Patents
Literature
1398 results about "Bipolar junction transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
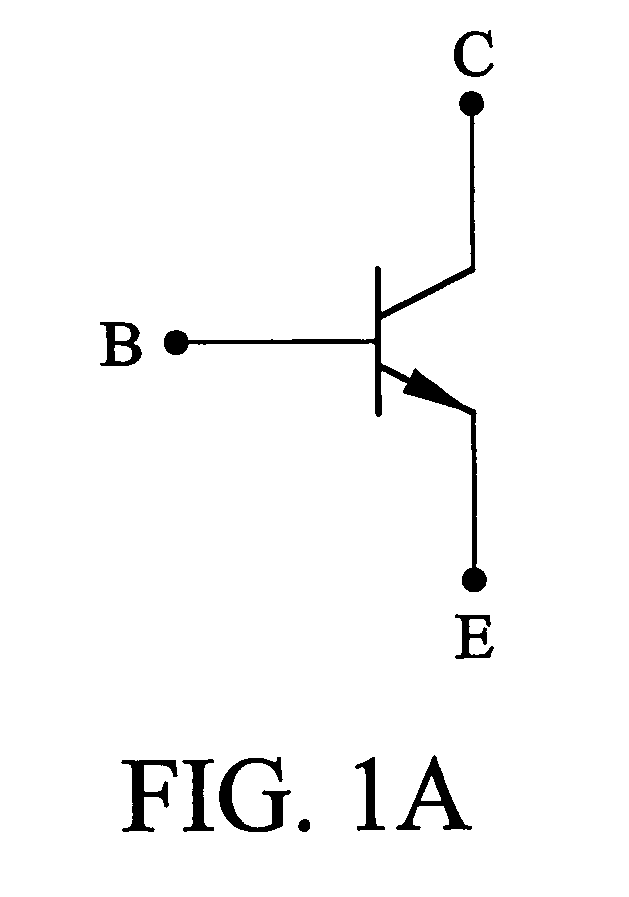
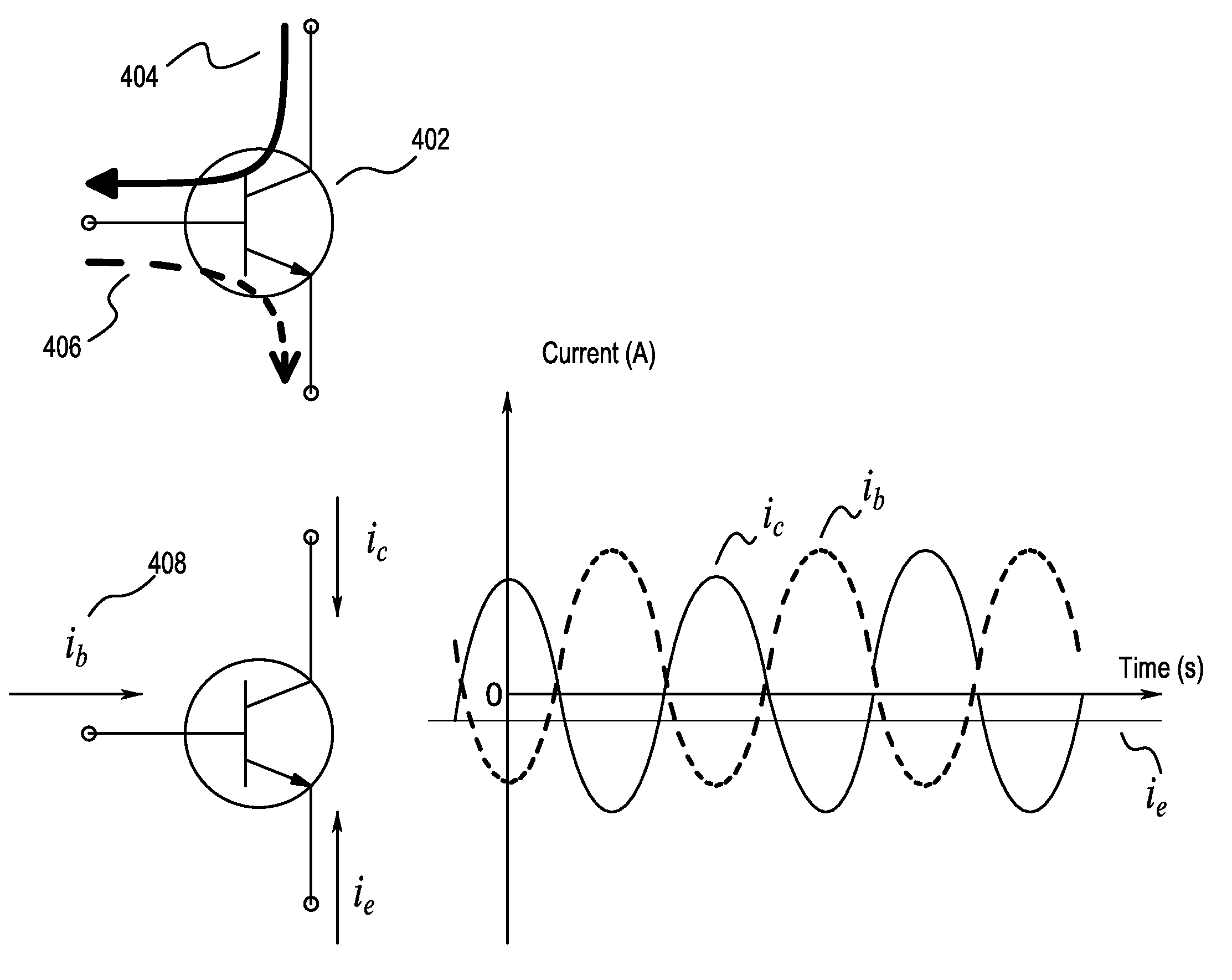
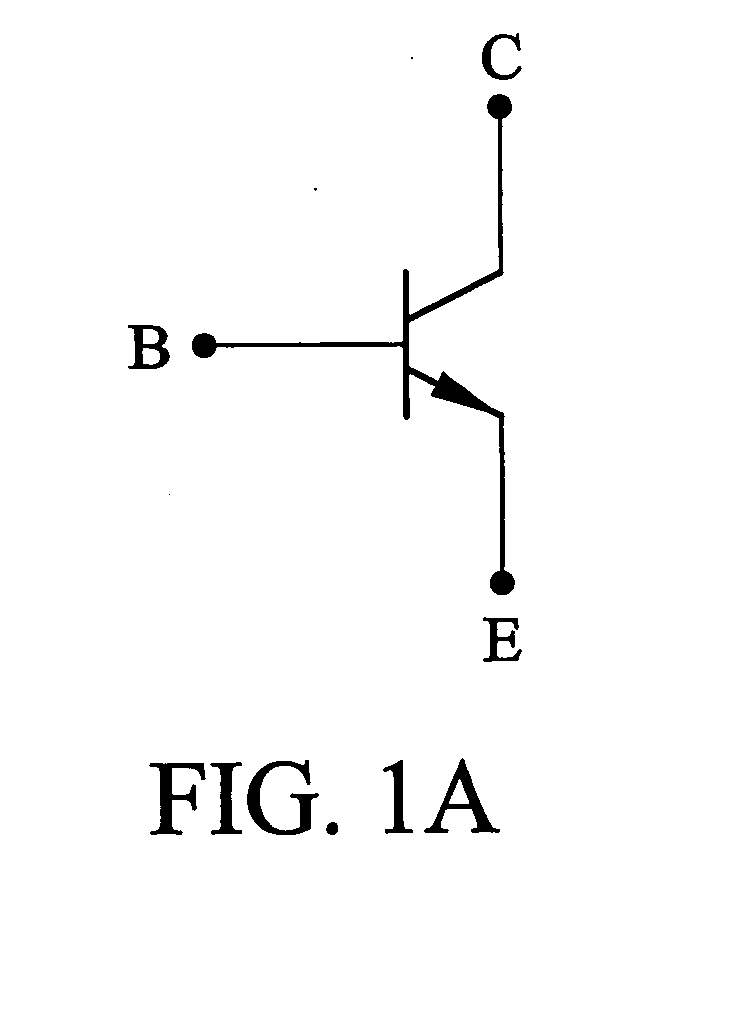
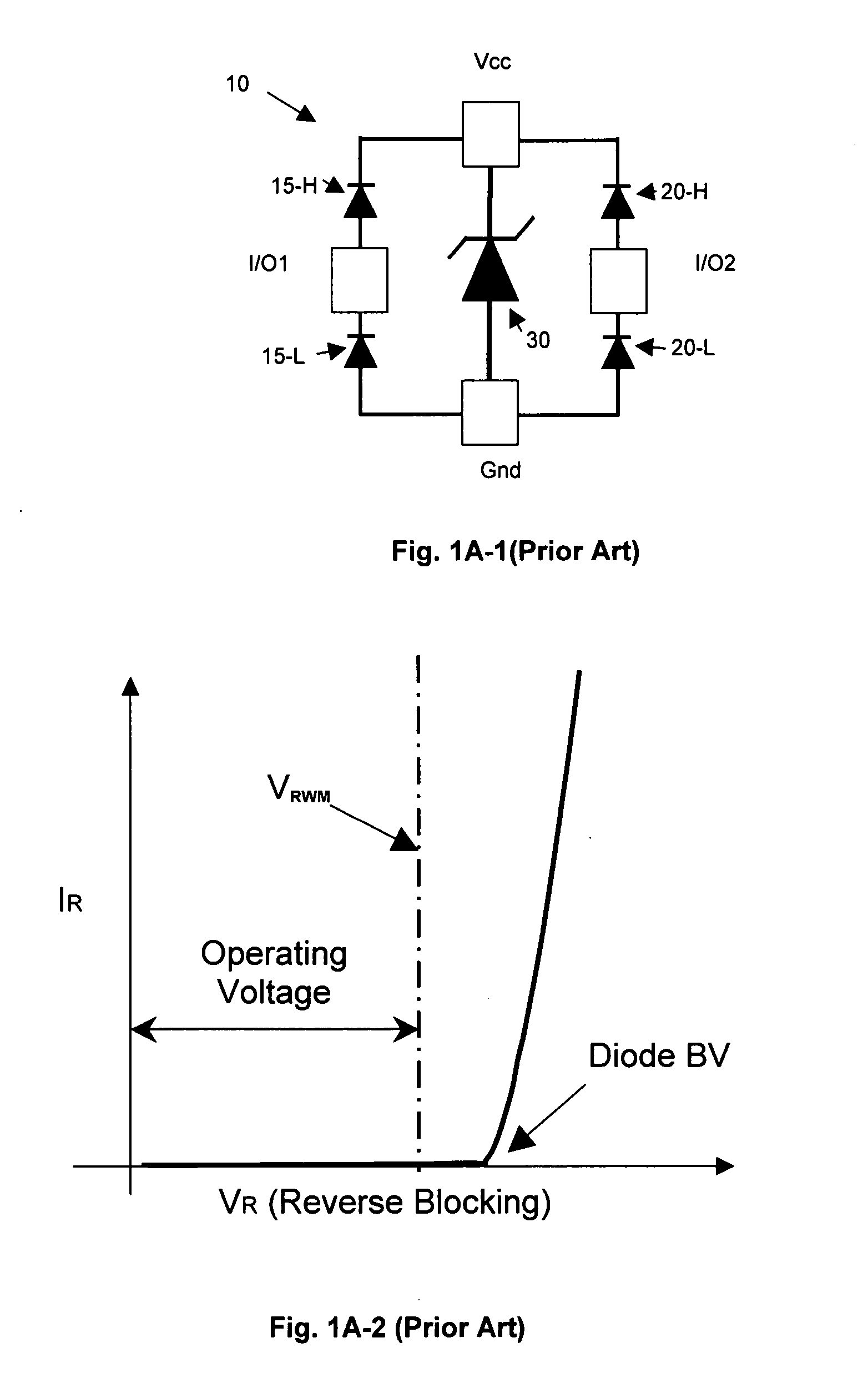
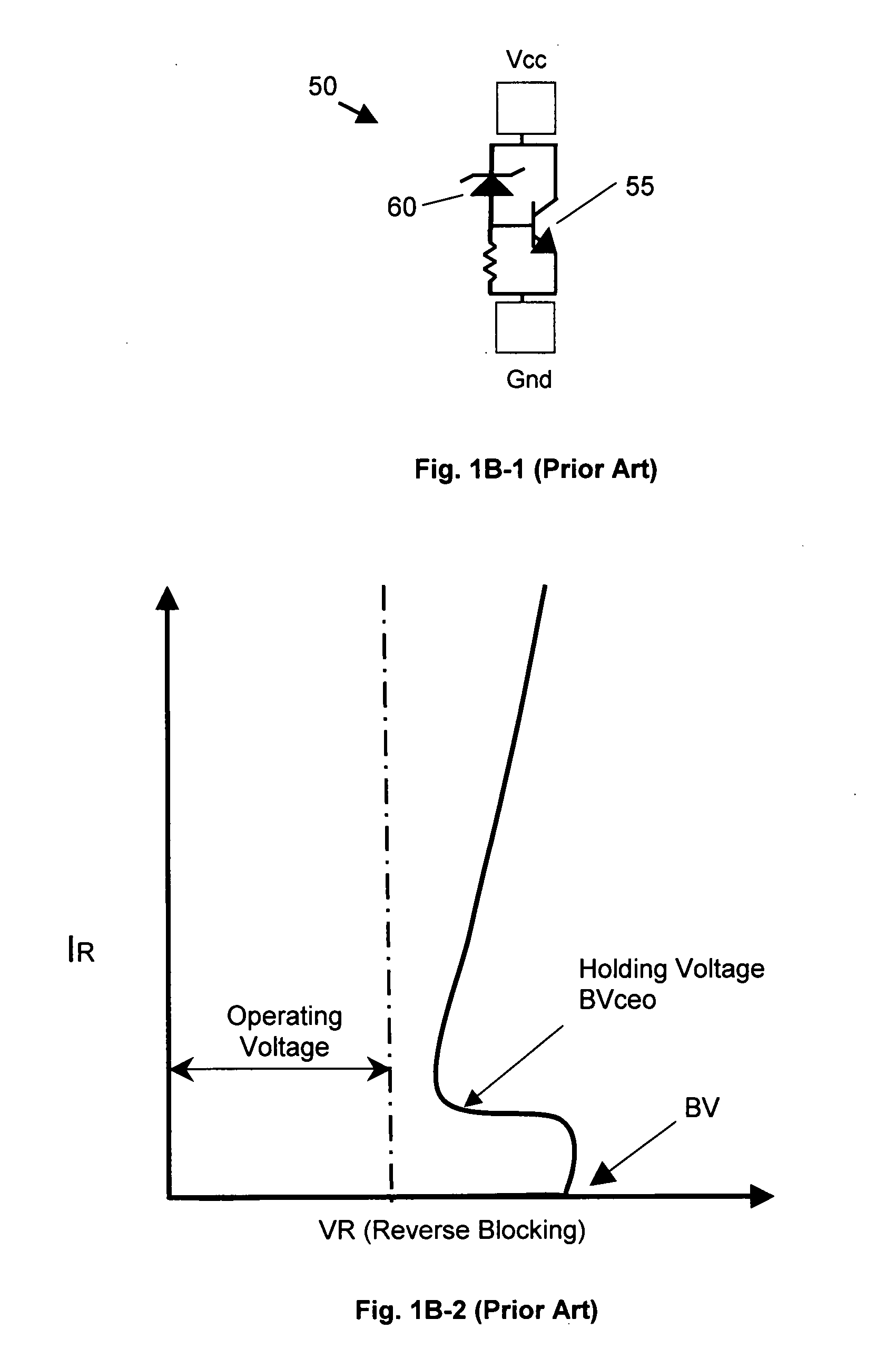
A bipolar junction transistor (bipolar transistor or BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and holes as charge carriers. Unipolar transistors, such as field-effect transistors, only use one kind of charge carrier. BJTs use two junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type.
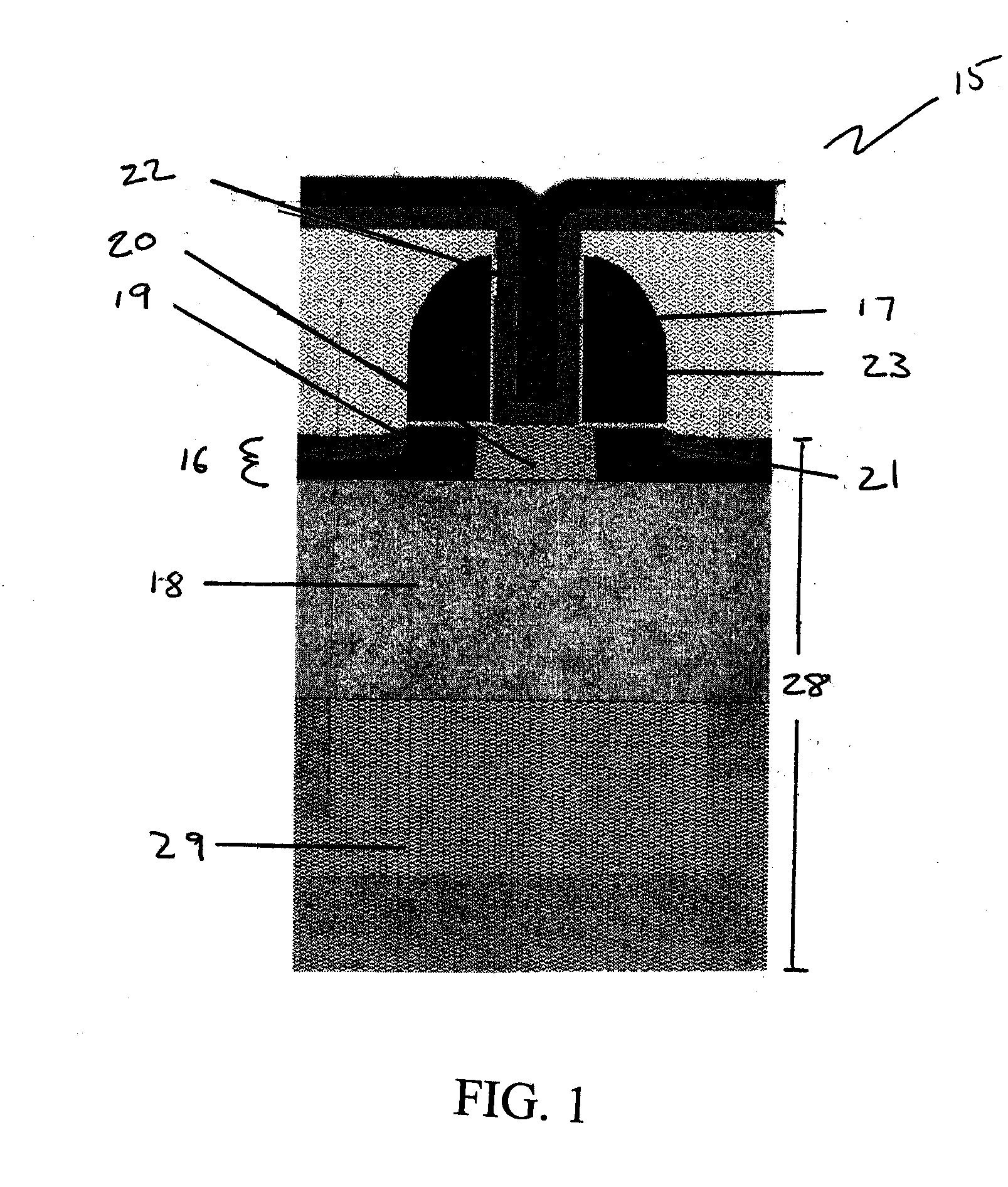
Bipolar Junction Transistor Based on CMOS Technology
InactiveUS20120032303A1Increase currentHigh base resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
The present invention relates to semiconductor technologies, and more particularly to a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) in a CMOS base technology and methods of forming the same. The BJT includes a semiconductor substrate having an emitter region, a base having a first contact, and a collector having a second contact and a well plug; a first silicide film on the first contact; a second silicide film on the second contact; a first silicide blocking layer on or over the semiconductor substrate between the first and second silicide films, and a second silicide blocking layer on the semiconductor substrate between the first silicide film and the emitter region.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
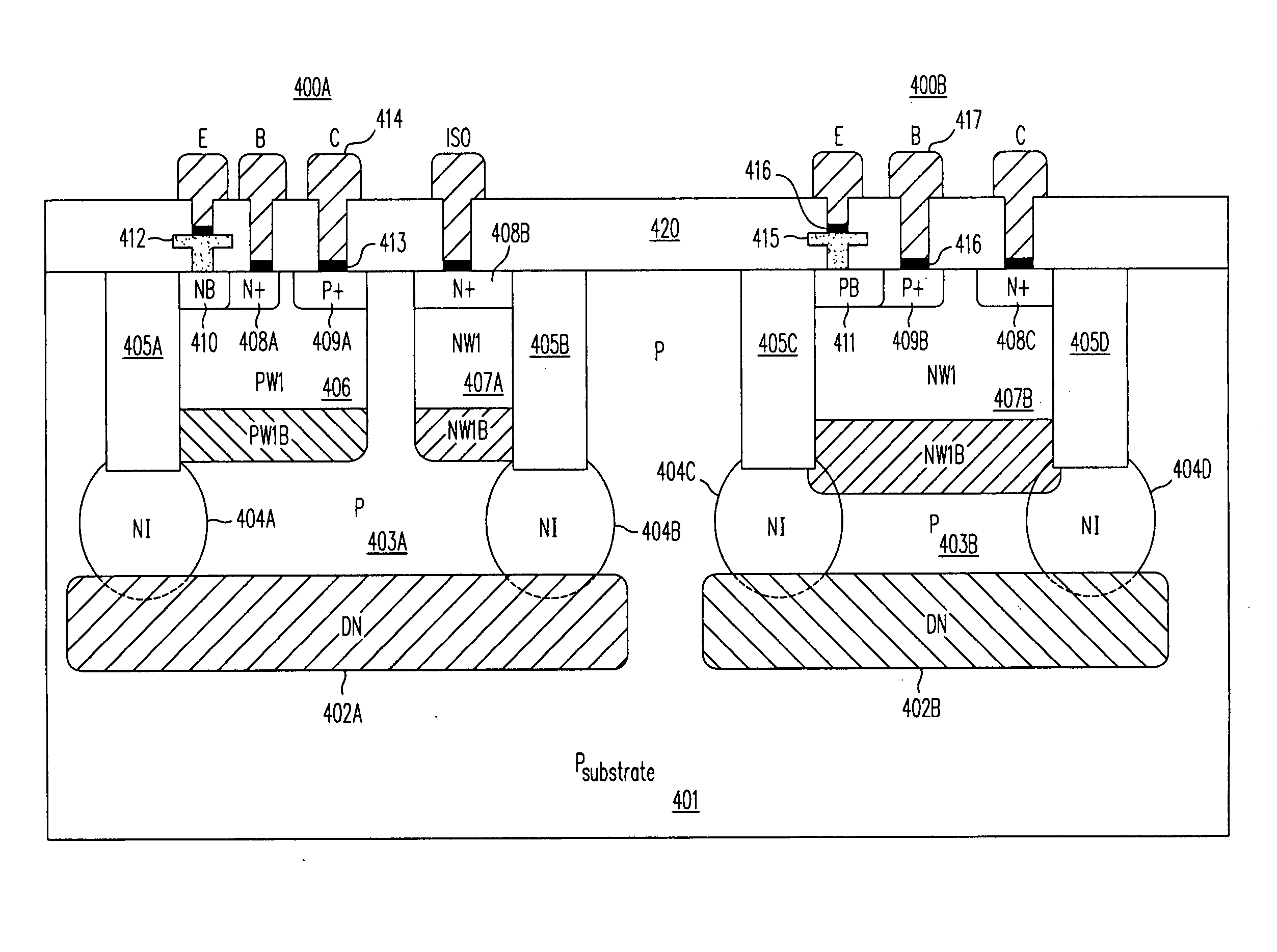
High-gain vertex lateral bipolar junction transistor
InactiveUS7701038B2Reduce parasitic effectsIncrease currentLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryEngineering
A lateral bipolar junction transistor having improved current gain and a method for forming the same are provided. The transistor includes a well region of a first conductivity type formed over a substrate, at least one emitter of a second conductivity type opposite the first conductivity type in the well region wherein each of the at least one emitters are interconnected, a plurality of collectors of the second conductivity type in the well region wherein the collectors are interconnected to each other, and a plurality of base contacts of the first conductivity type in the well region wherein the base contacts are interconnected to each other. Preferably, all sides of the at least one emitters are adjacent the collectors, and none of the base contacts are adjacent the sides of the emitters. The neighboring emitter, collectors and base contacts are separated by spacings in the well region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
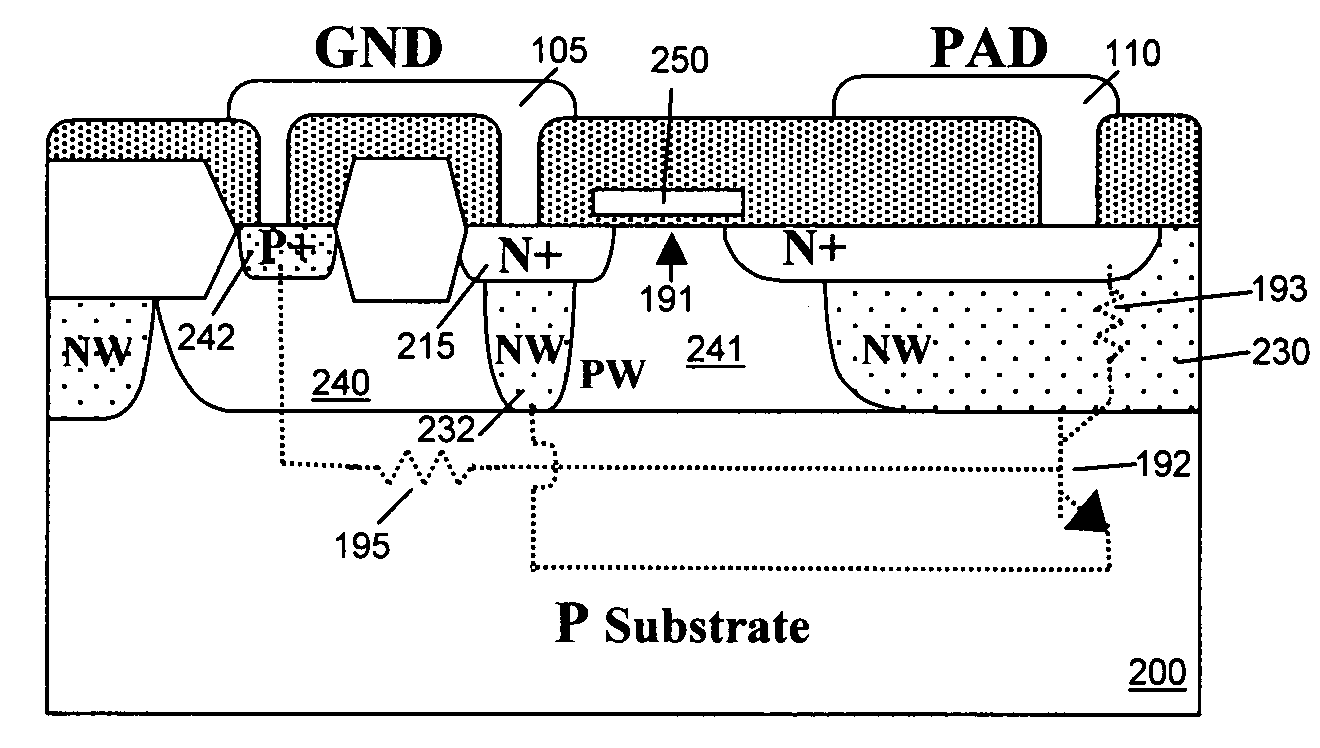
Electrostatic protection device
ActiveUS20110101444A1Easy to modifyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringImpurity
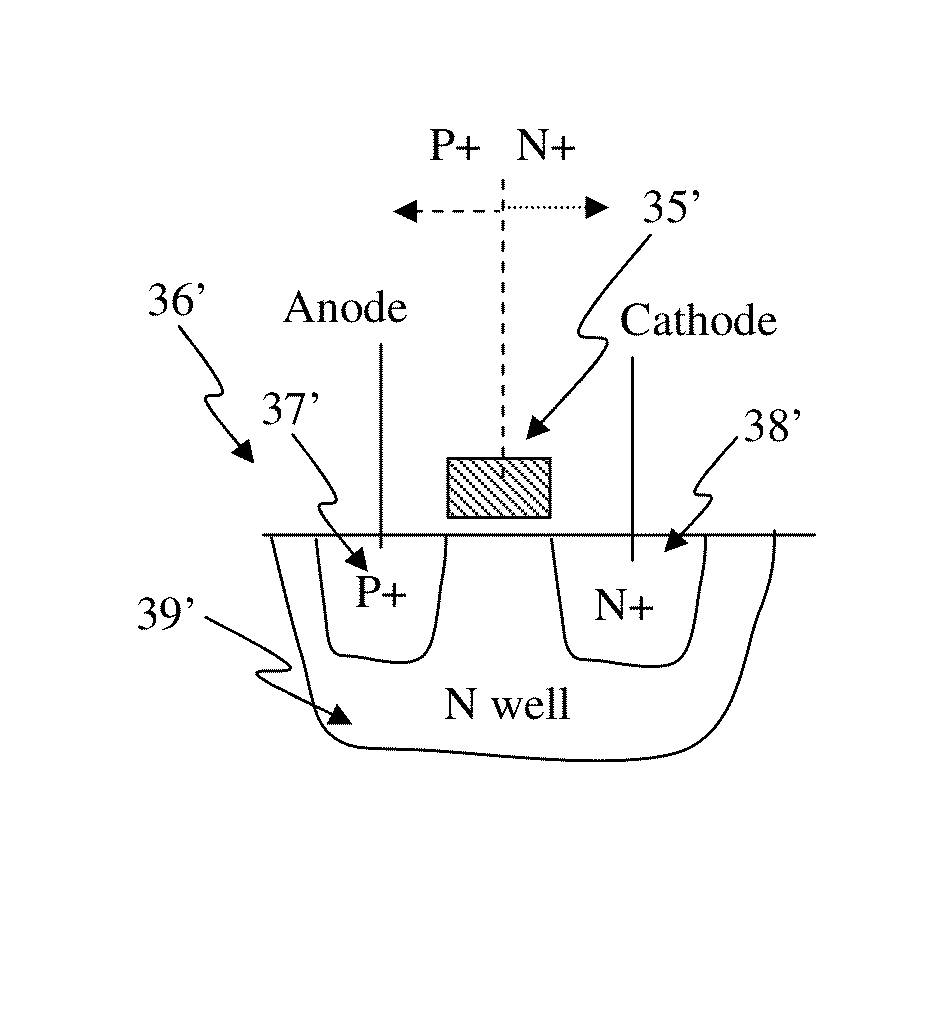
An apparatus including an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device comprising a semiconductor having first, second and third regions arranged to form a transistor, wherein the first region is doped with a first impurity of a first conductivity type and is separated from the second region which is doped with a second impurity of a second conductivity type opposite the first type, and wherein a dimensional constraint of the regions defines an operational threshold of the ESD protection device. In one example, the separation between a collector and an emitter of a bipolar transistor defines a trigger voltage to cause the electrostatic discharge protection device to become conducting. In another example, a width of a bipolar transistor base controls a holding voltage of the electrostatic discharge protection device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
