Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Good electric characteristic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
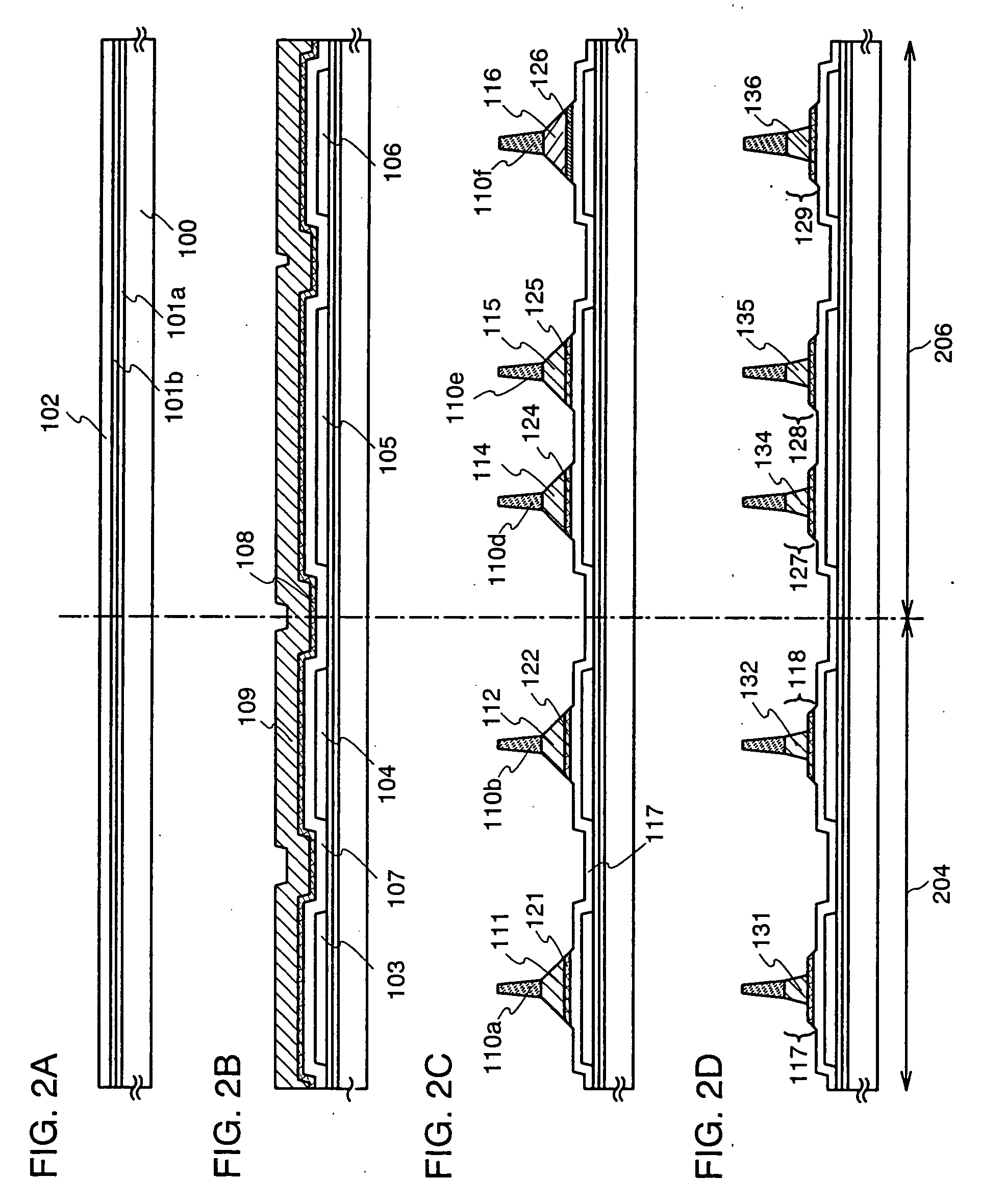
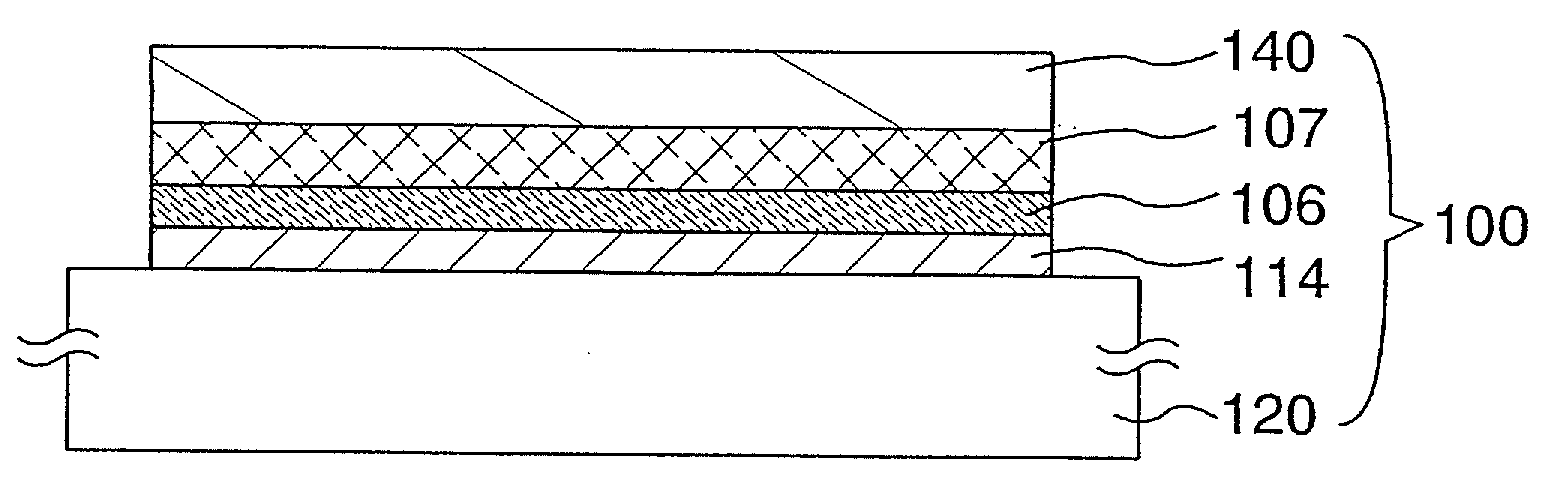
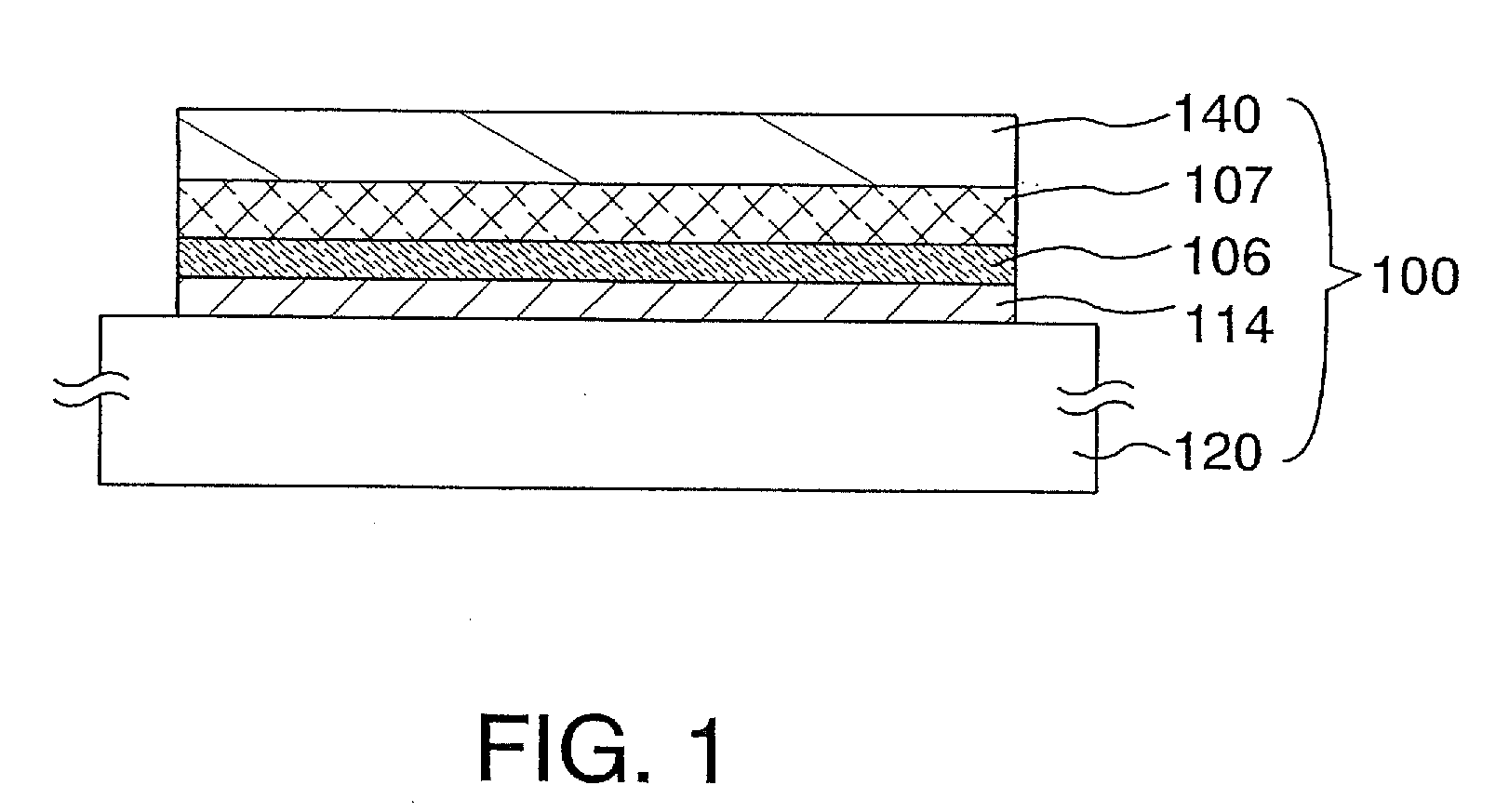
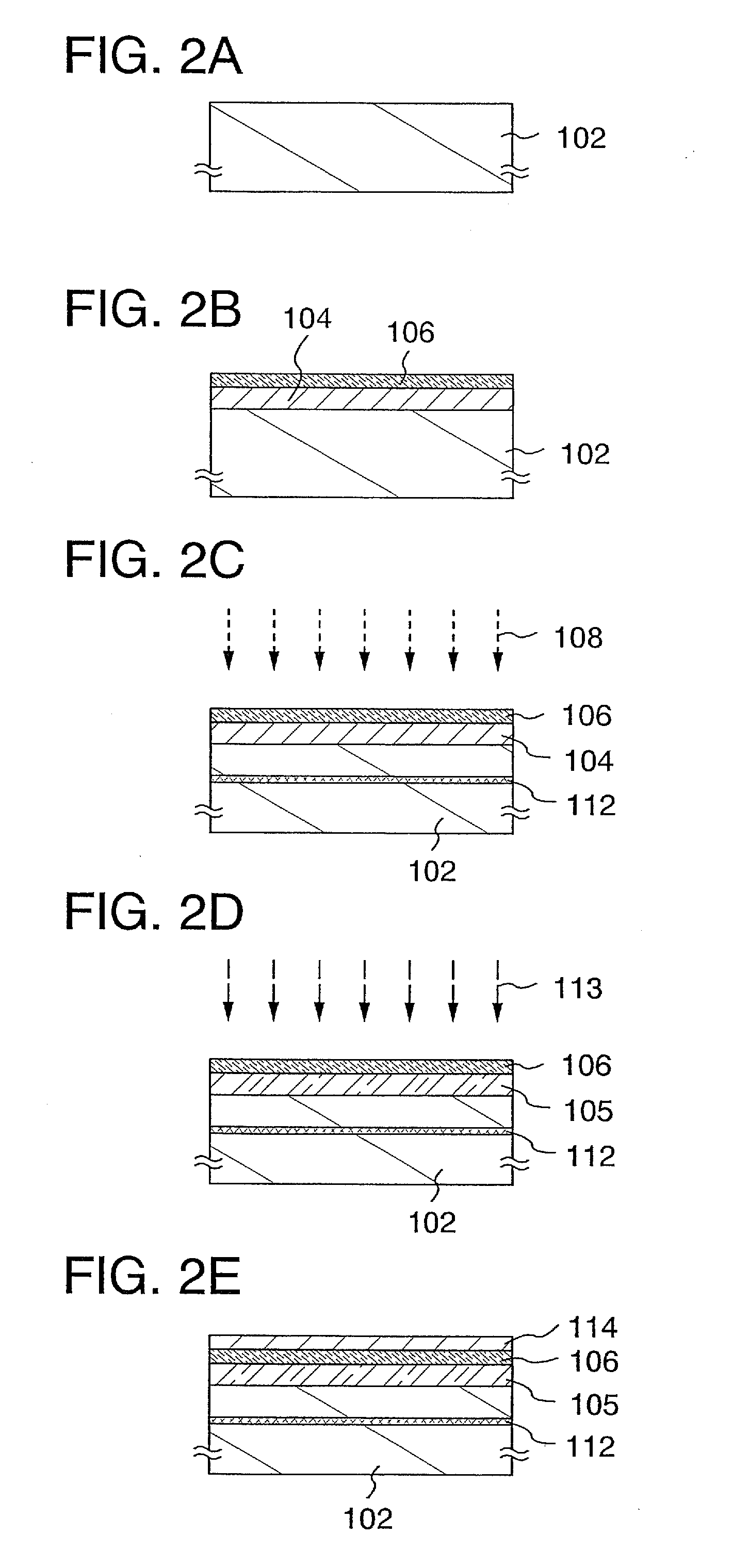
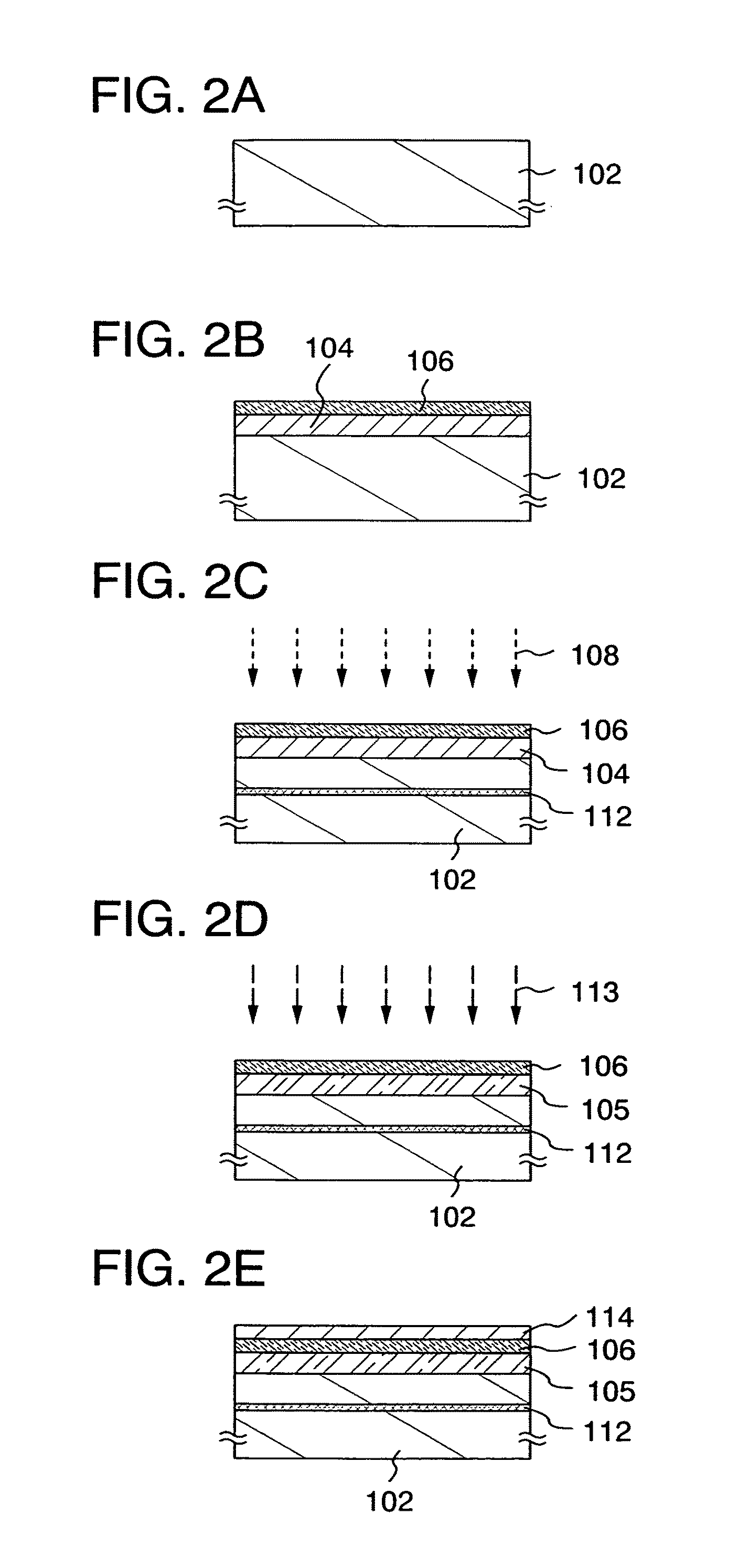
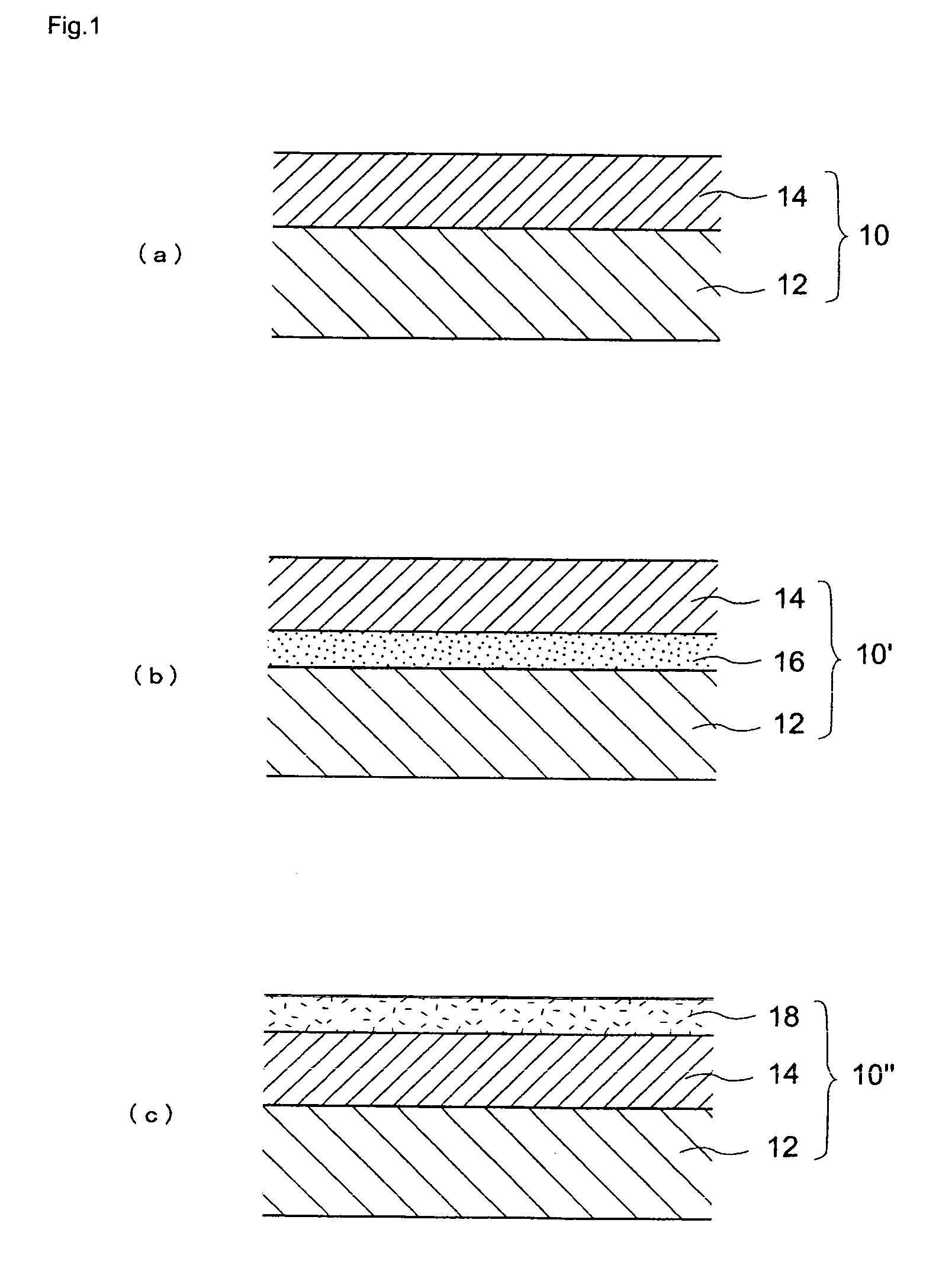
Semiconductor substrate and maehtod for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080315351A1Improve electrical characteristicsEasy to manufactureTransistorSolid-state devicesNitrogenSingle crystal
A semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing thereof are provided. The method includes a step of forming a first insulating film containing silicon and oxygen as its composition over a single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of forming a second insulating film containing silicon and nitrogen as its composition over the first insulating film, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with first ions to form a separation layer in the single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with second ions so that halogen is contained in the first insulating film, and a step of performing heat treatment to separate the single-crystal semiconductor substrate with a single-crystal semiconductor film left over the supporting substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device as well as solid-state image sensing device and method for producing the same
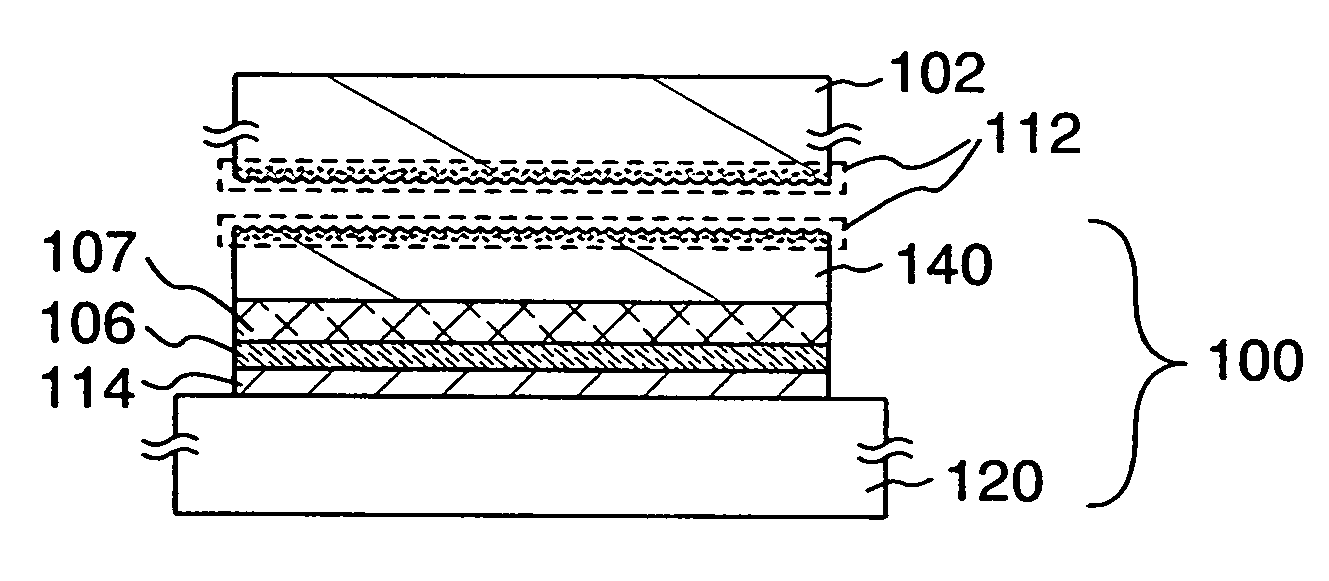
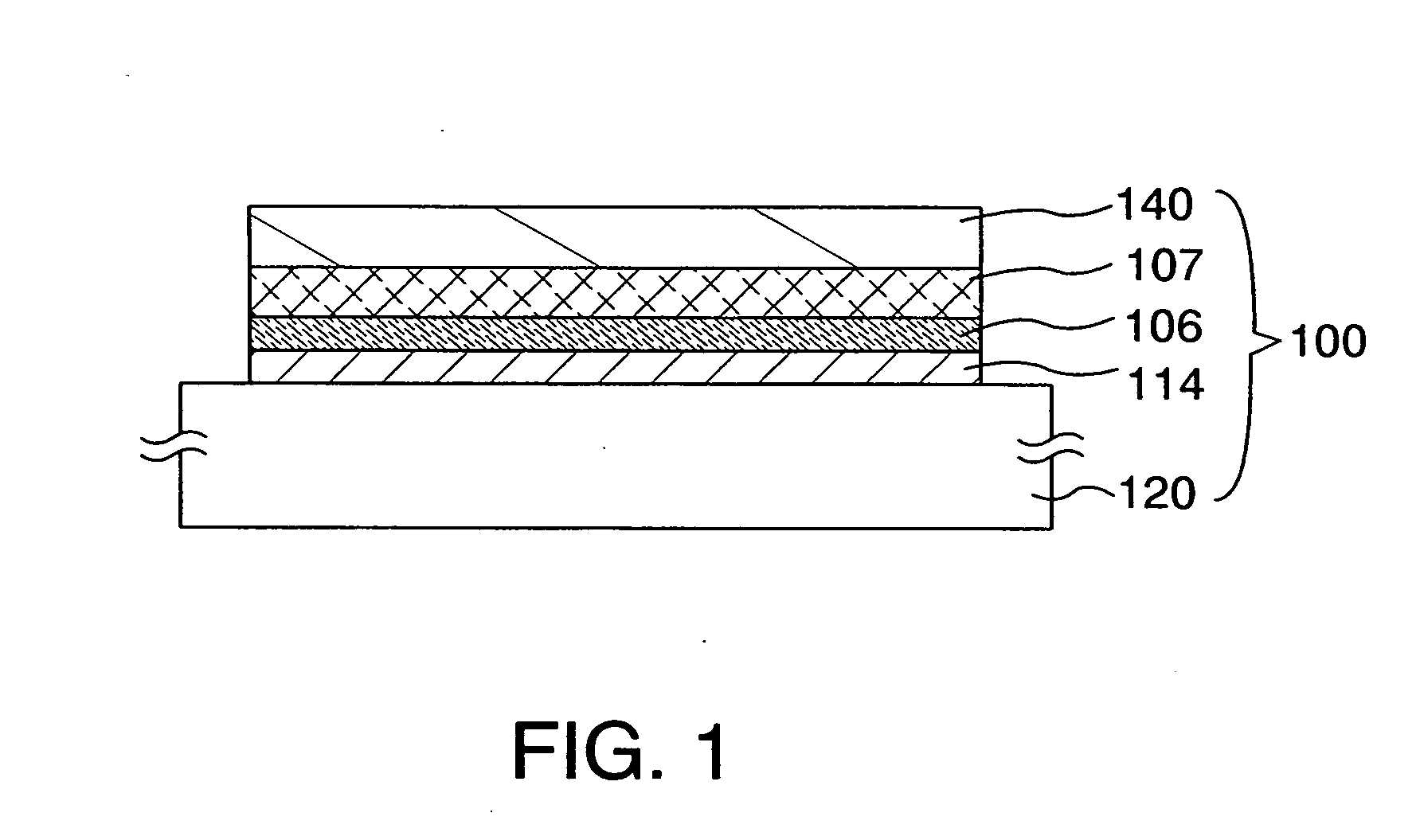
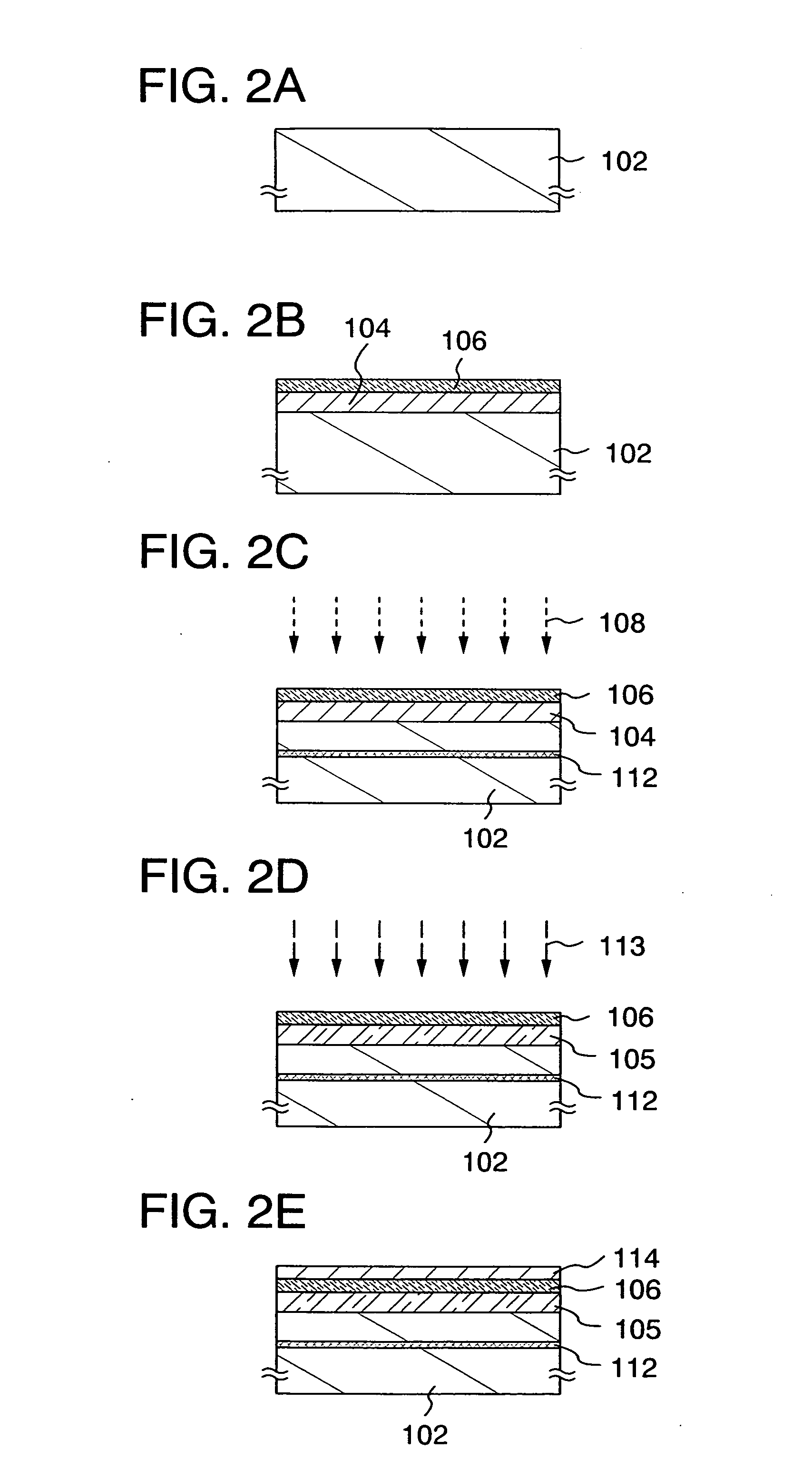
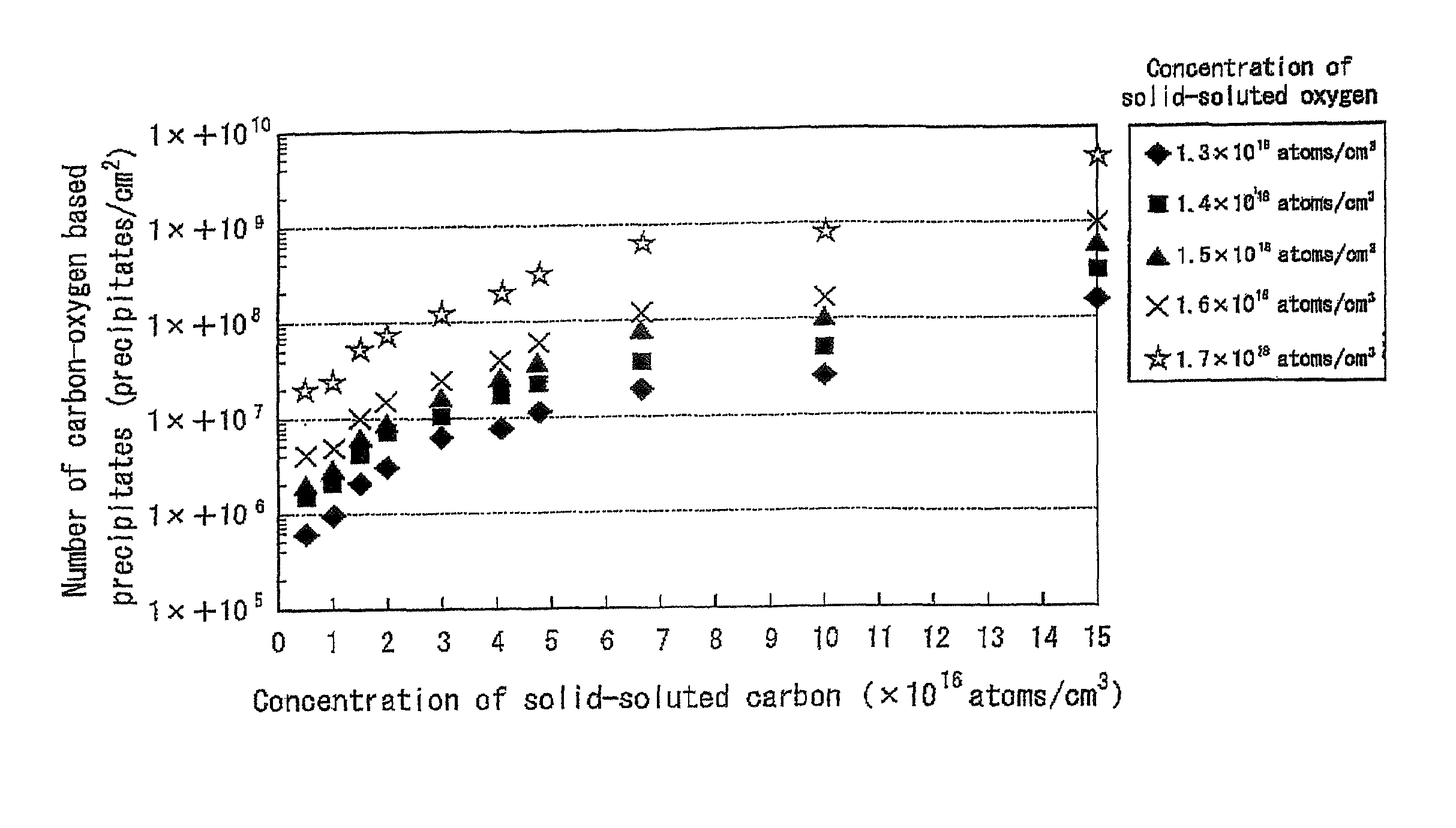
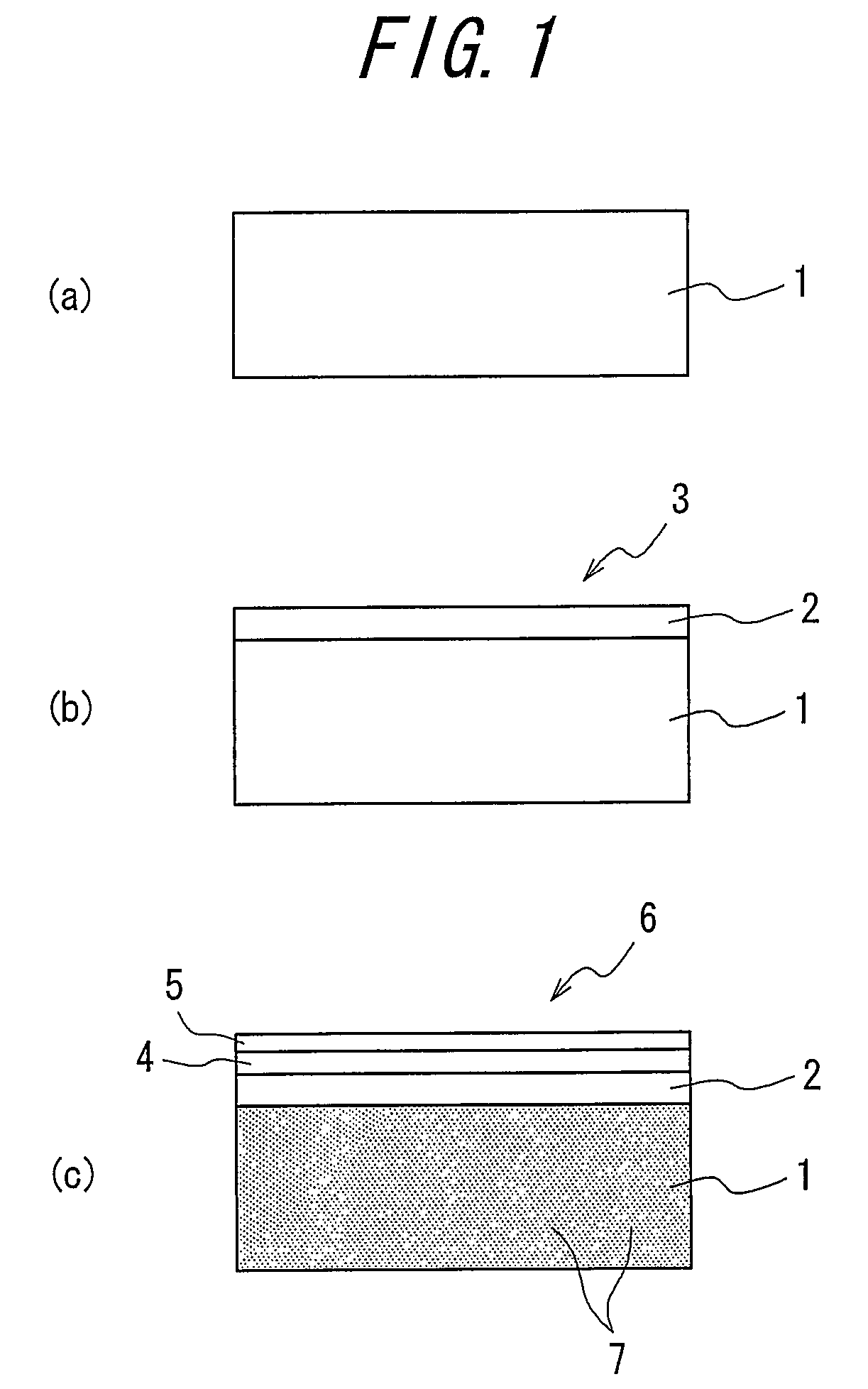
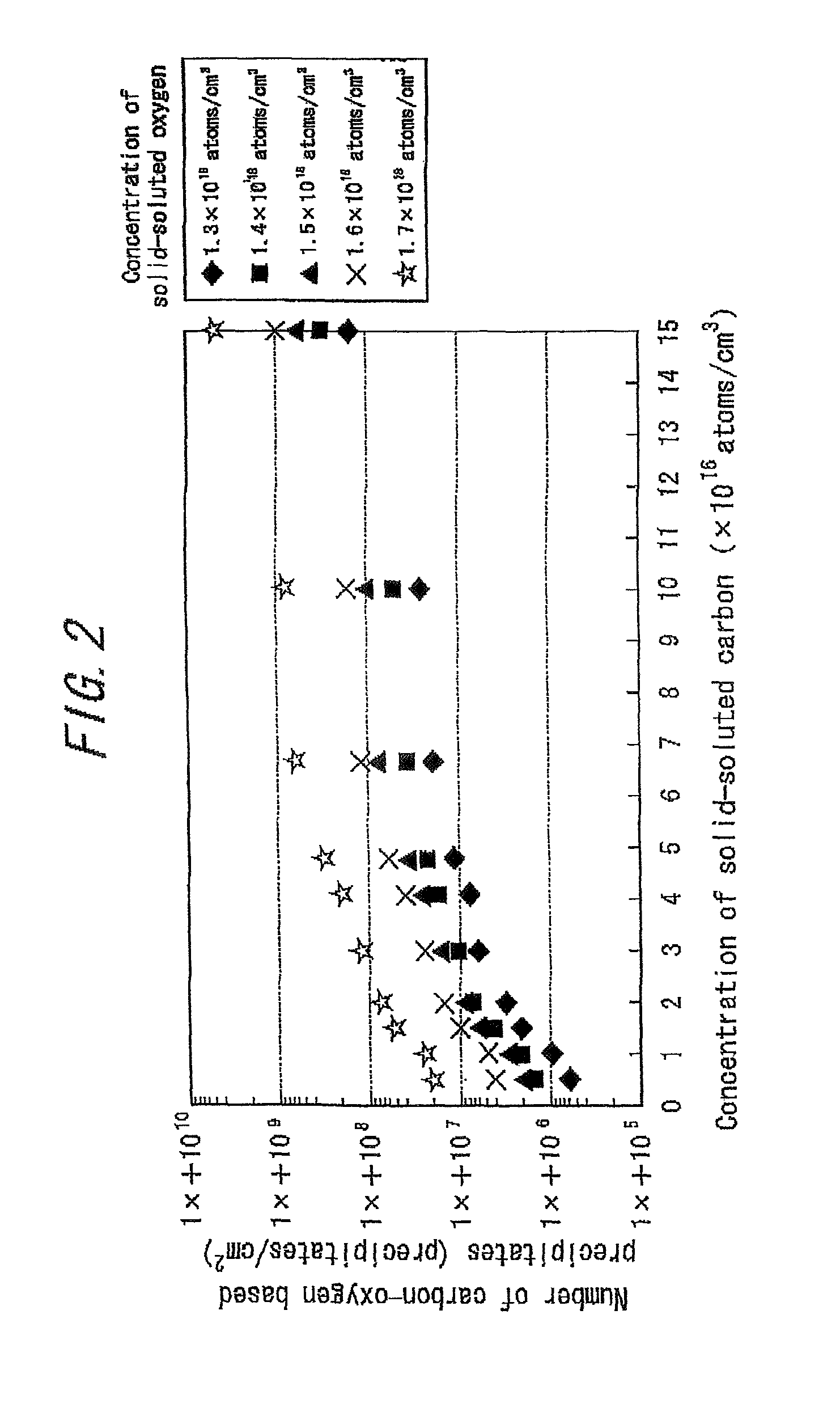
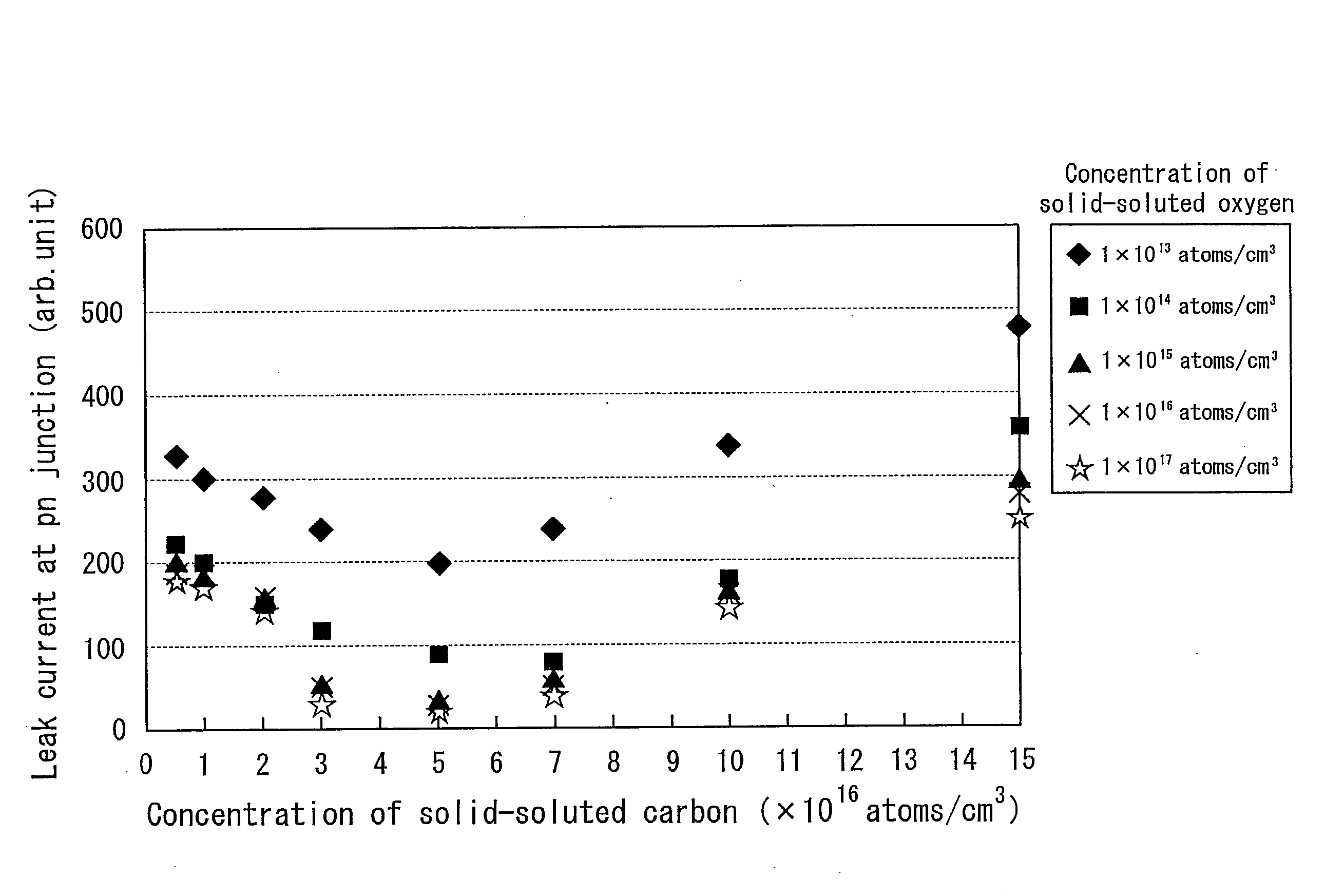
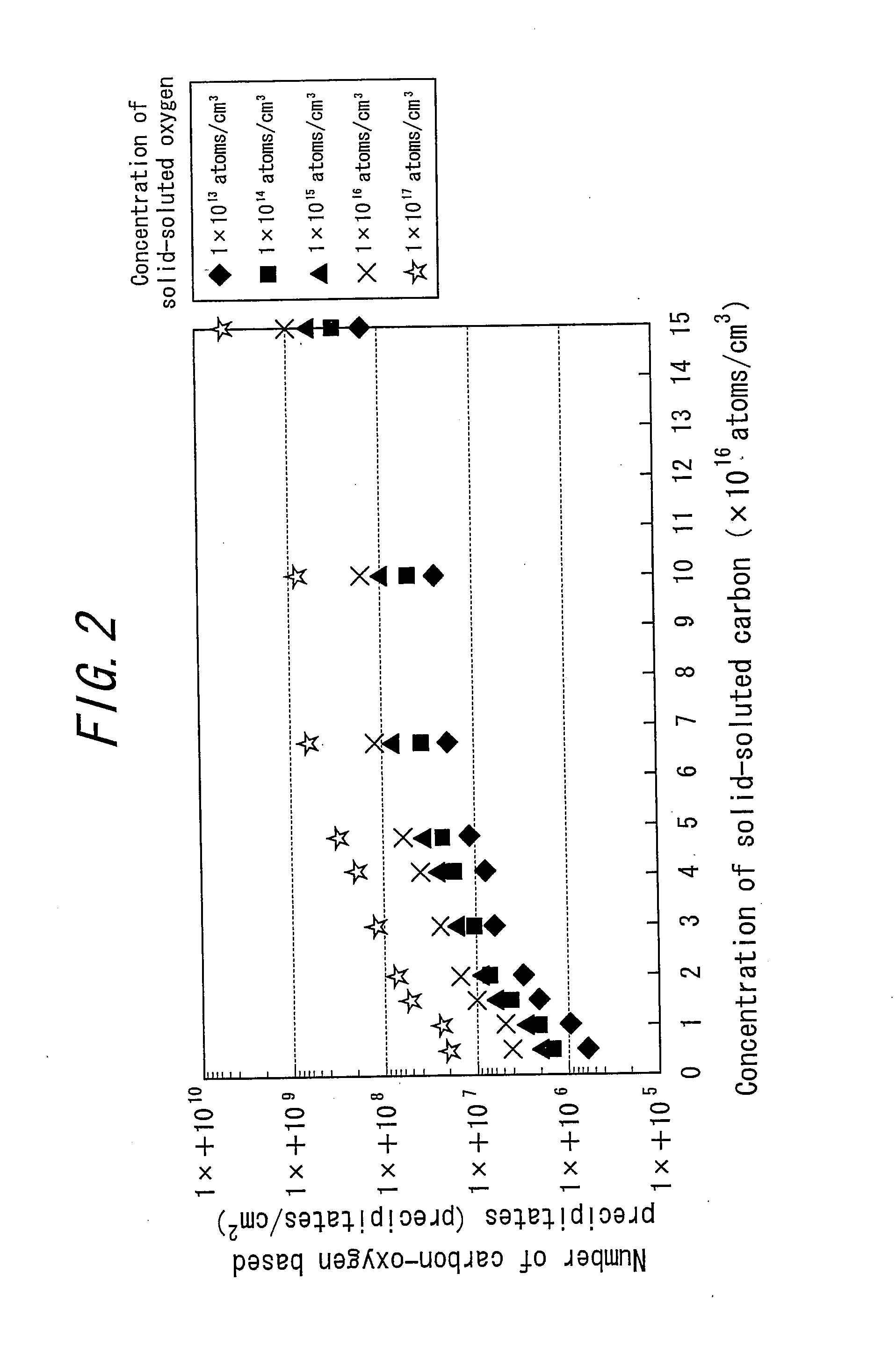
ActiveUS8063466B2Improve inhalation effectGood electric characteristicPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCarbon ionOxygen
There is provided a semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device in which the production cost is lower than that of a gettering method through a carbon ion implantation and problems such as occurrence of particles at a device production step and the like are solved.Silicon substrate contains solid-soluted carbon having a concentration of 1×1016-1×1017 atoms / cm3 and solid-soluted oxygen having a concentration of 1.4×1018-1.6×1018 atoms / cm3.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Display device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060091397A1Improve reliabilityHigh definitionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsDisplay device
