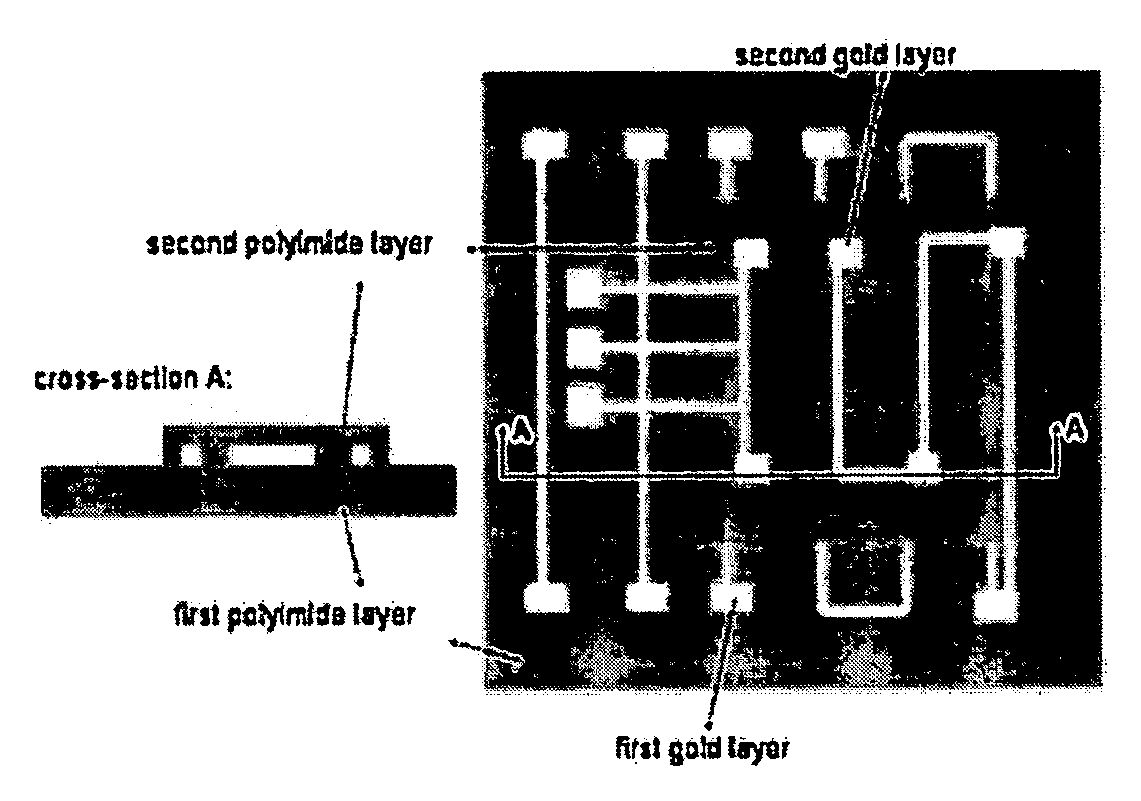
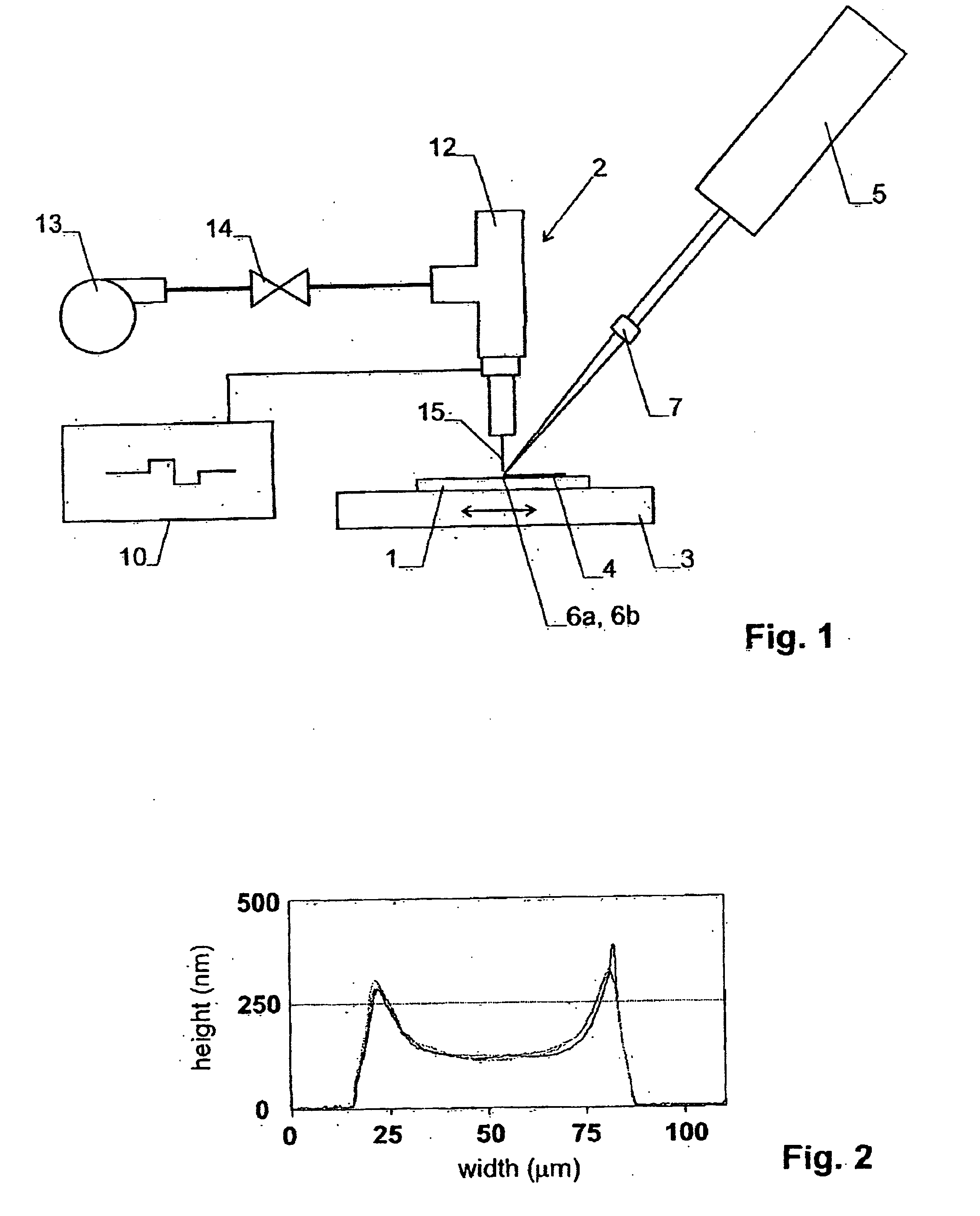
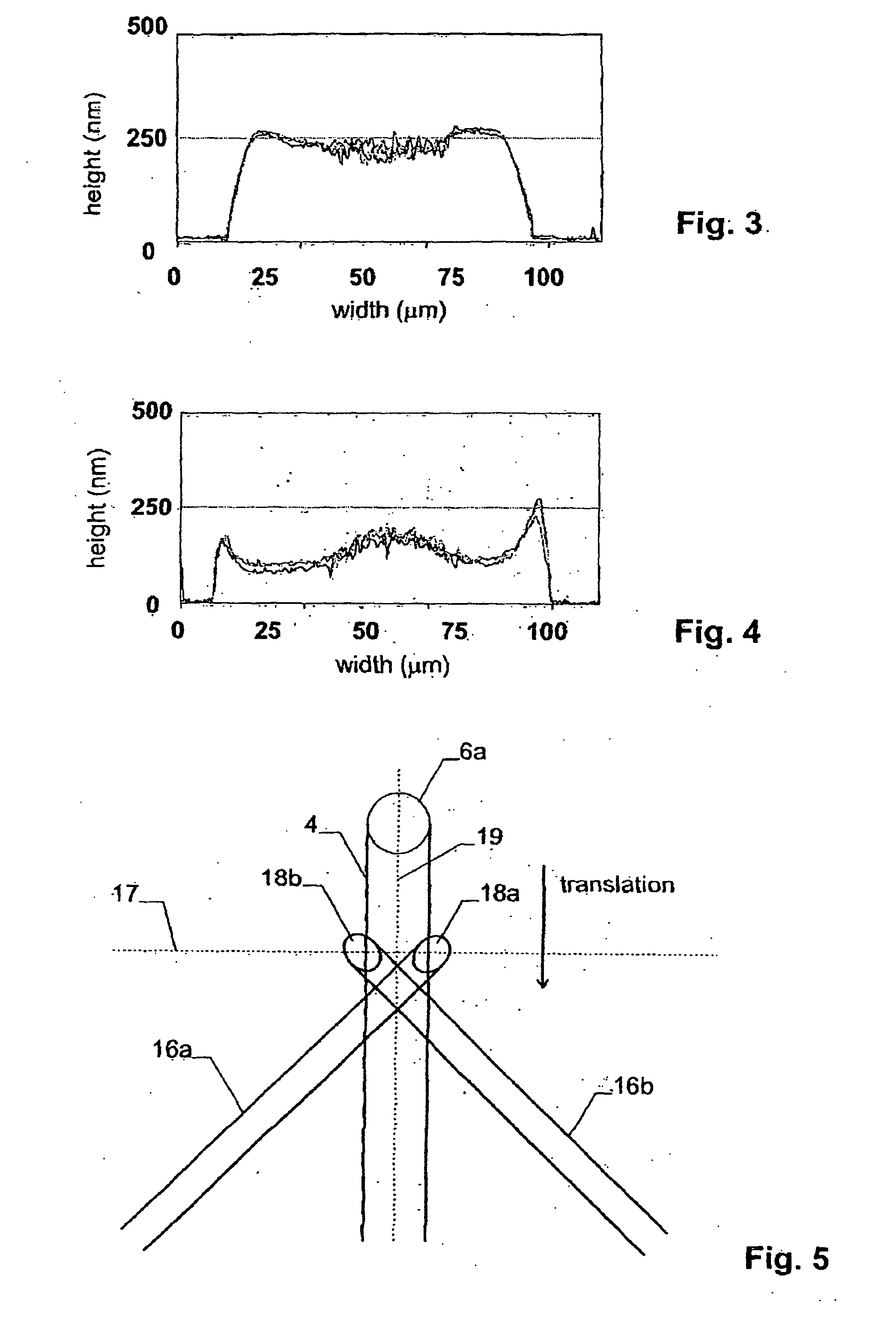
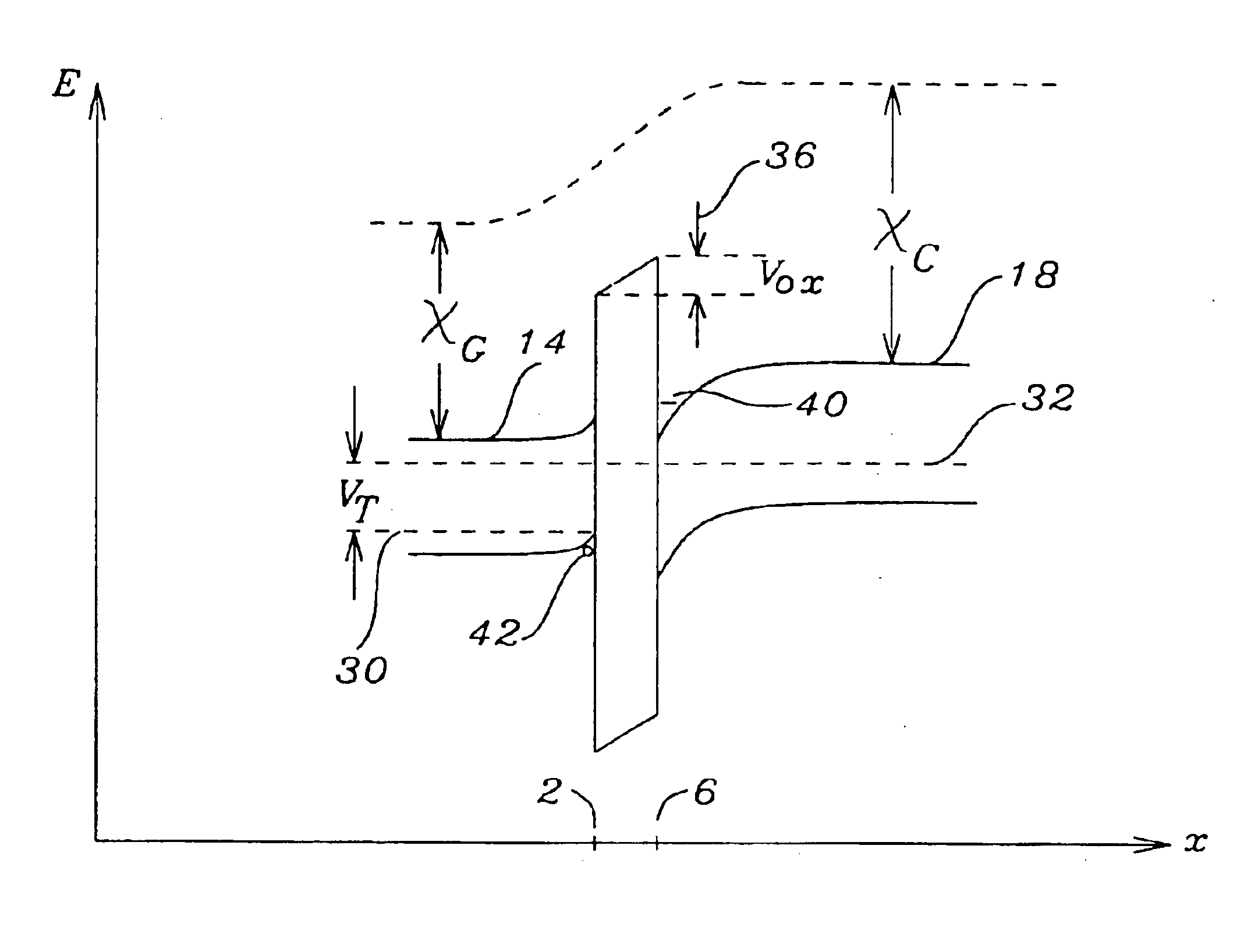
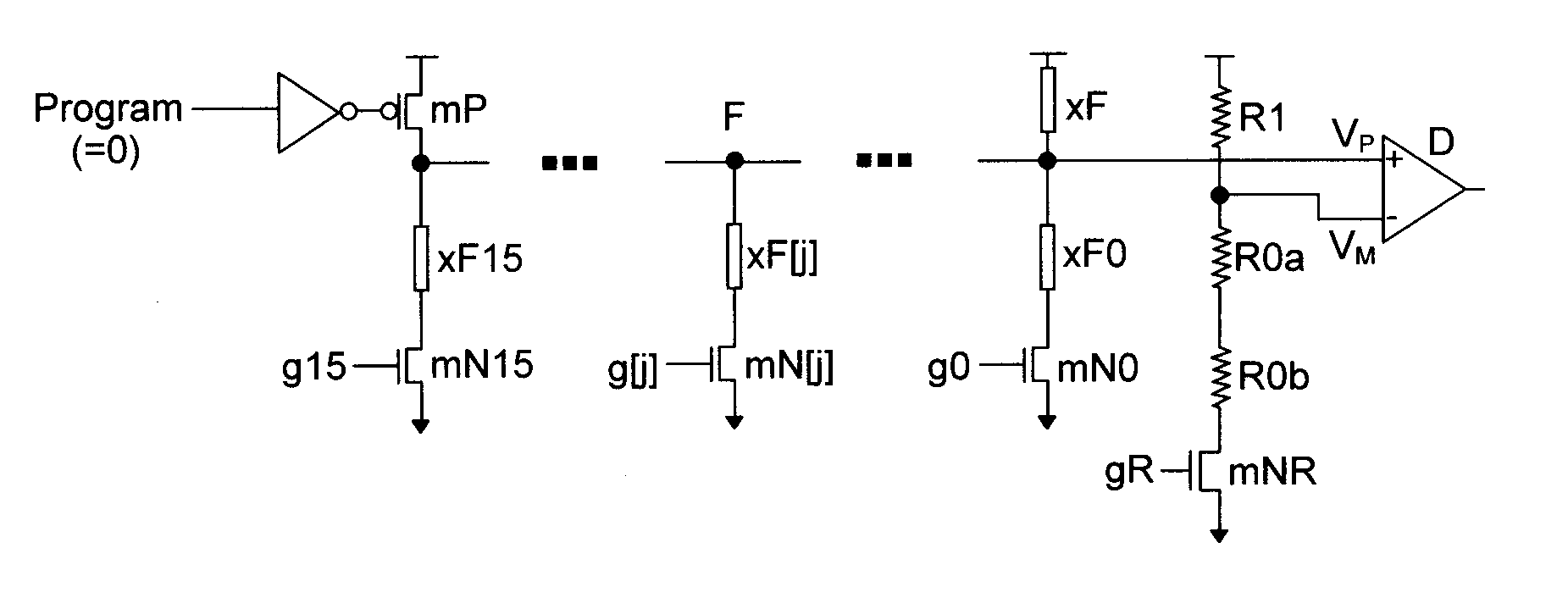Patents
Literature
738 results about "Electronic band structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
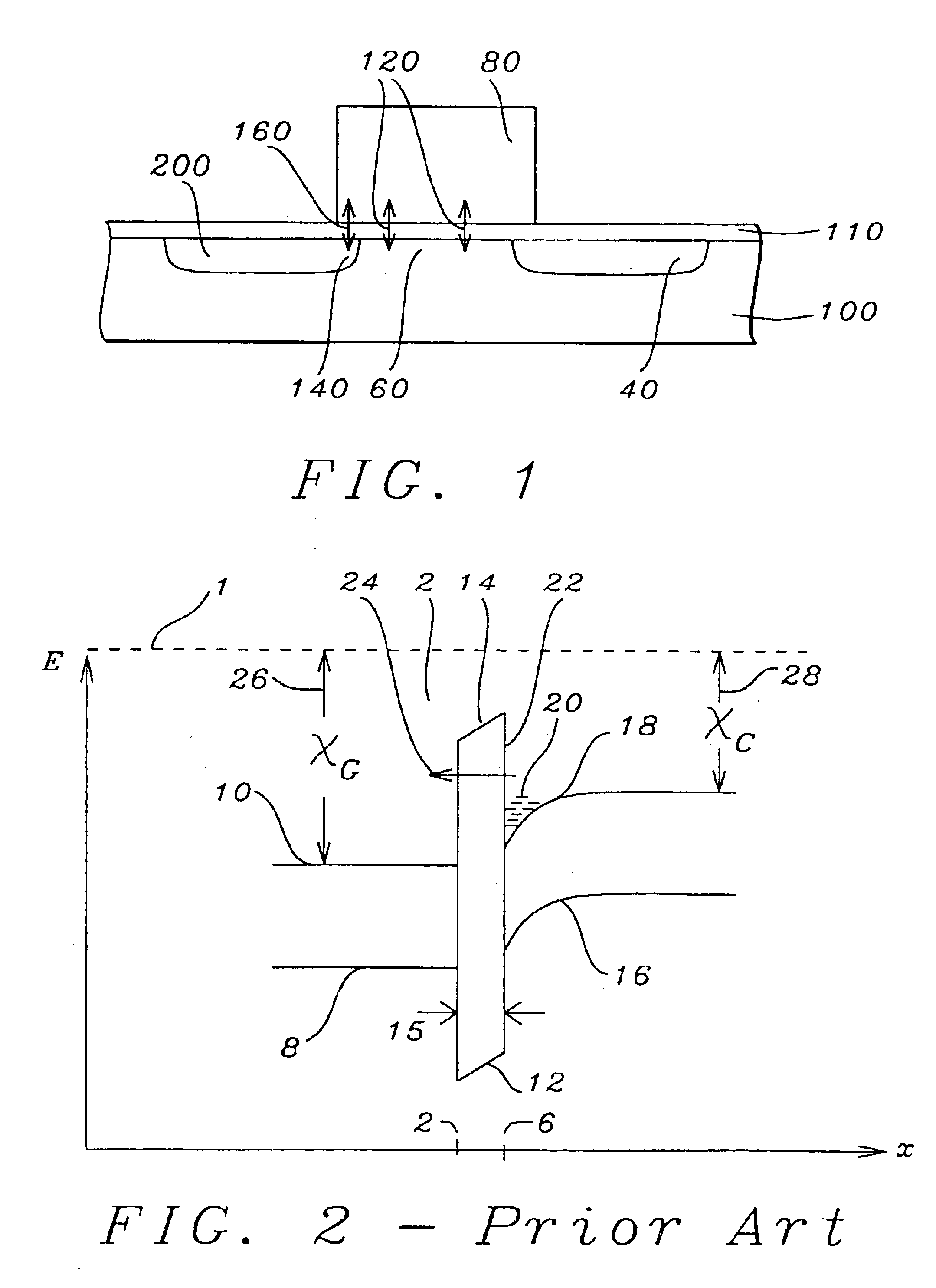
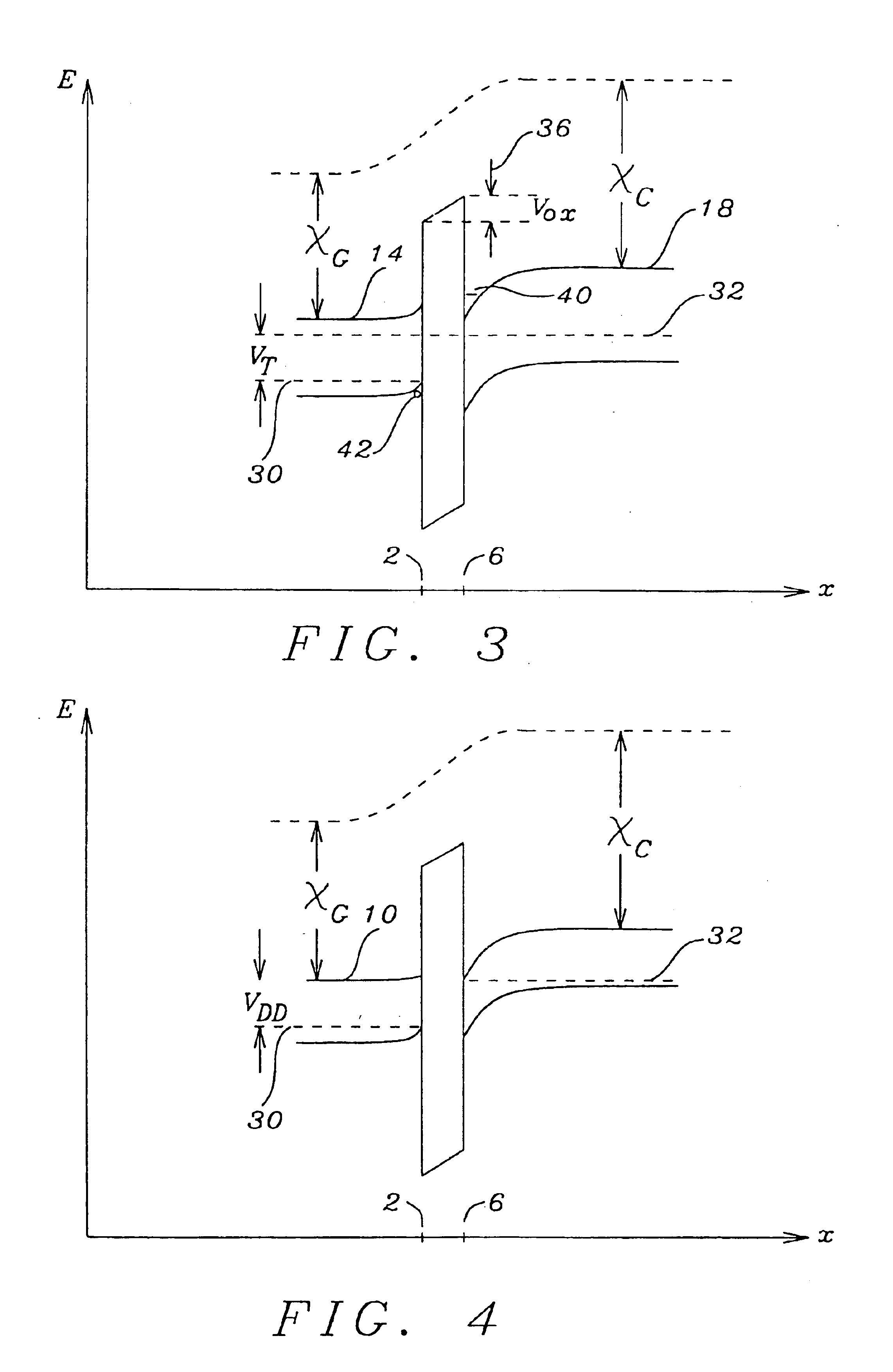
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a solid describes the range of energies an electron within the solid may have (called energy bands, allowed bands, or simply bands) and ranges of energy that it may not have (called band gaps or forbidden bands).
