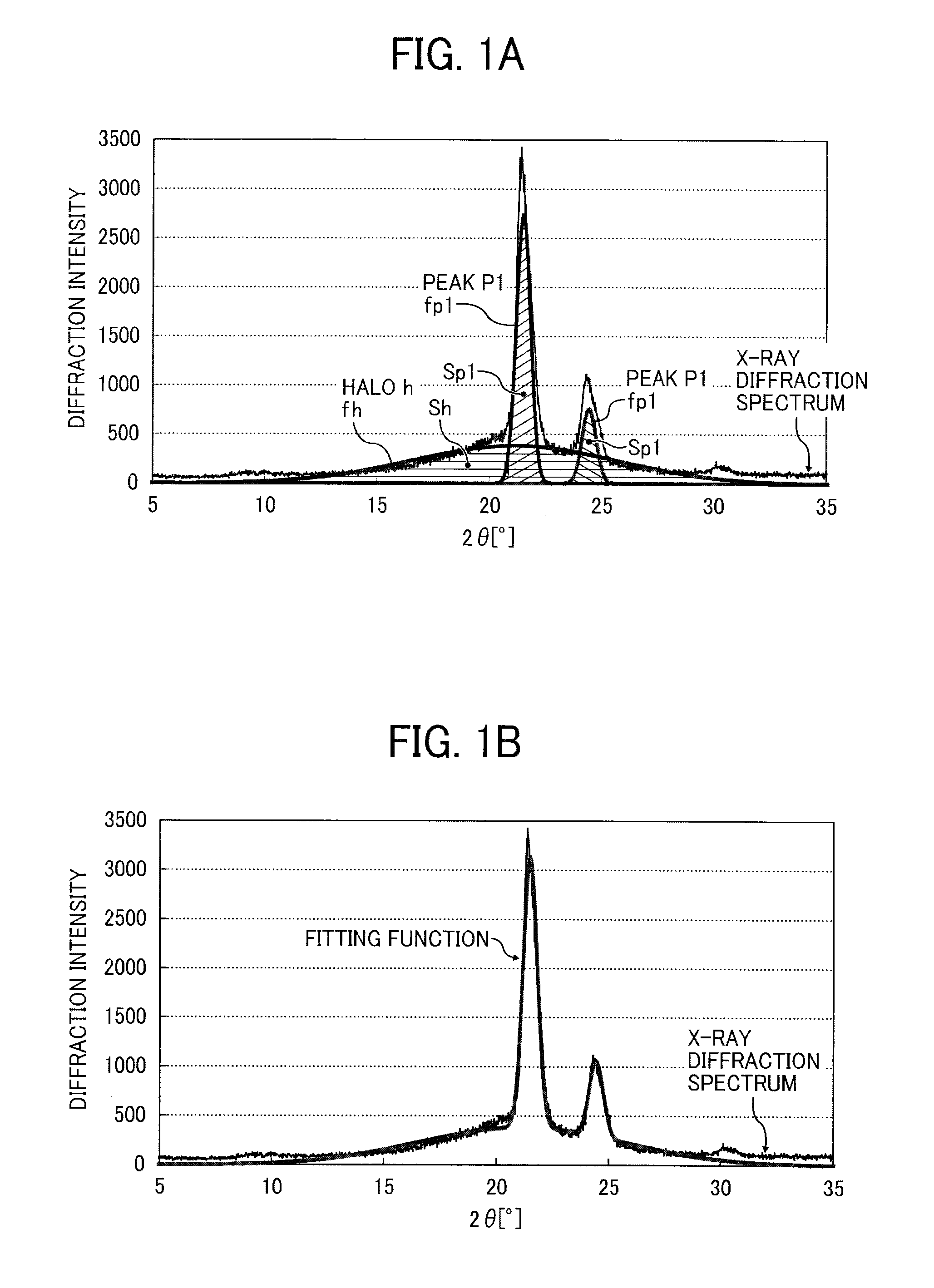
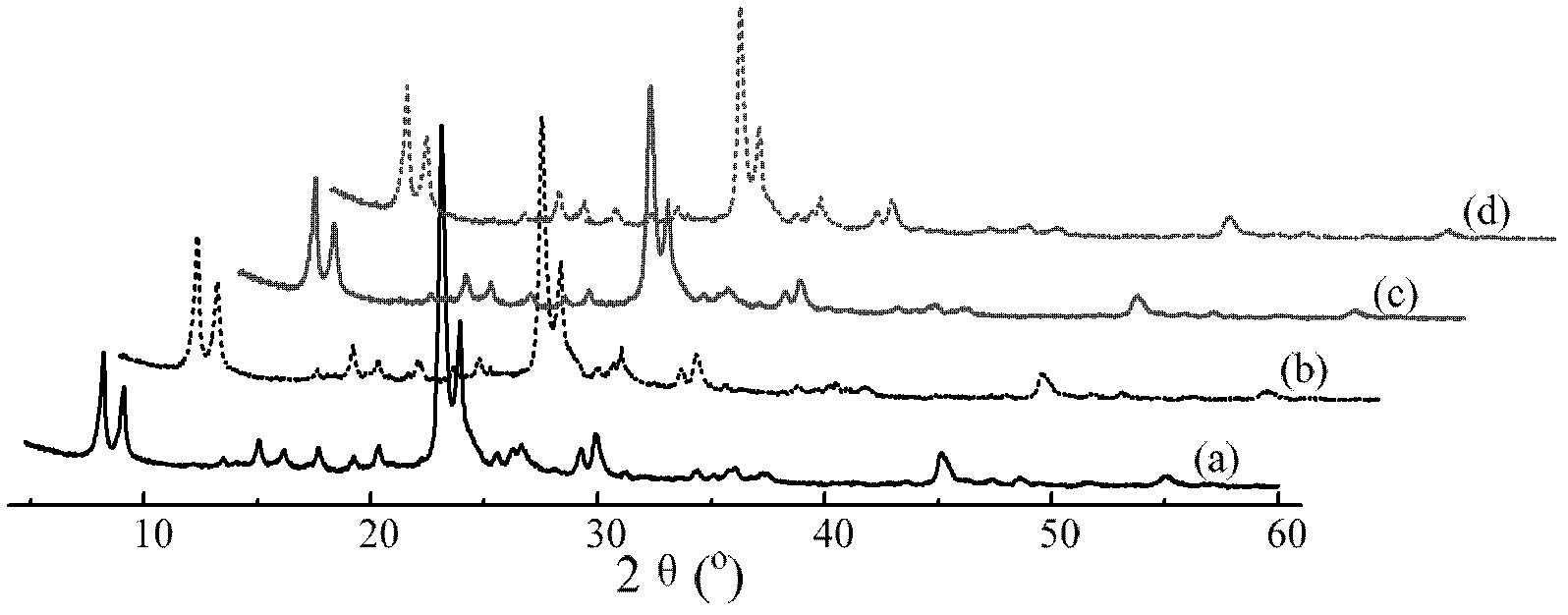
Patents
Literature
583 results about "Diffraction spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
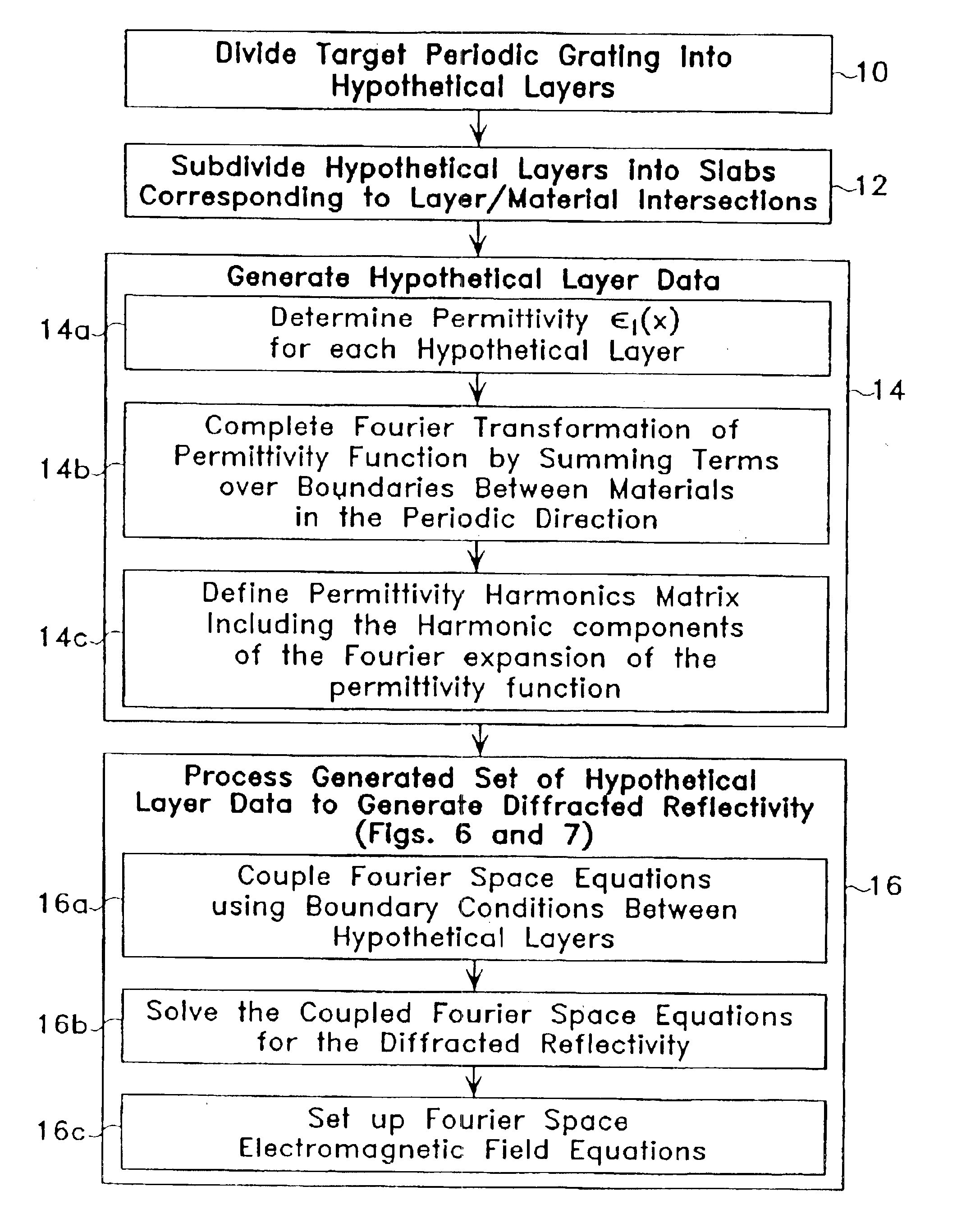
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
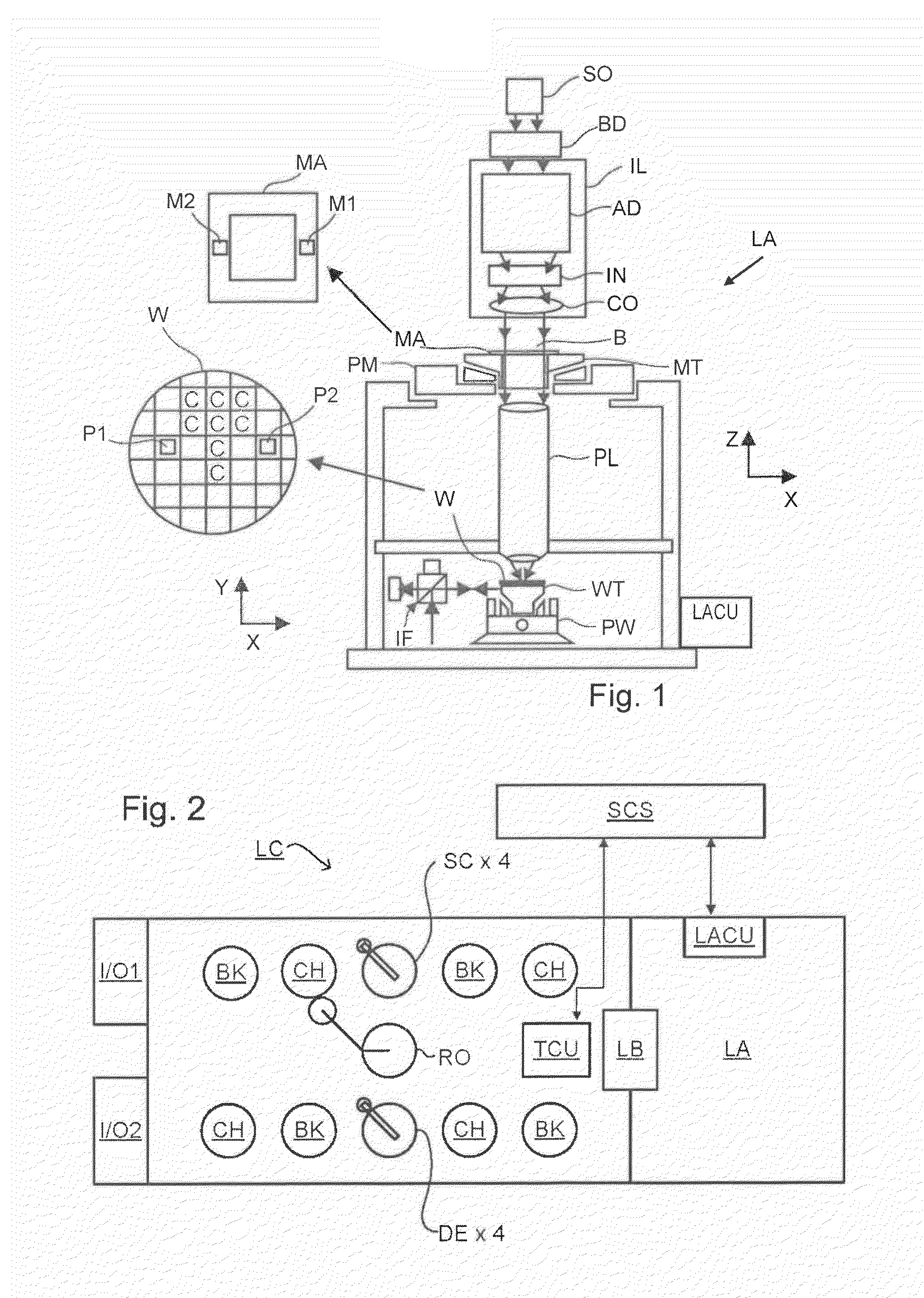
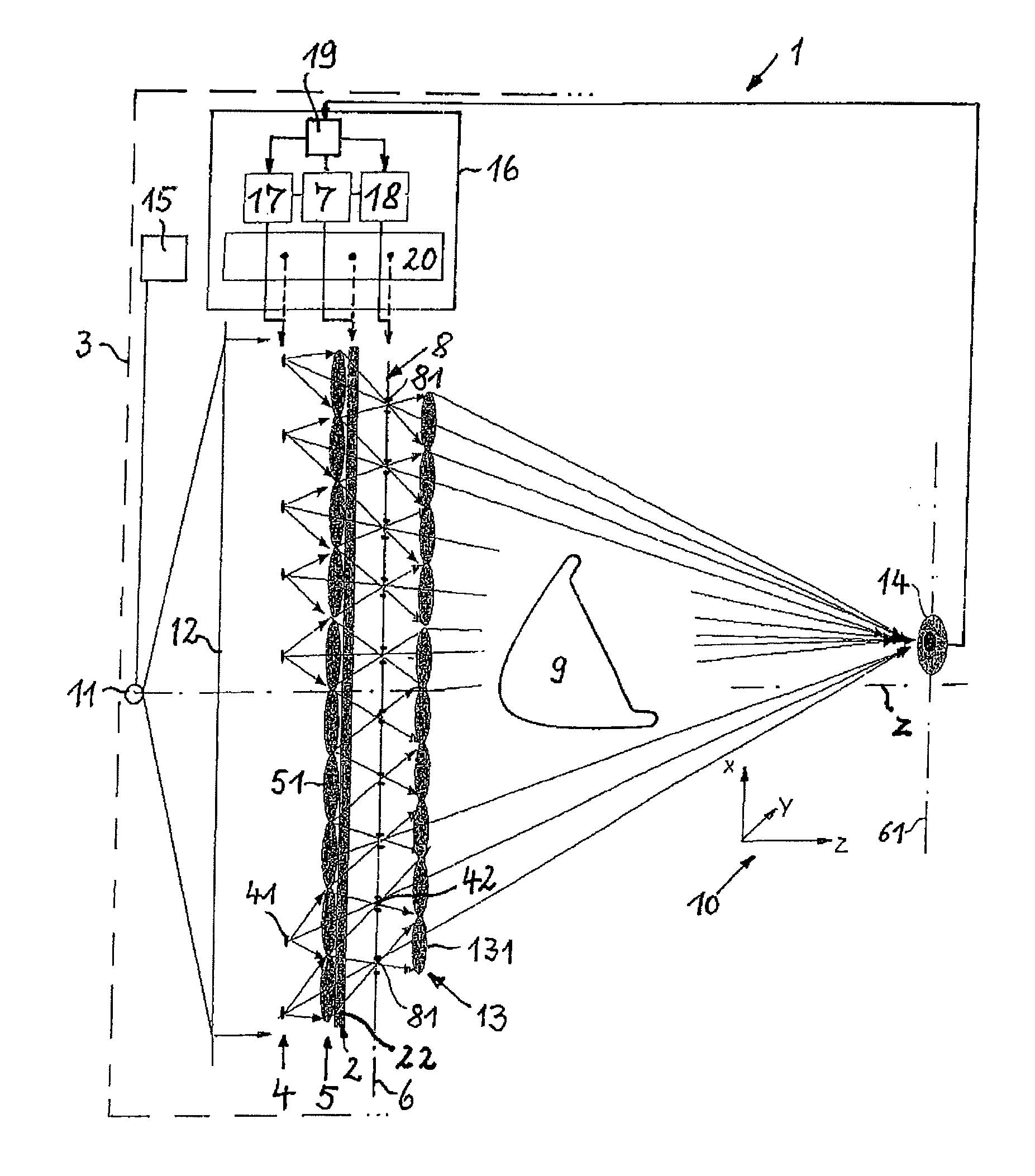
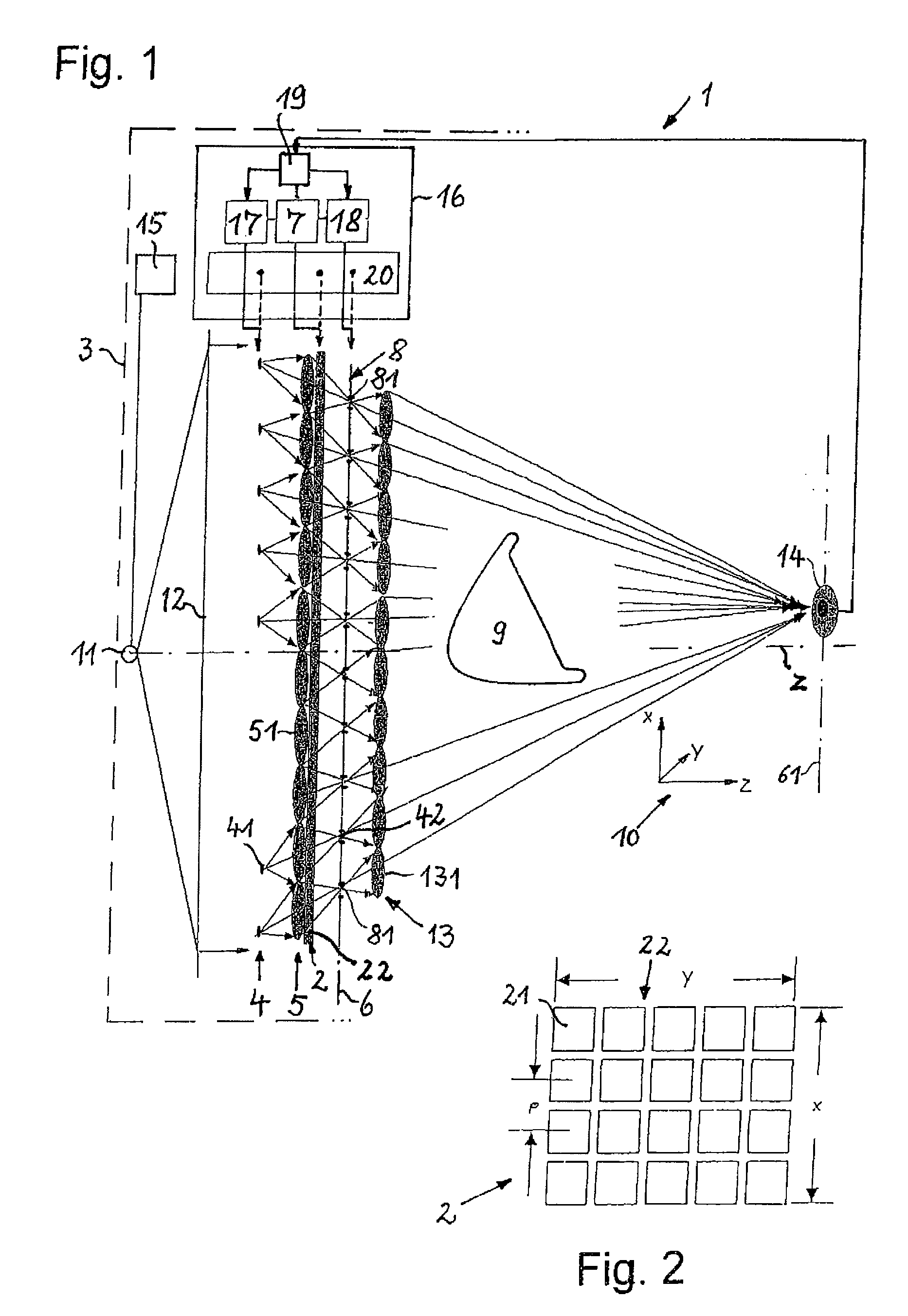
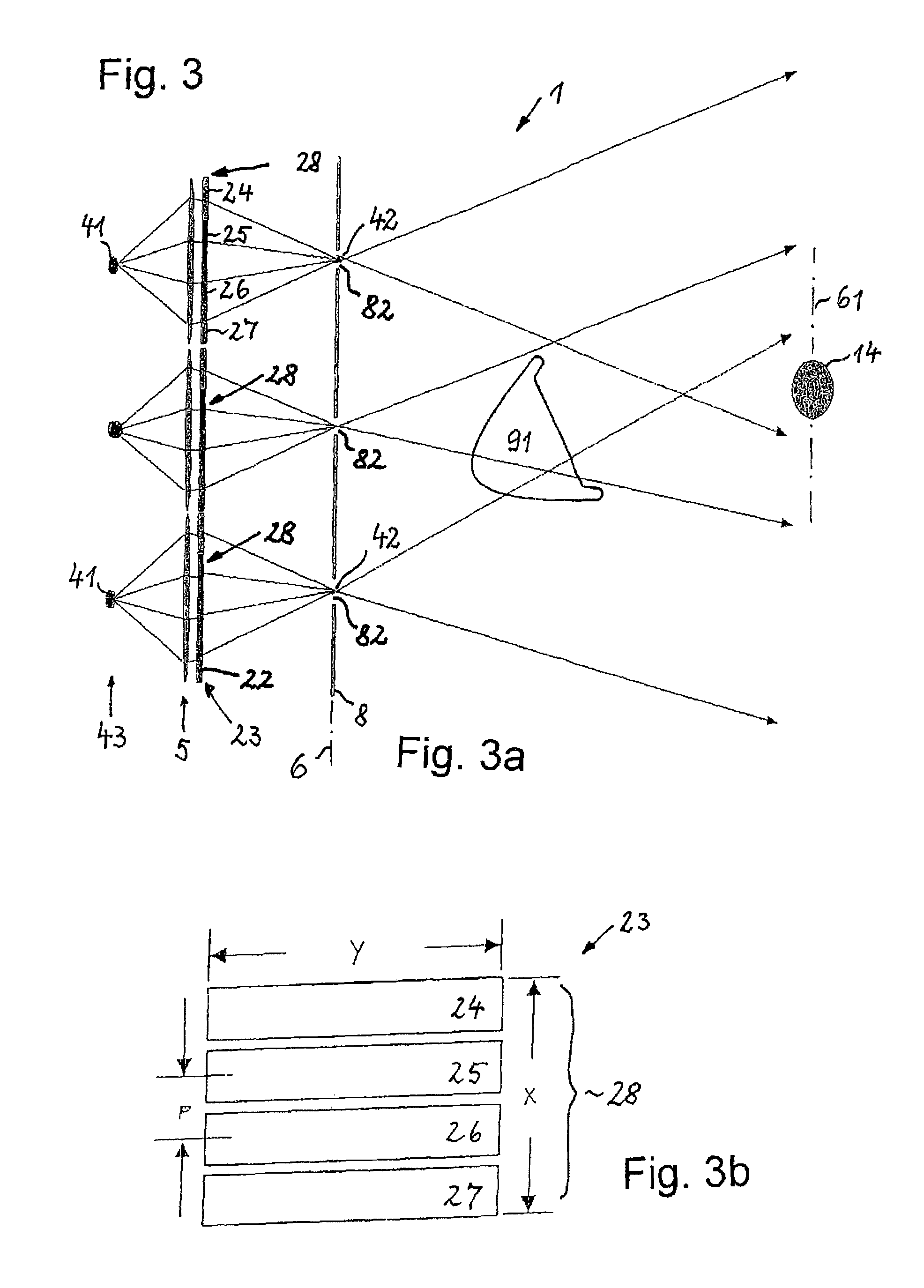
Methods and Scatterometers, Lithographic Systems, and Lithographic Processing Cells
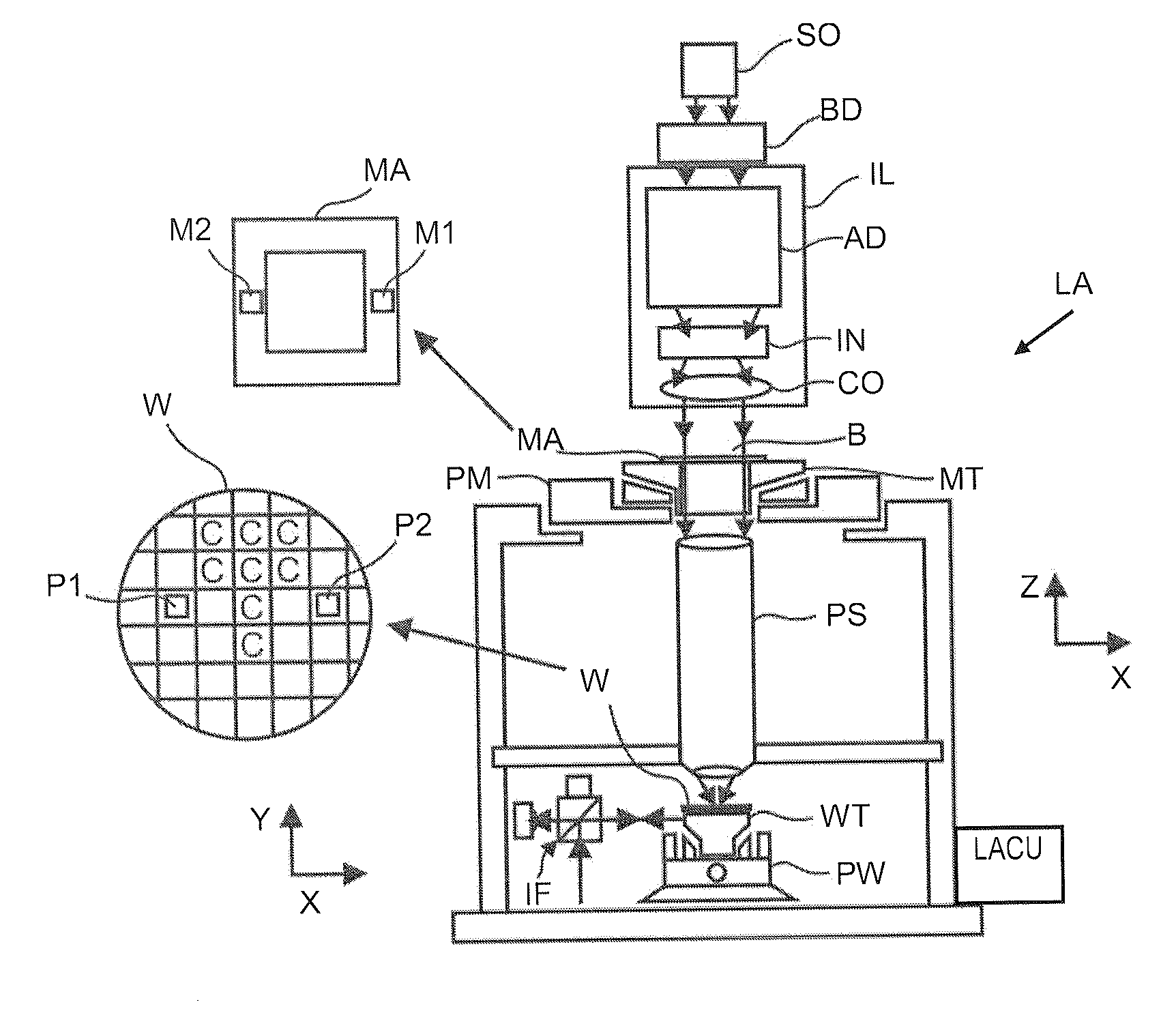
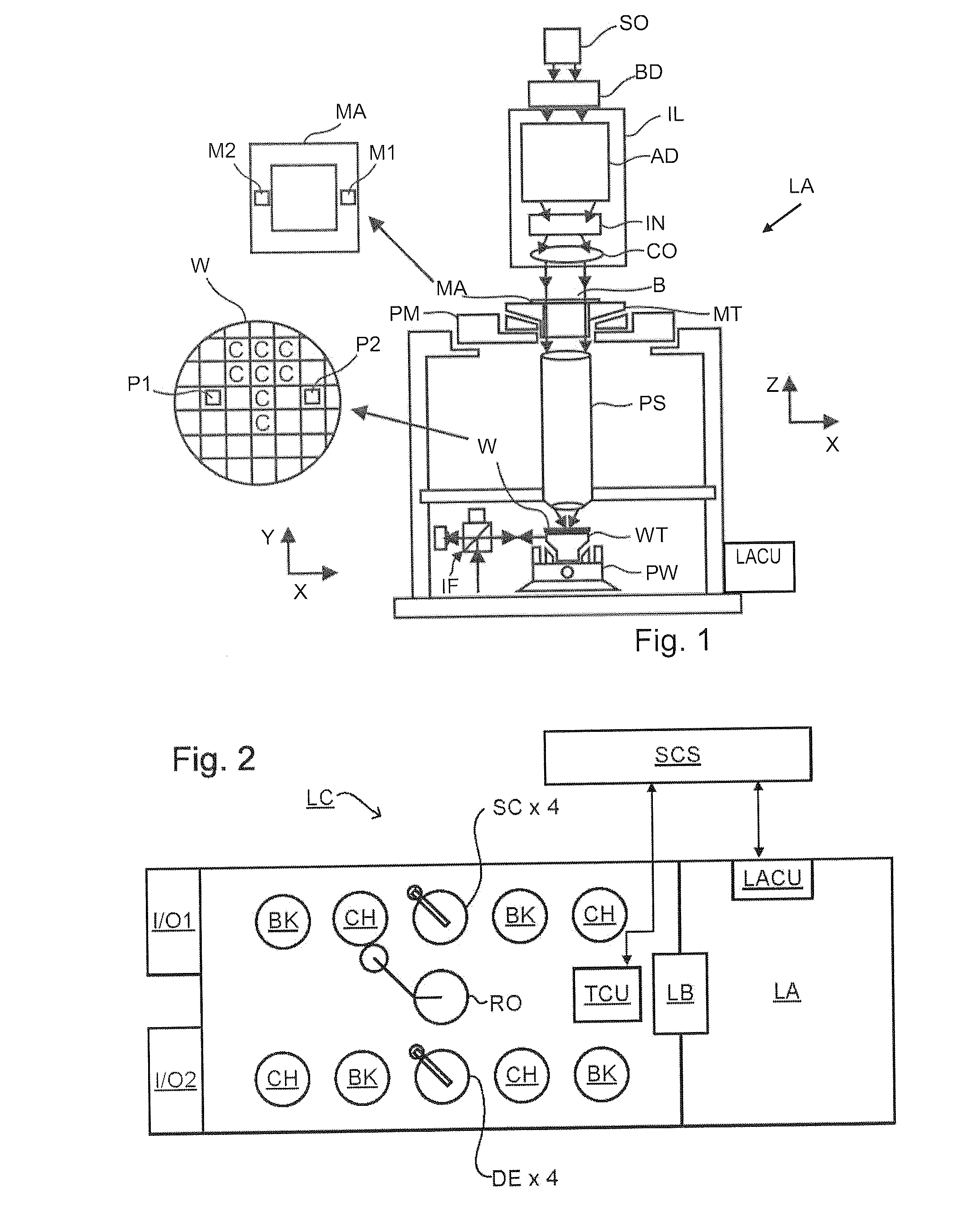
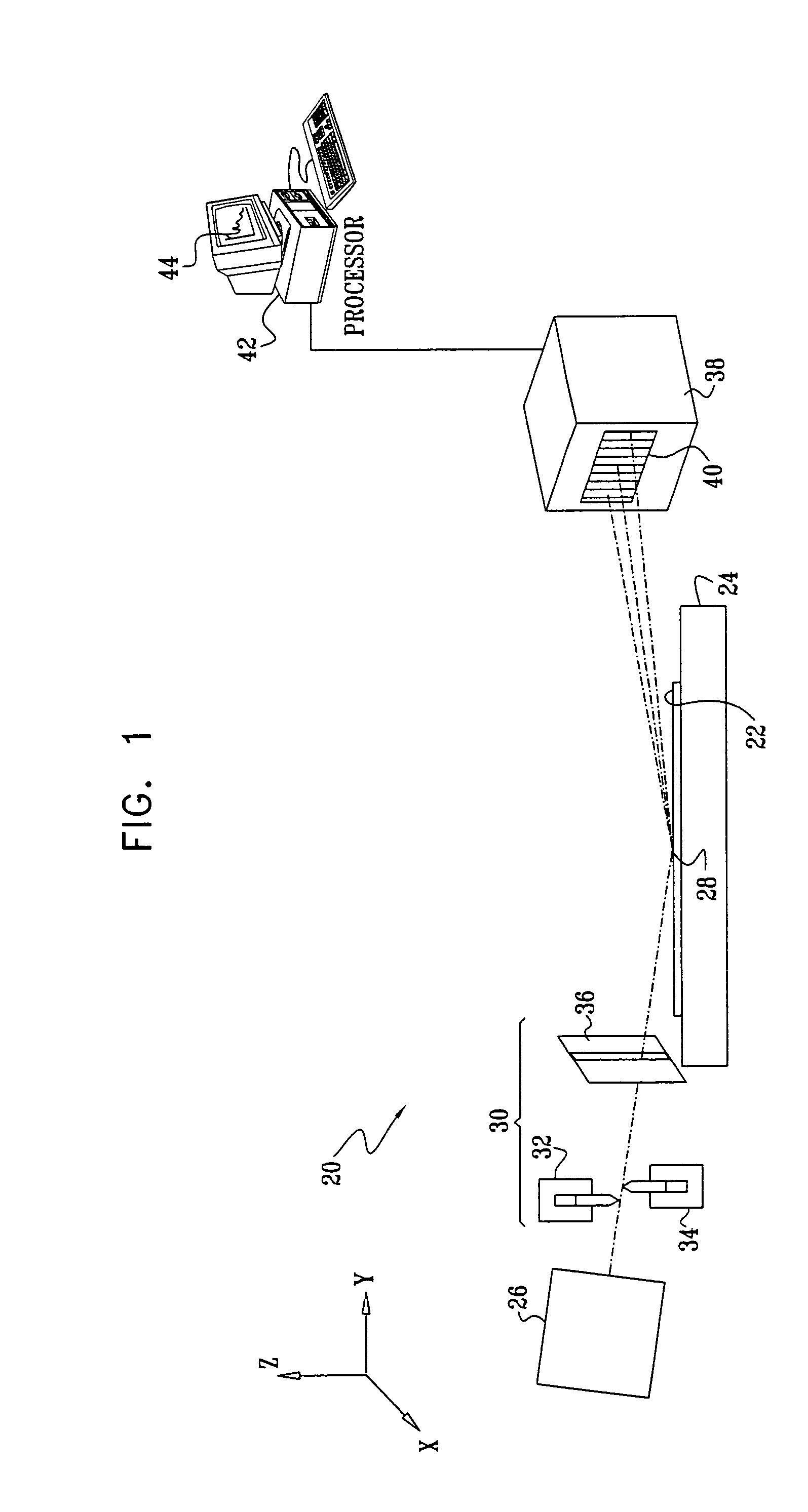
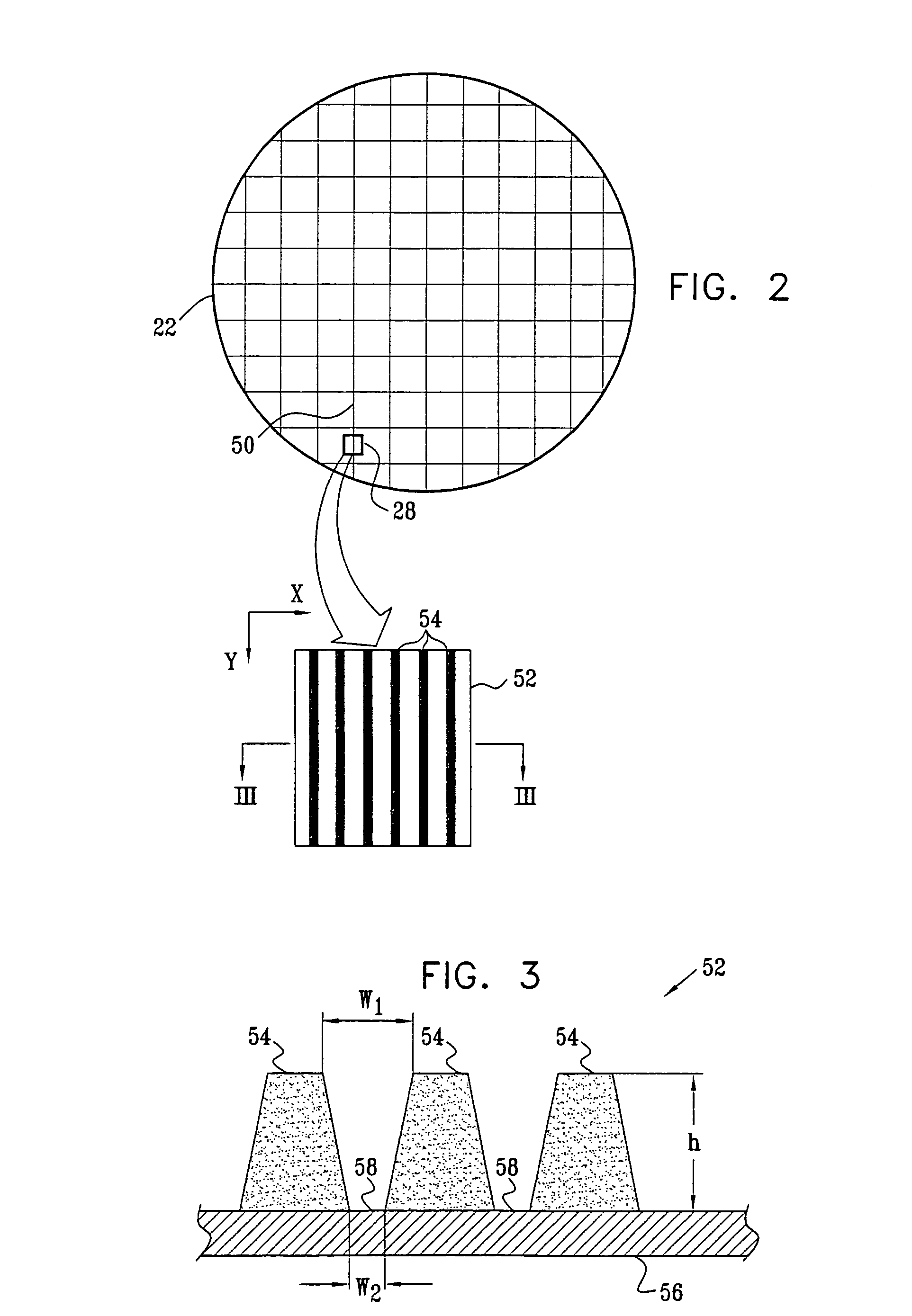
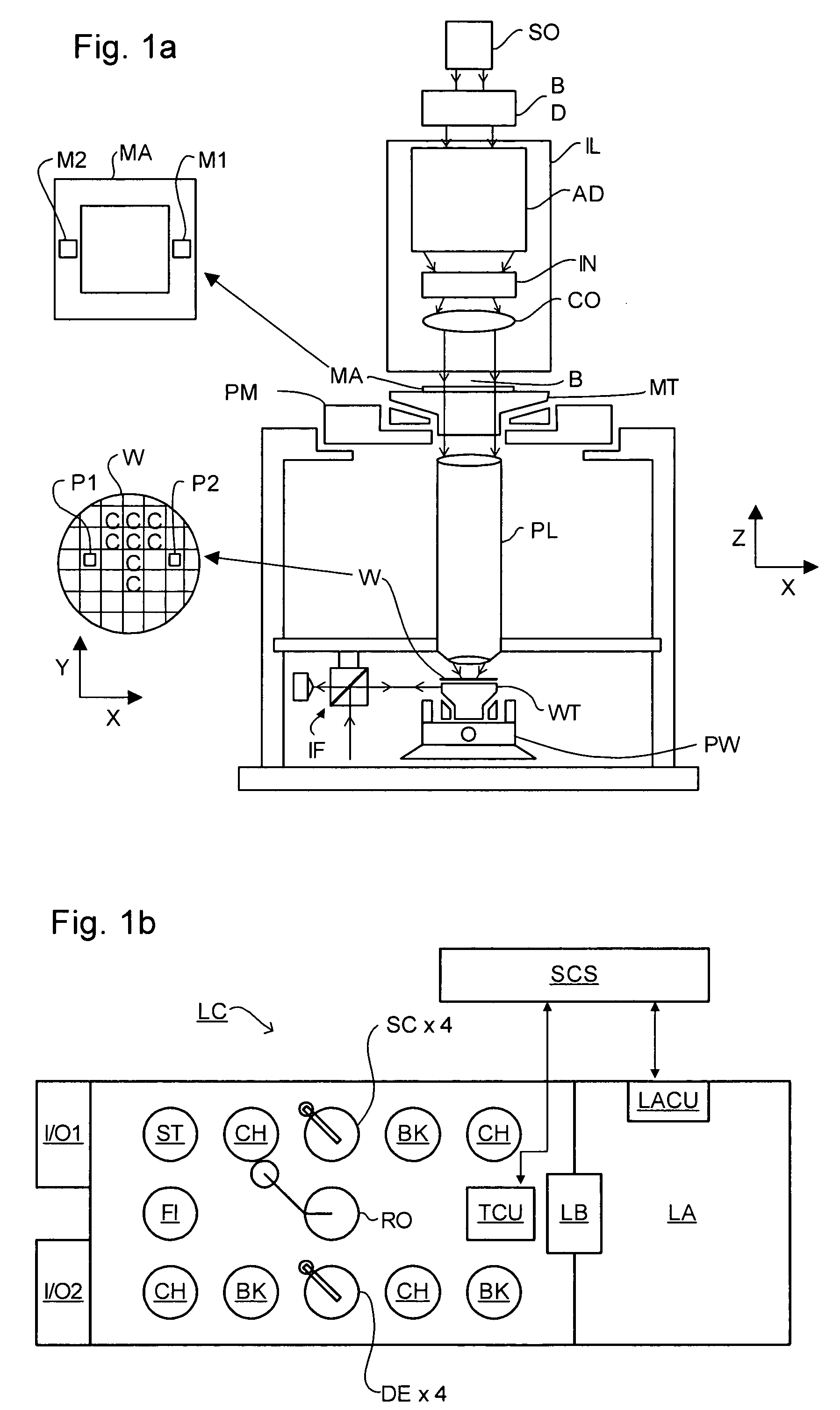
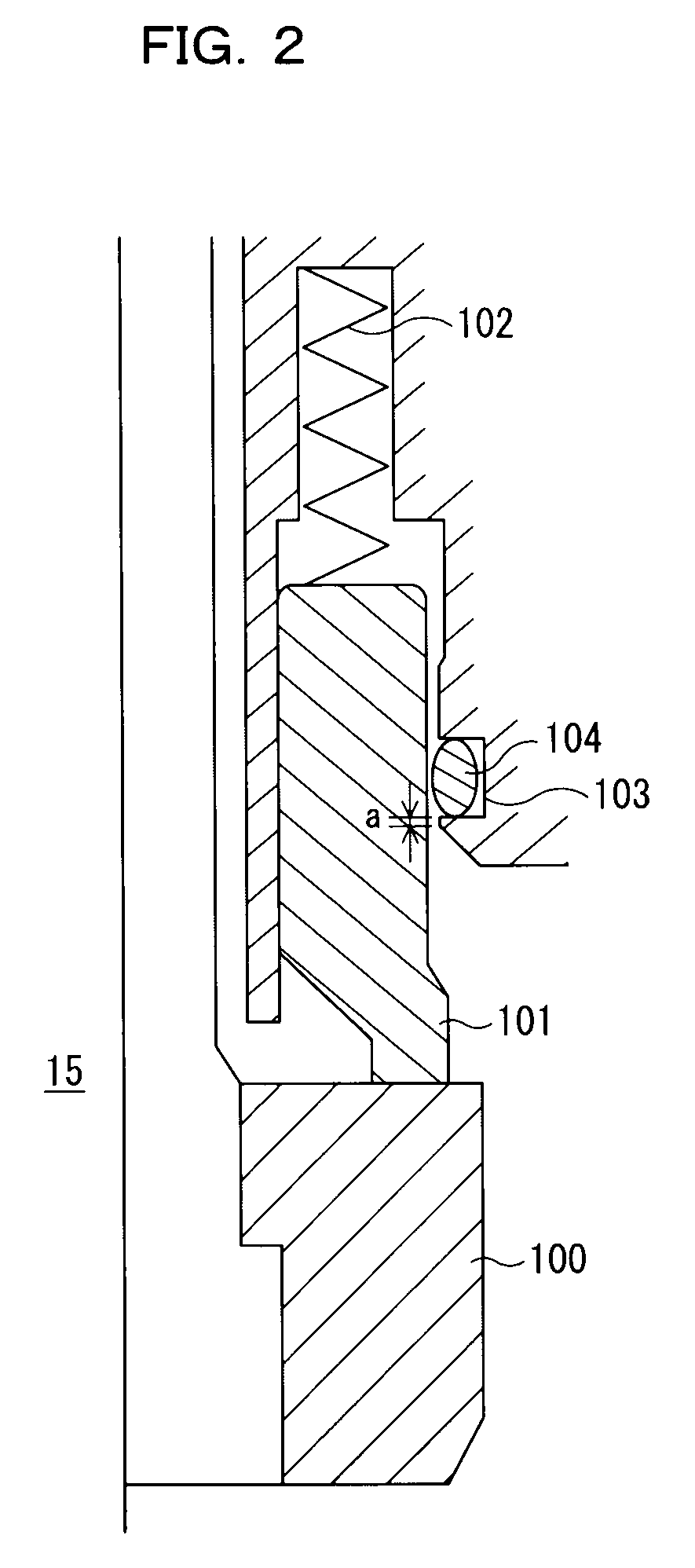
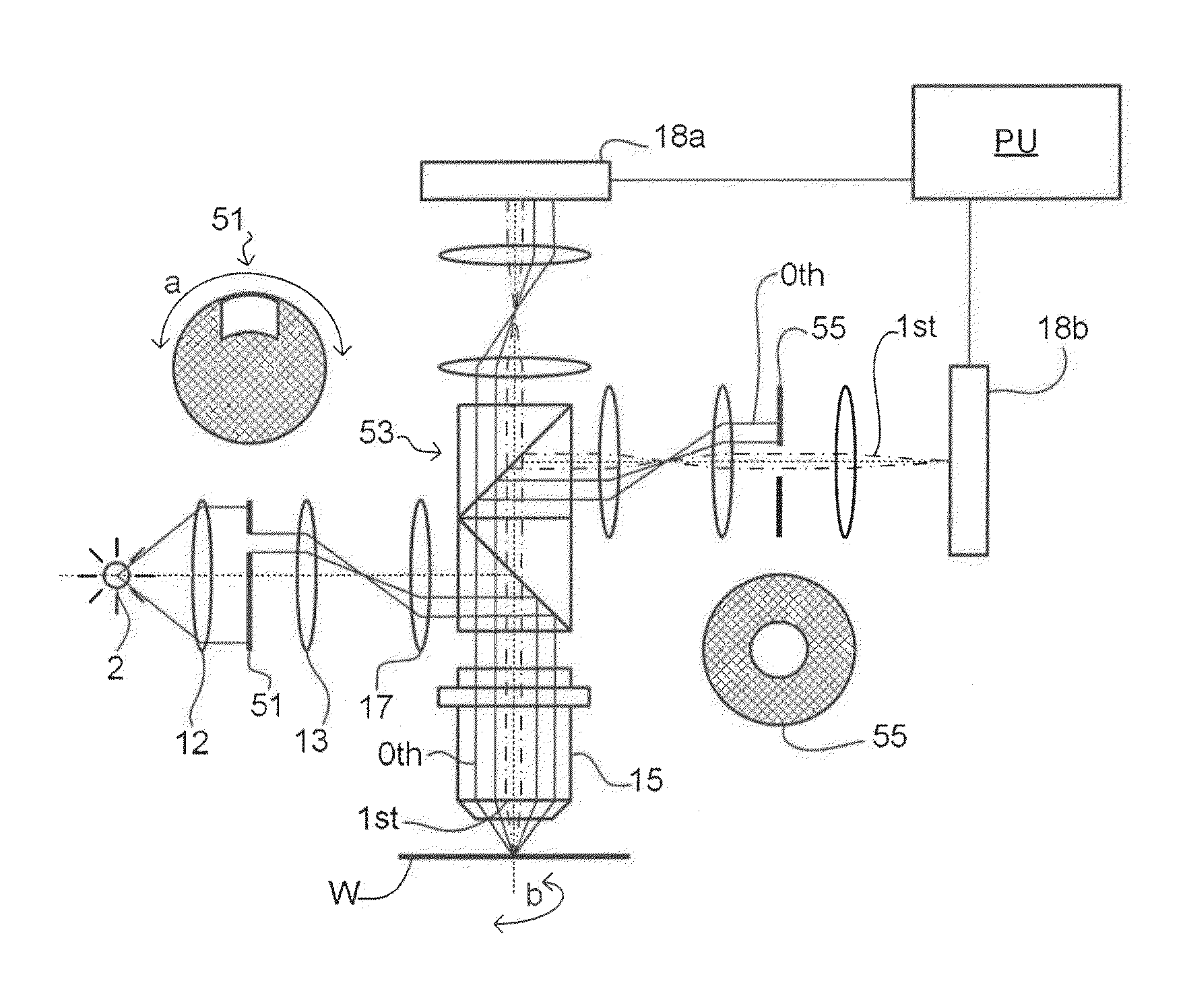
ActiveUS20110027704A1Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerEngineering
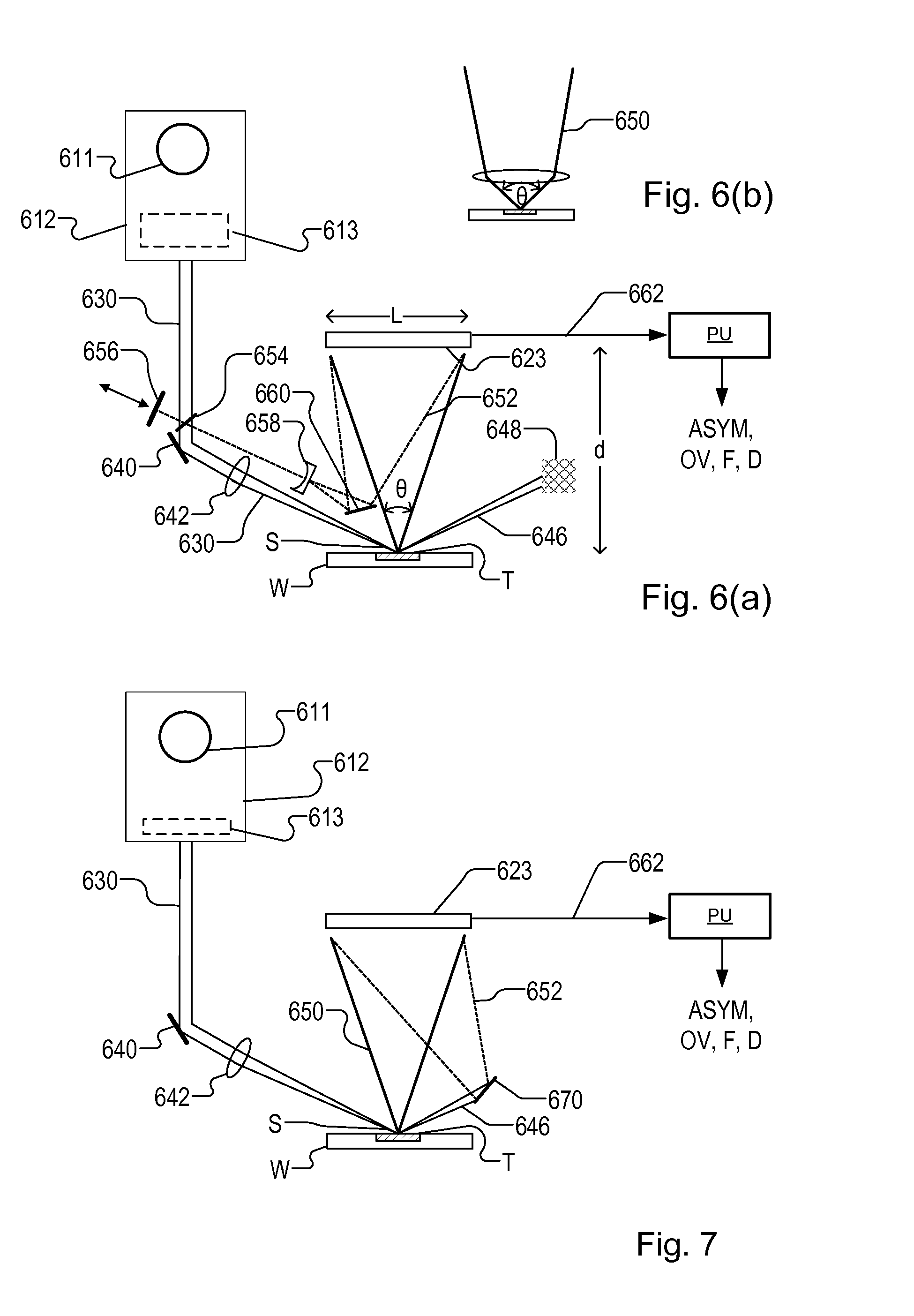
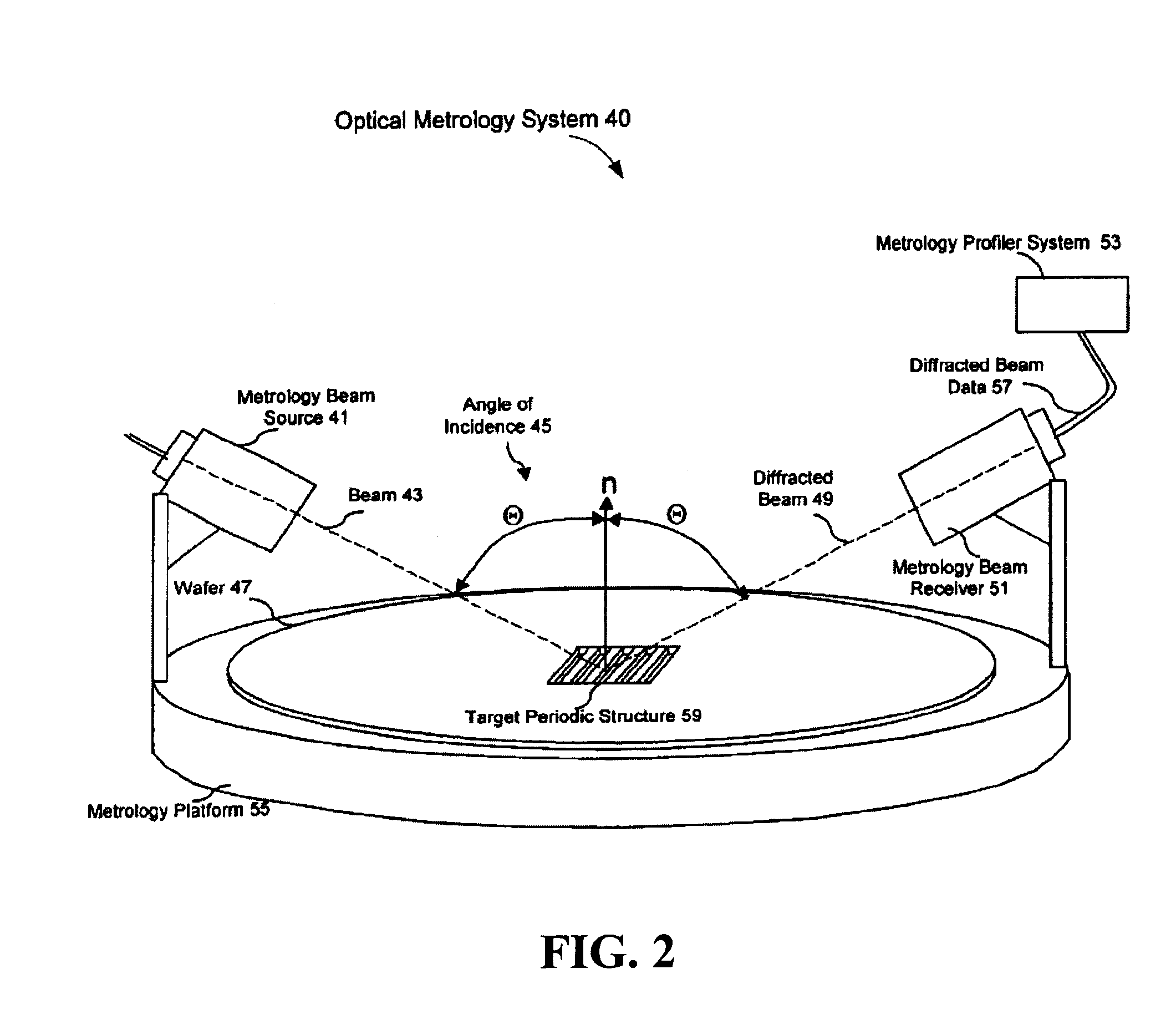
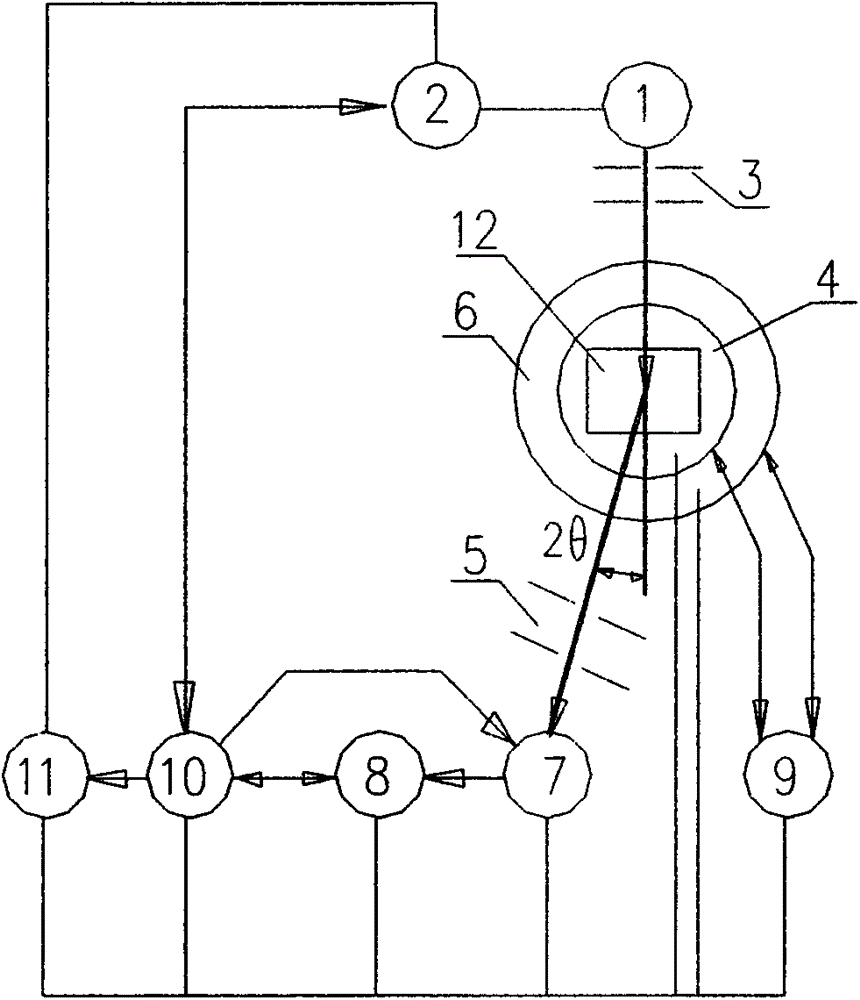
In a method of determining the focus of a lithographic apparatus used in a lithographic process on a substrate, the lithographic process is used to form a structure on the substrate, the structure having at least one feature which has an asymmetry in the printed profile which varies as a function of the focus of the lithographic apparatus on the substrate. A first image of the periodic structure is formed and detected while illuminating the structure with a first beam of radiation. The first image is formed using a first part of non-zero order diffracted radiation. A second image of the periodic structure is foamed and detected while illuminating the structure with a second beam of radiation. The second image is formed using a second part of the non-zero order diffracted radiation which is symmetrically opposite to the first part in a diffraction spectrum. The ratio of the intensities of the measured first and second portions of the spectra is determined and used to determine the asymmetry in the profile of the periodic structure and / or to provide an indication of the focus on the substrate. In the same instrument, an intensity variation across the detected portion is determined as a measure of process-induced variation across the structure. A region of the structure with unwanted process variation can be identified and excluded from a measurement of the structure.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Measurement of critical dimensions using X-ray diffraction in reflection mode
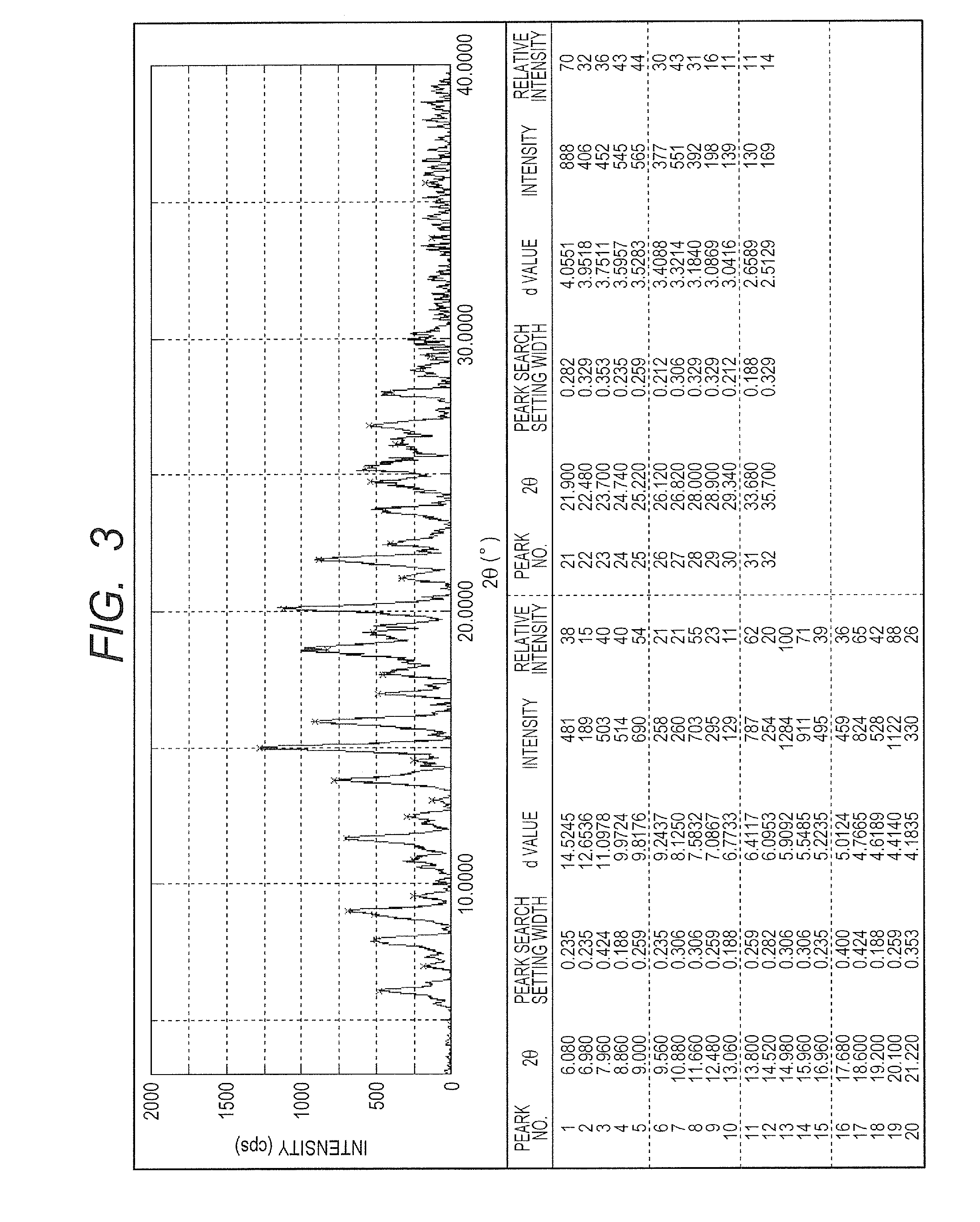
