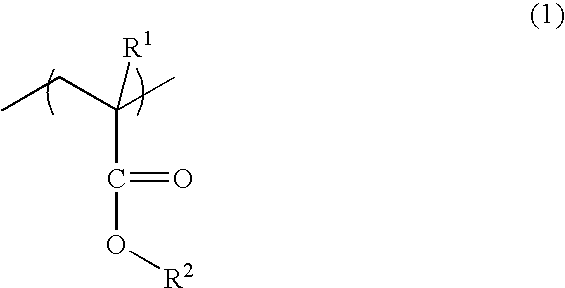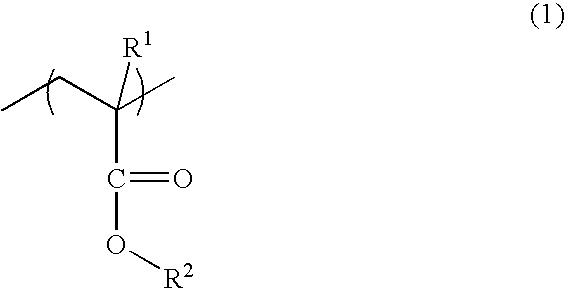Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Low propagation loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
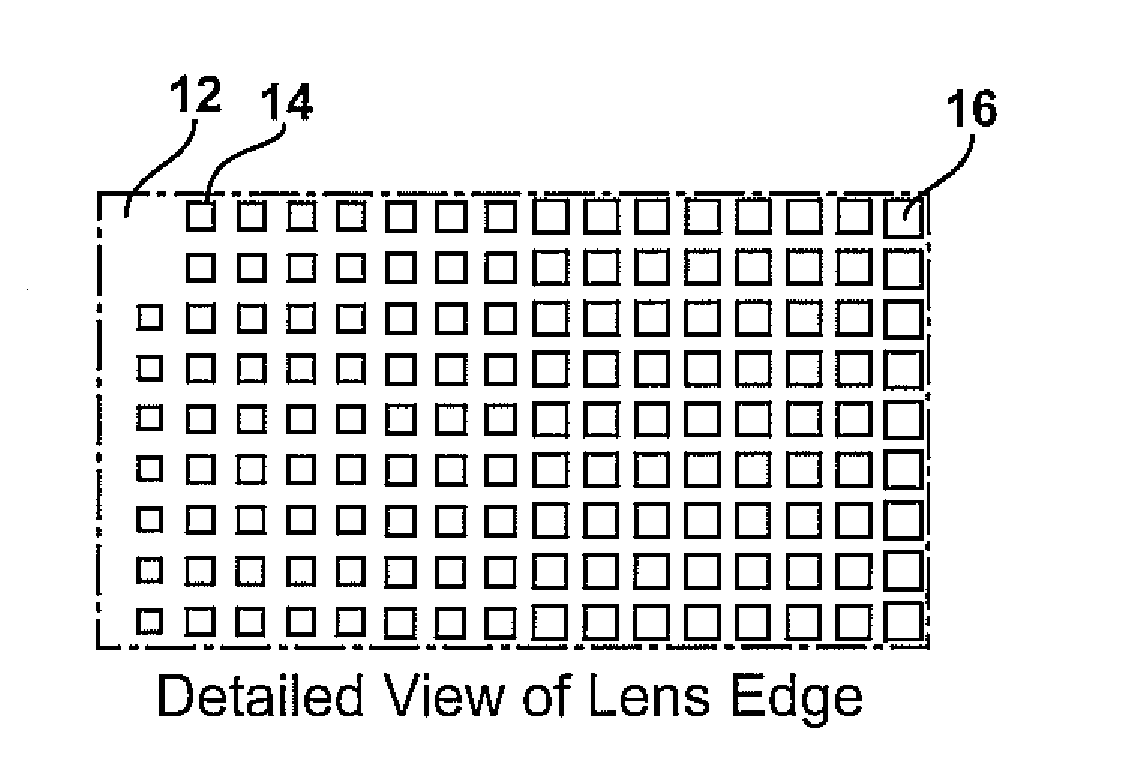
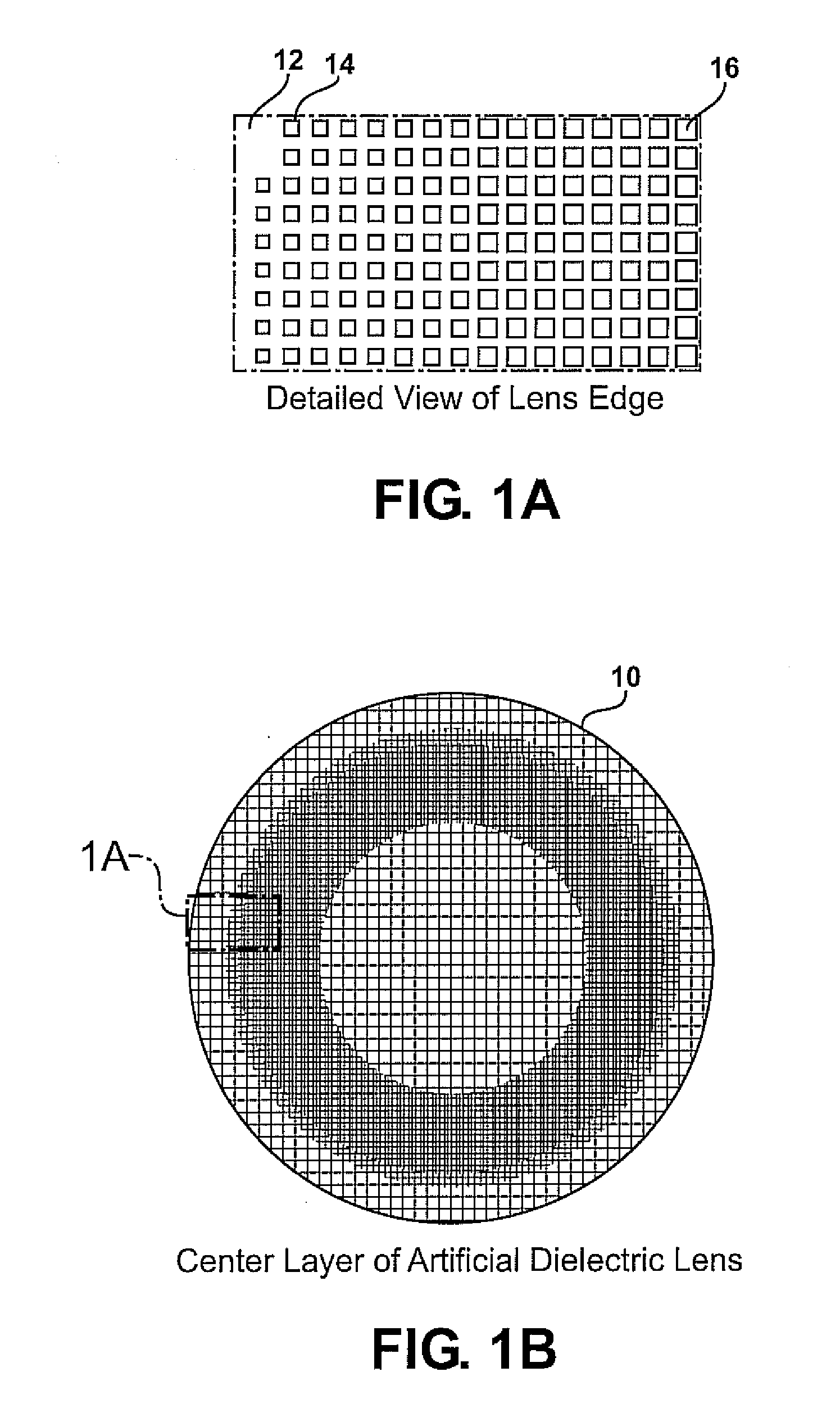
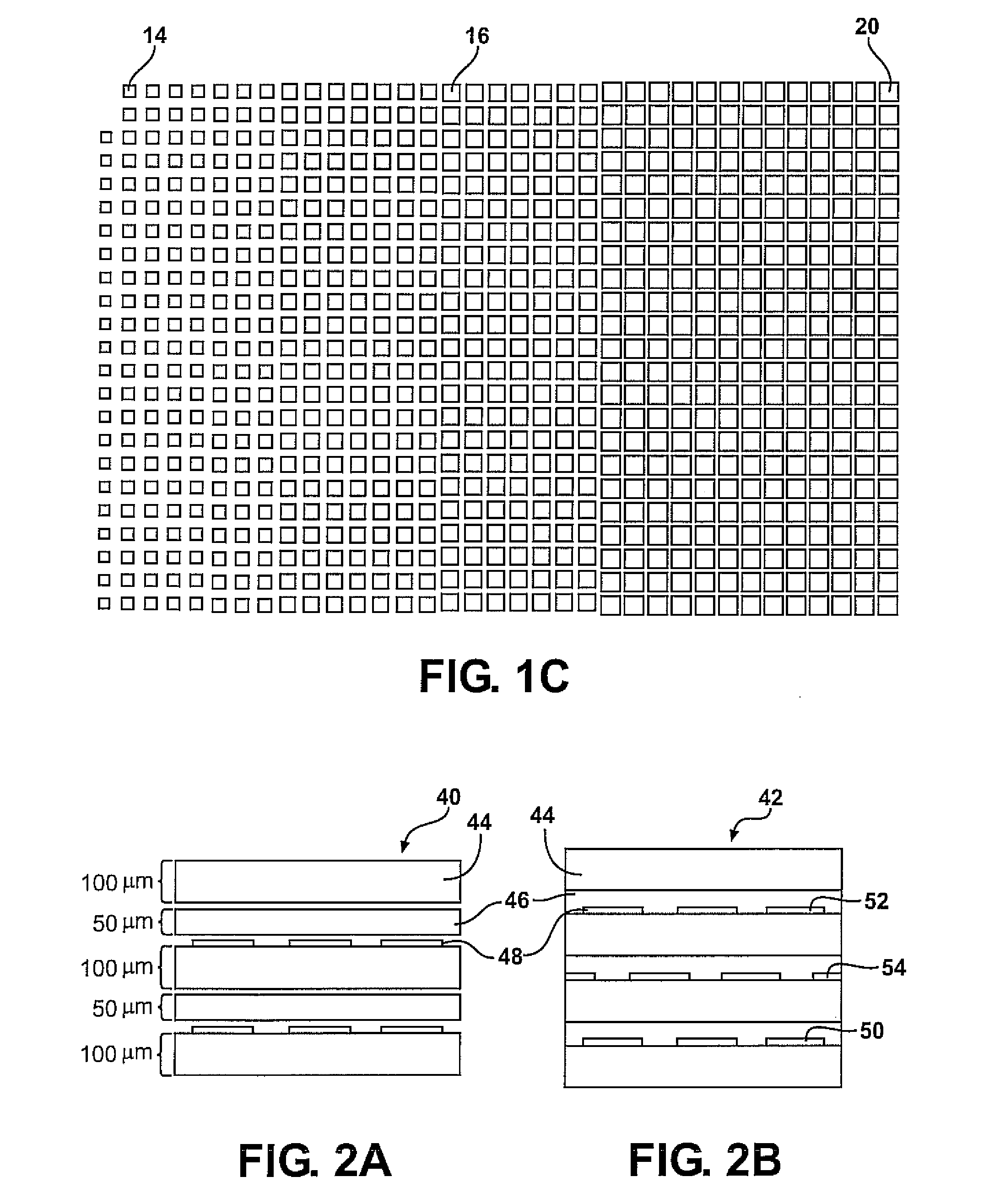
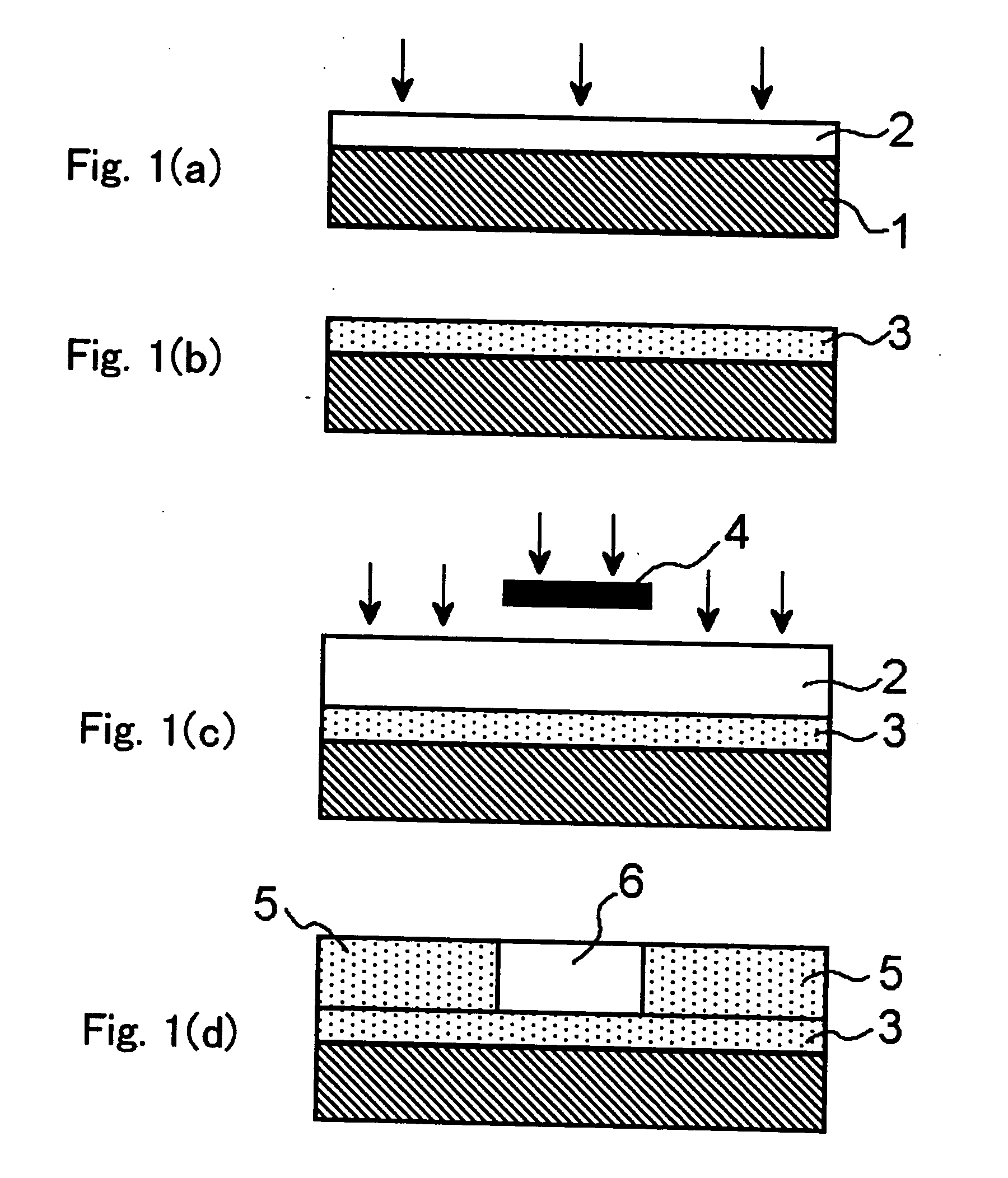
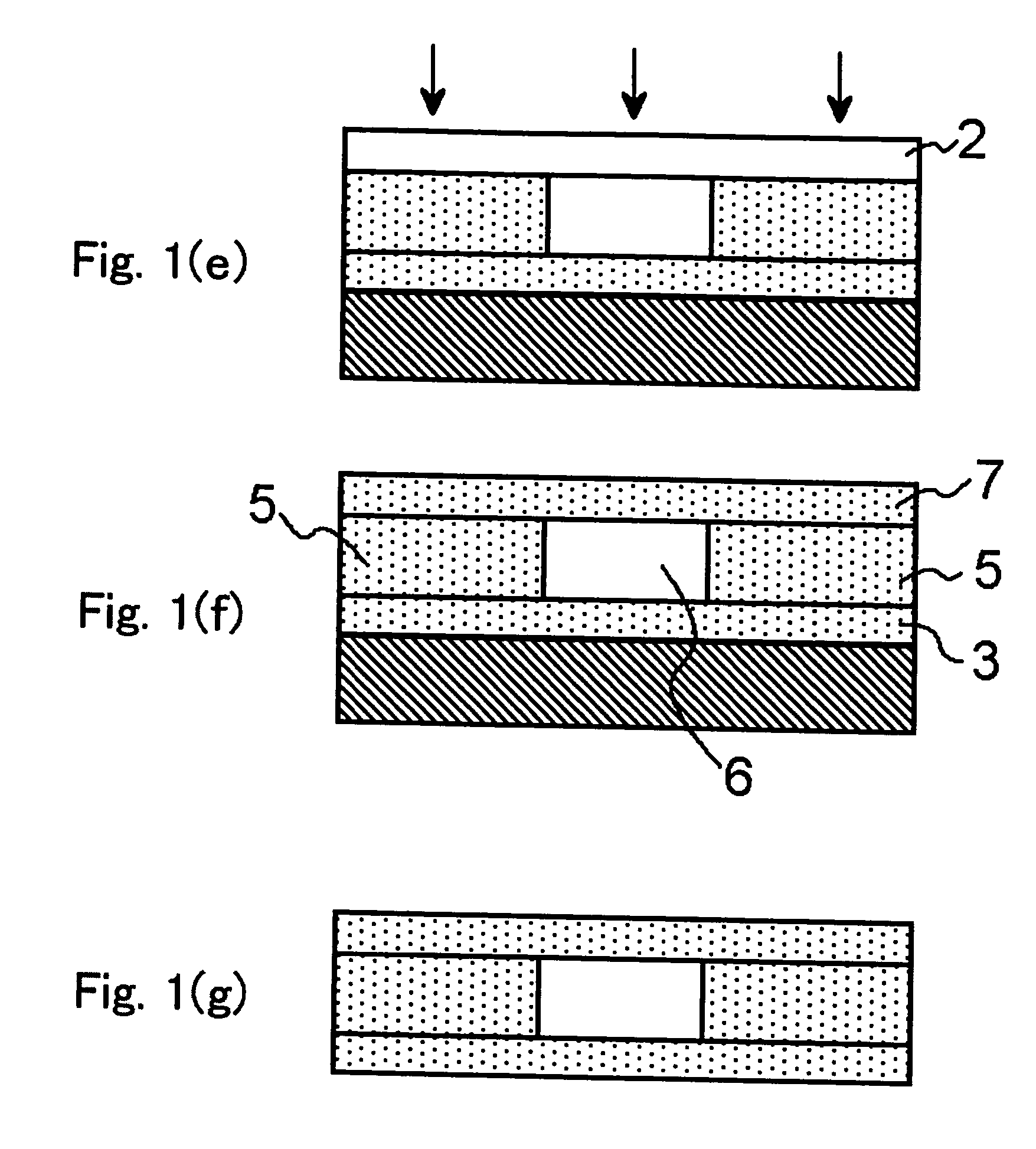
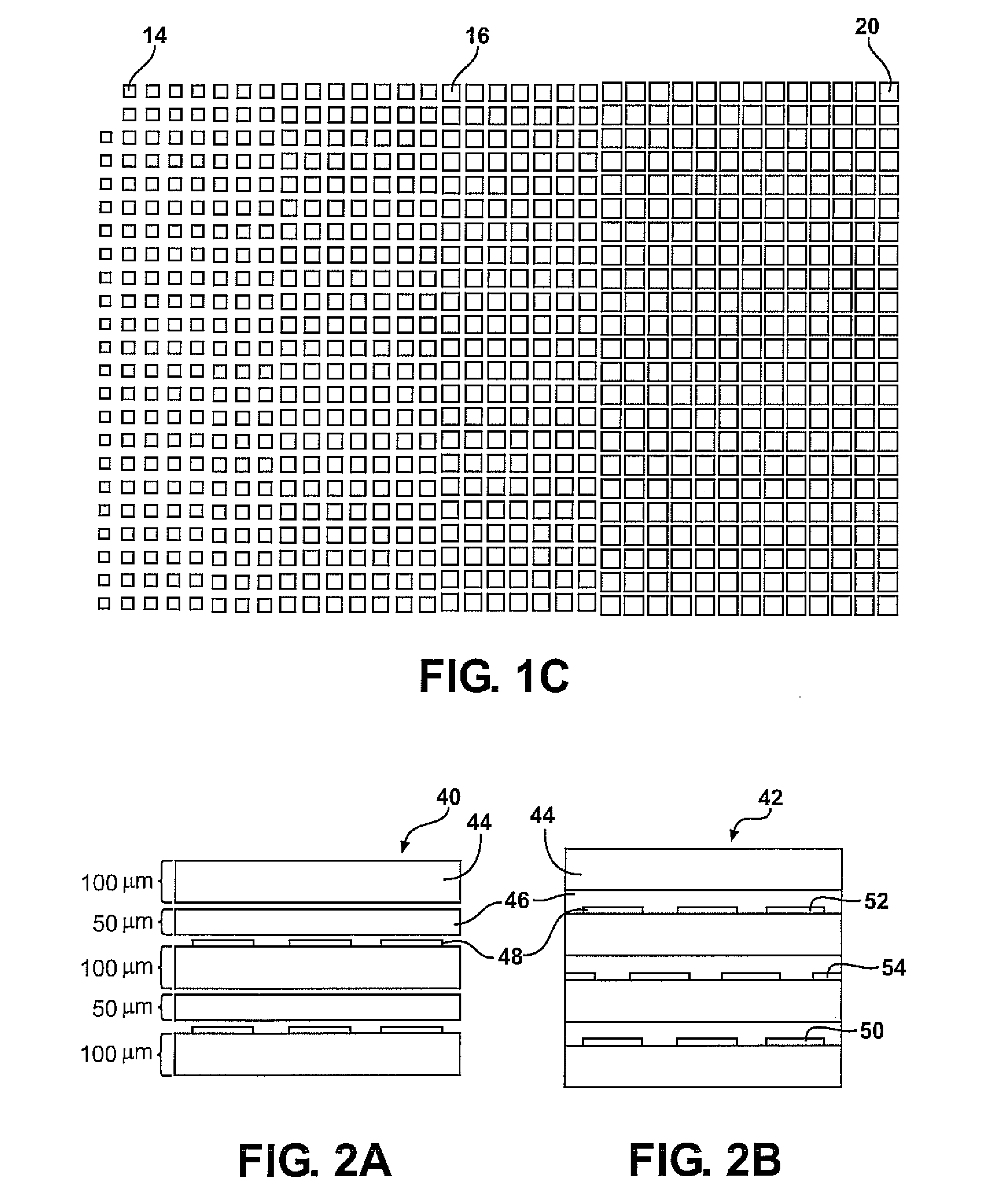
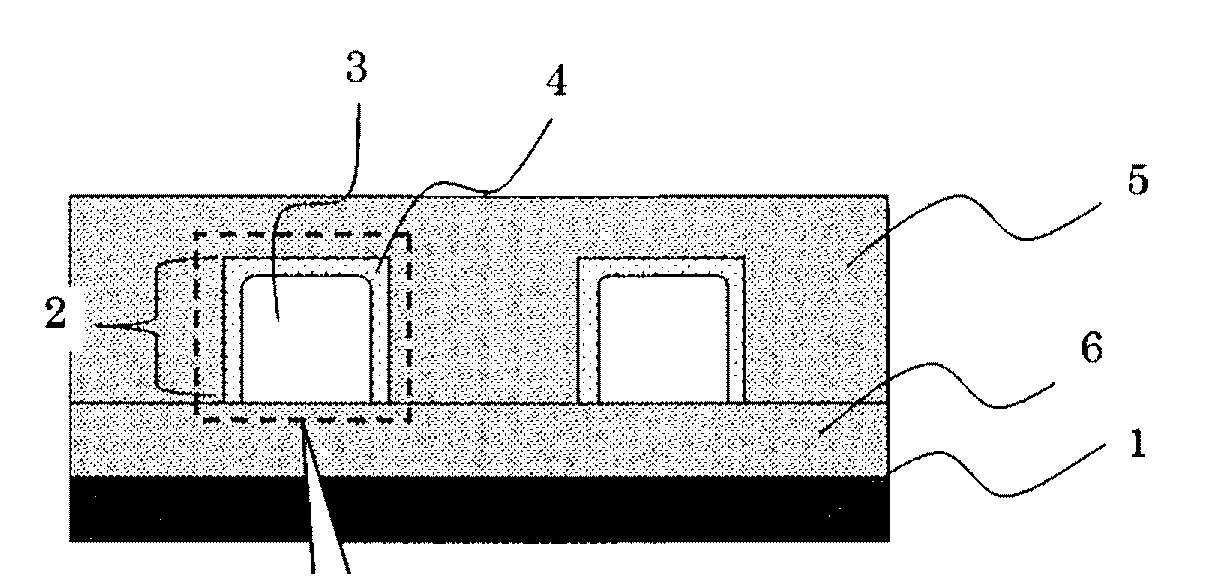
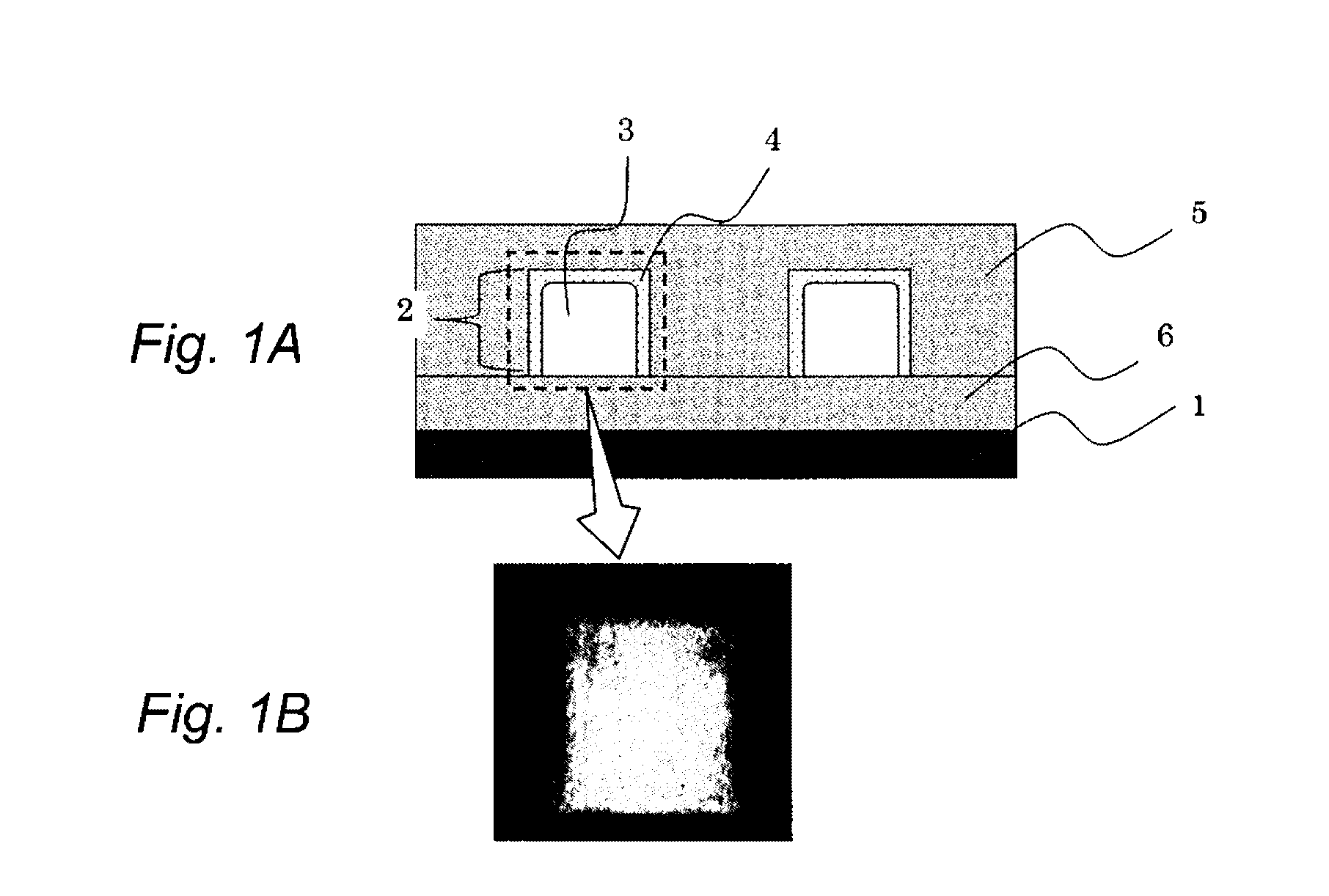
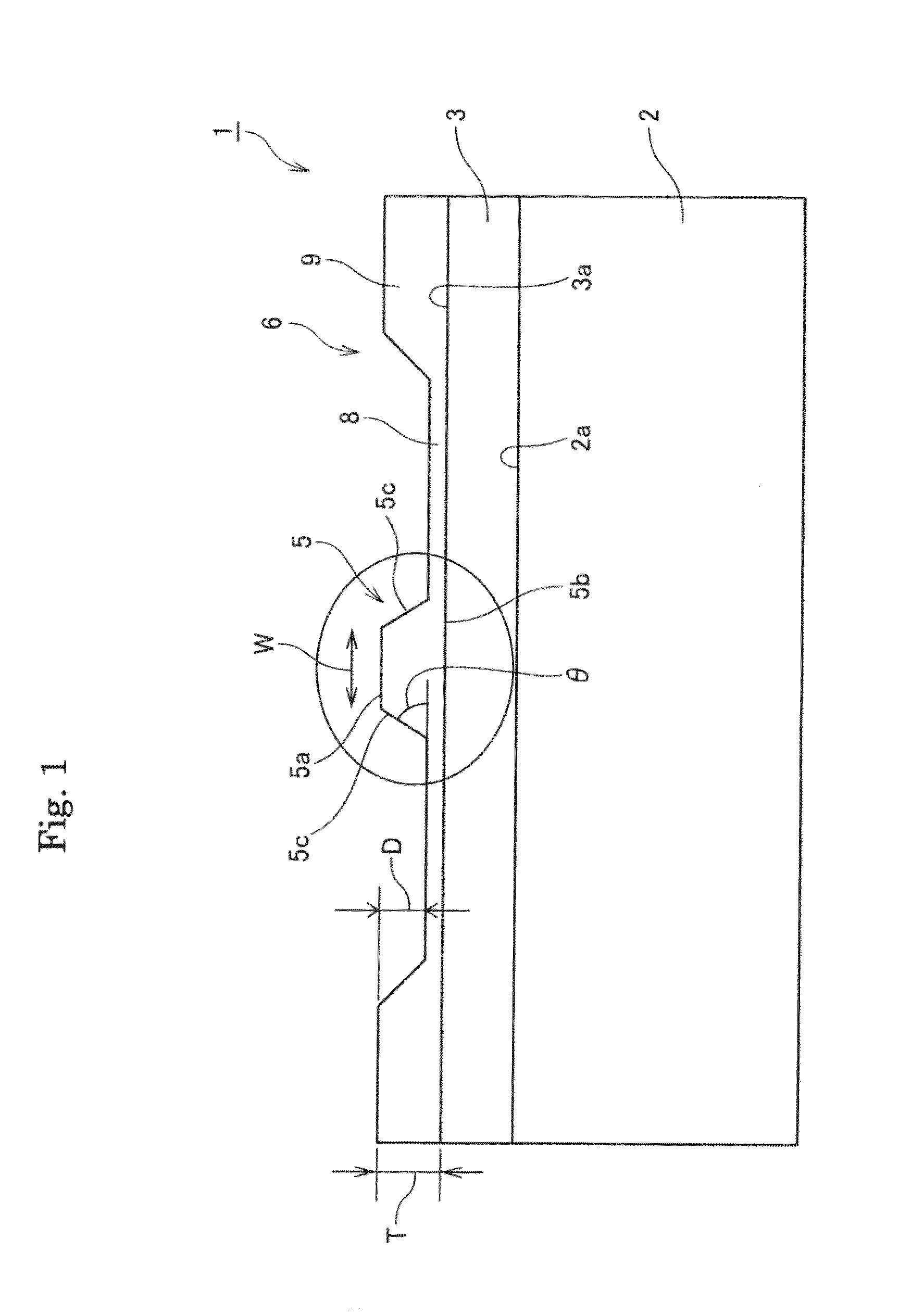
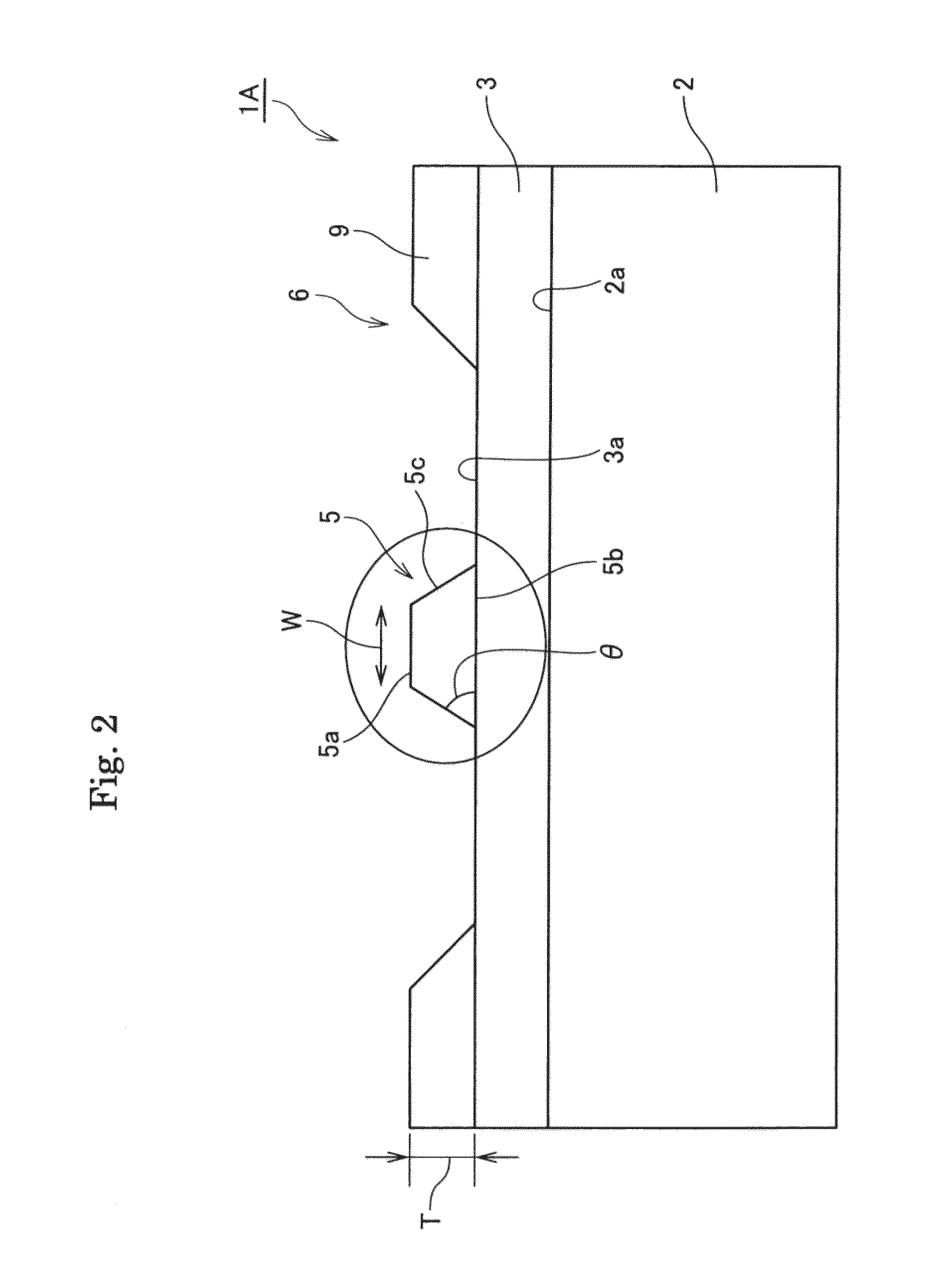
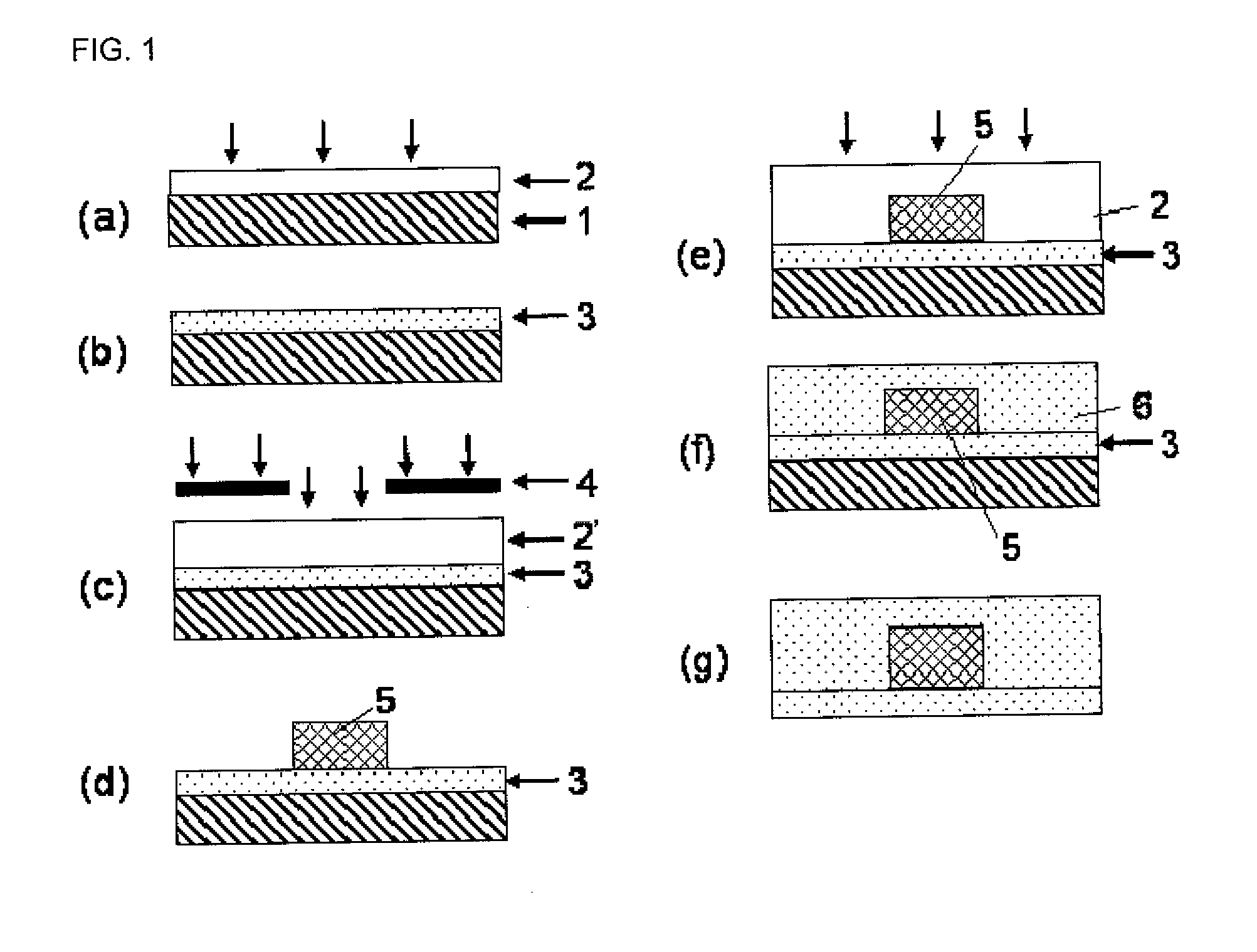
Planar gradient-index artificial dielectric lens and method for manufacture
A gradient index lens for electromagnetic radiation includes a dielectric substrate, a plurality of conducting patches supported by the dielectric substrate, the conducting patches preferably being generally square shaped and having an edge length, the edge length of the conducting patches varying with position on the dielectric substrate so as to provide a gradient index for the electromagnetic radiation. Examples include gradient index lenses for millimeter wave radiation, and use with antenna systems.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
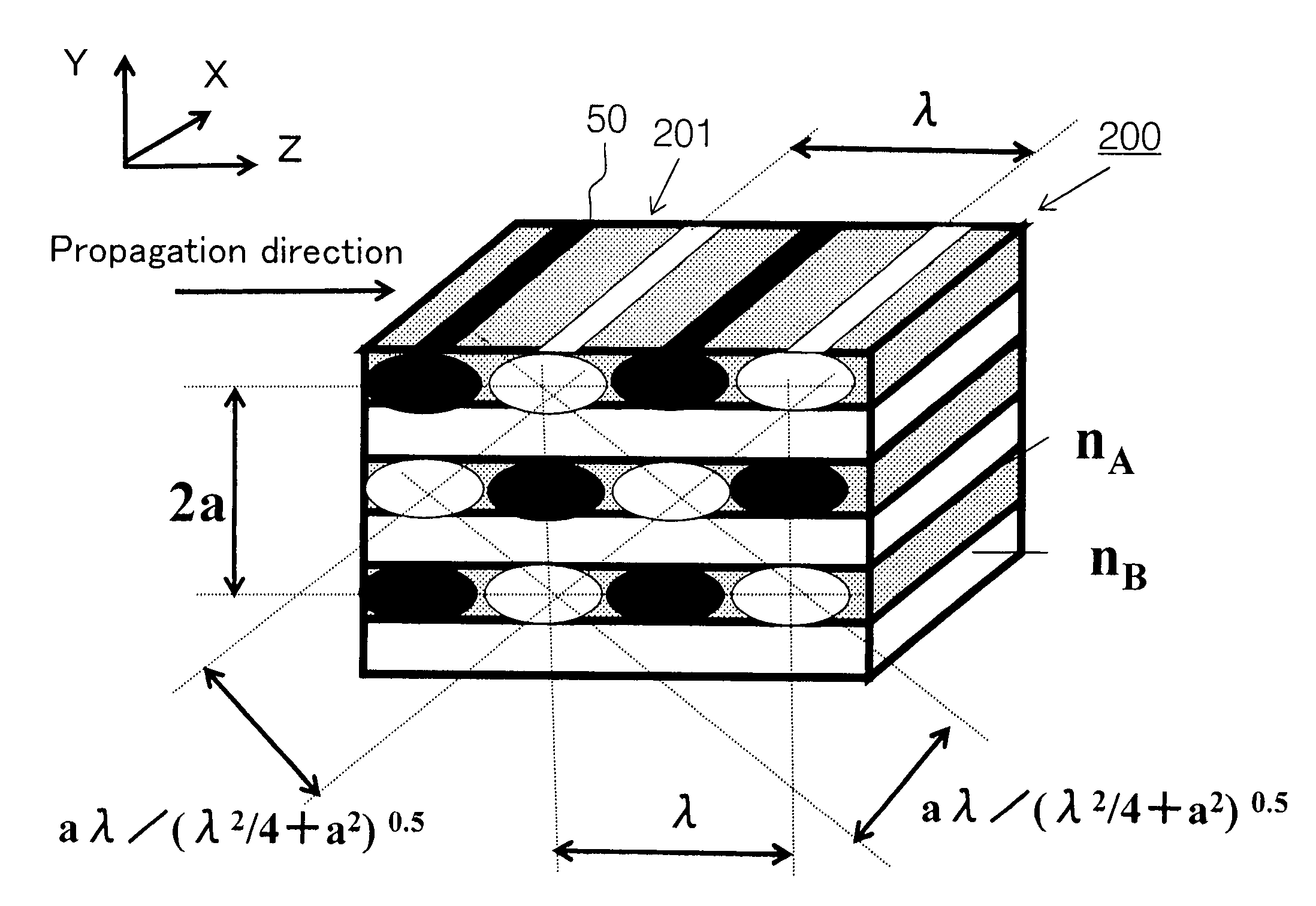
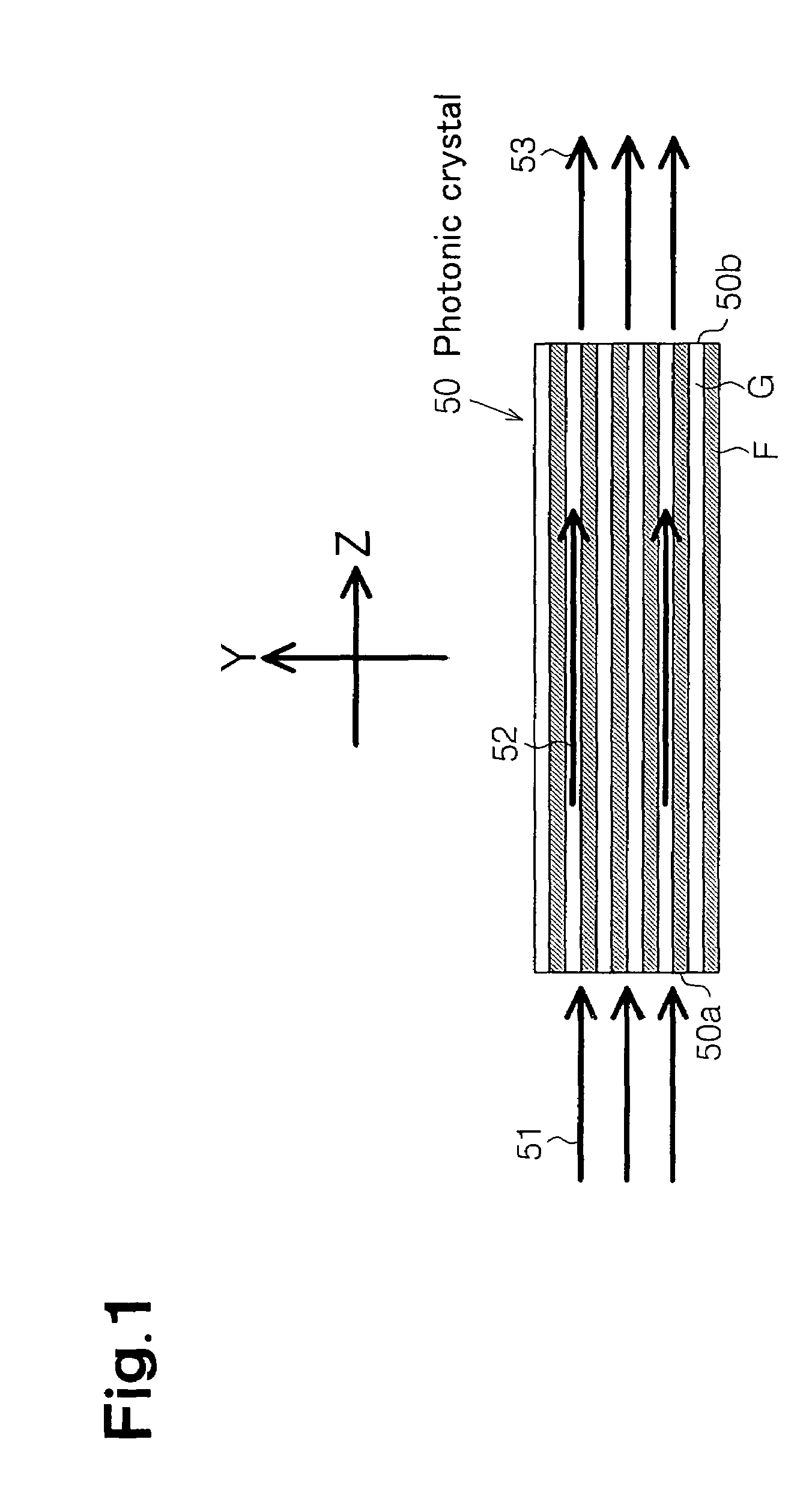
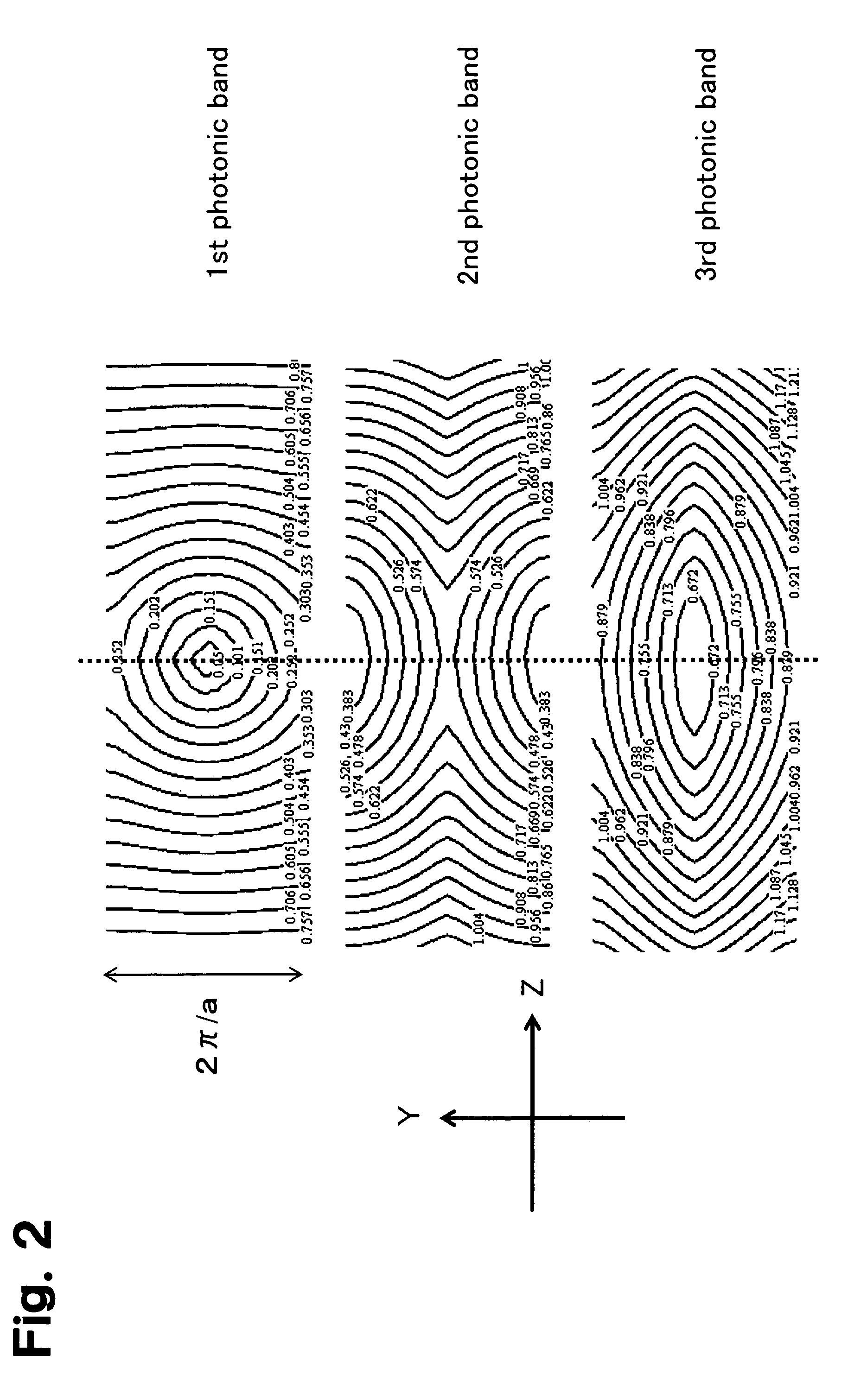
Photonic crystal waveguide, homogeneous medium waveguide, and optical device
