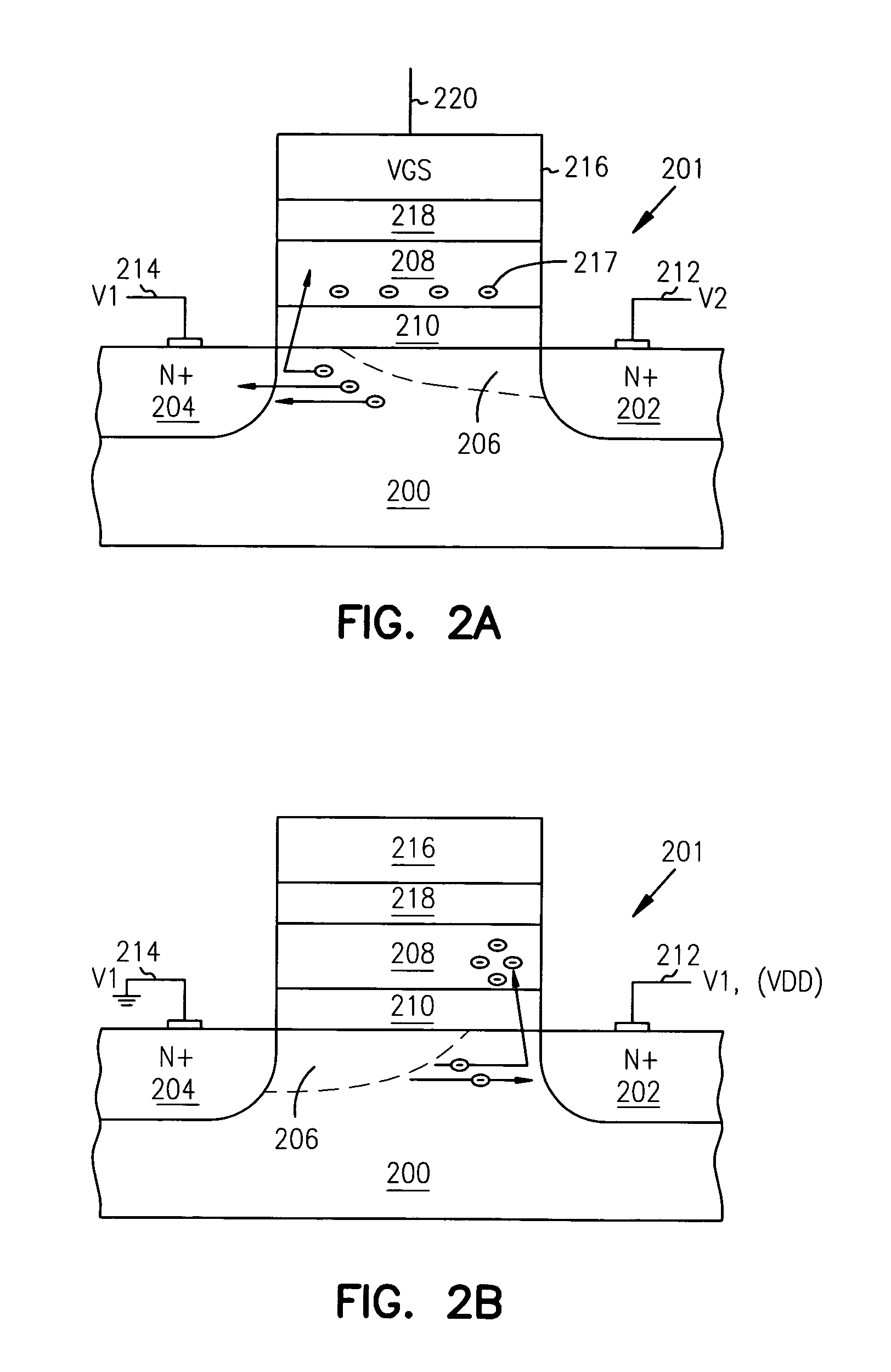
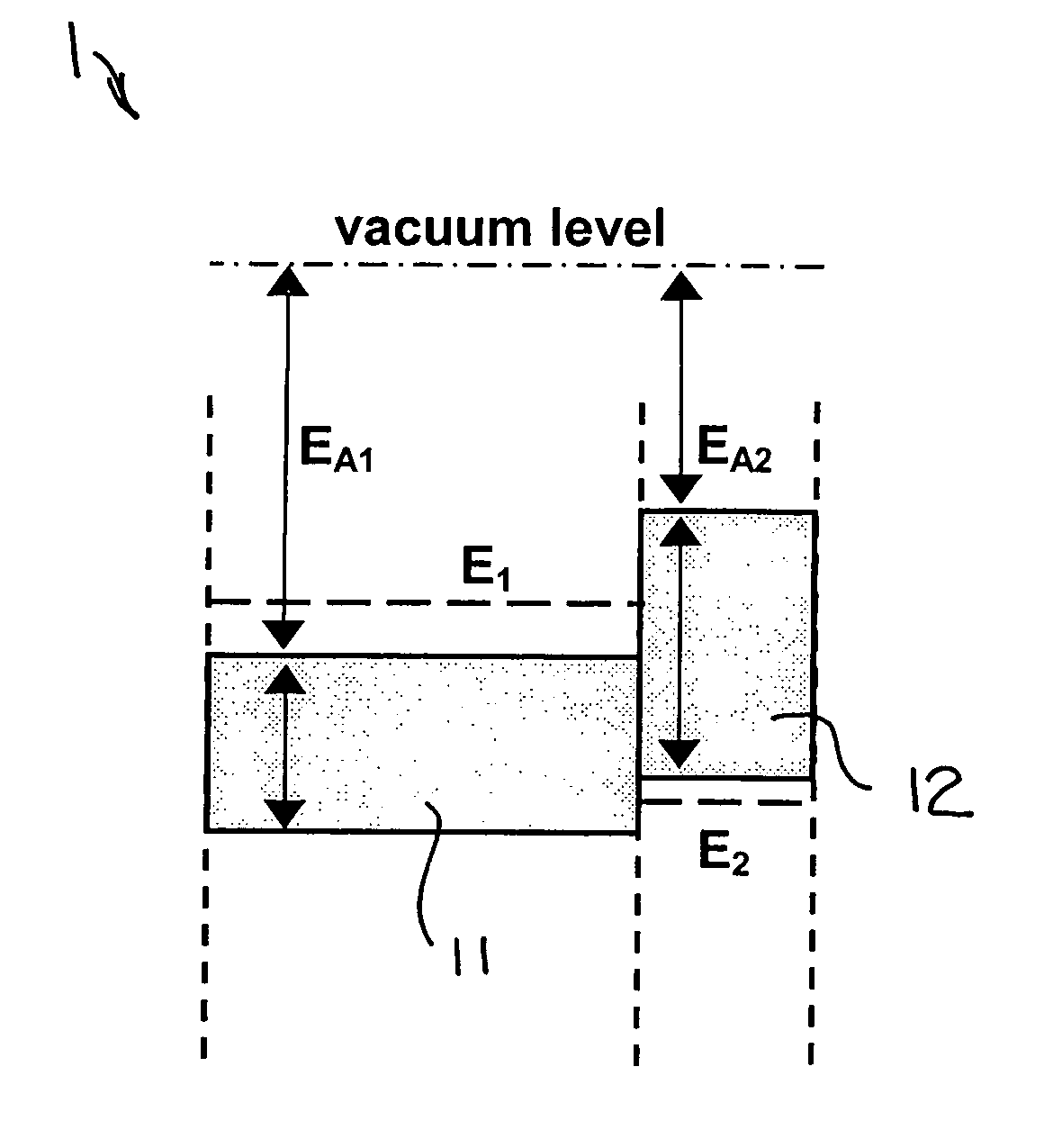
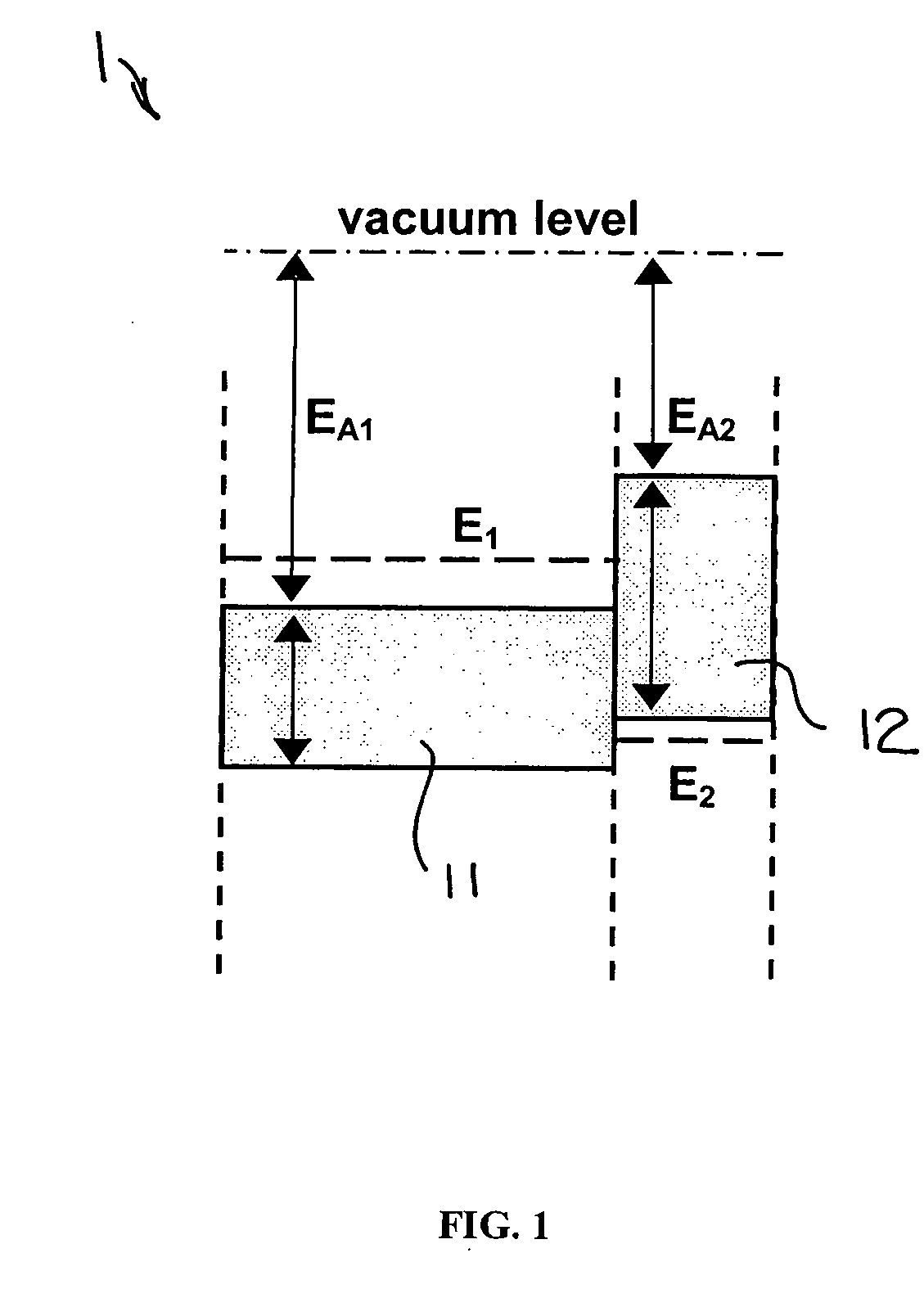
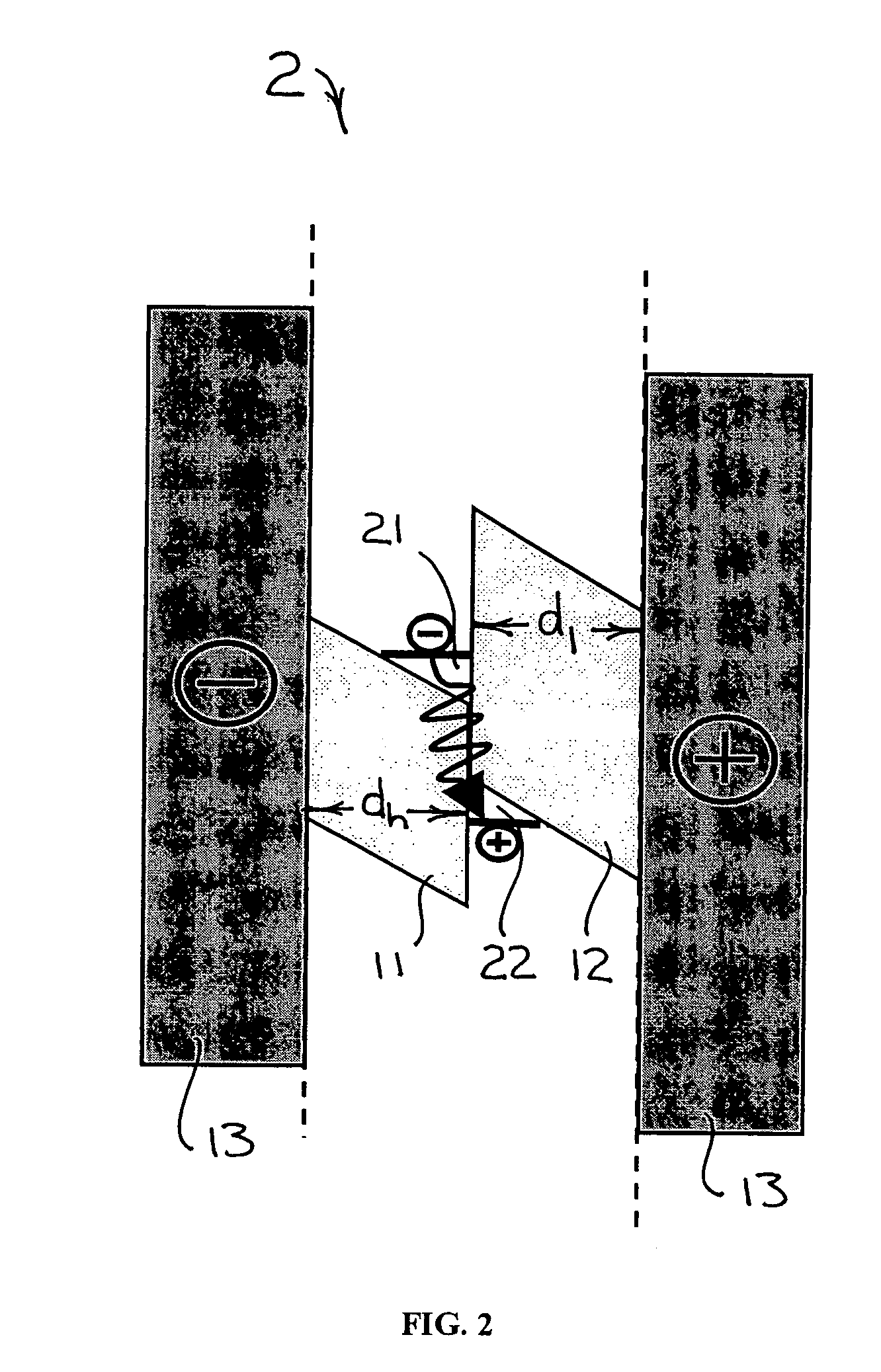
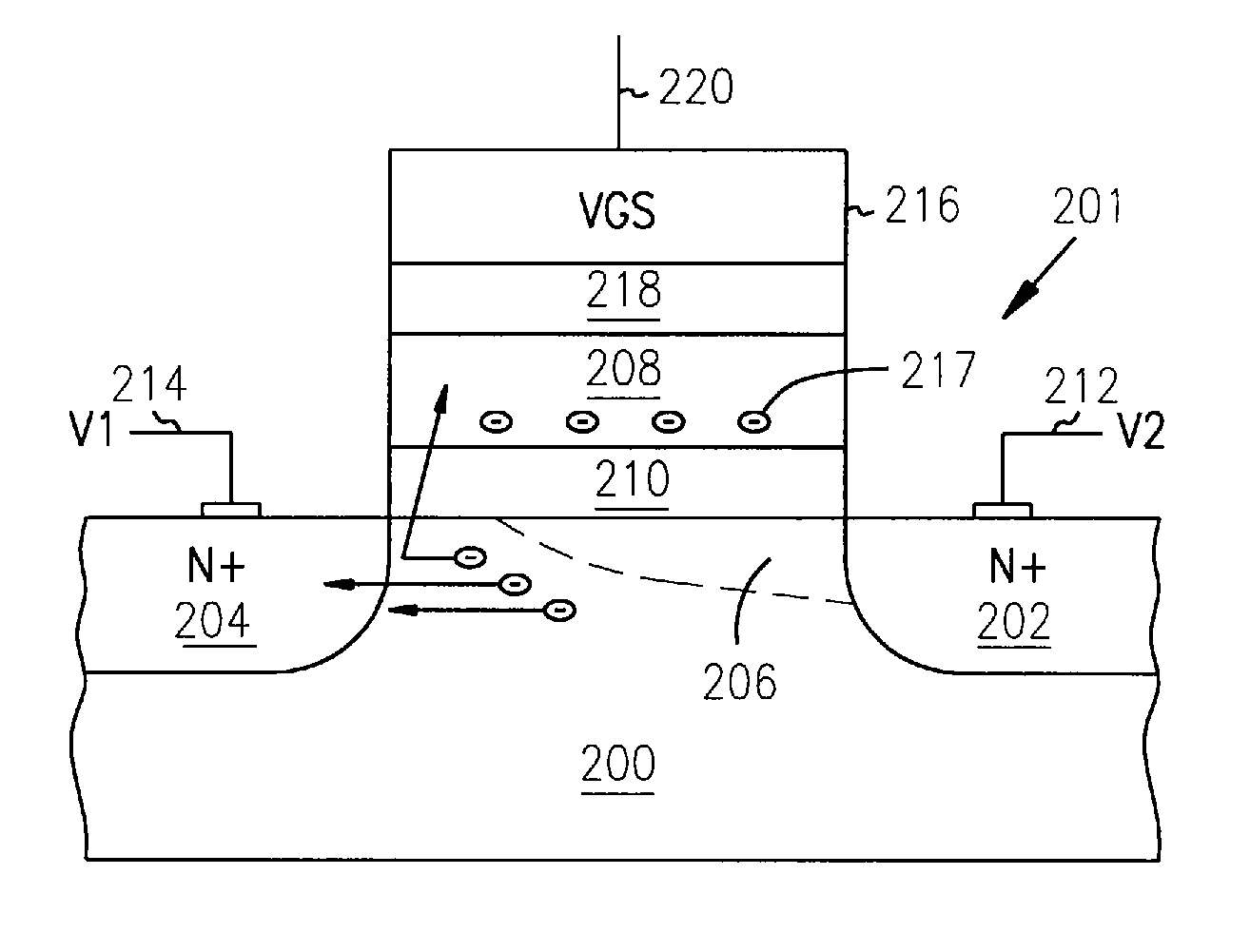
A potential well is the region surrounding a local minimum of potential energy. Energy captured in a potential well is unable to convert to another type of energy (kinetic energy in the case of a gravitational potential well) because it is captured in the local minimum of a potential well. Therefore, a body may not proceed to the global minimum of potential energy, as it would naturally tend to due to entropy.