ActiveUS7110491B2Material analysis using radiation diffractionCritical dimensionDiffraction spectrum
A method for X-ray analysis of a sample includes directing a beam of X-rays to impinge on an area of a periodic feature on a surface of the sample and receiving the X-rays scattered from the surface in a reflection mode so as to detect a spectrum of diffraction in the scattered X-rays as a function of azimuth. The spectrum of diffraction is analyzed in order to determine a dimension of the feature.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
Inspection Apparatus, Inspection Method And Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20160061750A1Avoid difficultyMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansGratingMetrology
Metrology targets are formed on a substrate (W) by a lithographic process. A target (T) comprising one or more grating structures is illuminated with spatially coherent radiation under different conditions. Radiation (650) diffracted by from said target area interferes with reference radiation (652) interferes with to form an interference pattern at an image detector (623). One or more images of said interference pattern are captured. From the captured image(s) and from knowledge of the reference radiation a complex field of the collected scattered radiation at the detector. A synthetic radiometric image (814) of radiation diffracted by each grating is calculated from the complex field. From the synthetic radiometric images (814, 814′) of opposite portions of a diffractions spectrum of the grating, a measure of asymmetry in the grating is obtained. Using suitable targets, overlay and other performance parameters of the lithographic process can be calculated from the measured asymmetry.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
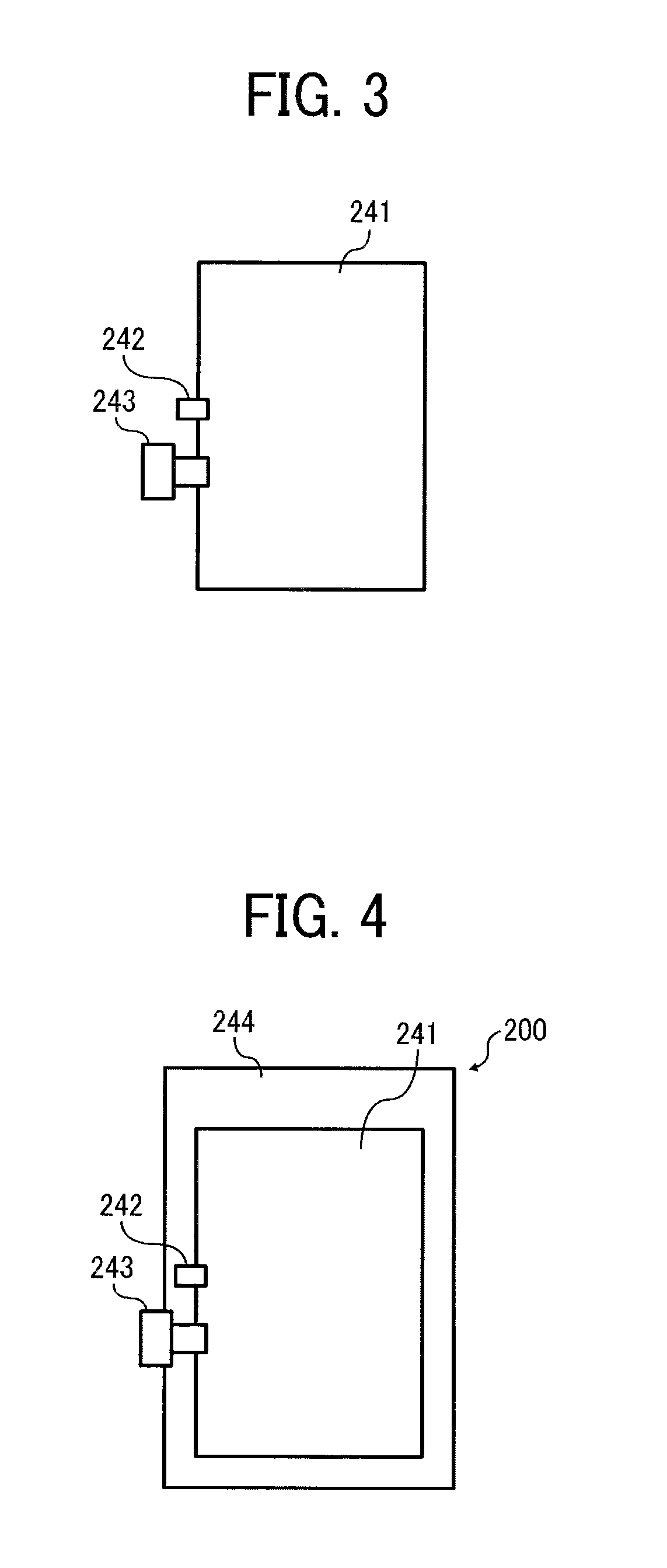
Aligning system of photoetching apparatus and steping combined system of said aligning system thereof
ActiveCN1949087ASolve absorptionSuppresses the effects of interference destructive effectsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFrequency spectrumLight beam
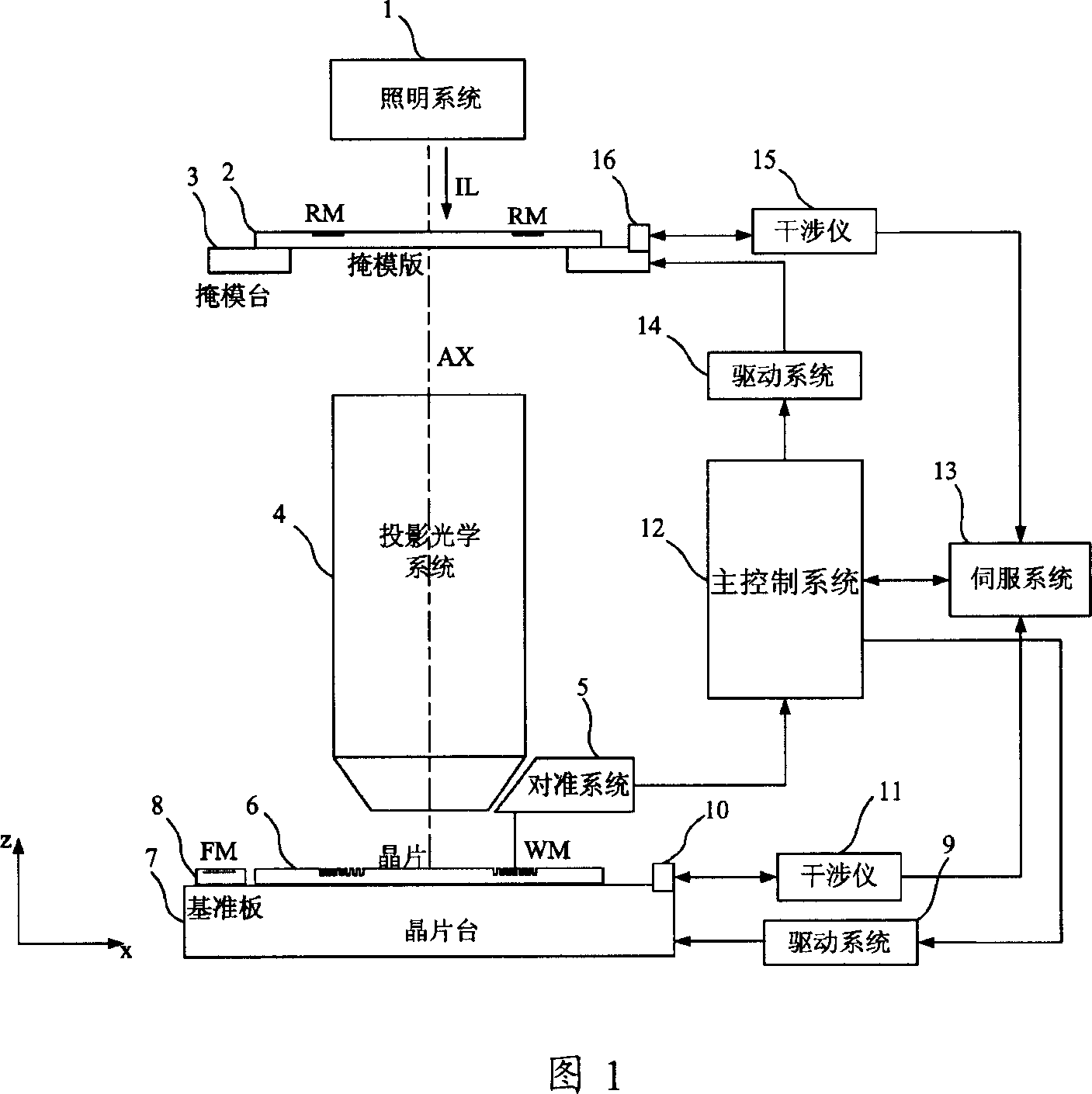
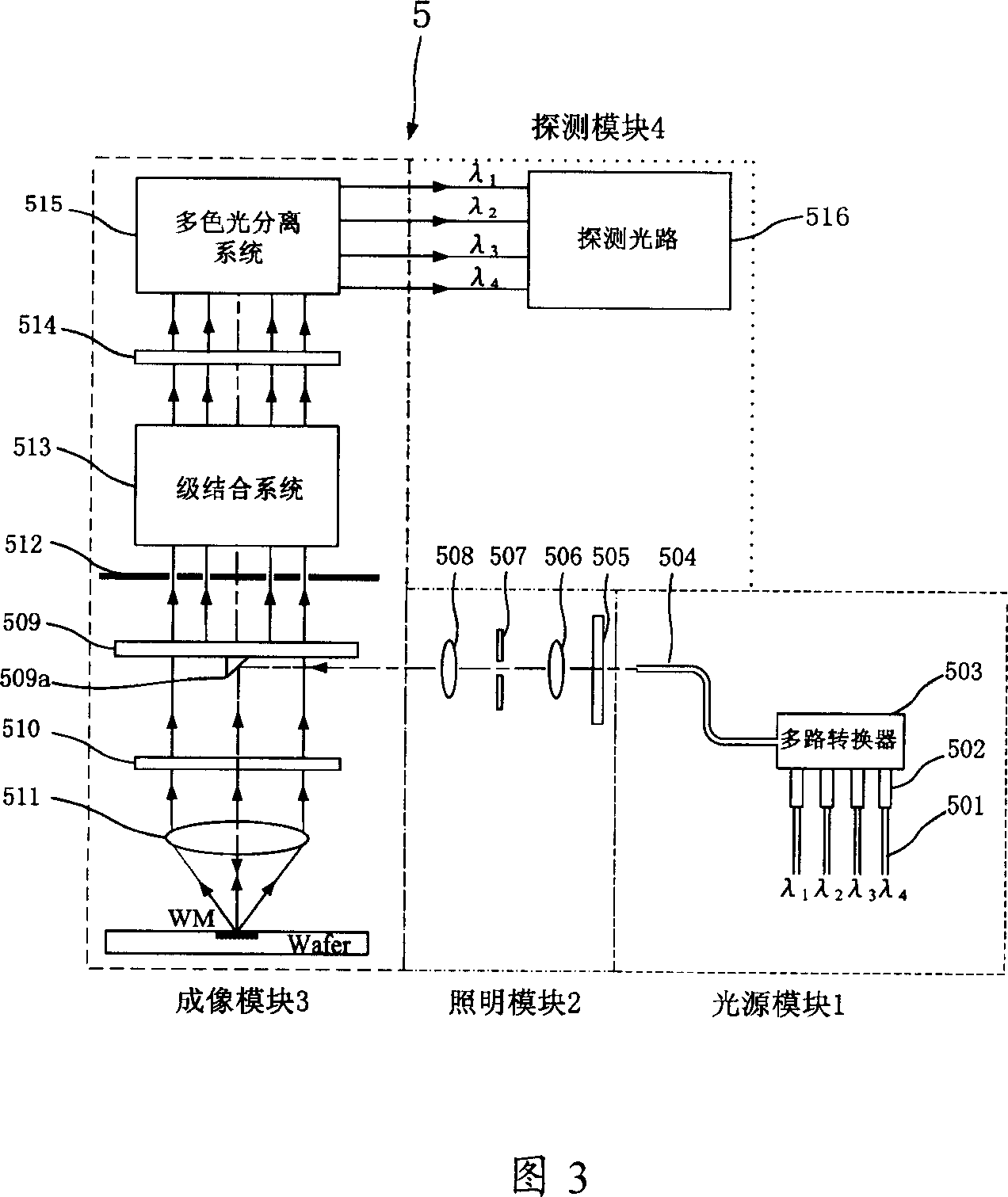
The invention discloses mask-alignment aligning system and its grade combining system. The aligning system includes light source module, illumination module, imaging module, and detecting module. The grade combining system makes positive negative grade frequency spectrum facula of the alignment mark diffraction spectrum process corresponding overlap coherent, uses polychromatic light separating system to separate multiple wavelength light signal, measures light intensity or phase change at the corresponding position of the multiple wavelength multistage secondary diffracted facula to gain alignment mark position information. The invention has high alignment precision and stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