It is an object of the invention to manufacture a highly reliable display device at a low cost with high yield. A display device of the invention includes: a first reflective electrode layer; and a second transparent electrode layer with an electroluminescent layer interposed therebetween, wherein the electroluminescent layer has a layer containing an organic compound and an inorganic compound, and the first electrode layer contains an aluminum alloy containing at least one or more selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, titanium, and carbon.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solar battery, method for manufacturing solar battery, method for manufacturing solar cell module, and solar cell module
ActiveUS20100200058A1Good electric characteristicHighly reliable connectionLamination ancillary operationsLaminationElectrical batteryElectricity
The present invention provides a solar battery including a solar cell; a wiring substrate having a wire to be electrically connected to an electrode provided in the solar cell; and an adhesive agent for adhering the solar cell and the wiring substrate to each other. The present invention also provides a method for manufacturing the solar battery, a method for manufacturing a solar cell module using the solar battery, and the solar cell module.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electrophotographic photoconductor and image formation method, image formation apparatus, and process cartridge for image formation apparatus using the electrophotographic photoconductor
InactiveUS20050221210A1Improve wear resistanceImprove smoothnessElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeElectrical conductorSurface layer
An electrophotographic photoconductor having at least a photoconductive layer on an electrically conductive support, wherein a surface layer of the photoconductive layer is a crosslinked layer obtainable by curing at least a three or more-functional radical-polymerizable monomer having no charge transporting structure and a charge transportation compound having a radical-polymerizable functional group by using an acylphosphine oxide compound as a photo-polymerization initiator under light energy irradiation.
