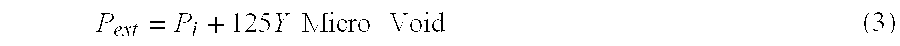Patents
Literature
6733results about "By pulling from melt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
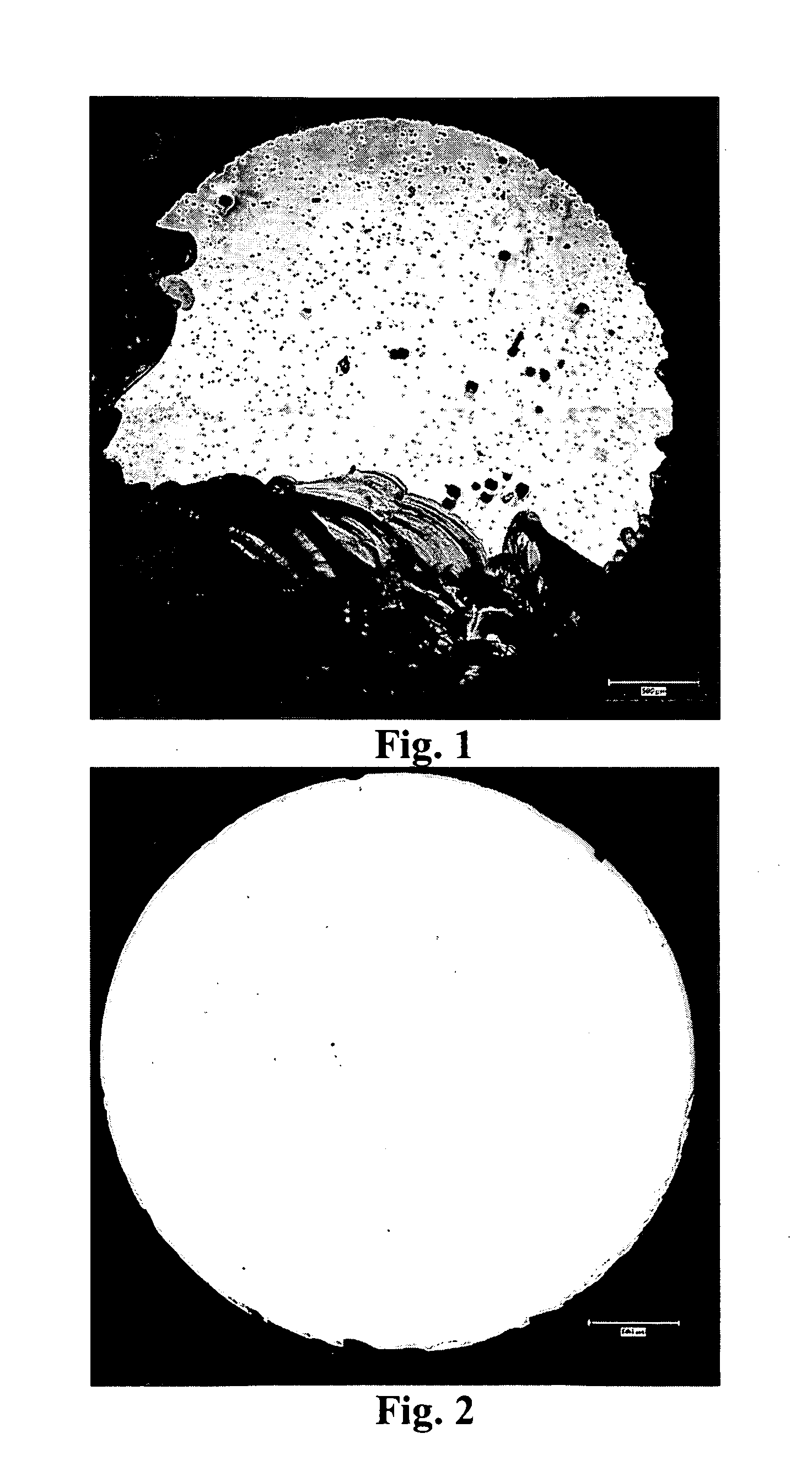
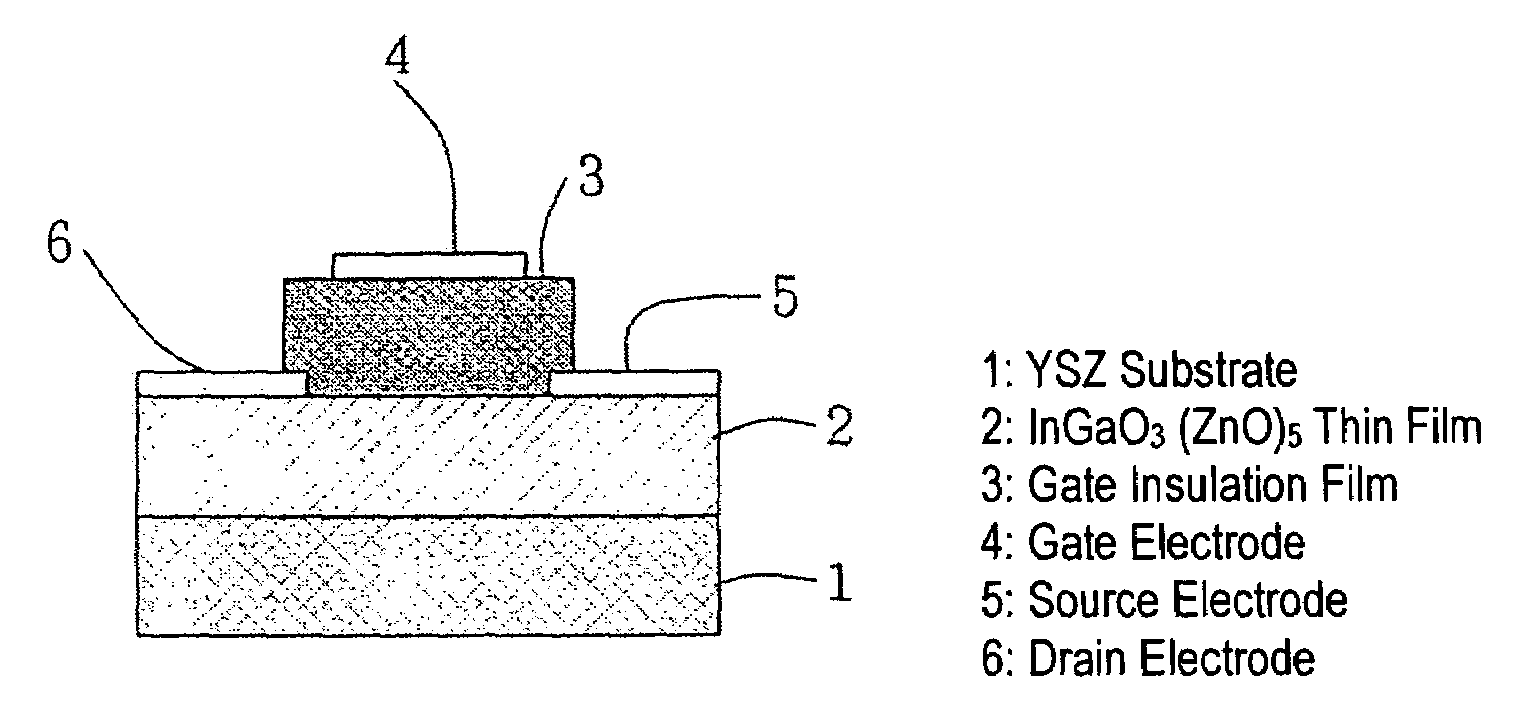
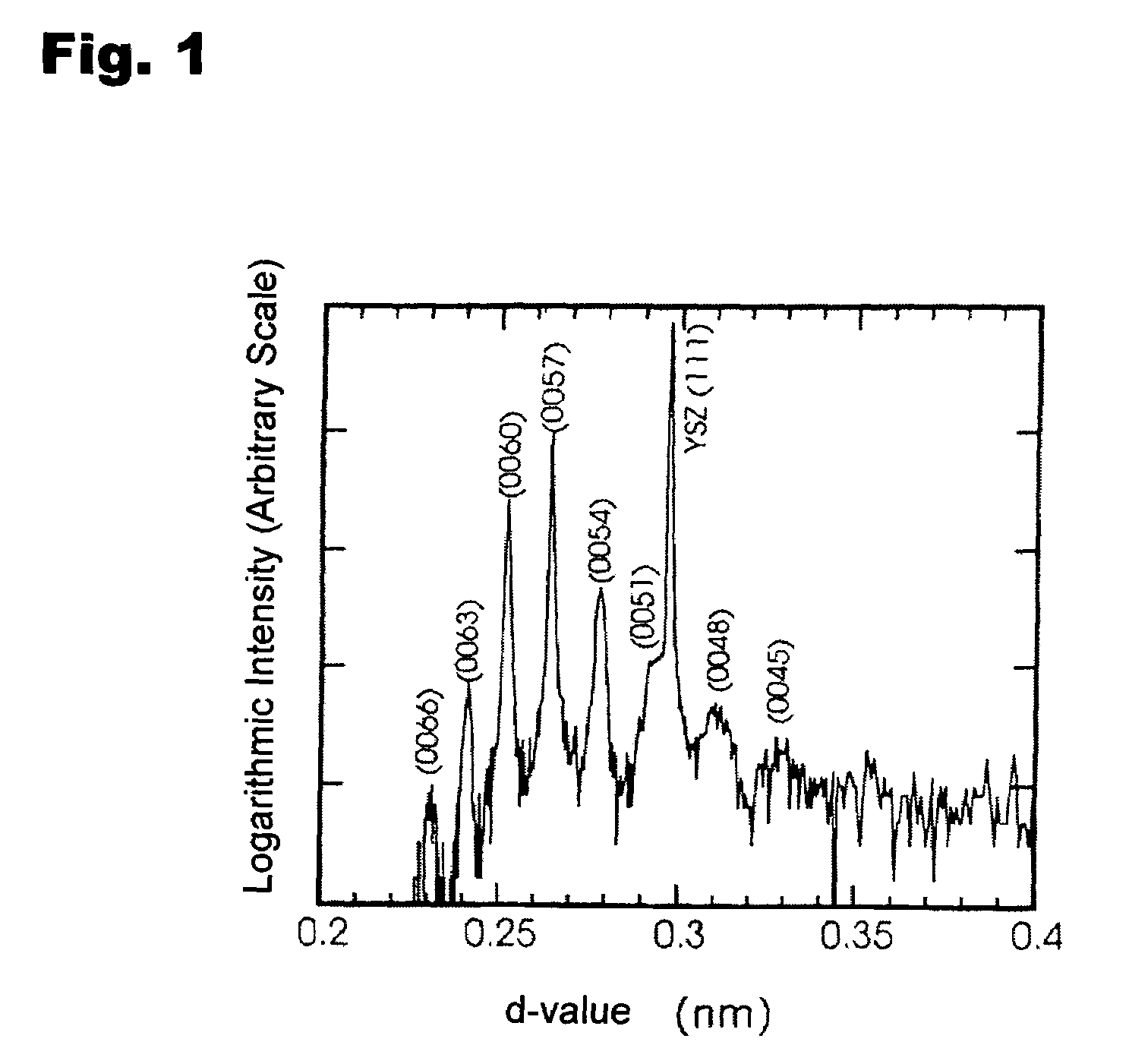
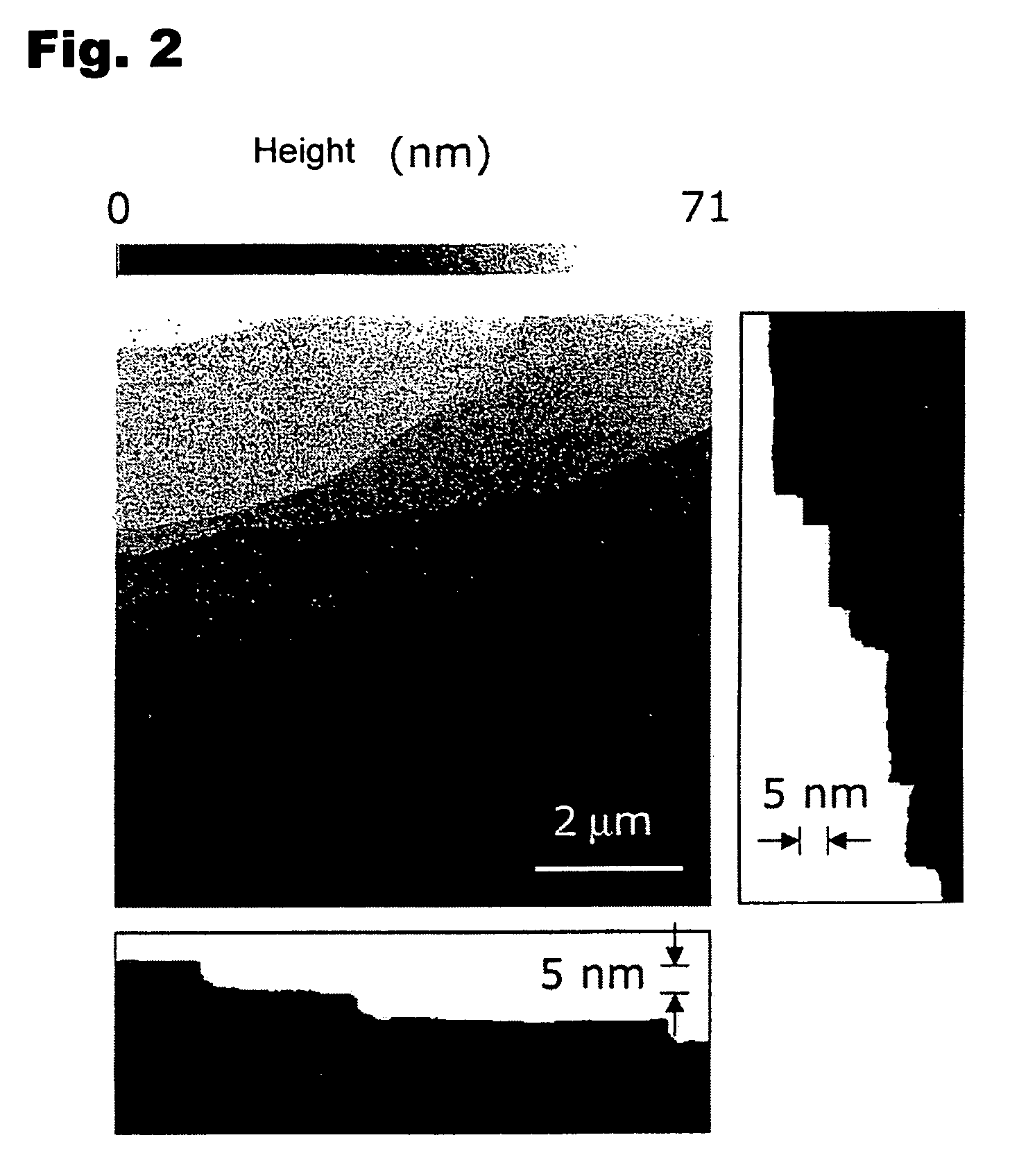
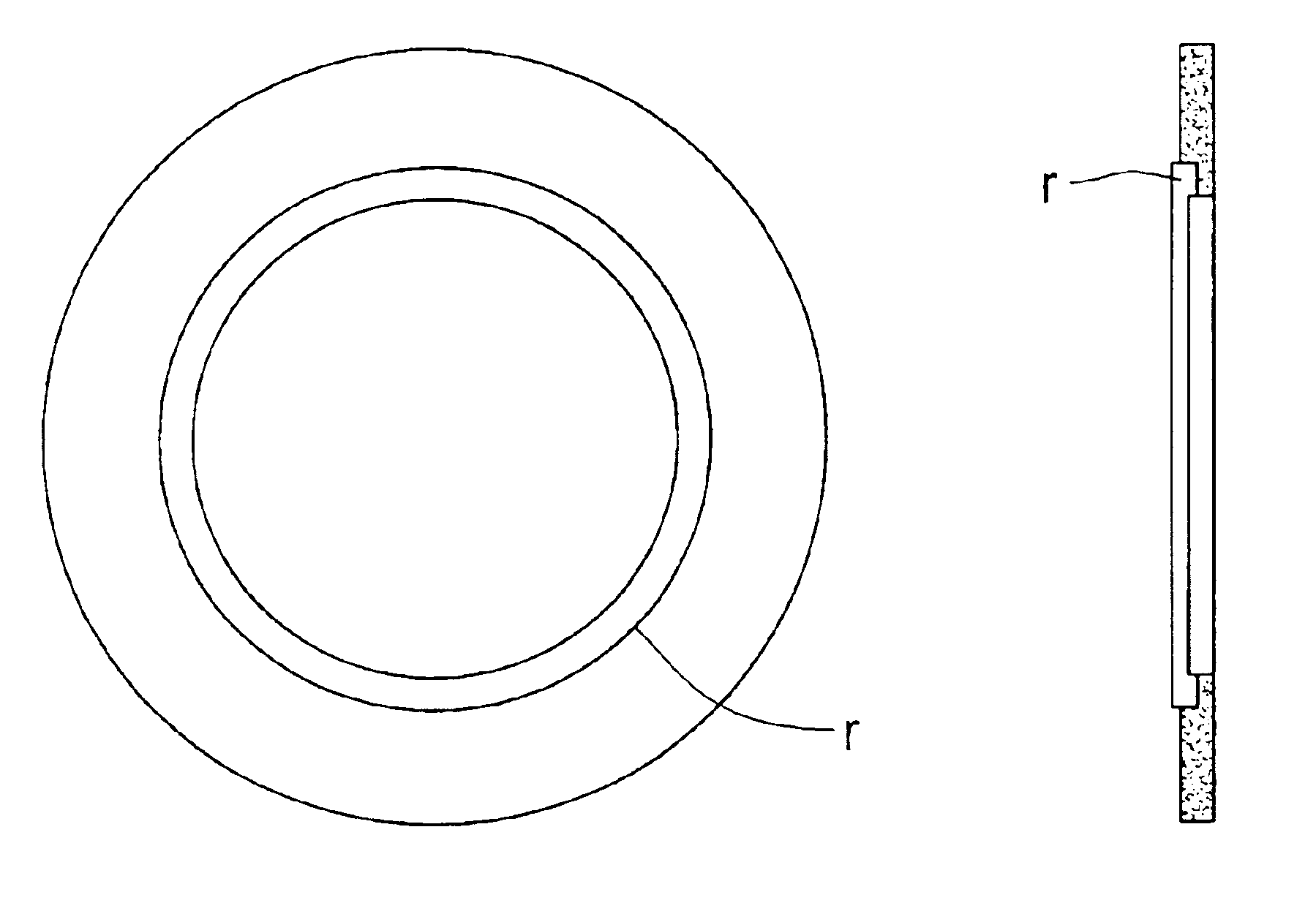
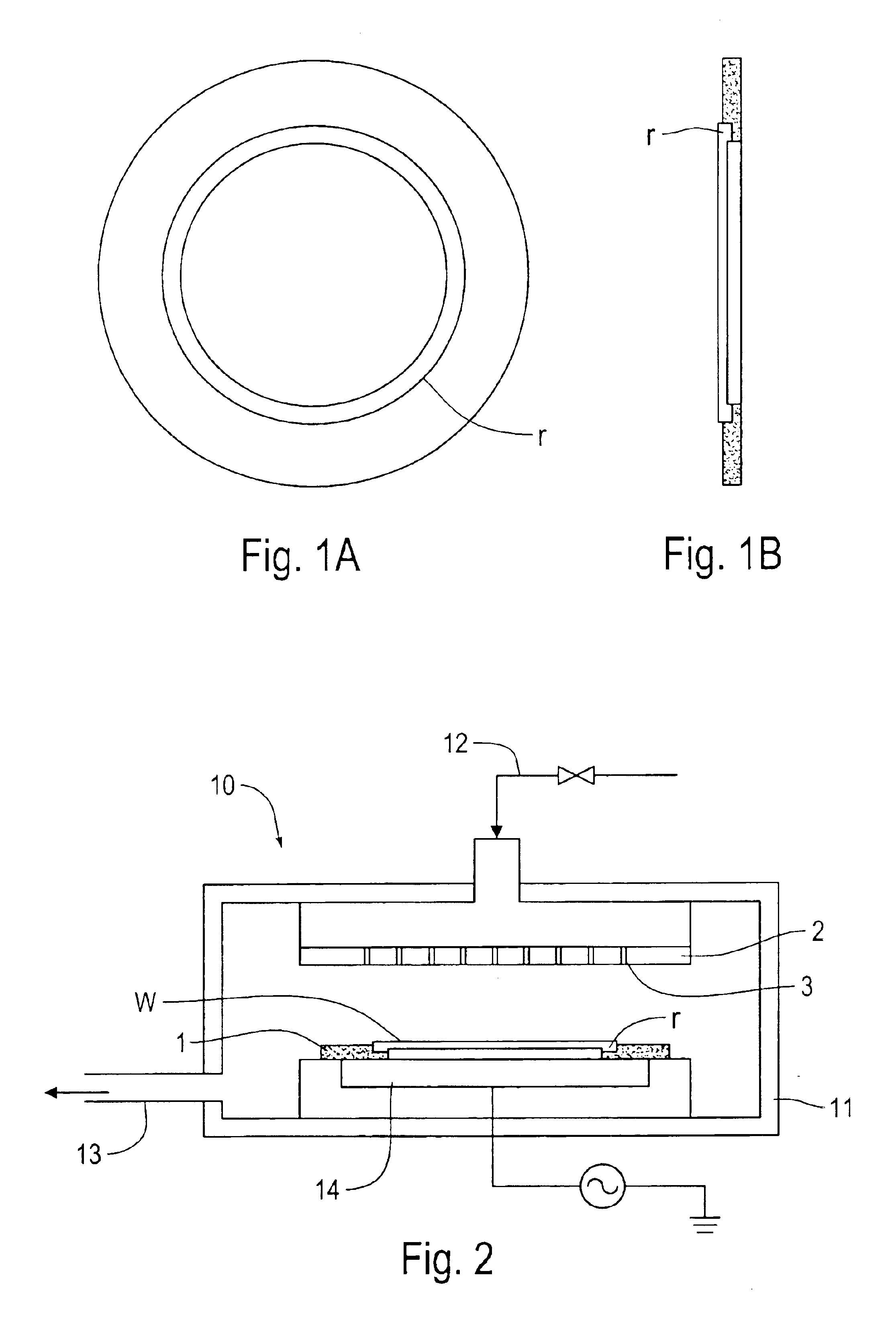
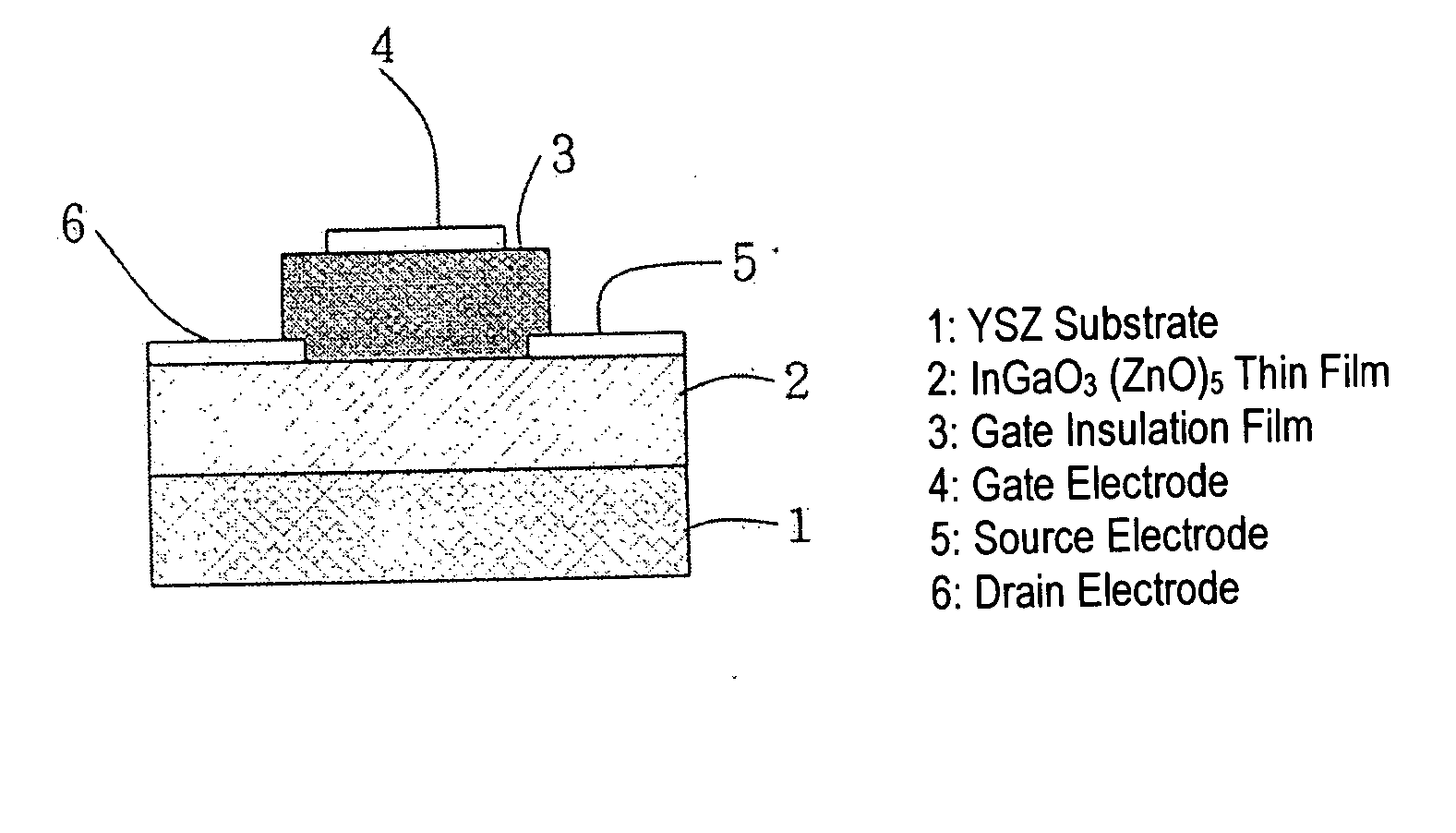
Natural-superlattice homologous single crystal thin film, method for preparation thereof, and device using said single crystal thin film
InactiveUS7061014B2Easy to controlSimple processTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
Disclosed is a natural-superlattice homologous single-crystal thin film, which includes a complex oxide which is epitaxially grown on either one of a ZnO epitaxial thin film formed on a single-crystal substrate, the single-crystal substrate after disappearance of the ZnO epitaxial thin film and a ZnO single crystal. The complex oxide is expressed by the formula: M1M2O3 (ZnO)m, wherein M1 is at least one selected from the group consisting of Ga, Fe, Sc, In, Lu, Yb, Tm, Er, Ho and Y, M2 is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mn, Fe, Ga, In and Al, and m is a natural number of 1 or more. A natural-superlattice homologous single-crystal thin film formed by depositing the complex oxide and subjecting the obtained layered film to a thermal anneal treatment can be used in optimal devices, electronic devices and X-ray optical devices.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
Ald Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20070269983A1Enhanced advantageMaterial utilization efficiency is increasedLiquid surface applicatorsBy zone-melting liquidsCompound (substance)Engineering
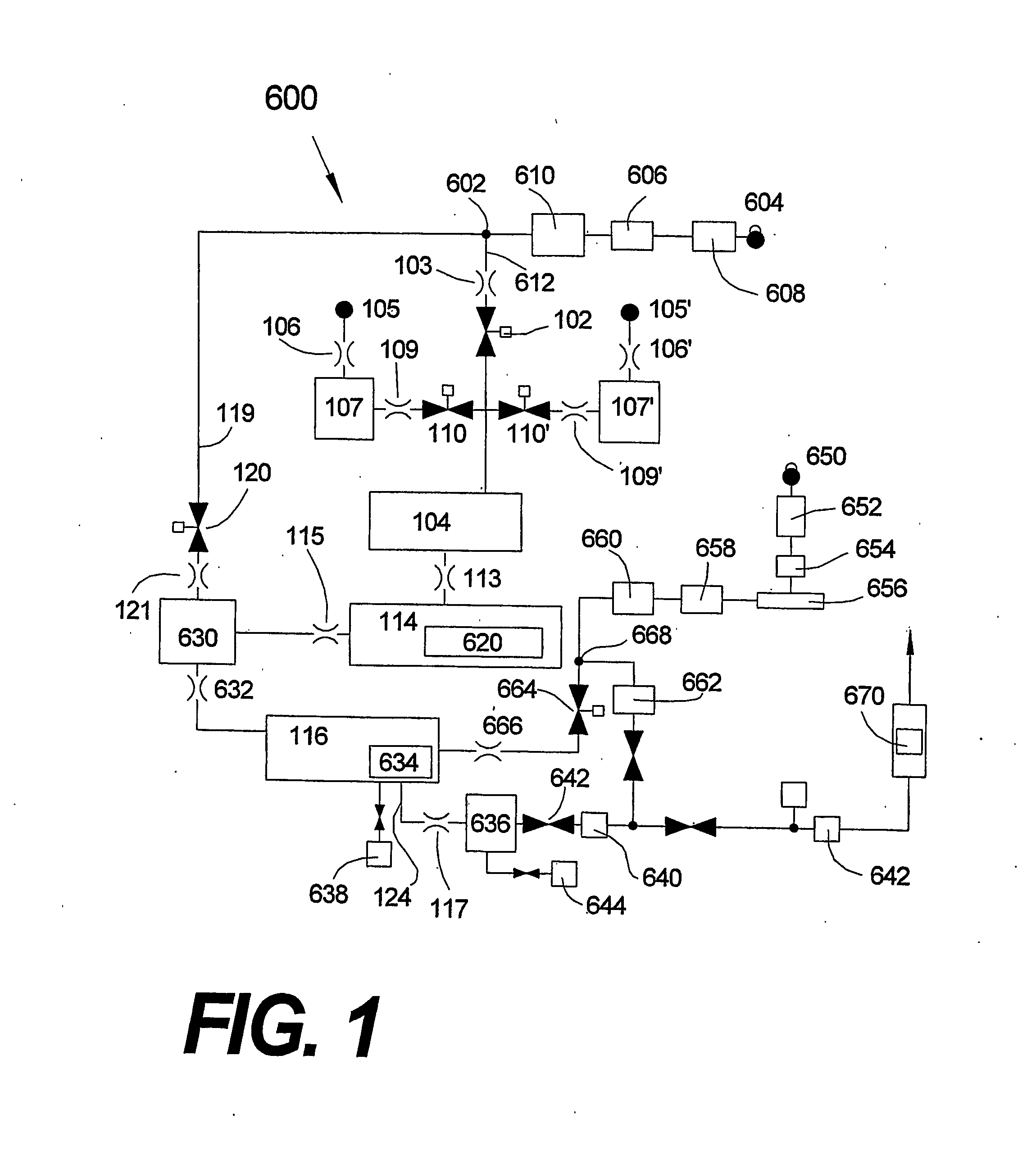
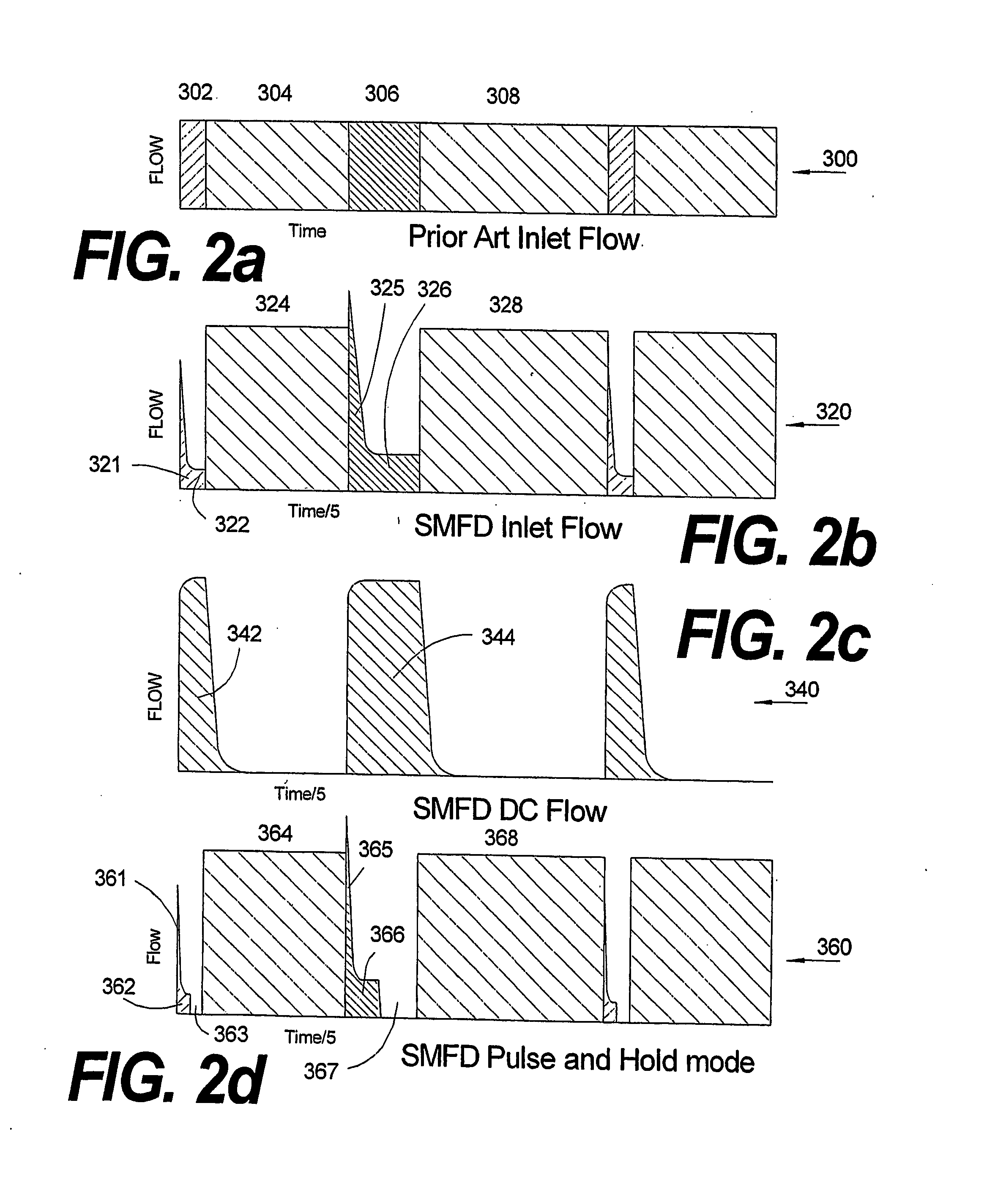
Improved apparatus and method for SMFD ALD include a method designed to enhance chemical utilization as well as an apparatus that implements lower conductance out of SMFD-ALD process chamber while maintaining full compatibility with standard wafer transport. Improved SMFD source apparatuses (700, 700′, 700″) and methods from volatile and non-volatile liquid and solid precursors are disclosed, e.g., a method for substantially controlling the vapor pressure of a chemical source (722) within a source space comprising: sensing the accumulation of the chemical on a sensing surface (711); and controlling the temperature of the chemical source depending on said sensed accumulation.
Owner:SUNDEW TECH
Single crystal and quasi-single crystal, composition, apparatus, and associated method
InactiveUS20060037529A1Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMischmetalSource material
Owner:SORAA
Resonant cavity light emitting devices and associated method
InactiveUS20060118799A1Increase probabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonant cavitySource material
A method may produce a resonant cavity light emitting device. A seed gallium nitride crystal and a source material in a nitrogen-containing superheated fluid may provide a medium for mass transport of gallium nitride precursors therebetween. A seed crystal surface may be prepared by applying a first thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material. Gallium nitride material may be grown on the prepared surface of the seed gallium nitride crystal by applying a second thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material while the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material are in the nitrogen-containing superheated fluid. A stack of group III-nitride layers may be deposited on the single-crystal gallium nitride substrate. The stack may include a first mirror sub-stack and an active region adaptable for fabrication into one or more resonant cavity light emitting devices.
