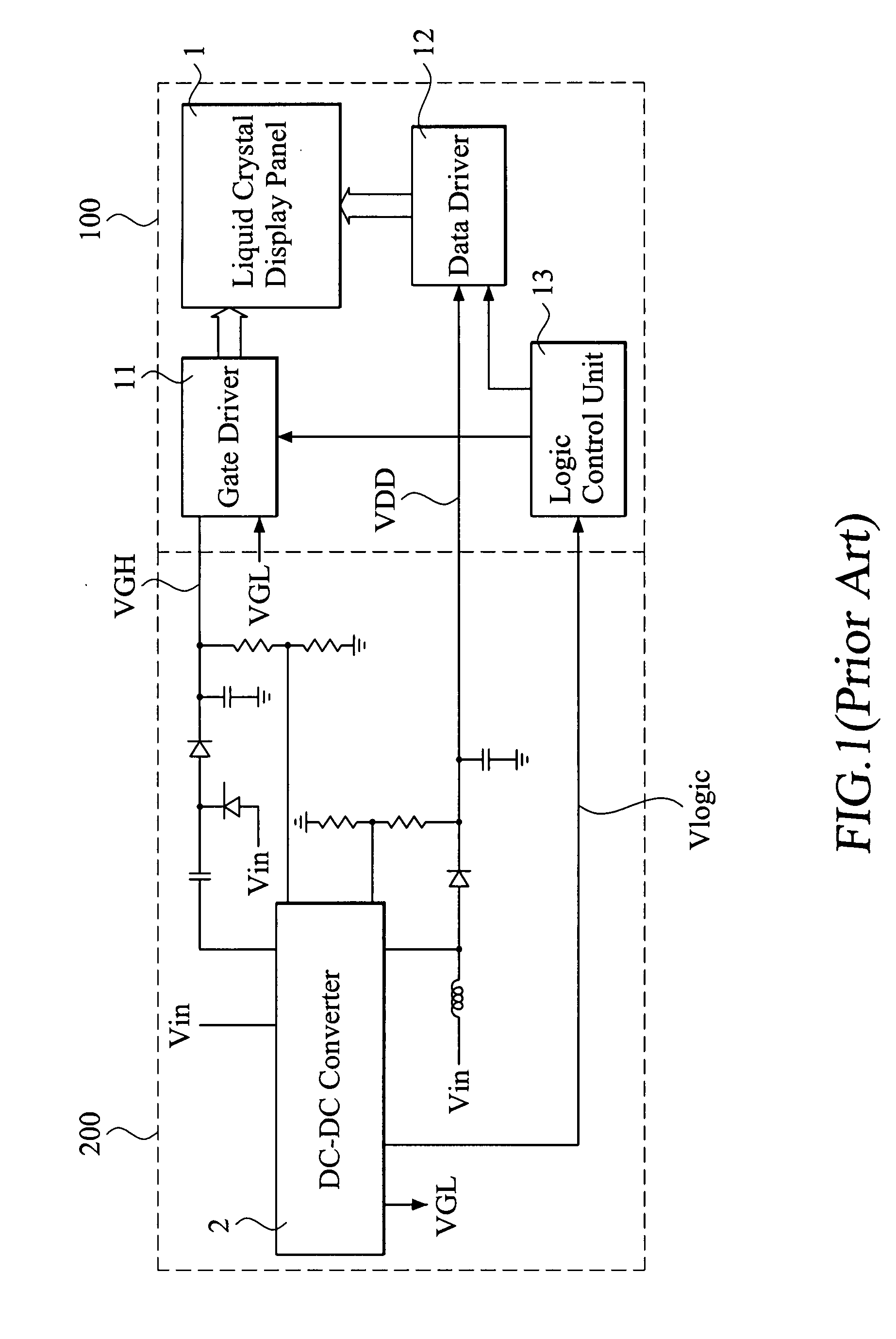
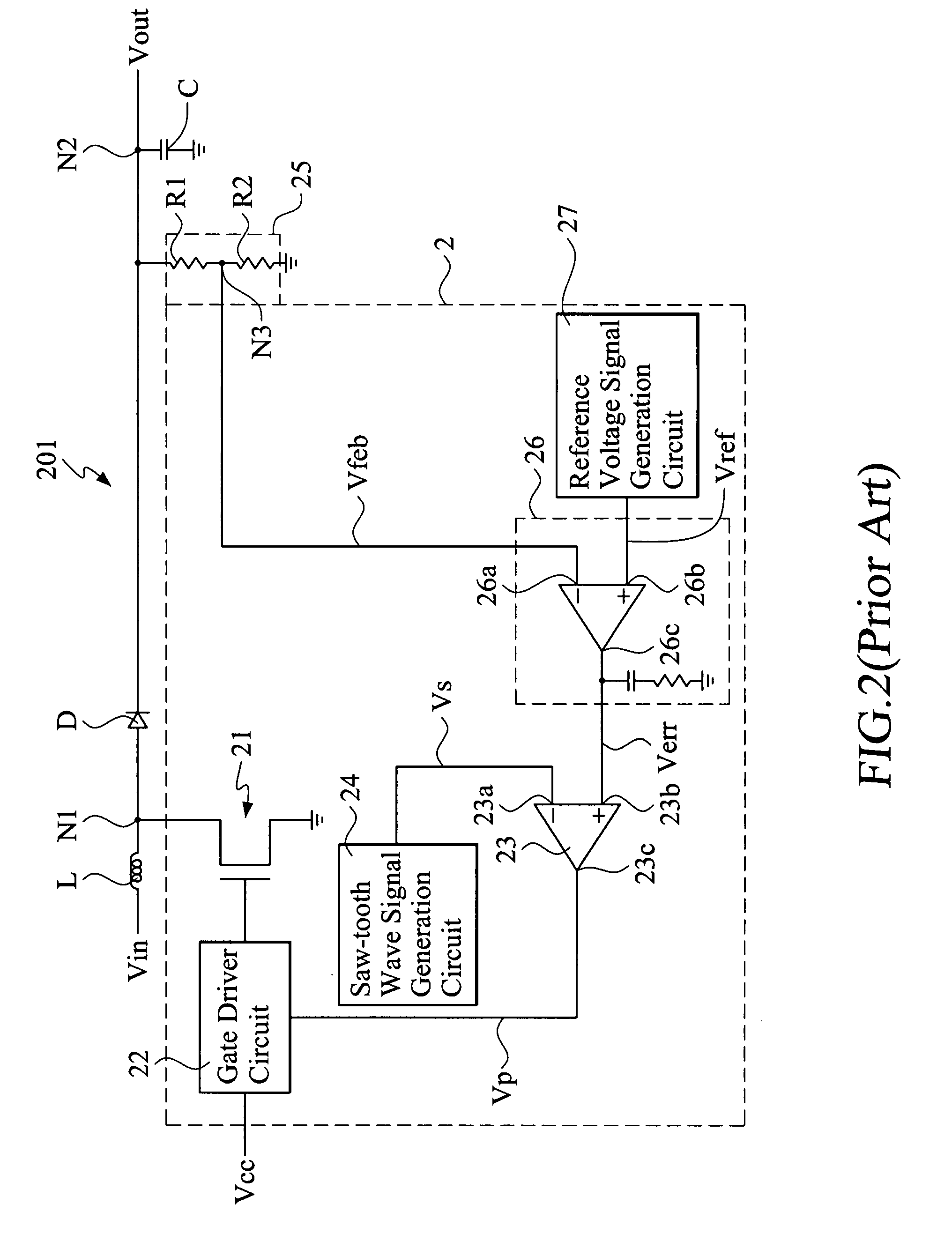
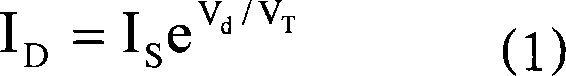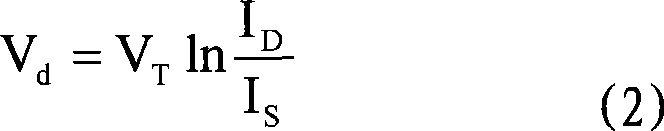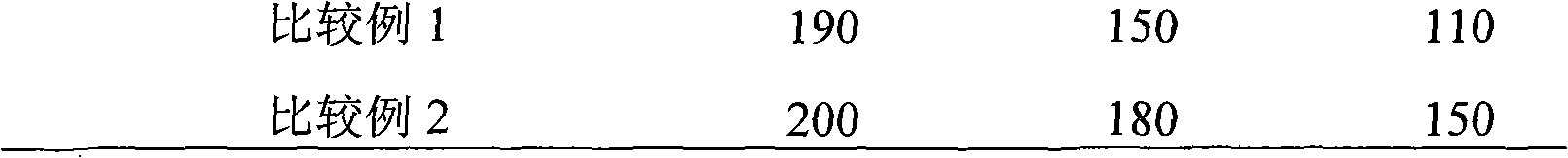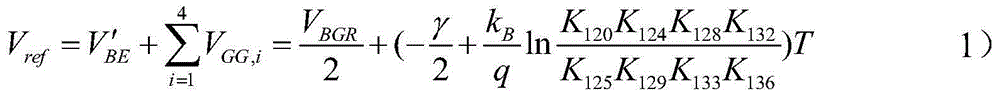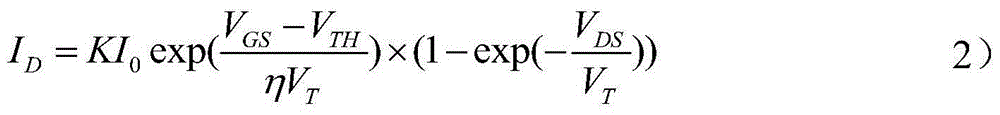Patents
Literature
1584 results about "Negative temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
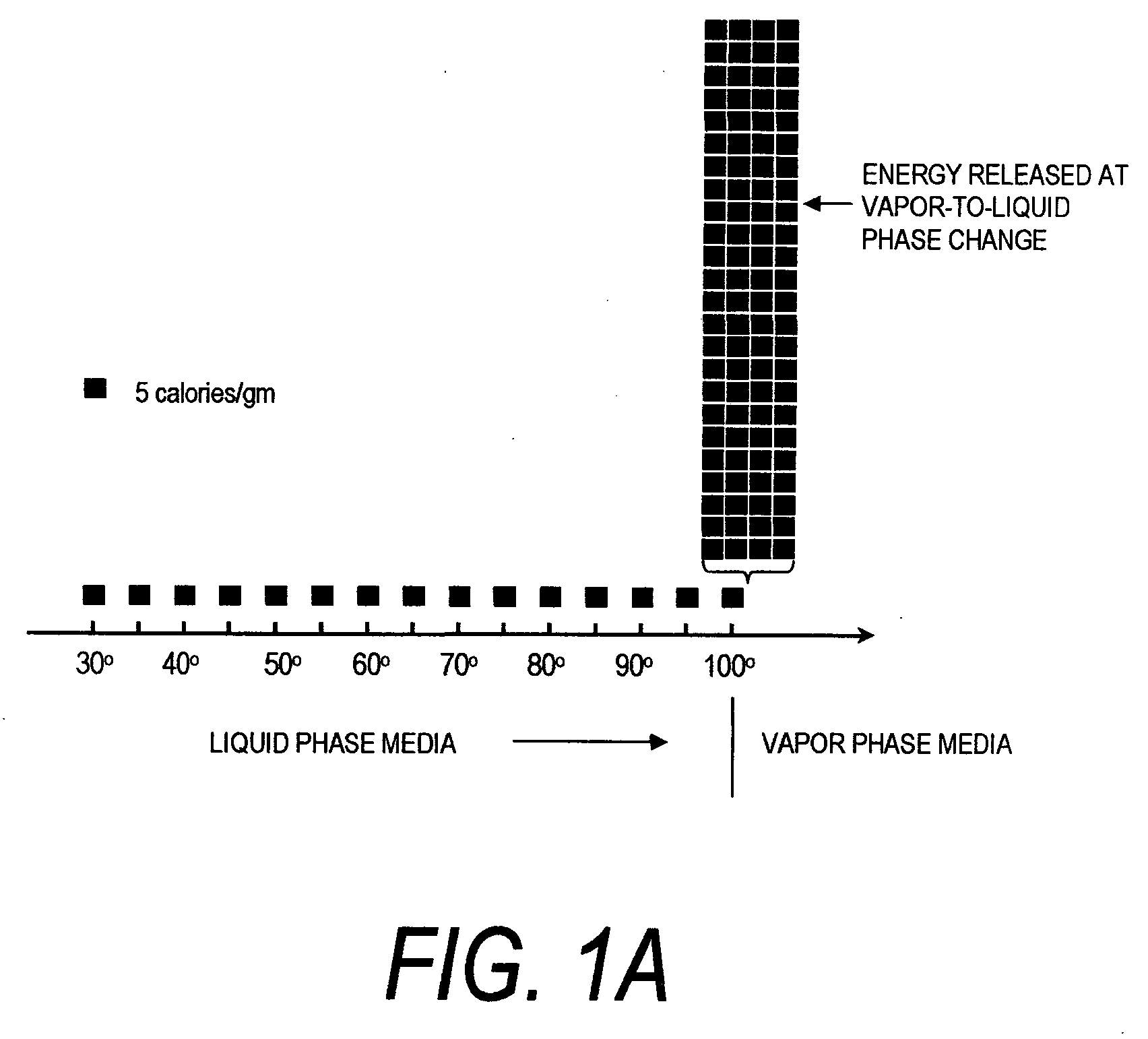
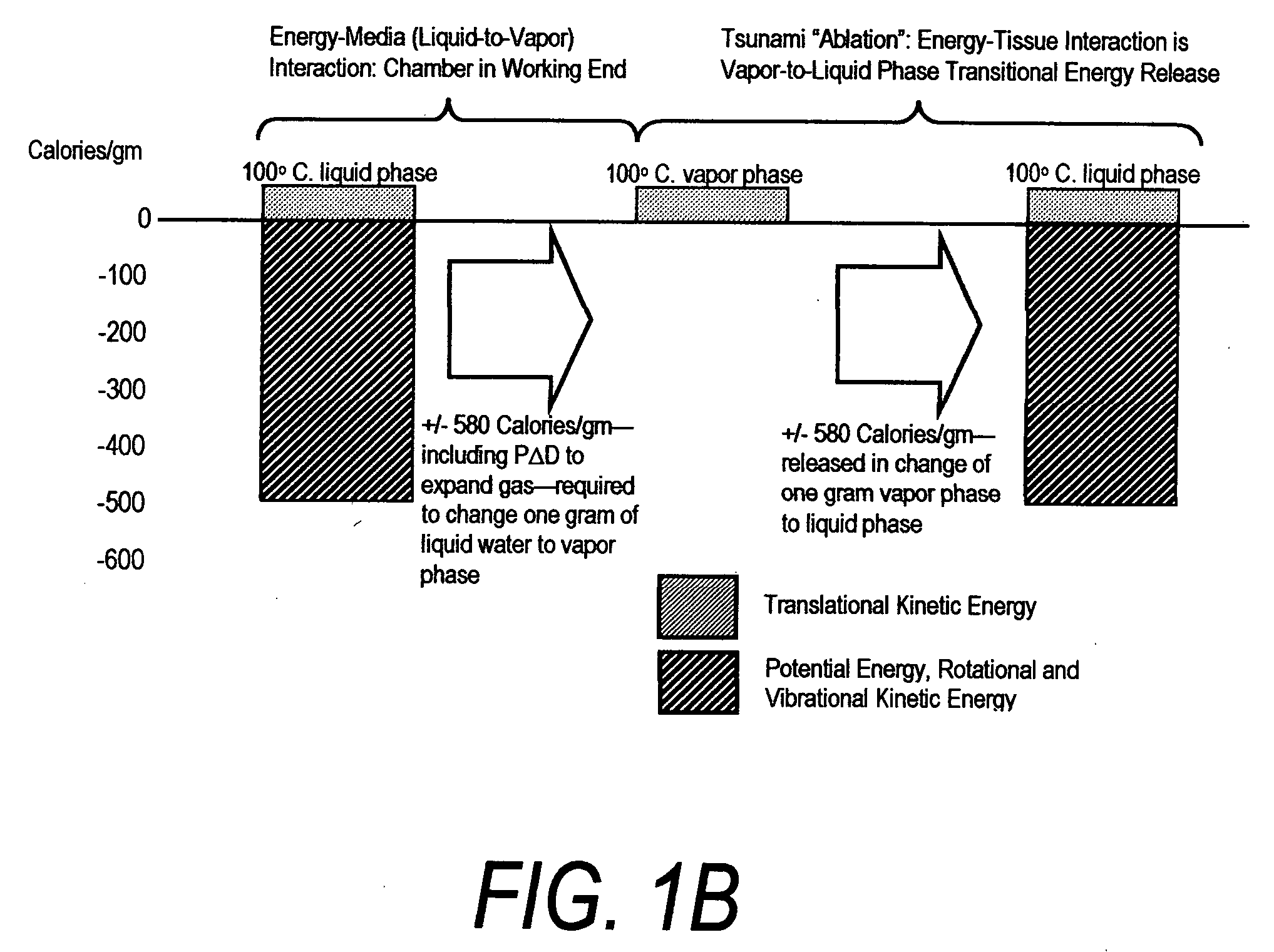
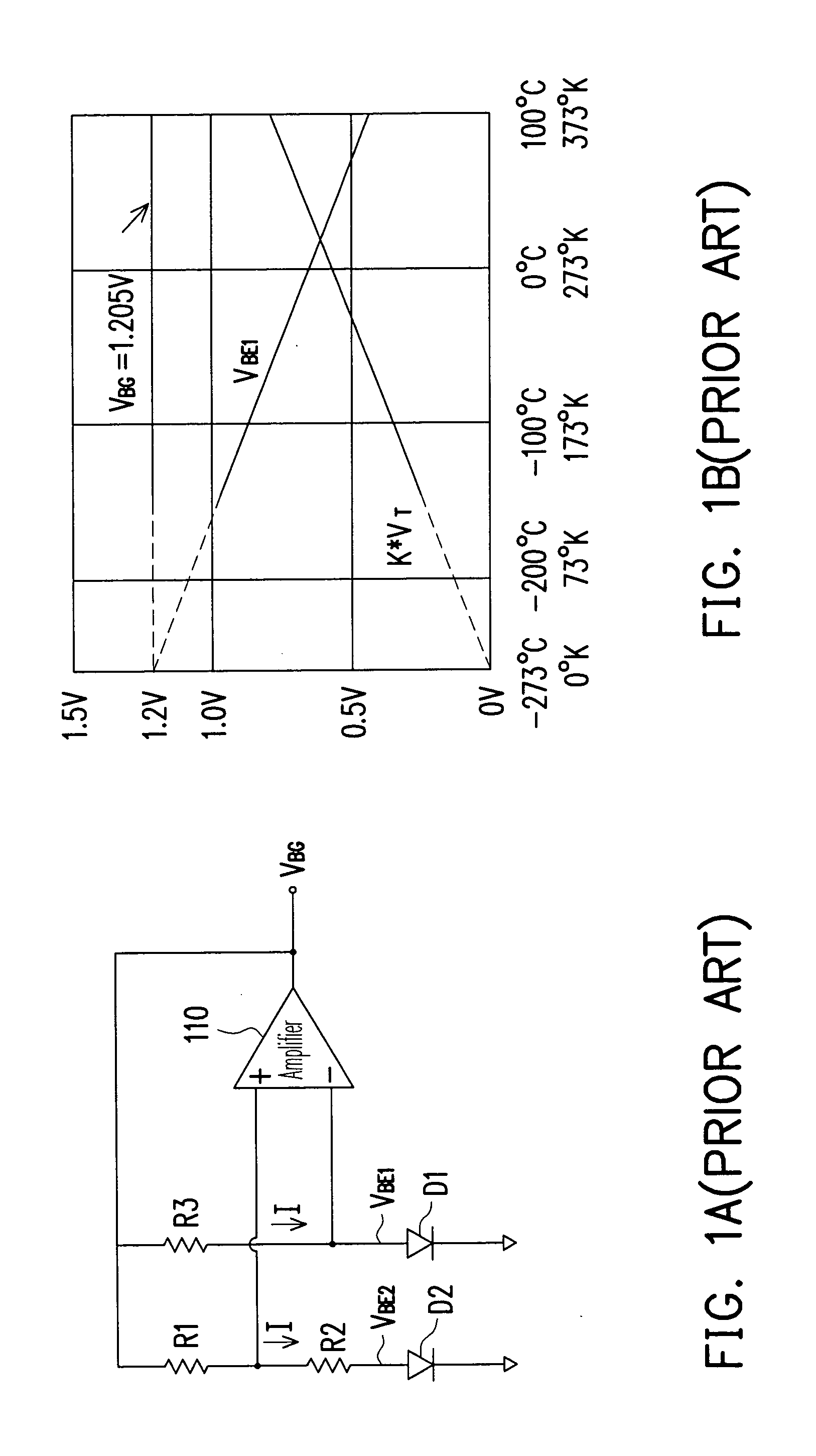
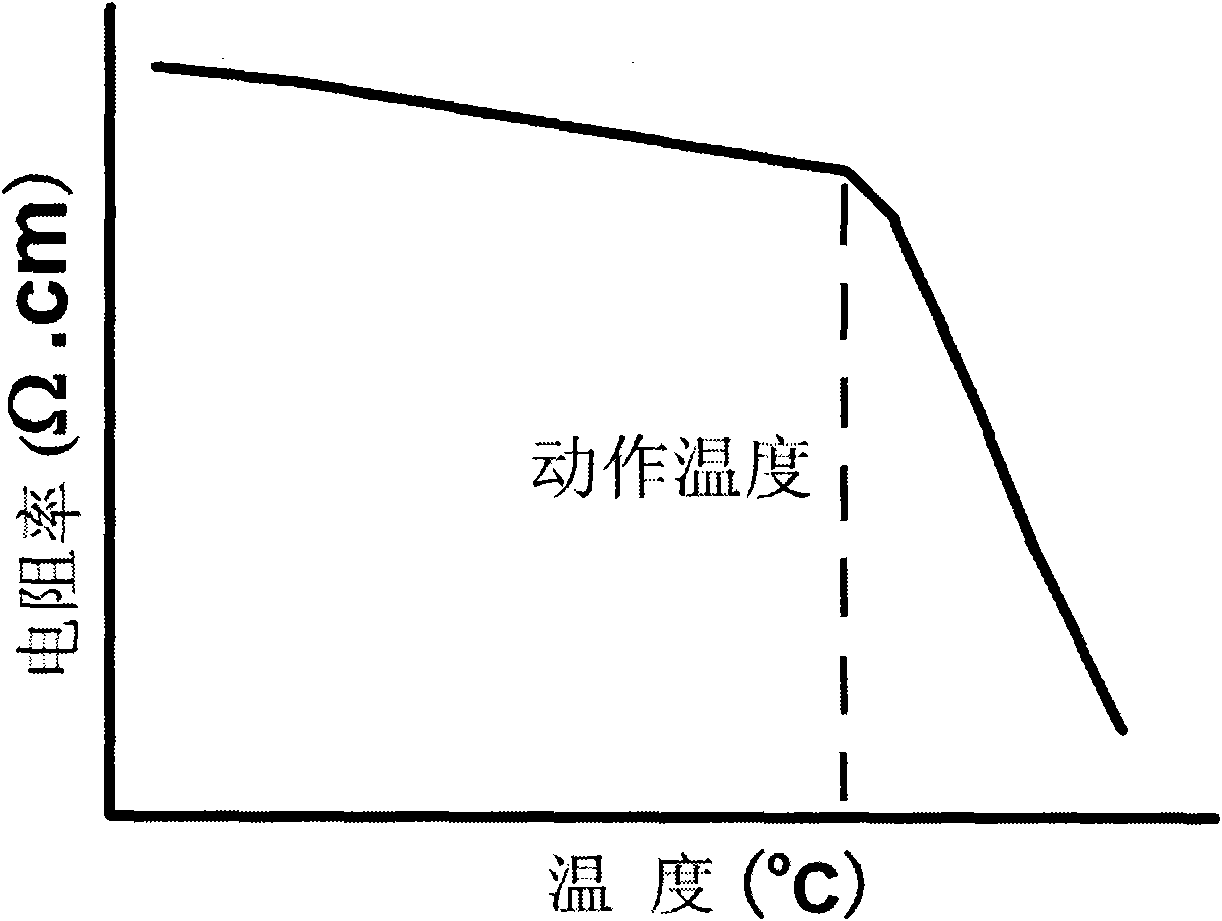
Certain systems can achieve negative temperature; that is, their temperature can be expressed as a negative quantity on the Kelvin or Rankine scales. The absolute temperature (Kelvin) scale can be understood loosely as a measure of average kinetic energy. Usually, system temperatures are positive. However, in particular isolated systems, the temperature defined in terms of Boltzmann's entropy can become negative.