Owner:RICOH KK
Semiconductor device fabrication method
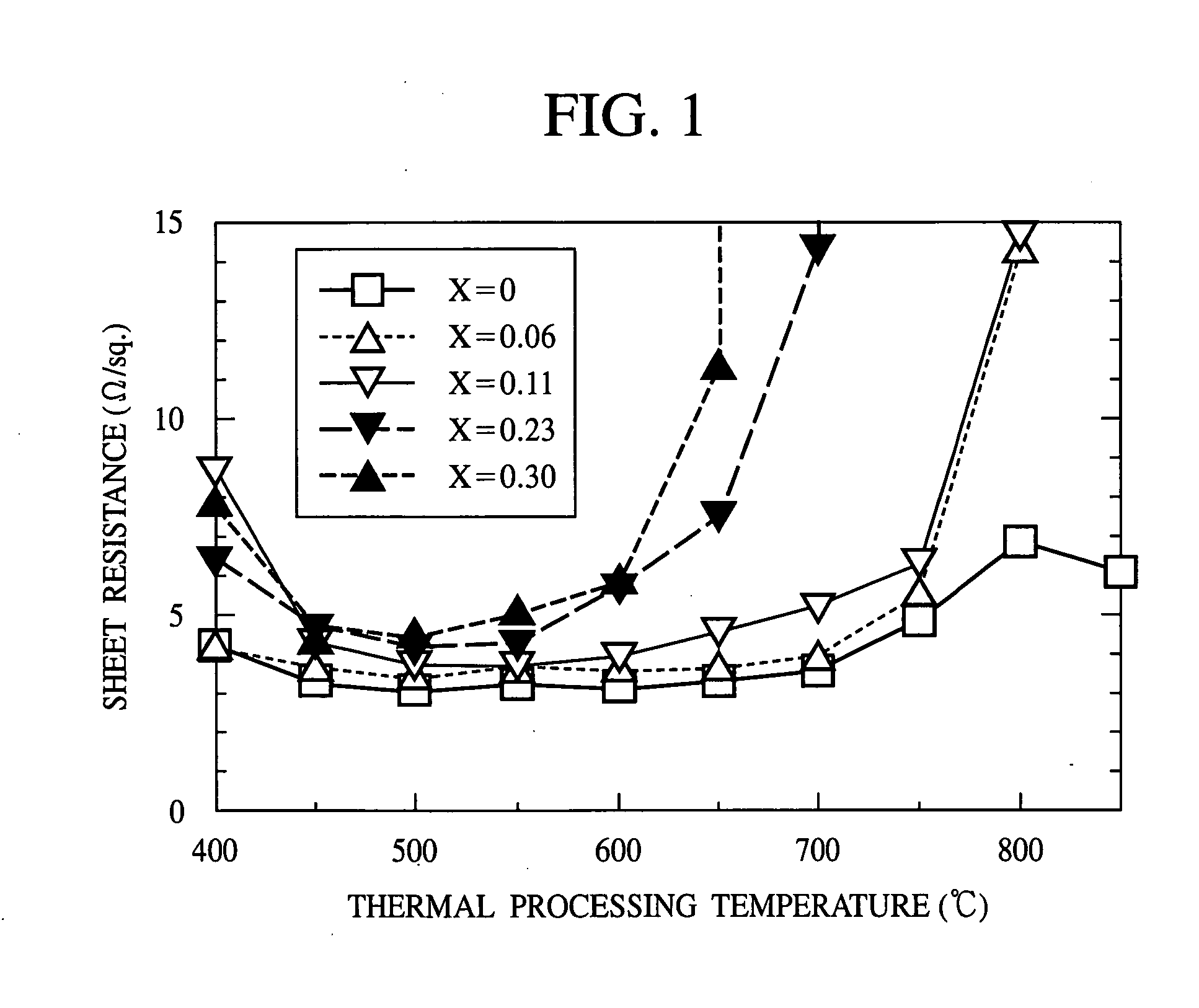
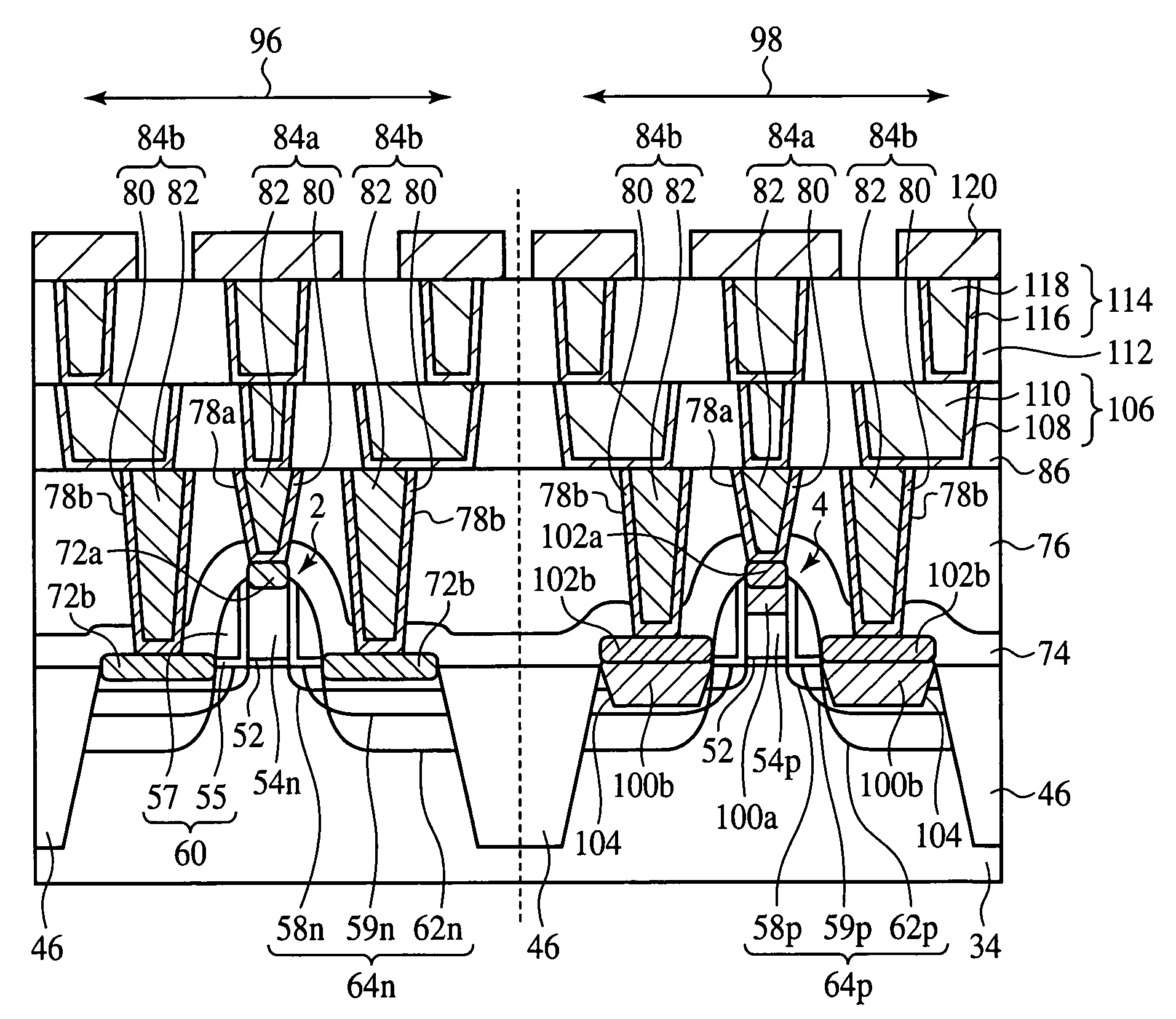
ActiveUS20060281288A1Improve electrical characteristicsReduce sheet resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorGrain boundary
The semiconductor device fabrication method comprising the step of forming a gate electrode 54p on a semiconductor substrate 34; the step of forming a source / drain diffused layer 64p in the semiconductor substrate 34 on both sides of the gate electrode 54p; the step of burying a silicon germanium layer 100b in the source / drain diffused layer 64p; the step of forming an amorphous layer at an upper part of the silicon germanium layer 101; the step of forming a nickel film 66 on the amorphous layer 101; and the step of making thermal processing to react the nickel film 66 and the amorphous layer 101 with each other to form a silicide film 102b on the silicon germanium layer 100b. Because of no crystal boundaries in the amorphous layer 101 to react with the nickel film 66, the silicidation homogeneously goes on. Because of no crystal faces in the amorphous layer 101, the Ni(Si1-xGex)2 crystals are prevented from being formed in spikes. Thus, even when the silicon germanium layer 100b is silicided by using a thin nickel film 66, the sheet resistance can be low, and the junction leak current can be suppressed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
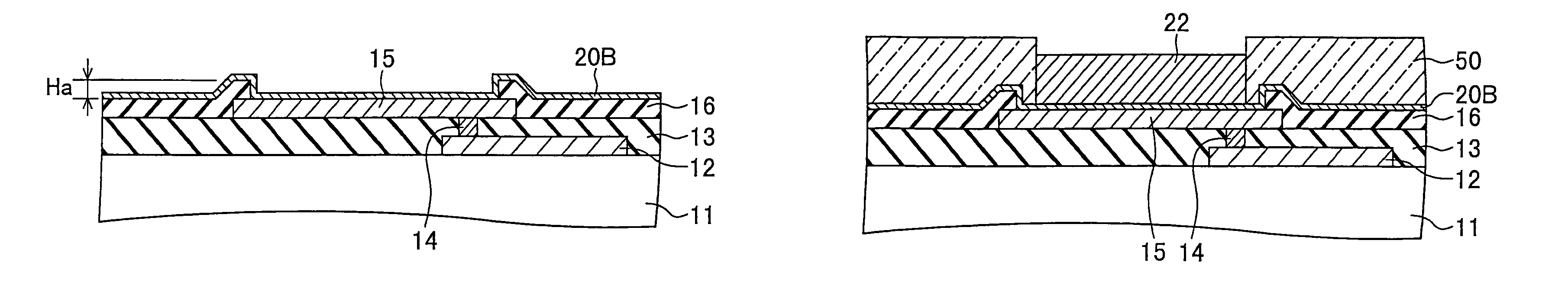
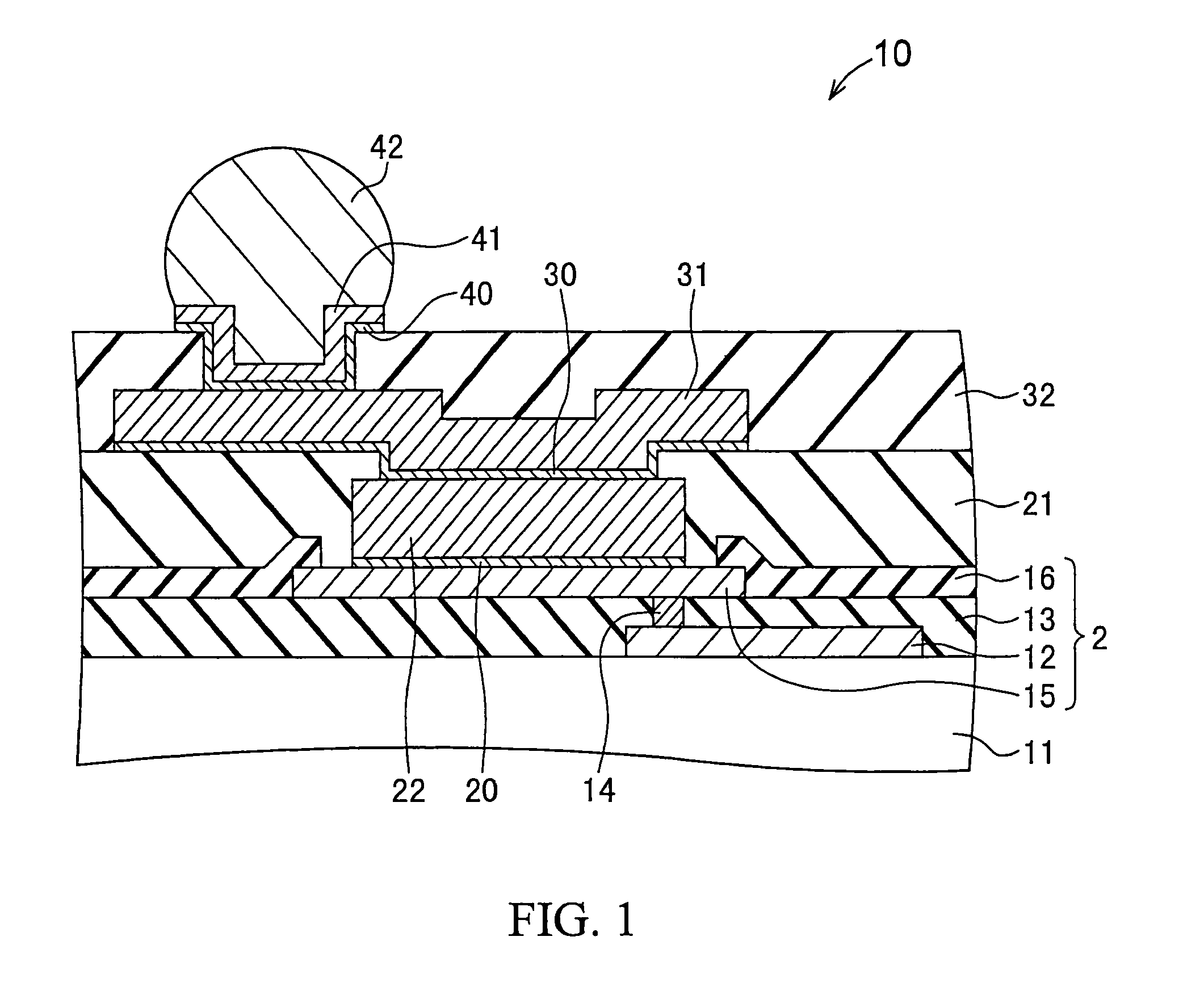
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating same
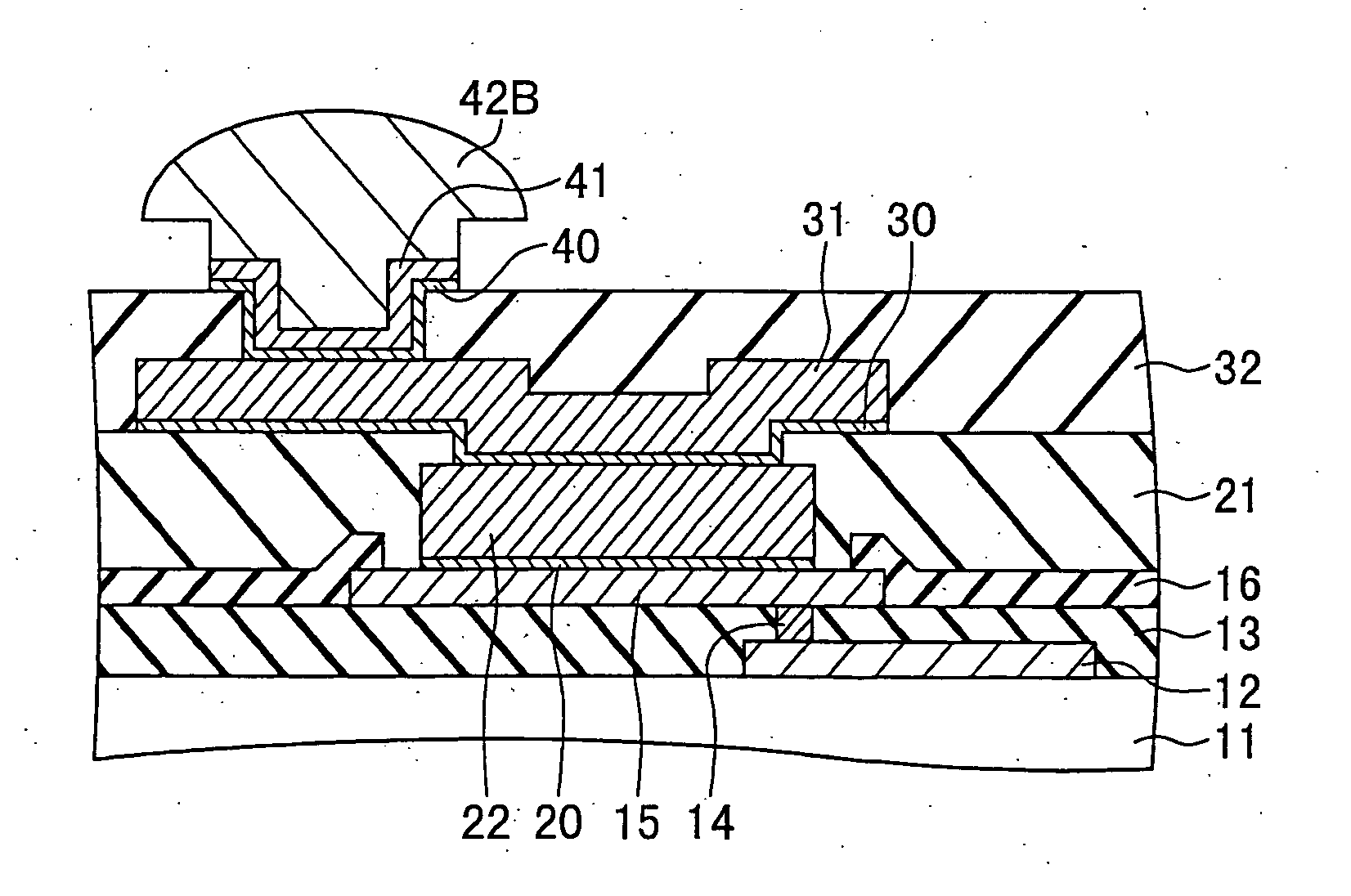
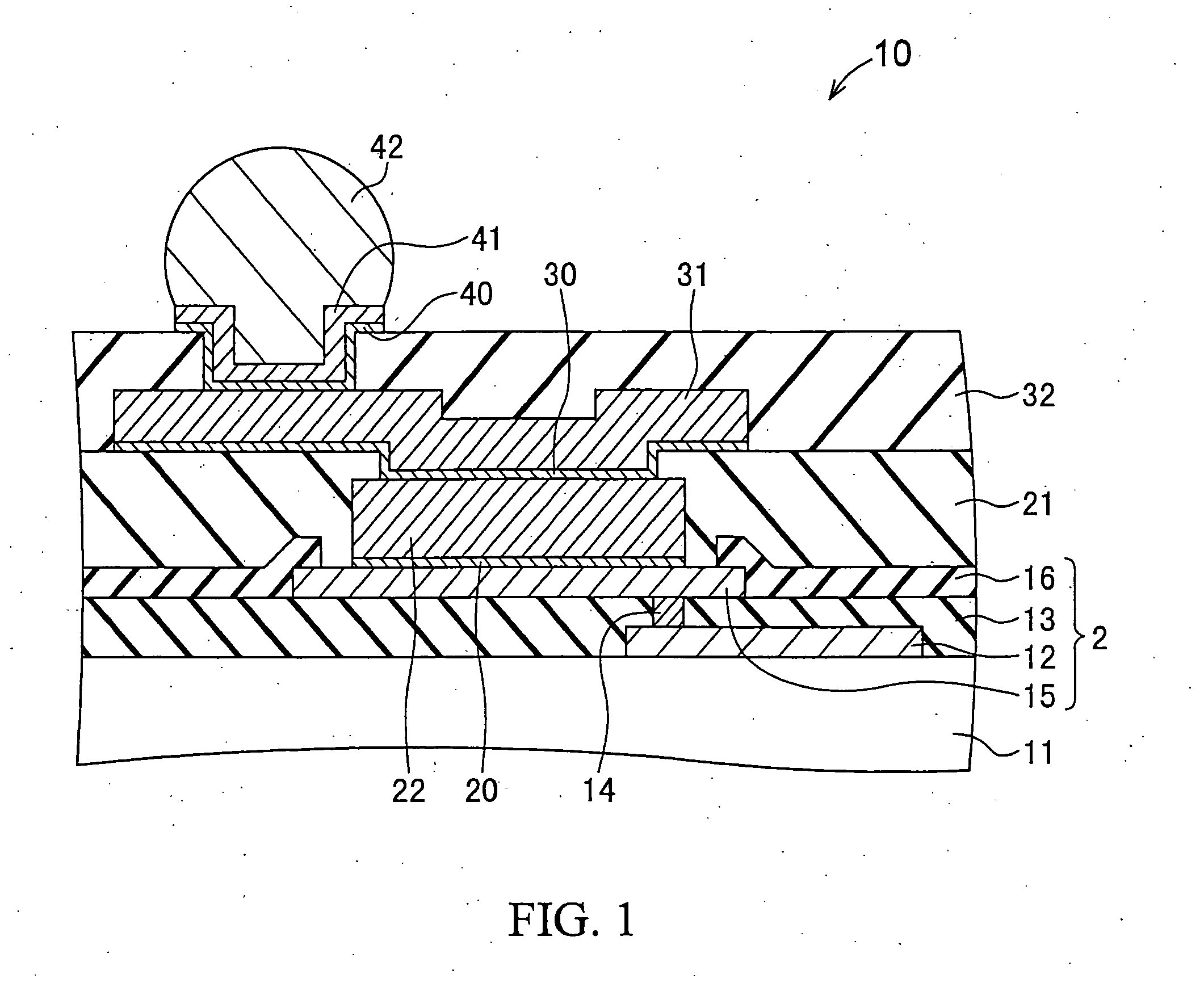
ActiveUS20110198748A1Avoid crackingImprove electrical characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricResist
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device includes: forming a semiconductor chip portion having an electrode on a main surface of a wafer; forming a first resist pattern having a first opening on the electrode; filling the first opening with a first electrically conductive material, thereby forming an electrically conductive post; removing the first resist pattern after said forming of the electrically conductive post; forming an interlayer dielectric film having a second opening positioned on the electrically conductive post; and forming an electrically conductive redistribution layer extending from an upper surface of the electrically conductive post over an upper surface of the interlayer dielectric film.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method for forming negative electrode and method for manufacturing lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20130212879A1Improve electrical characteristicsReduce the number of stepsContact member manufacturingElectrode thermal treatmentLithiumSlurry
The number of steps is reduced in the formation process of an electrode. Deterioration of the electrode is suppressed. A highly reliable lithium secondary battery is provided by suppressing the deterioration of the electrode. A method for forming a negative electrode and a method for manufacturing a lithium secondary battery including the negative electrode are provided. In the method for forming the negative electrode, graphene oxide, a plurality of particulate negative electrode active materials, and a precursor of polyimide are mixed to form slurry; the slurry is applied over a negative electrode current collector; and the slurry applied over the negative electrode current collector is heated at a temperature higher than or equal to 200° C. and lower than or equal to 400° C. so that the precursor of the polyimide is imidized. The graphene oxide is reduced in heating the slurry to imidize the precursor of the polyimide.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device fabrication method
ActiveUS7390707B2Suppress increase of sheet resistance and junction leak currentGood electric characteristicTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorHeat treated