Owner:SORAA
Silicon focus ring and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6815352B1Reduce Particle GenerationAvoid roughnessPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesCzochralski methodSingle crystal
There is disclosed a silicon focus ring consisting of silicon single crystal used as a silicon focus ring in a plasma apparatus, wherein concentration of interstitial oxygen contained in the silicon focus ring is not less than 5x10<17 >atoms / cm<3 >and not more than 1.5x10<18 >atoms / cm<3>, and a producing method for a silicon focus ring used for a plasma apparatus, wherein a single crystal silicon wherein concentration of interstitial oxygen contained in the silicon focus ring is not less than 5x10<17 >atoms / cm<3 >and not more than 1.5x10<18 >atoms / cm<3 >is grown by a Czochralski method, the single crystal silicon is processed in a circle, and a silicon focus ring is produced. There can be provided a silicon focus ring, which can prevent disadvantage due to impurities such as heavy metal.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Nitride semiconductor wafer
ActiveUS7390359B2Maintain good propertiesQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthAluminium silicatesPlane orientationSingle crystal
A nitride semiconductor substrate having properties preferable for the manufacture of various nitride semiconductor devices is made available, by specifying or controlling the local variation in the off-axis angle of the principal surface of the nitride semiconductor substrate. In a nitride semiconductor single-crystal wafer having a flat principal surface, the crystallographic plane orientation of the principal surface of the nitride semiconductor single-crystal wafer varies locally within a predetermined angular range.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Natural-superlattice homologous single crystal thin film, method for preparation thereof, and device using said single crystal thin film
InactiveUS20050039670A1Avoid large deviationImprove insulation performanceTransistorPolycrystalline material growthX-raySingle crystal substrate
Disclosed is a natural-superlattice homologous single-crystal thin film, which comprises a complex oxide which is epitaxially grown on either one of a ZnO epitaxial thin film formed on a single-crystal substrate, the single-crystal substrate after disappearance of the ZnO epitaxial thin film and a ZnO single crystal. The complex oxide is expressed by the a formula: M1M2O3 (ZnO)m, wherein M1 is at least one selected from the group consisting of Ga, Fe, Sc, In, Lu, Yb, Tm, Er, Ho and Y, M2 is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mn, Fe, Ga, In and Al, and m is a natural number of 1 or more. A natural-superlattice homologous single-crystal thin film formed by depositing the complex oxide and subjecting the obtained layered film to a thermal anneal treatment can be used in optimal devices, electronic devices and X-ray optical devices.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
Directed reagents to improve material uniformity
A method for locally controlling the stoichiometry of an epitaxially deposited layer on a semiconductor substrate is provided. The method includes directing a first reactant gas and a doping gas across a top surface of a semiconductor substrate and directing a drive gas and a second reactant gas against the substrate separately from the first reactant gas in a manner that rotates the substrate while introducing the second reactant gas at an edge of the substrate to control each reactant separately, thereby compensating and controlling depletion effects and improving doping uniformity in resulting epitaxial layers on the substrate.
