Titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, method for preparing the same and electrophotographic photoconductor
a technology of phthalocyanin and titanyl phthalocyanin, which is applied in the field of titanyl phthalocyanin crystal, can solve the problems of poor sensitivity characteristic of photosensitive layer to -type crystal, inability to form photosensitive layer having good electric characteristics, and inability to give good images, etc., to achieve excellent storage stability in organic solvents, enhance storage stability, and improve the effect of sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
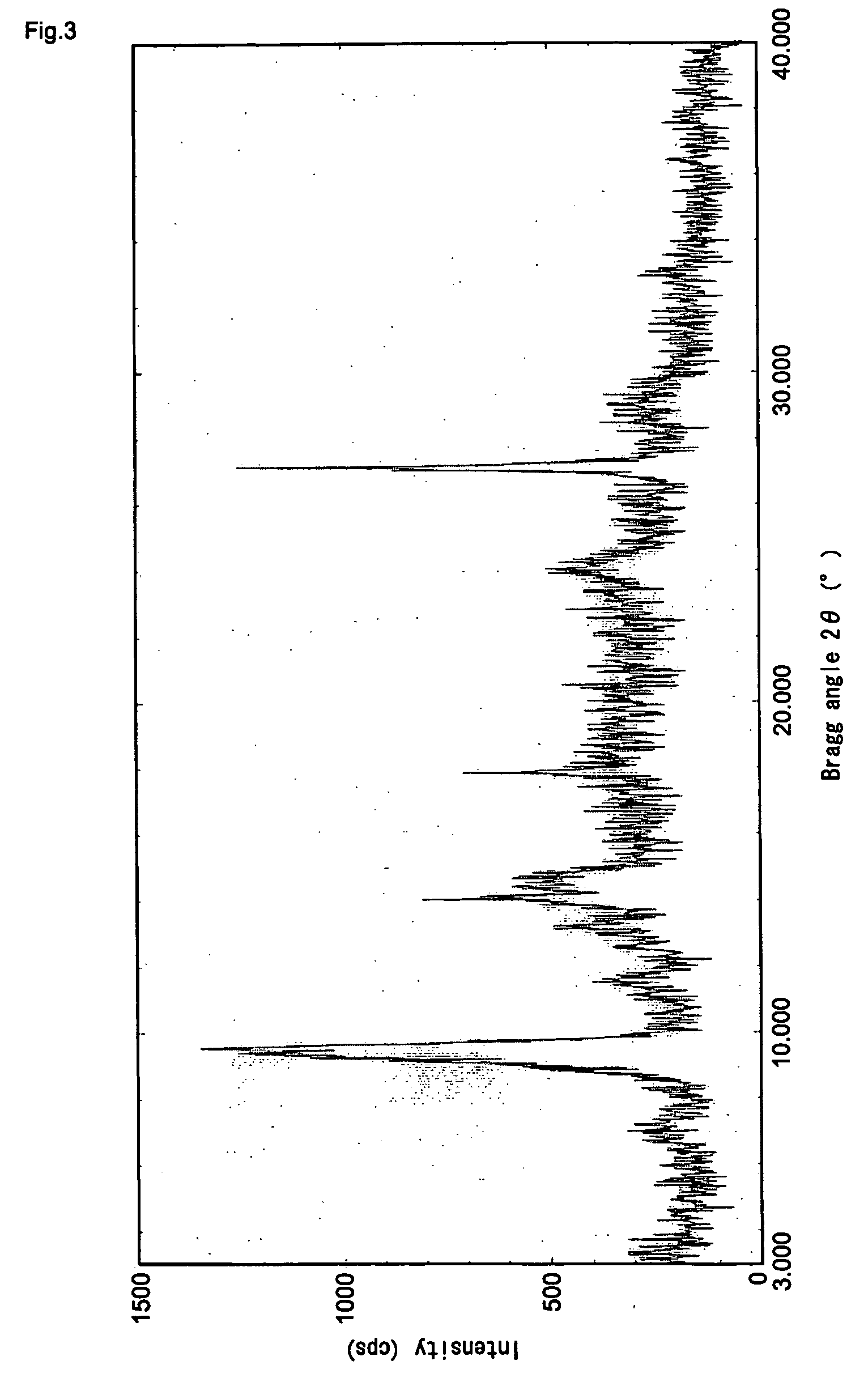
[0058] First Embodiment of the present invention is a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal characterized by having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=27.2° in the CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum and one peak within the range of 270 to 400° C. other than a peak accompanied by the vaporization of adsorbed water in the differential scanning calorimetric analysis. The titanyl phthalocyanin crystal of First Embodiment is described hereinafter by dividing it into components.
1. Optical Characteristics and Thermal Characteristics
(1) Optical Characteristics
[0059] The titanyl phthalocyanin crystal as present invention is characterized by having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=27.2° in the CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum as an optical characteristic (first optical characteristic). It is preferable that the crystal has no peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=26.2° in the CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum (second optical characteristic).
