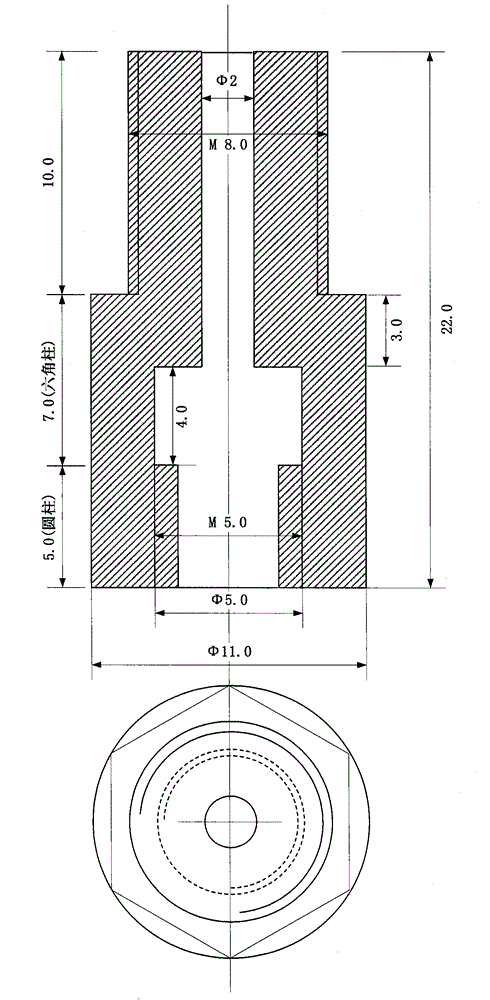
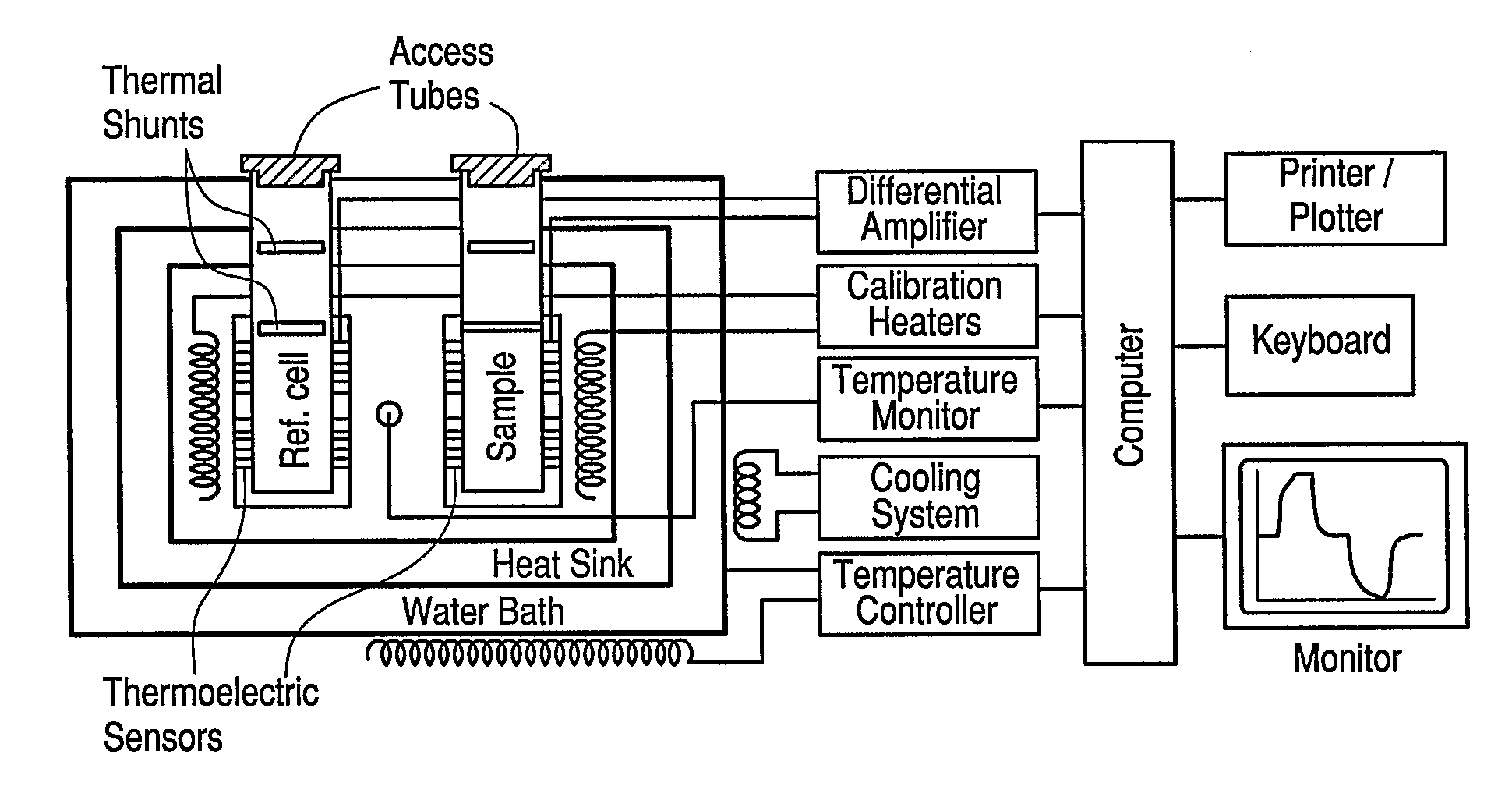
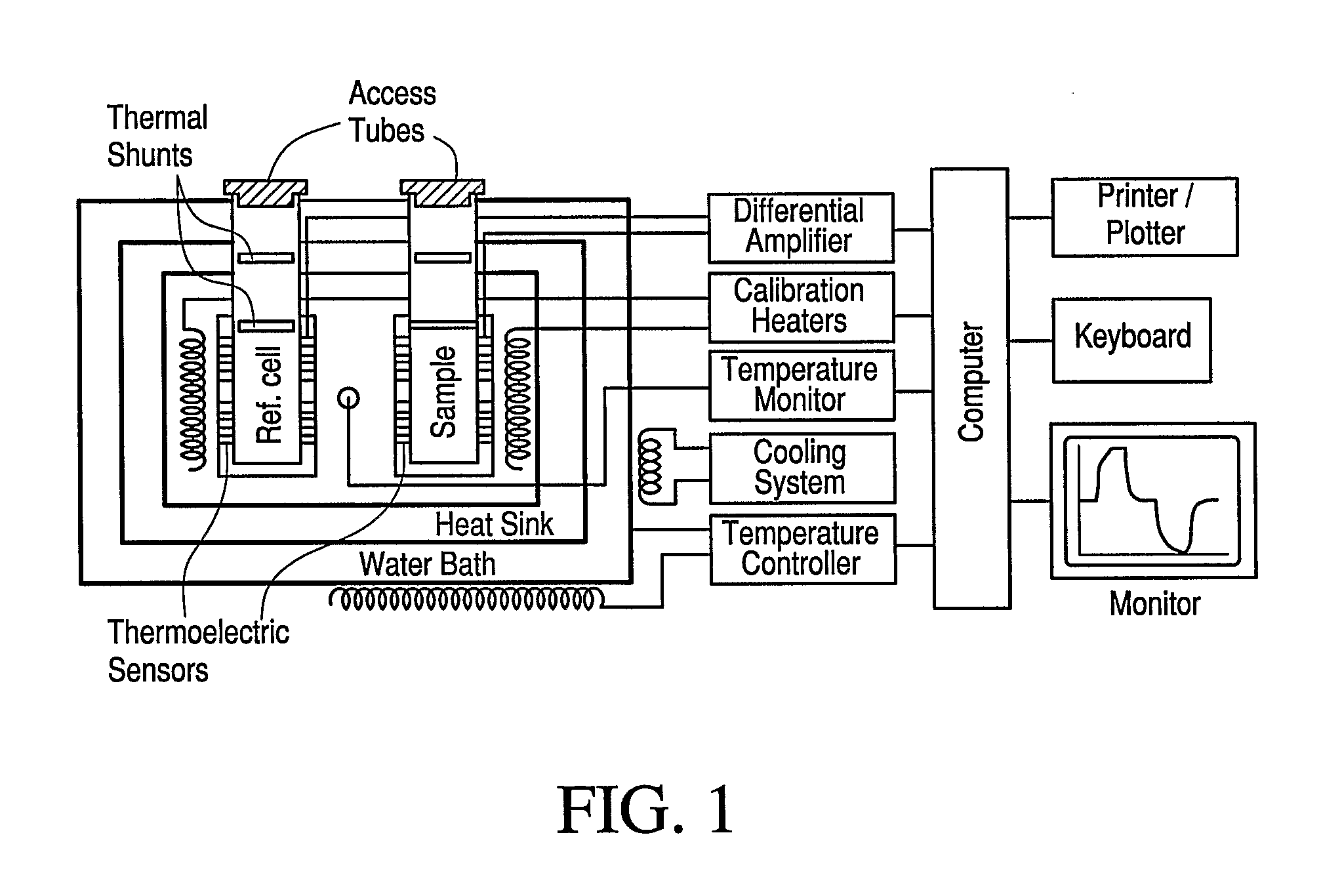
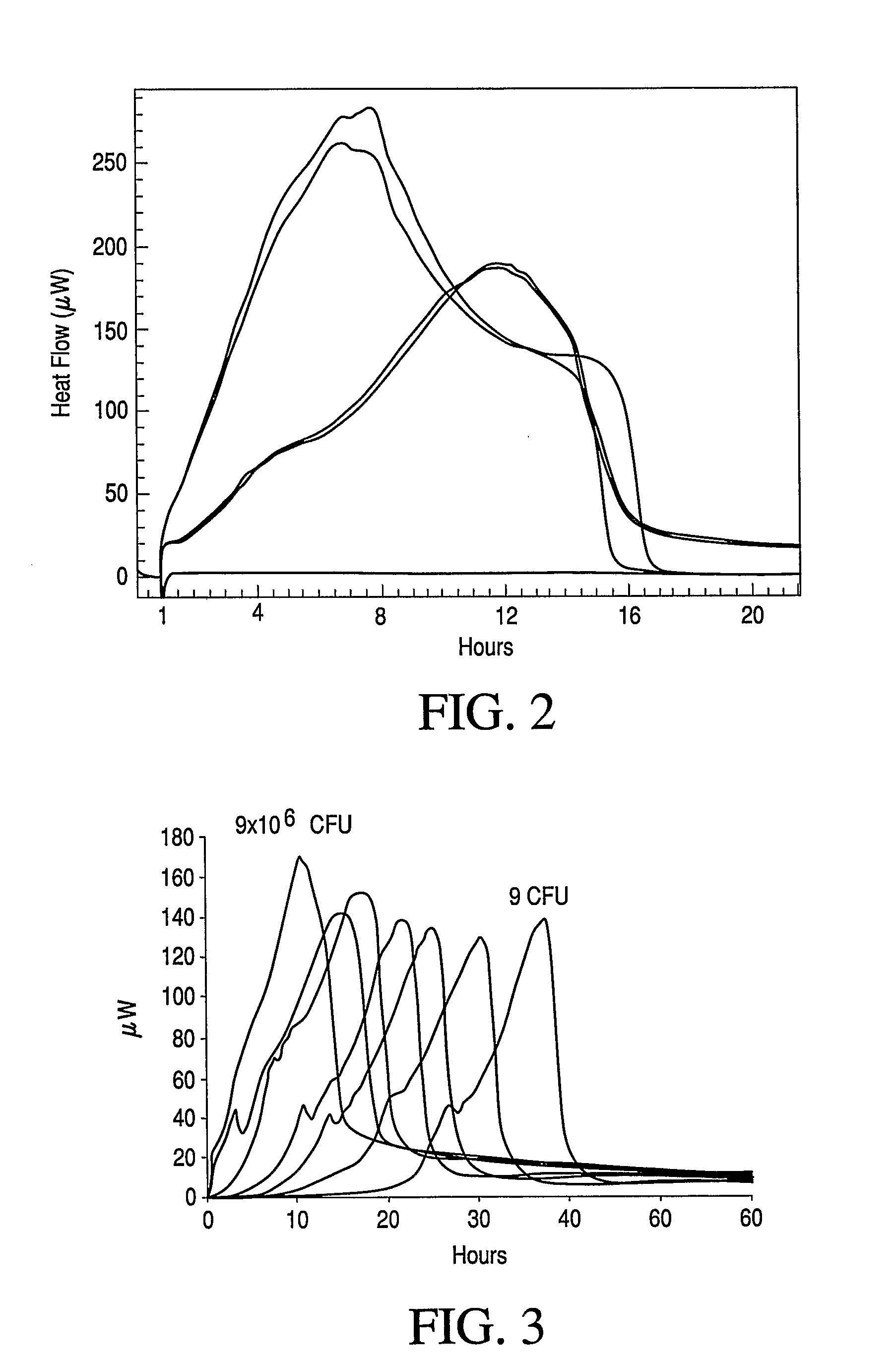
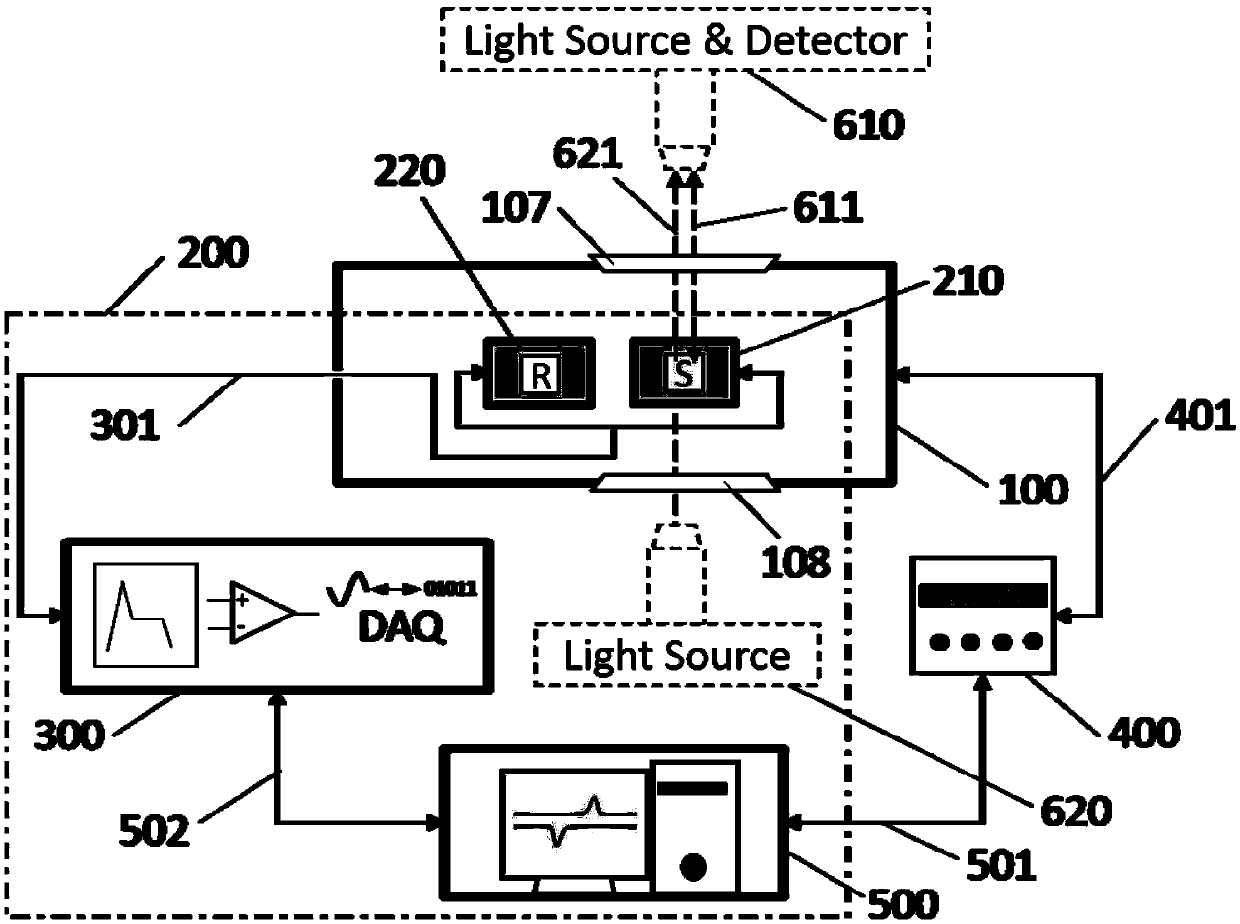
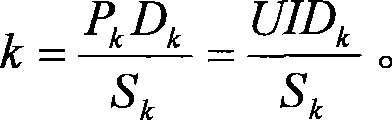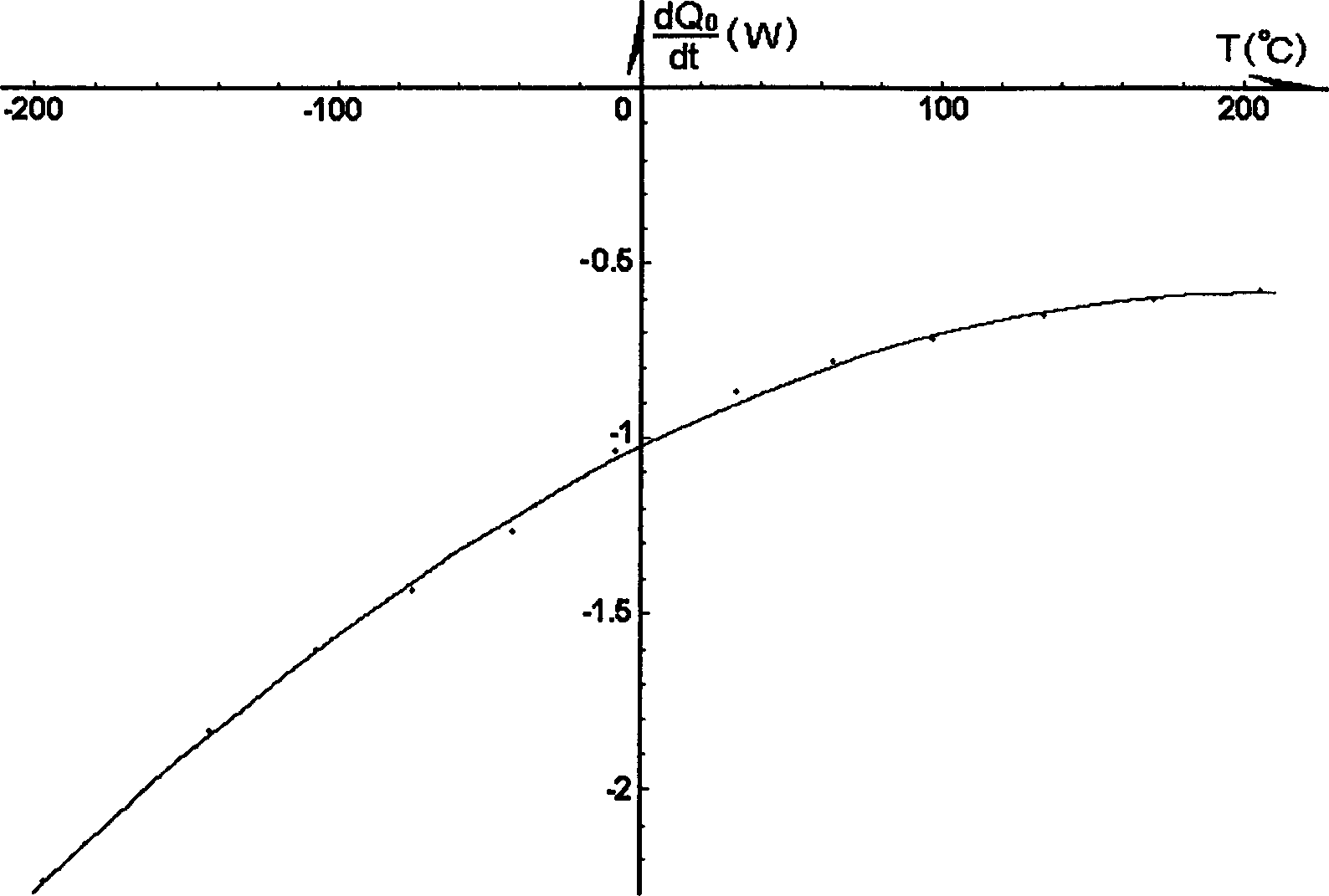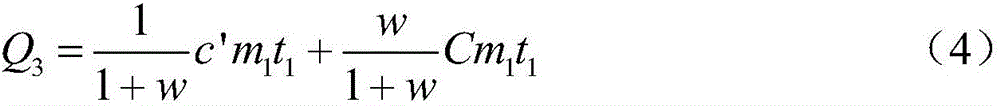Patents
Literature
196 results about "Calorimetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Calorimietry is the science or act of measuring changes in state variables of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due, for example, to chemical reactions, physical changes, or phase transitions under specified constraints. Calorimetry is performed with a calorimeter. The word calorimetry is derived from the Latin word calor, meaning heat and the Greek word μέτρον (metron), meaning measure. Scottish physician and scientist Joseph Black, who was the first to recognize the distinction between heat and temperature, is said to be the founder of the science of calorimetry.