Opto-electronic package structure having silicon-substrate and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20090273005A1Simplify component complexityIncrease heatSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureOpto electronic
Owner:TOUCH MICRO SYST TECH
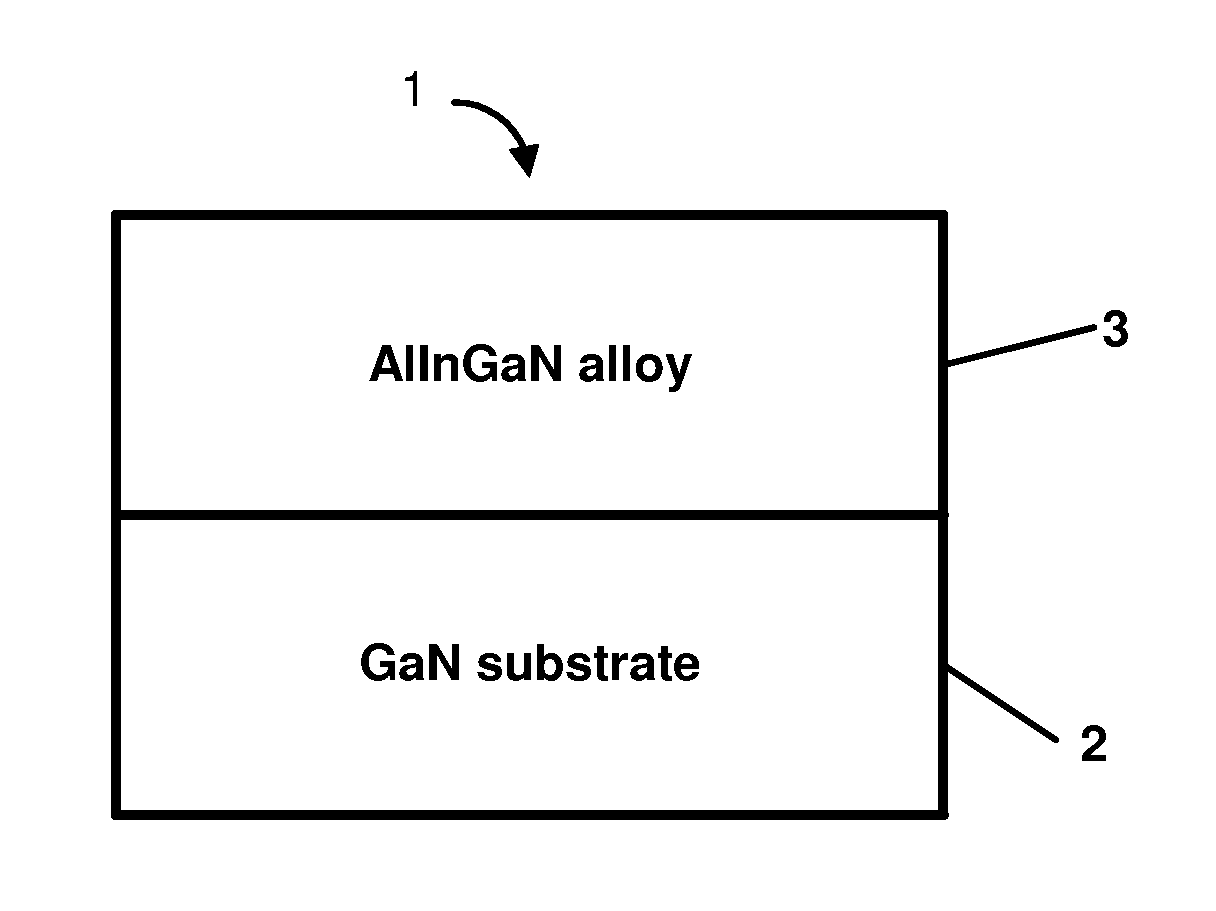
Formation of nitride-based optoelectronic and electronic device structures on lattice-matched substrates
InactiveUS20080303033A1Improve epitaxial layer qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsAlloy
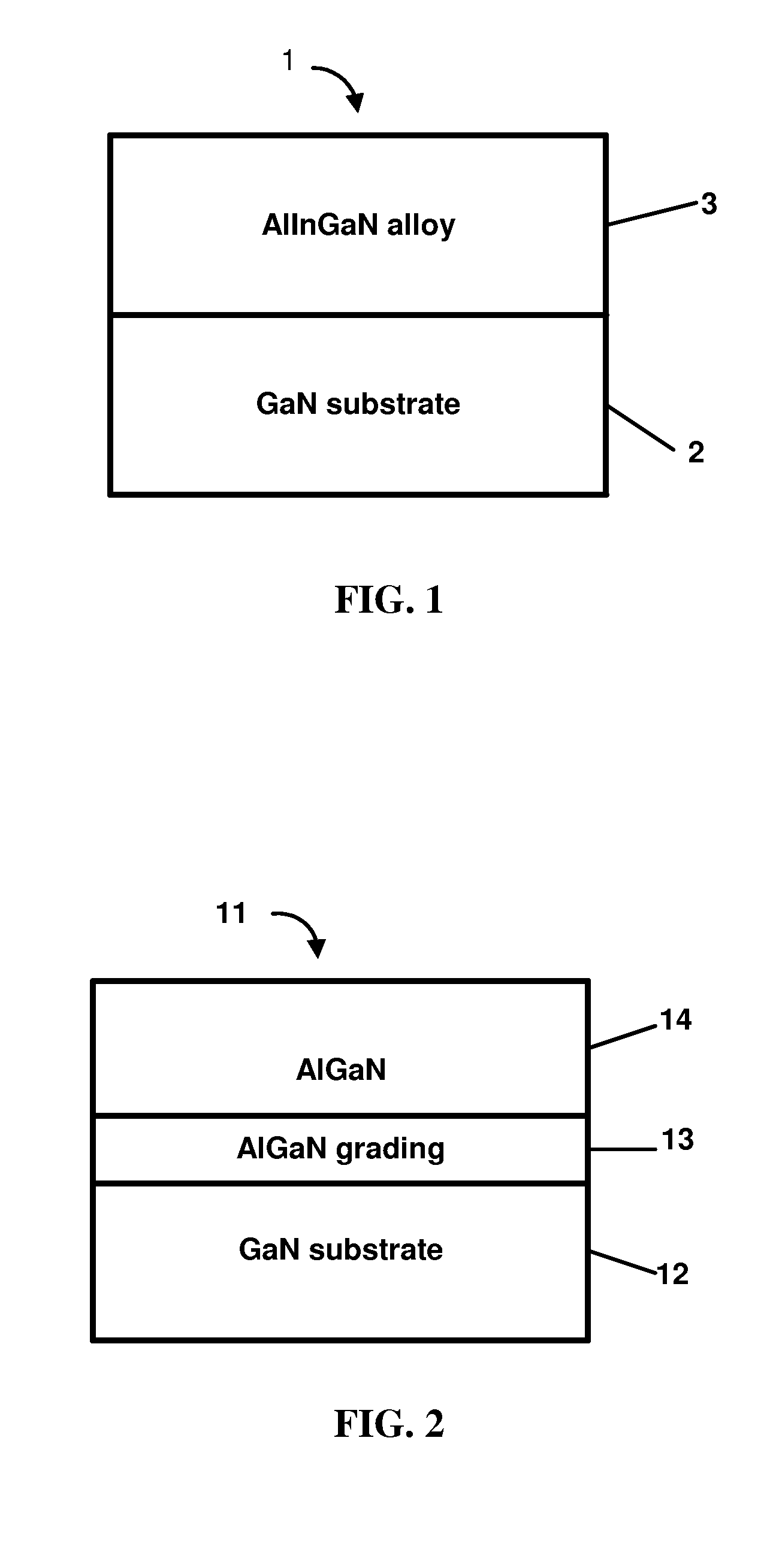
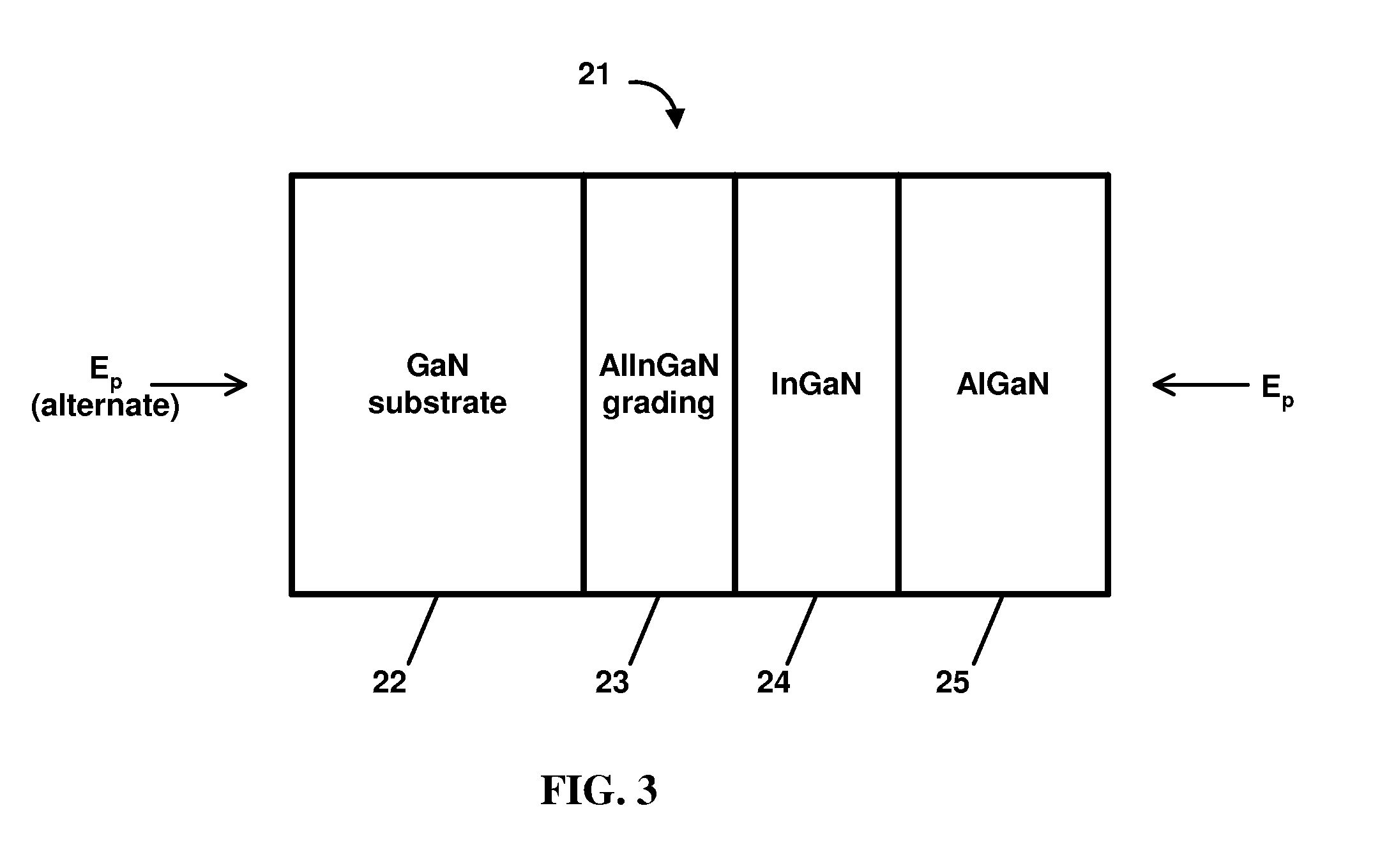
A method of forming an AlInGaN alloy-based electronic or optoelectronic device structure on a nitride substrate and subsequent removal of the substrate. An AlInGaN alloy-based electronic or optoelectronic device structure formed on a nitride substrate is freed from the substrate on which it was grown.
Owner:CREE INC
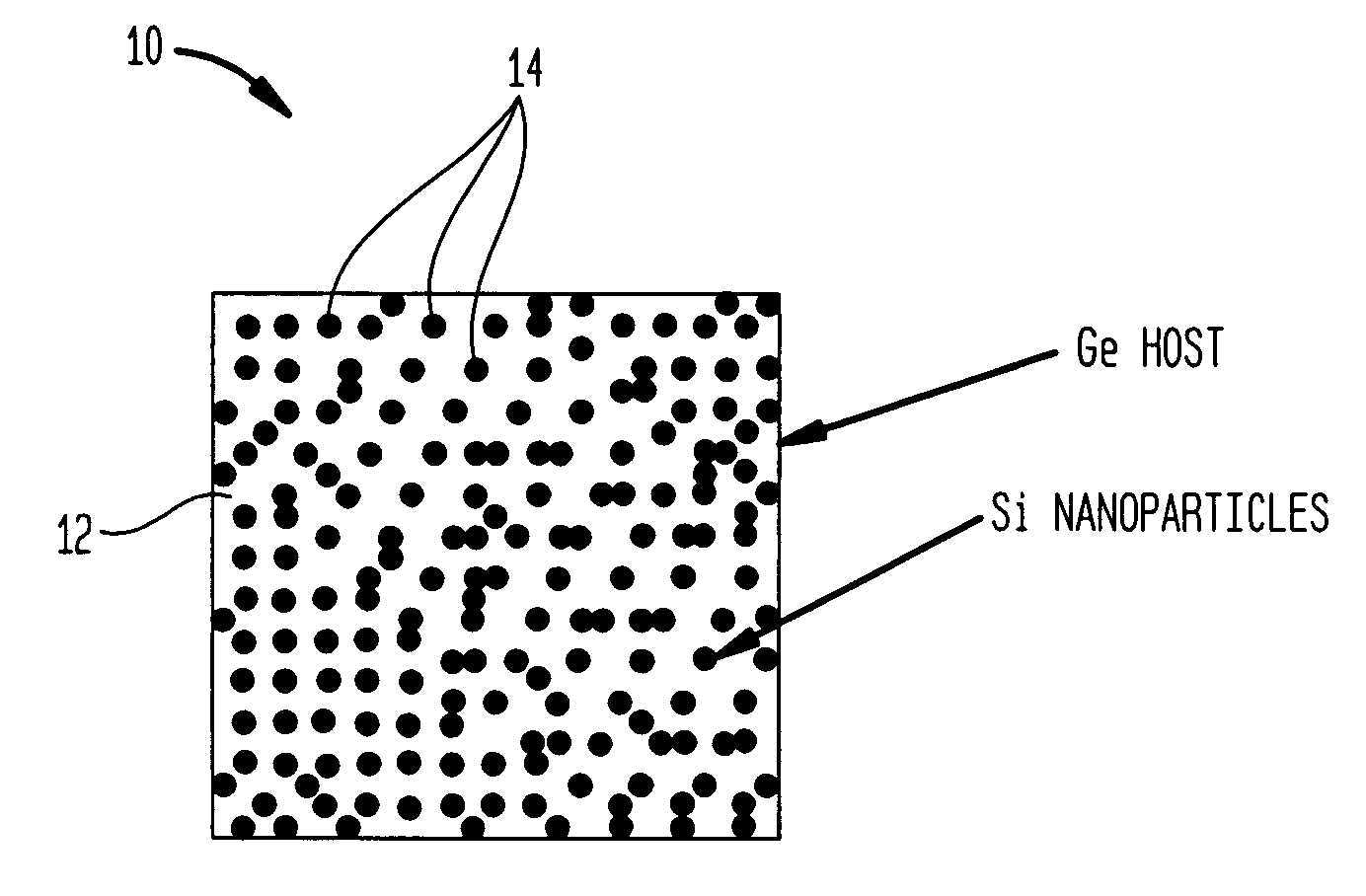
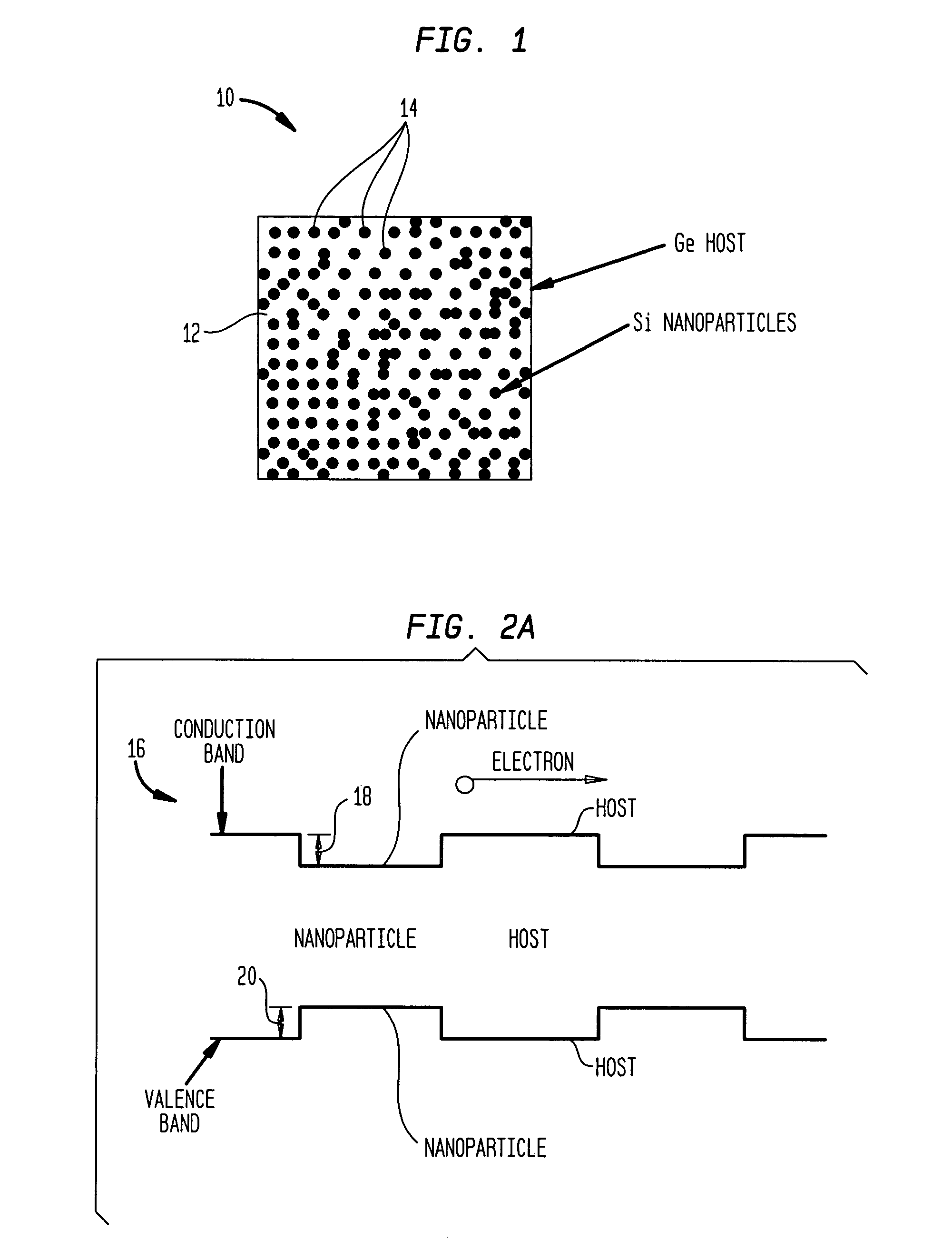
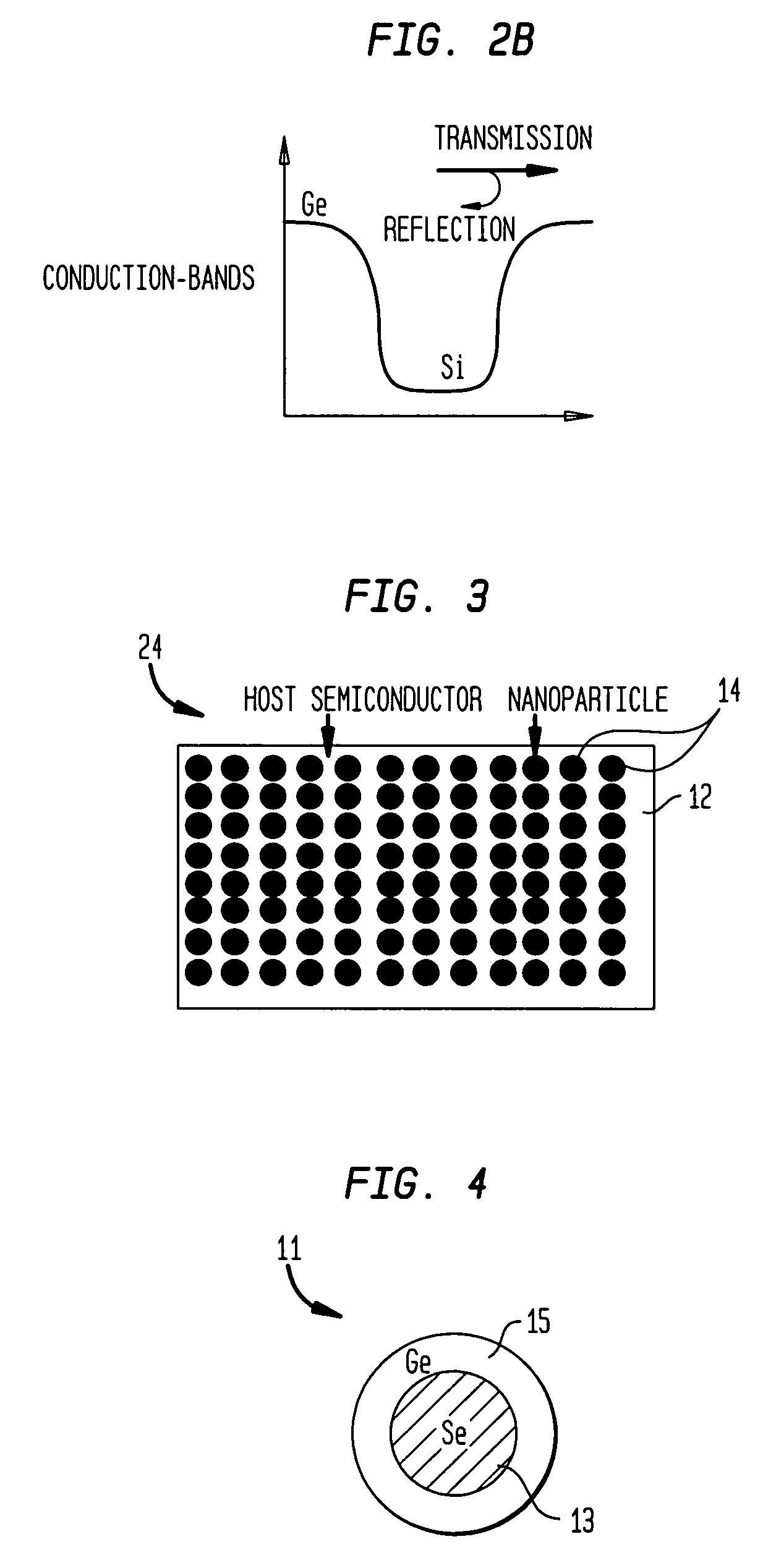
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
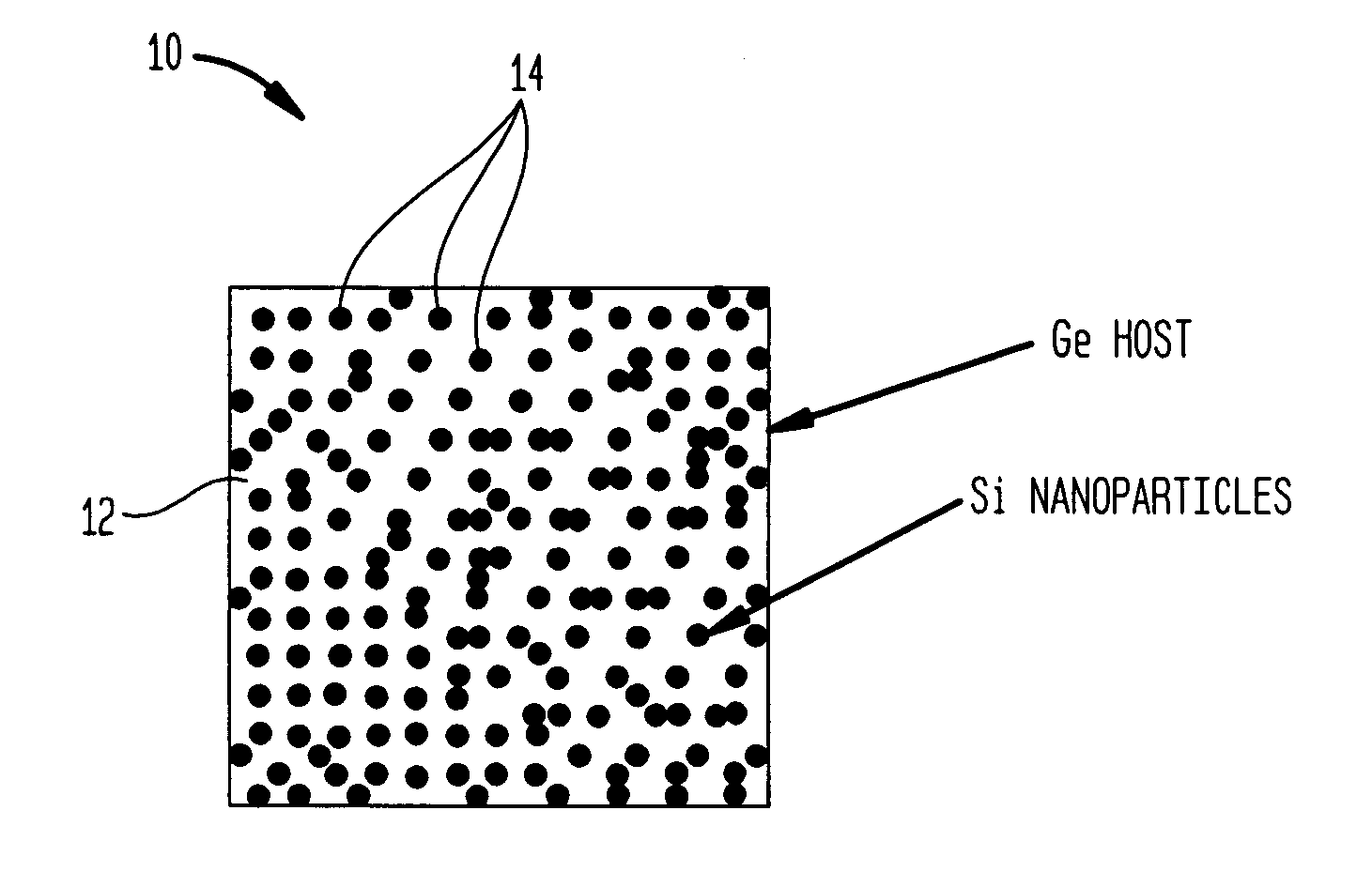
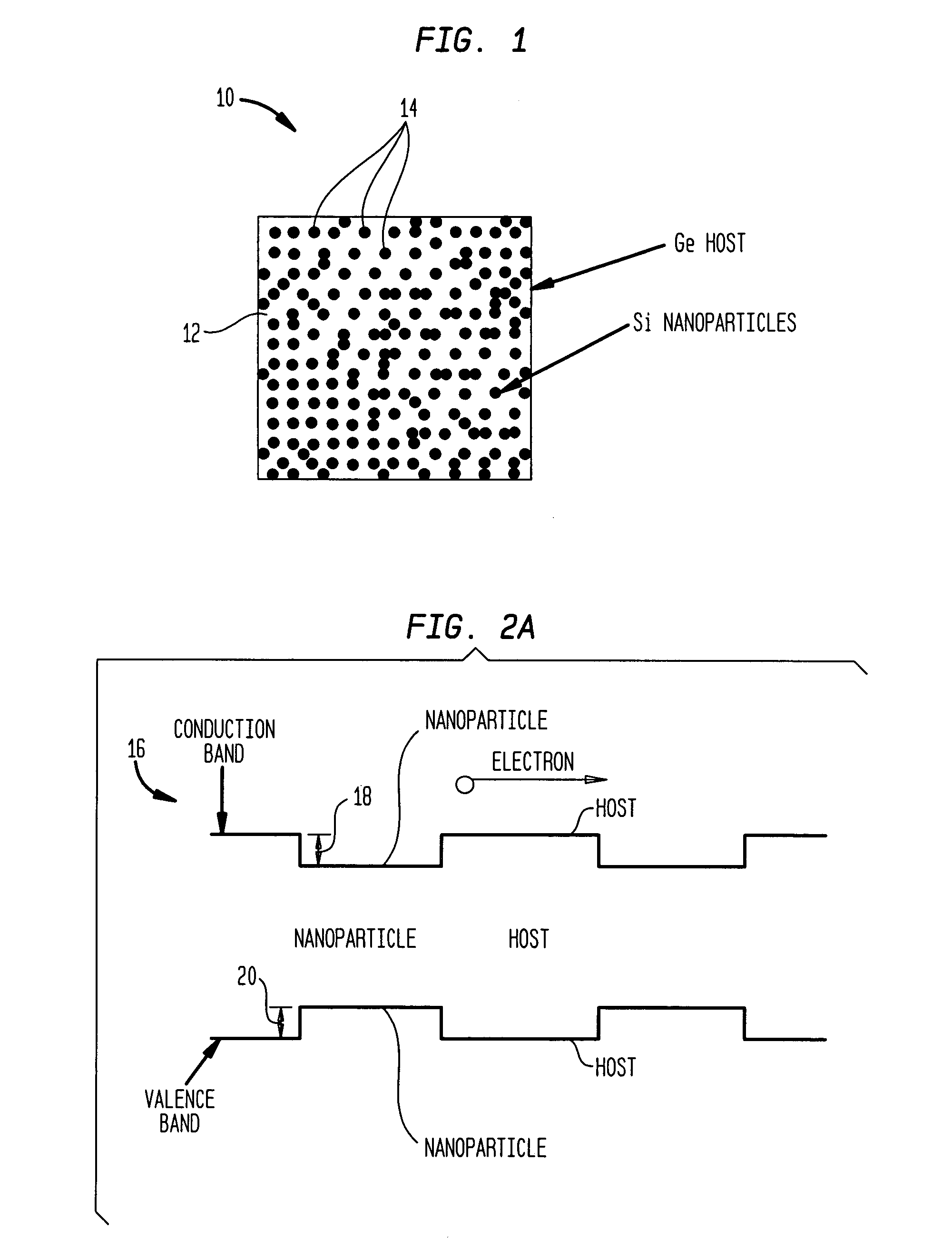
InactiveUS20060102224A1Improve thermoelectric performanceLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectValence bandConduction band
The present invention is generally directed to nanocomposite thermoelectric materials that exhibit enhanced thermoelectric properties. The nanocomposite materials include two or more components, with at least one of the components forming nano-sized structures within the composite material. The components are chosen such that thermal conductivity of the composite is decreased without substantially diminishing the composite's electrical conductivity. Suitable component materials exhibit similar electronic band structures. For example, a band-edge gap between at least one of a conduction band or a valence band of one component material and a corresponding band of the other component material at interfaces between the components can be less than about 5 kBT, wherein kB is the Boltzman constant and T is an average temperature of said nanocomposite composition.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
Tiled electronic display structure
InactiveUS6897855B1Television system detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceElectrical connection
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
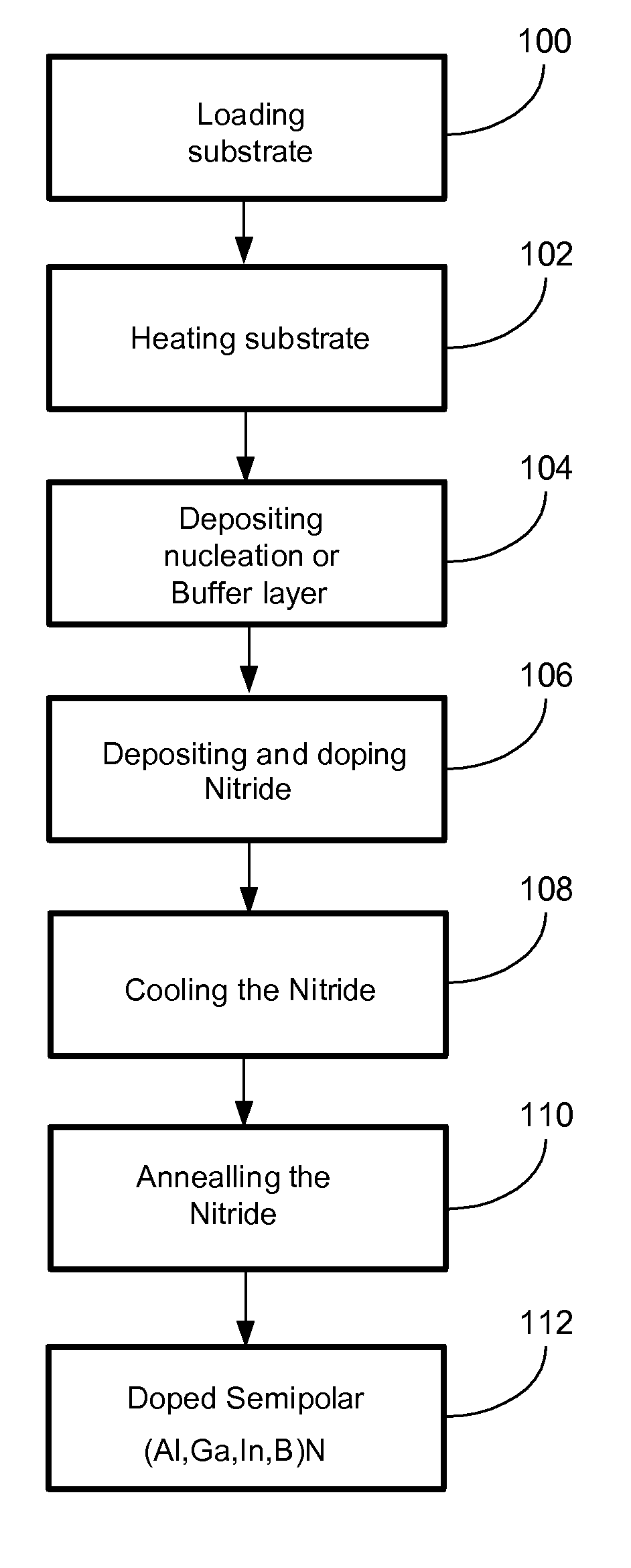
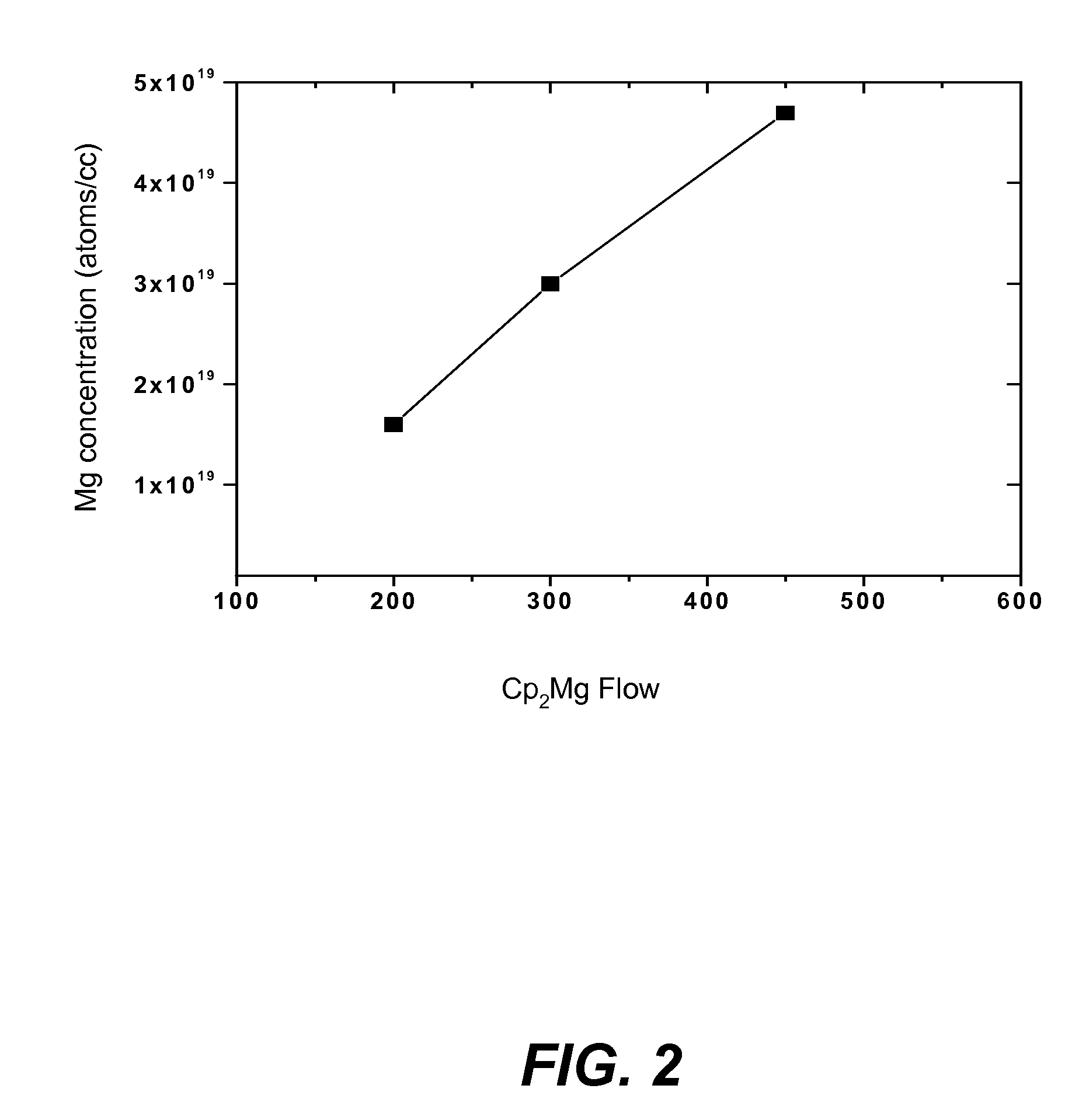
METHOD FOR CONDUCTIVITY CONTROL OF (Al,In,Ga,B)N