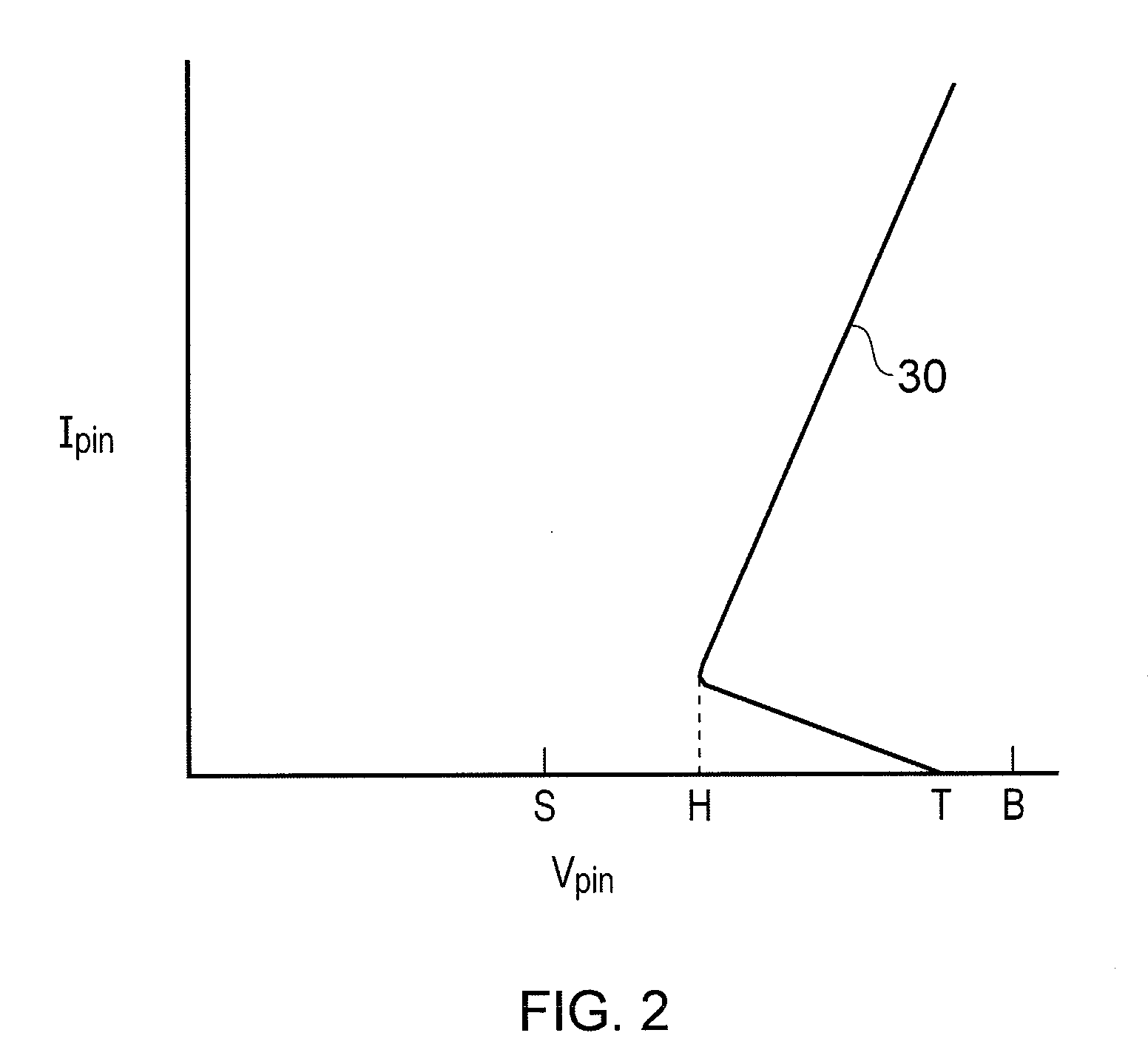
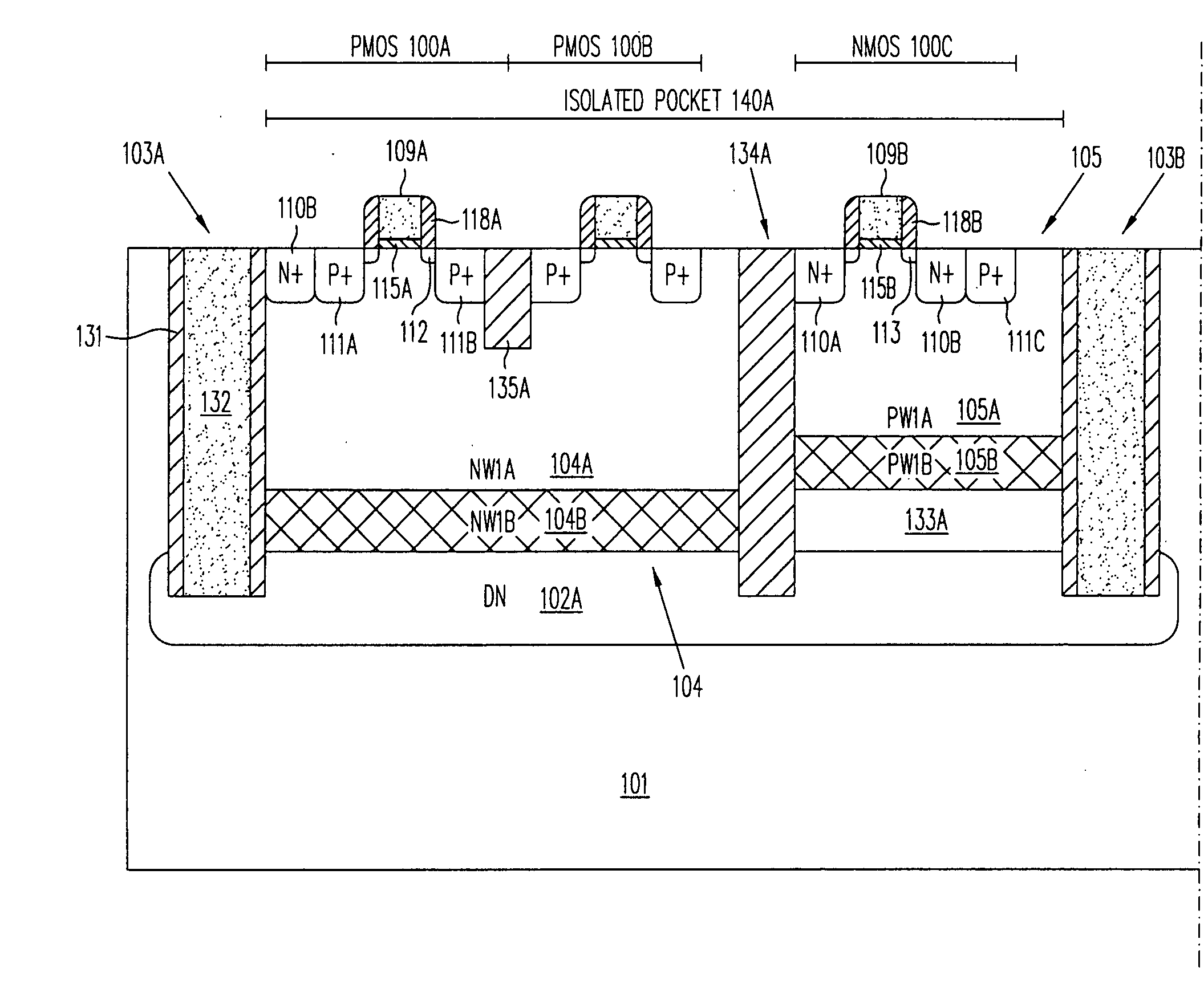
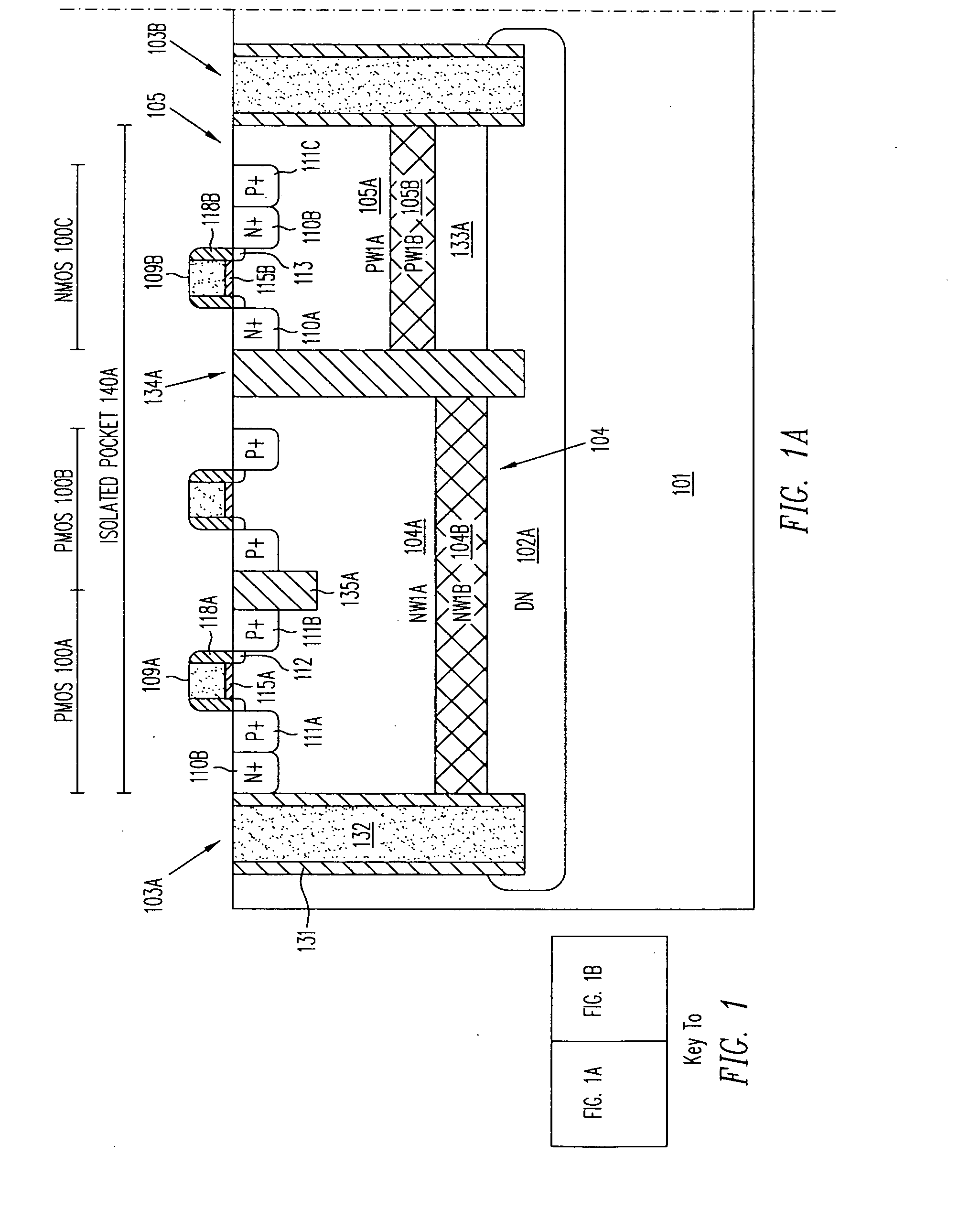
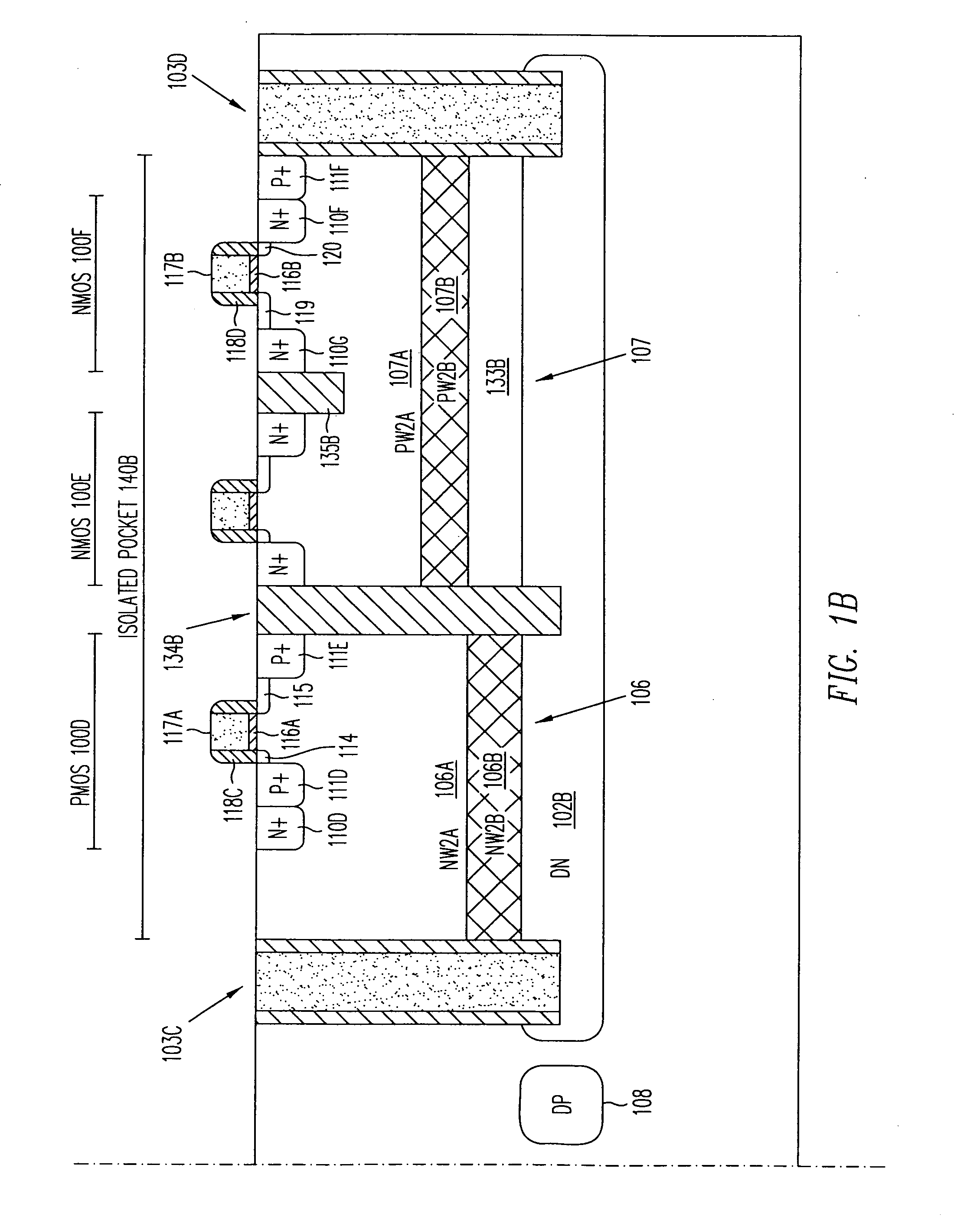
Isolated Bipolar Transistor
InactiveUS20080217699A1Avoid problemsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
An isolated bipolar transistor formed in a P-type semiconductor substrate includes an N-type submerged floor isolation region and a filled trench extending downward from the surface of the substrate to the floor isolation region. Together the floor isolation region and the filled trench form an isolated pocket of the substrate which contains the bipolar transistor. The collector of the bipolar transistor may comprise the floor isolation region. The substrate does not contain an epitaxial layer, thereby overcoming the many problems associated with fabricating the same.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Voltage reference circuit
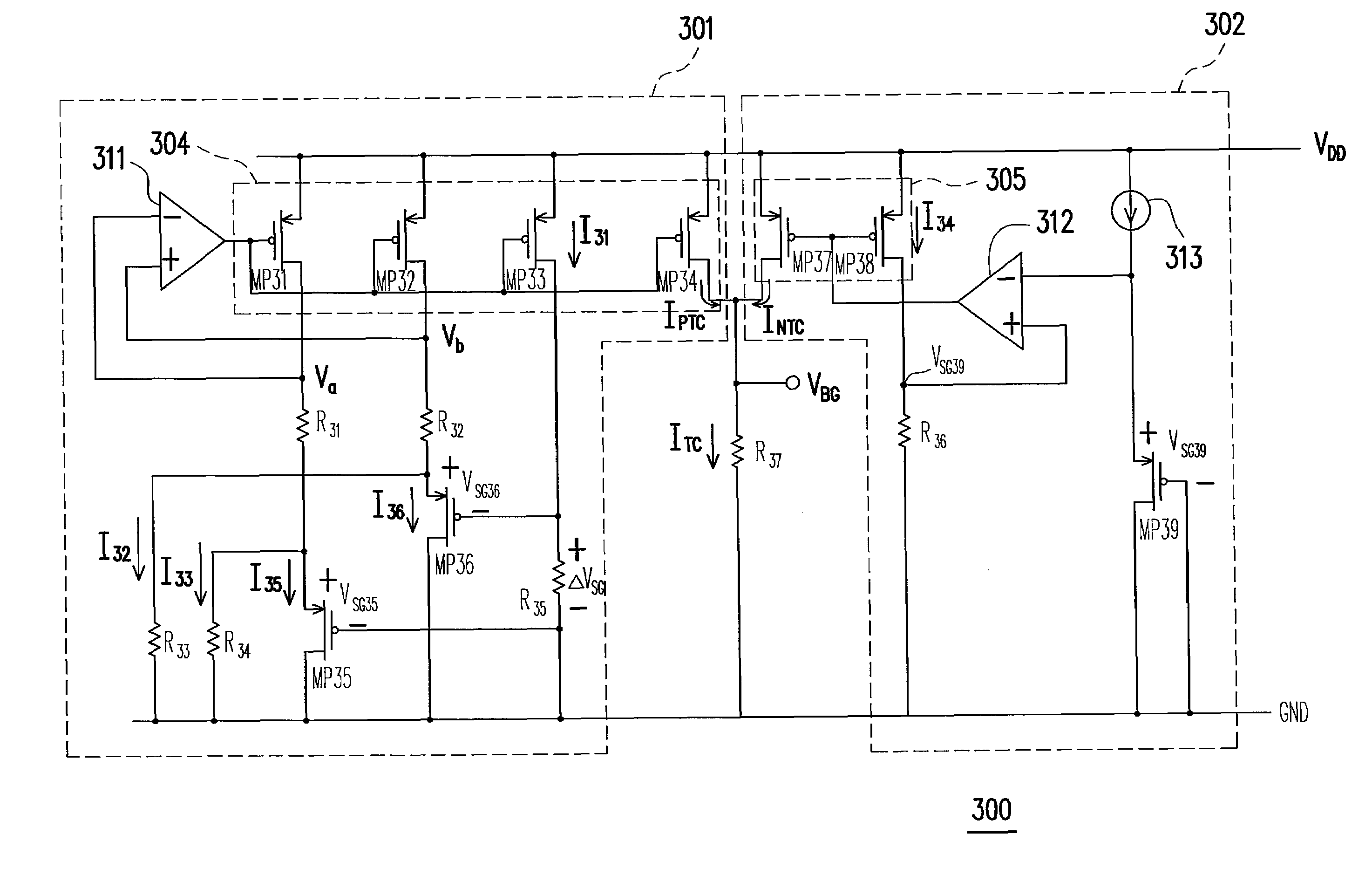
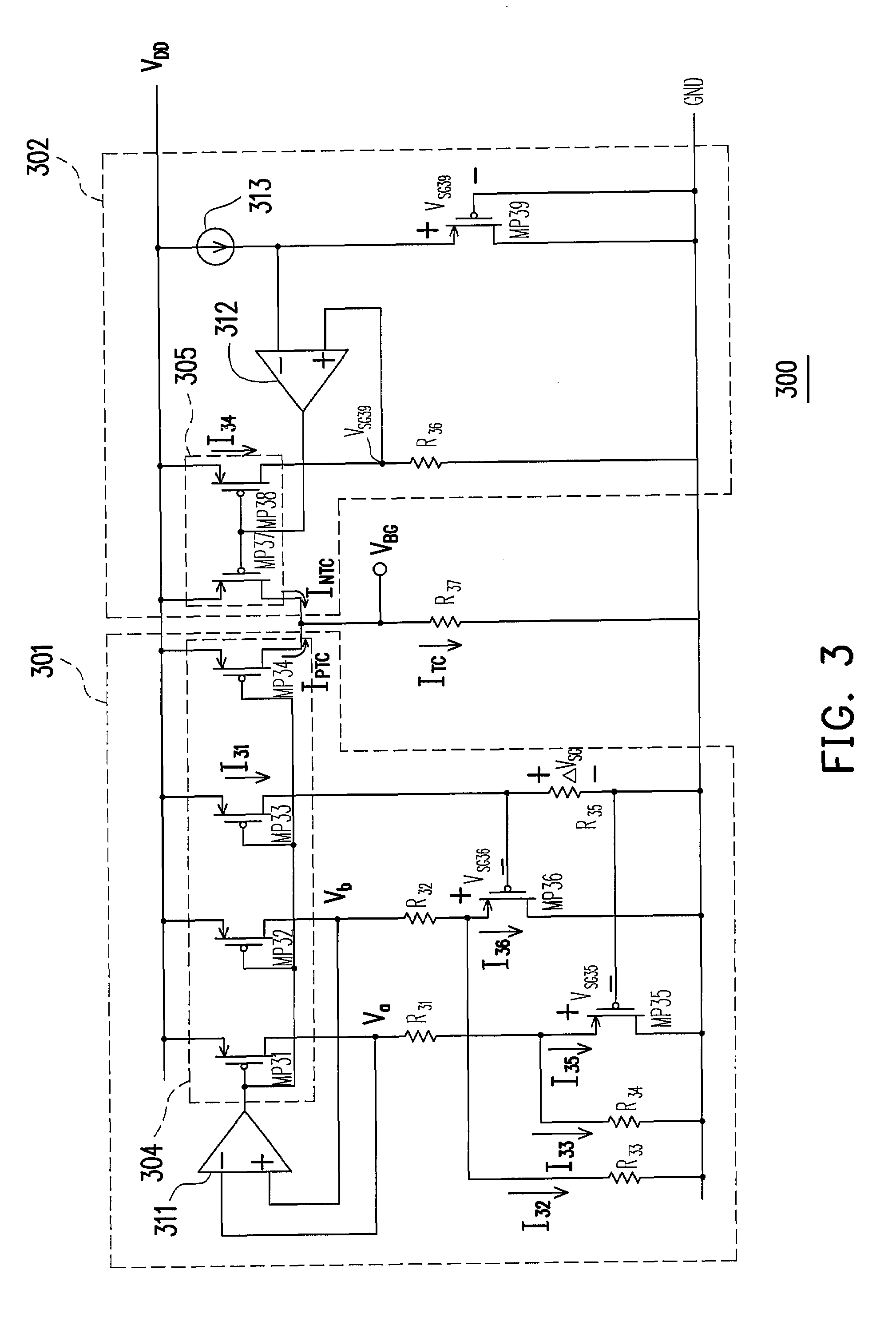
InactiveUS7301321B1Stable reference voltageReduce layout costsPower supply linesElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureVoltage drop
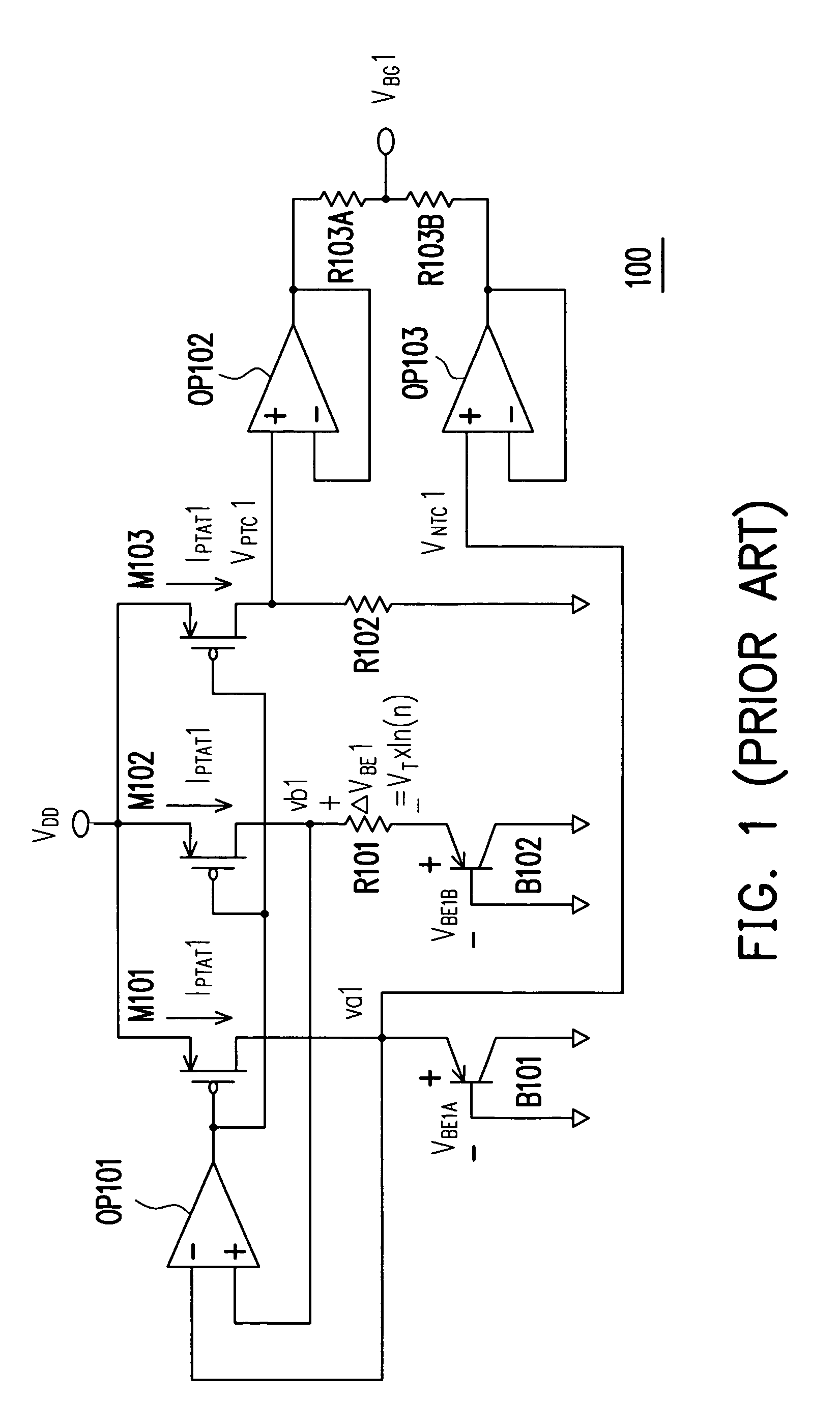
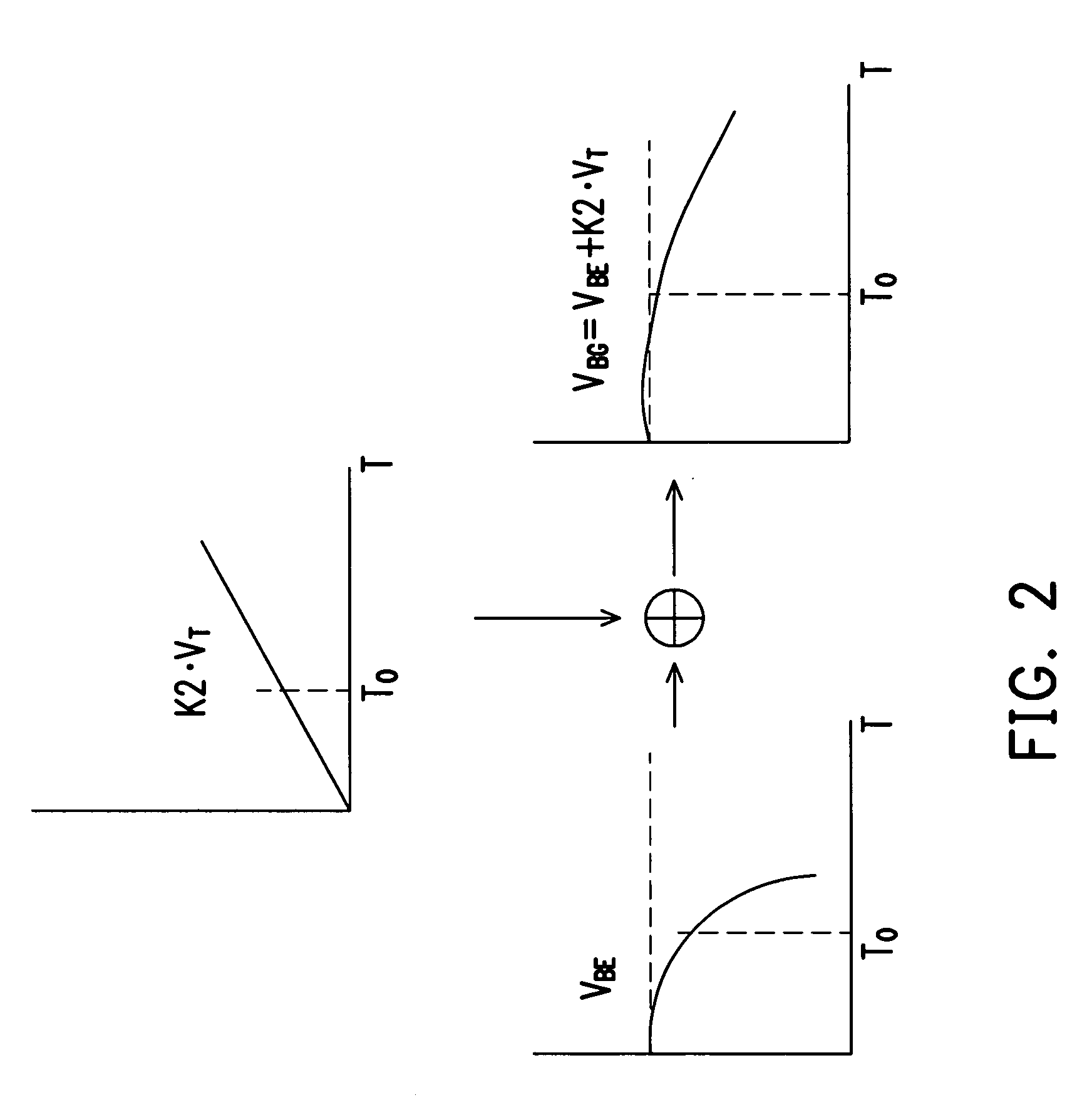
A voltage reference circuit including a positive temperature coefficient current generator, a negative temperature coefficient current generator, and a first resistor is provided. In the positive temperature coefficient current generator, two transistors are operated in the weak inversion region, and a second resistor is connected in series between the gates of the two transistors. The second resistor employs the characteristic that a transistor operated in weak inversion region acts like a bipolar junction transistor to generate a positive temperature coefficient current. The negative temperature coefficient current generator generates a negative temperature coefficient current in response to a negative temperature coefficient voltage drop on a third resistor. The positive temperature coefficient current and the negative temperature coefficient current flow through the first resistor together, thus producing a stable reference voltage.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
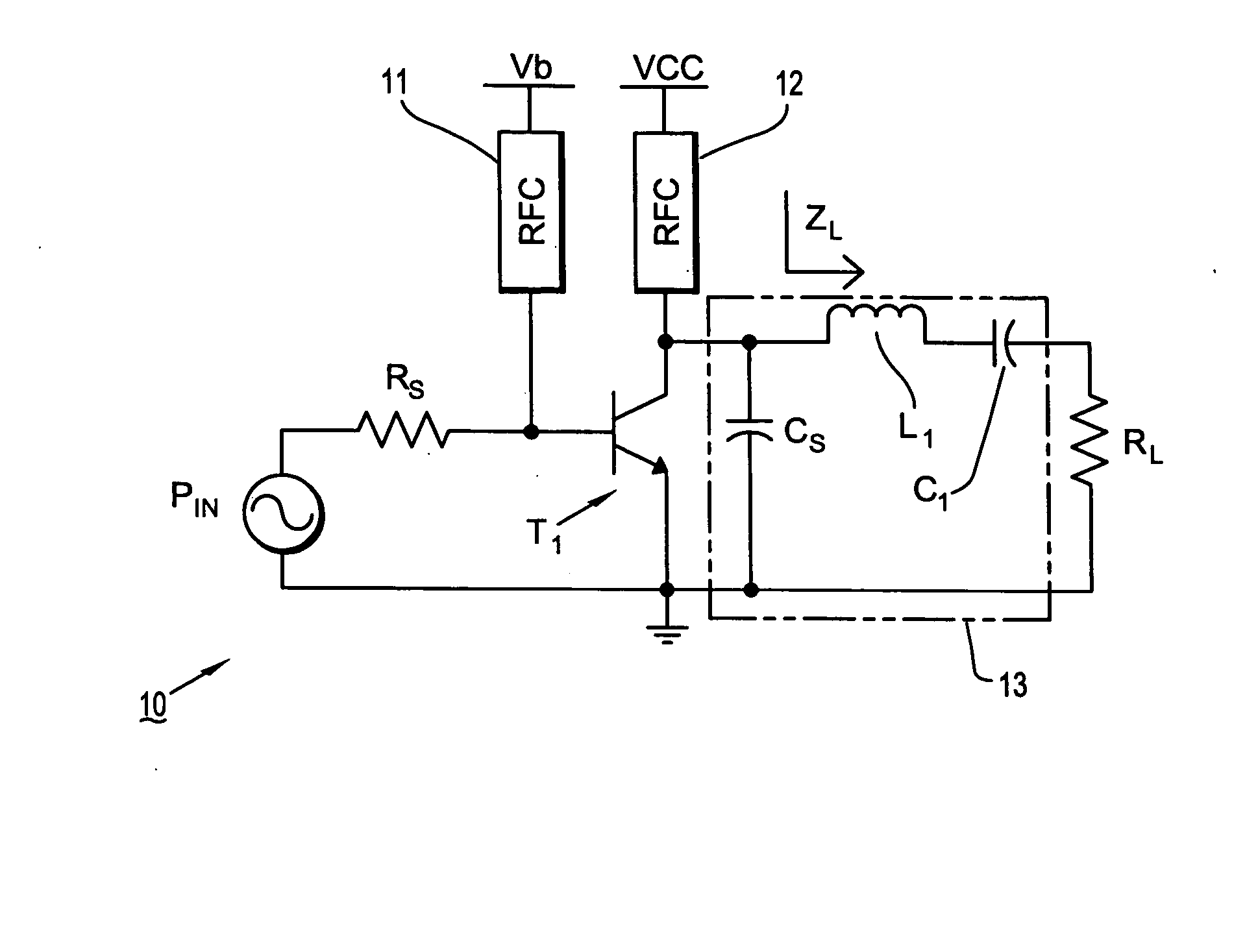
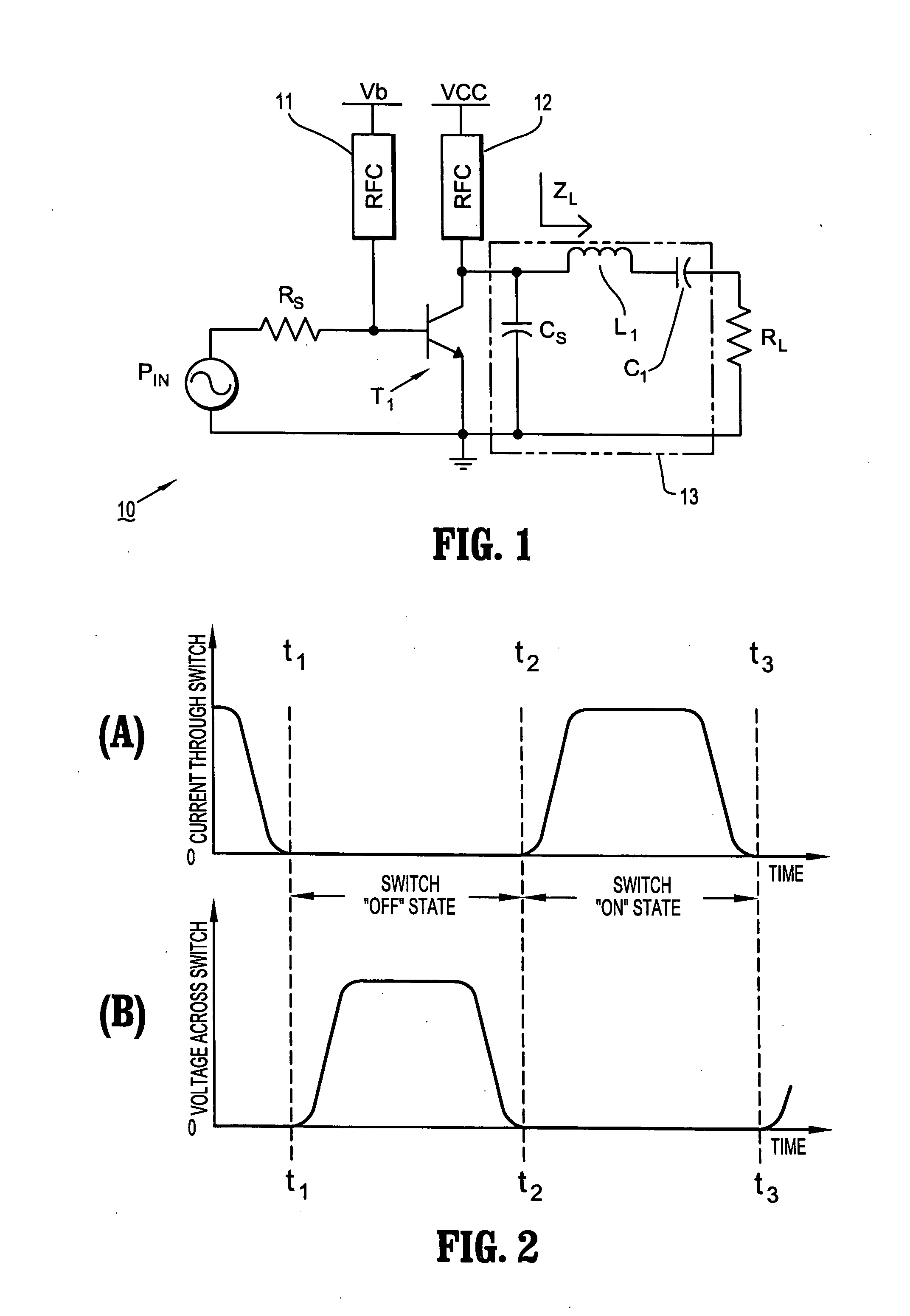
Impedance-Matching Network Using BJT Switches in Variable-Reactance Circuits
ActiveUS20120188007A1Reduce voltageTransistorMultiple-port networksVacuum variable capacitorImpedance matching
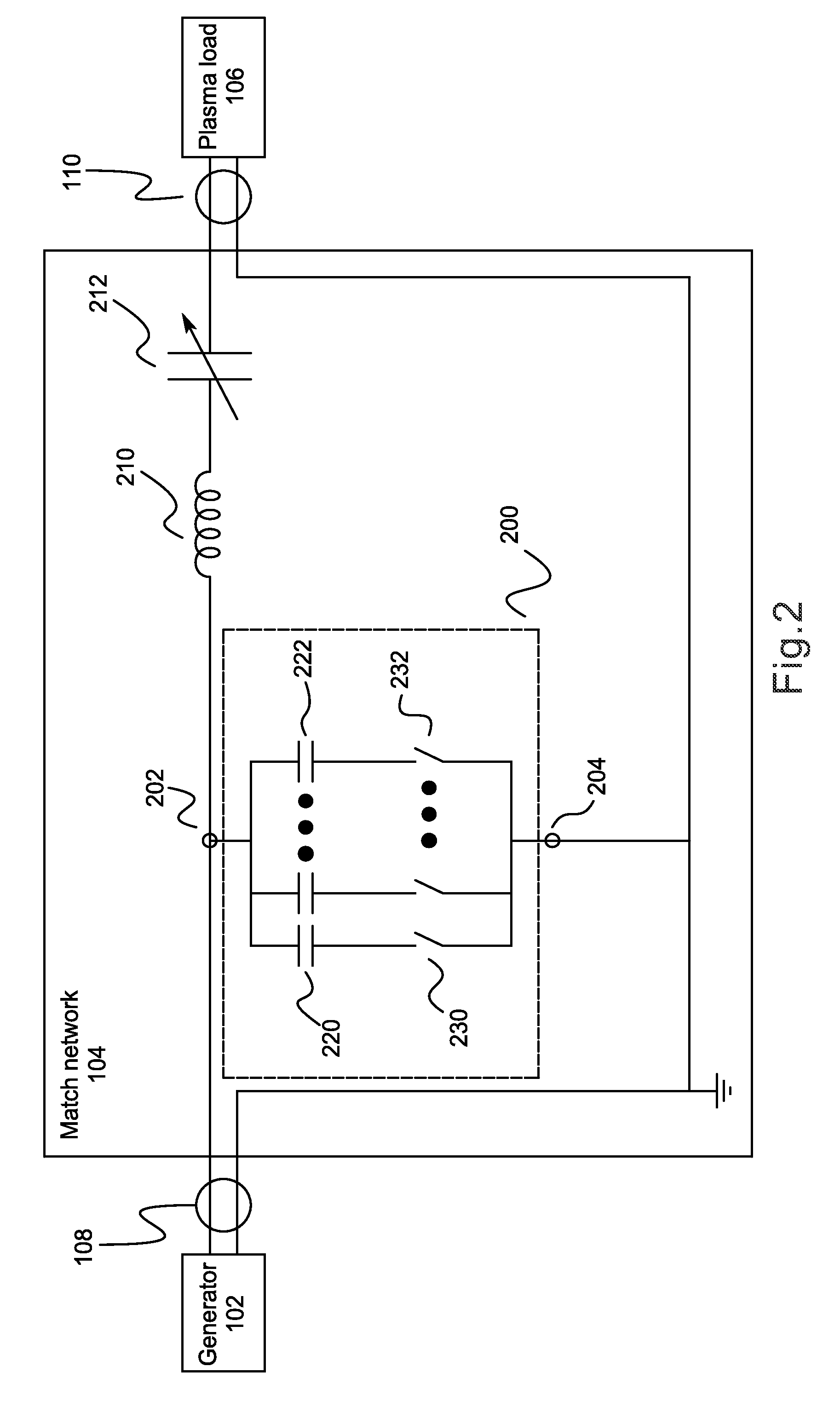
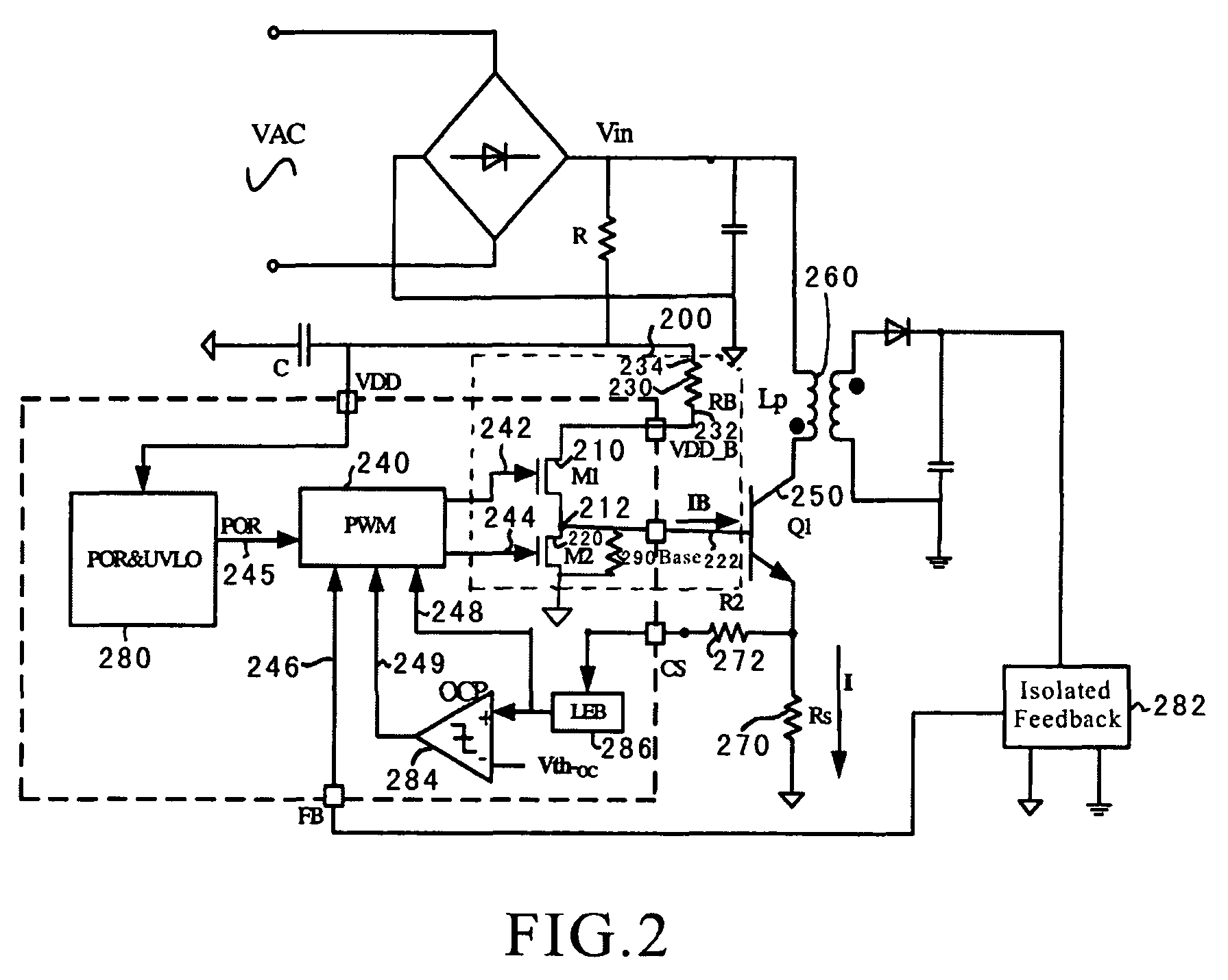
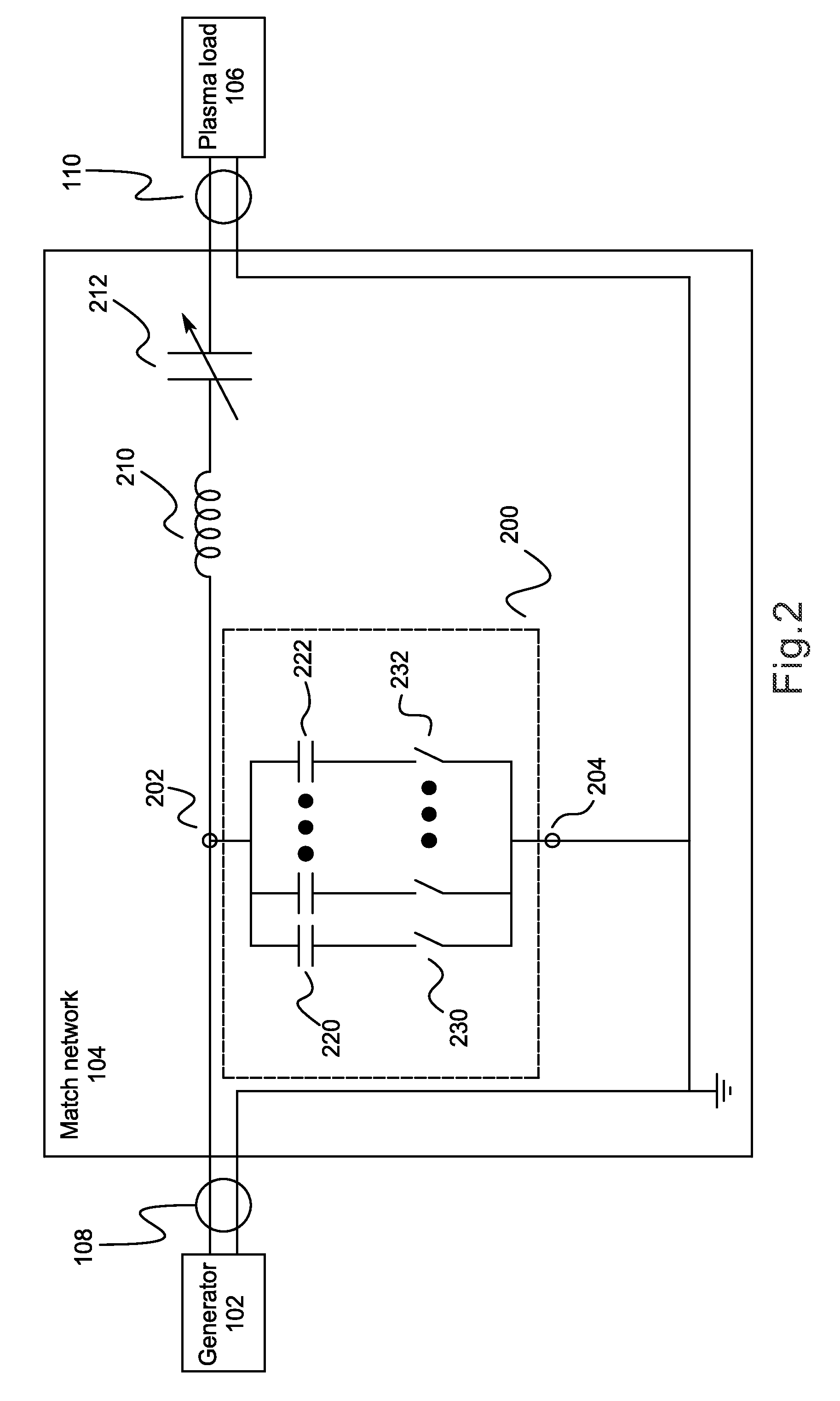