Systems and Methods for Controlling the Position of a Charged Polymer Inside a Nanopore
Techniques for controlling the position of a charged polymer inside a nanopore are provided. For example, one technique includes using electrostatic control to position a linear charged polymer inside a nanopore, and creating an electrostatic potential well inside the nanopore, wherein the electrostatic potential well controls a position of the linear charged polymer inside the nanopore.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Systems and Methods for Controlling the Position of a Charged Polymer Inside a Nanopore
Techniques for controlling the position of a charged polymer inside a nanopore are provided. For example, one technique includes using electrostatic control to position a linear charged polymer inside a nanopore, and creating an electrostatic potential well inside the nanopore, wherein the electrostatic potential well controls a position of the linear charged polymer inside the nanopore.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Memory utilizing oxide-conductor nanolaminates
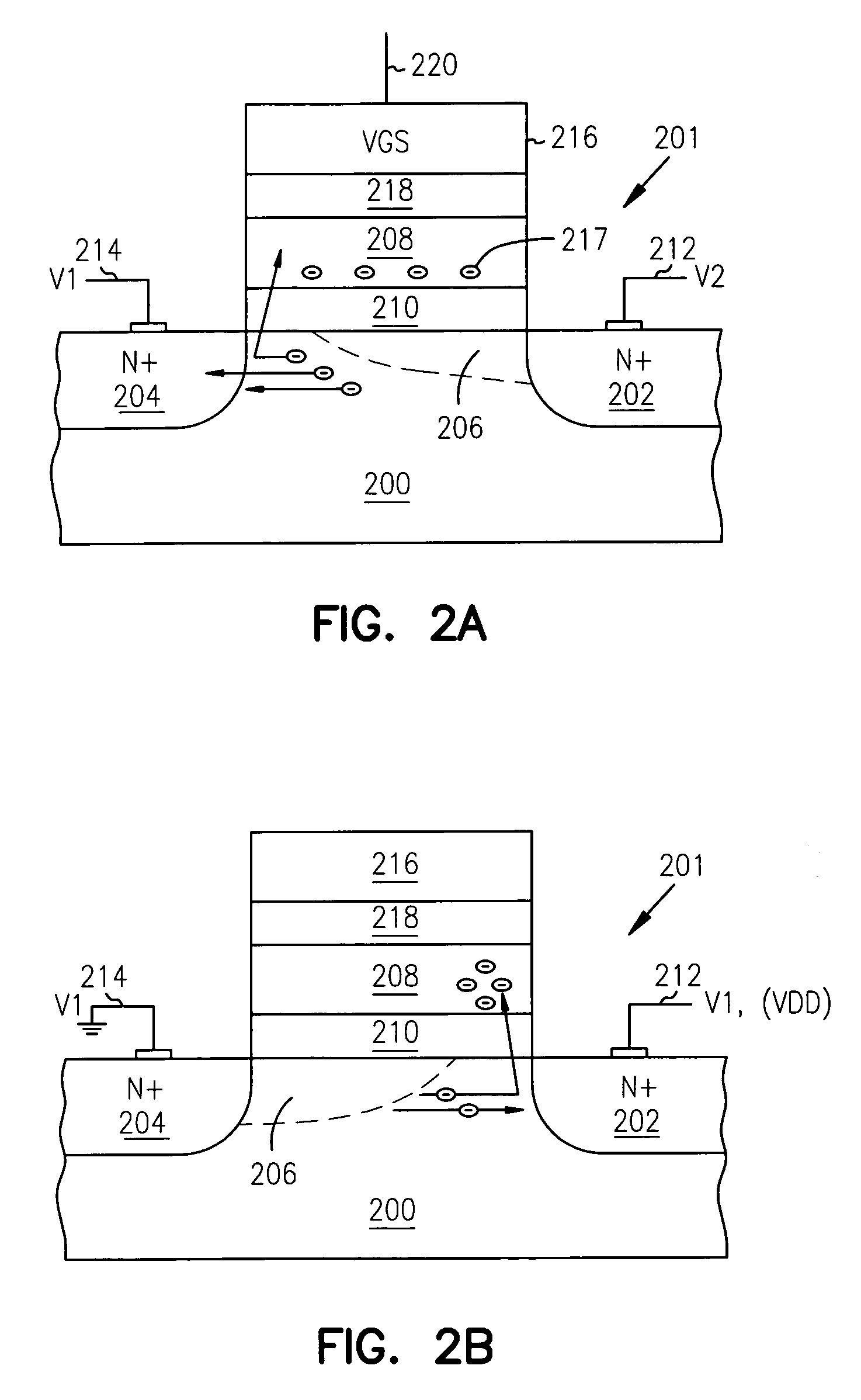
Structures, systems and methods for floating gate transistors utilizing oxide-conductor nanolaminates are provided. One floating gate transistor embodiment includes a first source / drain region, a second source / drain region, and a channel region therebetween. A floating gate is separated from the channel region by a first gate oxide. The floating gate includes oxide-conductor nanolaminate layers to trap charge in potential wells formed by different electron affinities of the oxide-conductor nanolaminate layers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Array of luminescent elements
Light emitting systems and method of fabricating the same are disclosed. The light emitting system includes two or more monolithically integrated luminescent elements. Each luminescent element includes an electroluminescent device and a dedicated switching circuit for driving the electroluminescent device. At least one luminescent element includes a potential well for down converting light emitted by the electroluminescent device in the luminescent element.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
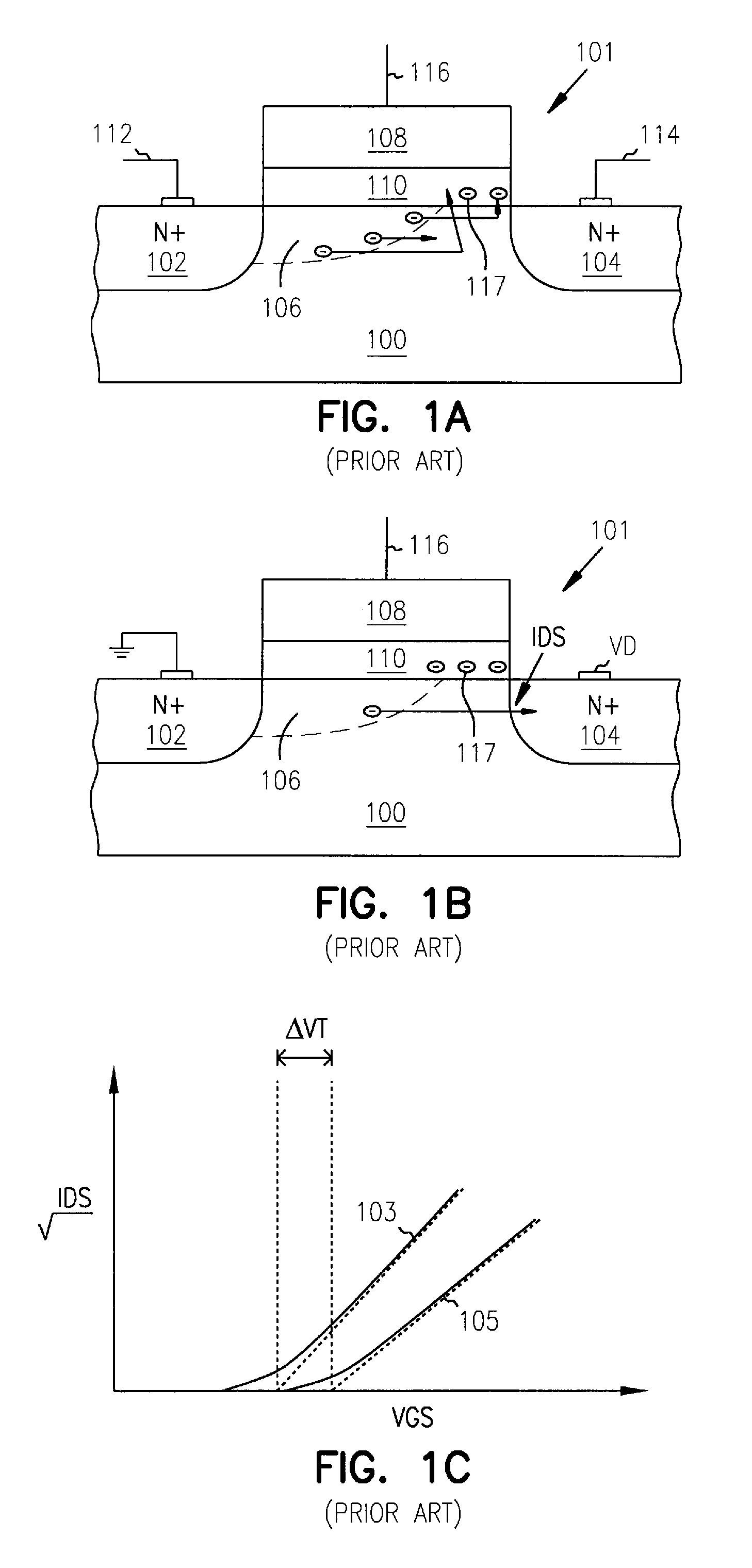
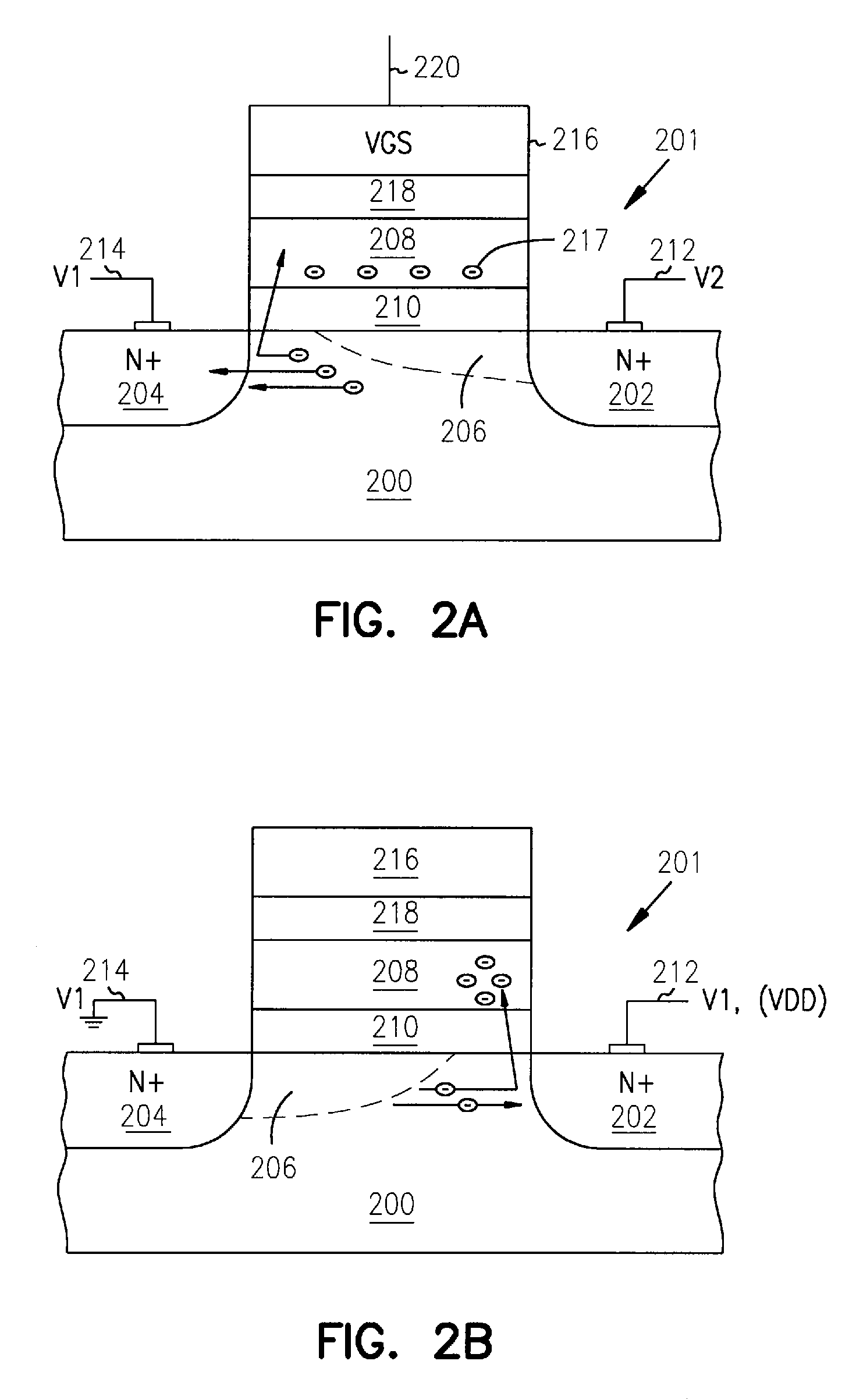
Complete-charge-transfer vertical color filter detector
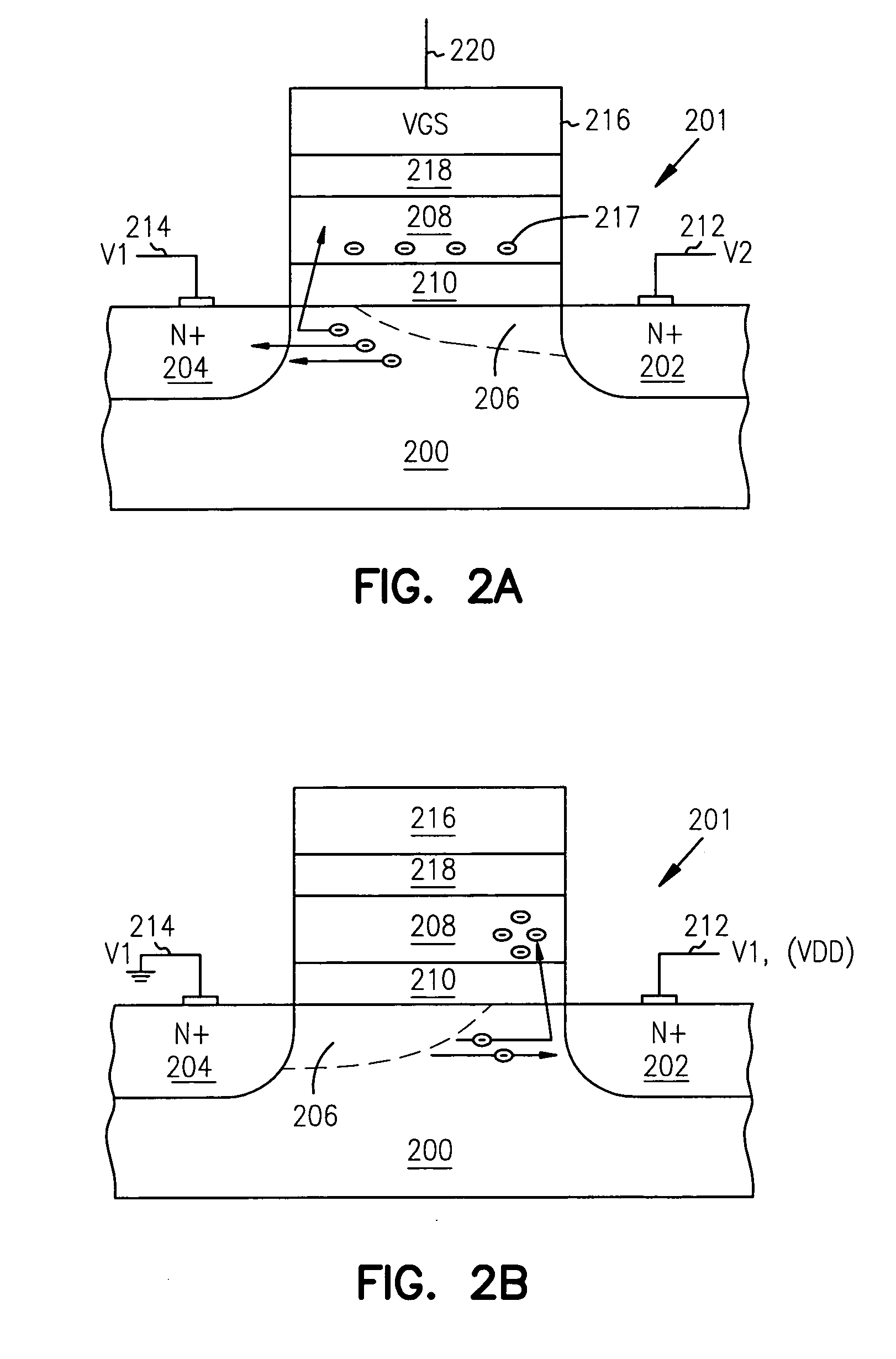
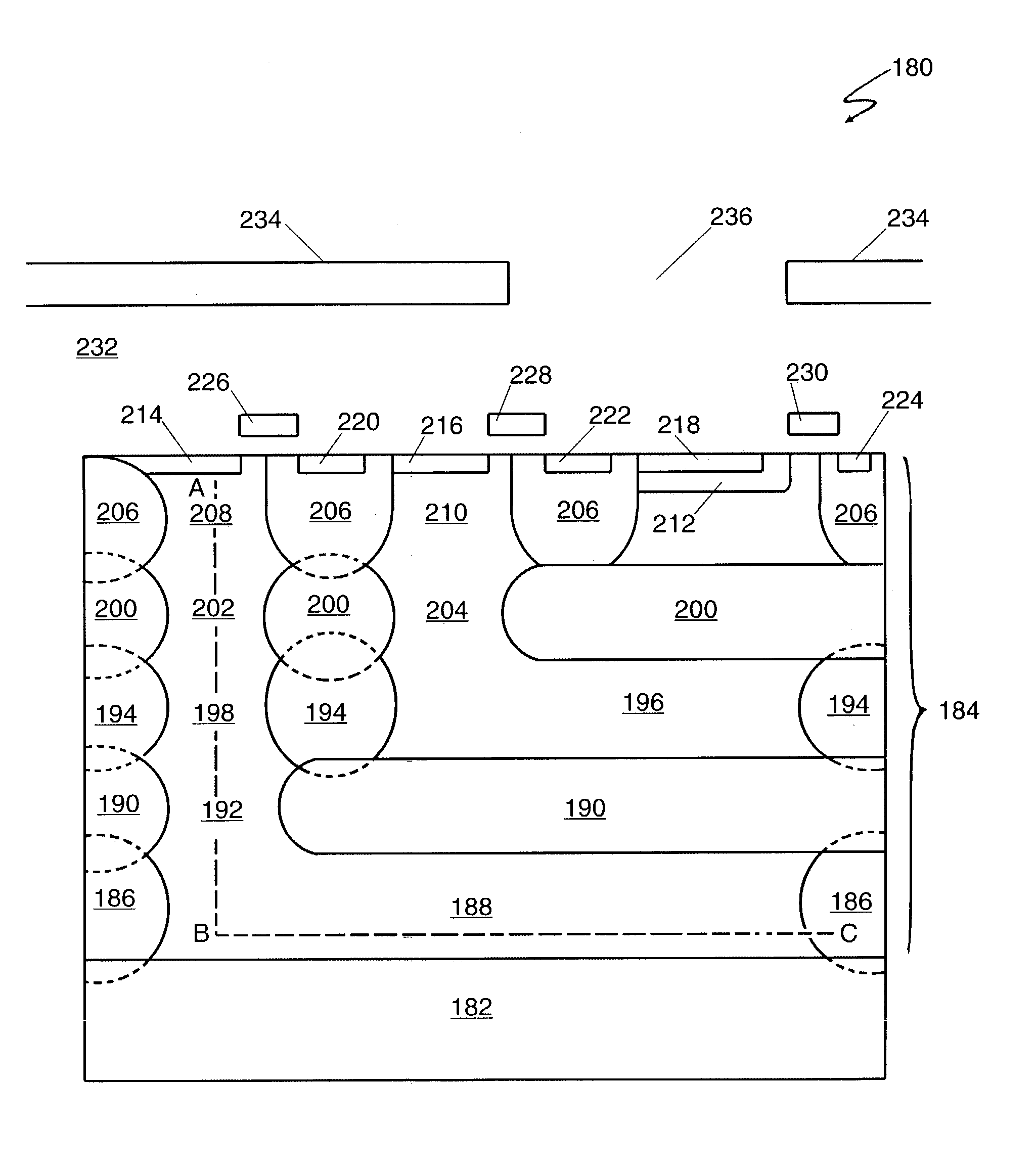
InactiveUS7132724B1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesPotential wellSemiconductor materials
A vertical-color-filter detector disposed in a semiconductor structure comprises a complete-charge-transfer detector comprising semiconductor material doped to a first conductivity type and has a horizontal portion disposed at a first depth in the semiconductor structure substantially below an upper surface thereof and a vertical portion communicating with the upper surface of the semiconductor structure. The complete-charge-transfer detector is disposed within a first charge container forming a potential well around it. The horizontal portion of the complete-charge-transfer detector has a substantially uniform doping density in a substantially horizontal direction and the vertical portion of the complete-charge-transfer detector has a doping density that is a monotonic function of depth and is devoid of potential wells. A first charge-transfer device is disposed substantially at an upper surface of the semiconductor structure and is coupled to the vertical portion of the complete-charge-transfer detector.