ActiveUS20070190758A1Improve conductivityEnhancing or tailoring conductivity propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectronic statesSpinel
A method of controlled p-type conductivity in (Al,In,Ga,B)N semiconductor crystals. Examples include {10 11} GaN films deposited on {100} MgAl2O4 spinel substrate miscut in the <011> direction. Mg atoms may be intentionally incorporated in the growing semipolar nitride thin film to introduce available electronic states in the band structure of the semiconductor crystal, resulting in p-type conductivity. Other impurity atoms, such as Zn or C, which result in a similar introduction of suitable electronic states, may also be used.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
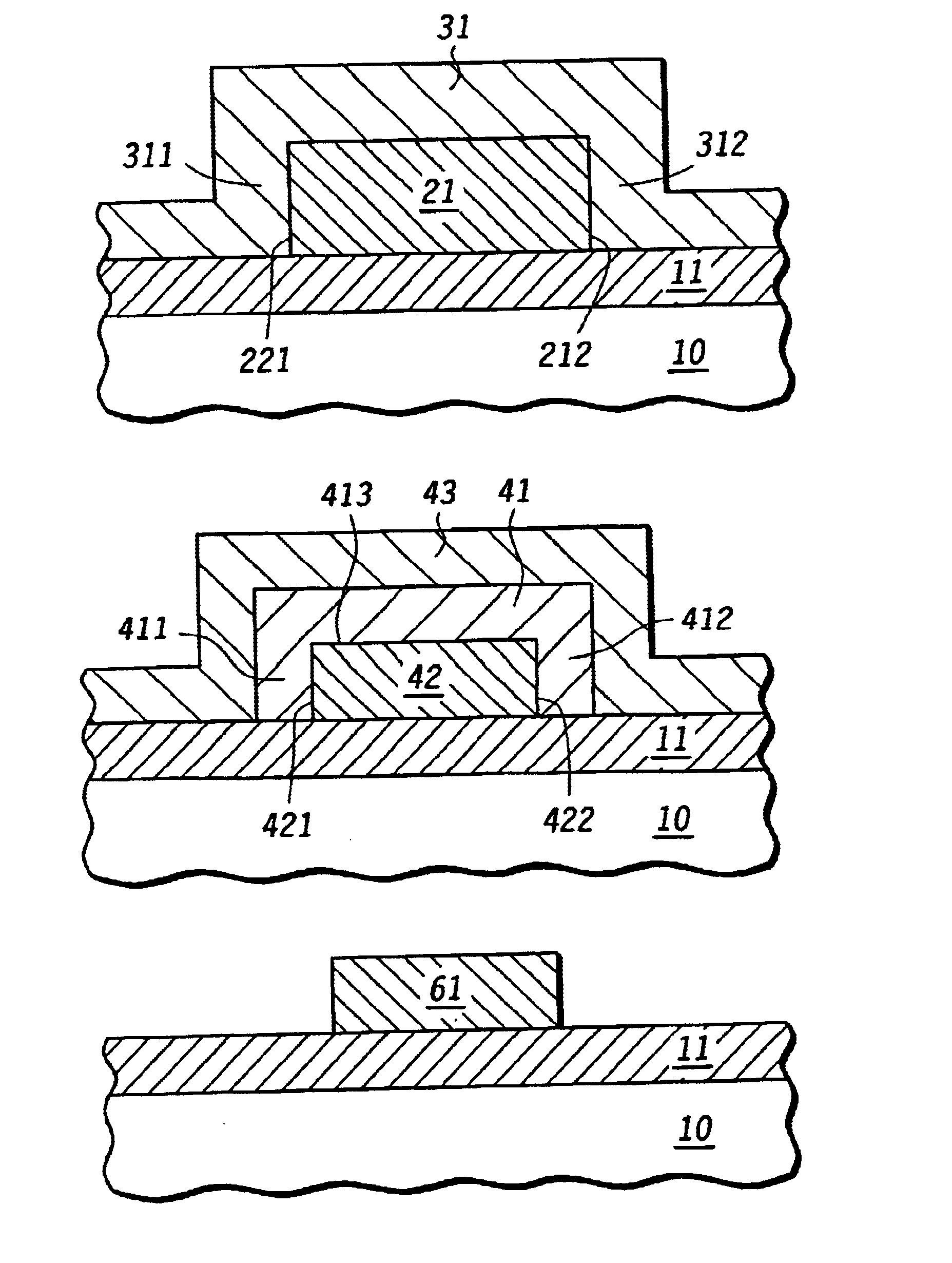
Method for forming an electronic structure using etch
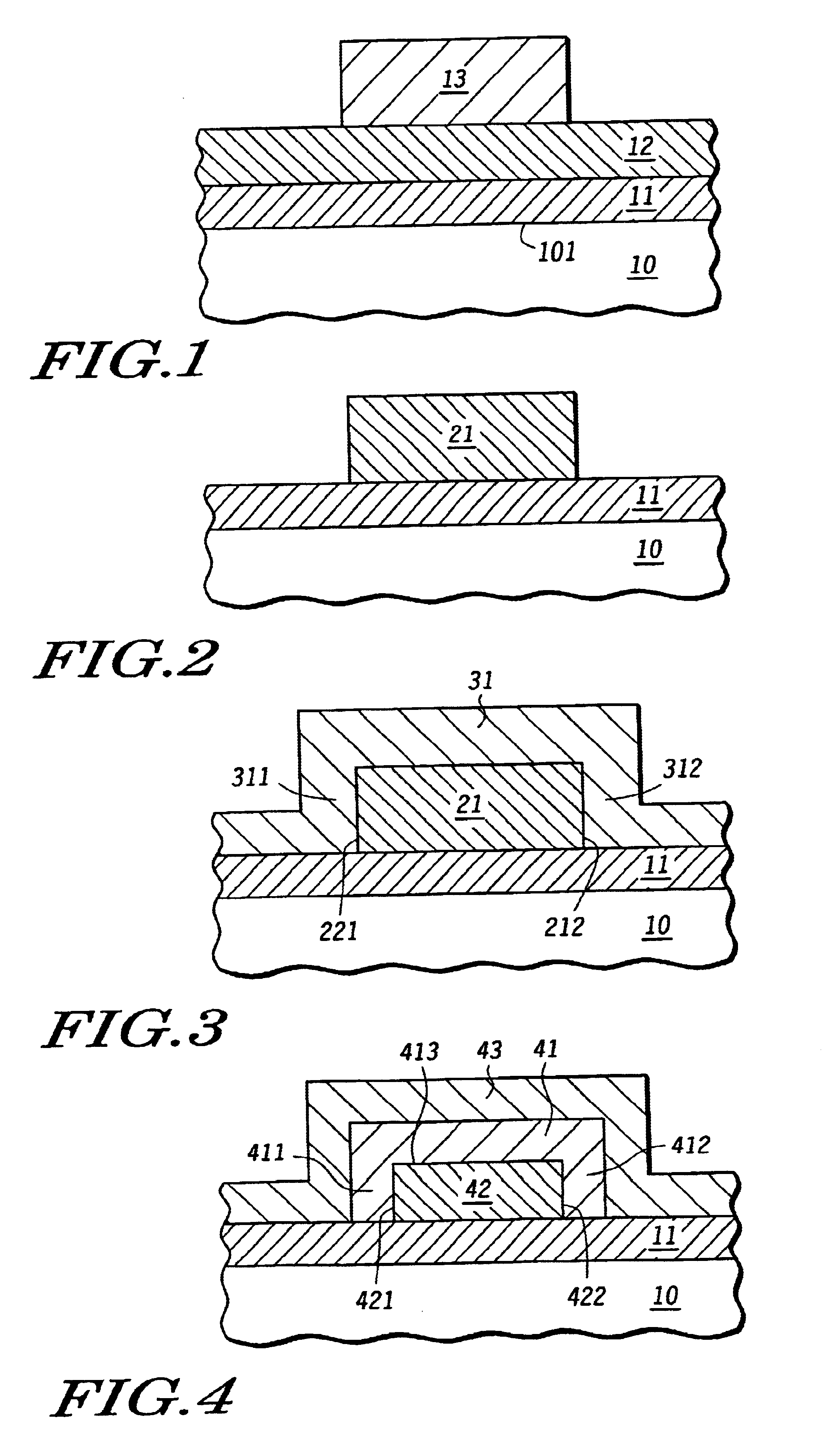
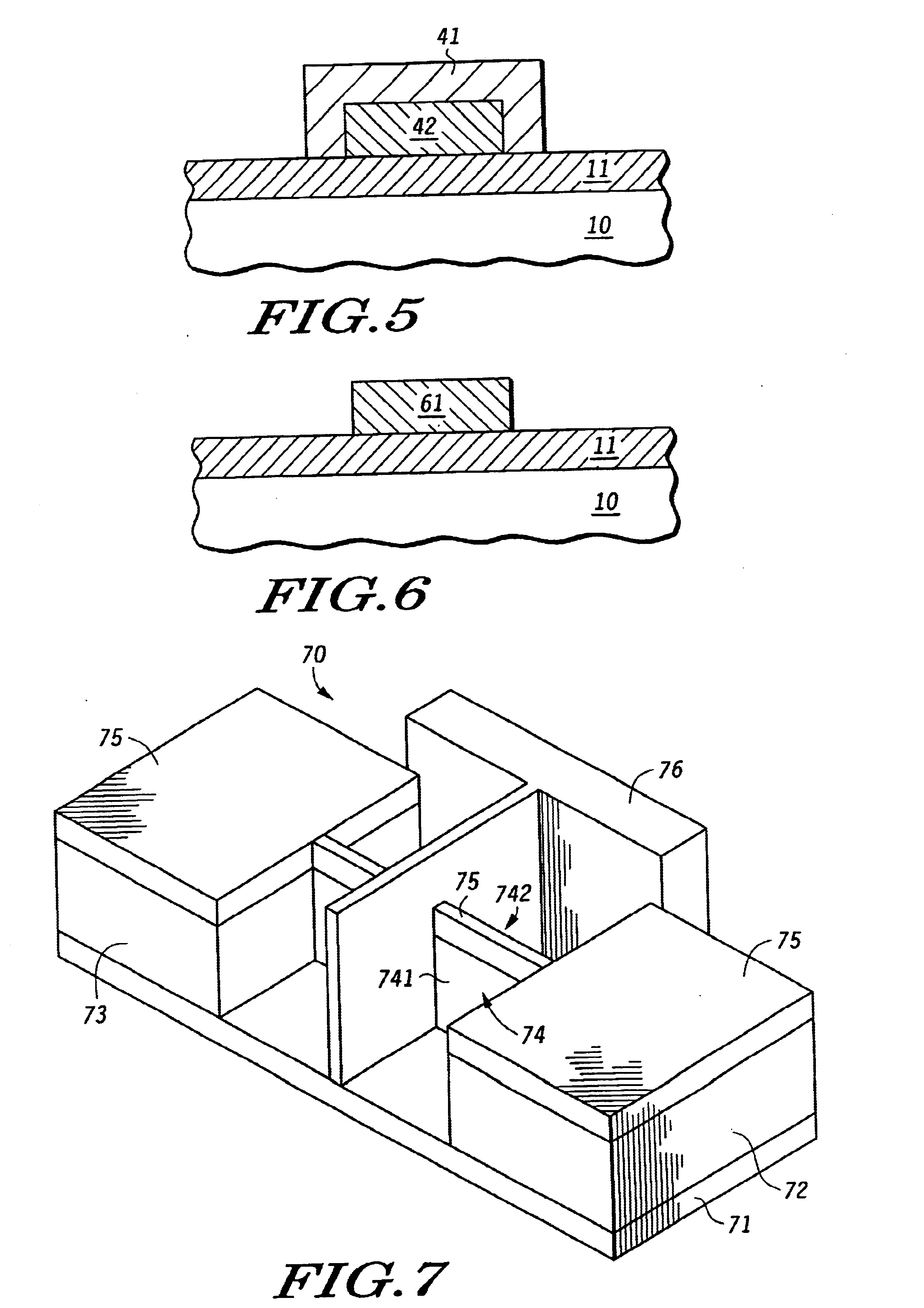
A method of forming a conductive structure having a length that is less than the length define by photolithographic patterning. A silicon layer (12) is formed in a MeOx dielectric layer (11) is photolithographically patterned to a predetermined first length. A metal layer (31) is formed conformally to at least the sidewalls of the silicon layer and then is reacted with the silicon to form a metal silicide (41). In particular, metal silicide abutments (411,412) are formed contiguous to sidewalls (421,422) of a reduced conductor (42). The remaining metal layer and the metal silicide are etched away, resulting in a conductor having predetermined second length that is less than the predetermined first length.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
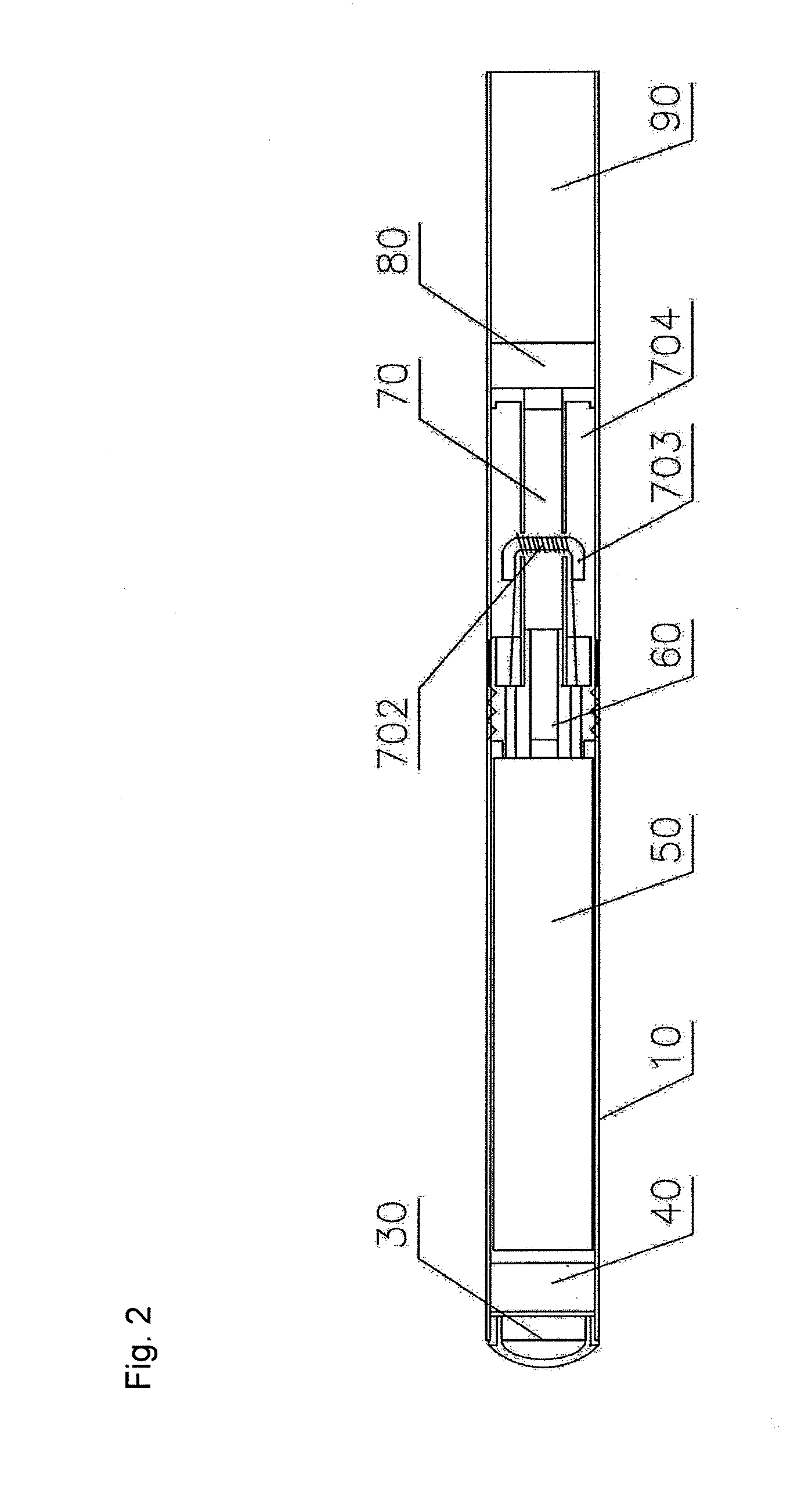
Electronic cigarette structure
InactiveUS20140048086A1Avoid possibilityEasy to useTobacco pipesTobacco devicesGlass fiberMouth piece
An electronic cigarette structure is described and relates to the field of electronic cigarette technology. The electronic cigarette structure includes a round tubular cigarette tube and a control board module, a battery, an atomizer base, a fibreglass tube and a sealing ring installed within said cigarette tube from front to back. A diametrical hole penetrates the fibre glass tube, that hole being internally equipped with a glass fibre rope around which heating wire is wrapped, the heating wire being connected to the atomizer base, there being a cigarette mouthpiece installed at the rear end of the cigarette tube on the outside of the sealing ring, said mouthpiece being an acetate fibre filter cotton mouthpiece.