Owner:CREE INC
Device and method for pressure-driven plug transport and reaction
ActiveUS20050087122A1Eliminate evaporationWell mixedMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsPressure.driveCarrier fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Single-source precursors for ternary chalcopyrite materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6992202B1Effective yieldFurnaces without endless coreMaterial nanotechnologyChalcopyriteQuantum dot
A single source precursor for depositing ternary I-III-VI2 chalcopyrite materials useful as semiconductors. The single source precursor has the I-III-VI2 stoichiometry “built into” a single precursor molecular structure which degrades on heating or pyrolysis to yield the desired I-III-VI2 ternary chalcopyrite. The single source precursors effectively degrade to yield the ternary chalcopyrite at low temperature, e.g. below 500° C., and are useful to deposit thin film ternary chalcopyrite layers via a spray CVD technique. The ternary single source precursors according to the invention can be used to provide nanocrystallite structures useful as quantum dots. A method of making the ternary single source precursors is also provided.
Owner:OHIO AEROSPACE INST +1
Method of manufacturing single crystal ingot, and single crystal ingot and wafer manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20140015108A1Increase productionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrucibleIngot
A method of manufacturing a single crystal ingot, and a single crystal ingot and a wafer manufactured thereby are provided. The method of manufacturing a single crystal ingot according to an embodiment includes forming a silicon melt in a crucible inside a chamber, preparing a seed crystal on the silicon melt, and growing a single crystal ingot from the silicon melt, and pressure of the chamber may be controlled in a range of 90 Torr to 500 Torr.
Owner:LG SILTRON
Method of growing a thin film onto a substrate
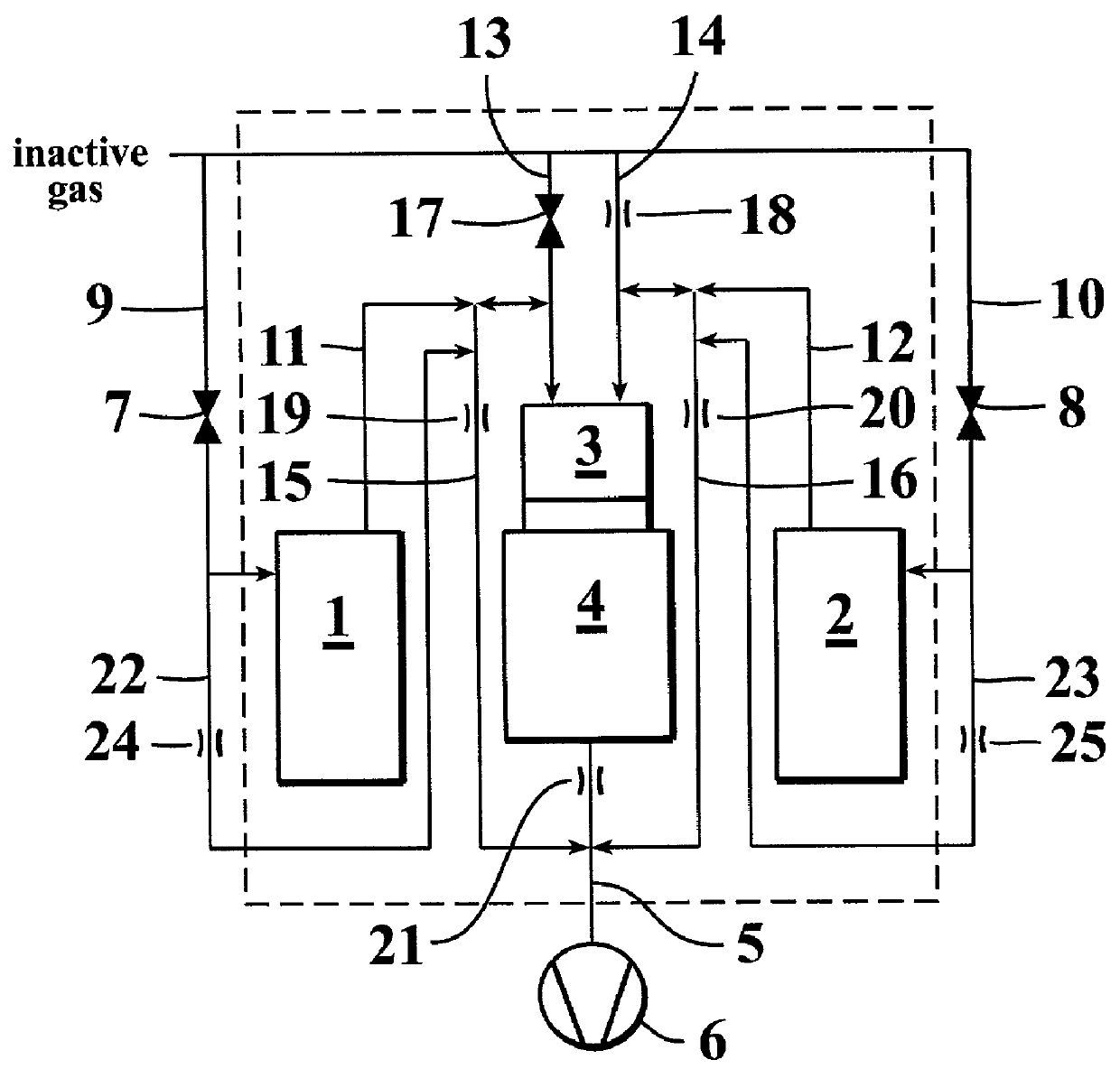
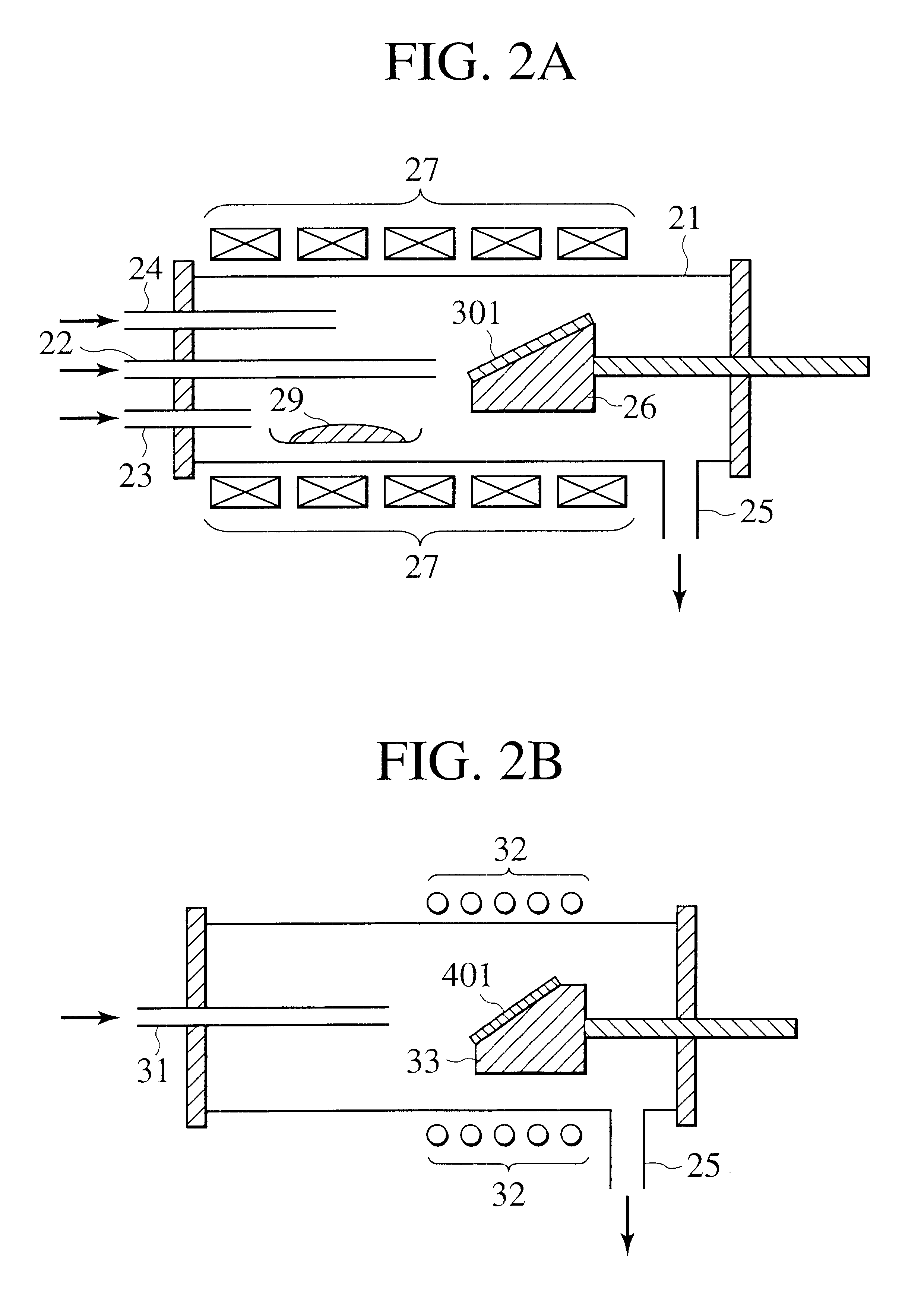
InactiveUS20010054377A1Reduce wasteGuaranteed uptimePressurized chemical processPolycrystalline material growthSurface reactionGas phase
A method of growing a thin film onto a substrate placed in a reaction chamber according to the ALD method by subjecting the substrate to alternate and successive surface reactions. The method includes providing a first reactant source and providing an inactive gas source. A first reactant is fed from the first reactant source in the form of repeated alternating pulses to a reaction chamber via a first conduit. The first reactant is allowed to react with the surface of the substrate in the reaction chamber. Inactive gas is fed from the inactive gas source into the first conduit via a second conduit that is connected to the first conduit at a first connection point so as to create a gas phase barrier between the repeated alternating pulses of the first reactant entering the reaction chamber. The inactive gas is withdrawn from said first conduit via a third conduit connected to the first conduit at a second connection point.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for preparing epitaxial-substrate and method for manufacturing semiconductor device employing the same
InactiveUS6627552B1Improve convenienceImprove surface morphologyPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystalSemiconductor
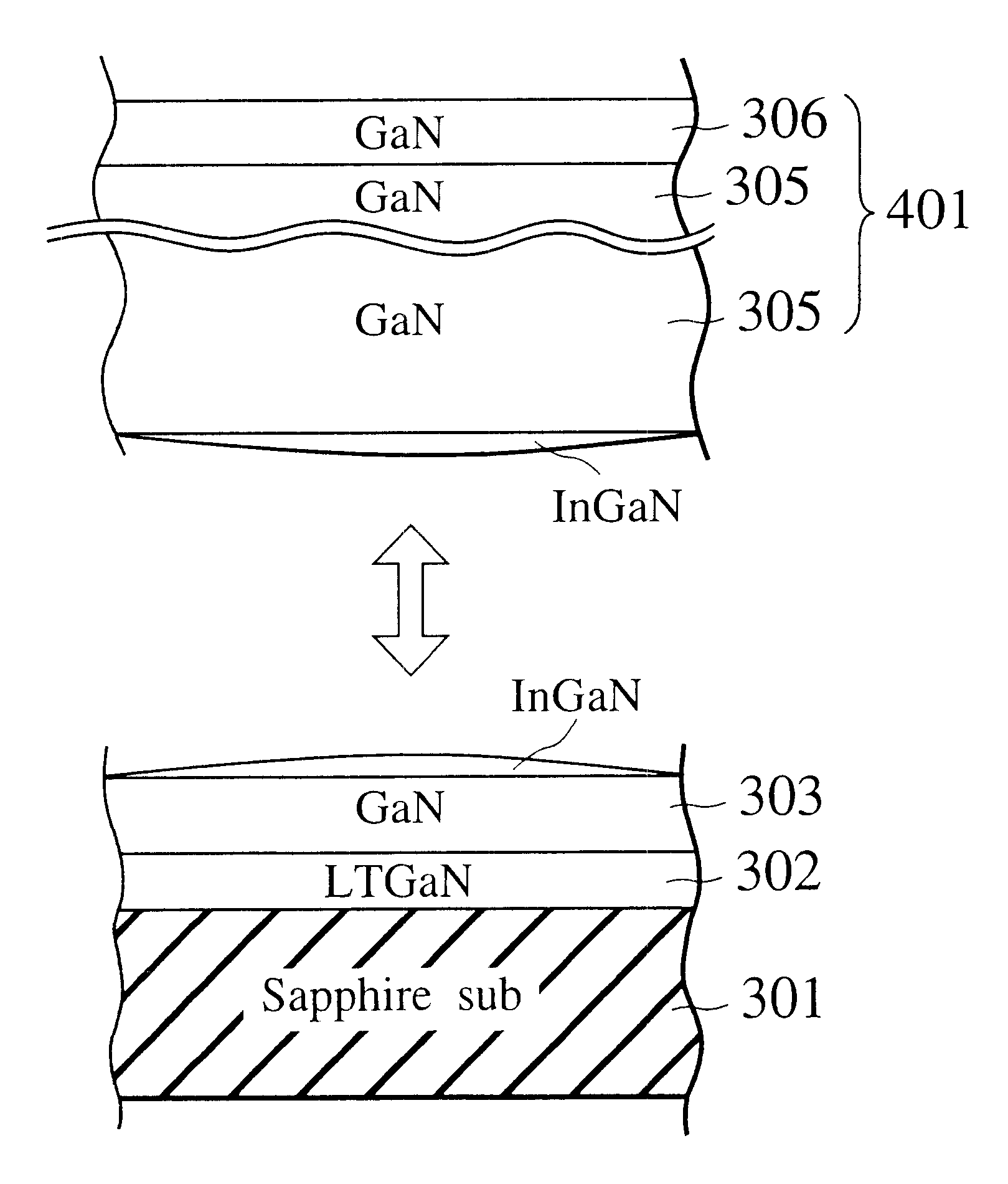
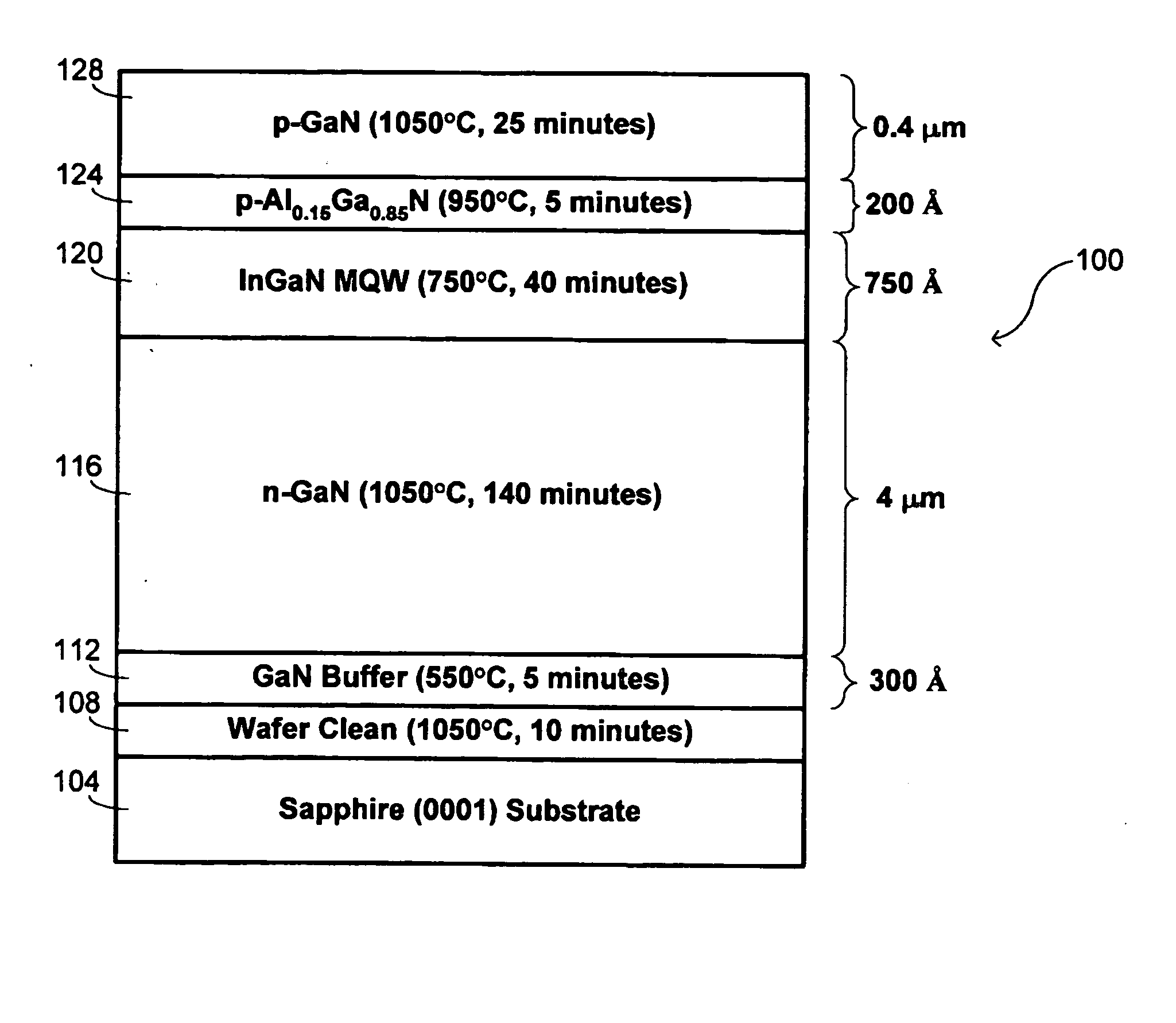
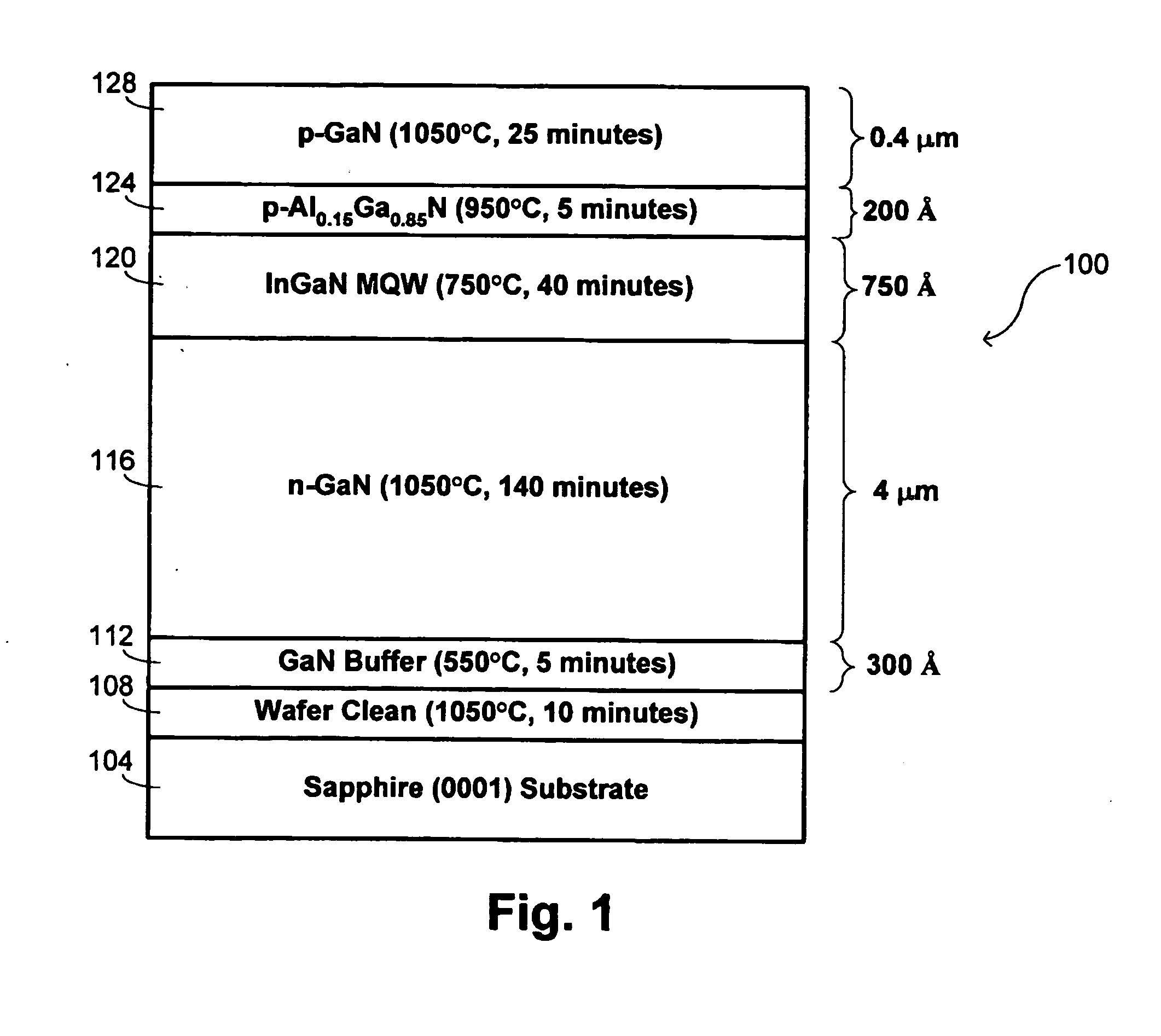
The present invention provides a method for preparing epitaxial-substrate, for growing a multilayered structure of GaN based semiconductor layers on the epitaxial-substrate so as to construct a semiconductor device such as blue-emitting laser diode and LED. The method for preparing the epitaxial-substrate encompasses (a) growing a first GaN based semiconductor layer on a bulk-substrate; (b) growing an InGaN based semiconductor layer on the first GaN based semiconductor layer; (c) growing a second GaN based semiconductor layer on the InGaN based semiconductor layer; and (d) separating the second GaN based semiconductor layer from the first GaN based semiconductor layer to provide the epitaxial-substrate. The epitaxial-substrate having a high crystallographic perfection and an excellent surface morphology is obtained simply and in a short time. The defect density of the single crystalline GaN based semiconductor layer film grown on the epitaxial-substrate is greatly reduced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Scintillating substance and scintillating wave-guide element