Owner:FOVEON
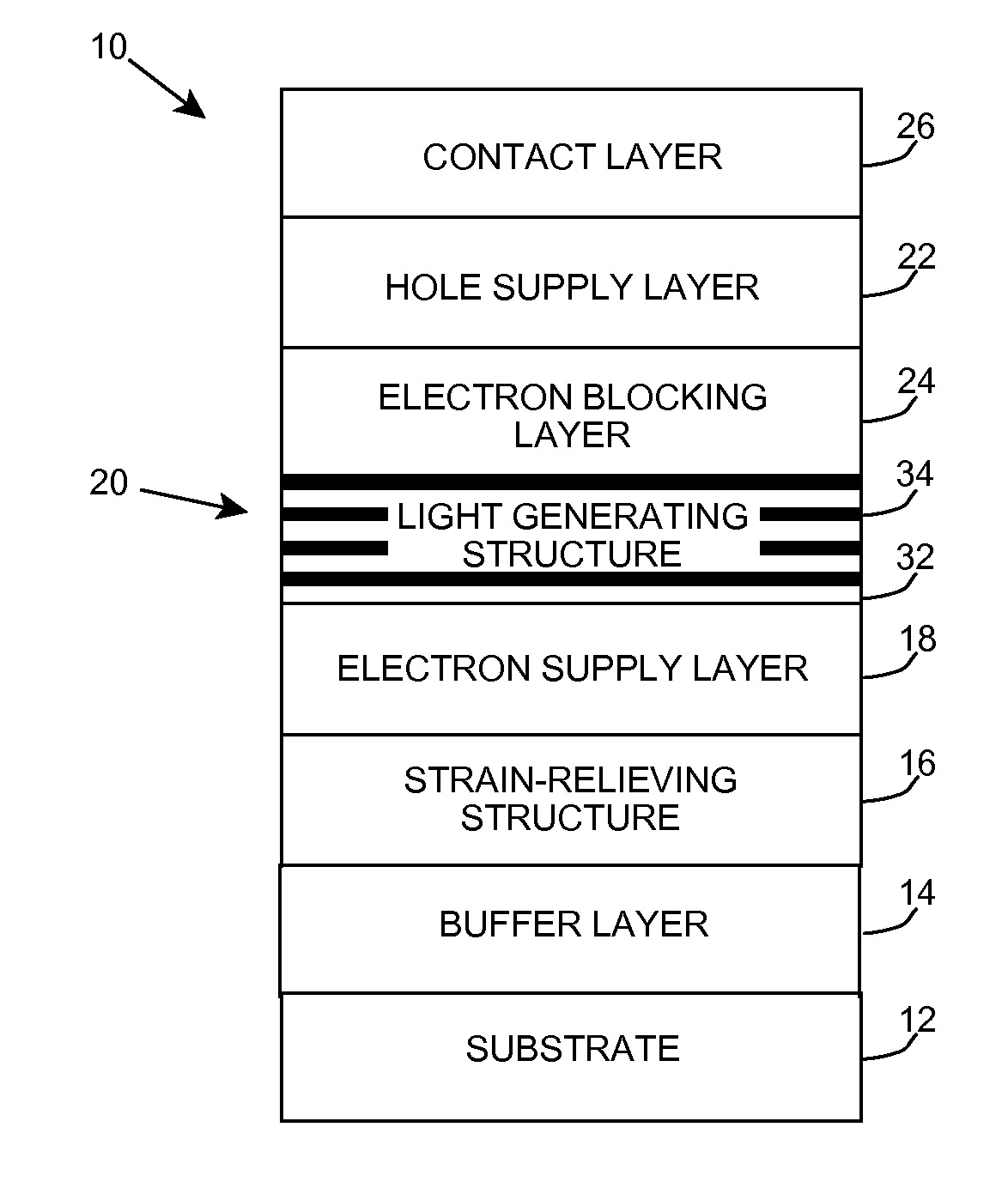
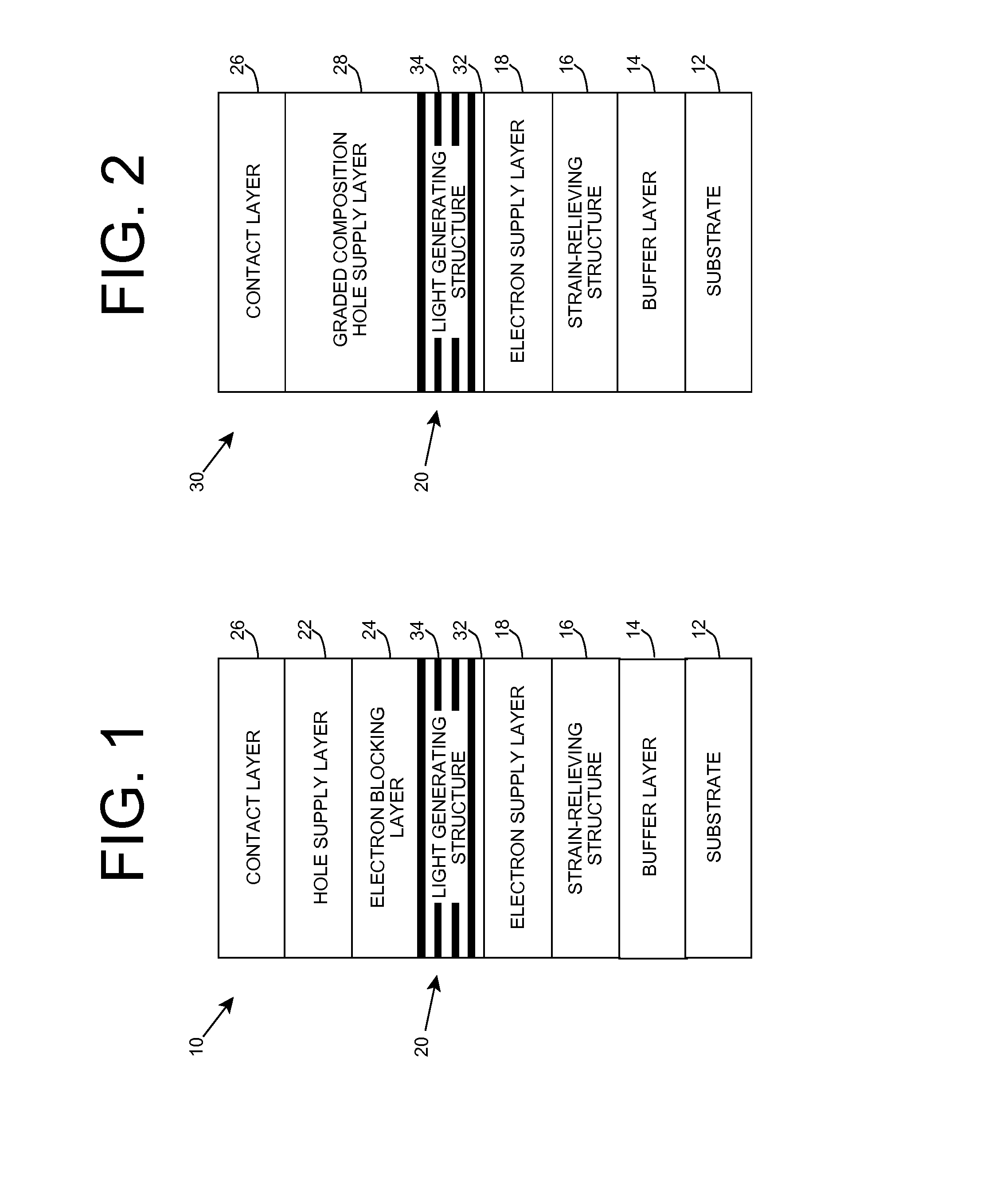
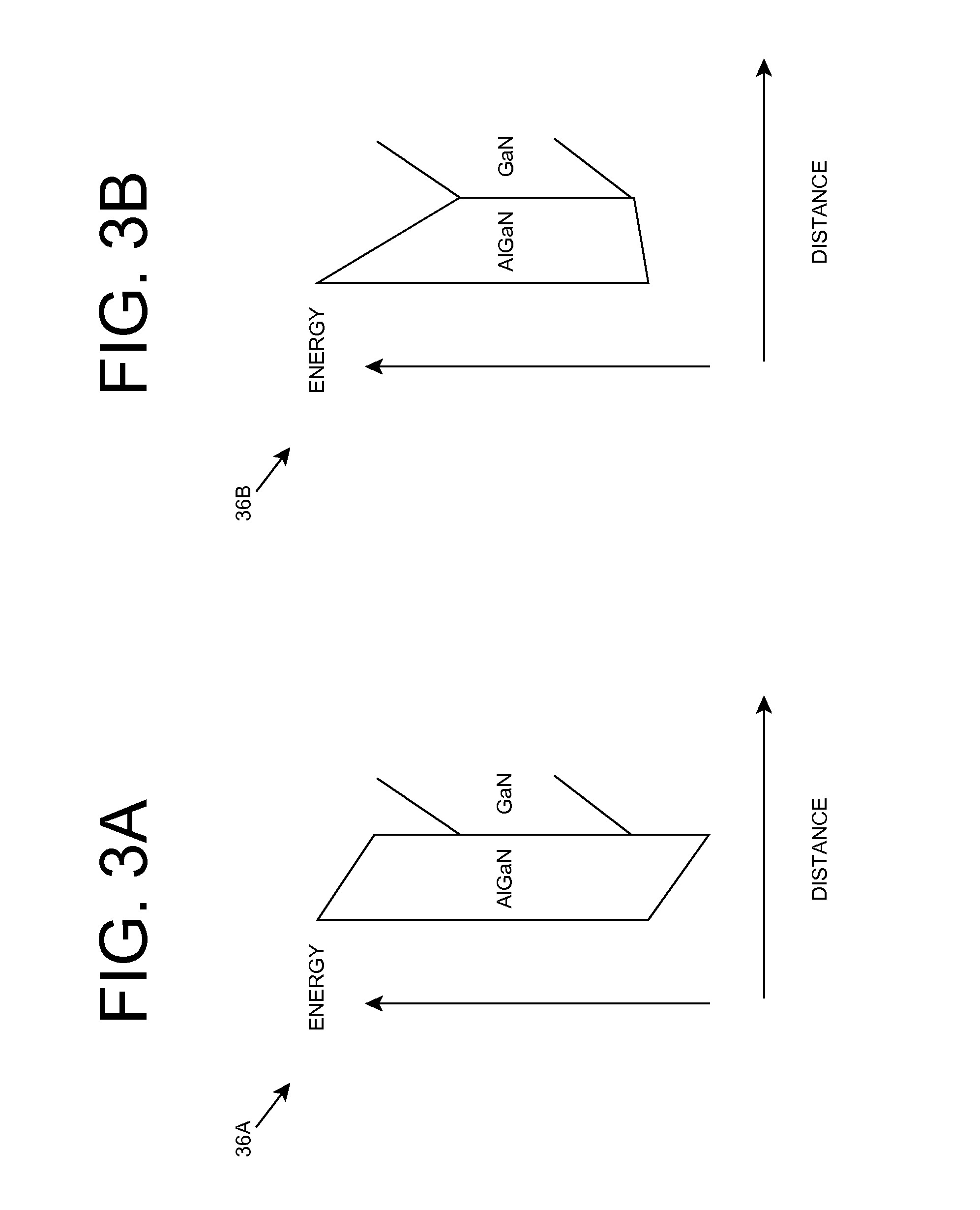
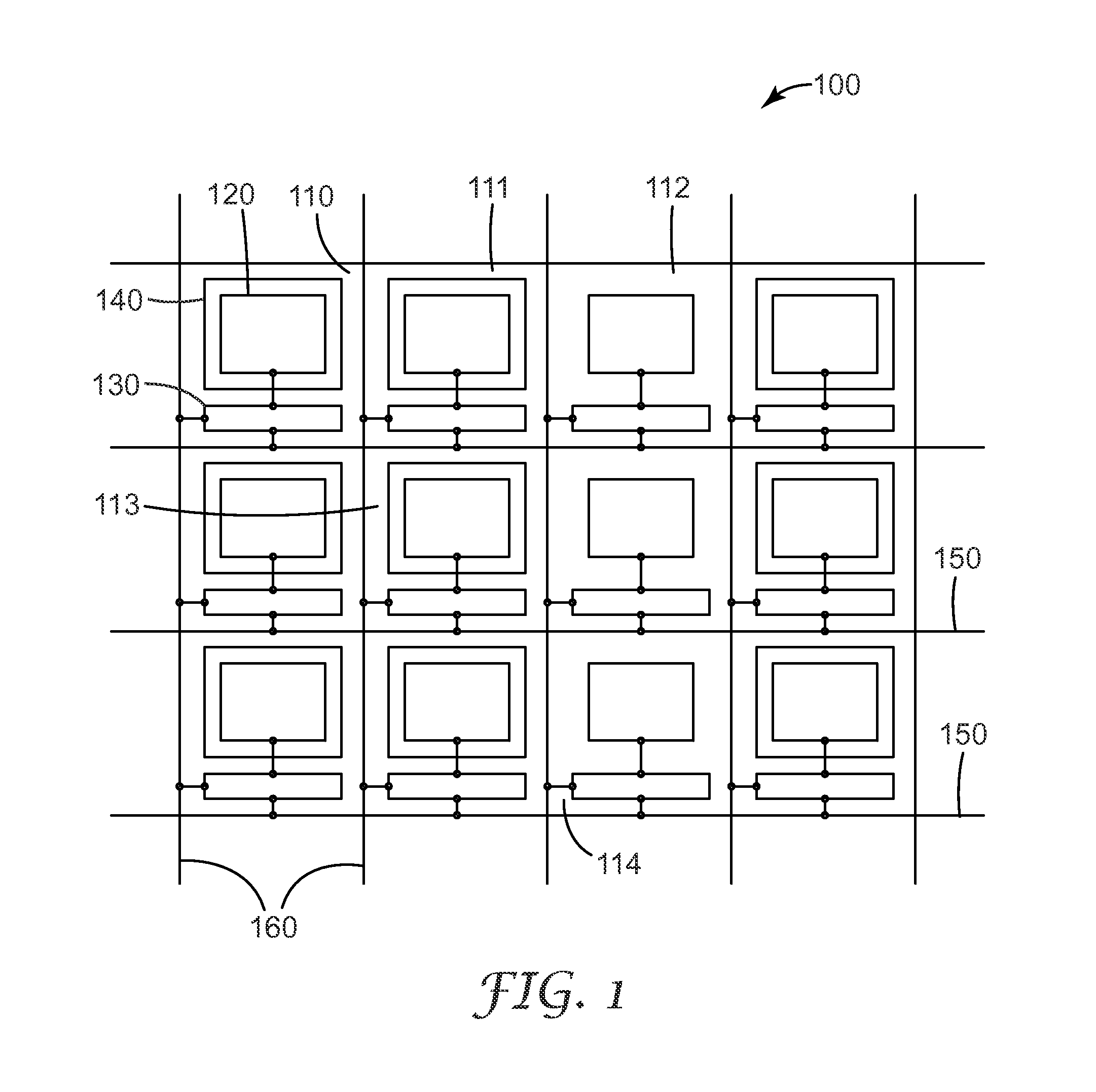
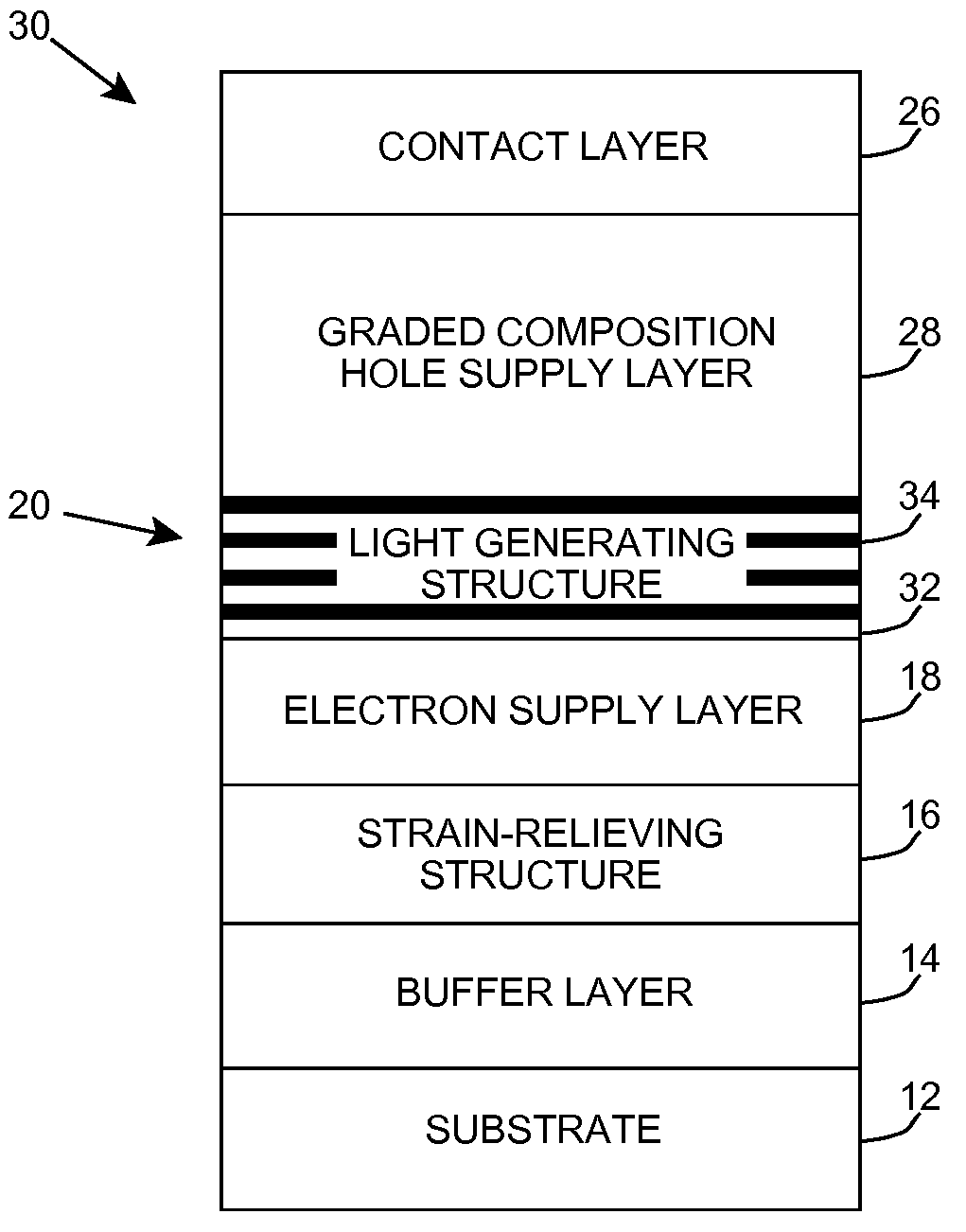
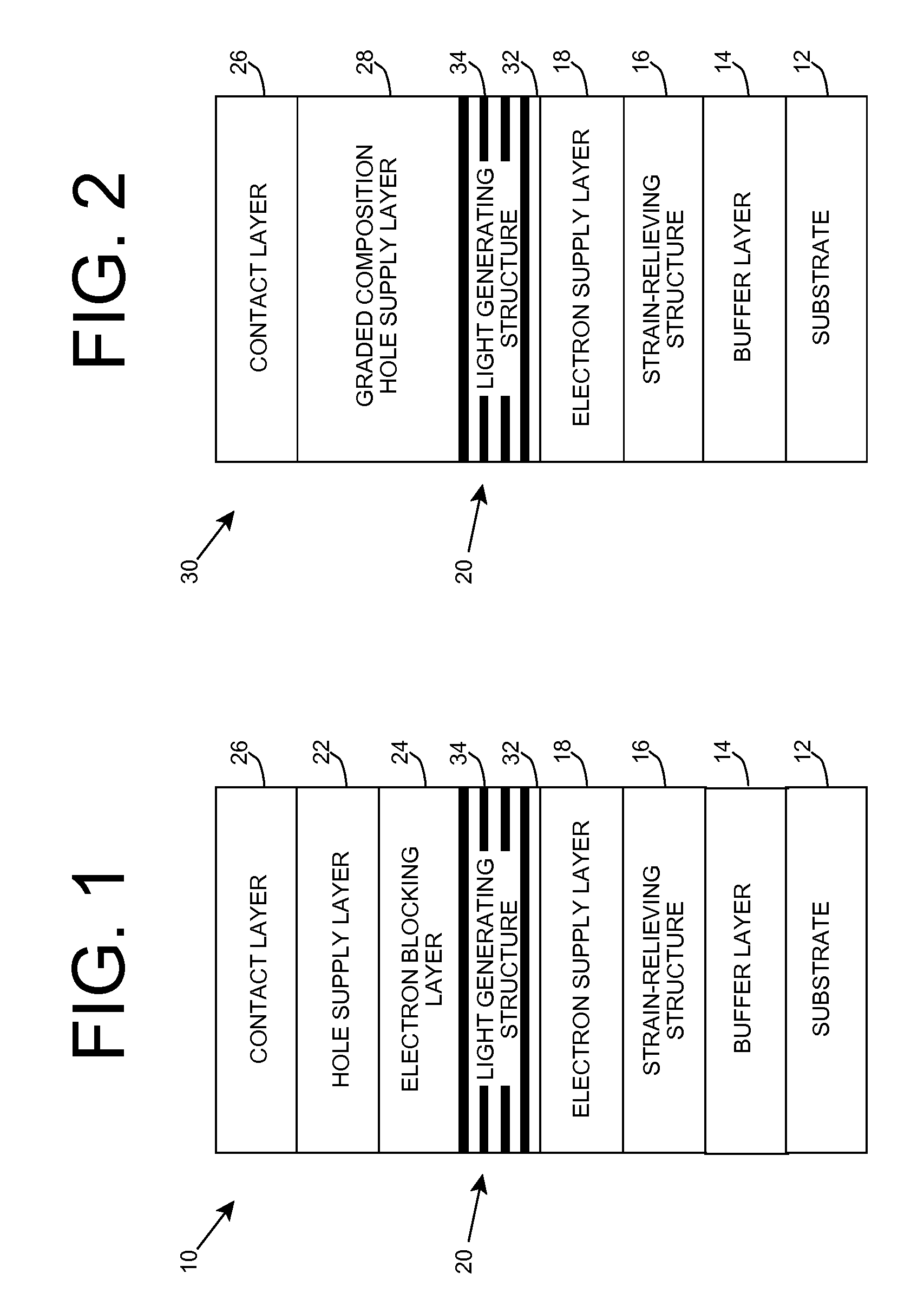
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
ActiveUS20070181869A1Improve featuresConvenient lightingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
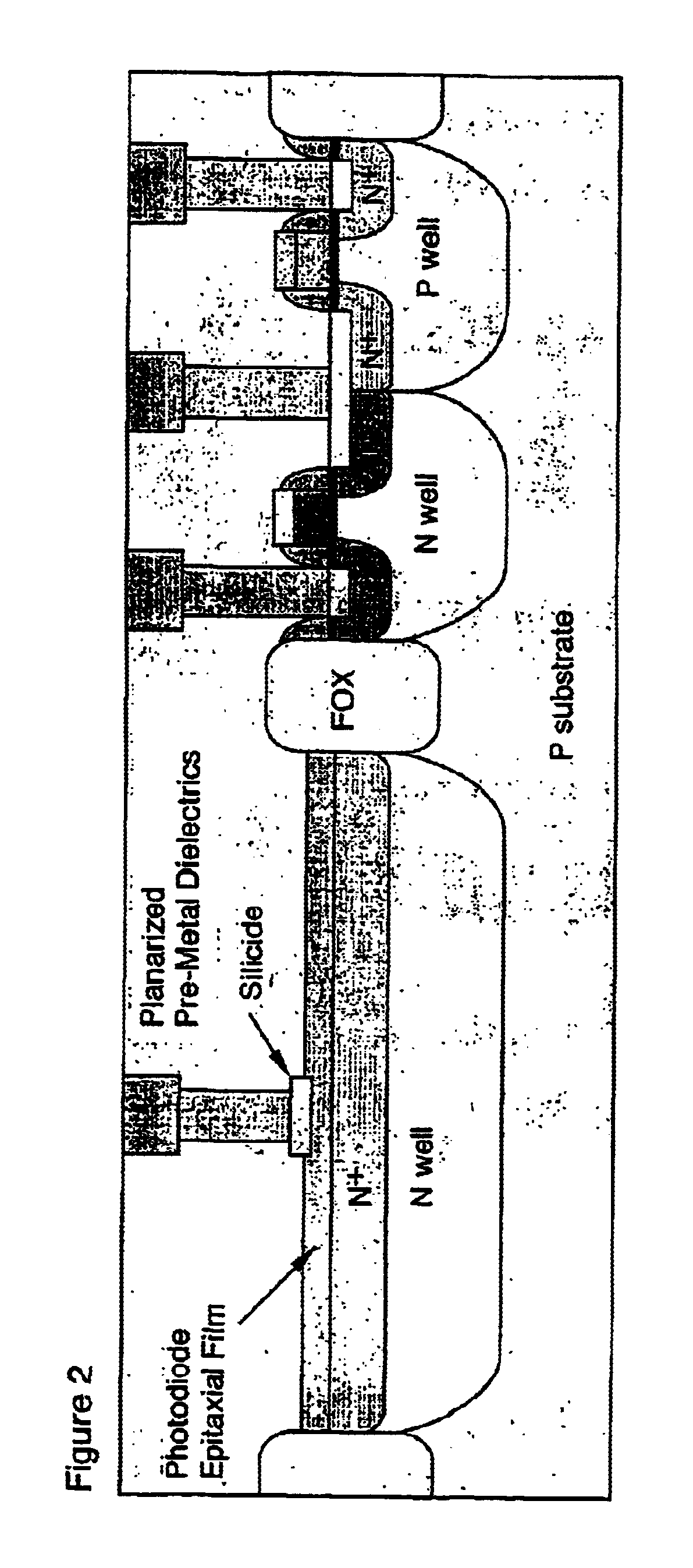
Method of fabricating heterojunction photodiodes integrated with cmos
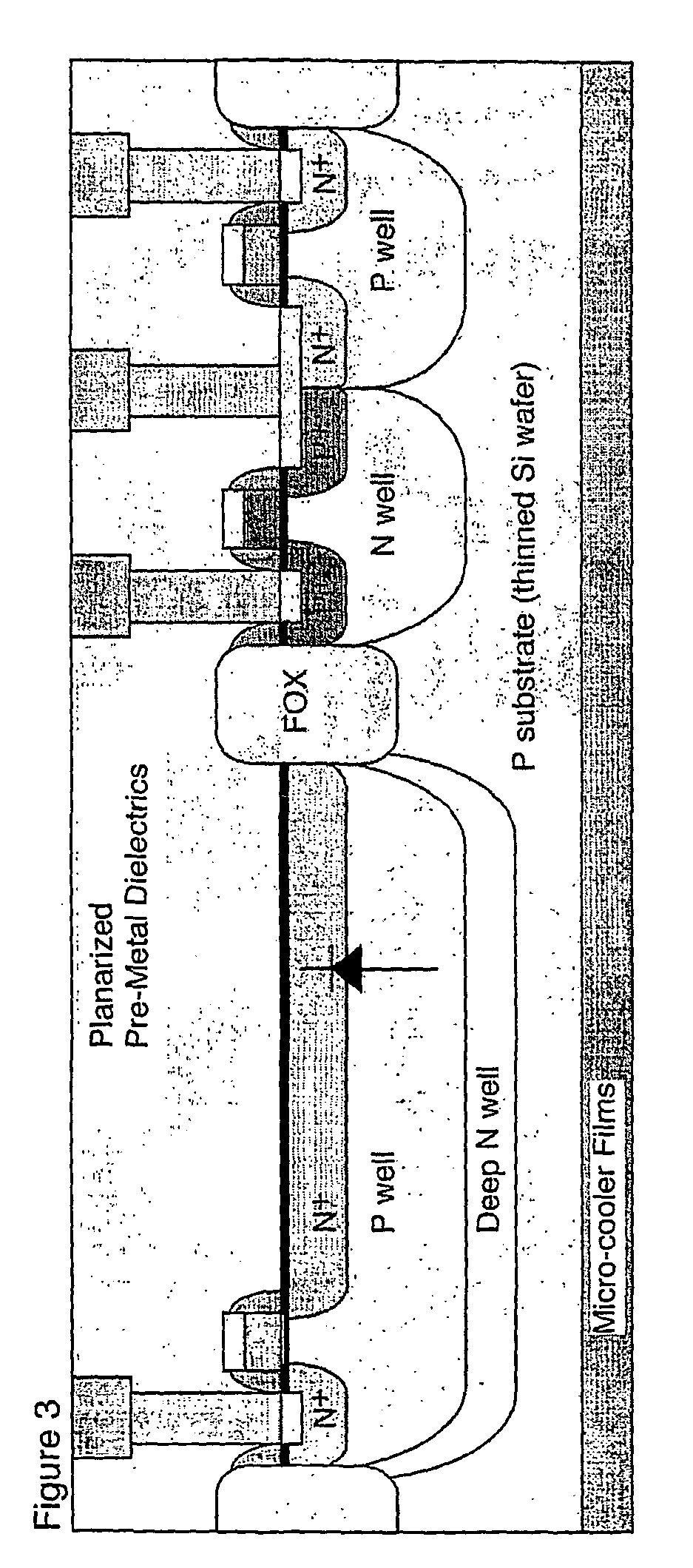
A method in which thin-film p-i-n heterojunction photodiodes are formed by selective epitaxial growth / deposition on pre-designated active-area regions of standard CMOS devices. The thin-film p-i-n photodiodes are formed on active areas (for example n<+>-doped), and these are contacted at the bottom (substrate) side by the "well contact" corresponding to that particular active area. There is no actual potential well since that particular active area has only one type of doping. The top of each photodiode has a separate contact formed thereon. The selective epitaxial growth of the p-i-n photodiodes is modular, in the sense that there is no need to change any of the steps developed for the "pure" CMOS process flow. Since the active region is epitaxially deposited, there is the possibility of forming sharp doping profiles and band-gap engineering during the epitaxial process, thereby optimizing several device parameters for higher performance. This new type of light sensor architecture, monolithically integrated with CMOS, decouples the photo-absorption active region from the MOSFETs, hence the bias applied to the photodiode can be independent from the bias between the source, drain, gate and substrate (well) of the MOSFETs.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Memory utilizing oxide nanolaminates
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
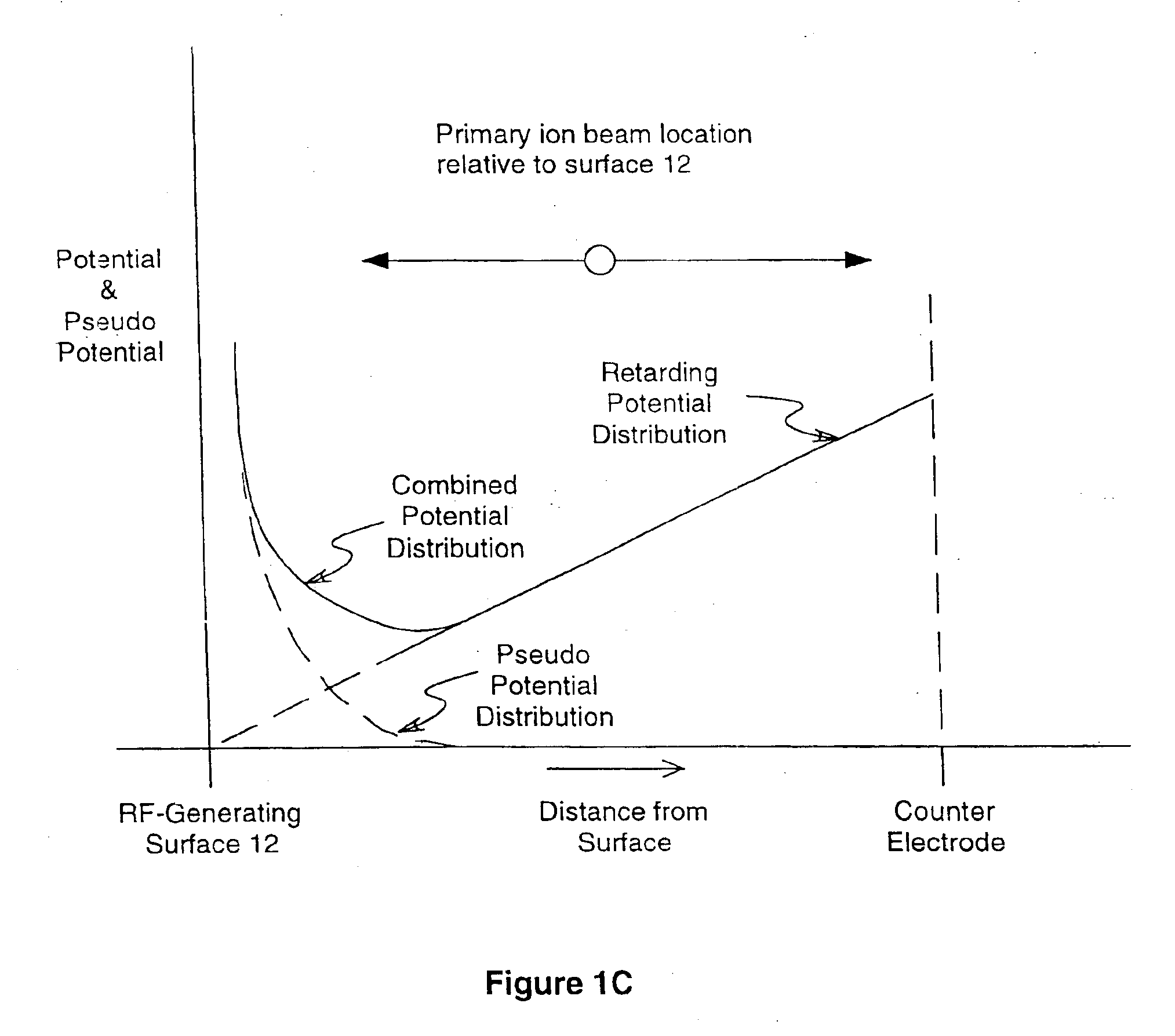
RF surfaces and RF ion guides
ActiveUS7365317B2Promote sportsFreedom of movementStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersPotential wellRf field
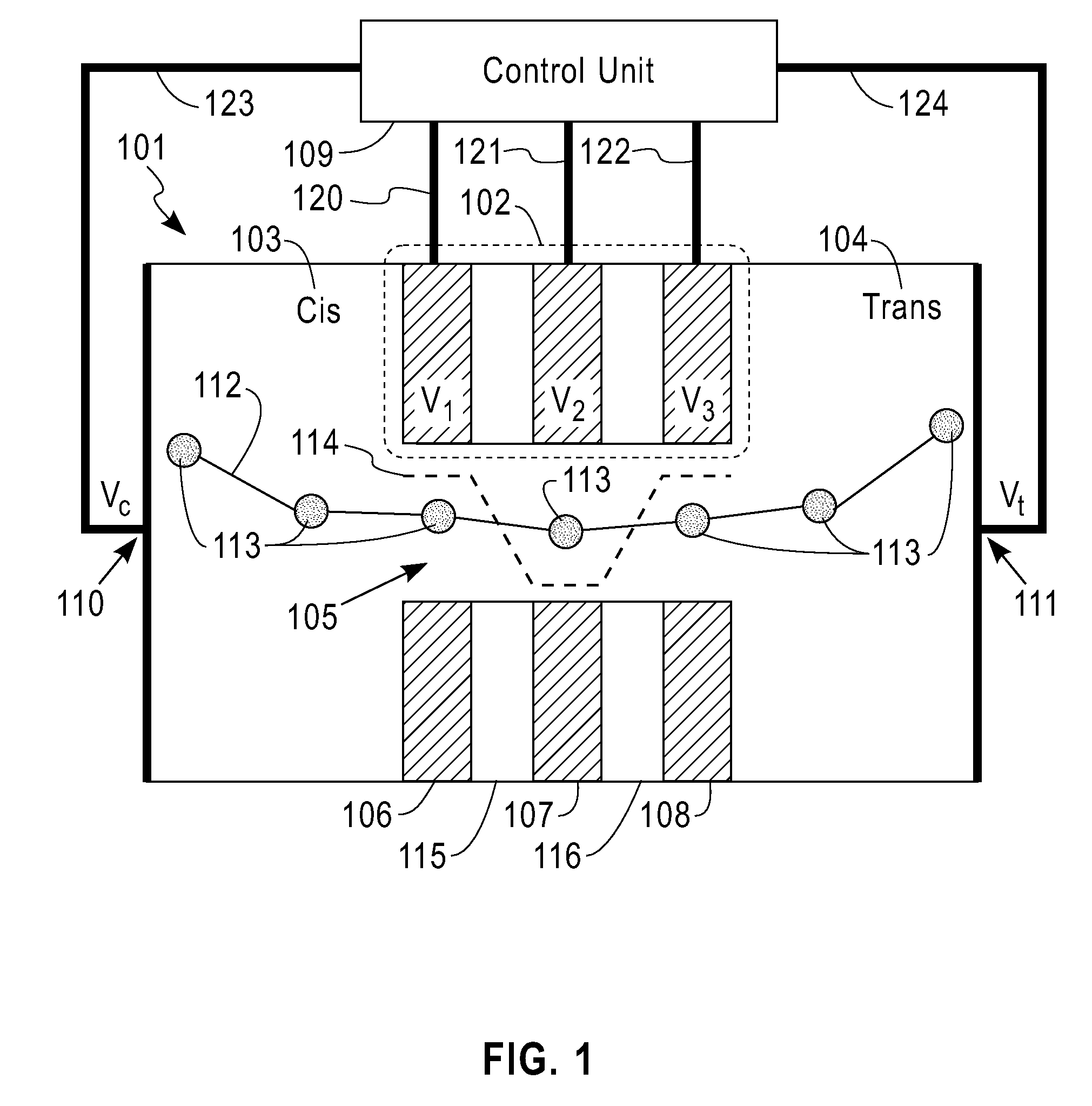
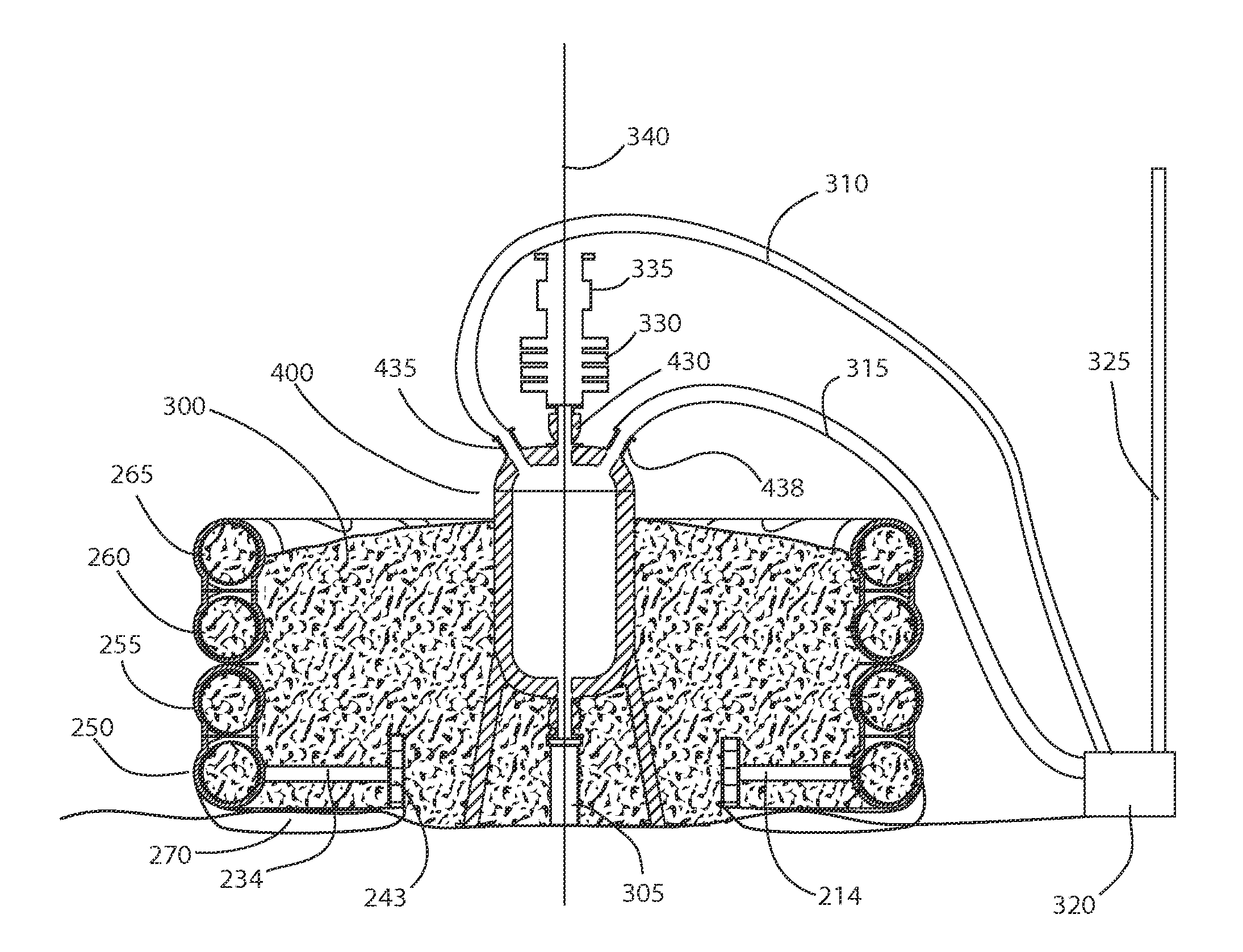
Apparatus and methods are provided for trapping, manipulation and transferring ions along RF and DC potential surfaces and through RF ion guides. Potential wells are formed near RF-field generating surfaces due to the overlap of the radio-frequency (RF) fields and electrostatic fields created by static potentials applied to surrounding electrodes. Ions can be constrained and accumulated over time in such wells. During confinement, ions may be subjected to various processes, such as accumulation, fragmentation, collisional cooling, focusing, mass-to-charge filtering, spatial separation ion mobility and chemical interactions, leading to improved performance in subsequent processing and analysis steps, such as mass analysis. Alternatively, the motion of ions may be better manipulated during confinement to improve the efficiency of their transport to specific locations, such as an entrance aperture into vacuum from atmospheric pressure or into a subsequent vacuum stage.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