[0060] ...
second embodiment
[0075] Second Embodiment is a method for preparing the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=27.2° in the CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum and one peak within the range of 270 to 400° C. other than a peak accompanied by the vaporization of adsorbed water in the differential scanning calorimetric analysis and is characterized by comprising the following processes (a) and (b);
[0076] (a) a process for preparing a titanyl phthalocyanin compound by adding a titanium alkoxide or titanium tetrachloride at a value within the range of 0.40 to 0.53 mole with respect to 1 mole of o-phthalonitrile or its derivative or 1,3-diiminoisoindoline or its derivative and adding a urea compound at a value within the range of 0.1 to 0.95 mole with respect to 1 mole of o-phthalonitrile or its derivative or 1,3-diiminoisoindoline or its derivative to react the compounds,
[0077] (b) a process for preparing a titanyl phthalocyanin crystal by performing a...
third embodiment
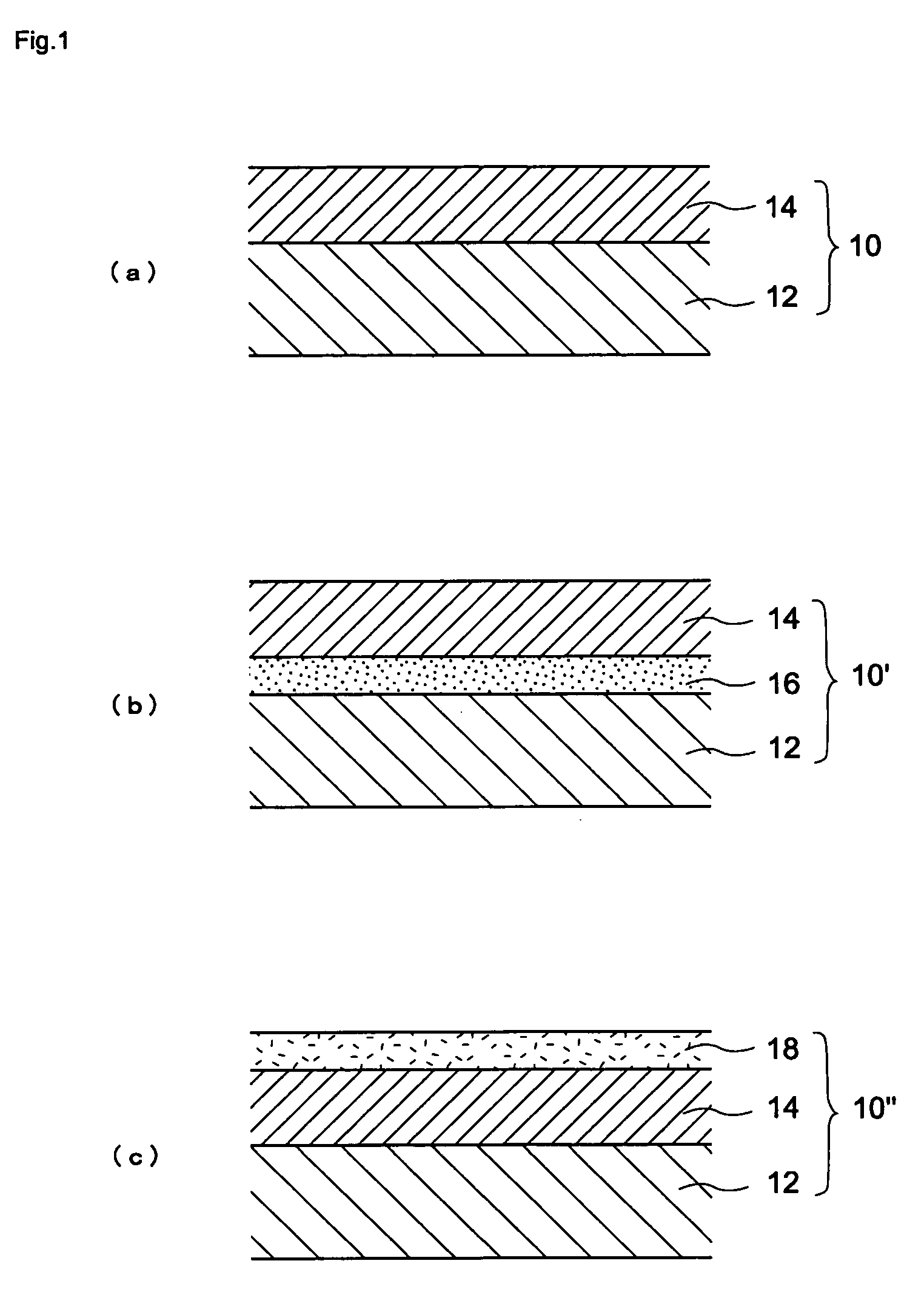
[0115] Third Embodiment is an electrophotographic photoconductor characterized in that a photosensitive layer is provided on a conductive substrate, and the photosensitive layer comprises the titanyl phthalocyanin crystal having the maximum peak at a Bragg angle 2θ±0.2°=27.2° in the CuKα characteristic X-ray diffraction spectrum and one peak in a range of 270 to 400° C. other than a peak accompanied by the vaporization of adsorbed water in the differential scanning calorimetric analysis within the range of 0.1 to 50 part by weight with respect to 100 part by weight of a binder resin forming the photosensitive layer.