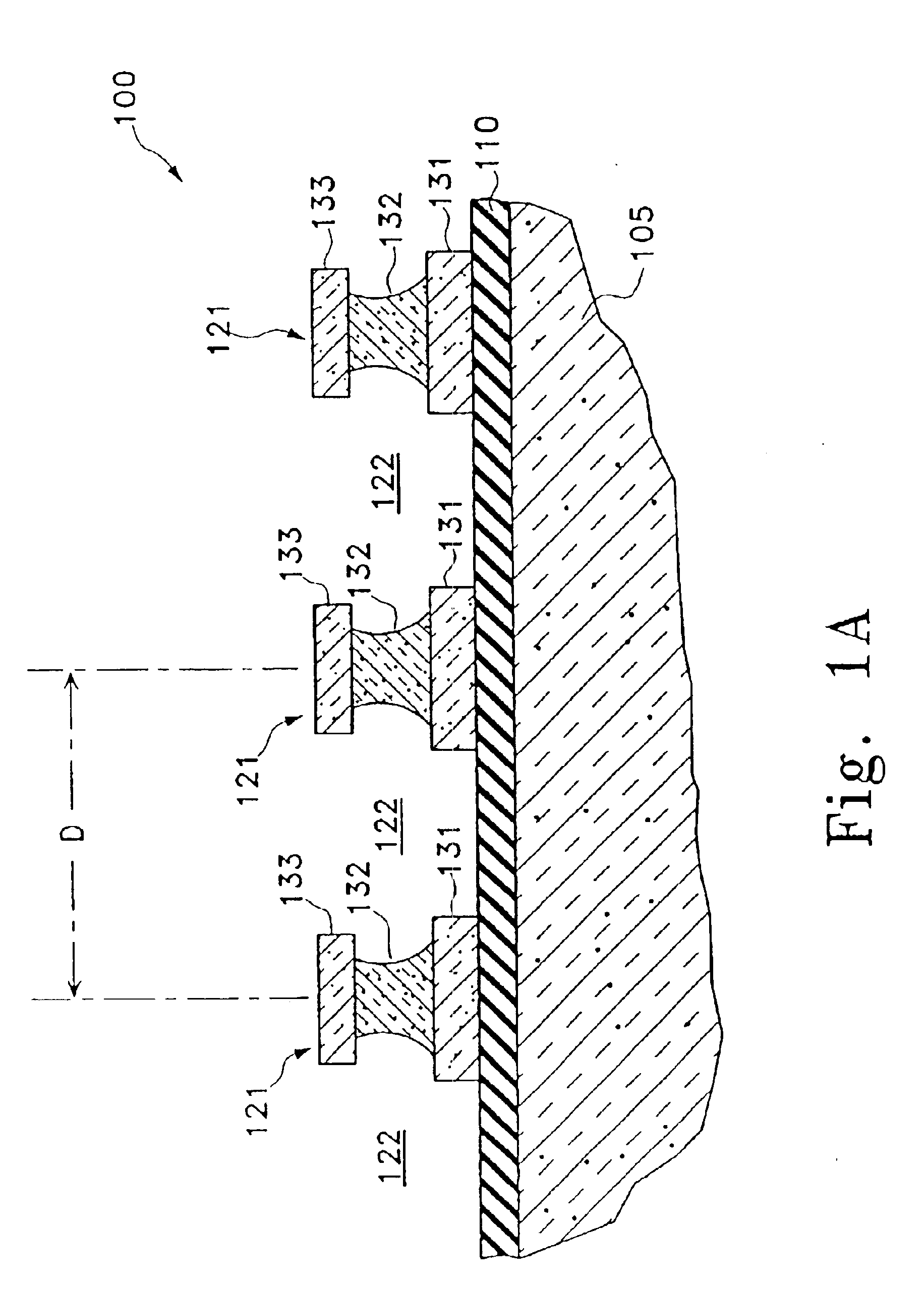
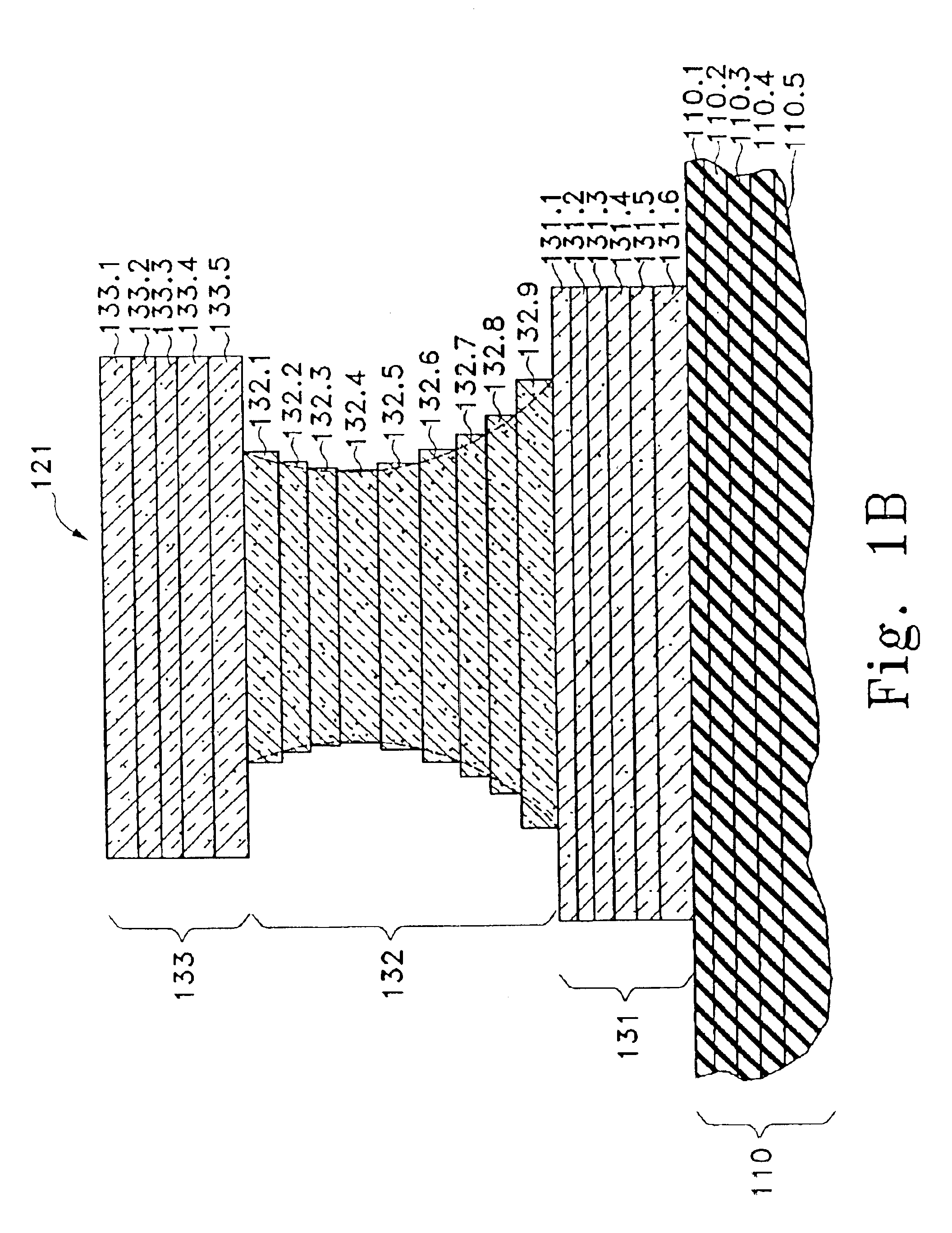
Optical profilometry of additional-material deviations in a periodic grating
Disclosed is a method and system for measurement of periodic gratings which have deviations which result in more than two materials occurring along at least one line in the periodic direction. A periodic grating is divided into a plurality of hypothetical layers, each hypothetical layer having a normal vector orthogonal to the direction of periodicity, each hypothetical layer having a single material within any line parallel to the normal vector, and at least one of the hypothetical layers having at least three materials along a line in the direction of periodicity. A harmonic expansion of the permittivity ε or inverse permittivity 1 / ε is performed along the direction of periodicity for each of the layers including the layer which includes the first, second and third materials. Fourier space electromagnetic equations are then set up in each of the layers using the harmonic expansion of the permittivity E or inverse permittivity 1 / ε, and Fourier components of electric and magnetic fields in each layer. The Fourier space electromagnetic equations are then coupled based on boundary conditions between the layers, and solved to provide the calculated diffraction spectrum.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
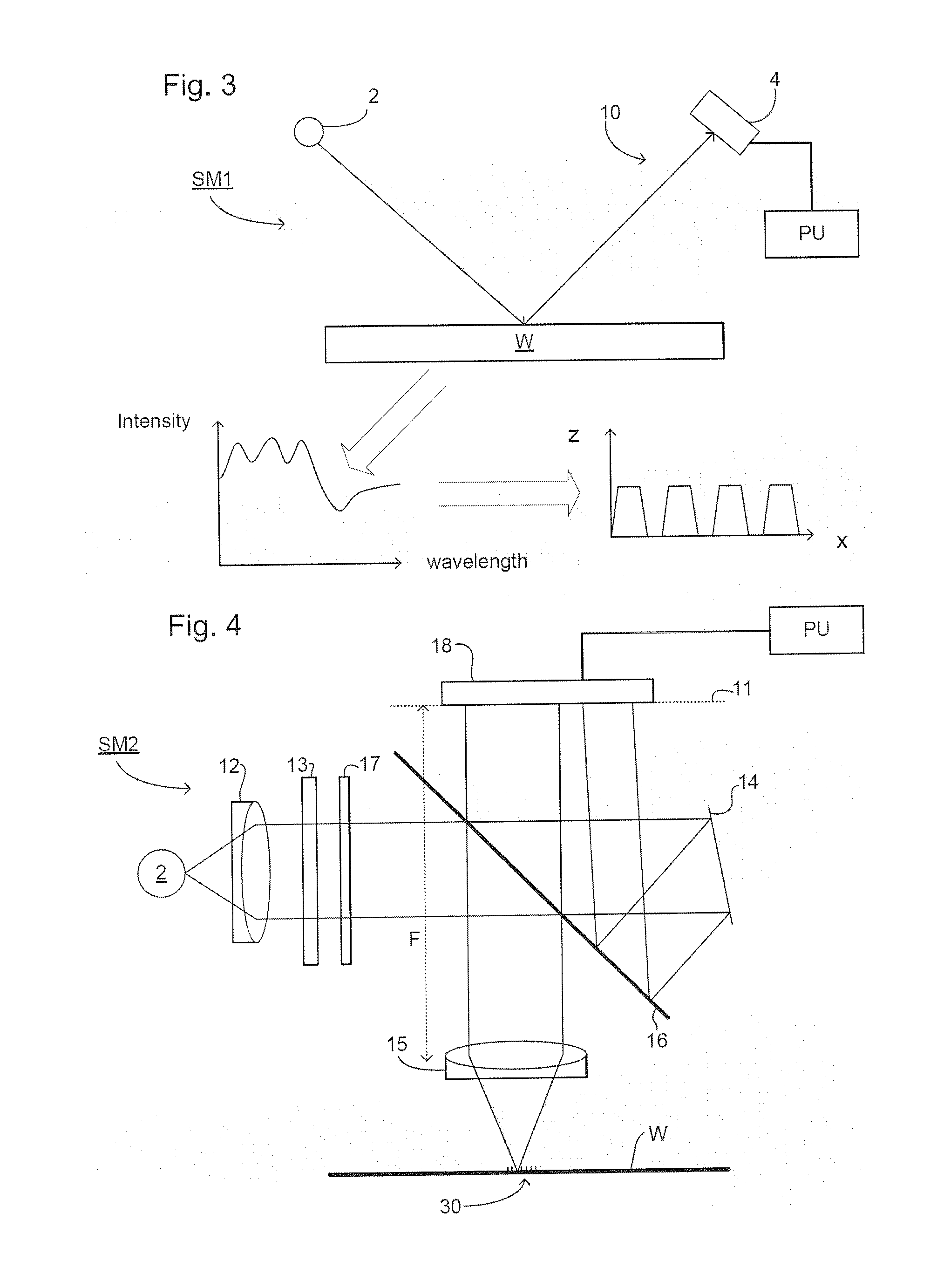
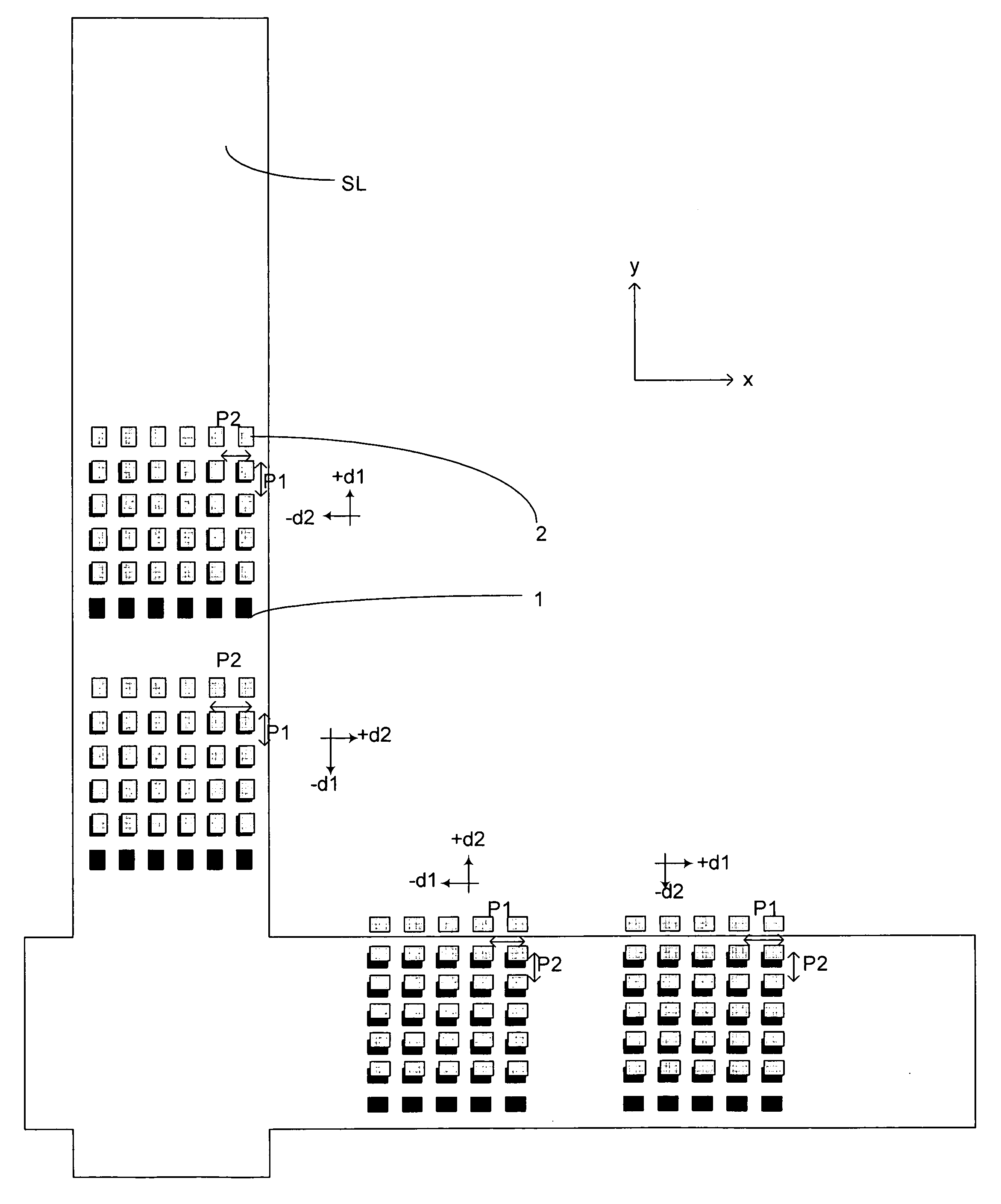
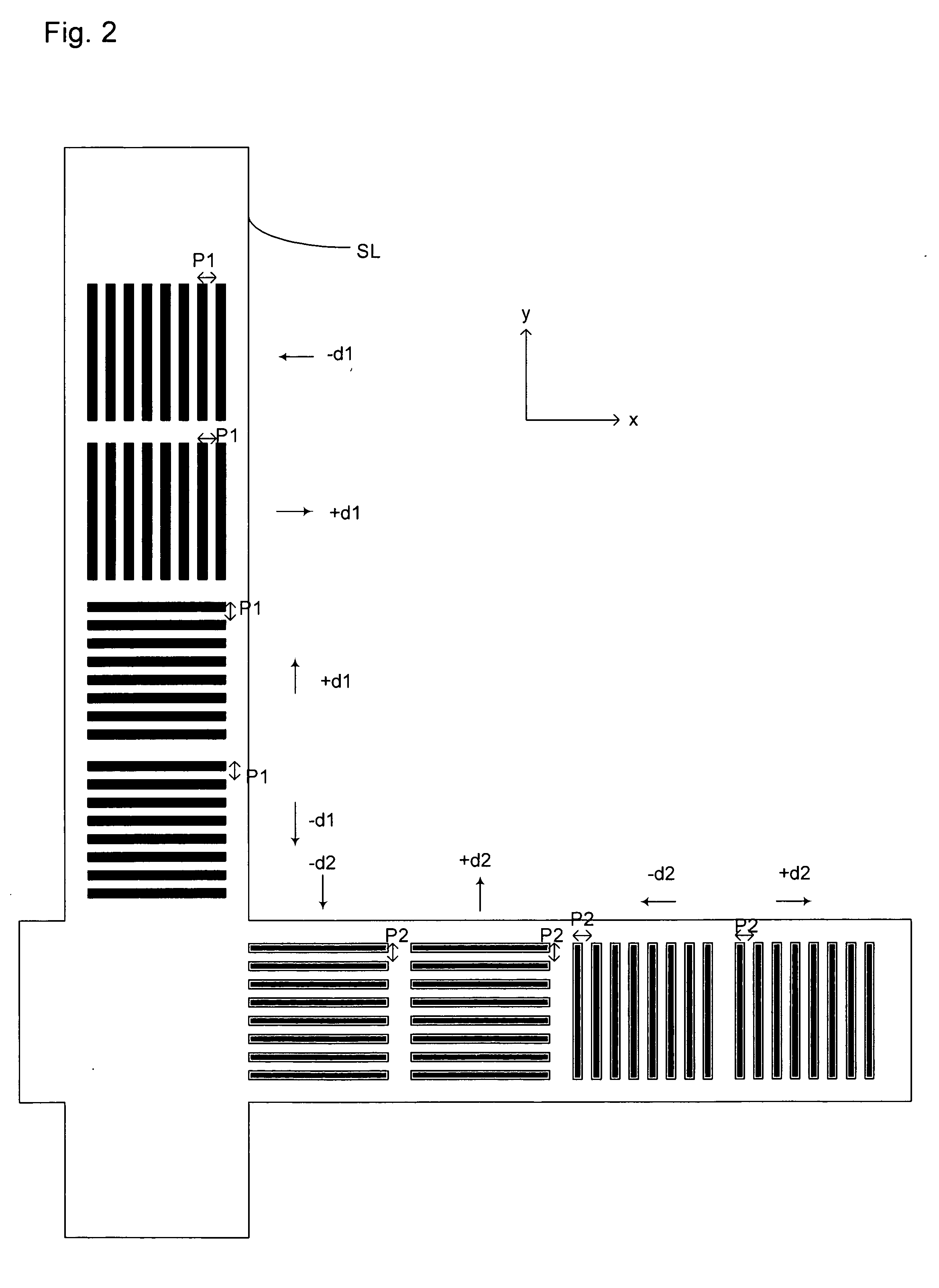
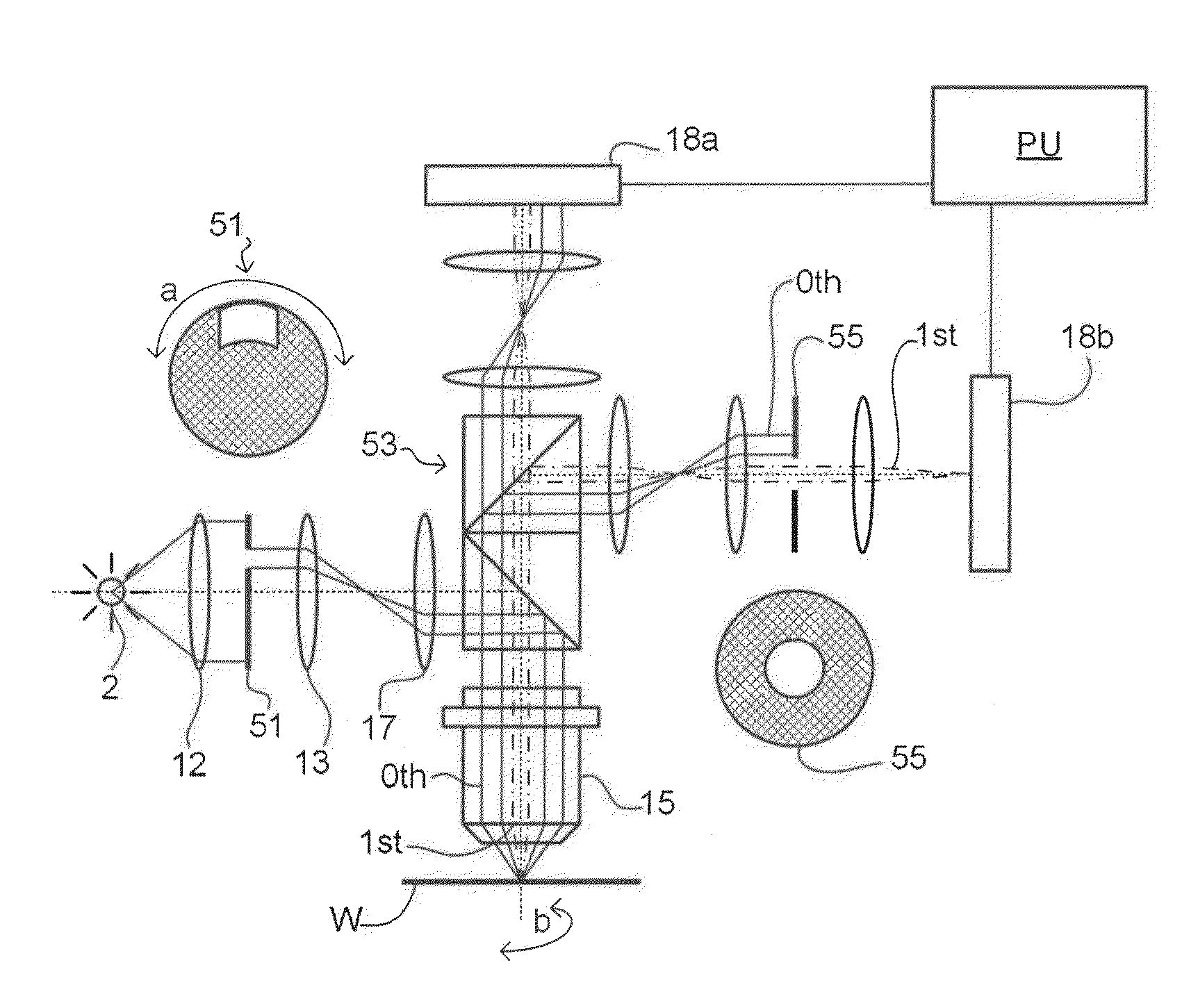
Method and apparatus for angular-resolved spectroscopic lithography characterization
An overlay target on a substrate includes two sets of gratings; the first set having a pitch P1 and the second set having a pitch P2 and each set including a grating with an orientation substantially perpendicular to the first grating of each set. When a layer of resist is to be aligned with the layer below it, the same overlay marks are provided on the upper layer and the relative positions of the overlay targets on the upper layer and the lower layer are compared by shining an overlay beam on to the overlay targets and measuring the diffraction spectrum of the reflected beam. Having two sets of overlay targets with different pitches in gratings enables the measurement of overlay errors that are greater than the pitch of either one of the overlay gratings.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Inkjet ink, ink cartridge, inkjet recording device, and inkjet printed matter