A photonic crystal waveguide and a homogeneous medium waveguide for enabling a steep bend and arrangement at an arbitrary angle with low propagation loss. A photonic crystal waveguide has a core formed by a photonic crystal having periodicity in the Y-direction. Electromagnetic wave is propagated by a band on the Brillouin zone boundary of the photonic band structure of the core. A side face of the core parallel to the Y-direction is in contact with a homogeneous medium having a refractive index of ns, and the condition of λ0 / ns>aλ / (λ2 / 4+a2)0.5 is satisfied when the wavelength in vacuum of the electromagnetic wave is represented by λ0, the period of the photonic crystal is represented by a, and the period in the XZ-plane direction of the wave propagated through the core is represented by λ.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
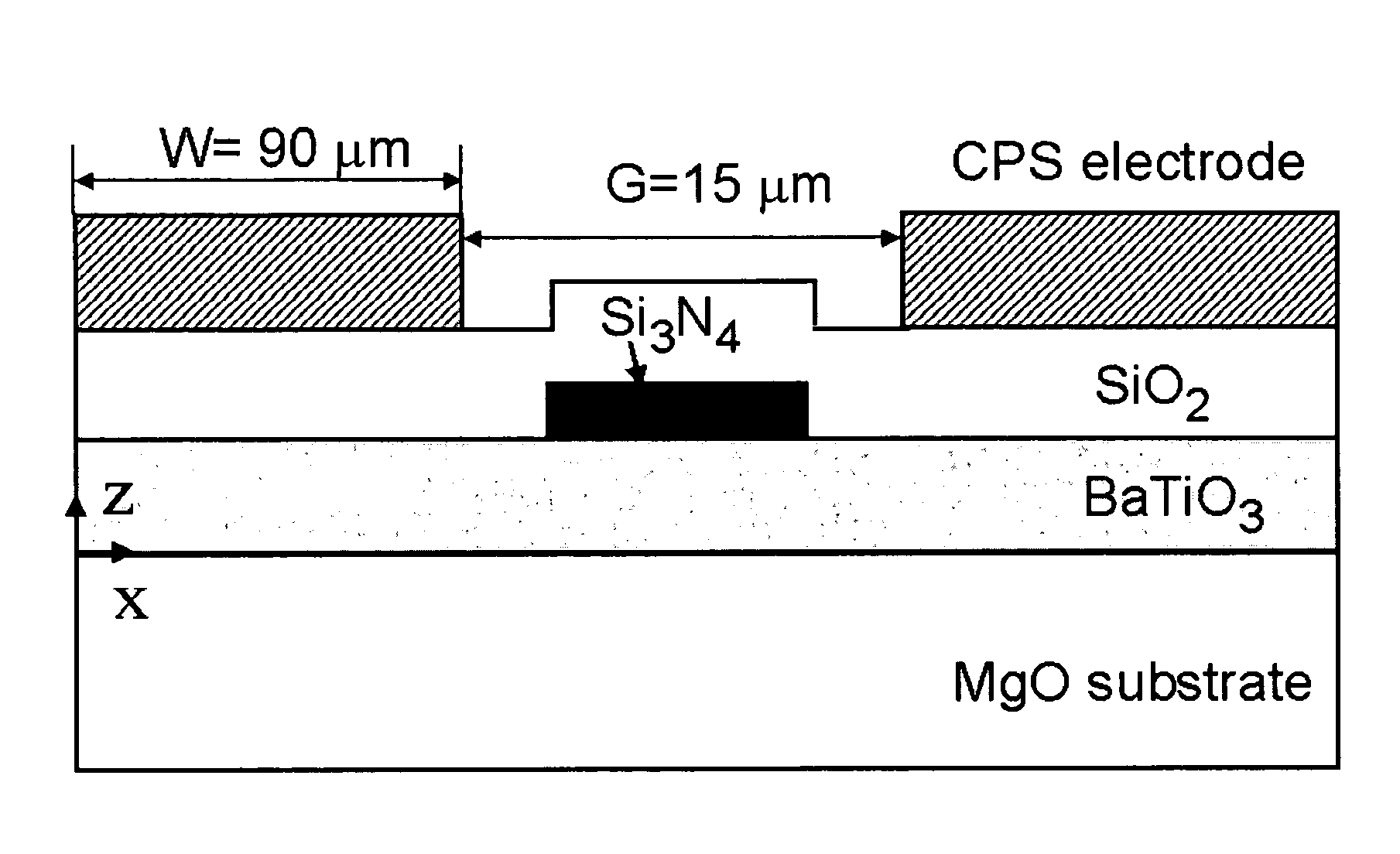
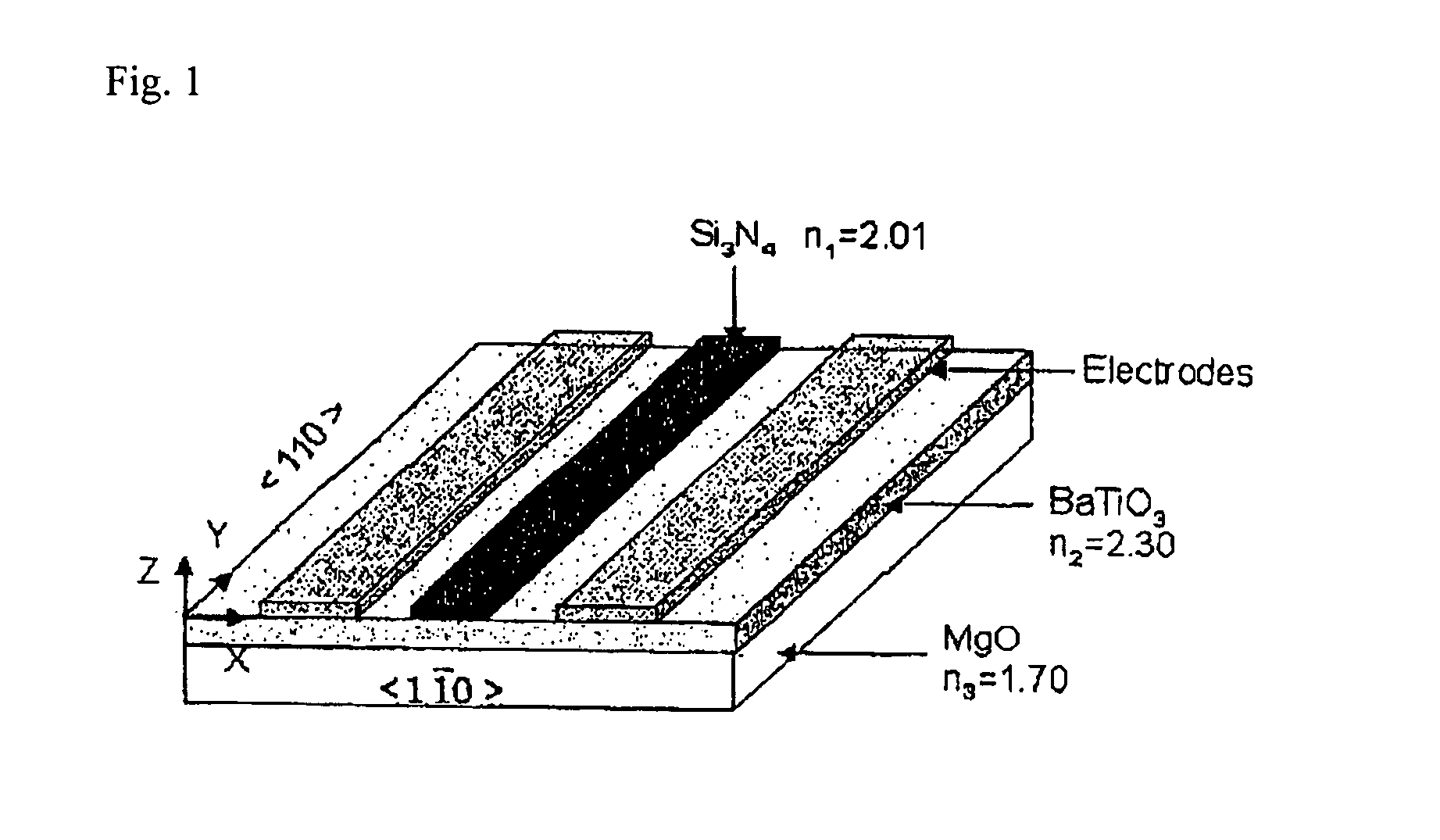
BaTiO3 thin film waveguides and related modulator devices
InactiveUS7224878B1Reduce polarizationReduce the driving voltageNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideElectro-optic modulator
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
High efficiency wavelength converters
InactiveUS7170671B2Efficiently obtainedAvoid surface damageAfter-treatment detailsBy pulling from meltEnergy transferHigh rate
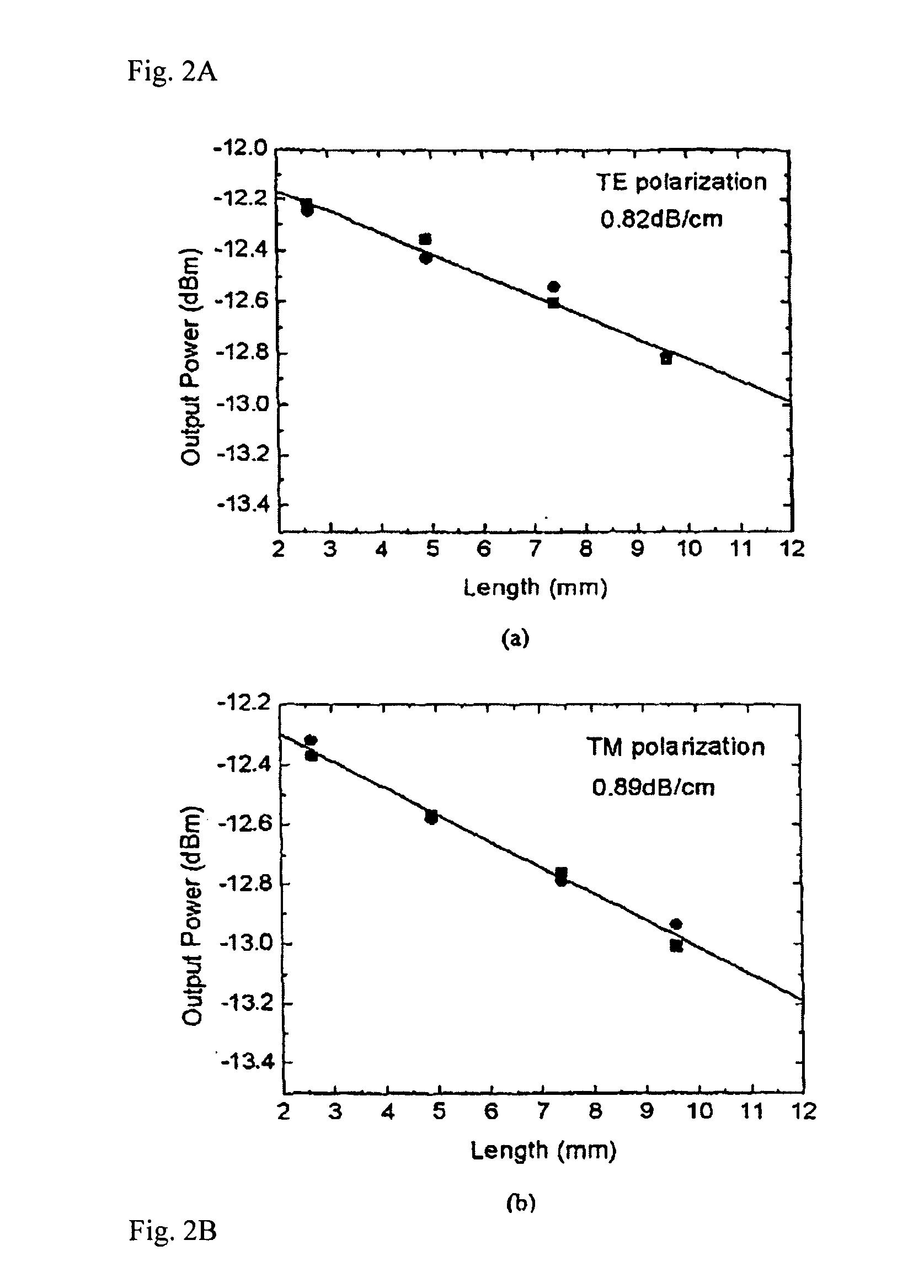
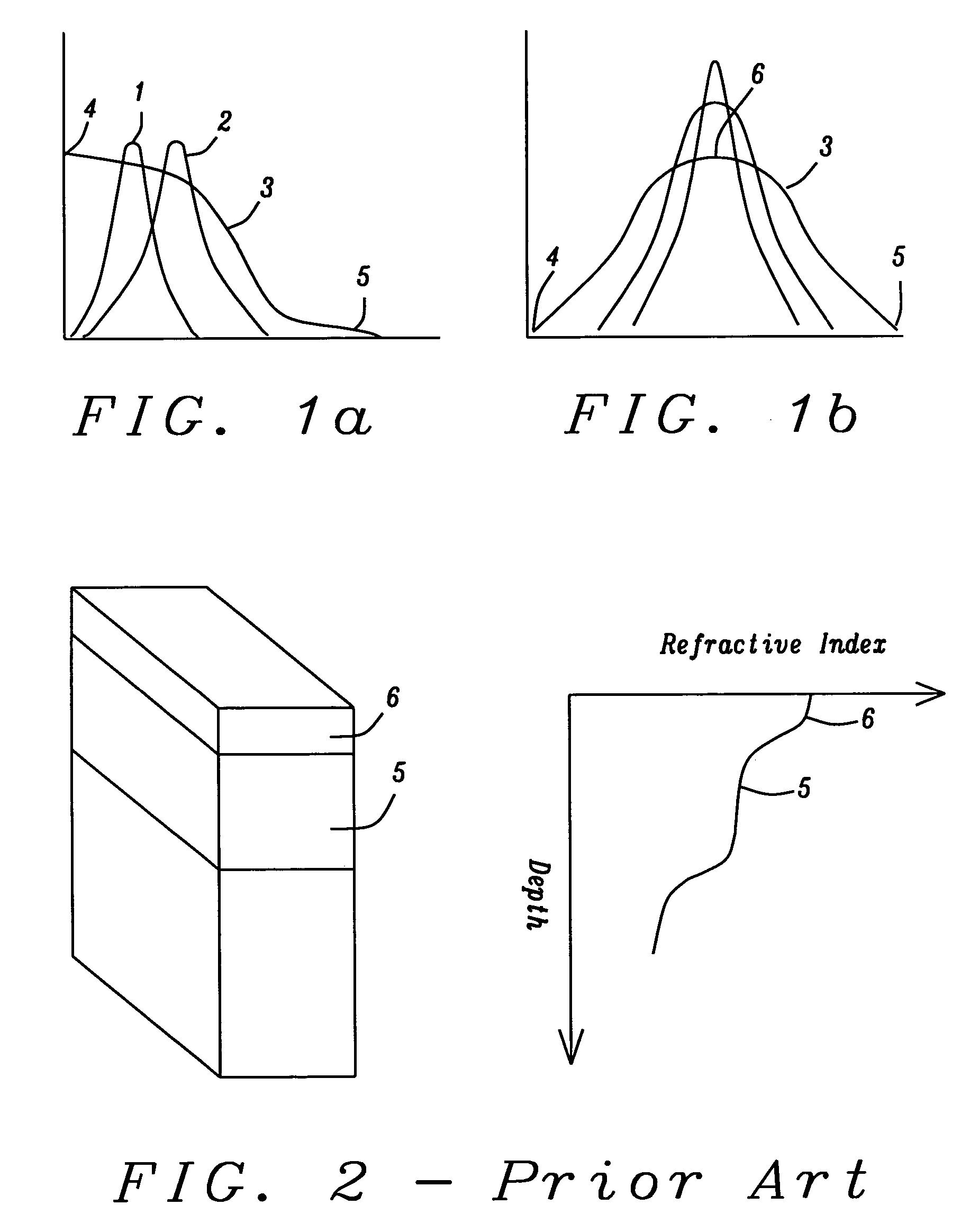