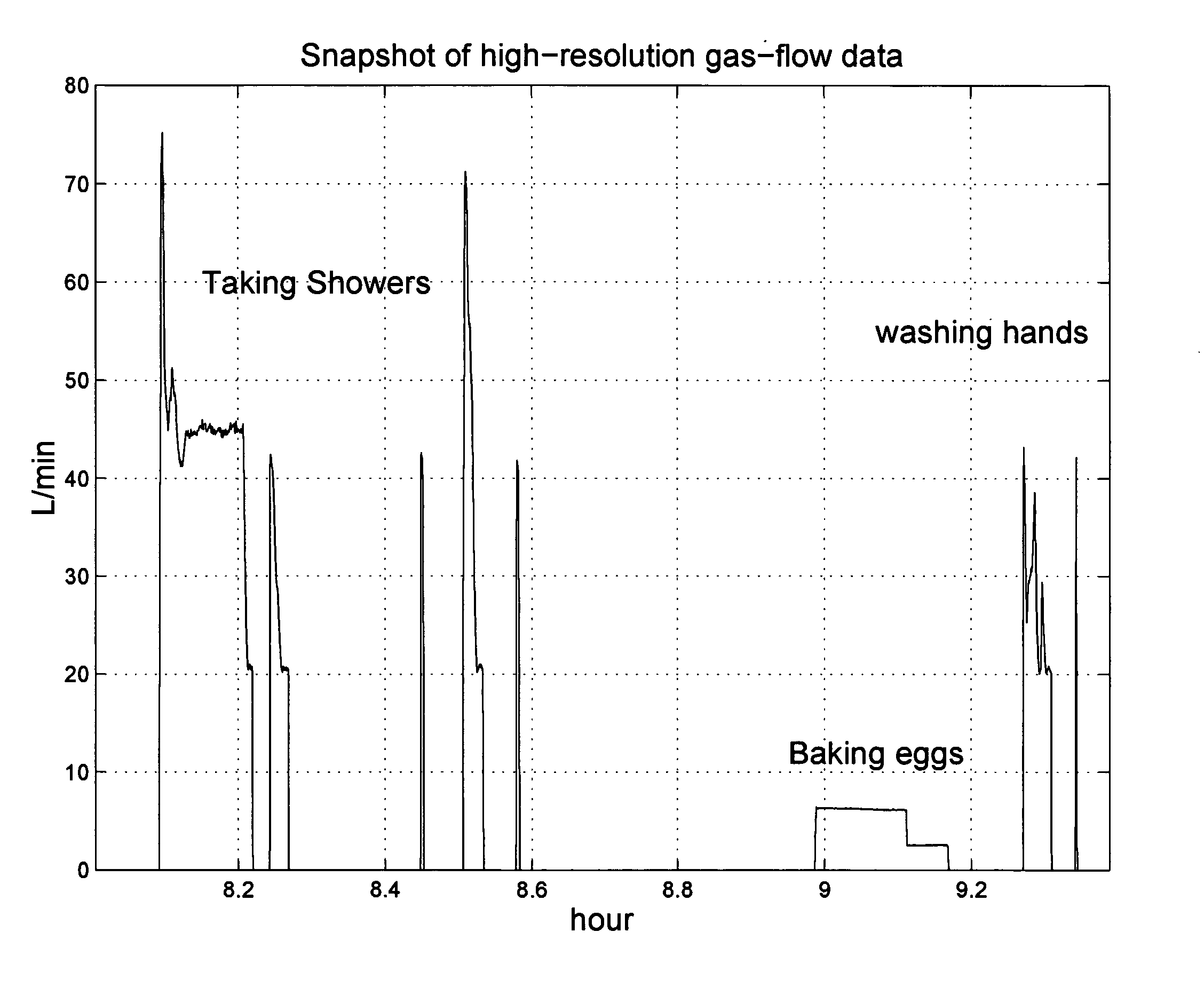
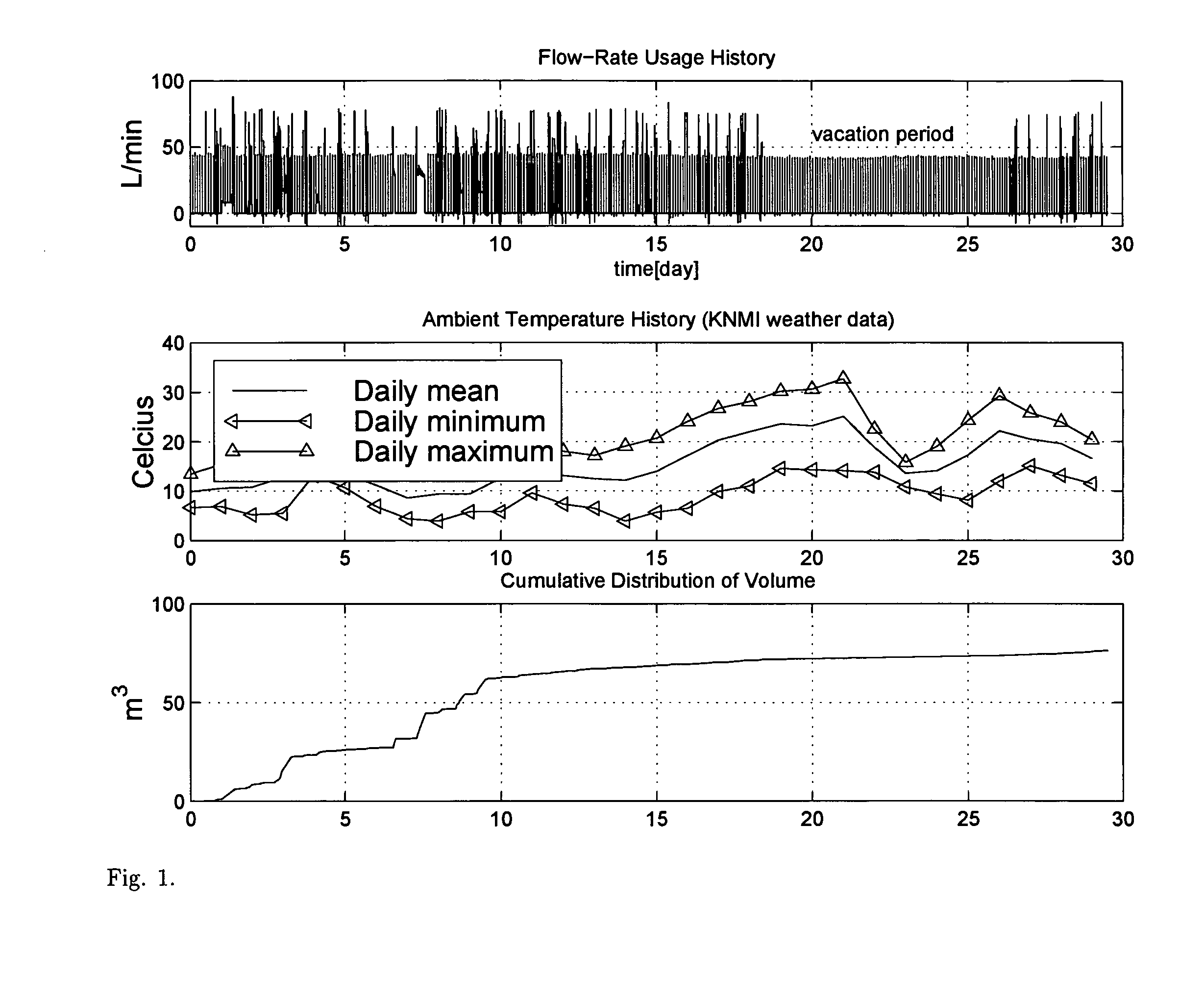
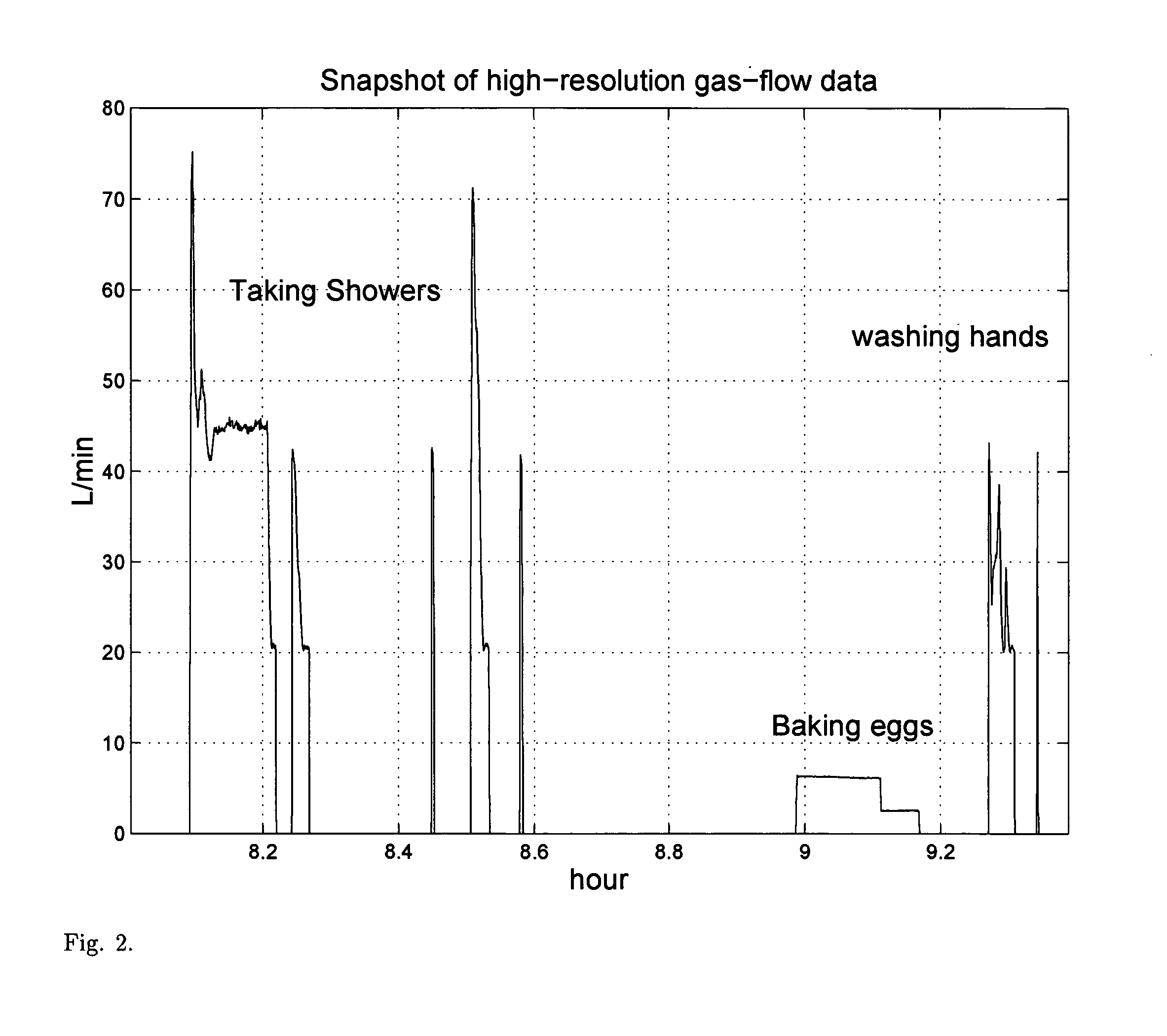
Gas-energy observatory
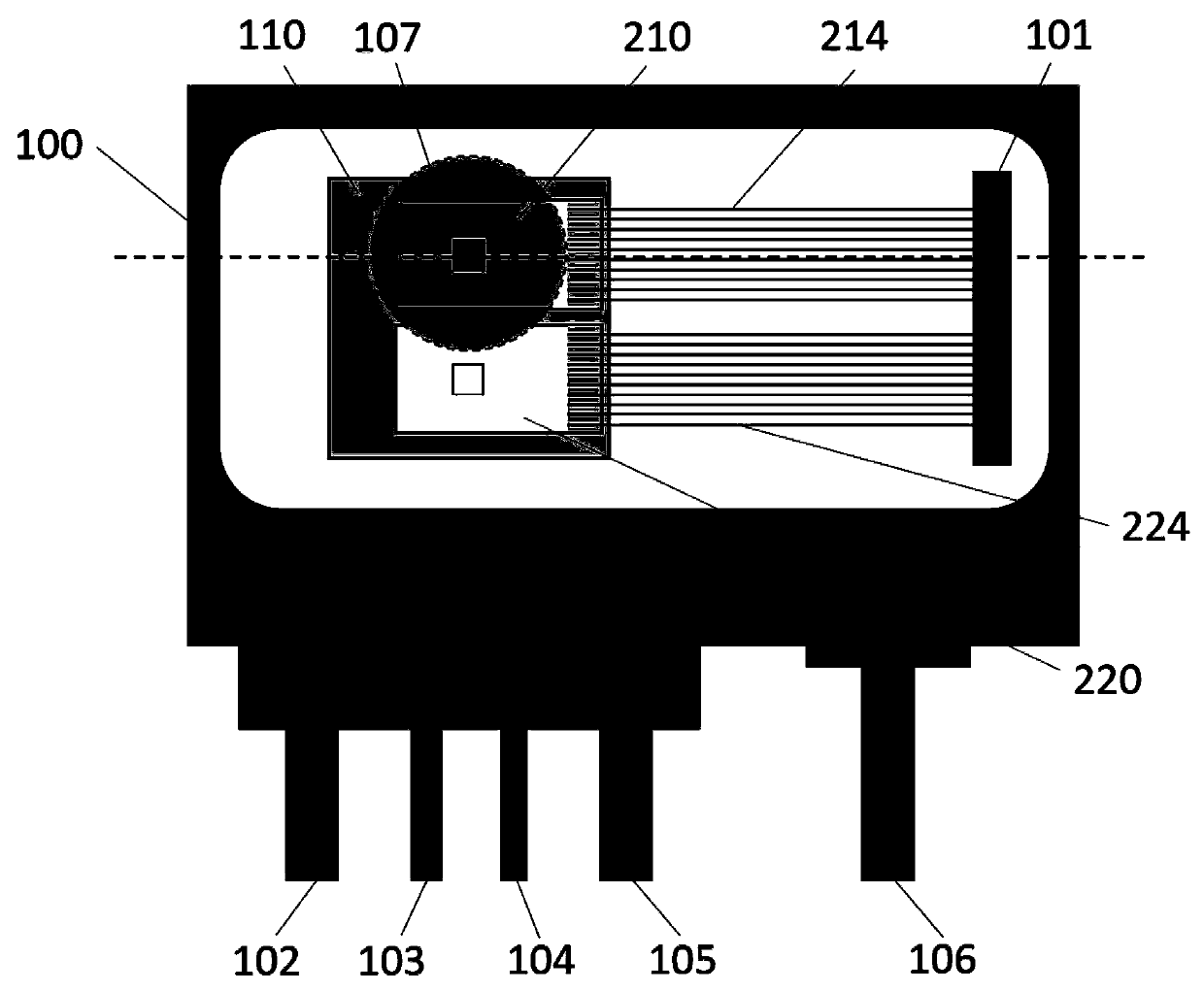
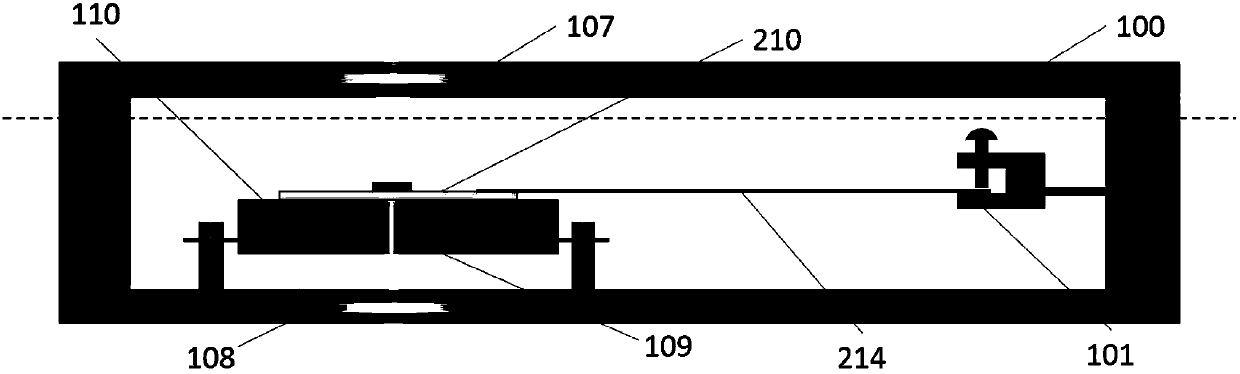
Heating is a significant factor in residential gas-energy usage. Saving energy on heating is receiving increasing attention with rising energy prices and the Kyoto Protocol on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Energy awareness and energy efficiency hereby become important qualifications for human behavior and residential building codes, and become a factor in the evolution of the global climate. Here, we describe a novel measurement and validation system for domestic gas-energy usage in combination with primary weather data. We disclose a gas-energy observatory which visualizes human behavior in gas-energy consumption associated with domestic facilities, and measures home energy efficiency by calorimetry. Weather-sensitivity analysis quantifies energy-usage as a function of small variations in room temperature and home energy efficiency. Weather-sensitivity data can be used to calculate changes in room-temperature settings or improvements in home insulation for a desired reduction in CO2-output. By public dissemination of its primary weather data, it creates in dual-use at no additional cost a novel in-situ climate observational systems with unprecedented wide-area coverage and spatial resolution.
Owner:VAN PUTTEN MAURITIUS H P M +3
Linear material for blood vessel stent and blood vessel stent utilizing same
InactiveUS7070615B1Good antithrombotic propertiesImprove physical functionStentsSurgeryCoronary arteriesBlood vessel spasm
Owner:KYOTO MEDICAL PLANNING
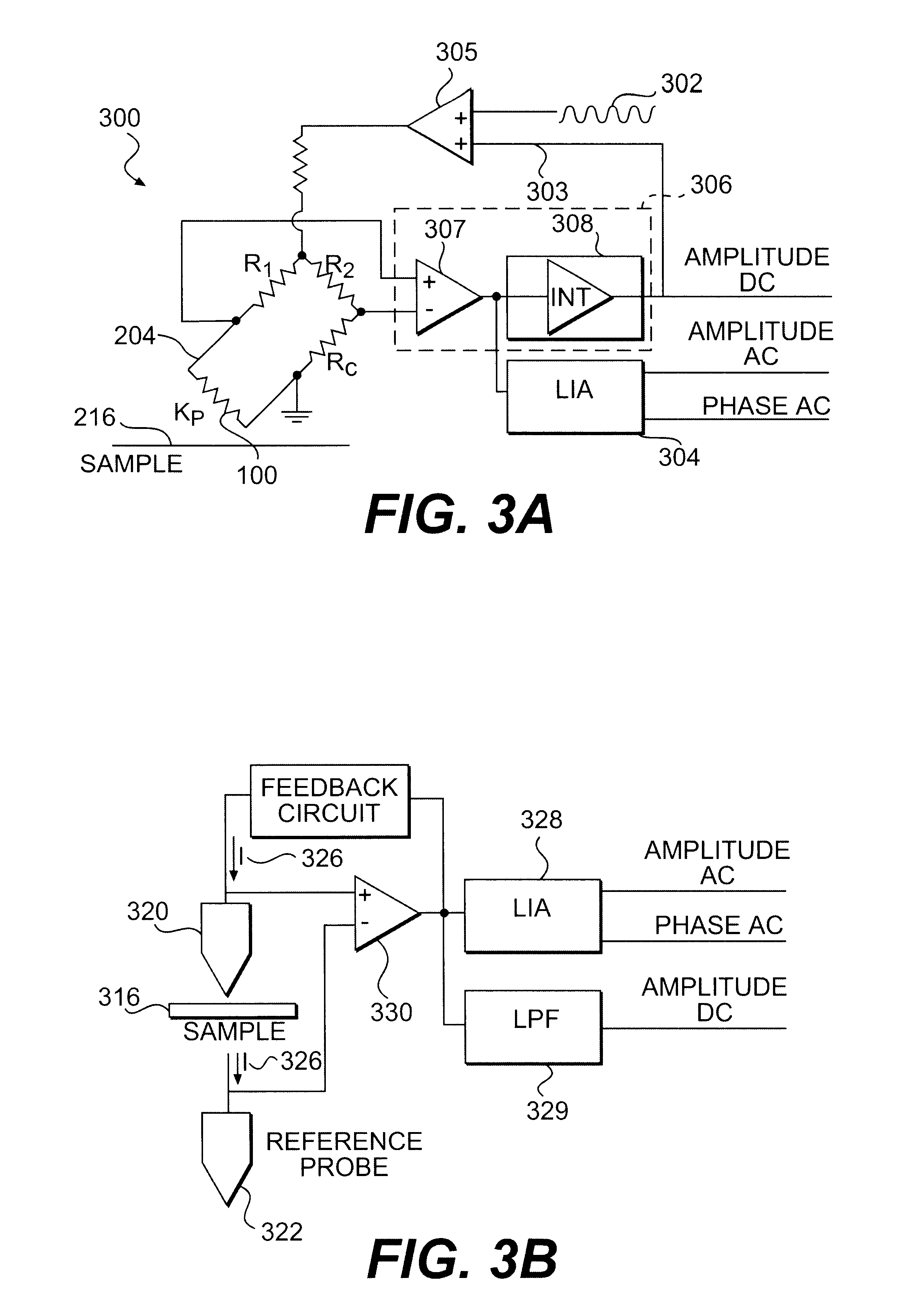
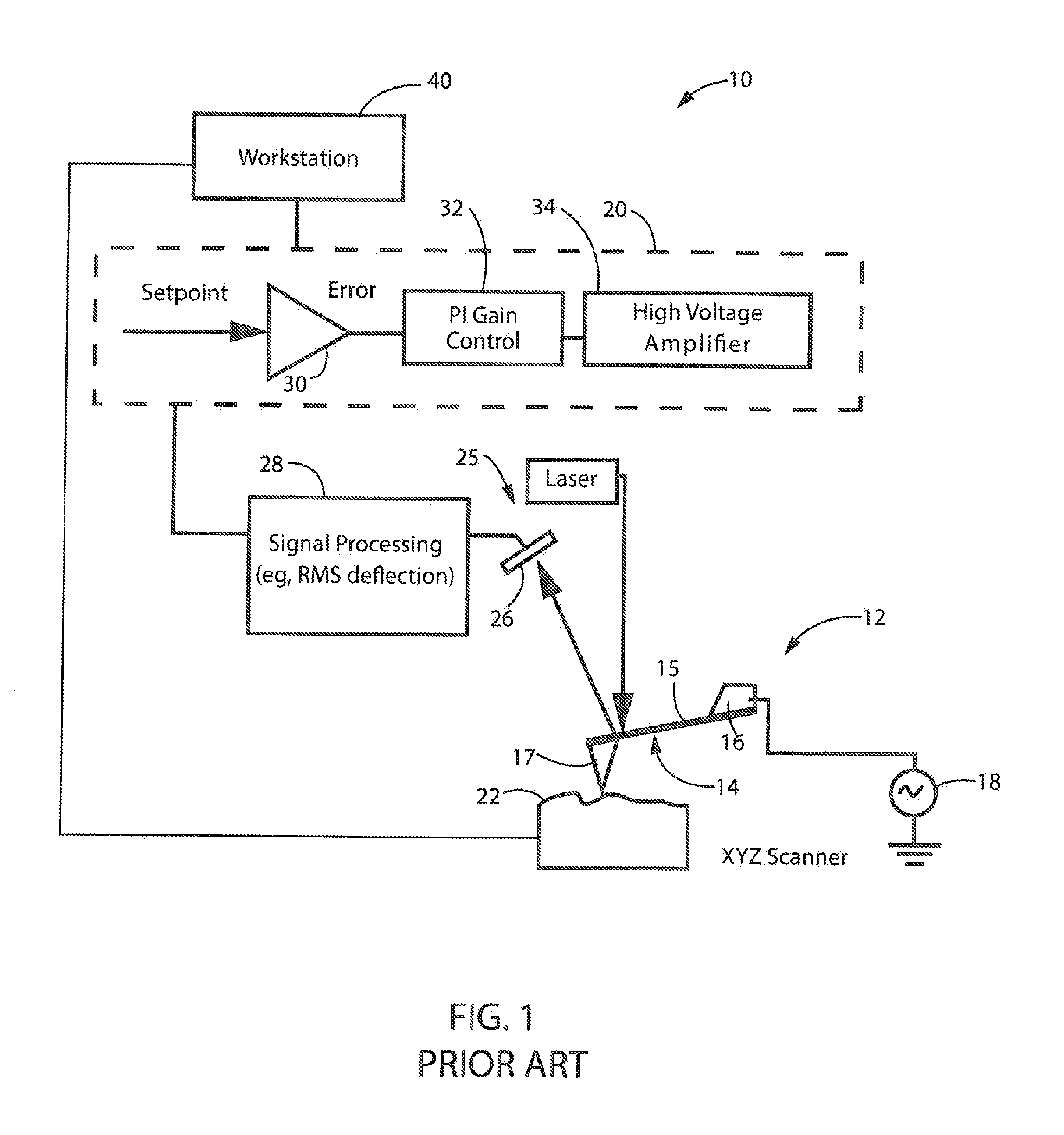
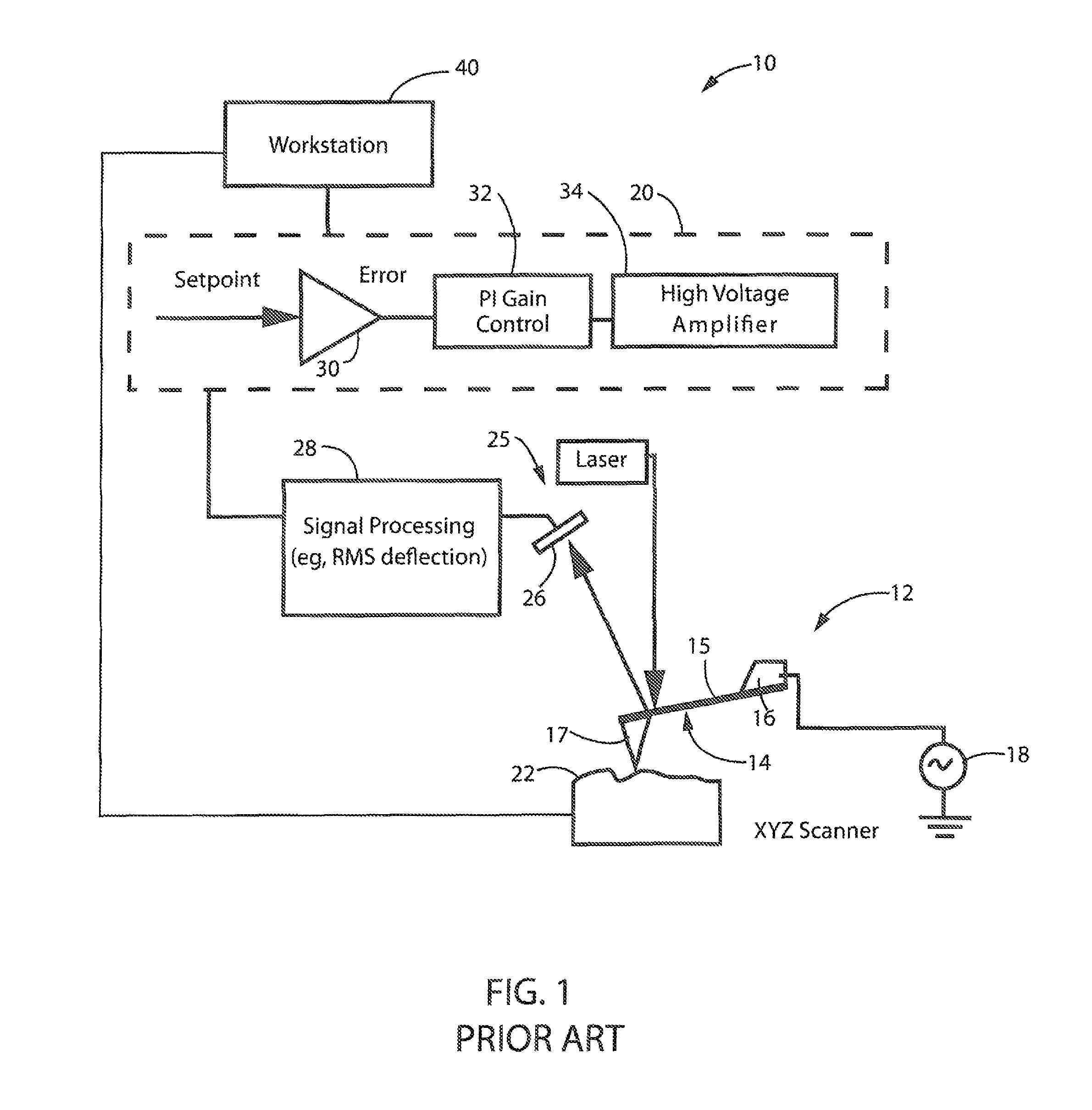
Method and apparatus for performing localized thermal analysis and sub-surface imaging by scanning thermal microscopy
InactiveUS6491425B1Reduce areaSuitable shapeNanotechMaterial heat developmentMaximum depthTemperature wave
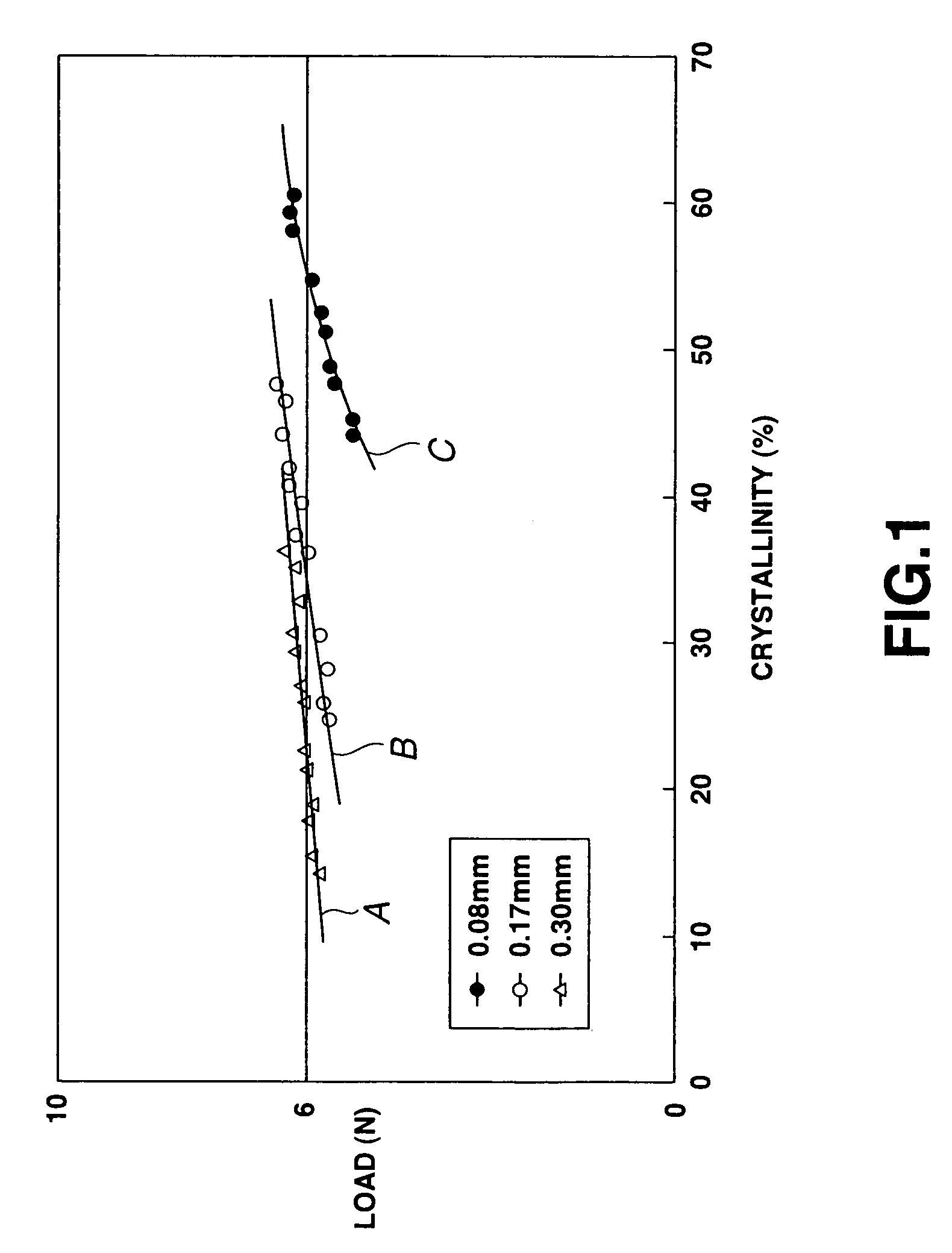
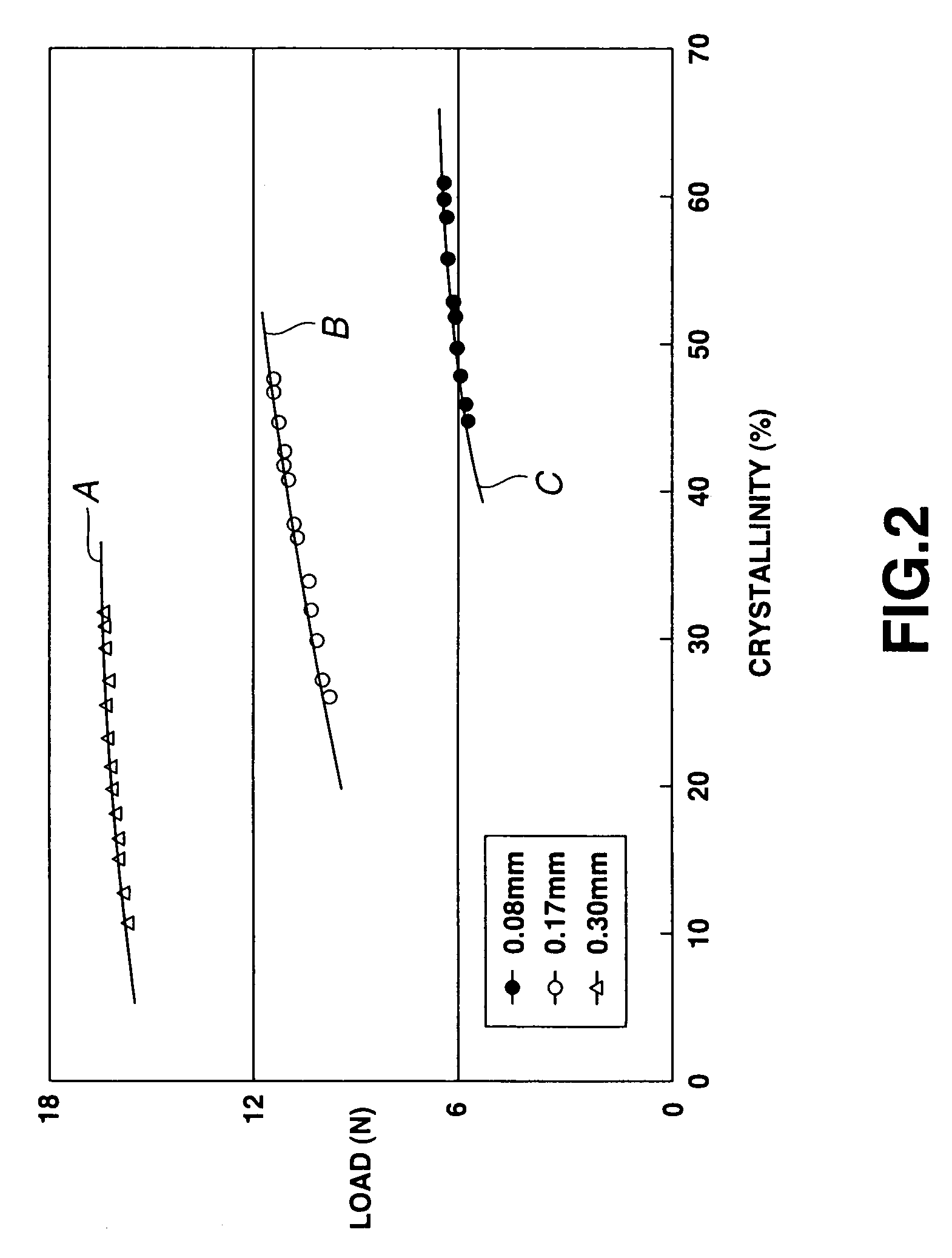
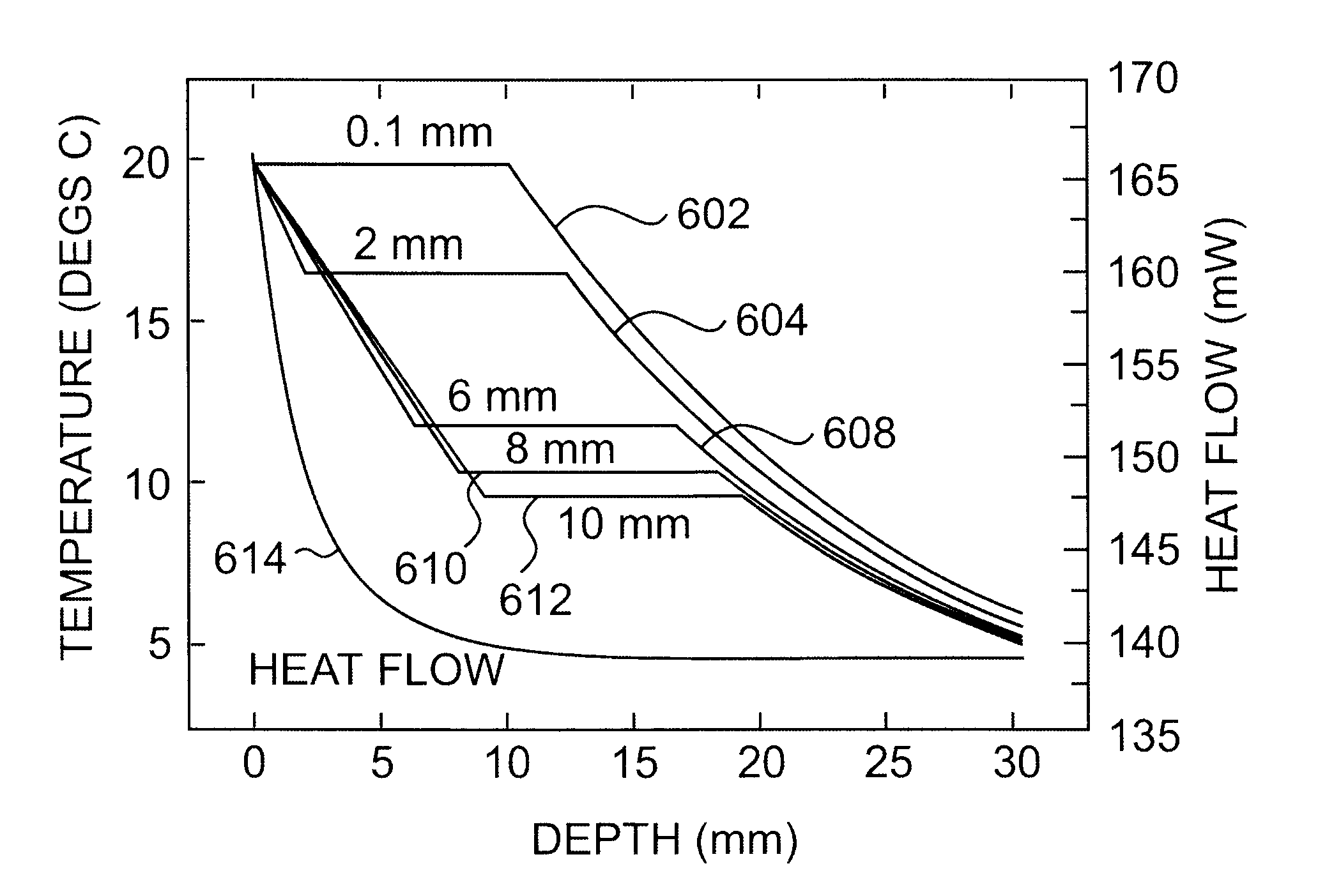
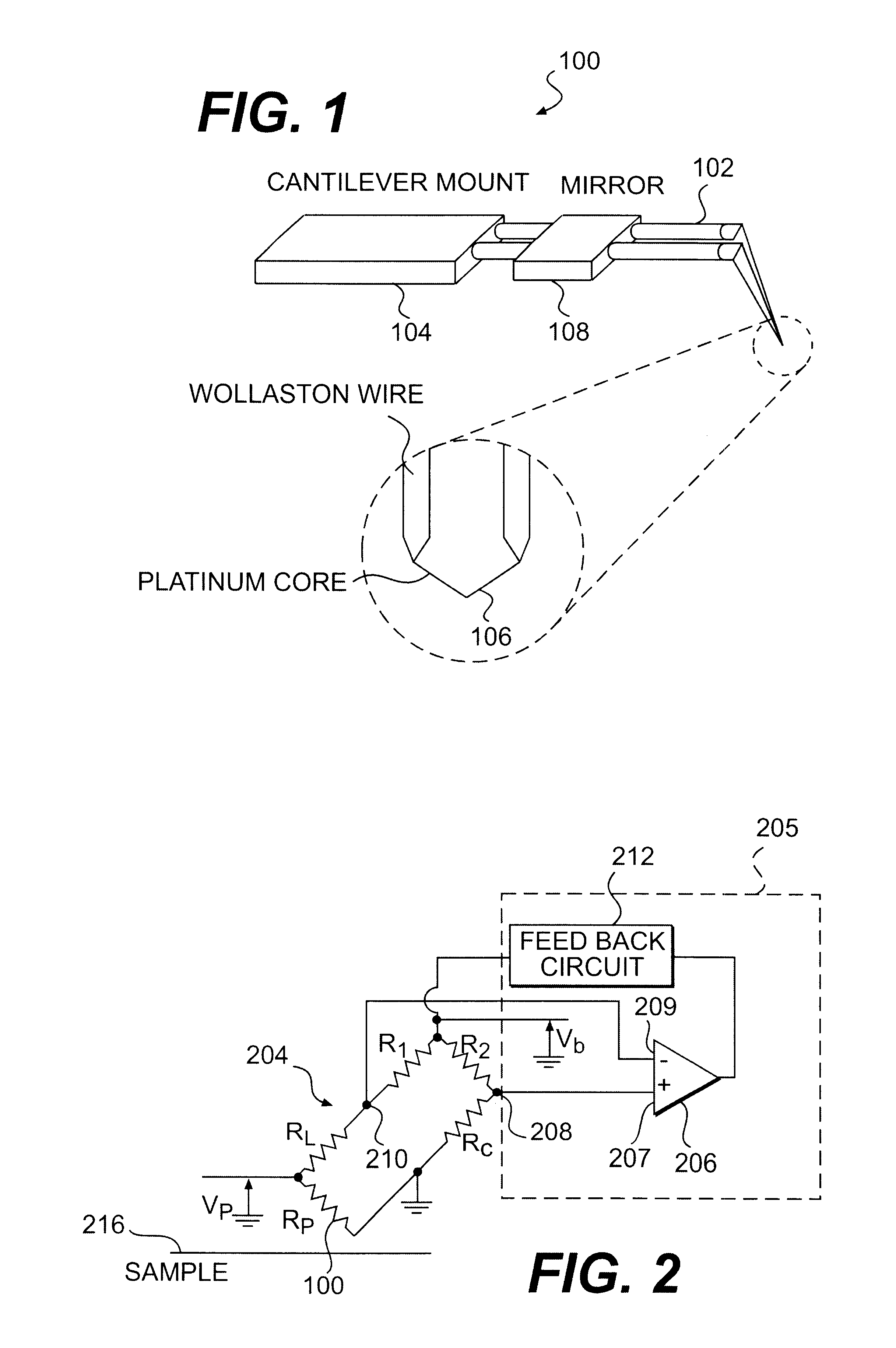