Owner:SHENZHEN CITY YUKANG TECH
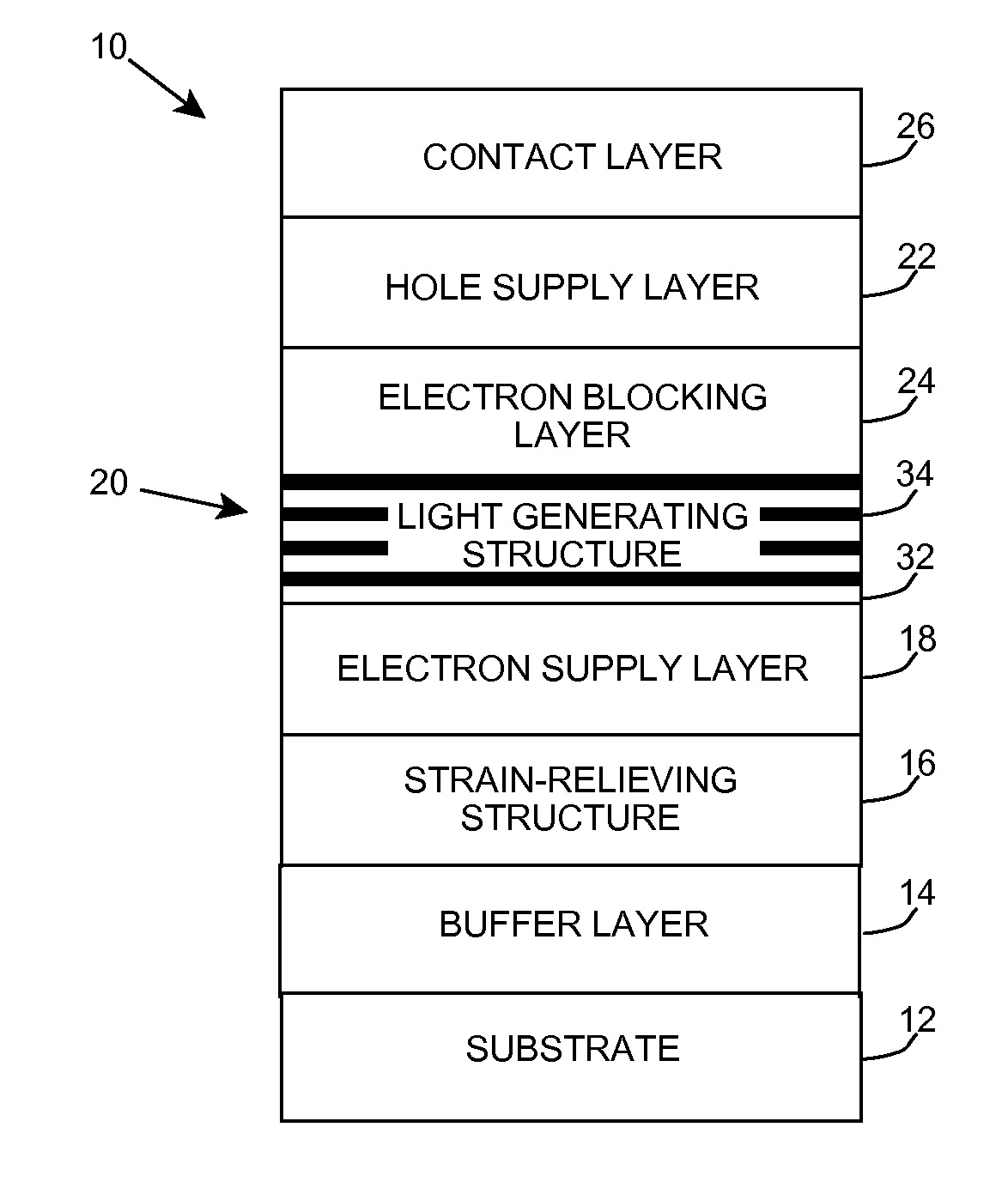
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
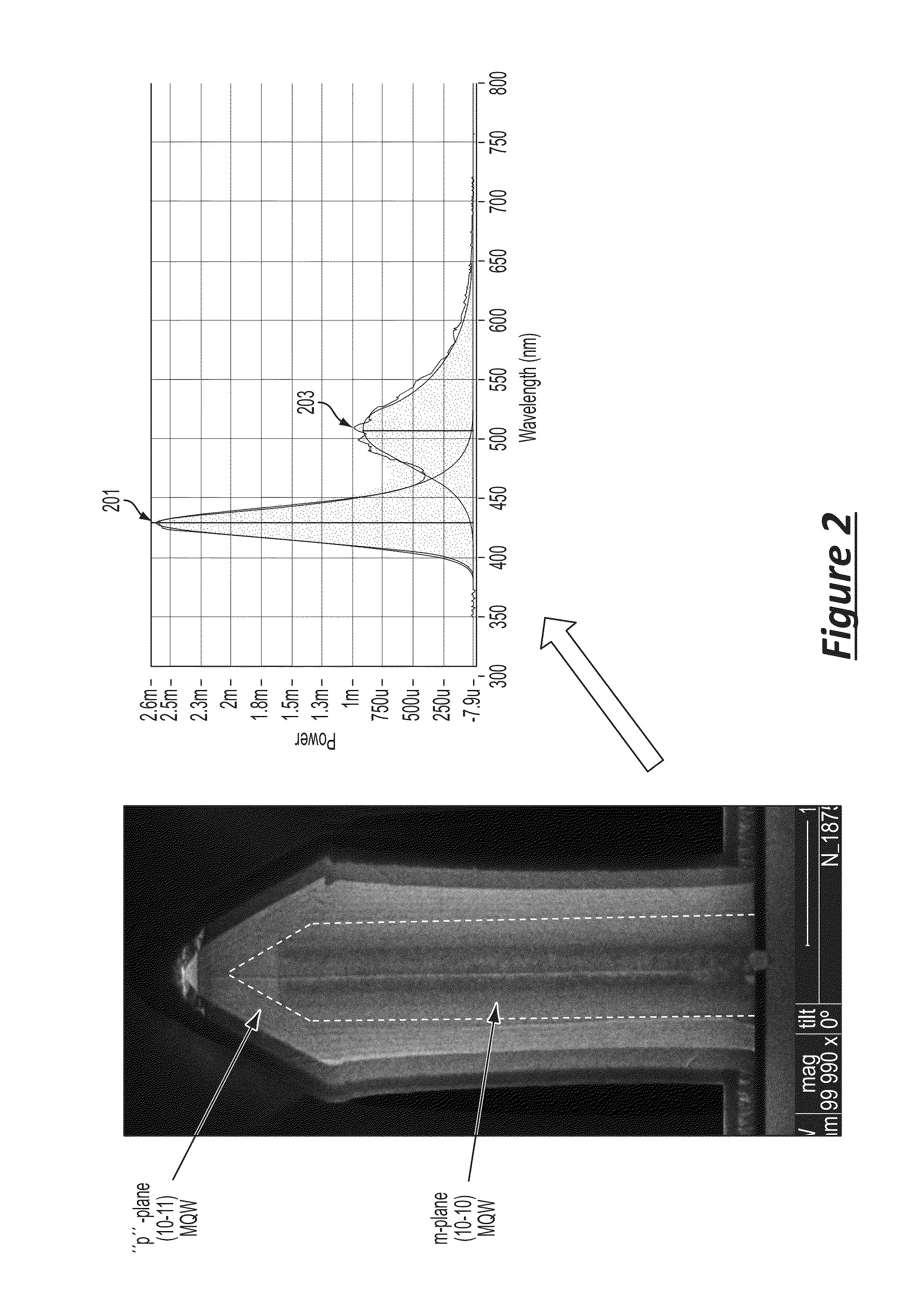
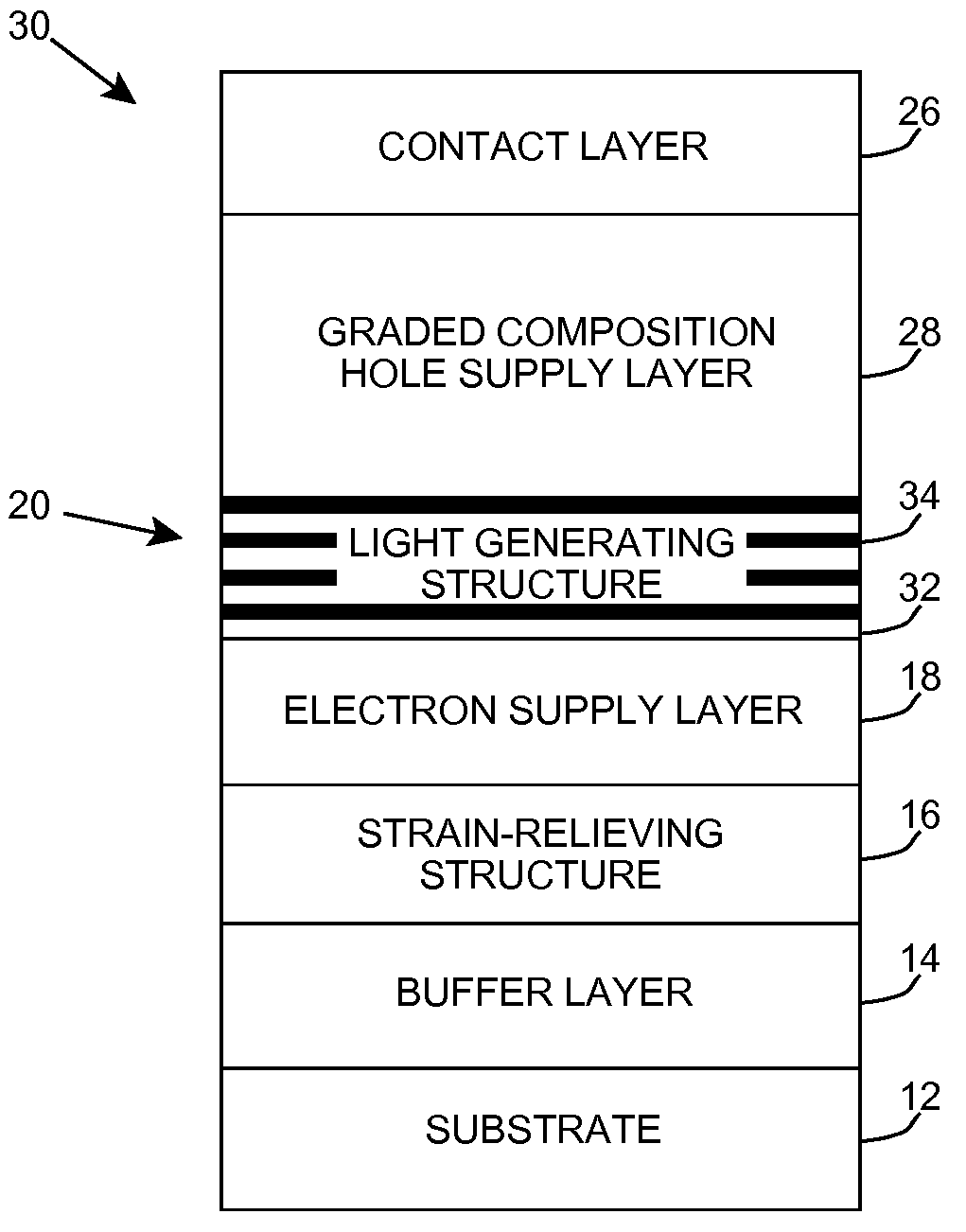
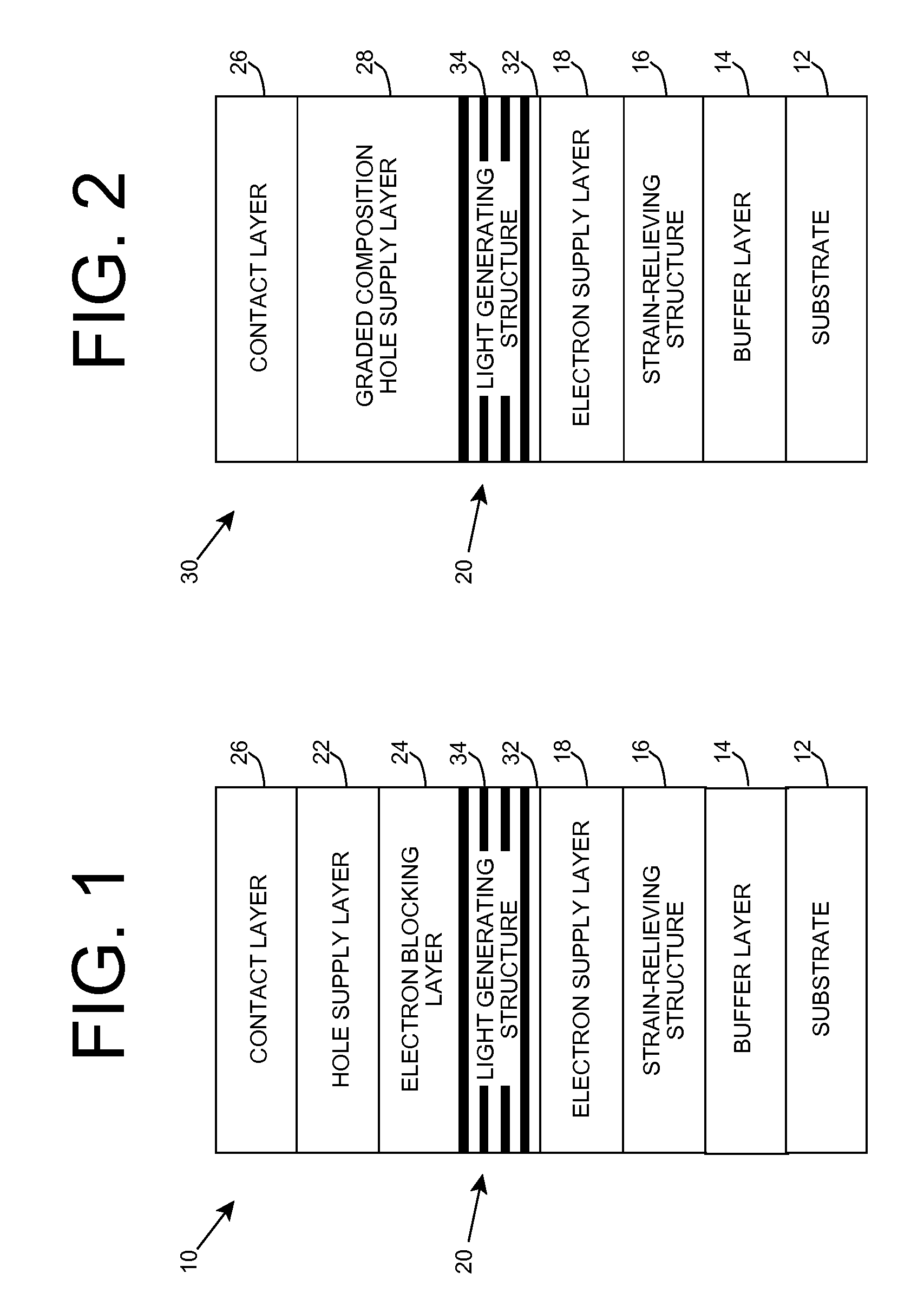
ActiveUS20070181869A1Improve featuresConvenient lightingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Maskless nanofabrication of electronic components
InactiveUS20100035375A1Reduce the amount requiredEfficient methodRadiation applicationsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureNanoparticle
The present invention relates to systems, materials and methods for the formation of conducting, semiconducting, and dielectric layers, structures and devices from suspensions of nanoparticles. Drop-on-demand systems are used in some embodiments to fabricate various electronic structures including conductors, capacitors, FETs. Selective laser ablation is used in some embodiments to pattern more precisely the circuit elements and to form small channel devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Suppression of MOSFET gate leakage current
InactiveUS6949769B2Reduce leakage currentReduce and eliminate leakage currentTransistorGate leakage currentMOSFET
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
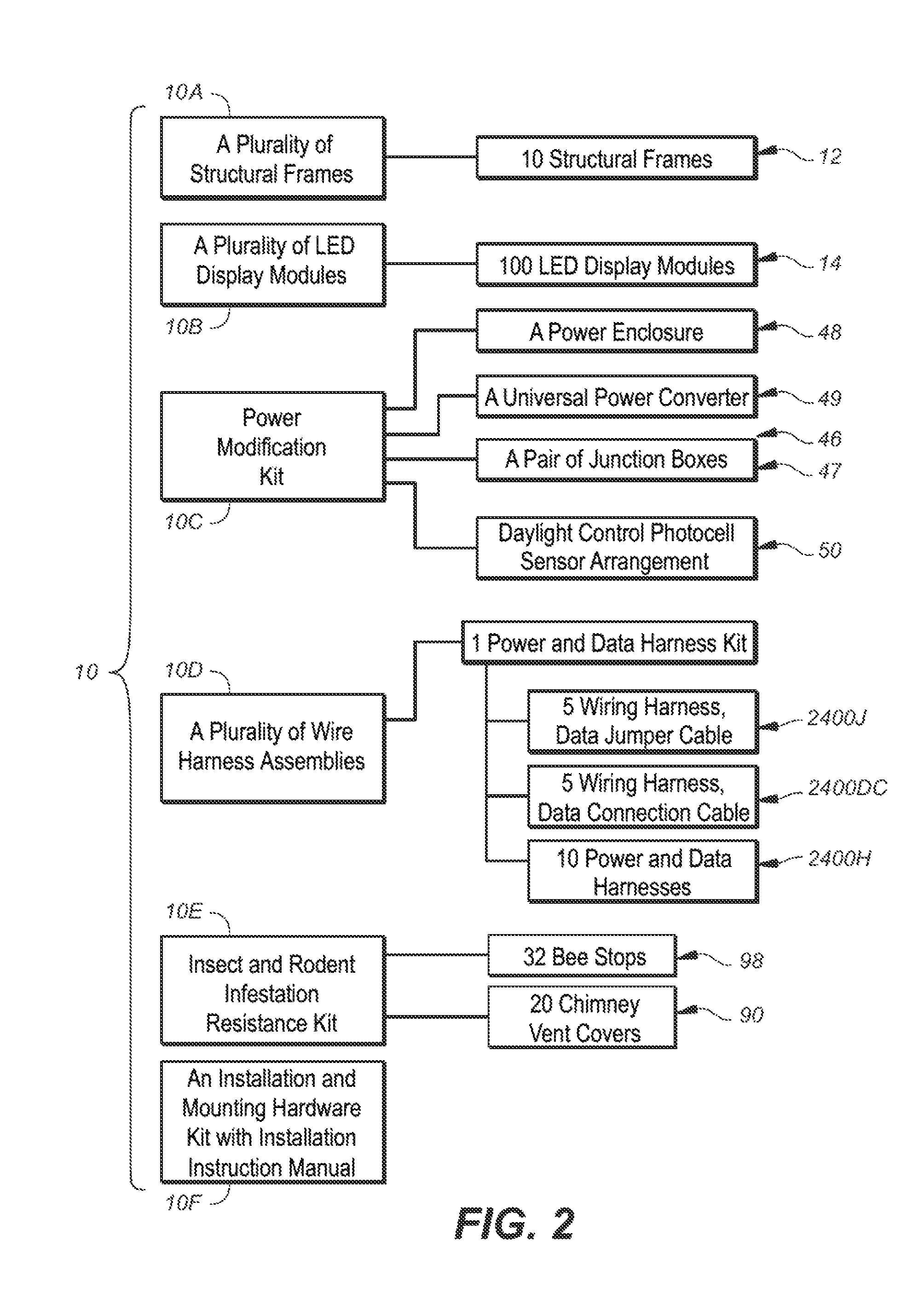
Modular installation and conversion kit for electronic sign structure and method of using same
InactiveUS8824125B1Facilitate dataImprove powerBus-bar/wiring layoutsSubstation/switching arrangement casingsElectronic structureModularity
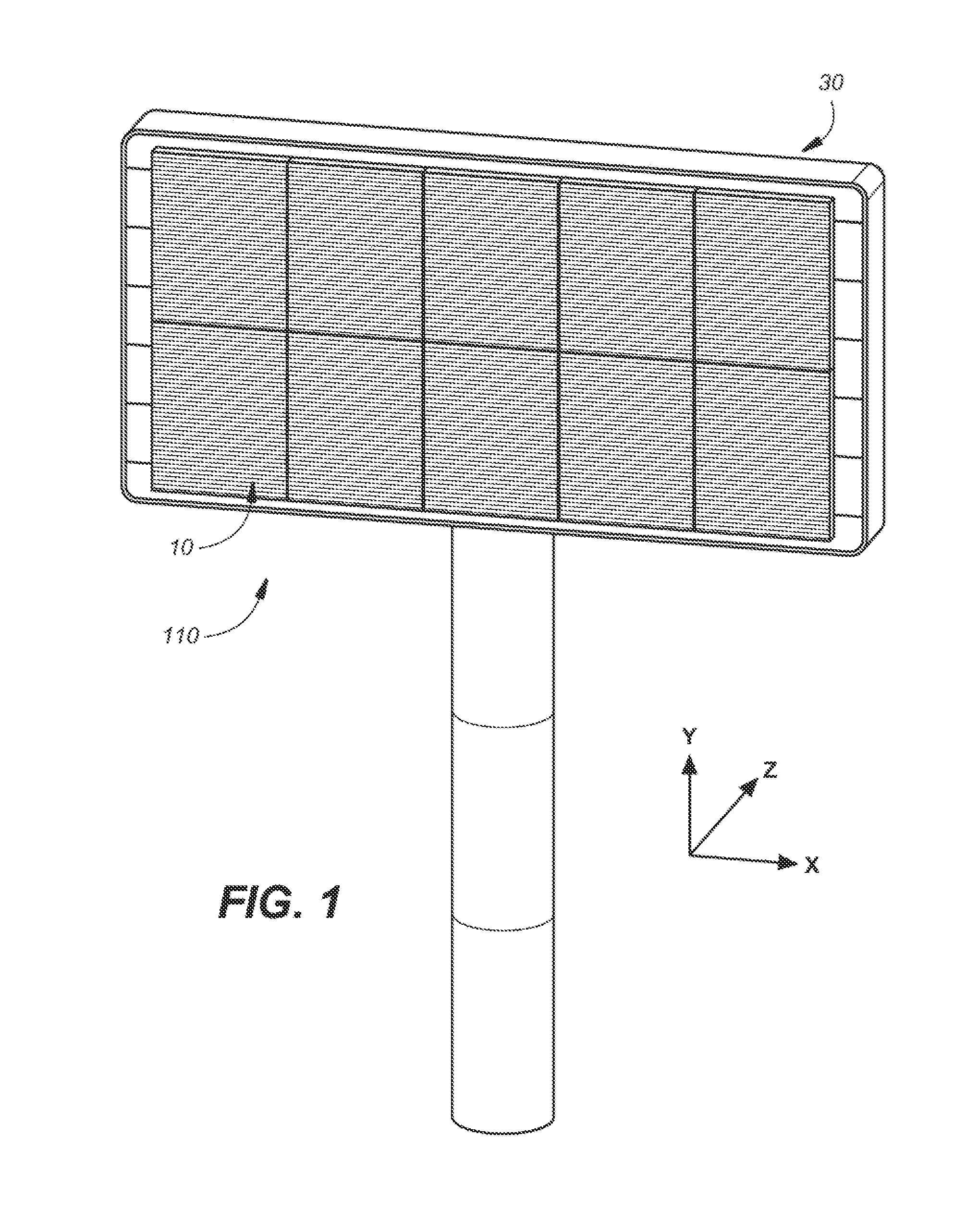
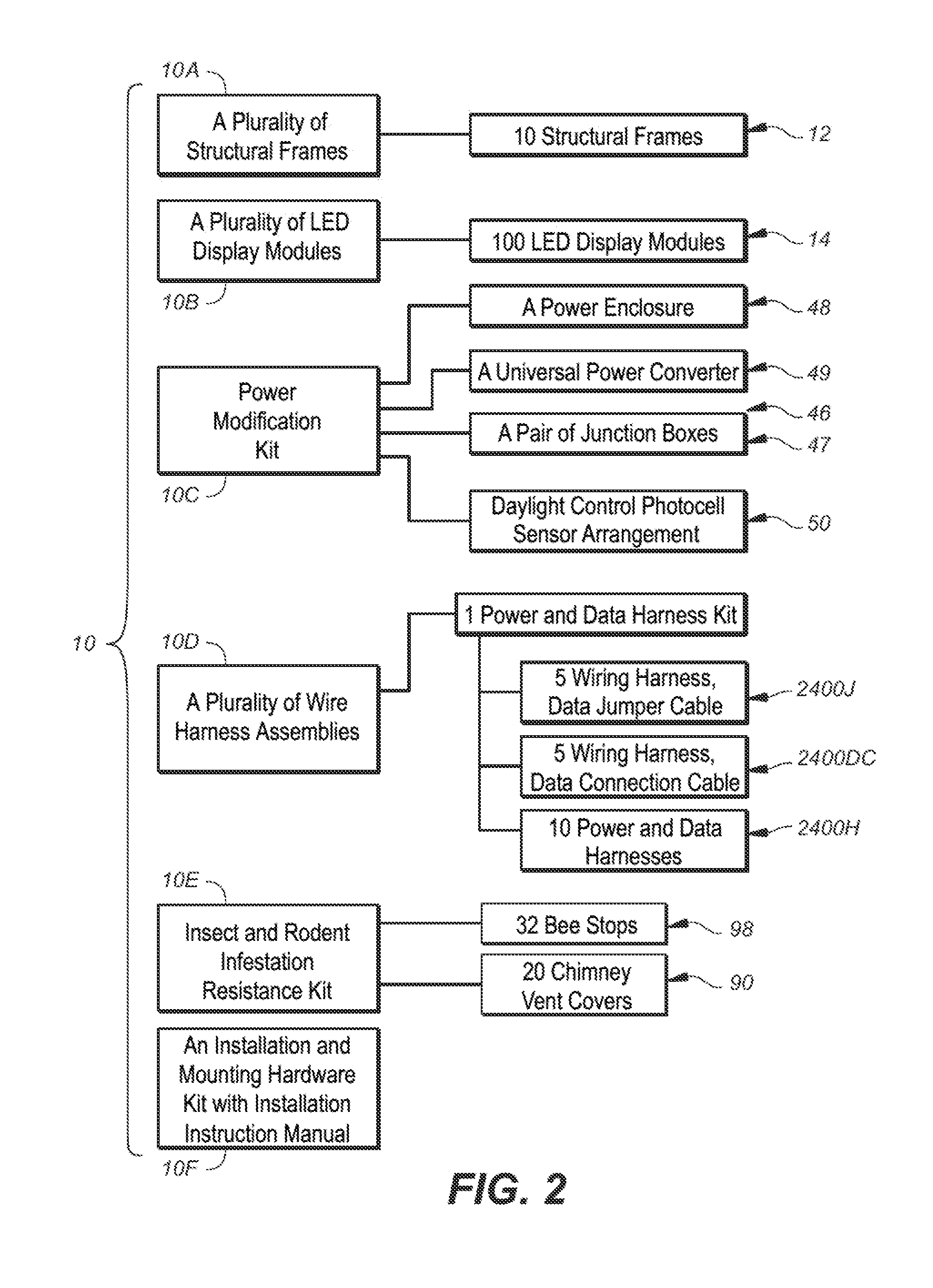
An out of the box signage kit facilitates in field conversion of a static billboard having an anchored planar mounting structure into a large format billboard type electronic sign that includes a plurality of interchangeable weatherized display modules; a plurality of hand mountable interchangeable structural frames for supporting the plurality of weatherized display modules, each structural frame having a back portion for mounting to a frontside of the anchored planar mounting structure and a front portion defining a plurality of bay members for receiving corresponding ones of said plurality of weatherized display modules; and a plurality of interchangeable wire harnesses, each individual wire harness including a first end for coupling to a power source mounted on a backside of the anchored planar mounting structure, each individual wire harness having a plurality of power extensions for coupling the power source to at least one of the display modules.