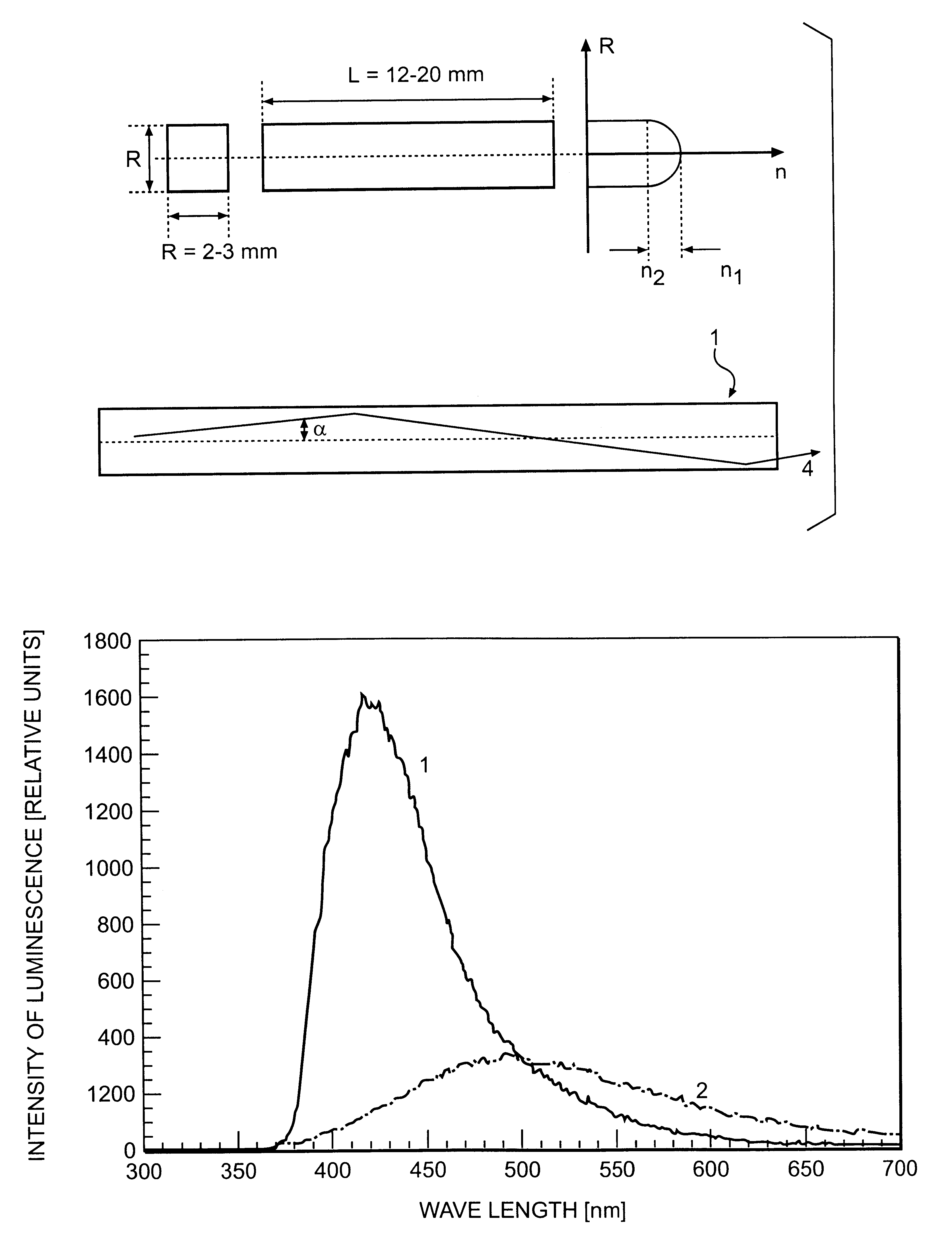
InactiveUS6278832B1Improve light outputShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberAdditive ingredient
The invention is related to nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry, namely to the measurement of x-ray, gamma and alpha radiation; control for trans uranium nuclides in the habitat of a man; non destructive control for the structure of heavy bodies; three dimensional positron-electron computer tomography, etc.The essence of the invention is in additional ingredients in a chemical composition of a scintillating material based on crystals of oxyorthosilicates, including cerium Ce and crystallized in a structural type Lu2SiO5.The result of the invention is the increase of the light output of the luminescence, decrease of the time of luminescence of the ions Ce3+, increase of the reproducibility of grown crystals properties, decrease of the cost of the source melting stock for growing scintillator crystals, containing a large amount of Lu2O3, the raise of the effectiveness of the introduction of SCintillating crystal luminescent radiation into a glass waveguide fibre, prevention of cracking of crystals during the production of elements, creation of waveguide properties in scintillating elements, exclusion of expensive mechanical polishing of their lateral surface.
Owner:SOUTHBOURNE INVESTMENTS
Nitride Single Crystal Seeded Growth in Supercritical Ammonia with Alkali Metal Ion
ActiveUS20080156254A1Increase in sizeShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsDissolutionSingle crystal
The present invention is related to a process for obtaining a larger area substrate of mono-crystalline gallium-containing nitride by making selective crystallization of gallium containing nitride on a smaller seed under a crystallization temperature and / or pressure from a supercritical ammonia-containing solution made by dissolution of gallium-containing feedstock in a supercritical ammonia-containing solvent with alkali metal ions, comprising: providing two or more elementary seeds, and making selective crystallization on the two or more separate elementary seeds to get a merged larger compound seed. The merged larger compound seed is used for a seed in a new growth process and then to get a larger substrate of mono-crystal gallium-containing nitride.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
Anneal of epitaxial layer in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7416605B2From gel statePolycrystalline material growthCharge carrier mobilityDegree Celsius
An anneal of an epitaxially grown crystalline semiconductor layer comprising a combination of group-IV elements. The layer contains at least one of the group of carbon and tin. The layer of epitaxially grown material is annealed at a temperature substantially in a range of 1,000 to 1,400 degrees Celsius for a period not to exceed 100 milliseconds within 10% of the peak temperature. The anneal is performed for example with a laser anneal or a flash lamp anneal. The limited-time anneal may improve carrier mobility of a transistor.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Semiconductor wafers with non-standard crystal orientations and methods of manufacturing the same
The crystal orientations of monocrystalline semiconductor wafers may be varied by four parameters. The first parameter is the type of crystal seed used to grow the monocrystalline semiconductor ingot from which the wafers are cut. The second parameter is the angle at which the wafer is sliced from the ingot. The third parameter is the crystal plane towards which the wafer is cut. And, the fourth parameter is the position of the orientation indication feature that is used to align the wafer during processing. Different combinations of these parameters provide variations of non-standard crystal orientations of monocrystalline semiconductor wafers and semiconductor-on-insulator substrates such as silicon-on-insulator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