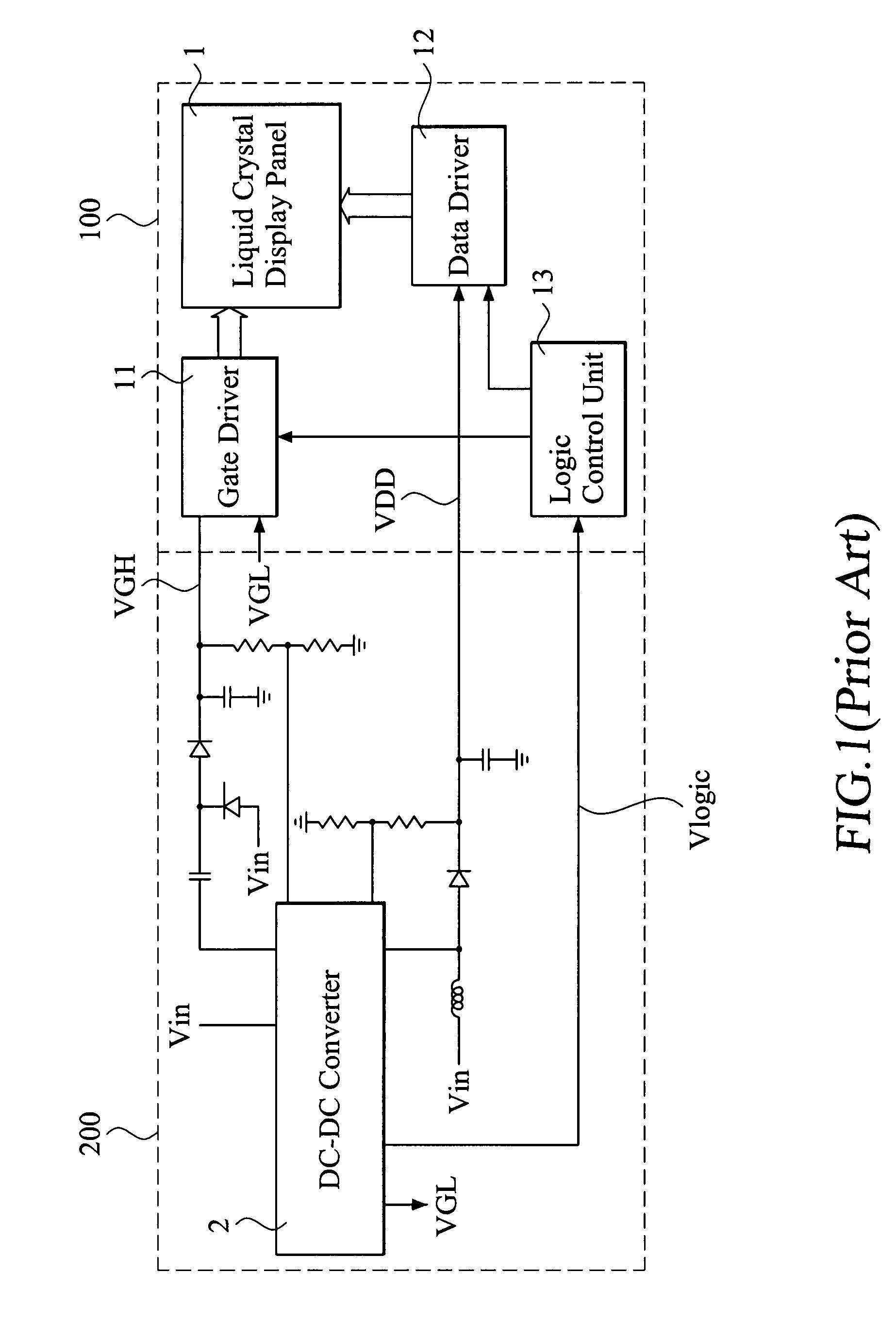
Medical instrument and method of use
ActiveUS20060224154A1Prevents desiccationPrevents escharSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal energyGas phase
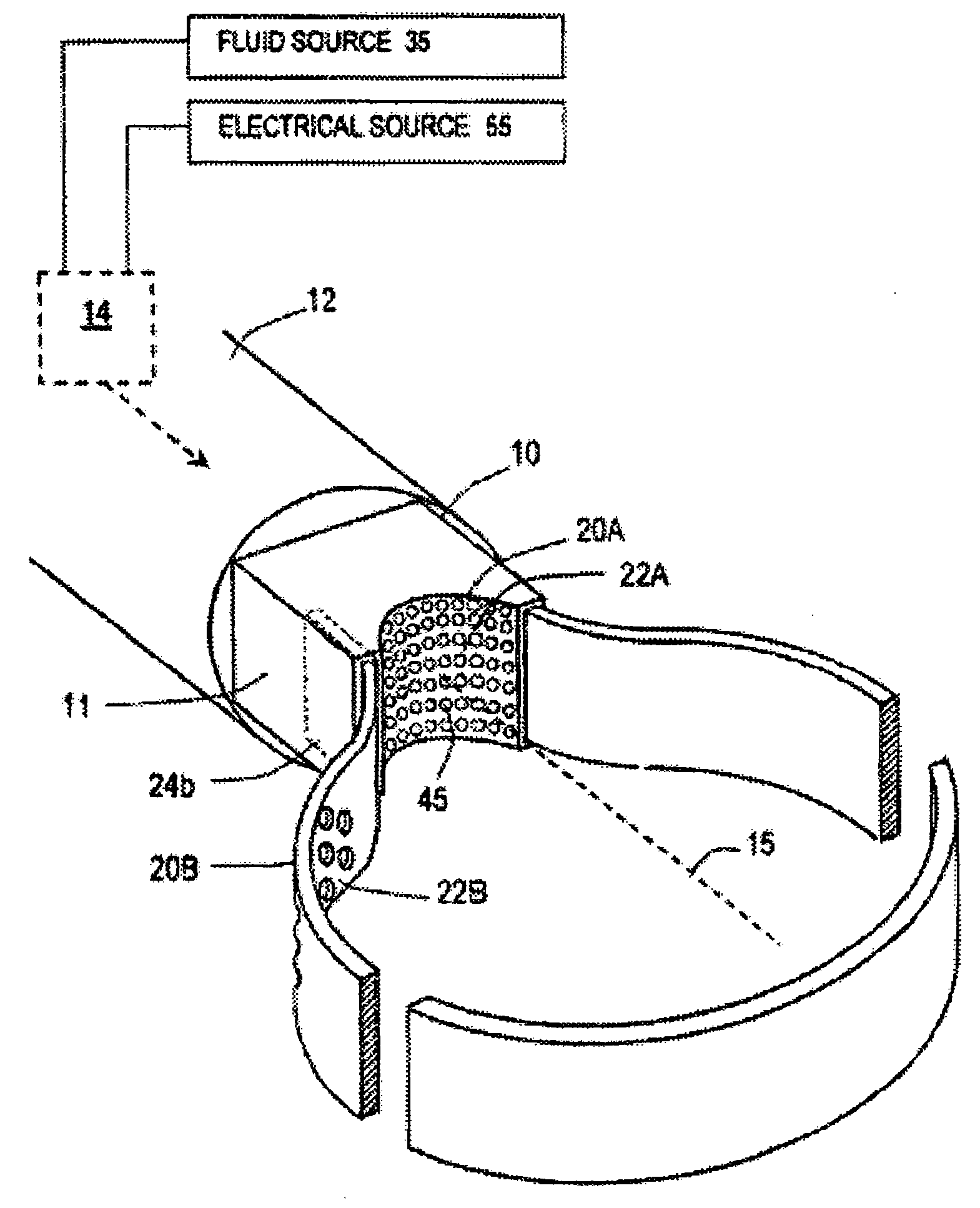
An instrument for thermally-mediated therapies in targeted tissue volumes or for volumetric removal of tissue. In one embodiment, the instrument has an interior chamber that includes a diffuser structure for diffusing a biocompatible conductive fluid that is introduced under high pressure. The interior chamber further includes surfaces of opposing polarity electrodes for vaporizing the small cross-section diffused fluid flows created within a diffuser structure. In one embodiment, the diffuser structure includes a negative temperature coefficient of resistance material between the opposing polarity surfaces. The NTCR structure can self-adjust the lengths of current paths between the opposing polarities to insure complete vaporization of the volume of flow of conductive fluid. The non-ionized vapor phase media is ejected from a working surface of the instrument and a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue applies thermal energy substantially equal to the heat of vaporization to ablate tissue. In another embodiment, the instrument provides voltage means for converting the non-ionized vapor phase media into an ionized media or plasma for applying energy to body structure.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
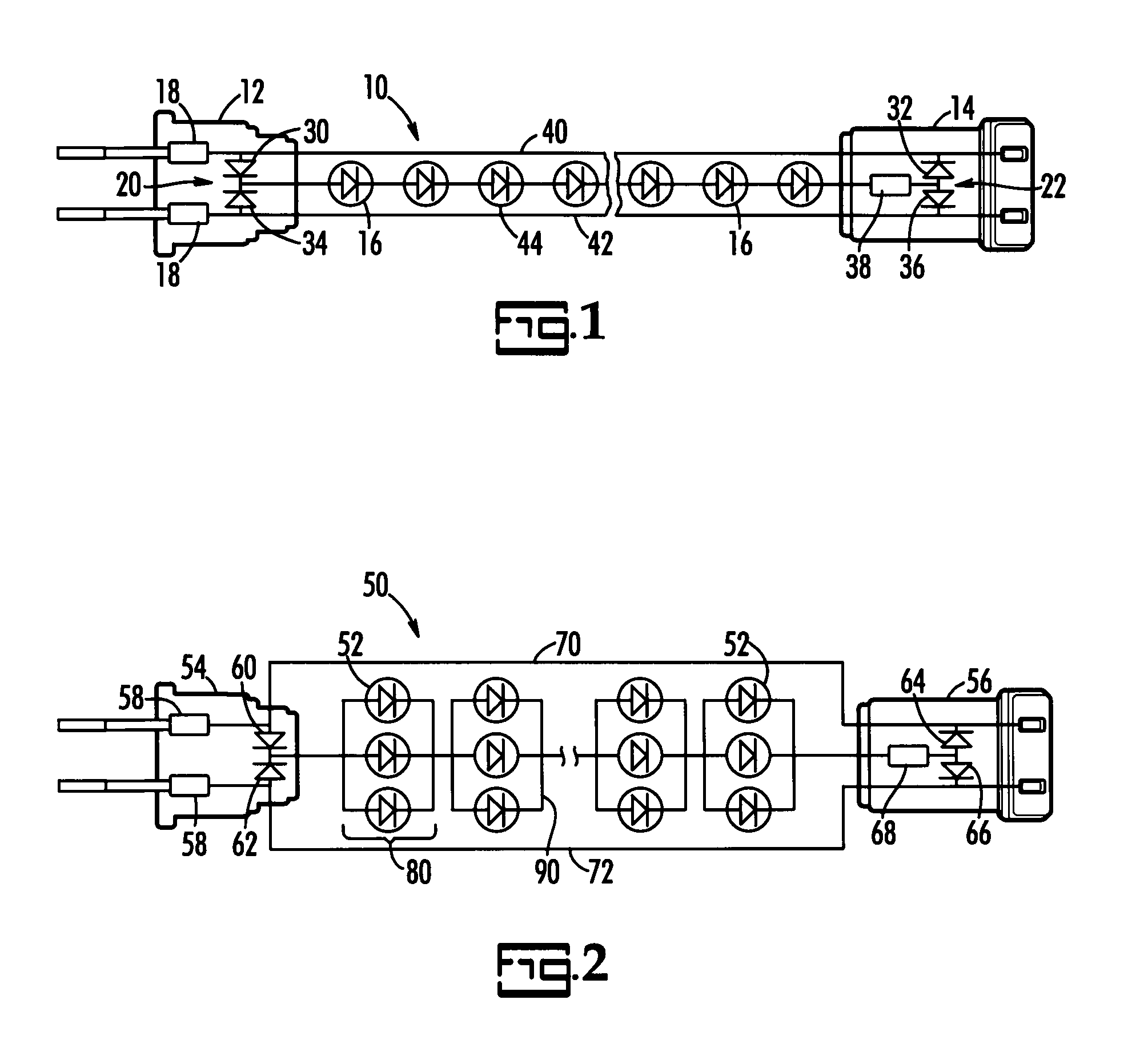
LED light string with split bridge rectifier and thermistor fuse
Owner:BEST POINT GROUP LTD
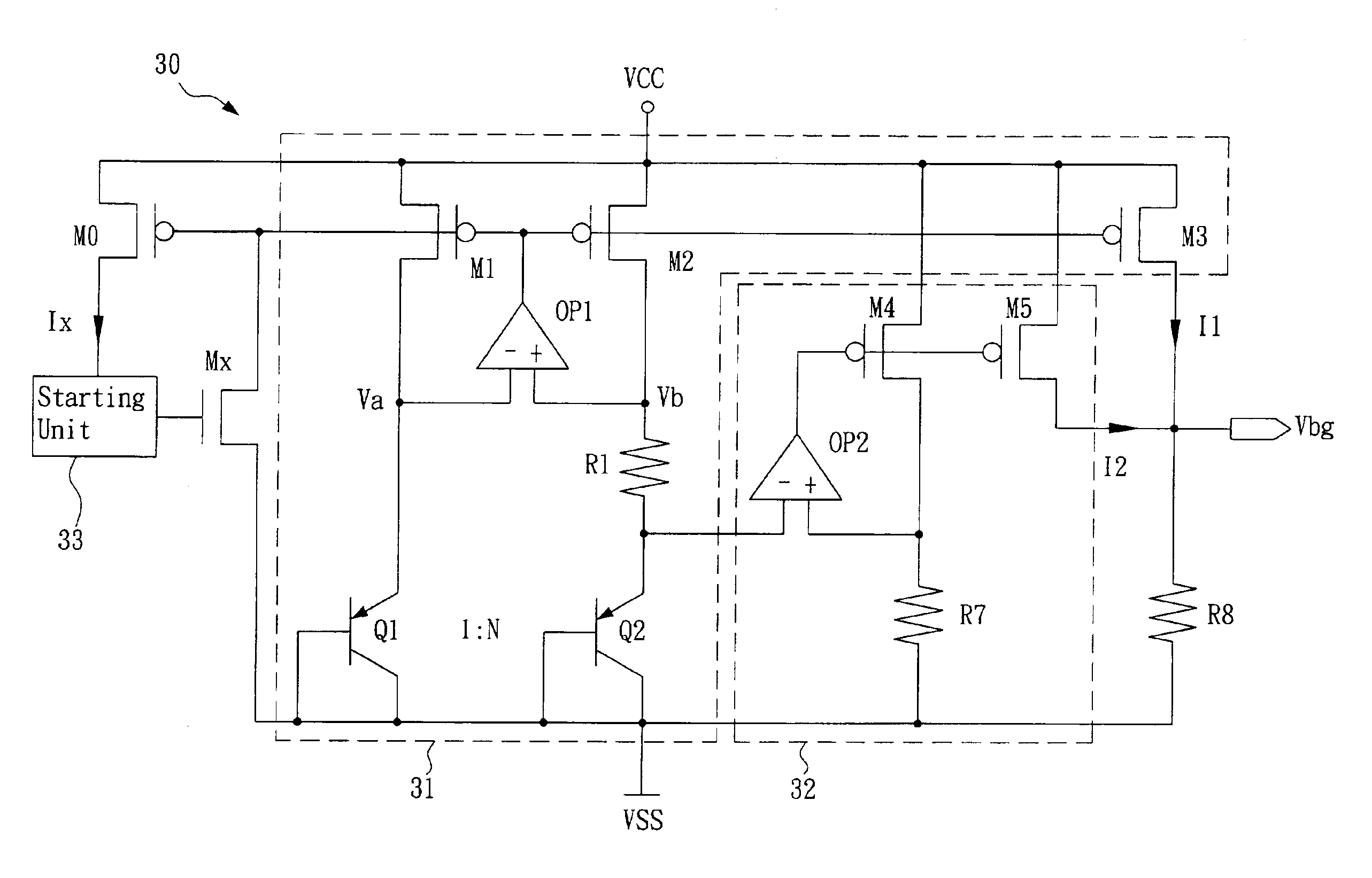
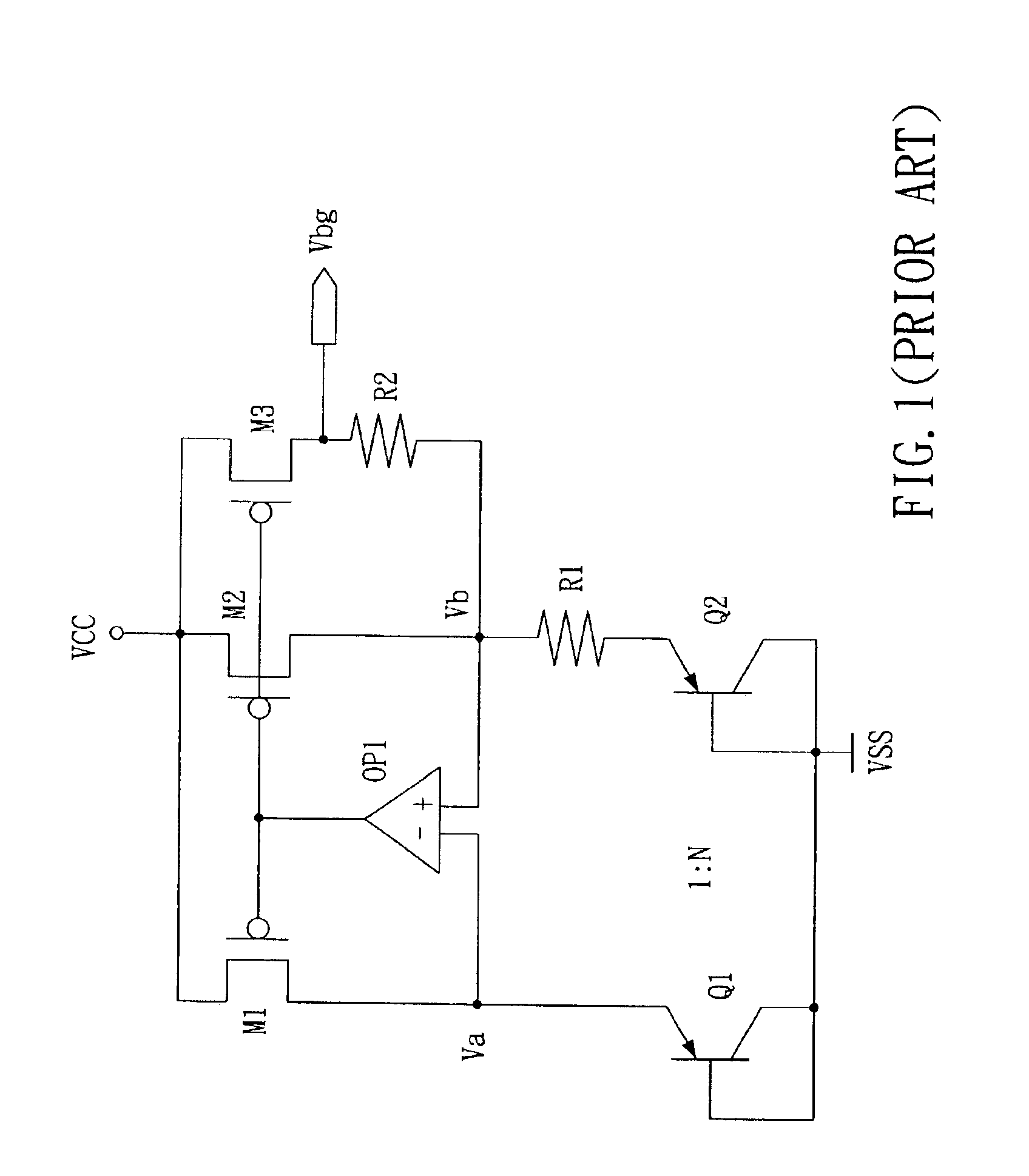
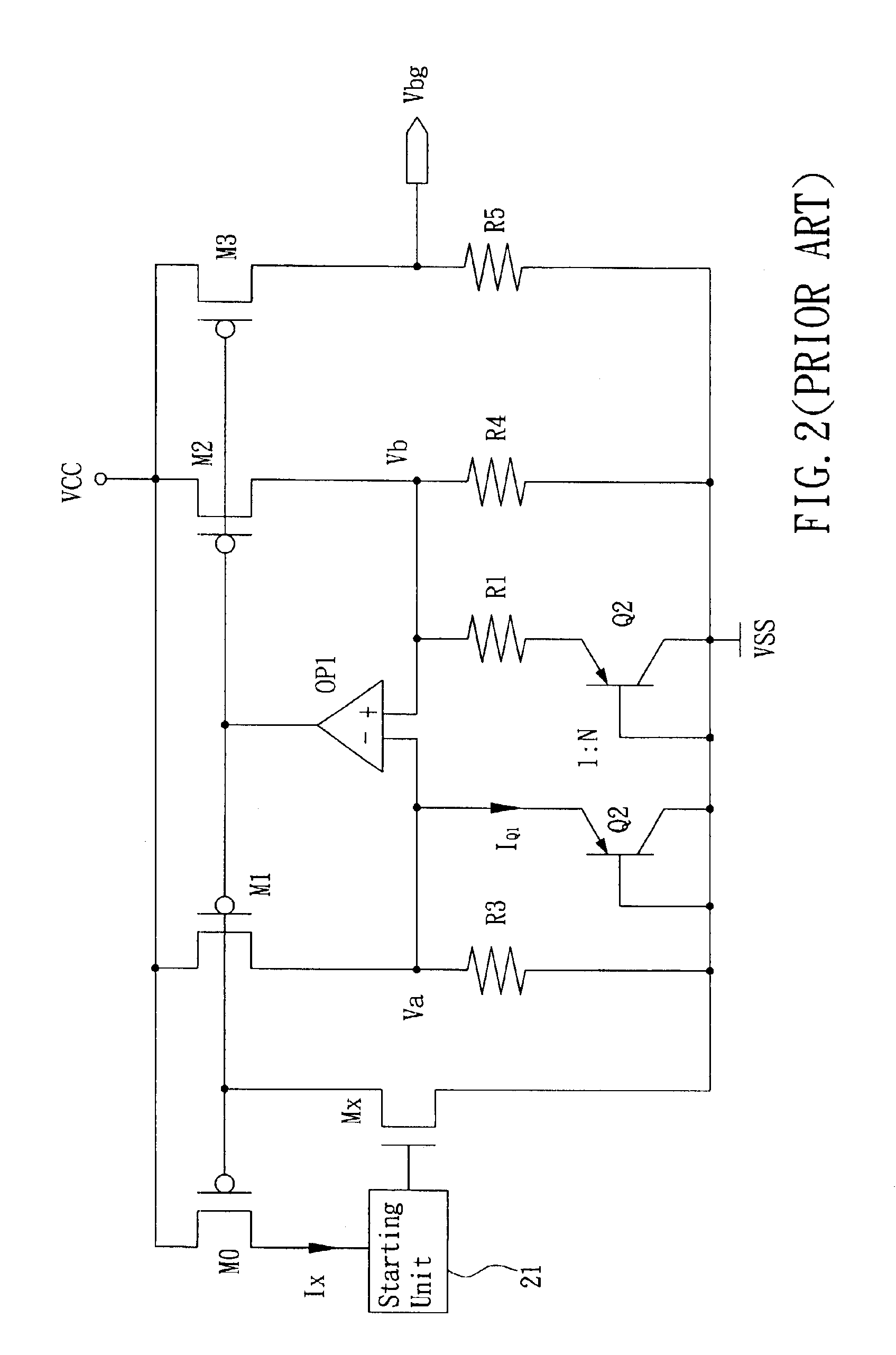
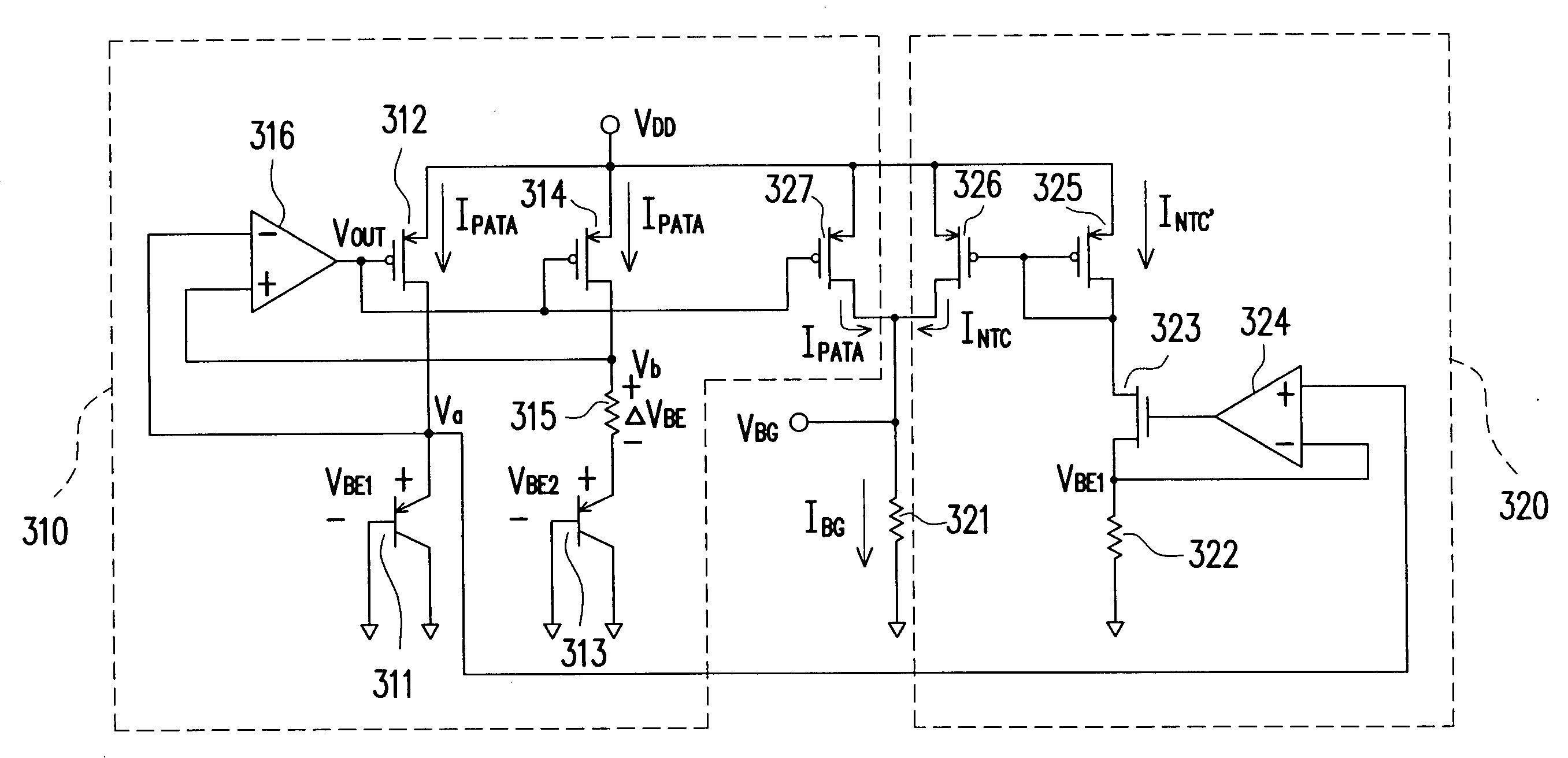
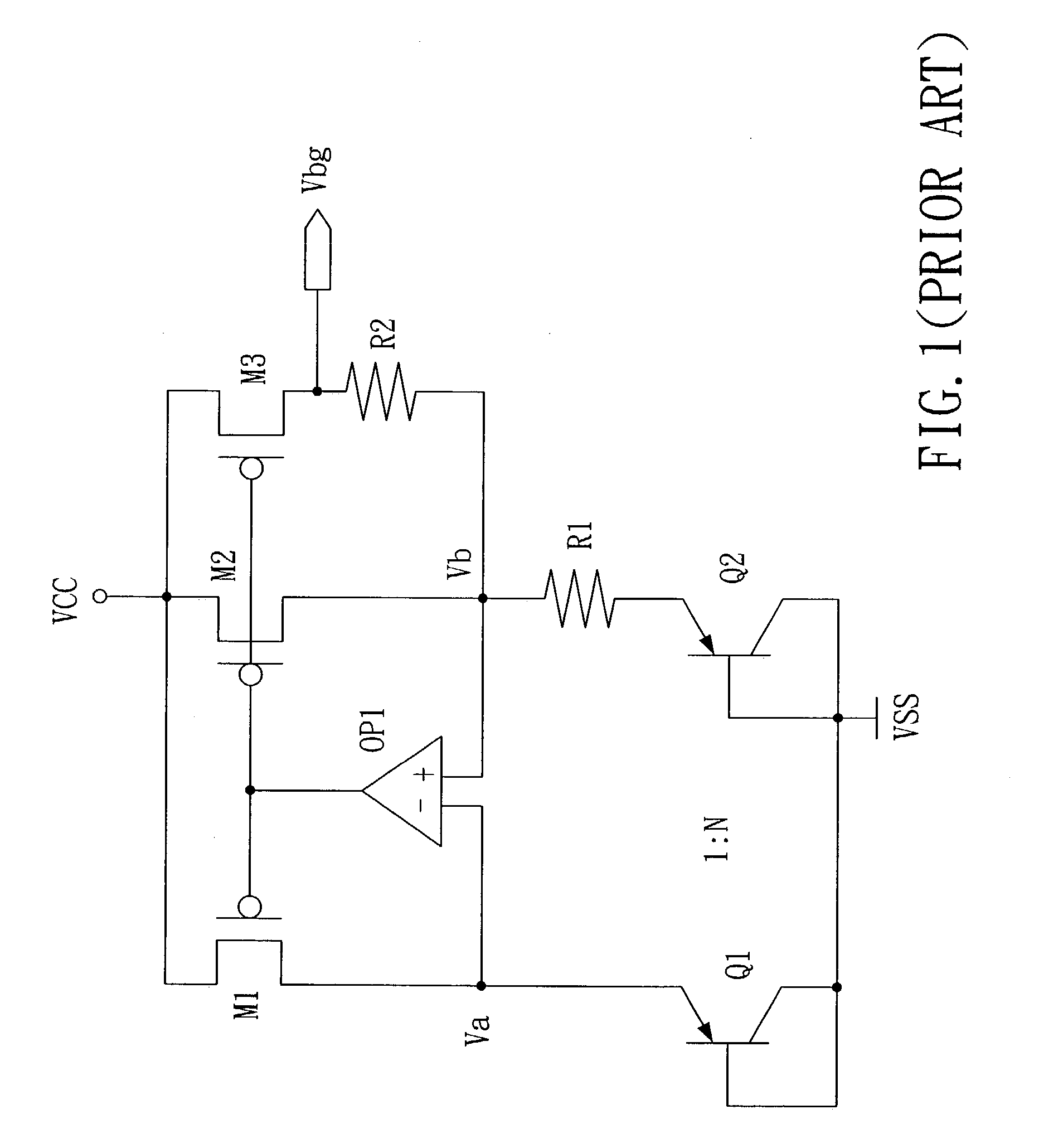
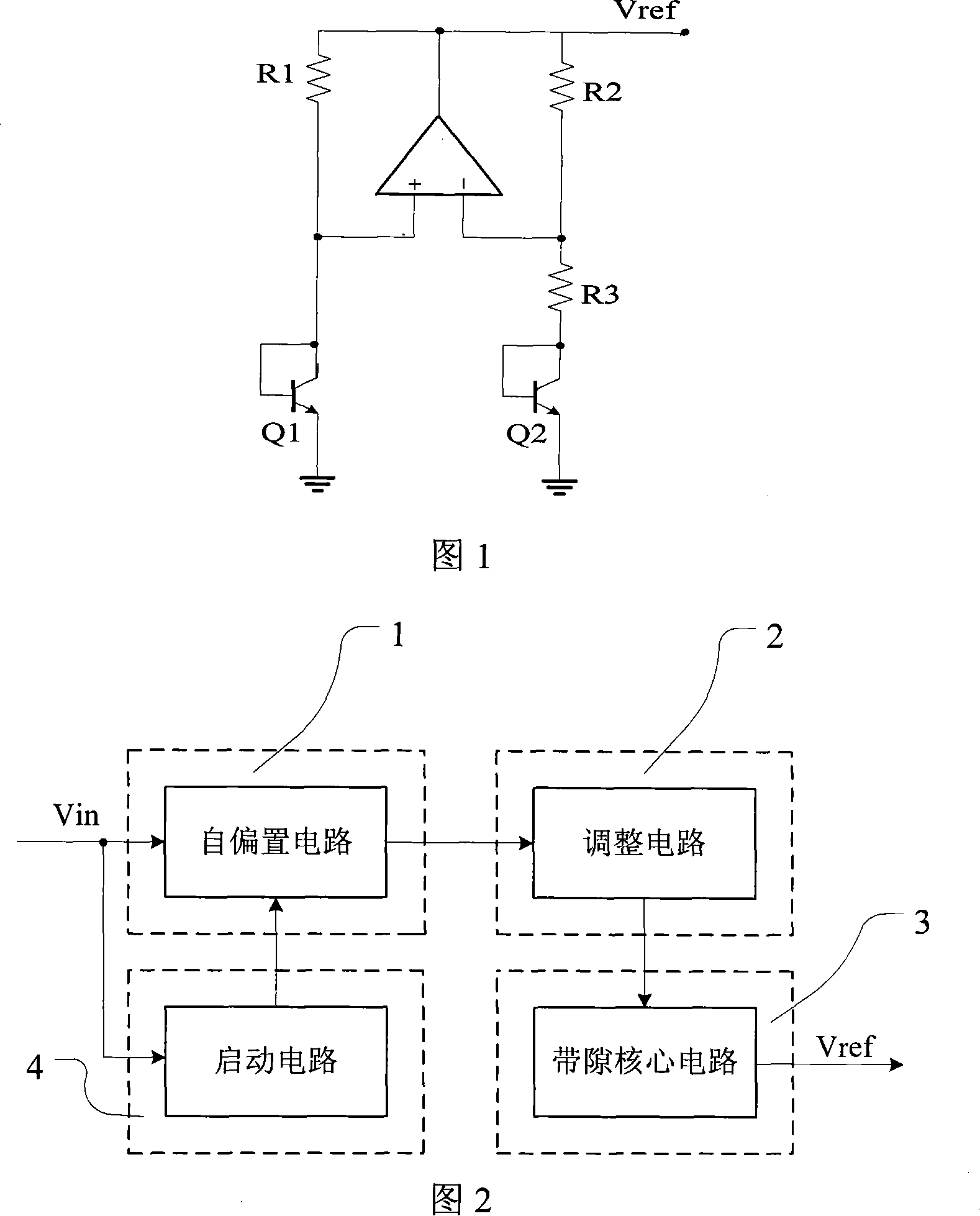
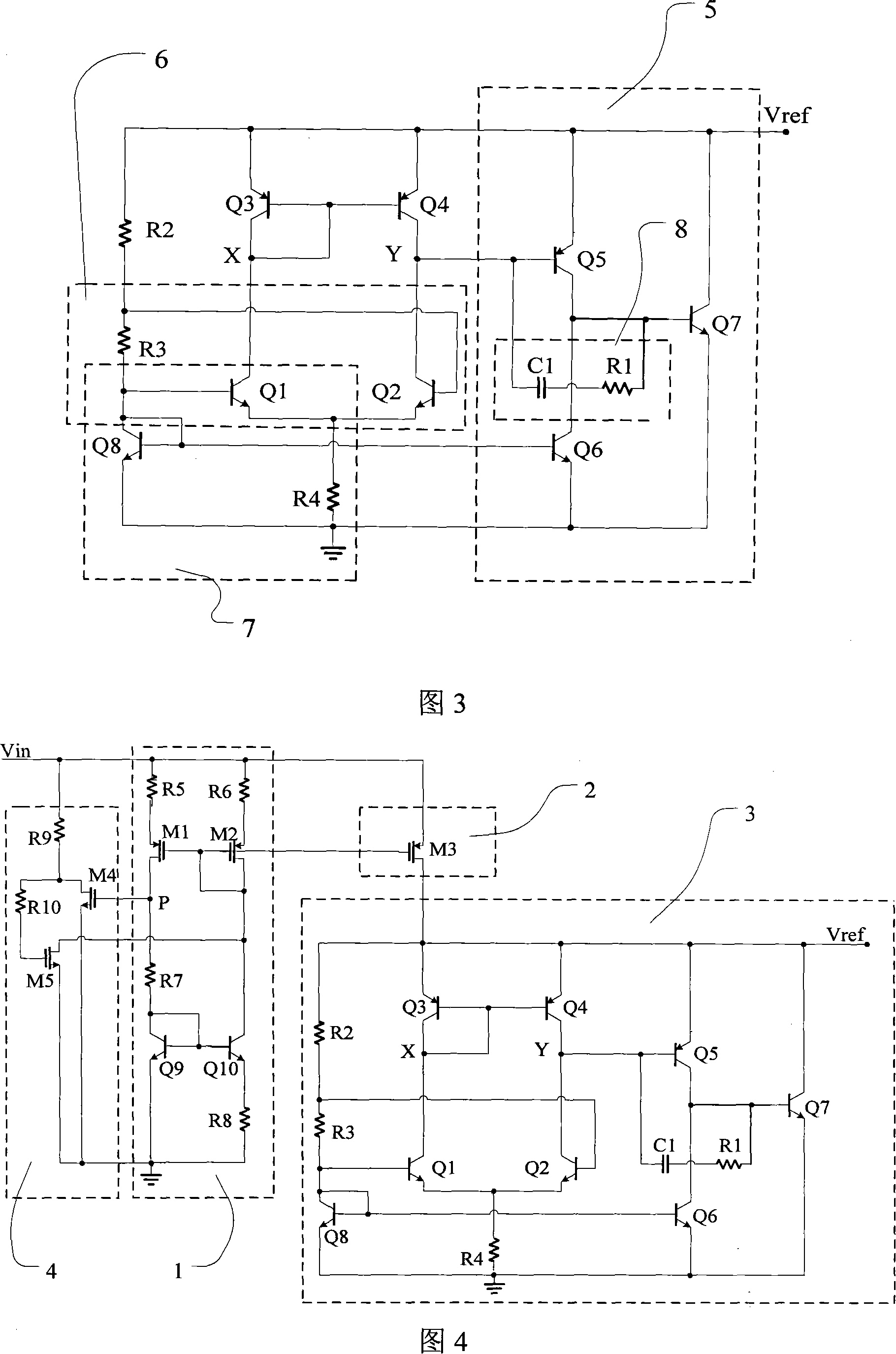
Fast start-up low-voltage bandgap voltage reference circuit
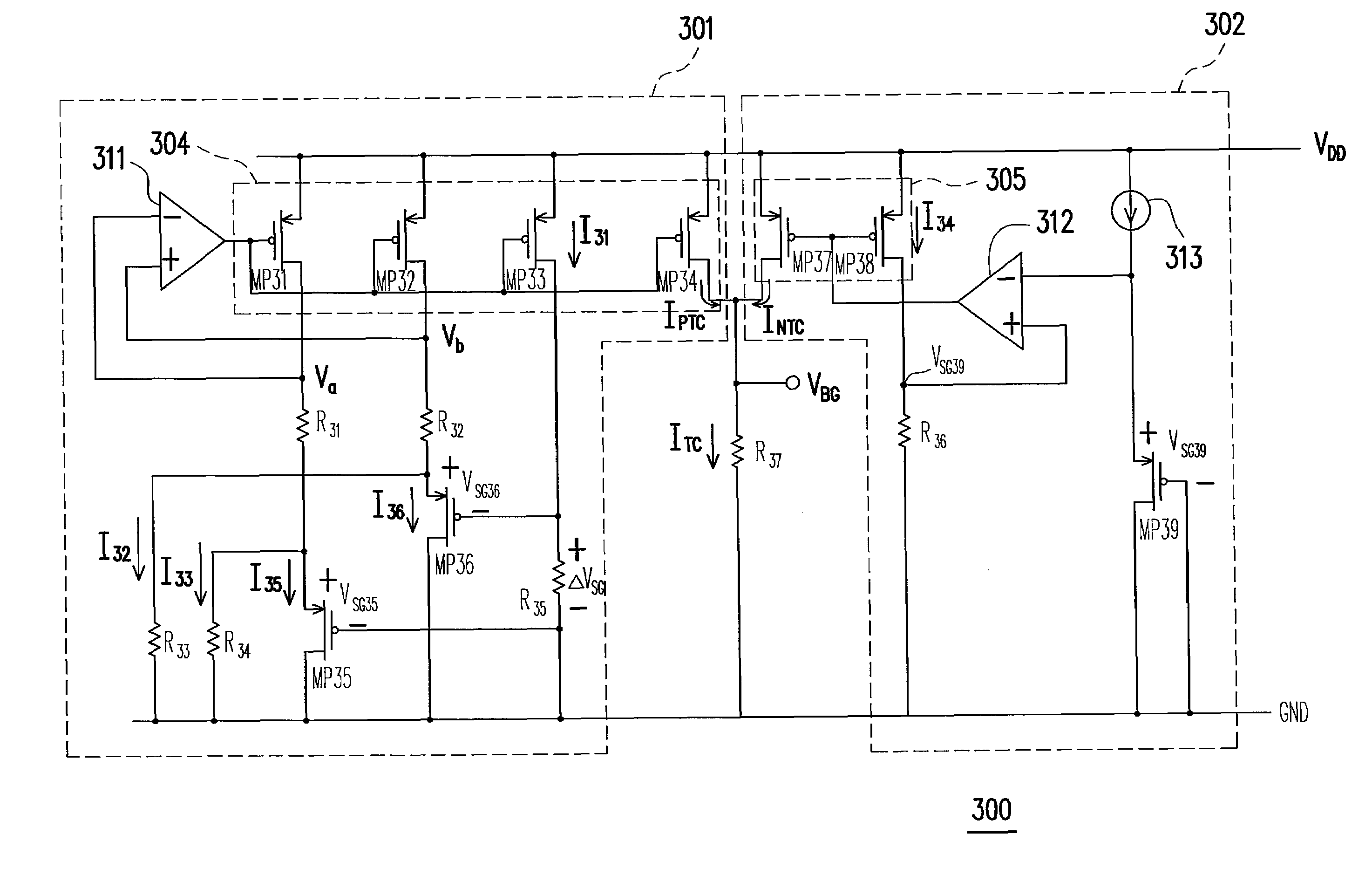
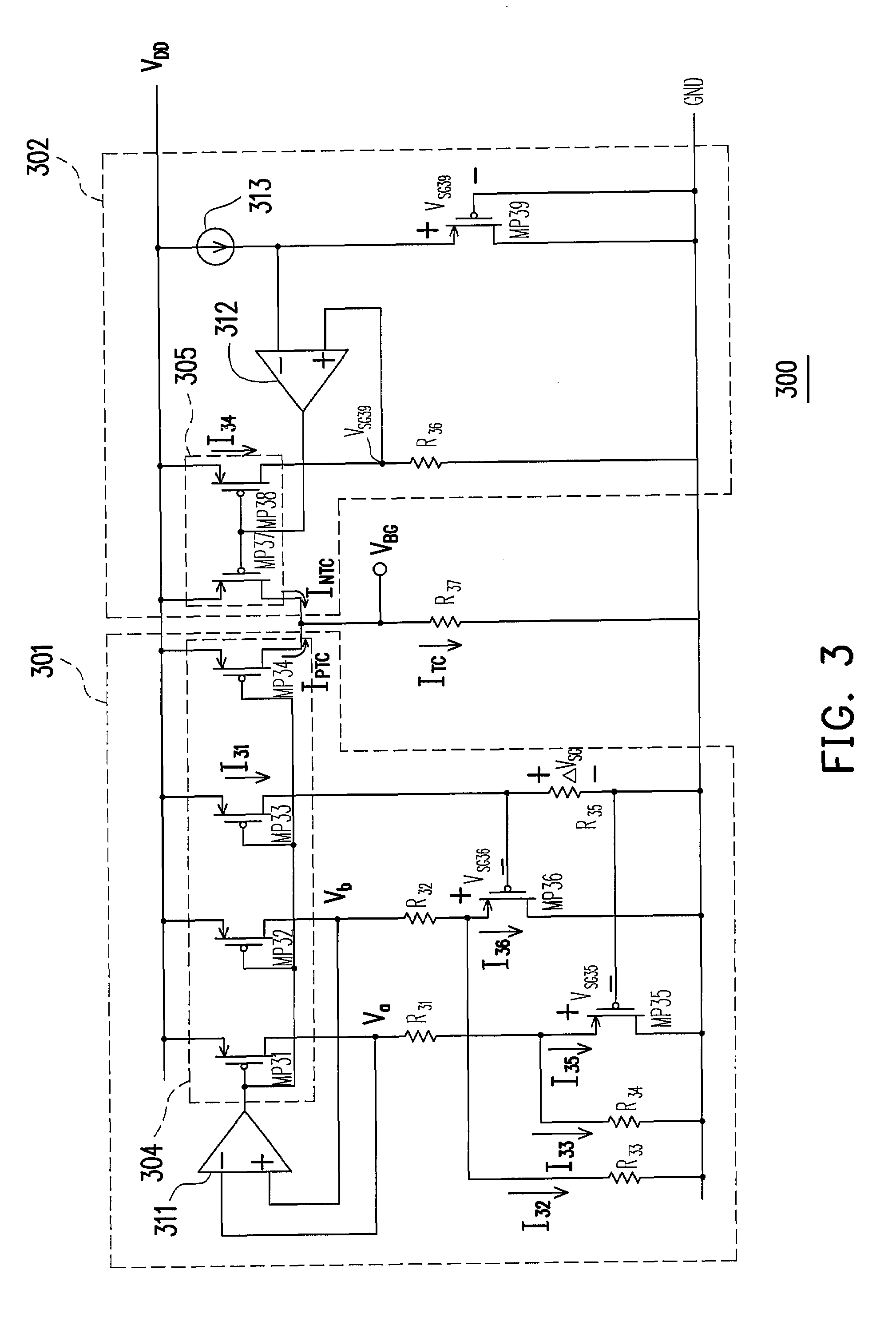
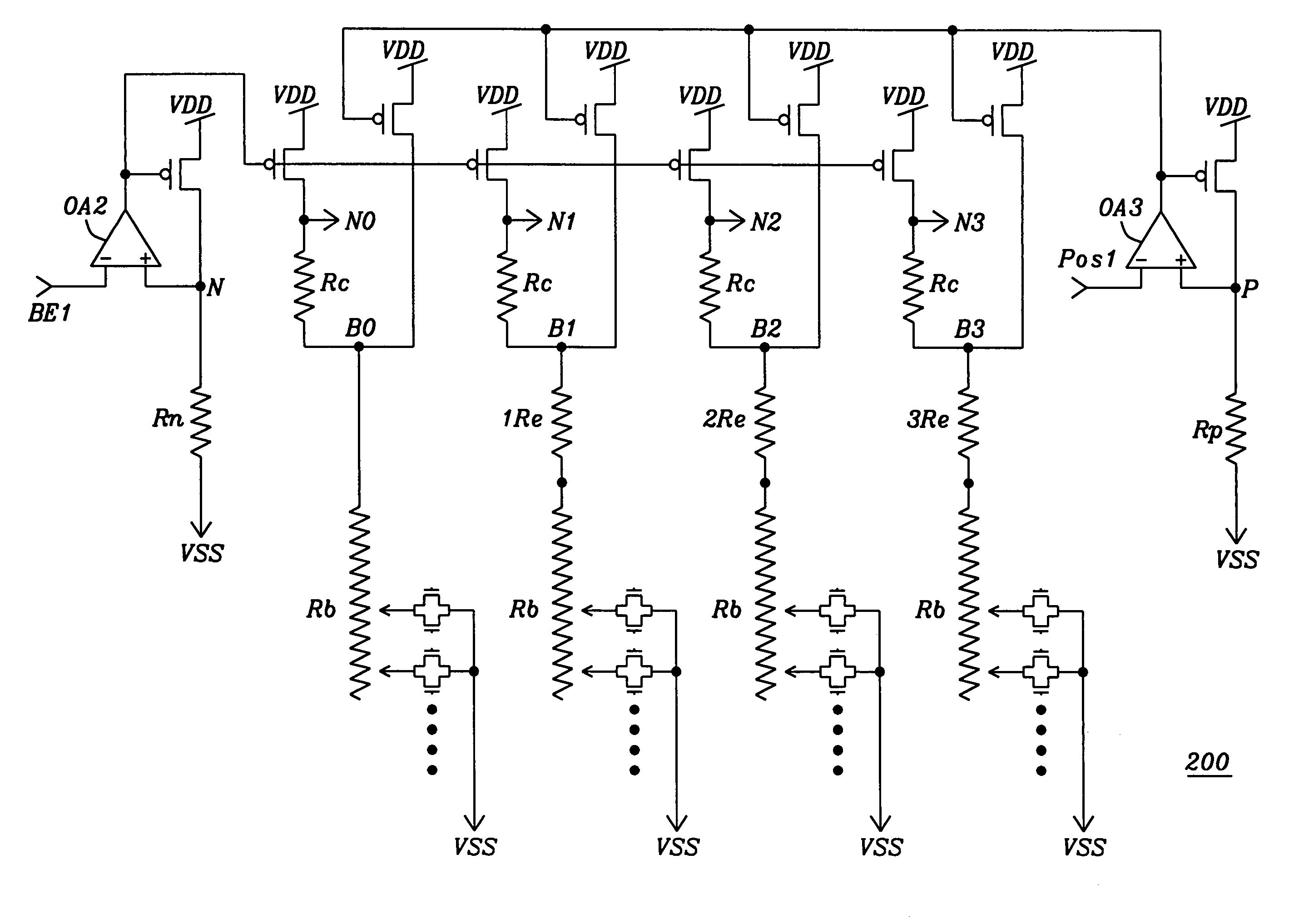
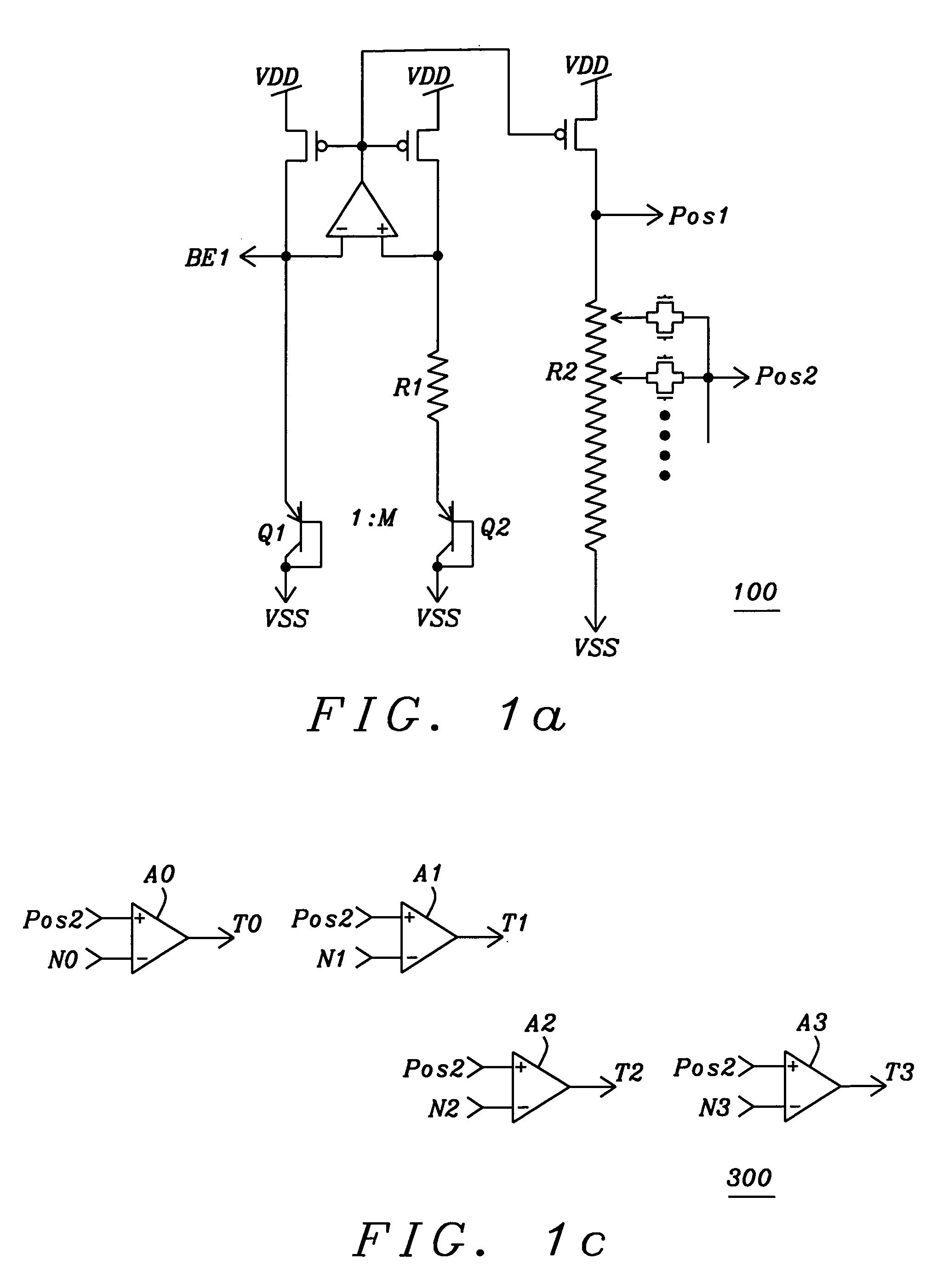
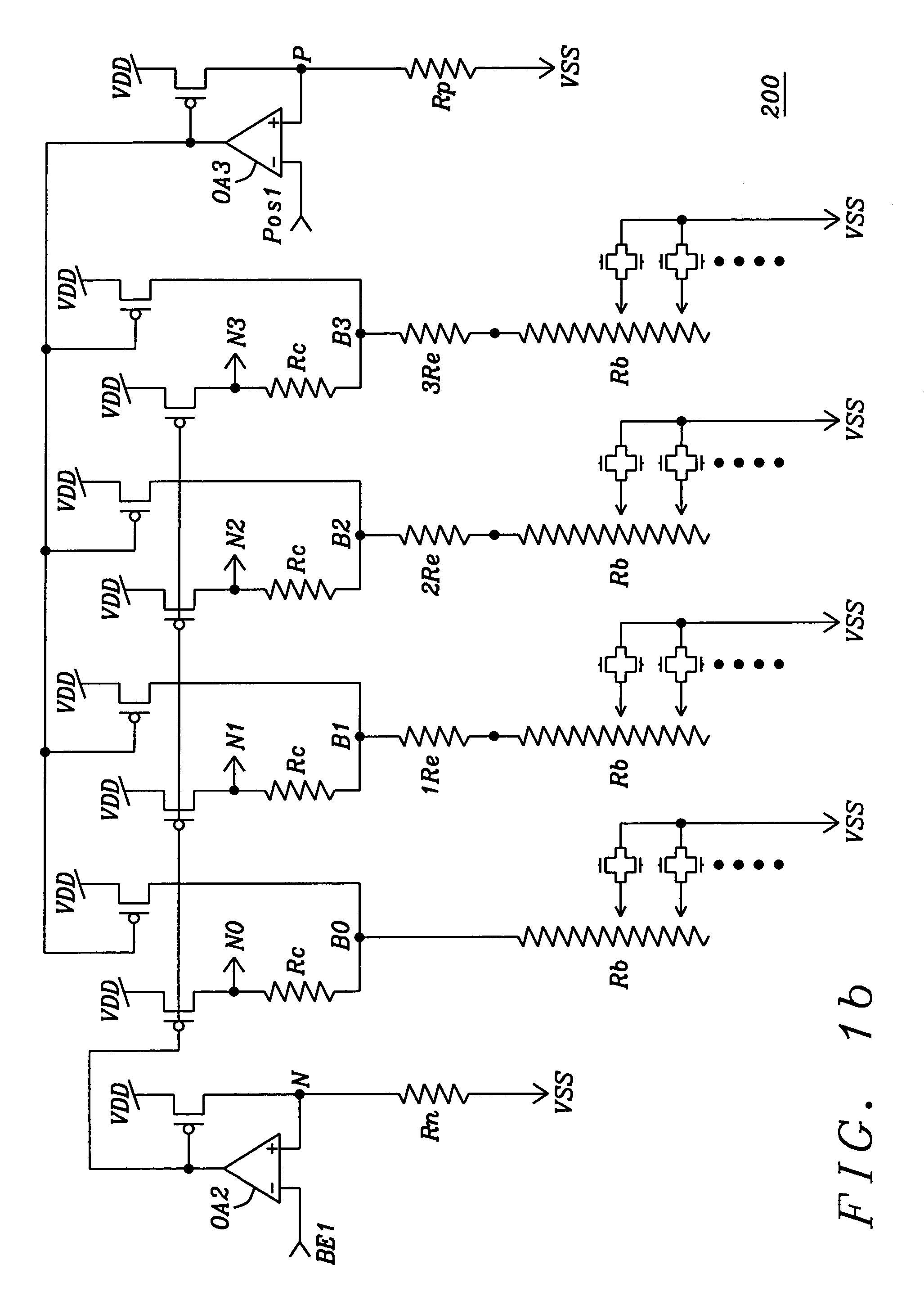
A fast start-up low-voltage bandgap voltage reference circuit is disclosed. The bandgap voltage reference circuit includes: a first current generator, which is implemented by a self-bias unit and a current mirror for generating a first reference current with positive temperature coefficient; a second current generator, which is connected to a point with negative temperature coefficient in the first current generator to generate a second reference current with negative temperature coefficient; and a resistor for converting the first reference current and the second reference current into a low-voltage bandgap voltage independent of temperature. Because the bandgap voltage reference circuit of the invention uses the resistor to convert the first reference current and the second reference current into voltage, the circuit can provide low-voltage bandgap voltage.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Color LED driver
ActiveUS20070171159A1Small sizeLow costStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentNegative temperature