Owner:ADTI MEDIA
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
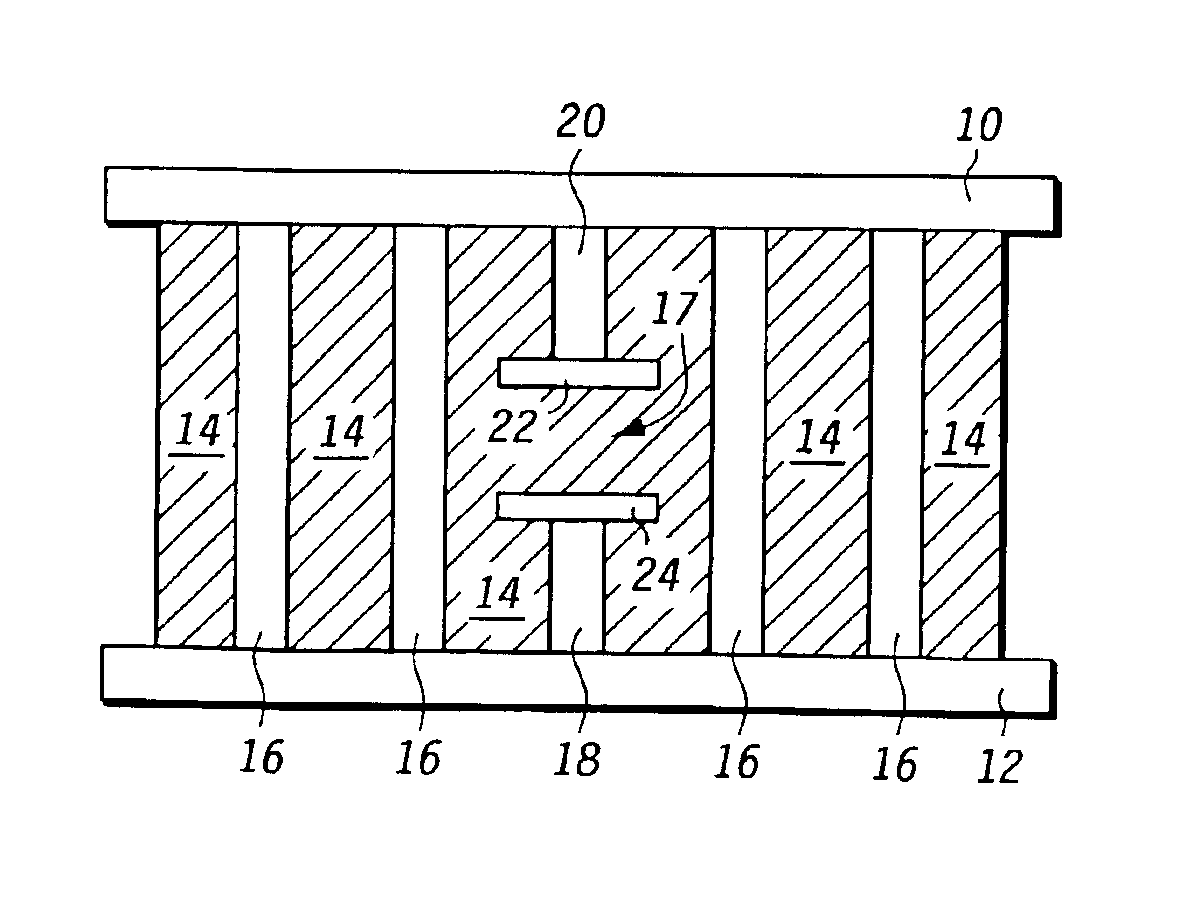
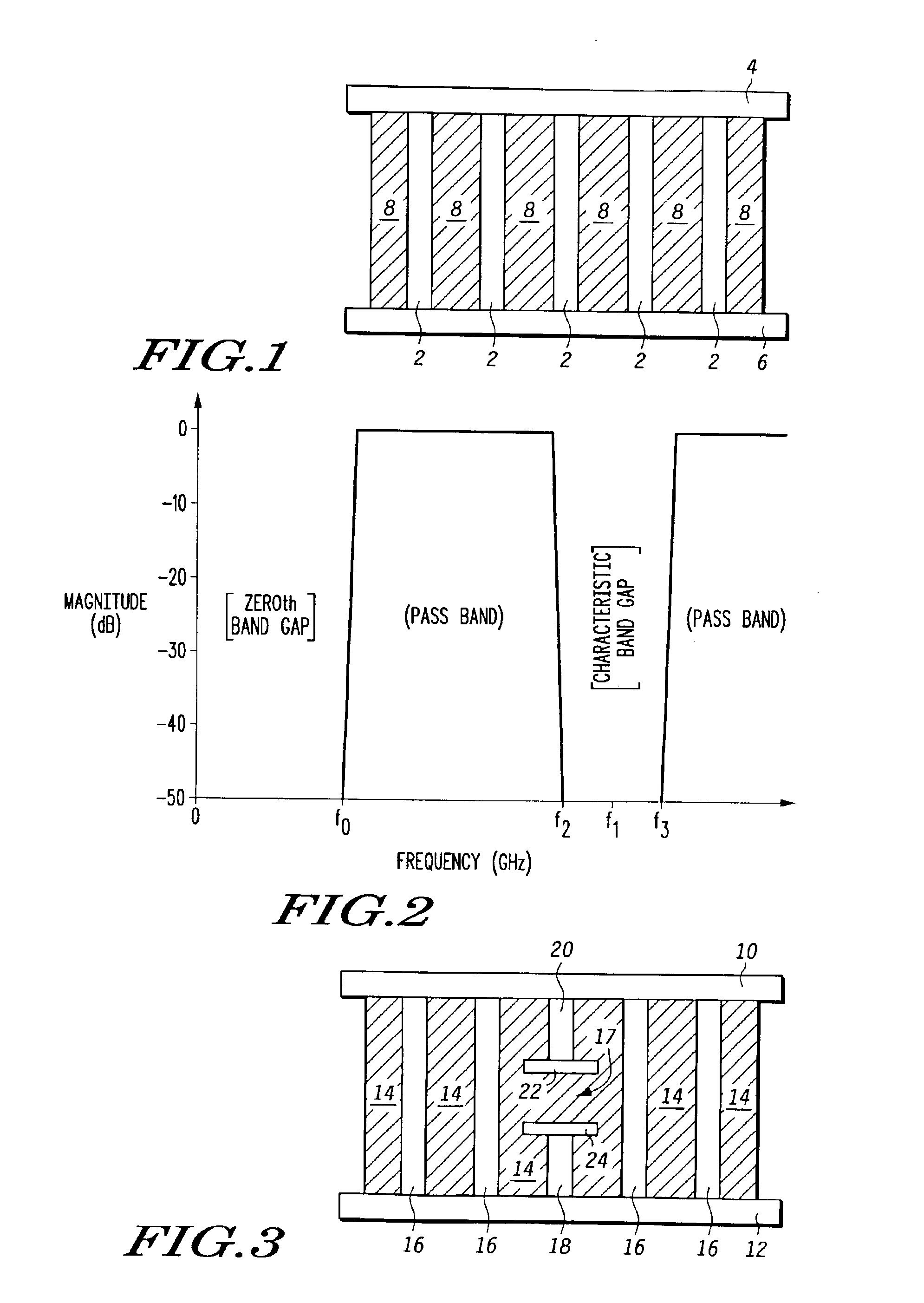
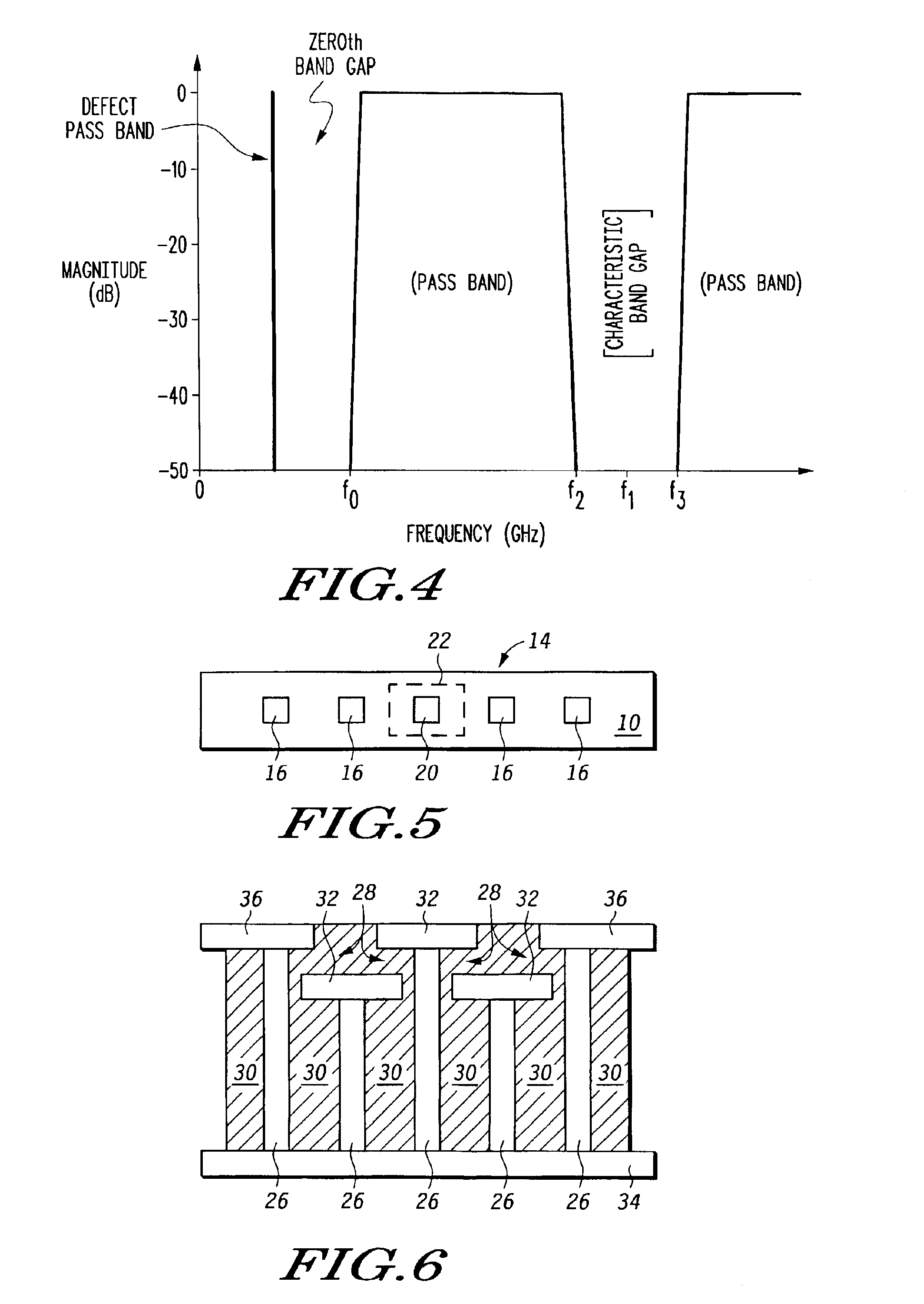
Electromagnetic band gap microwave filter
A microwave filter is formed from an electromagnetic band gap structure. The electromagnetic band gap structure includes a periodic array of metal features (16, 42, 44, 50) formed within a dielectric matrix (14, 52). A defect feature (17, 48) is formed within the periodic array of metal features (16, 42, 44, 50) in order to create a pass band within a stop band region.
Owner:NXP USA INC
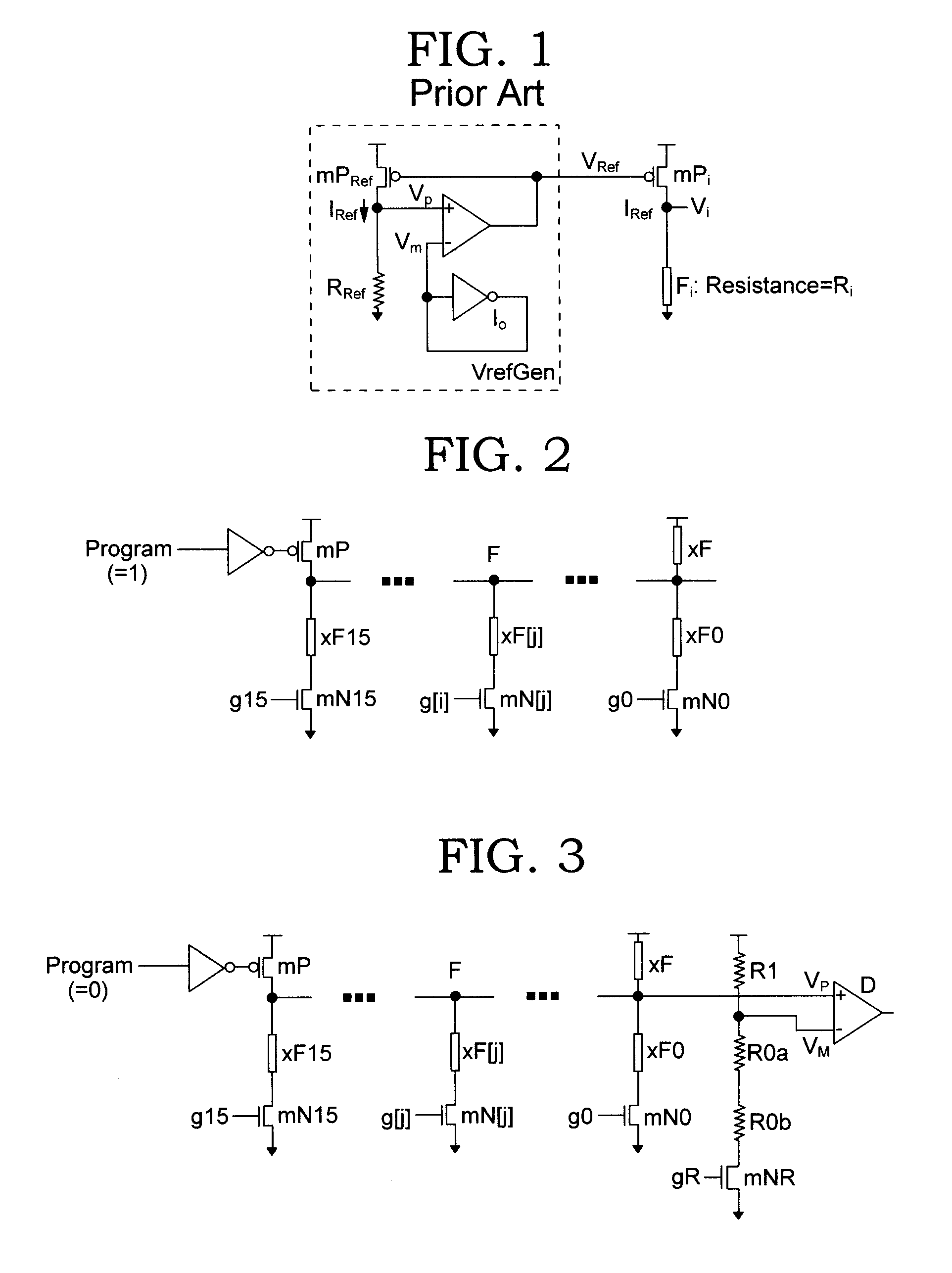
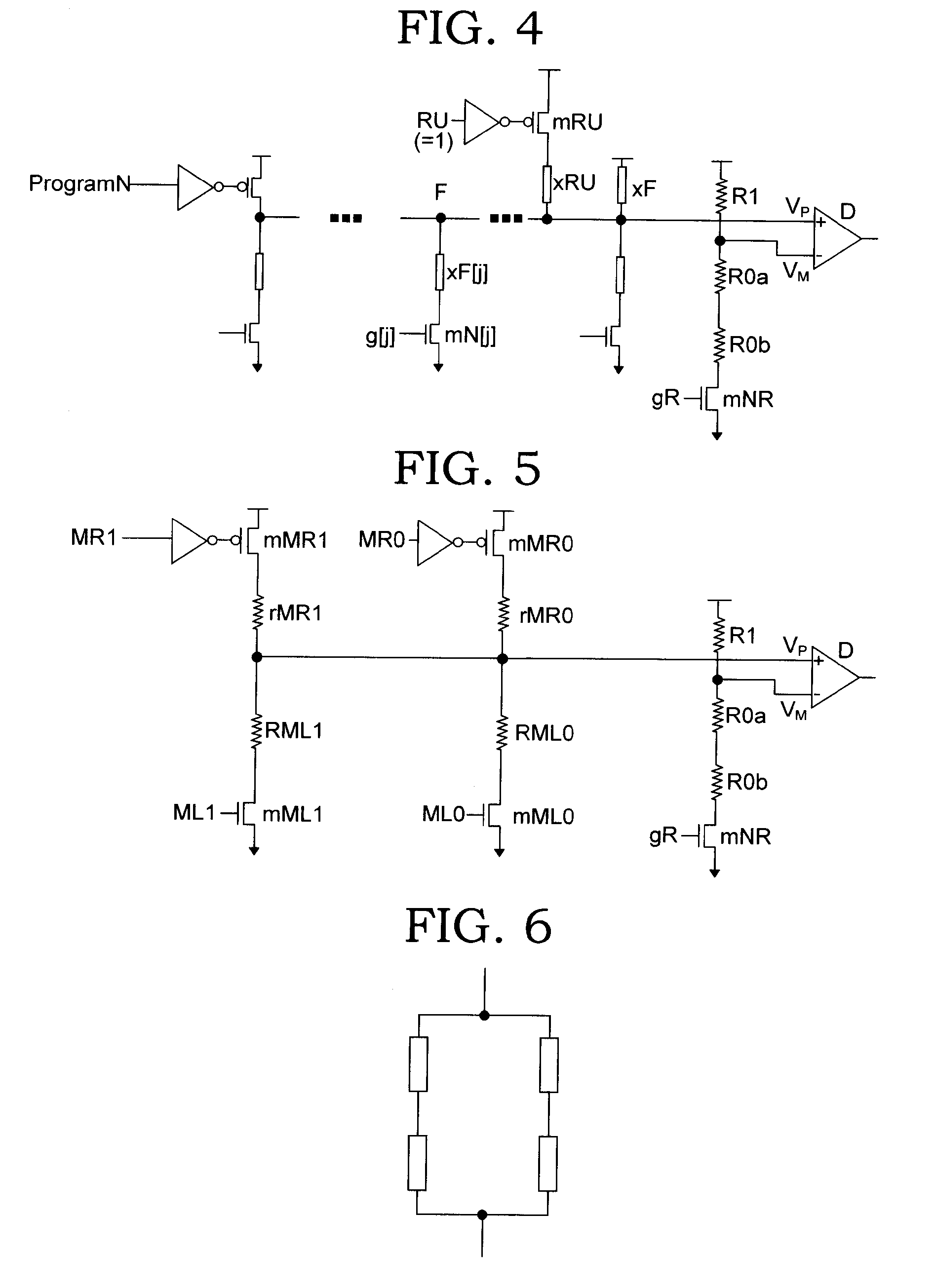
Low voltage programmable eFuse with differential sensing scheme
ActiveUS7098721B2Low level of resistanceEasy to operateSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectronic structure
An electronic fuse structure is disclosed for integrated circuits that is programmable with low voltage and incorporates a differential sensing scheme. The programming step is performed at about 1.5 times Vdd while the sense operation is performed at Vdd, which limits the resistance variation through the electronic fuse caused by the sense operation. During the sense operation a gating transistor emulates the voltage drop across a fuse select transistor for the case of an intact fuse. A circuit and method for characterizing the resistance of the electronic fuse is also disclosed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
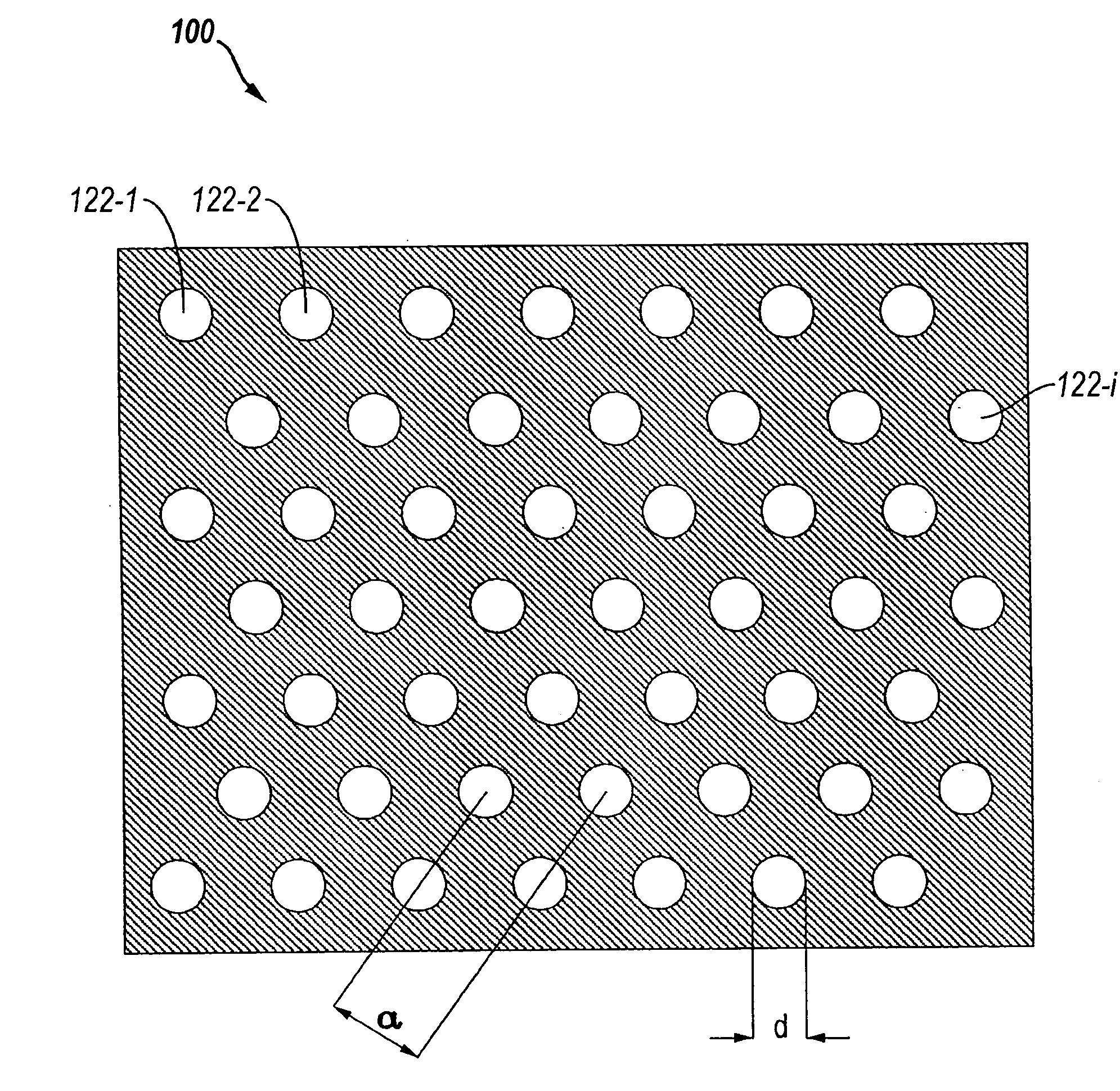
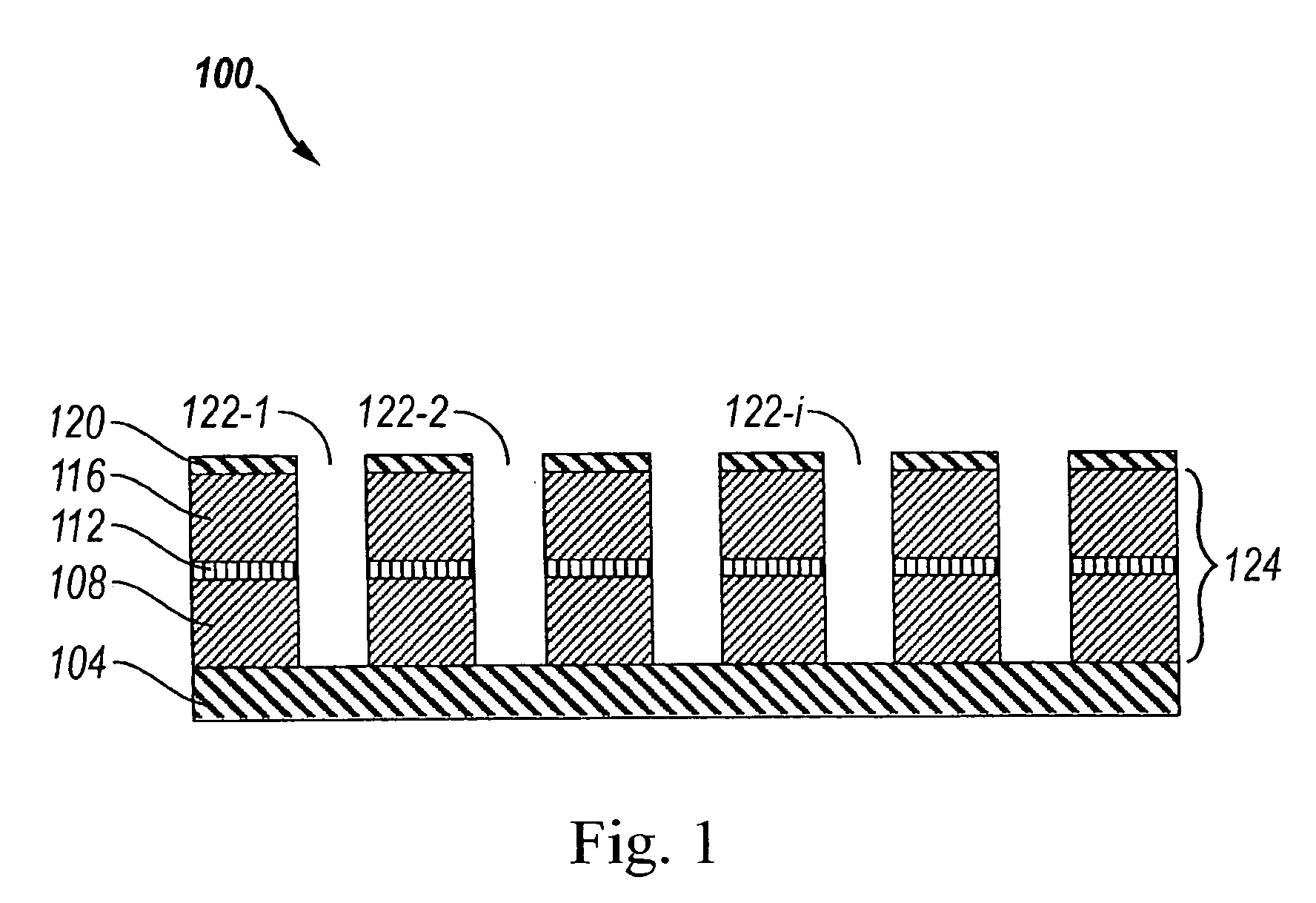
LED including photonic crystal structure
InactiveUS7279718B2Increase transmit powerMore energySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesManufacturing technologyLateral overgrowth
A photonic crystal light emitting diode (“PXLED”) is provided. The PXLED includes a periodic structure, such as a lattice of holes, formed in the semiconductor layers of an LED. The parameters of the periodic structure are such that the energy of the photons, emitted by the PXLED, lies close to a band edge of the band structure of the periodic structure. Metal electrode layers have a strong influence on the efficiency of the PXLEDs. Also, PXLEDs formed from GaN have a low surface recombination velocity and hence a high efficiency. The PXLEDs are formed with novel fabrication techniques, such as the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique over a patterned masking layer, yielding semiconductor layers with low defect density. Inverting the PXLED to expose the pattern of the masking layer or using the Talbot effect to create an aligned second patterned masking layer allows the formation of PXLEDs with low defect density.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Maskless nanofabrication of electronic components
InactiveUS7682970B2Reduce the amount requiredEfficient methodRadiation applicationsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureNanoparticle
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
LED including photonic crystal structure
InactiveUS7642108B2Increase transmit powerMore energySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyPhotonic crystal structure
A photonic crystal light emitting diode (“PXLED”) is provided. The PXLED includes a periodic structure, such as a lattice of holes, formed in the semiconductor layers of an LED. The parameters of the periodic structure are such that the energy of the photons, emitted by the PXLED, lies close to a band edge of the band structure of the periodic structure. Metal electrode layers have a strong influence on the efficiency of the PXLEDs. Also, PXLEDs formed from GaN have a low surface recombination velocity and hence a high efficiency. The PXLEDs are formed with novel fabrication techniques, such as the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique over a patterned masking layer, yielding semiconductor layers with low defect density. Inverting the PXLED to expose the pattern of the masking layer or using the Talbot effect to create an aligned second patterned masking layer allows the formation of PXLEDs with low defect density.