This disclosure describes systems, methods, and apparatuses for impedance-matching radio frequency power transmitted from a radio frequency generator to a plasma load in a semiconductor processing chamber. Impedance-matching can be performed via a match network having a variable-reactance circuit. The variable-reactance circuit can comprise one or more reactive elements all connected to a first terminal and selectively shorted to a second terminal via a switch. The switch can comprise a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) controlled via bias circuitry. In an on-state, the BJT base-emitter junction is forward biased, and AC is conducted between a collector terminal and a base terminal. Thus, AC passes through the BJT primarily from collector to base rather than from collector to emitter. Furthermore, the classic match network topology used with vacuum variable capacitors can be modified such that voltages do not overload the BJT's in the modified topology.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
System and method for driving bipolar transistors in switching power conversion
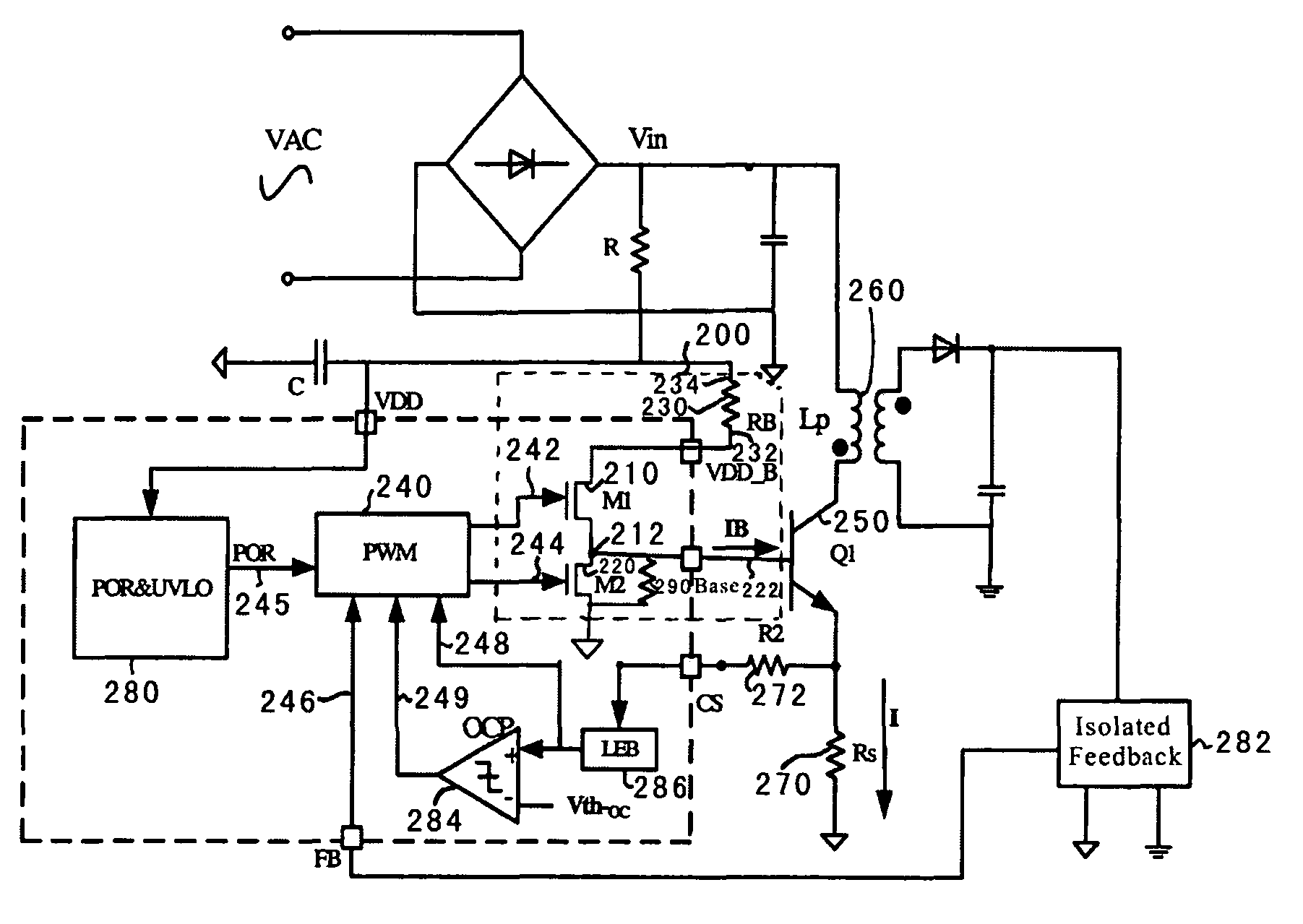
A system and method for driving a bipolar junction transistor is provided. The system includes a first transistor including a first gate, a first terminal, and a second terminal. The first gate is configured to receive a first control signal. Additionally, the system includes a second transistor including a second gate, a third terminal, and a fourth terminal. The second gate is configured to receive a second control signal. Moreover, the system includes a first resistor including a fifth terminal and a sixth terminal. The fifth terminal is connected to the first terminal, and the sixth terminal is biased to a first predetermined voltage. The fourth terminal is biased to a second predetermined voltage. The second terminal and the third terminal are connected at a node, and the node is connected to a base for a bipolar junction transistor.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Impedance-matching network using BJT switches in variable-reactance circuits
ActiveUS8416008B2Reduce voltageTransistorMultiple-port networksVacuum variable capacitorImpedance matching
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Radiation induced diode structure
ActiveUS20140124895A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric layerSemiconductor
A semiconductor device containing an NPN bipolar junction transistor may be formed by forming a p-type radiation induced diode structure (RIDS) region in an intrinsic p-type base region of the NPN bipolar junction transistor at a boundary of the intrinsic p-type base region with a dielectric layer over a substrate of the semiconductor device, between an emitter of the NPN bipolar junction transistor and an extrinsic p-type base region of the NPN bipolar junction transistor. The p-type RIDS region has a doping density high enough to prevent inversion of a surface of the p-type RIDS region adjacent to the dielectric layer when trapped charge is accumulated in the dielectric layer, while the intrinsic p-type base region may invert from the trapped charge forming the radiation induced diode structure. The p-type RIDS region is separated from the emitter and from the extrinsic base region by portions of the intrinsic base region.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
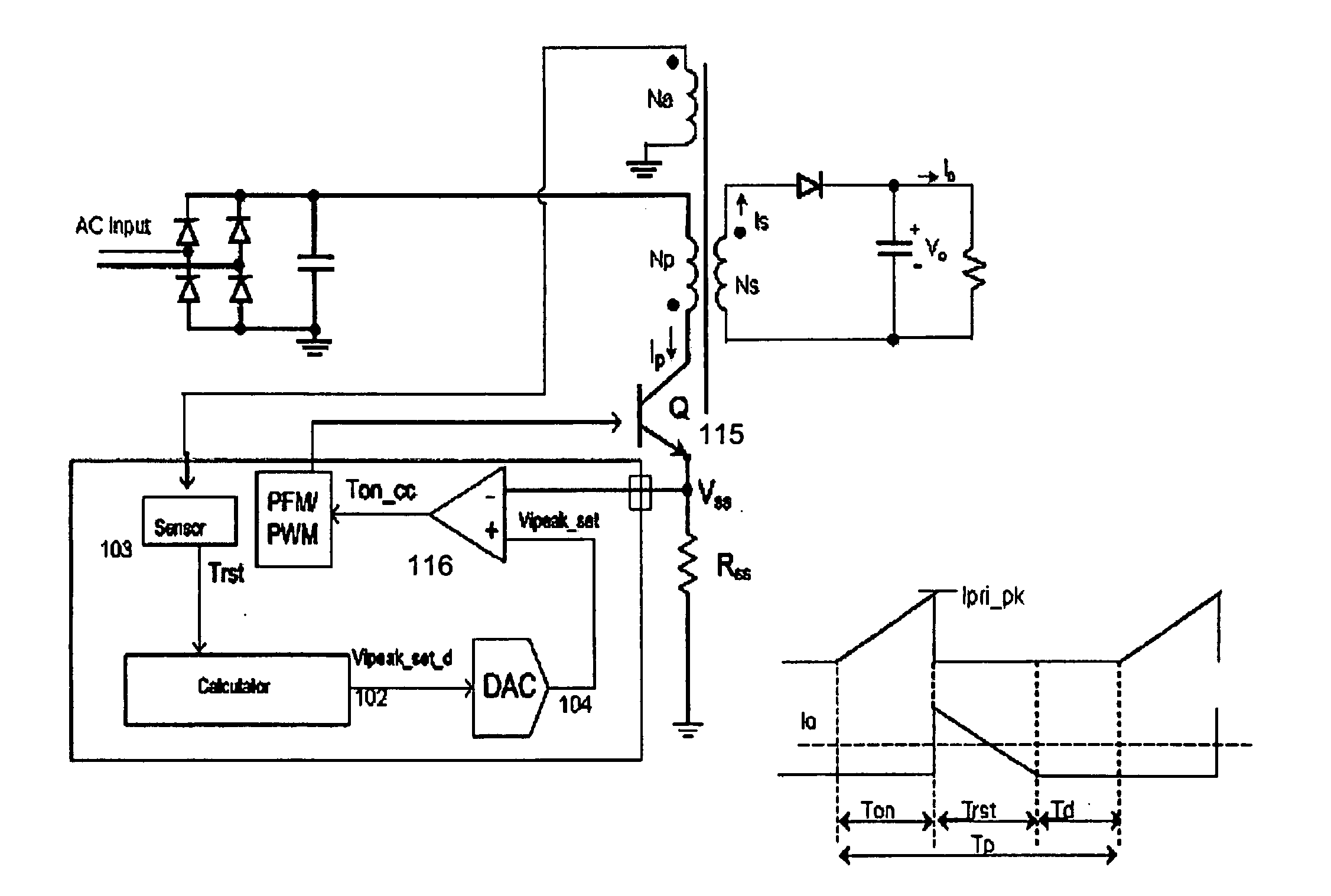
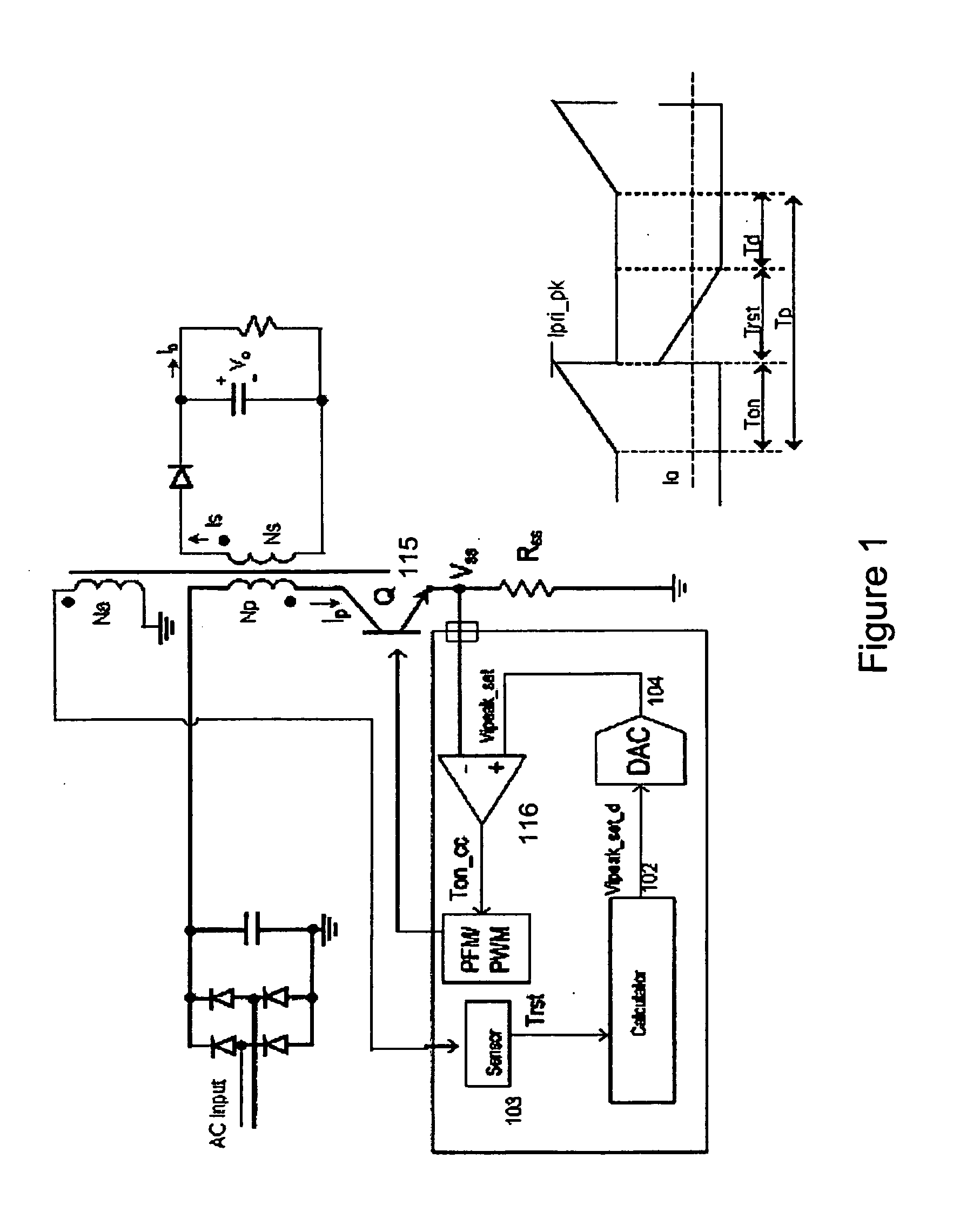
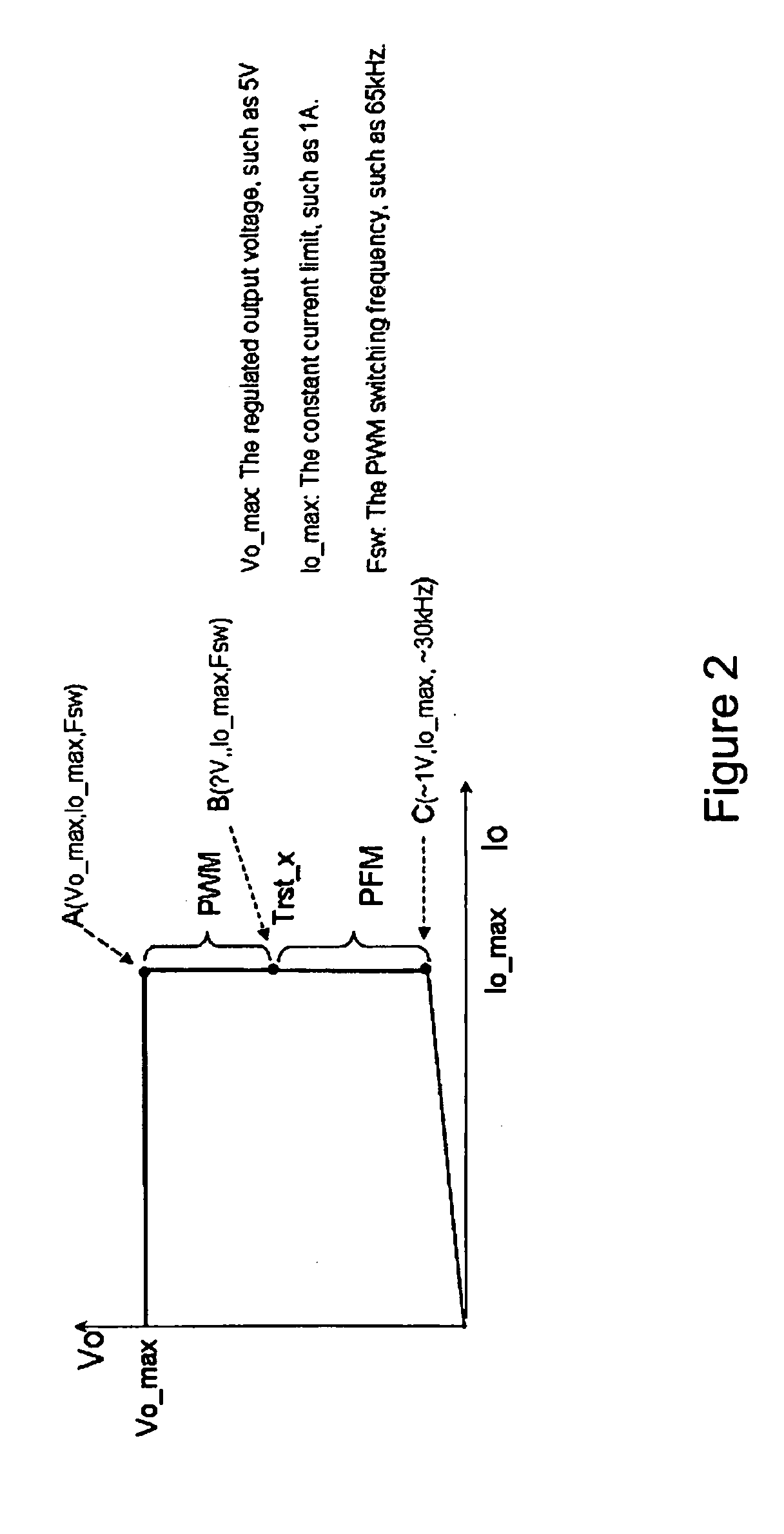
System And Method For Controlling A Current Limit With Primary Side Sensing Using A Hybrid PWM and PFM Control
ActiveUS20090059632A1Accurate constant current (CC) controlMinimizing leakage inductanceAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionEnergy transferCurrent limiting
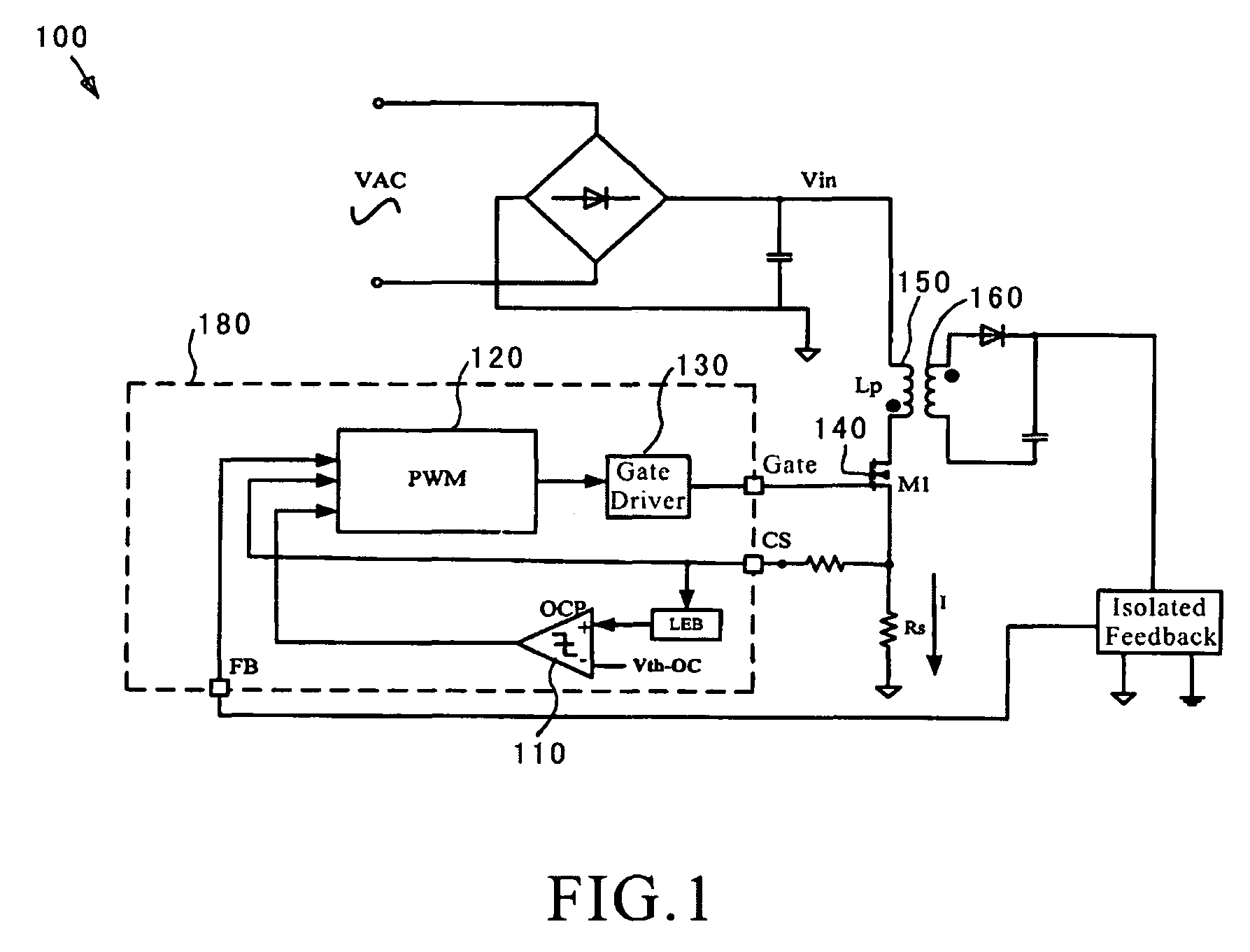