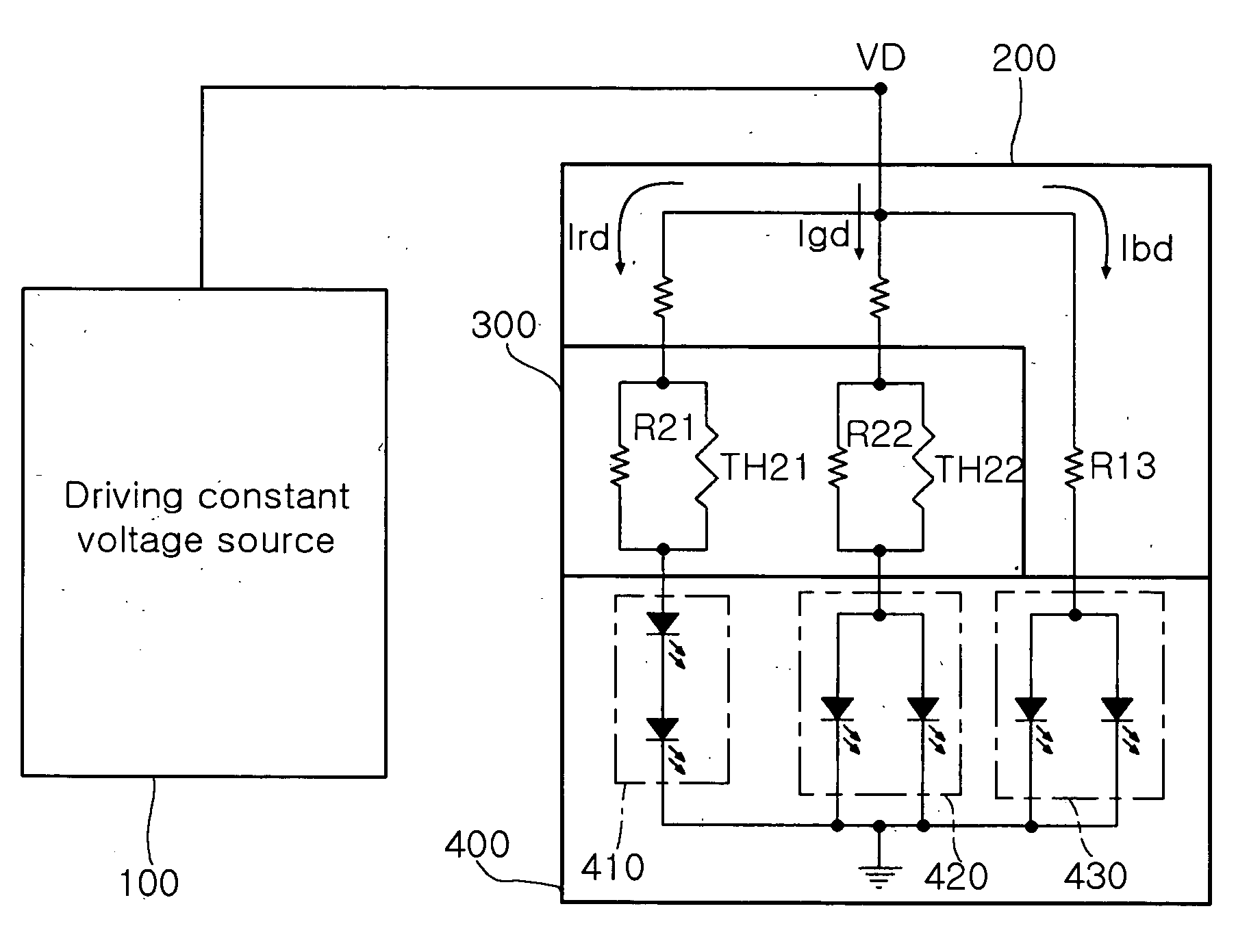
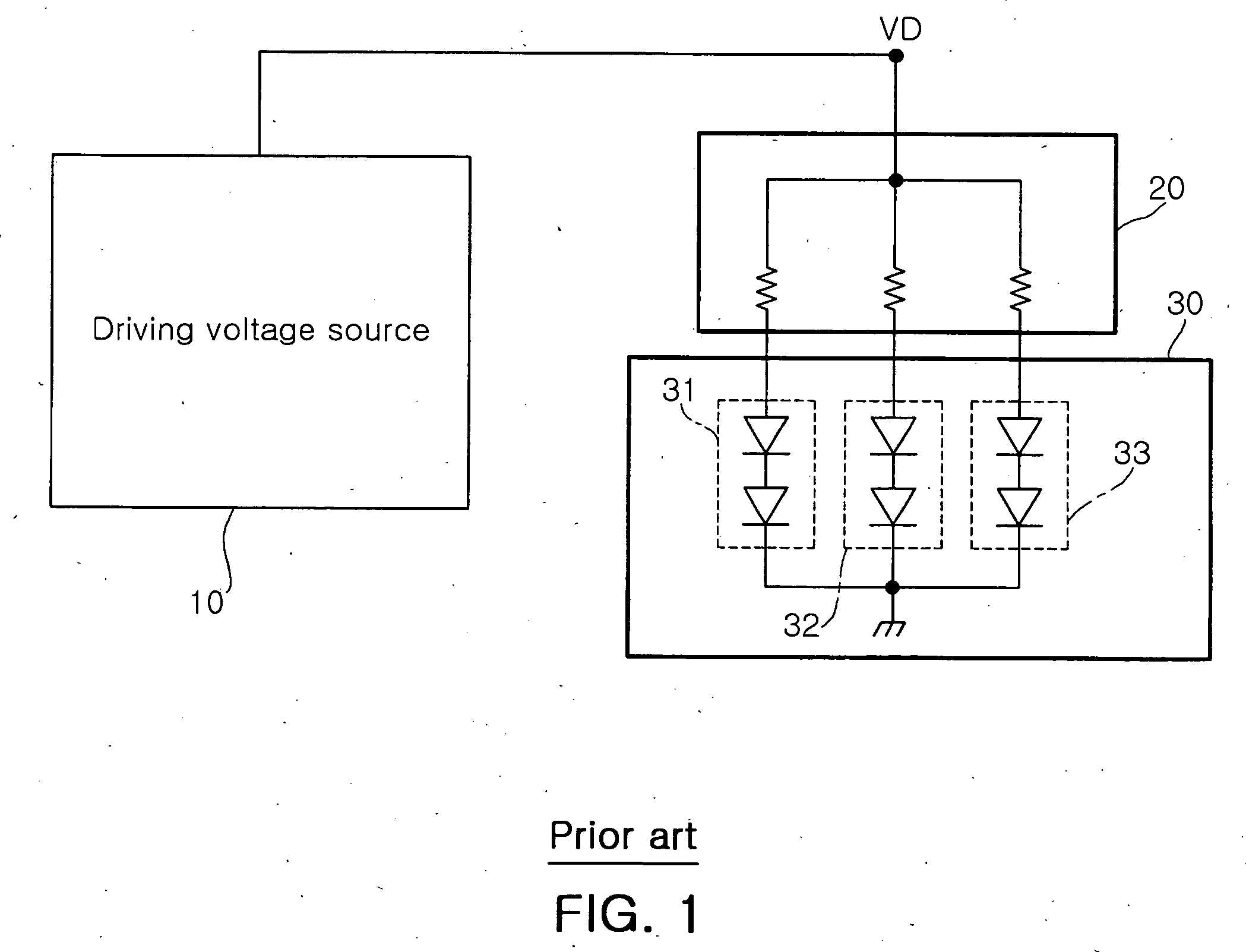
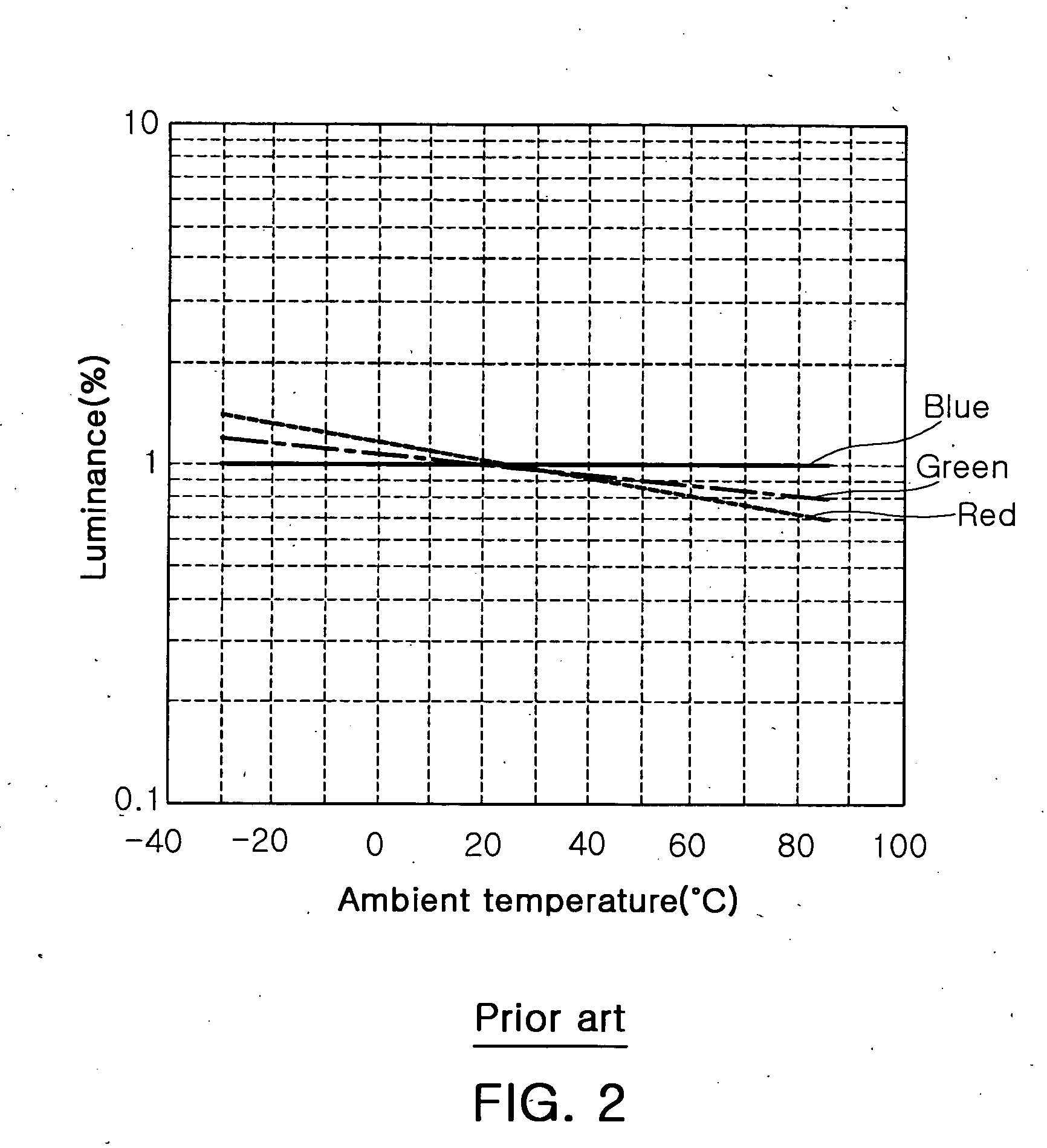
Disclosed herein is a color LED driver, which is capable of being implemented by a compact structure without a feedback structure and accompanying a small size and low cost, by directly connecting a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor to a driving current path of a color LED applied to an LCD backlight to compensate a characteristic variation of the LED due to a variation in a temperature. The color LED driver includes a driving constant voltage source 100 which supplies a predetermined driving constant voltage VD; a driving circuit 200 which converts the driving constant voltage VD of the driving constant voltage source 100 into a plurality of driving currents, for driving color LEDs, the plurality of driving currents including red LED driving current Ird, green LED driving current Igd and blue LED driving current Ibd; a temperature compensation unit 300 which compensates variations in the red LED driving current Ird and the green LED driving current Igd due to a variation in a temperature, among the plurality of driving currents from the driving circuit 200; and an LED unit 400 including a plurality of color LEDs which are turned on by the driving currents from the temperature compensation circuit 300 and the driving current from the driving circuit 200.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
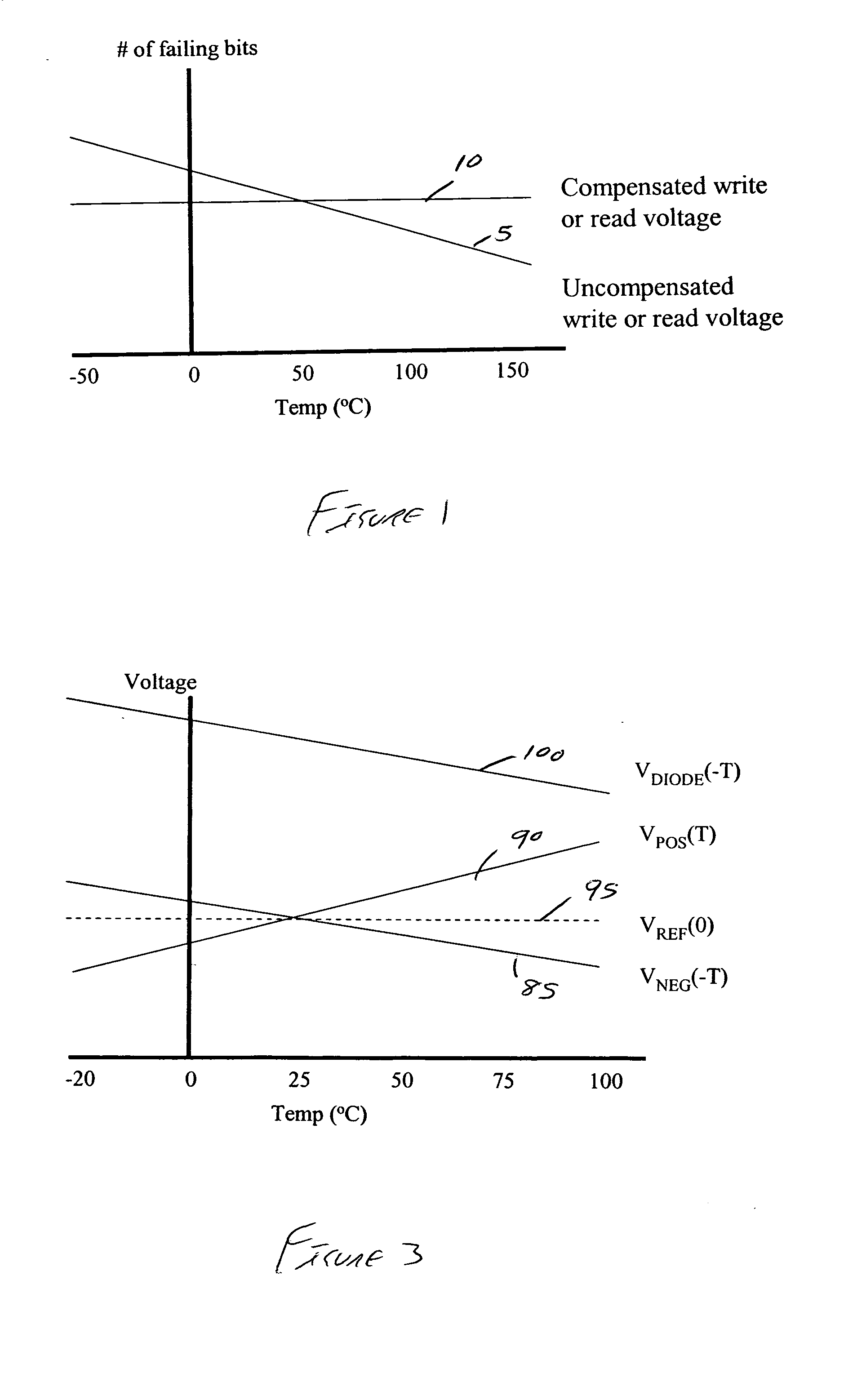
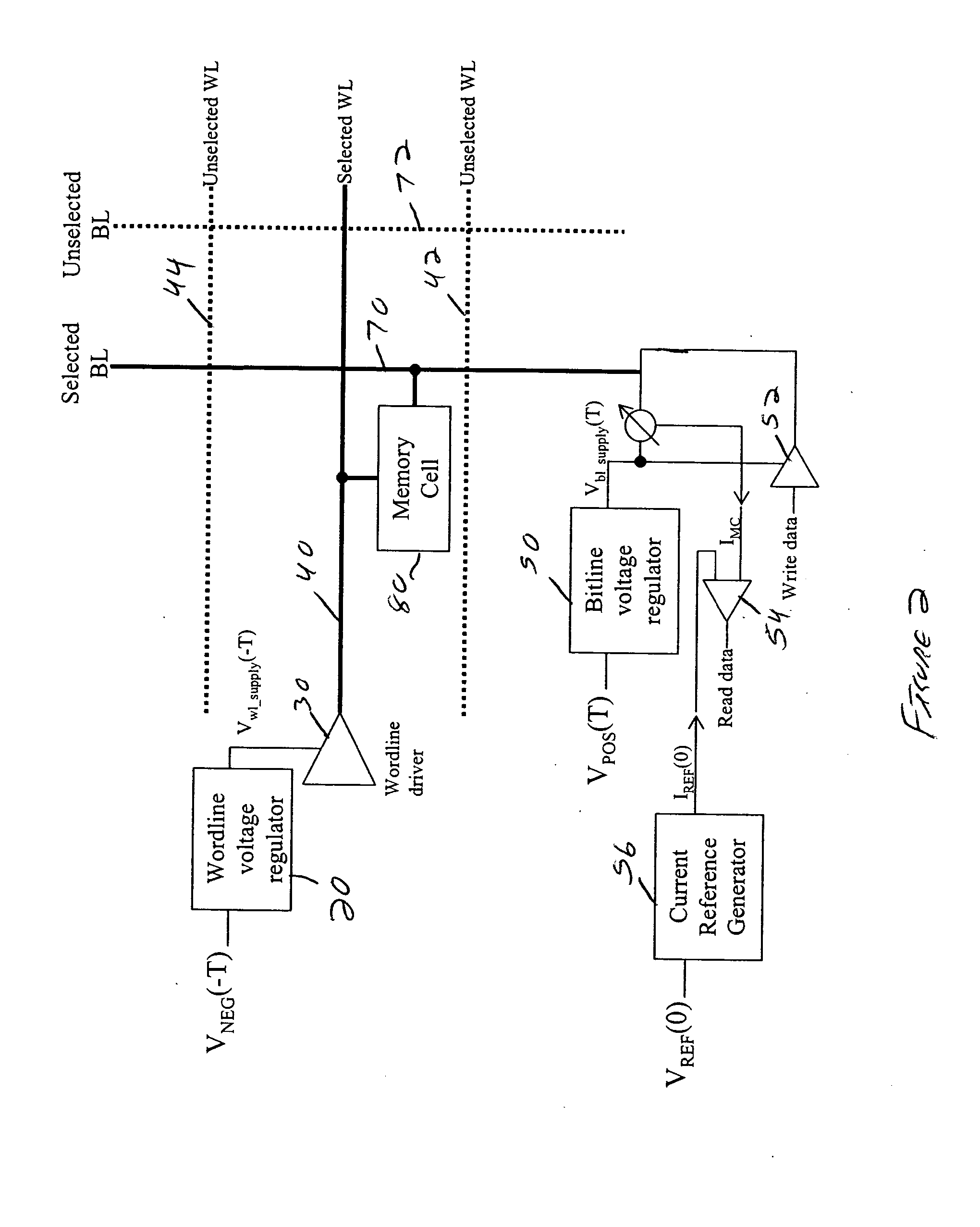
Method and system for temperature compensation for memory cells with temperature-dependent behavior
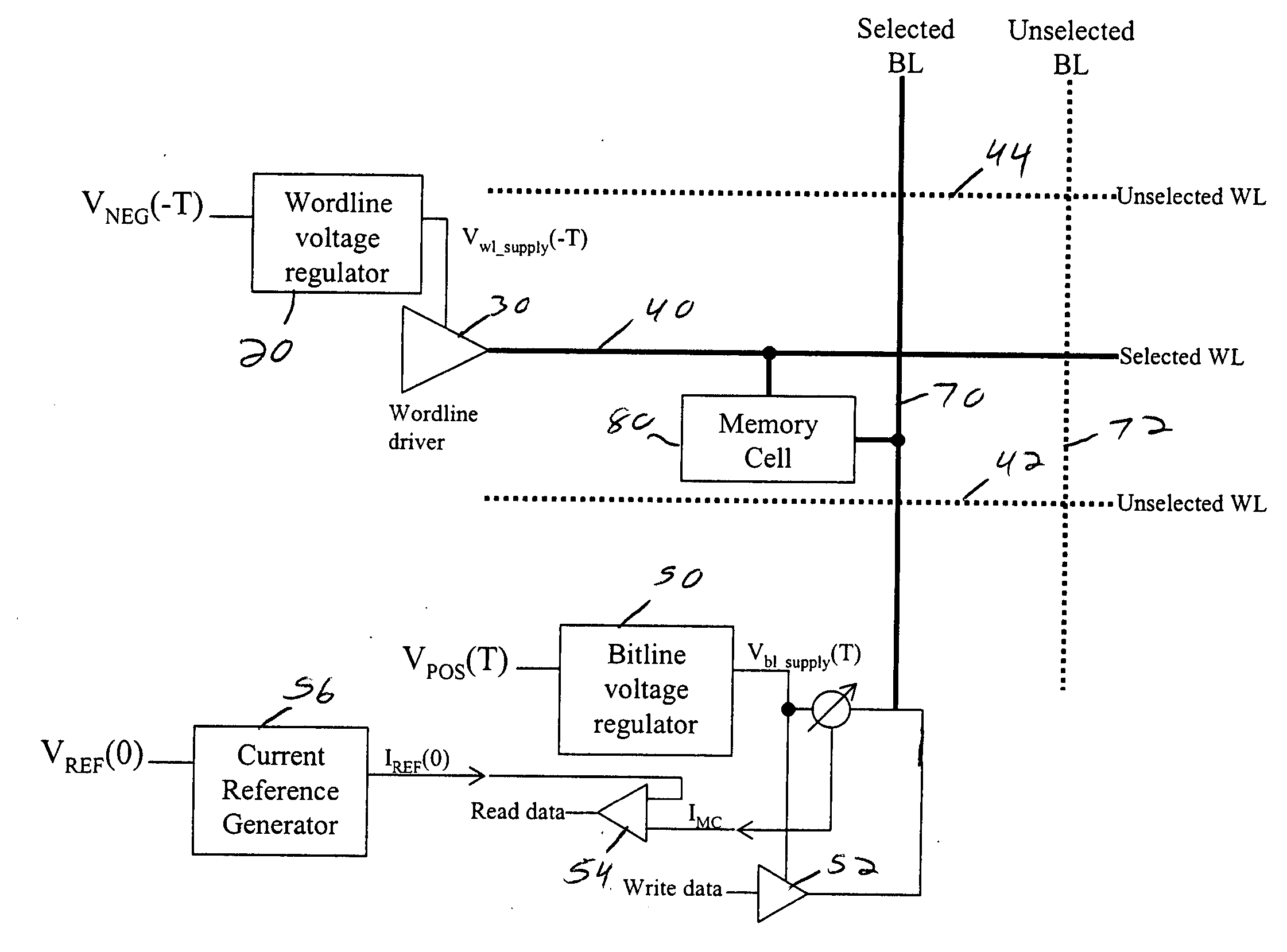
The preferred embodiments described herein relate to a method and system for temperature compensation for memory cells with temperature-dependent behavior. In one preferred embodiment, at least one of a first temperature-dependent reference voltage comprising a negative temperature coefficient and a second temperature-dependent reference voltage comprising a positive temperature coefficient is generated. One of a wordline voltage and a bitline voltage is generated from one of the at least one of the first and second temperature-dependent reference voltages. The other of the wordline and bitline voltages is generated, and the wordline and bitline voltages are applied across a memory cell. Other methods and systems are disclosed for sensing a memory cell comprising temperature-dependent behavior, and each of the preferred embodiments can be used alone or in combination with one another.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Heater with simultaneous hot spot and mechanical intrusion protection
InactiveUS6958463B1Excellent dielectric propertiesPreventing and minimizing current leakageHeating element shapesFiberElectrical conductor