The semiconductor device fabrication method comprising the step of forming a gate electrode on a semiconductor substrate; the step of forming a source / drain diffused layer in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate electrode; the step of burying a silicon germanium layer in the source / drain diffused layer; the step of forming an amorphous layer at an upper part of the silicon germanium layer; the step of forming a nickel film on the amorphous layer; and the step of making thermal processing to react the nickel film and the amorphous layer with each other to form a silicide film on the silicon germanium layer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
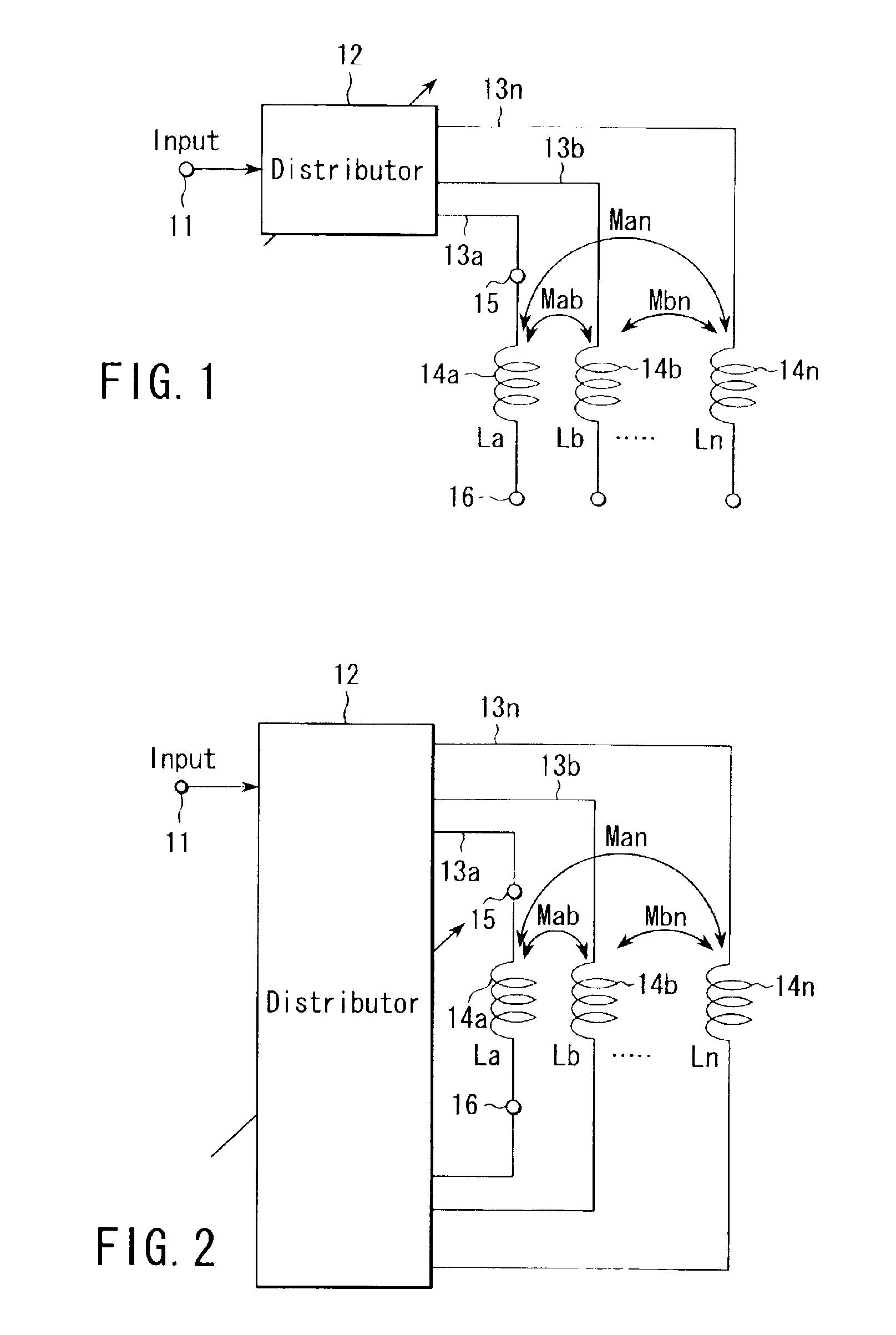
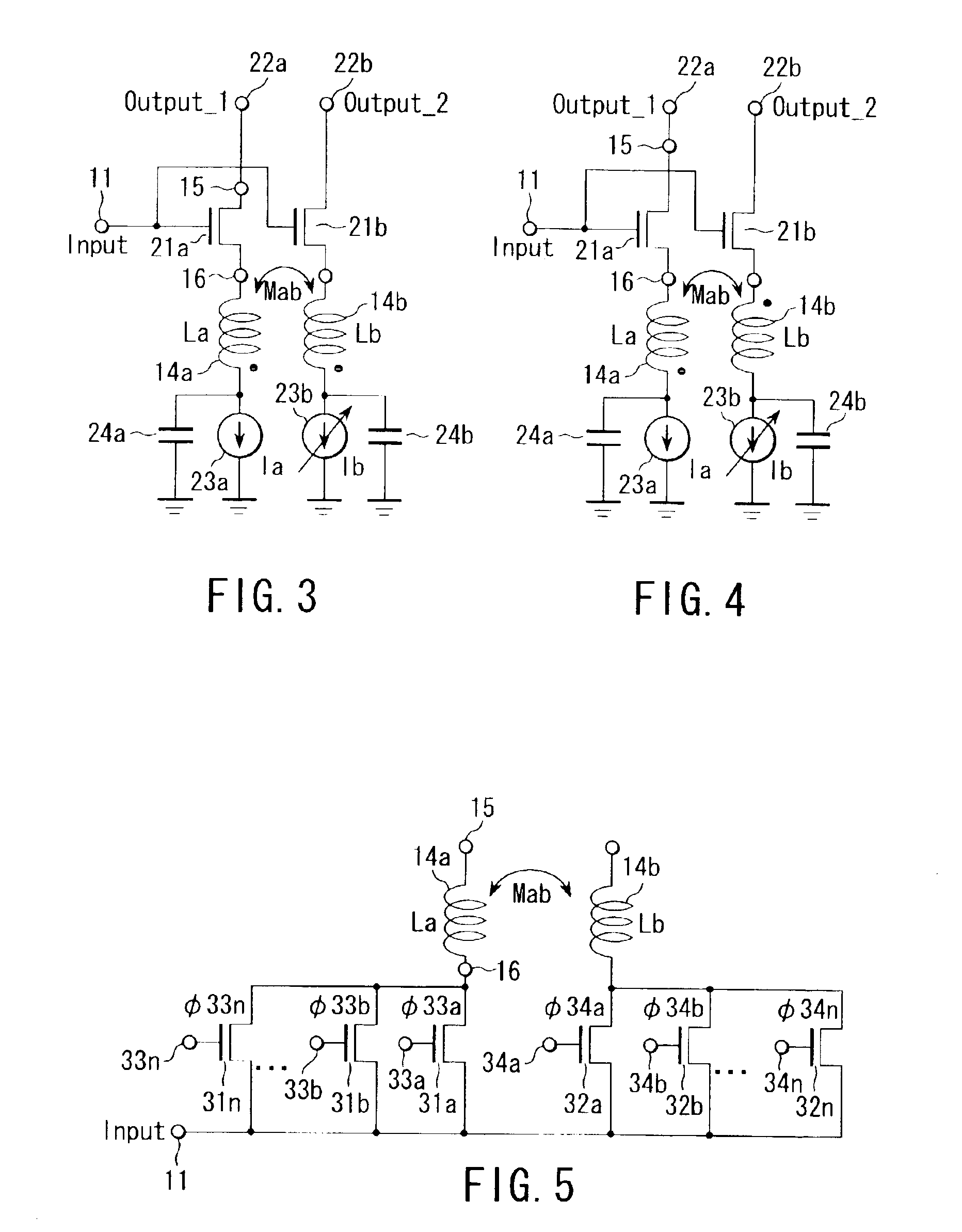
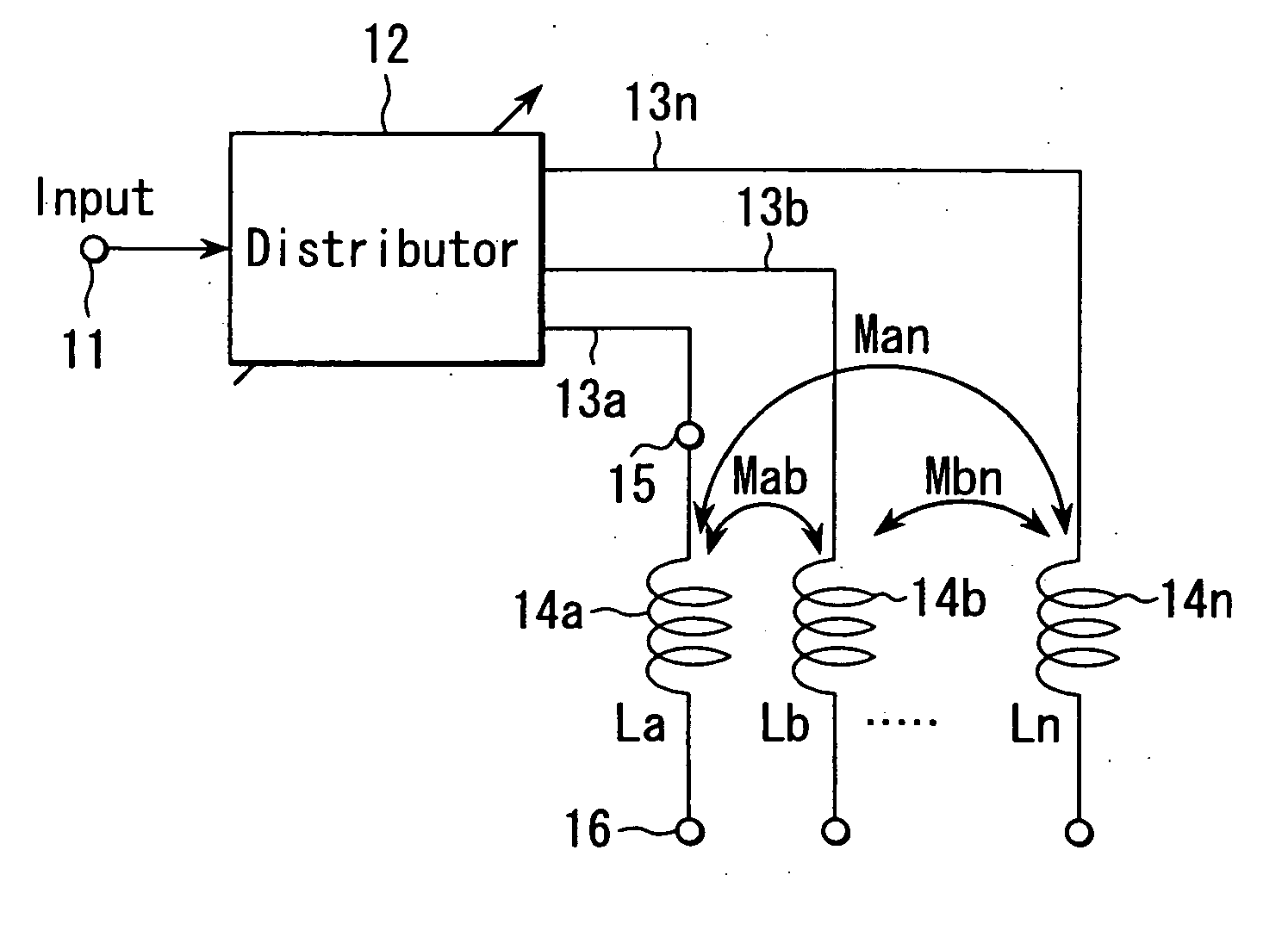
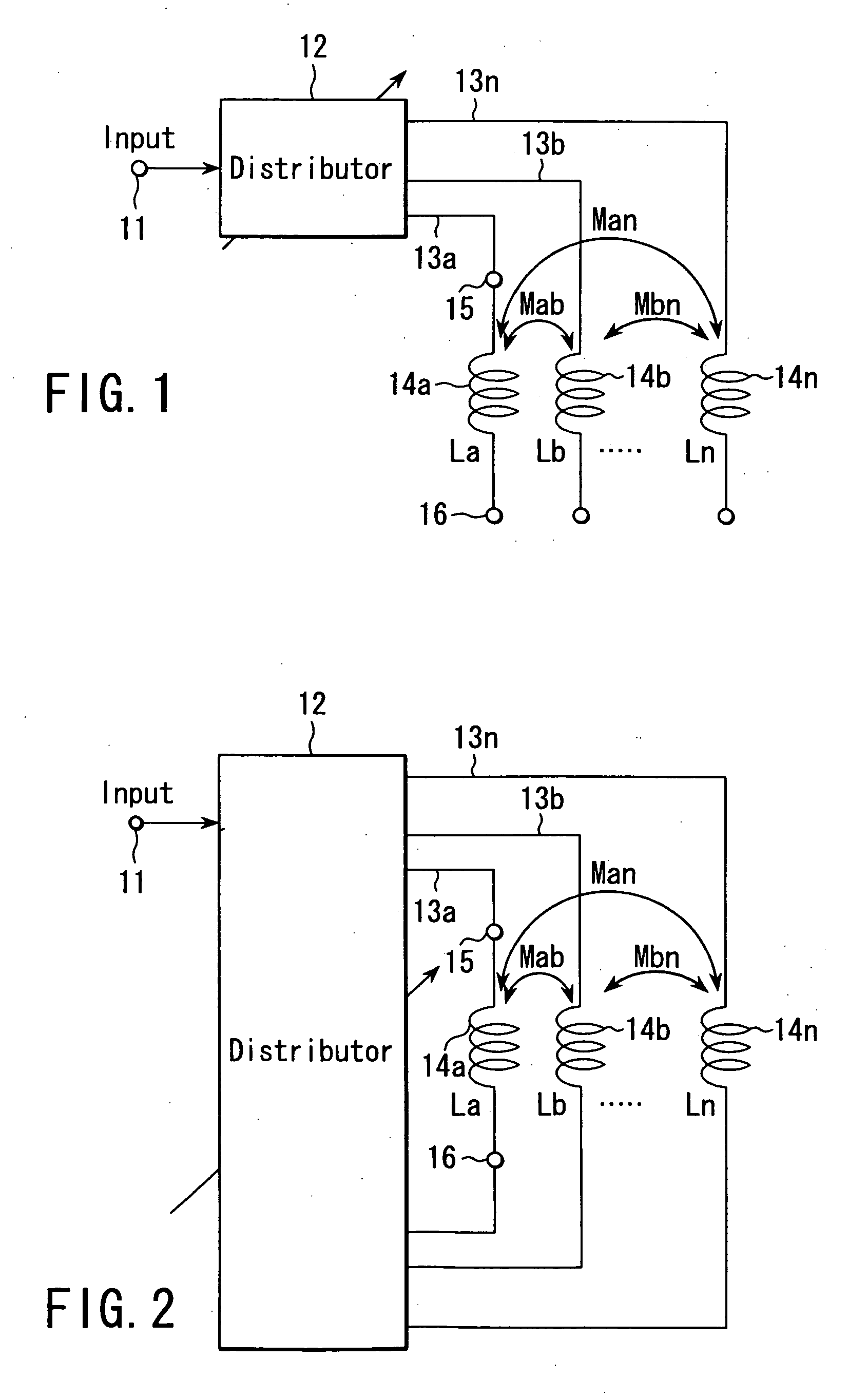
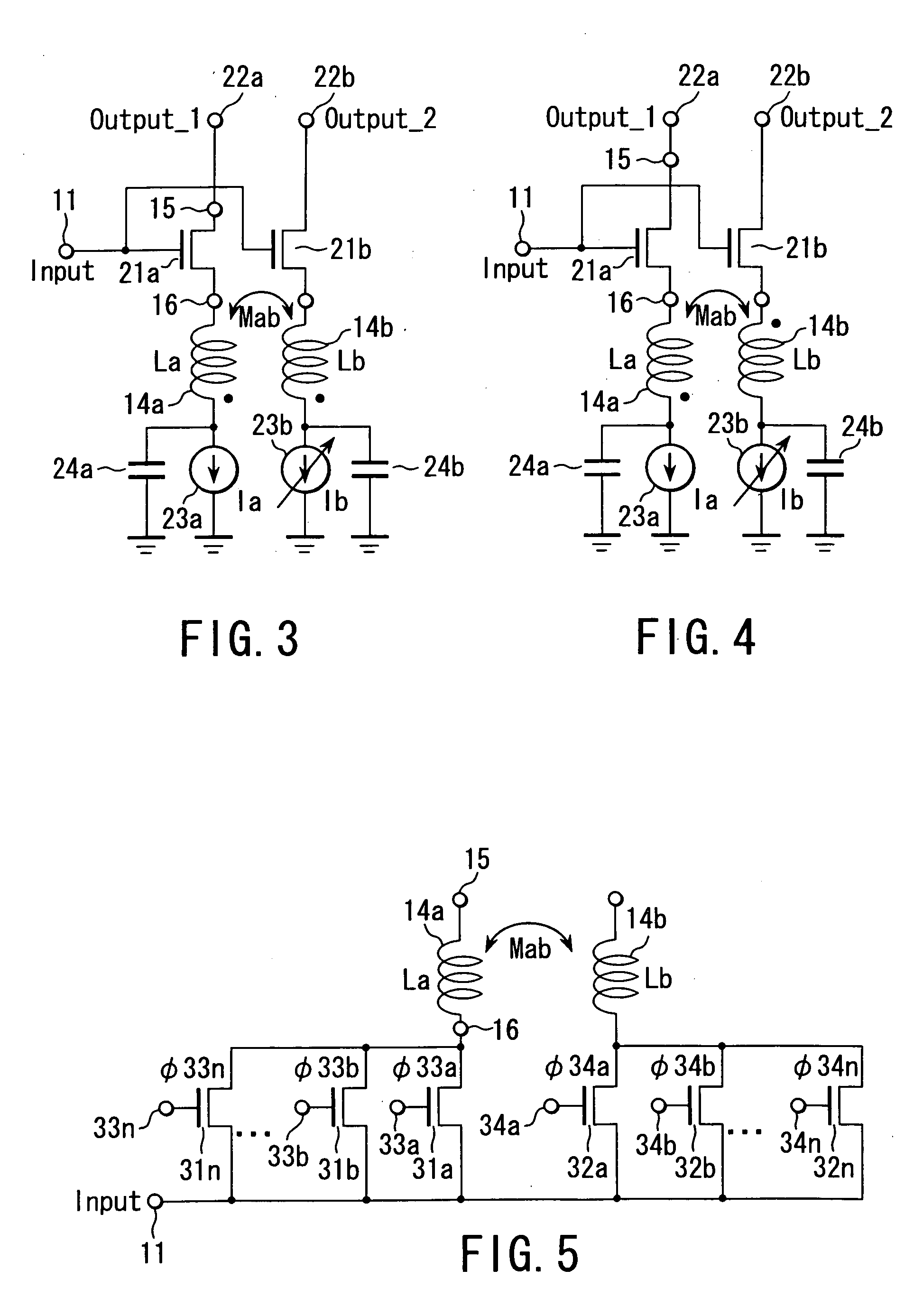
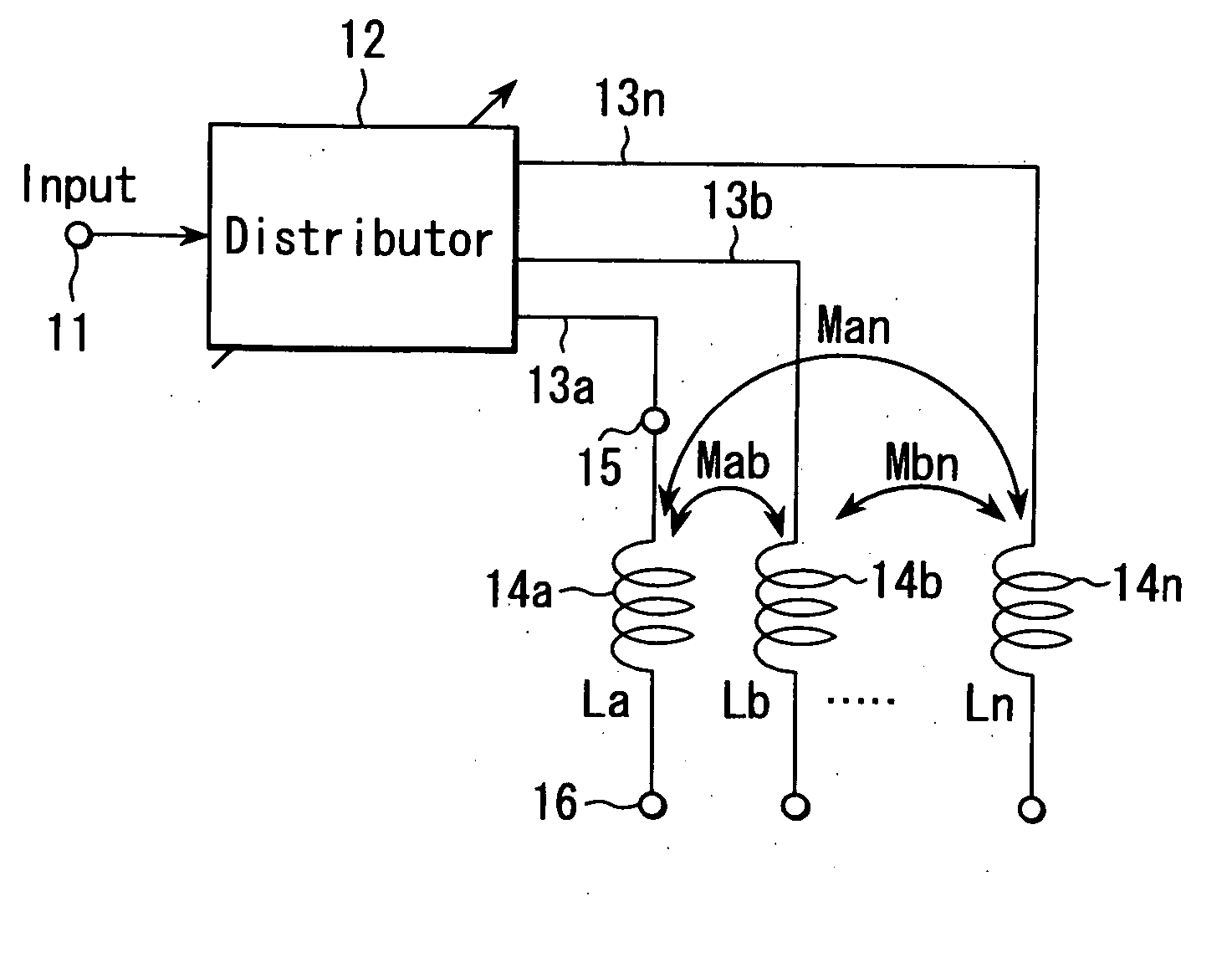
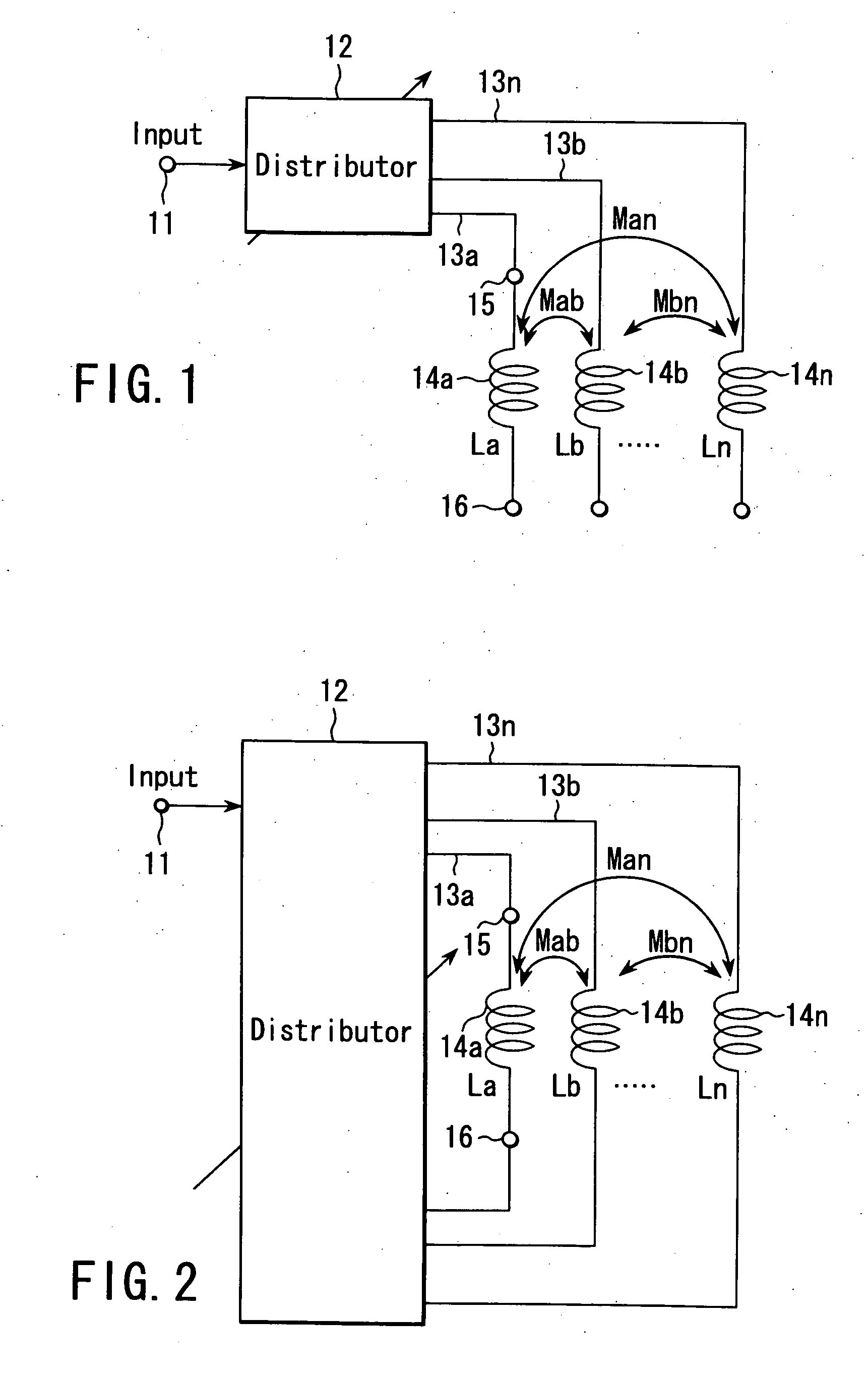
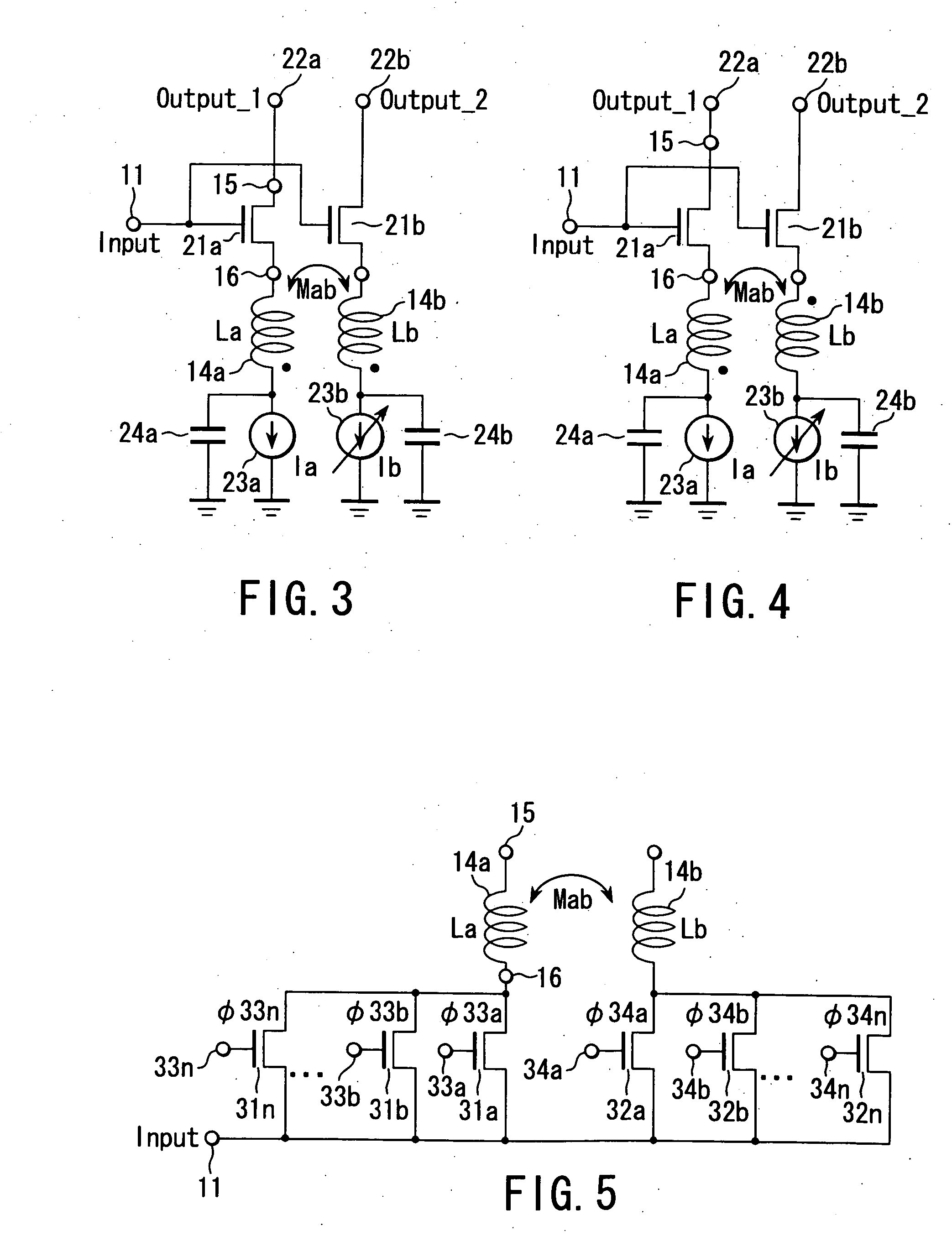
Variable inductor, oscillator including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this oscillator, and amplifier including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this amplifier
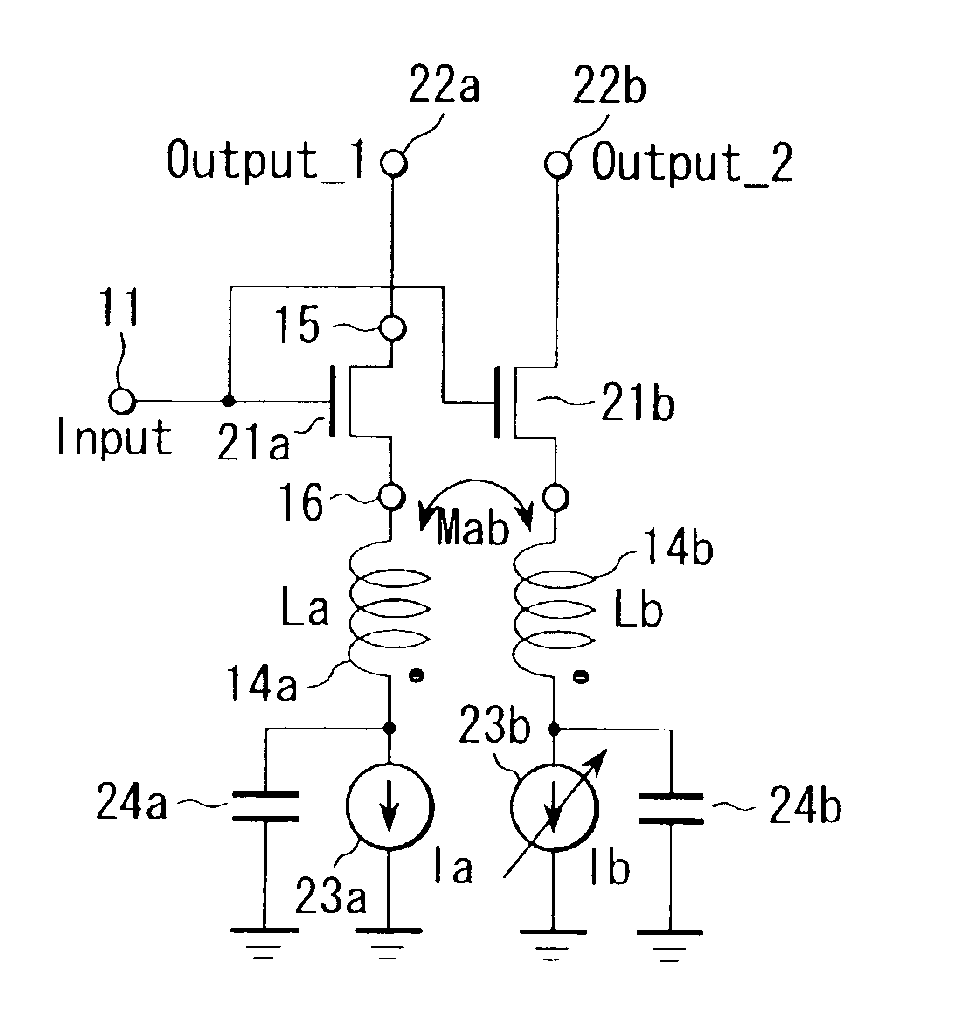
InactiveUS7098737B2Good electric characteristicMiniaturizationResonant circuit tuningGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierInductor
An amplifier comprises an amplifier circuit which comprises a first inductor as an impedance element for degeneration, and a control circuit which has a second inductor electro-magnetically connected to the first inductor, and changes a control current flowing through the second inductor to change an inductance value of the first inductor, thereby changing amplification characteristics of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
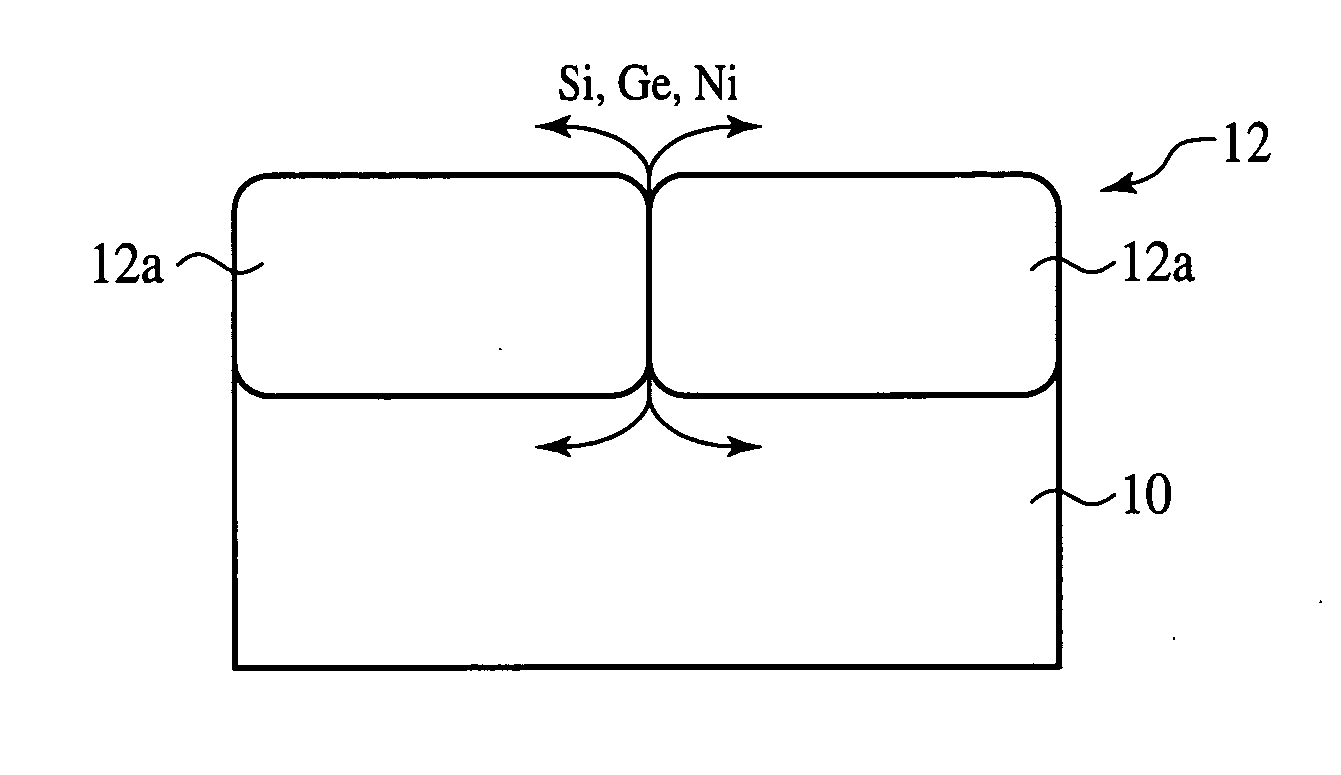
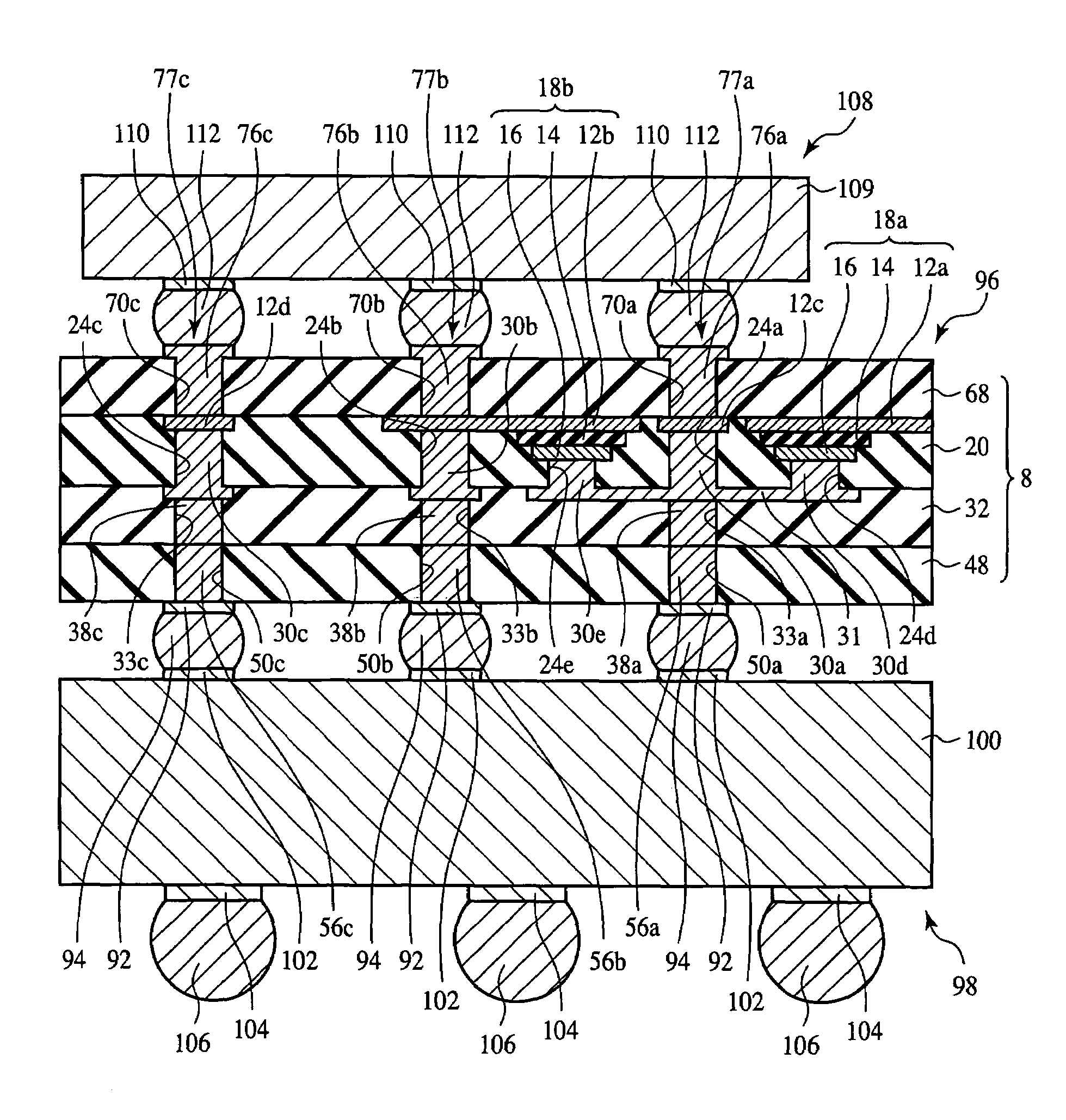
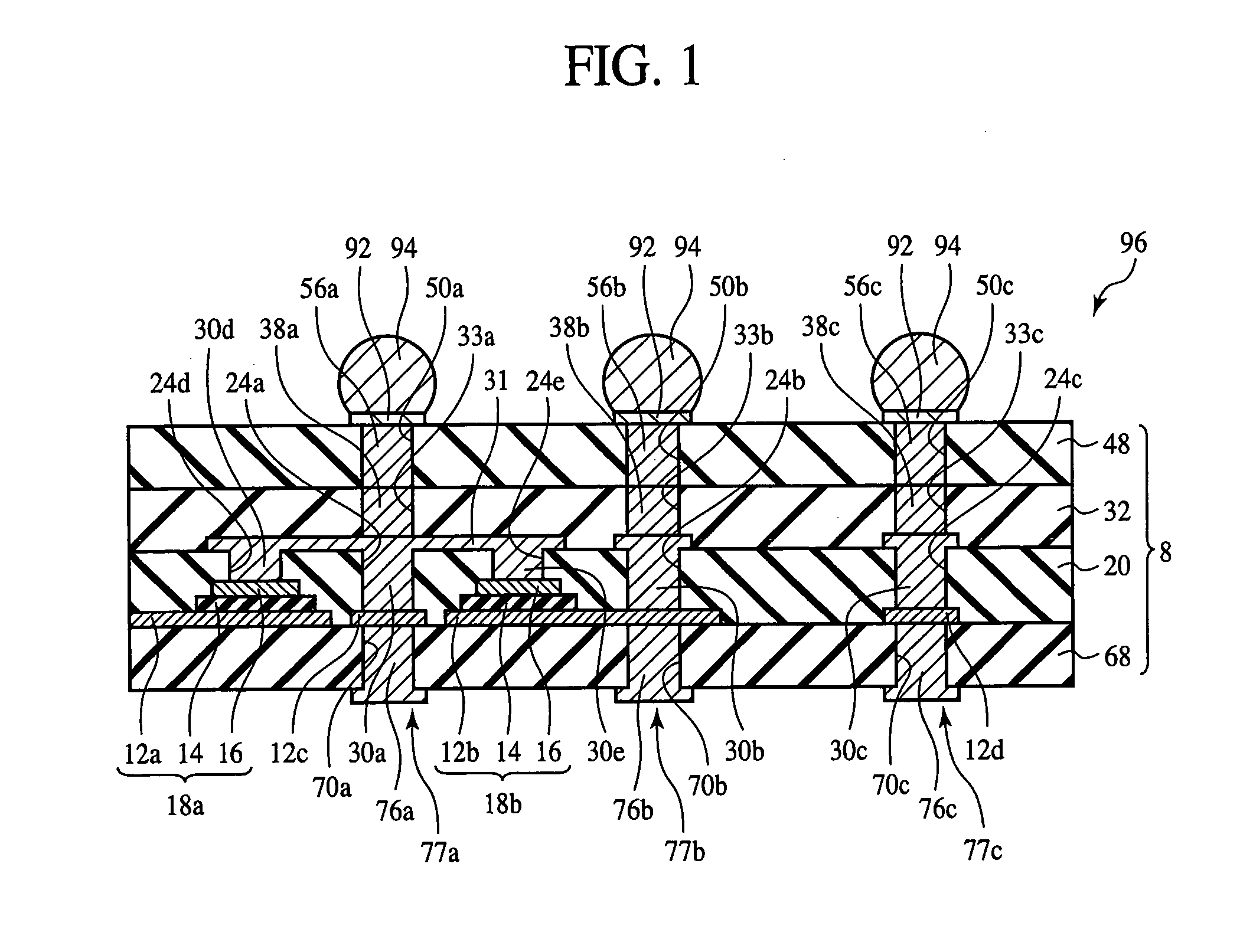
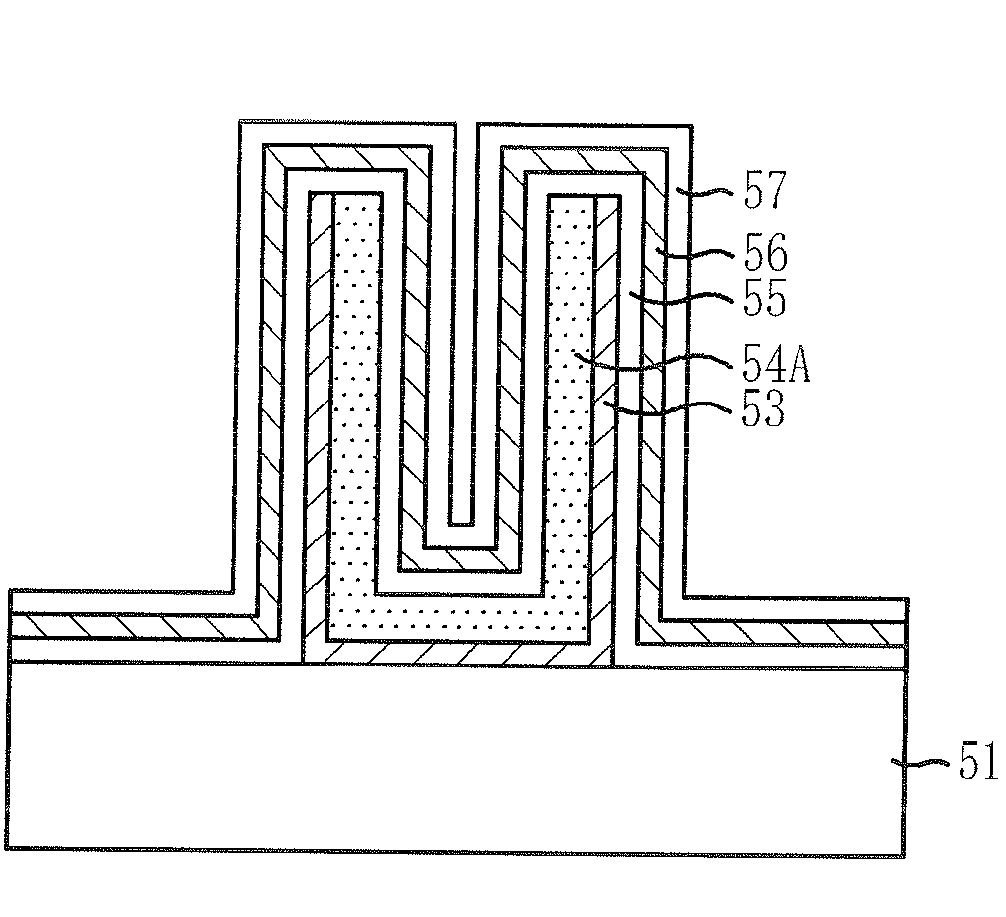
Interposer and method for fabricating the same
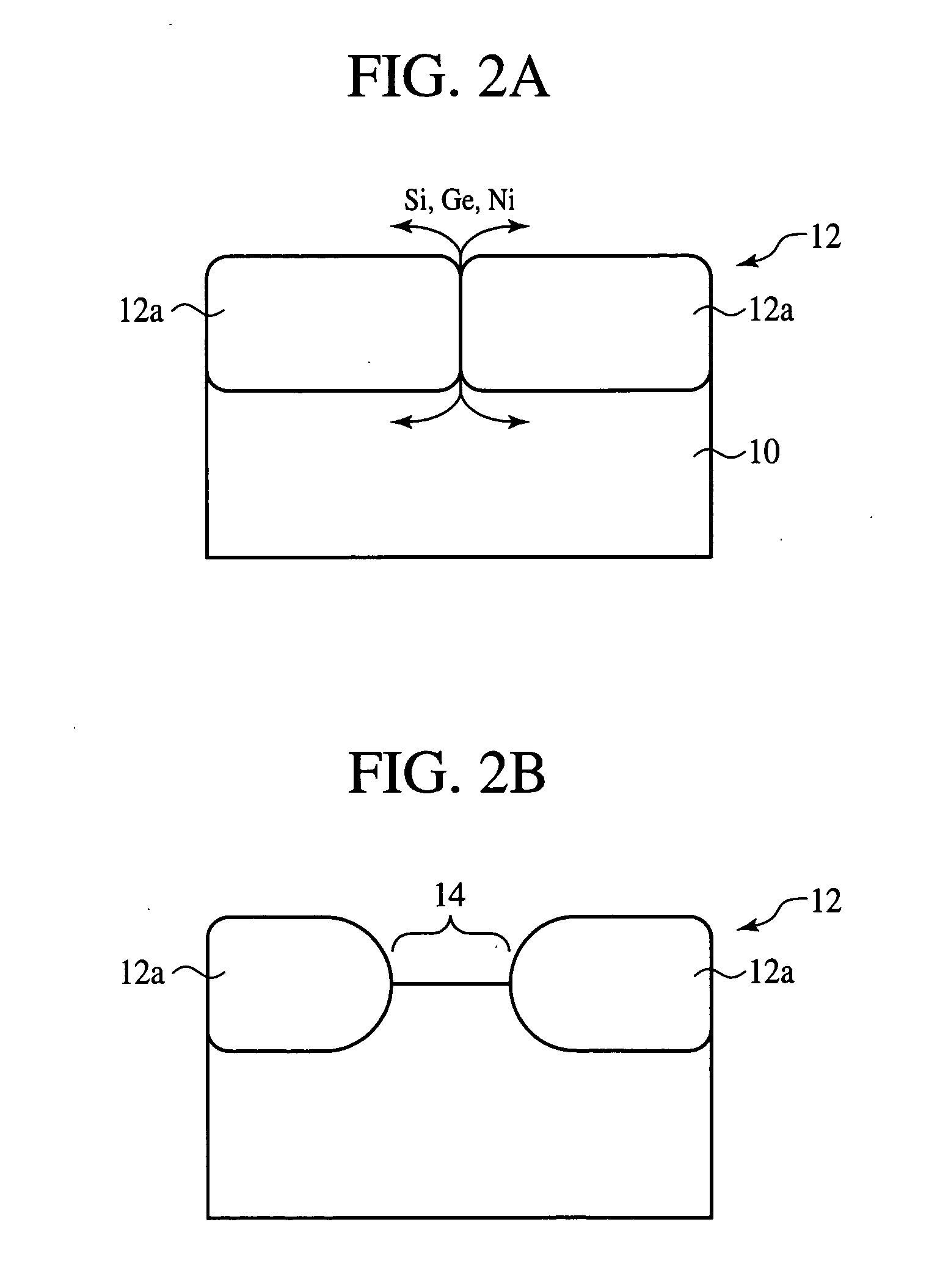
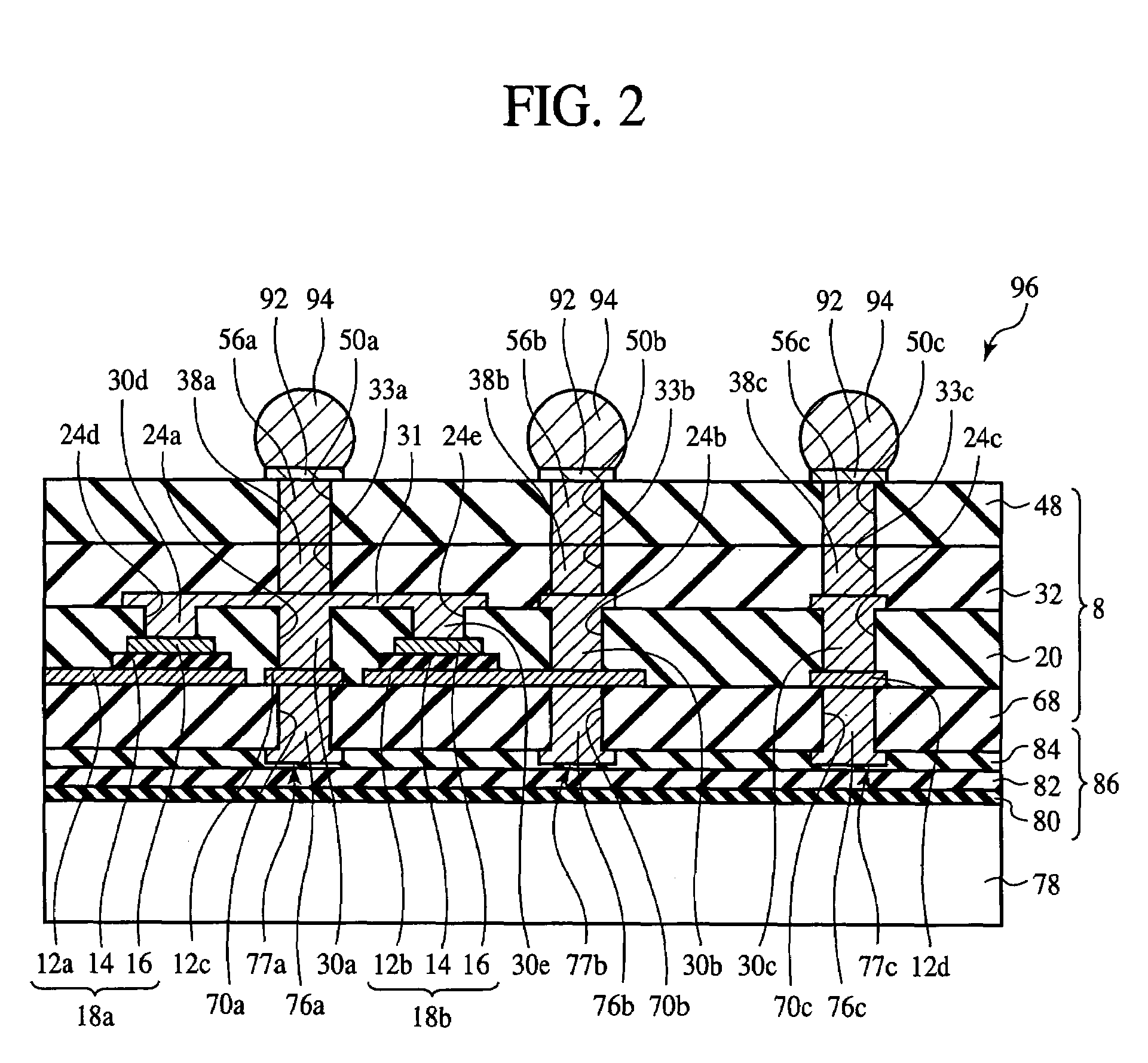
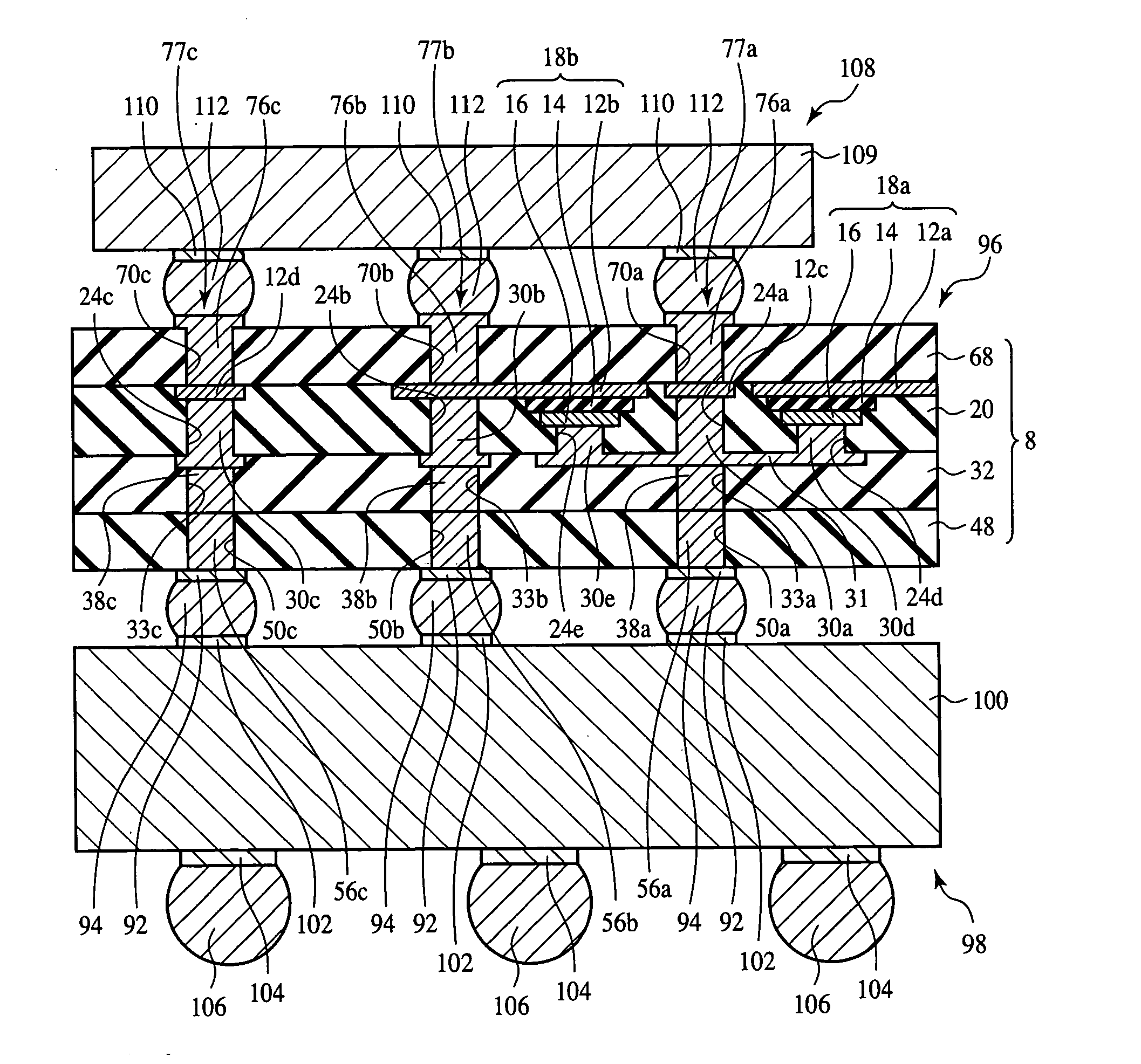