A hybrid constant current control system that uses both pulse width modulation (PWM) and pulse frequency modulation (PFM) control. When transitioning from constant voltage mode to constant current mode the present invention can continue to control using PWM. Thereafter, when the voltage has dropped, the present invention smoothly transitions to PFM mode. The point of transition is based upon the switching frequency and the lowest rated voltage of operation. The system and method avoids very short (narrow) Ton times which ensures accurate constant current (CC) control with bipolar junction transistor (BJT) devices. The present invention also avoids acoustic noise because the switching frequency is maintained at a high enough level to avoid such acoustic noise even when the energy transferred through the transformer is still substantial and the output voltage is not too low. In addition the output current limit is insensitive to variation in the inductance-input voltage ratio, and is minimized against leakage inductance.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
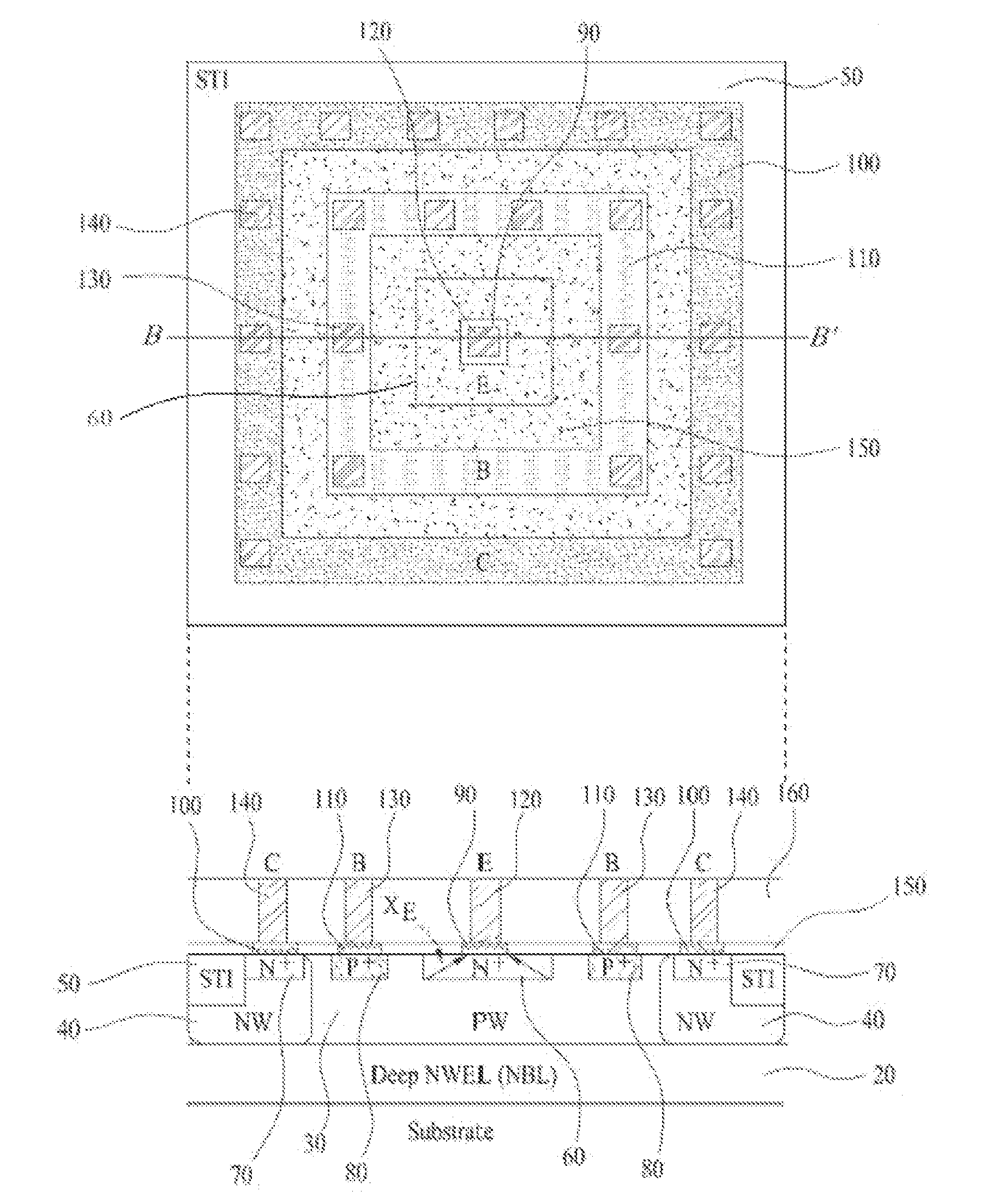
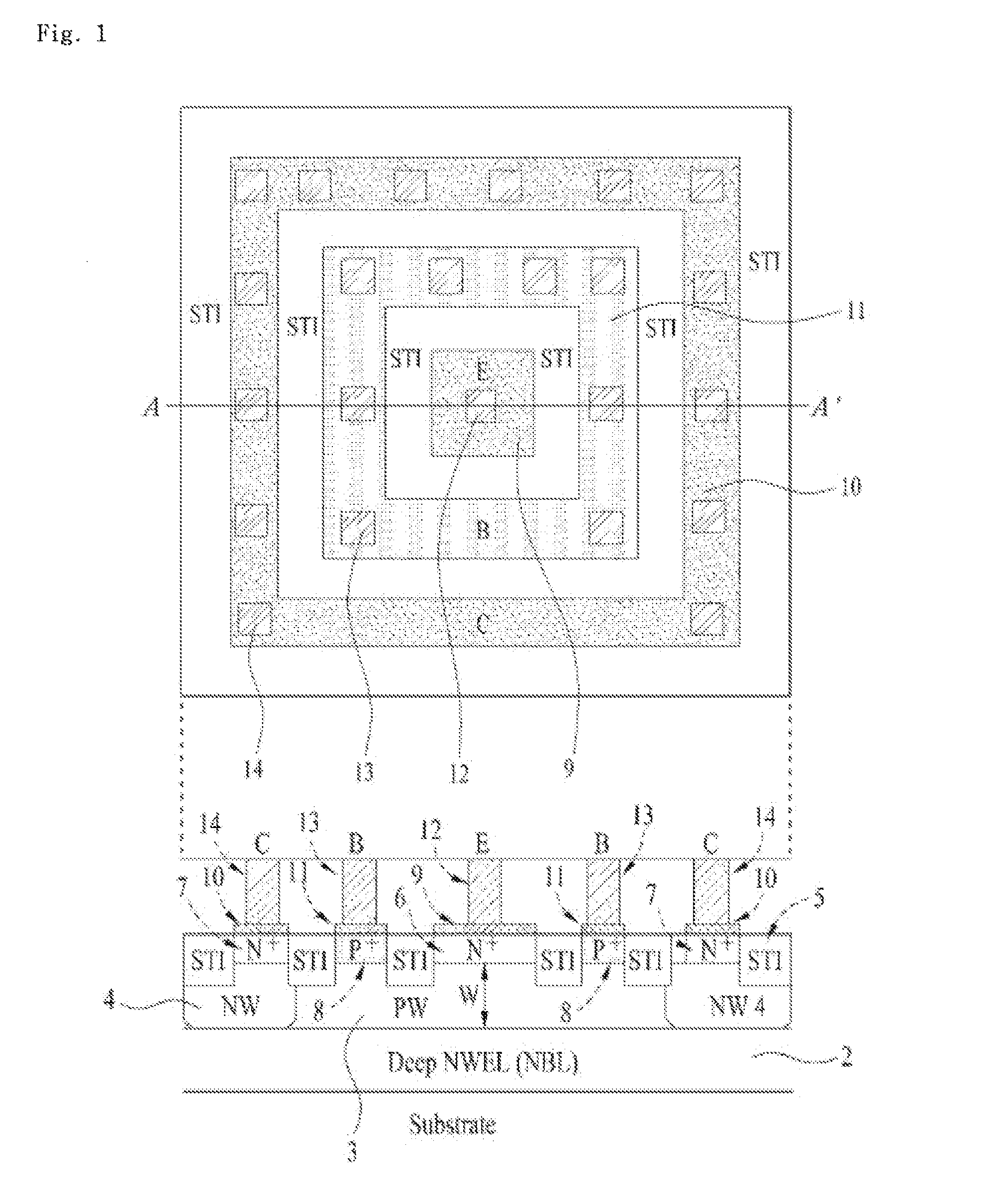
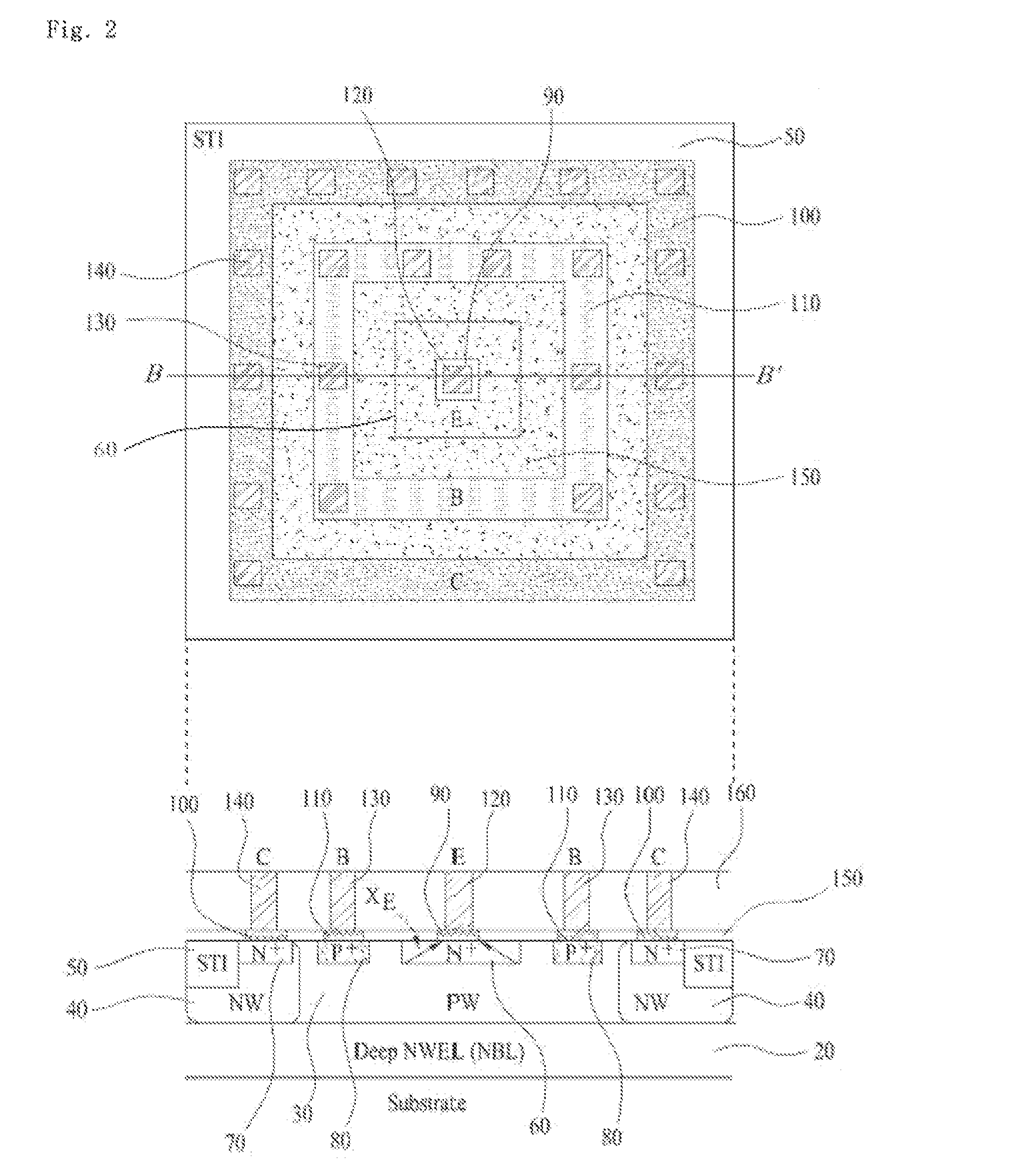
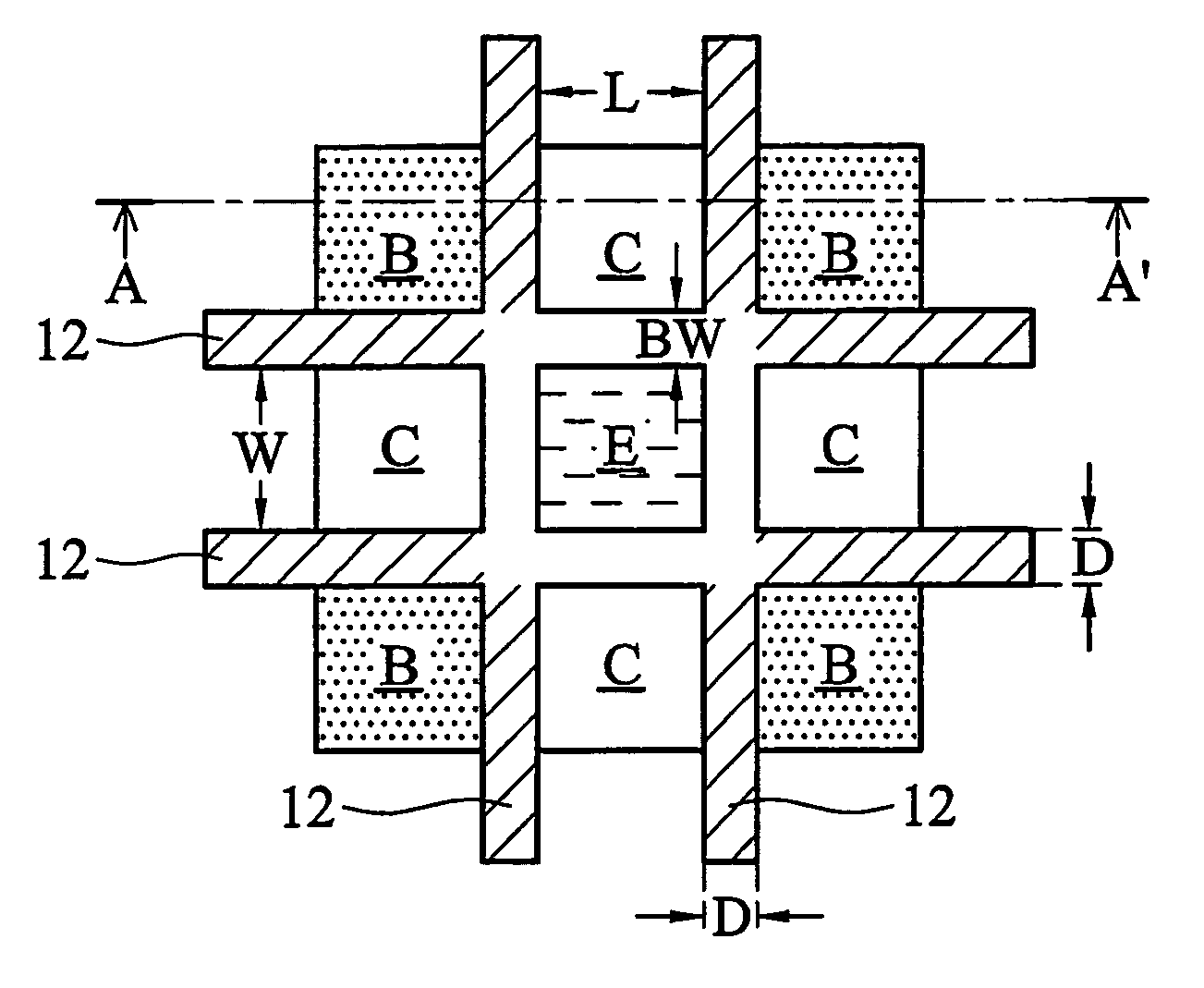
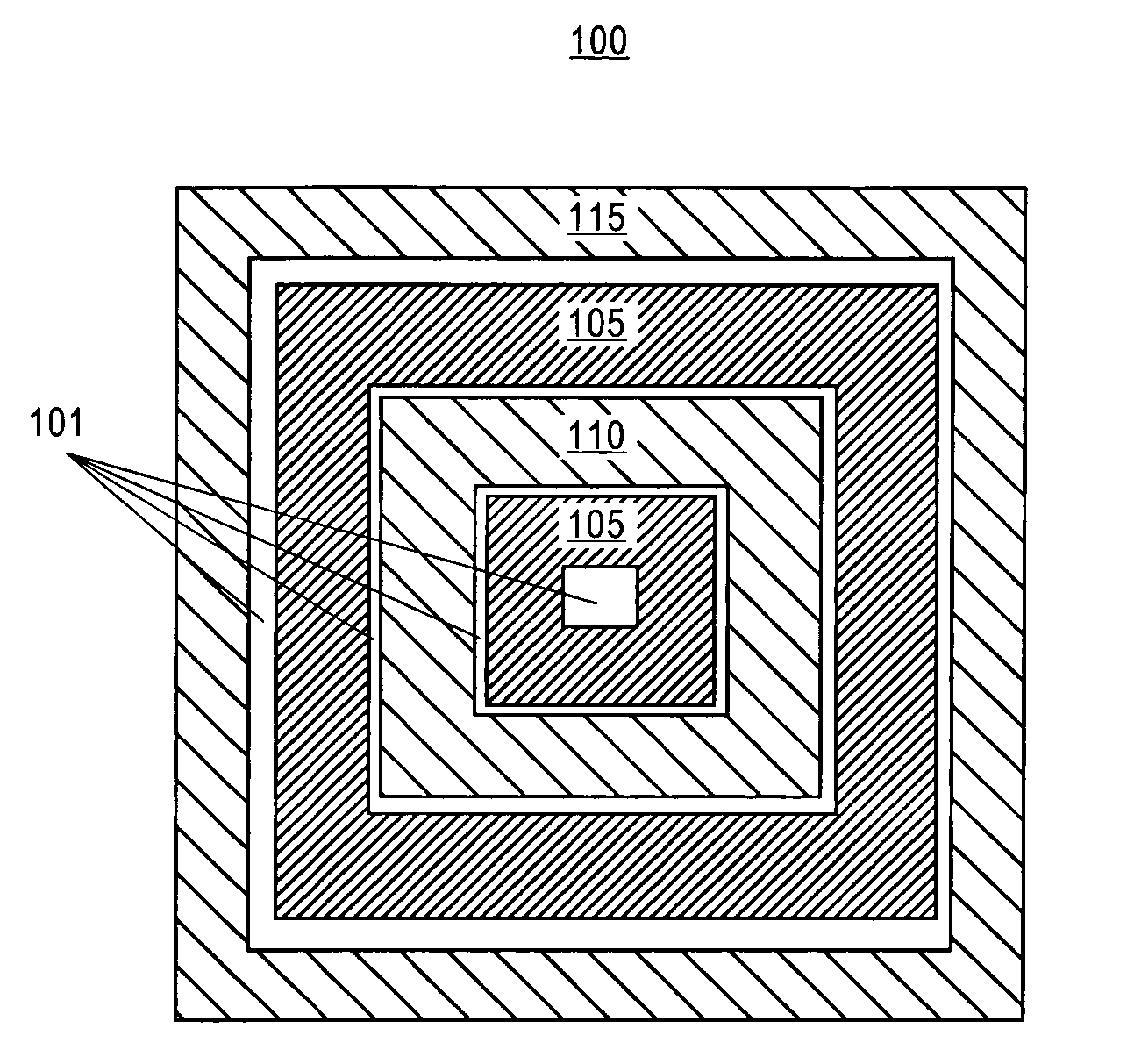
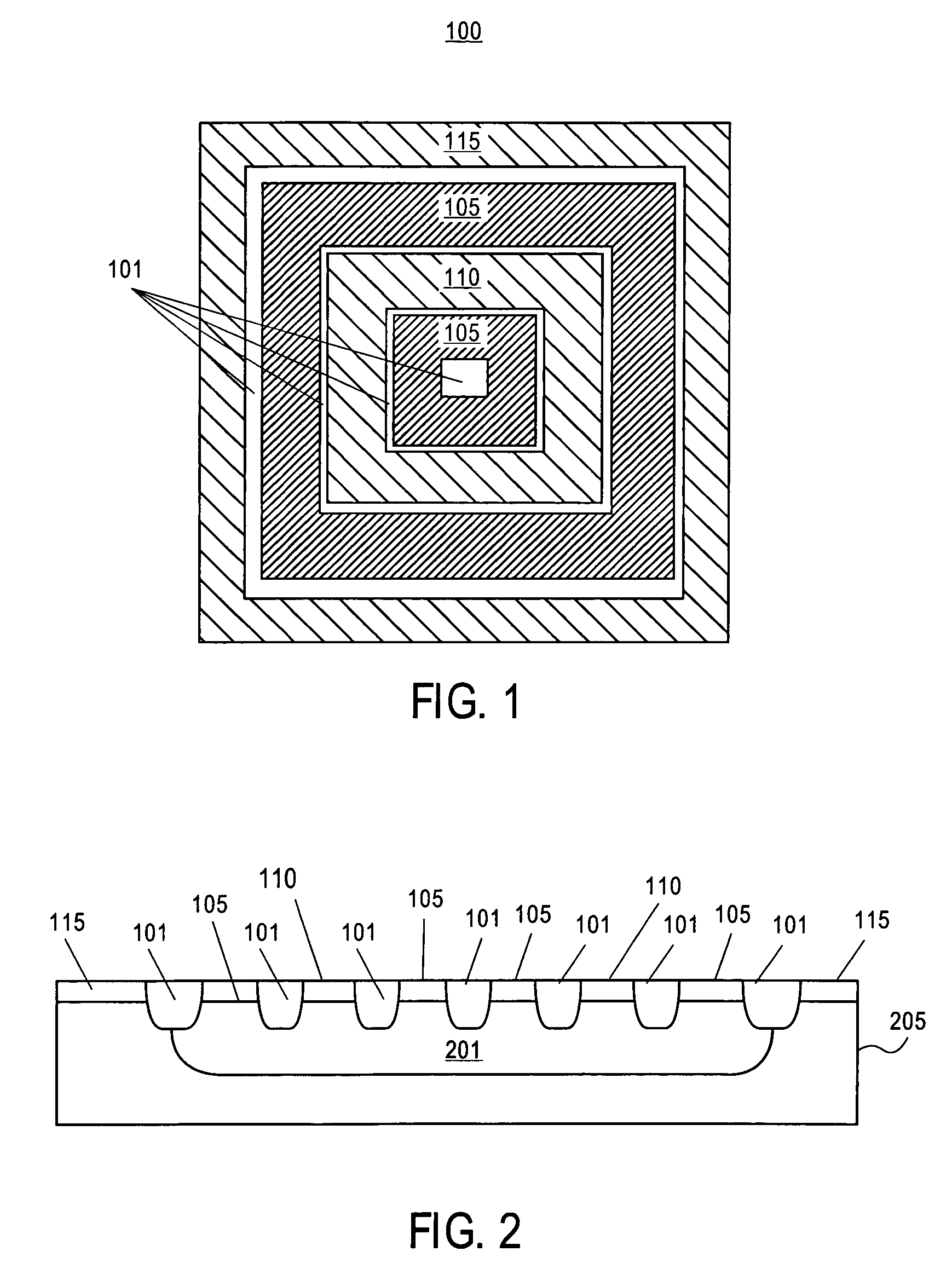
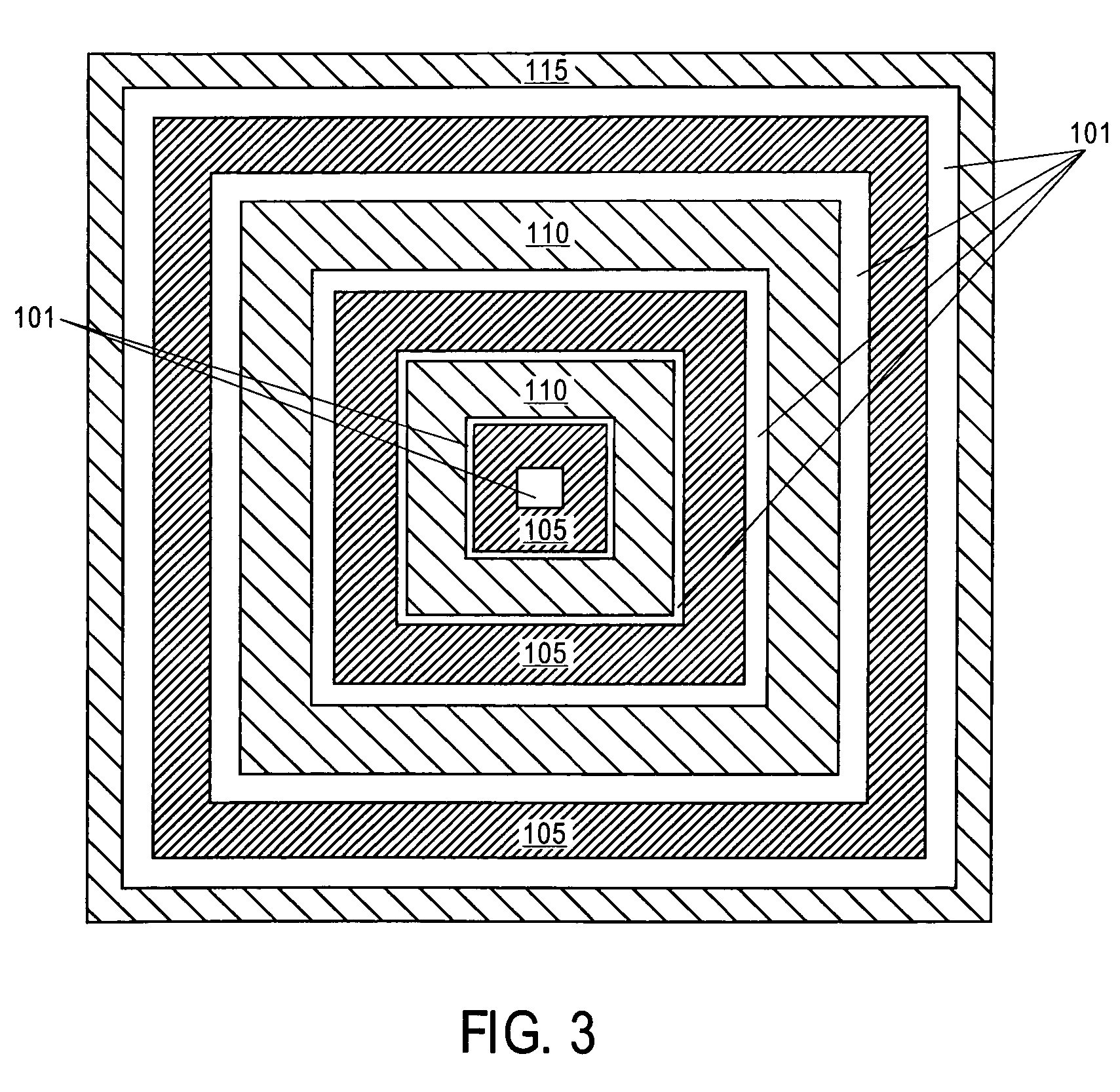
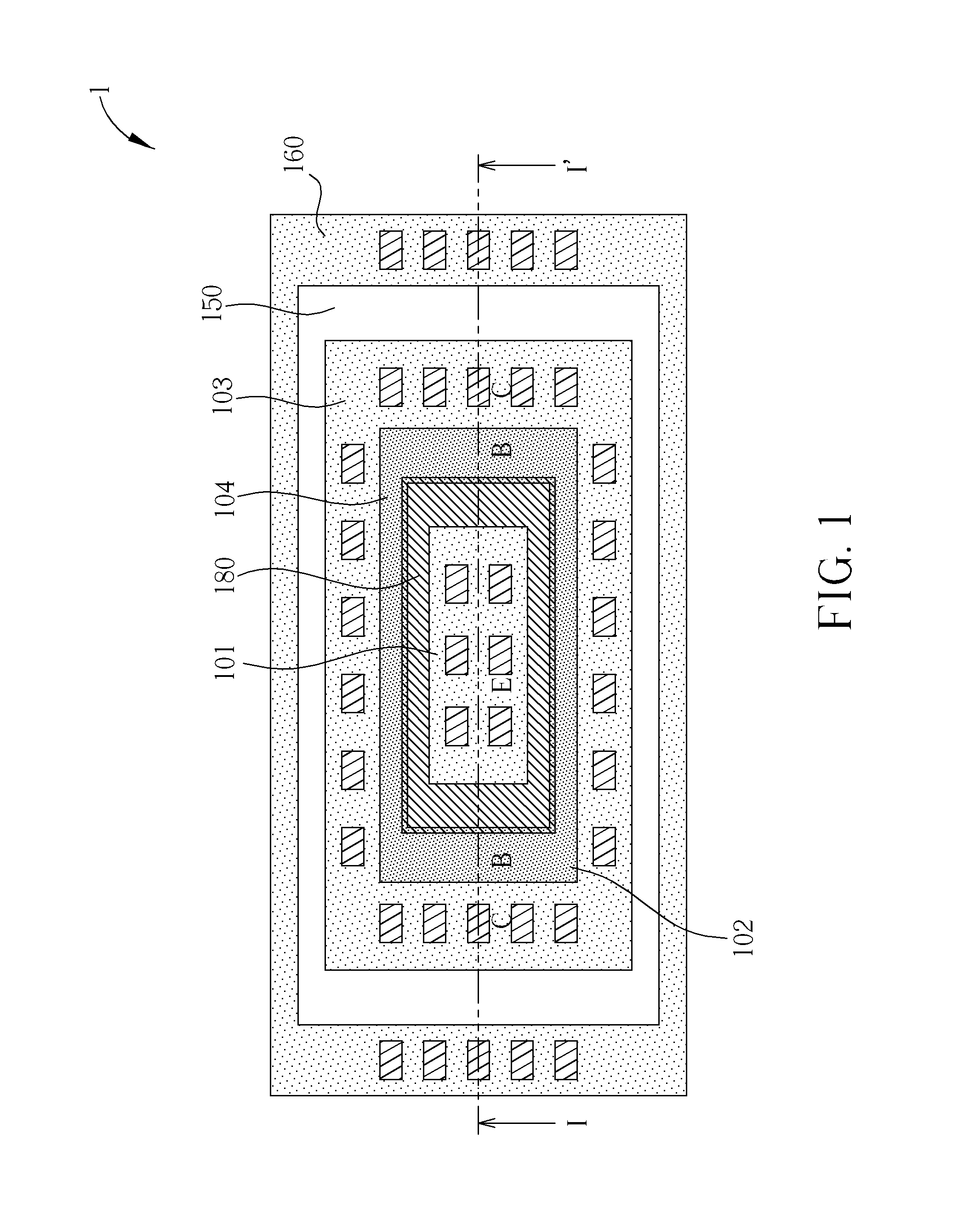
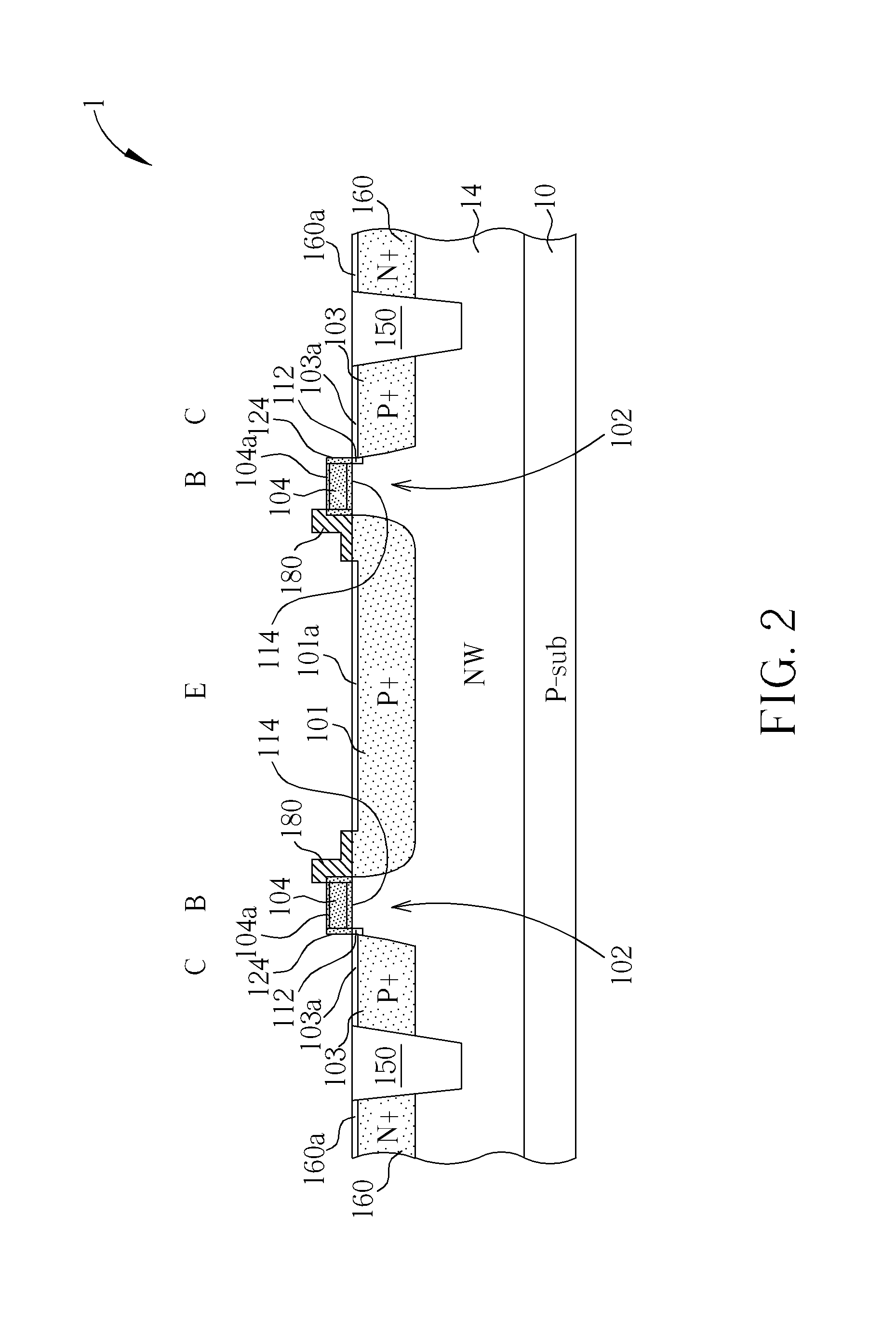
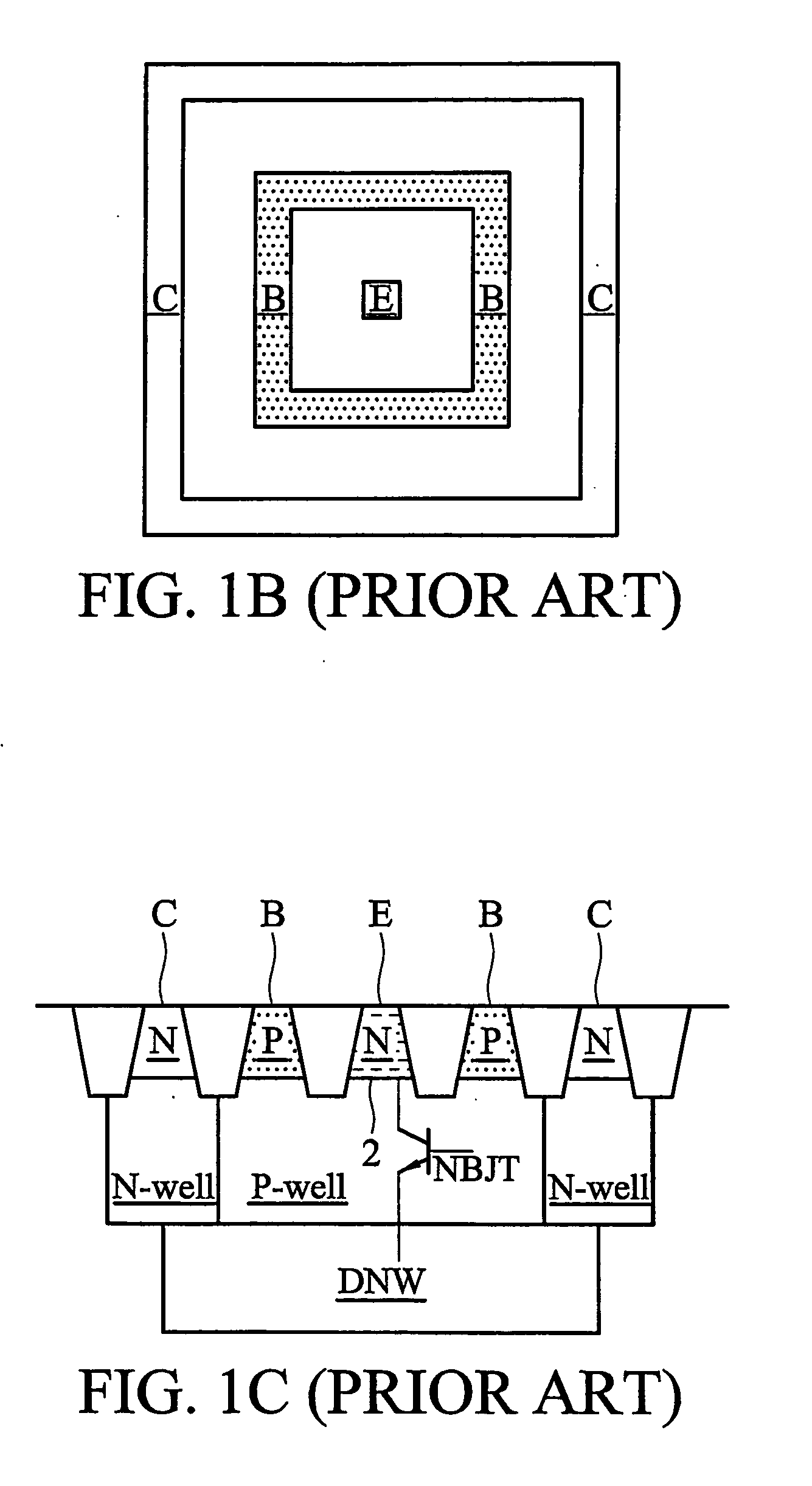
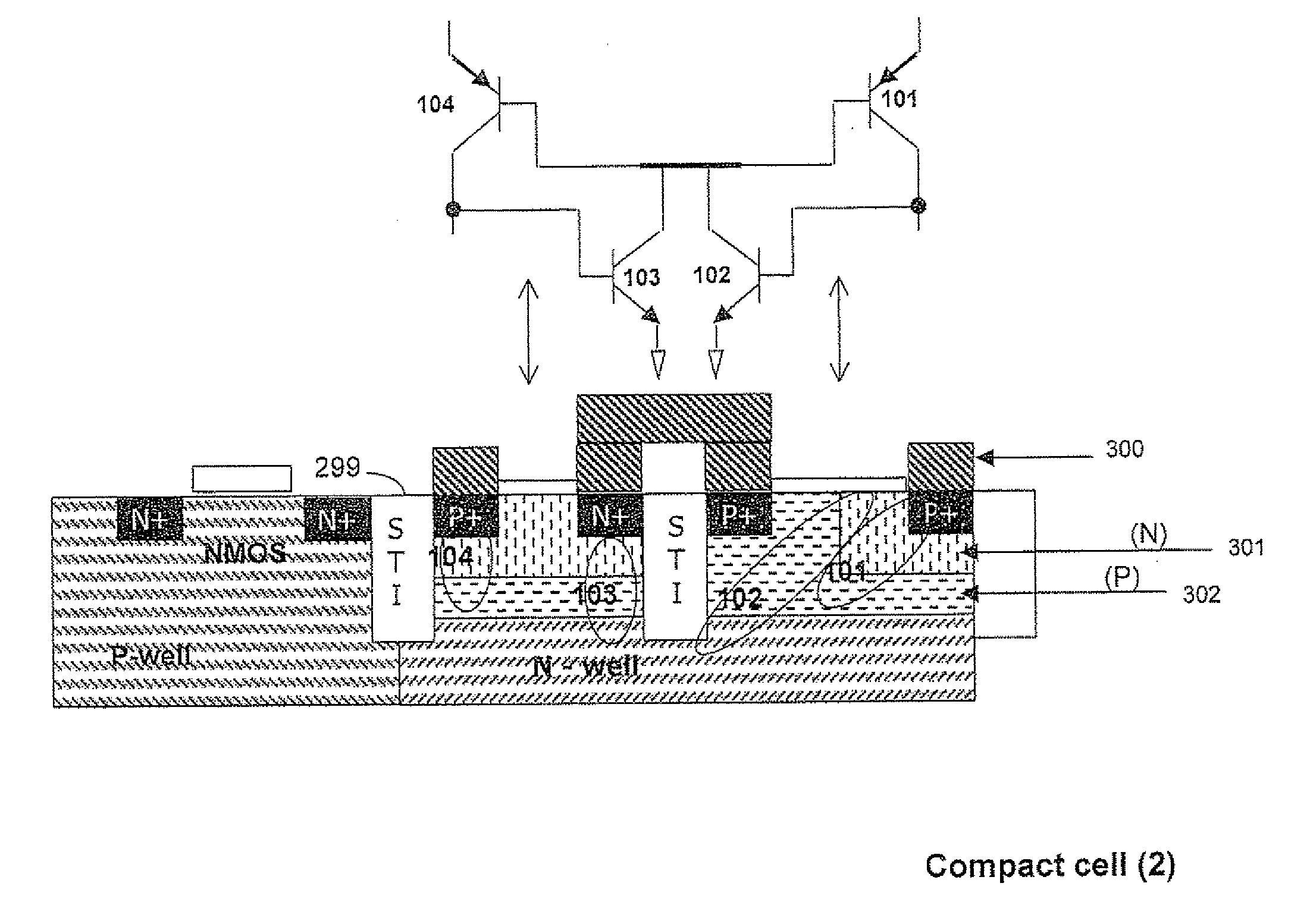
Symmetric bipolar junction transistor design for deep sub-micron fabrication processes
InactiveUS7439608B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBipolar junction transistor
Described herein are embodiments of a bipolar junction transistor including a plurality of base terminal rings having an emitter terminal ring between any two base terminal rings of the plurality of base terminal rings, and a collector terminal ring surrounding the plurality of base terminal rings and the emitter terminal ring and methods of manufacturing the same.
Owner:INTEL CORP
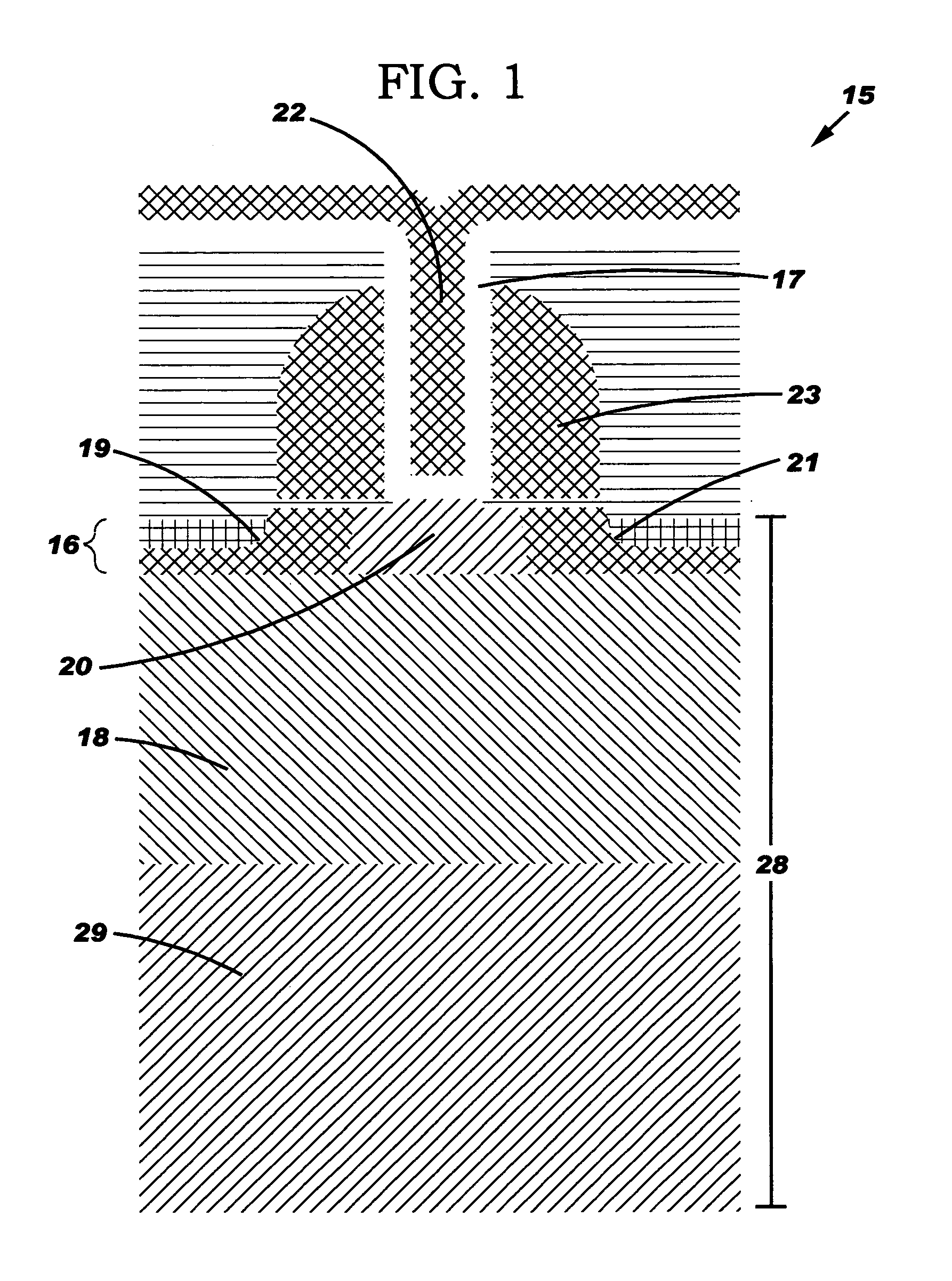
Isolated bipolar transistor
A bipolar transistor is formed in an isolation structure comprising a floor isolation region, a dielectric filled trench above the floor isolation region and a sidewall isolation region extending downward from the bottom of the trench to the floor isolation region. This structure provides a relatively deep isolated pocket in a semiconductor substrate while limiting the depth of the trench that must be etched in the substrate.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED +1
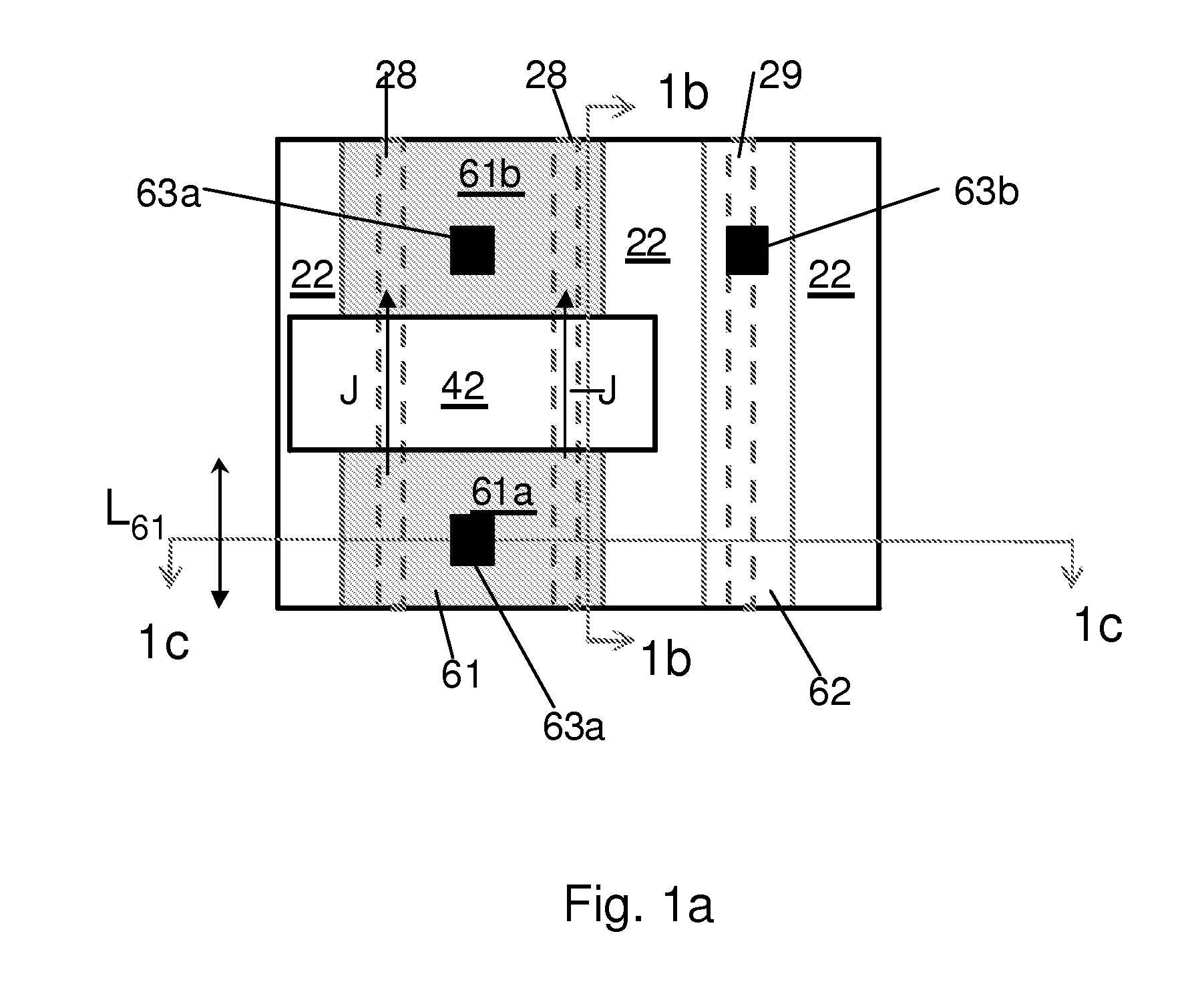
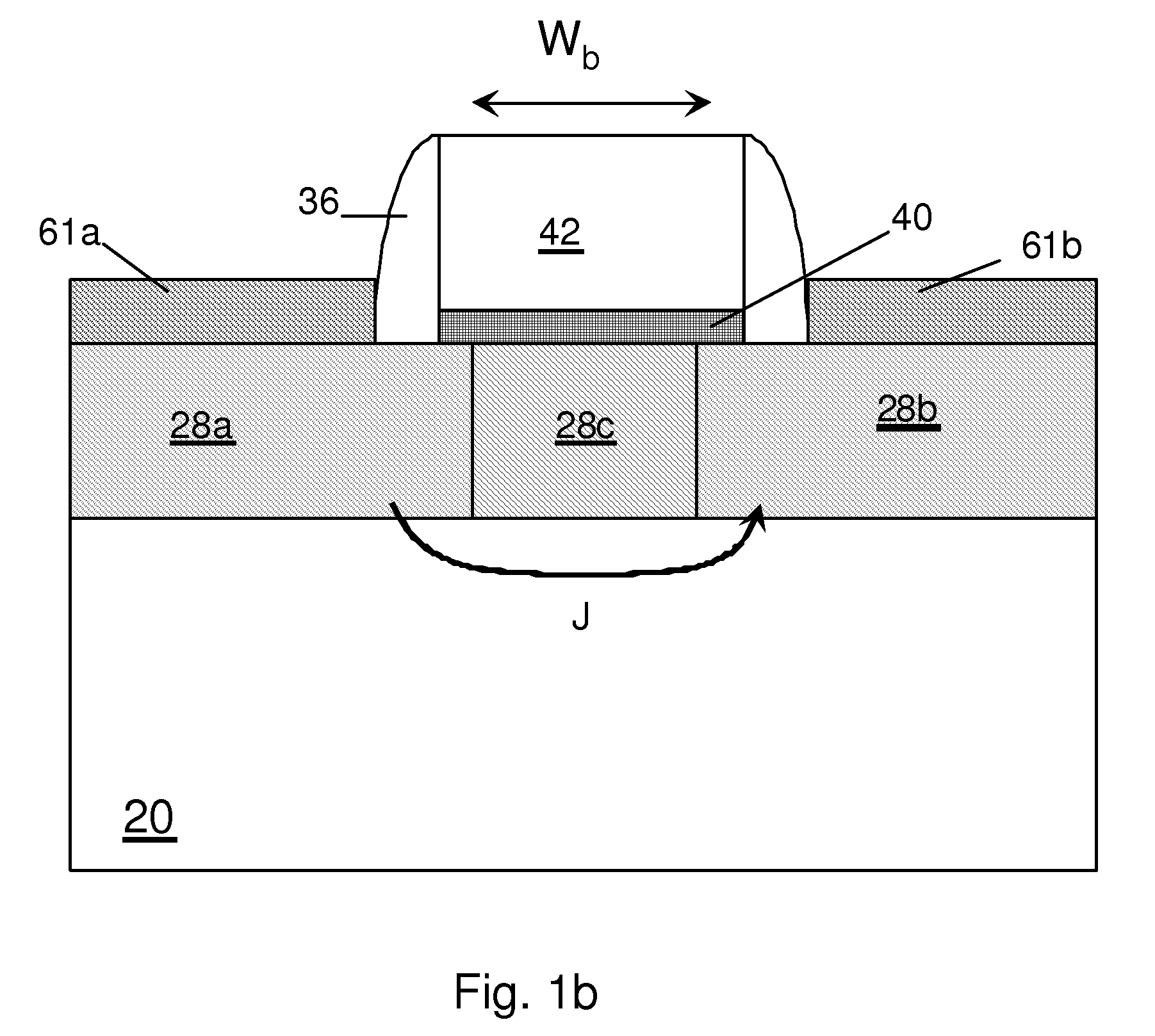
Structures and techniques for using semiconductor body to construct bipolar junction transistors
ActiveUS20140131711A1High ESD immunityReduce input capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBlock layerBipolar junction transistor
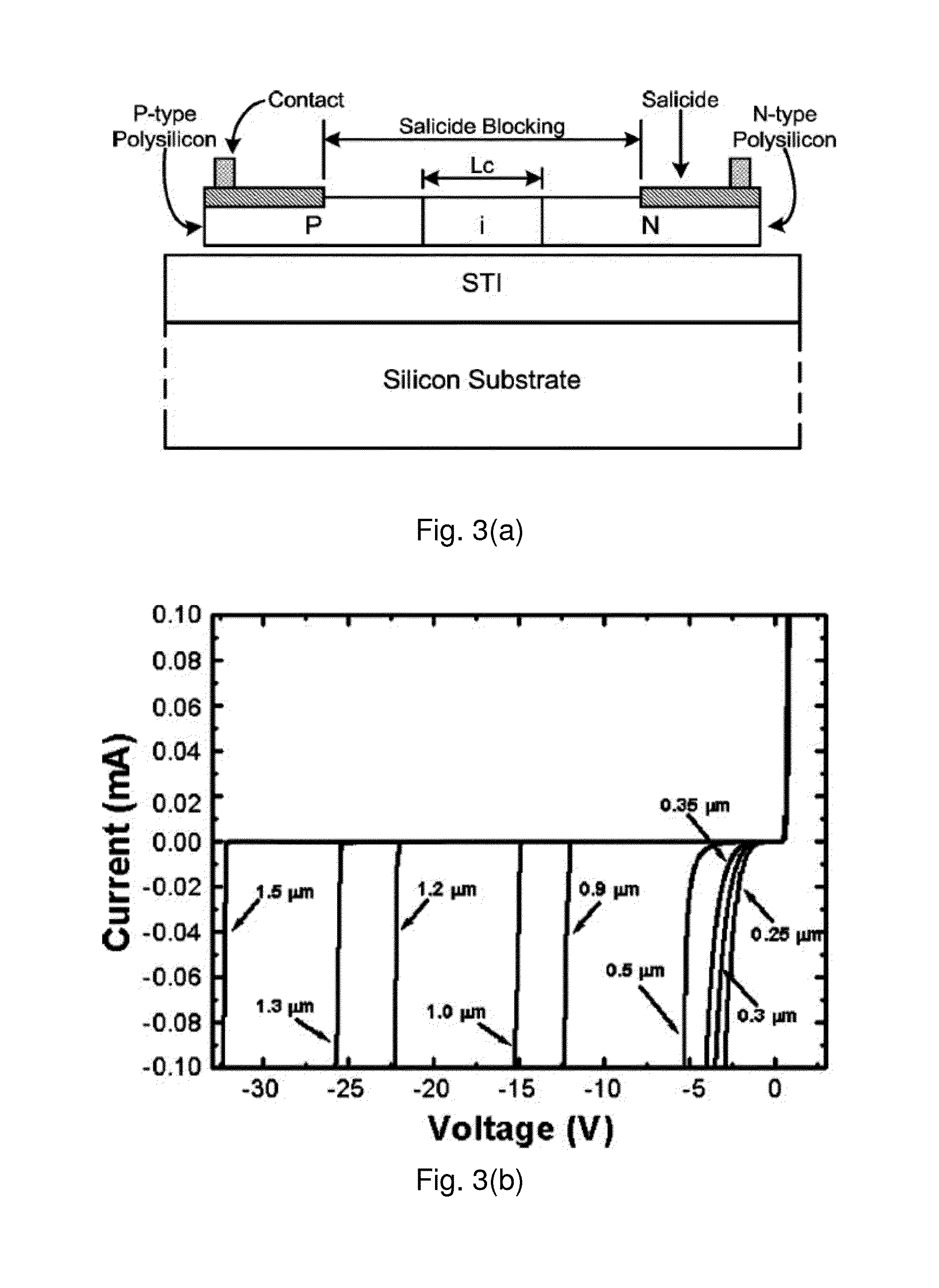
A bipolar junction transistor built with a mesh structure of cells provided on a semiconductor body is disclosed. The mesh structure has at least one emitter cell with a first type of implant. At least one emitter cell has at least one side coupled to at least one cell with a first type of implant to serve as collector of the bipolar. The spaces between the emitter and collector cells are the intrinsic base of a bipolar device. At least one emitter cell has at least one vortex coupled to at least one cell with a second type of implant to serve as the extrinsic base of the bipolar. The emitter, collector, or base cells can be arbitrary polygons as long as the overall geometry construction can be very compact and expandable. The implant regions between cells can be separated with a space. A silicide block layer can cover the space and overlap into at least a portion of both implant regions.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Bipolar Junction Transistors and Methods of Fabrication Thereof