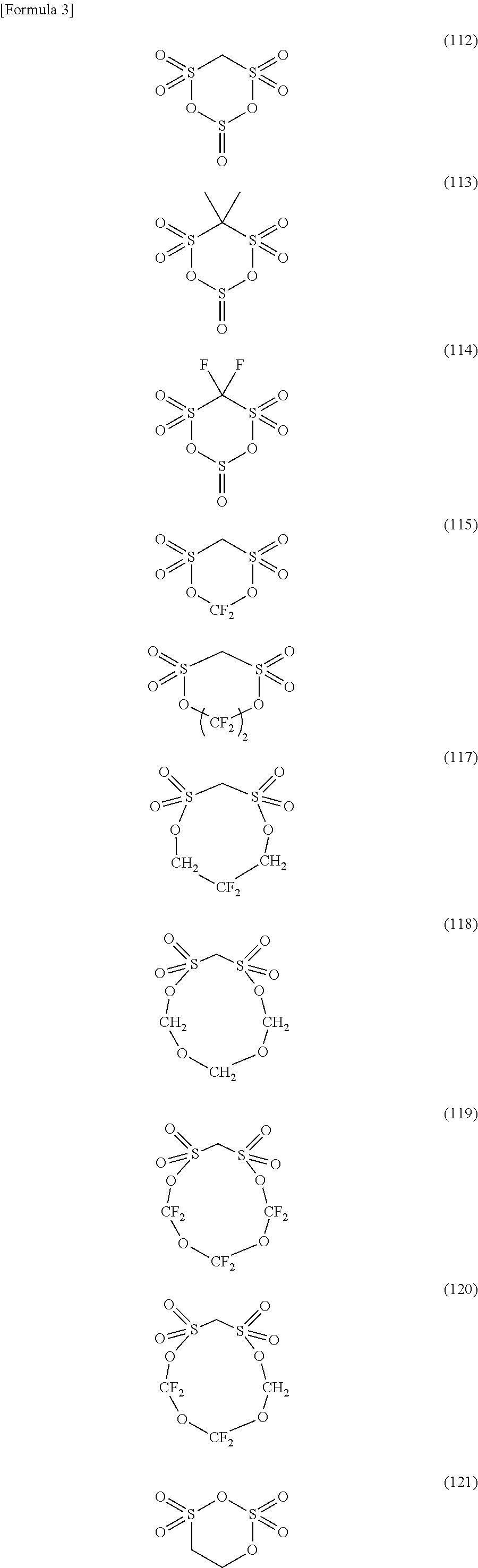
Inkjet ink contains a pigment, a hydrosoluble solvent, and water, wherein the pigment is represented by the following chemical formula 1 and has a CuKα X-ray diffraction spectrum having a wavelength of 1.541 Å such that no main peak is observed at a Bragg (2θ±0.2°) angle in a range of 2θ of from 28.0° to 29.0°,wherein R represents a hydrogen atom, a methyl group, or a chlorine atom.
Owner:RICOH KK
Methods and Scatterometers, Lithographic Systems, and Lithographic Processing Cells
ActiveUS20140139814A1Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerEngineering
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Toner, development agent, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
Toner contains a binder resin containing a crystalline resin having a urethane and / or urea bonding; and a colorant, wherein in a diffraction spectrum of the toner as measured by an X-ray diffraction instrument, a ratio {C / (C+A)} of an integral intensity C of the spectrum derived from the crystalline structure to an integral intensity A of the spectrum derived from the non-crystalline structure is 0.12 or greater, wherein the toner satisfies the following relation 1: T1−T2≦30° C. (Relation 1), where T1 represents the maximum endothermic peak in the first temperature rising from 0° C. to 100° C. at the temperature rising rate of 10° C. / min and T2 represents the maximum exothermic peak in the first temperature falling from 100° C. to 0° C. at the temperature falling rate of 10° C. / min as T1 and T2 are measured by diffraction scanning calorimetry (DSC).
Owner:RICOH KK
ZSM-11 molecular sieve with hierarchical porous structure and preparation method thereof
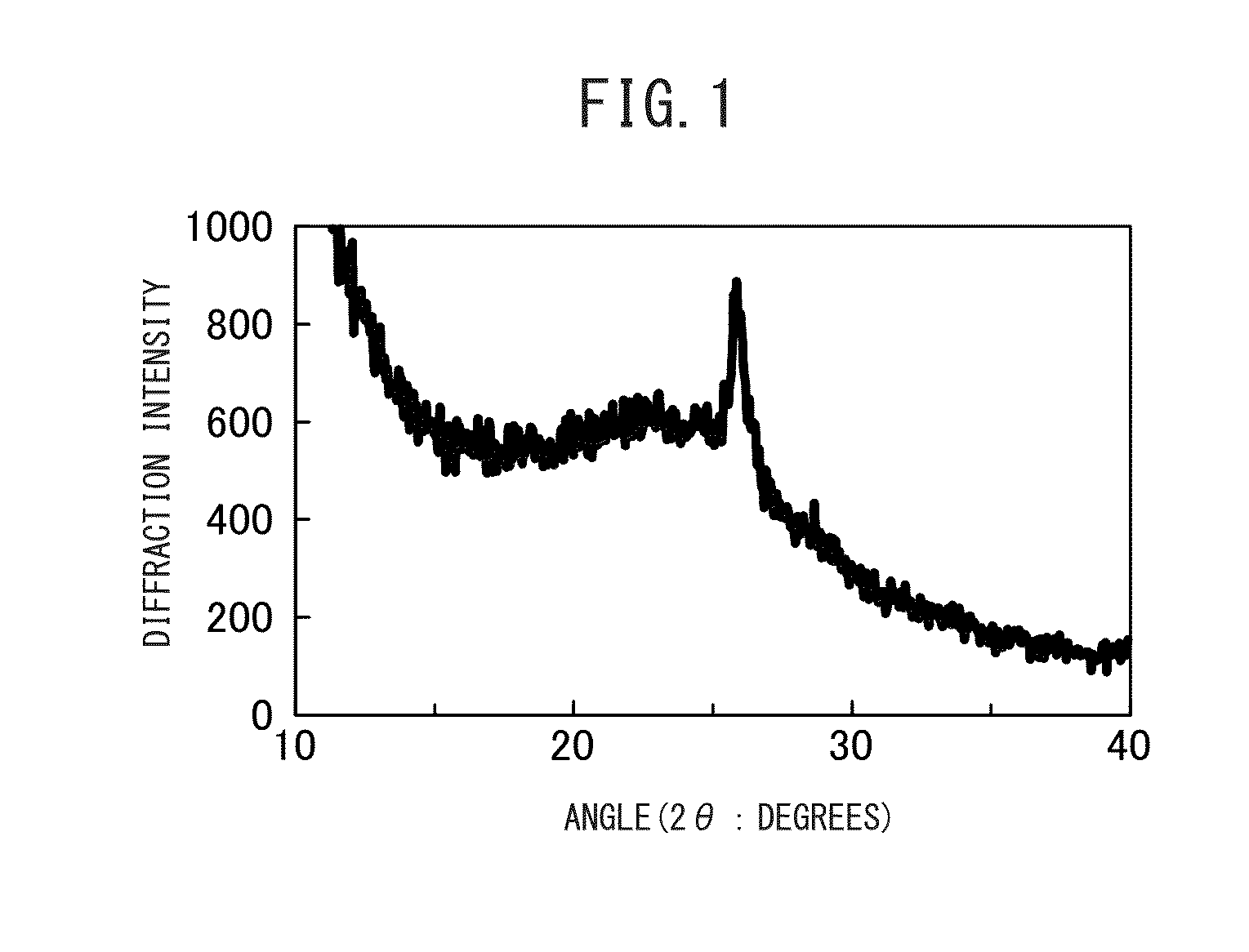
InactiveCN102557071AImprove diffusion abilityGood thermal and hydrothermal stabilityPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteX-rayHeat stability
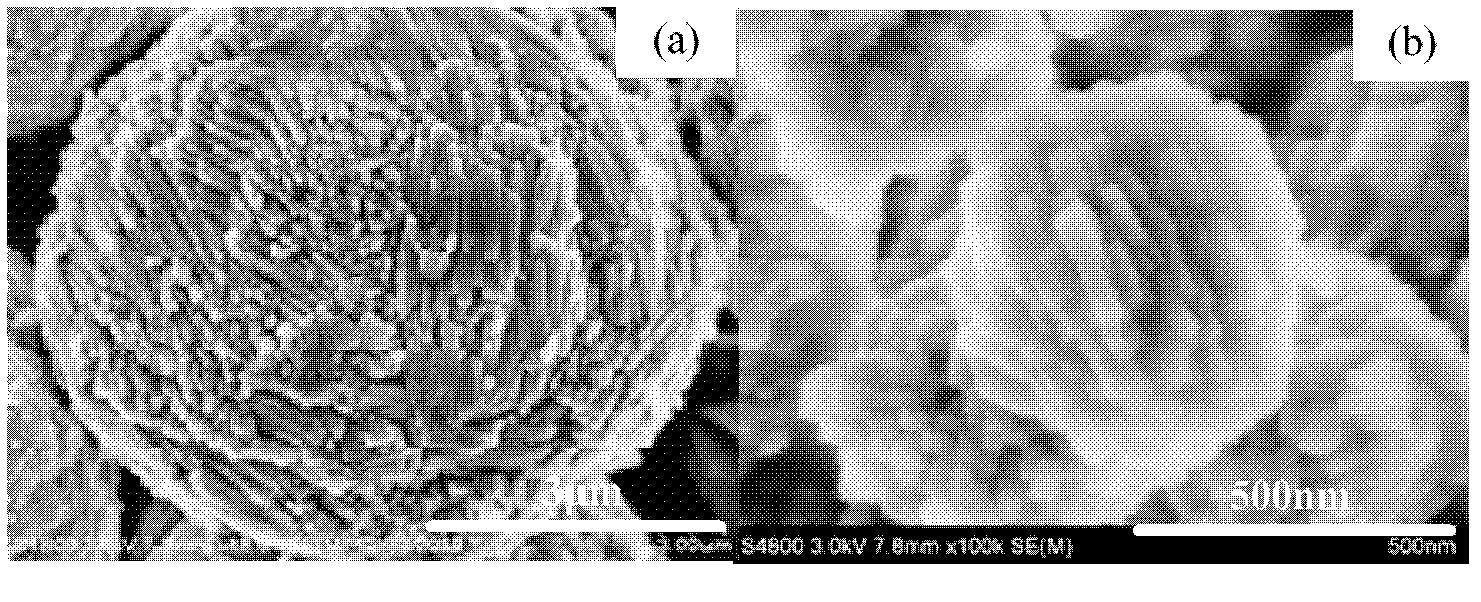
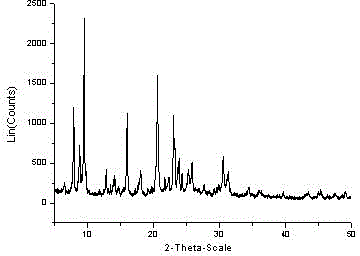
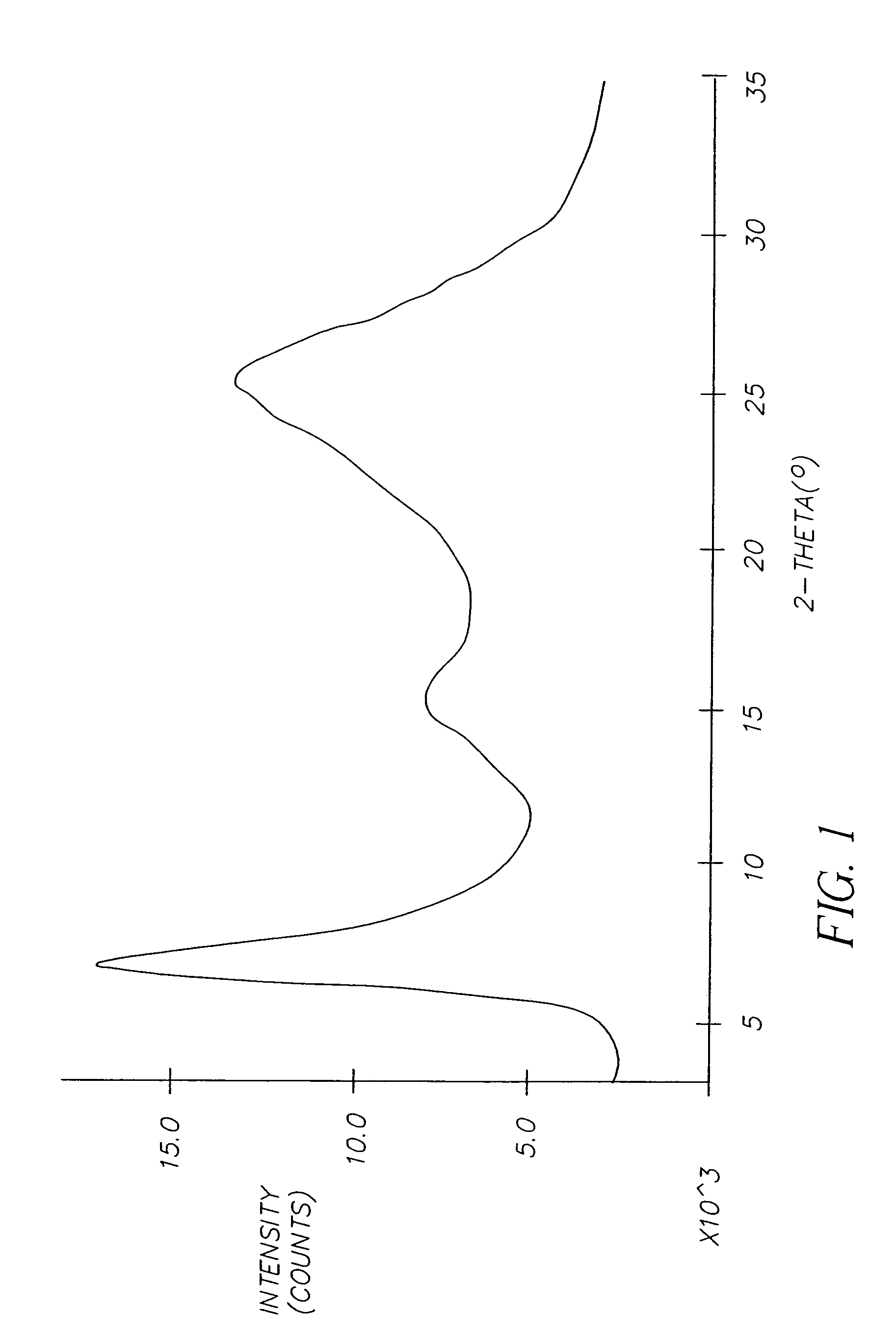
A ZSM-11 molecular sieve with a hierarchical porous structure is characterized in that X-X-ray diffraction spectrum of the molecular sieve is as shown in Figure 1(a) / table 1; the molecular sieve has an even spherical appearance, each ball is formed through self assembly of rod-shaped crystallites (Figure 2), the molecular sieve is formed by evenly mixing raw materials of substance containing