An electrical heater utilizes negative temperature coefficient material (NTC) and current imbalance between live and neutral ends of the heater to simultaneously protect the heater from the hot spot and mechanical intrusion into the heating cable. The NTC layer, separating the heating wire and current leakage conductor, becomes electrically conductive at the temperatures above 60° C., thus “leaking” the current to earth. The hot spot is detected by measuring the current imbalance between line and neutral connections of the heating cable. The mechanical intrusion into the heater, such as cable or insulation damage, water or sharp metal object penetration, is also simultaneously measured by the same current imbalance measuring system such as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). The optional return conductor and metal foil / mesh hot spot detection shields cancel electromagnetic field. The heater may contain positive temperature coefficient (PTC) continuous sensor to control the temperature in the heater. Such PTC sensor can be made of electrically conductive fibers and / or metal wires.
Owner:THERMOSOFT INT
Voltage reference circuit
InactiveUS7301321B1Stable reference voltageReduce layout costsPower supply linesElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureVoltage drop
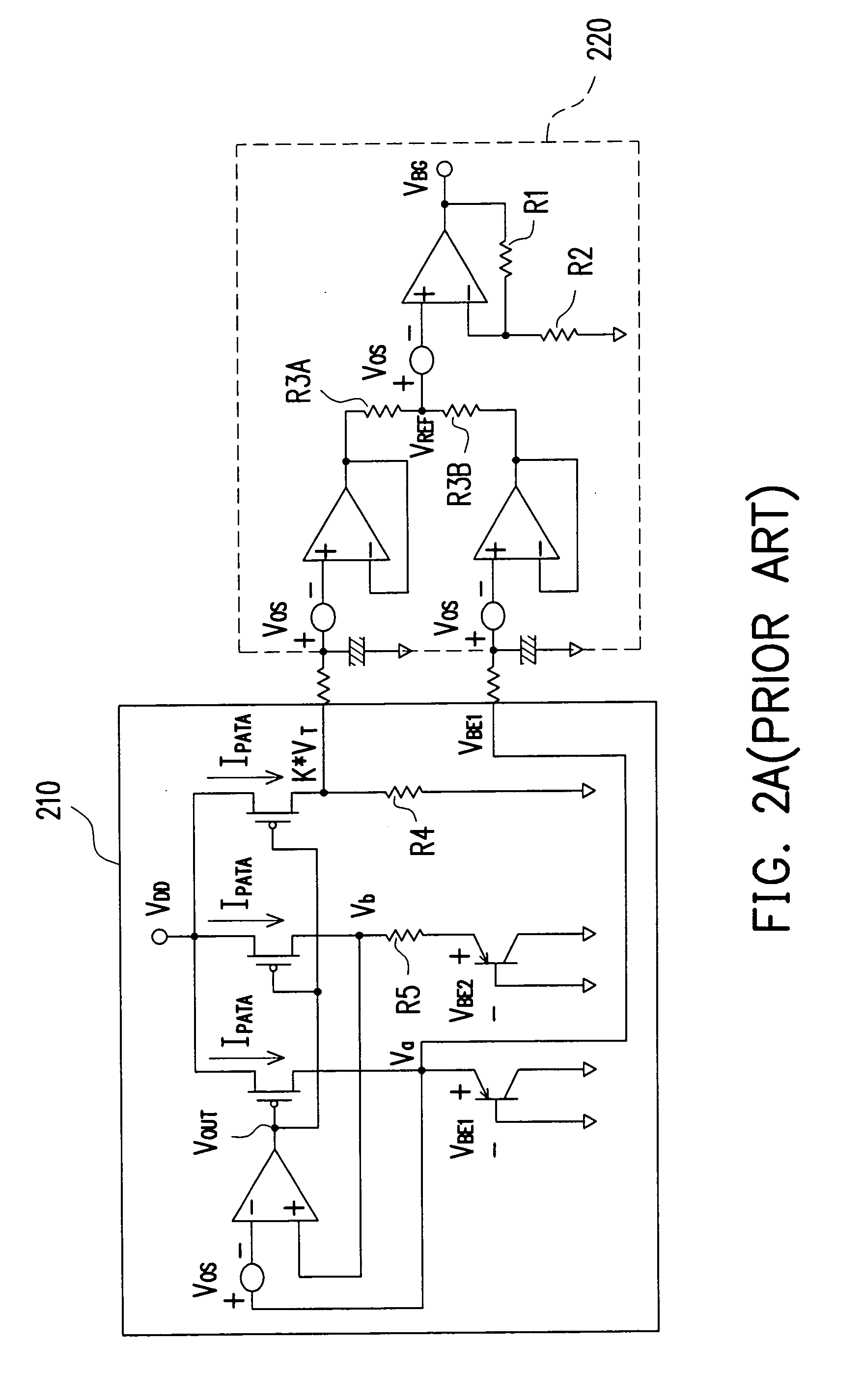
A voltage reference circuit including a positive temperature coefficient current generator, a negative temperature coefficient current generator, and a first resistor is provided. In the positive temperature coefficient current generator, two transistors are operated in the weak inversion region, and a second resistor is connected in series between the gates of the two transistors. The second resistor employs the characteristic that a transistor operated in weak inversion region acts like a bipolar junction transistor to generate a positive temperature coefficient current. The negative temperature coefficient current generator generates a negative temperature coefficient current in response to a negative temperature coefficient voltage drop on a third resistor. The positive temperature coefficient current and the negative temperature coefficient current flow through the first resistor together, thus producing a stable reference voltage.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
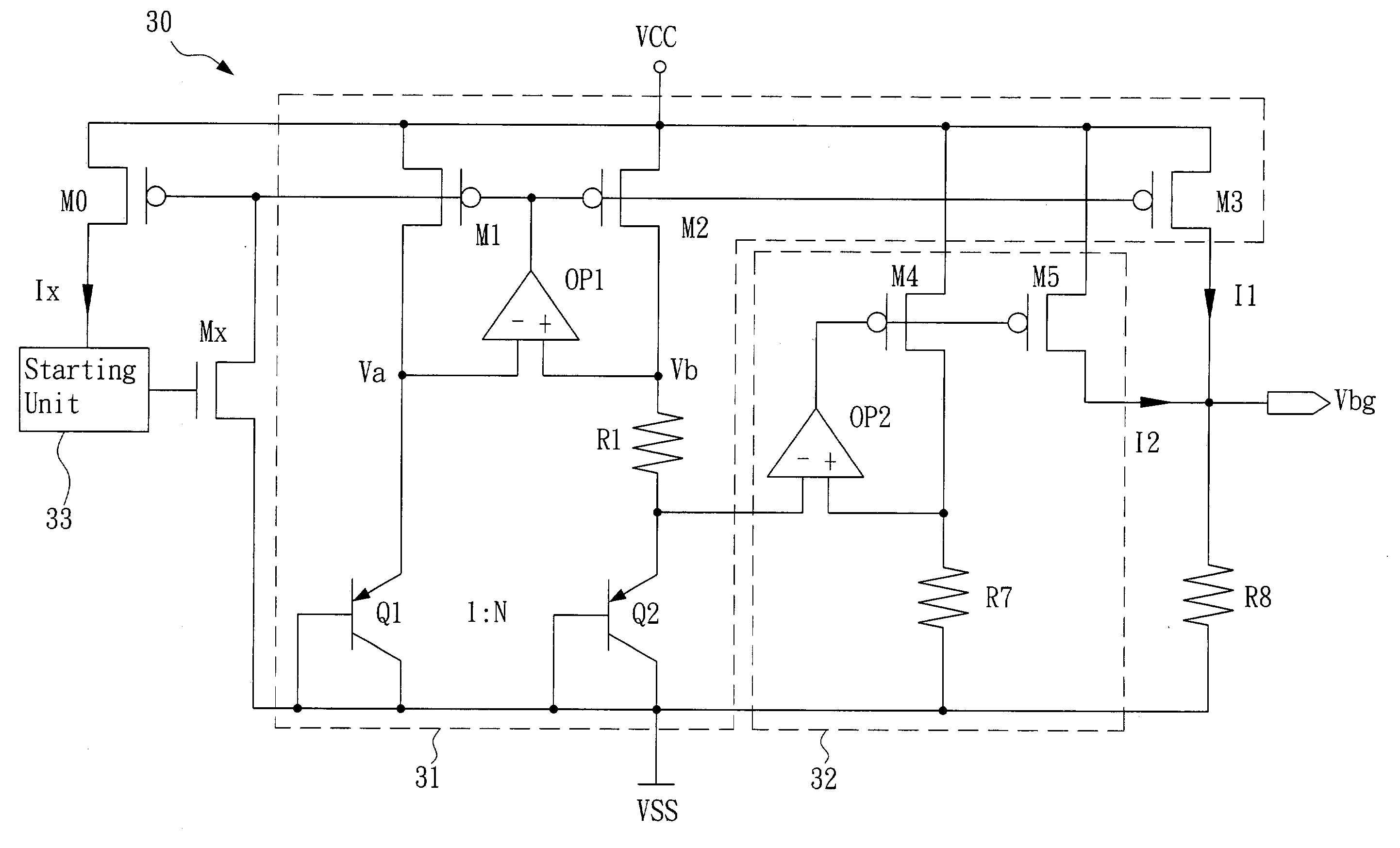
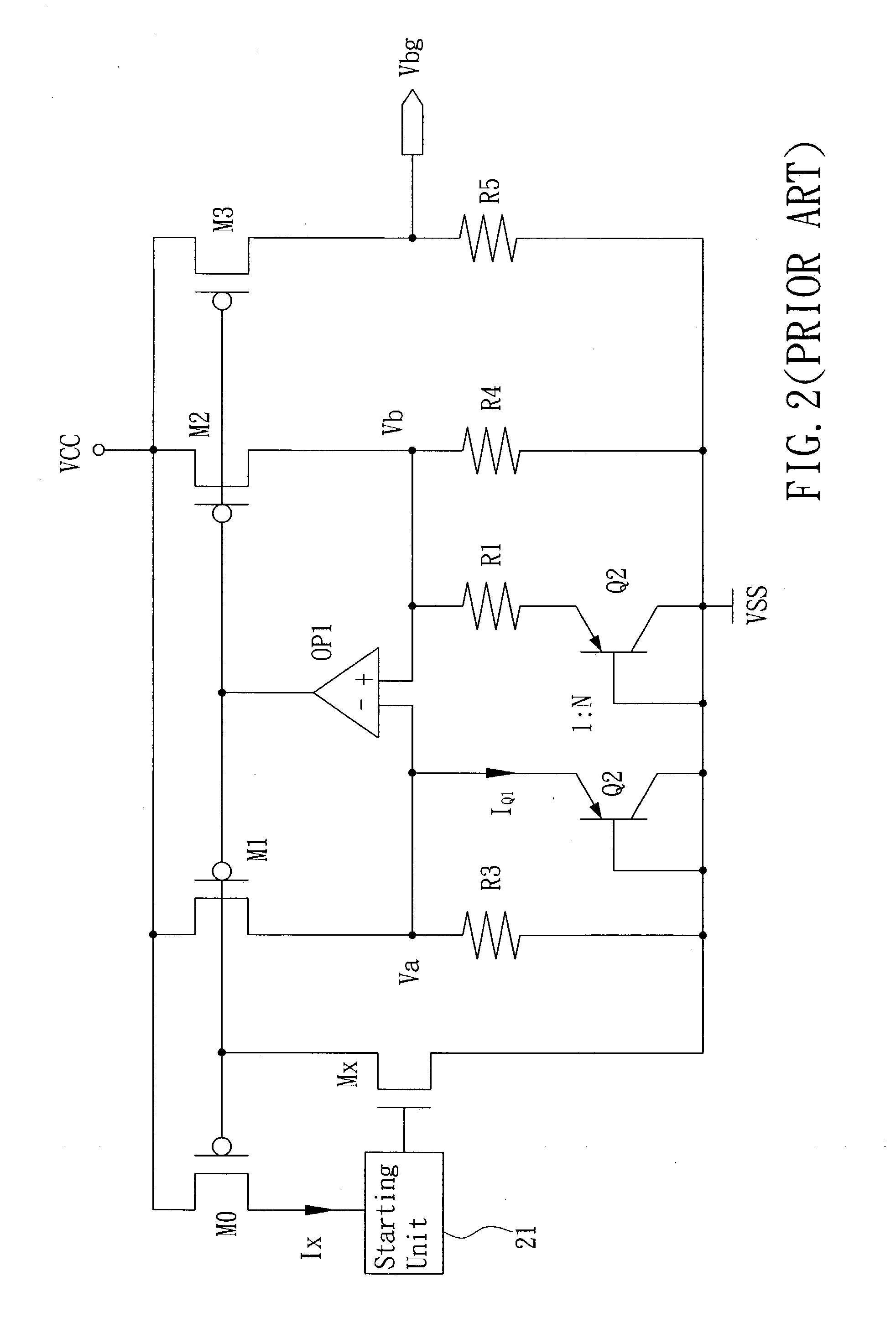
Low supply voltage band-gap reference circuit and negative temperature coefficient current generation unit thereof and method for supplying band-gap reference current
InactiveUS20080018319A1Reduce circuit areaLow costElectronic switchingPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesHigh resistanceLow voltage
A low supply voltage band-gap reference circuit is provided, which includes a positive temperature coefficient current generation unit and a negative temperature coefficient current generation unit, and it is implemented by way of current summing. Through the current-mode temperature compensation technique, the present invention is able to reduce the voltage headroom and the number of operational amplifiers required by the conventional voltage-summing method, as well as the influence to the output voltage due to the offset voltage, thereby providing a stable and low voltage band-gap reference voltage level. In addition, by reducing the number of operational amplifiers and resistors of high resistance, the circuit area is reduced, and chip cost is saved.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