Owner:LUMILEDS
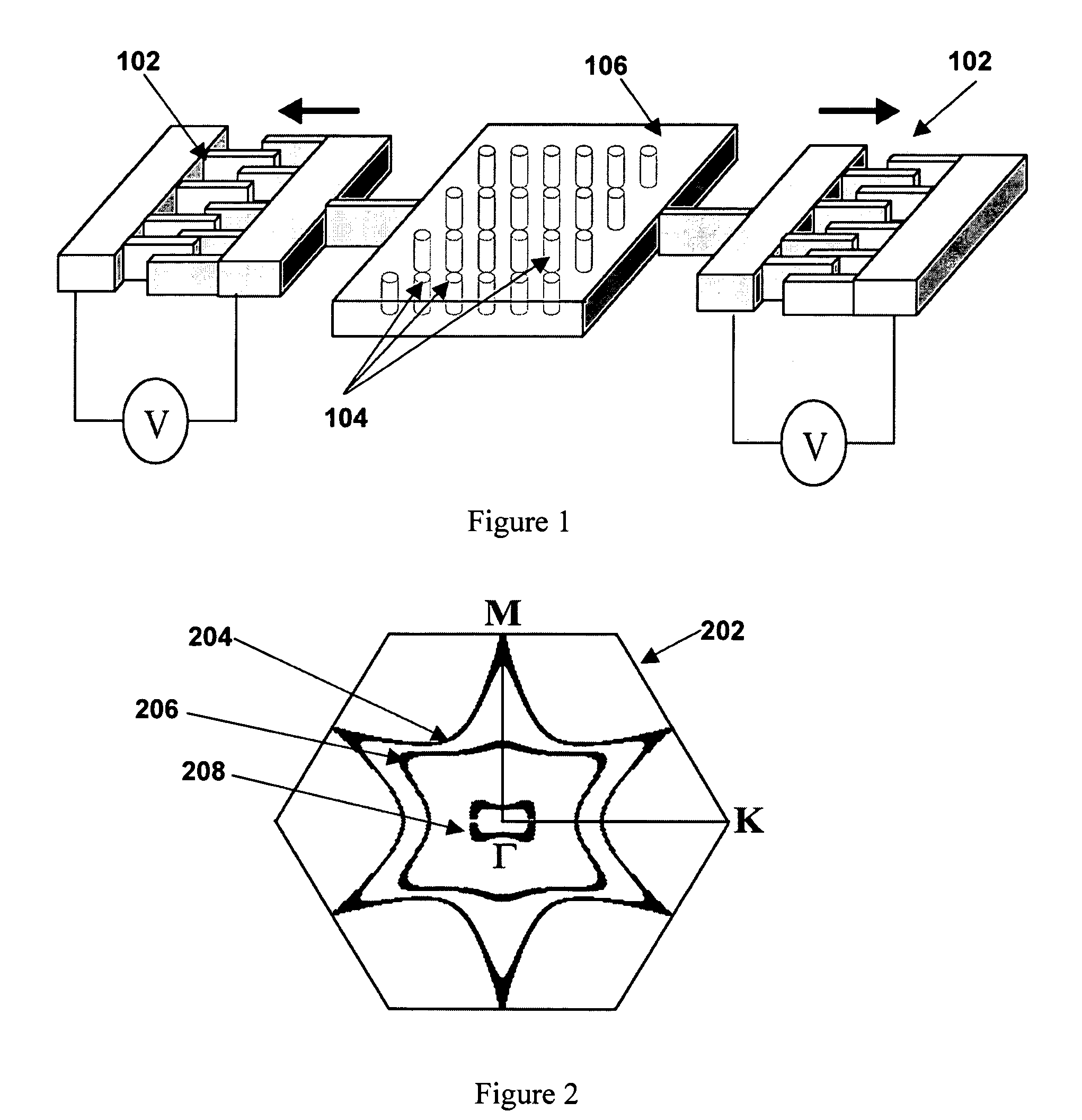
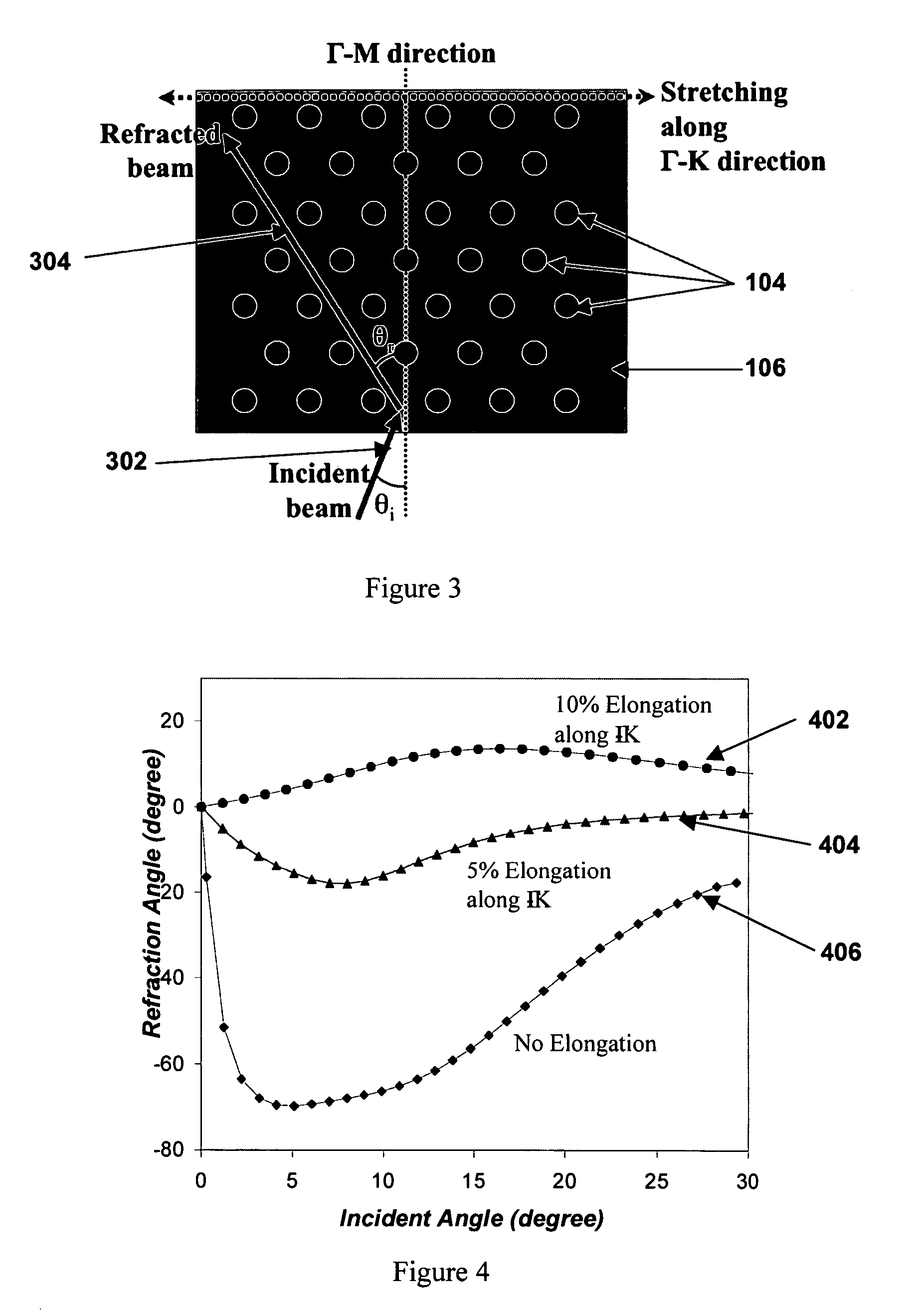
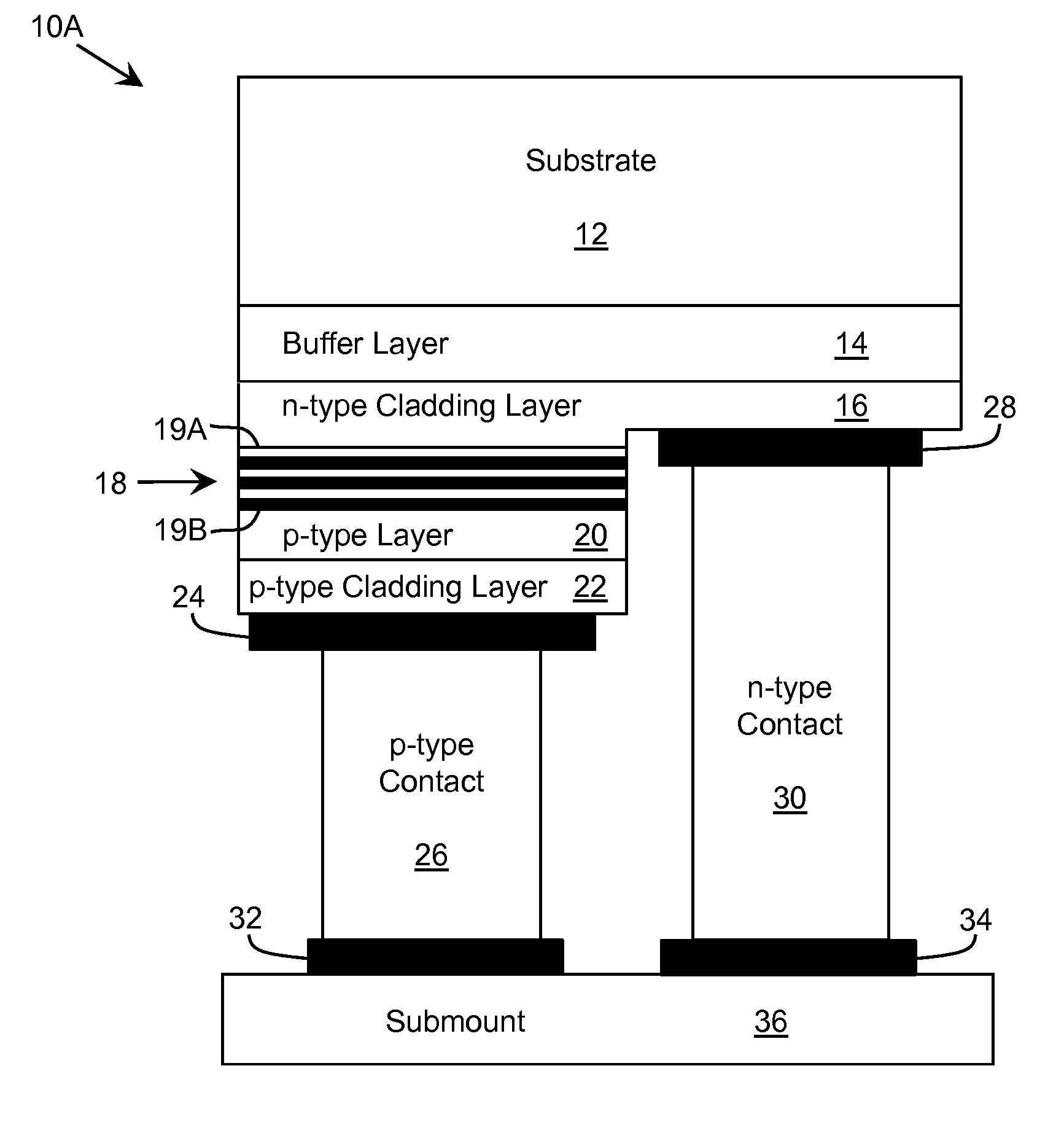
Strain tunable, flexible photonic crystals
A device is described based on flexible photonic crystal, which is comprised of a periodic array of high index dielectric material embedded in a flexible polymer. Dynamic, real time tunability is achieved by the application of a variable force with a MEMS actuator or other means. The force induces changes in the crystal structure of the photonic crystal, and consequently modifies the photonic band structure. The concept was demonstrated by a theoretical investigation on the effect of mechanical stress on the anomalous refraction behavior of the flexible PC, and a very wide tunability in beam propagation direction was observed. Experimental studies on fabrication and characterizations of the flexible photonic crystal structures were also carried out. High quality flexible PC structures were fabricated by e-beam lithography and anisotropic etching processes.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
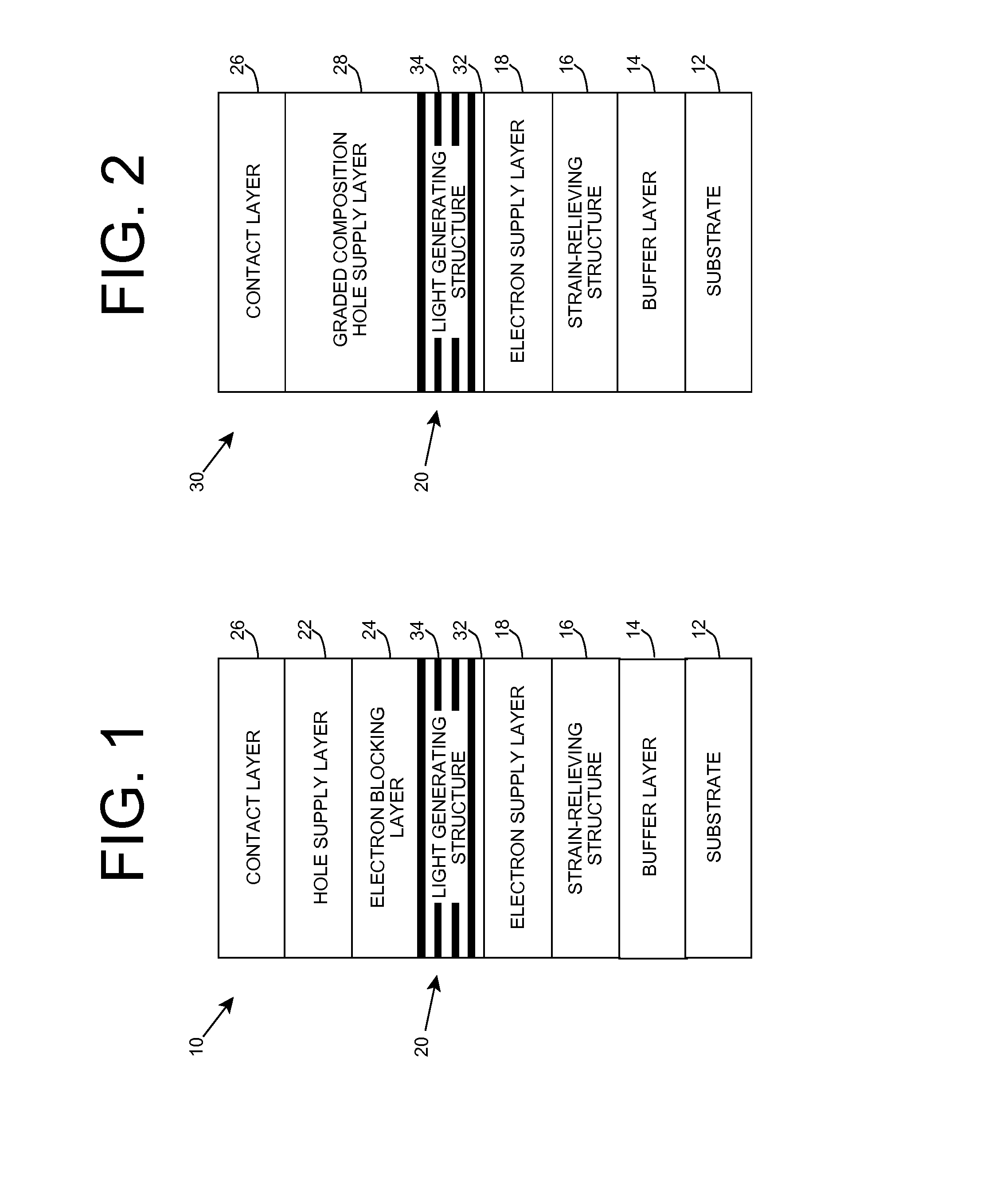
Light Emitting Diode with Polarization Control
ActiveUS20120217473A1Easy to optimizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersDelta dopingQuantum well
An improved light emitting heterostructure is provided. The heterostructure includes an active region having a set of barrier layers and a set of quantum wells, each of which is adjoined by a barrier layer. The quantum wells have a delta doped p-type sub-layer located therein, which results in a change of the band structure of the quantum well. The change can reduce the effects of polarization in the quantum wells, which can provide improved light emission from the active region.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Modular installation and conversion kit for electronic sign structure and method of using same
InactiveUS20140259645A1Facilitate dataImprove powerCircuit arrangements on insulating boardsMetal working apparatusElectronic structureComputer module
Owner:ADTI MEDIA
Resonant cavity enhanced multi-quantum well light modulator and detector
ActiveUS20060180830A1Increase contrastSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsTelecommunications linkSpatial light modulator
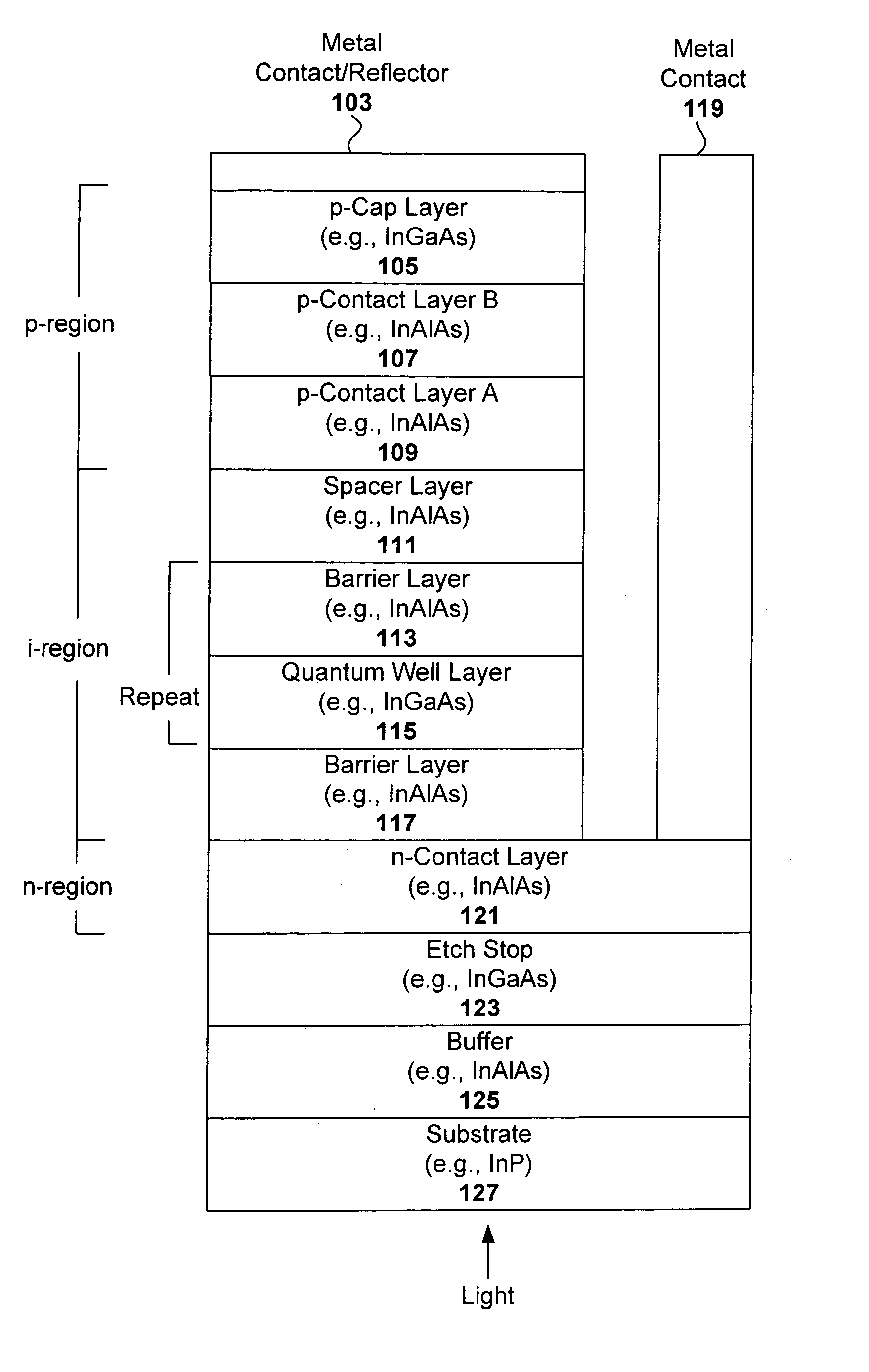
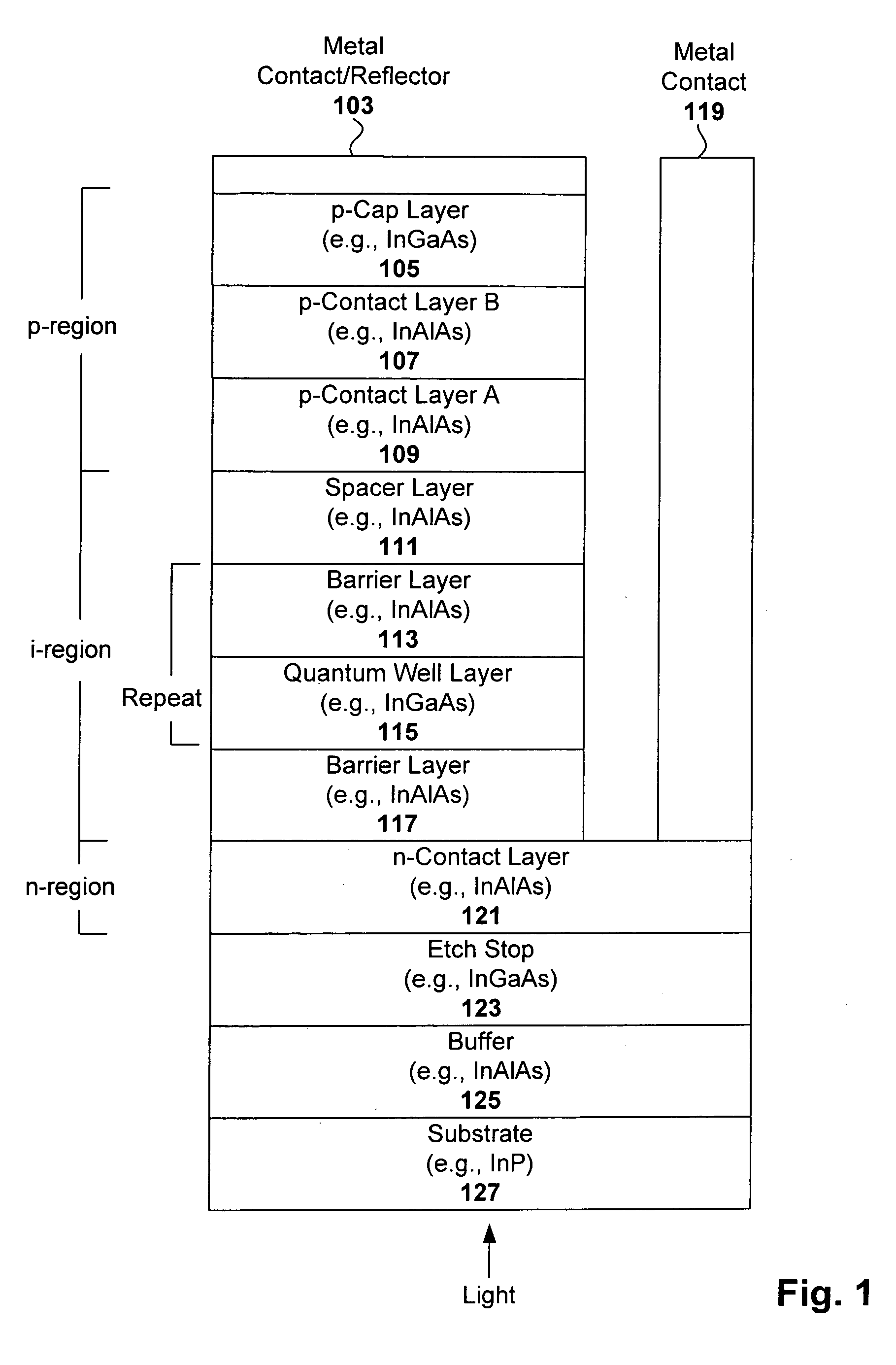
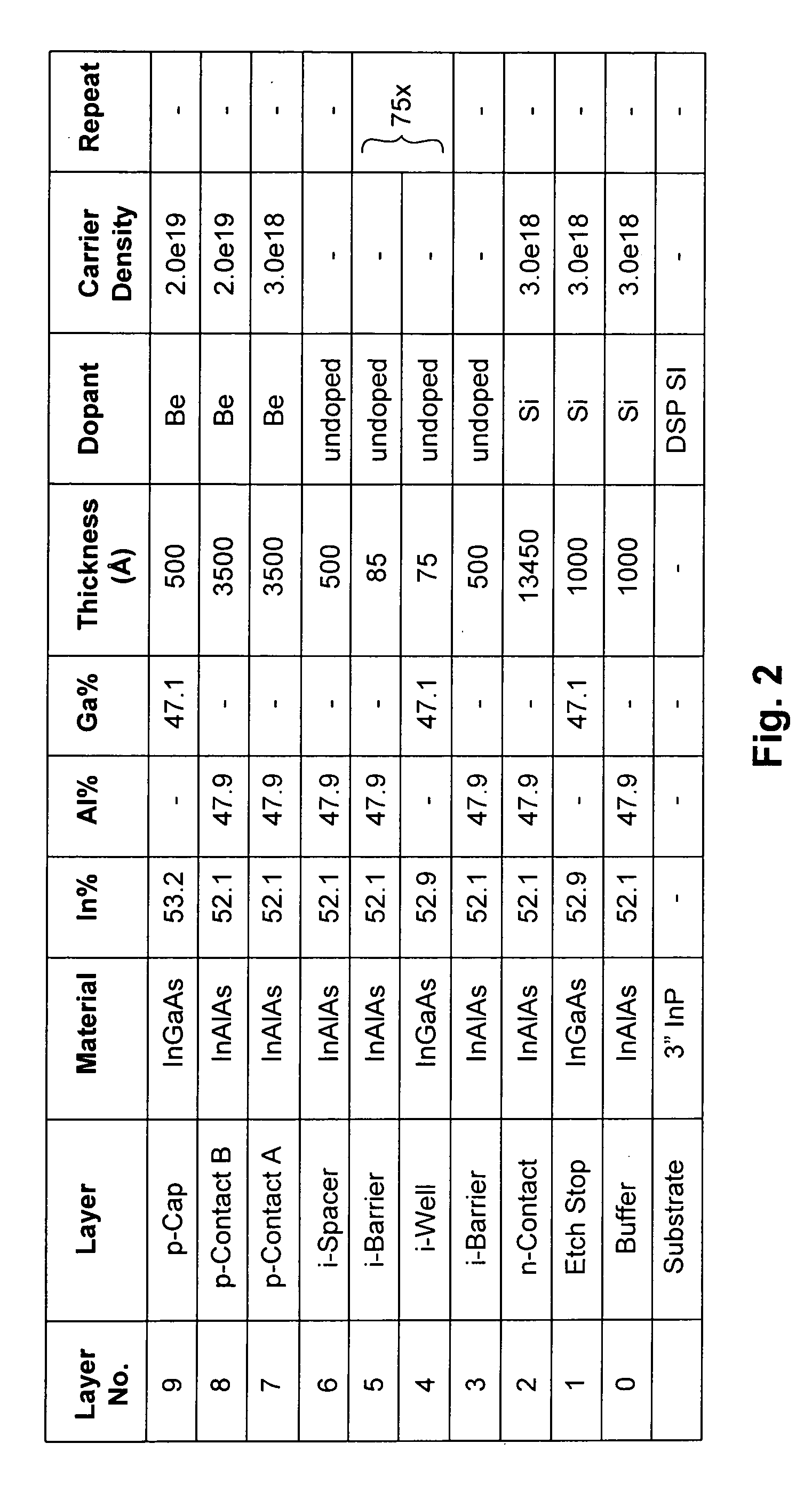
Multi-quantum well (MQW) spatial light modulator devices are disclosed that are capable of achieving reasonable quantum efficiencies and high contrast ratios in order to close an optical communication link by resolving the logical on or off state. The device both modulates and detects light through the use of the quantum well design and resonant cavity enhancement. Based on the materials (e.g., InGaAs / InAlAs) and their band structures, this device can be configured to communicate in the eye-safe wavelength range (e.g., 1550±20 nm). The device can be fabricated using standard photolithographic processes such as molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) and inductively coupled plasma (ICP) reactive ion etching (RIE).