A platinum / Rhodium resistance thermal probe is used as an active device which acts both as a highly localized heat source and as a detector to perform localized differential calorimetry, by thermally inducing and detecting events such as glass transitions, meltings, recystallizations and thermal decomposition within volumes of material estimated at a few mum3. Furthermore, the probe is used to image variations in thermal conductivity and diffusivity, to perform depth profiling and sub-surface imaging. The maximum depth of the sample that is imaged is controlled by generating and detecting evanescent temperature waves in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for performing localized thermal analysis and sub-surface imaging by scanning thermal microscopy
InactiveUS6095679AReduce areaSuitable shapeNanotechMaterial thermal conductivityMaximum depthTemperature wave
A platinum / Rhodium resistance thermal probe is used as an active device which acts both as a highly localized heat source and as a detector to perform localized differential calorimetry, by thermally inducing and detecting events such as glass transitions, meltings, recystallizations and thermal decomposition within volumes of material estimated at a few mu m3. Furthermore, the probe is used to image variations in thermal conductivity and diffusivity, to perform depth profiling and sub-surface imaging. The maximum depth of the sample that is imaged is controlled by generating and detecting evanescent temperature waves in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Optical detectors for infrared, sub-millimeter and high energy radiation
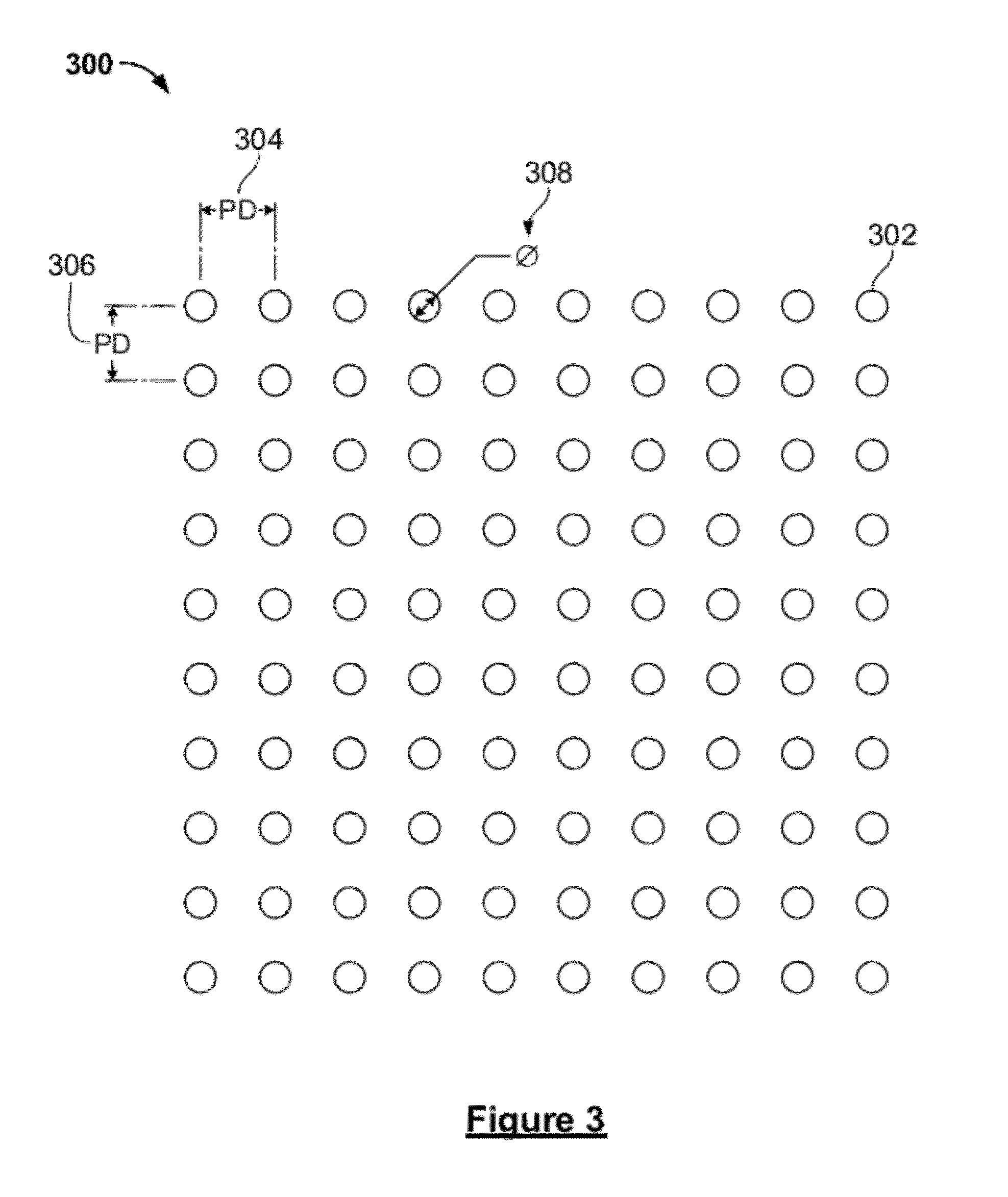
InactiveUS20060214113A1Reduce the total massSimpler and less-costlyRadiation pyrometryPhotometryHigh energyGram
Optical methods and devices for the thermal detection and imaging of infrared, sub-millimeter, millimeter and high energy radiation, wherein the thermal mass of the detector is minimized by the use of microscopic photoluminescent temperature probes having a weight mass which can be of the order of 10−11 grams or smaller. Used for detection of high energy radiation, including quantum calorimetry, said temperature probes allow non-contact measurements free of electrical sources of noise like Johnson noise or Joule heating.