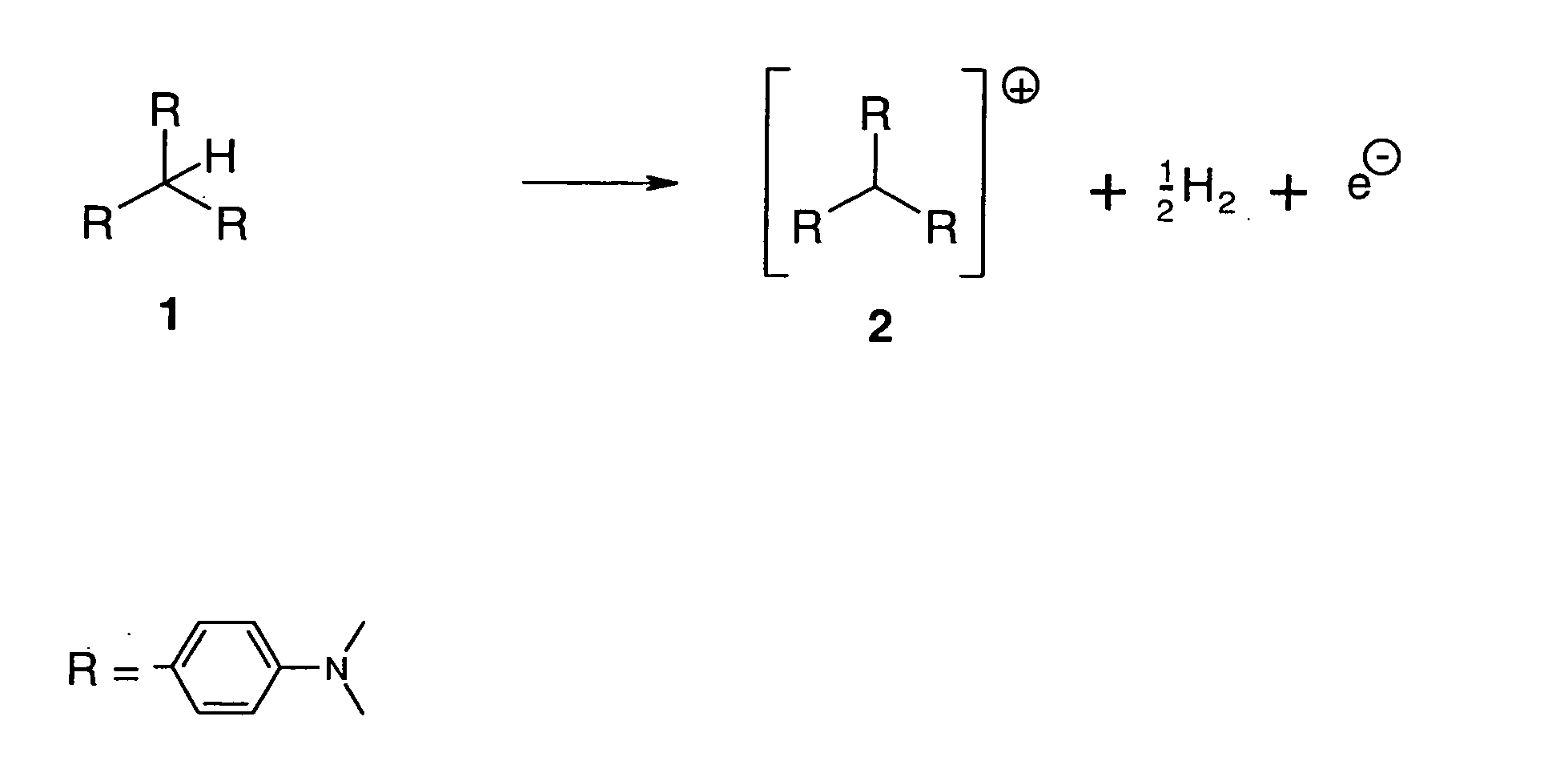
Doped organic semiconductor materials and process for their preparation
ActiveUS20050061232A1Simple materialHigh light efficiencyOrganic chemistryFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier mobility
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of doped organic semiconductor materials having an increased charge carrier density and effective charge carrier mobility, by doping with a dopant, a process in which after mixing the dopant into the organic semiconductor material, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, nitrogen or hydroxyl radicals are split off and at least one electron is transferred to the semiconductor material or from the semiconductor material. The process is distinguished by the fact that an uncharged organic compound is used as dopant. Doped organic semiconductor materials are obtainable by one of the processes. The semiconductor materials are distinguished by the fact that the doped layer contains cations of at least one organic compound, the uncharged form of the organic compound being unstable in air.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
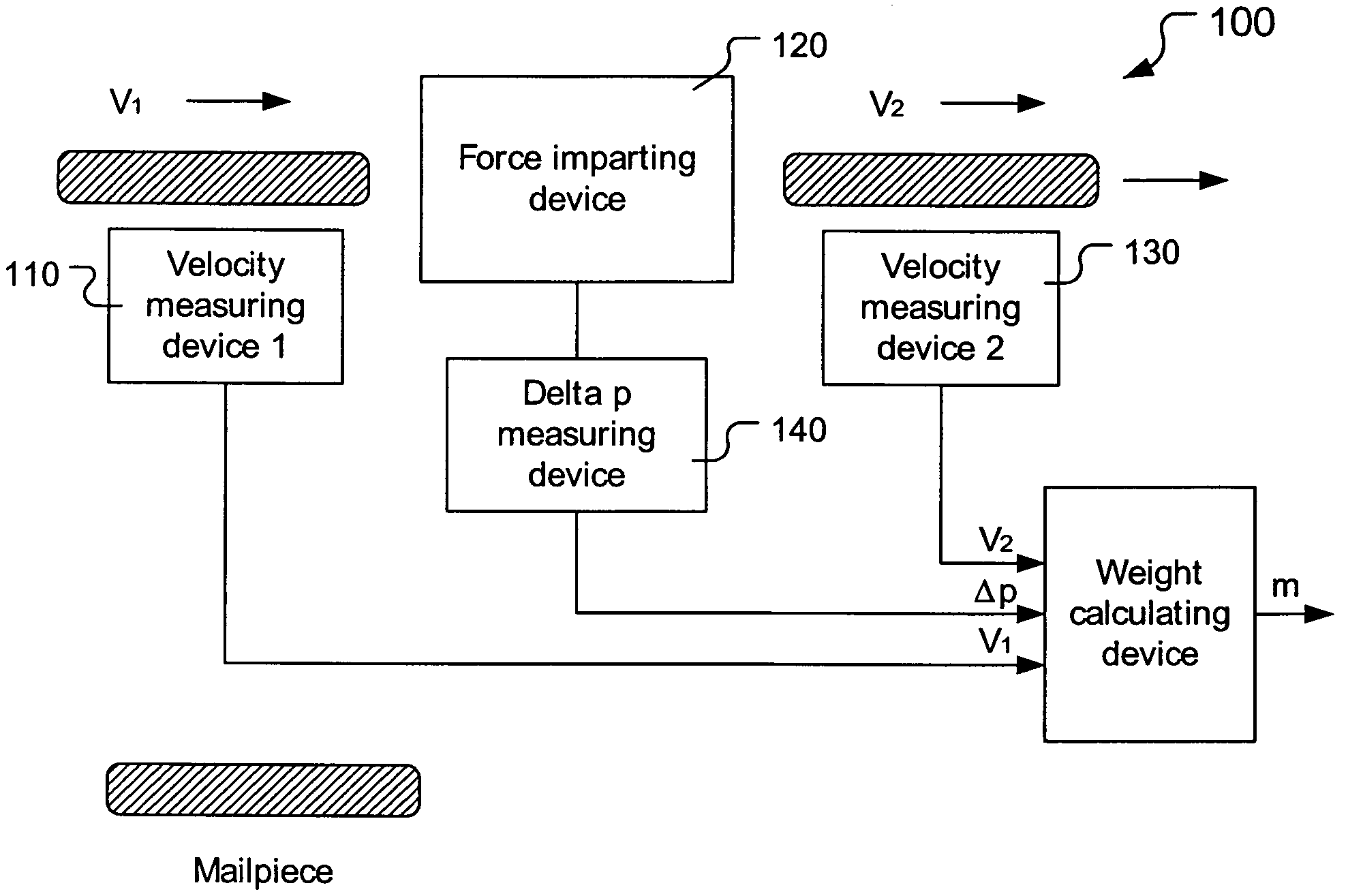
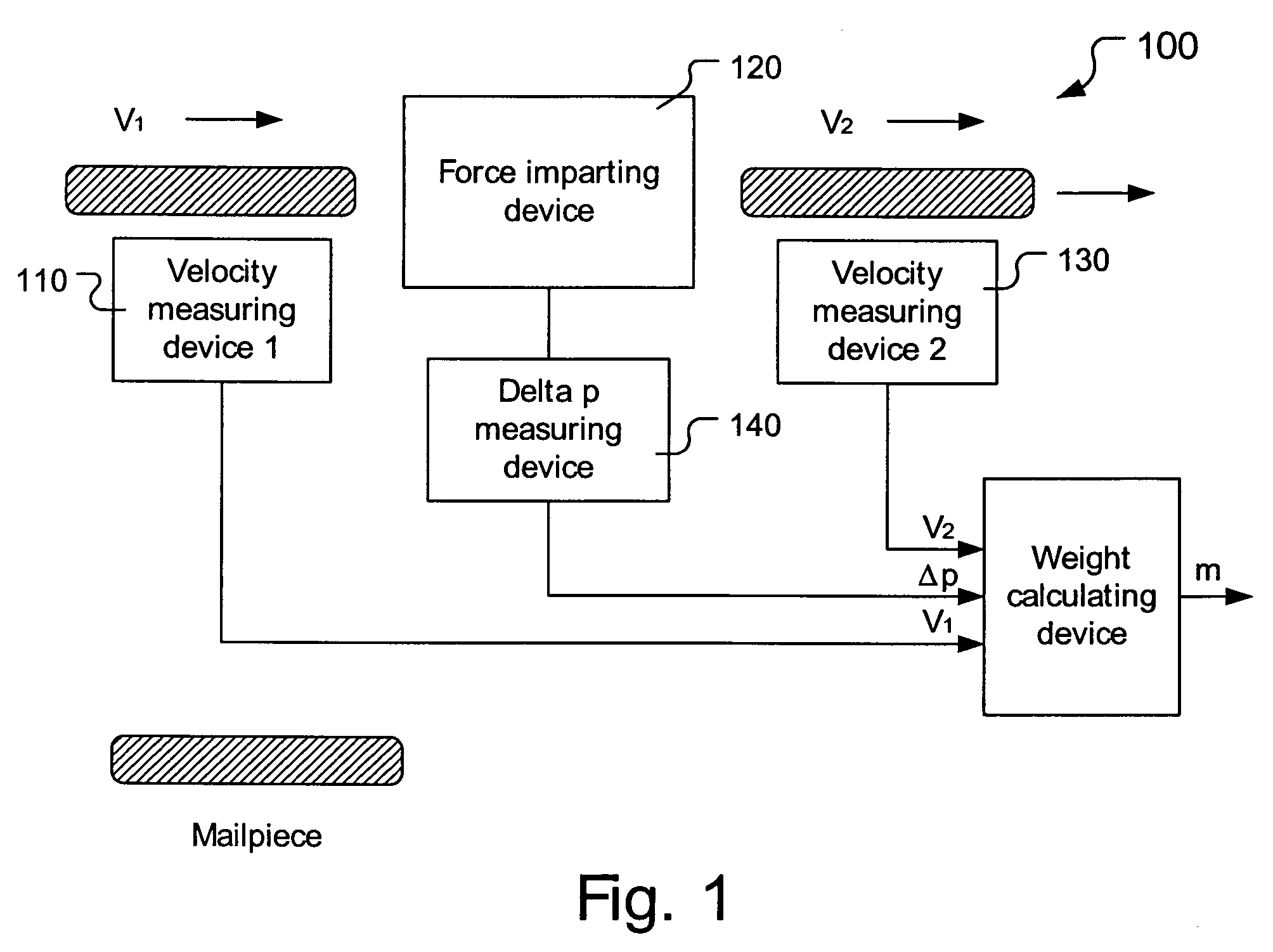
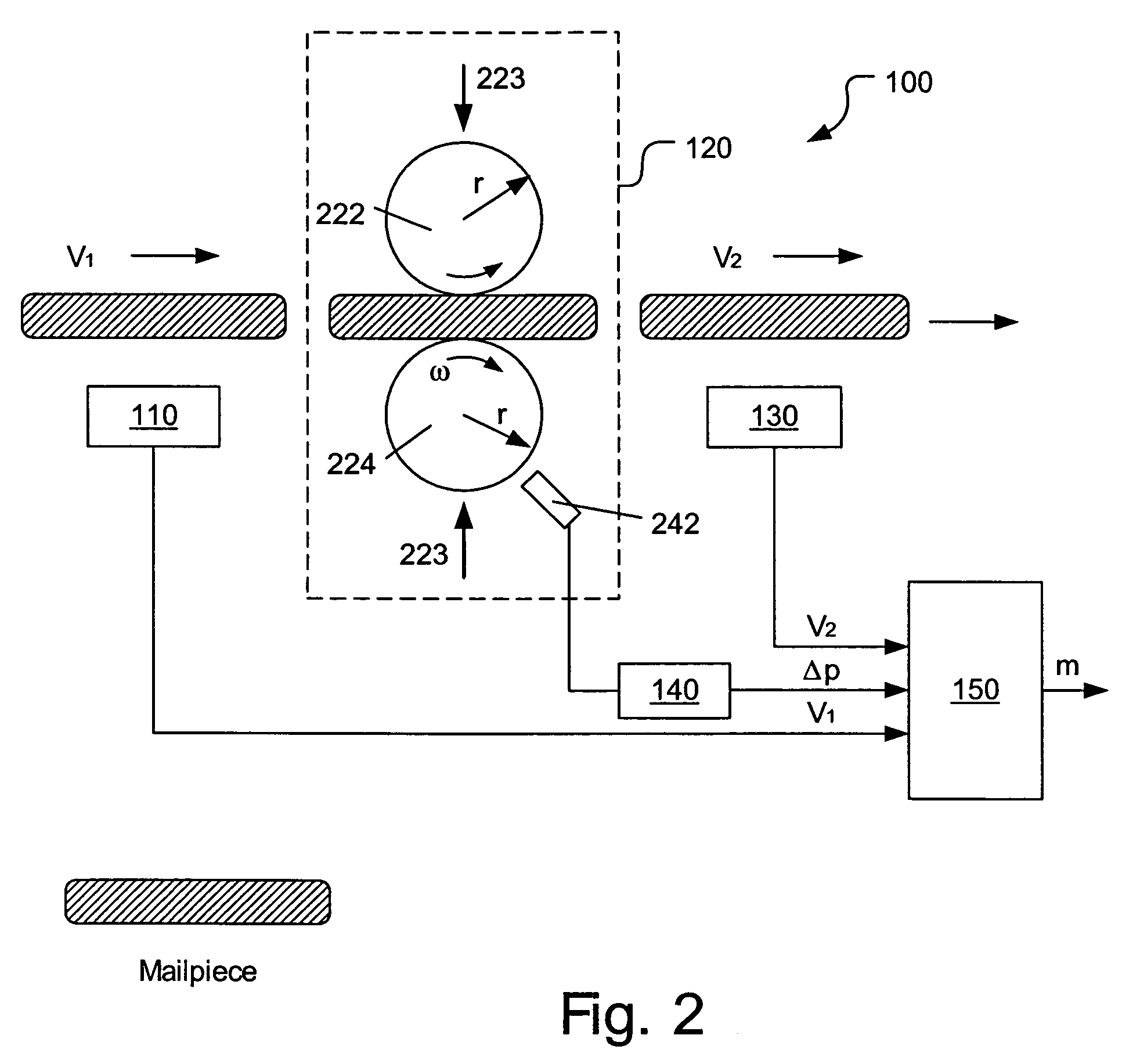
Method and apparatus for determining weight of moving mailpieces
The invention pertains to a mailpiece weight measuring apparatus for use with a high speed automatic mailpiece processing system. The weight measuring apparatus measures the inertial mass of the mailpiece as the weight equivalent. The apparatus includes a device for determining a first velocity of a mailpiece, a device for imparting a force to the mailpiece in a direction co-linear with the first velocity so that the mailpiece exits said force impacting device at a second velocity, a device for determining the second velocity of the mailpiece, a device for determining a change in a parameter proportional to the force imparted on the mailpiece, and a device for determining the weight of the mailpiece based upon the determined first velocity, second velocity and change in the parameter.
Owner:DMT SOLUTIONS GLOBAL CORP
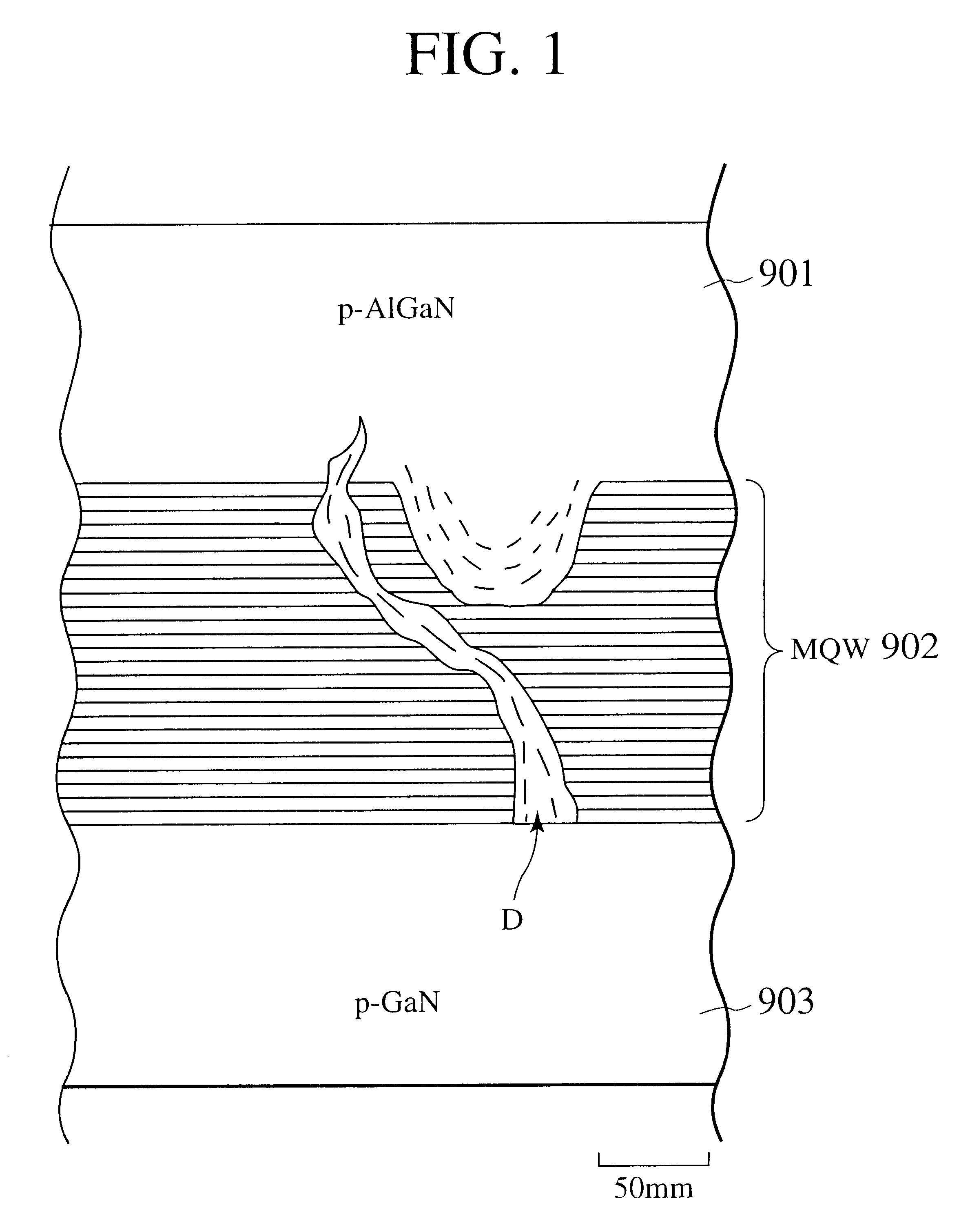
Epitaxial growth of compound nitride semiconductor structures
InactiveUS20070240631A1Quick upgradeImprove uniformityAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseThermal chemical vapor deposition
Apparatus and methods are described for fabricating a compound nitride semiconductor structure. Group-III and nitrogen precursors are flowed into a first processing chamber to deposit a first layer over a substrate with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process. The substrate is transferred from the first processing chamber to a second processing chamber. Group-III and nitrogen precursors are flowed into the second processing chamber to deposit a second layer over the first layer with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process. The first and second group-III precursors have different group-III elements.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Aluminum oxide material for optical data storage
InactiveUS6846434B2Increase of write/read rateHigh data storage densityPolycrystalline material growthPhotosensitive materialsVacancy defectDopant
The present invention provides aluminum oxide crystalline materials including dopants and oxygen vacancy defects and methods of making such crystalline materials. The crystalline materials of the present invention have particular utility in optical data storage applications.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device as well as solid-state image sensing device and method for producing the same
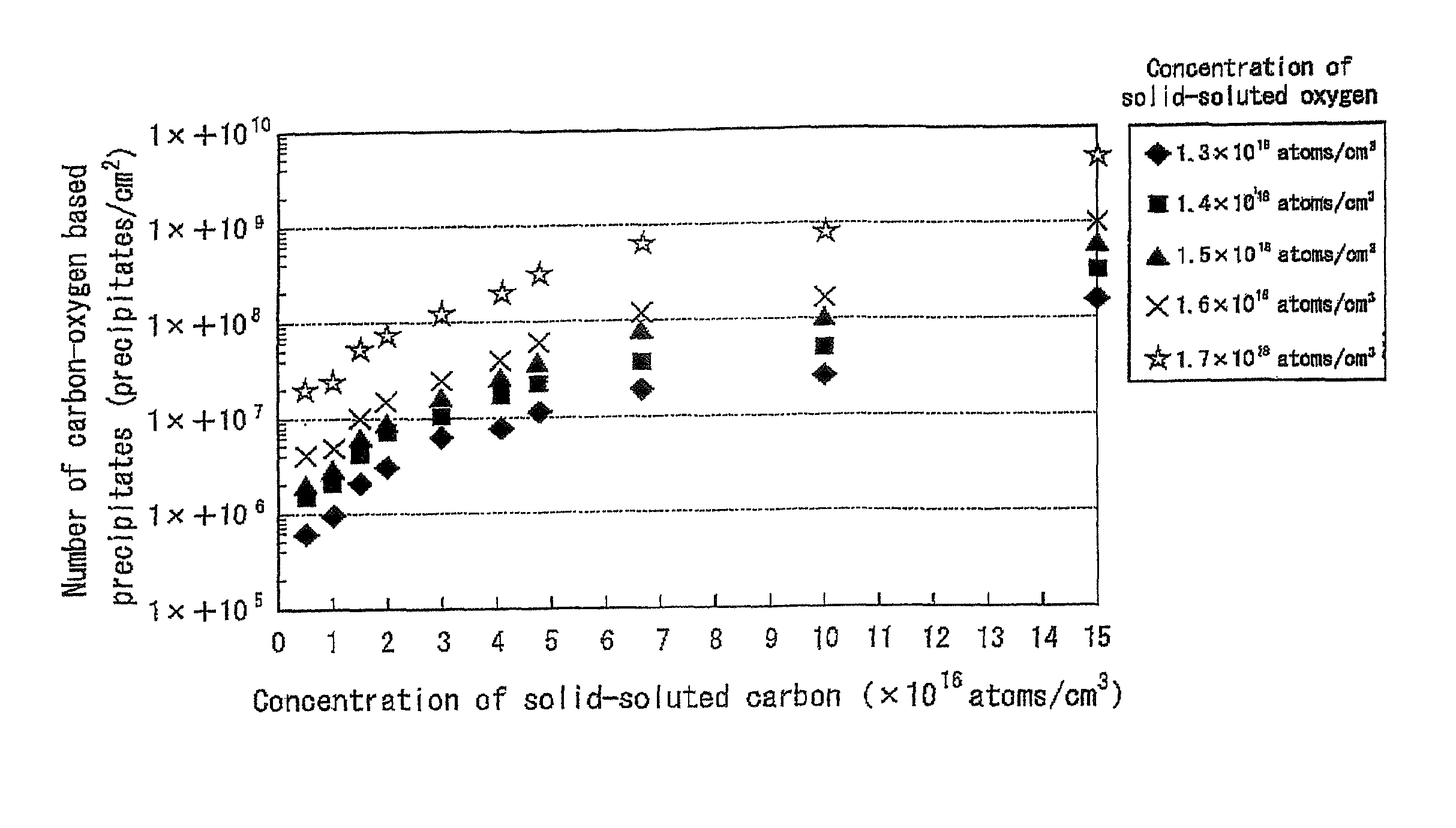
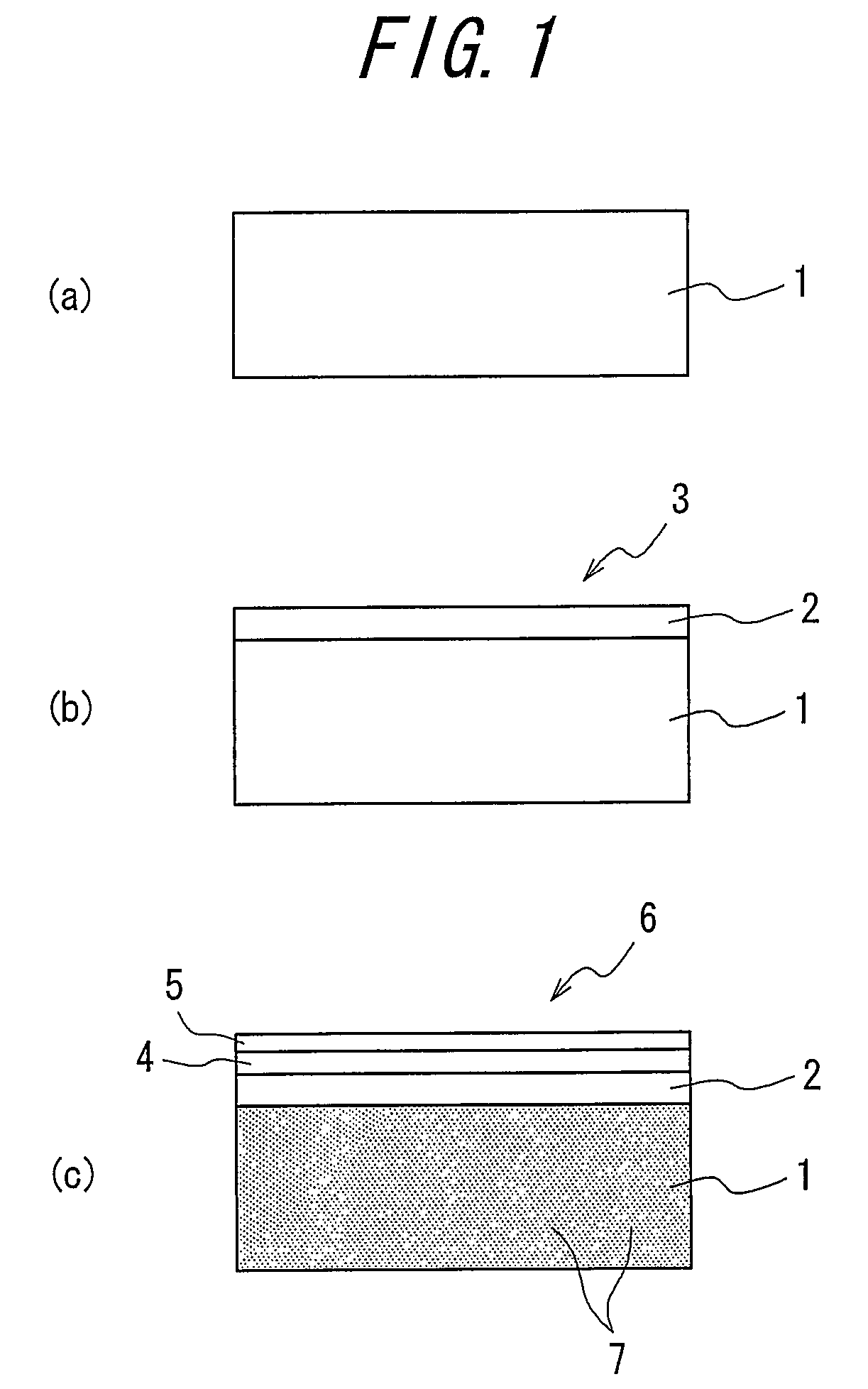
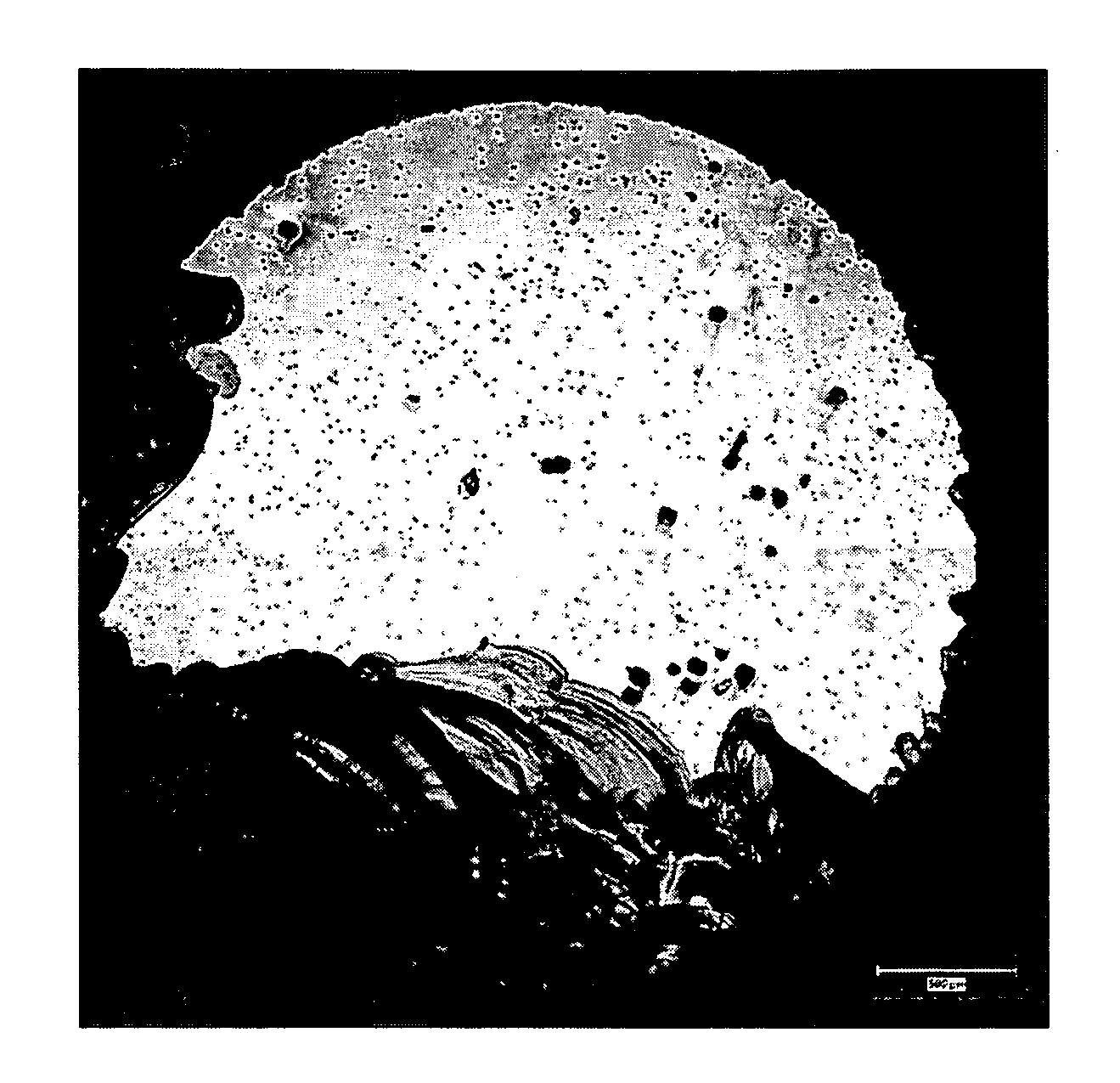
ActiveUS8063466B2Improve inhalation effectGood electric characteristicPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCarbon ionOxygen
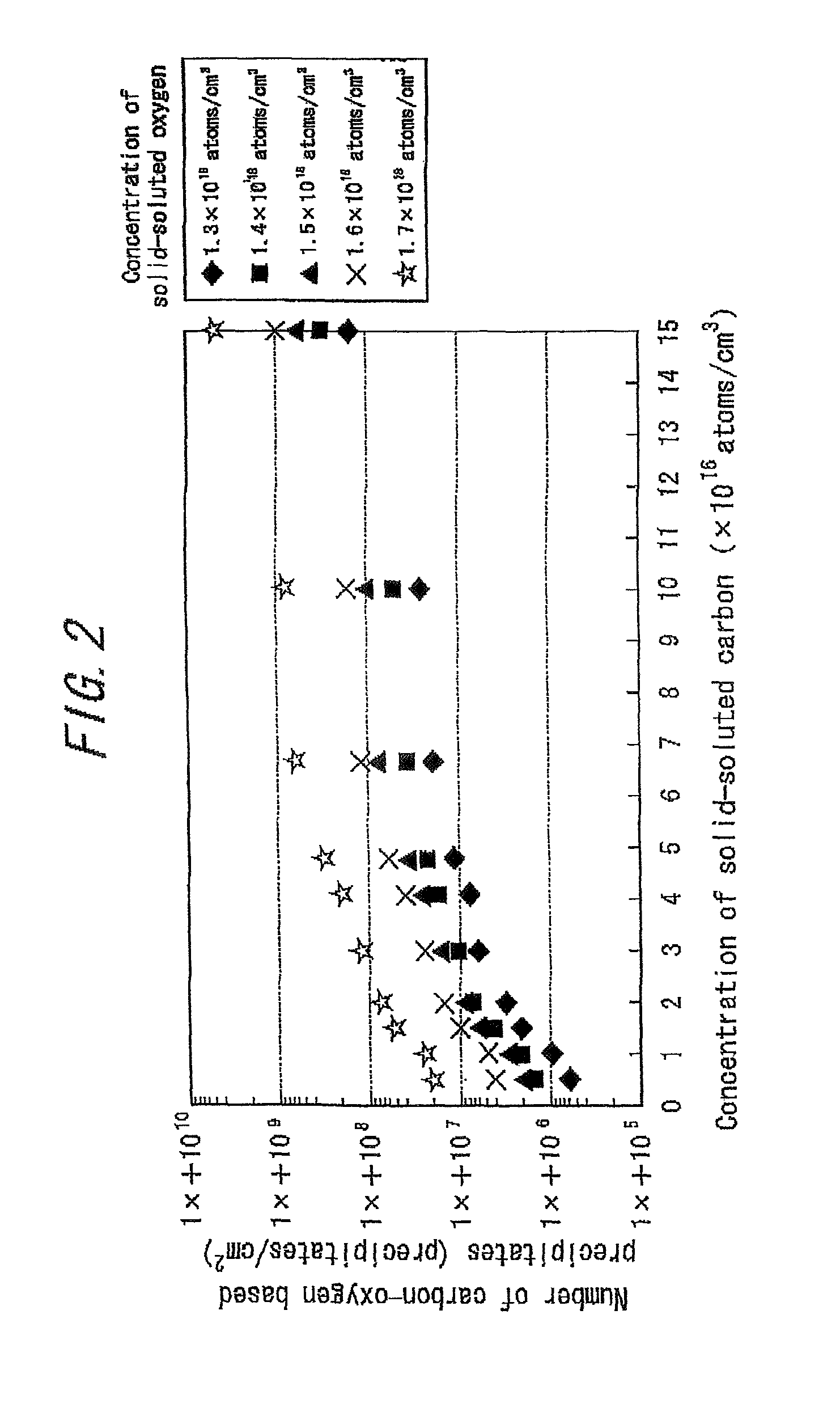