A method is provided for forming a waveguide region within a periodically domain reversed ferroelectric crystal wherein the waveguide region has a refractive index profile that is vertically and horizontally symmetric. The symmetric profile produces effective overlapping between quasi-phasematched waves, a corresponding high rate of energy transfer between the waves and a symmetric cross-section of the radiated wave. The symmetric refractive index profile is produced by a method that combines the use of a diluted proton exchange medium at a high temperature which produces a region of high index relatively deeply beneath the crystal surface, followed by a reversed proton exchange which restores the original crystal index of refraction immediately beneath the crystal surface.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
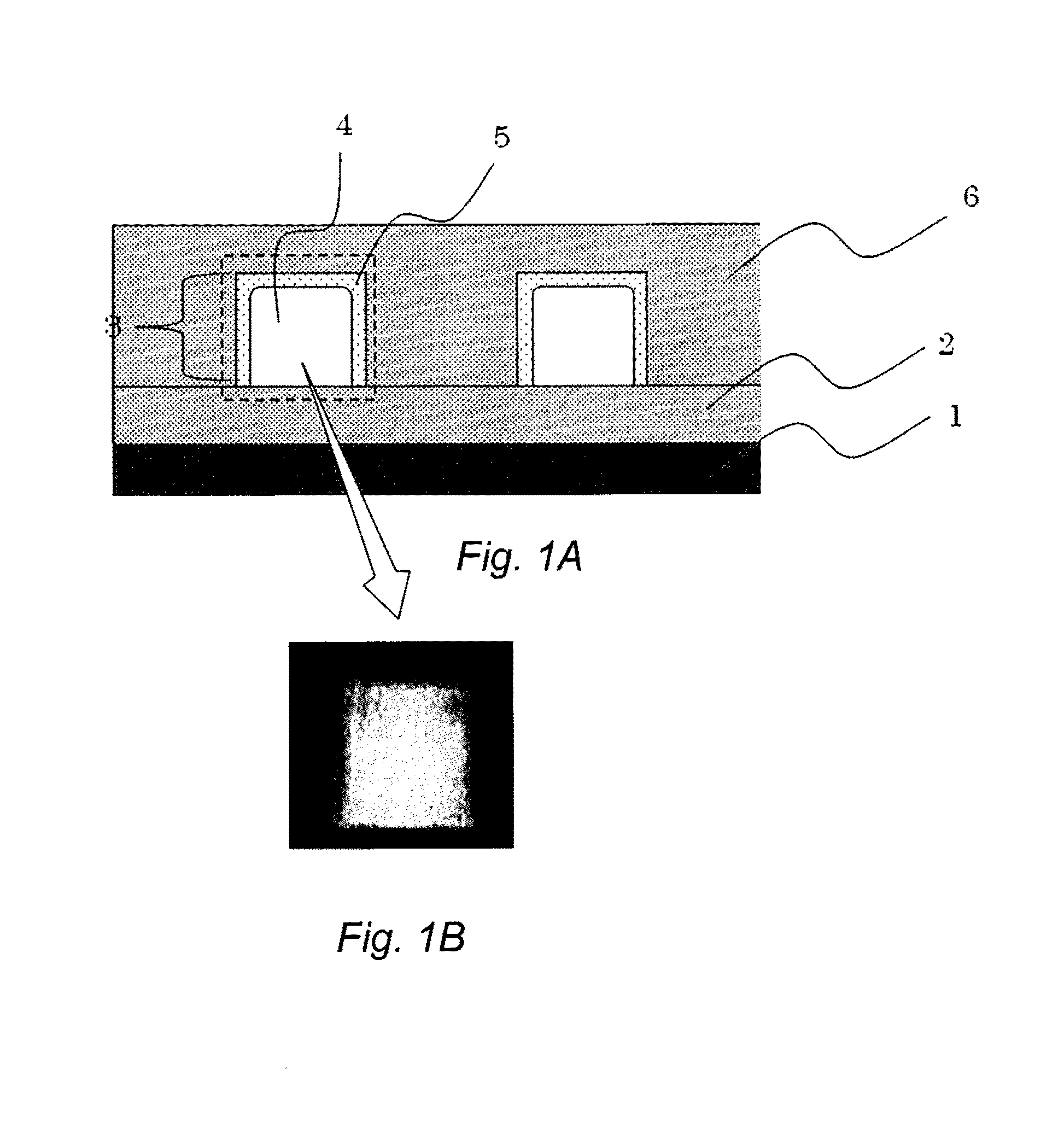
Diamond wafer, method of estimating a diamond wafer and diamond surface acoustic wave device
InactiveUS6210780B1Inexpensive and low-loss insulatorLow costVacuum evaporation coatingScattering properties measurementsThin metalDiamond crystal
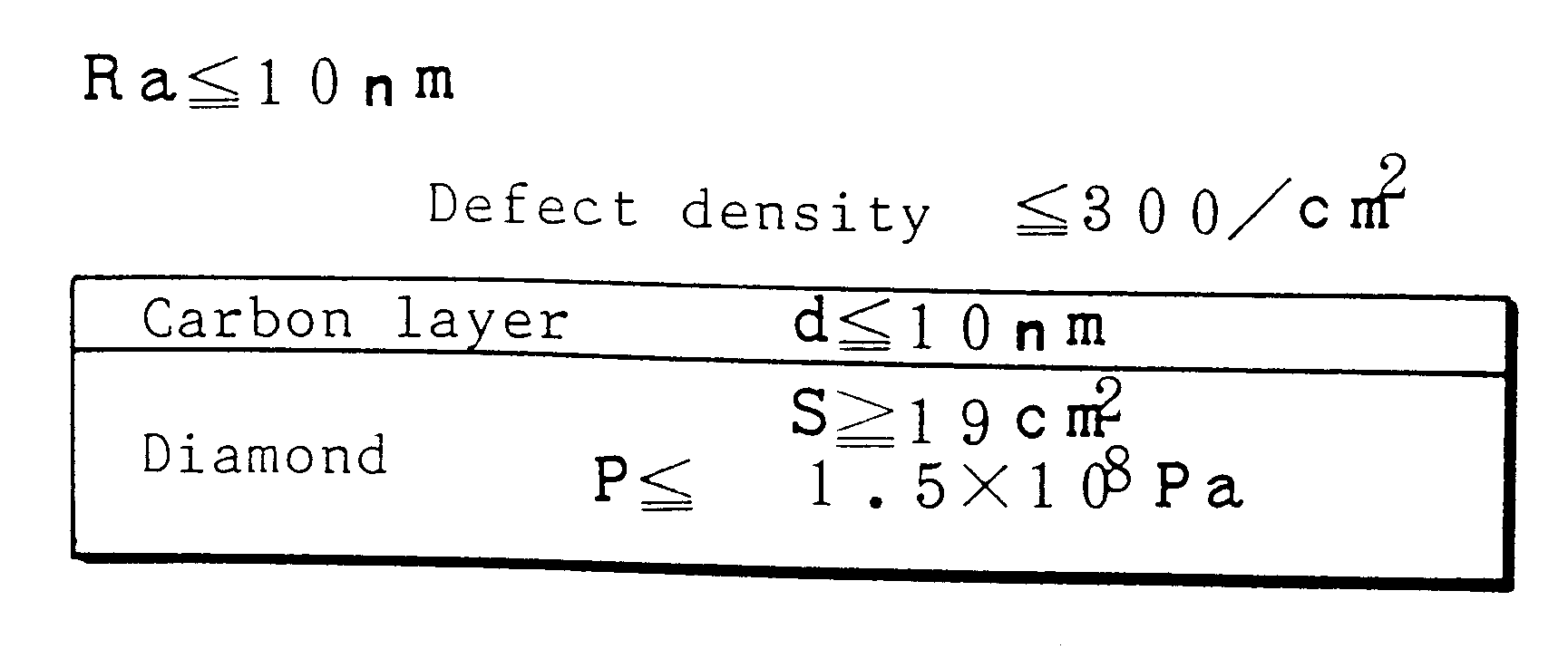
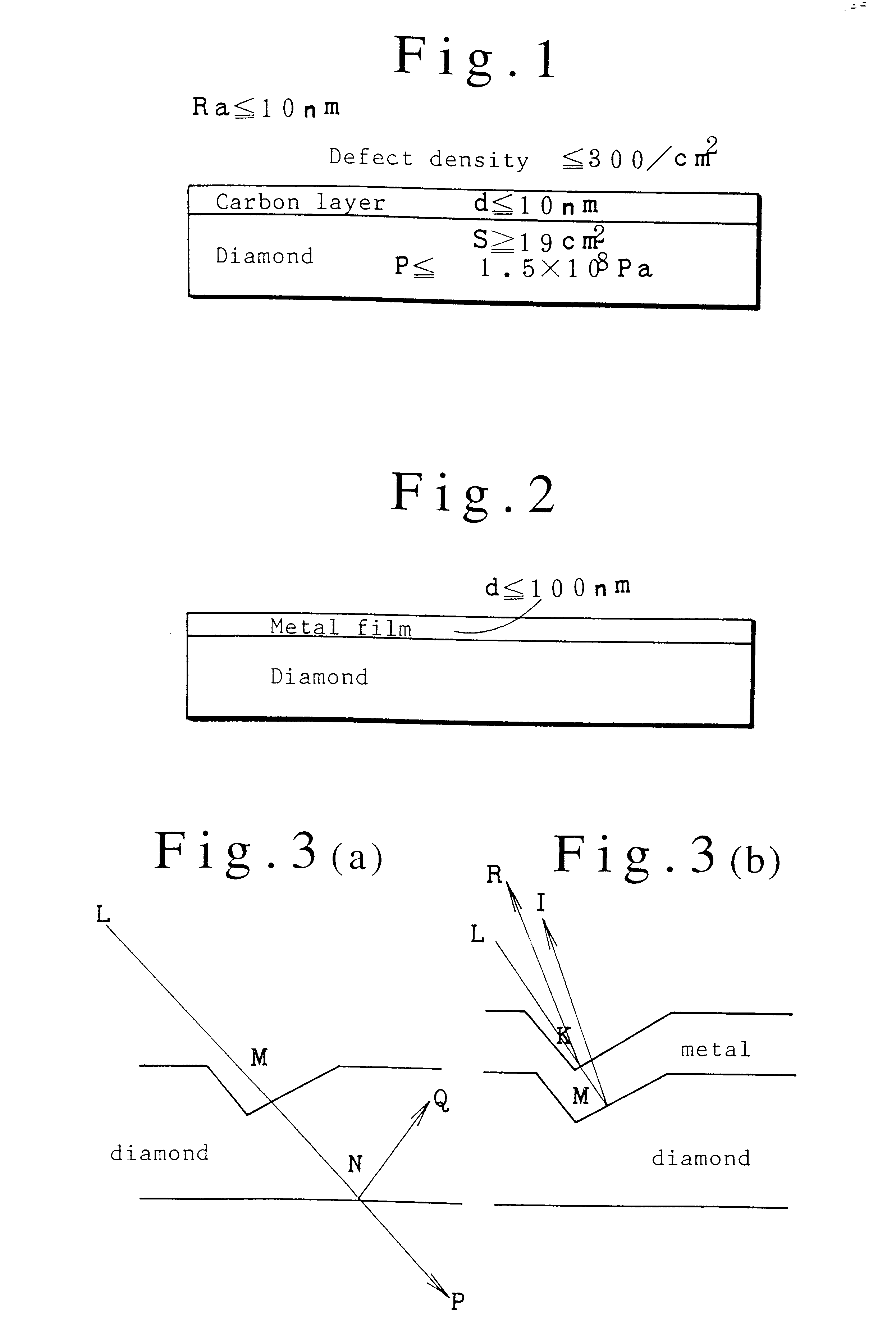
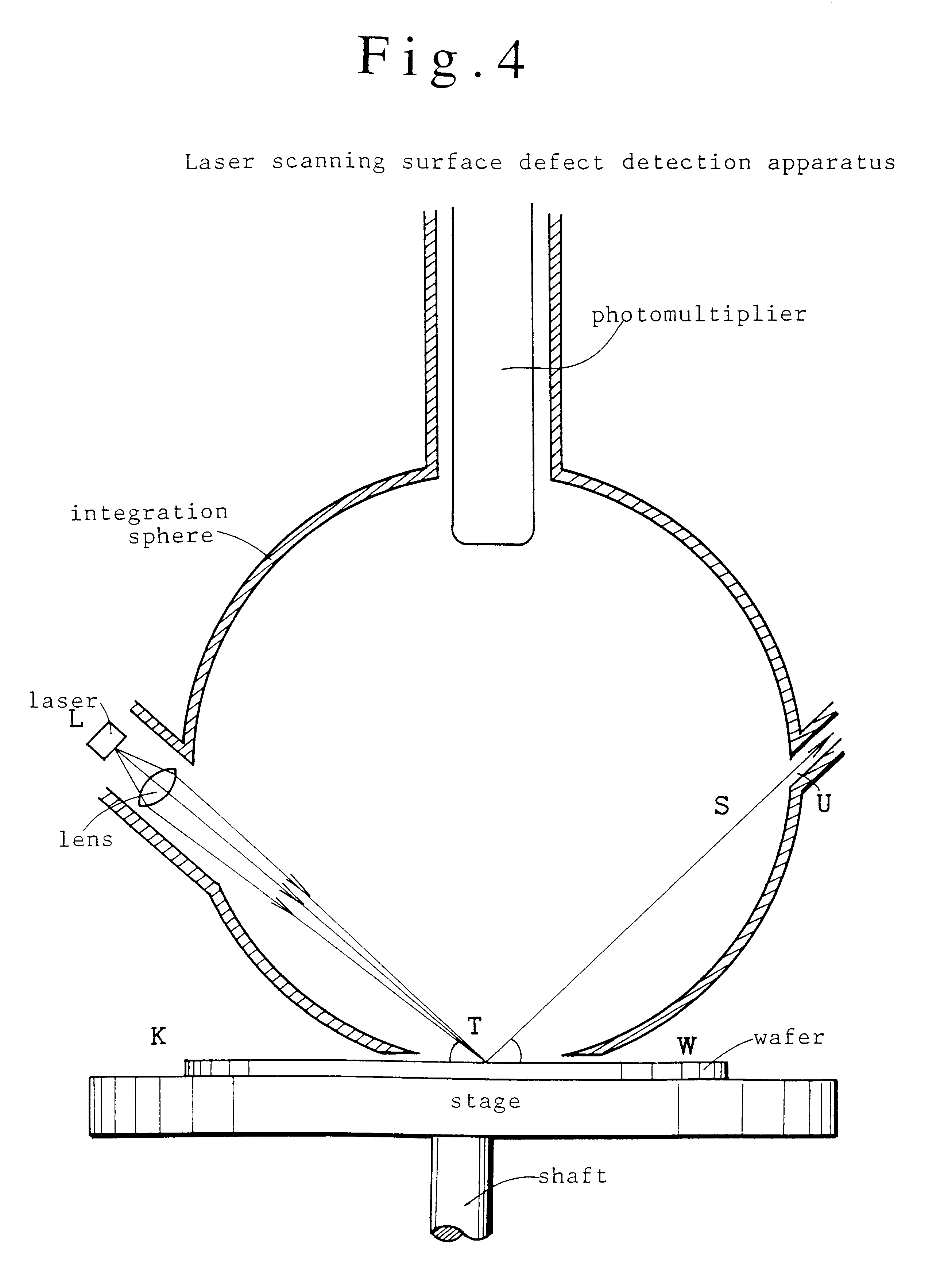
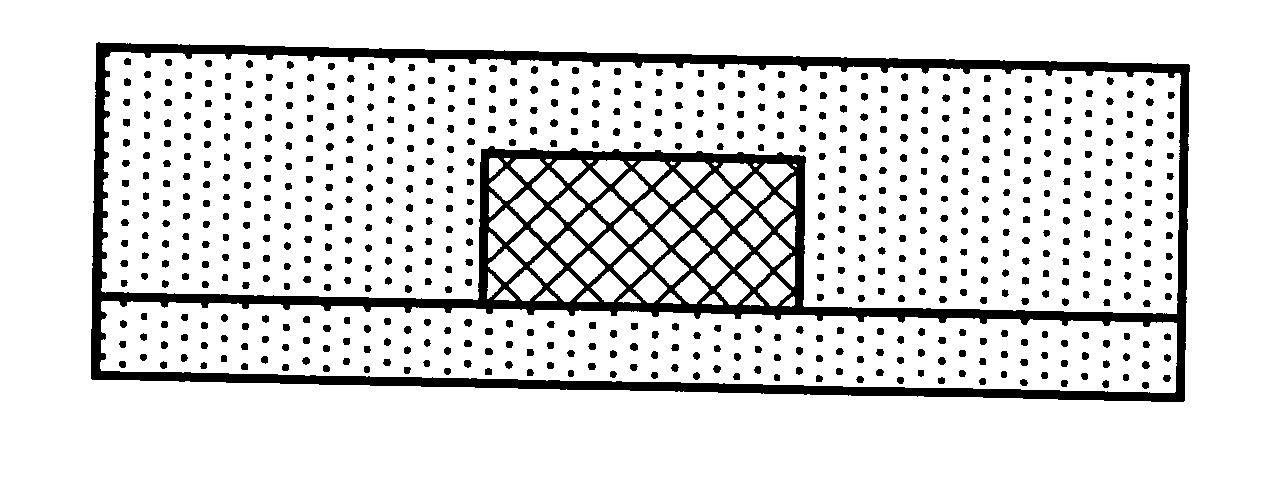
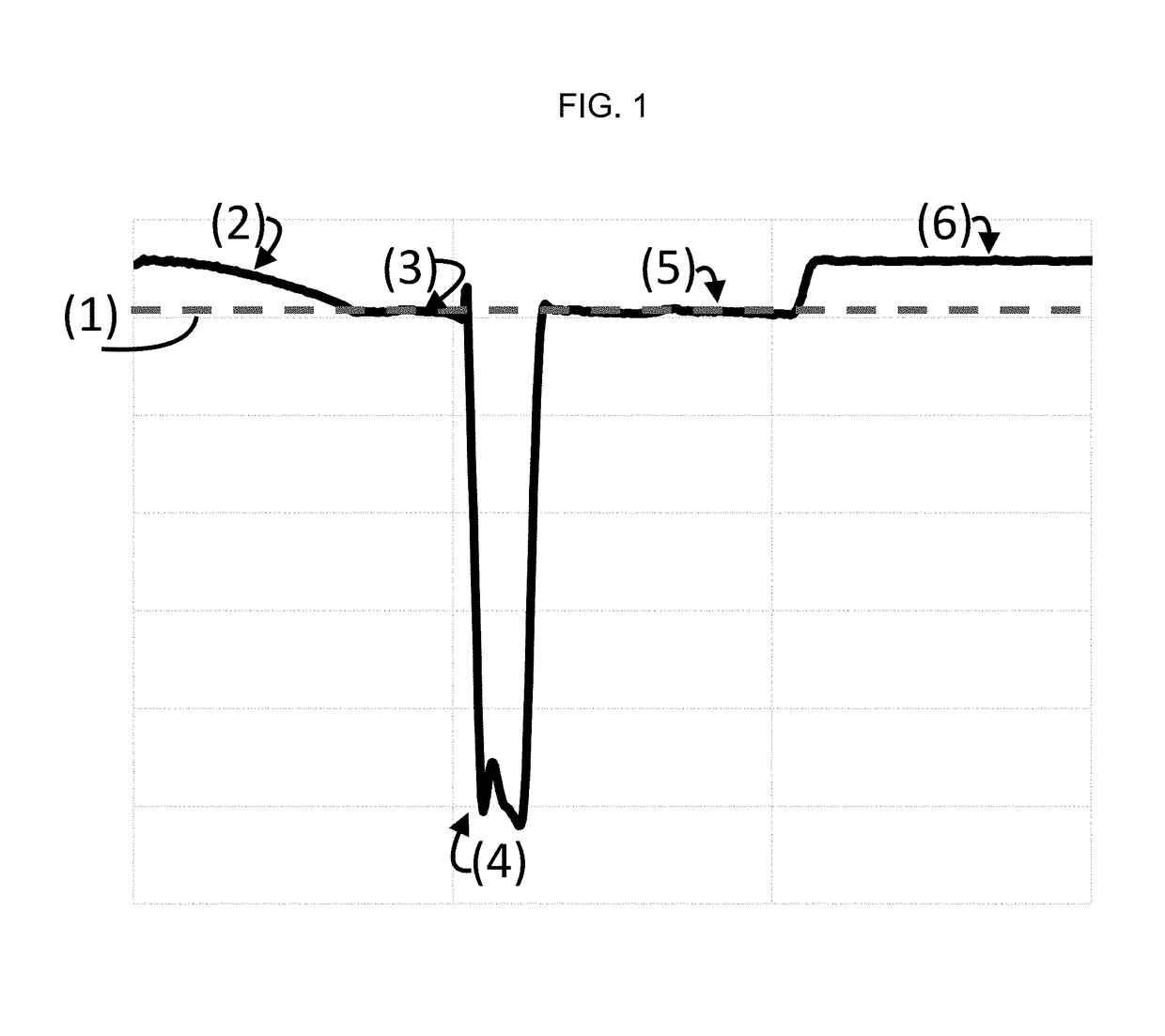
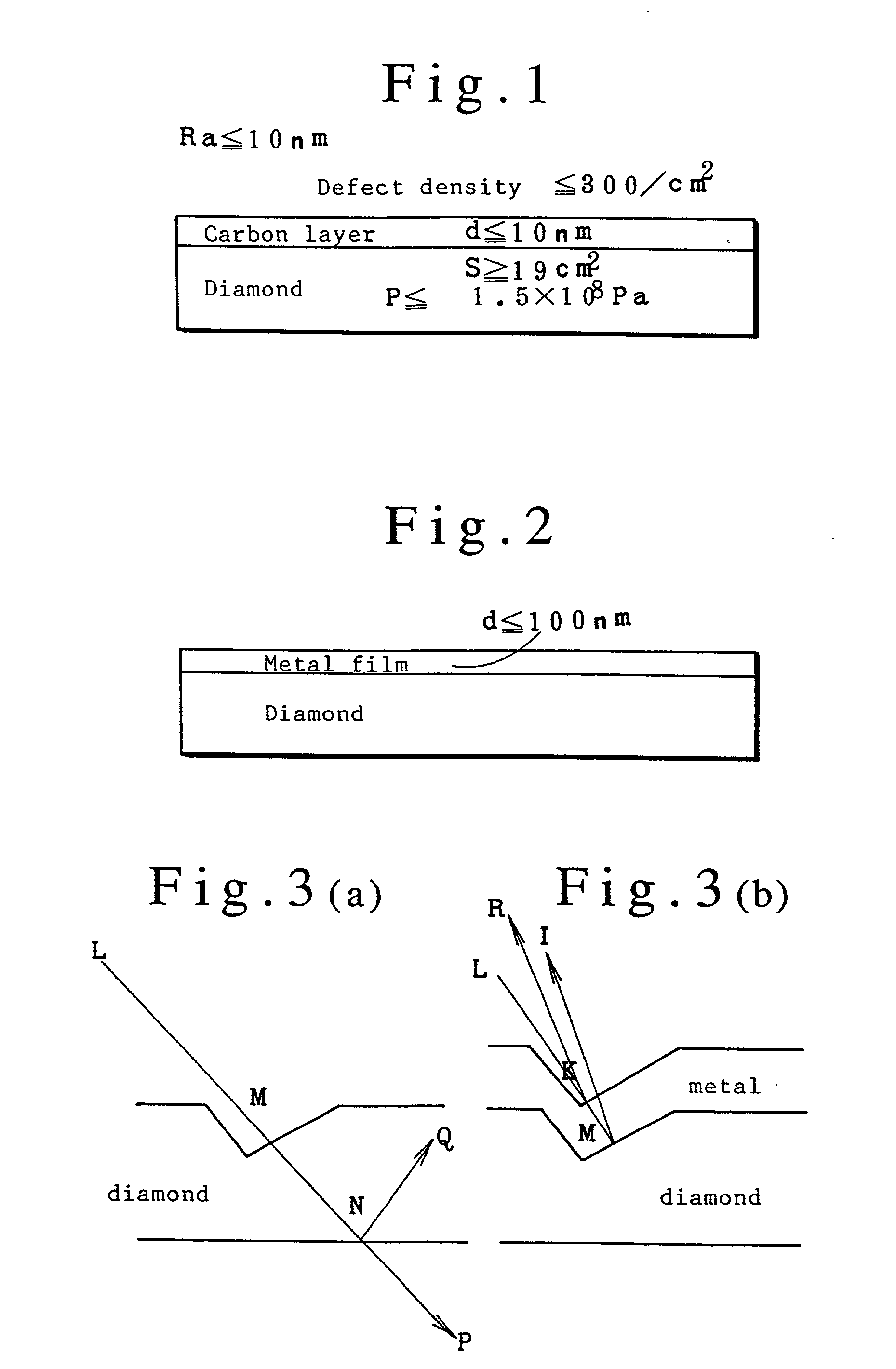
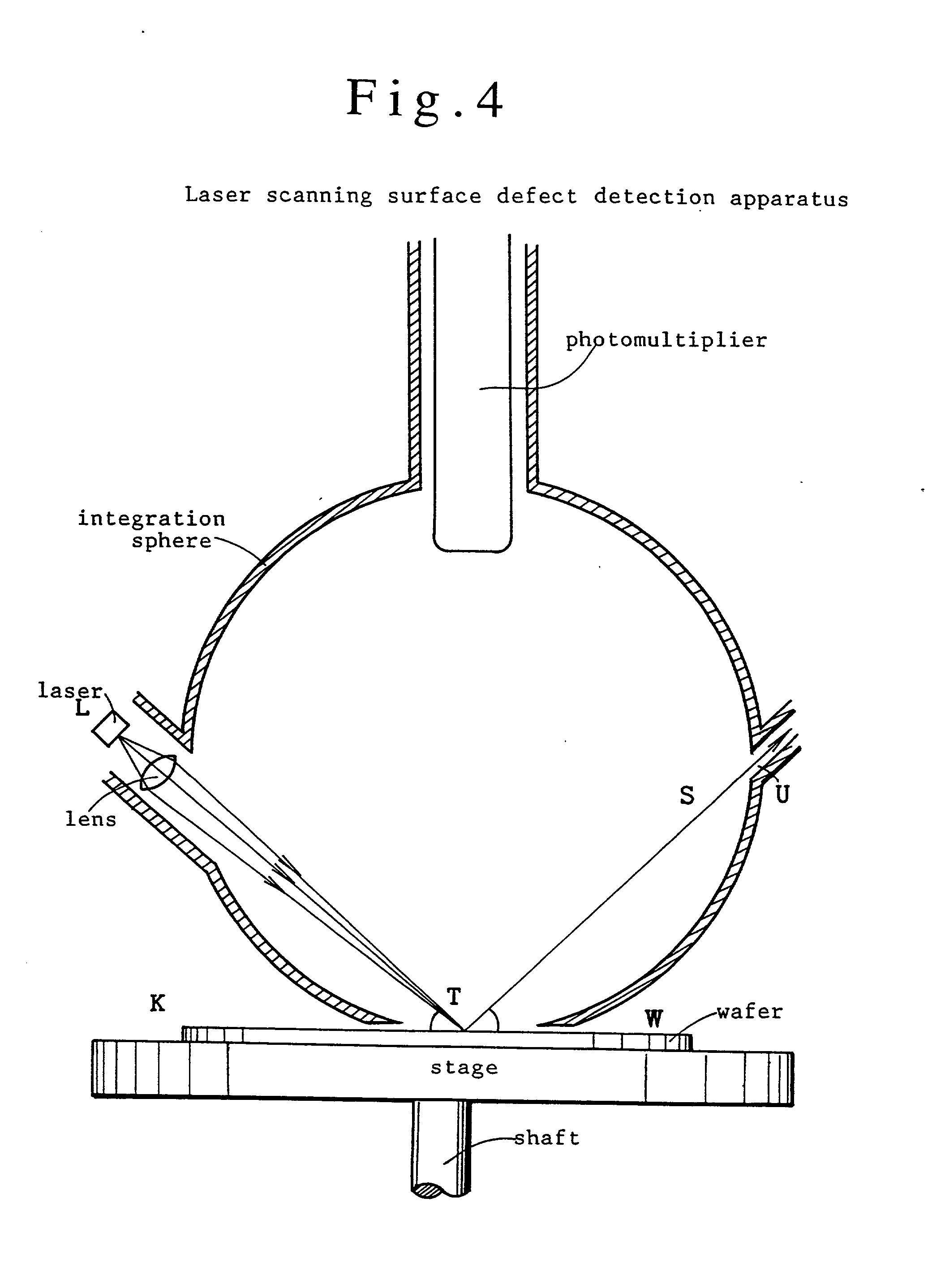