Owner:KLEINERMAN MARCOS Y
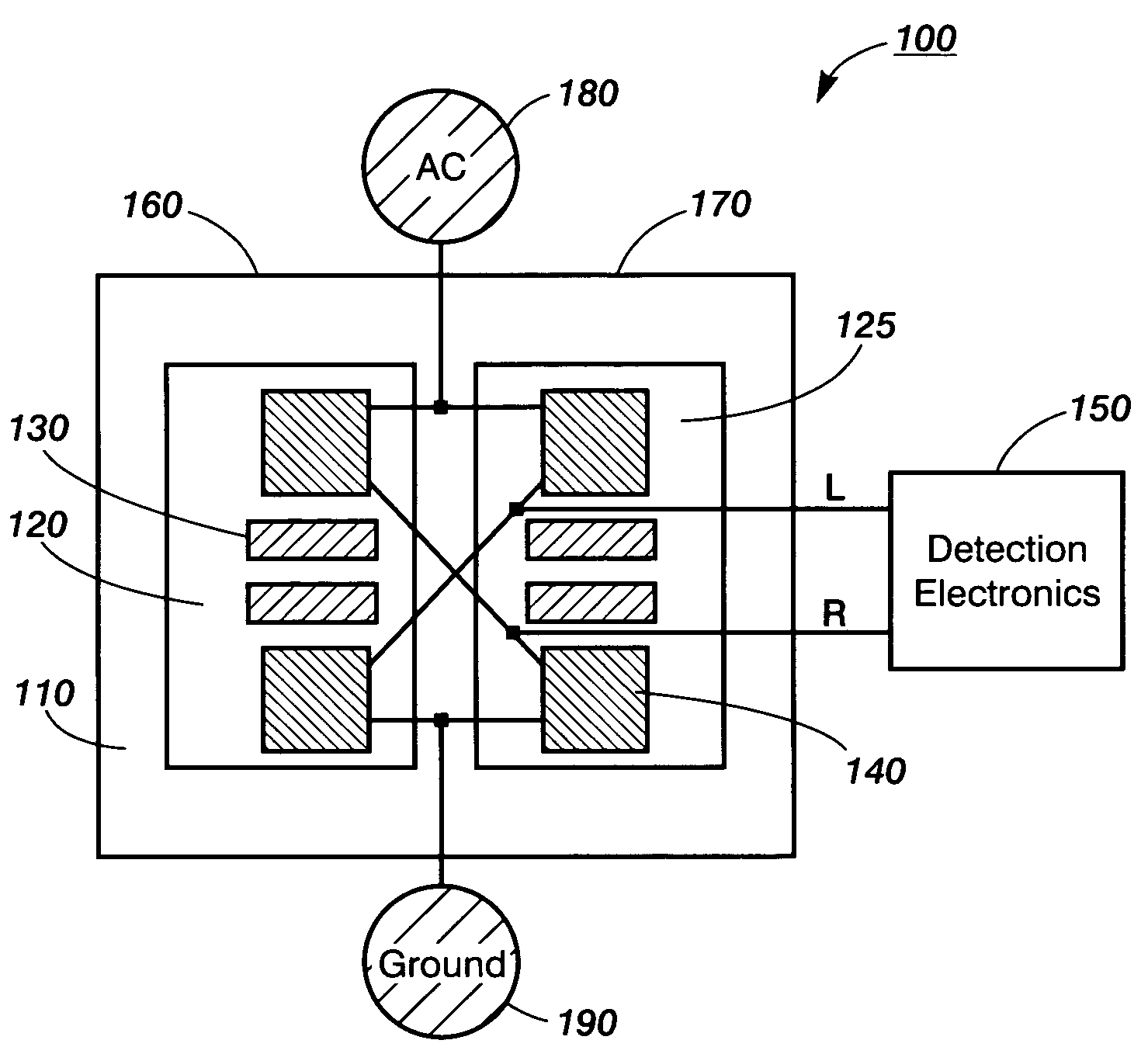
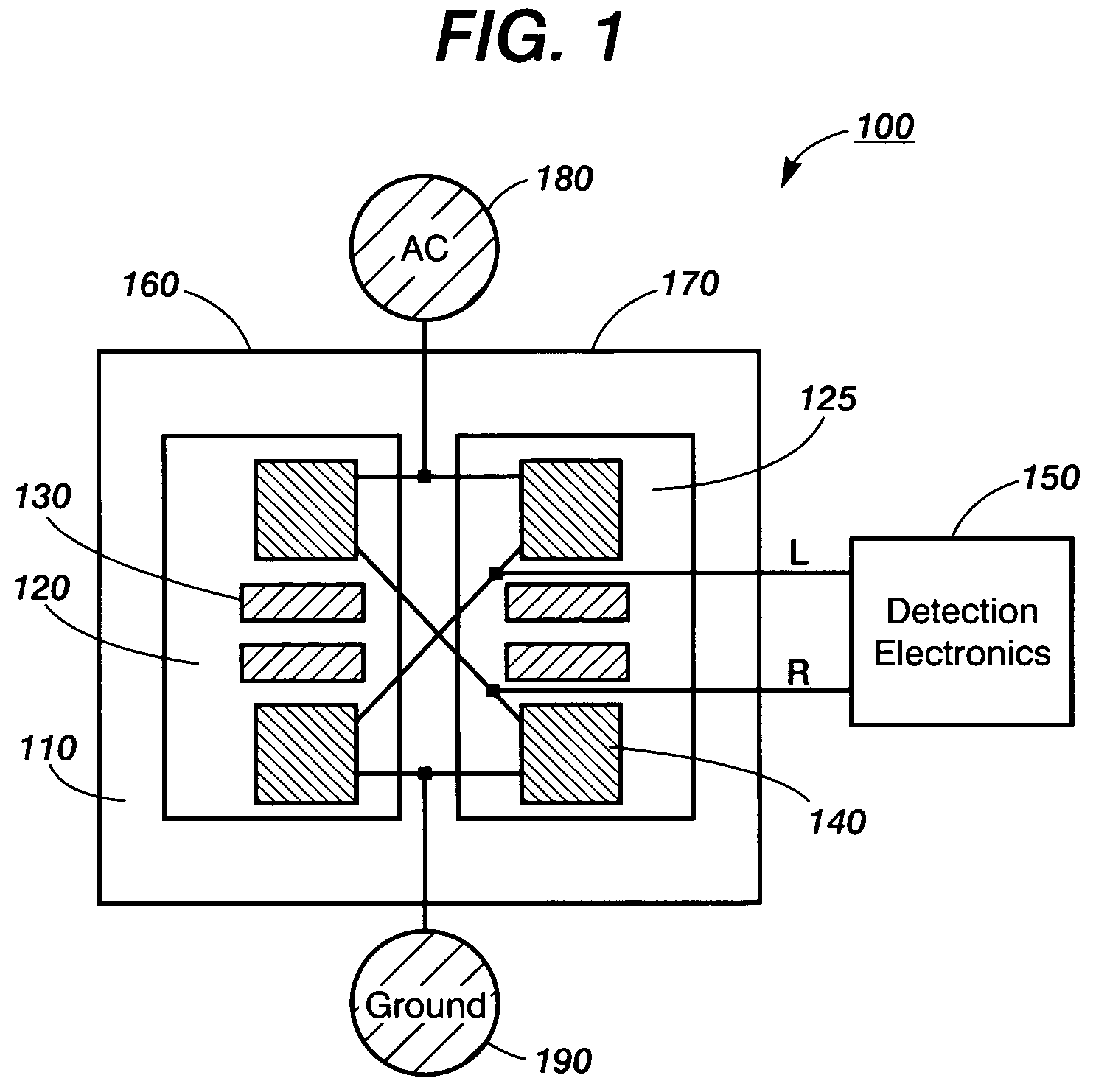
Resistive thermal sensing
Thermal sensors for calorimetry can include vanadium oxide, heavily p-doped amorphous silicon, or other materials with high temperature coefficients of resistivity. Such thermal sensors can have low noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD). For example, a thermal sensor with NETD no greater than 100 μK over a bandwidth range of approximately 3 Hz or more can include a thermistor including vanadium oxide sputtered at room temperature under conditions that yield primarily V2O5; more specifically, the NETD can be no greater than 35 μK, or even 10 μK over a bandwidth range of approximately 3 Hz or more. If a low noise thermal sensor has NETD no greater than 50 μK over such a bandwidth range, a low noise output circuitry connected to its thermistor can provide an electrical output signal that includes information about input thermal signal peaks with amplitude of approximately 100 μK.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
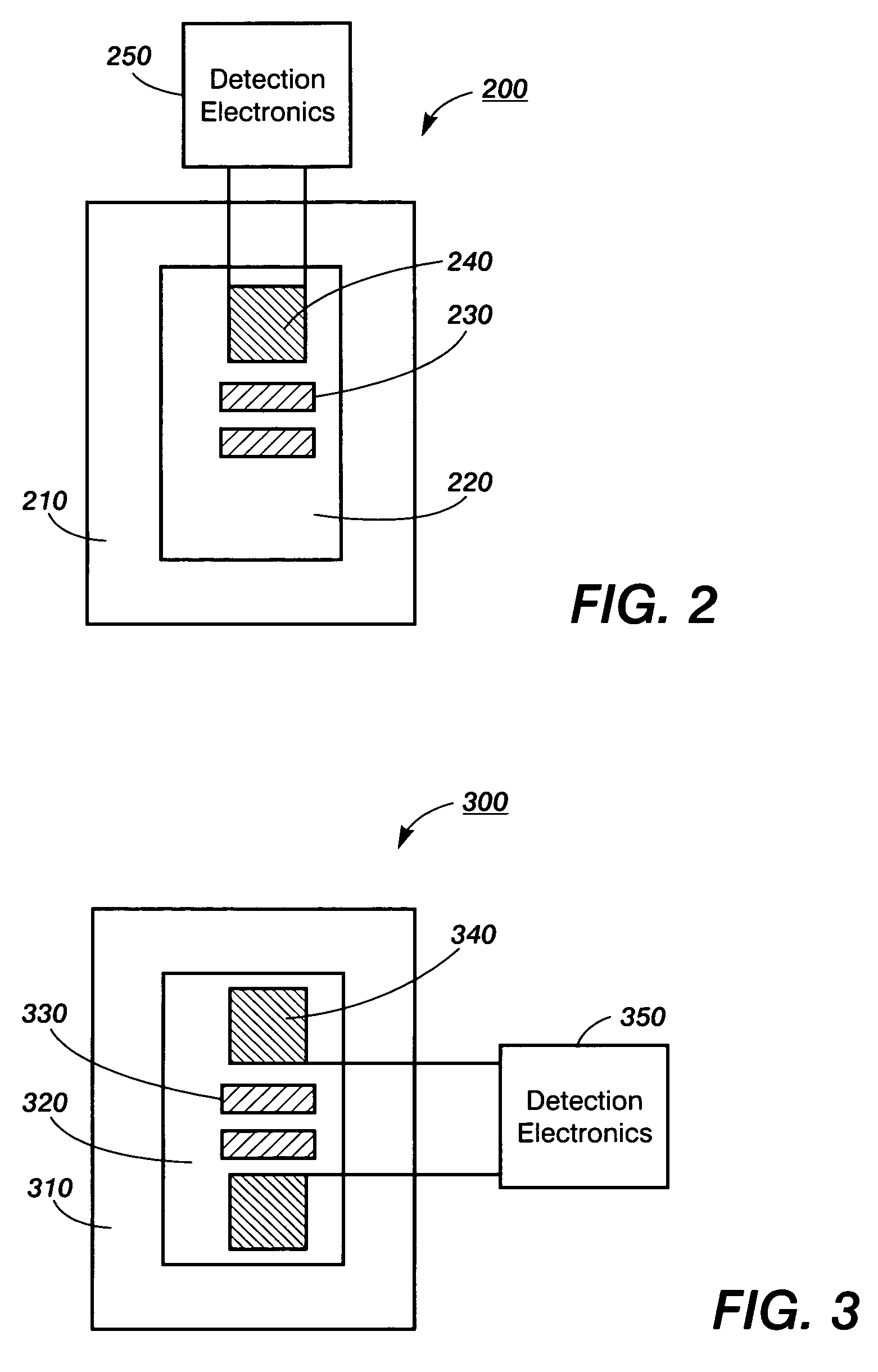
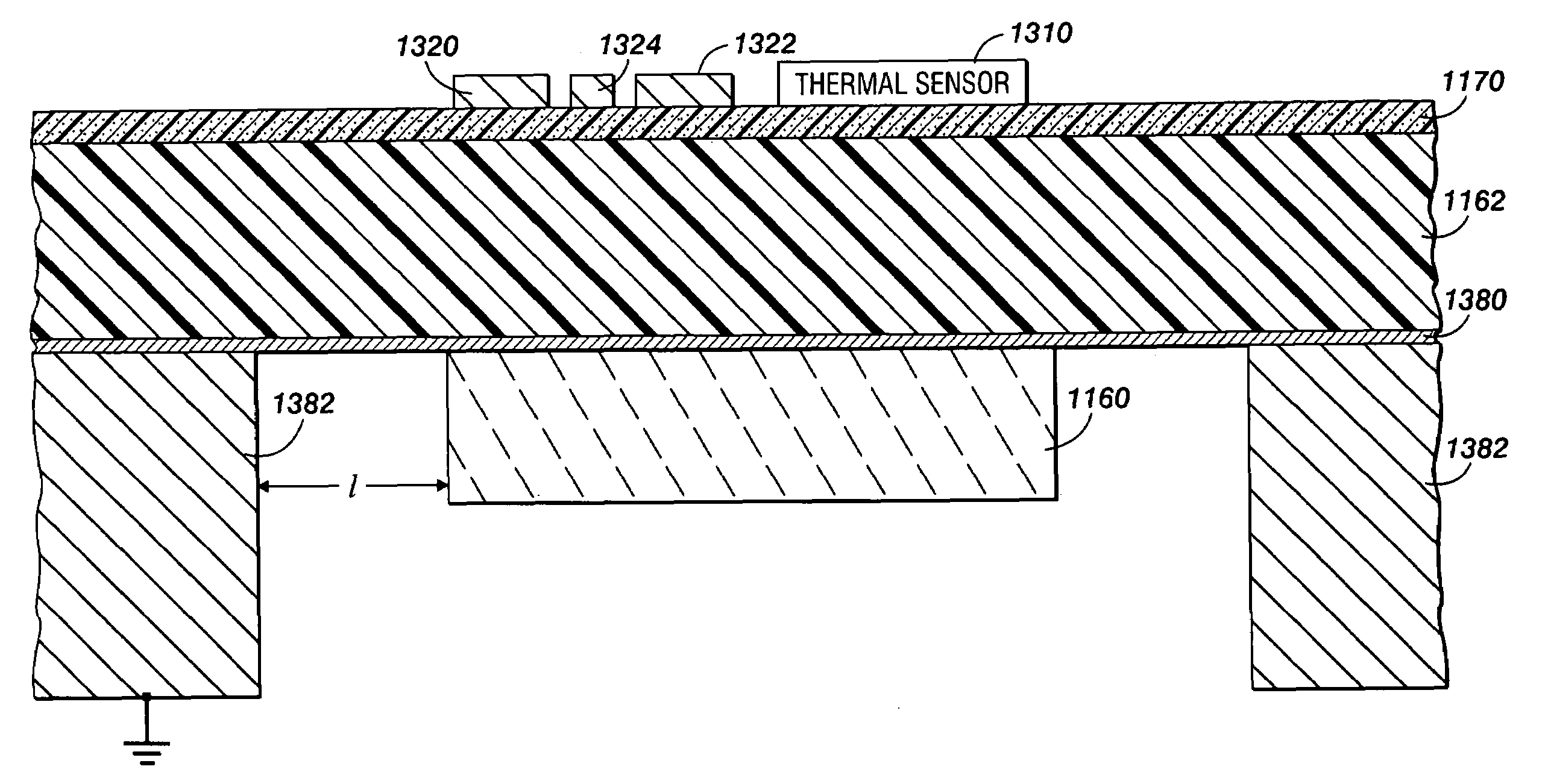
Thermal sensing
InactiveUS7473030B2Thermometer detailsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
In thermal sensing devices, such as for calorimetry, a support layer or central layer can have a thermometer element or other thermal sensor on one side and a thermally conductive structure or component on the other. The thermally conductive structure can conduct temperature or other thermal input signals laterally across the support layer or central layer. The temperature or signals can then be provided to the thermometer element, such as by thermal contact through the support layer. An electrically conducting, thermally isolating anti-coupling layer, such as of gold or chromium, can reduce capacitive coupling between the thermally conductive structure and the thermometer element or other thermal sensor.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Toner, development agent, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
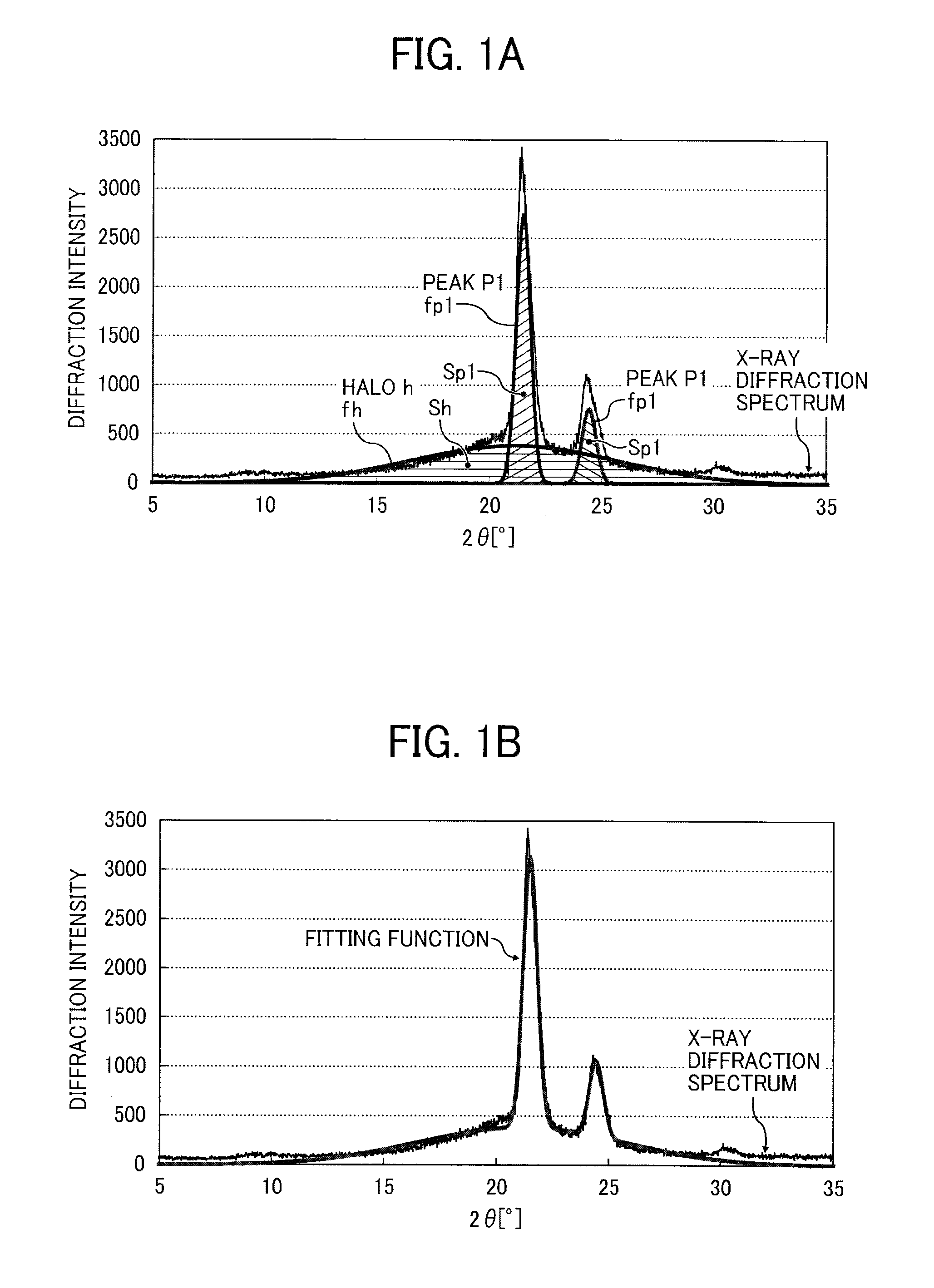
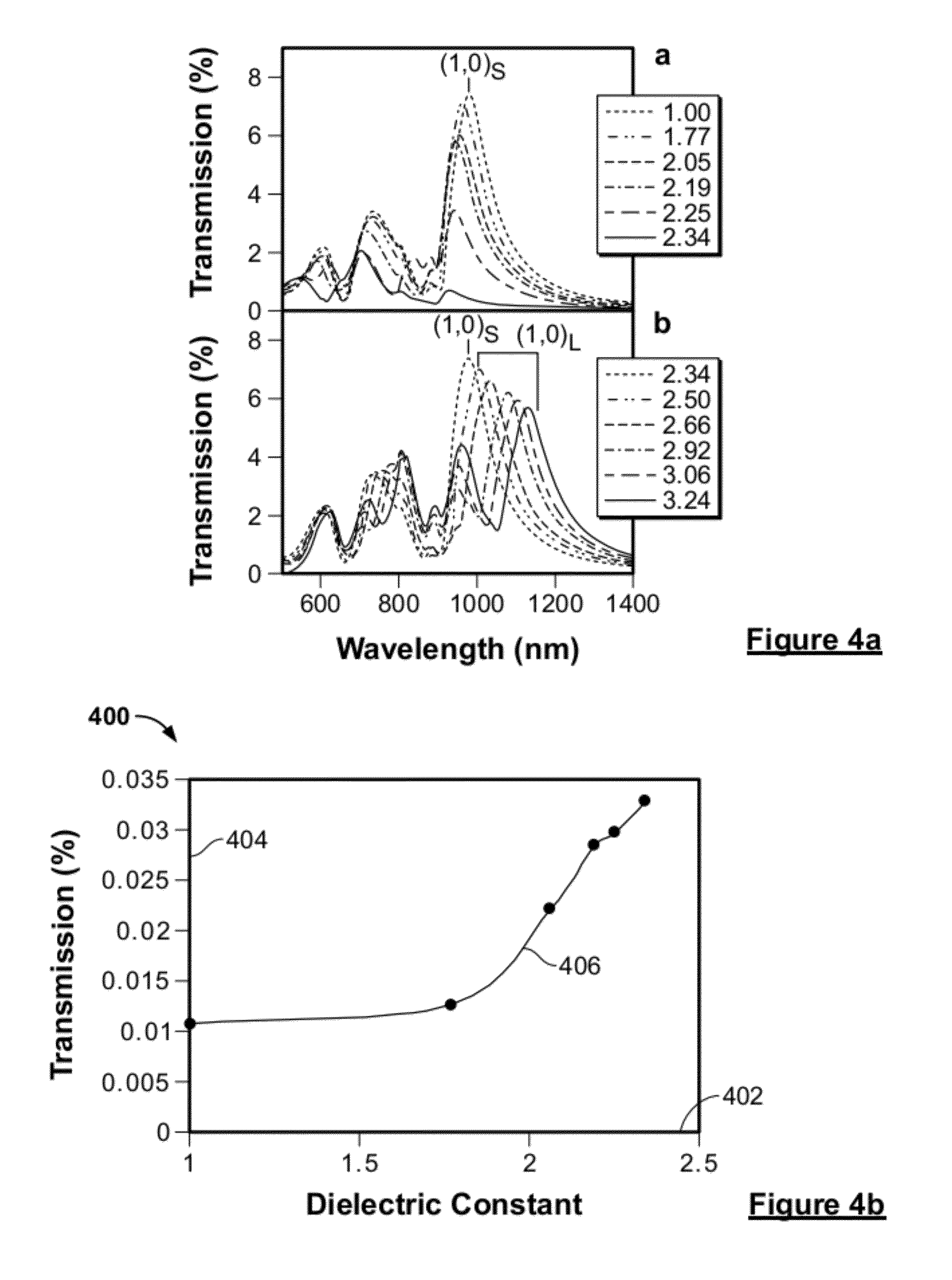
Toner contains a binder resin containing a crystalline resin having a urethane and / or urea bonding; and a colorant, wherein in a diffraction spectrum of the toner as measured by an X-ray diffraction instrument, a ratio {C / (C+A)} of an integral intensity C of the spectrum derived from the crystalline structure to an integral intensity A of the spectrum derived from the non-crystalline structure is 0.12 or greater, wherein the toner satisfies the following relation 1: T1−T2≦30° C. (Relation 1), where T1 represents the maximum endothermic peak in the first temperature rising from 0° C. to 100° C. at the temperature rising rate of 10° C. / min and T2 represents the maximum exothermic peak in the first temperature falling from 100° C. to 0° C. at the temperature falling rate of 10° C. / min as T1 and T2 are measured by diffraction scanning calorimetry (DSC).