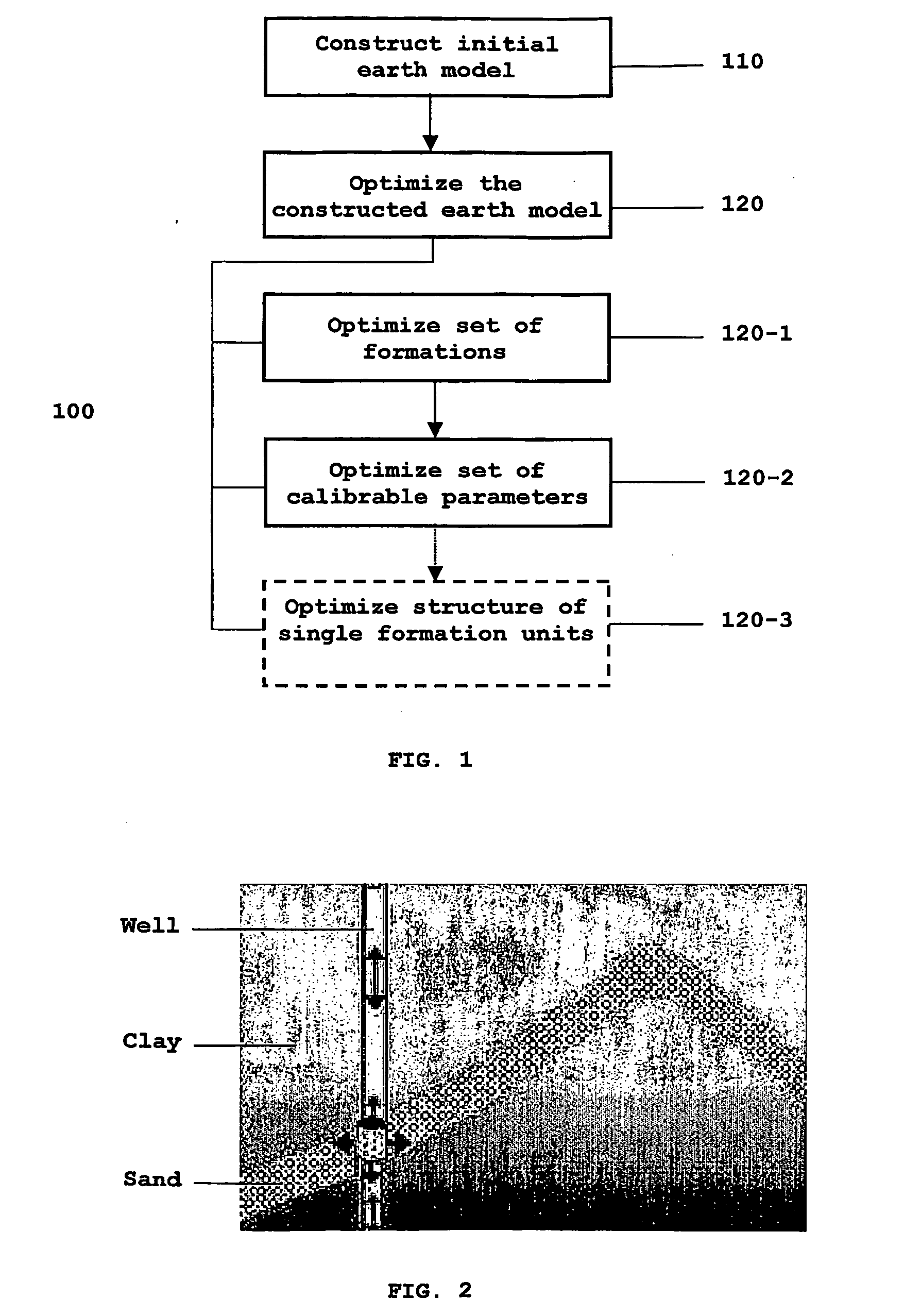
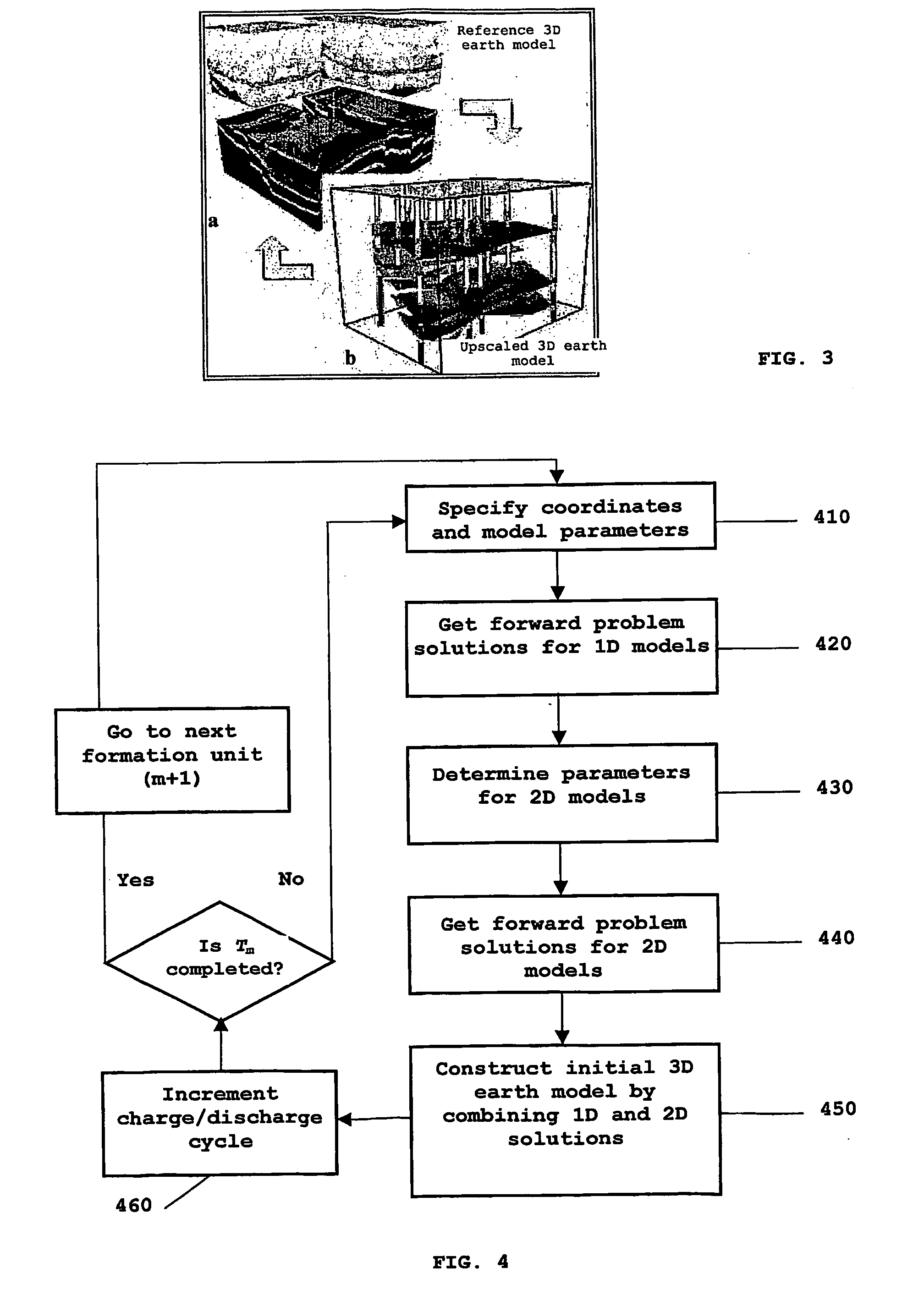
Method for Generating a 3D Earth Model
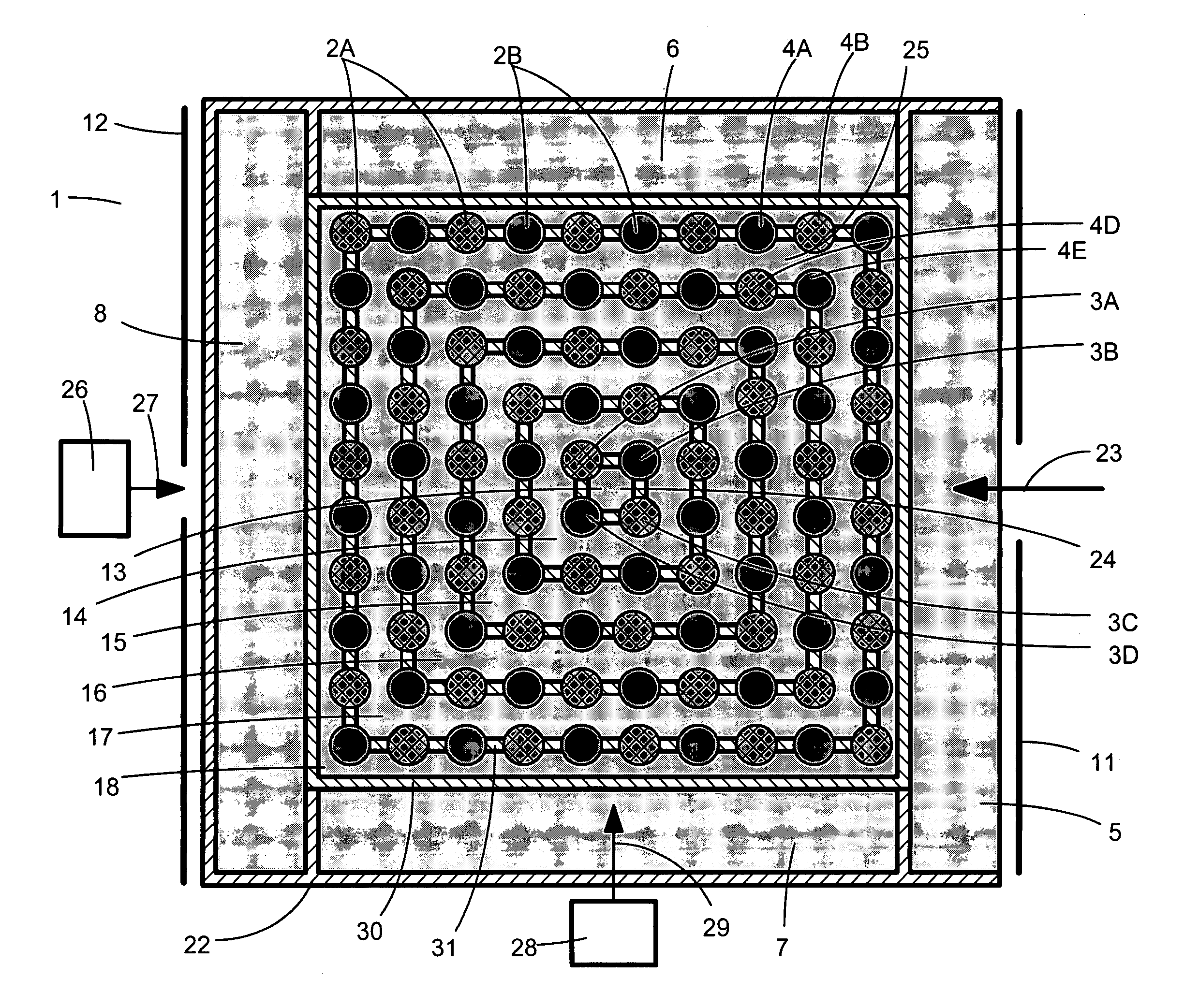
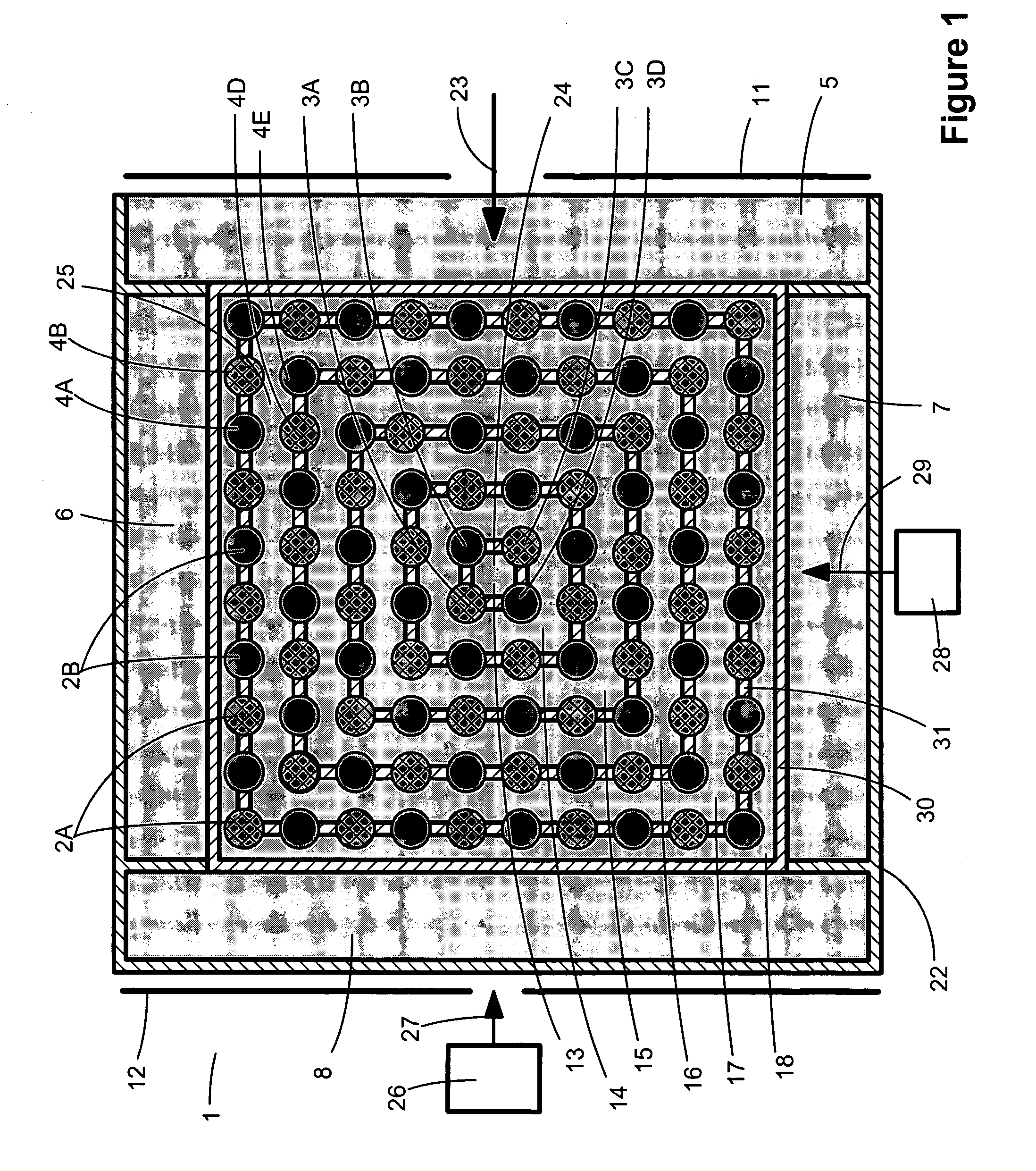
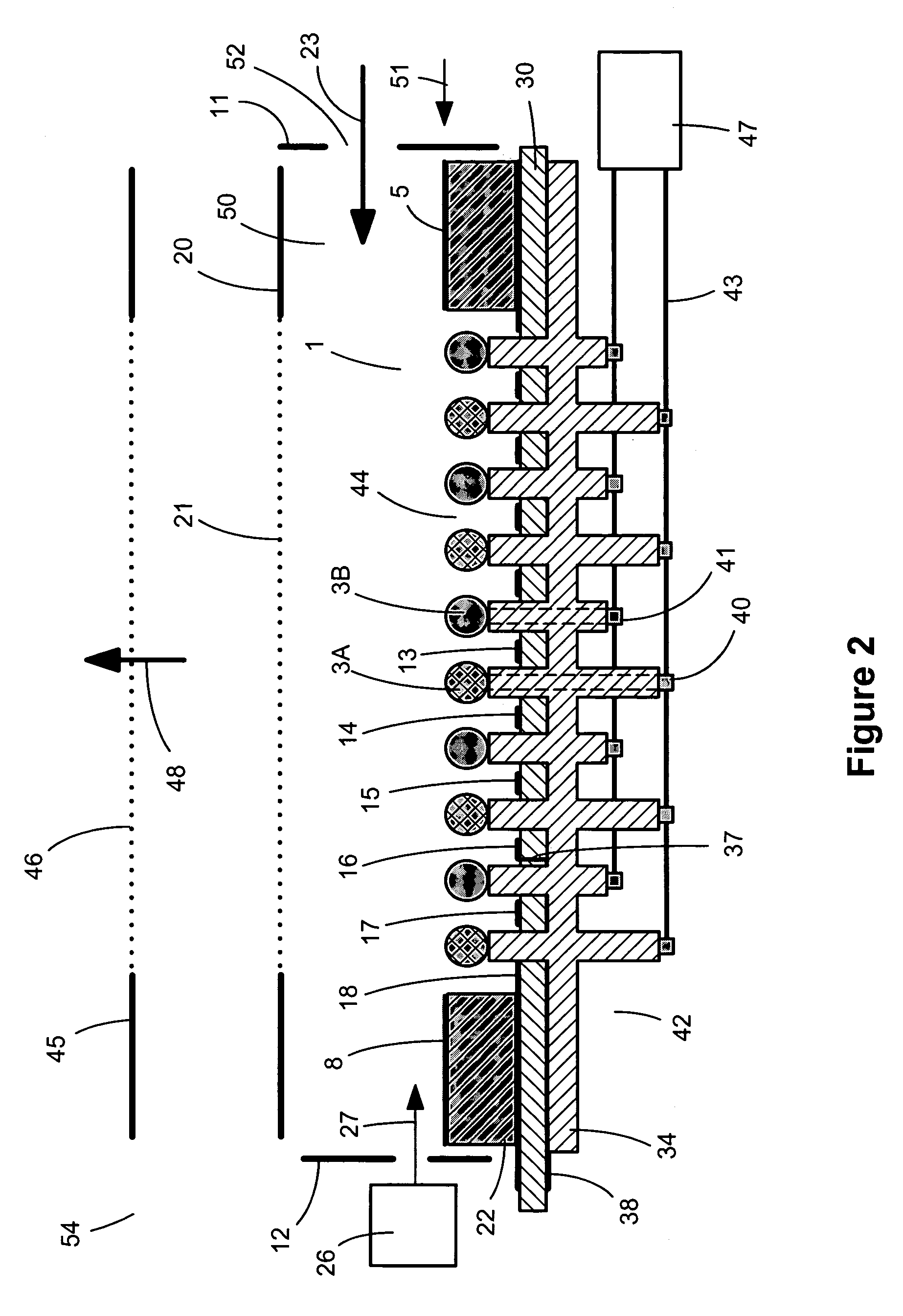
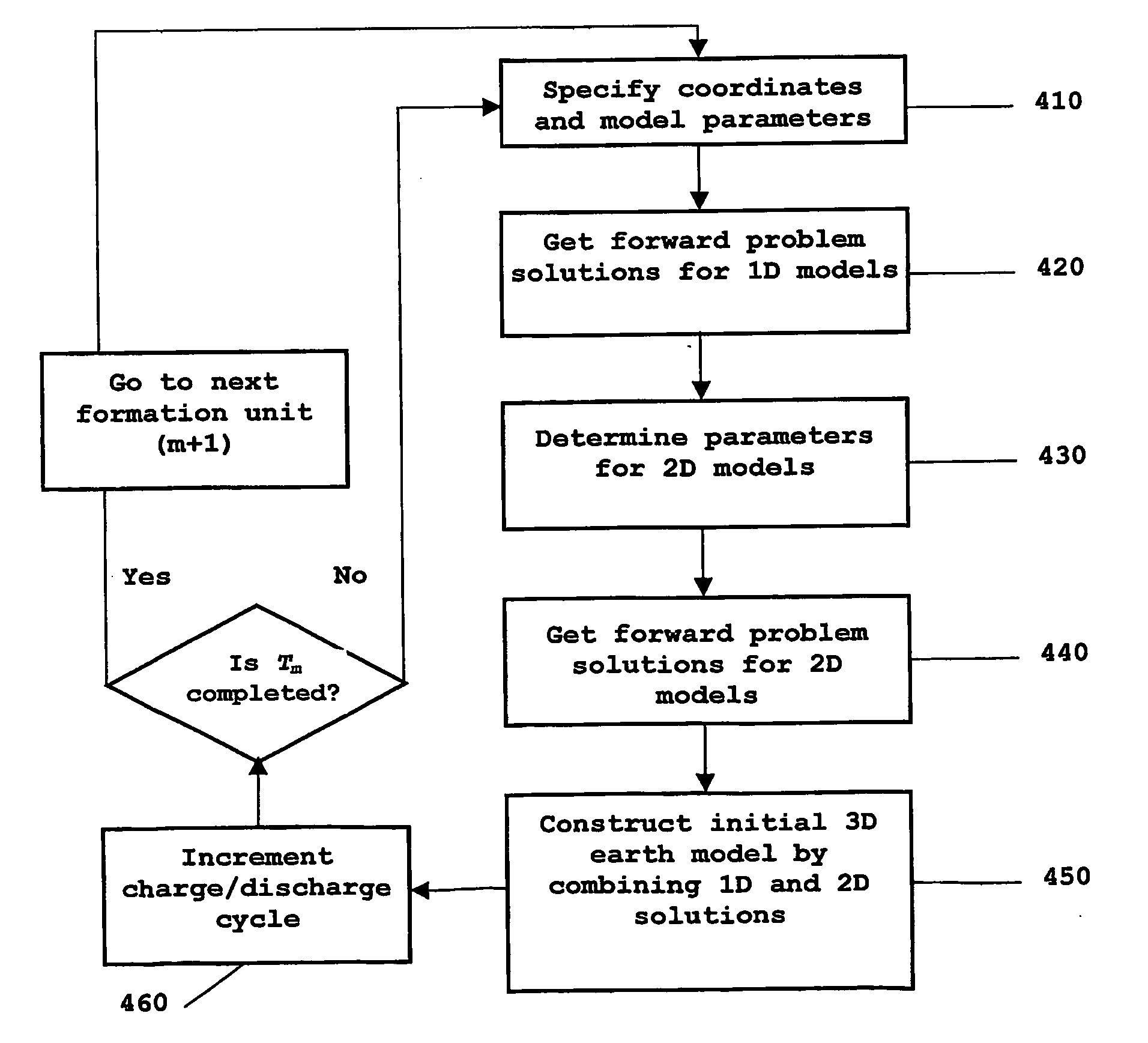
InactiveUS20090119076A1Improved drilling processEffective predictionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyPotential wellWell drilling
A method is provided for generating an invertible 3D hydrodynamic earth model suitable for defining target characteristics of a subsurface area formed by a plurality of formations and comprising drilling positions of potential and real wells. The method comprises constructing an initial 3D earth model by combining solutions for a set of single 1D models, each of the models corresponding to a real or potential well drilling position and covering the entire respective aggregate of formations along the wellbore, with solutions for a relevant set of 2D earth models which are constructed only for single formations, and optimizing the constructed initial 3D earth model by defining an optimal set of formations and an optimal set of calibratable model parameters. A method and system are also provided for application of the earth model construction method for predicting overpressure evolution before and during drilling. As the earth model constructed in accordance with the above method provides efficient inversion of data, in particular gathered while drilling, the prediction can be updated in real-time while drilling. The invention can ensure optimization of the drilling process and improves its safety.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Memory utilizing oxide-conductor nanolaminates
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for controlling position of charged polymer inside nanopore
Techniques for controlling the position of a charged polymer inside a nanopore are provided. For example, one technique includes using electrostatic control to position a linear charged polymer inside a nanopore, and creating an electrostatic potential well inside the nanopore, wherein the electrostatic potential well controls a position of the linear charged polymer inside the nanopore.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
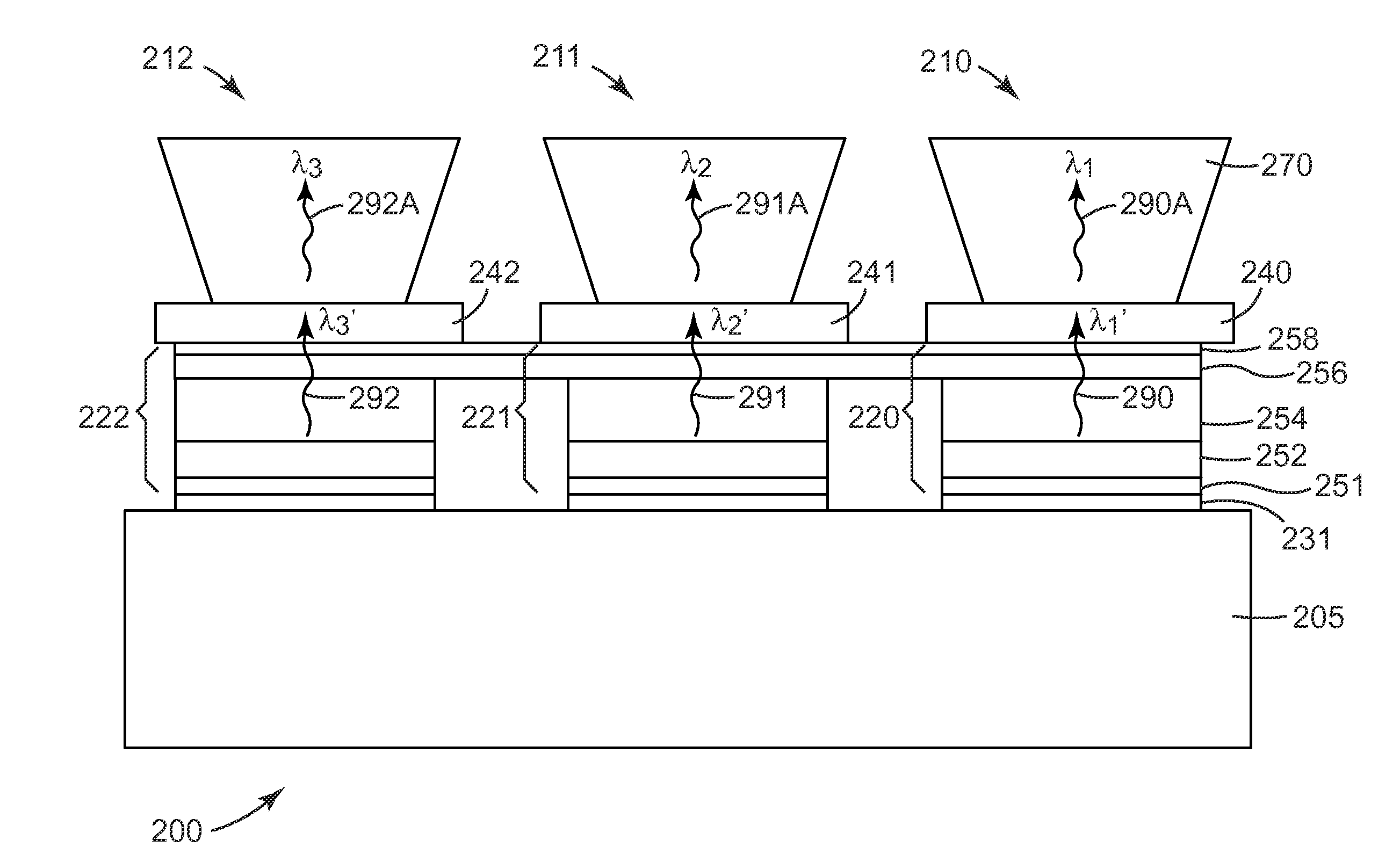
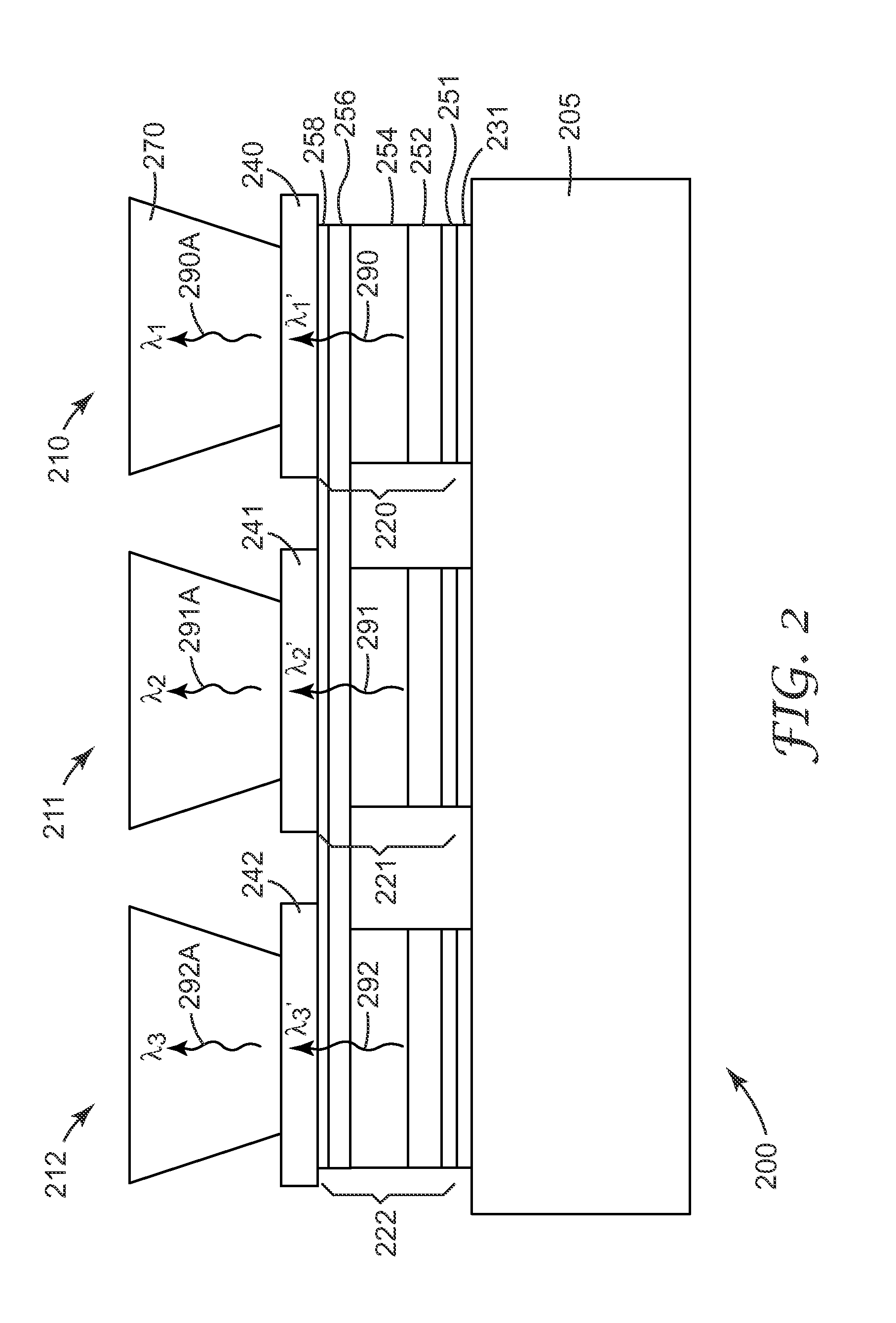
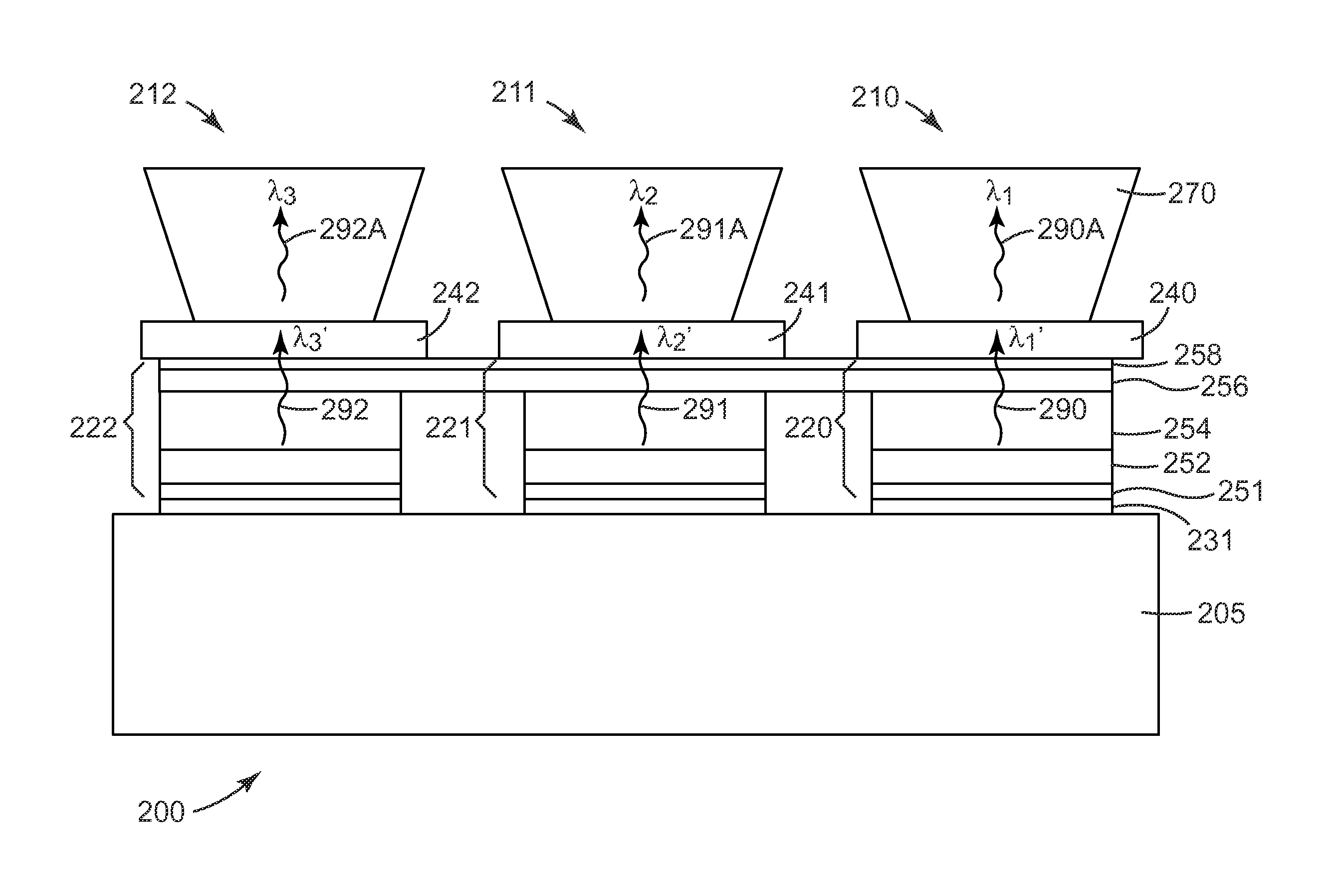
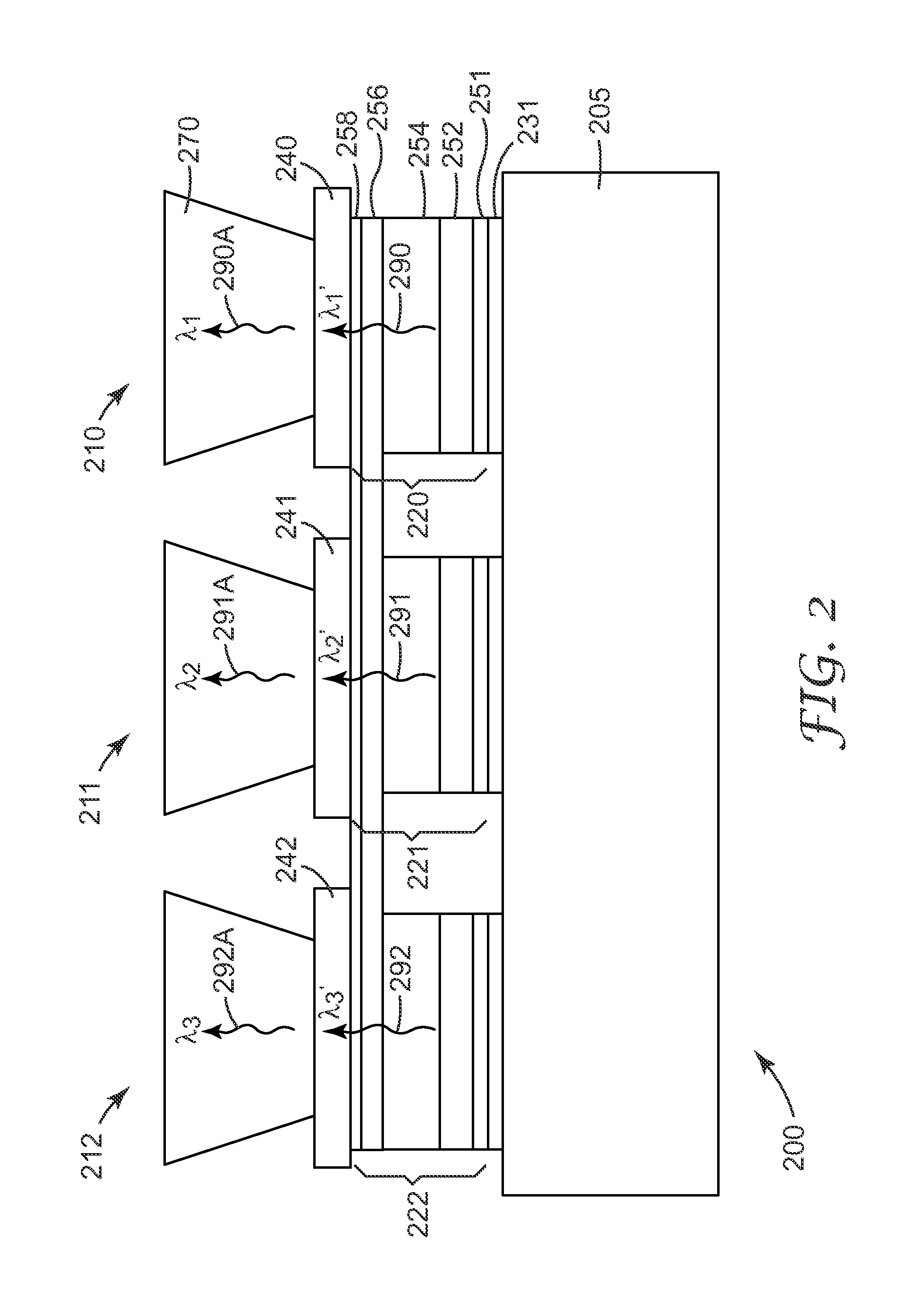
Semiconductor light source with electrically tunable emission wavelength
A semiconductor light source is disclosed comprising a substrate, lower and upper claddings, a waveguide region with imbedded active area, and electrical contacts to provide voltage necessary for the wavelength tuning. The active region includes single or several heterojunction periods sandwiched between charge accumulation layers. Each of the active region periods comprises higher and lower affinity semiconductor layers with type-II band alignment. The charge carrier accumulation in the charge accumulation layers results in electric field build-up and leads to the formation of generally triangular