Surfaces of diamond crystals are examined by coating the surfaces with thin metal films, launching laser beams to the diamond surfaces in a slanting angle, detecting defects and particles on the diamond surfaces by the scattering of beams and counting the defects and particles by a laser scanning surface defect detection apparatus. Diamond SAW devices should be made on the diamond films or bulks with the defect density less than 300 particles cm-2. Preferably, the diamond surfaces should have roughness less than Ra20 nm. Diamond SAW filters can be produced by depositing a piezoelectric film and making interdigital transducers on the low-defect density diamond crystals.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
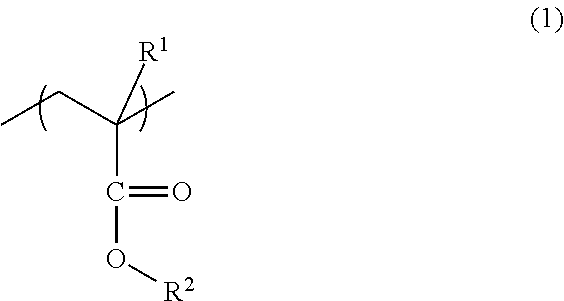
Photosensitive resin composition for forming optical waveguide, optical waveguide, and method for forming optical waveguide pattern
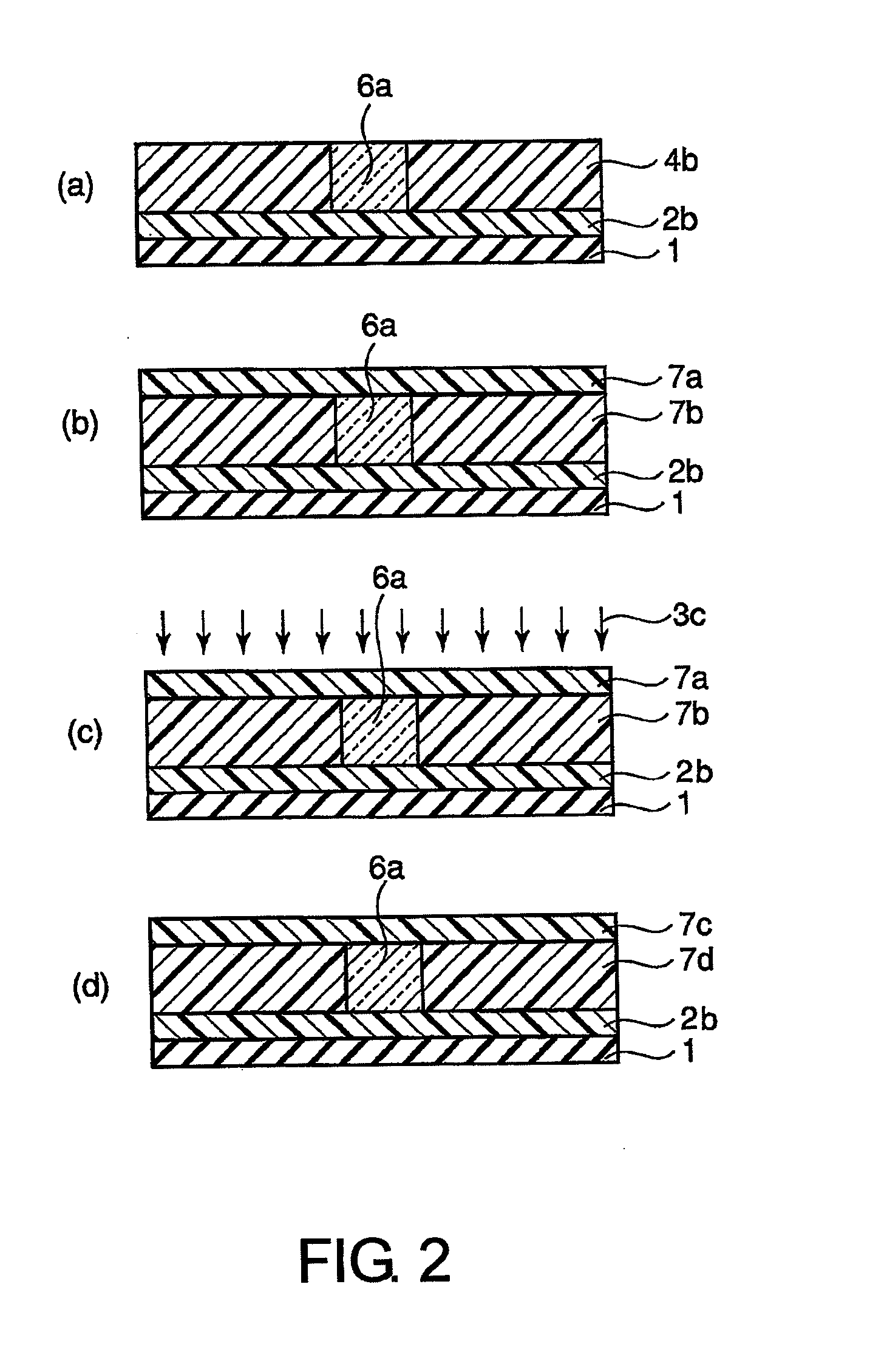
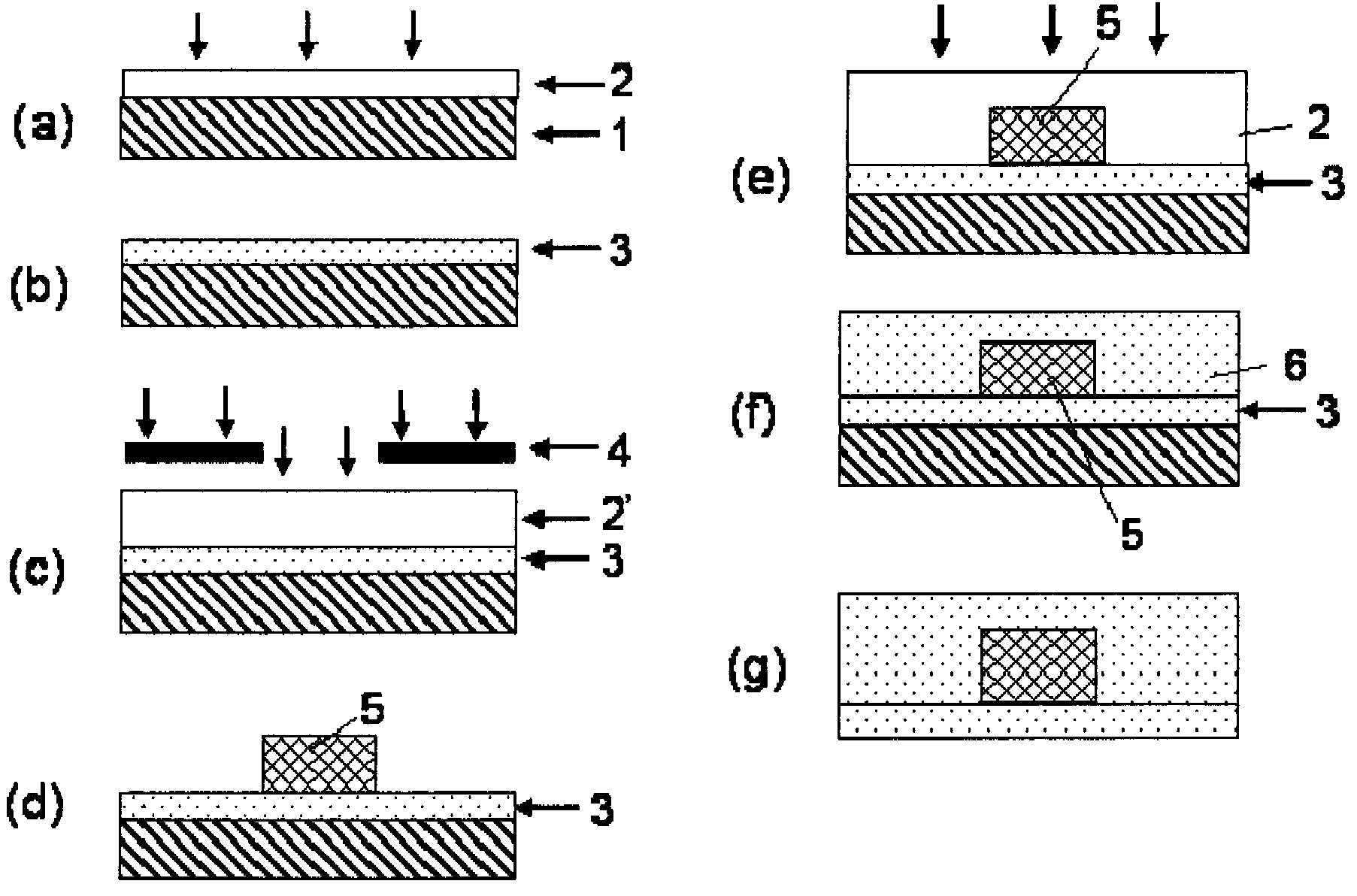
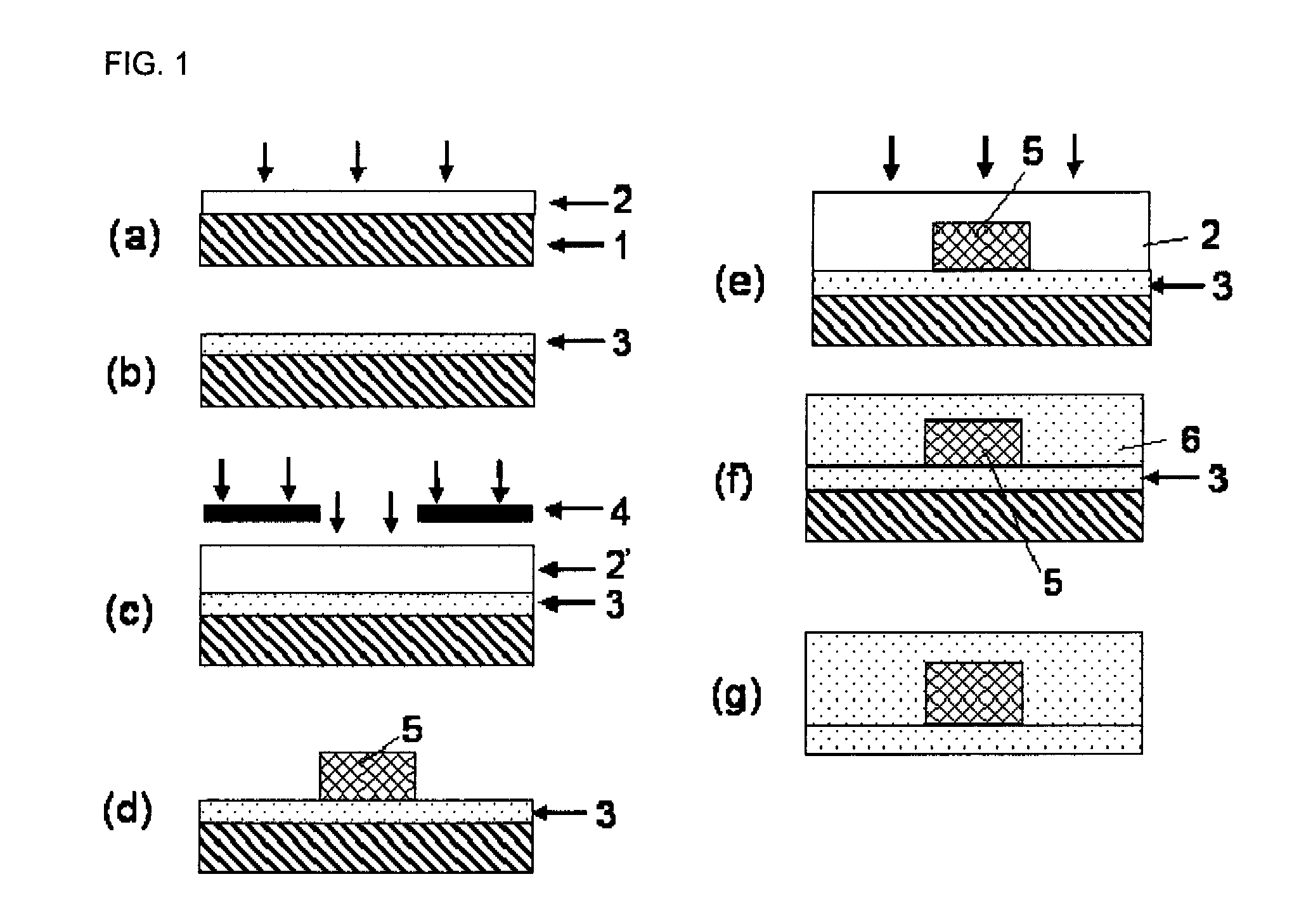
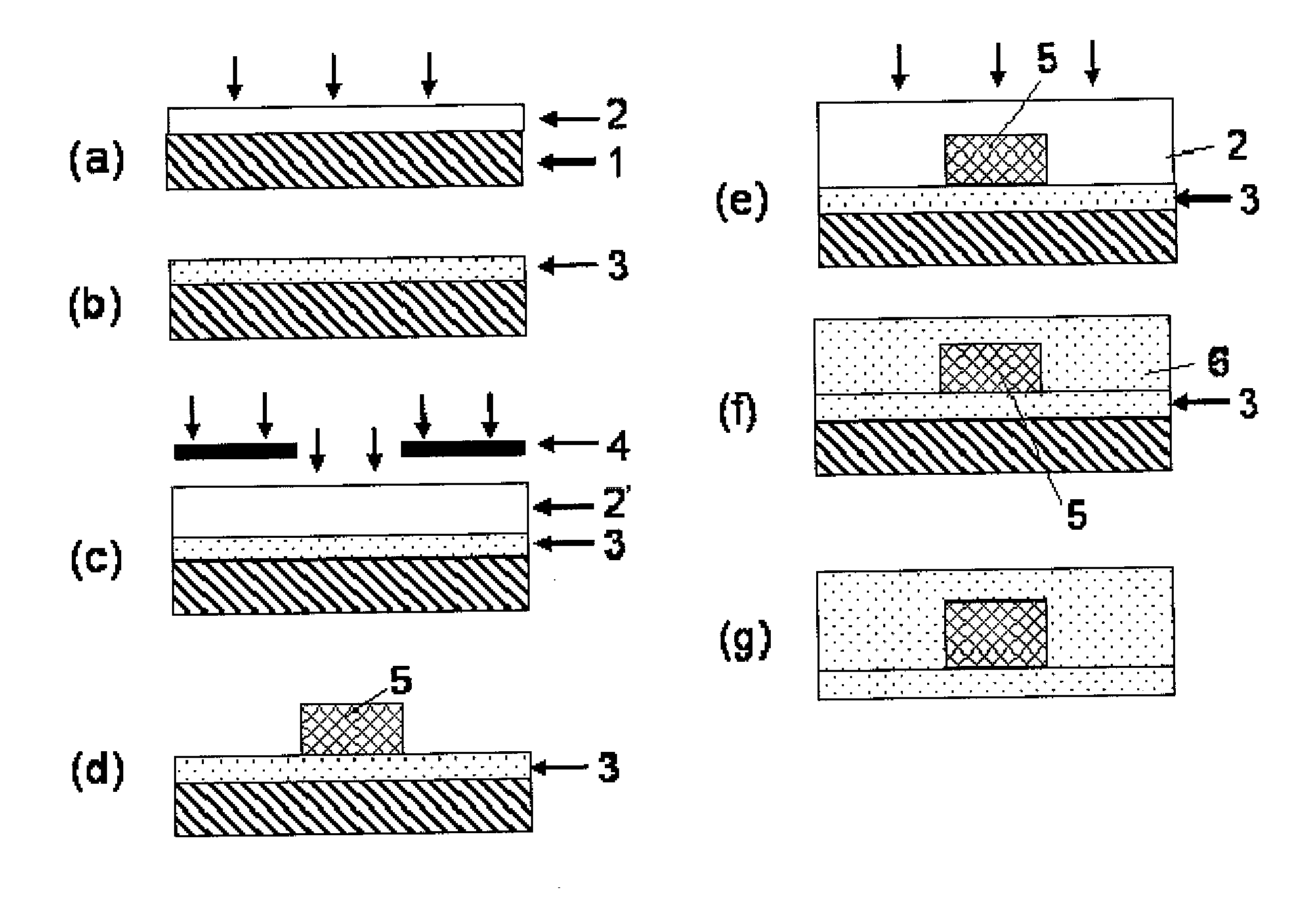
InactiveUS20070041698A1Improve transmission performanceLow propagation lossPhotomechanical apparatusOptical waveguide light guideHydrogen atomHalogen
A photosensitive resin composition for forming an optical waveguide comprises, at least, a polymer comprising at least one repeating structural unit represented by the following general formula (1): wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or methyl group; and R2 to R5 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a photoacid generator. This composition can form an optical waveguide pattern with excellent shape precision and at a low cost, and an optical waveguide of a low propagation loss.