Owner:RICOH KK
Thermal sensing
InactiveUS20050254552A1Thermometer detailsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsCapacitive couplingCalorimetry
In thermal sensing devices, such as for calorimetry, a support layer or central layer can have a thermometer element or other thermal sensor on one side and a thermally conductive structure or component on the other. The thermally conductive structure can conduct temperature or other thermal input signals laterally across the support layer or central layer. The temperature or signals can then be provided to the thermometer element, such as by thermal contact through the support layer. An electrically conducting, thermally isolating anti-coupling layer, such as of gold or chromium, can reduce capacitive coupling between the thermally conductive structure and the thermometer element or other thermal sensor.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
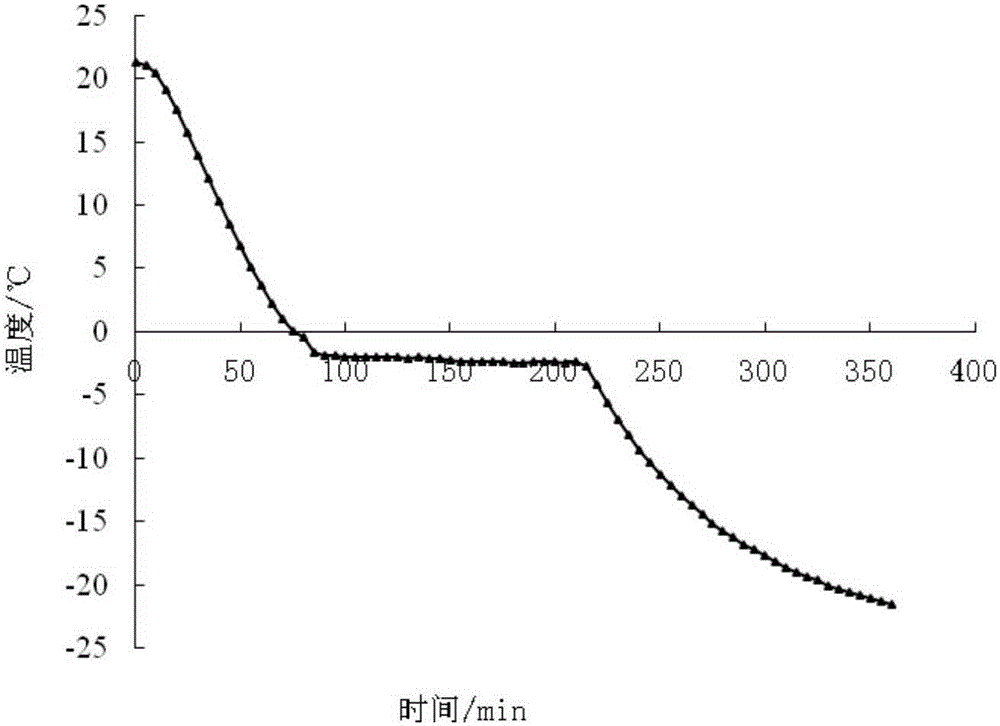
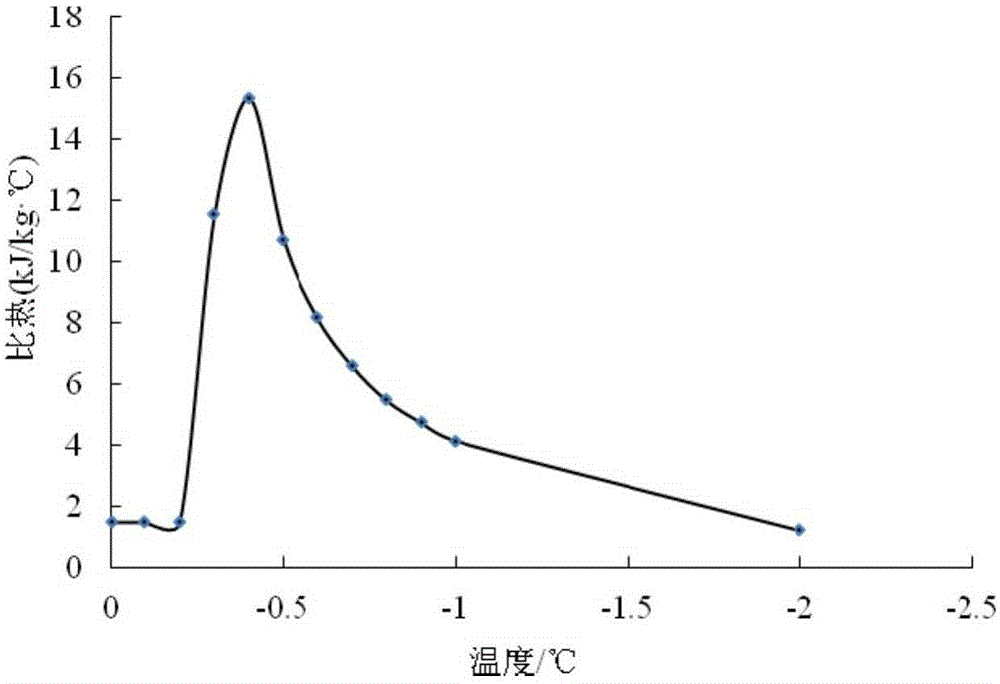
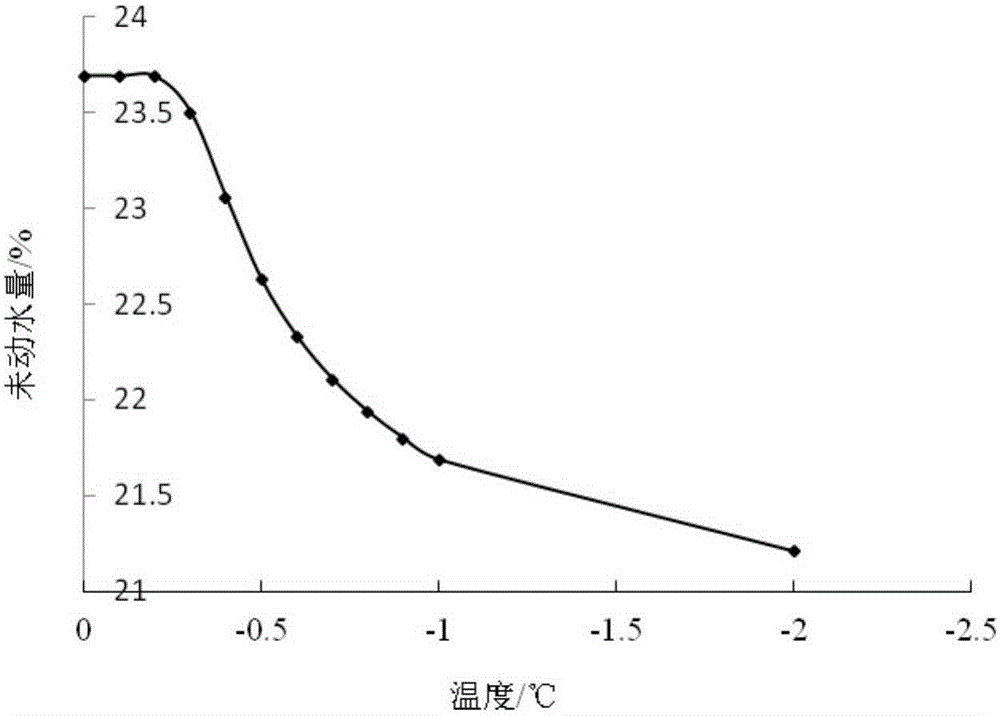
Method for determining content of unfrozen water in soil freezing process by using specific heat calculation
InactiveCN105241920ACalculations are clearThe theoretical basis is simple and sufficientMaterial heat developmentMaterial moisture contentPhase changePhysical property
The invention provides a method for determining the content of unfrozen water in a soil freezing process by using specific heat calculation. The method comprises the following steps: adopting the total heat of one temperature measuring point as the sum of soil particle heat, pore water heat, pore ice heat and heat released by phase change of water in soil; determining the physical properties of a soil sample by using indoor geotechnical test, and determining the phase change temperature range of the soil sample through freezing test; determining the specific heat of frozen heat at the corresponding temperature measuring point by using a calorimeter through mixed calorimetry; and expressing the four heats and the total heat by using the specific heat, deriving the unfrozen water content-specific heat function relation, and calculating to obtain the content of the unfrozen water at every temperature measuring point. The method for measuring the content of the unfrozen water has the advantages of simple operation and small test result error. General labs and construction units can use a simple calorimeter to measure and calculate the content of the unfrozen water.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
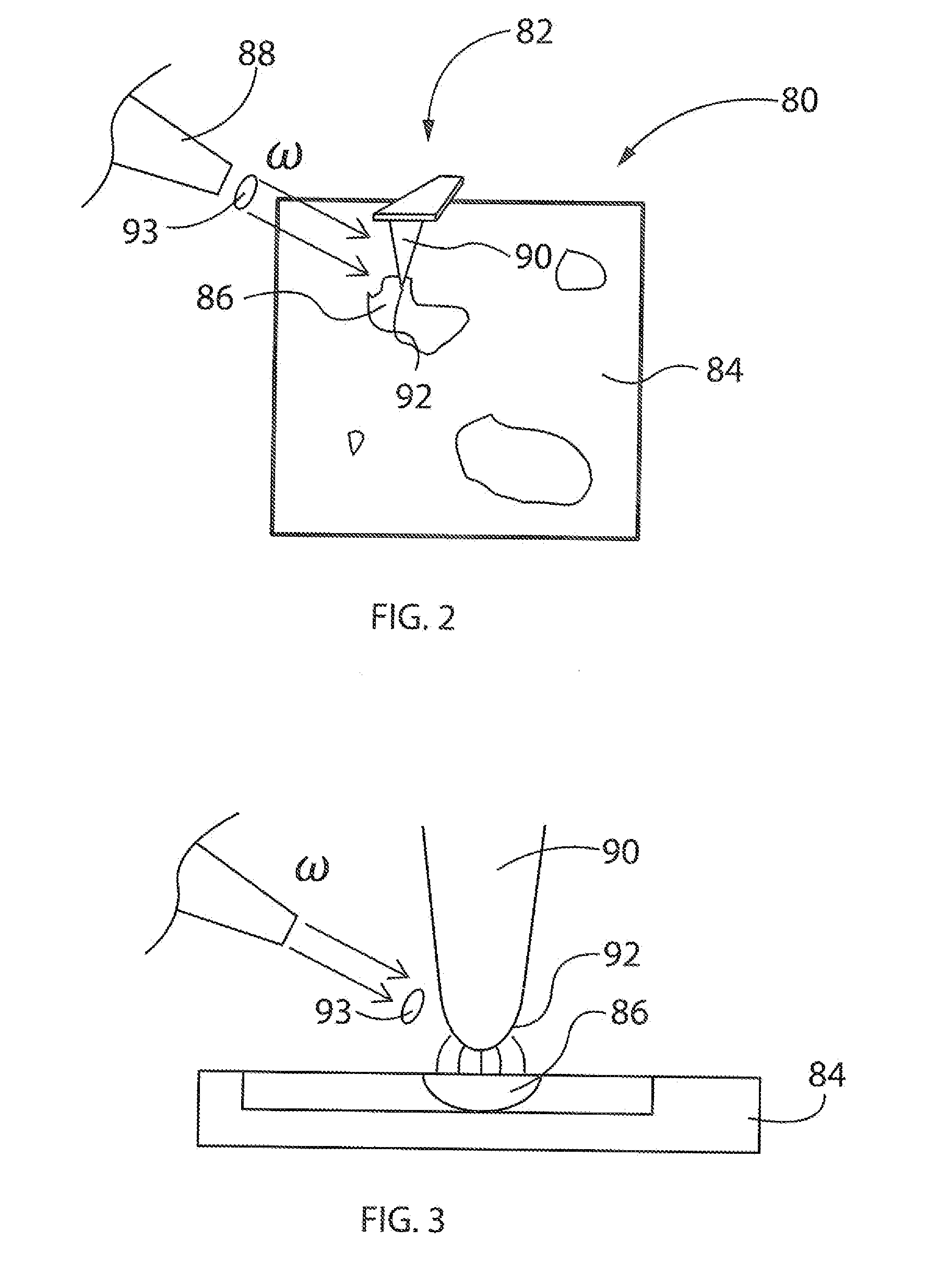
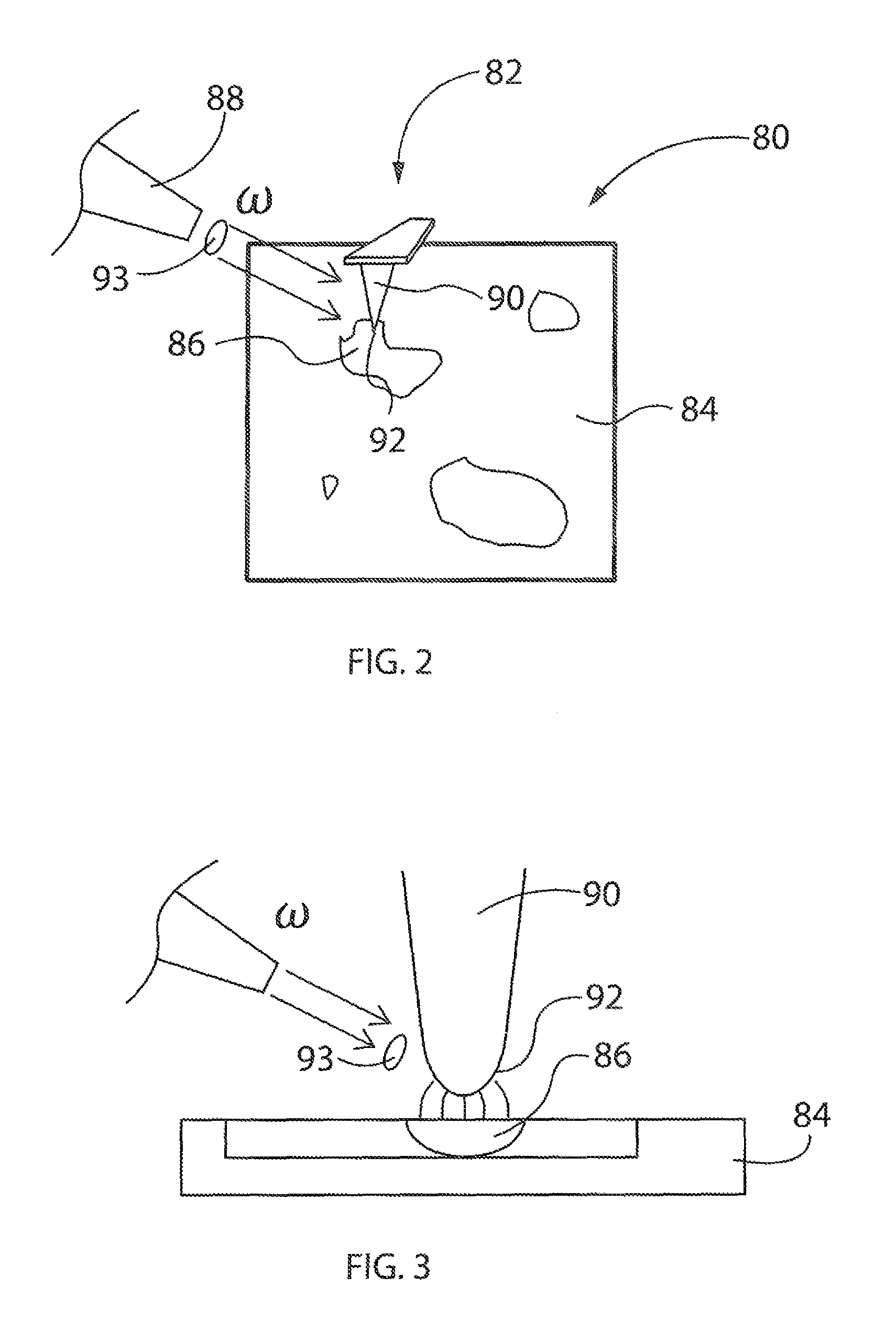
Peakforce Photothermal-Based Detection of IR Nanoabsorption
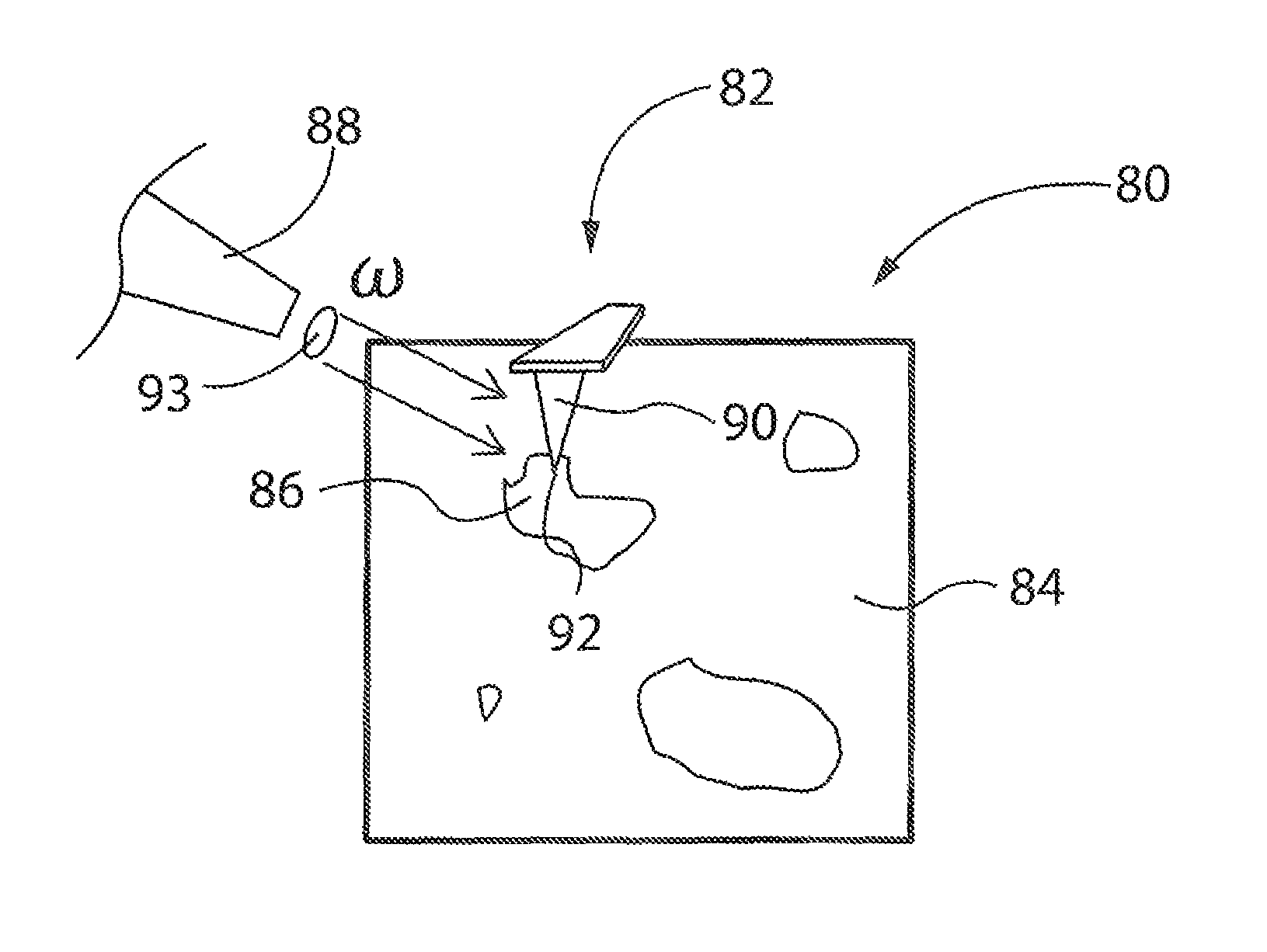
InactiveUS20140289912A1High resolutionSample preparation is minimizedMaterial analysis by optical meansNanotechnologyRegion of interestCalorimetry
An apparatus and method of performing photothermal chemical nanoidentification of a sample includes positioning a tip of a probe at a region of interest of the sample, with the tip-sample separation being less than about 10 nm. Then, IR electromagnetic energy having a selected frequency, ω, is directed towards the tip. Using PFT mode AFM operation, absorption of the energy at the region of interest is identified. Calorimetry may also be performed with the photothermal PFT system.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
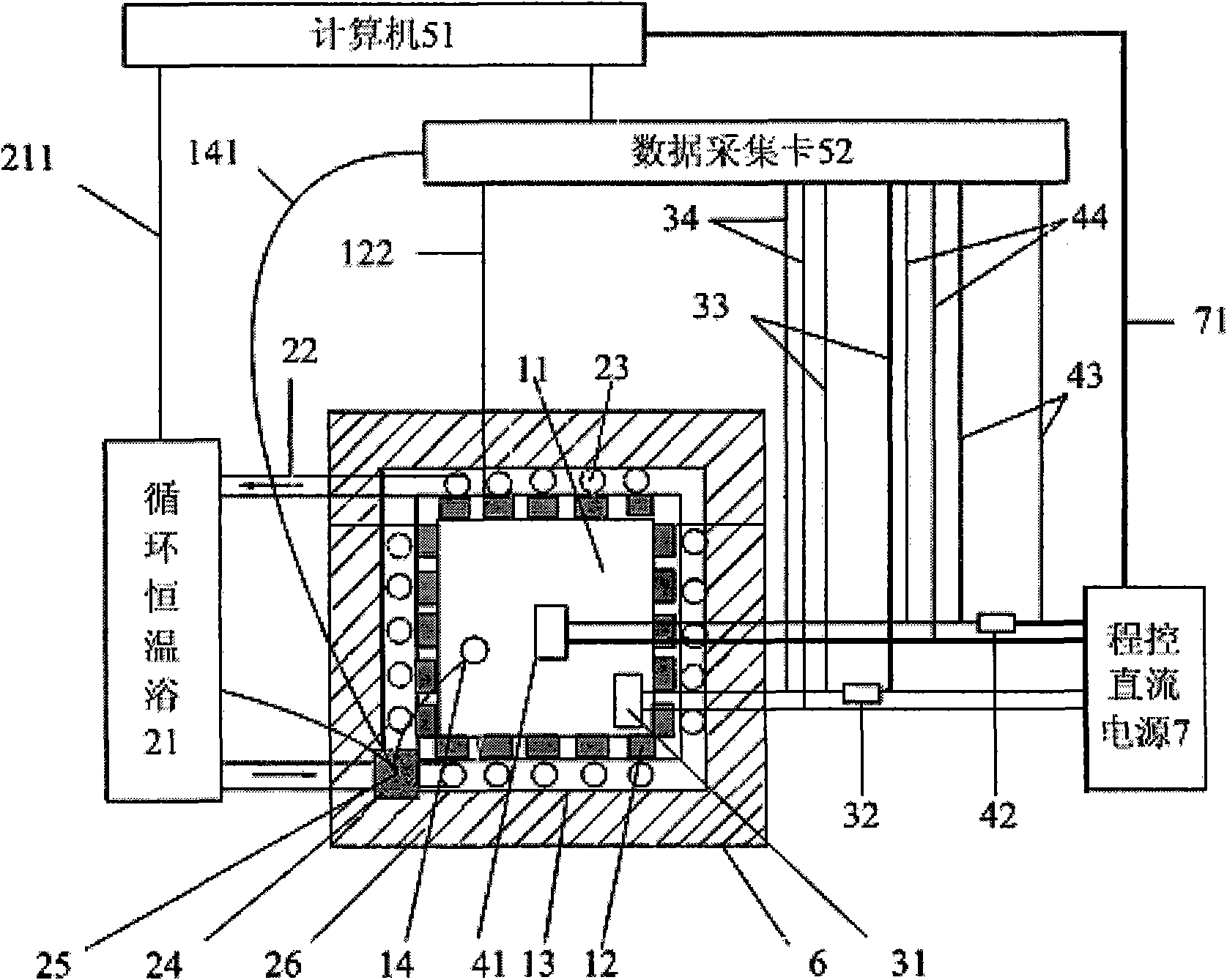
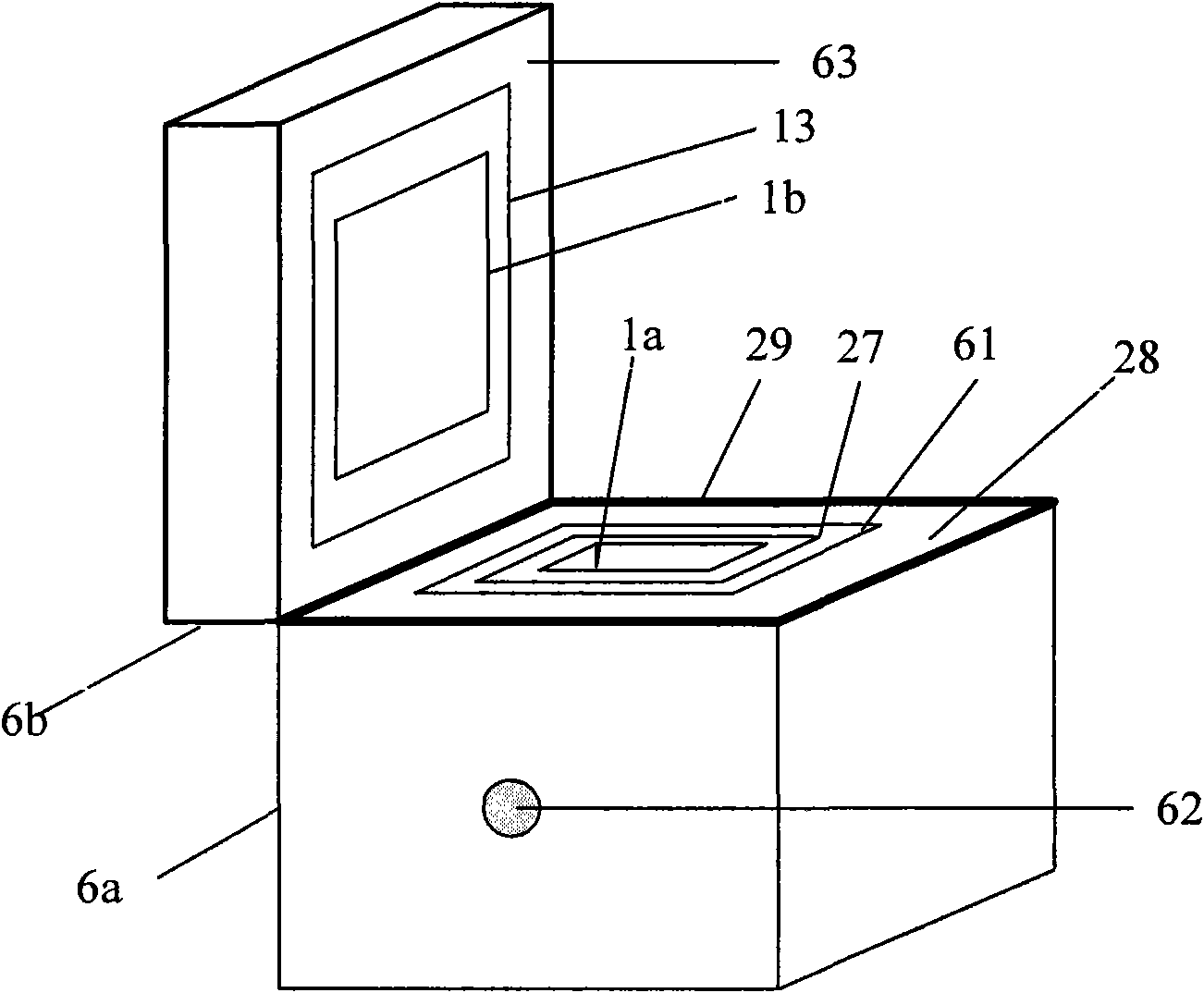
Thermal power measurement device
ActiveCN101576520AHigh sensitivityReduced position dependenceMaterial heat developmentElectrical testingWater bathsMeasurement device
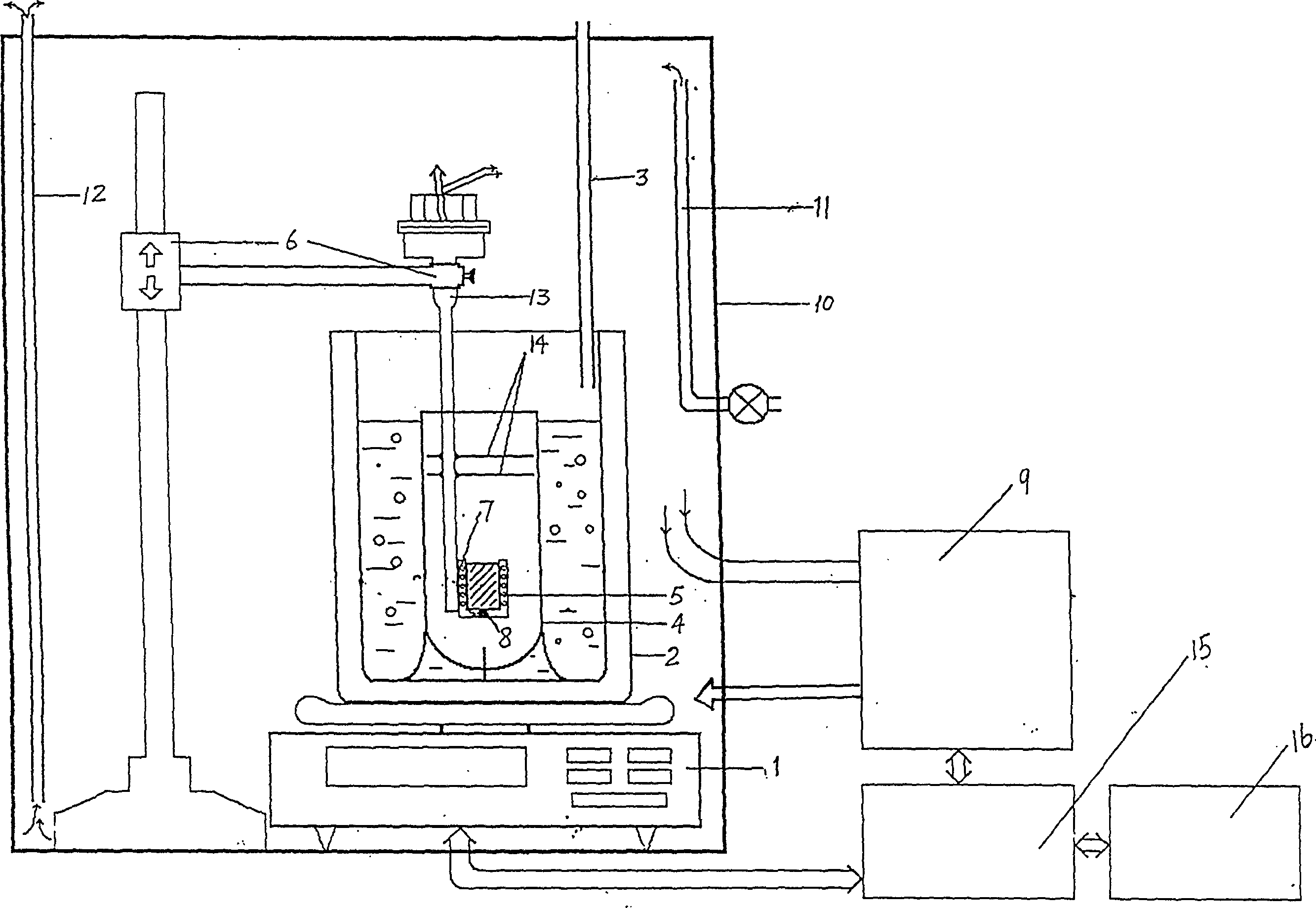
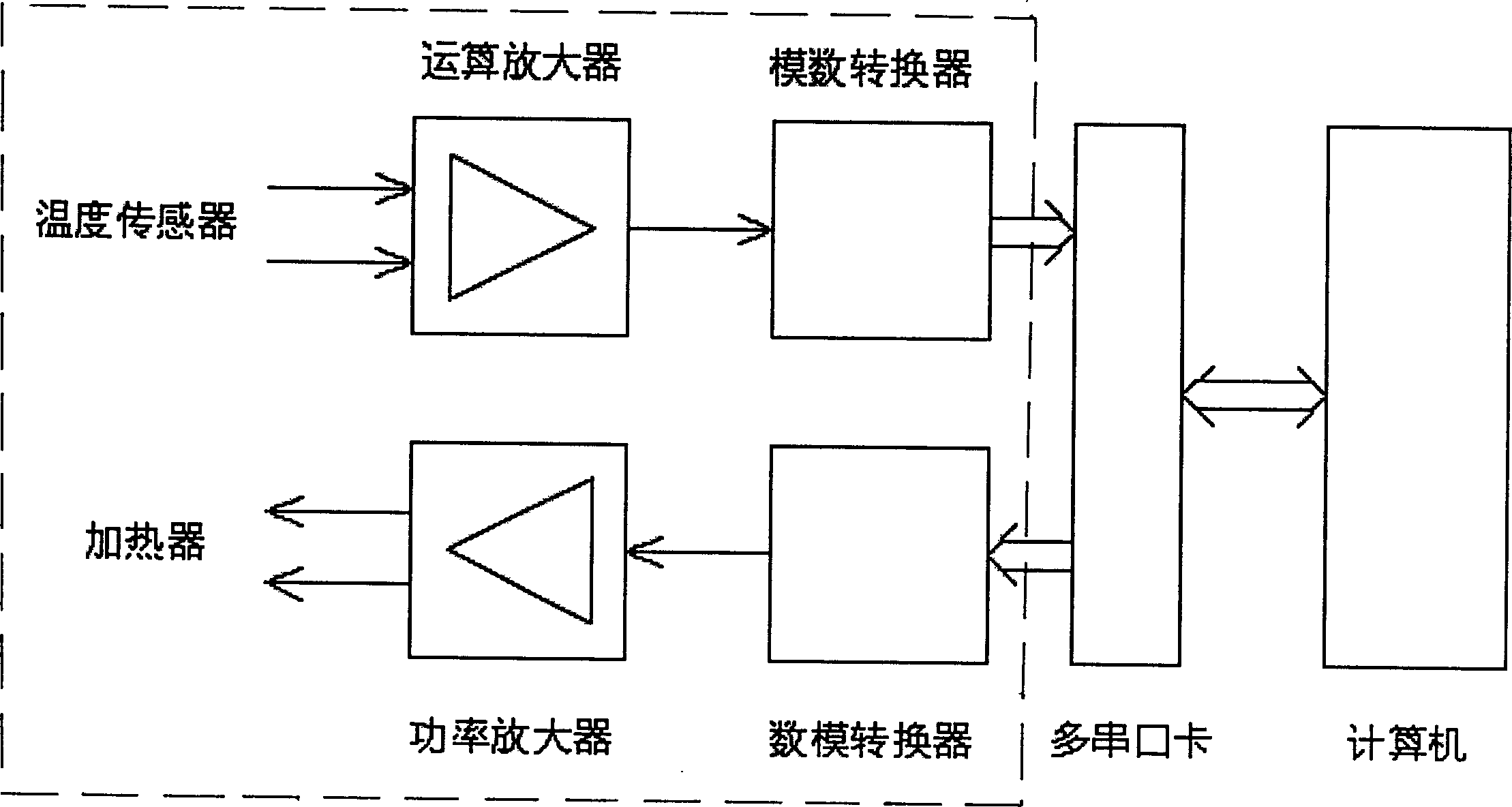