ActiveUS20100187656A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
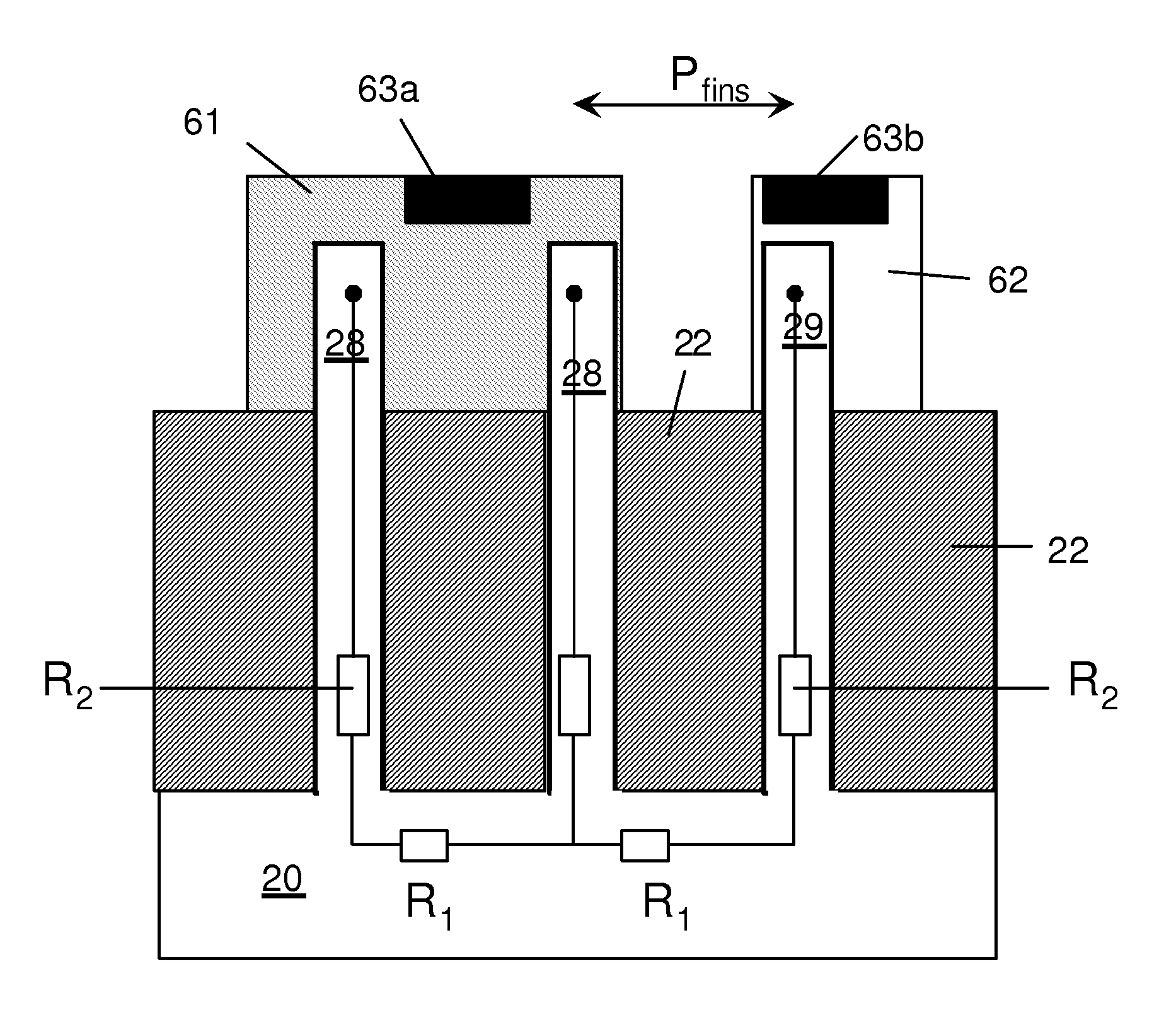
Design and methods for fabricating bipolar junction transistors are described. In one embodiment, a semiconductor device includes a first fin comprising a first emitter region, a first base region, and a first collector region. The first emitter region, the first base region, and the first collector region form a bipolar junction transistor. A second fin is disposed adjacent and parallel to the first fin. The second fin includes a first contact to the first base region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
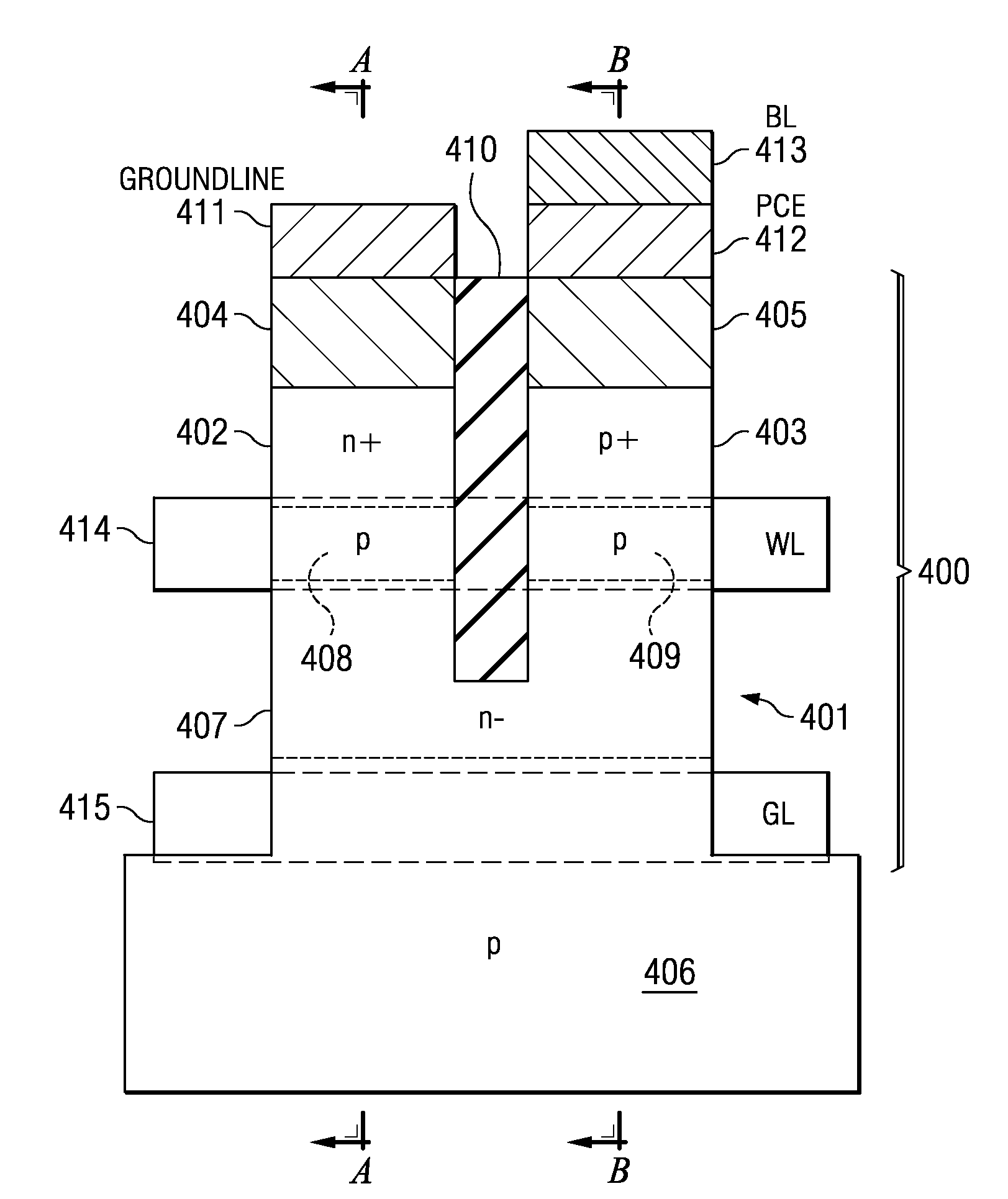
Phase change memory cell on silicon-on insulator substrate
ActiveUS7005665B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryElectrical conductor
The present invention includes a method for forming a phase change material memory device and the phase change memory device produced therefrom. Specifically, the phase change memory device includes a semiconductor structure including a substrate having a first doped region flanked by a set of second doped regions; a phase change material positioned on the first doped region; and a conductor positioned on the phase change material, wherein when the phase change material is a first phase the semiconductor structure operates as a bipolar junction transistor, and when the phase change material is a second phase the semiconductor structure operates as a field effect transistor.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Fuel cell anomaly detection method and apparatus
InactiveUS6953630B2Improve fuel cell system operating efficiencyEasy to operateFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsAnomaly detection
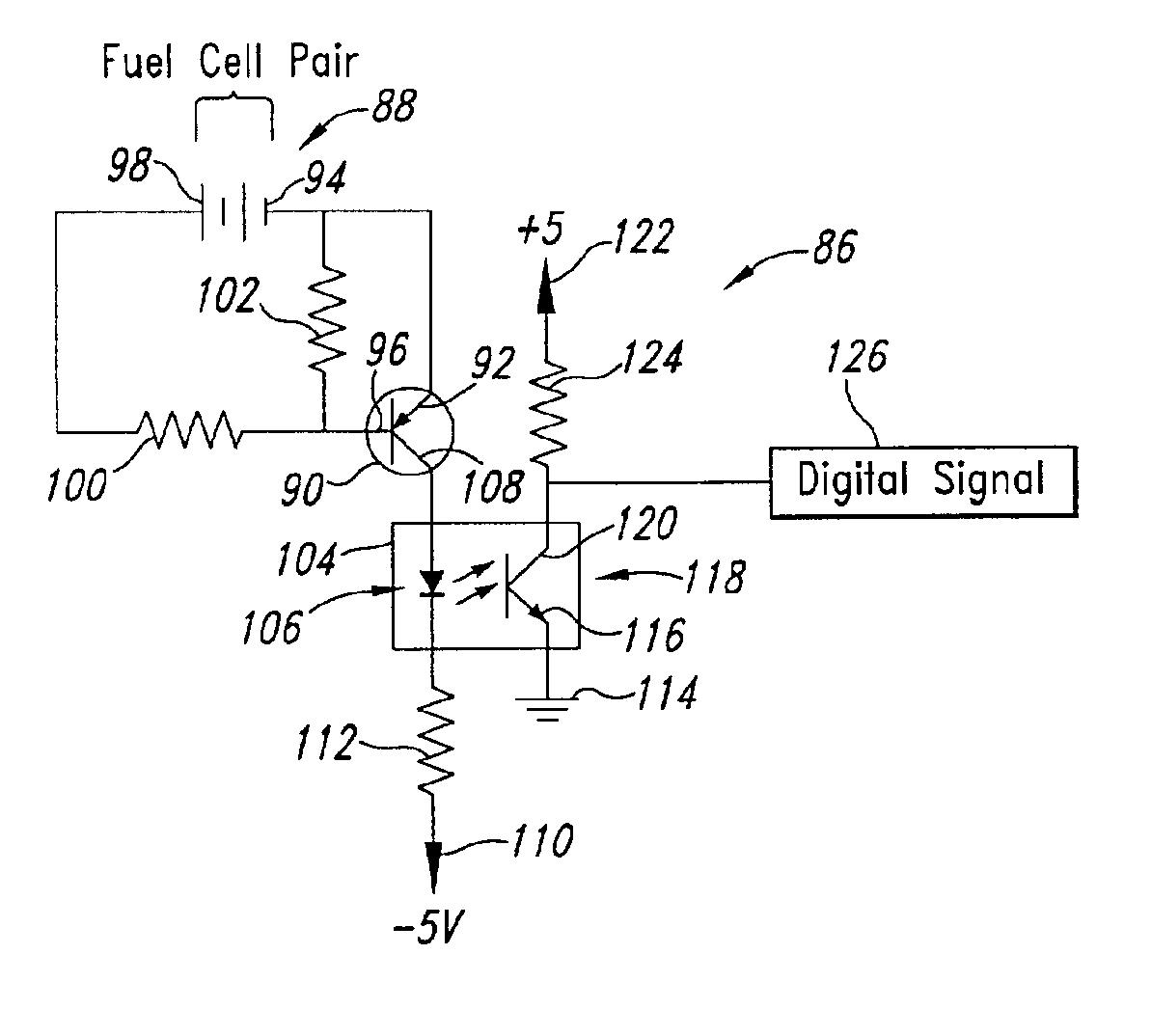
A respective bipolar junction transistor is coupled across pairs of fuel cells in a fuel cell stack to monitor the voltage across each fuel cell pairs for a drop in voltage below a threshold voltage. A respective optoisolator coupled to each of the transistors produces a digital signal corresponding to the status of the respective pair of fuel cells. An “AND” circuit produces a single digital signal corresponding to the status of one or more pairs of fuel cells.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
Vertical carbon nanotube transistor integration
ActiveUS20060169972A1High bulk densityOvercomes drawbackNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureCarbon nanotube
A hybrid semiconductor structure which includes a horizontal semiconductor device and a vertical carbon nanotube transistor, where the vertical carbon nanotube transistor and the horizontal semiconductor device have at least one shared node is provided. The at least one shared node can include, for example, a drain, source or gate electrode of a FET, or an emitter, collector, or base of a bipolar transistor. A method of forming the inventive hybrid semiconductor structure having at least one shared node between the vertical carbon nanotube transistor and the horizontal semiconductor device is also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Lateral bipolar junction transistor