Owner:NEC CORP
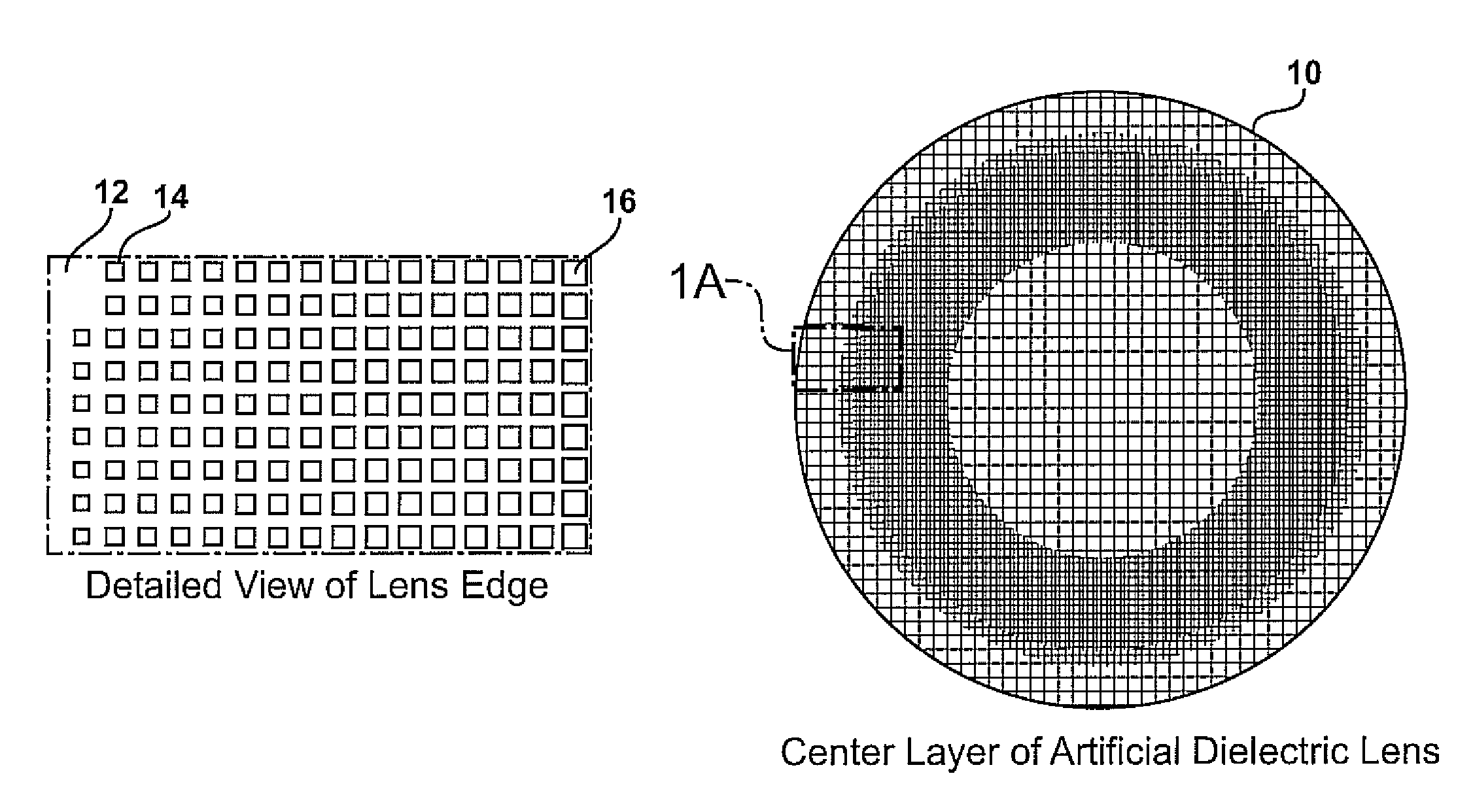
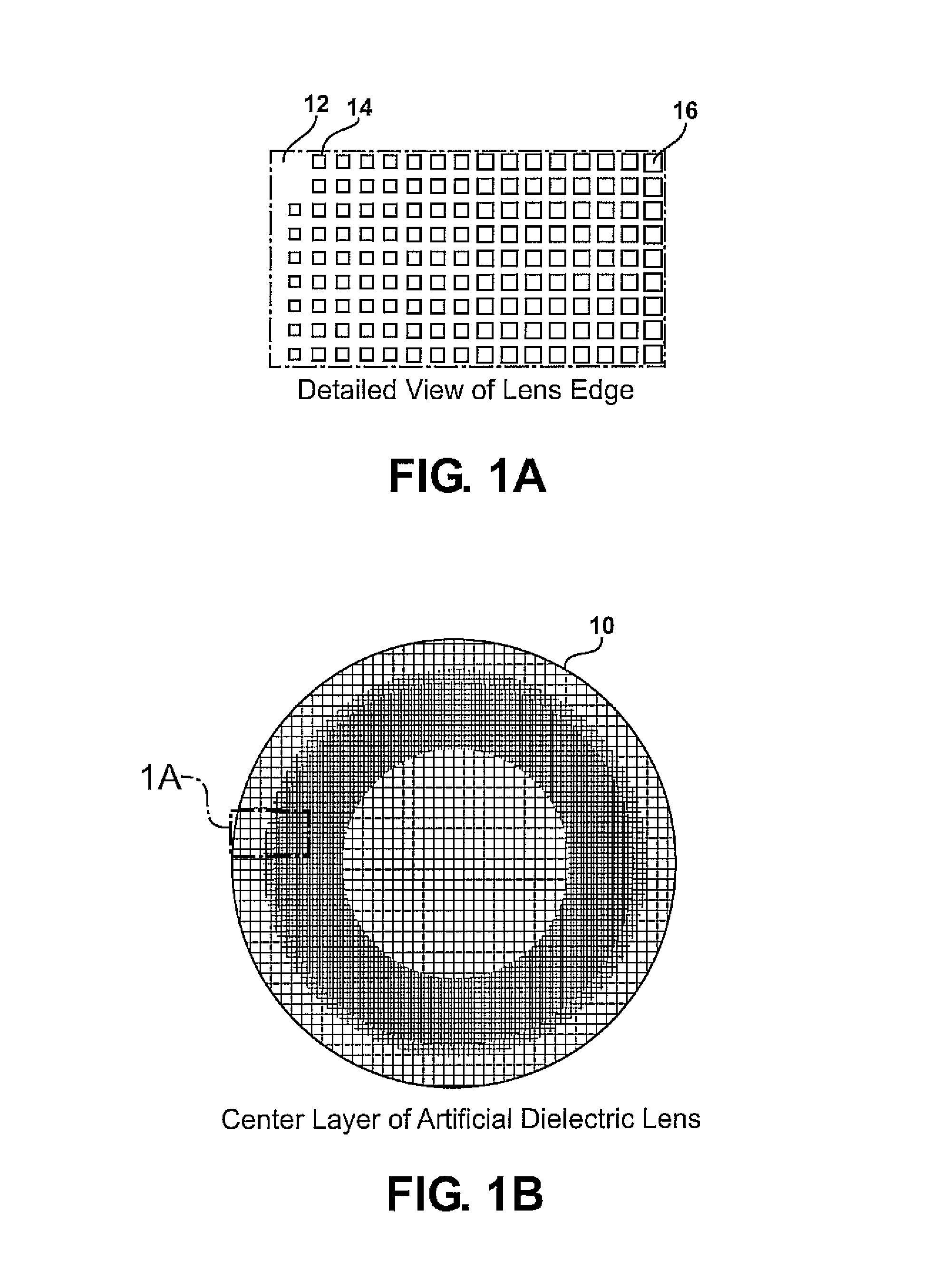
Planar gradient-index artificial dielectric lens and method for manufacture
InactiveUS8803738B2Easy to getLow propagation lossSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateRefractive index
A gradient index lens for electromagnetic radiation includes a dielectric substrate, a plurality of conducting patches supported by the dielectric substrate, the conducting patches preferably being generally square shaped and having an edge length, the edge length of the conducting patches varying with position on the dielectric substrate so as to provide a gradient index for the electromagnetic radiation. Examples include gradient index lenses for millimeter wave radiation, and use with antenna systems.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
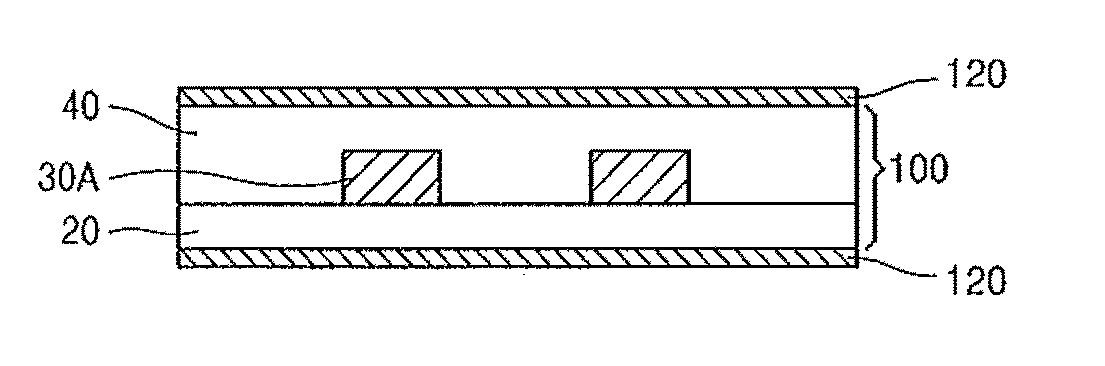
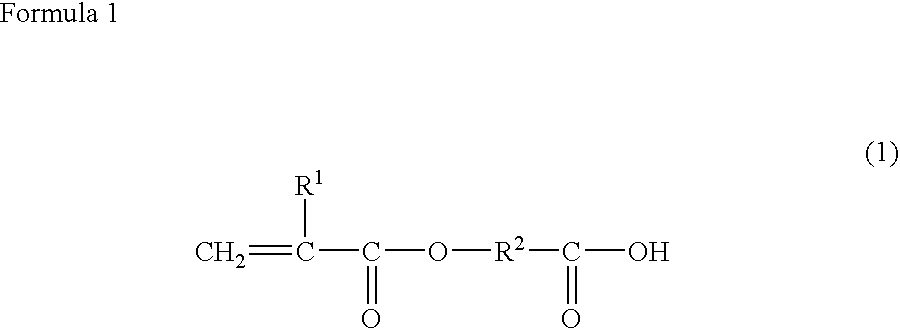
Compound containing crosslinkable moieties, prepolymer, blend and polymer sheet obtained therefrom, and waveguide for optical interconnection
ActiveUS20100172623A1Easy to useLow propagation lossOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHalogenHydrogen
A compound containing a crosslinkable moiety, a curable prepolymer, a blend, and a polymer sheet obtained therefrom, and an optical waveguide for optical interconnection. The compound is represented by the formula below:Ar—Hwherein Ar includes a crosslinkable moiety at one end, a moiety selected from the group consisting of —O—, —S—, —COO—, —CO—, —COS—, —SO2—, and —NH—, and one or two repeating units selected from the group consisting of the following repeating units:wherein A in the repeating unit is carbon or nitrogen, and X is hydrogen or halogen. At least one of the core and the cladding in the optical waveguide includes the polymer sheet.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multi-clad Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20190025502A1Low propagation lossHigh beam qualityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantHigh numerical aperture
A multi-clad optical fiber design is described in order to provide low optical loss, a high numerical aperture (NA), and high optical gain for the fundamental propagating mode, the linearly polarized (LP) 01 mode in the UV and visible portion of the optical spectrum. The optical fiber design may contain dopants in order to simultaneously increase the optical gain in the core region while avoiding additional losses during the fiber fabrication process. The optical fiber design may incorporate rare-earth dopants for efficient lasing. Additionally, the modal characteristics of the propagating modes in the optical core promote highly efficient nonlinear mixing, providing for a high beam quality (M2<1.5) output of the emitted light.
Owner:NUBURU INC
Diamond wafer, method of estimating a diamond wafer and diamond surface acoustic wave device
InactiveUS20010044029A1Inexpensive and low-loss insulatorLow costPolycrystalline material growthImpedence networksThin metalDiamond crystal
Surfaces of diamond crystals are examined by coating the surfaces with thin metal films, launching laser beams to the diamond surfaces in a slanting angle, detecting defects and particles on the diamond surfaces by the scattering of beams and counting the defects and particles by a laser scanning surface defect detection apparatus. Diamond SAW devices should be made on the diamond films or bulks with the defect density less than 300 particles cm-2. Preferably, the diamond surfaces should have roughness less than Ra20 nm. Diamond SAW filters can be produced by depositing a piezoelectric film and making interdigital transducers on the low-defect density diamond crystals.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
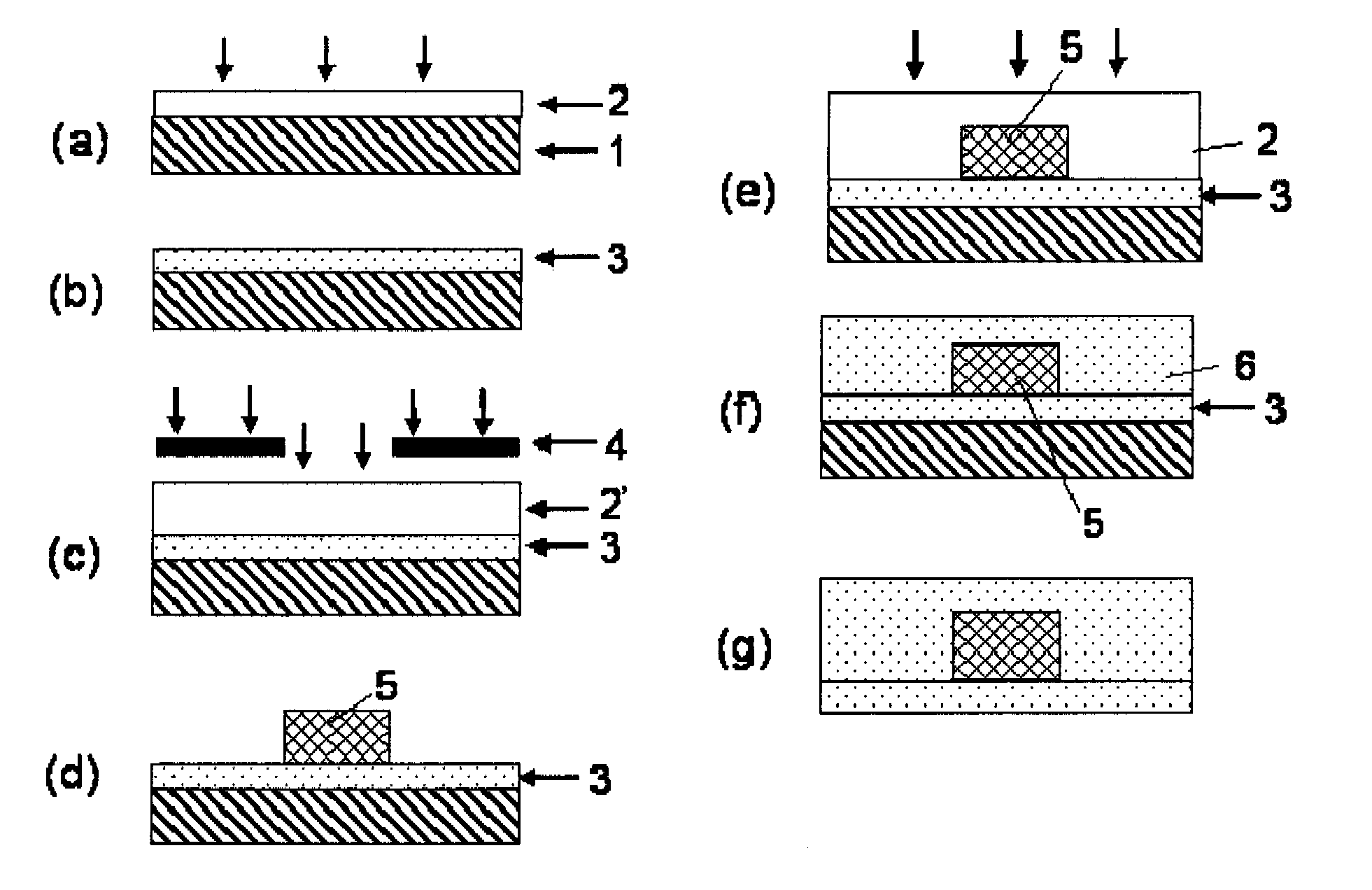
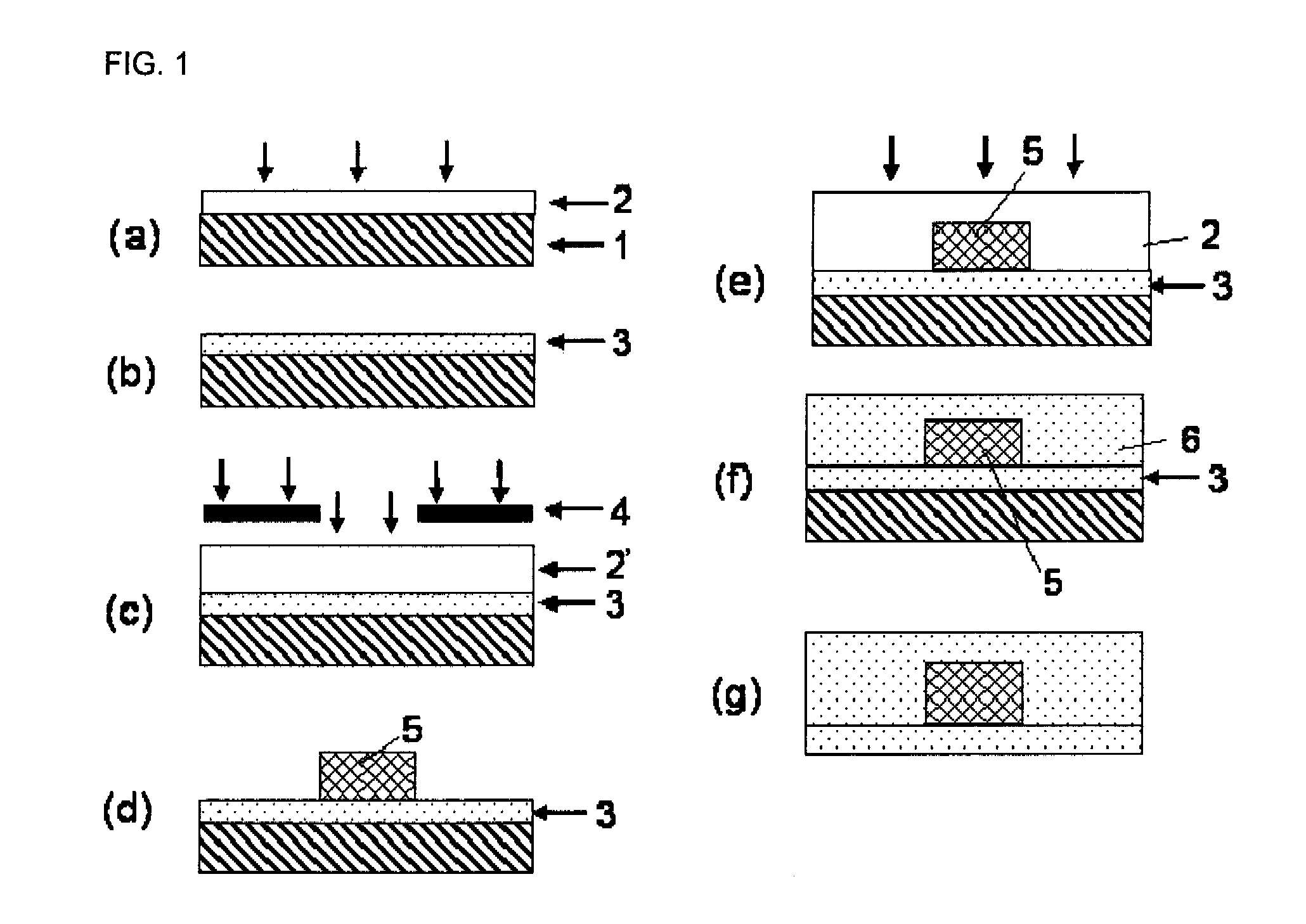
Optical deflection element and method of producing the same
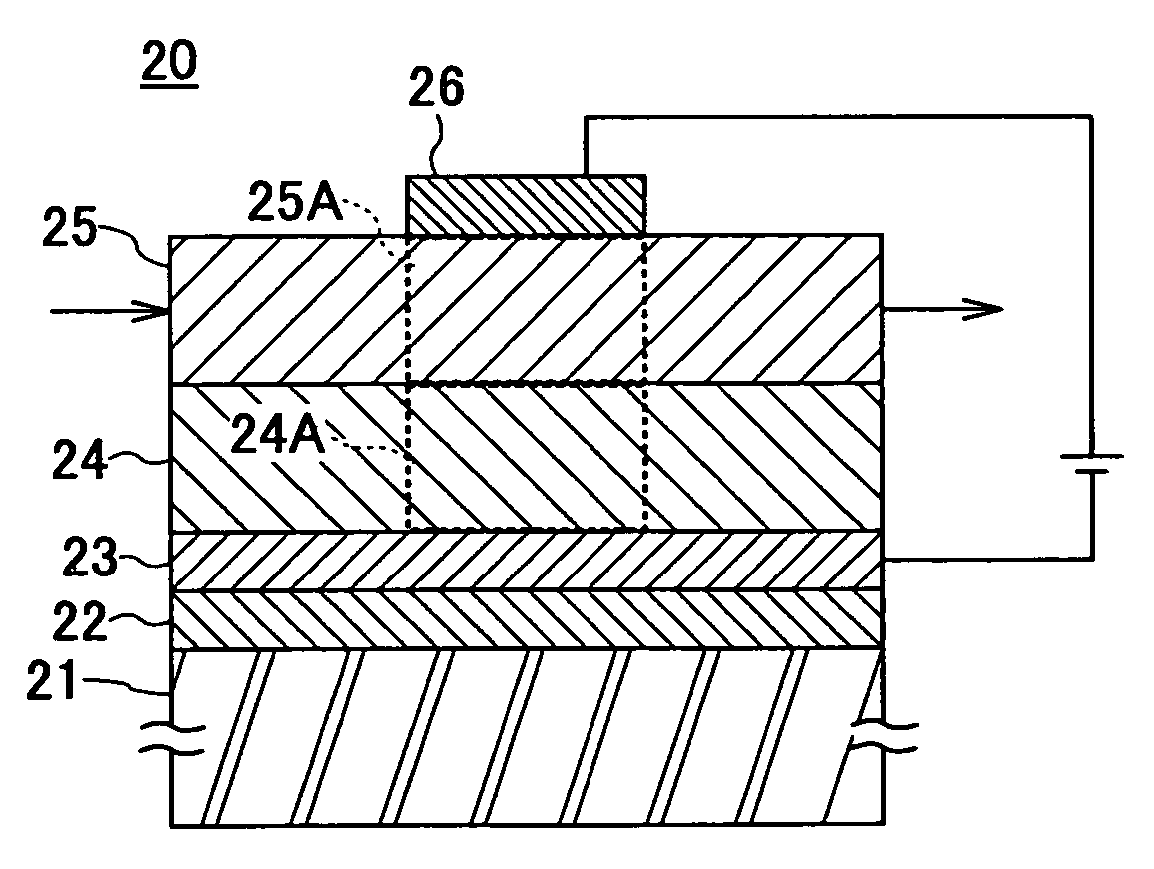
InactiveUS20050162595A1High crystallinityLow propagation lossNon-linear opticsSpinelRefractive index
A disclosed optical deflection element includes a magnesia spinel film 22, a lower electrode 23, a lower cladding layer 24, a core layer 25, and an upper cladding layer 26, which are sequentially stacked formed on a silicon single crystal substrate 21. The magnesia spinel film 22, the lower electrode 23, a PLZT film acting as the lower cladding layer 24, and a PZT film acting as the core layer 25 are epitaxially grown on respective underlying layers thereof. Because of a voltage applied between the lower electrode 23 and the upper electrode 26, refractive index variable regions 25A, 24A, in which the refractive index varies, are formed due to the electro-optical effect. Light incident into the core layer 25 is deflected at the interface between the core layer 25 and the refractive index variable regions 25A, 24A to the inner side relative to the surface of the core layer 25.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