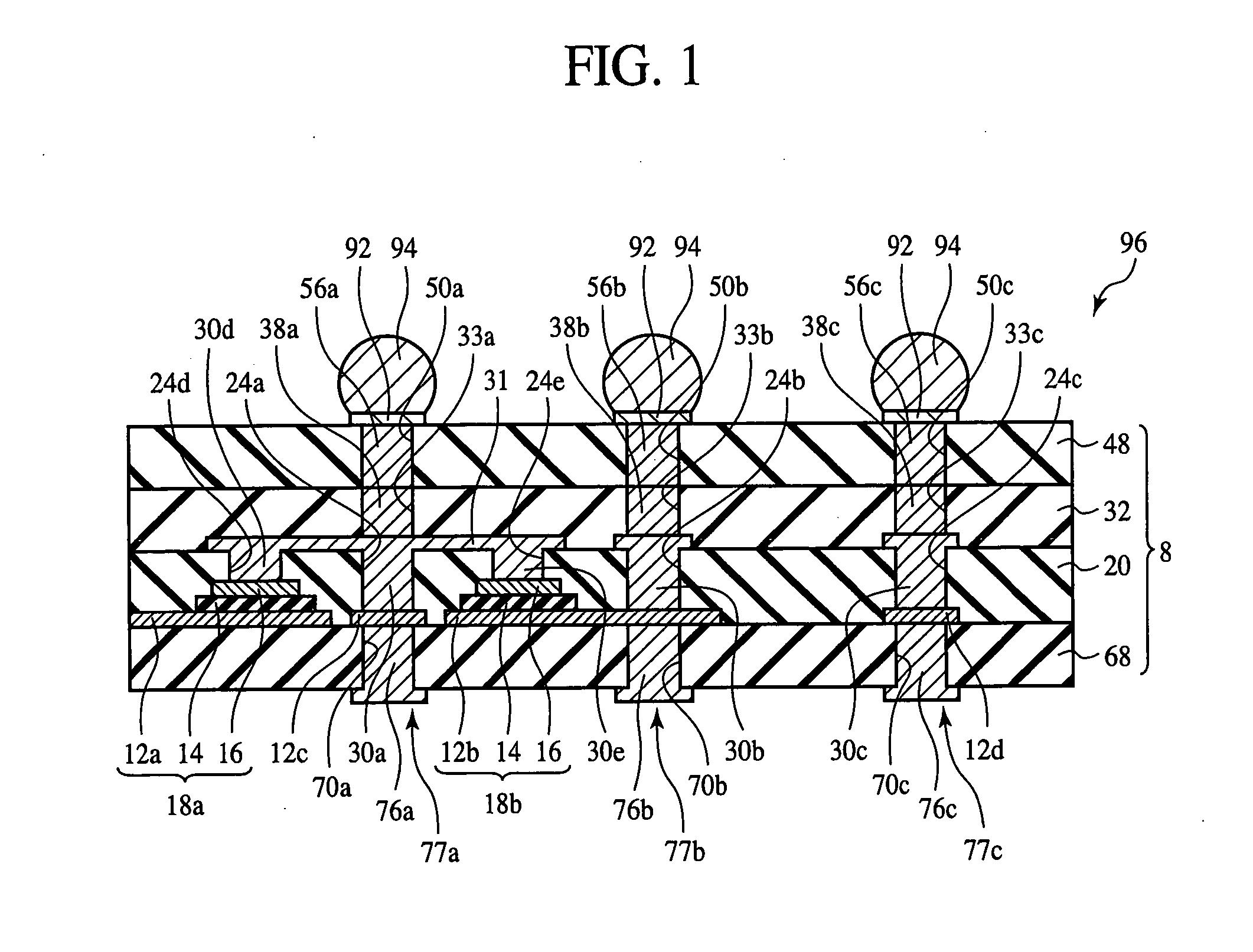
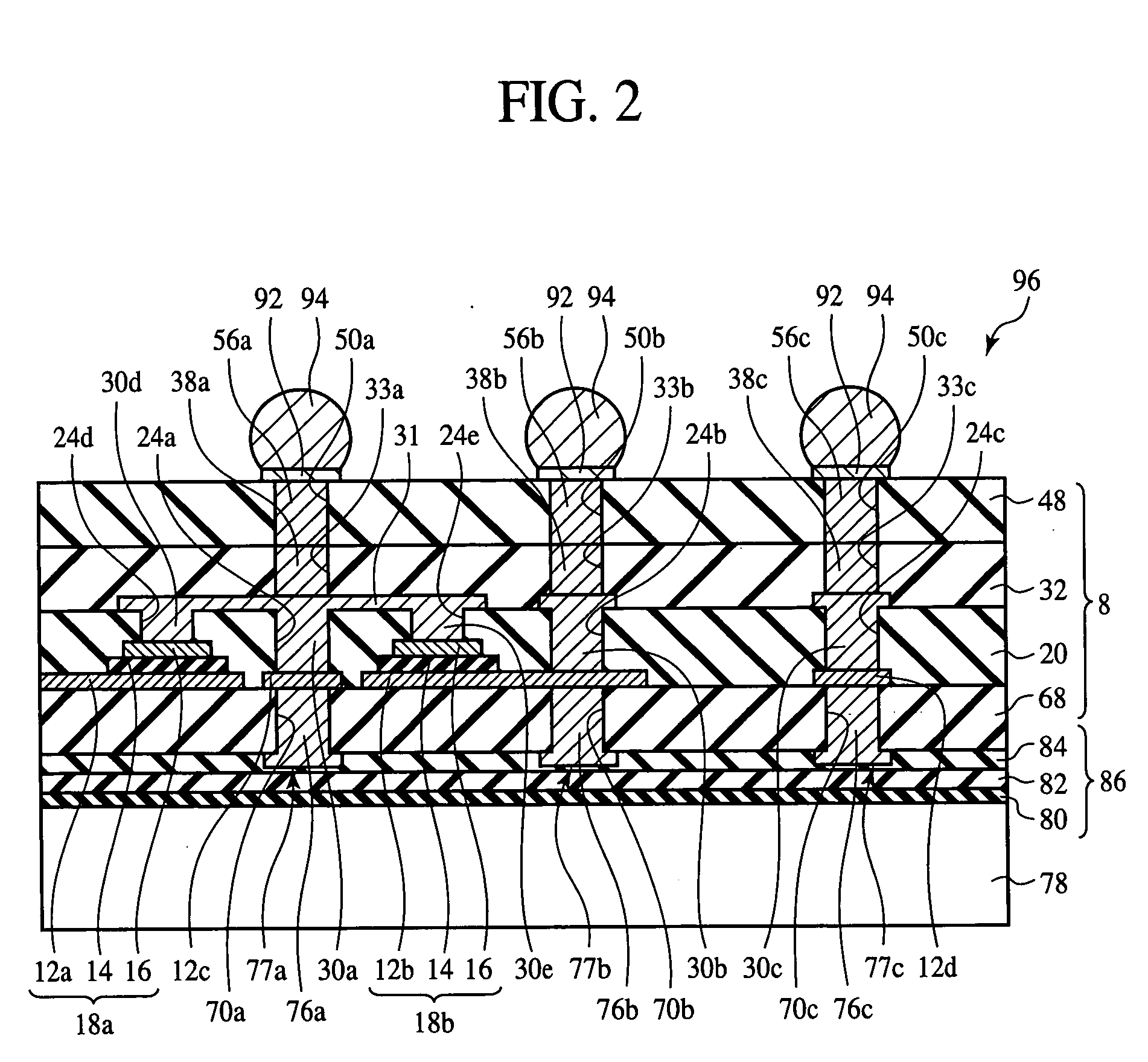
InactiveUS7355290B2Good electric characteristicLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsDielectricInterposer
The interposer comprises a base 8 formed of a plurality of resin layers 68, 20, 32, 48; thin-film capacitors 18a, 18b buried between a first resin layer 68 of said plurality of resin layers and a second resin layer 20 of said plurality of resin layers, which include first capacitor electrodes 12a, 12b, second capacitor electrodes 16 opposed to the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b and the second capacitor electrode 16, and a capacitor dielectric film 14 of a relative dielectric constant of 200 or above formed between the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b and the second capacitor electrode 16; a first through-electrode 77a formed through the base 8 and electrically connected to the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b; and a second through-electrode 77b formed through the base 8 and electrically connected to the second capacitor electrode 16.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for fabricating surface mountable chip inductor
InactiveUS20020013994A1Good electric characteristicTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresThermoplasticSurface mounting
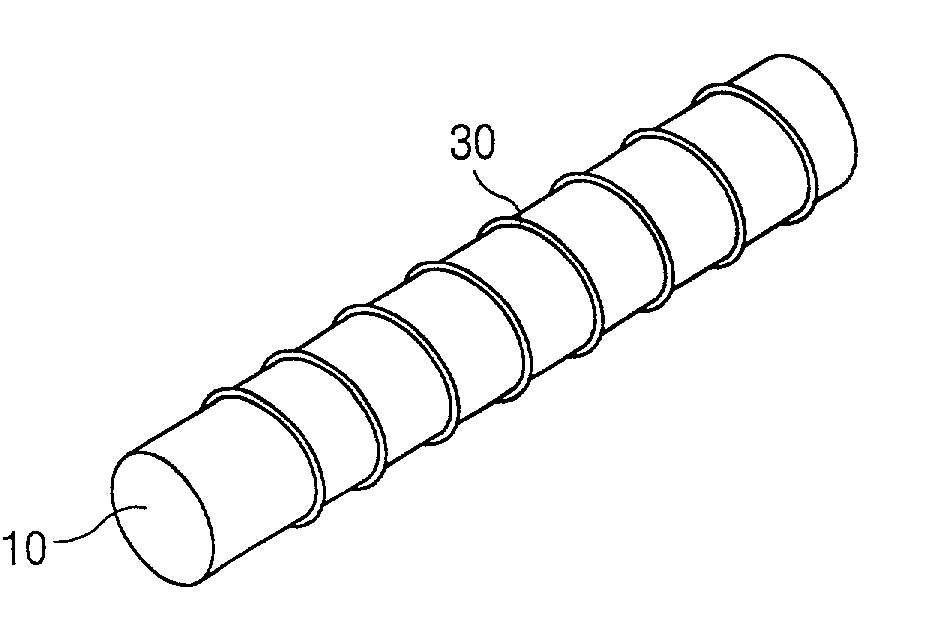
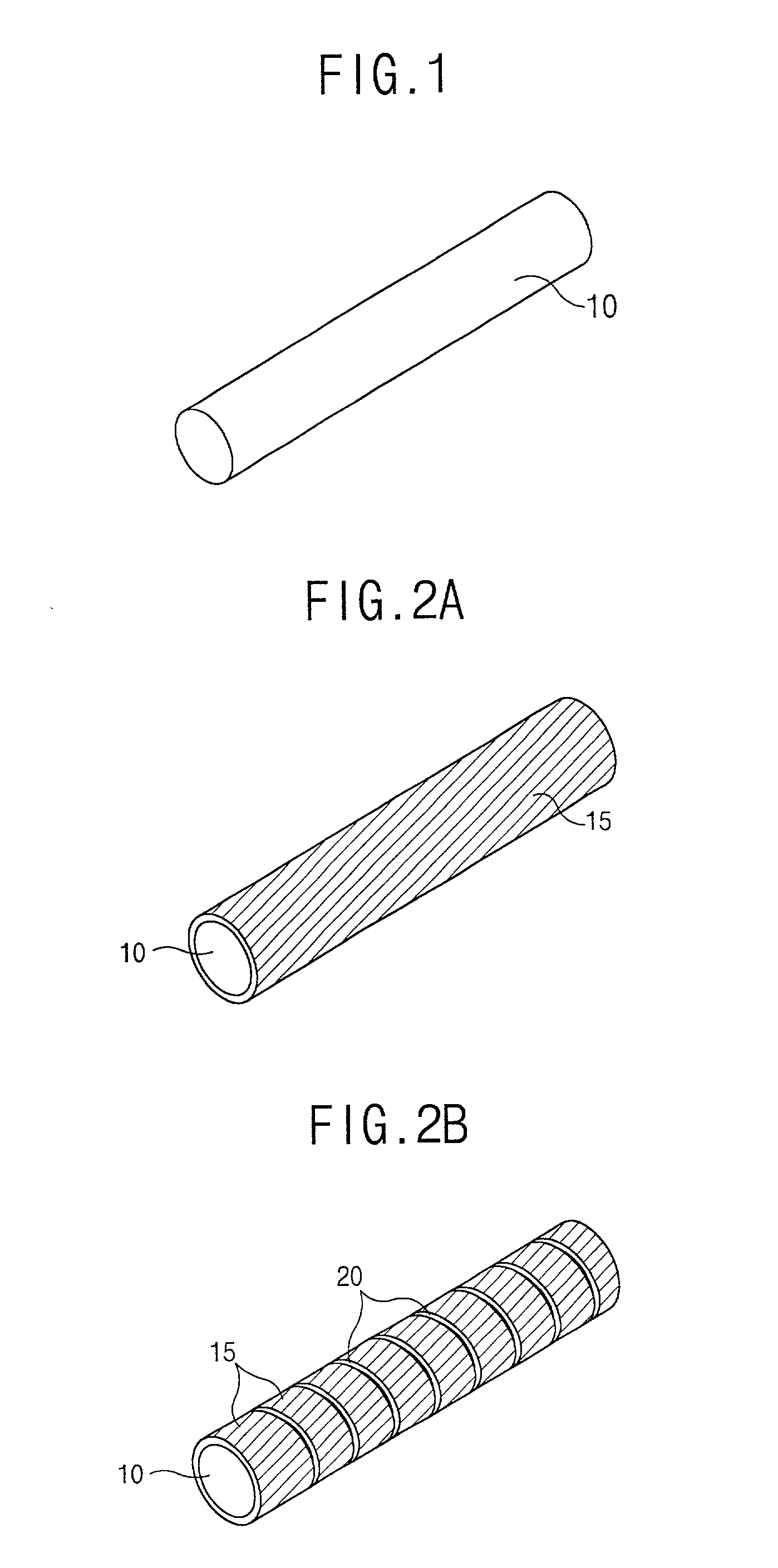
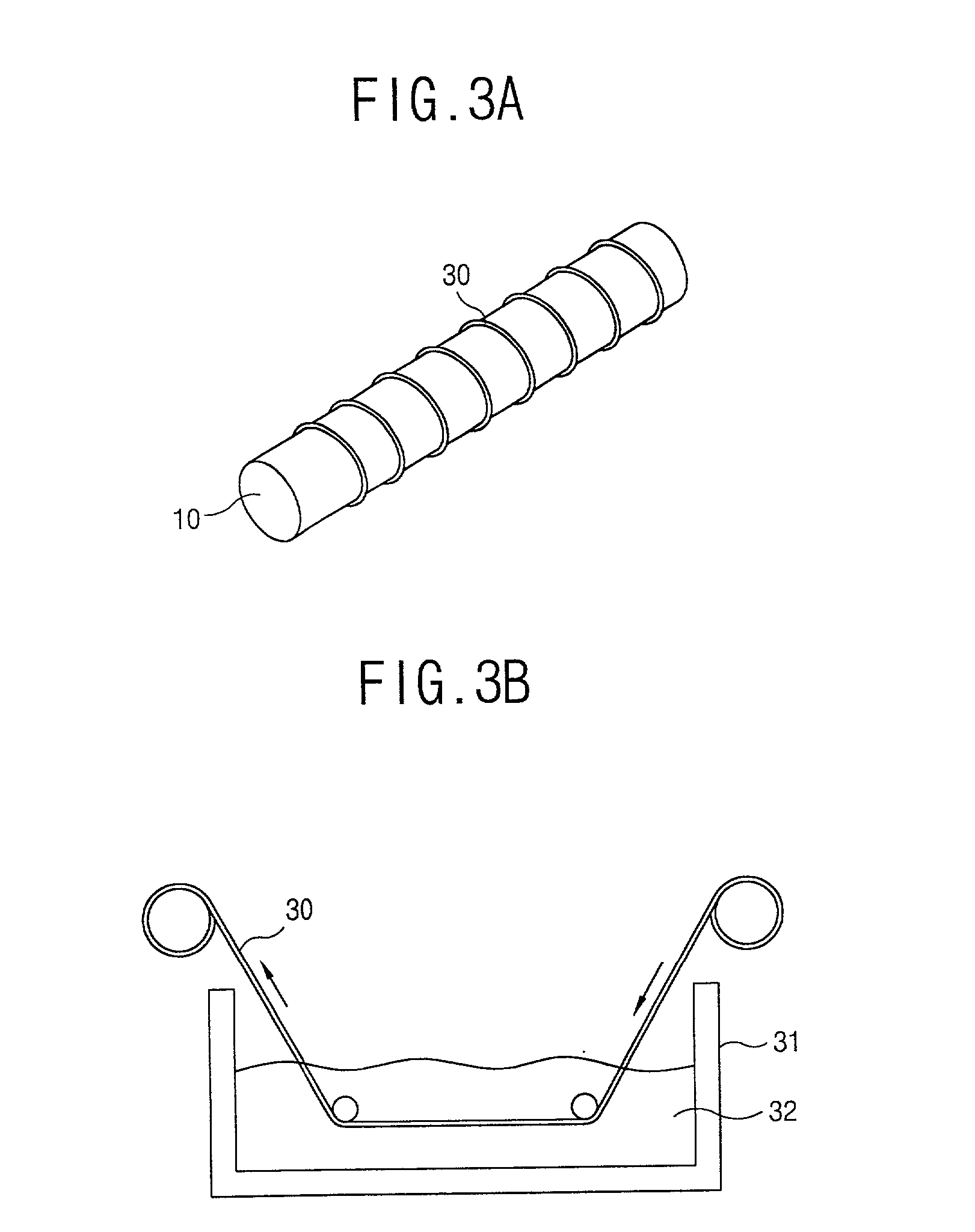
In a method for fabricating a surface mountable chip inductor, a spiral coil pattern is formed on a surface of a cylindrical body fabricated by mixing ferrite or ceramic powder with thermoplastic organic binder, the cylindrical body is transformed into a square-shaped body by being inserted into a square-shaped mold and being applied pressure at a certain temperature. An electric characteristic lowering problem can be prevented by forming the coil on the cylindrical body, and transforming the cylindrical body into a square-shaped body is advantageous to surface mounting.