High polymer-based graphene composite material with positive resistance temperature coefficient and preparation method
InactiveCN102532669AReduce dosageImprove conductivityState of artElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to a high polymer-based graphene composite material with positive resistance temperature coefficient, and a preparation method of the material. The composite material comprises a base body and conductive filler; the content of conductive material is 0.01-10wt%; all components are mixed uniformly and are formed through mold-pressing or extrusion / injection molding; and the formed material is irradiated after being dried, so that the high polymer-based graphene composite material with positive resistance temperature coefficient can be obtained. Compared with the prior art, the graphene composite material and the preparation method have the advantages that the manufacturing process is simple, less influence is caused to the performance of base material, oxidation is unlikely to occur, the resistivity is more stable, the circulation stability of the material is better, and NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) effect is not generated easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fast start-up low-voltage bandgap voltage reference circuit
A fast start-up low-voltage bandgap voltage reference circuit is proposed. The bandgap voltage reference circuit comprises: a first current generator, which is implemented by a self-bias unit and a current mirror for generating a first reference current with positive temperature coefficient; a second current generator, which is connected to a point with negative temperature coefficient in the first current generator to generate a second reference current with negative temperature coefficient; and a resister for converting the first reference current and the second reference current into a low-voltage bandgap voltage independent of temperature. Because the bandgap voltage reference circuit of the invention uses the resistor to convert the first reference current and the second reference current into voltage, the circuit can provide low-voltage bandgap voltage.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
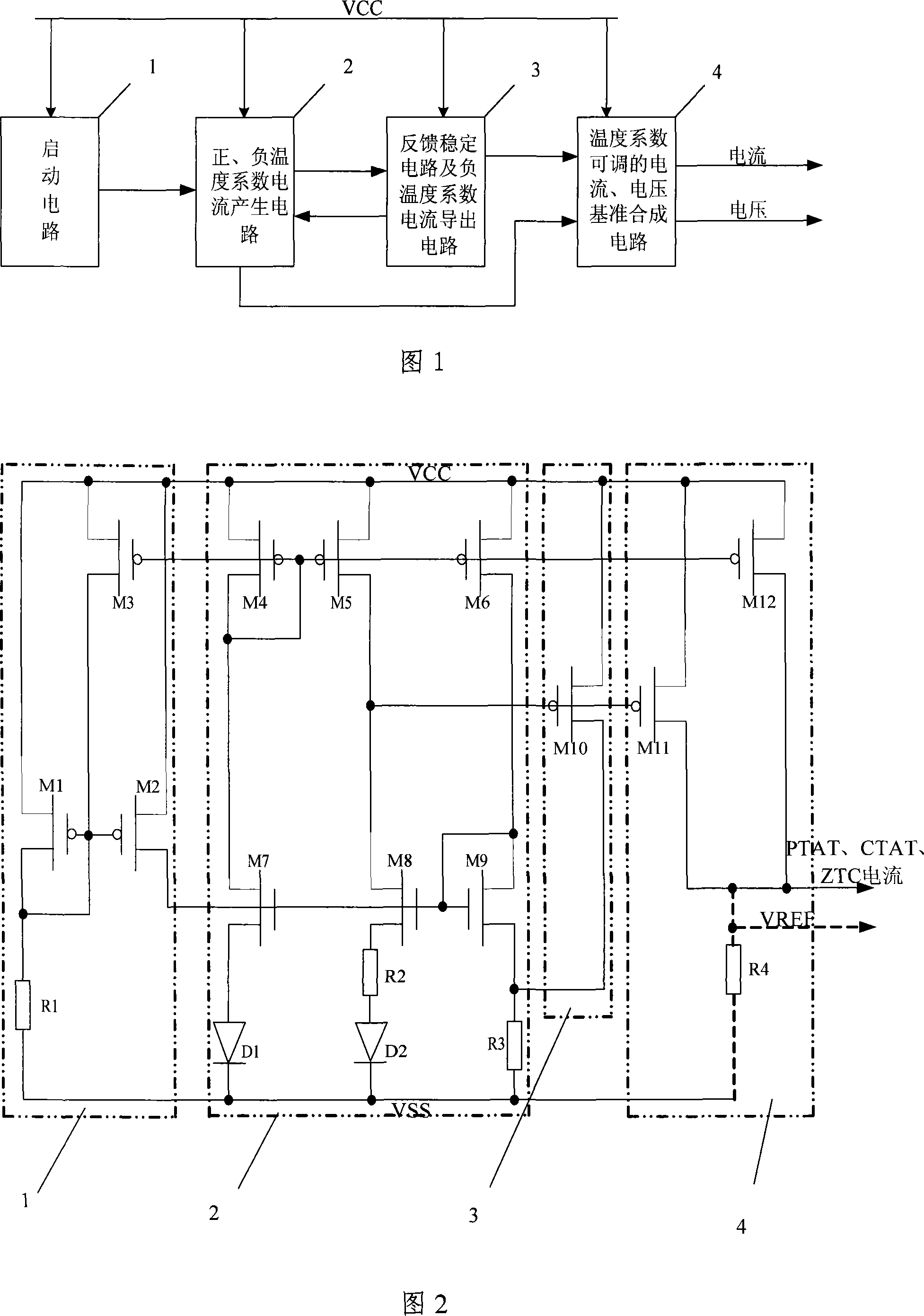
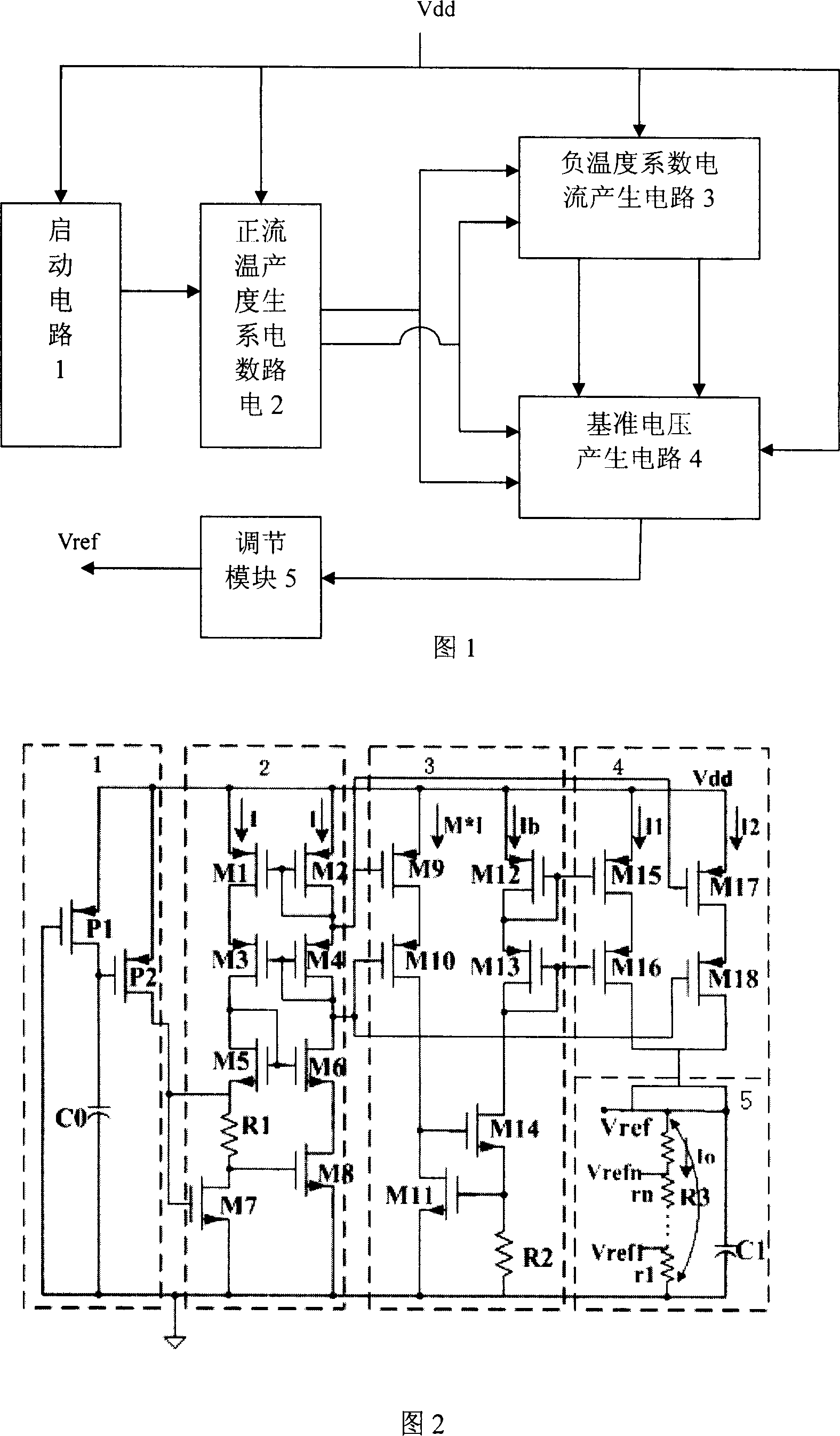
Circuit outputting adjustable positive and negative or zero-temperature coefficient electrical current and voltage reference
InactiveCN101178610ASimple structureReduce layout areaElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureReference current
The invention provides a circuit for outputting adjustable positive, negative or zero temperature coefficient current and voltage reference, including: a start-up circuit, a positive and negative temperature coefficient current generation circuit, a feedback stable and negative temperature coefficient current derivation circuit, and the temperature coefficient can be Adjusted current reference, voltage reference synthesis circuit. The invention is realized under the standard CMOS technology, has simple structure, low input voltage, and can generate current reference and voltage (VREF) reference with adjustable temperature coefficient, which can be positive, negative or zero temperature coefficient.