There is provided a semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device in which the production cost is lower than that of a gettering method through a carbon ion implantation and problems such as occurrence of particles at a device production step and the like are solved.Silicon substrate contains solid-soluted carbon having a concentration of 1×1016-1×1017 atoms / cm3 and solid-soluted oxygen having a concentration of 1.4×1018-1.6×1018 atoms / cm3.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for reducing defect concentration in crystals
ActiveUS20060096521A1Reduce defect concentrationRelieve pressureAfter-treatment detailsUltra-high pressure processesDiamond crystalHigh pressure cell
A method for removing defects at high pressure and high temperature (HP / HT) or for relieving strain in a non-diamond crystal commences by providing a crystal, which contains defects, and a pressure medium. The crystal and the pressure medium are disposed in a high pressure cell and placed in a high pressure apparatus, for processing under reaction conditions of sufficiently high pressure and high temperature for a time adequate for one or more of removing defects or relieving strain in the single crystal.
Owner:SLT TECH
Process and apparatus for large-scale manufacturing of bulk monocrystalline gallium-containing nitride
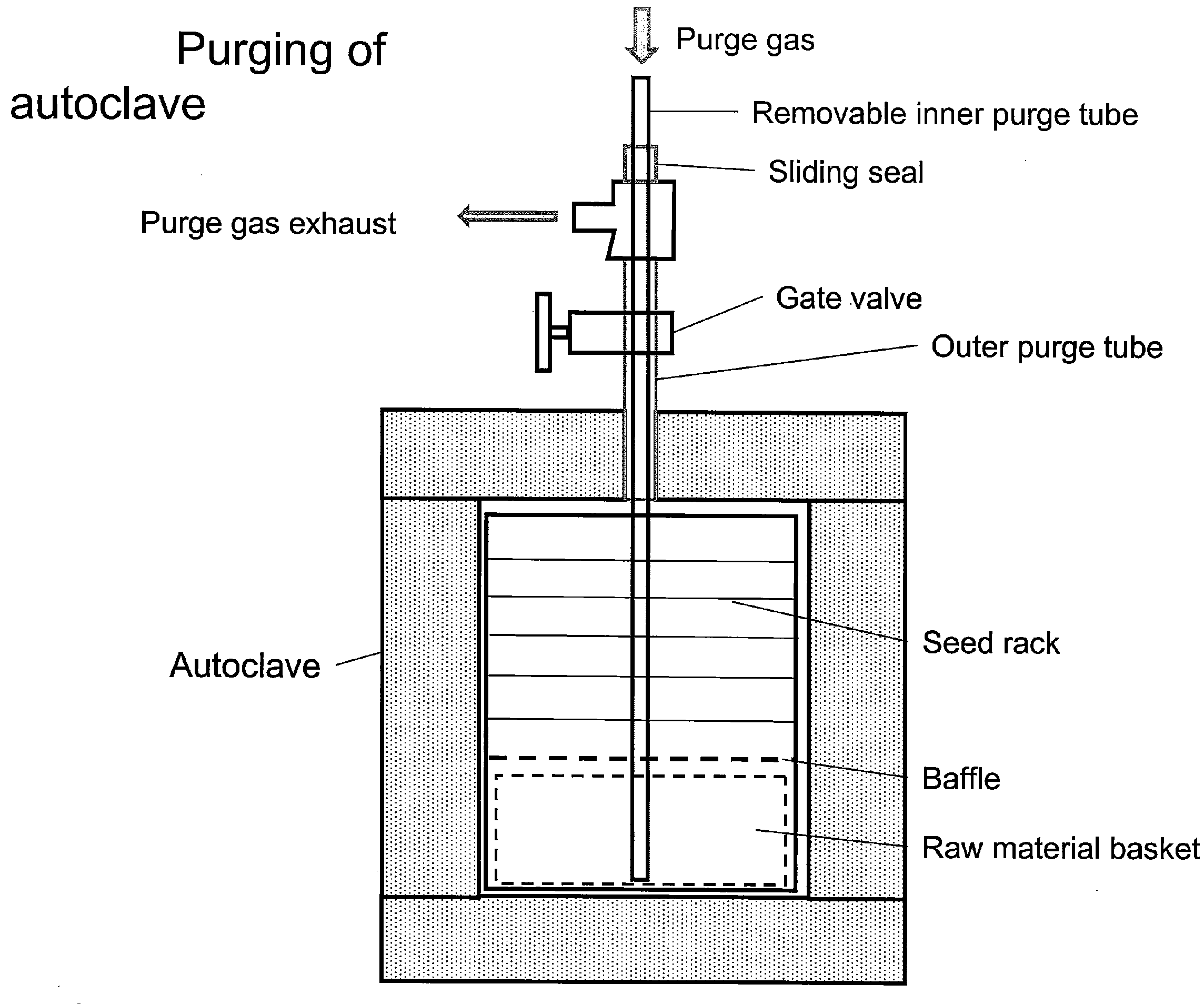
ActiveUS20100031876A1Cost-effectiveSimple and cost-effective to manufacturePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCost effectivenessSingle crystal
A method for large-scale manufacturing of gallium nitride includes a process for reducing and / or minimizing contamination in the crystals, for solvent addition to an autoclave, for improving or optimizing the solvent atmosphere composition, for removal of the solvent from the autoclave, and for recycling of the solvent. The method is scalable up to large volumes and is cost effective.
Owner:SLT TECH
Microvolume crystallization method employing multiple lumens
InactiveUS6872250B2Facilitates the device being rotatedMaterial crystallisationPolycrystalline material growthCrystallizationCrystal
A method for determining crystallization conditions for a material, the method comprising: taking a microfluidic device comprising one or more lumens having microvolume dimensions and a plurality of different crystallization samples within the one or more lumens, the plurality of crystallization samples comprising a material to be crystallized and crystallization conditions that vary among the plurality of crystallization samples; transporting the plurality of different crystallization samples within the lumens; and identifying a precipitate or crystal formed in the one or more lumens.
Owner:TAKEDA SAN DIEGO
High temperature high pressure capsule for processing materials in supercritical fluids
InactiveUS20050152820A1From normal temperature solutionsUltra-high pressure processesHigh pressureSolvent
A capsule for containing at least one reactant and a supercritical fluid in a substantially air-free environment under high pressure, high temperature processing conditions. The capsule includes a closed end, at least one wall adjoining the closed end and extending from the closed end; and a sealed end adjoining the at least one wall opposite the closed end. The at least one wall, closed end, and sealed end define a chamber therein for containing the reactant and a solvent that becomes a supercritical fluid at high temperatures and high pressures. The capsule is formed from a deformable material and is fluid impermeable and chemically inert with respect to the reactant and the supercritical fluid under processing conditions, which are generally above 5 kbar and 550° C. and, preferably, at pressures between 5 kbar and 80 kbar and temperatures between 550° C. and about 1500° C. The invention also includes methods of filling the capsule with the solvent and sealing the capsule, as well as an apparatus for sealing the capsule.
Owner:SLT TECH
Method for forming nitride crystals
A method for growing a nitride crystal and a crystalline composition selected from one of AlN, InGaN, AlGaInN, InGaN, and AlGaNInN is provided. The composition comprises a true single crystal, grown from a single nucleus, at least 1 mm in diameter, free of lateral strain and tilt boundaries, with a dislocation density less than about 104 cm−2.