Owner:CERATECH
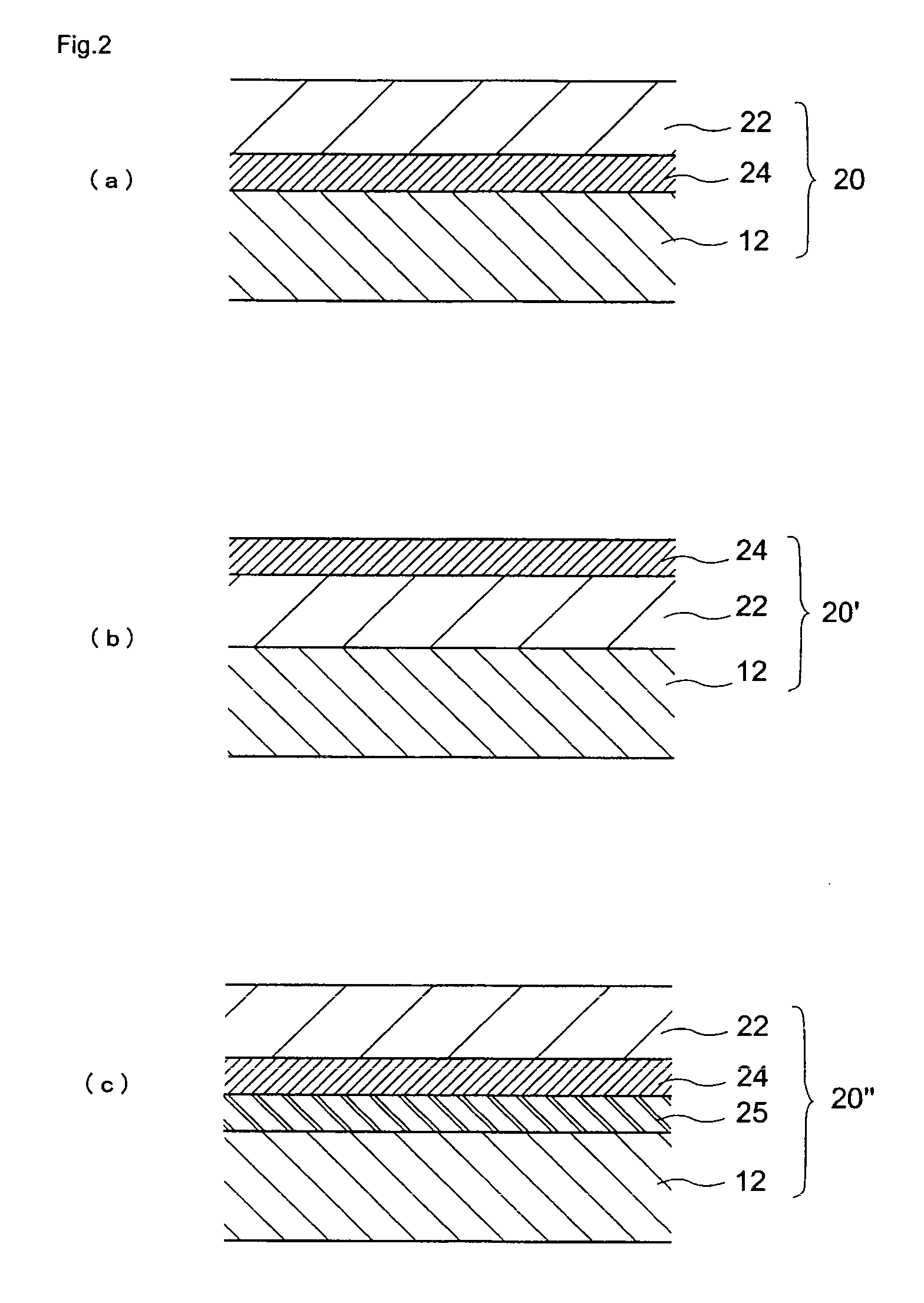
Semiconductor substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100237458A1Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialNitrogen
A semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing thereof are provided. The method includes a step of forming a first insulating film containing silicon and oxygen as its composition over a single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of forming a second insulating film containing silicon and nitrogen as its composition over the first insulating film, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with first ions to form a separation layer in the single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with second ions so that halogen is contained in the first insulating film, and a step of performing heat treatment to separate the single-crystal semiconductor substrate with a single-crystal semiconductor film left over the supporting substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080157278A1Improve electrical characteristicsImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsDielectric layerCapacitor
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7781306B2Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesNitrogenSingle crystal
A semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing thereof are provided. The method includes a step of forming a first insulating film containing silicon and oxygen as its composition over a single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of forming a second insulating film containing silicon and nitrogen as its composition over the first insulating film, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with first ions to form a separation layer in the single-crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of irradiating the second insulating film with second ions so that halogen is contained in the first insulating film, and a step of performing heat treatment to separate the single-crystal semiconductor substrate with a single-crystal semiconductor film left over the supporting substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
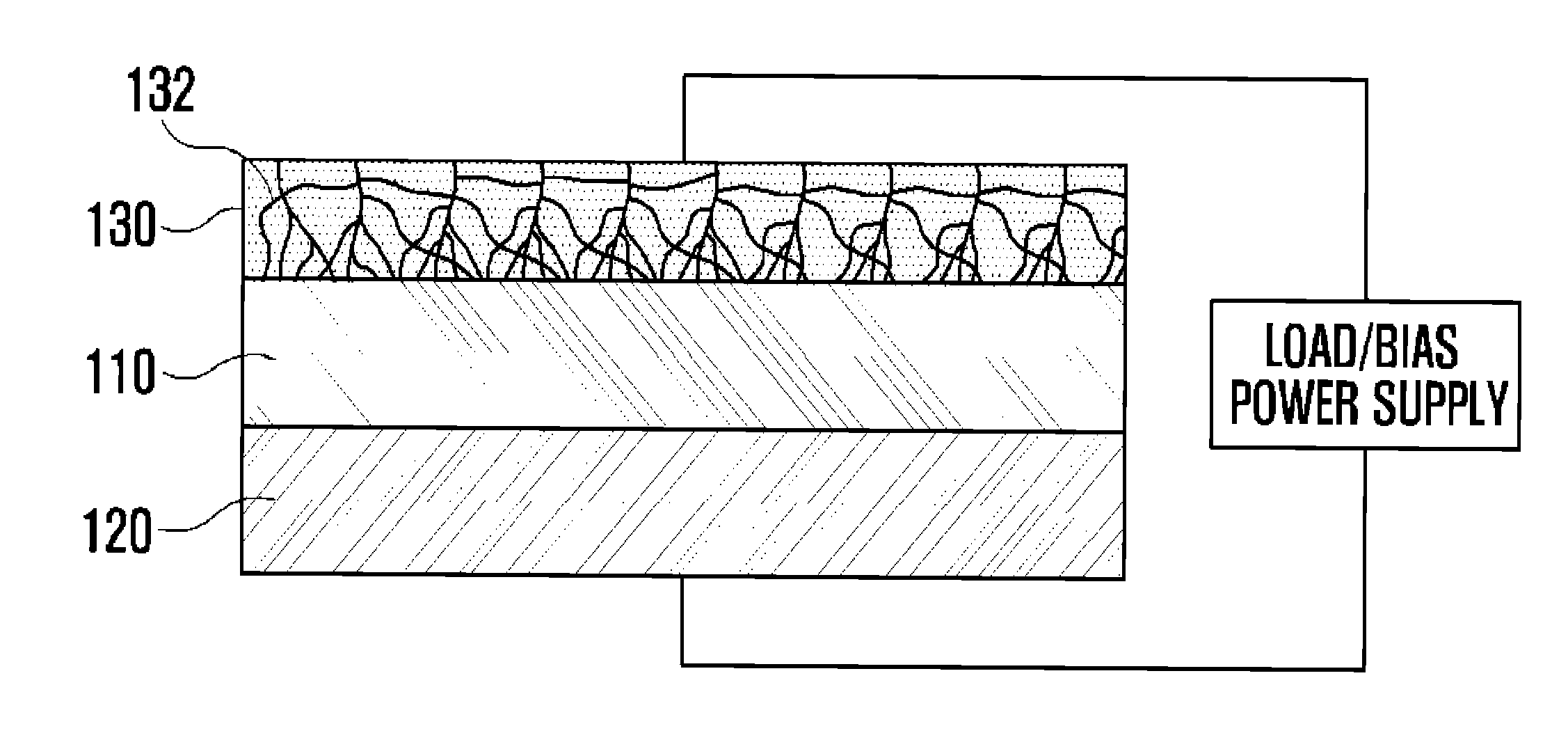
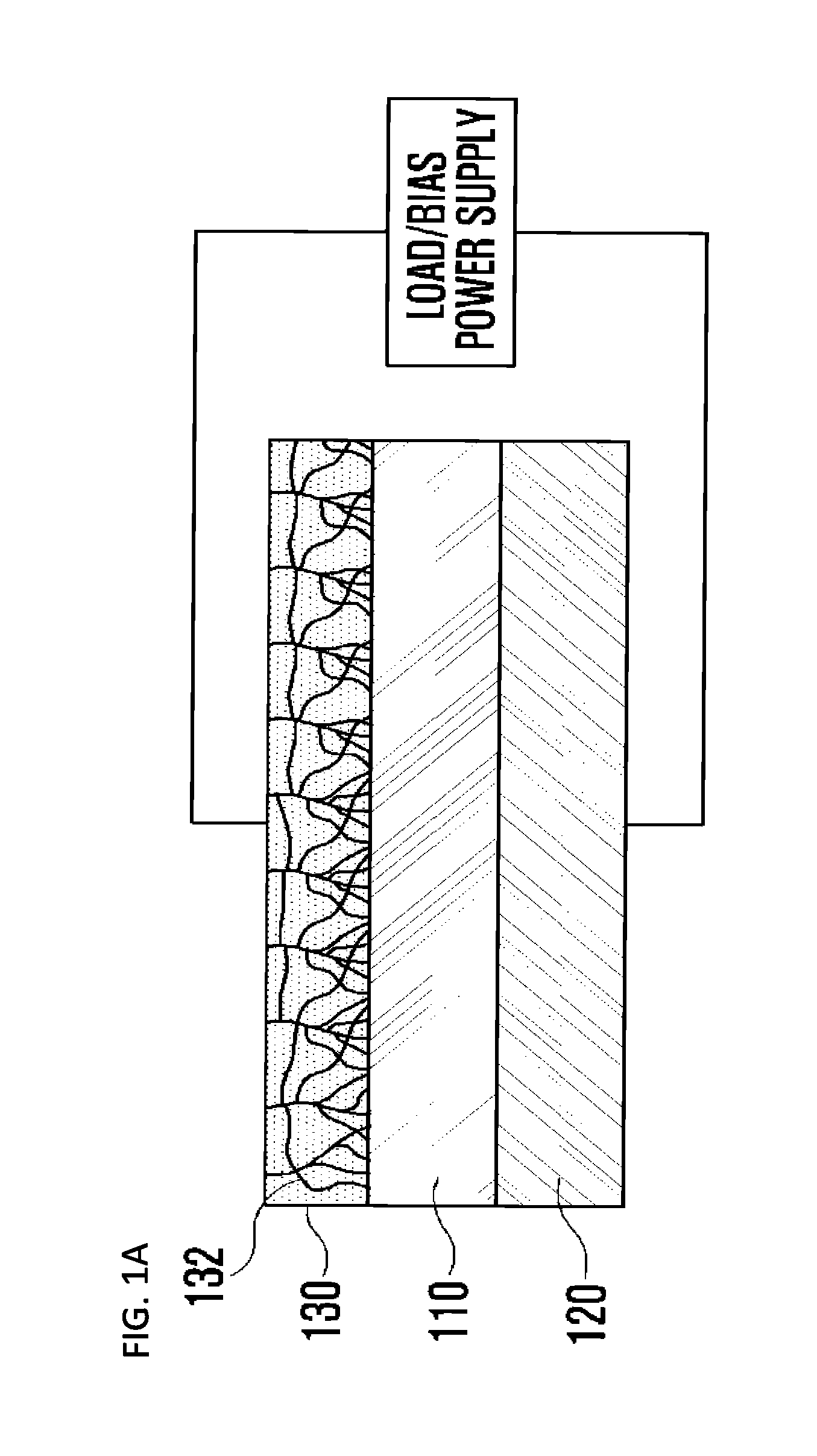
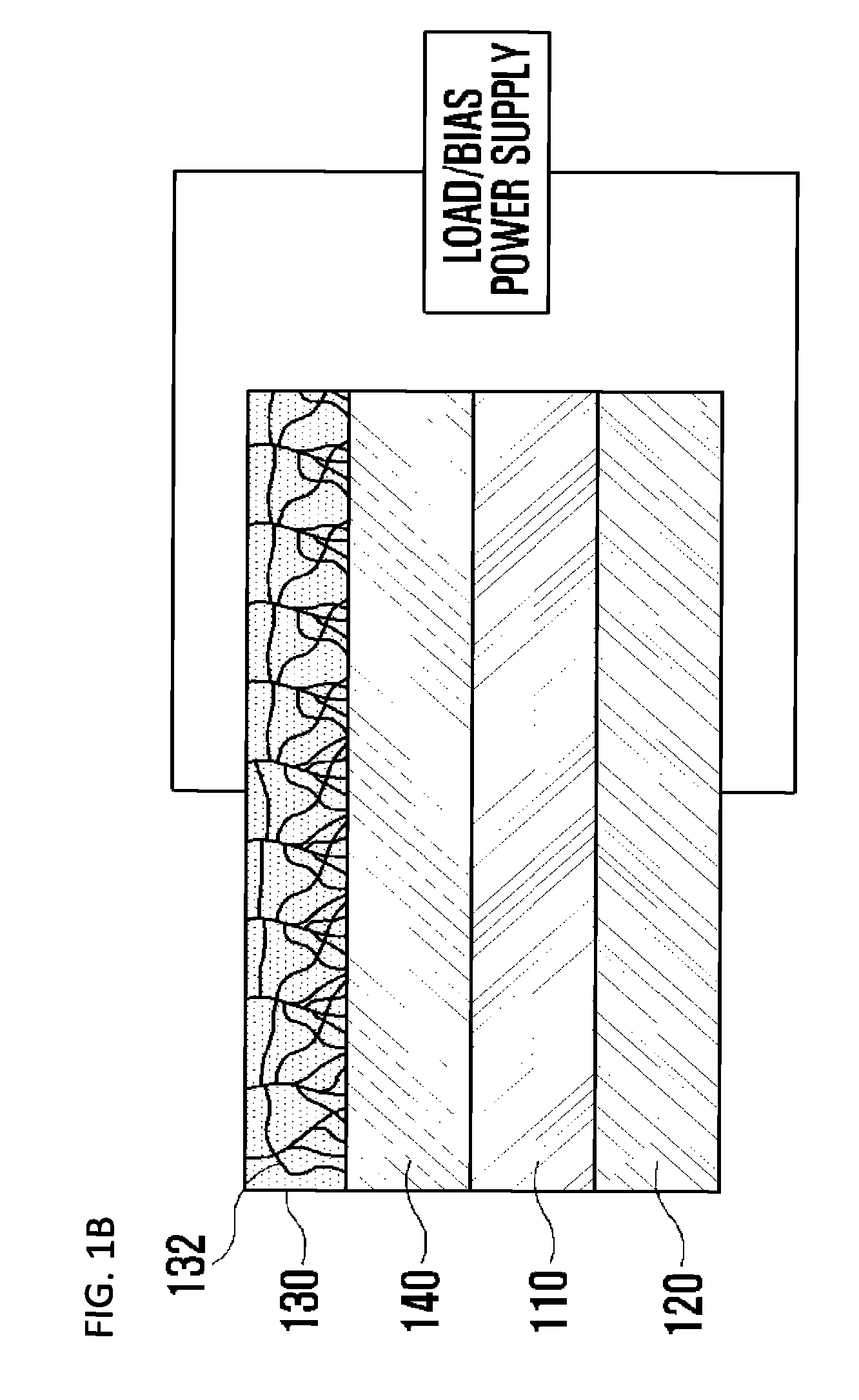
Light receiving device including transparent electrode and method of manufacturing light receiving device
ActiveUS20150380579A1Improve light transmission propertiesImprove electrical characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
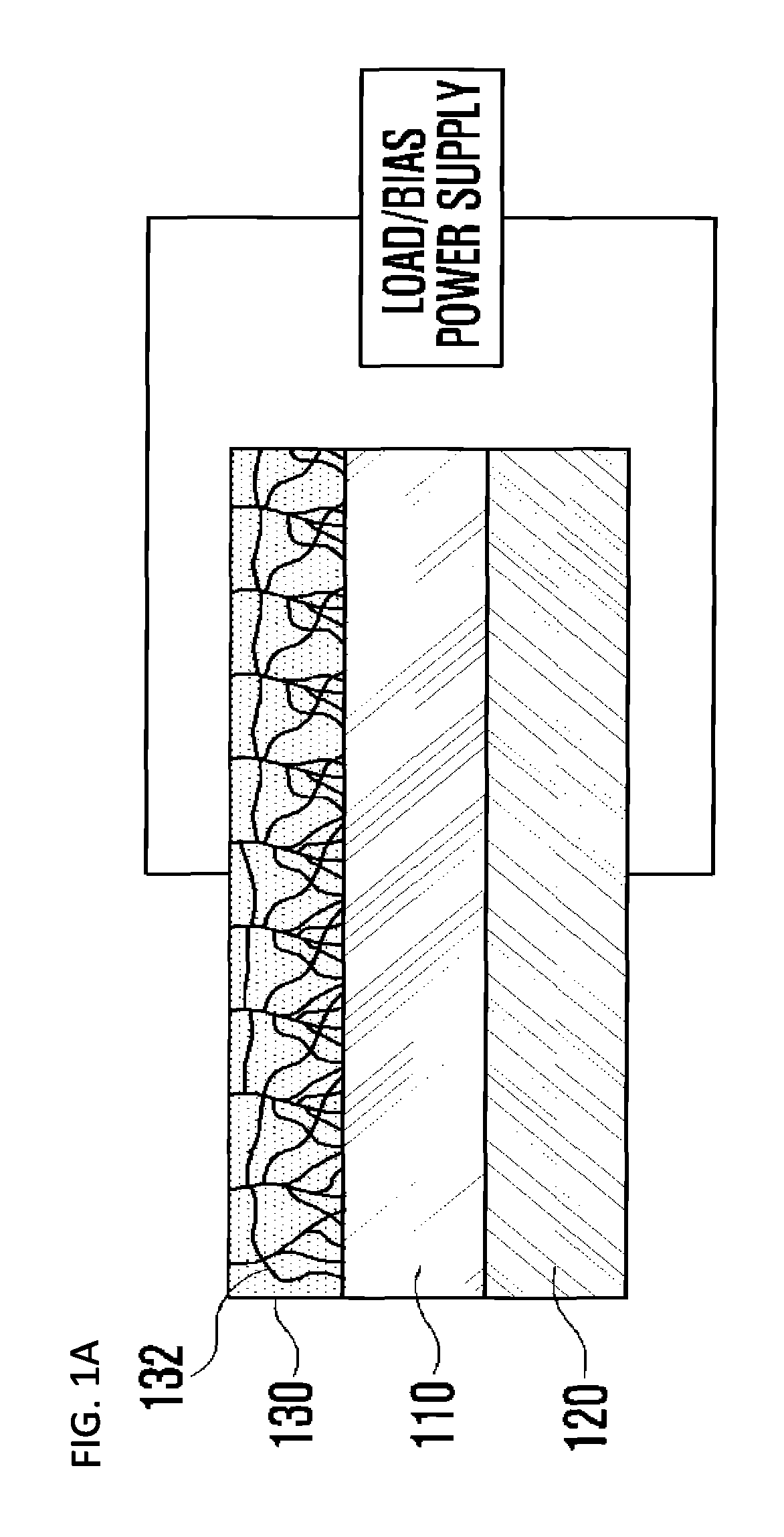
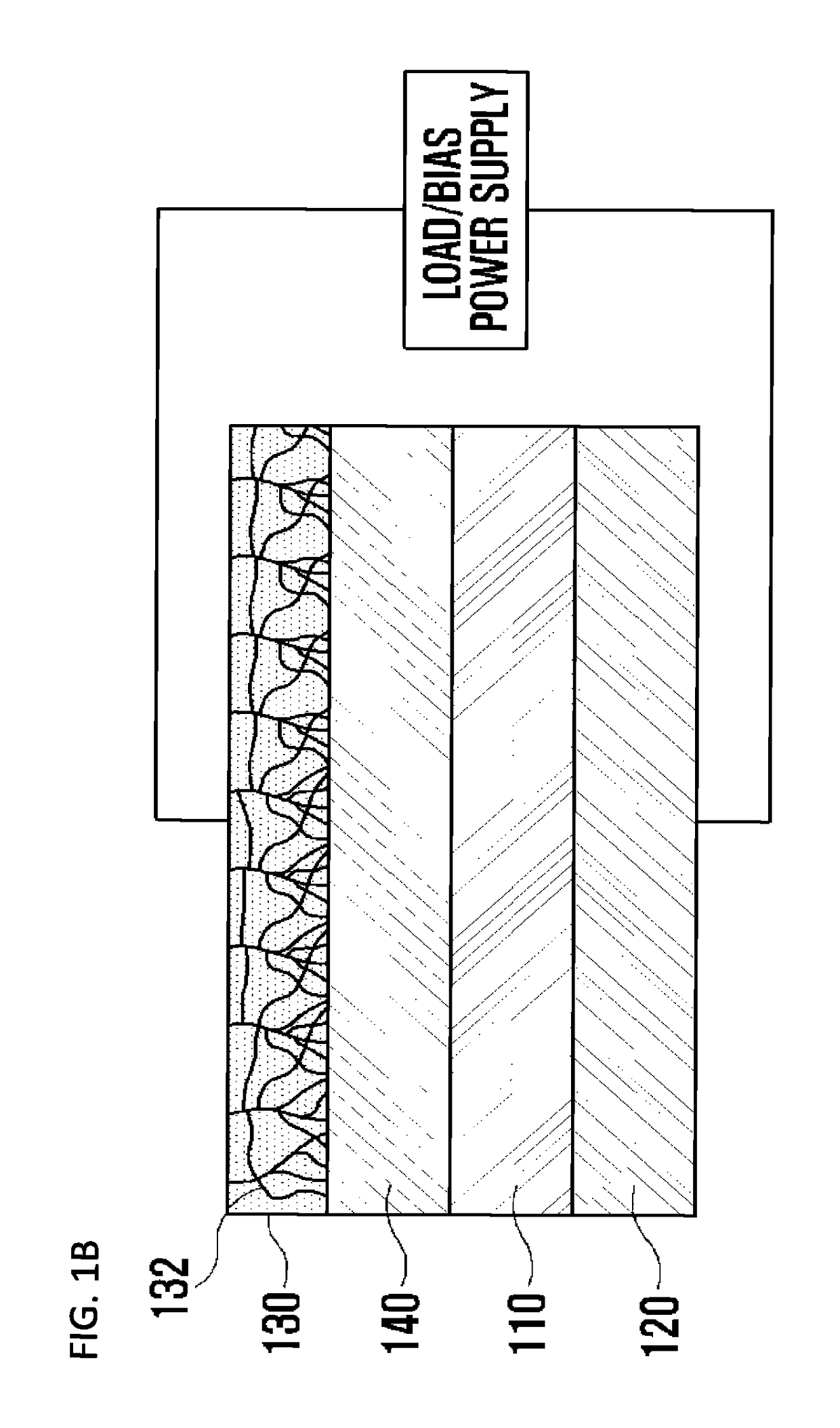
Provided is a light receiving device including a transparent electrode and a method of manufacturing the light receiving device. A transparent electrode is formed so as to be in contact with a photoelectric conversion layer which absorbs light to generate electric energy, and the transparent electrode is formed by using a resistance change material which has high transmittance with respect to light in the entire wavelength range and of which resistance state is to be changed from a high resistance state into a low resistance state if a voltage exceeding a threshold voltage inherent in the resistance change material so that conducting filaments are formed in the transparent electrode. Accordingly, since the transparent electrode has high transmittance characteristic with respect to the light in the entire wavelength range and high conductivity characteristic, the light receiving device also has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and good electric characteristics.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
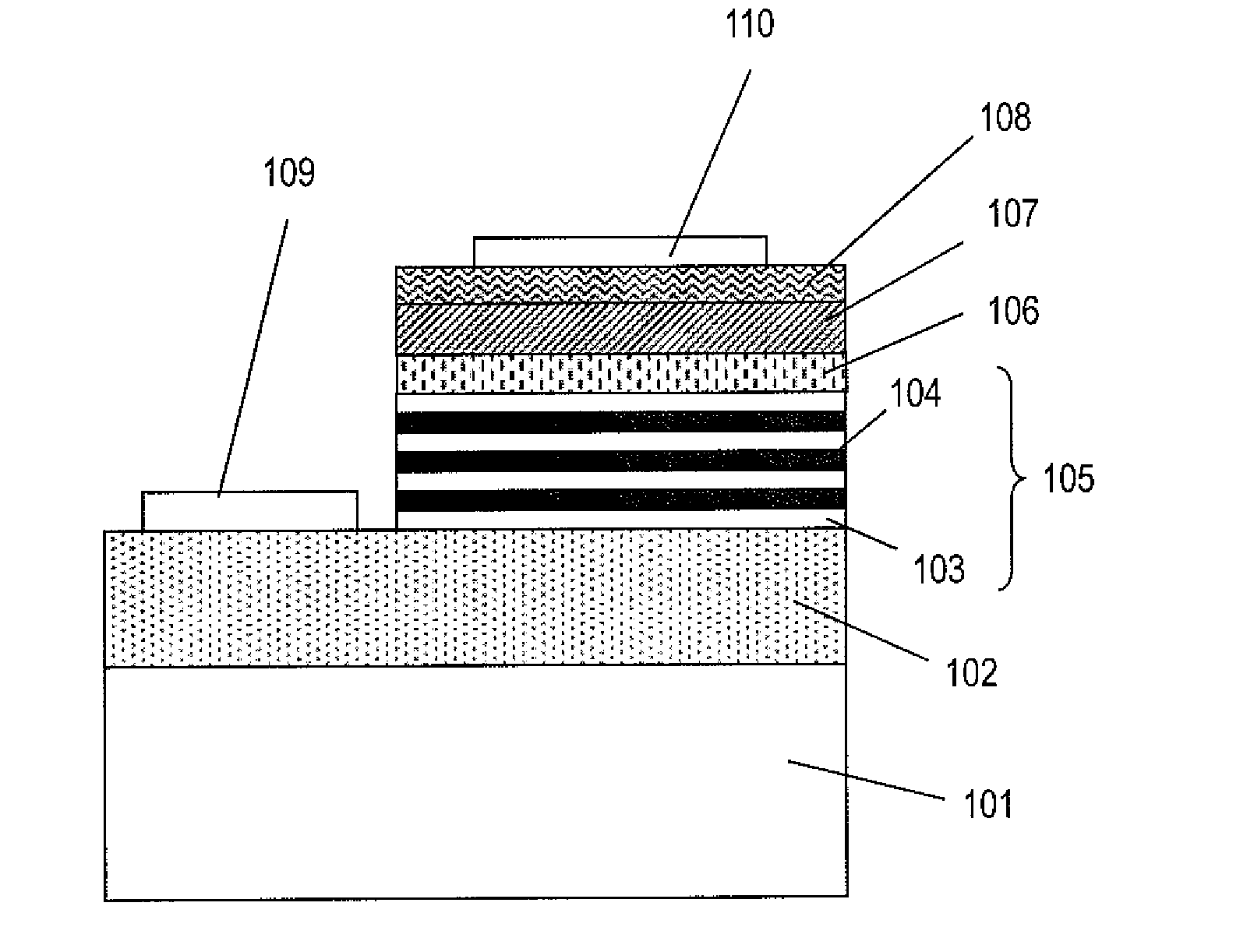
Gallium nitride based compound semiconductor light-emitting element and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20130234110A1Improve electrical characteristicsExcellent characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysical chemistryGallium nitride
A gallium nitride based compound semiconductor light-emitting element according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes: an n-type gallium nitride based compound semiconductor layer; a p-type gallium nitride based compound semiconductor layer; and an active layer which is arranged between the n- and p-type gallium nitride based compound semiconductor layers. The active layer and the p-type gallium nitride based compound semiconductor layer are m-plane semiconductor layers. The p-type gallium nitride based compound semiconductor layer includes magnesium at a concentration of 2.0×1018 cm−3 to 2.5×1019 cm−3 and oxygen, of which the concentration is 5% to 15% of the concentration of the magnesium.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Antenna control system and multi-frequency shared antenna
ActiveUS20150009078A1Horizontal plane half power beam width convergenceIncrease half power beam widthParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsControl systemOptoelectronics
A multi-frequency shared antenna comprises a low frequency radiation array and a first high frequency radiation array both of which are disposed on a reflection plate and provided with power by different feeding networks. The first high frequency radiation array comprises a number of high frequency radiation units, at least partial high frequency radiation units are arranged on a same axis which overlaps one of two axes of the low frequency radiation array, in all high frequency radiation units arranged on said axis, at least partial high frequency radiation units are nested with the low frequency radiation units arranged on the same axis, and the orthogonal projection area of these nested high frequency radiation units on the reflection plate falls within the orthogonal projection area of the corresponding low frequency radiation units on the same reflection plate.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, method for preparing the same and electrophotographic photoconductor
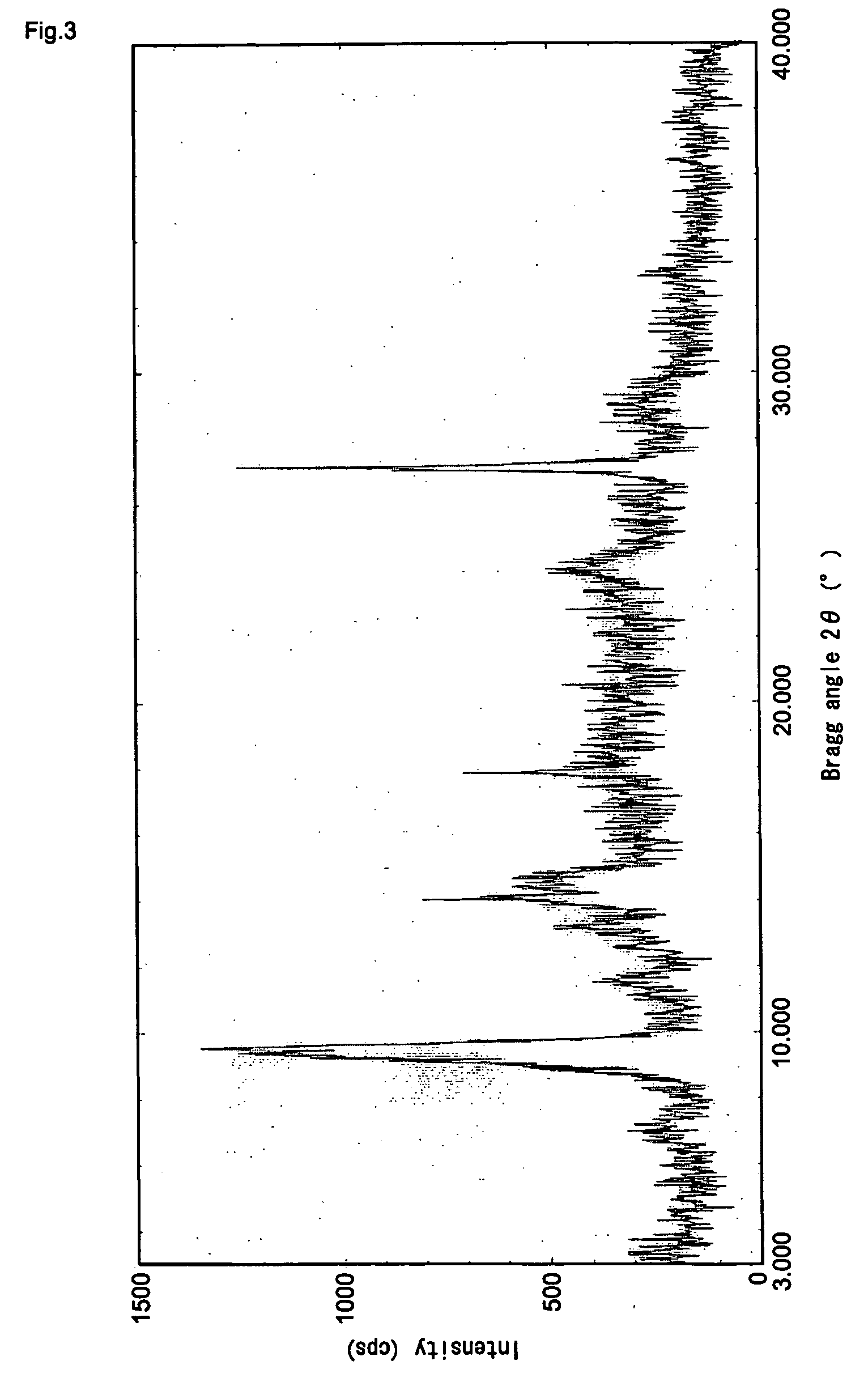
InactiveUS20070111123A1Enhance the imageGood storage stabilityOrganic chemistryReactive dyesCrystallographyElectrical conductor
According to the present invention, a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal excellent in storage stability in organic solvents, a method for preparing the same and an electrophotographic photoconductor using the same are provided. In the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, the method for preparing such a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal and the electrophotographic photoconductor using the same, the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal is characterized by having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=27.2° in a CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum and one peak within the range of 270 to 400° C. other than a peak accompanied by the vaporization of adsorbed water in a differential scanning calorimetric analysis.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Method for fabricating surface mountable chip inductor
InactiveUS6918173B2Good electric characteristicTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresThermoplasticSurface mounting
In a method for fabricating a surface mountable chip inductor, a spiral coil pattern is formed on a surface of a cylindrical body fabricated by mixing ferrite or ceramic powder with thermoplastic organic binder, the cylindrical body is transformed into a square-shaped body by being inserted into a square-shaped mold and pressure being applied at a certain temperature. An electric characteristic lowering problem can be prevented by forming the coil on the cylindrical body, and transforming the cylindrical body into a square-shaped body to improve surface mounting.