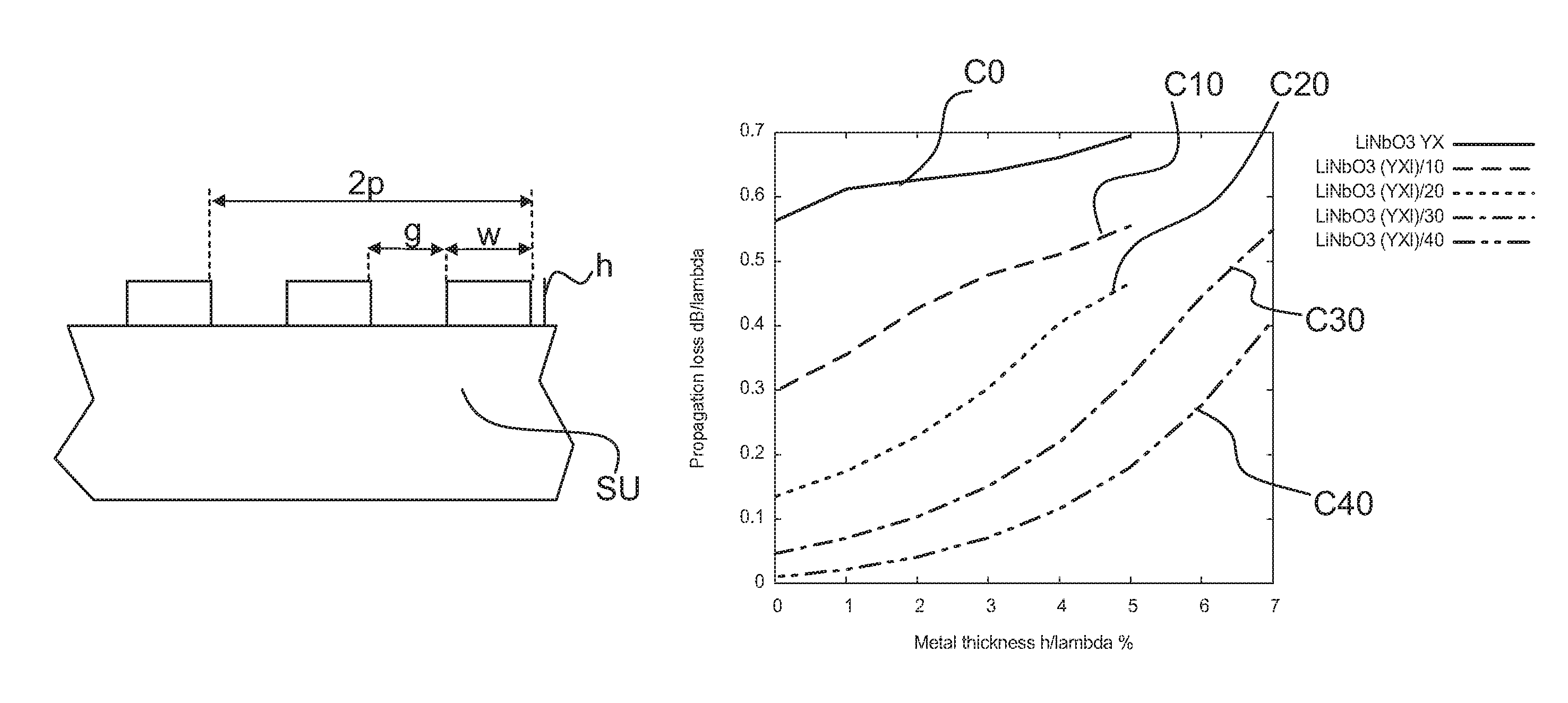
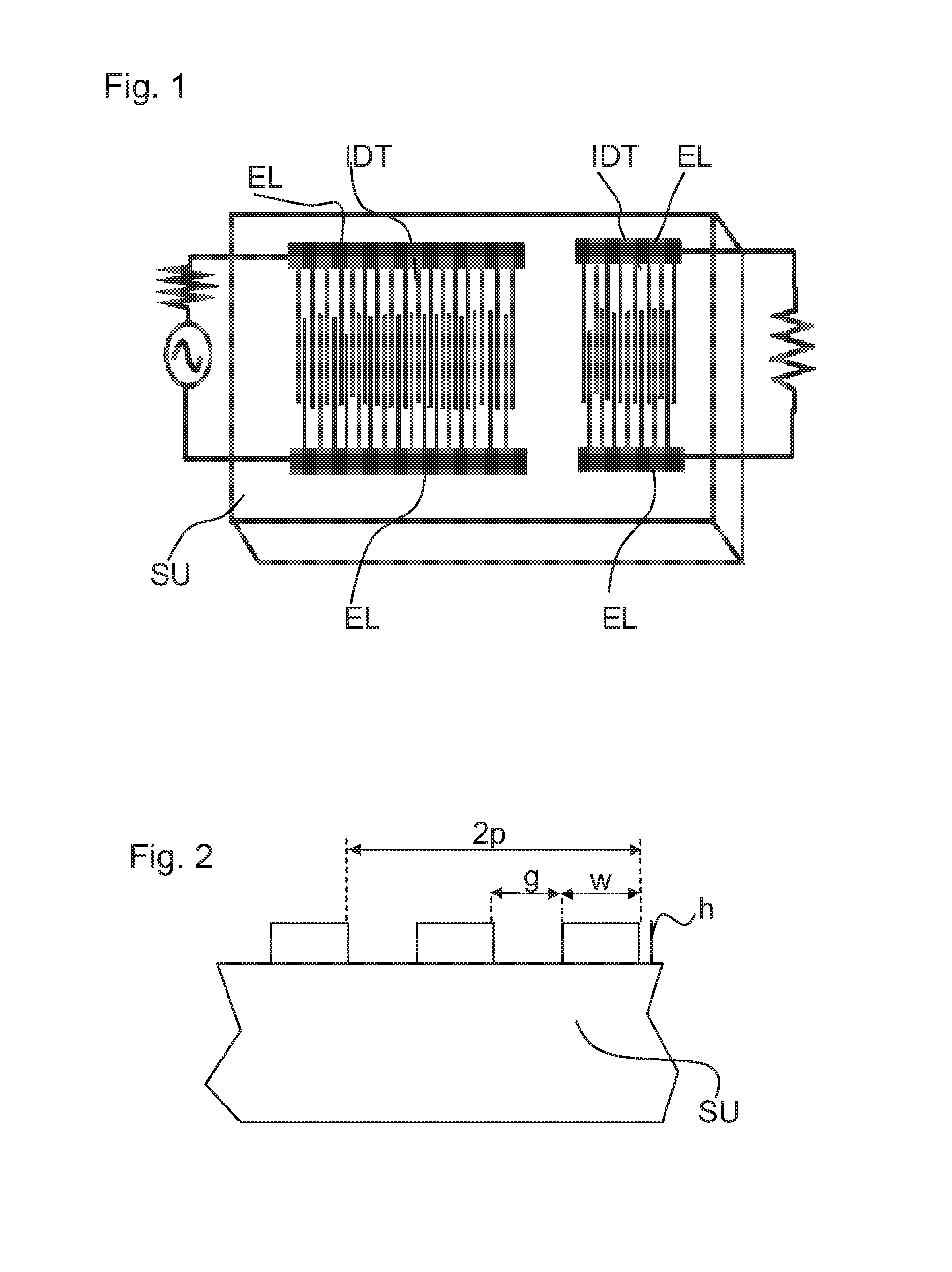
Surface Acoustic Wave Filter
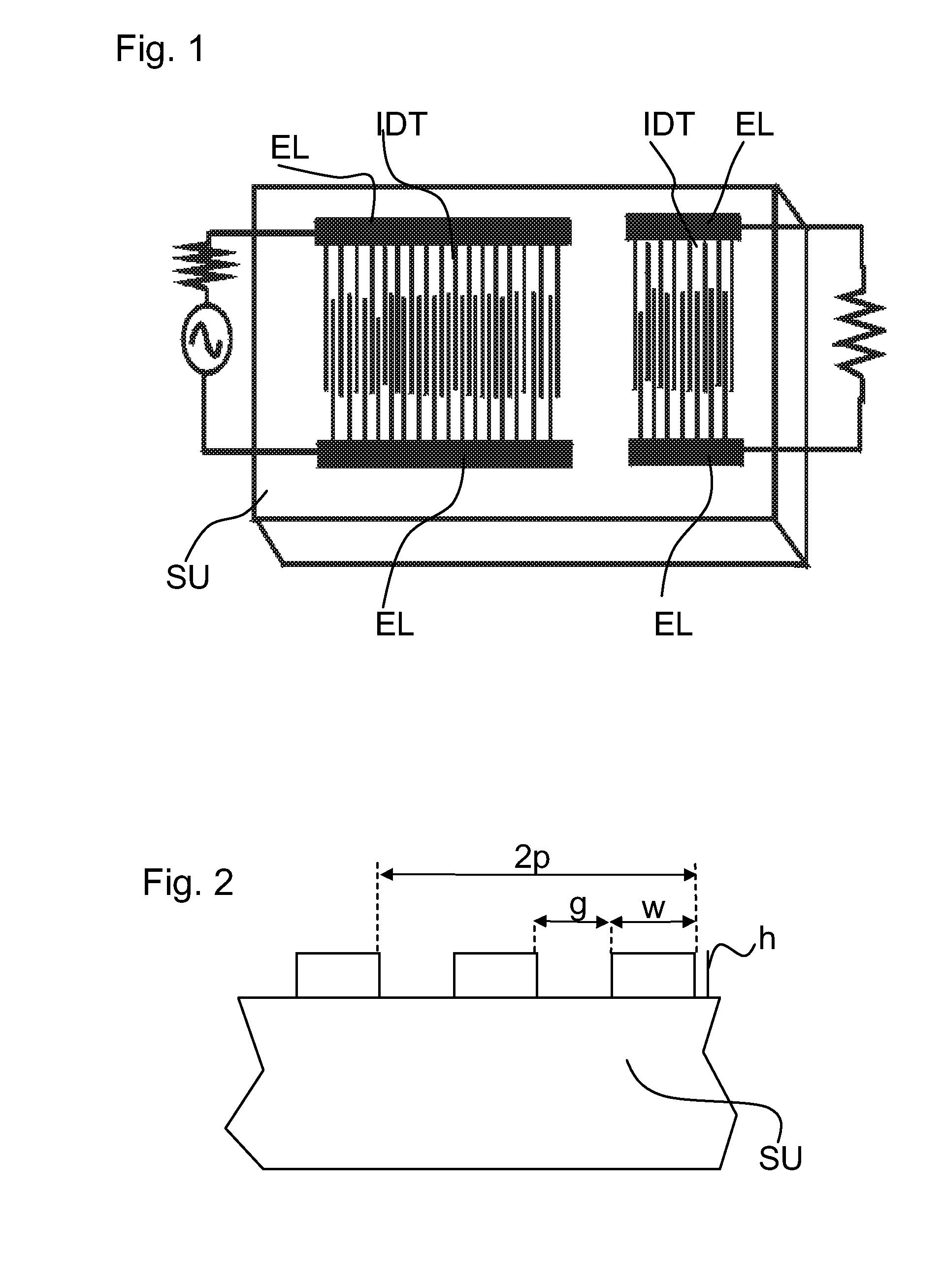
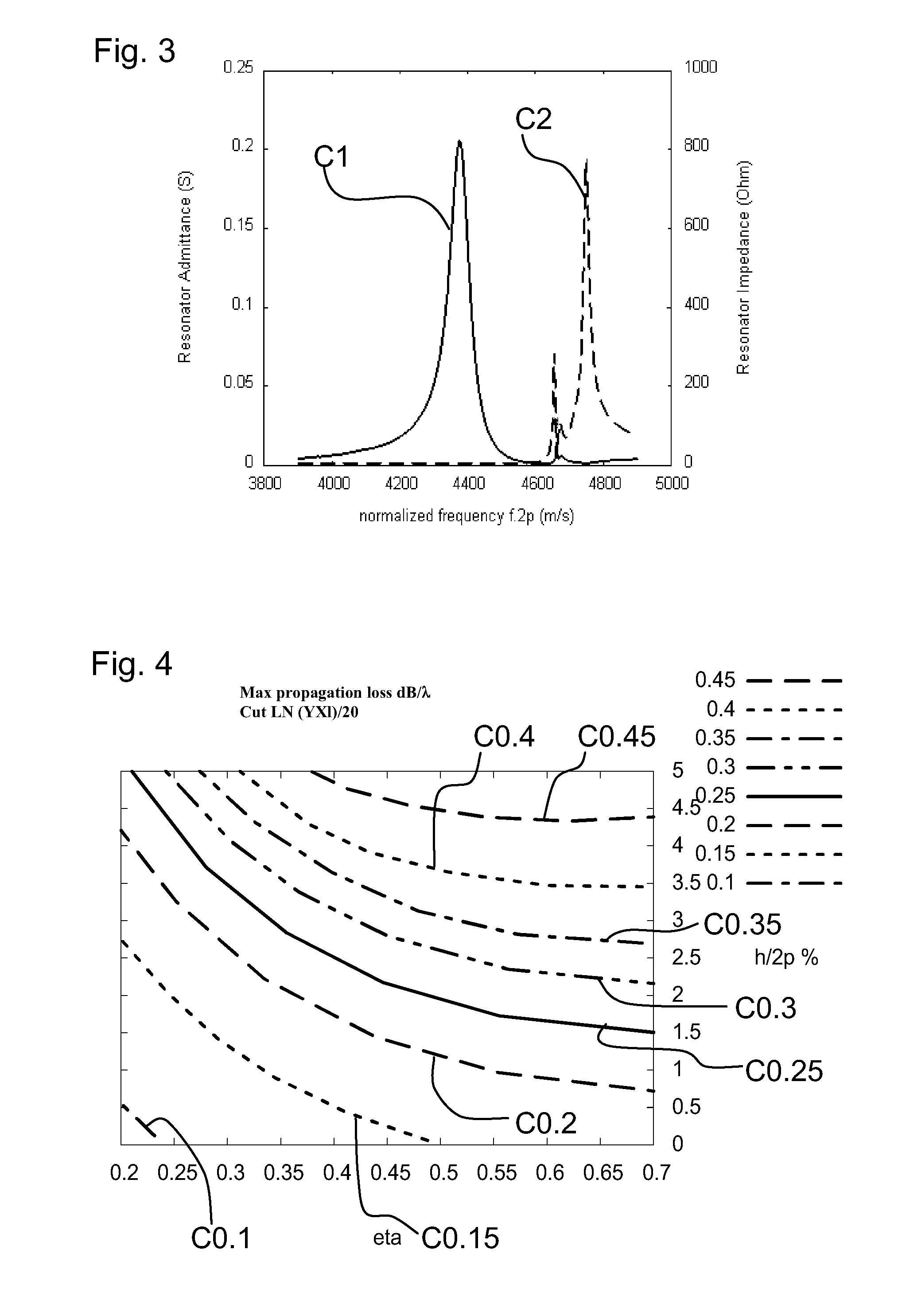
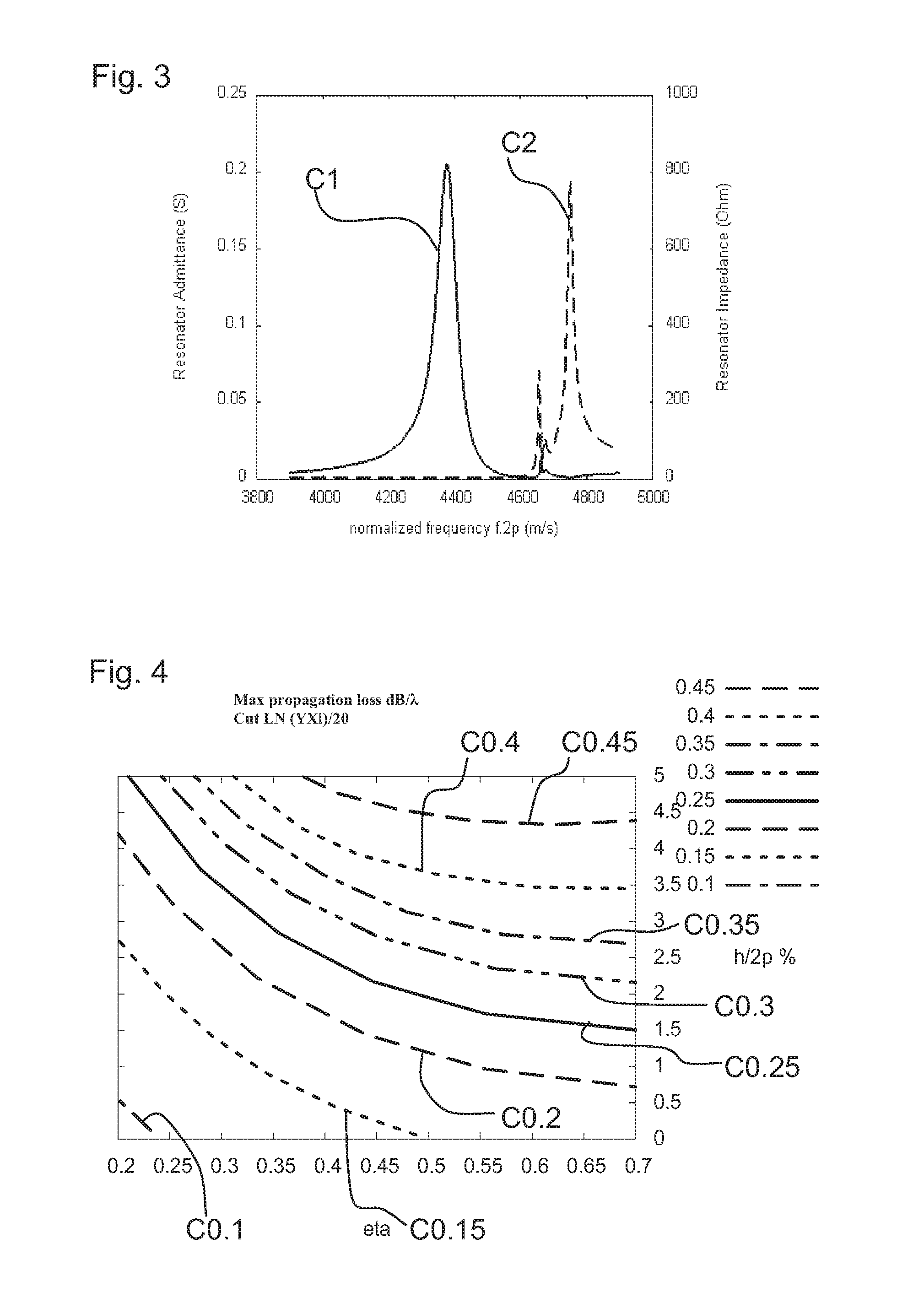
ActiveUS20140028414A1Low temperature dependenceEnhanced couplingImpedence networksLithium niobateInterdigital transducer
A surface acoustic wave filter includes a θ-rotated Y-cut X-propagation lithium niobate substrate. The cut angle ranges from 20° to 40°. An interdigital transducer can be used for exciting a surface acoustic wave that is formed on the substrate.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Photosensitive resin composition, method for control of refractive index, and optical waveguide and optical component using the same
InactiveUS20100329616A1Improve transmission characteristicsLow propagation lossCladded optical fibrePhotosensitive materialsChemical compoundRefractive index
Provided are: a resin composition for the formation of an optical waveguide, which shows low transmission loss and high heat stability and enables to form a waveguide pattern at high shape accuracy and at low cost; an optical waveguide; a method of forming an optical waveguide; and an optical element using the method. A photosensitive resin composition is used, which includes a polyamic acid represented by a general formula (I) or a polyamic acid ester (A), a compound (B) having an epoxy group, and a compound (C) which generates an acid by being exposed to light.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Paste composition for light guide and light guide utilizing the same
InactiveUS20090270541A1Good curabilityGood developabilityOptical waveguide light guideLight waveLight guide
Problems: an object of the present invention is to provide an optical waveguide-forming paste composition that allows short-time curing and provides excellent developability.Means for Solving: The present invention is directed to an optical waveguide-forming paste composition including (A) barium sulfate particles with a mean particle diameter of 1 nm or more to 50 nm or less, (B) a compound having a polymerizable group and a carboxyl group, or a phosphoric ester compound having a polymerizable group, and (C) an organic solvent.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Resin composition for forming optical waveguide, resin film for forming optical waveguide, and optical waveguide using the same
InactiveUS20160280829A1High transparencyPrecise patternCladded optical fibreLamination ancillary operationsOptical propagationPhoto irradiation
The present invention provides a resin composition for an optical waveguide and a resin film for optical waveguides, the composition and the film being soluble in an aqueous alkaline solution, being patternable as required by alkali development, and exhibiting a lower optical propagation loss at a wavelength of from 830 to 850 nm, and an optical waveguide using the composition or the film. The resin composition for an optical waveguide according to the present invention includes (A) a polymer, (B) a polymerizable compound, and (C) a polymerization initiator. A refractive index A of the film after irradiation with UV light and heat-curing and a refractive index B of the film after irradiation with UV light, immersion in an alkali developer, and then heat-curing satisfy the relationship of A>B. As an optical waveguide produced by alkali development using the resin composition according to the present invention has, on at least part of the periphery of a core pattern that forms a core layer, a portion having a refractive index that is lower than the refractive index of the central portion of the core pattern, the optical waveguide is effective in preventing light travelling through the core layer from leaking out into the cladding layer, which can lower optical propagation loss.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
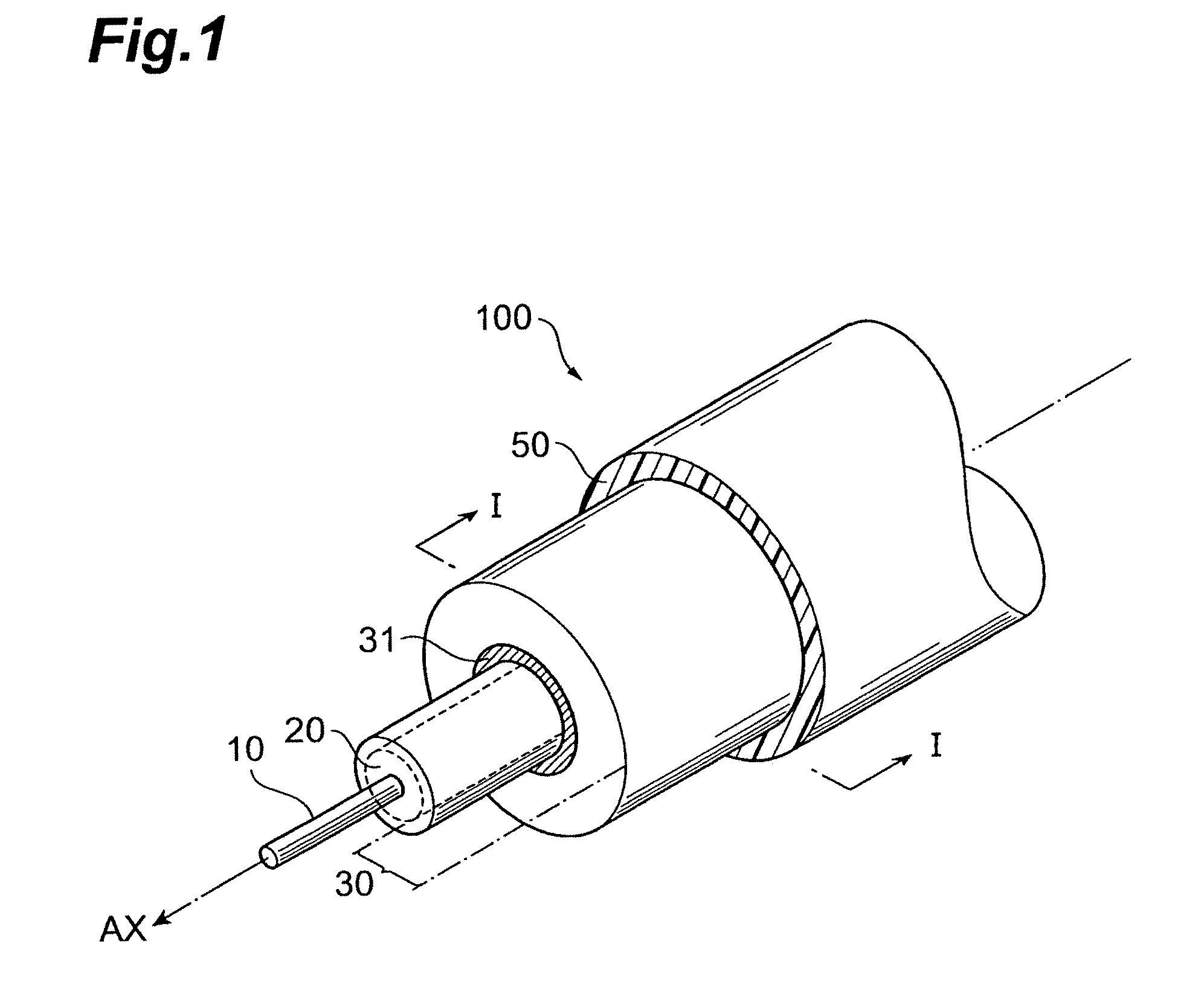
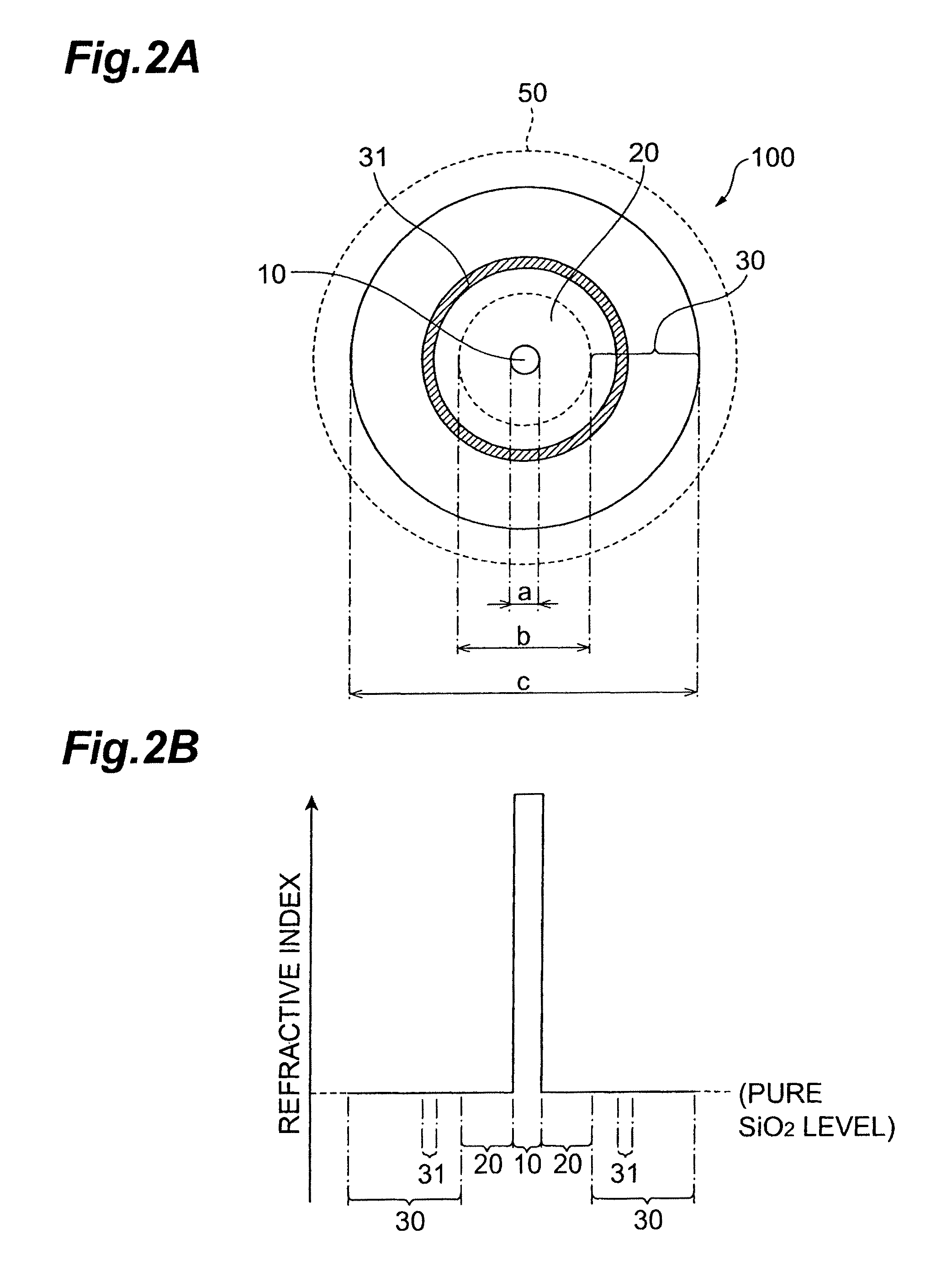
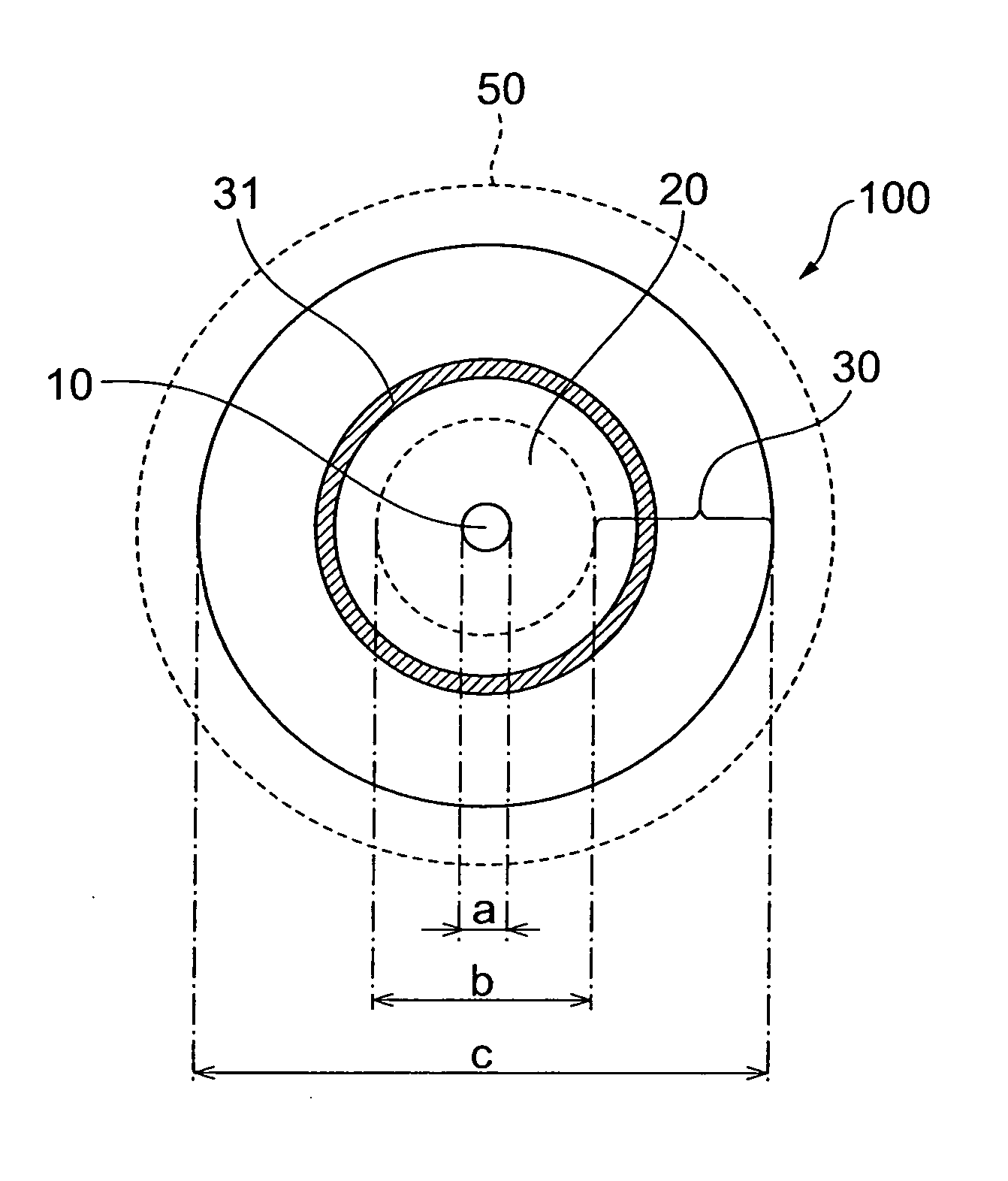
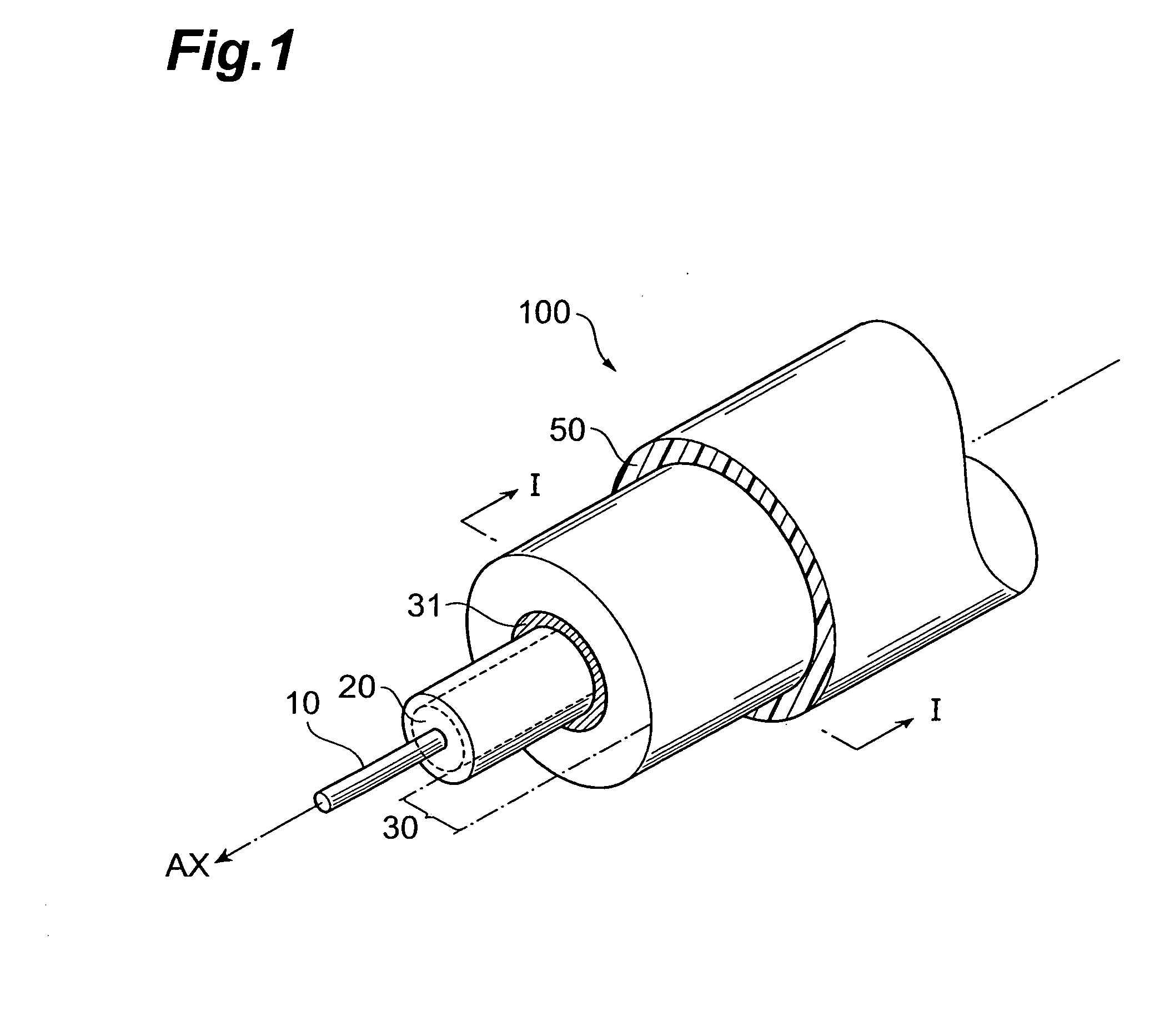
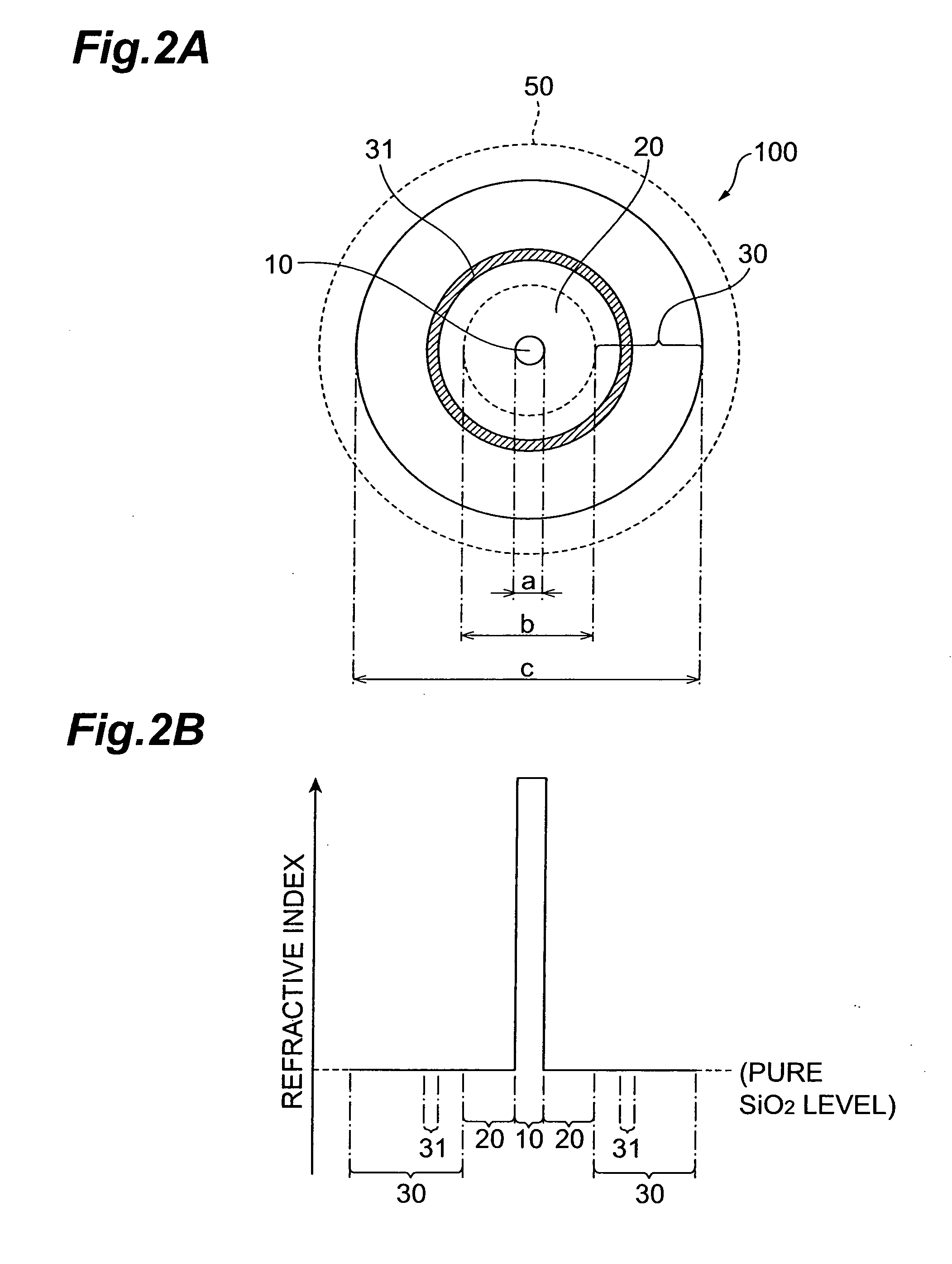
Optical fiber
ActiveUS8687931B2Reduced propagation lossIncrease capacityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesCombustionResin coating
The present invention relates to an optical fiber having a structure to enable both prevention of resin coating combustion due to leaked light, and low-loss light transmission. The optical fiber comprises a core region, and a cladding region. The cladding region is constituted by an optical cladding which affects the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region, and a physical cladding which does not affect the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region. Particularly, a leakage reduction portion is provided in the physical cladding so as to surround an outer periphery of the core region through the optical cladding. The leakage reduction portion functions to suppress propagation of the leaked light propagating from the core region toward outside the cladding region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