Owner:SLT TECH
Method and Device For Comminuting and Sorting Polysilicon
ActiveUS20070235574A1Increase productionPolycrystalline material growthSiliconEngineeringPolycrystalline silicon
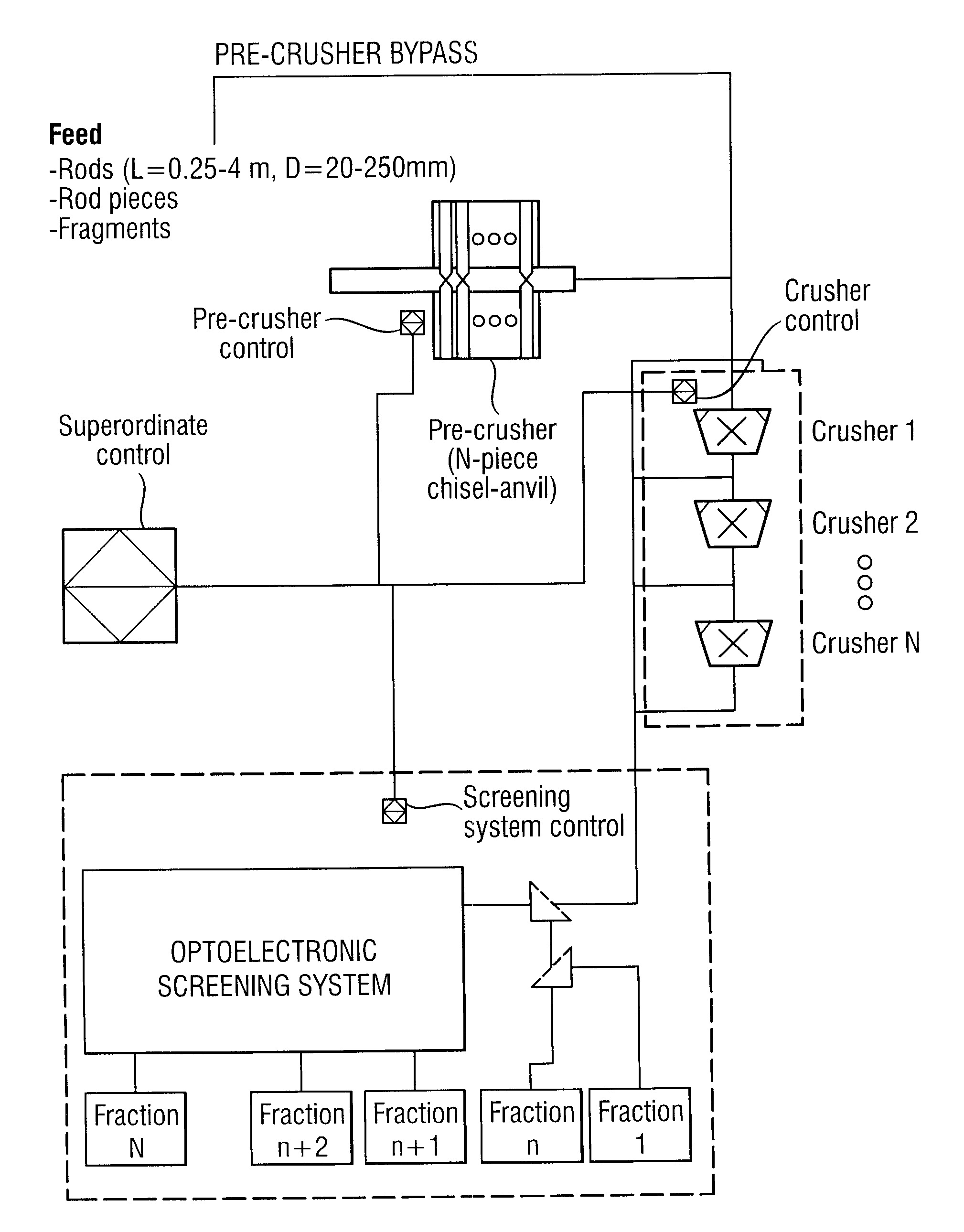
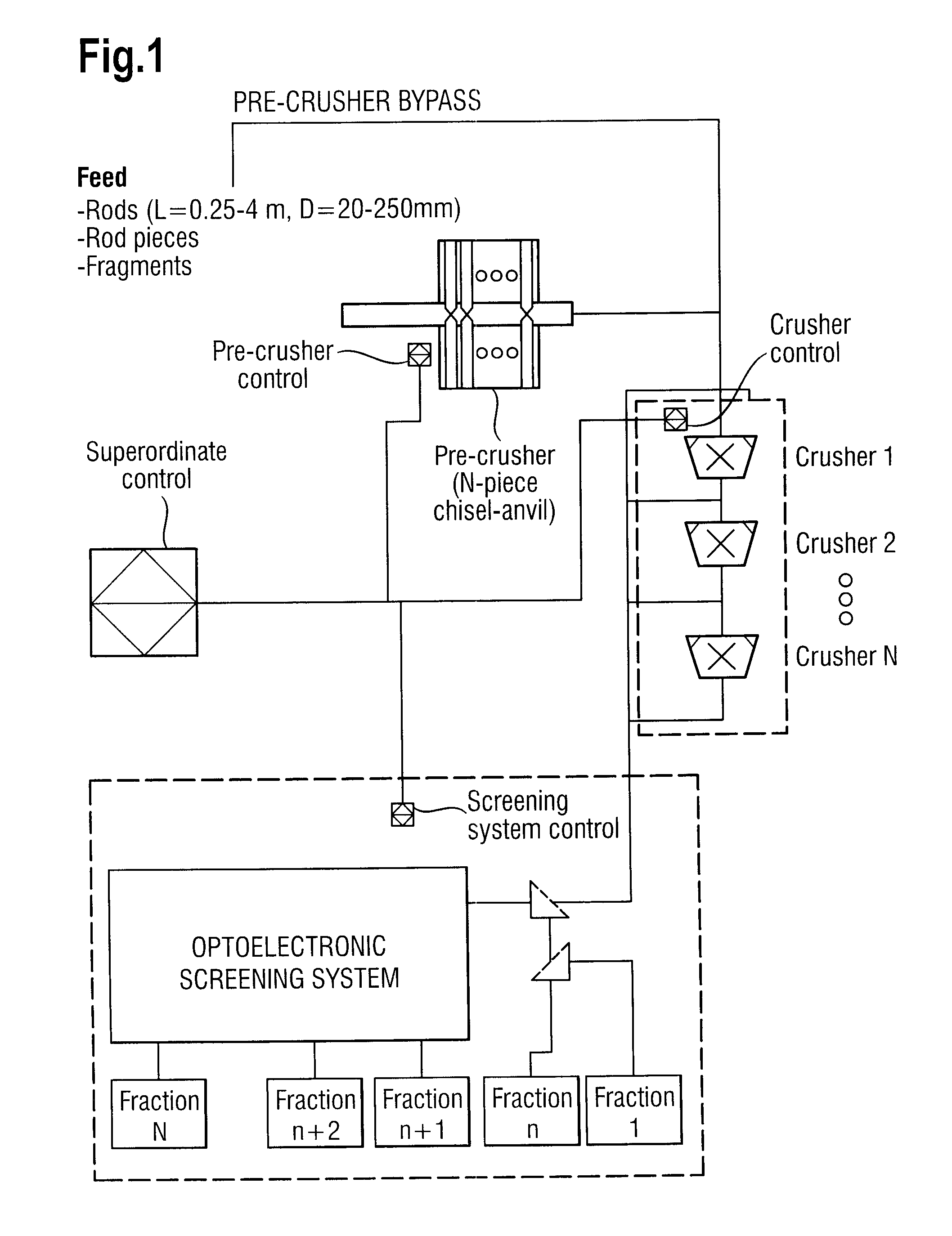
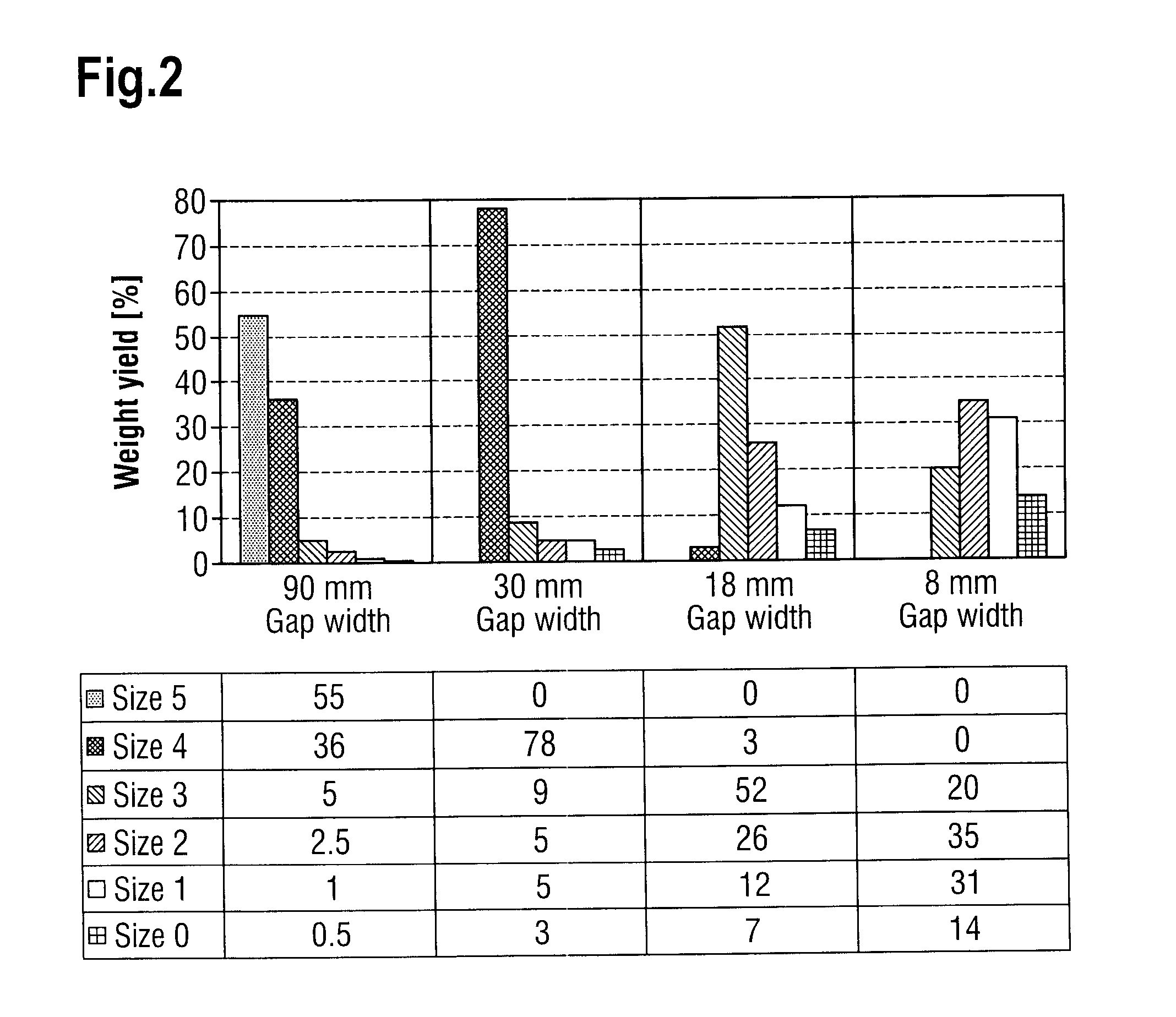
The invention relates to a device for comminuting and sorting polycrystalline silicon, comprising an instrument for feeding a coarse polysilicon fraction into a crushing system, the crushing system associated with a sorting system for classifying the polysilicon fraction, wherein the device is provided with a controller which allows variable adjustment of at least one crushing parameter in the crushing system and / or at least one sorting parameter in the sorting system.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Silicon Casting Apparatus and Method of Producing Silicon Ingot
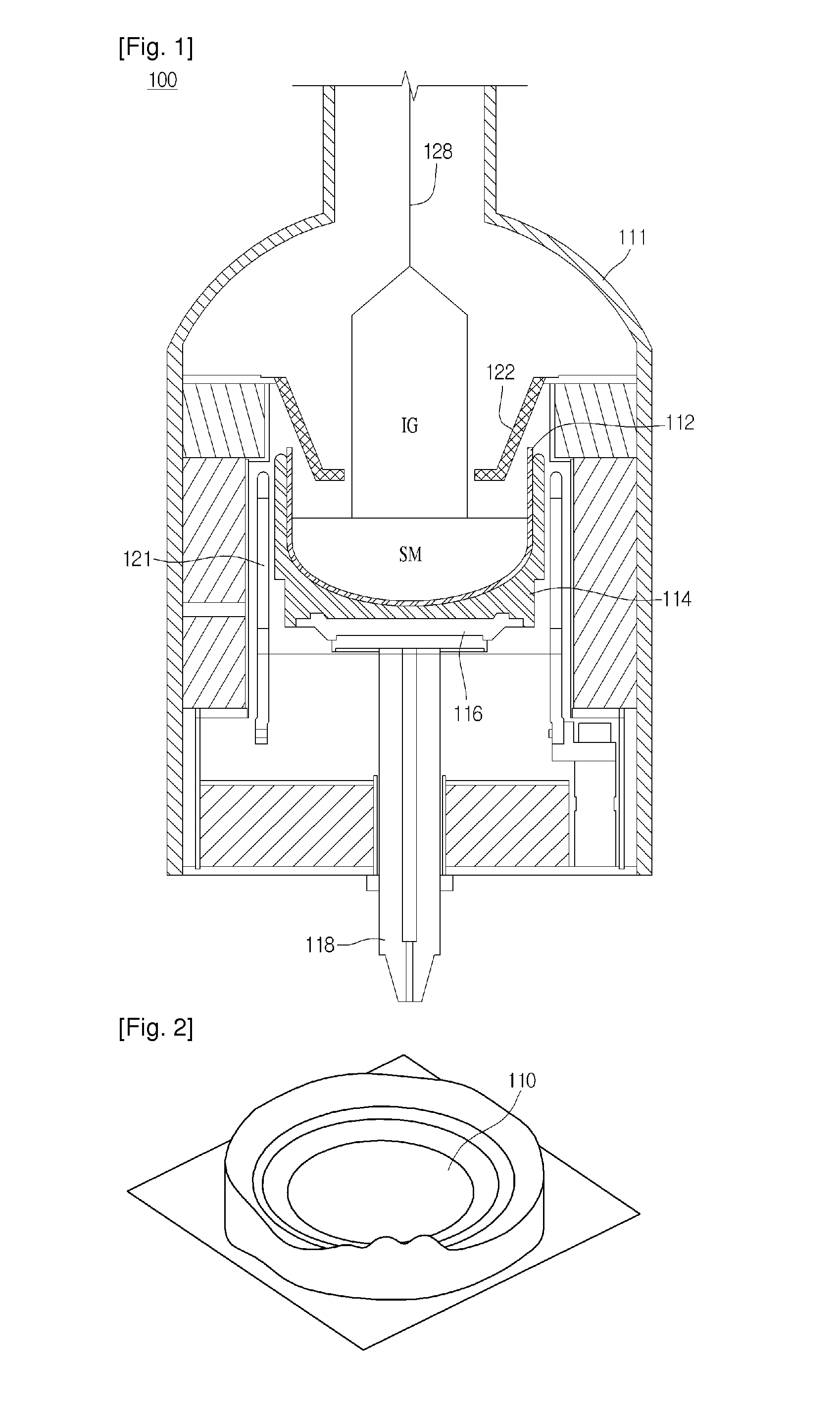
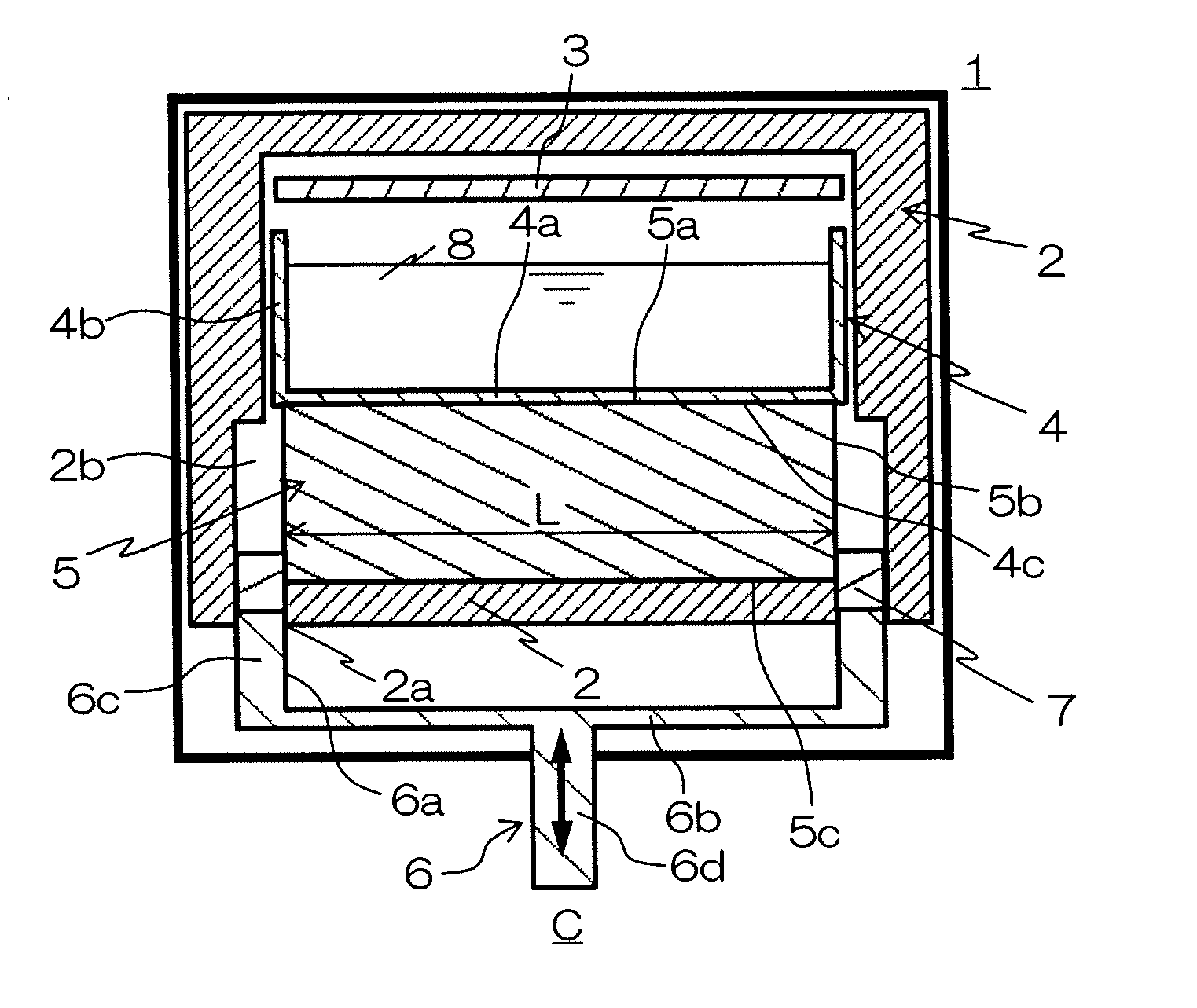
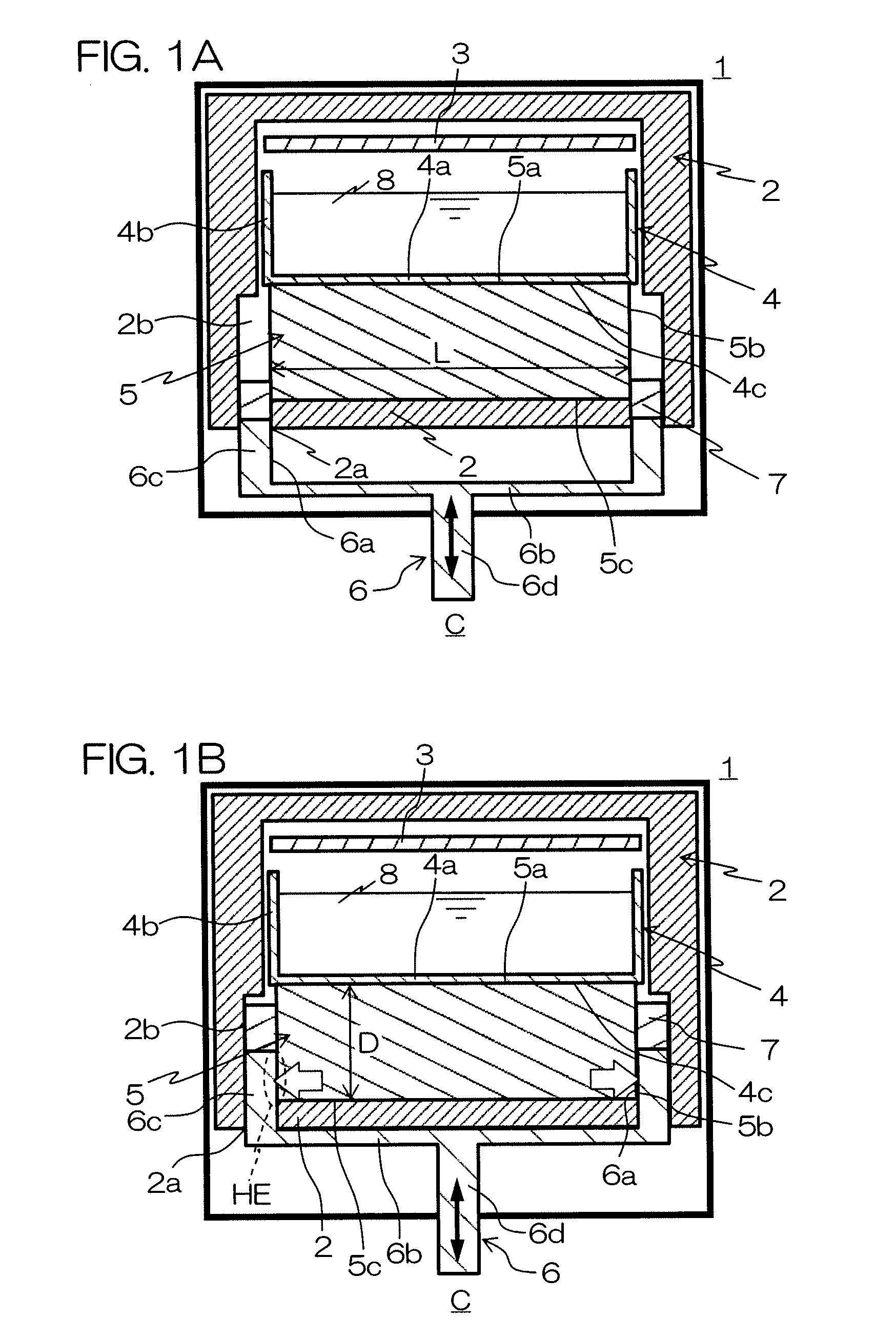
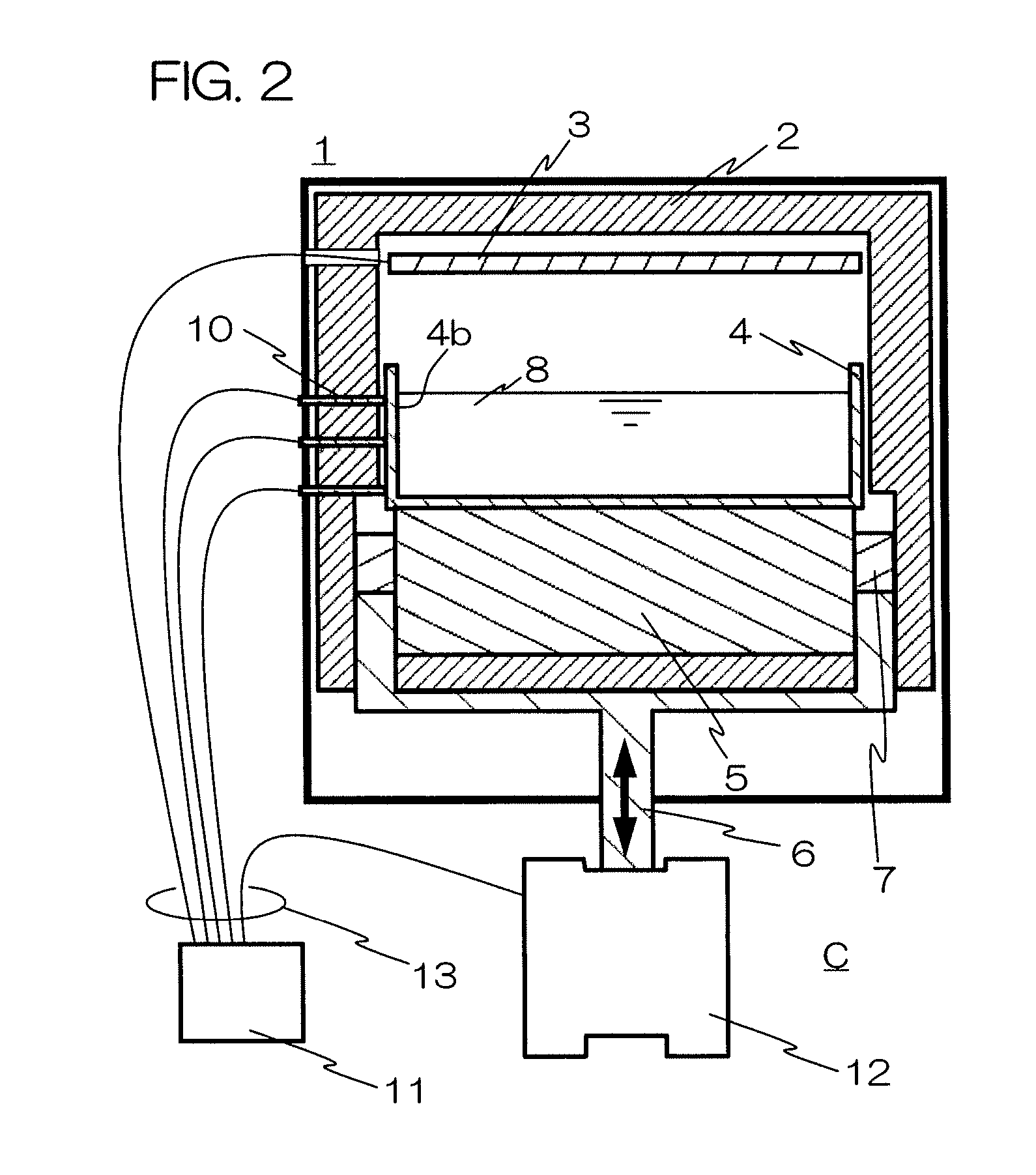
InactiveUS20070227189A1Good reproducibilityLow costFinal product manufactureGlass drawing apparatusIngotTemperature gradient
A silicon casting apparatus for producing polycrystal silicon ingot by heating a silicon melt (8) held in a mold (4) from above by a heater (3) and cooling it from below while changing the heat exchange area of a heat exchange region (HE), defined between a pedestal (5) having the mold (4) placed thereon and a bottom cooling member (6), in