Owner:XIAN BIAOXIN ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH
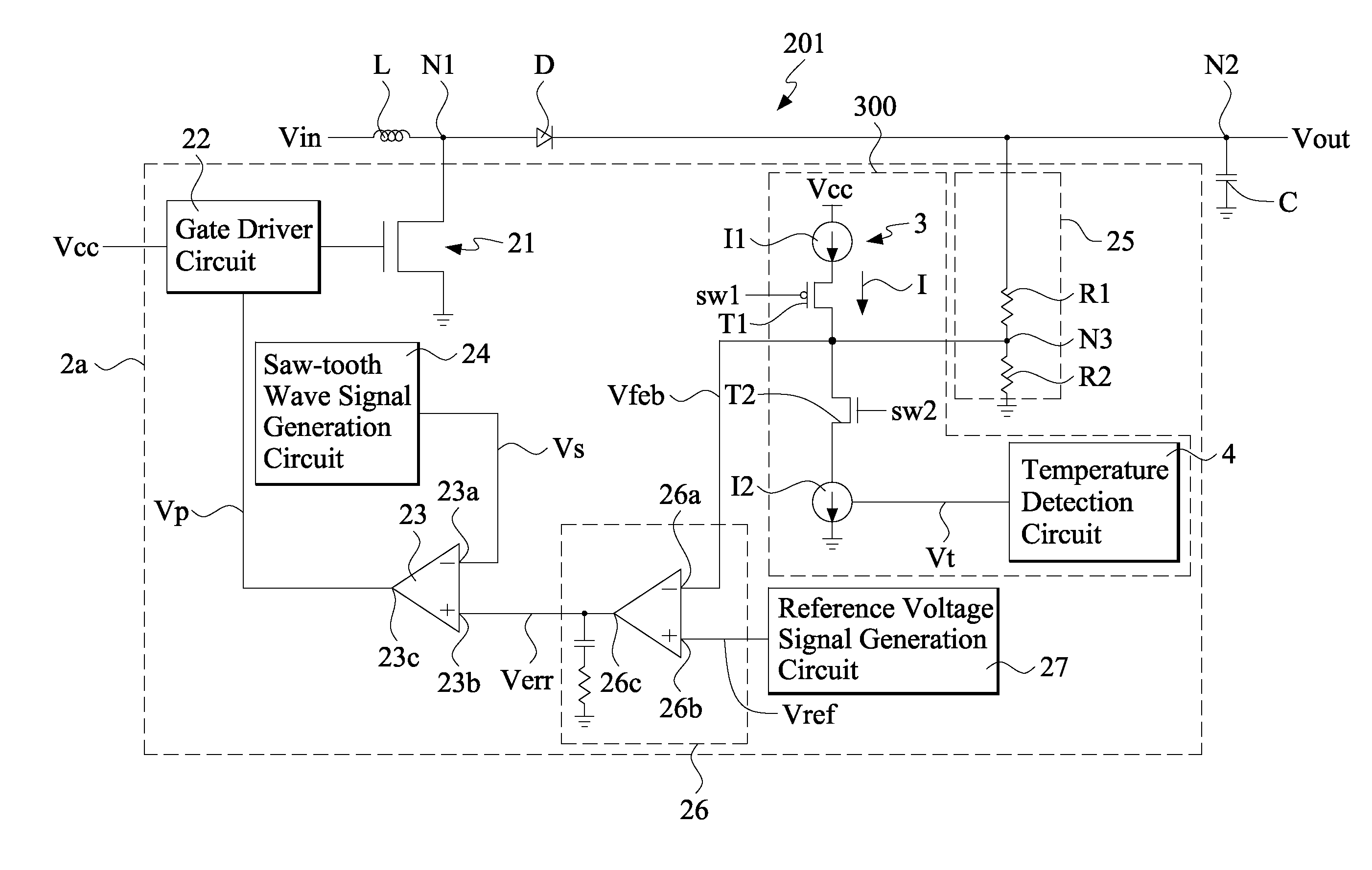
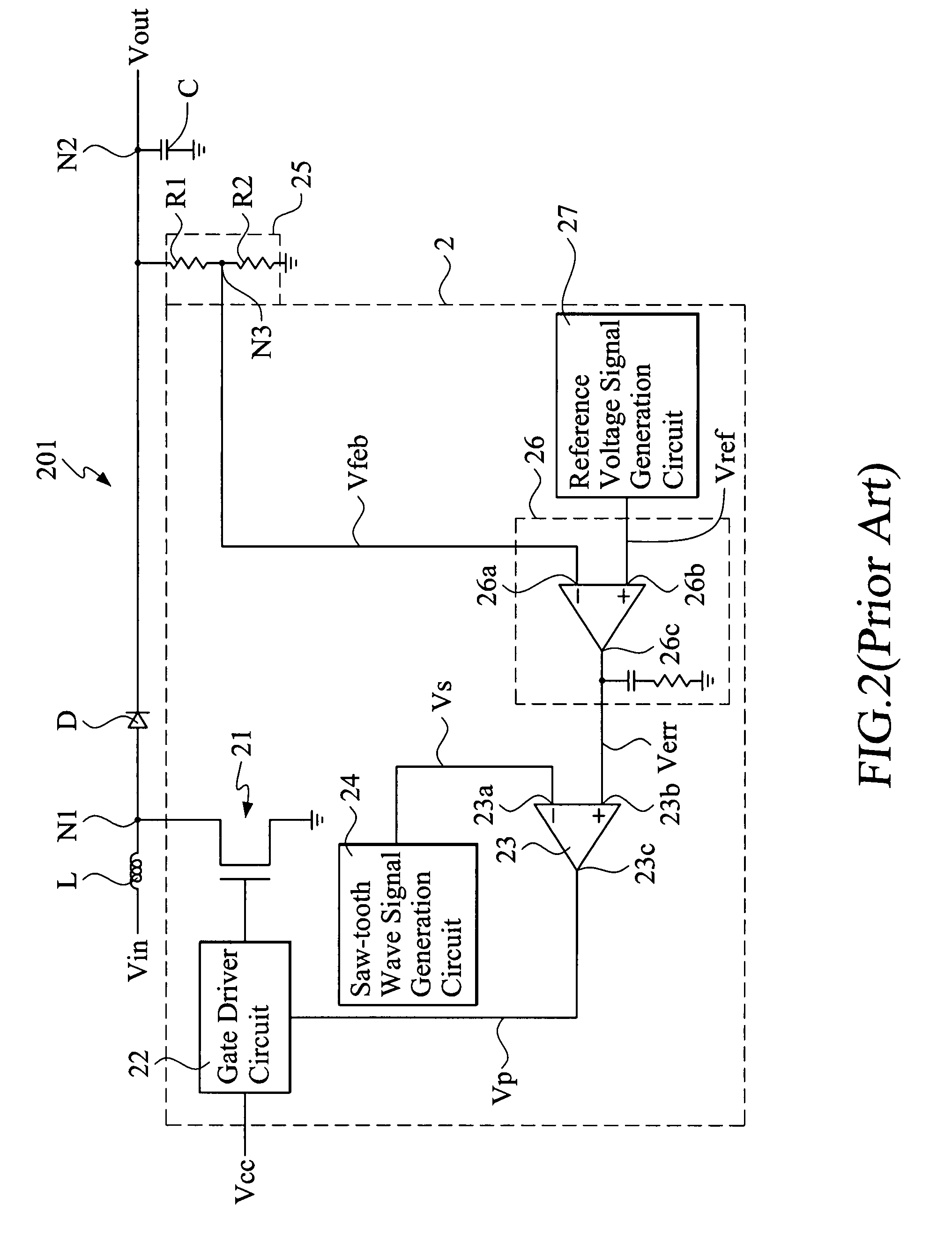
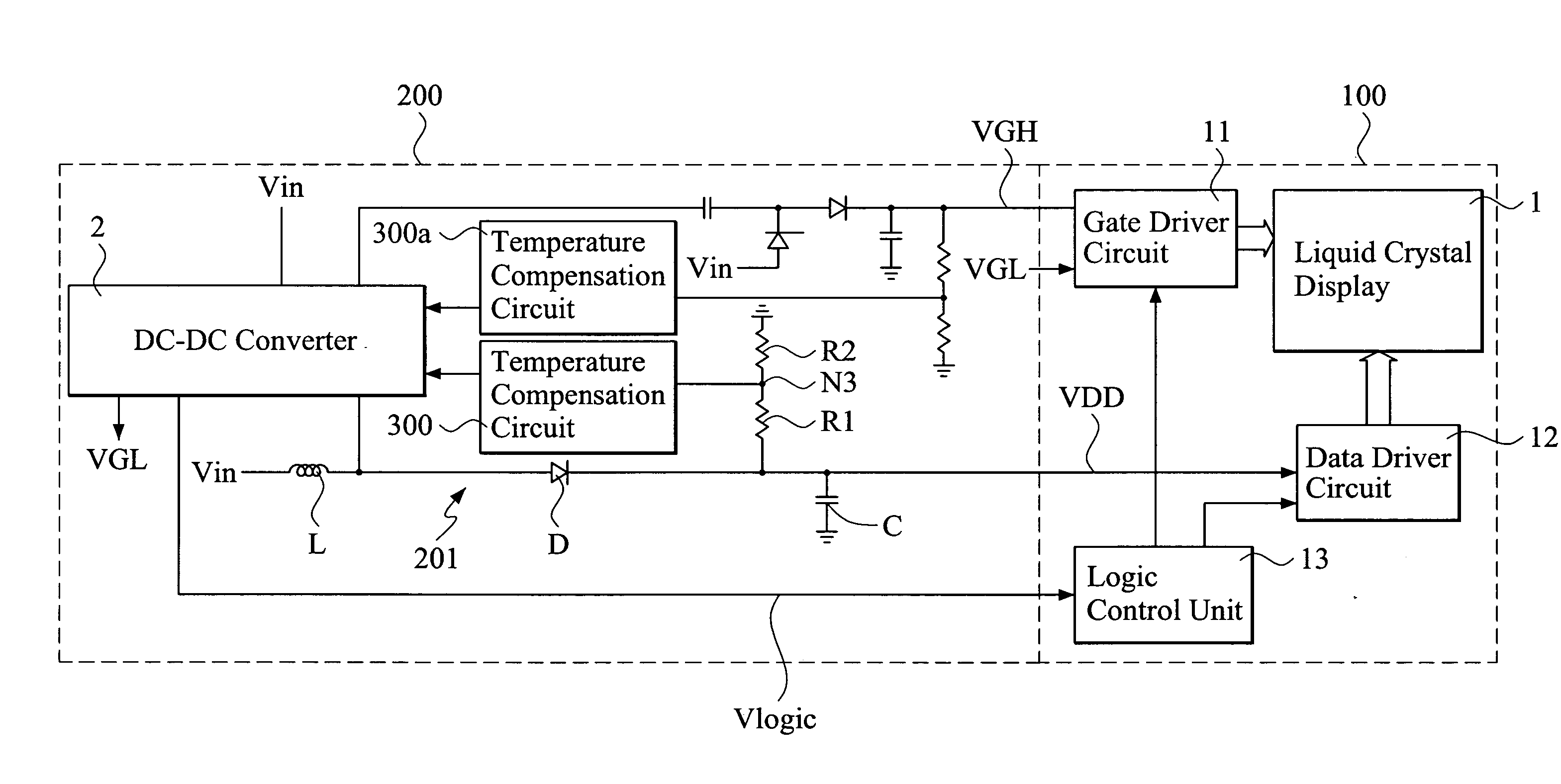
DC-DC converter with temperature compensation circuit
InactiveUS7859511B2Stable characteristicsEfficient supplyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDc dc converterNegative temperature
A DC-DC converter includes a temperature compensation circuit arranged between a feedback differential amplification circuit and an output voltage detection circuit to compensate the variation of the voltage level of the DC output voltage of the converter caused by ambient temperature changes. The temperature compensation circuit includes a temperature detection circuit that detects the ambient temperature and, in response thereto, generates a temperature signal; and a current source circuit that is connected between a feedback signal input terminal of the feedback differential amplification circuit and the output voltage detection circuit. The current source circuit, based on the temperature signal, generates an electrical current and a compensation voltage proportional to the electrical current. The compensation voltage is applied to the DC output voltage to thereby regulate the voltage level of the DC output voltage. The temperature signal is a temperature signal of positive temperature characteristics and / or a temperature signal of negative temperature characteristics.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
High evenness negative temperature coefficient heat-sensitive resistance material and its preparation method
ActiveCN101127266AImprove uniformityGood repeatabilityNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsMetal/alloy conductorsNegative temperatureHeat sensitive
The utility model relates to a thermistance material with high uniformity and negative temperature coefficient. The main formulation is one in the six systems of Mn-Ni-Cu, Mn-Co-Cu, Mn-Co-Ni-Cu, Mn-Co-Fe-Cu, Mn-Co-Ni or Mn-Co-Fe. The combination of at least two of the oxides as CaO, ZnO, SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, Cr2O3, TiO2, Sb2O3, Bi2O3, SrO, Nb2O5 and B2O3 are added to the main formulation. The utility model also relates to a preparation method for preparing the thermistance material with high uniformity and negative temperature coefficient, comprising the following steps: mixture making, primary wet milling, drying, calcining, and secondary wet milling, drying and granulating, pressing and forming, and sintering. The utility model has the advantages that: the thermistance material with negative temperature coefficient (NTCR) made by the method has high uniformity and high repeatability; the specific resistance uniformity of the same batch material is all better than plus or minus 1%; the specific resistance error of different batches does not exceed plus or minus 2%; the error of value B does not exceed plus or minus 1%; the utility model is suitable for mass and large-scale production.
Owner:山东中厦电子科技有限公司
Semiconductor ceramic with negative resistance temperature coefficient and negative temperature coefficient thermistor
InactiveCN1348192ALittle change in characteristicsInhibit swellingCeramicsNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative temperature
A semiconductor ceramic having a negative temperature coefficient of resistance, the element comprising about 0.1 to 20 mol % of AMnO3 (A represents at least one of Ca, Sr, Ba, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Th, Dy and Ho) and to a spinel composite oxide made of a solid solution of Mn and at least one element in Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mg and Al. As a perovskite Mn composite oxide, one or more of CaMnO3, SrMnO3, BaMnO3, LaMnO3, PrMnO3, NdMnO3, SmMnO3, EuMnO3, GdMnO3, TbMnO3, DyMnO3 and HoMnO3 may be used.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
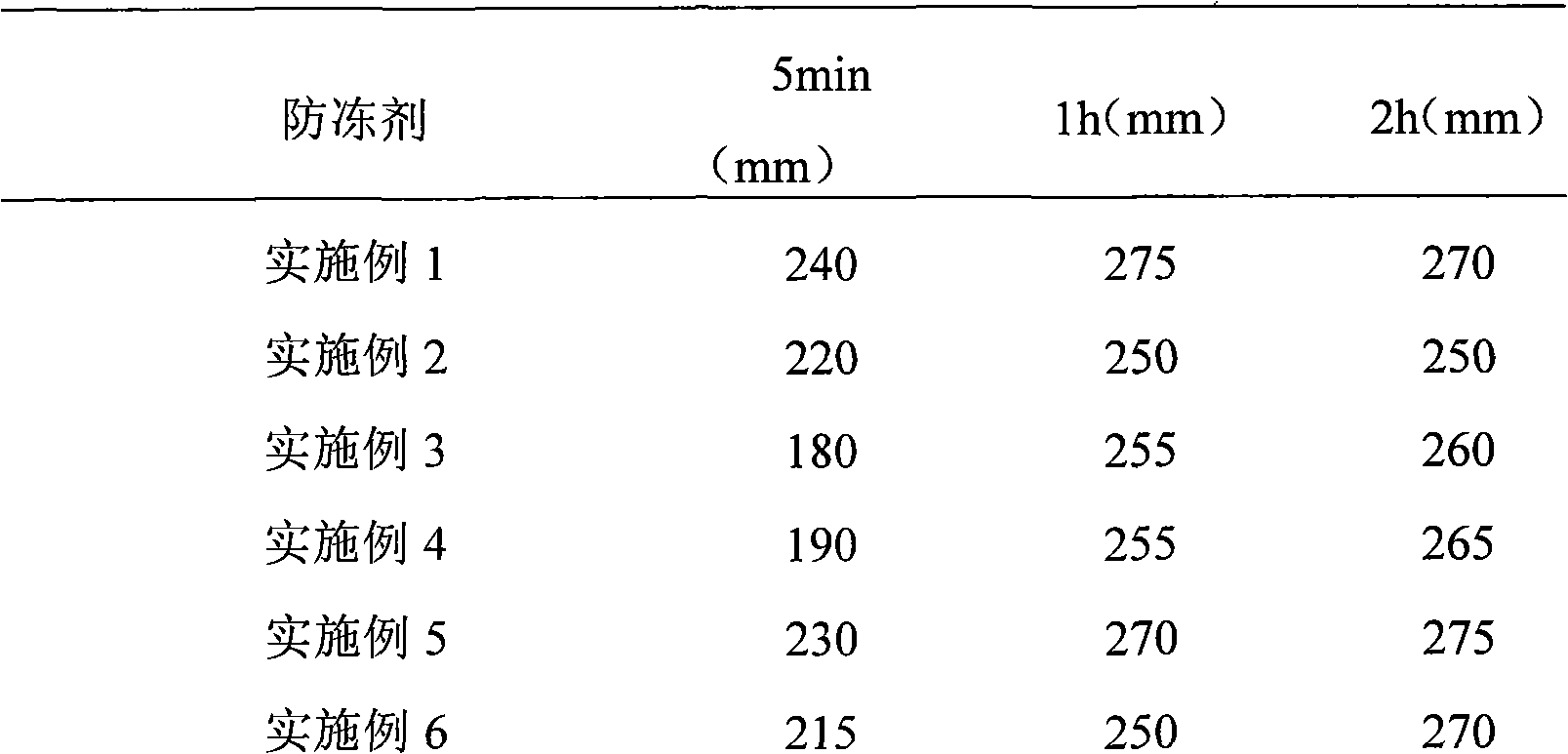
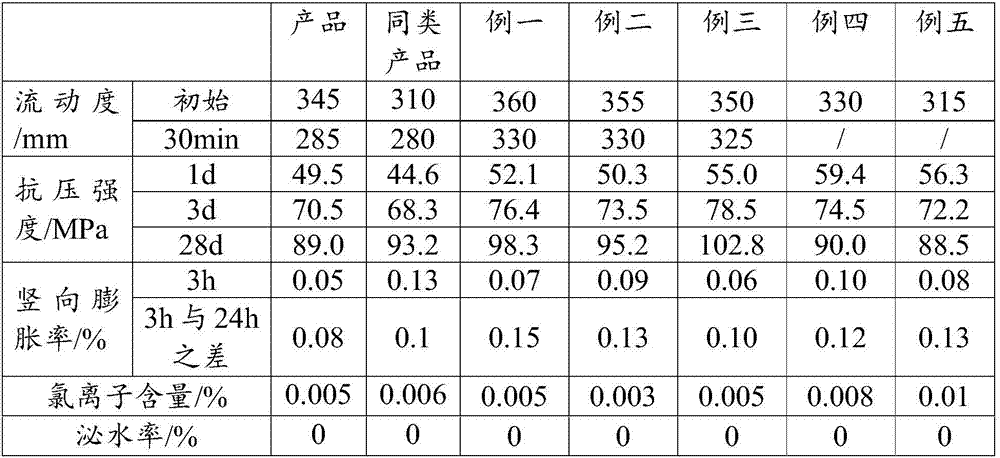
Polycarboxylic acids anti-freeze agent for cement concrete and method for preparing same
The invention relates to poly carboxylic acid system antifreeze applied to cement concrete and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the building material field. The antifreeze is prepared by the optimal combination of an efficient water reduce of poly carboxylic acid, organic alcohol amine, low-carbon alcohol, sulfocyanide and formate. The preferred proportion of the components is that the efficient water reducer to the organic alcohol amine to the low-carbon alcohol to the sulfocyanide to the calcium formate to water is equal to (3.0-8.0) to (0.5-2.0) to (0.0-2.0) to (10.0-20.0) to (0.0-6.0) to (65.0-75.0) (by mass percentage). Compared with the existing antifreeze, the antifreeze of the system has the advantages of high water reducing rate and comparatively good workability and quick growth of strength at negative temperature. The antifreeze has the advantages of low intermingled quantity in the cement concrete, good water solubility, low alkali content, high strength at the early stage and at the later stage of the cement concrete but no chlorine and is applicable to the preparation of various cement concrete at the negative temperature ranging from negative 5 DEG C to negative 20 DEG C in winter in the north area.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
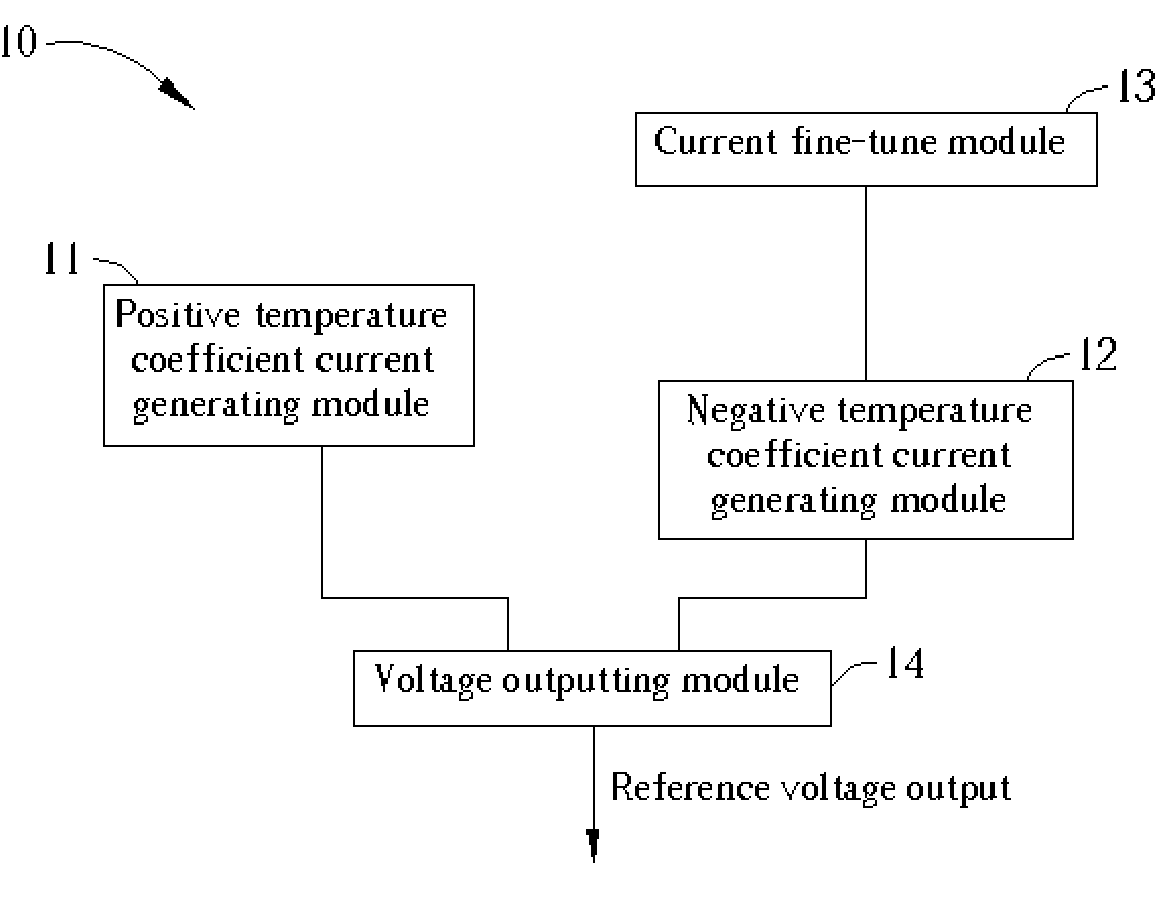
Voltage generating apparatus with a fine-tune current module
ActiveUS6958597B1Increase currentTotal current dropPower supply linesElectric variable regulationSub thresholdNegative temperature
Voltage generating apparatus includes a positive temperature coefficient current generating module, a negative temperature coefficient current generating module, a fine-tune current module and a voltage output module. The function of the positive temperature coefficient current generating module and the negative temperature coefficient current generating module, which take advantage of characteristics of MOS devices operated in the sub-threshold region, is to generate a stable current of positive temperature coefficient and a stable current of negative temperature coefficient, respectively. The current fine-tune module increases or decreases output current of the negative temperature coefficient current generating module. The voltage output module sums two output currents of the positive temperature coefficient current generating module and the negative temperature coefficient current generating module and transforms the total current into output voltage that is stable under temperature and process variation.