A thermal power measurement device is characterized in that the device comprises a calorimetry cylinder, a constant-temperature and heat-insulation system, a temperature equalization system, a calibration system, a signal processing and controlling system and a box body, wherein the calorimetry cylinder is a three-layer embedded composite structure; the inner-most layer is a sample chamber, the middle layer is semiconductor thermoelectric modules that are connected in series and the external wall is a constant-temperature layer; the sample chamber is internally provided with a thermocouple and a thermal resistor; the semiconductor thermoelectric modules are fixedly arranged between the sample chamber and the external wall by a mechanical method; the constant-temperature and heat-insulation system comprises a constant-temperature system and a heat insulation system; the constant-temperature system comprises a circular constant-temperature bath and a red copper fluid pipe; the red copper fluid pipe is closely attached to the external wall of the calorimetry cylinder; the inlet of the red copper fluid pipe is connected with the circular constant-temperature bath by a constant-temperature trough; the constant-temperature trough is internally provided with a remote temperature probe that is connected with the circular constant-temperature bath; the temperature equalization system comprises a fan that is arranged in the sample chamber; the calibration system comprises the thermal resistor; and the signal processing and controlling system comprises a computer and a data collecting card and is used for collecting signals in real time and controlling the fan power, calibration power and water bath temperature.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
M-w grade microwave power instrumentation system based on calorimetric method
ActiveCN101126780AEnhanced radio frequency high voltage tolerance limitSmall temperature rangeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical testingElectricityWater flow
The utility model belongs to a microwave power measurement system, specifically discloses a megawatt grade impulse microwave power measurement system based on calorimetric method, wherein an outlet temperature pickup is arranged on the stream outlet of a water pipe and an electric heater is arranged in the water pipe; the electric heater is connected with a rated power electricity supply; a microwave detecting device is arranged on the inlet of a microwave power absorbing device; the water runs through the inwall water pipe of the power absorbing device and an inlet temperature pickup is arranged on the stream inlet of the water pipe; an NTC thermal resistance R3 of the inlet temperature pickup is connected with a equilibrium resistance R1, while an NTC thermal resistance R4 of the outlet temperature pickup is connected with a equilibrium resistance R2; the NTC thermal resistance R3, the NTC thermal resistance R4, the equilibrium resistance R1 and the equilibrium resistance R2 form a Winston bridge and the Winston bridge is connected with a differential amplifying circuit. The utility model can measure the multiplex pulse high-power microwave power in millimetric wave band and the measuring range can be one kilowatt up to two or three megawatt.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
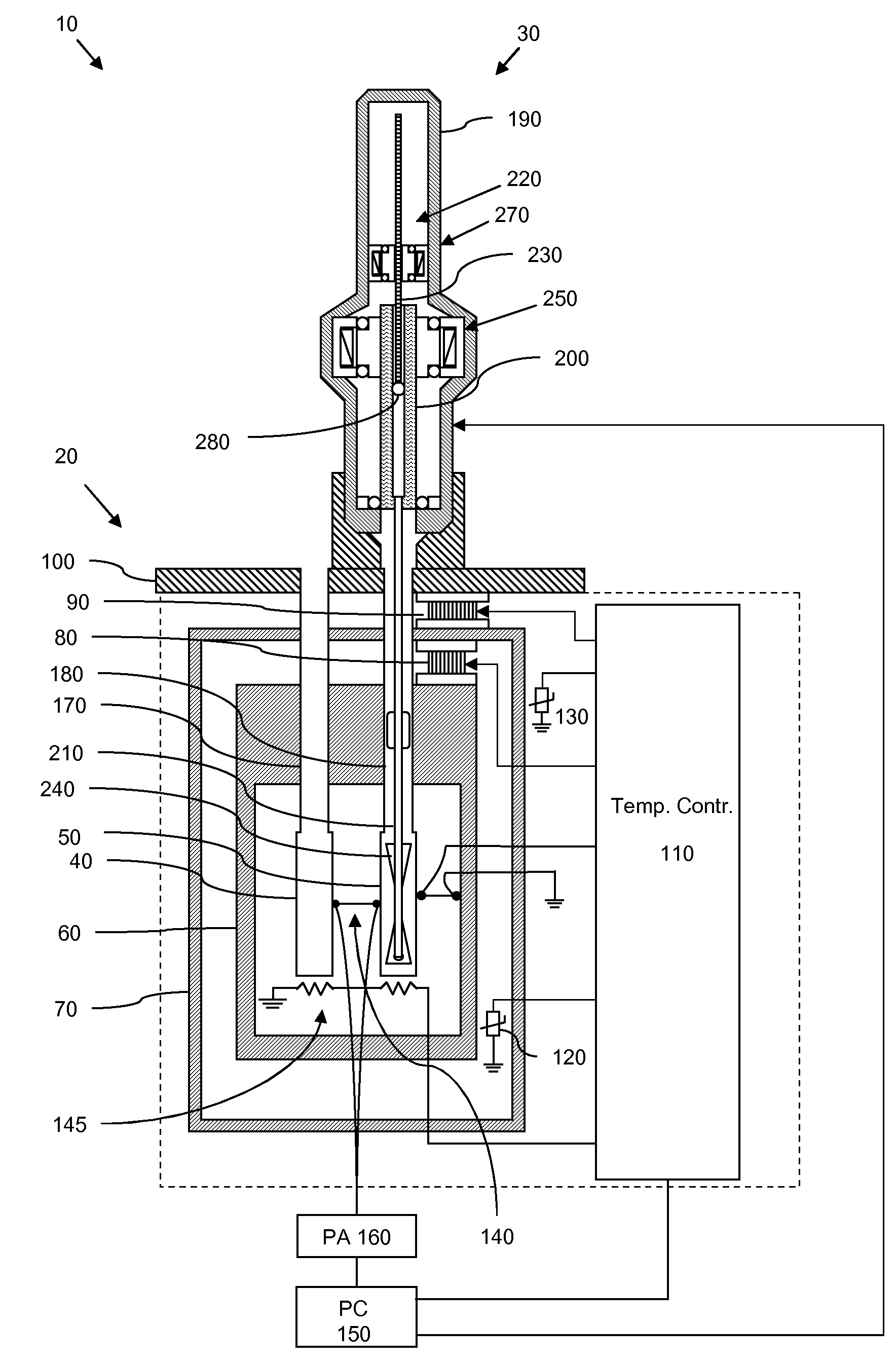
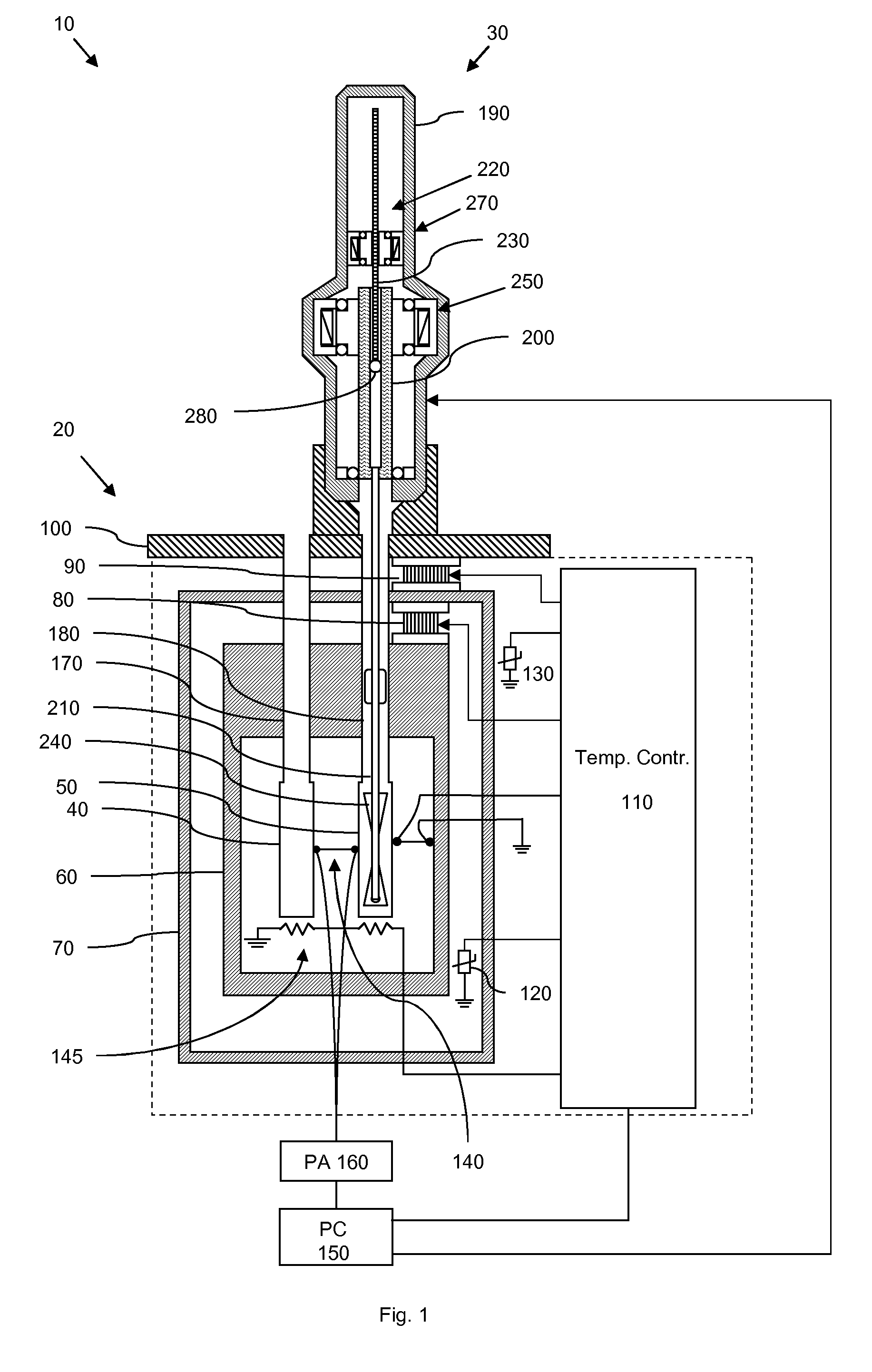
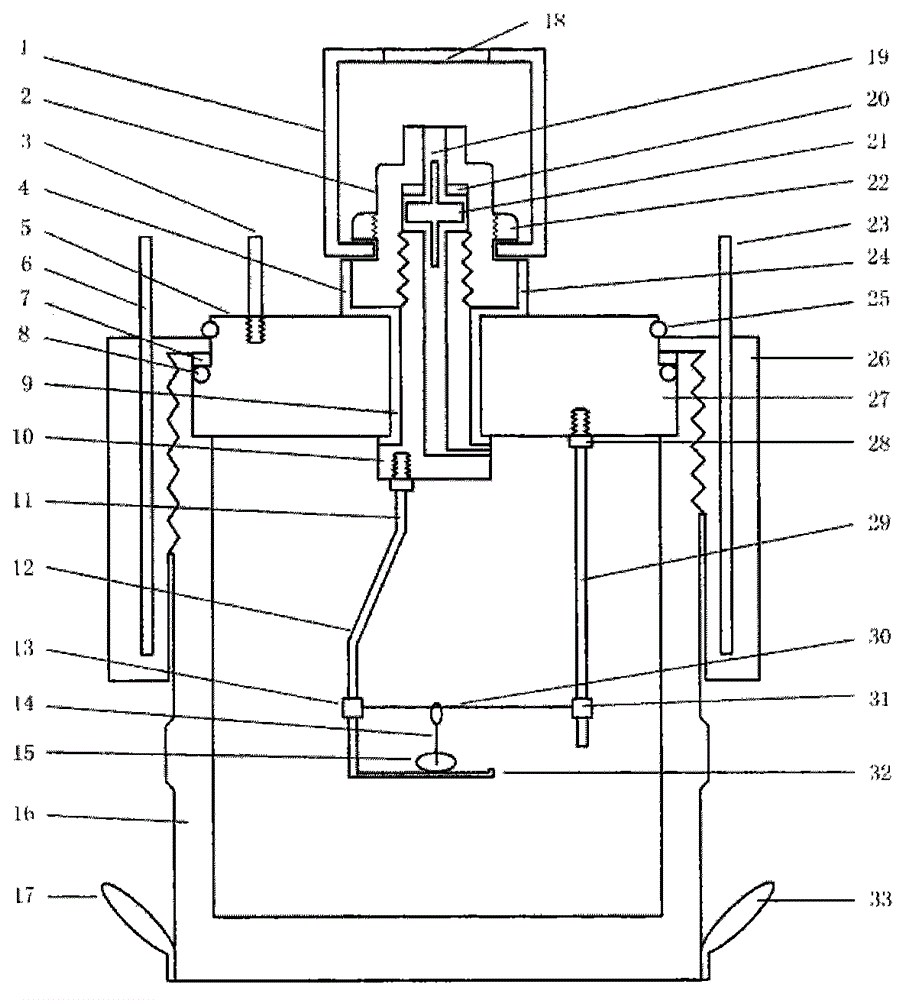
Automatic isothermal titration microcalorimeter apparatus and method of use
ActiveUS20100135853A1Less timeReduced cell volumeReagent containersBurette/pipette supportsPipetteDriver syringe
Automated isothermal titration micro calorimetry (ITC) system comprising a micro calorimeter with a sample cell and a reference cell, the sample cell is accessible via a sample cell stem and the reference cell is accessible via a reference cell stem. The system further comprises an automatic pipette assembly comprising a syringe with a titration needle arranged to be inserted into the sample cell for supplying titrant, the pipette assembly comprises an activator for driving a plunger in the syringe, a pipette translation unit supporting the pipette assembly and being arranged to place pipette in position for titration, washing and filling operations, a wash station for the titrant needle, and a cell preparation unit arranged to perform operations for replacing the sample liquid in the sample cell when the pipette is placed in another position than the position for titration.