electron and hole potential wells in the higher and lower affinity layers. Nonequillibrium carriers can be created in the active region by means of electrical injection or optical pumping. Radiative recombination occurs between the electrons and holes, accumulated in the ground states of the triangular potential wells formed in the high- and low-affinity layers of each active region periods. The ground state energy in the triangular wells and the radiation wavelength can be tuned by changing the voltage drop across the active region.
Owner:MAXION TECH +1
Memory utilizing oxide nanolaminates
Structures, systems and methods for transistors utilizing oxide nanolaminates are provided. One transistor embodiment includes a first source / drain region, a second source / drain region, and a channel region therebetween. A gate is separated from the channel region by a gate insulator. The gate insulator includes oxide insulator nanolaminate layers with charge trapping in potential wells formed by different electron affinities of the insulator nanolaminate layers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method of fabricating heterojunction photodiodes integrated with CMOS
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Memory utilizing oxide-nitride nanolaminates
Structures, systems and methods for transistors utilizing oxide-nitride nanolaminates are provided. One transistor embodiment includes a first source / drain region, a second source / drain region, and a channel region therebetween. A gate is separated from the channel region by a gate insulator. The gate insulator includes oxide-nitride nanolaminate layers to trap charge in potential wells formed by different electron affinities of the oxide-nitride nanolaminate layers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
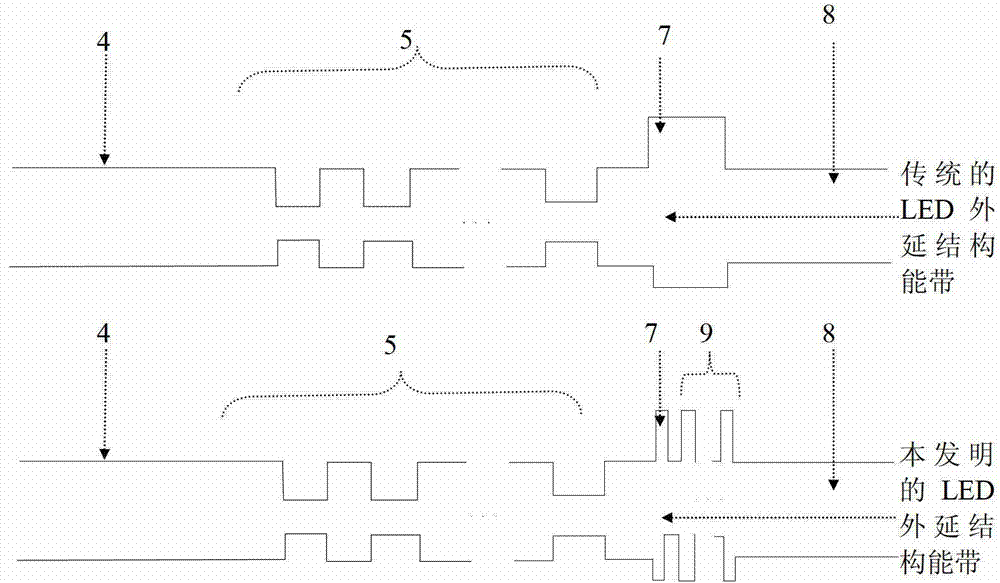
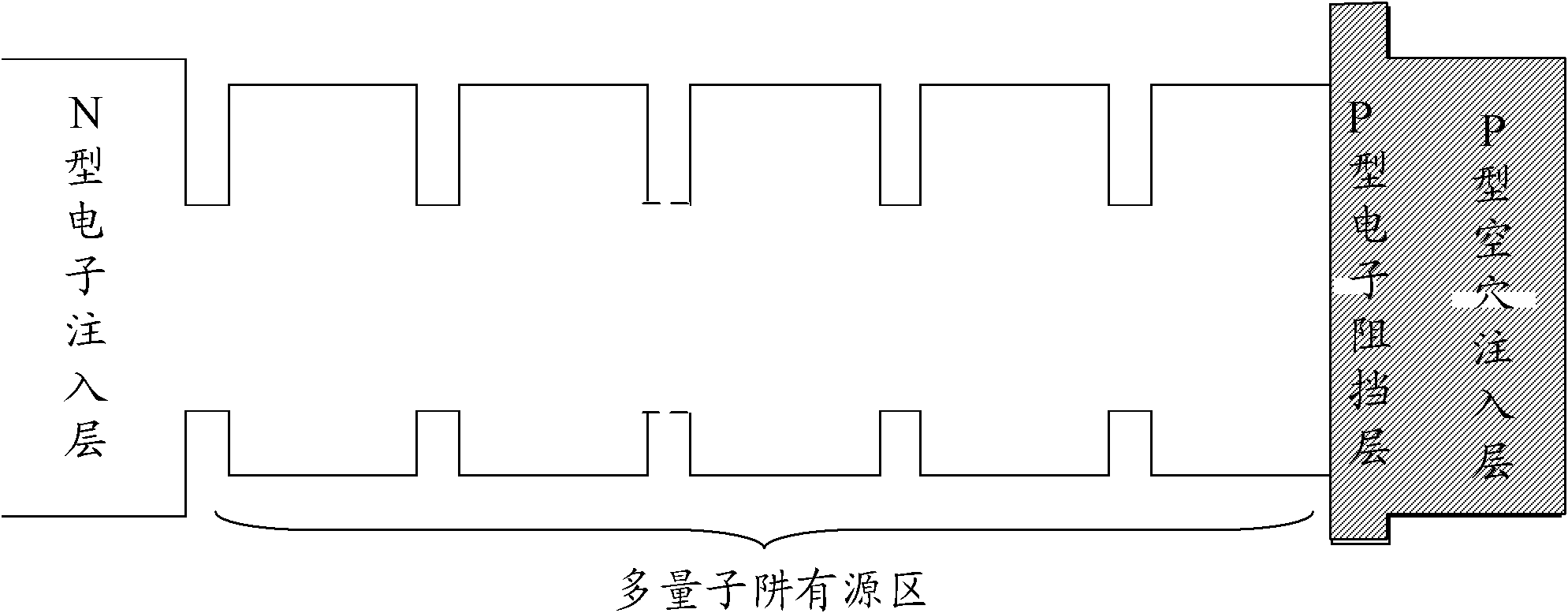
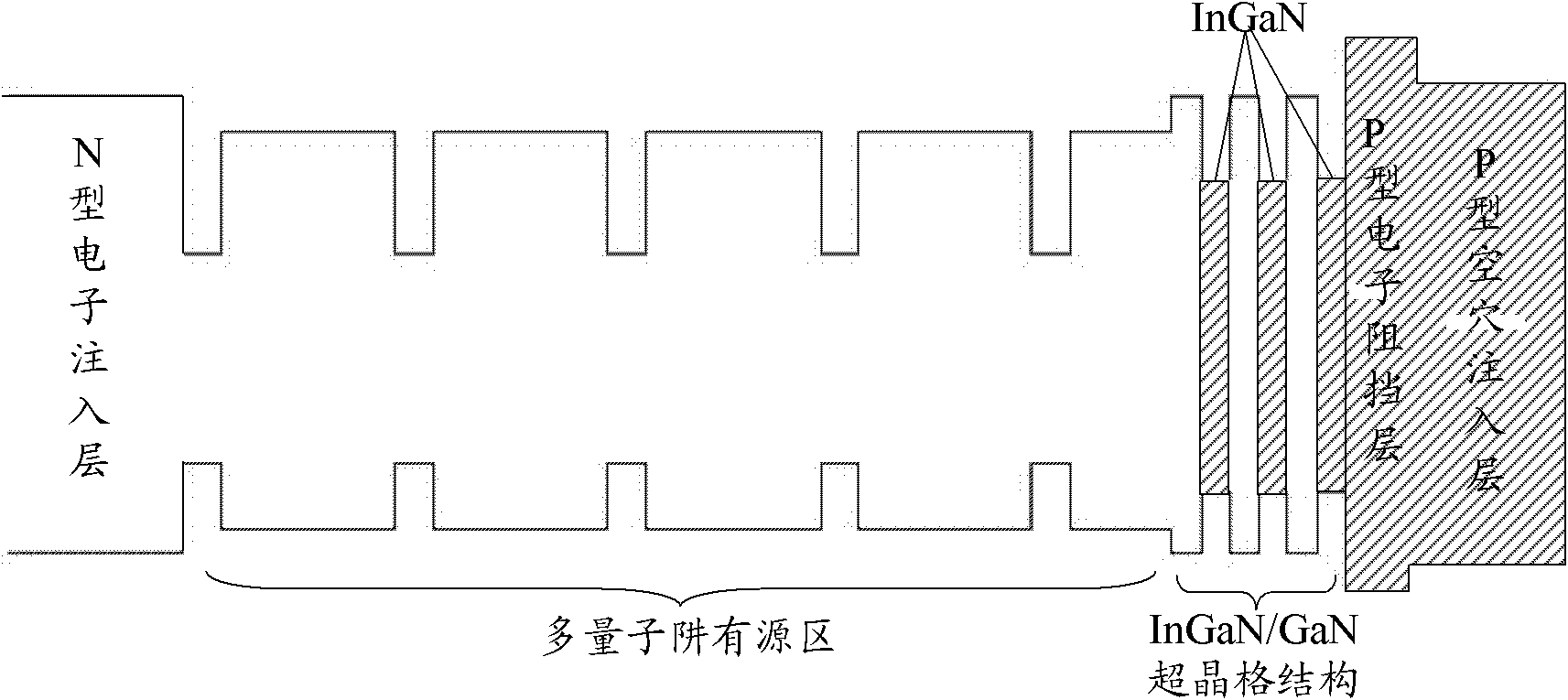
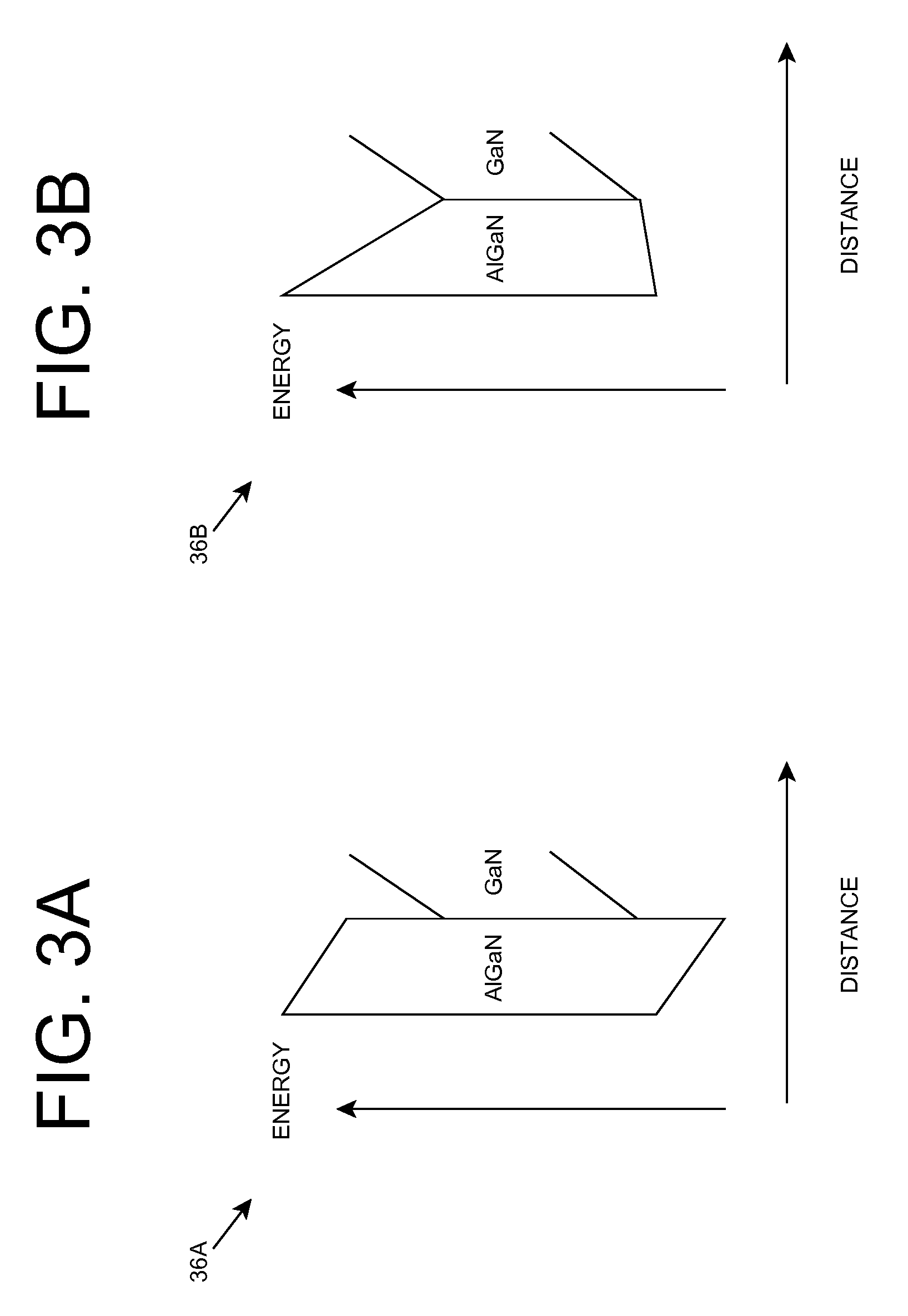
Epitaxial structure and growing method for improving gallium nitride (GaN) based light-emitting diode (LED) lighting efficiency
InactiveCN103066174AImprove crystal qualityStress reliefSemiconductor devicesPotential wellEffect light
The invention discloses an epitaxial structure and a growing method for improving gallium nitride (GaN) based light-emitting diode (LED) lighting efficiency. The order of the epitaxial structure from bottom to up is that a substrate, a low-temperature GaN buffer layer, a GaN non-doping layer, a N-shaped GaN layer, a multiple quantum well (MQW) structure, a multiple quantum well active layer, a low-temperature P-shaped GaN layer, a P-shaped aluminum (AL) GaN layer, a high-temperature P-shaped GaN layer and a P-shaped contact layer, wherein the order of the multiple quantum well active layer from bottom to up comprises a InyGa1-yN potential well layer, a InN layer and a barrier layer in sequence. The growing method of the multiple quantum well active layer structure is that by inserting the InN layer and a low-temperature annealing step in the growing process of a InyGa1 potential well layer and a GaN barrier layer, so that the composition of In quantum dot in the barrier layer is advanced and crystalline quality of the quantum well is improved, therefore, gallium nitride based LED lighting efficiency is improved.