Owner:EMEMORY TECH INC
DC-DC converter with temperature compensation circuit
InactiveUS20080309608A1Stable characteristicsEfficient supplyTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDc dc converterNegative temperature
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
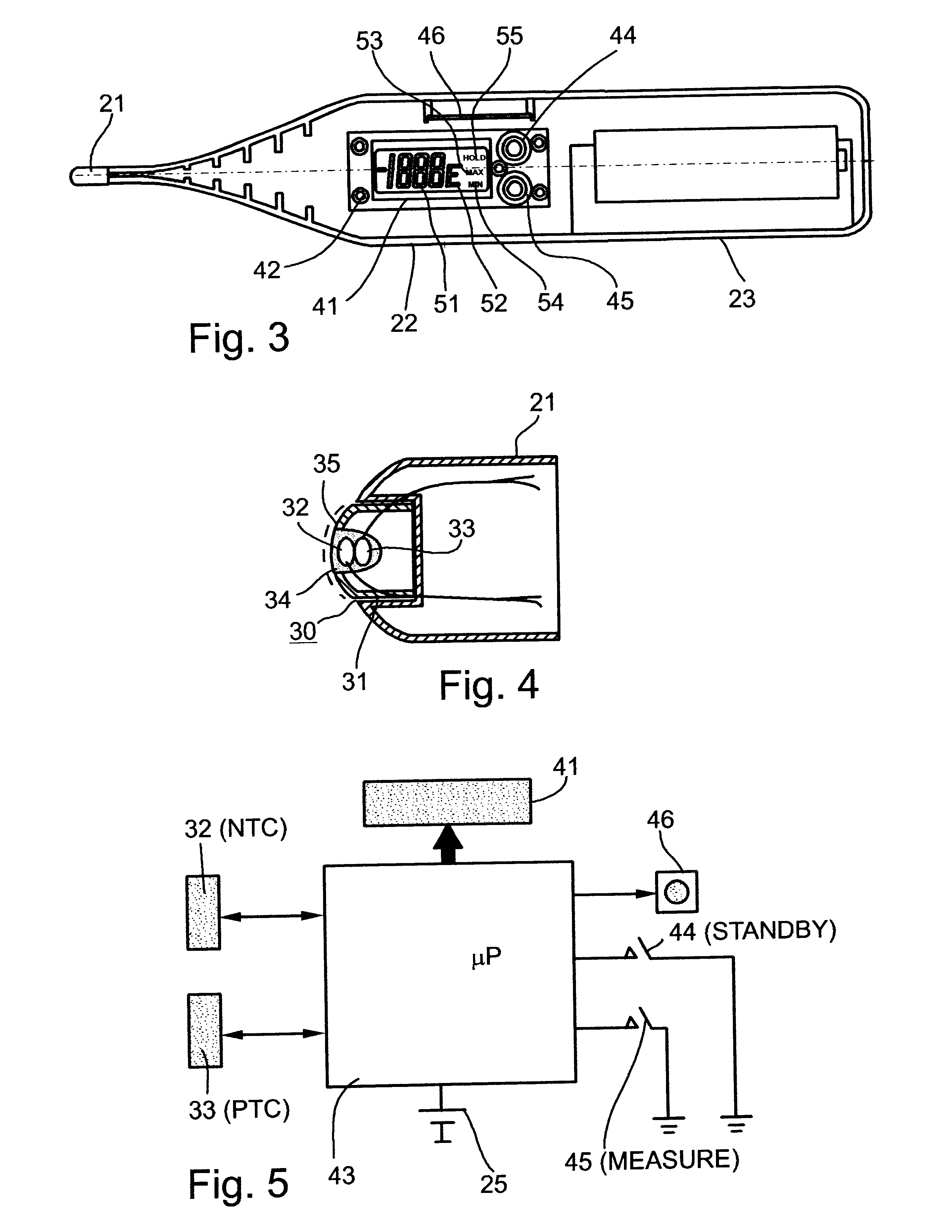
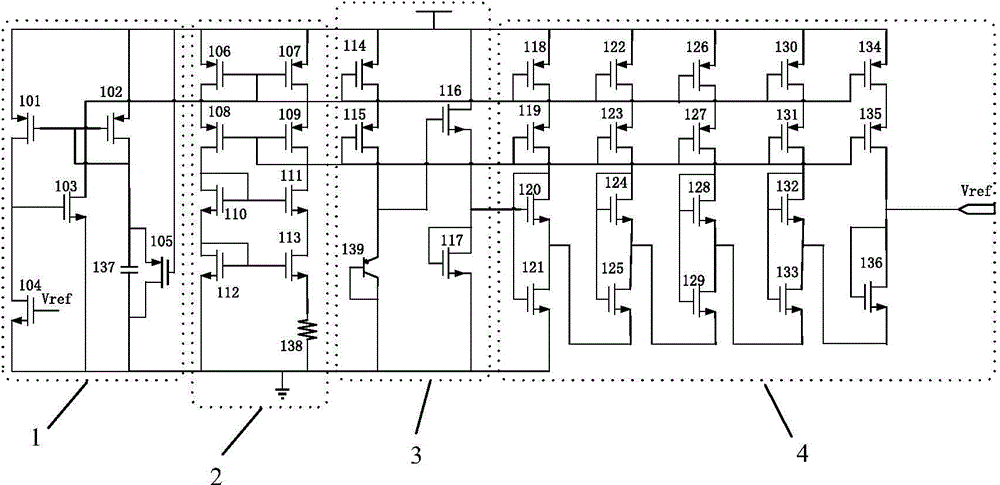
Electronic thermometer with preheating
InactiveUS6250802B1Accurate measurementLower resistanceThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An electronic thermometer for measuring the temperature of a body, includes a probe having a heating element for preheating the probe to the approximate temperature of the body, and a temperature measuring element for measuring the precise temperature the body. The heating element is a relatively low-resistance thermistor having a positive temperature coefficient (PTC), and the temperature measuring element is a relatively high-resistance thermistor having a negative temperature coefficient (NTC).
Owner:HOMECARE TECH
Low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit
ActiveCN104950971AReduce power consumptionLow working voltageElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of simulation integrated circuits, and discloses a low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit. The circuit comprises a start circuit, a reference current source generation circuit, a voltage division circuit and a reference voltage output circuit. The start circuit is used for enabling a reference voltage source to get rid of a zero degeneracy point and to work under specific work voltage. The reference current source generation circuit is used for generating current to provide bias for a rear end circuit, and MOS transistors in the rear end circuit all work in a sub-threshold region. The voltage division circuit is used for enabling an output circuit to reach required technical indexes and generating a negative temperature coefficient. The reference voltage output circuit is used for generating voltage with a positive temperature coefficient and making the output voltage Vref have the zero temperature characteristic. The low-power-consumption sub-threshold type CMOS band gap reference voltage circuit has the advantages of being low in work voltage, low in power consumption and low in temperature coefficient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
DC-DC converter with temperature compensating circuit
InactiveCN101330252AAppropriate working voltageStatic indicating devicesApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDc dc converterNegative temperature
The invention relates to a DC-to-DC converter with a temperature compensation circuit. The temperature compensation circuit is arranged between a feedback differential amplification circuit and an output voltage detection circuit of the DC-to-DC converter and is used for compensating the voltage level of the DC output voltage of the DC-to-DC converter caused by the change of the environmental temperature. The temperature compensation circuit comprises a temperature detection circuit used for detecting the environmental temperature and generating a temperature signal according to the detection result, and a current source circuit connected between the feedback signal input terminal of the feedback differential amplification circuit and the output voltage detection circuit, wherein the current source circuit can generate a current value according to the temperature signal generated by the temperature detection circuit, form a compensative voltage proportion to the current value and apply the compensative voltage to the DC output voltage, thereby regulating the voltage value of the DC output voltage. The temperature signal generated by the temperature detection circuit is a temperature signal with positive temperature characteristics or a temperature signal with negative temperature characteristics.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Negative temperature coefficient polymer composite material for temperature sensing cable and preparation method
InactiveCN101654530AImprove structural stabilityGood repeatabilityNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsNegative temperatureThermoplastic elastomer
The invention relates to a negative temperature coefficient polymer composite material for temperature sensing cables and a preparation method, belonging to the field of the preparation of macromolecule functional composite material and process technology of polymers; the invention has the characteristics that: rubber or thermoplastic elastomers are combined with different auxiliary polymers, conducting particles are added to prepare the macromolecule composite material with the characteristic of negative temperature coefficient. The material has the characteristics that the resistance changeis low below the room temperature and operating temperature, and then is rapidly reduced after reaching the operating temperature, and overcomes the disadvantages that the traditional NTC macromolecule composite material has obvious resistance change below the room temperature and the operating temperature, and the resistance change is low close to the operating temperature, so as to lead the prepared temperature sensing cables to have high sensitivity, to have little effect to environment temperature and good repetitiveness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
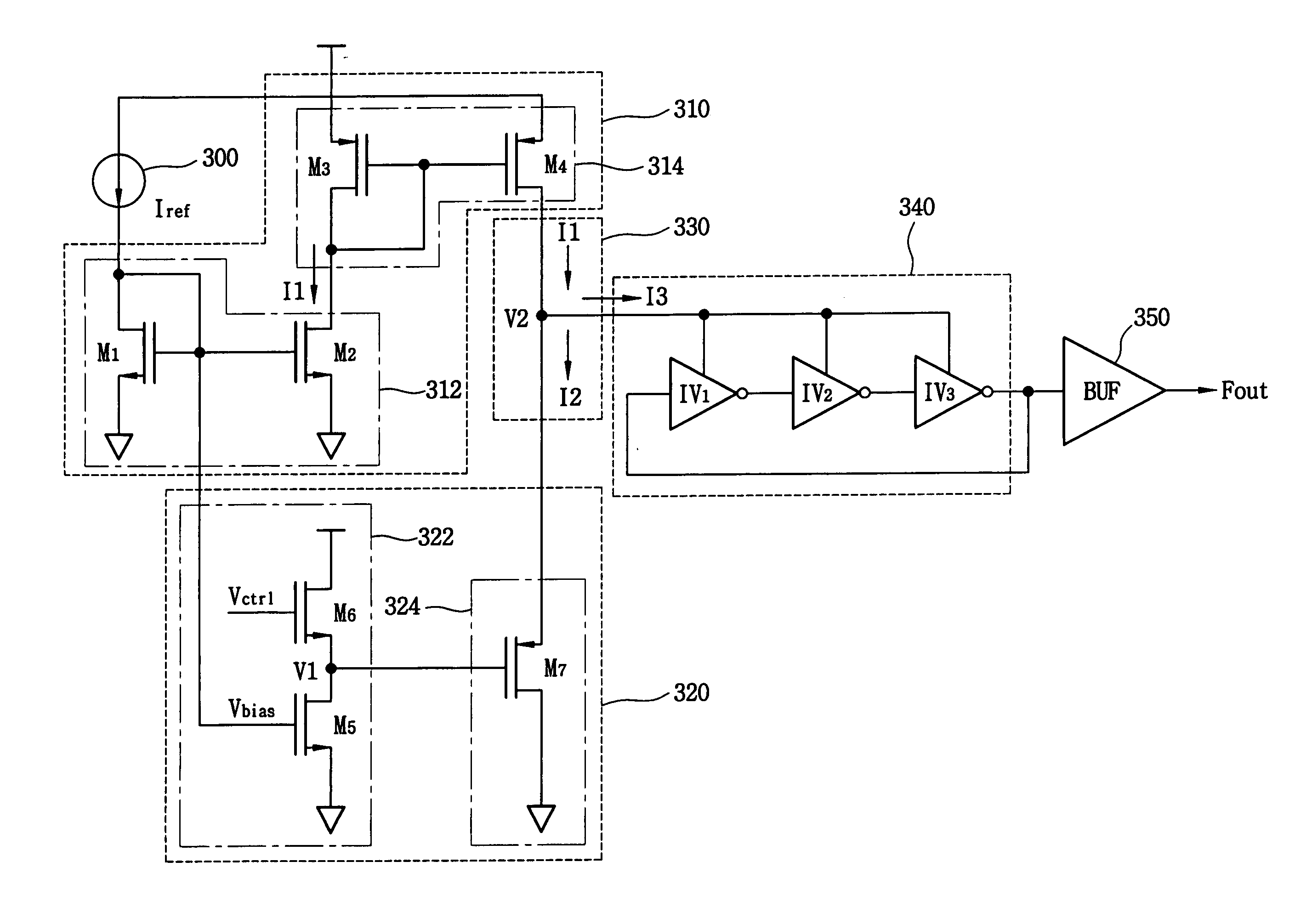
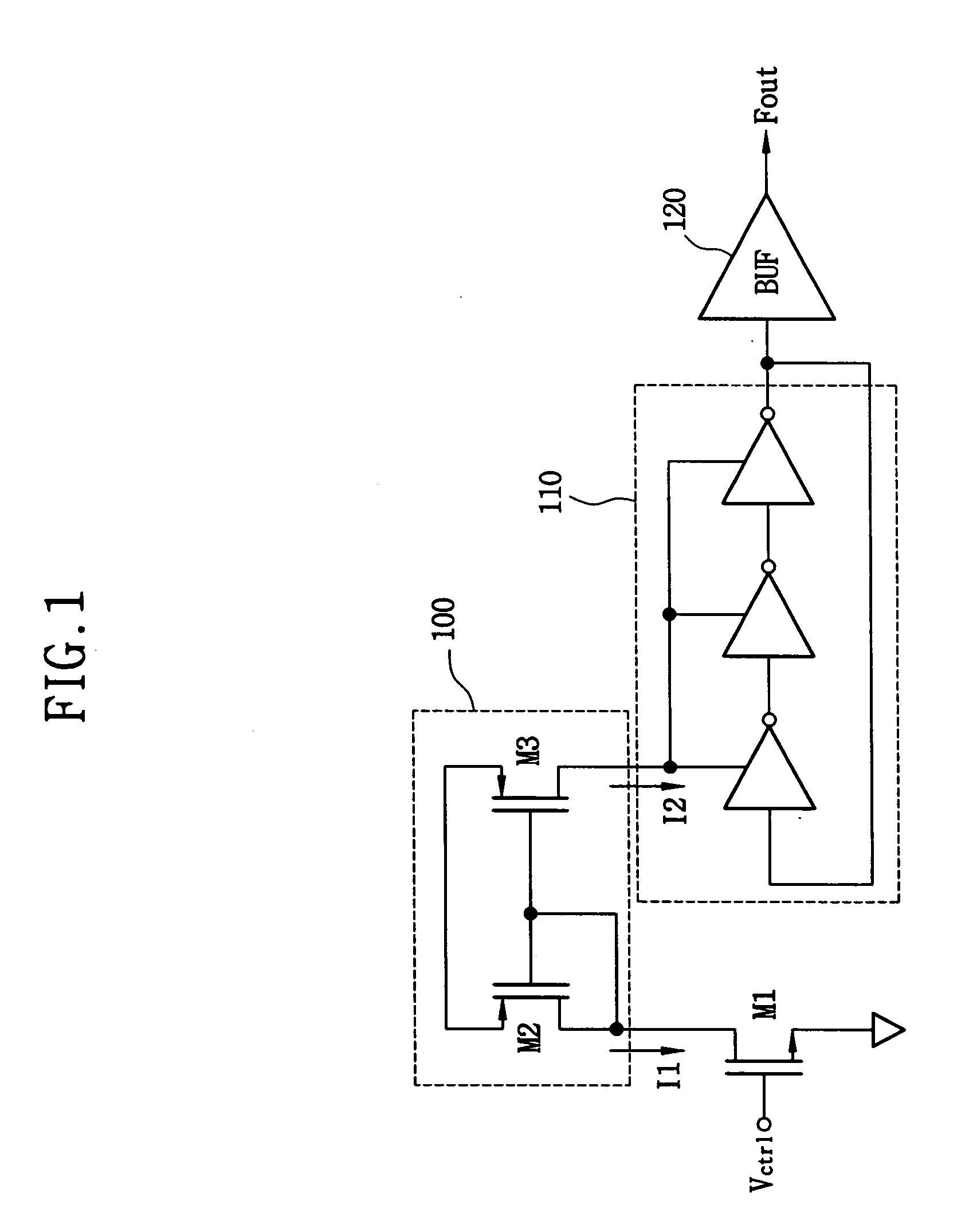
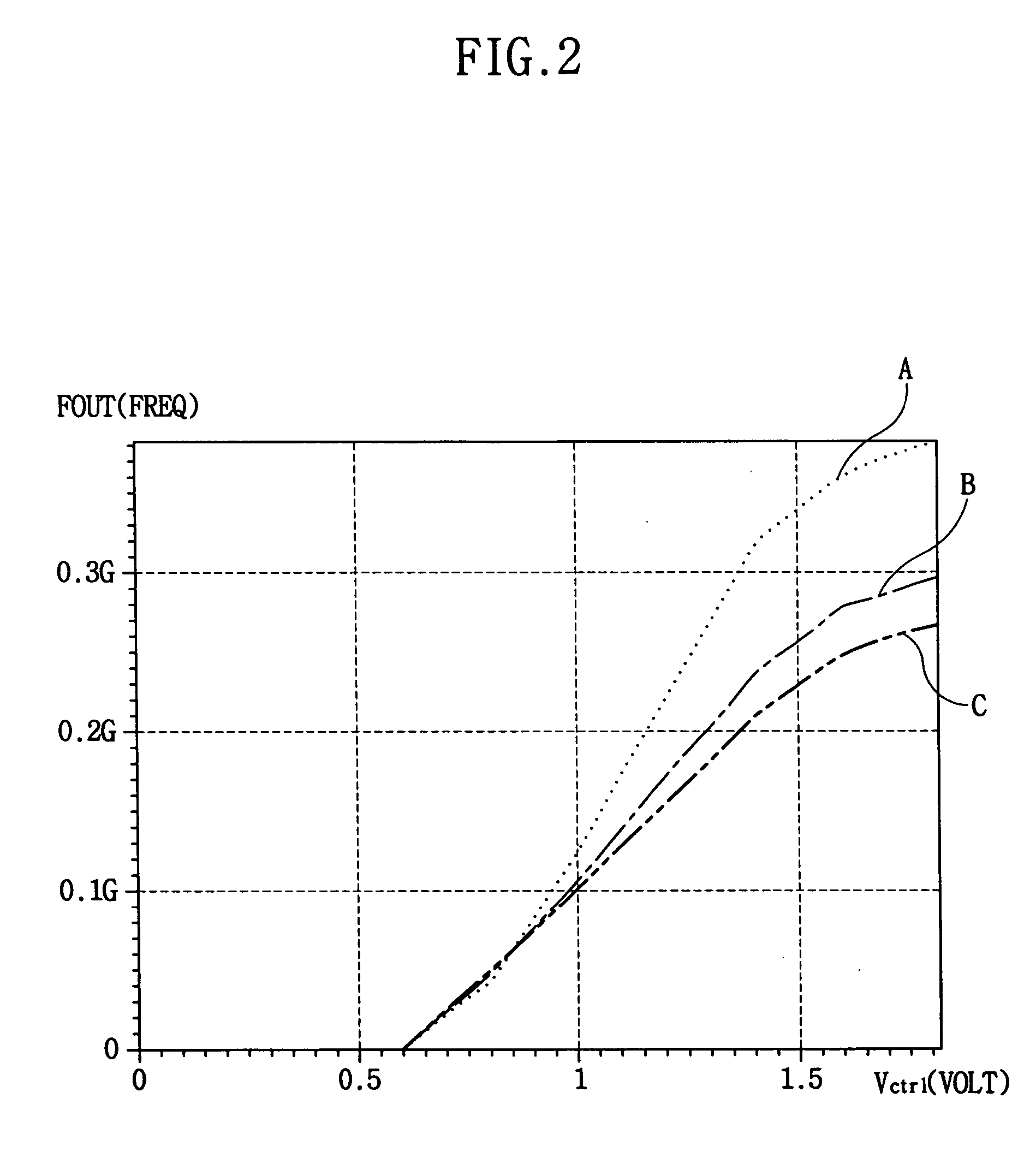
Voltage controlled oscillator and method of generating an oscillating signal
ActiveUS20050030109A1Frequency stabilityPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationNegative temperatureEngineering
A voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) includes a current source, a current sink and a frequency generator. The current source generates a first current having a first negative temperature coefficient. The current sink generates a second current. A current level of the second current varies in response to a first voltage level of a control voltage, and the second current has a second negative temperature coefficient. The frequency generator generates an oscillating signal having a frequency corresponding to a difference between the first and second currents. The VCO generates the oscillating signal having a stable frequency that is independent of temperature variation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Band-gap reference source with high power supply restraint
InactiveCN101131592ASimple structureReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsNegative feedbackFrequency compensation
There is a sort of reference source which has the crack by checking the high electrical source, and it consists of the self-polarization circuit, the regulating circuit, the kernel circuit which has the crack, and the startup circuit. The IPTAT generating circuit of the kernel circuit which has the crack makes the collector current of the Q1 and Q2 of the NPN pipe to equal by that the degenerative feedback which is magnified adjusts its quiescent point, the IPTAT current and the VBE of the Q8 of the NPN transistor which has the negative temperature coefficient in the constant-current circuit are progressed the first compensation of the temperature, at the same time they debase the temperature coefficient. The constant-current circuit produces the polarization by itself, and provides the polarization current to the IPTAT generating current. The operational amplifier circuit advances the plus for the two-stage operational amplifier, the compensation current progresses the frequency compensation for the two-stage operational amplifier. The generating circuit removes the dependency of the reference export VREF to supply voltage by negative feedback effect in order advance the PSRR. The startup circuit removes the degeneration polarization point and it drives the self-polarization circuit to work. The self-polarization circuit provides the polarization voltage for the regulating circuit. The circuit configuration of this invention is simple and new, it does not need the external polarization, the area of this circuit is small, and it has the good temperature coefficient.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
CMOS reference voltage source with adjustable output voltage
InactiveCN101013331ASmall temperature coefficientFast switching speedElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureEngineering
The invention provides an output voltage adjustable CMOS reference voltage source to facilitate the realization of the standard CMOS process, which includes the start circuit, the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit, the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit, and the reference voltage generating circuit; the output of the start circuit connecting with the input of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit, the first output of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively connecting with the first input of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit and the third input of the reference voltage generating circuit, the second output of the positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively connecting with the second input of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit and the fourth input of the reference voltage generating circuit, the first and second outputs of the negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit respectively corresponding connecting with the first and second inputs of the reference voltage generating circuit, and the reference voltage generating circuit has the reference voltage output to output reference voltage.