[0116] The contents already described in Embodiments 1 and 2 are omitted and the above-mentioned method for preparing titanyl phthalocyanin crystal is described as Third Embodiment hereinafter.
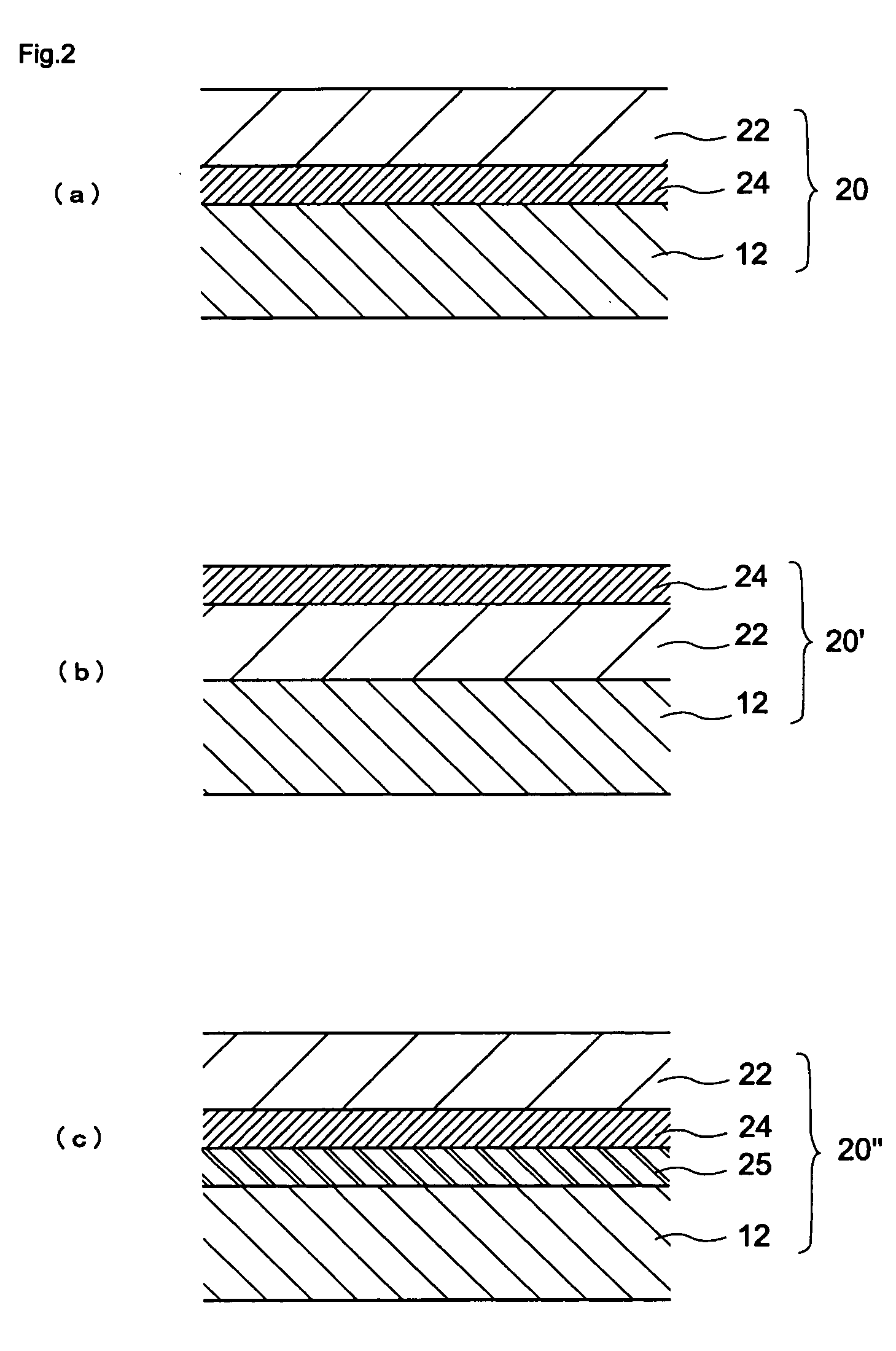
[0117] There are a single layer photoconductor and a laminated layer photoconductor in organic photoconductors, and the present invention is applicable to the both photoconductors...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bragg angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bragg angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bragg angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com