A lateral bipolar junction transistor includes an emitter region; a base region surrounding the emitter region; a gate disposed at least over a portion of the base region; and a collector region surrounding the base region; wherein the portion of the base region under the gate does not under go a threshold voltage implant process.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
High-gain vertex lateral bipolar junction transistor
InactiveUS20070105301A1Improved current gainReduce parasitic effectsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBipolar junction transistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A lateral bipolar junction transistor having improved current gain and a method for forming the same are provided. The transistor includes a well region of a first conductivity type formed over a substrate, at least one emitter of a second conductivity type opposite the first conductivity type in the well region wherein each of the at least one emitters are interconnected, a plurality of collectors of the second conductivity type in the well region wherein the collectors are interconnected to each other, and a plurality of base contacts of the first conductivity type in the well region wherein the base contacts are interconnected to each other. Preferably, all sides of the at least one emitters are adjacent the collectors, and none of the base contacts are adjacent the sides of the emitters. The neighboring emitter, collectors and base contacts are separated by spacings in the well region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
MOS transistor triggered transient voltage supressor to provide circuit protection at a lower voltage
ActiveUS20080218922A1Reduce leakageSuppress the I/O-to-I/O latch-upTransistorWave amplification devicesLow voltageDevice form
An electronic device formed as an integrated circuit (IC) wherein the electronic device further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit. The TVS circuit includes a triggering MOS transistor connected between an emitter and a collector of a first bipolar-junction transistor (BJT) coupled to a second BJT to form a SCR functioning as a main clamp circuit of the TVS circuit. The TVS circuit further includes a triggering circuit for generating a triggering signal for the triggering MOS transistor wherein the triggering circuit includes multiple stacked MOS transistors for turning into a conductive state by a transient voltage while maintaining a low leakage current.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Phase Change Memory Cell with MOSFET Driven Bipolar Access Device
InactiveUS20100061145A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPhase-change memory
Embodiments are directed to memory devices comprising a bipolar junction transistor having an emitter, a base and a collector; a first side of a resistance changing memory element coupled to the emitter of the bipolar junction transistor; and a MOSFET coupled to the base of the bipolar junction transistor.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Phase Change Memory Cell On Silicon-On Insulator Substrate
ActiveUS20050208699A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorPhase-change memory