Owner:南通金石工贸有限公司 +1
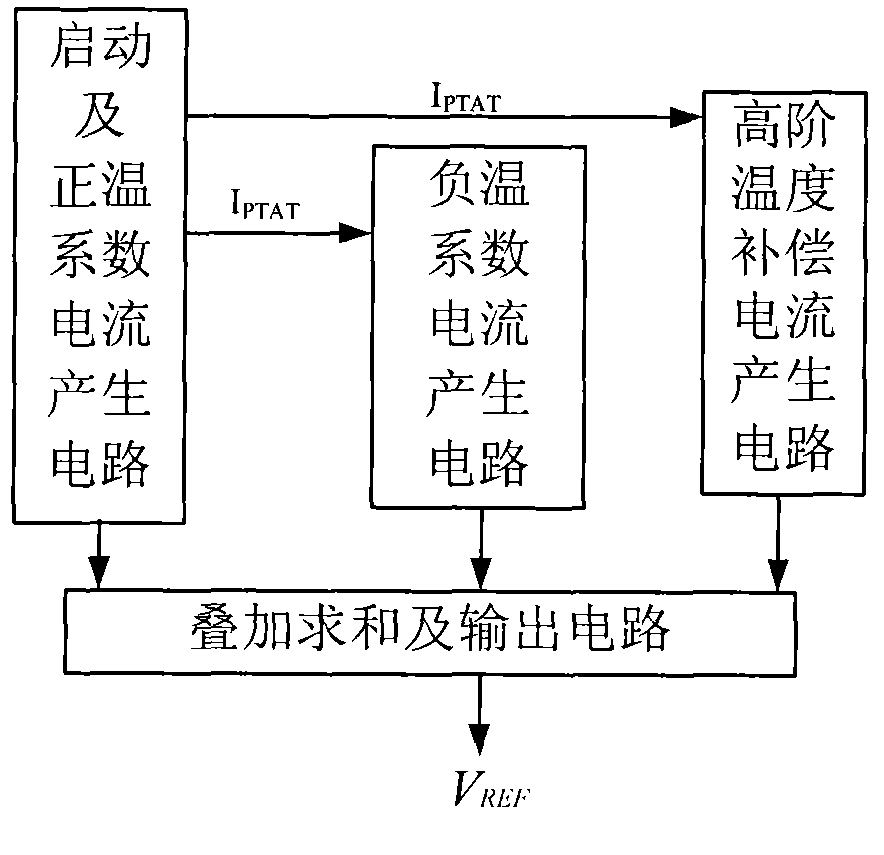
Voltage reference source with high-order temperature compensation circuit
InactiveCN101950191AElimination of Higher Order Temperature CoefficientsSmall temperature driftElectric variable regulationReference circuitElectron
A voltage reference source with high-order temperature compensation circuit belongs to the electronic technical field. The voltage reference source comprises a starting current and positive temperature coefficient current generating circuit, a negative temperature coefficient current generating circuit, a high-order temperature compensation current generating circuit and a superimposition and summation output circuit. The added high-order temperature compensation current generating circuit performs linearization to the breakover voltage VBE between the voltage of the base and emitter of a triode to obtain a high-order compensation amount which is in agreement with the high-order temperature amount of the PN junction voltage, and the high-order temperature coefficient of the PN junction voltage can be eliminated fundamentally after proportional offset, thus realizing a CMOS voltage reference source with the lower temperature coefficient. The voltage reference source is prepared by the common CMOS technology with lower cost, has extremely low temperature coefficient, less power consumption and smaller area, and can be used in the reference circuits such as analog circuits and digital-analog hybrid circuits which are required to have low temperature coefficients.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
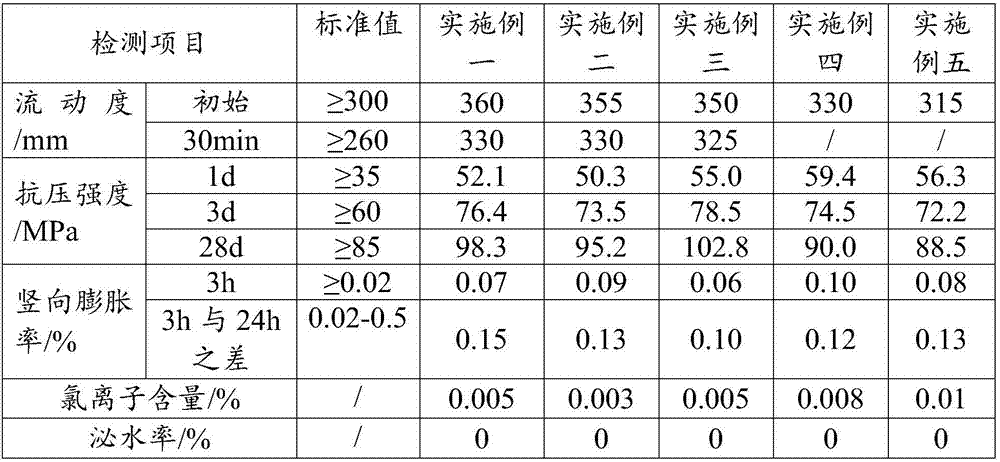
Sleeve grouting material for steel bar connection and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a sleeve grouting material for steel bar connection and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of construction engineering. The sleeve grouting materialfor the steel bar connection is mainly prepared from raw materials including cement, aggregate, an admixture, a polycarboxylic water reducer, a plastic expanding agent, a compound expanding agent, aregulator and the like; the sleeve grouting material has great machine discharging flowability and flowability after 30min, slight expansion, early strength and high strength, is easy to produce and construct in the aspect of construction and has the advantages of reliable quality, low cost, shortened construction period, convenience for utilization and the like; the sleeve grouting material has long working time and strong environmental adaptability. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and easy to operate; the sleeve grouting material for the steel bar connection, whichis applicable to room-temperature, low-temperature and negative-temperature conditions, can be prepared through regulating the ratio.
Owner:CNBM ZHONGYAN TECH
Precise temperature sensor with smart programmable calibration
ActiveUS7204638B2Easy CalibrationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNegative temperatureEngineering
A temperature sensor with a plurality of temperature sense points based on a bandgap reference circuit providing negative temperature coefficient reference voltages and a positive temperature coefficient reference voltage. All negative temperature coefficient reference voltages have the same slope and the same spacing from each other. The intercept points between the negative temperature coefficient reference voltages and the positive temperature coefficient reference voltage determine the temperature sense points. Efficient calibration of the spacing of the temperature sense points is provided by a tap on a programmable resistor in the positive temperature coefficient reference circuit. Efficient calibration of the absolute temperature is provided by second programmable resistors in a circuit driven by two current sources. The calibration of one temperature point equally applies to all other second programmable resistors.
Owner:ETRON TECH INC
Temperature sensor
InactiveUS20040004992A1Guaranteed uptimeEasy to adjustThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNegative temperatureEngineering
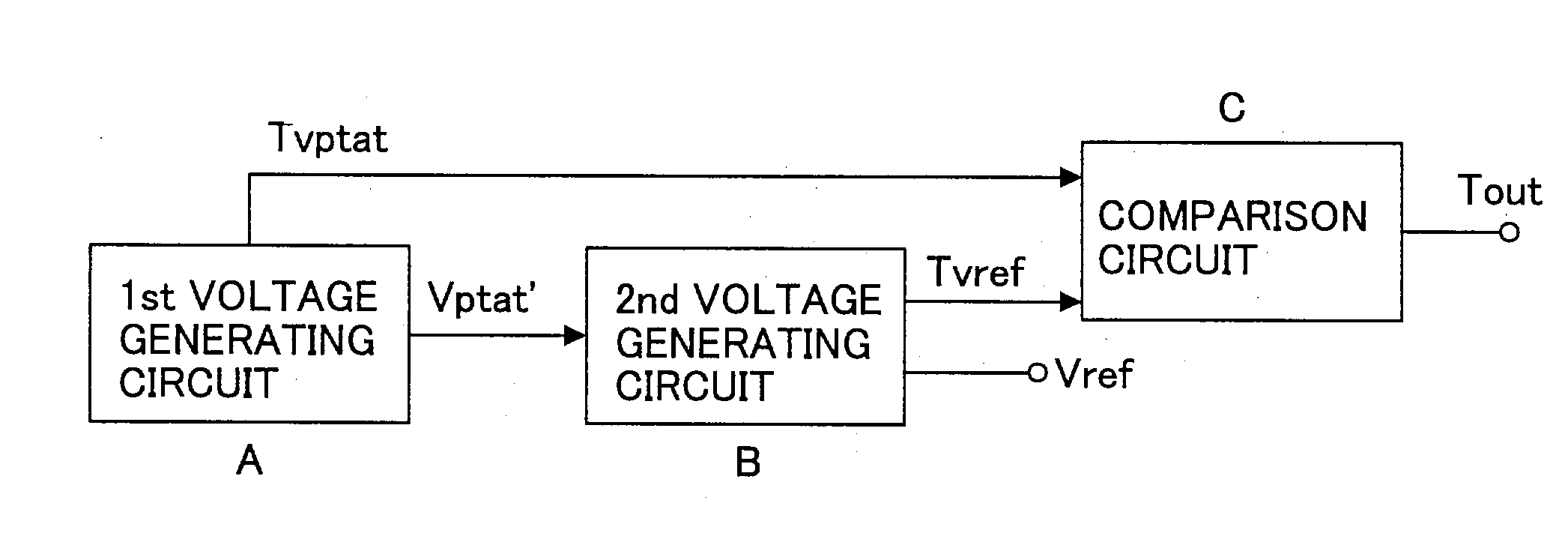
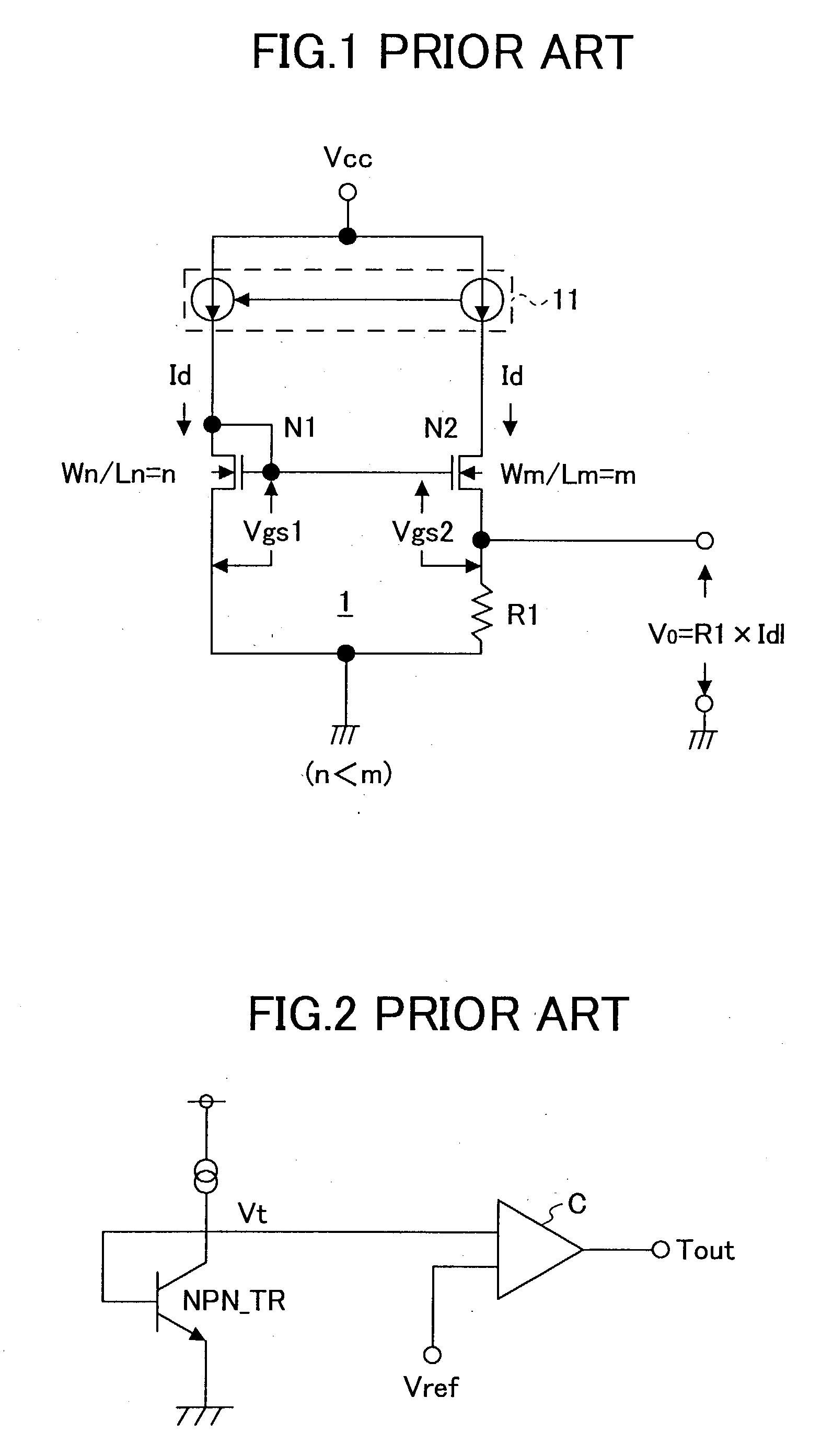
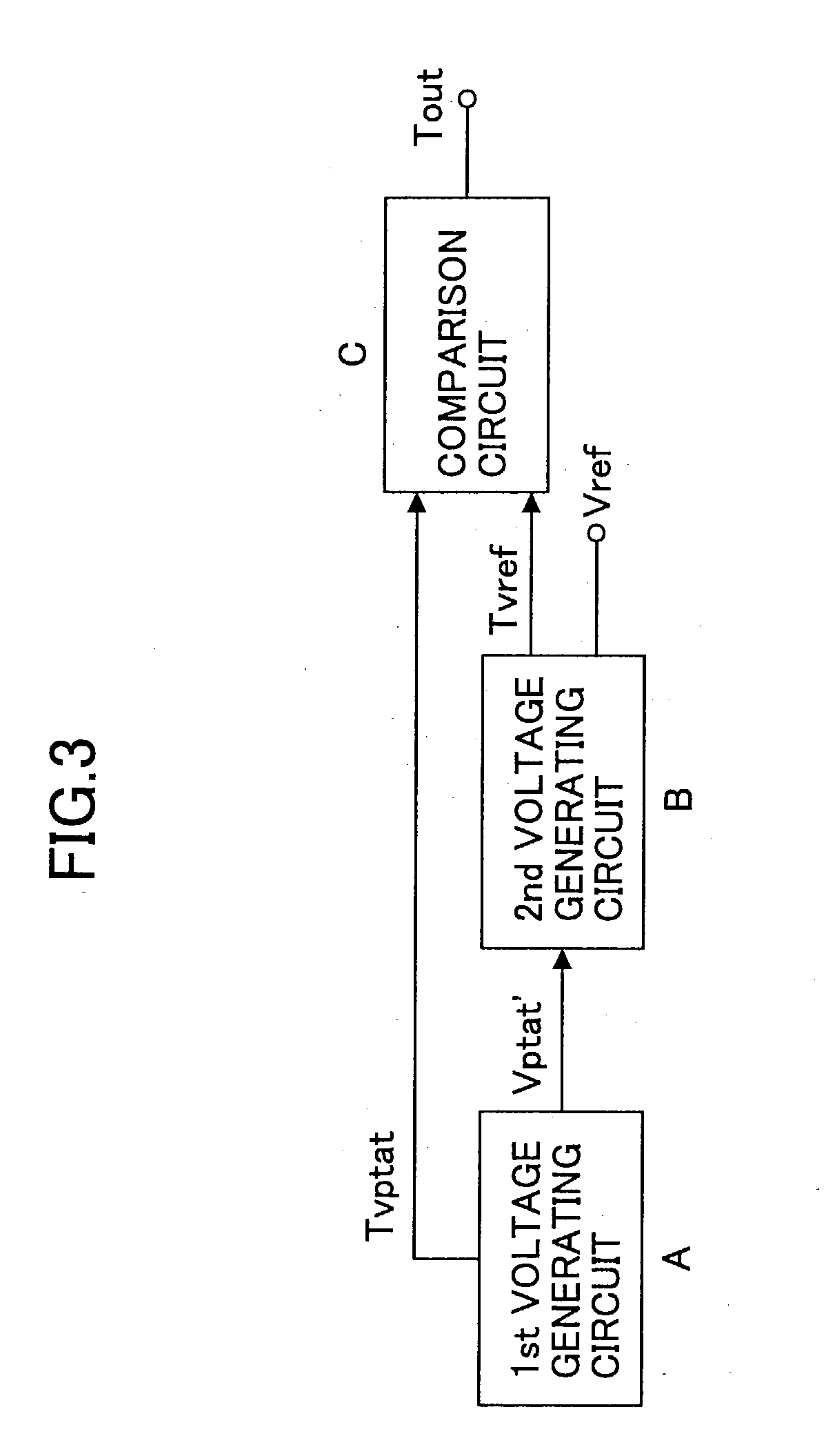
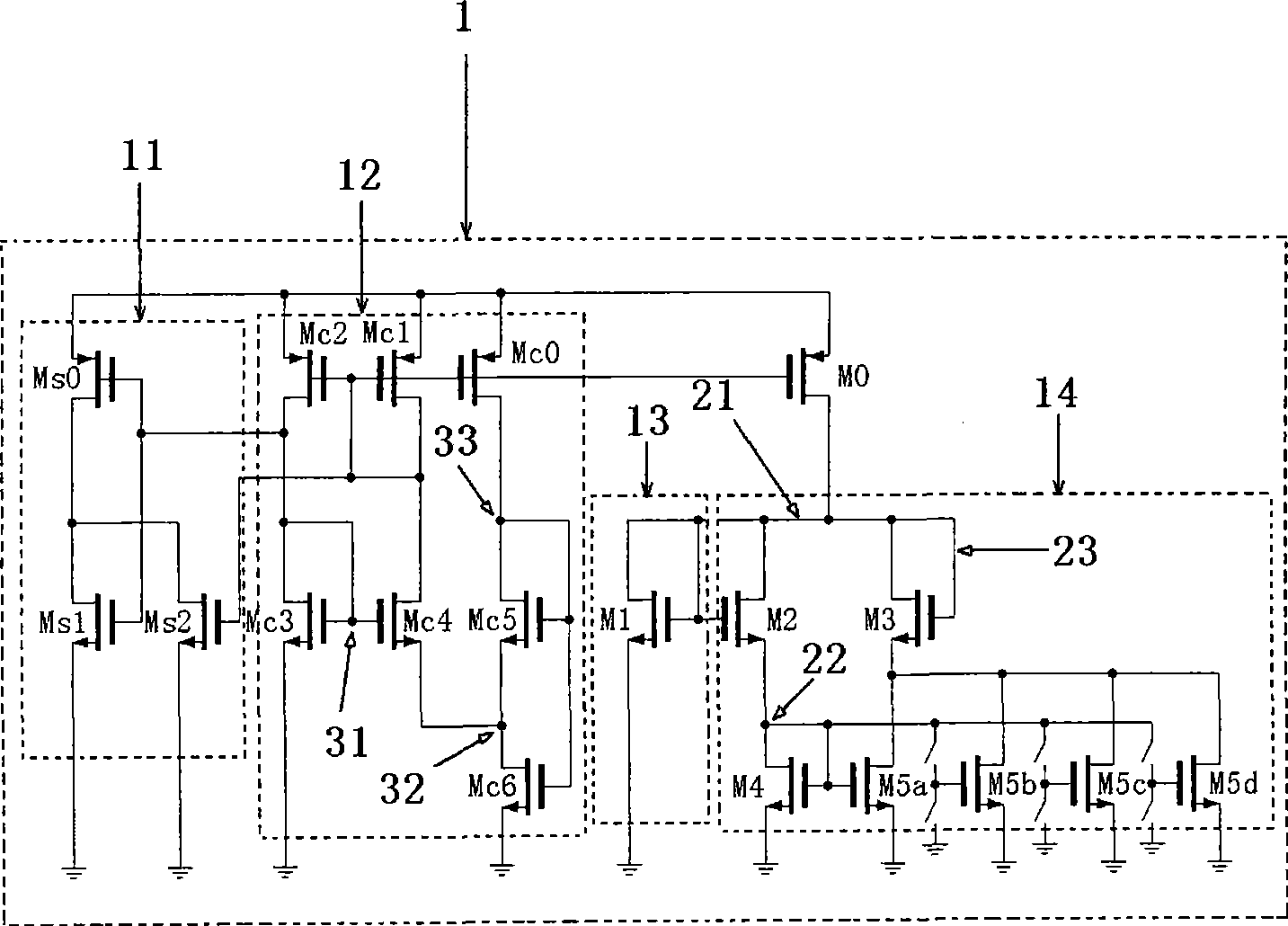
A temperature sensor comprises (a) a first voltage generating circuit that generates and outputs a first voltage having a positive or negative temperature coefficient in proportion to the absolute temperature; (b) a second voltage generating circuit that generates a second voltage having an opposite sign of temperature coefficient compared to the first voltage and outputs a reference voltage that does not have a temperature coefficient based on the second voltage; and (c) a comparator that compares the first voltage output from the first voltage generating circuit with the reference voltage output from the second voltage generating circuit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Low-voltage low-power consumption CMOS voltage reference circuit
ActiveCN101470459AReduce power supply voltageReduce voltageElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention discloses a low-voltage low-power-consumption CMOS voltage reference circuit, which is used for generating a voltage reference. The CMOS voltage reference circuit comprises a starting circuit 11, a self-bias current source 12, a voltage generator 13 with negative temperature coefficient, a voltage reference regulator 14 and a single-tube current mirror MOS transistor M0. The CMOS voltage reference circuit adopts an MOS transistor operating at a sub-threshold area to generate a voltage with negative temperature coefficient, utilizes a sleeve and a folded structure of the MOS transistor operating at the sub-threshold area to substitute a resistance for amplifying a voltage with positive temperature coefficient, thereby offsetting the voltage with positive temperature coefficient by the voltage with negative temperature coefficient, and generating a temperature-independent voltage reference. The CMOS voltage reference circuit eliminates the use of passive devices and an operation amplifier, wherein the passive devices relate to a resistance, a capacitor and the like, thereby greatly reducing the component number of the circuit and the static operating current, and reducing the power consumption and the area of the circuit.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD
Image heating apparatus and heater used in the apparatus
InactiveUS8592726B2Inhibit temperature riseLow costHeater elementsElectrographic process apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An image heating apparatus includes: an endless belt; a heater, contacted to a surface of the endless belt, provided so that a longitudinal direction thereof is parallel to a generating line direction of the endless belt; and a pressing member for forming a nip together with the endless belt. The heater includes: an elongated substrate; a first heat generating line, provided on the substrate along a longitudinal direction of the substrate, including first heat generating resistors having a negative temperature coefficient of resistance and being electrically connected in series; and a second heat generating line, provided on the substrate along the longitudinal direction of the substrate, electrically connected to the first heat generating line in parallel. The second heat generating line includes a plurality of second heat generating resistors having the negative temperature coefficient of resistance and being electrically connected in series.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com