Owner:合肥彩虹蓝光科技有限公司
Charged particle trapping in near-surface potential wells
InactiveUS6872941B1Low efficiencyQuality improvementStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial nanotechnologyPotential wellHigh energy
A Time-Of-Flight mass spectrometer is configured with a pulsing region and electronic controls that generate a potential well for ions in the pulsing region, due to the repelling effect of a high-frequency electric field that is created in the space immediately proximate to a surface, and an additional static electric field that accelerates ions toward the surface. Ions can be constrained and accumulated over time in the potential well prior to acceleration into the Time-Of-Flight tube for mass analysis. Ions can also be directed to collide with the surface with high energy to cause Surface Induced Dissociation (SID) fragmentation, or with low energy to effect collisional cooling, hence, better spatial focusing, prior to mass analysis. The apparatus and method described in the invention result in refined control of ion fragmentation energy and improved Time-Of-Flight mass analysis performance.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
LED (Light Emitting Diode) epitaxial structure with P (Positive) type superlattice and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103050592AStop SpillFacilitate horizontal expansionSemiconductor devicesPotential wellHigh density
The invention discloses an LED (Light Emitting Diode) epitaxial structure with a P (Positive) type superlattice and a preparation method thereof. The epitaxial structure comprises a substrate, wherein a GaN (Gallium Nitride) buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer, an n (negative) type GaN layer, a multi-quantum well luminous layer, a first P type GaN layer, a P type AlGaN (Aluminium Gallium Nitride) electronic blocking layer and a second P type GaN layer are sequentially arranged on the substrate from bottom to top, and the P type superlattice formed by a PInGaN (P type Indium Gallium Nitride) potential well layer and a PAlGaN potential barrier layer in a periodic interactive overlapping way is arranged between the P type AlGaN electronic blocking layer and the second P type GaN layer. The PInGaN potential well layer in the P type superlattice generates and constrains a great number of holes for the formation of a two-dimensional hole high-density state; the PAlGaN potential barrier layer hinders the escape of the holes; in such a way, the transverse spreading of the holes is improved, the electron overflow can be prevented, the hole injection efficiency is increased and the electron and hole recombination probability is improved; and therefore, the brightness of a chip can be improved by 5-10%.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
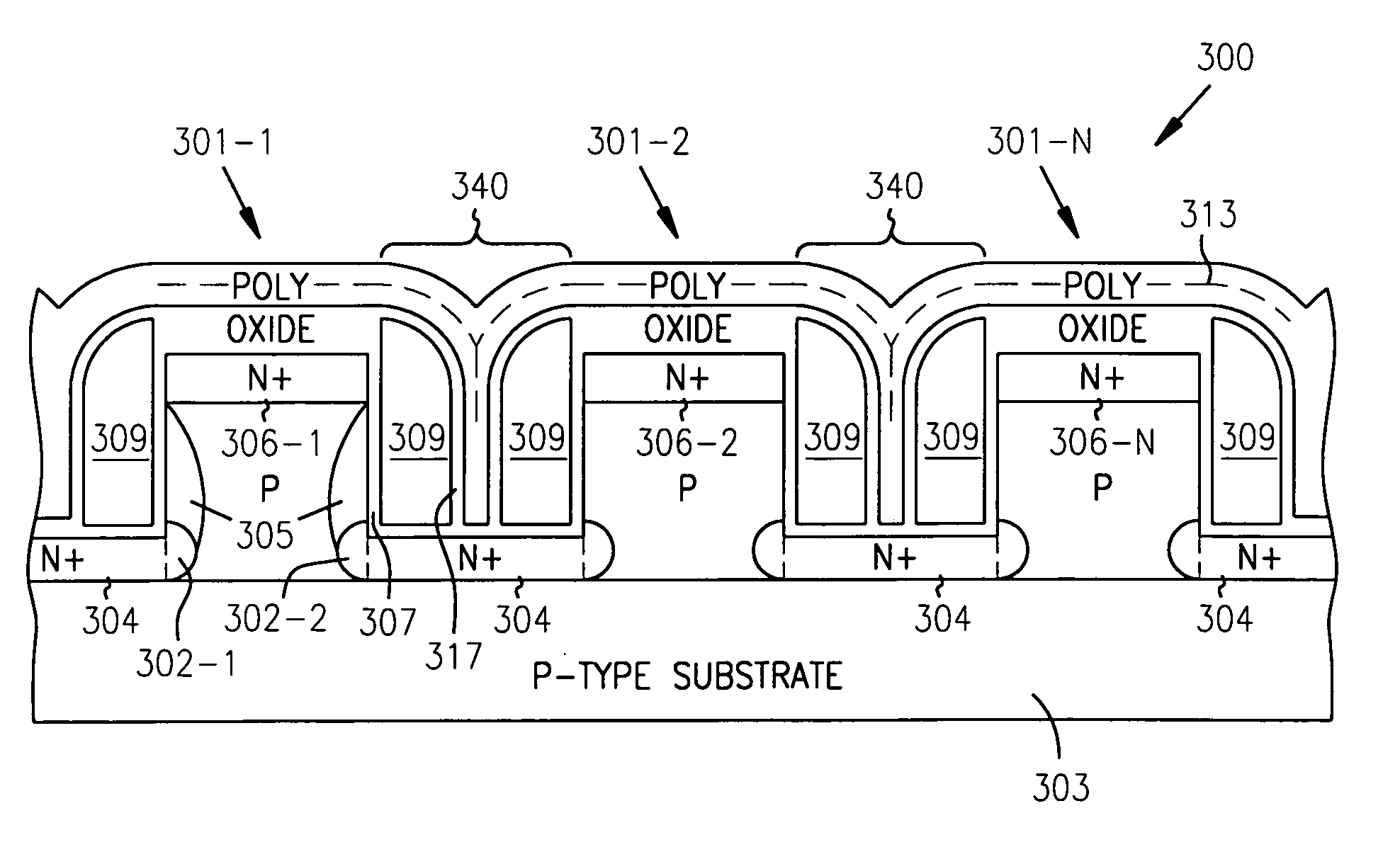
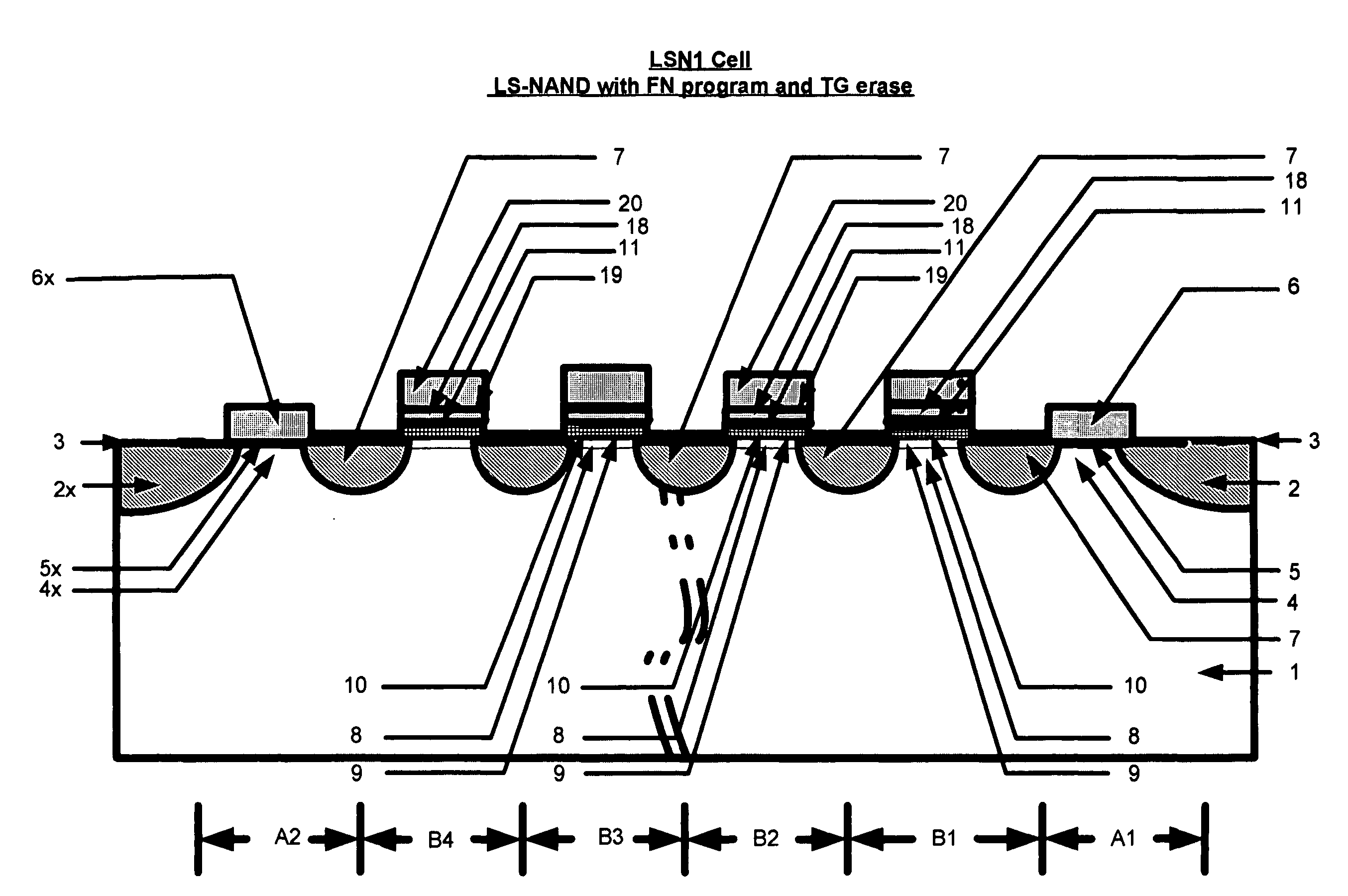
Location-specific NAND (ls NAND) memory technology and cells
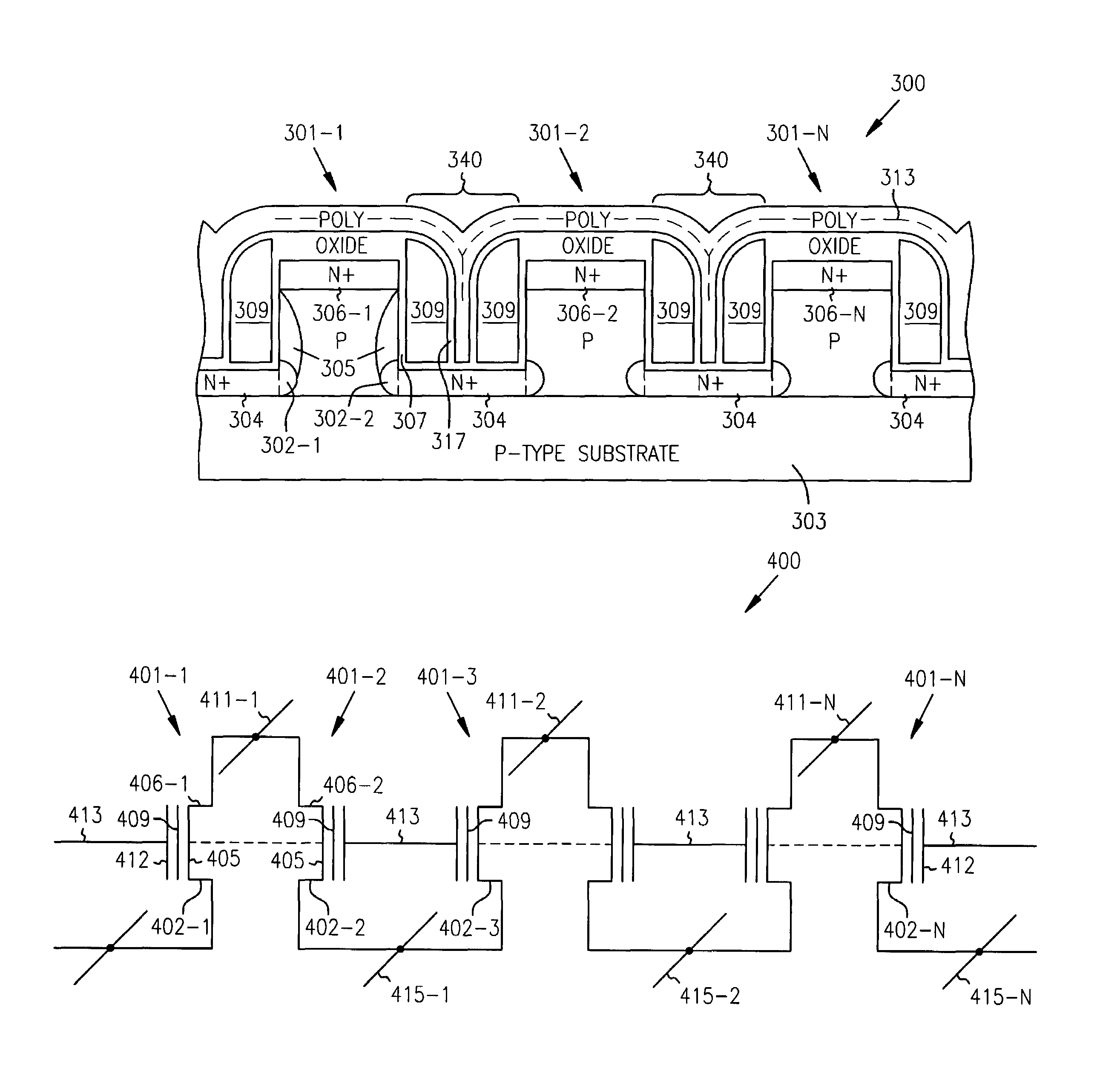
The use of a Nitride layer or a silicon-nodule layer capable of location-specific (LS) charge storage, allow easy vertical scaling and implementation of NOR and NAND NVM array and technology. If the charge is stored in the traps in the Nitride storage layer, a Oxide Nitride Oxide is used as the storage element and if charge is stored in potential wells of discrete silicon-nodules, or Carbon Bucky-ball layers, an Oxide silicon-nodule Oxide storage element, or an Oxide Bucky-ball Oxide layer is used as the storage element. The problem of location-specific NAND memory is the inability to erase the cells with repeatable results. A novel erase method, Tunnel Gun (TG) method, that generate holes for consistent erase of LS storage elements and typical NAND Cells that erase by the disclosed method and programmed by either by Fouler-Nordheim (FN) tunneling or Low Current Hot Electron (LCHE) method are disclosed.