The present invention includes a method for forming a phase change material memory device and the phase change memory device produced therefrom. Specifically, the phase change memory device includes a semiconductor structure including a substrate having a first doped region flanked by a set of second doped regions; a phase change material positioned on the first doped region; and a conductor positioned on the phase change material, wherein when the phase change material is a first phase the semiconductor structure operates as a bipolar junction transistor, and when the phase change material is a second phase the semiconductor structure operates as a field effect transistor.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
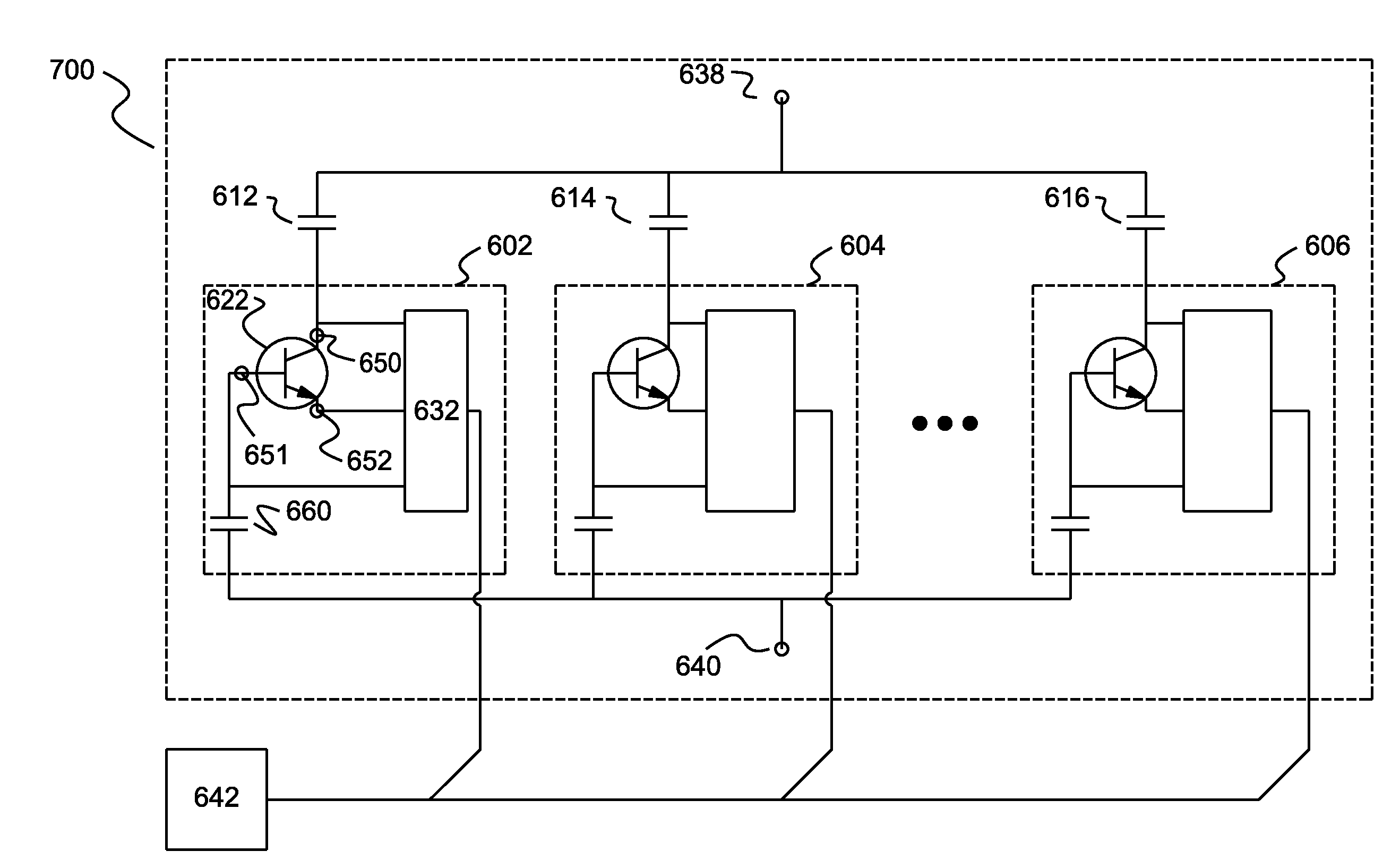
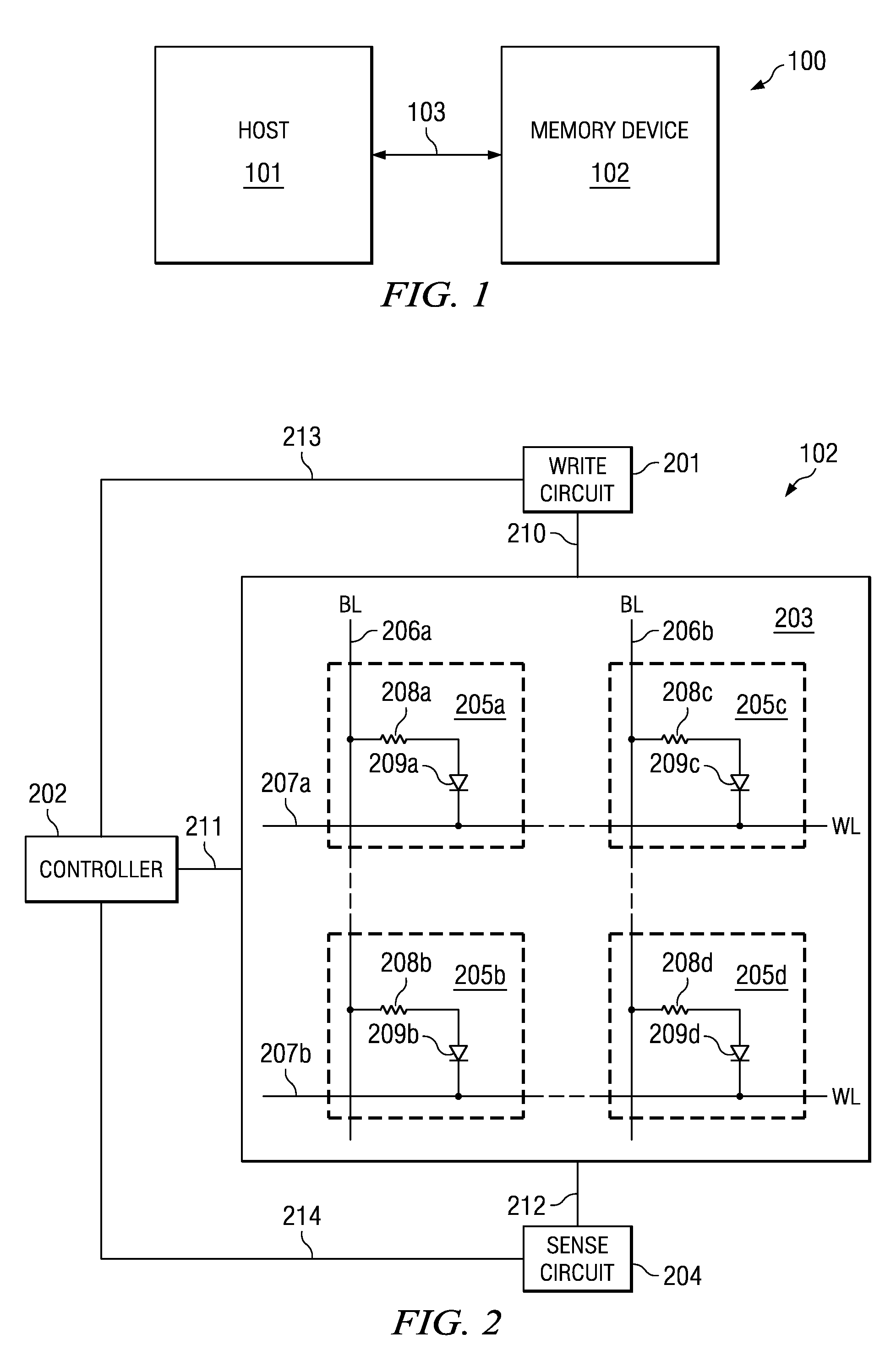
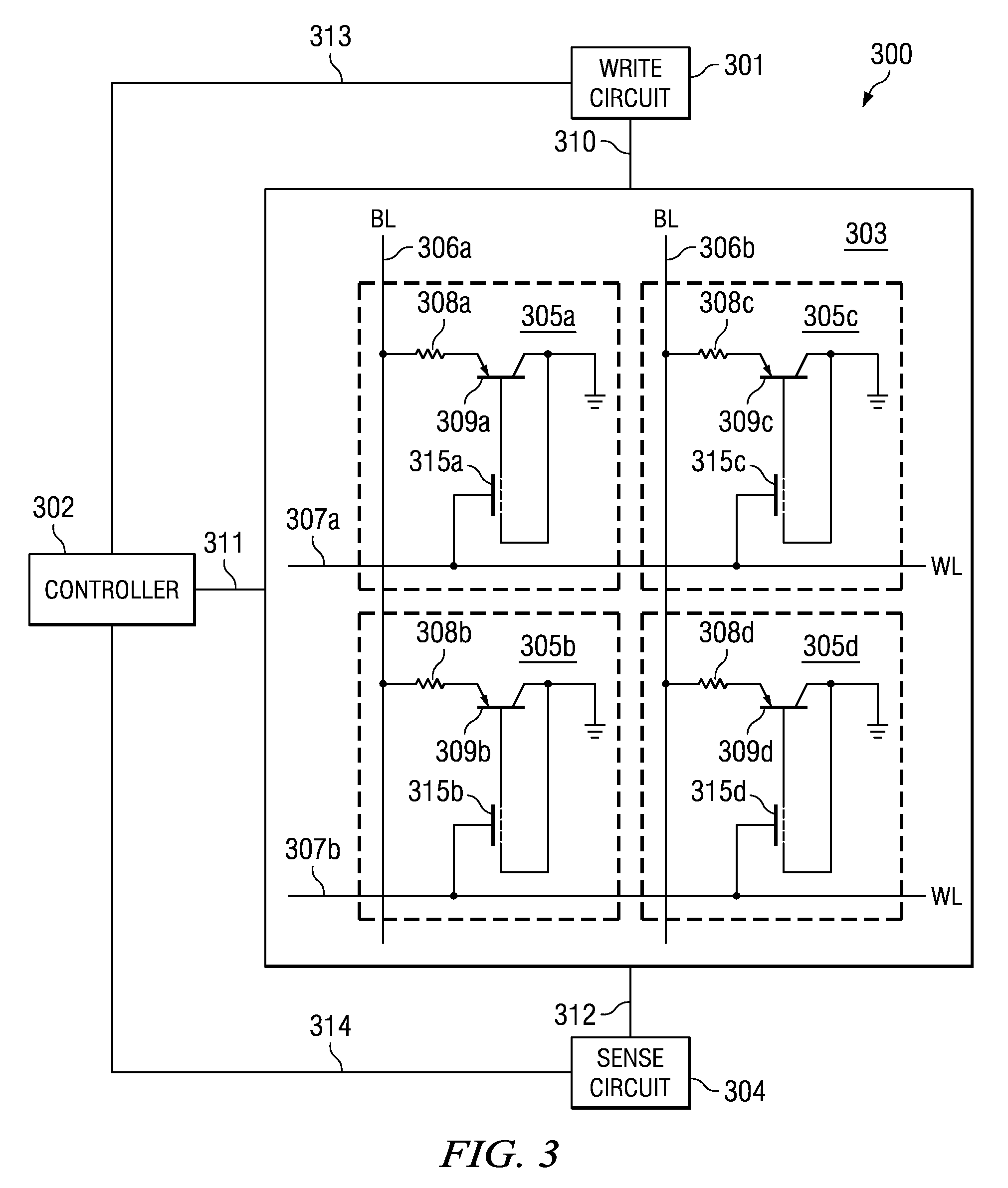
Memory cell structures, memory arrays, memory devices, memory controllers, and memory systems, and methods of manufacturing and operating the same
Example embodiments are directed to memory cell structures, memory arrays, memory devices, memory controllers, and memory systems using bipolar junction transistor (BJT) operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure and method of forming a bipolar transistor having a void between emitter and extrinsic base
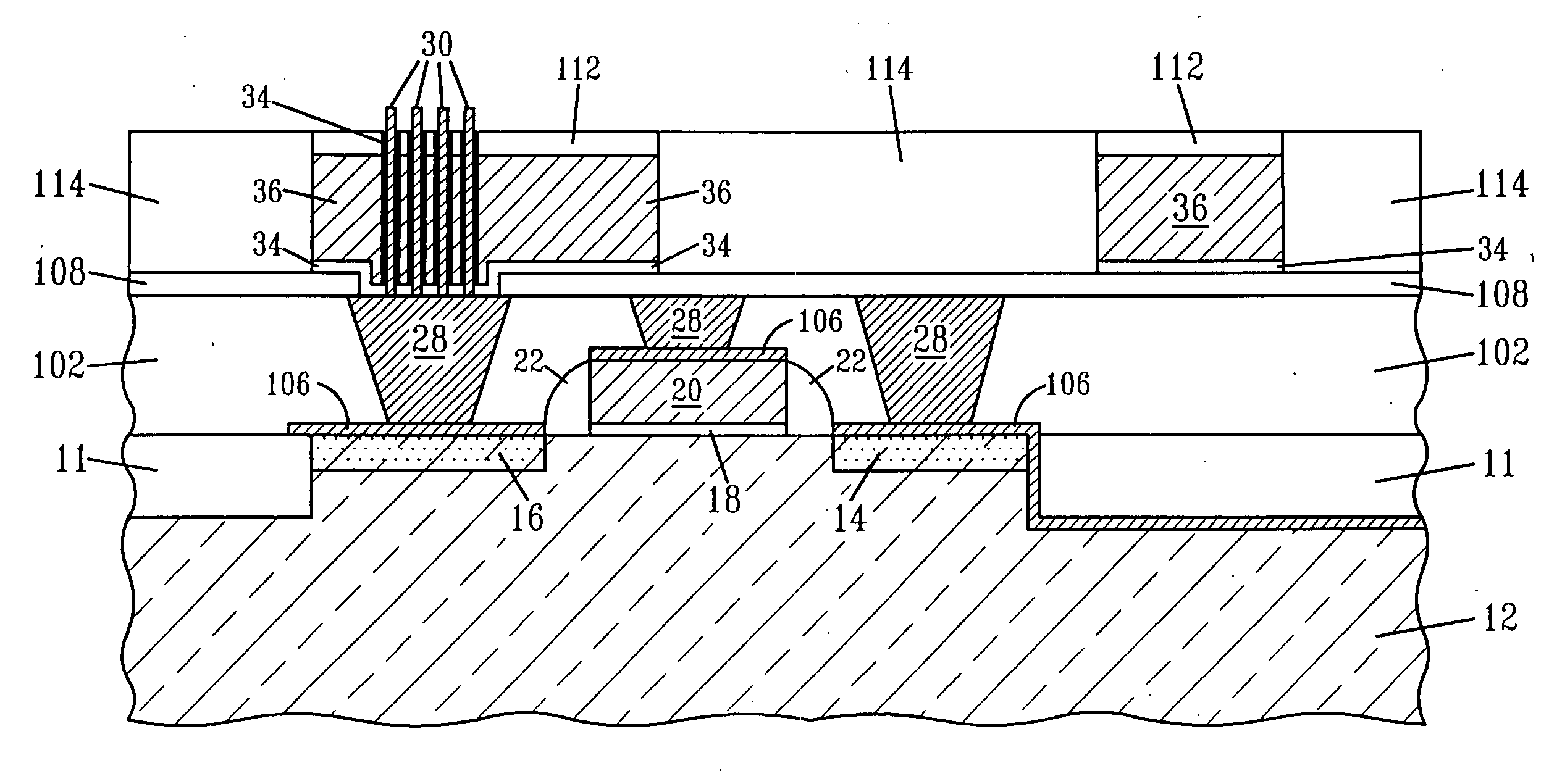
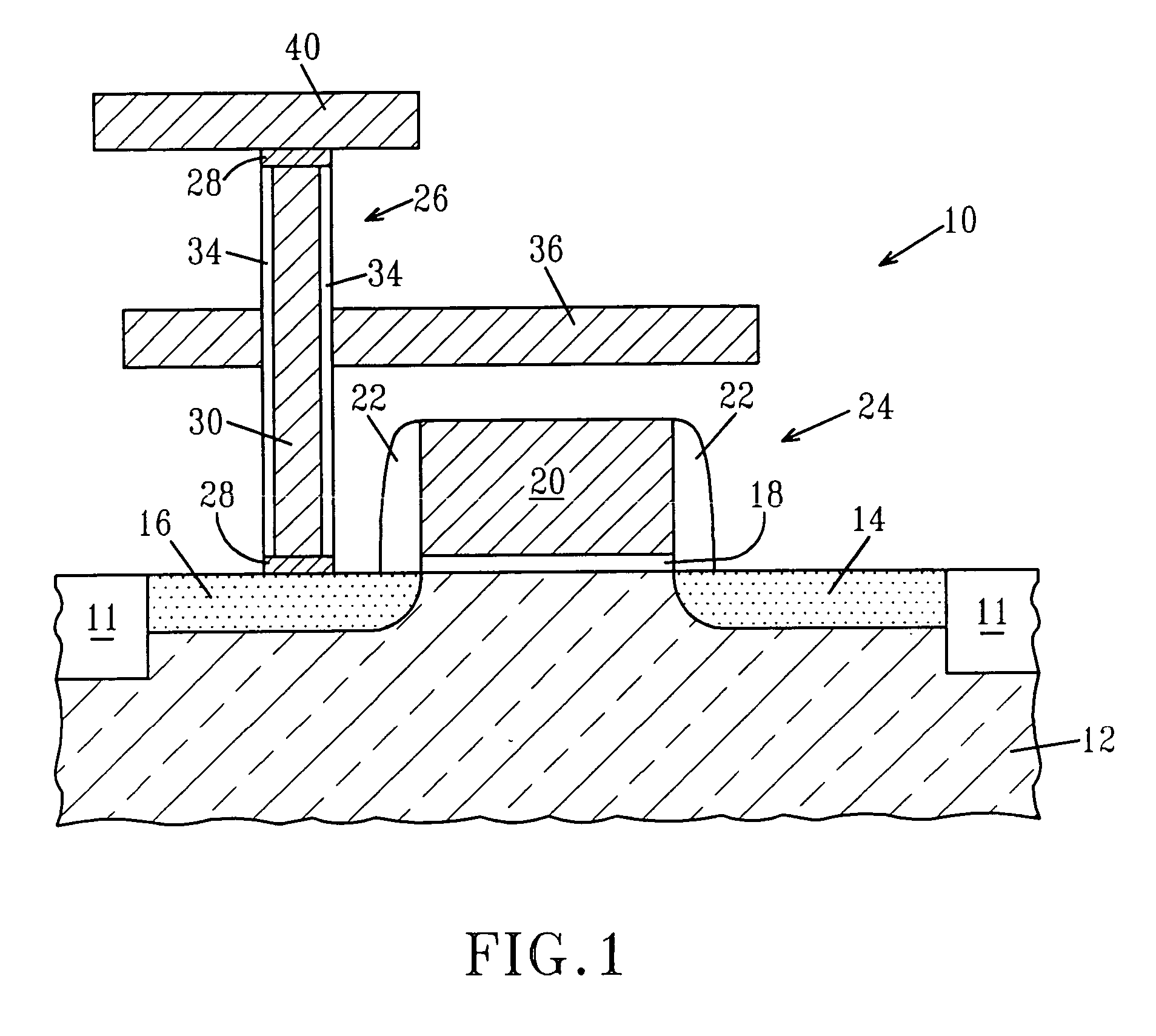
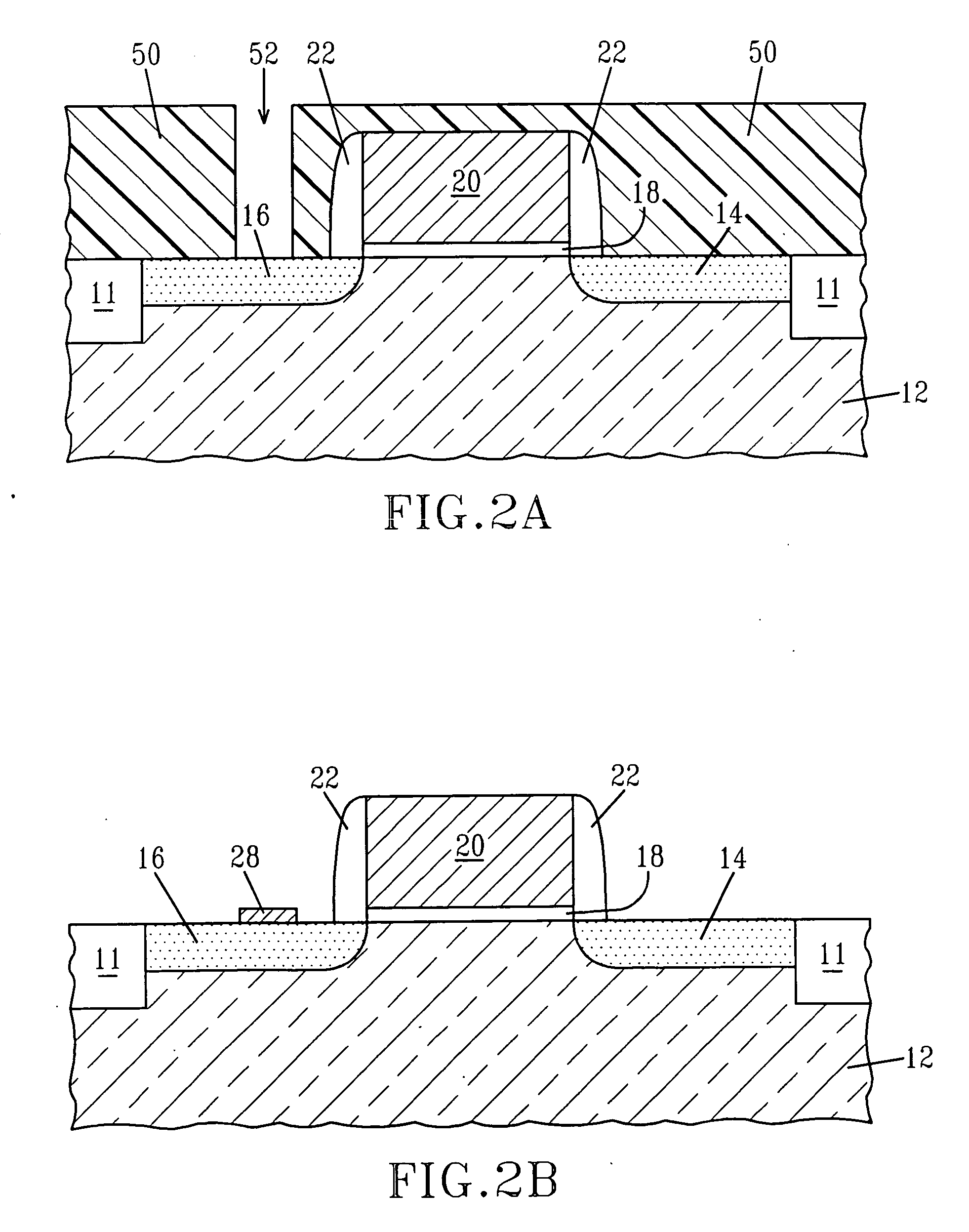
Structure and a method are provided for making a bipolar transistor, the bipolar transistor including a collector, an intrinsic base overlying the collector, an emitter overlying the intrinsic base, and an extrinsic base spaced from the emitter by a gap, the gap including at least one of an air gap and a vacuum void.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
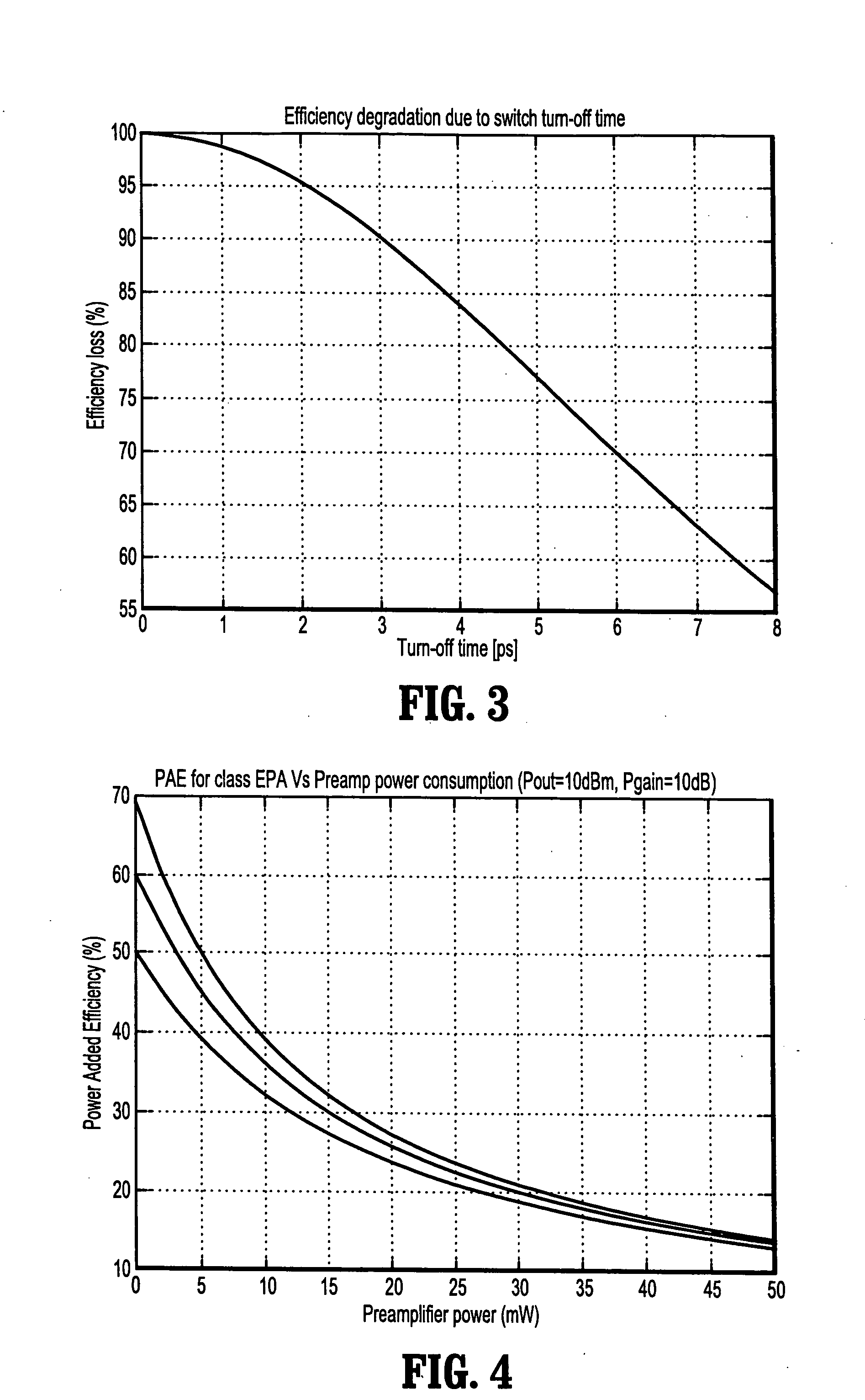
Circuits and methods for implementing power amplifiers for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS20060261890A1Improve driving conditionsPower added efficiencyRF amplifierAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Circuits and methods are provided for implementing highly efficient switch-mode power amplifiers using BJTs (bipolar junction transistors) as active switching devices at millimeter-wave frequencies. More specifically, circuits and methods are provided for driving power amplifiers with BJT switching devices to achieve highly efficient switch-mode (e.g., Class E) operation at millimeter wave frequencies (e.g., 60 GHz).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
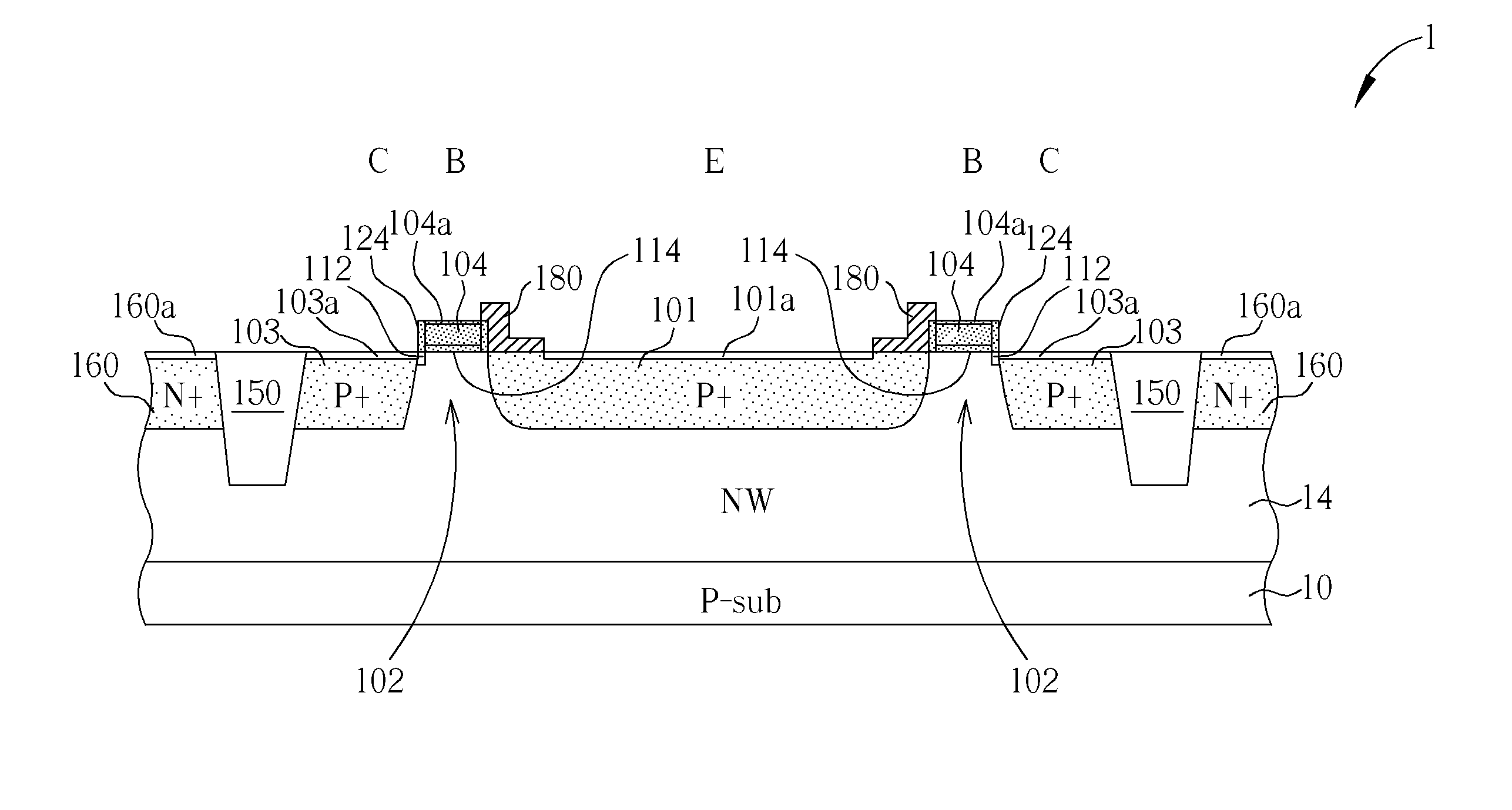
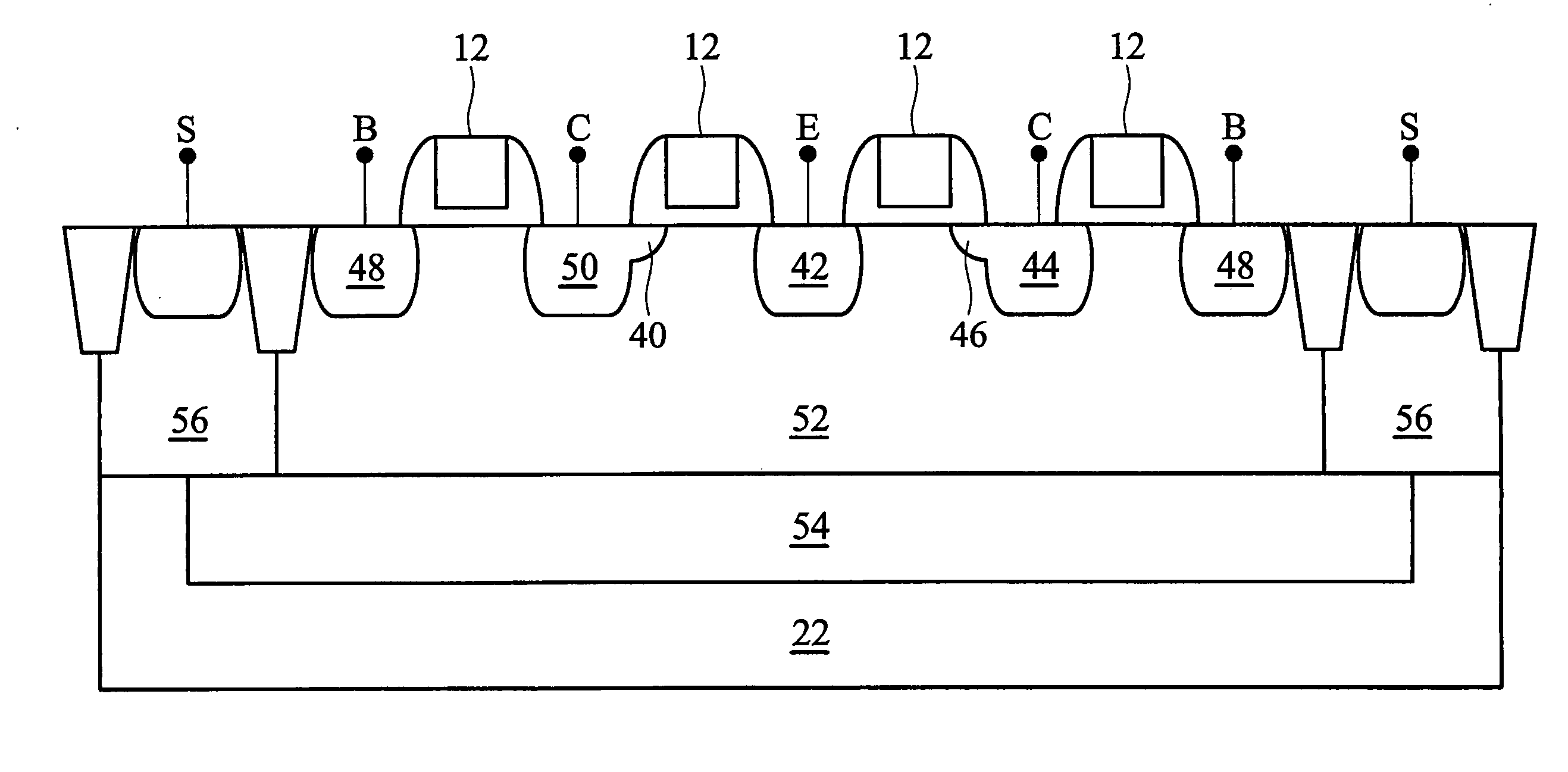
Four-transistor and five-transistor bjt-cmos asymmetric SRAM cells
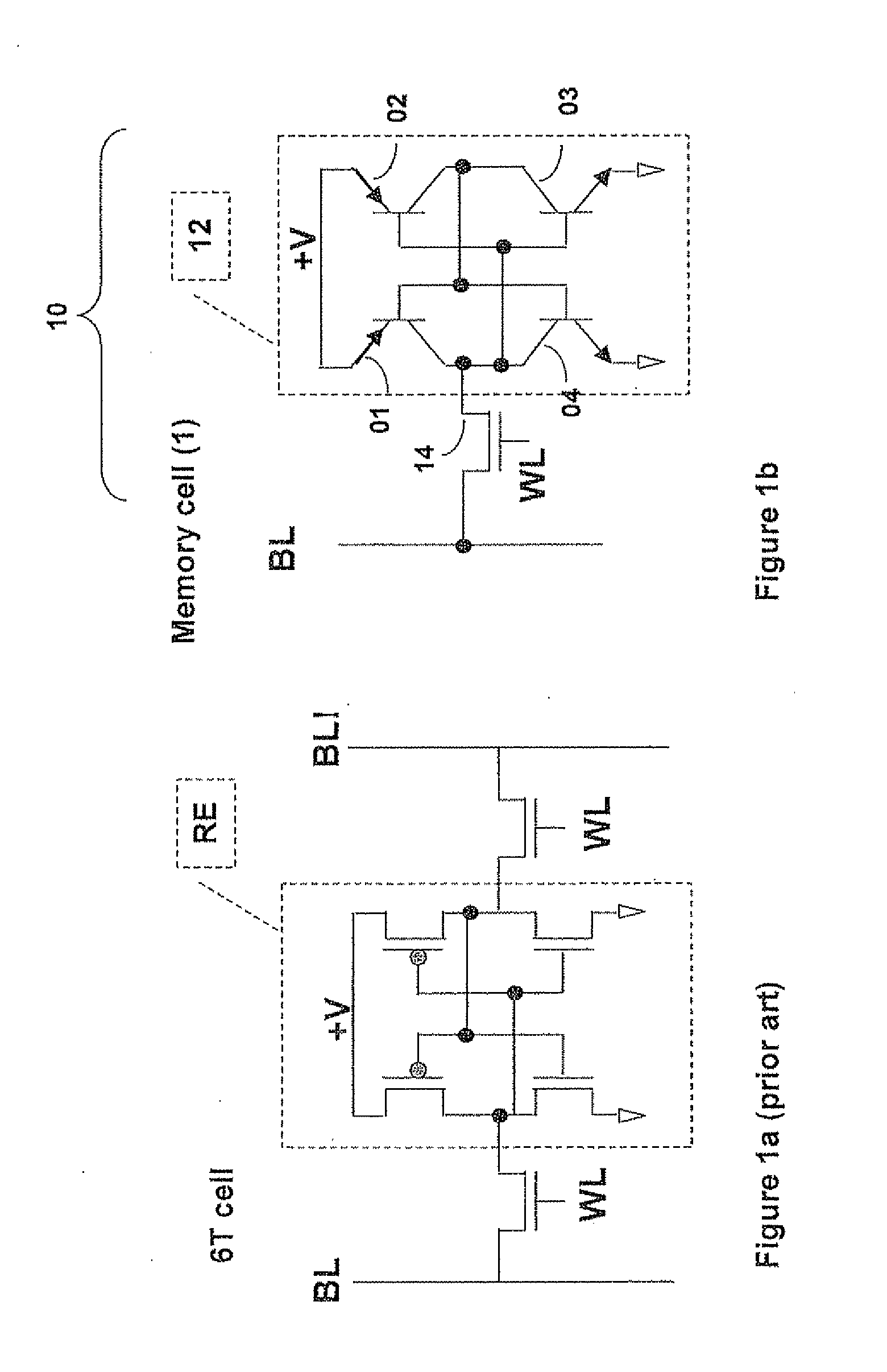
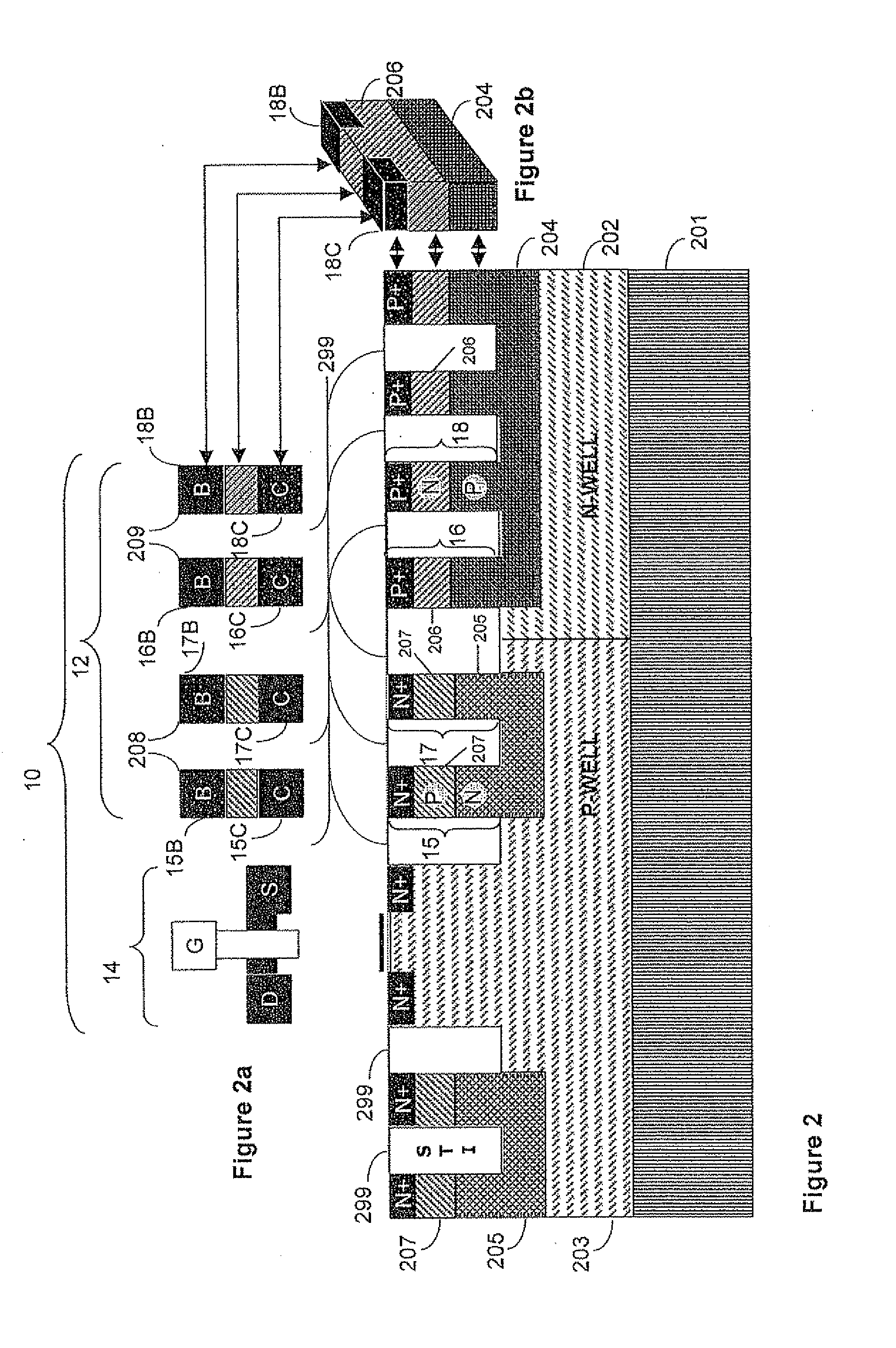
A memory cell comprises asymmetric retention elements formed of bipolar junction transistors integrated with a CMOS transistor. The BJT transistors of the retention element may be vertically stacked. In one embodiment, the N region of two adjacent NPN BJT transistors may be connected to ground and may form a common emitter of the NPN BJT transistors while the P region of two adjacent PNP BJT transistors may be connected to high voltage and may form a common emitter of the PNP BJT transistors. For further compactness in one embodiment a base of one transistor doubles as a collector of another transistor. The retention element may have only a single bit line and a single write line, with no negative bit line. In some embodiments, a single inverter and only three transistors may form the retention element. Memory space may be cut approximately in half.