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
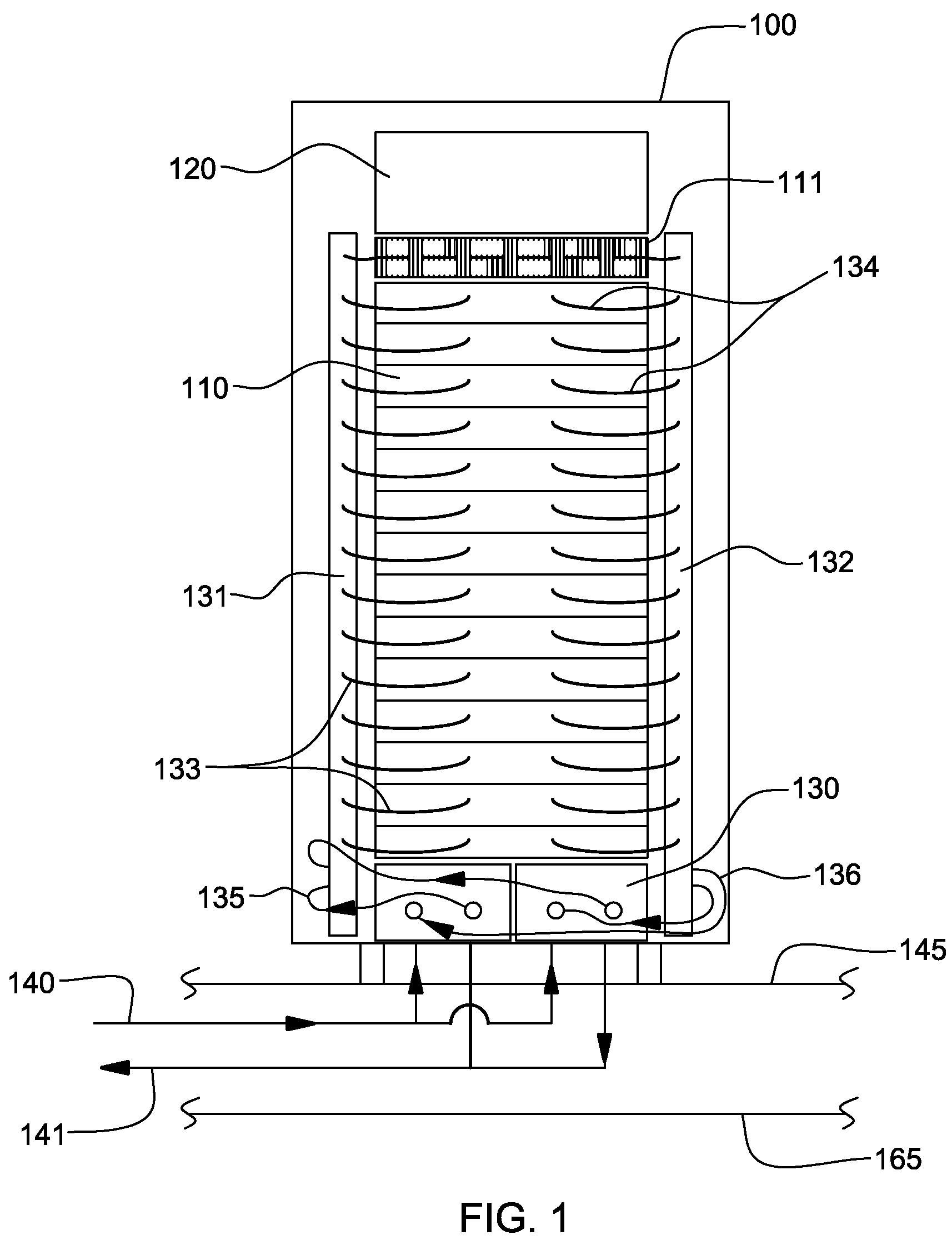
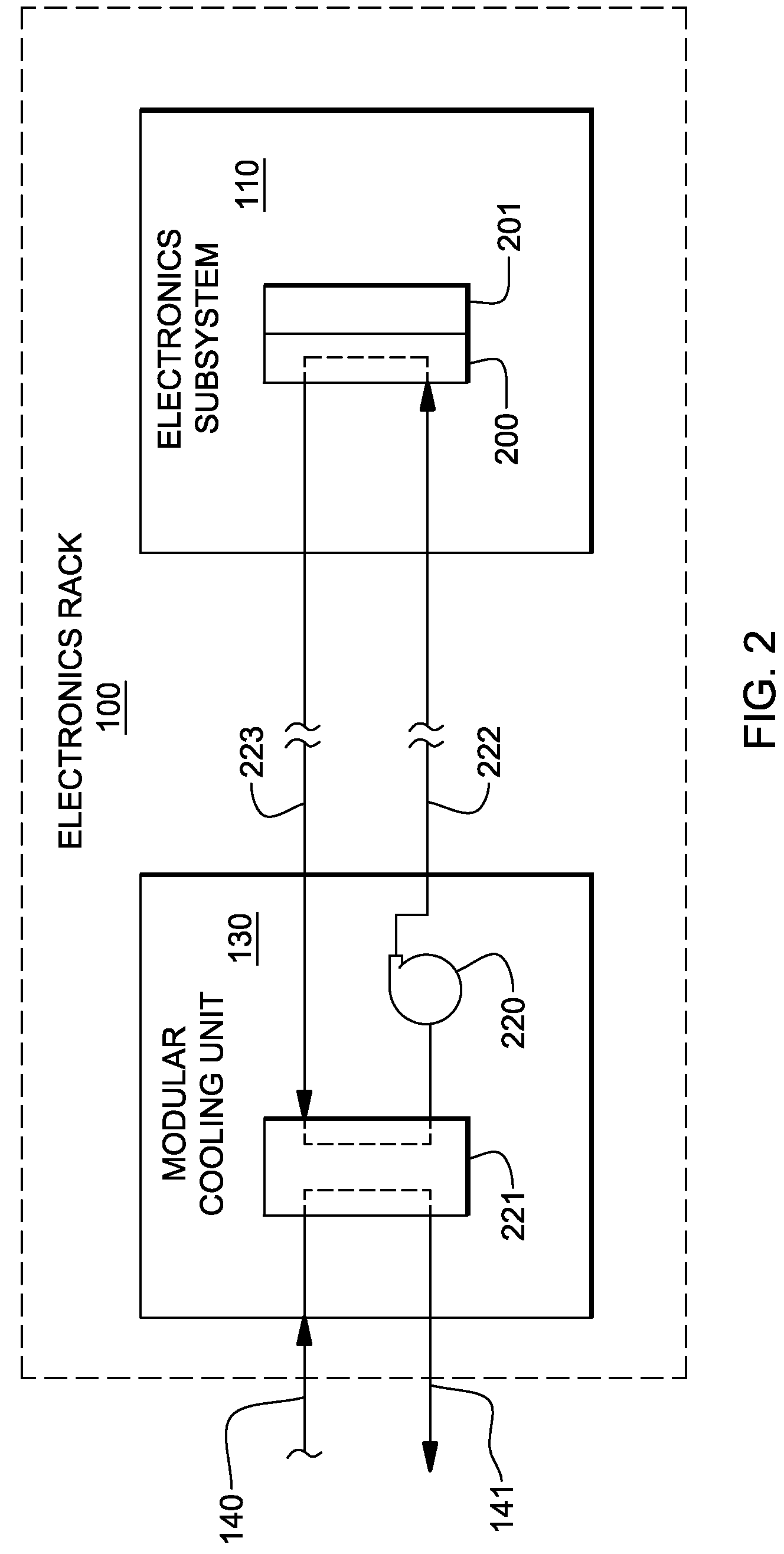
Compliant conduction rail assembly and method facilitating cooling of an electronics structure
InactiveUS8094453B2Heat transfer modificationCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectronic structureEngineering
Compliant conduction rail assembly and method are provided for facilitating cooling of an electronics structure. The rail assembly includes a first thermally conductive rail mounted to a surface of the electronics structure, a second thermally conductive rail thermally conductively interfaced to the first rail, and a biasing mechanism biasing the second rail away from the first rail. The first and second rails and the biasing mechanism are configured for slidable insertion into a housing with the electronics structure, the housing containing a liquid-cooled cold plate(s). With insertion of the electronics structure into the housing, the second rail engages the liquid-cooled cold plate and is forced by the biasing mechanism into thermal contact with the cold plate, and is forced by the cold plate towards the first rail, which results in a compliant thermal interface between the electronics structure and the liquid-cooled cold plate of the housing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
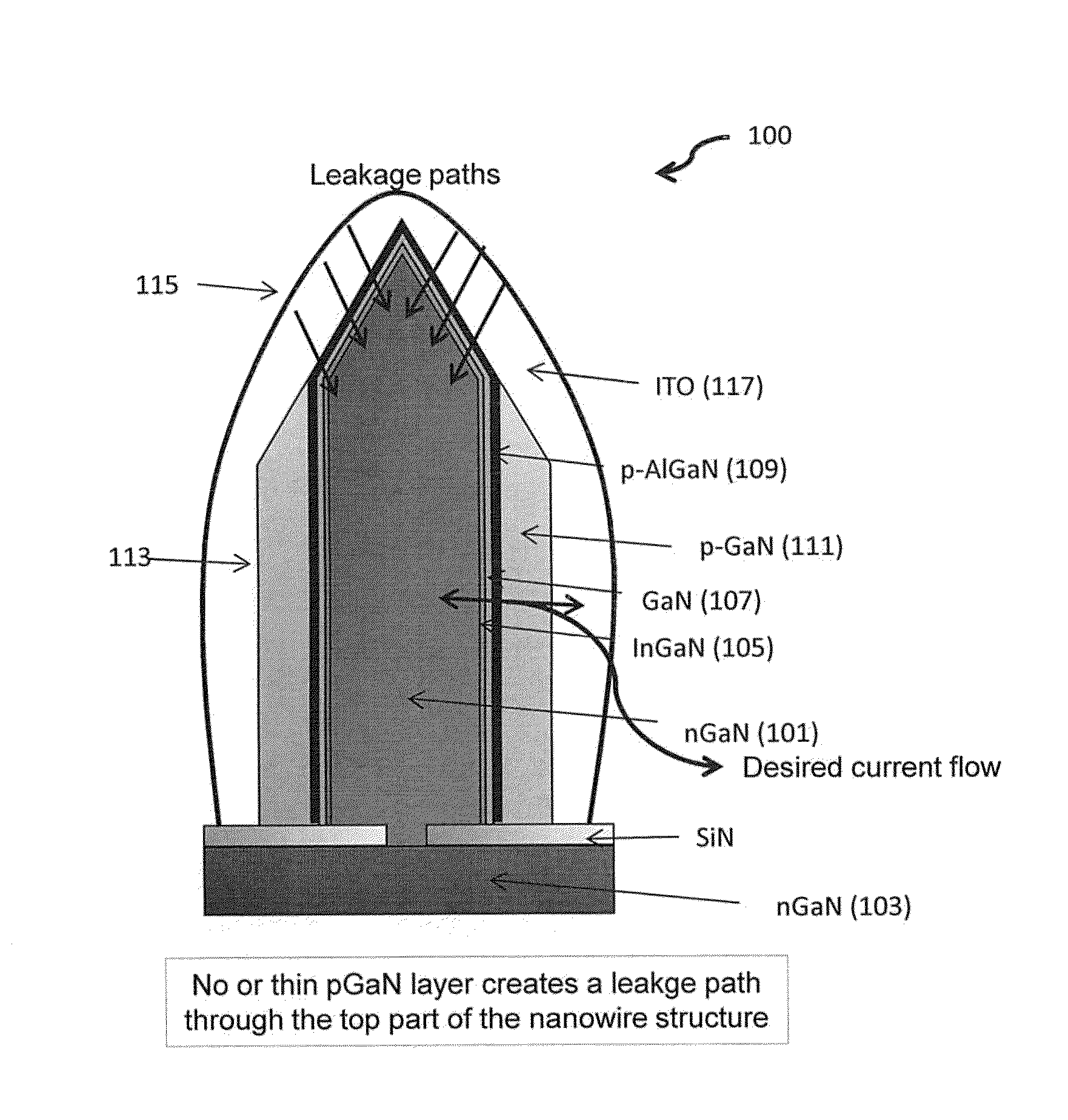
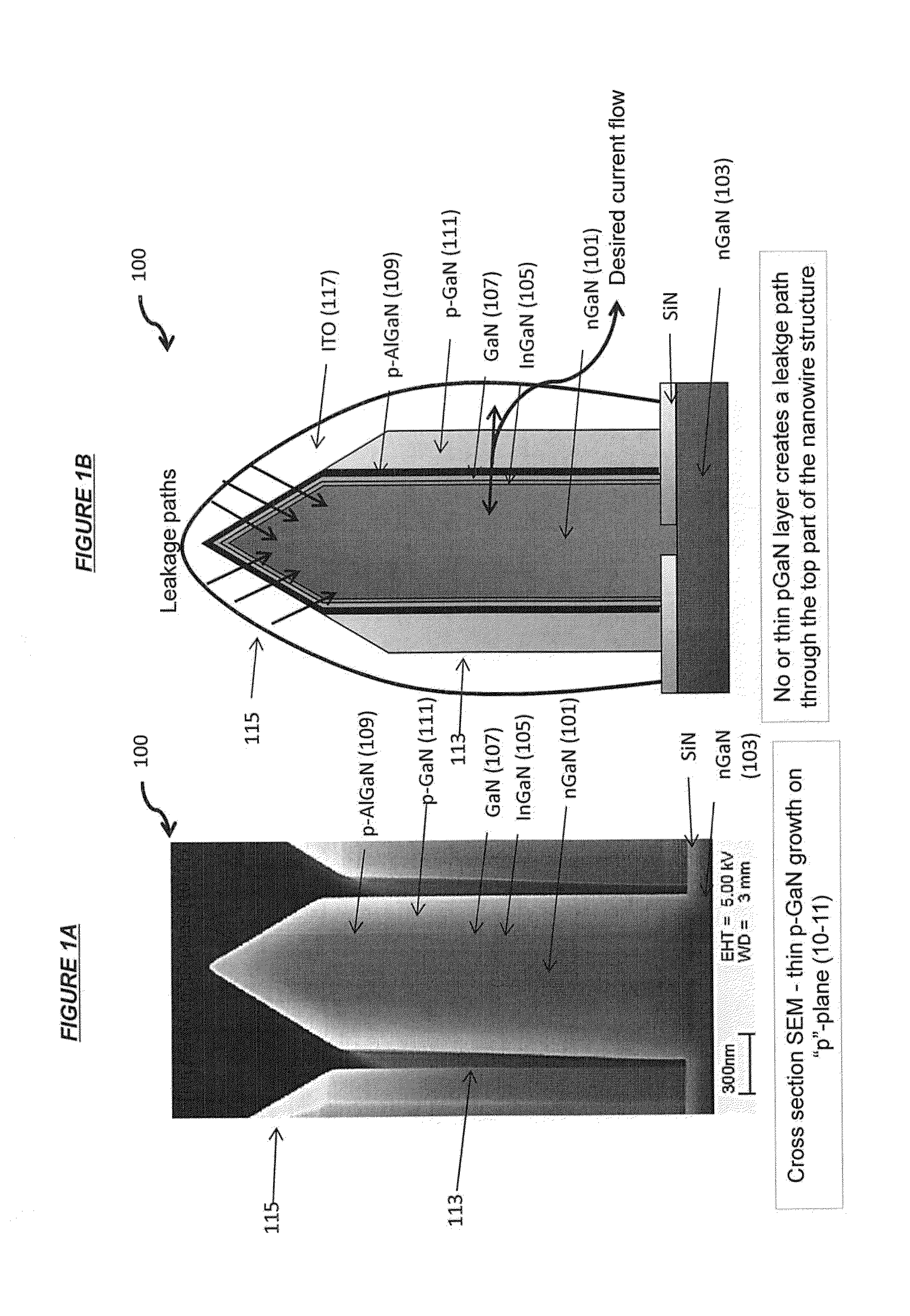
Nanowire Sized Opto-Electronic Structure and Method for Modifying Selected Portions of Same
ActiveUS20140138620A1Reducing and eliminating conductivityReduce conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsElectronic structureNanowire
A LED structure includes a support and a plurality of nanowires located on the support, where each nanowire includes a tip and a sidewall. A method of making the LED structure includes reducing or eliminating the conductivity of the tips of the nanowires compared to the conductivity of the sidewalls during or after creation of the nanowires.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
ActiveUS7619238B2Convenient lightingImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Preparation method of multiple quantum well structure for photoelectric device
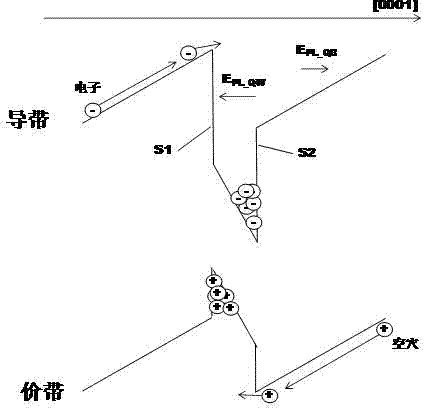
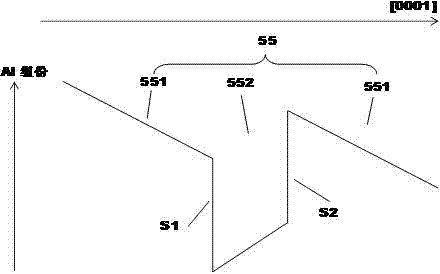
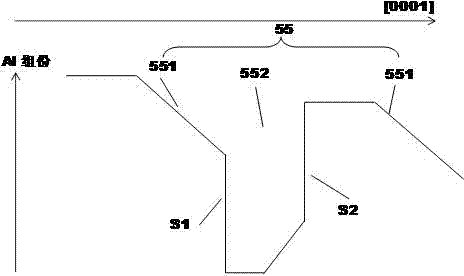
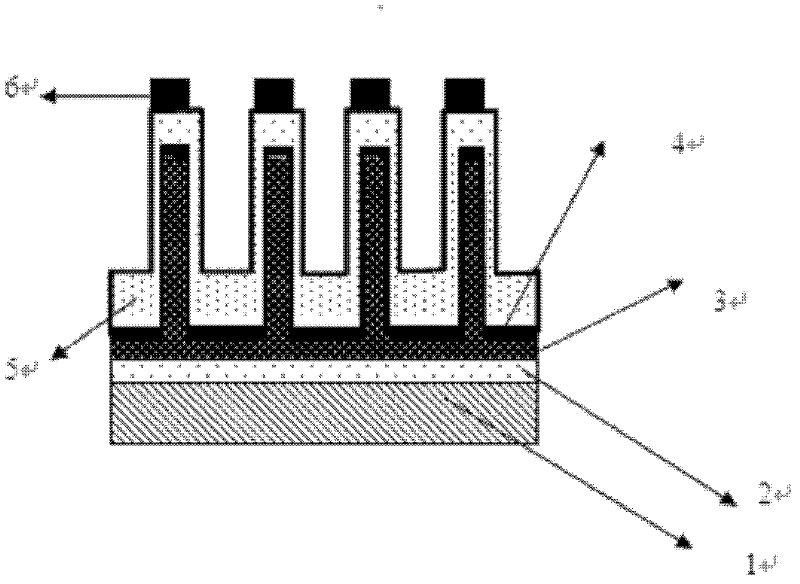
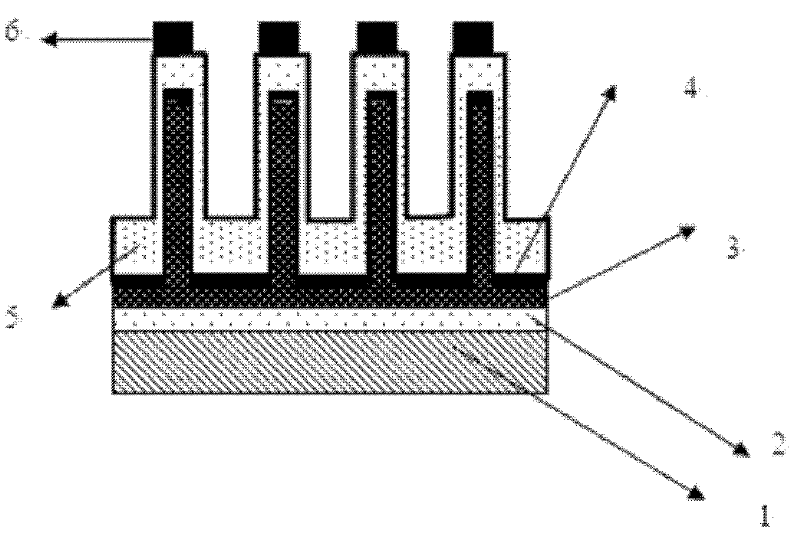
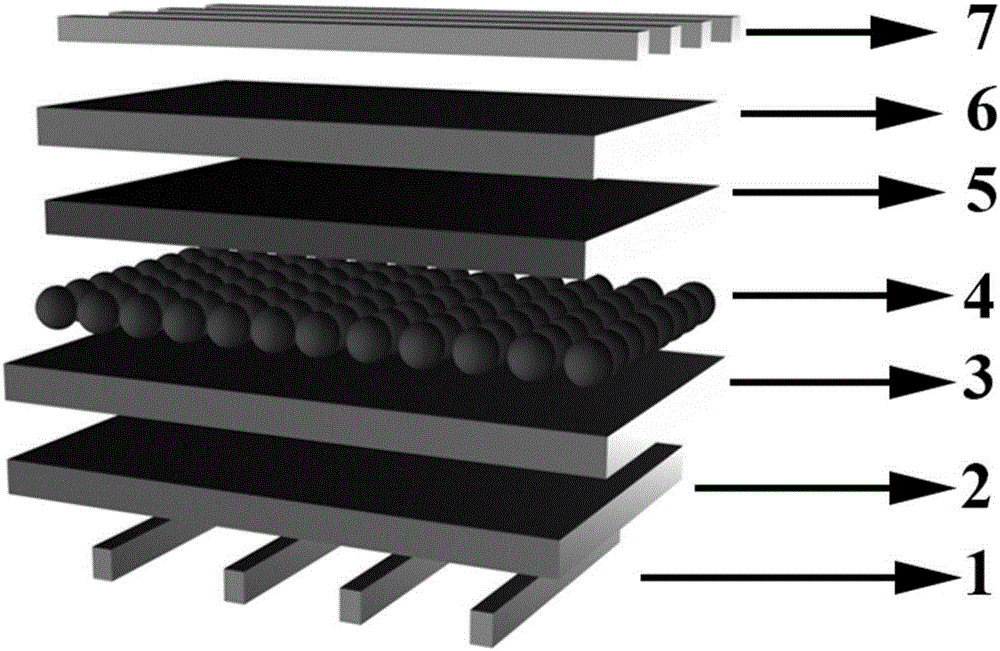
ActiveCN102103990AImprove the broadening effectImprove life test performanceLaser detailsFinal product manufacturePotential wellElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multiple quantum well structure for a photoelectric device. The multiple quantum well structure comprises n quantum well structures which are overlapped in sequence, and each quantum well structure is formed by sequential growth of potential well layers and potential barriers, wherein the growth of each potential well layer comprises the following steps: 1, first growing an NixGa1-xN potential well layer, wherein x is more than 0.1 and less than 0.45; 2, growing a GaN insert layer; and 3, growing the InxGa1-xN potential well layer, wherein x is more than 0.1 and less than 0.45. When the potential well layer grows, one or more than two of GaN insert layers with energy band width different from that of the InxGa1-xN potential well layer and an In treatment layer grow alternately. On the one hand, the In treatment layer can stabilize the structure of the InxGa1-xN, ensures the stability of quantum well components, and controls the stability and consistency of wavelength; on the other hand, the GaN insert layer disturbs the energy band structure of a quantum well region to improve the composite rate of electron hole pairs, so that the internal quantum efficiency of device illumination is improved, and as the brightness is improved, the life test performance of the device can be improved.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH +1
High Throughput Thin Film Characterization And Defect Detection
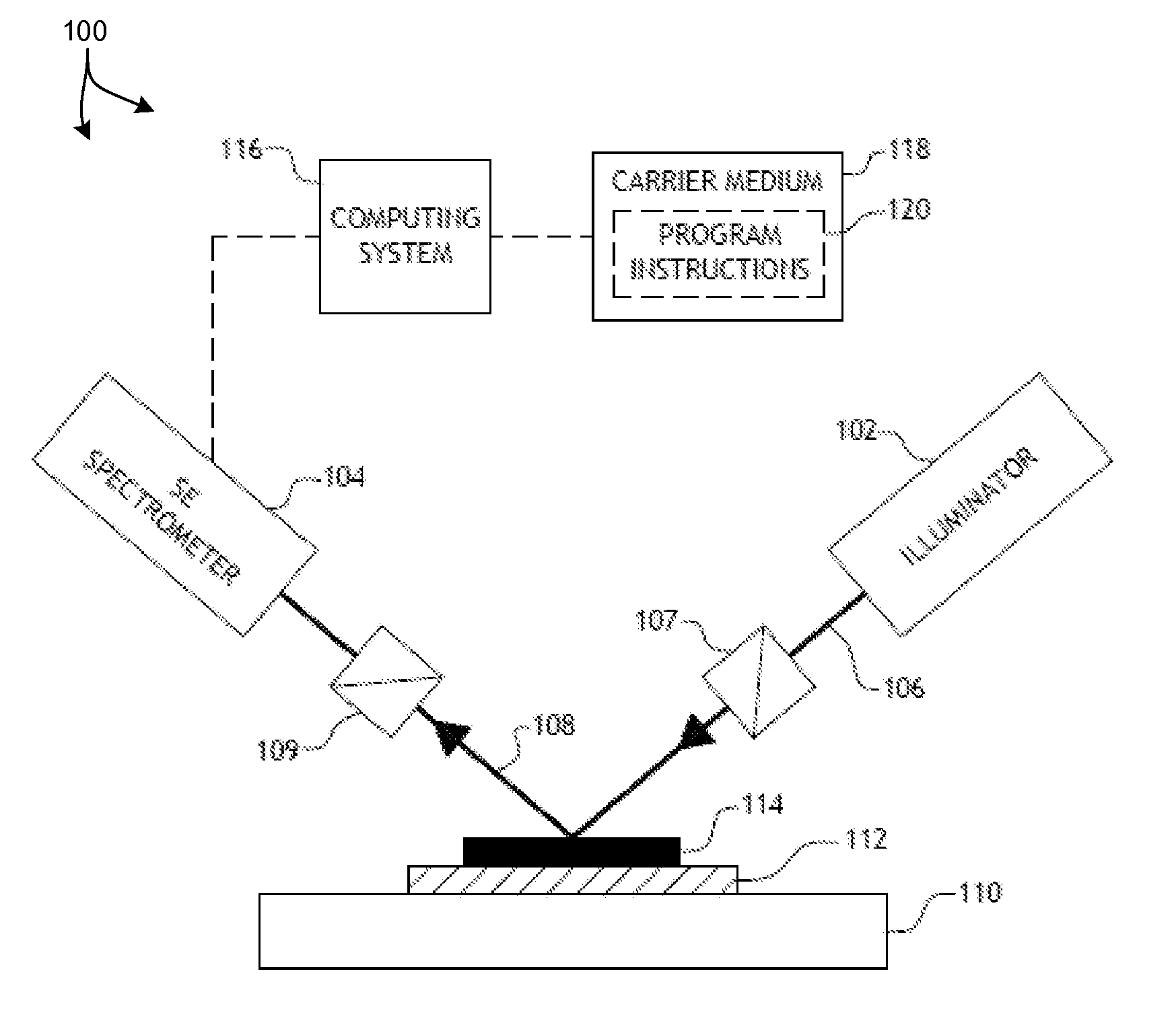
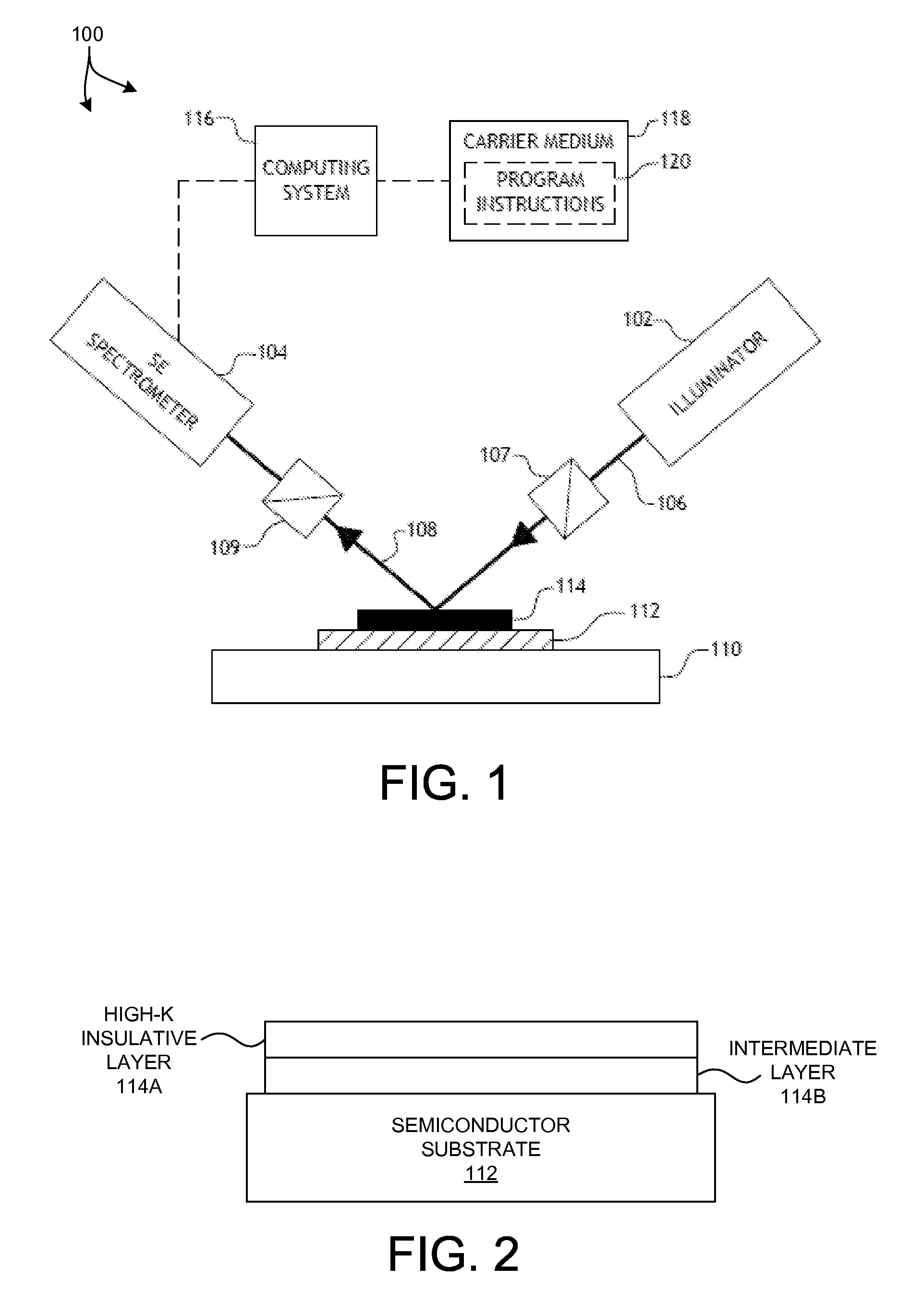
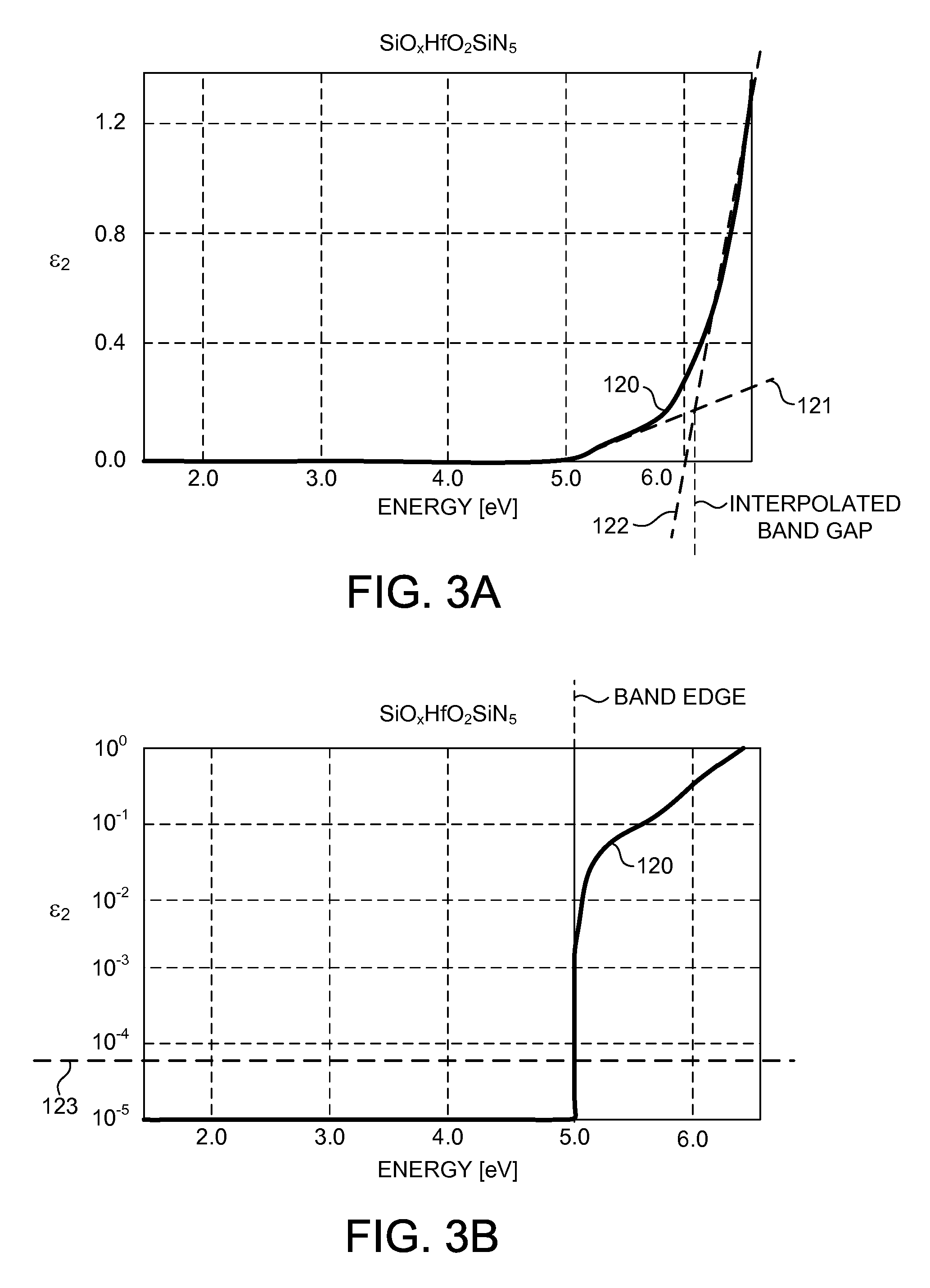
ActiveUS20130083320A1Quick measurementData can be usedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDielectricSpectral response
Methods and systems for determining band structure characteristics of high-k dielectric films deposited over a substrate based on spectral response data are presented. High throughput spectrometers are utilized to quickly measure semiconductor wafers early in the manufacturing process. Optical dispersion metrics are determined based on the spectral data. Band structure characteristics such as band gap, band edge, and defects are determined based on optical dispersion metric values. In some embodiments a band structure characteristic is determined by curve fitting and interpolation of dispersion metric values. In some other embodiments, band structure characteristics are determined by regression of a selected dispersion model. In some examples, band structure characteristics indicative of band broadening of high-k dielectric films are also determined. The electrical performance of finished wafers is estimated based on the band structure characteristics identified early in the manufacturing process.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Photonic crystal waveguide, homogeneous medium waveguide, and optical device