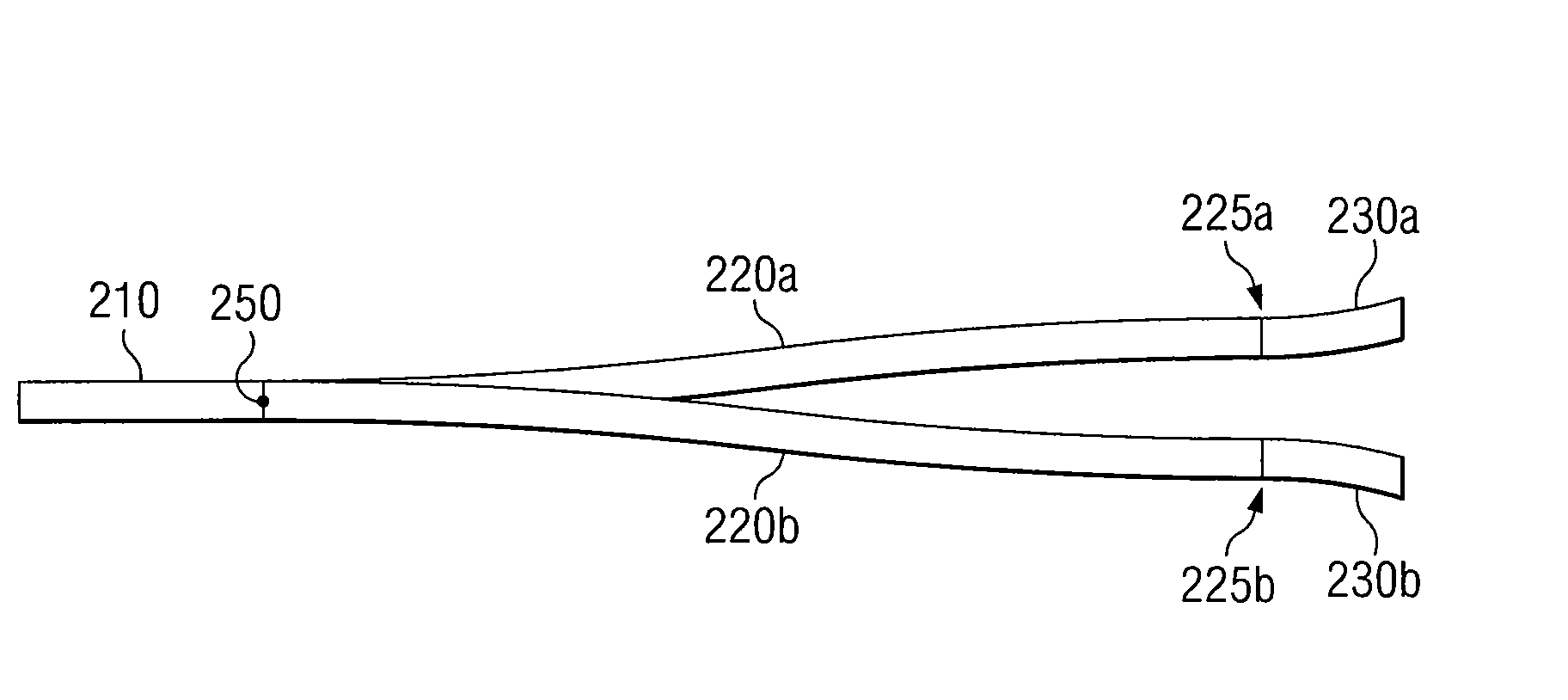
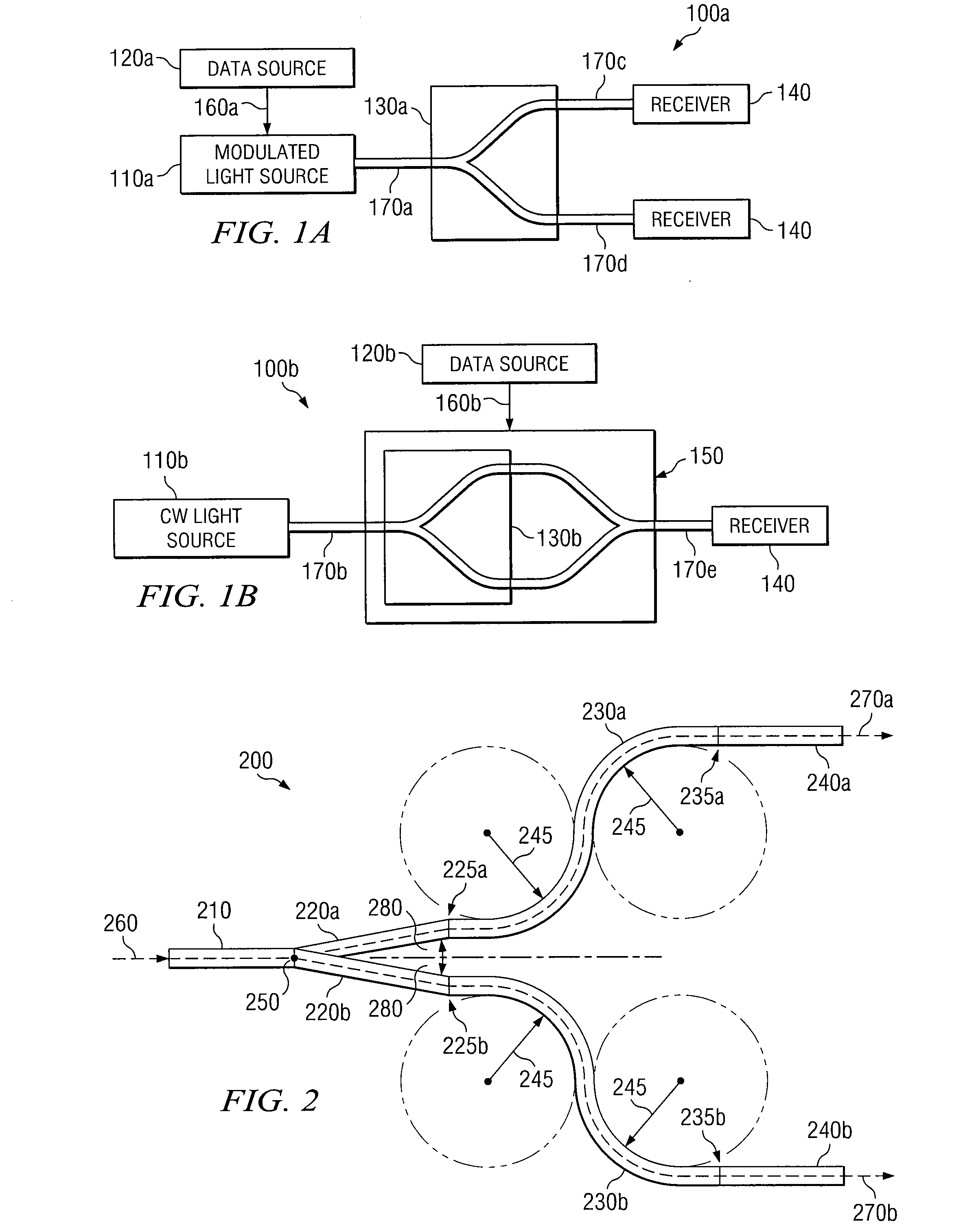
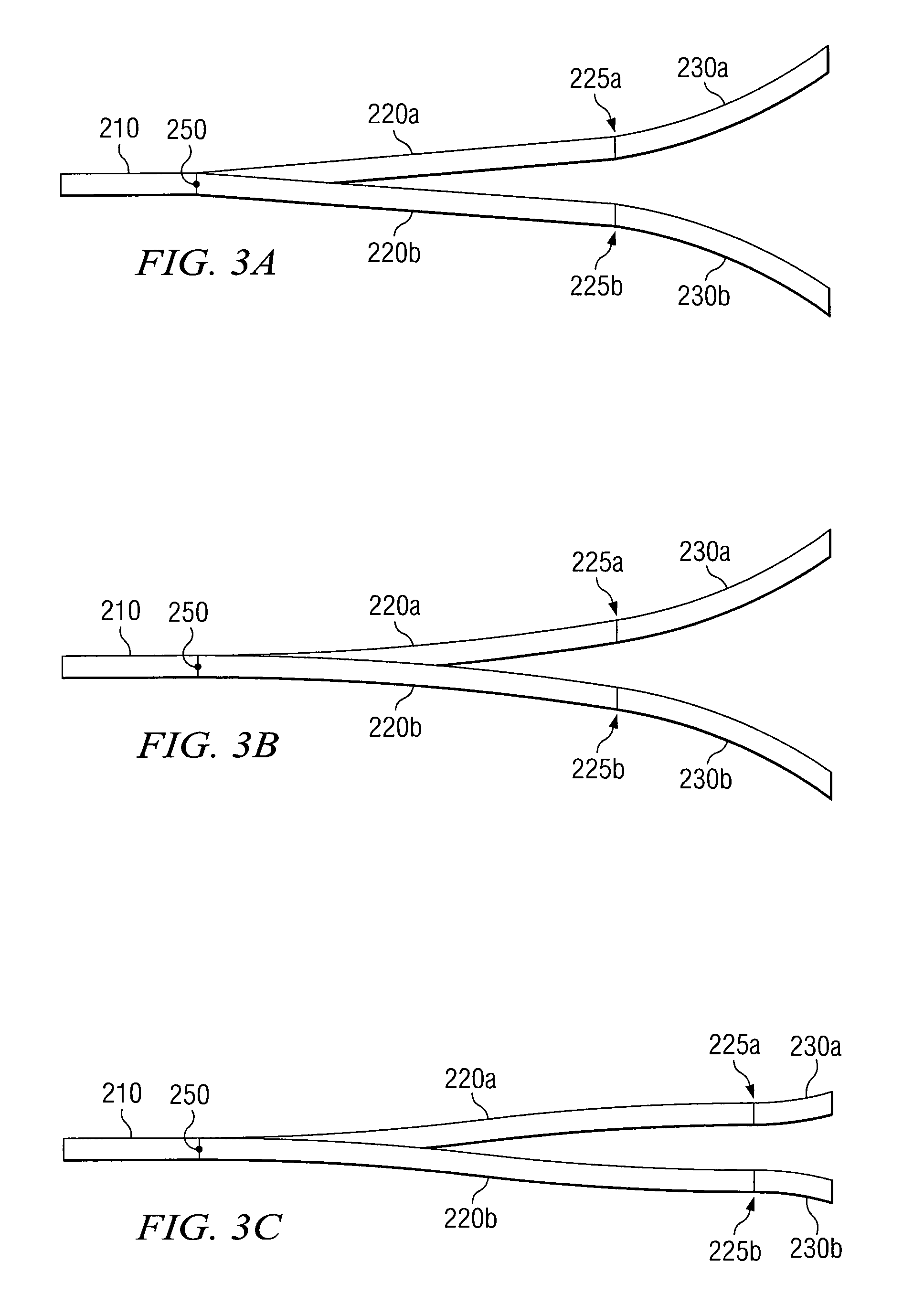
Optical Beam Splitter
InactiveUS20100046890A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLight beamWaveguide
An optical beam splitter includes an input waveguide, two or more branching arms, two or more fan-out arms, and two or more output waveguides. The input waveguide receives an input light beam. The two or more branching arms are coupled to the input waveguide at a separation point and split the input light beam at the separation point into two or more light beams. Each fan-out arm is coupled to one of the branching arms and fans-out one of the two or more light beams to a predetermined output pitch. Each output waveguide is coupled to one of the fan-out arms and transmits one of the two or more light beams out of the optical beam splitter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical fiber
InactiveUS20100183272A1Reduced propagation lossIncrease capacityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideCombustionResin coating
The present invention relates to an optical fiber having a structure to enable both prevention of resin coating combustion due to leaked light, and low-loss light transmission. The optical fiber comprises a core region, and a cladding region. The cladding region is constituted by an optical cladding which affects the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region, and a physical cladding which does not affect the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region. Particularly, a leakage reduction portion is provided in the physical cladding so as to surround an outer periphery of the core region through the optical cladding. The leakage reduction portion functions to suppress propagation of the leaked light propagating from the core region toward outside the cladding region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical waveguide-forming composition
ActiveUS20180305488A1Excellent optical propertiesLow light propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideCompound aEthyl group
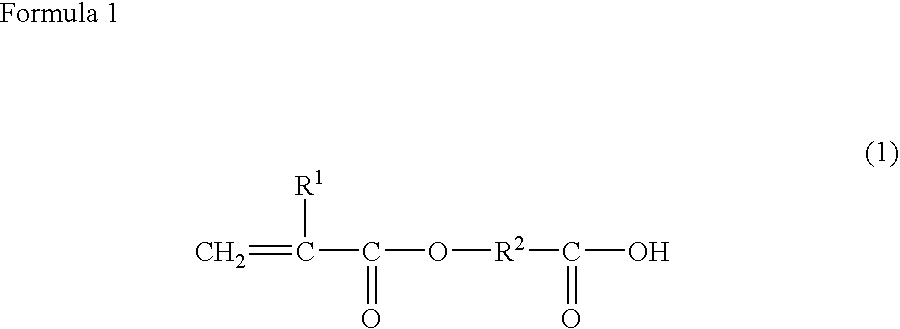
An optical waveguide-forming composition: 100 parts by mass of a reactive silicone compound (a) composed of a polycondensate of a diarylsilicic acid compound A of Formula [1]Ar1 and Ar2 are a phenyl, naphthyl or a biphenyl group optionally substituted, and an alkoxy silicon compound B of Formula [2]Ar3—Si(OR1)aR23-a [2]Ar3 is a phenyl, naphthyl or biphenyl group having at least one group having a polymerizable double bond, R1 is methyl or ethyl group, R2 is methyl, ethyl, or vinylphenyl group, and a is 2 or 3, and 1 part by mass to 200 parts by mass of a di(meth)acrylate compound (b) of Formula [3].R3 and R4 are a hydrogen atom or methyl group, R5 is a hydrogen atom, methyl group, or ethyl group, L1 and L2 are an alkylene group, and m and n are 0 or a positive integer, wherein m+n is 0 to 20.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
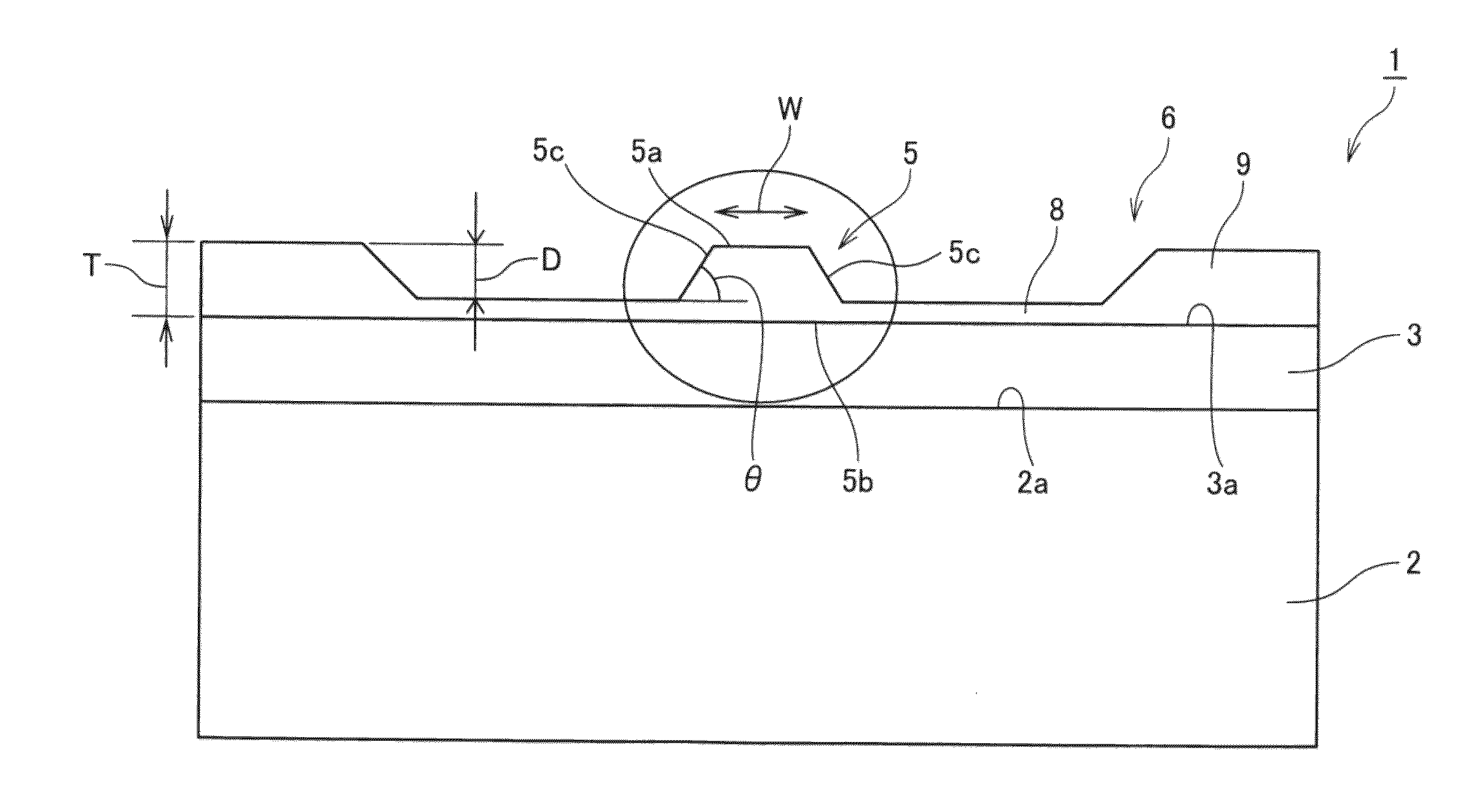
Optical Waveguide Devices
ActiveUS20150147038A1Design freedomReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsTungstatePotassium
An optical waveguide device 1 includes a thin layer 3 and a ridge portion 5 loaded on the thin layer 3. The thin layer 3 is made of an optical material selected from the group consisting of lithium niobate, lithium tantalate, lithium niobate-lithium tantalate, yttrium aluminum garnet, yttrium vanadate, gadolinium vanadate, potassium gadolinium tungstate; and potassium yttrium tungstate. The ridge portion 5 is made of tantalum pentoxide and has a trapezoid shape viewed in a cross section perpendicular to a direction of propagation of light. The ridge portion is not peeled off from the thin layer in a tape peeling test.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Photosensitive resin composition for optical waveguide formation, optical waveguide and method for producing optical waveguide
InactiveUS20090046986A1High shape accuracyImprove transmission performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsOptical articlesMethacrylateMeth-
The present invention has an object to provide a photosensitive resin composition for optical waveguide formation, which has low transmission loss and can form a waveguide pattern with high shape accuracy at low cost; an optical waveguide; and a method for producing an optical waveguide. The present invention provides a photosensitive resin composition for optical waveguide formation comprising at least: a polymer containing at least a (meth)acrylate structure unit having an epoxy structure, and a (meth)acrylate structure unit having a lactone structure and / or a vinyl monomer structure unit having an aromatic structure; and a photoacid generator, of which one or both of a core layer and a cladding layer are formed of a cured product.