IVA elements, substance containing IIIA element, alkali metal hydroxide, template and water, and then through two stages of crystallization processes, the molecular sieve product has pure crystalling phase, is relatively high in degree of crystallinity, and has an excellent heat and water heat stability, namely, the method is relatively low in cost, the performance of the ZSM-11 molecular sieve is excellent, and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
SAPO-34/ZSM-5 composite molecular sieve and synthesis method of composite molecular sieve
InactiveCN104556143AAdjustable acid distributionWide distribution of acidityMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular sieveMaterial Pore Size
The invention relates to an SAPO-34 / ZSM-5 composite molecular sieve and a synthesis method of the composite molecular sieve, solving the problems of single pore diameter, low acidity and low reaction activity of the porous materials which are synthesized by the prior art. The synthesis method of the composite molecular sieve comprises the following steps: firstly mixing a silicon source, an aluminum source, a phosphorus source and an organic template agent according to a certain ratio, then adding a certain quantity of ZSM-5 molecular sieves, uniformly mixing and carrying out hydrothermal crystallization, and synthesizing the SAPO-34 / ZSM-5 composite molecular sieve by controlling nucleation and crystal growth conditions, wherein the composite molecular size is adjustable in ratio of two phases; an XRD diffraction spectrum of the composite molecular size has a maximum d interval at the positions of 7.92+ / -0.1, 8.79+ / -0.1, 9.52+ / -0.1, 12.85+ / -0.1, 16.00+ / -0.1, 20.56+ / -0.1, 23.01+ / -0.05, 23.24+ / -0.05, 23.86+ / -0.05, 25.83+ / -0.1, 30.55+ / -0.1 and 31.32+ / -0.1. The composite molecular sieve can be applied to industrial production for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by reacting methyl alcohol / dimethyl ether.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Toner
InactiveUS20150220013A1Excellent developabilityExcellent offset resistanceDevelopersCharge controlEngineering
Provided is a toner that shows both developability and electrostatic offset resistance. The toner includes a charge controlling agent that is represented by the following formula (1), and that has peaks at 15.000°±0.150° and 20.100°±0.150° in CuKα X-ray diffraction spectrum obtained in 2θ range of 10° or more to 40° or less where θ represents Bragg angle, one of the peaks being a peak having a maximum intensity and the other being a peak having a second maximum intensity.