Owner:MALVERN PANALYTICAL INC
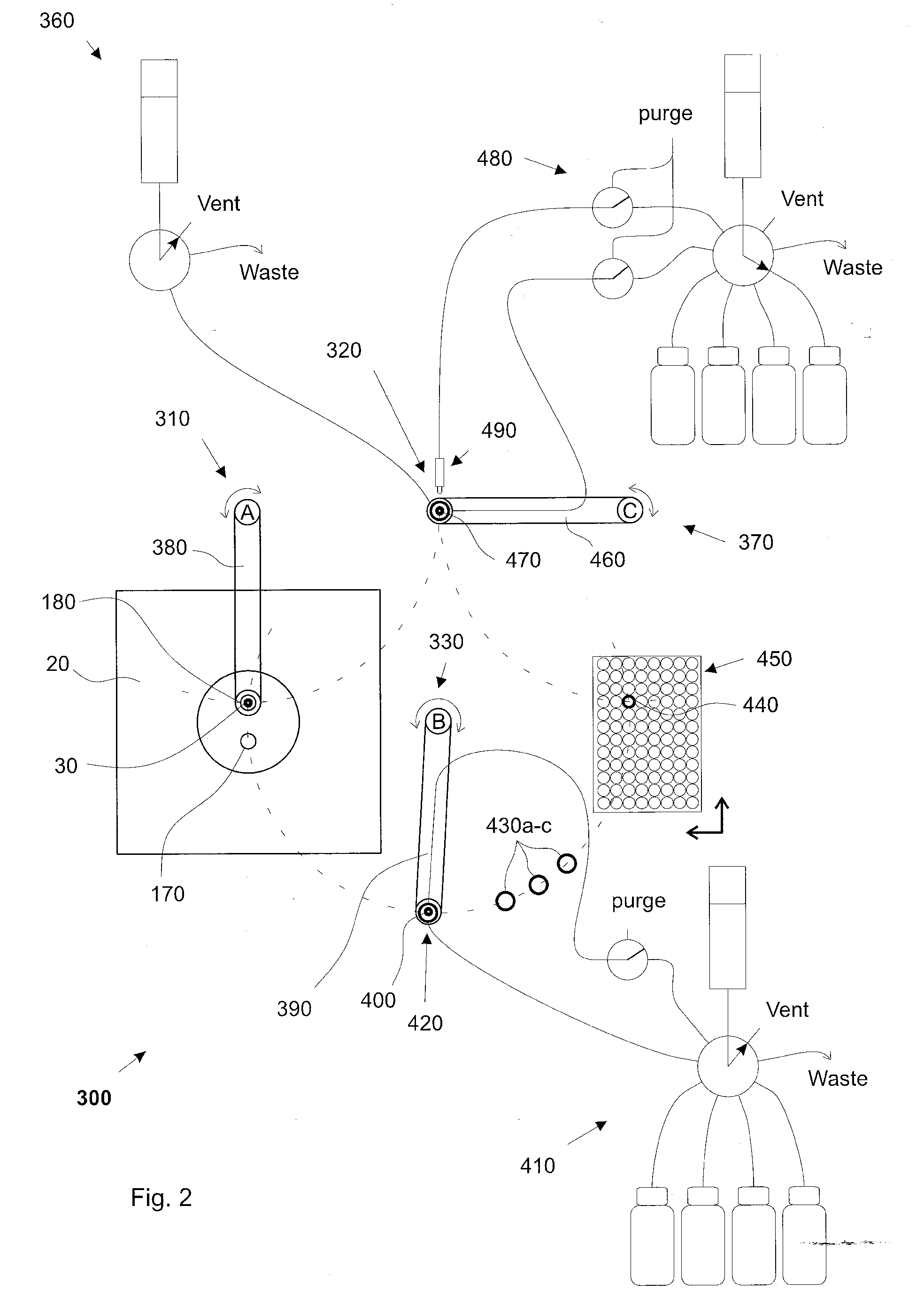
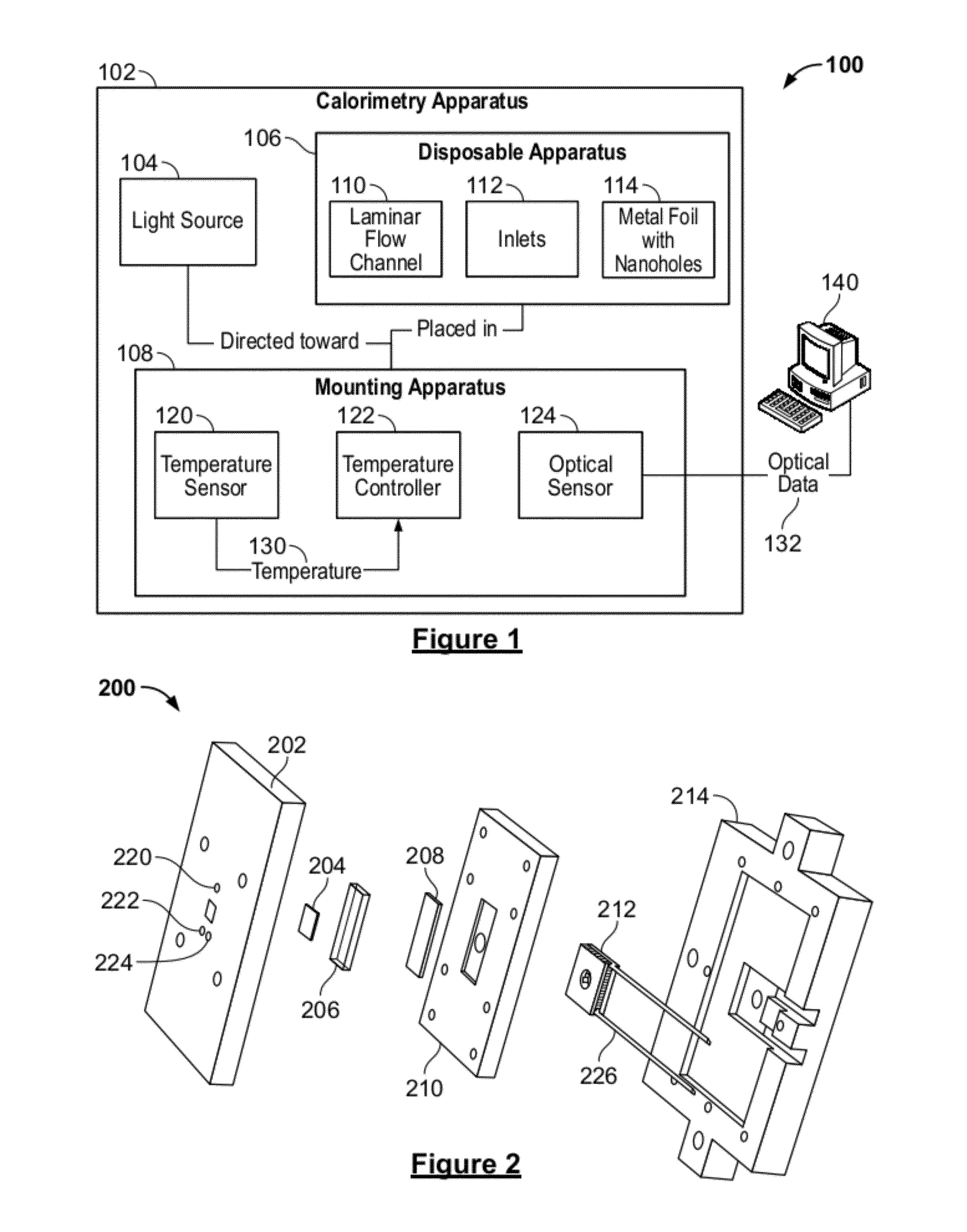
System and method for a microfluidic calorimeter
ActiveUS20120264224A1Reduce noise and errorMaterial heat developmentMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringCalorimetric measurement
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for a microfluidic calorimeter apparatus. A microfluidic calorimeter system includes a calorimetry apparatus and a processor in connection with the apparatus. The apparatus includes a microfluidic laminar flow channel connected to two inlets for flowing fluid into the laminar flow channel. Below the laminar flow channel is a plurality of microscale temperature sensors at known positions in the channel. The processor is in connection with the discrete temperature sensors and determines a calorimetry measurement based on local temperatures derived from data output by the microscale temperature sensors and the respective positions of the sensors in the channel.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Liquid nitrogen gasification scanning calorimetry method and liquid nitrogen gasification calorimeter
The invention discloses a liquid nitrogen gasification scan heat measuring method and the device. The invention uses process of heat exchange between the sample and the liquid nitrogen, and carries on sample heat measuring; it also discloses two kinds of optimized projects, namely: carries on heat compensation or overheat compensation in the process, in order to upgrade the heat measuring precision. At the same time, the invention also discloses a device based on the method. The invention is simple, quick and accurate, the device is simple, and the consumed nitrogen is little.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
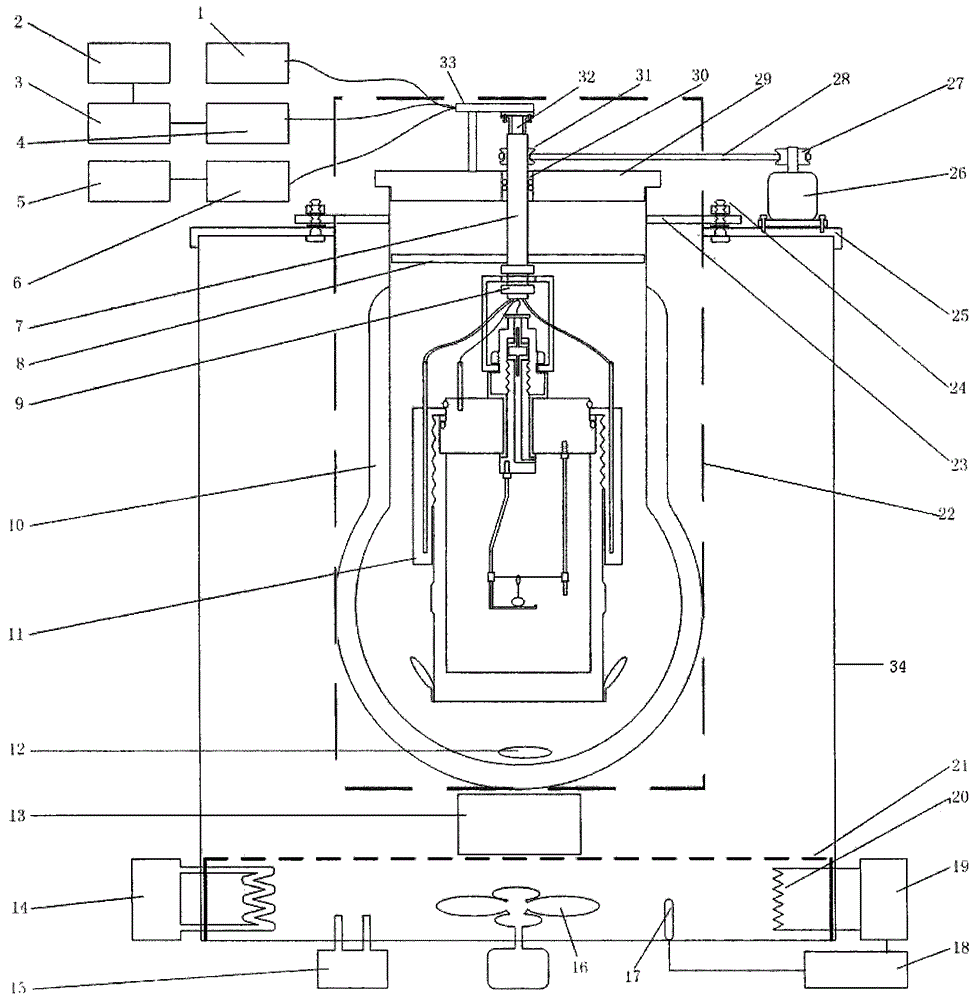
Adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter with dynamic thermal inertia correction features
ActiveCN109974902AReduce the impactKinetic parameter improvementMaterial heat developmentCalorimeterData displayChemical reaction
The invention discloses an adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter with dynamic thermal inertia correction features. The adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter comprises highly symmetrical dual testchannels, a standard heater, an external plugging type spherical reaction cell, a temperature and power measurement module, a system circuit board, and control software for data display and recording.The differences between the adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter and a classical adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter in structure and data processing are that: in terms of calorimetry, the adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter can obtain dynamic thermal inertia factors in an adiabatic reaction process in real time by utilizing heating power of the standard heater measured by means of thetwo channel symmetric structure; and in terms of thermal analysis, for the deficiency that a thermal inertia factor is considered as a constant in the existing thermal analysis kinetics solving method based on adiabatic accelerated calorimetry, a novel kinetics solving method considers the dynamic changes of the thermal inertia factor and combines a non-linear fitting method for kinetics solution. The adiabatic accelerating rate calorimeter is higher in applicability, and is of great significance for improving the accuracy of the chemical reaction heat risk assessment.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method and system for calorimetry probe
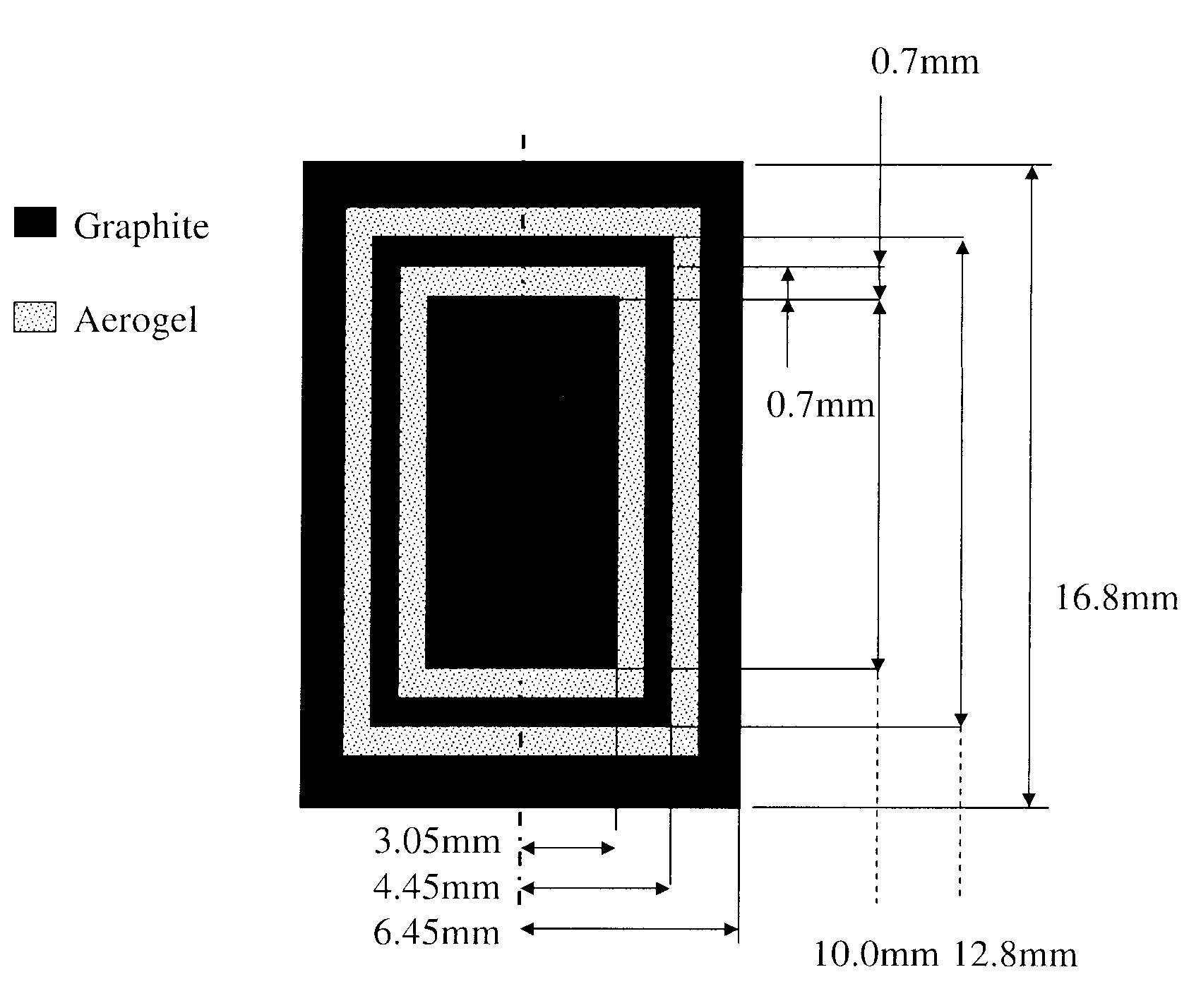
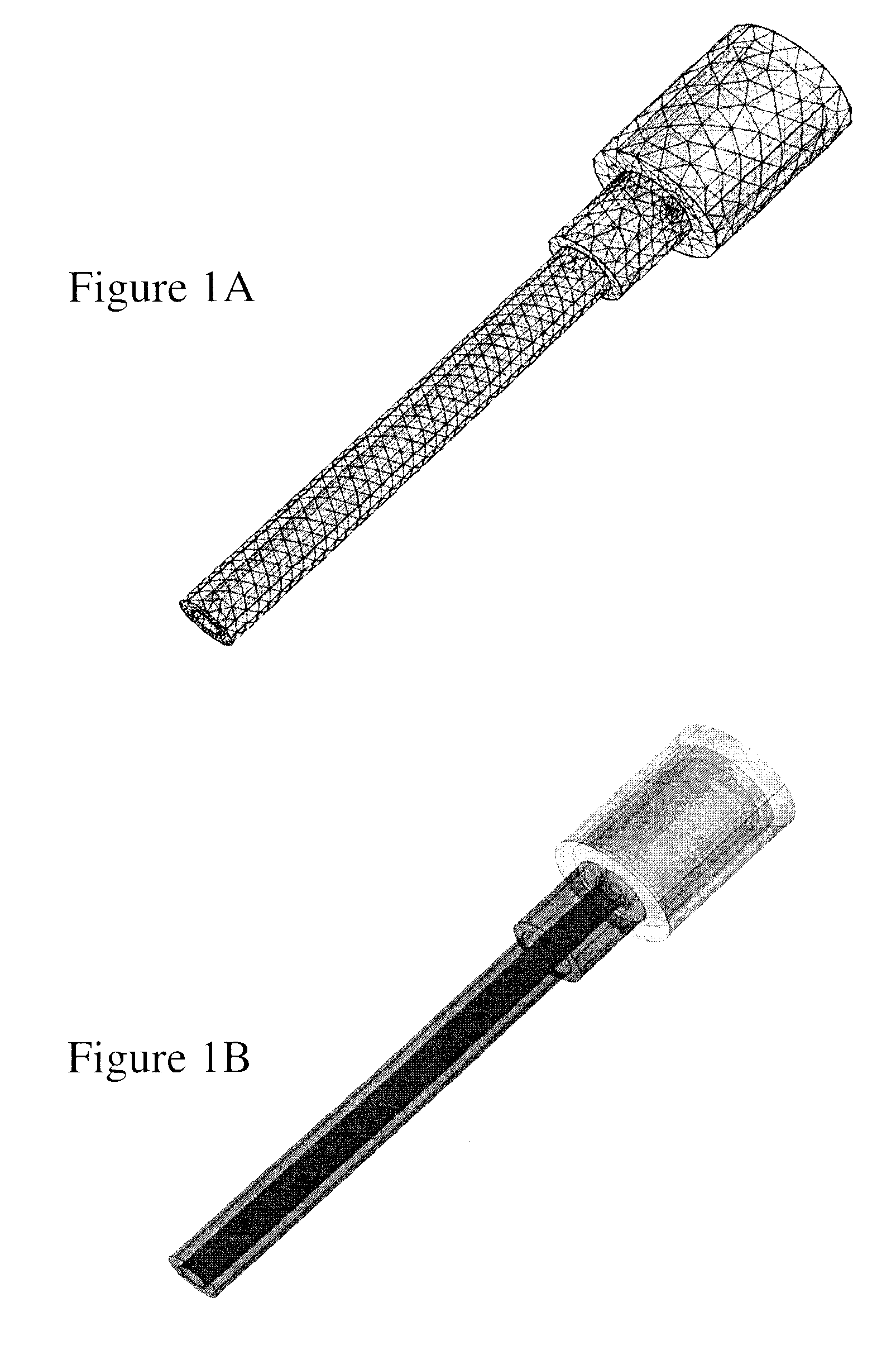
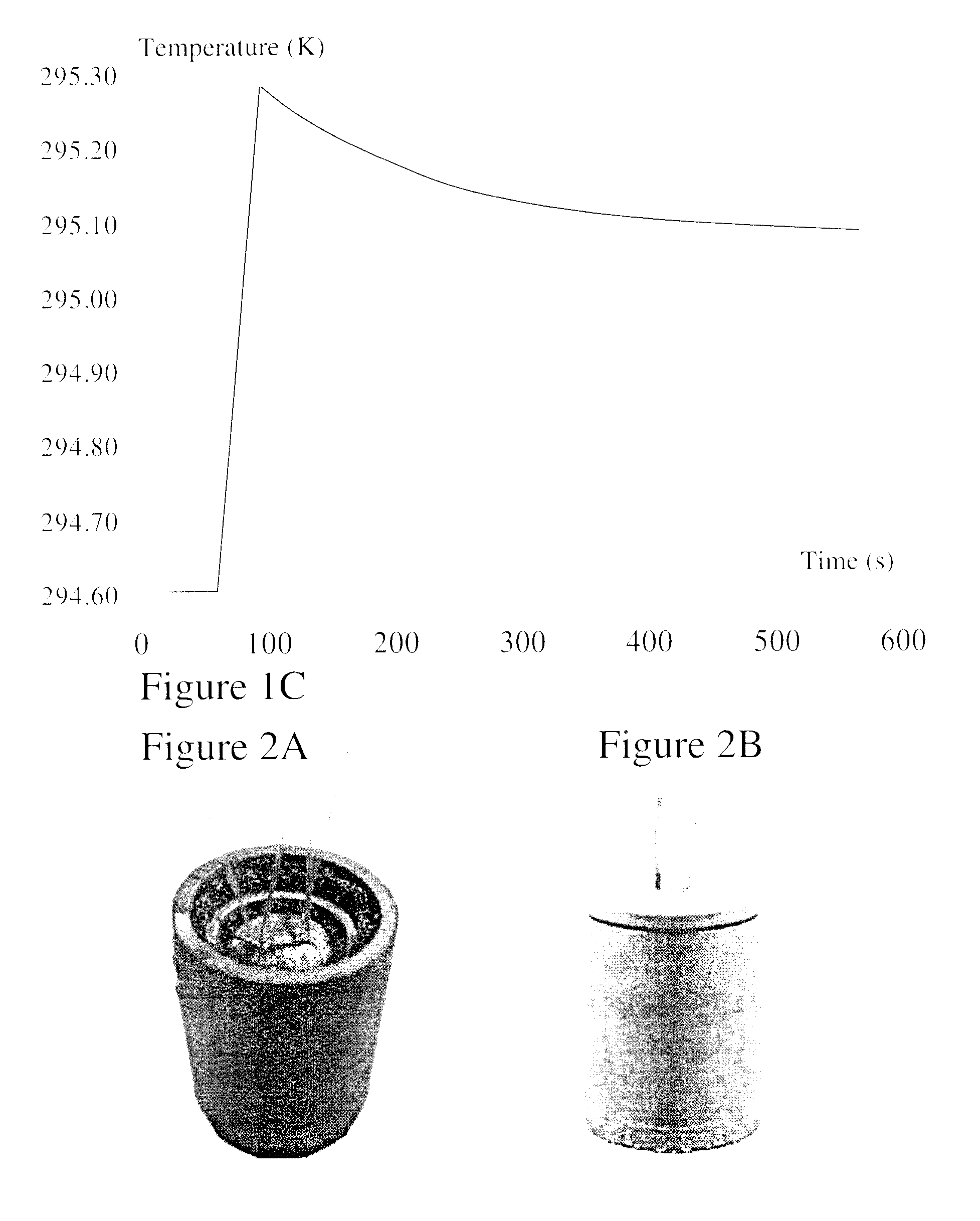
InactiveUS9586060B2Calorimetric dosimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDosimetry radiationEquipment Operator
Radiotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for cancer and its success depends critically on accurate targeting and delivery of the correct radiation dose. Accurate dosimetry is therefore essential to maintain and improve patient survival rates. However, size and long wait times currently limit water and graphite based calorimeters to standards laboratories leaving field-based dosimetry to ionization chamber measurements which depend upon a reference field-specified calibration factor. It would therefore be beneficial to provide radiotherapy equipment operators a direct approach of clinical reference dosimetry wherein the dosimeter provides increased independence on dose, dose rate, radiation energy, and energy type, etc. It would be further beneficial for such novel clinical dosimeters to be compact, function as secondary standards used routinely for measurements and allow radiotherapy doses to be measured directly and in an absolute manner. According to embodiments of the invention novel compact graphite probe calorimeters are provided.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
Peakforce photothermal-based detection of IR nanoabsorption
InactiveUS8955161B2High resolutionSample preparation is minimizedRadiation pyrometryNanotechnologyRegion of interestCalorimetry
An apparatus and method of performing photothermal chemical nanoidentification of a sample includes positioning a tip of a probe at a region of interest of the sample, with the tip-sample separation being less than about 10 nm. Then, IR electromagnetic energy having a selected frequency, ω, is directed towards the tip. Using PFT mode AFM operation, absorption of the energy at the region of interest is identified. Calorimetry may also be performed with the photothermal PFT system.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Development of rotating miniature combustion bomb
InactiveCN104155340ASmall volumeOvercoming the need for large sample volumesMaterial heat developmentTwo temperatureEngineering
The invention relates to development and design of a horizontal rotating miniature combustion bomb and a rotation system thereof. The invention consists of two parts, the structure of the combustion bomb and the rotation system. The structure of the combustion bomb has the characteristics of: single head; barrel volume of about 7.30 cm<3>; two temperature measurement thermistors and two thermal resistances on the combustion bomb cover; a mixing blade at the lower part of the bomb body in order to stir a calorimetry agent to flip upwards during rotation and reach quick temperature equilibrium; bomb body made of high temperature high pressure resistant 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel material; platinum or platinum rhodium alloy containing 3-1 / 2% of rhodium on the inner wall of the combustion bomb barrel; and electrode and crucible made of platinum or a platinum rhodium alloy material containing 3-1 / 2 % of rhodium. The rotation system has the characteristics of: rotation of the combustion bomb greater than 360 degrees; three circuits on the combustion bomb (temperature measurement circuit, heating circuit and ignition circuit) connected with the external circuit by using 24 path pure gold contactor collecting ring to ensure smooth circuit; and stepless speed regulation.