Owner:THOMAS MAMMEN
Mass spectrometry method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050121609A1Improve trapping efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyStability-of-path spectrometersPotential wellMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A mass spectrometer 10 comprises an ion source 12 which generates nebulized ions which enter an ion cooler 20 via an ion source block 16. Ions within a window of m / z of interest are extracted via a quadrupole mass filter 24 and passed to a linear trap 30. Ions are trapped in a potential well in the linear trap 30 and are bunched at the bottom of the potential well adjacent an exit segment 50. Ions are gated out of the linear trap 30 into an electrostatic ion trap 130 and are detected by a secondary electron multiplier 10. By bunching the ions in the linear trap 30 prior to ejection, and by focussing the ions in time of flight (TOF) upon the entrance of the electrostatic trap 130, the ions arrive at the electrostatic trap 130 as a convolution of short, energetic packets of similar m / z. Such packets are particularly suited to an electrostatic trap because the FWHM of each packet's TOF distribution is less than the period of oscillation of those ions in the electrostatic trap.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
CMOS image sensor with reset shield line
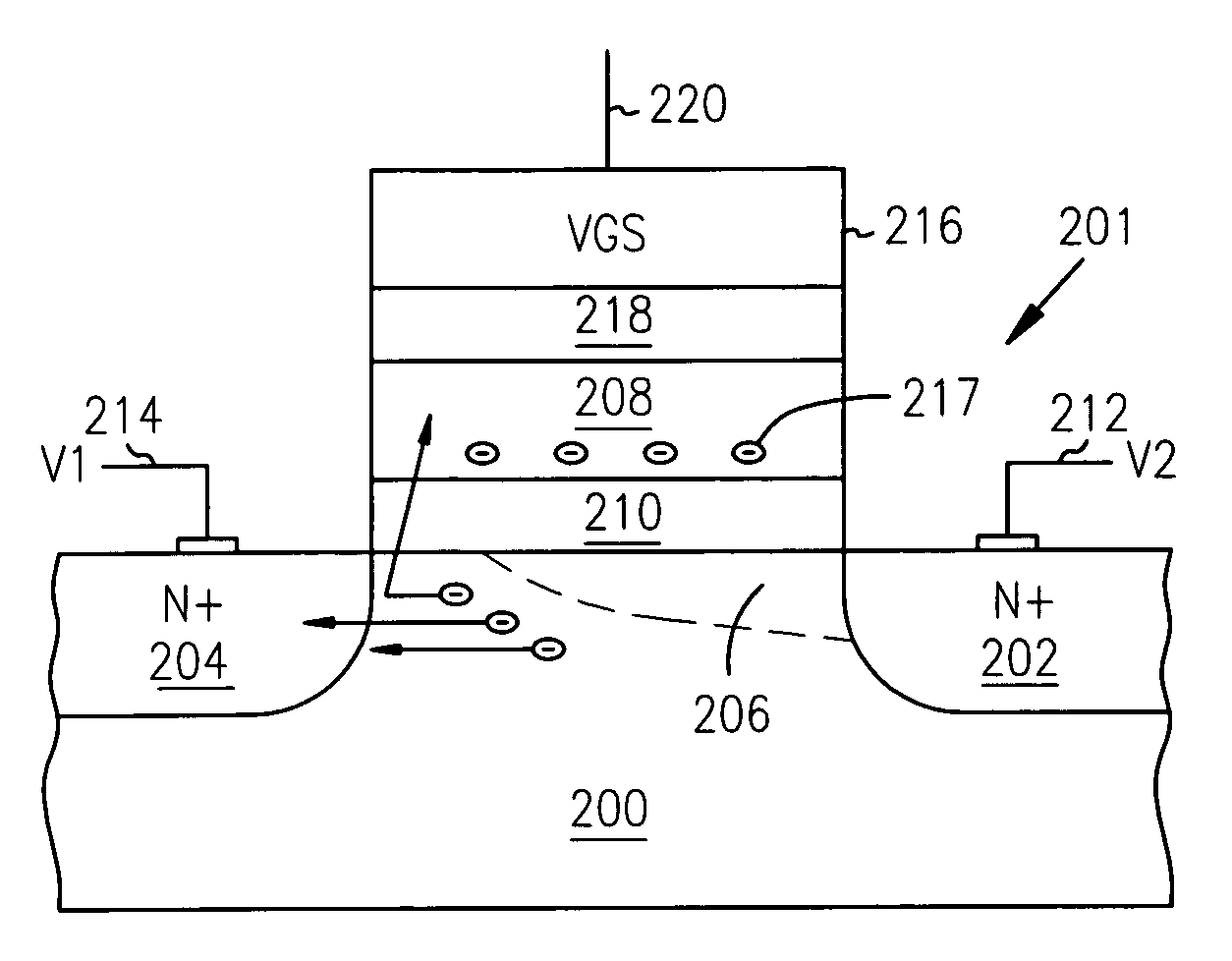
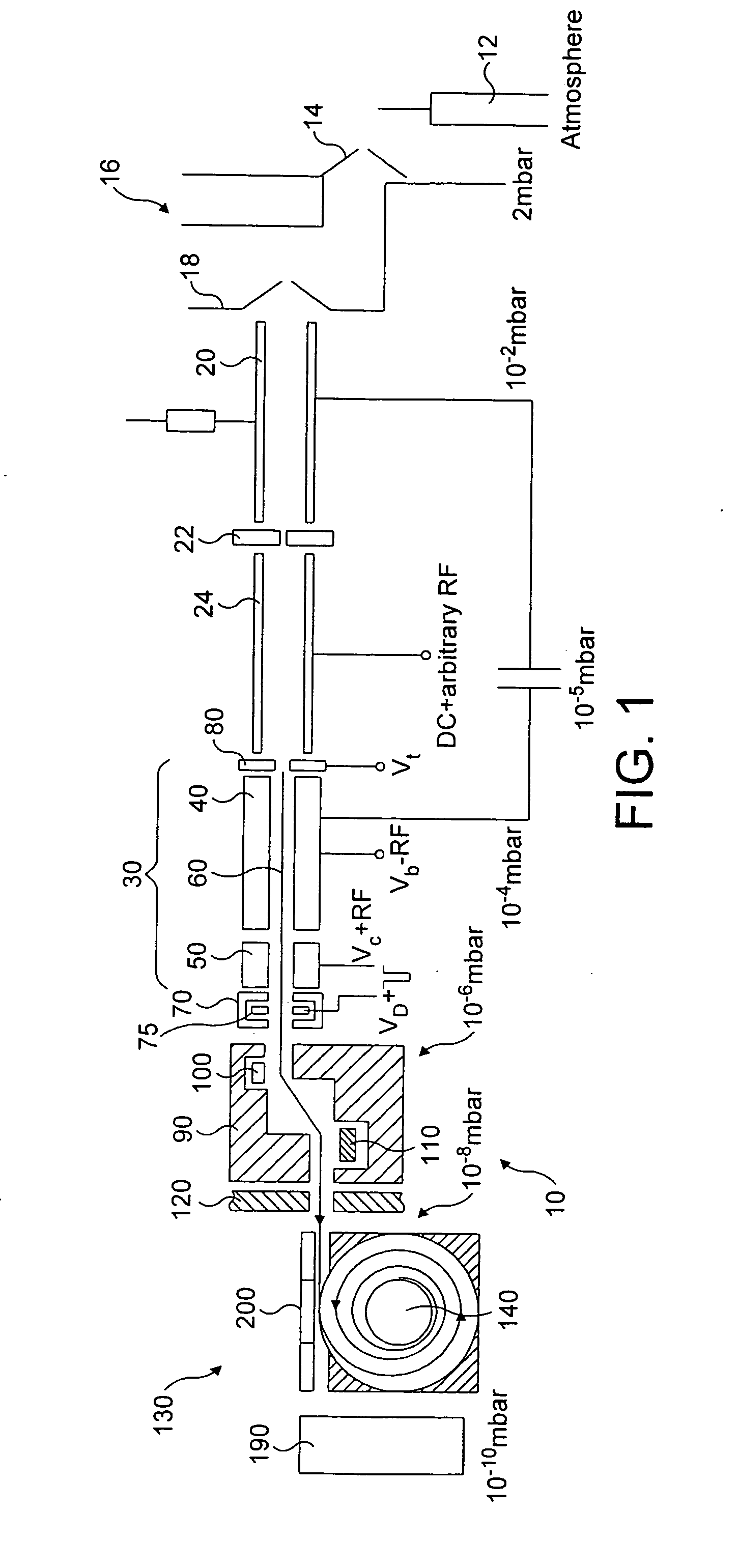
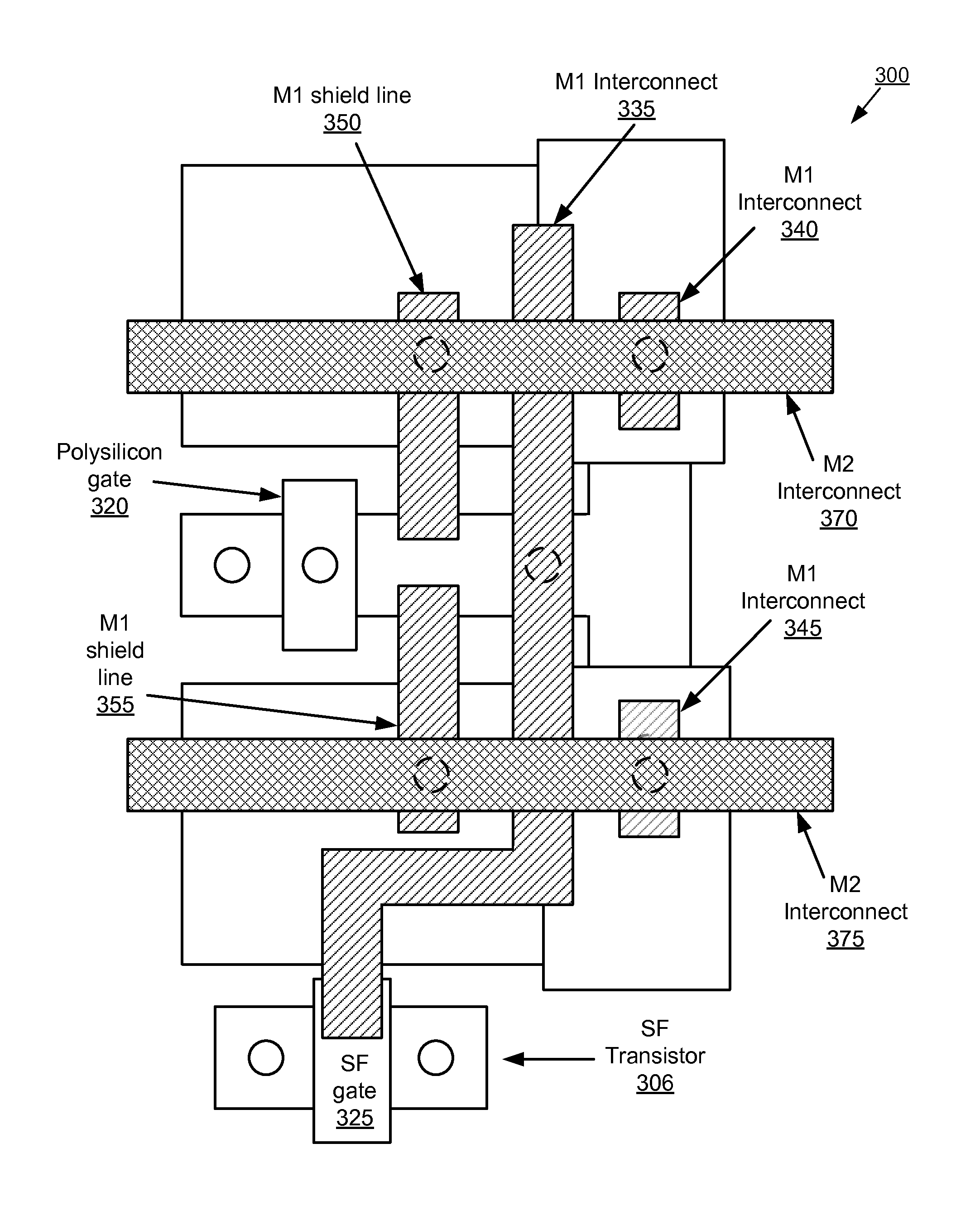
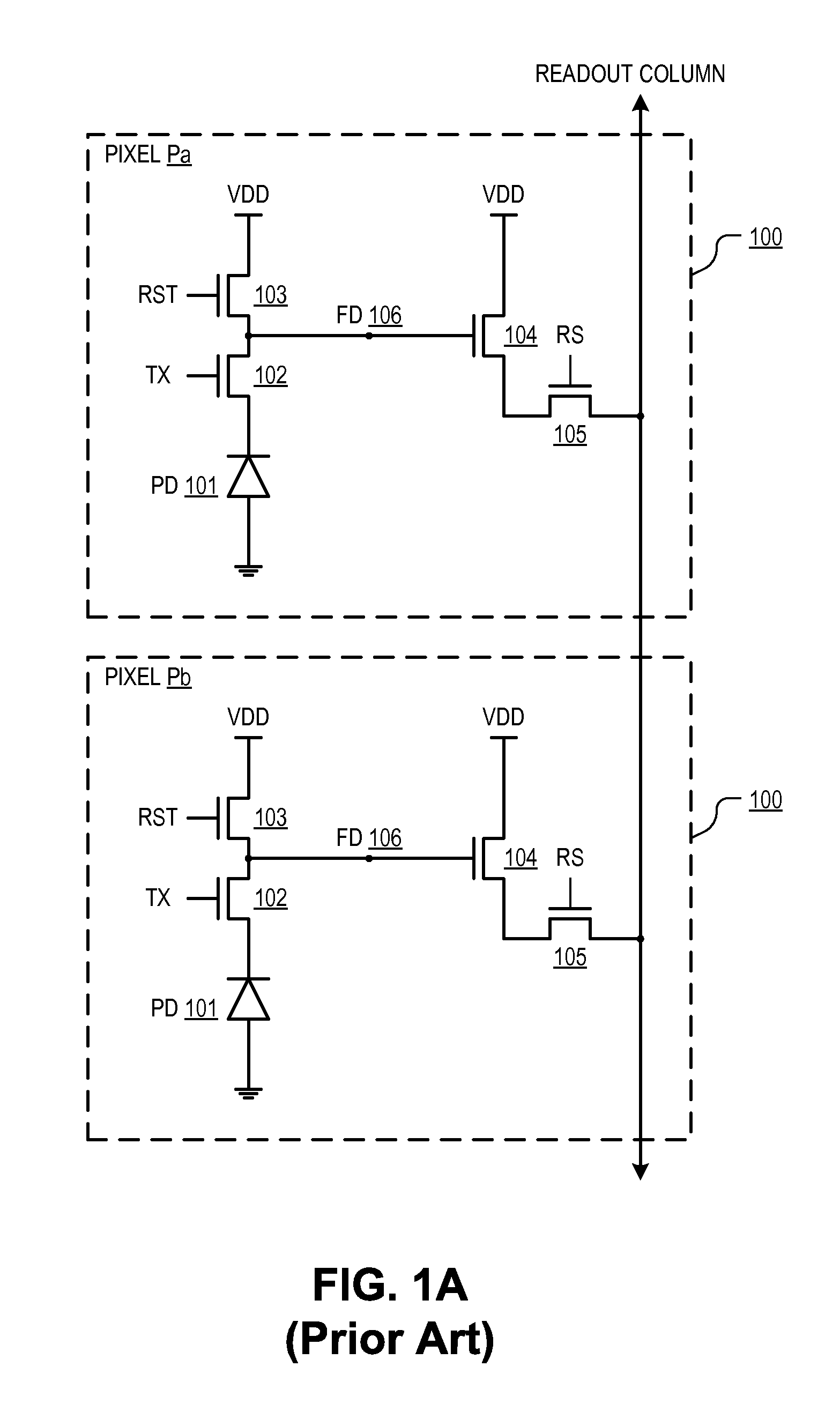
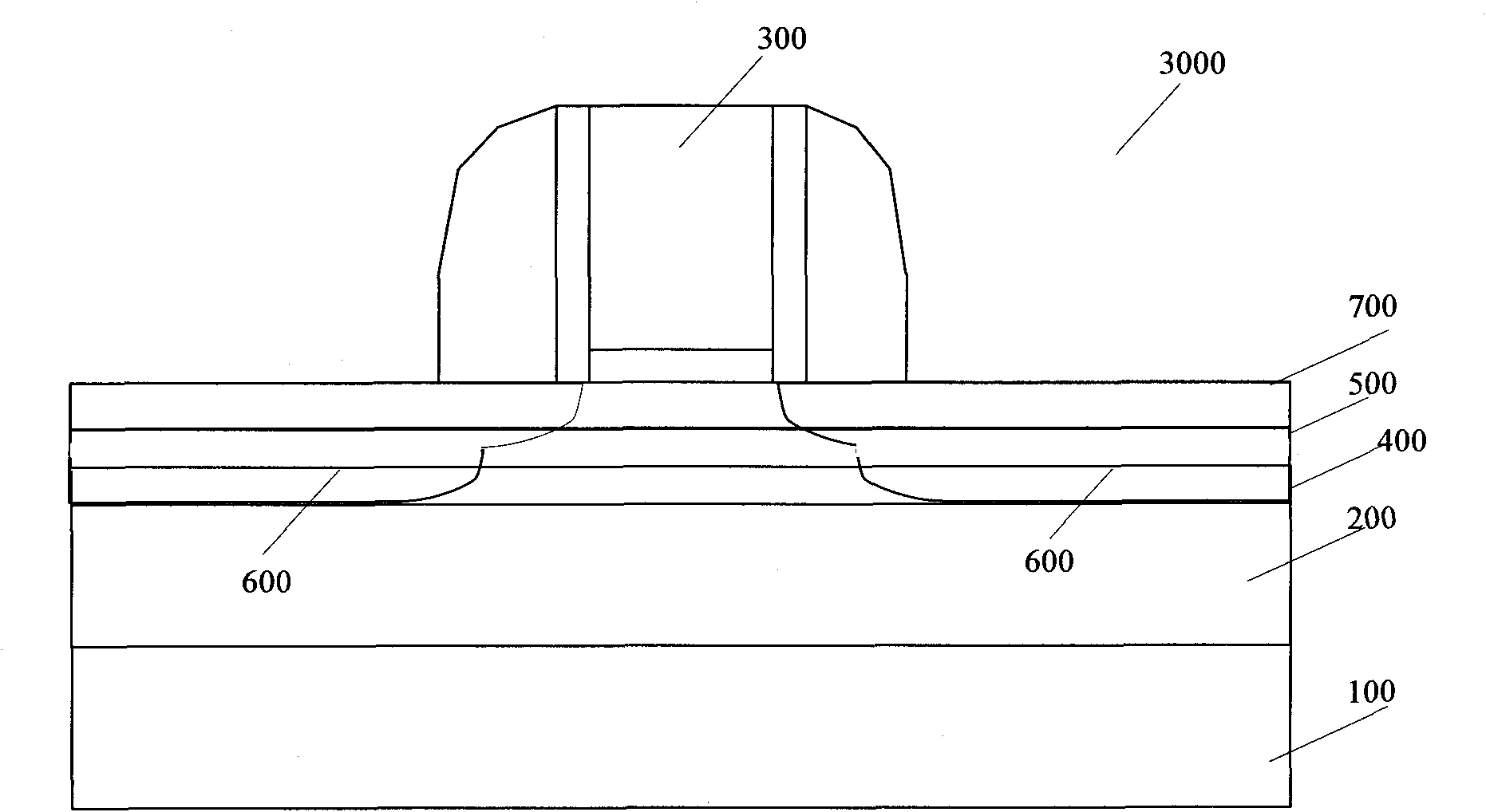
Techniques and mechanisms to improve potential well characteristics in a pixel cell. In an embodiment, a coupling portion of a pixel cell couples a reset transistor of the pixel cell to a floating diffusion node of the pixel cell, the reset transistor to reset a voltage of the floating diffusion node. In another embodiment, the pixel cell includes a shield line which extends athwart the coupling portion, where the shield line is to reduce a parasitic capacitance of the reset transistor to the floating diffusion node.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Image pick-up device and image pick-up system using the image pick-up device
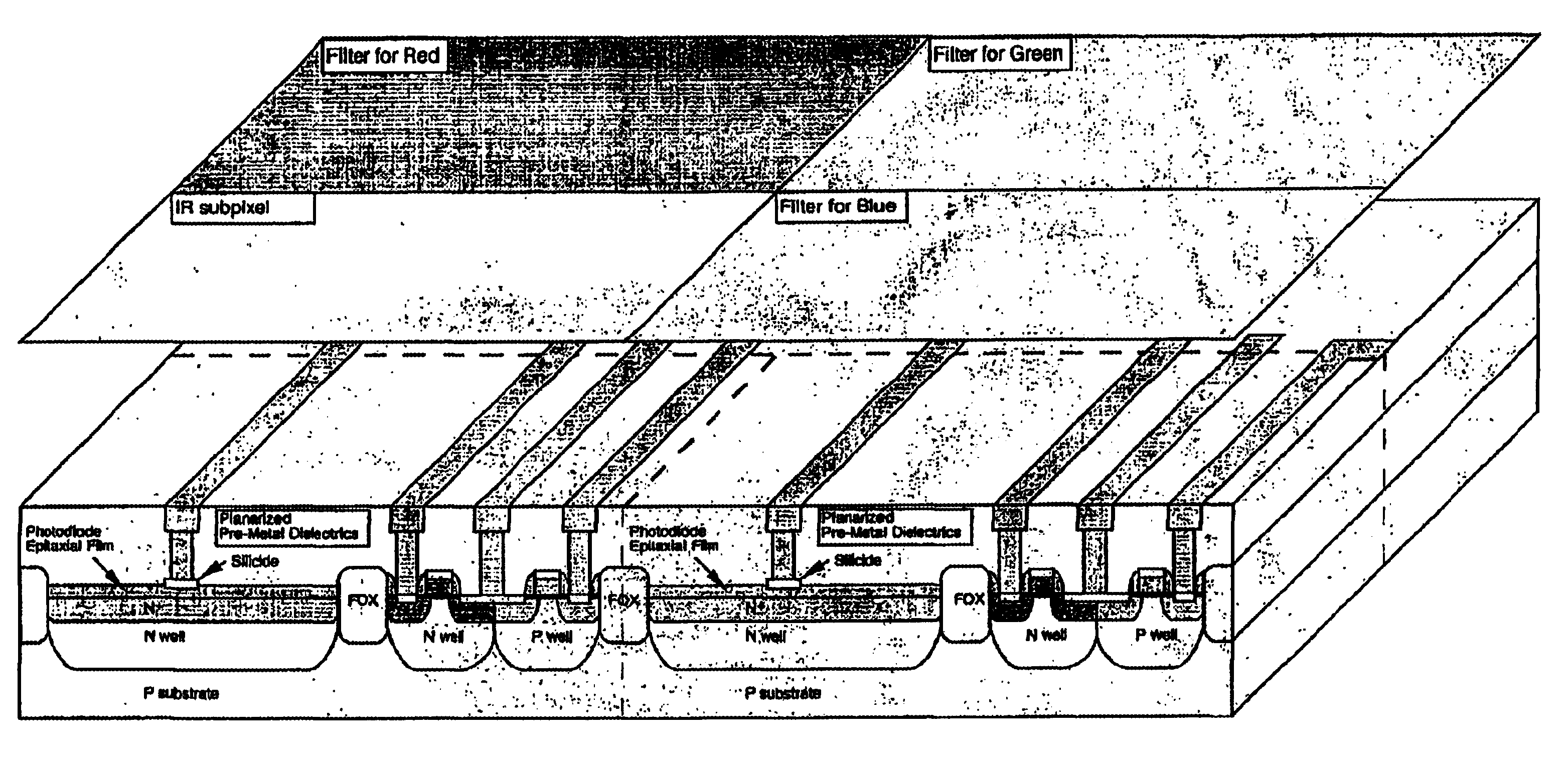
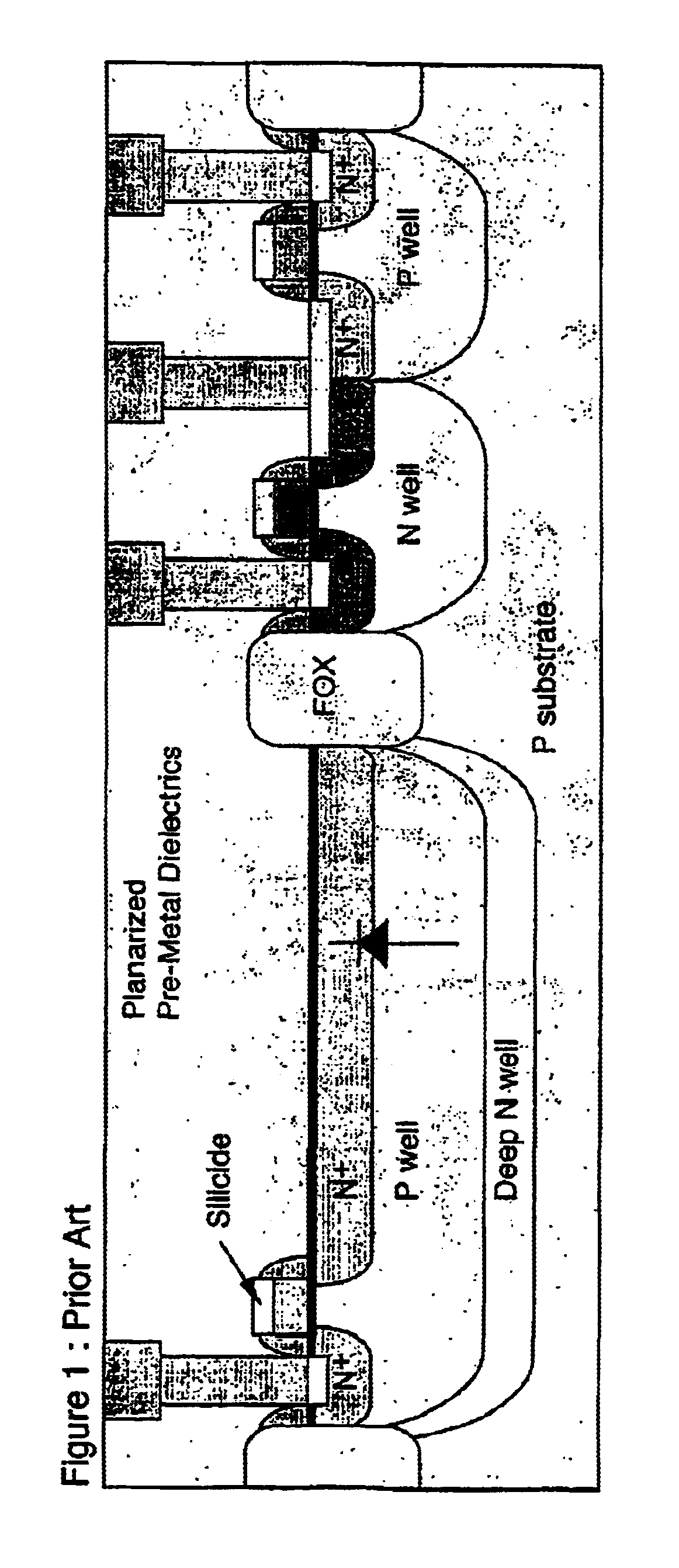
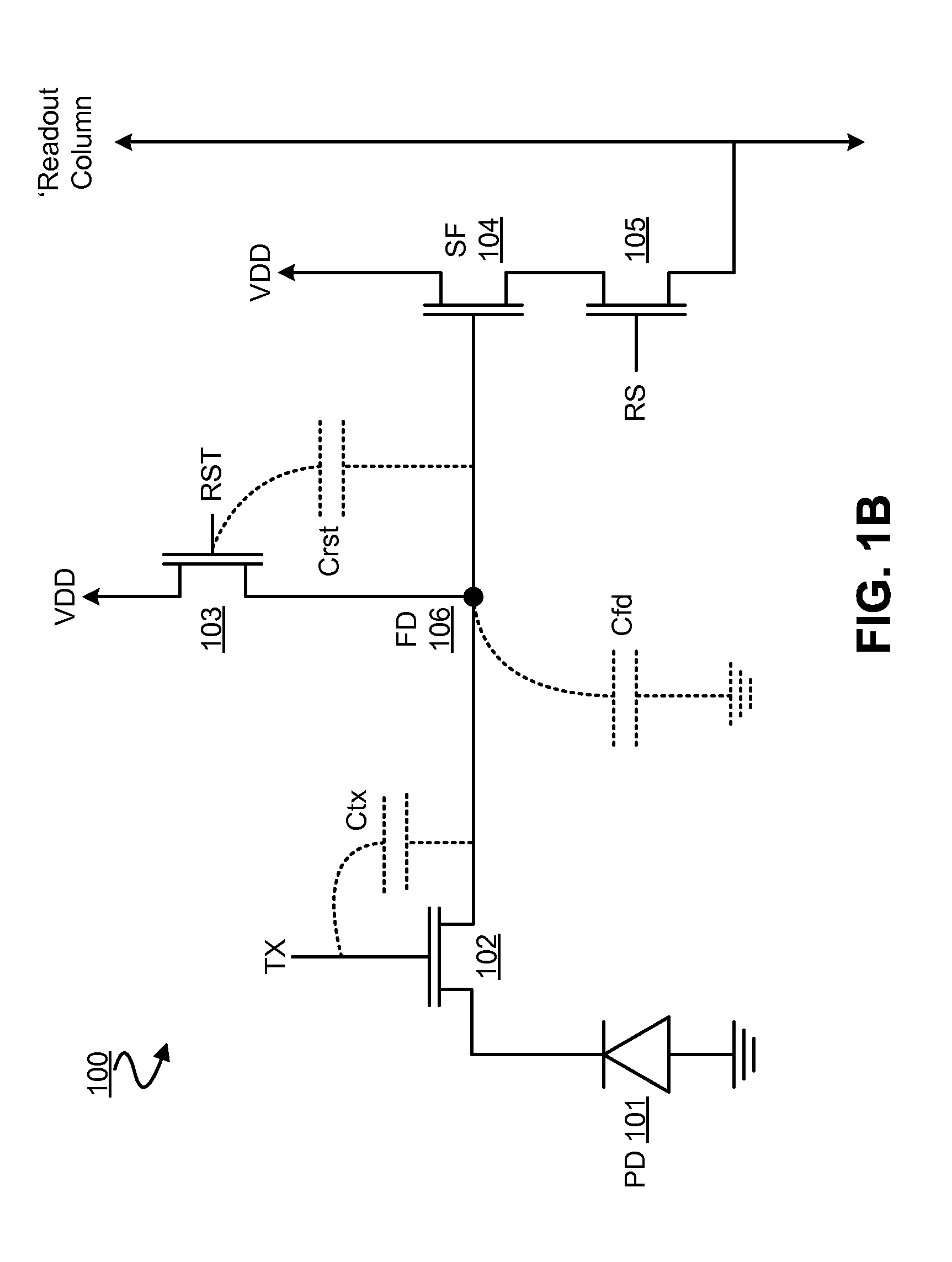
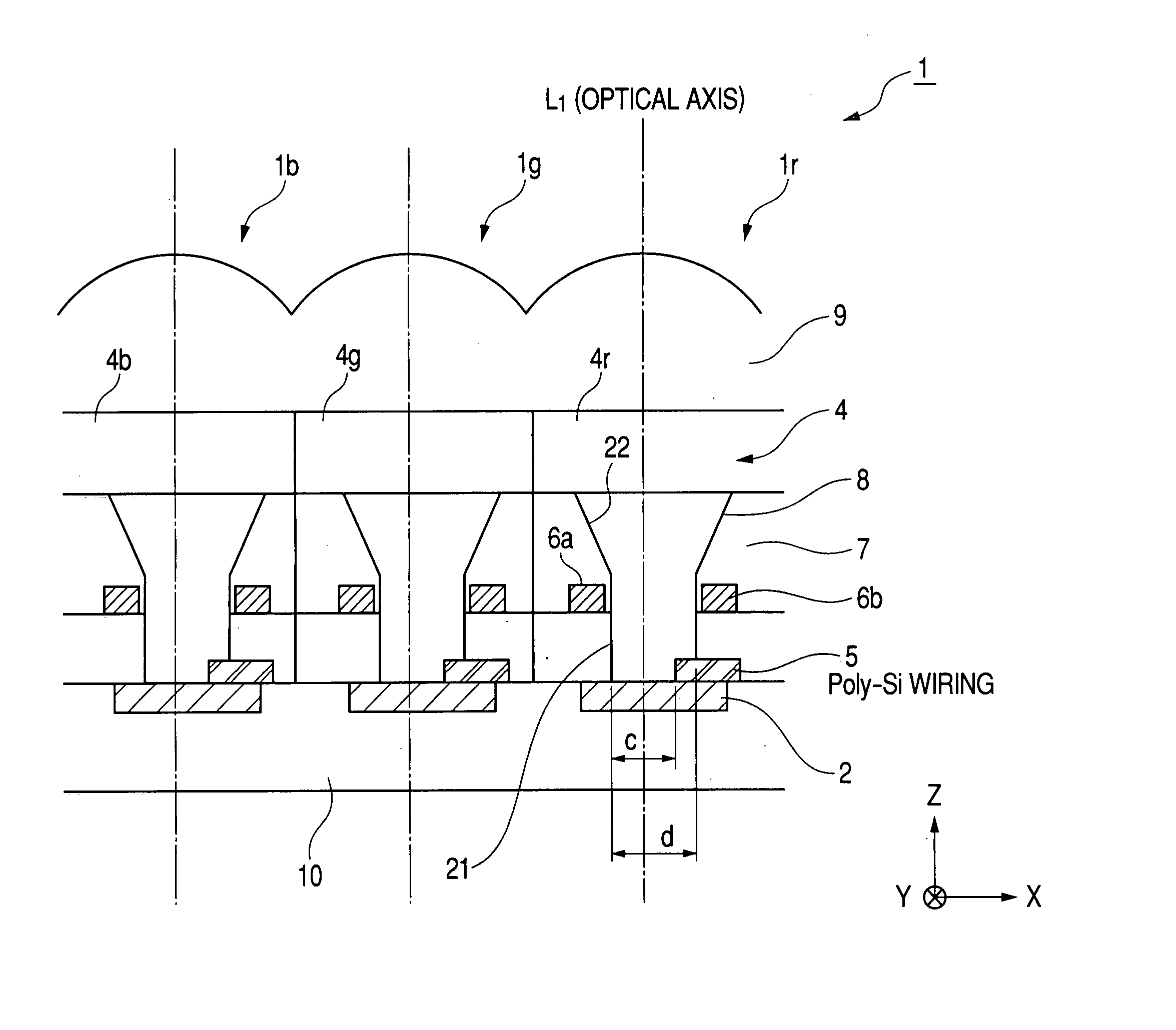
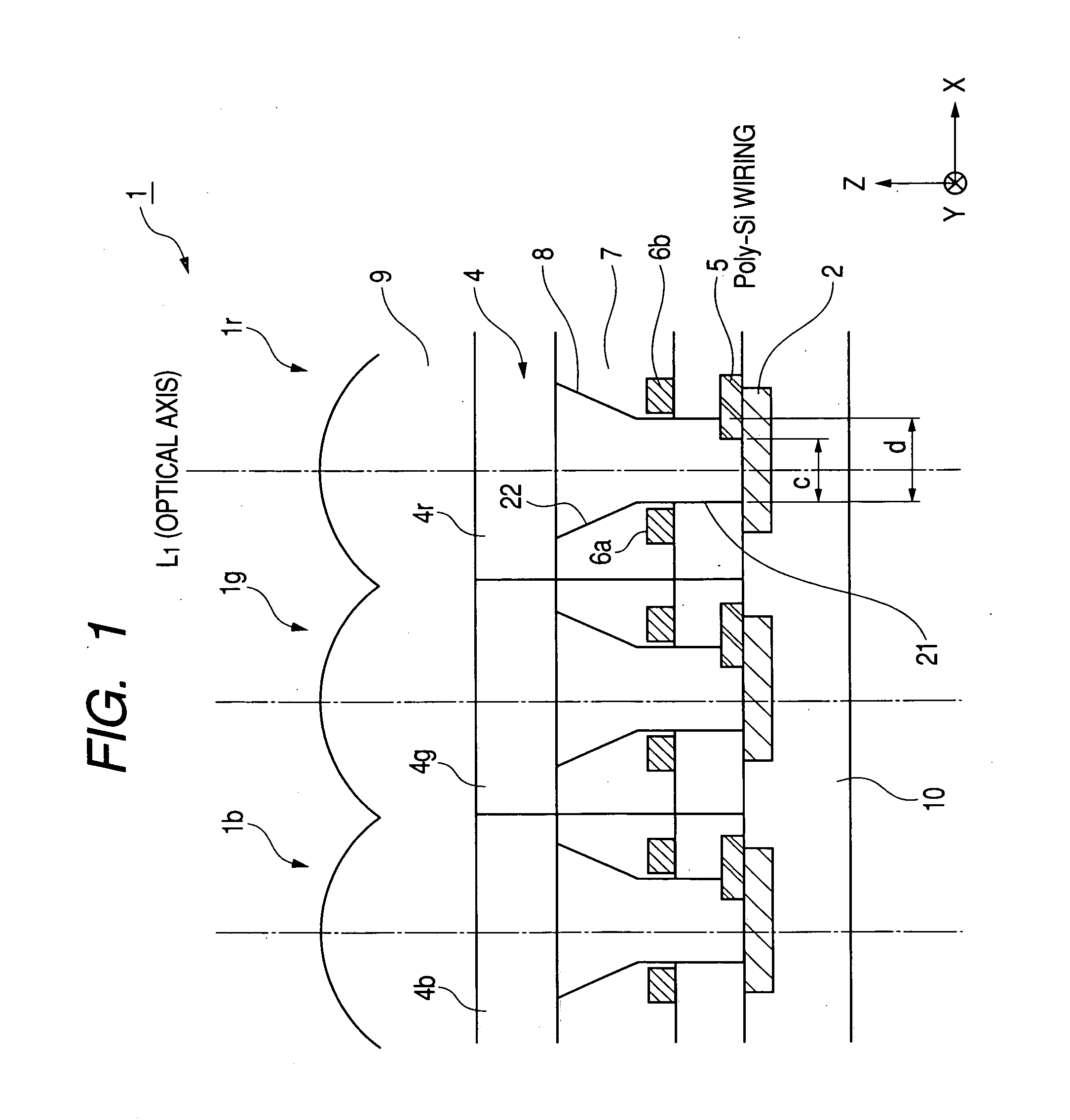
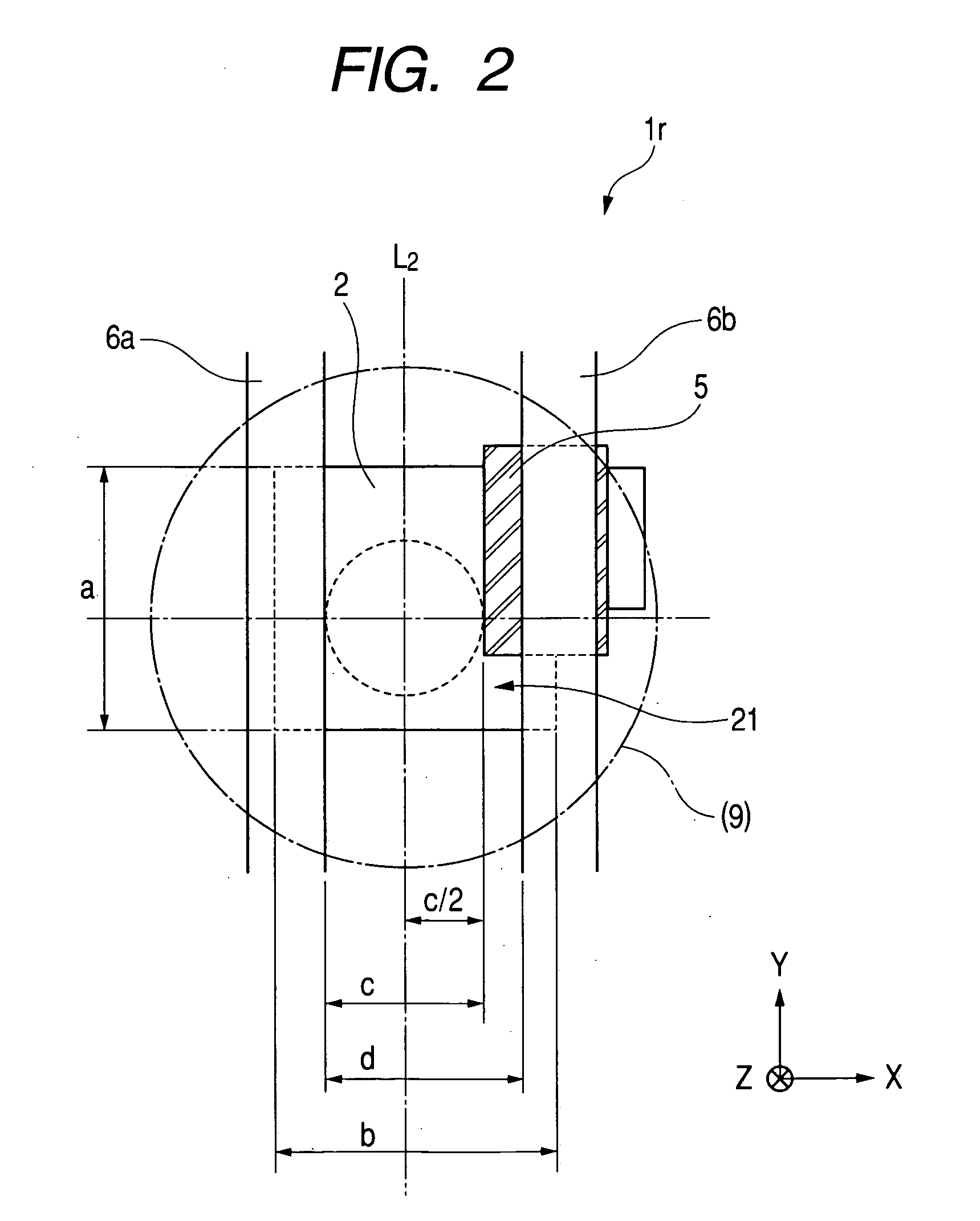
InactiveUS20050072906A1High sensitivityLight collection efficiency is improvedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPotential wellEngineering
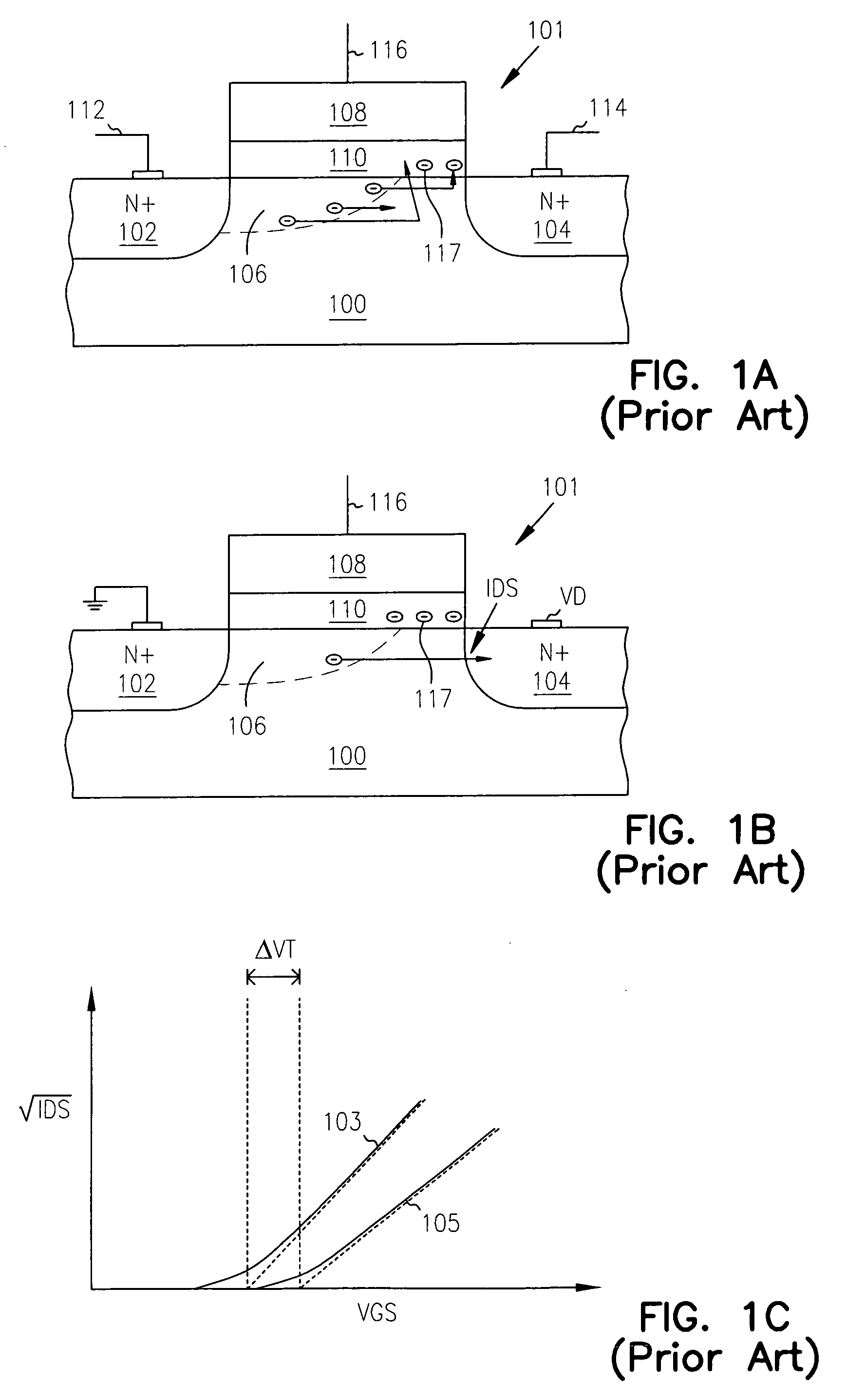
With an aim of receiving a subject image at good sensitivity by improving the light collection efficiency of incident light, an image pick-up element includes a light-receiving portion, poly-silicon wiring formed on the light-receiving portion, and a potential well structure. The poly-silicon wiring is arranged so as to be overlapped with at least a part of the light-receiving portion, and is electrically connected to the light-receiving portion to perform the control of electric charges generated at the light-receiving portion, the switching of the light-receiving portion, and the like. The potential well structure is formed in at least a part of the area of the light-receiving portion in which the poly-silicon wiring is arranged, and the opened area of the potential well structure is sufficiently secured. The incident light entering the potential well structure is totally reflected by the inner wall of the potential well structure, and reaches the light-receiving portion or the poly-silicon wiring. The incident light reaching the poly-silicon wiring is transmitted through the poly-silicon wiring to be received by the light-receiving portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Nitride LED (light-emitting diode) structure and nitride LED structure preparing method
InactiveCN102185057AIncrease hole concentrationImprove internal quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesPotential wellQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses a nitride LED (light-emitting diode) structure. A P-type doped InGaN / GaN superlattice structure is inserted between a multiple quantum well active layer and an electronic barrier layer so as to improve the hole concentration and reduce the dosage concentration of the P-type hole injection layer; the superlattice structure has polarization effect, thus being capable of improving the doping efficiency and reducing the P-type impurity concentration; and impurity atoms are prevented from being diffused to the potential well, and the inner quantum efficiency and the luminous efficiency of the device can be improved. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the nitride LED structure, through inserting the P-type doped InGaN / GaN superlattice structure between the multiple quantum well active layer and the electronic barrier layer, the hole concentration can be improved, and the dosage concentration of the P-type hole injection layer can be reduced; since the superlattice structure has polarization effect, the doping efficiency can be improved and the P-type impurity concentration can be reduced; and the impurity atoms are prevented from being diffused to the potential well, and the inner quantum efficiency and the luminous efficiency of the device can be improved.
Owner:ENRAYTEK OPTOELECTRONICS
Array of luminescent elements