Owner:CANON KK
Device for the production of holographic reconstructions with light modulators
InactiveUS8218212B2Arrangement is expensiveImprove diffractionHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsDiffraction orderImage plane
A device for the production of holographic reconstructions having light modulators is disclosed. The device comprises at least one pixelated light modulator illuminated by at least one light source, and a focusing optical element field arrangement which images the light sources in an image plane after the light modulator. For the reconstruction, only one order of diffraction of the Fourier spectrum of the hologram should be used. The light modulator is provided with an assigned filter-aperture field arrangement which is located in the area of the image plane of the light source images and which has a plurality of aperture openings. Said aperture openings are designed in such a way that they each allow the passage of a prespecified area of the overall dimensions either smaller or the same as a diffraction order of the diffraction spectrum following Fourier transformation and produced from the holographic coding of the light modulator.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
High heat-resistant member, method for producing the same, graphite crucible and method for producing single crystal ingot
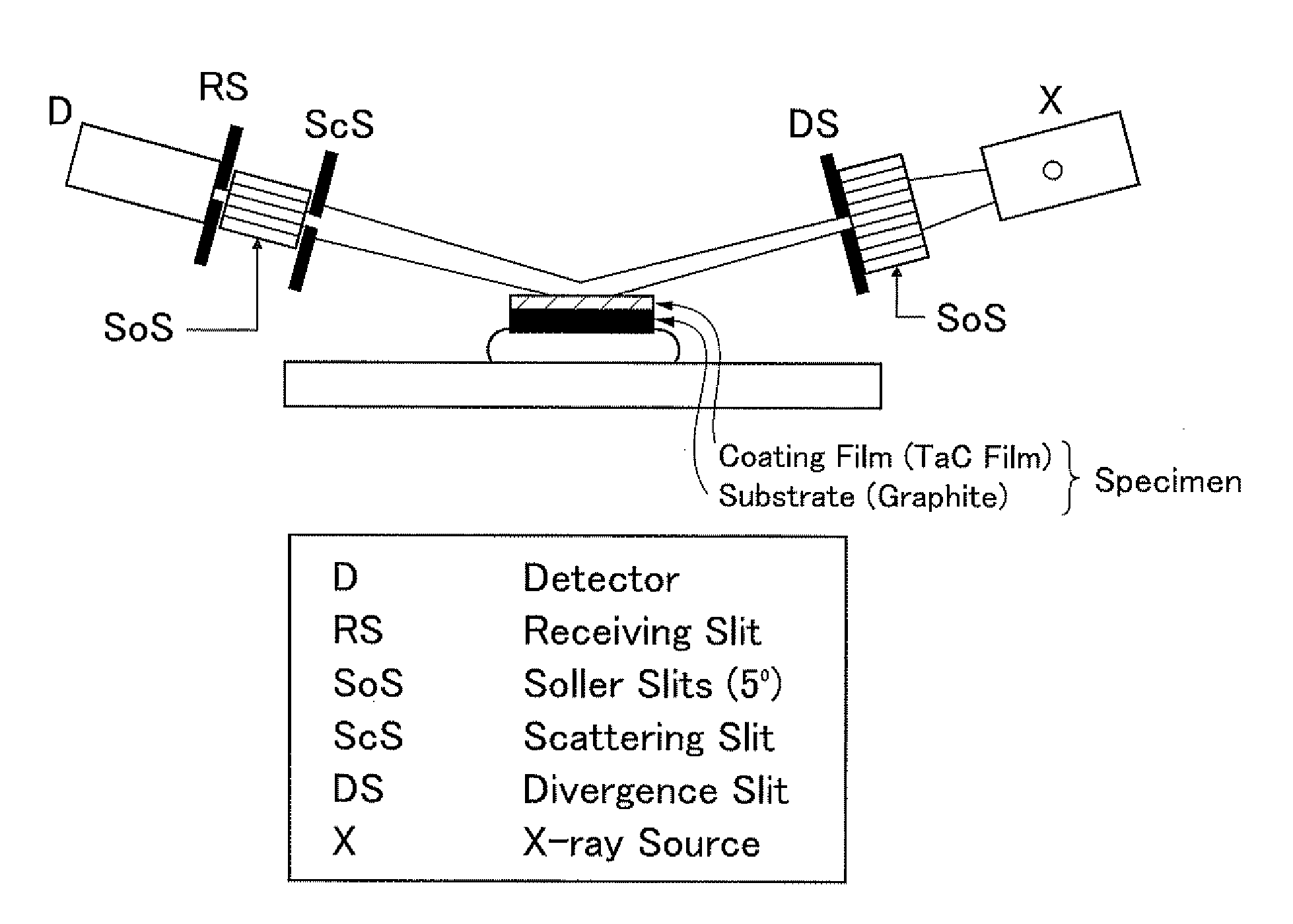
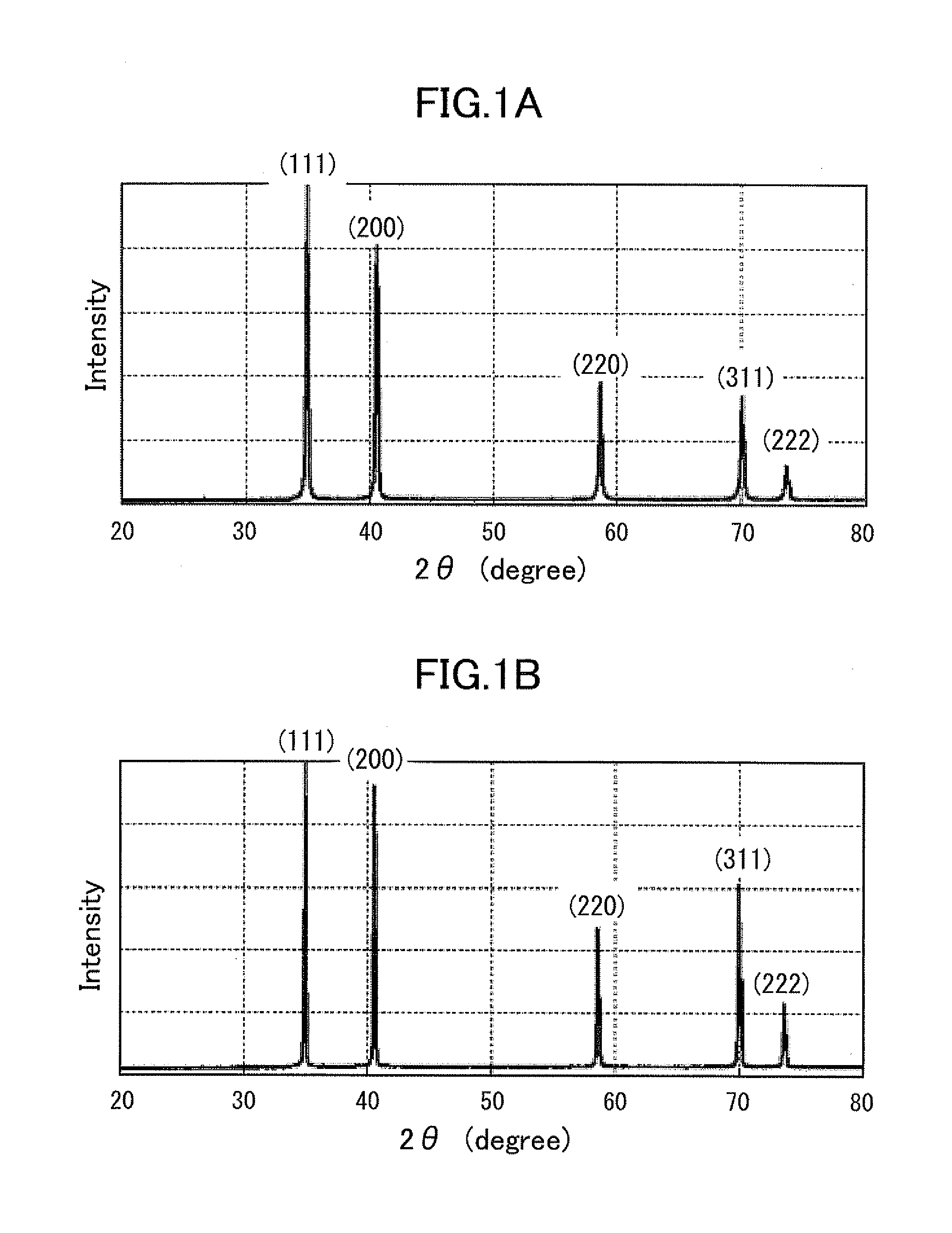
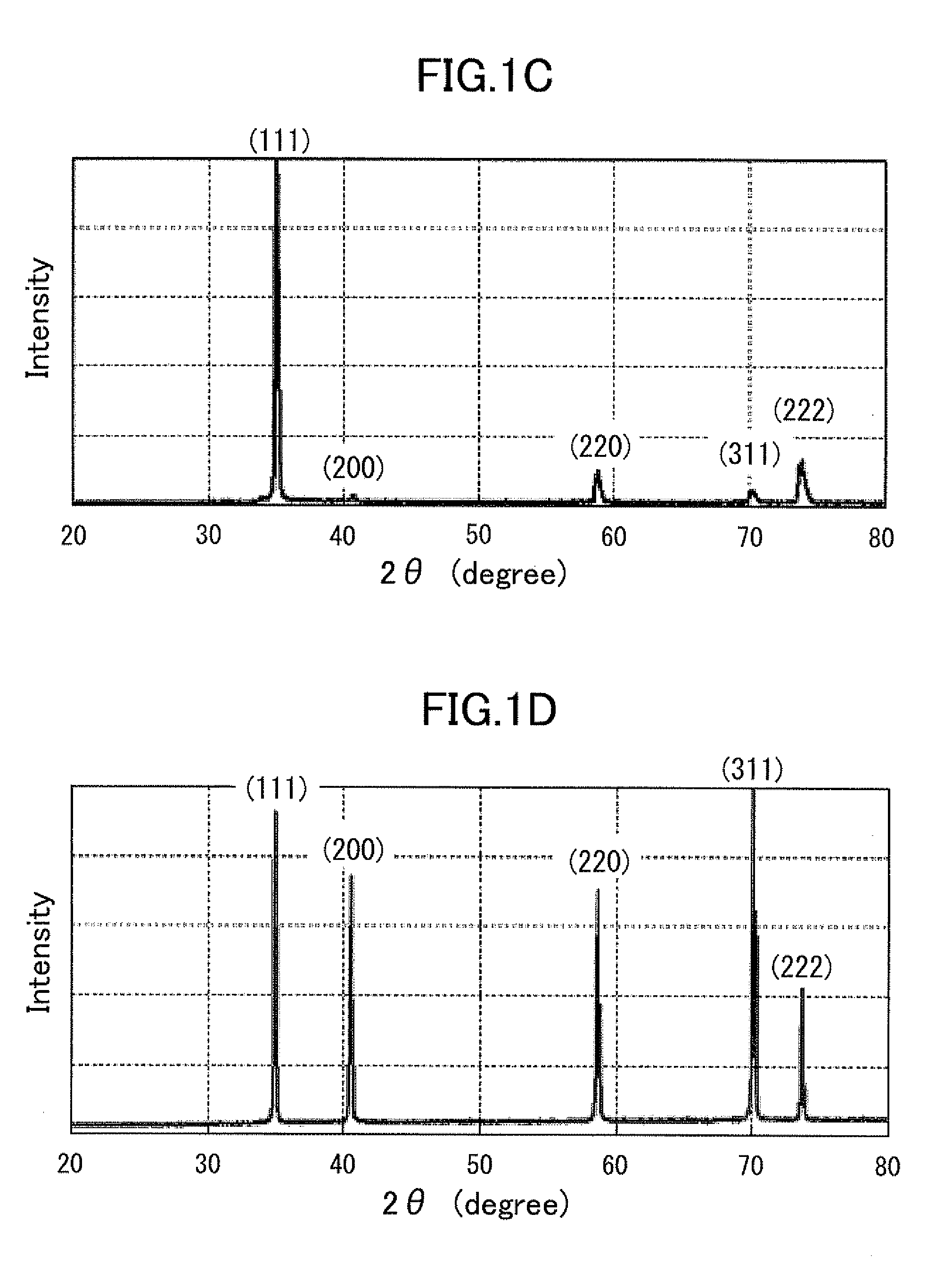
ActiveUS20130061800A1Improve heat resistanceIncreased durabilityAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCarbide coatingX-ray
A high heat-resistant member includes a graphite substrate including isotropic graphite and a carbide coating film including a carbide, such as tantalum carbide, and covering a surface of the graphite substrate, the carbide coating film having a randomly oriented isotropic grain structure in which crystallites having a size indexed by a full width at half maximum of a diffraction peak of an X-ray diffraction spectrum of not more than 0.2° from (111) planes are accumulated at substantially random. The orientation of the carbide coating film is determined by whether degree of orientation (F) in any Miller plane calculated based on an XRD spectrum using the Lotgering method is within a range from −0.2 to 0.2.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Carbon material for catalyst support use
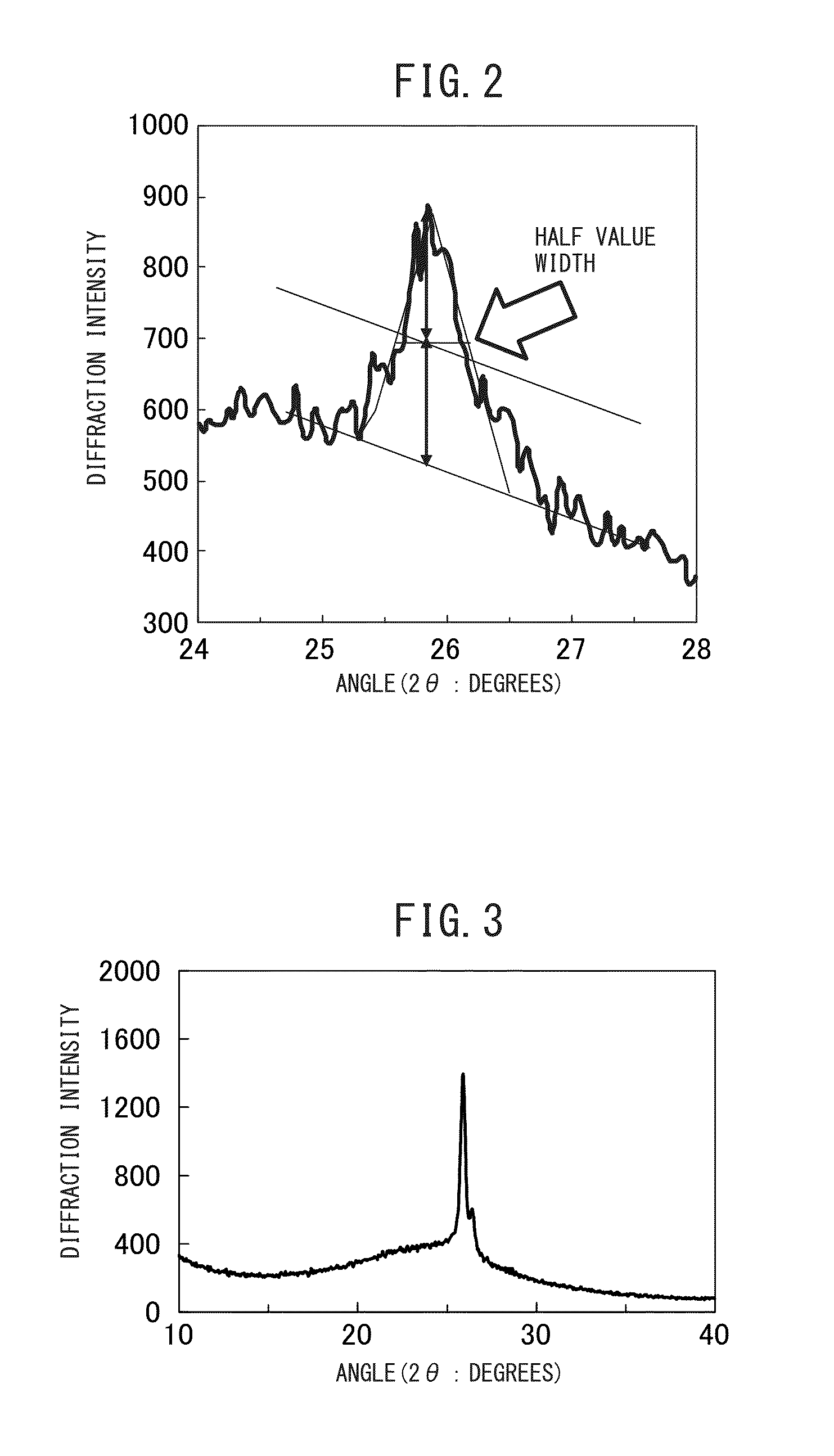
A carbon material for catalyst support use which, when used as a catalyst support, maintains a high porosity while being stable chemically, having electrical conductivity, being excellent in durability, and being excellent in diffusibility of the reaction starting materials and reaction products is provided. It is characterized by comprising dendritic carbon mesoporous structures which have 3D structures of branched carbon-containing rod shapes or carbon-containing ring shapes, having a pore size of 1 to 20 nm and a cumulative pore volume of 0.2 to 1.5 cc / g found by analyzing a nitrogen adsorption isotherm by the Dollimore-Heal method, and having a powder X-ray diffraction spectrum which has a peak corresponding to a 002 diffraction line of graphite between diffraction angles (2θ: degrees) of 20 to 30 degrees and has a peak with a half value width of 0.1 degree to 1.0 degree at 25.5 to 26.5 degrees.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Method for determining unknown crystal Bravais lattice by electric back scattering diffraction
InactiveCN101413906ARealize analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBravais latticeReal time analysis
The invention provides a method used for determining Bravais lattice of unknown crystal by electron backscatter diffraction. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the steps as follows: 1) an electron backscatter diffraction spectrum is obtained and the crystal diffraction information in the diffraction spectrum is measured; 2) a two-dimensional reciprocal surface of the crystal is obtained; 3) a three-dimensional reciprocal primitive cell is reconstructed by the two-dimensional reciprocal surface; 4) the cell parameter of the three-dimensional reciprocal primitive cell s worked out according to the width of the Kikuchi band and the angle between the Kikuchi bands in the same Kikuchi electrode; 5) a reciprocal reduced cell of the crystal is solved; 6) the Bravais lattice of the crystal is determined in the reciprocal space; 7) the Bravais lattice of the crystal is determined. In the method, only a scanning electron microscope and an electron backscatter diffraction accessory are used to realize the analysis on unknown lattice of bulk crystals, and the exponential of the Kikuchi band and the Kikuchi electrode in the electron backscatter diffraction spectrum is marked at the same time. The method has no special requirement on the samples to be analyzed, is suitable for quickly analyzing bulk samples, and can be used for analyzing the microstructure morphologies and crystal structure in the buck samples.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for measuring speed and frequency of ultrasonic traveling wave in liquid
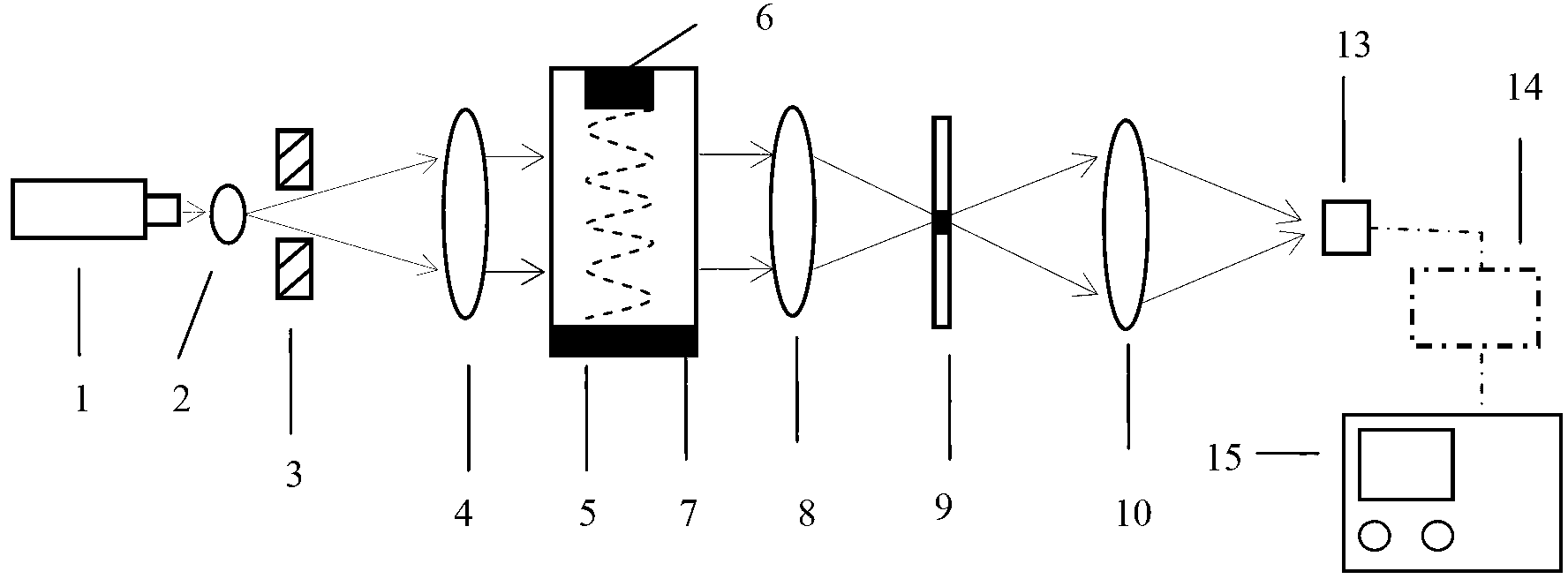
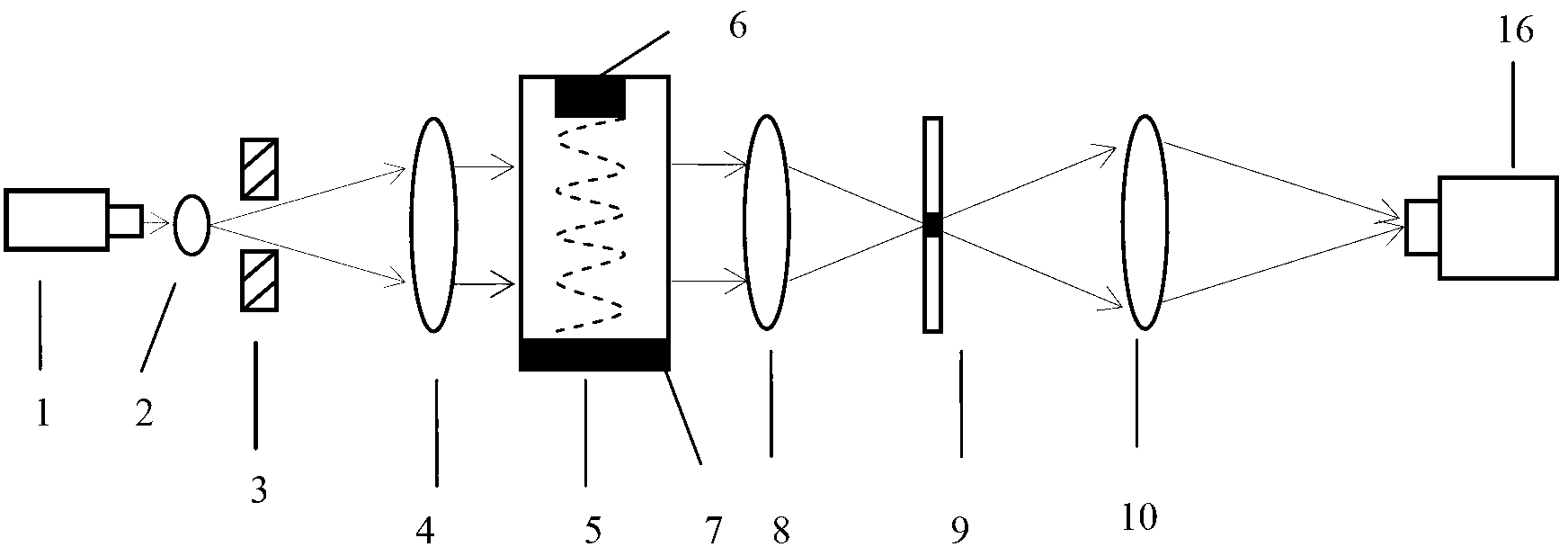
InactiveCN103308142ASimple light pathFast measurementVelocity propogationUsing wave/particle radiation meansMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring the speed and frequency of ultrasonic traveling wave in a liquid. The method comprises the following steps that a monochromatic parallel light beam is vertical to an ultrasonic transmission direction and radiates a dynamic ultrasonic grating that the ultrasonic wave forms in the liquid; the dynamic ultrasonic grating penetrates through a lens and the diffraction spectrum of a traveling wave ultrasonic phase grating is formed; the spectrum is processed and imaged through an amplitude filter and an imaging lens, and a spectrum image of the ultrasonic traveling wave grating is obtained; the spacing of two adjacent spectral lines on the spectrum image is measured, and the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave in the liquid is calculated; the change of an electrical signal after the previous level of spectrum and zero level spectrum of the spectrum image are mixed is detected or recorded, and the frequency of the ultrasonic wave is worked out; the speed of the ultrasonic wave in the liquid is worked out through the wavelength and the frequency. The device for realizing the method comprises a light source, a transparent sink, a lens I, the amplitude filter, the imaging lens and the measuring device which are sequentially connected, and a sound-absorbing medium and the ultrasonic transducer are arranged in the transparent sink and are respectively arranged on both sides.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20130011747A1Excellent cycle characteristicsShorten the timeAlkaline accumulatorsGraphiteLithiumX-ray