such a manner as to keep pace with the rise of the solid-liquid interface of the silicon melt (8), thereby causing unidirectional solidification upward along the mold (4); and a method of producing polycrystal silicon ingot using such apparatus. According to this production method, the temperature gradient given to the silicon melt (8) can be maintained at constant by adjusting the heat exchange area, so that polycrystal silicon ingot having good characteristics can be produced with good reproducibility.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Silicon purifying method, slag for purifying silicon and purified silicon
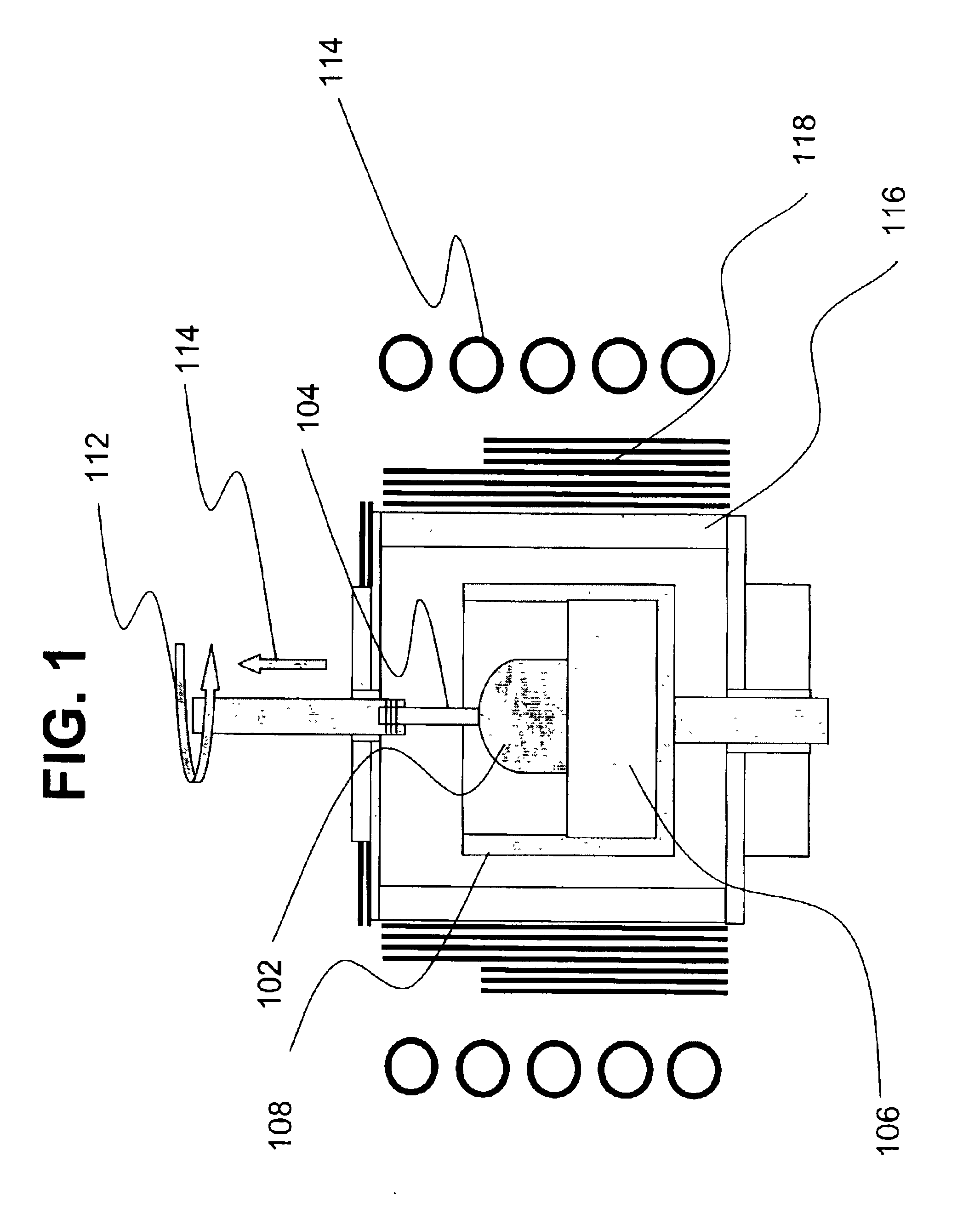
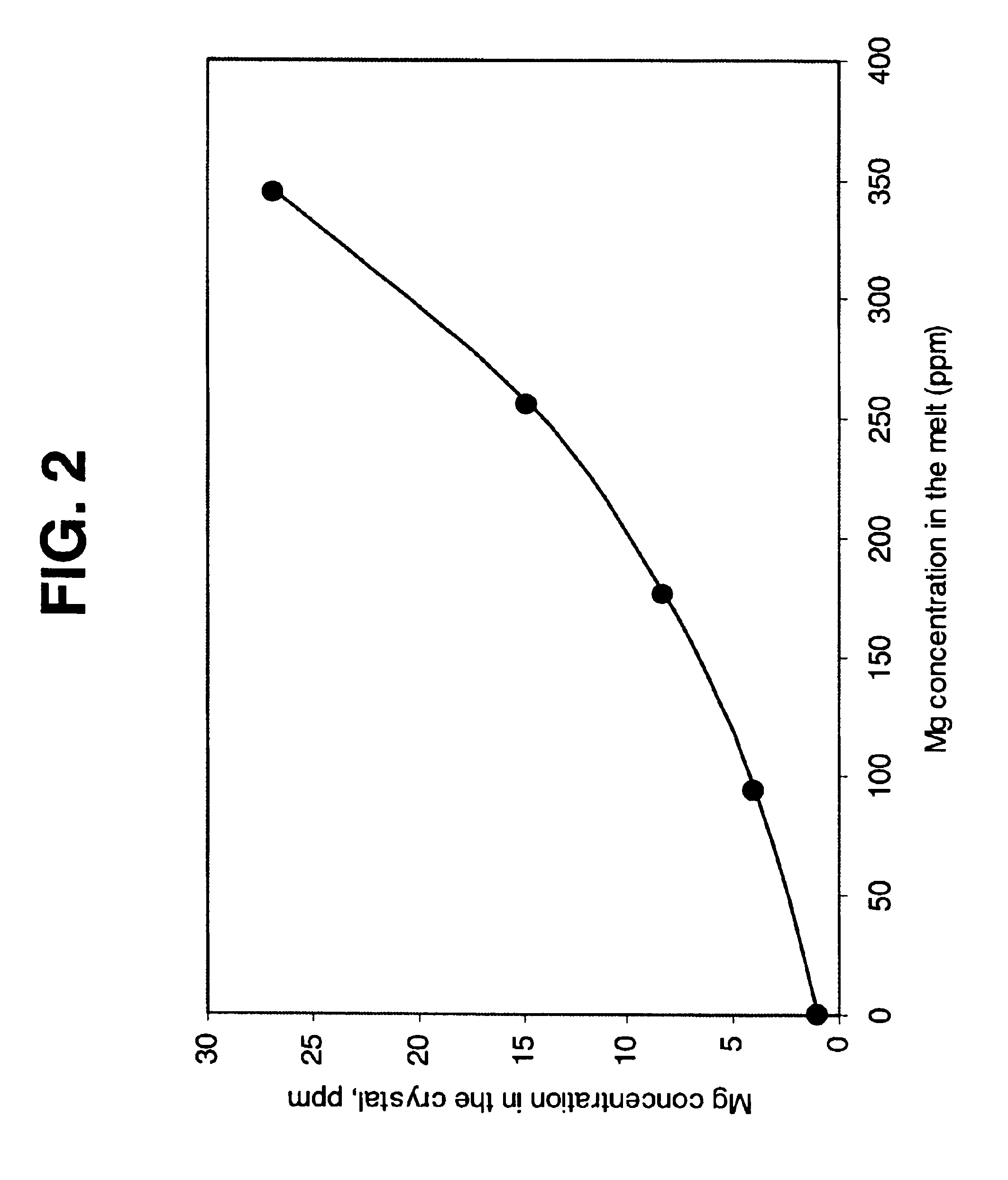
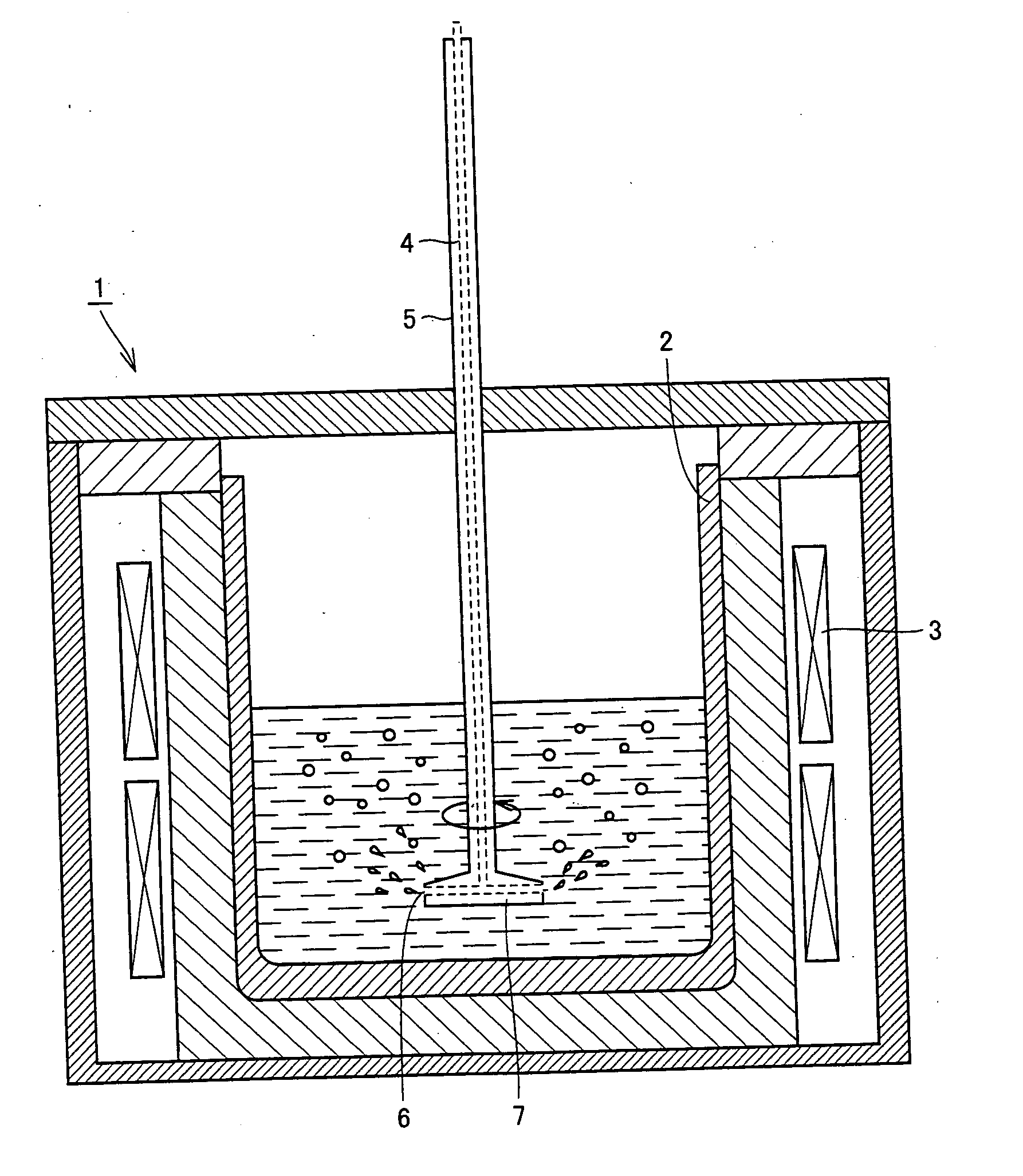
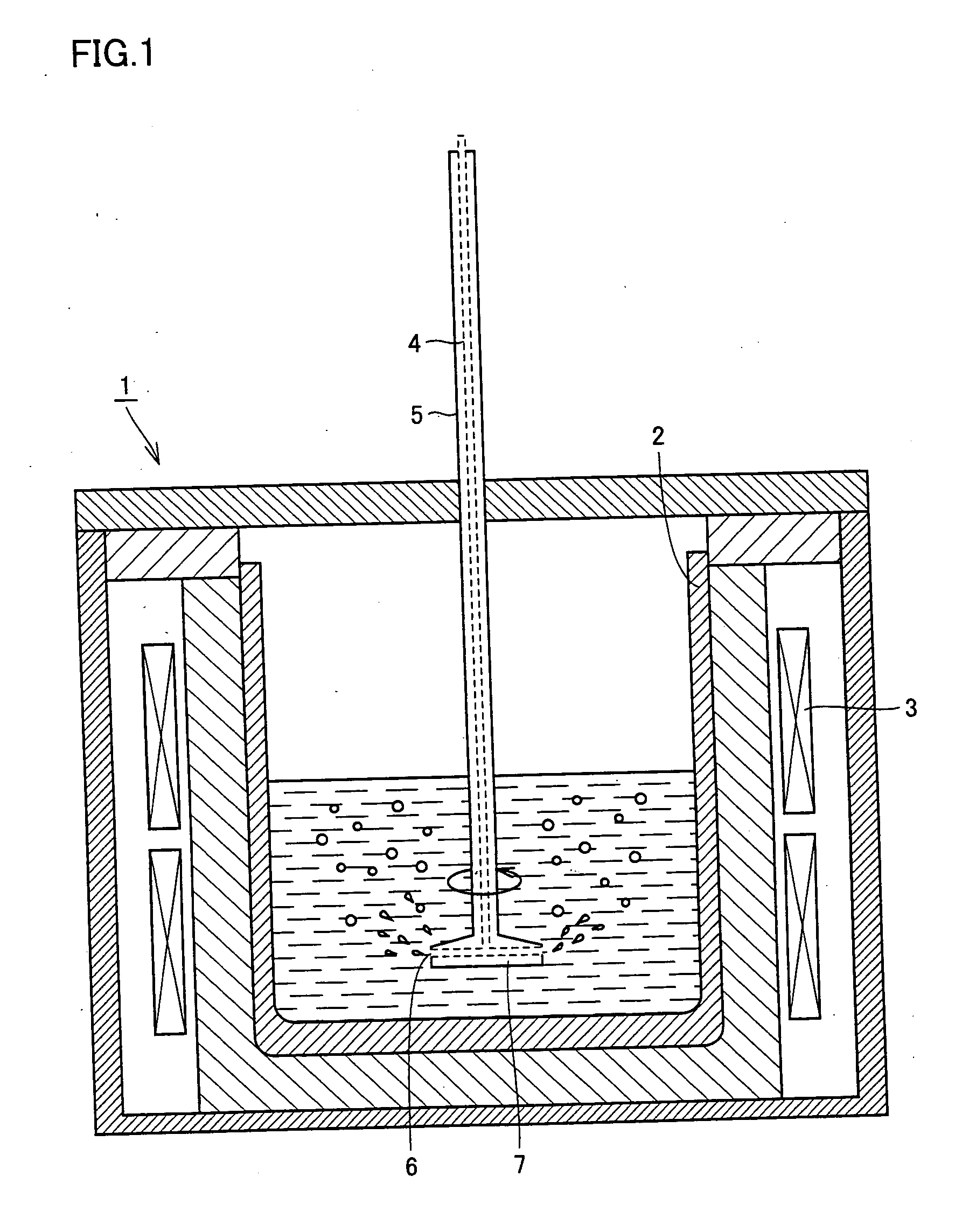
InactiveUS20050139148A1Low-priced processEfficient purificationPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltWater vaporSilicon oxide
Method capable of preparing silicon having purity of about 6N applied to a solar cell efficiently at a low cost. Raw silicon containing boron and a slag are melted and a shaft is rotated by a rotating / driving mechanism for stirring the molten silicon. The molten slag is dispersed in the molten silicon, thereby accelerating the boron removal reaction. It is further effective to use a slag containing at least 45 percent by mass of silicon oxide or to blow gas mixed with water vapor into the molten silicon for refining reaction.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com