Light emitting systems and method of fabricating the same are disclosed. The light emitting system includes two or more monolithically integrated luminescent elements. Each luminescent element includes an electroluminescent device and a dedicated switching circuit for driving the electroluminescent device. At least one luminescent element includes a potential well for down converting light emitted by the electroluminescent device in the luminescent element.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
ActiveUS7619238B2Convenient lightingImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
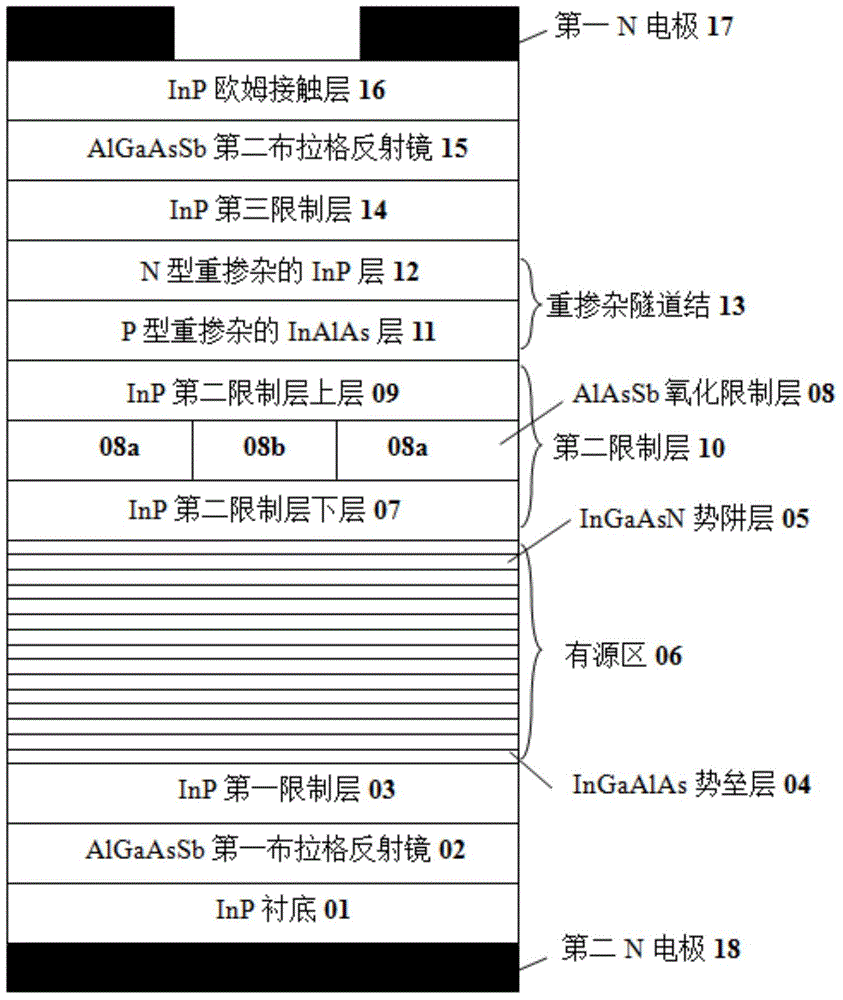
InactiveCN104577711AHigh gainEffective limitLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPotential well
The invention discloses a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser which comprises a substrate, a first Bragg reflector, a first limiting layer, an active region, a second limiting layer, a second Bragg reflector and an Ohmic contact layer which are arranged in a laminated manner, wherein the active region adopts a quantum well structure, a potential barrier layer is made of InGaAlAs, and a potential well layer is made of InGaAsN; a heavily-doped tunnel junction and a third limiting layer are also arranged between the second limiting layer and the second Bragg reflector; an oxidized limiting layer is also arranged in the second limiting layer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the laser. The laser has the advantages that the laser uses an InGaAsN / InGaAlAs material system as the active region, has large conduction band order ratio and can effectively limit injected carriers, so that the threshold current is reduced, and the laser gain is improved; on an isometric wavelength band of 1550 nm, the content of N required by an active region material is lower, and devices with high material quality are easy to obtain.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
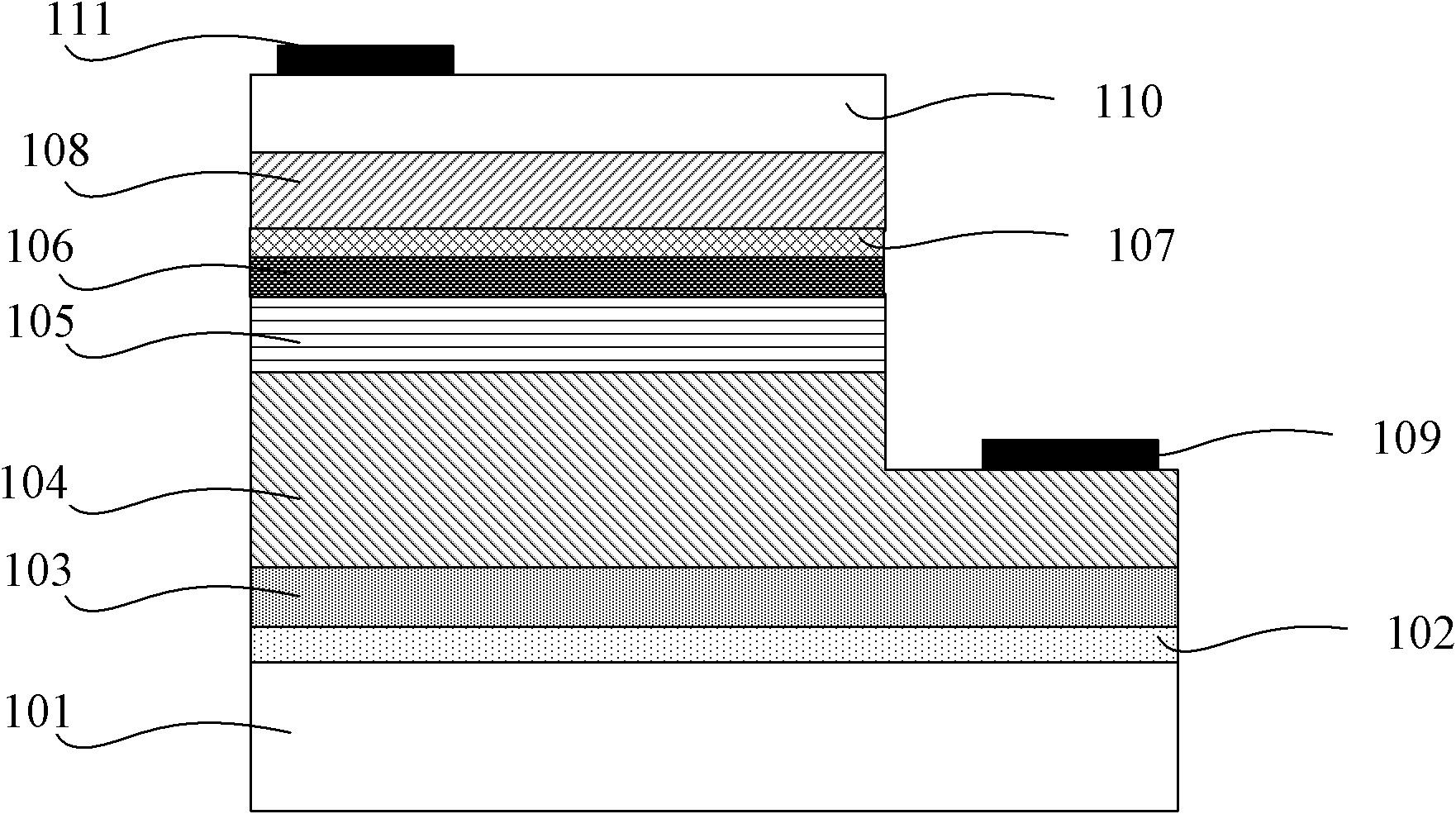
Semiconductor structure
The invention provides a semiconductor structure which comprises a substrate, a transition layer or an insulating layer formed on the substrate, a first strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer, a strain narrow bandgap semiconductor layer, a second strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer, a grid stacking layer formed on the second strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein the first strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer, the strain narrow bandgap semiconductor layer and the second strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer are sequentially formed on the transition layer or the insulating layer; and the source electrode and the drain electrode are formed in the first strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer, the strain narrow bandgap semiconductor layer and the second strain wide bandgap semiconductor layer. The semiconductor structure not only can suppress the generation of two kinds of BTBT (Band-to-Band Tunneling) electric leakages, but also can generate a cavity potential well in the middle strain narrow bandgap semiconductor layer (such as a strain GE layer or a strain SiGe layer) so as to improve the mobility of carriers and the property of devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of multiple quantum well structure for photoelectric device
ActiveCN102103990AImprove the broadening effectImprove life test performanceLaser detailsFinal product manufacturePotential wellElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multiple quantum well structure for a photoelectric device. The multiple quantum well structure comprises n quantum well structures which are overlapped in sequence, and each quantum well structure is formed by sequential growth of potential well layers and potential barriers, wherein the growth of each potential well layer comprises the following steps: 1, first growing an NixGa1-xN potential well layer, wherein x is more than 0.1 and less than 0.45; 2, growing a GaN insert layer; and 3, growing the InxGa1-xN potential well layer, wherein x is more than 0.1 and less than 0.45. When the potential well layer grows, one or more than two of GaN insert layers with energy band width different from that of the InxGa1-xN potential well layer and an In treatment layer grow alternately. On the one hand, the In treatment layer can stabilize the structure of the InxGa1-xN, ensures the stability of quantum well components, and controls the stability and consistency of wavelength; on the other hand, the GaN insert layer disturbs the energy band structure of a quantum well region to improve the composite rate of electron hole pairs, so that the internal quantum efficiency of device illumination is improved, and as the brightness is improved, the life test performance of the device can be improved.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH +1
Method and system for confining and salvaging oil and methane leakage from offshore locations and extraction operations
A method of, and system for, collecting and controlling hydrocarbons leaking from offshore sea bottom environments entail providing a concrete containment barrier and catenary gasket around the leak source, pumping concrete onto the catenary gasket, opening ports and valves in a containment vessel while it is positioned over the leak source, at least partially embedding the containment vessel in the pumped concrete, closing the ports and valves to capture leaking fluids, and communicating the fluids to the surface for further processing. The modular containment barrier may be placed around an existing or potential well site, or an operating well, abandoned well or sea bottom fissure to facilitate implementation of the method in the event of a leak.
Owner:BREY ARDEN L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com