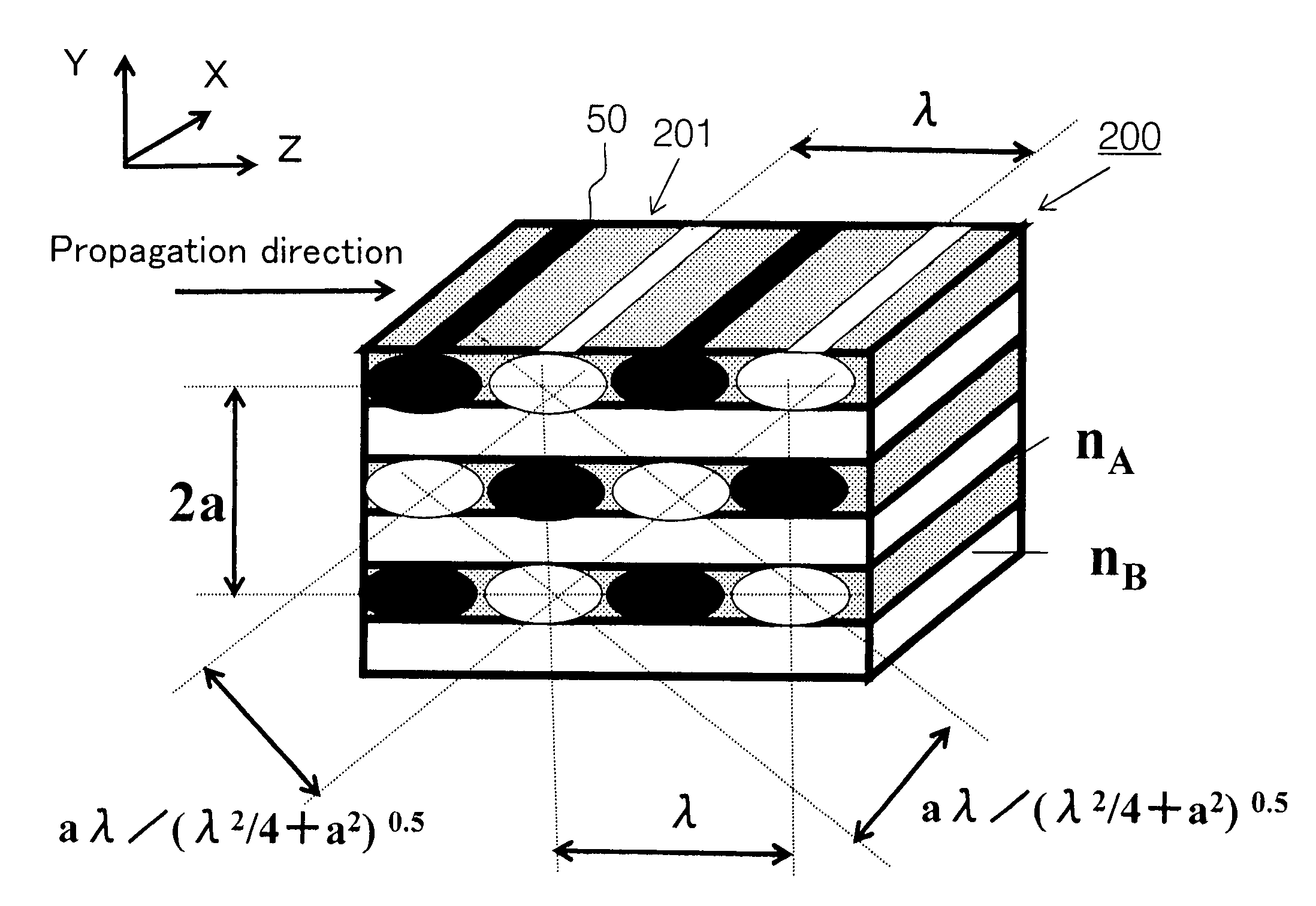
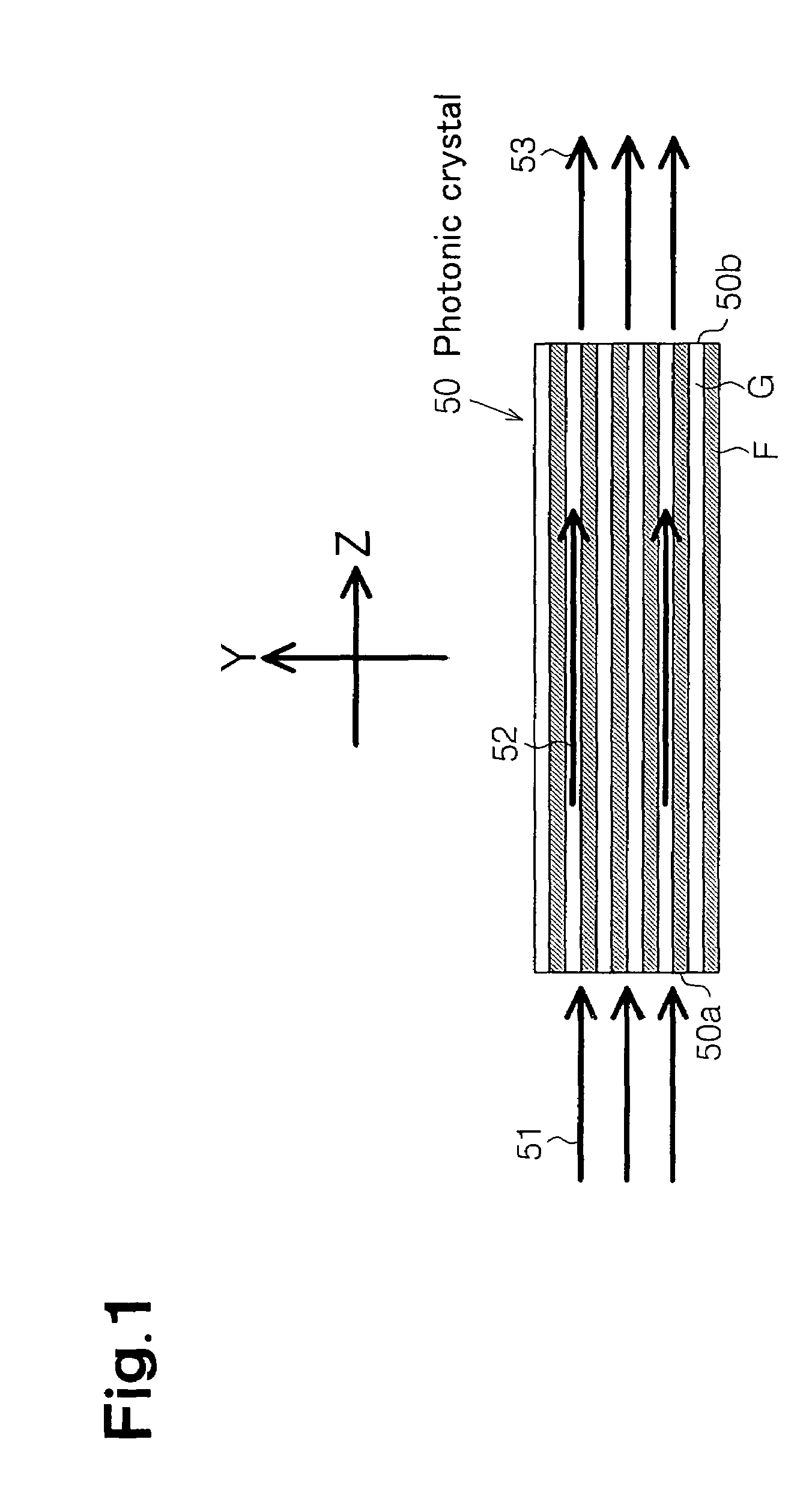
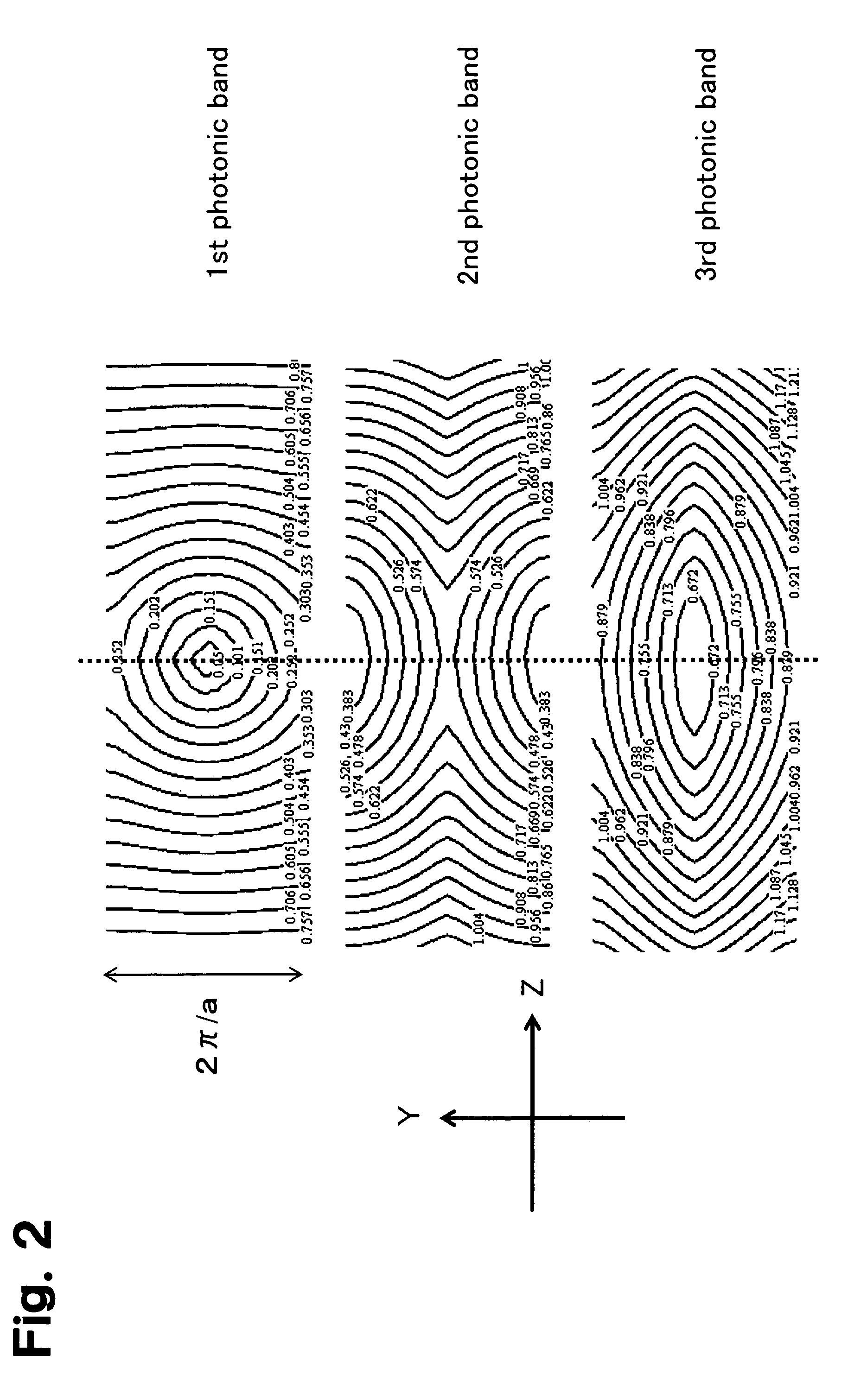
A photonic crystal waveguide and a homogeneous medium waveguide for enabling a steep bend and arrangement at an arbitrary angle with low propagation loss. A photonic crystal waveguide has a core formed by a photonic crystal having periodicity in the Y-direction. Electromagnetic wave is propagated by a band on the Brillouin zone boundary of the photonic band structure of the core. A side face of the core parallel to the Y-direction is in contact with a homogeneous medium having a refractive index of ns, and the condition of λ0 / ns>aλ / (λ2 / 4+a2)0.5 is satisfied when the wavelength in vacuum of the electromagnetic wave is represented by λ0, the period of the photonic crystal is represented by a, and the period in the XZ-plane direction of the wave propagated through the core is represented by λ.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Semiconductor ultraviolet source device
ActiveCN103247728AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce tiltSemiconductor devicesUltravioletElectronic band structure
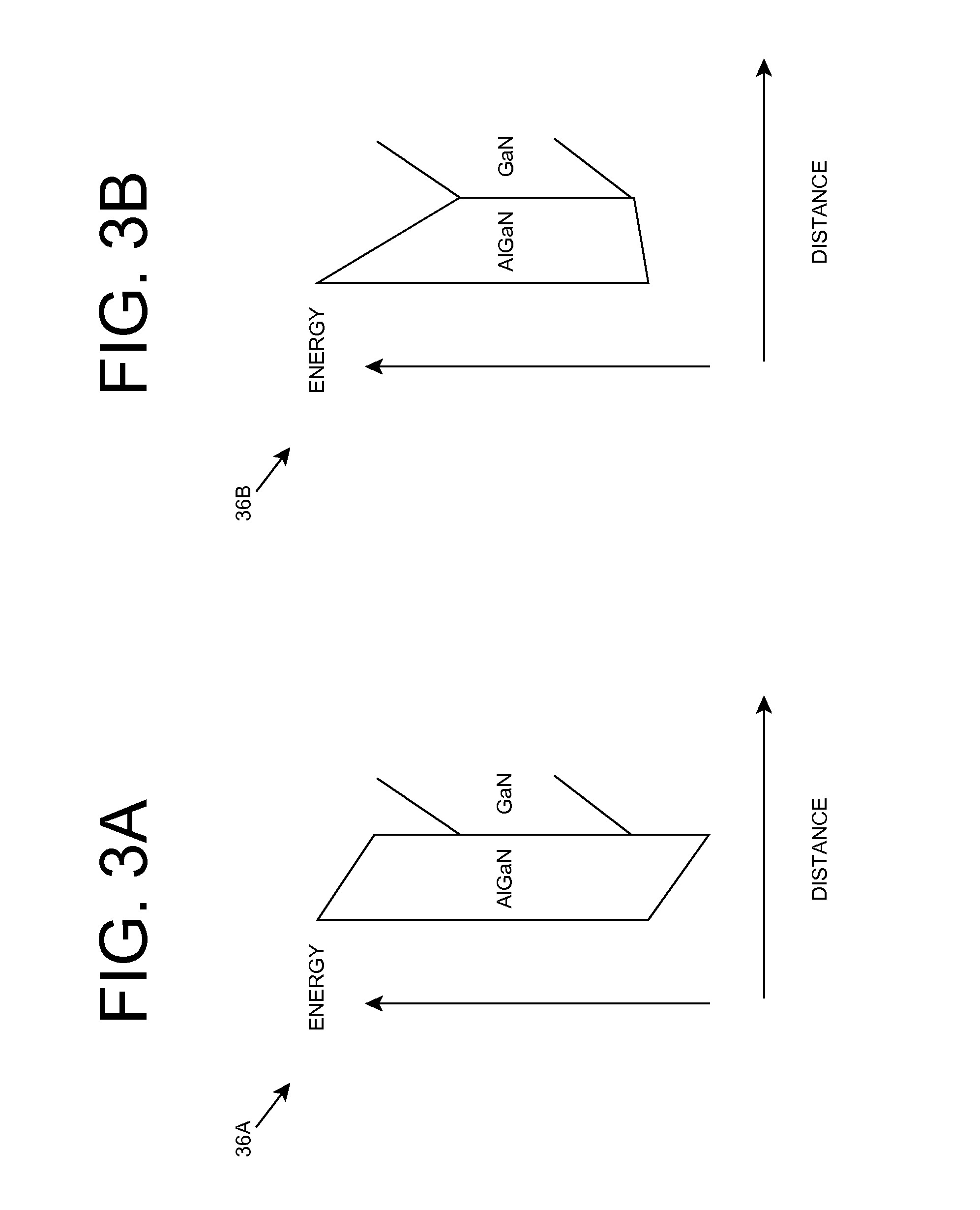
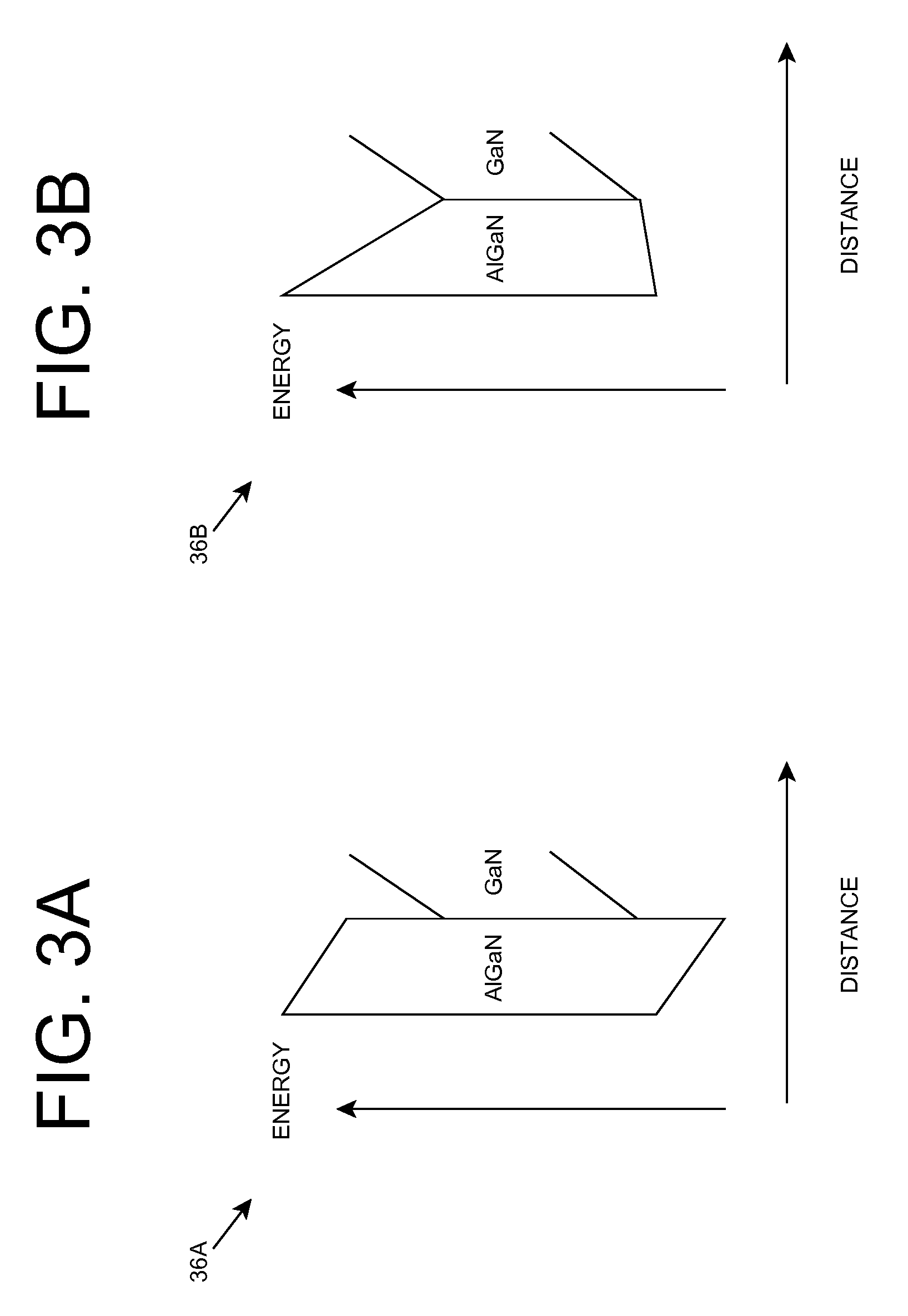
The invention provides a semiconductor ultraviolet source device. A quantum well and a quantum barrier in the epitaxial growth structure of the device have component gradients in the epitaxial growth direction, and the directions of the component gradients of the quantum well and the quantum barrier in the epitaxial growth direction are opposite. Heterostructures such as the energy band structures of multiple quantum wells are regulated through using the variation of the Al (aluminum) component of AlInGaN material, the energy band edge inclination of the quantum well and the quantum barrier is reduced, electrons and holes injected to the barrier are reduced, the positive working voltage of an ultraviolet LED (light emitting diode) is reduced, and the light emitting efficiency of the quantum well is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO JASON ELECTRIC
Thin-film solar photovoltaic cell with nano wire array structure and preparation method for thin-film solar photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN102569508ALow costImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseCuprous sulfide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thin-film solar photovoltaic cell with a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) nano wire array structure. The method comprises the following steps of: growing a large-area cuprous sulfide or copper sulfide nano wire array by adopting a gas-solid reaction method, and converting the cuprous sulfide or copper sulfide nano wire array into a CIGS nano wire array by physical vapor deposition and heat treatment methods. The component, the phase structure and the energy band structure of the semiconductor nano wire array can be regulated by controlling the categories of deposition elements, the deposition sequence, the deposition process, post treatment and the like, so that solar photovoltaic cells with different structures and properties are prepared. Through the cell, light reflection is reduced, light absorption is increased, the probability of producing current carriers can be increased, the probability of recombination of holes and electrons is reduced, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved. The method is low in cost, the preparation processes are controllable, the prepared nano wire array is uniform in structure distribution, and preparation of the nano structural thin-film solar photovoltaic cell with large area and high photoelectric conversion efficiency can be realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Efficient blue-light quantum dot light emitting diode and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN106549110AImprove luminous efficiencyLong application lifeMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesHole transport layerElectronic band structure
The invention discloses an efficient blue-light quantum dot light emitting diode and a preparation method therefor. The diode comprises a negative electrode, an electron transport layer, a surface modification layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer, a hole transport layer, a hole injection layer and a positive electrode formed on a substrate, wherein the negative electrode is placed at the bottom layer; the electron transport layer, the surface modification layer, the quantum dot light emitting layer, the hole transport layer, the hole injection layer and the positive electrode are arranged from the bottom up in sequence; and the surface modification layer can balance the electron and hole injection of the quantum dot light emitting diode by modification of the electron transport layer on the lower side, so as to improve the light emitting efficiency of a device. By adoption of the efficient blue-light quantum dot light emitting diode and the preparation method therefor, the light emitting efficiency of the device can be effectively improved, and the service life of the device is prolonged and other performance of the device is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com