There is provided a lithium ion secondary battery excellent in cycle characteristics in which the conductivity of an electrode using a graphite material which is less deformed and oriented by pressurization is improved. A negative electrode mixture which includes at least a negative electrode active material comprising graphite as a main component, a binder, and a conductive aid has a ratio of a peak intensity of a (002) plane to a peak intensity of a (110) plane in an X-ray diffraction spectrum of 30 or more and 70 or less, the spectrum being measured after the negative electrode mixture is pressed at 98 MPa (1000 kgf / cm2), and the conductive aid includes carbon black having a DBP absorption (cm3 / 100 g) of 250 or more and 500 or less.
Owner:NEC ENERGY DEVICES LTD
Negative active material, method of preparing the negative active material, negative electrode and lithium battery
The present invention provides a negative active material, a method of preparing the negative active material, a negative electrode including the negative active material, and a lithium battery comprising the electrode. The negative active material including: a composite including a matrix comprising silicon oxide, silicon carbide, carbon and silicon particles dispersed in the matrix; and a carbon coating film formed on a surface of the composite, wherein an intensity ratio of a SiC peak to a Si peak in an X-ray diffraction spectrum is at least 1.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Heat-induced formation of co-crystalline composition containing titanyl phthalocyanine and titanyl fluorophthalocyanine
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
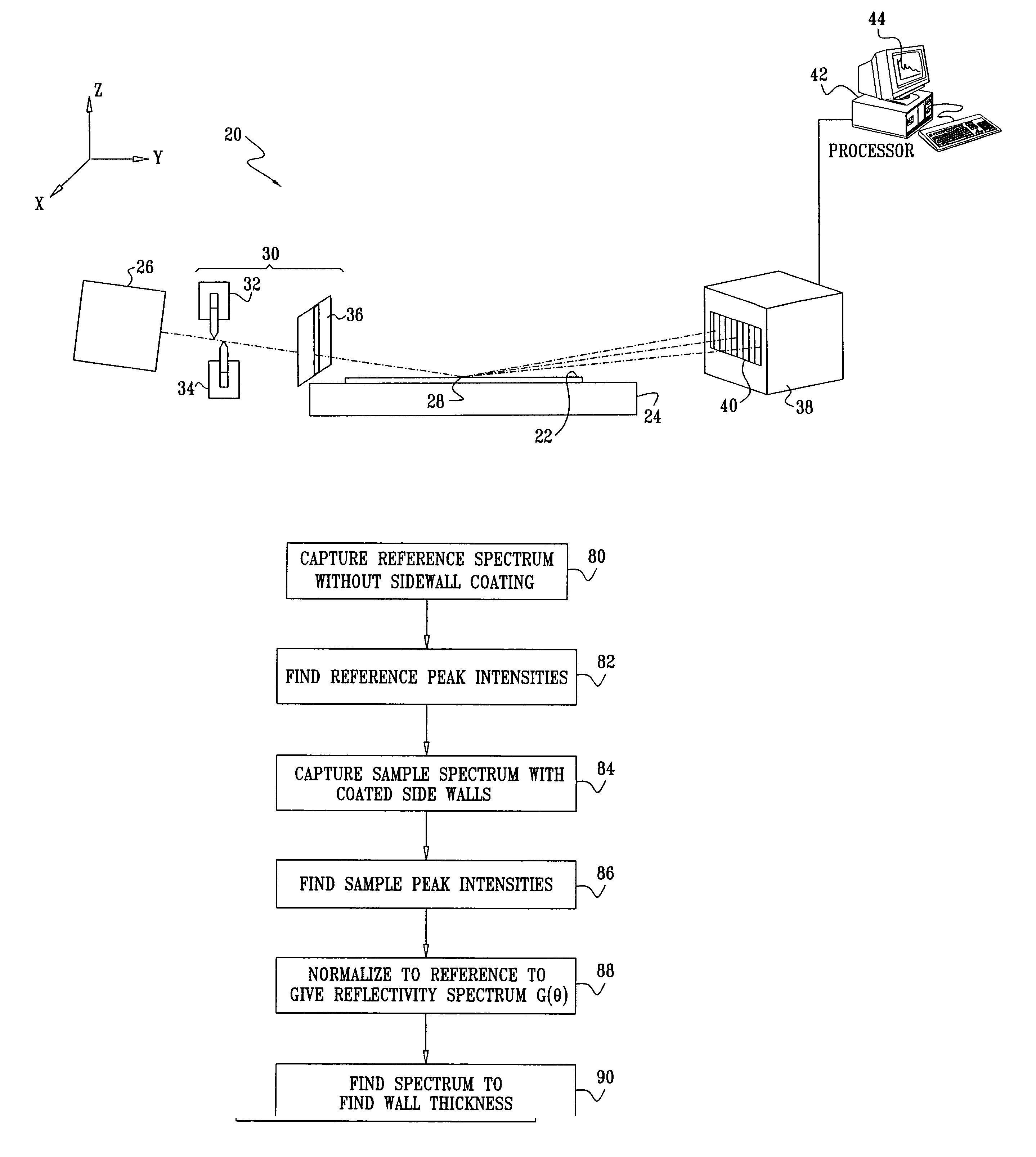
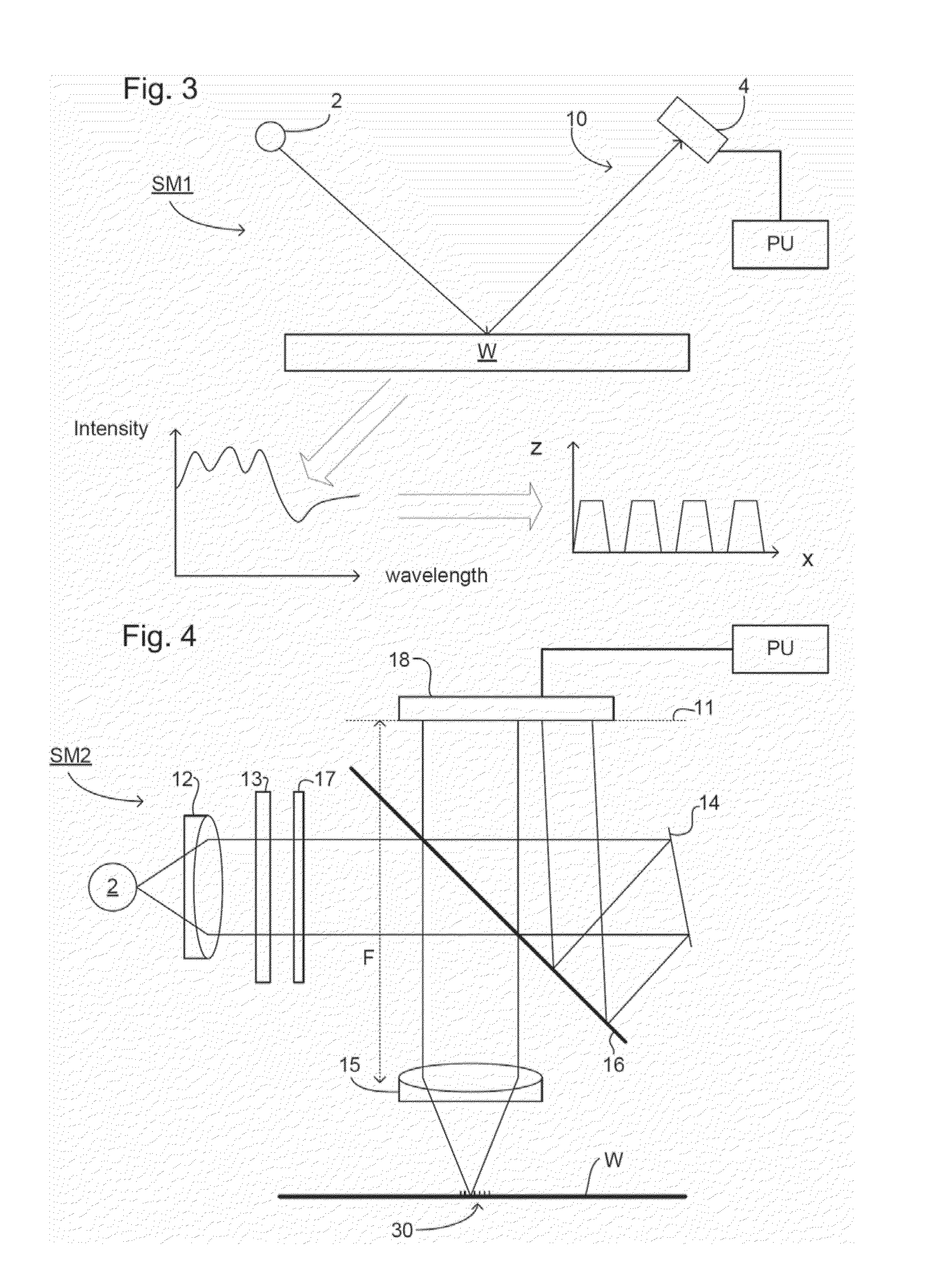
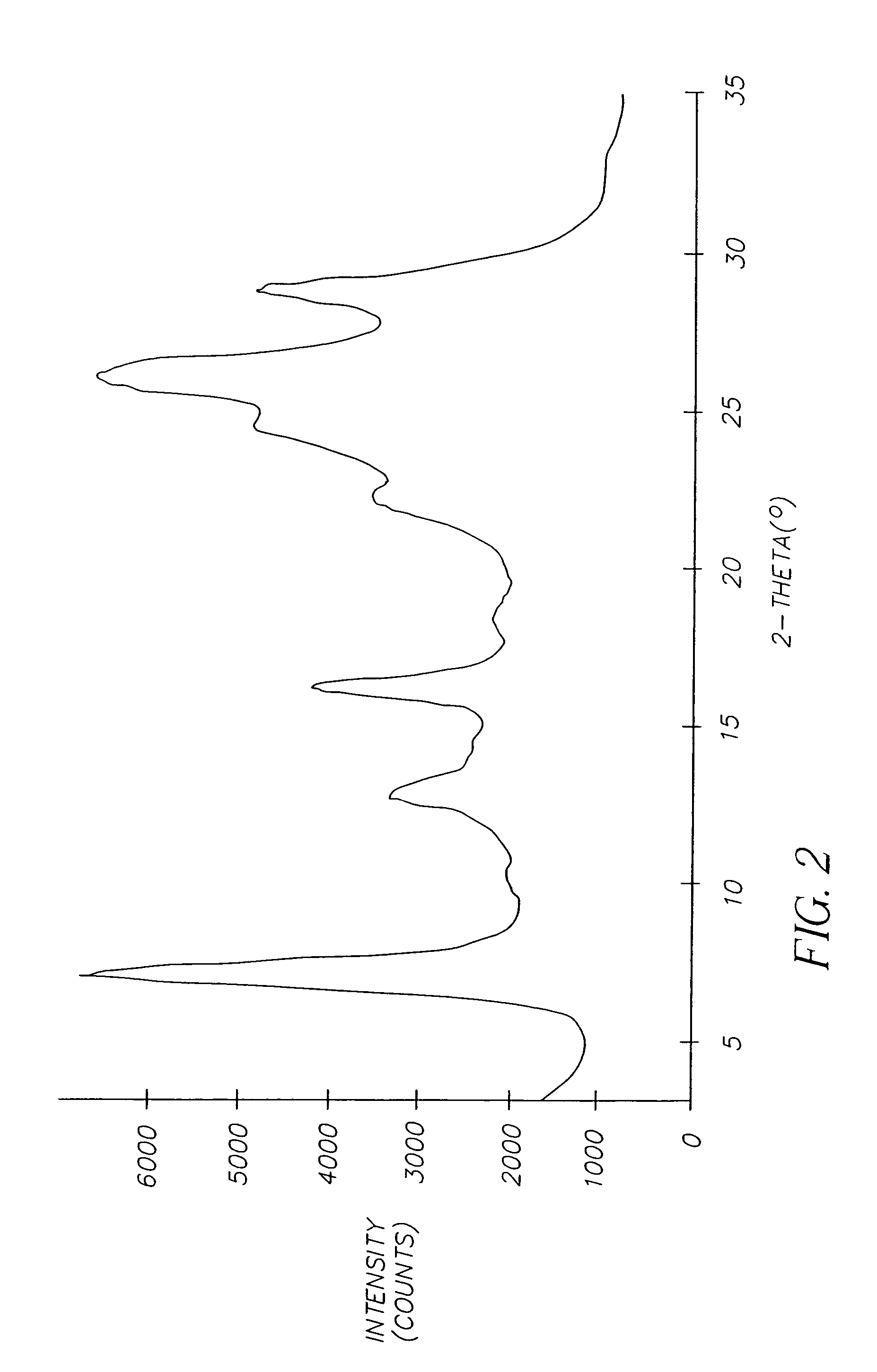
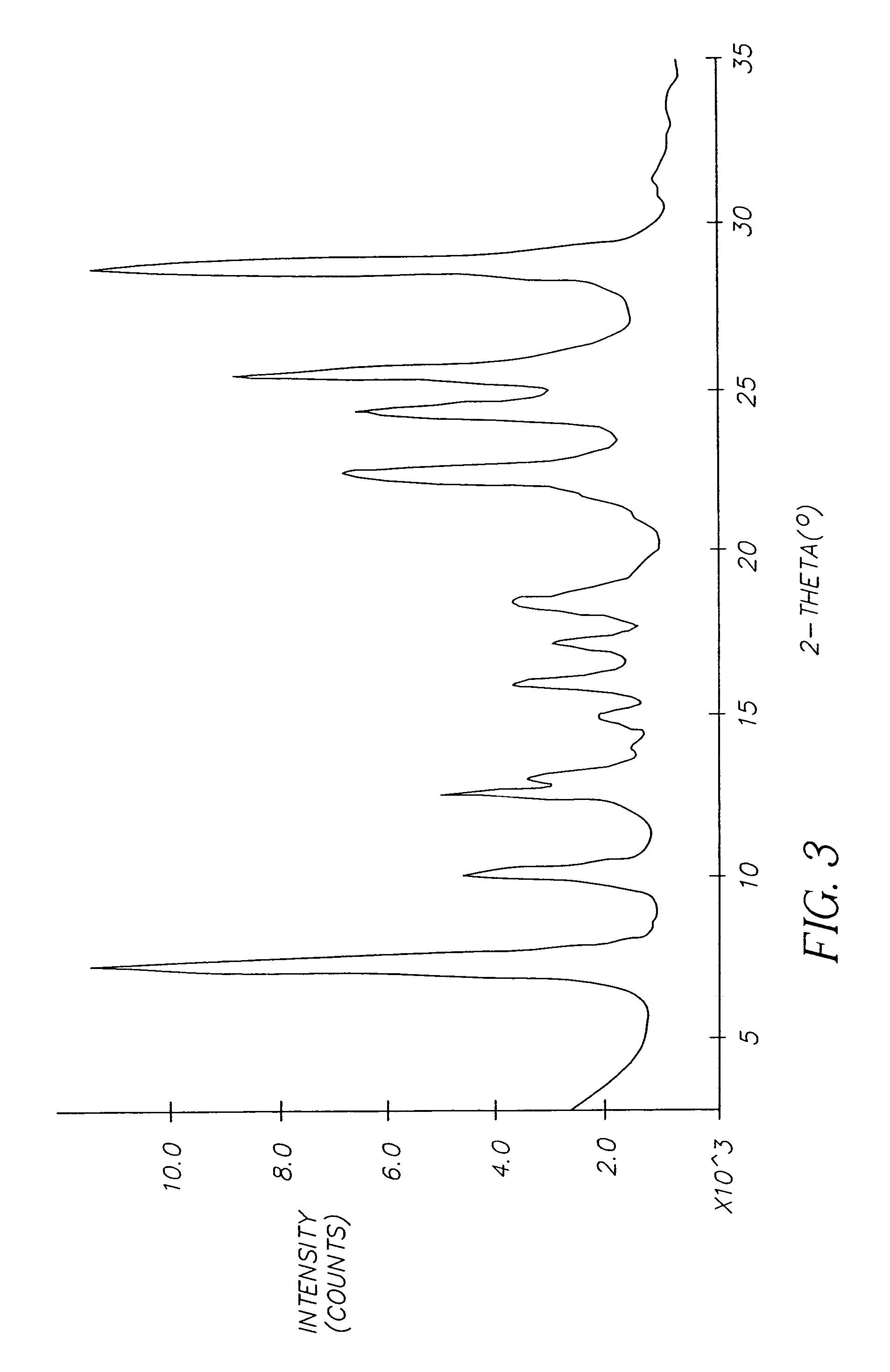
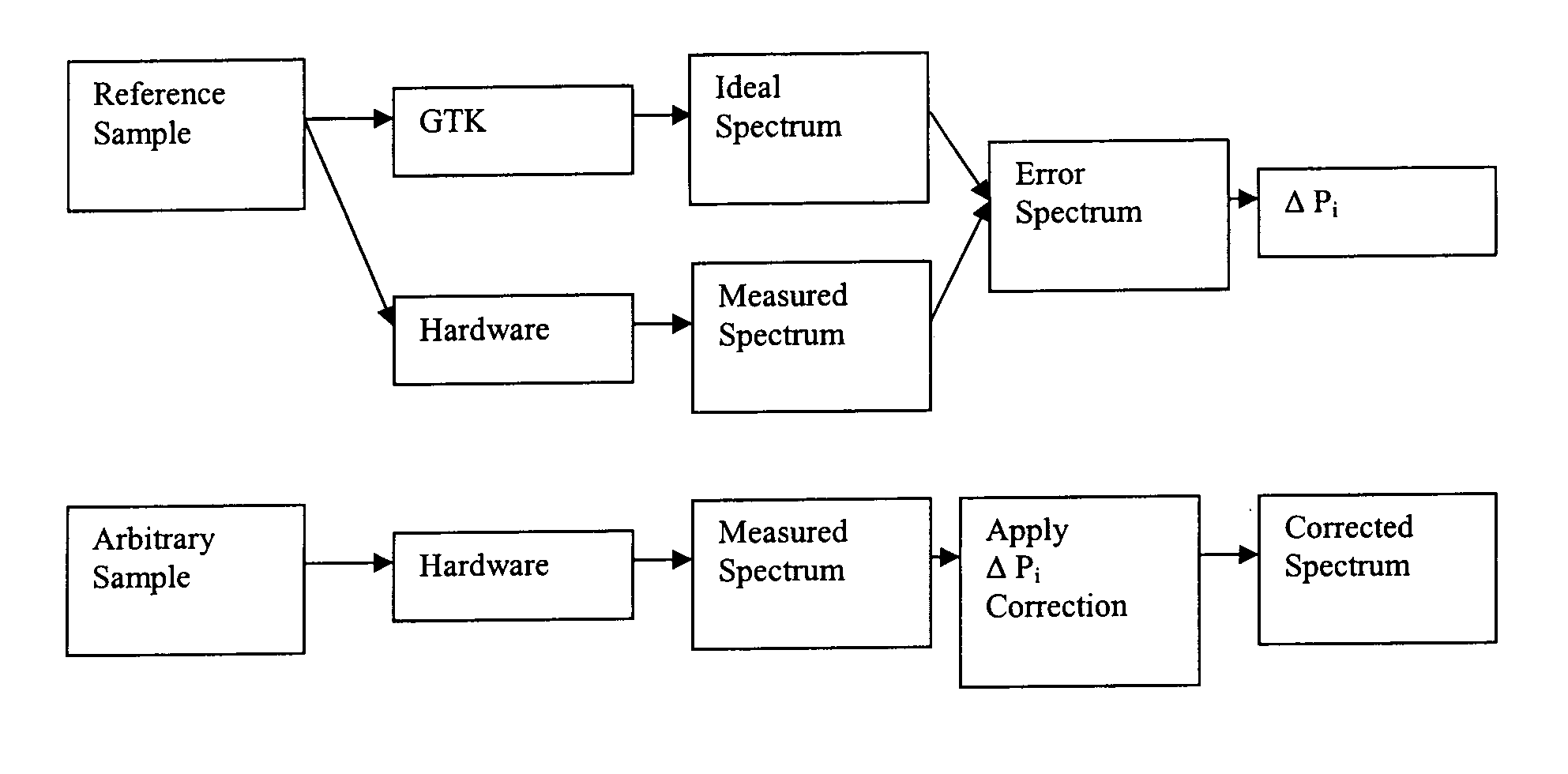
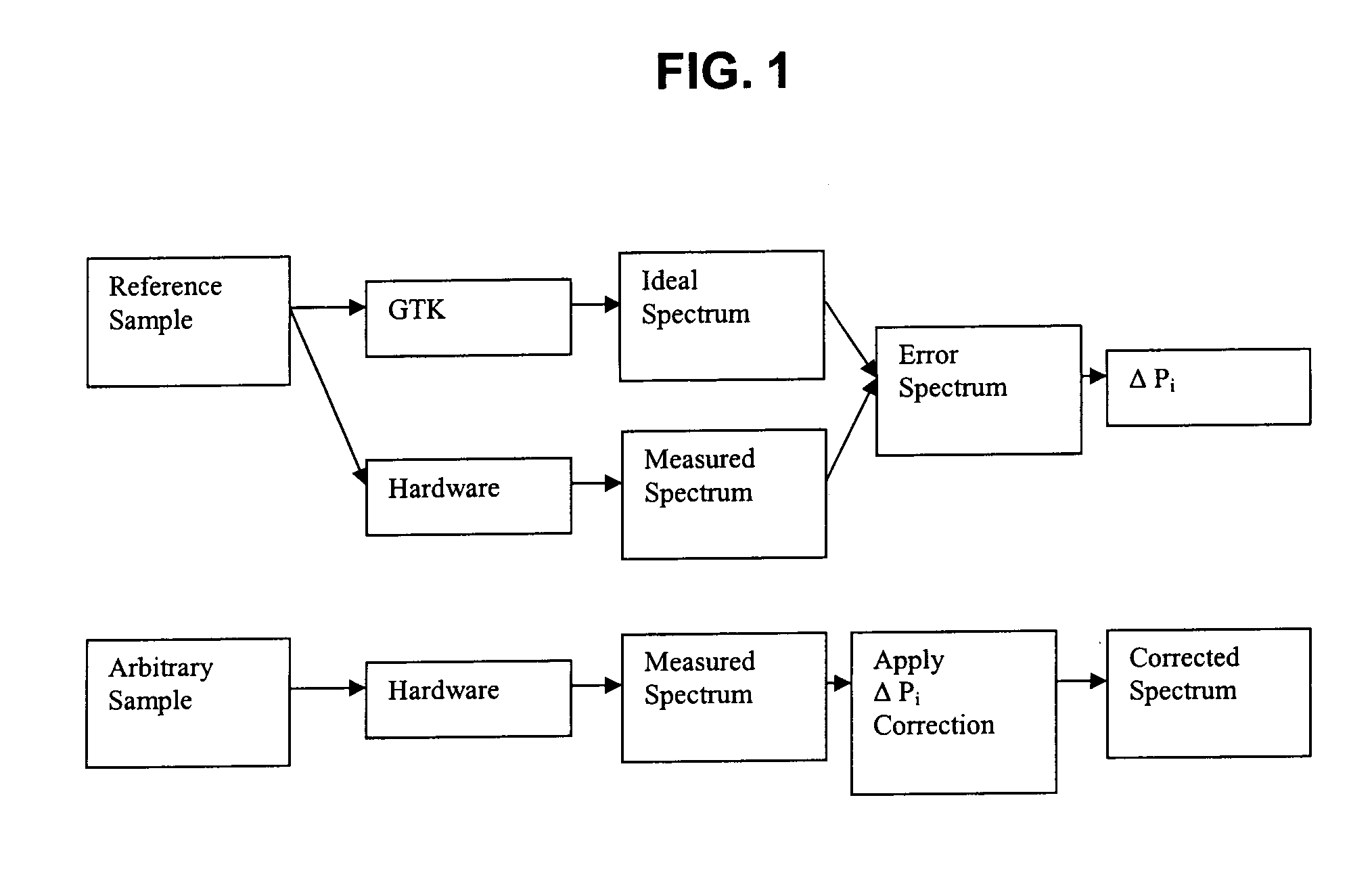
Method of correcting systematic error in a metrology system
A method for correcting systematic errors in an optical measurement tool in which a first diffraction spectrum is measured from a standard substrate including a layer having a known refractive index and a known extinction coefficient by exposing the standard substrate to a spectrum of electromagnetic energy. A tool-perfect diffraction spectrum is calculated for the standard substrate. A hardware systematic error is calculated by comparing the measured diffraction spectrum to the calculated tool-perfect diffraction spectrum. A second diffraction spectrum from a workpiece is measured by exposing the workpiece to the spectrum of electromagnetic energy, and the measured second diffraction spectrum is corrected based on the calculated hardware systematic error to obtain a corrected diffraction spectrum.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060197823A1High imagingIncrease speedElectrographic process apparatusPrintingX-rayImage formation
An image forming apparatus including an image bearing member to operate at a linear velocity of at least 300 mm / sec, which includes an electroconductive substrate, a charge blocking layer located overlying the electroconductive substrate, a moiré prevention layer located overlying the charge blocking layer, and a photosensitive layer located overlying the moiré prevention layer. The photosensitive layer contains titanyl phthalocyanine having a primary particle diameter of not greater than 0.25 μm and having a crystal form having a CuKα X ray diffraction spectrum having a wavelength of 1.542 Å such that the maximum diffraction peak is observed at a Bragg (2θ) angle of 27.2±0.2°, main peaks are observed at a Bragg (2θ) angle of 9.4±0.2°, 9.6±0.2°, and 24.0±0.2°, and a peak is observed at a Bragg (2θ) angle of 7.3±0.2° as the lowest angle diffraction peak, while there is no peak between 9.4±0.2 and 7.3±0.2 and there is no peak at 26.3±0.2°).
Owner:RICOH KK
Zeolite containing catalytic dewaxing catalyst
InactiveCN1448484AHigh selectivityHigh yieldCatalyst carriersPetroleum wax recoveryRare earthDiffraction spectrum
The dewaxing catalyst contains one kind of zeolite carrier and hydrogenating metal component, and the zeolite is one kind of RE containing high-silicon zeolite in five membered ring structure and hassilica / alumina molar ratio of 20-100, RE oxide content in 0.1-2.5 wt% and sodium oxide content of 0.1-1.5 wt%. The zeolite has special X-ray diffraction spectrum line and relatively high selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Toner
ActiveUS10295920B2Improve development performanceSuppress appearanceDevelopersStrontium titanateX-ray
Provided is toner that contains a toner particle, and an external additive containing a strontium titanate particle, wherein the toner has an average circularity of at least 0.935 and not more than 0.995, the strontium titanate particle has a number-average primary particle diameter of at least 10 nm and not more than 60 nm, the strontium titanate particle has a peak in the range of 39.700°±0.150° and a peak in the range of 46.200°±0.150° in a CuKα x-ray diffraction spectrum obtained in the 2θ range of at least 10° and not more than 90° where θ is the Bragg angle, and the ratio of the area Sb of the peak at 46.200°±0.150° to the area Sa of the peak at 39.700°±0.150° is at least 1.80 and not more than 2.30.
Owner:CANON KK
Crystalline oxotitanylphthalocyanine and electrophotographic photoreceptor using the same