Owner:ASA GIL
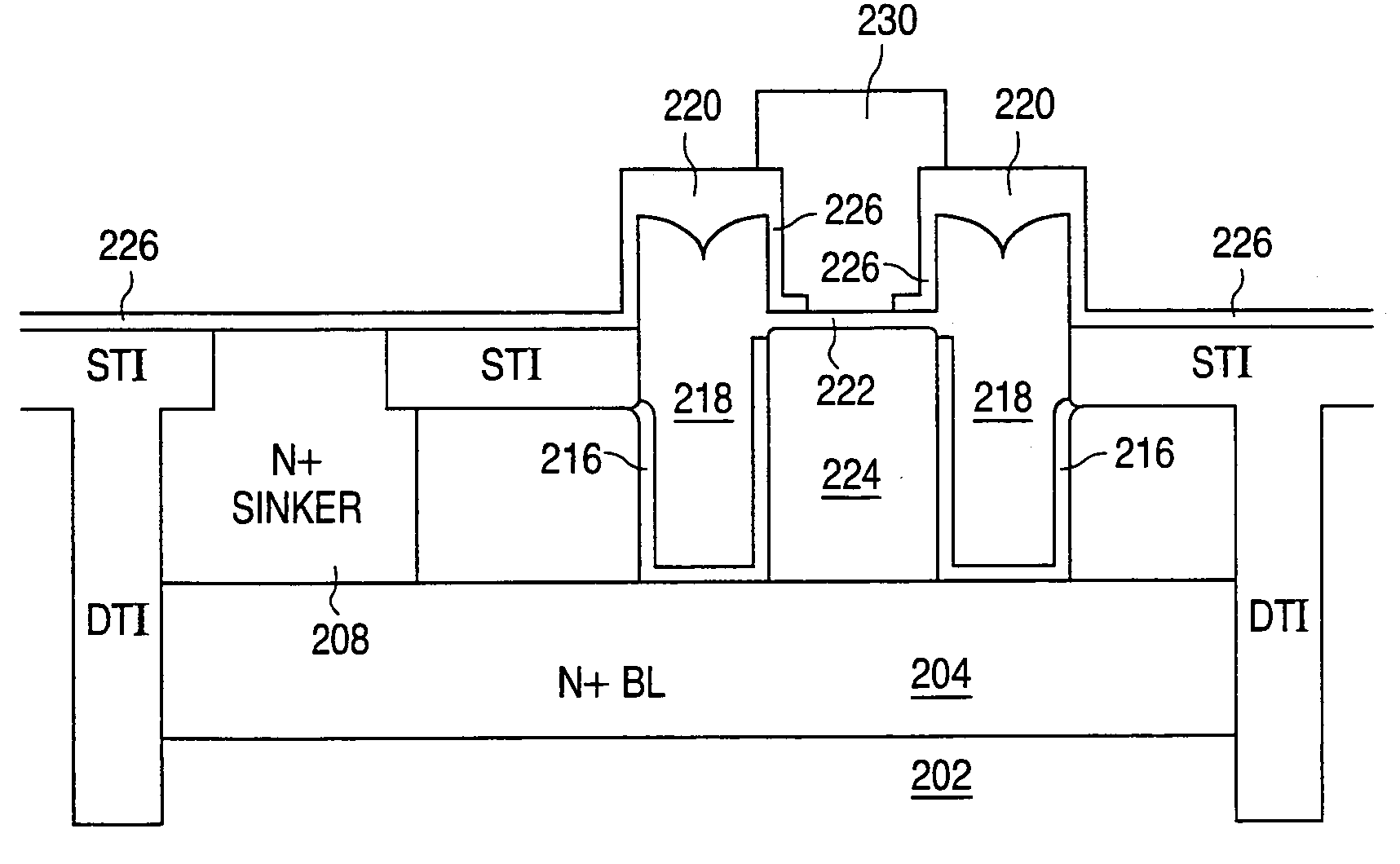
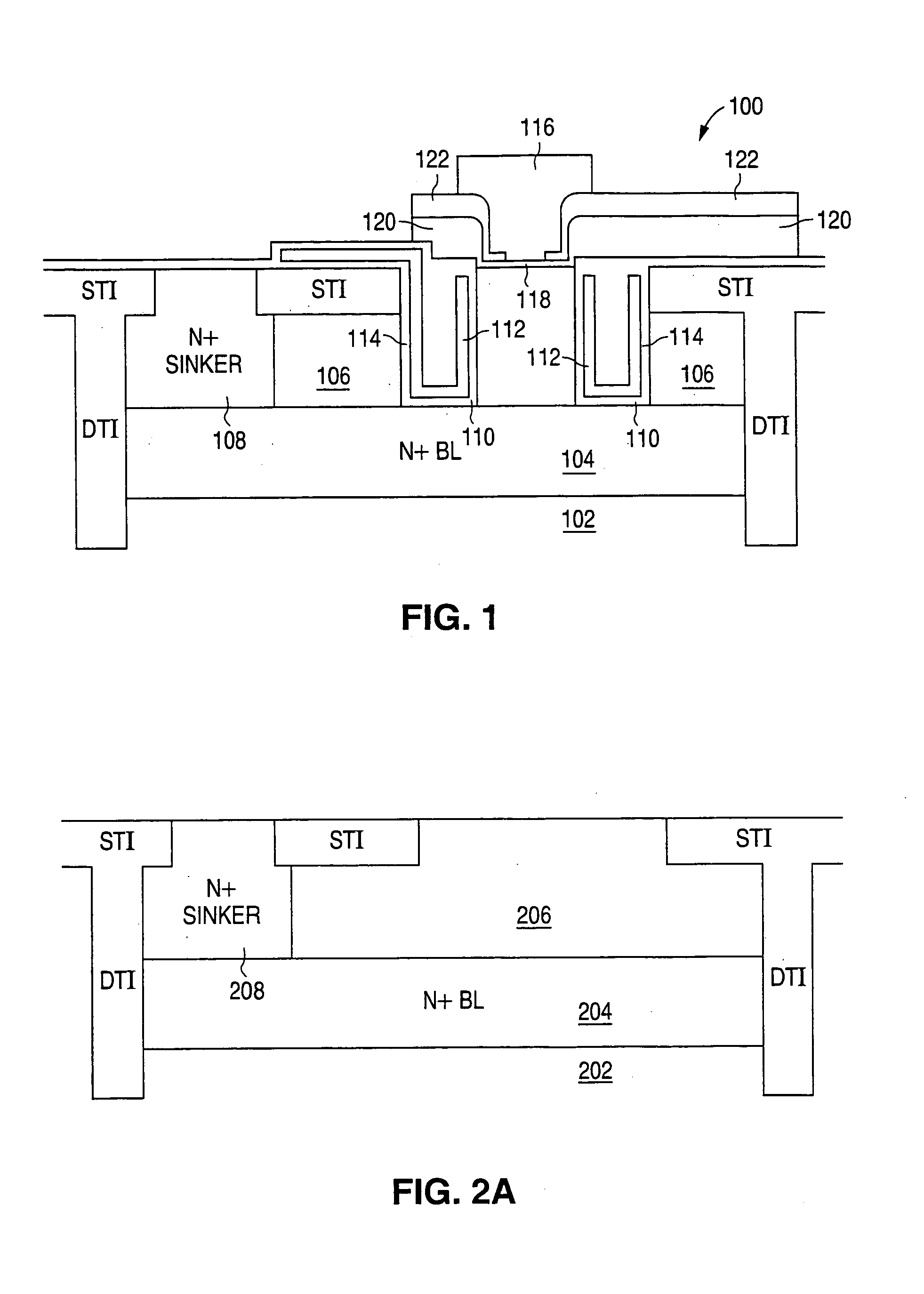
Super self-aligned BJT with base shorted field plate and method of fabricating
ActiveUS7132344B1Raise the ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVertical fieldSubstrate surface
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) structure and fabrication method are provided in which a doped polysilicon filled trench is utilized to form both the extrinsic base contact region and a vertical field plate. A sacrificial mandrel of dielectric material is formed over regions that will become the BJT active area. This allows the polysilicon filled trench to be extended above the original semiconductor substrate surface. In this way, the base-collector and emitter-base junctions are both self-aligned to the field plate trench. The field plate is utilized to control and shape the electric field in the base-collector depletion region, allowing heavier collector well doping for the same breakdown voltage. This results in improvement in both the breakdown / Ron ratio and the fT*BVcbo product.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
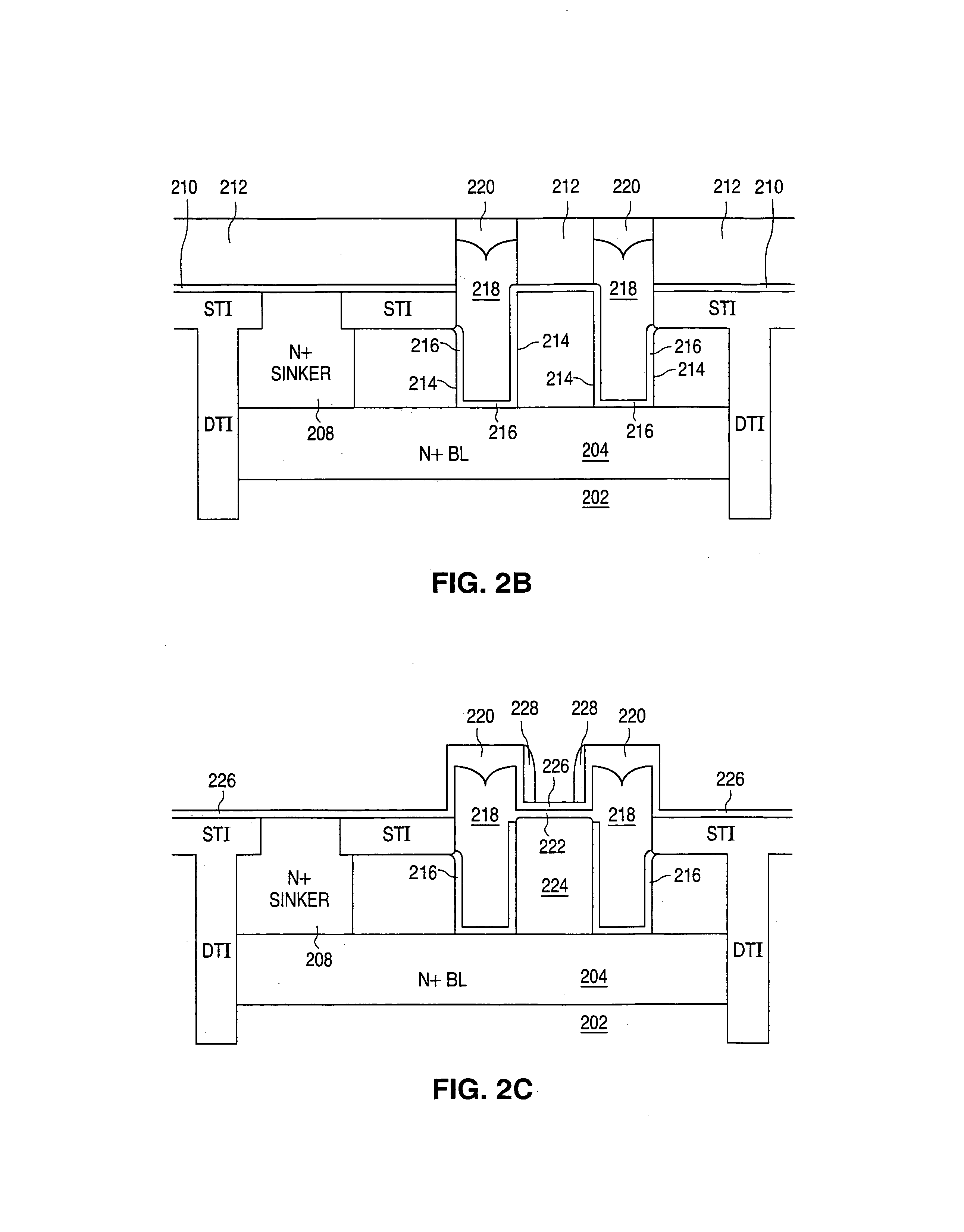
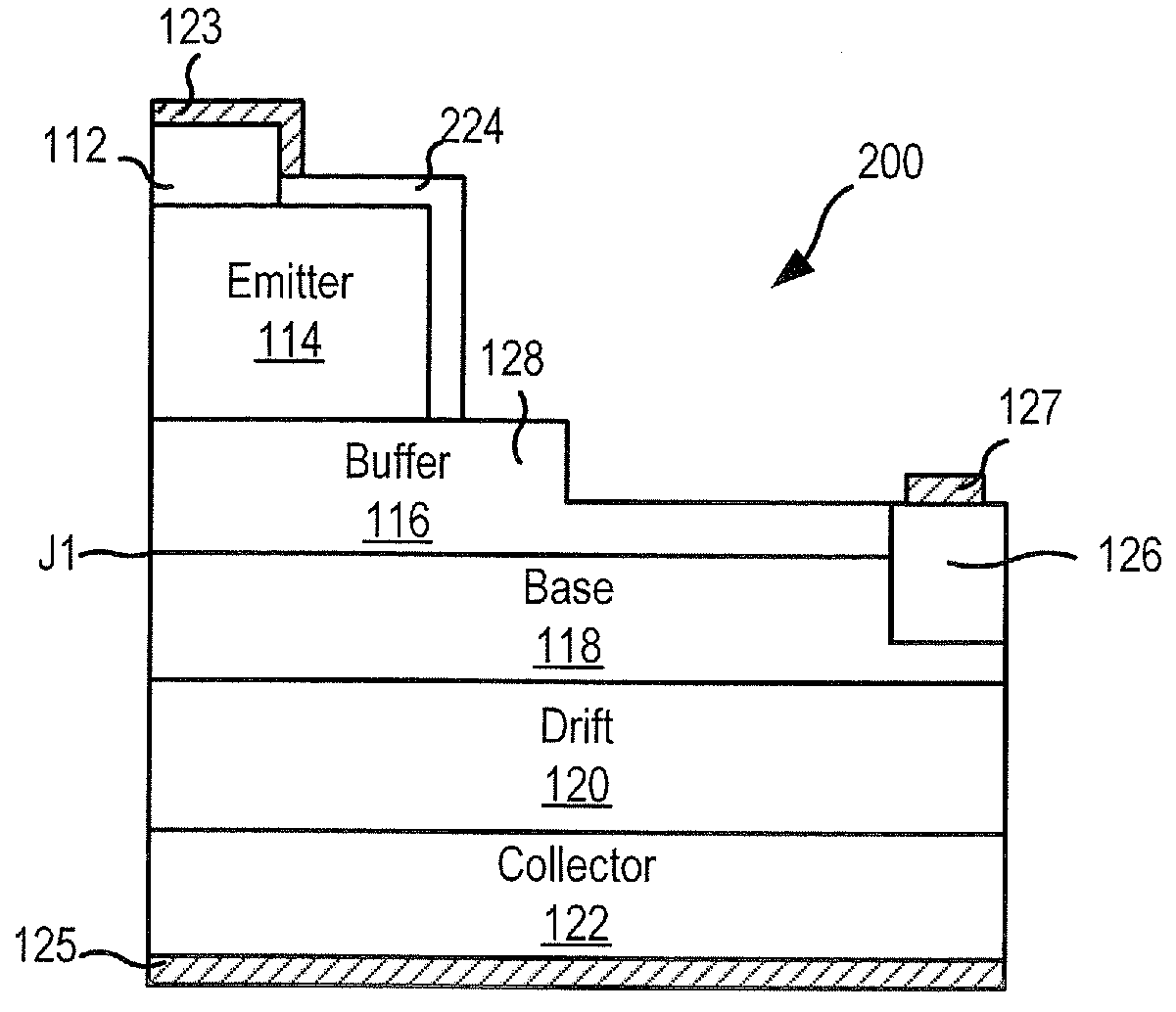
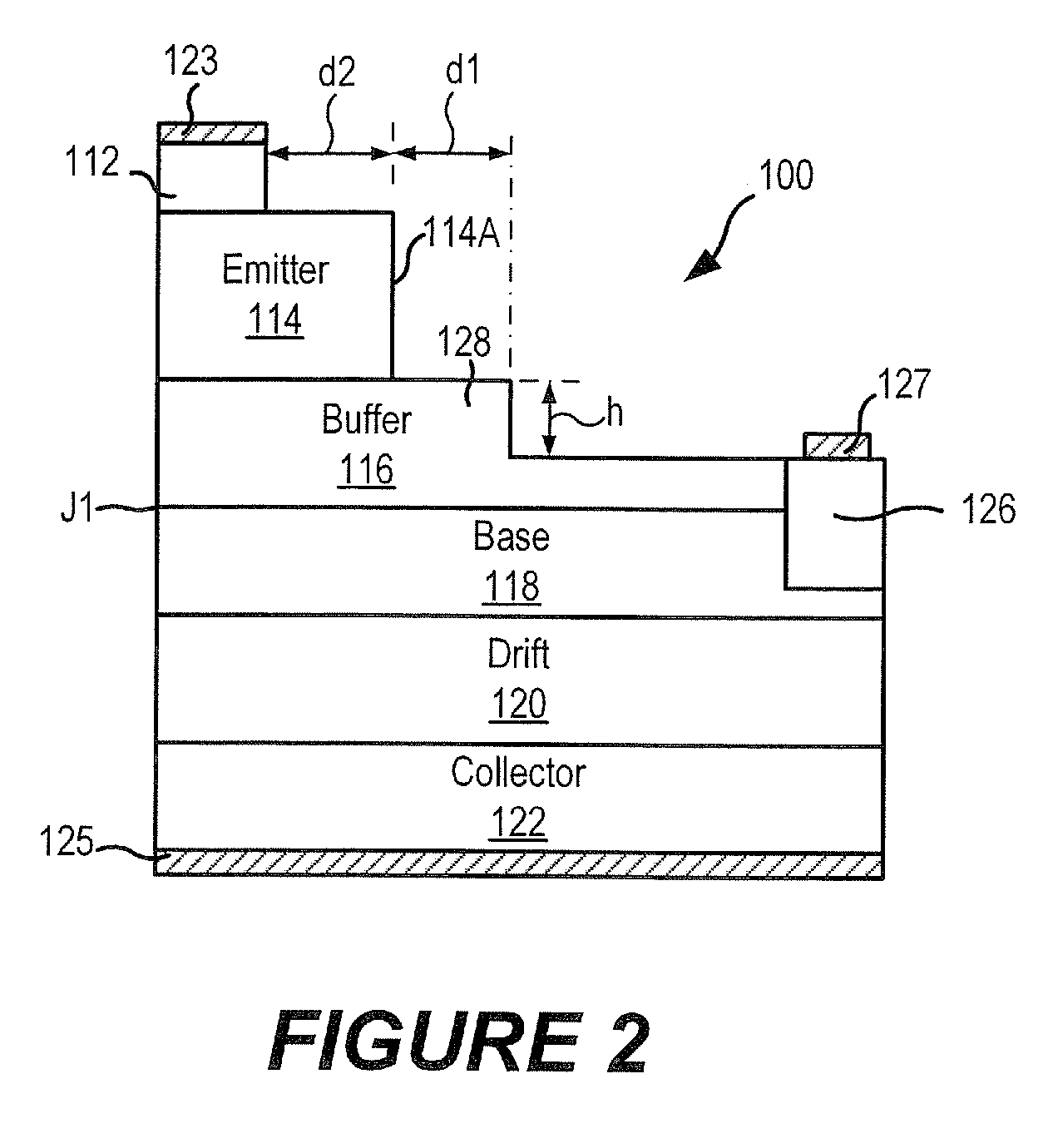
Power semiconductor devices with mesa structures and buffer layers including mesa steps
A bipolar junction transistor includes a collector having a first conductivity type, a drift layer having the first conductivity type on the collector, a base layer on the drift layer and having a second conductivity type opposite the first conductivity type, a lightly doped buffer layer having the first conductivity type on the base layer and forming a p-n junction with the base layer, and an emitter mesa having the first conductivity type on the buffer layer and having a sidewall. The buffer layer includes a mesa step adjacent to and spaced laterally apart from the sidewall of the emitter mesa, and a first thickness of the buffer layer beneath the emitter mesa is greater than a second thickness of the buffer layer outside the mesa step.
Owner:CREE INC
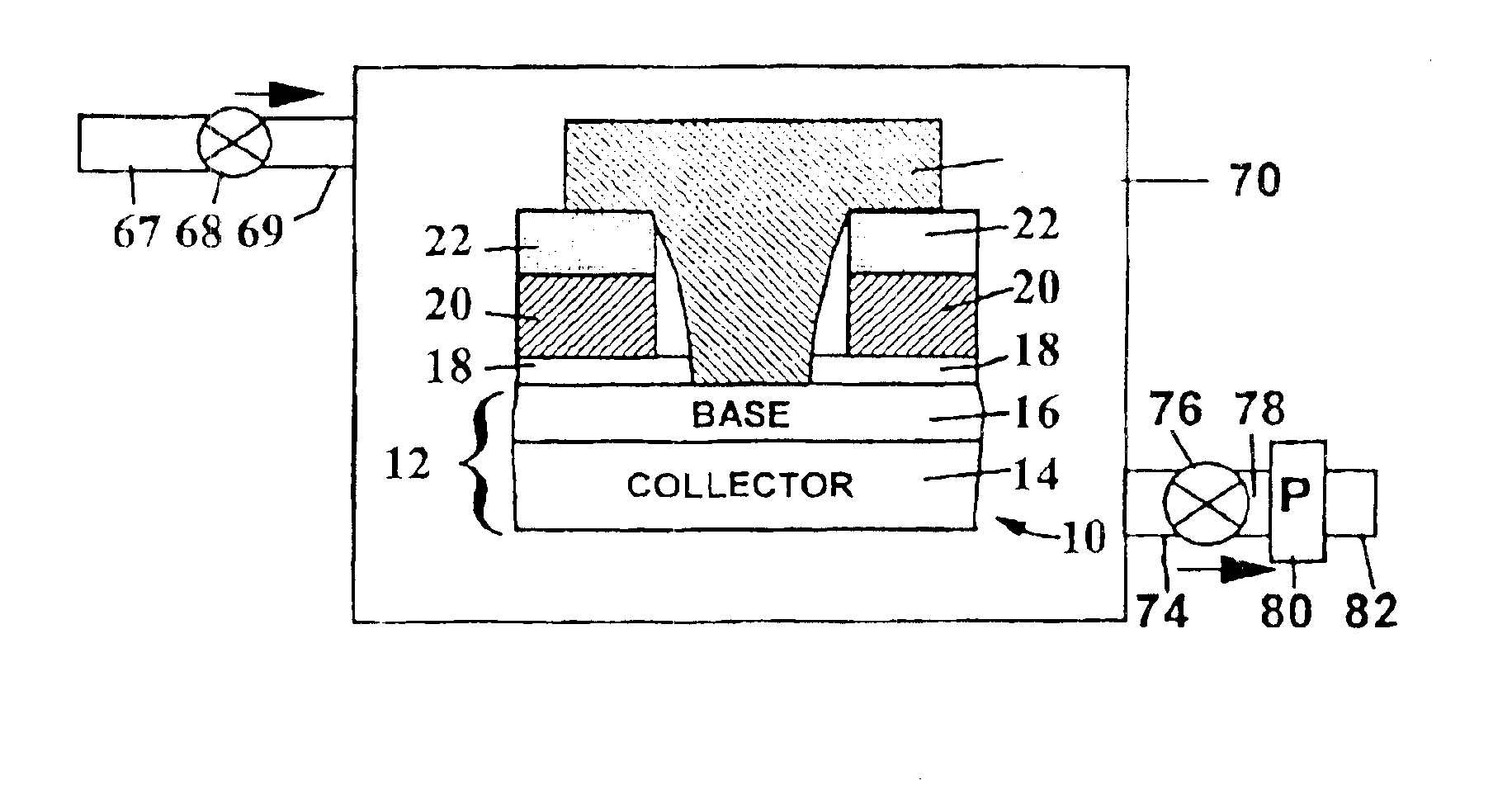
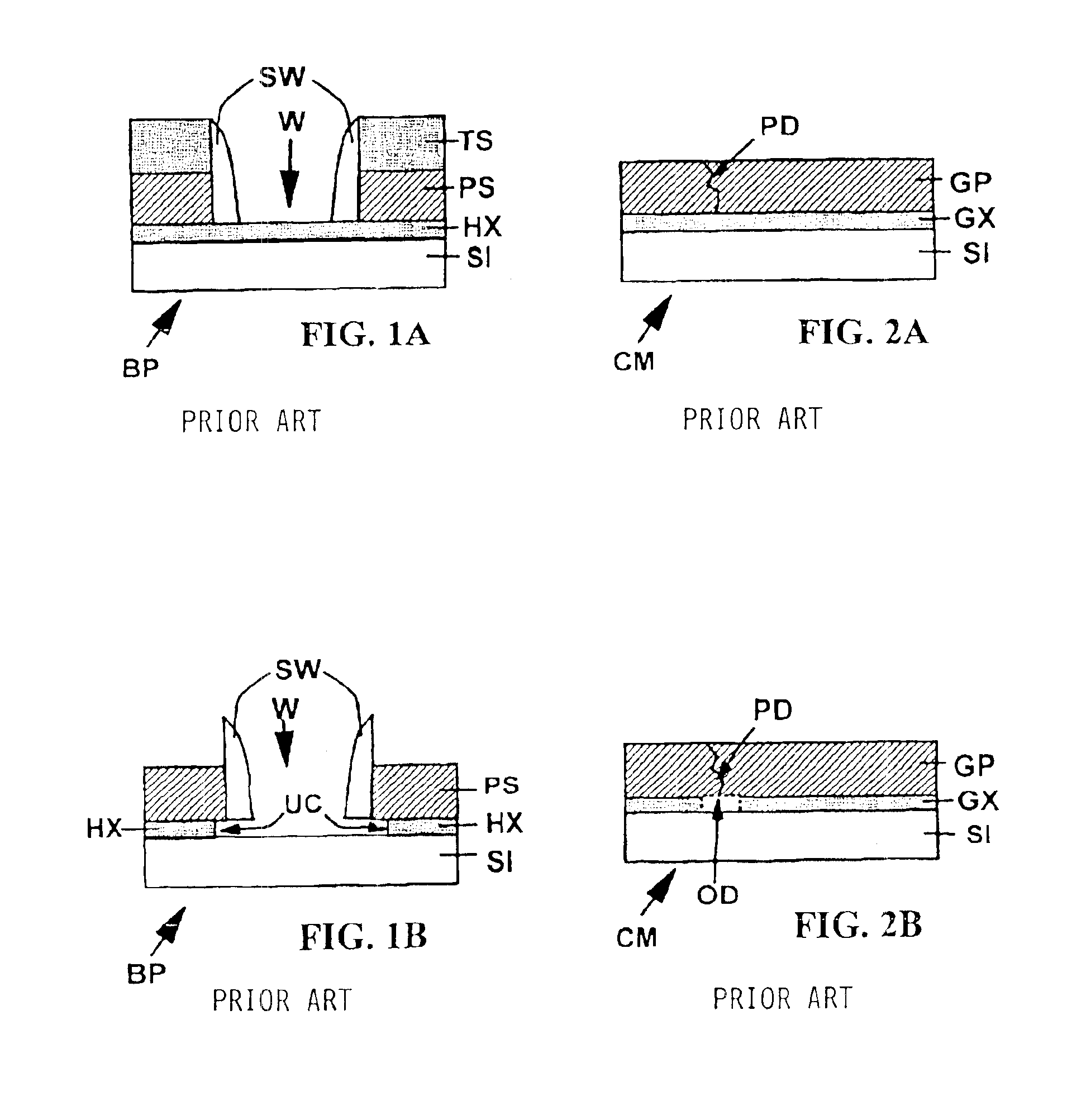
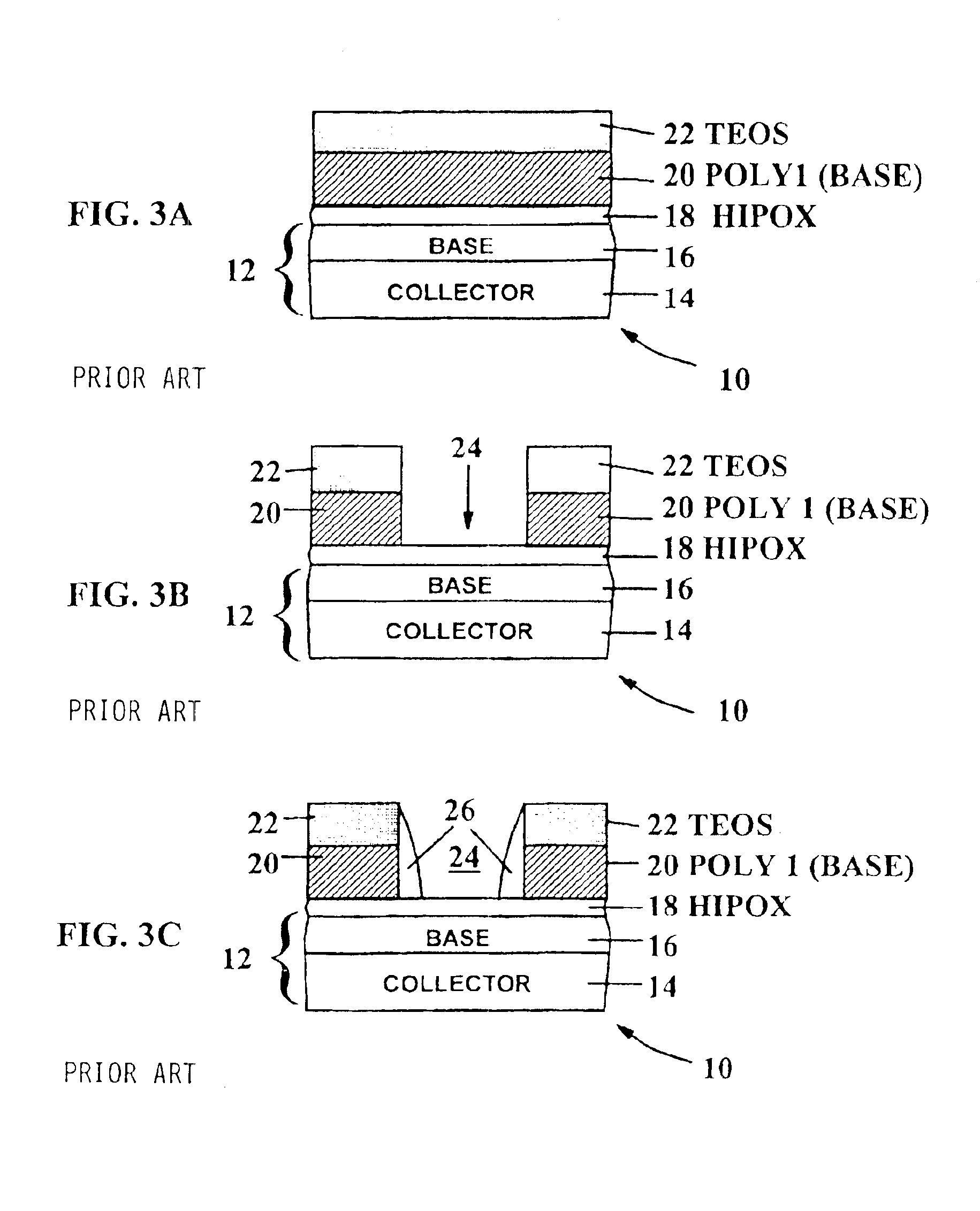
Low defect pre-emitter and pre-base oxide etch for bipolar transistors and related tooling
InactiveUS6858532B2Adverse side-effectSuppressed undercutSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceEngineering
An oxide etch process is described which may be used for emitter and base preparation in bipolar SiGe devices. The low temperature process employed produces electrical insulation between the emitter and base by a COR etch which preserves insulating TEOS glass. The insulating TEOS glass provides reduced capacitance and helps to achieve high speed. An apparatus is also described for practicing the disclosed process.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
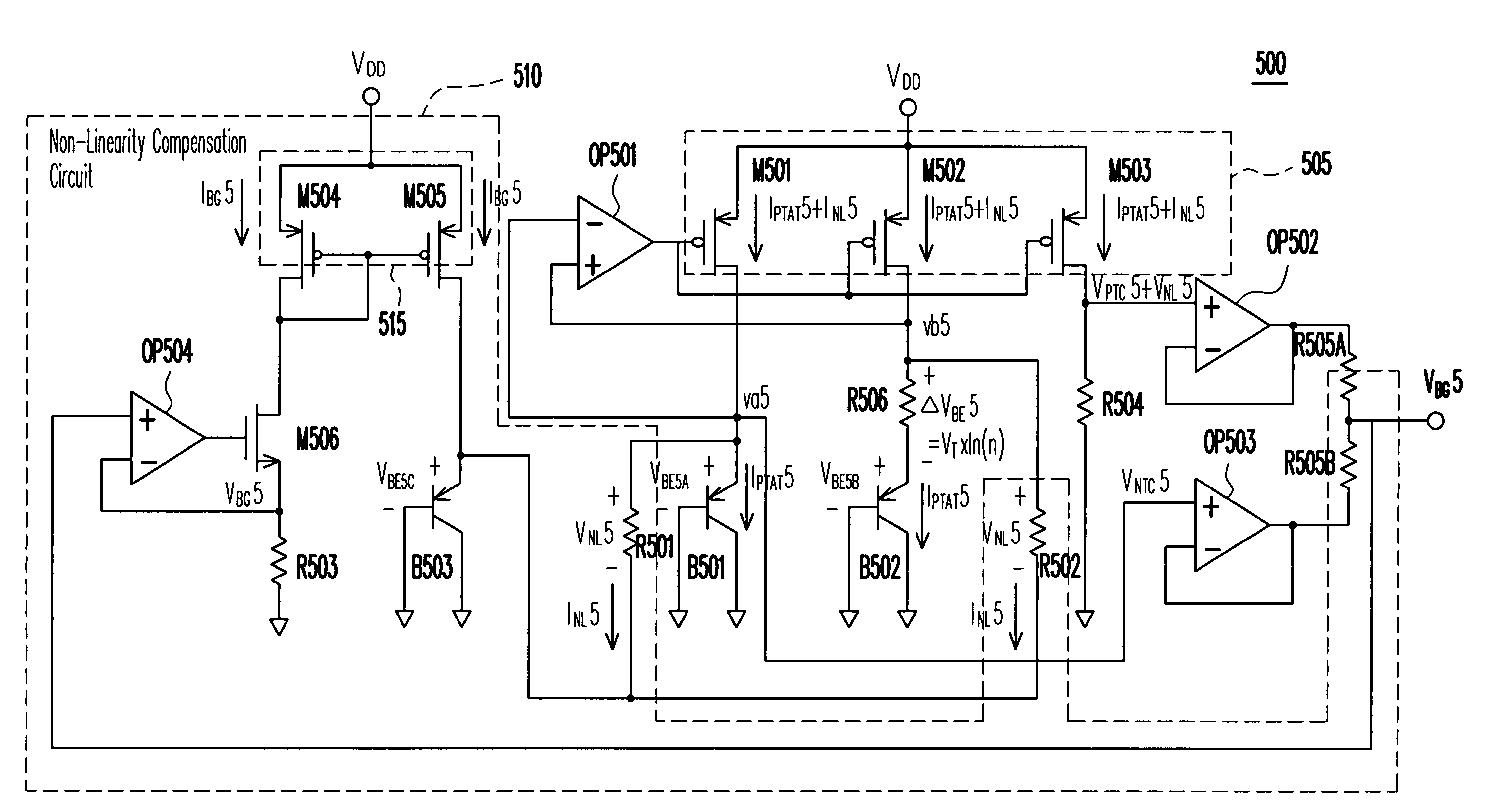
Non-linearity compensation circuit and bandgap reference circuit using the same
InactiveUS7411380B2High precisionLow costPower supply linesElectric variable regulationEngineeringReference circuit
A non-linearity compensation circuit and a bandgap reference circuit using the same for compensating non-linear effects of a reference voltage are provided. In the non-linearity compensation circuit, the reference voltage is transformed into a temperature independent current. A current mirror mirrors the temperature independent current for biasing a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). Further, two resistors are used for estimating a non-linear voltage, so as to compensate the reference voltage.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com