Owner:李强国
Mixed calorimetry based specific heat calculating method for frozen soil
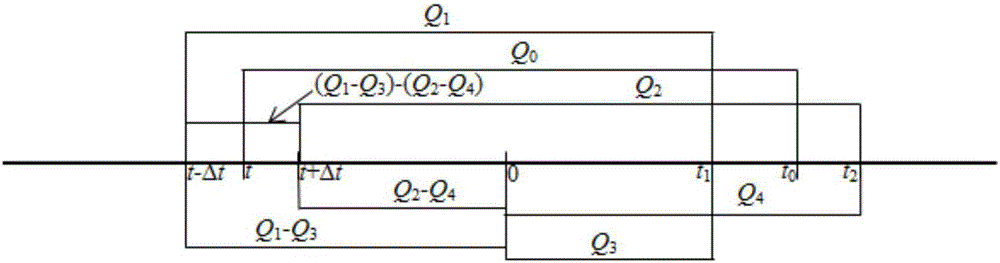
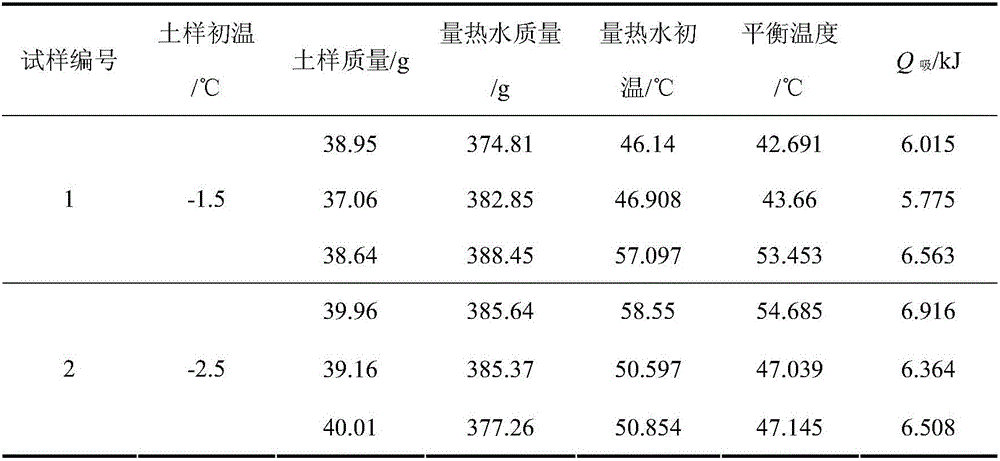
ActiveCN106770436ARaise the temperature field to predict the temperatureEnsure safetyMaterial heat developmentPreparing sample for investigationMaximum errorSoil science
The invention provides a mixed calorimetry based specific heat calculating method for frozen soil. The method comprises the following steps: a soil sample with the mass of m is taken, and water content w of the soil sample is measured; the soil sample is placed in a freezer at the constant negative temperature t lower than 0 DEG C for 60 h, and the total heat Q0 of the frozen soil sample is acquired; the frozen soil sample is placed in the freezer for 60 h; the total heat Q1 and Q2 required by the soil sample at the constant negative temperature (t-delta t) and (t+ delta t) for being heated to heat exchange balance temperature t1 and t2 from initial temperature are calculated respectively; the heat Q3 and Q4 are determined by measuring specific heat and content of soil particles and water; the specific heat c of the frozen soil sample at the specific negative temperature t is obtained according to a formula. The method has the beneficial effects that the specific heat of the frozen soil sample at a certain temperature point can be calculated precisely, conventional errors caused by thermal calculation based on average specific heat are improved, the minimum error is 0.039 DEG C, the maximum error is 0.5955 DEG C, and actual engineering needs can be met. Predicted temperature of a temperature field in a freezing method construction process can be increased to a larger extent by aid of precision improvement, and the safety of freezing method construction is guaranteed.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
Benzene imide structure based high-temperature self-crosslinking copolyester with effects of flame retardancy, smoke suppression and melt drop resistance and preparation method of copolyester
ActiveCN108359084APreserve thermoplastic processabilityIncrease melt viscosityStructural unitStructure based
The invention discloses a benzene imide structure based high-temperature self-crosslinking copolyester with effects of flame retardancy, smoke suppression and melt drop resistance. Copolyester is prepared from structural units represented by I, II and III or structural units represented by I, II and IV through random copolymerization, wherein the characteristic viscosity [eta] of copolyester is 0.41-1.12 dL / g, and the limit oxygen index is 24.2%-38.7%; the vertical combustion class is in a range from V-2 to V-0; the p-HRR (peak of heat release rate) in a cone calorimetry test is reduced by 7.1%-72.1% as compared with that of pure PET, and total smoke release is decreased by 2.0%-59.2% as compared with that of pure PET. The invention further discloses a preparation method of copolyester. Ahigh-temperature self-crosslinking group introduced in the preparation process is a benzene imide group, and prepared copolyeste cannot be subjected to crosslinking during processing and polymerization, so that thermoplastic processability of polyester is retained; meanwhile, due to the tackifying effect and high charring property brought by the self-crosslinking action at high temperature or during combustion, prepared copolyester has excellent flame retardancy, smoke suppression and melt drop resistance effects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
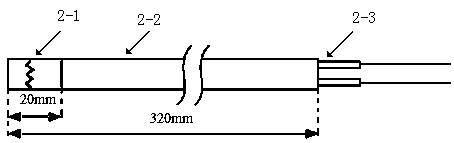
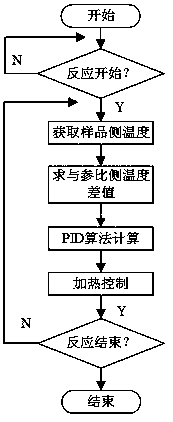
Method for measuring and calculating dynamic heat capacity of adiabatic reaction calorimetry samples
The invention discloses a method for measuring and calculating dynamic heat capacity of adiabatic reaction calorimetry samples. The method is provided with an adiabatic reaction calorimetry device with two-channel asymmetric sample pool structures, data of adiabatic condition reaction process and path offset reaction process can be measured by the adiabatic reaction calorimetry device and are processed by the aid of an energy-balance equation, and a specific heat capacity-temperature variation function of the samples close to real rules is acquired by the aid of constant approximation of an interpolation function and a dynamic estimation method of reactant concentration. According to the method, approximate heat capacity-temperature variation rules of the samples of the adiabatic reaction process can be acquired, key index-reaction heat calculated according to the heat capacity-temperature variation rules is closer to real conditions, and more accurate reference is provided for heat hazard evaluation of reactants.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
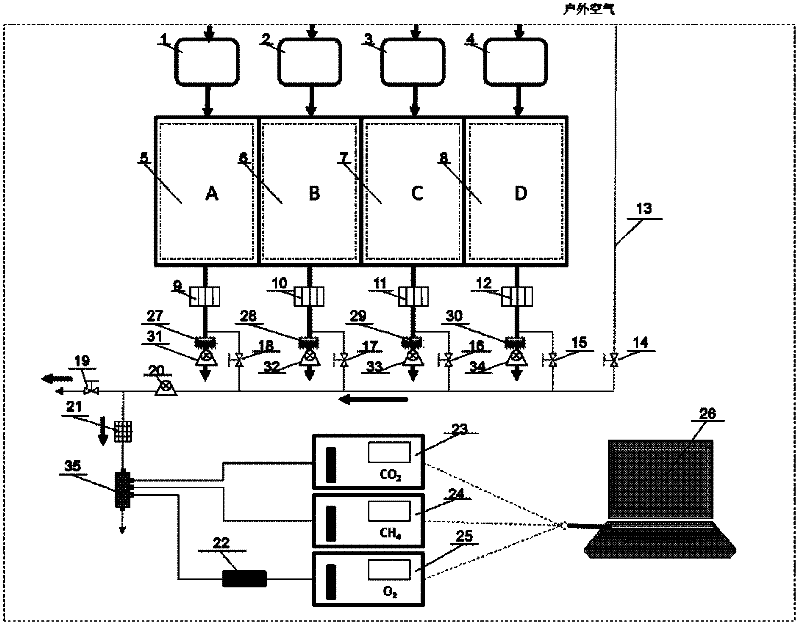
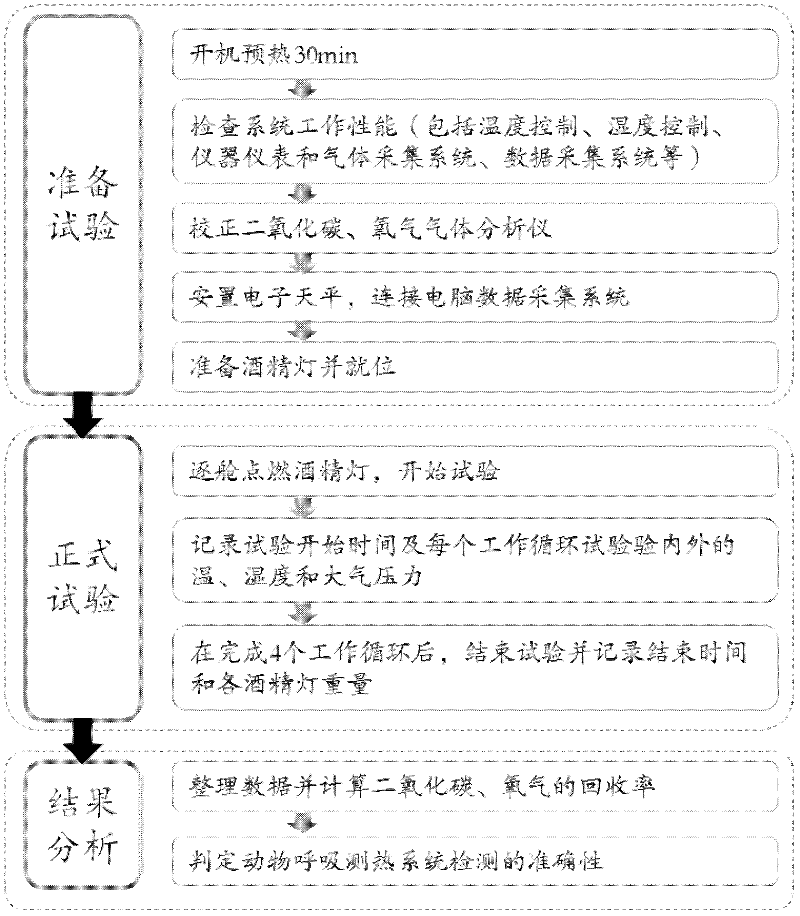
A method for testing accuracy of animal breath calorimetry system
InactiveCN102261970AReduce mistakesMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateMaterial analysisStart timeTest chamber
The invention discloses a method for inspecting the detection accuracy of an animal respiratory calorimetry system, which comprises the following steps: accurately weighing an alcohol lamp, wherein an appropriate amount of anhydrous alcohol is filled in the alcohol lamp; putting the alcohol lamp into a test chamber of a respiratory calorimetry system to be detected, and igniting the alcohol lamp to start a compensation test of the system; recording the start time and the internal and external temperatures, humidities and atmospheric pressures of the test chamber; after the system runs four operating cycles, extinguishing the alcohol lamp to complete the test; recording the end time, and weighing the alcohol lamp; and finally, according to the data acquired by the system, such as gas concentration, air mass flow, anhydrous alcohol consumption, burning time and the like, calculating the recovery ratios of carbon dioxide and oxygen, and then judging the detection accuracy of the animal respiratory calorimetry system. In the method disclosed by the invention, through burning the anhydrous alcohol, an animal respiratory test is simulated so as to rapidly and accurately assess the accuracy of detection results of the animal respiratory calorimetry system, thereby providing an important method and a technical means for the development of the verification test of the system.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breath Monitoring Apparatus and Method
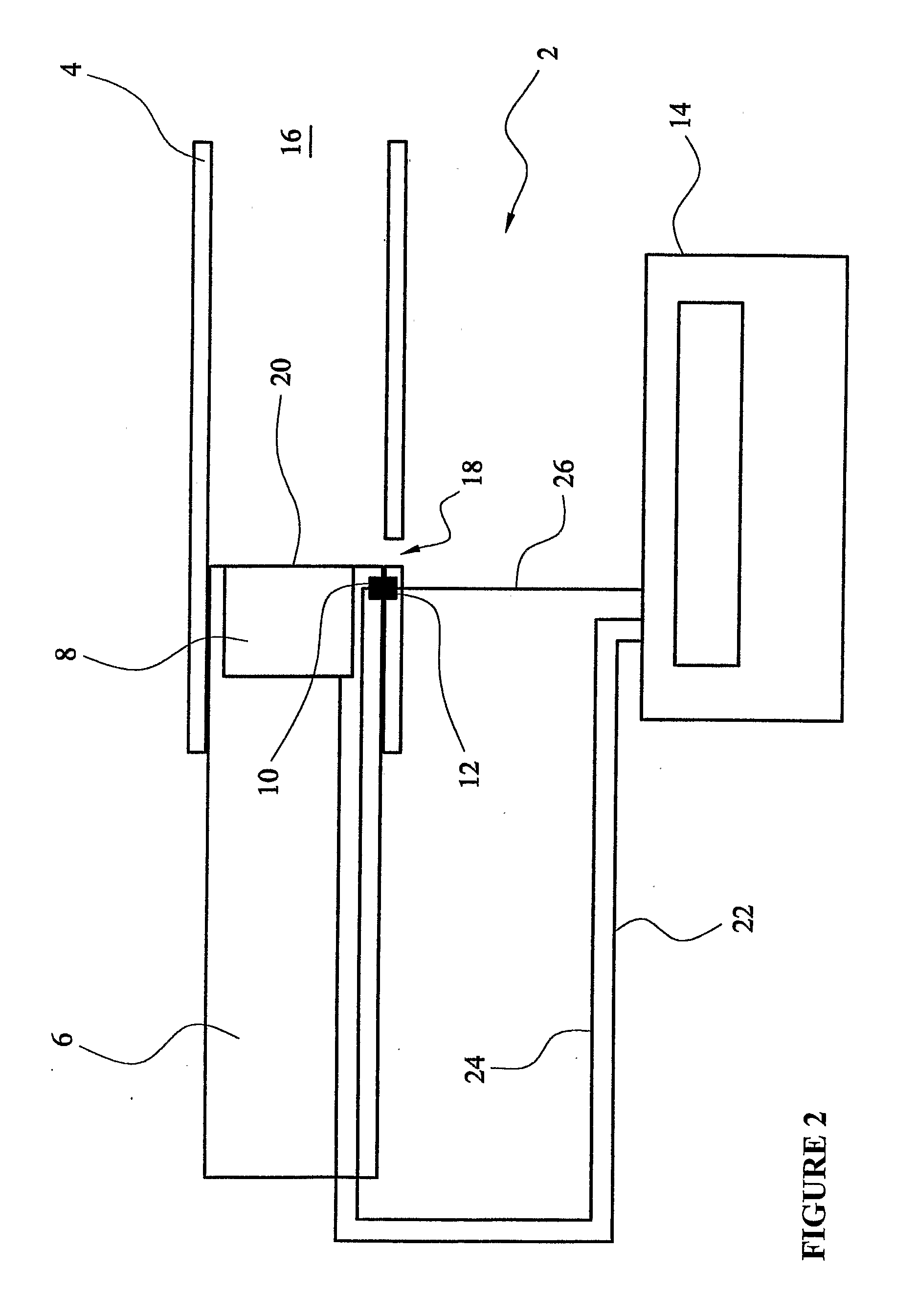
InactiveUS20080161709A1Effective monitoringStay focusedRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsCalorimetryEnvironmental health
A breath monitoring apparatus is provided comprising a housing (4) on which is mounted, a means (6, 10, 12) to measure the volume of an inhaled breath of the user; and a means (8) to measure the gas content of an exhaled breath of a user. There is further provided a method of monitoring breaths, the method comprising the steps of calculating the volume of an inhaled breath of a user and calculating the gas content of an exhaled breath of the user. The apparatus and method relate in particular to indirect calorimetry.
Owner:NUTREN TECH
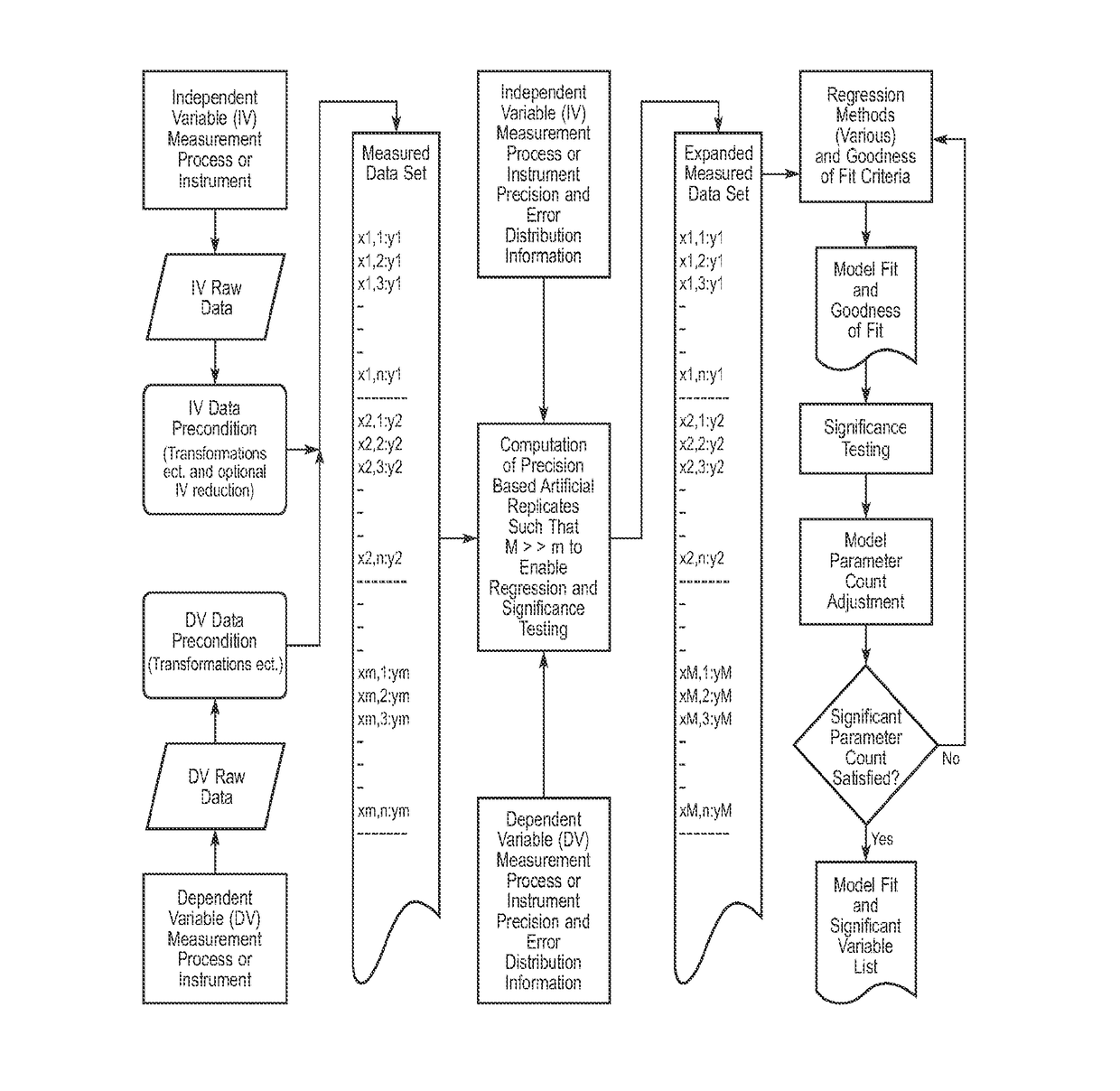
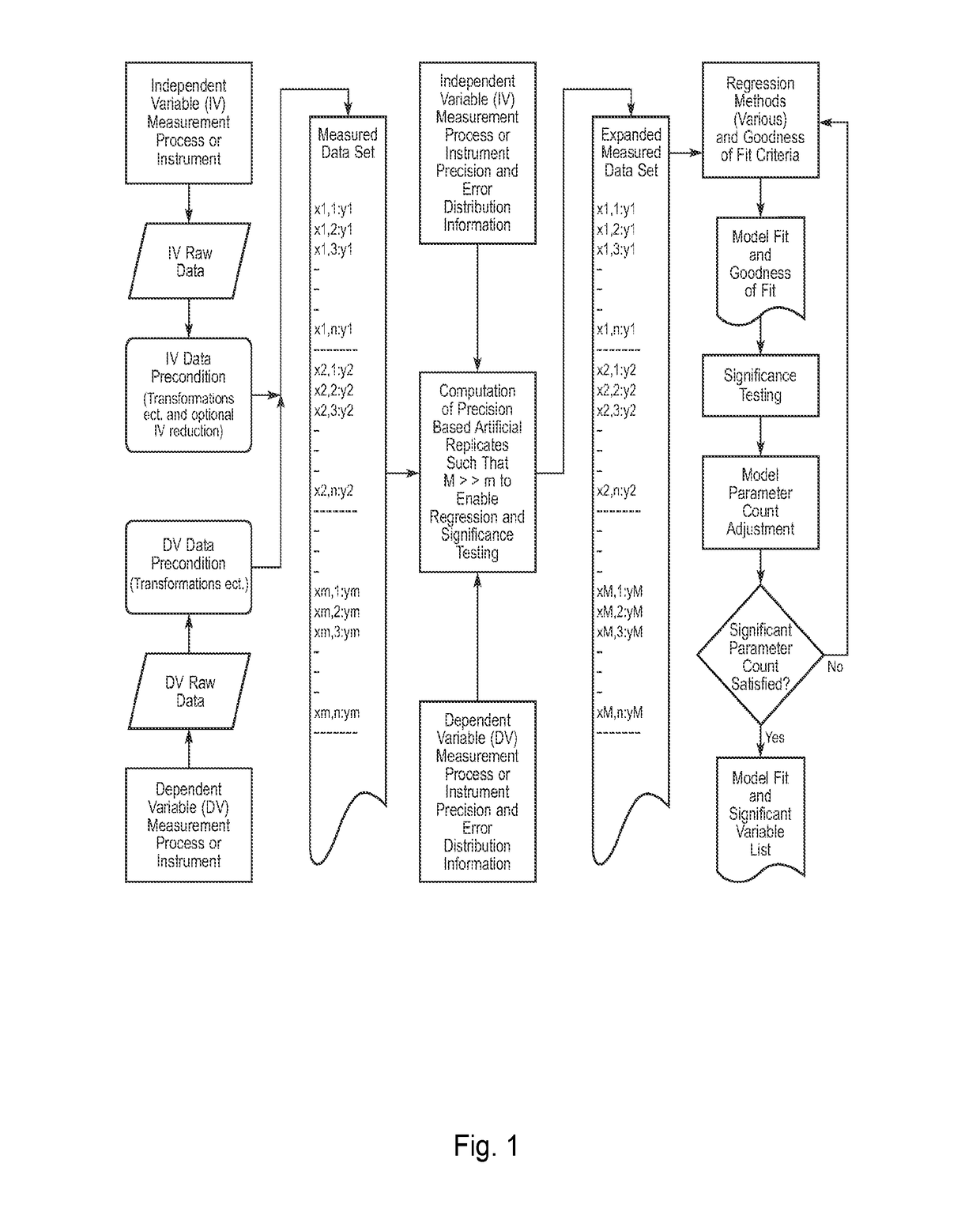
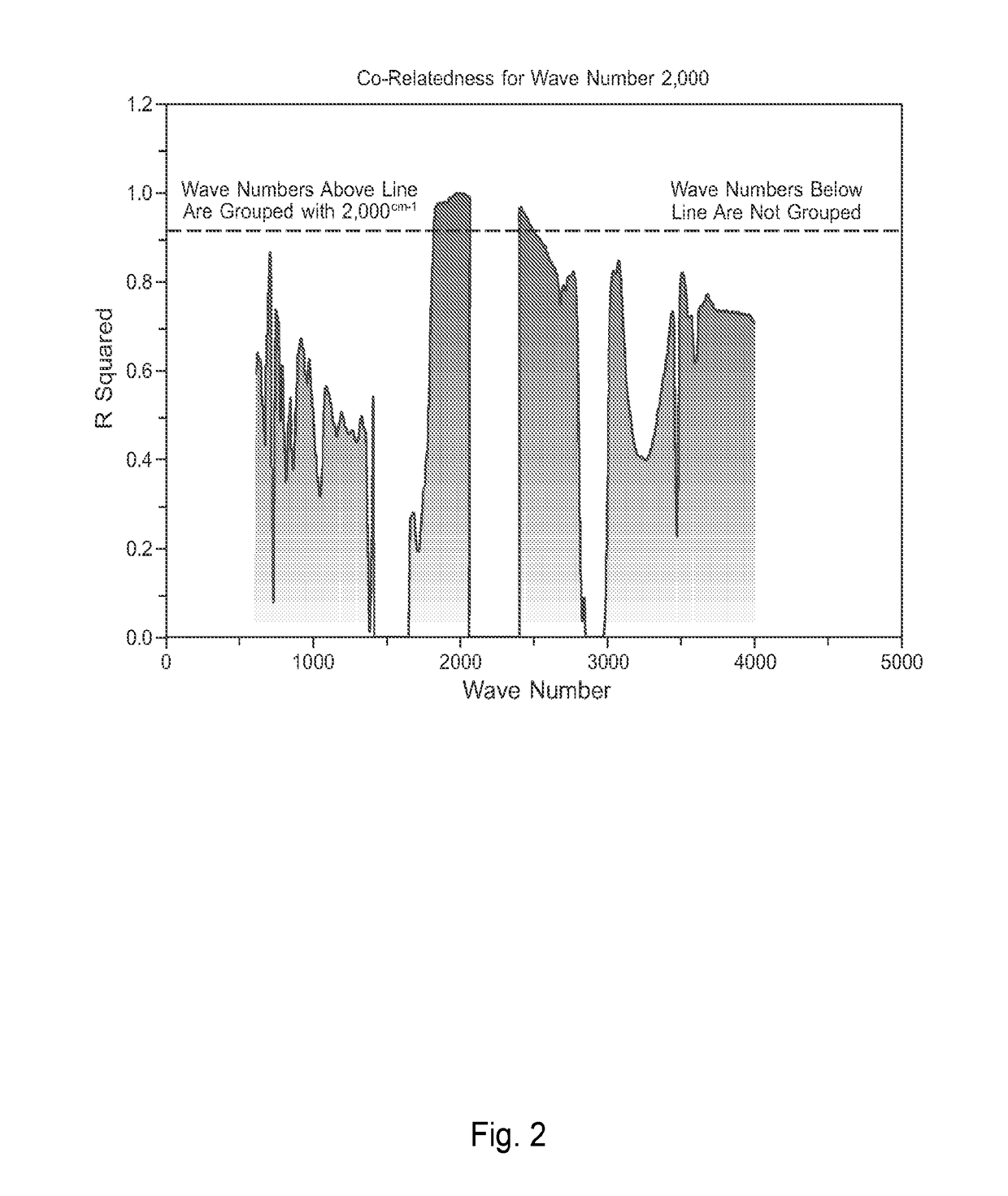
Method for Correlating Physical and Chemical Measurement Data Sets to Predict Physical and Chemical Properties
InactiveUS20180196778A1Material testing goodsComplex mathematical operationsData setChemical physics
The present invention is generally related to the correlation of physical and / or chemical measurements with other physical and / or chemical measurements and the application of the correlation to transform a product or process (e.g., to formulate, mix, blend compounds or materials of various natures and origins) upon predicting / estimating certain property(ies) and / or performance index(ices) as indicated by a dependent variable estimate. Embodiments of the inventive technology applies specifically to the problem of producing a correlation when the independent variables of interest exceed the number of observations. This situation is common in many fields of science and technology, such as, but not limited to, spectroscopy, calorimetry, thermogravimetric, chromatography and others. A perhaps primary advantage of embodiments of the inventive method over prior art is the ability to generate correlations directly in terms of measured variables.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
Calorimetric assessment of microorganisms and use thereof
InactiveUS20090317859A1Promoting and suppressing growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobiology
Methods, integrated kits and systems for the rapid detection, identification and / or quantification of microorganisms in samples such as blood samples via calorimetry are disclosed.
Owner:DANIELS ALMA U +2
Cold-hot stage type high-speed calorimeter capable of being combined with other microstructure characterization techniques
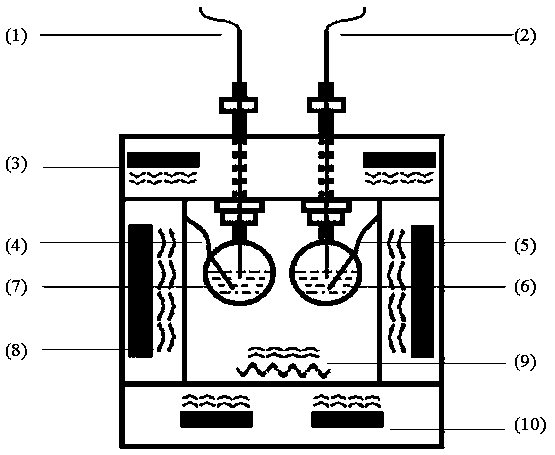
ActiveCN103743775ATemperature monitoringAvoid affecting test resultsMaterial heat developmentCalorimeterTemperature controlLight reflection
The invention discloses a cold-hot stage type high-speed calorimeter capable of being combined with other microstructure characterization techniques, and relates to the phase and microstructure analysis device technology field. The cold-hot stage type high-speed calorimeter includes a sample chamber having a light transmission transparent window and a light reflection transparent window on the wall, a cold-hot stage having the interior including a heating element and a refrigerant circulation pipeline for controlling the temperature and having a transmission hole, a sample chamber temperature control system and a high-speed calorimetric system. The cold-hot stage type high-speed calorimeter has the advantages that: 1, the high-speed calorimetric system having the temperature rising / dropping rate is miniaturized to the cold-hot stage, and with utilization of the reflection window, the transmission window and the cold-hot stage transmission hole, on-site combination of calorimetry and microstructure characterization are carried out; and 2, response is rapid through programmable control, sample temperature disturbance caused by incident light in structure measurement is dynamically compensated, the sample temperature is stabilized, thereby being conveniently used for researches on a metastable state.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Calorimetry
According to the present invention in a first aspect, there is provided an apparatus for determining the type of fuel burnt by a user, the apparatus comprising an oxygen sensor and a carbon dioxide sensor, and wherein the oxygen sensor and the carbon dioxide sensor are operable to establish the type of fuel burnt by a user of the apparatus.
Owner:NUTREN TECH
Optical detectors for infrared, sub-millimeter and high energy radiation
Optical methods and devices for the thermal detection and imaging of infrared, sub-millimeter, millimeter and high energy radiation, wherein the thermal mass of the detector is minimized by the use of microscopic photoluminescent temperature probes having a weight mass which can be of the order of 10−11 grams or smaller. Used for detection of high energy radiation, including quantum calorimetry, said temperature probes allow non-contact measurements free of electrical sources of noise like Johnson noise or Joule heating.
Owner:KLEINERMAN MARCOS Y
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com