An object of the invention is to improve the photosensitivity characteristics, characteristics on repeated use and stability of a photoreceptor. A photosensitive layer formed on a conductive support of a photoreceptor contains crystalline oxotitanylphthalocyanine having major peaks in an X-ray diffraction spectrum at Bragg angles (2theta±0.2°) of 7.3°, 9.4°, 9.6°, 11.6°, 13.3°, 17,9°, 24.1° and 27.2°, wherein a peak bundle formed by overlapping the peaks at 9.4° and 9.6° is the largest peak, and the peak at 27.2° is the secondary largest peak as a charge generating substance. Furthermore, it contains a bisamine compound, an N,N'-bisenamine compound, a styryl compound, an amine-hydrazone compound, a benzofuran-bishydrazone compound, a bisenamine compound, a benzofuran-bishydrazone compound or a benzofuran-bis-cyclic hydrazone compound represented by the particular structural formulae as a charge transporting substance.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic Semiconductor Thin Film, Organic Semiconductor Device, Organic Thin Film Transistor and Organic Electronic Luminescence Element
An organic semiconductor thin film, comprising an organic semiconductor compound, wherein the organic semiconductor thin film is manufactured by a process of forming a film by using a solution or a dispersion at room temperature prepared by mixing the organic semiconductor compound and an organic solvent, and the half width of a diffraction peak having the maximum intensity is 0.4° or less in an X-ray diffraction spectrum of the film.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Device and method for measuring multi-wavelength characteristic X ray diffraction
InactiveCN104634799AHigh diffraction intensityEliminate attenuationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayHigh pressure
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring multi-wavelength characteristic X ray diffraction of an X ray diffraction spectrum of a measured crystal material sample by selecting a certain characteristic X ray of an X ray tube anode target within a relatively wide wavelength range. The device comprises an X ray tube, a high-pressure generator, a silt, an angle measurer, a detector, a multi-path analyzer, and the like. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, large-scale attenuation of the characteristic X ray diffraction due to use of a filter sheet or a crystal monochromator and the like is avoided; required characteristic X rays for measuring needed wavelength can be selected by regulating the tube voltage of the X ray tube and upper and lower thresholds of the multi-path analyzer, so that diffraction rays (characteristic X rays with relatively large wavelengths) on the surface of a sample can be measured in a nondestructive manner, and the diffraction rays (characteristic X rays with relatively small wavelengths) inside the sample can be measured in the nondestructive manner. Moreover, the device is simple and convenient to operate, relatively short in detection time; the characteristic X ray diffraction spectrums obtained by scanning are real and reliable.
Owner:郑琪
Toner
ActiveUS20180246432A1Improve development performanceSuppress appearanceDevelopersStrontium titanateX-ray
Provided is toner that contains a toner particle, and an external additive containing a strontium titanate particle, wherein the toner has an average circularity of at least 0.935 and not more than 0.995, the strontium titanate particle has a number-average primary particle diameter of at least 10 nm and not more than 60 nm, the strontium titanate particle has a peak in the range of 39.700°±0.150° and a peak in the range of 46.200°±0.150° in a CuKα x-ray diffraction spectrum obtained in the 2θ range of at least 10° and not more than 90° where θ is the Bragg angle, and the ratio of the area Sb of the peak at 46.200°±0.150° to the area Sa of the peak at 39.700°±0.150° is at least 1.80 and not more than 2.30.
Owner:CANON KK
Electrophotographic photoreceptor, image-forming apparatus, and electrophotographic cartridge
ActiveUS20090136861A1Excellent in electric characteristicHigh sensitivityElectrographic process apparatusCoatingsX-ray1-Propanol
An electrophotographic photoreceptor having high sensitivity and low residual potential is provided. The electrophotographic photoreceptor includes an undercoat layer containing metal oxide particles and a binder resin on an electroconductive substrate, and a photosensitive layer disposed on the undercoat layer, wherein the metal oxide particles have a volume average particle diameter of 0.1 μm or less and a 90% cumulative particle diameter of 0.3 μm or less which are measured by a dynamic light-scattering method in a liquid of the undercoat layer dispersed in a solvent mixture of methanol and 1-propanol at a weight ratio of 7:3; and the photosensitive layer contains crystalline phthalocyanine showing at least one distinct main diffraction peak at a Bragg angle (2θ±0.2°) of 27.0° to 29.0° in an X-ray diffraction spectrum.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
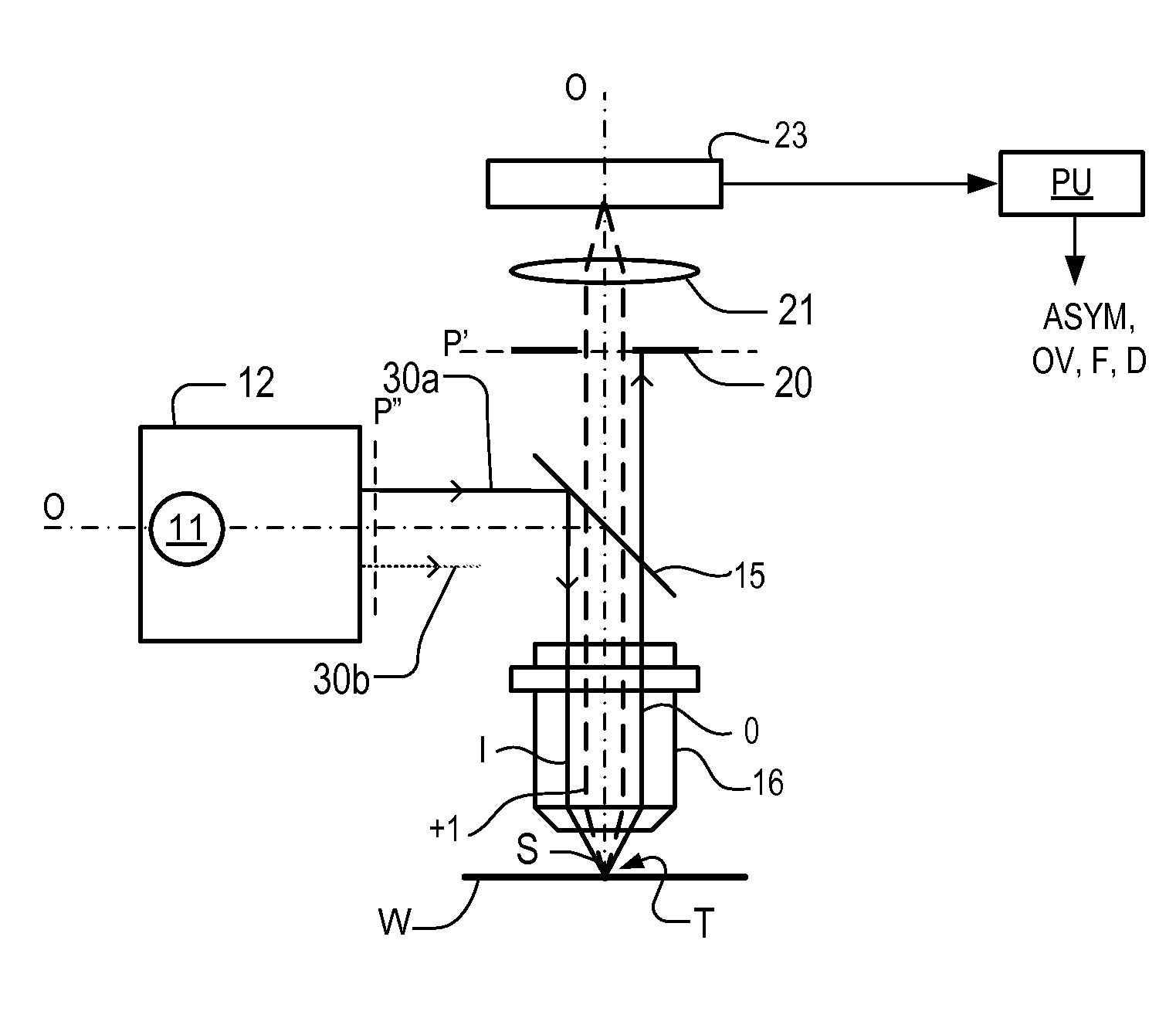
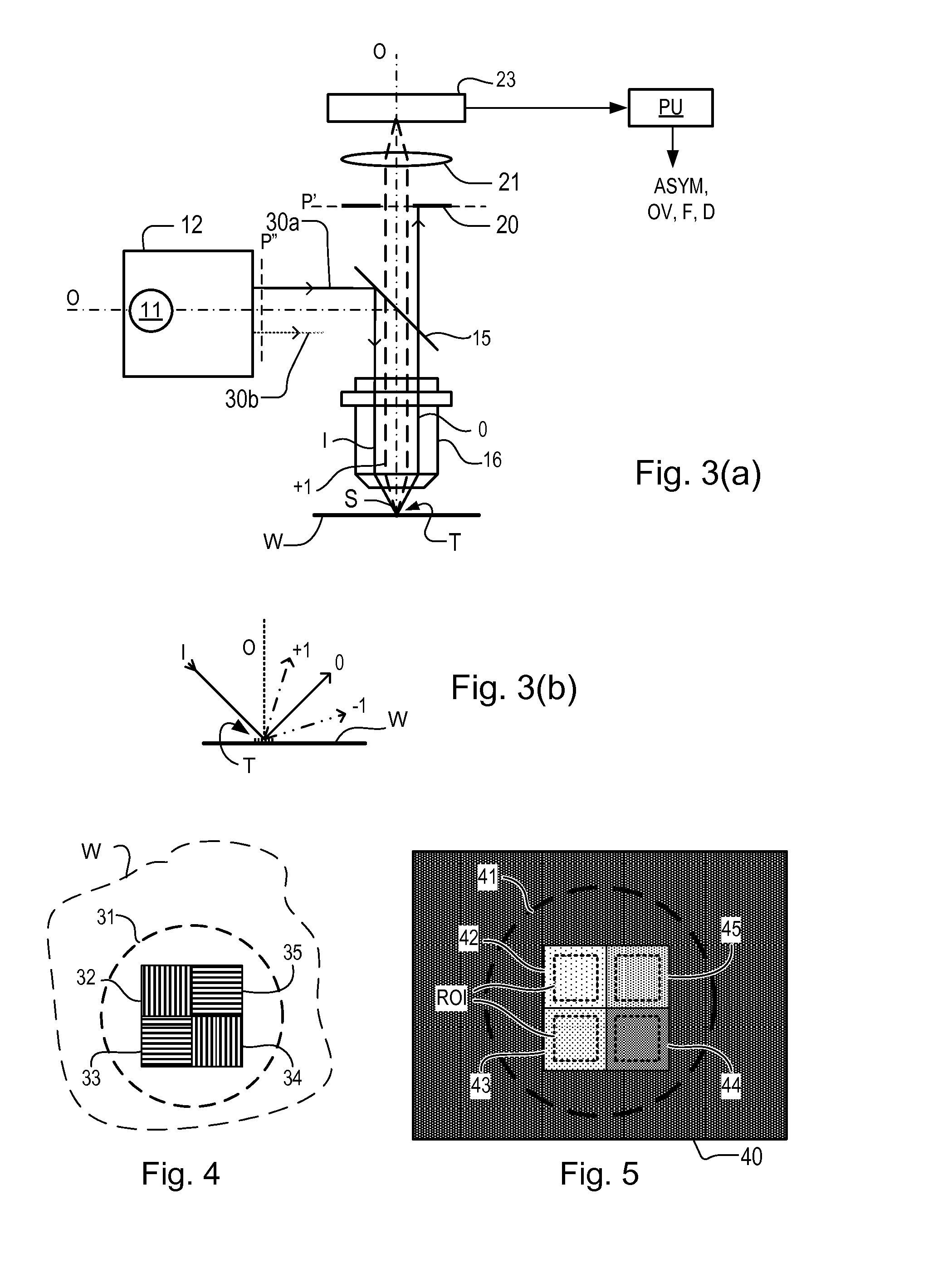
Methods and scatterometers, lithographic systems, and lithographic processing cells
ActiveUS8994944B2Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScatterometerEngineering
In a method of determining the focus of a lithographic apparatus used in a lithographic process on a substrate, the lithographic process is used to form a structure on the substrate, the structure having at least one feature which has an asymmetry in the printed profile which varies as a function of the focus of the lithographic apparatus on the substrate. A first image of the periodic structure is formed and detected while illuminating the structure with a first beam of radiation. The first image is formed using a first part of non-zero order diffracted radiation. A second image of the periodic structure is formed and detected while illuminating the structure with a second beam of radiation. The second image is formed using a second part of the non-zero order diffracted radiation which is symmetrically opposite to the first part in a diffraction spectrum. The ratio of the intensities of the measured first and second portions of the spectra is determined and used to determine the asymmetry in the profile of the periodic structure and / or to provide an indication of the focus on the substrate. In the same instrument, an intensity variation across the detected portion is determined as a measure of process-induced variation across the structure. A region of the structure with unwanted process variation can be identified and excluded from a measurement of the structure.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com