Owner:CERATECH
Interposer and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070090546A1Improve electrical characteristicsLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsDielectricInterposer
The interposer comprises a base 8 formed of a plurality of resin layers 68, 20, 32, 48; thin-film capacitors 18a, 18b buried between a first resin layer 68 of said plurality of resin layers and a second resin layer 20 of said plurality of resin layers, which include first capacitor electrodes 12a, 12b, second capacitor electrodes 16 opposed to the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b and the second capacitor electrode 16, and a capacitor dielectric film 14 of a relative dielectric constant of 200 or above formed between the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b and the second capacitor electrode 16; a first through-electrode 77a formed through the base 8 and electrically connected to the first capacitor electrode 12a, 12b; and a second through-electrode 77b formed through the base 8 and electrically connected to the second capacitor electrode 16.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Variable inductor, oscillator including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this oscillator, and amplifier including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this amplifier
InactiveUS20060033584A1Improve electrical characteristicsMiniaturizationGated amplifiersSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAudio power amplifierInductor
An amplifier comprises an amplifier circuit which comprises a first inductor as an impedance element for degeneration, and a control circuit which has a second inductor electro-magnetically connected to the first inductor, and changes a control current flowing through the second inductor to change an inductance value of the first inductor, thereby changing amplification characteristics of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
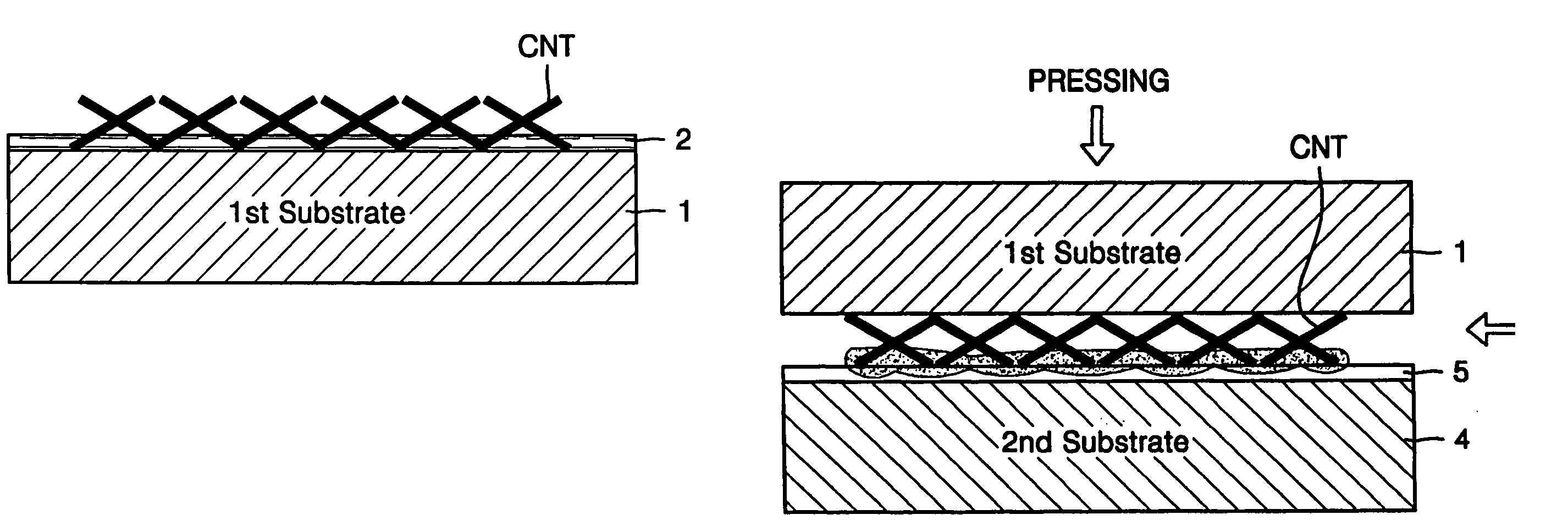
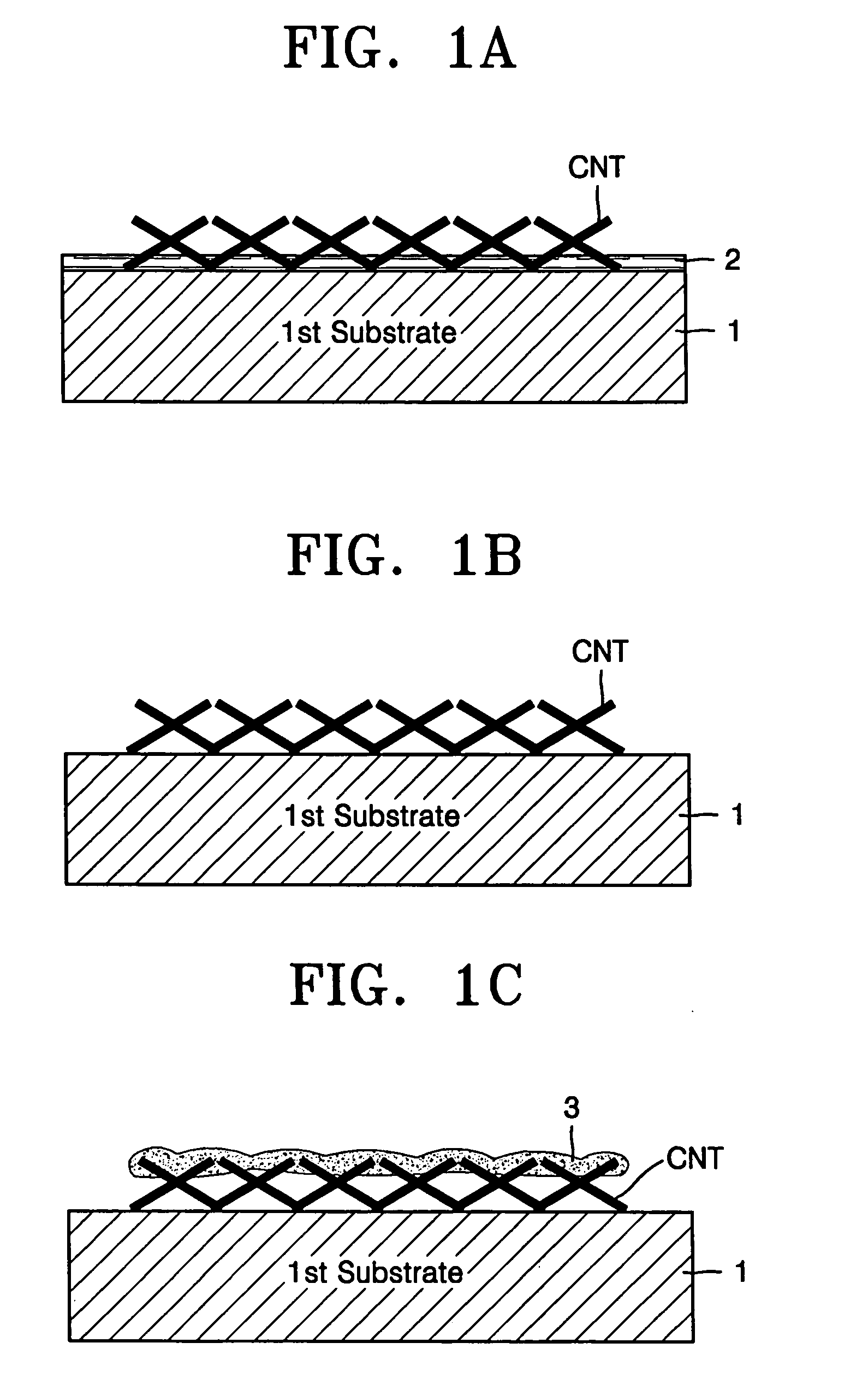
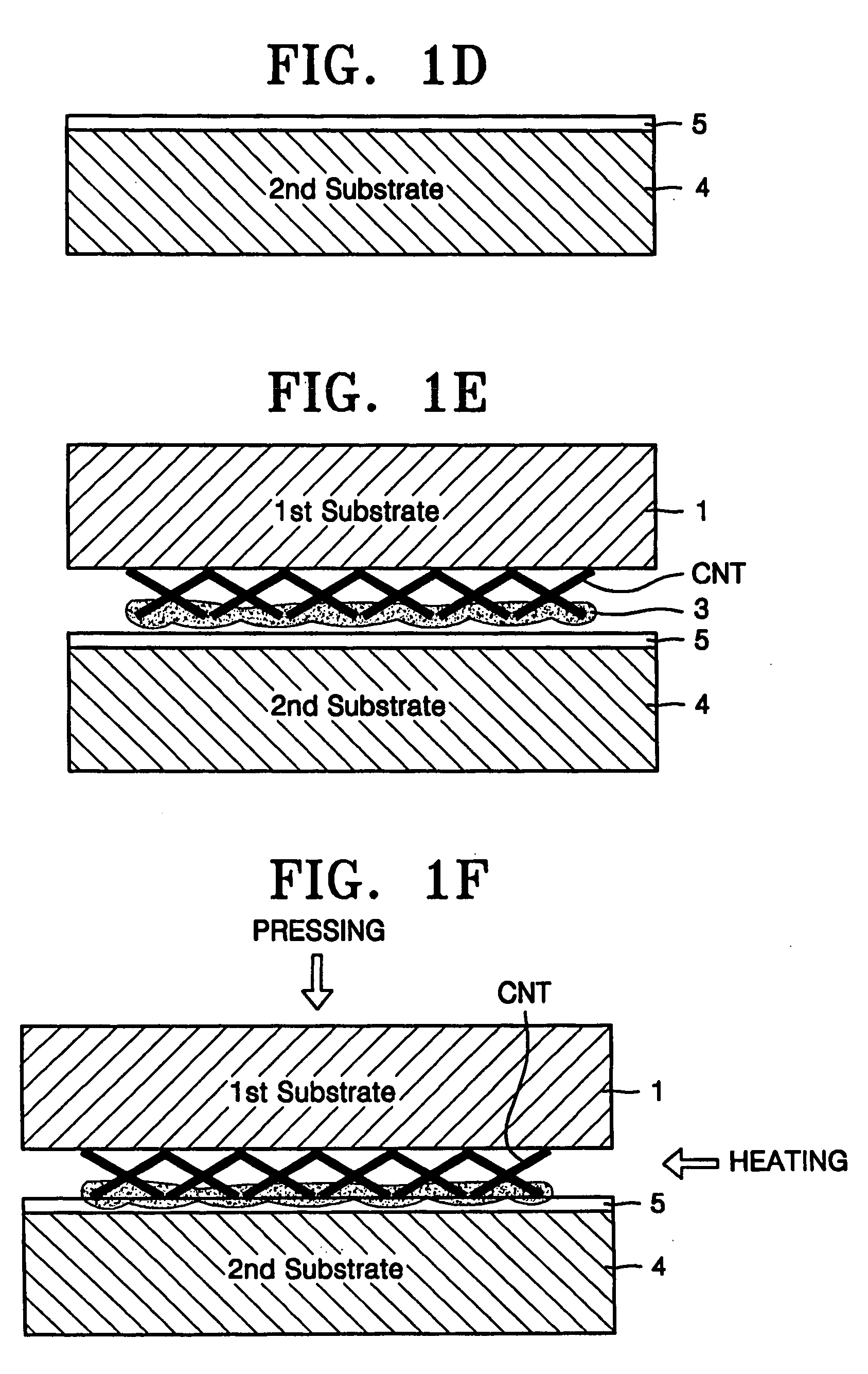
Method of manufacturing carbon nanotube field emission device
InactiveUS20060079012A1Simple methodHigh purityWater closetsElectric discharge tubesField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube emitter and a method of manufacturing a carbon nanotube field emission device using the carbon nanotube emitter. Powdered carbon nanotubes are adsorbed onto a first substrate. A metal is deposited on the carbon nanotubes. The resultant structure is pressure-bonded to a surface of a cathode. The first substrate is spaced apart from a second substrate to tense the carbon nanotubes, so that the carbon nanotubes are perpendicular to the first substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
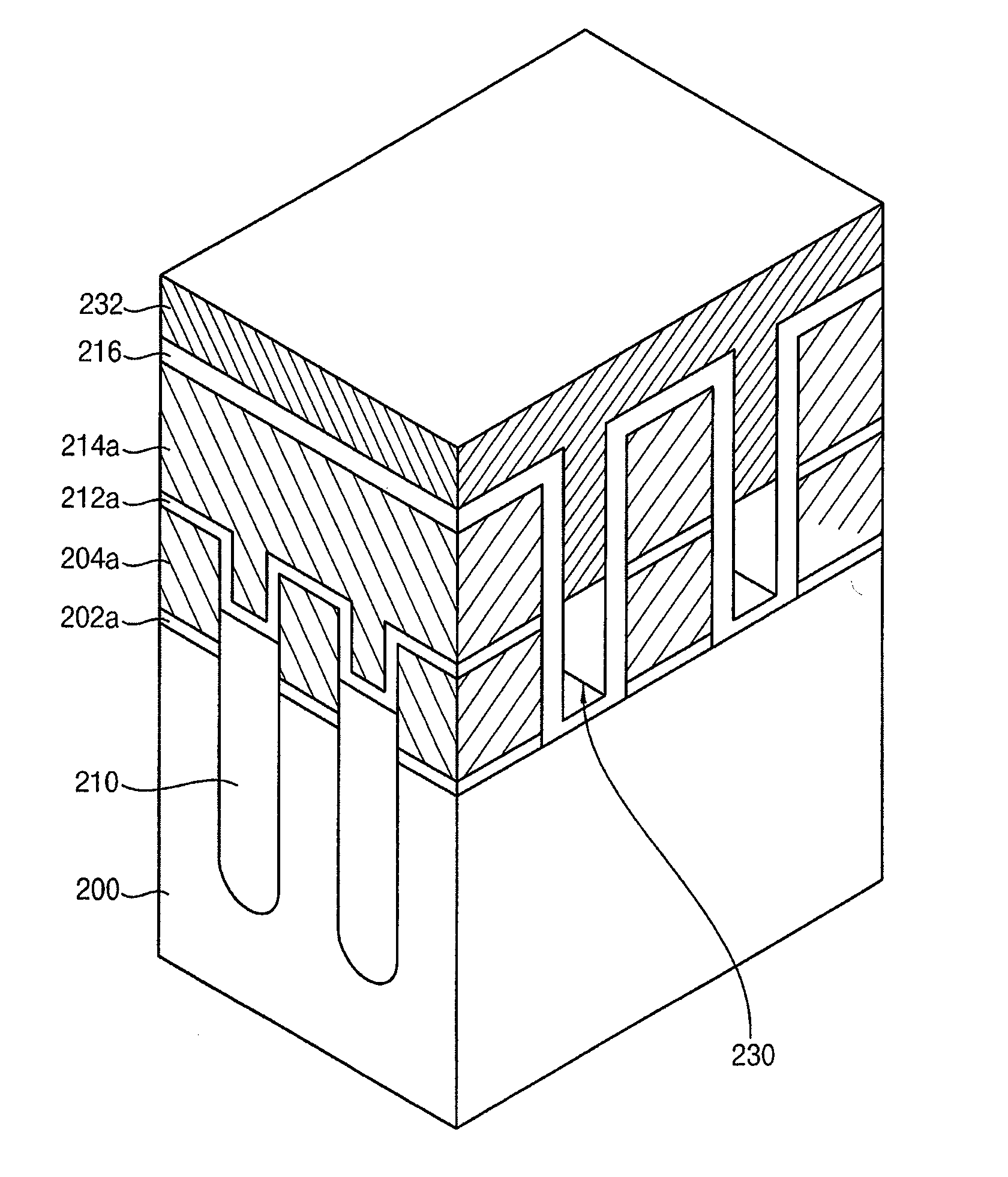
Non-volatile memory devices and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120223379A1Coupling ratioCoupling ratio is reducedTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringDielectric layer
A non-volatile memory device includes a substrate including a plurality of active regions and a plurality of device isolating trenches formed between a respective one of each of the active regions along a first direction in the substrate. A plurality of gate structures each including a tunnel insulating layer pattern, a floating gate electrode, a dielectric layer pattern and a control gate electrode is formed on the substrate. A first insulating layer pattern is provided within the device isolating trenches. A second insulating layer pattern is formed along an inner surface portion of a gap between the gate structures. An impurity doped polysilicon pattern is formed on the second insulating layer pattern in the gap between the gate structures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Variable inductor, oscillator including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this oscillator, and amplifier including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this amplifier
InactiveUS20060170500A1Good electric characteristicMiniaturizationResonant circuit tuningGain controlAudio power amplifierInductor
An amplifier comprises an amplifier circuit which comprises a first inductor as an impedance element for degeneration, and a control circuit which has a second inductor electro-magnetically connected to the first inductor, and changes a control current flowing through the second inductor to change an inductance value of the first inductor, thereby changing amplification characteristics of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, method for preparing the same and electrophotographic photoconductor
ActiveUS20100081073A1Enhance the imageGood storage stabilityPorphines/azaporphinesElectrographic process apparatusOrganic solventElectrical conductor
According to the present invention, a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal excellent in storage stability in organic solvents, a method for preparing the same and an electrophotographic photoconductor using the same are provided. In the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, the method for preparing such a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal and the electrophotographic photoconductor using the same, the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal is characterized by having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2 θ±0.2°=27.2° in a CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum and one peak within the range of 270 to 400° C. other than a peak accompanied by the vaporization of adsorbed water in a differential scanning calorimetric analysis.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Method of fabricating a conductive post on an electrode
ActiveUS8183147B2Avoid crackingGood electric characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsResistDielectric
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device includes: forming a semiconductor chip portion having an electrode on a main surface of a wafer; forming a first resist pattern having a first opening on the electrode; filling the first opening with a first electrically conductive material, thereby forming an electrically conductive post; removing the first resist pattern after said forming of the electrically conductive post; forming an interlayer dielectric film having a second opening positioned on the electrically conductive post; and forming an electrically conductive redistribution layer extending from an upper surface of the electrically conductive post over an upper surface of the interlayer dielectric film.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device as well as solid-state image sensing device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20100148297A1Improve inhalation effectAvoid defectsPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCarbon ionOxygen
There is provided a semiconductor substrate for solid-state image sensing device in which the production cost is lower than that of a gettering method through a carbon ion implantation and problems such as occurrence of particles at a device production step and the like are solved.Silicon substrate contains solid-soluted carbon having a concentration of 1×1016-1×1017 atoms / cm3 and solid-soluted oxygen having a concentration of 1.4×1018-1.6×1018 atoms / cm3.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for forming negative electrode and method for manufacturing lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS9680272B2Reduce the number of stepsGood electric characteristicContact member manufacturingElectrode thermal treatmentSlurryLithium-ion battery
The number of steps is reduced in the formation process of an electrode. Deterioration of the electrode is suppressed. A highly reliable lithium secondary battery is provided by suppressing the deterioration of the electrode. A method for forming a negative electrode and a method for manufacturing a lithium secondary battery including the negative electrode are provided. In the method for forming the negative electrode, graphene oxide, a plurality of particulate negative electrode active materials, and a precursor of polyimide are mixed to form slurry; the slurry is applied over a negative electrode current collector; and the slurry applied over the negative electrode current collector is heated at a temperature higher than or equal to 200° C. and lower than or equal to 400° C. so that the precursor of the polyimide is imidized. The graphene oxide is reduced in heating the slurry to imidize the precursor of the polyimide.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light receiving device including transparent electrode and method of manufacturing light receiving device
ActiveUS9793423B2Improve light transmission propertiesGood electric characteristicFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Provided is a light receiving device including a transparent electrode and a method of manufacturing the light receiving device. A transparent electrode is formed so as to be in contact with a photoelectric conversion layer which absorbs light to generate electric energy, and the transparent electrode is formed by using a resistance change material which has high transmittance with respect to light in the entire wavelength range and of which resistance state is to be changed from a high resistance state into a low resistance state if a voltage exceeding a threshold voltage inherent in the resistance change material so that conducting filaments are formed in the transparent electrode. Accordingly, since the transparent electrode has high transmittance characteristic with respect to the light in the entire wavelength range and high conductivity characteristic, the light receiving device also has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and good electric characteristics.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com