Owner:NEC CORP
High efficiency wavelength converters
InactiveUS20060044644A1Speed up the conversion processLow refractive indexBy pulling from meltLight demodulationHigh rateWavelength
A method is provided for forming a waveguide region within a periodically domain reversed ferroelectric crystal wherein the waveguide region has a refractive index profile that is vertically and horizontally symmetric. The symmetric profile produces effective overlapping between quasi-phasematched waves, a corresponding high rate of energy transfer between the waves and a symmetric cross-section of the radiated wave. The symmetric refractive index profile is produced by a method that combines the use of a diluted proton exchange medium at a high temperature which produces a region of high index relatively deeply beneath the crystal surface, followed by a reversed proton exchange which restores the original crystal index of refraction immediately beneath the crystal surface.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
Photosensitive resin composition for optical waveguide formation, optical waveguide and method for producing optical waveguide
InactiveUS7847017B2High shape accuracyImprove transmission performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsOptical articlesMethacrylateMeth-
Owner:NEC CORP
Photosensitive resin composition for optical waveguide formation, optical waveguide and method for producing optical waveguide
InactiveUS20110044597A1High shape accuracyImprove transmission performanceCladded optical fibrePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMeth-Photoacid generator
Owner:NEC CORP
Paste composition for light guide and light guide utilizing the same
InactiveUS7960462B2Improve curing effectExcellent developabilityOptical waveguide light guidePhosphoric Acid EstersOrganic solvent
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Optical fiber
ActiveUS20140064684A1Reduced propagation lossIncrease capacityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideCombustionResin coating
The present invention relates to an optical fiber having a structure to enable both prevention of resin coating combustion due to leaked light, and low-loss light transmission. The optical fiber comprises a core region, and a cladding region. The cladding region is constituted by an optical cladding which affects the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region, and a physical cladding which does not affect the transmission characteristics of light propagating in the core region. Particularly, a leakage reduction portion is provided in the physical cladding so as to surround an outer periphery of the core region through the optical cladding. The leakage reduction portion functions to suppress propagation of the leaked light propagating from the core region toward outside the cladding region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
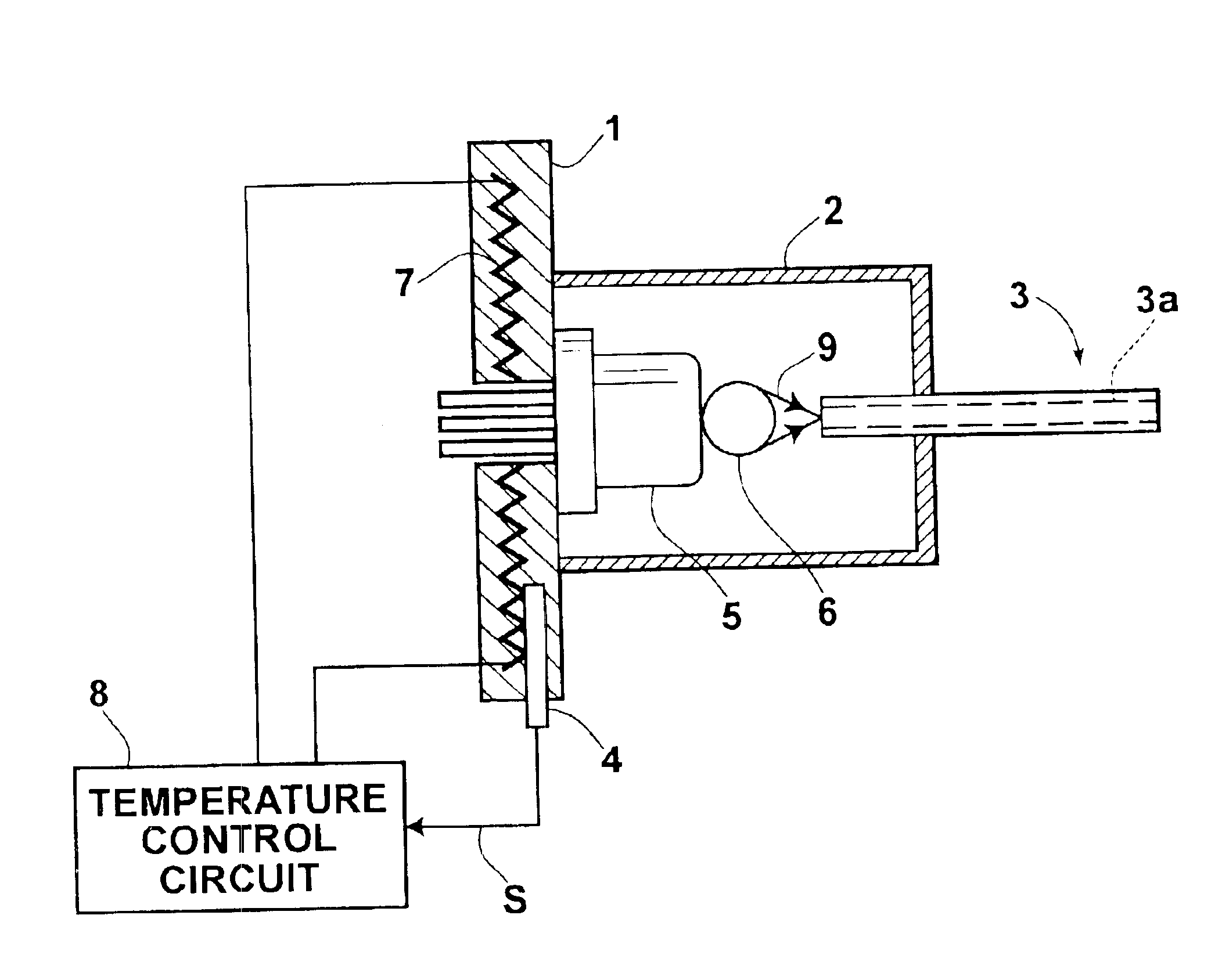
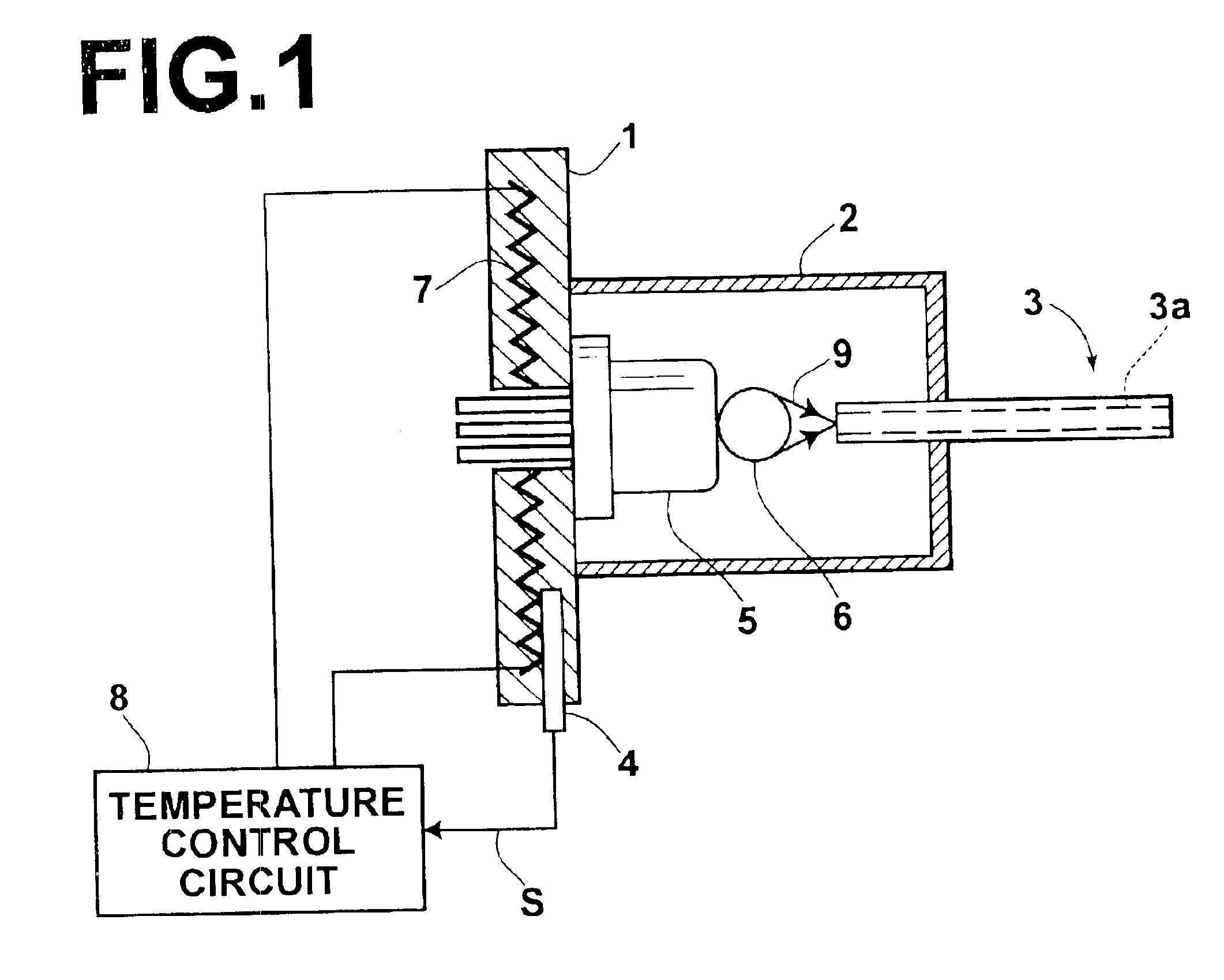
Transmission apparatus using a plastic fiber
InactiveUS6874951B2Stable transmission characteristicsReduce transmission costsLaser detailsCladded optical fibrePolymethyl methacrylateEngineering
Light, which has been produced by a semiconductor device and has wavelengths falling within the range of 630 nm to 680 nm, is propagated through a plastic fiber provided with a core containing a polymethyl methacrylate as a principal constituent. The temperature of the semiconductor device is adjusted by a temperature adjusting system comprising a heater for heating the semiconductor device, a temperature detector for detecting the temperature of the semiconductor device and feeding out a temperature detection signal, and a control circuit for controlling actuation of the heater in accordance with the temperature detection signal in order to set the temperature of the semiconductor device at a predetermined target value that is lower than the highest temperature assumed to occur under an environment, in which the semiconductor device is located.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
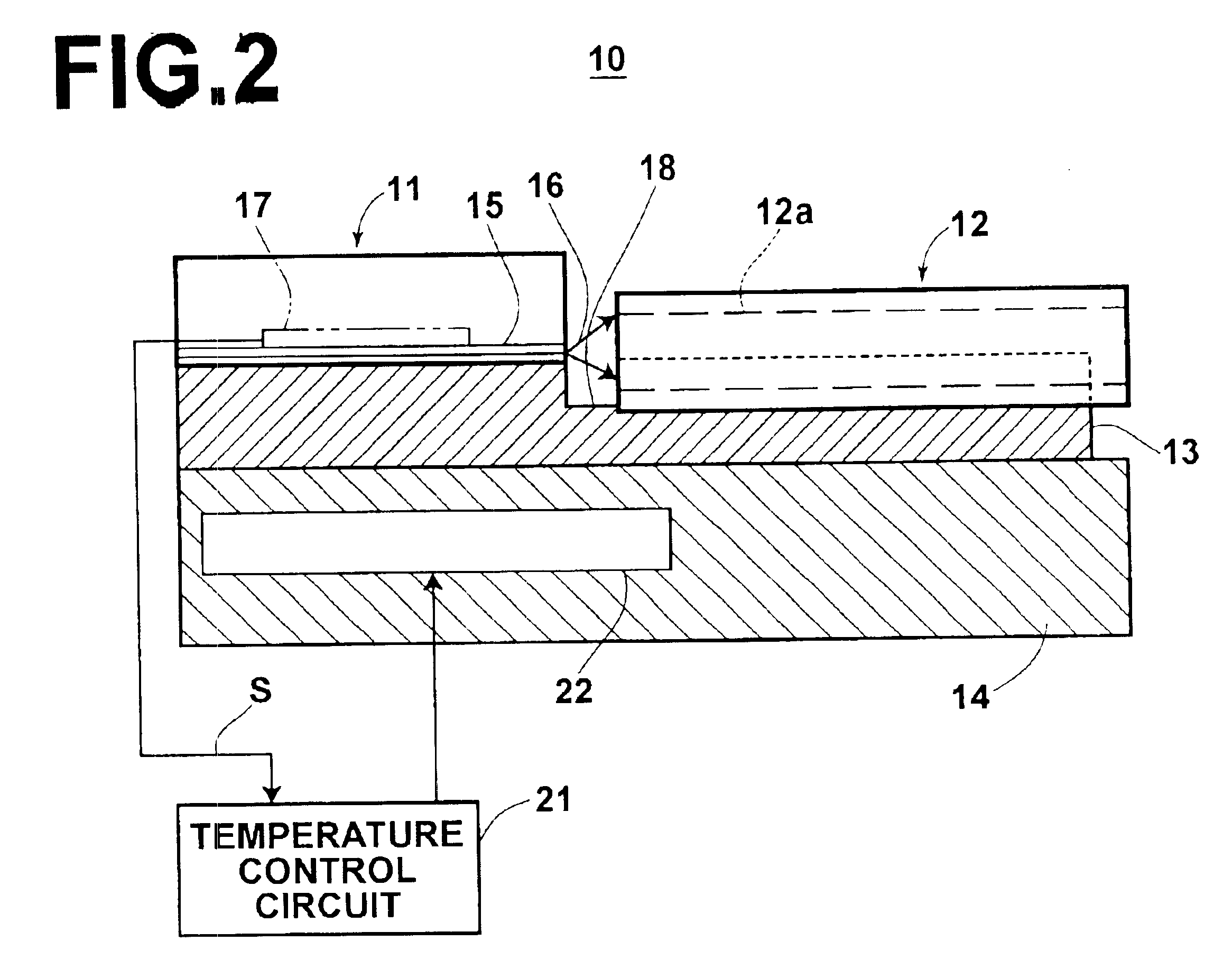
Method for manufacturing optical member, and optical member, transparent member for forming optical member, optical waveguide and optical module
InactiveUS20160209591A1Improve batch productivityLow optical propagation lossOptical articlesCoatingsRefractive index profileLight wave
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing an optical member and an optical waveguide having a low optical loss. The provided method is capable of highly accurately controlling the positional configuration of refractive index distribution in the surface layer, including its vicinity, and the center portion of the core pattern in a transparent member. The method for manufacturing the optical member by the present invention has a Process A, in which the transparent member is exposed to a solution and thereby the refractive index of the surface layer of the transparent member exposed to the solution is substantially lower than that of the center portion of the transparent member not exposed to the solution. The substantial lowering of the refractive index of the surface layer is achieved by making the refractive index regulating agent exert its function by being included in the surface layer of the transparent member. The optical waveguide by the present invention has such a feature that surface layers of two or more sides on the circumference of the core pattern forming the core part have a refractive index lower than that of the center portion of the core pattern. The surface layer includes a refractive index regulating agent for lowering the refractive index. Further, a lower clad layer or an upper clad layer, or both, are provided outside the surface layer of low refractive index, wherein the refractive index of these clad layers are lower than that of the surface layer.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Surface acoustic wave filter on a lithium niobate substrate
ActiveUS9391589B2Enhanced couplingMaximise couplingImpedence networksLithium niobateInterdigital transducer
Owner:SNAPTRACK
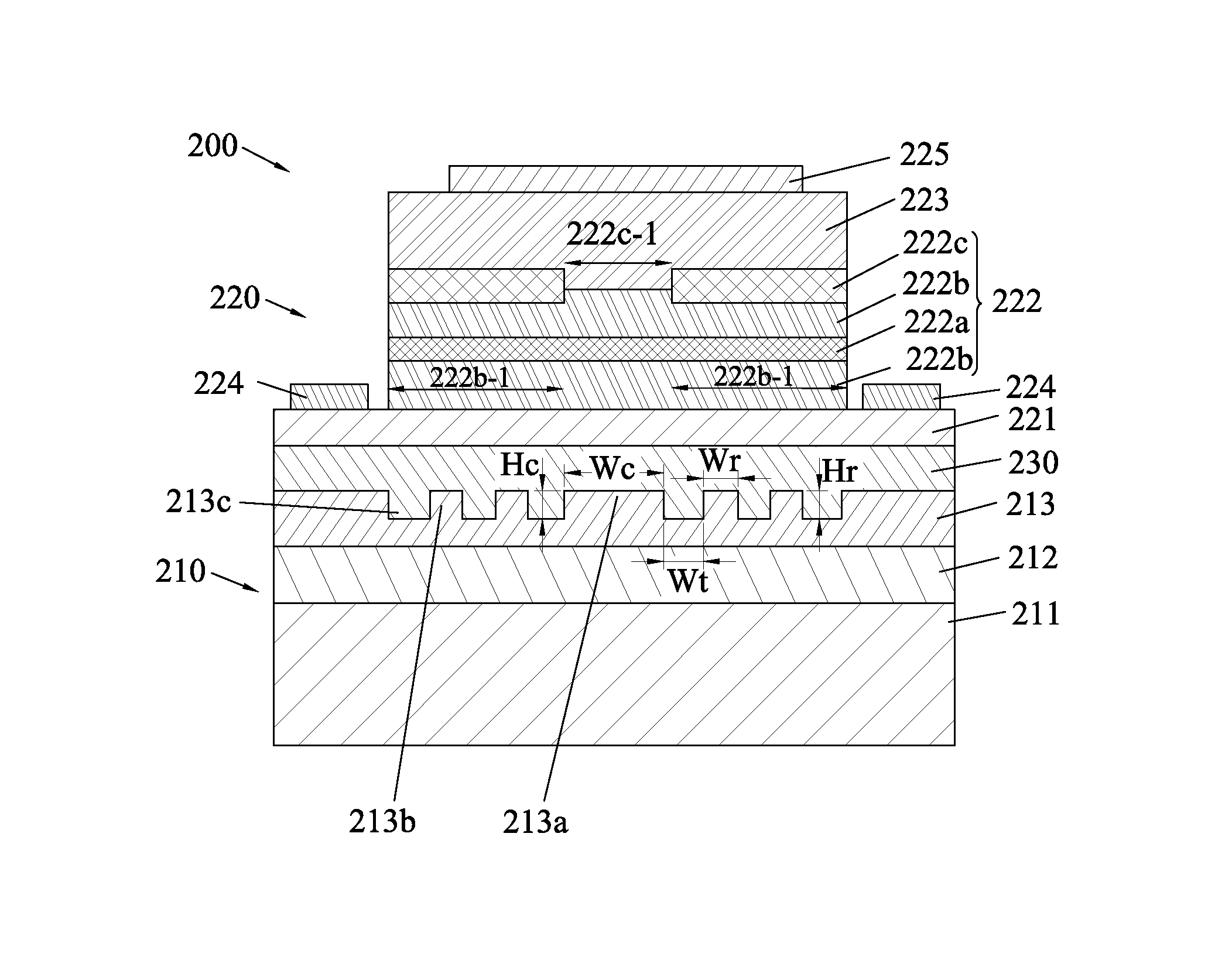
Semiconductor laser apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS9484711B2Low propagation lossEfficient heat dissipationLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSingle mode laserMechanical bond
A semiconductor laser apparatus includes a silicon-on-insulator assembly and an edge-emitting semiconductor laser assembly integrated on the silicon-on-insulator assembly. The silicon-on-insulator assembly includes an optical waveguide at the top which is bonded to the edge-emitting semiconductor laser assembly and configured to couple a laser light emitted from the edge-emitting semiconductor laser assembly, and the optical waveguide includes a core portion located in the middle of the optical waveguide; and at least one vertical rib configured on two sides of the core portion respectively, with a width narrower than that of the core portion. The apparatus obtains a single mode laser operation and has low propagation loss and high mechanical bond strength.
Owner:CLOUD LIGHT TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com